Patents
Literature
82 results about "P53 proteins" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
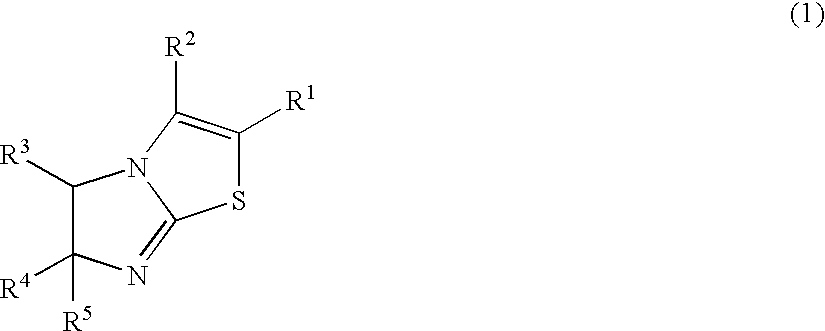
Imidazothiazole derivatives
There is provided a novel compound that inhibits interaction between murine double minute 2 (Mdm2) protein and p53 protein and exhibits anti-tumor activity. The present invention provides an imidazothiazole derivative represented by the following formula (1) having various substituents that inhibits interaction between Mdm2 protein and p53 protein and exhibits anti-tumor activity:wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, and R5 in the formula (1) each has the same meaning as defined in the specification.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
Sequence specific DNA binding by p53
InactiveUS7087583B2Inhibit tumor growthLoss of functionOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsHuman DNA sequencingCancer cell
Specific sequences in the human genome are the sites of strong binding of wild-type p53 protein, but not mutant forms of the protein. These sequences are used diagnostically to detect cells in which the amount of wild-type p53 is diminished. The sequences can also be used to screen for agents which correct for loss of wild-type p53 to DNA in cancer cells.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Methods and composition for restoring conformational stability of a protein of the p53 family
InactiveUS20020048271A1Wide applicabilityInhibit tumor growthBiocideSenses disorderMutated proteinWild type
The invention is in the field of cancer treatment. In particular, the present invention provides pharmaceutical compounds capable of interacting with mutant and non-mutant forms of cancer-related regulatory proteins such that the mutant protein regains the capacitv to properly interact with other macromolecules thereby restoring or stabilizing all or a portion of its wild type activity. Regulatory proteins include members of the p53 protein family such as. for example, p53, p63 and p73. The compounds of the invention are useful for cancer treatment. Methods for screening for such pharmacological compounds are also provided.
Owner:RASTINEJAD FARZAN +3
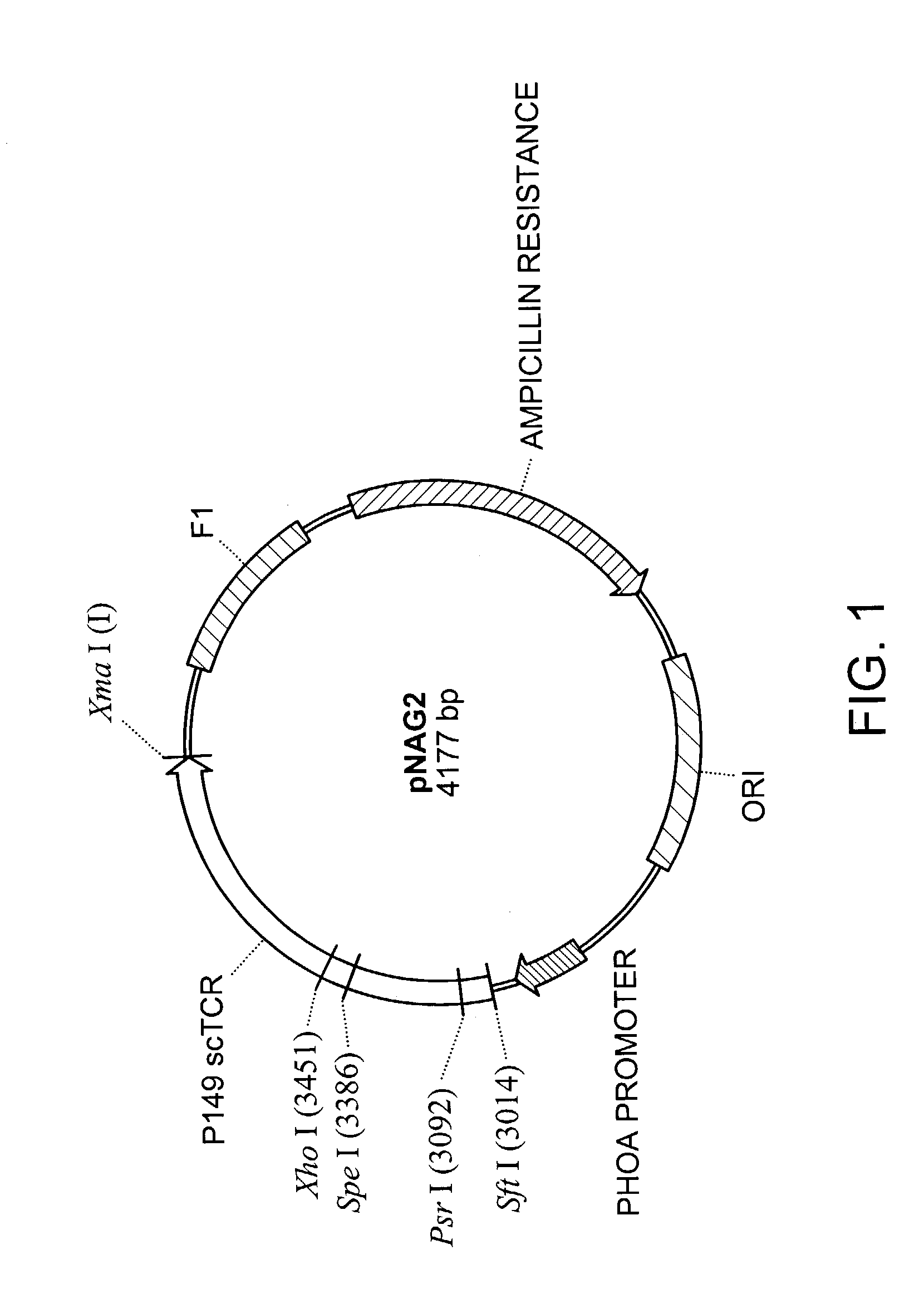
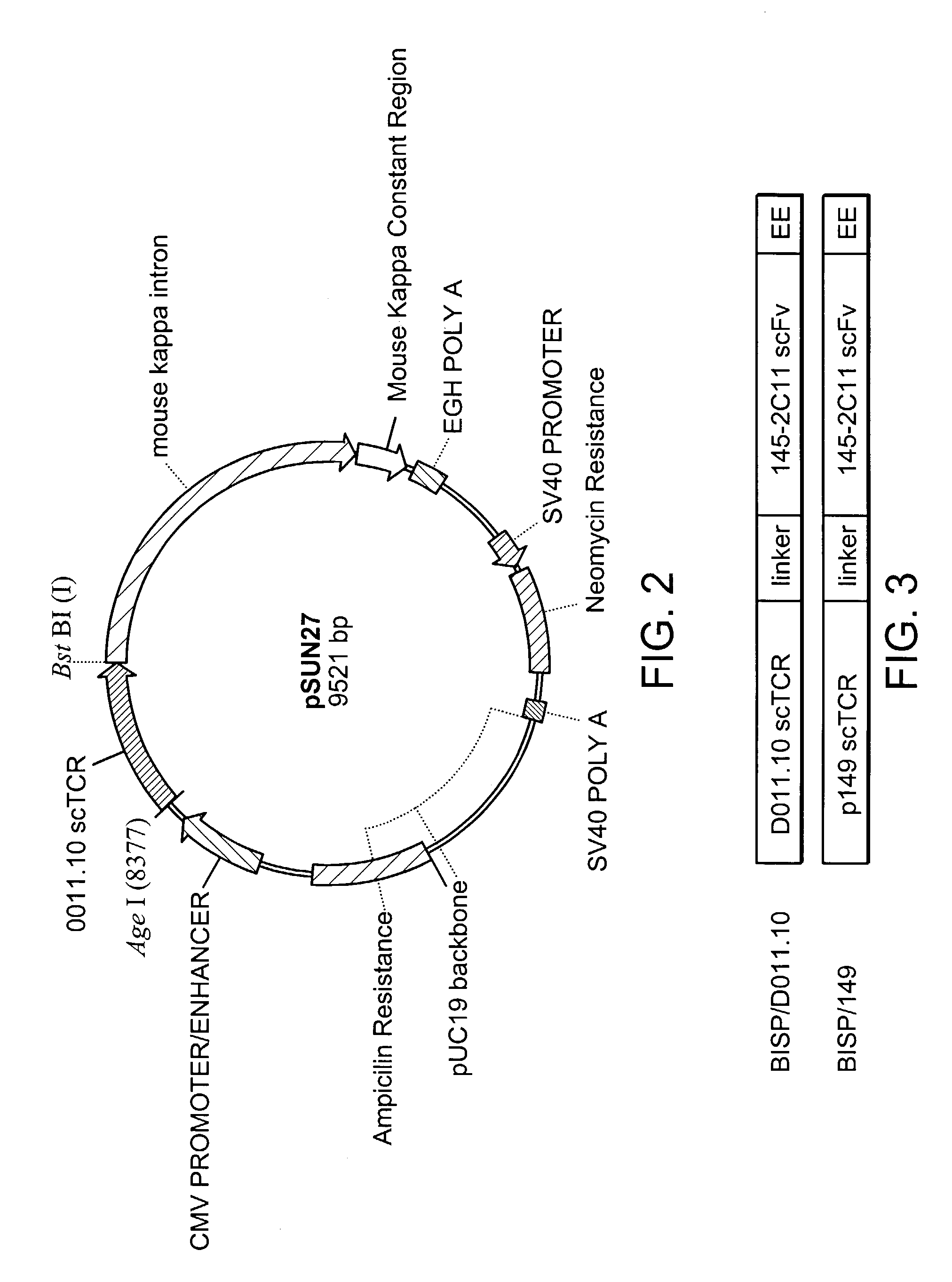
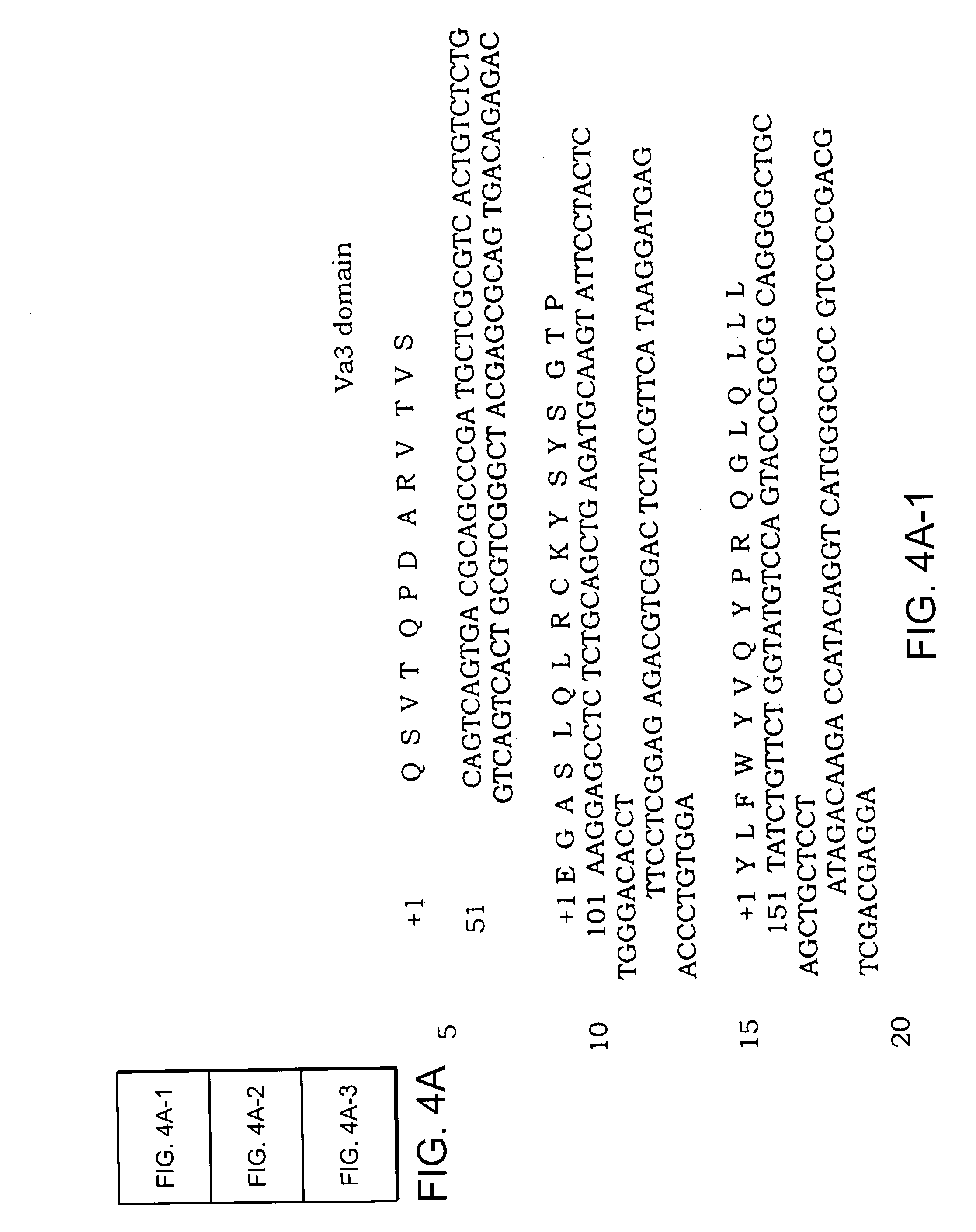
P53 binding T cell receptor molecules
InactiveUS7456263B2Avoid developmentEasily substitutedImmunoglobulin superfamilyFungiP53 bindingBinding peptide
The invention provides T-cell receptor (TCR) molecules comprising a Vα chain and a Vβ chain that bind peptides derived from the p53 protein, preferably, the human p53 protein. The TCR molecules include both heterodimeric molecules and single chain molecules which specifically bind a sequence preferably spanning about amino acid positions 264-272 of the p53 protein displayed in the context of an HLA molecule, preferably, HLA-A2.1. Also disclosed are methods for making and using such TCR molecules. The invention has a wide spectrum of useful application including therapeutic uses and use in the detection of cells expressing p53 protein.
Owner:ALTOR BIOSCI LLC +1
Treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus by down-regulating the autoimmune response to autoantigens
InactiveUS20060030524A1Improving immunogenicityEasily raisedAntipyreticGenetic material ingredientsAntigenDNA-binding domain
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) can be prevented or treated by down-regulating the autoimmune response to the C-terminal-DNA-binding domain of the p53 protein (p53) by an active principle selected from the group consisting of: (i) a peptide of, or comprising, the C-terminal DNA-binding domain of the p53 protein; (ii) a monoclonal antibody (mAb) specific for said domain of p53 (Ab1), and fragments thereof; (iii) an mAb specific for Ab1 (hereinafter Ab2), and fragments thereof; (iv) a peptide based on a complementarity determining region (CDR) of the heavy or light chain of said Ab1 or Ab2; (v) a DNA molecule coding for (i) and (iv) of for the variable region of said Ab1 and Ab2 of (ii) and (iii); and (vi) T cells specific for (i) to (iv), fragments thereof, T cell receptor (TCR) thereof and peptides comprising the variable region of said TCR. SLE can also be diagnosed by assaying for antibodies (Ab1) against the C-terminal DNA-binding domain of p53 or antibodies (Ab2) specific to the Ab1 antibodies.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
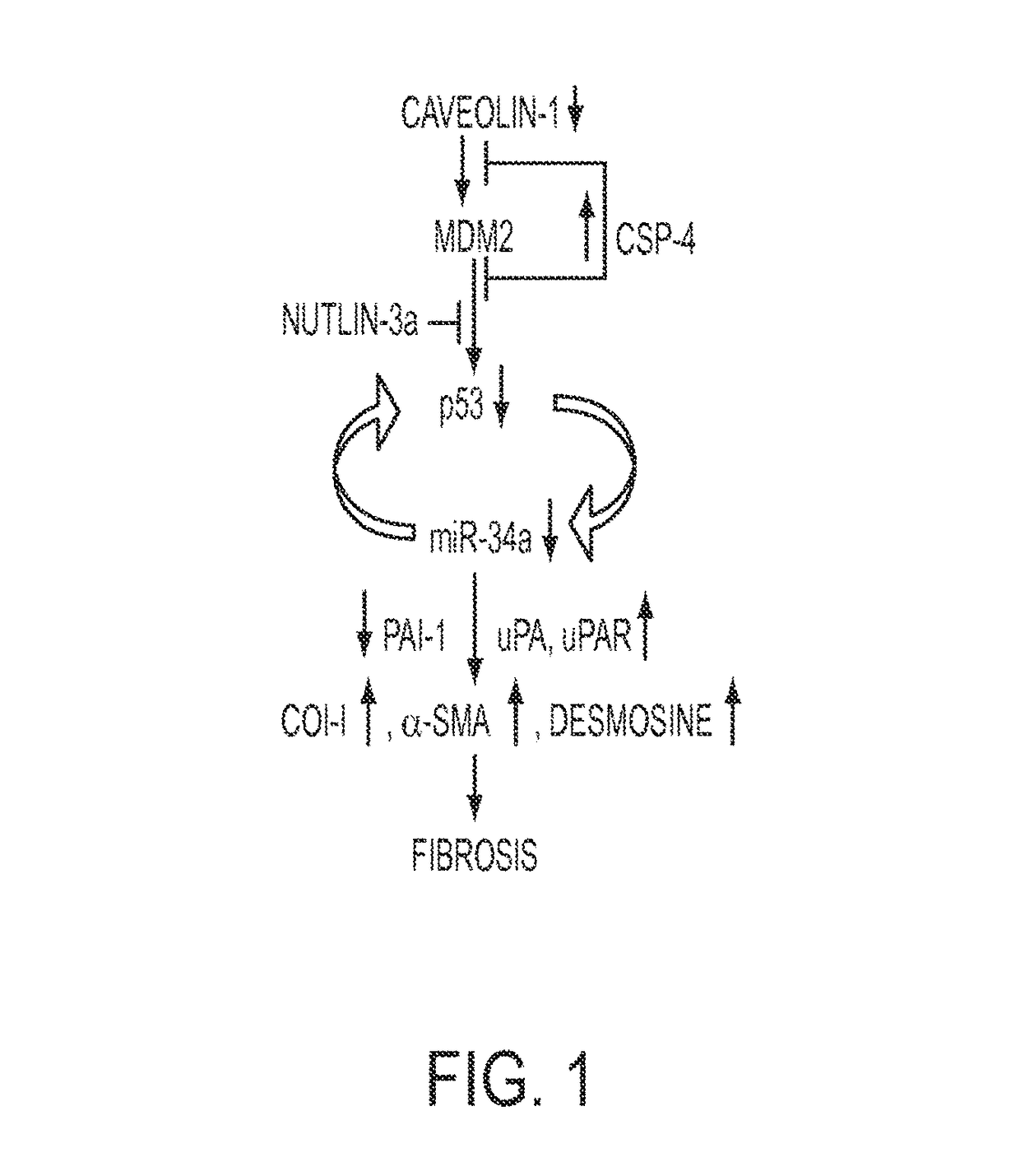
Inhibition of pulmonary fibrosis with nutlin-3A and peptides
ActiveUS9630990B2Effective treatmentPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifOrganic active ingredientsCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
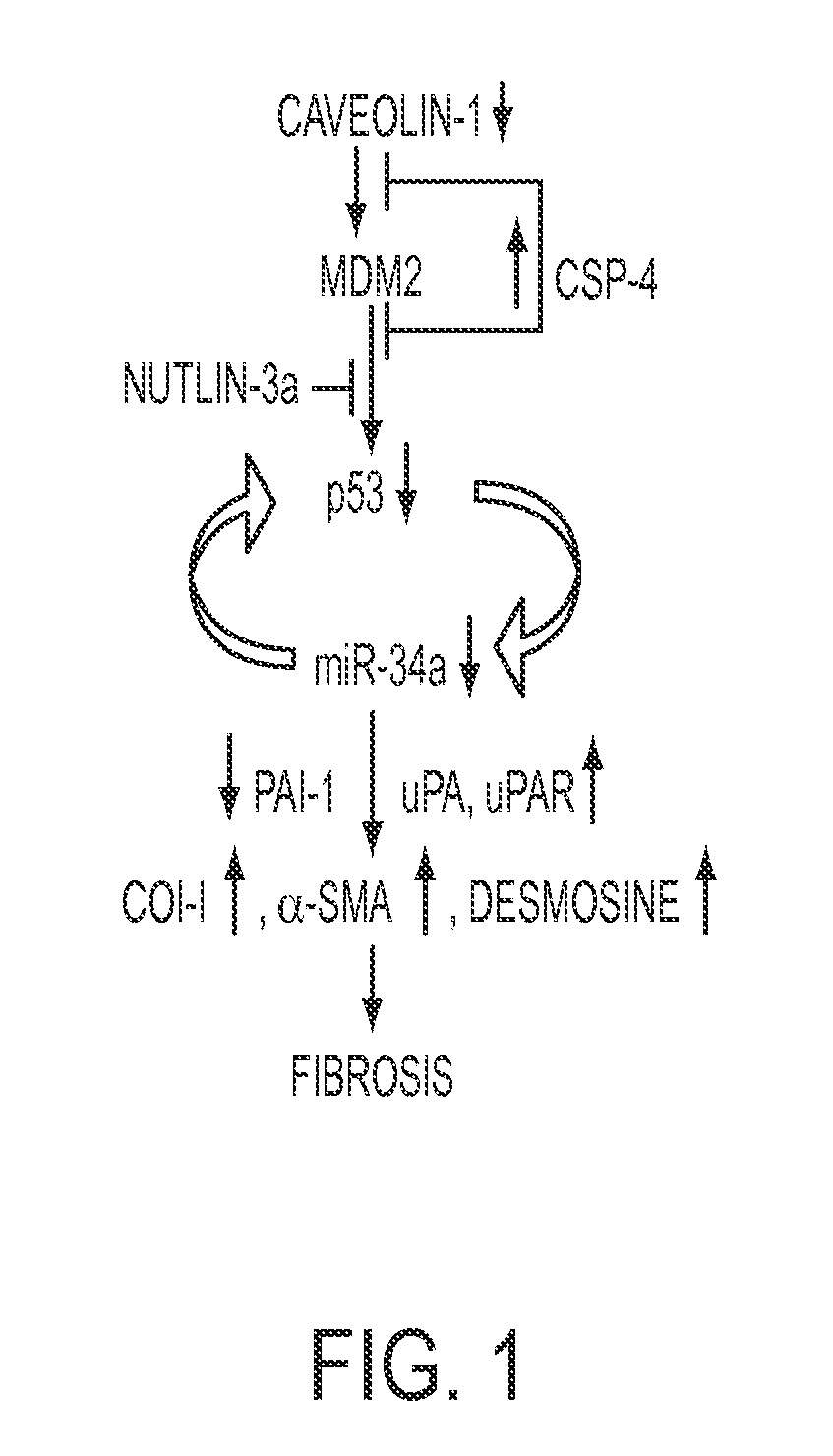
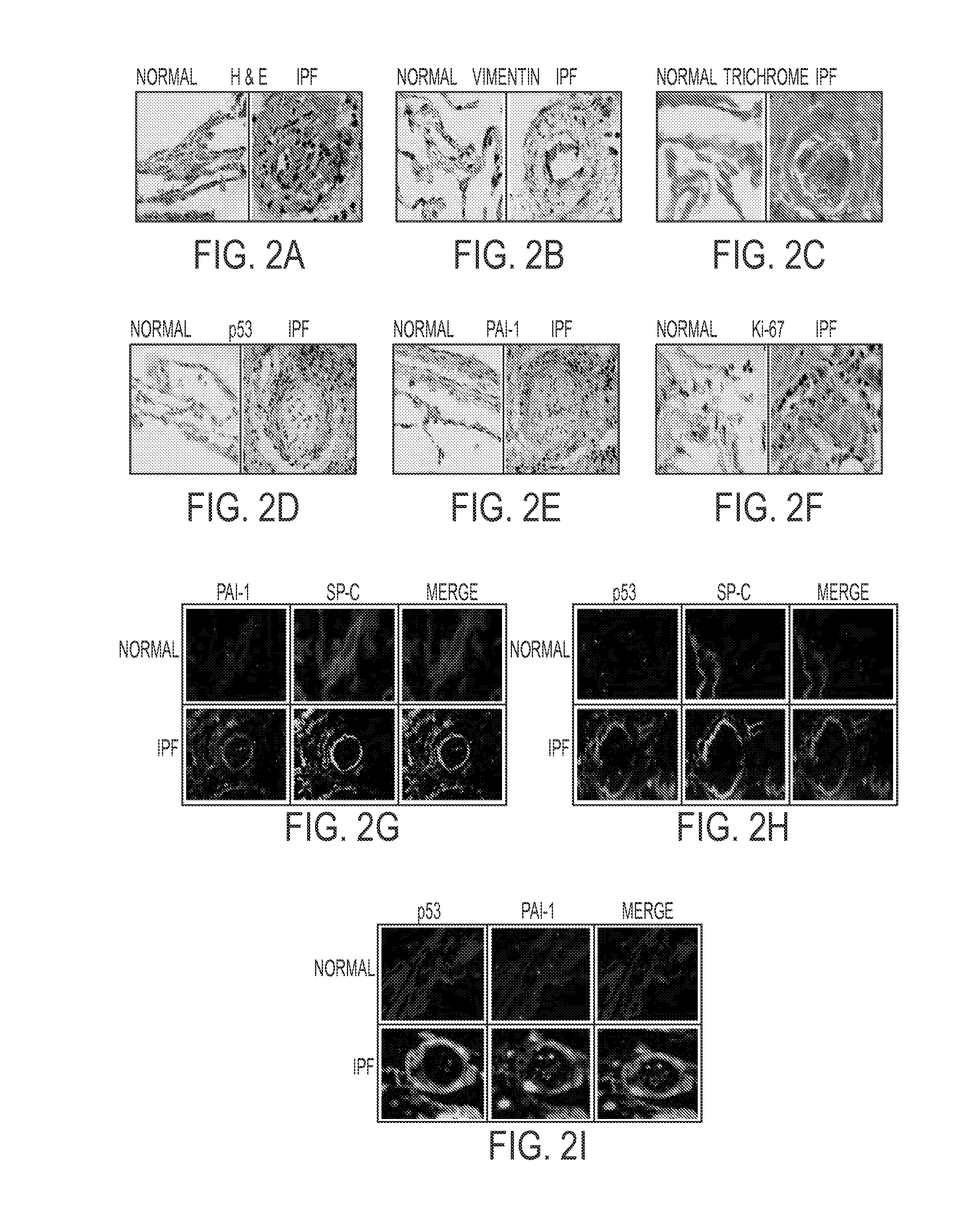
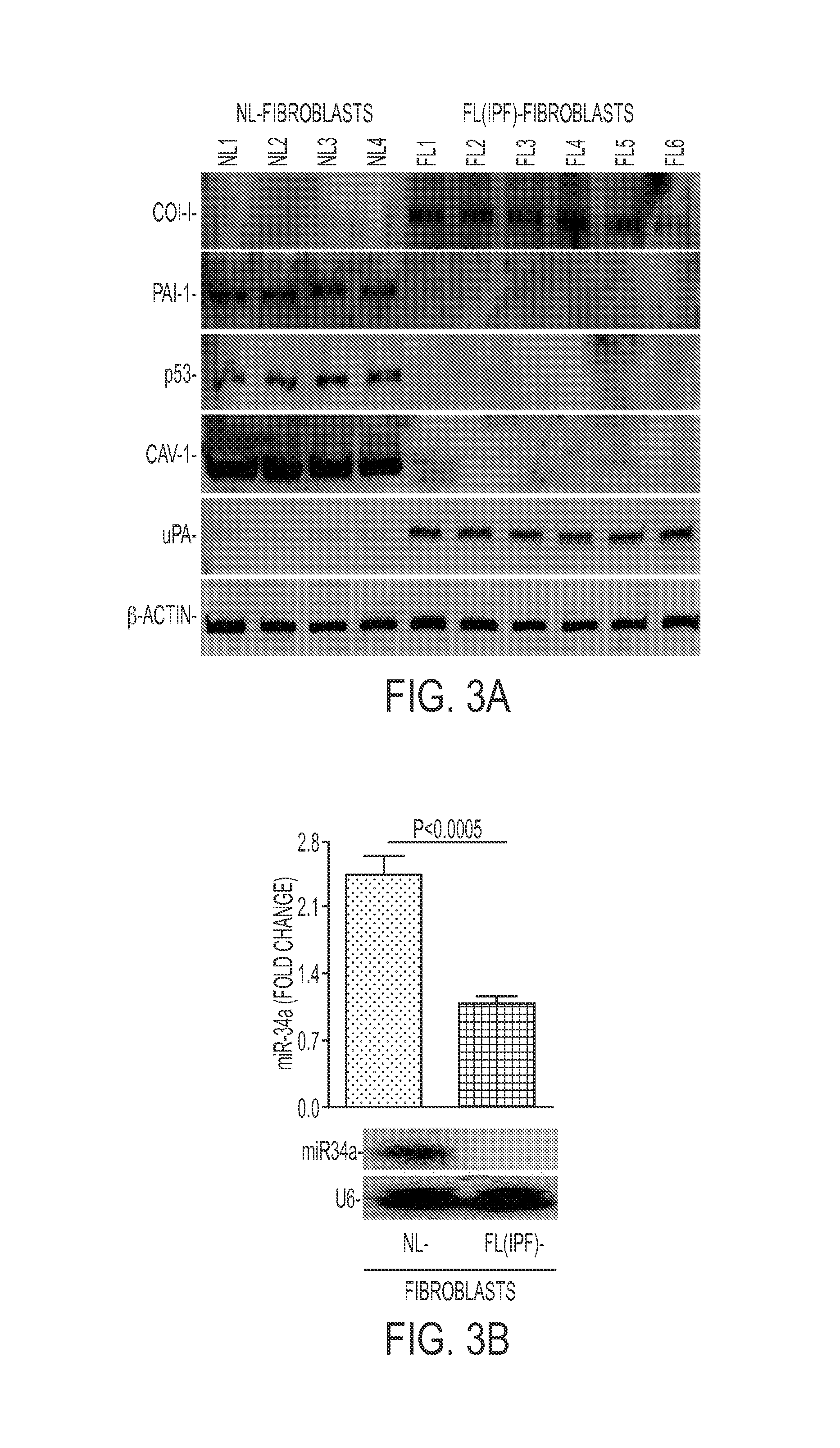
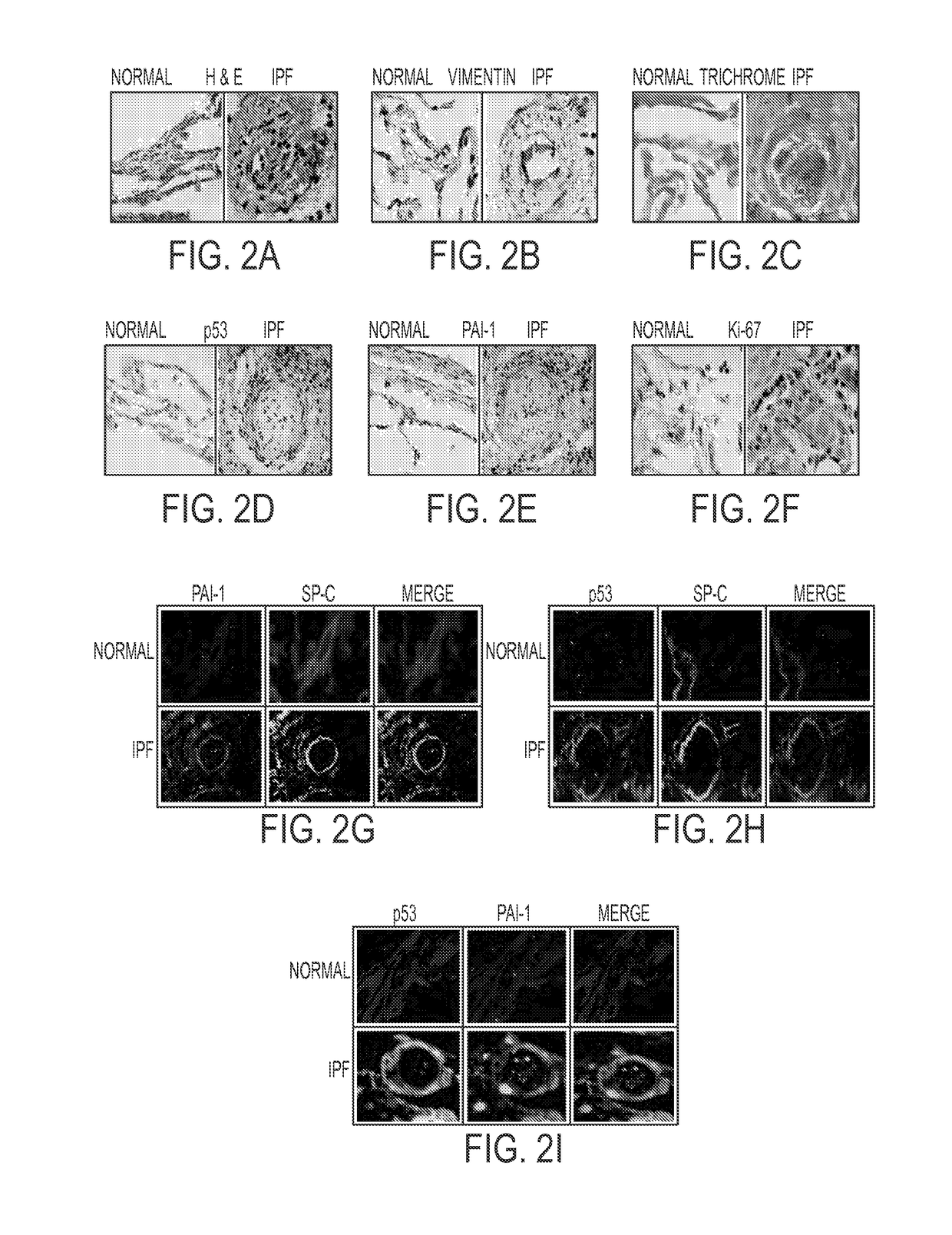
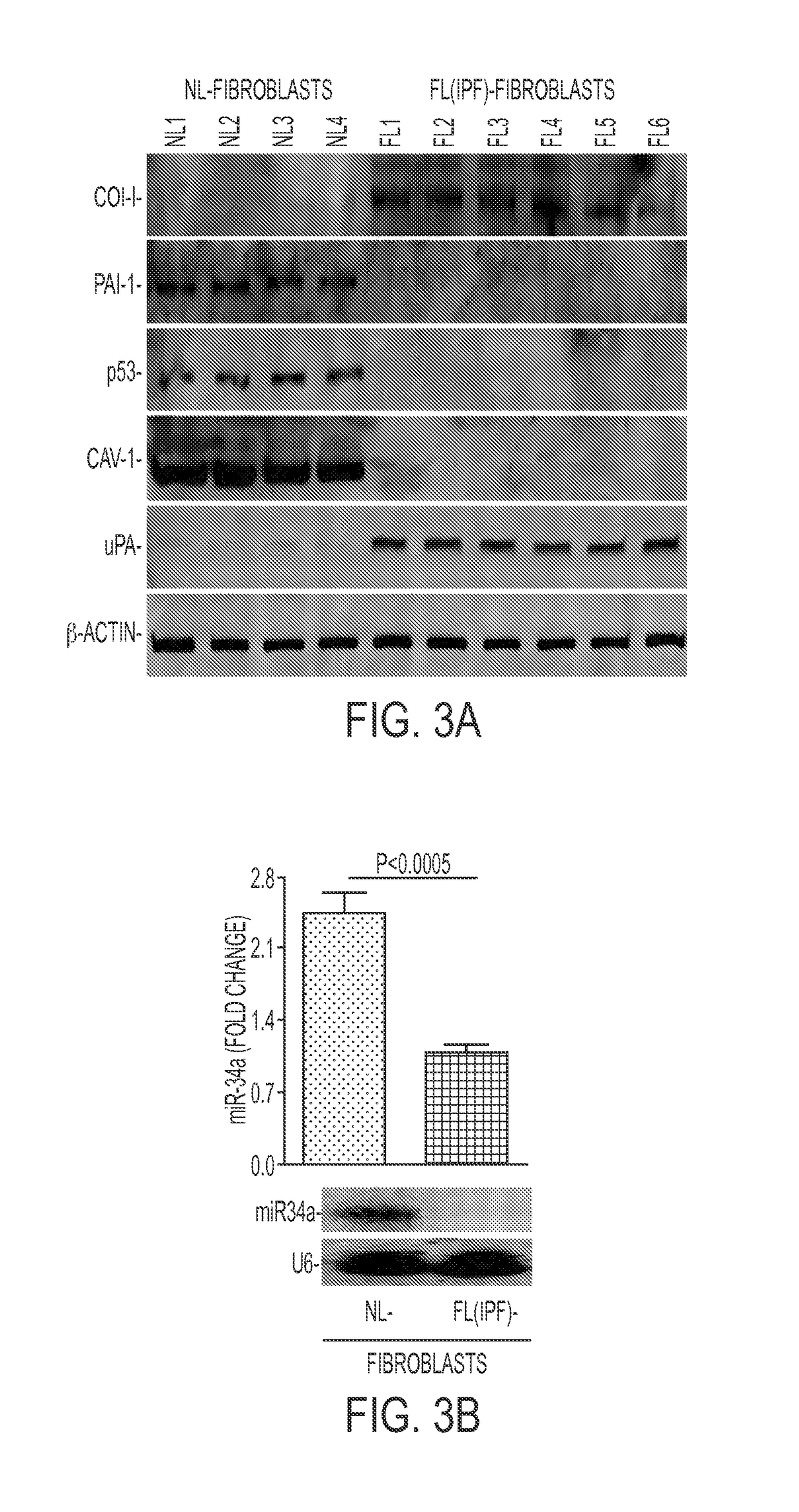
In fibrotic lung fibroblasts, basal levels of p53 protein (and miR-34a) are markedly suppressed, leading to reduced p53-mediated inhibition of uPA and uPAR, or concurrent induction of PAI-1. These changes contribute to excessive FL-fibroblast proliferation and production of extracellular matrix (ECM), and, therefore, pulmonary fibrosis. These processes are reversed by treating the cells, and treating subjects suffering from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) with the small organic molecule nutlin-3a (NTL) or with a peptide, CSP-4 (SEQ ID NO:1), or variants or derivatives or multimers of this peptide, which increase p53 levels by inhibiting MDM2-mediated degradation of p53 protein. Use of these compounds serves as a new approach to the treatment of IPF, they restore p53 expression and p53-mediated changes in the uPA-fibrinolytic system in FL-fibroblasts and restrict production and deposition of ECM.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Peptidomimetic macrocycles
ActiveUS9505804B2Stabilize alpha-helical secondary structureImprove biological activityP53 proteinPeptide preparation methodsCross-linkDisease
Provided herein are peptidomimetic macrocycles containing amino acid sequences with at least two modified amino acids that form an intramolecular cross-link that can help to stabilize a secondary structure of the amino acid sequence. Suitable sequences for stabilization include those with homology to the p53 protein. These sequences can bind to the MDM2 and / or MDMX proteins. Also provided herein are methods of using such macrocycles for the treatment of diseases and disorders, such as cancers or other disorders characterized by a low level or low activity of a p53 protein or high level of activity of a MDM2 and / or MDMX protein.
Owner:AILERON THERAPEUTICS INC
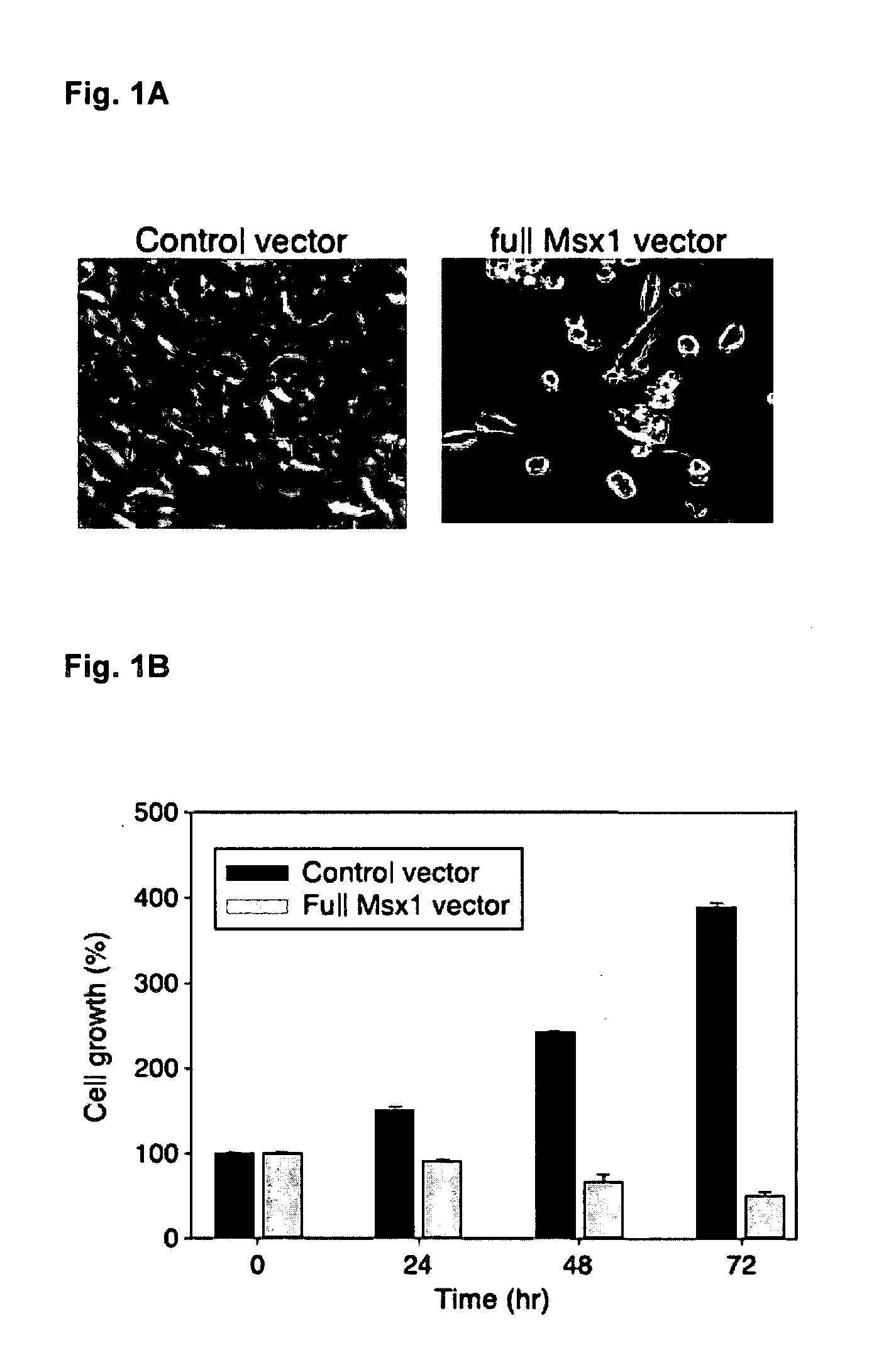
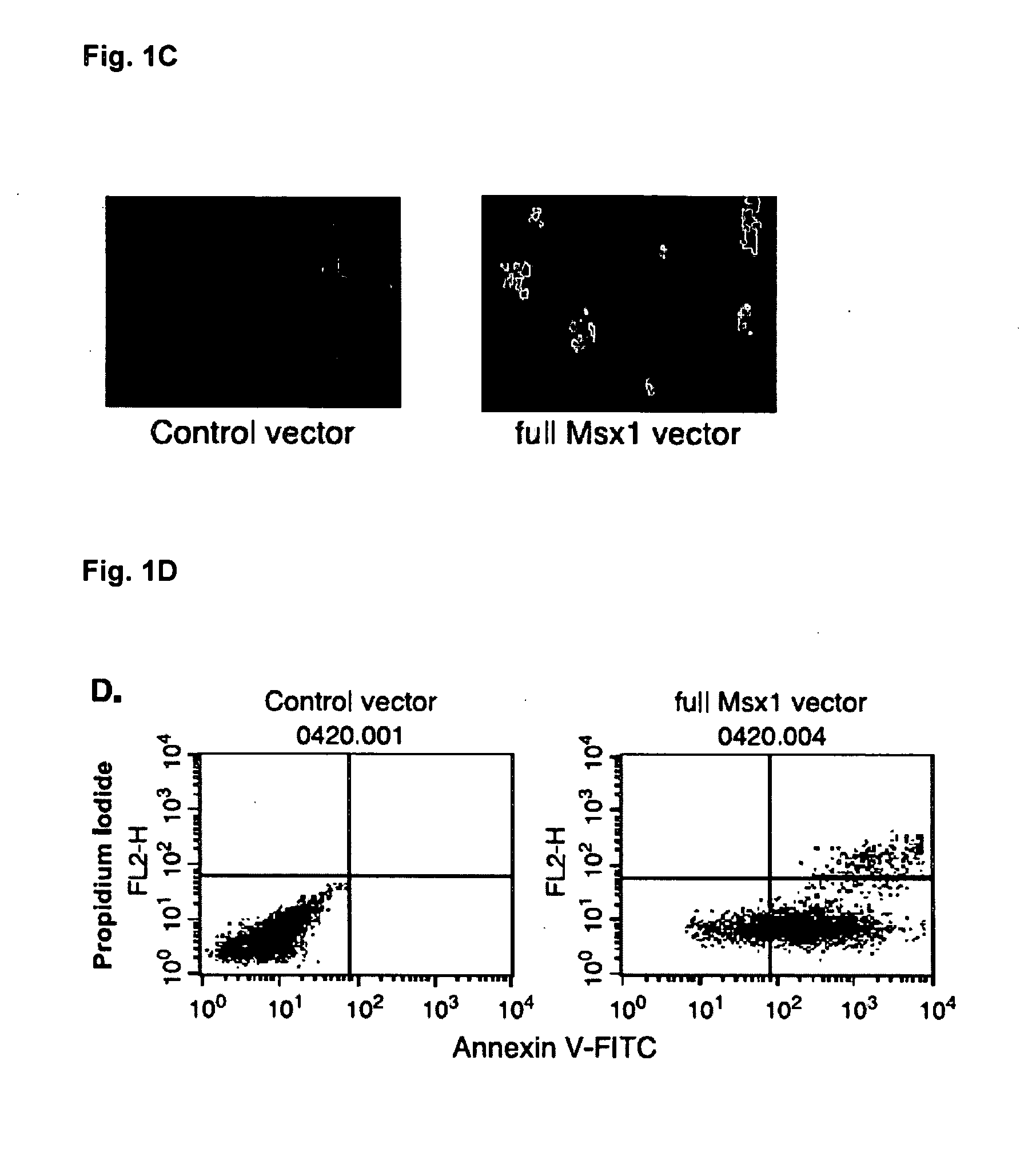
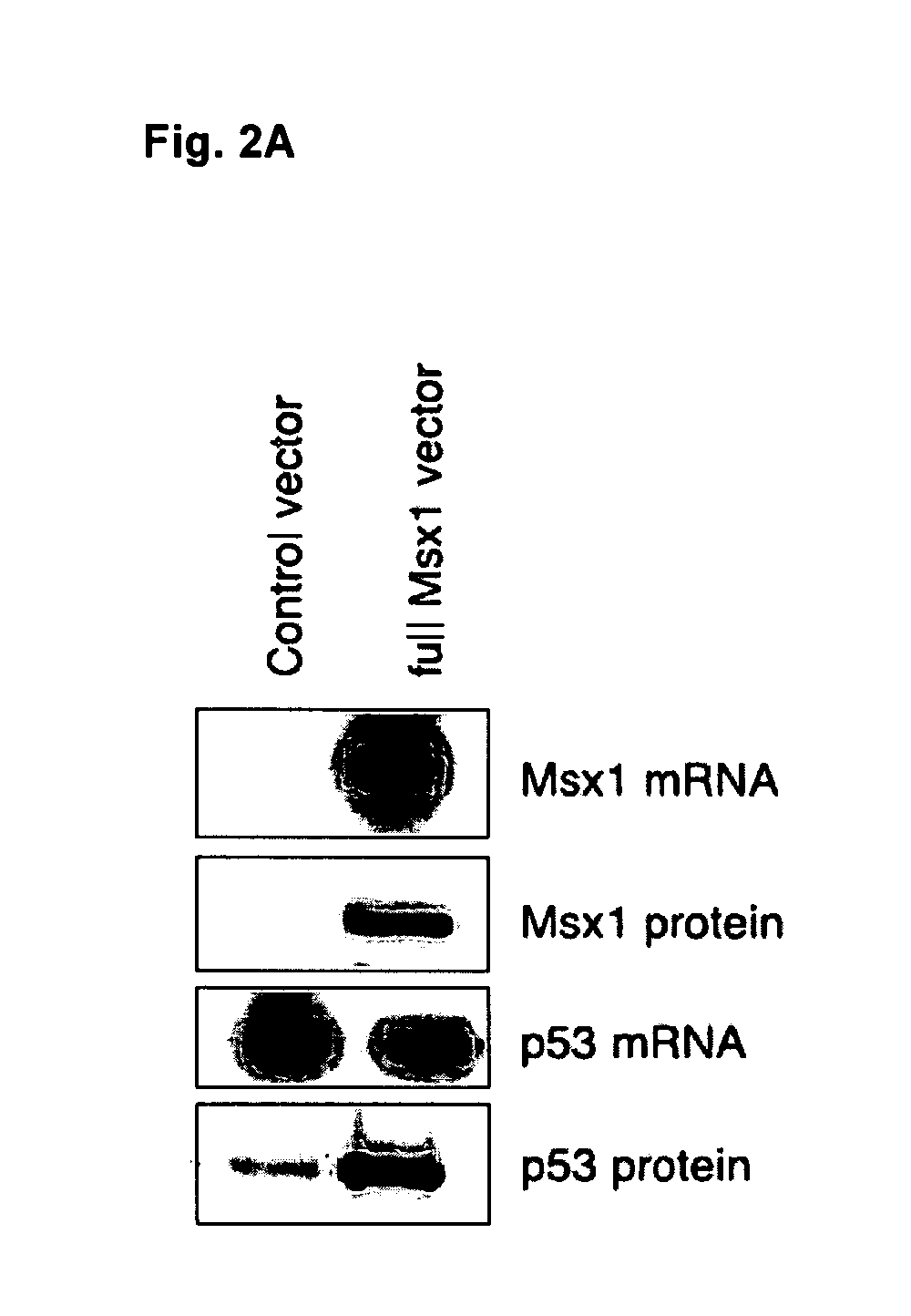
Novel agent for inducing apoptosis comprising Msx1 or a gene encoding the same as an active ingredient
InactiveUS20070021337A1Effectively modulating apoptosisEffectively induce apoptosisPeptide/protein ingredientsEnzymesAbnormal tissue growthBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The present invention relates to a novel use of Msx1 protein or a nucleotide encoding the same for inducing apoptosis. The Msx1 of the present invention induces apoptosis through direct interaction with p53 via a homeodomain and such interaction leads to increased stability, and / or nuclear localization of p53 in cells. The Msx1 or homeodomain thereof can be effectively used for the treatment of tumors, in which wild-type p53 protein has lost its function by some mechanism that inactivates p53 proteins.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUNDATION SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
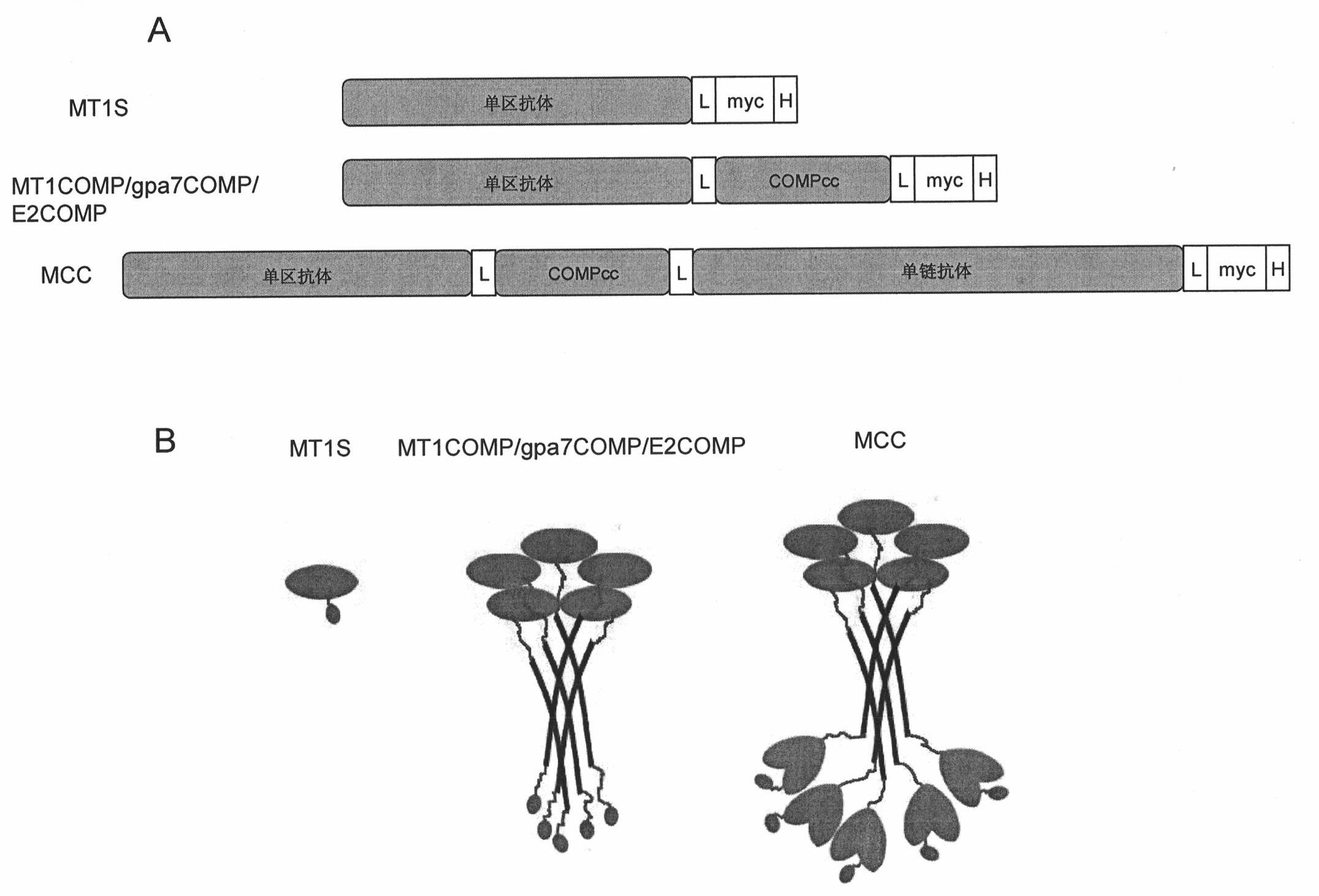
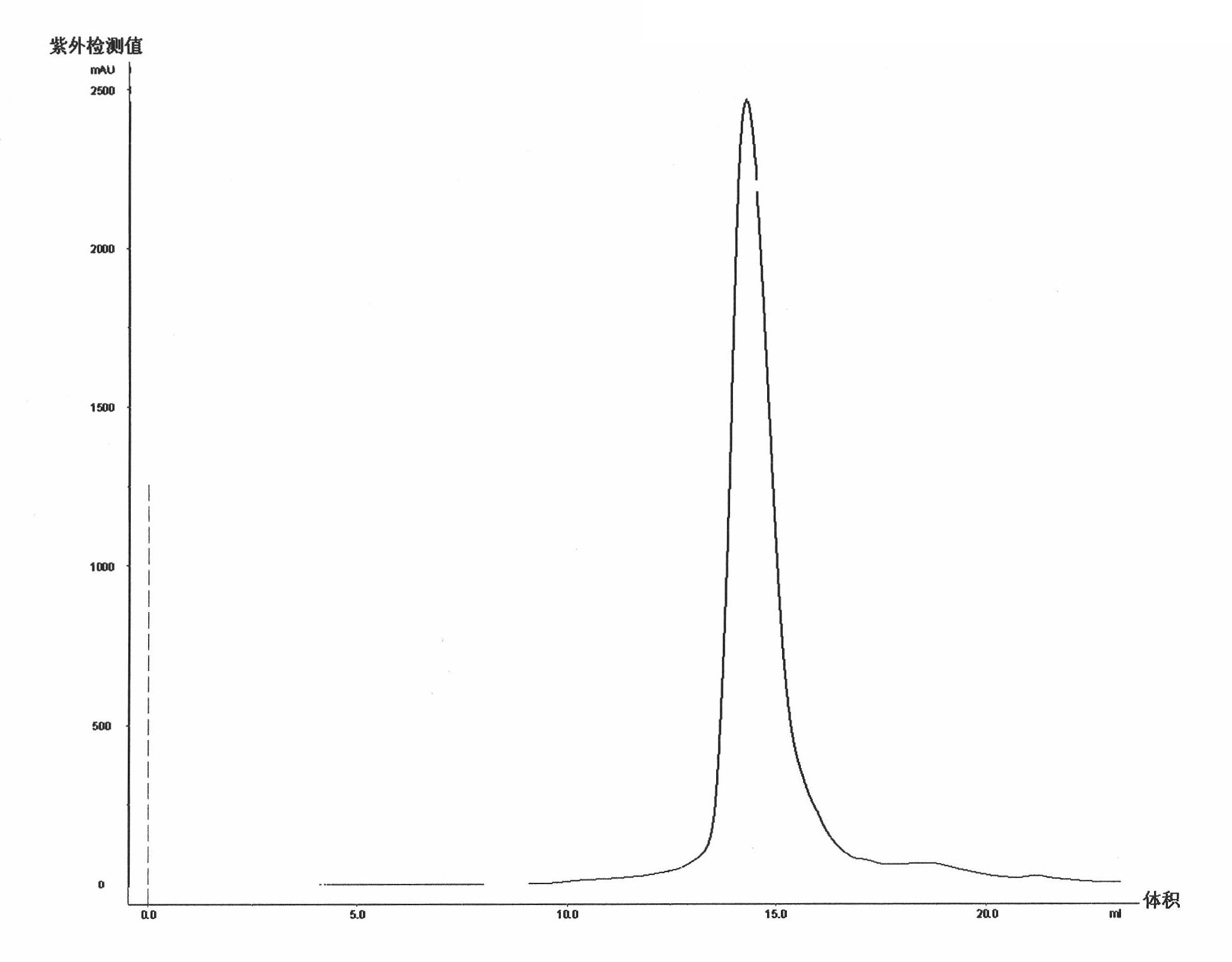
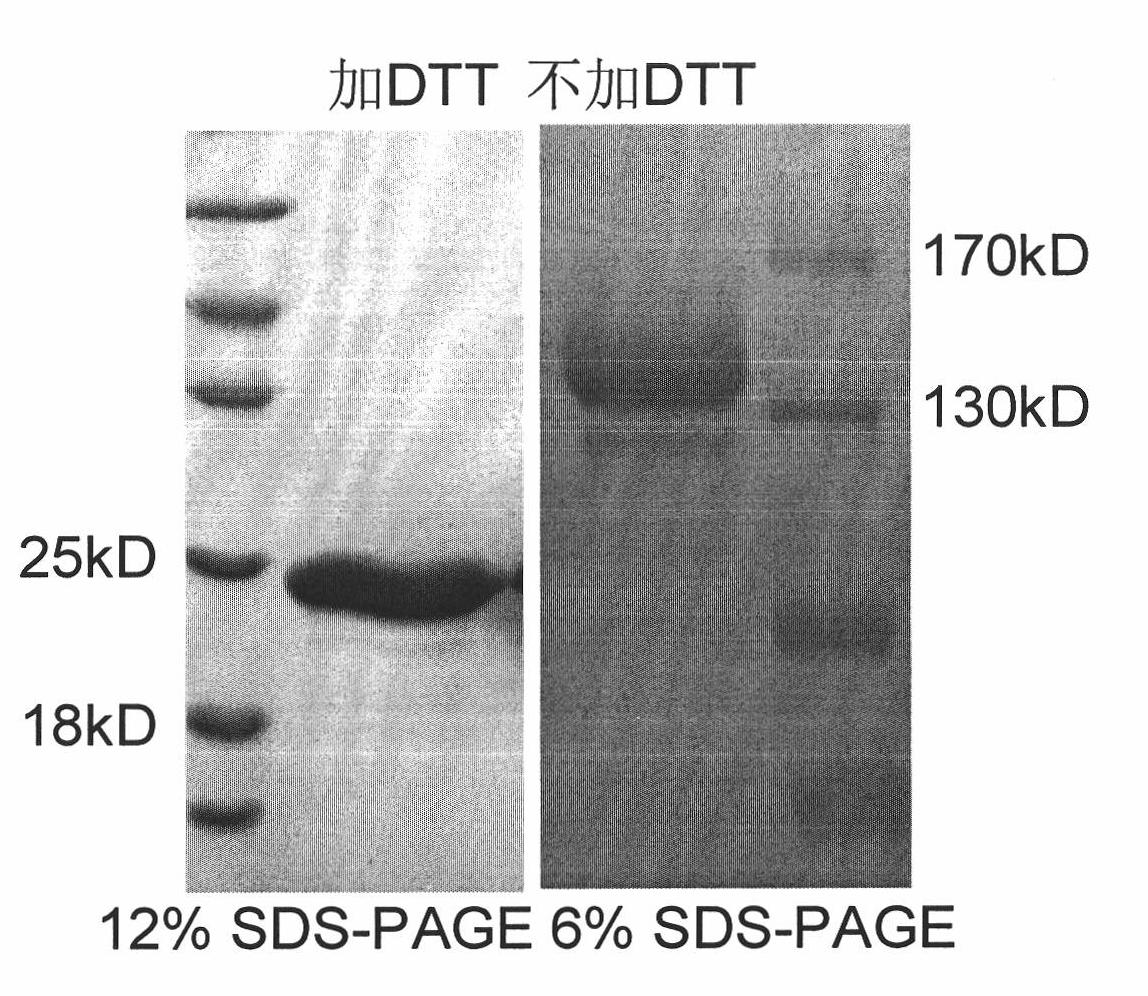
Fusion protein polymer
InactiveCN101830986AImprove solubilityImprove biological activityFungiBacteriaEscherichia coliMelanoma
The invention relates to a fusion protein polymer. The fusion protein polymer consists of a component A and a component B, wherein the component A is a single domain antibody, while the component B is peptide sequences which perform multimerization on fusion protein and are derived from TNF alpha protein, ACRP30 protein, P53 protein, COMP protein, C4BP protein and mutants of the TNF alpha protein, the ACRP30 protein, the P53 protein, the COMP protein and the C4BP protein. The fusion protein polymer has the advantages of successful expression in Escherichia coli, high expression quantity, relatively simple preparation and low cost. Poly-antibodies of the fusion protein polymer have high dissolubility and biological activity and greatly improve the affinity of antibody protein. The fusion protein polymer can be prepared into various biotech products such as diagnostic reagents used for diagnosing melanoma and the like, and used for target treatment of the melanoma and the like by carrying a therapeutic medicament. When the poly-antibodies based on the fusion protein polymer are clinically applied, the problem of strong immunogenicity can be solved.
Owner:北京表源生物技术有限公司
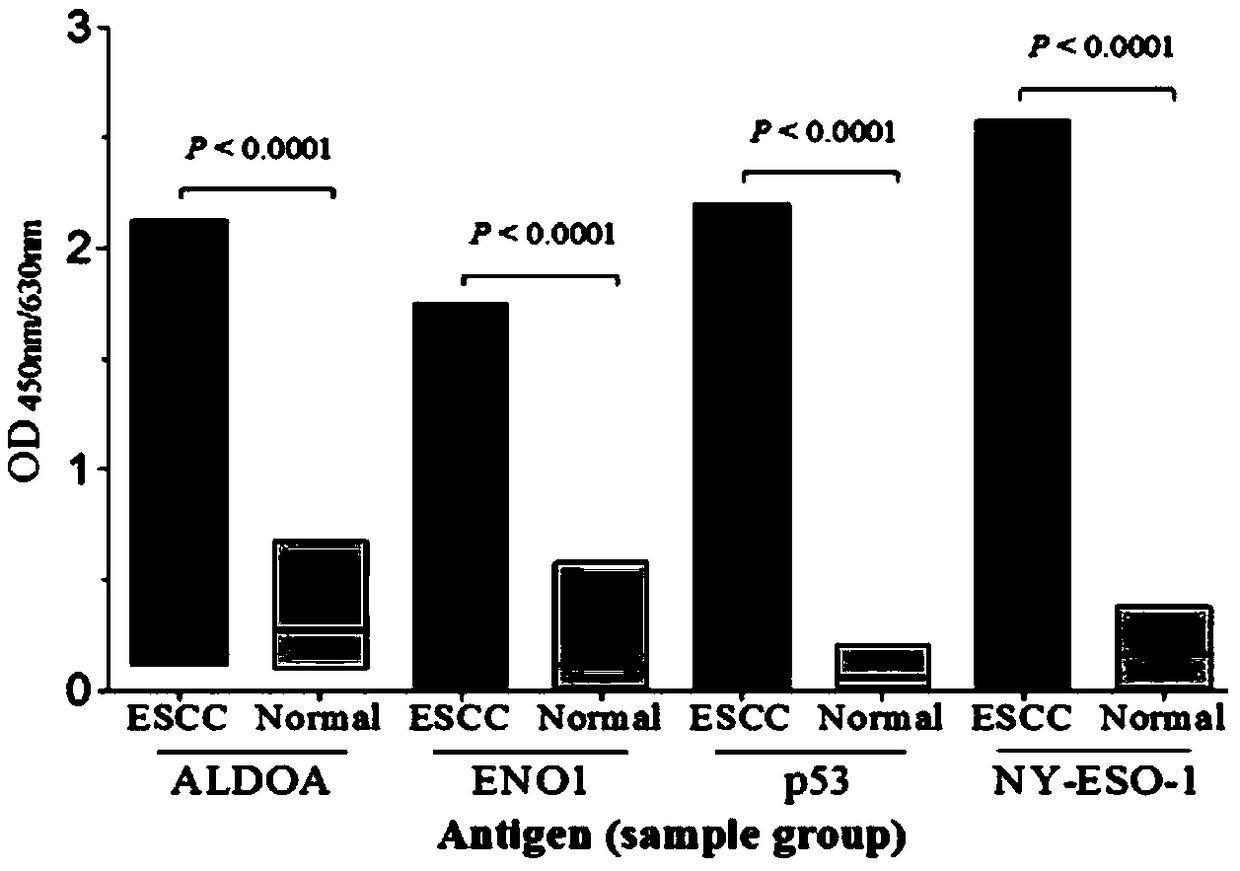
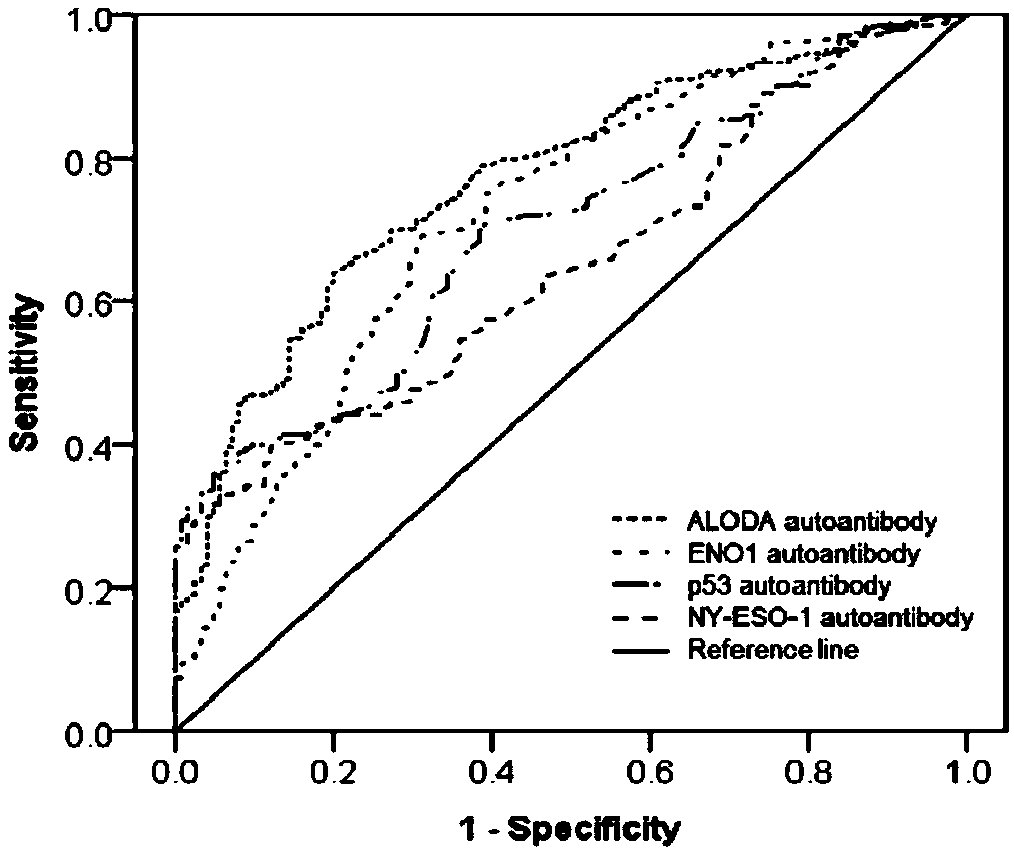
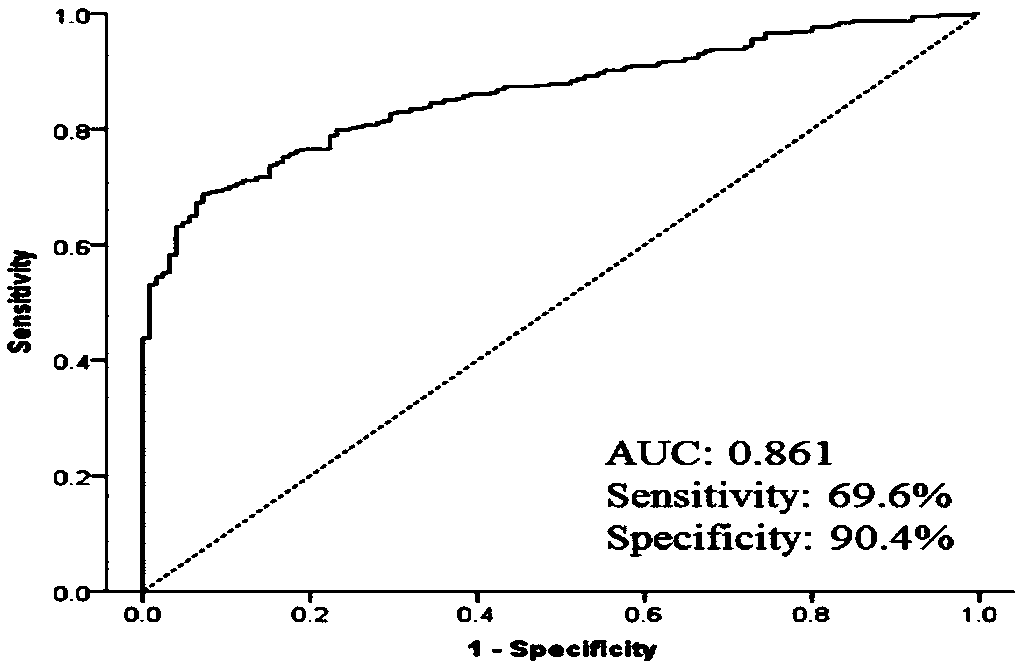
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma autoantibody molecular marker model and application thereof
ActiveCN109342727AGood distinctionIncreased sensitivityDisease diagnosisStage I Esophageal Squamous Cell CarcinomaAutoantibody production
The invention relates to an esophageal squamous cell carcinoma autoantibody molecular marker model and an application thereof. The molecular model mainly comprises an ALDOA autoantibody, an ENO1 autoantibody, a p53 autoantibody, and an NY-ESO-1 autoantibody, and can be used for preparing a kit for distinguishing esophageal squamous carcinoma patients and healthy medical examiners. The kit for detecting esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients mainly comprises recombinant ALDOAD protein, recombinant ENO1 protein, recombinant p53 protein, and recombinant NY-ESO-1 protein. According to the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma autoantibody molecular marker model and the application thereof, the ENO1 autoantibody is found to be elevated in serum level in the esophageal squamous carcinoma patients for the first time, and is jointly detected with the ALDOA autoantibody, the p53 autoantibody, and the NY-ESO-1 autoantibody for distinguishing the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients andthe healthy medical examiners, and has a better distinguishing effect than a single index detection; and in addition, the detection method adopted by the invention is an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay indirect method, is simple and convenient to implement, has good sensitivity and specificity, and is a method which is mature and reliable and can be widely used in base layer hospitals.
Owner:汕头市颂美恩生物科技有限公司
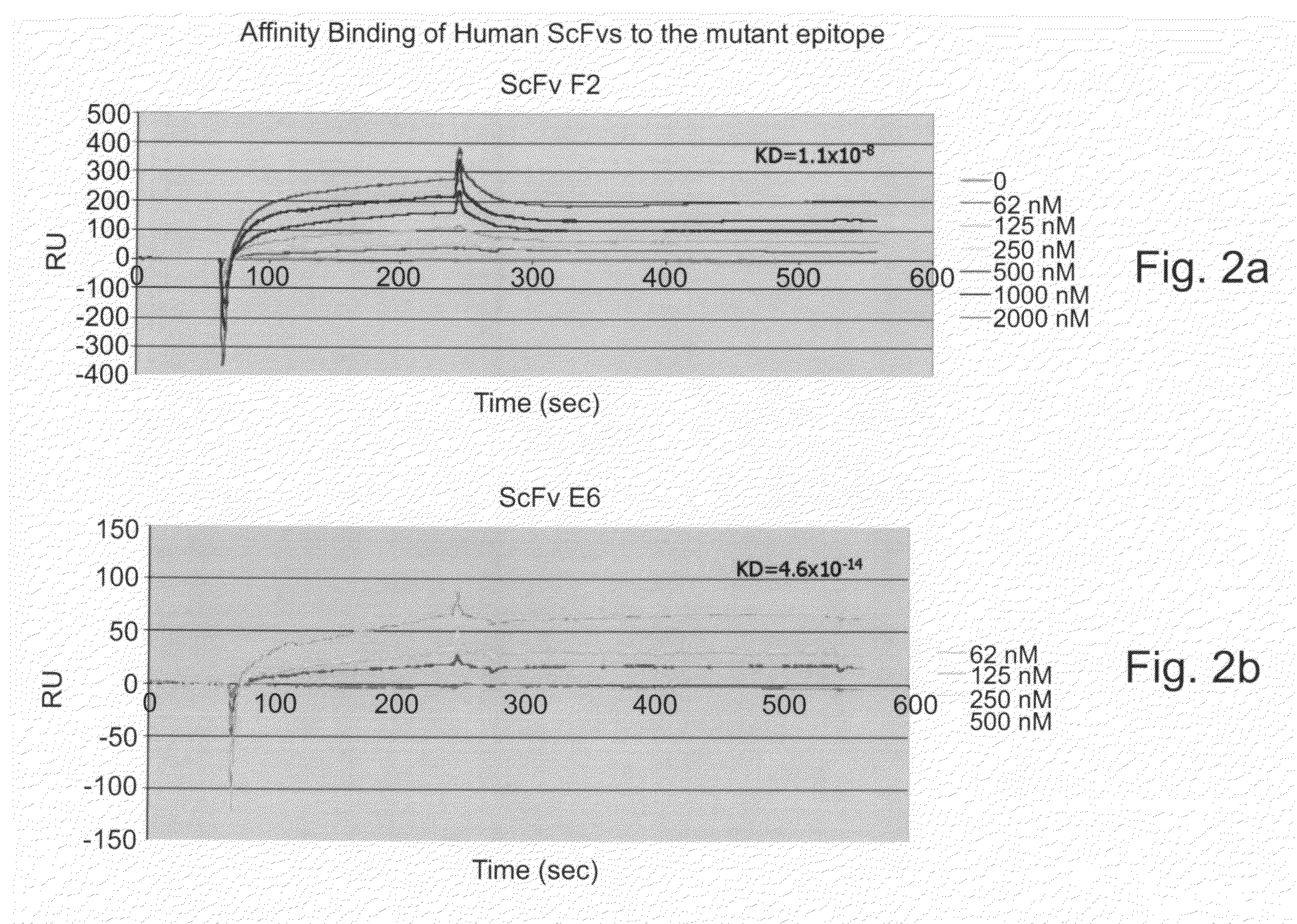
Human synthetic single-chain antibodies directed against the common epitope of mutant P53 and their uses
Isolated polypeptides, isolated polynucleotides or expression vectors encoding same, viral display vehicles which can be specifically bind an exposed epitope shared by mutant, but not wild type, p53 protein are provided. Also provided are methods of inducing apoptosis and treating cancer as well as diagnosing a p53-related cancer using the isolated polypeptides uncovered by the present invention.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
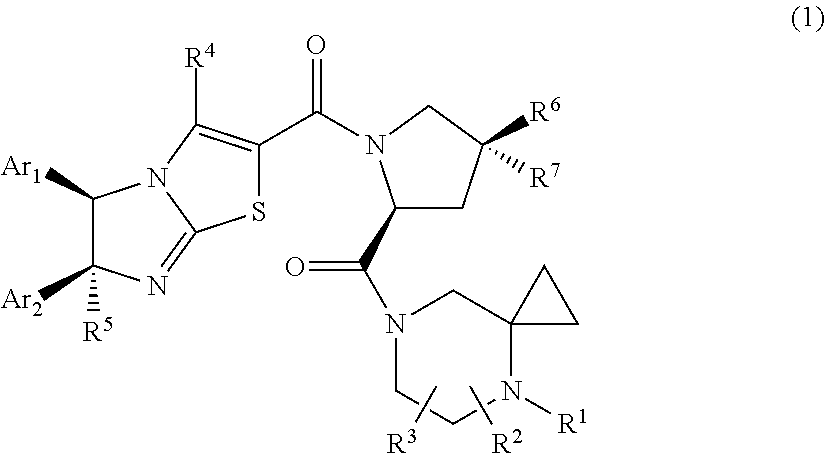
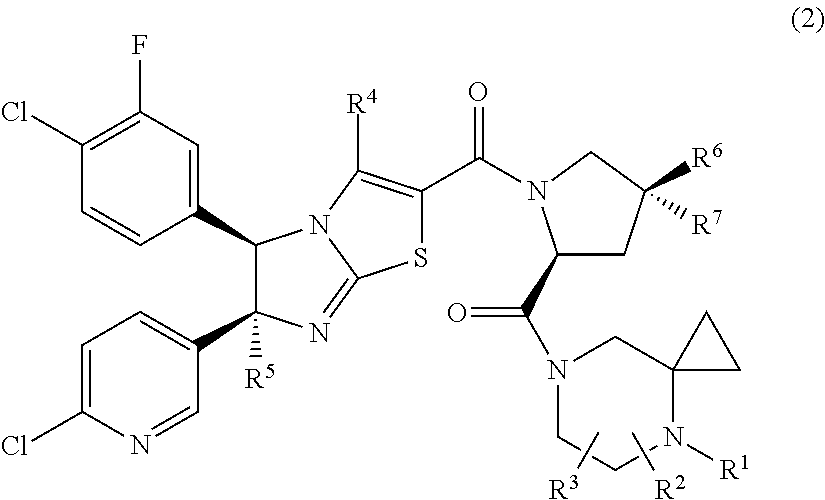
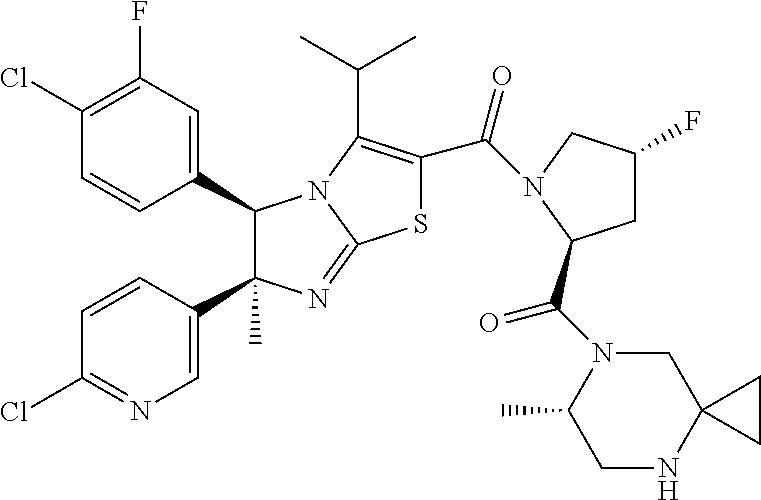
Imidazothiazole derivatives having proline ring structure
InactiveUS20110301176A1Organic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryMdm2 ProteinImidazothiazole derivatives
There is provided compounds that inhibit interaction between murine double minute 2 (Mdm2) protein and p53 protein and exhibits anti-tumor activity. Compounds include imidazothiazole derivatives that can inhibit interaction between Mdm2 protein and p53 protein and exhibits anti-tumor activity.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
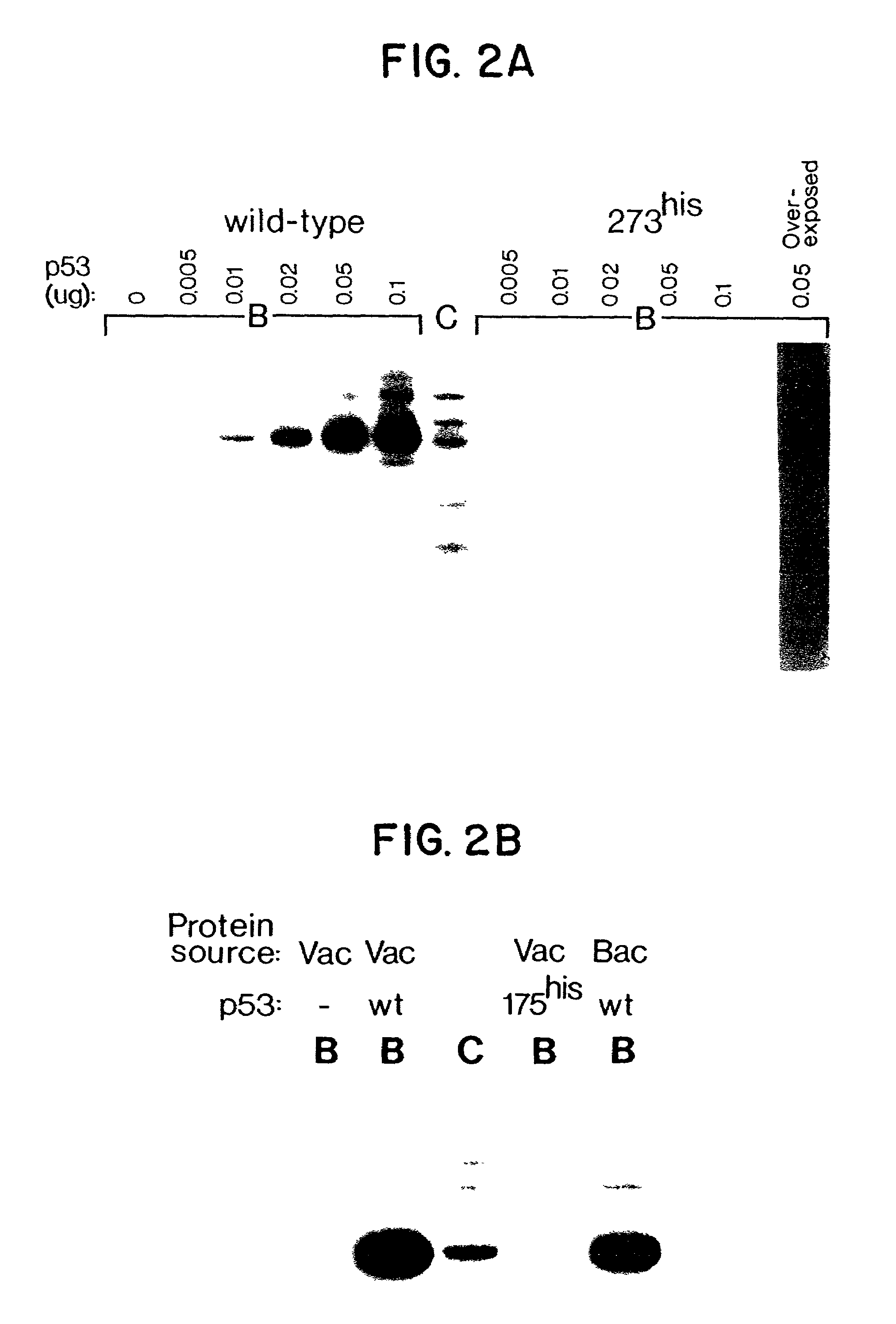
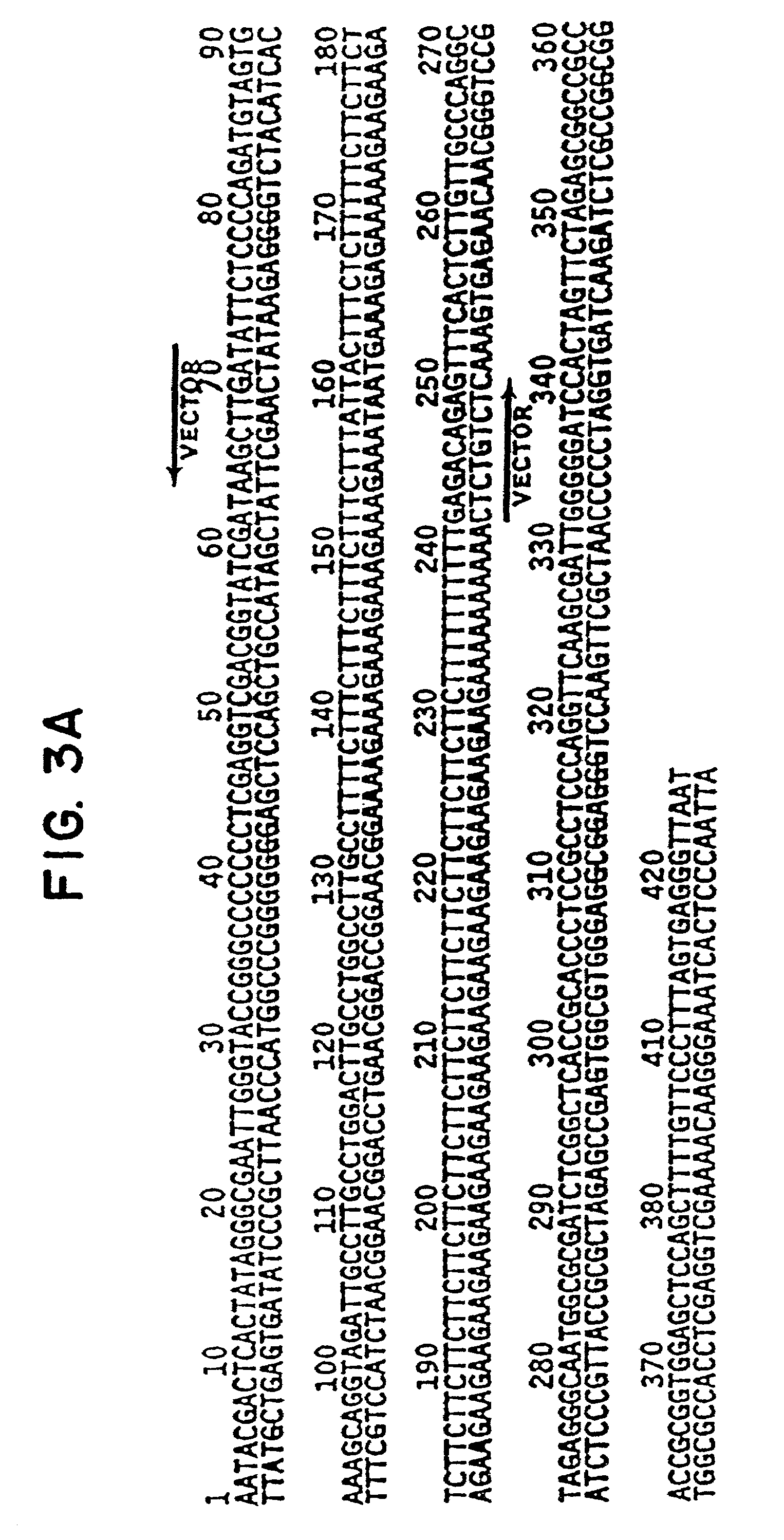
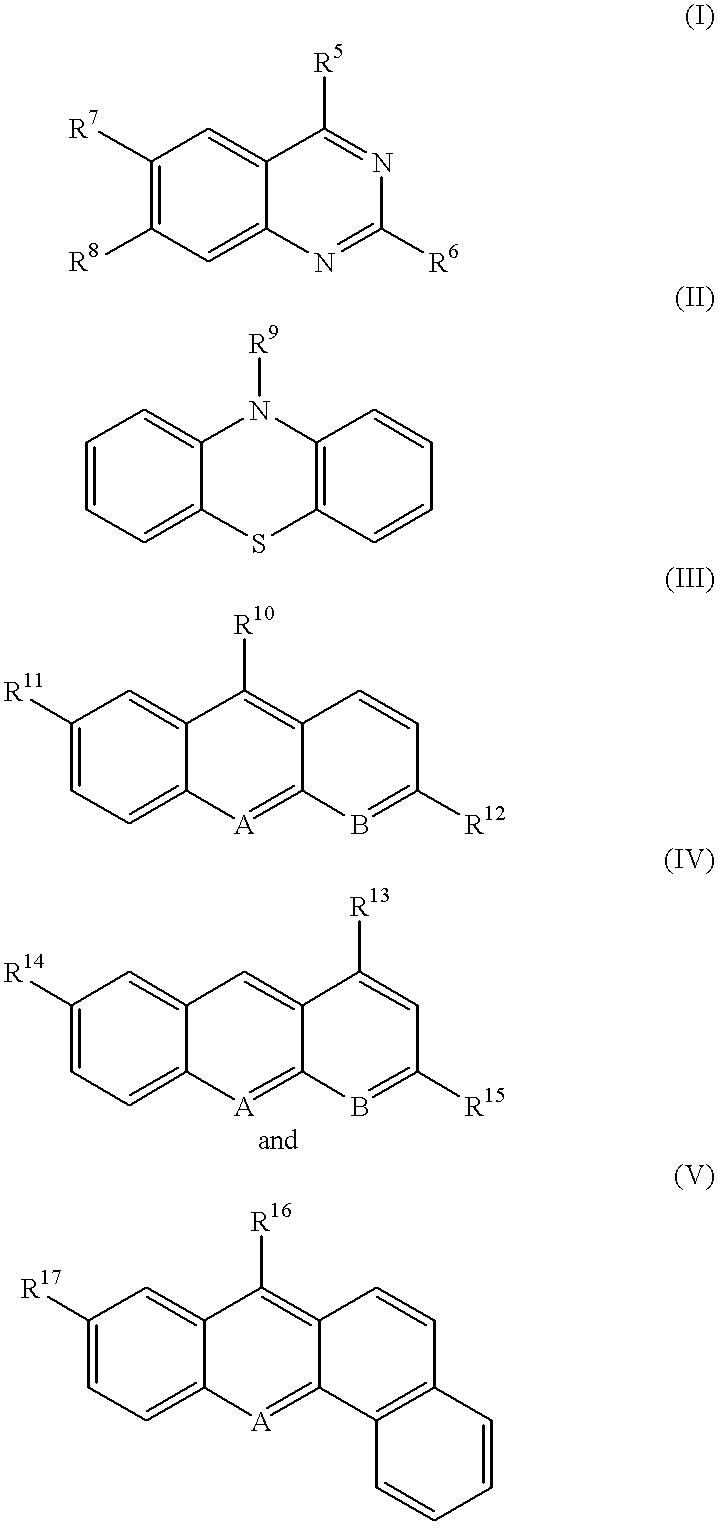
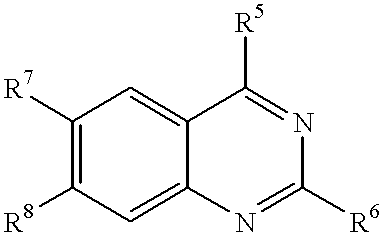
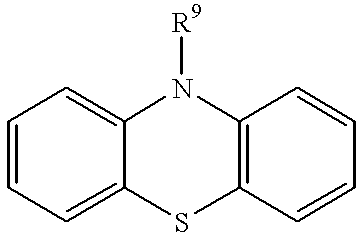
1-Azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-one derivatives and maleimide derivatives and their use for treating cancer tumors
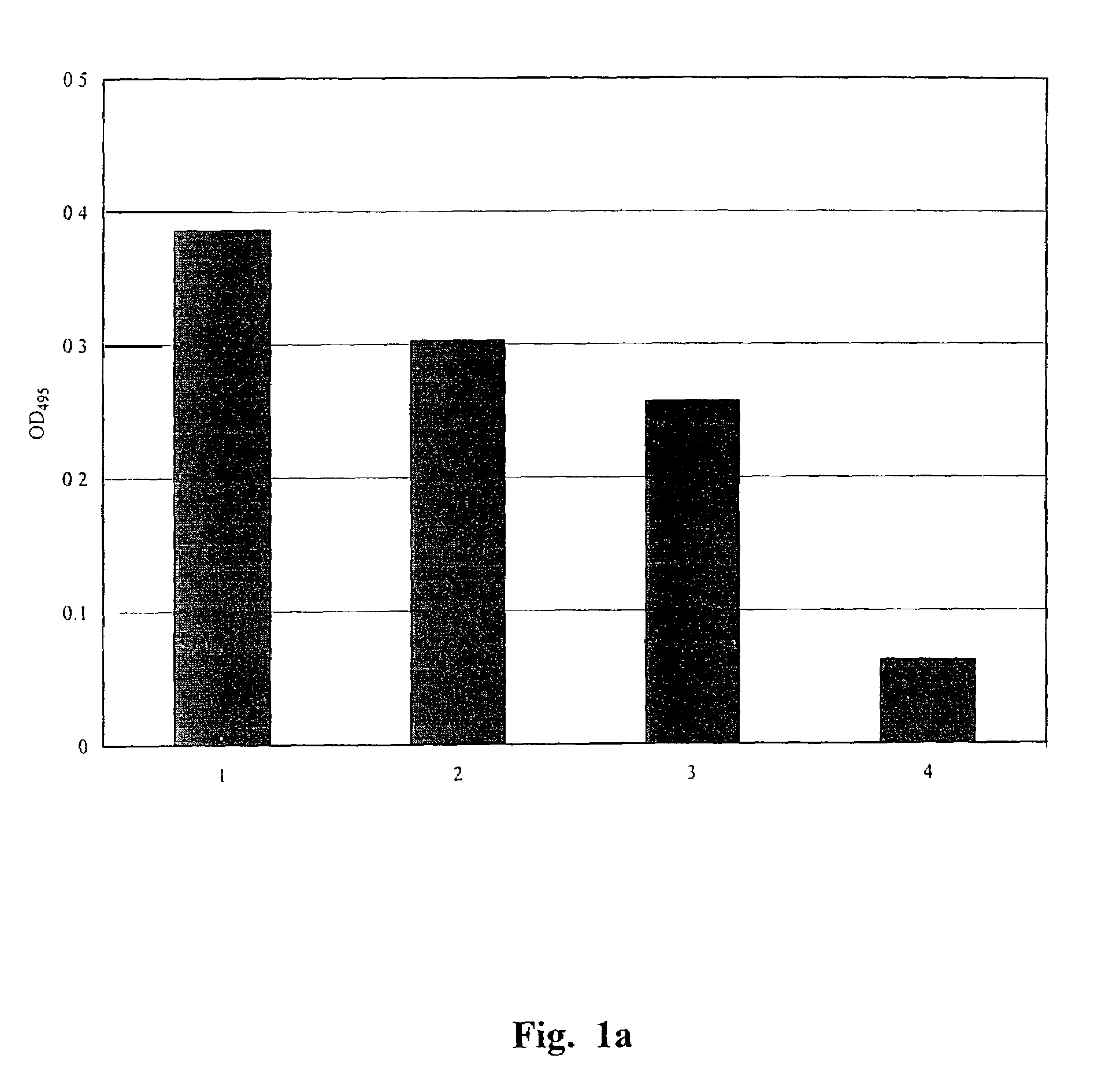
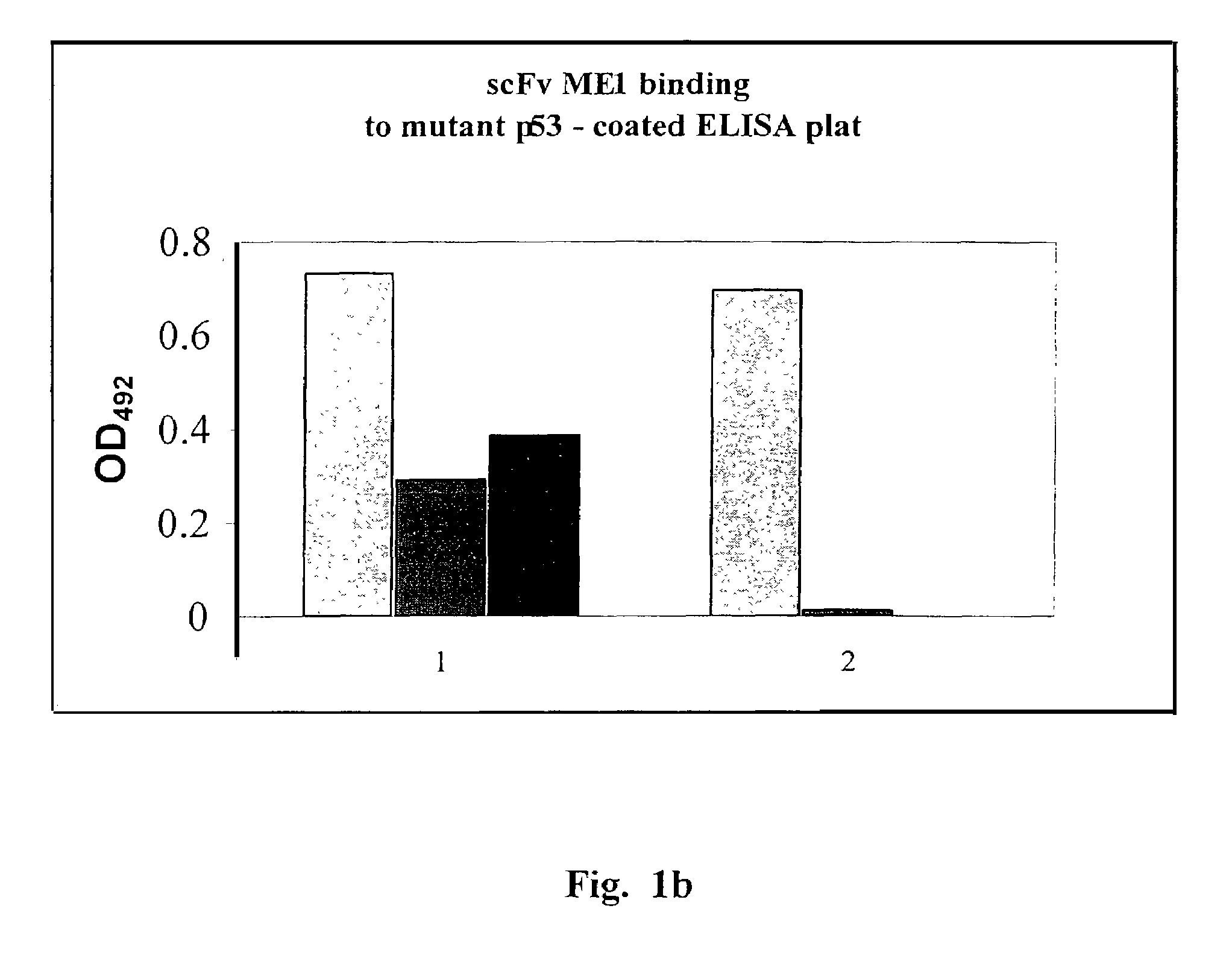
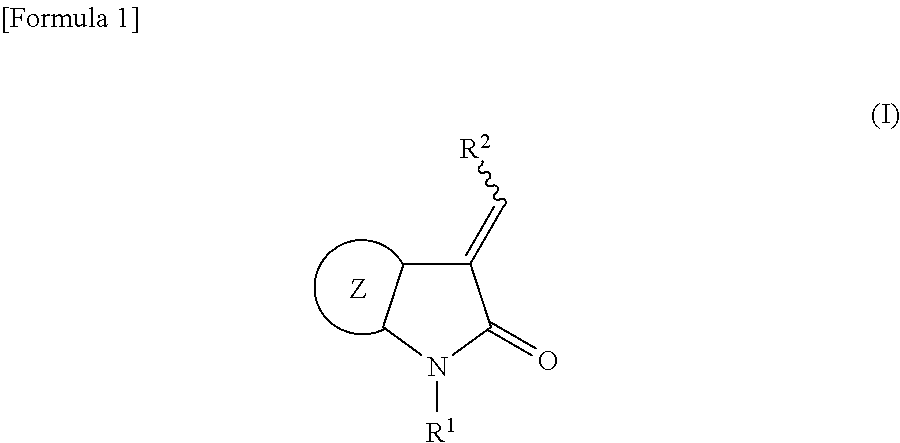
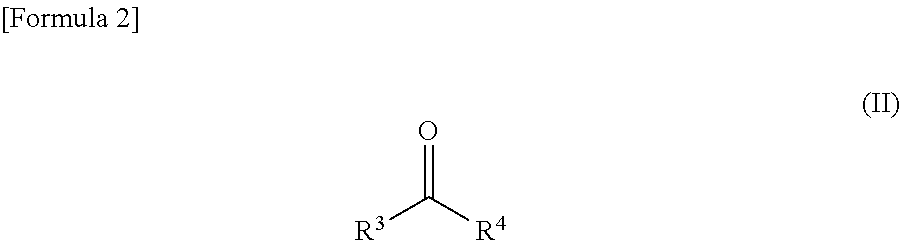
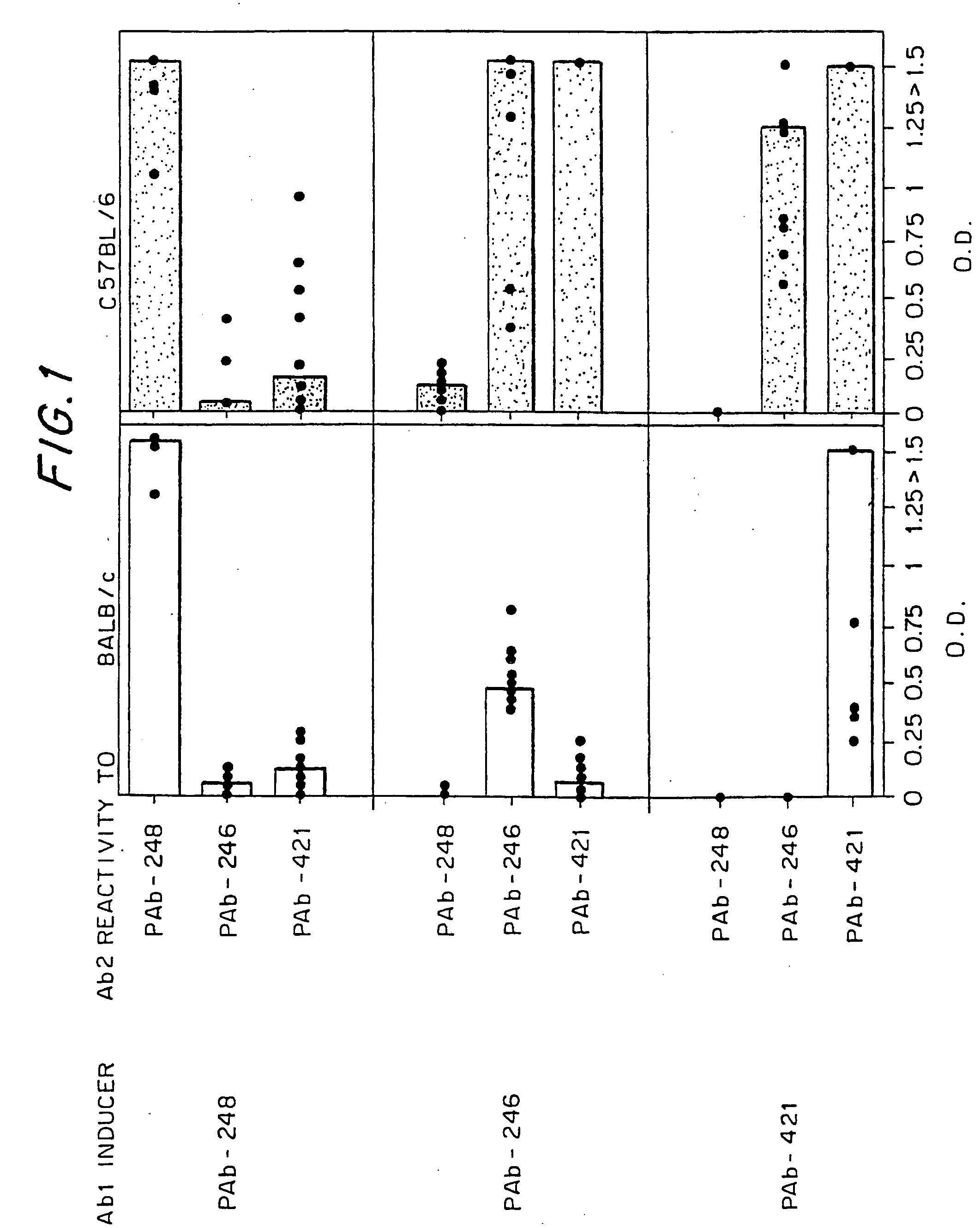
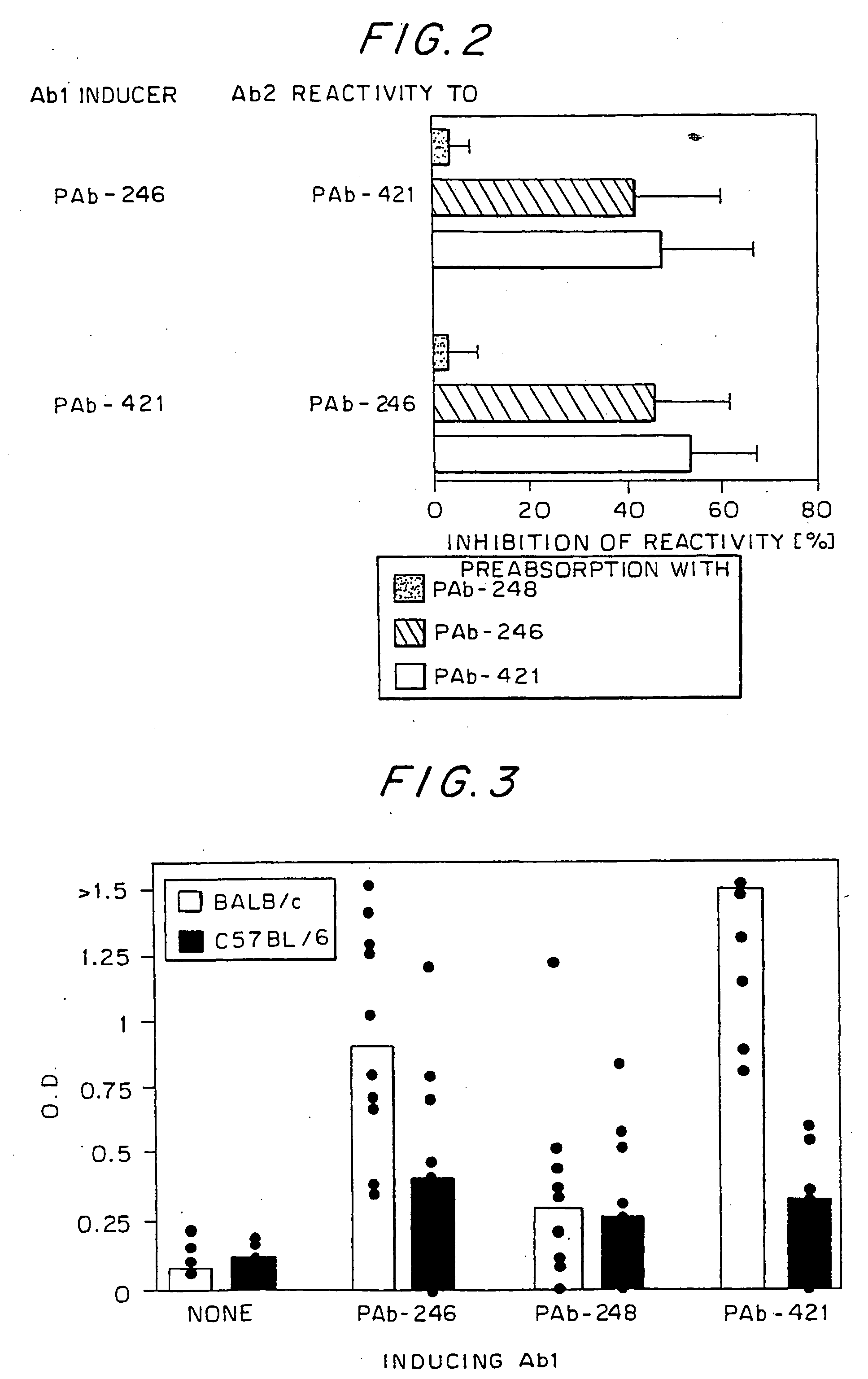
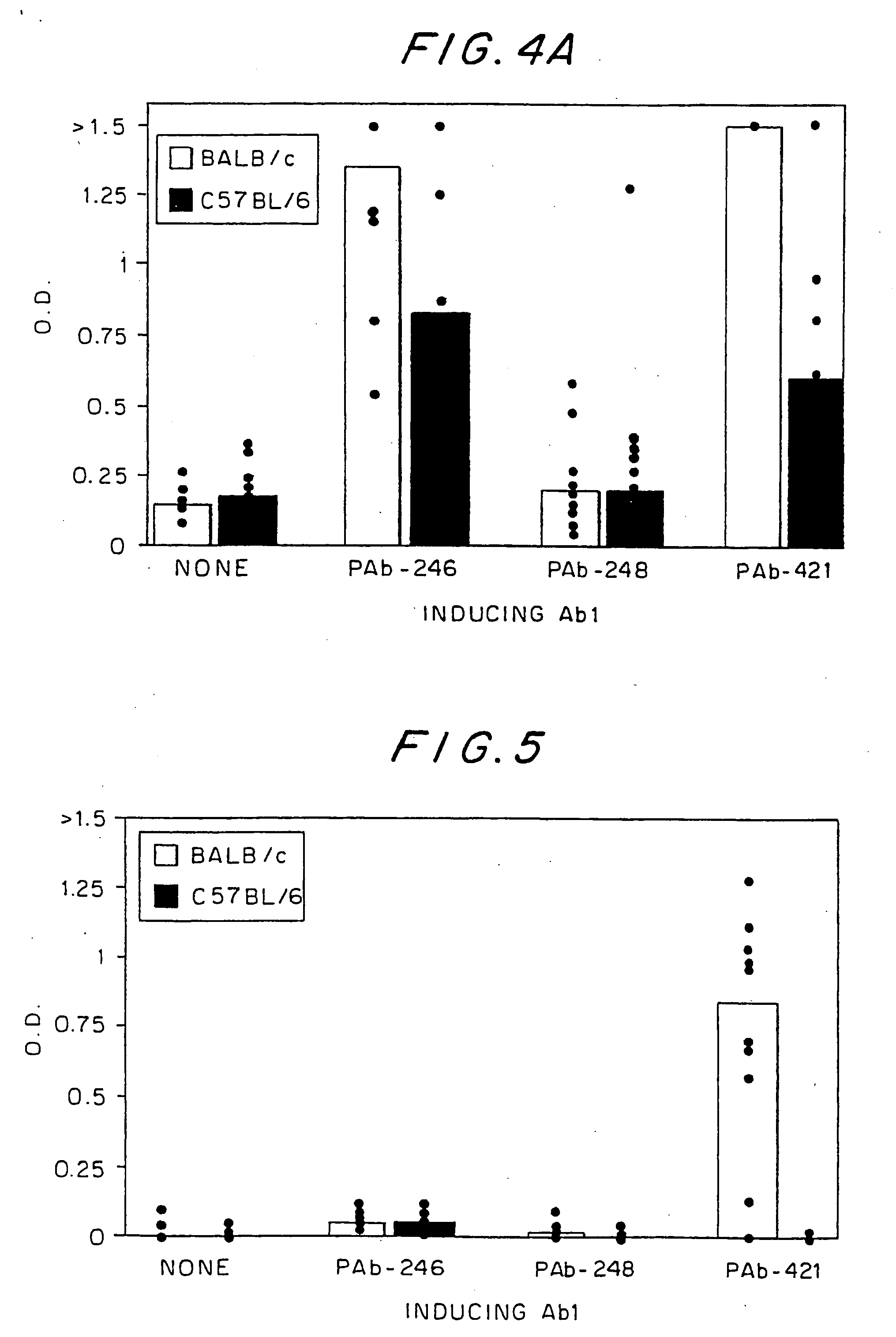
The present invention provides novel compounds, corresponding to formulae I and II, respectively, which are able to reactivate the apoptosis-inducing function of mutant p53 proteins. This reactivation is provided by restoration of sequence-specific DNA-binding activity and transcriptional transactivation function to mutant p53 proteins, and modulation of the conformation-dependent epitopes of the p53 protein. Accordingly, the substances according to the invention will be used in pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treatment of patients suffering from various types of tumors.
Owner:APREA THERAPEUTICS AB
High-sensitivity protein detection method
InactiveCN103276087ALow costGood effectMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingCross-linkProtein detection
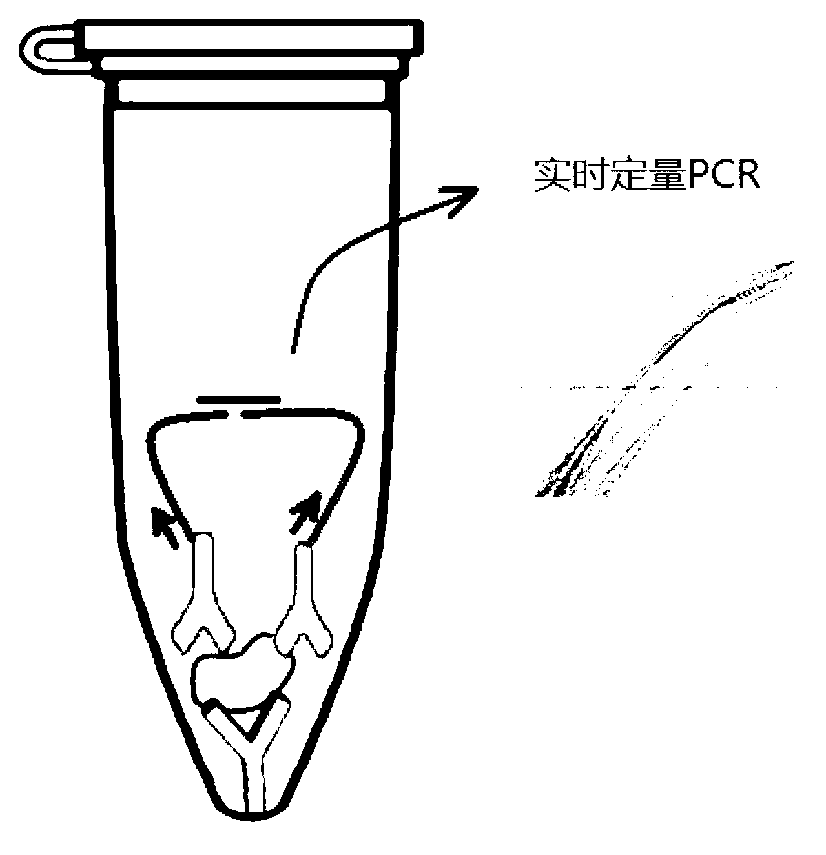
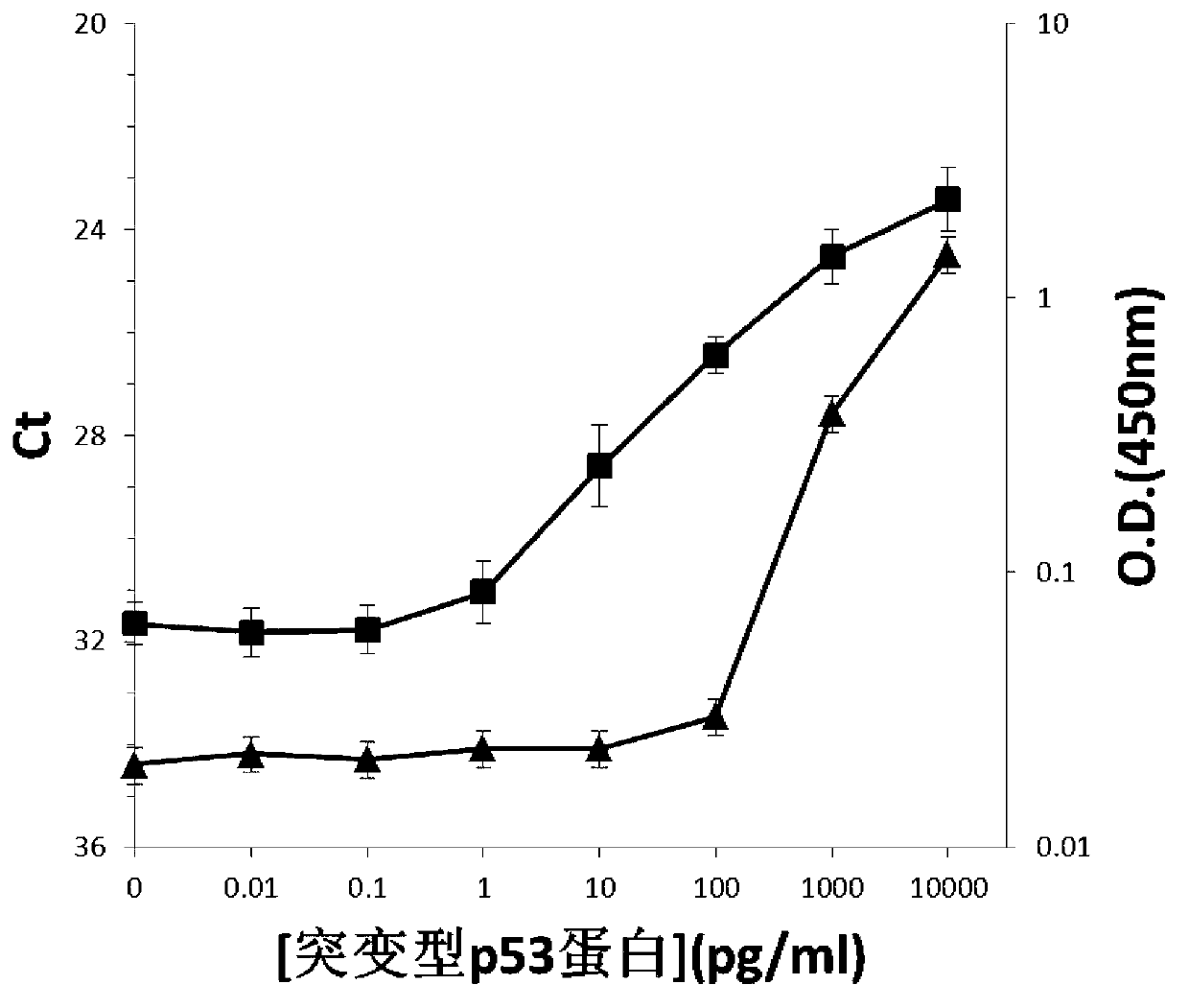
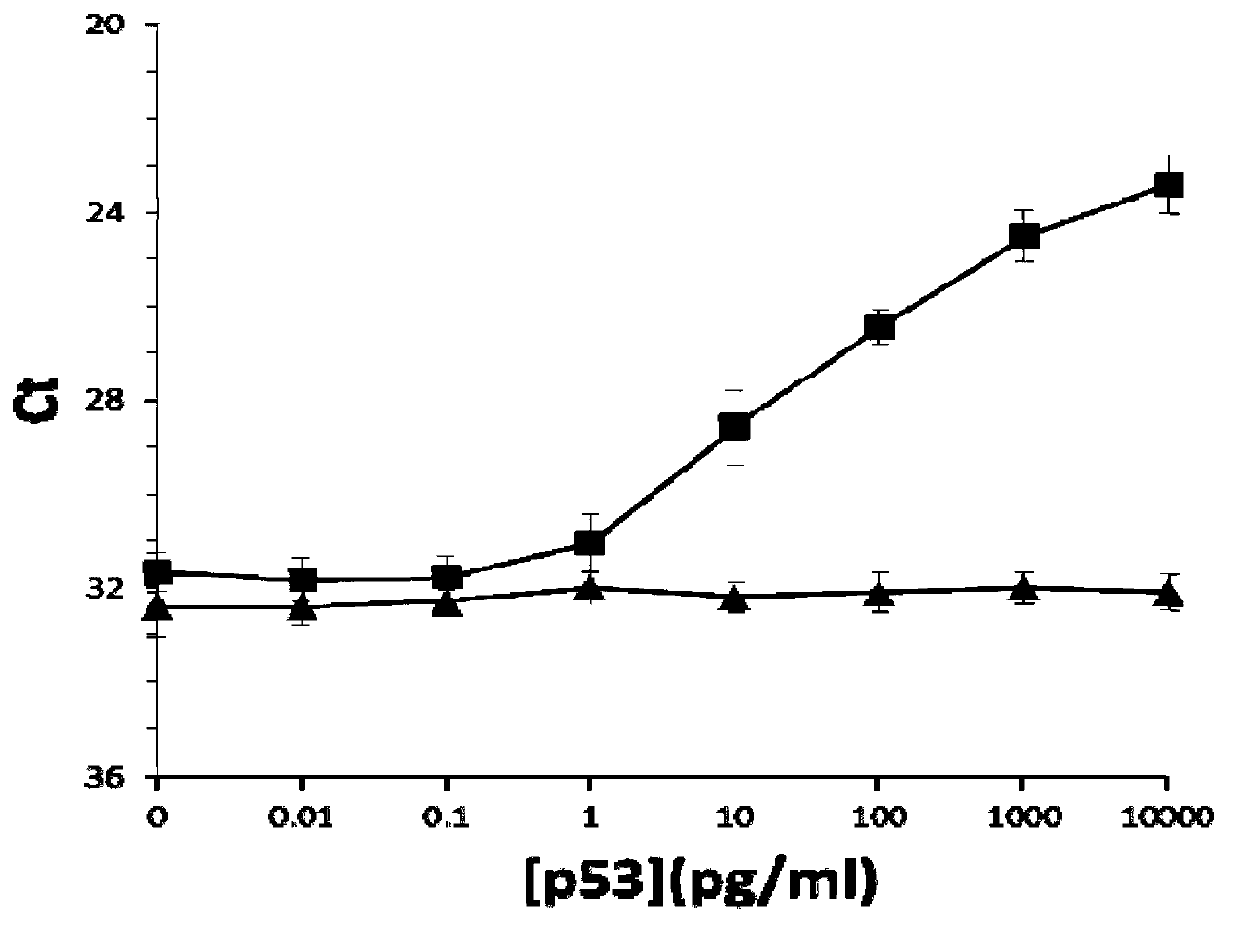
The invention discloses a high-sensitivity protein detection method, wherein one of the following modes is selected optionally: mode 1, performing a tube wall solid phase PLA (proximity ligation assay) by a direct coating method, namely, directly adsorbing the protein or the antibody to a real-time fluorescence quantification PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) tube wall to perform PLA detection; and mode 2, performing a tube wall solid phase PLA by a cross-linking agent fixing method, namely, cross-linking the protein or the antibody to the real-time fluorescence quantification PCR tube wall by glutaraldehyde to perform PLA detection. Specifically, the method comprises the following steps of: using a monoclonal antibody pab240, and sequentially establishing PLA detection of P53 protein (P53 protein mutant) and cTnI (cardiac troponin I). According to the method disclosed by the invention, the antibody is fixed on a PCR tube so as to perform protein PLA detection, magnetic beads are not needed in the detection process, defects caused by application of the magnetic beads are overcome, and the detection sensitivity to the protein is also improved greatly.
Owner:HANGZHOU JINXI BIOLOGICAL TECH
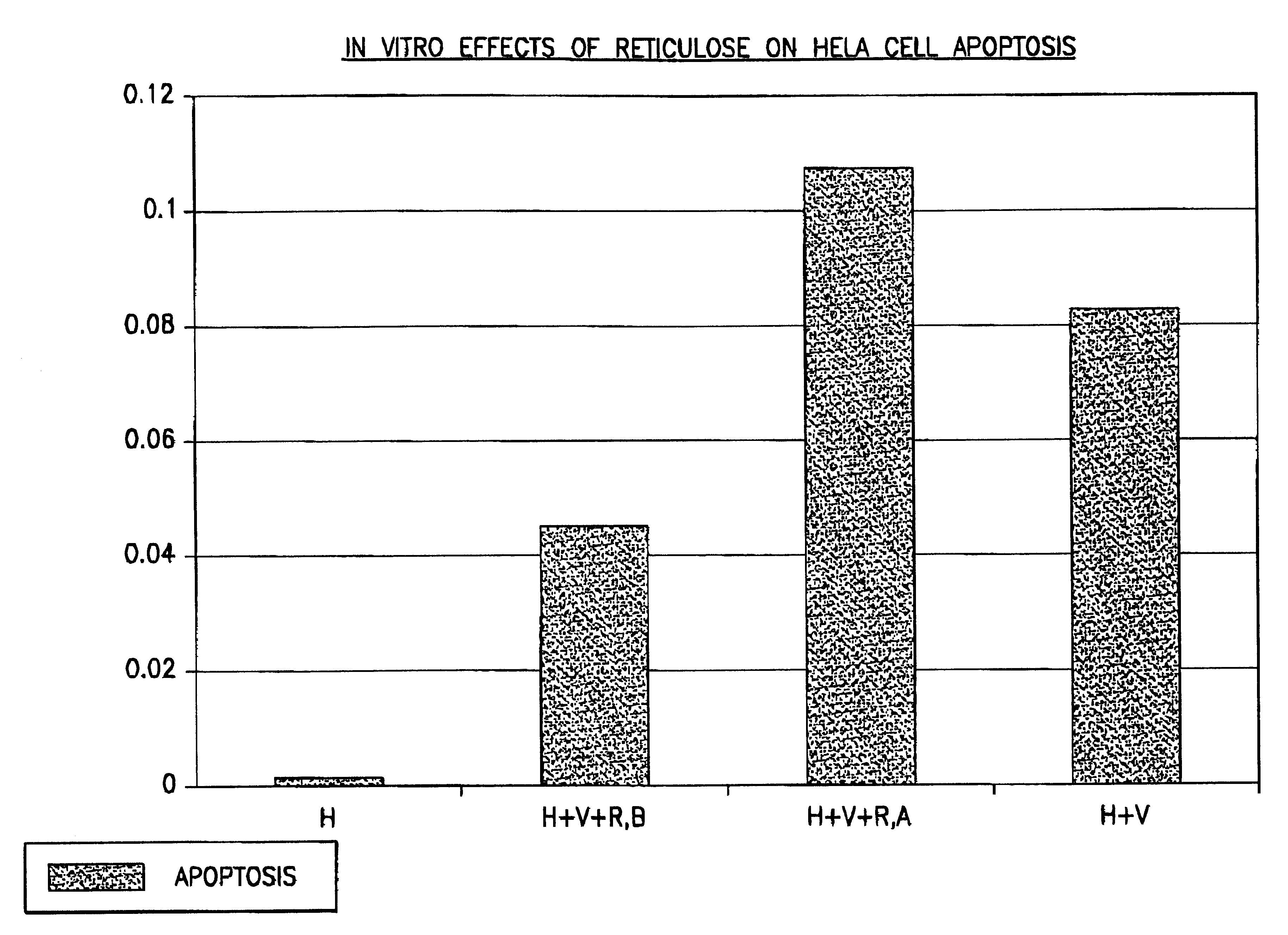
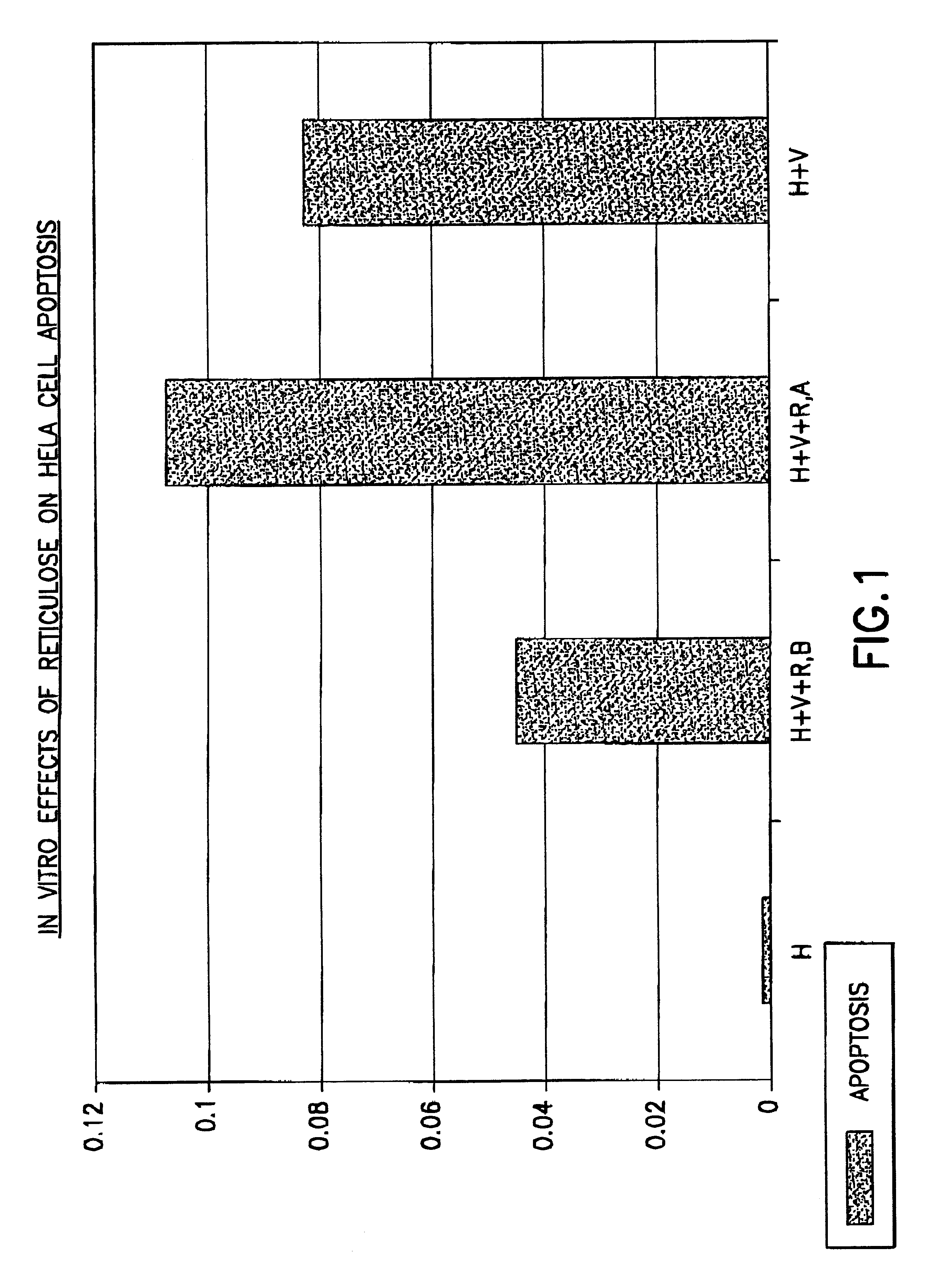
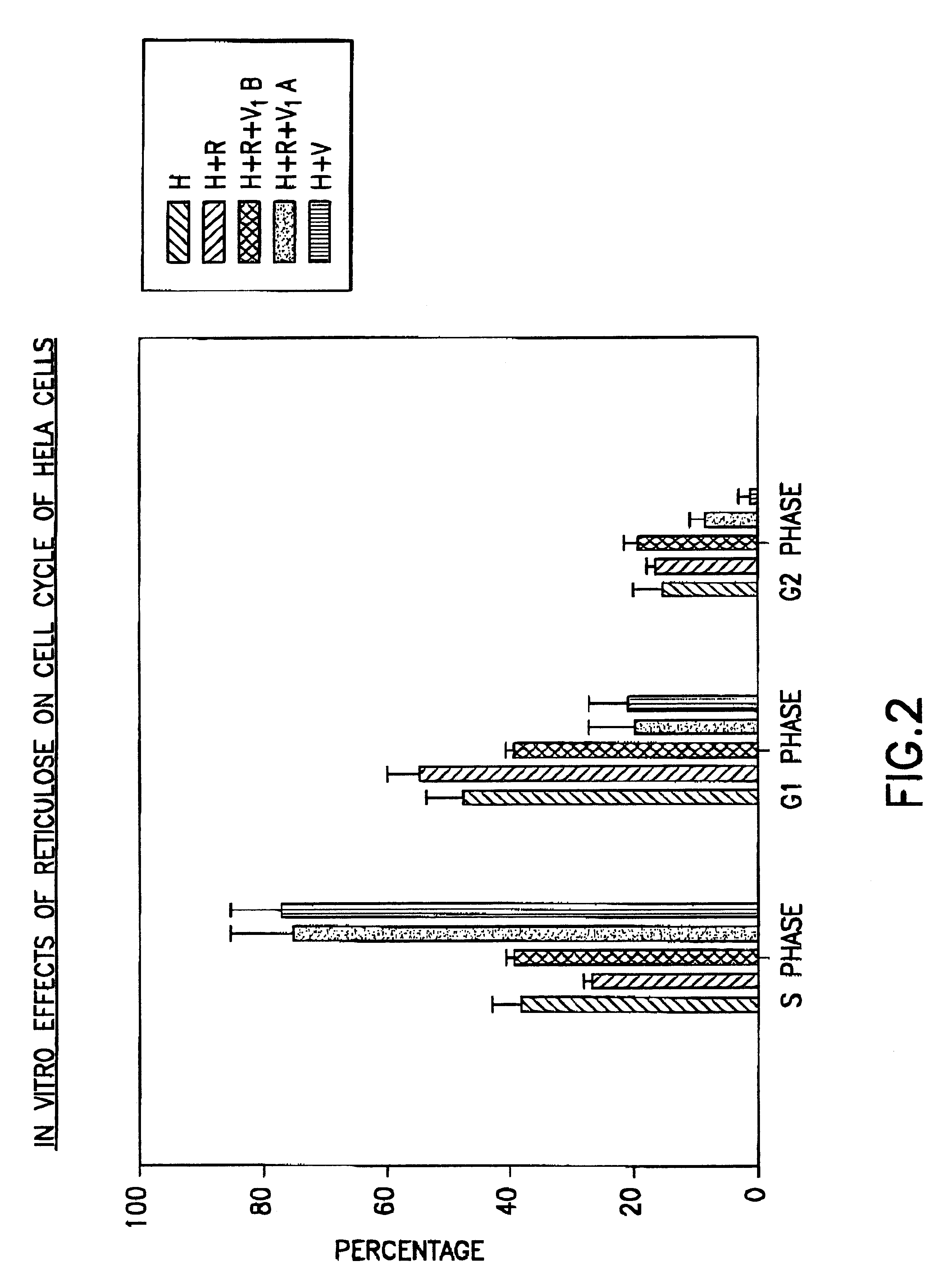
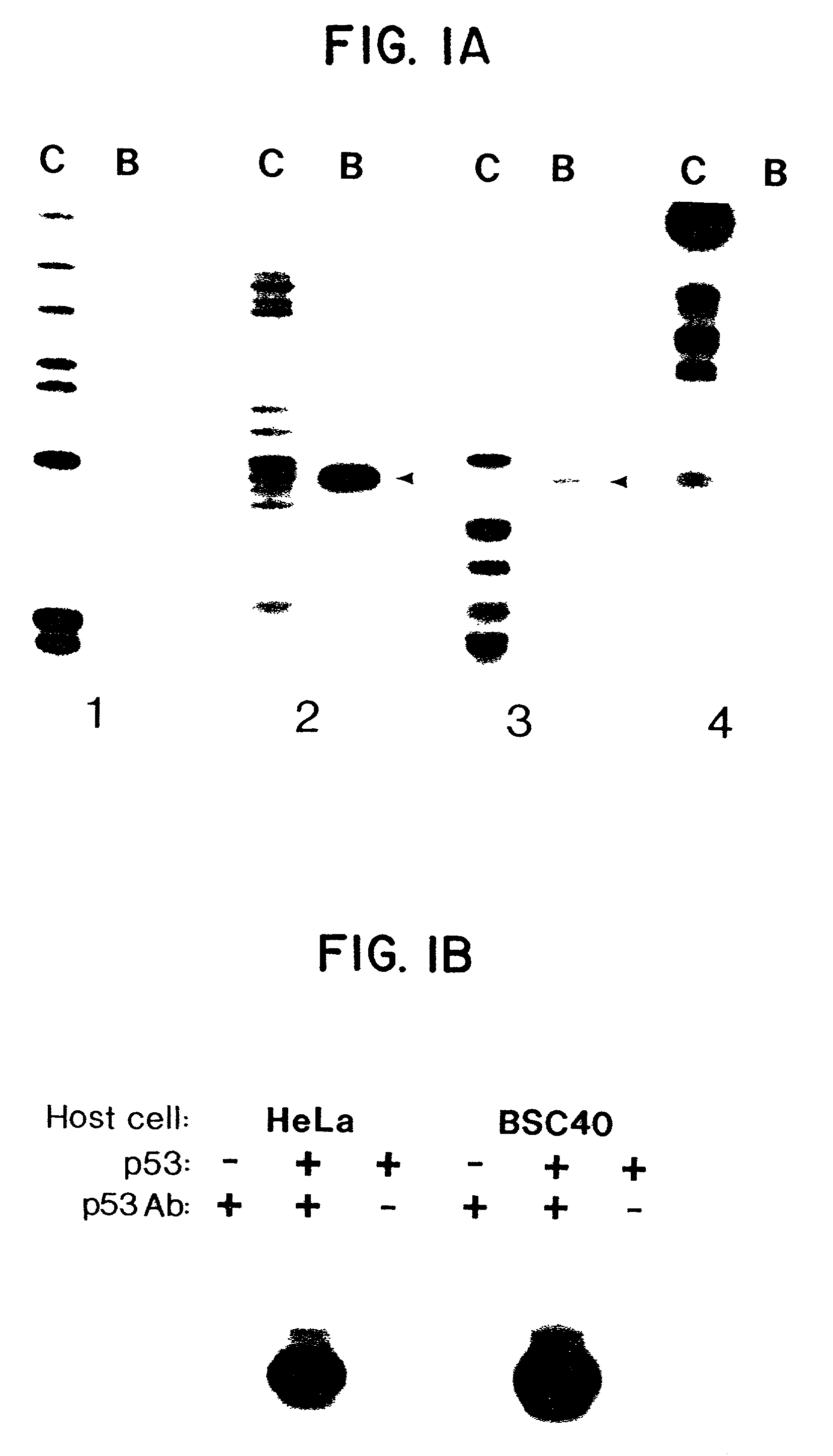
Assay method for determining Product R's effect on adenovirus infection of Hela cells
InactiveUS6440658B1Avoid virus infectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingDNA fragmentationAdenovirus diseases
An assay method for determining the effect of Product R on virus infection of Hela cells. The method comprising the following step: (1) dividing Hela cells into several groups, (2) treating one group with Product R prior to infecting the cells with a virus and treating another group with Product R after the cells being infected with the virus, and (3) determining the effects of Product R on virus infection by comparing the changes in the cell cycle, DNA fragmentation and p53 protein in cells undergone the different treatments in step (2).
Owner:BBM HLDG
Method for Treating Cancer Harboring a p53 Mutation
InactiveUS20130281493A1Preventing or delaying the onset (or reoccurrence)Reduce the possibilityBiocideOrganic chemistryCancer cellFhit gene
A method for determining if a subject with cancer or precancerous lesions or a benign tumor, will respond to treatment with an inhibitor selected from the group comprising an inhibitor of one or more enzymes in the mevalonate pathway, an inhibitor of geranylgeranyl transferase, an inhibitor of farnesyl transferase or an inhibitor of squalene synthase, by (i) obtaining a sample of the cancer cells, precancerous cells or benign tumor cells from the subject, (ii) assaying the cells in the sample for the presence of a mutated p53 gene or a mutant form of p53 protein or a biologically active fragment thereof, and (iii) if the cells have the mutated p53 gene or mutant form of the p53 protein, then determining that the subject will respond to treatment with the inhibitor or combinations thereof. Some embodiments are directed to treatment with the inhibitors.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
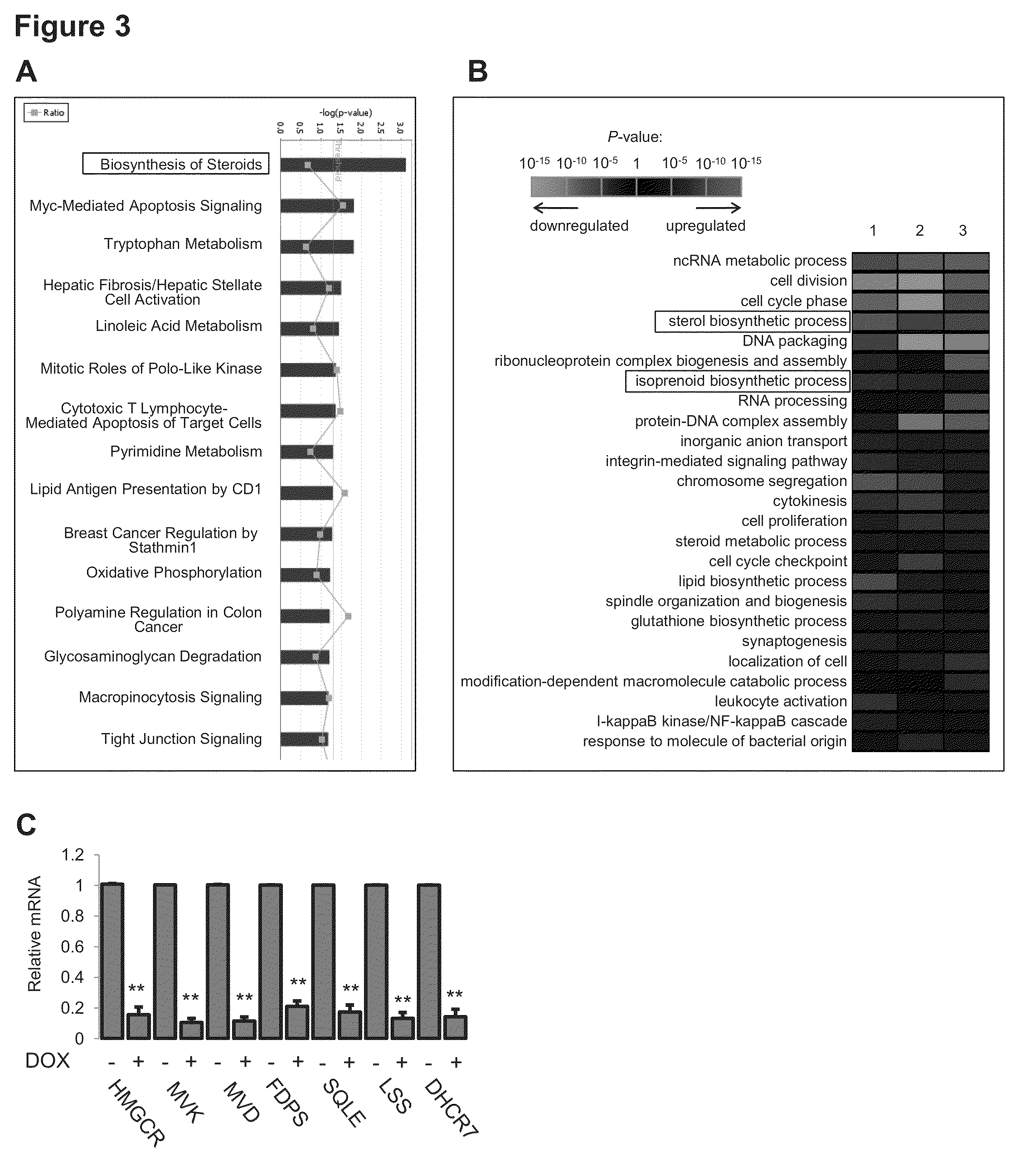
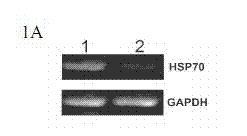
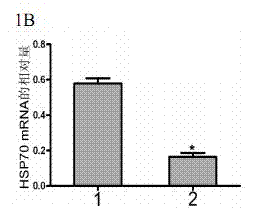
Method for regulating expression, quantity and activity of heat shock protein 70 and application thereof
ActiveCN102816792AIncreased sensitivityAdded treatment strategyPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsDeath ReceptorsTranscription Factor NF-kB
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and in particular relates to a method for regulating expression, quantity and activity of a heat shock protein 70 and application thereof. The method provided by the invention can also regulate tumor tissue, activity of a transcription factor NF-kB, expression and activity of a death receptor DR4 and DR5, phosphorylation and activity of JNK and c-Jun, expression and activity of a p53 protein, expression and proapoptotic activity of proapoptotic molecules Bax, Bid, t-Bid, capsase 3, capsase 8 and capsase 9, and expression and activity of c-FLIP and Bcl-2, and promote apoptosis of tumor tissues and cells. The invention also relates to application of the above method to preparation of drugs cooperatively applied with cell apoptosis induced drug.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
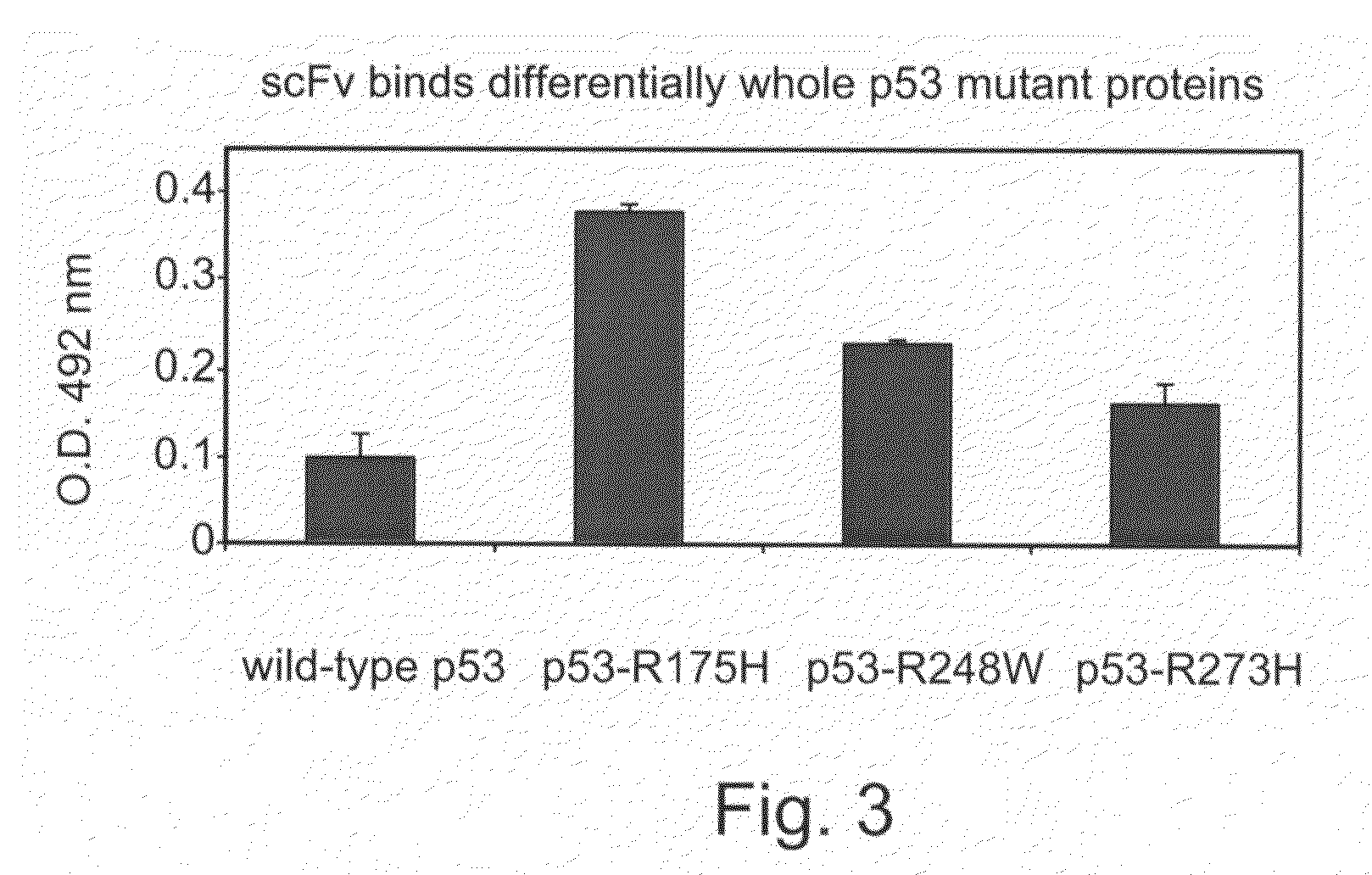
Single chain antibody against mutant p53
InactiveUS7288637B2Strong specificityImprove effectivenessAnimal cellsSugar derivativesEpitopeSingle-Chain Antibodies
More than 90% of mutations found in the p53 protein produce a conformational change in p53 which results in the exposure of an epitope, which is otherwise hidden in the hydrophobic core of the molecule. A single chain antibody (scFv) which specifically recognizes this common mutant epitope in mutant p53 but not in wild type p53 is disclosed. Also described are a DNA molecule encoding the scFv, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the antibody and methods of treatment using the pharmaceutical compositions.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Method for producing spirooxindole derivative
ActiveUS20160194331A1Efficient and inexpensive mannerAvoid interactionOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalytic reactions1,3-Dipolar cycloadditionMdm2 Protein
The present invention is intended to provide a method for efficiently producing and providing a compound having a spirooxindole skeleton, for example, a compound having a spirooxindole skeleton and having antitumor activity that inhibits the interaction between Mdm2 protein and p53 protein, or an intermediate thereof, using an asymmetric catalyst. A compound having an optically active tricyclic dispiroindole skeleton is efficiently obtained through a catalytic asymmetric 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reaction using ketimine as a reaction substrate and using a chiral ligand and a Lewis acid.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
PEPTIDES CAPABLE OF REACTIVATING p53 MUTANTS
ActiveUS20190315804A1Efficiently reactivatePromote activationPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemDiseaseWild type
The invention provides peptides that can reactivate p53 mutants efficiently and specifically, as well as methods that allow the identification, selection and isolation of such peptides, in a precise, cost and time effective manner. In particular, there are provided mutant p53 reactivating peptides that can restore the native wild type p53 folding, and hence the tumor suppressor activity, to the mutant p53 protein. Such peptides are useful for treating various conditions and diseases in which p53 is mutated.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Inhibition of pulmonary fibrosis with nutlin-3a and peptides
ActiveUS20160272678A1Prevent proliferationEffective treatmentPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifOrganic active ingredientsCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
In fibrotic lung fibroblasts, basal levels of p53 protein (and miR-34a) are markedly suppressed, leading to reduced p53-mediated inhibition of uPA and uPAR, or concurrent induction of PAI-1. These changes contribute to excessive FL-fibroblast proliferation and production of extracellular matrix (ECM), and, therefore, pulmonary fibrosis. These processes are reversed by treating the cells, and treating subjects suffering from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) with the small organic molecule nutlin-3a (NTL) or with a peptide, CSP-4 (SEQ ID NO:1), or variants or derivatives or multimers of this peptide, which increase p53 levels by inhibiting MDM2-mediated degradation of p53 protein. Use of these compounds serves as a new approach to the treatment of IPF, they restore p53 expression and p53-mediated changes in the uPA-fibrinolytic system in FL-fibroblasts and restrict production and deposition of ECM.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
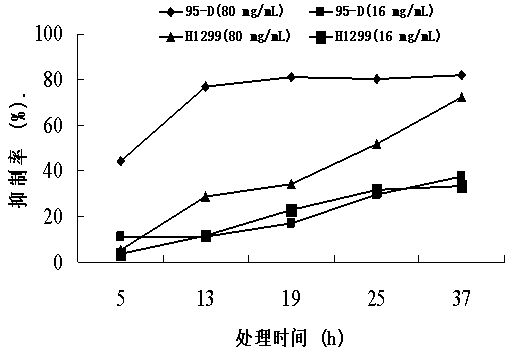
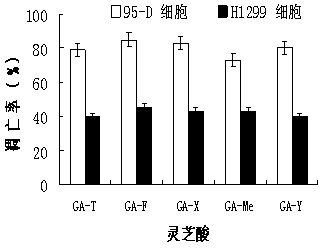
Inhibitor by virtue of interaction of P53-MDM2 and applications of inhibitor
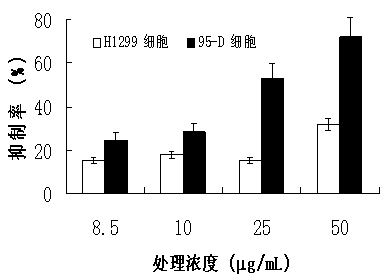
InactiveCN104188976AInhibitory activityPromote apoptosisOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsGanoderic acid TPharmacometrics
The invention discloses an inhibitor by virtue of interaction of P53-MDM2 and applications of the inhibitor. The inhibitor by virtue of interaction of P53-MDM2 is ganoderic acid X, ganoderic acid Me, ganoderic acid Y, ganoderic acid T or ganoderic acid F or a composition formed by combining one of ganoderic acid X, ganoderic acid Me, ganoderic acid Y, ganoderic acid T and ganoderic acid F with pharmacologically acceptable additive components. The inhibitor by virtue of interaction of P53-MDM2, disclosed by the invention, is applied to promotion of the apoptosis of tumor cells and particularly applied to promotion of the apoptosis of the 95-D lung cancer cells expressing P53 proteins or H1299 lung cancer cells not expressing the P53 proteins; the inhibitor by virtue of interaction of P53-MDM2, disclosed by the invention, has the effects of remarkably inhibiting the activity of MDM2 in human malignant lung cancer cells, thereby inhibiting the degradation of the P53 proteins and further promoting the apoptosis of the tumor cells containing P53.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
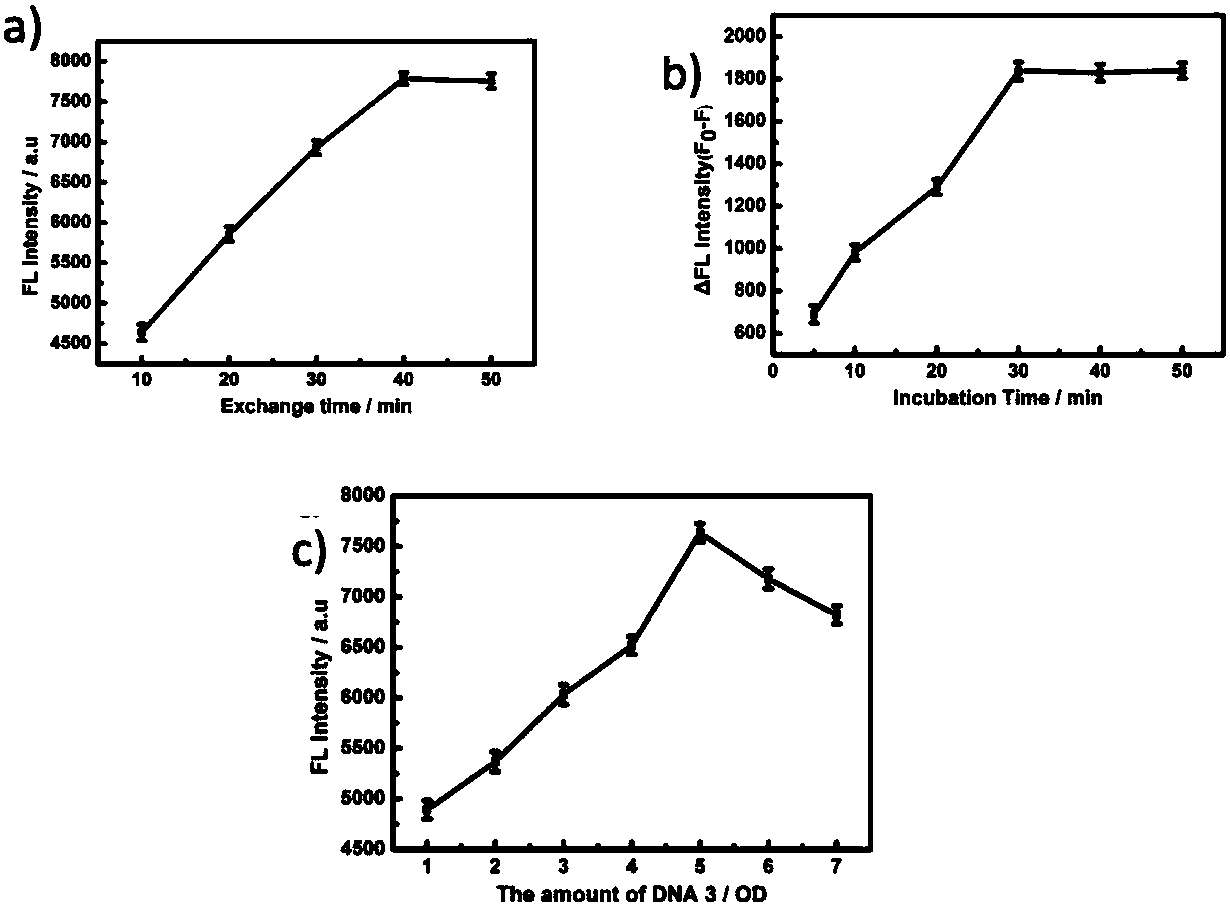
Fluorescence detection agent for p53 protein, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a fluorescence detection agent for a p53 protein. The fluorescence detection agent comprises a magnetic nano-particle, double-stranded DNA, and a functional layer coating the surface of the magnetic nano-particle and connected with the double-stranded DNA; the double-stranded DNA is obtained through hybridizing DNA-1 single strand and DNA-2 single strand; the DNA-1 is a carboxyl oligonucleotide probe, and the sequence is COOH-(CH2)6-TTT TTT TCC GGG CAT GCC CGG CAT TGC-3'; and the DNA-2 is the partial complementary sequence of the DNA-1, and the sequence is 5'-GGG CAT GCC C-3'. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the fluorescence detection agent, and an application of the fluorescence detection agent in the detection of the wild p53 protein. The agent has the advantages of low preparation cost, realization of sensitive, rapid and accurate capture of the p53 protein, realization of ultra-sensitive, highly- selective and highly-accurate detection of the p53 protein, low detection limit, and realization of quantitative analysis and detection of the p53 protein in normal cells and cancer cell lysate, and can be used in clinical diagnosis and early detection of cancers.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Hybrid protein of p53 protein epitope(SQAMDDLMLS) and filobactivirus gene 8 protein and application thereof
This invention belongs to the DNA recombination field in bioengineering. Wherein, with the recombination technique, inserting the gene fragment of B cell epitope composed by 37-46 peptide fragments on N-end of P53 protein into the carrier integrated with main coat protein gene of filamentous phage to form the new recombinant plasmid; in host, secreting the epitope gene product out of the cell to assemble in coat protein and form heterozygous protein that can be used as a antigen to detect antibody in clinical tumor patient serum (such as, gastric cancer, liver cancer, breast cancer and lung cancer).
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
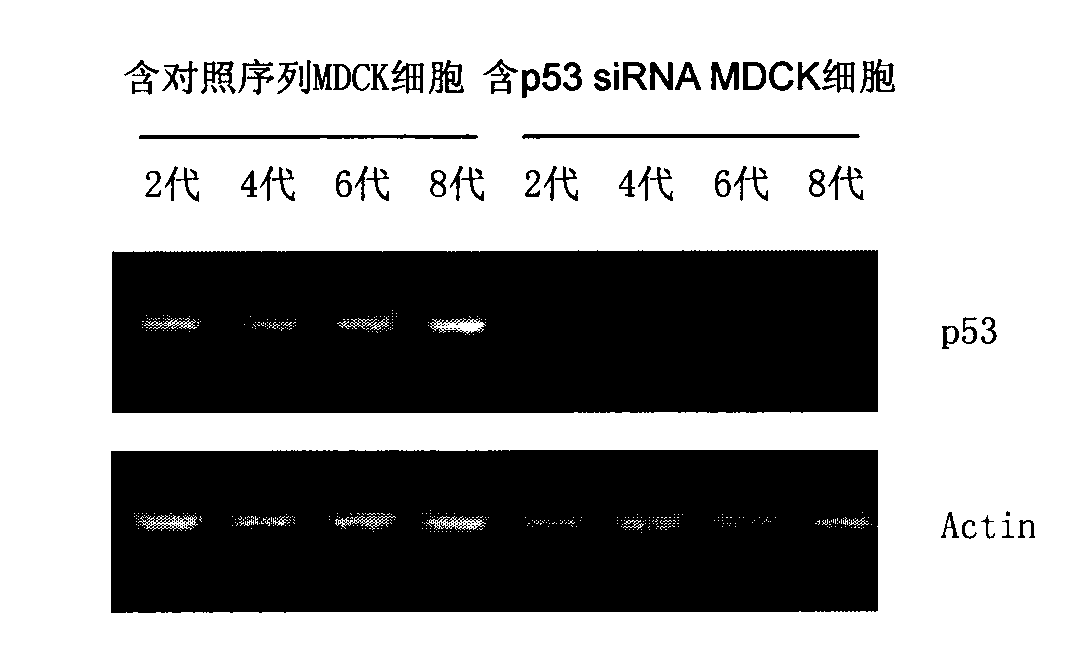
SiRNA for inhibiting canine p53 gene expression and canine cell model of p53 gene silence
The invention discloses a small interfering RNA (siRNA) for inhibiting canine p53 gene expression. The sequence of the siRNA is shown as SEQ ID No: 1 or SEQ ID No: 2 in a sequence table. The invention also discloses a DNA for coding the siRNA and a recombinant vector containing the siRNA or the DNA. Preferably, the recombinant vector is a slow virus vector for infecting a canine cell to obtain a canine cell model of p53 gene silence. The canine p53 gene siRNA sequence can effectively degrade mRNA of p53 genes so as to inhibit the expression of the p53 genes. By using the siRNA sequence for interfering with the expression of the canine p53 genes, on the one hand, a treatment medicament for diseases related with the p53 genes such as cell apoptosis related diseases can be prepared; and on the other hand, the established p53 knock down cell model has great significance for researching the effect of p53 protein on innate immunity of cells and possible specific mechanisms.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Separation and purification method of wild-type p53 protein
InactiveCN102212525AKeep aliveHigh yieldPeptide preparation methodsFermentationHigh concentrationProtein target
The invention belongs to the related fields of biomedical products and clinical detection and the like, and mainly relates to a new method for separating and purifying wild-type p53 protein. The separation and purification method of the wild-type p53 protein comprises cloning of a p53 gene, construction of recombinant expression plasmid, protein induced expression and purification, prokaryotic system-based inducible expression, ultrasonic cracking of thalli, and separation and purification of the p53 protein in the obtained cracked supernate by using nickel column affinity chromatography. High-concentration active target protein is separated and purified by the prokaryotic system-based inducible expression and the nickel column affinity chromatography in the ultrasonic cracked thalli supernate. Denaturation and renaturation of inclusion bodies are not performed, and the protein is directly purified from the ultrasonic cracked supernate, so that the activity of the target protein is furthest kept; and compared with the conventional method, the method has the advantage that: the yield of the target protein is greatly improved by optimizing the inducible expression and using a purification scheme.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Application of knocking out p53 gene in inhibiting proliferation and metastasis of glioma cells
ActiveCN107384956AGrowth inhibitionReduce proliferationGenetically modified cellsP53 proteinLymphatic SpreadWilms' tumor
The invention belongs to the technical field of tumor cells, and particularly relates to application of knocking out p53 genes in inhibiting proliferation and metastasis of glioma cells. According to technical scheme, the p53 genes in malignant glioma cells in a human body change by knocking out the p53 genes, thus p53 protein expression is reduced even completely deleted, and the purpose of inhibiting proliferation and metastasis of the glioma cells is achieved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
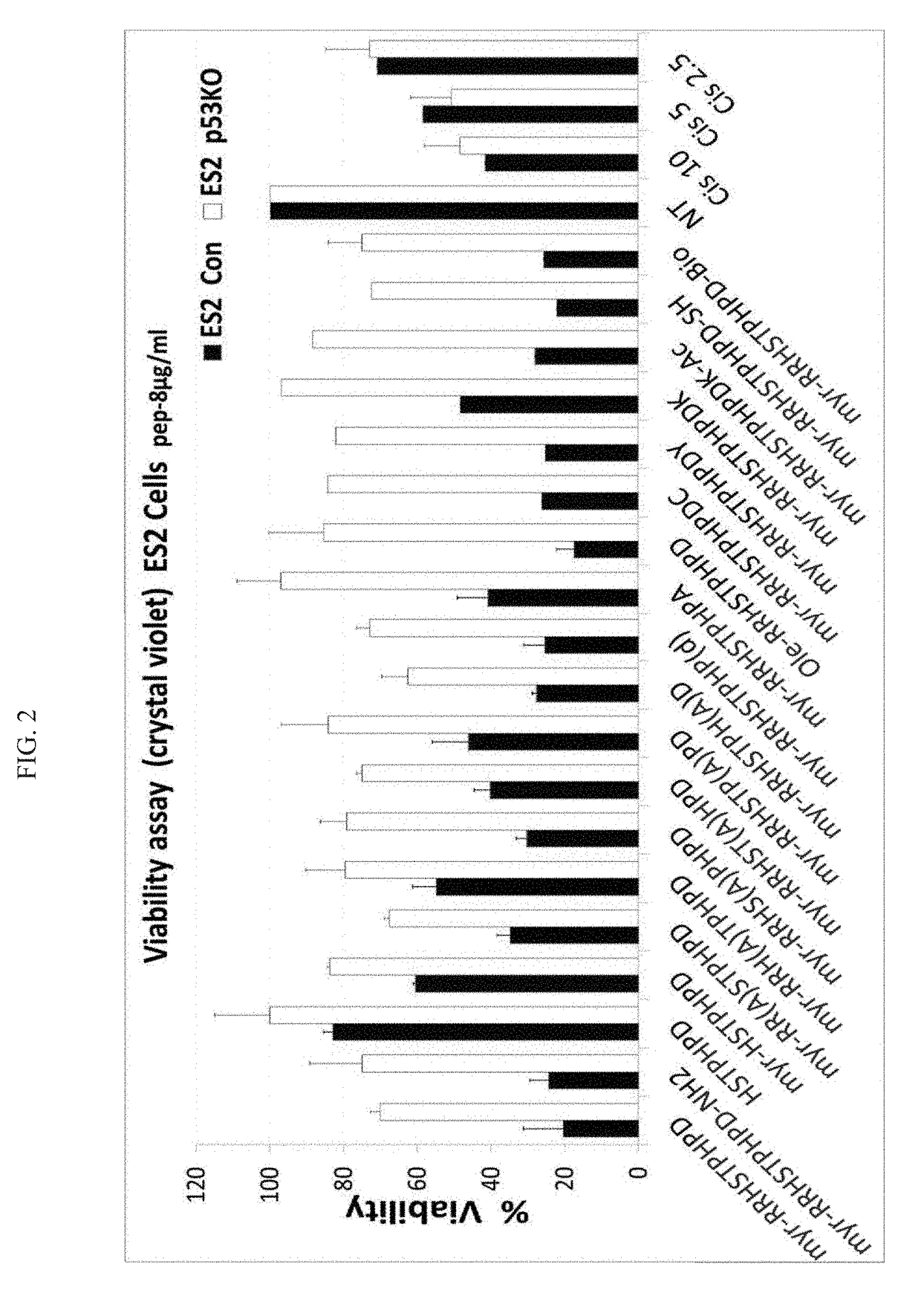
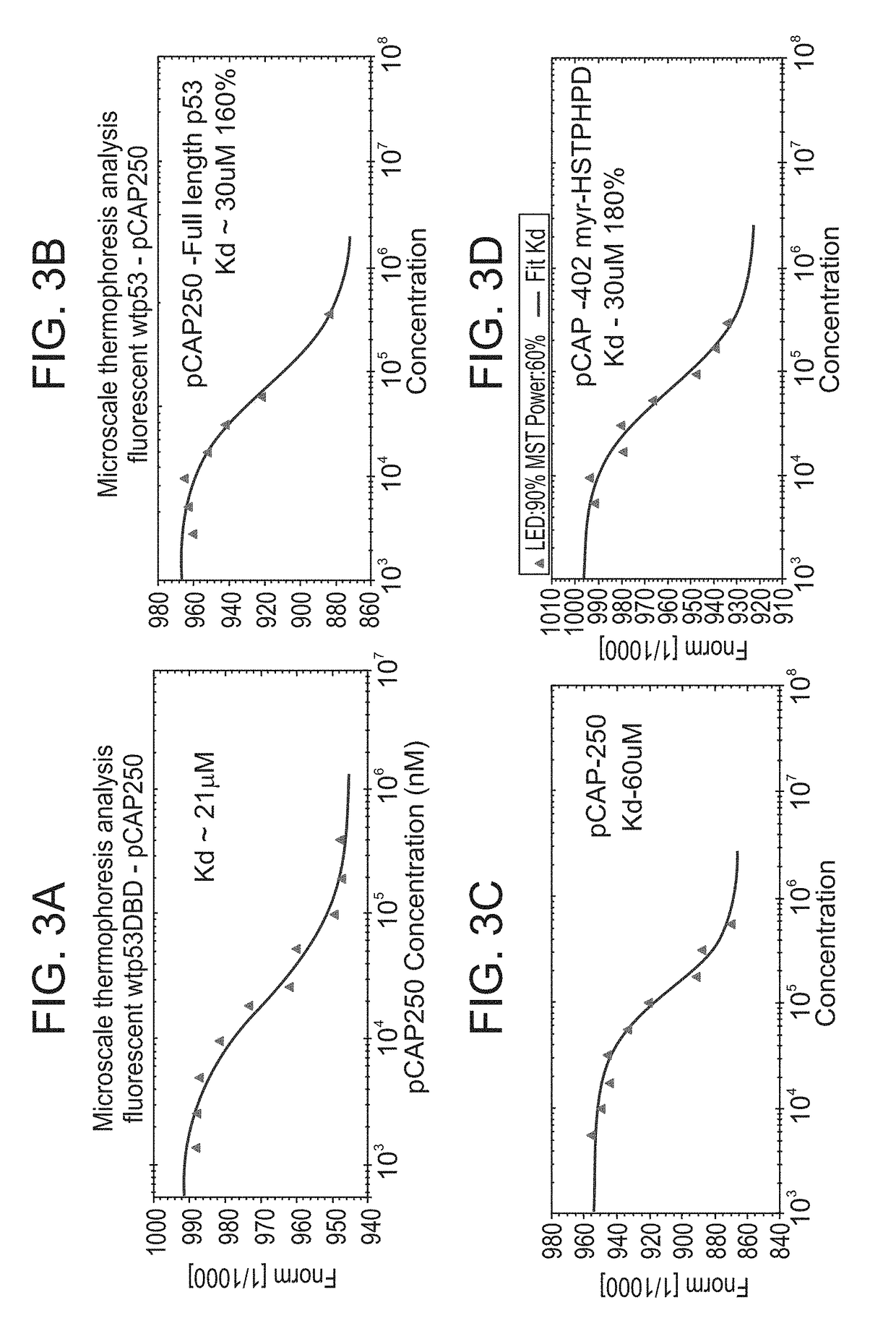
Peptides and use of same in the treatment of diseases, disorders or conditions associated with a mutant p53
ActiveUS20190048053A1Reduce cell viabilityReturn to normal activitiesPeptide/protein ingredientsP53 proteinDiseaseActivating mutation
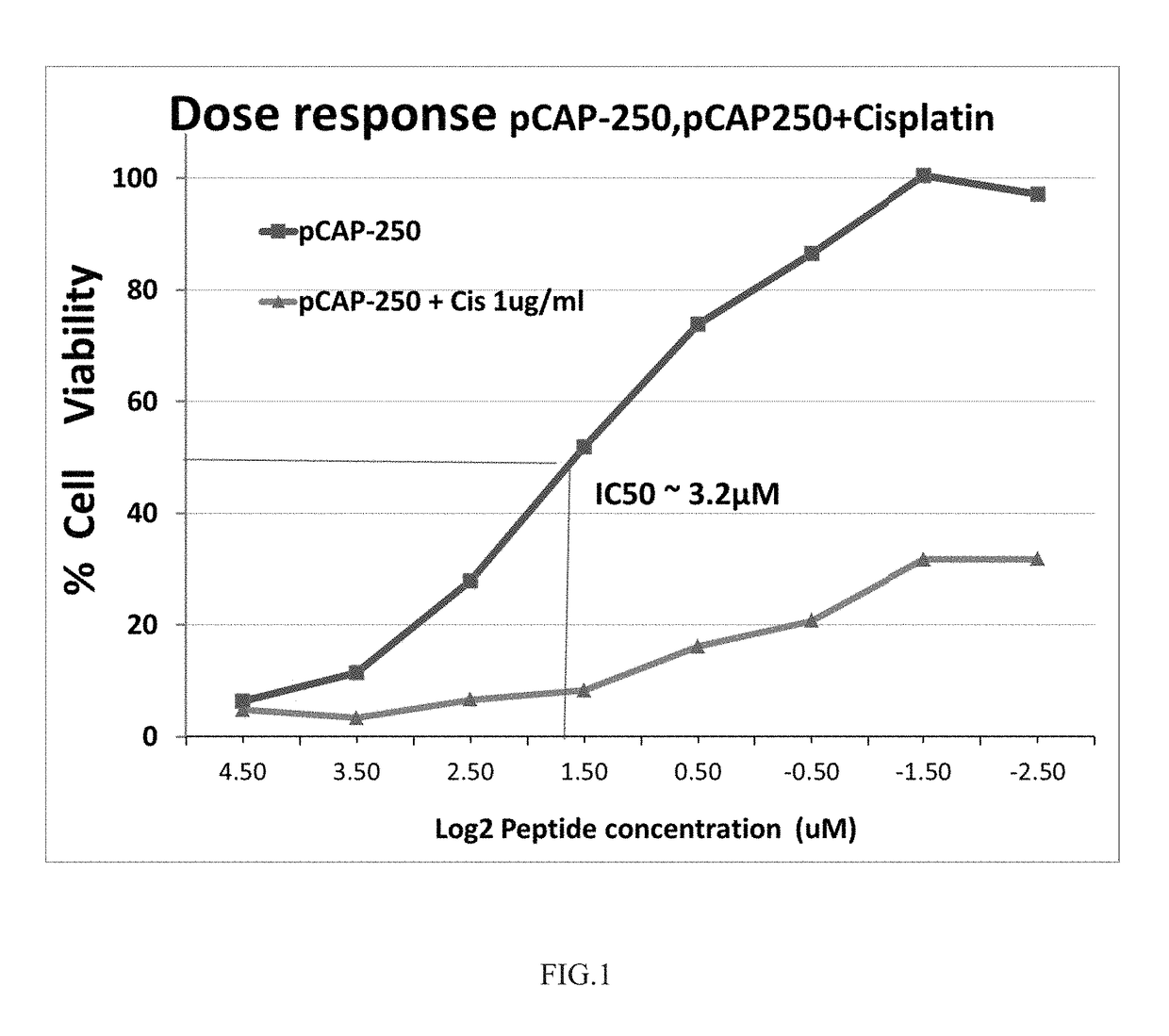
An isolated peptide is provided. The peptide comprises an amino acid sequence arranged in a space and configuration that allow interaction of the peptide with the DNA Binding Domain (DBD) of p53 through at least one residue of the DBD by which pCAP 250 (SEQ ID NO: 1) binds the DBD, wherein the peptide at least partially reactivates a mutant p53 protein, with the proviso that the peptide is not SEQ ID NO: 59-382.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
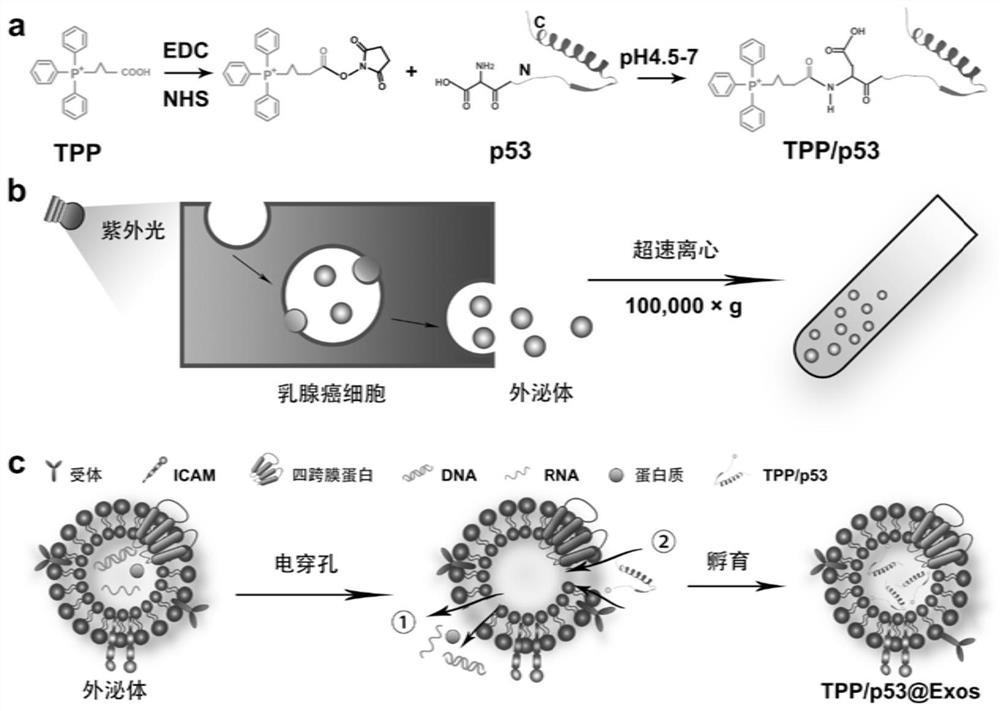
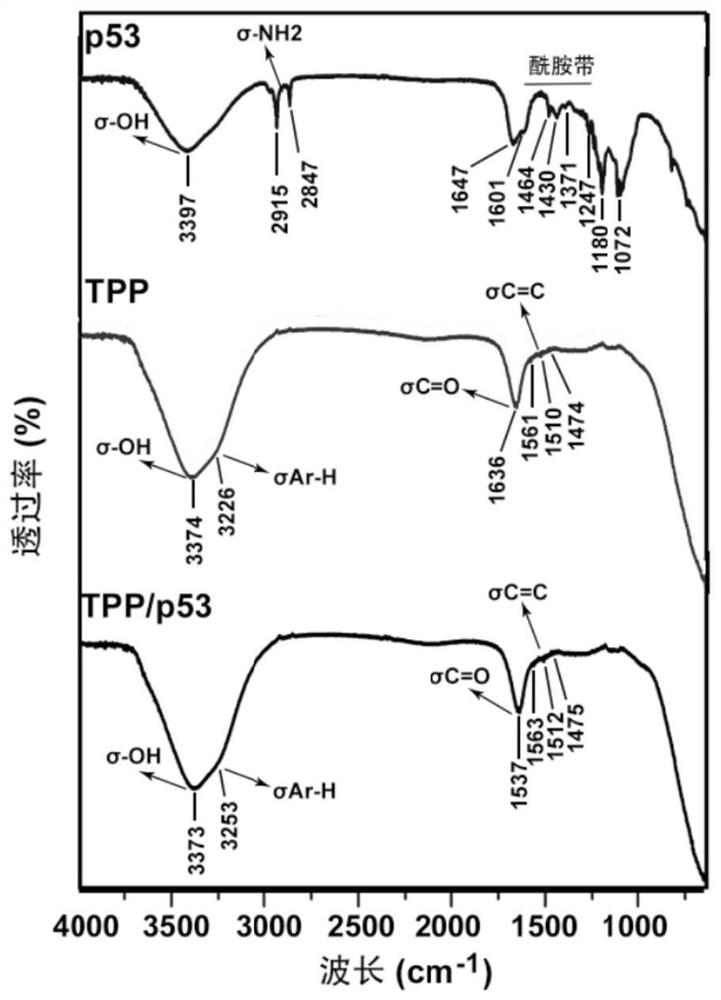
Protein nano-drug for cancer targeted therapy and preparation method thereof
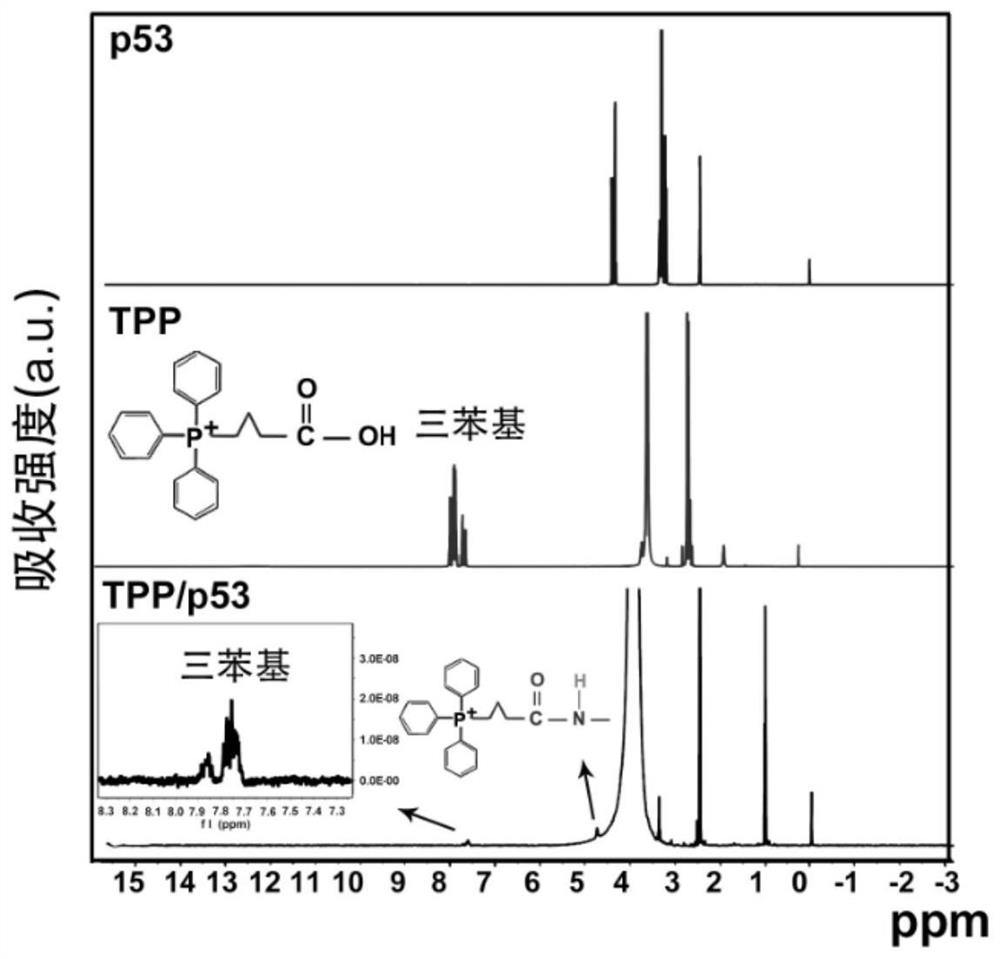
ActiveCN111905105AImprove delivery efficiencyMaintain membrane protein integrityNanomedicineMacromolecular non-active ingredientsCancer cellApoptosis pathways
The invention discloses a protein nano-drug for cancer targeted therapy and a preparation method thereof. The protein nano-drug is an exosome of humanized p53 protein transferred with covalent cross-linked triphenylphosphine (TPP). A protein nano-drug delivery system TPP / p53@Exos developed by the invention can recognize specific cancer cells in a targeted manner, efficiently inhibits the growth ofthe cancer cells by activating endogenous apoptosis pathways of the cells, has no toxic or side effect, and provides a new means for cancer treatment. The preparation method of the nano-drug deliverysystem has a high protein loading rate (about 75%), and can also be used for protection and targeted delivery of other protein drugs.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Recombinant protein G3P20-31, and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN111100209AEasy to makeStrong specificityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVirus peptidesEpitopePeptide fragment
The invention discloses a recombinant protein G3P20-31, and a preparation method and an application thereof, belonging to the technical field of DNA recombination in bioengineering. According to the invention, a phage display technology is utilized to clone a gene segment for encoding a P53 protein N-terminal 20-31 peptide fragment into a filamentous phage vector PIII protein gene, and a recombinant protein for displaying the P53 protein epitope is prepared and displayed onto the surface of bacteriophage, so the recombinant protein is used for detecting the serum p53 antibody of a tumor patient. The invention also discloses an application of the recombinant protein G3P20-31 in preparation of a biological product for detecting a tumor patient serum p53 antibody. The biological product has the advantages of strong specificity, high sensitivity, simple preparation, low cost and the like.
Owner:XINXIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
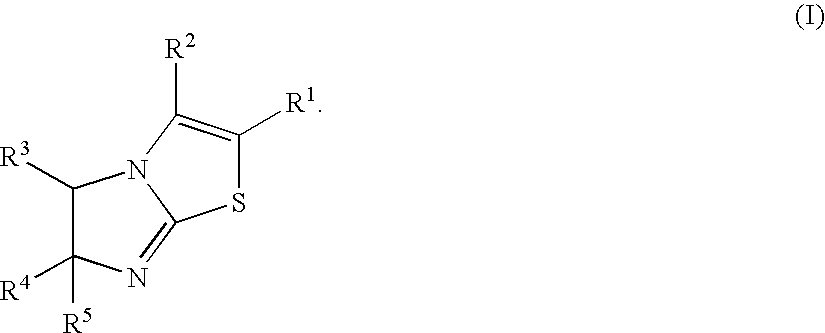
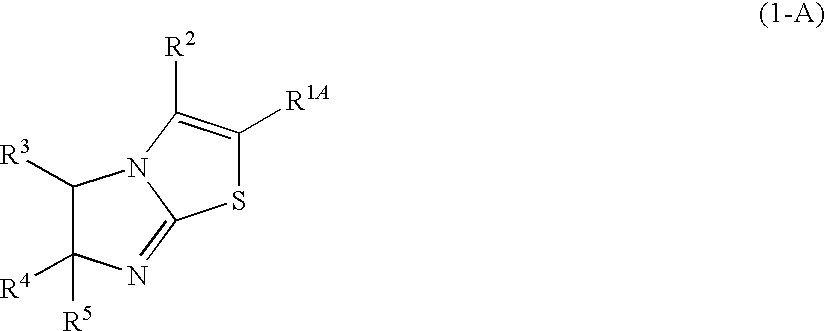

![1-Azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-one derivatives and maleimide derivatives and their use for treating cancer tumors 1-Azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-one derivatives and maleimide derivatives and their use for treating cancer tumors](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/42082f5c-c7d0-421d-b391-520197caf426/US06921765-20050726-D00001.png)
![1-Azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-one derivatives and maleimide derivatives and their use for treating cancer tumors 1-Azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-one derivatives and maleimide derivatives and their use for treating cancer tumors](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/42082f5c-c7d0-421d-b391-520197caf426/US06921765-20050726-D00002.png)
![1-Azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-one derivatives and maleimide derivatives and their use for treating cancer tumors 1-Azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-one derivatives and maleimide derivatives and their use for treating cancer tumors](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/42082f5c-c7d0-421d-b391-520197caf426/US06921765-20050726-D00003.png)