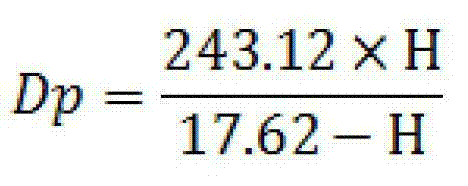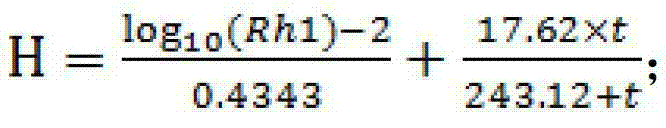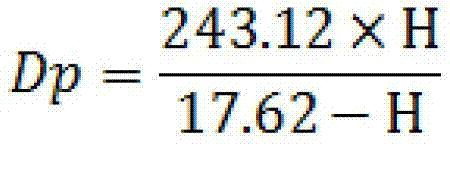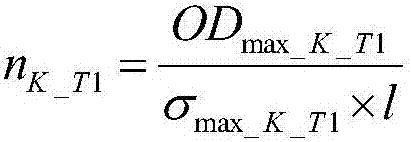Patents
Literature
37 results about "Stagnation temperature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In thermodynamics and fluid mechanics, stagnation temperature is the temperature at a stagnation point in a fluid flow. At a stagnation point the speed of the fluid is zero and all of the kinetic energy has been converted to internal energy and is added to the local static enthalpy. In incompressible fluid flow, and in compressible flow, the stagnation temperature is equal to the total temperature at all points on the streamline leading to the stagnation point. See gas dynamics.
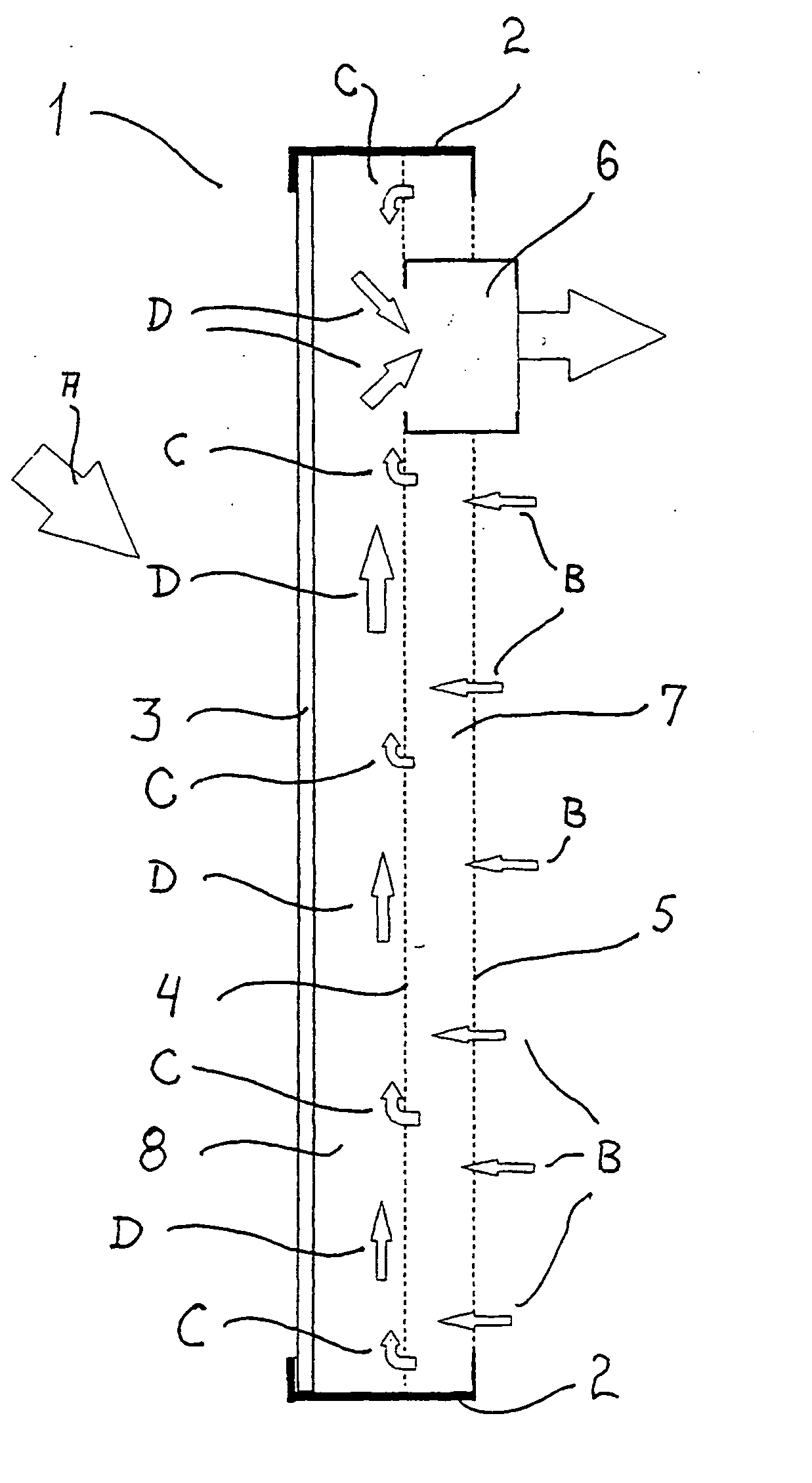
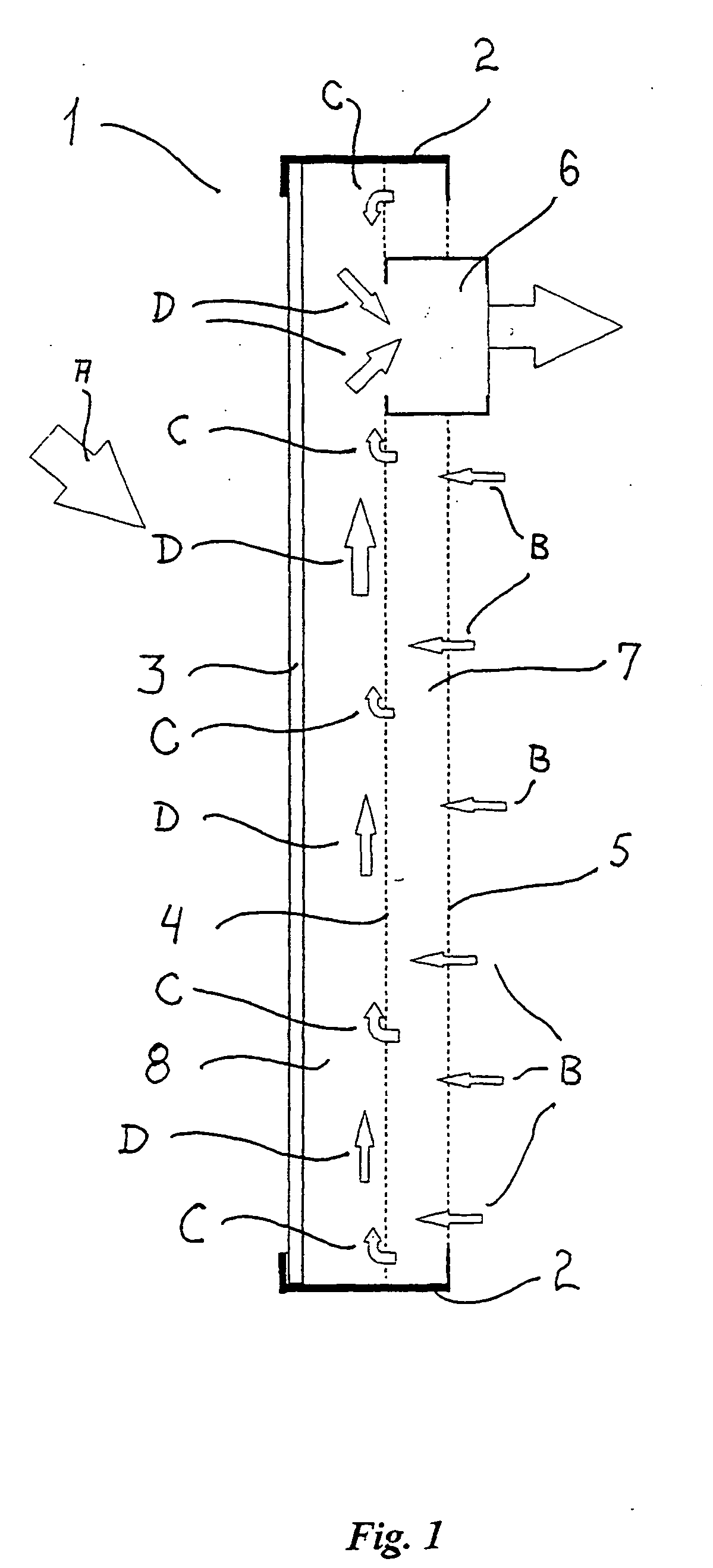
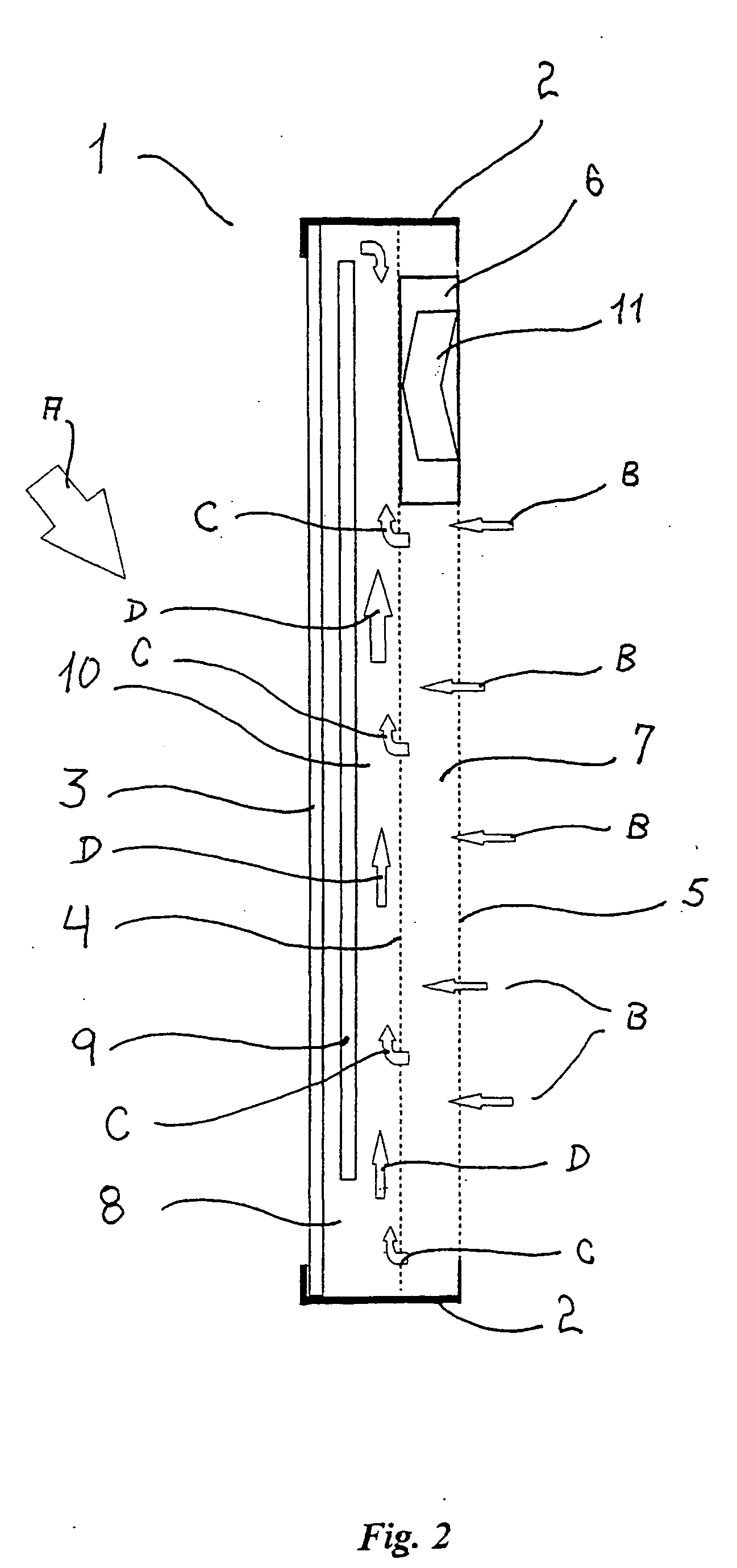
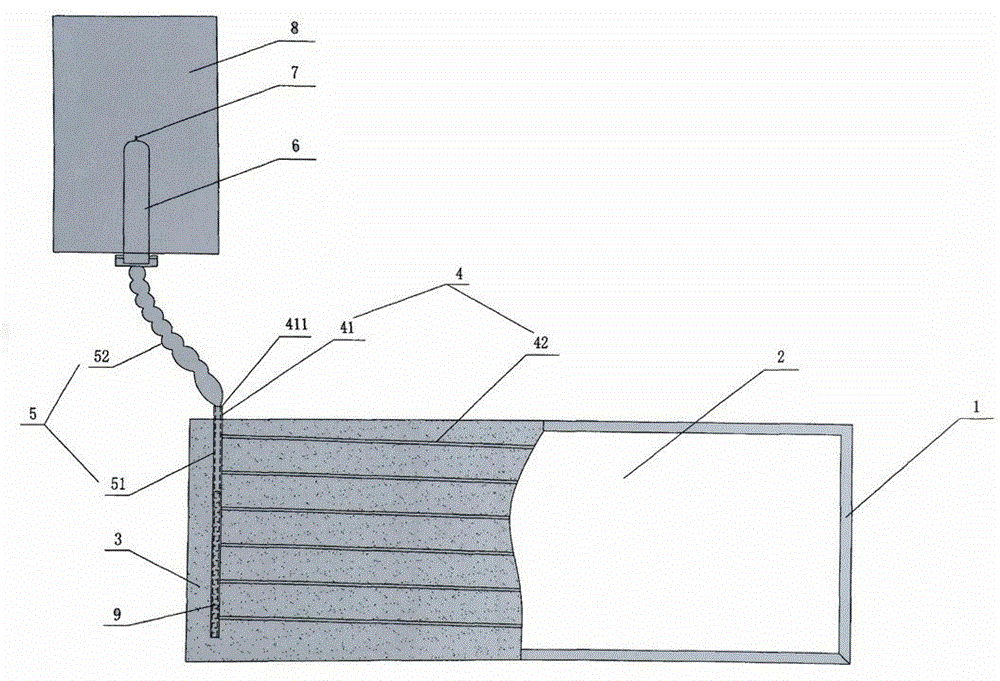
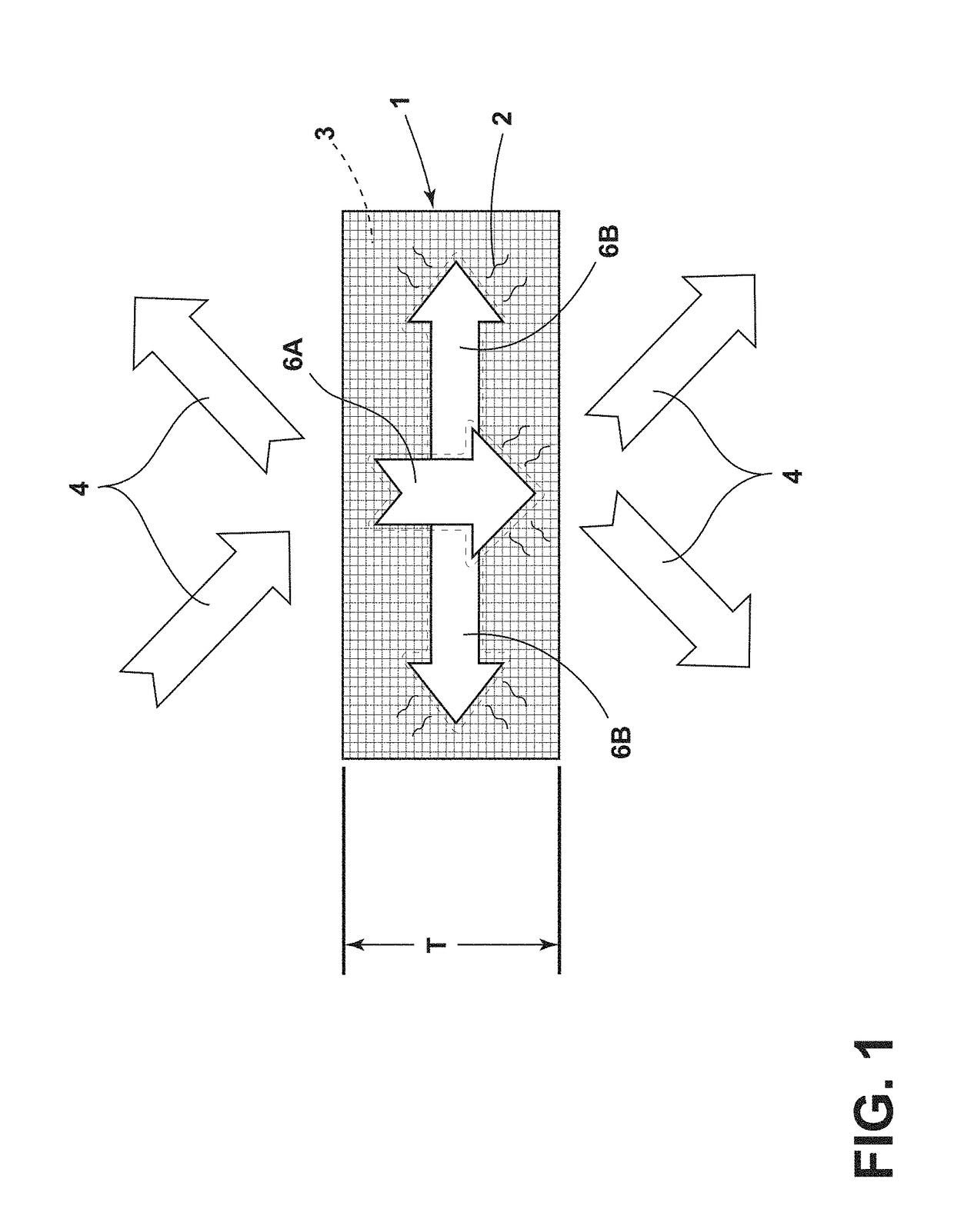
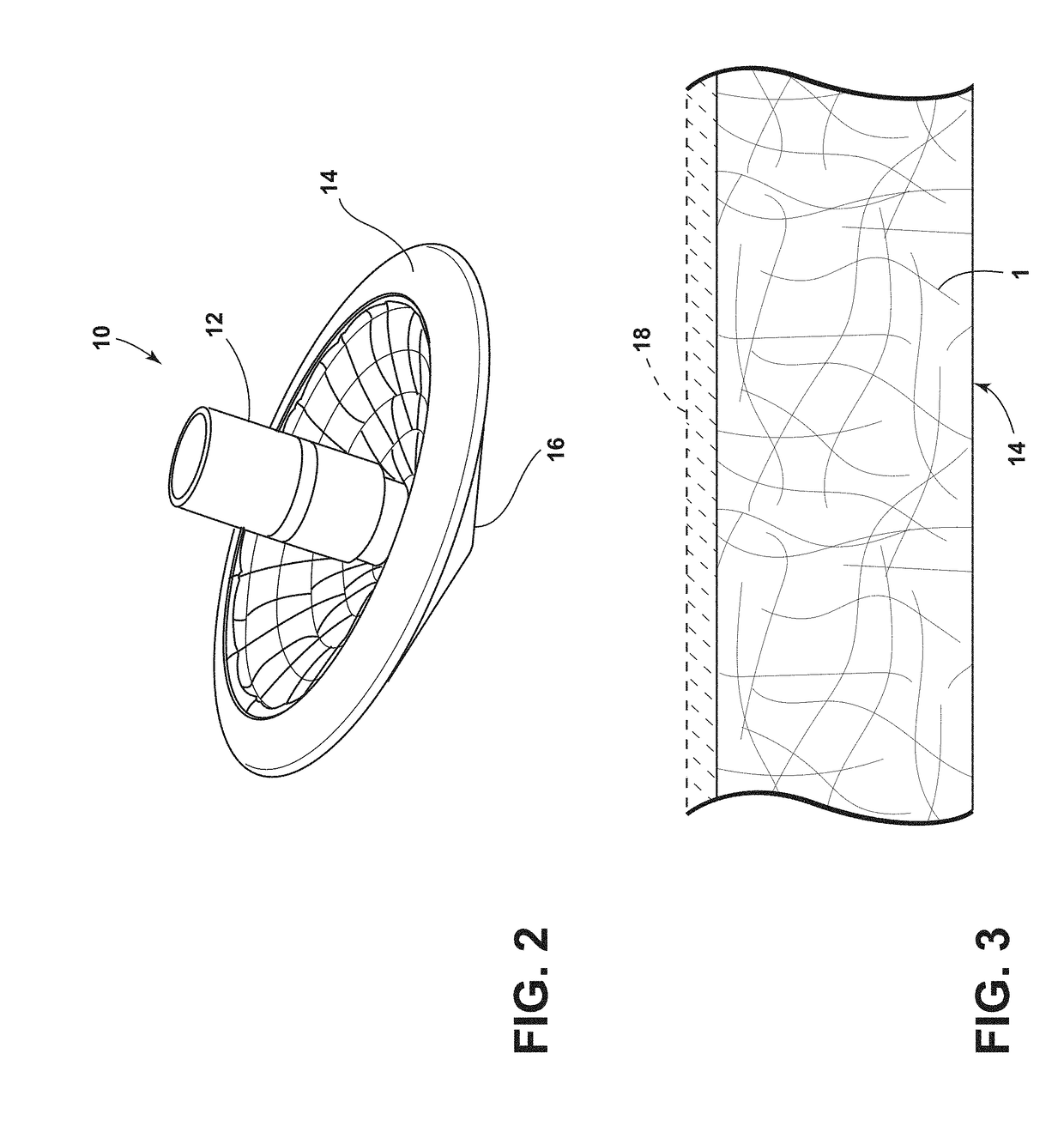
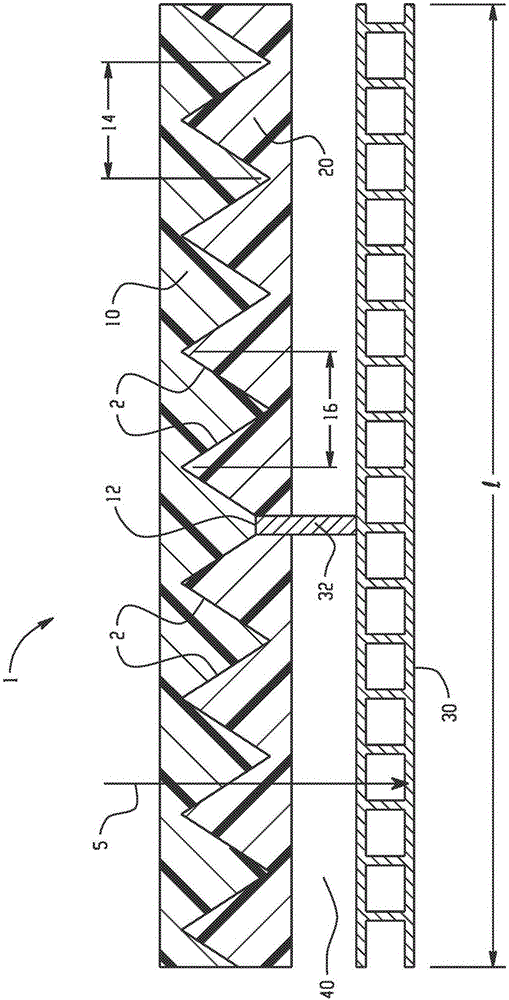
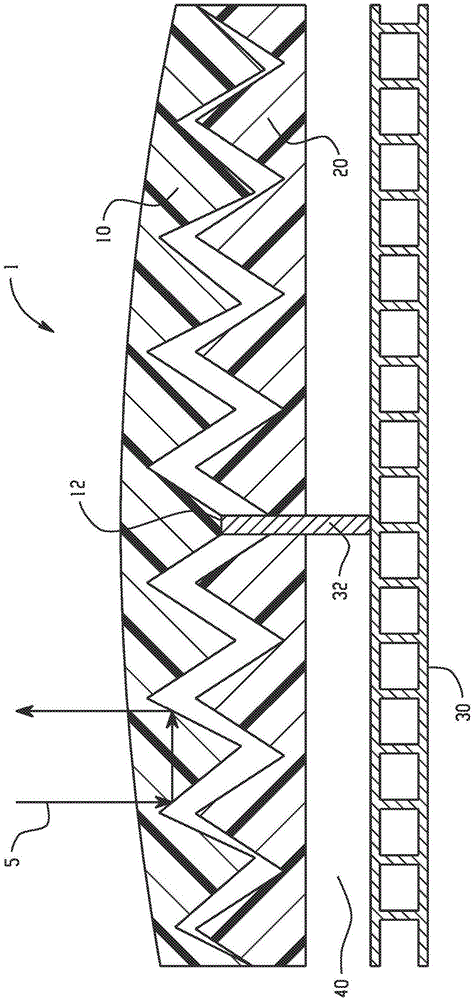
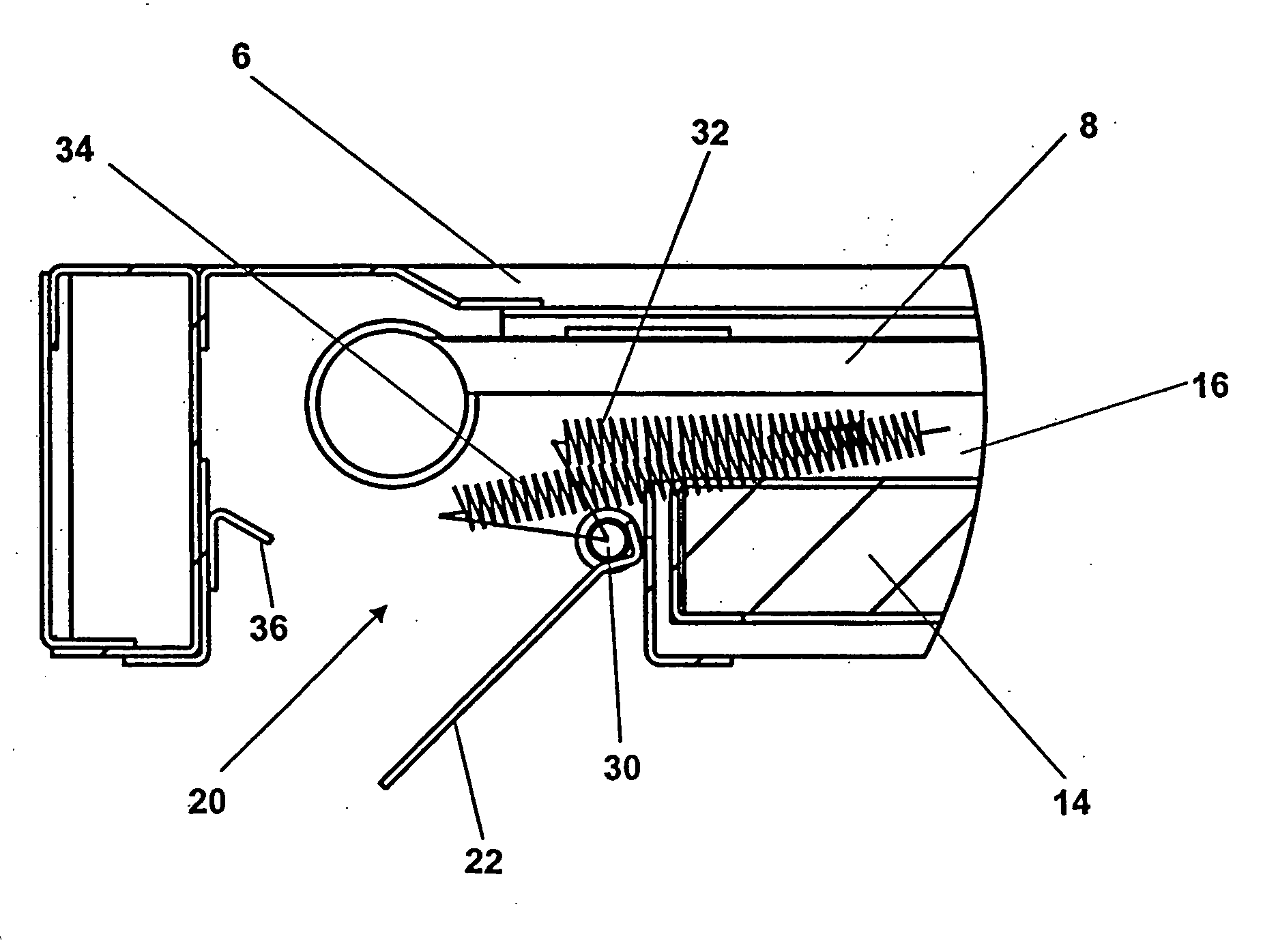
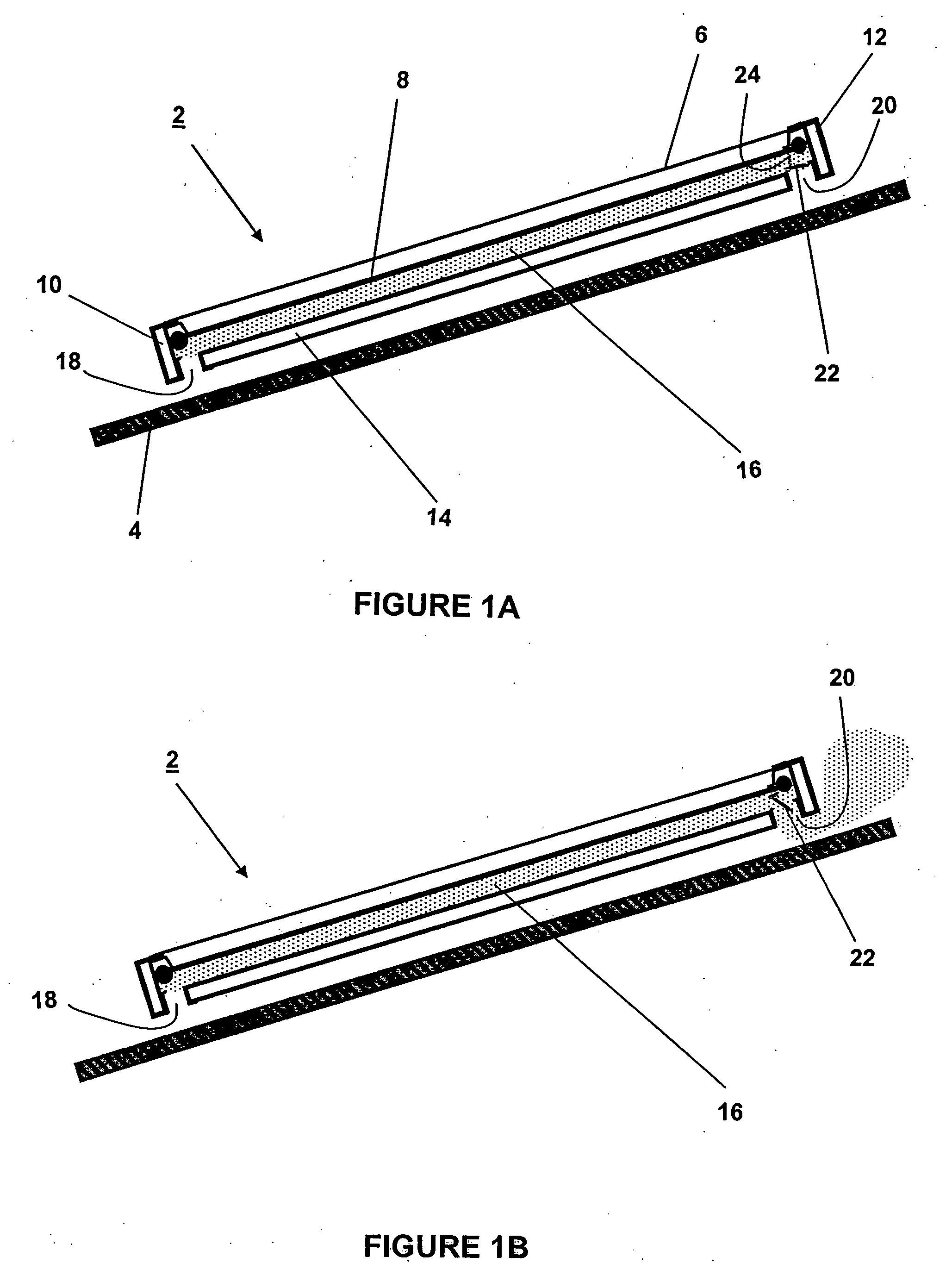
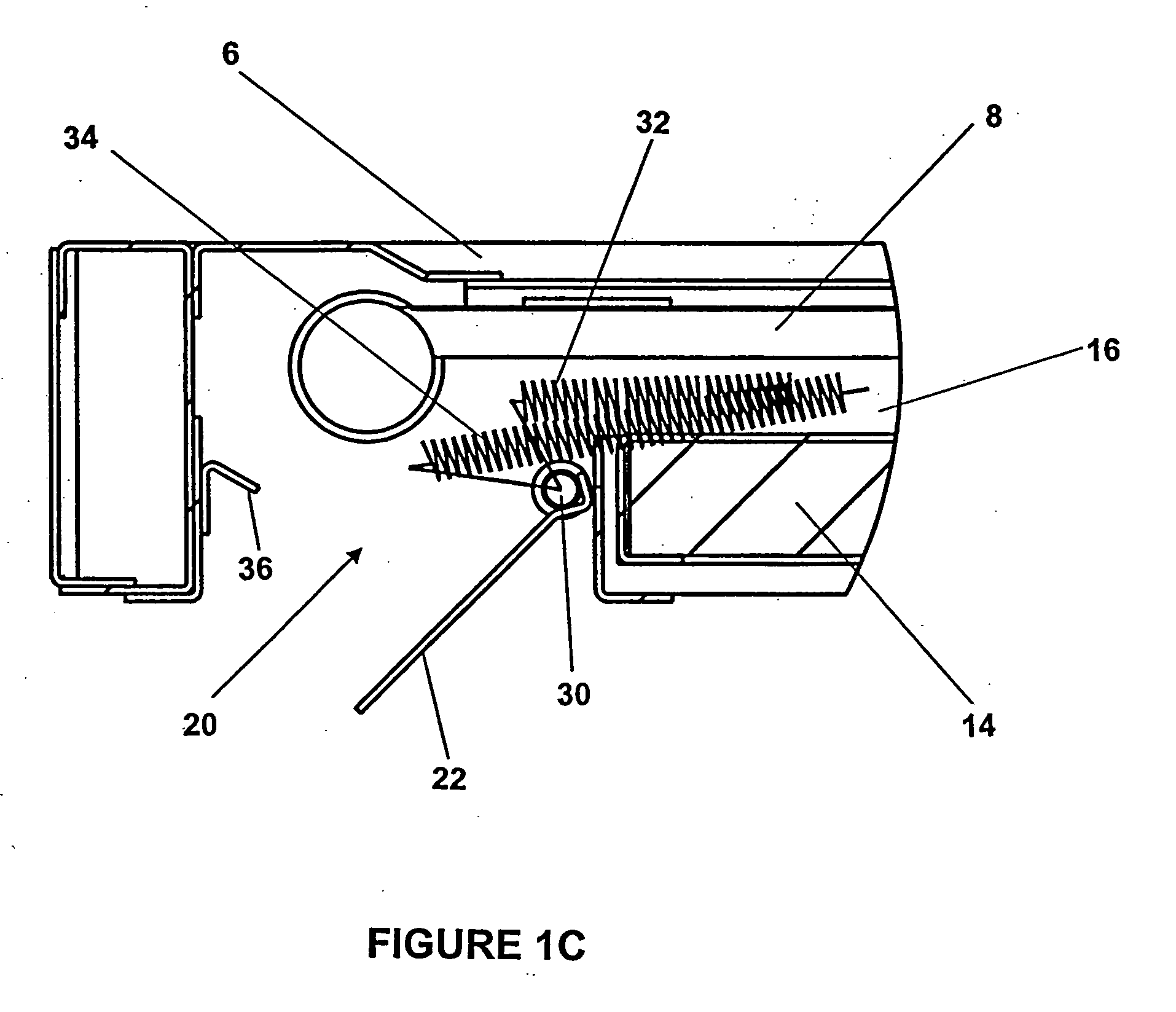
Solar collector panel for heating ventilation air
ActiveUS20050061311A1Reduce quality problemsGood effectRoof covering using slabs/sheetsSolar heating energyRadiative heat lossElectricity
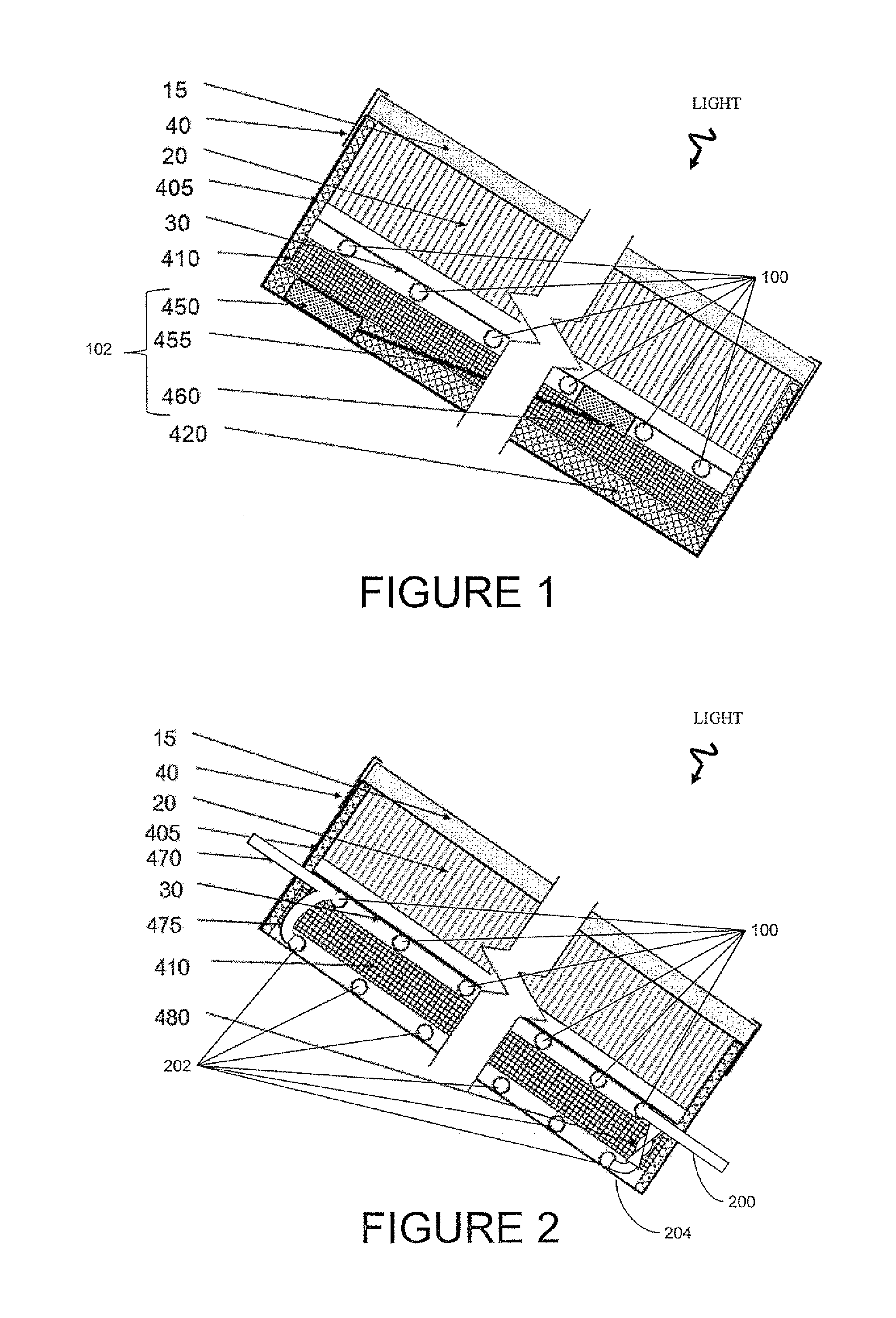
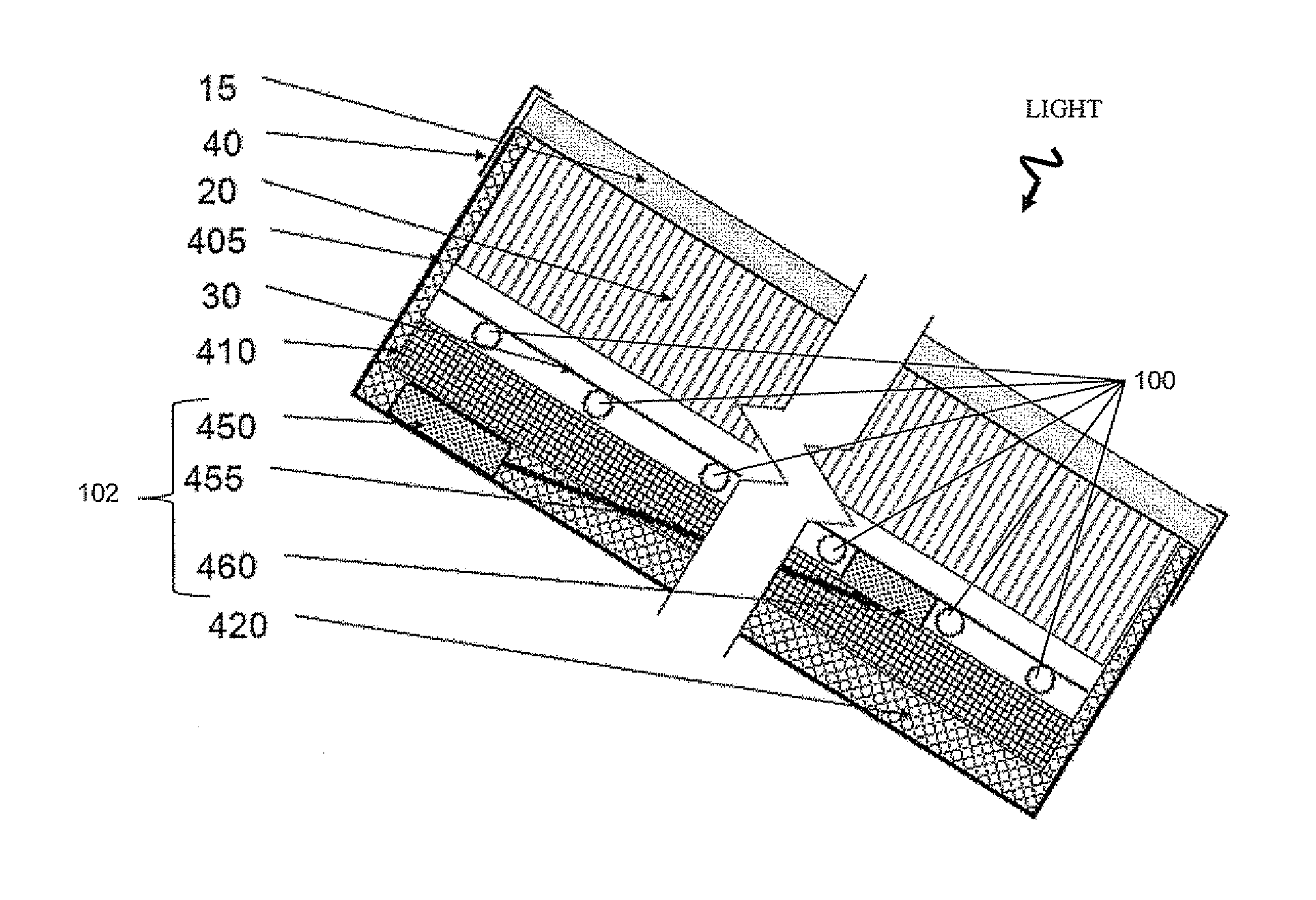
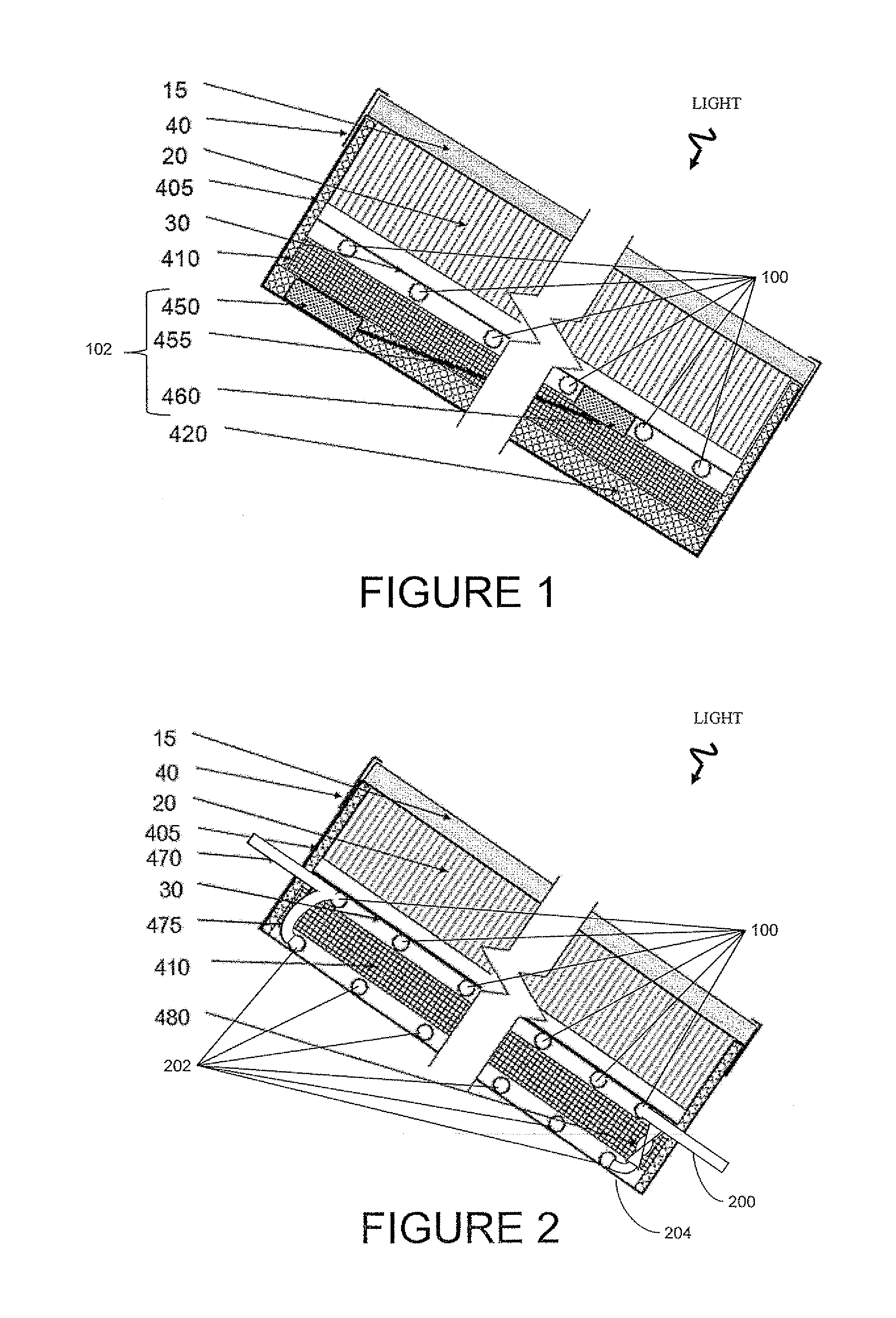
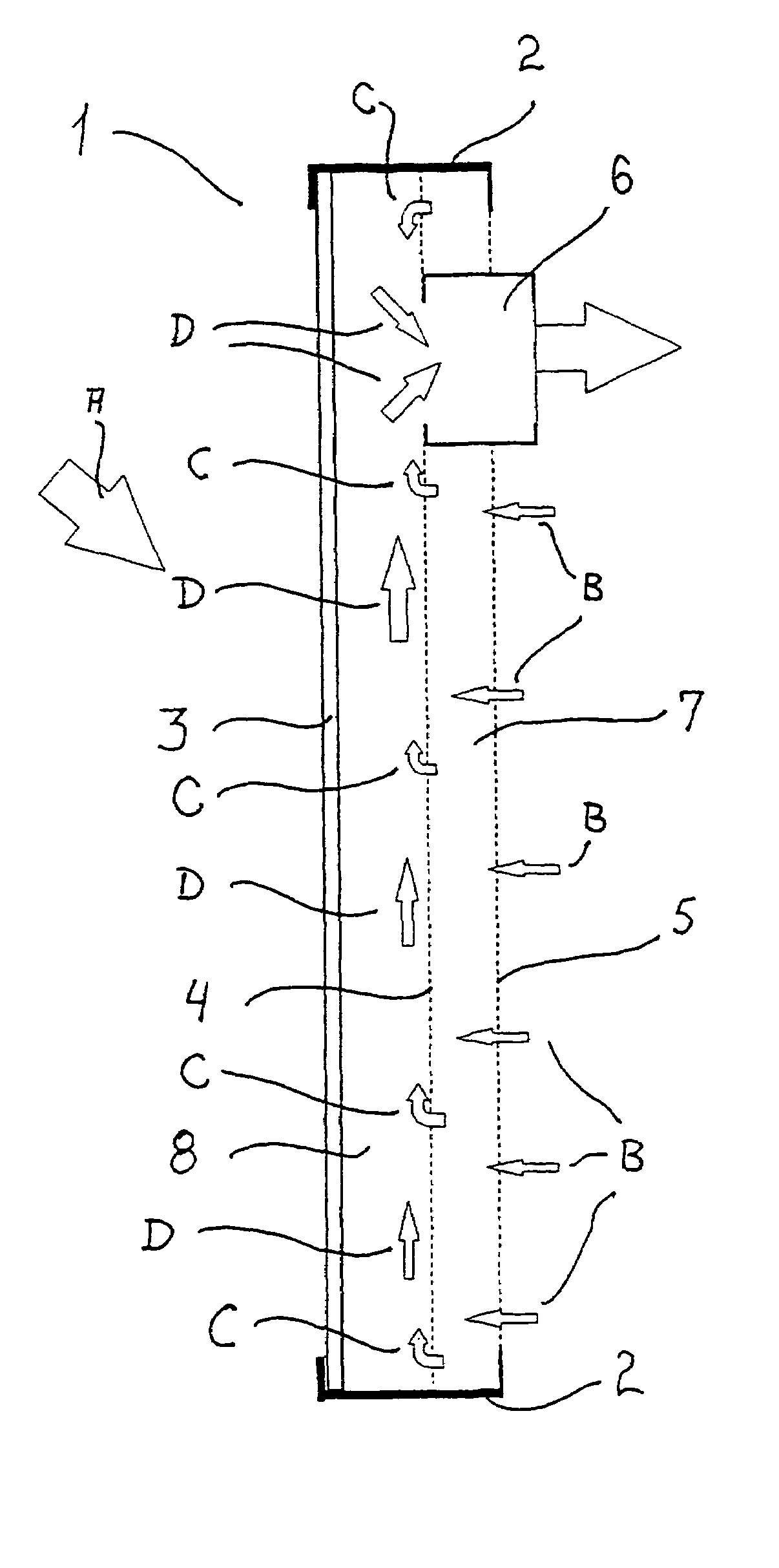
A solar collector panel is disclosed for heating of air, in which the conventional insulation material on the back panel facing away from the sun is replaced by a spacing between a permeable back panel and a permeable heat absorber means, so that a heat convection airflow through the back panel and into the interior of the solar energy panel against the temperature gradient prevents the convection heat loss in the opposite direction. The back panel also reduces the radiation heat loss from the heat absorber means. Furthermore, in case the flow of air through the solar energy panel is stopped, the convection-insulation will no longer be effective, and a photovoltaic cell panel placed within the solar energy panel and generating electricity from the solar radiation will not be subjected to the damaging high stagnation temperature of a traditionally insulated solar collector panel.
Owner:NORTON CHRISTENSEN INC
Simulating experiment method of rock natural seepage ability
The invention discloses a simulating experiment method of rock natural seepage ability, and the simulating experiment method comprises the following steps: properly preparing a dynamic high-temperature and high-pressure water rock simulation experiment set used in the simulating experiment method; placing a sample rock core column into a reaction kettle; injecting a prepared solution filled in a solution container into the reaction kettle via a transmission pump, performing rock core confining pressure and internal pressure control in the reaction kettle to keep the pressure of the sample rock core column to be consistent with that of a real formation; using a temperature control system to set reaction temperature, heating the reaction kettle; using a counterbalance valve for regulating the pressure of the reaction kettle to a formation pressure demanded by an experiment; after an experiment fluid flows out via the sample rock core column in the reaction kettle, recording liquid out-letting amount of an outlet liquid in even space to obtain the rock core column seepage ability, namely seepage velocity with the unit of ml / min; according to the rock core column seepage ability and an actual wellbore oil drainage area, extrapolating daily fluid production rate of every unit thickness per meter. The method can truly and directly reflect rock actual seepage ability, so that the purpose of effectiveness evaluation of a reservoir stratum can be achieved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Multi-loop cable steady-state temperature rise acquisition method adapting to various boundary conditions
ActiveCN106021189ASimple calculationAccurate calculationDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsHeat flowSteady state temperature
The invention relates to a multi-loop cable steady-state temperature rise acquisition method adapting to various boundary conditions. The method comprises the following steps: 1) constructing a multi-loop cable steady-state temperature rise model adapting to various boundary conditions according to a thermal field superposition principle; 2) acquiring an initial temperature rise matrix T<0> according to a set initial heat flow matrix Q<0>; 3) performing reduction according to the initial temperature rise matrix T<0> and the boundary conditions to form a reduced heat flow matrix Q<1>; 4) acquiring a next-step temperature rise matrix T<1> according to the reduced heat flow matrix Q<1>; and 5) judging whether a maximum difference value among all elements which correspond to the initial temperature rise matrix T<0> and the next-step temperature rise matrix T<1> is greater than a convergence threshold or not, if so, substituting T<0> with T<1> and returning to the step 3), and otherwise, judging that a current corresponding temperature rise matrix is a steady-state temperature rise matrix. Compared with the prior art, the multi-loop cable steady-state temperature rise acquisition method has the advantages of easiness and accuracy in calculation, high calculation efficiency, advanced algorithm, adaptability to various boundary conditions, and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
Absorbent material and solar panel using such a material
ActiveUS9671137B2Enhanced radiationGood emissivitySolar heating energyMirrorsTransmittanceAbsorbent material
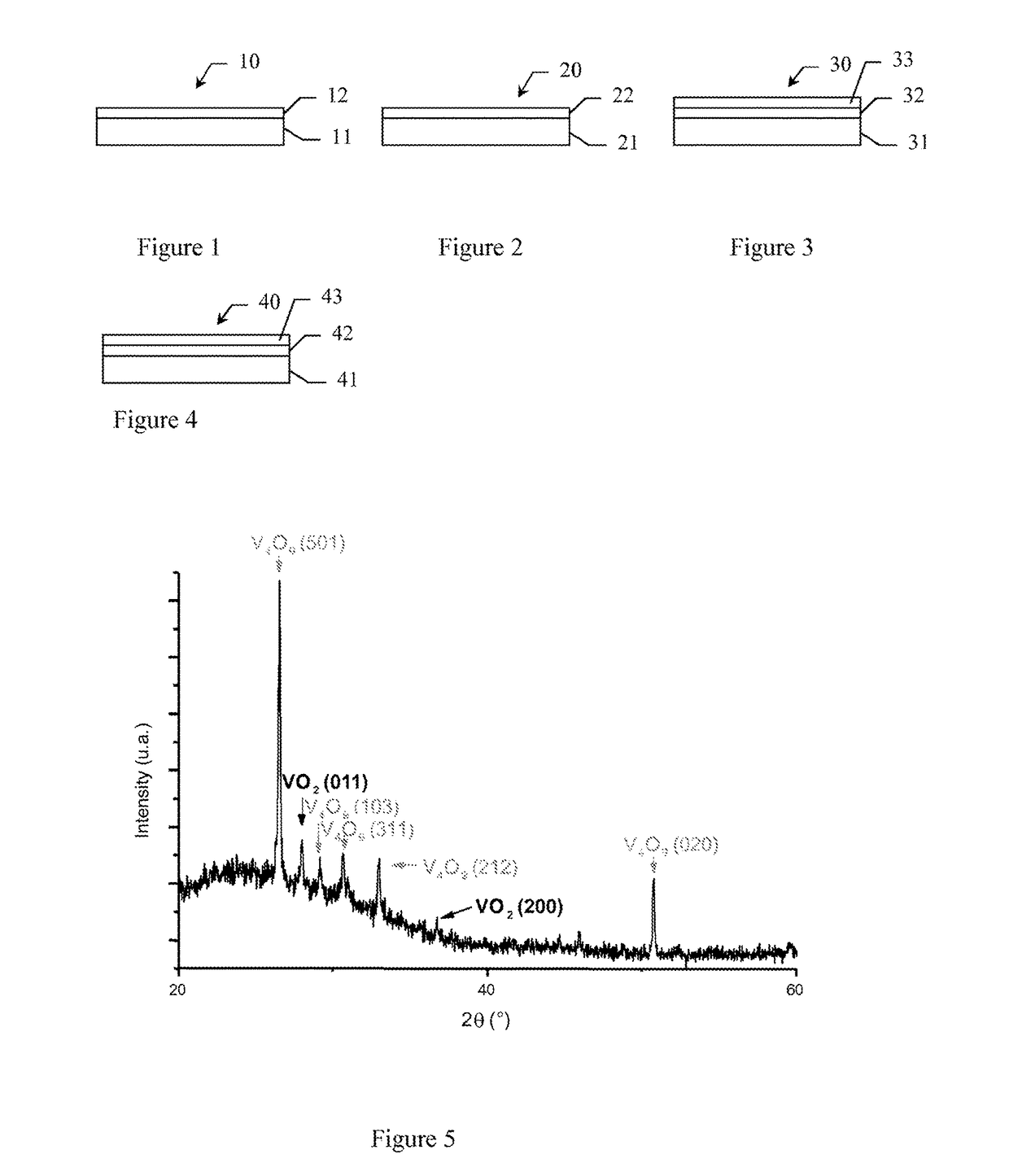
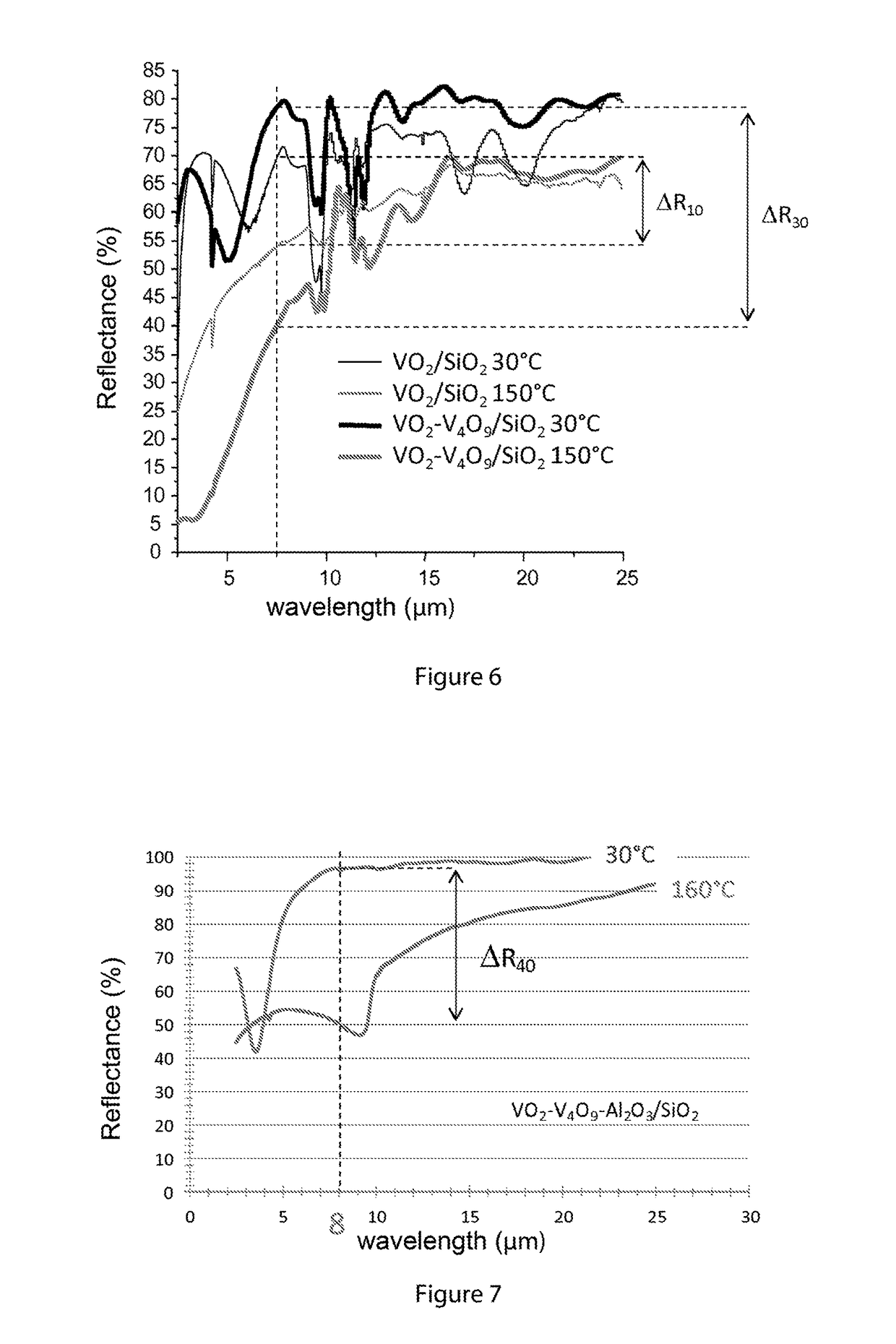
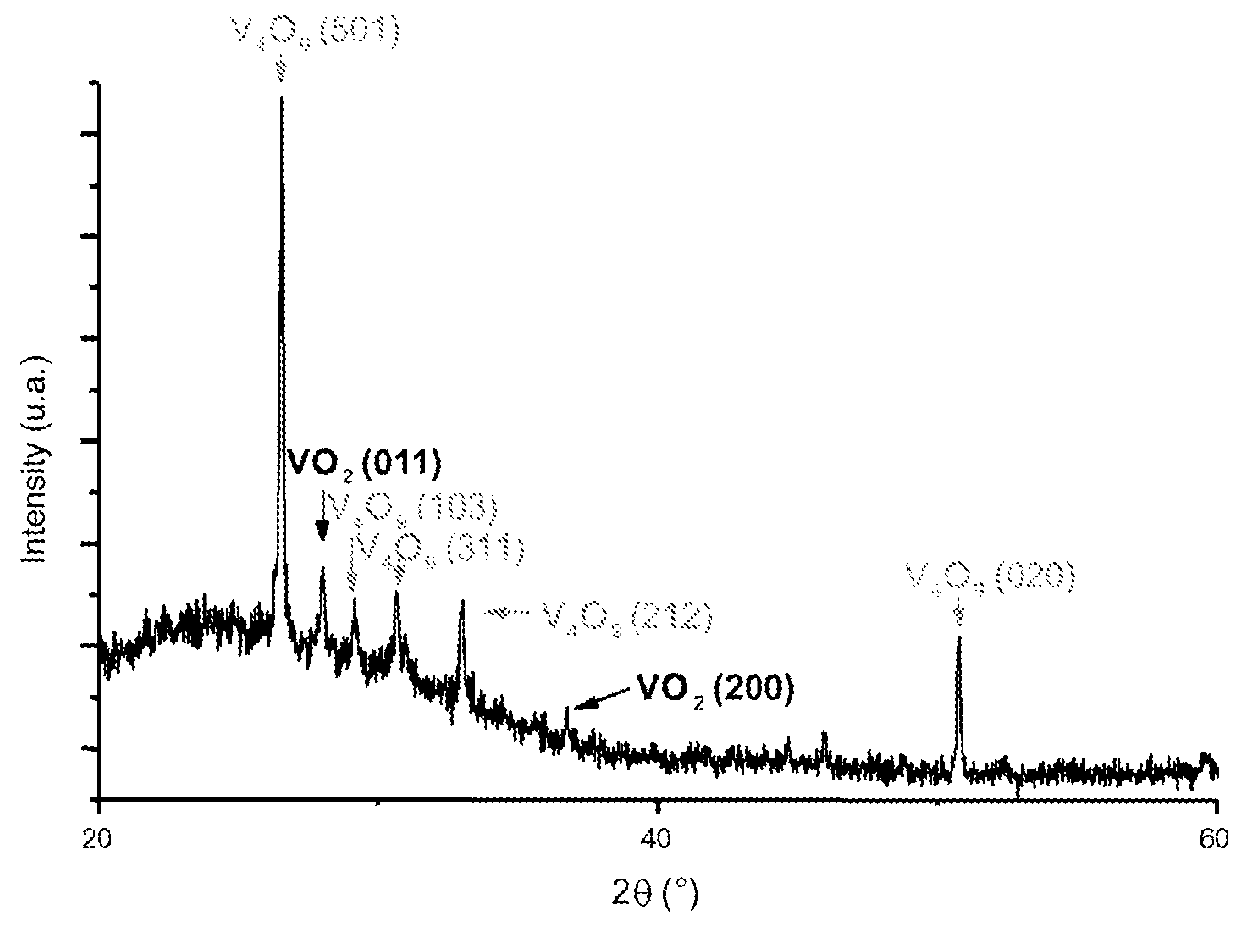
The invention concerns a multilayer material comprising at least:a support having a reflectance R higher than 80% for radiations of wavelengths higher than 5 μm,a selective layer comprising a combination of Vanadium oxides VO2 and VO2O2n+ / −1, with n>1, said selective layer having an absorbance higher than 75% for radiations of wavelengths comprised between 0.4 and 2.5 μm, regardless of the temperature T, and having, for radiations of wavelengths comprised between 6 and 10 μm, a transmittance Tr such that:Tr>85% for T<Tc, a critical temperature,20%≦Tr≦50% for T>Tc.Application to the production of thermal solar panels having a low stagnation temperature and high performance.
Owner:VIESSMANN FAULQUEMONT +2
Intelligent dew removing method and intelligent dew removing device for glass door body of wine cabinet
InactiveCN103206826AEasy to useSolve the problem of condensationLighting and heating apparatusDefrostingEngineeringStagnation temperature
The invention relates to an intelligent dew removing device and an intelligent dew removing method for a glass door body of a wine cabinet. The glass door body can be intelligently heated by using the method or the wine cabinet provided with the device, and when temperature of the glass door body is higher than condensation stagnation temperature, heating automatically stops, and the wine cabinet automatically exits a dew removing program. Due to the fact that condensation can not be generated on the door body when the temperature of the door body is higher than the condensation stagnation temperature, the problem that the condensation can be generated on the glass door body can be fundamentally solved, and normal use of the wine cabinet can not be influenced, and furthermore energy consumption during the actual use process of the wine cabinet and life of a glass door are benefited.
Owner:HEFEI HUALING CO LTD
System and method for temperature limiting in a sealed solar energy collector
Insulated solar panels provide that provide a solar thermal collector with means for limiting stagnation temperatures and preventing damage include: temperature limiting is provided by the insulated solar panel, isolating internal components from the environment, using passive closed systems within the sealed solar thermal collector, while also allowing alternative implementations as active systems and / or portions of the temperature limiting system outside the sealed solar thermal collector. A heat pipe can be used as a passive thermal switch, where the temperature induced action at a predetermined temperature causes an abrupt transition from a state of thermal isolation to a state of strong thermal coupling. Additionally, a set of siphon circulation pipes provides a passive closed system for temperature limiting.
Owner:TIGI
System and method for temperature limiting in a sealed solar energy collector
Insulated solar panels provide that provide a solar thermal collector with means for limiting stagnation temperatures and preventing damage include: temperature limiting is provided by the insulated solar panel, isolating internal components from the environment, using passive closed systems within the sealed solar thermal collector, while also allowing alternative implementations as active systems and / or portions of the temperature limiting system outside the sealed solar thermal collector. A heat pipe can be used as a passive thermal switch, where the temperature induced action at a predetermined temperature causes an abrupt transition from a state of thermal isolation to a state of strong thermal coupling. Additionally, a set of siphon circulation pipes provides a passive closed system for temperature limiting.
Owner:TIGI
Preparation method of ESH-state C19400 copper alloy strips
InactiveCN110172601AImprove performance indicatorsMeet ESH status requirementsFurnace typesMetal rolling arrangementsPerformance indexNational standard
The invention relates to a modifying method of C 19400 copper alloy strips, in particular to a preparation method of ESH-state C19400 copper alloy strips. In the method, alloys are smelted as follows:microelements are fed on the basis of the contents of Cu, Fe and P elements meeting the national standard, and are one or combinations of different types of Si, Co, Sn, Zn, Ni and Mg; the total content of the microelements is controlled to be not more than 0.2%; the smelting temperature is 1150-1300 DEG C; and the insulation time is not shorter than 20 min; solid-solution treatment: the solid-solution temperature is controlled within 600-900 DEG C; the solid-solution time is not shorter than 30 s; and the temperature is not higher than 200 DEG C after quenching; aging: a graded aging mode isadopted; the first-grade and second-grade aging temperatures are controlled in a range of 400-600 DEG C; and the insulation time is 2 min to 10 h; and cold rolling of finished products: the finished product machining rate is in a range of 10-60%. The performance indexes of the C 19400 copper alloy strips are improved; the ESH-state requirements are met; the HV reaches above 150; and the tensile strength reaches 550 MPa to meet special function requirements.
Owner:TAIYUAN JIN XI CHUNLEI COPPER CO LTD
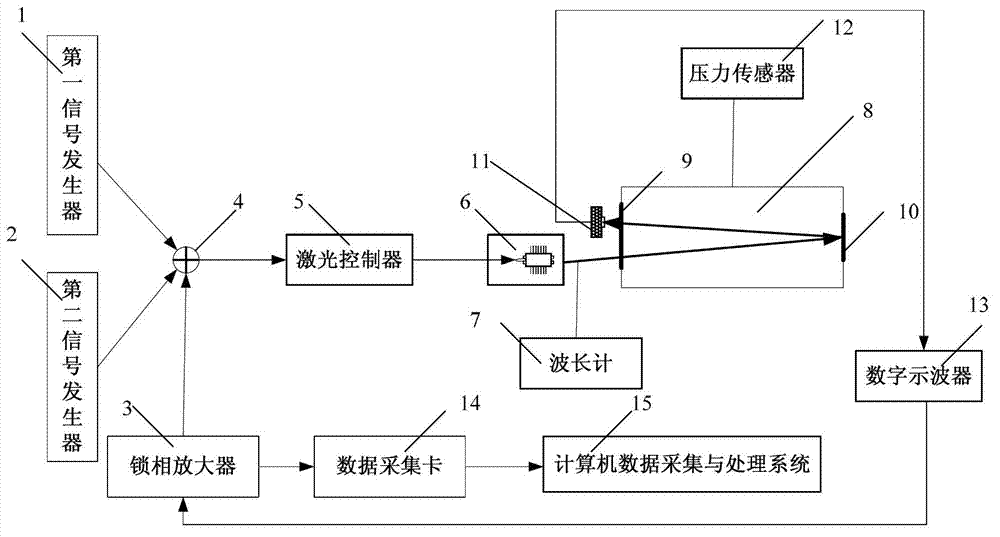
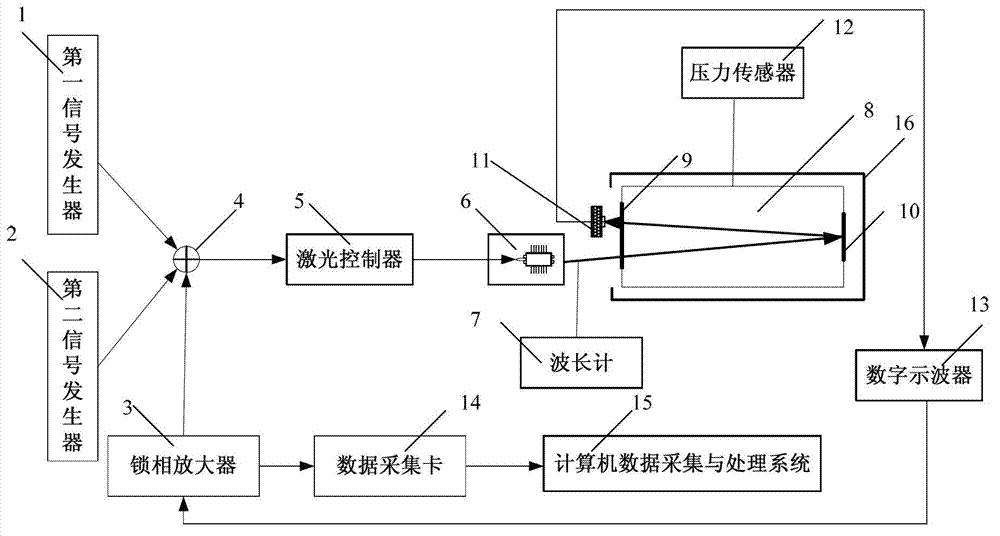
Method for measuring temperature in vacuum environment based on wavelength modulation spectrum technology
InactiveCN103308186AReduce the effects of stressReduce measurement errorRadiation pyrometryTwo temperatureWavelength modulation
The invention discloses a method for measuring a temperature in a vacuum environment based on a wavelength modulation spectrum technology, and belongs to the technical field of tunable laser diode absorption spectroscopy. According to the method, a laser is modulated by utilizing a high-frequency sine wave, a low-frequency triangular wave and a low-frequency square wave based on the wavelength modulation spectrum technology, so that selected two temperature measurement spectral lines appear at a high level position and a low level position respectively; spectral line scanning is realized by the triangular wave; the second harmonic signal ratio of the two spectral lines is obtained by experimental measurement; the rotational temperature of gas molecules is determined by comparing the second harmonic signal ratio with a theoretical calculating value; and the rotational temperature and a translational temperature (the classical thermodynamic temperature) are kept balance all the time, so that the temperature of gas can be measured. By the method, the problems of surface material analysis and temperature traceability of a current contact temperature sensor applied in the vacuum environment are solved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
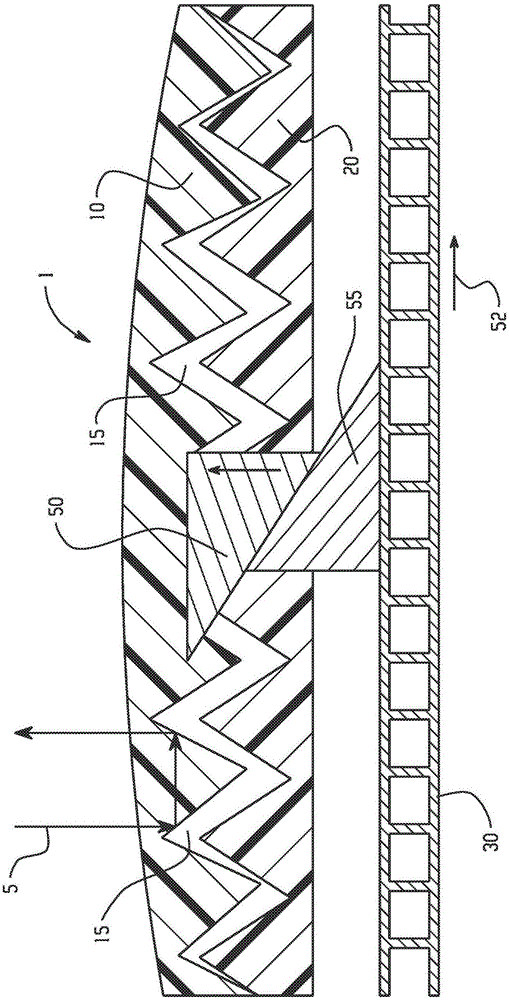
Solar collector panel for heating ventilation air
ActiveUS7694672B2Easy to manufactureImprove reliabilityRoof covering using slabs/sheetsSolar heating energyRadiative heat lossEngineering
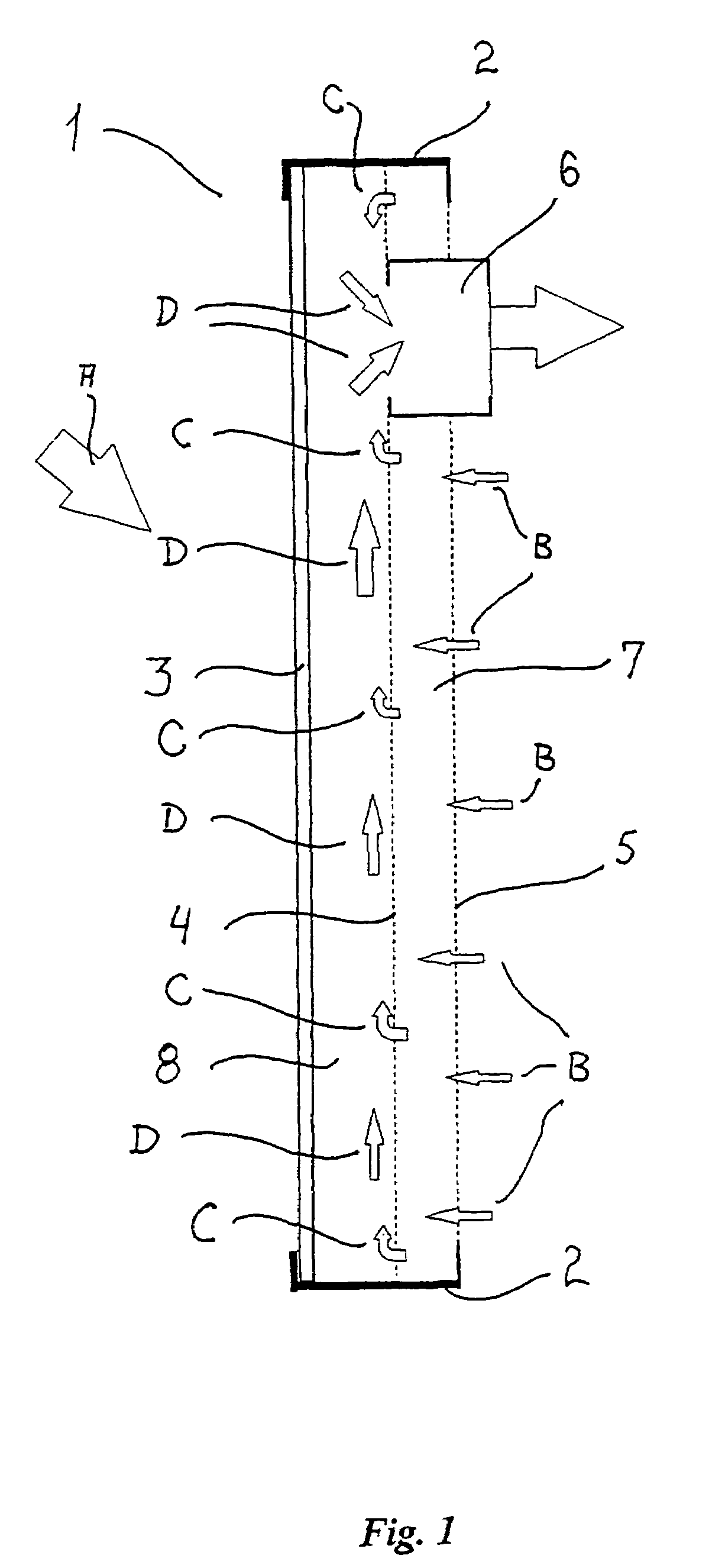
A solar collector panel is disclosed for heating of air, in which the conventional insulation material on the back panel facing away from the sun is replaced by a spacing between a permeable back panel and a permeable heat absorber means, so that a heat convection airflow through the back panel and into the interior of the solar energy panel against the temperature gradient prevents the convection heat loss in the opposite direction. The back panel also reduces the radiation heat loss from the heat absorber means. Furthermore, in case the flow of air through the solar energy panel is stopped, the convection-insulation will no longer be effective, and a photovoltaic cell panel placed within the solar energy panel and generating electricity from the solar radiation will not be subjected to the damaging high stagnation temperature of a traditionally insulated solar collector panel.
Owner:NORTON CHRISTENSEN INC
Absorbent material and solar panel using such a material
ActiveUS20160033174A1Enhanced radiationGood emissivitySolar heating energyMirrorsTransmittanceAbsorbent material
The invention concerns a multilayer material comprising at least:a support having a reflectance R higher than 80% for radiations of wavelengths higher than 5 μm,a selective layer comprising a combination of Vanadium oxides VO2 and VO2O2n+ / −1, with n>1, said selective layer having an absorbance higher than 75% for radiations of wavelengths comprised between 0.4 and 2.5 μm, regardless of the temperature T, and having, for radiations of wavelengths comprised between 6 and 10 μm, a transmittance Tr such that:Tr>85% for T<Tc, a critical temperature,20%≦Tr≦50% for T>Tc.Application to the production of thermal solar panels having a low stagnation temperature and high performance.
Owner:VIESSMANN FAULQUEMONT +2
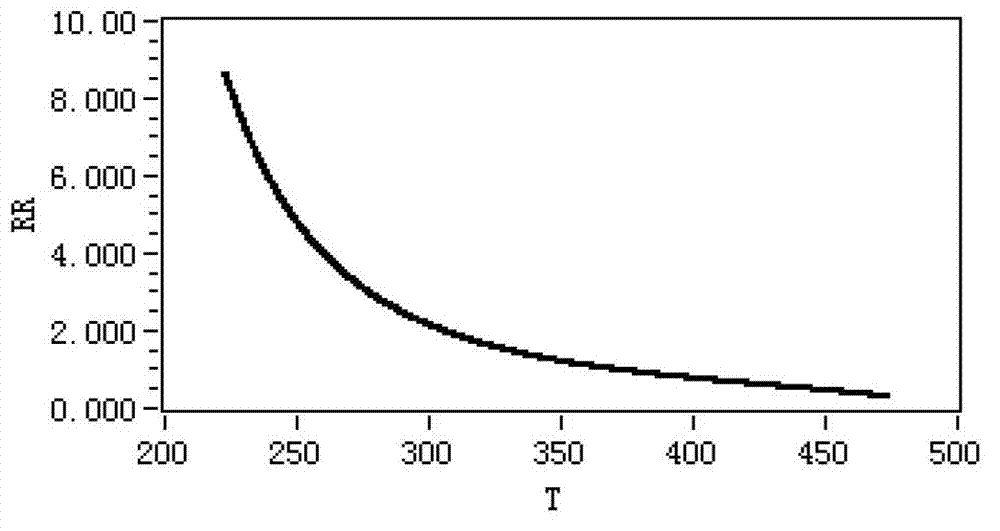
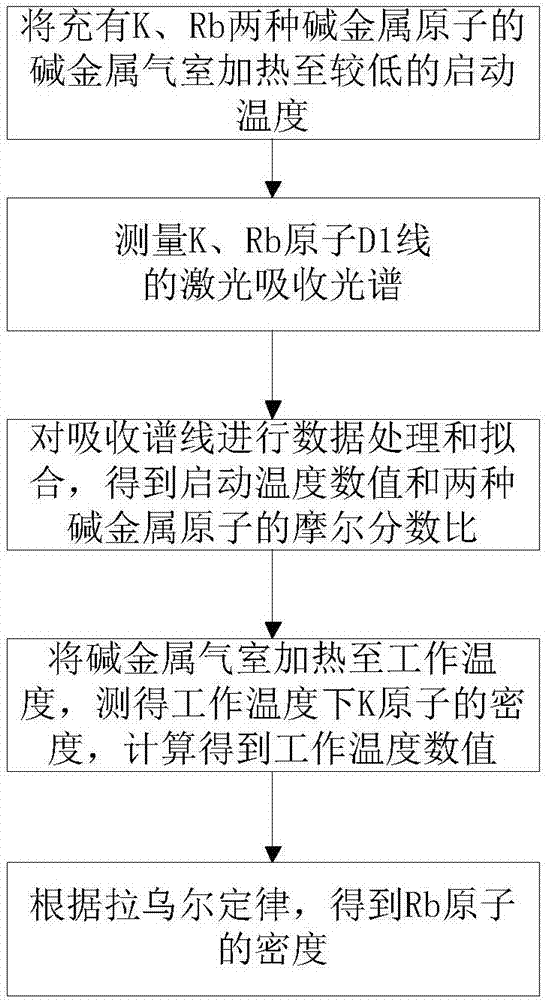
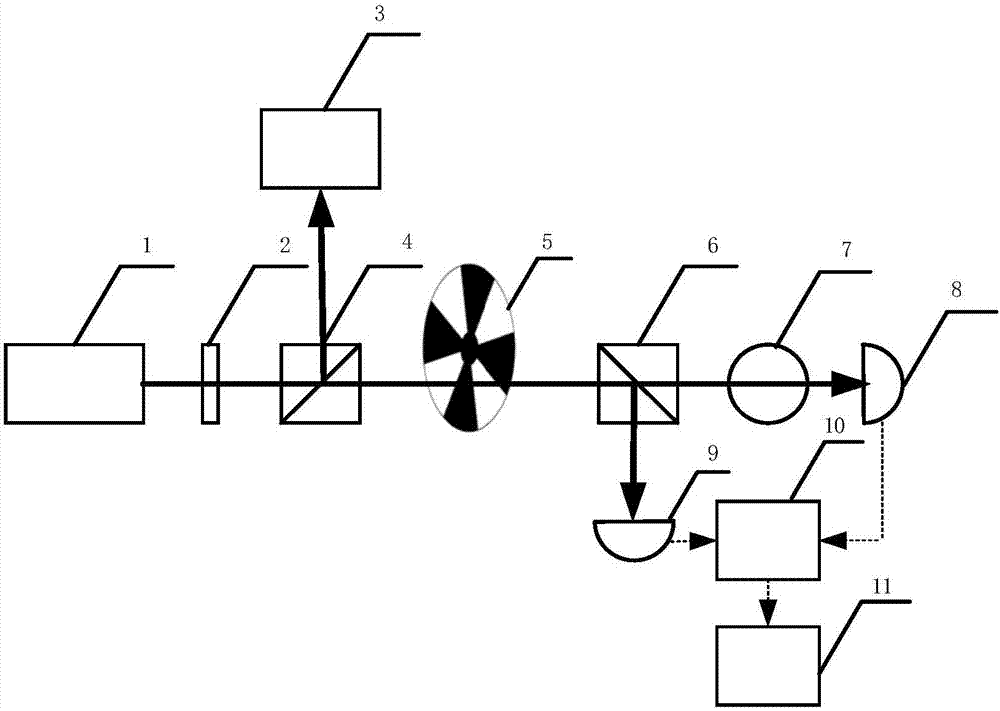
Hybrid optical pumping-based accurate atomic density measurement method
ActiveCN107167437AHigh measurement accuracyColor/spectral properties measurementsCurve fittingWorking temperature
The invention relates to a hybrid optical pumping-based accurate atomic density measurement method. The method comprises the steps of heating an alkali metal gas chamber filled with K and Rb up to starting temperature, and measuring to obtain laser absorption spectrums of the K and the Rb to obtain densities of the K and the Rb at the starting temperature, and associating Raoult's law to obtain the starting temperature as well as ratios of saturated vapor pressures to molar fractions of the K and the Rb at the starting temperature; heating the gas chamber up to working temperature, wherein the density of the Rb is very high and the absorption is very strong near a resonance point in an SERF state, carrying out curve fitting to obtain a greater deviation of the density of the Rb, and accordingly obtaining the density of the K by means of a spectral absorbing method; combining the known molar fraction of the K, and calculating to obtain the working temperature; combining the molar fraction of the Rb to obtain the saturated vapor pressure of the Rb at the working temperature, and further obtaining the density of the Rb at the working temperature. The hybrid optical pumping-based accurate atomic density measurement method is suitable for the situation that during hybrid optical pumping, the saturation absorption spectrum is very high in atomic number density and is very strong in absorption at the both sides of a resonant peak, so that the density is difficult to obtain by means of a fitted curve.
Owner:杭州诺驰生命科学有限公司
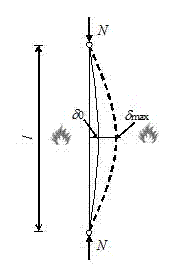
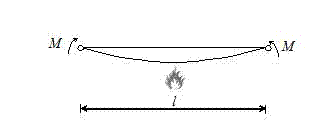
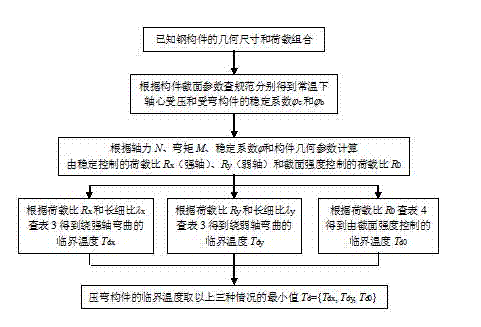
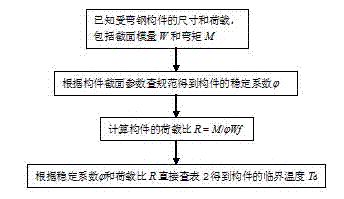
Stagnation temperature computing method of bending steel members
The invention relates to a practical fire resisting design method of a construction steel structure, and particularly relates to a stagnation temperature computing method of bending steel members. According to the method provided by the invention, stagnation temperatures of the bending steel members with different stability coefficients and load ratios can be directly obtained through checking a table. The method comprises the following specific steps of: respectively computing stagnation temperatures for bending a steel member around a strong shaft and a weak shaft under stable control and stagnation temperatures under section intensity control, wherein the minimum value of the stagnation temperatures under the three destruction is taken as a stagnation temperature of a bending framework. The method provided by the invention determines to reduce steel product strength at a high temperature according to a great quantity of test data, and the stability coefficients of bending steel members at a high temperature is directly obtained through checking the table. The method provided by the invention gives out the stagnation temperatures of the bending steel members through a form mode, a complicated numerical calculation process is avoided, and a steel structure fire resisting design method provided by the invention is convenient and reliable.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Superconductive flat plate solar water heater
InactiveCN104864612AEasy to moveAchieve heatingSolar heating energySolar heat devicesSolar waterEngineering
The invention discloses a superconductive flat plate solar water heater and belongs to the field of flat plate solar water heaters. The superconductive flat plate solar water heater comprises a water tank, a superconductive pipe, a condenser and a heat collector, wherein the condenser is provided with a capillary. A heat collecting pipe of the heat collector is composed of a thick copper pipe in the vertical direction and a plurality of thin copper pipes, one end of each thin copper pipe is sealed, the other end of each thin copper pipe is communicated with a pipe wall of the thick copper pipe, each thin copper pipe forms an included angle of 1-5 degrees with the horizontal direction, and the sealed ends of the thin copper pipes are located below the horizontal line. The bottom end of the thick copper pipe is sealed, the top end of the thick copper pipe is provided with an opening, one end of the superconductive pipe is inserted in the thick copper pipe in a matched mode through an opening, the other end of the superconductive pipe is communicated with the condenser, the condenser is installed in the water tank, and superconductive liquid is injected into the superconductive pipe. The superconductive flat plate solar water heater is in split type design and is simple in structure and convenient to install, the maintenance rate is zero; and the superconductive flat plate solar water heater runs at a stagnation temperature, is high in heat-collecting efficiency, absorbs heat quickly and is longer in service life.
Owner:HAINING YINUO ELECTRIC
Method for controlling stagnation temperature of solar vacuum tube
InactiveCN102589166AControl air drying temperatureExtended service lifeSolar heat devicesSolar thermal energy generationManufacturing cost reductionEmissivity
The invention provides a method for controlling a stagnation temperature of a solar vacuum tube. The method controls the stagnation temperature of the solar vacuum tube by changing emissivity of a back surface of a heat absorbing body of the solar vacuum tube. The inventive method can effectively control the stagnation temperature of a vacuum heat collecting tube, and make the stagnation temperature lower than a bearable set temperature of a solar vacuum heat collecting tube system, to thereby prolong the service life and lower manufacture cost of the system.
Owner:KINCAID ENERGY & TECH DEV
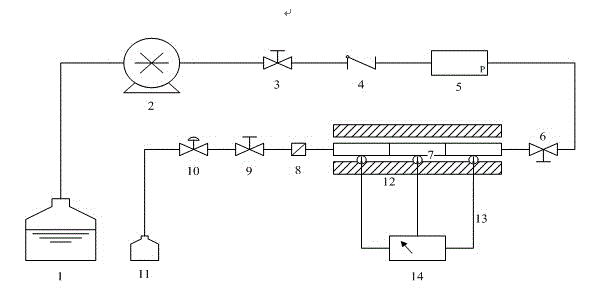
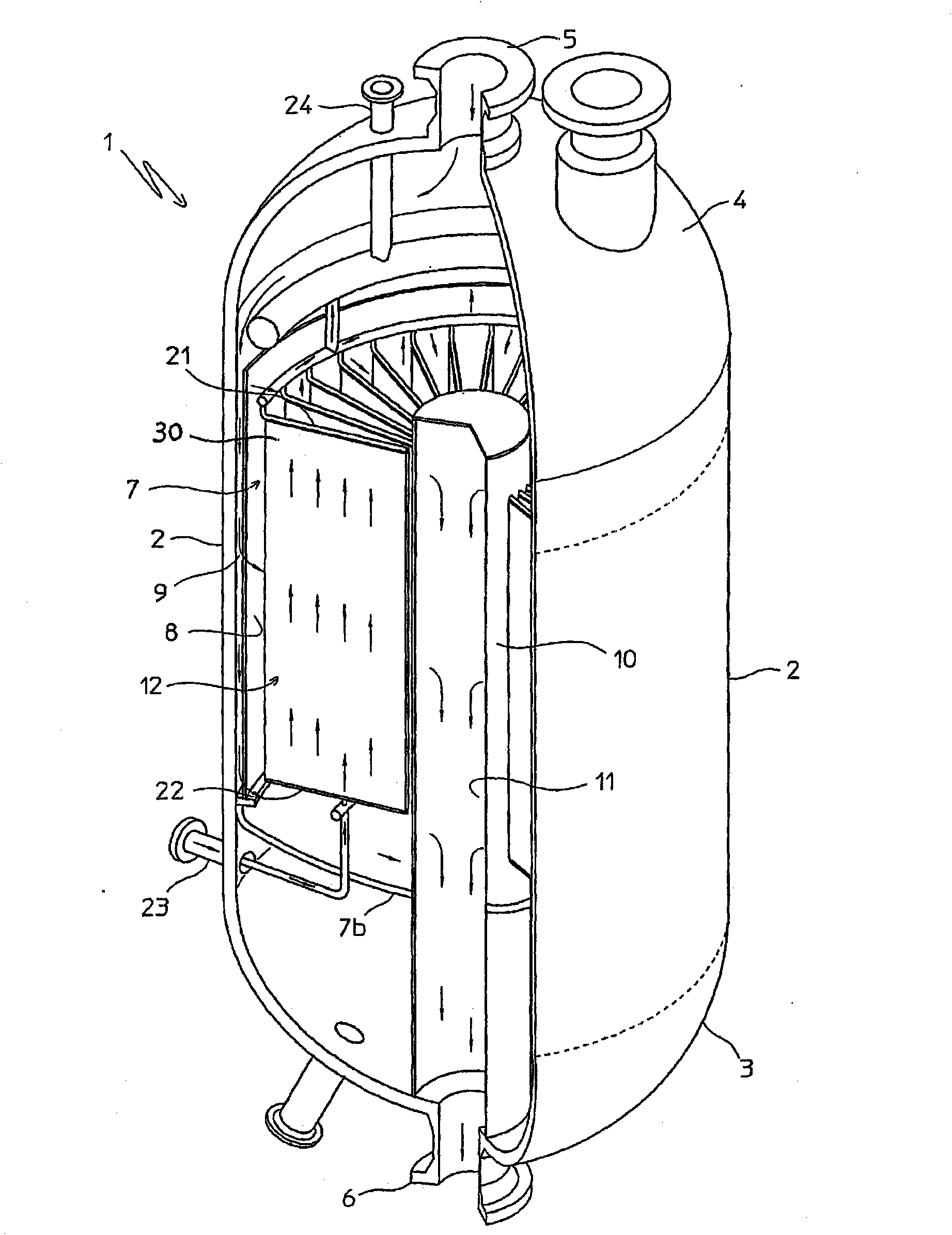
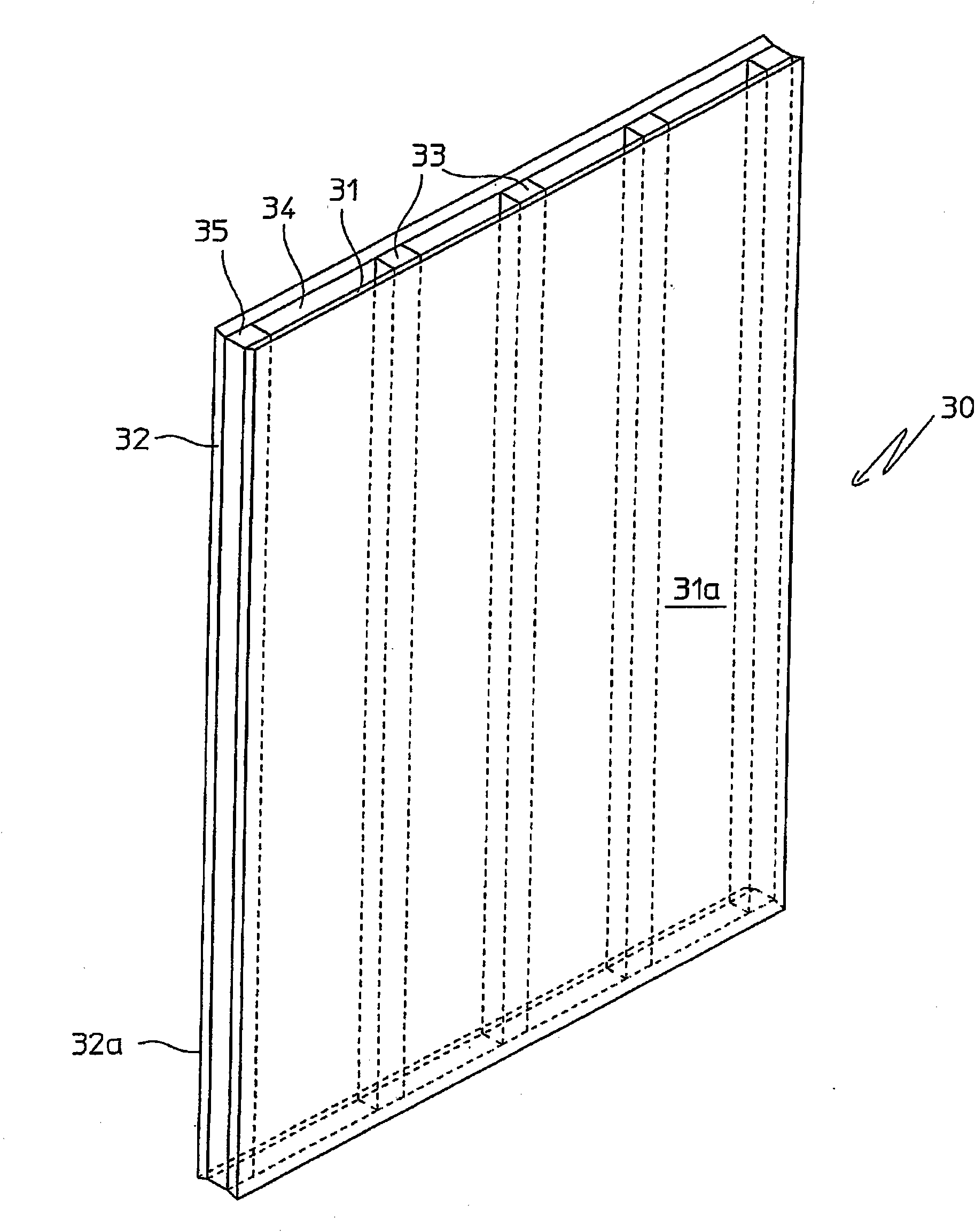
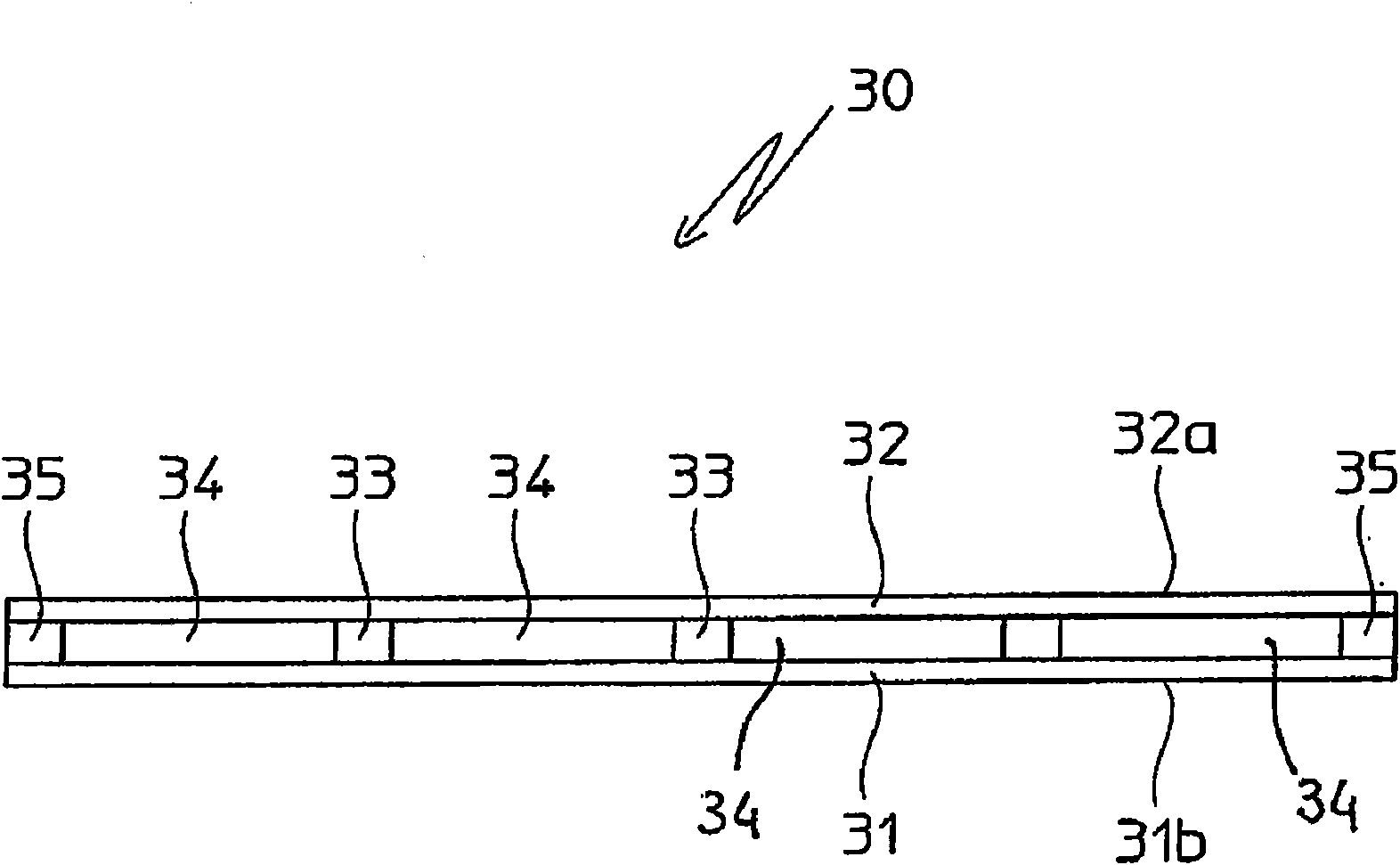
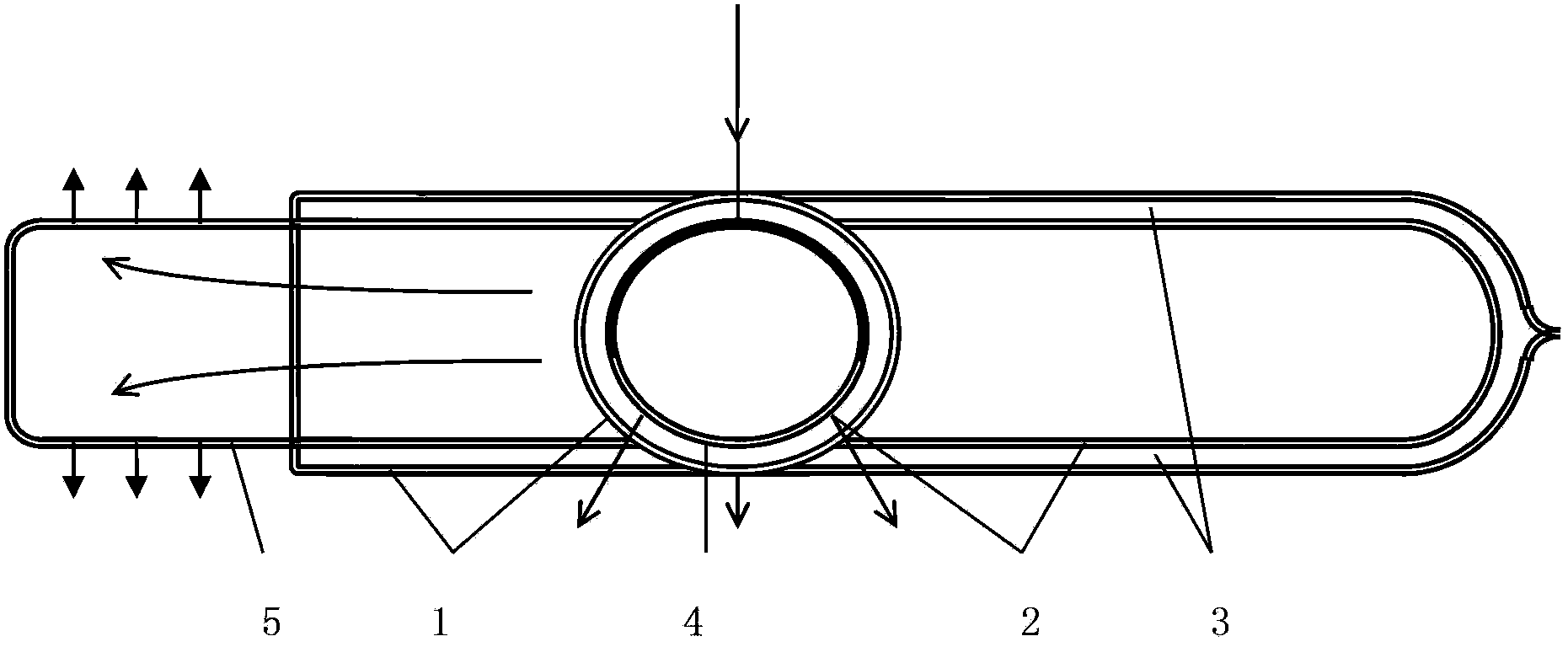
Chemical reactor with plate type heat exchange unit
InactiveCN101873889AHigh mechanical strengthReduce the distance (spacingSpacing meansChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsChemical reactorReaction temperature
An isothermal chemical reactor (1) is described comprising a plate (30) heat exchange unit (12), immersed in a catalytic bed (7) and destined to heat or cool the reagents in order to maintain the reaction temperature in a predetermined range; said plates (30) are formed by two flat walls (31, 32) and longitudinal spacers (33), with obtainment of parallel channels (34) for the circulation of a heat exchange fluid.
Owner:METHANOL CASALE SA
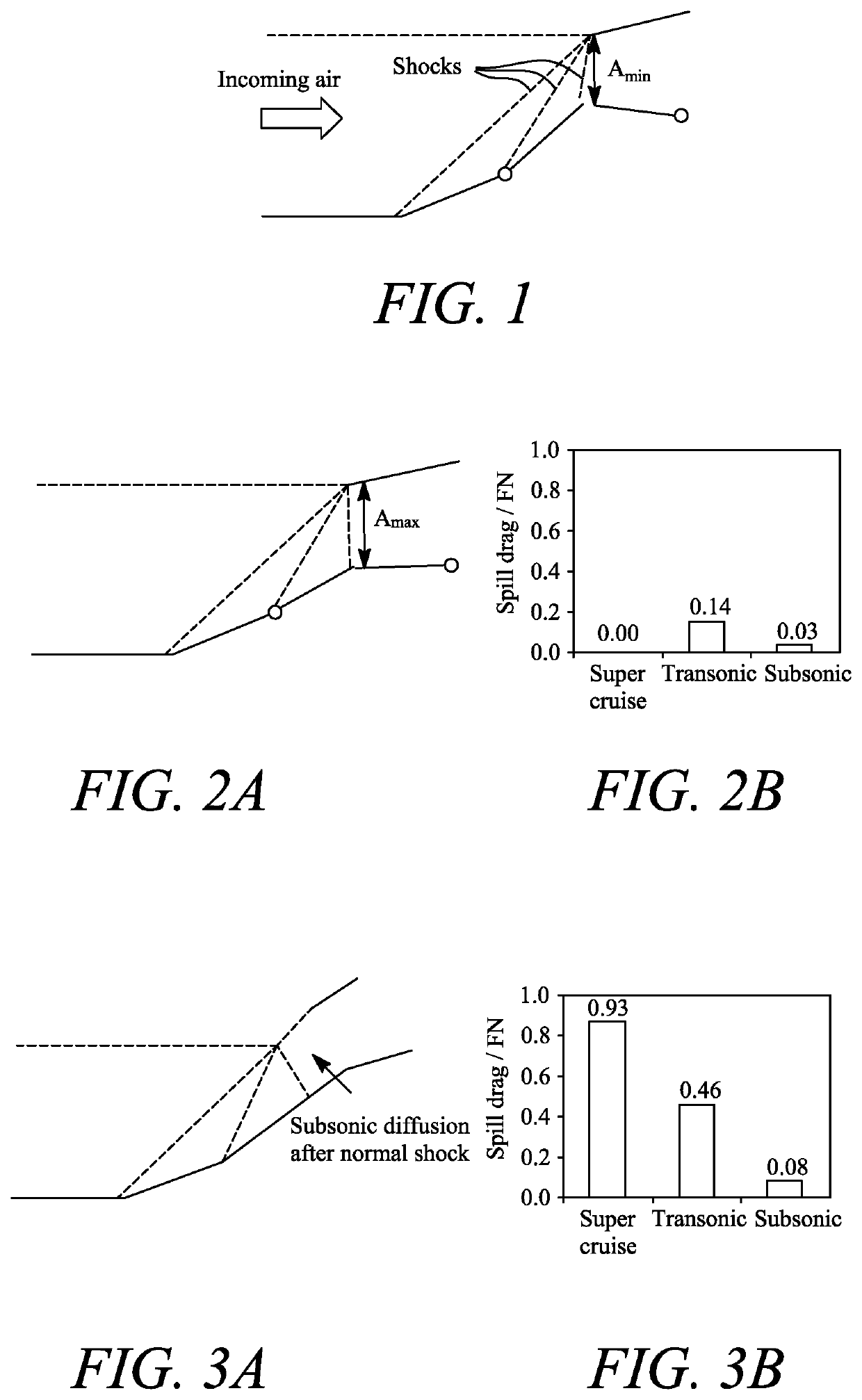
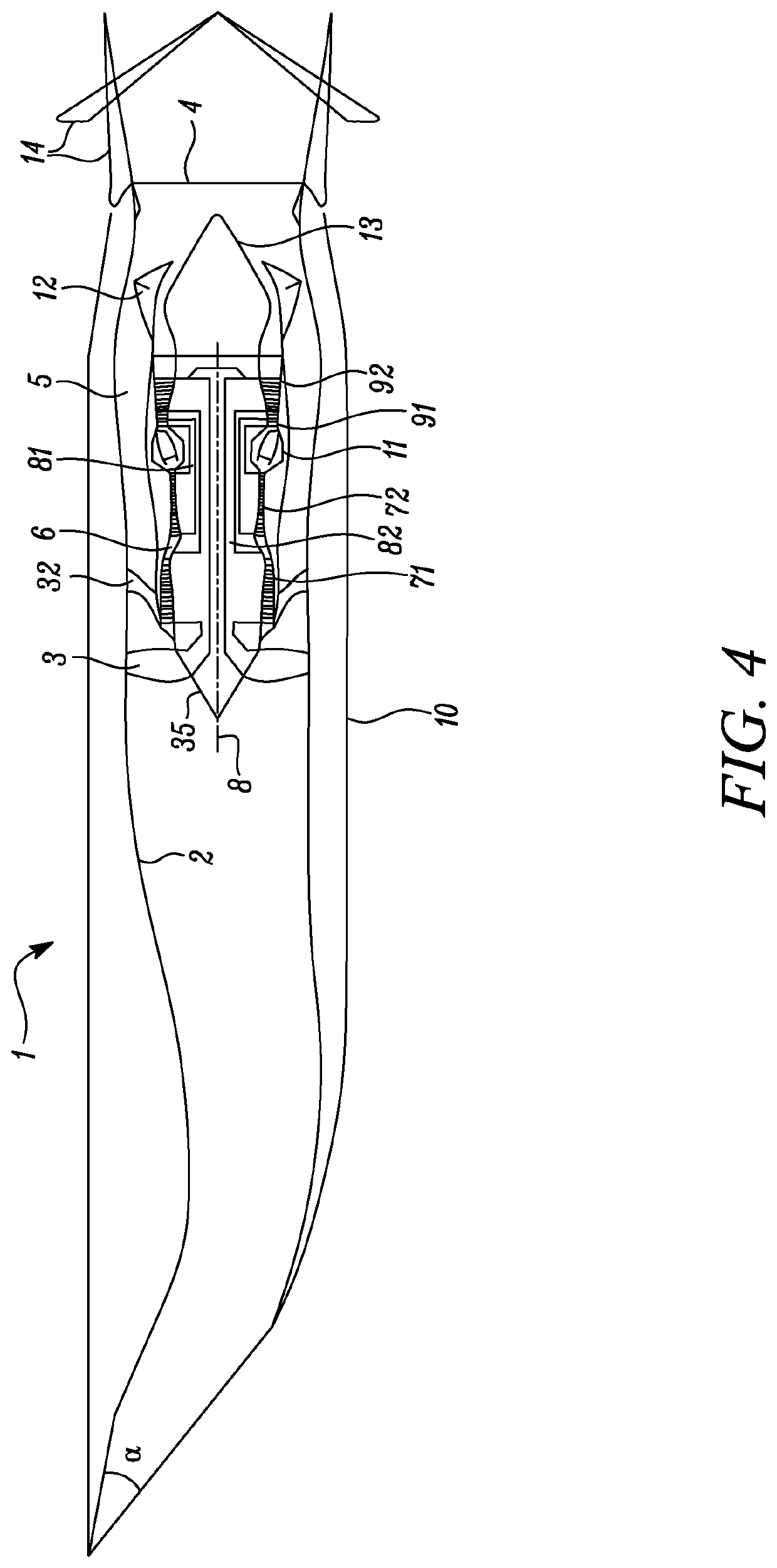
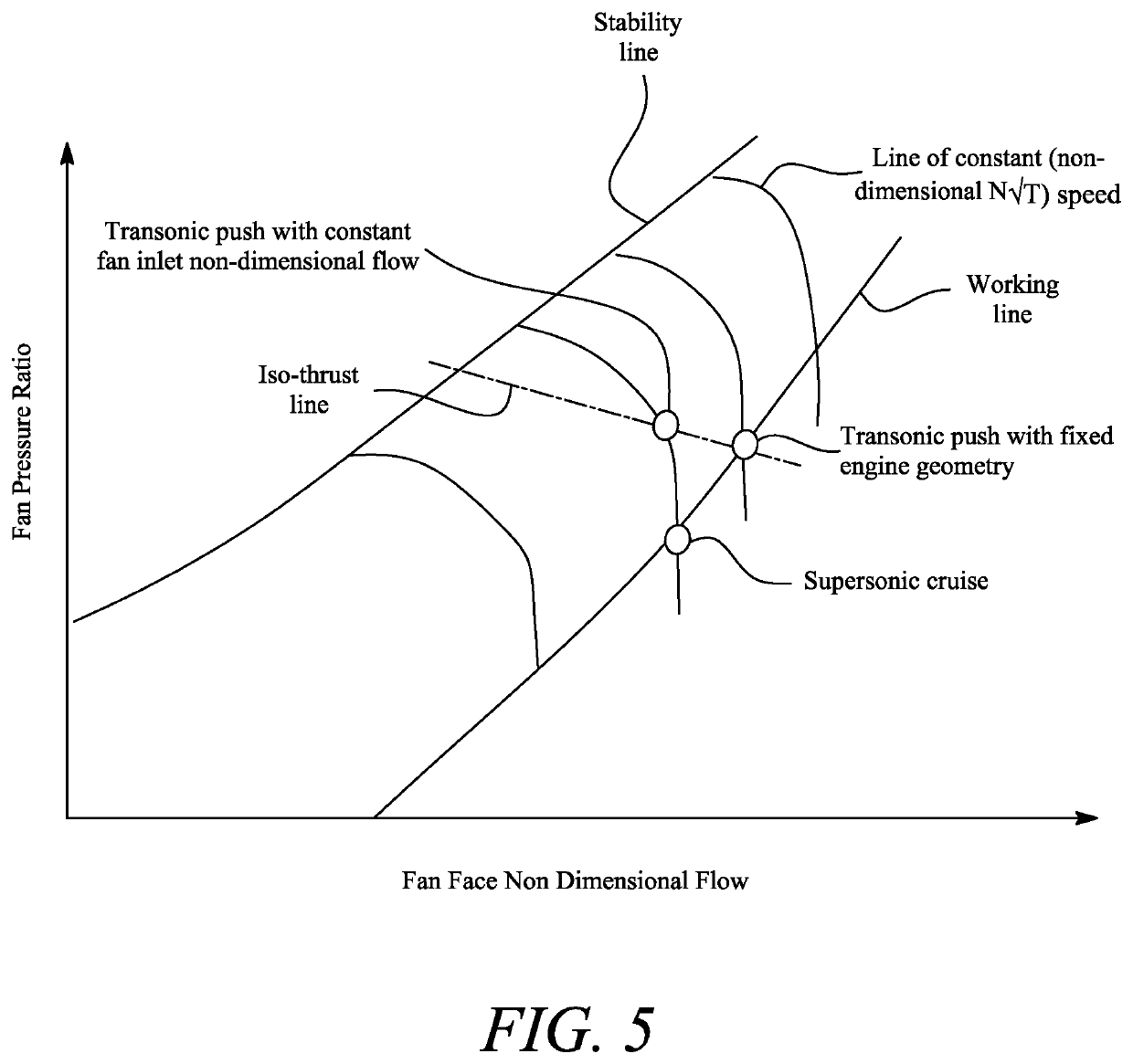
Supersonic aircraft turbofan engine
PendingUS20200023986A1Improve engine efficiencyReduce thrustEngine manufactureTurbine/propulsion air intakesCombustion chamberTurbofan
Engine has core compressor, combustor and turbine, fan located upstream of core and supersonic intake for slowing down incoming air at inlet formed by intake, bypass duct surrounding engine core, fan generates airflow to engine core and bypass airflow through bypass duct. Engine has mixer for exhaust gas flow exiting engine core, bypass airflow exiting bypass duct, thrust nozzle for discharging mixed flows, and controller for thrust produced by engine. To change level of engine thrust between transonic push operation and supersonic cruise operation, controller adjusts one or more components which vary relative areas available for hot exhaust gas flow and cold bypass airflow at mixer while holding fan inlet non-dimensional mass flow w √{square root over ( )} T / P substantially constant, where w is mass flow of incoming air at fan inlet, T is stagnation temperature of incoming air at fan inlet and P is stagnation pressure of incoming air at fan inlet.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
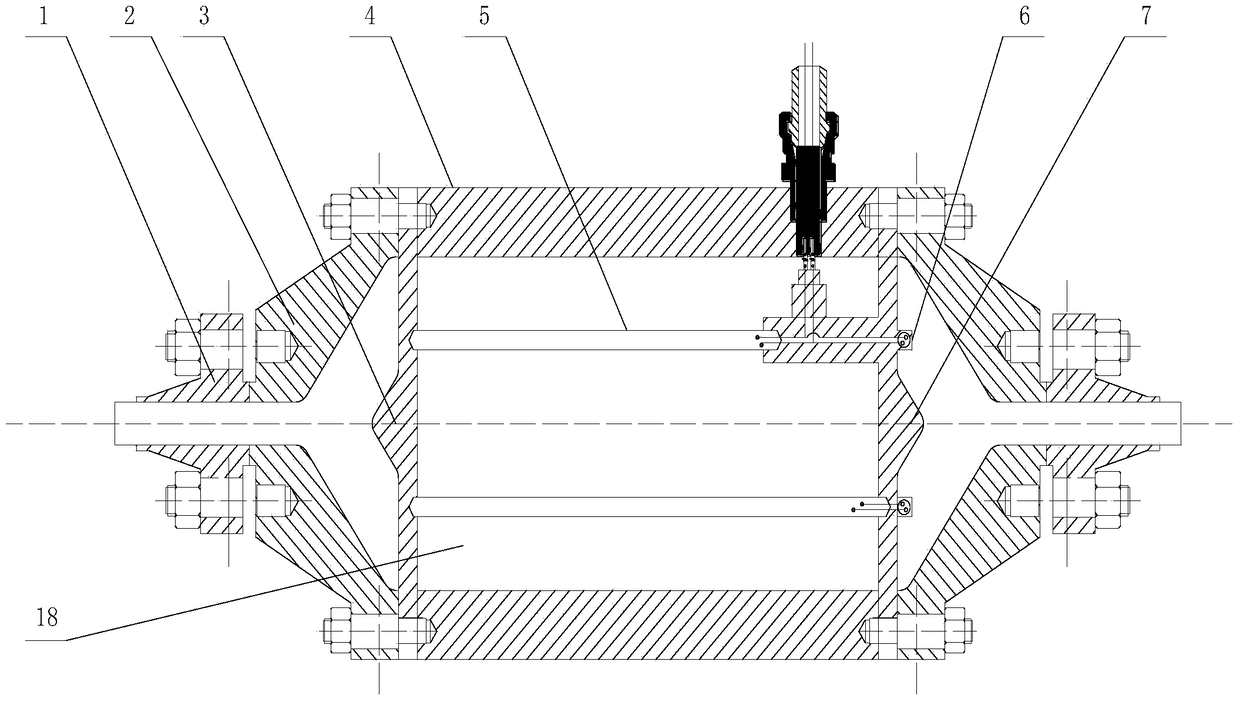
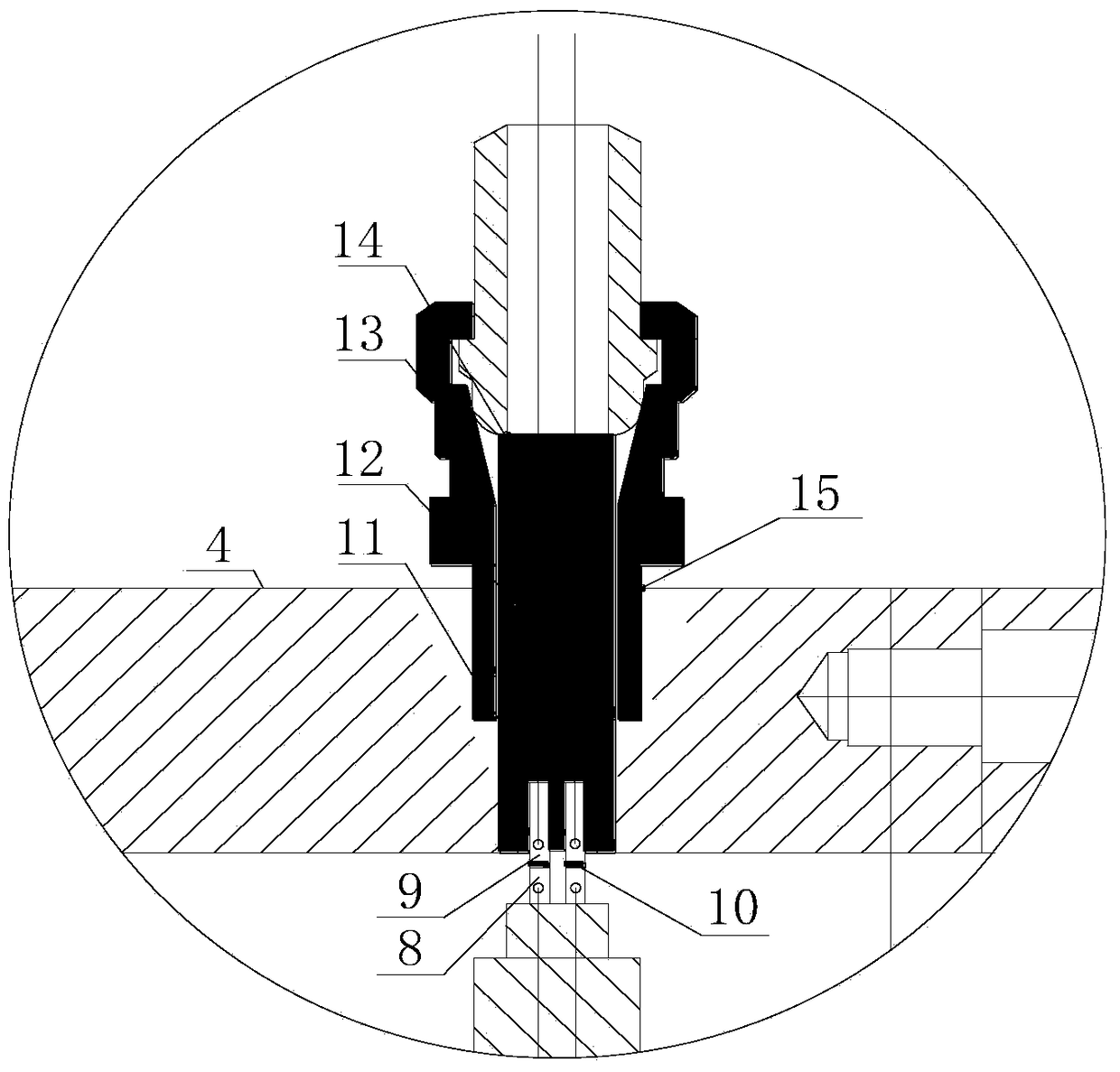
A high-pressure orifice gas stagnation temperature control device and method
ActiveCN106444889BControllable temperature parametersAvoid Measuring InaccuraciesTesting/calibration apparatusTemperature control using electric meansVena contracta diameterTemperature control
The present invention belongs to the orifice plate gas flow measurement technical field and relates to a high-pressure orifice plate gas stagnation temperature control device and method. The control device is a temperature control gas tank; a temperature control gas tank inlet flange is externally connected with the outlet of a gas source; a front porous rectifying plate is clamped to a temperature control gas tank wall through a temperature control gas tank inlet expanding type clamp plate flange by means of bolts; electric heating rods are fixedly clamped to a rear porous rectifying plate through the front porous rectifying plate; line collection rings are located on the rear porous rectifying plate; electrode springs are clamped between electric heating rod inner electrodes and external electrodes; the external electrodes are embedded in insulating materials; the insulating materials are embedded in metal plugs; the metal plugs are welded to ball head-taper surface sealing structures; the ball head-taper surface sealing structures are welded to the temperature control gas tank wall; and outer periphery flow guiding holes and inner periphery flow guiding holes are located on the rear porous rectifying plate. With the high-pressure orifice plate gas stagnation temperature control device and method of the invention adopted, gas temperature at the inlet of an orifice plate can be effectively compensated in a certain range, the accuracy of key parameter measurement participating in the calculation of the discharge coefficient of the orifice plate can be ensured, and the accuracy of the calibration of the discharge coefficient of the orifice plate can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE INST FOR METROLOGY & MEASUREMENT TECH +1
Method for computing stagnation temperature of flexural steel member
InactiveCN103207205AEasy to calculateBuilding constructionsInvestigating phase/state changeLoad ratioStability coefficient
The invention relates to a practical fire resisting design method of a construction steel structure, and particularly relates to a method for computing stagnation temperature of a flexural steel member. According to the method provided by the invention, aiming at different stability coefficients and load ratios, the stagnation temperature of the flexural steel member can be directly taken through checking a table; and the reduction in the steel product strength at a high temperature is determined according to a great quantity of test data, and the stability coefficient of the flexural steel member at the high temperature is directly taken through checking the table. According to the method provided by the invention, the stagnation temperature of the flexural steel member is given out through a form mode, and the complicated numerical calculation process is avoided; and the invention provides a convenient and reliable steel structure fire resisting design method.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
In-Situ Passivation and Insulation Layer for a Flexible Thermal Protection System (FTPS)
A lightweight flexible BNNT mat or fabric provides improved thermal stability and shielding capabilities under a hypersonic thermal flux. The BNNT mat reduces the stagnation temperature and maintains a low regression rate. An in-situ passivation layer may be formed on the BNNT mat or fabric under high thermal flux. The passivation layer minimizes or prevents penetration of the atmosphere (air or gas) as well as heat and radiation through the thickness of the BNNT material, and it effectively diffuses heat throughout the mat or fabric laterally and radially to minimize localized excessive heat. A BNNT mat according to the present disclosure may also efficiently transfer heat from the BNNT material via radiation due to the high thermal emissivity (0.92) of the BNNT material.
Owner:NAT INST AEROSPACE ASSOC +1
Total temperature probe device with high precision and low self-loss
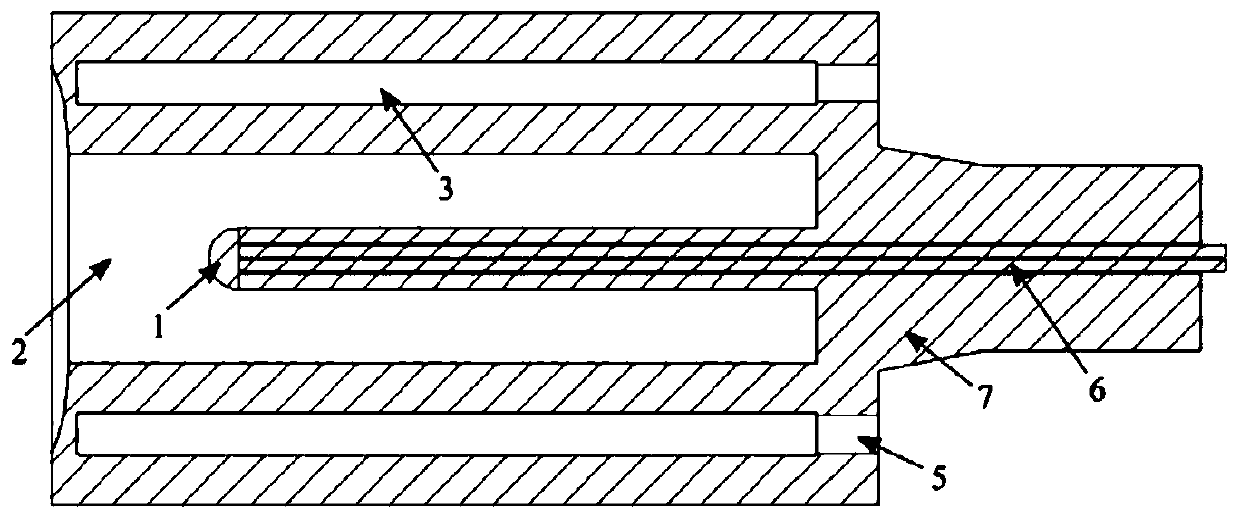
PendingCN110160667AReduce measurement errorAccurate measurementThermometer detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsLeading edgeInsulation layer
The invention discloses a total temperature probe device with high precision and low self-loss. The total temperature probe device is installed at the leading edge of a rotating mechanical blade of anaerospace vehicle and comprises a probe body, wherein the probe body is defined with two layers of chambers, which are respectively recorded as a stagnation layer and a heat insulation layer; the heat insulation layer is sleeved outside the stagnation layer, the stagnation layer contains a temperature sensor, a first through hole is defined between the stagnation layer and the heat insulation layer, and a second through hole is defined at the bottom of the heat insulation layer in the direction of the blade pitch. The purpose of the total temperature measuring device provided by the inventionis to accurately measure the stagnation temperature of the leading edge of the blade, reduce the loss caused by the temperature measuring device, and obtain a more accurate total temperature measurement when the influence on the original flow field is as small as possible.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Flow measurement for a gas turbine engine
PendingUS20220074772A1Reduce rotation speedReduce speedGas-turbine engine testingEngine fuctionsThermodynamicsEngineering
A method of thermodynamic assessment of flow through a turbomachine having a compressor, comprising: receiving sensor readings from a plurality of acoustic sensors located about an intake for the turbomachine upstream of the compressor; and receiving pressure and stagnation temperature readings for the flow into the intake. A static temperature is determined for the flow into the intake and an average velocity of the flow over a flow area of the intake upstream of the compressor using the acoustic sensor readings. A mass flow rate of the flow through the intake is determined using the average velocity of the flow and the stagnation pressure.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Passive stagnation control for solar collectors
InactiveCN105992918ASolar heating energySolar heat collector controllersActuatorSolar energy harvesting
A method for controlling stagnation in a solar collector, comprises: providing an solar energy absorbing substrate and a first layer; providing a second layer disposed between the first layer and the solar energy absorbing substrate; coupling an actuator to the solar energy absorbing substrate; and expanding the actuator when the solar collector is exposed to a stagnation temperature to form a gap between the first layer and the second layer.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
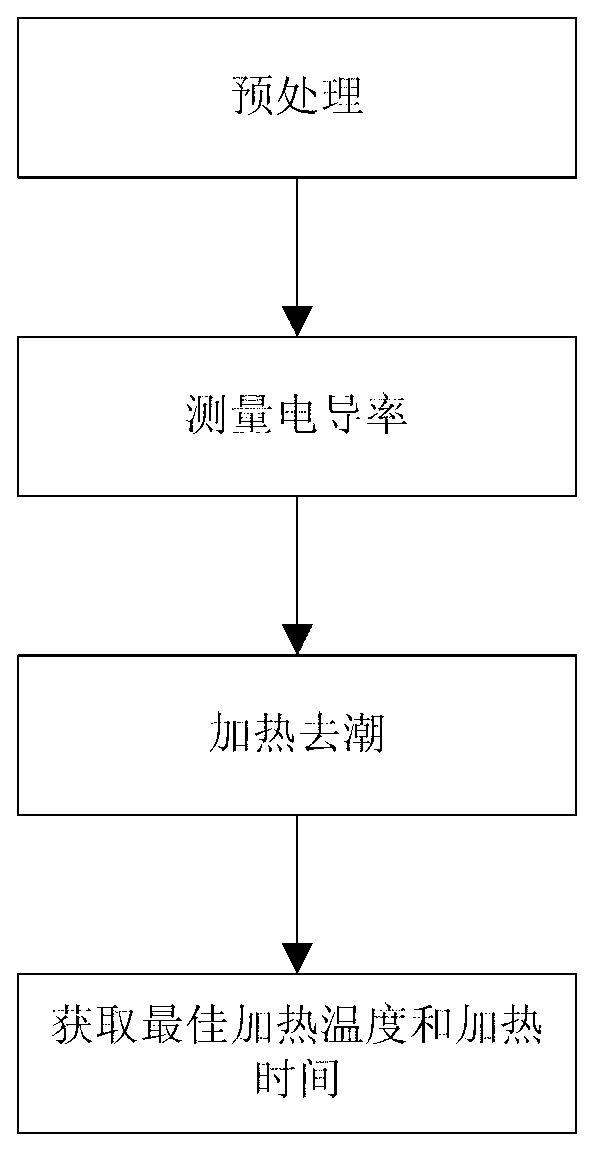
Damp removal and straightening experimental method for damp solid cables
InactiveCN103063711ADetermine the temperatureDetermine the timeMaterial resistanceInsulation layerExperimental methods
The invention relates to a damp removal and straightening experimental method for damp solid cables. The method comprises the following steps: 1) the damp solid cables to be detected and brand new solid cables as straightening standard are pre-treated, so that main insulation layers are exposed on the surfaces of the solid cables as measurement sections; 2) the electric conductivities of the measurement sections on the damp solid cables to be detected and the brand new solid cables are measured respectively; 3) the damp solid cables to be detected are heated with constant temperature under different temperatures, and the electric conductivities of the measurement sections are detected in a real-time manner in the heating process; and 4) the electric conductivities obtained in a real-time manner are compared with that of the measurement sections on the brand new solid cables to obtain the optimal damp removal and straightening temperature and time. Compared with the prior art, the method can quickly and accurately determine the optimal damp removal and straightening temperature and time for the damp solid cables.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ELECTRIC POWER CO +2
Method and apparatus for solar collector with integral stagnation temperature control
InactiveUS20070272233A1Avoid overall overheatingSolar heating energySolar heat collector controllersEngineeringSolar energy harvesting
This invention relates to a method and apparatus for a solar collector having intergral control of the maximum temperature that it can reach, thereby avoiding excessive stagnation temperatures in the collector. In one embodiment, a solar collector comprises a top portion comprising glazing, a bottom portion; an absorber disposed between said top portion and said bottom portion for absorbing solar energy received through said glazing, said absorber in a spaced relationship above said bottom portion such that a channel is defined between a lower surface of said absorber and an upper surface of said bottom portion; an inlet and an outlet associated with and at substantially opposite ends of said channel between said absorber and said bottom portion, for ventilating said channel; and a damper for opening said outlet at a temperature equal to or above a first selected temperature and for closing said outlet at a temperature equal to or below a second selected temperature; wherein said first and second selected temperatures are below a stagnation temperature of the solar collector.
Owner:QUEENS UNIV OF KINGSTON
High-emissivity low-stagnation-temperature all-glass evacuated collector tube
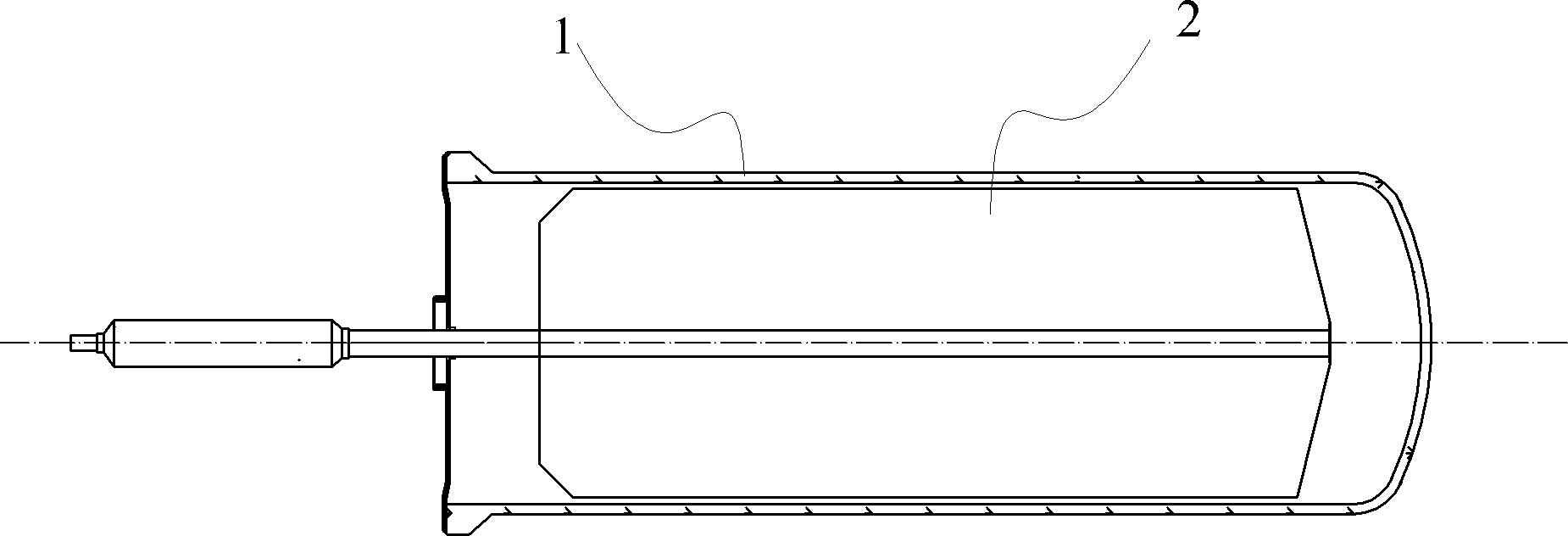
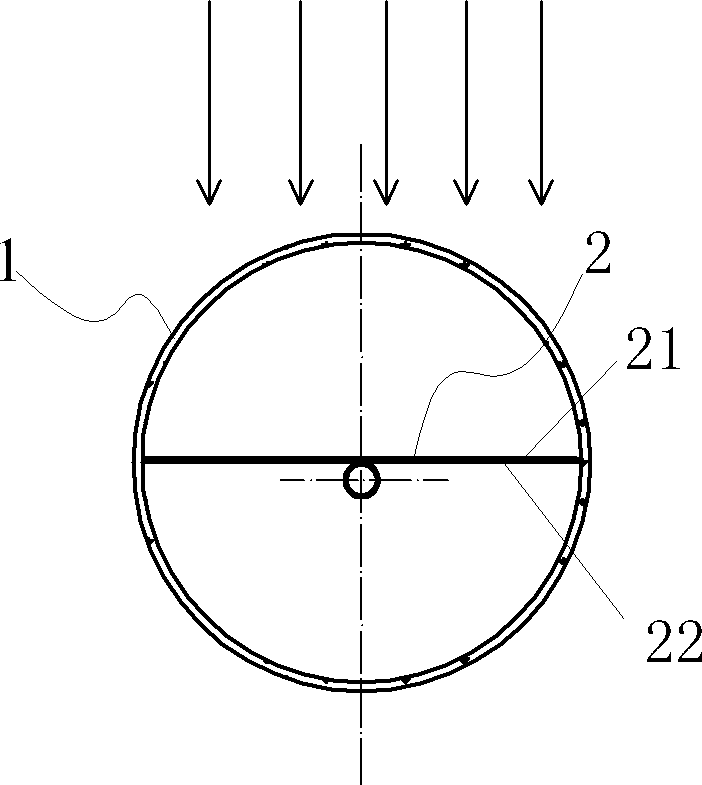
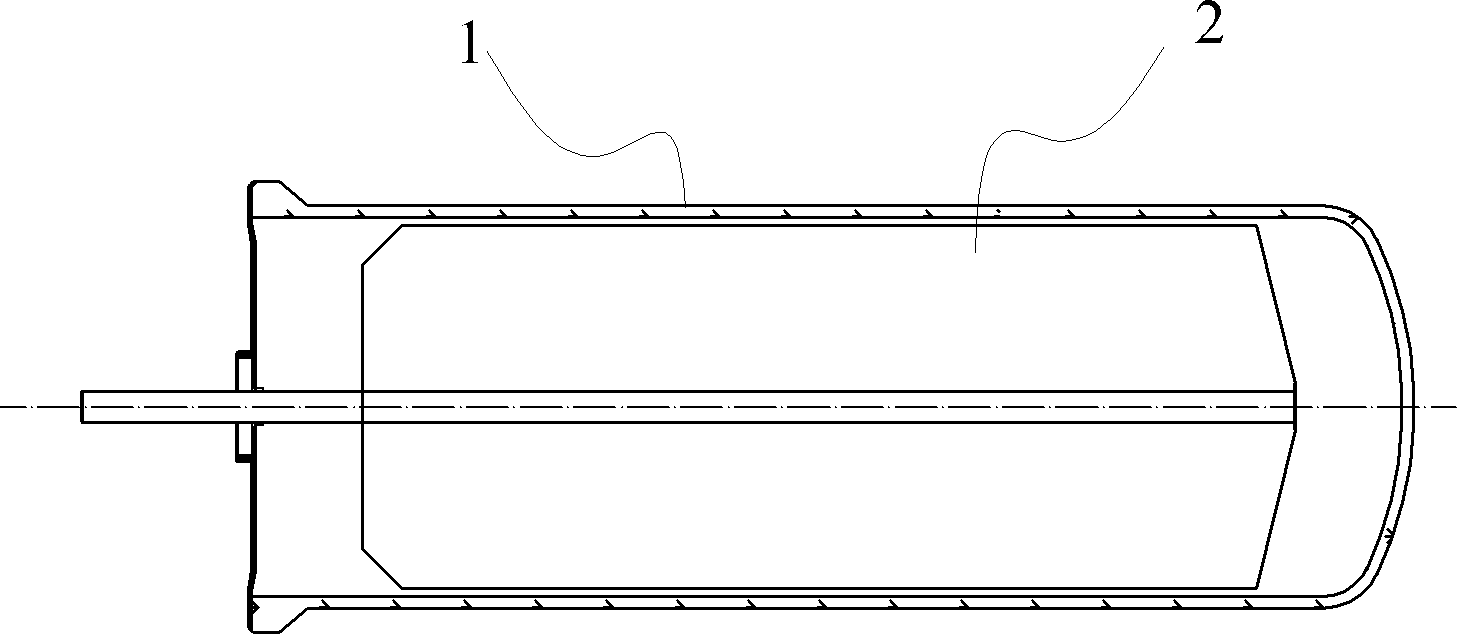
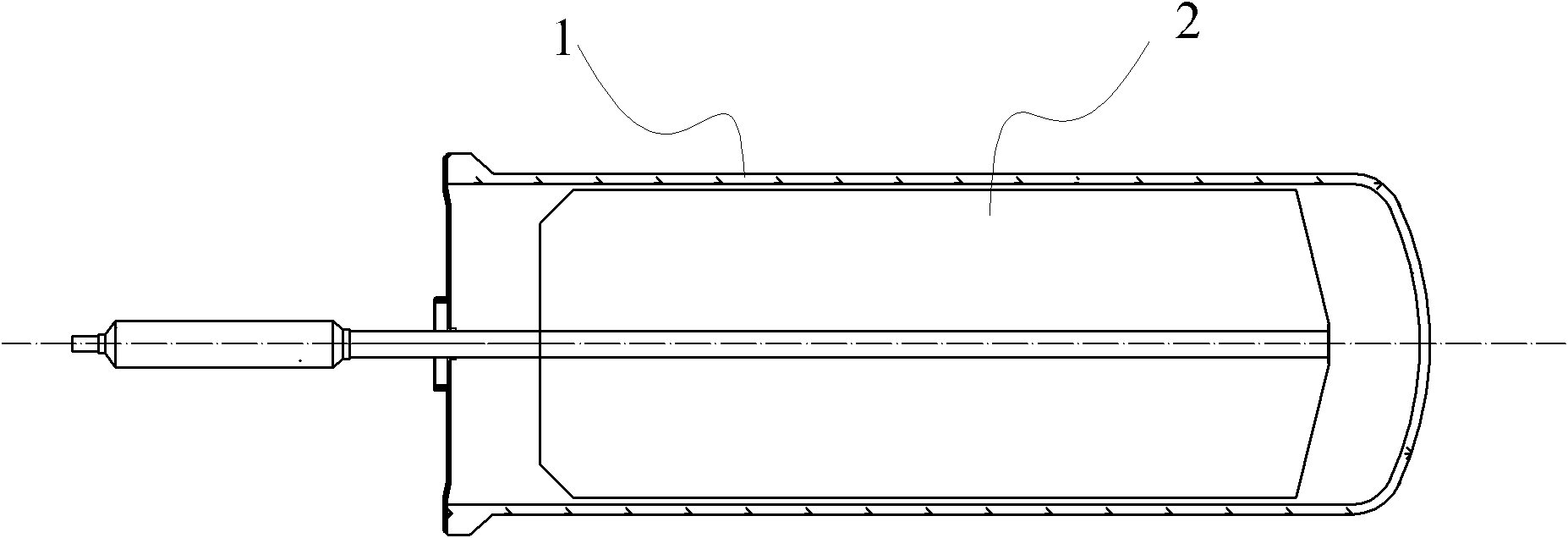
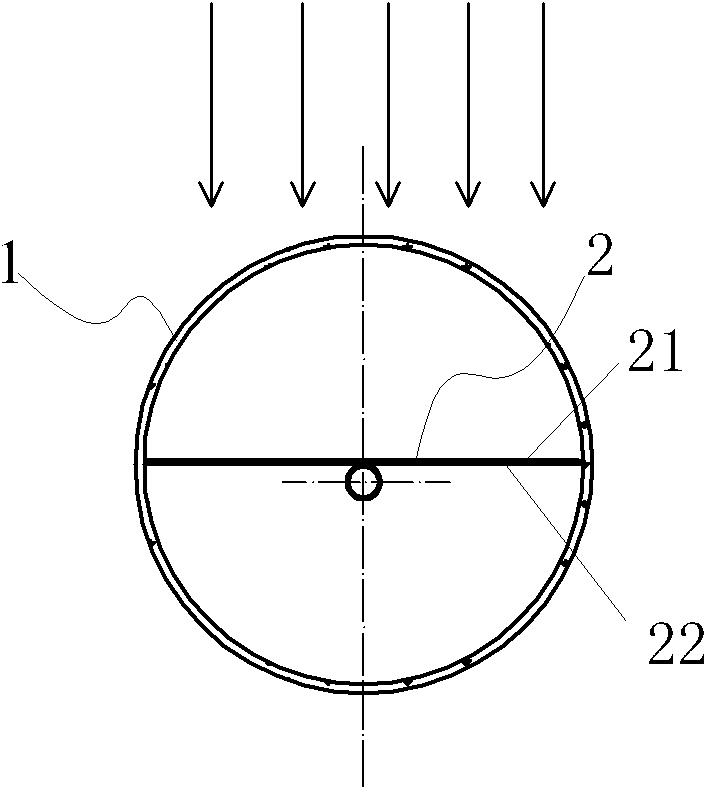
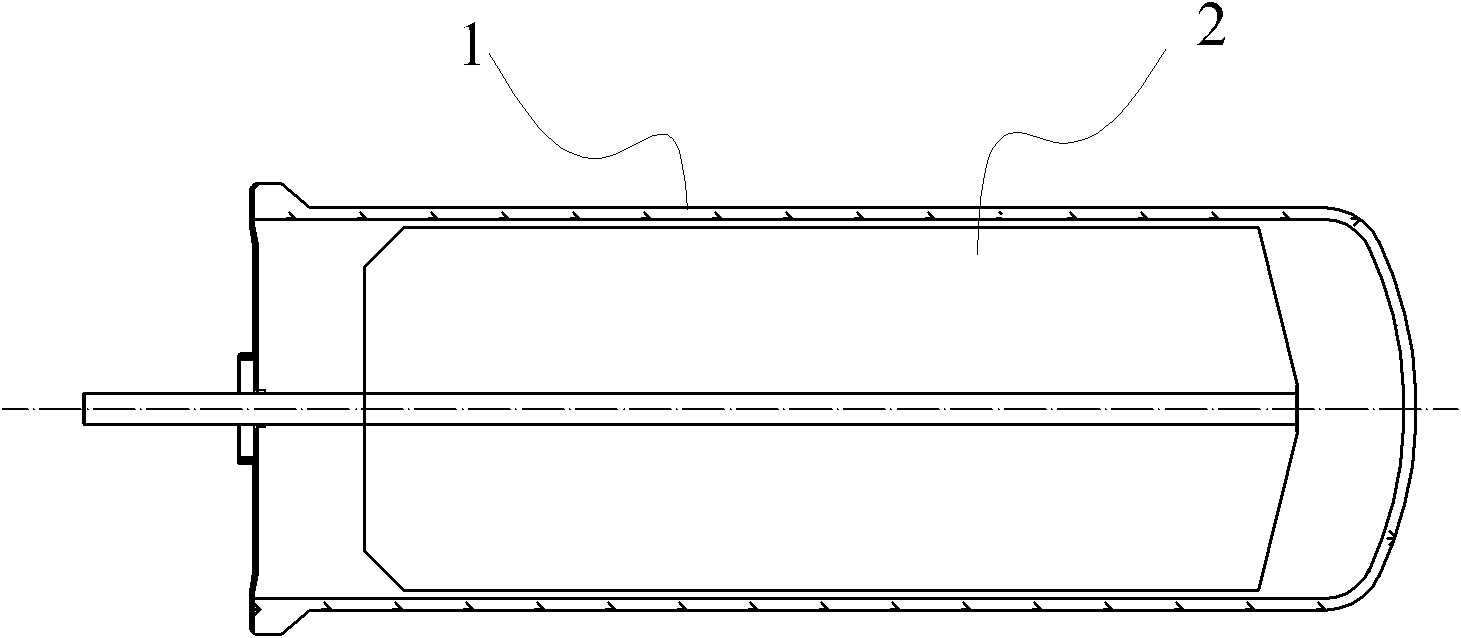
InactiveCN103423898ALower air drying temperatureSolar heat devicesSolar thermal energy generationSteam pressureEmissivity
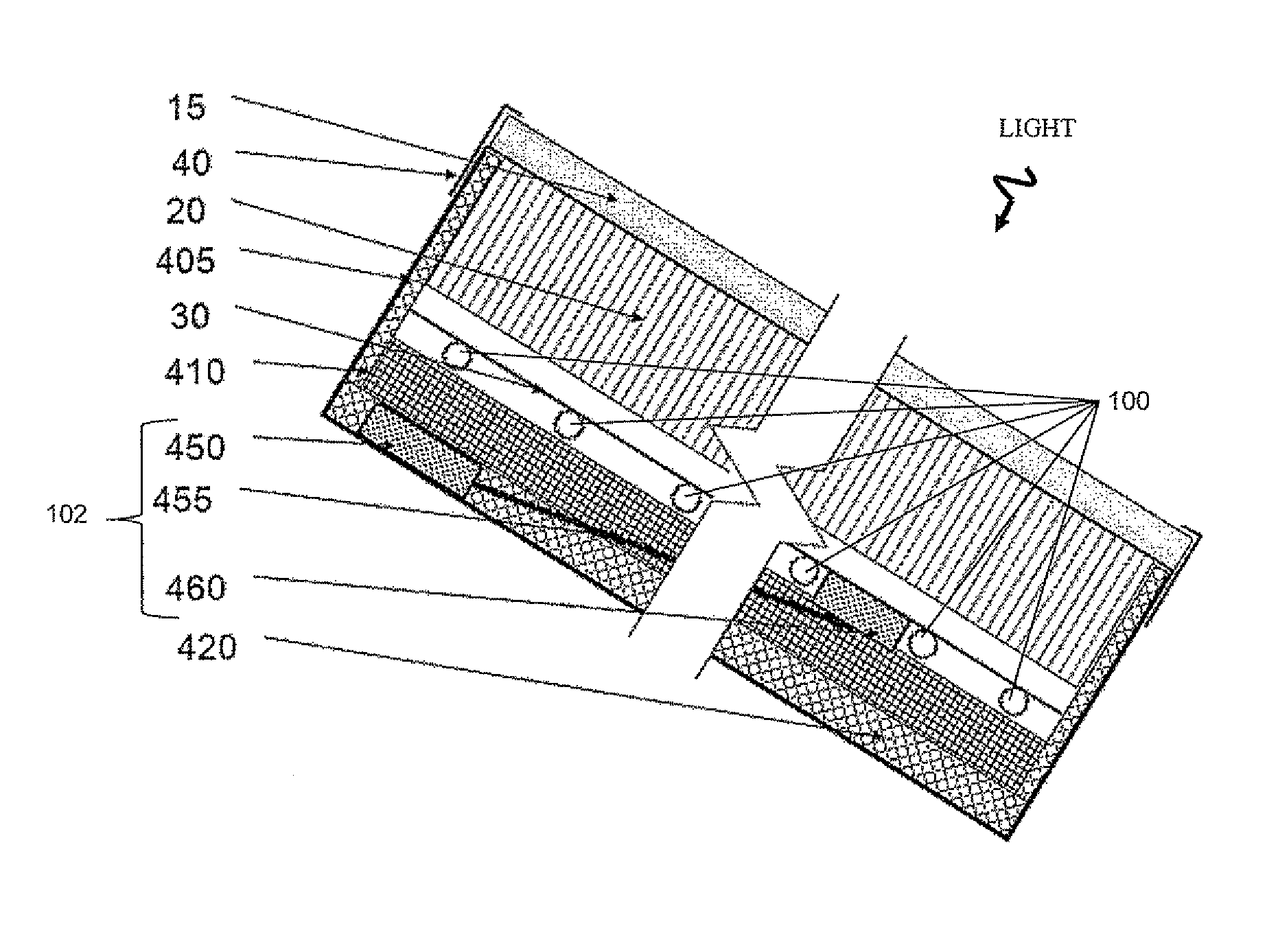
The invention relates to a high-emissivity low-stagnation-temperature all-glass evacuated collector tube. The all-glass evacuated collector tube is made by concentrically connecting a cover glass tube 1 with an inner glass tube 2 to form a jacket and vacuumizing the jacket to form a vacuum heat-insulating layer 3. Ashady face of the outer surface of the inner glass tube 2 comprises an uncoated area 4 provided with a circumferential angle of about 140 degrees and represented by double lines. A film is deposited on the sunny face of the inner glass tube 2. The inner glass tube 2 extends outwards by a section and is sealed to make a heat tube. As shown in figure 1, a working principle is characterized in that sunlight penetrates the cover glass tube 1 to be converted into heat energy on the film of the inner glass tube 2, and the heat energy is outputted through a cold end 5; during normal heat collecting, heat energy radiated through the uncoated area 4 is little; during stagnation, the surface temperature of the inner glass tube 2 is very high, heat energy radiated through the uncoated area 4, with emissivity of 92%, namely, the surface of the inner glass tube 2 is increased, excessive rising of the stagnation temperature is limited, and steam pressure inside the heat tube cannot be too high.
Owner:徐秀萍
Manufacturing method of dried basil
InactiveCN105231343AFragrance effect is goodKeep for a long timeFood preservationSurface layerEngineering
The invention provides a manufacturing method of dried basil, and relates to the technical field of food processing. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: (1) picking fresh and high-quality basils as the raw material, washing basils, and draining; (2) degrading the water on the surface layer of basils for 6 hours in a room with a constant temperature of 42 to 45 DEG C; (3) carrying out dehydration by a dehydrating machine for 45 minutes under a rotation speed of 220 r / min, and then degrading water for the second time; (4) putting the basils into the room with a constant temperature, adjusting the temperature to 32-35 DEG C, and then degrading water for the third time for 12 hours; (5) fixing color and morphology of basils at a constant temperature of 60 DEG C, and degrading the water of basils until the water content reaches 60%; (6) quantitatively packing basils into vacuum bags, storing the products in a freezing chamber with a temperature lower than 0 DEG C, and delivering the products to all parts of the country. The shelf life of basil is largely prolonged, fresh basil can be stored for only three days, the processed basil can be stored for one year or more, moreover, the fragrance is preserved, and the basils will not be crushed or broken.
Owner:HEFEI QICHAO FOOD CO LTD
High-temperature muffle furnace nine-time thermometry
ActiveCN103090663BEasy to controlAvoid abnormal fluctuationsMuffle furnacesRetort furnacesThermal ageingTest efficiency
The invention relates to a high-temperature muffle furnace nine-time thermometry. Specifically, the high-temperature muffle furnace nine-time thermometry is used for achieving accuracy control of each area temperature in a high-temperature muffle furnace. The high-temperature muffle furnace nine-time thermometry comprises steps of getting the point, testing the stagnation temperature, looking up a table of the stagnation temperature test, testing aging temperature, looking up a table of the aging temperature test, comparing the stagnation temperature and comparing the aging temperature. The high-temperature muffle furnace nine-time thermometry is convenient for the accuracy control of the thermal ageing temperature of a catalytic agent, supplies reliable temperature data to a catalytic agent thermal ageing test, avoids abnormal fluctuation of the aging test, reduces the cost of repeating aging, saves the test time and improves the test efficiency.
Owner:WUXI WEIFU ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION CATALYST
Method for controlling stagnation temperature of solar vacuum tube
InactiveCN102589166BControl air drying temperatureExtended service lifeSolar heat devicesSolar thermal energy generationManufacturing cost reductionEmissivity
The invention provides a method for controlling a stagnation temperature of a solar vacuum tube. The method controls the stagnation temperature of the solar vacuum tube by changing emissivity of a back surface of a heat absorbing body of the solar vacuum tube. The inventive method can effectively control the stagnation temperature of a vacuum heat collecting tube, and make the stagnation temperature lower than a bearable set temperature of a solar vacuum heat collecting tube system, to thereby prolong the service life and lower manufacture cost of the system.
Owner:KINCAID ENERGY & TECH DEV
Aircraft standing point temperature calculation method based on two-dimensional search
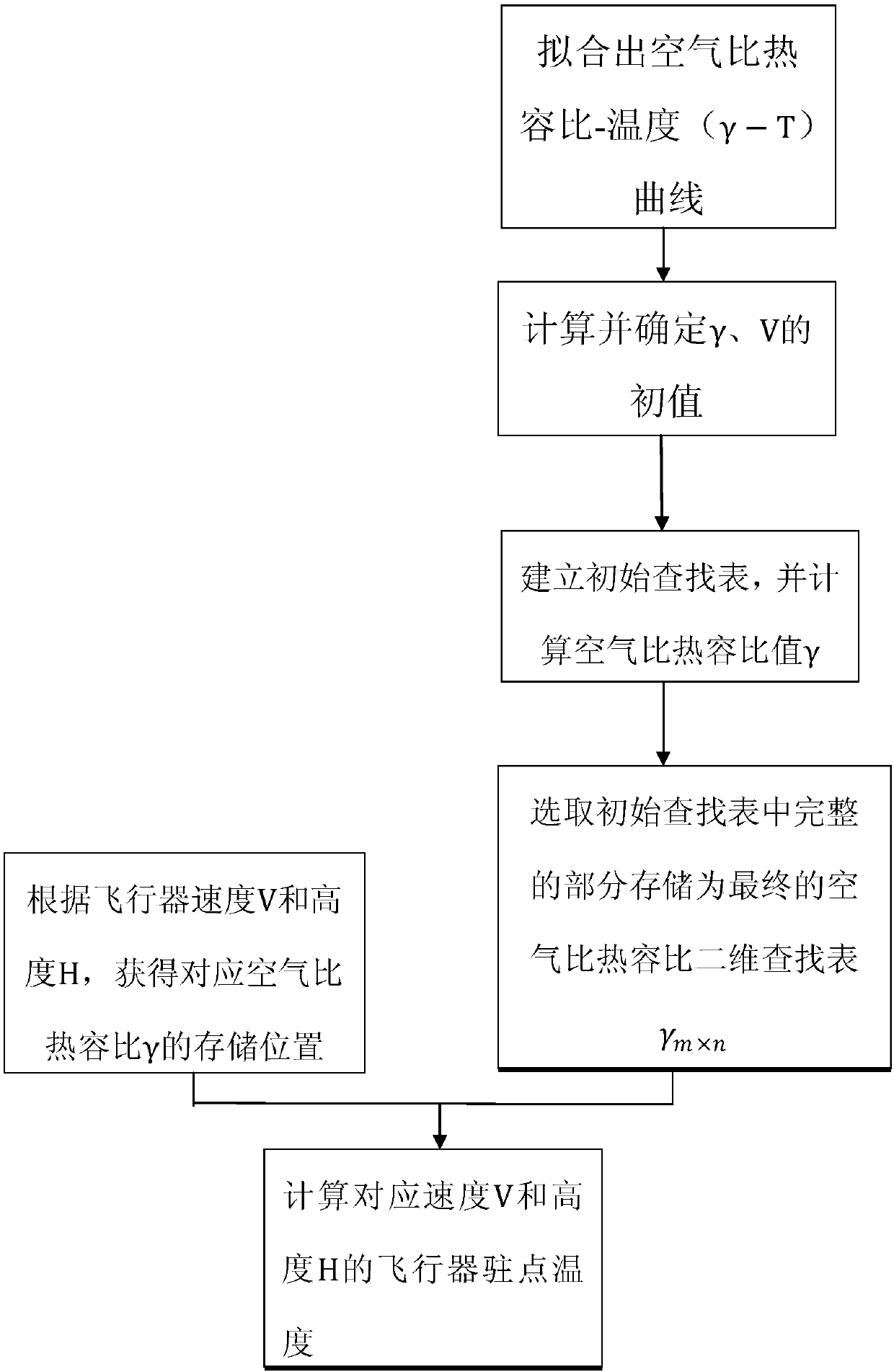
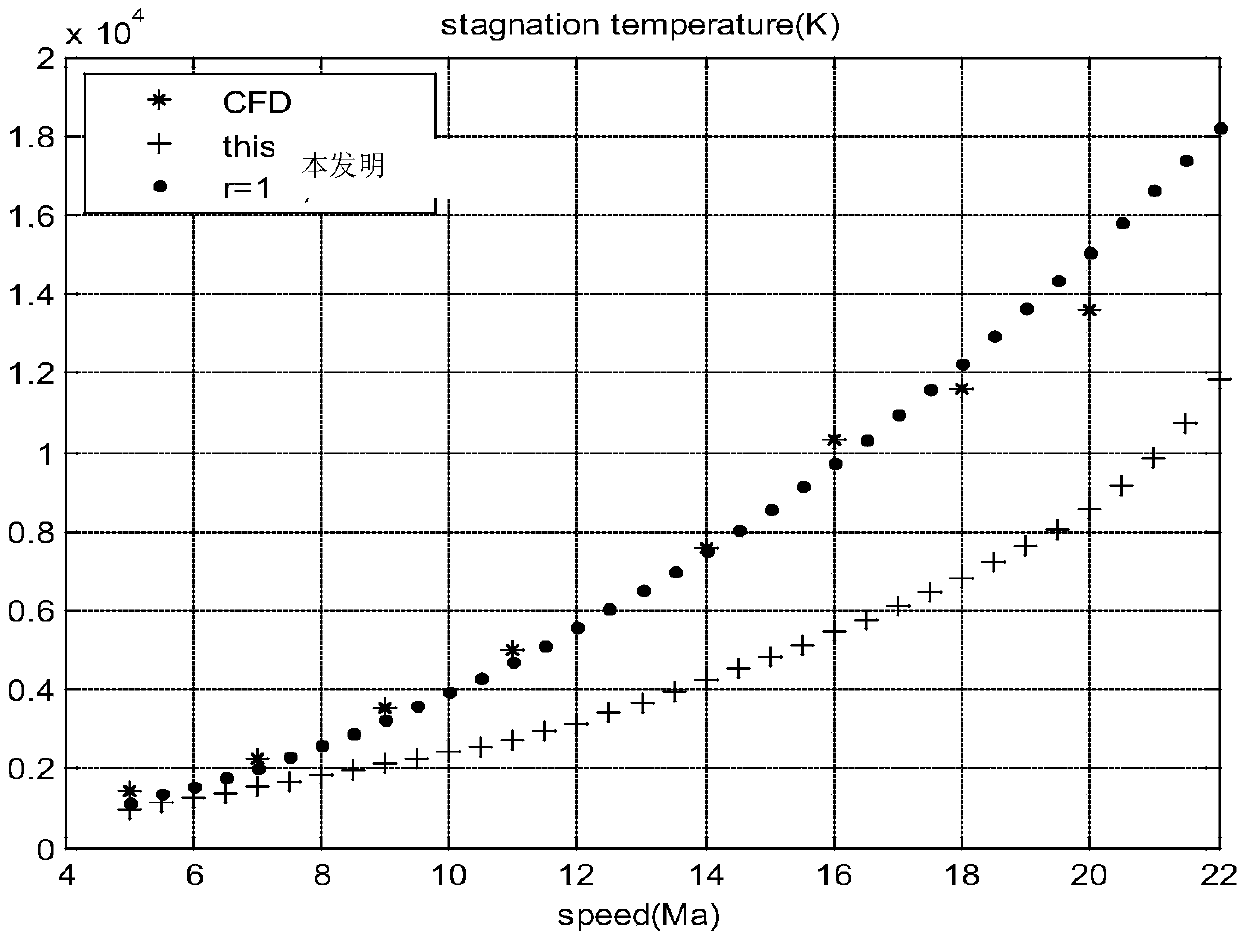
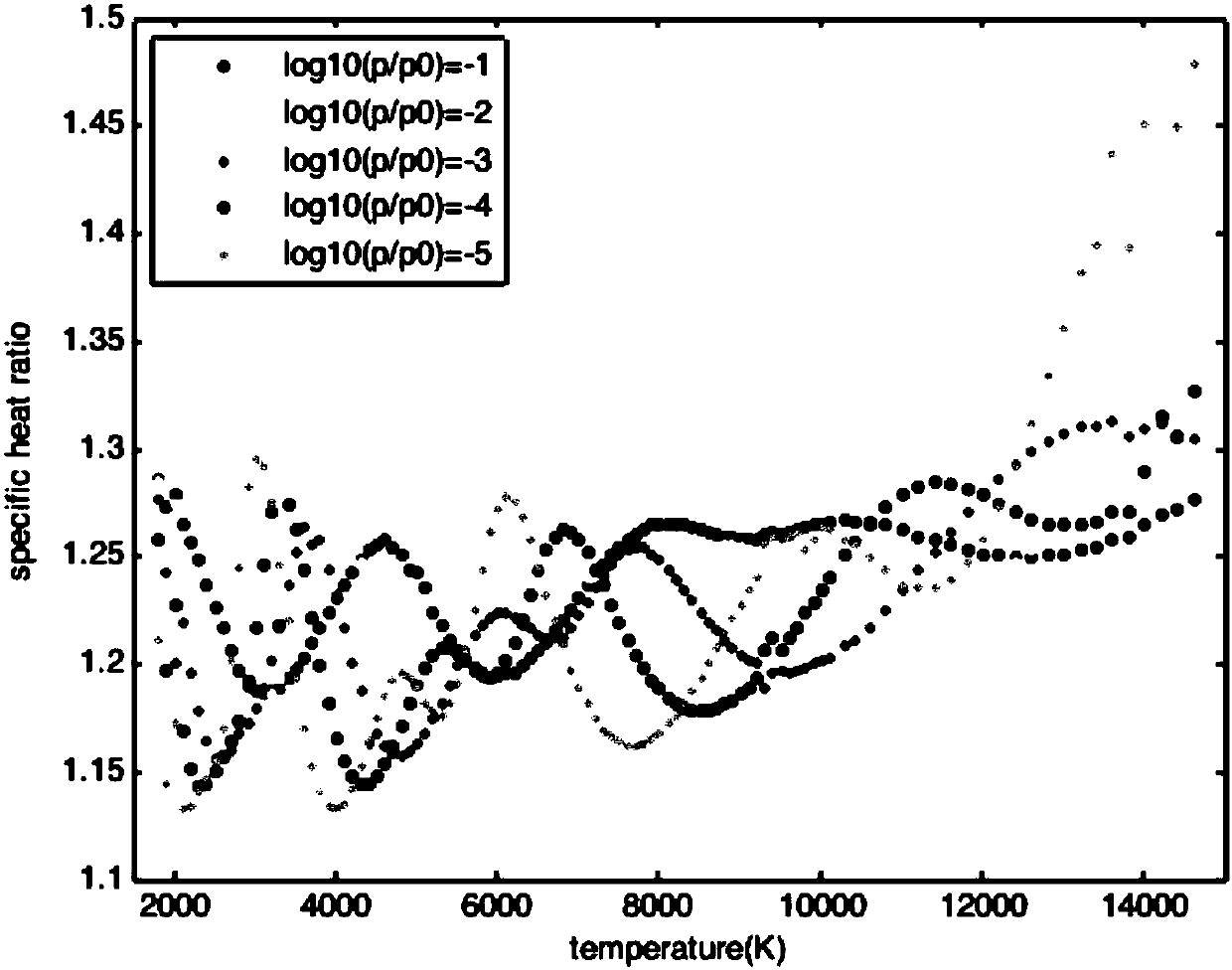
ActiveCN107563145AConvenient and practical heightConvenient and practical speedSpecial data processing applicationsCurve fittingLookup table
The invention discloses an aircraft standing point temperature calculation method based on two-dimensional search. A look-up table is established; a gamma-T curve is fitted out; the gamma-T curve is converted into the look-up table, and the temperature value T is used as a searching condition, and a corresponding air specific heat capacity ratio gammaT can be found out; the standing point temperature value when V=5Ma is calculated, according to the temperature value, a gamma value is selected, the standing point temperature is repeatedly calculated, and the gamma initial value is determined; the air specific heat capacity ratios gammai and gammaj are calculated; the flight speed V and the height H are used as conditions, the air specific heat capacity ratio gamma is searched in the two-dimensional look-up table, the aircraft standing point temperature T at the corresponding speed and height is calculated, and finally, when the height is within 20-70 km and the speed is within 5-22 Ma,the aircraft standing point temperature can be obtained. The problems that in the prior art, the aircraft standing point temperature is not accurate and calculation is discontinuous are solved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com