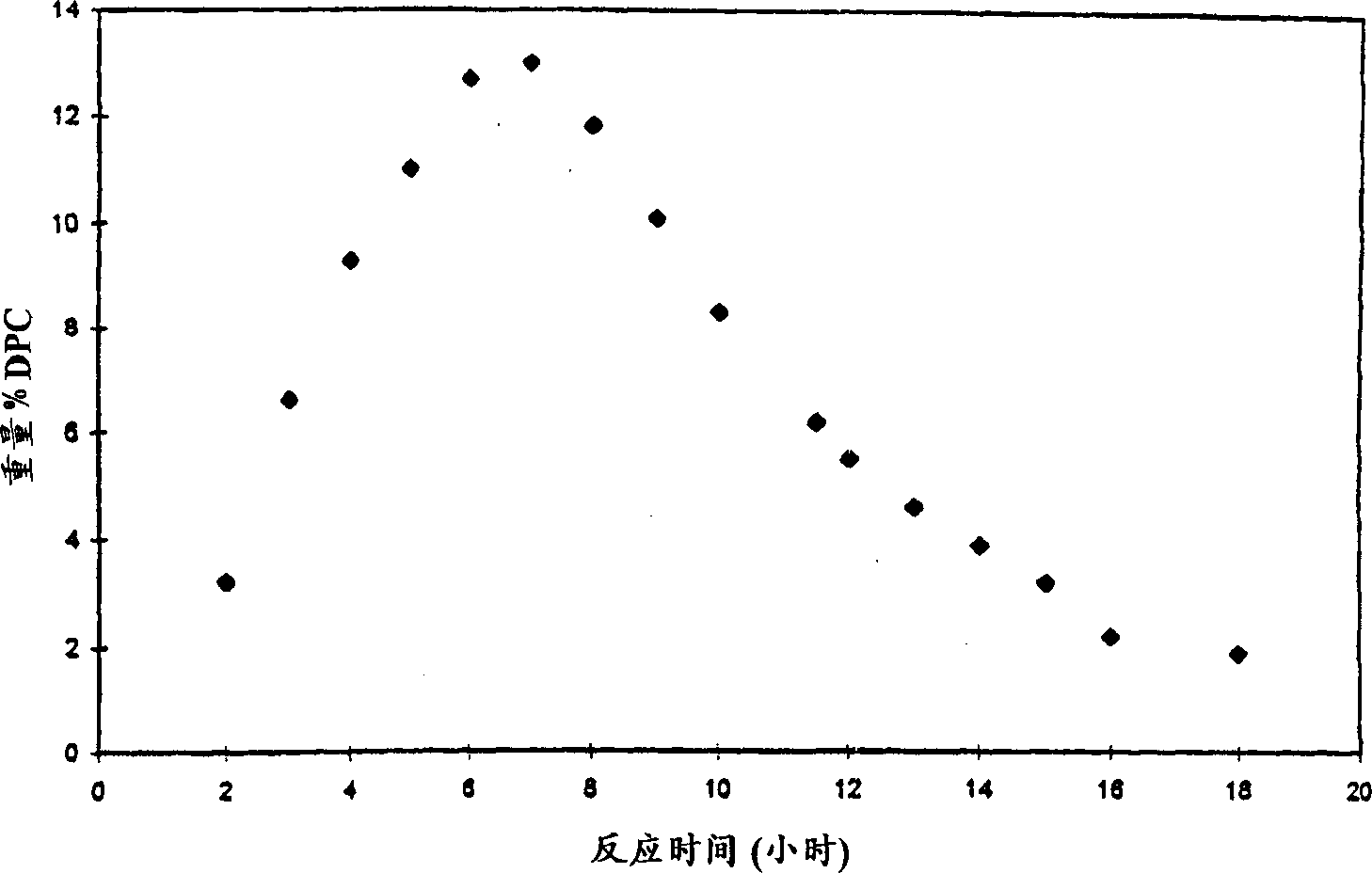
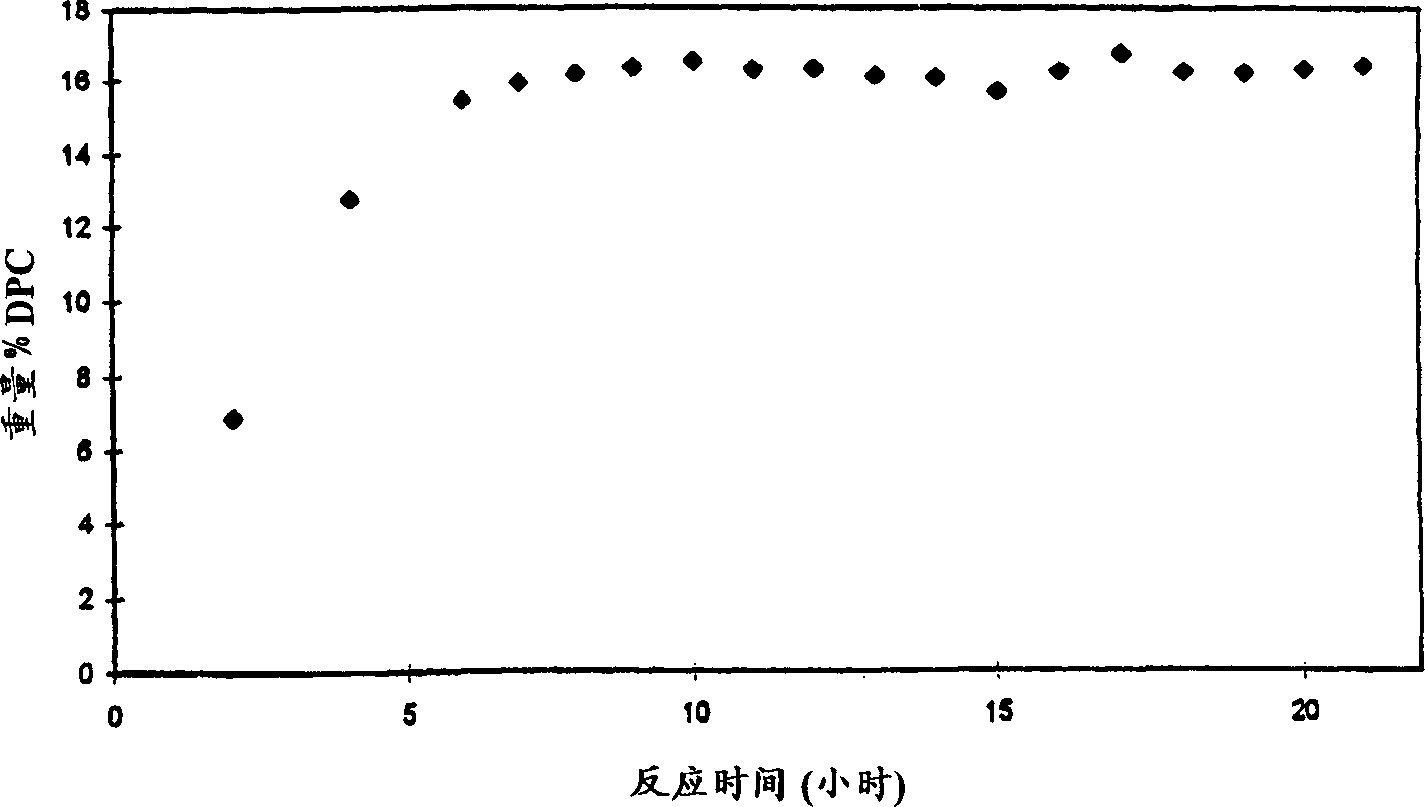
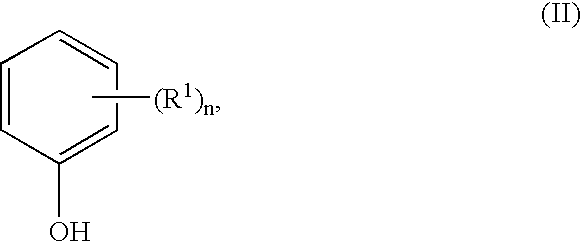Patents
Literature
52 results about "Aromatic hydroxylation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
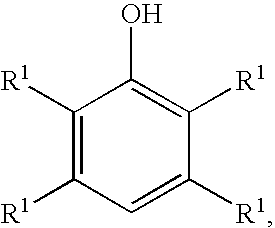
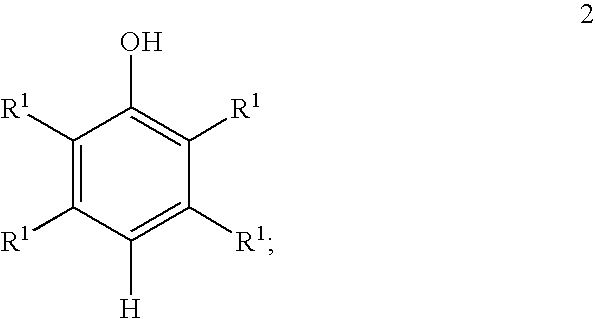
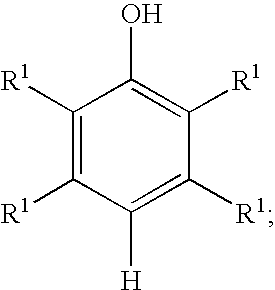
Selective hydroxylation of aromatic compounds is among the most challenging chemical reactions in synthetic chemistry and has gained steadily increasing attention during recent years, particularly because of the use of hydroxylated aromatics as precursors for pharmaceuticals.
Process for producing isocyanates using diaryl carbonate
ActiveUS20110054211A1Efficient productionOrganic compound preparationPreparation from carbamatesArylCarbamate
An object of the present invention is to provide a process that enables isocyanate to be produced stably over a long period of time and at high yield without encountering problems of the prior art during production of isocyanate without using phosgene. The present invention provides an isocyanate production process including the steps of: obtaining a reaction mixture containing an aryl carbamate having an aryl group originating in a diaryl carbonate, an aromatic hydroxy compound originating in a diaryl carbonate, and a diaryl carbonate, by reacting a diaryl carbonate and an amine compound in the presence of a reaction solvent in the form of an aromatic hydroxy compound; transferring the reaction mixture to a thermal decomposition reaction vessel; and obtaining isocyanate by applying the aryl carbamate to a thermal decomposition reaction, wherein the reaction vessel in which the reaction between the diaryl carbonate and the amine compound is carried out and the thermal decomposition reaction vessel for the aryl carbamate are different.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI CHEM CORP
Process for preparing diaryl carbonates or alkyl aryl carbonates from dialkyl carbonates
Owner:COVESTRO DEUTSCHLAND AG
Resin for producing an inorganic fiber material
InactiveUS20100310867A1Emission reductionSynthetic resin layered productsAldehyde/ketone condensation polymer adhesivesFiberProtein materials
A water dilutable binder resin for use in an inorganic fiber material; wherein the binder resin is prepared by reacting at least the following components in any order: (a) proteinaceous material which is substantially soluble in water at 20° C. and has a viscosity of <50 mPa*s for a 25 wt % aqueous solution, (b) an aromatic hydroxyl compound, and (c) an aldehyde, and wherein the water dilutable binder resin has a property of having a viscosity of <100 mPa*s when measured at a concentration of 50 wt % at 20° C. During curing, the resin thus produced gives lower phenol emissions. Also, the formaldehyde and ammonia emissions are dramatically lower when compared to conventional resins.
Owner:DYNEA
Negative photosensitive resin composition and application thereof
ActiveUS20150044790A1Excellent peelabilityAccelerate evaporationPhotosensitive materialsSolid-state devicesXylylenePolymer science
A negative photosensitive resin composition including an alkali-soluble resin (A), a photoacid generator (B), a basic compound (C), a cross-linking agent (D), and a solvent (E) is provided. The alkali-soluble resin (A) includes an acrylate resin (A-1) and a novolac resin (A-2). The acrylate resin (A-1) is synthesized by polymerizing a monomer for polymerization, wherein the monomer for polymerization includes an unsaturated carboxylic acid or unsaturated carboxylic acid anhydride monomer (a-1-1) and a monomer (a-1-2). The monomer (a-1-2) includes a compound (a-1-2-1) with a tricyclodecane or dicyclopentadiene structure, a compound (a-1-2-2) represented by formula (1), or a combination of both. The novolac resin (A-2) is synthesized by polymerizing an aldehyde compound with an aromatic hydroxy compound, wherein the aromatic hydroxy compound includes a xylenol compound.
Owner:CHI MEI CORP
Method of separating metallic catalyst constituents from reaction mixtures
InactiveUS20050014965A1Effect reactivityEffect selectivityOrganic compound preparationPreparation from carbon monoxide and oxygenReaction temperatureSolvent
A process for the preparation of an aromatic carbonate is disclosed. The process entails reacting in the presence of a catalyst system an aromatic hydroxy compound with carbon monoxide and oxygen, and optionally in one or more solvents to produce a liquid phase. At least a portion of the liquid phase is subjected to a treatment to obtain a treated liquid phase. The treatment entails at least one of (a) heating to a temperature that is at most mean reaction temperature without passing oxygen thereto, and (b) adding one or more protic compounds thereto, and (c) passing through it one or more inert or reducing gases. Solid metallic catalyst constituents are then separated from the treated liquid phase.
Owner:BAYER MATERIALSCIENCE AG
Alcohol-removal-free preparation method for rapidly-synthesized high-framework-titanium-content titanium silicalite molecular sieve
ActiveCN105800637AEasy to synthesizeShort crystallization timeOrganic chemistryMolecular sieve catalystsAlkaneKetone
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a rapidly-synthesized high-framework-titanium-content titanium silicalite molecular sieve. An organic compound of a non-surfactant is added to a synthetic glue solution, so that generation of extra framework titanium is restrained, and growth of a molecular sieve structure is promoted. A certain quantity of an organic compound of one or more non-surfactants is added to the TS-1 synthetic glue solution, polymerization of silicon-titanium species in the synthetic glue solution is affected through the hydrogen-bond interaction, agglomeration of titanium species is restrained accordingly, the speed at which titanium enters a molecular sieve framework is increased, and formation of the molecular sieve framework structure is promoted. Compared with a conventional method for hydro-thermal synthesis of the TS-1 molecular sieve, no alcohol removal is needed in the process of preparing the TS-1 synthetic glue solution through the method, the synthesis process is simplified, and industrial production is convenient. The content of framework titanium in the TS-1 prepared through the method is high, catalytic activity and selectivity are obviously improved, and the method is mainly shown in reactions such as olefin epoxidation, aromatic hydroxylation, hydroxylation of phenol, ammonia ketone oximation and alkane oxidation.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Negative photosensitive resin composition and application thereof
ActiveCN104345557ASolid-state devicesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusCross-linkPhotoacid generator
A negative photosensitive resin composition including an alkali-soluble resin (A), a photoacid generator (B), a basic compound (C), a cross-linking agent (D), and a solvent (E) is provided. The alkali-soluble resin (A) includes an acrylate resin (A-1) and a novolac resin (A-2). The acrylate resin (A-1) is synthesized by polymerizing a monomer for polymerization, wherein the monomer for polymerization includes an unsaturated carboxylic acid or unsaturated carboxylic acid anhydride monomer (a-1-1) and a monomer (a-1-2). The monomer (a-1-2) includes a compound (a-1-2-1) with a tricyclodecane or dicyclopentadiene structure, a compound (a-1-2-2) represented by formula (1), or a combination of both. The novolac resin (A-2) is synthesized by polymerizing an aldehyde compound with an aromatic hydroxy compound, wherein the aromatic hydroxy compound includes a xylenol compound.
Owner:CHI MEI CORP
Negative photosensitive resin composition and application thereof
InactiveUS20140363915A1Poor strippabilityPhotosensitive materialsSolid-state devicesCross-linkPhotoacid generator
Owner:CHI MEI CORP
Processes for preparing diaryl and/or alkylaryl carbonates from dialkyl carbonates
Processes comprising: reacting a dialkyl carbonate and an aromatic hydroxy compound in the presence of a transesterification catalyst in a first reaction column, the first reaction column comprising a top section, a bottom section, a rectifying section in an upper portion of the column and a reaction zone below the rectifying section; feeding a bottom product from the first reaction column to a further reaction column; the bottom product comprising a diaryl carbonate, an alkylaryl carbonate, or both, and residual unreacted dialkyl carbonate and aromatic hydroxy compound; the further reaction column comprising a top section, a rectifying section in an upper portion of the column and a reaction zone below the rectifying section; and reacting the residual reacted dialkyl carbonate and aromatic hydroxy compound in the further reaction column; feeding a process stream to a distillation column, the process stream comprising a mixture of unreacted dialkyl carbonate and one or more reaction-product alcohols drawn from the first reaction column, the further reaction column, or both, such that the unreacted dialkyl carbonate is separated from the one or more reaction-product alcohols; and recycling the separated, unreacted dialkyl carbonate to the first reaction column; wherein the further reaction column comprises one or more condensers, and heat of condensation from the one or more condensers is fed back into the process.
Owner:COVESTRO DEUTSCHLAND AG
Allergen inhibitor, allergen-inhibiting method, allergen-inhibiting fiber and allergen-inhibiting sheet
InactiveUS20050095222A1Excellent allergen-inhibiting effectInhibition is effectiveBiocideAnimal repellantsSulfateCompound (substance)
The allergen inhibitor of this invention comprises at least one compound selected from the group consisting of an aromatic hydroxy compound, an alkali metal carbonate, alum, lauryl benzene sulfonate, lauryl sulfate, polyoxyethylene lauryl ether sulfate, and a divalent or more sulfate having either or both of a polyoxyethylene chain and a polyethylene chain in the molecule thereof.
Owner:SEKISUI CHEM CO LTD
Air cleaner, functional filter and method of manufacturing the filter, air cleaning filter, and air cleaner device
InactiveCN1805776ADispersed particle filtrationLighting and heating apparatusWater insolubleAir cleaning
An air cleaner, wherein an inlet port and an outlet port are formed, an antiallergic filter having an aromatic hydroxyl compound is installed in the air flow passage of an air blow means in a body, and the inlet port is formed at the front lower part of the air cleaner, whereby pollen and dead tick near a floor surface can be efficiently sucked to inactivate antiallergic activation. A treating solution is conditioned by dissolving and / or dispersing a water soluble material and a water insoluble material in the mixed solvent of water, celosolves and / or carbitols. A functional filter can be manufactured by adding the treatment solution to a filter base material. An air cleaner device is formed by disposing the functional filter between the inlet port and the outlet port for air or water. An air cleaning filter is formed by adding two or more raw materials selected from a raw material having antiallergic properties, a raw material having antibacterial properties, a raw material having antivirus properties, and a raw material having mildewproofing properties. The air cleaning device is formed by disposing the air cleaning filter between the inlet port and the outlet port for air.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Isocyanate production process using composition containing carbamic acid ester and aromatic hydroxy compound, and composition for transfer and storage of carbamic acid ester
ActiveUS20100113823A1Efficient productionAvoid reactionCarbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationCarbamatePhosgene
An object of the present invention is to provide an isocyanate production process, which is free of the various problems found in the prior art, and which uses a composition containing a carbamic acid ester and an aromatic hydroxy compound when producing isocyanate without using phosgene, as well as a carbamic acid ester composition for transferring or storing carbamic acid ester. The present invention discloses an isocyanate production process including specific steps and using a composition containing a carbamic acid ester and an aromatic hydroxy compound, as well as a composition for transfer or storage of carbamic acid ester comprising the carbamic acid ester and the specific aromatic hydroxy compound.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI CHEM CORP
Polycarbonate preparation system
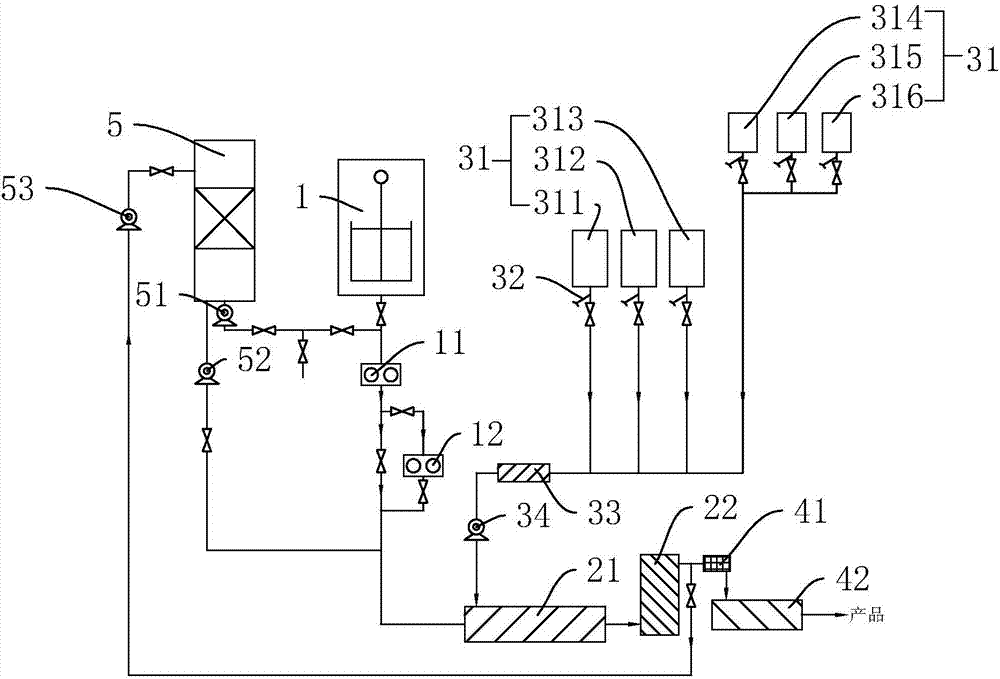
The invention discloses a polycarbonate preparation system which solves the problem that environment stress is increased as cleaning needs a great number of aromatic hydroxyl compounds. According to the technical scheme adopted by the invention, the key point is that the system comprises a polycondensation reaction mechanism, an additive adding mechanism, a mixing filtering mechanism and an extruding pelletizing mechanism; a phenol cleaning mechanism is further connected between the polycondensation reaction mechanism and the extruding pelletizing mechanism; the phenol cleaning mechanism comprises a phenol recycling tank connected between a melt filter and the extruding pelletizing mechanism; a heating device is arranged on the bottom of the phenol recycling tank; the phenol recycling tank is connected between a polycondensation reactor and a static mixer through a cooling pipeline; and a first booster ump is arranged on the cooling pipeline. The polycarbonate preparation system avoids waste of phenol, increases a utilization rate of phenol, and reduces pressure, caused on environment, of waste liquor generated by cleaning equipment.
Owner:NINGBO ZHETIE DAPHOON CHEM
Processes for preparing benzoquinones and hydroquinones
InactiveUS20050137409A1Speed up the conversion processHigh selectivityPhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic compound preparationHydroquinone CompoundCopper
A process for the preparation of benzoquinones and hydroquinones includes oxidizing an aromatic hydroxy compound with oxygen or an oxygen containing gas, a copper containing catalyst, and optionally a promoter to form the benzoquinone. A reduction reaction is employed to form the hydroquinone.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Processes for preparing benzoquinones and hydroquinones
InactiveUS20050137380A1Speed up the conversion processHigh selectivityPhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic compound preparationHydroquinone CompoundCopper
A process for the preparation of benzoquinones and hydroquinones includes oxidizing an aromatic hydroxy compound with oxygen or an oxygen containing gas, a copper containing catalyst, and a promoter to form the benzoquonone. A reduction reaction is employed to form the hydroquinone.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
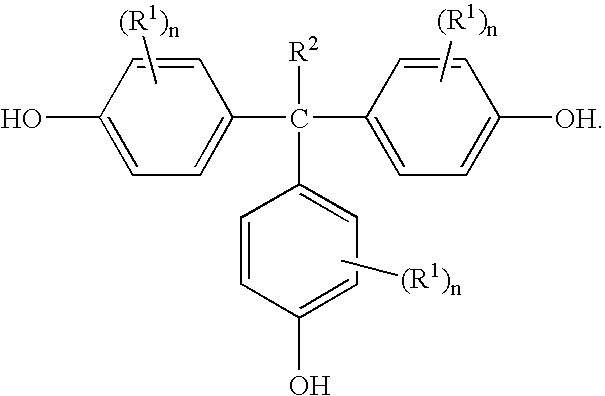
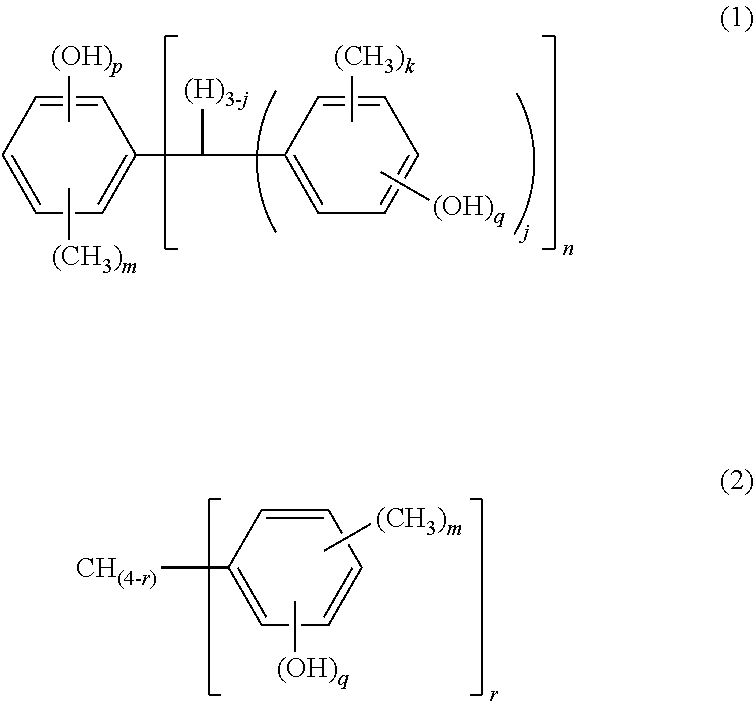
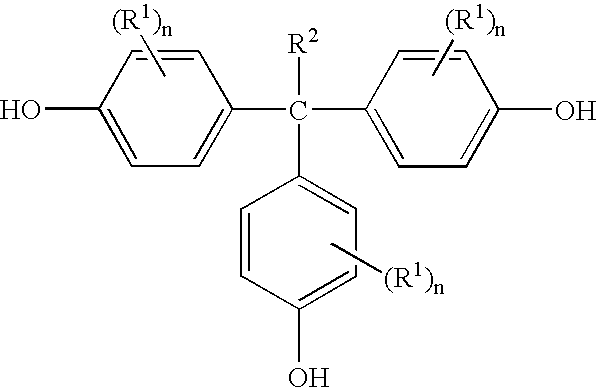
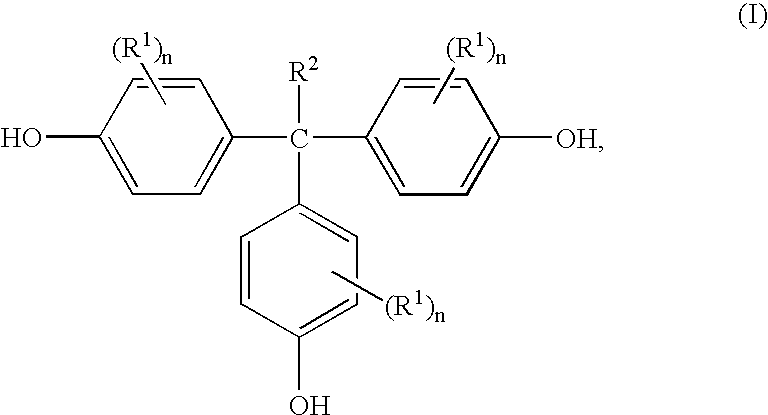
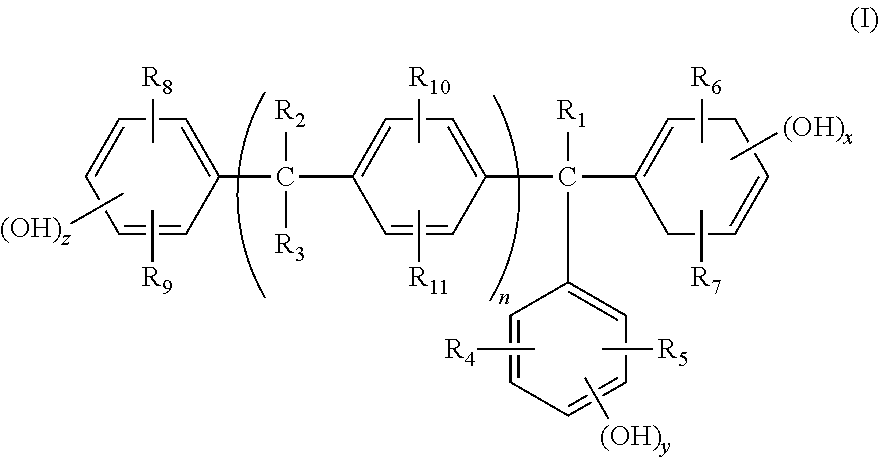
Methods for preparing 1,1,1-tris(4-hydroxyphenyl)alkanes
A method for preparing 1,1,1,-tris(4-hydroxyphenyl)alkanes generally comprises reacting a mixture of an aromatic hydroxy compound and a ketone in the presence of at least one sulfonic acid catalyst and a mercaptan co-catalyst to produce the 1,1,1-tris(4-hydroxyphenyl)alkanes of formula:
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Positive lift-off resist composition and patterning process
ActiveUS20120129106A1High sensitivityElectric discharge tubesDiazo compound compositionsResistCellulose
A positive lift-off resist composition is provided comprising (A) an alkali-soluble novolac resin, (B) a quinonediazidosulfonate photosensitive agent, (C) an alkali-soluble cellulose resin, and (D) an aromatic hydroxy compound having a formula weight of 180-800. The composition has shelf stability, high sensitivity, and a film retention after development of at least 95% and is used to form a lift-off resist pattern of fully undercut profile.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
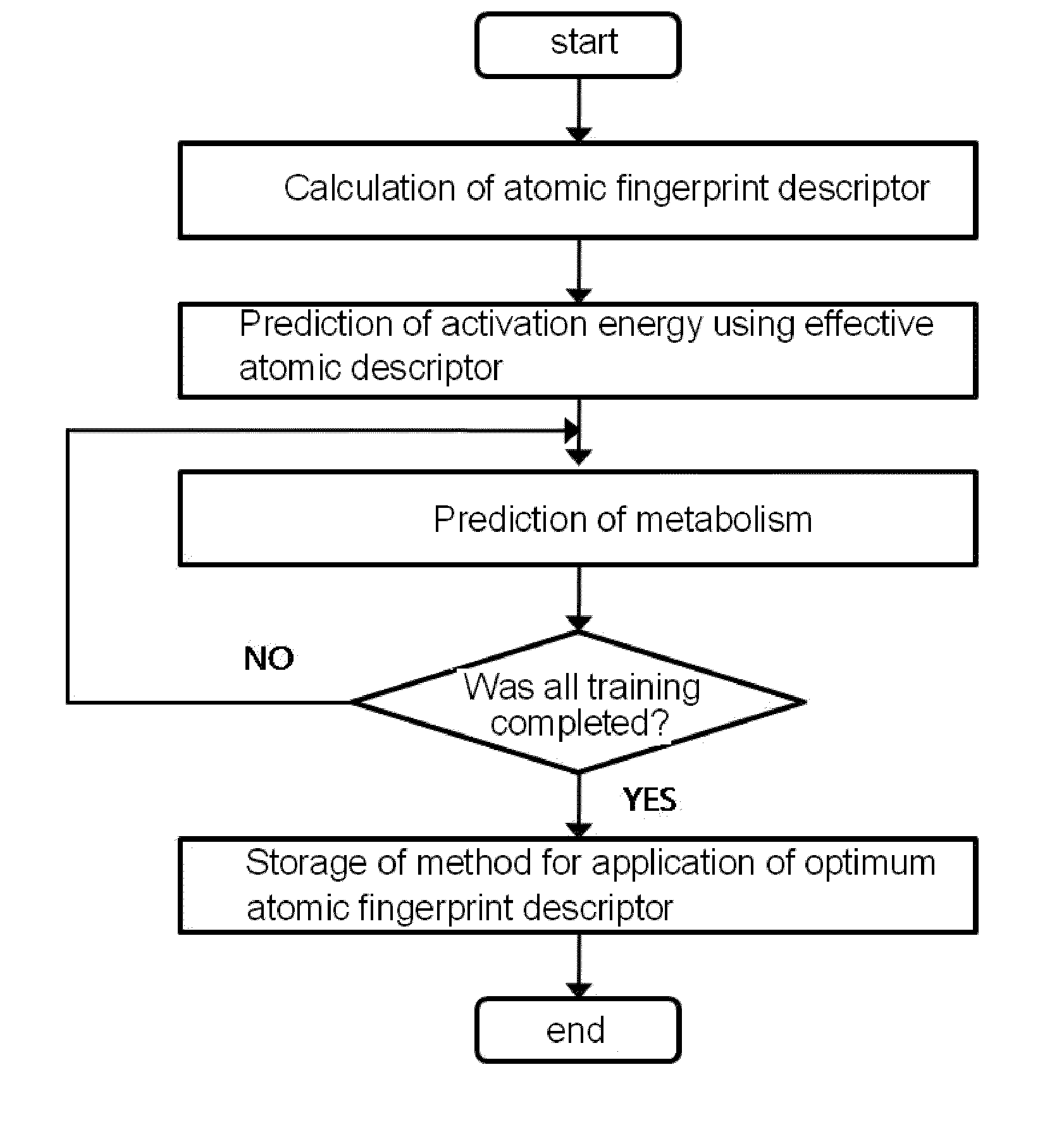
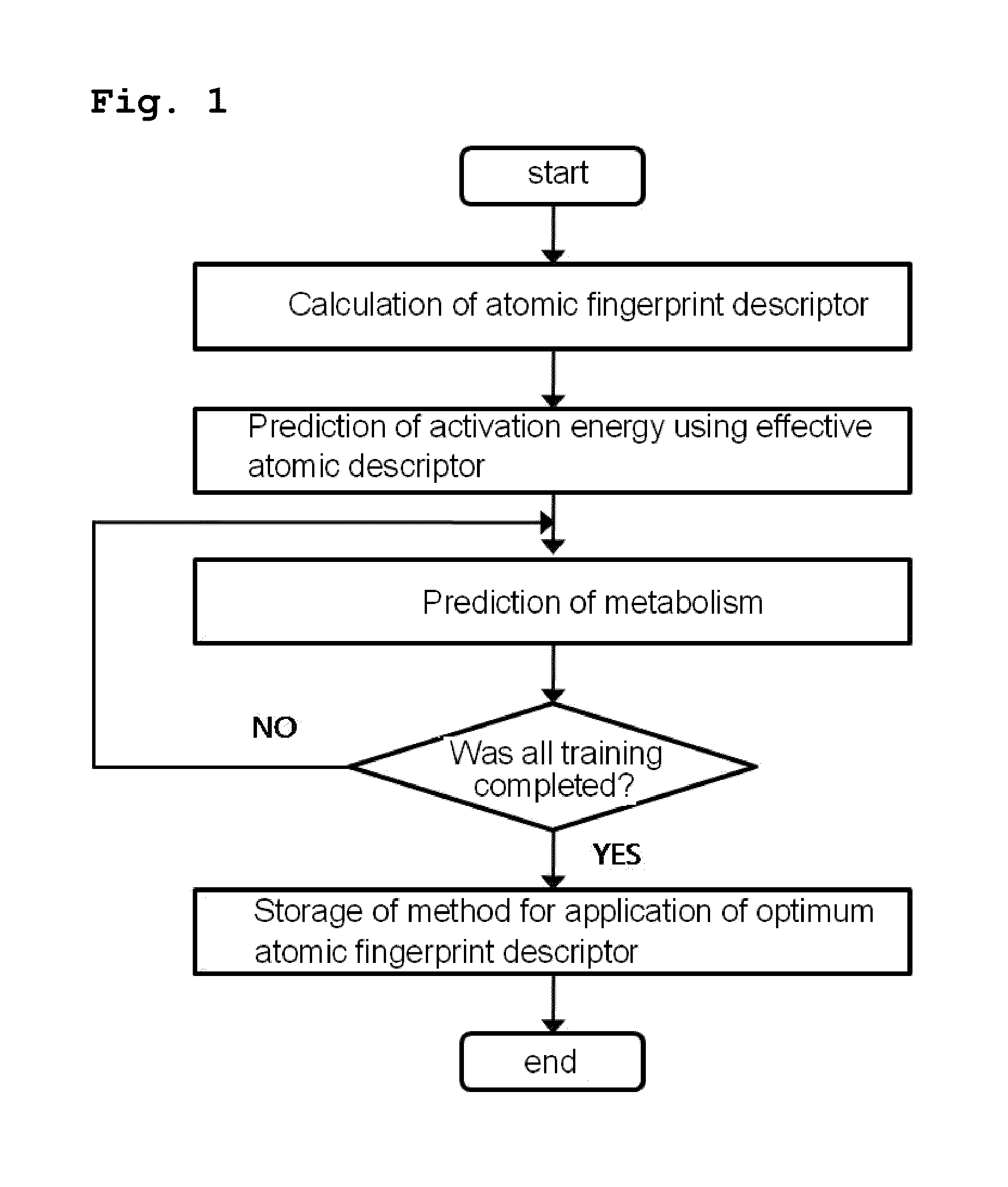
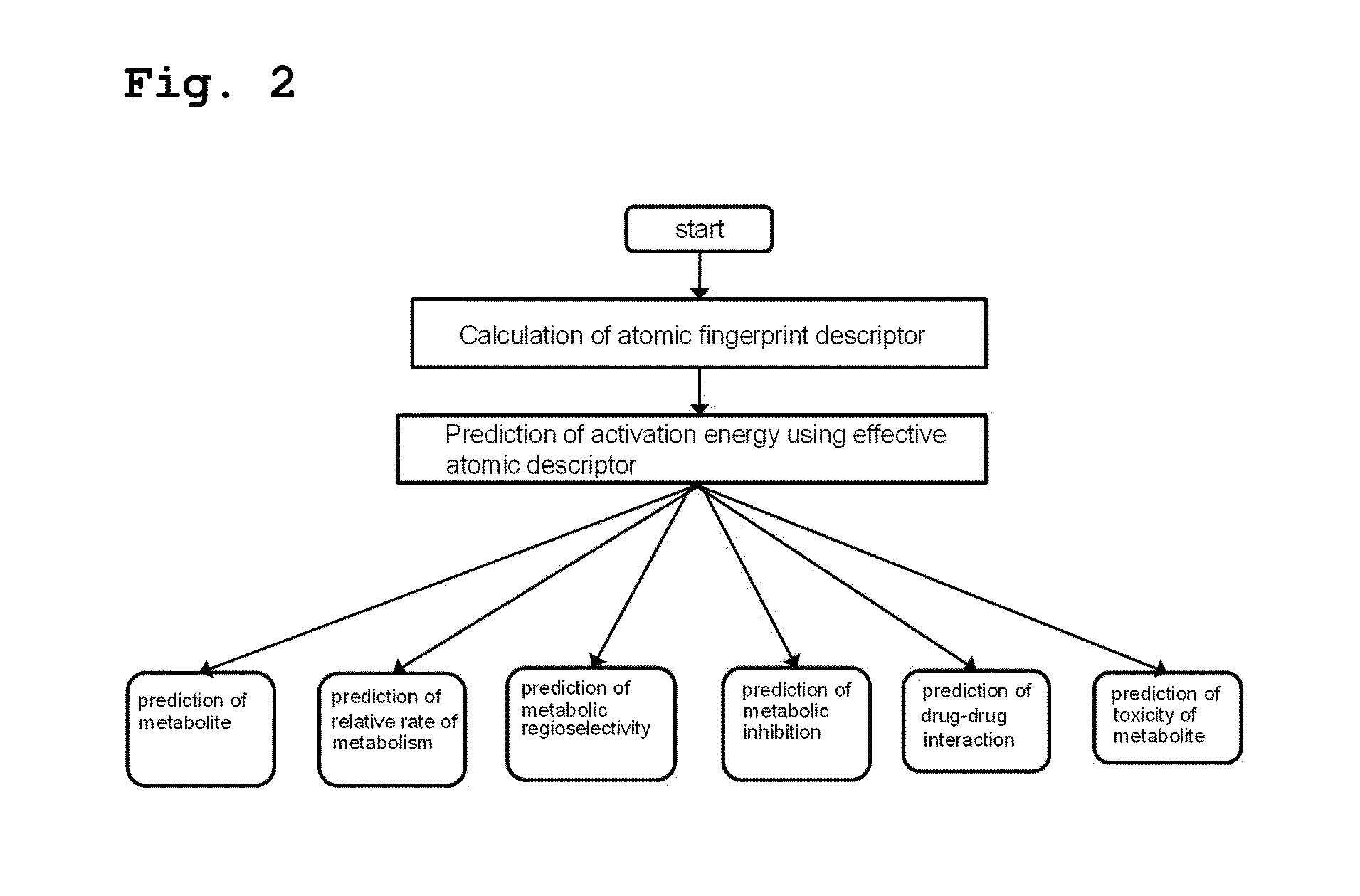
Method for predicting activation energy using an atomic fingerprint descriptor or an atomic descriptor
InactiveUS20110213558A1The process is fast and accurateChemical property predictionMolecular designMetaboliteChemical reaction
The present invention provides a method for constructing a database of atomic fingerprint descriptors. The invention provides a method for predicting activation energy using an atomic fingerprint descriptor and an atomic descriptor, the method comprising the steps of: (i) calculating the atomic fingerprint descriptor of a substrate; (ii) comparing the calculated atomic fingerprint descriptor with the constructed atomic fingerprint descriptor database to select an atomic position where cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism occurs; and (iii) predicting activation energy for the selected atomic position using an atomic descriptor. Also, the invention provides a method of predicting the activation energy of CYP450-mediated phase I metabolism using effective atomic descriptors. Specifically, the invention provides a method of predicting the activation energy either for cytochrome P450-mediated hydrogen abstraction or for tetrahedral intermediate formation in cytochrome P450-aromatic hydroxylation using equations including effective atomic descriptors. The method of the invention can rapidly predict activation energy for phase I metabolites at a practical level without having to perform a docking experiment between any additional CYP450 and the substrate, or a quantum mechanical calculation, thereby making it easier to develop new drugs using a computer. Also, the present invention may propose a strategy for increasing the bioavailability of drugs through the avoidance of metabolites based on the possibility of drug metabolism. Furthermore, the method of the present invention proposes new empirical approaches which can also be easily applied to activation energies for various chemical reactions, and makes it possible to explain physical and chemical factors that determine activation energy. In addition, through the prediction of activation energy according to the present invention, it is possible to predict i) metabolic products, ii) the relative rate of metabolism, iii) metabolic regioselectivity, iv) metabolic inhibition, v) drug-drug interactions, and vi) the toxicity of a metabolite.
Owner:BIOINFORMATICS & MOLECULAR DESIGN RES CENT
Methods for preparing 1,1,1-tris(4-hydroxyphenyl)alkanes
A method for preparing 1,1,1,-tris(4-hydroxyphenyl)alkanes generally comprises reacting a mixture of an aromatic hydroxy compound and a ketone in the presence of at least one ion exchange resin catalyst and optionally a co-catalyst to produce the 1,1,1-tris(4-hydroxyphenyl)alkanes of formula:
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
Negative photosensitive resin composition and application thereof
ActiveUS9366959B2Excellent peelabilityAccelerate evaporationSolid-state devicesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusXylylenePolymer science
A negative photosensitive resin composition including an alkali-soluble resin (A), a photoacid generator (B), a basic compound (C), a cross-linking agent (D), and a solvent (E) is provided. The alkali-soluble resin (A) includes an acrylate resin (A-1) and a novolac resin (A-2). The acrylate resin (A-1) is synthesized by polymerizing a monomer for polymerization, wherein the monomer for polymerization includes an unsaturated carboxylic acid or unsaturated carboxylic acid anhydride monomer (a-1-1) and a monomer (a-1-2). The monomer (a-1-2) includes a compound (a-1-2-1) with a tricyclodecane or dicyclopentadiene structure, a compound (a-1-2-2) represented by formula (1), or a combination of both. The novolac resin (A-2) is synthesized by polymerizing an aldehyde compound with an aromatic hydroxy compound, wherein the aromatic hydroxy compound includes a xylenol compound.
Owner:CHI MEI CORP
Isocyanates and Aromatic Hydroxy Compounds
ActiveUS20110319648A1Efficient productionCarbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationPolymer scienceCarbamate
Owner:ASAHI KASEI CHEM CORP
Method for producing water-soluble homopolymers or copolymers which comprise (meth)acrylamide
A process for preparing water-soluble homo- or copolymers comprising (meth)acrylamide by free-radical polymerization of an aqueous solution of monoethylenically unsaturated monomers comprising at least (meth)acrylamide in the presence of at least one stabilizer for prevention of polymer degradation by molecular oxygen. The stabilizer is preferably one selected from the group of sulfur compounds, sterically hindered amines, N-oxides, nitroso compounds, aromatic hydroxyl compounds and ketones, more preferably 2-mercaptobenzothiazole or a salt thereof.
Owner:BASF AG
Positive photosensitive resin composition and method for forming patterns by using the same
InactiveUS20140242504A1Sure easyImproved profilePhotosensitive materialsPhotosensitive material processingBenzaldehydeOrtho-naphthoquinone
The present invention relates to a positive photosensitive resin composition and a method for forming patterns by using the same. The positive photosensitive resin composition includes a novolac resin (A), an ortho-naphthoquinone diazide sulfonic acid ester (B), a hydroxycompound (C) and a solvent (D). The novolac resin (A) further includes a hydroxy-type novolac resin (A-1) and a xylenol-type novolac resin (A-2). The hydroxy-type novolac resin (A-1) is synthesized by condensing hydroxyl benzaldehyde compound with aromatic hydroxyl compound. The xylenol-type novolac resin (A-2) is synthesized by condensing aldehyde compound with xylenol compound. The postbaked positive photosensitive resin composition can be beneficially formed to patterns with high film thickness and well cross-sectional profile.
Owner:CHI MEI CORP
Composition, pattern forming method, and manufacturing methods of crystal particles and display device
The invention provides a negative photosensitive resin composition, a pattern forming method, a metal pattern forming method, a manufacturing method of light emitting diode crystal particles and a manufacturing method of an organic light emitting display device. The negative photosensitive resin composition including a novolac resin (A), a photoacid generator (B), a basic compound (C), a cross-linking agent (D), and a solvent (E). The novolac resin (A) includes a hydroxy-type novolac resin (A-1) and a xylenol-type novolac resin (A-2). The hydroxy-type novolac resin (A-1) is synthesized by polycondensing a hydroxybenzaldehyde compound and an aromatic hydroxy compound. The xylenol-type novolac resin (A-2) is synthesized by polycondensing an aldehyde compound and a xylenol compound.
Owner:CHI MEI CORP
Processes for preparing benzoquinones and hydroquinones
ActiveUS20060025634A1Organic compound preparationQuinone preparation by oxidationPhosphateHydroquinone Compound
A process for the preparation of hydroquinone compounds comprising, reacting an aromatic hydroxy compound with an oxidizing agent in a biphasic solvent system. The reaction is carried out in the presence of a transition metal hydroxy phosphate catalyst to produce the corresponding hydroquinone compound.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
Positive photosensitive resin composite and method for forming pattern
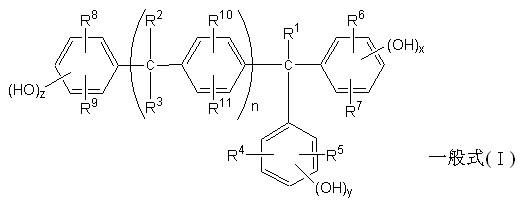
ActiveCN102566273APhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolventAromatic hydroxylation
The invention relates to a positive photosensitive resin composite and a method for forming a pattern and especially to a positive photosensitive resin composite having good anti-cracking performance and a method for using the composite to form the pattern. The positive photosensitive resin composite contains novolac resin (A), epoxy resin (B) having epoxy propyl, naphthoquinone sulfoacid ester (C) and solvent (D), wherein the novolac resin (A) contains hydroxy novolac resin (A-1). The hydroxy novolac resin (A-1) is prepared by condensing hydroxy benzaldehyde compound and aromatic hydroxyl compound.
Owner:CHI MEI CORP
Process for producing aromatic compounds
InactiveUS20060106261A1Efficient productionSimple and easy procedureCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationCompound aArame
A process produces an aromatic compound by bringing an aromatic compound (B) into contact with molecular oxygen (C) in the presence of a catalyst (A) comprising at least one of (A1) a heteropolyacid and / or a salt thereof, and (A2) a mixture of oxoacids and / or salts thereof containing, as a whole, one of P and Si and at least one selected from V, Mo and W to thereby yield another aromatic compound (G) than the aromatic compound (B). The process can produce, for example, a corresponding aromatic hydroxy compound (G1) by allowing the aromatic compound (B) to react with the molecular oxygen (C) further in the presence of a reducing agent (D).
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
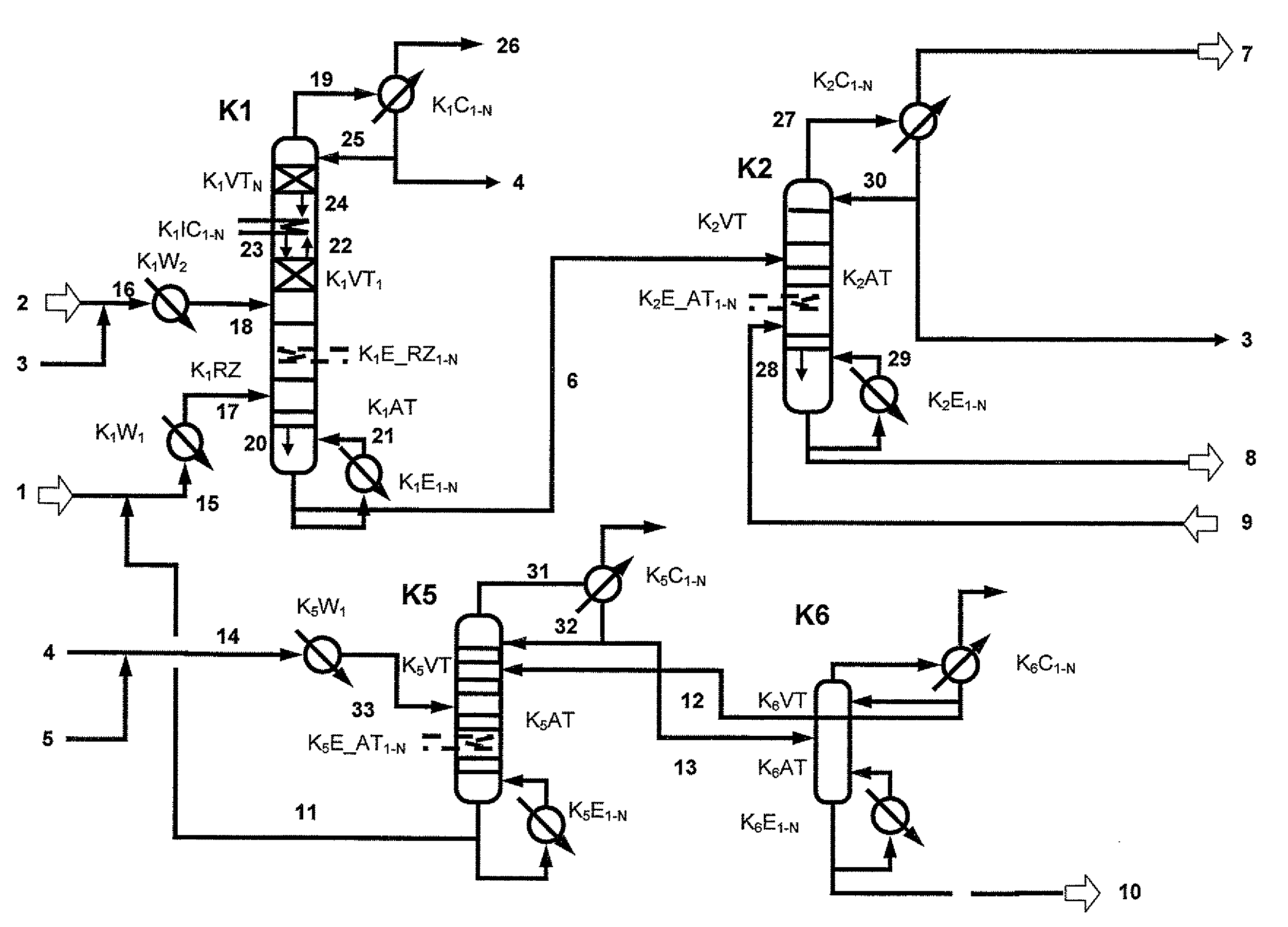
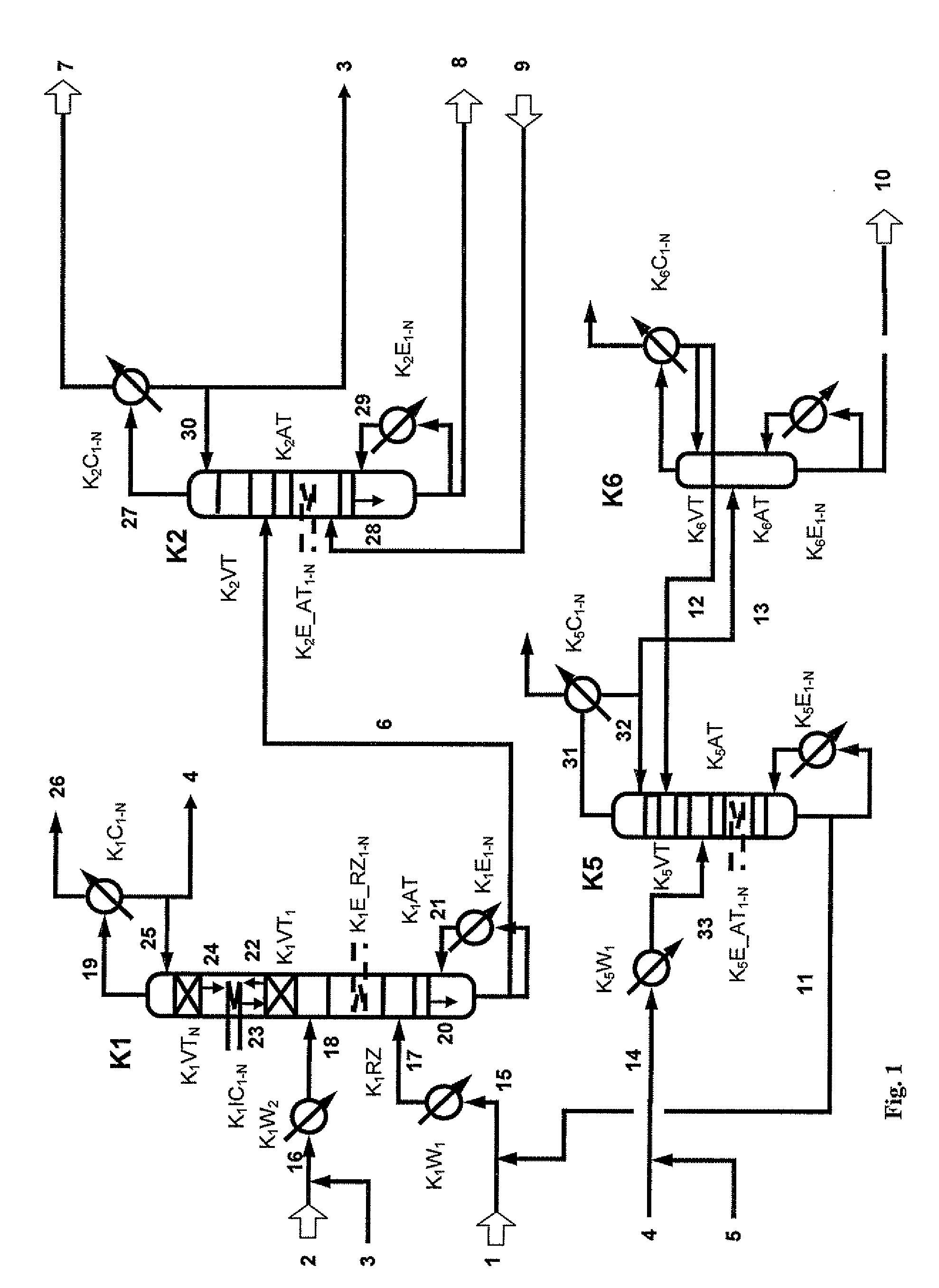
Continuous method for preparing aromatic carbonate using a heterogeneous catalyst and a reaction apparatus for the same
ActiveUS20050240046A1Low costMinimizing processOrganic chemistry methodsPreparation from organic carbonatesDistillationHomogeneous catalysis
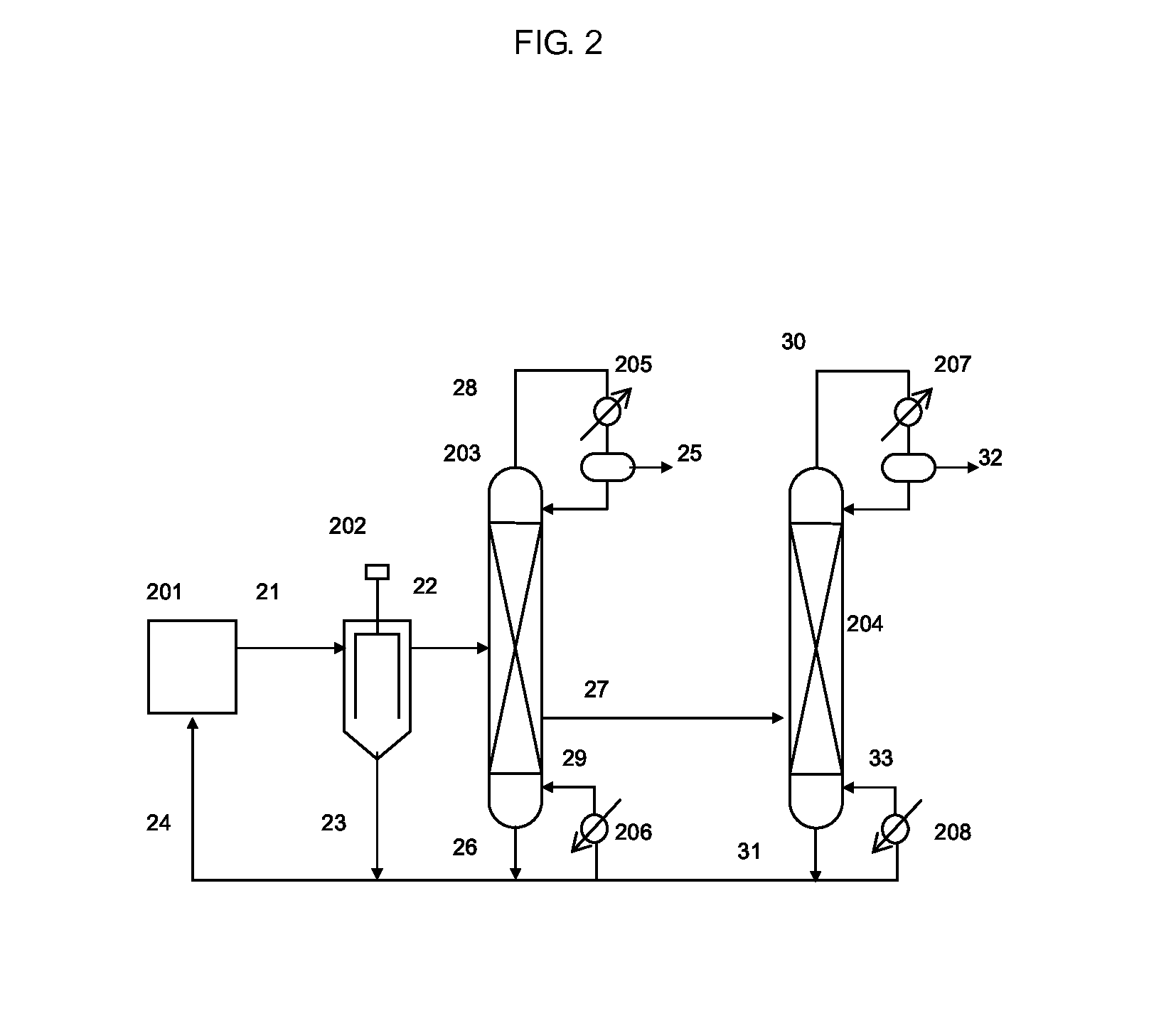
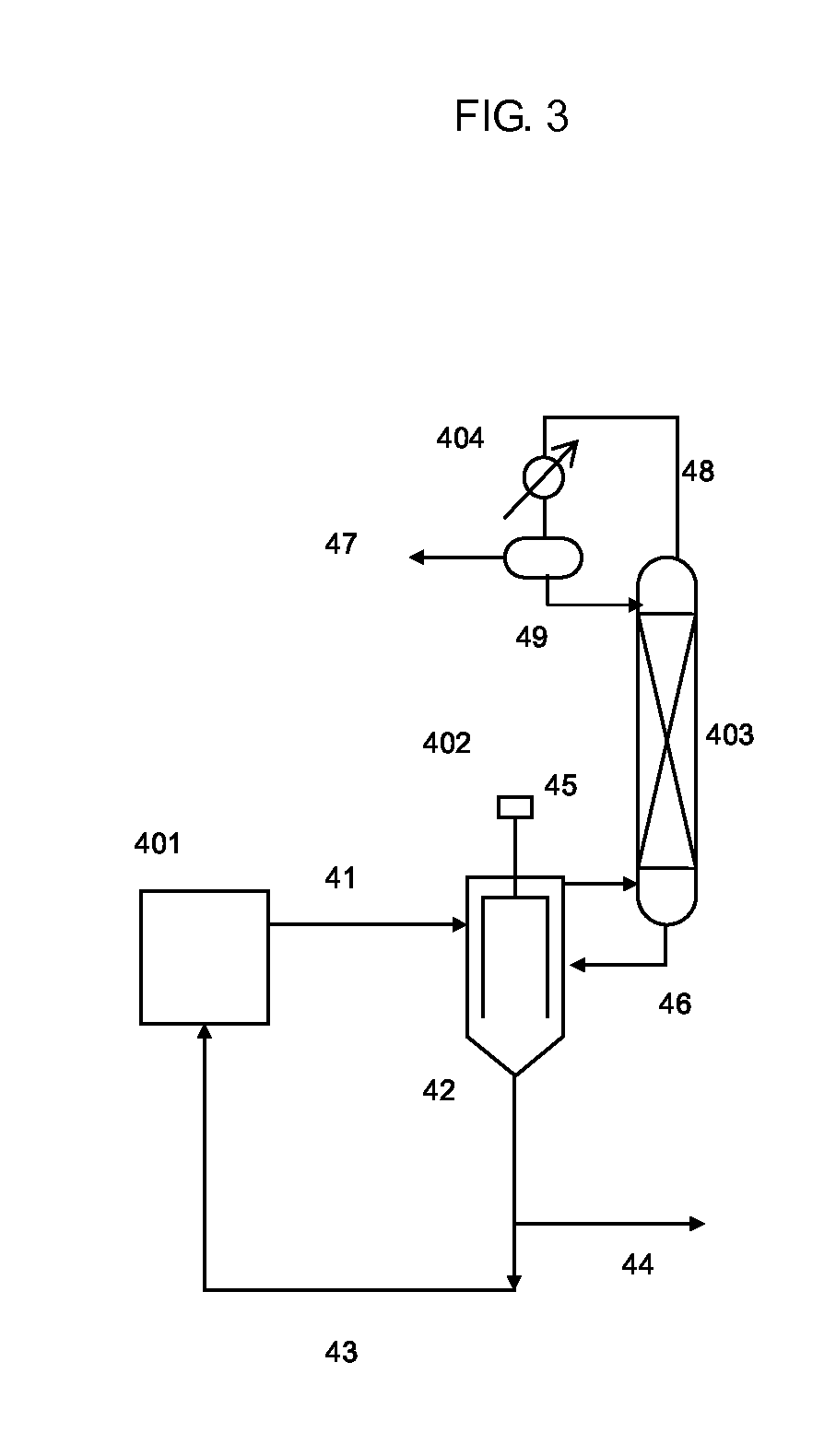
The present invention relates to a continuous method for the preparation of an aromatic carbonate by reacting a dialkyl carbonate and an aromatic hydroxy compound in the presence of a heterogeneous catalyst, and a reaction apparatus for the same. The continuous method comprises the step of reacting dialkyl carbonate and an aromatic hydroxy compound in the presence of the heterogeneous catalyst in a loop-type, catalyst-containing reaction apparatus, wherein a reactor equipped with a filter in which the catalyst is contained is connected with a heat exchanger portion for providing necessary heat during the reaction, reaction solution is circulated between the catalyst-containing portion and heat exchanger via a circulation pump, and by-products can be eliminated via a distillation column connected with the reactor.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Process for producing diaryl carbonates
InactiveUS6852872B2High selectivityYield of productOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsPtru catalystCombinatorial chemistry
A process for producing diaryl carbonate is disclosed. The process entails forming a reaction mixture wherein reacting are an aromatic hydroxy compound corresponding to the formulaR—O—H (II),wherein R denotes a C6-22-aromatic hydrocarbon radical, with CO and O2 in the presence of a catalyst system. The catalyst system contains components a) a Group VIII B metal compound, b) at least one second metal compound, c) a bromide compound, and d) a base. The process entails introduction of one or more of components a) to d) to the reaction mixture in more than one increment in the course of the reaction.
Owner:BAYER AG
Method for making aromatic carbonates
InactiveCN1332718AEconomically viable to produceIncrease reaction rateOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsReaction rateDesiccant
The present invention relates to an improved process for the production of aromatic carbonates by reacting aromatic hydroxyl compounds, carbon monoxide and oxygen in the presence of a catalyst system comprising at least one palladium or palladium compound, at least one lead compound, at least one halide Source and at least one desiccant, wherein the optimum ratio of lead co-catalyst to palladium catalyst equivalents can increase the reaction rate and also make aromatic carbonates available in an economically viable continuous process.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com