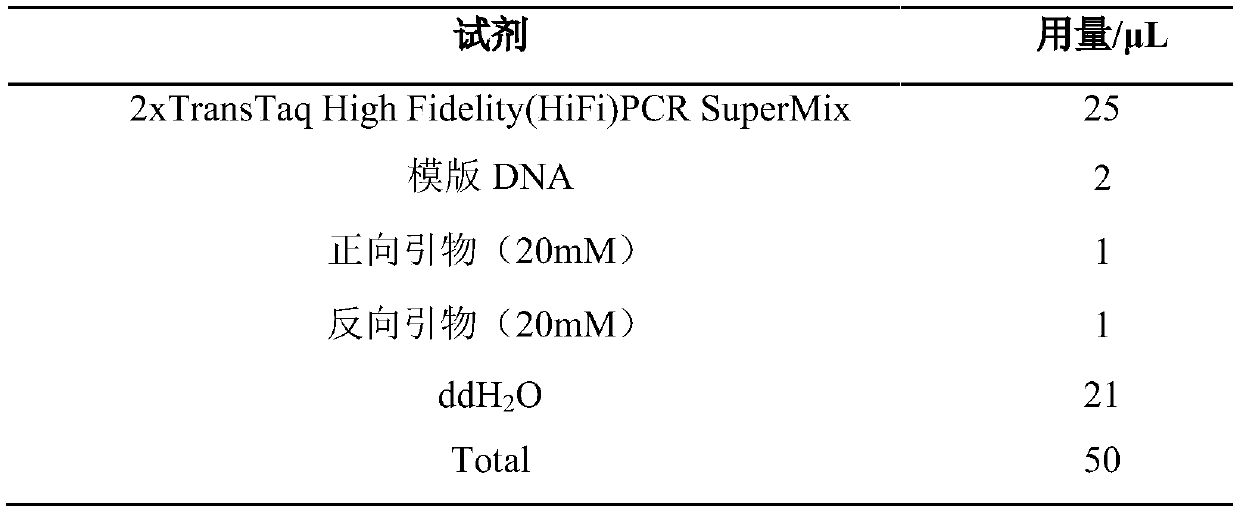
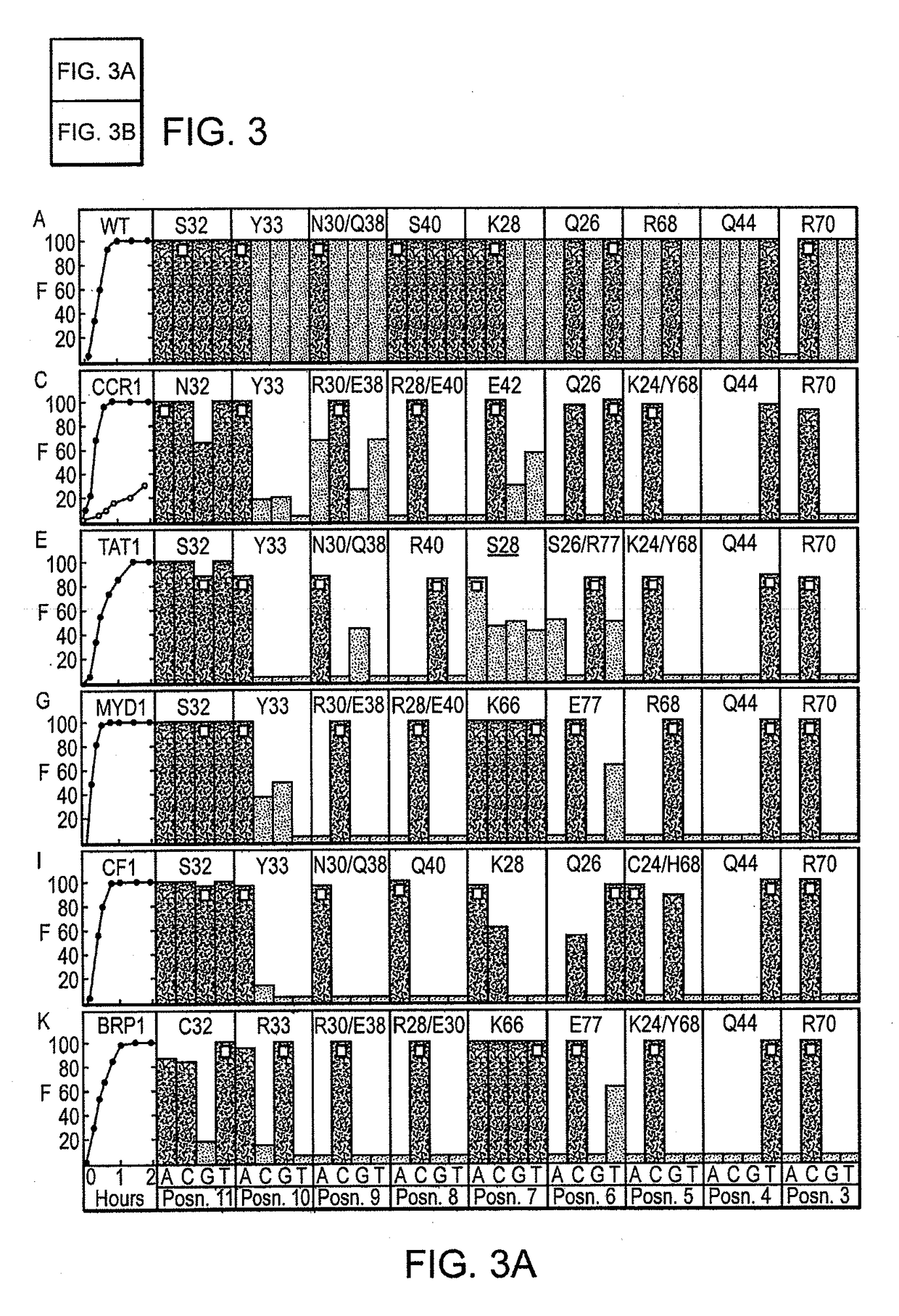
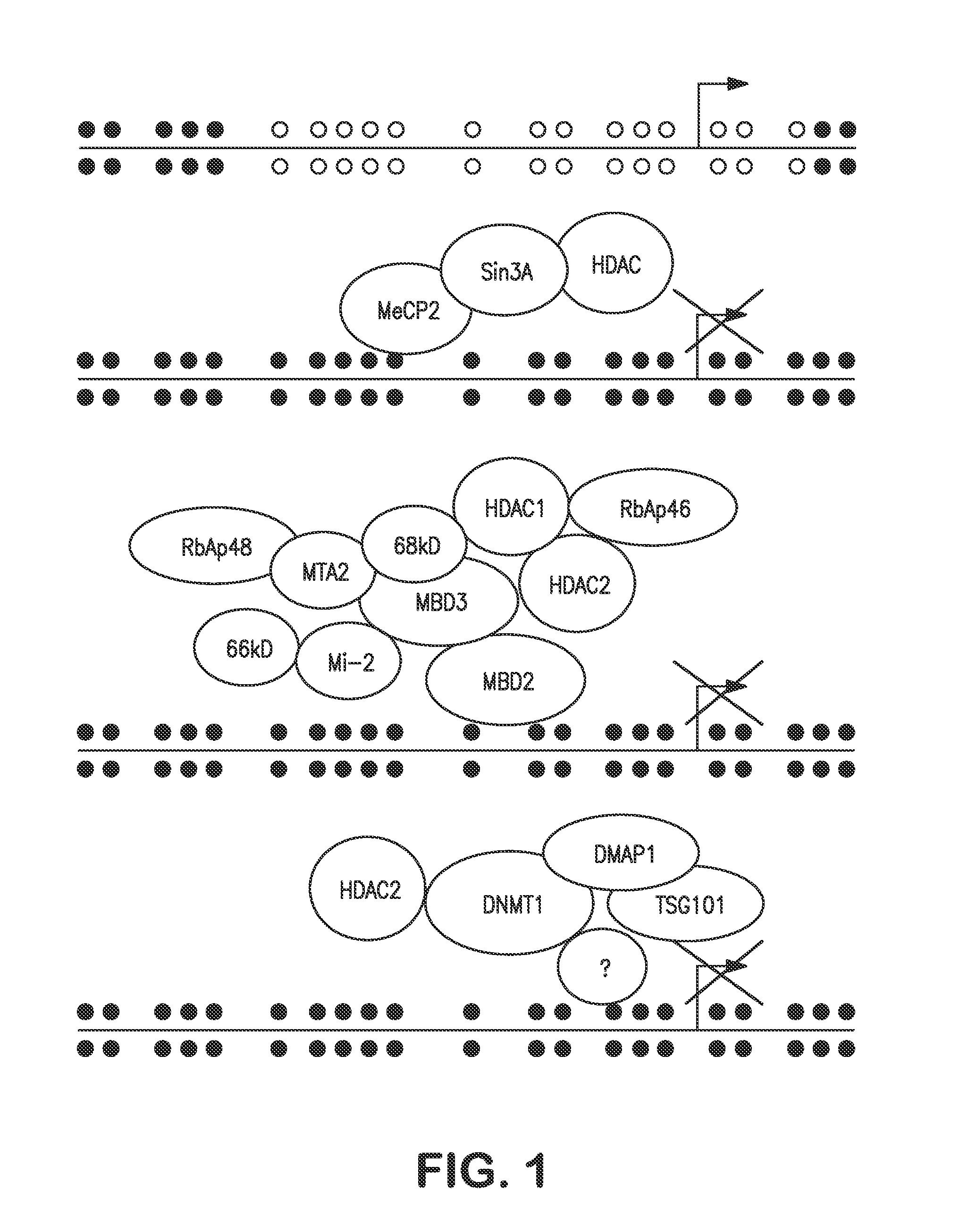
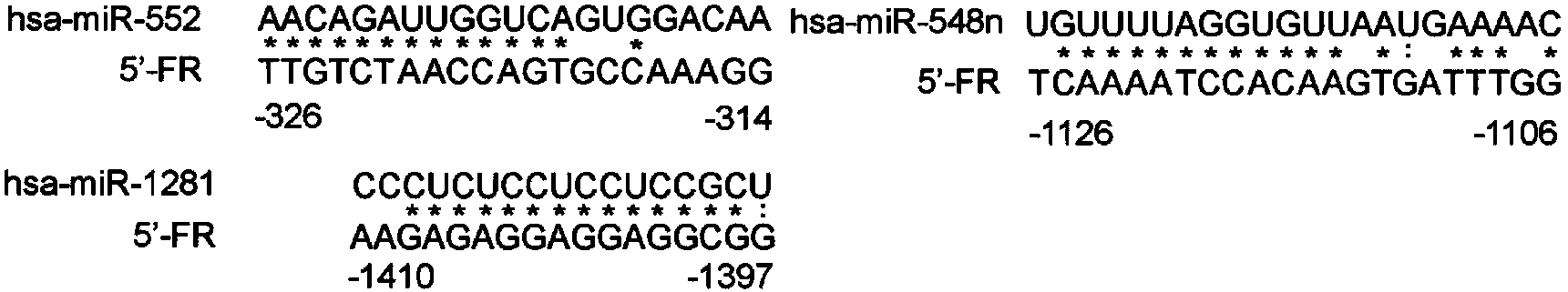Patents
Literature
38 results about "Transcription Repression" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
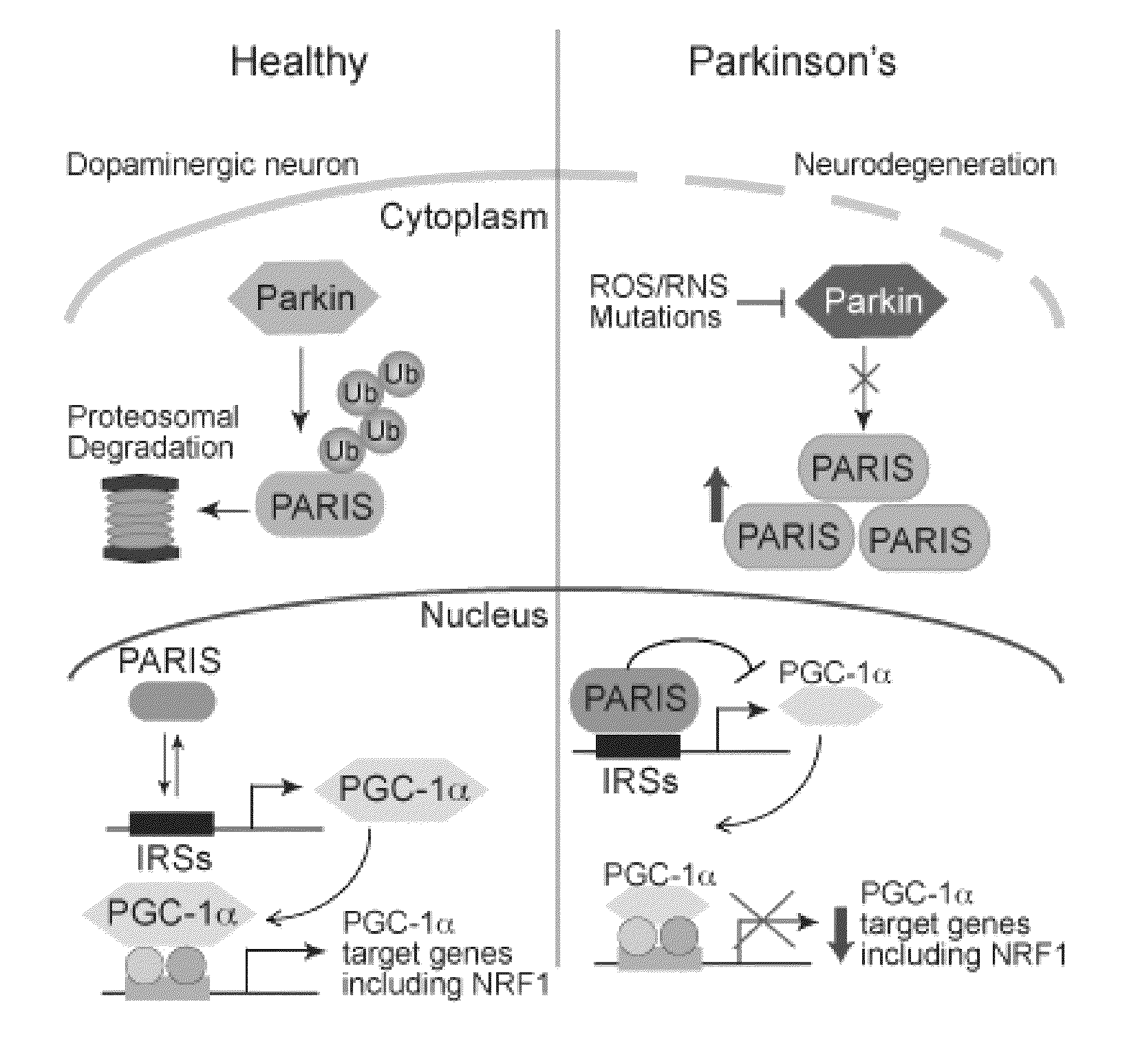
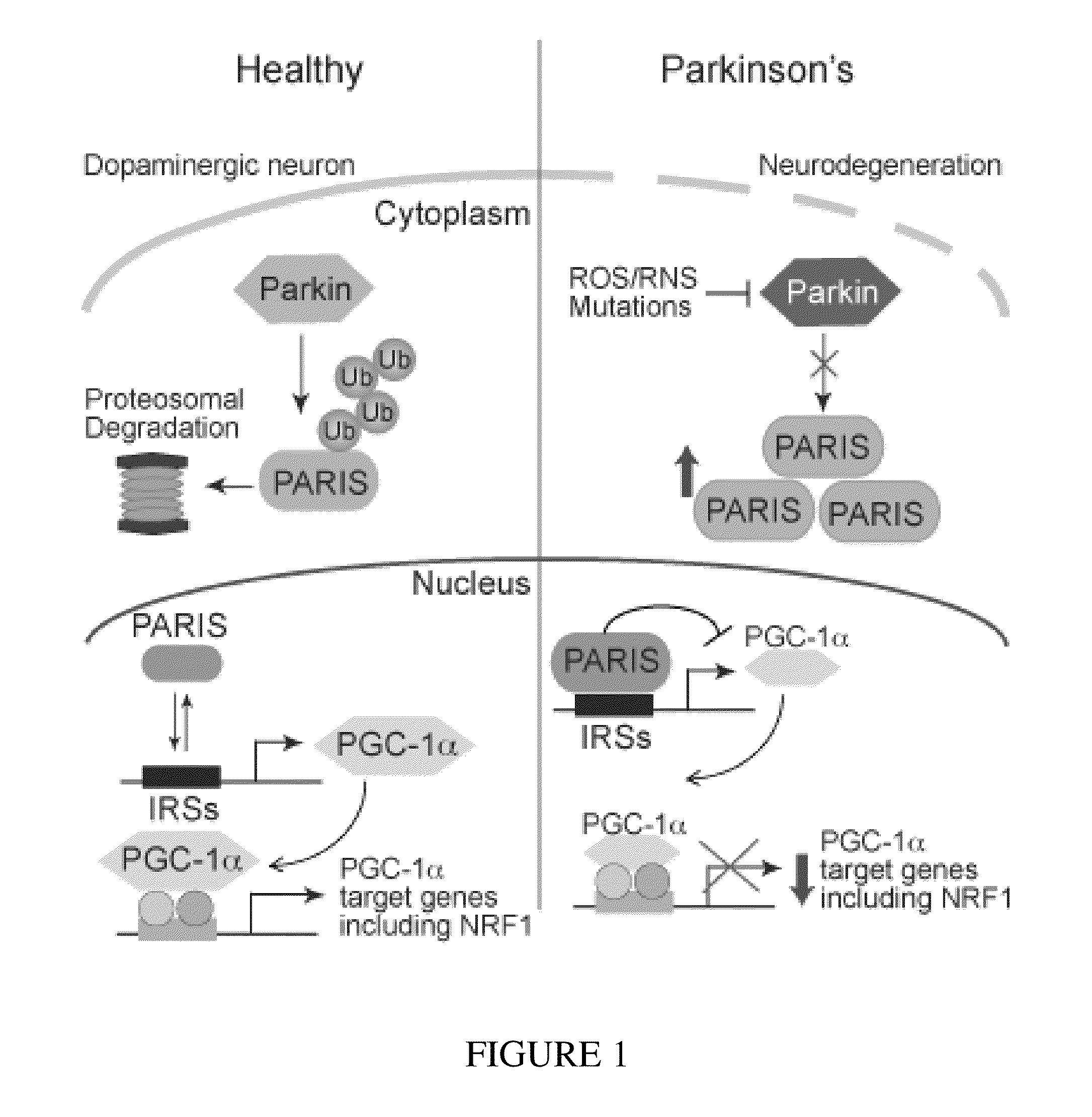
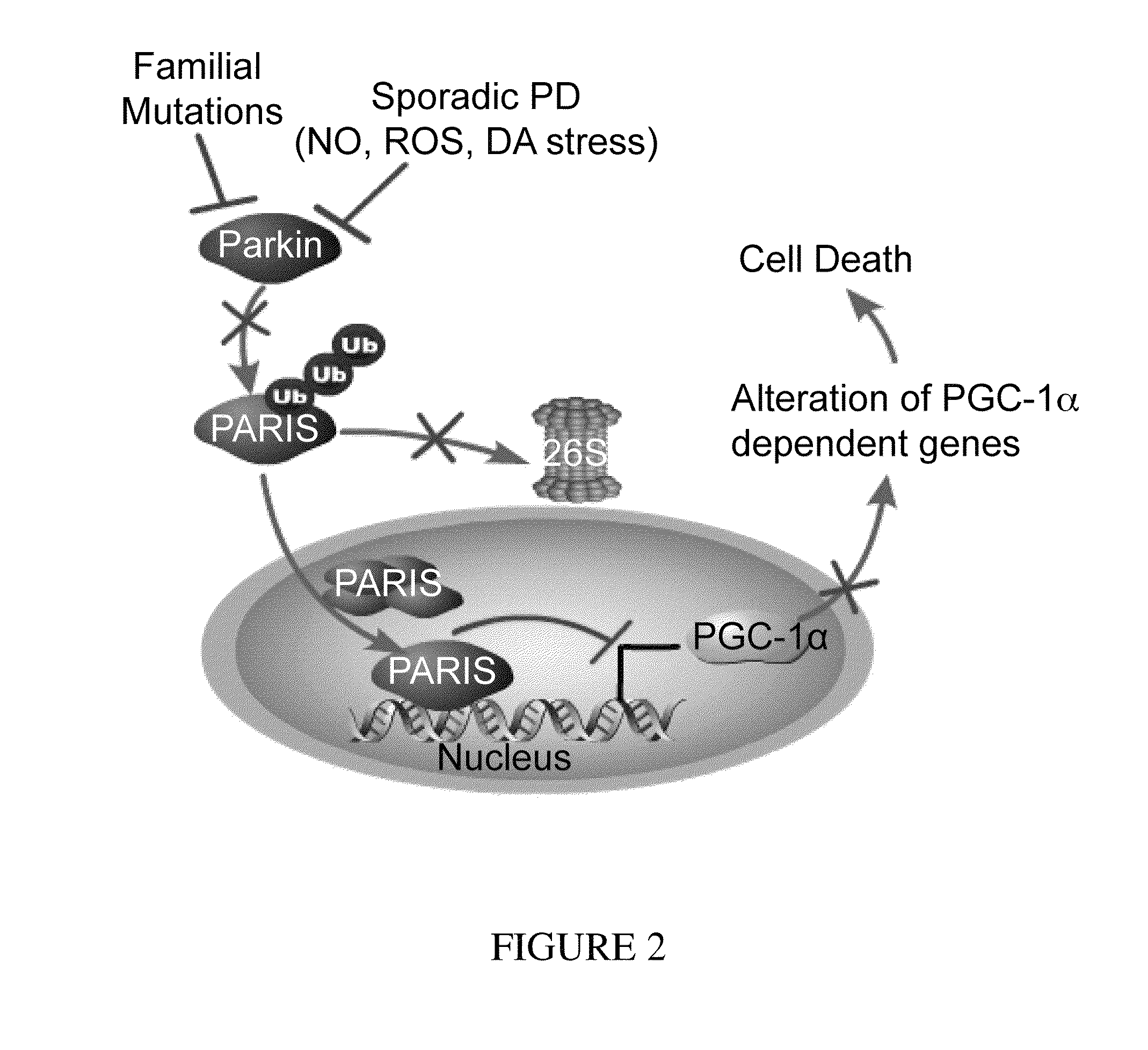
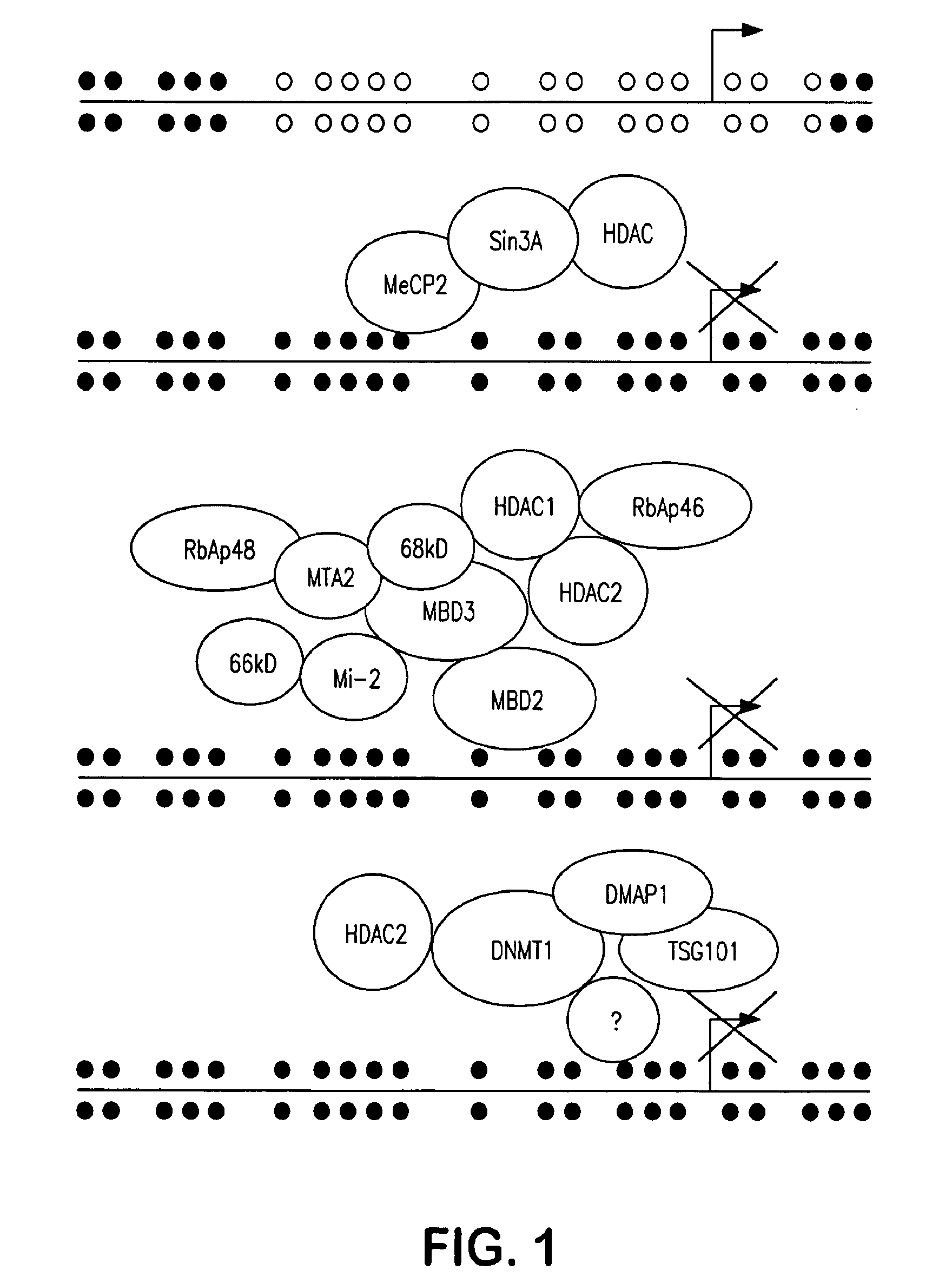
Gene-specific repression of transcription plays a central role in gene regulation. This is true for the spatial control of gene activity in development, during which boundaries of gene expression are often determined by the spatially restricted localization or activity of transcriptional repressors (Mannervik et al.
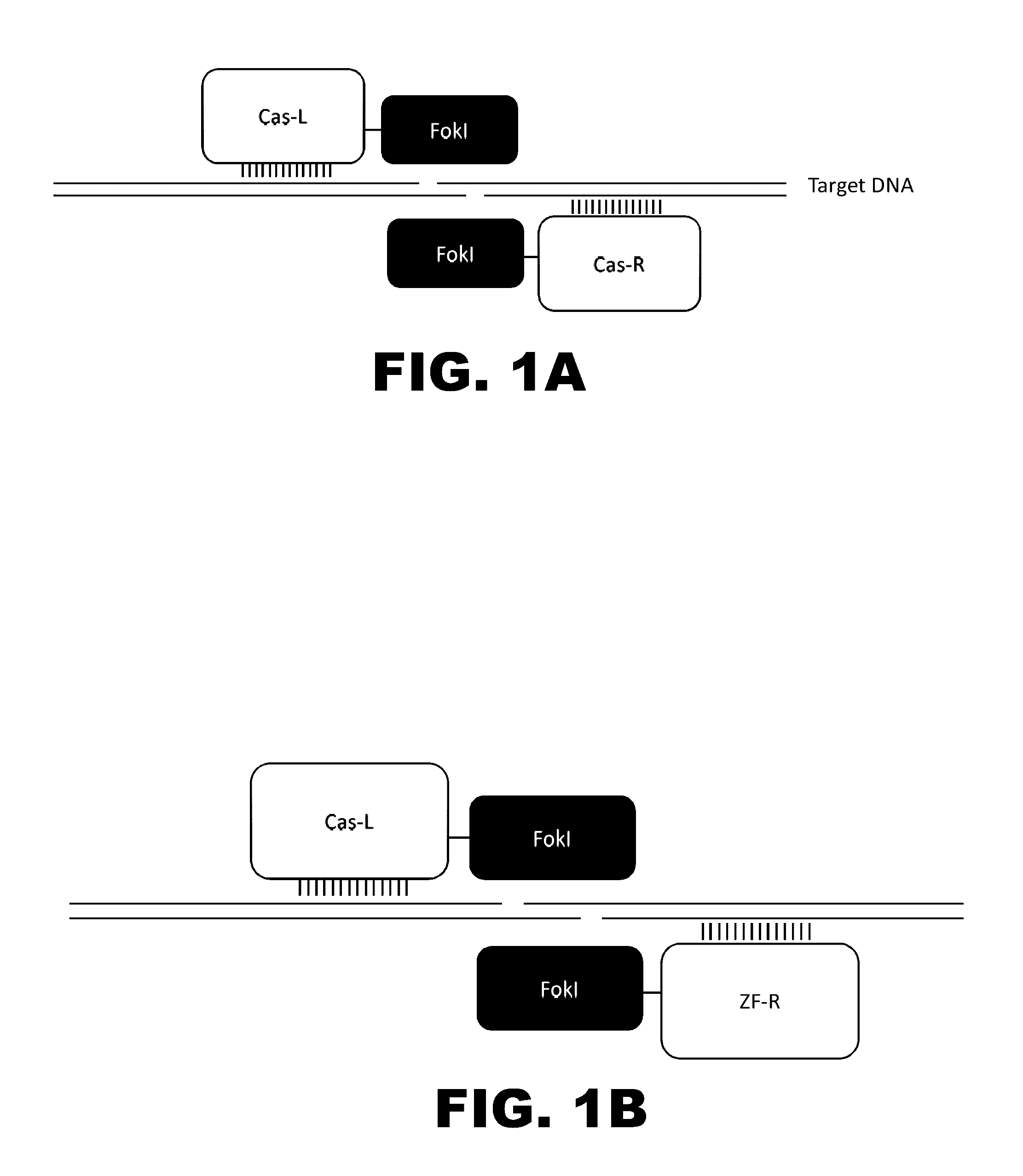
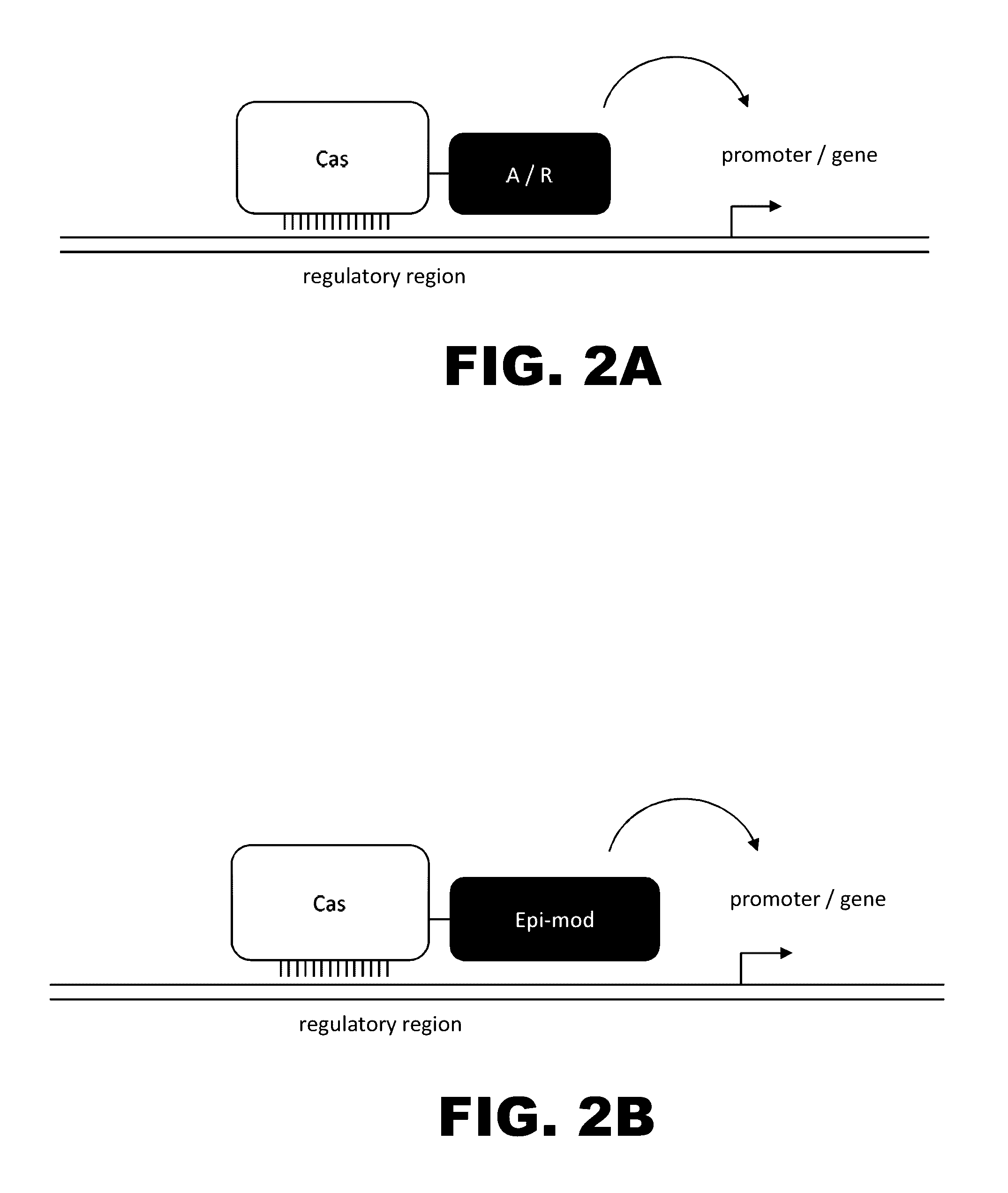
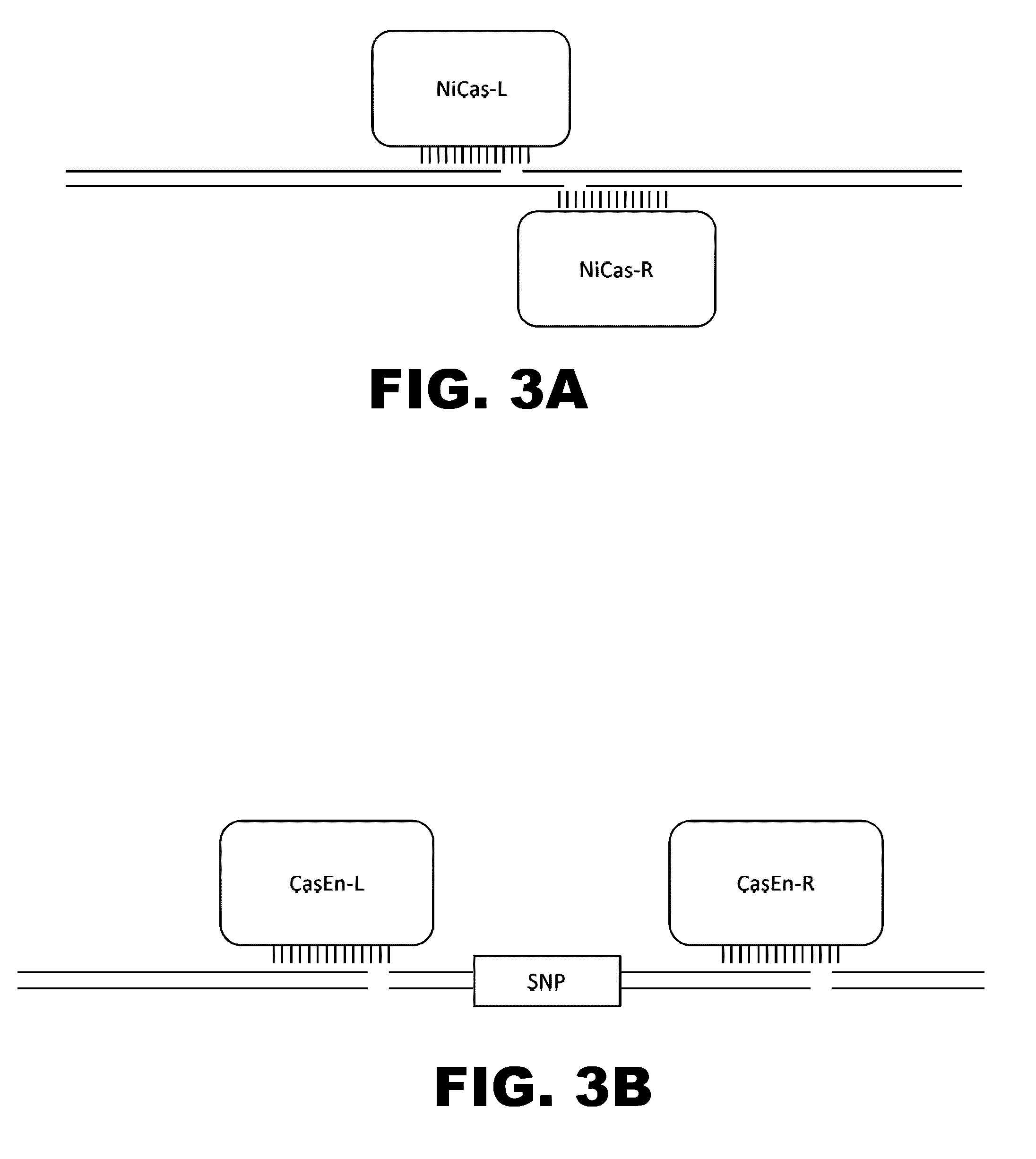
Crispr-based genome modification and regulation
The present invention provides RNA-guided endonucleases, which are engineered for expression in eukaryotic cells or embryos, and methods of using the RNA-guided endonuclease for targeted genome modification in in eukaryotic cells or embryos. Also provided are fusion proteins, wherein each fusion protein comprises a CRISPR / Cas-like protein or fragment thereof and an effector domain. The effector domain can be a cleavage domain, an epigenetic modification domain, a transcriptional activation domain, or a transcriptional repressor domain. Also provided are methods for using the fusion proteins to modify a chromosomal sequence or regulate expression of a chromosomal sequence.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Sid-polyamide fusions: a potent method of regulating gene expression
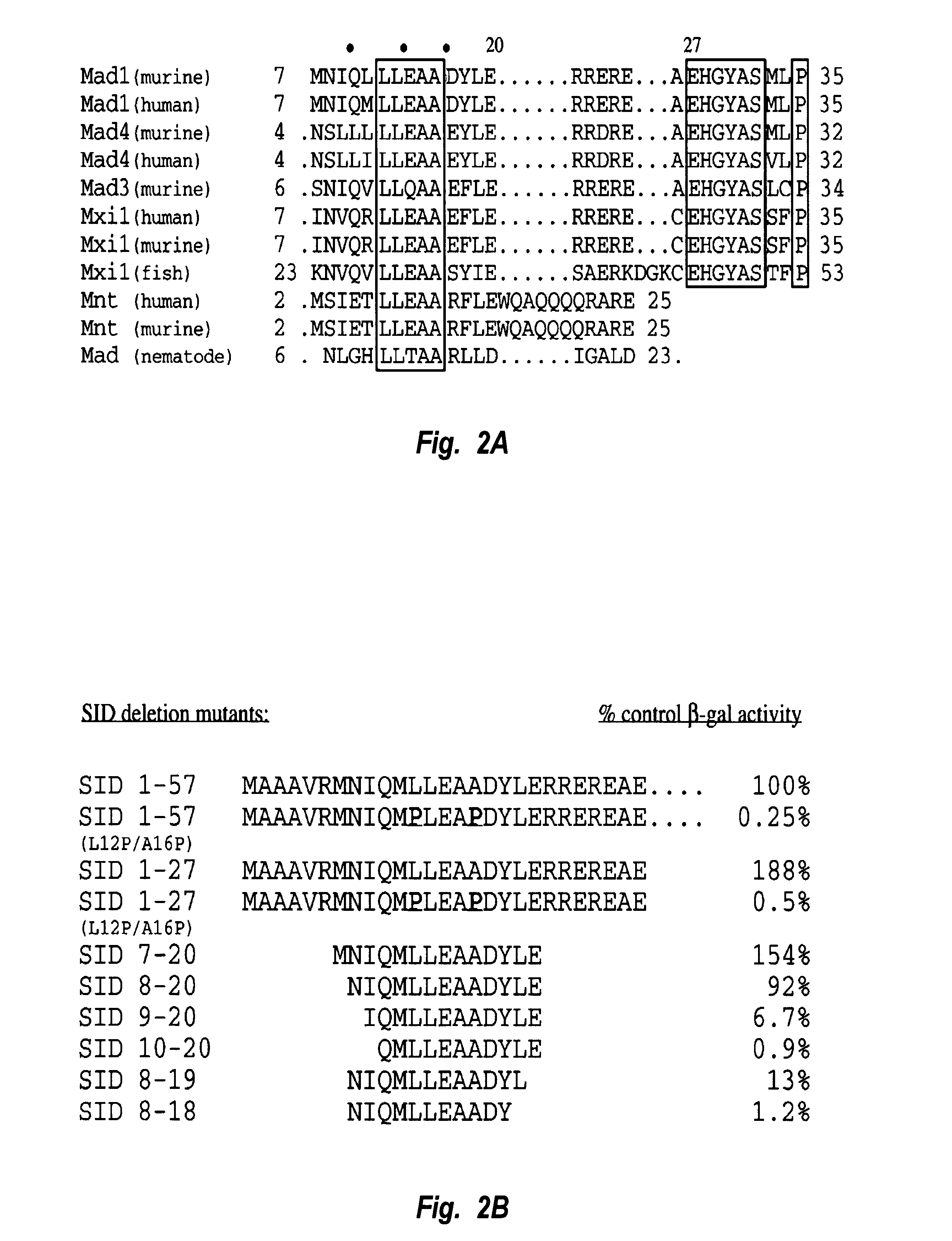
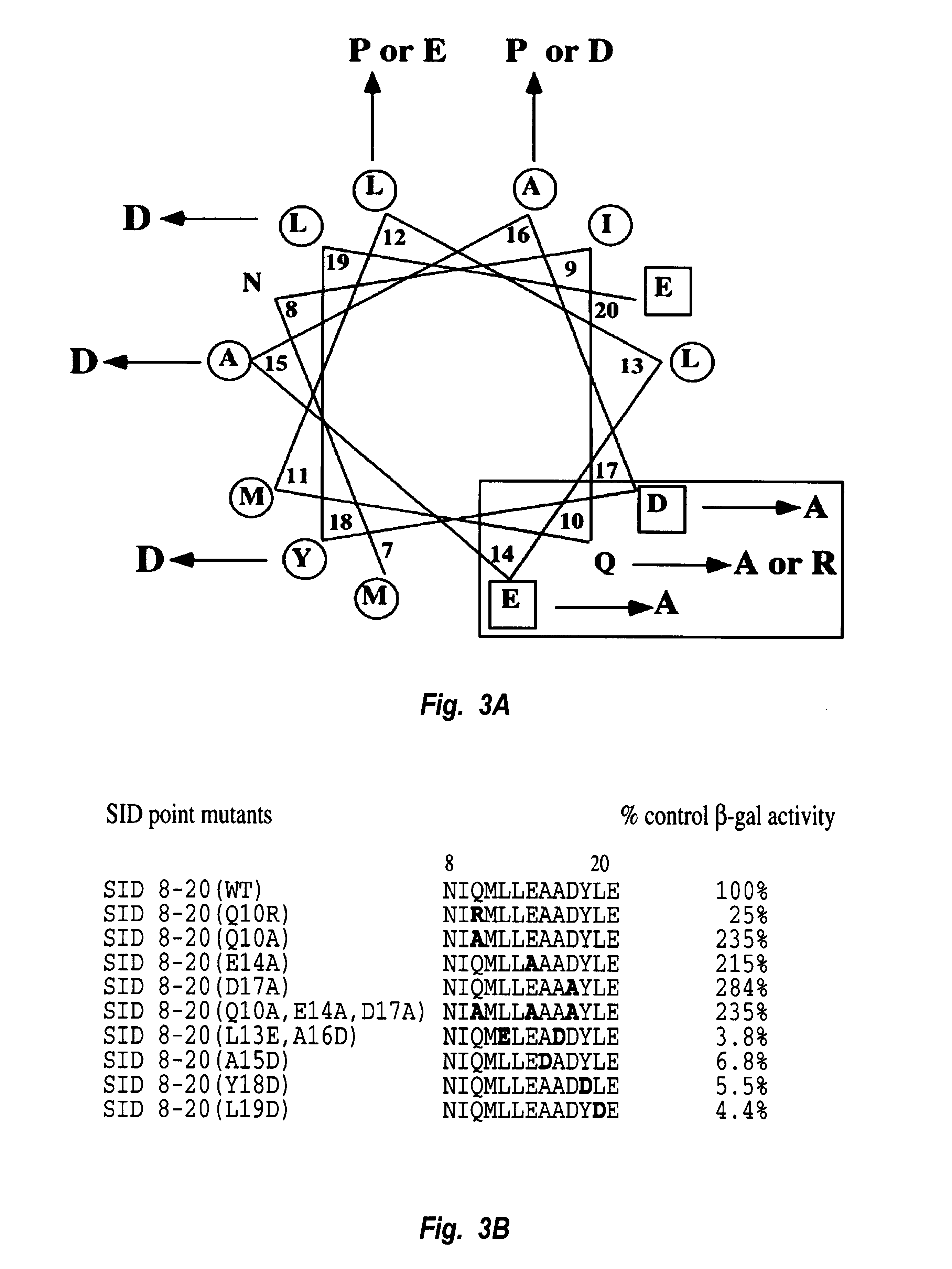
This invention relates to a thirteen amino acid polypeptide sequence which is able to autonomously function as a transcription repression domain through its ability to bind mSin3A. Disclosed herein are compounds and methods for regulating transcription of a selected gene. Compounds include fusions of this repression domain to a DNA-binding domain, such as a polyamide or zinc finger domain. Methods are provided for constructing and for using such compounds to regulate transcription of a selected gene.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Construction method and application of high-yield L-threonine gene engineering bacterium
ActiveCN109735478APromote growthEnhanced circulation fluxBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismAgricultural science
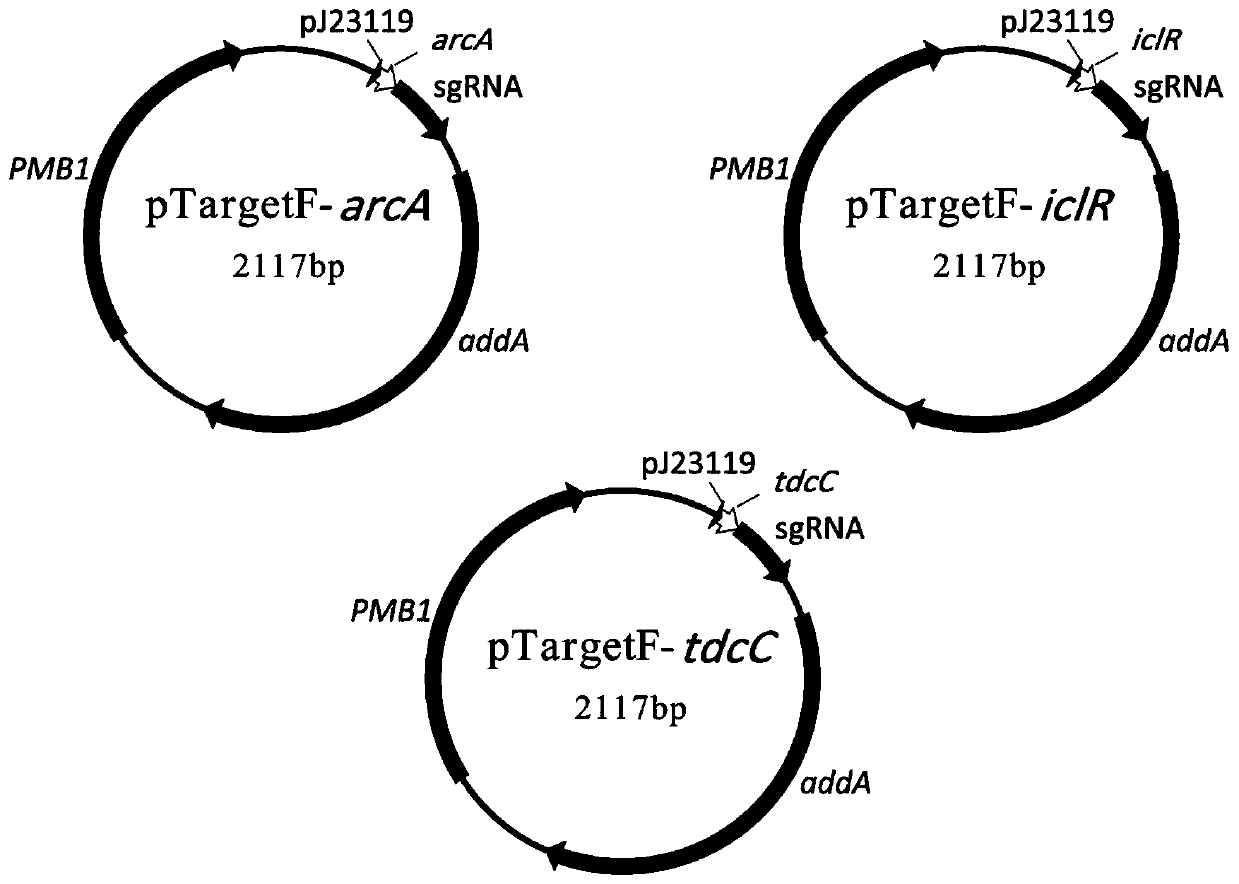
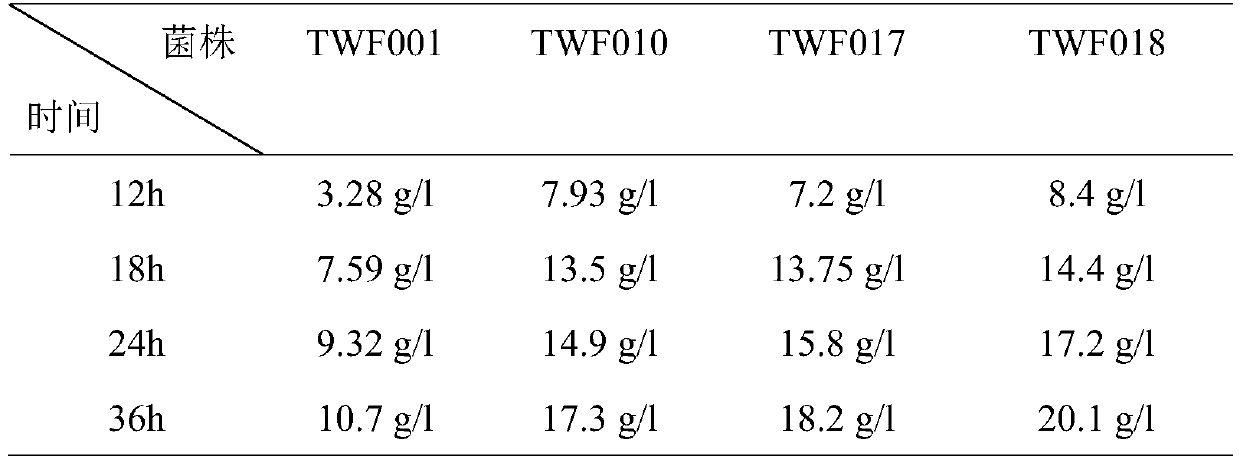
The invention discloses a construction method and application of a high-yield L-threonine gene engineering bacterium and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering and microbial fermentation.By means of deletion of an arcA gene encoding a transcription regulatory factor, deletion of an iclR gene encoding transcription repression and deletion of a tdcC gene encoding a threonine transporter, the yield of L-threonine is greatly improved, the yield of L-threonine is increased to 20.1 g / L after 36 hours of fermentation, and the conversion rate reaches 0.67.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
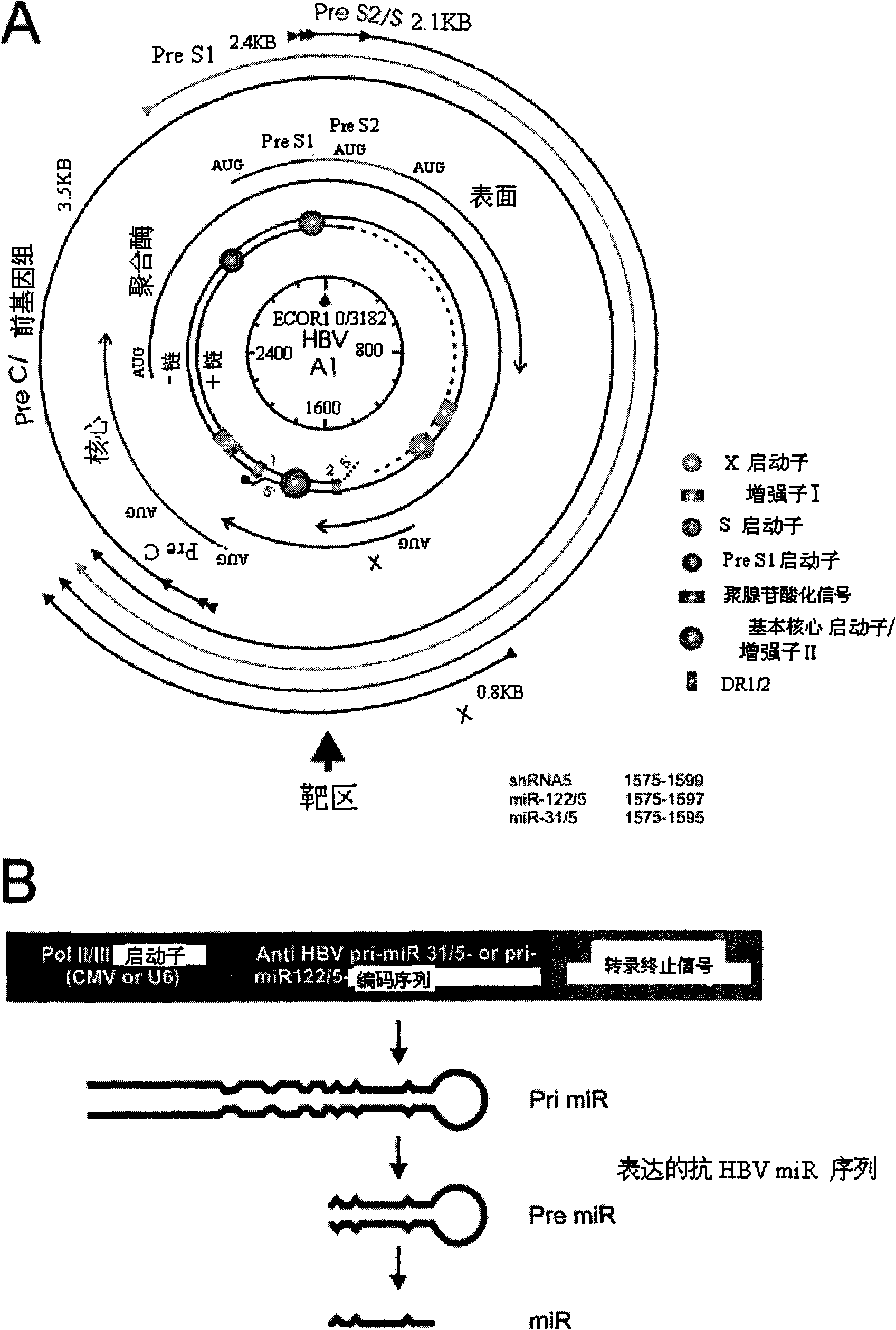
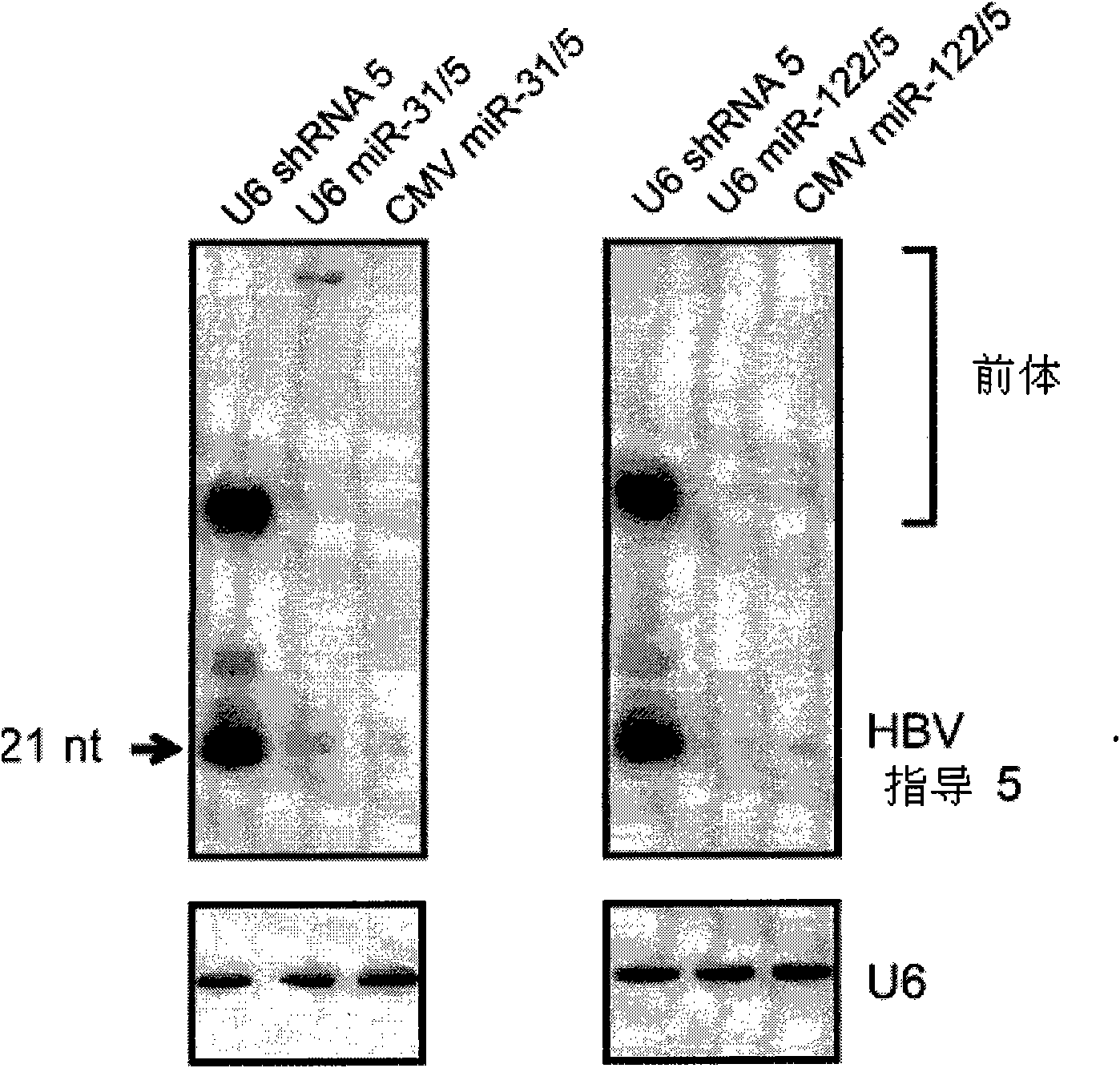
A primary micro RNA expression cassette
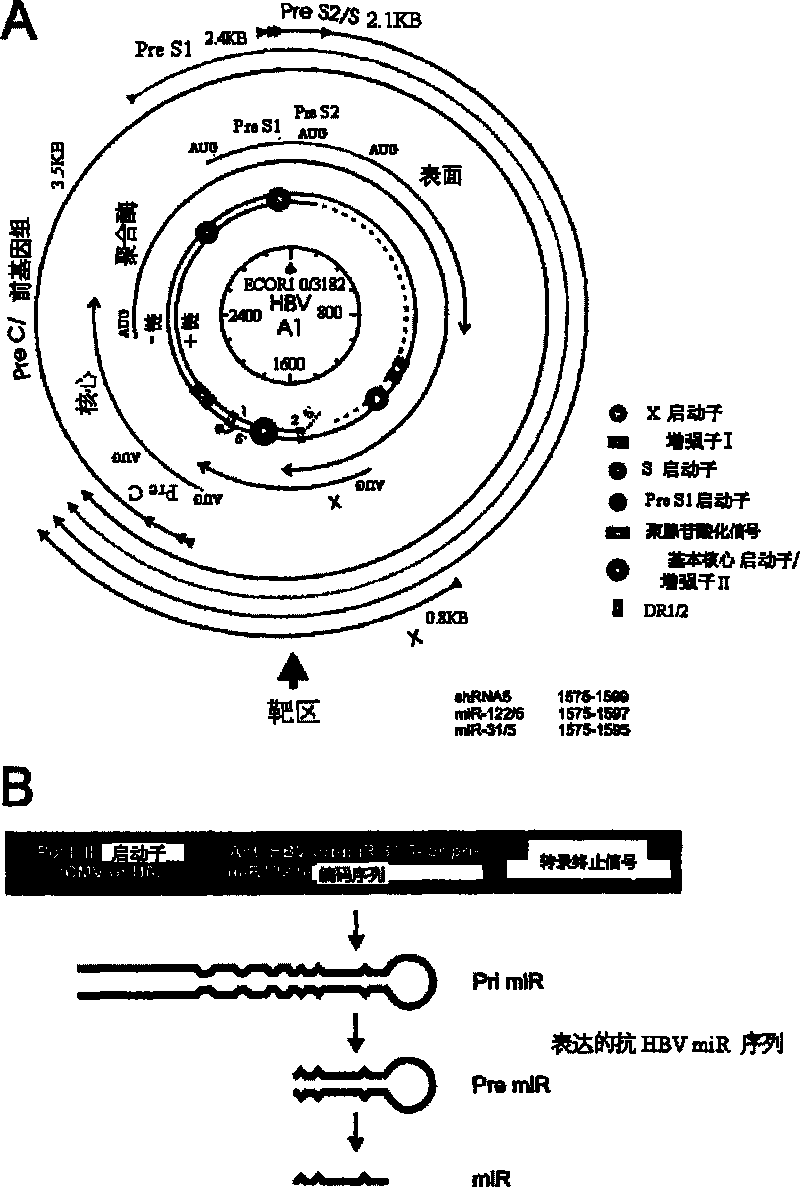
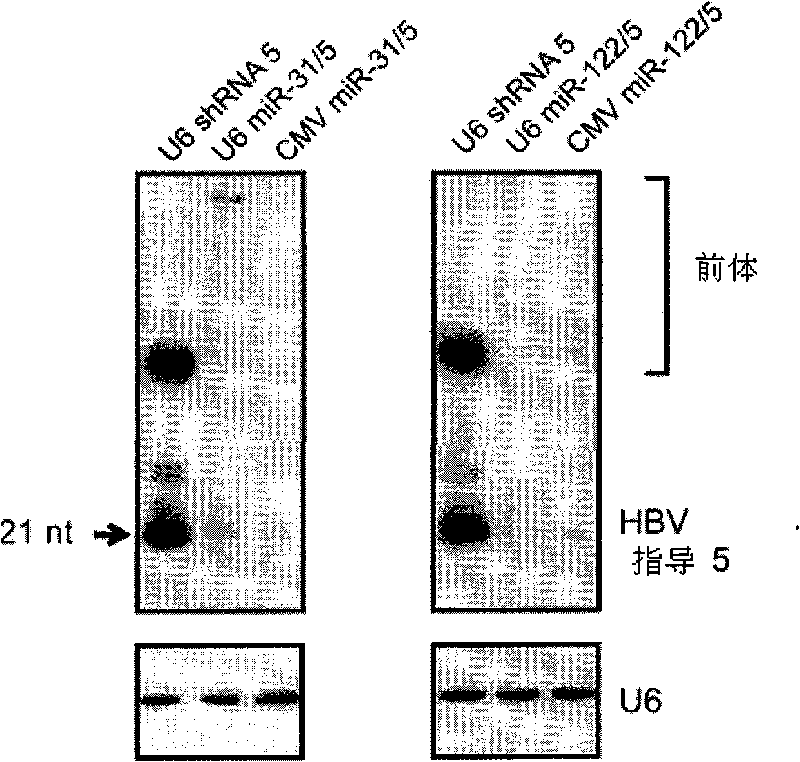
This invention relates to inhibition of hepatitis gene expression. More specifically, the invention relates to a method of using RNA sequences to inhibit Hepatitis B and C Virus replication. Expression cassettes that include DNA sequences derived from endogenous micro RNAs (miRs) are used in the method and are transcribed by Pol Il promoters, and then processed to generate sequences that are specific to target hepatitis virus sequences (RNAi effecter sequences). The RNAi effecter sequences can target the selected hepatitis virus sequences resulting in gene silencing or transcriptional inhibition of the hepatitis virus gene. The expression cassettes may be delivered in vitro or in vivo to host cells. A pharmaceutical composition containing the expression cassettes is also claimed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF THE WITWATERSRAND
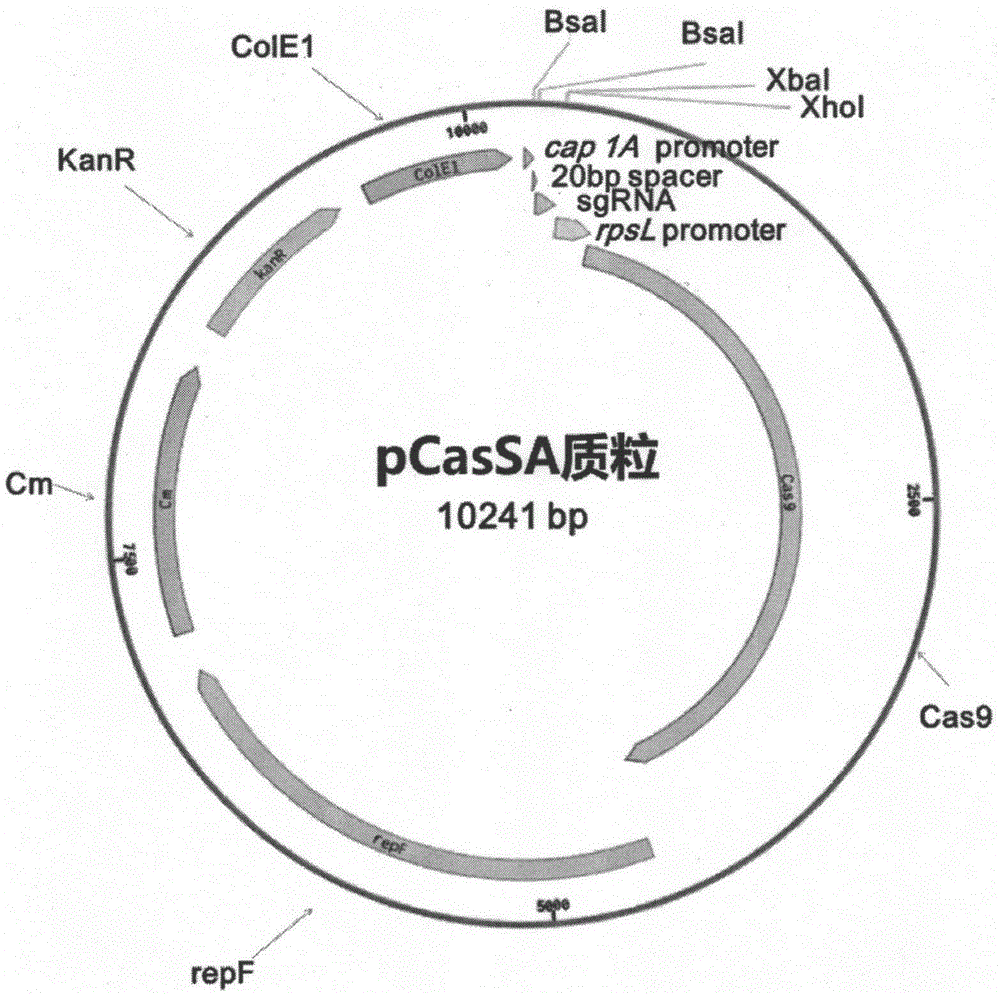
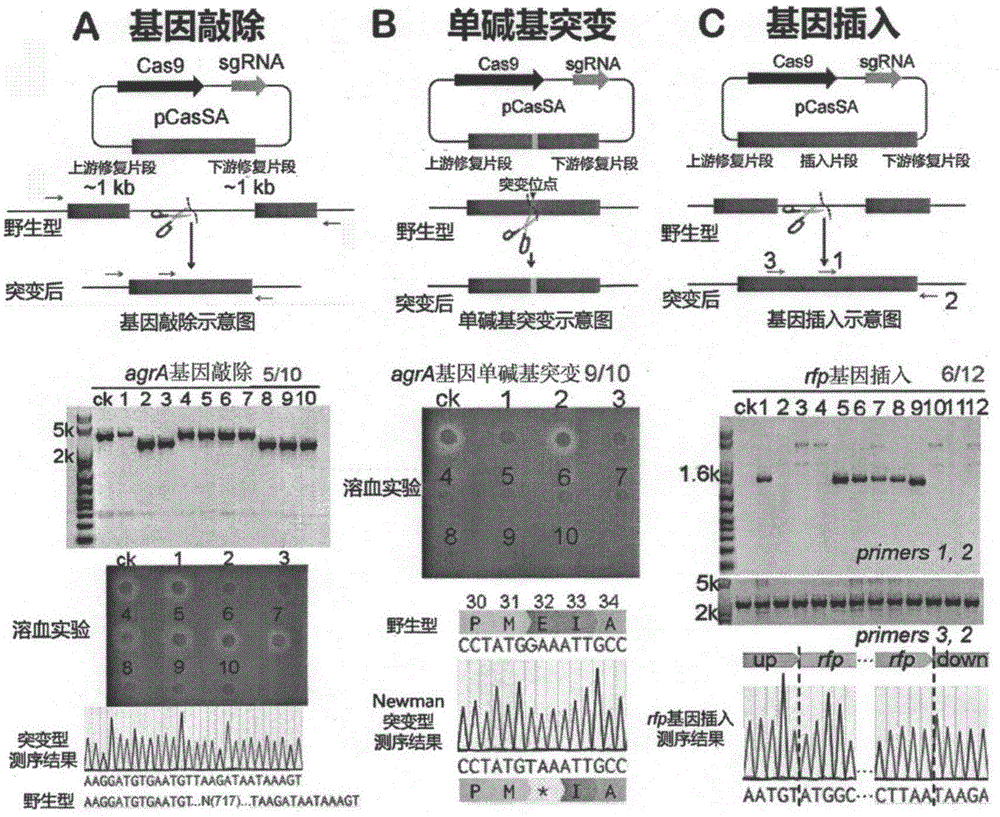
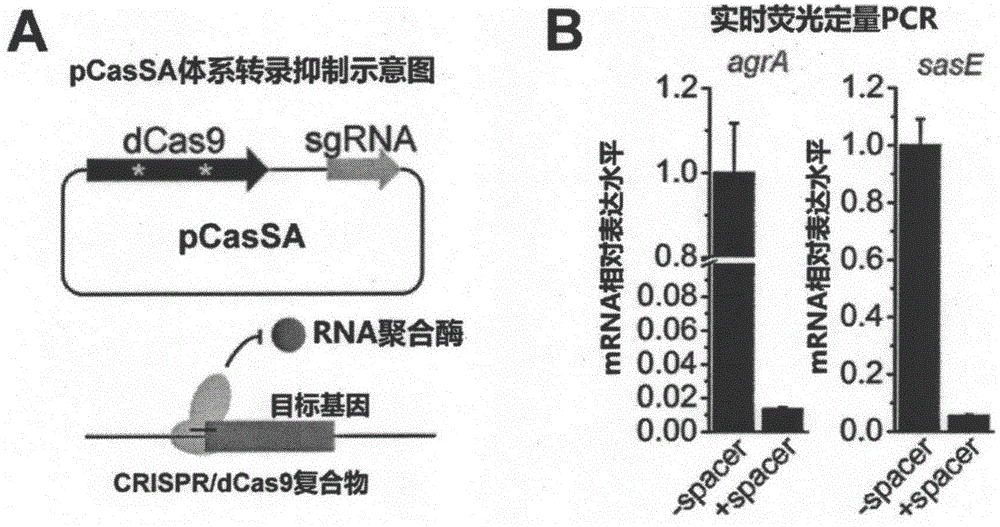
pCasSA plasmid and application thereof
ActiveCN106834330AEfficient editingEfficient transcriptional repressionVectorsBacteriaStaphylococcus cohniiStaphylococcus pseudintermedius
The invention provides pCasSA plasmid and an application thereof. The sequence of the pCasSA plasmid is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. The pCasSA plasmid is capable of (1) effectively and rapidly editing genomes of various staphylococcus aureus strains, including gene knockout, single base mutation and gene insertion, and (2) having an efficient transcription inhibition function on target genes. The technique has wide application prospects in such aspects as staphylococcus aureus infection treatment, medicine target discovery, medicine development and staphylococcus aureus physiological study.
Owner:SHANGHAI TECH UNIV
Promoter regions of the mouse and human telomerase RNA component genes
InactiveUS7084267B1Increase and decrease promoter activityIncrease and decrease magnitudeOrganic active ingredientsFungiTelomerasePromoter activity
The present invention relates to the identification of the genomic promoter region of the human and mouse telomerase RNA gene. Telomerase activity is necessary for the unrestricted proliferative capacity of many human cancers. It is proposed that mutation or dysregulation of the telomerase repression pathway may cause reactivation or upregulation of telomerase expression in cancer. The invention provides details of elements important for the regulation of telomerase RNA genes, including the Sp family of transcription factors. There is further provided methods for screening elements having the ability for suppressing telomerase RNA gene promoter activity and use of such elements in the treatment of cancers. In addition, evidence is also provided for the development of new transcription based therapies for cancer and for genetic approaches to targeting therapeutic genes to cancer cells. Namely, (1) transcriptional repression and the disruption of signal transduction pathways regulating telomerase activation. (2) Tumour specific gene expression for genetic therapy via telomerase RNA gene promoters.
Owner:THE UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF GLASGOW
Aptazyme modified sgRNA carrier with theophylline regulated expression and application
The invention discloses an aptazyme modified sgRNA carrier with theophylline regulated expression. Aptazyme P1-F5 is inserted to tetraloop and stem loop 2 positions of an expressed sgRNA-AZ 2.0 skeleton; by means of Kpn I and EcoR I sites, and EcoR I and Spe I sites, a U6 promoter and the sgRNA-AZ 2.0 skeleton are connected into the carrier pUC19 / EKSHL in order to obtain the carrier pU6-sgRNA-AZ 2.0; using Bsa I for enzyme digestion of the carrier pU6-sgRNA-AZ 2.0, and using cohesive end design and connecting an sgRNA sequence directing at the target gene so as to obtain the pU6-sgRNA-AZ 2.0-target site. The carrier can effectively mediate the genome editing function of Cas9 protein, and bring the editing activity under regulation of theophylline, also can mediate the transcription inhibition of dCas9-KRAB protein to the target gene, and enables regulation of inhibitory activity by theophylline.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
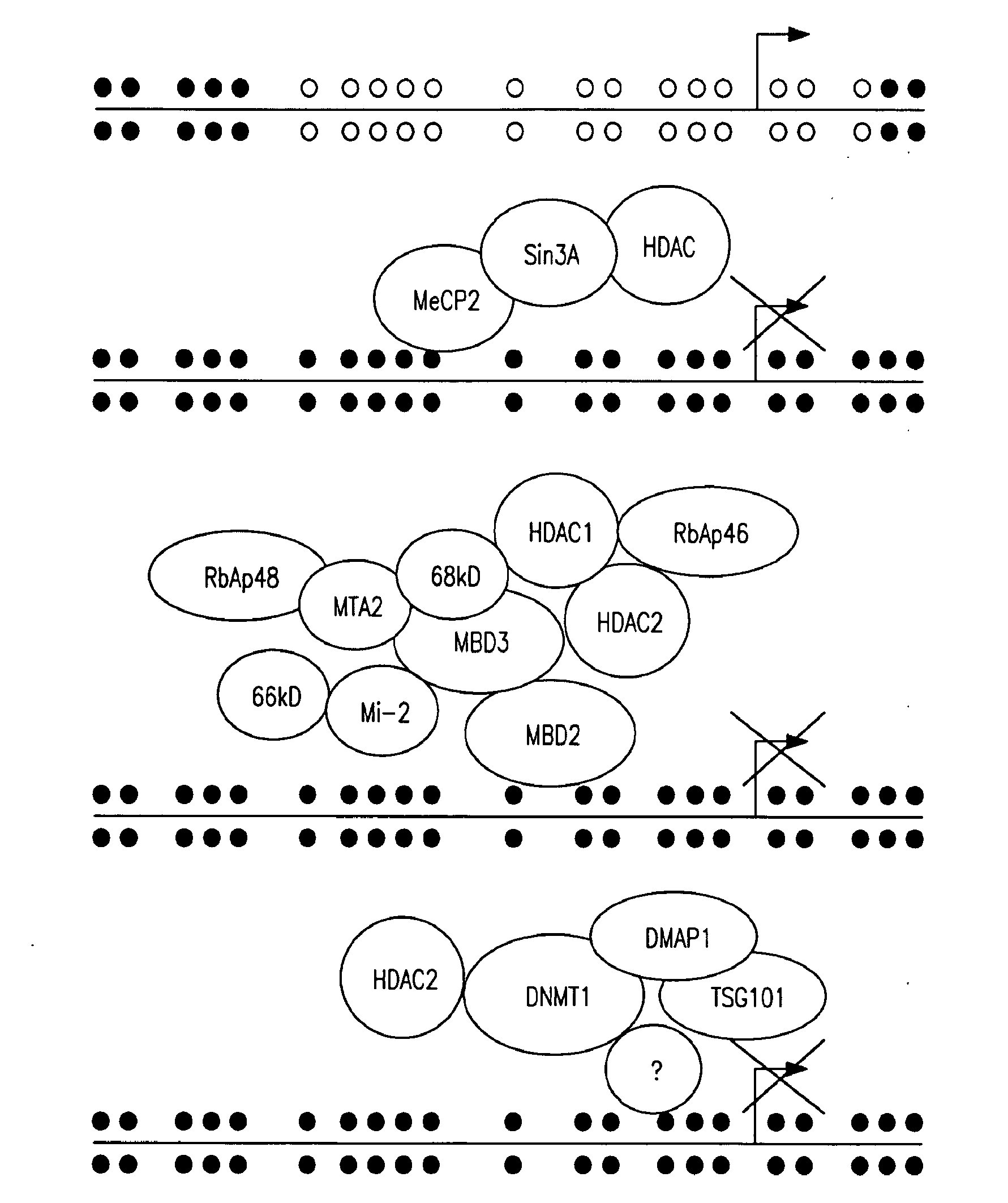
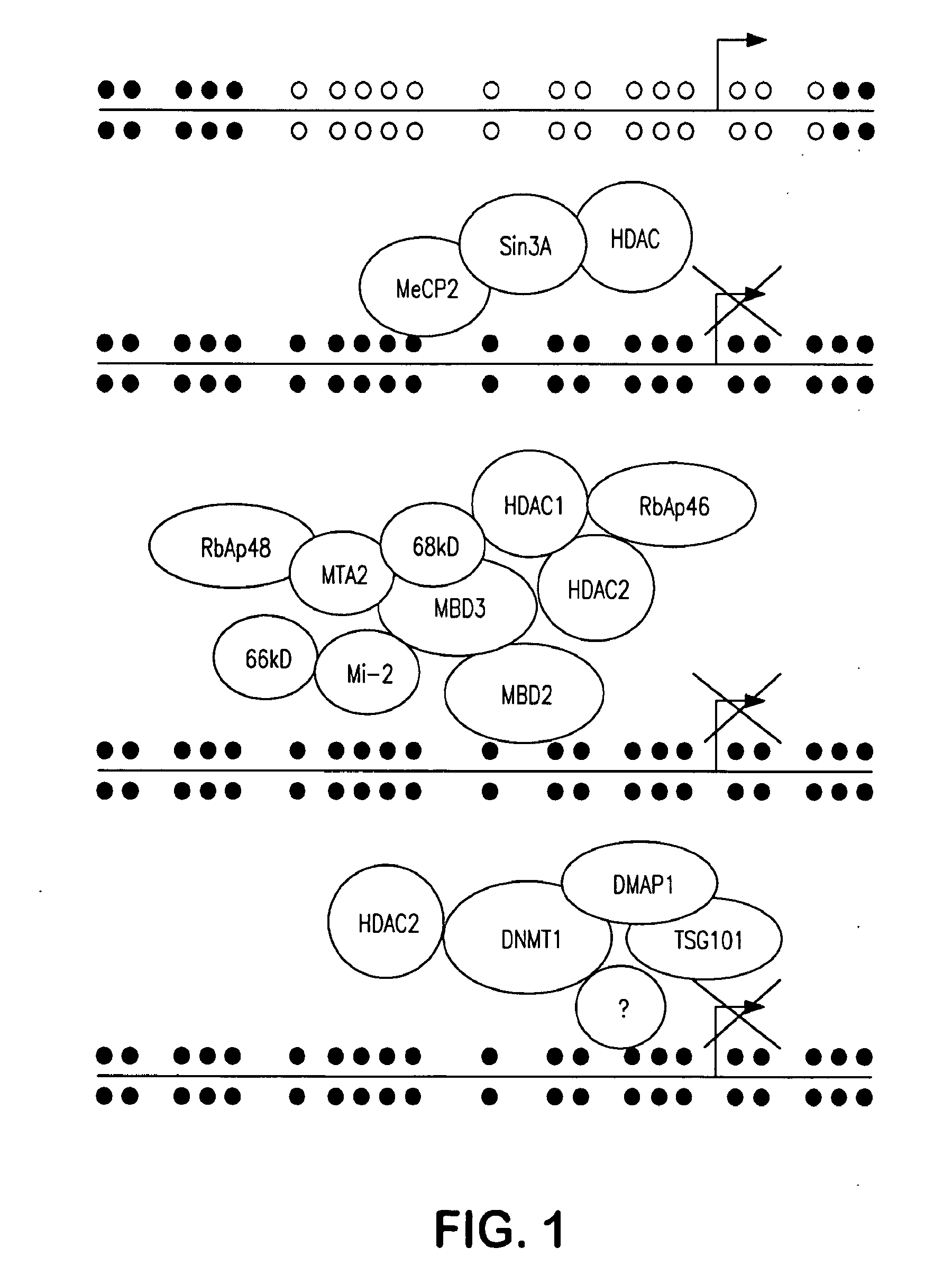
Agents for Reversing Epigenetic Silencing of Genes
ActiveUS20100093768A1Increase transcriptionPreventing and treating cancerCompound screeningBiocideSickle cell anemiaGenomic DNA
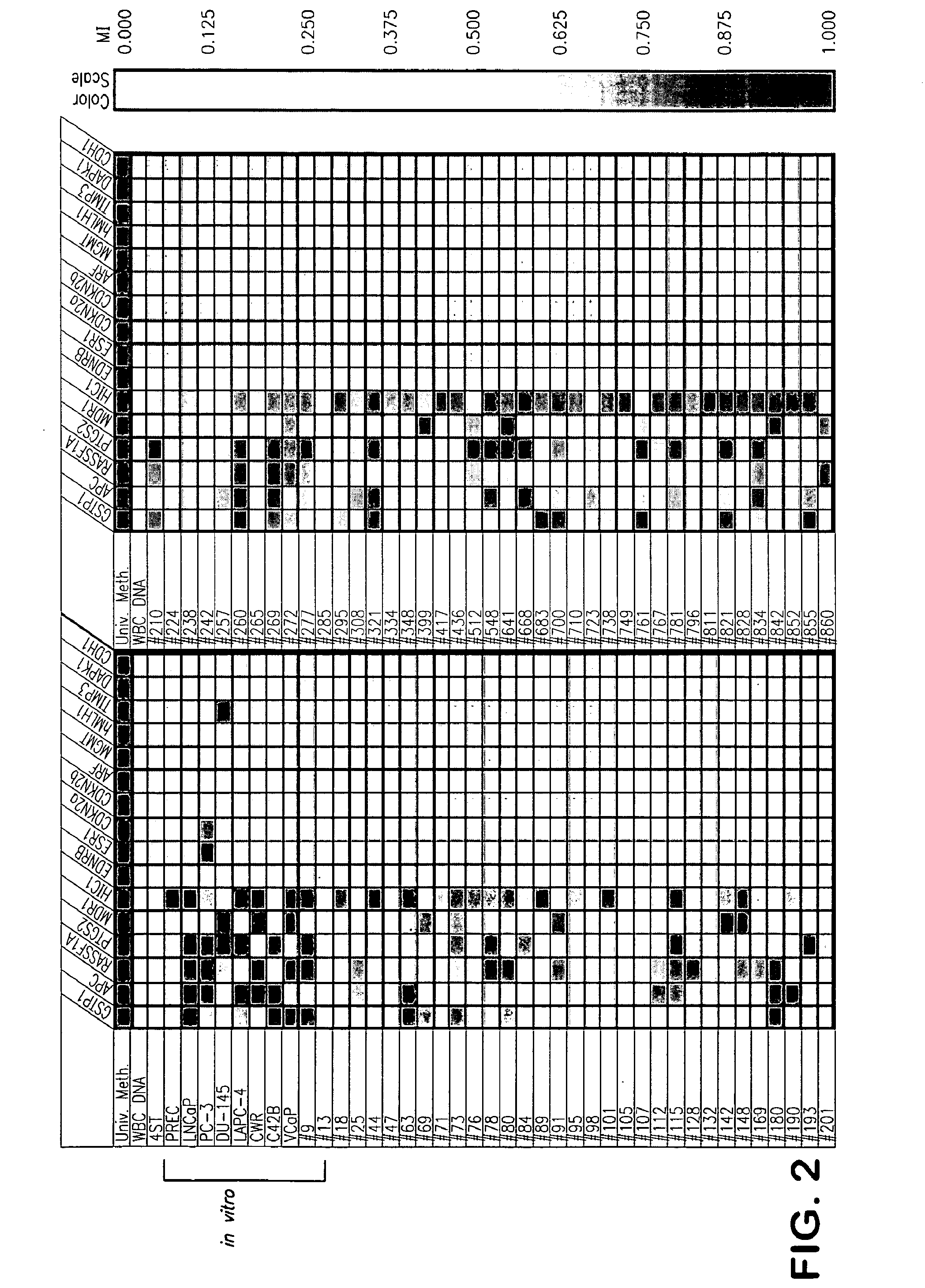
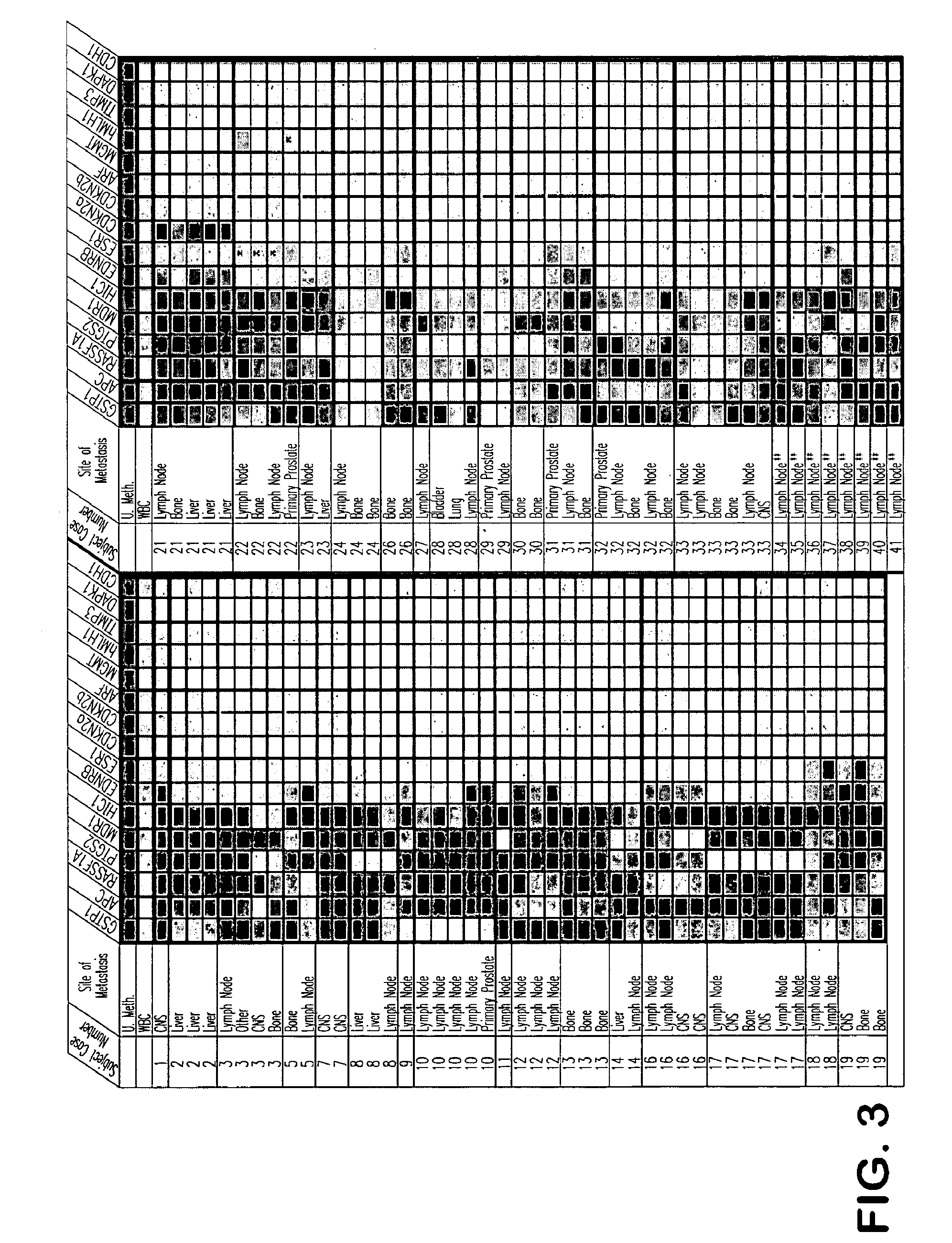
The present invention provides methods for discovering agents that are effective in reversing epigenetic silencing by inhibiting the interaction of methyl-binding (MBD) proteins with methylated genomic DNA. Also provided are methods for reactivating silenced genes having CpG island hypermethylation along with methods for treatment and prevention of diseases, such as cancer and sickle cell anemia, by administering an agent that modulates methyl-binding domain (MBD) protein-mediated transcriptional repression, thereby increasing gene transcription to prevent or treat disease. Additionally, compounds identified by the present invention useful for treatment and prevention of diseases, such as cancer and sickle cell anemia, are provided.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
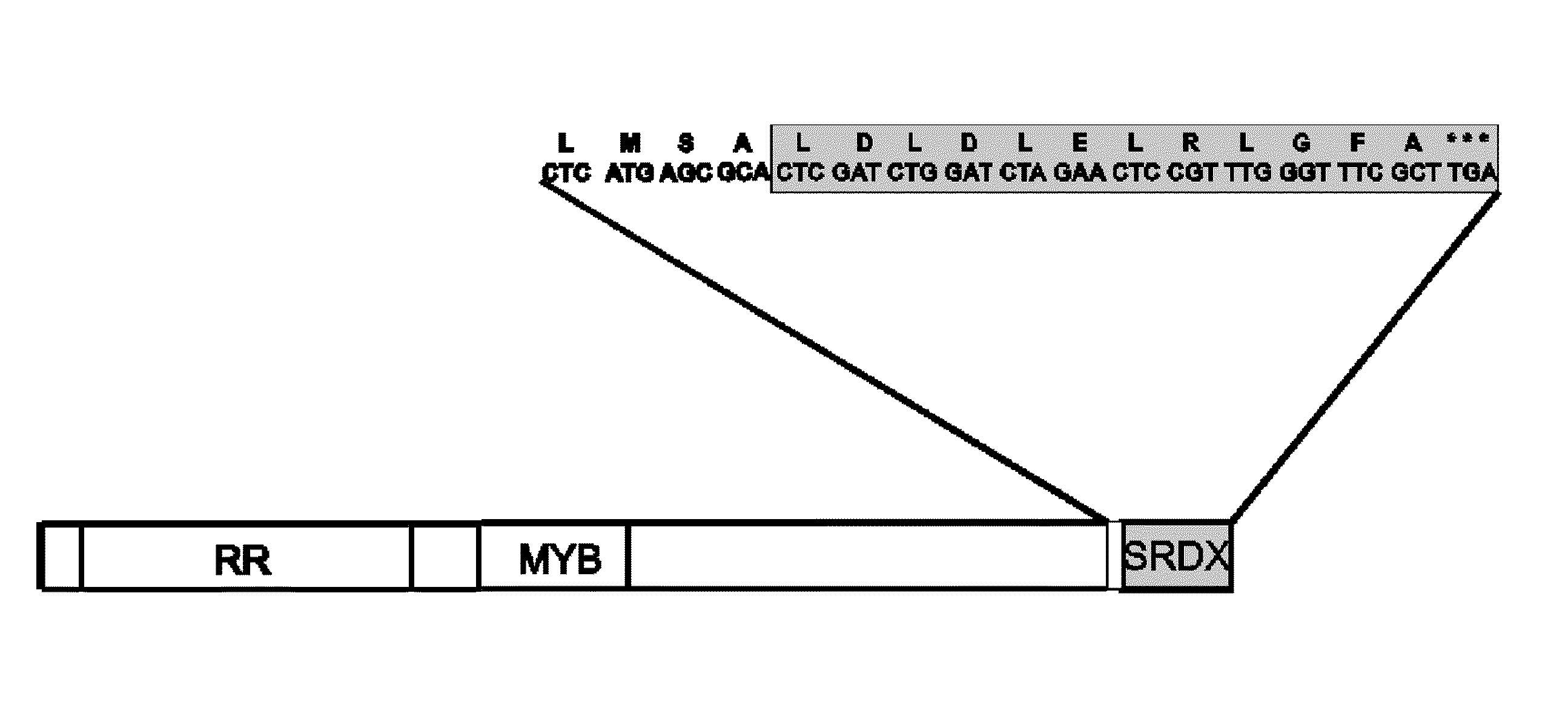
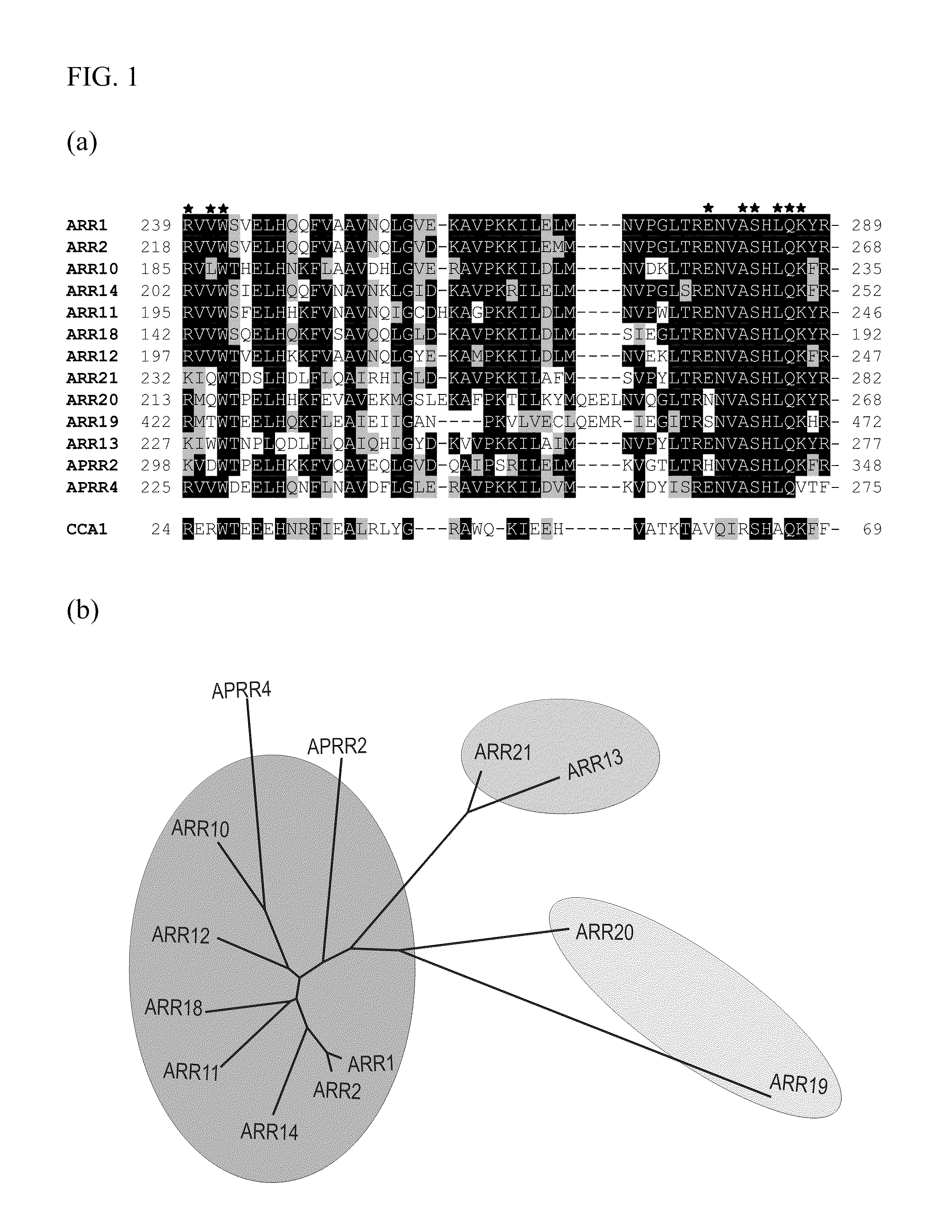
Transcriptional Repressors of Cytokinin Signaling and Their Use
ActiveUS20100115666A1Shorten germination timeReduce time lossFusion with DNA-binding domainImmunoglobulinsPolynucleotideTransgene
The invention relates to fusion proteins capable of acting as transcriptional repressors of cytokinin signaling, to polynucleotides encoding these fusion proteins, to vectors and cells comprising these polynucleotides, and to transgenic plants and parts thereof comprising these polynucleotides, vectors, and cells.The invention further relates to a process for making these transgenic plants and to the use of these transgenic plants for producing seeds of enhanced size, with enhanced seed filling, with reduced seed loss and / or with more rapid germination, and / or for producing a live root system with increased root mass, root length and / or root branching. The invention also relates to a method for enhancing the seed size, for enhancing seed filling, for reducing seed loss, and / or for reducing germination time and / or reproduction time, and / or for enhancing the root mass, root length and / or root branching of a plant and to seeds obtainable by the methods of the present invention.
Owner:SCHMULLING THOMAS +2
Repressors for hiv transcription and methods thereof
InactiveUS20040126877A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAcquired immunodeficiencyProtein C
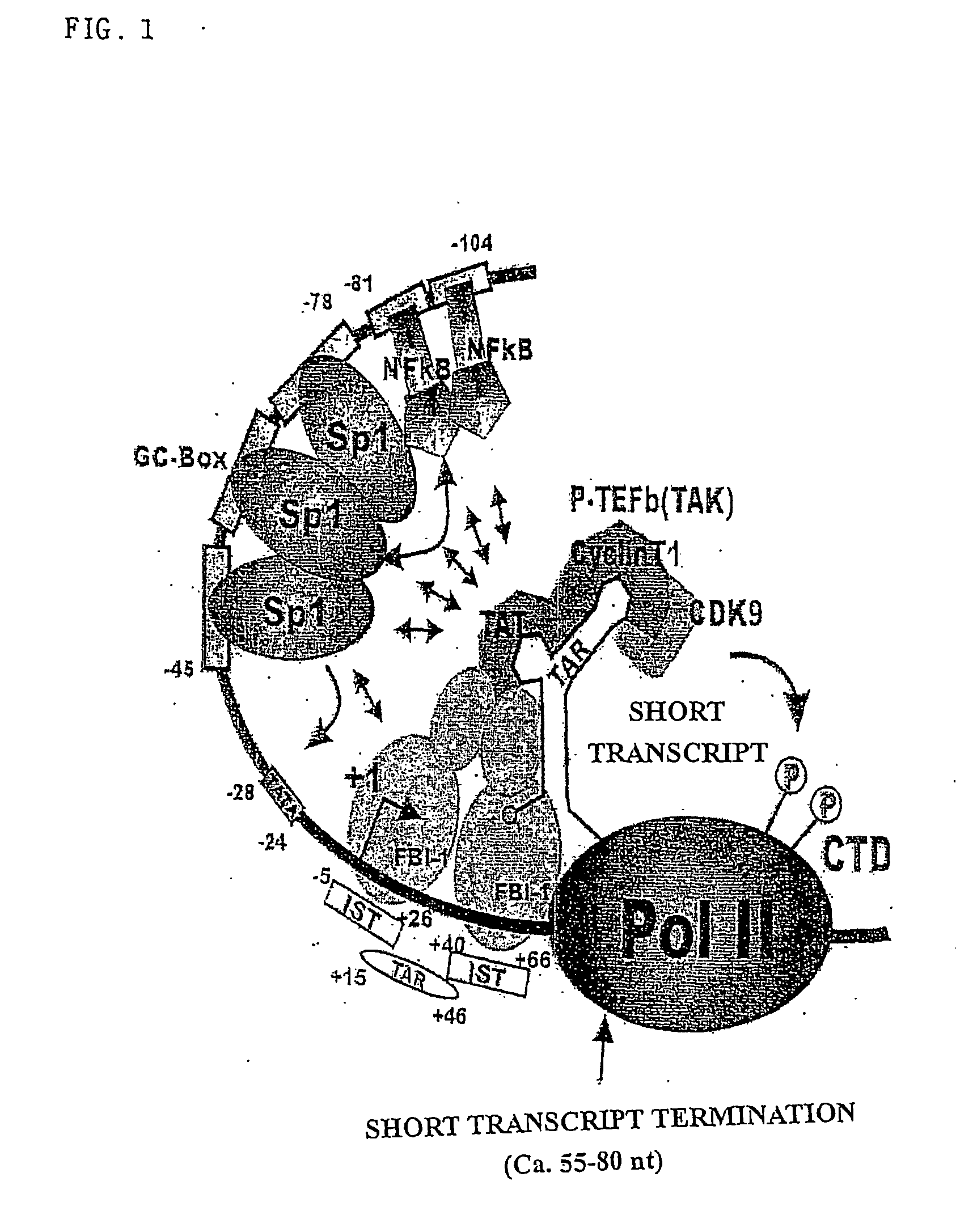
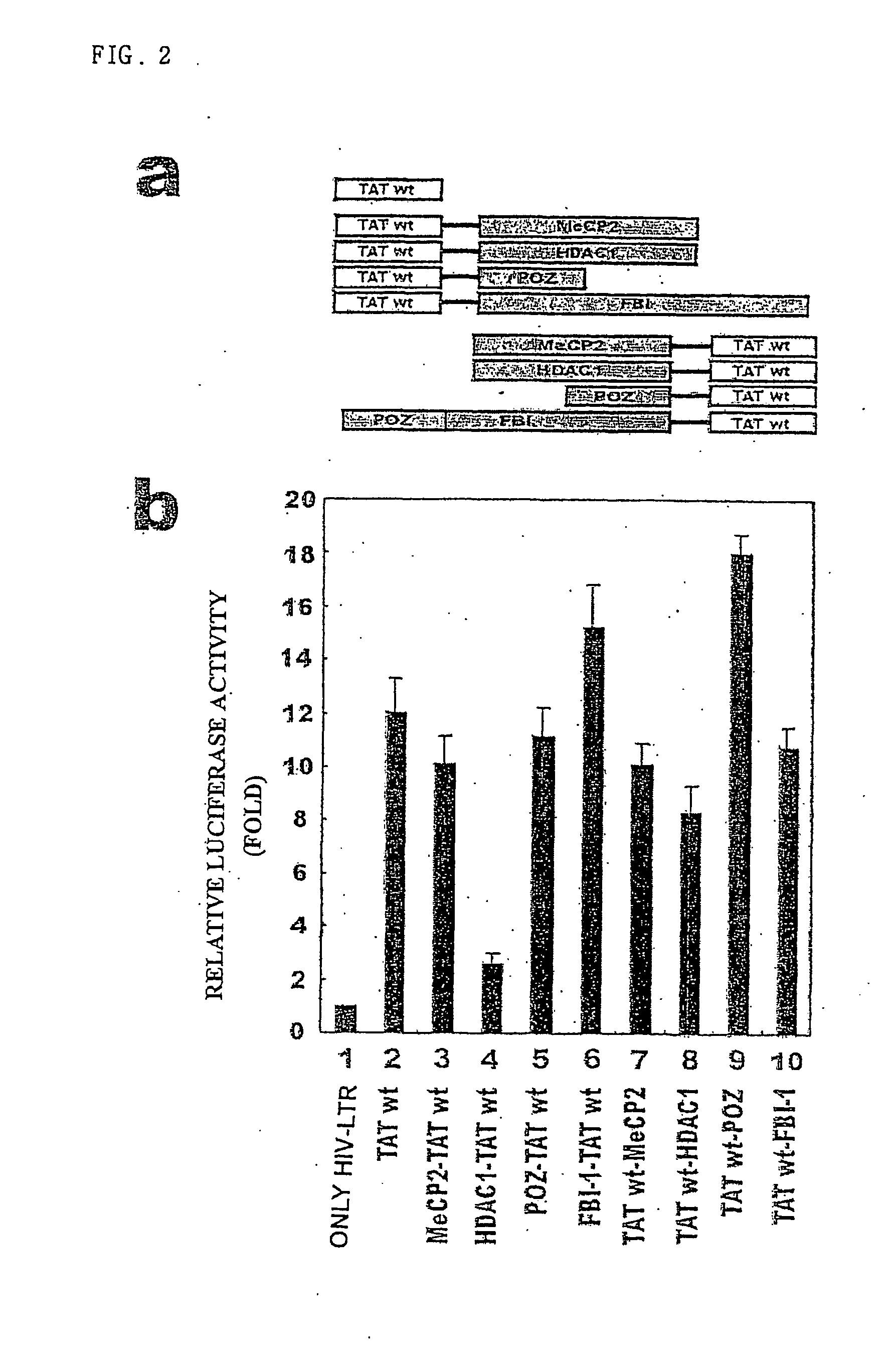
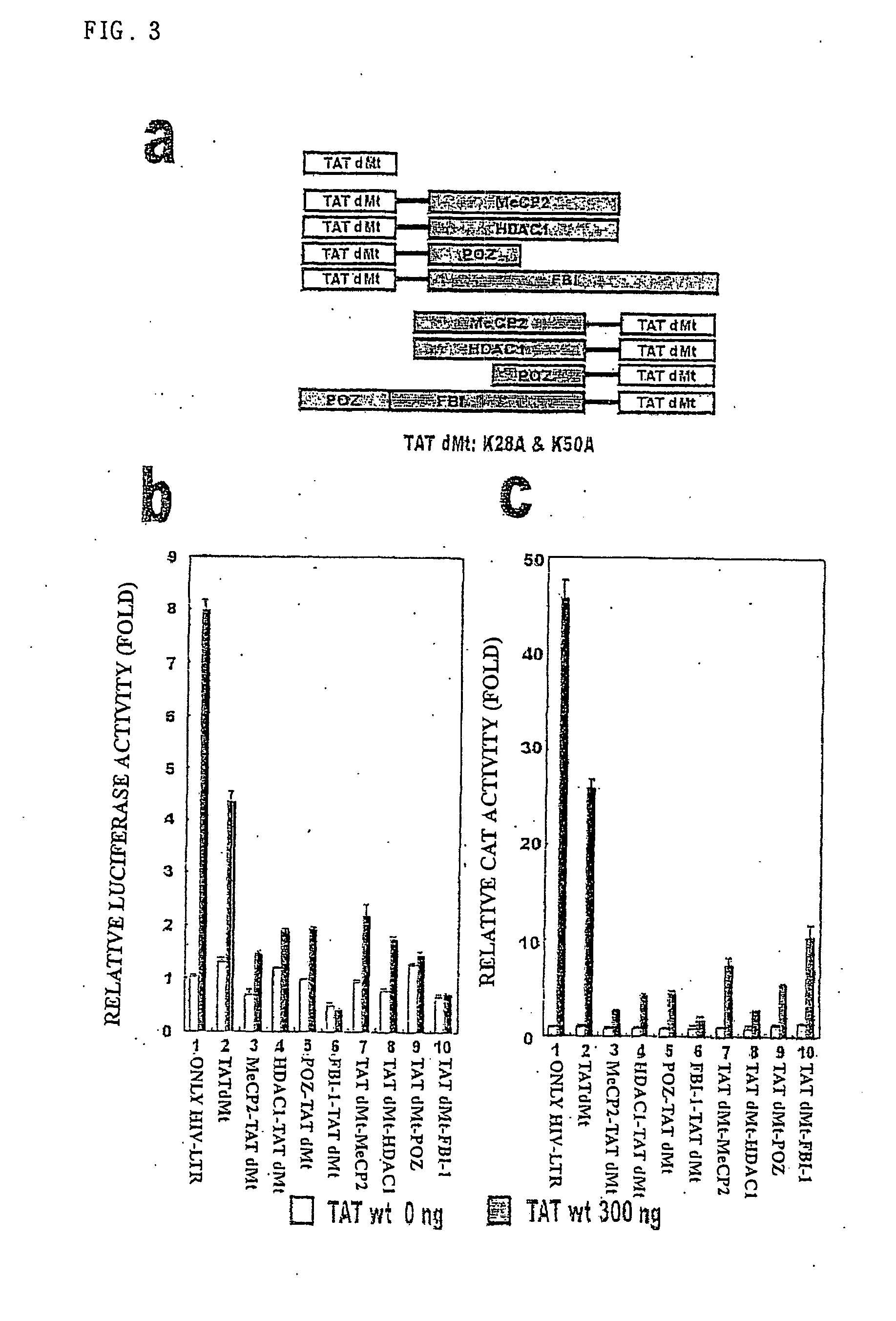
The present invention relates to repressors suppressing production of acquired immune deficiency syndrom (AIDS) viral genome (RNA) and methods repressing transcription thereof. The invention, more specifically, relates to fusion proteins repressing AIDS viral genomes (RNA) of a protein selected from group consisting of proteins strongly repressing activities of proteins such as Sp1, NF-kB, proteins repressing transcriptional activities by strongly condensing chromatin, and proteins which are able to bind around AIDS viral promoter; and protein (for example Tat or Tat derivatives) recognizing short RNA strand (TAR) and methods repressing transcription using same. The said fusion proteins dramatically show effect repressing production of HIV-1 genome (RNA) by delivering repressing proteins like Sp1, NF-k B to HIV-1 LTR using protein recognizing short RNA strand as a carrier. The invention shows transcription inhibitory effect of HIV by targeting transcription-repressing fusion proteins to HIV LTR.
Owner:HUR MAN WOOK
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing L-threonine as well as construction method and application of genetically engineered bacterium
InactiveCN112481179AIncrease productionImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSaccharic acidThreonine
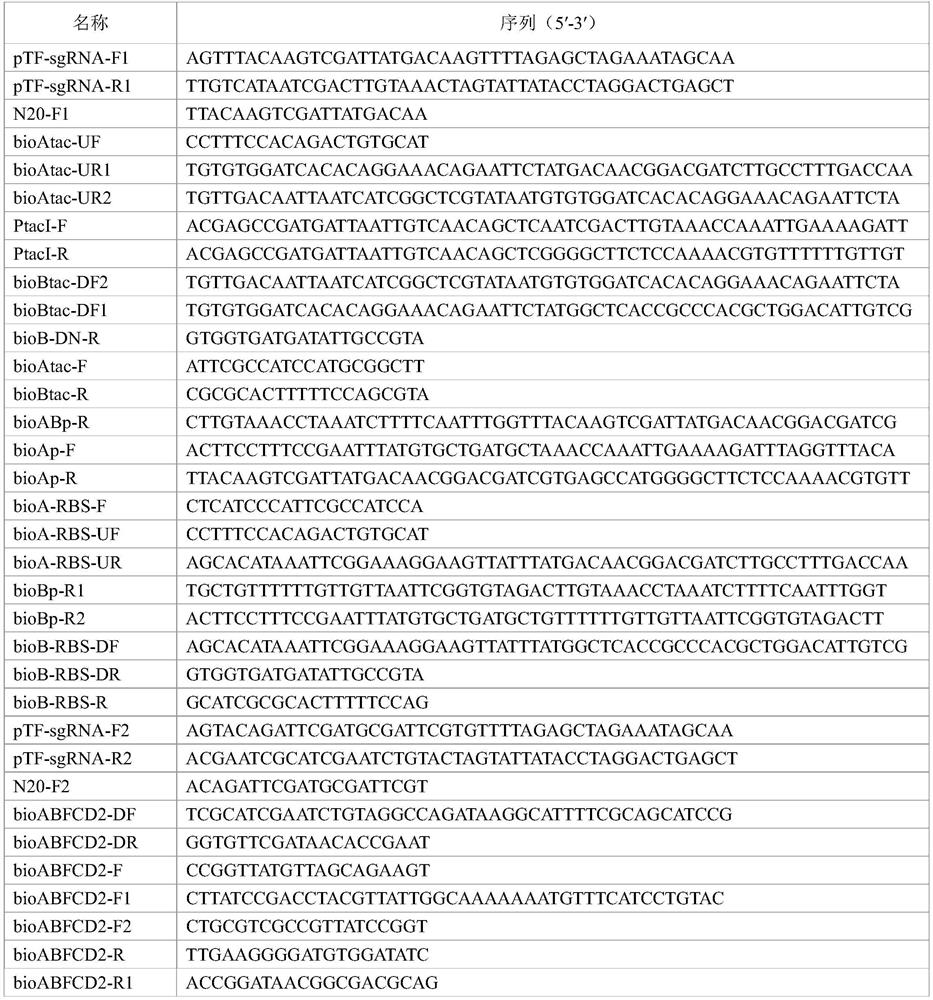
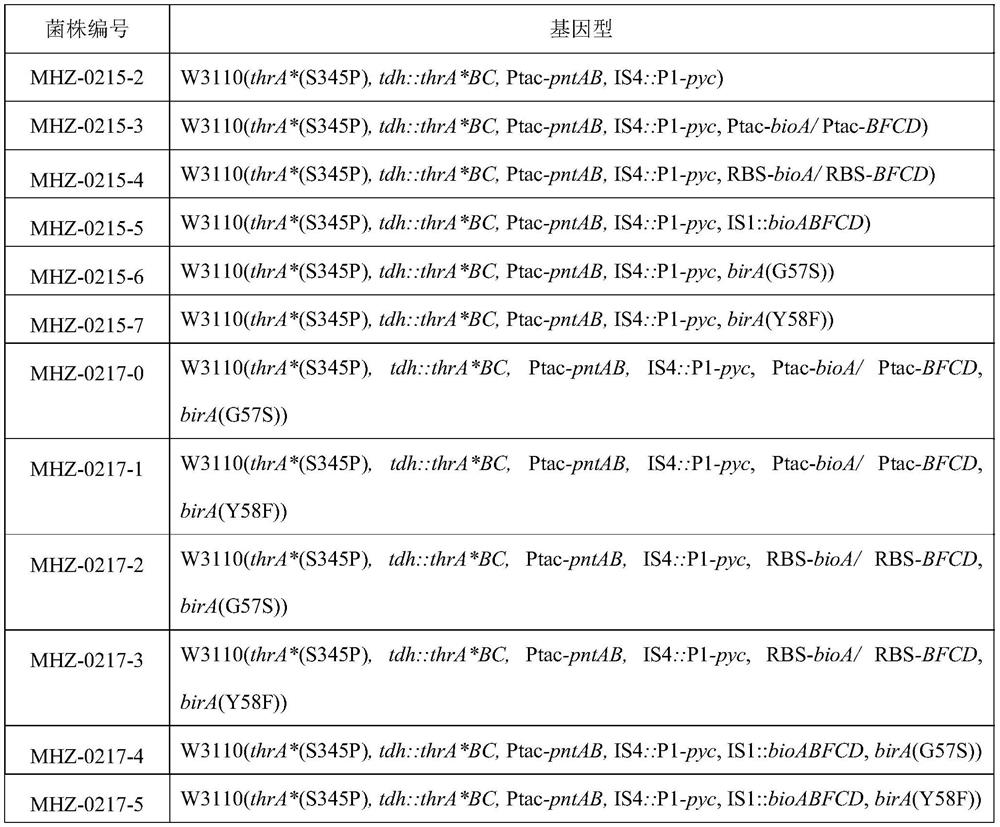
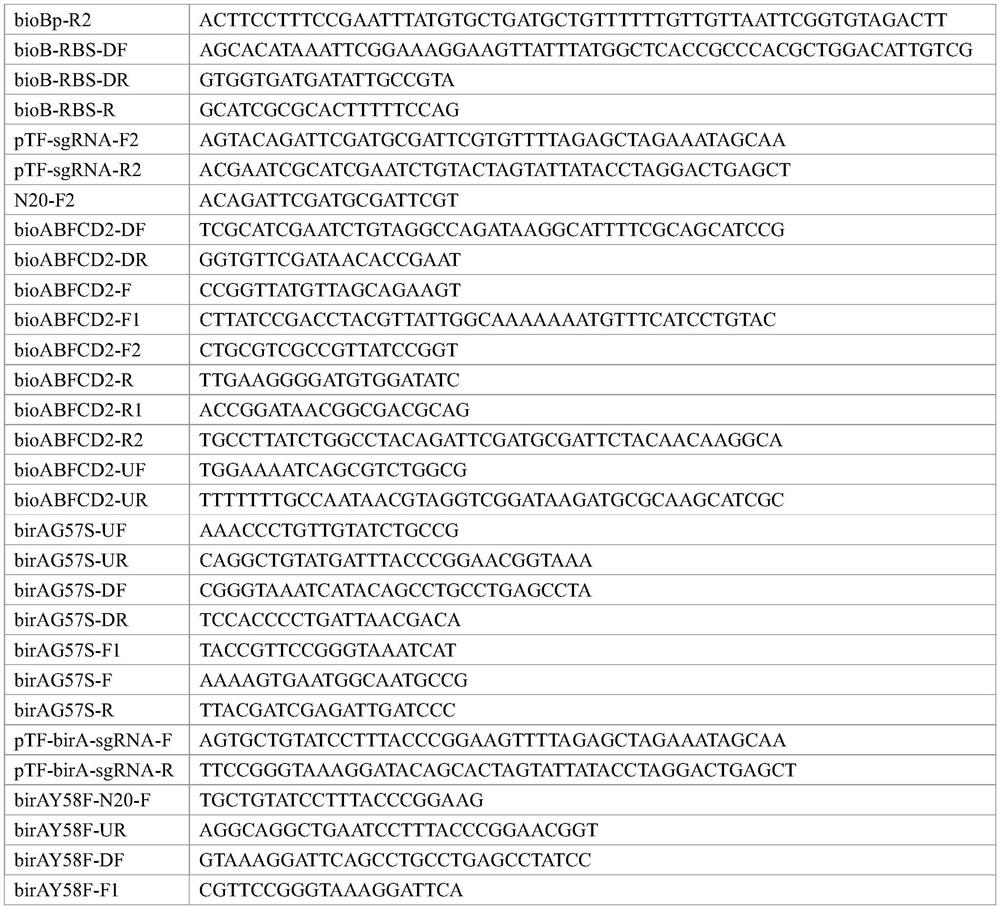
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for producing L-threonine as well as a construction method and application of the genetically engineered bacterium. The biotin synthesis of the L-threonine producing strain is enhanced, especially the pyc gene of the strain is enhanced, and the adopted specific means is to enhance the bioABFCD gene (including promoter enhancement, RBS sequence enhancement and multi-copy), release the transcription repression of the brA gene, and release the transcription repression of the brA while enhancing the bioABFCD. According to the constructed genetically engineered bacterium for producing the L-threonine, through fermentation culture, the yield of the L-threonine can reach 20.2 g / L, and the conversion rate of saccharic acid can reach 23.8%.
Owner:MEIHUA BIOTECH LANGFANG CO LTD
Method for screening microRNA having transcribing and post-transcriptional gene silencing functions
ActiveCN103571839AGood gene silencing effectImprove adaptabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening processGeneticsScreening method
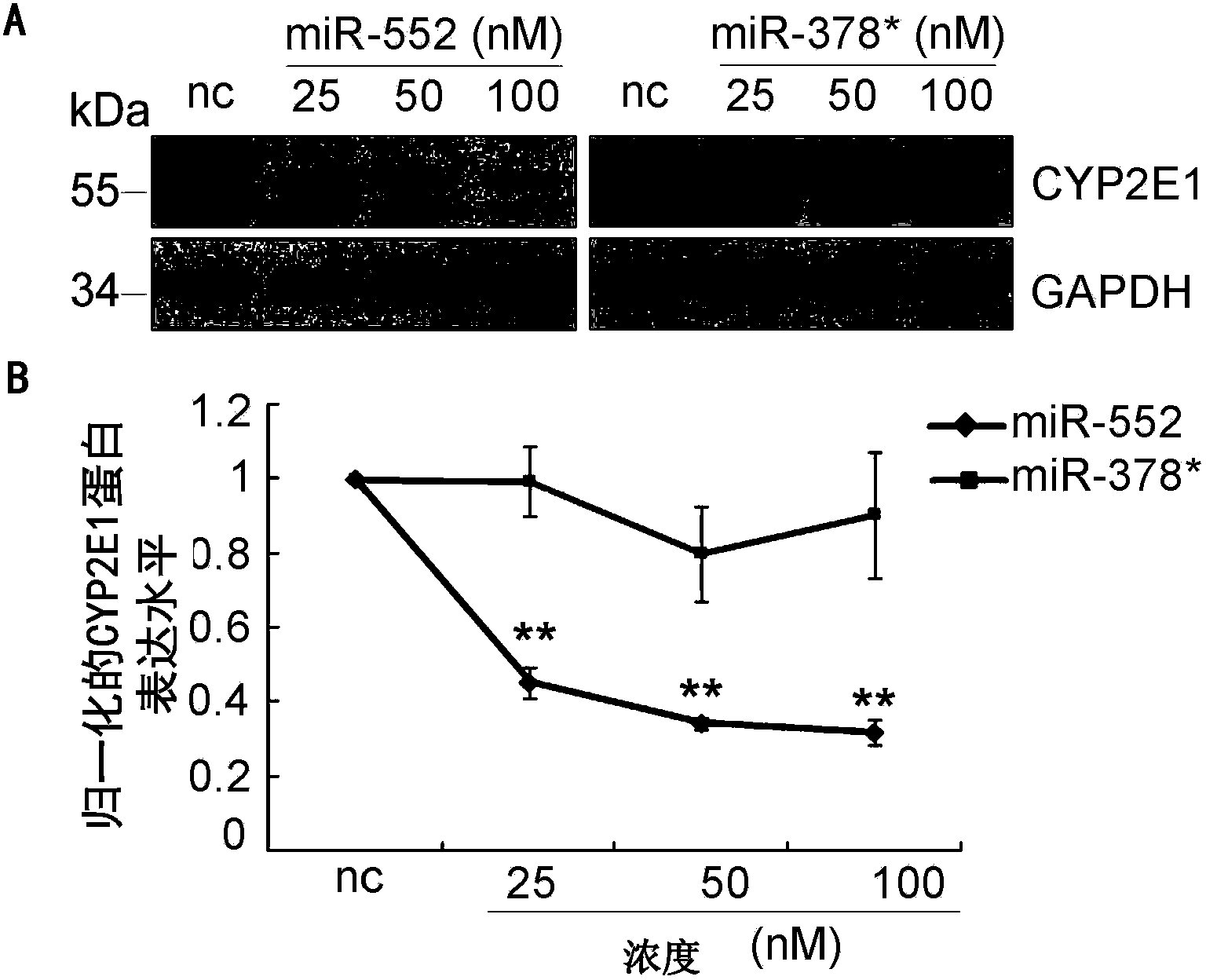
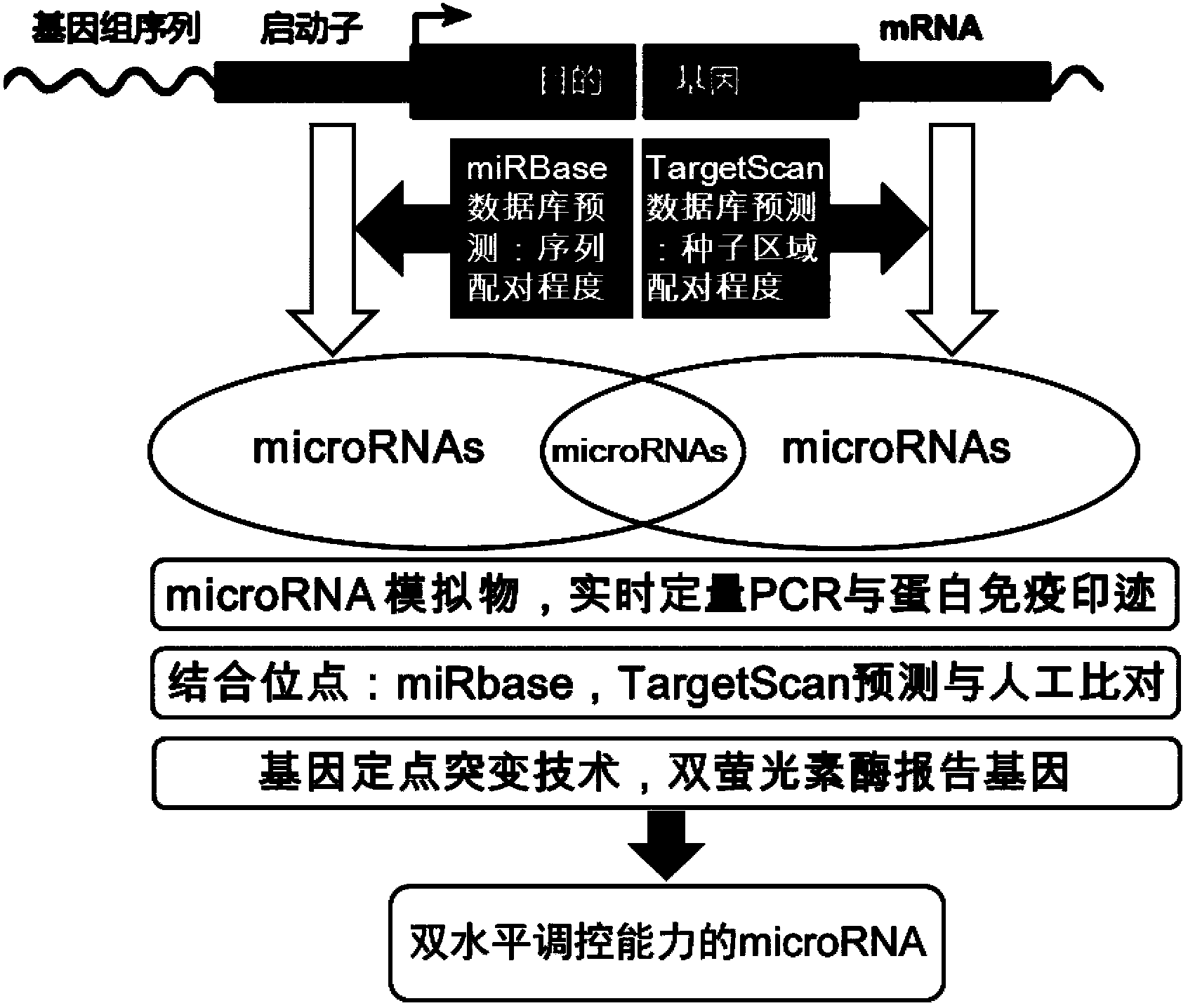
The invention provides a method for screening microRNA having transcribing and post-transcriptional gene silencing functions. The microRNA obtained by screening through the method can be combined with 5' flanking region specific sites to reduce the target gene mRNA expression (having a transcription inhibition capability), and can also be combined with 3' non-translational region specific sites to reduce the target gene protein expression effect (having a post-transcriptional / translational inhibition capability).
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
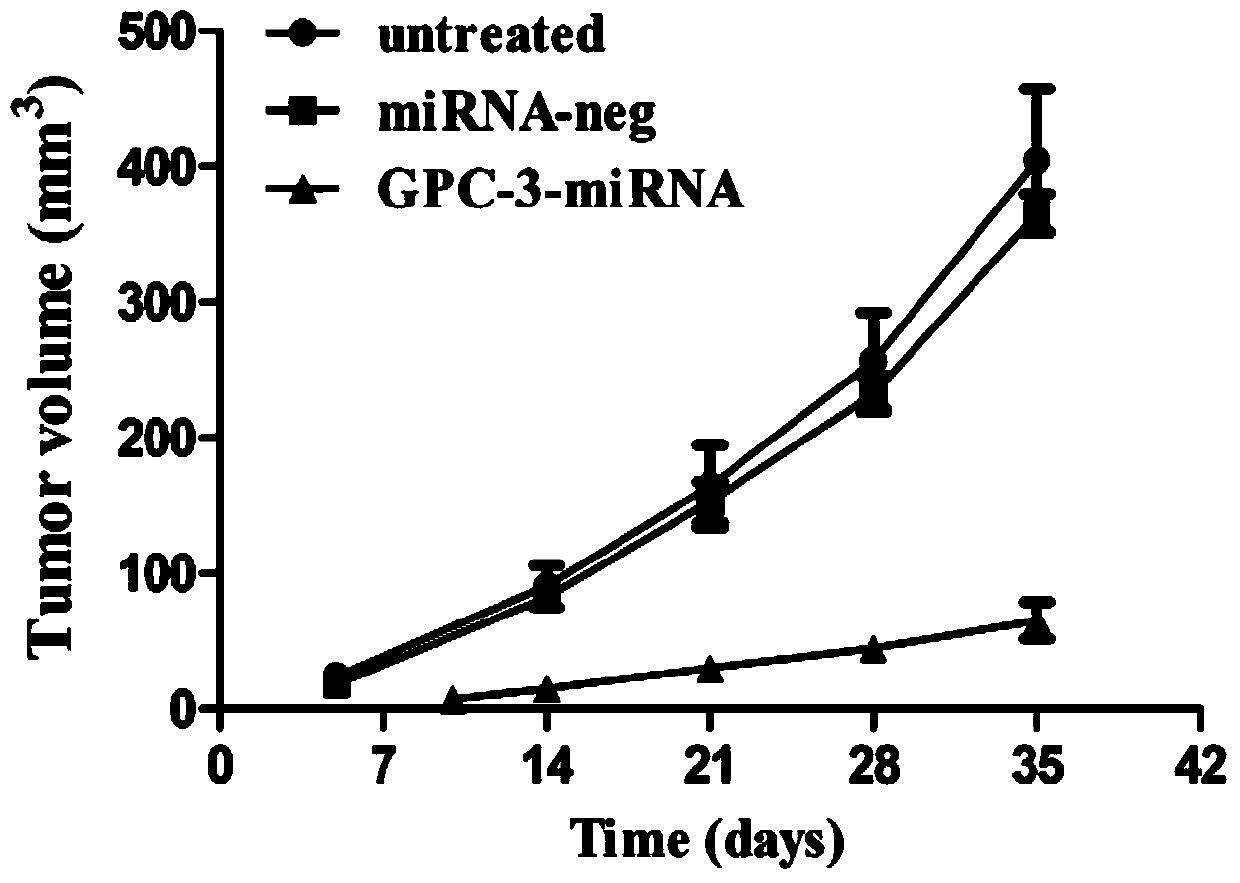
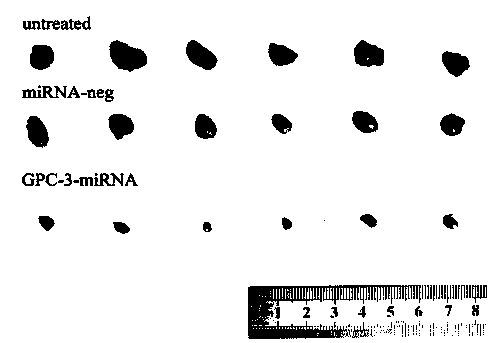
Method for detecting inhibiting ability of silent GPC-3 gene transcription on hepatocellular carcinoma transplanted tumor in nude mouse
InactiveCN103743902ASimple methodVector-based foreign material introductionMaterial analysisFluorescenceHepg2 cells
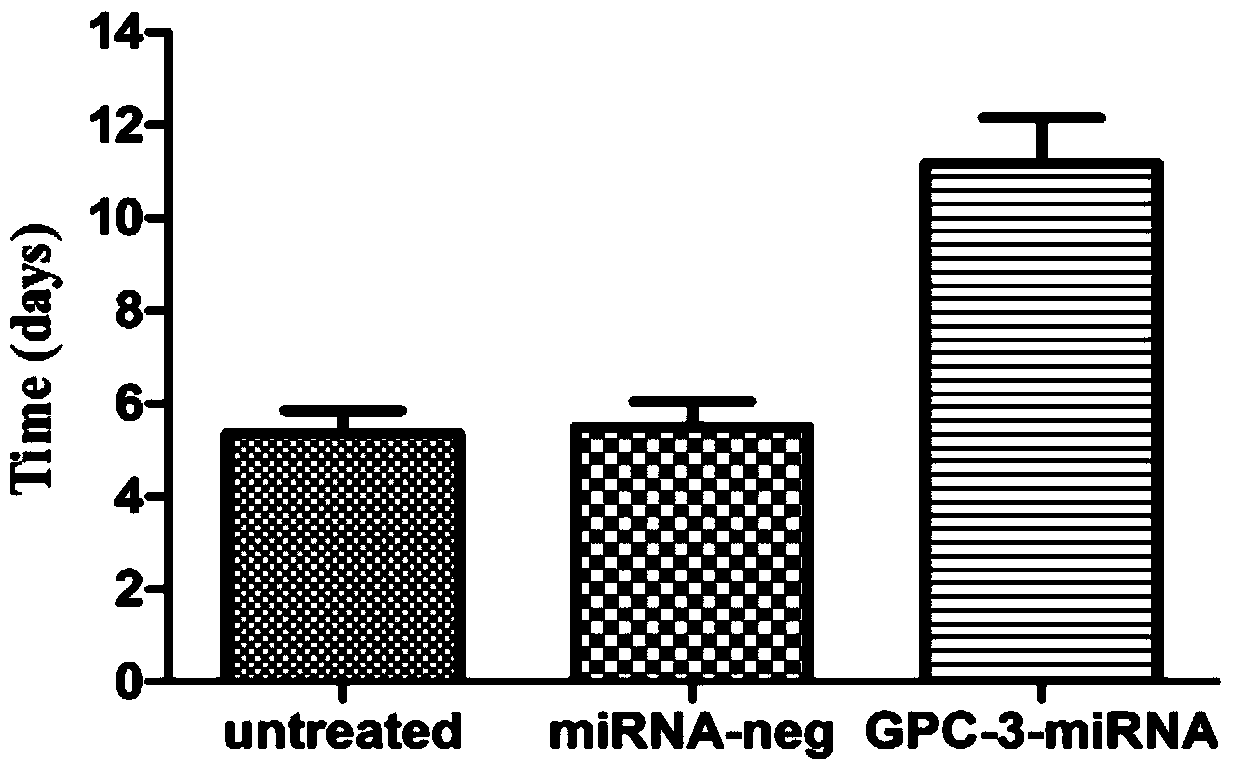
The invention discloses a method for detecting the inhibiting ability of silent GPC-3 (glypican-3) gene transcription on a hepatocellular carcinoma transplanted tumor in a nude mouse. The method includes: 1) designing and synthesizing 4 pairs of miRNA oligomeric single-strand DNA specific to a target gene consensus sequence, then synthesizing the corresponding dsDNA, inserting the dsDNA into a vector to construct 4 recombinant plasmids, and picking out the recombinant plasmid with the highest interference efficiency through fluorescence quantitative PCR; 2) transfecting the recombinant plasmid with the highest interference efficiency into HepG2 cells to construct transfected HepG2 cells, and performing screening, thus obtaining a stably transfected HepG2 cell; 3) inoculating the stably transfected HepG2 cell to the nude mouse subcutaneously to construct a human hepatocellular carcinoma tumor-bearing nude mouse model; and 4) then determining the growth state of the stably transfected HepG2 cell in the human hepatocellular carcinoma tumor-bearing nude mouse model. The method provided by the invention can be employed to detect the inhibiting ability of silent GPC-3 gene transcription on a hepatocellular carcinoma transplanted tumor in the nude mouse, and can be used for research of GPC-3 on transplanted tumors.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF NANTONG UNIV
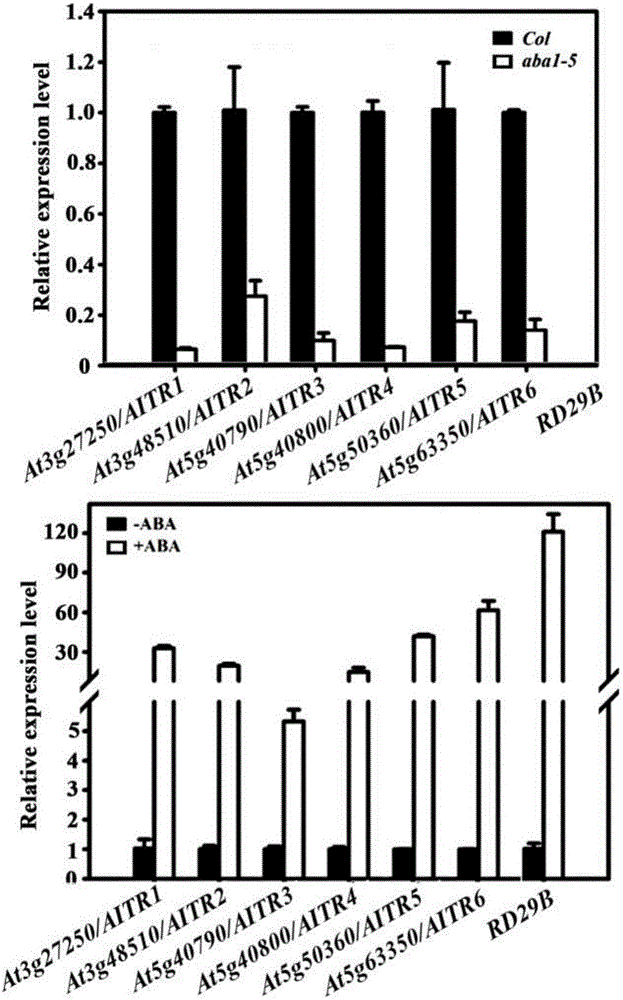
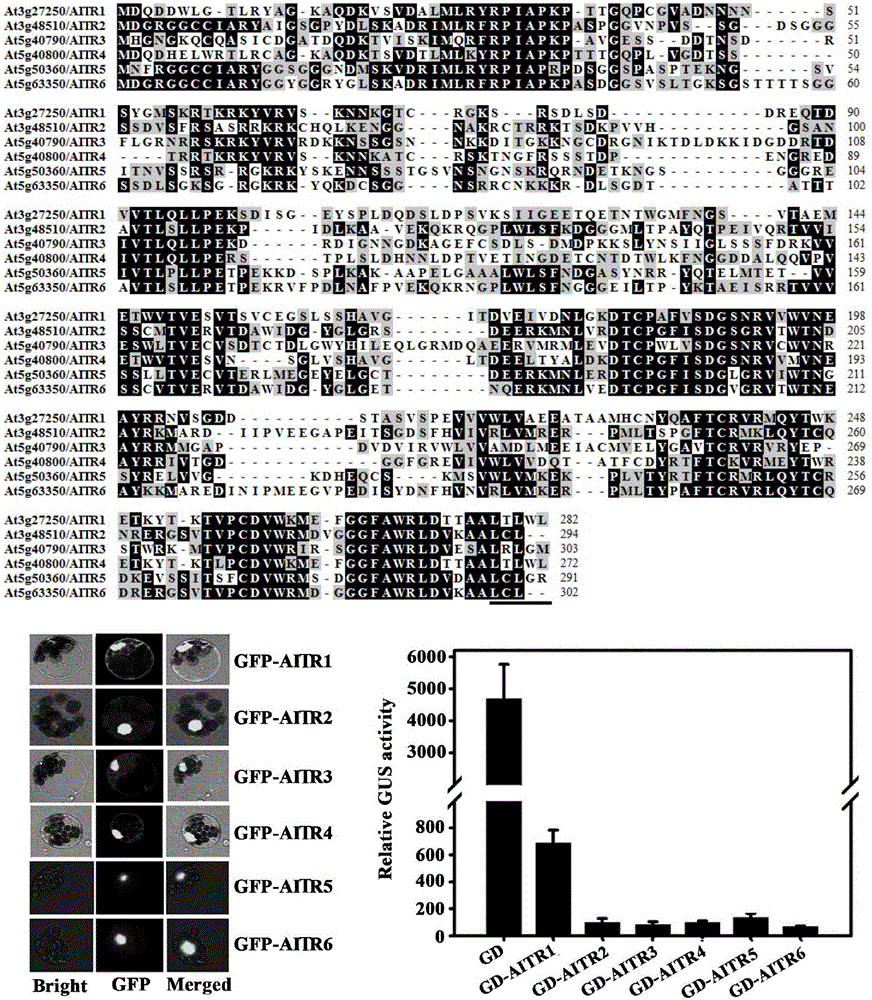
Transcription inhibitor family gene and application thereof
The invention relates to discovery of a transcription factor family gene specific to angiosperms, detection on transcription inhibition activity of an encoding protein, and application of the transcription factor family gene in improving plant stress resistance. An experiment on AITRs (ABA-induced transcription repressors) gene knocked-out arabidopsis mutant is utilized to verify enhanced resistance of the mutant to ABA and an abiotic stress. AITRs are further discovered to be widely present in the angiosperms. Based on experiments taking tomatoes and soybeans as examples, expression of AITRs gene of the tomatoes is induced by the ABA, and a protoplast transfection experiment proves that the AITRs of both the tomatoes and the soybeans are transcription inhibitors, which indicates that the AITRs are a novel transcription factor family conserved in the angiosperms, and knocking out corresponding AITRs gene of a plant can enhance resistance of the plant to the abiotic stress. Therefore, the invention provides a transcription factor gene family which can be applied to genetic modification to enhance resistance of the plant to adverse environment.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
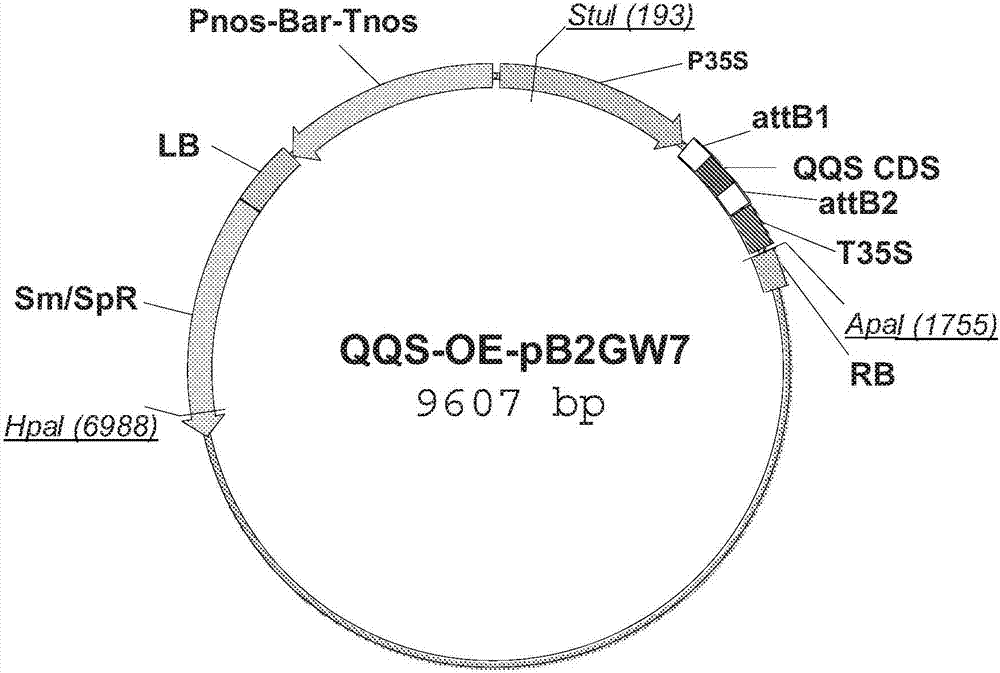
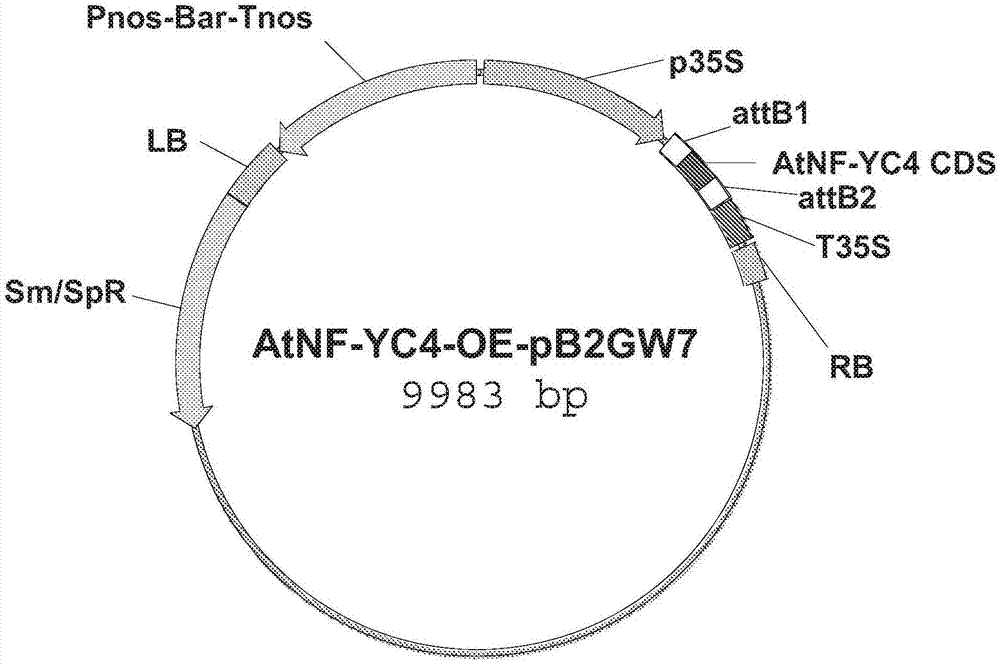
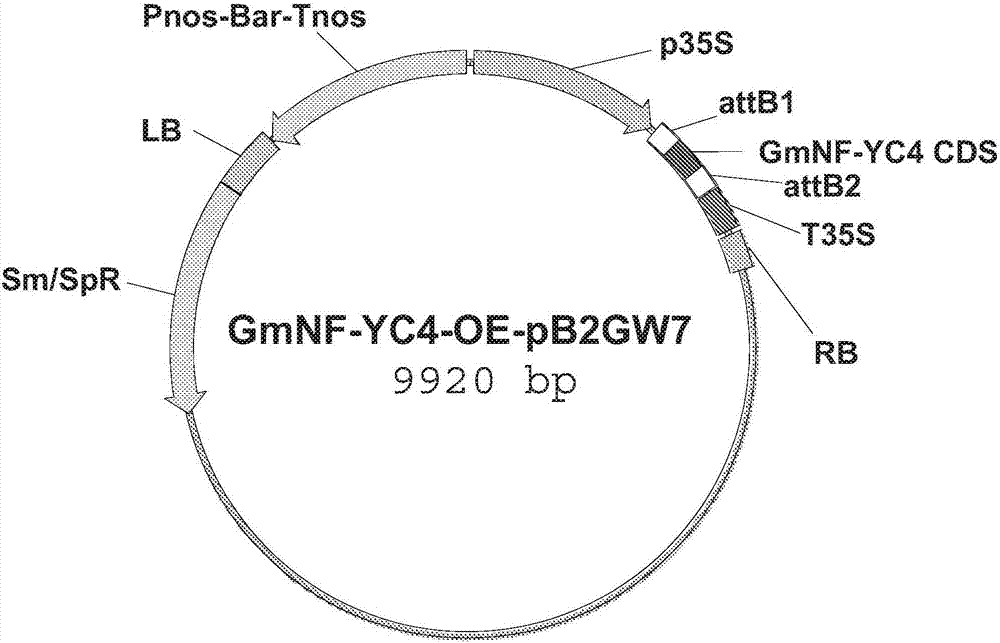
Modification of transcriptional repressor binding site in NF-YC4 promoter for increased protein content and resistance to stress
Method of increasing protein content in a eukaryotic cell comprising an NF-YC4 gene comprising modifying the transcriptional repressor binding site; method of producing a plant with increased proteincontent comprising crossing and selecting for increased protein content; method of increasing resistance to a pathogen or a pest in a plant comprising an NF-YC4 gene comprising modifying the transcriptional repressor binding site, alone or in further combination with expressing QQS in the plant; method for producing a plant with increased resistance to a pathogen or a pest comprising crossing andselecting for increased resistance to the pathogen or the pest; a cell, collection of cells, tissue, organ, or organism in which the NF-YC4 gene comprises a promoter comprising a transcriptional repressor binding site that has been modified so that the transcriptional repressor cannot prevent transcription of the NF-YC4; hybrid plants; and seeds.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing L-threonine as well as construction method and application of genetically engineered bacterium
PendingCN114015632AIncrease productionImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSaccharic acidThreonine
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for producing L-threonine as well as a construction method and application of the genetically engineered bacterium. According to the invention, biotin synthesis of an L-threonine production strain is enhanced, and specific means of enhancing bioABFCD gene (including promoter enhancement, RBS sequence enhancement and multi-copy), relieving BirA gene transcription repression, and relieving BirA transcription repression while enhancing bioABFCD are adopted. The constructed genetically engineered bacterium for producing the L-threonine is subjected to fermentation culture, the yield of the L-threonine can reach 20.2 g / L, and a saccharic acid conversion rate can reach 23.8%.
Owner:MEIHUA BIOTECH LANGFANG CO LTD
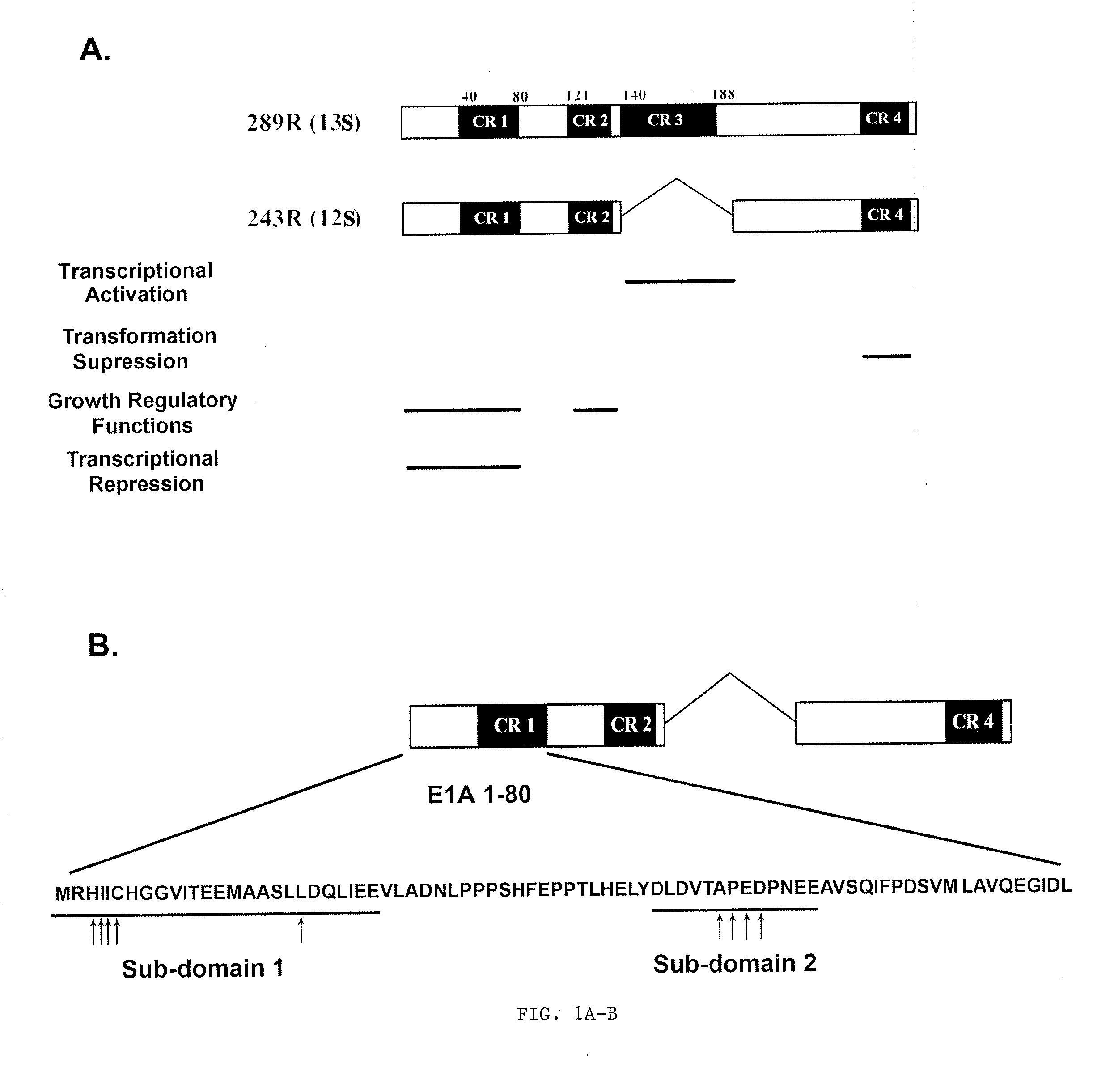
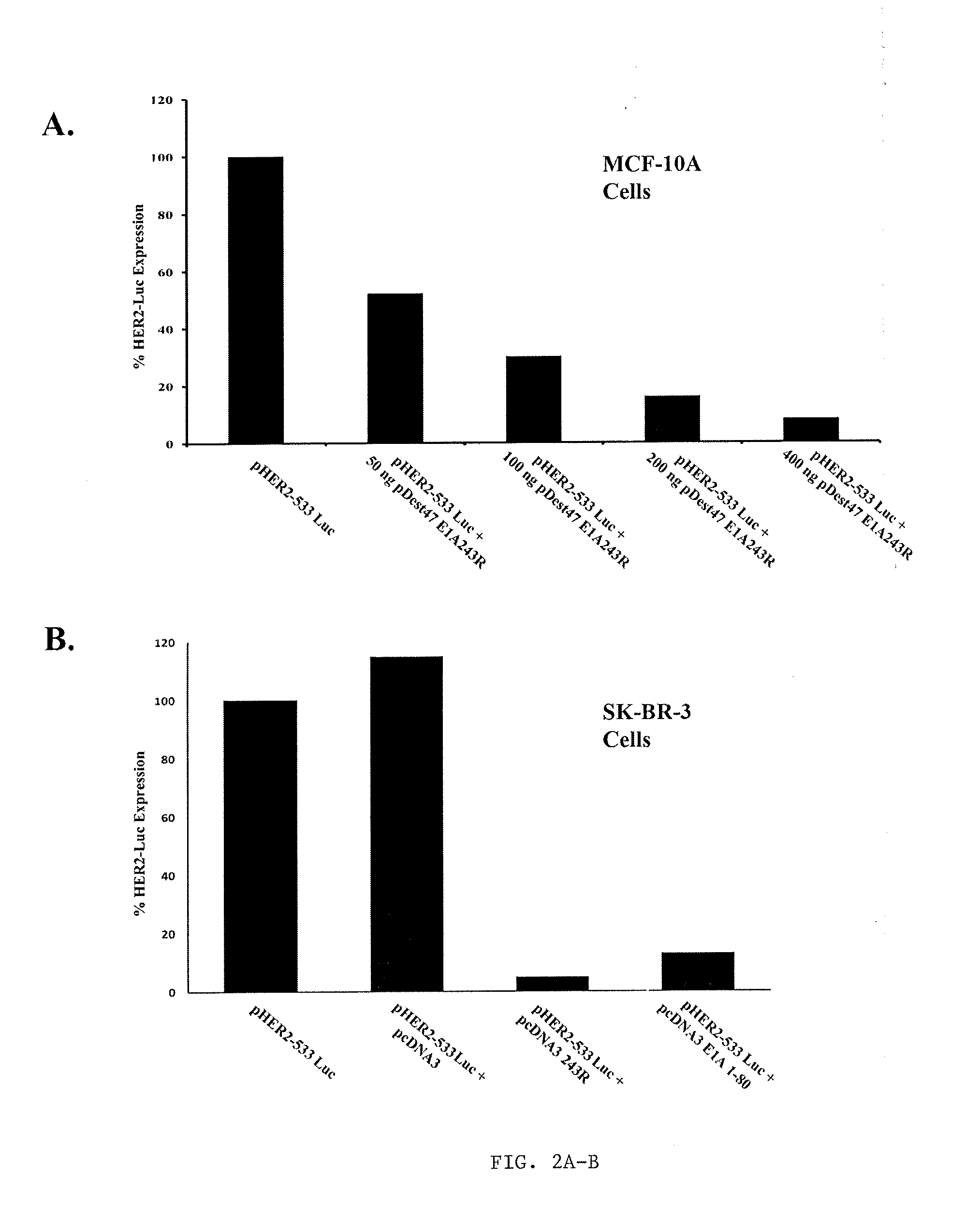
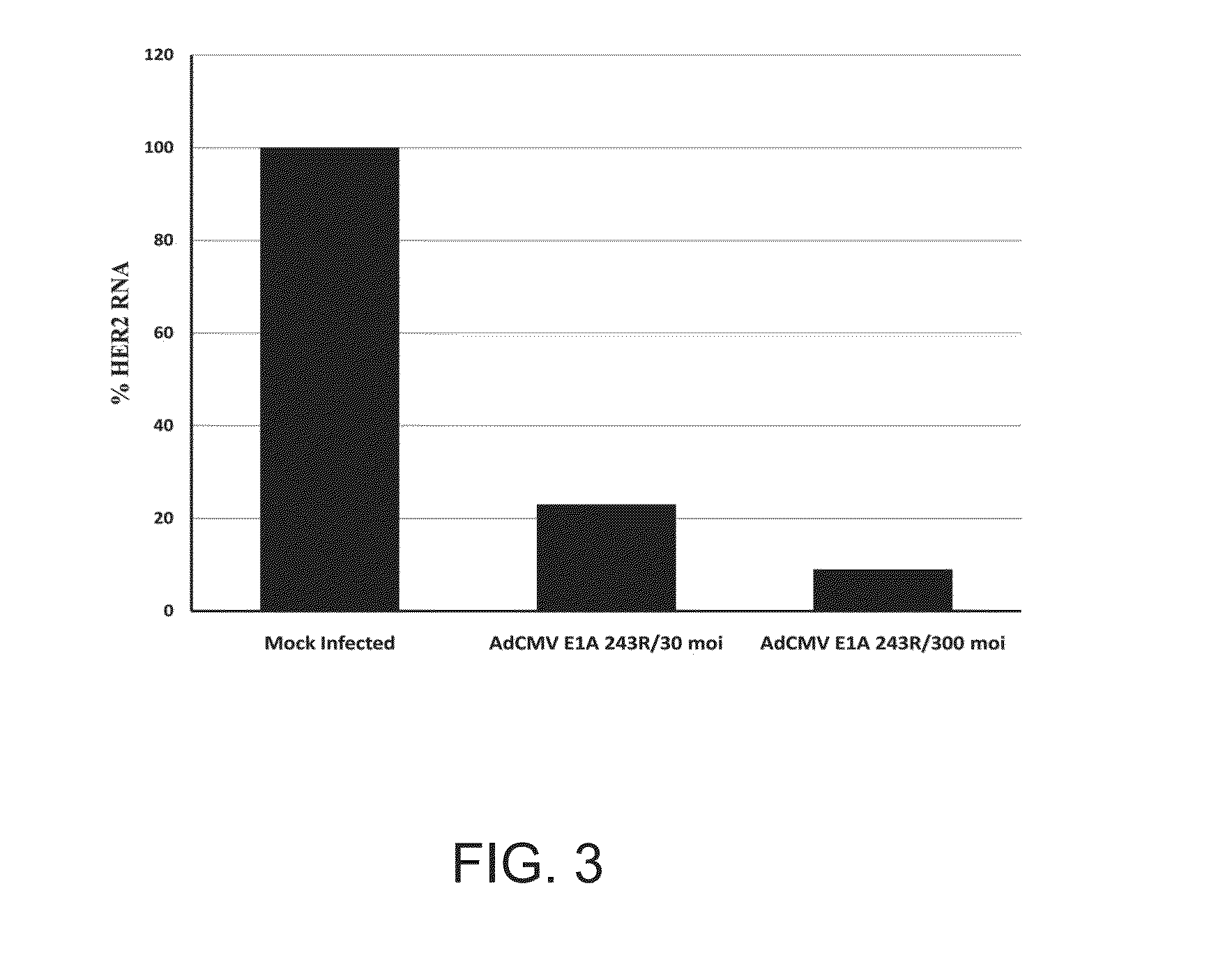
Adenovirus E1A Fragments for Use in Anti-Cancer Therapies
InactiveUS20130023481A1Improve the quality of lifeImprove survivalNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsCo administrationAnti her2
The present invention relates to an improved cancer therapy comprising co-administration with the E1A 1-80 transcription-repression domain activity. In addition, E1A 1-80 can act as a monotherapy against cancers that express elevated HER2 / Neu or in combination with anti-HER2 / Neu, chemo- or radiotherapeutic treatments.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
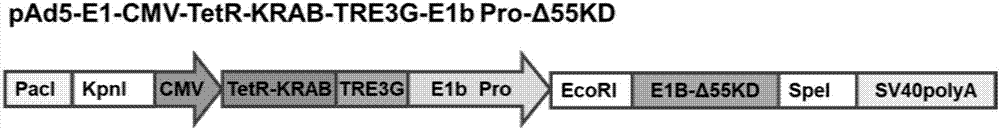
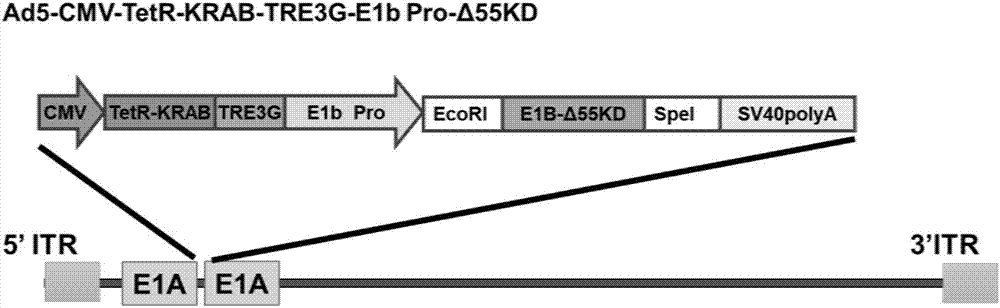
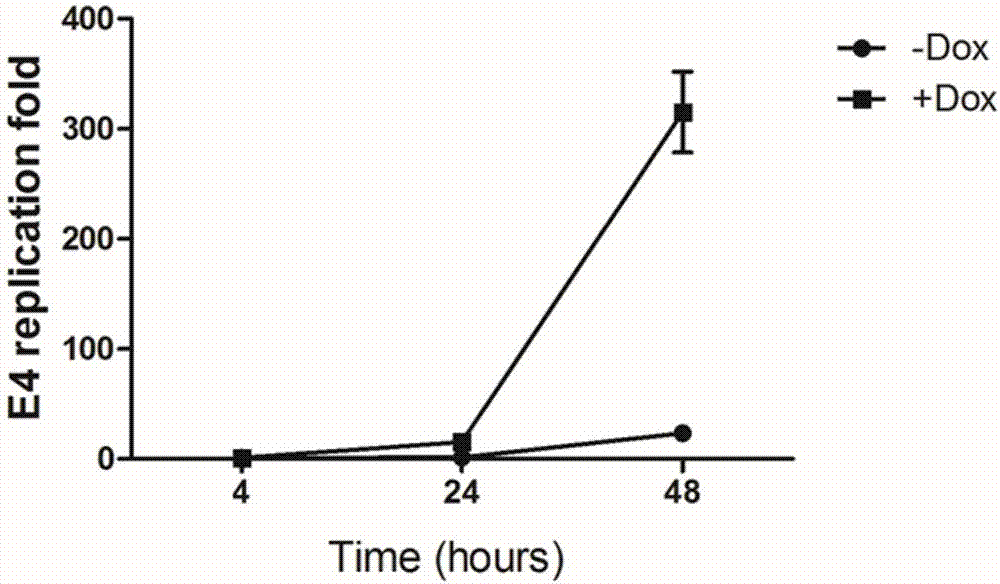
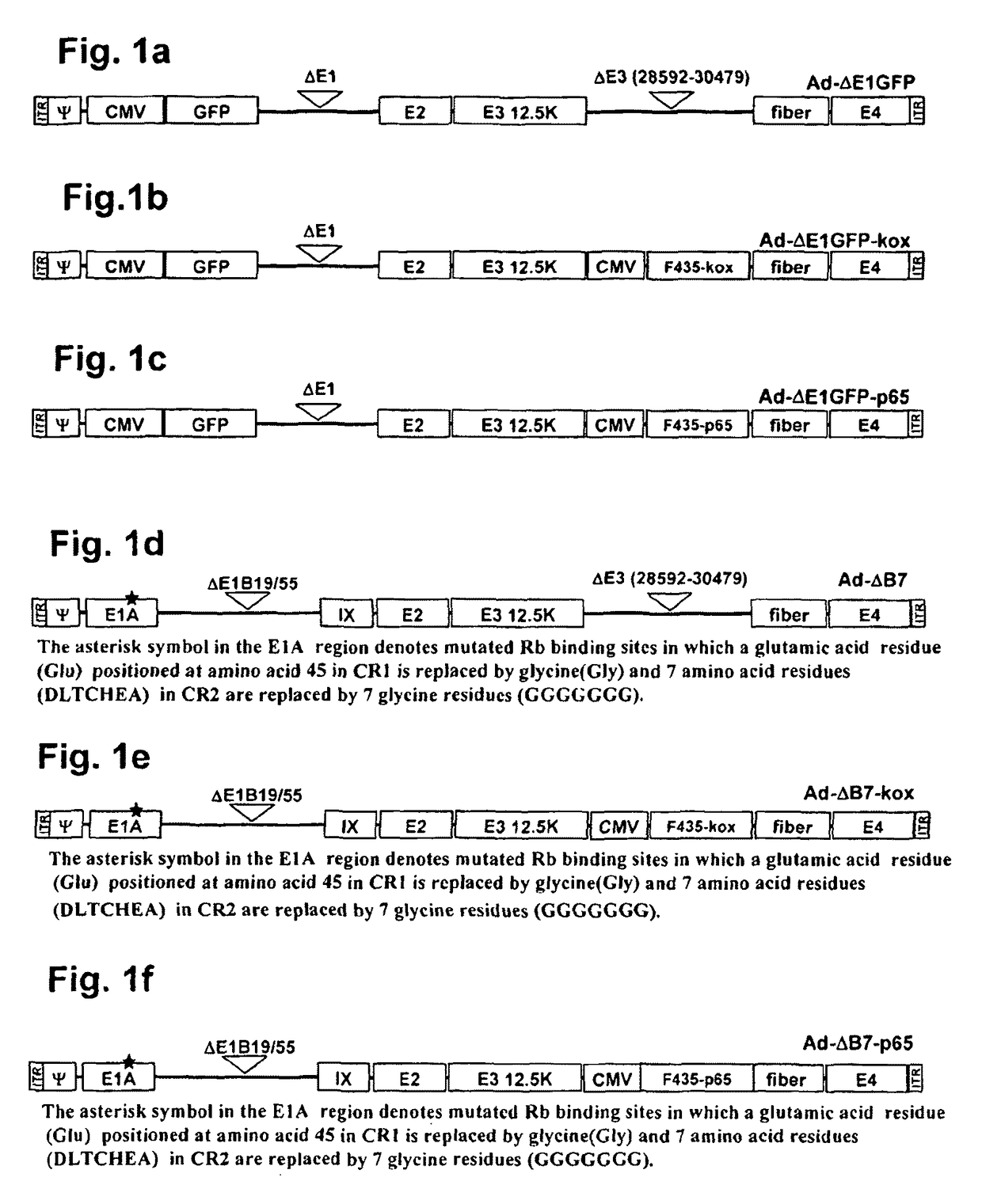
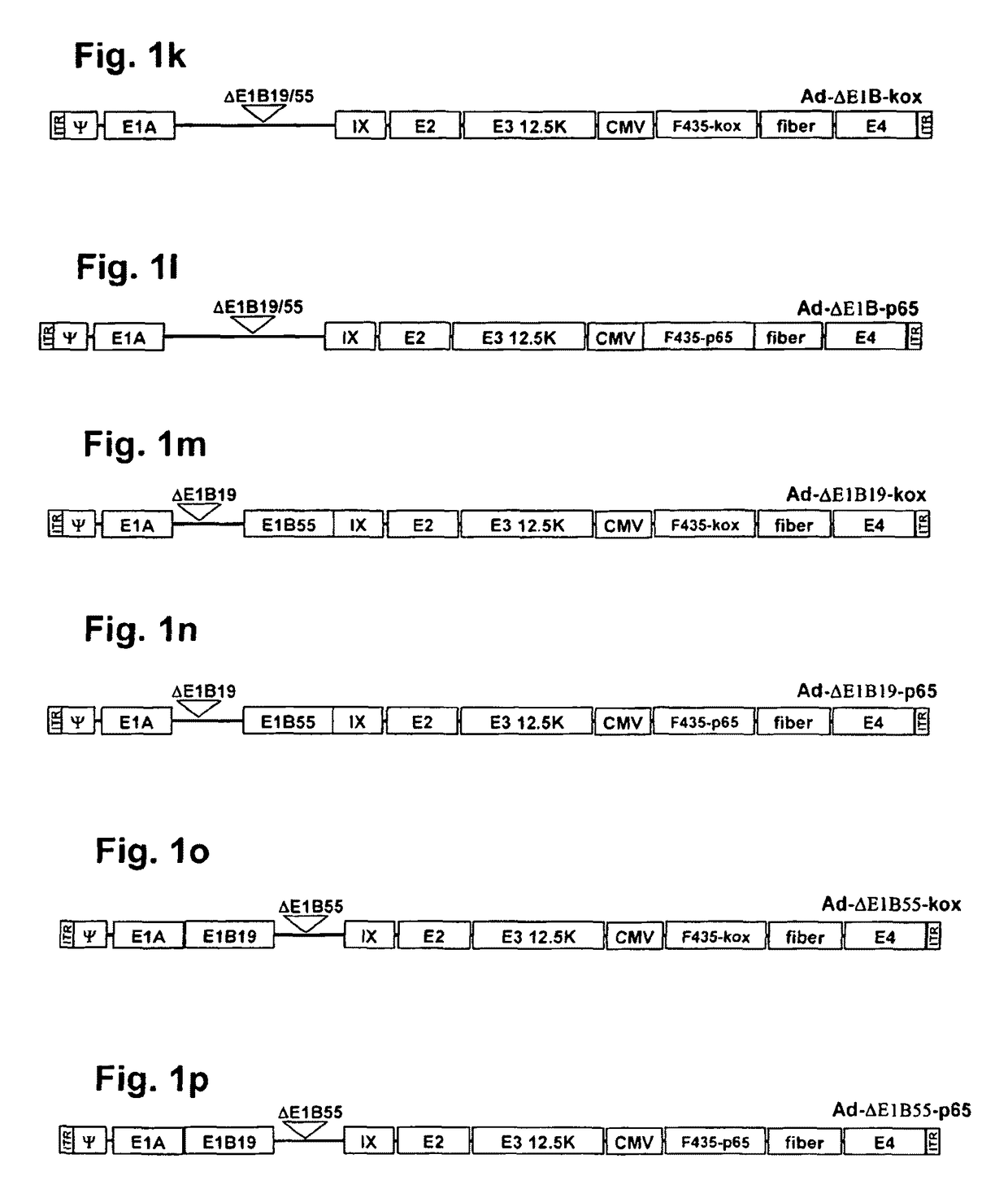
Conditionally replicating adenovirus vector for viral replication regulated by transcription inhibition type Tet-On system and application
The invention discloses a conditionally replicating adenovirus vector for virus replication regulated by a TetR-KRAB-mediated transcription inhibition type Tet-On system, adenovirus E1 region comprises the following components in the following connection sequence: 5'-CMV promoter, TetR-KRAB gene, promoter TRE3G-E1b Pro containing a tetracycline responsive element, EcoR I enzyme cutting site, E1B Delta 55KD protein-deleted adenovirus E1A-E1B19KD gene sequence, enzyme cutting site Spe I and mRNA transcription termination signal SV40polyA-3'; the CMV promoter expresses transcription inhibitor TetR-KRAB; a gene sequence inserted into the two enzyme cutting sites of the EcoR I and the Spe I is a gene fragment from adenovirus E1A translation initiation site to adenovirus E1B19KD protein termination codon, the promoter TRE3G-E1b Pro containing the tetracycline responsive element expresses adenovirus E1A gene, adenovirus E1B19KD gene is expressed by the own promoter of the adenovirus E1B19KD, and the packed adenovirus is named as Ad5-CMV-TetR-KRAB-TRE3G-E1bPro-Delta 55KD. Tests show that the virus can be loaded into mesenchymal stem cells for application in study of tumor therapy.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Recombinant adenoviruses capable of regulating angiogenesis
ActiveUS9850500B2Effective supervisionEasy to superviseBiocideSenses disorderDNA-binding domainNucleotide
The present invention relates to a recombinant adenovirus capable of regulating angiogenesis, which comprises (a) an adenoviral UR (inverted terminal repeat) nucleotide sequence; and (b) a transcription regulatory sequence for a VEGF-A (vascular endothelial growth factor-A) gene comprising (i) a nucleotide sequence encoding a DNA binding domain comprising a zinc finger domain to bind to a site in a VEGF-A promoter sequence as set forth in nucleotides 1-2362 of SEQ ID NO:1, and (ii) a transcription activation domain or a transcription inhibitory domain linked to the nucleotide sequence encoding the DNA binding domain; and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the recombinant adenovirus.
Owner:GENEMEDICINE CO LTD
Transcriptional repression domain as well as encoding genes and application thereof
ActiveCN108727480ADecreased transcriptional activation activityReduced inhibitory activityPlant peptidesFermentationGMO PlantsTranscriptional repression
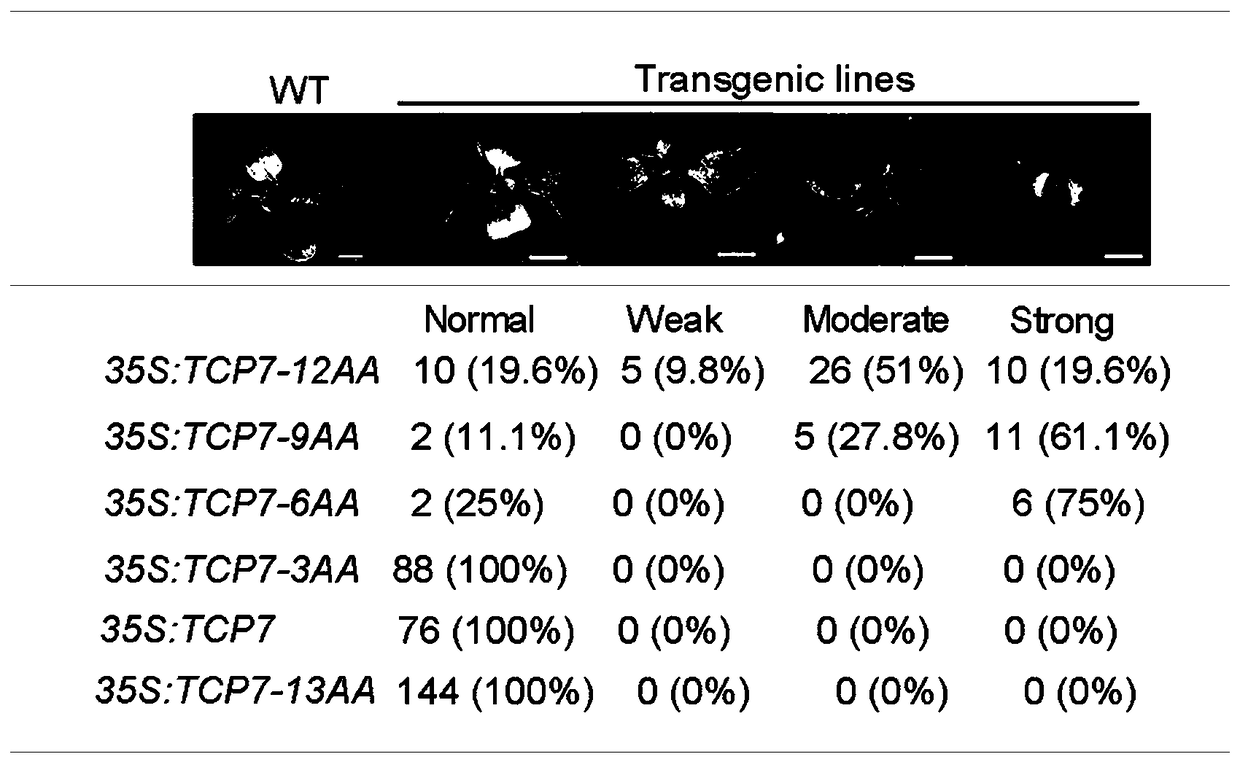
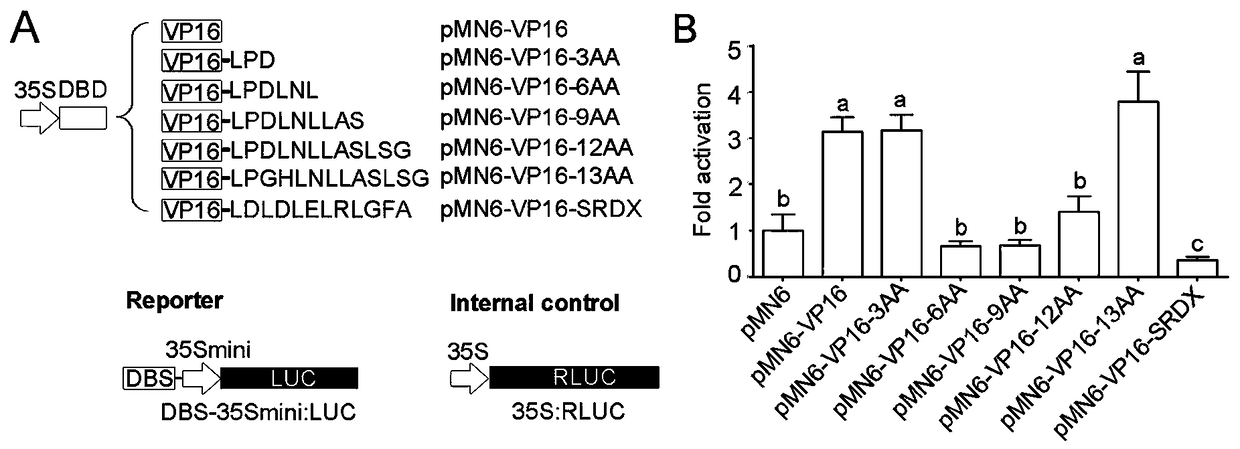
The invention discloses a transcriptional repression domain as well as encoding genes and application thereof in regulating stress tolerance of plants. The transcriptional repression domain comprisesamino acid sequences as shown in SEQ ID NO:1 or SEQ ID NO:2 or SEQ ID NO:3. Since the transcriptional inhibitory activity of the existing SRDX is too strong, transgenic plants in which certain transcription factors are fused with the SRDX may not survive. By contrast, inhibitory sequences provided by the invention have transcriptional inhibitory activity, but the transcriptional inhibitory activity is lower than that of the SRDX; and the transcriptional repression domain is of great scientific research and practical value to explore the function of transcription factors and gene expression regulation.
Owner:HEBEI NORMAL UNIV
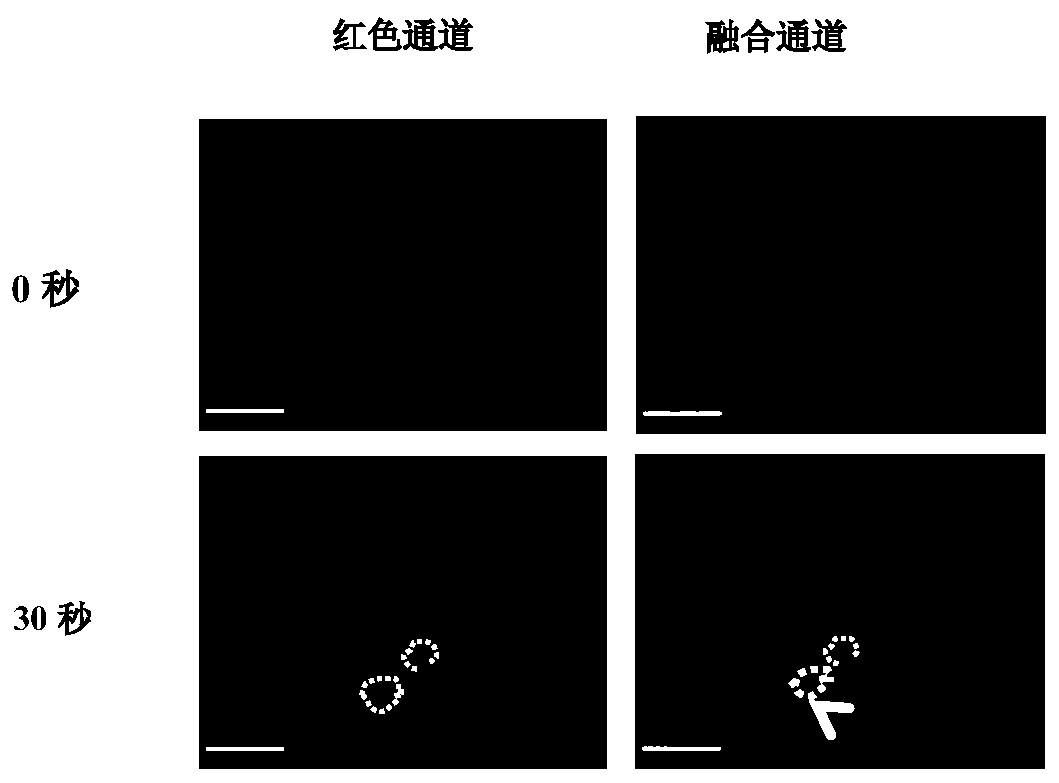
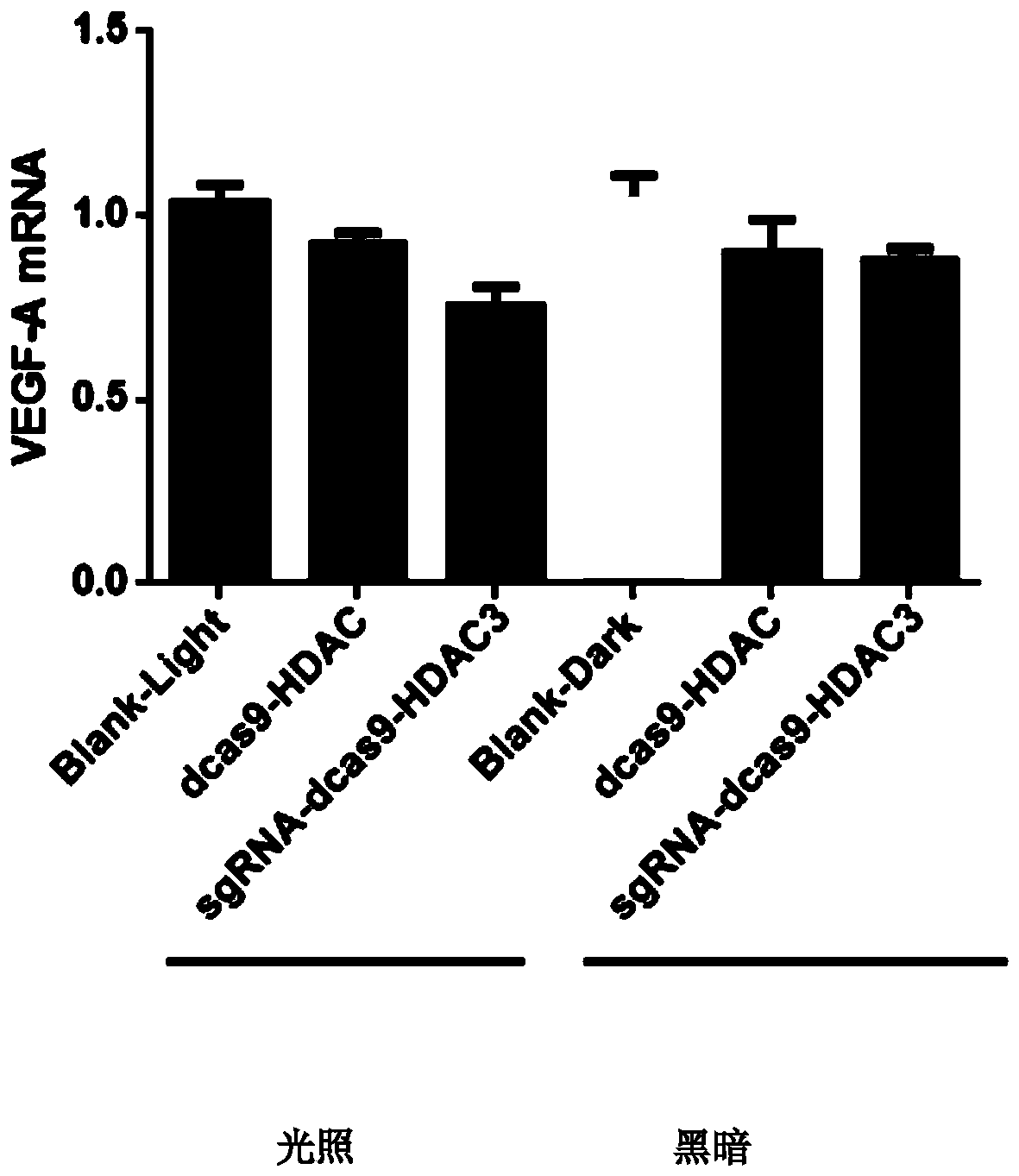
Optically controlled gene transcription inhibition system and method, and construction method for optically controlled gene transcription inhibition system
InactiveCN110628820ARealize dynamic real-time controllable adjustmentRealize precise regulationVector-based foreign material introductionGrowth factors/regulatorsGene targetsHistone deacetylase
The invention discloses an optically controlled gene transcription inhibition system and method, and a construction method for the optically controlled gene transcription inhibition system. A CRISPR (Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) system is mainly used to design genes which are targeted by different sgRNAs (small guide Ribonucleic Acid) and have different purposes. An optically controlled transcription inhibition system is introduced, blue light dependence responsive proteins cibl and cry2 mutually act under different illumination conditions to drive HDAC (histone deacetylase) to indirectly act on a target gene, the HDAC is combined to a target gene site, histone is subjected to deacetylation, and gene transcription is inhibited so as to realize optically controlled gene transcription inhibition. A "CRISPR gene targeting-optogenetic gene regulation and control" technology is used for realizing the accurate targeting of a VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) and a receptor gene. Meanwhile, an optogenetic regulation and control technology is used for realizing the dynamic real-time controllable regulation of the VEGF and a receptor molecule accordingto individual differences.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
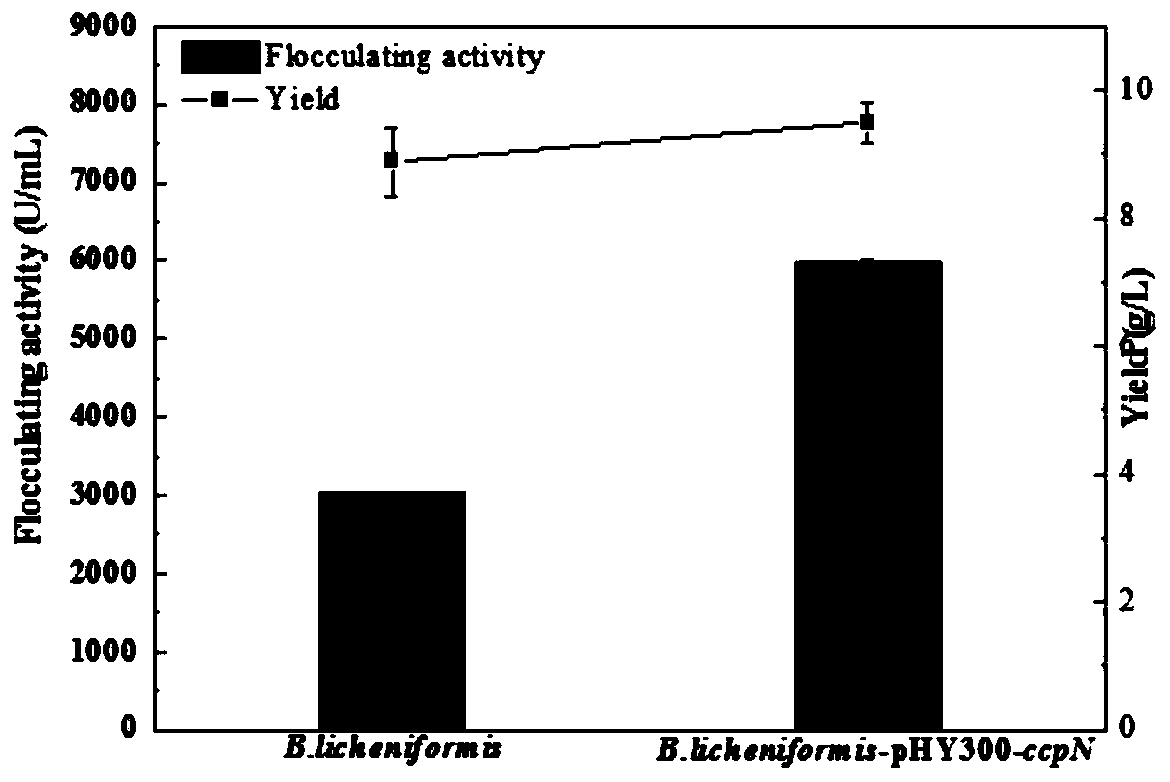
Engineering bacterium over-expressing carbon catabolite repression effect transcription inhibitor gene and construction method thereof
ActiveCN110029081AIncrease productionHigh activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBacillus licheniformis
The invention relates to an engineering bacterium over-expressing carbon catabolite repression effect transcription inhibitor gene and a construction method thereof. The over-expressed carbon catabolite repression effect transcription inhibitor gene ccpN is obtained by cloning polysaccharide flocculant by using PCR amplification in a synthesis pathway, the nucleotide sequence is as shown in SEQ IDNo.1. The carbon catabolite repression effect transcription inhibitor gene ccpN is cloned by using PCR amplification, the gene ccpN fragment are ligated into an expression vector, and introduced intoBacillus licheniformis, and the engineering bacterium of the target gene is obtained by tetracycline resistance screening. The construction method is as follows: designing PCR primers; inserting thetarget gene into downstream multiple cloning sites of PHY300PLK-PamyL-TTamyL constitutive promoter PamyL so as to obtain expression plasmids, and introducing the plasmids into escherichia coli DH5alpha for amplification; and transferring the over-expressed plasmids by electric shock into the Bacillus licheniformis, selecting transformants, and performing verification to obtain recombinant bacteriaof Bacillus licheniformis.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
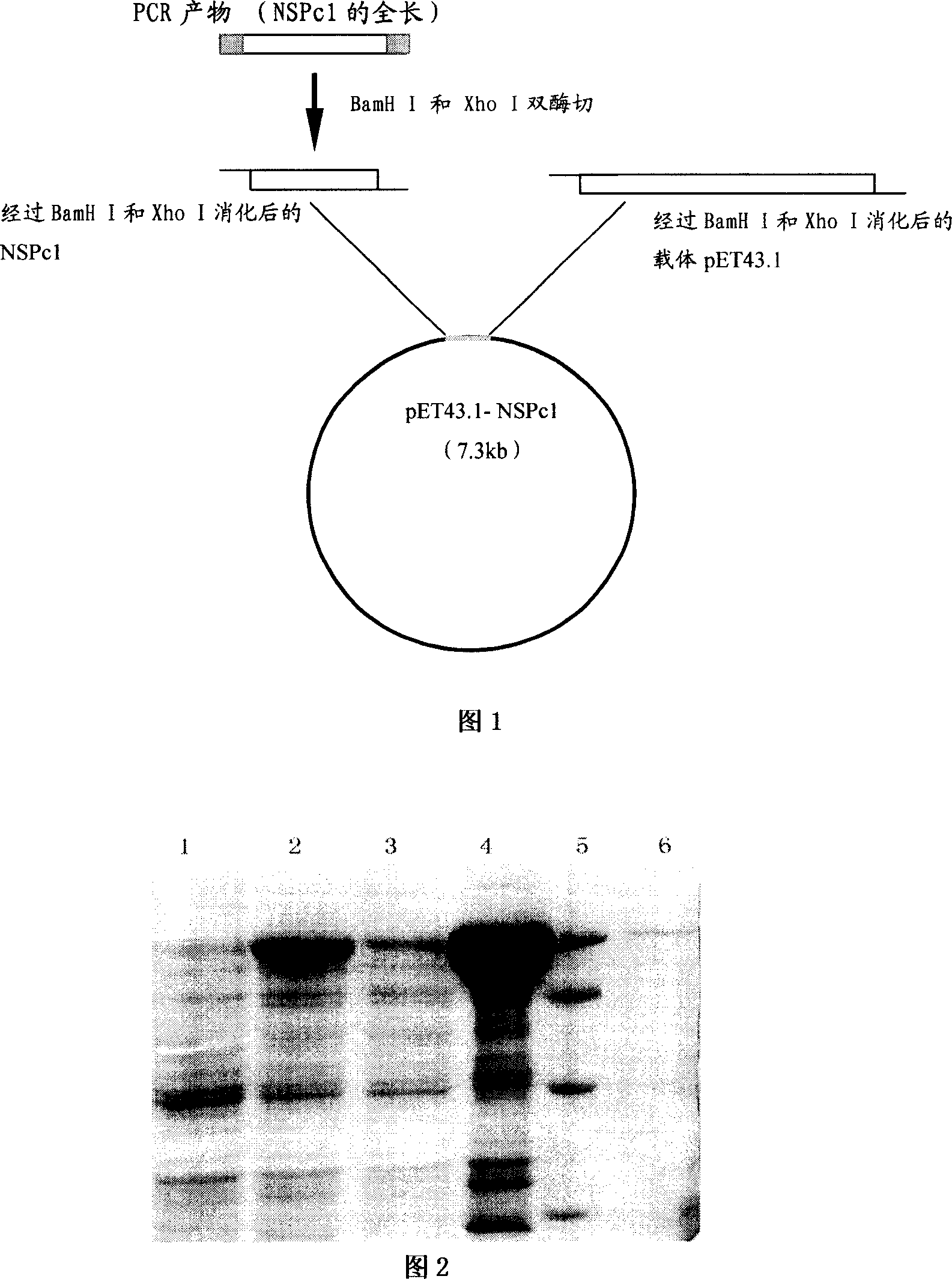
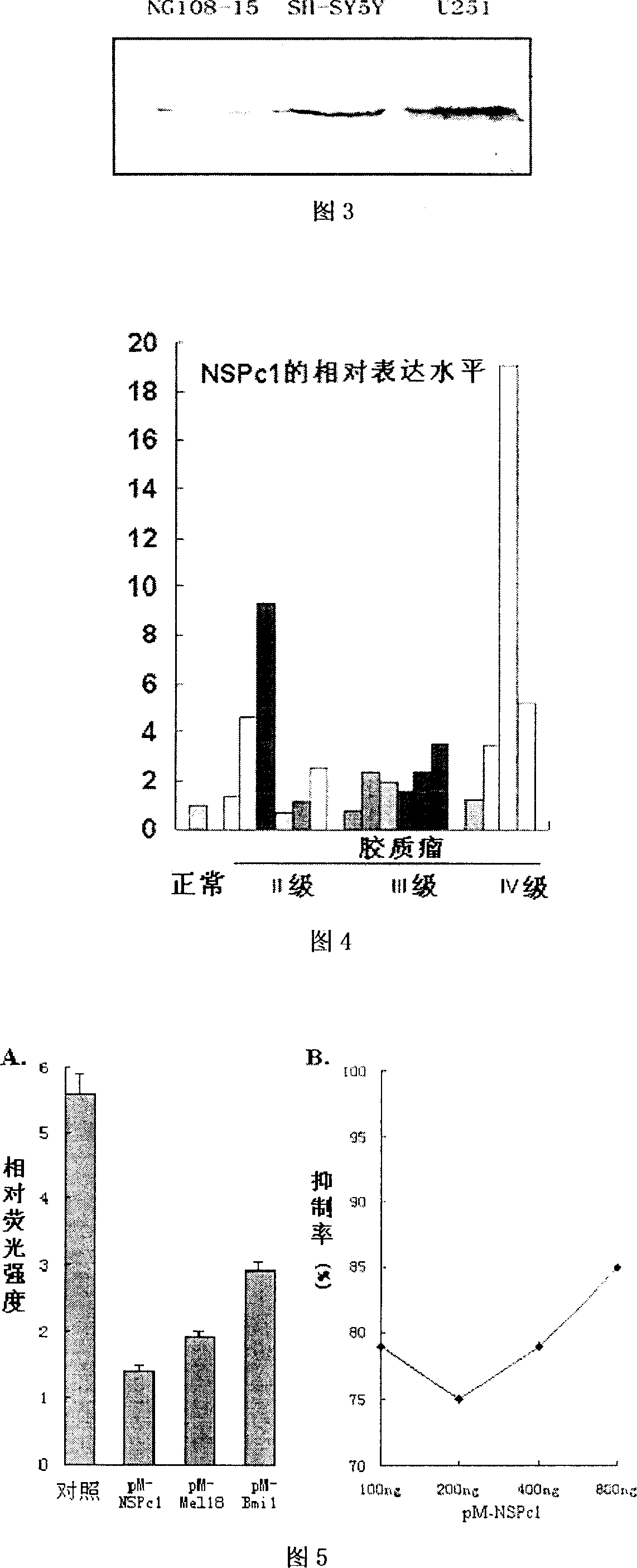
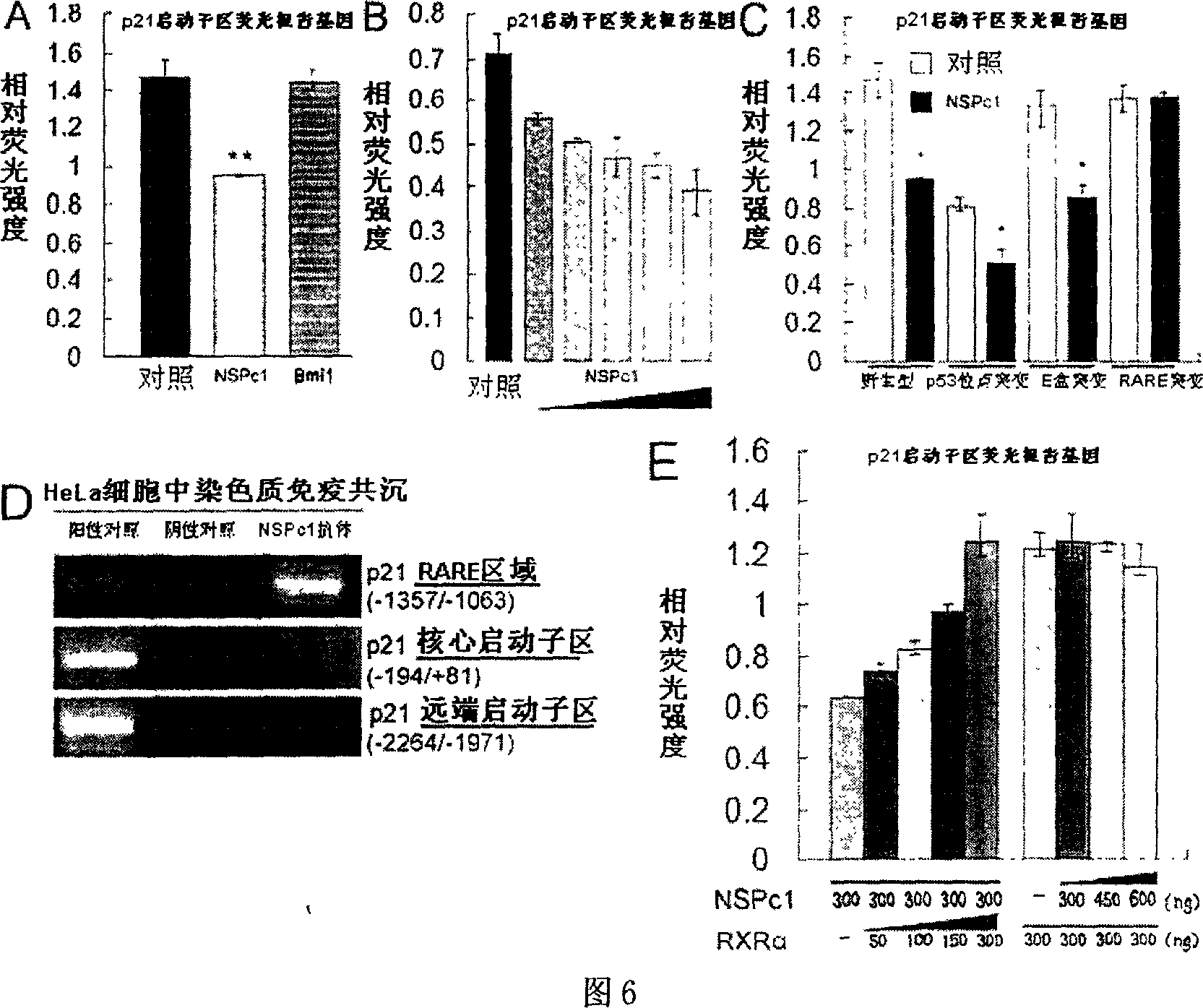
Neural protein NSPc1 having influence on nerve tumor cell differentiation by tretinoin signal pathway
InactiveCN1952131AEfficient detectionSerum immunoglobulinsMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliAntigen
It is found out in the invention that the poly-comb protein NSPc1 of the neural system can highly express in the tumor cell lines from a variety source of neural system using the Western blot technique, it is also found out that the expression level of NSPc1 in human gliocytoma sample is far higher than that in the normal tissue around the cancer and it goes up as the grading increase of the neurogliocytoma pathology using the Real-time PCR technique. NSPc1 is found to have transcription inhibition capacity using the fluorescence detection of reporting gene technology, and p21Waf1 / Cip1 is found to be the target controlled gene of NSPc1. Promoter sequence mutation experiments and chromatin co-immunoprecipitation experiments of P21Waf1 / Cip1 showed that the inhibition effect of NSPc1 on the transcription of p21Waf1 / Cip1 depends on retinoic acid response elements (RARE). Overexpressions of retinoic acid receptor RXRalphacan eliminate the inhibition activity of NSPc1 on p21Waf1 / Cip1 promoter. These results indicate that NSPc1 highly expressing in nerve tumor inhibits the transcription of p21Waf1 / Cip1 through interfering the controlling access of the retinoic acid thus affects the differentiation of the nervous system tumor. Therefore, not only can NSPc1 be used as candidate markers for grouping diagnostic of nervous system malignant tumor type, but also can serve as a target of gene therapy. Meanwhile, in the invention, building the plasmid for prokaryotic expressing of full-length protein of NSPc1, transforming Escherichia coli to express the corresponding protein; After purifying the protein it can be used for the preparation of high-quality antibodies, as well as applied to the nervous system tumor diagnosis.
Owner:THE INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Methods and compositions for inhibiting herpesviral replication
InactiveUS7179619B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingViral replicationTranscriptional repression
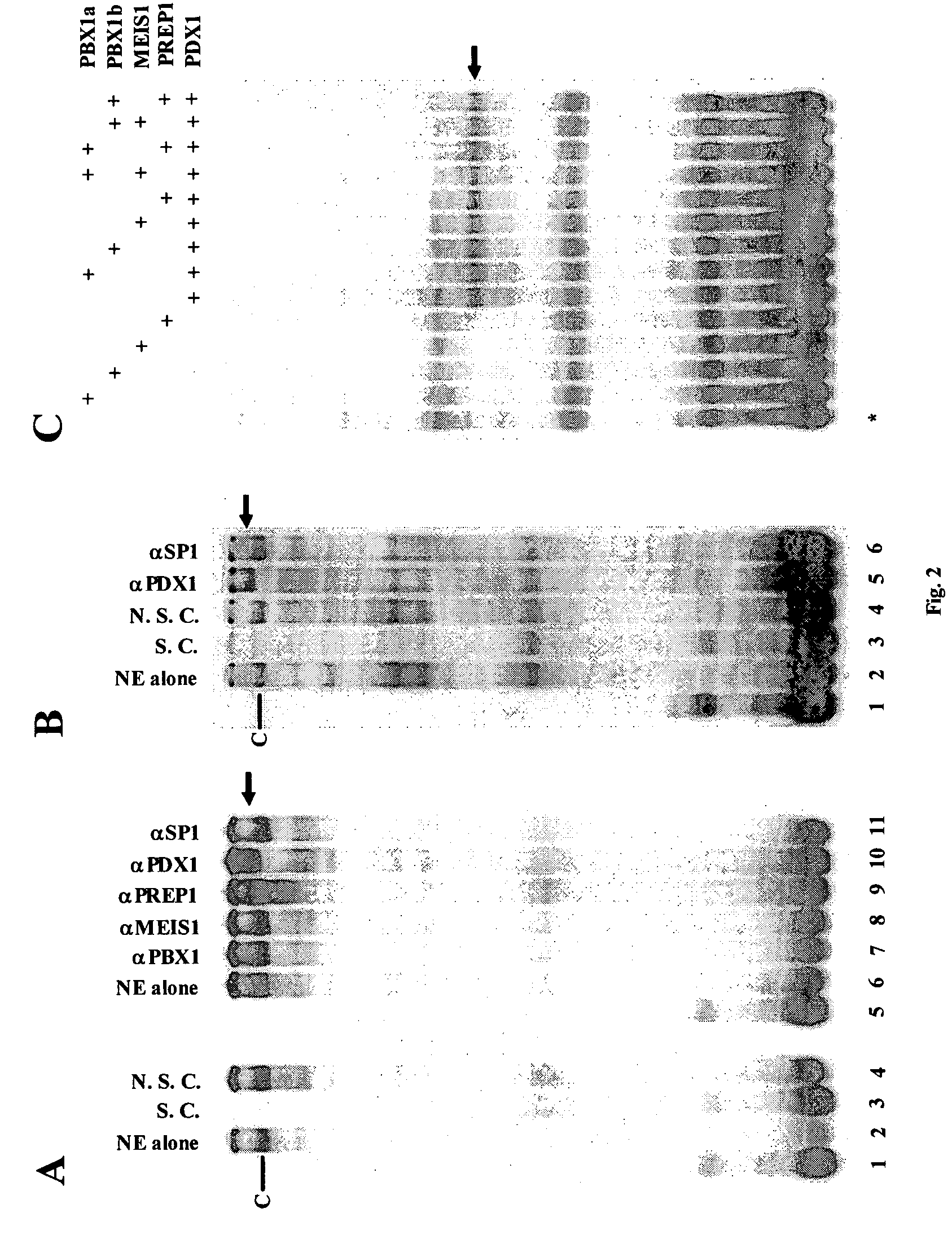
This invention provides methods of screening for compounds that inhibit herpesviral transcription and replication. The methods comprise screening test compounds for ability to enhance the activity of homeodomain transcription factor PDX1 in repressing transcription of herpesviral genes (e.g., the IE gene of cytomegalovirus). Transcriptional repression by PDX1 can be monitored using an expression vector comprising a reporter gene operably linked to a PDX1-binding, upstream transcription regulatory sequence of the herpesvirus. The invention further provides methods and pharmaceutical compositions for stimulating PDX1-mediated transcriptional repression in a subject and for treating diseases and conditions associated with herpesviral infection.
Owner:IRM
D-psicose biosensor and application thereof
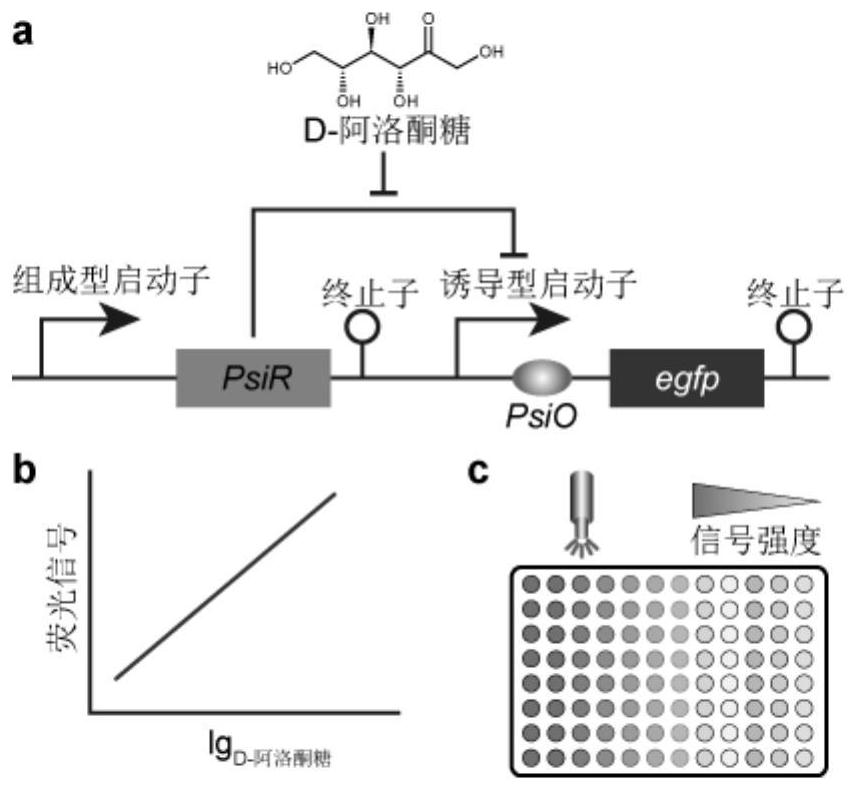
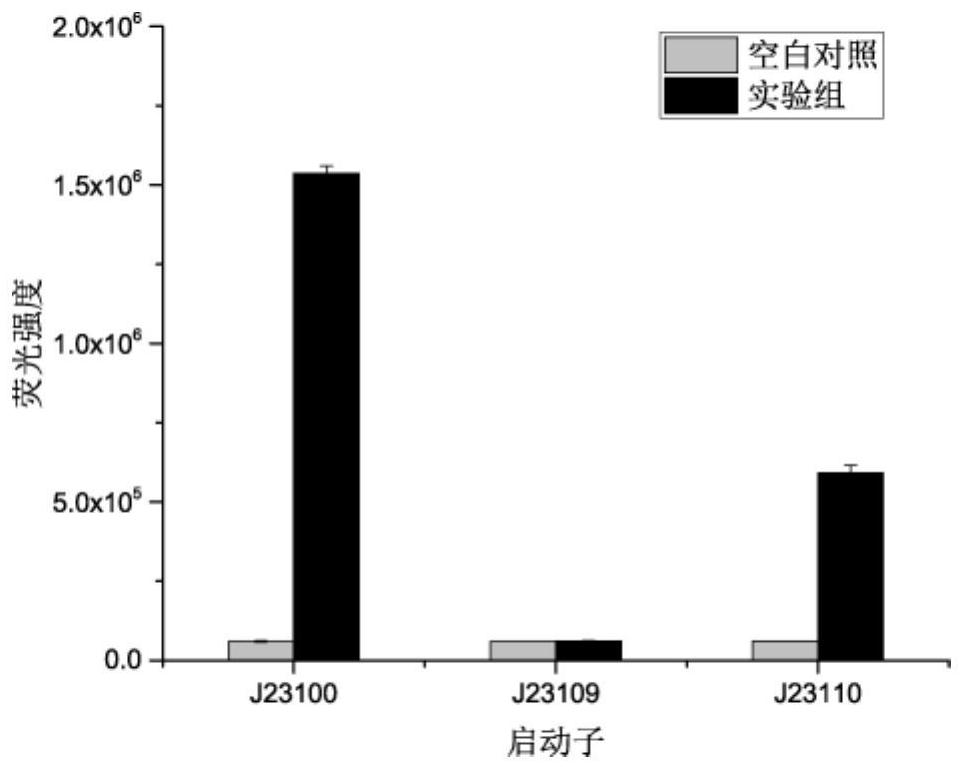
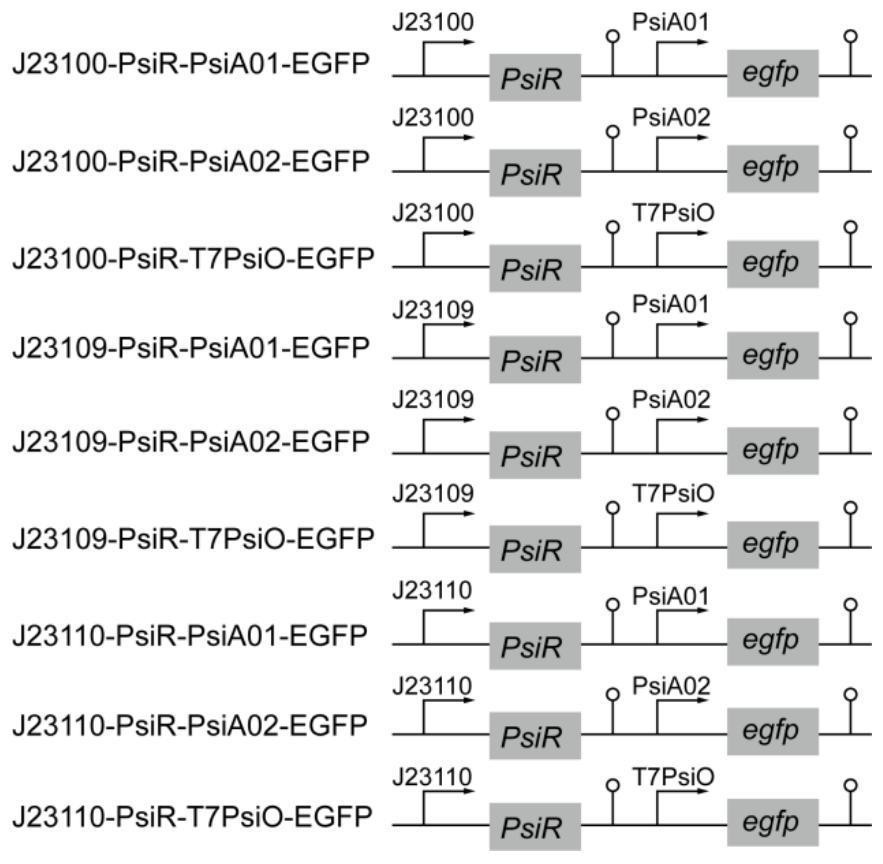
PendingCN114317387AEnable high-throughput analysisNo sampling requiredBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBinding site
The invention provides a D-psicose biosensor which can be used for detecting the content of D-psicose in vivo and in vitro of microorganisms, and belongs to the field of synthetic biology and biochemical engineering. The biosensor takes escherichia coli as a chassis, and consists of a constitutive promoter, a transcription factor PsiR, an inducible promoter and a reporter gene egfp. Wherein the constitutive promoter is used for controlling expression of a transcription factor PsiR, and the inducible promoter is used for controlling expression of a reporter gene egfp. When the D-psicose does not exist, the PsiR is combined with the regulation site PsiO of the inducible promoter to repress the transcription of a downstream reporter gene; when D-psicose exists, PsiR is not combined with PsiO any more, transcription repression of a downstream reporter gene is relieved, and a fluorescence signal is generated. In a certain range, the signal intensity of the reporter gene is in direct proportion to the logarithm of the concentration of the D-psicose, so that the concentration of the D-psicose can be calculated by monitoring the fluorescence signal intensity. According to the present invention, the binding site PsiO of the transcription factor FdeR is fused with the strong promoter to construct the artificial chimeric promoter, such that the sensitivity and the monitoring range of the sensor are optimized; the biosensor constructed by the invention not only can be used for monitoring the concentration of D-psicose in the environment, but also can be used for monitoring the yield of a D-psicose production strain, and has great application potential in the fields of biochemical engineering, industrial microorganisms and food.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Primary micro RNA expression cassette
This invention relates to inhibition of hepatitis gene expression. More specifically, the invention relates to a method of using RNA sequences to inhibit Hepatitis B and C Virus replication. Expression cassettes that include DNA sequences derived from endogenous micro RNAs (miRs) are used in the method and are transcribed by Pol II promoters, and then processed to generate sequences that are specific to target hepatitis virus sequences (RNAi effecter sequences). The RNAi effecter sequences can target the selected hepatitis virus sequences resulting in gene silencing or transcriptional inhibition of the hepatitis virus gene. The expression cassettes may be delivered in vitro or in vivo to host cells. A pharmaceutical composition containing the expression cassettes is also claimed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF THE WITWATERSRAND
Fusion molecules of rationally-designed dna-binding proteins and effector domains
InactiveUS20180023065A1Affect specificityAffect activityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFusion with DNA-binding domainDNA-binding domainTranscription Repressor
Targeted transcriptional effectors (transcription activators and transcription repressors) derived from meganucleases are described. Also described are nucleic acids encoding same, and methods of using same to regulate gene expression. The targeted transcriptional effectors can comprise (i) a meganuclease DNA-binding domain lacking endonuclease cleavage activity that binds to a target recognition site; and (ii) a transcription effector domain.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Agents for reversing epigenetic silencing of genes
The present invention provides methods for discovering agents that are effective in reversing epigenetic silencing by inhibiting the interaction of methyl-binding (MBD) proteins with methylated genomic DNA. Also provided are methods for reactivating silenced genes having CpG island hypermethylation along with methods for treatment and prevention of diseases, such as cancer and sickle cell anemia, by administering an agent that modulates methyl-binding domain (MBD) protein-mediated transcriptional repression, thereby increasing gene transcription to prevent or treat disease. Additionally, compounds identified by the present invention useful for treatment and prevention of diseases, such as cancer and sickle cell anemia, are provided.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Agents for reversing epigenetic silencing of genes
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com