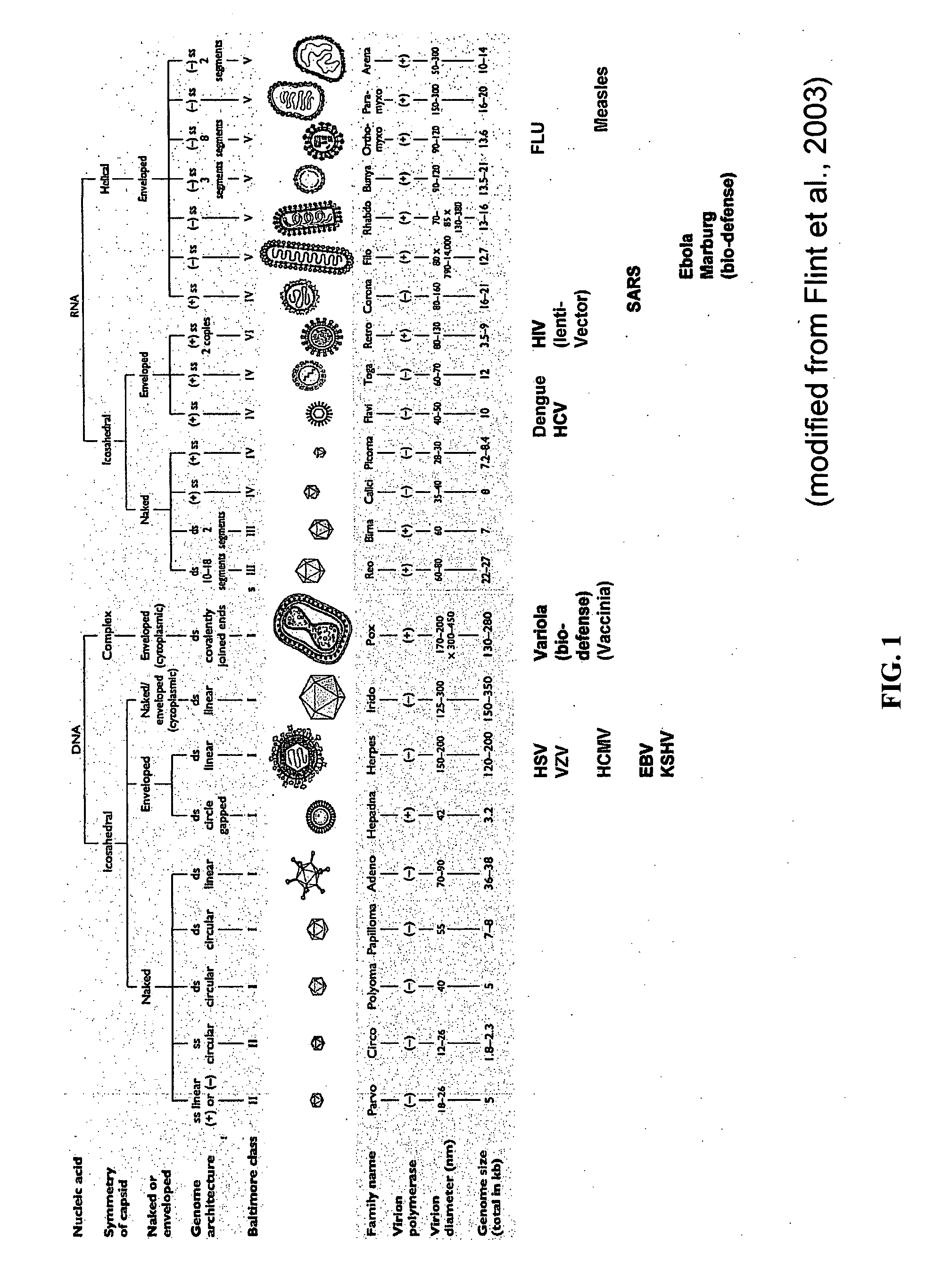
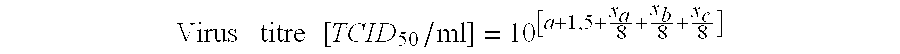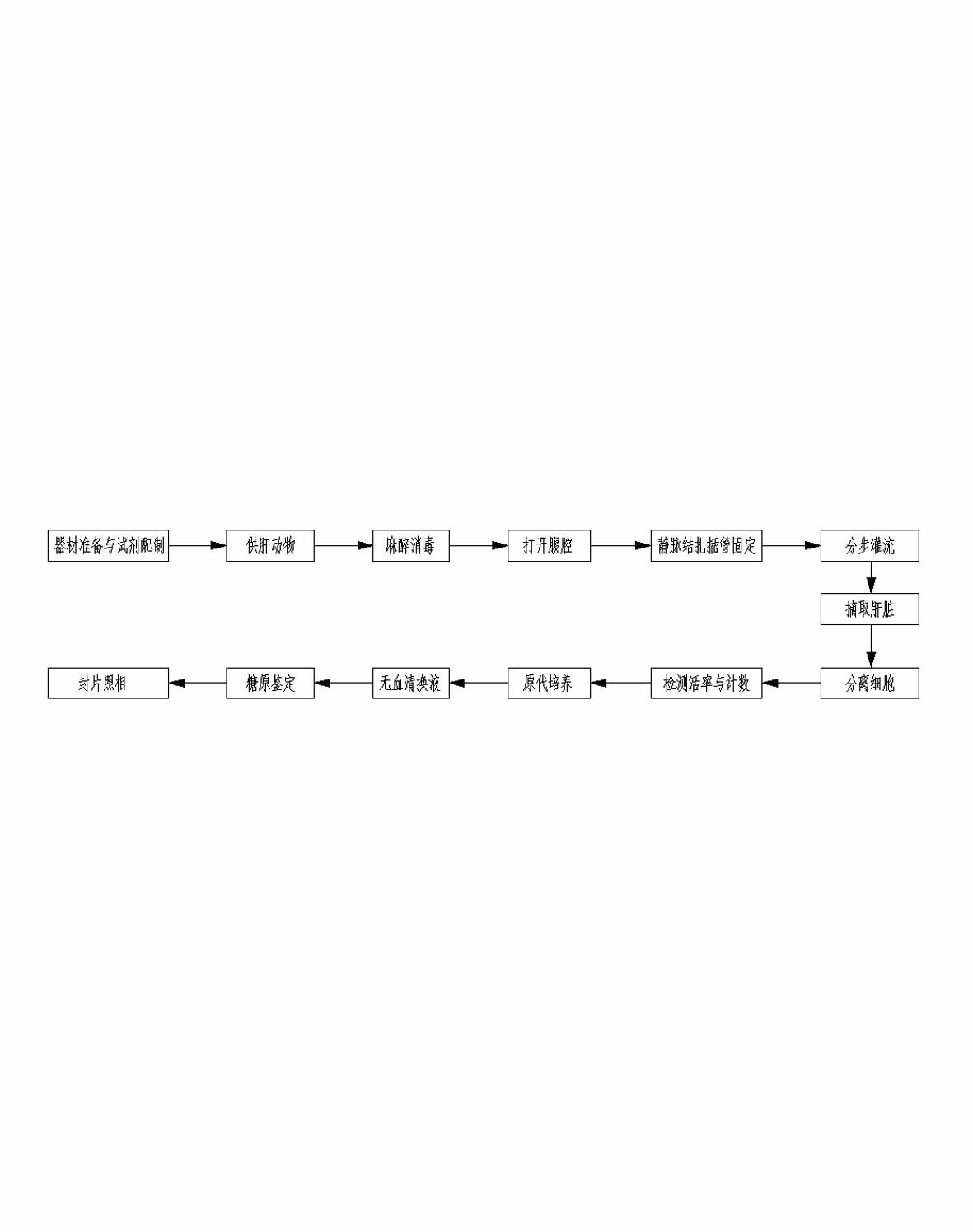Patents
Literature
253 results about "Virus infected cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for the generation of antigen-specific lymphocytes
InactiveUS20070116690A1Function increaseEnhancing function of T cellBiocideVirusesAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
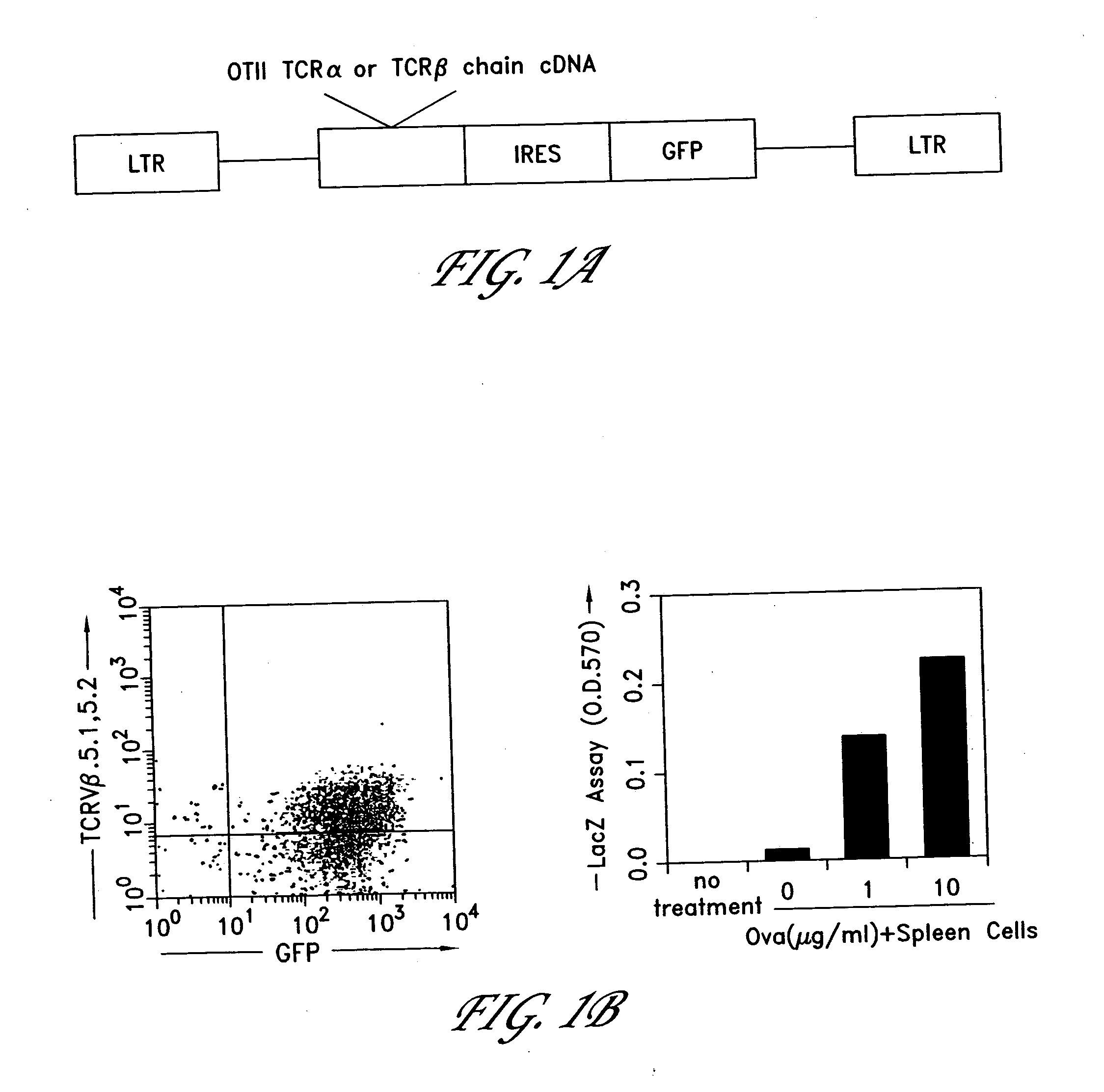
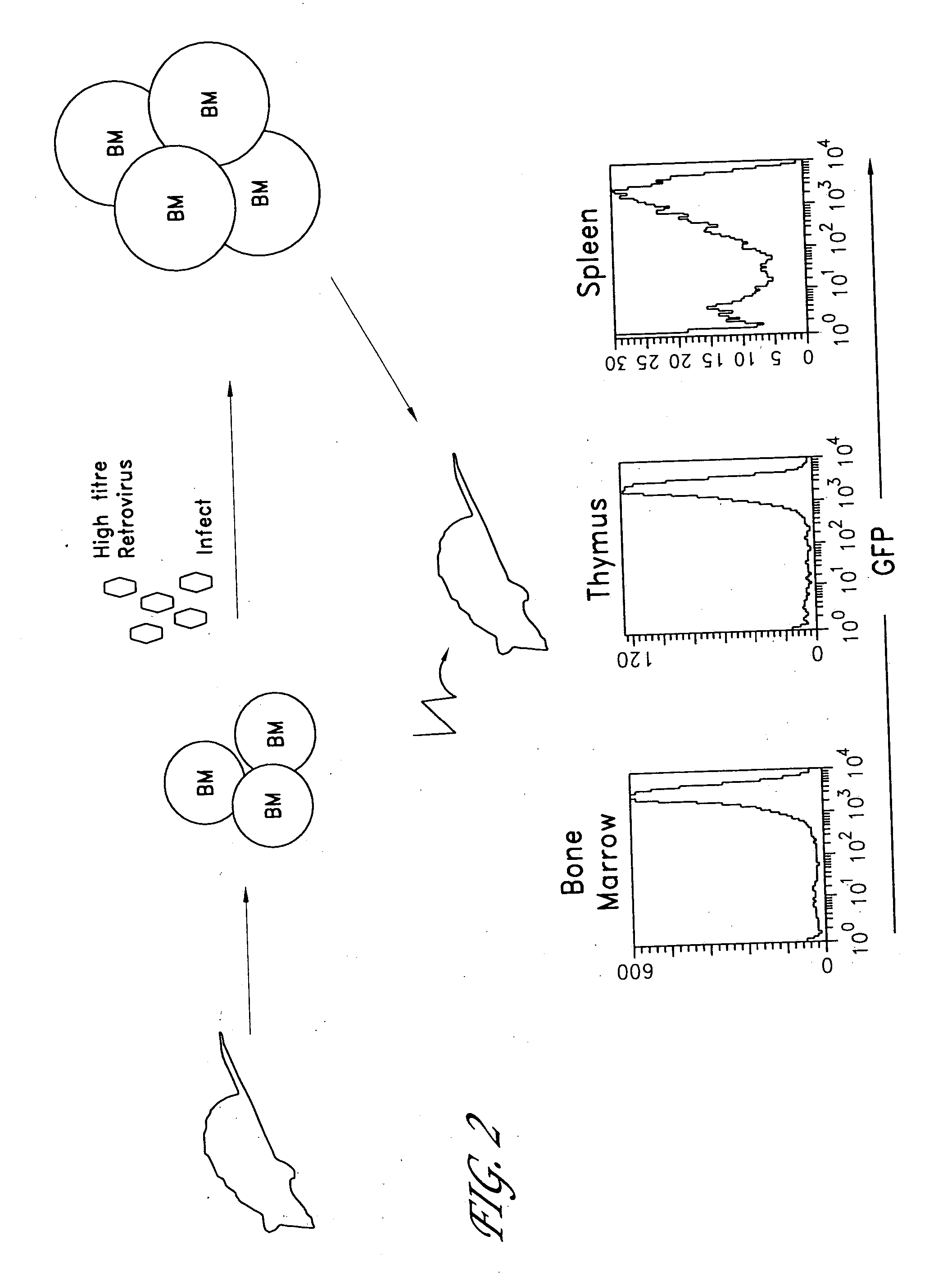
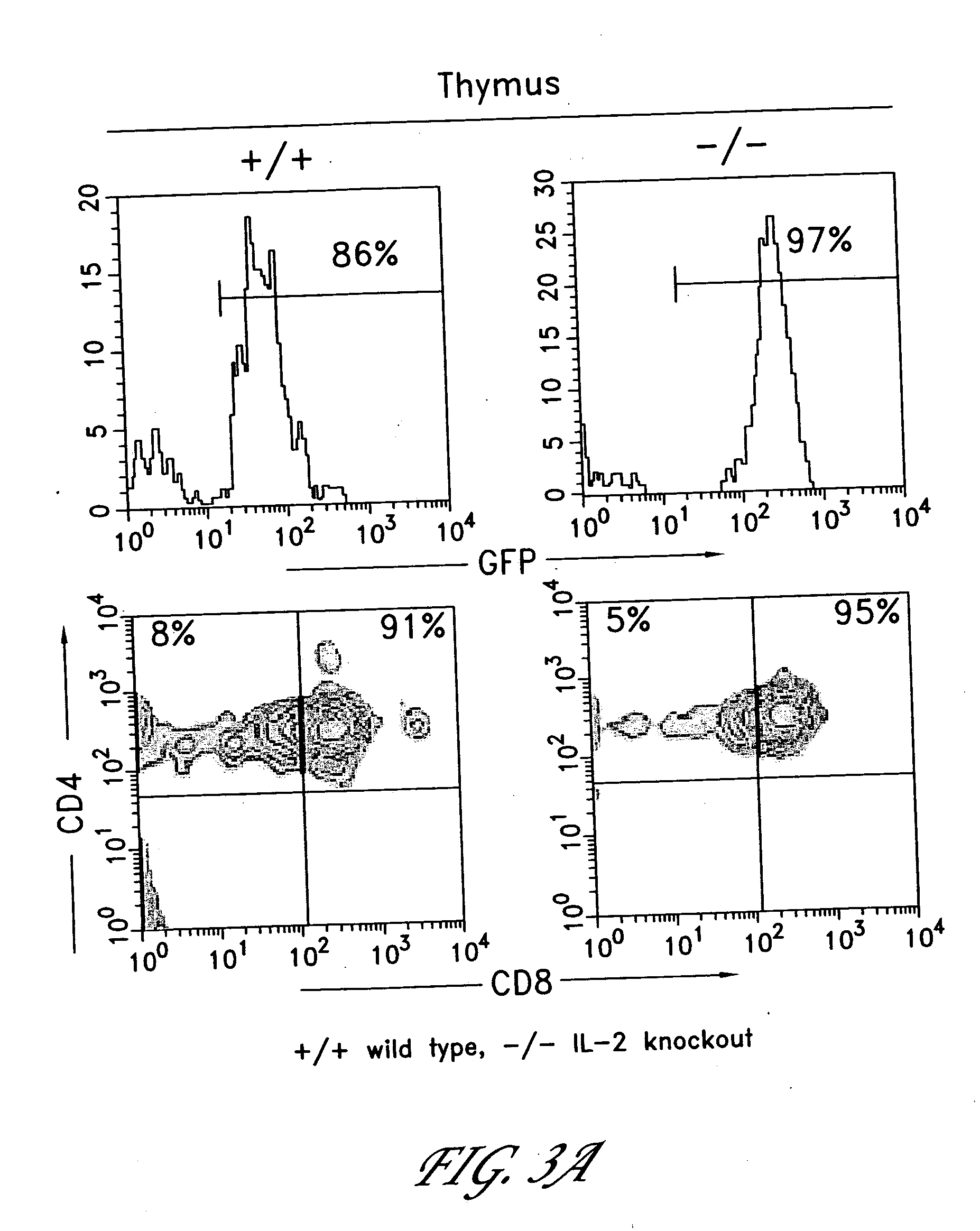
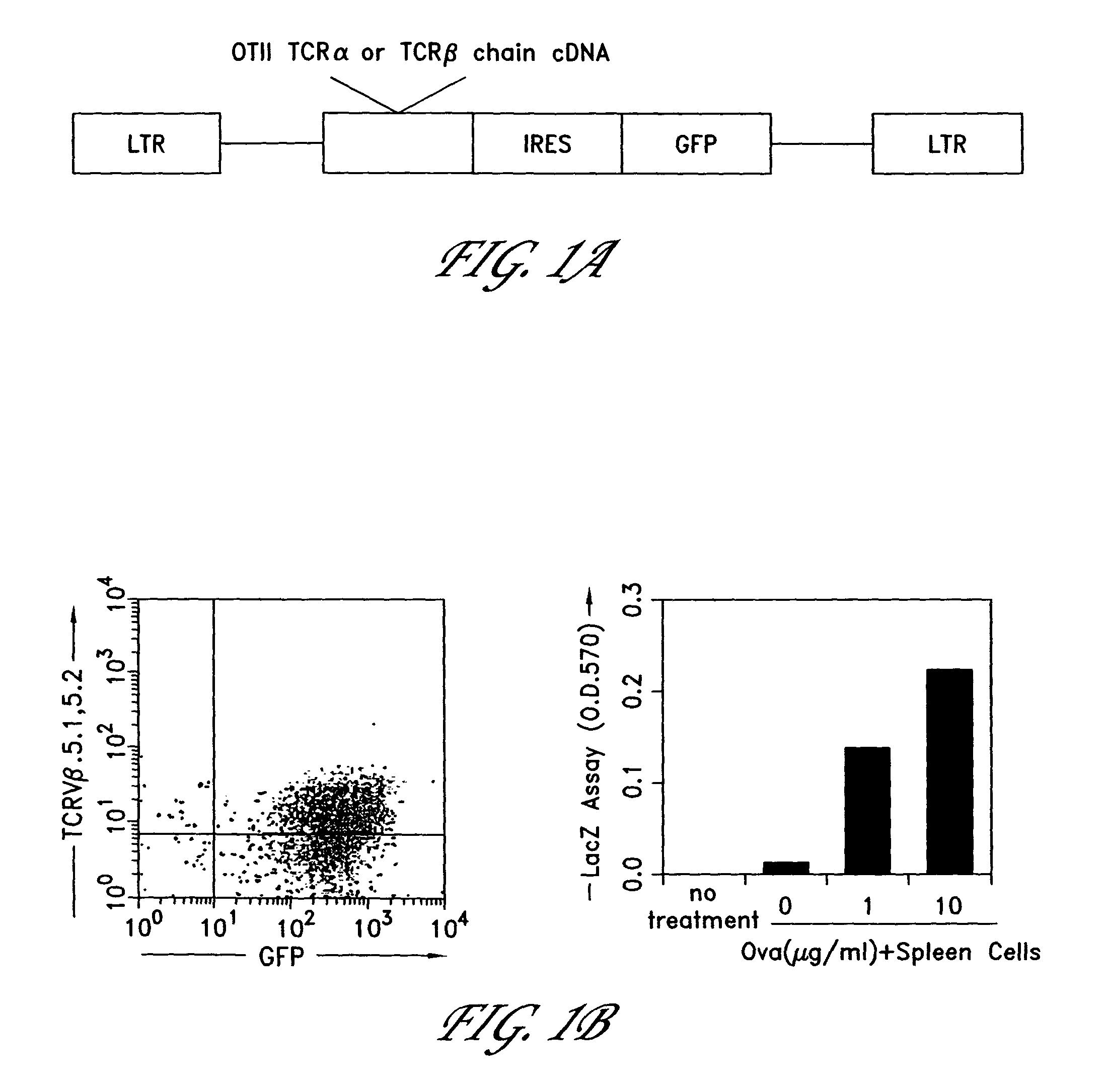
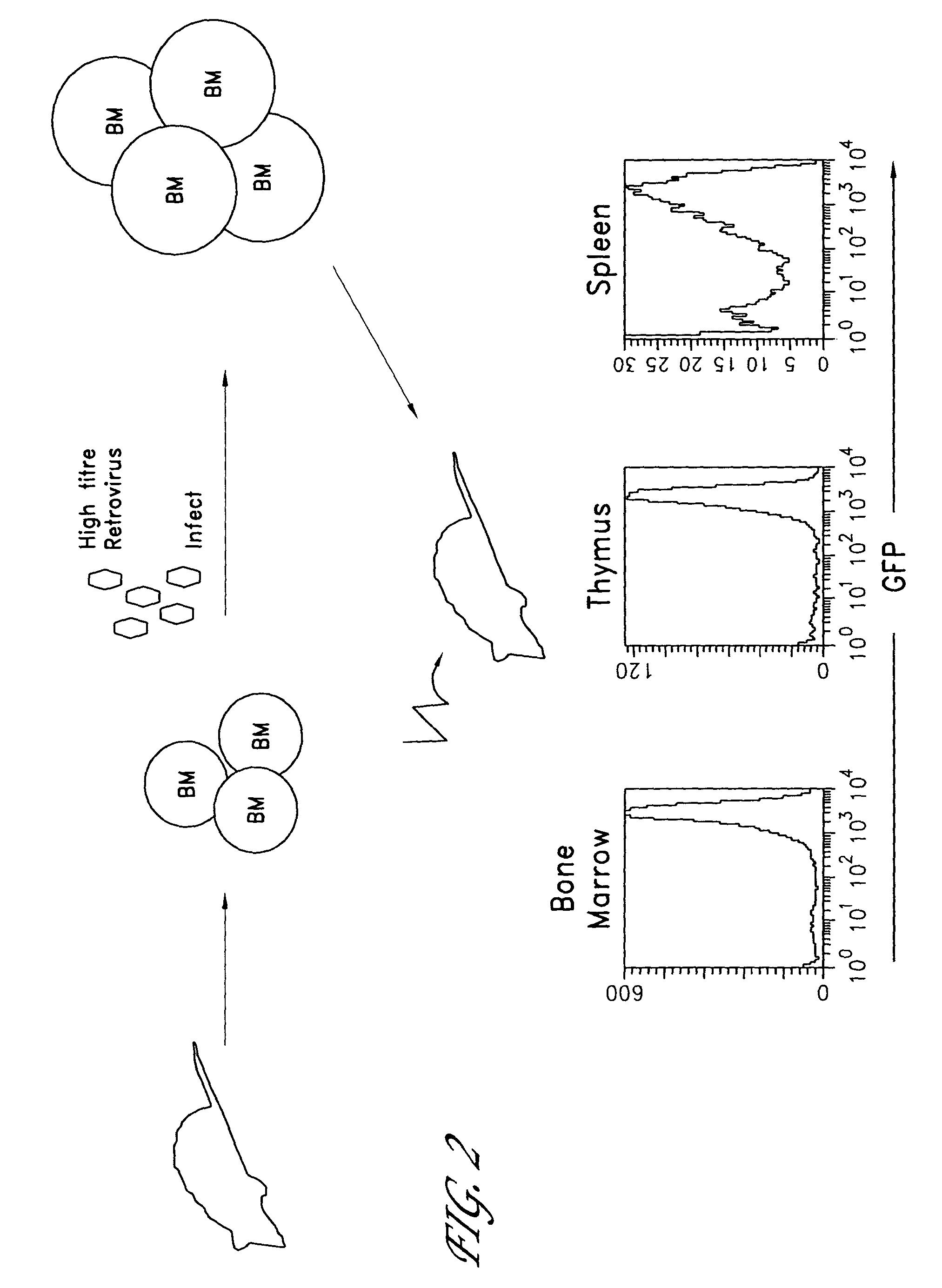
The invention provides systems and methods for the generation of lymphocytes having a unique antigen specificity. In a preferred embodiment, the invention provides methods of virally infecting cells from bone marrow with one or more viral vectors that encode antigen-specific antibodies for the production of, for example B cells and T cells. In some embodiments, the viral vectors include an IRES or 2A element to promote separation of, for example, the α subunit and β subunit of a T cell receptor (TCR) or heavy and light chains of a B-cell antibody. The resulting lymphocytes, express the particular antibody that was introduced in the case of B cells and TCR in the case of T cells. The lymphocytes generated can be used for a variety of therapeutic purposes including the treatment of various cancers and the generation of a desired immune response to viruses and other pathogens. The resulting cells develop normally and respond to antigen both in vitro and in vivo. We also show that it is possible to modify the function of lymphocytes by using stem cells from different genetic backgrounds. Thus our system constitutes a powerful tool to generate desired lymphocyte populations both for research and therapy. Future applications of this technology may include treatments for infectious diseases, such as HIV / AIDS, cancer therapy, allergy, and autoimmune disease.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Compositions and methods to enhance the immune system
InactiveUS8728476B2Enhance in vivo efficacyImprove immunityOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsTherapeutic antibodyCancer cell
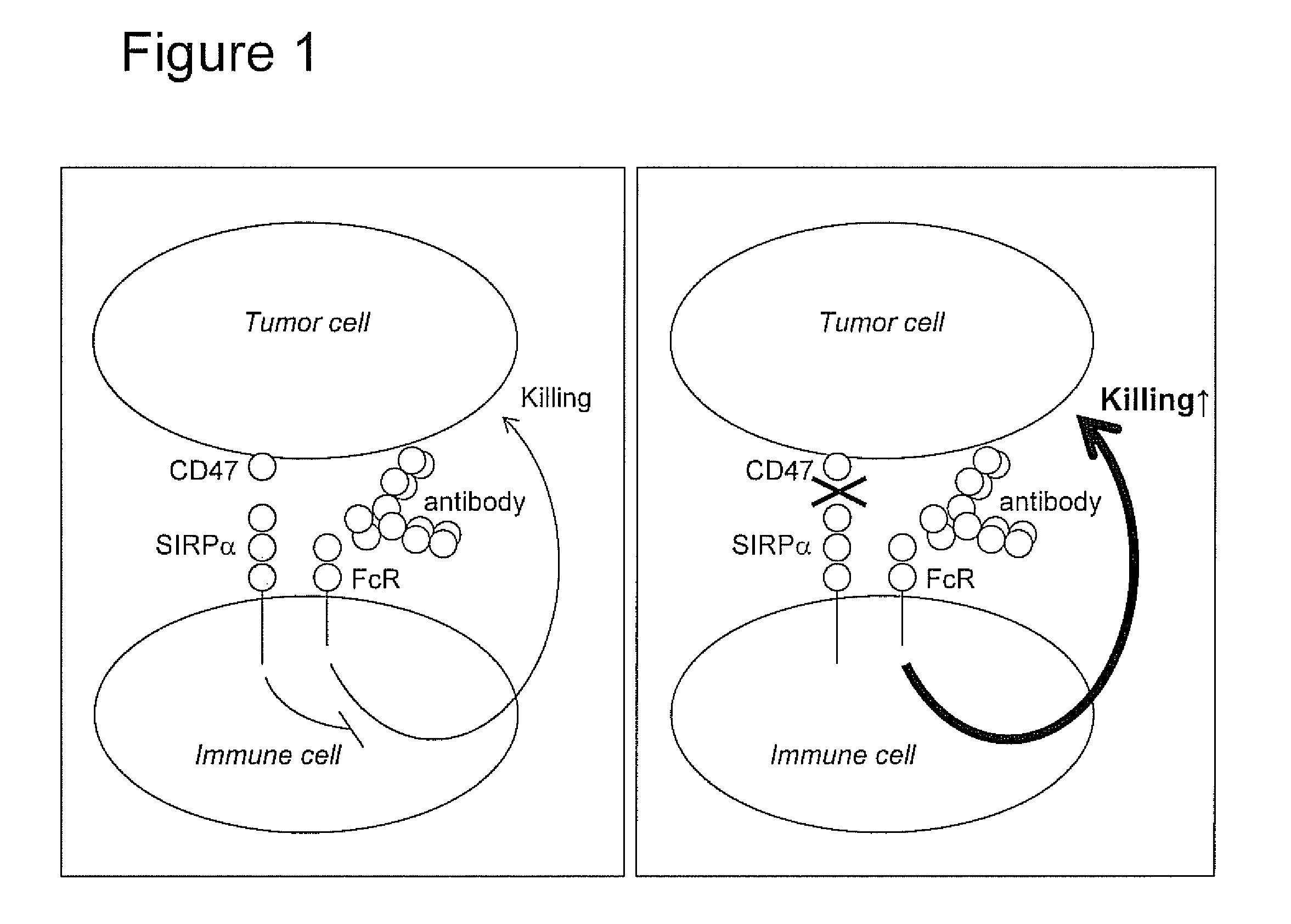
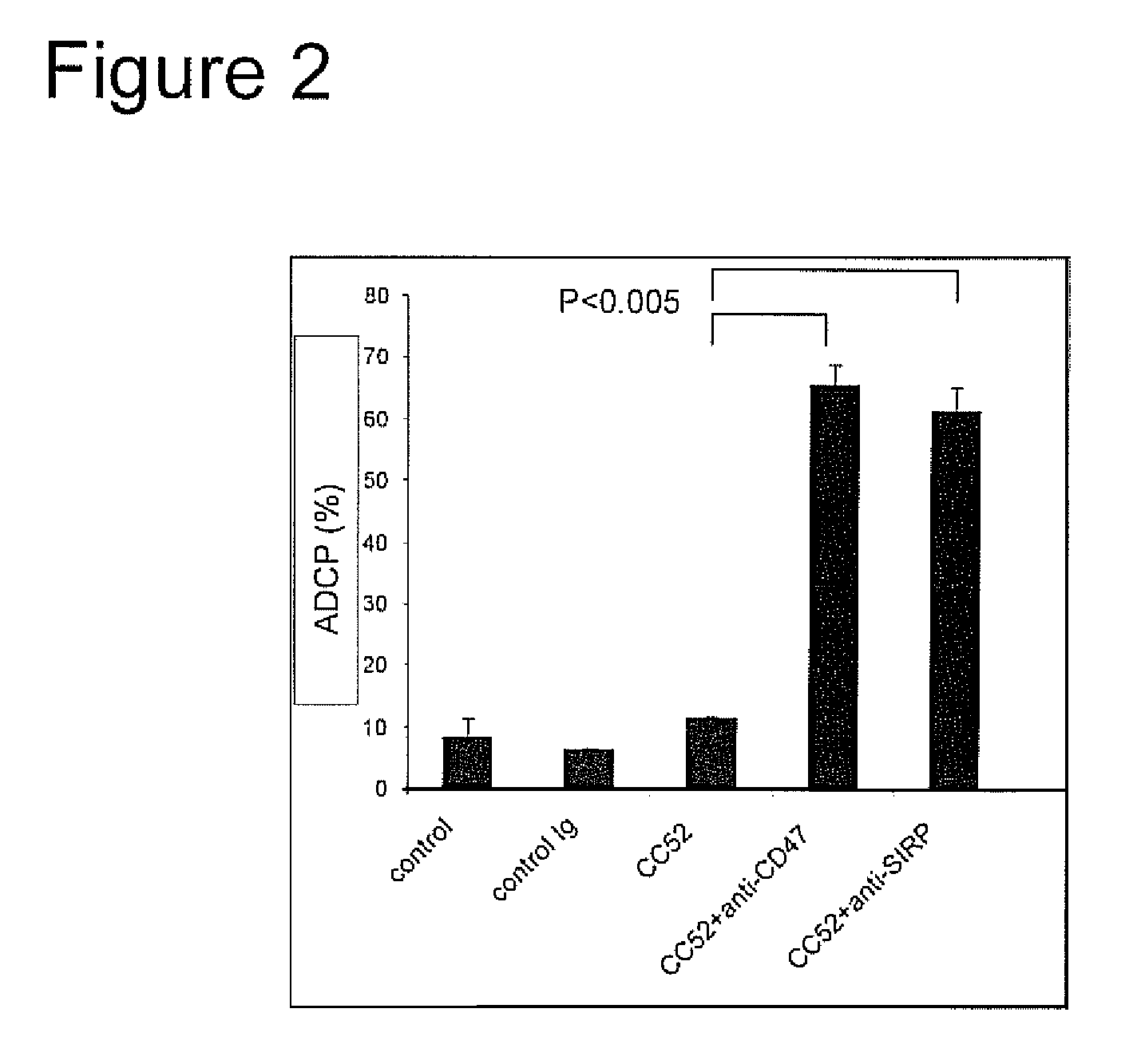
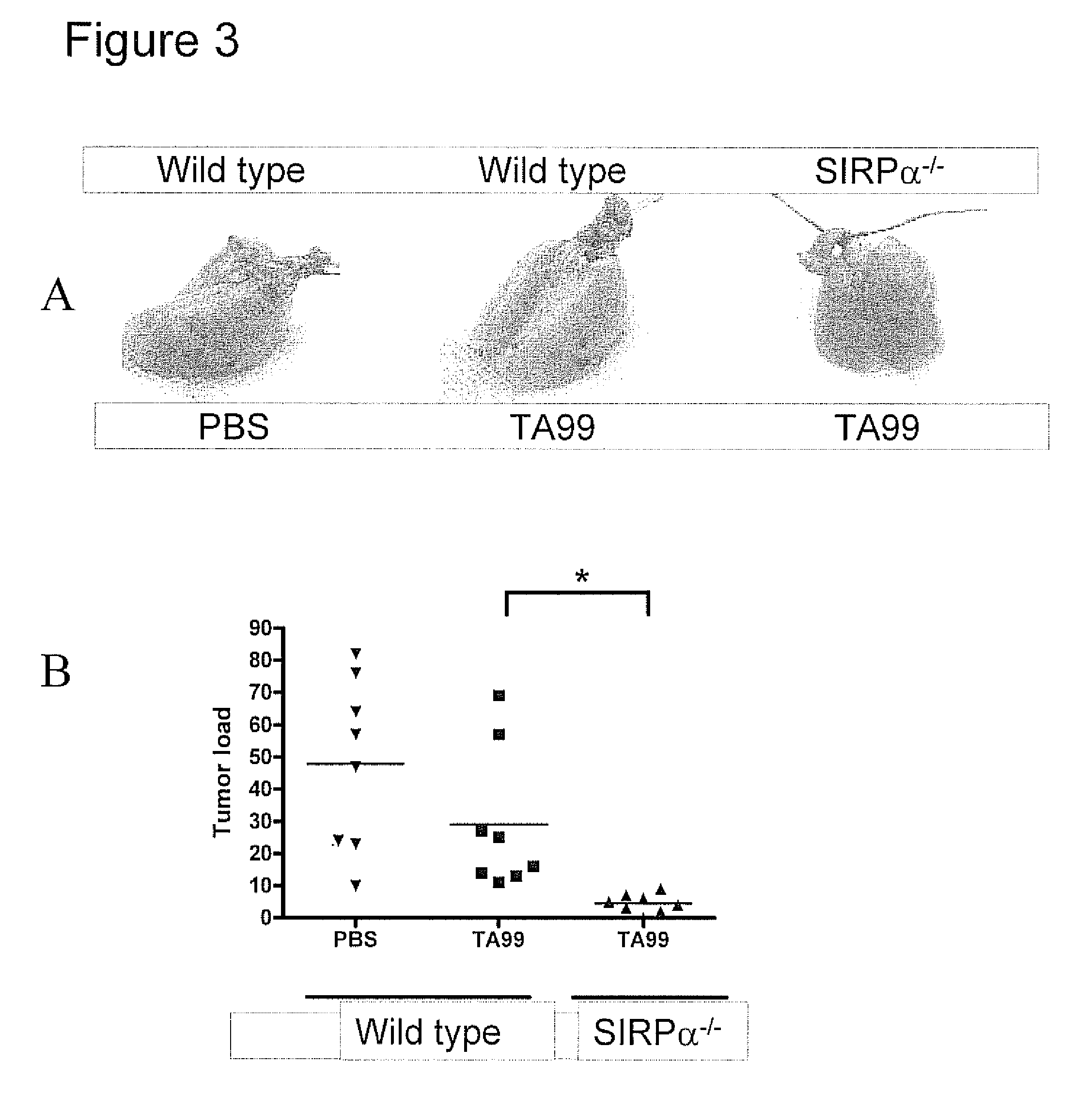
The invention relates to the field of molecular medicine. In particular, it relates to compositions and methods to enhance the clearance of aberrant cells, e.g. cancer cells or virus-infected cells, by the host's immune system. Provided is a composition comprising (i) a therapeutic compound that can trigger a host's immune effector cells against an aberrant cell, such as a therapeutic antibody, and (ii) at least one agent capable of reducing or preventing inhibitory signal transduction initiated via SIRPalpha.
Owner:STICHTING SANQUIN BLOEDVOORZIENING
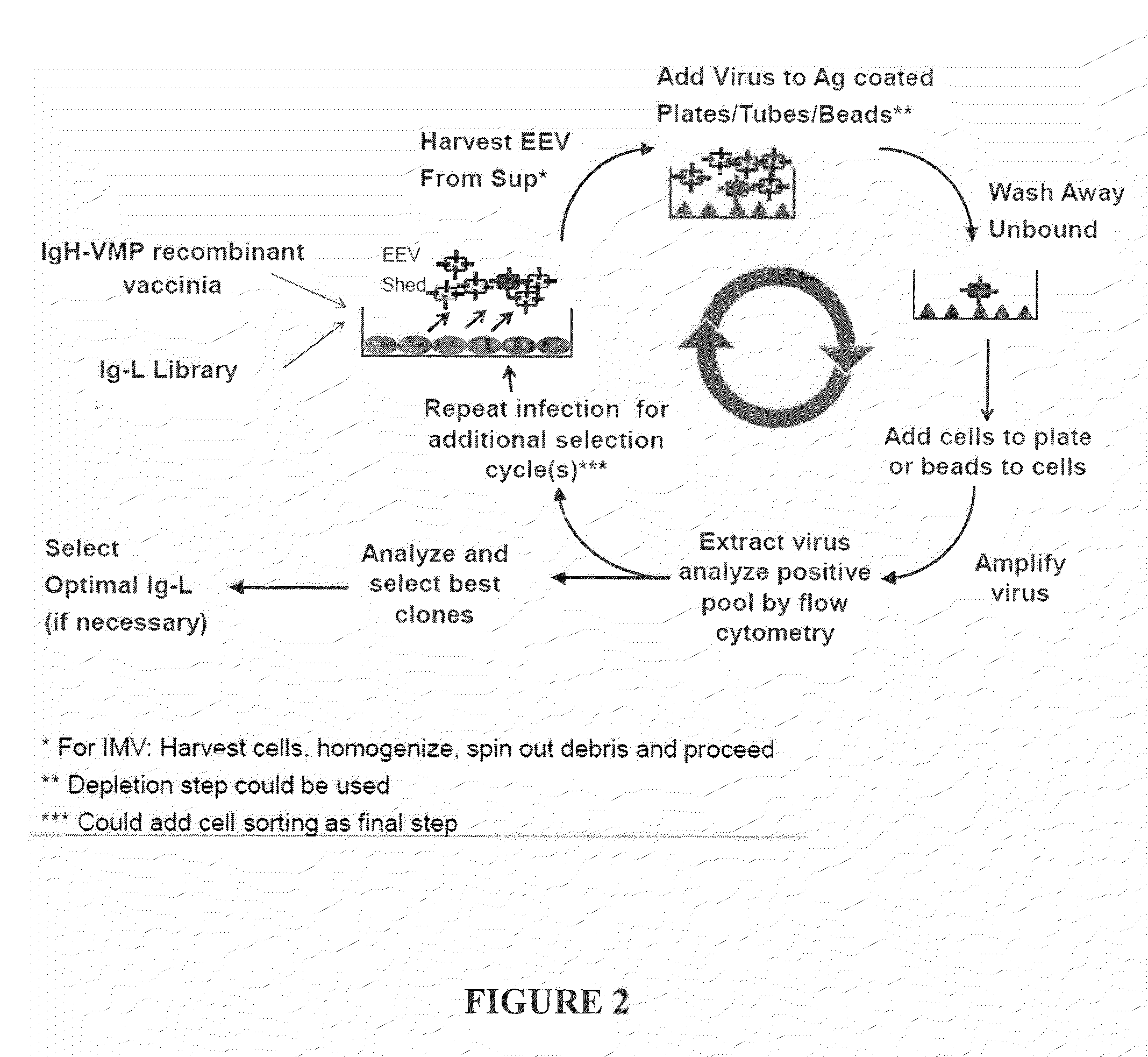
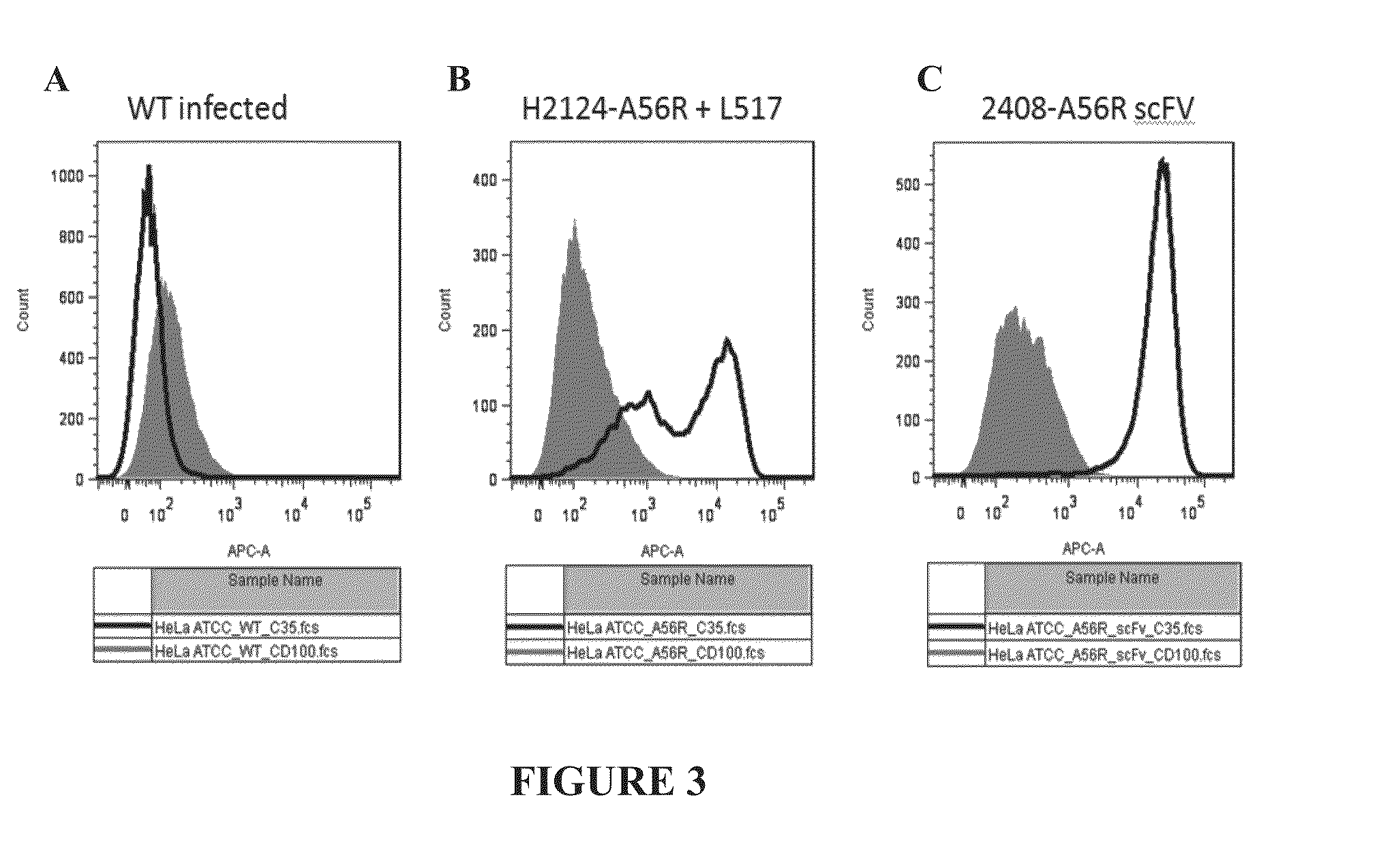
Fusion Proteins to Facilitate Selection of Cells Infected with Specific Immunoglobulin Gene Recombinant Vaccinia Virus
ActiveUS20130288927A1Library screeningVirus peptidesImmunoglobulin heavy chainRecombinant vaccinia virus
The present invention relates to a high efficiency method of expressing immunoglobulin molecules in eukaryotic cells. The invention is further drawn to a method of producing immunoglobulin heavy and light chain libraries, particularly using the trimolecular recombination method, for expression in eukaryotic cells. The invention further provides methods of selecting and screening for antigen-specific immunoglobulin molecules, and antigen-specific fragments thereof. The invention also provides kits for producing, screening and selecting antigen-specific immunoglobulin molecules. Finally, the invention provides immunoglobulin molecules, and antigen-specific fragments thereof, produced by the methods provided herein.
Owner:VACCINEX
Nucleic acid molecules, polypeptides, antibodies and compositions containing same useful for treating and detecting influenza virus infection
Polynucleotides and polypeptides which participate in influenza virus infection of cells and nucleic acid molecules, which include a polynucleotide sequence capable of specifically binding the polypeptides of the present invention. Also provided are methods of using such nucleic acid molecules, polynucleotides and antibodies directed thereagainst for diagnosing, treating and preventing influenza virus infection.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Use of polymeric nanoparticles for vaccine delivery
InactiveUS20080044484A1Enhance antigen presentationImprove efficiencyBiocidePowder deliveryCancer cellT lymphocyte
The invention relates generally to the treatment and prevention of human cancer and viral diseases. More specifically, this invention relates to development of a new generation of vaccines that rely on eliciting cellular immune responses, specifically induction of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL), against cancer cells and virus-infected cells via administration of a polymeric nanoparticle containing a vaccine comprising a fusion peptide or a modified peptide. Such a fusion peptide is composed of an insertion signal sequence and a peptide derived from a tumor antigen or a viral antigen, which improves antigen presentation and induces CTL with higher efficiency against cancer cells and virus-infected cells. An exemplary peptide utilized in the invention is Mart-1:27-35 peptide.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Cytotoxic t-cell epitope peptides that specifically attack epstein-barr virus-infected cells and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090305324A1Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsEpitopeNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory Receptors
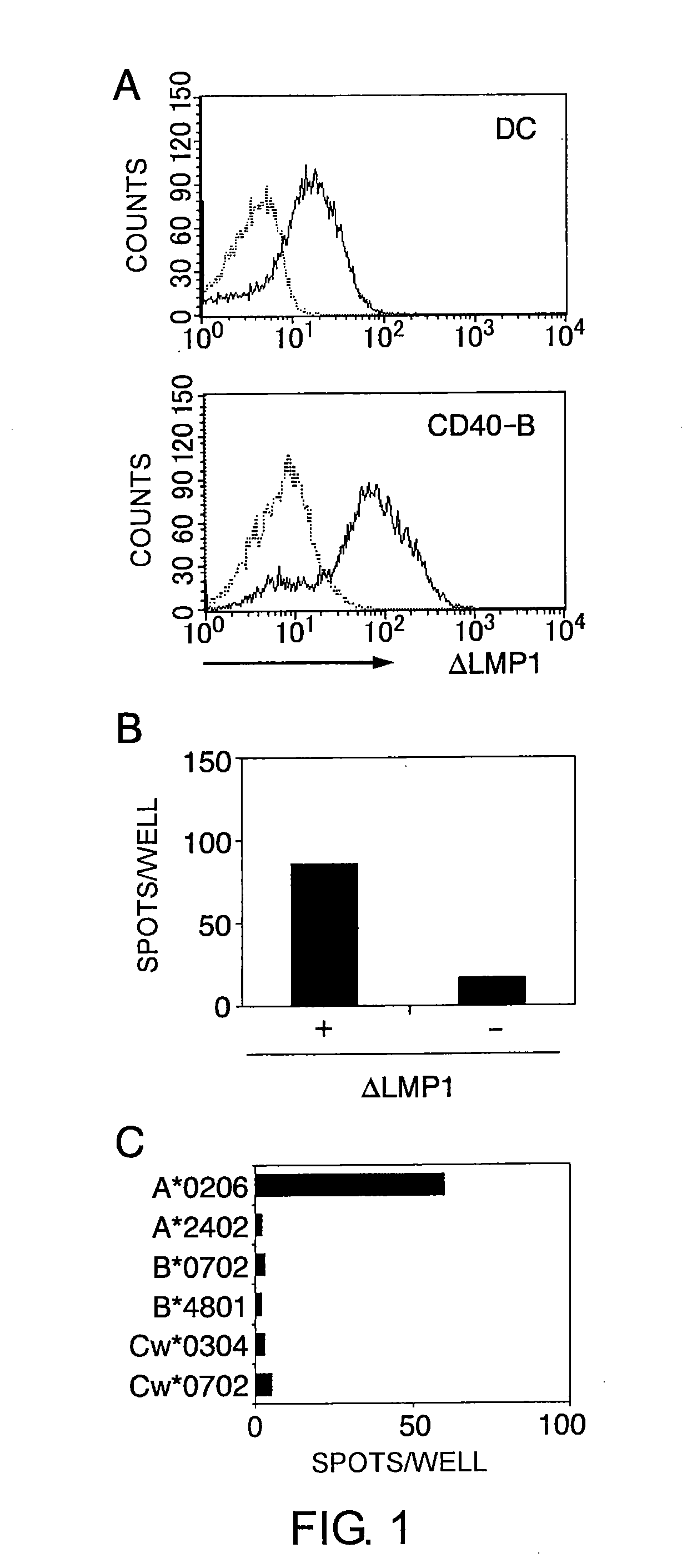
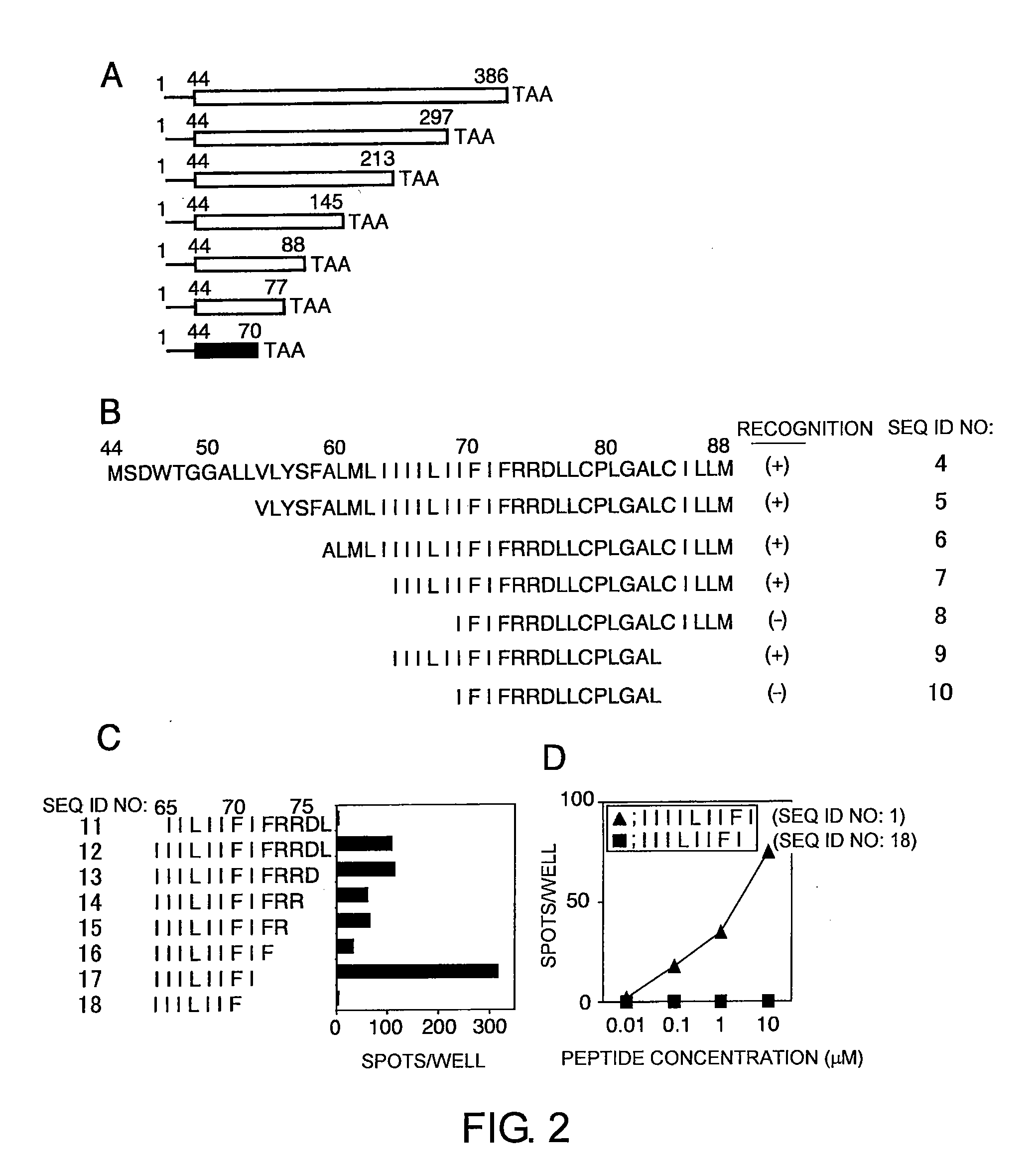
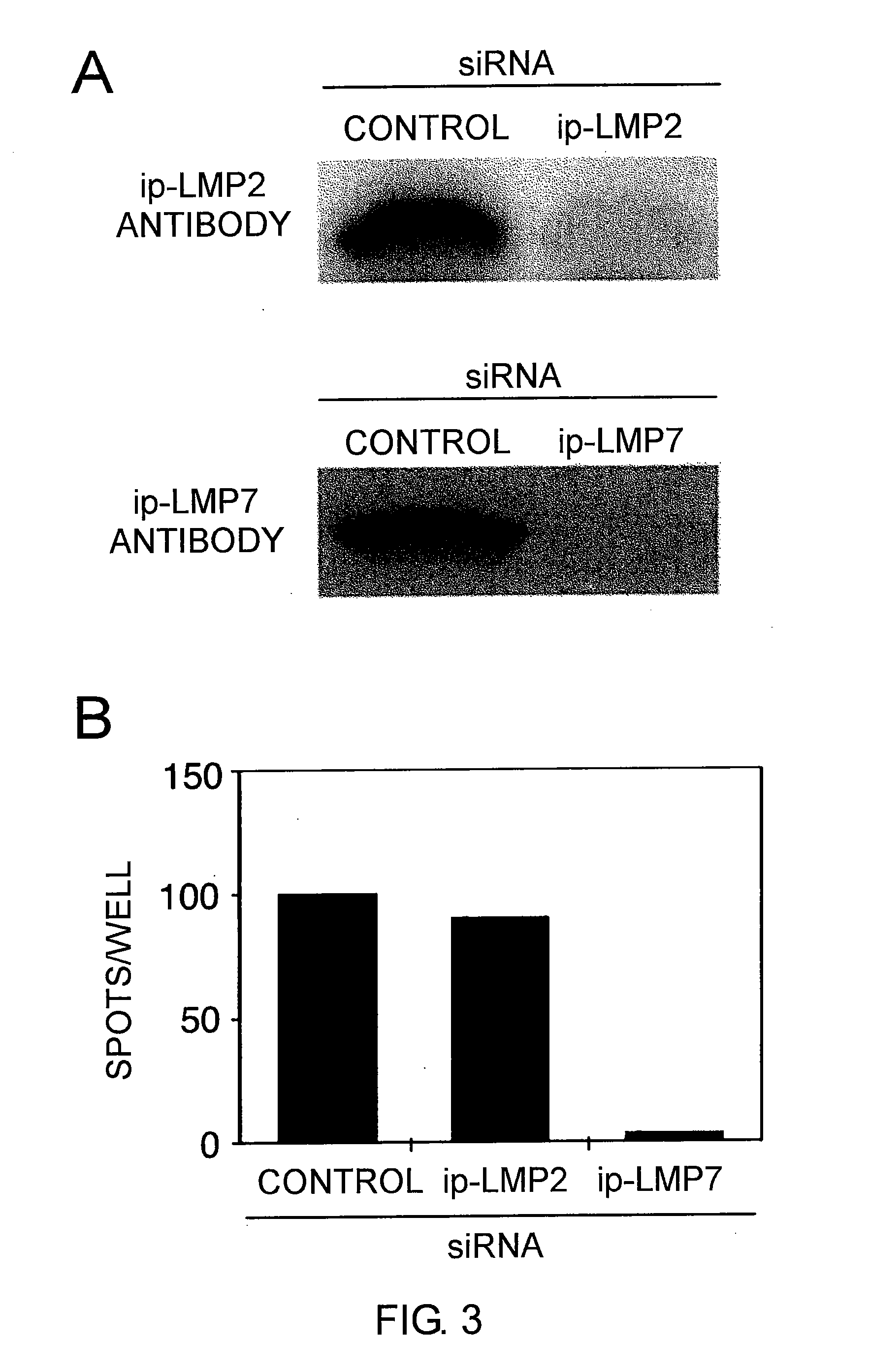
The present inventors introduced mRNAs for the Epstein-Barr virus proteins LMP1 and EBNA1 into antigen-presenting cells, and as a result, demonstrated that the cells induced Epstein-Barr virus-specific cytotoxic T cells. The present inventors also demonstrated that the cytotoxic T cells recognized epitope peptides presented via HLA-A*0206, HLA-Cw*0303, or HLA-Cw*0304, inhibited the outgrowth of Epstein-Barr virus-infected B cells, and lysed Epstein-Barr virus-infected NK lymphomas and NK cells.
Owner:AICHI PREFECTURE +1
Method for the recovery and purification of poxviruses from infected cells
InactiveUS7056723B2Easy to controlImprove scalabilityViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsInfected cellVaccinia
Owner:BAVARIAN NORDIC AS
Method for the generation of antigen-specific lymphocytes
InactiveUS7939059B2Function increaseEnhancing function of T cellBiocideVirusesDiseaseAutoimmune disease
The invention provides systems and methods for the generation of lymphocytes having a unique antigen specificity. In a preferred embodiment, the invention provides methods of virally infecting cells from bone marrow with one or more viral vectors that encode antigen-specific antibodies for the production of, for example B cells and T cells. In some embodiments, the viral vectors include an IRES or 2A element to promote separation of, for example, the α subunit and β subunit of a T cell receptor (TCR) or heavy and light chains of a B-cell antibody. The resulting lymphocytes, express the particular antibody that was introduced in the case of B cells and TCR in the case of T cells. The lymphocytes generated can be used for a variety of therapeutic purposes including the treatment of various cancers and the generation of a desired immune response to viruses and other pathogens. The resulting cells develop normally and respond to antigen both in vitro and in vivo. We also show that it is possible to modify the function of lymphocytes by using stem cells from different genetic backgrounds. Thus our system constitutes a powerful tool to generate desired lymphocyte populations both for research and therapy. Future applications of this technology may include treatments for infectious diseases, such as HIV / AIDS, cancer therapy, allergy, and autoimmune disease.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Enhancing Class I Antigen Presentation With Synthetic Sequences
InactiveUS20080206270A1Enhance antigen presentationInduces antitumor and antiviral CTLTumor rejection antigen precursorsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsCancer cellT lymphocyte
The invention relates generally to the treatment and prevention of human cancer and viral diseases. More specifically, this invention relates to development of a new generation of vaccines that rely on eliciting cellular immune responses, specifically induction of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL), against cancer cells and virus-infected cells via administration of a vaccine comprising a fusion peptide or a modified peptide. Such a fusion peptide is composed of an insertion signal sequence and a peptide derived from a tumor antigen or a viral antigen, which improves antigen presentation and induces CTL with higher efficiency against cancer cells and virus-infected cells. An exemplary antigen utilized in the invention is HER2 / neu. The peptides peptide vaccines of the invention are derived from the antigens PRAME, OFA / iLRP, STEAP and SURVIVIN.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
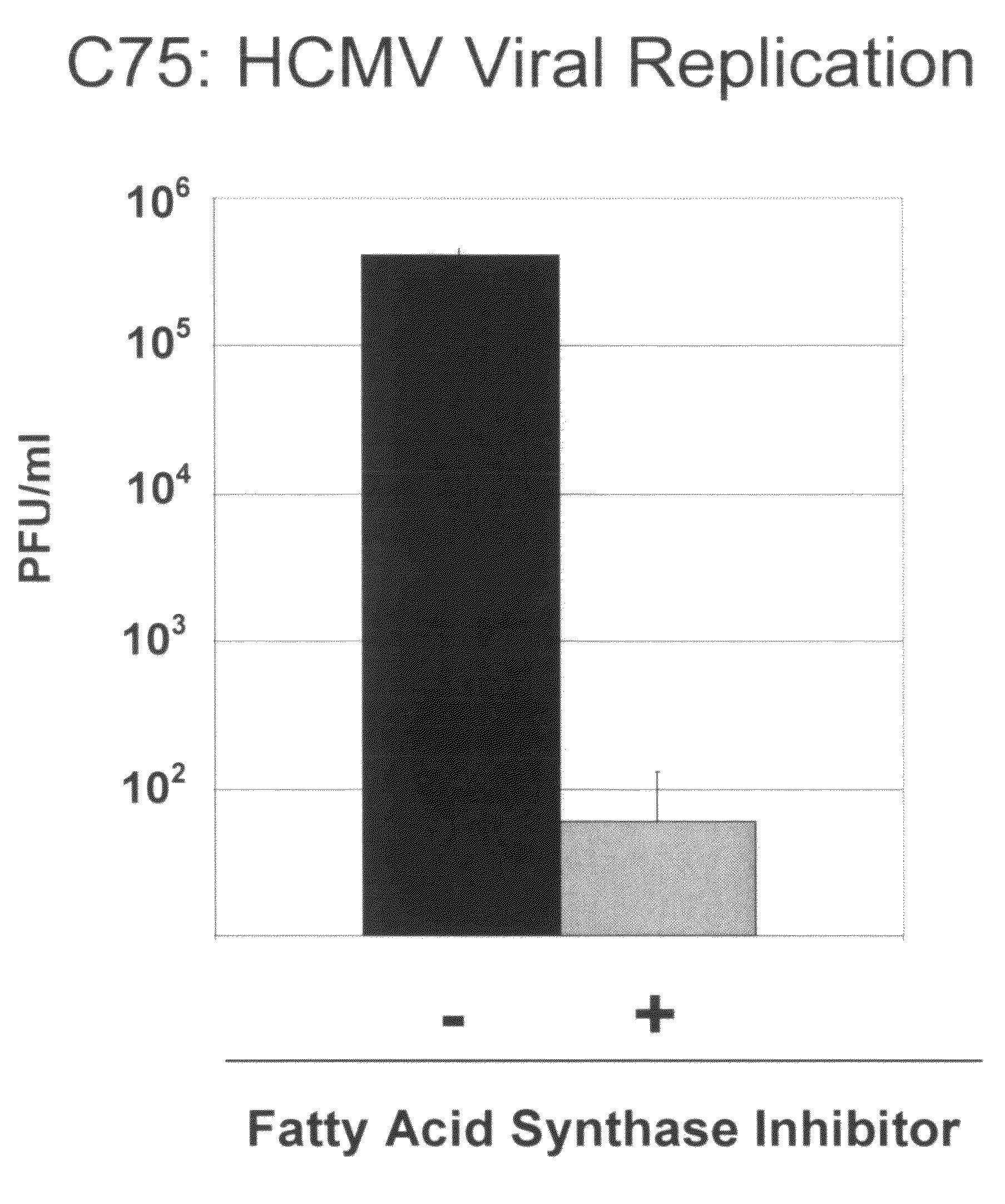
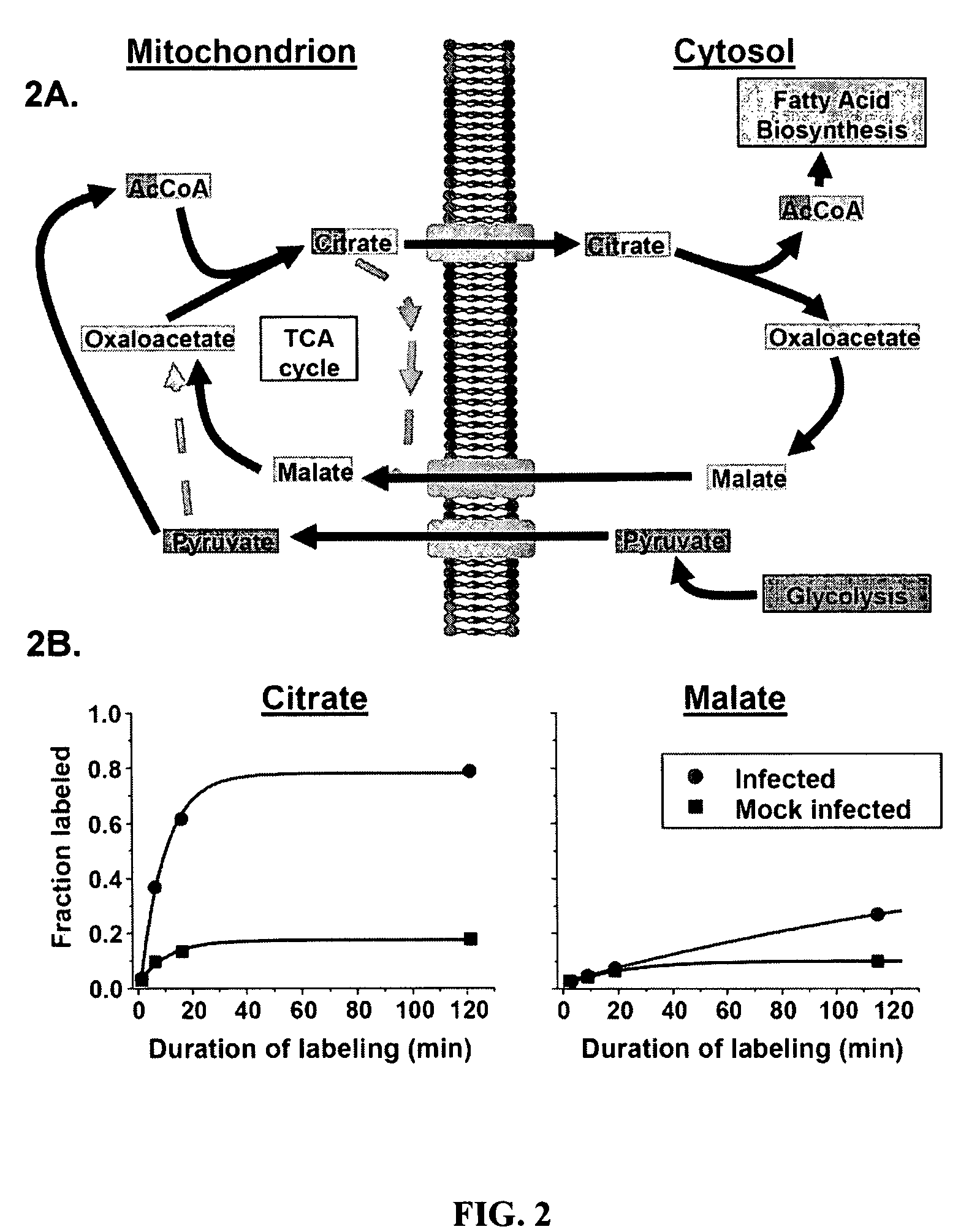
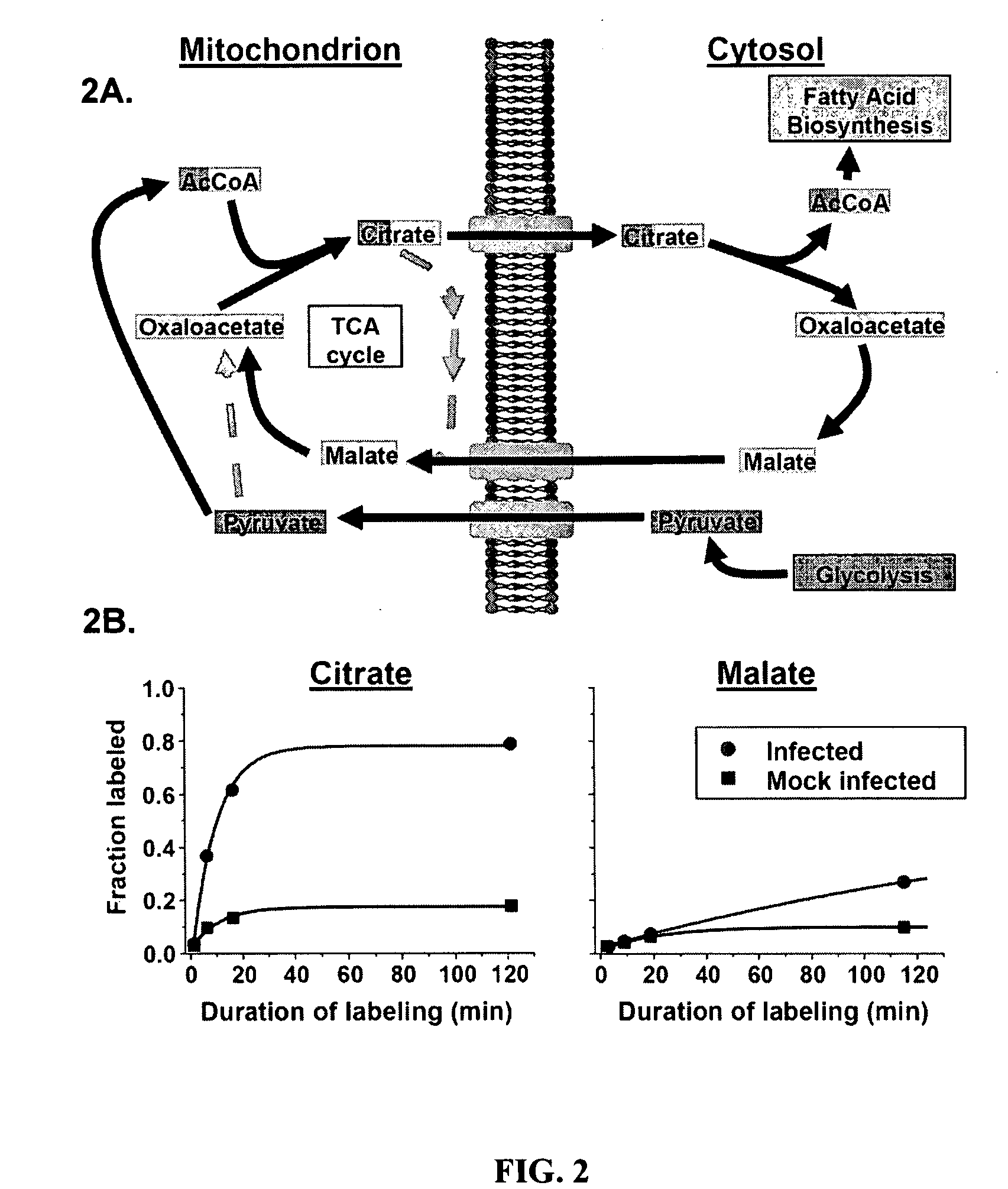
Treatment of viral infections by modulation of host cell metabolic pathways
InactiveUS8158677B2Reduce severityImprove survivalBiocideDigestive systemCritical control pointMetabolite
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Treatment of viral infections by modulation of host cell metabolic pathways
InactiveUS20090239830A1Reduction and amelioration of severityShorten the construction periodBiocideDigestive systemCritical control pointAntiviral drug
Alterations of certain metabolite concentrations and fluxes that occur in response to viral infection are described. Host cell enzymes in the involved metabolic pathways are selected as targets for intervention; i.e., to restore metabolic flux to disadvantage viral replication, or to further derange metabolic flux resulting in “suicide” of viral-infected cells (but not uninfected cells) in order to limit viral propagation. While any of the enzymes in the relevant metabolic pathway can be selected, pivotal enzymes at key control points in these metabolic pathways are preferred as candidate antiviral drug targets. Inhibitors of these enzymes are used to reverse, or redirect, the effects of the viral infection. Drug candidates are tested for antiviral activity using screening assays in vitro and host cells, as well as in animal models. Animal models are then used to test efficacy of candidate compounds in preventing and treating viral infections. The antiviral activity of enzyme inhibitors is demonstrated.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
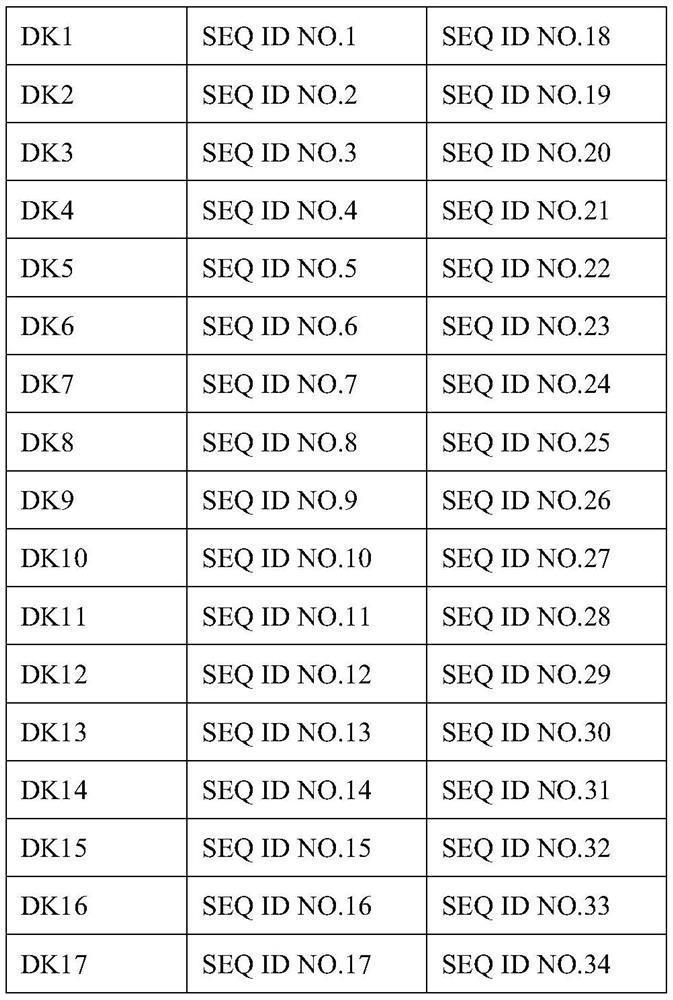
Monoclonal antibody for resisting antigen of RBD structural domain of novel coronavirus
ActiveCN111978395AStrong ability to resist novel coronavirusGood effectImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsAntigenHeavy chain
The invention discloses a monoclonal antibody for resisting an antigen of a RBD structural domain of novel coronavirus and belongs to the field of biological products. According to the monoclonal antibody disclosed by the invention, an amino acid sequence of a heavy-chain variable region of the monoclonal antibody is represented by any of SEQ ID No. 1-17, and an amino acid sequence of a light-chain variable region of the monoclonal antibody is represented by any of SEQ ID No. 18-34. The monoclonal antibody disclosed by the invention has good ability for preventing RBD of the novel coronavirusfrom bonding with an acceptor of the RBD; and verified by experiments, the coronavirus can be effectively prevented from infecting cells.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
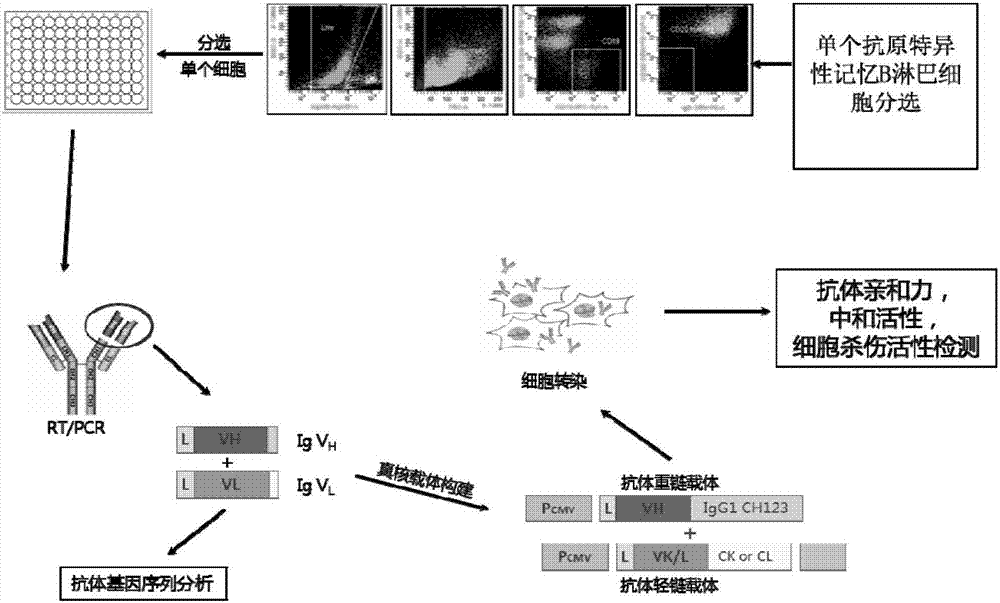
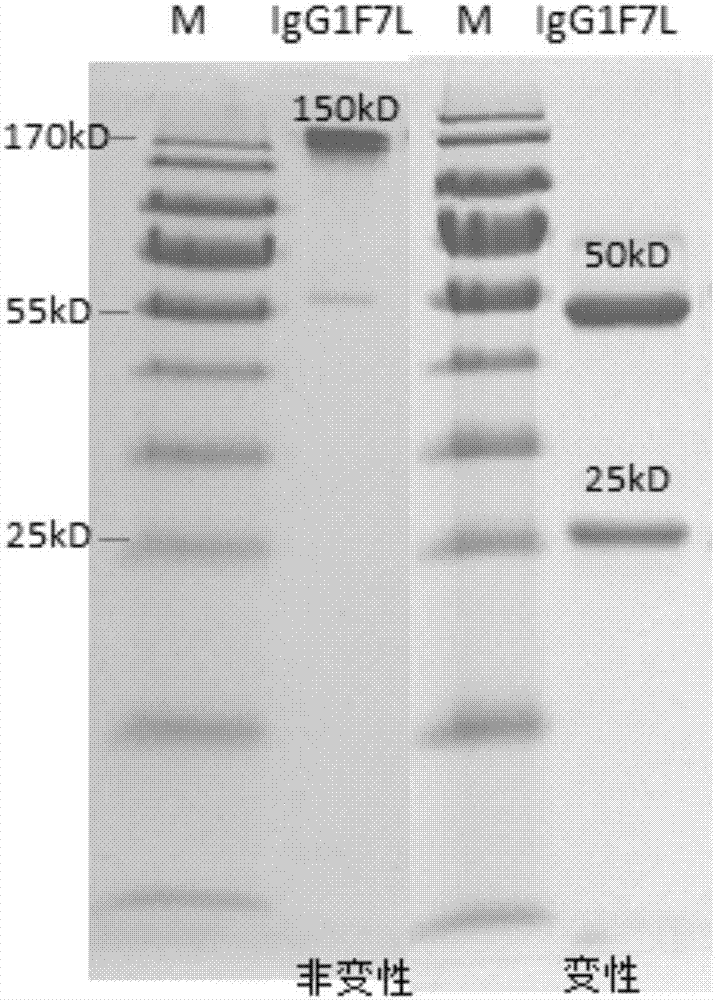
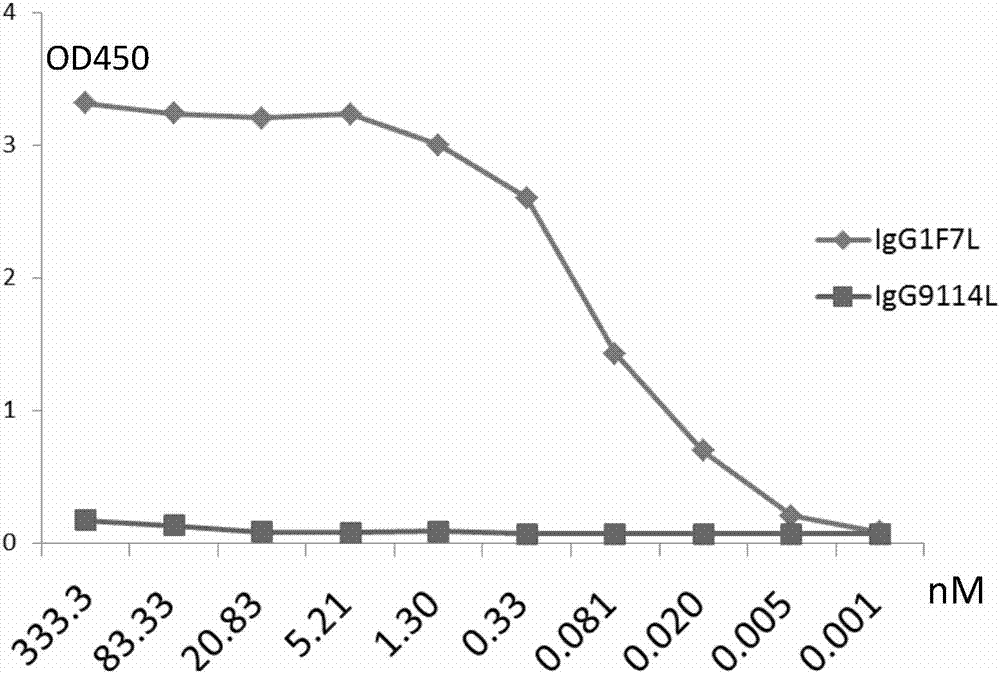
Human anti-H7N9 avian influenza virus neutralizing antibody 1F7L and its use
InactiveCN107226861AEffective neutralizationAvoid infectionImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory ReceptorsNeutralizing antibody
The invention discloses a human anti-H7N9 avian influenza virus neutralizing antibody 1F7L screened by a single cell sorting technology. The amino acid sequences in the light and heavy chain variable regions are shown in the formulas of SEQ ID No. 2 and SEQ ID No. 5. The antibody has the ability to neutralize the H7N9 influenza viruses in vitro and mediates the killing (ADCC) of the H7N9 influenza virus-infected cells with effector cells mainly comprising NK cells. The antibody can be used as a treatment drug for highly pathogenic avian influenza infection and can also be used for the development of H7N9 influenza virus antigen detection reagents.
Owner:THE THIRD PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF SHENZHEN
Method to block the infection by flaviviruses, molecules and uses
ActiveUS20110212105A1Modulate the DV infectionReducing and increasing interactionSsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsMolecular biologyCarrier protein
The present invention is related to a method for blocking the infection of cells by dengue virus, based on interfering the direct interaction of the viral envelope protein with a cellular receptor or its indirect interaction with said cellular receptor through a carrier protein, as well as related uses; wherein said cellular receptor is the alpha-2 macroglobulin receptor, also known as the low density receptor-related protein or as CD91, and said carrier protein is human alpha-2 macroglobulin.
Owner:CENT DE ING GENETICA & BIOTECNOLOGIA
Fish interferon gene and use thereof
InactiveCN101054584AGood effectReduce investmentGenetic material ingredientsAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyAnti virus
The present invention discloses a fish interferon gene and its uses. A gene represented by SEQ ID NO:1, a protein represented by SEQ ID NO:2. The gene can express obviously in virus-infected cell and stably transplanted interferon gene cell strain. The gene expression product has anti-virus infection function in cultured cell and fish body. The crucian interferon gene can be utilized and developed in prokaryotic, eukaryotic expression system (fish cell expression system and yeast cell expression system). The product can also be used as anti-virus biological agent and pharmaceutical feedstuff additive which is convenient for use and has obvious and take effect quickly.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
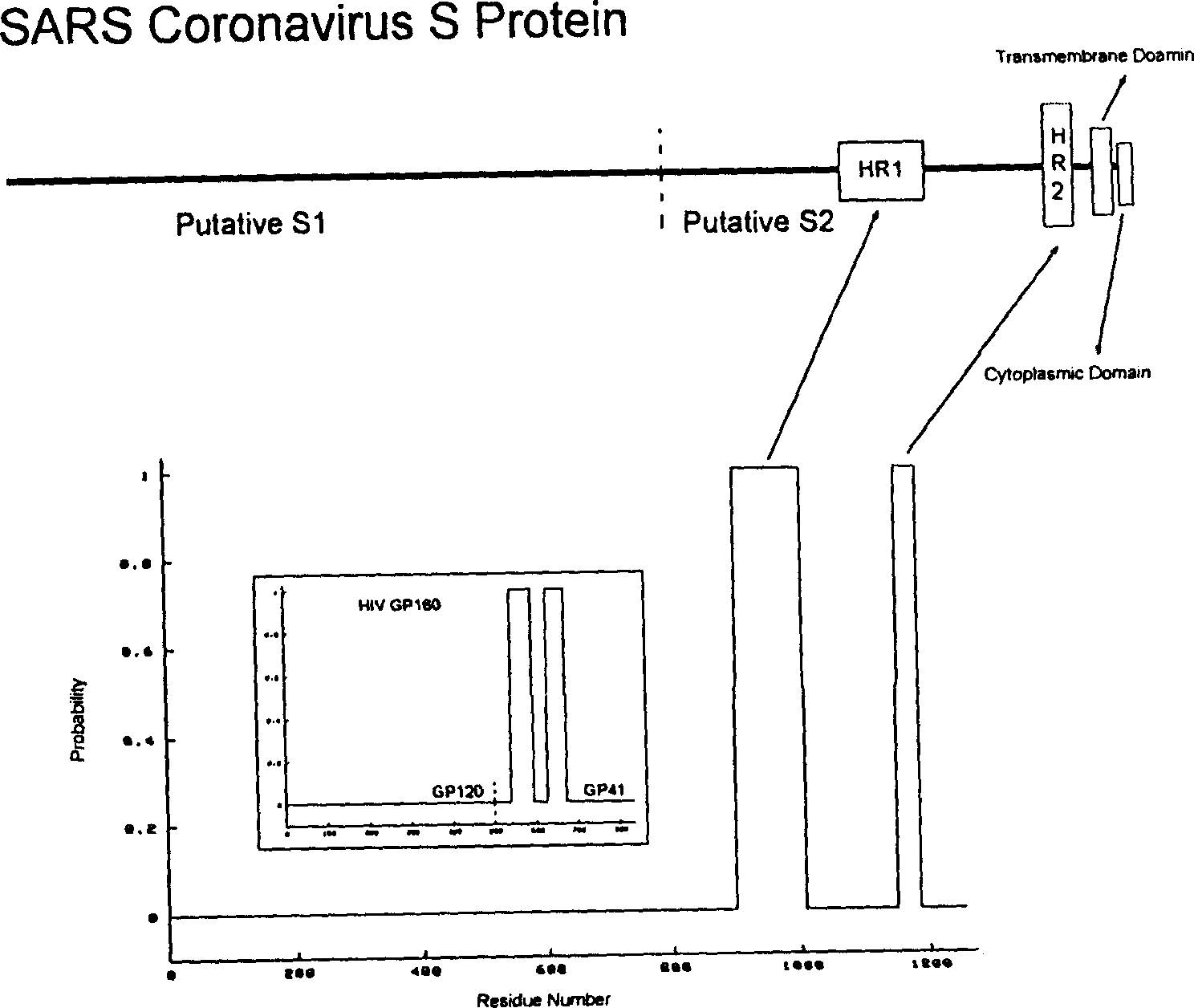
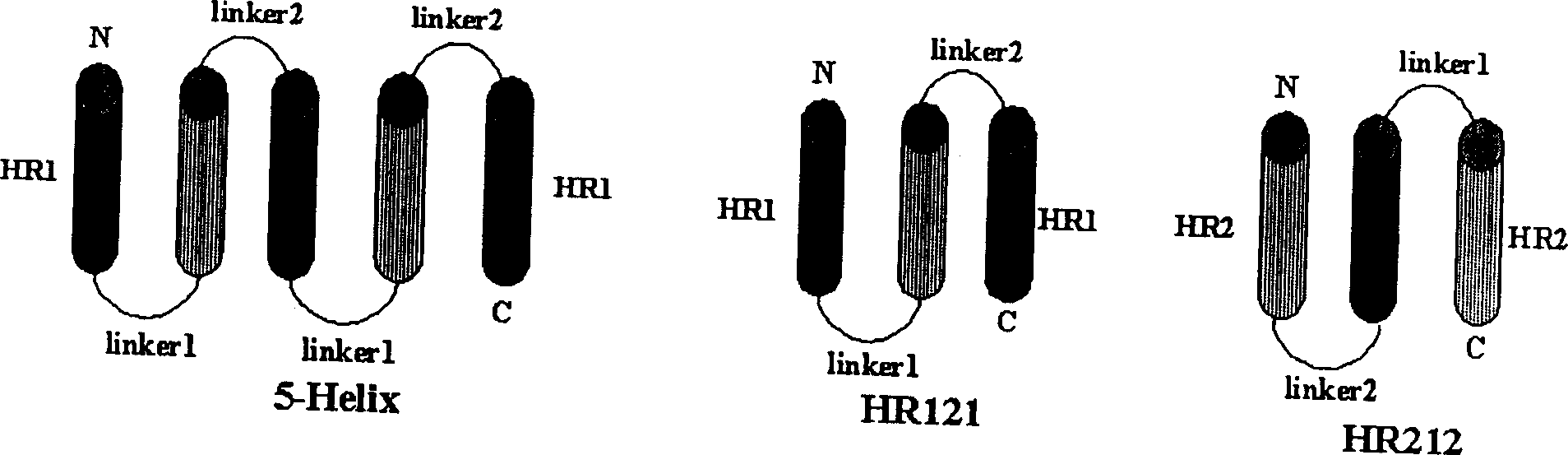
Polypeptide medicine for inhibiting SARS coronavirus, and derivatives and use thereof
The invention provides a method for blocking SARS coronavirus to infect cell with polypeptide or its derivative. The cistine series of polypeptide comes from two heptad repeat districts HR1 and HR2 of SARS coronavirus spike(S) protein. The invention also provides a method for producing the functional similarity with HR1 and HR2. the invention provides a method for producing HR polypeptide and its derivant with coalescence expression method. All the peptides have rejection capability to SARS.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Removing Cells from an Organism
InactiveUS20130197296A1Enhance initial association and complex formationImproved kineticsElectrotherapyEnergy modified materialsTreatment choicesOrganism
A minimally invasive method to eliminate circulating agents from an organism to prevent and treat diseases is disclosed. The method utilizes immunomagnetic methods to concentrate and localize disease-associated agents in a small region of the body. Subsequently, the complexes are removed from the body. Removal of disease-causing or disease-promoting agents (circulating tumor cells, bacteria, viruses and virus-infected cells, certain immune cells) would add a significant new option for intervention of disease progression and supplement other therapeutic options.
Owner:OTT KARL HEINZ +1
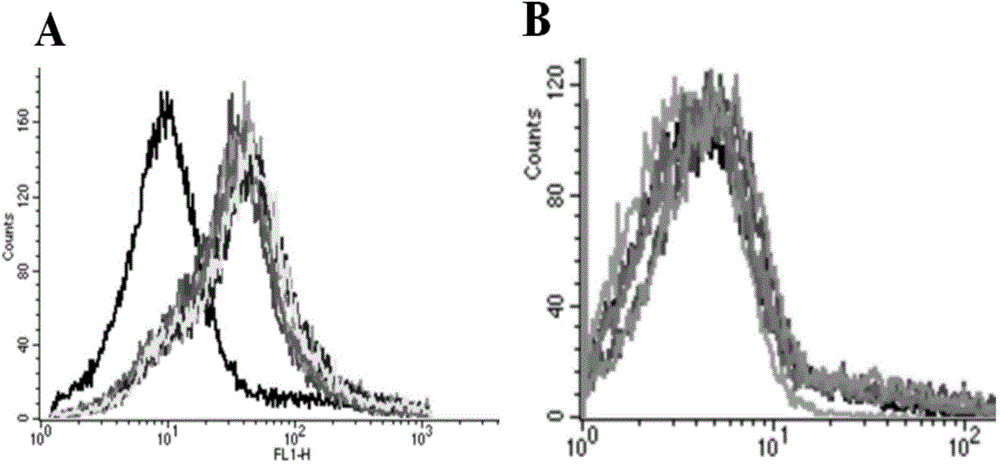
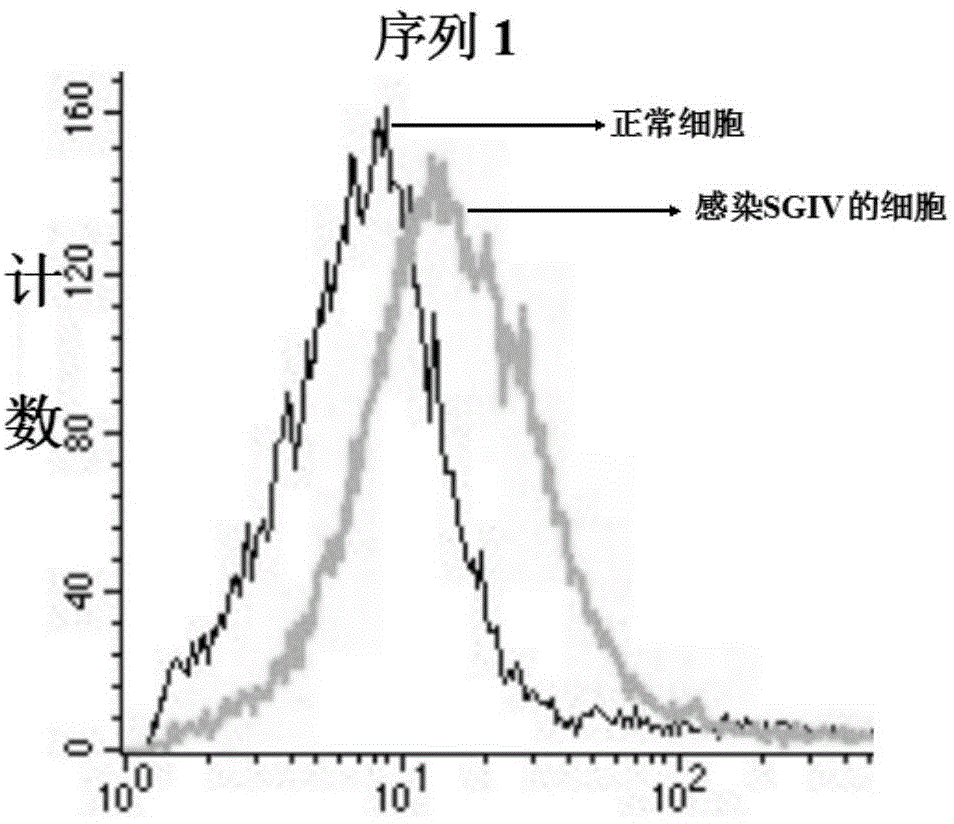
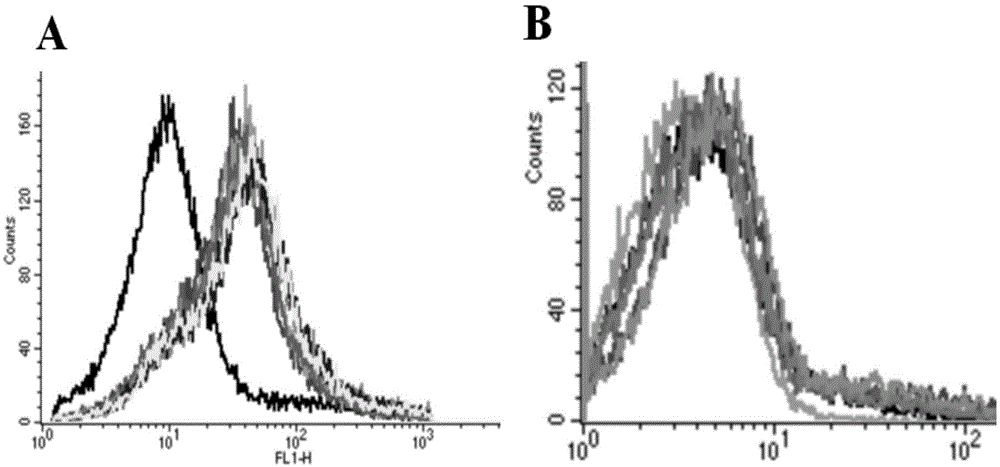
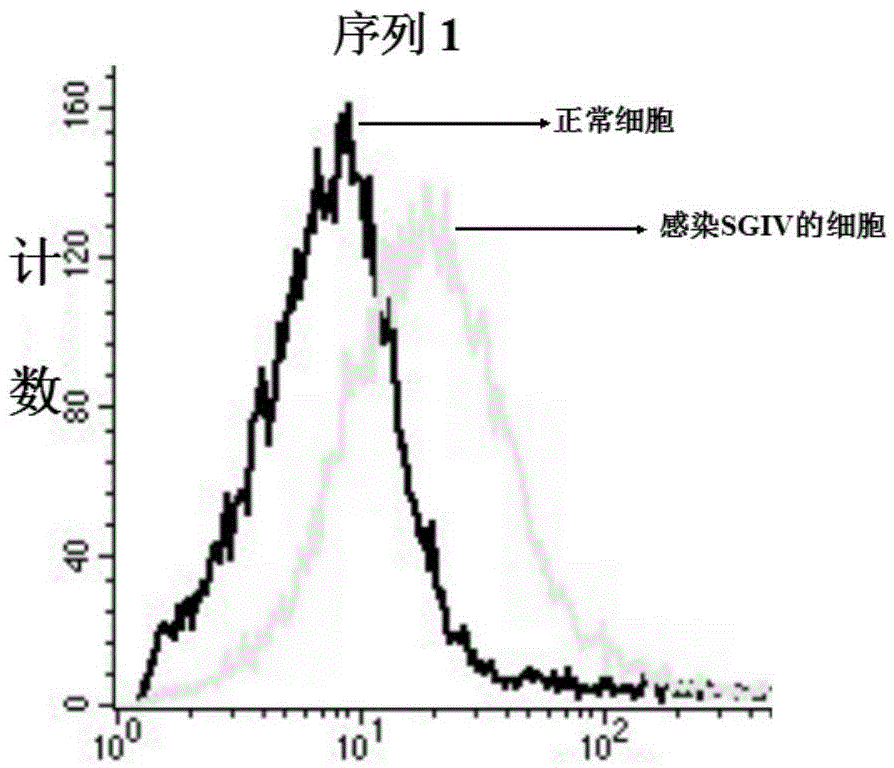
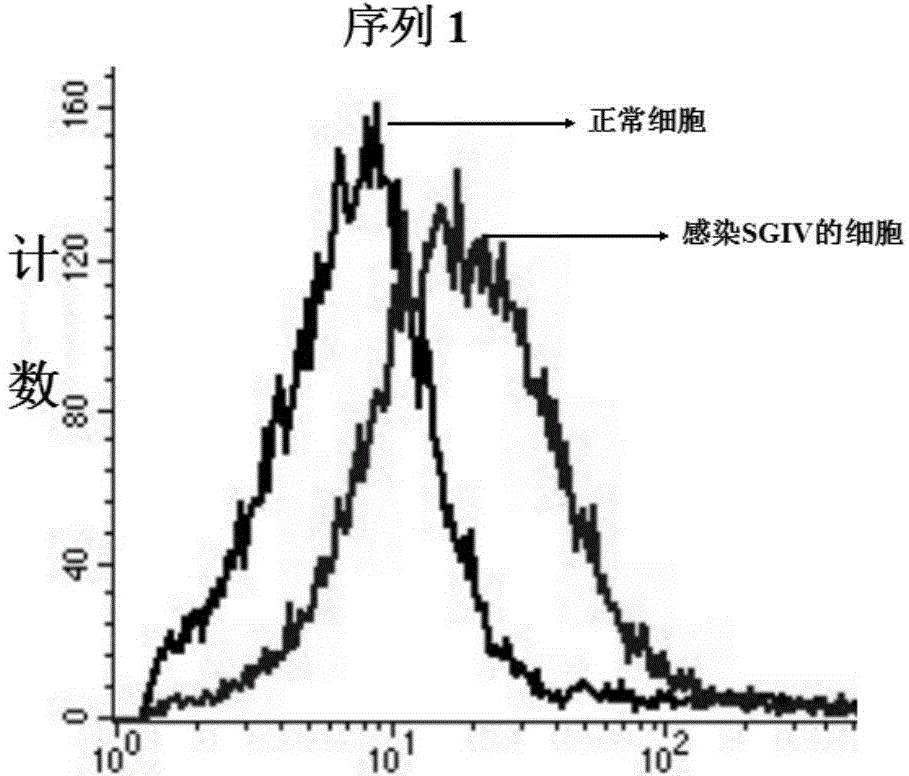
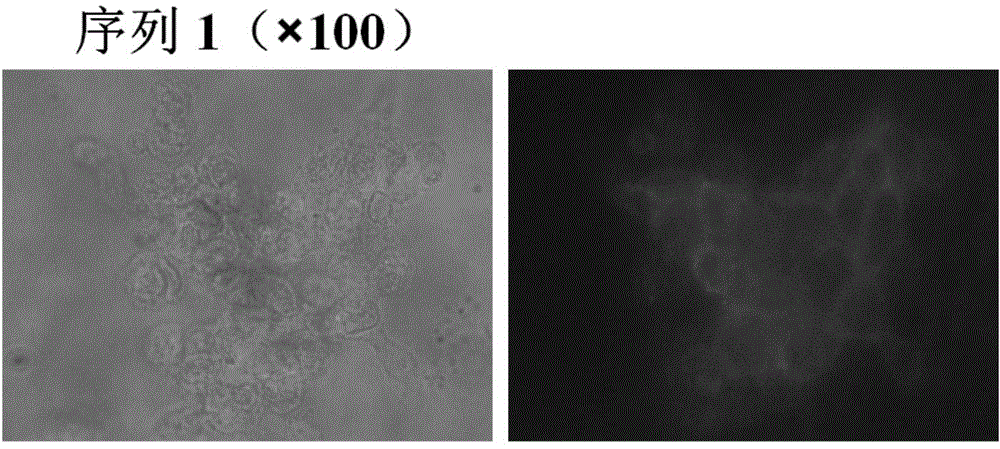
DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) aptamer for detecting grouper iridovirus infection, as well as screening method and application of DNA aptamer
ActiveCN104789696AHigh affinityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysis3-deoxyriboseDNA Aptamers
The invention discloses a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) aptamer for detecting grouper iridovirus infection, as well as a screening method and an application of the DNA aptamer. Two inverse screening steps are introduced in each screening process; first, a single-stranded DNA library of the former screening process is bound with normal cells to remove nonspecific ssDNA (single-stranded DNA) bound with the normal cells of a grouper; then, supernatant is bound with grouper iridovirus infected cells for screening; and ssDNA separated from the grouper iridovirus infected cells is bound with the normal cells for separation to obtain the supernatant. A PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification library prepares the single-stranded DNA library. The above screening flow is repeated; compared with the number of the normal cells in the first screening process, the number of the normal cells in the screening process is increased by 2-6 times; compared with binding time of the library and the cells in the first screening process, the binding time of the library and the cells in the subsequent screening process is increased to 1h from 0.5h; and the binding time of the library and the virus infected cells is shortened to 0.5h from 1h to improve the screening efficiency of each process.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) aptamer for detecting grouper iridovirus infection, as well as screening method and application of DNA aptamer
ActiveCN104789569AHigh affinityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processes3-deoxyriboseDNA Aptamers
The invention discloses a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) aptamer for detecting grouper iridovirus infection, as well as a screening method and an application of the DNA aptamer. Two inverse screening steps are introduced in each screening process; first, a single-stranded DNA library of the former screening process is bound with normal cells to remove nonspecific ssDNA (single-stranded DNA) bound with the normal cells of a grouper; then, supernatant is bound with grouper iridovirus infected cells for screening; and ssDNA separated from the grouper iridovirus infected cells is bound with the normal cells for separation to obtain the supernatant. A PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification library prepares the single-stranded DNA library. The above screening flow is repeated; compared with the number of the normal cells in the first screening process, the number of the normal cells in the screening process is increased by 2-6 times; compared with binding time of the library and the cells in the first screening process, the binding time of the library and the cells in the subsequent screening process is increased to 1h from 0.5h; and the binding time of the library and the virus infected cells is shortened to 0.5h from 1h to improve the screening efficiency of each process.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) aptamer for detecting grouper iridovirus infection, as well as screening method and application of DNA aptamer
ActiveCN104789568AHigh affinityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processes3-deoxyriboseDNA Aptamers
The invention discloses a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) aptamer for detecting grouper iridovirus infection, as well as a screening method and an application of the DNA aptamer. Two inverse screening steps are introduced in each screening process; first, a single-stranded DNA library of the former screening process is bound with normal cells to remove nonspecific ssDNA (single-stranded DNA) bound with the normal cells of a grouper; then, supernatant is bound with grouper iridovirus infected cells for screening; and ssDNA separated from the grouper iridovirus infected cells is bound with the normal cells for separation to obtain the supernatant. A PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification library prepares the single-stranded DNA library. The above screening flow is repeated; compared with the number of the normal cells in the first screening process, the number of the normal cells in the screening process is increased by 2-6 times; compared with binding time of the library and the cells in the first screening process, the binding time of the library and the cells in the subsequent screening process is increased to 1h from 0.5h; and the binding time of the library and the virus infected cells is shortened to 0.5h from 1h to improve the screening efficiency of each process.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Anti-TSG101 antibodies and their uses for treatment of viral infections
InactiveUS20040223972A1Sufficient amountMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against virusesInfected cellViral infection
The present invention provides methods of using antibodies that bind a TSG101 protein to inhibit or reduce viral production. The invention also provides methods of using the TSG101 antibodies for the treatment of viral infections, including HIV infection. The invention further provides methods of detecting viral infected cells using TSG101 antibodies.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
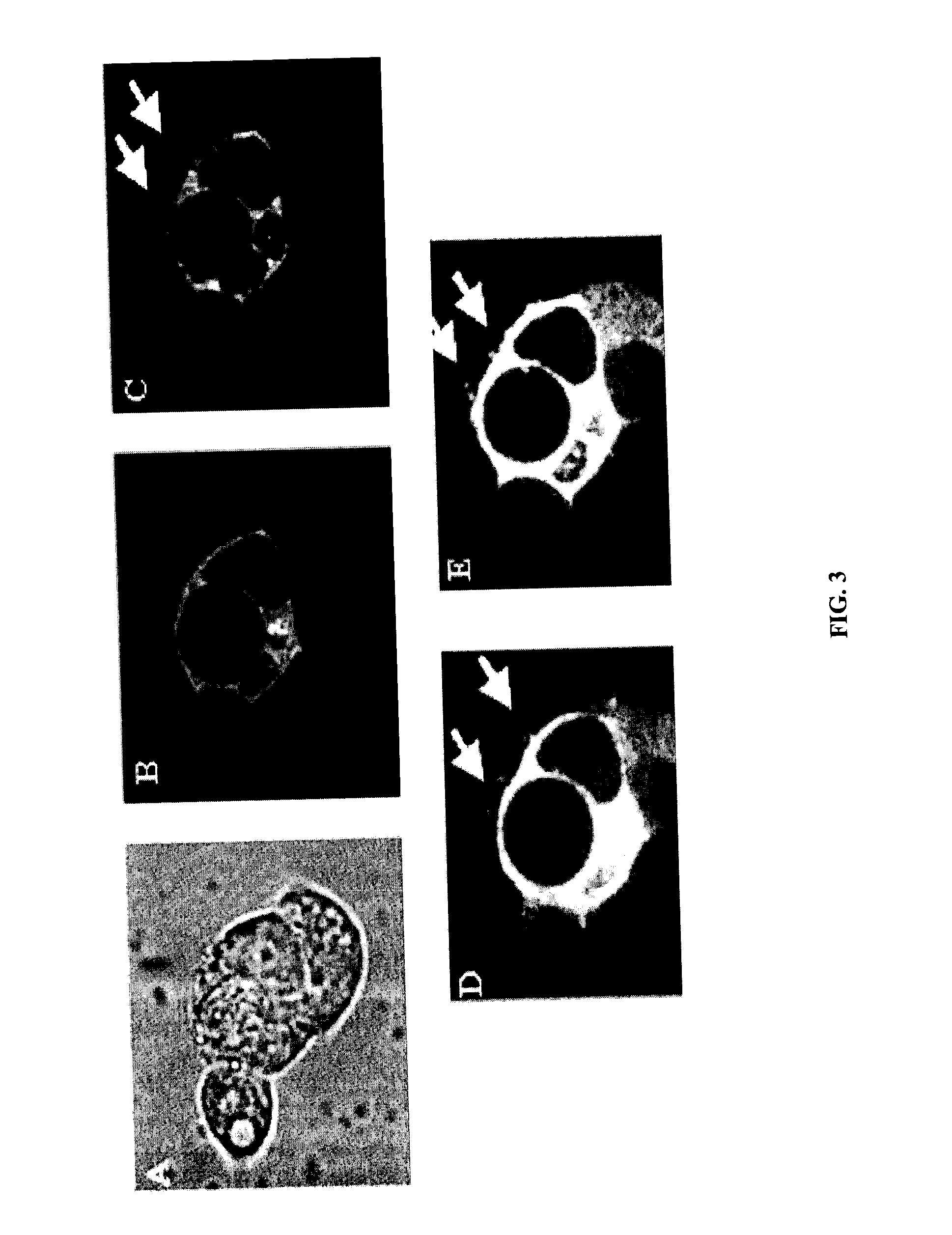
Method for separating, culturing and identifying primary hepatic cells of livestock and fowl
InactiveCN102643778AIncreased dispersionHigh purityMicrobiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsBiotechnologyDisease
The invention relates to a method for separating, culturing and identifying primary hepatic cells of livestock and fowl, which integrates a chelation process and an in-situ two-step perfusion process. Ca<2+> and Mg<2+> in hepatic tissues of livestock and fowl are previously removed so that the hepatic tissues maximally release the primary hepatic cells; and the formula of additives of the culture fluid is adjusted to perfect the serum-free culture system and identify the glycogen of the obtained primary hepatic cells. The invention can effectively enhance the quantity, motility and purity of the separated primary hepatic cells of livestock and fowl, and is applicable to various animals; and the obtained primary hepatic cells have the advantages of fewer traumas, high wall attaching tendency and high activity, can be widely used for physiological function adjustment, metabolic diseases, and pharmacological and toxicological mechanisms of hepatic cells of livestock and fowl, can establish a virus infected cell model, and can be used for research in the fields of physics and chemistry, toxicant factor influence and the like.
Owner:SHAOGUAN COLLEGE
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus diluent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105505887APromote growthGuaranteed normal growthSsRNA viruses positive-senseMicroorganism based processesCymbopogon distansPhosphate
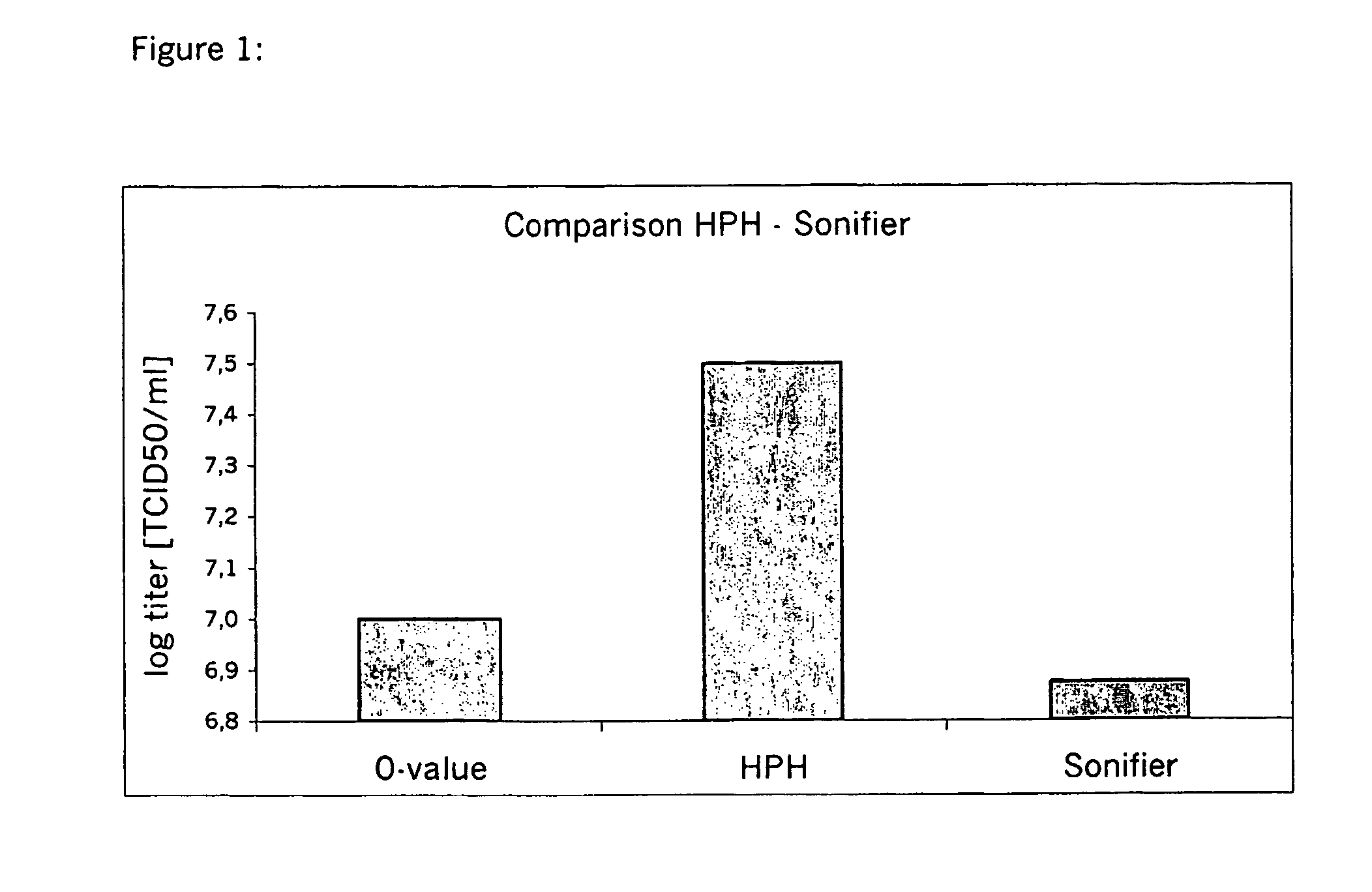
The invention provides a porcine and respiratory syndrome virus diluent and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of veterinary biological products. Every 1000 ml phosphate buffer of the diluent is prepared from, by weight, 10-30 g of amino acid combination, 10-30 g of compound traditional Chinese medicine polysaccharides and 10-30 g of liposome, wherein the amino acid combination comprises folic acid, riboflavin sodium phosphate, dexpanthenol and ascorbic acid, and the compound traditional Chinese medicine polysaccharides are extracted from pubescent angelica roots, Cymbopogon distans (Nees)A. Camus, chastetree fruit, butterflybush flowers, radix scrophulariae and red peony roots. The diluent has the advantages that after virus inoculation, cell growth can be promoted, and normal growth of cells can be maintained; viruses can infect the cells more easily after processing, and the probability that the viruses infect the cells is greatly increased; virus titer can be greatly increased in the same culture time, and virus content is increased by 10-100 times.
Owner:浙江美保龙生物技术有限公司
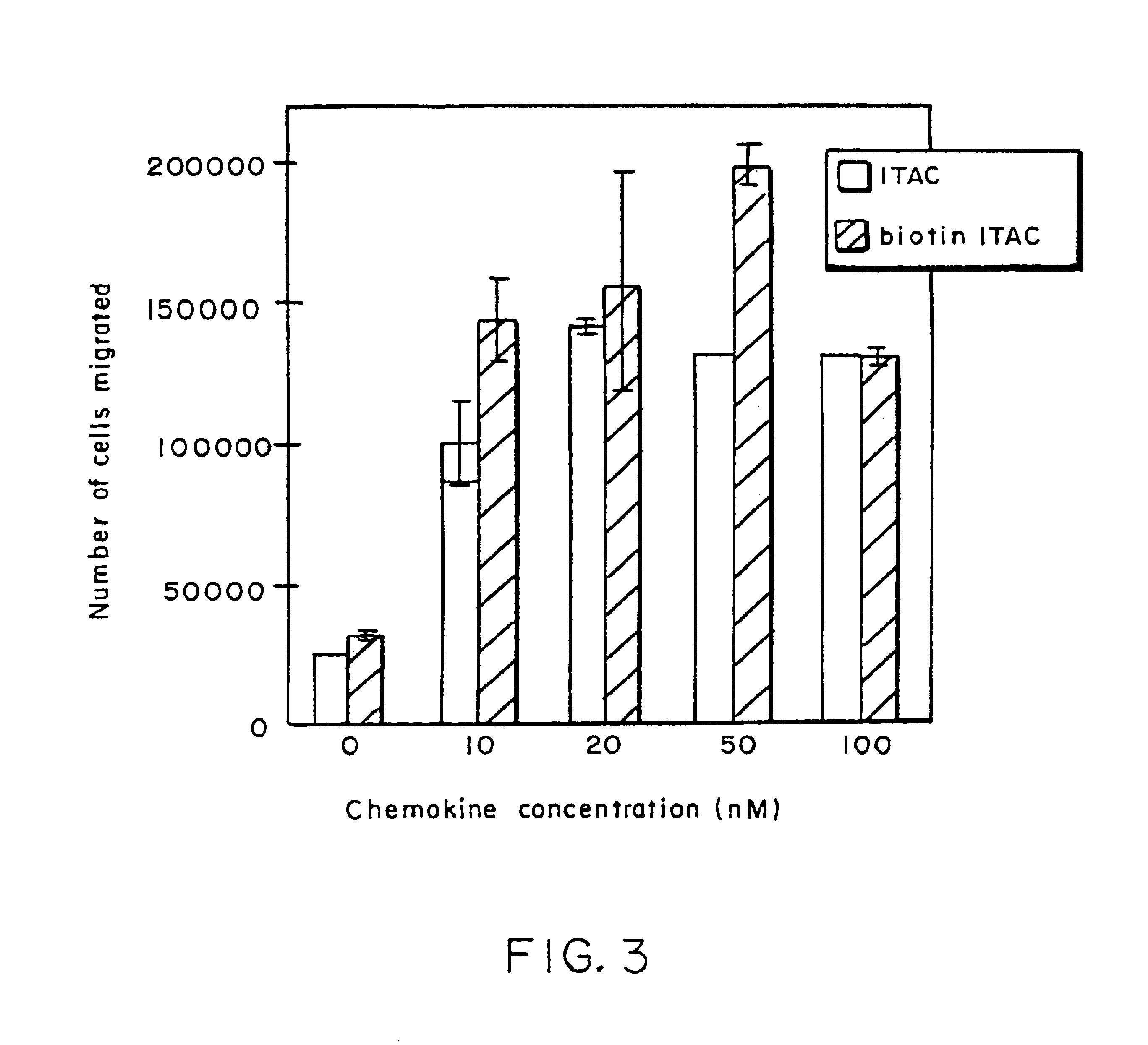
Biotinylated-chemokine antibody complexes
InactiveUS6869606B1Rapid down regulationConcentration adjustableBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsActive agentBiotin
Biotinylated pharmacologically active agents and complexes containing same are disclosed. In particular, biotinylated-chemokines are described. The complexes further include an anti-biotin antibody that selectively binds to biotin. The complex can be dissociated by contact with free biotin. The complexes are particularly useful for enhancing an immune response to tumor cells and virus-infected cells, in vivo or in vitro.
Owner:MILLENNIUM PHARMA INC
i(in Vitro) induction of antigen-specific T-cells using dendritic cell-tumor cell or dendritic cell-viral cell derived immunogens
Antigen-specific T-cells prepared by culturing T-cells in formulations comprising combinations of DCs and either tumor cells or virally infected cells are disclosed. These formulations generally comprise hybridoma of at least one dendritic cell fused to either at least one tumor cell or at least one virally infected cell, or co-cultures of dendritic cells and either tumor cells or virally infected cells. The resulting T-cells can then be used in immunotherapy methods through adoptive transfer of autologous antigen-specific T-cells into patients using well-established techniques, as agents to identify tumor antigens, and to establish animal models.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) primer, kit and method for detecting virus titer of slow viruses
ActiveCN108559792AReflect the real infection vitalityAffect extraction efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFluorescenceDNA extraction
The invention discloses a real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) primer, a kit and a method for detecting the virus titer of slow viruses. The primer falls on an envelope of the slow viruses, and the titer can be detected without a fluorescent label. In addition, the successfully integrated viruses infecting cells are detected, the real infection vitality of the virusescan be embodied, and the primer cannot be affected by cell genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) extraction efficiency and has the advantages of simplicity and convenience in operation and high sensitivity.
Owner:YUNZHOU BIOSCIENCES (GUANGZHOU) INC
Systems and Methods for Virus Propagation in Cell Cultures for Vaccine Manufacture
ActiveUS20150064768A1Improve the immunityEliminate wasteSsRNA viruses negative-senseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsInfected cellSystems design
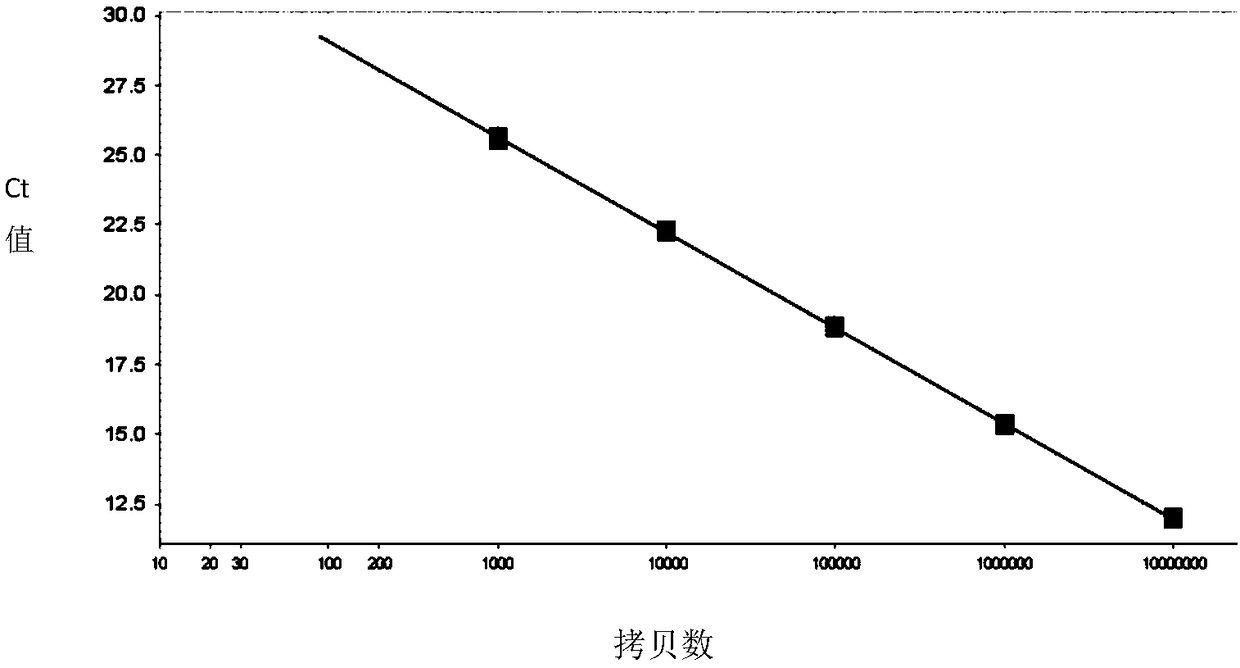
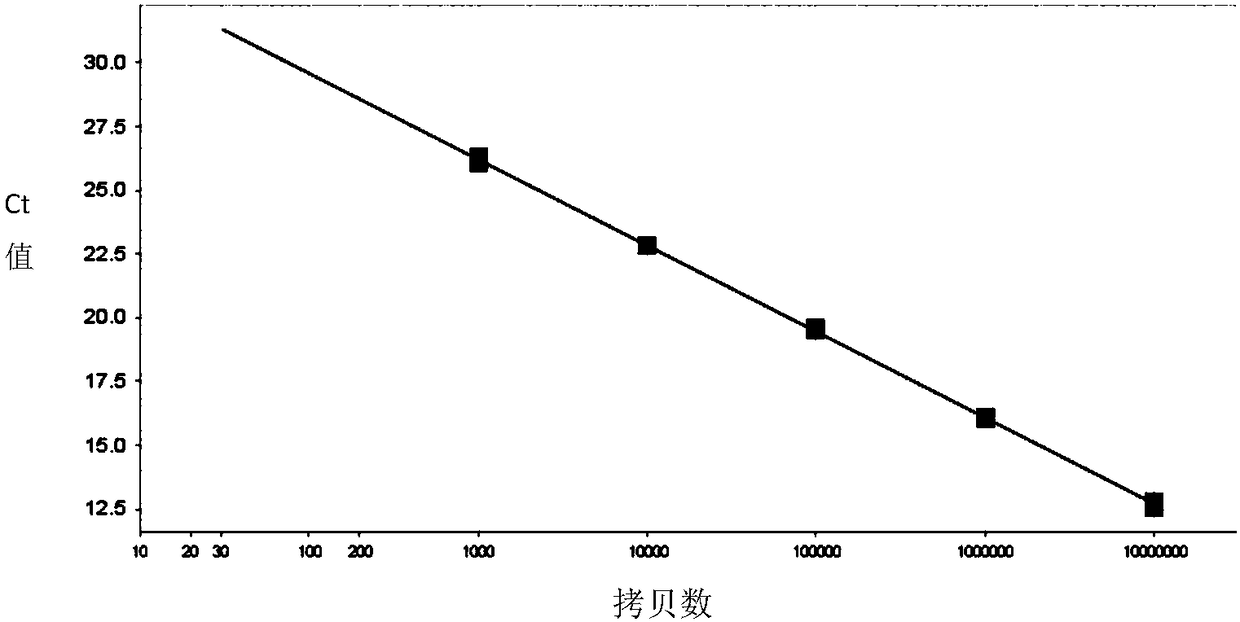
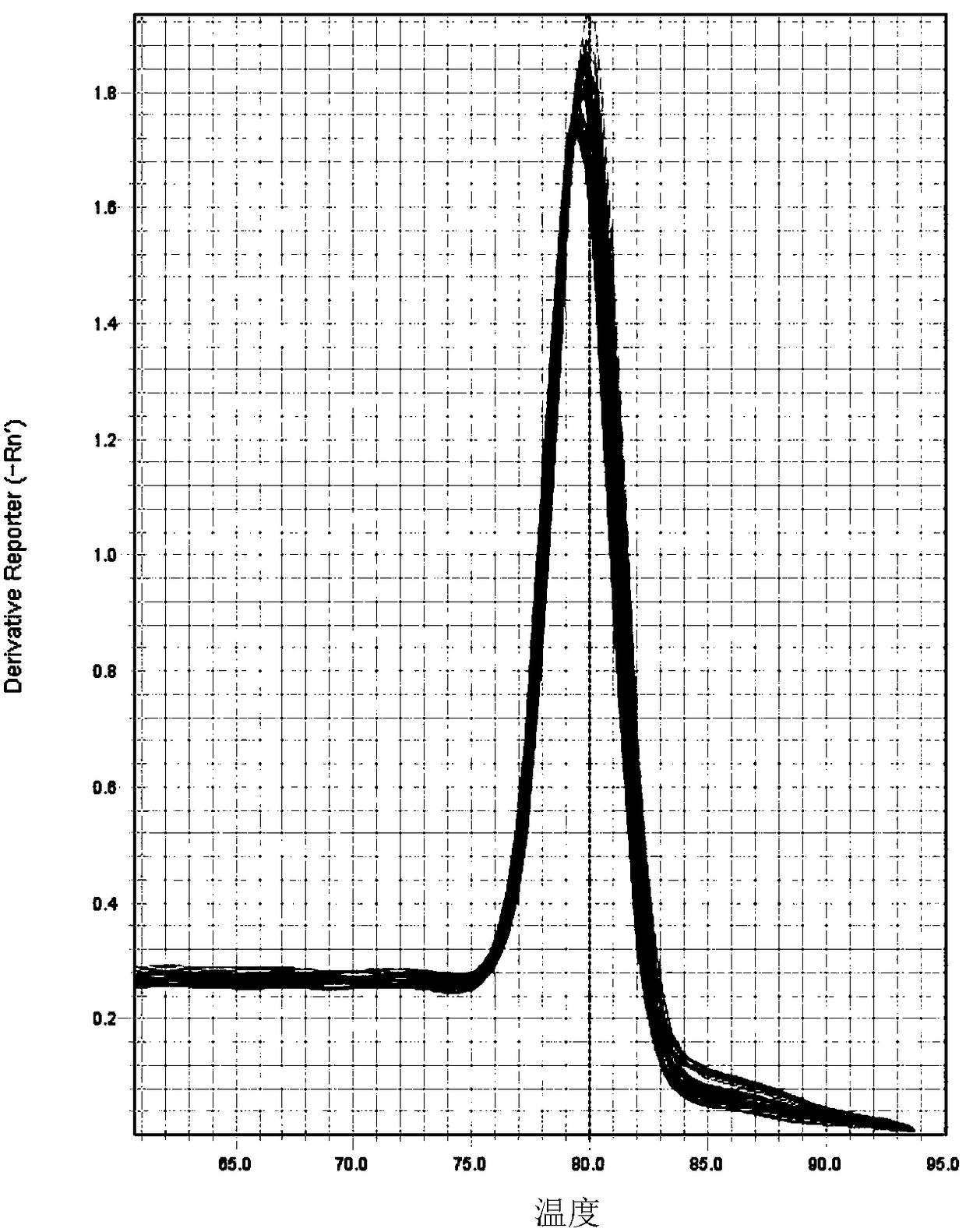
The present invention provides a closed system to propagate virus-infected cells without the effect of shear force, while providing quicker access to nutrients than is available conventionally. This system design allows for a high density of infected cell growth to increase the virus yields and to maintain homogeneity of the contents of the main container. The system further provides a nuclease to degrade the cellular DNA prior for purification of the virus or viral components. As the system is designed for maximum containment at low risk, the live virus can be a hazardous virus such as a Bio-safety Level 3 (BSL 3), BSL 4 or BSL5 virus.
Owner:INVENTPRISE INC
Anti-TSG101 antibodies and their uses for treatment of viral infections
InactiveUS7427468B2Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against virusesInfected cellViral infection
The present invention provides methods of using antibodies that bind a TSG101 protein to inhibit or reduce viral production. The invention also provides methods of using the TSG101 antibodies for the treatment of viral infections, including HIV infection. The invention further provides methods of detecting viral infected cells using TSG101 antibodies.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
In vitro induction of antigen-specific T-cells using dendritic cell-tumor cell or dendritic cell-viral cell derived immunogens
InactiveUS20050170503A1Provide immunityEliminate needGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsInfected cellAbnormal tissue growth
Antigen-specific T-cells prepared by culturing T-cells in formulations comprising combinations of DCs and either tumor cells or virally infected cells are disclosed. These formulations generally comprise hybridoma of at least one dendritic cell fused to either at least one tumor cell or at least one virally infected cell, or co-cultures of dendritic cells and either tumor cells or virally infected cells. The resulting T-cells can then be used in immunotherapy methods through adoptive transfer of autologous antigen-specific T-cells into patients using well-established techniques, as agents to identify tumor antigens, and to establish animal models.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
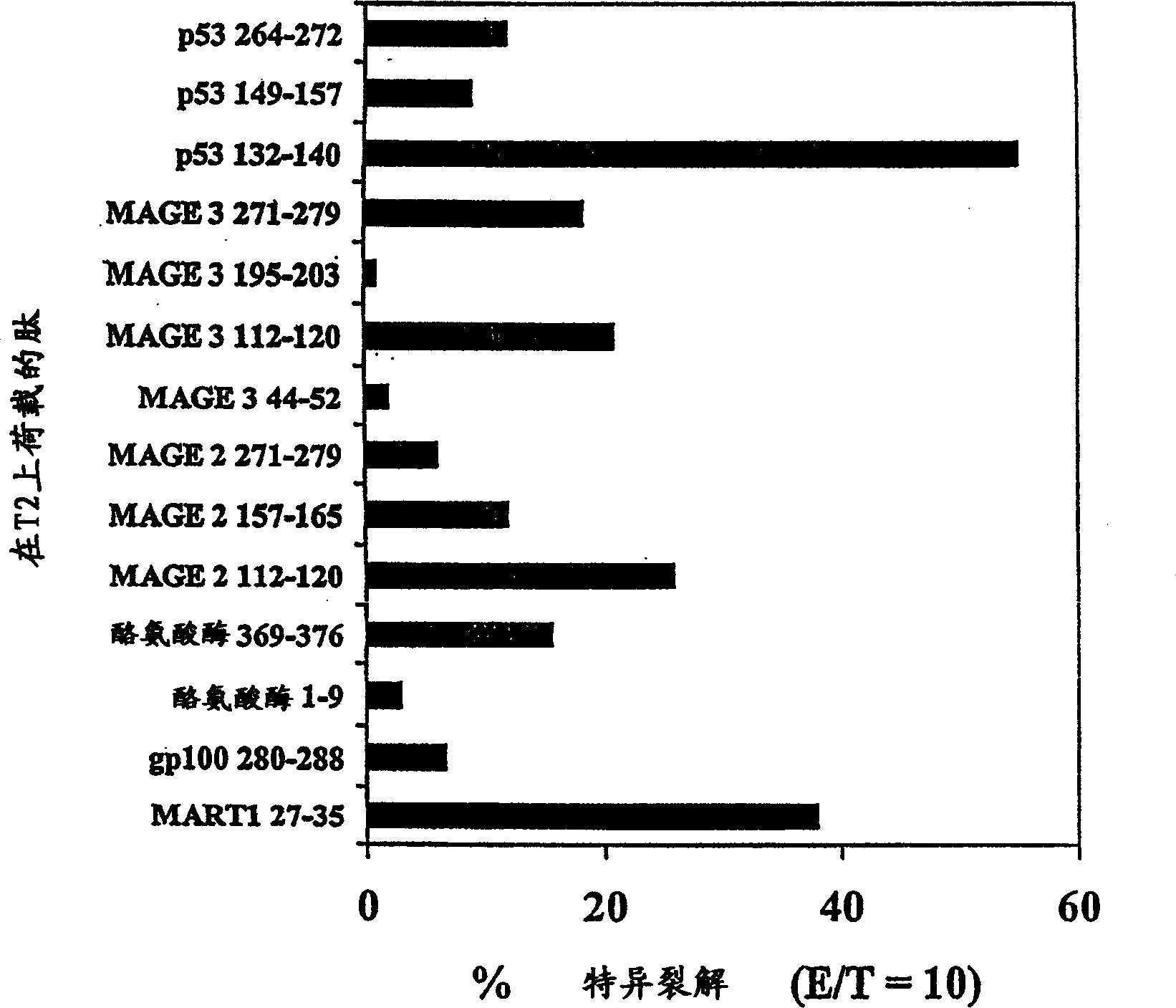
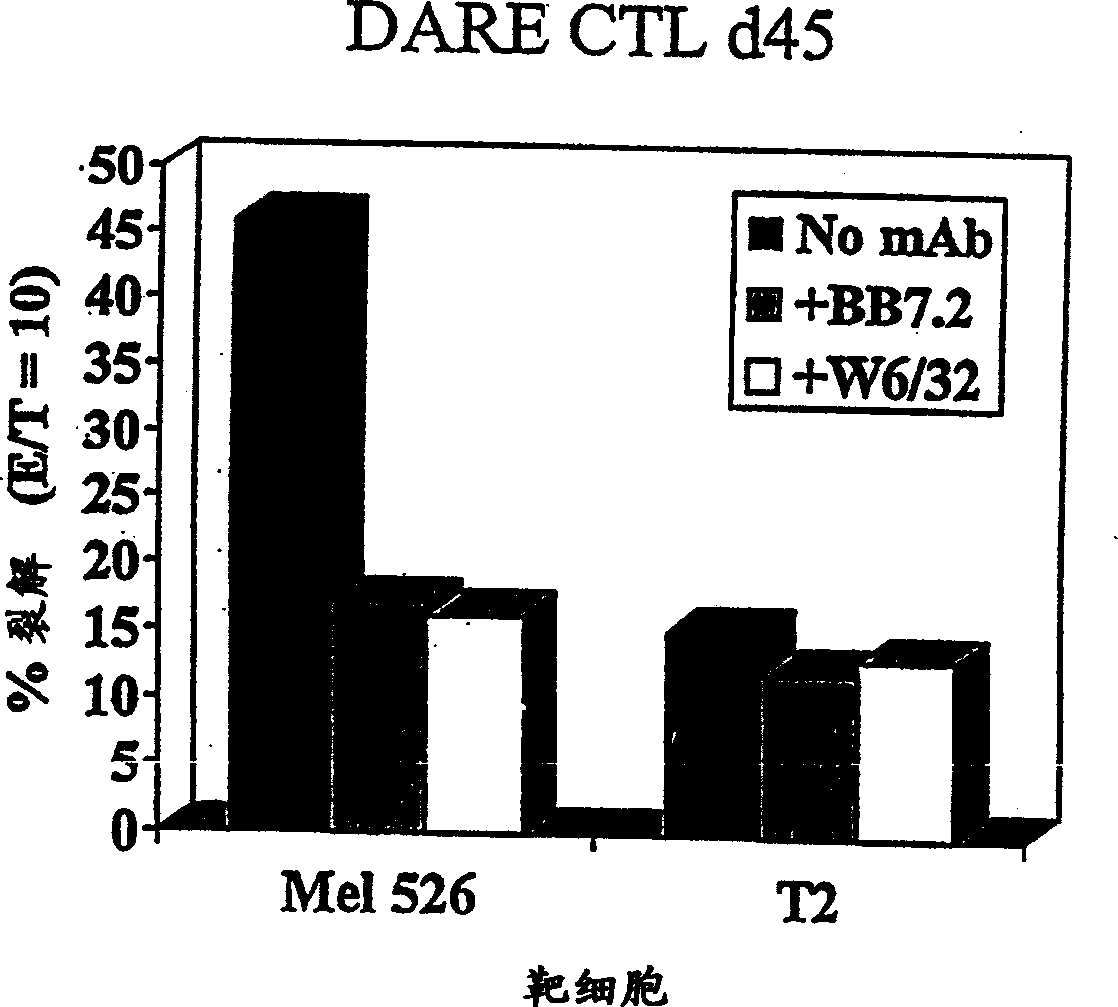
Methods and compositions using peptide-pulsed dendritic cells for stimulating cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for tumor cells or virus-infected cells
InactiveUS20030032050A1Easy to synthesizePrevent proliferationBacterial antigen ingredientsViral antigen ingredientsDendritic cellT lymphocyte
A novel method of immunization, which can be used either prophylactically or therapeutically, is described. The method comprises coating of antigen presenting cells with a peptide and administering the peptide-coated cells to a mammalian subject to provoke an immune response. Useful peptides include peptides derived from viral or bacterial antigens or mutant oncogene or tumor suppressor gene products. Immunogens, constituted by the peptide-coated cells, are also described.
Owner:THE GOVT OF THE US REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF H & H SERVICES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com