Patents
Literature
419results about "Liquid degasification regulation/control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
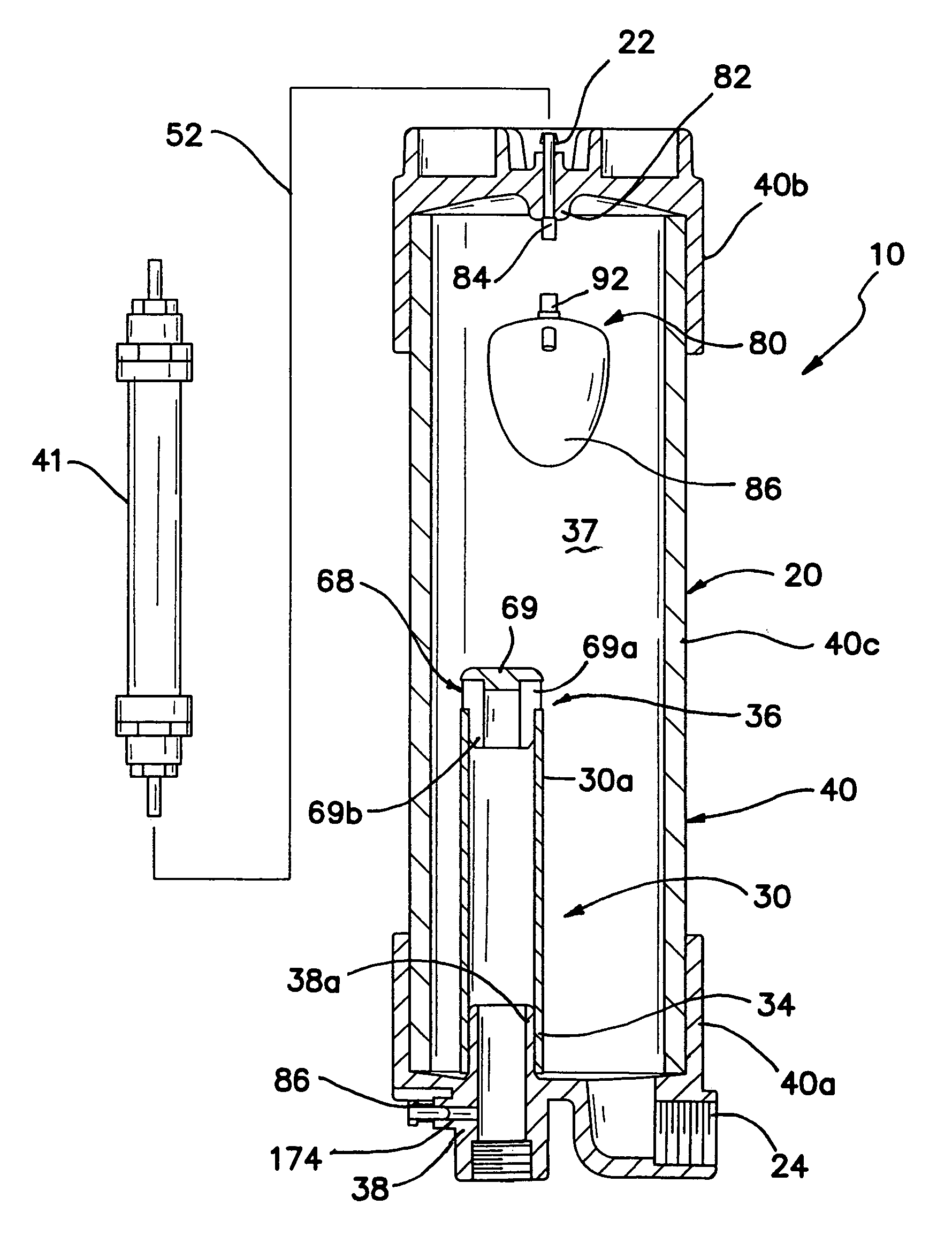
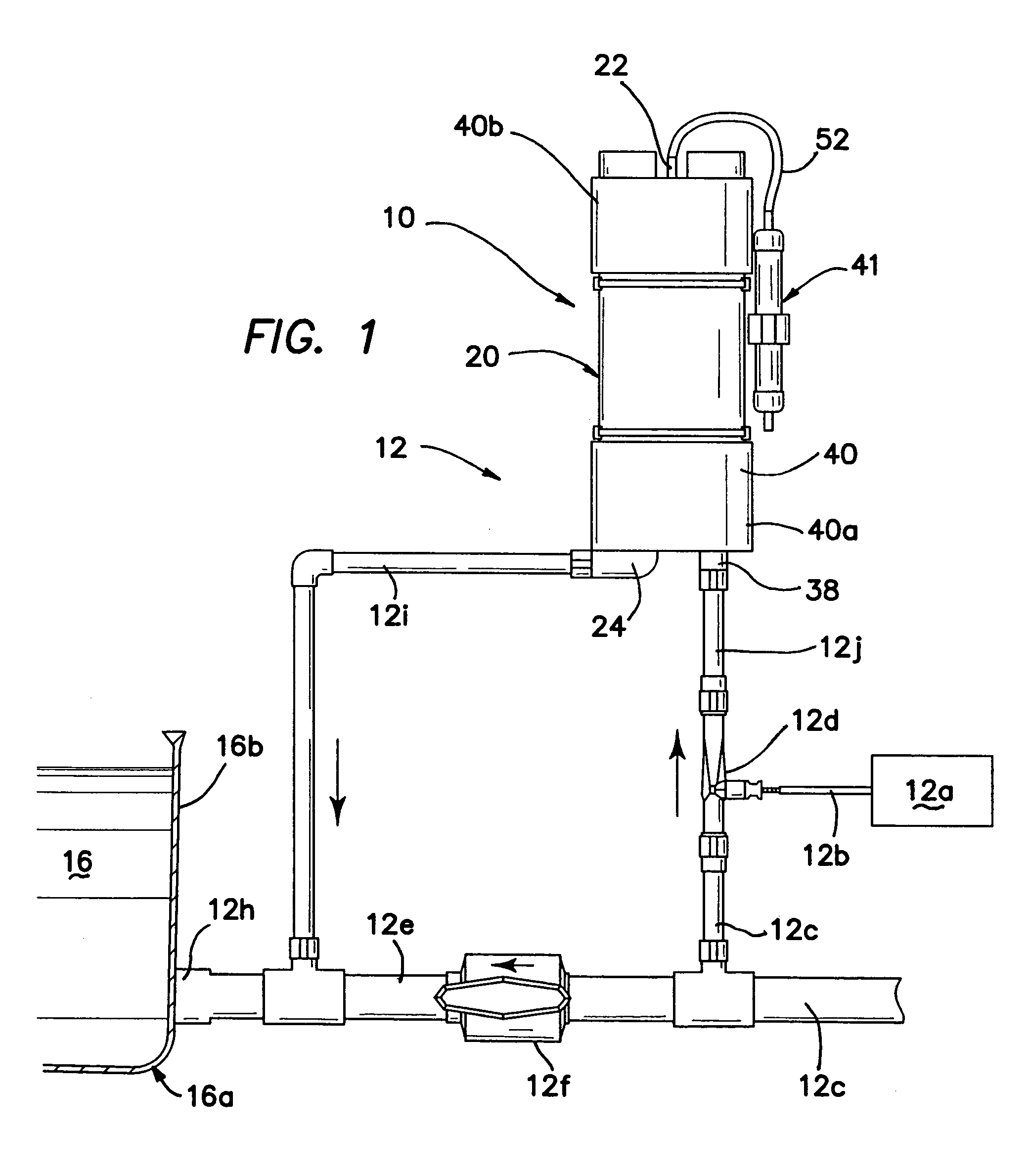
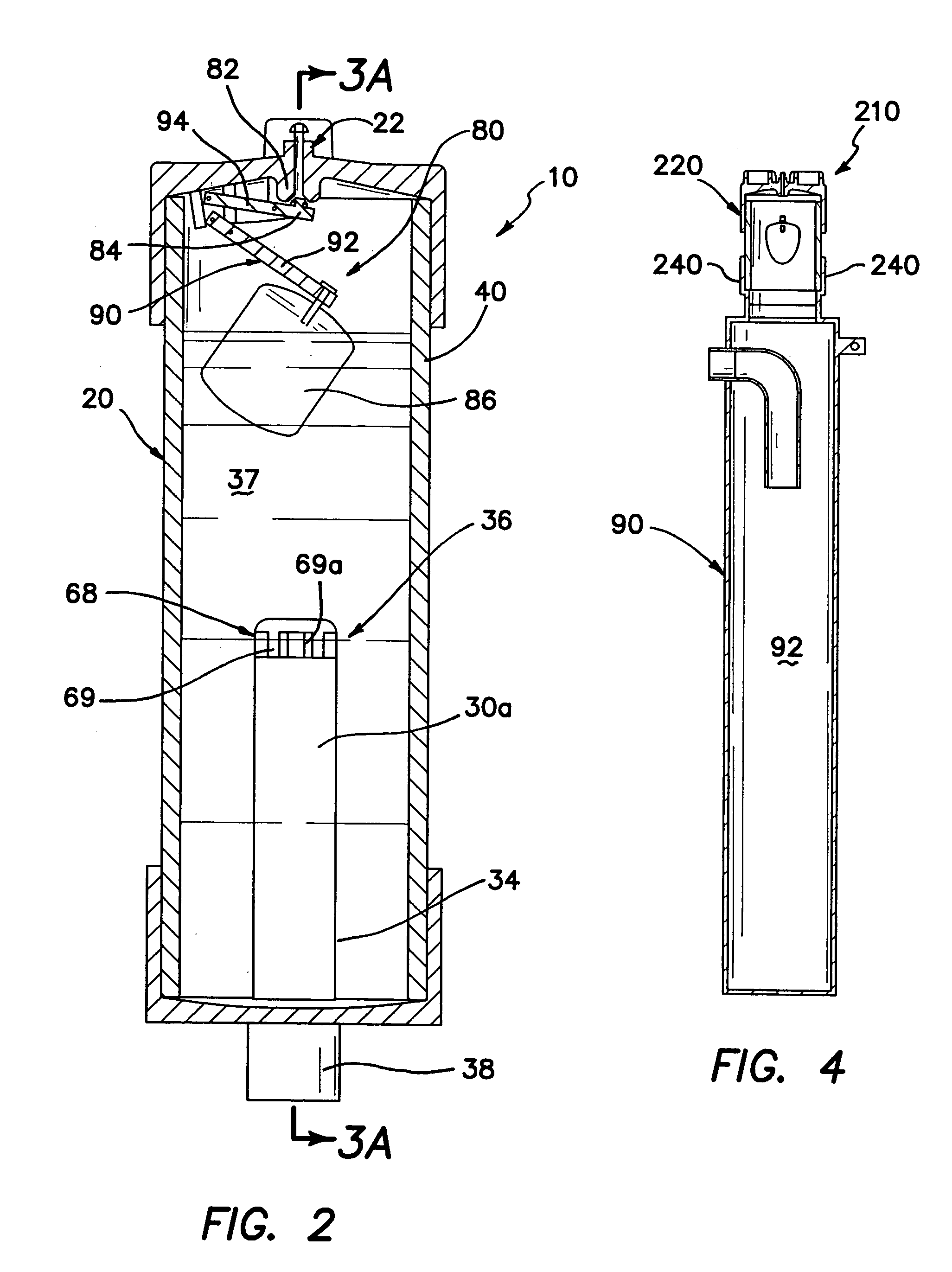
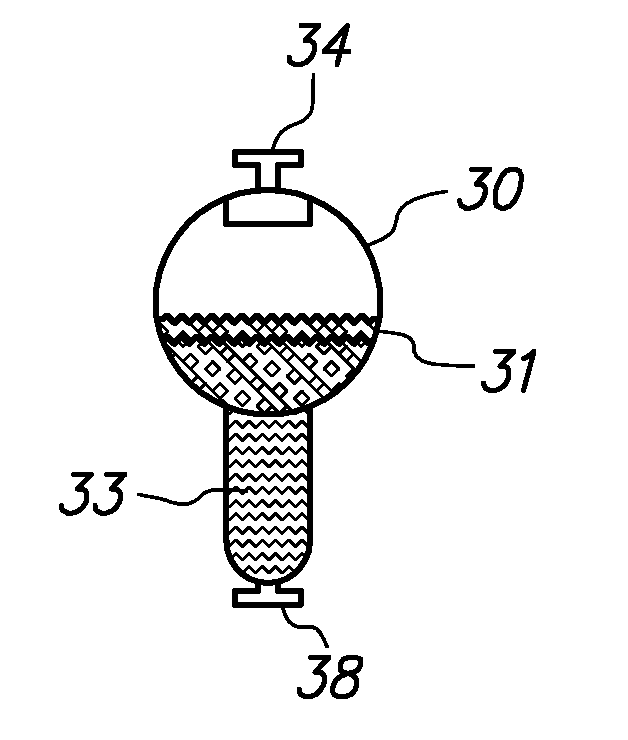
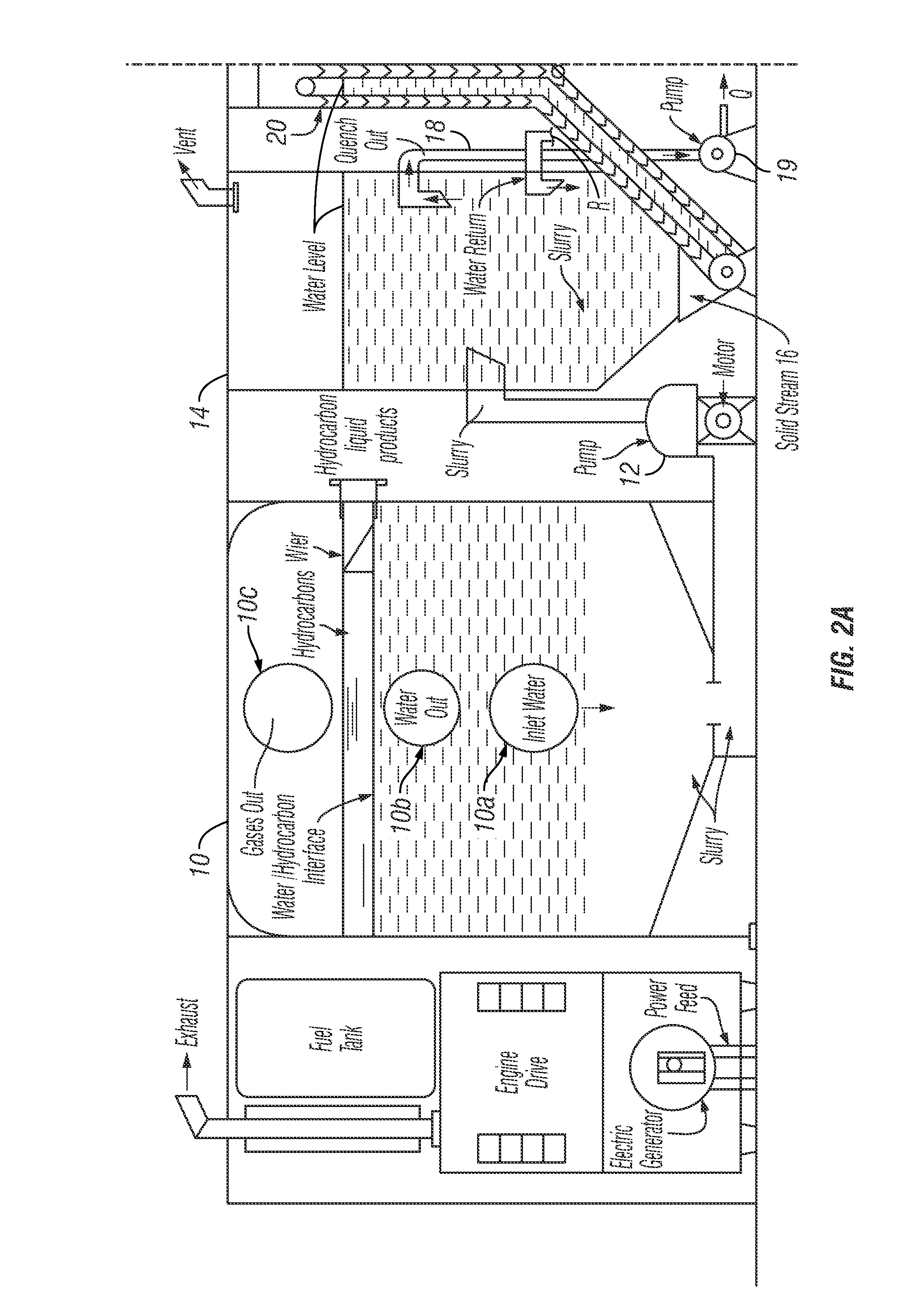
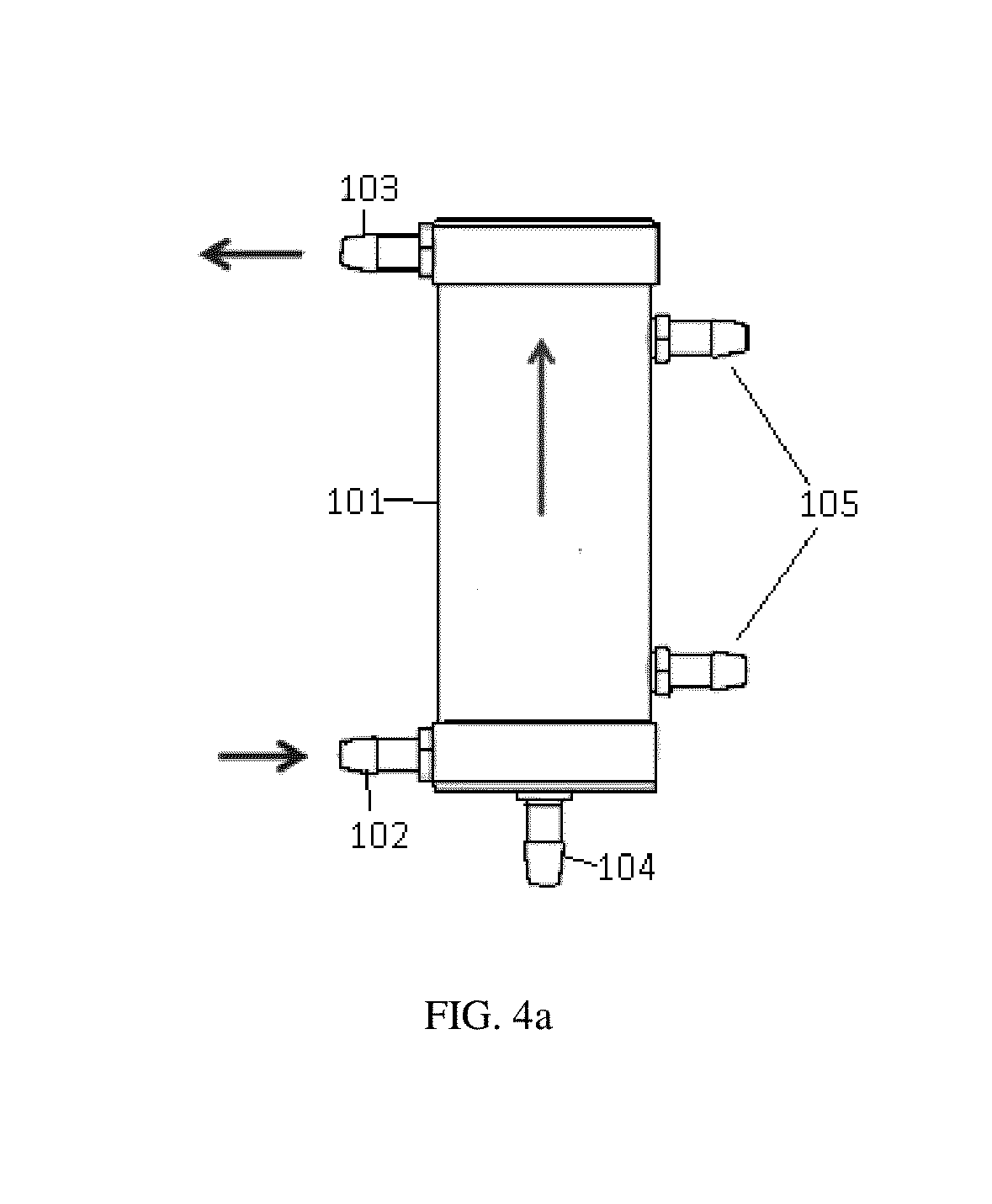
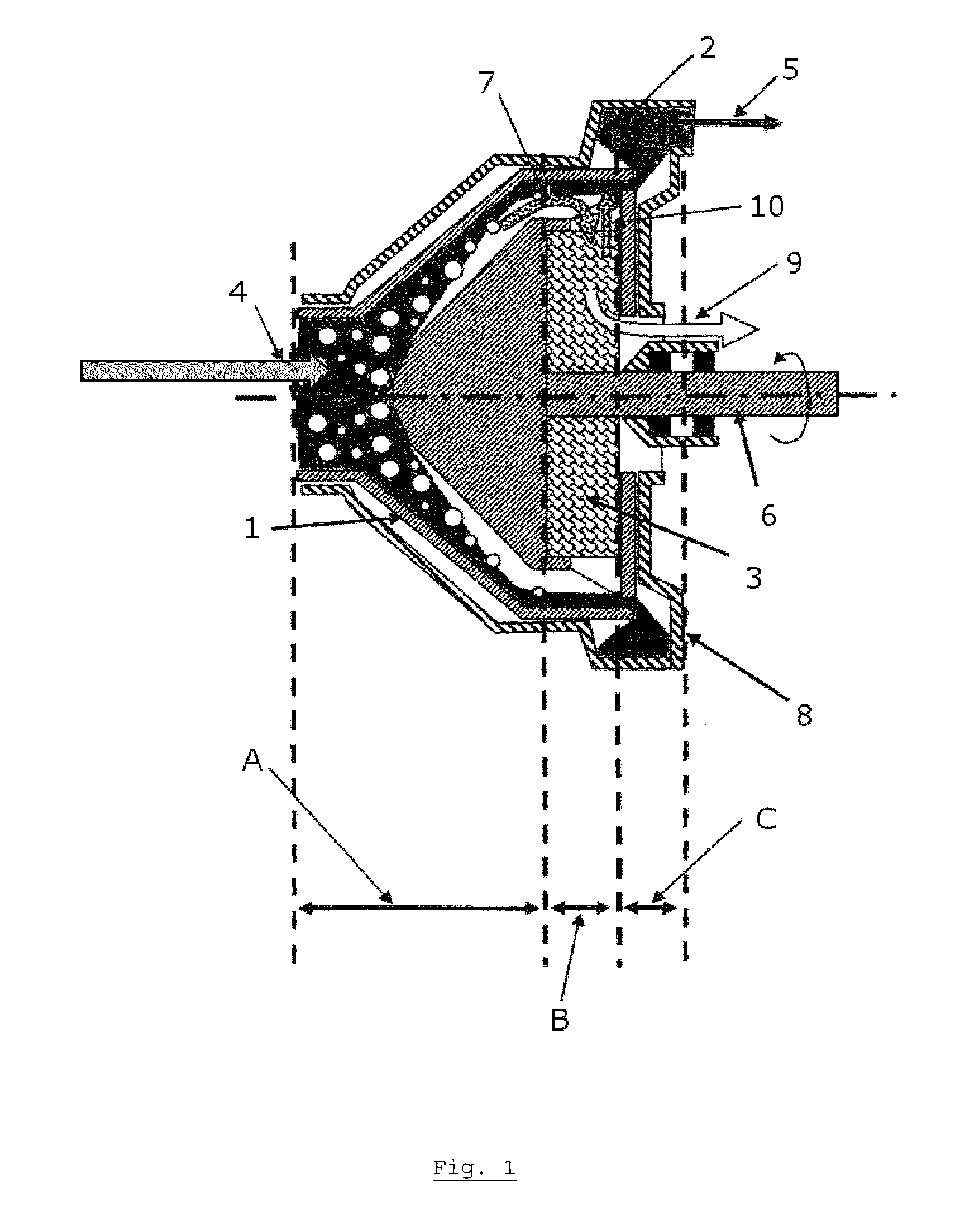
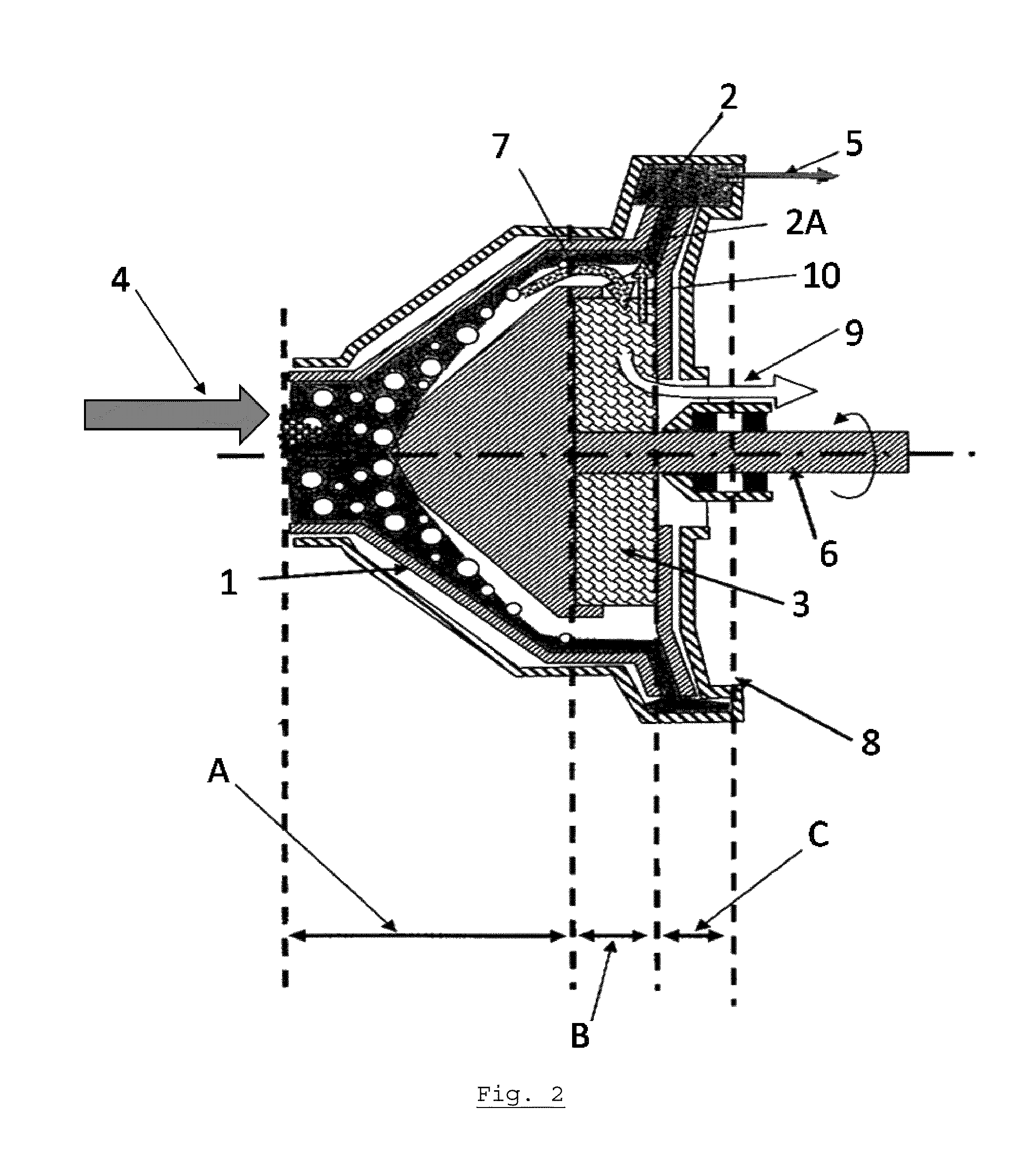
Water ozonation mixing and degassing system
ActiveUS7022225B1Straightforward in constructionEasy to useOther chemical processesDispersed particle separationLiquid waterExhaust fumes
An apparatus and system for mixing and separating ozonated water is provided. The apparatus is especially useful as a component of a system for cycling sanitizing ozonated water to a body of water such as a pool, spa or pond. The apparatus generally includes a separating vessel including a mixing tower, preferably located substantially entirely within the separating vessel and including a diffuser element for enhancing mixing of ozonated water without increasing turbulence in the separating vessel. Preferably, the apparatus includes a seal mechanism that substantially prevents liquid water from escaping the separating vessel with vented off-gas. The invention further provides an ozone destruct assembly including a condensate collection portion, and may also include a return line for passing a treated off-gas into the body of water.
Owner:CUSTOM MOLDED PROD
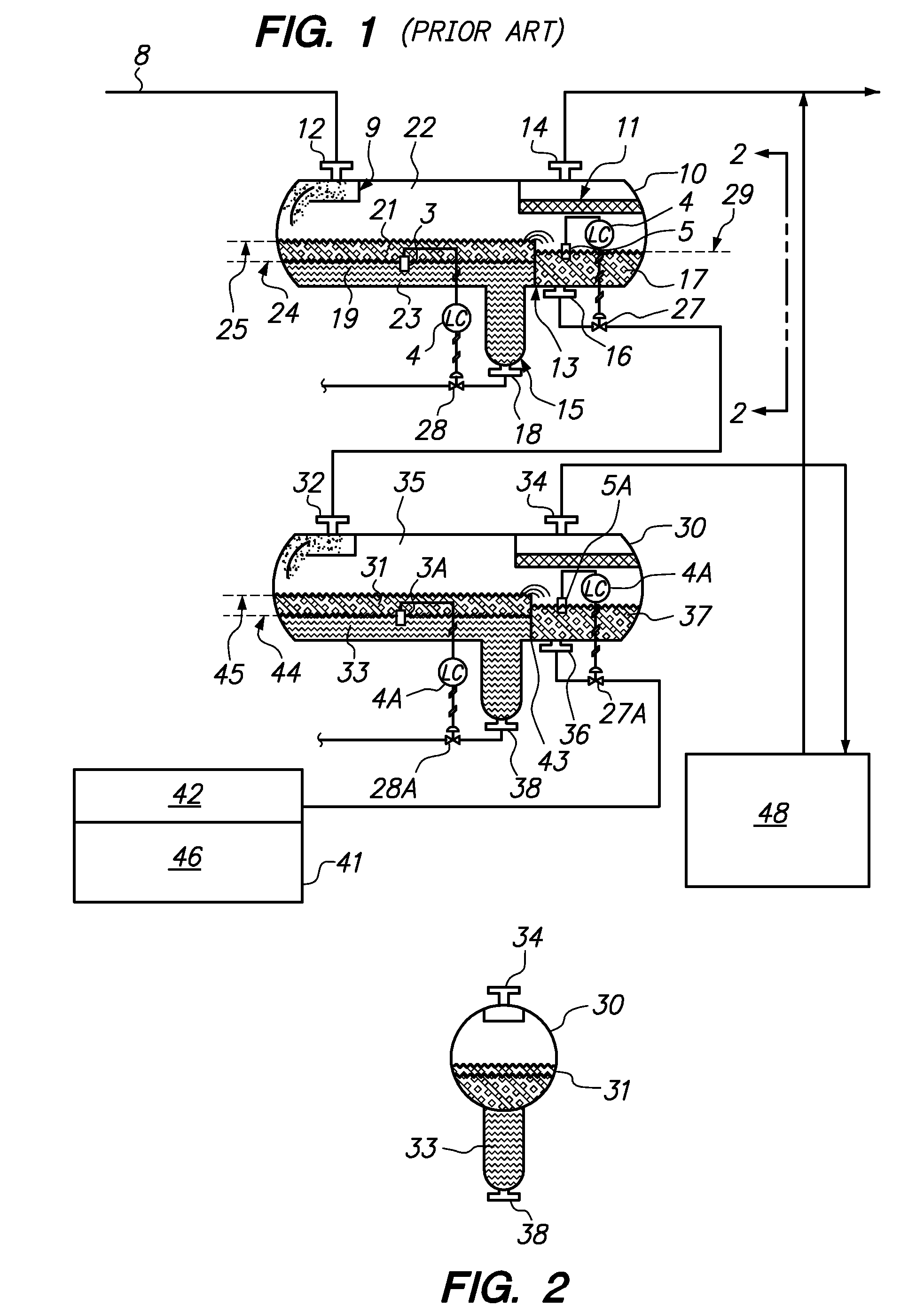
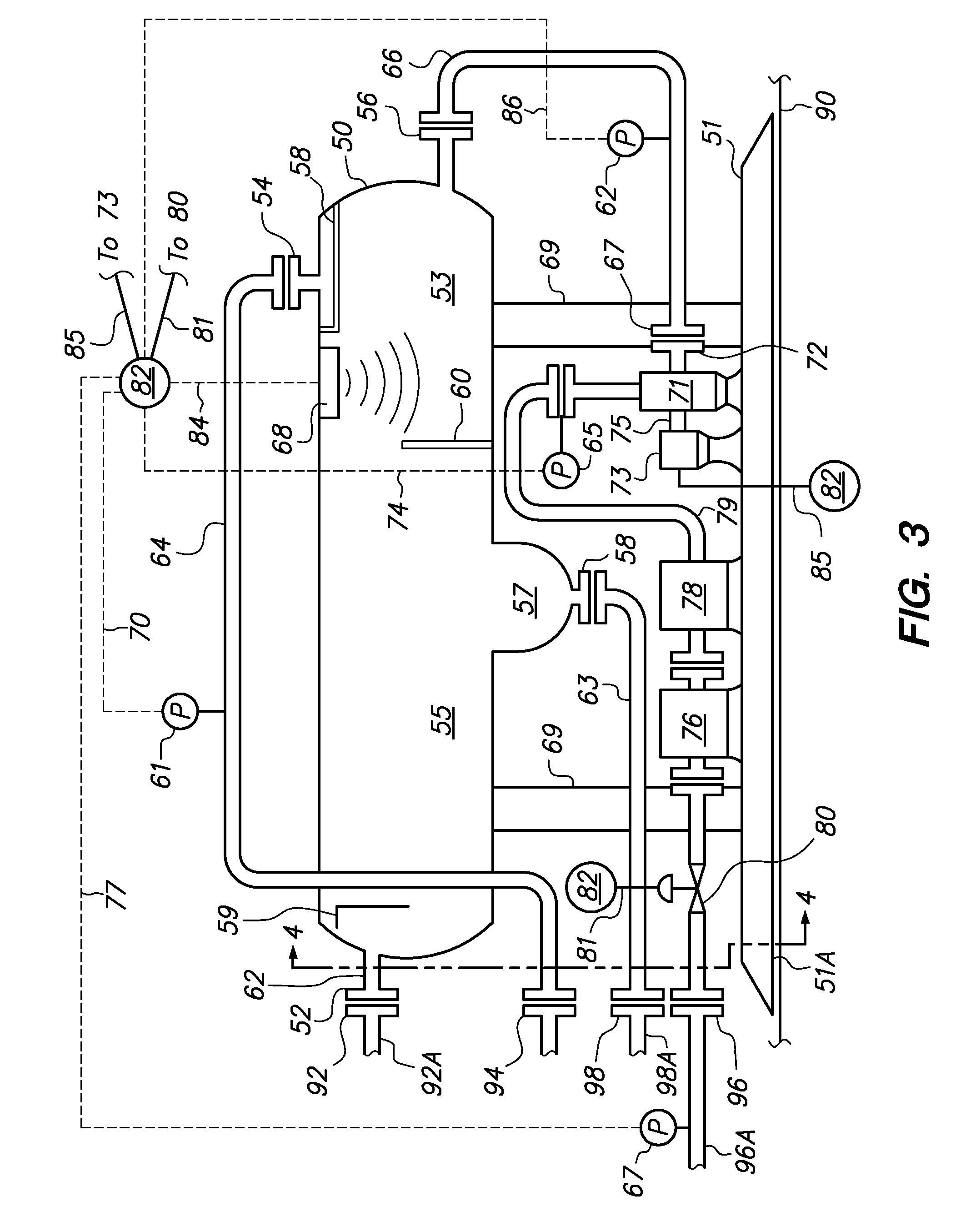
System and method to measure hydrocarbons produced from a well
InactiveUS20120285896A1Accurate measurementReduce environmental emissionsLiquid separation auxillary apparatusConstructionsProduct gasEngineering
A method and system for metering liquid production at a well comprises an actuated back pressure control valve, a liquid pump, a liquid flow meter and a pressure sensor, both intermediate the liquid pump and the back pressure control valve, and a separator having a liquid discharge conduit, a pressure sensor and a liquid / gas interface sensor disposed to monitor a section of the separator. The liquid pump receives a stream of liquid removed from the monitored section of the separator and moves the liquid stream through the flow meter and the back pressure control valve. A controller receives signals from the pressure sensors and the interface sensor, and operates the liquid pump at a speed to maintain an interface in the monitored section within a predetermined range while positioning the back pressure control valve to maintain the pressure at the flow meter above a pressure at which bubbles may form.
Owner:CROSSSTREAM ENERGY
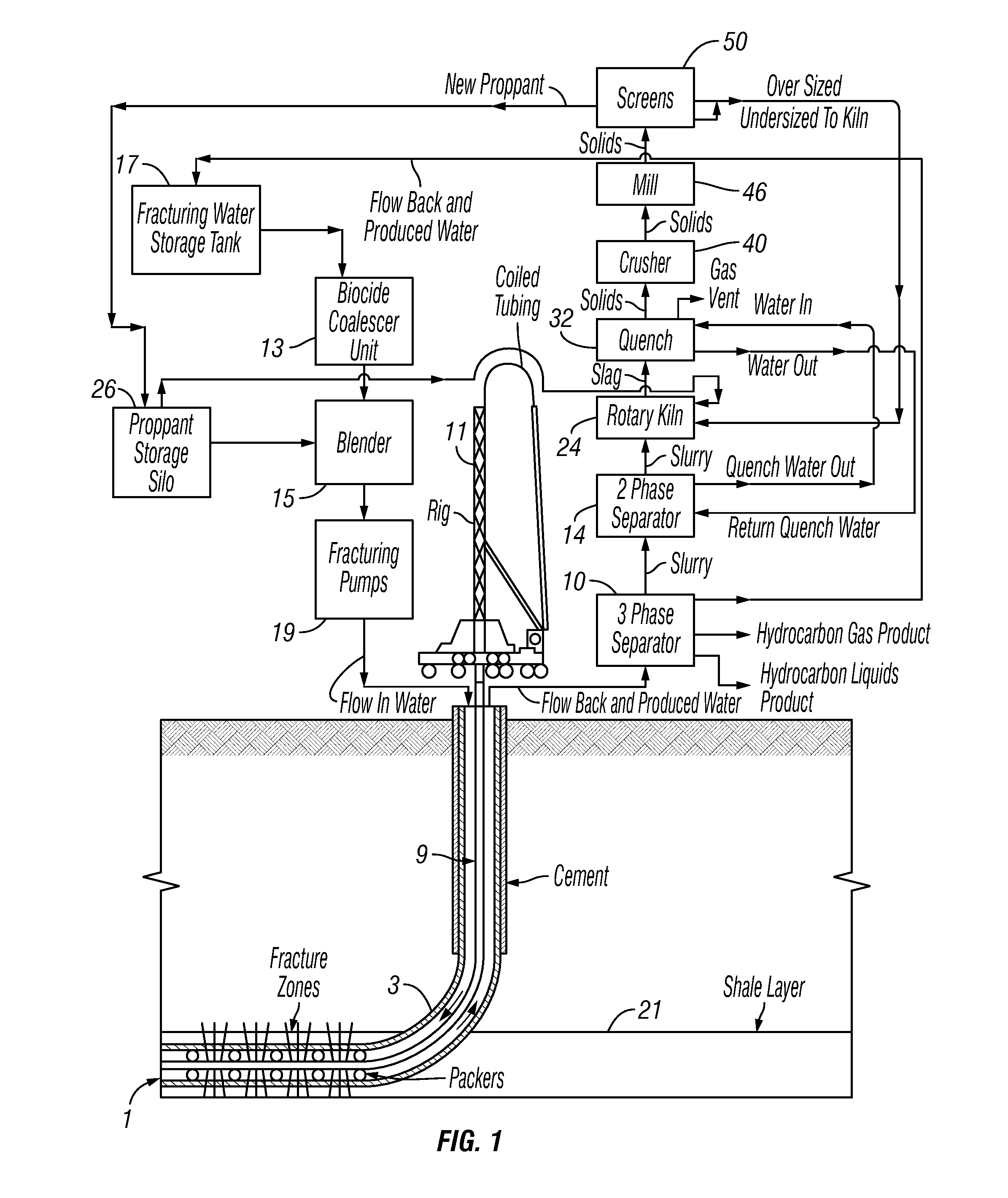
Fracture Water Treatment Method and System
InactiveUS20140027386A1Inhibition formationEliminate needWaste water treatment from quariesLiquid separation auxillary apparatusProduced waterHydrocarbon
A method and system for treatment of flow-back and produced water from a hydrocarbon well in which fracturing operations are carried out using a phase separation and creating of positive charge in the water.
Owner:MBJ WATER PARTNERS
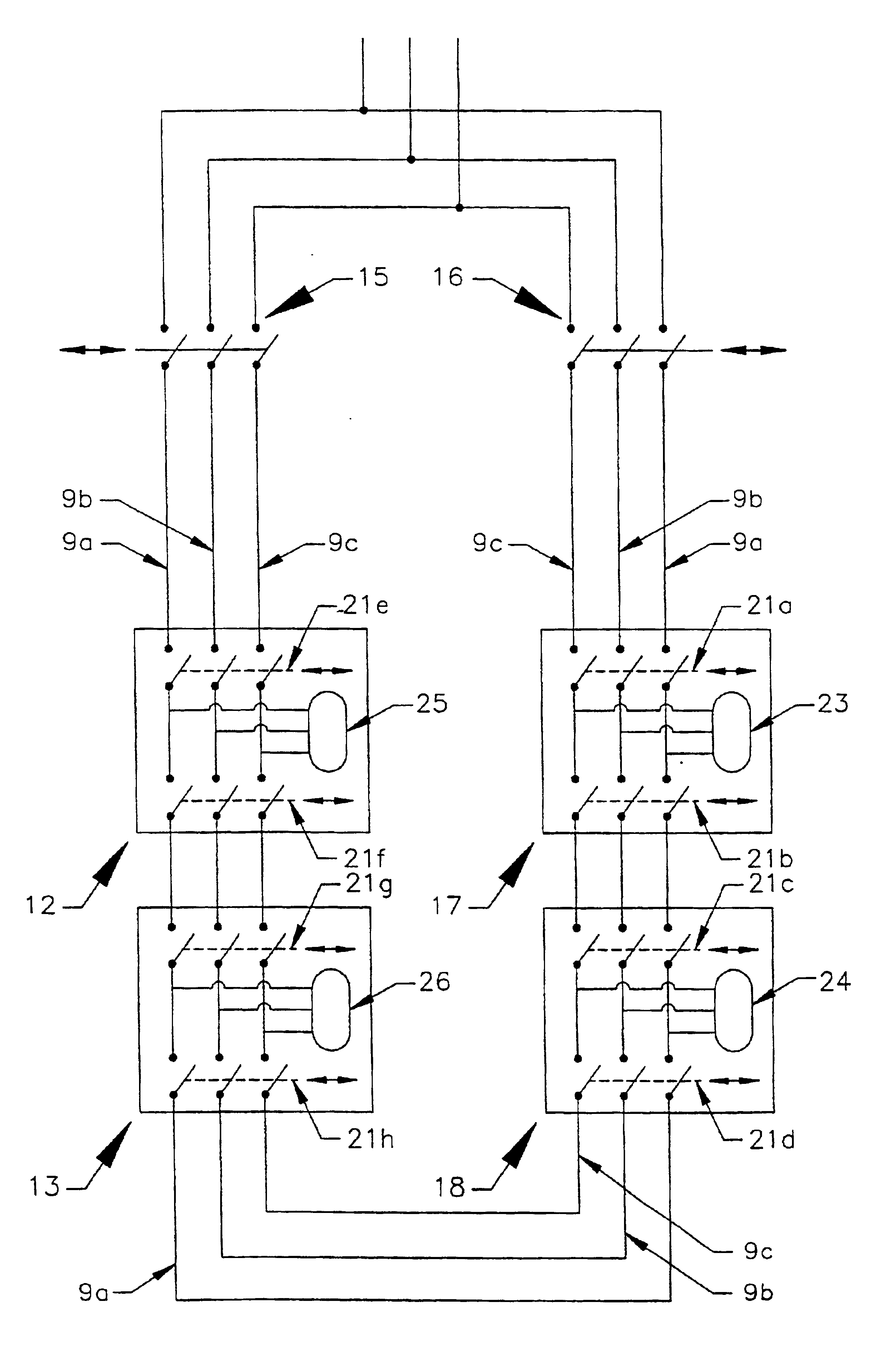
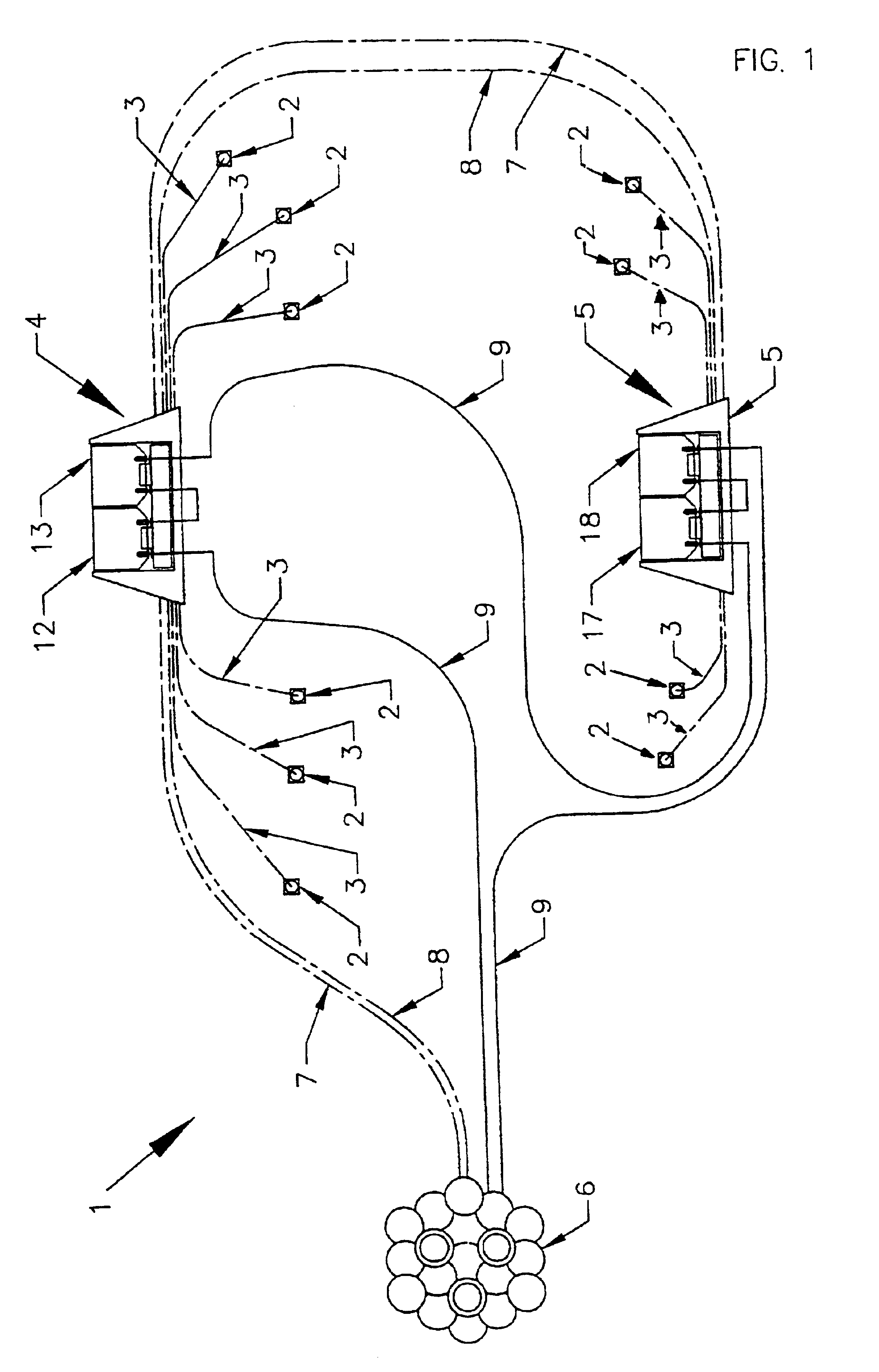
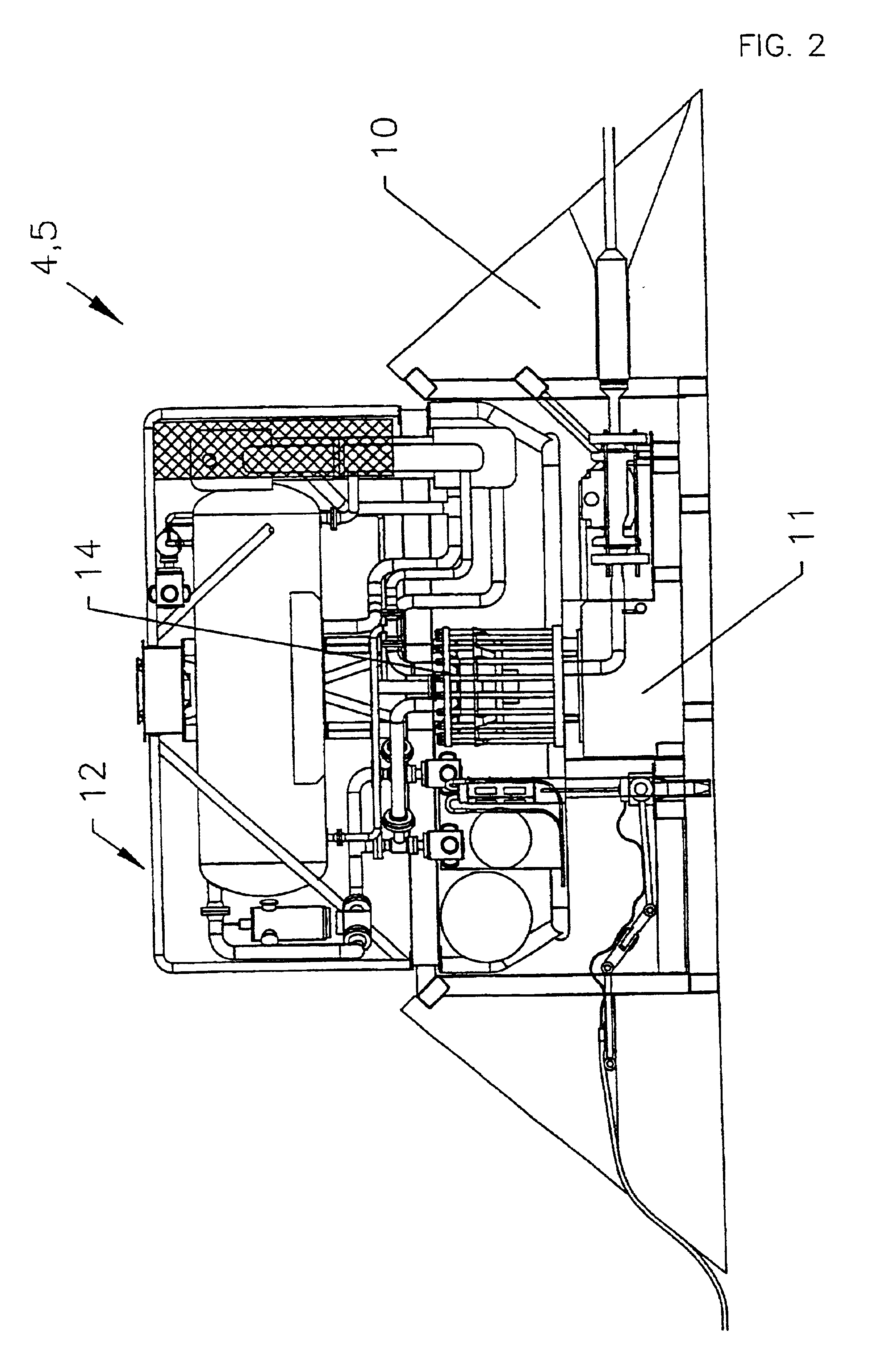
Electrical power distribution suitable for a substantially underwater system
InactiveUS6873063B1Liquid separation auxillary apparatusLiquid degasification regulation/controlElectricityUnderwater
A substantially underwater system comprises a plurality of retrievable substantially autonomous subsea modules (12, 13, 17, 18) and switchgear (15, 16, 21a . . . h). A host facility (6) and the modules are connected in series so as to form a circuit, the host facility providing power to all of the modules. Operation of the switchgear electrically isolates a module or a plurality of serially adjacent modules so that the module or modules can be removed without cutting off the power supply to any of the remaining modules of the system. Module based parts of the switchgear (21a . . . h) only or a combination of module based parts (21a . . . h) and host facility based parts (15, 16) of the switchgear are actuated depending on which module or modules are isolated and removed.
Owner:ALPHA THAMES LTD
Dialysis system and methods
InactiveUS20150314055A1Prevent backflowFlow imbalanceDialysis systemsMedical devicesUltrafiltrationDynamic balance
Dialysis systems and methods are described which can include a number of features. The dialysis systems described can be to provide dialysis therapy to a patient in the comfort of their own home. The dialysis system can be configured to prepare purified water from a tap water source in real-time that is used for creating a dialysate solution. The dialysis systems described also include features that make it easy for a patient to self-administer therapy. For example, the dialysis systems include disposable cartridge and patient tubing sets that are easily installed on the dialysis system and automatically align the tubing set, sensors, venous drip chamber, and other features with the corresponding components on the dialysis system. Methods of use are also provided, including automated priming sequences, blood return sequences, and dynamic balancing methods for controlling a rate of fluid transfer during different types of dialysis, including hemodialysis, ultrafiltration, and hemodiafiltration.
Owner:OUTSET MEDICAL
Control system and method for continuous mixing of slurry with removal of entrained bubbles
InactiveUS6994464B2Easy to controlControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsRotary stirring mixersSurge tankControl system
The present invention comprises a control system and method for the continuous mixing of slurry while removing entrained bubbles. The control system for continuous mixing of slurry with removal of entrained bubbles comprises a power and fluid rate control, wherein the powder and fluid rate control is coupled to a mixer through a powder feeder and a liquid pump. A fluid level control is coupled to the mixer and a surge tank, and a flow rate is coupled to the surge tank. The present invention also comprises a method for controlling the continuous mixing of slurry while removing entrained bubbles comprising providing a powder and fluid rate control, wherein the powder feeder and fluid rate control is coupled to a mixer through a powder feeder and a liquid pump. A fluid level coniol is coupled to the mixer and a surge tank and flow rate control is coupled to the surge tank.
Owner:MOBIUS TECH
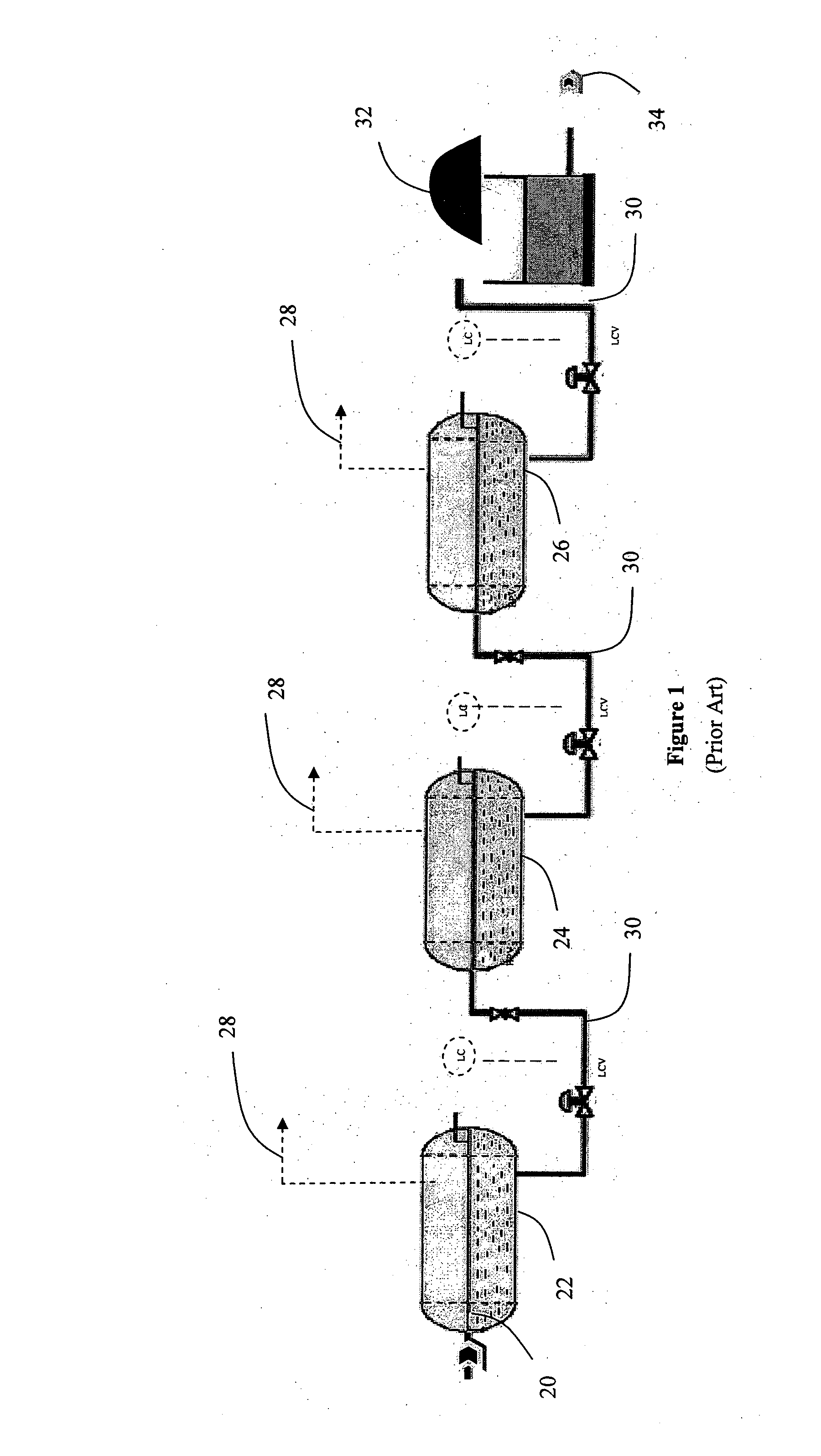
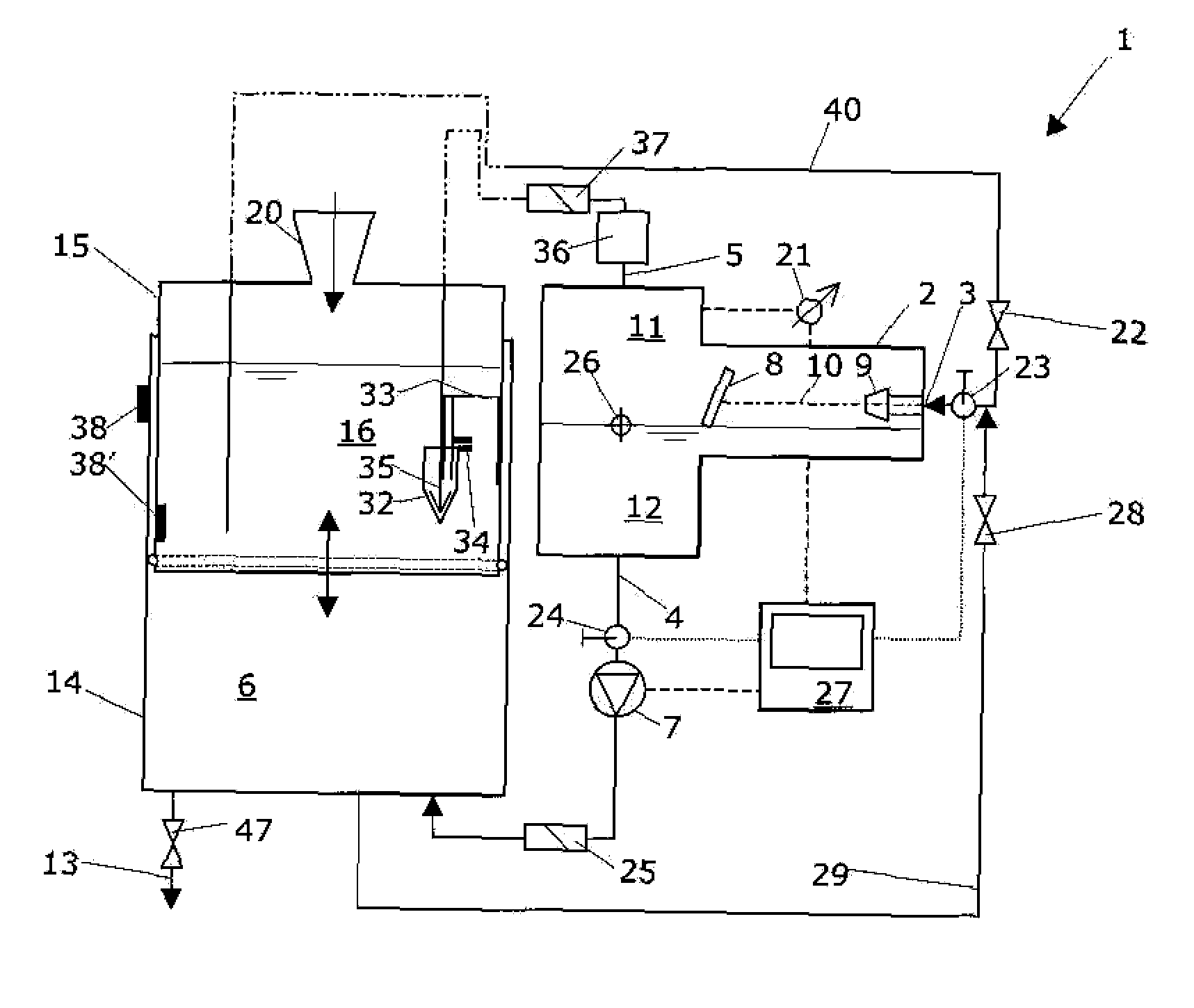
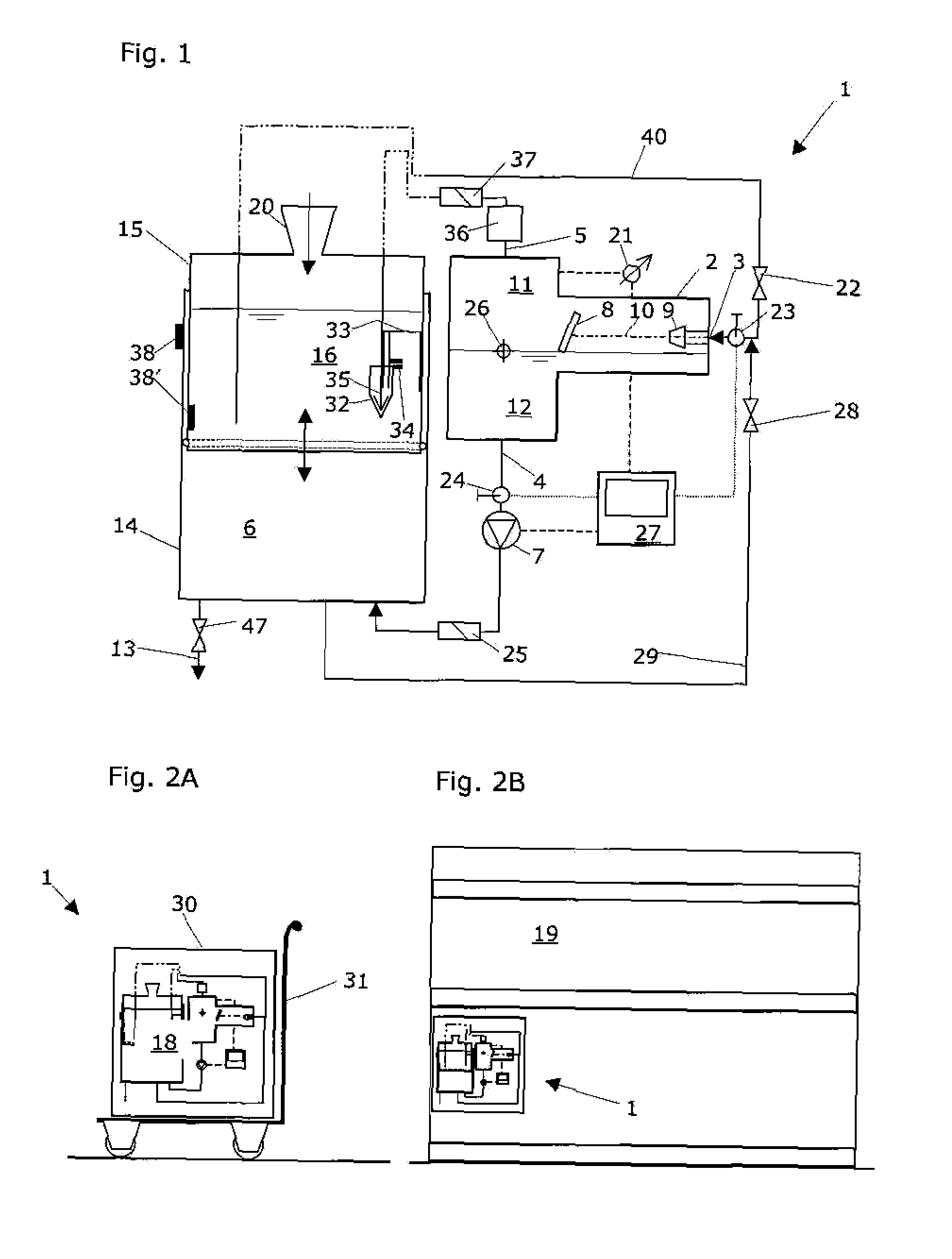
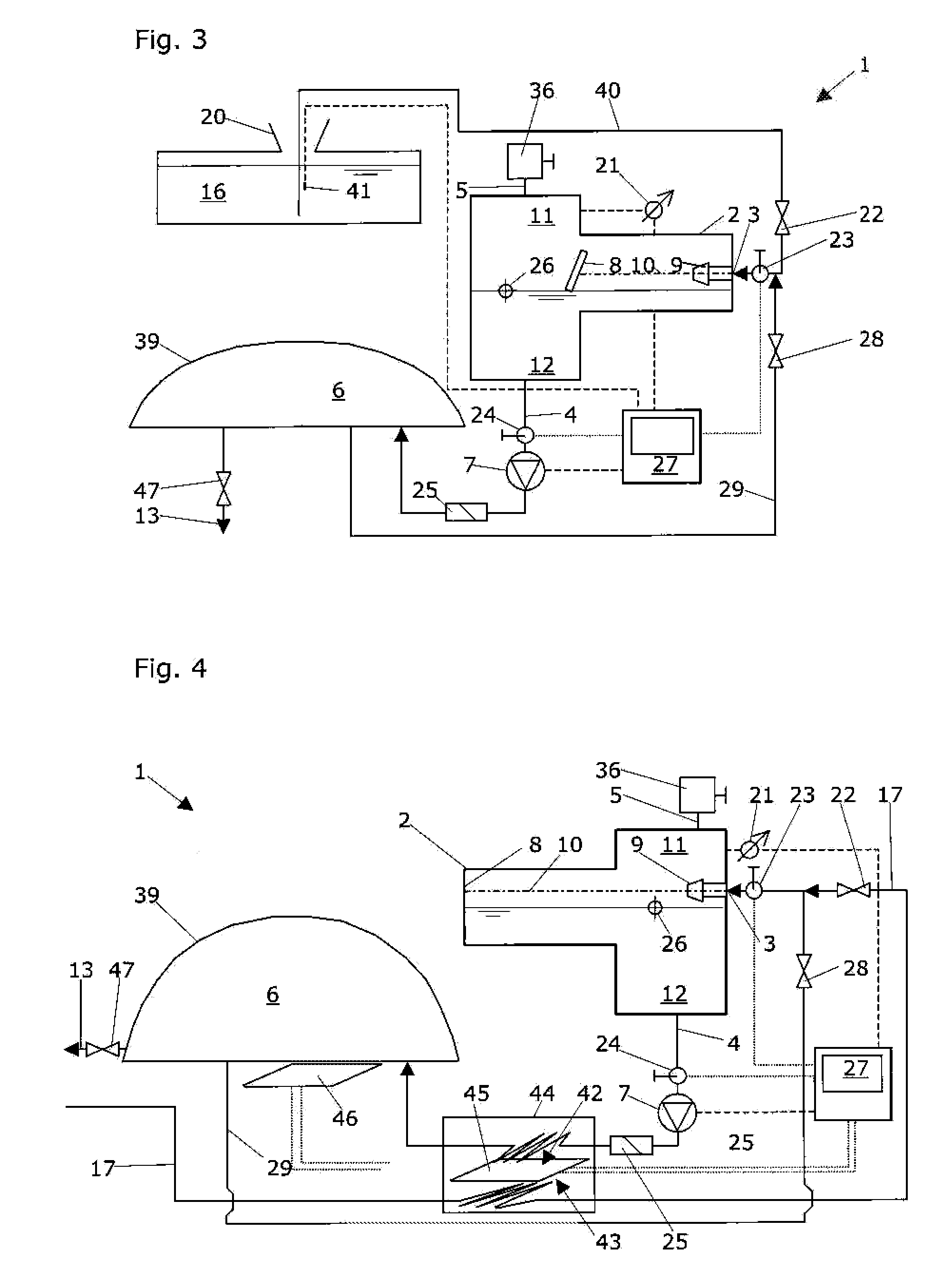
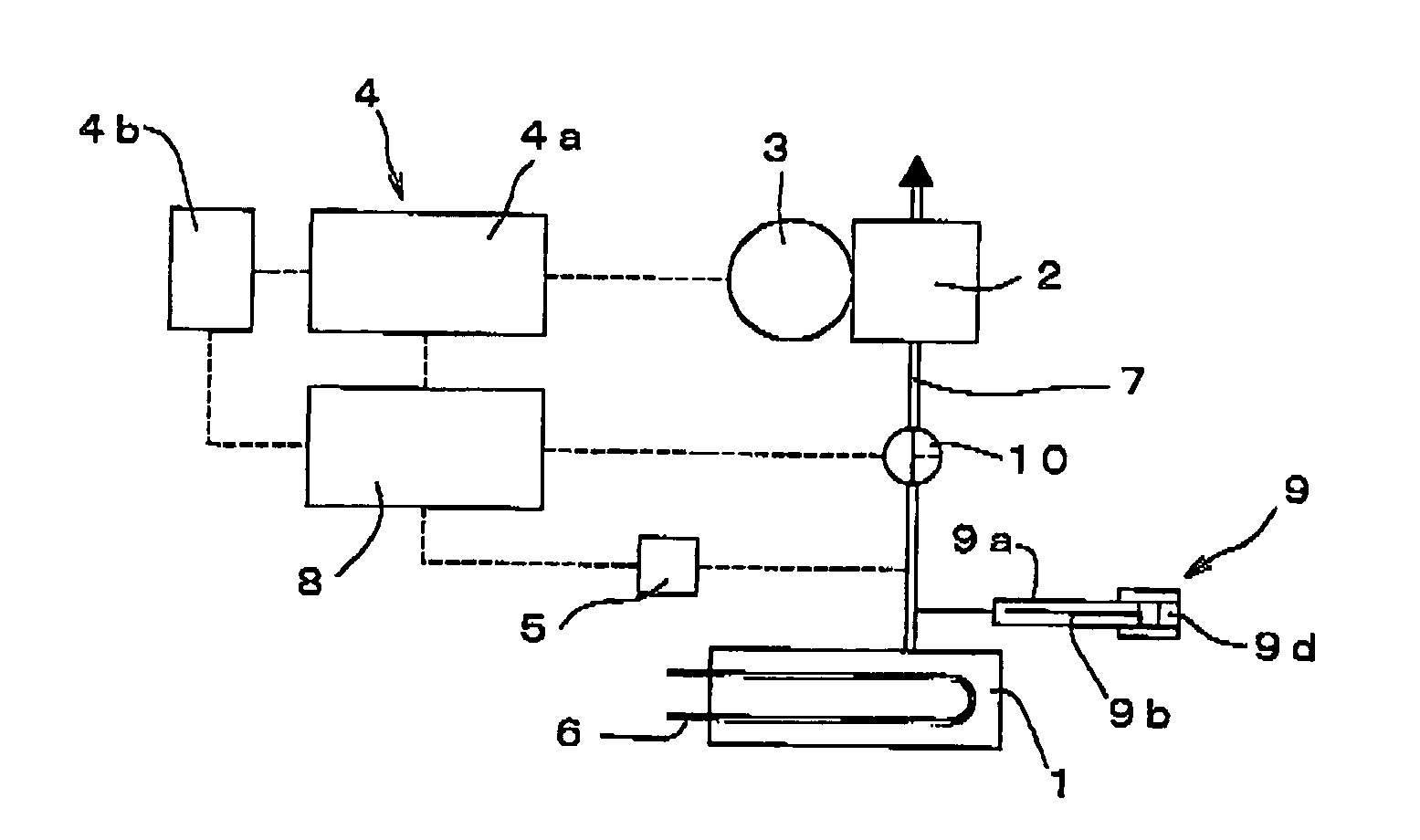
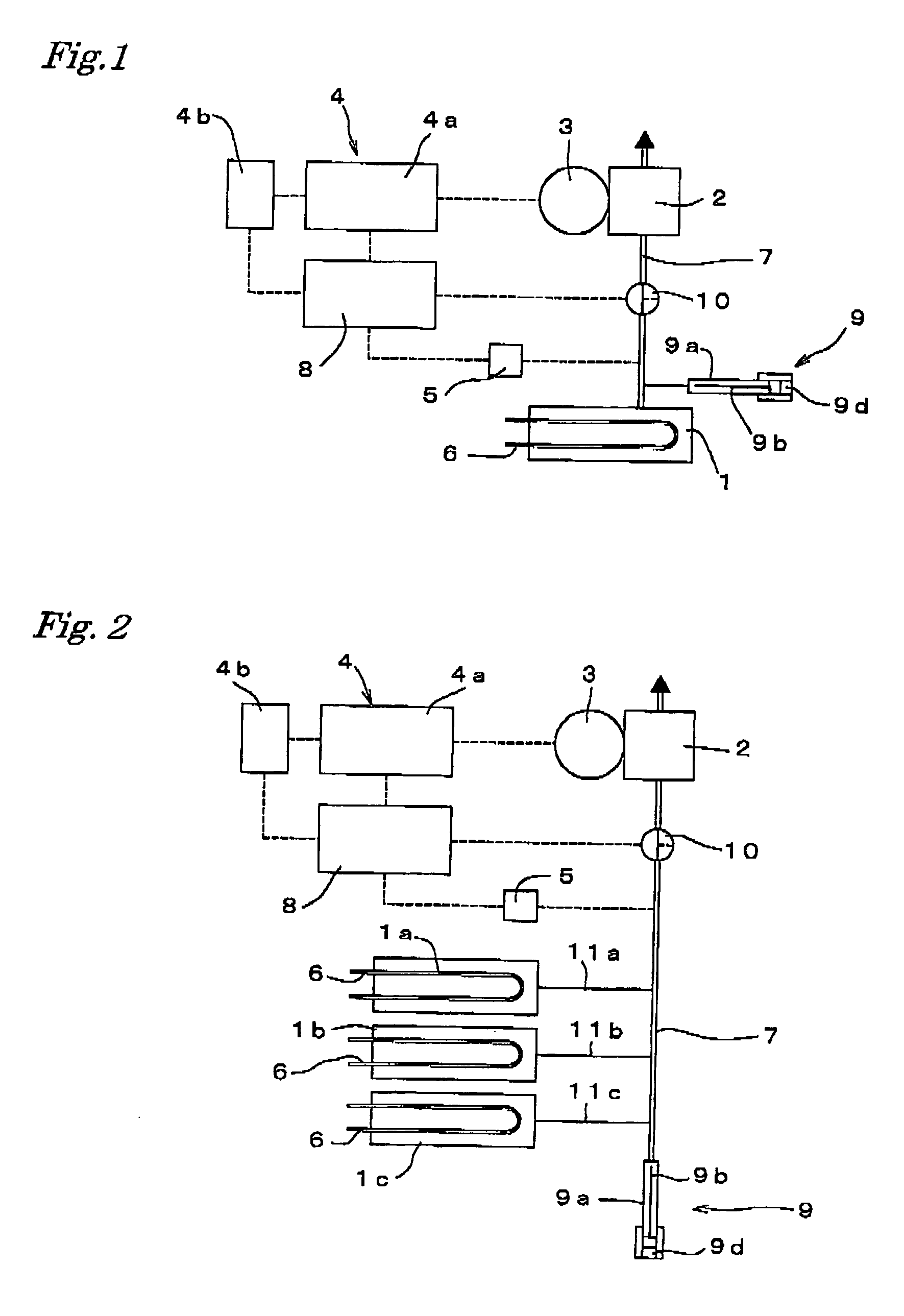
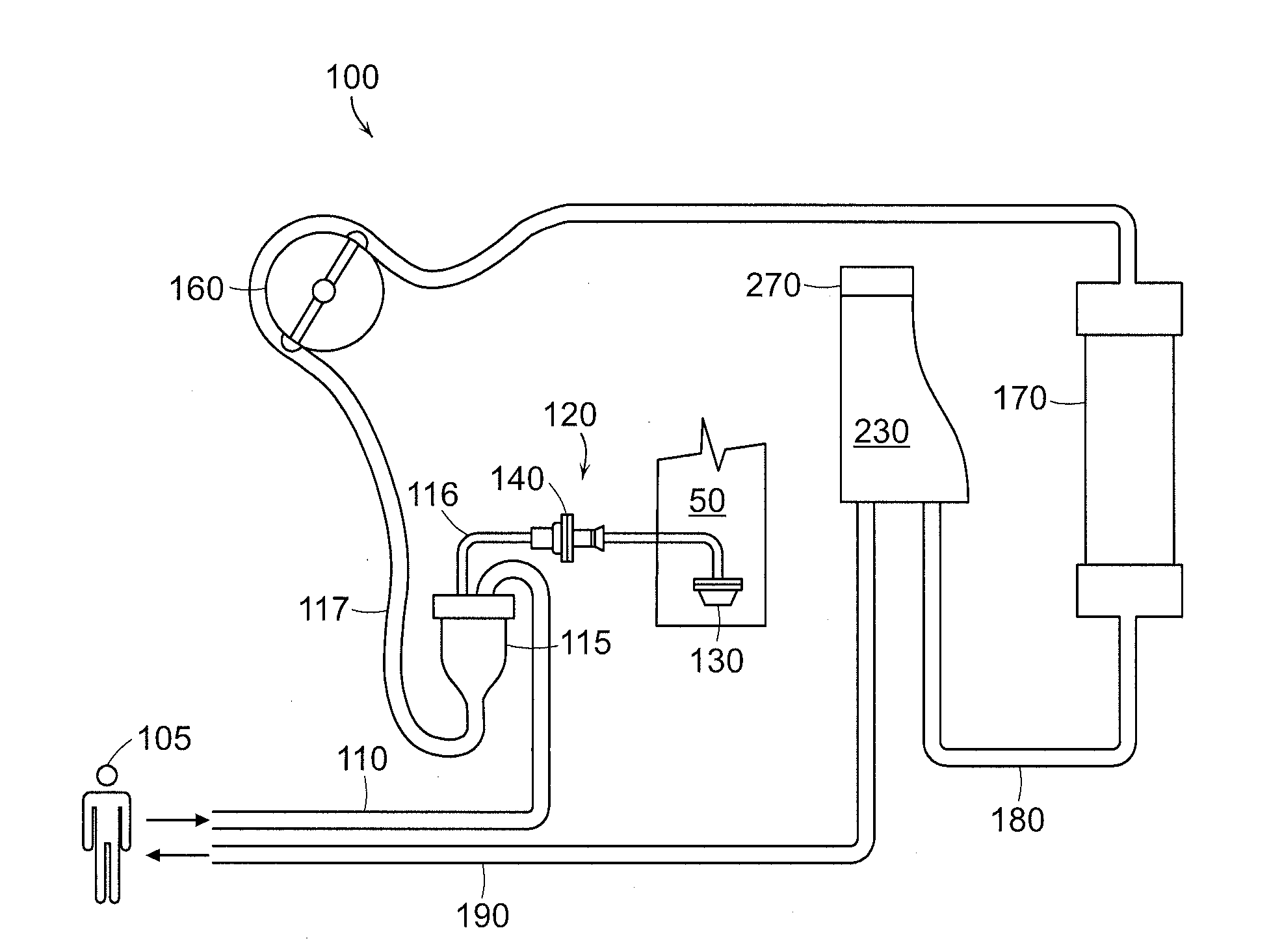
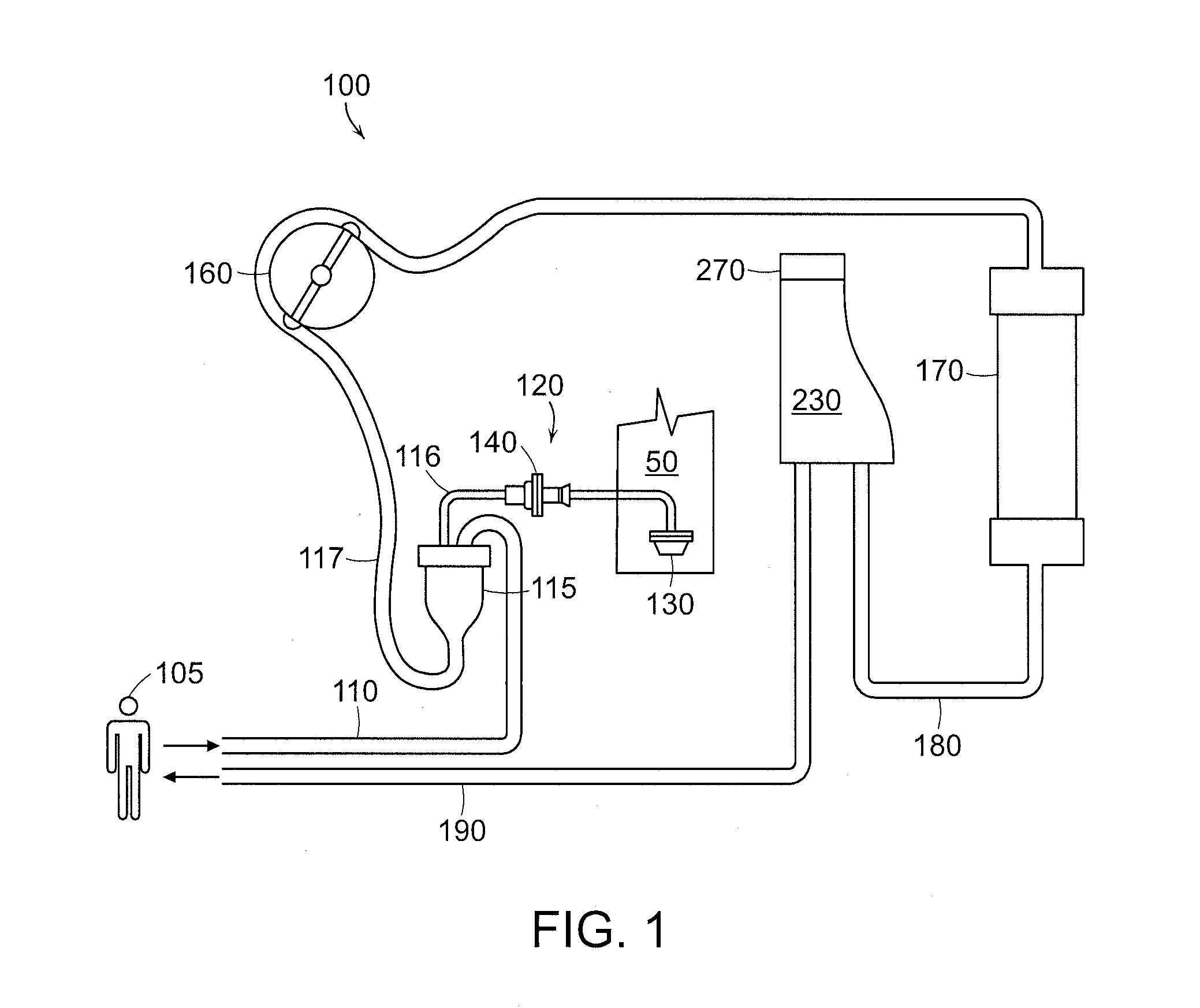
Degassing system for dialysis
The degassing system can include a degassing vessel and can utilize a vacuum pump and a fluid pump located downstream of the degassing vessel to control the pressure within the degassing vessel in order to control the concentration of gases in fluid exiting the degassing system. The degassing system can further comprise sensors in communication with the pumps to control the rate of flow and pressure through the degassing system. The degassing system may be placed in a dialysate flow path to remove dissolved gases including carbon dioxide from the dialysate.
Owner:MOZARC MEDICAL US LLC
System and process for an active drain for gas-liquid separators
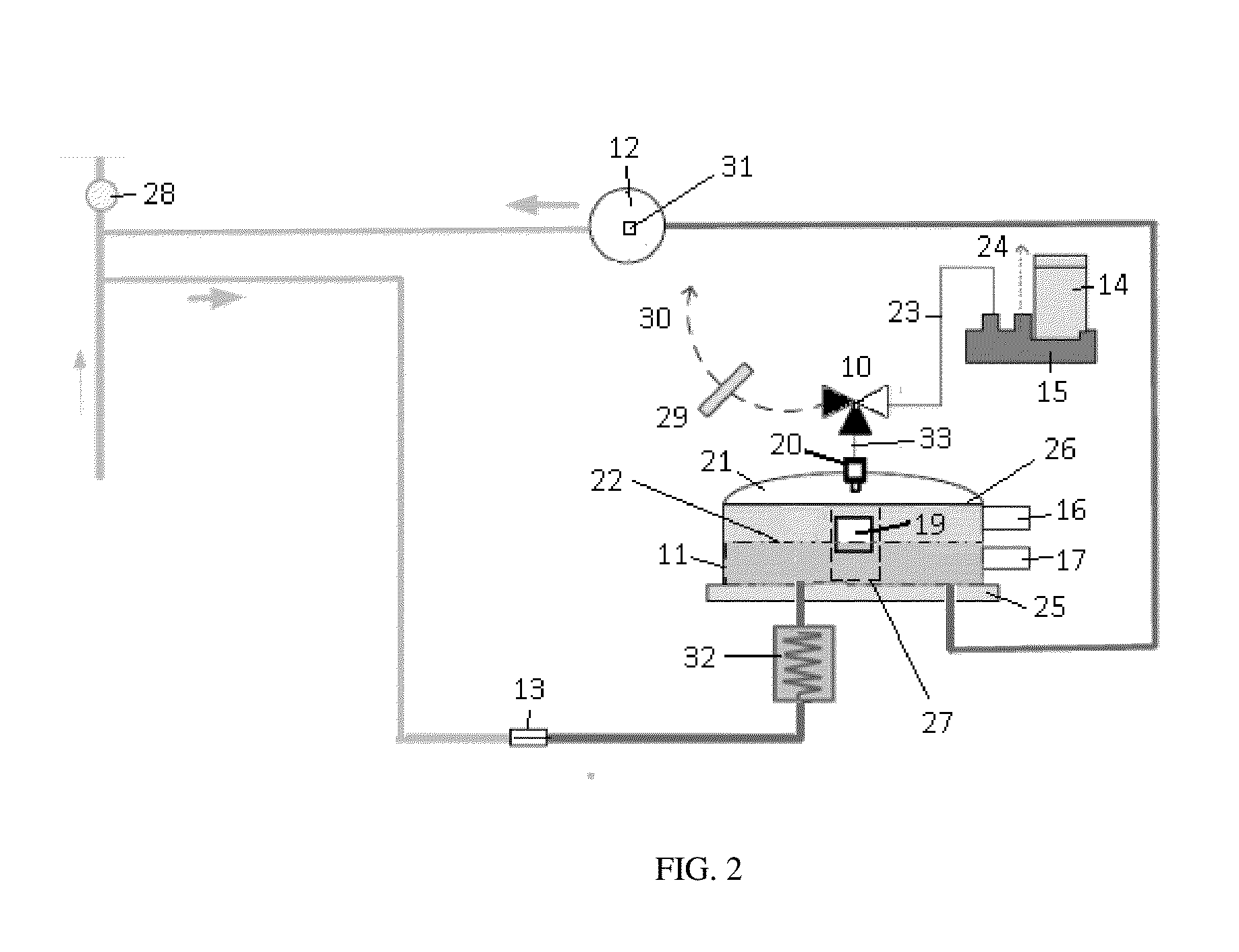
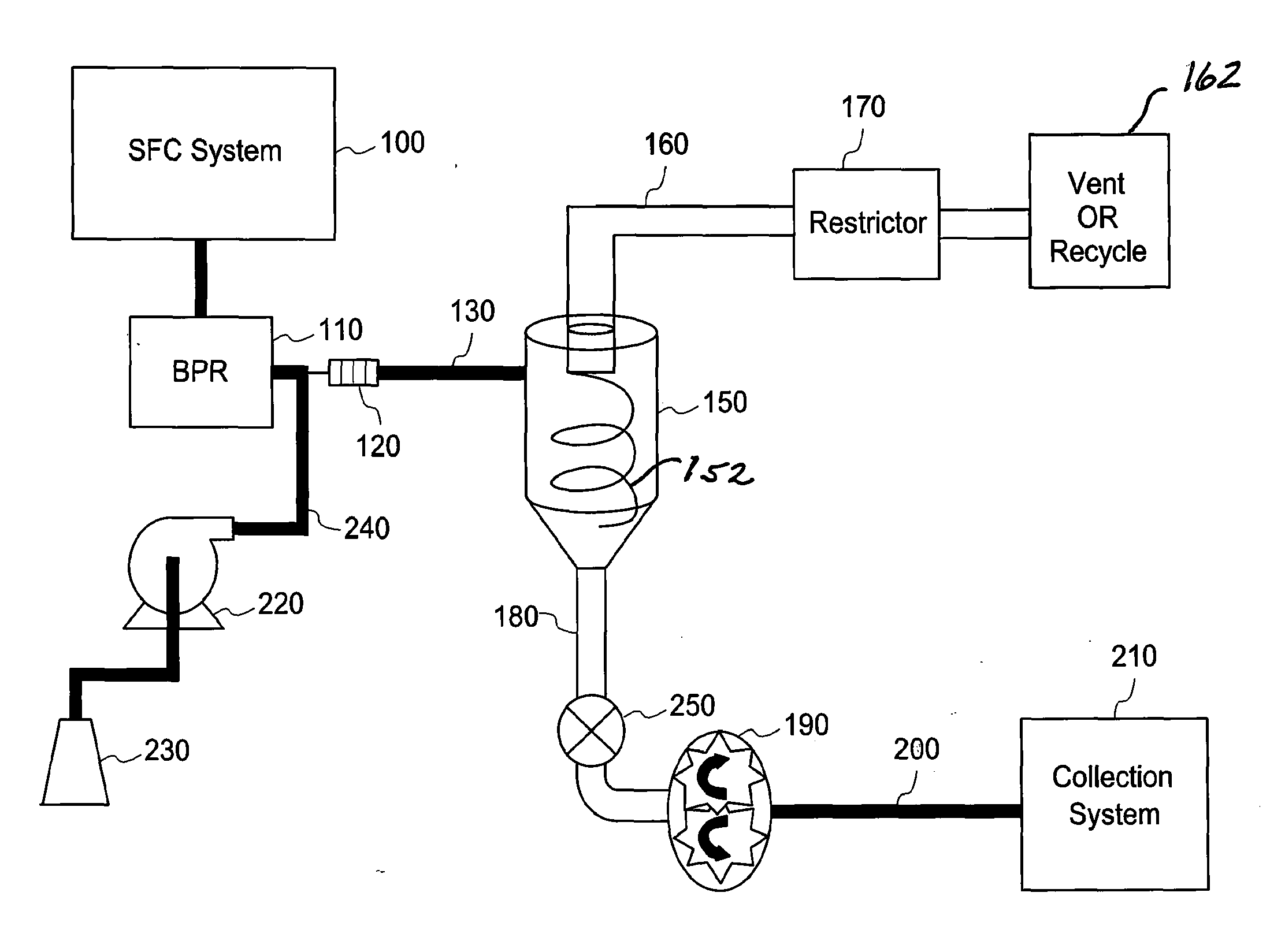
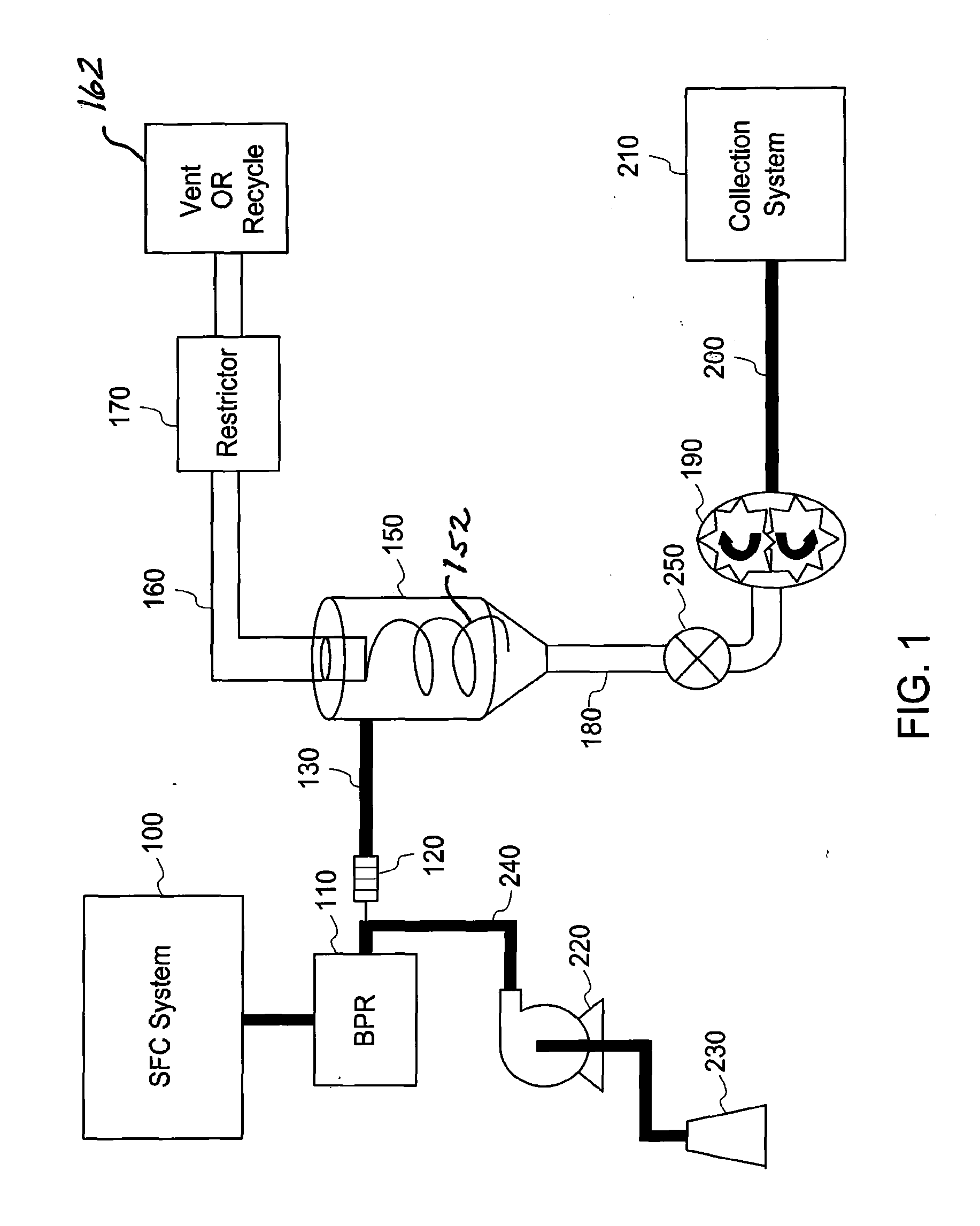
ActiveUS20130180404A1Deterministic drainingSolid sorbent liquid separationLiquid degasification regulation/controlIsolation valveVapor–liquid separator
An apparatus and process to effectively create an active drain for high and low pressure gas-liquid separator. The invention accomplishes a deterministic drainage rate of variable volume and viscosity liquid fractions from the separator. The mechanisms and methods thereof create a flow path from the separator that dramatically favors controlled liquid flow over a wide range of flow rates and viscosities while restricting gas flow. The invention is a superior method of drainage over conventional systems that employ pressure, vacuum, isolation valves and / or passive flow restrictors to achieve drainage of the separators. The embodiments are primarily directed to the fields of preparative supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) and supercritical fluid extraction (SFE). An advantage of one embodiment allows the economical conversion of typical HPLC systems to state of-the-art supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) systems with minimal modification to system components.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
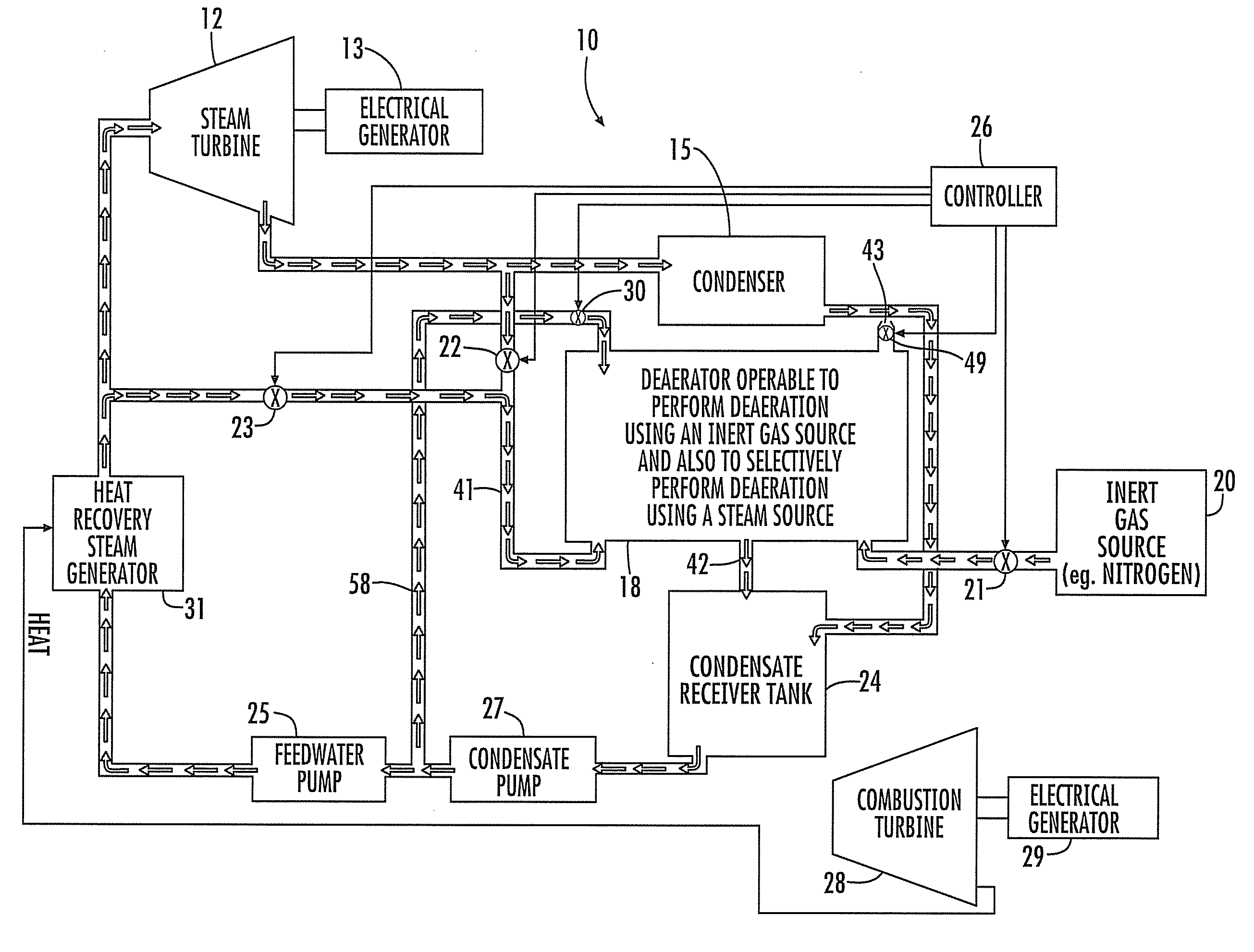
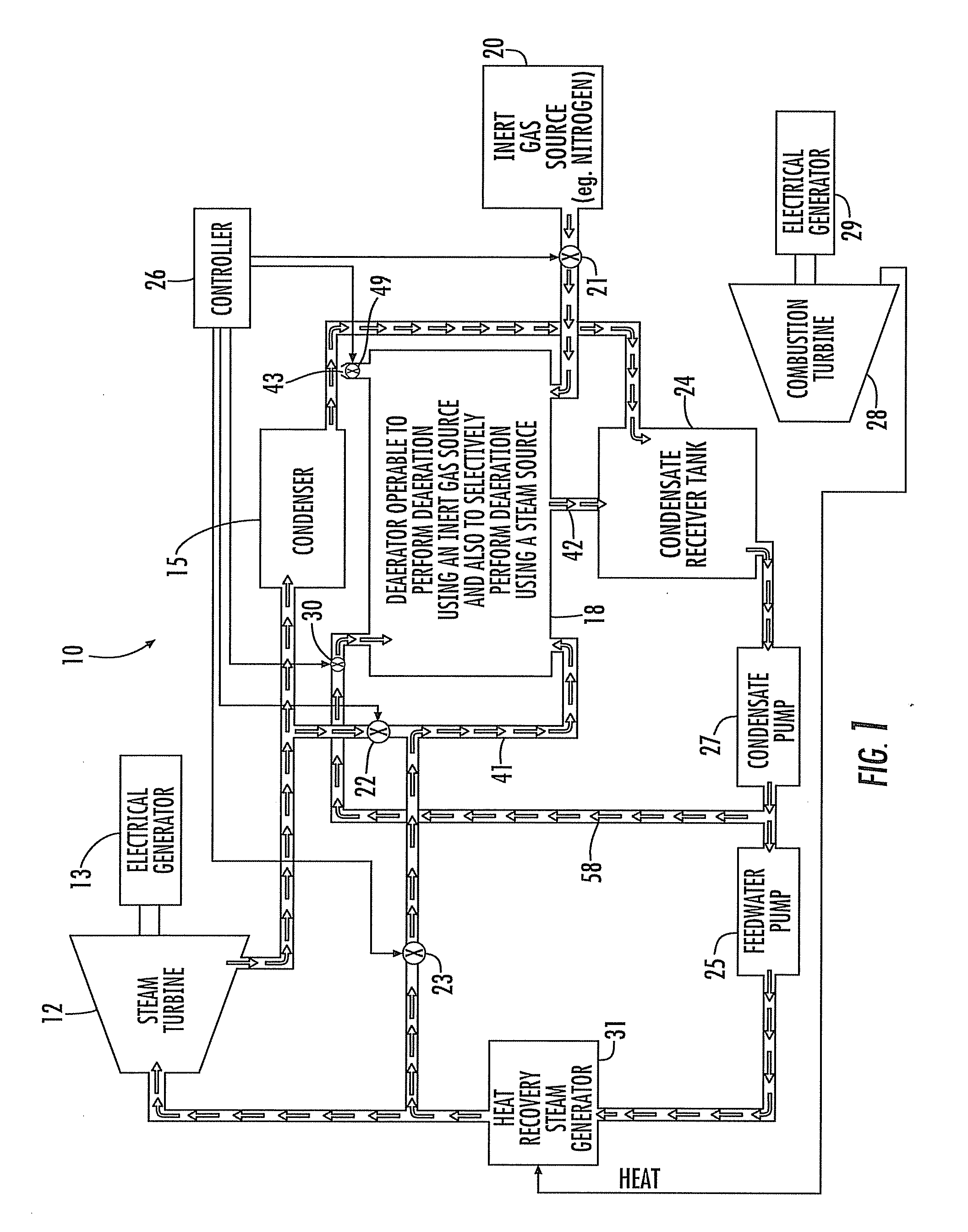
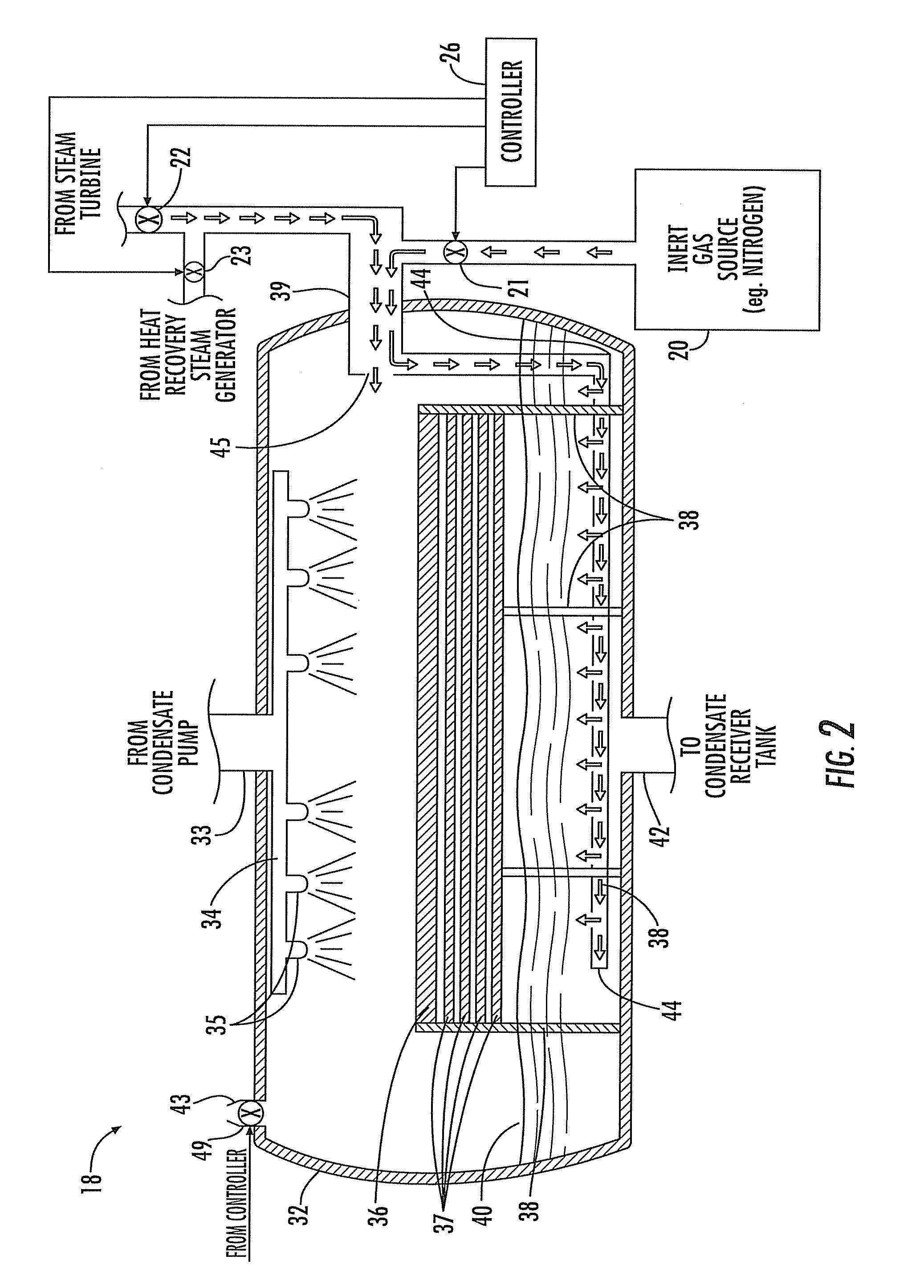
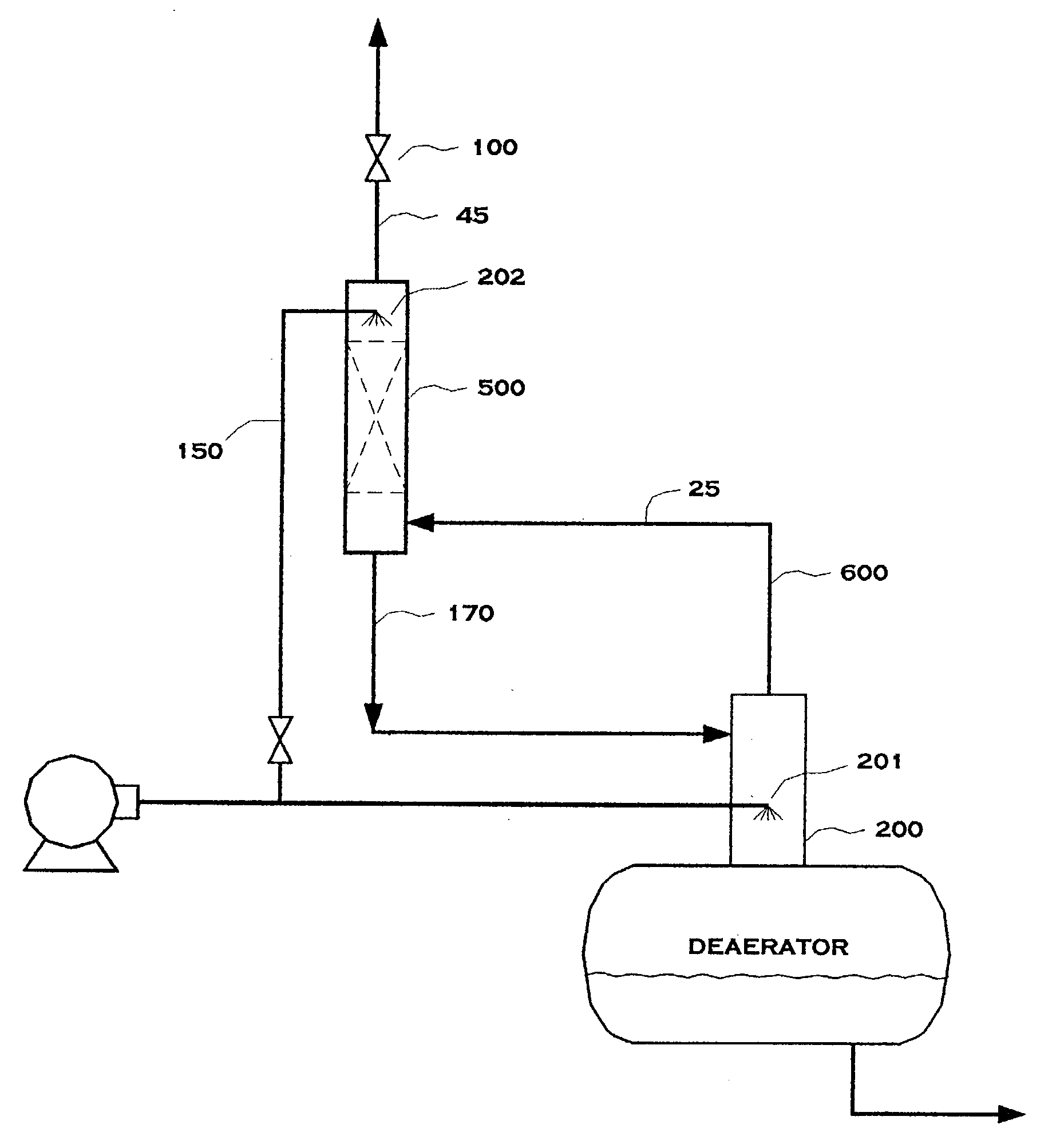
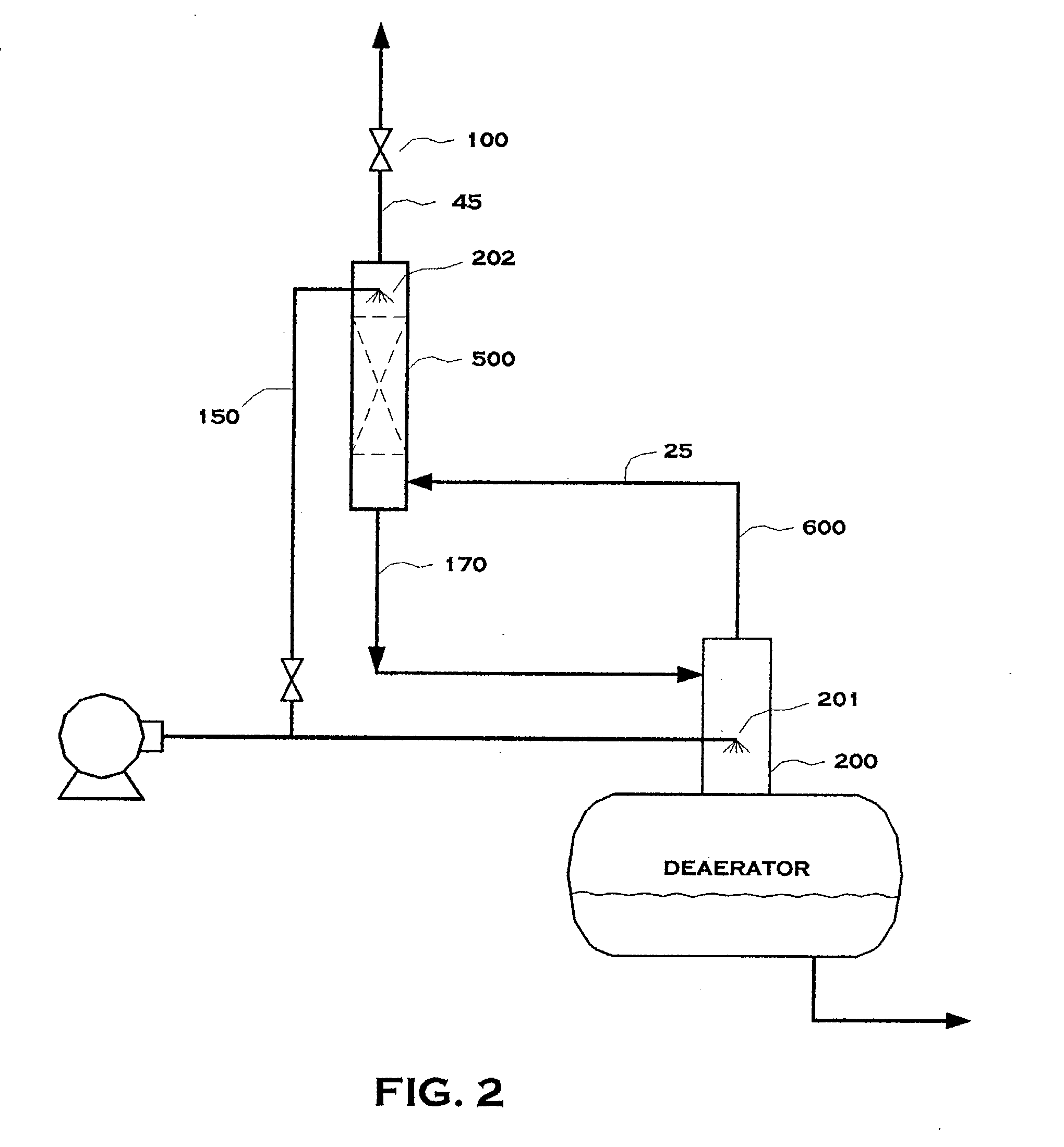
Power Generation Plant Having Inert Gas Deaerator and Associated Methods
InactiveUS20100199670A1Extend lifetimeExtend service intervalSteam regenerationLiquid degasification regulation/controlPower stationEngineering
A power generation plant includes a steam turbine and an electrical generator driven thereby. A condenser is downstream from the steam turbine. Moreover, the power generation plant includes a steam source and an inert gas source. A deaerator downstream from the condenser and is operable to perform deaeration using the inert gas source and is also selectively operable to perform deaeration using the steam source.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Bubble separator
InactiveUS20090120296A1Avoid damagePrevent overcoolingLiquid degasification regulation/controlEngineeringMechanical engineering
A bubble separator is a cyclone-type bubble separator having a cooling mechanism (oil cooler) connected downstream thereof, and is provided with a relief mechanism that operates when the interior pressure in a main body increases. The fluid inside the main body escapes downstream of the cooling mechanism due to the operation of the cooling mechanism. In particular, preferably the relief mechanism is provided in a gas discharge portion that is connected to the main body.
Owner:TOYOTA BOSHOKU KK
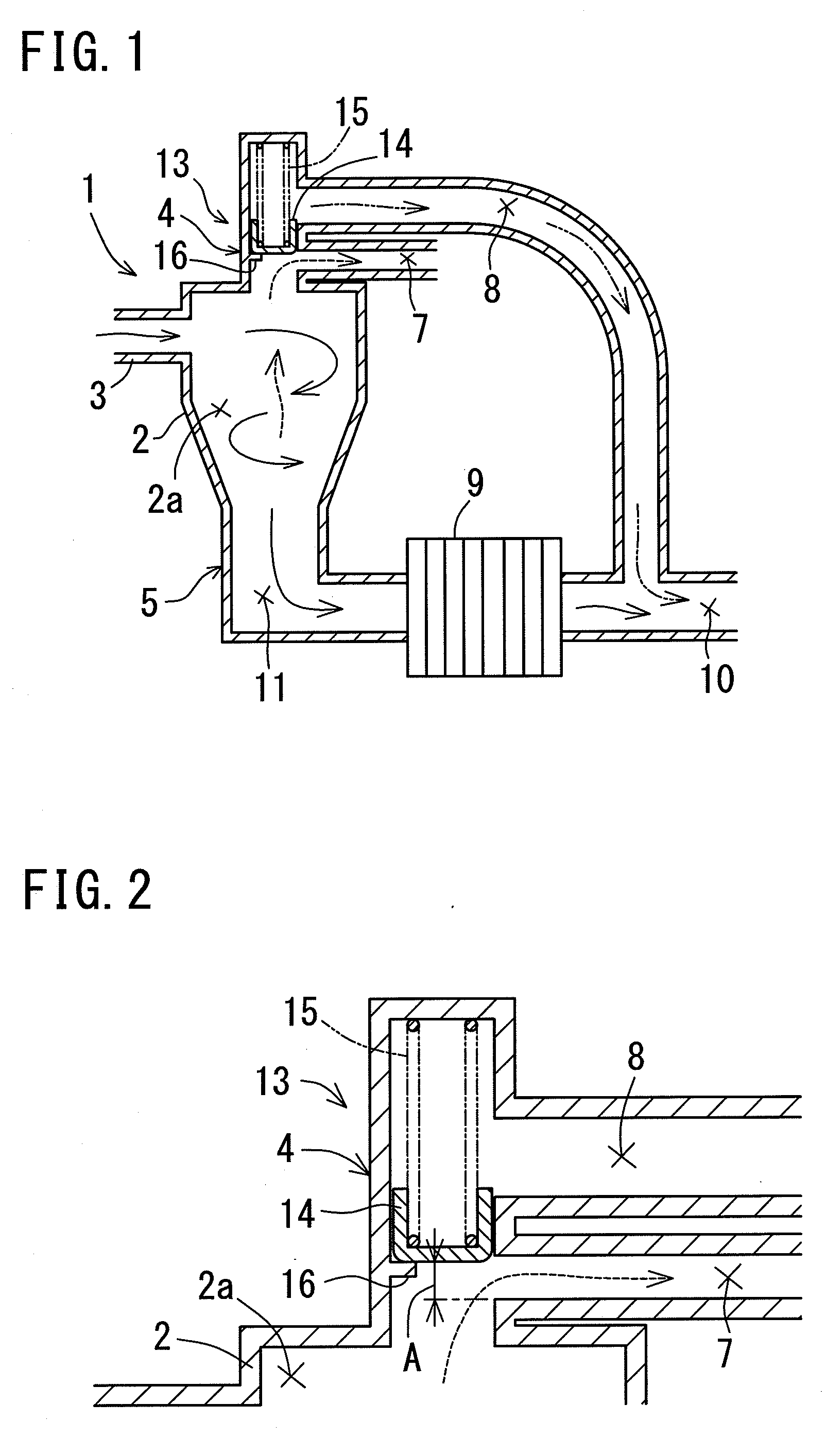
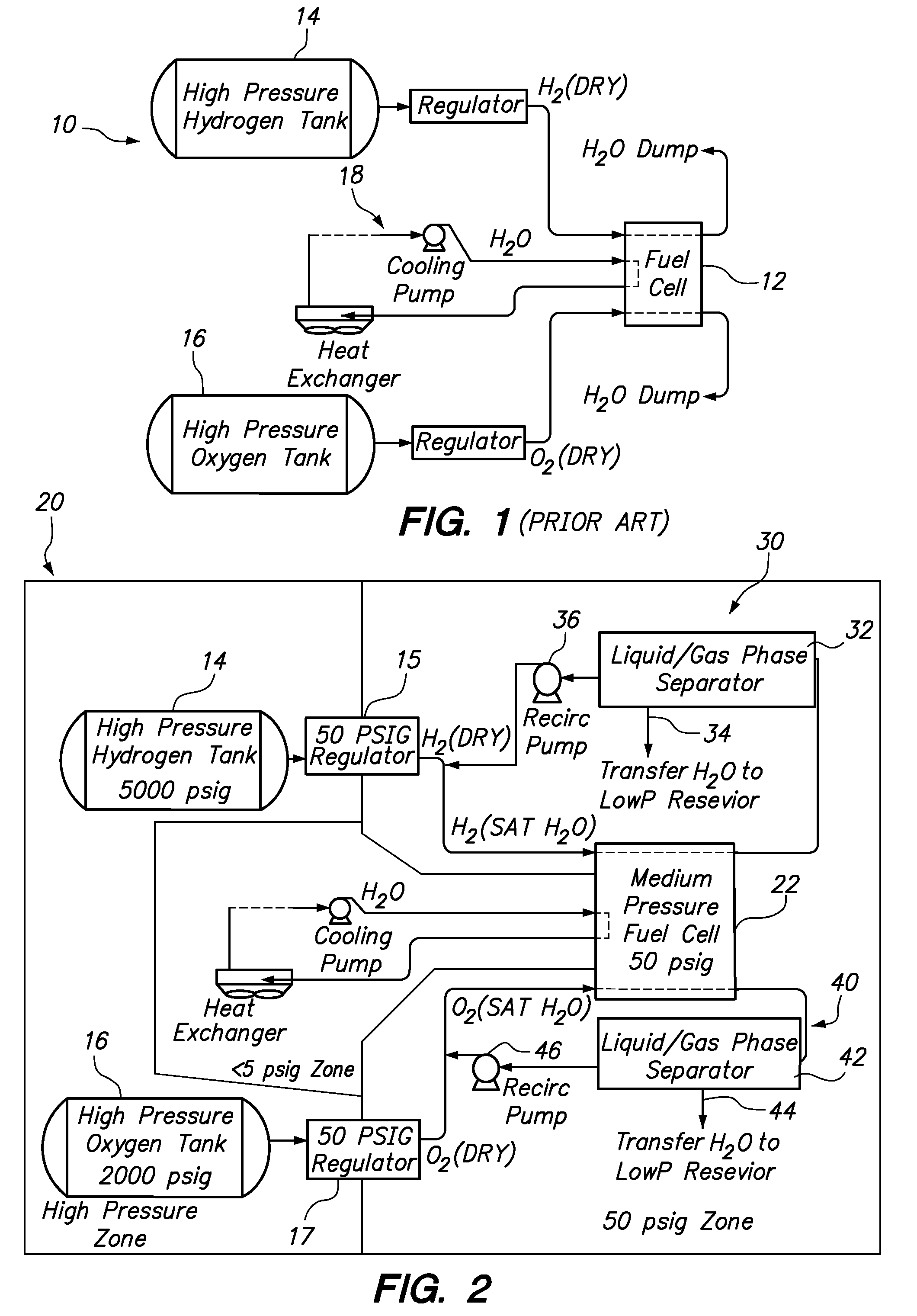
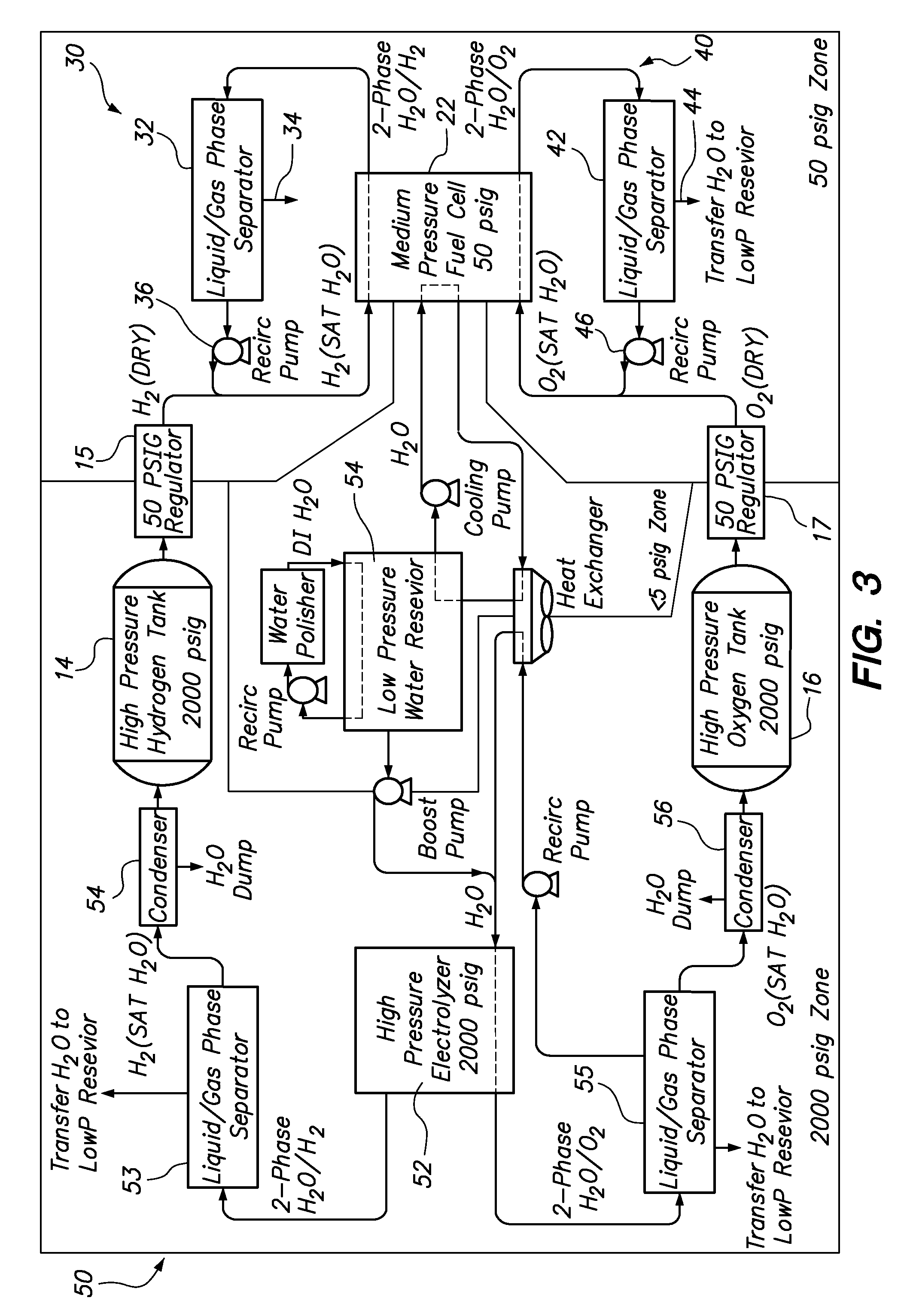
Fuel cell emergency power system
Fuel cell emergency power systems comprising a fuel cell having an anode and a cathode, a power distribution unit for selectively directing electrical current from the fuel cell to one or more consuming device, a hydrogen gas control system and an oxygen gas control system. The hydrogen gas control system includes a pressurized hydrogen tank providing hydrogen gas in selective fluid communication to the anode, a hydrogen gas-liquid water phase separator in downstream fluid communication with the anode, and a hydrogen recirculation pump for recirculating substantially liquid water-free hydrogen from the hydrogen gas-liquid water phase separator to the anode. Similarly, the oxygen gas control system includes a pressurized oxygen tank providing oxygen gas in selective fluid communication to the anode, an oxygen gas-liquid water phase separator in downstream fluid communication with the anode, and an oxygen recirculation pump for recirculating substantially liquid water-free oxygen from the oxygen gas-liquid water phase separator to the anode.
Owner:LYNNTECH
System to remove Dissolved Gases Selectively from Liquids
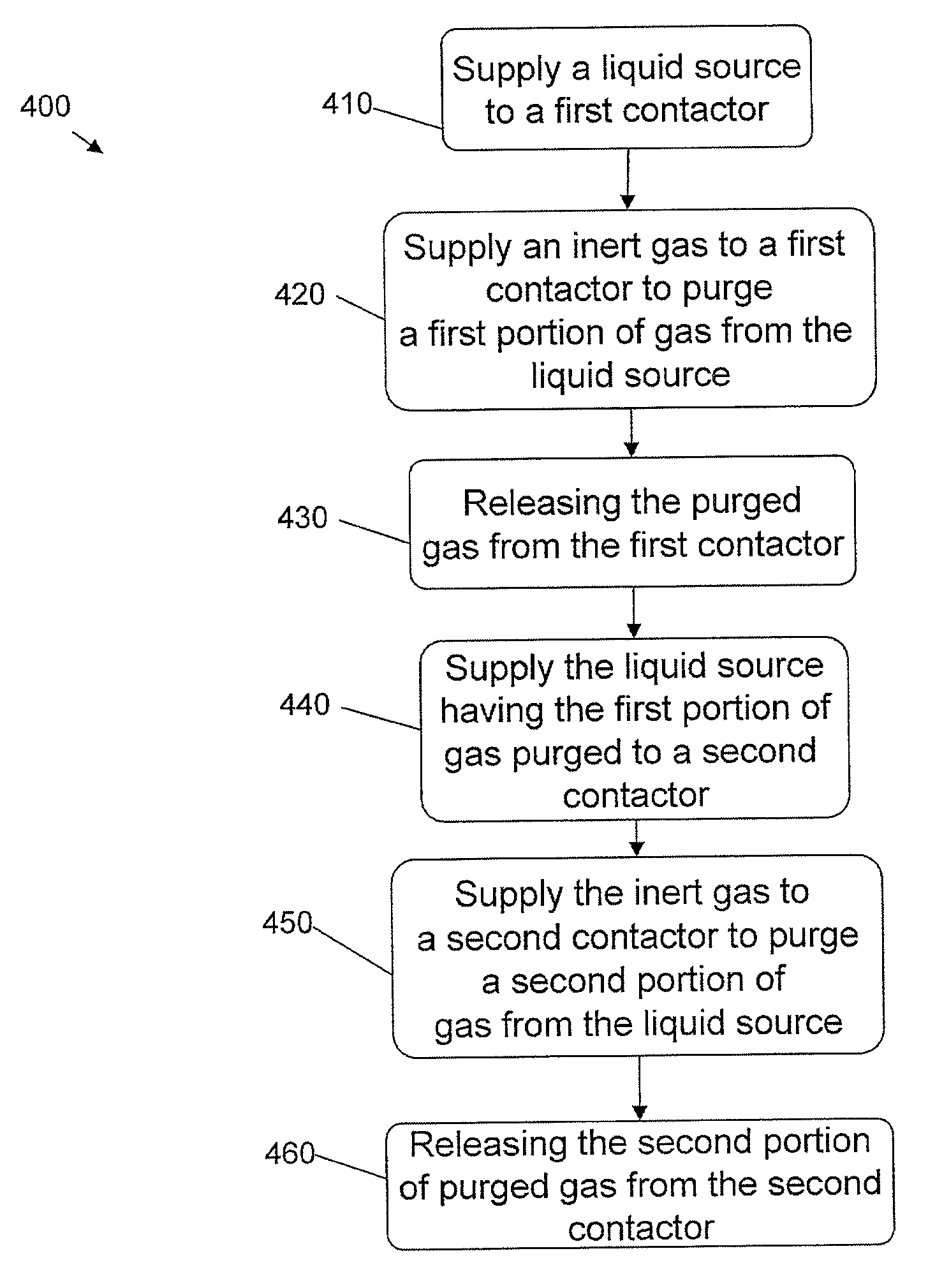
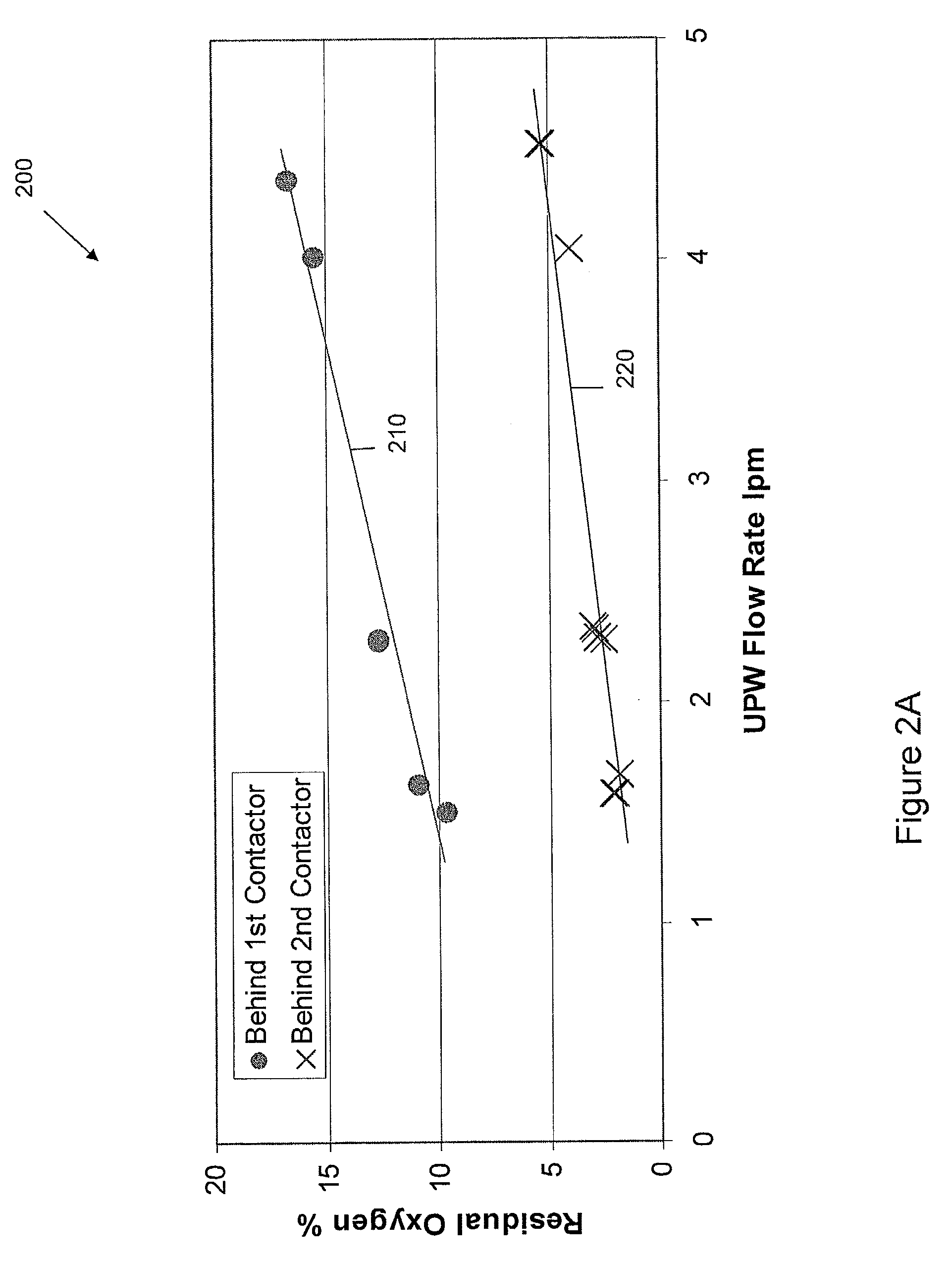
ActiveUS20120279396A1Reduce consumptionExtend your lifeLiquid degasification with auxillary substancesUsing liquid separation agentEnvironmental engineeringContactor
A system to purge dissolved gases selectively from liquids can include a first contactor having two first contactor inlets and two first contactor outlets. The first contactor can receive liquid from a liquid source at a first inlet of the first contactor and an inert gas source at a second inlet of the first contactor, the inert gas can purge a first portion of gas from the liquid source. The first portion of purged gas exits the first contactor at a first outlet of the first contactor. The second contactor can receive input from the second outlet of the first contactor and the inert gas, the inert gas purges a second portion of the gas from the liquid source. The second portion of purged gas can exit the second contactor at a first outlet of the second contactor.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
Apparatus and method for real time determination of density and related parameters in manufacturing processes
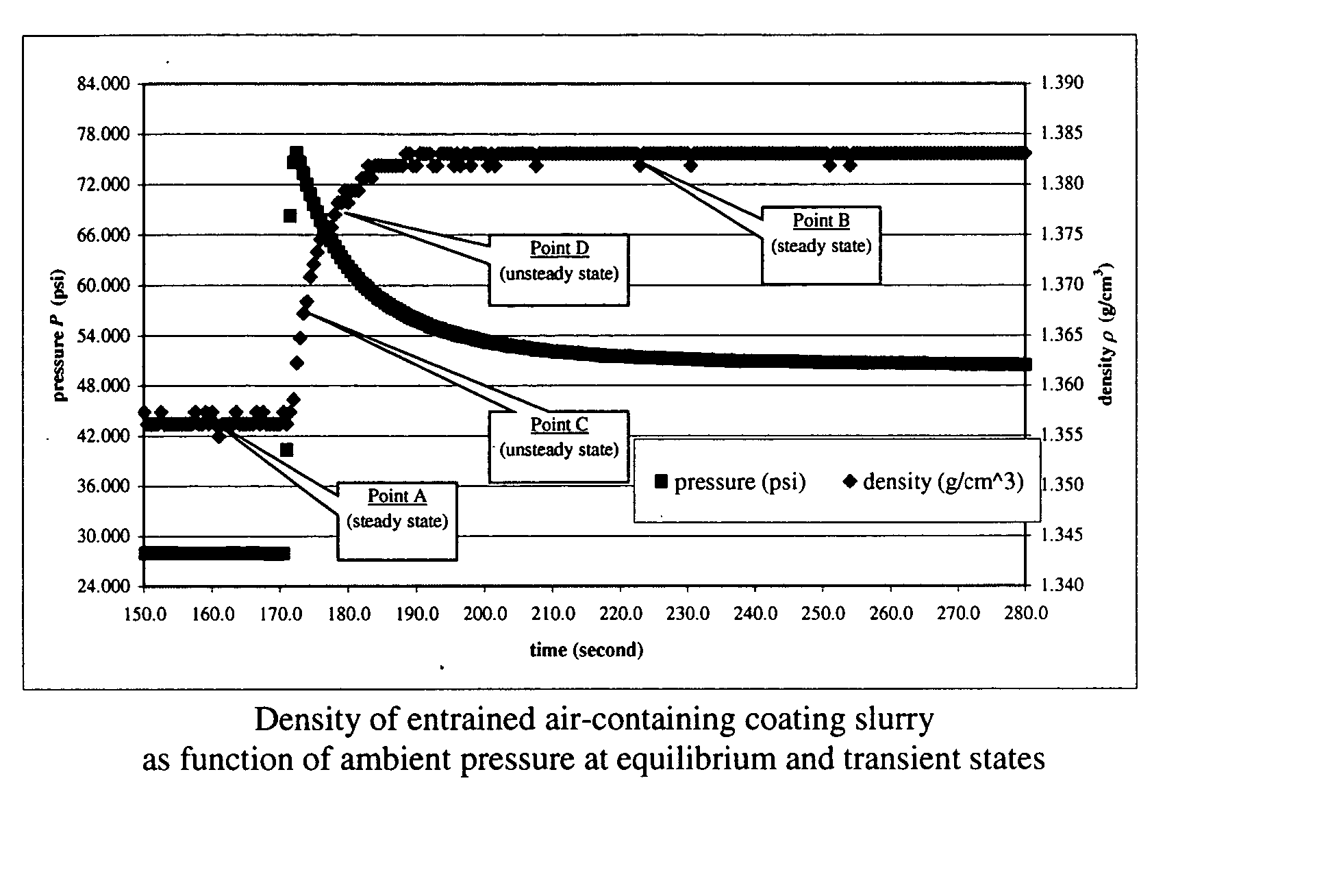
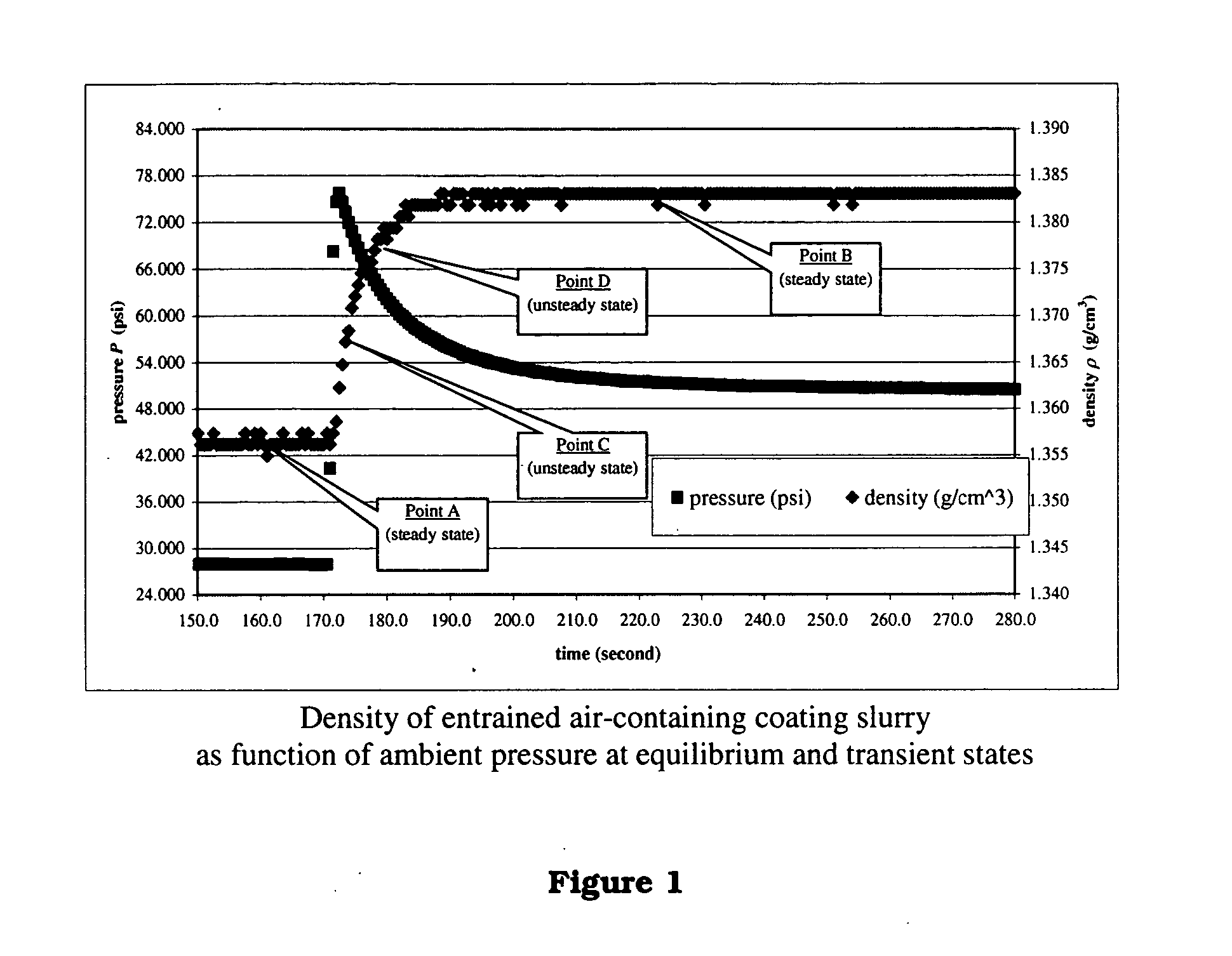
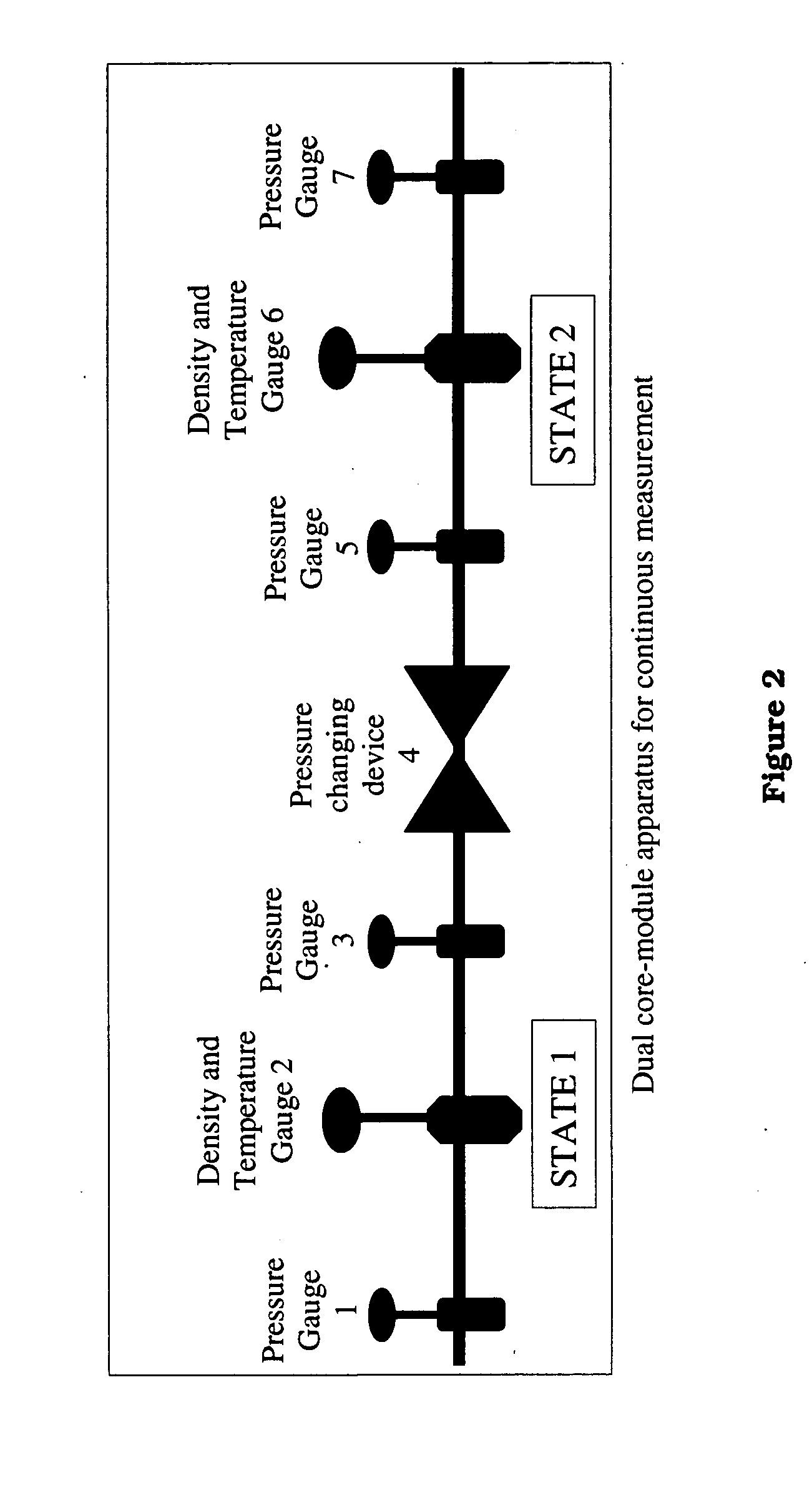
InactiveUS20050043900A1Easy to controlEffectively monitor processTransportation and packagingMixing methodsObservational errorKaolin clay
Methods and apparati for measuring entrained gas content. One of the disclosed apparatus embodiments includes a chamber and piping for process fluid, the piping including two different sectors each comprising a density and temperature gauge having a pressure gauge located upstream and a second pressure gauge located downstream, the two sectors being operatively joined together by a pressure-changing device. The pressure measurement feature may be incorporated into the combination density and temperature gauge, eliminating the need for separate pressure gauges. Data generated by this invention reduces measurement error caused by the dissolving or exsolving of gases with changes in pressure of a fluid, while providing instantaneous measurement, through apparatuses that measure system conditions at each of two pressure states within a very short period of time. For instance, in the context of continuously coating a substrate, the method of this invention comprises: a.) setting a quantitative target for weight-% of one or more solids, e.g. kaolin clay, calcium carbonate, titanium dioxide, or alumina trihydrate, to be coated onto a substrate such as a paper web; b.) continuously applying the solids to the substrate via a carrier fluid; c.) measuring the apparent density of the slurry; d.) determining the true density of the slurry; e.) calculating the weight-% of solids in the slurry as disclosed above; f.) comparing the calculated weight-% solids to the target weight-% solids; and, g.) if the calculated weight-% is greater or less than the target weight-%, lowering or raising the amount of solids applied in step b.). Many other method and apparatus embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:APPVION OPERATIONS INC
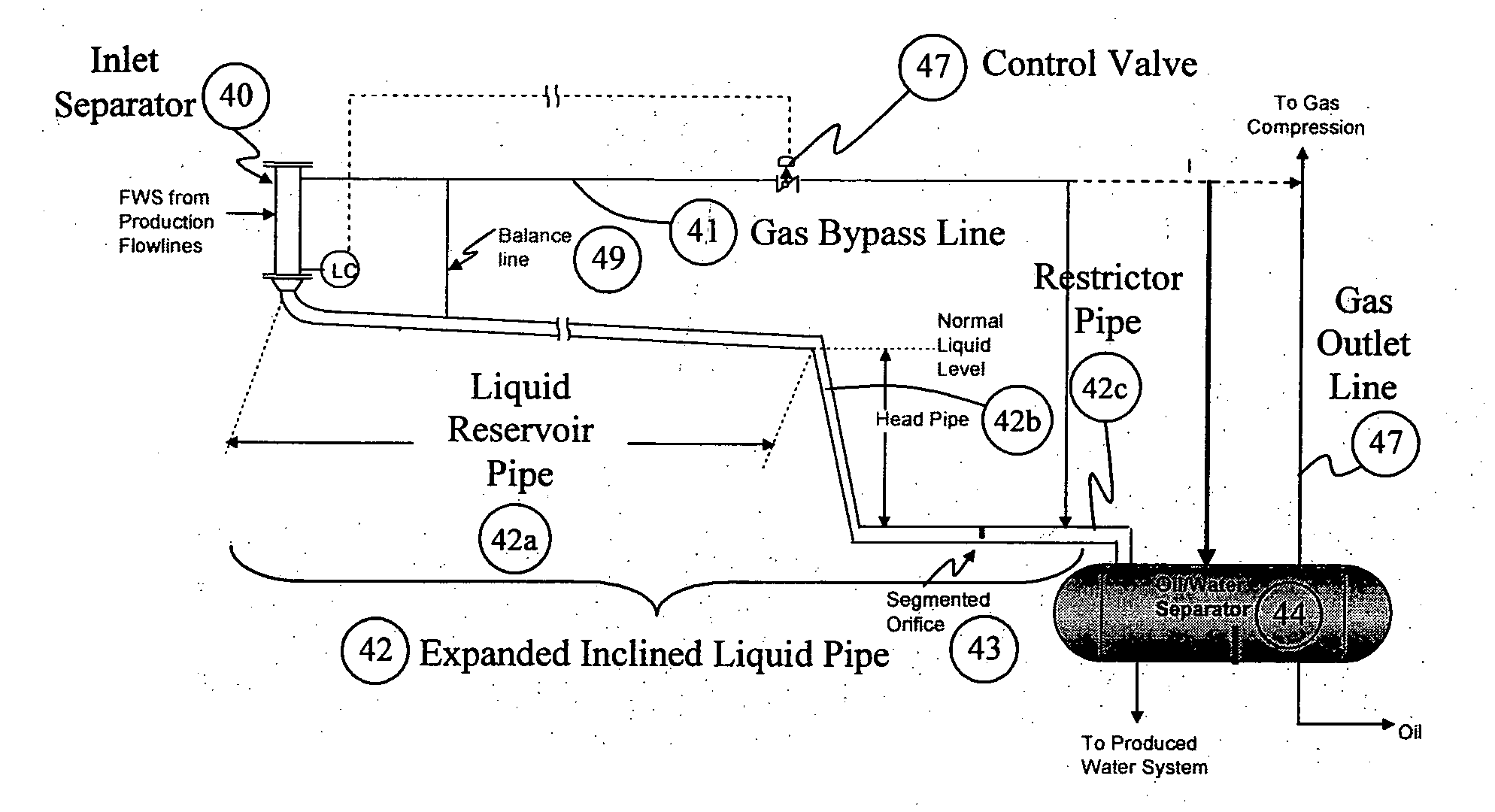
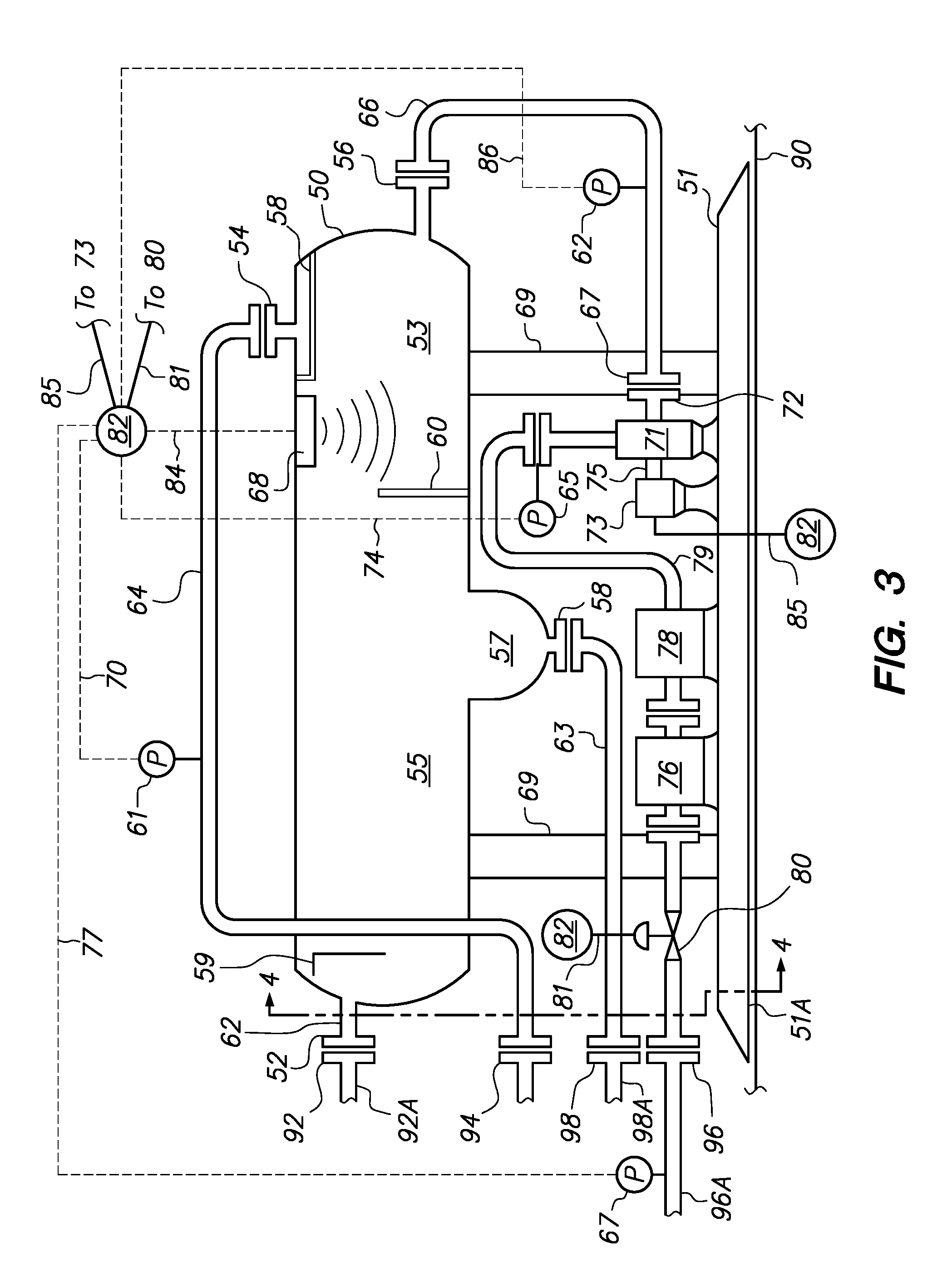
Slug Suppressor Apparatus and Crude Oil Stabilization Assembly and Process Therefor
InactiveUS20120160103A1Effective functionMinimal controlLiquid degasification regulation/controlFlash degasificationEngineeringSuppressor
A slug suppressor apparatus comprising an inlet separator capable of gas-liquid separation of full well stream fluid and expanded inclined liquid pipe for dampening slugs. The inlet separator has an inlet for receiving the full well stream fluid, a separated gas outlet in its upper section, and a separated liquid outlet in its lower section. The separated gas outlet and the separated outlet are operationally connected to a gas bypass line and the expanded inclined liquid pipe respectively. The expanded inclined liquid pipe has means for dampening liquid slugs and is connectable to a 3-Phase separator.
Owner:NGLTECH
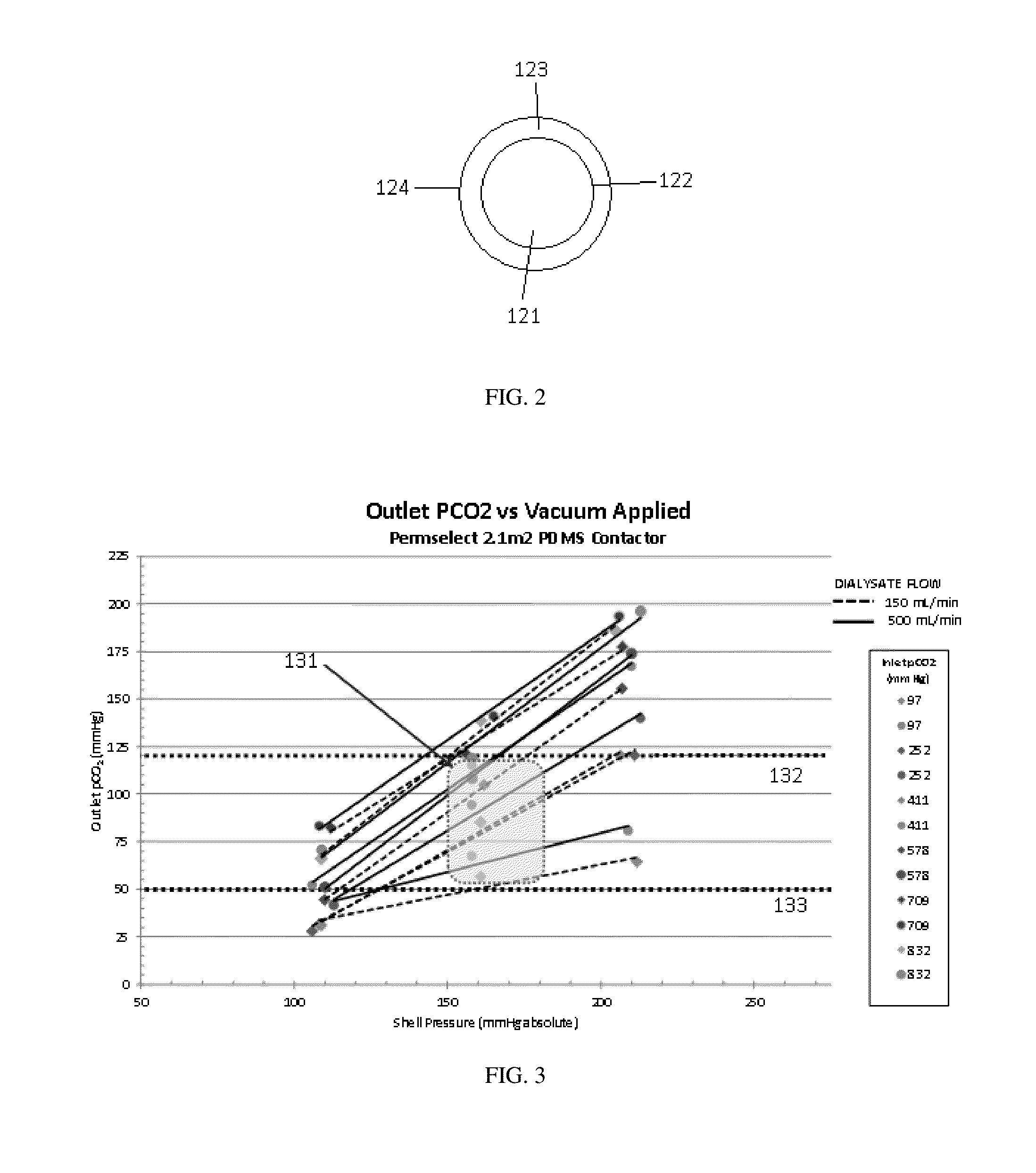
Degassing membrane for dialysis
The degasser can have a degassing membrane that can be constructed from non-porous silica. The degassing membrane can be highly permeable to carbon dioxide but less permeable oxygen or nitrogen gases. Pressure in the dialysate and the degasser can be controlled in order to control the amount of carbon dioxide and other gases in dialysate leaving the degasser. The degassing membrane may be placed in a degassing module in a dialysate flow path to remove dissolved carbon dioxide from the dialysate.
Owner:MOZARC MEDICAL US LLC
Conditioning device for liquid handling system liquids
InactiveUS20070140916A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsLiquid degasification regulation/controlLine tubingEngineering
A device for conditioning a system liquid for a liquid handling apparatus has a degassing chamber for degassing the system liquid, with a system liquid injection point, a system liquid drain line and a gas train line. The device has a collection chamber for degassing liquid, which is separated from the degassing chamber and is connected via a recirculation pump to the system liquid drain line. At least one such device can be integrated into a mobile facility for conditioning a system liquid for a liquid handling apparatus. A liquid handling workstation having at least one such liquid handling apparatus for pipetting or dispensing liquid samples with the aid of a system liquid or such a liquid handling apparatus may also comprise at least one such device.
Owner:TECAN TRADING AG
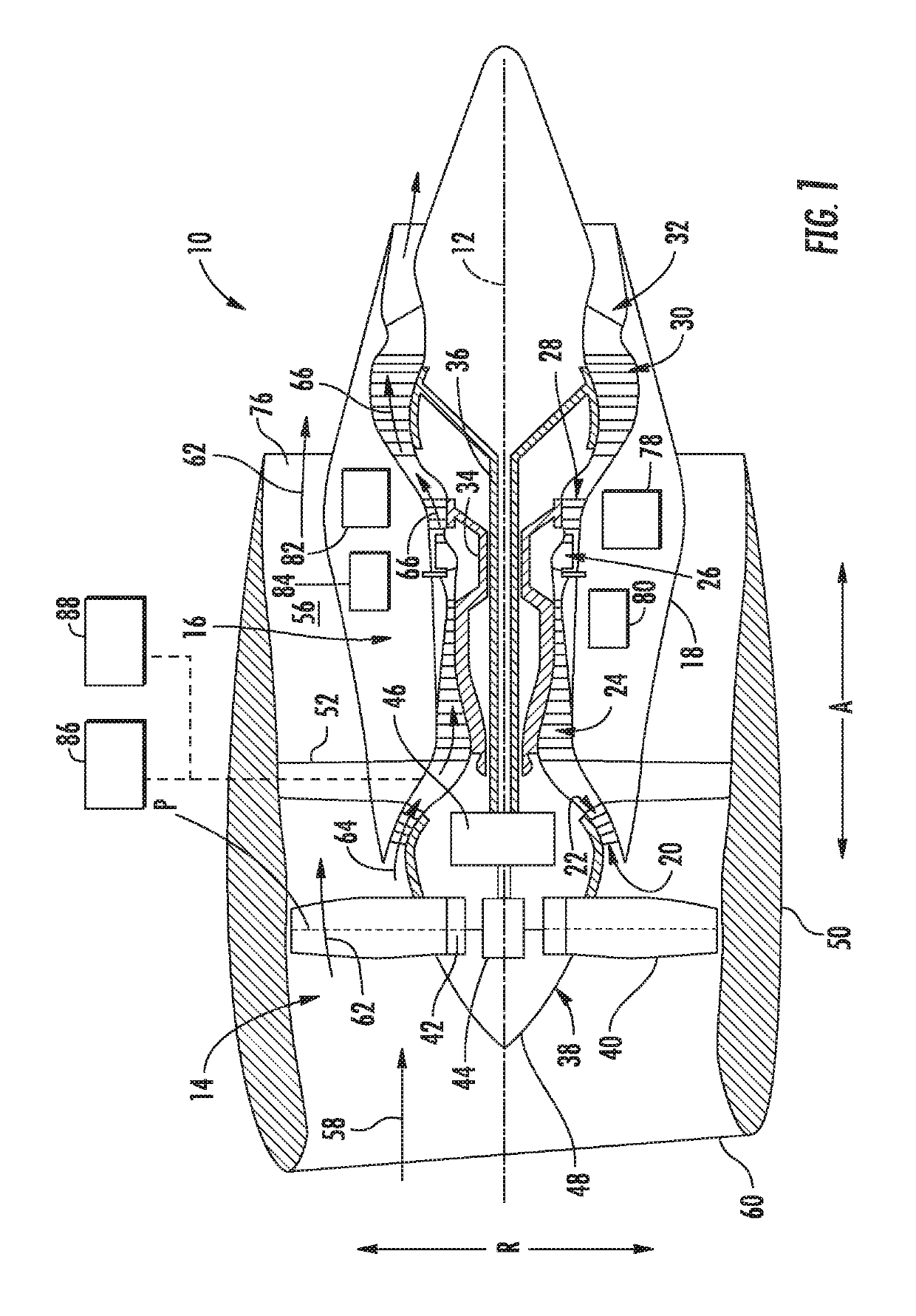
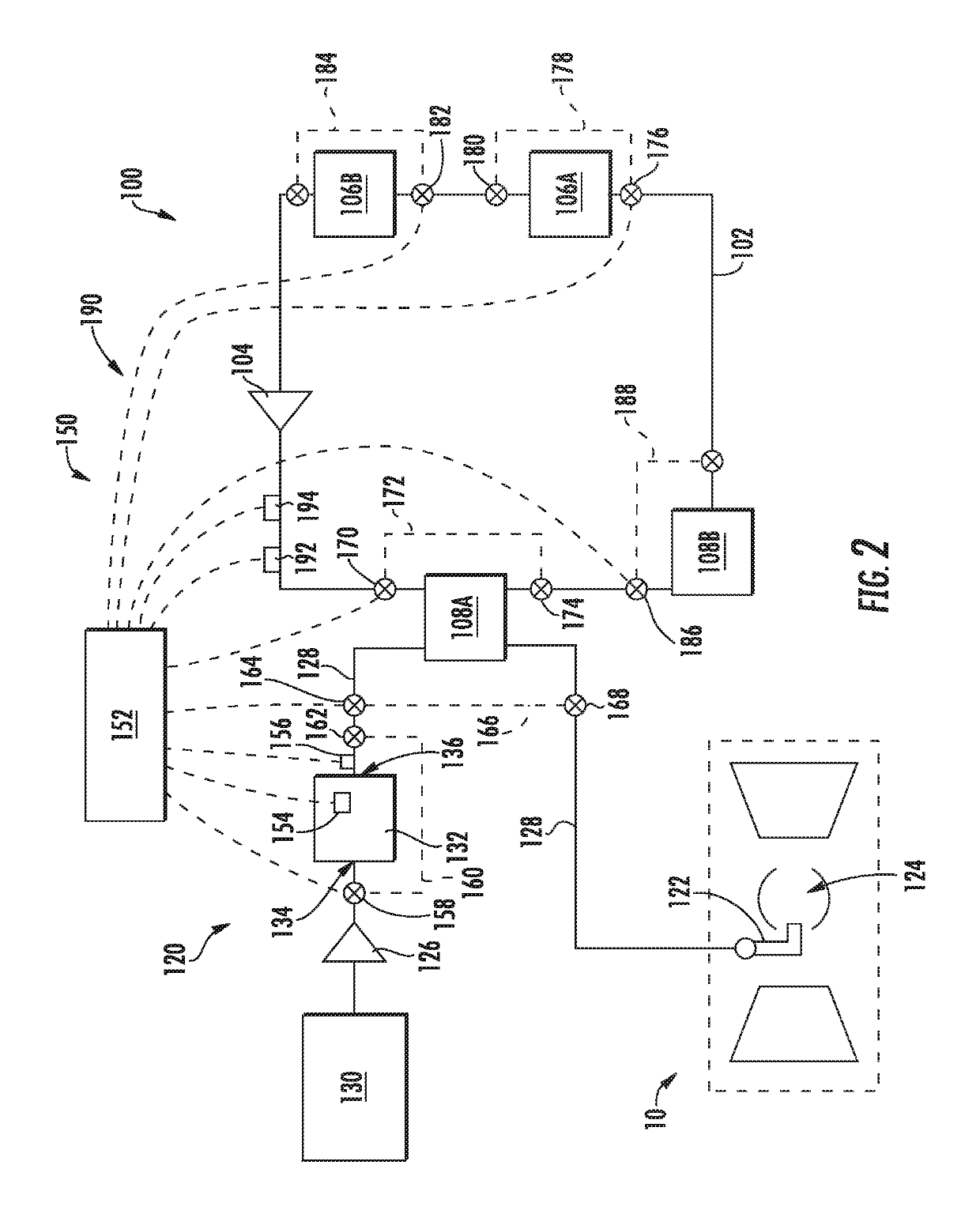
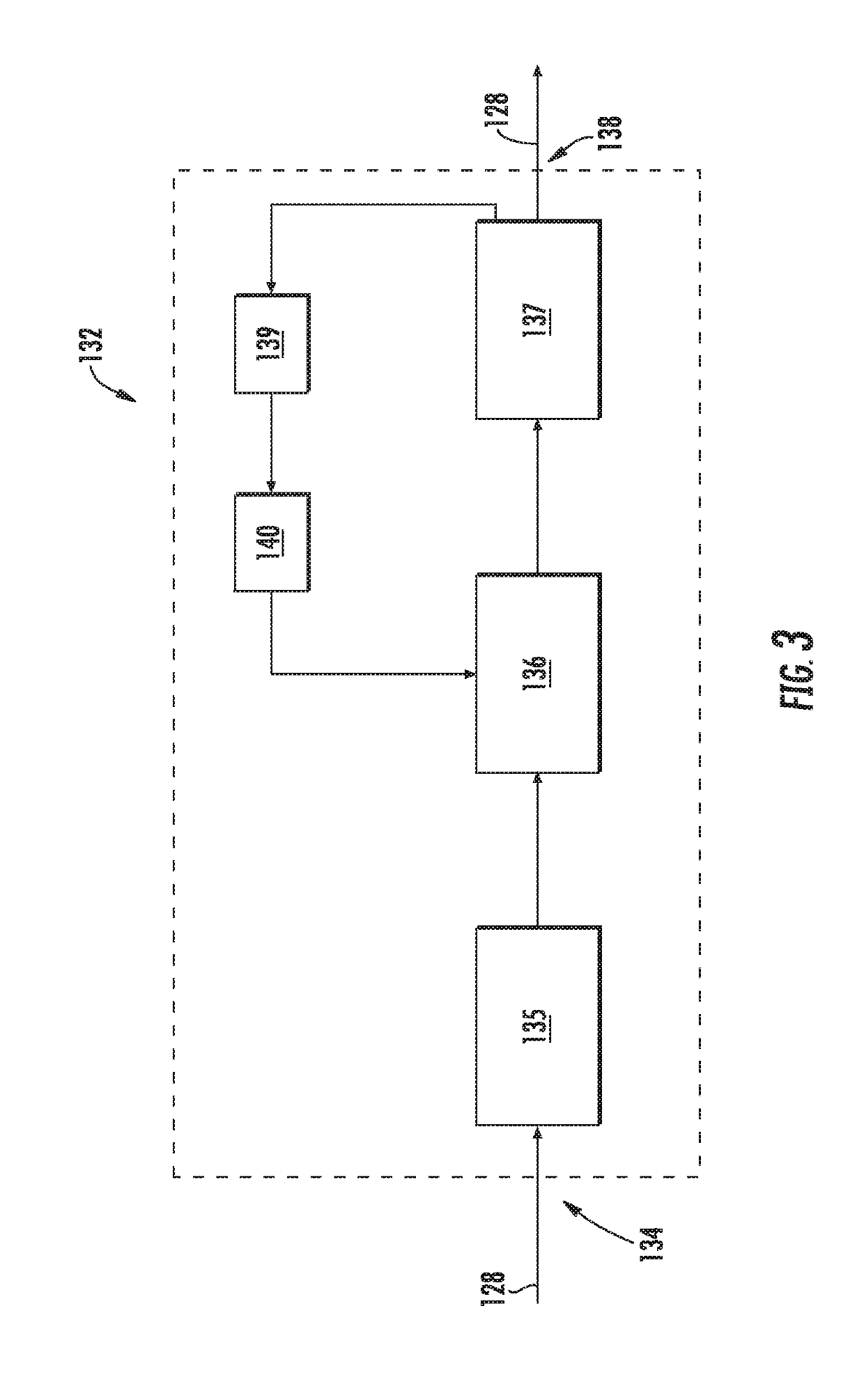
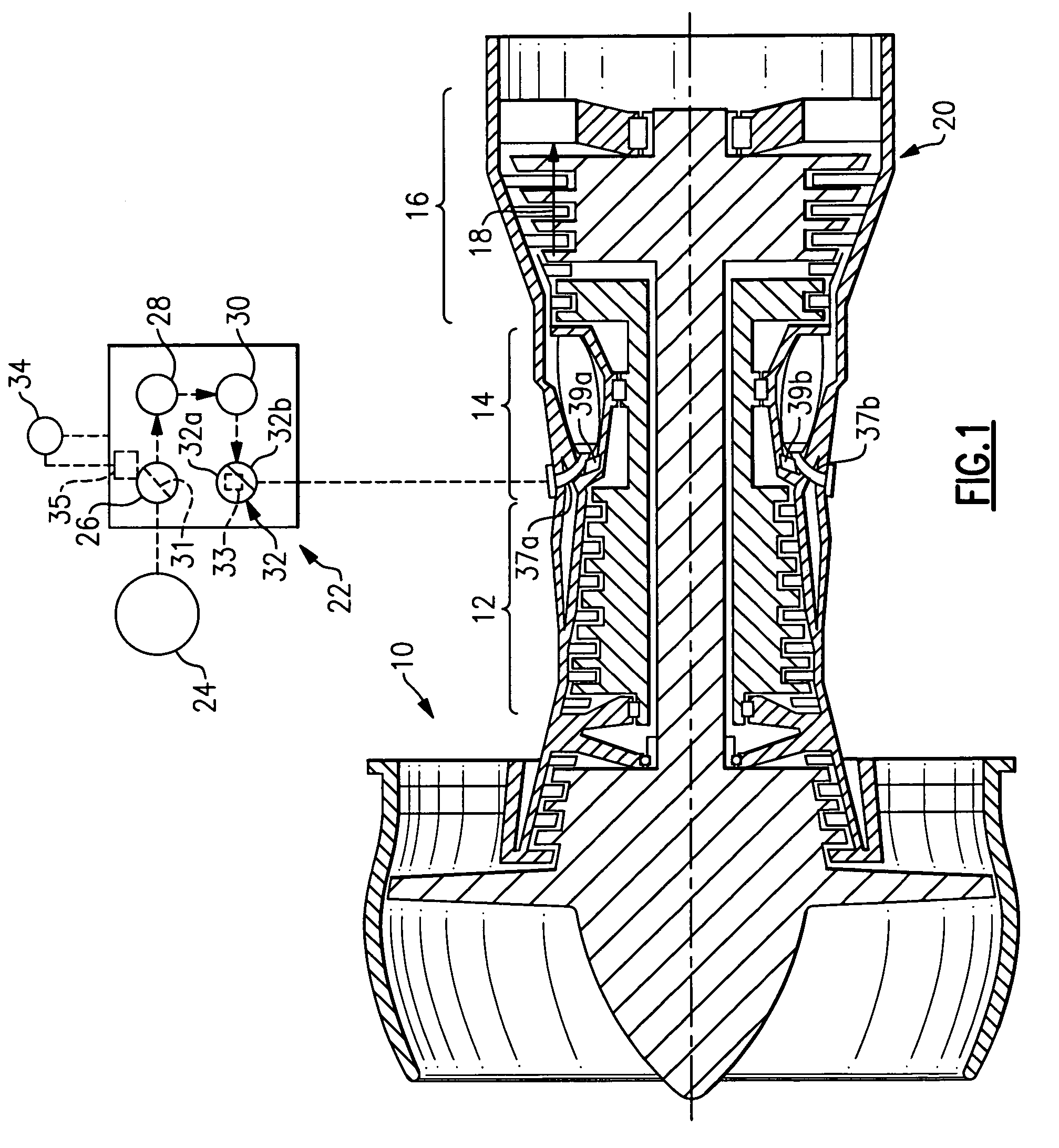
Thermal management system
ActiveUS20190153952A1Reduces fuel contentLiquid degasification with auxillary substancesTurbine/propulsion engine coolingEngineeringThermal management system
A combustion engine includes a combustion section; a fuel delivery system for providing a fuel flow to the combustion section, the fuel delivery system including an oxygen reduction unit for reducing an oxygen content of the fuel flow; a thermal management system including a heat sink heat exchanger, the heat sink heat exchanger in thermal communication with the fuel delivery system at a location downstream of the oxygen reduction unit; and a control system including a sensor operable with the fuel delivery system for sensing data indicative of an operability of the oxygen reduction unit and a controller operable with the sensor, the controller configured to initiate a corrective action based on the data sensed by the sensor indicative of the operability of the oxygen reduction unit.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
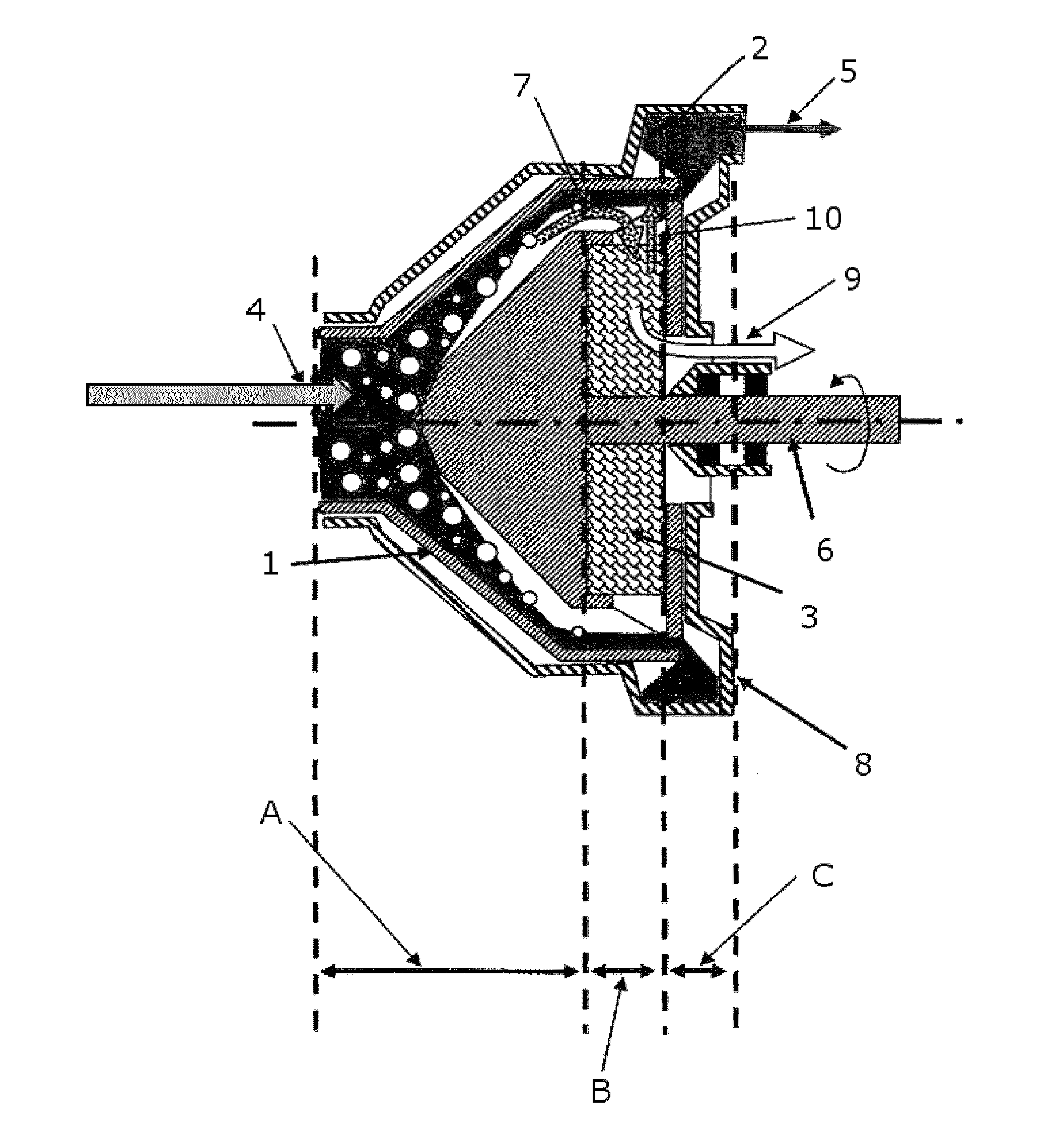
Combined pumping and separating machine for the oil circuit of a turbojet
A combined machine for pumping and separating into two distinct and purified phases a two-phase liquid / gas mixture or fluid, is provided. A first stage of the combined machine is equipped with an intake for the two-phase fluid, in which the two-phase fluid is sucked, pumped and partially separated into two distinct phases. One phase is mainly liquid and the other phase is mainly gaseous. A second stage of the combined machine includes two zones, which includes a first zone and a second zone. In the first zone, the mainly liquid phase extracted from the first stage is degassed. In the second zone, the mainly gaseous phase extracted from the first stage is dried. In a third stage of the combined machine, the degassed liquid is forced back and pressurized.
Owner:TECHSPACE AERO
Vacuum control system
ActiveUS20050079074A1Effectively and accurately removingDegree of vacuum in vacuum can be keptLiquid degasification regulation/controlFluid dynamicsInternal pressureRotatory power
There is provided a vacuum control system for allowing the degree of vacuum in a vacuum vessel to be kept constant, effectively and accurately removing vaporized components degassed into the vacuum vessel through a gas permeation diaphragm by stably introducing a very small amount of air into a vacuum exhaust path, and thus operating stably, and a vacuum degassing apparatus employing the vacuum control system. The vacuum control system controls the rotatory power of a DC brushless motor, continuously controls displacement of a vacuum pump, and thus keeps the degree of vacuum in a vacuum vessel constant, by decompressing the inside of the vacuum vessel using an exhaust vacuum pump which operates with the DC brushless motor, monitoring the inside pressure of the vacuum vessel using a pressure sensor, and controlling a voltage applied to the DC brushless motor on the basis of an output signal resulting from measurement of the inside pressure of the vacuum vessel by the pressure sensor.
Owner:ERC
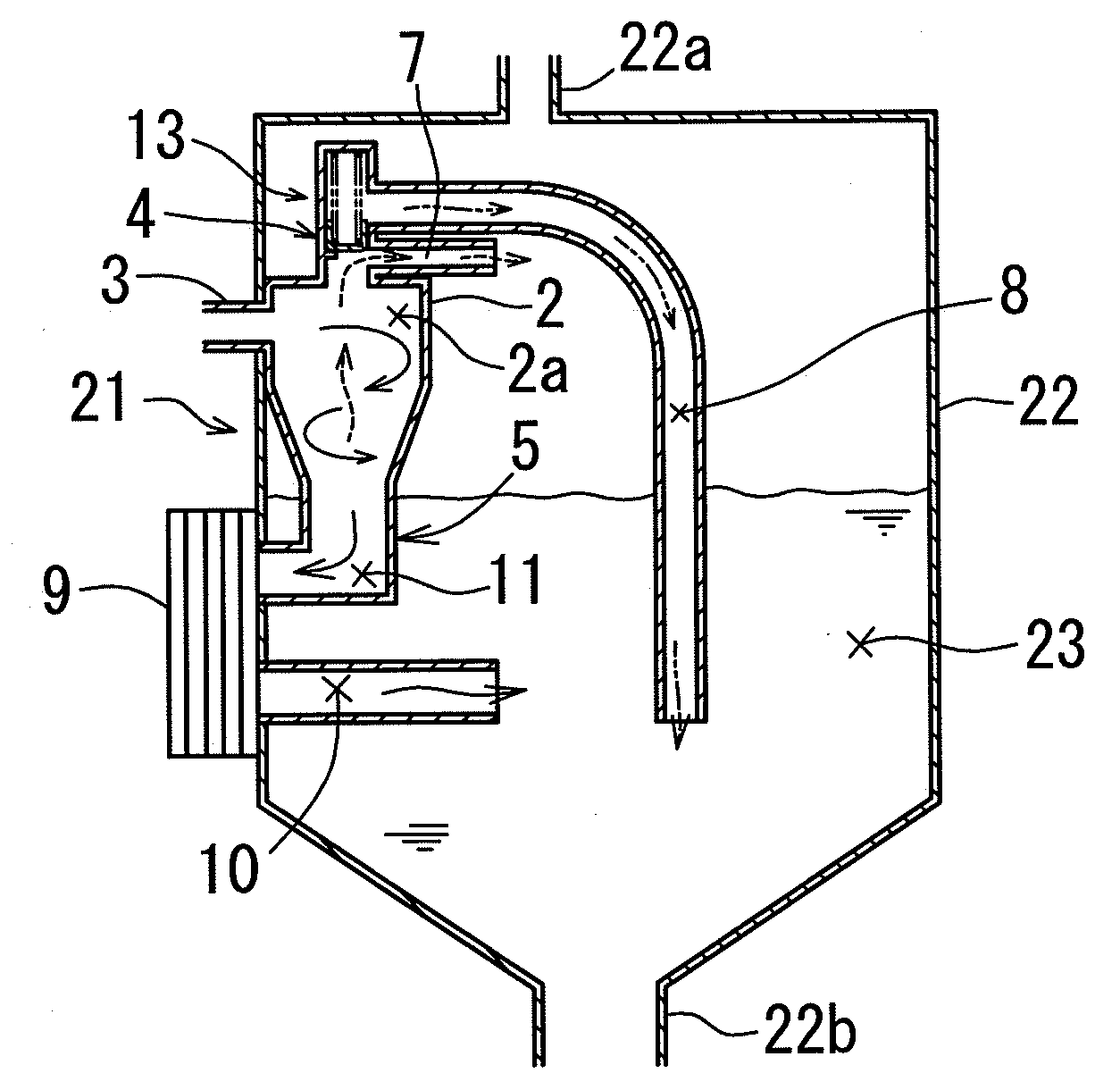
Oil/gas production apparatus
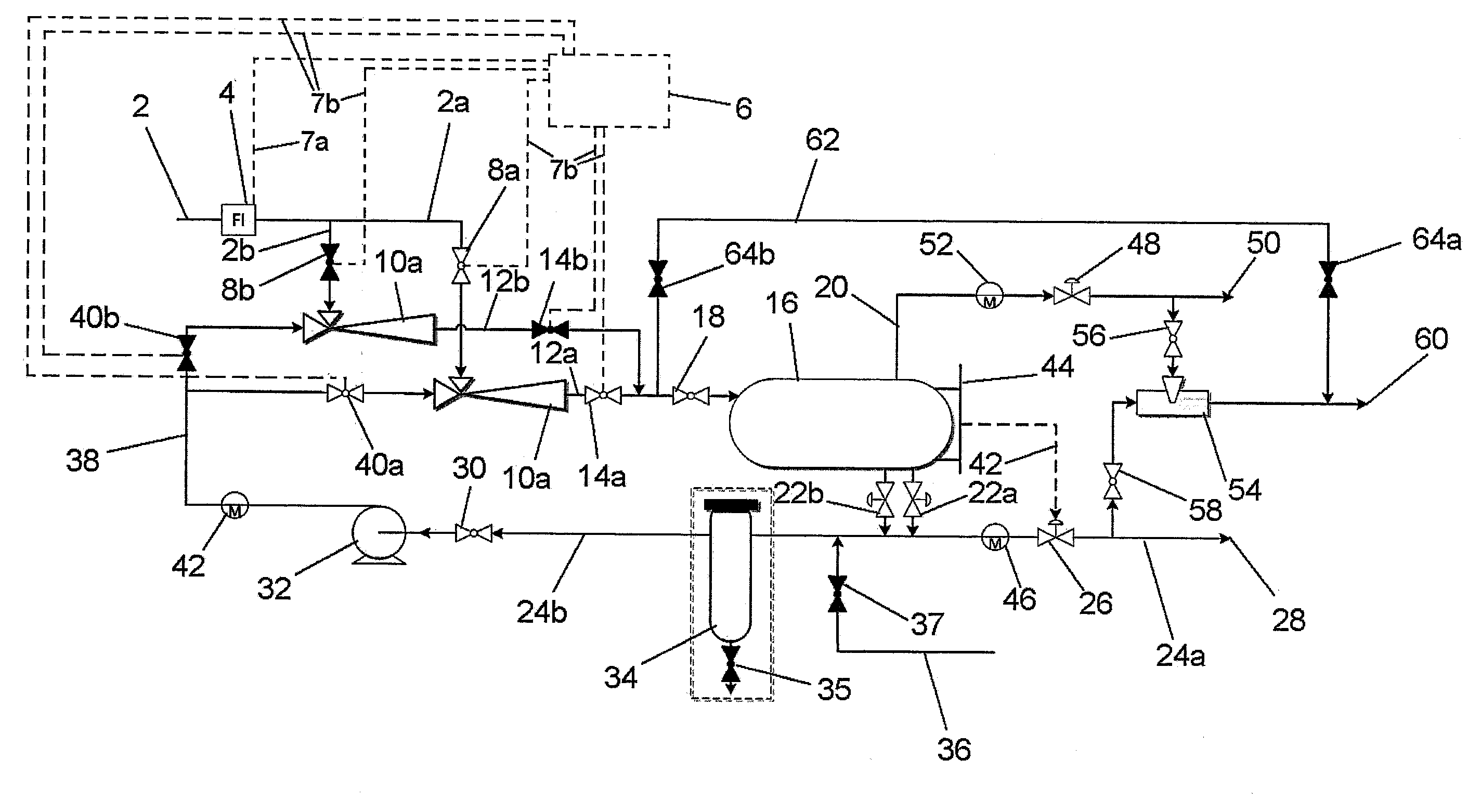
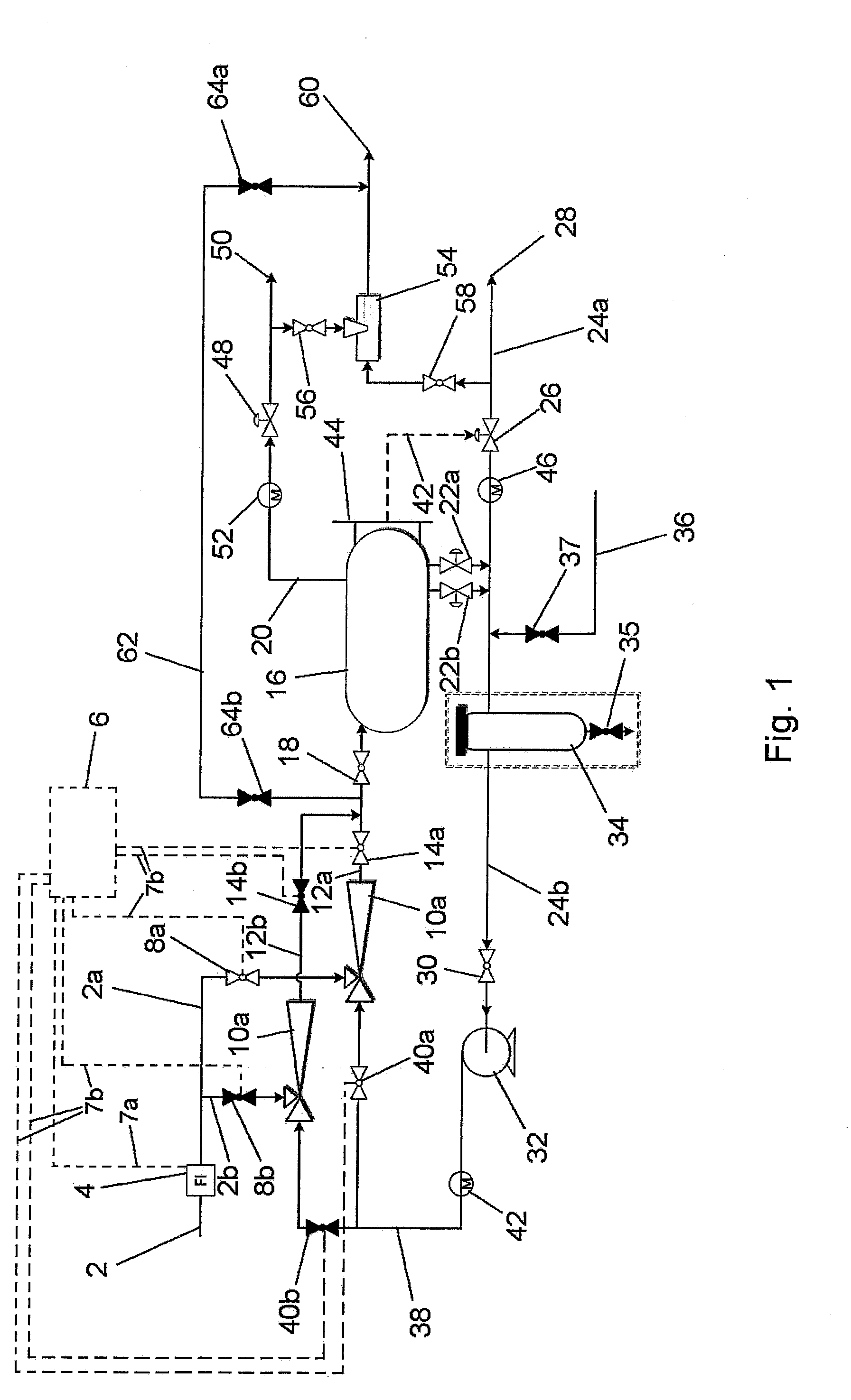
ActiveUS20160265322A1Mitigate aforesaid disadvantageReduce back pressureLiquid degasification regulation/controlJet pumpsFluid phaseControl system
An apparatus for boosting the pressure of flowing fluids includes a plurality of jet pumps (10a, 10b), each having a LP inlet for LP fluid, a HP inlet for HP liquid and a MP outlet for MP fluid. A fluid separator device (16) is connected to receive the MP fluid from the outlets of the jet pumps, a gas outlet line (20) for a separated gas phase and a liquid outlet (22a, 22b) for separated liquid phase. A liquid return line (24b, 38) is connected to the liquid outlet of the fluid separator device and the HP inlets of the jet pumps (10a, 10b) for returning at least some of the separated liquid phase from the fluid separator device to the HP inlets of the jet pumps, and a mechanical pump (32) is connected into the liquid return line for boosting the pressure of the liquid delivered to the HP inlets of the jet pumps. A flow control system (6) is provided for controlling the flow of fluids through the respective jet pumps (10a, 10b).
Owner:CALTEC PRODN SOLUTIONS LTD
Apparatus and method for gas-liquid separation
ActiveUS20140260993A1Raise the ratioEfficient separationCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentVapor–liquid separatorPhase splitter
A multi-phase separation apparatus shapes fluid flow in a flow shaping line preferably shaped to have a plurality of loops with consecutively decreasing diameters. Shaping the two-phase flow drives the heavier, denser fluids to the outside wall of the flow shaping line and allows the lighter, less dense fluids such as gas to occupy the inner wall of the flow shaping line. With the gas positioned on the inner wall, an exit port on the inner wall permits a majority, if not all, of the gas, along with a minimal amount of liquid, to be diverted to a conventional gas-liquid separator at a flow rate much lower than the total flow rate within the flow shaping line. The remaining liquid flow in the flow shaping line is subsequently introduced into an adjustable phase splitter to separate different liquid components from one another.
Owner:HAVEN TECH SOLUTIONS LLC
System and method to measure hydrocarbons produced from a well
InactiveUS20160129371A1Accurate measurementReduce capital investmentLiquid separation auxillary apparatusConstructionsEngineeringControl valves
Owner:CROSSSTREAM ENERGY
Vacuum control system
ActiveUS7686590B2Effectively and accurately removingDegree of vacuum in vacuum can be keptLiquid degasification regulation/controlFluid dynamicsInternal pressureBrushless motors
Owner:ERC
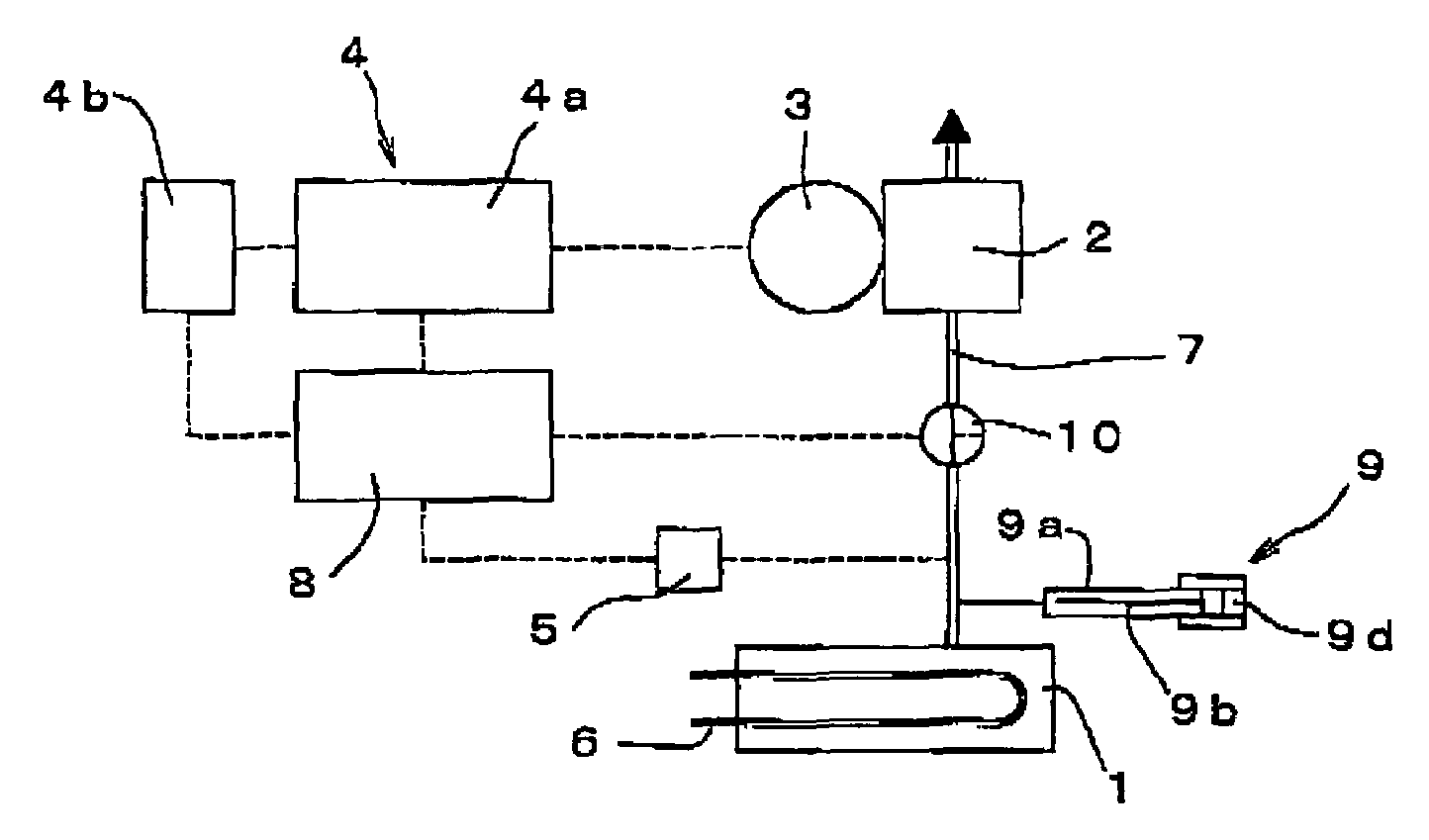
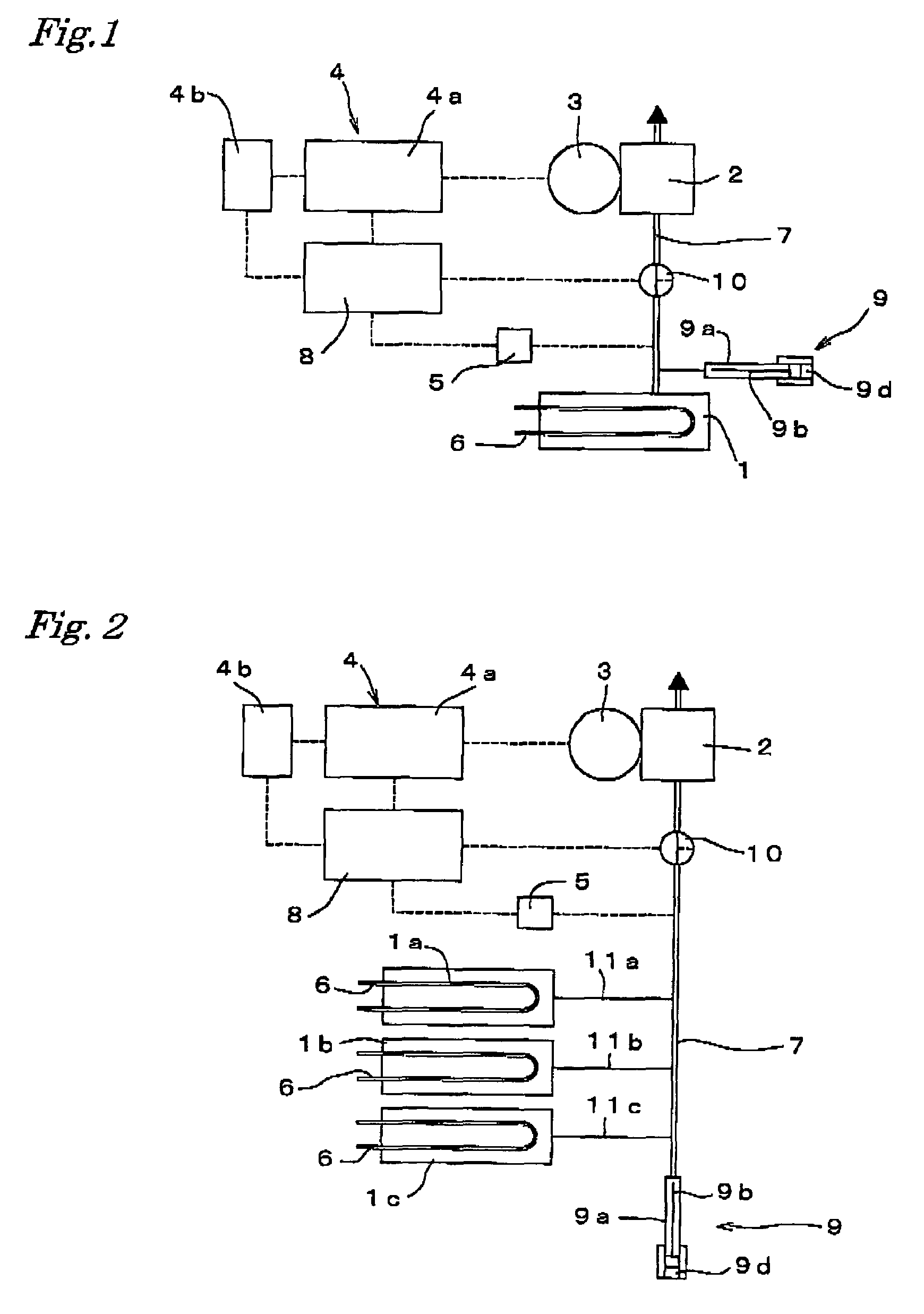
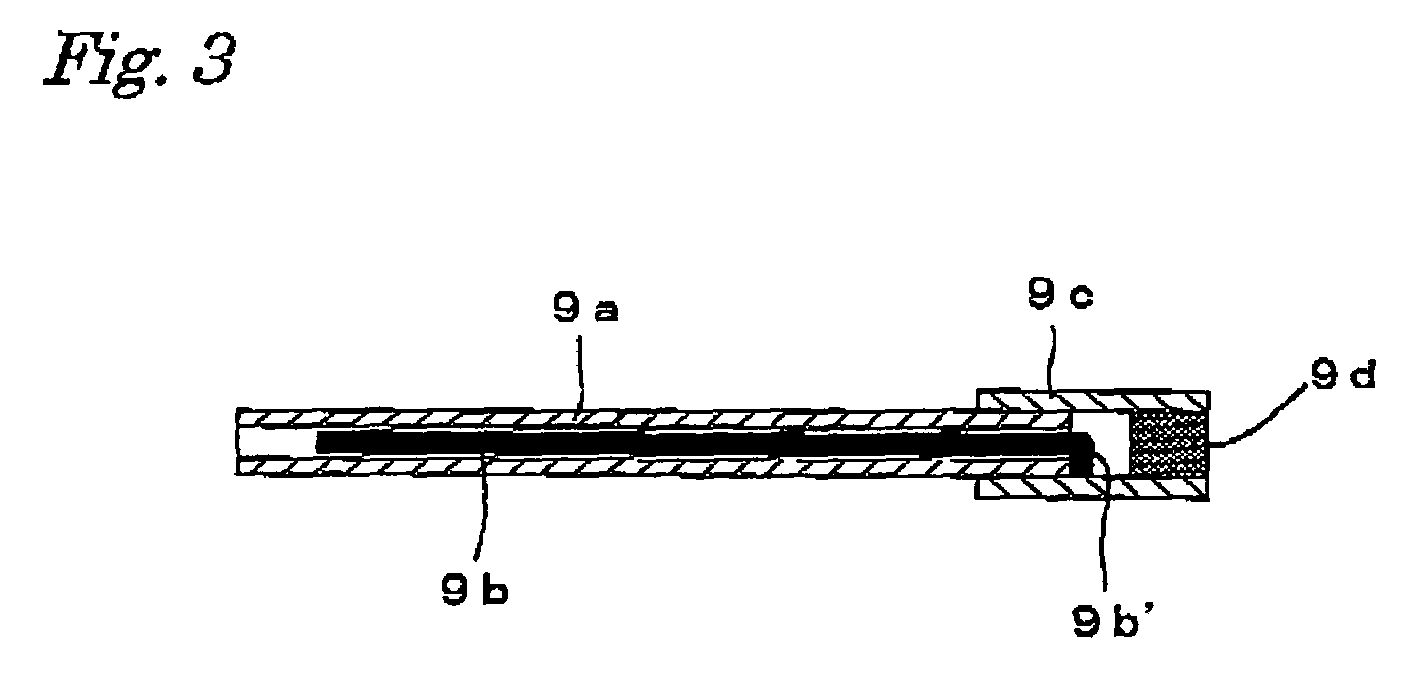
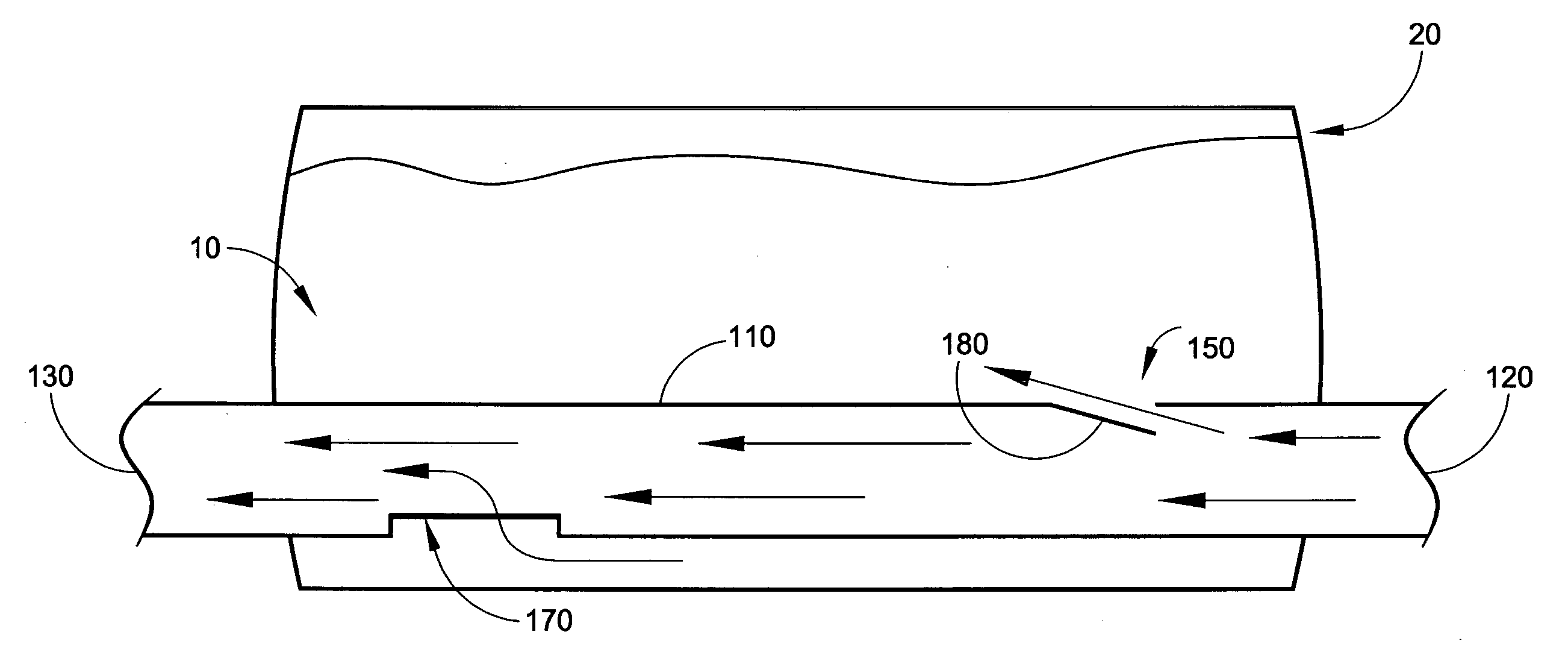
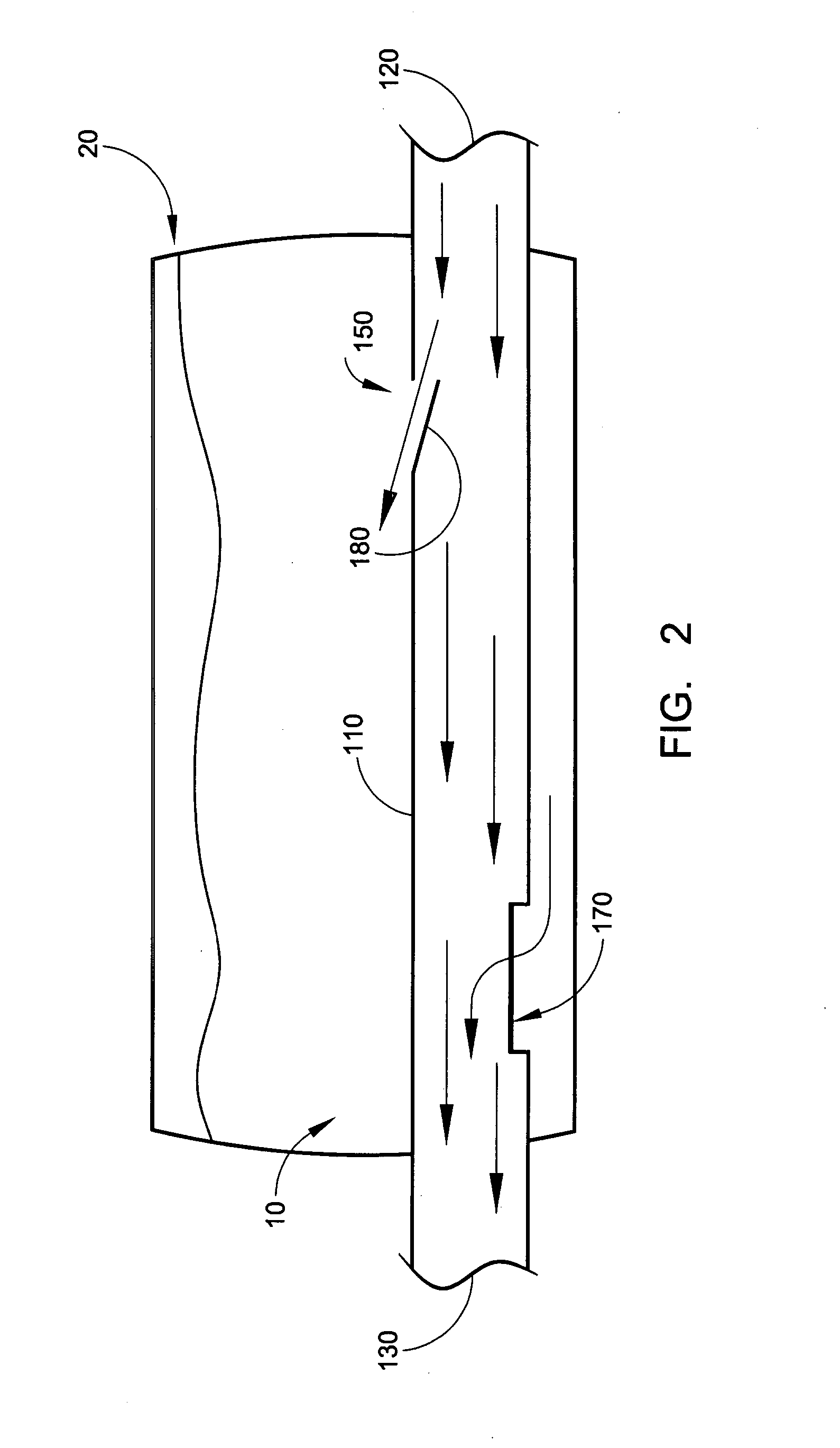
Deaeration Device and Method of Use
InactiveUS20080110344A1Promote escapeLower energy requirementsLiquid coolingLiquid degasification regulation/controlCoolant flowEngineering
A deaeration device for deaerating coolant fluid flow in a recirculation cooling system, where the recirculation cooling system includes a cooling fluid reservoir adapted to receive the deaeration device submerged within cooling fluid therein, includes an elongated deaeration tube including a fluid outlet and a deaerating skimming shaped slot for skimming air bubbles and cooling fluid from cooling fluid flow flowing through the deaeration tube, and including a fluid inlet for allowing the same amount of fluid that is skimmed off and removed through the top fluid outlet to re-enter the deaeration tube to maintain mass balance in the cooling fluid flow.
Owner:SHEPPARD MULLIN RICHTER & HAMPTON
Fuel system and method of reducing emission
InactiveUS7537646B2Emission reductionEasy to operateCombination devicesBurnersEngineeringLiquid fuel
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
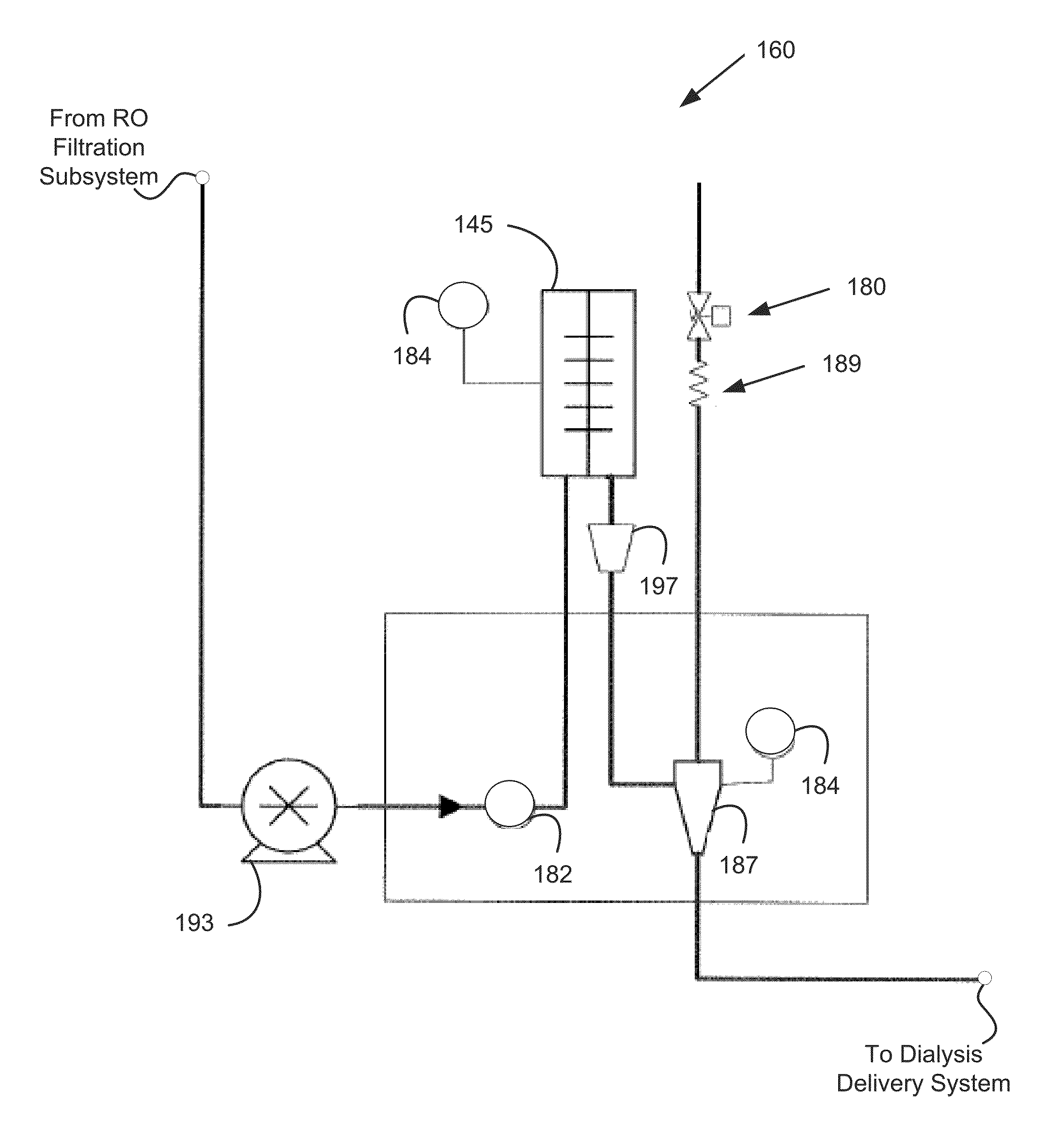
Apparatus and method for venting gas from a liquid
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
Method for receiving fluid from a natural gas pipeline
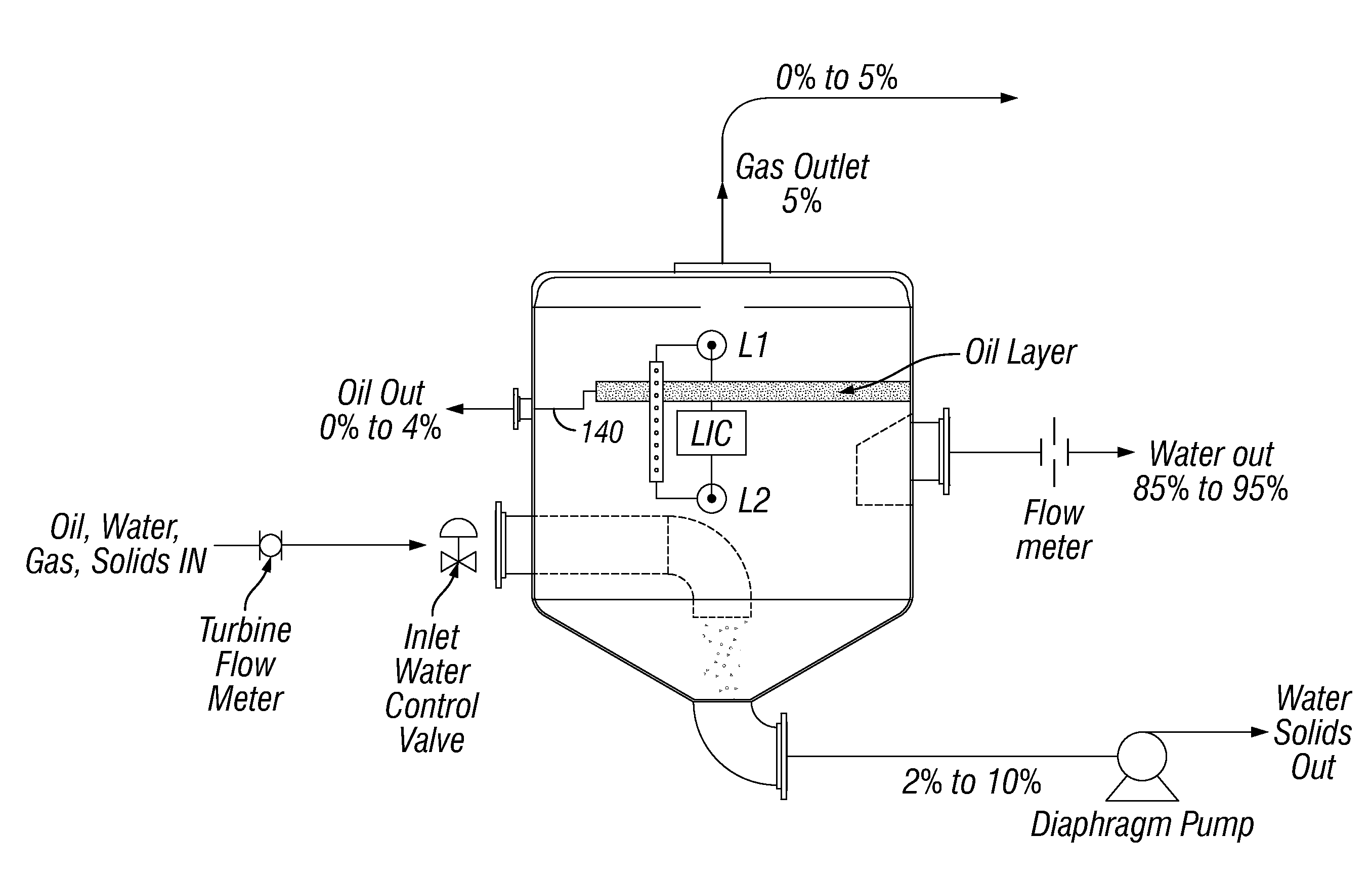
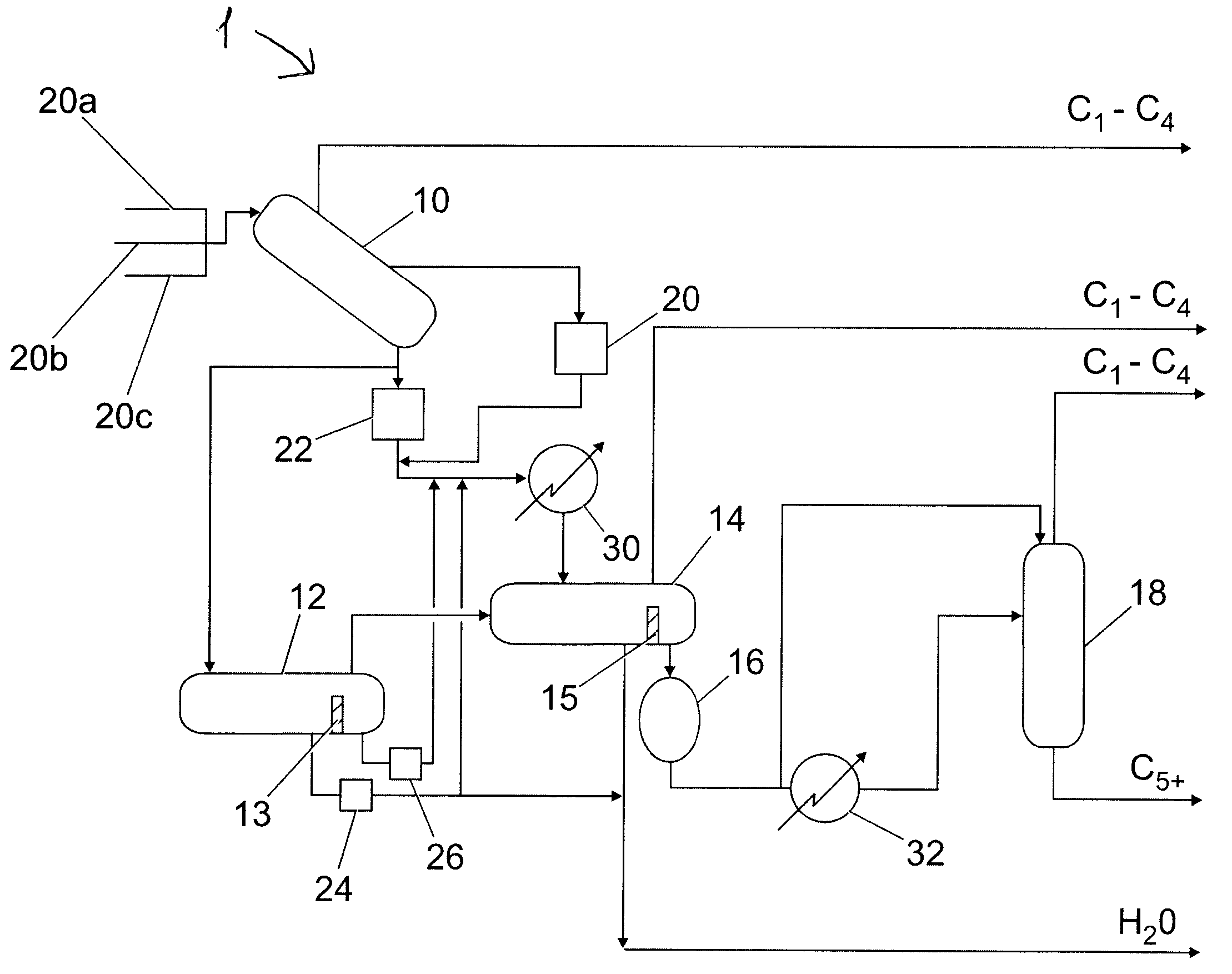
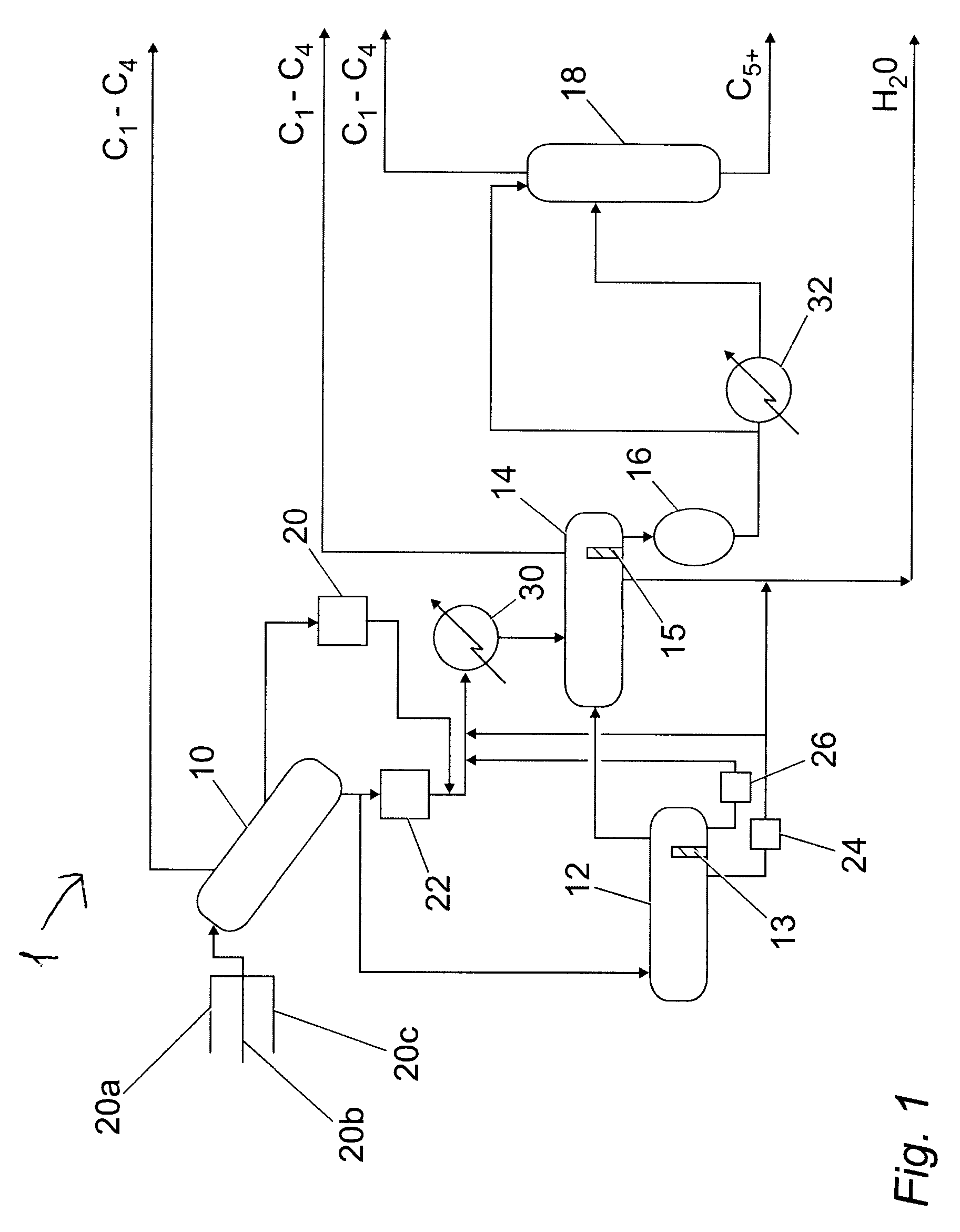
ActiveUS20090133578A1Less expensiveLiquid degasification regulation/controlFluid removalLiquid hydrocarbonsThree-phase
A method for receiving fluid from a natural gas pipeline, the fluid comprising gaseous hydrocarbons, liquid hydrocarbons, water and optionally solids, the method comprising: (a) in a slug catcher (10), receiving the fluid comprising gaseous hydrocarbons, liquid hydrocarbons, water and optionally solids from at least one pipeline (20a, 20b, 20c) (b) in the slug catcher (10), separating at least a portion of the gaseous hydrocarbons from the rest of the fluid to leave a liquid mixture or a liquid / solid mixture; (c) directing at least a portion of the liquid mixture or liquid / solid mixture to a separation vessel (14), preferably a three-phase separation vessel; and (d) in the event of a surge of liquids and optionally solids to the slug catcher (10), directing at least a portion of the liquid mixture or the liquid / solid mixture from the slug catcher (10) to a surge vessel (12).
Owner:SHELL USA INC
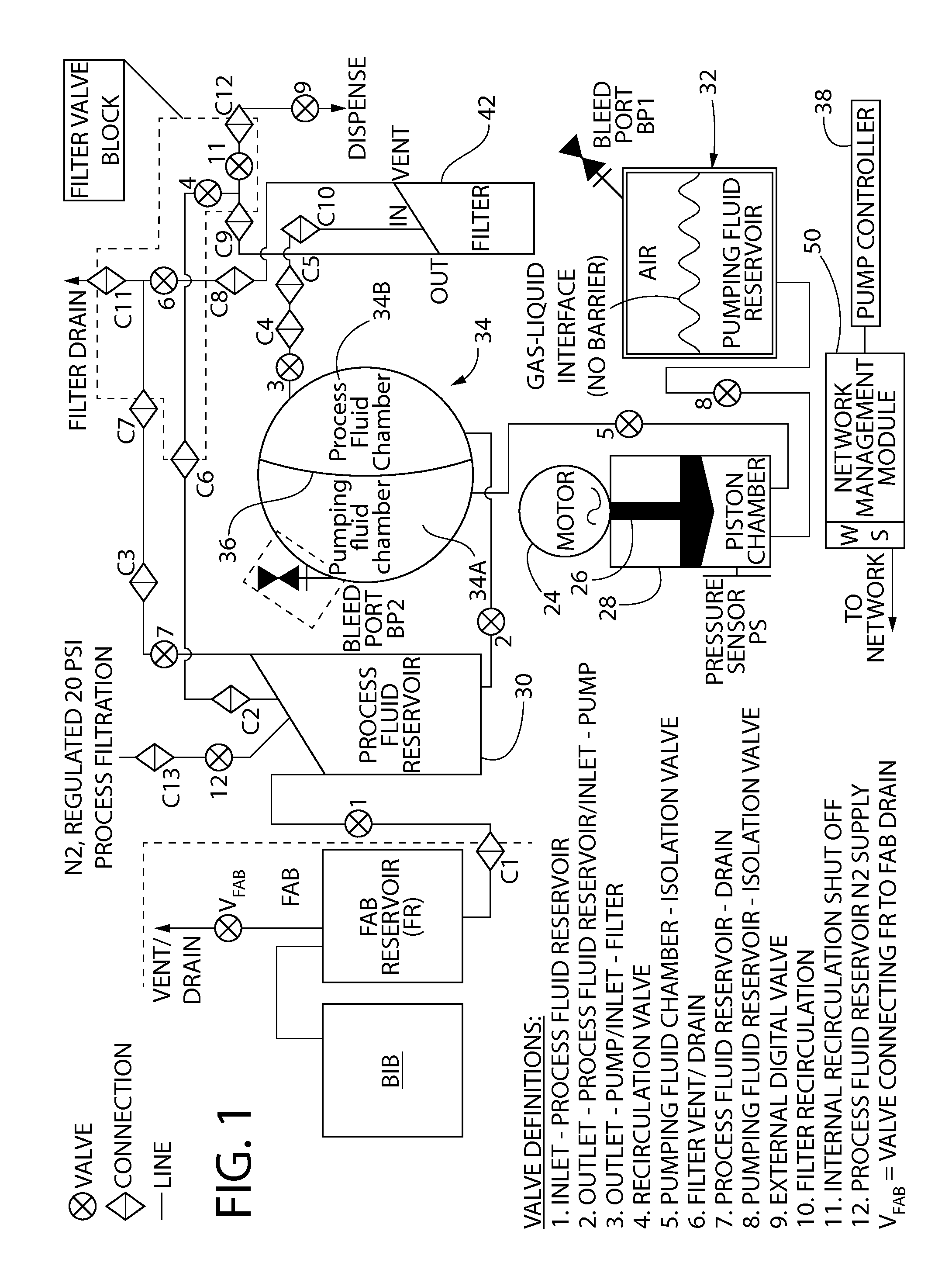
Pump having an automated gas removal and fluid recovery system and method
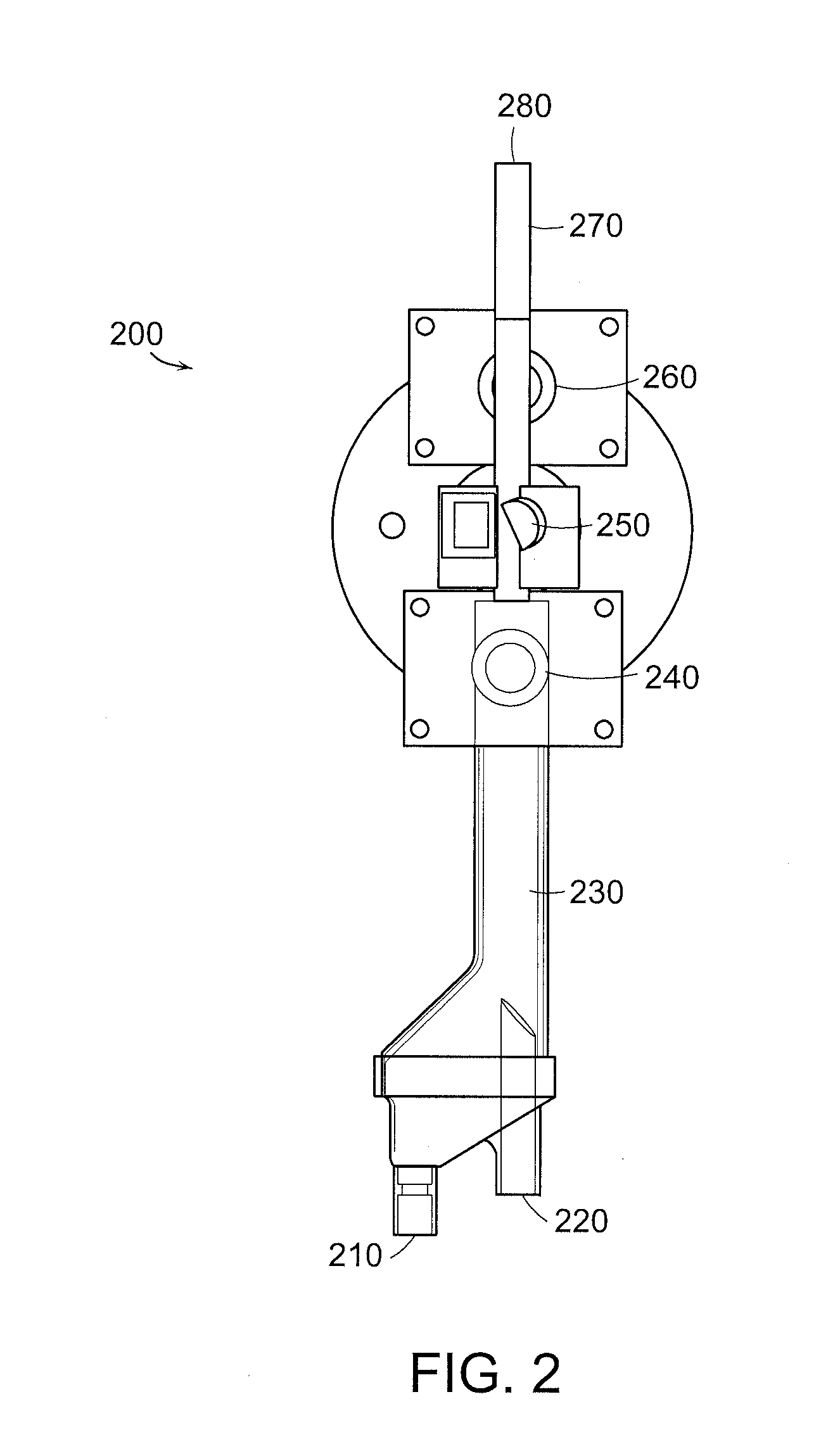
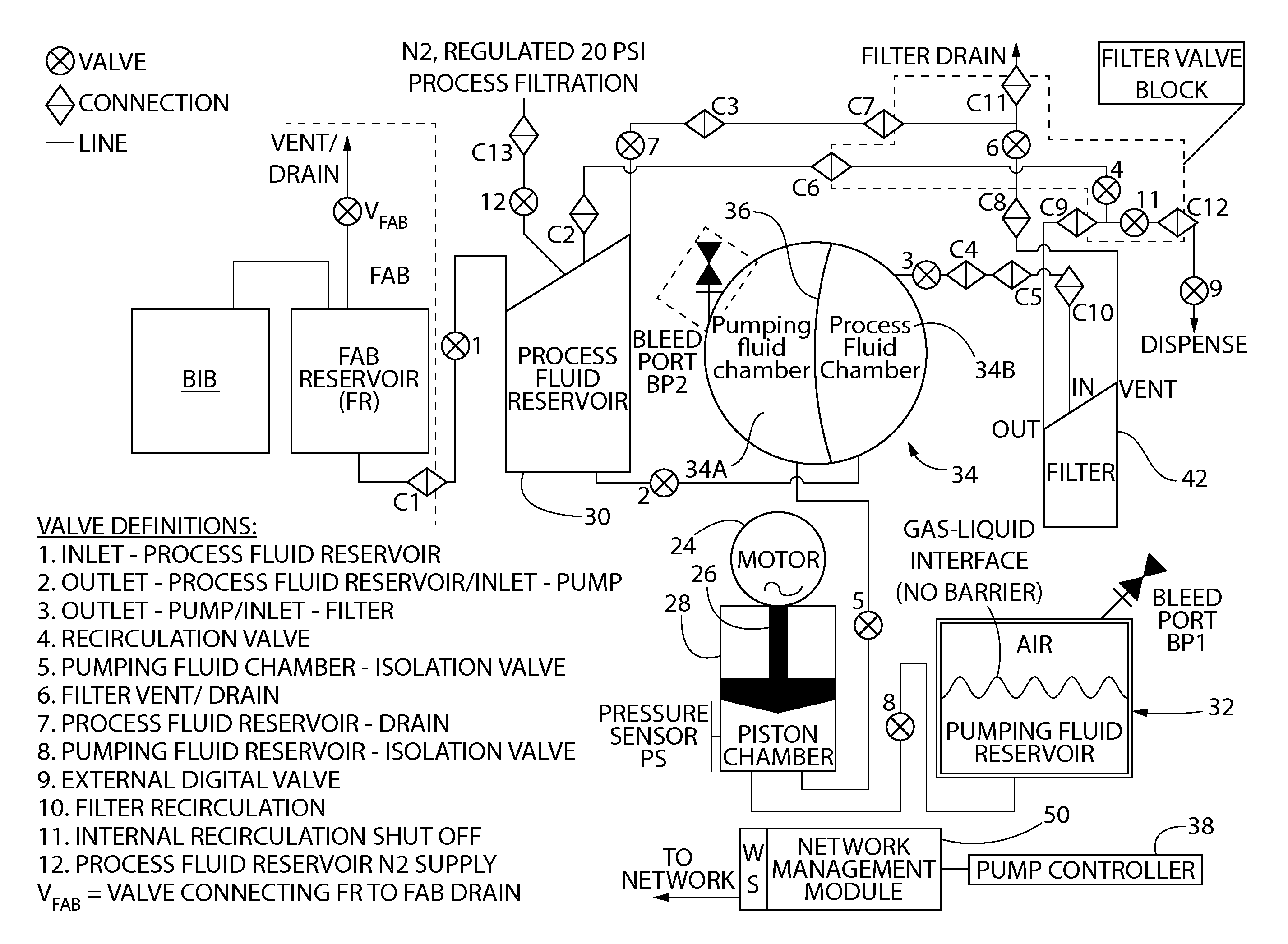
ActiveUS20140271252A1Programme controlPositive displacement pump componentsThe InternetProcess engineering
A precision pump system having a motor driver for accurately and repeatedly delivering process fluid, (e.g., photo chemicals) using a pumping fluid with minimal process fluid loss to a fabrication process and whereby the motor driver can be easily and quickly replaced without interrupting the fluid flow path. This is accomplished with the use of a process fluid reservoir and a pumping fluid reservoir that are associated with the pump, either integrated with the pump or closely adjacent. In addition, this precision pump system can be remotely monitored, viewed and controlled over the Internet. In addition, trapped process fluid within a downstream filtering block can be recirculated to the process fluid reservoir when trapped gas in the filter is removed. Furthermore, a nitrogen gas source is connected to the process fluid reservoir via a valve in case a need to insert a gas is required.
Owner:TELEDYNE DIGITAL IMAGING US INC
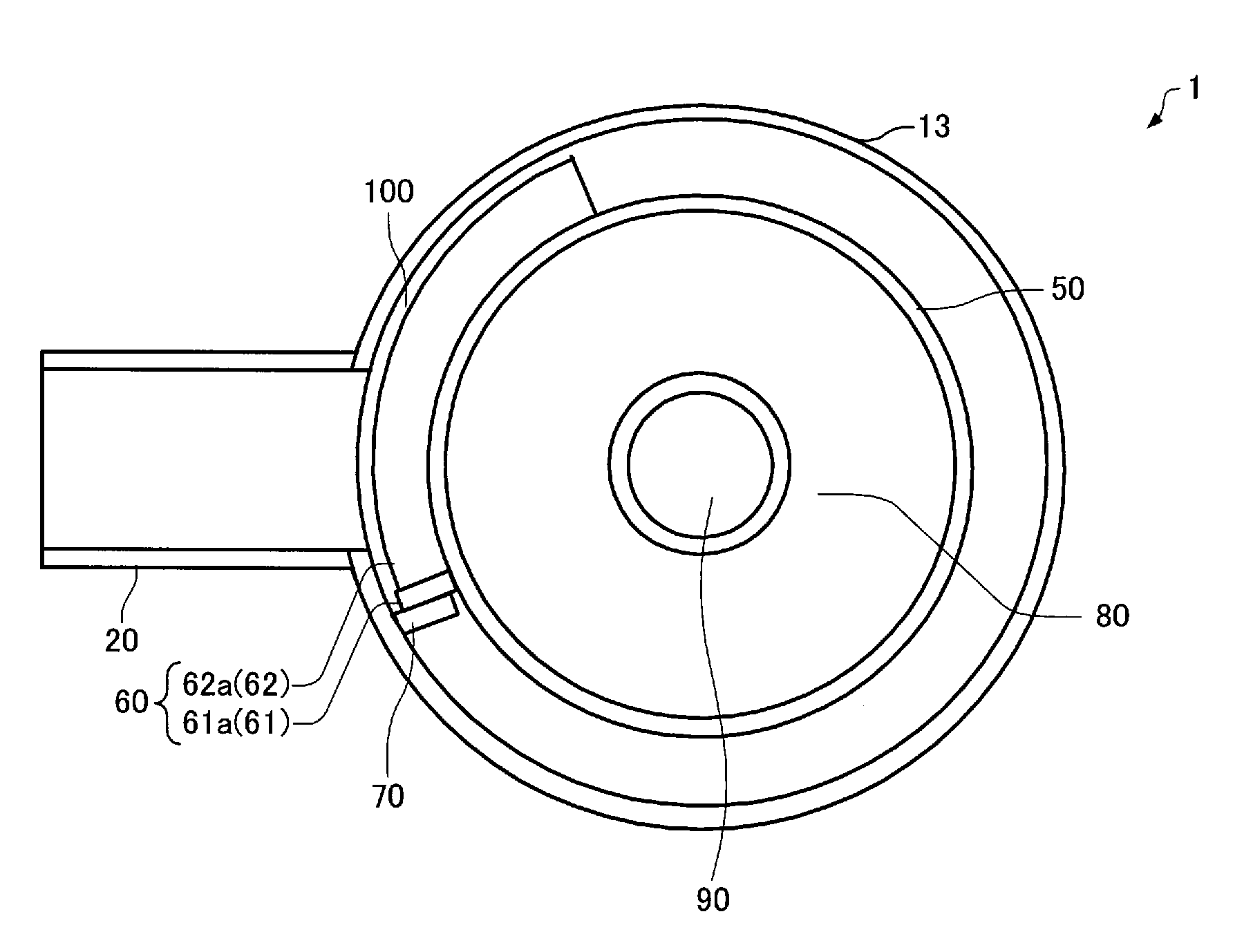
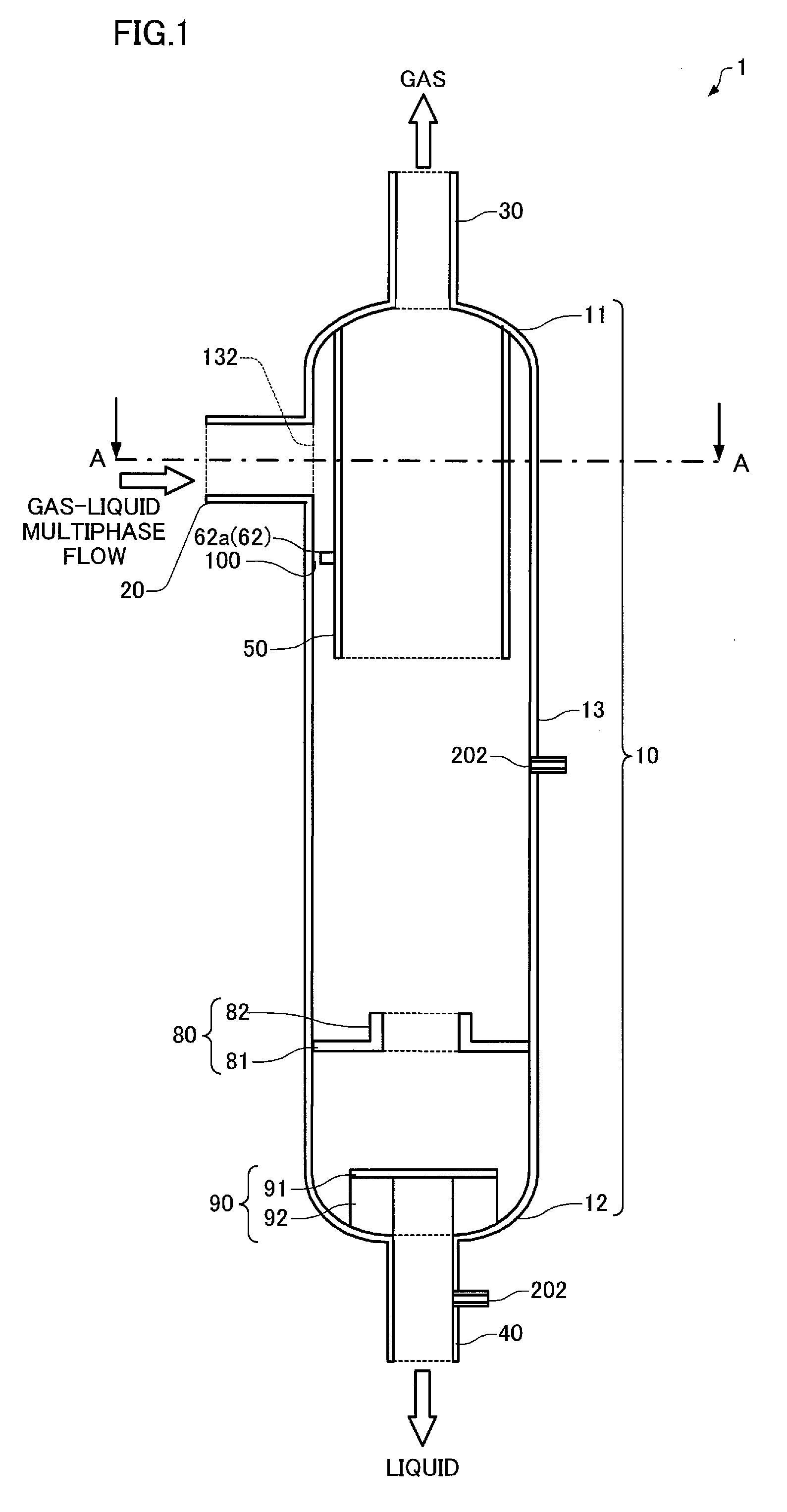
Gas-liquid separator and multiphase flow rate measurement device
InactiveUS20120297986A1Simple configurationSafely and efficiently separateReversed direction vortexDispersed particle separationVapor–liquid separatorMeasurement device
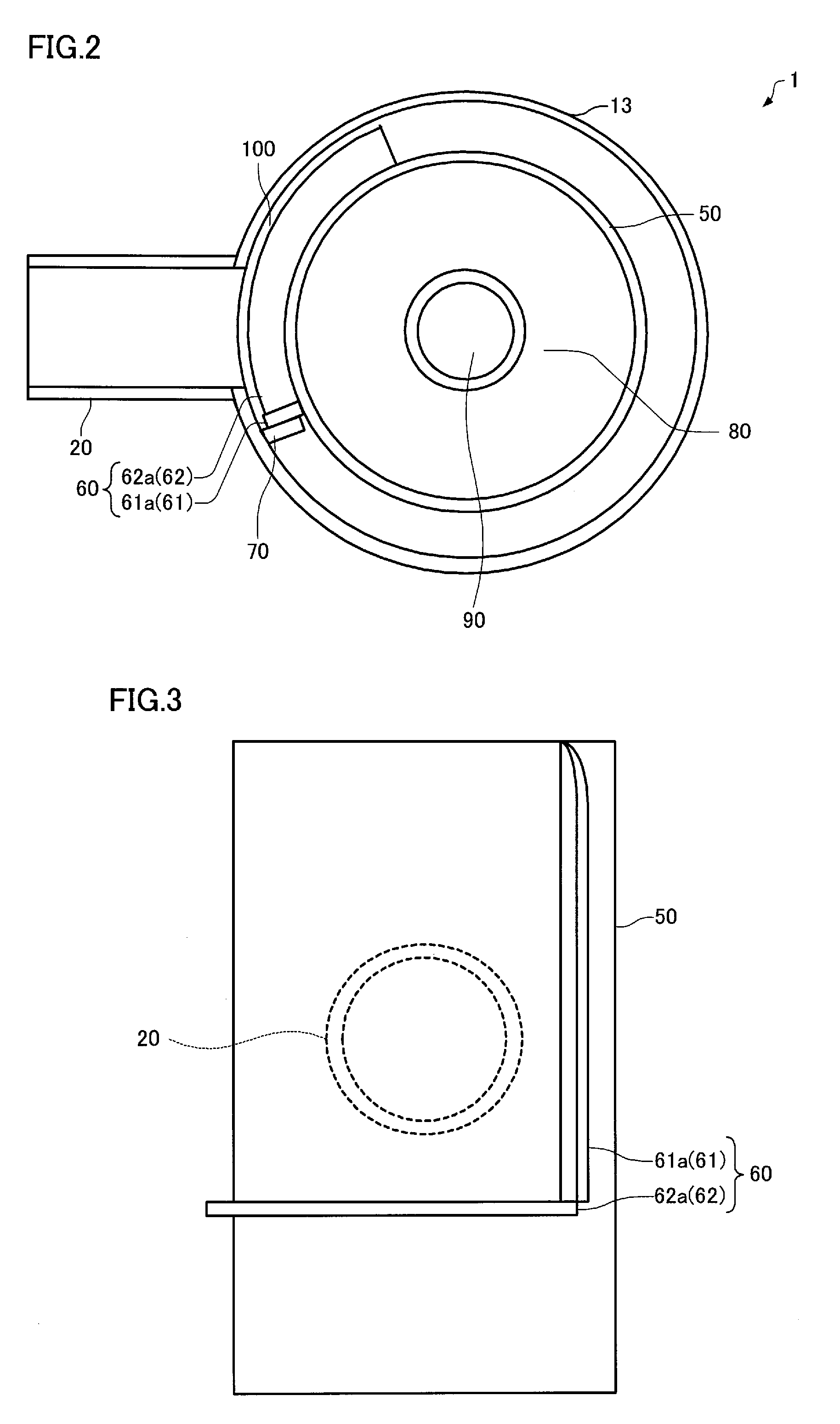
A gas-liquid separator (1) is configured so that the inner side surface of a body section (13) and the outer side surface of an inner pipe (50) are concentric when viewed from above, an inlet pipe (20) extending toward the center axis of the body section (13) when viewed from above, a guide plate (60) including a guide plate side section (61) that extends in a non-horizontal direction, and a guide plate lower section (62) that extends in a non-vertical direction and is continuous with the guide plate side section (61), the guide plate side section (61) being at least disposed on the inner side surface of the body section (13) at a position on one side of an inlet opening (132), or on the outer side surface of the inner pipe (50) at a position on one side of an area opposite to the inlet opening (132), the guide plate lower section (62) being at least disposed on the outer side surface of the inner pipe (50) at a position directly under an area opposite to the inlet opening (132) and along the outer side surface of the inner pipe (50) when viewed from above, and a space (100) being at least partially formed between the guide plate lower section (62) and the body section (13).
Owner:JAPAN OIL GAS & METALS NAT CORP
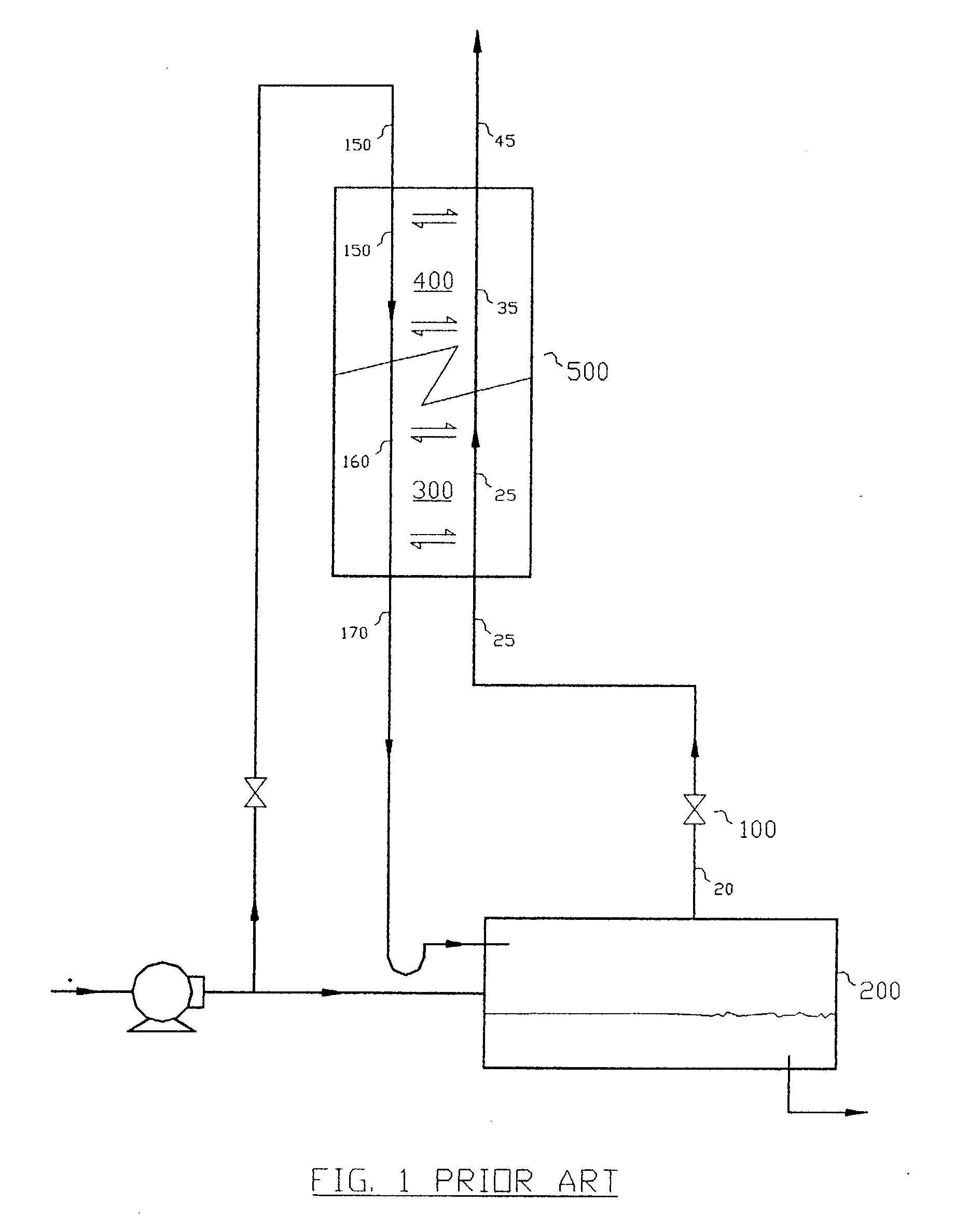
Staged heat and mass transfer applications
InactiveUS20040168900A1Easy to operateImprove reliabilityDistillation regulation/controlDistillation in boilers/stillsParticulatesSteam condensation
This invention exploits the concept of Staged Heat and Mass Transfer (SHMT) to enhance operability, control robustness and intrinsic safety in preventing corrosion while recovering material, and energy if desirable, in process waste streams. Two applications illustrating the improvements based on the SHMT concept are given. One application illustrates novel design features to recover vent from a steam boiler deaeration system, positively eliminating the risk of oxygen and carbon dioxide accumulation in deaerator. The other application illustrates process adaptations of the same SHMT concept to recover steam, steam condensate, and fugitive emissions involving particulate materials if desirable, from any process vents from vessels that are opened to the atmosphere. Again, without the risk of corrosion by atmospheric oxygen.
Owner:TUNG PETER
Popular searches
Treatment with anaerobic digestion processes Multistage water/sewage treatment Waste water treatment from bathing facilities Water/sewage treatment by degassing Water/sewage treatment apparatus Water/sewage treatment by oxidation Settling tanks feed/discharge Water/sewage treatment Loose filtering material filters Pumps
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com