Patents
Literature
54results about How to "Small contamination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
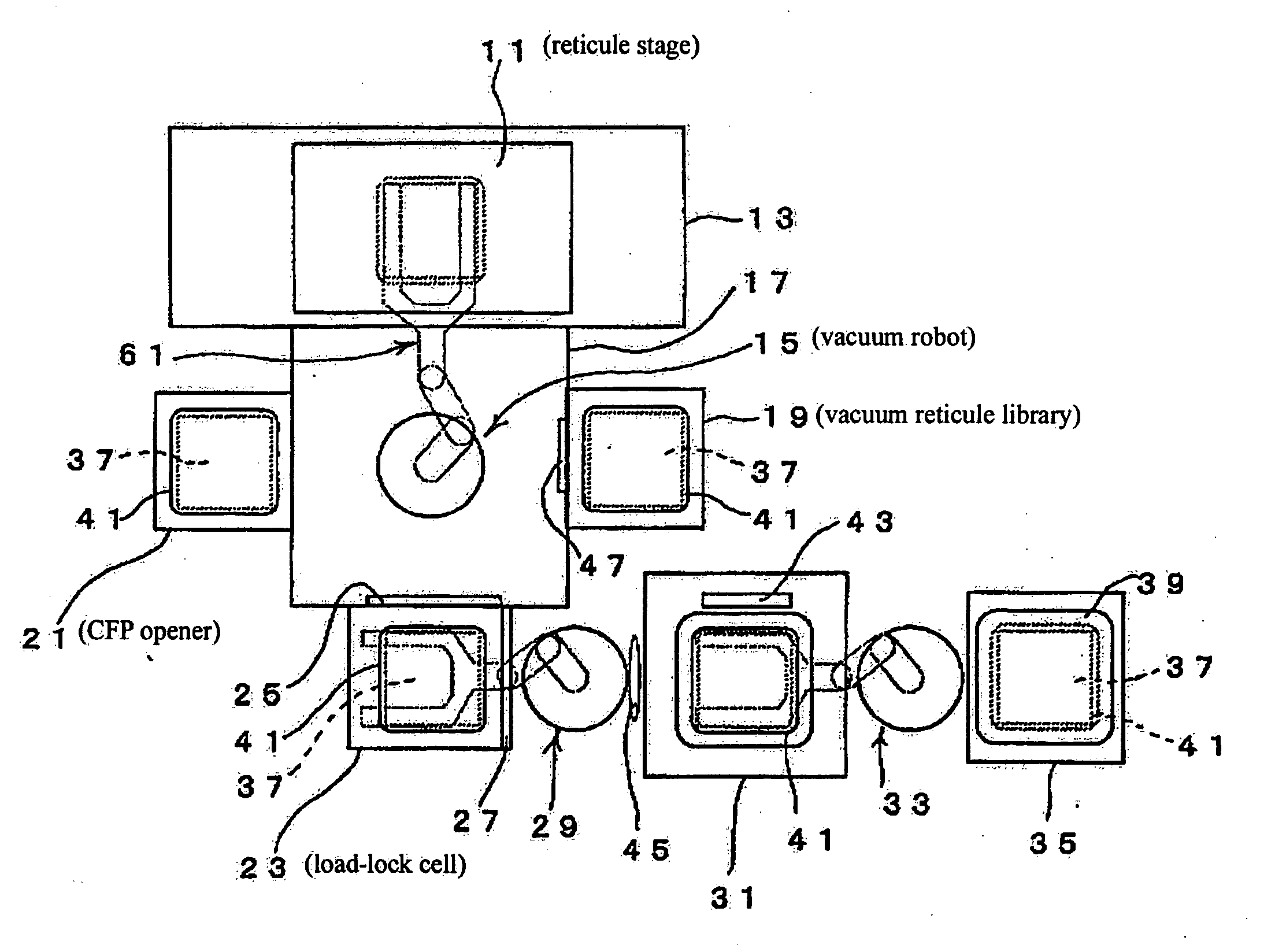
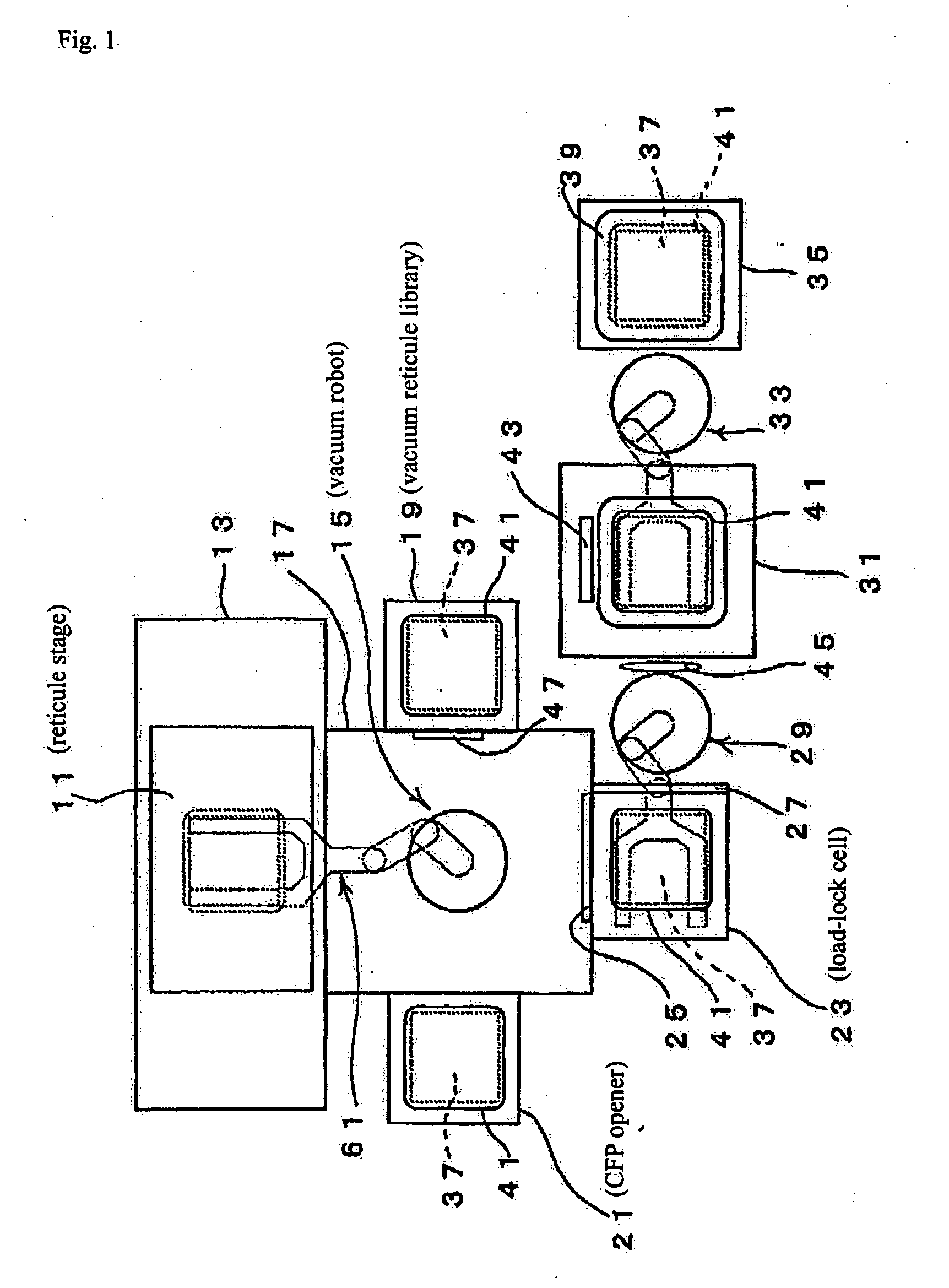
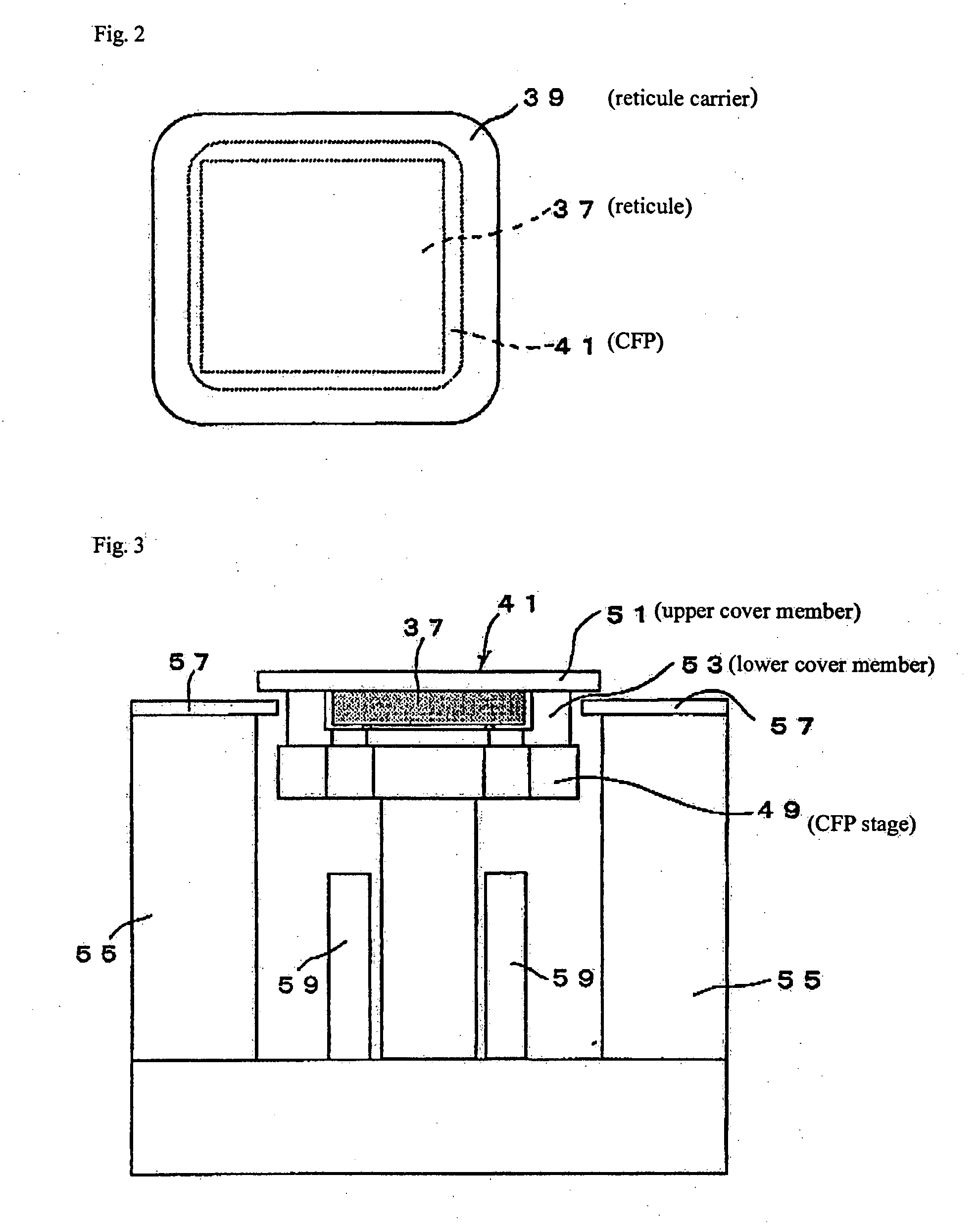
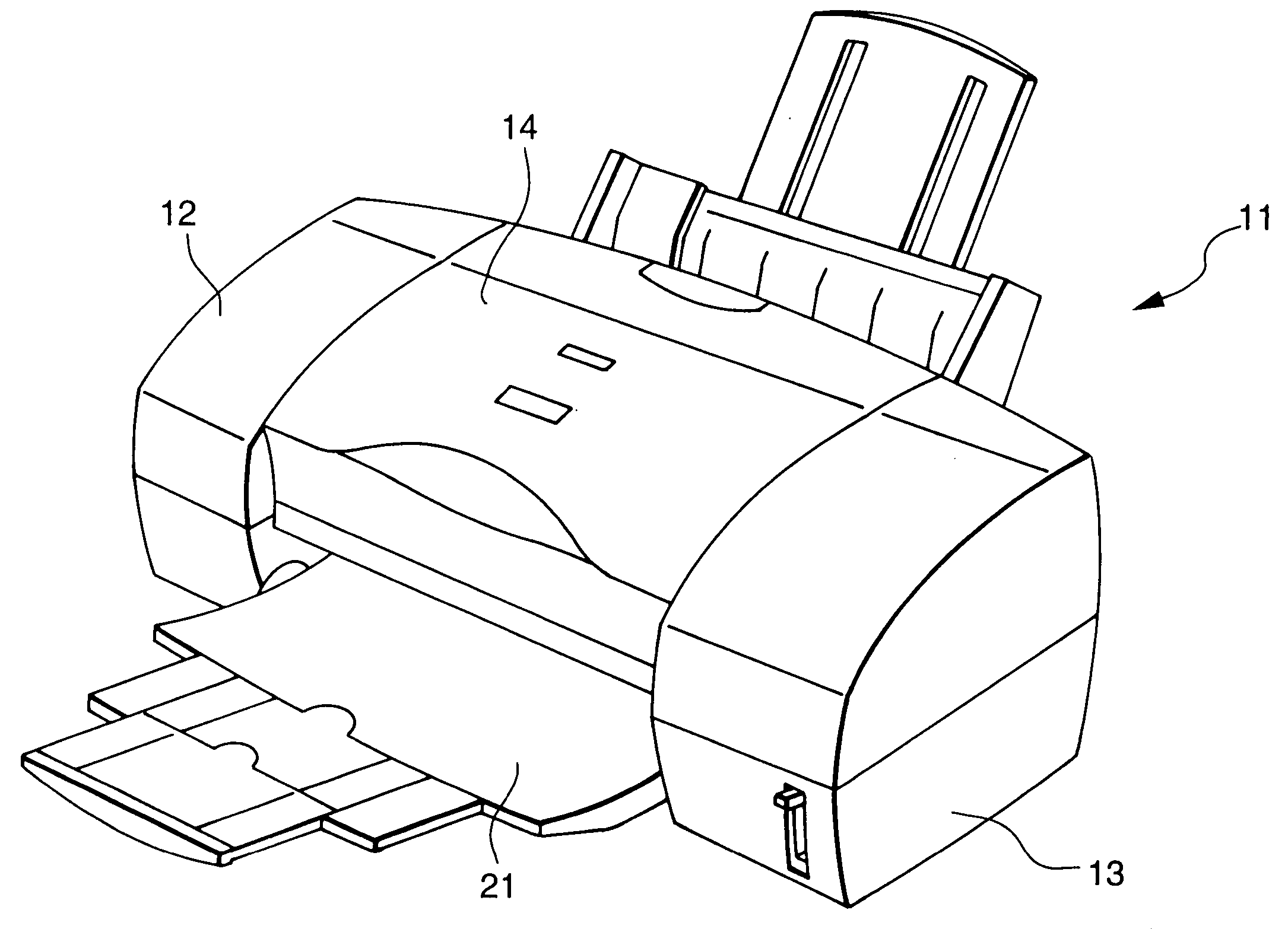
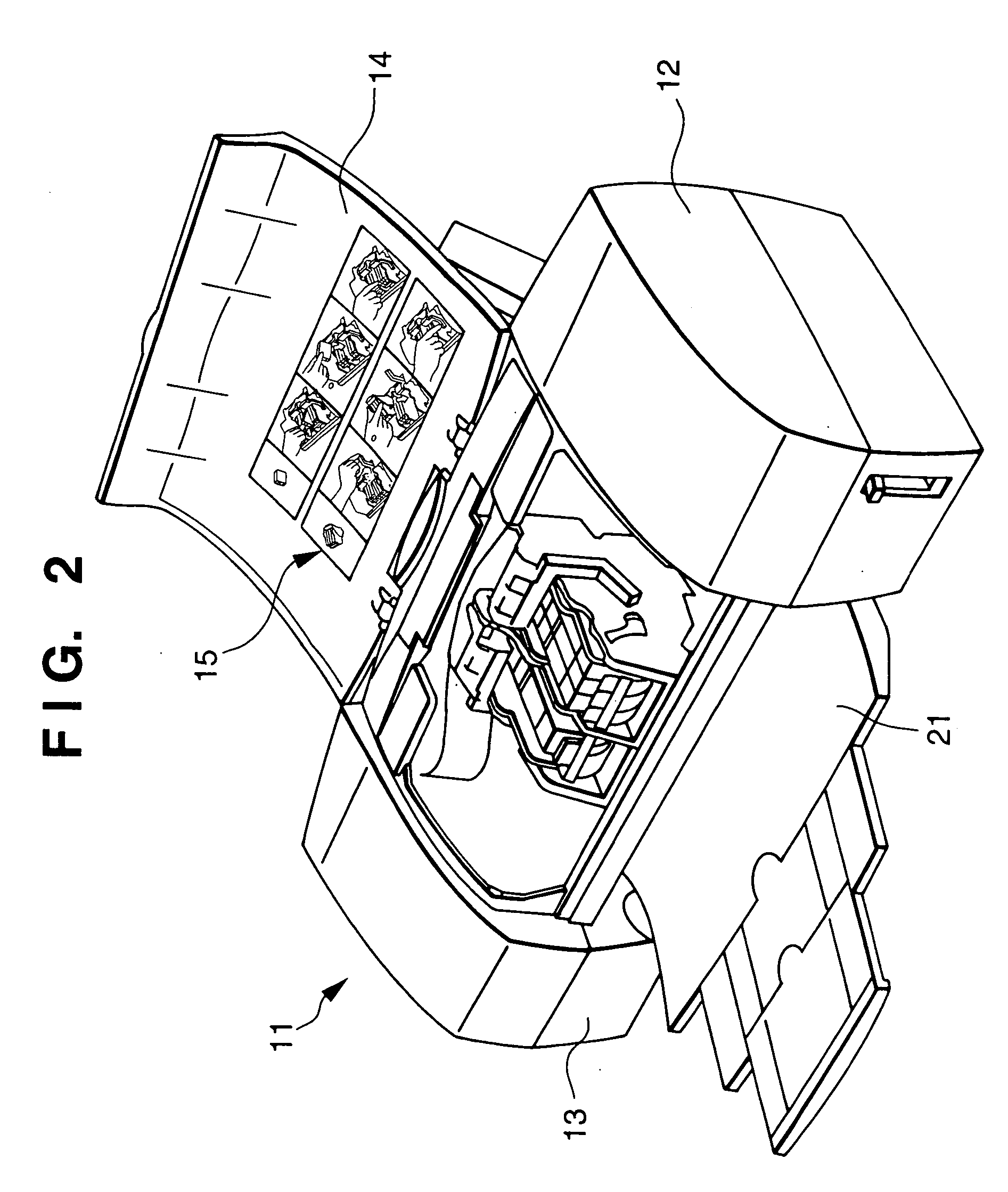
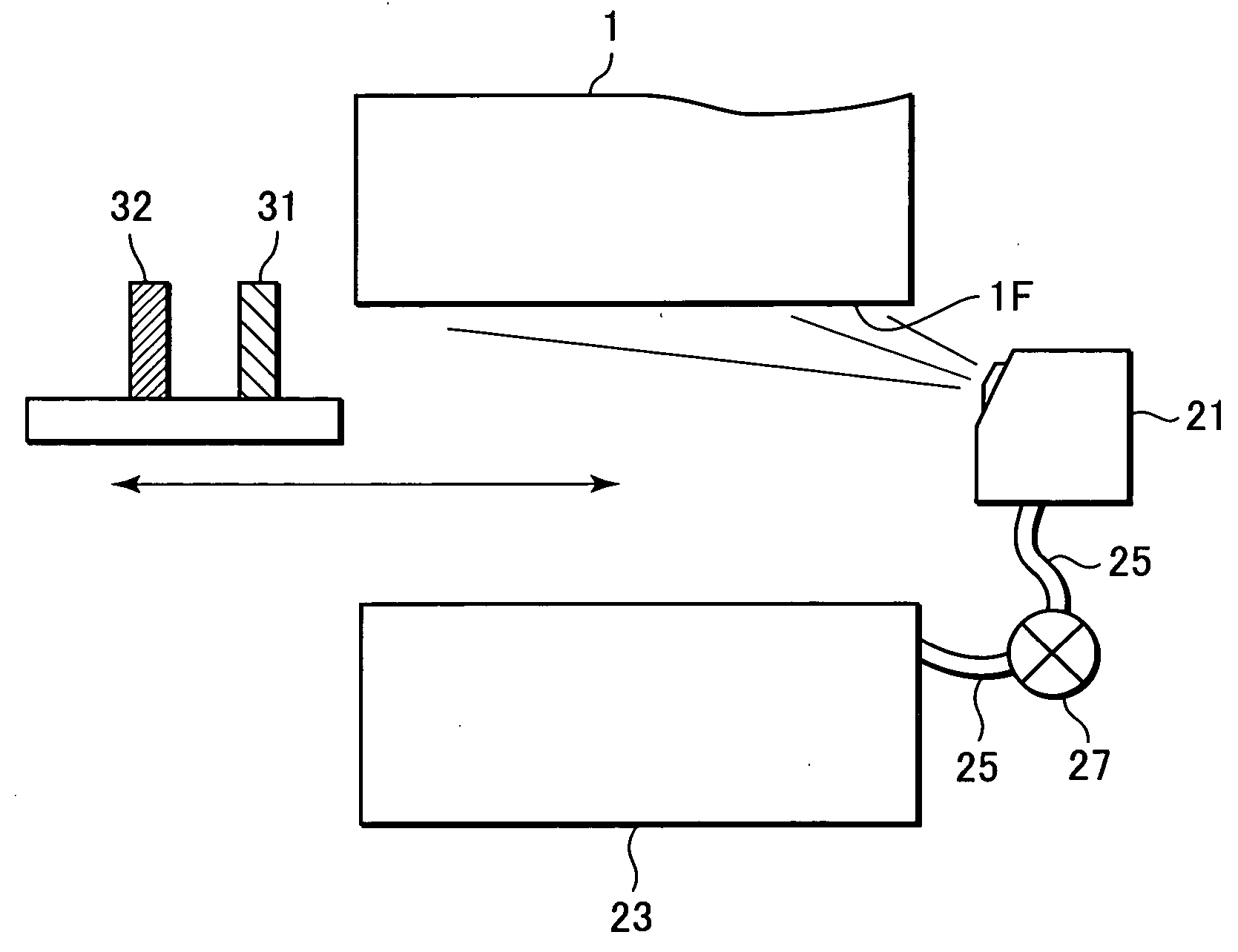
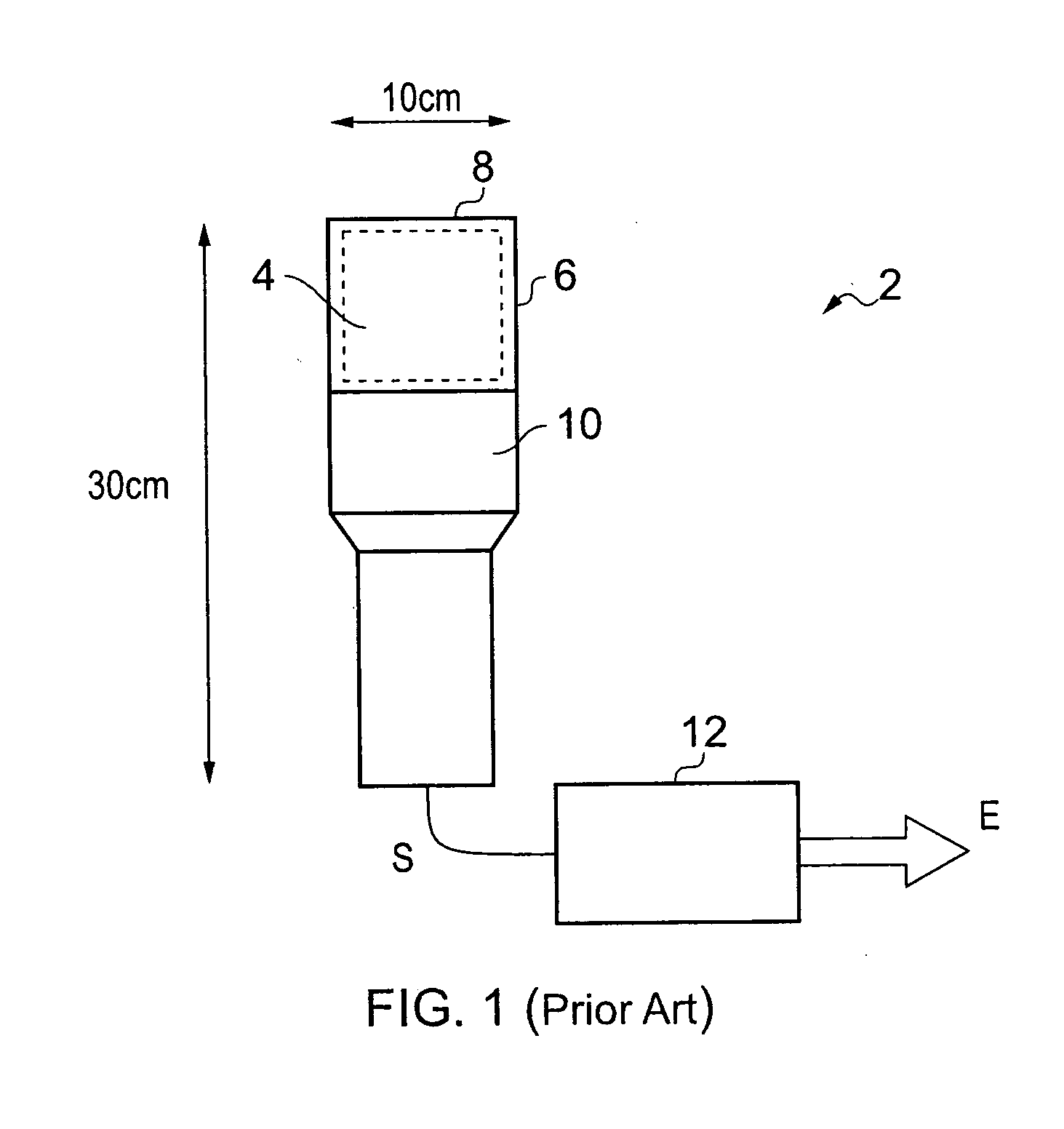
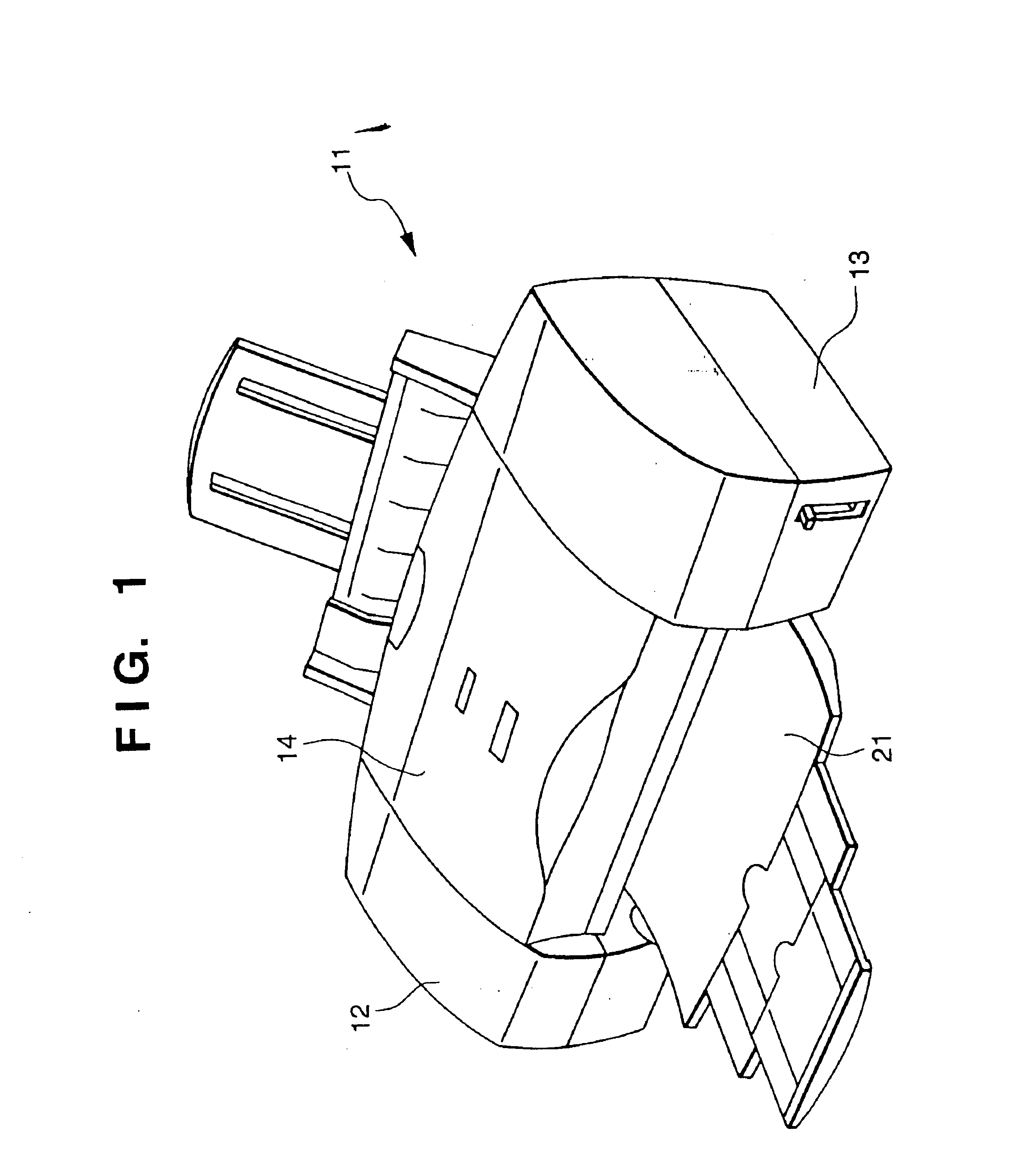
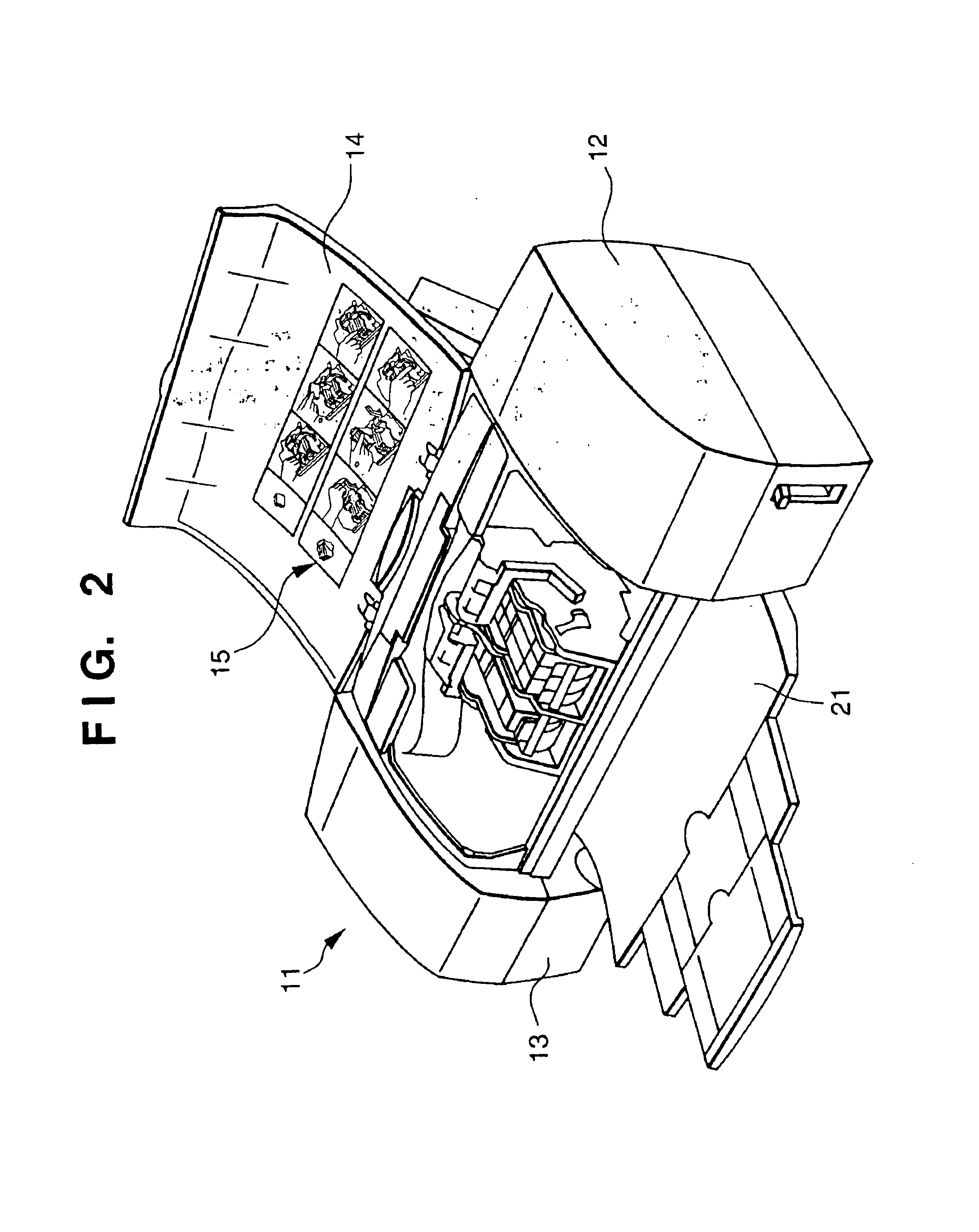
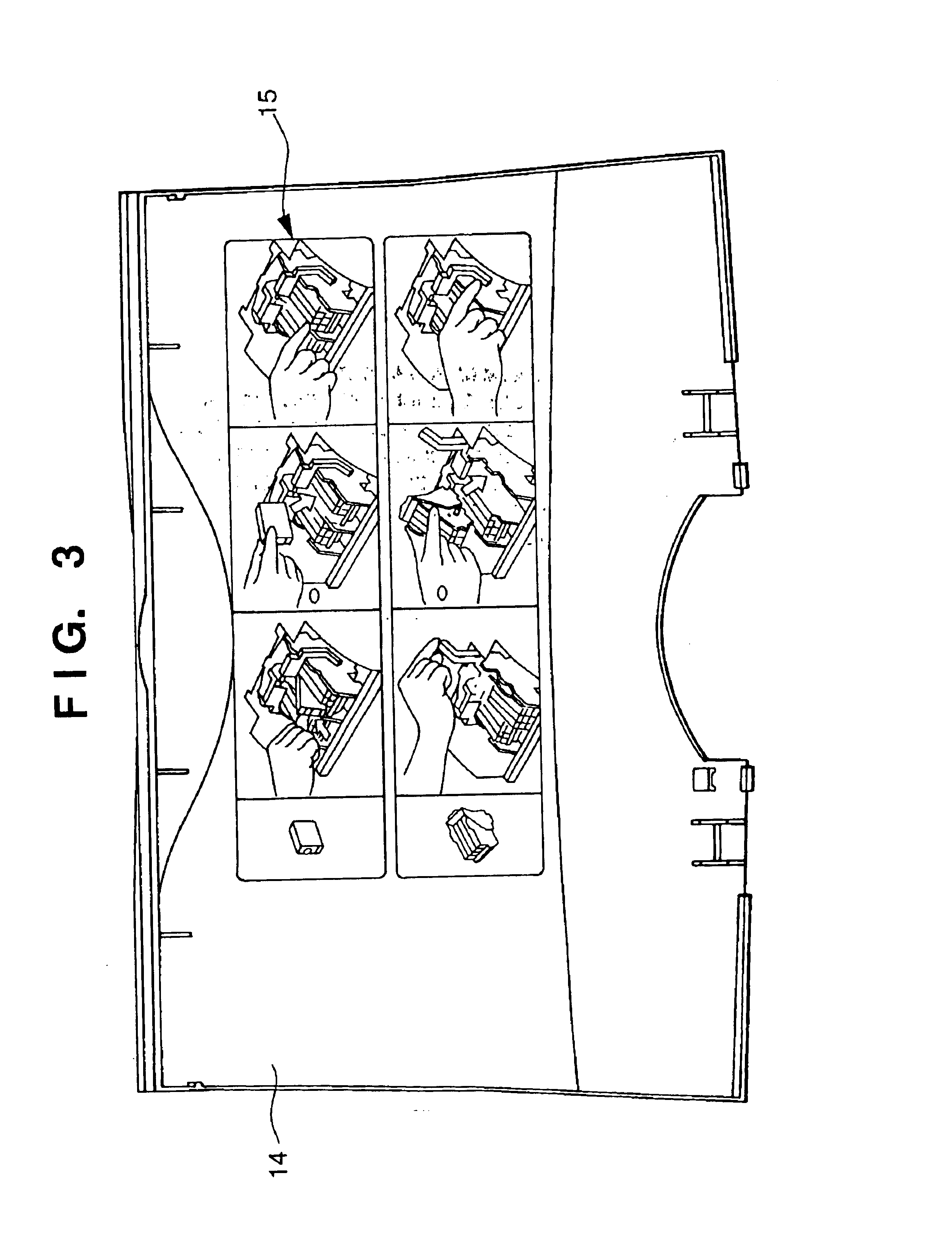
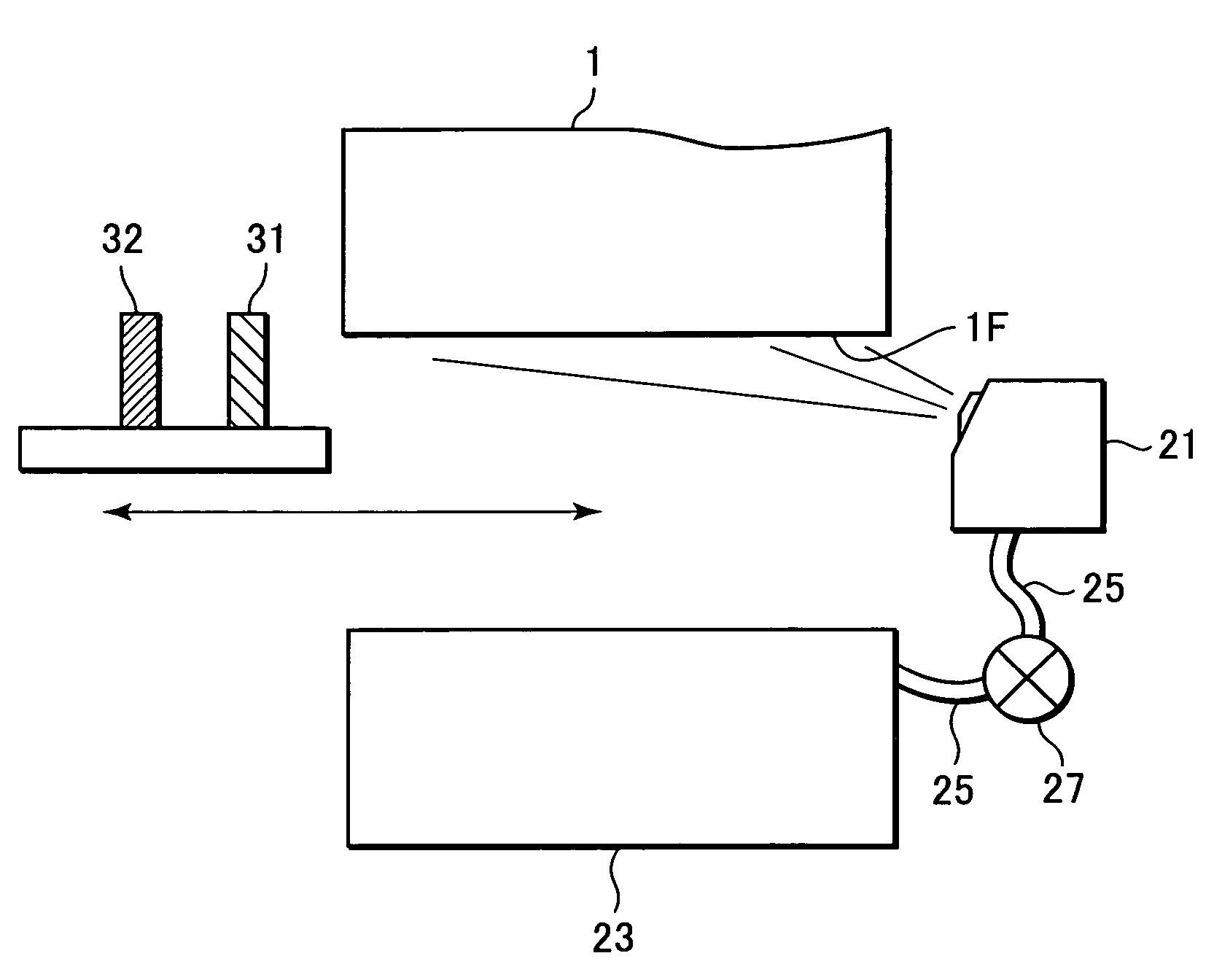
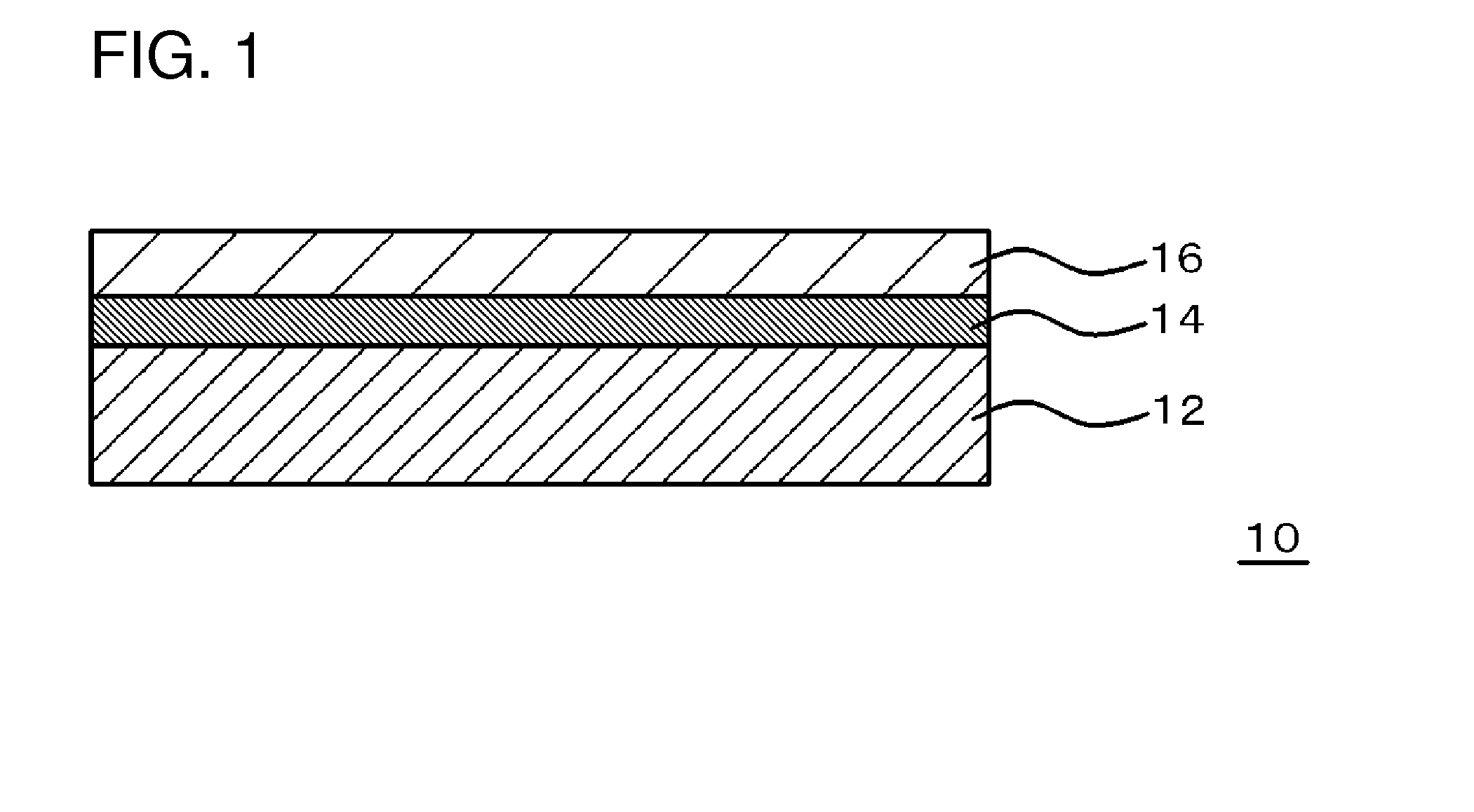
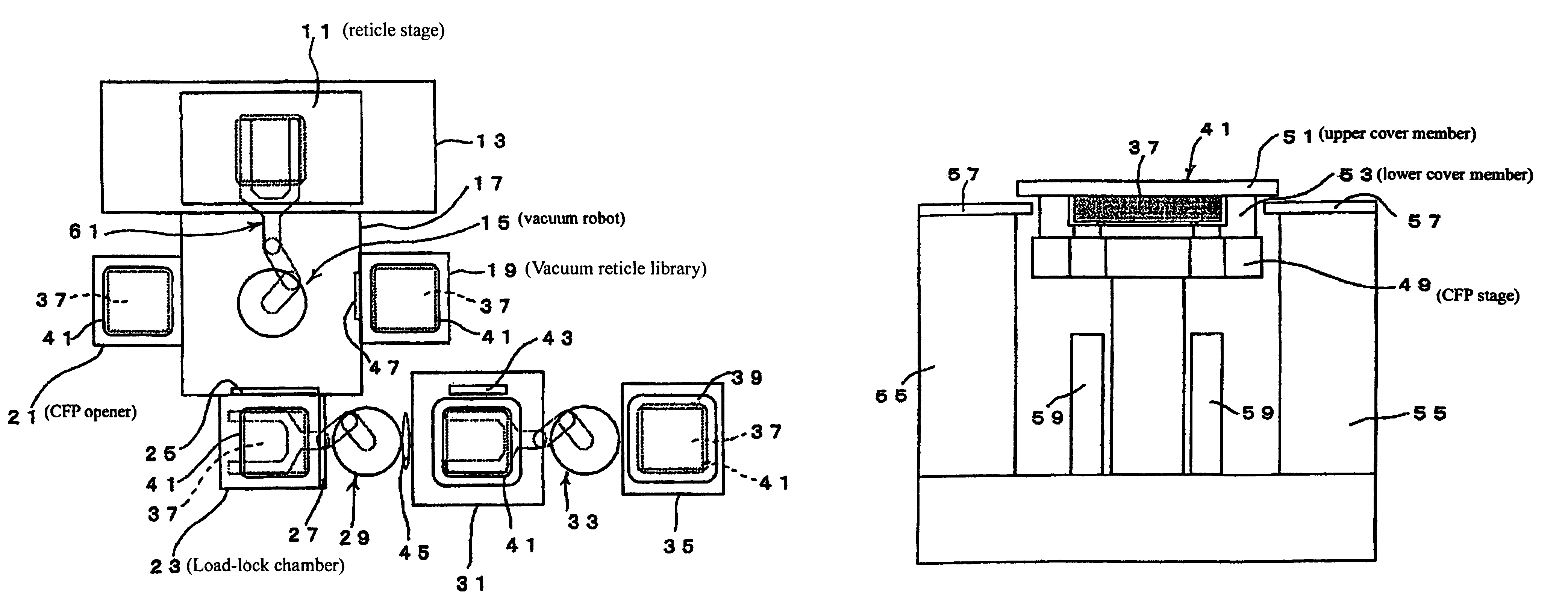
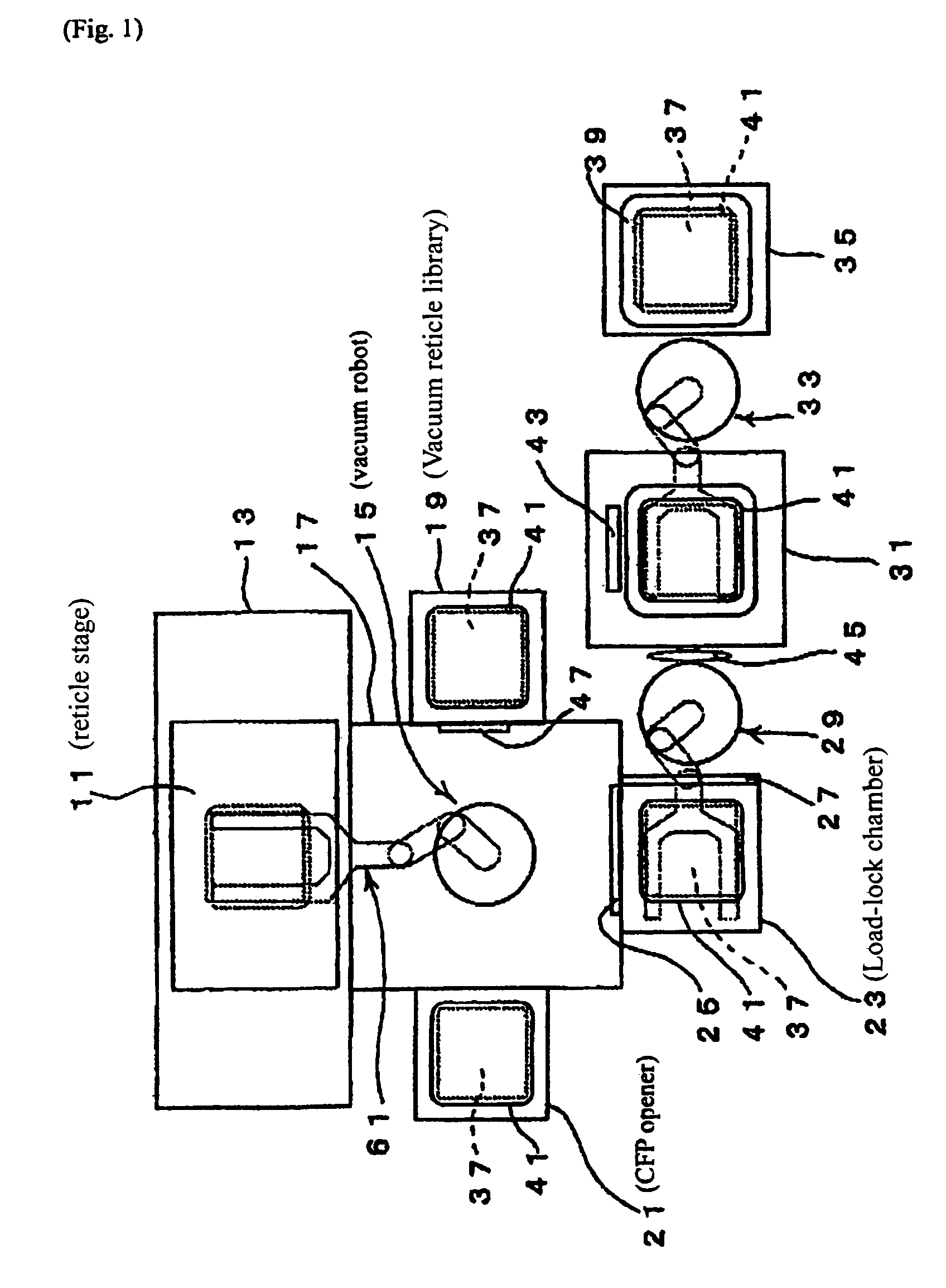
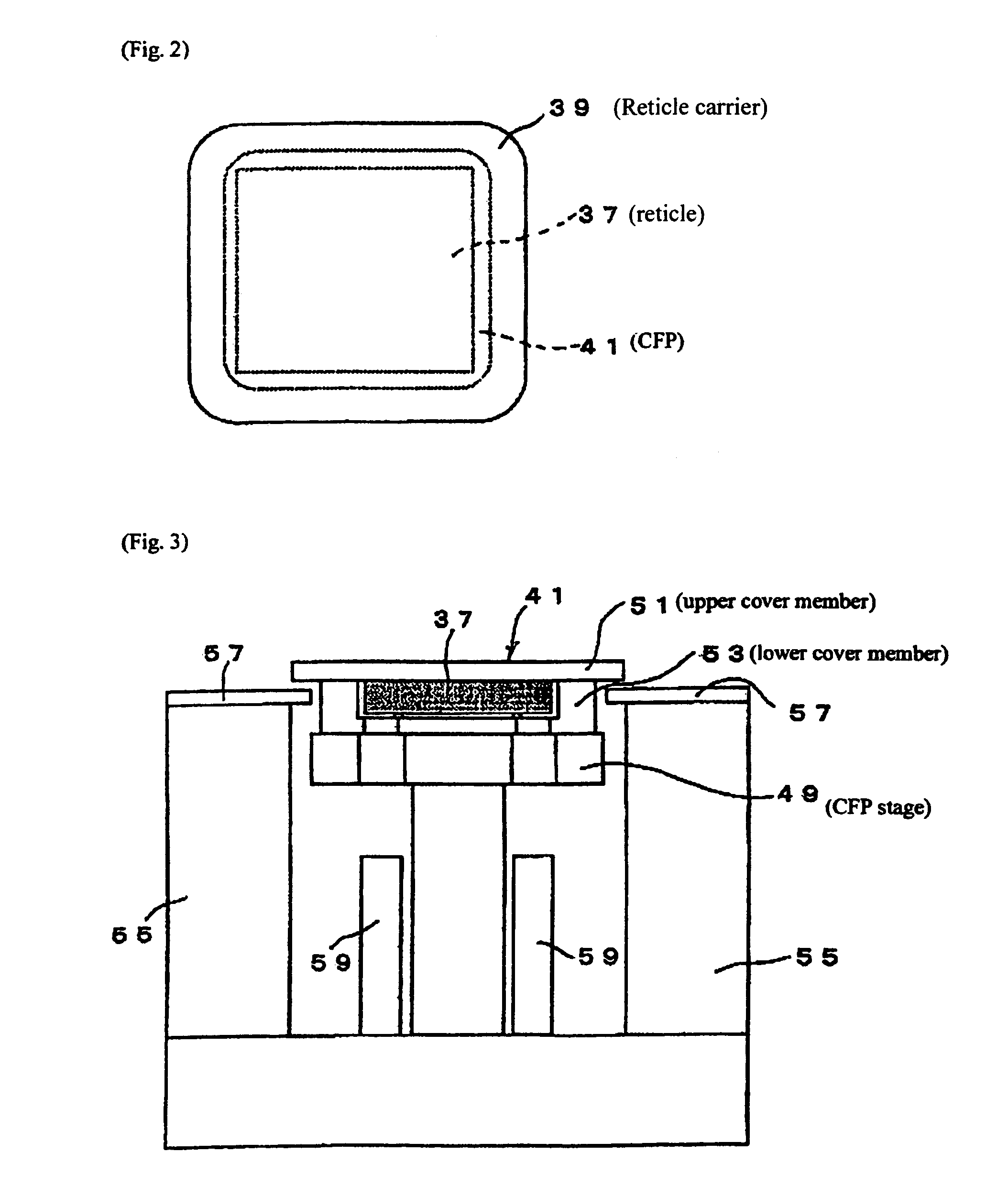
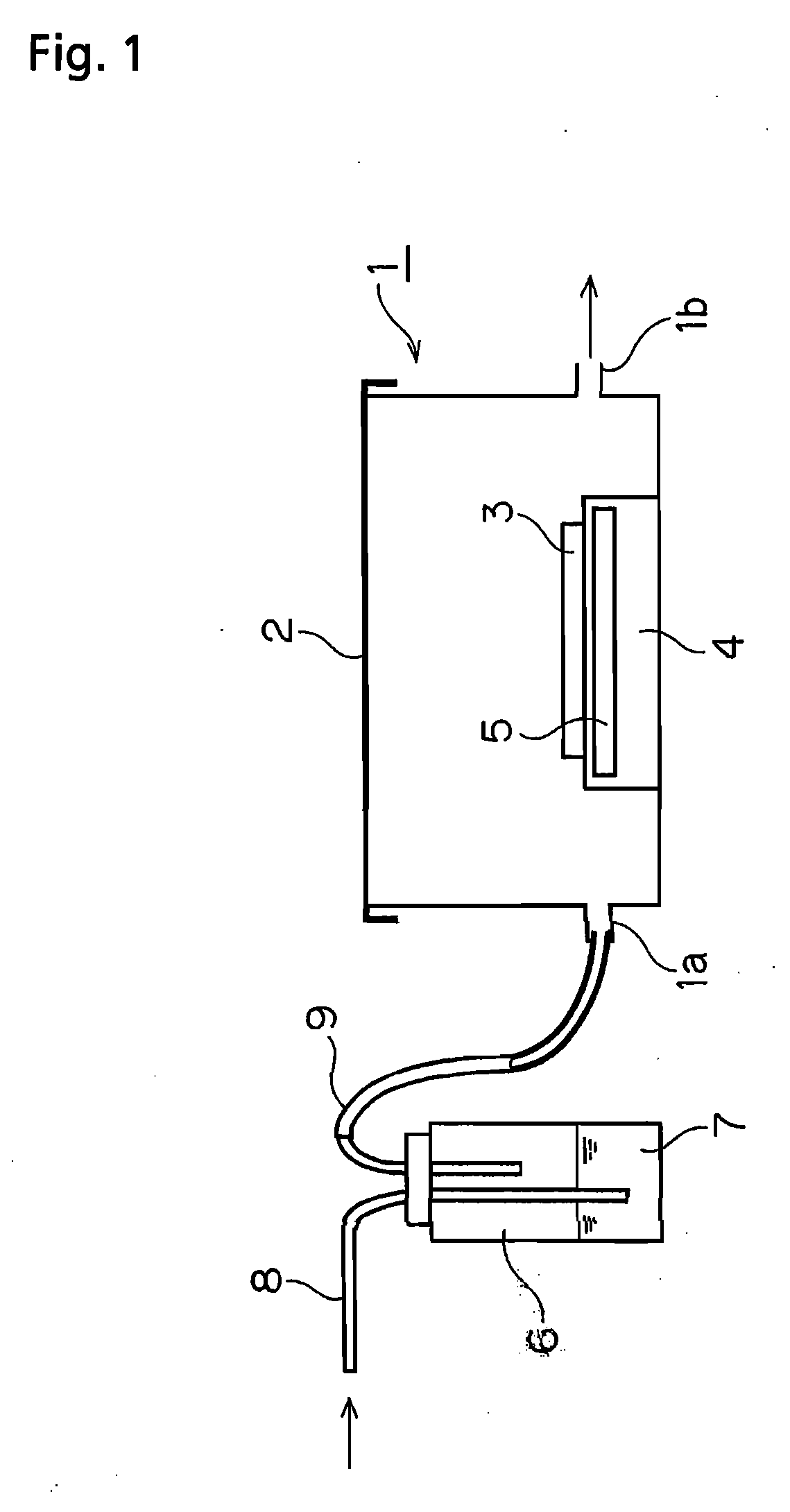
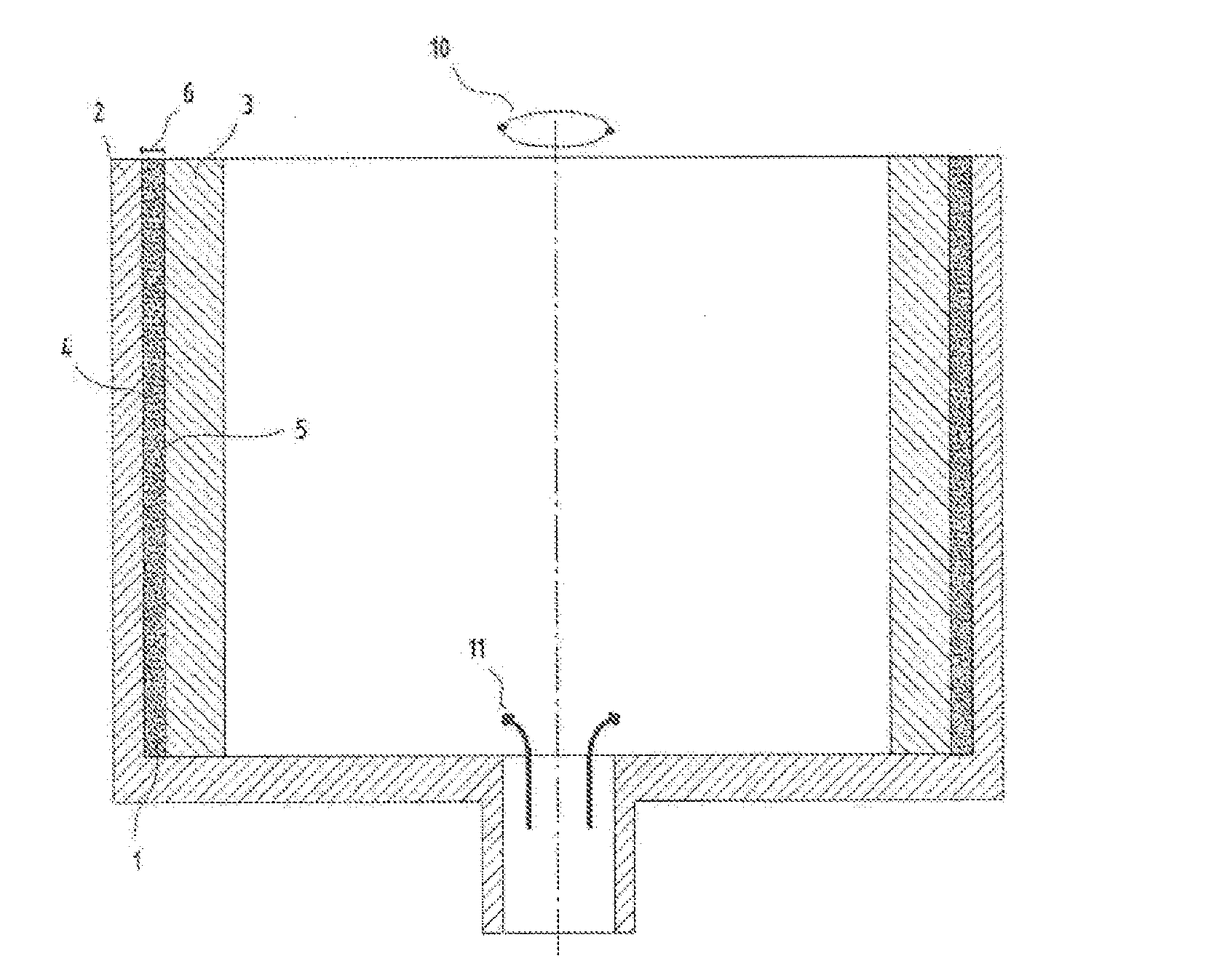
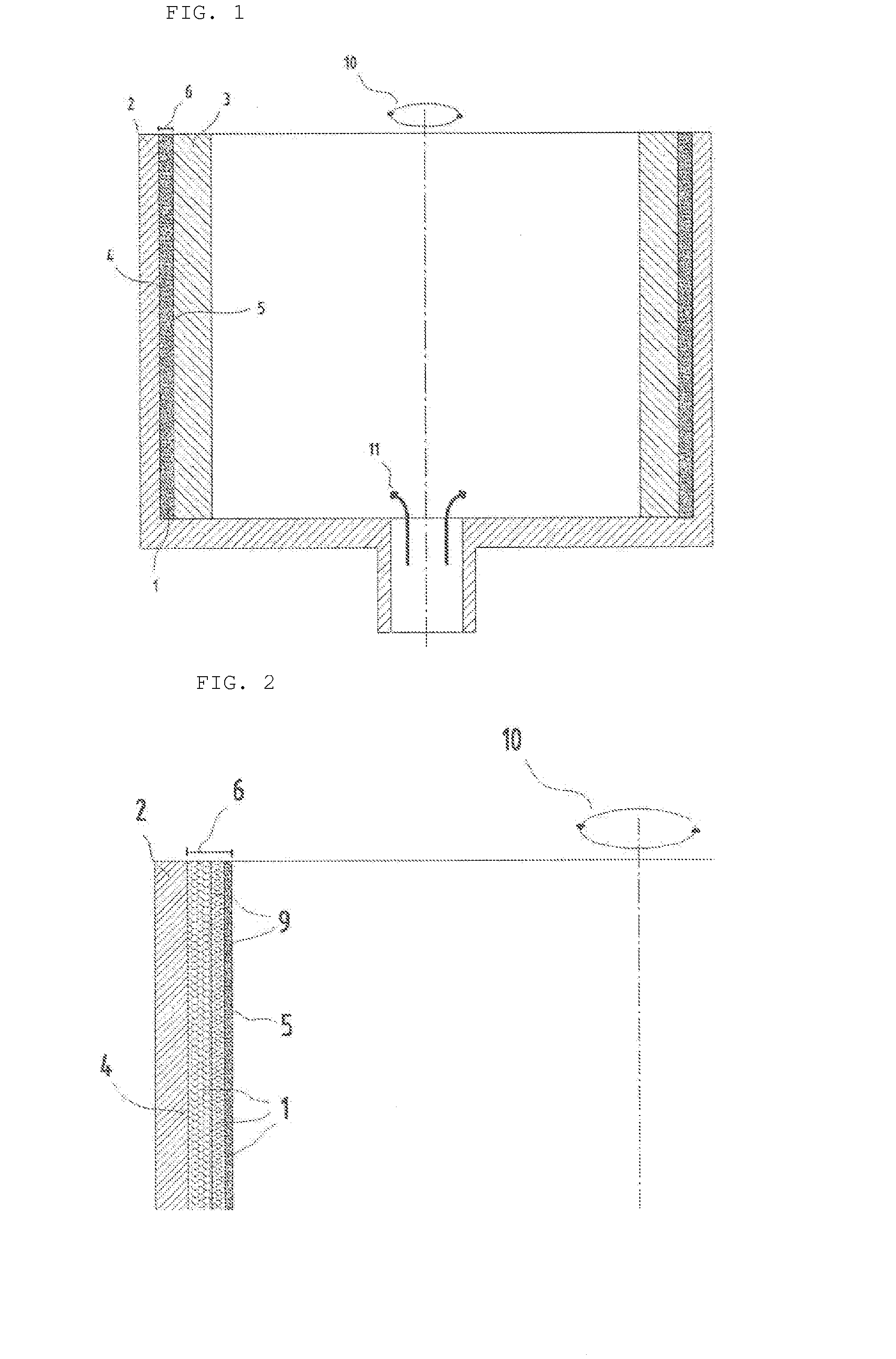
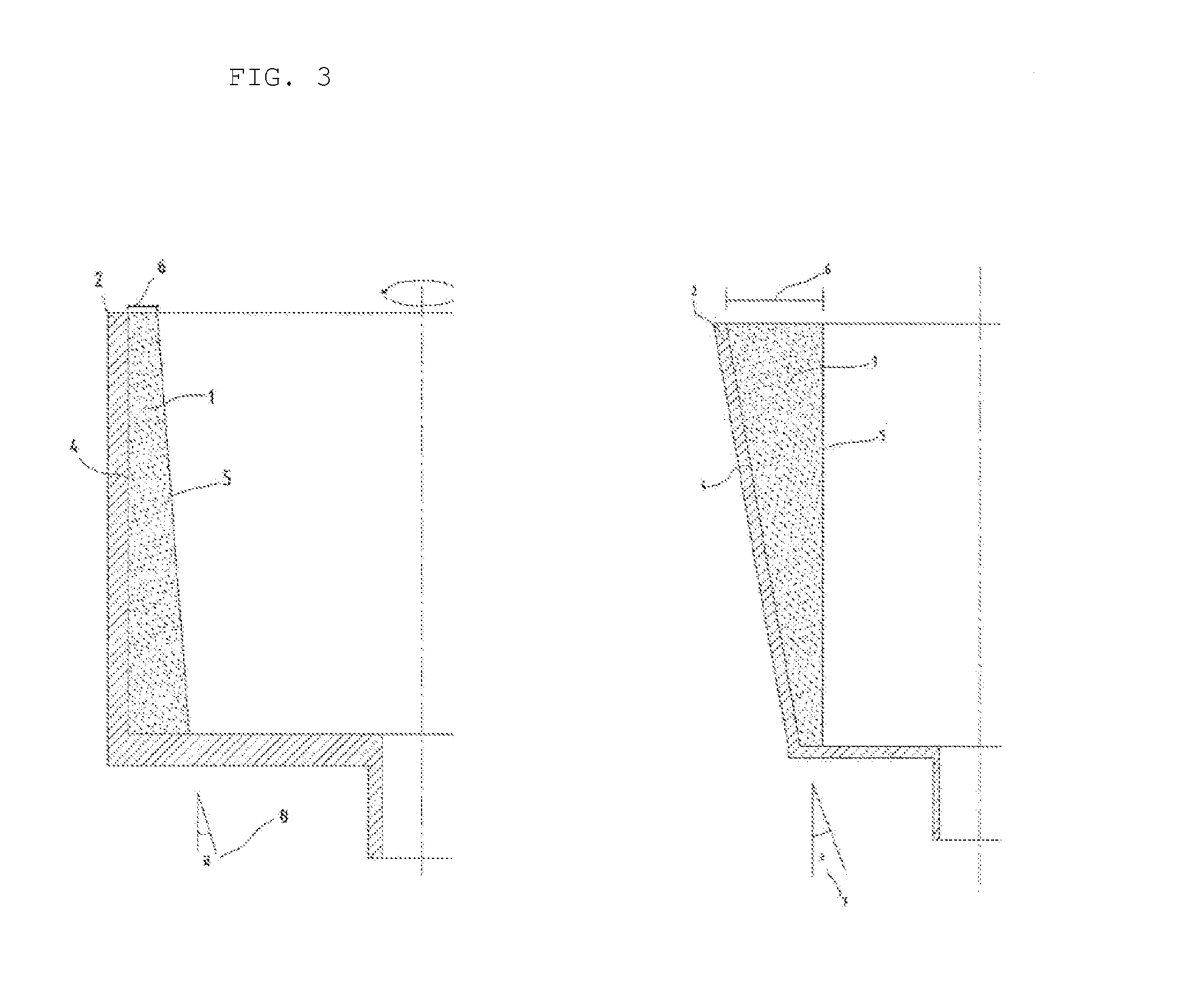
Substrate conveyor apparatus, substrate conveyance method and exposure apparatus
ActiveUS20060087638A1High yieldSmall contaminationNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineering
Owner:NIKON CORP
Disperse black and blue dye composition
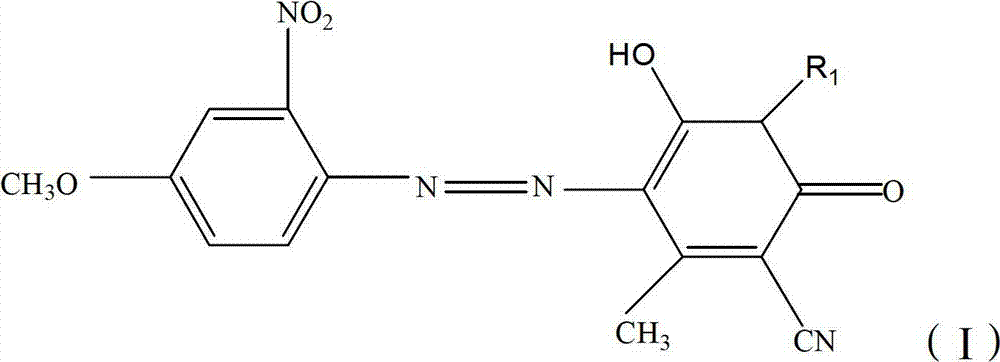
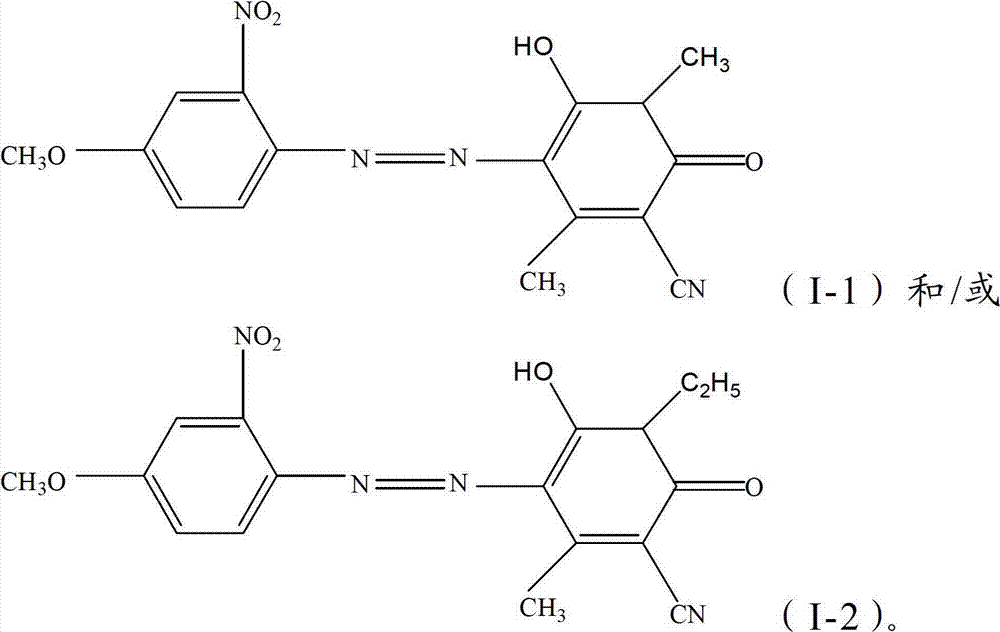
ActiveCN102352125ASmall contaminationGood washing fastnessOrganic dyesDyeing processSunlightContamination
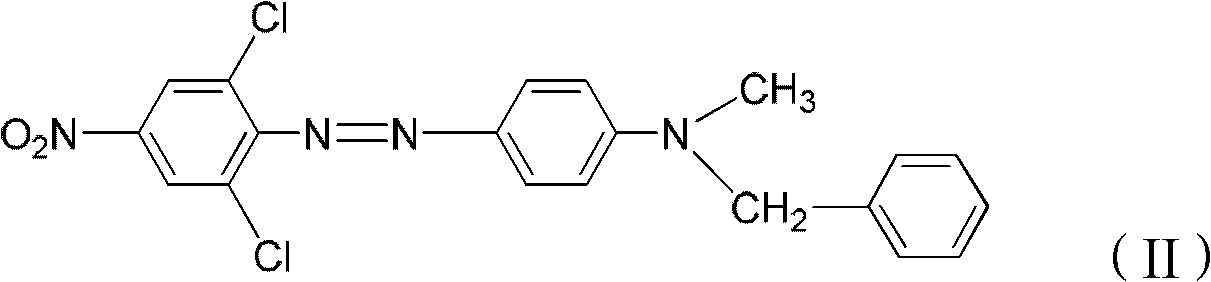
The invention discloses a disperse black and blue dye composition which basically comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 20-80% of component A, 15-40% of component B, 1-35% of component C, 0-10% of component D and 0-5% of component E, wherein the component A is one or more than one of compounds represented by formula (I); the component B is a compound represented by formula (II); the component C is one or more than one of compounds represented by formula (III); the component D is one or more than one of compounds represented by formula (IV); and the component E is one or more than one of compounds represented by formula (V). The disperse black and blue dye composition provided by the invention has small contamination to spandex, excellent compatibility and high dye uptake rate, various fastnesses such as sunlight fastness, rubbing fastness, sublimation fastness and the like of dyeing on terylene / spandex fabrics are excellent, and especially the washing fastness isextremely good.
Owner:ZHEJIANG RUNTU
Recycled plastic material, electronic apparatus having the recycled plastic material, method of manufacturing plastic part, method of manufacturing the recycled plastic material, and method of reusing plastic material
InactiveUS20050051919A1Easy to recycleDeterioration of the hue of the obtained recycled plastic material can be preventedGas current separationLayered productsThermoplasticPolymer science
A recycled plastic material is made from laser-engraved thermoplastic, metal-containing thermoplastic, thermoplastic used in an inkjet apparatus, or thermoplastic to which an ink or its composition have stuck. This recycled plastic material is manufactured by pulverizing any of these thermoplastics, cleaning the pulverized thermoplastic, removing a cleaning solution from the cleaned thermoplastic to dry it, and removing the dried thermoplastic solid matter other than the thermoplastic.
Owner:CANON KK
Ink jet printing apparatus
An ink jet printing apparatus can prevent or suppress the generation, by a reaction liquid and ink, of a reaction product on the face surface of a discharge head, and can remove the ink, the reaction liquid or the reaction product adhering to the face surface so as to constantly maintain a stable printing quality. Immediately before a printing operation is initiated, an anti-coagulation liquid is sprayed on the face surface of a discharge head, and the discharge head performs the discharge operation (printing operation) with the anti-coagulation liquid applied to the face surface. When the printing operation has been completed, or when the printing of a predetermined amount of data has been performed, the face surface of the discharge head is wiped by blades to remove the ink and the reaction liquid. Since the anti-coagulation liquid is applied to the face surface in advance, the generation of the reaction product on the face surface is prevented or suppressed. Furthermore, even when a reaction product is adhered to the face surface, the coagulation of this product on the face surface can be prevented.
Owner:CANON KK
Carrier for holding an object to be polished
InactiveUS20050202758A1Increased durabilityIncrease resistanceRevolution surface grinding machinesGrinding drivesDiamond-like carbonCarbon coated
To provide a diamond-like carbon coated carrier for holding an object to be polished used for double-sided polishing, and a manufacturing method therefor. A carrier for holding an object to be polished according to the present invention has a substrate whose entire surface is coated with diamond-like carbon. A method of the present invention includes coating the entire carrier surface with diamond-like carbon using a surface coating apparatus using plasma CVD.
Owner:SPEEDFAM CO LTD
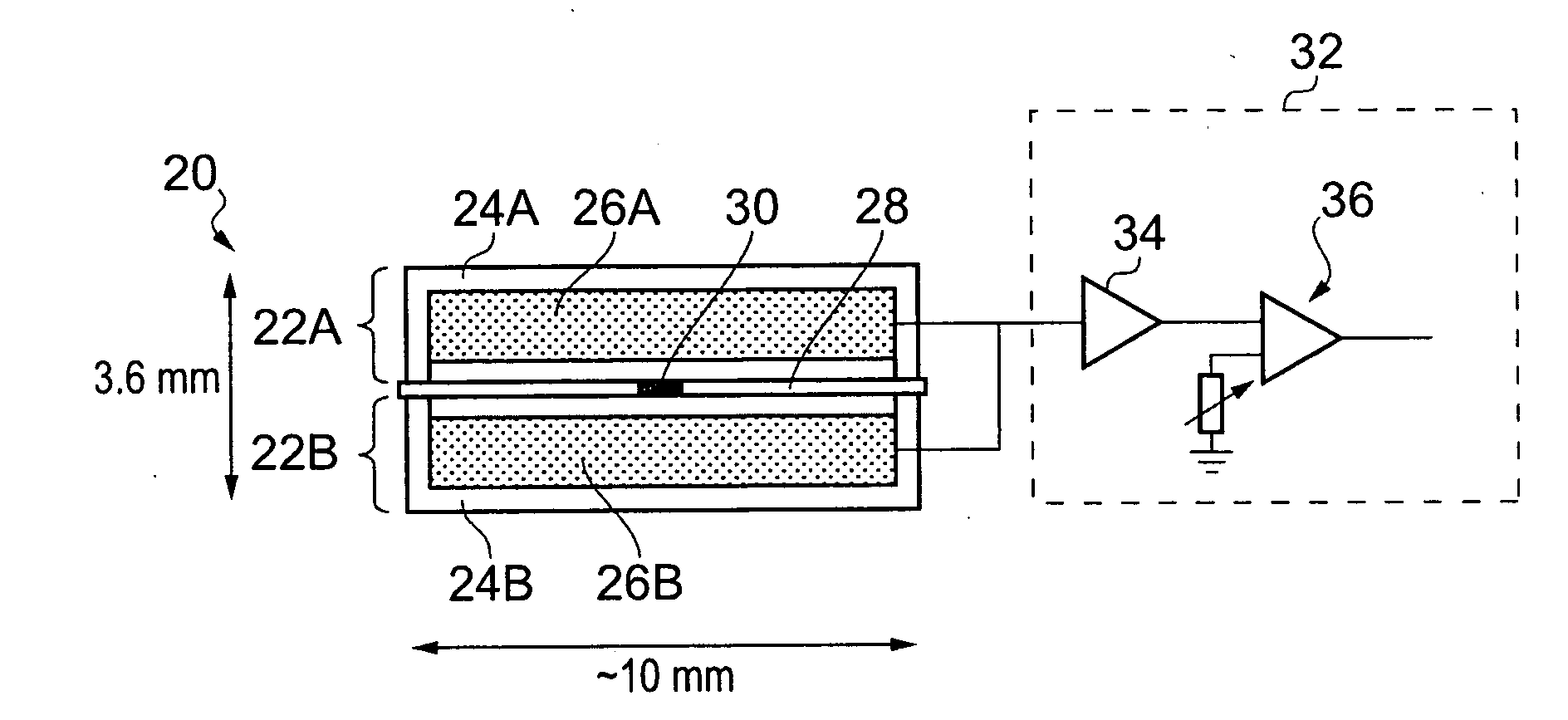
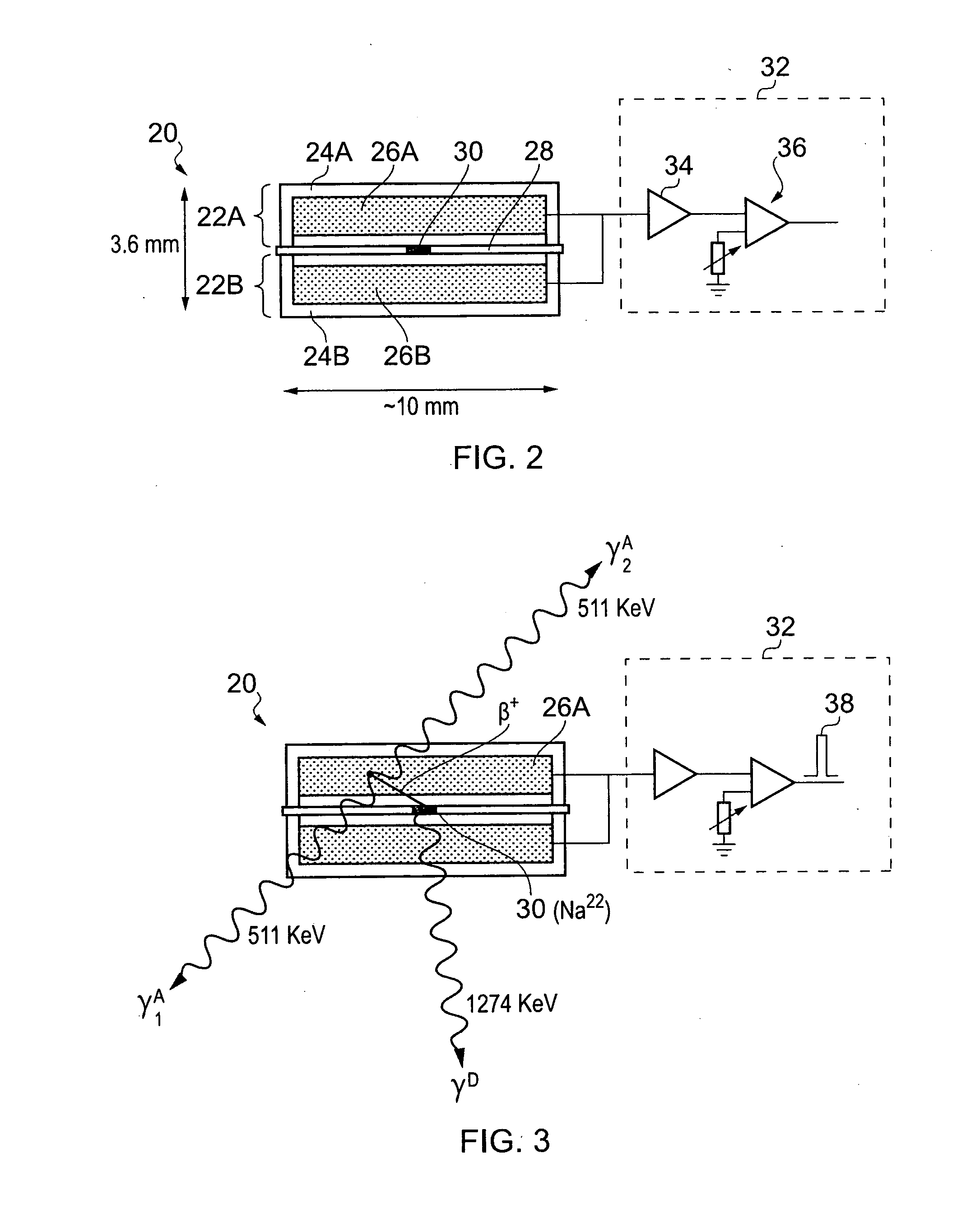
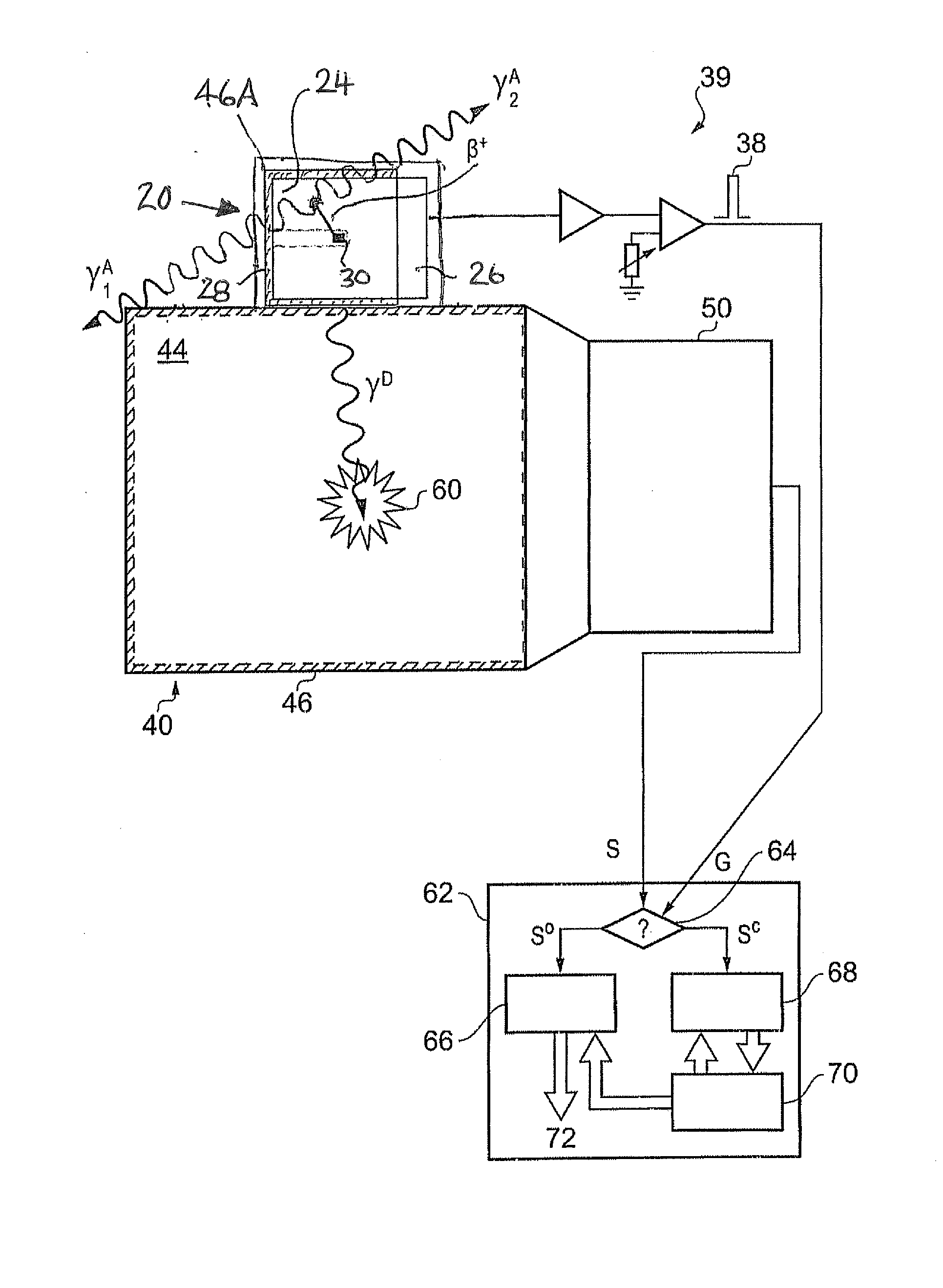
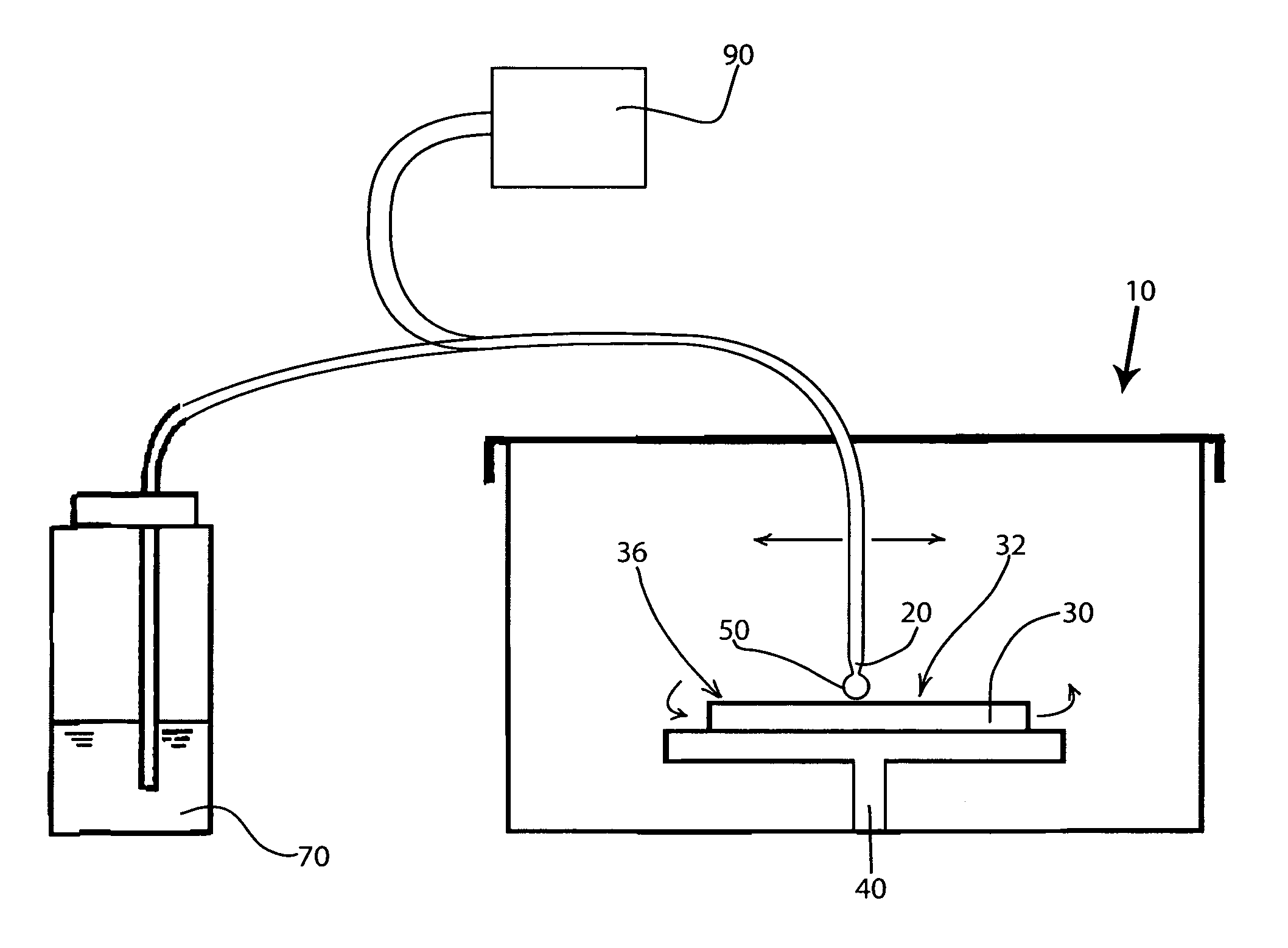
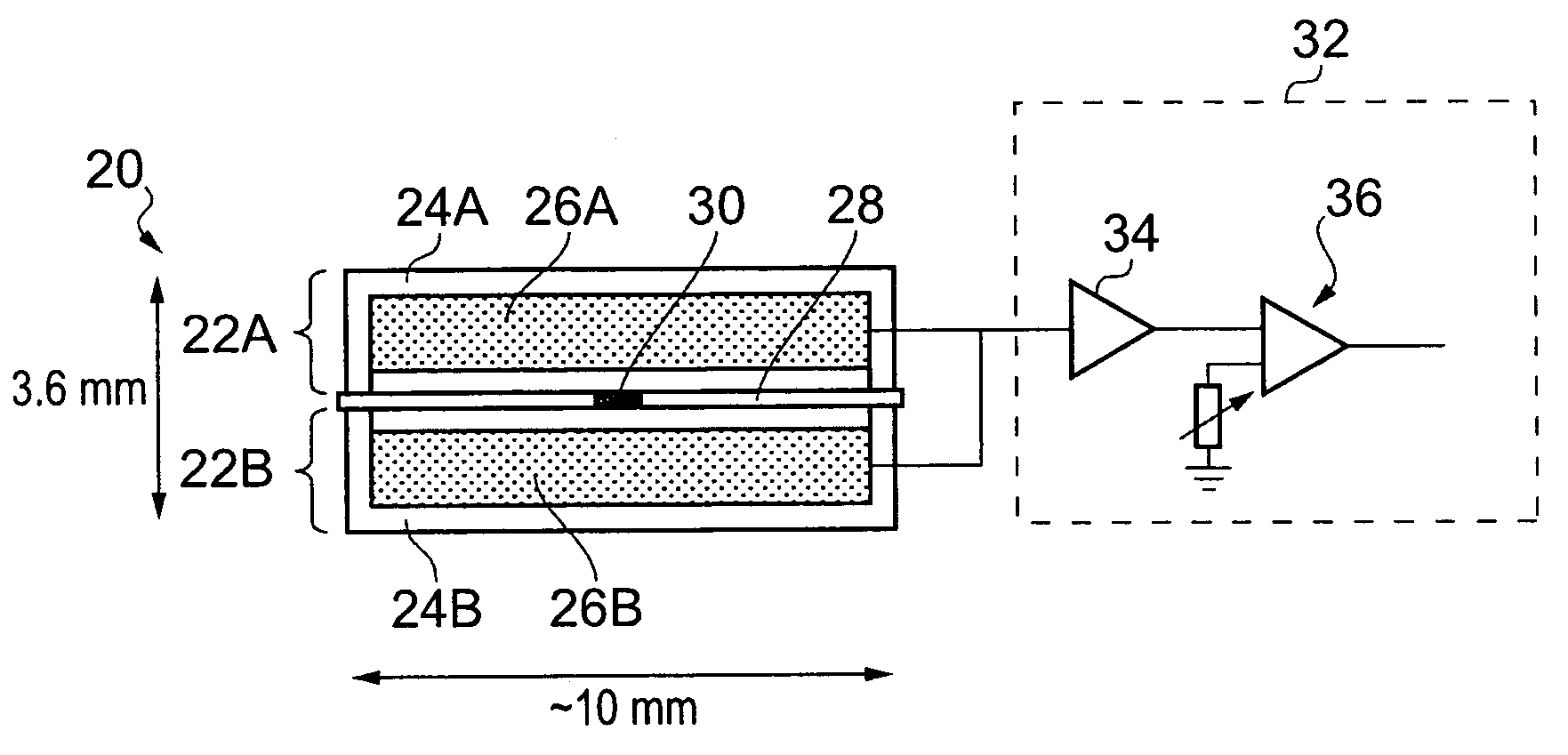
Stabilization in gamma-ray spectometry
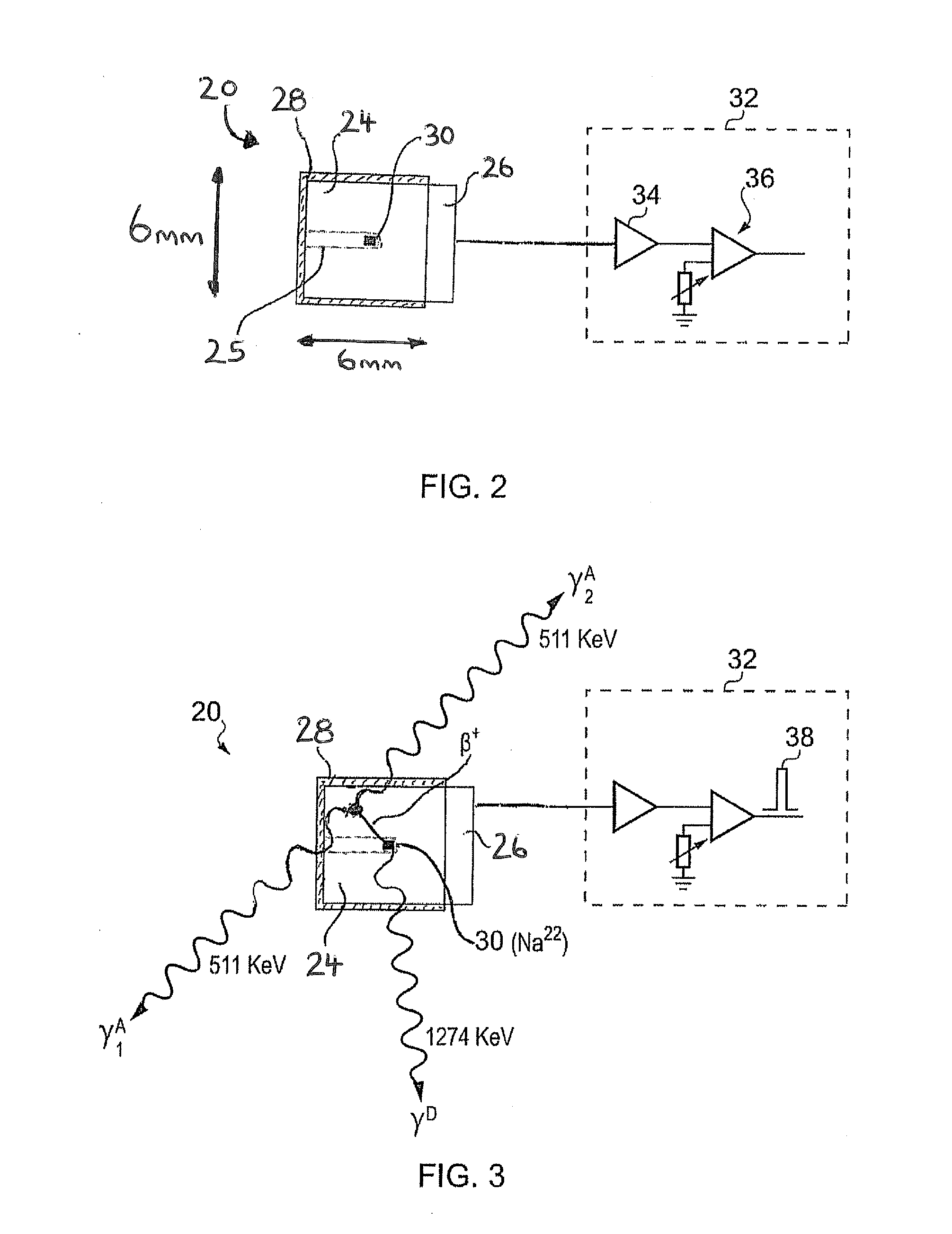
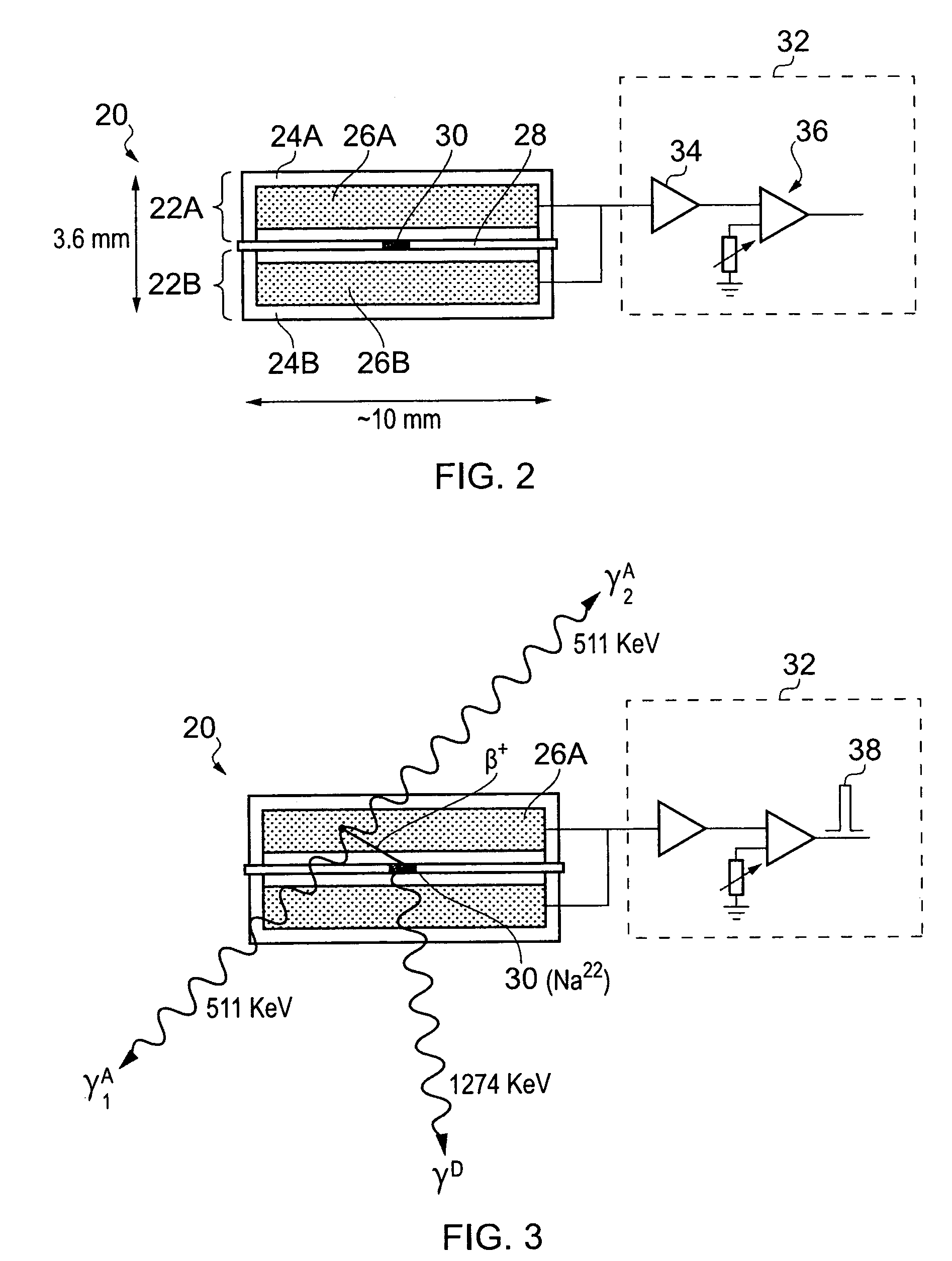
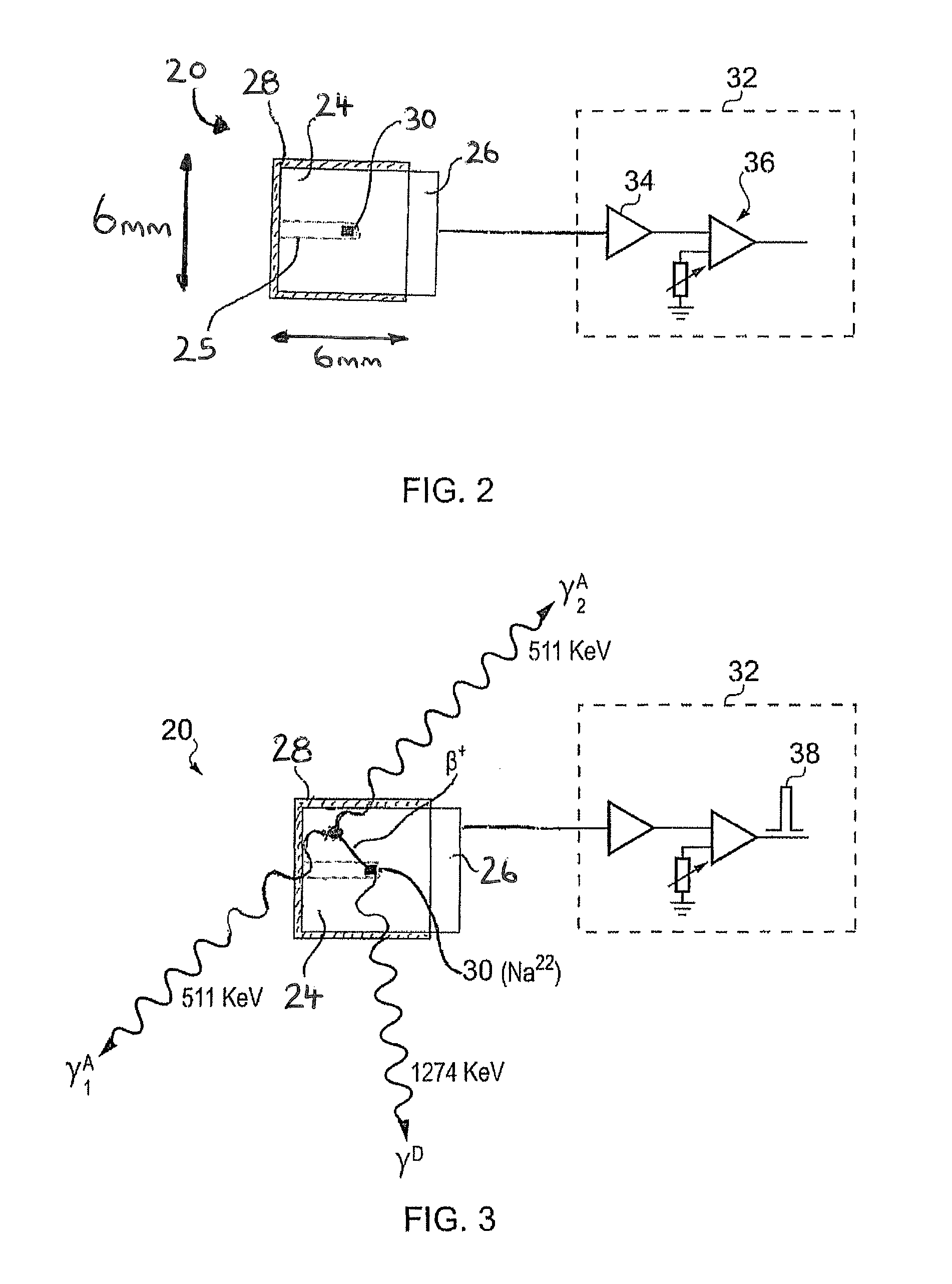
ActiveUS20110211675A1Easy to escapeSmooth responseX-ray spectral distribution measurementCalibration apparatusSolid state detectorGamma ray spectrometer
A calibration source (20) for a gamma-ray spectrometer (40) is provided. The calibration source comprises a radioactive material (30) comprising a radioactive isotope having a decay transition associated with emission of a radiation particle and a gamma-ray having a known energy, e.g. Na-22, and a solid-state detector (26A, 26B), e.g. a PIN photodiode, arranged to receive radiation particles emitted from the radioactive material. A gating circuit (32) is coupled to the solid-state detector and is operable to generate a gating signal in response to detection of a radiation particle in the solid-state detector. The gating signal may thus be used as an indicator that an energy deposit in a nearby gamma-ray spectrometer is associated with a decay transition in the radioactive isotope. Since these energy deposits are of a known energy, they can be used as reference points to calibrate the spectrometer response. Thus with calibration sources according to embodiments of the invention, spectral stabilization (i.e. accounting for a changing spectrometer response, as well as base calibration) may be performed in real time and in parallel with obtaining a spectrum of observed signal events (i.e. the spectrum of interest). Furthermore, this is achieved with little contamination of the spectrum events of interest.
Owner:SYMETRICA
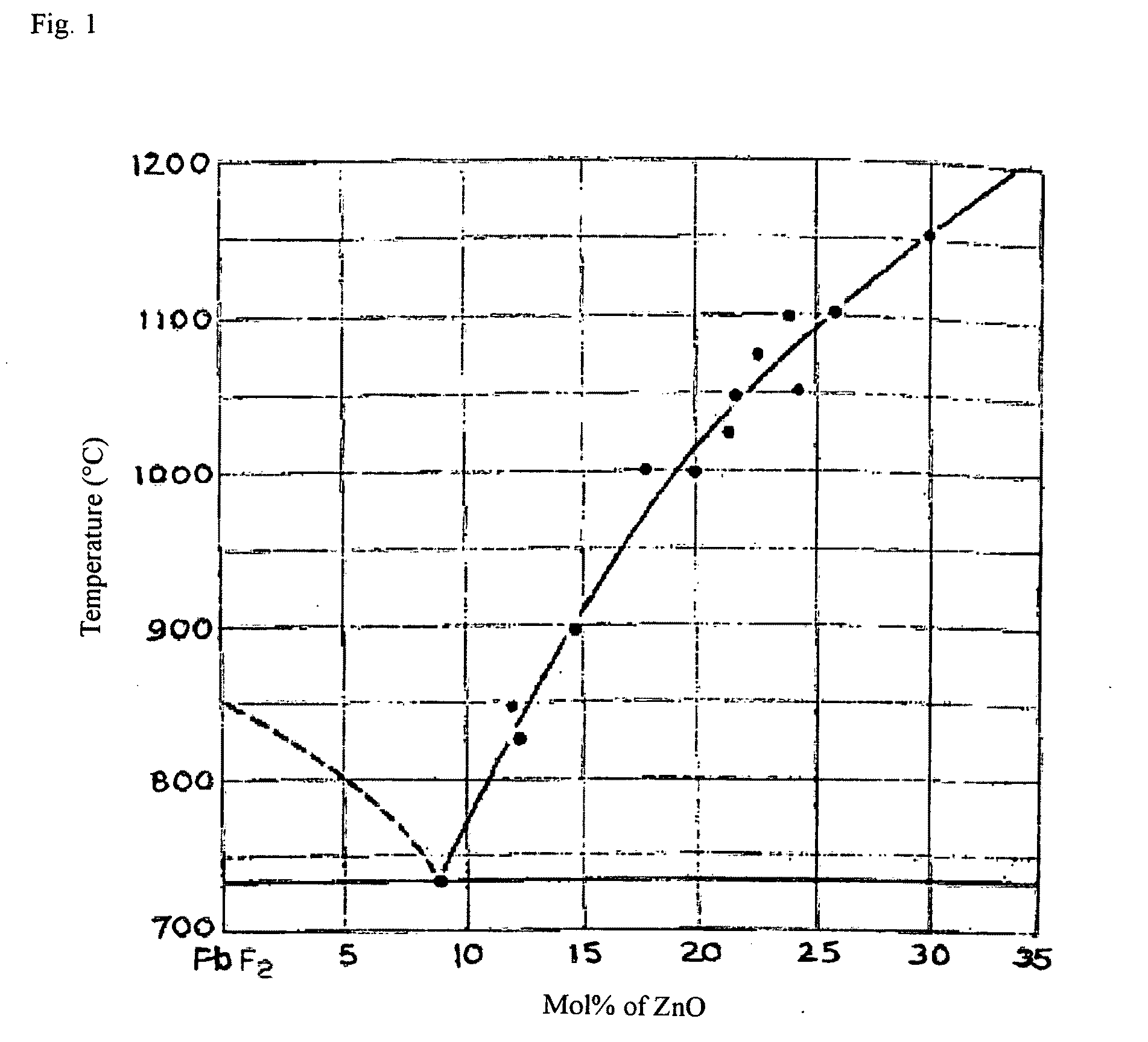
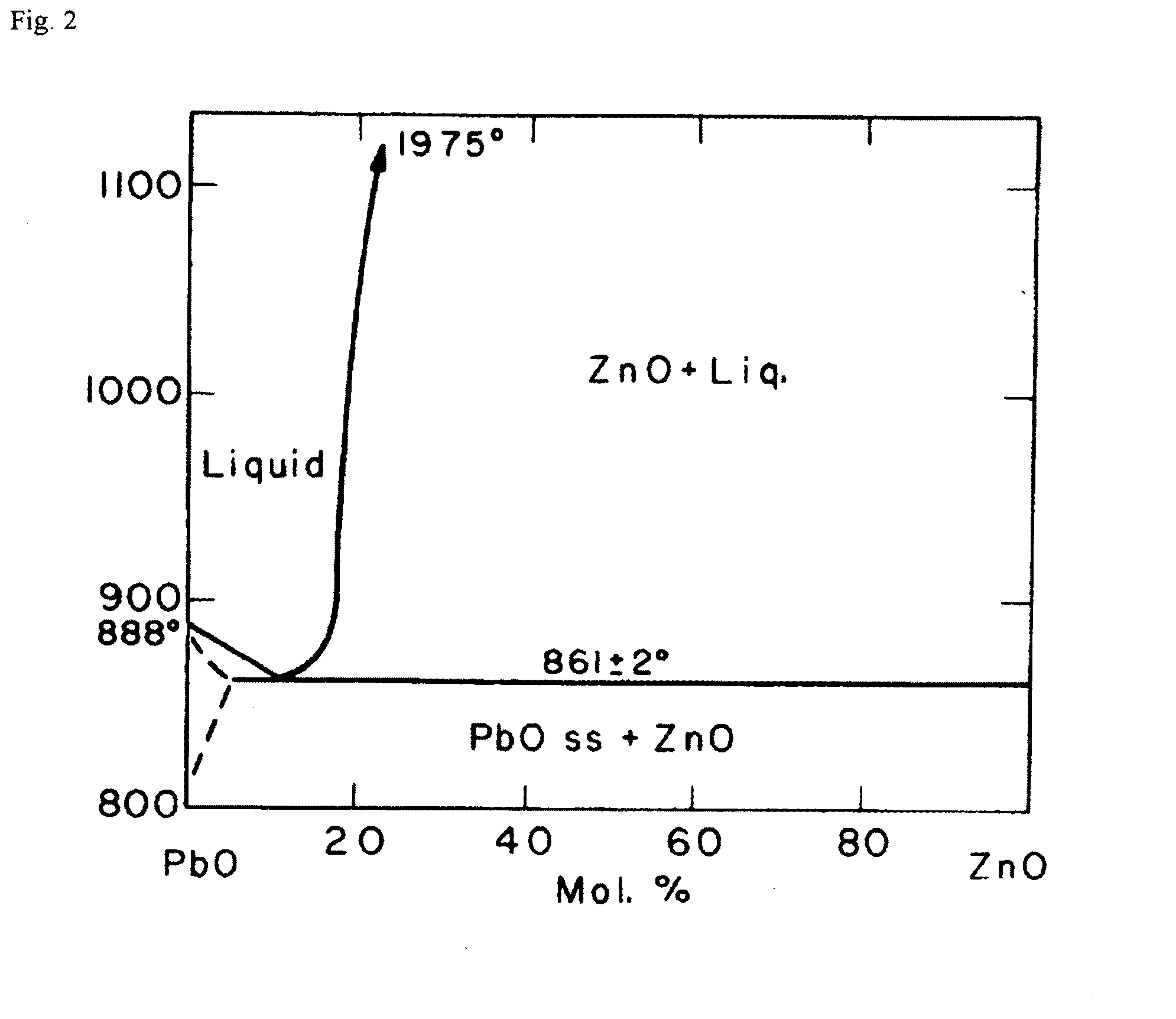
Process for Producing Zno Single Crystal According to Method of Liquid Phase Growth
InactiveUS20090044745A1Few dislocationFew defectPolycrystalline material growthLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthSolventSeed crystal
A method for producing a ZnO single crystal by a liquid phase growth technique, comprising the steps of: mixing and melting ZnO as a solute and PbF2 and PbO as solvents; and putting a seed crystal or substrate into direct contact with the obtained melted solution, thereby growing a ZnO single crystal on the seed crystal or substrate.
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
Recycled plastic material, electronic apparatus having the recycled plastic material, method of manufacturing plastic part, method of manufacturing the recycled plastic material, and method of reusing plastic material
InactiveUS6864294B2Easy to spreadEasy to useGas current separationPlastic recyclingThermoplasticPlastic materials
A recycled plastic material is made from laser-engraved thermoplastic, metal-containing thermoplastic, thermoplastic used in an inkjet apparatus, or thermoplastic to which an ink or its composition have stuck. This recycled plastic material is manufactured by pulverizing any of these thermoplastics, cleaning the pulverized thermoplastic, removing a cleaning solution from the cleaned thermoplastic to dry it, and removing the dried thermoplastic solid matter other than the thermoplastic.
Owner:CANON KK
Low gain pressure relief valve for a fluid pump
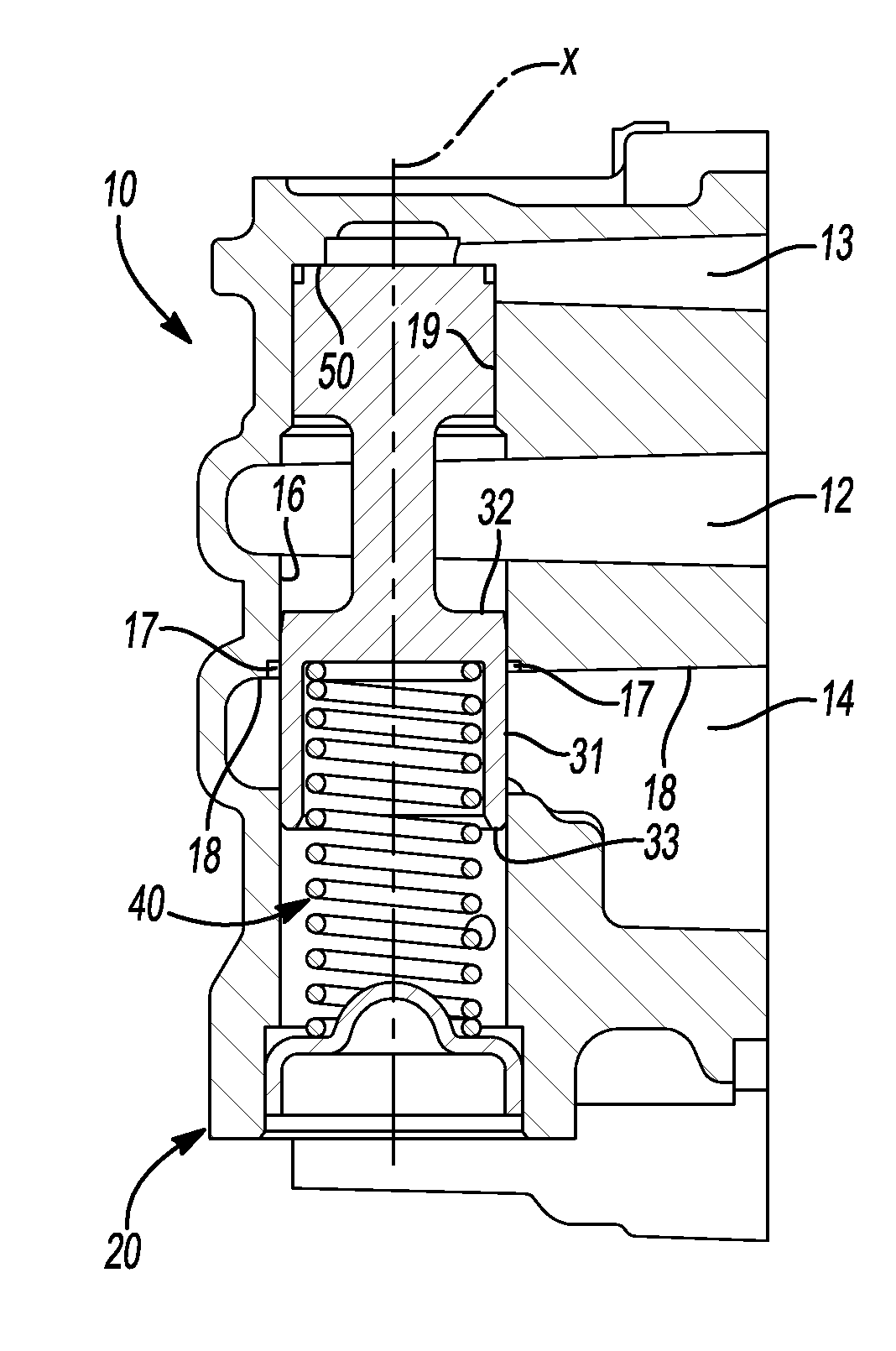
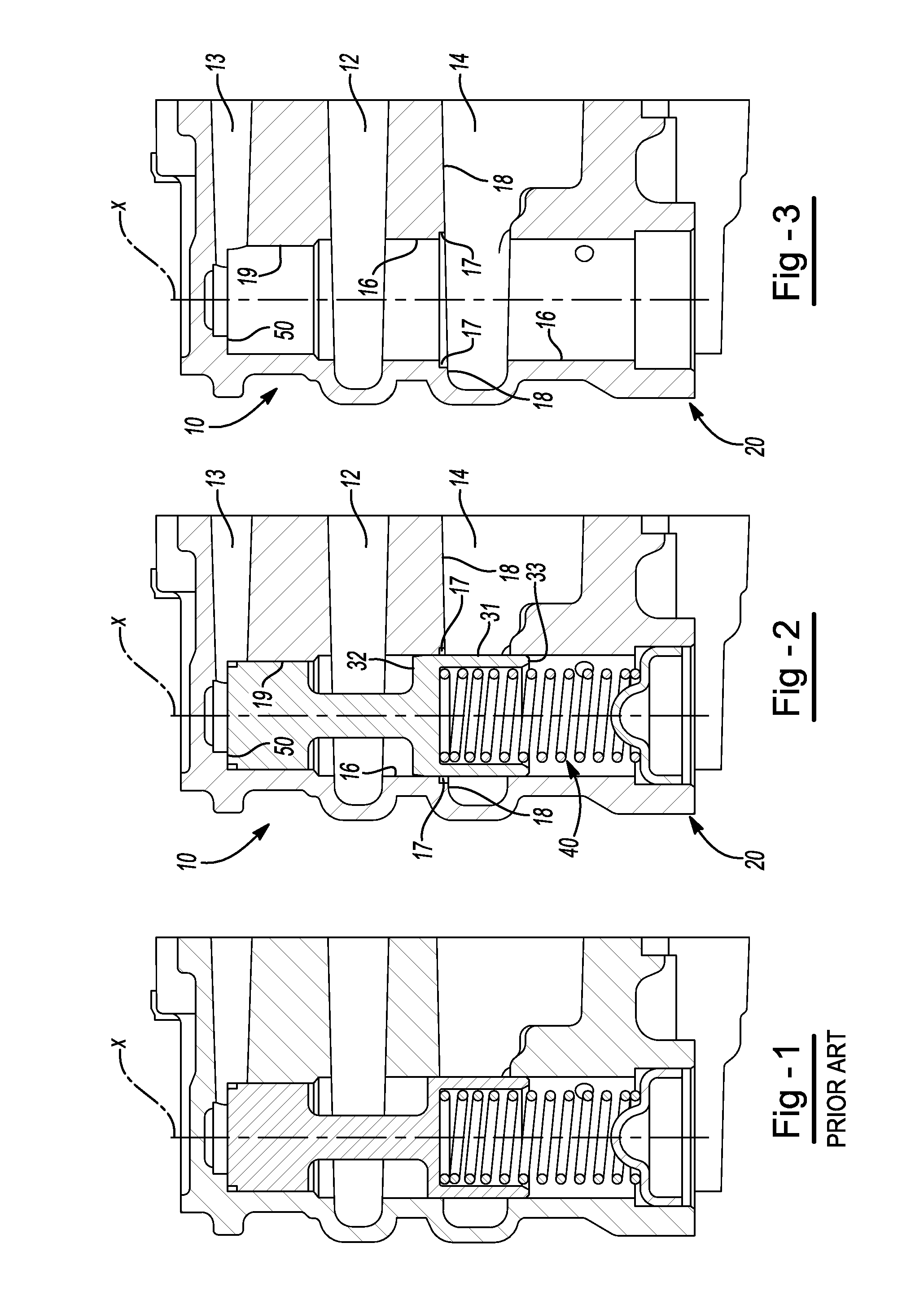
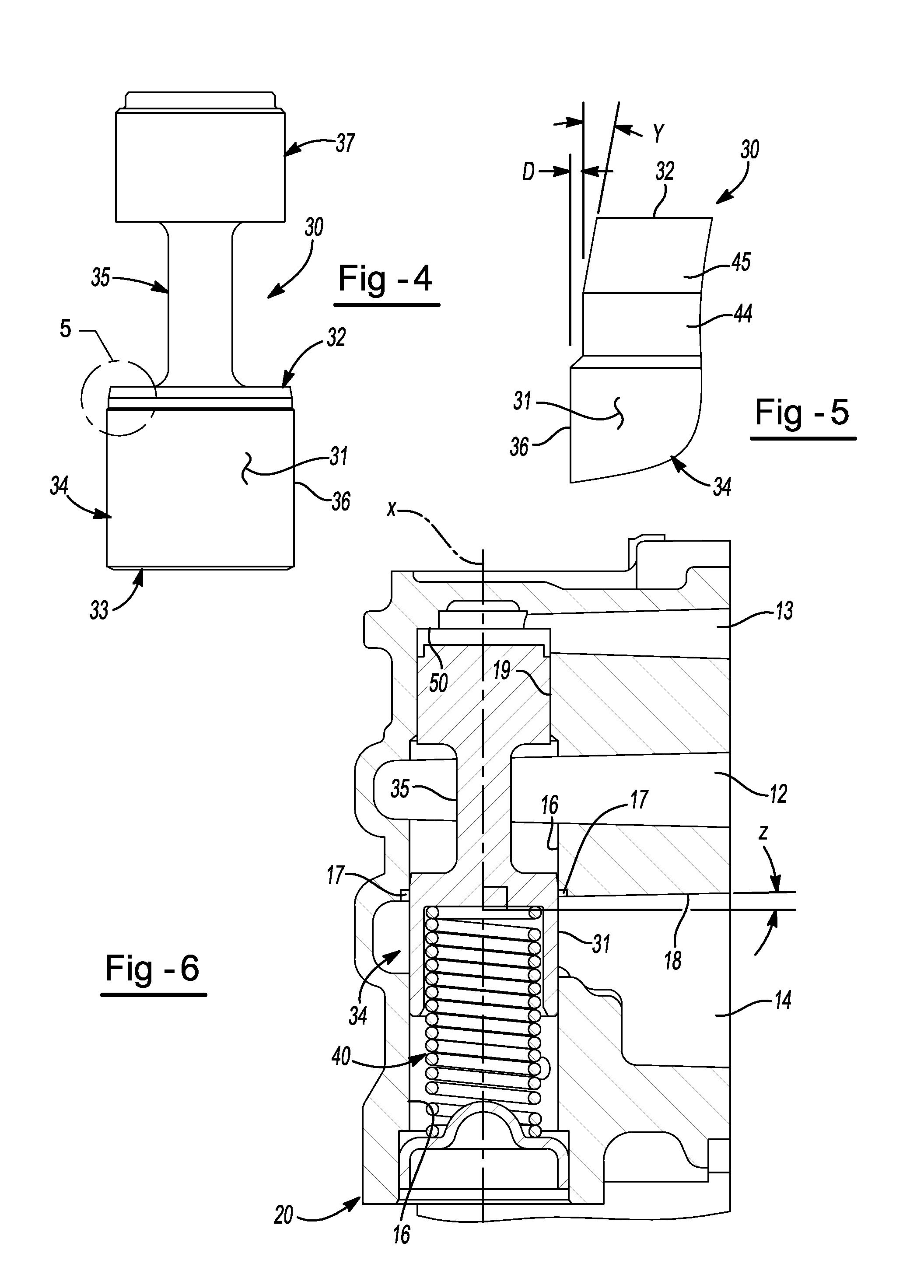
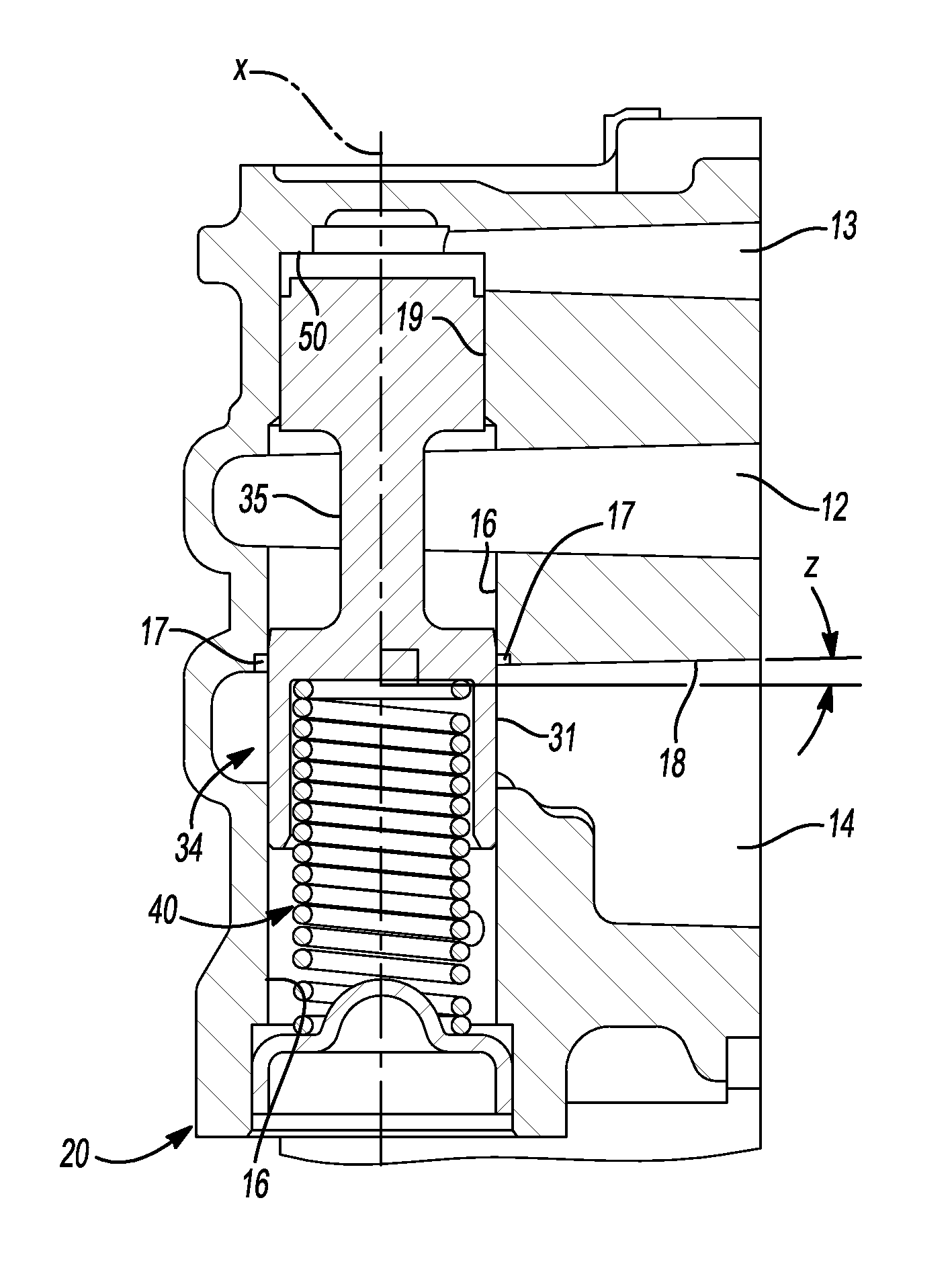
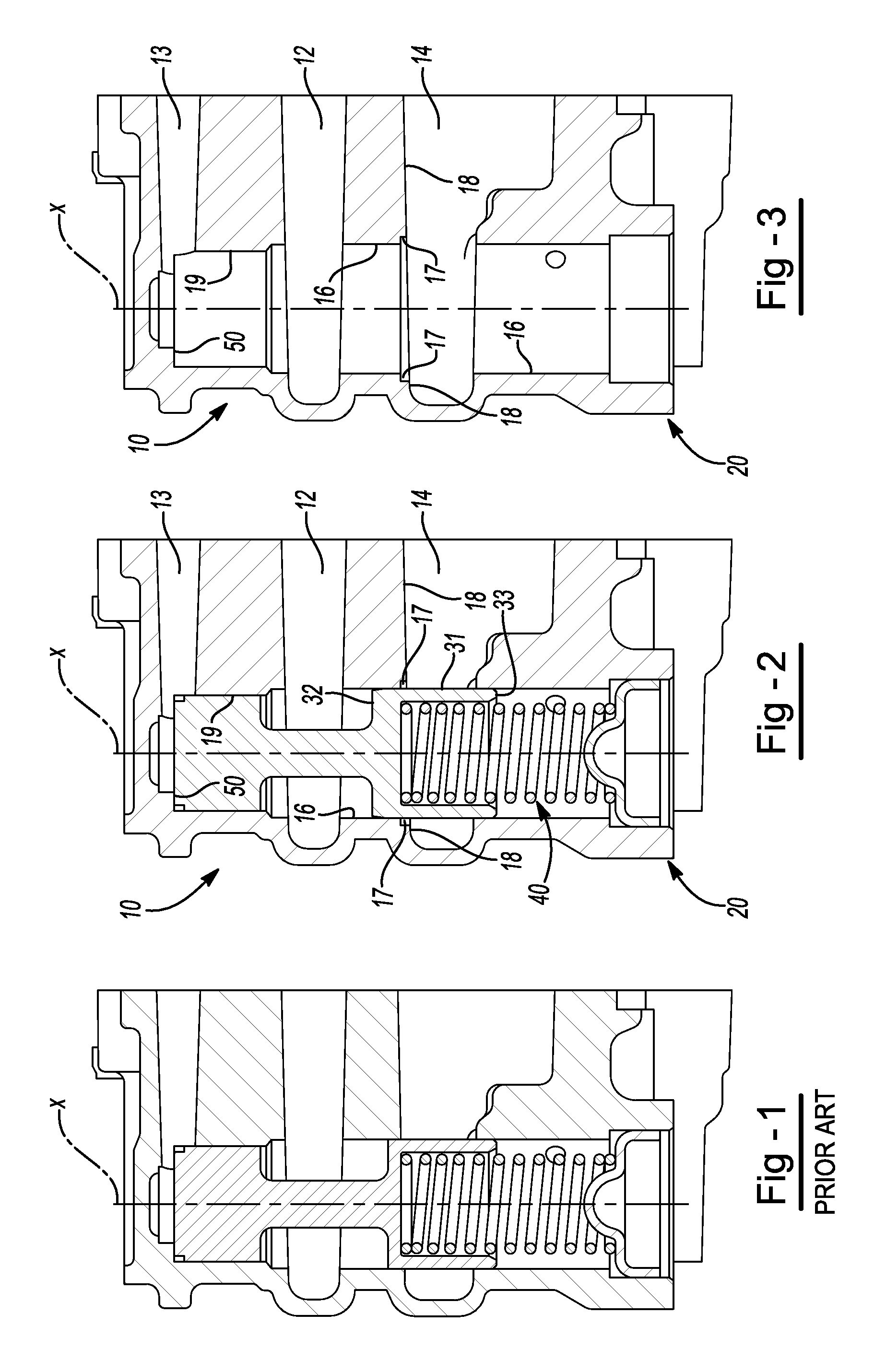
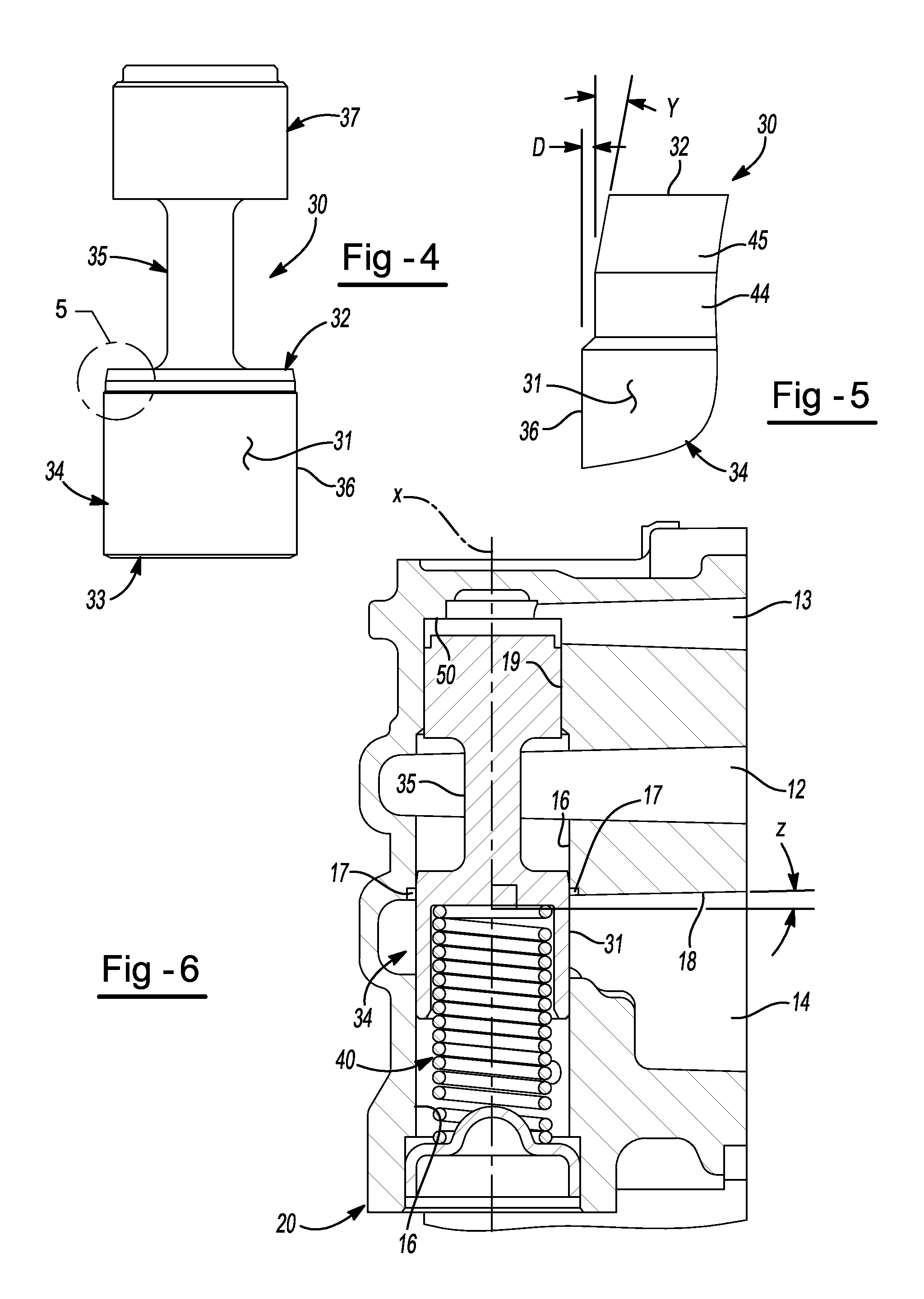
ActiveUS20120248362A1Reduce gainPreserving good robustness against small particle contaminationCheck valvesEqualizing valvesMetallic materialsEngineering
A pressure relief valve for use in regulating discharge fluid pressure of a pump includes a casted, metal material housing including a passage therein along a longitudinal axis and inlet and outlet ports substantially perpendicular to the longitudinal axis and each having walls that are at an angle less than perpendicular to the longitudinal axis wherein the angle of the wall from being perpendicular to the longitudinal axis is substantially equal to the draft angle from the casting of the housing. A first wall of the outlet intersects with the wall of the passage of the pressure relief valve. A valve body disposed in the passage is movable in the passage against the biasing force of a spring biasing the valve body in a first or closed direction wherein the inlet port and the outlet port are disconnected, until the force at the inlet applied to the valve body overcomes the biasing Force of the spring and the inlet fluid is communicated through the passage and to the outlet. The housing includes a counterbore at the intersection of the wall of the passage and the wall of the outlet port to provide a counterbore surface that is perpendicular to the wall of the passage around the outer circumference of the valve body. The top end of the valve body includes a reduced diameter portion and a tapered portion between the reduced diameter portion and the top of the valve body.
Owner:HANON SYST EFP CANADA LTD
High temperature-resistant fireproof coating and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108504257AGood weather resistanceImprove performance such as salt spray resistanceFireproof paintsEpoxy resin coatingsFiberAcrylic resin
The invention relates to the technical field of coatings, in particular to a high temperature-resistant fireproof coating and a preparation method thereof. The high temperature-resistant fireproof coating is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: acrylic resin, inorganic filler, a thickener, a flame-retardant agent, a ceramic additive, fireproof short fibers, a crosslinkingagent, a coupling agent, a flatting agent, a defoaming agent, a wetting agent, a film forming additive, other additives and solvents. The high temperature-resistant fireproof coating has the advantages that high temperature can be endured, the flame-retardant property is good, the propagation of fire condition is well blocked, and the fireproof property is excellent; the effect of resisting long-time impact by 1100 DEG C hydrocarbon high-temperature fire hazard is realized; the weather-resistant property and waterproof property are realized, the shrinkage is avoided, the coating strength is high, and the surface is flat.
Owner:GUANGDONG ZHICHENG CHEM +1
Gamma-Ray Spectrometry
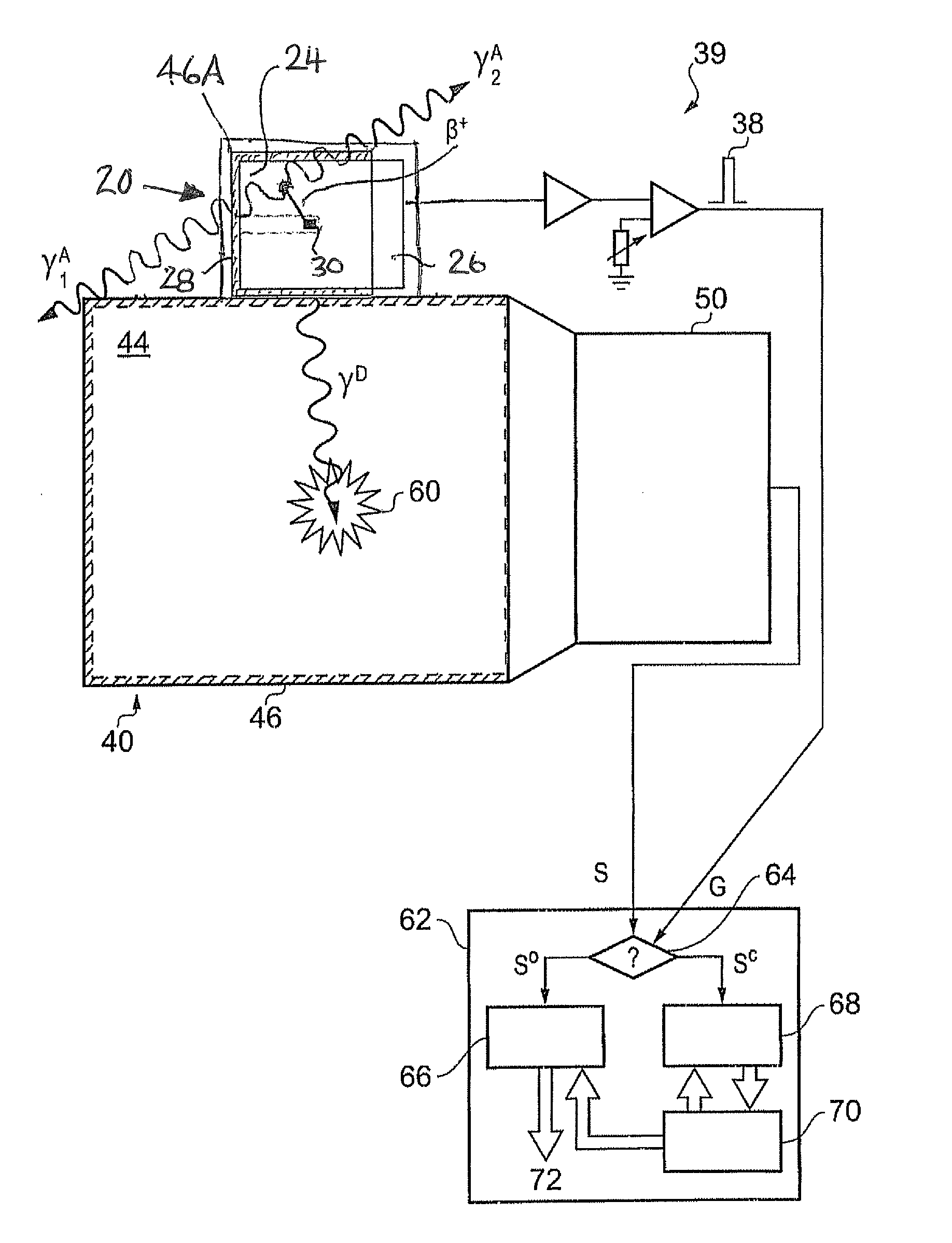
ActiveUS20150316665A1Smooth responseSmall contaminationX-ray spectral distribution measurementRadiation intensity measurementAmount of substanceGamma ray spectrometer
A calibration source for a gamma-ray spectrometer is provided. The calibration source comprises a scintillator body having a cavity in which a radioactive material is received. The scintillator body may be generally cuboid and the cavity may be formed by a hole drilled into the scintillator body. The radioactive material comprises a radioactive isotope having a decay transition associated with emission of a radiation particle and a gamma-ray having a known energy e.g. Na-22. A photodetector, for example a silicon photomultiplier, is optically coupled to the scintillator body and arranged to detect scintillation photons generated when radiation particles emitted from the radioactive material interact with the surrounding scintillator bod. A gating circuit is arranged to receive detection signals from the photodetector and to generate corresponding gating signals for a data acquisition circuit of an associated gamma-ray spectrometer to indicate that gamma-ray detections in the gamma-ray spectrometer occurring within a time window defined by the gating signal are associated with a decay transition in the radioactive isotope. Thus a calibration source is provided based around a simple scintillator body design. Furthermore, the radioactive material may be introduced into the scintillator body in a separate step after manufacture of the scintillator body, thereby reducing the risk of radioactive contamination during manufacture.
Owner:SYMETRICA
Silicon wafer reclamation method and reclaimed wafer
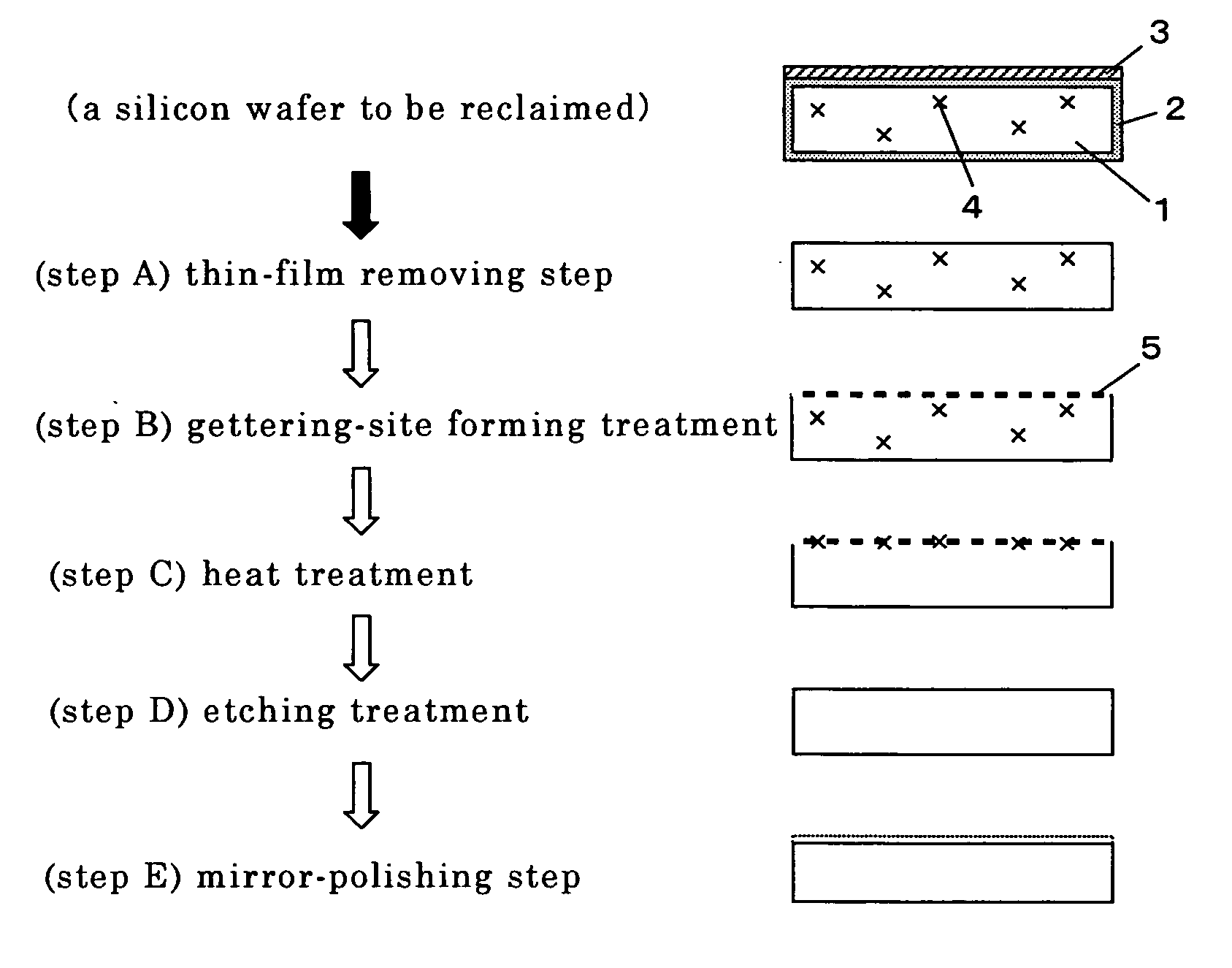
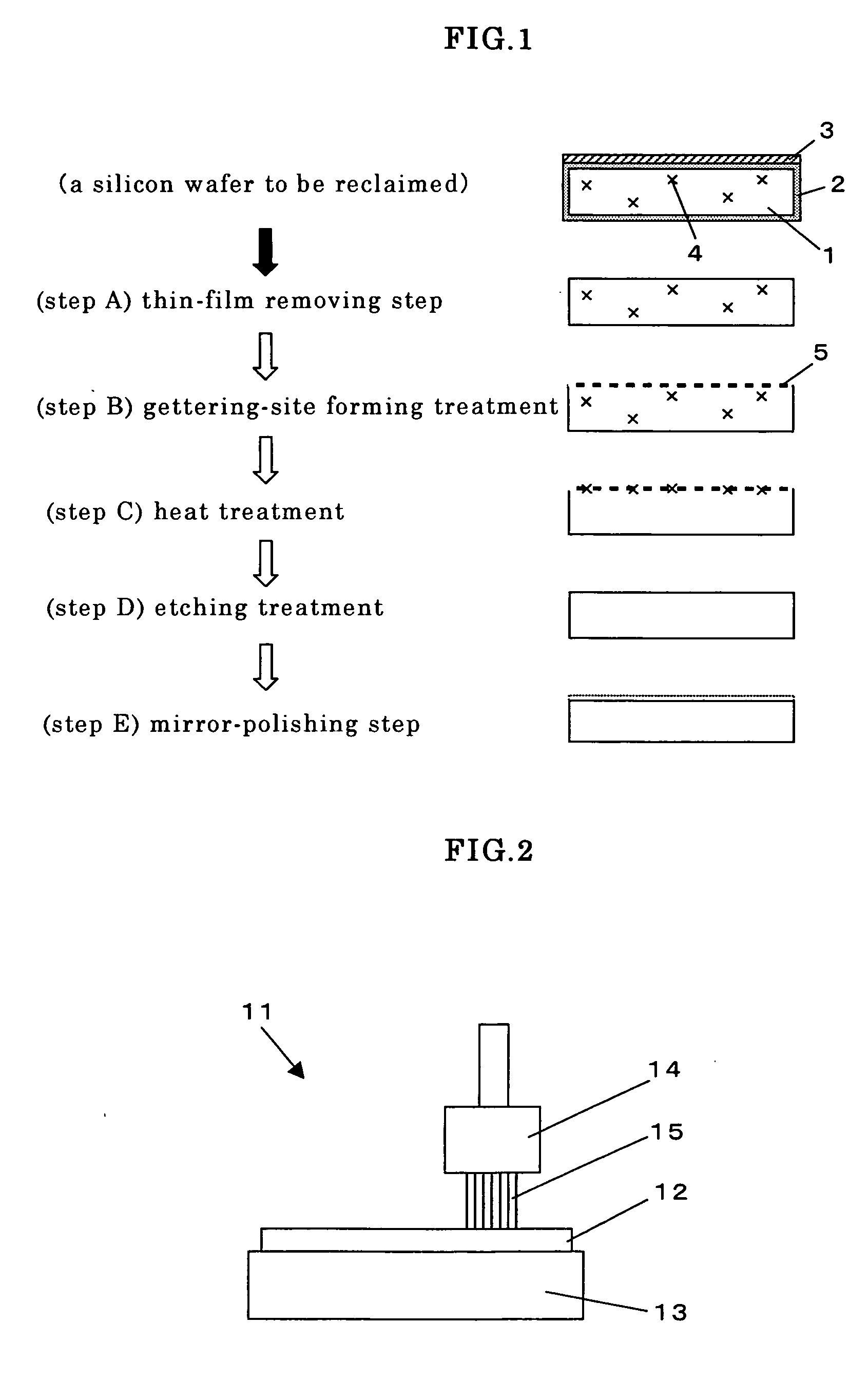
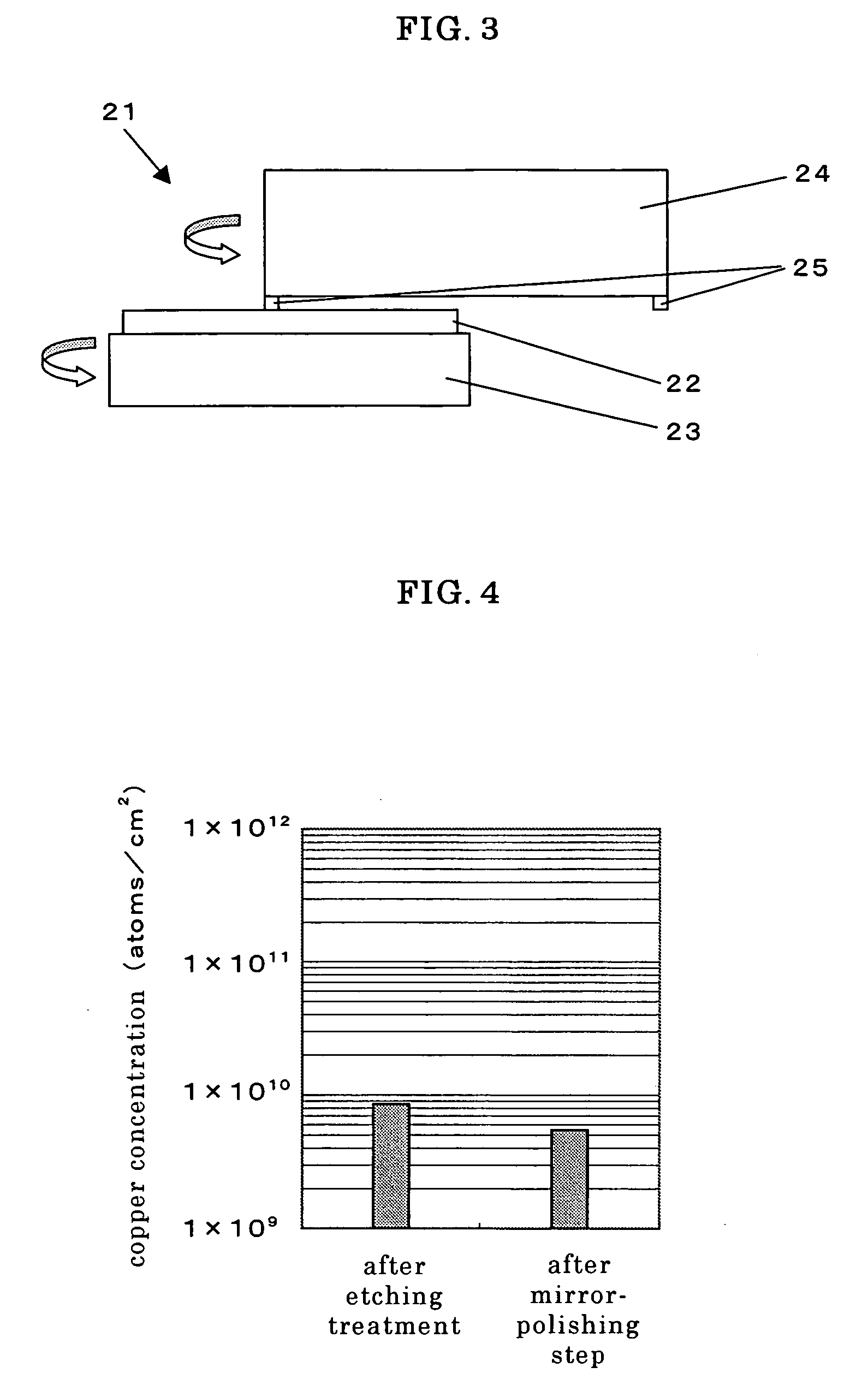
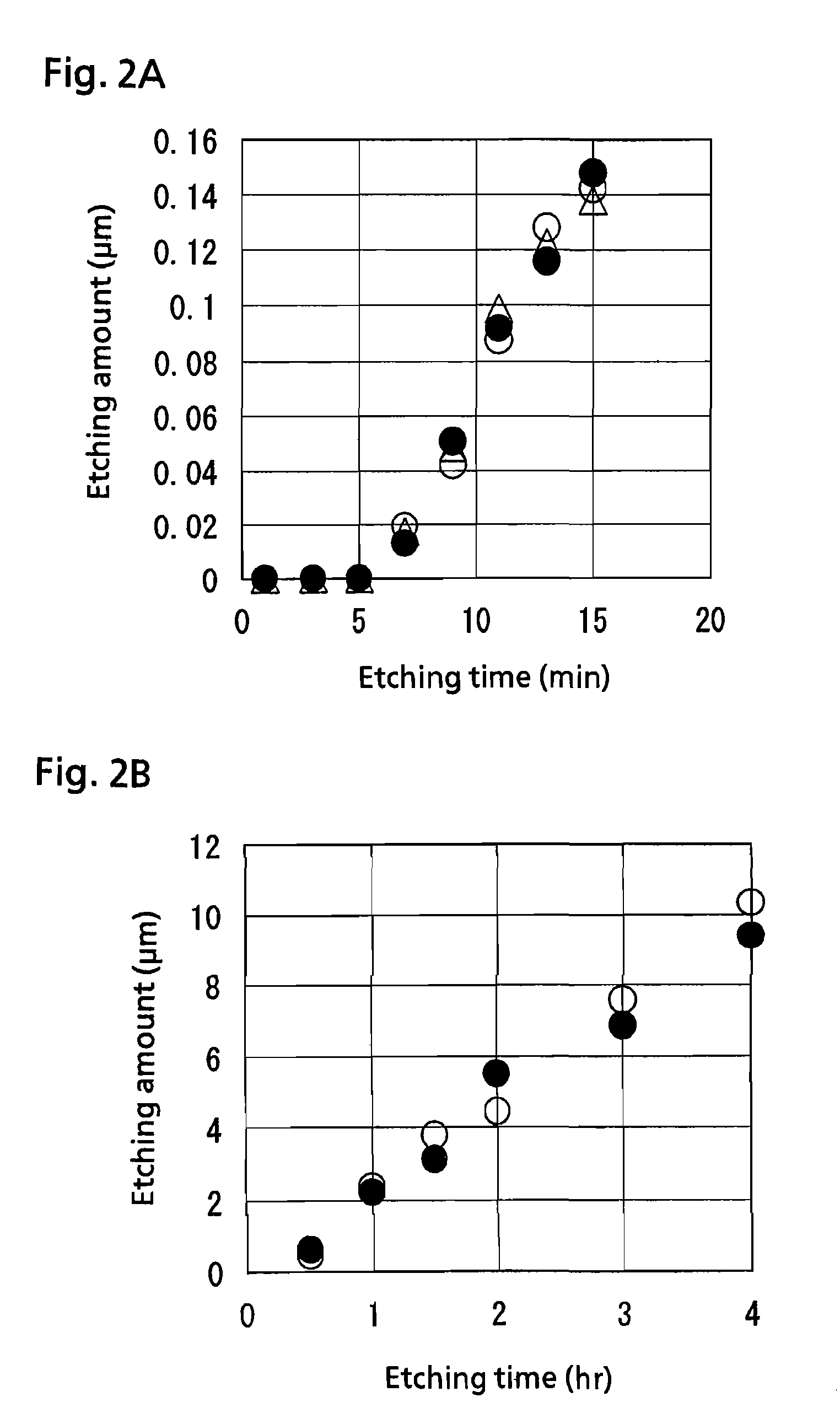
InactiveUS20070007245A1Small contaminationGet stableDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRecovery methodWafering
The present invention is a method for reclaiming a silicon wafer in which a thin film has been formed on its surface, at least, comprising a thin-film removing step for removing the thin film having been formed on the silicon wafer and a mirror-polishing step for mirror-polishing at least one side of the thin-film-removed silicon wafer, wherein, before performing the mirror-polishing step, gettering-site forming treatment for applying damage load to at least one side of the silicon wafer is performed and then the silicon wafer is subjected to heat treatment, thereby impurities inside the silicon wafer are reduced. Thereby, there is provided a method for reclaiming a silicon wafer, in which a thin film such as a metal thin film having been formed on a silicon wafer can be removed, and impurities having diffused inside the wafer can be also reduced, thereby silicon wafers having very little metal contamination can be stably obtained.
Owner:MIMASU SEMICON IND CO LTD
Ink jet printing apparatus
InactiveUS7314267B2Suppress and prevent generationImprove printing qualityPrintingEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
An ink jet printing apparatus can prevent or suppress the generation, by a reaction liquid and ink, of a reaction product on the face surface of a discharge head, and can remove the ink, the reaction liquid or the reaction product adhering to the face surface so as to constantly maintain a stable printing quality. Immediately before a printing operation is initiated, an anti-coagulation liquid is sprayed on the face surface of a discharge head, and the discharge head performs the discharge operation (printing operation) with the anti-coagulation liquid applied to the face surface. When the printing operation has been completed, or when the printing of a predetermined amount of data has been performed, the face surface of the discharge head is wiped by blades to remove the ink and the reaction liquid. Since the anti-coagulation liquid is applied to the face surface in advance, the generation of the reaction product on the face surface is prevented or suppressed. Furthermore, even when a reaction product is adhered to the face surface, the coagulation of this product on the face surface can be prevented.
Owner:CANON KK
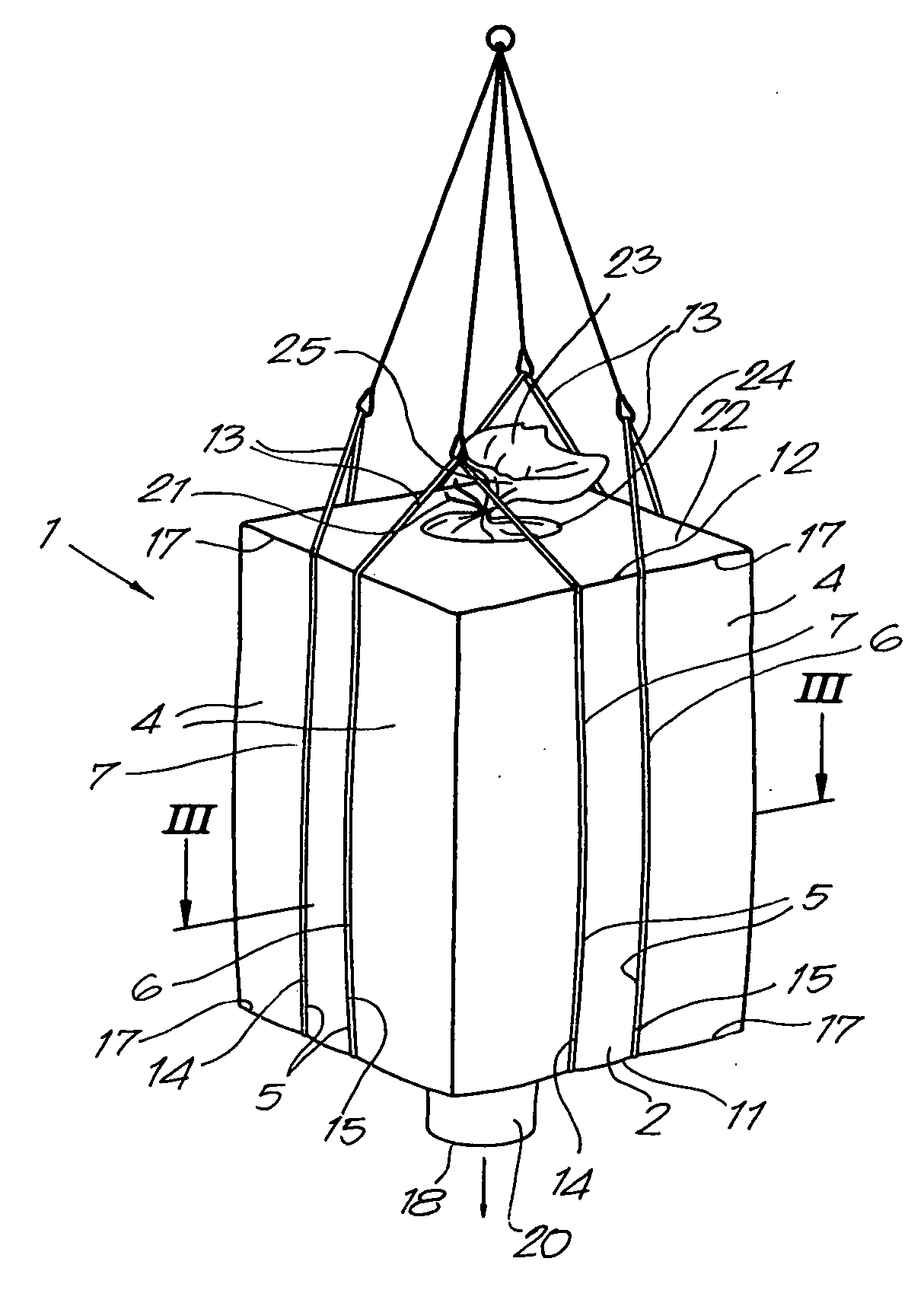
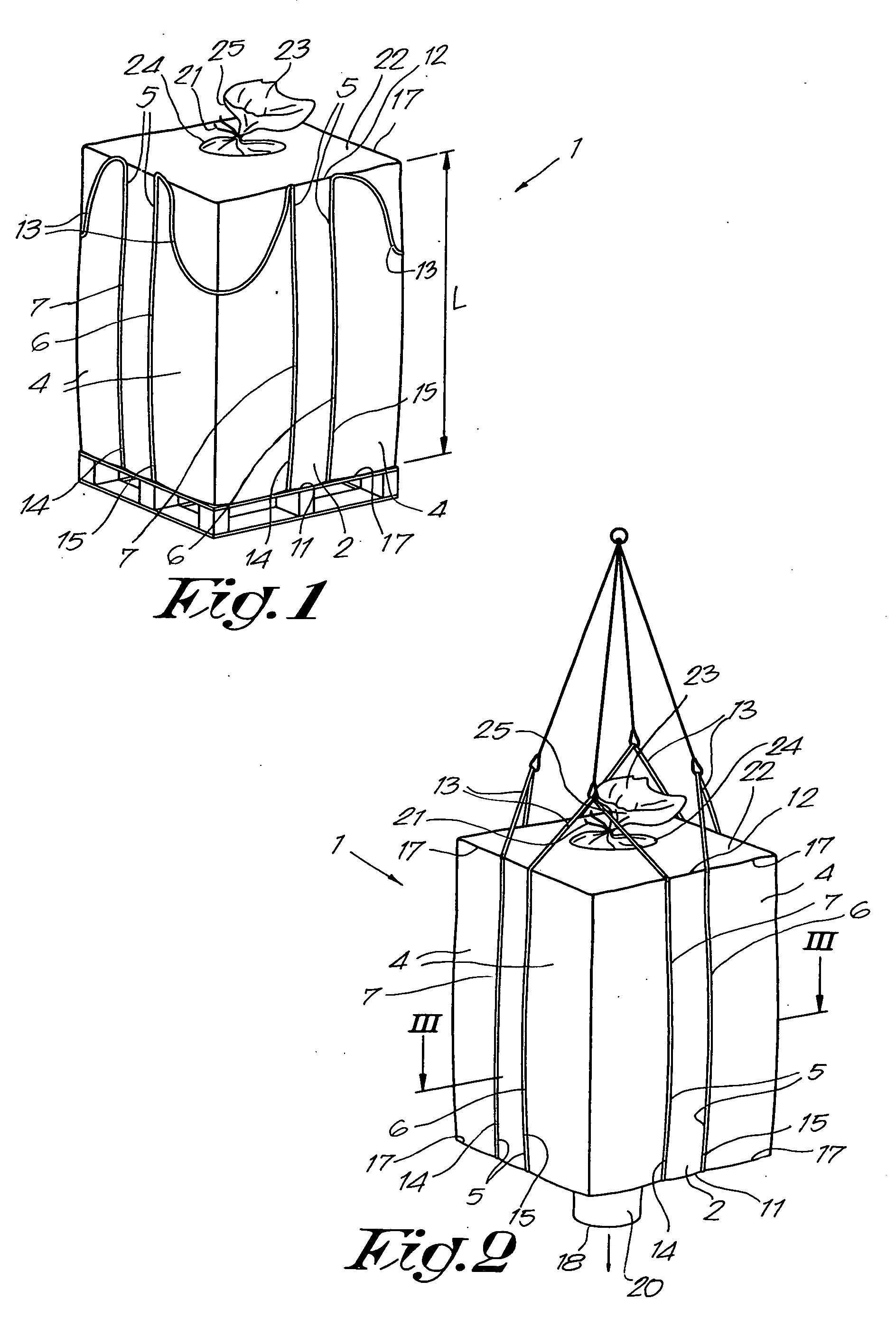
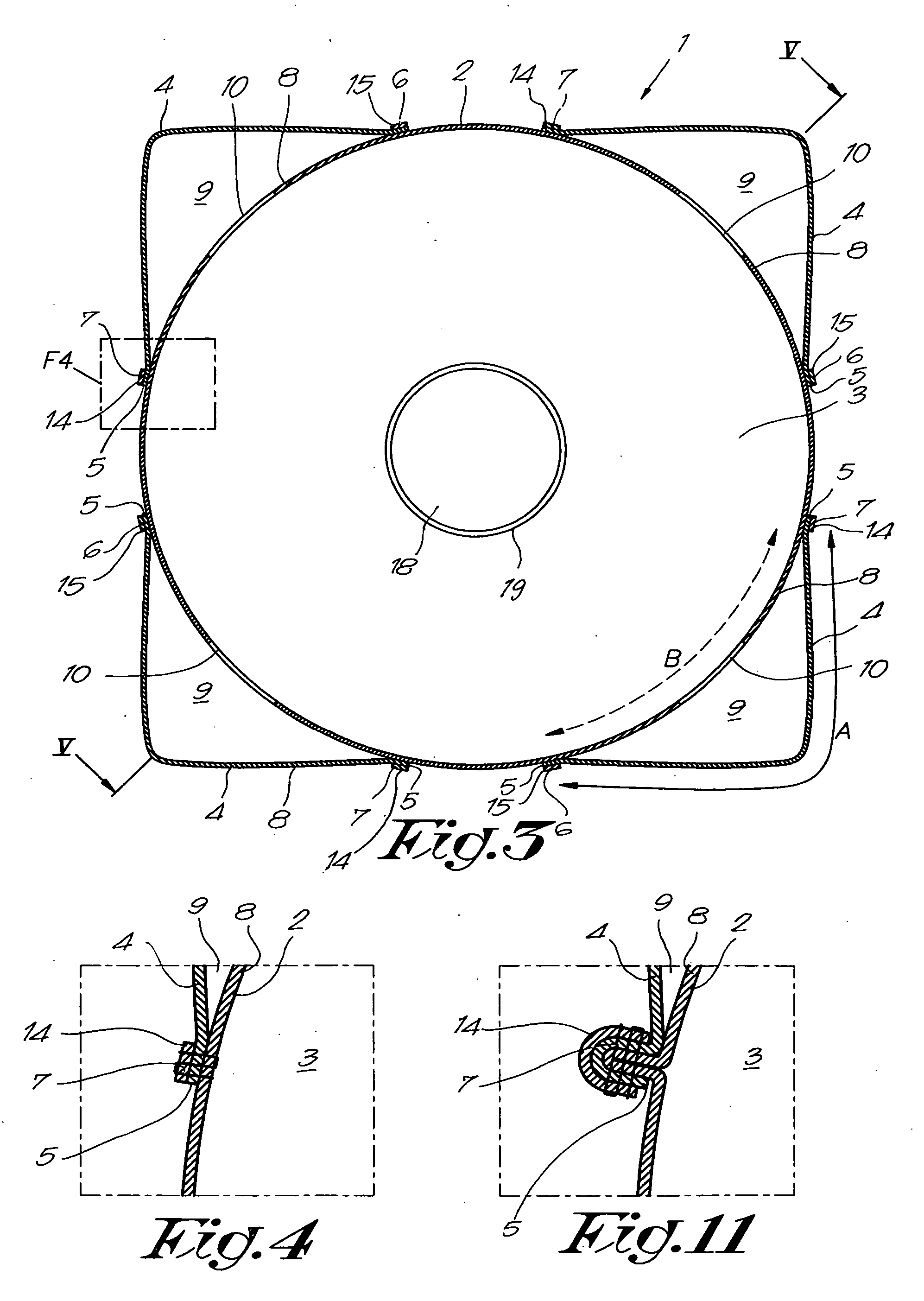
Container bag
InactiveUS20060104546A1Little risk of contaminationManufacturing a container bagBagsLarge containersMechanical engineeringEngineering
Owner:COMBES TRADING
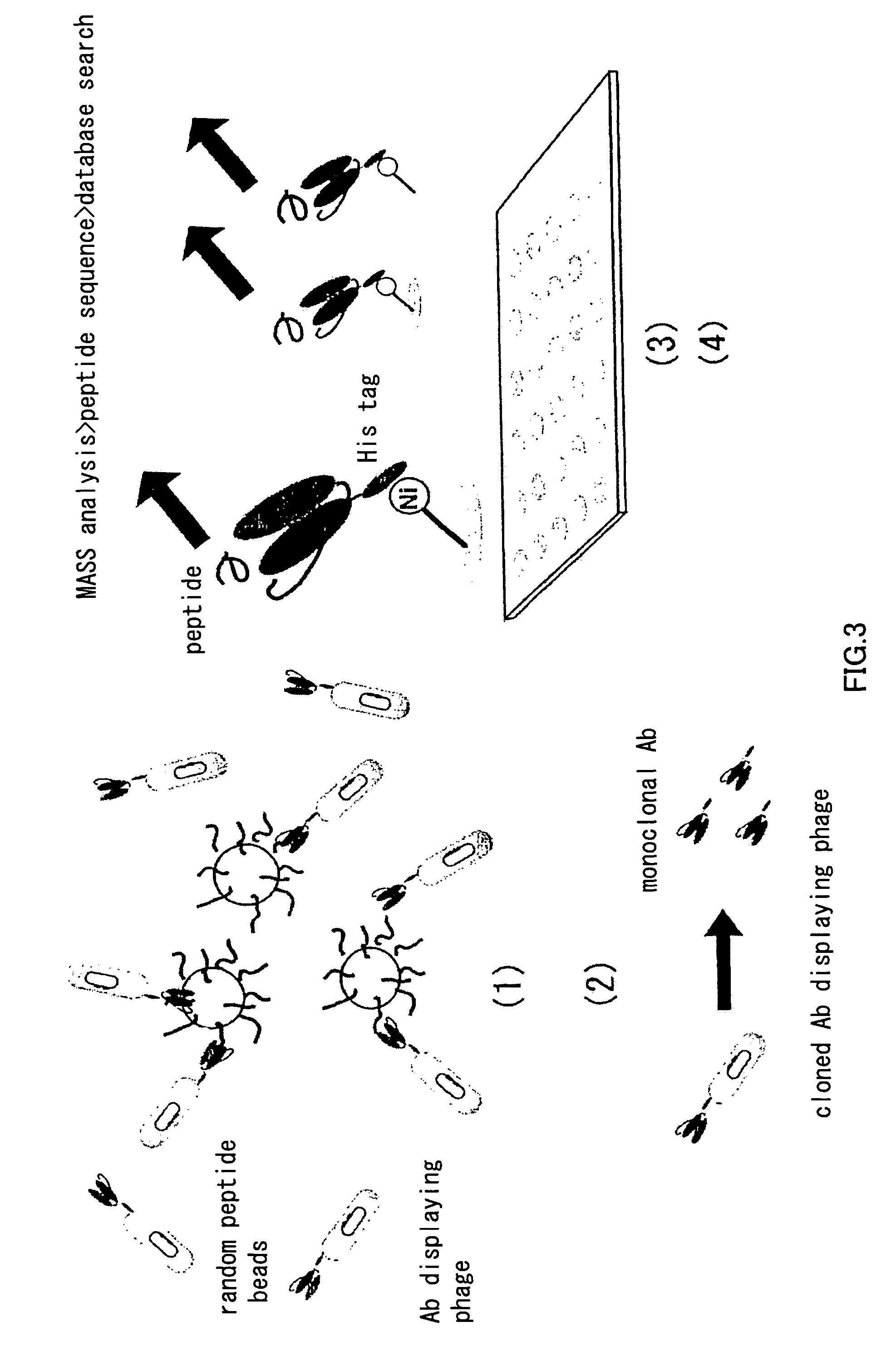
Artificial antibody library with super-repertory
ActiveUS8178320B2Improve stabilityProvide stableCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCDNA libraryPcr method
Owner:SHIMIZU NOBUYOSHI +1
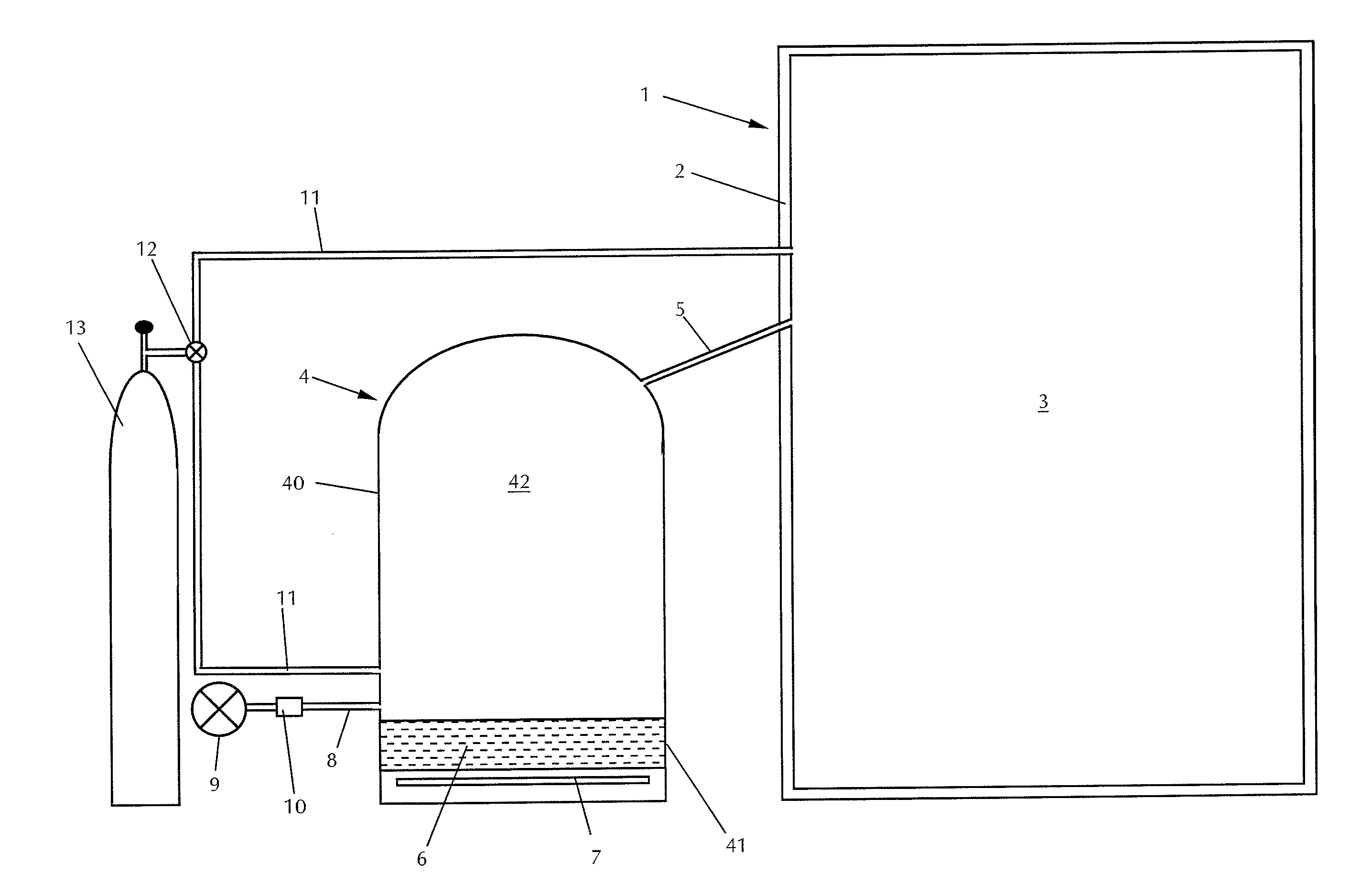
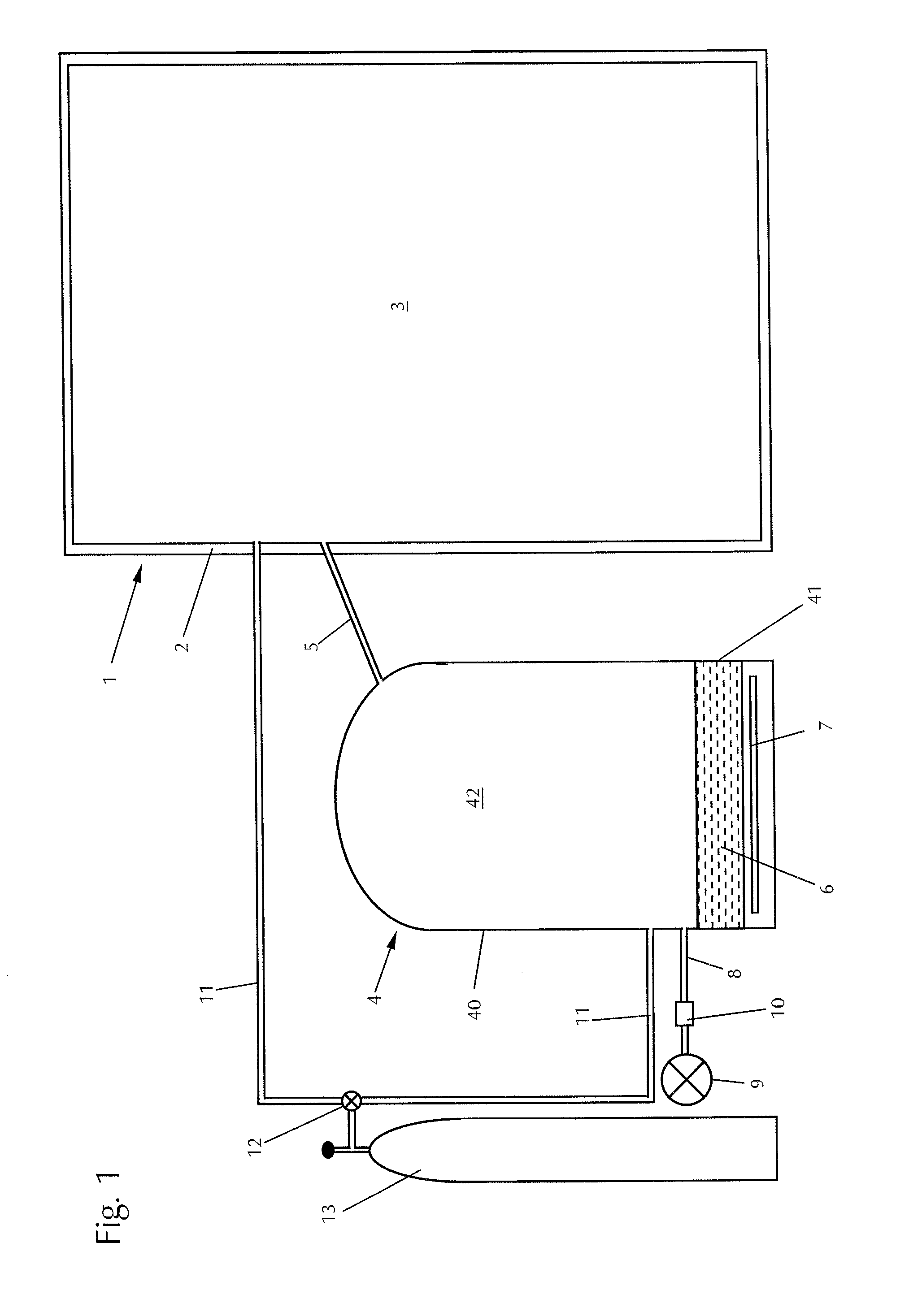
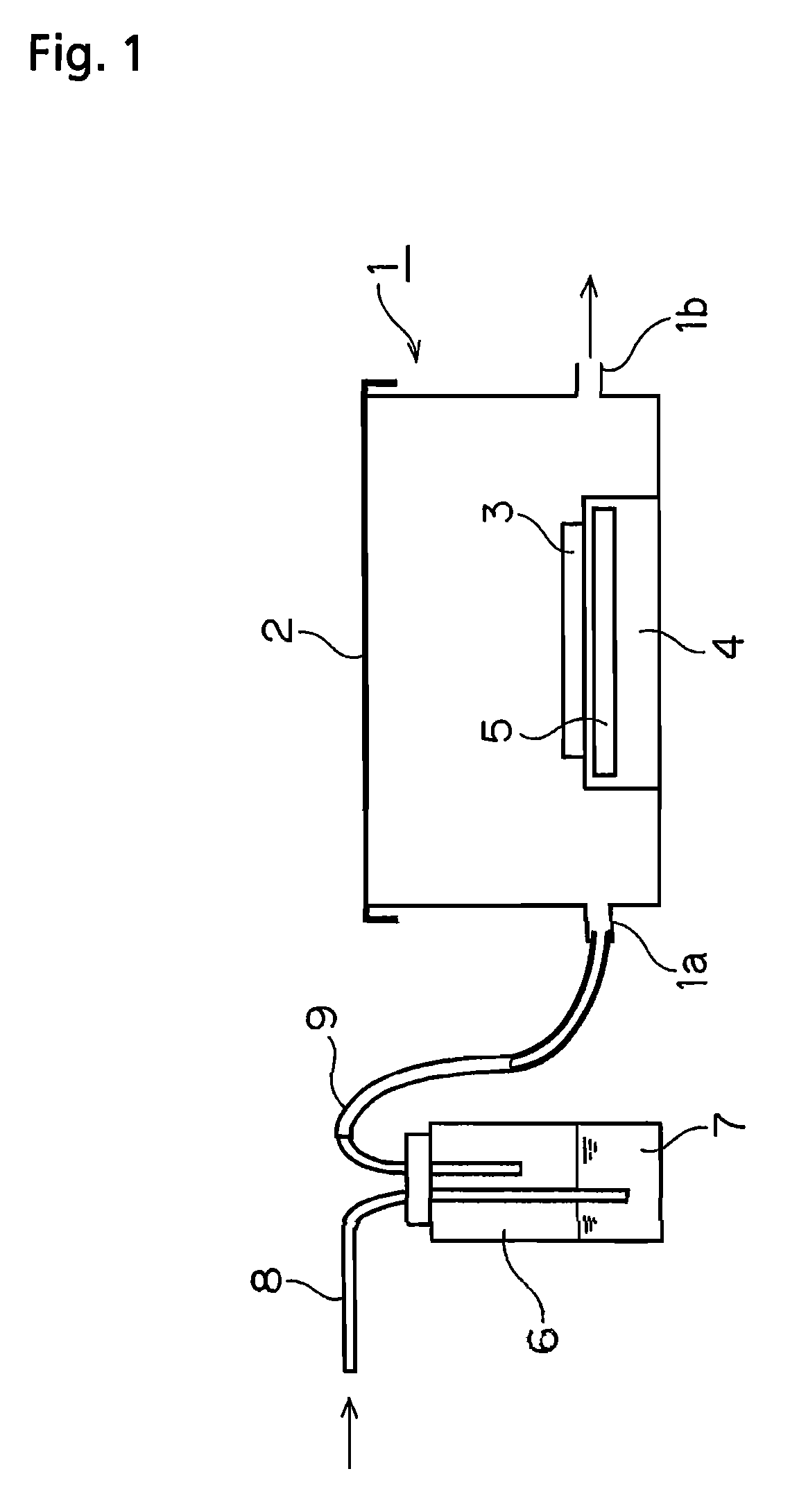
Laboratory Incubator Having Improved Interior Humidification
InactiveUS20130052101A1Easily carry outPrevent contaminationBiochemistry apparatusLaboratory glasswaresSteam engineWater reservoir
The invention relates to a laboratory climatic cabinet, in particular a gassed incubator, having an interior enclosed by a housing and the steam generator arranged outside the interior, which is connected to the interior via a steam feed line. The steam generator is designed as an essentially unpressurized container having a base area and a steam region located above it, the base area being designed to accommodate a water reservoir and being provided with a heating device for heating the water reservoir, the steam feed line leaving the steam generator in the area of the steam region and an air feed line opening into the steam generator, in order to feed ambient air to the steam generator and to introduce air enriched with water steam via the steam feed line in essentially unpressurized form into the interior of the incubator.
Owner:THERMO ELECTRONICS LED GMBH
Preparation method of low-contamination lignosulfonate
The invention discloses a preparation method of low-contamination lignosulfonate. The method comprises the steps as follows: after precipitating slurrying waste liquor for 0.5-2 h, removing water insoluble matter and cellulose impurities by a filter; condensing the slurrying waste liquor by membrane filter equipment to increase the concentration of the slurrying waste liquor from 8wt%-15wt% to 15wt%-30wt%; putting a sulfonating agent accounting for 5wt%-40wt% of concentrated liquor and a condensing agent accounting for 5wt%-40wt% of concentrated liquor once, conducting a reaction at 70-100 DEGC for 1-6 h, and performing sulfonation and polycondensation on the concentrated liquor; adding 0-10wt% of a reaction reagent to the concentrated liquor after sulfonation and polycondensation reaction, and conducting a reaction at 40-80 DEG C for 1-5 h; performing spray drying by a hot blast stove reaction solution to obtain lignosulfonate powder with finer particles. The invention also relates to lignosulfonate prepared with the preparation method. The low-contamination lignosulfonate is prepared from the slurrying waste liquor, particularly soda process slurrying waste liquor, waste utilization is realized, and the lignosulfonate has high thermal stability, good dispersity and low contamination while environmental pollution is reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGFA NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
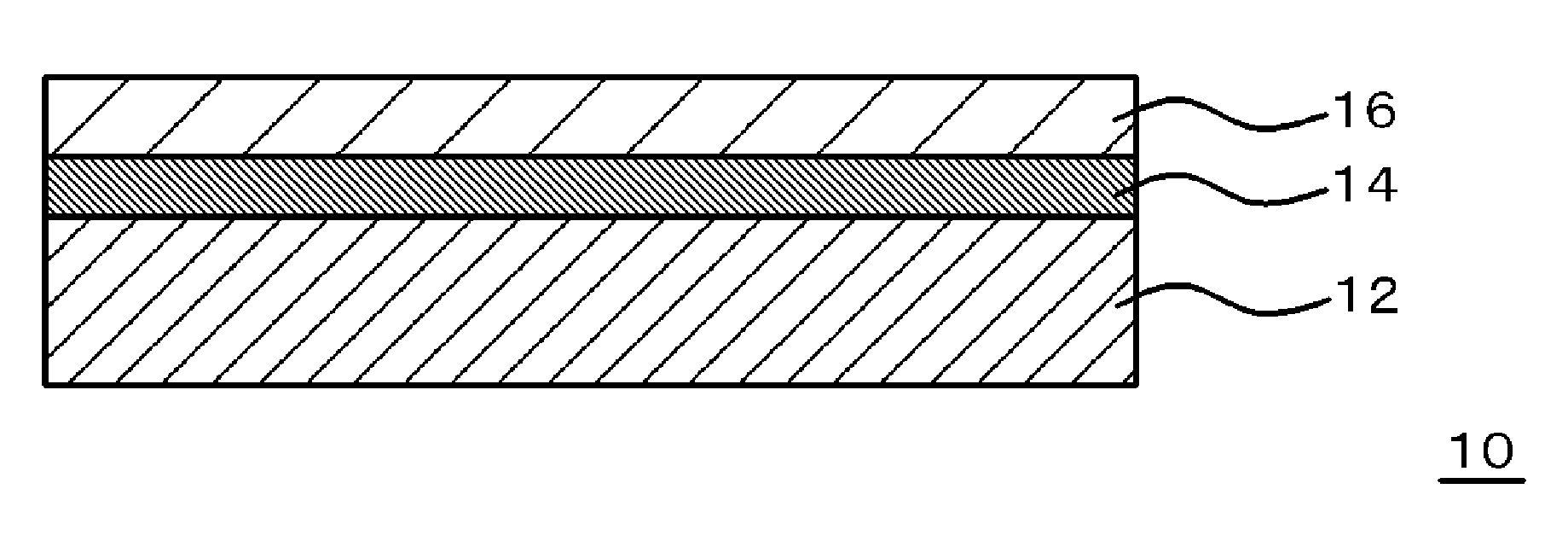
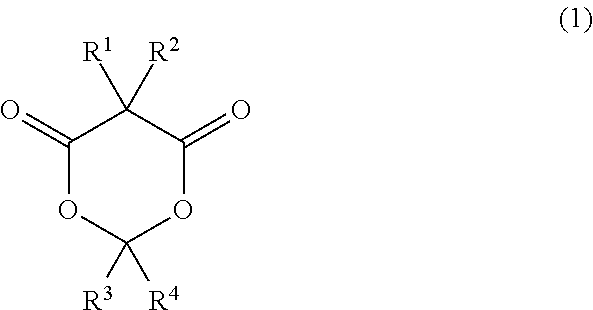
Adhesive resin composition, laminate, and self-stripping method
InactiveUS20140322474A1Promote decompositionEasily contaminatedOrganic chemistryNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesPolymer scienceAcid derivative
An adhesive resin composition of the present invention includes an expandable sticky polymer having a structure derived from a Meldrum's acid derivative, or a Meldrum's acid derivative represented by the following general formula (1) and an adhesive resin.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM TOHCELLO INC
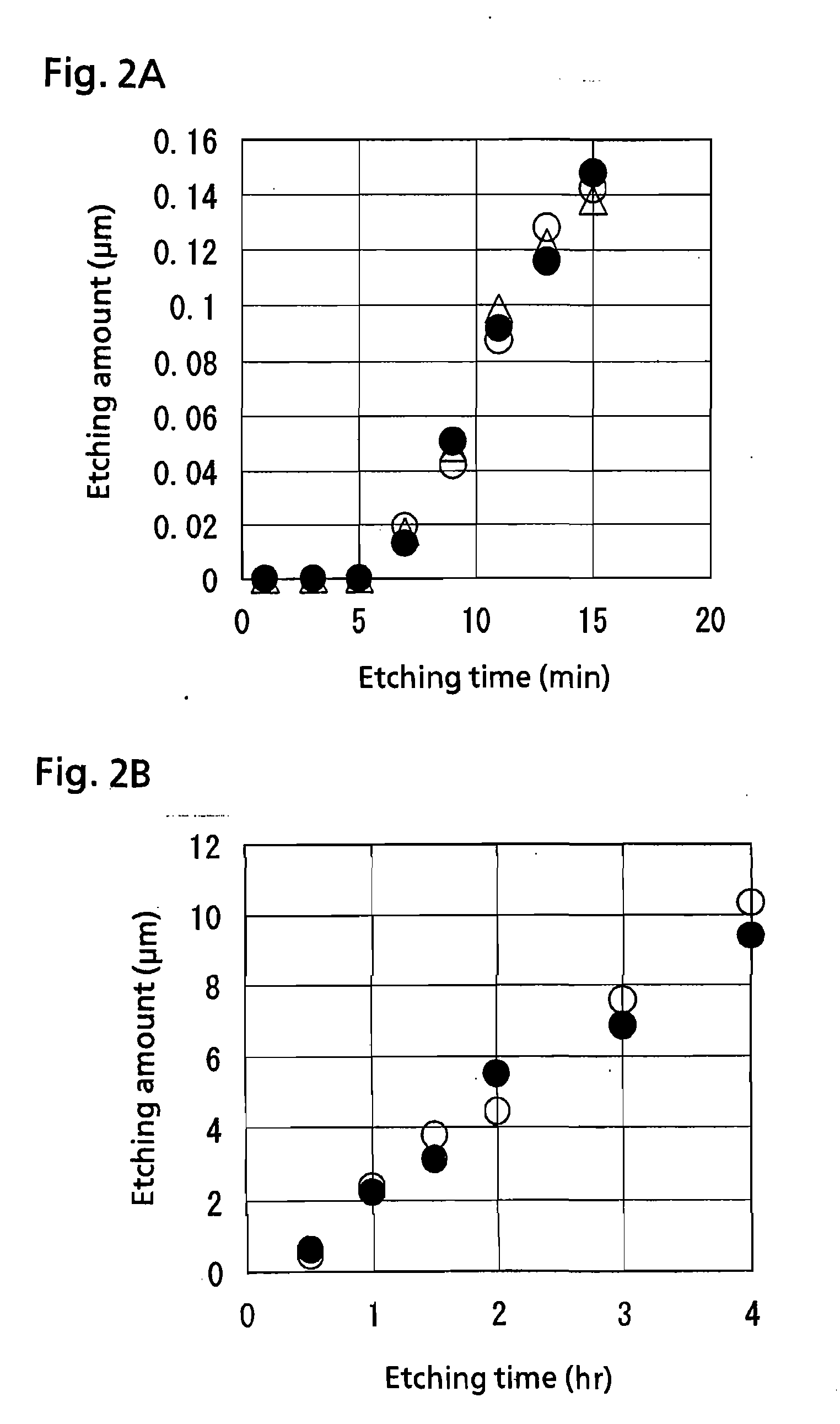
Silicon wafer etching method and apparatus, and impurity analysis method
ActiveUS7686973B2Small contaminationImprove smoothnessSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDecorative surface effectsHydrofluoric acidProduct gas
A wafer etching and impurity analysis method is presented in which a wafer is held in a vessel having gas introduction and exhaust ports, a solution including a mixture of hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid alone or together with sulfuric acid is bubbled with a carrier gas without being heated, which generates a gas containing vaporized hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid, and the inside of the vessel is purged so that the amount of gas supplied is kept constant at all times. All or a specific portion of the wafer is cooled to a specific temperature. Consequently, the gas is condensed on the surface of the wafer, which allows the required portion of the wafer to be etched. The method reduces the amount of liquid needed for residue recovery, the amount of admixed silicon during impurity analysis, and the concentration time.
Owner:SUMITOMO MITSUBISHI SILICON CORP
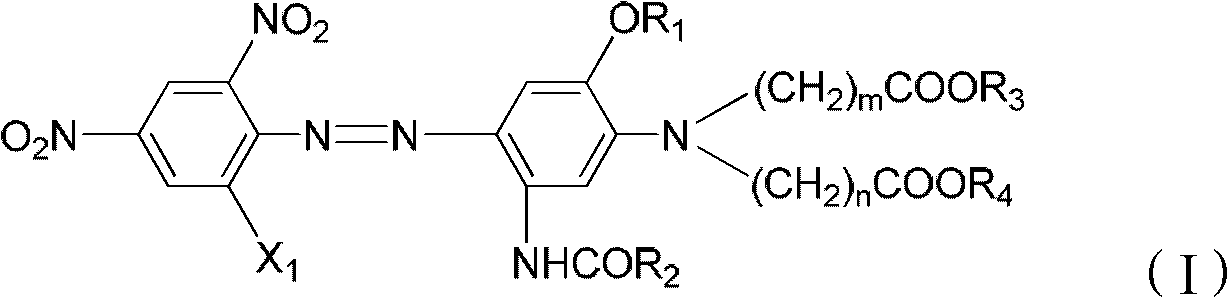
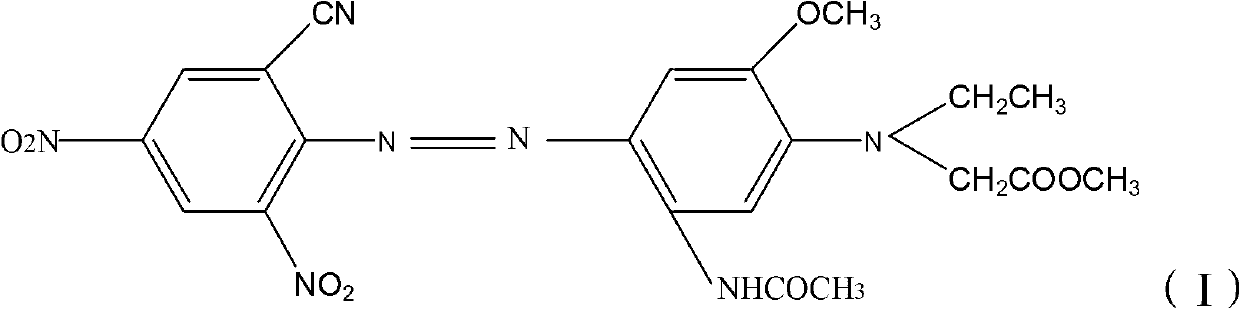
Dispersed black dye composition, dispersed black dye, and preparation method and application thereof
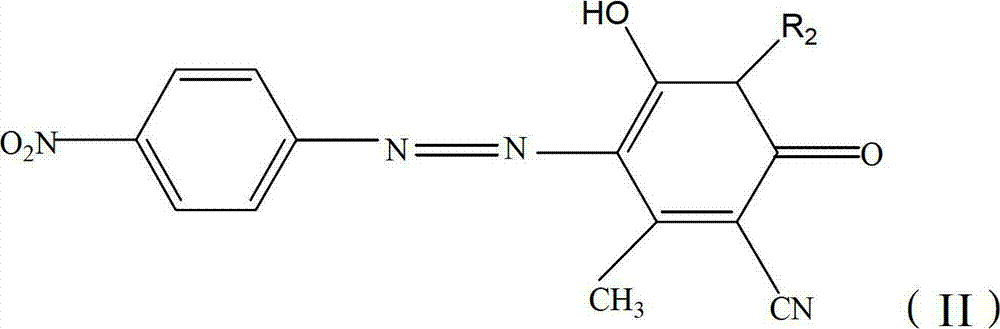
ActiveCN103044966AImprove washing fastnessSmall contaminationOrganic dyesDyeing processPolyesterNH3 compound
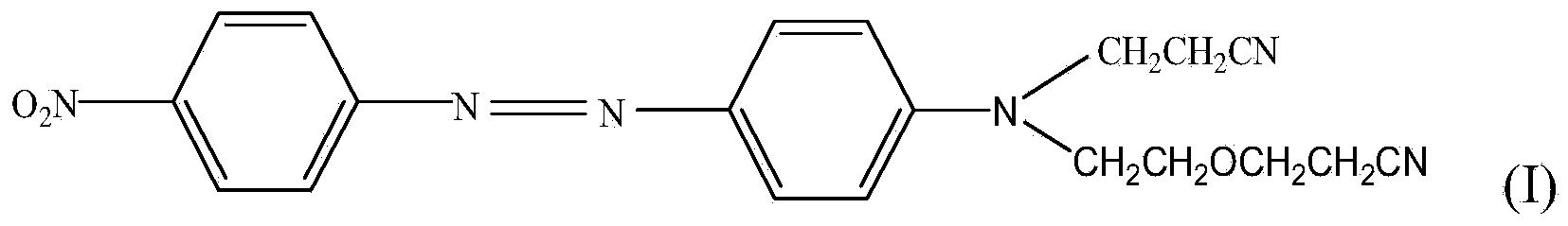
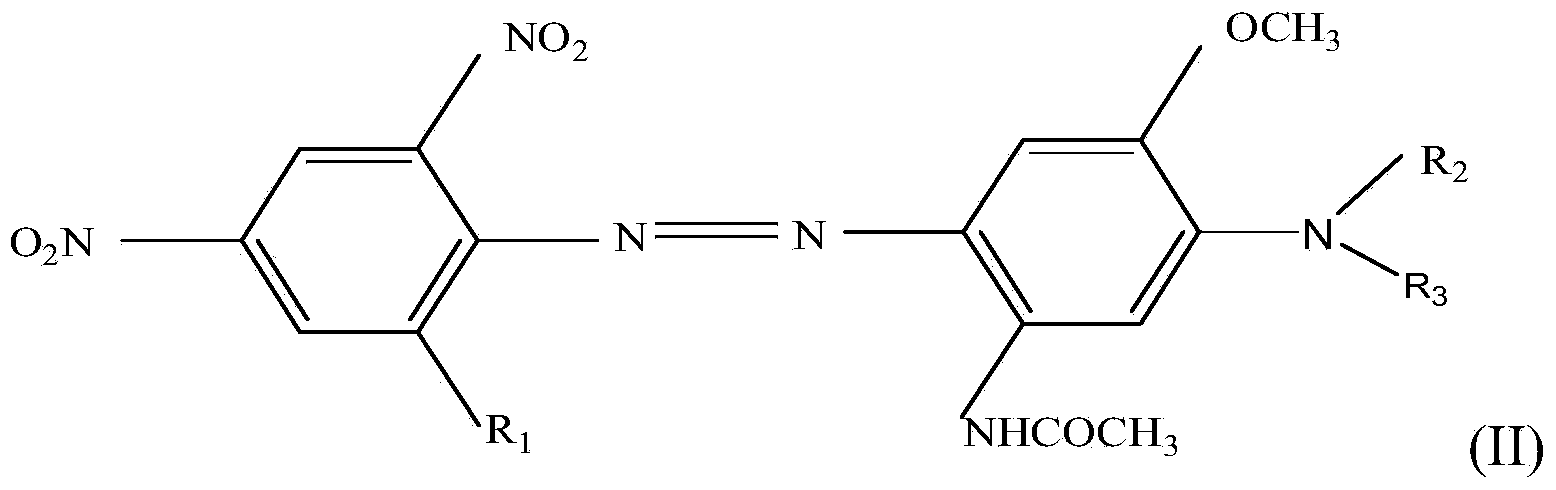
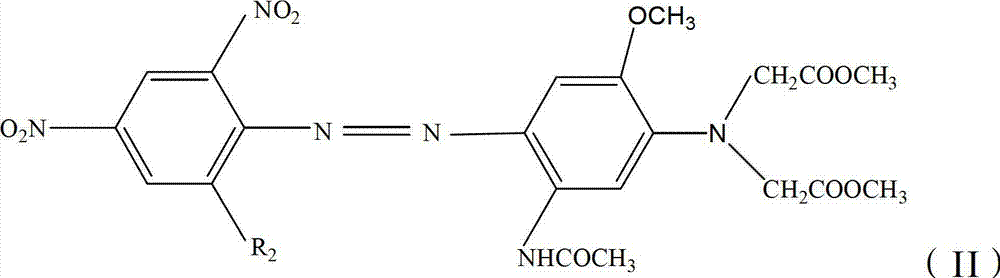
The invention relates to a dispersed black dye composition, dispersed black dye, and a preparation method and application thereof. Based on the total weight of the dispersed black dye composition, the dispersed black dye composition comprises 5 to 13 weight percent of component A shown as a formula (I), 5 to 14 weight percent of component B shown as a formula (II), 3 to 8 weight percent of component C shown as a formula (III), 5 to 10 weight percent of component D shown as a formula (IV), 50 to 80 weight percent of component E shown as a formula (V) and 2 to 5 weight percent of component F shown as a formula (VI). The dispersed black dye consists of the dispersed black dye composition and auxiliary materials, has high washing fastness and sublimation fastness and has low contamination property on polyester ammonia cotton and blended fabric thereof.
Owner:ZHEJIANG RUNTU
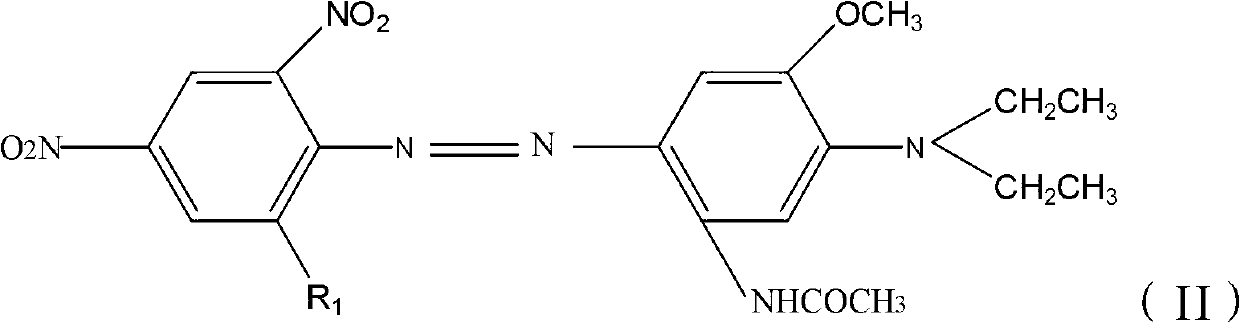
Disperse dye as well as preparation method and application thereof and disperse black dye composition
ActiveCN103709789AHigh sublimation fastnessSmall contaminationOrganic dyesDyeing processDisperse dyeHydrogen
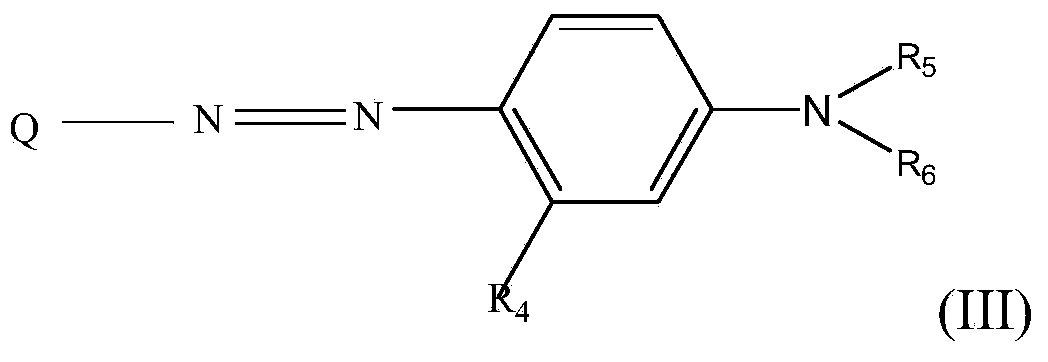
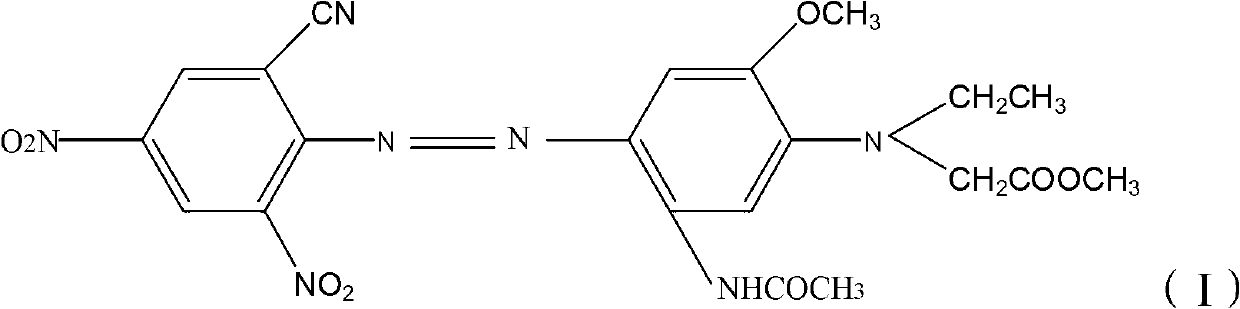
The invention provides a disperse dye as well as a preparation method and an application thereof and a disperse black dye composition with high sublimation fastness. The disperse dye comprises the composition. Based on the total weight of the composition, the composition comprises 30-50wt% of component A in the formula (I) in the specification, 35-70wt% of component B in the formula (II) in the specification and 0-15wt% of component C in the formula (III) in the specification, wherein in the formulas, R1 is Cl or Br; R2 and R3 are respectively and independently -CH2CH2OCOCH3 or -CH2COOCH3; Q is shown in the structural formula in the specification; X1 is Cl or Br; R4 is H, -NHCOR7 or C1-C4 alkyl; R5 and R6 are respectively and independently C1-C4 alkyl, C1-C4 alkyl with one hydrogen replaced by cyano group or -CH2CH2OCOCH3; and R7 is C1-C4 alkyl.
Owner:JIANGSU YUANZHENG CHEM
Substrate conveyor apparatus, substrate conveyance method and exposure apparatus
ActiveUS7483123B2Easily and reliably prevent contaminationContamination can be easilyNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineering
Owner:NIKON CORP
Disperse blue dye composition and disperse blue dye and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102993778AImprove washing fastnessSmall contaminationOrganic dyesDyeing processDisperse dyePhotochemistry
The invention discloses a disperse blue dye composition and a disperse blue dye and a preparation method and an application thereof. Based on the total weight of the disperse blue dye composition, the disperse blue dye composition comprises 60-90 percent of a component A and 10-40 percent of a component B, wherein the component A is the compound shown in the formula (I), and the component B is one or two of the compounds shown in the formula (II), wherein R1 is Cl or Br. The disperse blue dye comprises the disperse blue dye composition and auxiliary materials, and has good washing fastness and less staining to polyester / polyurethane cotton or blended fabrics thereof.
Owner:ZHEJIANG RUNTU
Dispersed black dye composition, dispersed black dye, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103044967AImprove washing fastnessSmall contaminationOrganic dyesDyeing processPolyesterContamination
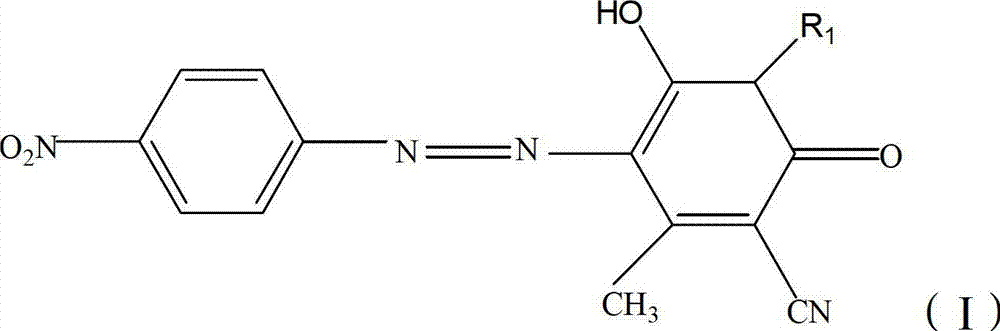
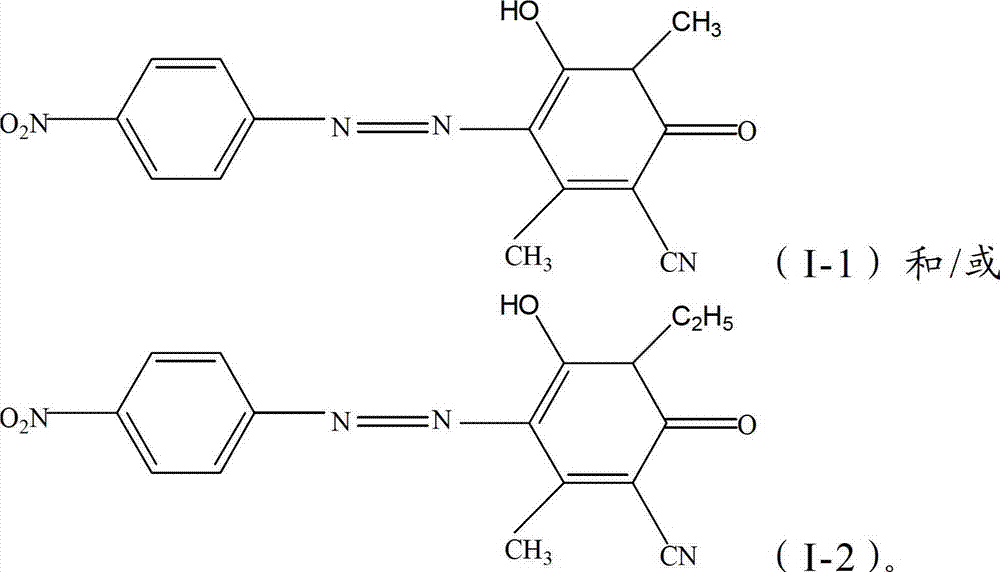
The invention relates to a dispersed black dye composition, dispersed black dye, and a preparation method and application thereof. Based on the total weight of the dispersed black dye composition, the dispersed black dye composition comprises 5 to 15 weight percent of component A shown as a formula (I), 35 to 60 weight percent of component B shown as a formula (II), 20 to 35 weight percent of component C shown as a formula (III) and 5 to 15 weight percent of component D shown as a formula (IV). The dispersed black dye consists of the dispersed black dye composition and auxiliary materials, has high washing fastness and sublimation fastness and has low contamination property on polyester ammonia cotton and blended fabric thereof. R in the formula (I) is alkyl of C1-C2 and R2 in the formula (II) is Cl or Br.
Owner:ZHEJIANG RUNTU
Environment-friendly conductive protective paint for furniture and preparation method of paint
InactiveCN106147305AEasy to separateNo loss of acidityElectrically-conductive paintsPolyvinyl butyralAdhesive
The invention discloses an environment-friendly conductive protective paint for furniture and a preparation method thereof, which is characterized in that the components of the raw materials are composed as follows in parts by weight: 15-20 parts of polymerized rosin, 10-15 parts of polyvinyl butyral, 10-15 parts of methyl methacrylate, 12-15 parts of linseed oil, 2-4 parts of quick-drying glue, 5-7 parts of styrene, 2-4 parts of polyethylene wax, 8-12 parts of acetaldehyde, dispersant VXW6208 0.6-0.8 parts, defoamer BYK-044 0.5-0.7 parts, PU thickener 1.2-1.4 parts. The invention prepares polymerized rosin through a catalytic process. The catalyst is easily separated from the product and can be reused. When applied on wood furniture, the conductivity of the paint film after hard drying can reach <1.5Ω / cm, making the formed paint film Not prone to cracking and deterioration, resulting in a long service life, it is resistant to blistering and exhibits low water absorption, low mold growth, low staining, and high color retention.
Owner:QINGDAO LANNONGGU AGRI PROD RES & DEV
Low gain pressure relief valve for a fluid pump
ActiveUS8720849B2Reduce gainSmall contaminationOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPressure relieving devices on sealing facesEngineeringCounterbore
A pressure relief valve for use in regulating discharge fluid pressure of a pump. A first wall of the outlet intersects with the wall of the passage of the pressure relief valve. The housing includes a counterbore at the intersection of wall of the passage and the first wall of the outlet port to provide a counterbore surface that is perpendicular to the wall of the passage around the outer circumference of the valve body. The top end of the valve body includes a reduced diameter portion and a tapered portion between the reduced diameter portion and the top of the valve body.
Owner:HANON SYST EFP CANADA LTD
Silicon wafer etching method and apparatus, and impurity analysis method
ActiveUS20080047934A1Little contaminationSmall contaminationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDecorative surface effectsChemistryEtching
A wafer etching and impurity analysis method is presented in which a wafer is held in a vessel having gas introduction and exhaust ports, a solution including a mixture of hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid alone or together with sulfuric acid is bubbled with a carrier gas without being heated, which generates a gas containing vaporized hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid, and the inside of the vessel is purged so that the amount of gas supplied is kept constant at all times. All or a specific portion of the wafer is cooled to a specific temperature. Consequently, the gas is condensed on the surface of the wafer, which allows the required portion of the wafer to be etched. The method reduces the amount of liquid needed for residue recovery, the amount of admixed silicon during impurity analysis, and the concentration time.
Owner:SUMITOMO MITSUBISHI SILICON CORP
Stabilization in gamma-ray spectometry
ActiveUS8384016B2Smooth responseSmall contaminationX-ray spectral distribution measurementCalibration apparatusGamma ray spectrometerFrequency spectrum
A calibration source comprises a radioactive material comprising a radioactive isotope having a decay transition associated with emission of a radiation particle and gamma-rays having a known energy and a solid-state detector, arranged to receive radiation particles emitted from the radioactive material. A gating circuit is coupled to the solid-state detector and is operable to generate a gating signal in response to detection of a radiation particle in the solid-state detector. The gating signal may thus be used as an indicator that an energy deposit in a nearby gamma-ray spectrometer is associated with a decay transitions in the radioactive isotope. Since these energy deposits are of a known energy, they can be used as reference points to calibrate the spectrometer response. Thus with calibration sources according to embodiments of the invention, spectral stabilization may be performed in real time and in parallel with obtaining a spectrum of observed signal events.
Owner:SYMETRICA
Gamma-ray spectrometry
ActiveUS9535177B2Smooth responseSmall contaminationX-ray spectral distribution measurementRadiation intensity measurementPhotodetectorRadioactive agent
A calibration source for a gamma-ray spectrometer is provided, comprising a scintillator body having a cavity in which a radioactive material is received. A scintillator body may be cuboid and the cavity may be a hole drilled into the scintillator body. The radioactive material comprises an isotope having a decay transition associated with emission of a radiation particle and a gamma-ray of known energy. A photodetector is optically coupled to the scintillator body and arranged to detect scintillation photons generated when radiation particles emitted from the radioactive material interact with the surrounding scintillator. A gating circuit is arranged to receive detection signals to generate corresponding gating signals for a data acquisition circuit of an associated gamma-ray spectrometer to indicate that gamma-ray detections in the gamma-ray spectrometer occurring within a time window defined by the gating signal are associated with a decay transition in the radioactive isotope.
Owner:SYMETRICA
Reactor and method for production of silicon by chemical vapor deposition
ActiveUS20140242783A1Equally distributedSmall contaminationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon compoundsProcess engineeringChemical vapor deposition
The invention provides a reactor for the manufacture of silicon by chemical vapour deposition (CVD), the reactor comprises a reactor body that can rotate around an axis with the help of a rotation device operatively arranged to the reactor, at least one sidewall that surrounds the reactor body, at least one inlet for reaction gas, at least one outlet for residual gas and at least one heat appliance operatively arranged to the reactor. The reactor is characterised in that during operation for the manufacture of silicon by CVD, the reactor comprises a layer of particles on the inside of at least, one sidewall.
Owner:DYNATEC ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com