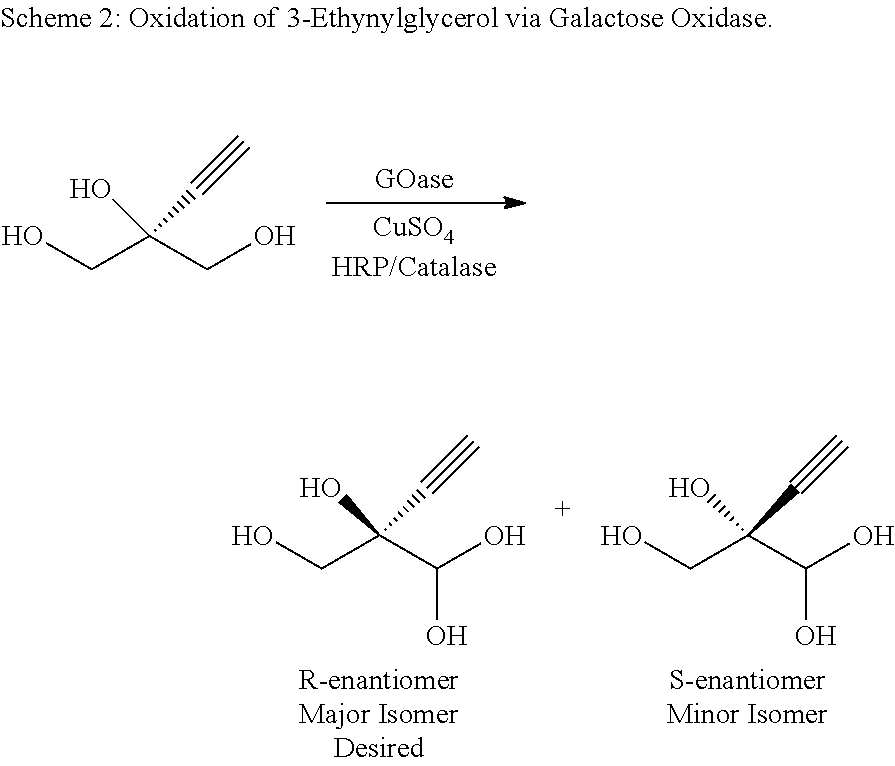
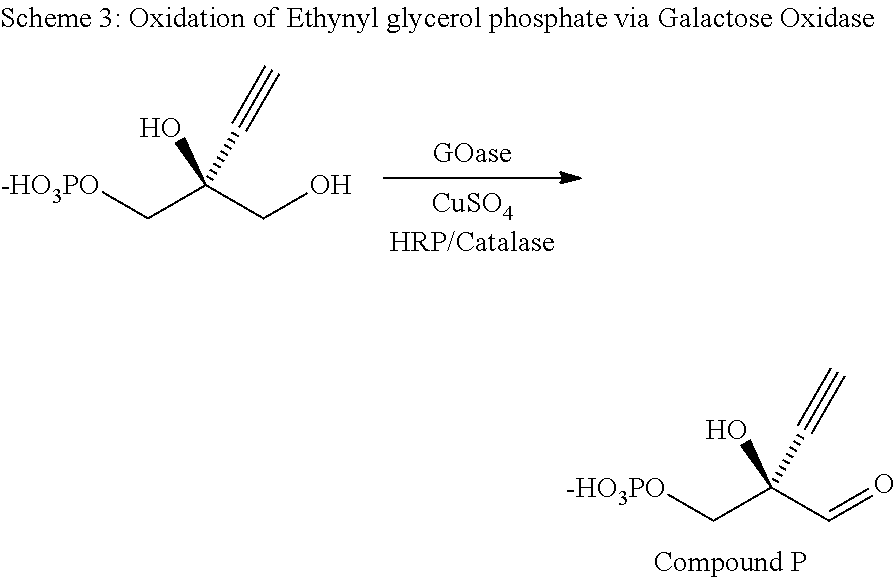
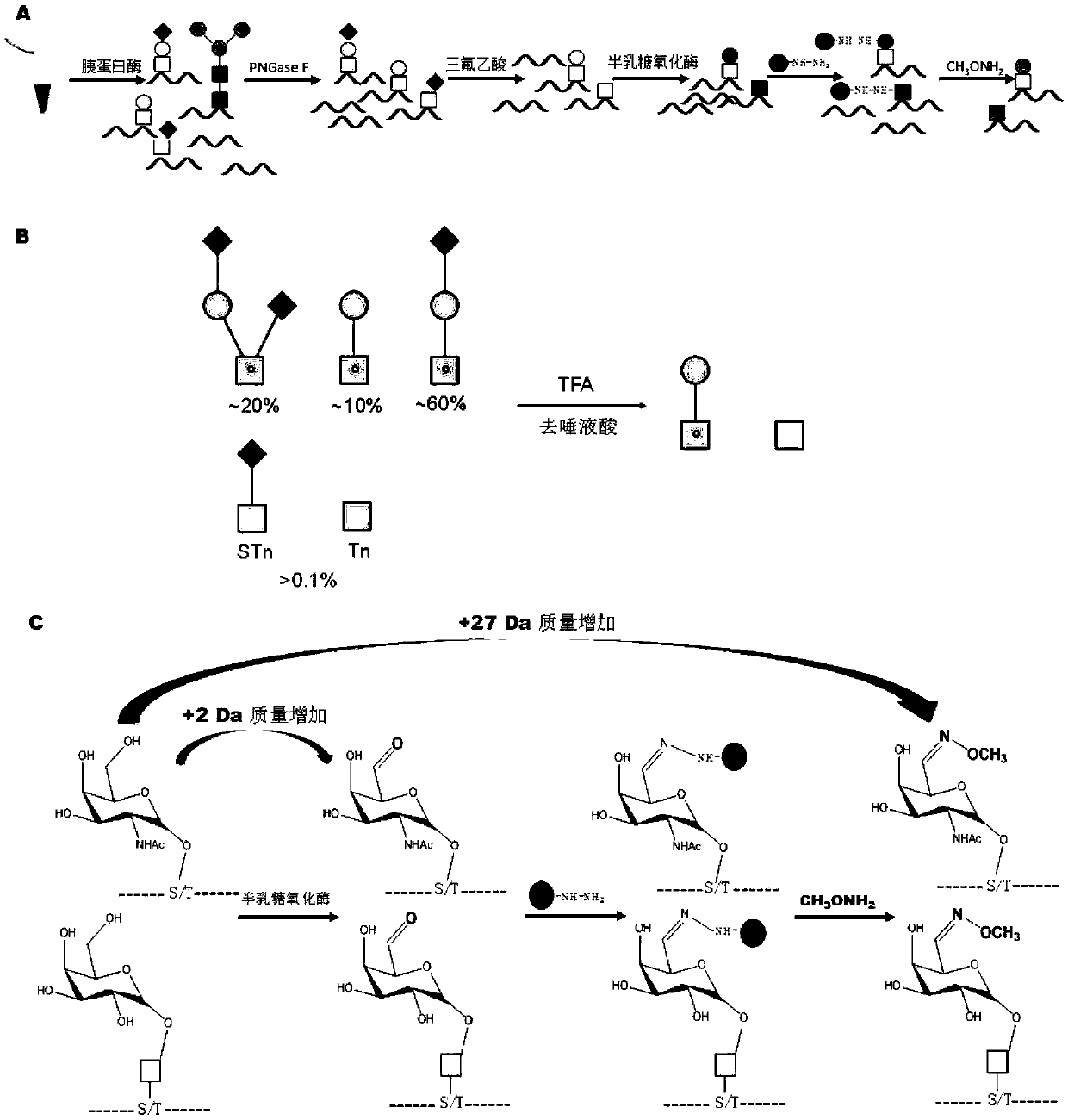
Patents
Literature
40 results about "Galactose oxidase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
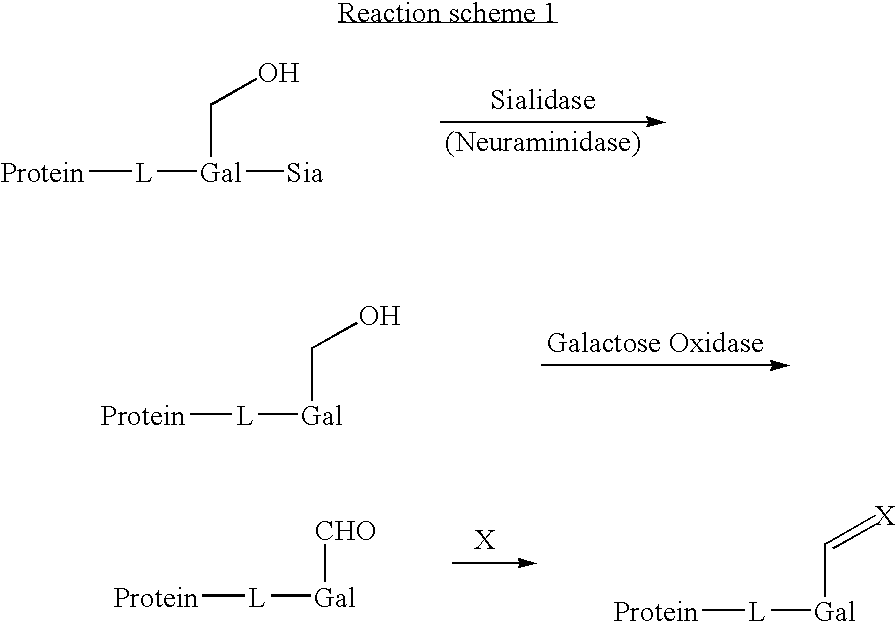
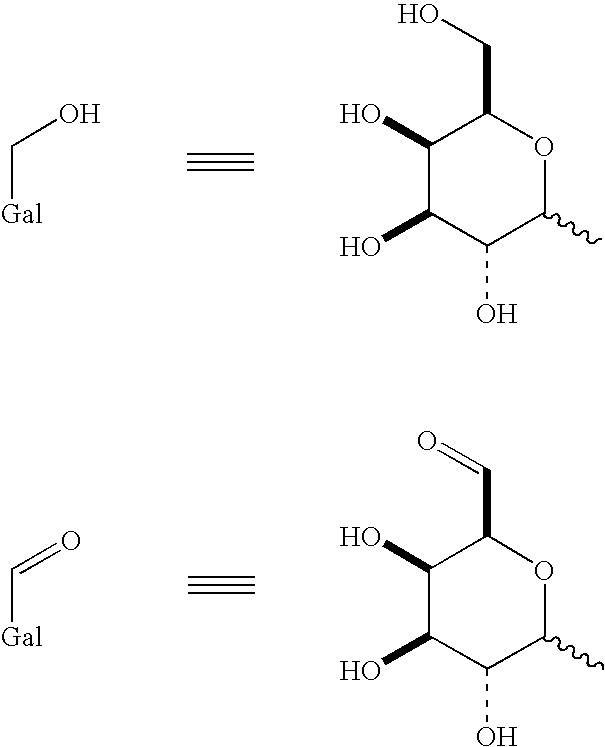
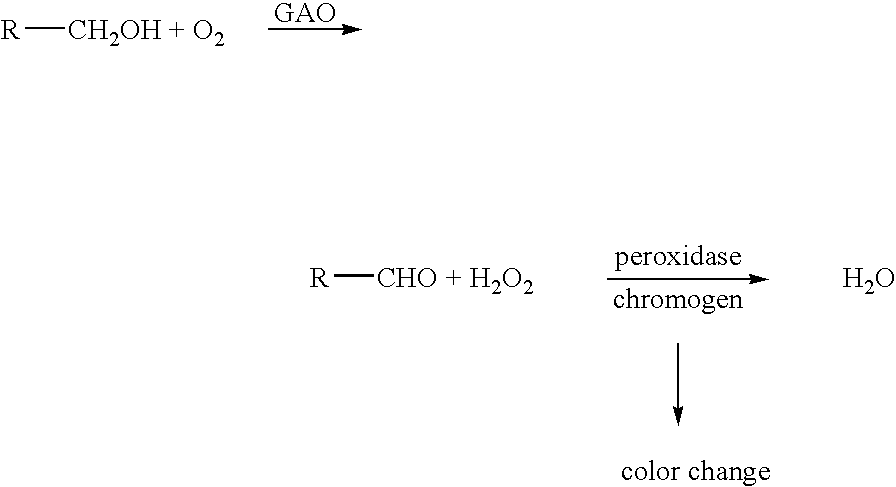
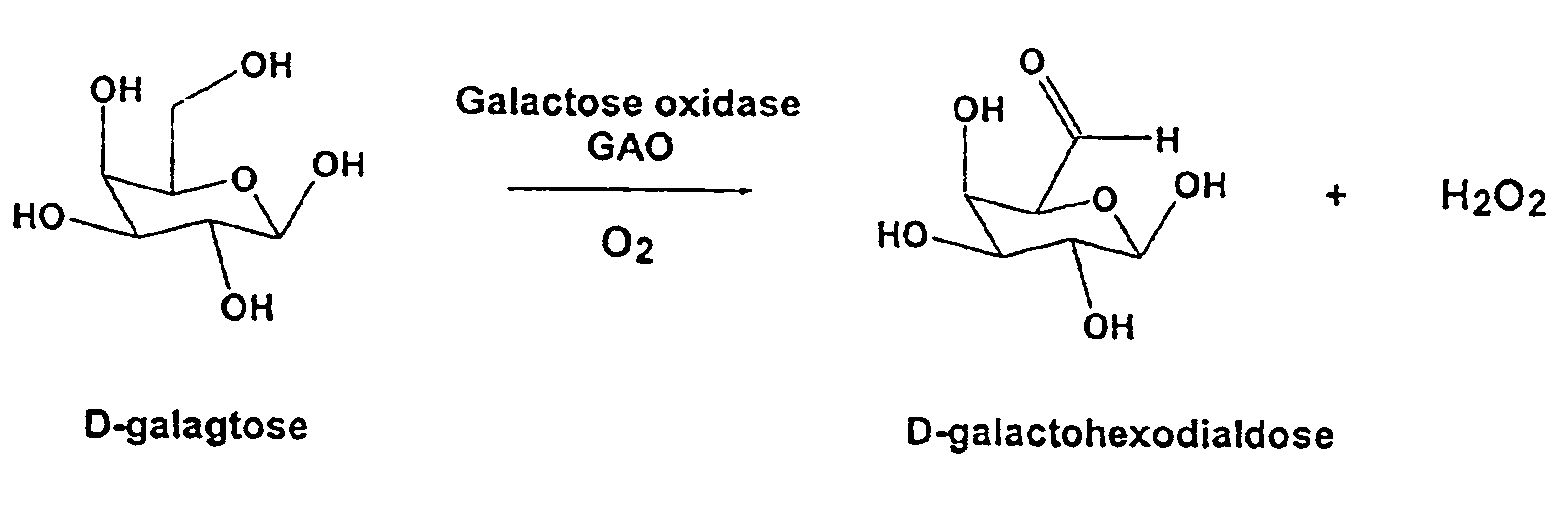
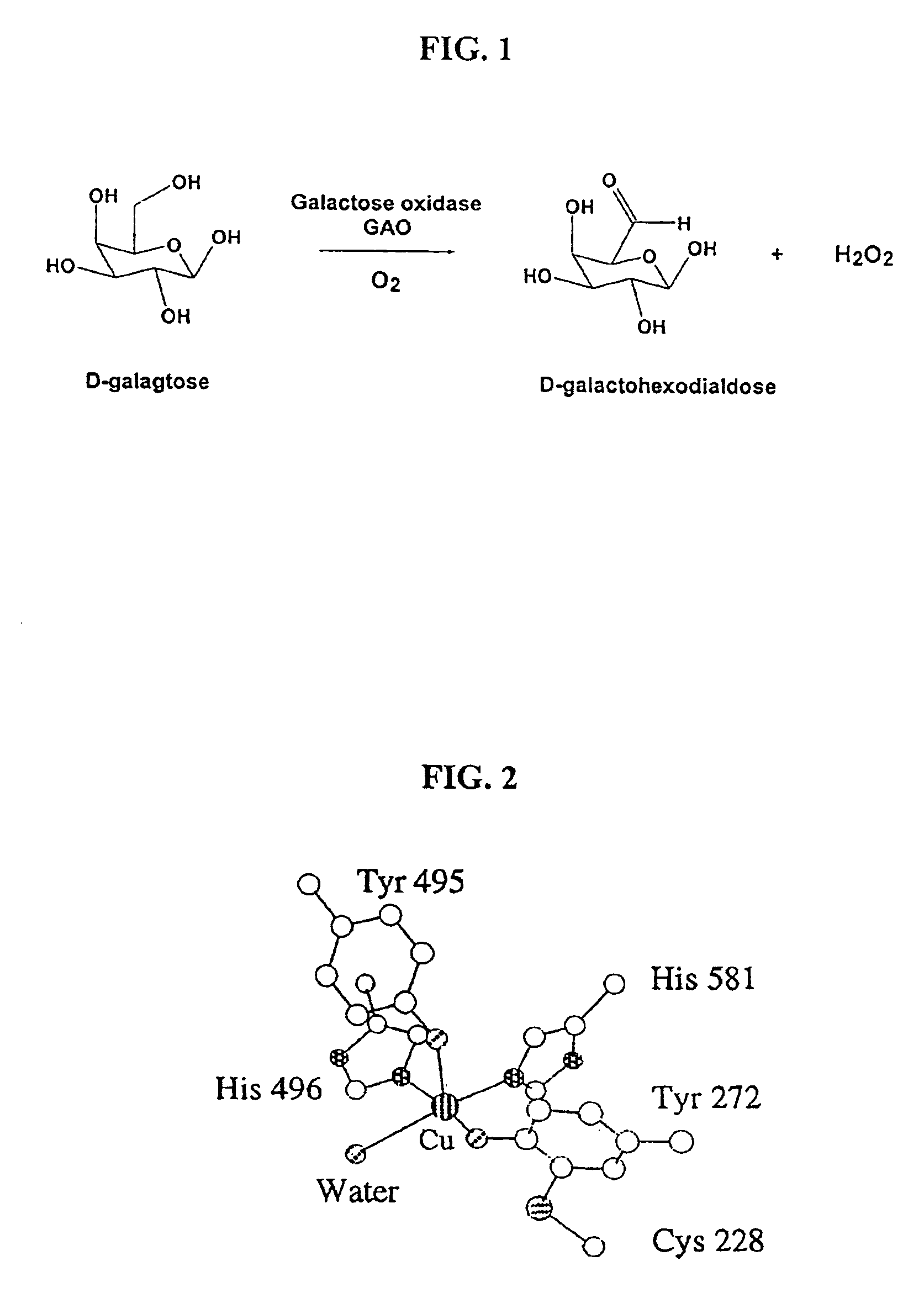
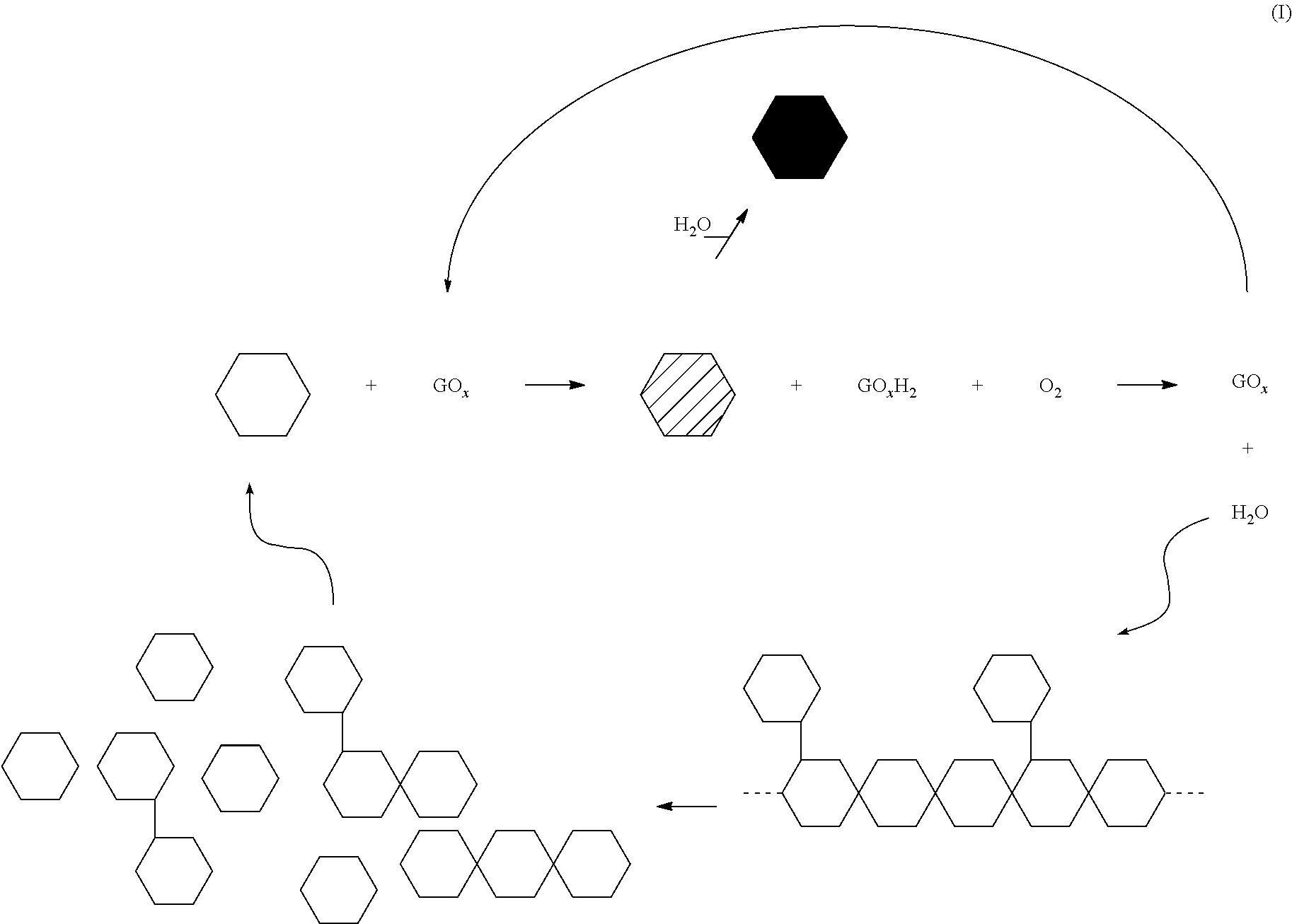
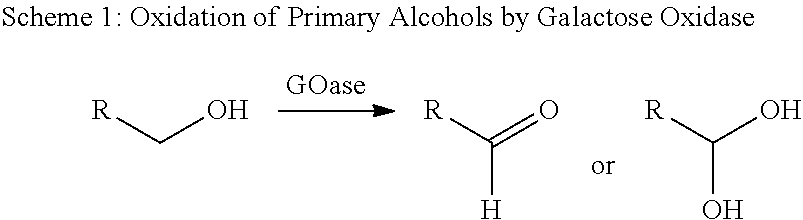
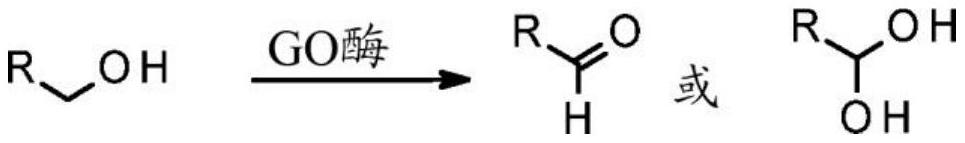
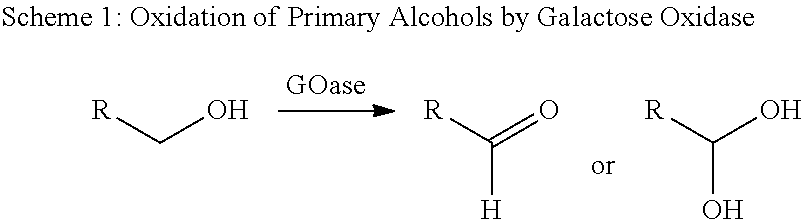
Galactose oxidase (D-galactose:oxygen 6-oxidoreductase, D-galactose oxidase, beta-galactose oxidase; abbreviated GAO, GAOX, GOase; EC 1.1.3.9) is an enzyme that catalyzes the oxidation of D-galactose in some species of fungi.
Use of galactose oxidase for selective chemical conjugation of protractor molecules to proteins of therapeutic interest
InactiveUS20060198819A1Extended half-lifeLittle or no maintenancePeptide/protein ingredientsAnimal repellantsTherapeutic intentBiochemistry
This invention relates to novel compounds, methods for selective chemical conjugation of protractor molecules and the use thereof for diagnostic and / or therapeutic purposes.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK HEALTH CARE AG
Directed evolution of oxidase enzymes
InactiveUS7098010B1Improve propertiesHigh expressionSugar derivativesBacteriaLactose oxidaseNucleotide
This invention relates to the expression of improved polynucleotide and polypeptide sequences encoding for eukaryotic enzymes, particularly oxidase enzymes. The enzymes are advantagoeusly produced in conventional or facile expression systems. Various methods for directed evolution of polynucleotide sequences can be used to obtain the improved sequences. The improved characteristics of the polypeptides or proteins generated in this manner include improved expression, enhanced activity toward one or more substrates, and increased thermal stability. In a particular embodiment, the invention relates to improved expression of the galactose oxidase gene and galactose oxidase enzymes. GAO mutants that are highly active and / or thermostable are disclosed.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method for determining galactose concentration and galactose diagnosis/determination reagent kit
InactiveCN101324580AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsELISA unitLactose
The invention relates to a kit for diagnosing / mensurating galactose by utilizing the technologies of the enzymic colorimetric method and the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The invention further relates to a method, a principle and the composition and the components of a reagent for mensurating the concentration of the galactose, and belongs to the technology field of medical / food inspection and measurement. The main components of the kit include a buffer solution, reduced coenzyme, galactose oxidase, NADH peroxidase and a stabilizer. Through mixing a sample and the reagent by a certain volume ratio, a series of enzymatic reactions occur, then the reactant is placed under an ultraviolet / visible light analyzer, and the degree / velocity of the decrease in absorbance at 340nm of the dominant wavelength is detected, thereby mensurating the concentration of the galactose.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Method for preparing high-curing modified-guar-gum contained aqueous solution
ActiveCN1936179AHigh solid contentLow viscosityWater-repelling agents additionPaper/cardboardAqueous solutionViscosity
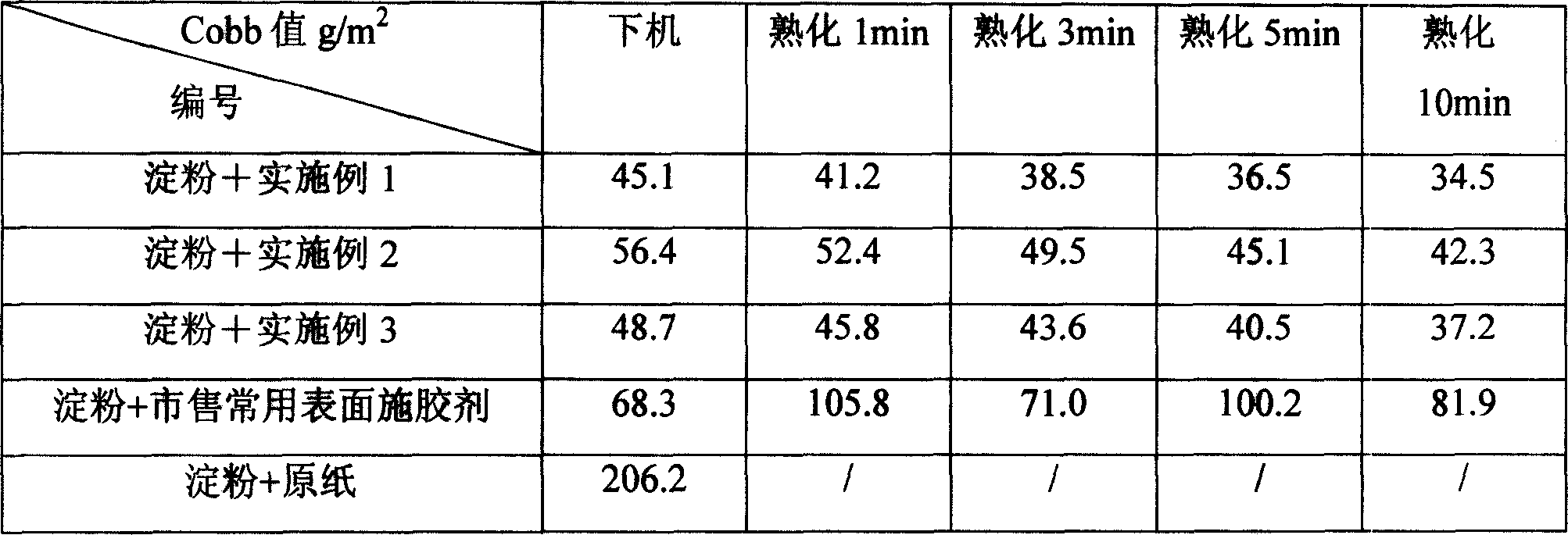
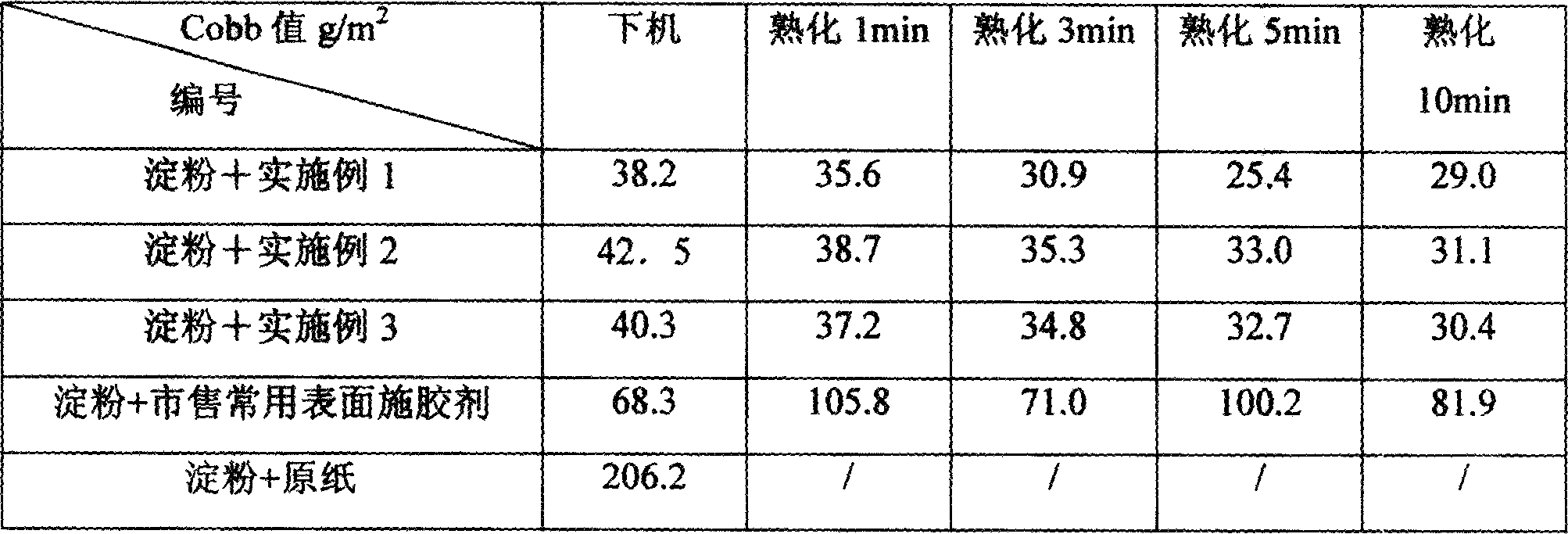
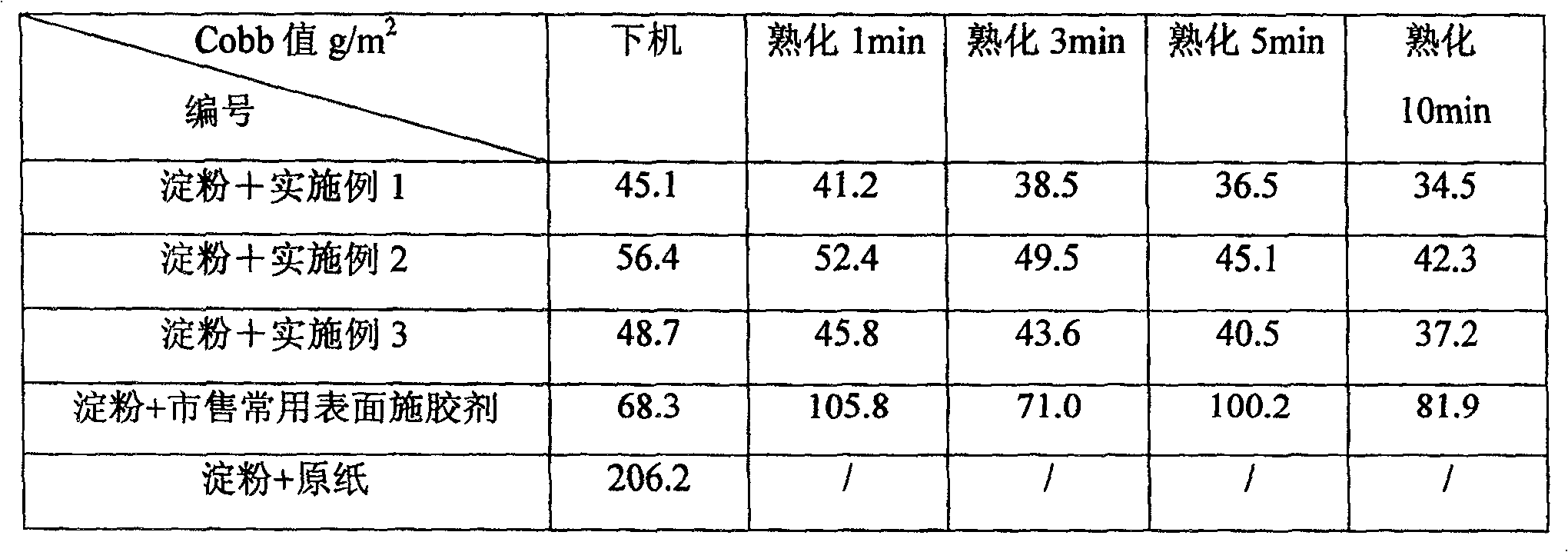
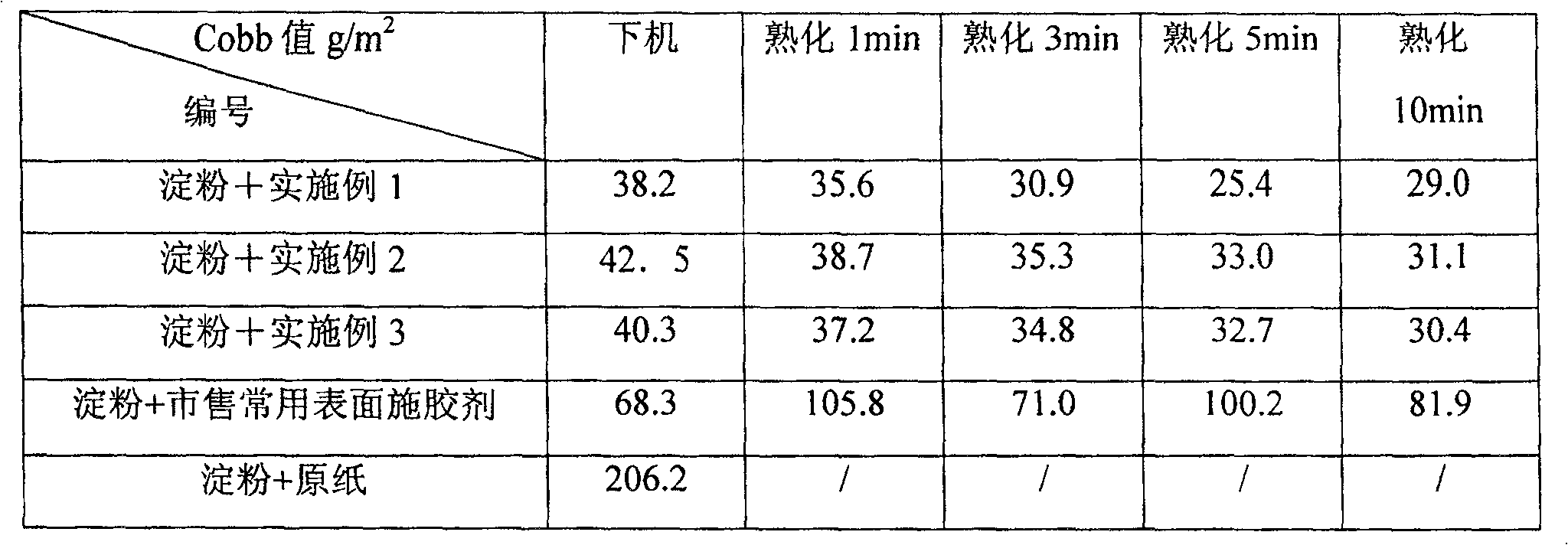
The invention discloses a high content modified guar gum solution manufacture method. The modified guar gum powder could be hydroxide propyl guar gum, positive ion guar gum or the mixture. It includes the following steps: adding positive ion oxidation guar gum powder into water to make the viscosity over 3000mpa.s, adding mannose enzyme solution, adding galactose oxidase solution, heating to 40-60 degree centigrade and reacting for 4-8 hours to gain modified guar gum solution that has viscosity at about 200-500mpa.s, content is 10-25%. The invention could be used to make paper making sizing agent. Comparing to simply using AKD, the sheet and the Cobb value after aging is obviously decreased.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGFA NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Test paper for detecting lactose content of sample and preparation method of test paper
ActiveCN106645132ARapid responseHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorLactasePolyvinyl chloride
Test paper for detecting lactose content of a sample and a preparation method of the test paper are provided; the test paper is made by: selecting filter paper, making a substrate carrier, adding lactase to the filter paper, drying by using a drying technique, adding TMB, horse radish peroxidase and galactose oxidase sequentially to another filter paper, drying step by step, selecting a PVC (polyvinyl chloride) board to fix the dried filter paper, and cutting; the test paper made herein is suitable for detecting the presence of lactose in a sample; as enzymatic reaction is used, the reaction is quick and the sensitivity is high; by using test paper method, it is possible to finish detection by one-time sample adding; results are judged through color variation so that detection is simple and easy; the preparation method of the test paper is simple, the cost is low, and the test paper is easy to popularize and suitable for quickly detecting whether a sample contains lactose or not.
Owner:XIAMEN SCIENDOX BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Conjugation of streptococcal capsular saccharides
ActiveUS8513392B2Avoid disruptionImproving immunogenicityAntibacterial agentsImmunoglobulinsStreptococcus agalactiaeLactose oxidase
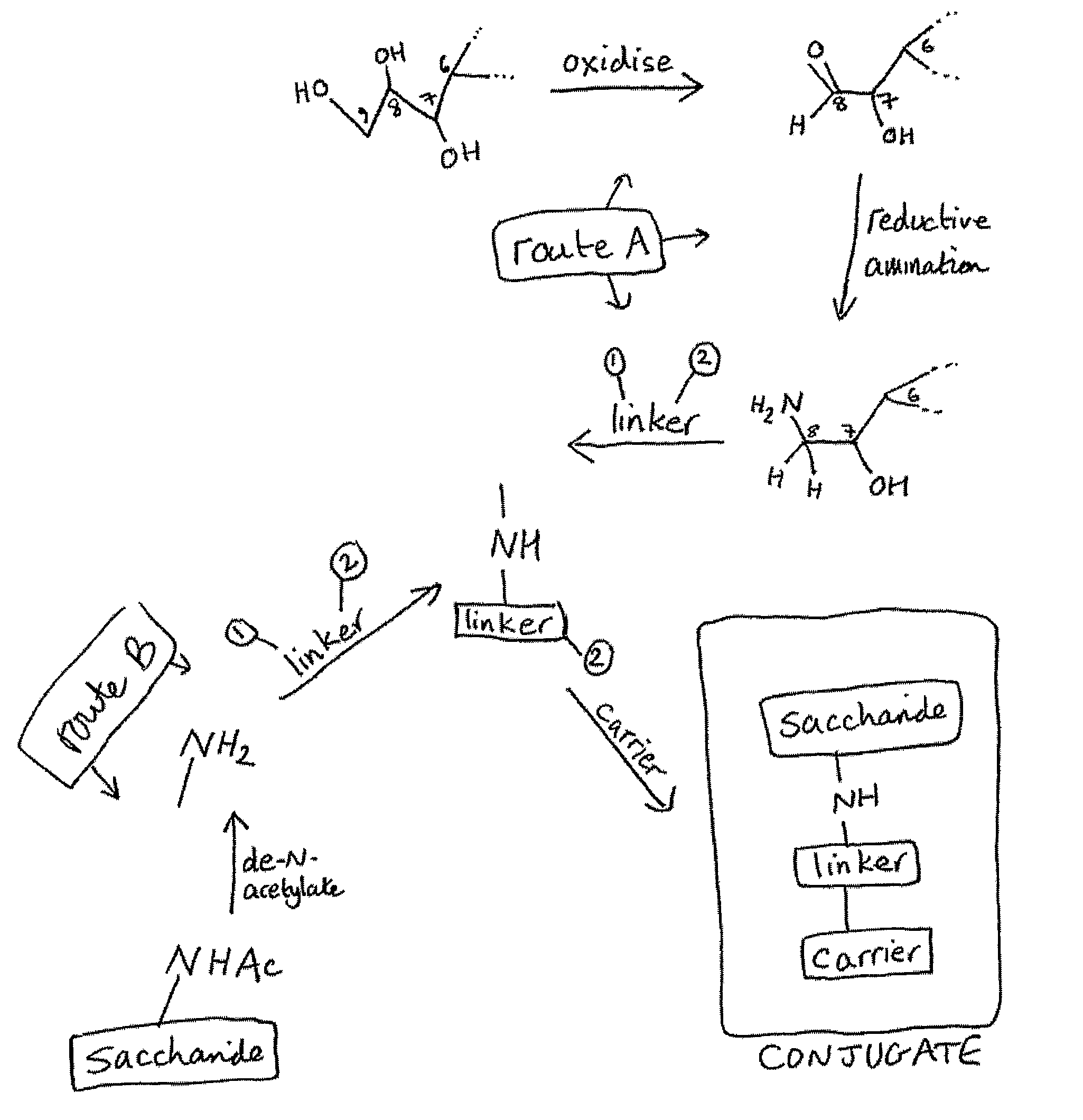
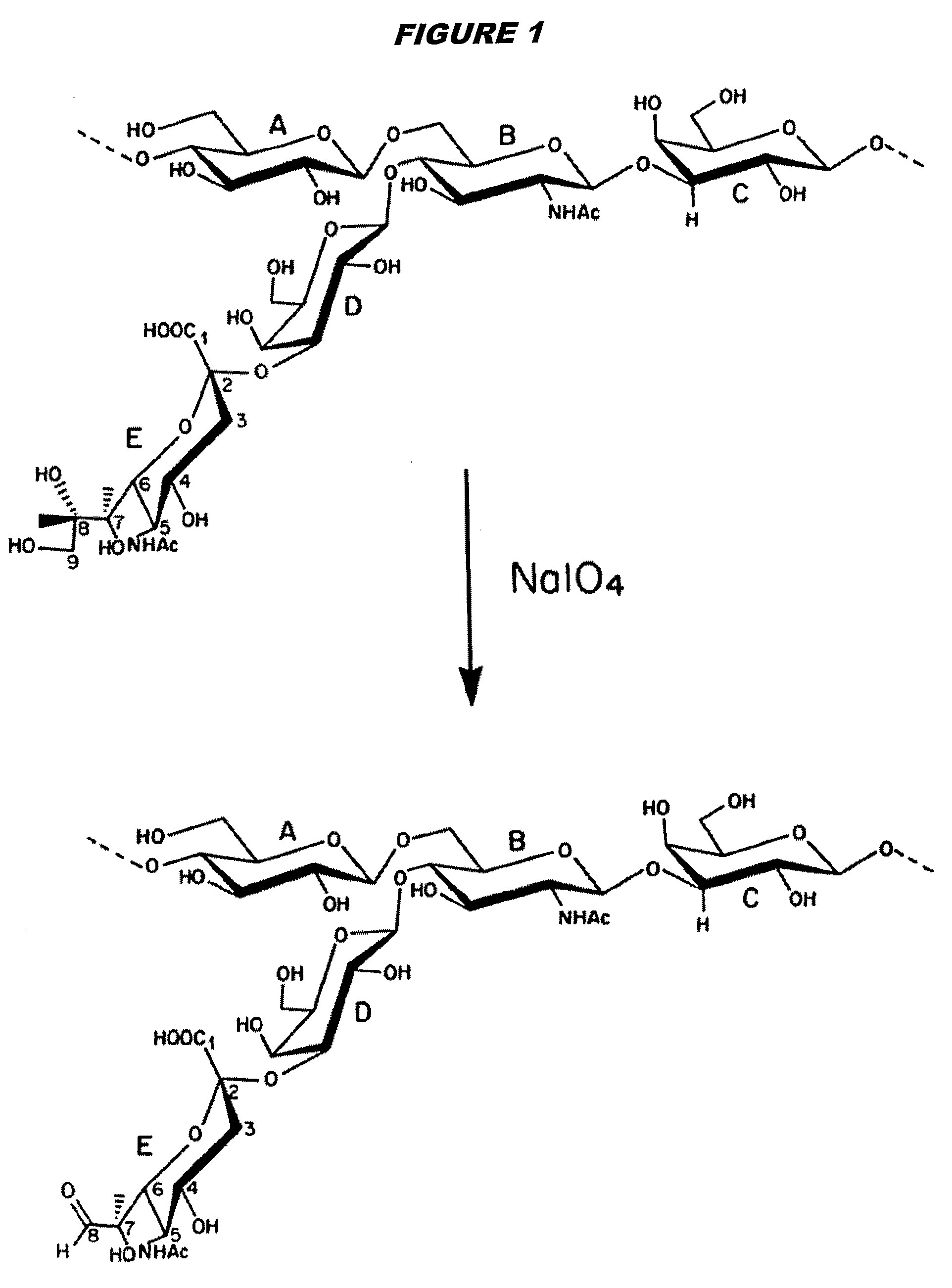
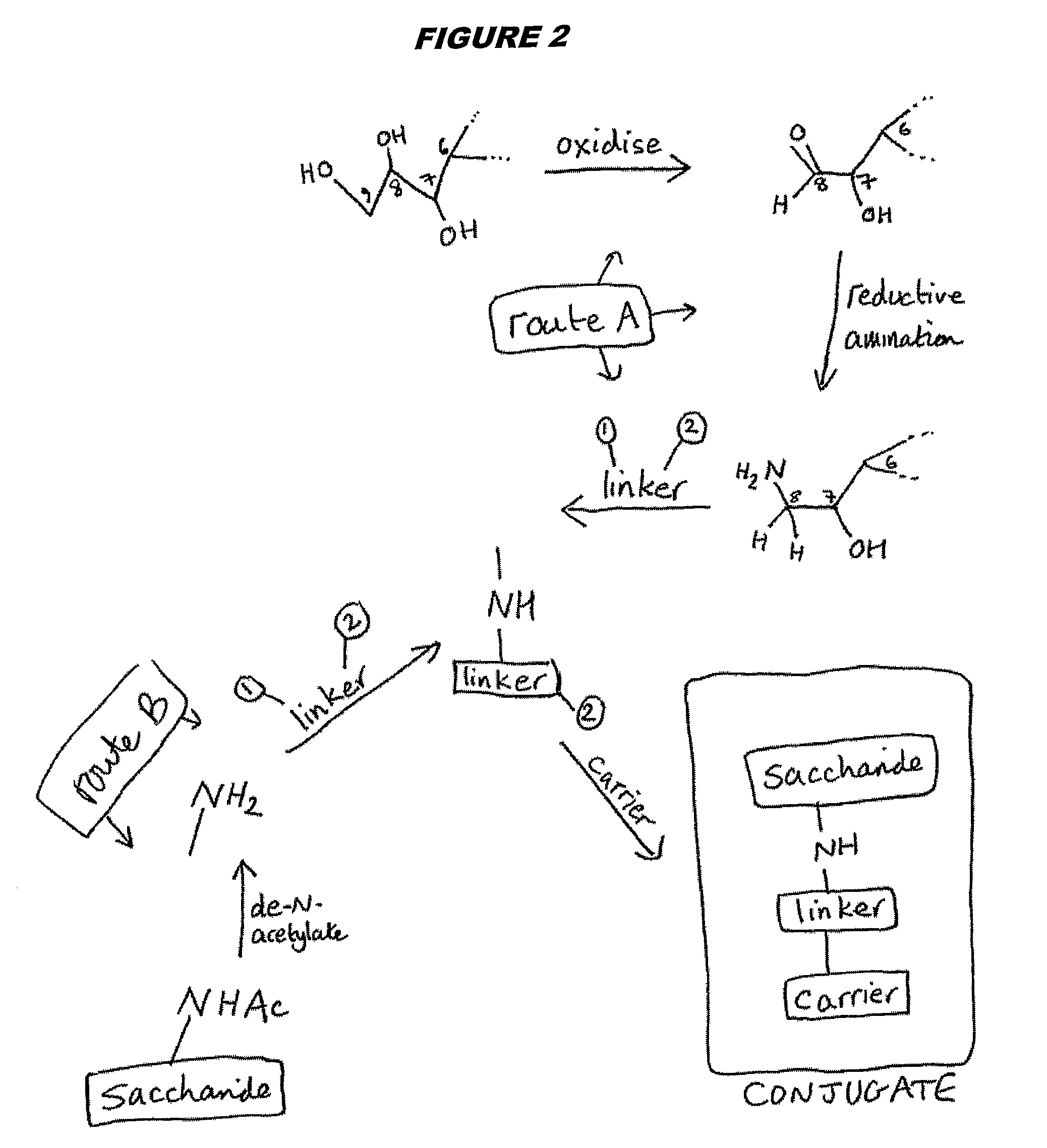
Three conjugation methods for use with the capsular saccharide of Streptococcus agalactiae. In the first method, reductive animation of oxidized sialic acid residue side chains is used, but the aldehyde groups are first aminated, and then the amine is coupled to a carrier via a linker. In the second method, sialic acid residues and / or N-acetyl-glucosamine residues are de-N-acetylated to give amine groups, and the amine groups are coupled to a carrier protein via a linker. In the third method, linkage is via galactose residues in the capsular saccharide rather than sialic acid residues, which can conveniently be achieved using galactose oxidase.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
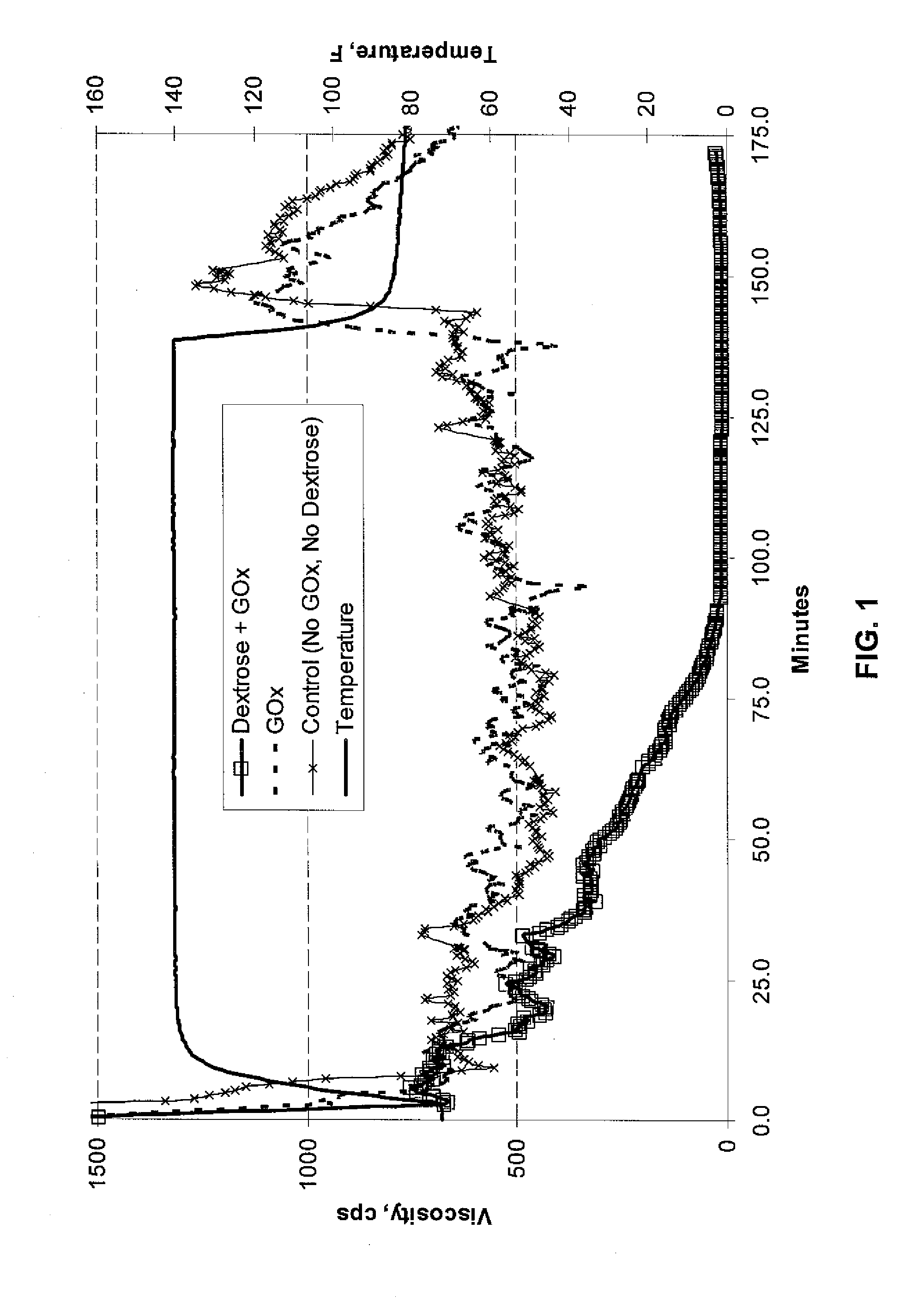
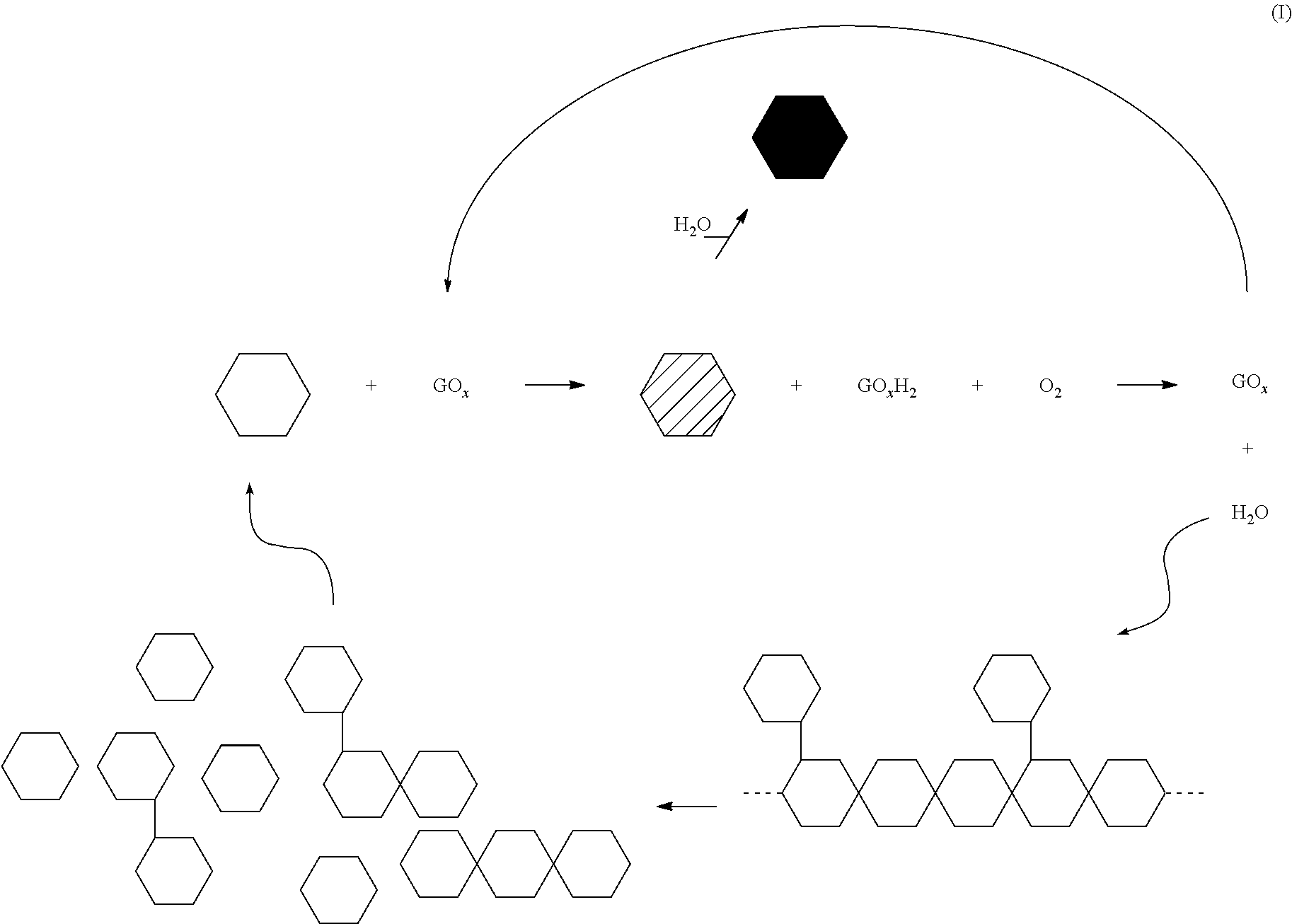
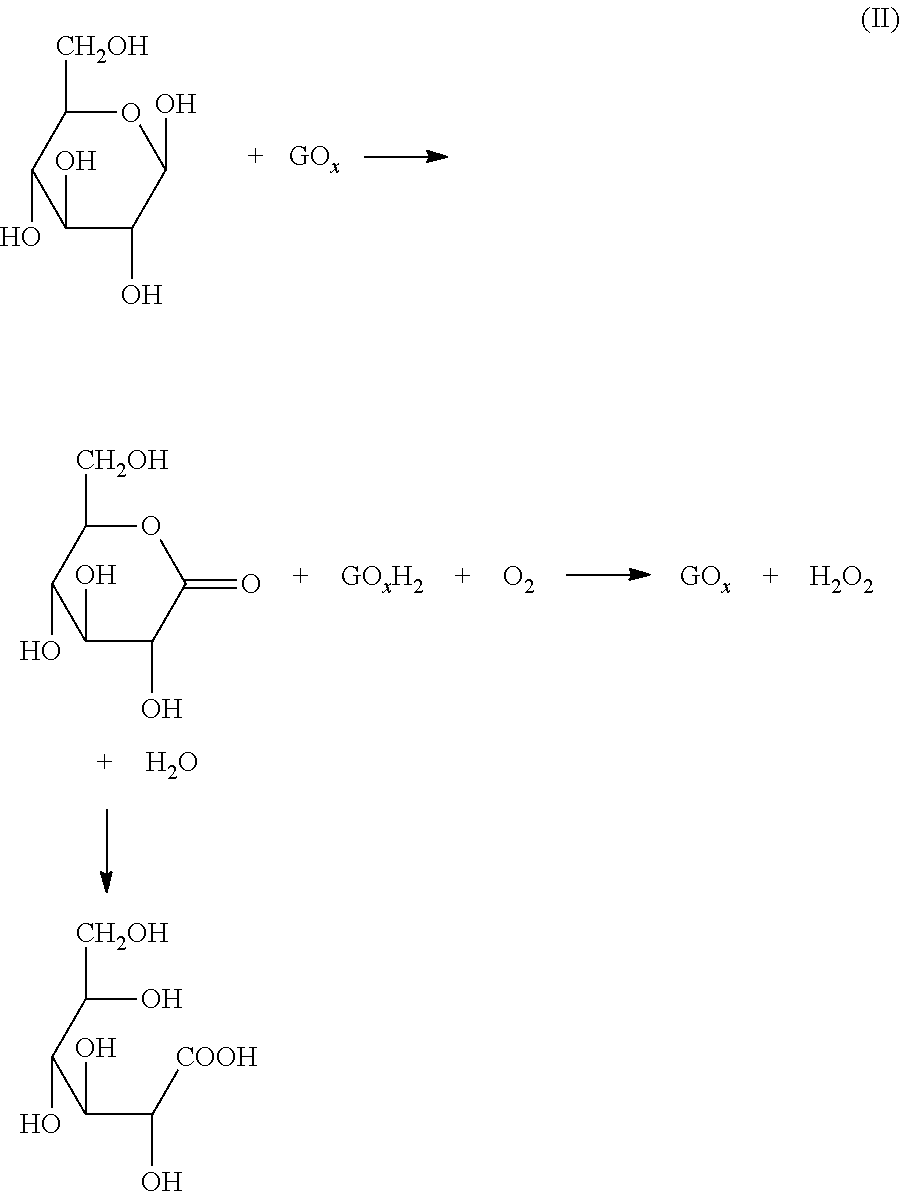
Use of Hexose Oxidases to Create Hydrogen Peroxide in Aqueous Well Treatment Fluids
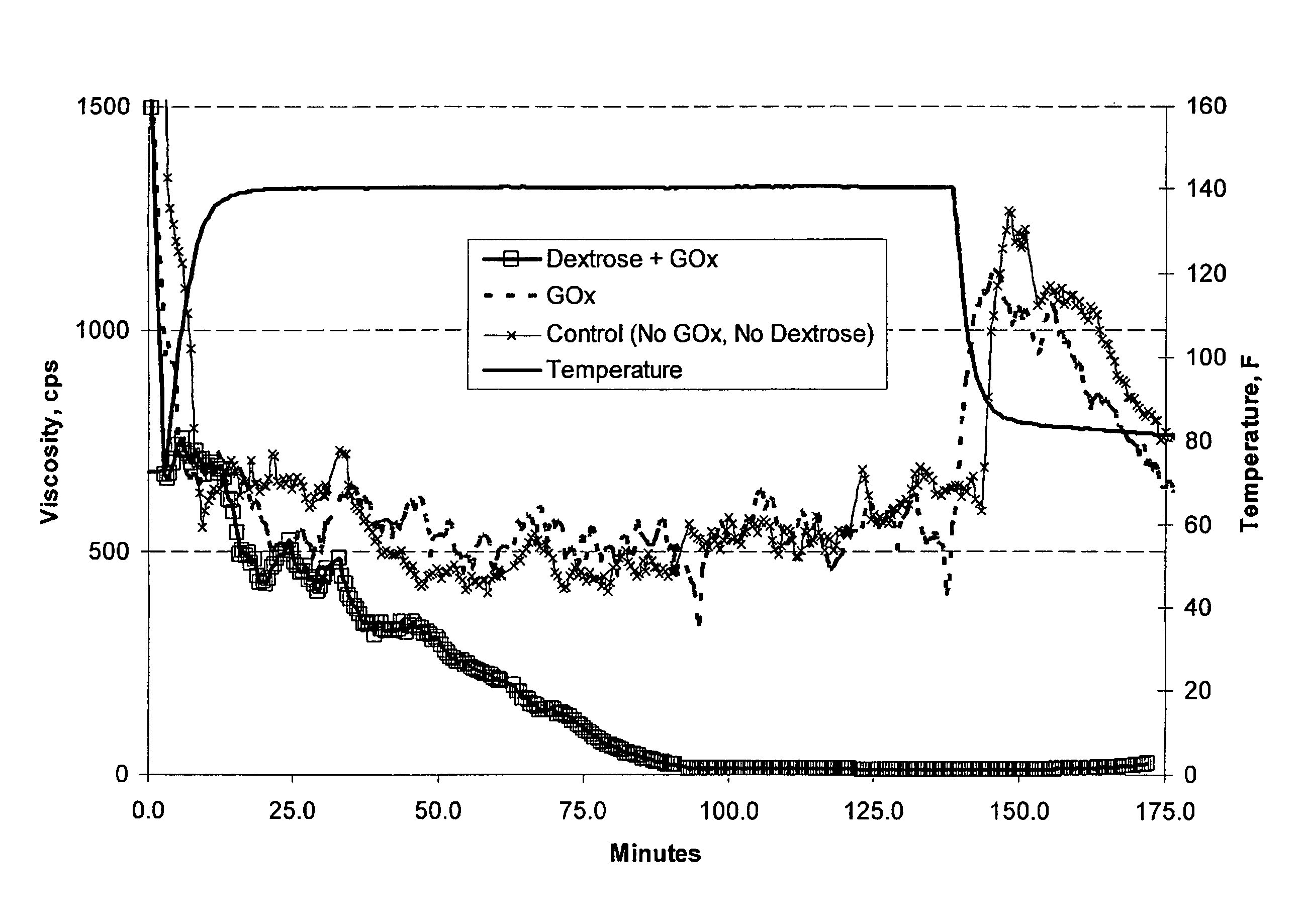
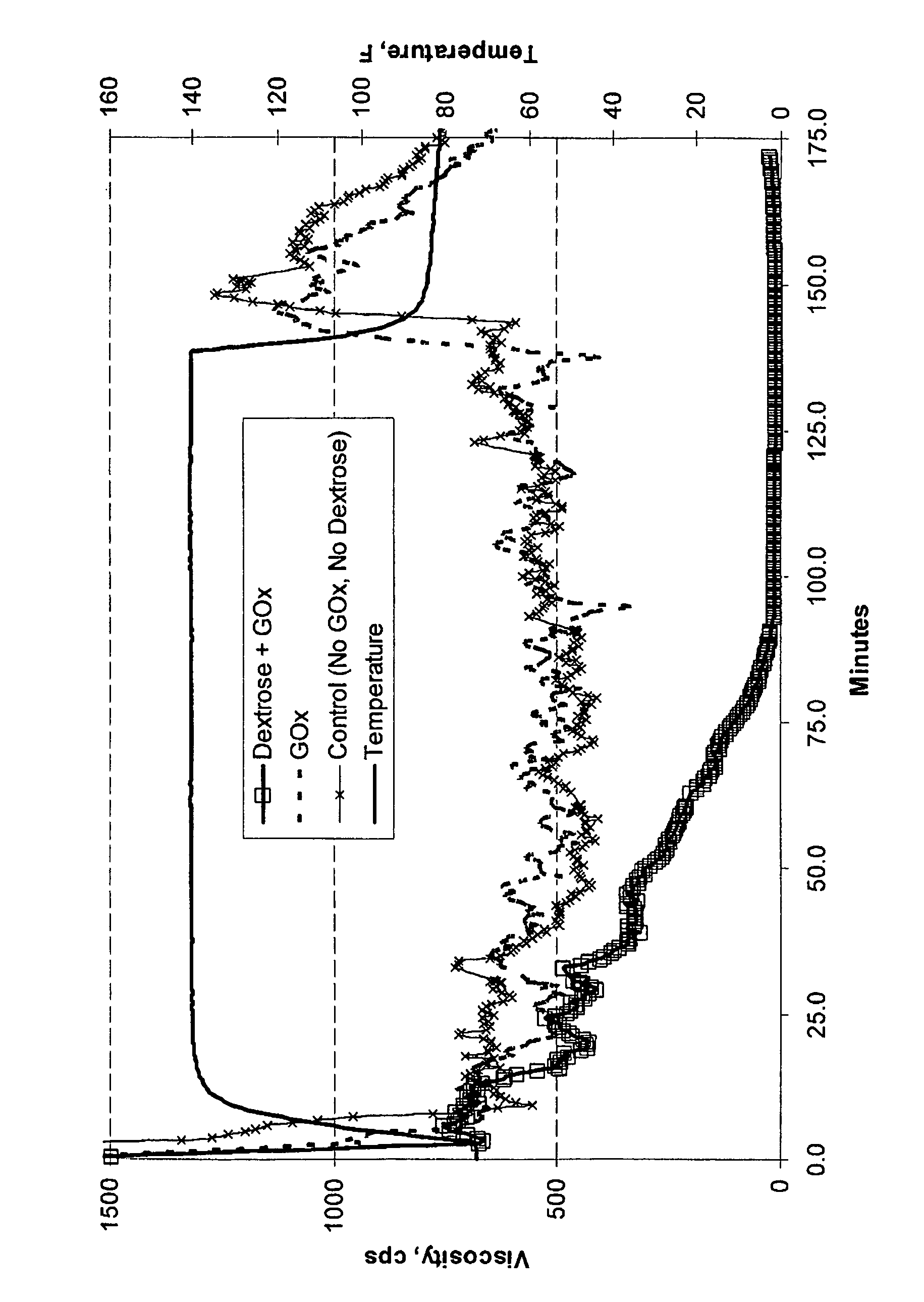
A hydrocarbon-bearing subterranean formation may be treated with an aqueous well treatment fluid which contains a hexose oxidase, such as glucose oxidase, mannose oxidase or galactose oxidase. The aqueous well treatment fluid further may contain a viscosifying polymer and an aldohexose. The aldohexose reacts in-situ with the hexose oxidase and molecular oxygen to produce hydrogen peroxide. The hydrogen peroxide may then act as a breaker.
Owner:BJ SERVICES LLC +1
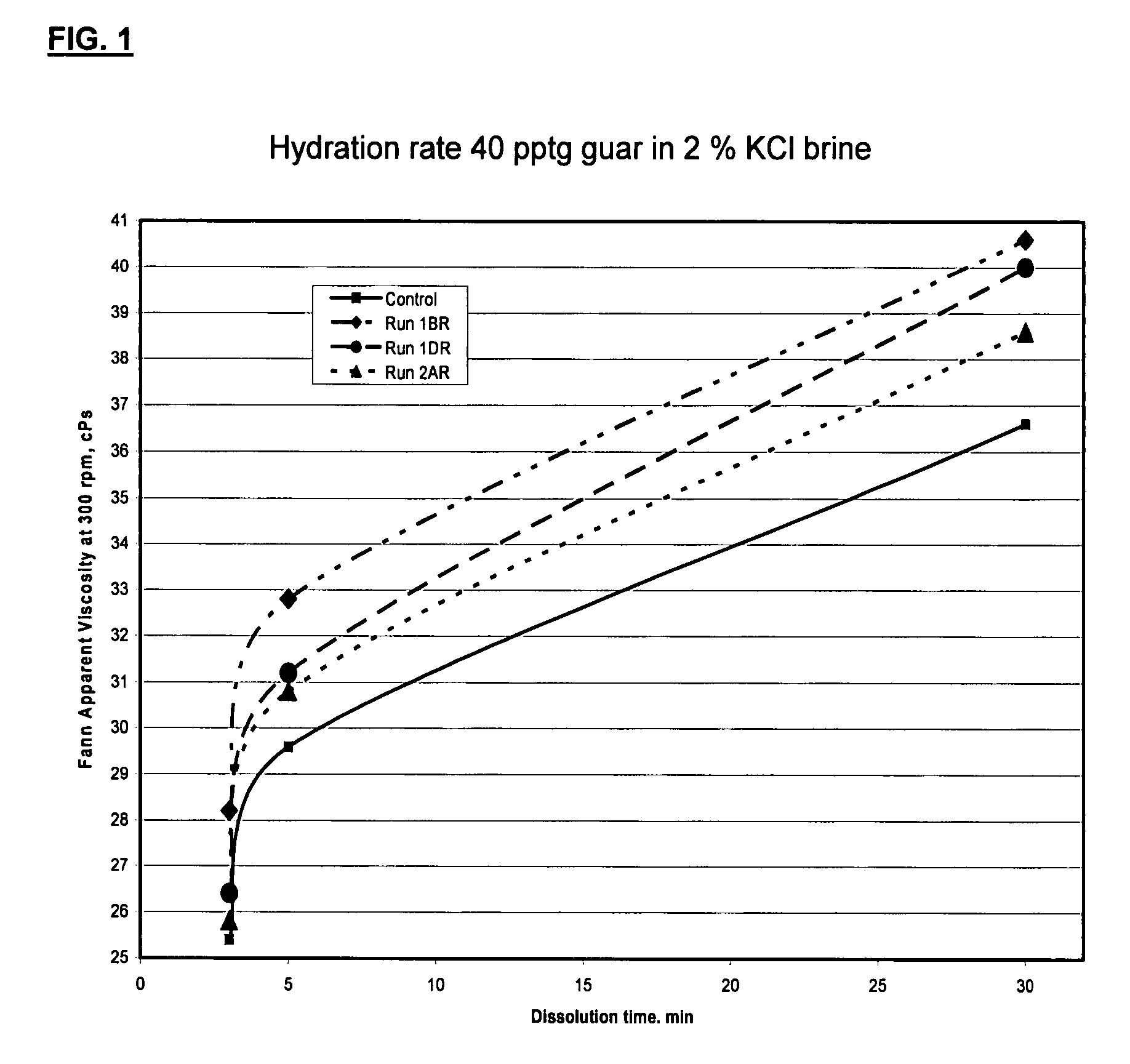
Oxidized guar for oilfield servicing fluids
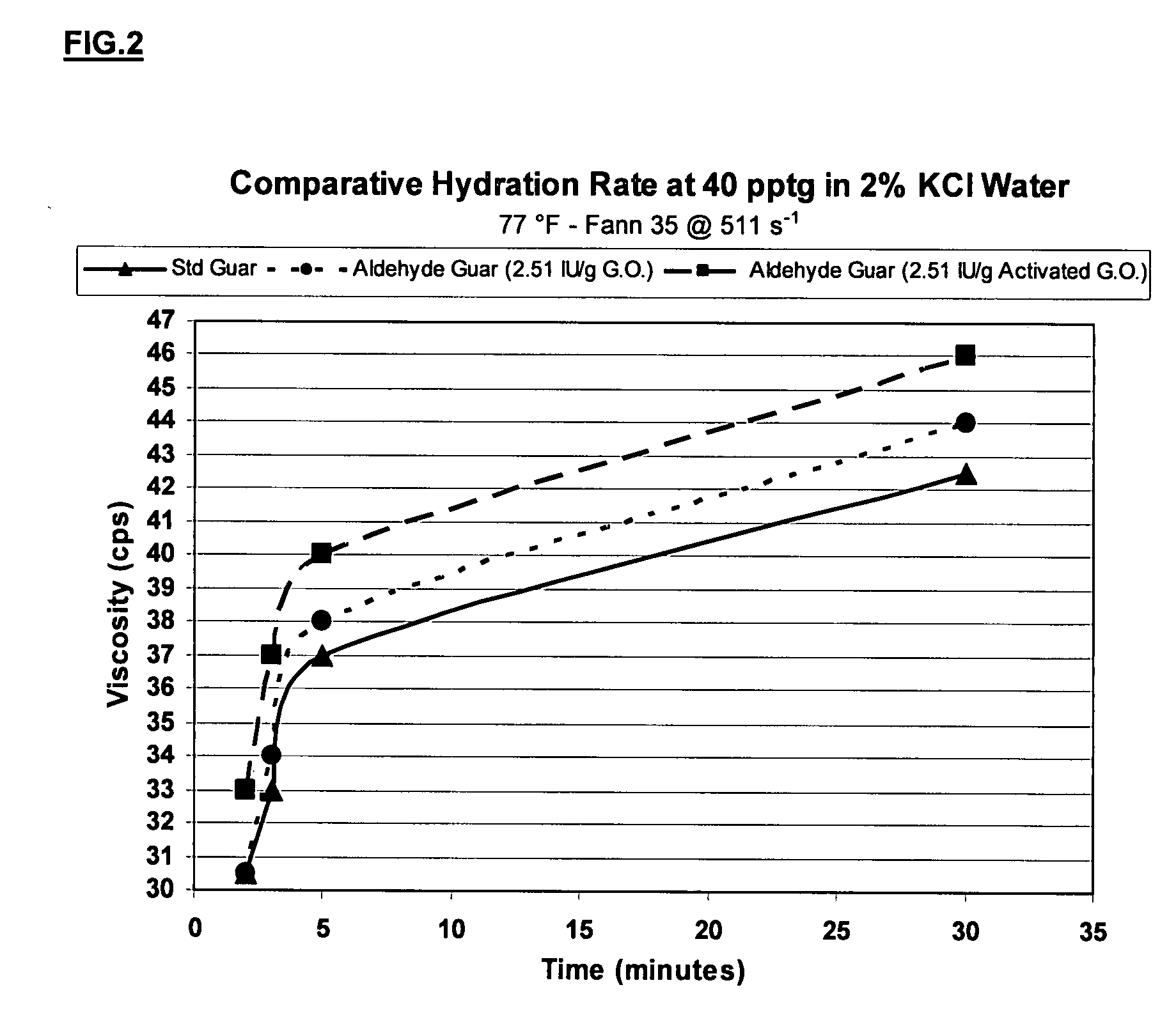
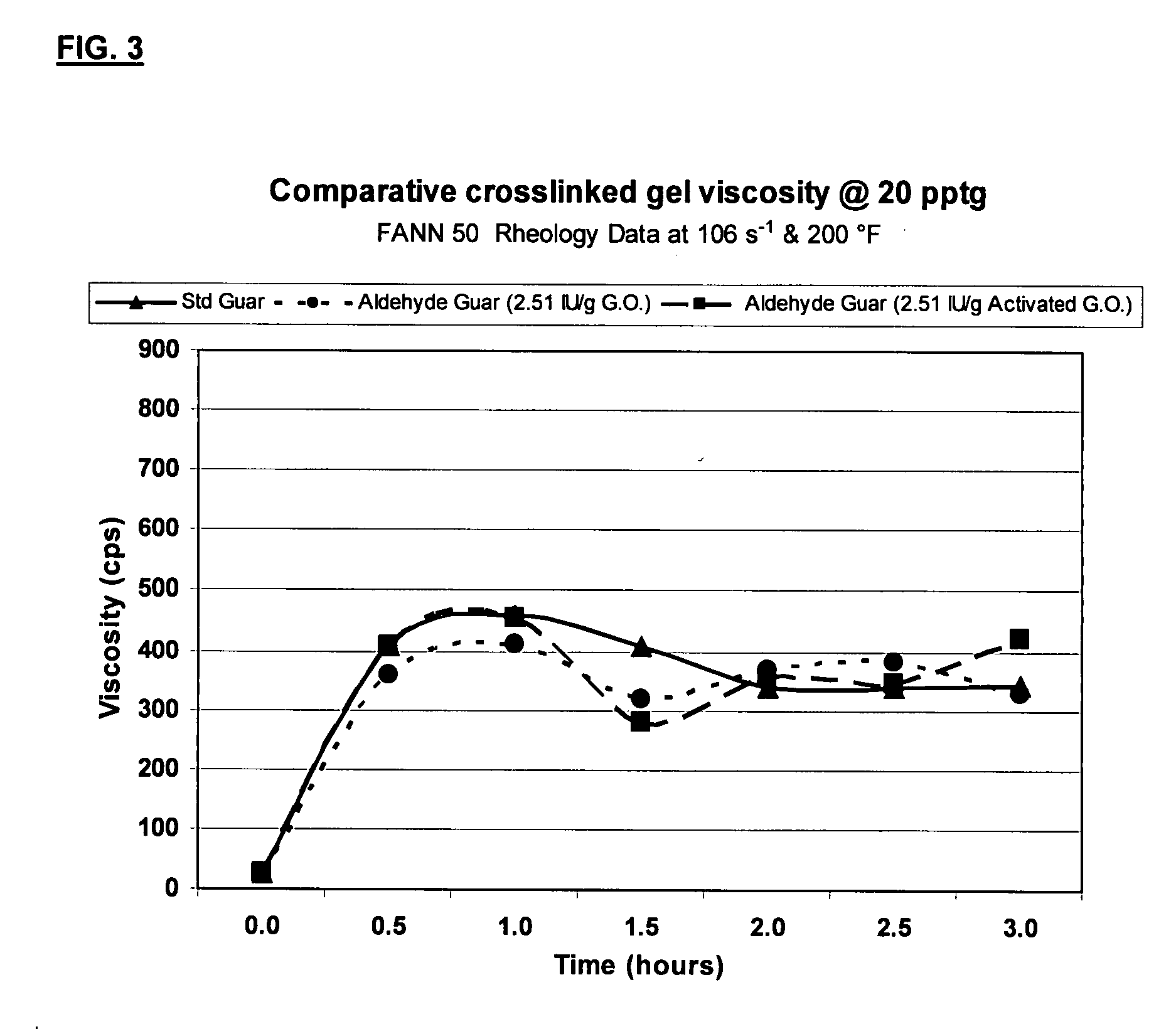
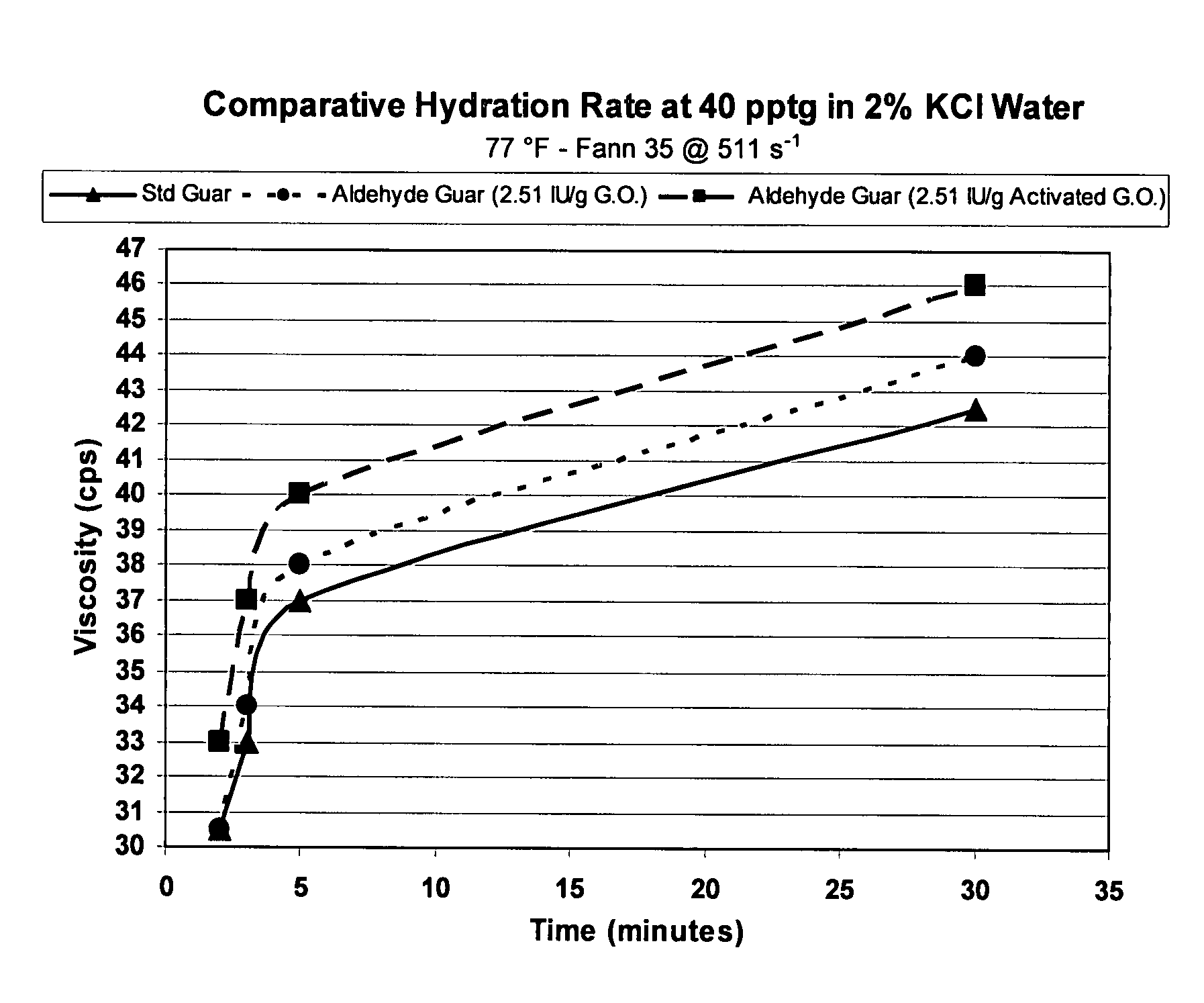
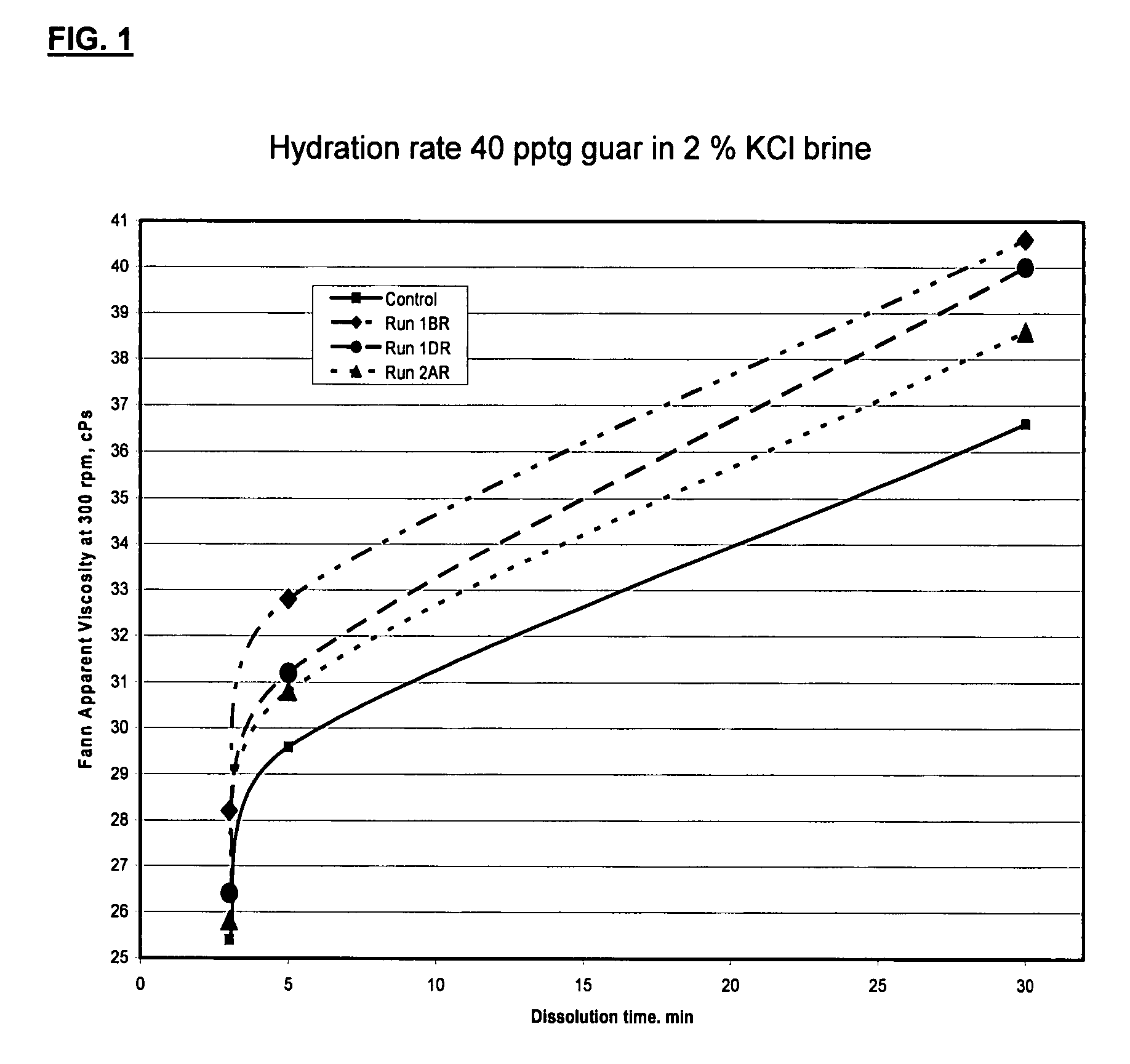
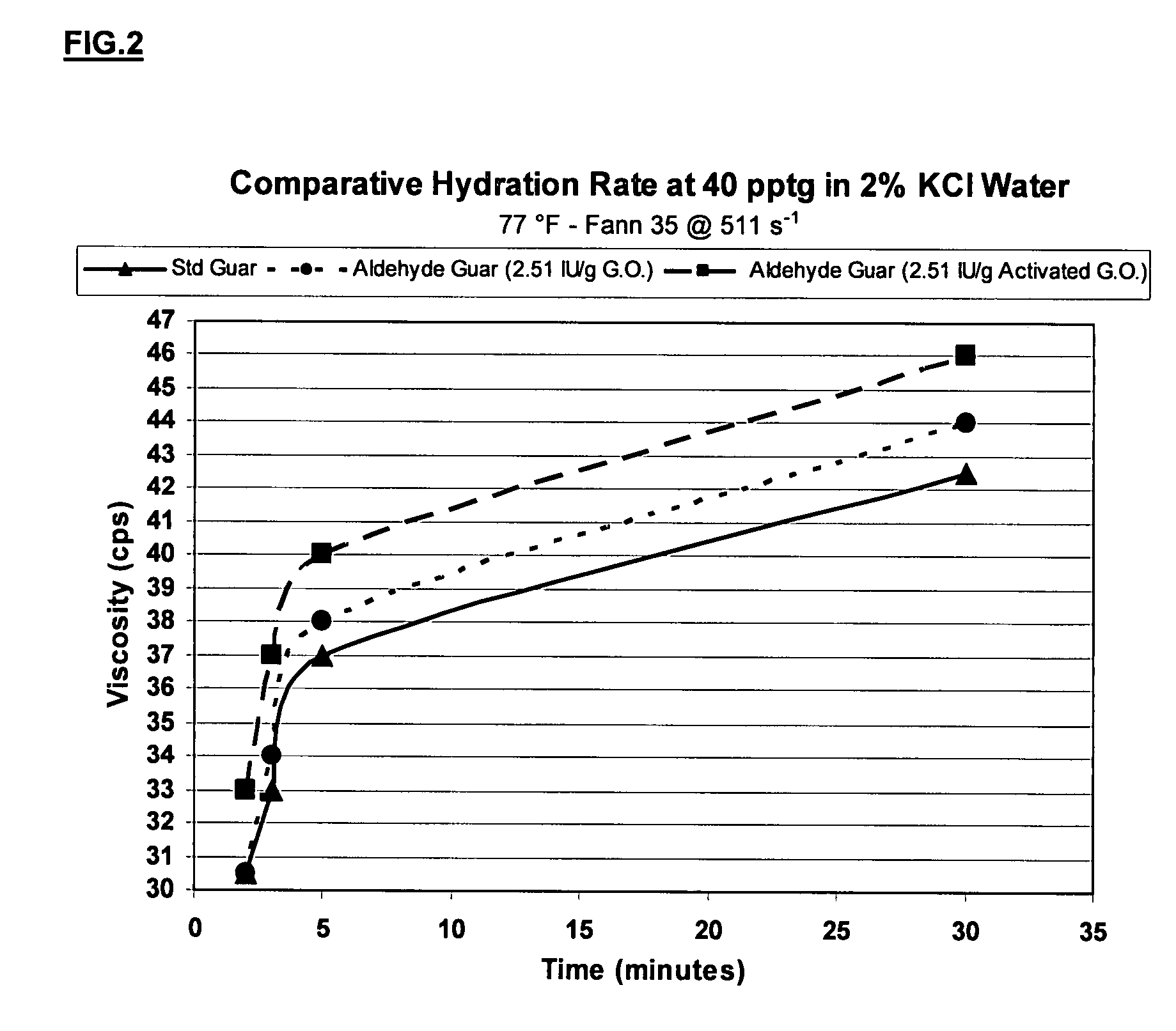
ActiveUS20070275862A1High viscositySolve insufficient capacityFluid removalFlushingPeroxidaseHydraulic fracturing
An oilfield servicing fluid composition containing an aldehyde guar produced by enzymatic oxidation of a non-derivatized, straight guar or of a guar derivative. The enzyme used to oxidize the guar to the aldehyde guar is galactose oxidase, which may be combined with catalase or catalase and peroxidase. The aldehyde guar is useful as an effective gelling agent for oilfield servicing fluids such as hydraulic fracturing fluids and stimulation fluids.
Owner:HERCULES LLC
Urine galactose test reagent kit
InactiveCN1811395AGood removal effectTest results have no effectMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsFiberChemical reaction
The present invention relates to a urinary galactose determination kit. It includes urine purification device, dry chemical reaction device and standard liquor. The urine purification device is a titration type container in which a selective specific adsorbent is held. Said selective specific adsorbent is formed from aluminium oxide, purification active carbon and galactose adsorption agonist. Besides, said invention also provides the concrete structure of said dry chemical reaction device and concrete composition of said standard liquor. Said kit can completely remove interference substance from urine, so that it can greatly raise accuracy of determination.
Owner:北京中生金域诊断技术股份有限公司
High-curing modified-guar-gum-contained aqueous solution and preparing method
ActiveCN1936178AReduce the Cobb valueIncrease the amount of dissolutionWater-repelling agents additionPaper/cardboardGuar gumAqueous solution
The invention discloses a high content modified guar gum solution and the manufacture method. It includes the following steps: adding positive ion oxidation guar gum powder into water, adding pH retarding agent to adjusting pH value of the system is 7-8, adding mannose enzyme solution, adding galactose oxidase solution, heating to 40-60 degree centigrade and reacting for 4-8 hours, heating to 90-95 degree centigrade keeping for 10-50 minutes to gain modified guar gum solution. The invention could be used to make paper making sizing agent. Comparing to simply using AKD, the sheet and the Cobb value after aging is obviously decreased.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGFA NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
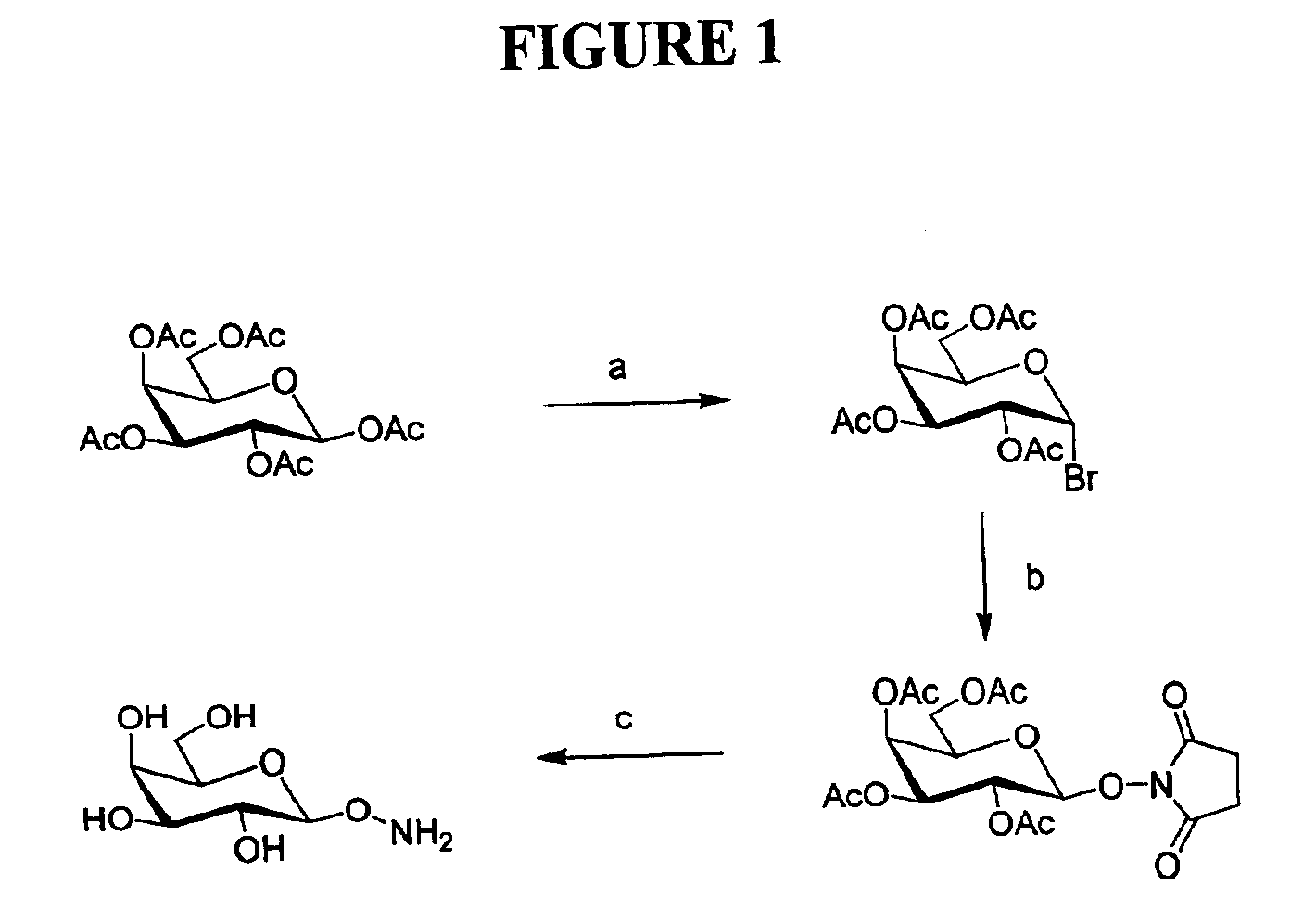
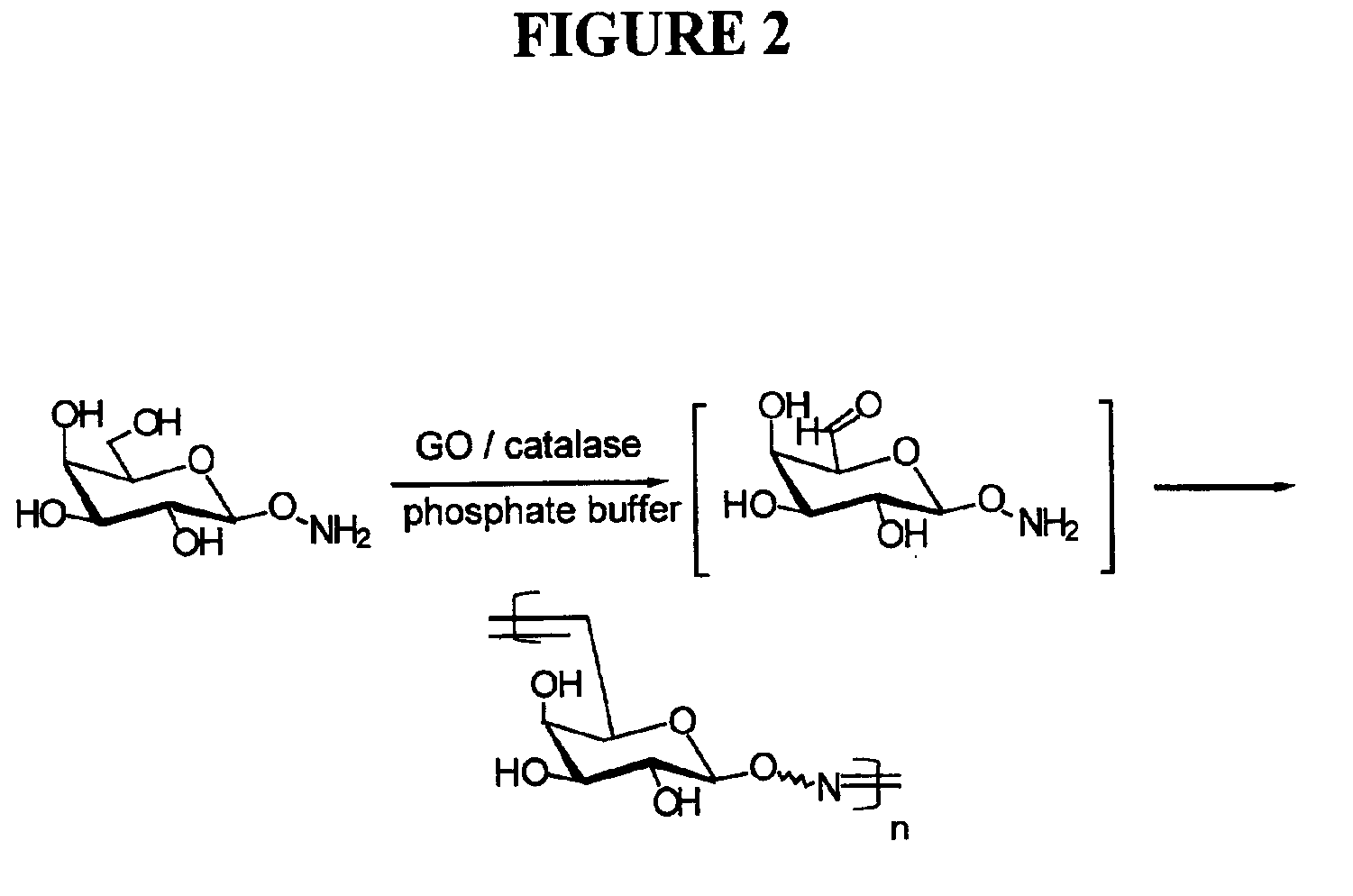
Oxime-linked polysaccharides and methods of preparing the same
Polysaccharides comprising one or more oxime linkages are provided. Methods for their preparation include the polycondensation of saccharides bearing oxime-forming substituents. In some embodiments, polymerization is conducted in the presence of galactose oxidase. The resulting oxime-linked polysaccharides have desirable properties and are useful in numerous applications including paper manufacturing and drug delivery vehicles.
Owner:HERCULES INC
Reagent card used for detecting faeces lactose contents, and faeces lactose content detection method based on reagent card
PendingCN109557088AAvoid interferenceAvoid influenceMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorLactaseFeces
The invention discloses a reagent card used for detecting faeces lactose contents. The reagent card comprises a sample pad, a reaction pad and a color development pad, wherein the sample pad, the reaction pad and the color development pad are connected in sequence; the sample pad bears lactase, the reaction pad bears galactose oxidase, and the color development pad bears color developing agent. Byuse of the reagent card, lactose in the faeces can be effectively measured, and therefore, the reagent card is simple in clinical operation and high in specificity. The invention also discloses a faeces lactose content detection method.
Owner:SICHUAN ORIENTER BIOLOGICAL TECH
Method for determining galactose concentration and galactose diagnosis/determination reagent kit
InactiveCN101324582AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsAssayEnzyme catalysis
The invention relates to a kit for diagnosing / mensurating galactose by utilizing the technologies of the enzymic colorimetric method and the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The invention further relates to a method, a principle and the composition and the components of a reagent for mensurating the concentration of the galactose, and belongs to the technology field of medical / food inspection and measurement. The main components of the kit include a buffer solution, coenzyme, galactose oxidase, NAD(P)H oxidase and a stabilizer. Through mixing a sample and the reagent by a certain volume ratio, a series of enzymatic reactions occur, then the reactant is placed under an ultraviolet / visible light analyzer, and the degree / velocity of the increase in absorbance at 340nm of the dominant wavelength is detected, thereby mensurating the concentration of the galactose.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Method of using hexose oxidases to create hydrogen peroxide in aqueous well treatment fluids
A hydrocarbon-bearing subterranean formation may be treated with an aqueous well treatment fluid which contains a hexose oxidase, such as glucose oxidase, mannose oxidase or galactose oxidase. The aqueous well treatment fluid further may contain a viscosifying polymer and an aldohexose. The aldohexose reacts in-situ with the hexose oxidase and molecular oxygen to produce hydrogen peroxide. The hydrogen peroxide may then act as a breaker.
Owner:BJ SERVICES LLC +1
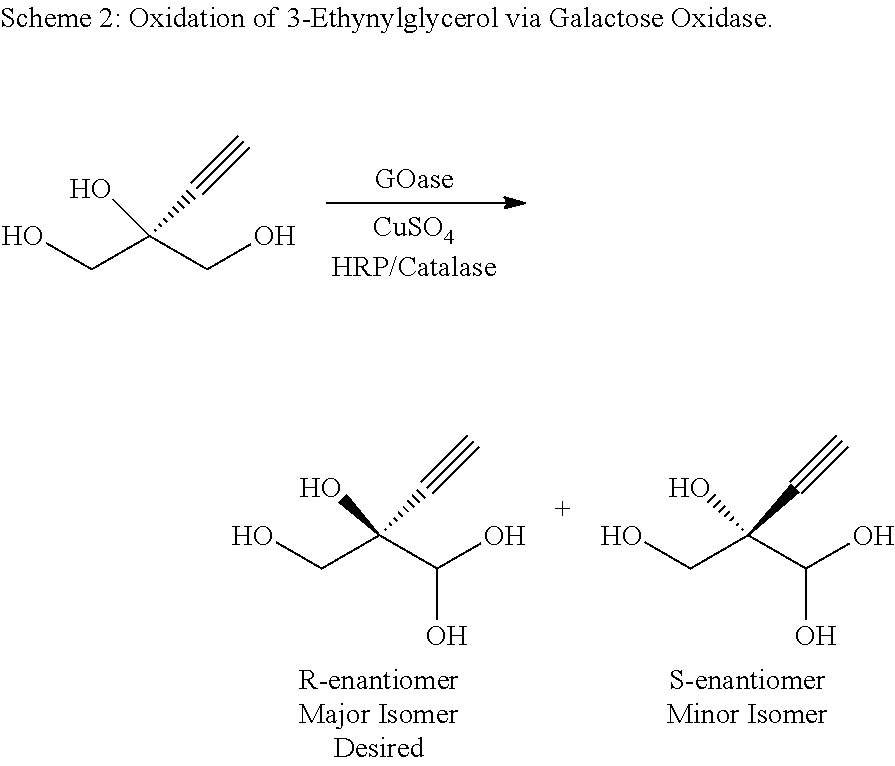
Engineered galactose oxidase variant enzymes
ActiveUS20200010869A1High activityHigh stereoselectivityOxidoreductasesFermentationOxidative enzymePolynucleotide
The present invention provides engineered galactose oxidase (GOase) enzymes, polypeptides having GOase activity, and polynucleotides encoding these enzymes, as well as vectors and host cells comprising these polynucleotides and polypeptides. Methods for producing GOase enzymes are also provided. The present invention further provides compositions comprising the GOase enzymes and methods of using the engineered GOase enzymes. The present invention finds particular use in the production of pharmaceutical and other compounds.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
Human serum O-glycosylation identification method based on chemical enzymatic catalysis
InactiveCN111157736AHigh analytical sensitivityStrong specificityComponent separationBiological testingChemical reactionLactose oxidase
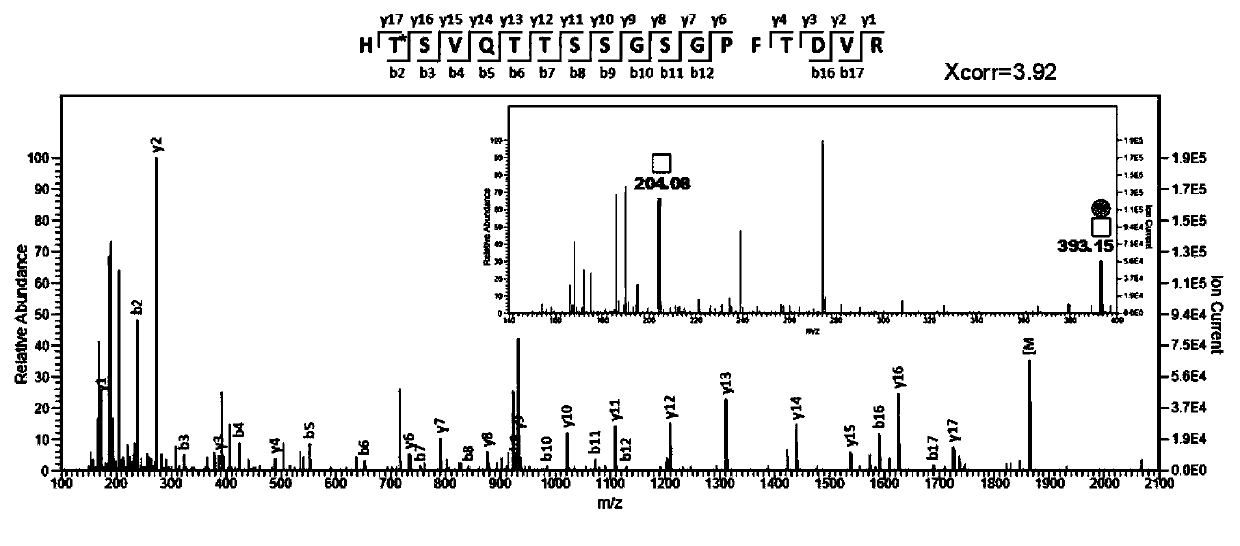
The invention relates to a method for detecting mucoprotein type O-linked glycosylation (O-GalNAc type). The method is based on a strategy of combining biological enzyme selective oxidation and biological orthogonal chemical reaction; alactose 6-hydroxyl is oxidized into an aldehyde group by utilizing galactose oxidase, the glycopeptides are specifically captured and released through hydrazide chemistry, the O-GalNAc glycoform high sensitivity analysis is achieved by using the mass spectrometry-based detection method, and 59 O-GalNAc glycosylation modification sequences can be detected from 50[mu] L of human serum, and can correspondingly exceed 30 O glycated proteins. The method has the characteristics of high detection sensitivity, high enrichment specificity and the like, and is an important means for analyzing the existing endogenous O-GalNAc type glycosylated protein / peptide fragment.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
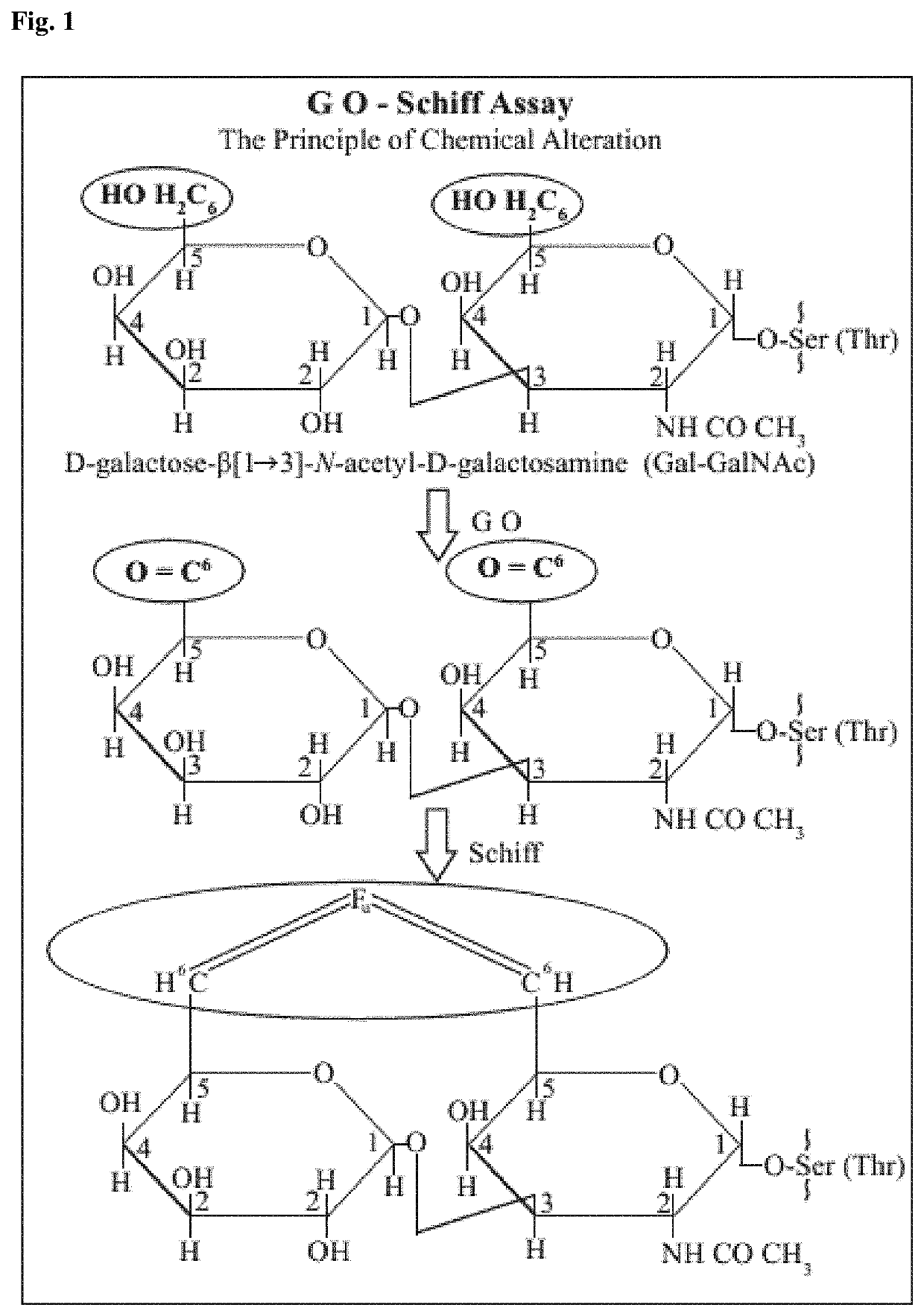
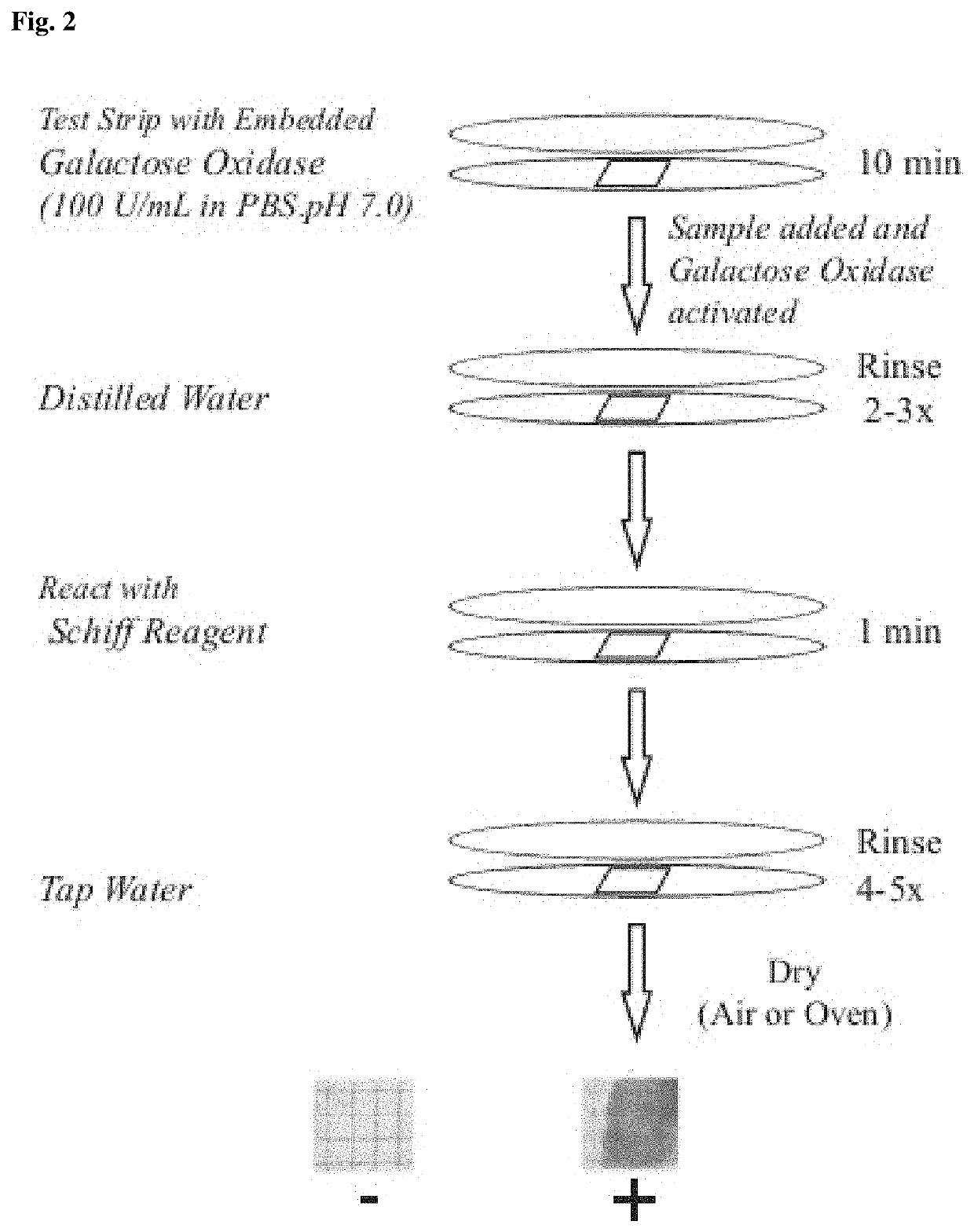
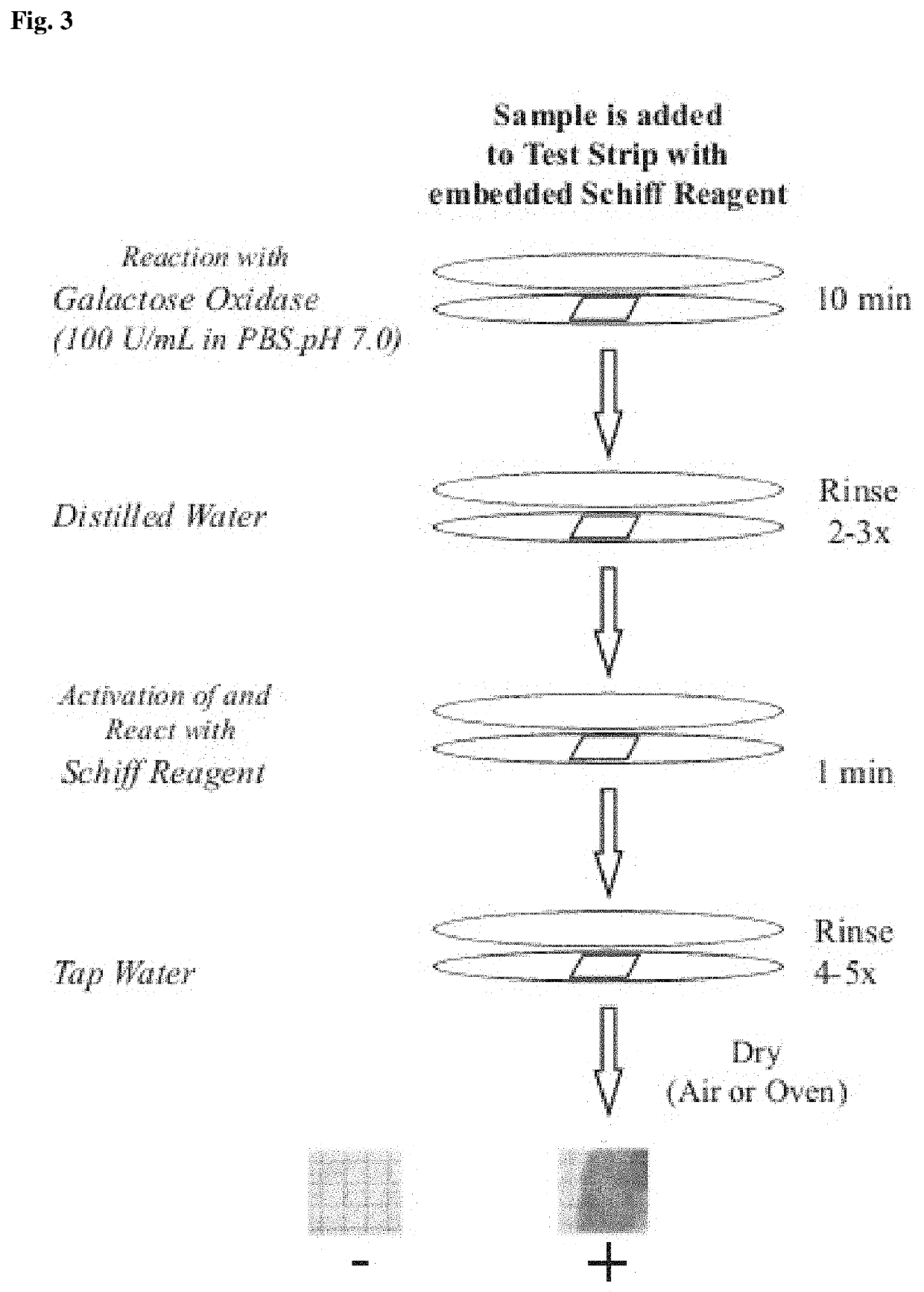
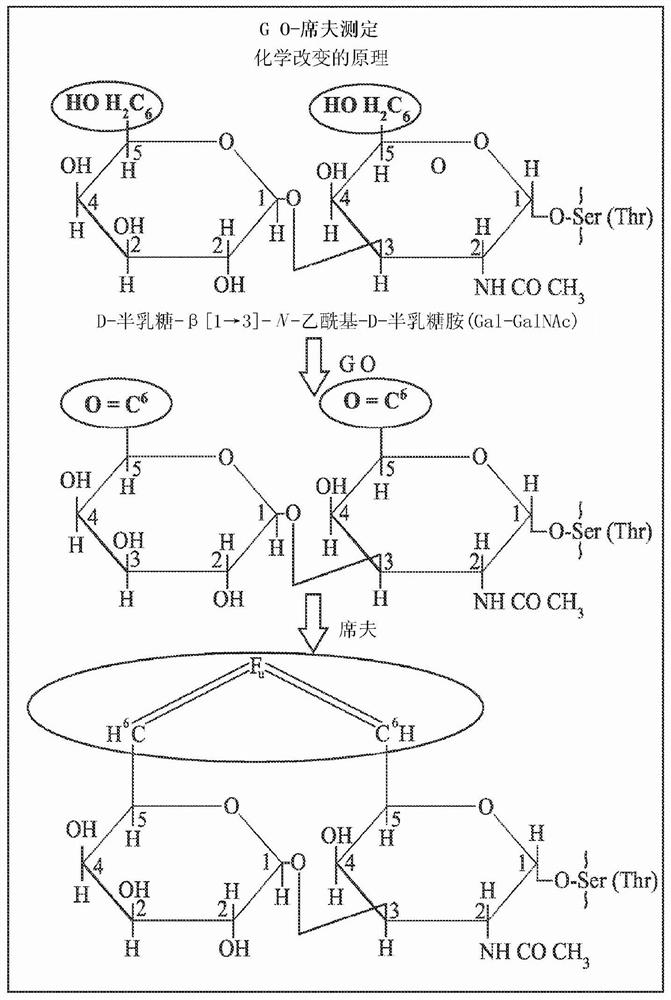
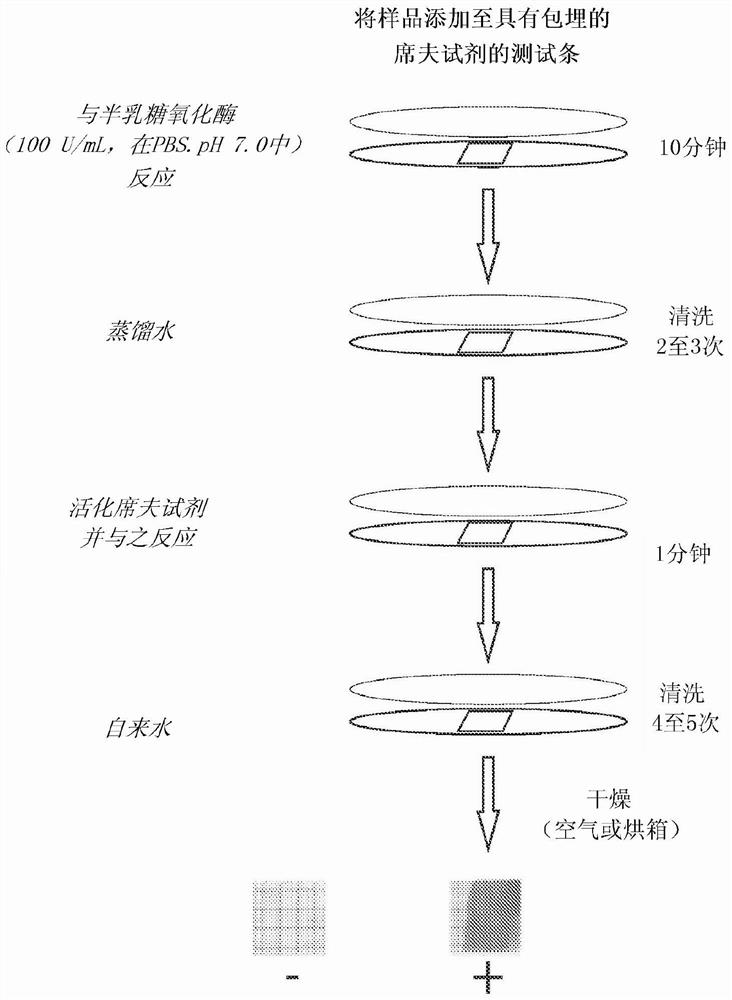
Liquid-phase galactose oxidase-schiff's assay
InactiveCN101305100ARemove uncertaintyEnsure mixabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisLactose oxidaseOxidative enzyme
The invention provides an improved method for detecting cancer or a precancerous condition in a sample using an oxidation agent, such as galactose oxidase, and an aldehyde detection agent, such as Schiffs reagent that does not require the sample to be immobilized onto a solid support. The invention also provides kits comprising the components necessary for carrying out the methods of the invention.
Owner:PREMD INC
Method for preparing high-curing modified-guar-gum contained aqueous solution
ActiveCN100547160CHigh solid contentLow viscosityWater-repelling agents additionPaper/cardboardEmulsionPapermaking
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGFA NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Oxidized guar for oilfield servicing fluids
ActiveUS7851416B2High viscositySolve insufficient capacityFluid removalFlushingPeroxidaseHydraulic fracturing
An oilfield servicing fluid composition containing an aldehyde guar produced by enzymatic oxidation of a non-derivatized, straight guar or of a guar derivative. The enzyme used to oxidize the guar to the aldehyde guar is galactose oxidase, which may be combined with catalase or catalase and peroxidase. The aldehyde guar is useful as an effective gelling agent for oilfield servicing fluids such as hydraulic fracturing fluids and stimulation fluids.
Owner:HERCULES LLC
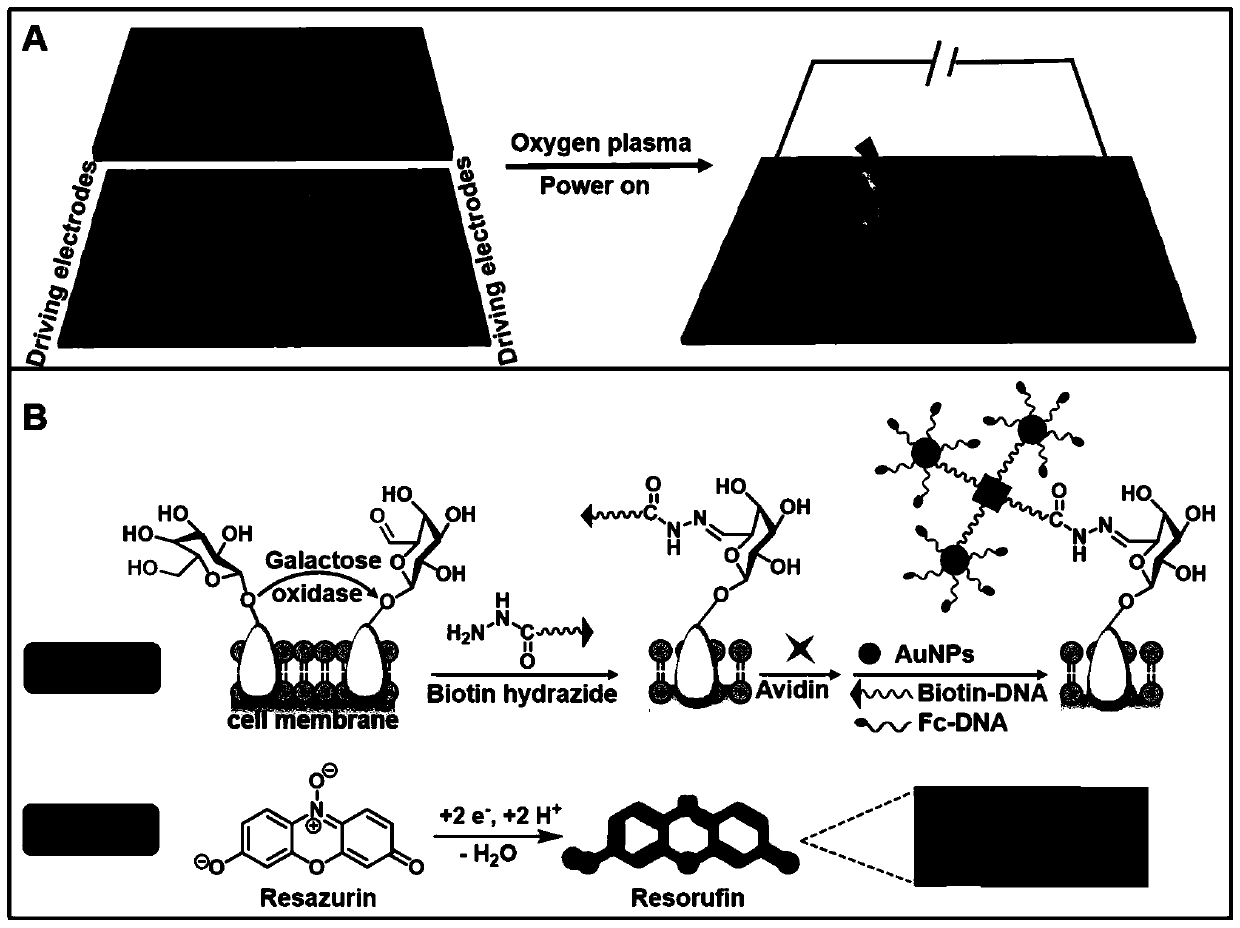
Cell surface glycan in-situ electrogenerated fluorescence imaging analysis method based on a bipolar electrode
PendingCN111323463AReduce consumptionHigh sensitivityFluorescence/phosphorescenceMaterial electrochemical variablesResolution (mass spectrometry)Oxidative enzyme
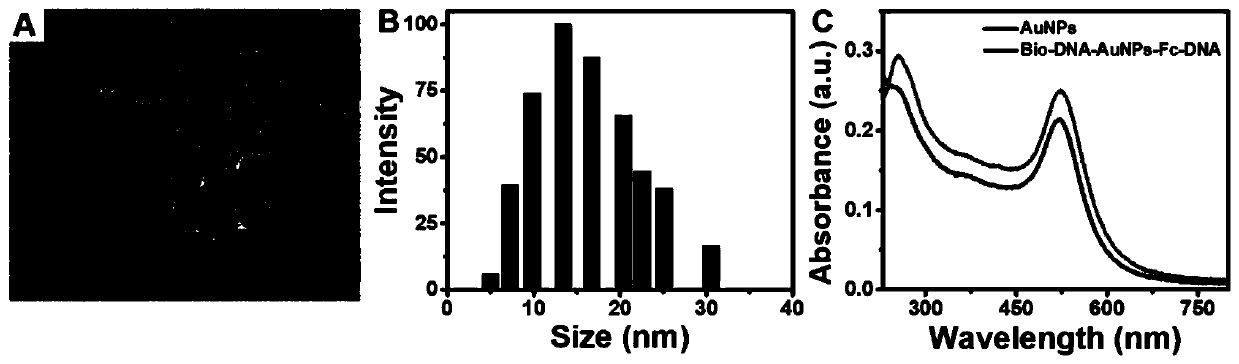
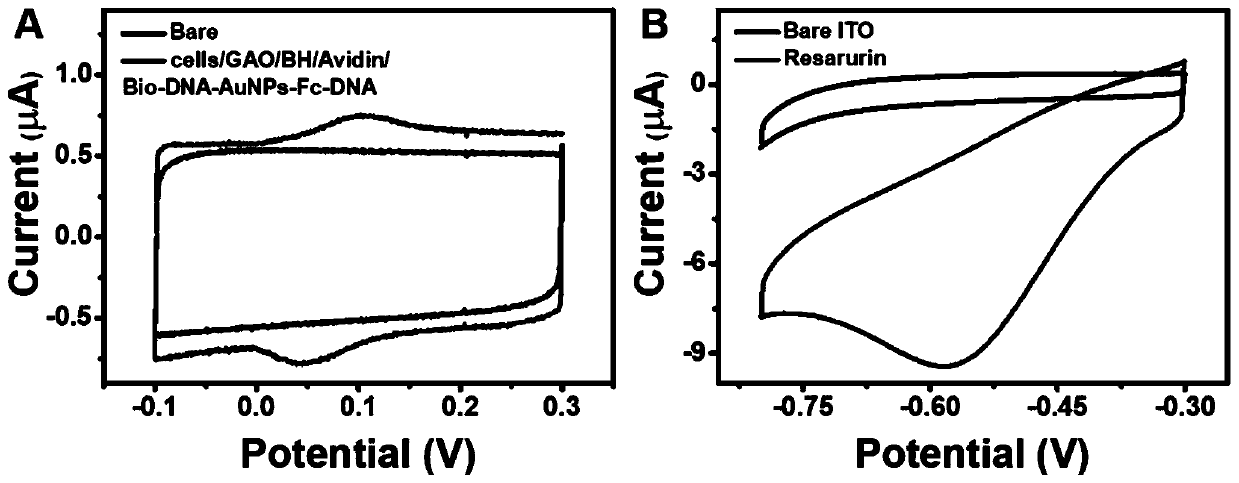
The invention discloses a cell surface glycan in-situ electrogenerated fluorescence imaging analysis method based on a bipolar electrode. The method comprises the following steps: 1) preparing a bipolar electrode micro-fluidic chip; (2) preparing a Bio-DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)-AuNPs (gold nanoparticles)-Fc-DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) nanoprobe; 3, incubating HepG2 cells in situ in an anode channel of the bipolar electrode, adding galactose oxidase to oxidize hydroxyl on galactose on the surfaces of the cells into aldehyde groups, aniline catalyzes a biotin hydrazide reaction to form a hydrazone compound, avidin serves as a bridge, and the hydrazone compound is combined with the Bio-DNA-AuNPs-Fc-DNA nanoprobe; 4) adding azure molecules into a cathode pool of the bipolar electrode, oxidizing Fc introduced by the anode under the potential of 2.4 V, reducing azure of the cathode into high-fluorescence resorufin, and quantitatively detecting the galactose expression level on the surfaceof the anode cell through the fluorescence intensity of the cathode; according to the method, the damage of fluorescence labeling or mass spectrometry to cells is avoided by utilizing a mild enzymaticoxidation method, and a sensitive electrochemical signal is converted into a visual optical signal by combining the bipolar electrode, so that high-resolution fluorescence imaging is realized.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method, device, and kit for population screening for cancer, cancer recurrence and precancerous conditions in symptom free individuals
PendingUS20210263036A1Quick testEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisOncologyPrecancerous condition
This disclosure relates to a screening test method, device, and kit for carbohydrates found in a biological sample and associated conditions including, cancerous and precancerous conditions. Specifically, the method tests abnormal carbohydrates in a biological sample using reagents of galactose oxidase, and Schiff's Reagent. The screening test method, device, and kit provides expanded testing capabilities across a range of known conditions and in an otherwise healthy population. This disclosure further relates to the use of the device or kit for an initial evaluation for cancerous and precancerous conditions in people without obvious signs and symptoms, and cancer recurrence in at point-of-care facility or at home.
Owner:CANCER PREVENTION LLC
Method for determining galactose concentration and galactose diagnosis/determination reagent kit
InactiveCN101324581AMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsPeroxidaseELISA unit
The invention relates to a kit for diagnosing / mensurating galactose by utilizing the technologies of the enzymic colorimetric method and the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The invention further relates to a method, a principle and the composition and the components of a reagent for mensurating the concentration of the galactose, and belongs to the technology field of medical / food inspection and measurement. The main components of the kit include a buffer solution, galactose oxidase, peroxidase, a reduced chromogen combination and a stabilizer. Through a series of enzymatic reactions, the colorless reduced chromogen combination is finally oxidized into the colored dyes, thereby mensurating the content of the dyes at 400nm-700nm of the wavelength by a visible light analyzer and further reflecting the concentration of the galactose directly.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Engineered galactose oxidase variant enzymes
PendingCN112673097AReduce or prevent reactivityOxidoreductasesFermentationDrug compoundOxidative enzyme
The present invention provides engineered galactose oxidase (GOase) enzymes, polypeptides having GOase activity, and polynucleotides encoding these enzymes, as well as vectors and host cells comprising these polynucleotides and polypeptides. Methods for producing GOase enzymes are also provided. The present invention further provides compositions comprising the GOase enzymes and methods of using the engineered GOase enzymes. The present invention finds particular use in the production of pharmaceutical and other compounds.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
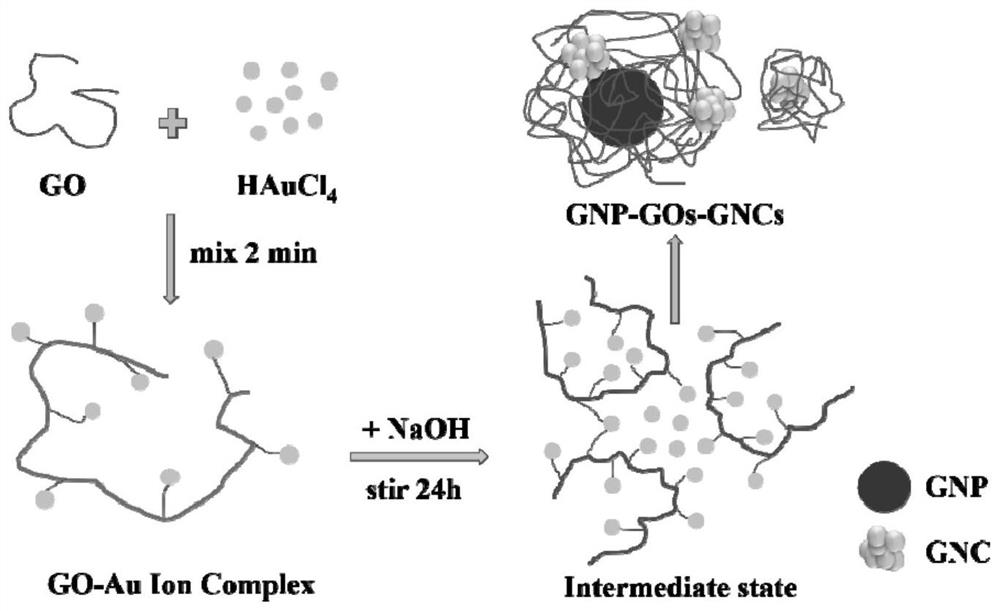
Gold nanoparticle-gold nanocluster composite material as well as preparation method and application thereof
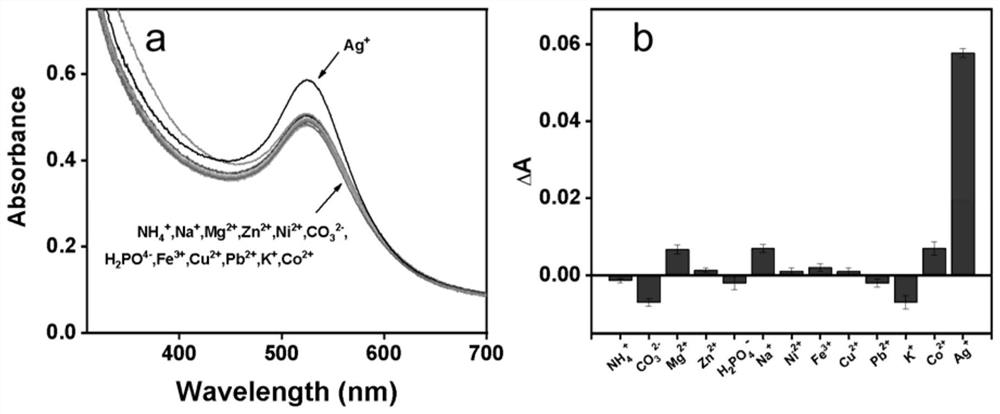
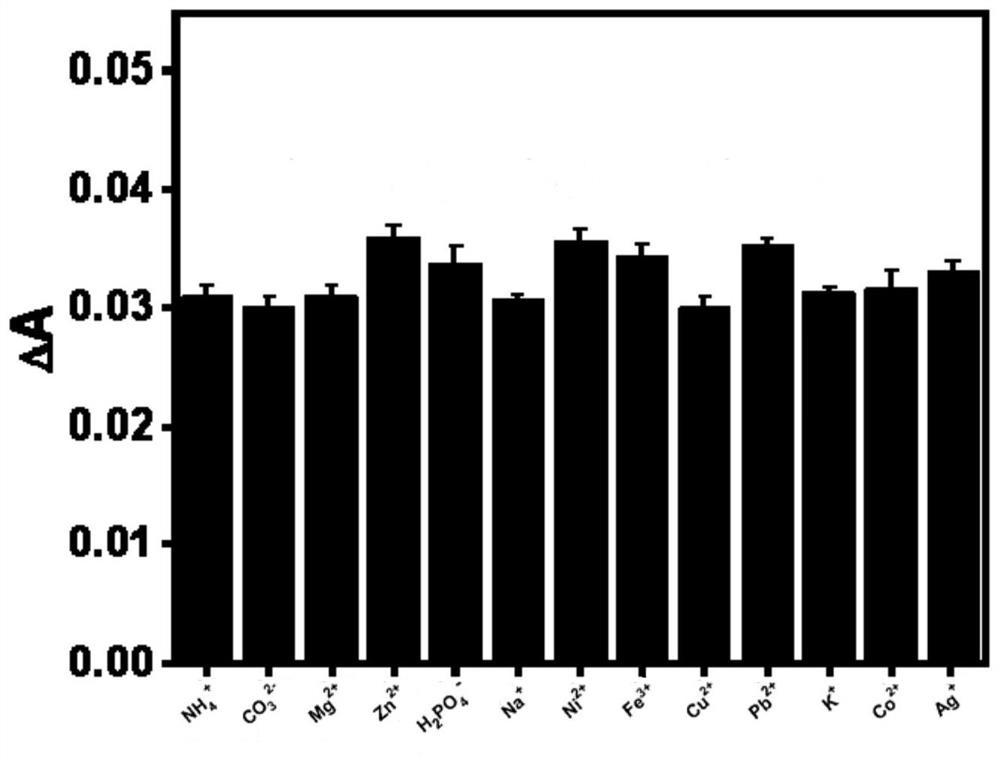
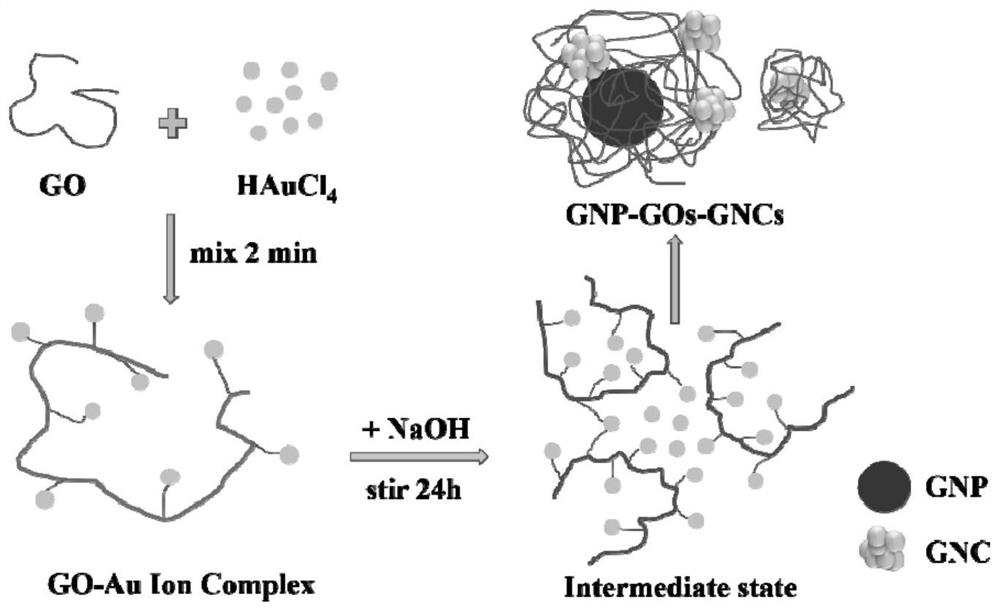
ActiveCN113199035AEfficient detectionEasy to prepareMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingNanoparticleOxidative enzyme
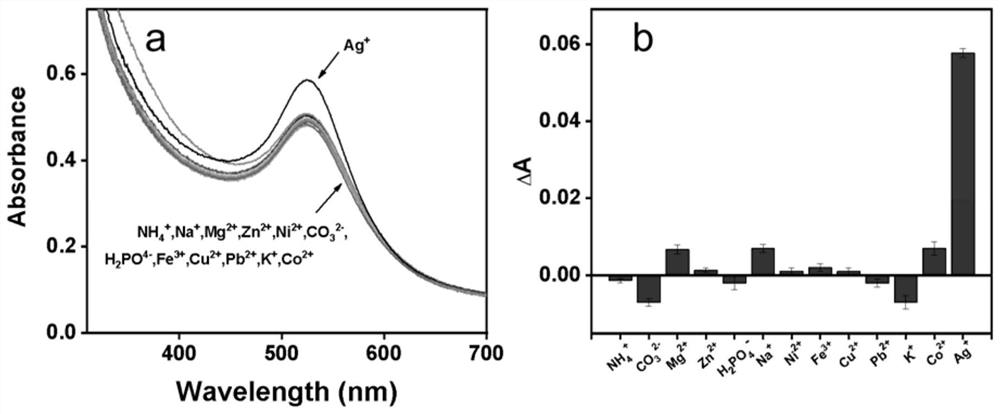
The invention discloses a gold nanoparticle-gold nanocluster composite material as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of nano materials. The composite material is prepared by the following steps of, S1, a HAuCl4 aqueous solution is mixed with a galactose oxidase (GO) solution to obtain a mixed solution; S2, the pH value of the mixed solution is adjusted to 11.0 to 12.0; and S3, the mixed solution with the adjusted pH is subjected to a reaction at the temperature of 35 DEG C to 40 DEG C, and the gold nanoparticle-gold nanocluster composite material is obtained. The invention further discloses application of the gold nanoparticle-gold nanocluster composite material in Ag < + > detection. The composite material can be used for directly detecting low-concentration Ag < + >.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
High-curing modified-guar-gum-contained aqueous solution and preparing method
ActiveCN100547159CIncrease the amount of dissolutionReduce dosageWater-repelling agents additionPaper/cardboardEmulsionDegree of substitution
The invention discloses a high-solid-content modified guar gum aqueous solution and a preparation method thereof, comprising the following steps: adding cationic oxidized guar gum powder with a cationic substitution degree of 0.05 to 0.2 into water, adding a pH buffering agent, and adjusting the pH of the system 7-8, add mannosidase aqueous solution, add galactose oxidase aqueous solution, heat up to 40-60°C and react for 4-8 hours, then heat up to 90-95°C and keep for 10-50 minutes to obtain modified guar gum aqueous solution . The modified guar gum aqueous solution of high solid content prepared by the present invention can be used as papermaking sizing agent, and compared with pure AKD (emulsion, Cobb value can be significantly reduced; Compared with commercially available surface sizing agent, After sizing, the Cobb value of the paper after off-machine and aging decreased significantly.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGFA NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Screening methods, devices and kits for detecting mucous membrane carbohydrates and related conditions
PendingCN114787375AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisOxidative enzymeCarcinomatoses
The present disclosure relates to screening test methods, devices, and kits for mucosal carbohydrates and related conditions, including cancerous and pre-cancerous conditions. In particular, the method uses a galactose oxidase reagent and a Schiff reagent for testing abnormal carbohydrates in mucus or bodily fluids. The screening test methods, devices, and kits provide improved accuracy and minimize processing procedures. The present disclosure also relates to the use of the device or kit in a health care facility for the preliminary evaluation of cancerous and pre-cancerous conditions.
Owner:阿布卡拉姆·穆罕默德·沙姆斯丁
Engineered galactose oxidase variant enzymes
The present invention provides engineered galactose oxidase (GOase) enzymes, polypeptides having GOase activity, and polynucleotides encoding these enzymes, as well as vectors and host cells comprising these polynucleotides and polypeptides. Methods for producing GOase enzymes are also provided. The present invention further provides compositions comprising the GOase enzymes and methods of using the engineered GOase enzymes. The present invention finds particular use in the production of pharmaceutical and other compounds.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
A kind of gold nanoparticle-gold nanocluster composite material and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN113199035BEfficient detectionEasy to prepareMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingNanoparticleOxidative enzyme
The invention discloses a gold nanoparticle-gold nanocluster composite material, a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of nanomaterials. The composite material is prepared by the following steps: S1, HAuCl 4 The aqueous solution is mixed with a galactose oxidase (GO) solution to obtain a mixed solution; S2, the pH value of the mixed solution is adjusted to 11.0-12.0; S3, the pH-adjusted mixed solution is reacted at 35-40 °C to obtain The gold nanoparticle-gold nanocluster composite material. The present invention also includes that the gold nanoparticle-gold nanocluster composite material is used for detecting Ag + applications in . The composite material can directly realize low-concentration Ag + detection.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Sodium (ion) diagnosis/measuring reagent kit and sodium (ion) concentration determination method
InactiveCN101464362AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsEnzymatic ColorimetryAbsorbance
The invention relates to a kit for diagnosing / measuring sodium (ions) by utilizing the technologies of the enzymic colorimetry and the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. The invention further relates to a method, a principle and the composition and the components of a reagent for measuring the concentration of sodium (ions), and belongs to the technical field of medical / food / environmental inspection and measurement. The main components of the kit include a buffer solution, reduced coenzyme, lactose, beta-galactosidase, galactose oxidase, NADH oxidase and a stabilizer. Through mixing a sample and the reagent by a certain volume ratio, a series of enzymatic reactions occur, then the reactant is placed under an ultraviolet / visible light analyzer, and the degree / velocity of the decrease in absorbance at 340 nm of the dominant wavelength is detected, thereby measuring the concentration of sodium (ions).
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Reagent (kit) for diagnosing/determining amino acid and method for determining concentration of amino acid
InactiveCN101750368AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsGalactose dehydrogenaseEnzymatic Colorimetry
The invention relates to a reagent (kit) for diagnosing / determining amino acid by using an enzyme colorimetric method and an enzyme link method, and also discloses a method for determining the concentration of the amino acid, a composition and components of the reagent, belonging to the technical field of medicine / food / environmental test determination. The reagent (kit) comprises the main components: a buffer solution, a coenzyme, a galactose hexose dialdose, an amino acid oxidase, a galactose oxidase, a galactose dehydrogenase and a stabilizing agent. A sample and the reagent are mixed according to a certain volume ratio to generate a series of enzymatic reactions, and reactants are placed under an ultraviolet / visible light analyzer for detecting the degree of absorbance rise at the dominant wavelength of 340 nm, thereby measuring and calculating the concentration of the amino acid.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com