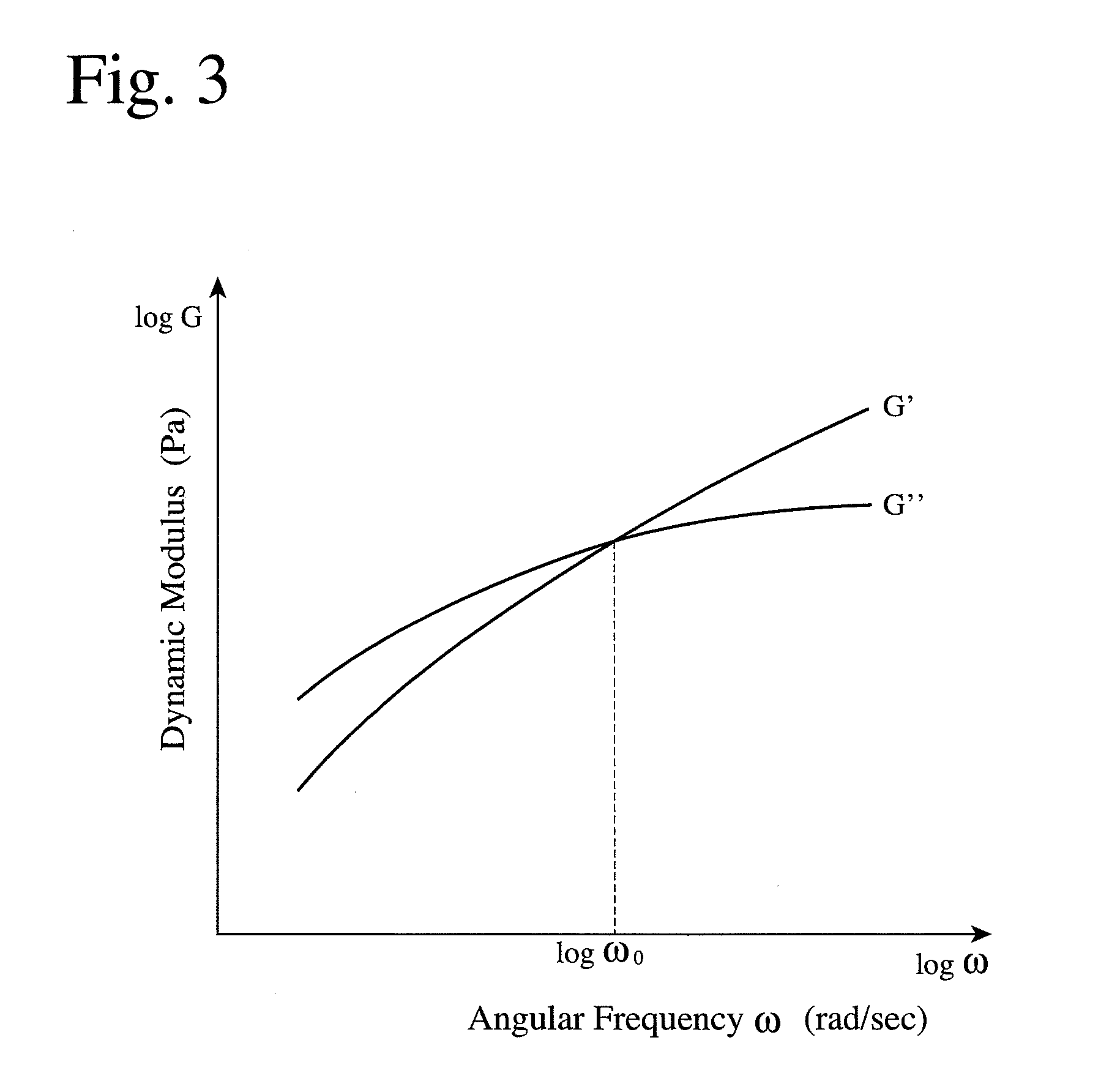
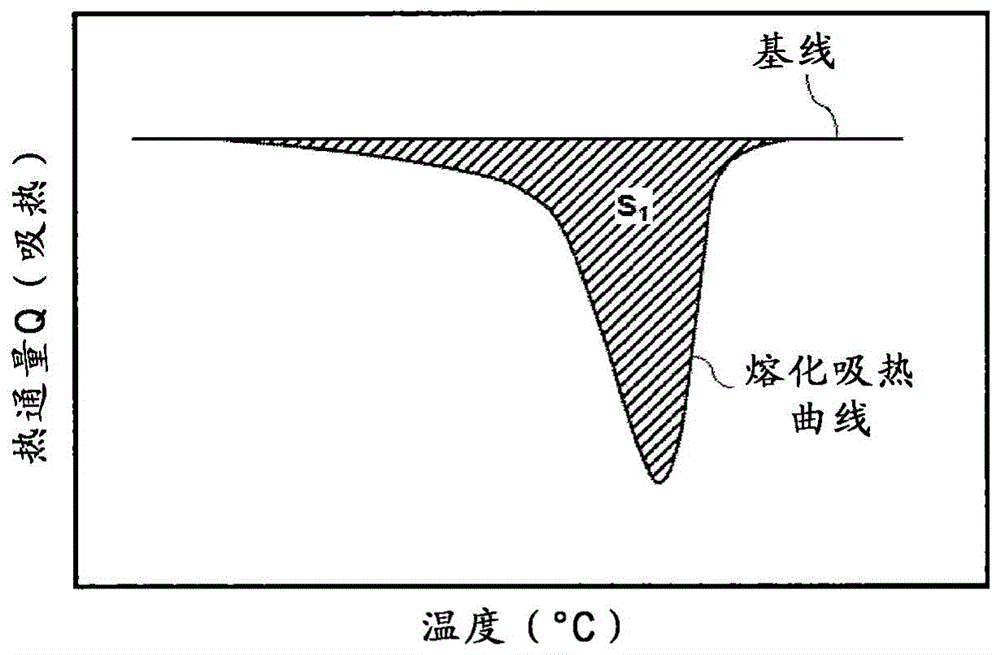
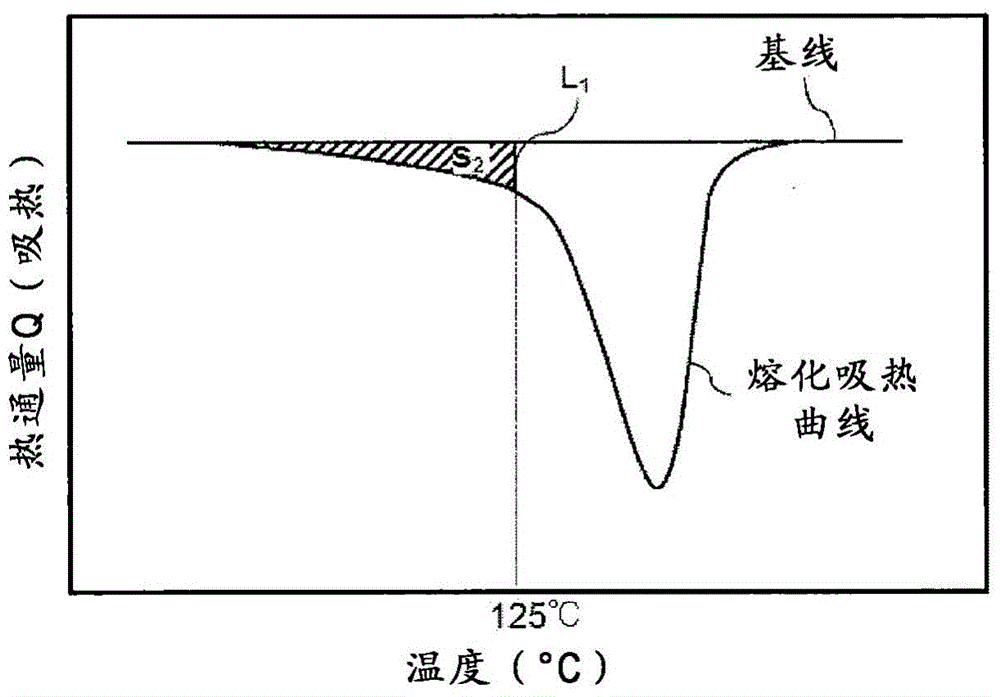
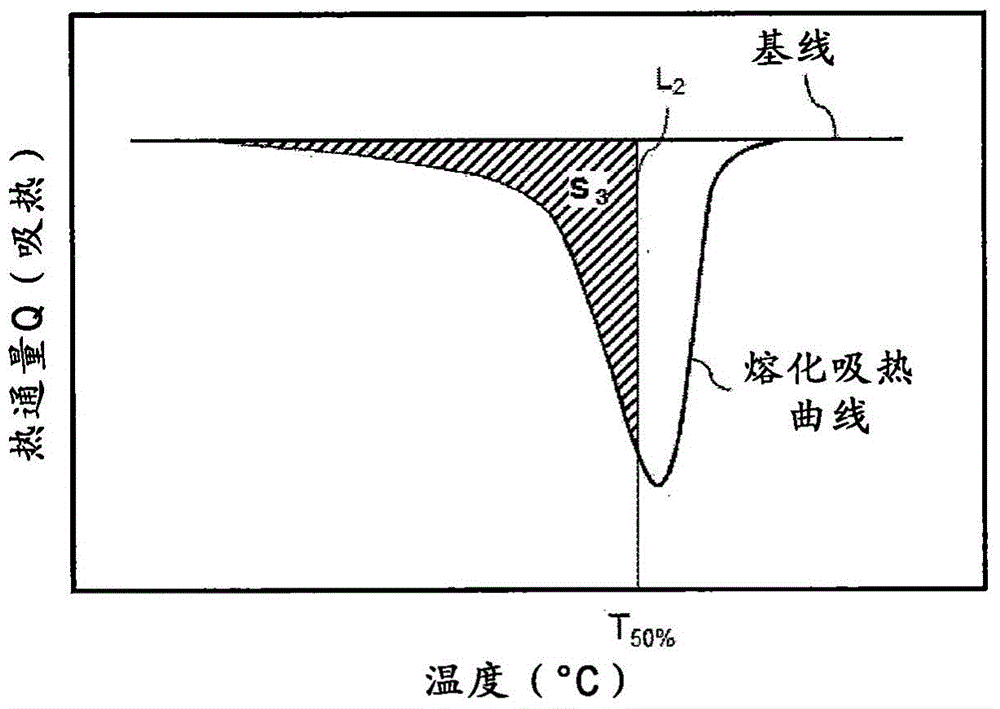
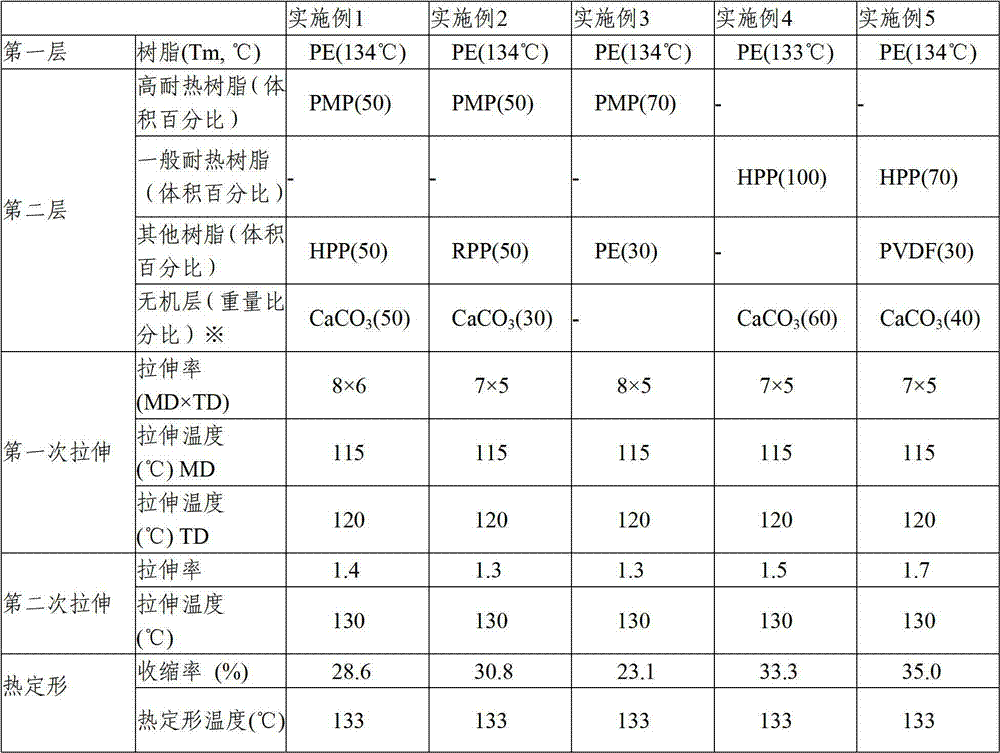
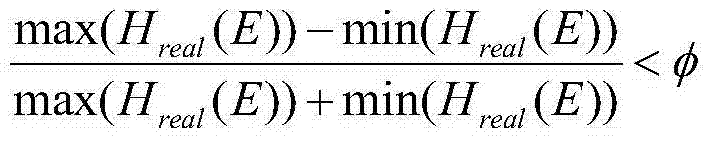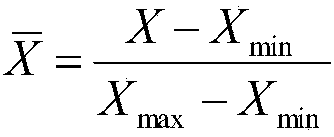Patents
Literature
105 results about "Thermomechanical analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
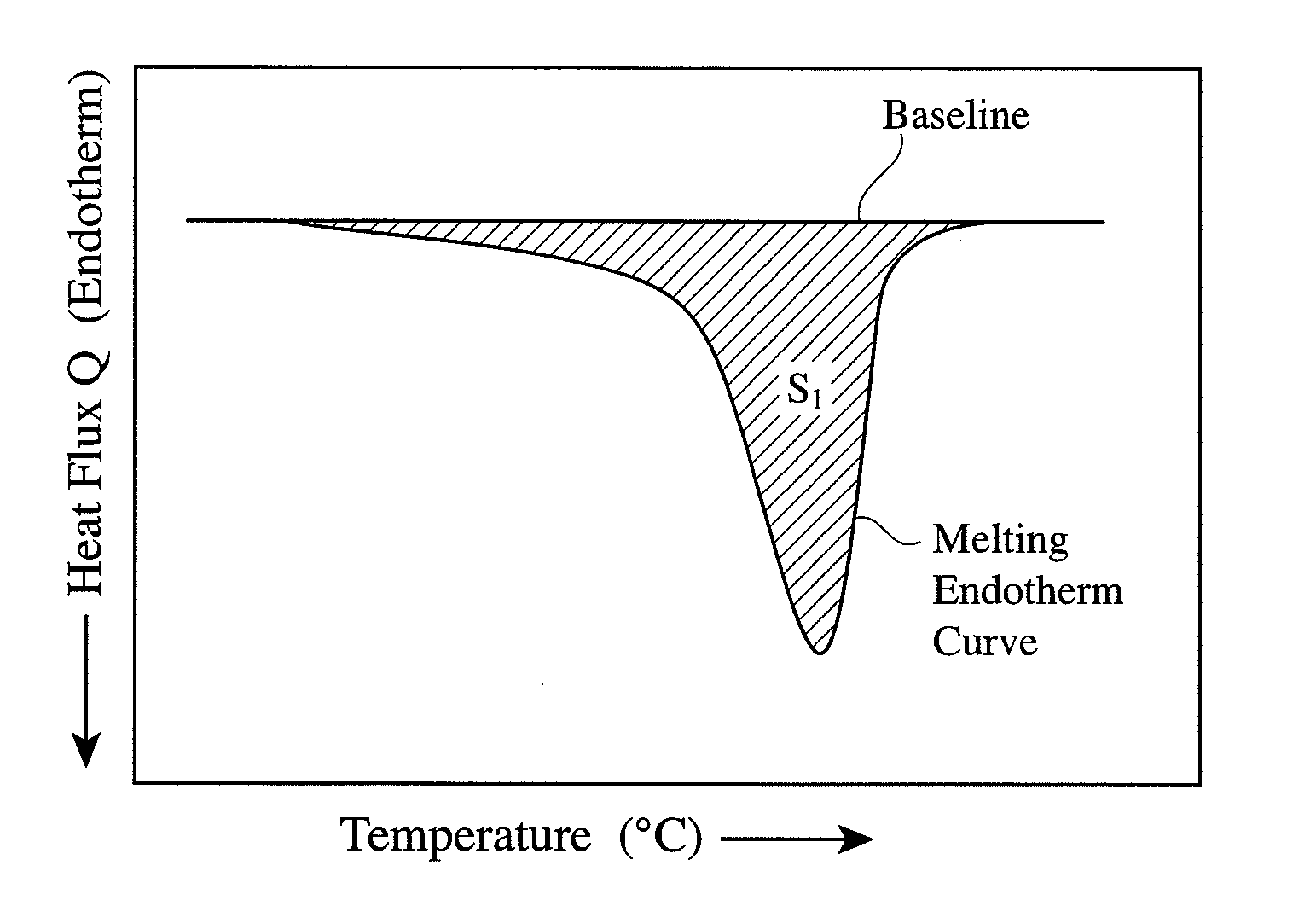
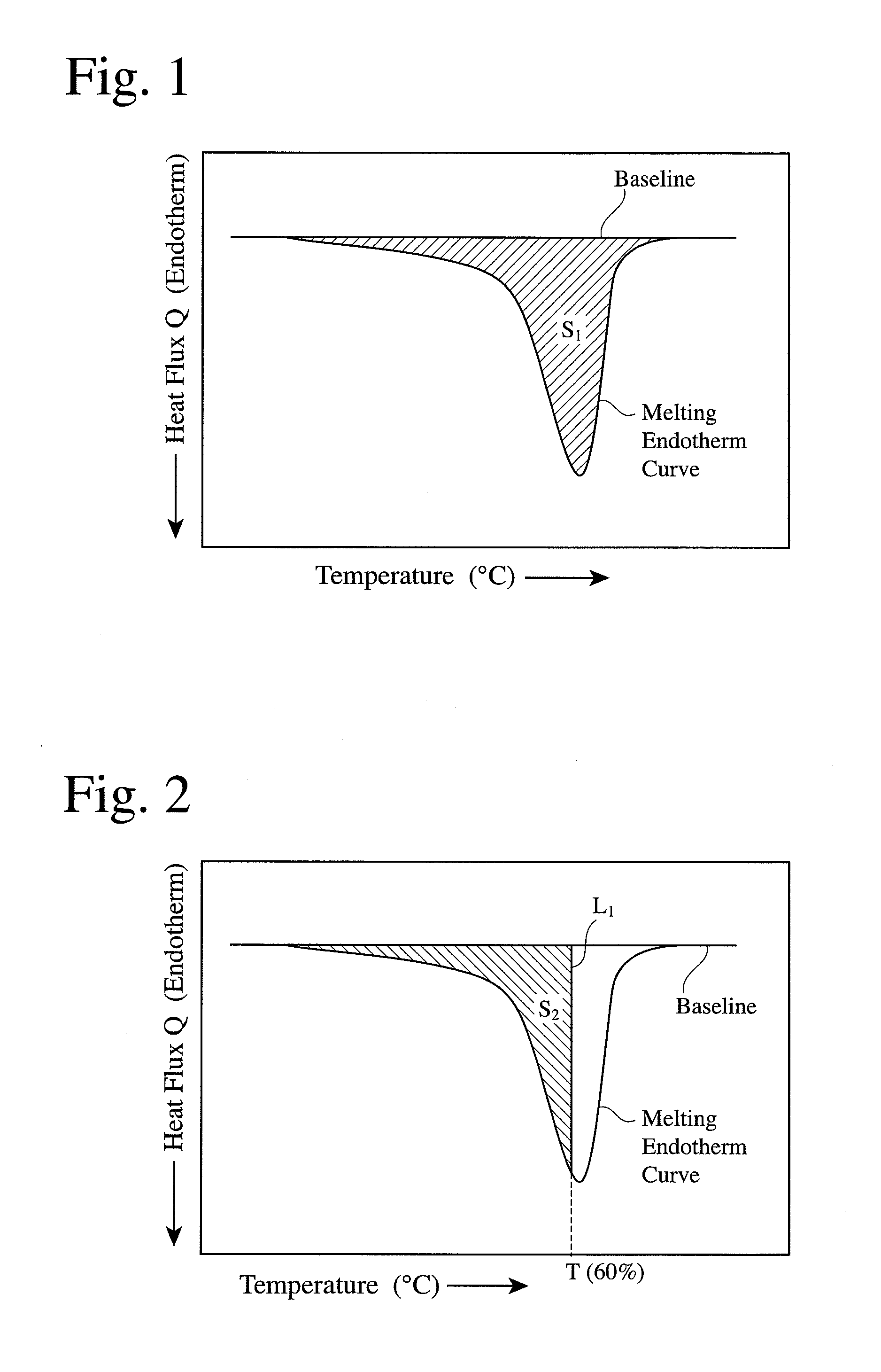
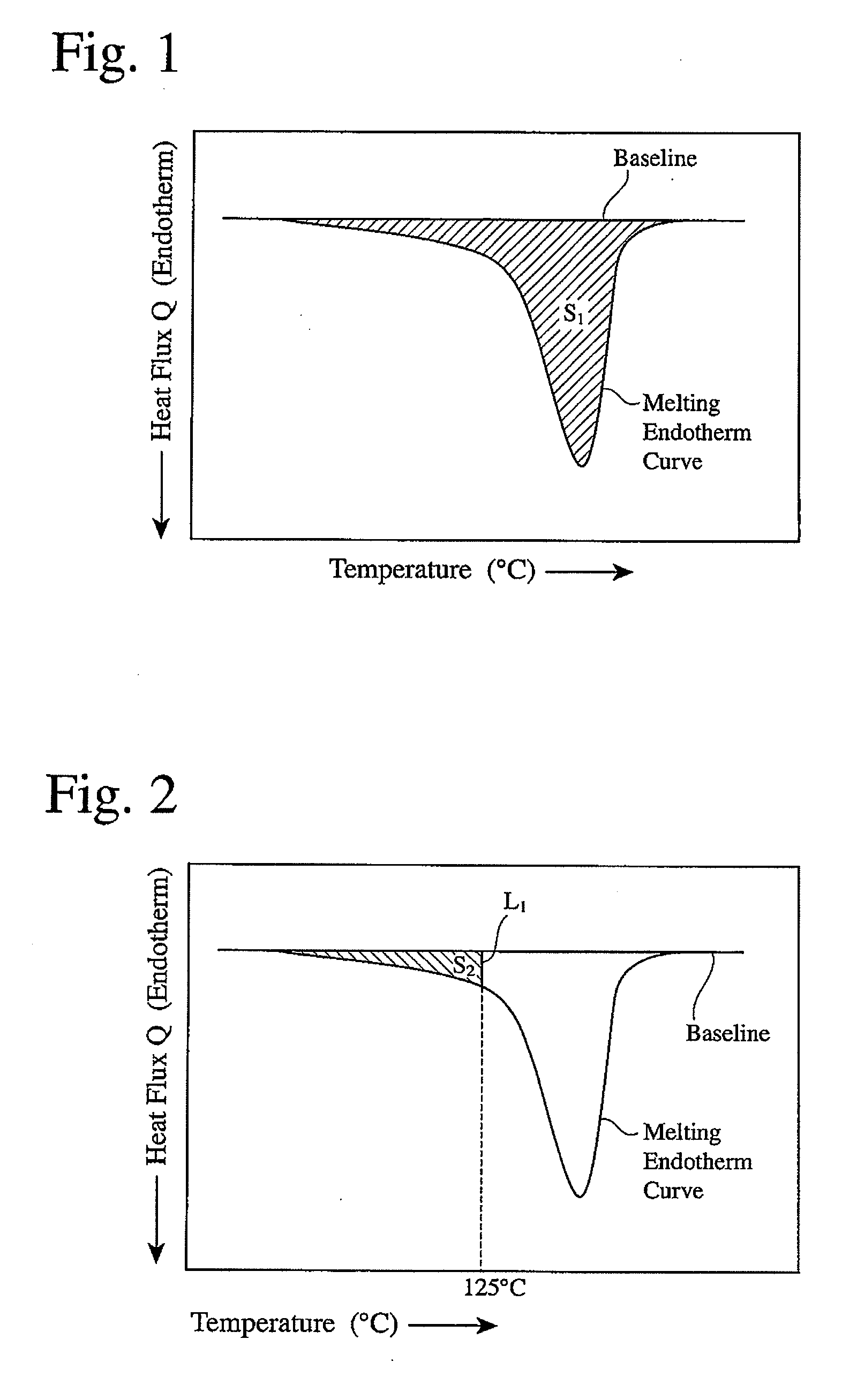
Thermomechanical analysis (TMA) is a technique used in thermal analysis, a branch of materials science which studies the properties of materials as they change with temperature. Thermomechanical analysis is a subdiscipline of the thermomechanometry (TM) technique.
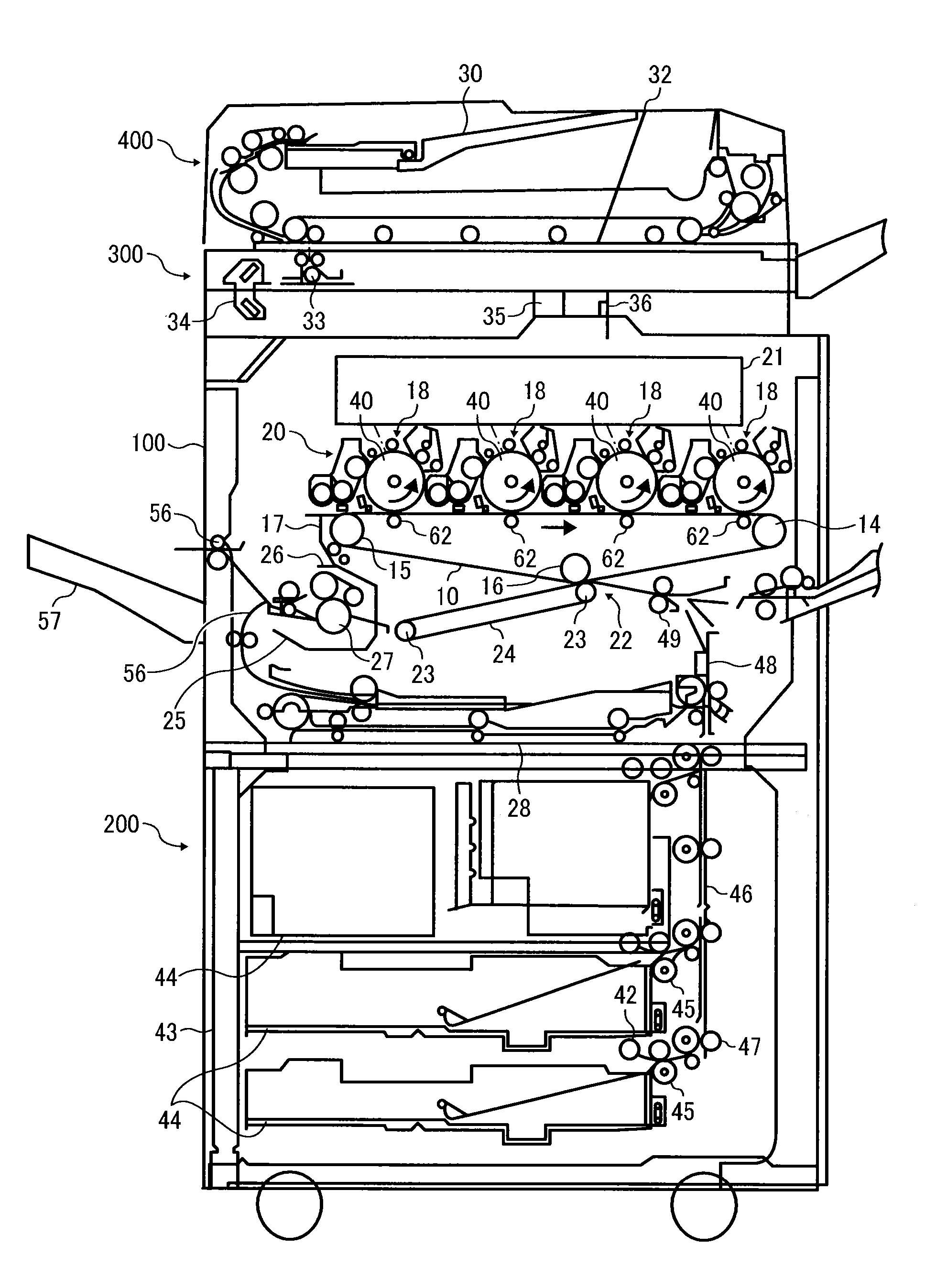
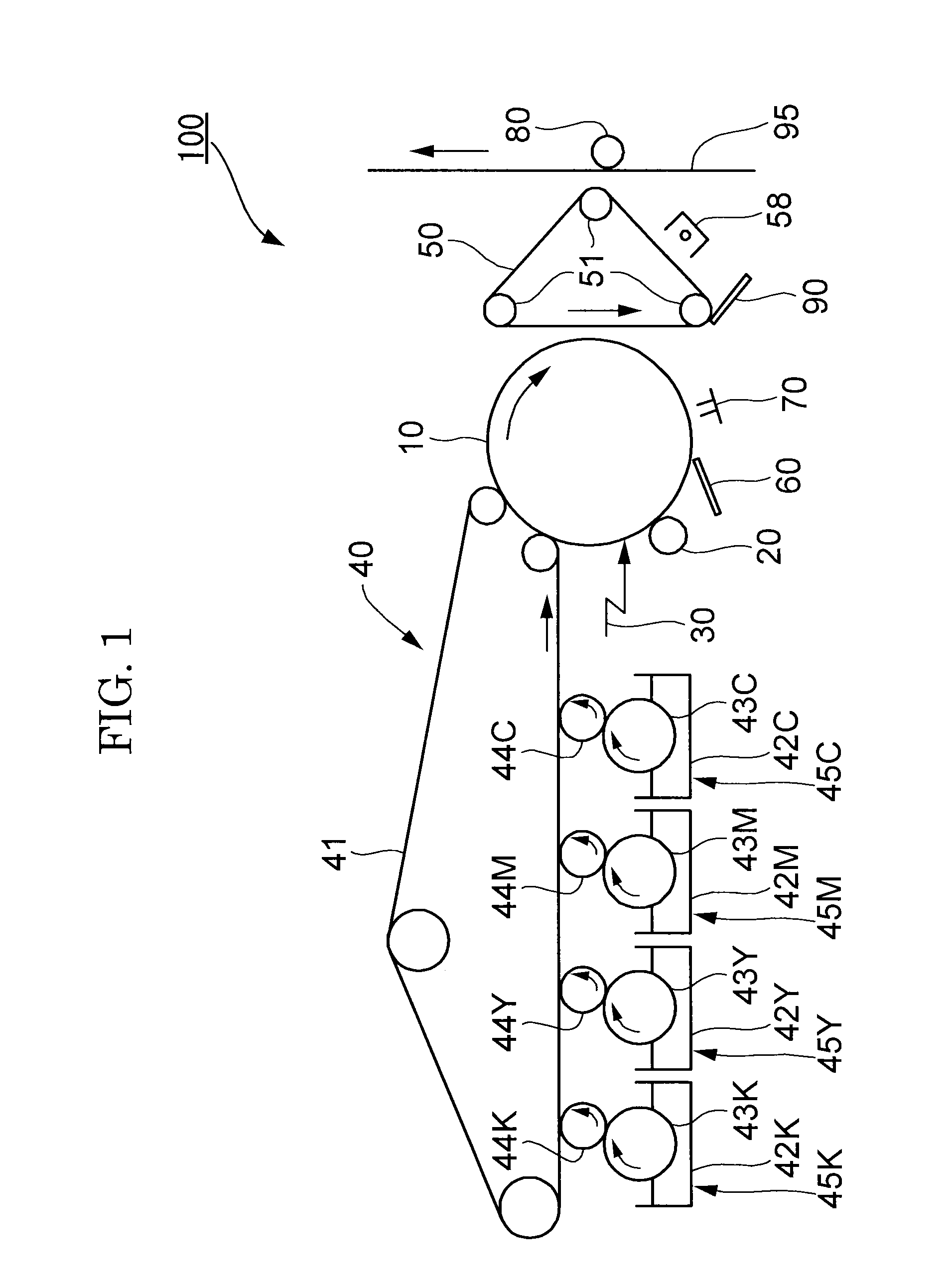
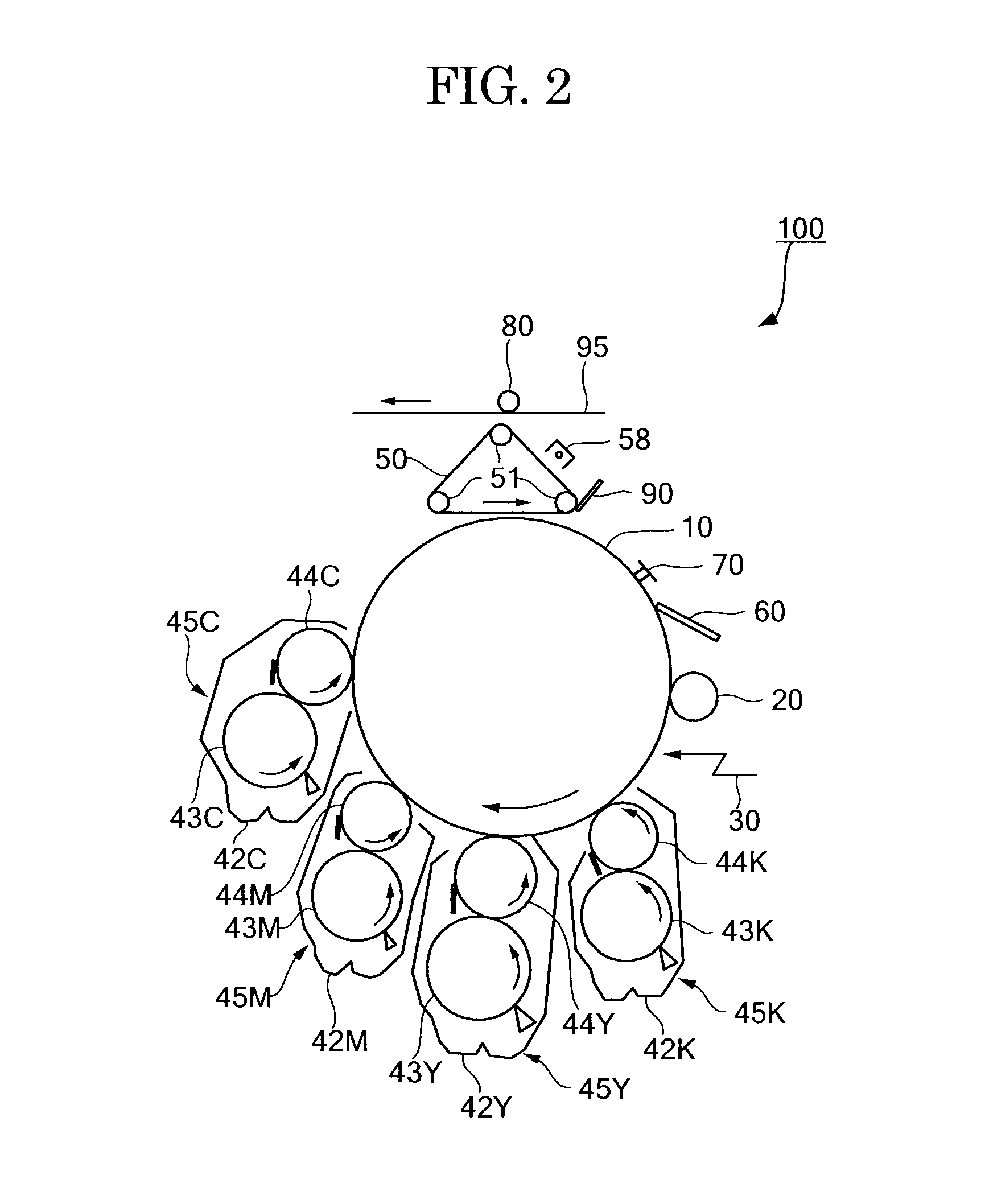
Toner, development agent, image forming apparatus, and image forming method
InactiveUS20140080050A1Toner accumulatingLow viscosityElectrographic process apparatusDevelopersPulse nuclear magnetic resonanceImage formation
Toner contains a binder resin, wherein the binder resin contains a block copolymer A containing a crystalline segment X and a non-crystalline segment Y, wherein the toner has a thermo-mechanical analysis (TMA) compressive deformation amount (TMA %) of 10% or less at 50° C. and a relative humidity of 90%, wherein the toner has a spin-spin relaxation time (t130) of 10 ms or greater at 130° C. as measured by pulse nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), wherein the toner has a spin-spin relaxation time (t′70) of 1 ms or less at 70° C. as measured by pulse NMR when descending from 130° C. to 70° C.
Owner:RICOH KK
Toner, developer and image forming apparatus
ActiveUS20130337374A1Excellent low temperature fixabilityHigh temperature-resistant offset propertyElectrographic process apparatusDevelopersImaging equipmentThermomechanical analysis
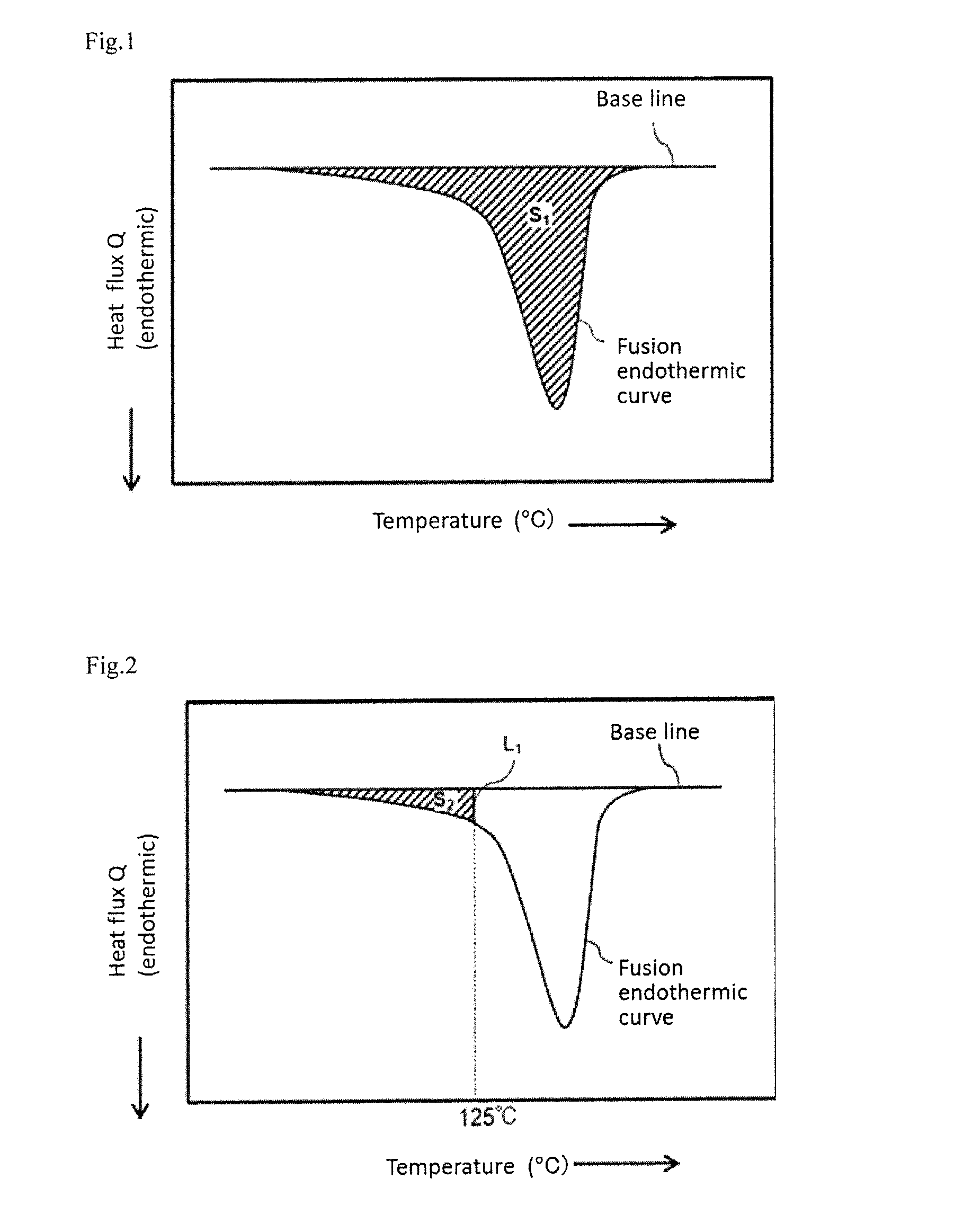
To provide a toner including a binder resin and a colorant, wherein the toner has a glass transition temperature by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) of 20° C. or greater and less than 50° C., an endothermic peak temperature by DSC of 50° C. or greater and less than 80° C. and an amount of compressive deformation at 50° C. by a thermomechanical analysis of 5% or less.
Owner:RICOH KK
Adhesive-carrying porous film for battery separator and use thereof
InactiveUS20070184340A1Efficiently manufactureReduce or preventCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersFilm/foil adhesivesIsocyanate compoundAdhesive
The invention provides an adhesive-carrying porous film for use as a battery separator, which comprises: a substrate porous film such that when a probe of a probe penetrating thermomechanical analyzer, said probe having a diameter of 1 mm, is placed on the porous film under a load of 70 g to measure a thickness thereof while heating the porous film from room temperature at a rate of 2° C. / minute, a temperature at which the thickness of the porous film decreases to a half of the thickness of the porous film when the probe was initially placed thereon is 200° C. or more; and a partially crosslinked adhesive carried on the substrate porous film, the partially crosslinked adhesive being prepared by reacting a reactive polymer having a functional group capable of reacting with an isocyanate group therein with a polyfunctional isocyanate so that the reactive polymer is partially crosslinked. Such a porous film (a separator) is temporarily bonded to an electrode to provide an electrode / separator laminate. In manufacturing a battery, the use of the laminate makes it possible to manufacture a battery efficiently with no mutual slip movement between the electrode and the separator, and is addition, the porous film (the separator) itself, after manufacturing a battery, functions as a separator which does not melt or break, and has a small heat shrinkage under high temperatures
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Microporous polyolefin membrane, its production method, battery separator and battery
InactiveUS20100069596A1Improve balanceMaintain good propertiesSemi-permeable membranesMembranesPolymer sciencePolyolefin
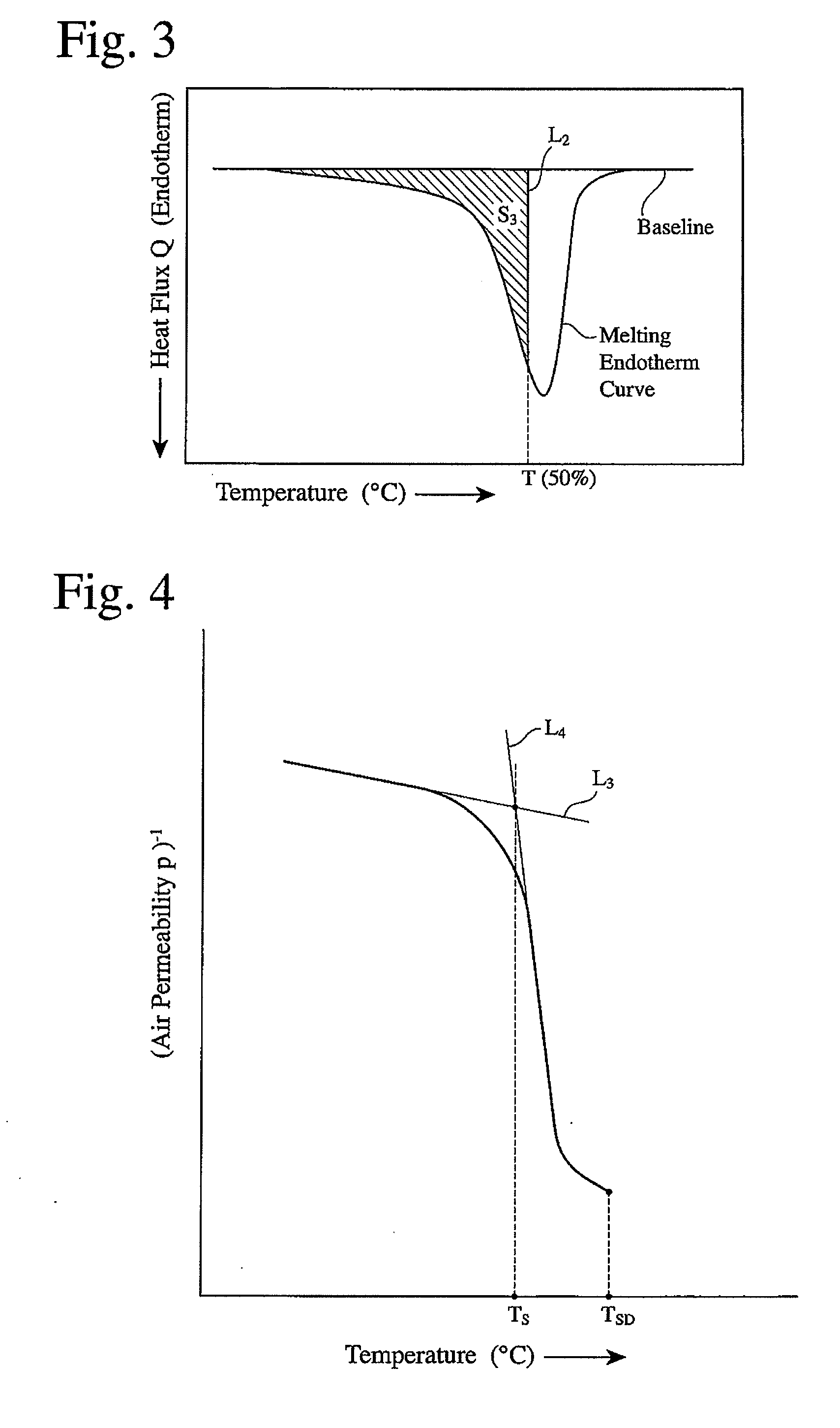
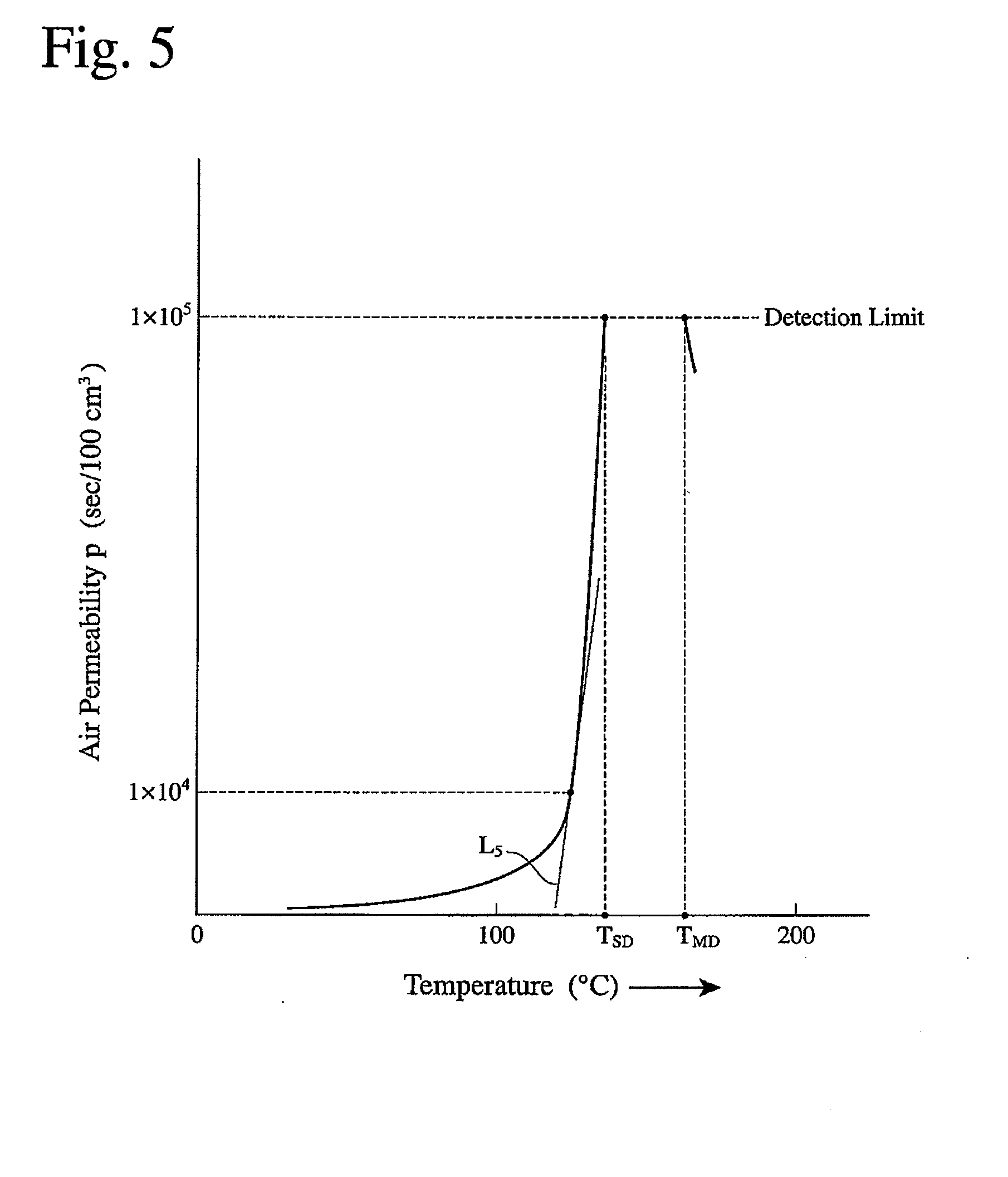
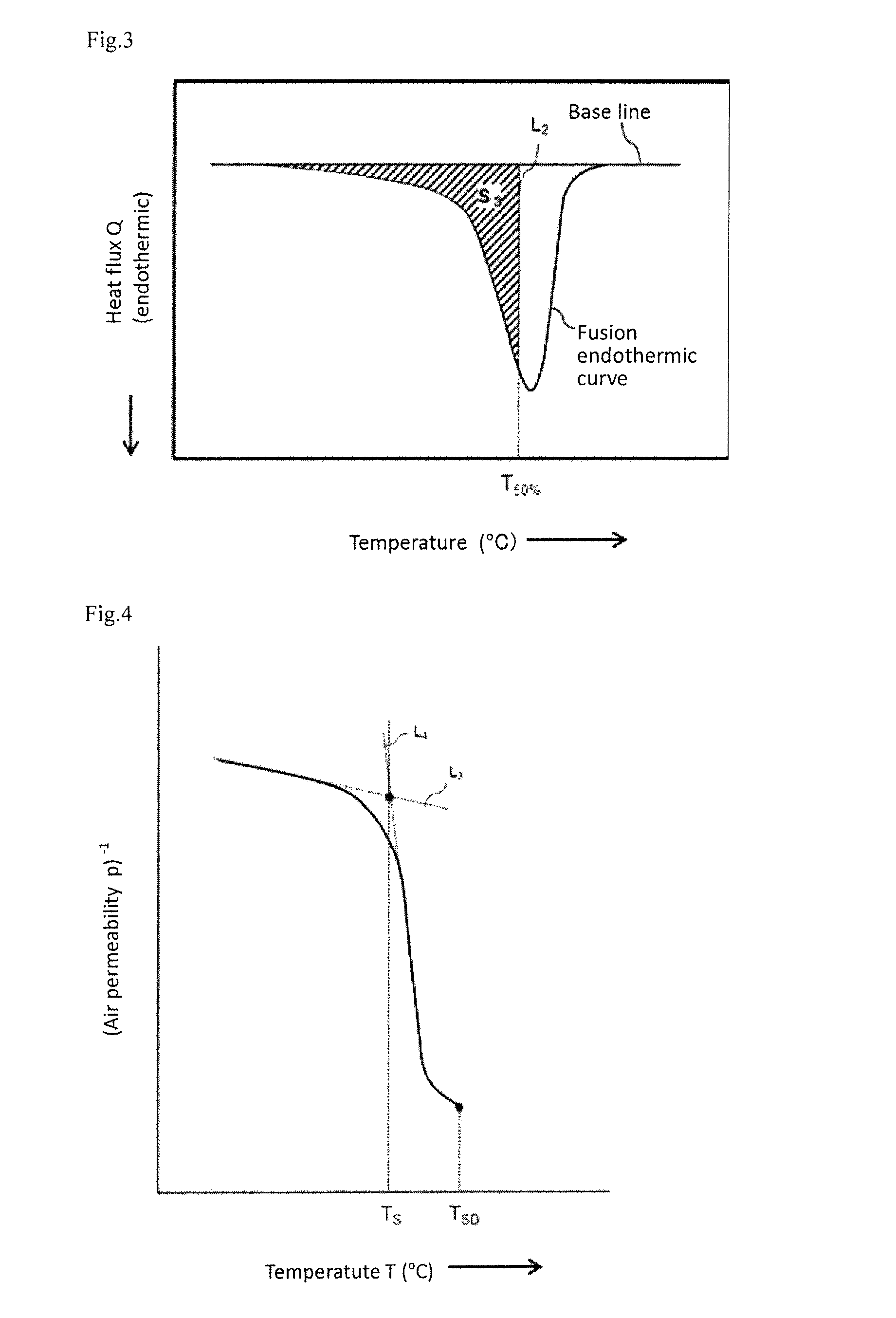
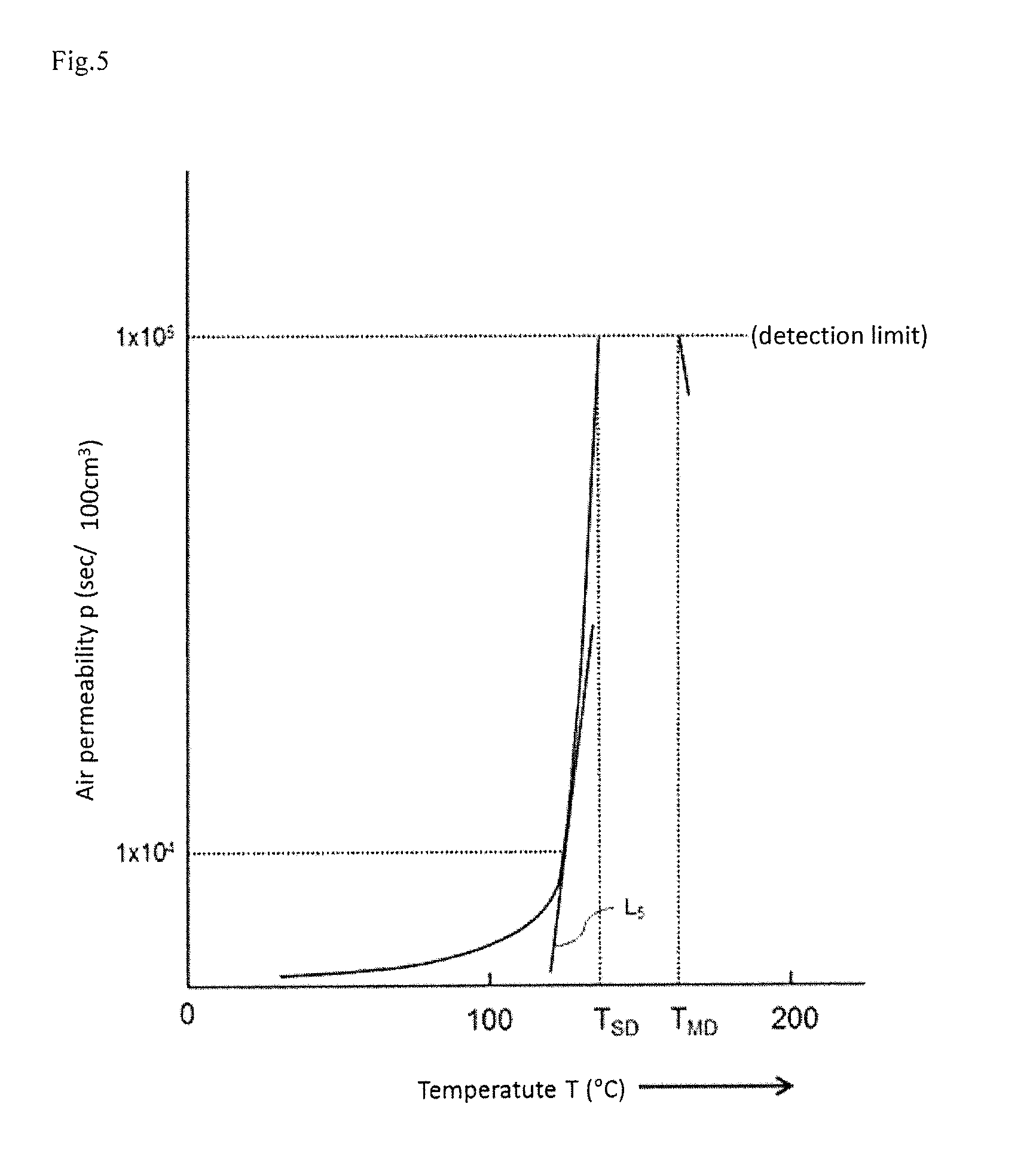
A microporous polyolefin membrane comprising a polyethylene resin, and having (a) a shutdown temperature of 135° C. or lower, at which the air permeability measured while heating at a temperature-elevating speed of 5° C. / minute reaches 1×105 sec / 100 cm3, (b) a maximum melting shrinkage ratio of 40% or less in a transverse direction in a temperature range of 135 to 145° C., which is measured by thermomechanical analysis under a load of 2 gf and at a temperature-elevating speed of 5° C. / minute, and (c) a meltdown temperature of 150° C. or higher, at which the air permeability measured while further heating after reaching the shutdown temperature becomes 1×105 sec / 100 cm3 again.
Owner:TONEN CHEM CORP
Battery separator and method for producing same
ActiveCN104428921AExcellent adhesionImprove permeabilityFinal product manufactureSecondary cellsPolyolefinPolymer science
Owner:TORAY IND INC
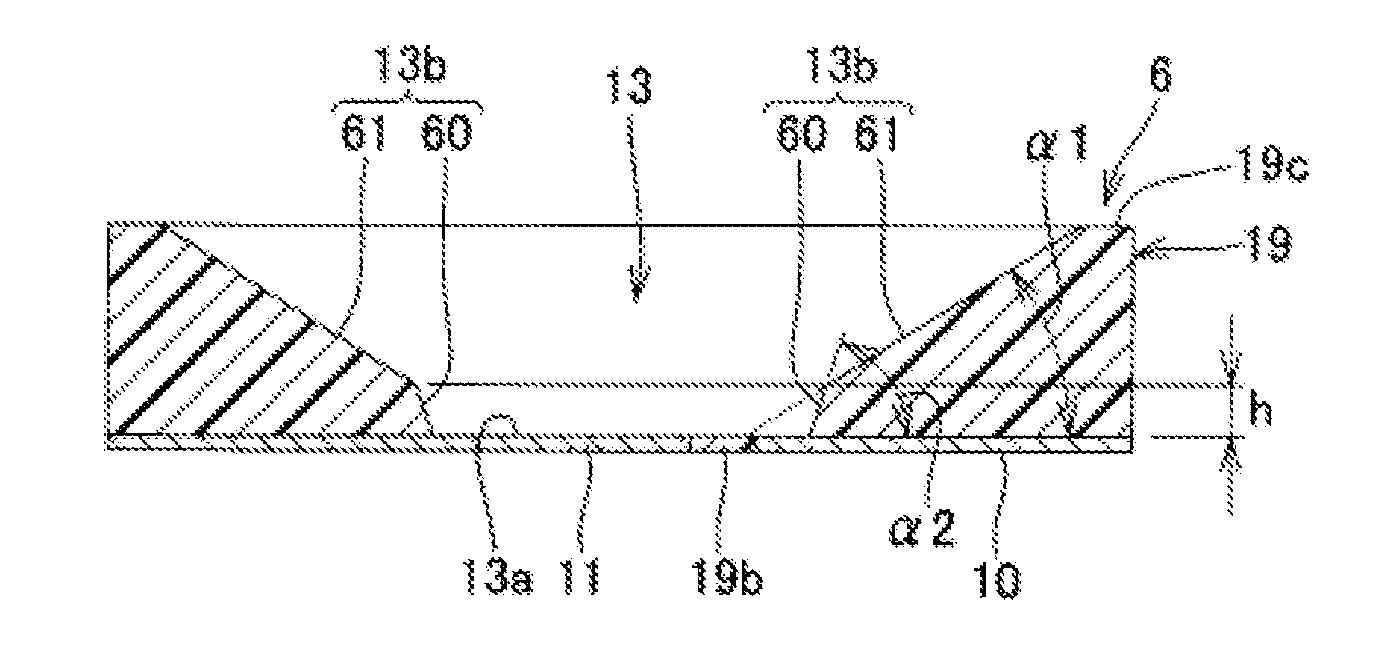
Molded resin body for surface-mounted light-emitting device, manufacturing method thereof, and surface-mounted light-emitting device
InactiveUS20150008455A1High light reflectivitySuitable for mass productionSolid-state devicesCoatingsSurface mountingEngineering
A molded resin body for surface-mounted light-emitting device has cured resin body integrally molded with a plurality of leads and a concave portion to which the plurality of leads are exposed at the bottom portion, in which the ten-point average roughness (Rz) of the opening surface of the concave portion is 1 μm to 10 μm, the glass transition temperature of the cured resin body is 10° C. or higher and the glass transition temperature is a value measured using a thermomechanical analyzer (TMS) under the conditions of a temperature range of −50 to 250° C., a temperature elevation rate of 5° C. / min, and a sample size length of 1 to 5 mm, and the optical reflectance at 460 nm of the opening surface of the concave portion is 80% or more and the optical reflectance retention rate on the opening surface after heating the molded resin body at 180° C. for 72 hours is 90% or more.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Microporous polyolefin membrane, its production method, battery separator and battery
InactiveUS20090042008A1Improve breathabilityExcellent heat shrinkage resistanceAlkaline accumulatorsAnimal housingPolymer sciencePolyolefin
A microporous polyolefin membrane comprising a polyethylene resin, and having (a) a shutdown temperature of 135° C. or lower, at which the air permeability measured while heating at a temperature-elevating speed of 5° C. / minute reaches 1×105 sec / 100 cm3, (b) a maximum melting shrinkage ratio of 40% or less in a transverse direction in a temperature range of 135 to 145° C., which is measured by thermomechanical analysis under a load of 2 gf and at a temperature-elevating speed of 5° C. / minute, and (c) a meltdown temperature, at which the air permeability measured while further heating after reaching the above shutdown temperature becomes 1×105 sec / 100 cm3 again, being 150° C. or higher.
Owner:TORAY BATTERY SEPARATOR FILM
Porous multi-layer film with improved thermal properties
ActiveCN102742045AGood quality and stabilityImprove permeabilityCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersSynthetic resin layered productsPorosityThermal stability
Provided is a porous multi-layer film having two or more layers that is used as a separator for battery. In the film, more than 2 layers have different porosities and pore sizes. The film has a thickness of 9 to 50?, a machine direction (MD) loop stiffness of 0.008mg / ? or more, puncture strength of 0.15N / ? or more, permeability of 1.5 x 10-5Darcy or more, shut-down temperature of 140? or less, melt-down temperature of 170? or more, a transverse direction (TD) maximum shrinkage of 25% or less in Thermomechanical Analysis (TMA) under a load of 1mN / (1? x 6mm), and melt down temperature of 160? or more. Since the porous multi-layer film shows excellent thermal stability at high temperature and electrolyte retaining property due to a dual pore structure, the film shows a superior effect when used as a separator for high-capacity / high-power lithium ion battery.
Owner:SK INNOVATION CO LTD +1
Biaxially oriented polyester film which is matt on one side and has characteristic shrinkage properties, process for its preparation and its uses
InactiveUS6913817B2High degreeLow transparencyFlexible coversWrappersPolyesterThermomechanical analysis
Biaxially oriented polyester films which have a polyester-containing base layer (B) and a matt overlayer (A), and are characterized by the following features: a) the transverse shrinkage of the film is between 1 and 2.3%, b) the transverse linear expansion of the film during thermo-mechanical analysis is smaller than or equal to 0.2%, c) the matt overlayer comprises particles, preferably SiO2, whose median diameter is from 2 to 10 μm and whose SPAN98 is smaller than or equal to 2, and d) the matt overlayer (A) comprises a polyester which has from 4 to 30 mol % of isophthalic acid units are notable in particular for low opacity, high transparency and low gloss of the overlayer (A), and are therefore suitable as flexible packaging films and for the purposes of hot lamination.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POLYESTER FILM
Microporous polyolefin film possessing good mechanical properties and thermal stability
ActiveUS20090148685A1Excellent characteristicsImprove high temperature safetyMembranesSemi-permeable membranesPorosityPolyolefin
The present invention relates to a microporous polyolefin film suitable as a separator for batteries and thermal properties thereof. A microporous polyolefin film according to the present invention has a film thickness of 5-40 μm, a porosity of 30%-60%, a permeability of 2.0×10−5-8.0×10−5 Darcy, a maximum pore size determined by the bubble point method of not more than 0.1 μm, a puncture strength of 0.20 N / μm or more at room temperature and 0.05 N / μm or more at 120° C., and a maximum shrinkage ratio in the transverse direction (TD) when subjected to a thickness-normalized external force in TMA (thermo-mechanical analysis) of not more than 0%. With excellent thermal stability at high temperature as well as superior puncture strength and gas permeability, the microporous polyolefin film according to the present invention is suitable for high-capacity, and high-power batteries.
Owner:SK INNOVATION CO LTD +1
Porous Multi-Layer Film with Improved Thermal Properties
ActiveUS20120301698A1Improve thermal stabilityImprove permeabilityCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersSynthetic resin layered productsPorosityThermal stability
Provided is a porous multi-layer film having two or more layers that is used as a separator for battery. In the film, more than 2 layers have different porosities and pore sizes. The film has a thickness of 9 to 50 μm, a machine direction (MD) loop stiffness of 0.008 mg / μm or more, puncture strength of 0.15 N / μm or more, permeability of 1.5×10−5 Darcy or more, shut-down temperature of 140° C. or less, melt-down temperature of 170° C. or more, a transverse direction (TD) maximum shrinkage of 25% or less in Thermomechanical Analysis (TMA) under a load of 1 mN / (1 μm×6 mm), and melt down temperature of 160° C. or more. Since the porous multi-layer film shows excellent thermal stability at high temperature and electrolyte retaining property due to a dual pore structure, the film shows a superior effect when used as a separator for high-capacity / high-power lithium ion battery.
Owner:SK INNOVATION CO LTD +1
Substrate with transparent electrode and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20140370275A1Simple stepsIncrease production capacityFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingCharge-carrier densityFilm base
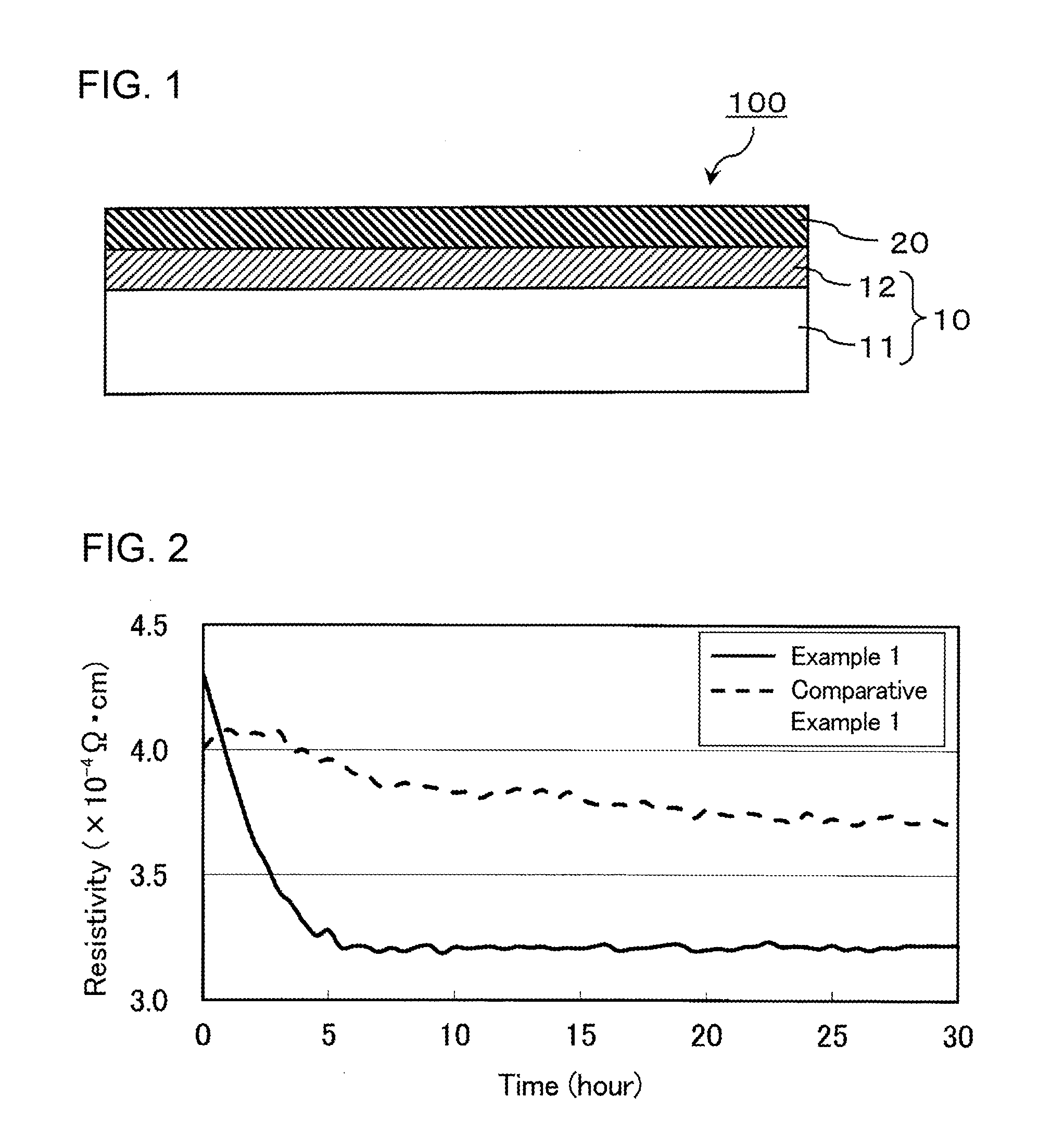
The present invention relates to a substrate with a transparent electrode, which has a transparent electrode layer on at least one surface of a transparent film base material. The transparent film base material has a transparent dielectric material layer containing an oxide as a main component on a surface at the transparent electrode layer side. In one embodiment of the present invention, the transparent electrode layer is a crystalline transparent electrode layer that has a crystallinity degree of 80% or more. In this embodiment, the crystalline transparent electrode layer has a resistivity of 3.5×10−4 Ω·cm or less, a thickness of 15 nm to 40 nm, an indium oxide content of 87.5% to 95.5%, and a carrier density of 4×1020 / cm3 to 9×1020 / cm3, and the substrate with the transparent electrode preferably has a heat shrinkage start temperature of 75° C. to 120° C. as measured by thermomechanical analysis.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Multilayered wiring board and semiconductor device
InactiveCN101785373AEasy to storeImprove installation reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsElectrical conductorEngineering
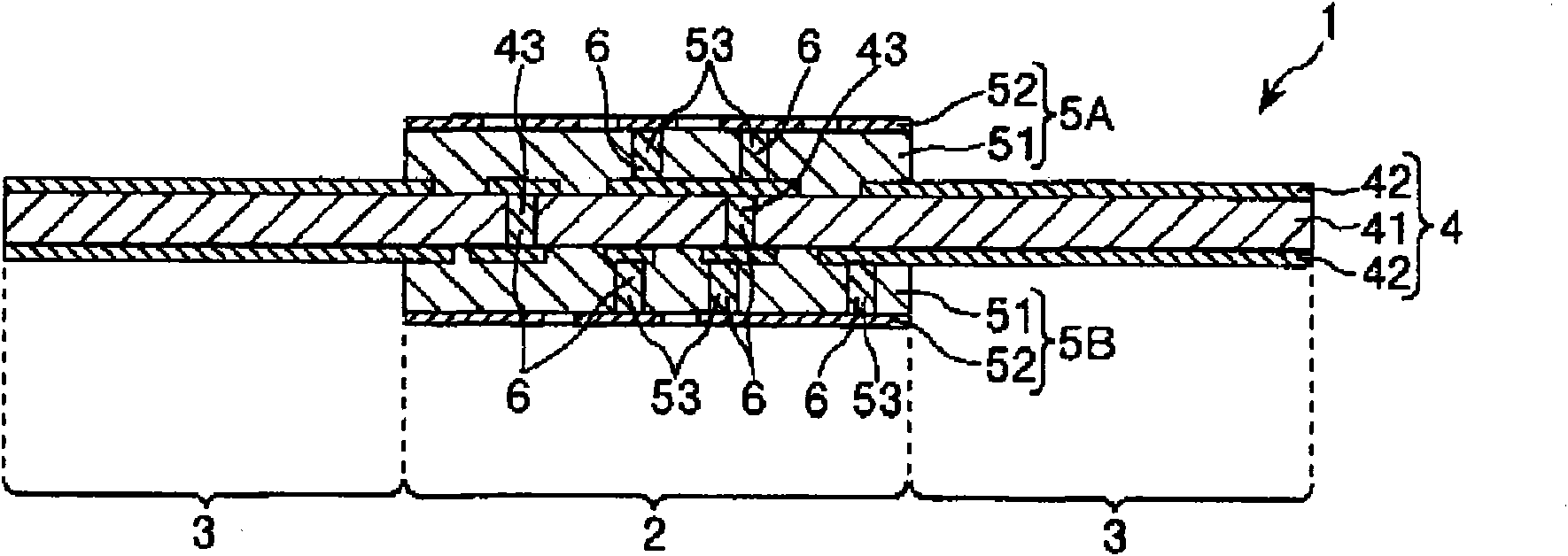
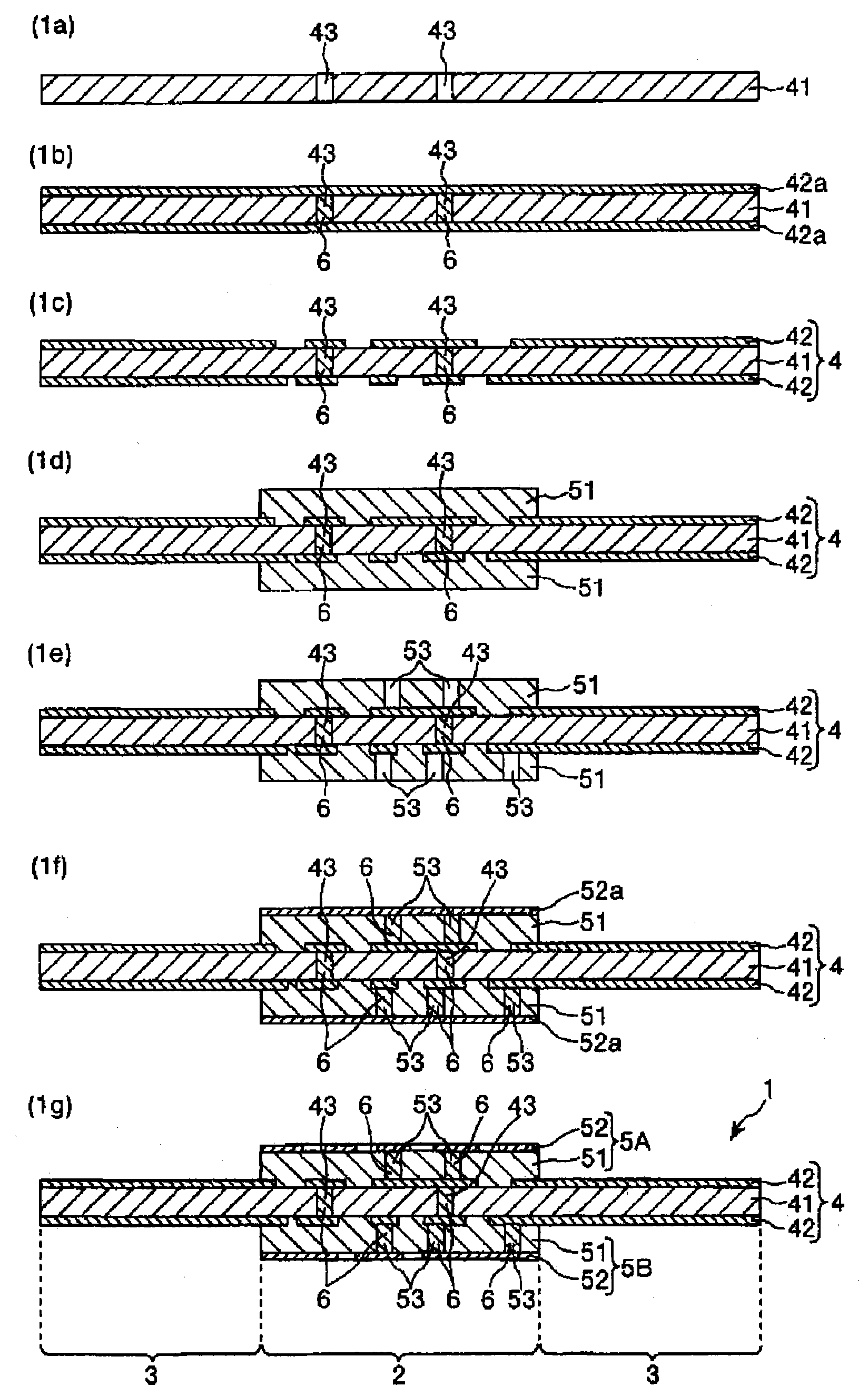
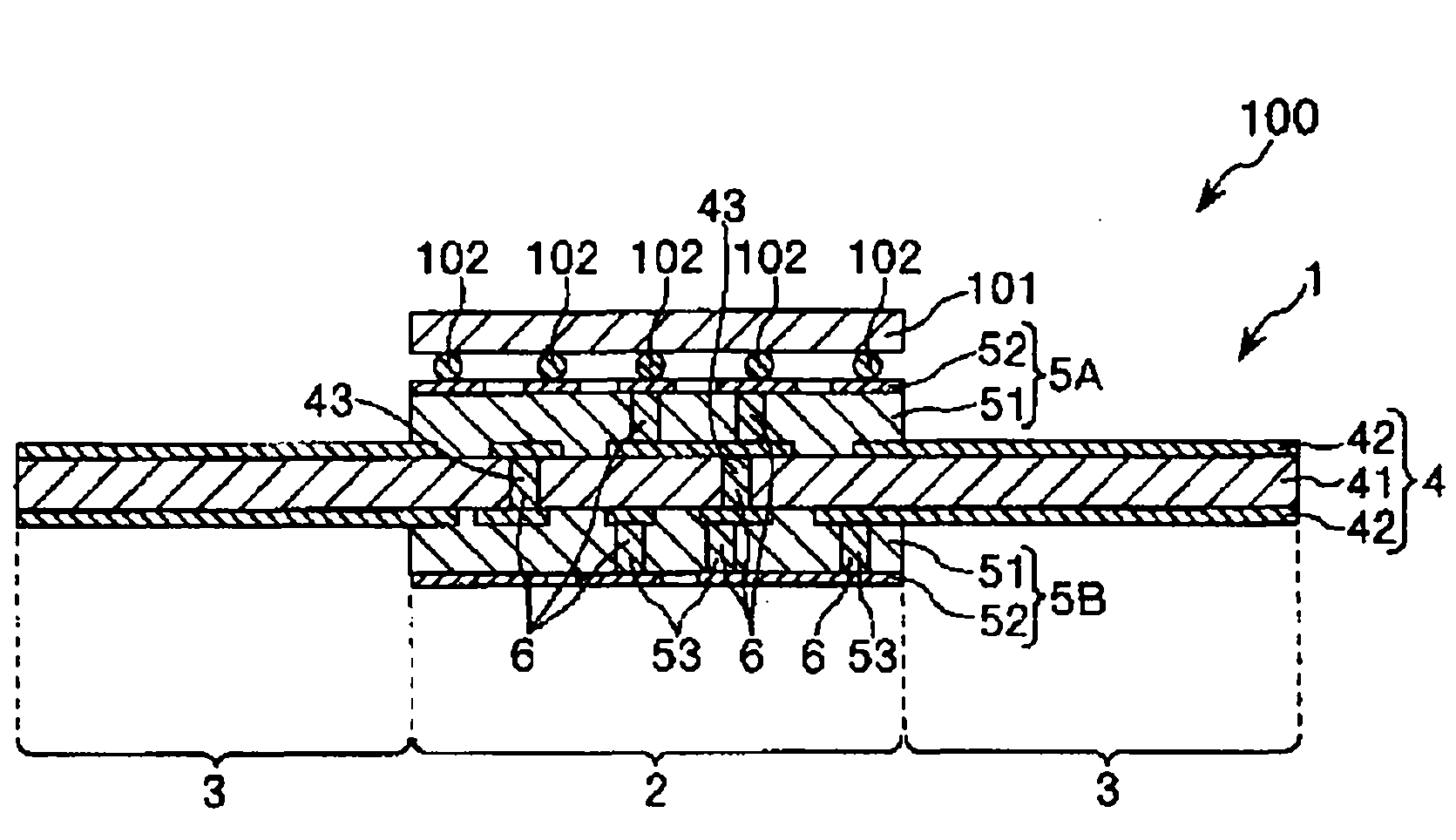
This invention provides a multilayered wiring board (1) comprising a rigid part (2) and a flexible part (3). The rigid part (2) comprises a first base material (4) and a second base material (5A). The first base material (4) comprises a first insulating layer (41) and a first conductor layer (42) and is flexible. The second base material (5A) comprises a second insulating layer (51) and a second conductor layer (52) bonded to at least one side of the first base material (4) and has a higher rigidity than the first base material (4). The flexible part (3) is extended continuously from the rigid part (2) and is formed of the first base material (4). The second insulating layer (51) has a coefficient of thermal expansion of not more than 13 ppm / DEG C as measured in a facial direction by a thermomechanical analysis in a predetermined temperature range and a coefficient of thermal expansion of not more than 20 ppm / DEG C in the thickness-wise direction as measured by a thermomechanical analysis according to JIS C 6481 in a predetermined temperature range.
Owner:SUMITOMO BAKELITE CO LTD
Highly functional polyethylene fiber, and dyed highly functional polyethylene fiber
ActiveUS20140000007A1Slow changeGood dimensional stabilityFibre typesGlovesFiberThermomechanical analysis
The present invention provides a highly functional polyethylene fiber exhibiting reduction of change in their physical properties in a wide range of temperatures for processing for products and in a wide range of temperatures for usage as products, thereby enabling improvement of dimensional stability. In addition, the present invention provides a highly functional polyethylene fiber exhibiting a high degree of dye exhaustion to be obtained in a simple dyeing operation, and excellent color fastness. The highly functional polyethylene fiber of the present invention is characterized in that an intrinsic viscosity [η] is higher than or equal to 0.8 dL / g, and not higher than 4.9 dL / g, ethylene is substantially contained as a repeating unit thereof, and a maximum thermal shrinkage stress is less than or equal to 0.4 cN / dtex in TMA (thermo-mechanical analysis), and a thermal shrinking percentage at 100° C. is less than or equal to 2.5%.
Owner:TOYOBO MC CORP
Battery separator and method of producing the same
InactiveUS20160126520A1Improve heat resistanceImprove physical strengthFinal product manufactureSecondary cellsPolymer sciencePolyolefin
A battery separator which is a laminated polyolefin microporous membrane, comprising a polyolefin microporous membrane, and a modifying porous layer comprising a water-soluble resin or water-dispersible resin, and fine particles, the modifying porous layer being laminated on at least one surface of the polyolefin microporous membrane, wherein the polyolefin microporous membrane comprises a polyethylene resin and has (a) a shutdown temperature (a temperature at which an air resistance measured while heating the polyolefin microporous membrane at a temperature rise rate of 5° C. / min reaches 1×105 sec / 100 cc) of 135° C. or lower, (b) a rate of air resistance change (a gradient of a curve representing dependency of the air resistance on temperature at an air resistance of 1×104 sec / 100 cc) of 1×104 sec / 100 cc / ° C. or more, (c) a transverse shrinkage rate at 130° C. (measured by thermomechanical analysis under a load of 2 gf at a temperature rise rate of 5° C. / min) of 20% or less, and a thickness of 16 μm or less, the shutdown temperature difference between the polyolefin microporous membrane and the laminated polyolefin microporous membrane being 4.0° C. or less. A method of producing the same.Provided is a battery separator with excellent adhesion and shutdown properties comprising a modifying porous layer and a polyolefin microporous membrane.
Owner:TORAY BATTERY SEPARATOR FILM
Easily handleable electrolytic copper foil, electrode comprising the same, secondary battery comprising the same, and method for manufacturing the same
An easily handleable electrolytic copper foil securing a highly durable secondary battery, an electrode including same, a secondary battery including same, and a method of manufacturing same. The electrolytic copper foil including first and second surfaces includes a copper layer including a matte surface facing the first surface and a shiny surface facing the second surface, a first protective layer formed on the matte surface of the copper layer, and a second protective layer formed on the shiny surface of the copper layer. A coefficient of thermal expansion of the electrolyte copper foil measured using thermomechanical analyzer while heating the electrolytic copper foil from 30 to 190 DEG C. at 5 DEG C per min ranges from 16 to 22 [mu]m / (m*DEG C), tensile strength of the electrolytic copper foil measured after heat treatment at 190 DEG C, ranges from 21 to 36 kgf / mm2, and weight deviation of the electrolytic copper foil is 5% or less.
Owner:SK NEXILIS CO LTD
Method for measuring expansibility of catalytic converter seal gasket
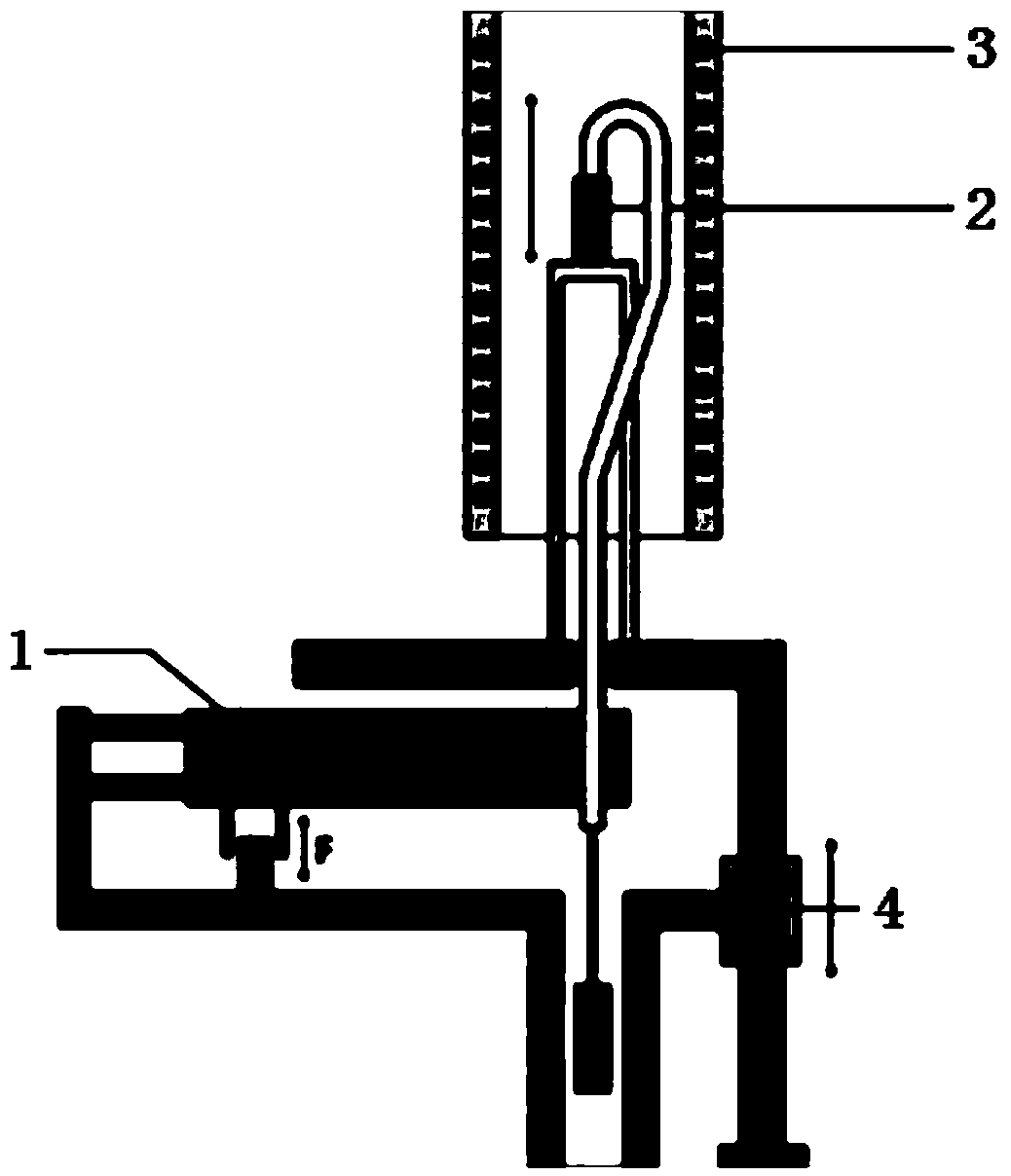
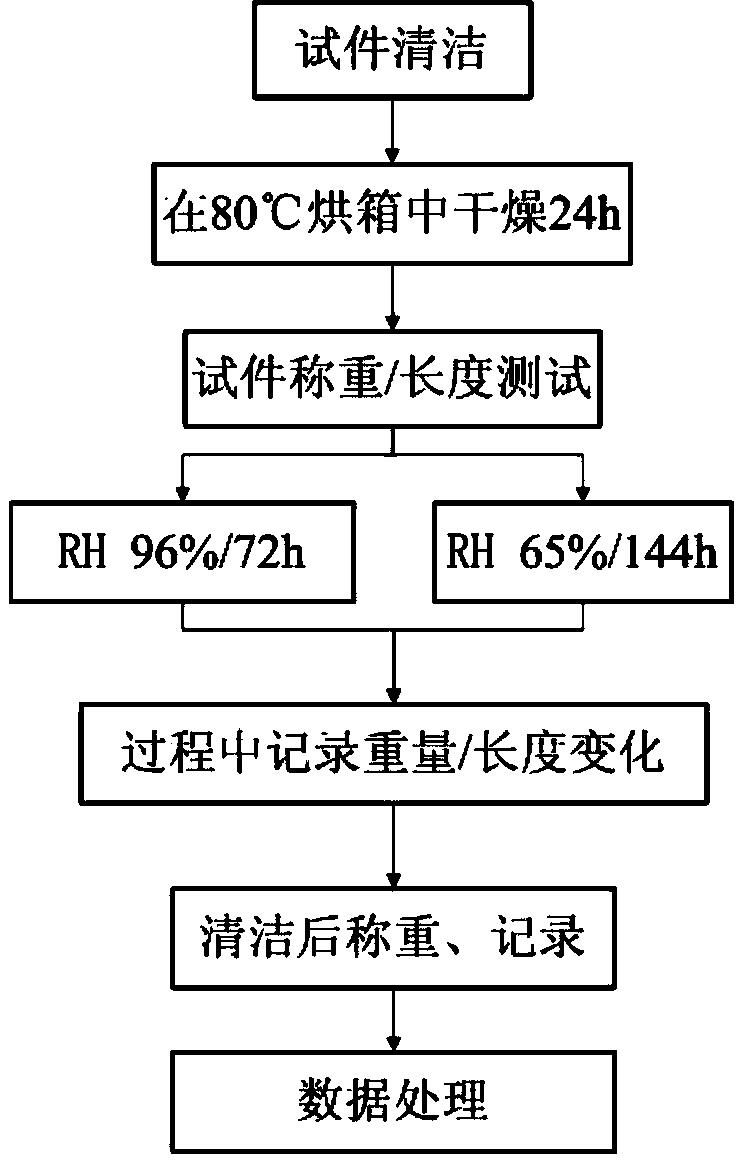
InactiveCN103969286AGuide implementationAccurate implementationMaterial thermal coefficient of expansionTemperature controlTest sample
The invention discloses a method for measuring expansibility of catalytic converter seal gasket. The method comprises the following steps: (1) sampling; (2) preparing test samples; (3) placing the samples: the test samples are placed under the movable end of a quartz glass rod in a thermal expansion analyzer and pressure of 1345 g is provided above the quartz glass rod; (4) then switching on a heating switch of a heating device in the thermal expansion analyzer and heating at the heating speed of 15 / min until the temperature reaches 750 DEG C; recording primary measuring data by a recorder in a thermal mechanical analyzer; when the temperature is reduced to the indoor temperature, heating continuously, controlling the temperature between 200 DEG C and 700 DEG C and conducting the circulation test for 50 times; after the circulation is over, the thermal expansion analyzer is automatically closed by the system and the samples are taken out after the temperature the device is reduced naturally; recording the data measured for 50 times by the recorder in the thermal expansion analyzer; (5) calculating thermal expansion performance parameters. The measuring method provided by the invention is simple, convenient and high in precision.
Owner:上海伊索热能技术股份有限公司
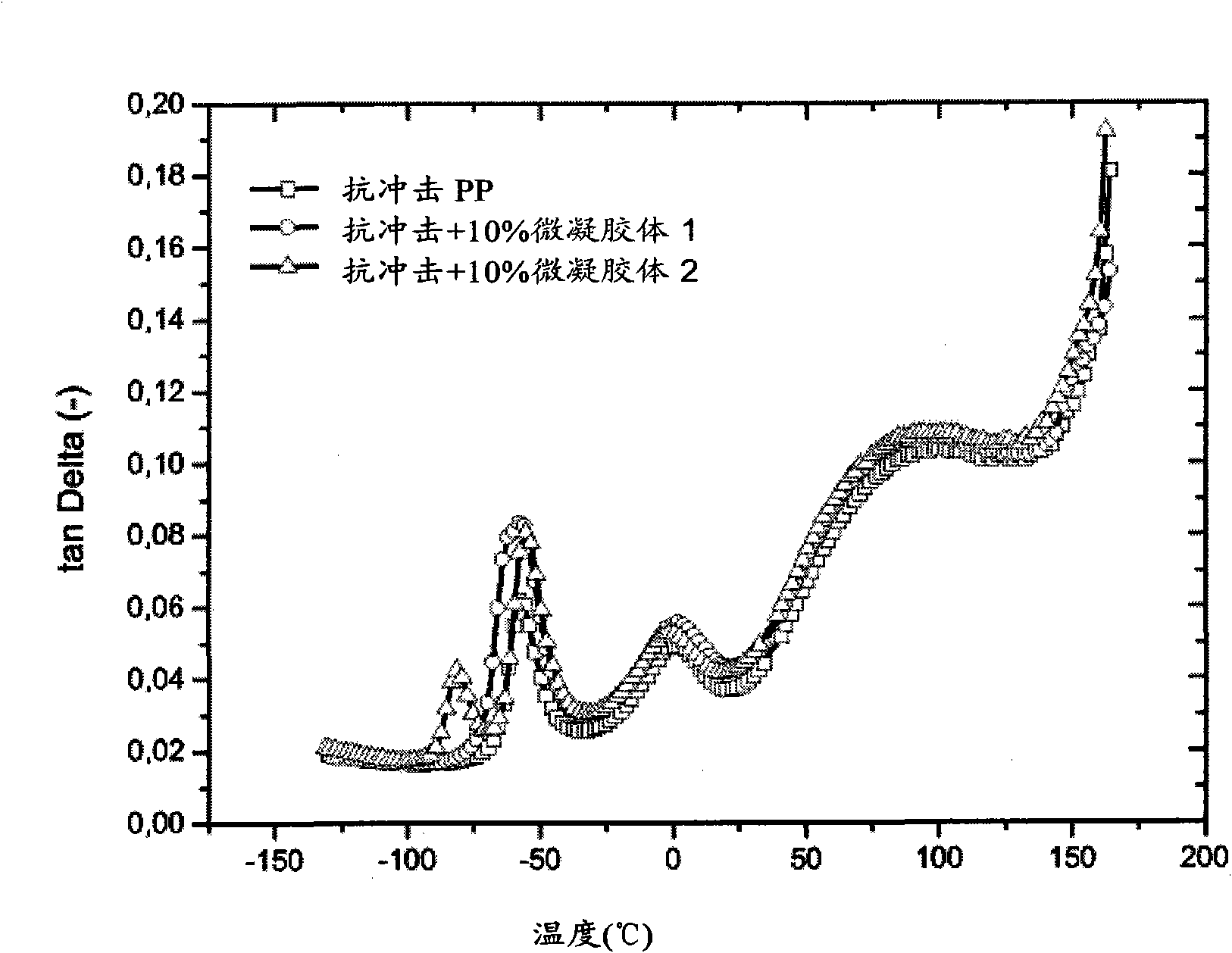
Impact-modified polypropylene
The present invention relates to a polymer composition, comprising: (i) a polypropylene matrix; (ii) a first elastomeric phase dispersed within the matrix and having a glass transition temperature Tg1, measured with dynamical mechanical thermal analysis according to ISO 6721-2, wherein the first elastomeric phase comprises an ethylene copolymer having comonomer units derived from C3 to C8 olefins; (iii) a second elastomeric phase dispersed within the matrix, wherein the second elastomeric phase is crosslinked and has a glass transition temperature Tg2, measured with dynamical mechanical thermal analysis according to ISO 6721-2, within the range of - 70 DEG C to -90 DEG C, wherein the difference between Tg1 and Tg2 is at least 15 DEG C and Tg1 is higher than Tg2.
Owner:ボレアリステクノロジーオイ
Method and device for correcting temperature of thermal mechanical analyzer tensile fixture
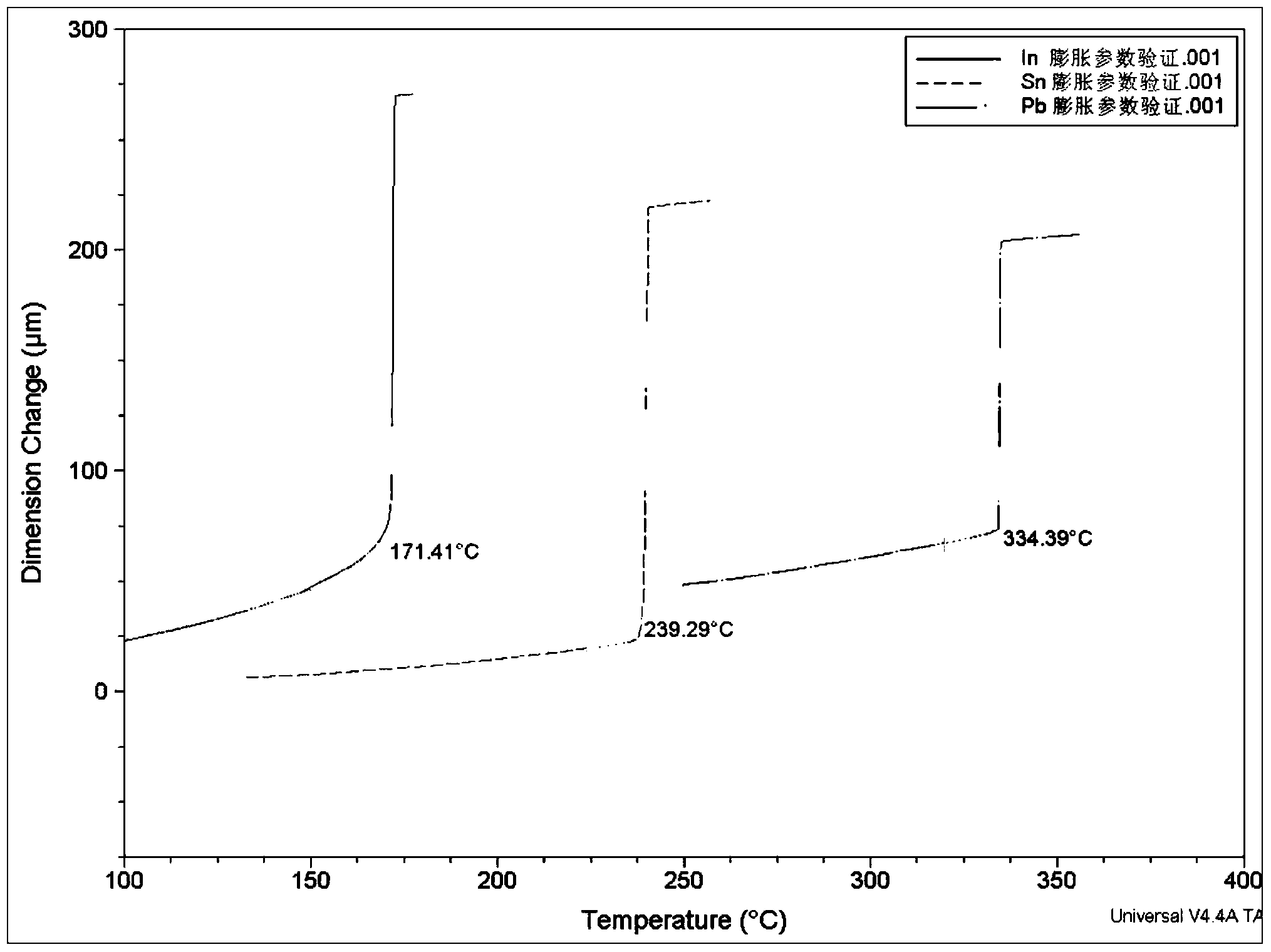
ActiveCN103471622AImprove stabilityEasy to markMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMitigation of undesired influencesThermocoupleThermomechanical analysis
The invention discloses a method and device for correcting temperature of a thermal mechanical analyzer tensile fixture. According to the method, a metal sample with a known melting point is fixed in a sample support of the tensile fixture, a probe is made to be in direct contact or indirect contact with the sample, when the sample is heated to be in a melting state, the probe can induct the sudden change of displacement, the temperature of the sample at the moment is measured through a thermocouple, and the temperature value and the actual melting point of the sample are compared and analyzed so that temperature correction can be carried out. Before a tensile mode is carried out by a thermal mechanical analyzer, temperature correction is carried out on the thermal mechanical analyzer with the metal sample with the known melting point, temperature parameters can be more accurate when the tensile mode is carried out, and the fact that the testing result of the tensile mode is more accurate is guaranteed.
Owner:GUANGDONG SHENGYI SCI TECH
Thermally expandable microcapsule and foam-molded article
InactiveUS20110263746A1Improve heat resistanceHigh expansion rateOther chemical processesMicroballoon preparationHeat resistanceShell molding
The present invention has its object to provide a thermally expandable microcapsule, which shows excellent heat resistance and a high expansion ratio and thereby can be suitably used for molding processes involving high shearing force, such as kneading molding, calender molding, extrusion molding, and injection molding. The present invention also has its object to provide a foamed product using the thermally expandable microcapsule. The present invention relates to a thermally expandable microcapsule, which comprises: a shell made of a polymer; and a volatile expansion agent as a core agent encapsulated in the shell, the storage elastic modulus (E′) of the shell at a temperature of 200° C. and a frequency of 10 Hz being 1×105 N / m2 or more, the storage elastic modulus (E′) of the shell at a temperature of 250° C. and a frequency of 10 Hz being 1×105 N / m2 or more, and a maximum displacement amount measured by thermomechanical analysis being 300 μm or more.
Owner:SEKISUI CHEM CO LTD
Highly functional polyethylene fiber, and dyed highly functional polyethylene fiber
ActiveCN102812170AHigh exhaustion rateLittle change in physical propertiesWeft knittingFibre typesFiberPolymer science
Provided is a highly functional polyethylene fiber which is small in changes of physical properties and has excellent dimensional stability over a wide range of product processing temperature and a wide range of product's service temperature. Also provided is a highly functional polyethylene fiber which is capable of achieving a high dye exhaustion ratio by a simple dyeing operation and has excellent color fastness. The highly functional polyethylene fibers of the present invention are characterized by having a limiting viscosity [n] of 0.8 dL / g to 4.9 dL / g (inclusive), a repeating unit that is substantially composed of ethylene, a maximum contraction stress as determined by TMA (thermomechanical analysis) of 0.4 cN / dtex or less and a thermal shrinkage at 100 DEG C of 2.5% or less.
Owner:TOYOBO MC CORP
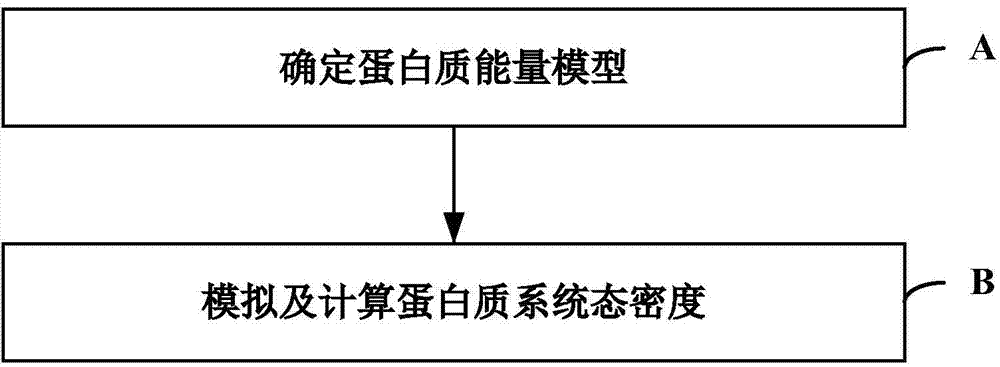
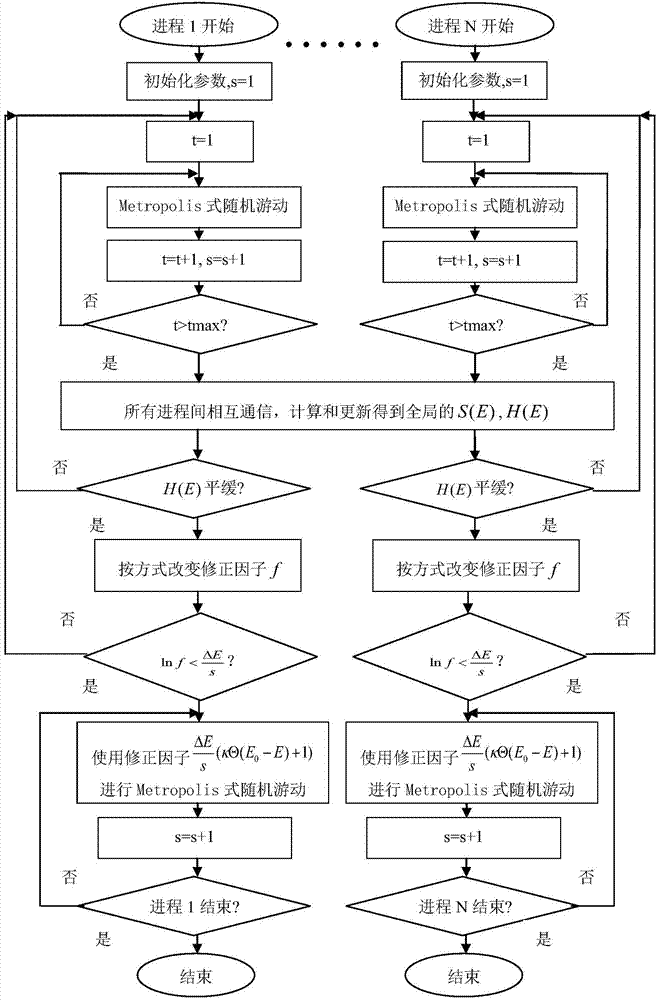
Monte Carlo simulation-based protein thermomechanical-analysis method
ActiveCN103699816AEfficient analysisSpeed up searchSpecial data processing applicationsSimulation basedProtein thermodynamics
The invention relates to the technical fields of biological computing and Monte Carlo simulation, and particularly discloses a Monte Carlo simulation-based protein thermomechanical-analysis method, which comprises the following steps of A, determining a protein energy model; B, simulating and calculating the state density of a protein system. According to the method, the whole thermomechanical process of protein folding can be efficiently analyzed and researched to further explore and research a protein folding process.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Device and method for testing wet expansion coefficient of carbon fiber composite material
The invention discloses a device and a method for testing the wet expansion coefficient of a carbon fiber composite material. The main body of the device adopts a thermal mechanical analyzer (TMA), the device is improved based on the TMA and equipped with a set of humidity controller for controlling humidity precision, the humidity controller comprises a water steam boiler and a humidity sensor, and the humidity control range is within 5-100 percent; within a certain humidity range, a wet deformation test is performed by using a displacement sensor and a mechanical sensor of the TMA. The device for testing the wet deformation has the characteristics of high testing speed, wide testing range, high resolution ratio and the like, and the requirement for the wet deformation test of various composite materials can be satisfied.
Owner:SHANGHAI COMPOSITES SCI & TECH CO LTD
Adhesive-carrying porous film for cell separator and its application
InactiveCN1771616AImprove securityFinal product manufactureSynthetic resin layered productsCross-linkPolymer science
According to the present invention, the following adhesive-loaded porous membrane is provided: using a needle probe type thermomechanical analyzer, a probe with a diameter of 1 mm is placed on the porous membrane under a load of 70 g, and the temperature is raised from room temperature at a rate of The porous membrane was heated at 2°C / min to measure its thickness, and a porous membrane at a temperature equal to or higher than 200°C when the thickness of the porous membrane became 1 / 2 of the thickness when the probe was placed at this time was used as a base material A porous membrane, a partially crosslinked adhesive formed by reacting a polyfunctional isocyanate with a reactive polymer having a functional group capable of reacting with an isocyanate group is supported on the porous membrane of the base material, and a part of it is crosslinked to form a battery Adhesive-loaded porous membrane for separators. Such a porous film (separator) is temporarily bonded to the electrodes to form an electrode / separator laminate. By using this laminate in the manufacture of batteries, there is no mutual slippage between the electrodes and the separator, and batteries can be manufactured efficiently. Moreover, the porous membrane (separator) itself does not melt or break at high temperature after the battery is manufactured, and also plays the role of a separator with little heat shrinkage.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Transparent electrode
InactiveUS20110171445A1Improve heat resistanceImprove conductivityGas discharge electrodesLayered productsHeat resistanceConductive materials
Disclosed herein is a transparent electrode, including: a polyimide film having an average linear thermal expansion coefficient of 50.0 ppm / ° C. or less, which is measured by thermo-mechanical analysis based on a film thickness of 50˜100 μm at a temperature of 50˜250° C., and a yellowness of 15 or less; and an electrode layer including a conductive material and a polyimide resin having an average linear thermal expansion coefficient of 50.0 ppm / ° C. or less, which is measured by thermo-mechanical analysis based on a film thickness of 50˜100 μm at a temperature of 50˜250° C., and a yellowness of 15 or less. The transparent electrode is advantageous in that a problem of a short circuit does not occur even when apparatuses including this transparent electrode are over-heated because it has excellent heat resistance, and in that it is transparent and has high electroconductivity.
Owner:KOLON IND INC
Liquid crystal polyester and its molded composition and use
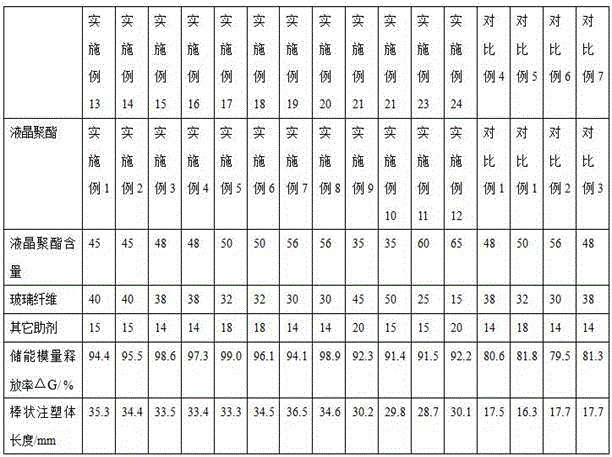
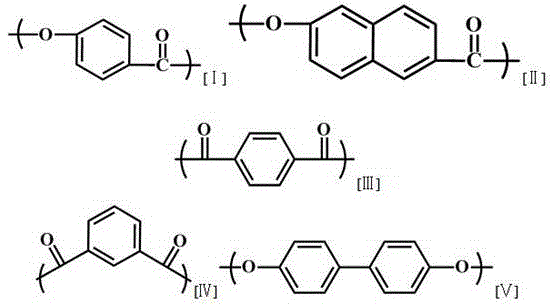
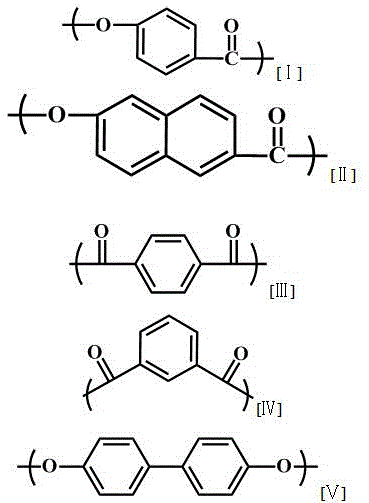
ActiveCN105837803AImprove liquidityImprove melting propertiesLiquid crystal compositionsPolyesterThermomechanical analysis
The invention discloses a liquid crystal polyester and its molded composition and use. The liquid crystal polyester comprises repeated structural units [I]-[IV]. A dynamic thermomechanical analysis (DMA) test proves that the liquid crystal polyester has a storage modulus release rate delta G greater than or equal to 95.0% and less than or equal to 99.4% defined in the formula (1) of delta G=[G(-50)-G(melting point)] / G(-50)*100%. The liquid crystal polyester has a storage modulus release rate delta G greater than or equal to 95.0% and less than or equal to 99.4%. The liquid crystal polyester and the liquid crystal polyester molded composition have good fluidity and excellent melting characteristics. A small thin wall molded product has high stability and is especially suitable for a thin wall electronic product.
Owner:KINGFA SCI & TECH CO LTD
Polyurethane urea elastic fiber
ActiveUS20090286441A1Improve heat resistanceImprove recoverabilityMonocomponent polyurethanes artificial filamentWarp knittingFiberThermomechanical analysis
Disclosed is a polyurethane urea elastic fiber containing 5-40% by weight of a polyurethane compound, wherein the compression deformation starting temperature determined by thermomechanical analysis (TMA) is not less than 150° C. but not more than 180° C. and time for thermal cutting at 180° C. is not less than 30 seconds.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI FIBERS CORPORATION
Method for analyzing melting characteristics of biomass ash
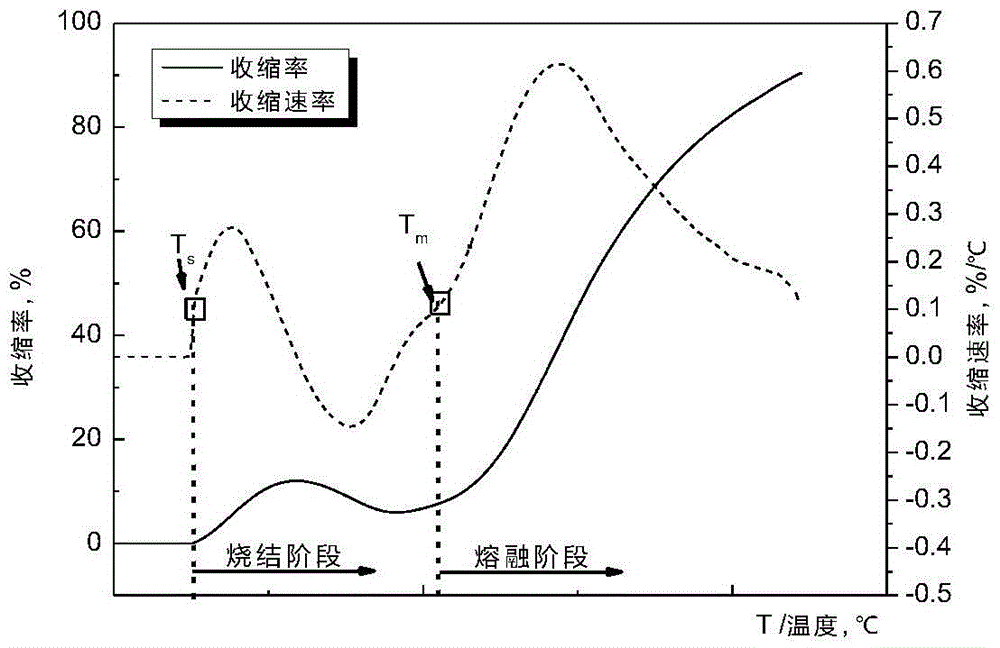
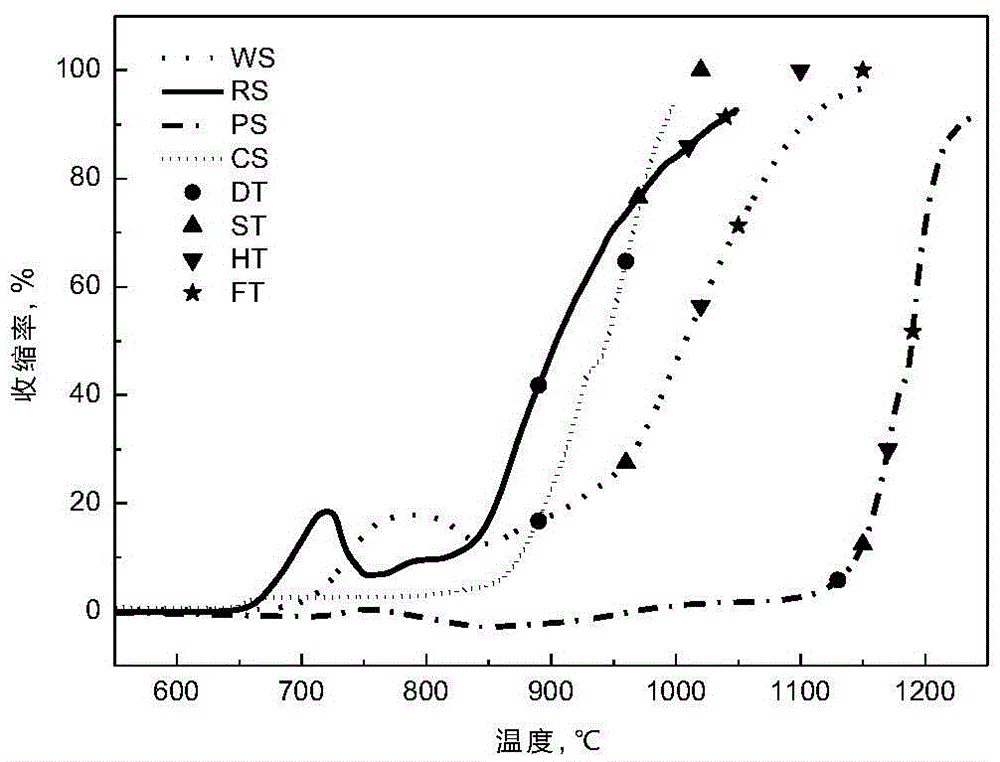
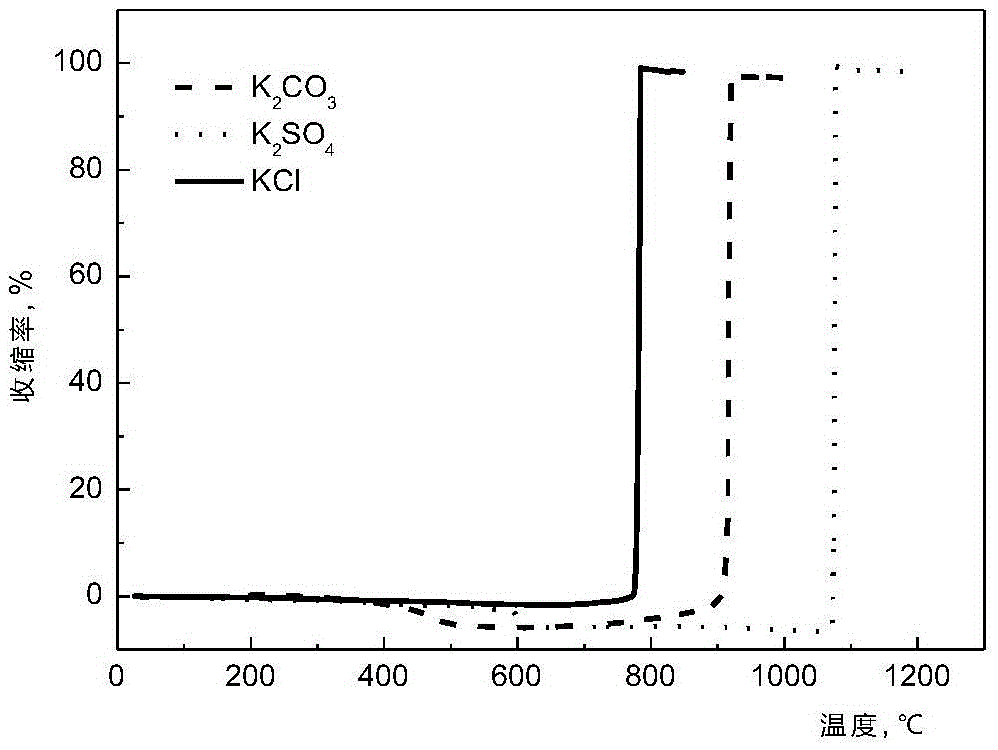
ActiveCN105527312AMelting properties reflectGood repeatabilityInvestigating phase/state changeThermomechanical analysisRepeatability
The invention relates to the field of gasifying of biomass energy sources, in particular to a method for analyzing melting characteristics of biomass ash. The method uses a thermal mechanical analyzer to test, and specifically comprises the following steps of preparing a biomass ash sample, testing the melting characteristics of the biomass ash, and analyzing a curve of the melting characteristics of the biomass ash; respectively defining the feature temperature Ts of a biomass ash sintering phase and the feature temperature Tm of a biomass ash melting phase, and utilizing the feature temperatures to analyze and evaluate the melting characteristics of the biomass ash; utilizing the feature temperature Tm to predict the agglomeration flow loss temperature caused by the melting of the biomass ash in the combusting and gasifying processes of a fluidized bed. The method has the advantages that the melting characteristics of the biomass ash in the whole heating process can be continuously observed, and the change caused by the viscosity and temperature characteristics of the biomass ash under high-temperature condition can be presented in the test process, so that when a thermal mechanical analyzing method is used for testing the melting characteristics of the biomass ash, the melting characteristics of the biomass ash can be more objectively and comprehensively reflected; the repeatability is good, and the accuracy is high.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Porous multi-layer film with improved thermal properties
ActiveUS8920913B2Improve permeabilityImprove propertiesCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersSynthetic resin layered productsPorosityThermal stability
Provided is a porous multi-layer film having two or more layers that is used as a separator for battery. In the film, more than 2 layers have different porosities and pore sizes. The film has a thickness of 9 to 50 μm, a machine direction (MD) loop stiffness of 0.008 mg / μm or more, puncture strength of 0.15 N / μm or more, permeability of 1.5×10−5 Darcy or more, shut-down temperature of 140° C. or less, melt-down temperature of 170° C. or more, a transverse direction (TD) maximum shrinkage of 25% or less in Thermomechanical Analysis (TMA) under a load of 1 mN / (1 μm×6 mm), and melt down temperature of 160° C. or more. Since the porous multi-layer film shows excellent thermal stability at high temperature and electrolyte retaining property due to a dual pore structure, the film shows a superior effect when used as a separator for high-capacity / high-power lithium ion battery.
Owner:SK INNOVATION CO LTD +1
Method for predicting output power of organic Rankine cycle on basis of BP neural network
InactiveCN108564172AQuick forecastAccurate predictionNeural learning methodsNerve networkOrganic Rankine cycle
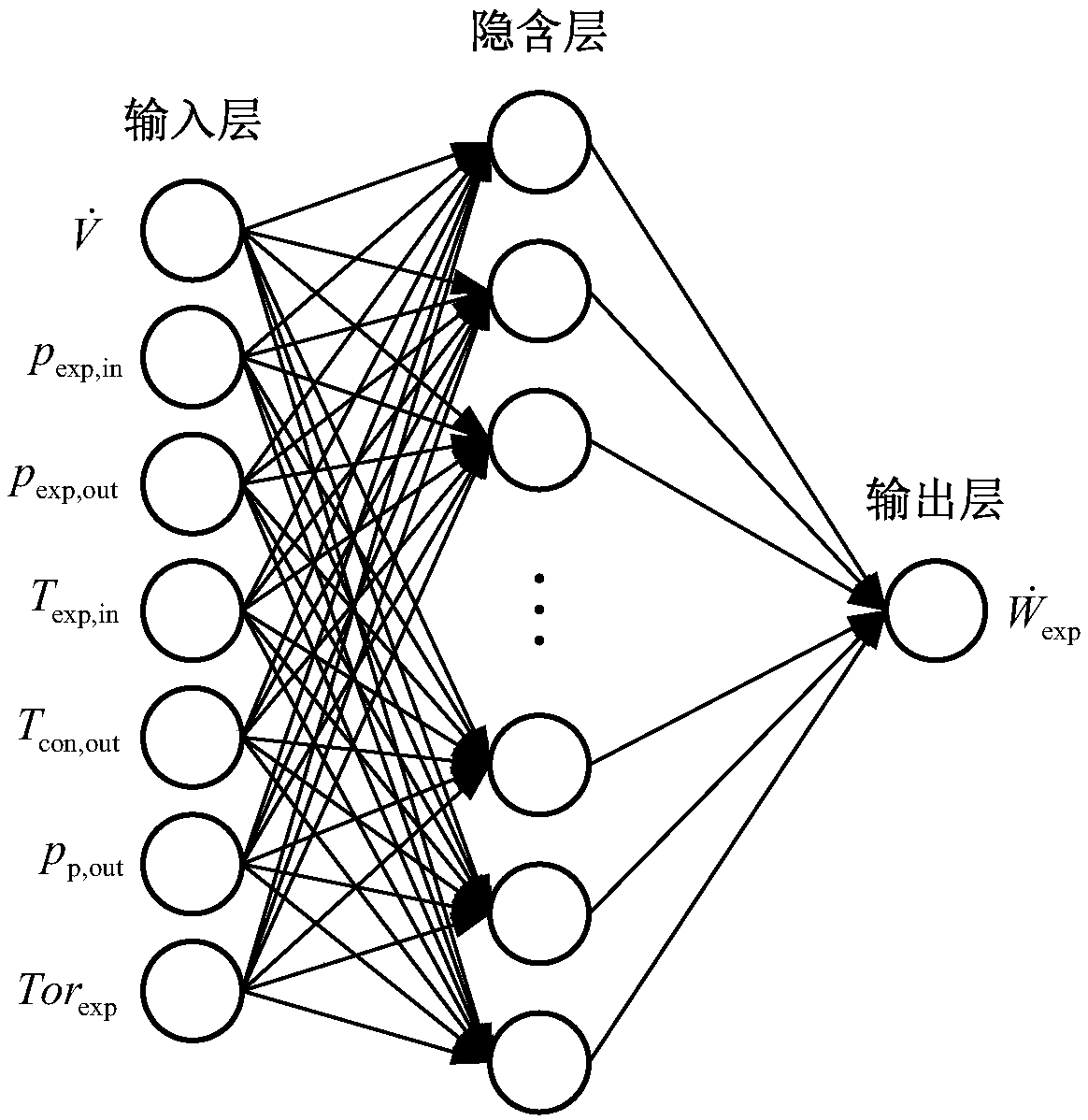
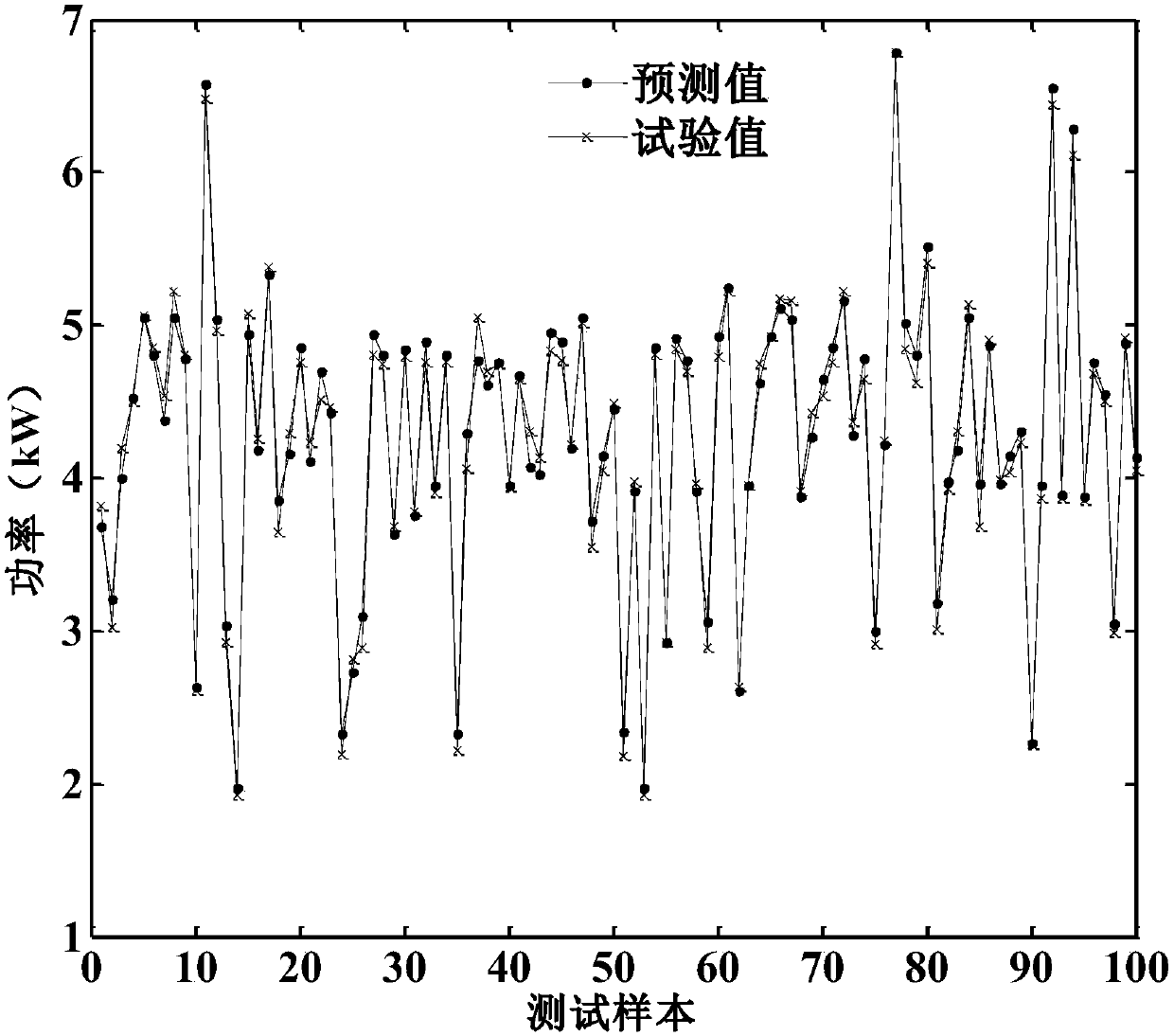
The invention relates to a method for predicting output power of organic Rankine cycle on the basis of a BP neural network and belongs to the field of thermal power engineering. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring multiple groups of organic Rankine cycle operation data, wherein each group comprises the following parameters: the volume flow of an organic working medium, the torque of an expansion machine, the inlet pressure of the expansion machine, the outlet pressure of the expansion machine, the inlet temperature of the expansion machine, the outlet temperature of a condenser, the outlet pressure of a working medium pump and the output power of the expansion machine; performing normalization processing on the acquired data; establishing the BP neural network; training andtesting the neural network; and performing inverse normalization processing on the output power of the expansion machine, namely the output data of the neural network, in the test data. Compared withthe traditional thermomechanical analysis method, the constructed neural network model can predict the output power of the organic Rankine cycle rapidly and accurately, can avoid research on the operation mechanism of each part of the system, can obviously improve the working efficiency and the prediction precision and provides reliable guidance for optimization of the organic Rankine cycle.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com