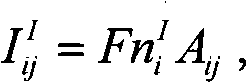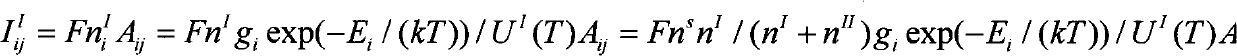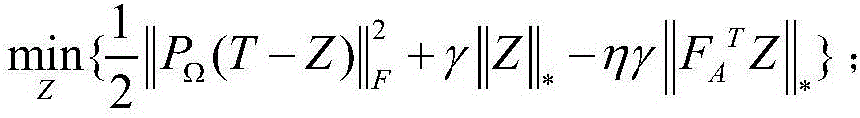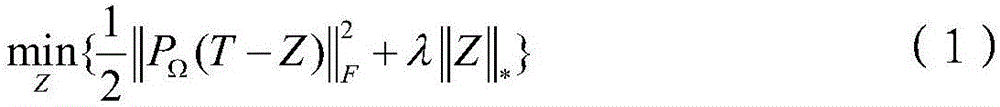Patents
Literature
74 results about "Lamé parameters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In continuum mechanics, the Lamé parameters (also called the Lamé coefficients, Lamé constants or Lamé moduli) are two material-dependent quantities denoted by λ and μ that arise in strain-stress relationships. In general, λ and μ are individually referred to as Lamé's first parameter and Lamé's second parameter, respectively. Other names are sometimes employed for one or both parameters, depending on context.
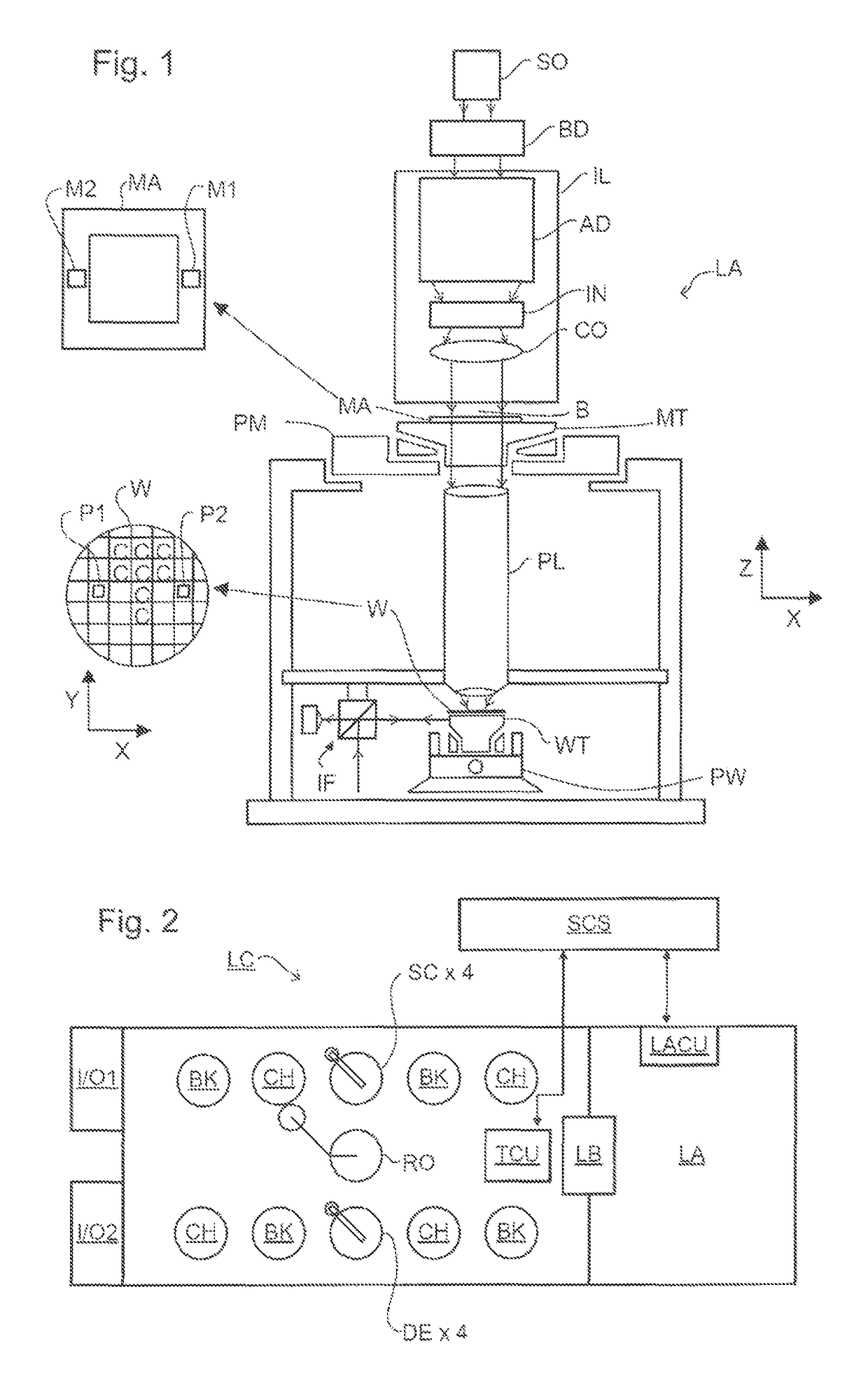
Method and Apparatus for Measuring a Structure on a Substrate, Computer Program Products for Implementing Such Methods and Apparatus
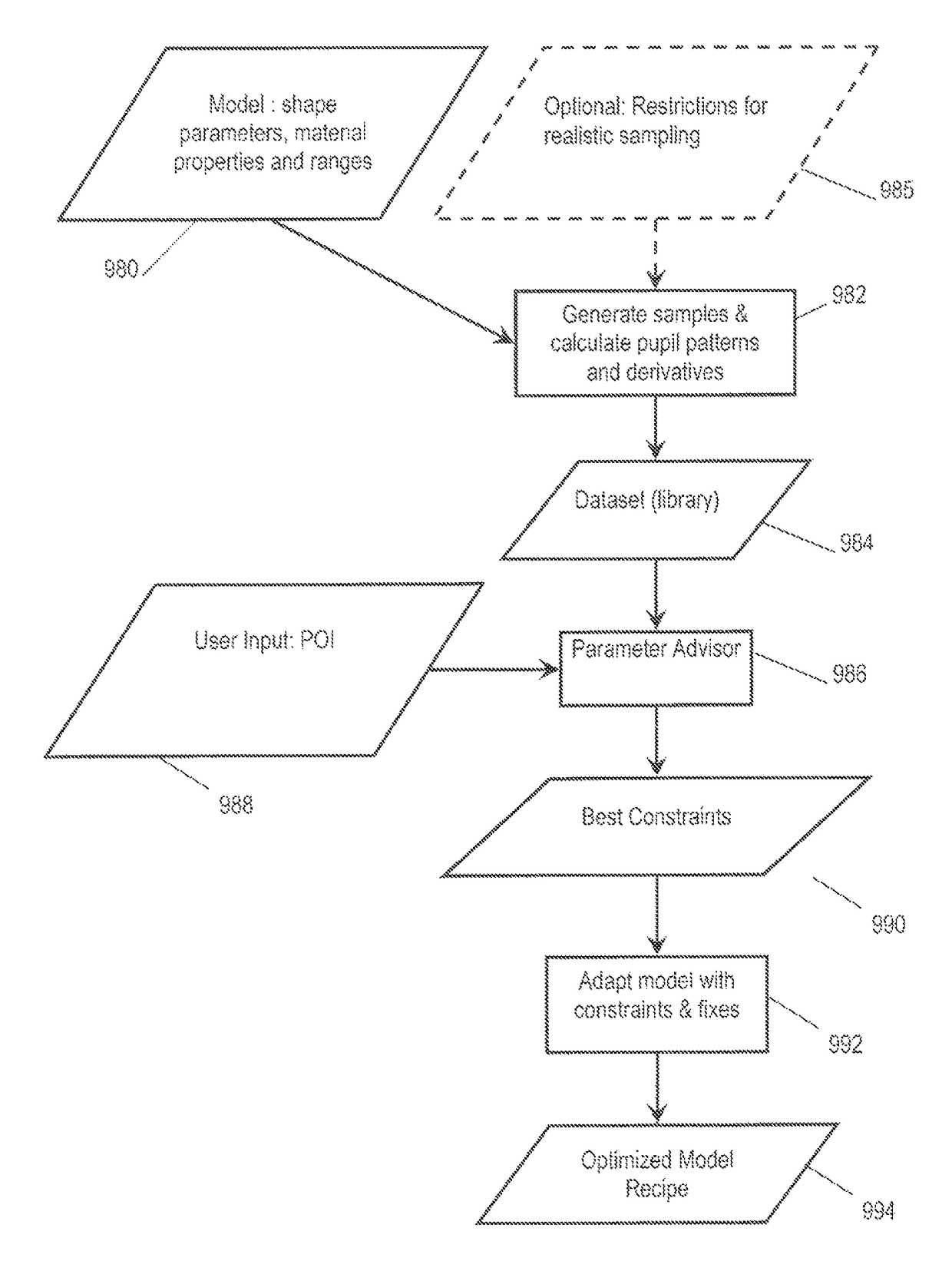
ActiveUS20120123748A1Degree of freedom is loweredReduce in quantityMaterial analysis by optical meansComputation using non-denominational number representationAlgorithmUser input
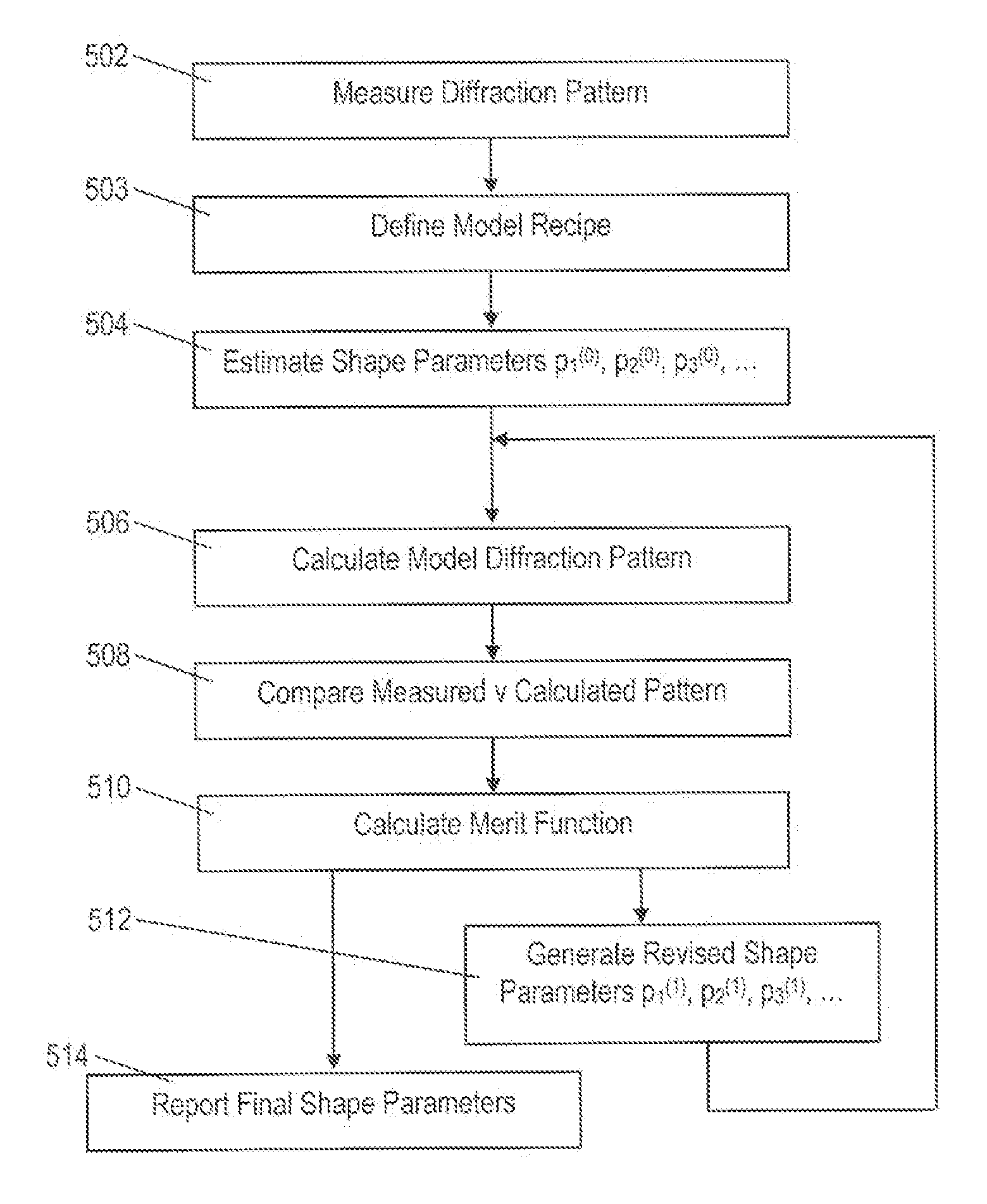
Diffraction models and scatterometry are used to reconstruct a model of a microscopic structure on a substrate. A plurality of candidate structures are defined, each represented by a plurality of parameters (p1, p2, etc.)). A plurality of model diffraction signals are calculated by simulating illumination of each of the candidate structures. The structure is reconstructed by fitting one or more of the model diffraction signals to a signal detected from the structure. In the generation of the candidate structures, a model recipe is used in which parameters are designated as either fixed or variable. Among the variable parameters, certain parameters are constrained to vary together in accordance with certain constraints, such as linear constraints. An optimized set of constraints, and therefore an optimized model recipe, is determined by reference to a user input designating one or more parameters of interest for a measurement, and by simulating the reconstruction process reconstruction. The optimized model recipe can be determined automatically by a parameter advisor process that simulates reconstruction of a set of reference structures, using a plurality of candidate model recipes. In the generation of the reference structures, restrictions can be applied to exclude unrealistic parameter combinations.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Spectral standardization-based coal quality on-line detection method
ActiveCN101949852AHigh precisionEliminate experimental parameter fluctuationsAnalysis by thermal excitationDensity ratioElectronic density
The invention relates to a spectral standardization-based coal quality on-line detection method, which can be used for coal quality on-line detection based on a laser induced plasma spectra principle. In the method, a calibrating model is established by using the intensity of an atomic characteristic spectral line after spectral standardization as a vertical coordinate and using the concentration of an element corresponding to the atomic characteristic spectral line as a horizontal coordinate. When the coal with unknown components is detected, the concentration of an element to be tested can be obtained according to the calibrating model after the spectral standardization. In the method, plasma temperature, electronic density, density ratio of ion to atom of the same element and a boltzmann's law are taken into consideration, so that the fluctuation of experiment parameters is compensated and the measuring precision is improved. The method can also be applied to the similar occasions requiring on-line real-time detection of chemical components.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Well-constrained pre-stack elastic parameter inversing method for modulating supplemented subspace
InactiveCN102169190AWave group details are not richHigh-resolutionSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingImage resolutionRunning time
The invention relates to a well-constrained pre-stack elastic parameter inversing method for modulating supplemented subspace, belonging to the field of seismic log. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that: the computation time is shortened so that the running time is shortened and the cost is reduced; the processing parameters can be adjusted so that a better processing result can be obtained; the frequency-increasing data wave group detailed information is not abundant so that the wave group characteristics of original seismic events and the interlaminar information of original profiles are maintained and the resolution of the profiles is enhanced; the undue dependence on a stratified model is avoided to ensure that the information of combined reconstruction beside the well is preferably fitted with the log information, and the non-stratified information contained in seismic data can be fully reflected outside the well; therefore, the problem of matching the seismic data of reservoir stratums (stratums such as fluvial facies reservoir stratum, carbonatite pore and fissure and hole intensive belt and the like ) with reticular characteristics with the well information is solved.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
3DMIMO channel modeling method
InactiveCN105553584AVariable speedReduce complexityTransmission monitoringNetwork planningSimulationShort terms
The invention relates to a 3D MIMO channel modeling method. The method includes the following steps that: (1) simulated scenes and network layout are determined, large-scale parameters are calculated according to the scenes and calculated correlations; (2) small-scale parameters are generated sequentially based on the large-scale parameters, a probability density function and the scenes; (3) a channel coefficient is calculated; (4) the small-scale parameters are updated according to a calculation result, and a drift model is built; and (5) time evolution is carried out according to the drift model, and then, modeling is carried out. According to the 3D MIMO channel modeling method of the invention, short-term time evolution of the channel coefficient is realized through updating time delay, a departure angle, an arrival angle, polarization, shadow fading and a K factor; smooth transition between adjacent channel segments is supported; a visual-range scene and a non-visual-range scene are simulated jointly by a common framework structure, and therefore, the complexity of a model can be reduced, and multi-unit scenes can be configured freely; and an algorithm of position graph generation is expanded, and diagonal angle movement directions are considered, and smoother output is created.
Owner:YANTAI POWER SUPPLY COMPANY OF STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER +1
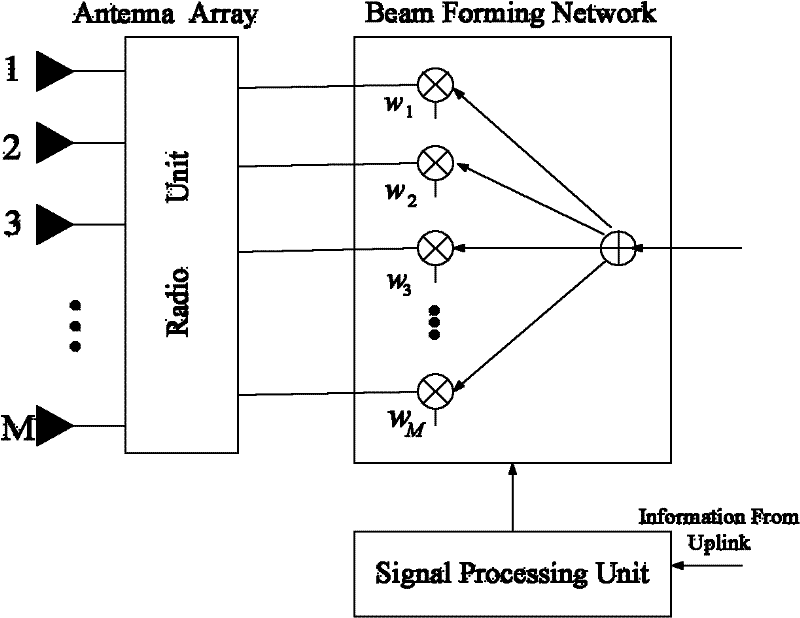
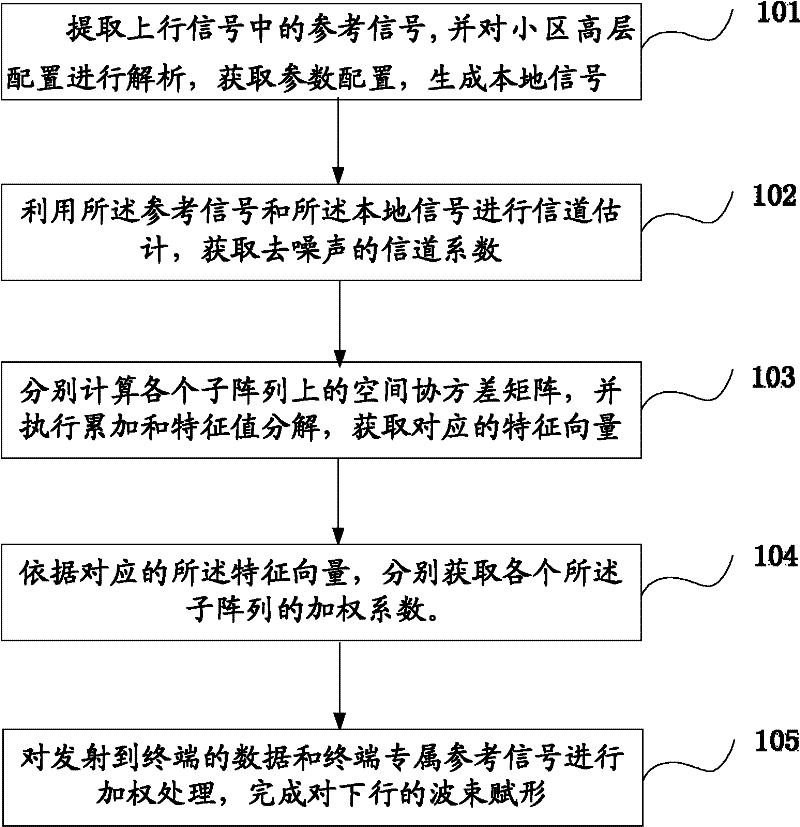
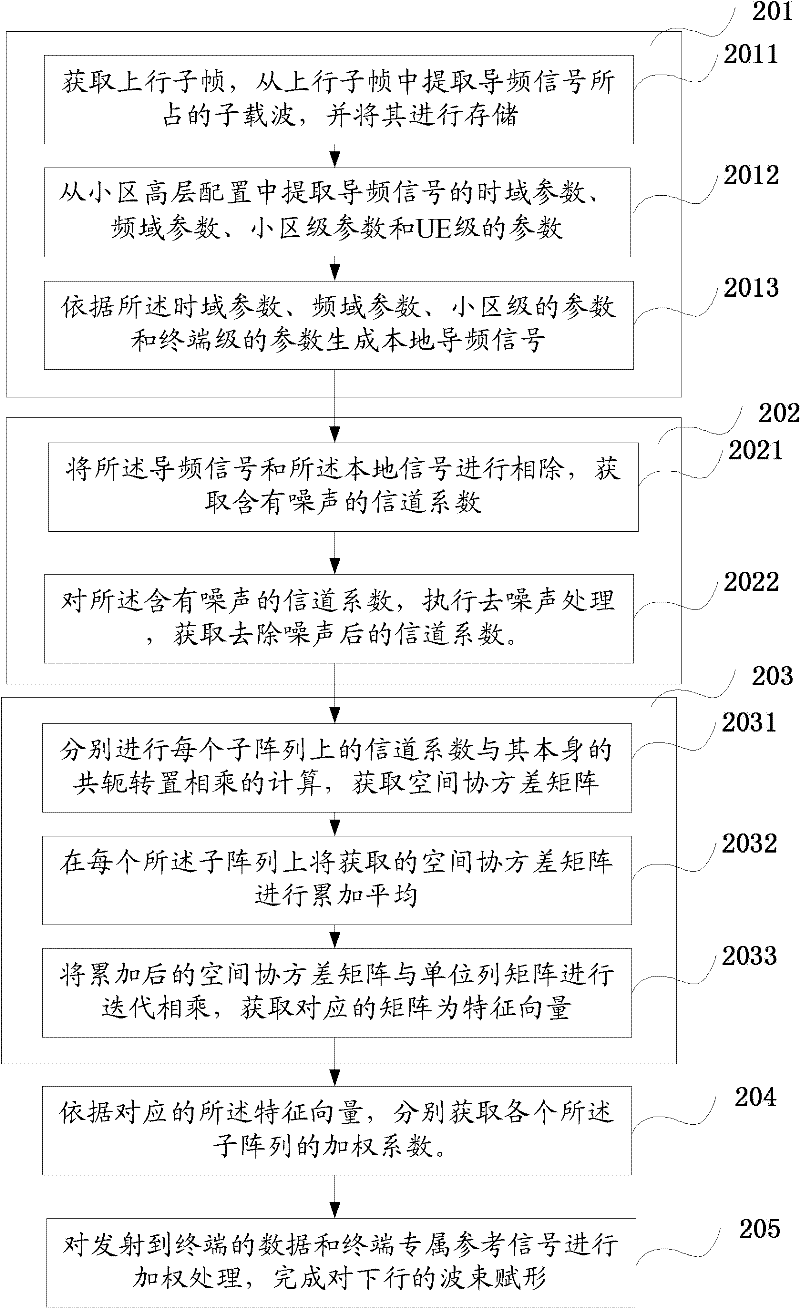
Beam-forming method of and device
ActiveCN102237922AHigh speedImprove implementation speedSpatial transmit diversityFeature vectorDecomposition
The invention discloses a beam-forming method and device. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting a reference signal from uplink signals and resolving the high-level configuration of a cell to obtain the parameter configuration of the reference signal and generate a local signal; performing channel estimation by using the reference signal and the local signal to obtain a denoised channel coefficient; calculating a space covariance matrix on each subarray by using the channel coefficient; performing characteristic value decomposition on the covariance matrix to obtain a characteristic vector and further obtain a weighting coefficient accordingly; and weighting data transmitted to a terminal and an exclusive reference signal of the terminal by using the weighting coefficient to finish beam forming of a downlink. Due to the adoption of the steps in the method, the calculation process of beam forming is simplified, the beam forming realization speed can be effectively increased under the condition of ensuring a certain beam-forming accuracy, the time delay of a system is reduced, and the aims of pointing at a target terminal, reducing the signal demodulation errors and lowering the interference on other terminals are fulfilled.
Owner:WUHAN HONGXIN TELECOMM TECH CO LTD
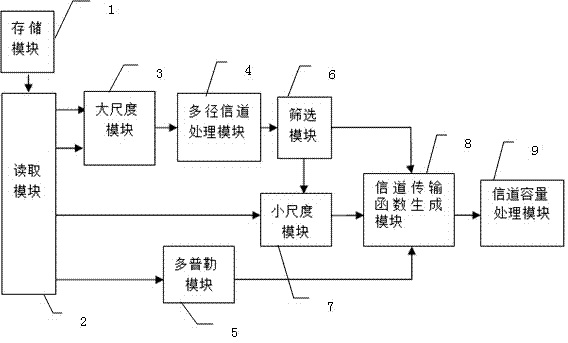
Time-variant underwater acoustic channel capacity simulation model
ActiveCN104734795AOvercome uncertaintyImprove Simulation ResultsTransmission monitoringTime delaysChannel parameter
The invention discloses a time-variant underwater acoustic channel capacity simulation model. The time variant underwater acoustic channel capacity simulation model comprises a storage module for storing various parameters, a reading module for reading the various parameters stored in the storage module, a large-scale module for obtaining random channel parameters subjected to large-scale transformation through first-order AR transformation, a multipath channel processing module for obtaining path information of multiple paths of the random channel parameters based on a ray tracing model, a screening module for screening out three to ten important paths, a small-scale module for calculating small-scale attenuation coefficients of multiple micro-paths according to small-scale parameters, a Doppler module for processing Doppler parameters to calculate an effective Doppler matrix, a channel transmission function generating module for obtaining a total channel transmission matrix of a multipath time delay acoustic channel according to comprehensively-obtained various parameter, and a channel capacity processing module for conducting processing transformation on channel transmission functions in the total transmission matrix and obtaining pulse response, channel gain and channel capacity of the acoustic channel through calculation.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
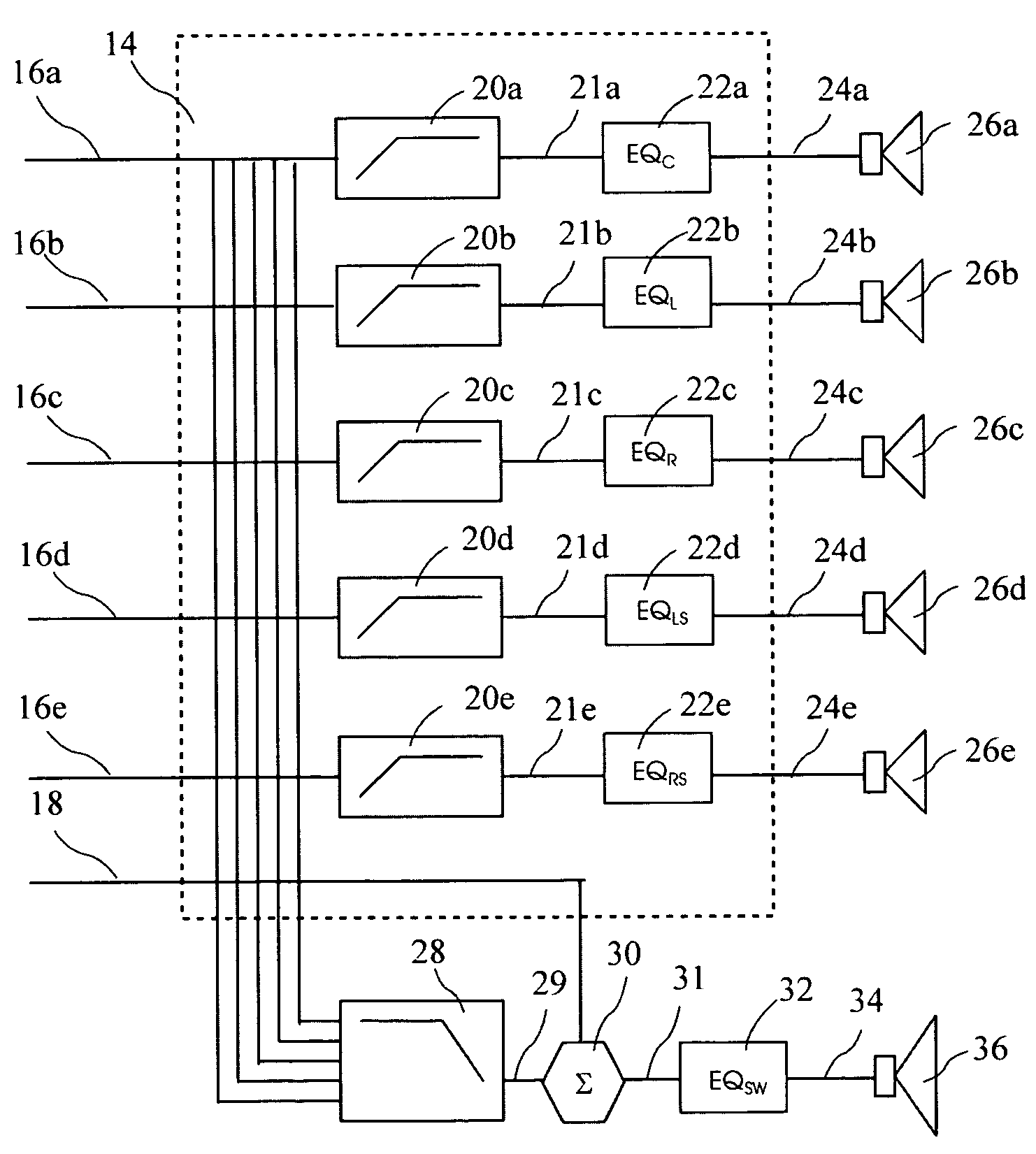
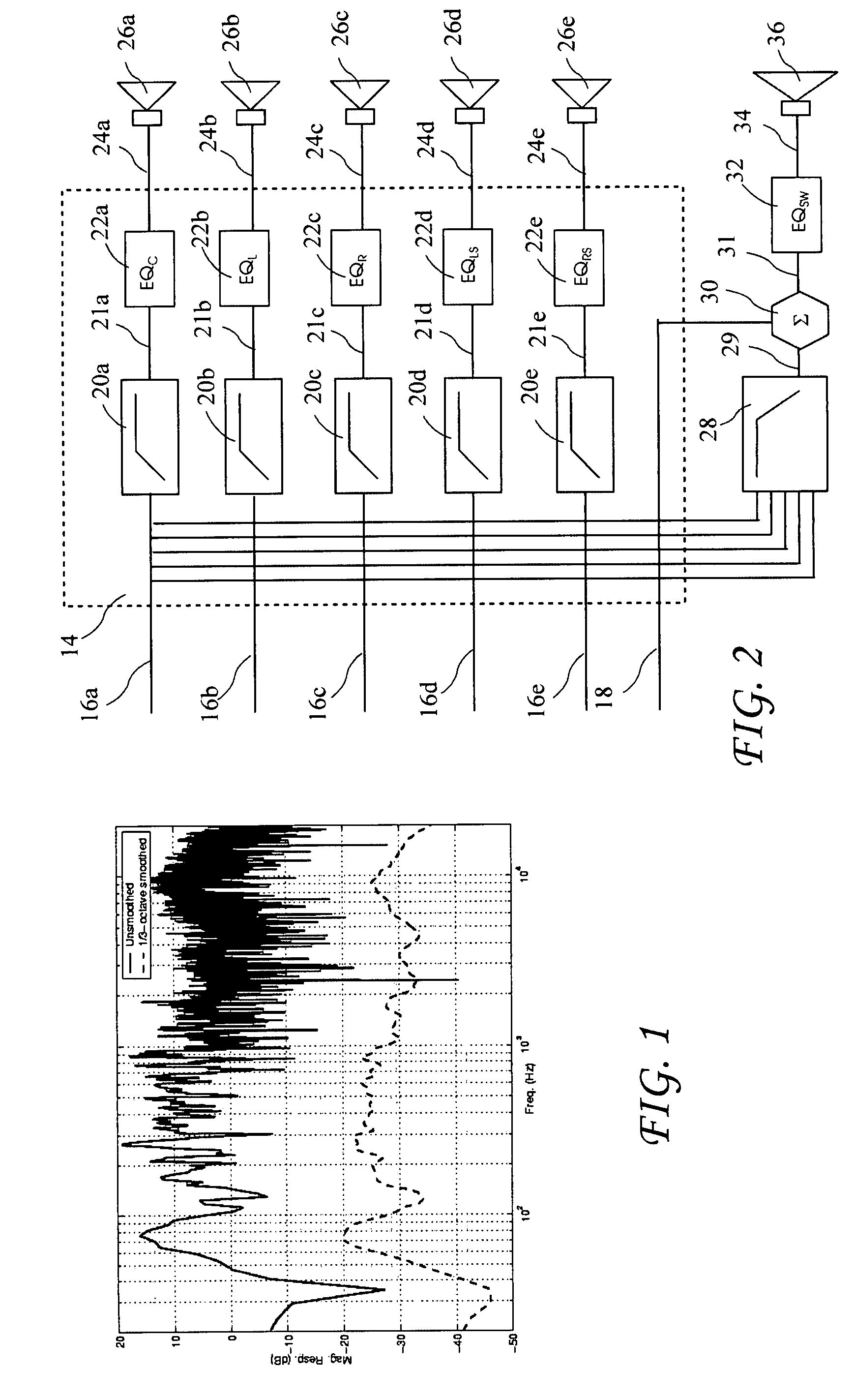
Room acoustic response modeling and equalization with linear predictive coding and parametric filters
A method for determining coefficients of a family of cascaded second order Infinite Impulse Response (IIR) parametric filters used for equalizing a room response. The method includes determining parameters of each IIR parametric filter from poles or roots of a reasonably high-order Linear Predictive Coding (LPC) model. The LPC model is able to accurately model the low-frequency room response modes providing better equalization of loudspeaker and room acoustics, particularly at the low frequencies. Advantages of the method include fast and efficient computation of the LPC model using a Levinson-Durbin recursion to solve the normal equations that arise from the least squares formulation. Due to possible band interactions between the cascaded IIR parametric filters, the method further includes optimizing the Q value of each filter to better equalize the room response.
Owner:AUDYSSEY LABORATORIES
Radiographic apparatus and an image processing method therefore
ActiveUS20140205058A1Securing convergence accuracySpeedReconstruction from projectionRadiation/particle handlingImaging processingTomography
Initial values Â1P̂1M̂1 . . . ÂnP̂nM̂n of parameters representing a geometric relationship between an X-ray tube, a stage and a flat panel X-ray detector are estimated, a least squares solution (p̂w)i of characteristic point three-dimensional coordinates is estimated, and only limited parameters are updated until reprojection square errors converge. Thus, based on known radiographic conditions, initial values of the parameters are estimated, and a nonlinear optimization operation is carried out on only the parameters considered, in view of mechanisms and drive characteristics of the apparatus, to have large errors between the initial values of the parameters and the parameters at a time when radiography is actually carried out. As a result, the calculation can be speeded up, while securing the convergence accuracy of the nonlinear optimization operation, by using the radiographic conditions, i.e. information on tomography.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Locomotive traction motor bearing degradation monitoring method
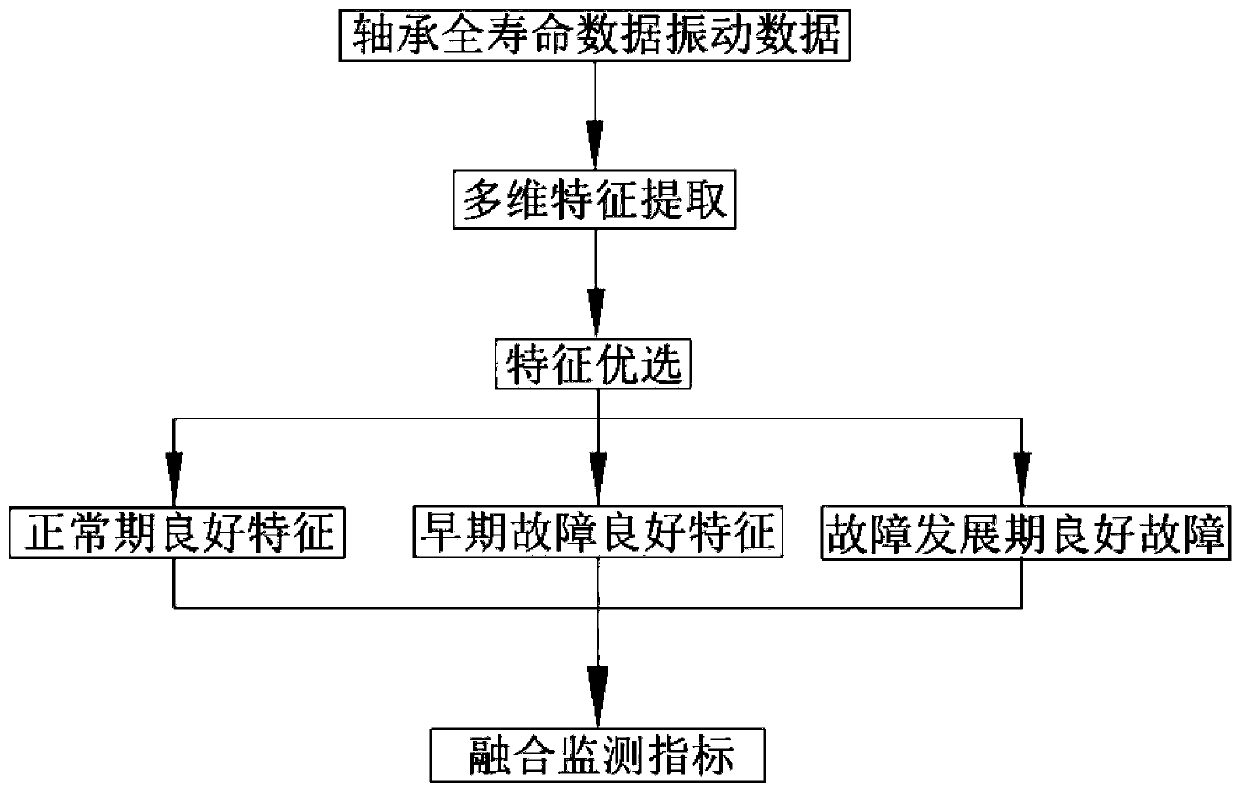
ActiveCN110057584AWell-characterized performance degradationLow reliabilityMachine part testingFeature setEngineering
The invention discloses a locomotive traction motor bearing degradation monitoring method. The locomotive traction motor bearing degradation monitoring method comprises the steps thata motor bearing is measured to obtain full-life time domain vibration signal u(i); multiple time domain features, multiple frequency domain features, and multiple time-frequency domain multi-dimensional features are extracted based on the full-life time domain vibration signal u(i) to form a high-dimensional feature set, and normalization processing is conducted; from the three aspects of normal operation period,early failure, and failure development period, 10 features of each of three types are optimally selected for the high-dimensional feature set, an autoencoder network is used for de-redundancy processing correspondingly to obtain three features ofx<1>, x<2>, and x<3>, then the Mahalanobis distance formula is used for calculating the distance between samples to obtain the Mahalanobis distance d<ij>between each sample, similarity coefficient alpha<ij> and similarity coefficient mean value M are calculated; an adaptive neighborhood K is initially constructed and corrected, the corrected K is subjected to LLE fusion indexconstruction, a fusion index Z is obtained, processed, and exponentially fitted, exponential fit parameters are calculated, and the final fusion index is obtained; and thefinal fusion index is used for determiningdivision threshold values of four degradation stagesof the normal operation period, the early failure period, the failure development period, and a failure period.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
System and method for free-space method dielectric constant measurement through addition of polarization grid
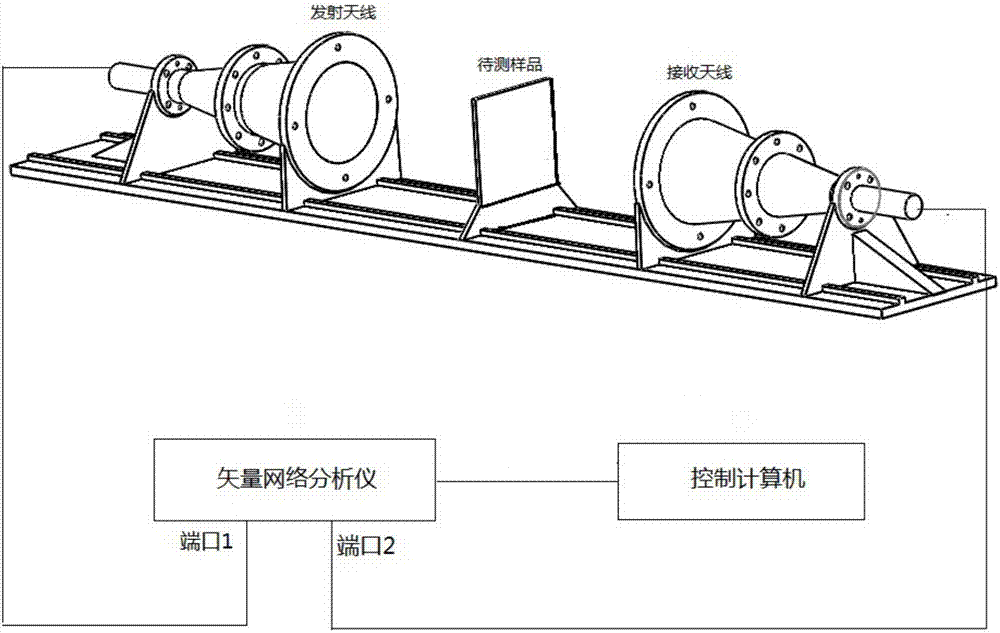
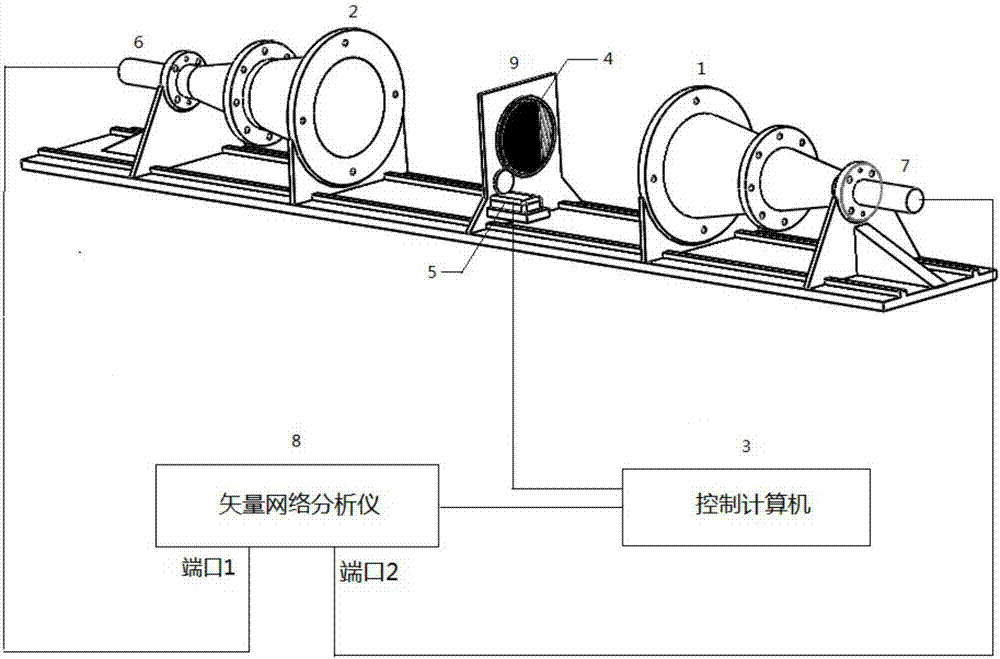
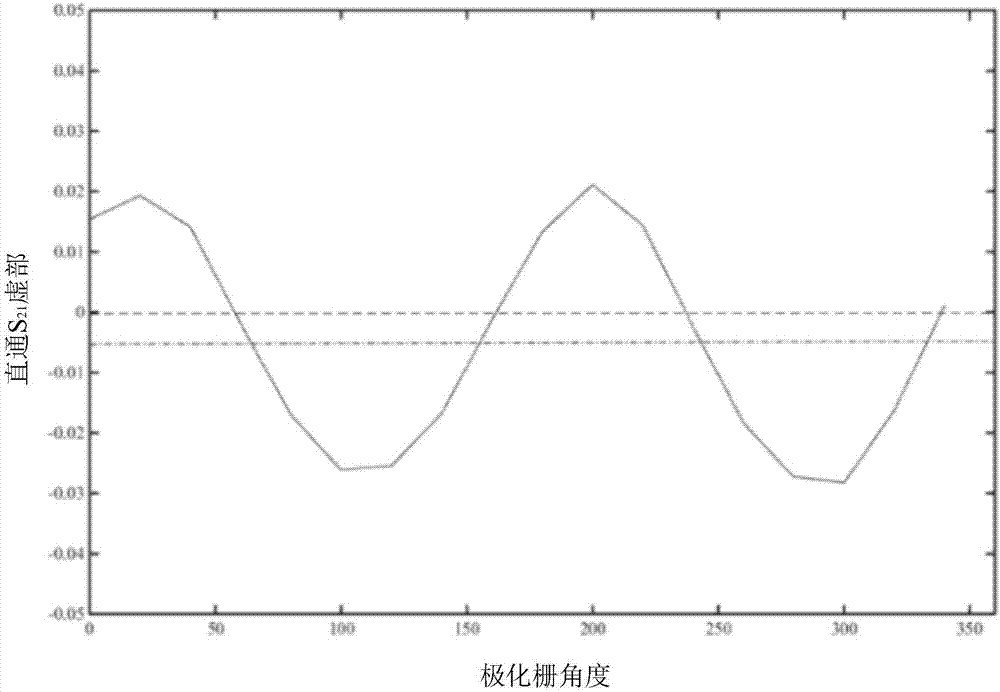
InactiveCN107202942AReduce the impactReduce back-and-forth reflectionsTesting dielectric strengthDielectricComputational physics
The present invention discloses a system and method for free-space method dielectric constant measurement through addition of a polarization grid, belonging to the electromagnetic field and microwave technology field. On the basis of the current free-space method measurement system, a polarization grid mesh is added next to one side of a sample to be measured, a changing curve of reflection parameters and transmission parameters of the network with the angle of the polarization grid mesh is measured to distinguish the electromagnetic wave penetrating into the electromagnetic wave of the grid mesh from the invariable electromagnetic waves of other paths; and the changing signals carry the dielectric information of the sample to be measured, and the coefficients such as the amplitude in the changing curve are employed to perform evolution of the dielectric constant of the sample to be measured. In a stable environment, the changing of the network parameters with the polarization grid angle is not sensitive to the electromagnetic environment, and therefore the influences of the electromagnetic wave diffraction and diffraction in the experiment environment is effectively reduced. Besides, focusing lens antennas employ lossy material polylactic acid (PLA) to effectively reduce the multiple reflection of electromagnetic wave between the antennas to allow an experiment result to be more accurate.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for increasing seismic imaging resolution ratio
ActiveCN103424777AHigh-resolutionEasy to identifySeismic signal processingImage resolutionElastica theory
The invention discloses a method for increasing a seismic imaging resolution ratio and is applied to reflection seismic data processing in seismic exploration . The method includes that by performing frequency-dependent amplitude recovery and frequency dispersion correction on migration stack data volume, the resolution ratio of imaging is increased integrally, and the imaging resolution ratios of middle and deep structures are enabled to be close to the imaging resolution ratio of a shallow structure; amplitude recovery and frequency dispersion correction are performed based on a viscoelastic theory, but a nonuniform Q value field does not need to be provided in advance; viscous absorption of seismic waves is described by introducing an equivalence Q value, and the nonuniform equivalent Q value field needed for calculation is acquired by establishing a single numerical indicator and by utilizing parameter scanning. Compared with methods like unsteady-state deconvolution, the method has the advantages that high-frequency information is restored while frequency dispersion correction is completed; a stable control algorithm is introduced, so that stability of calculation is guaranteed. By the method, breaking of the middle and deep structures and stratum deposition forms can be indicated better; and the method has important application value for oil-gas and mineral resource exploration.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
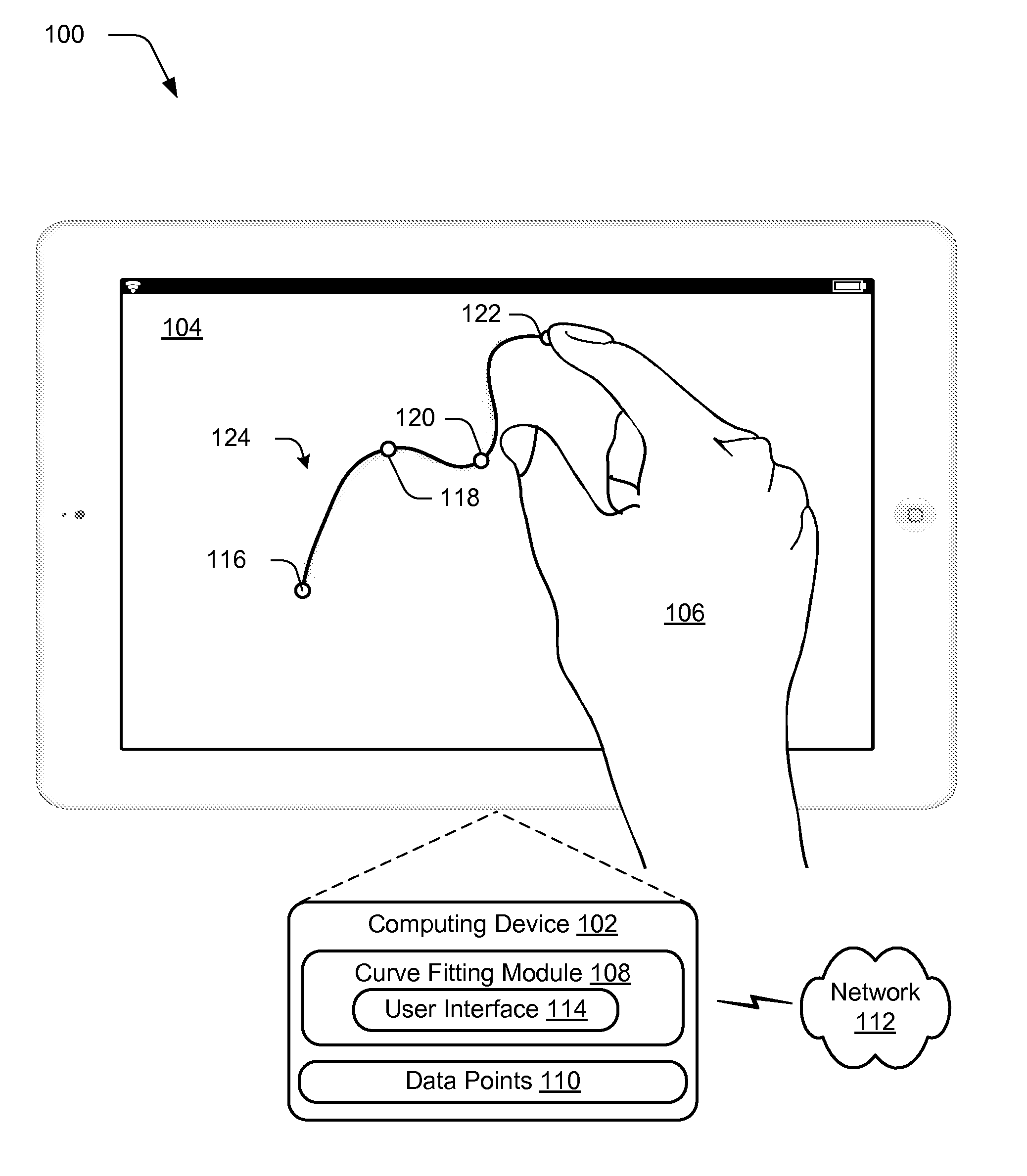
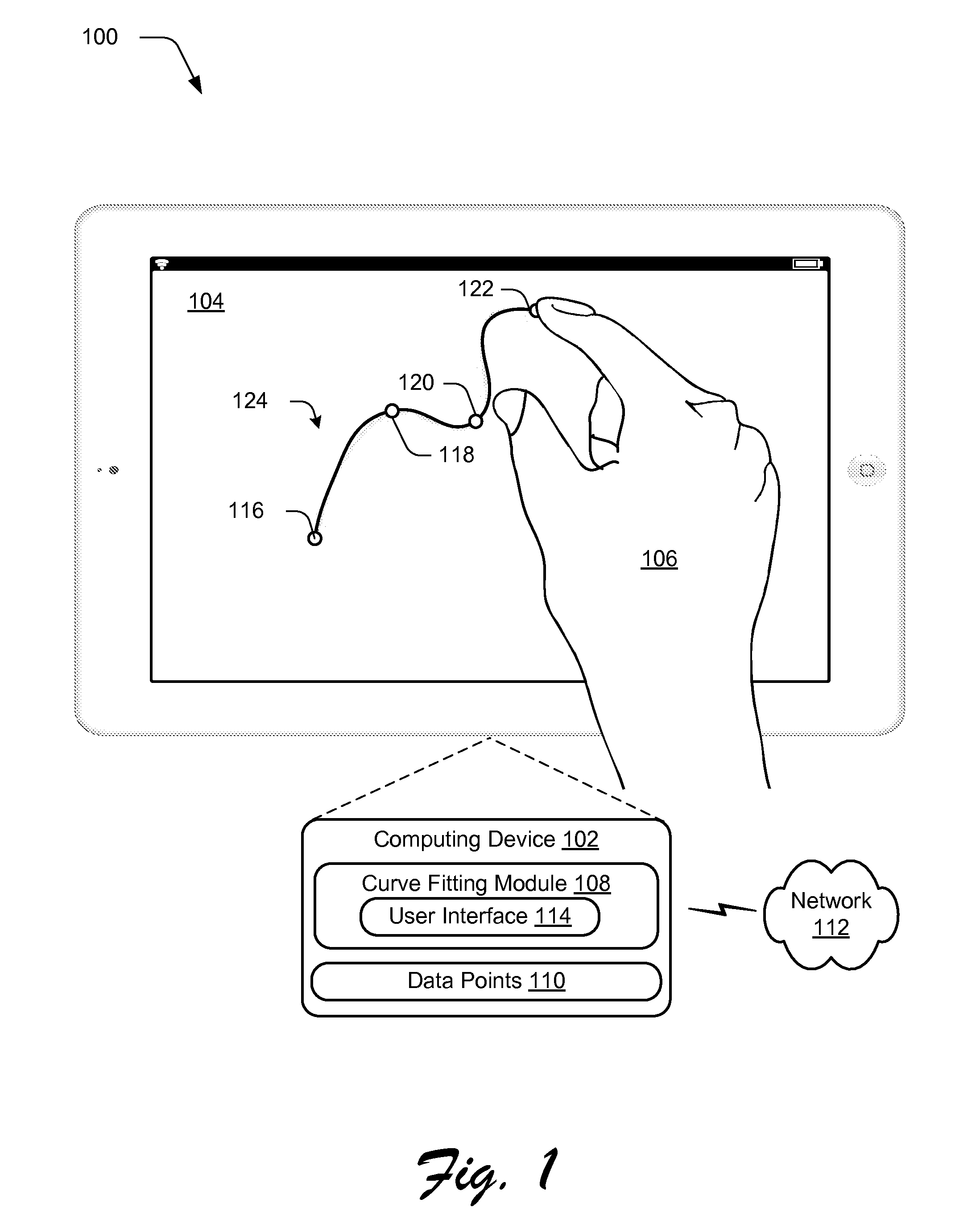
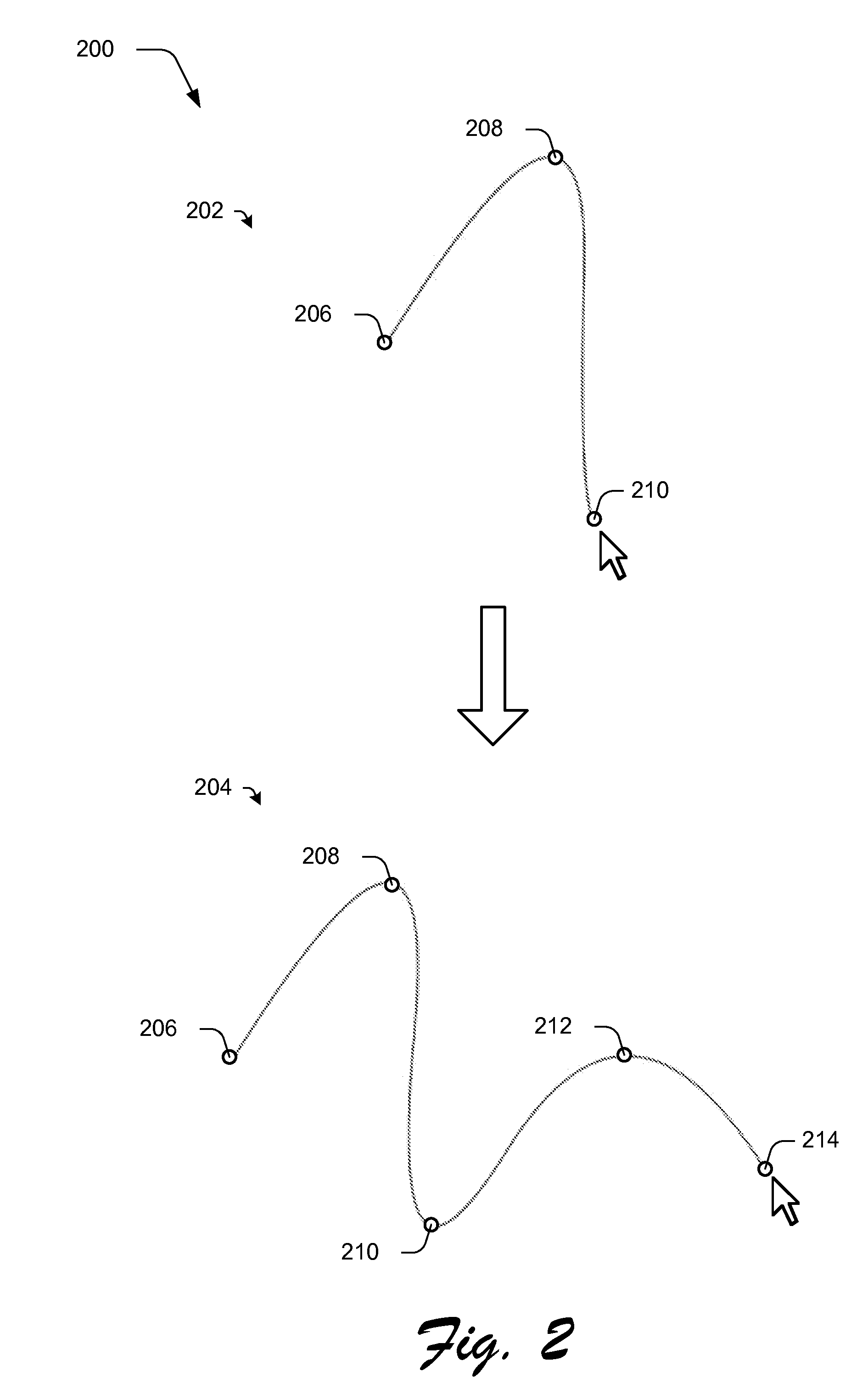
Fitting a Parametric Curve using Maximum Curvature
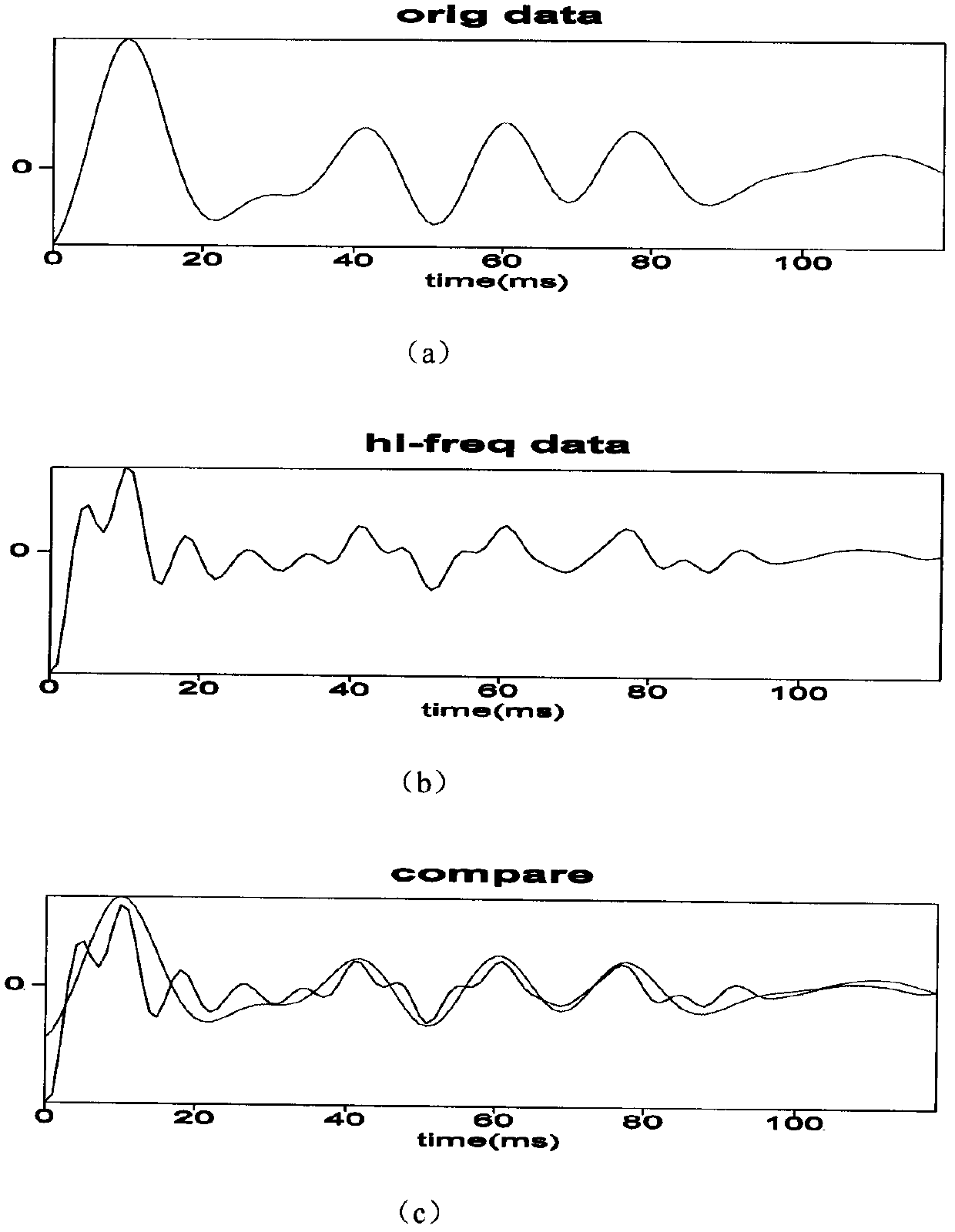
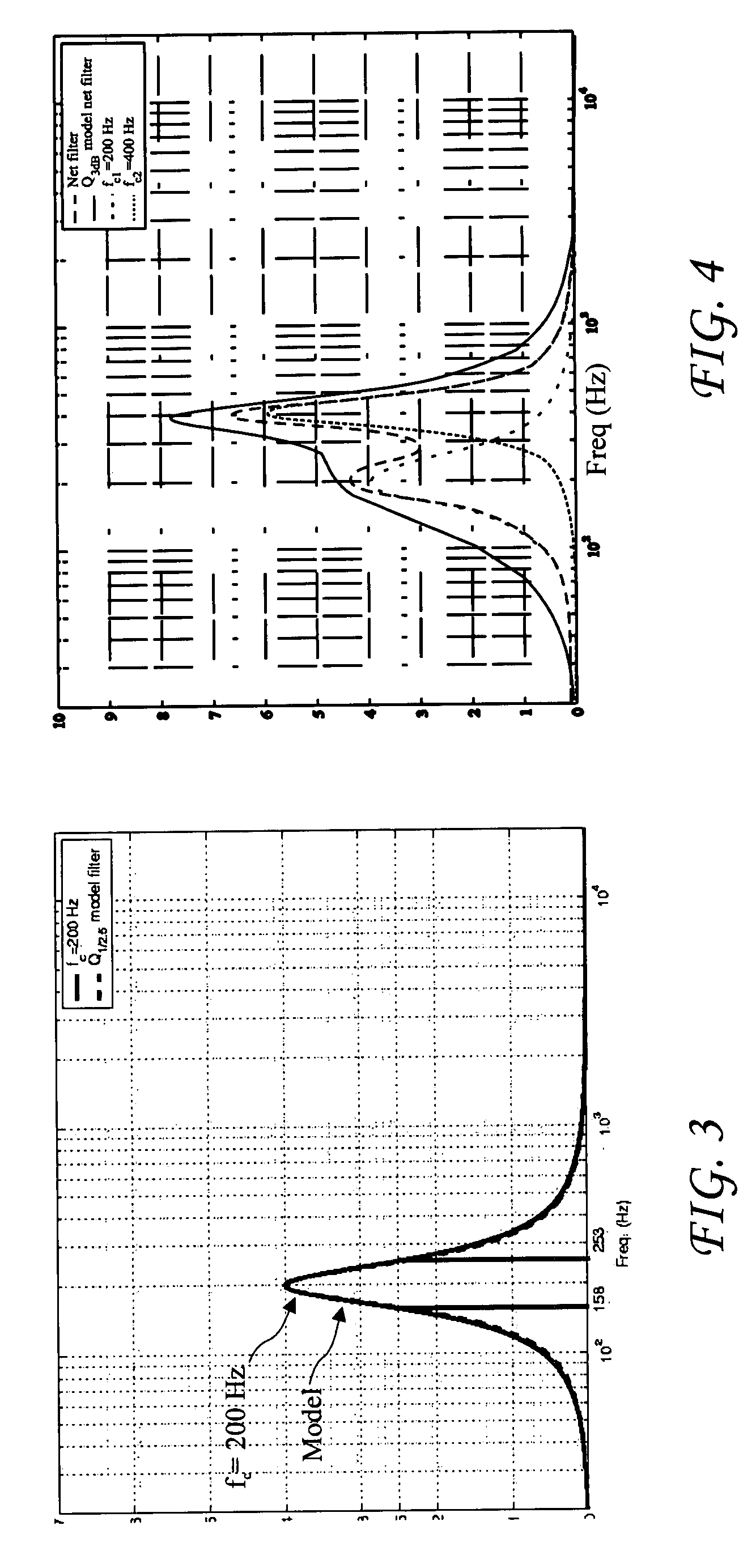
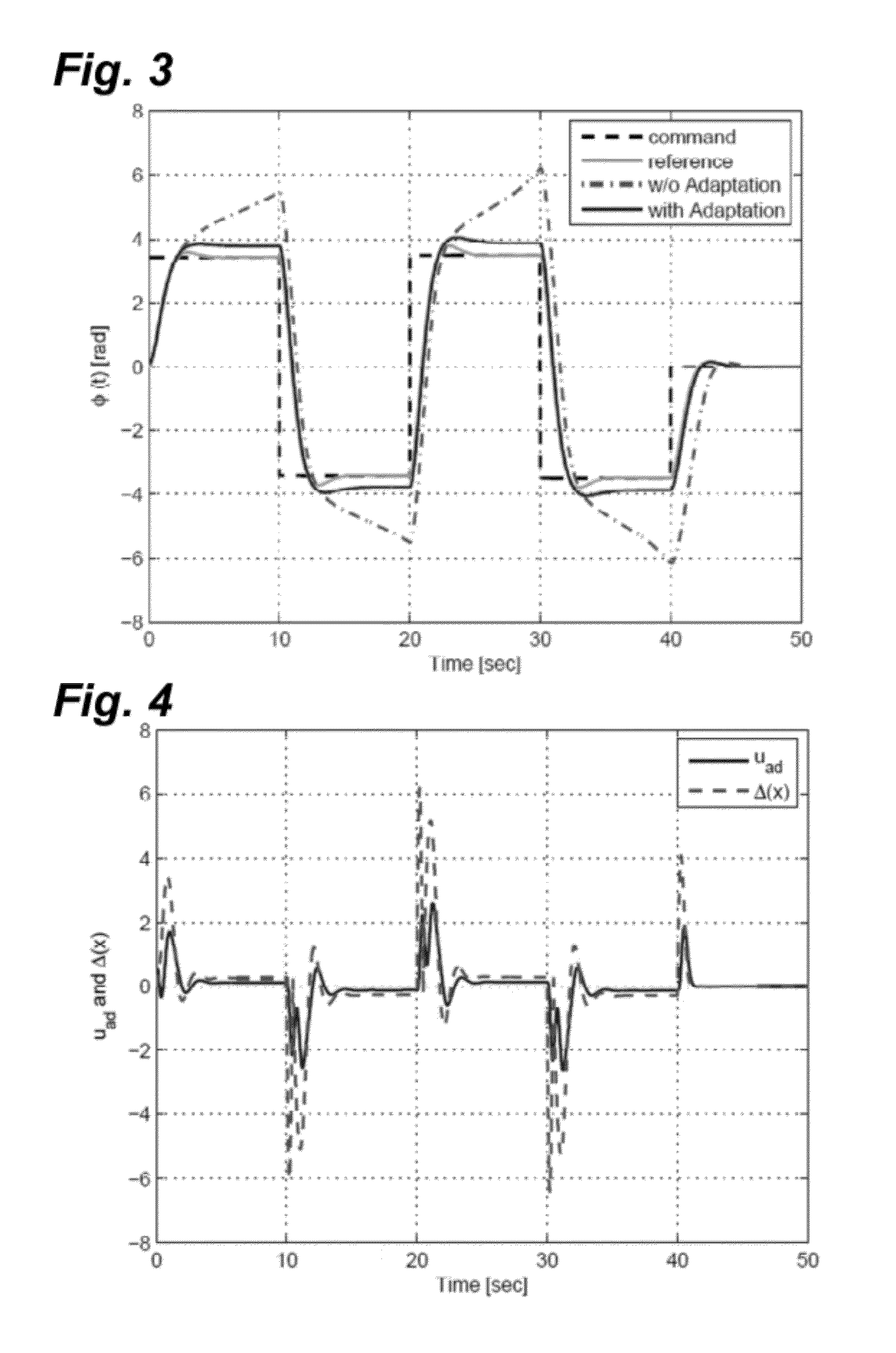
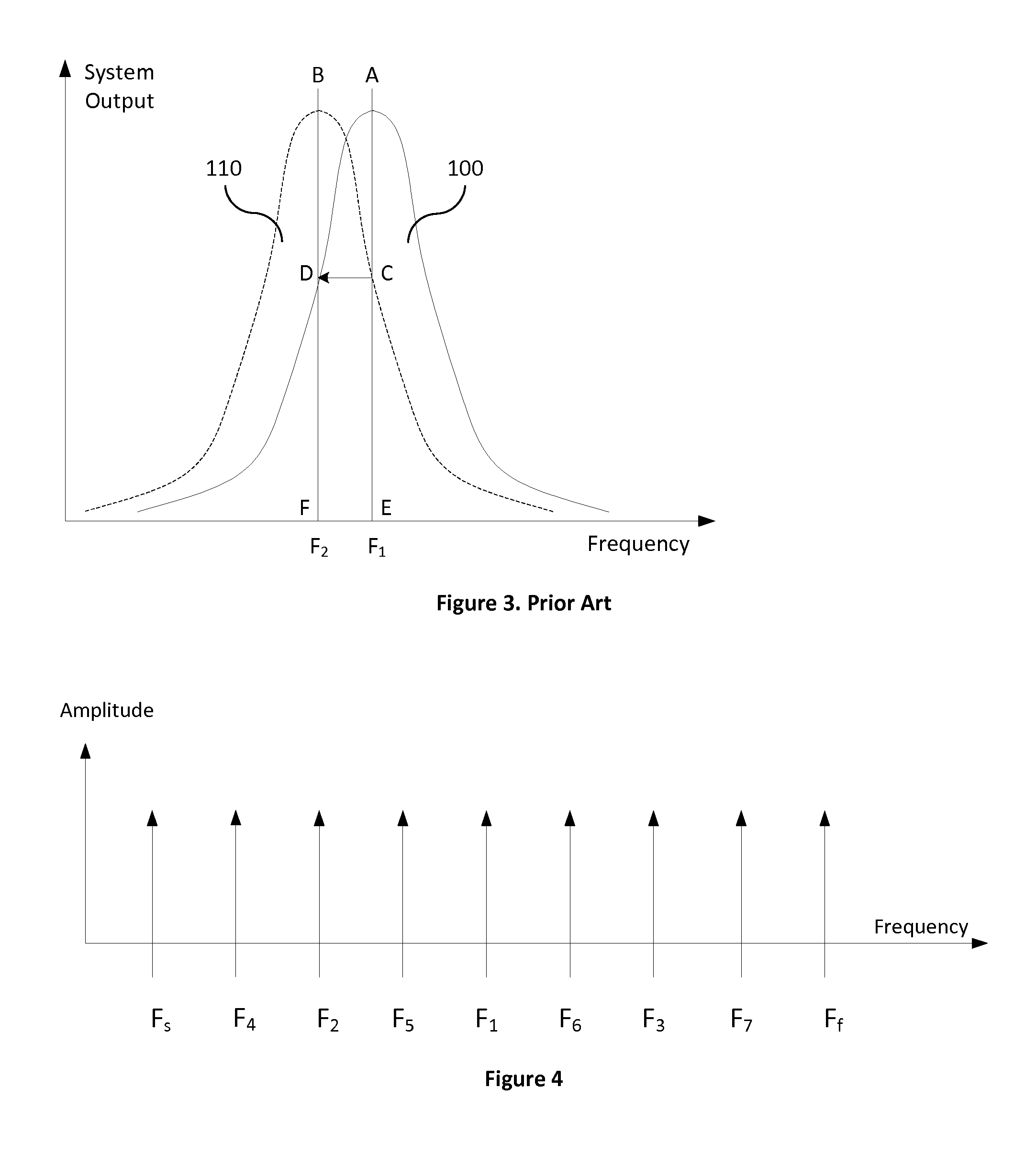
ActiveUS20150062129A1Well formedDrawing from basic elementsImage analysisCurve fittingLamé parameters
Parametric curve fitting using maximum curvature techniques are described. In one or more implementations, a parametric curve is fit to a segment of a plurality of data points that includes a first data point disposed between second and third data points by setting a point of maximum curvature for the segment of the curve at the first data point. A result of the fitting is output by the computing device.
Owner:ADOBE INC
Method for determining Avrami mathematical model coefficient of metal dynamic recrystallization volume fraction
PendingCN110245382AReduce consumptionSimple calculationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMathematical modelStress–strain curve
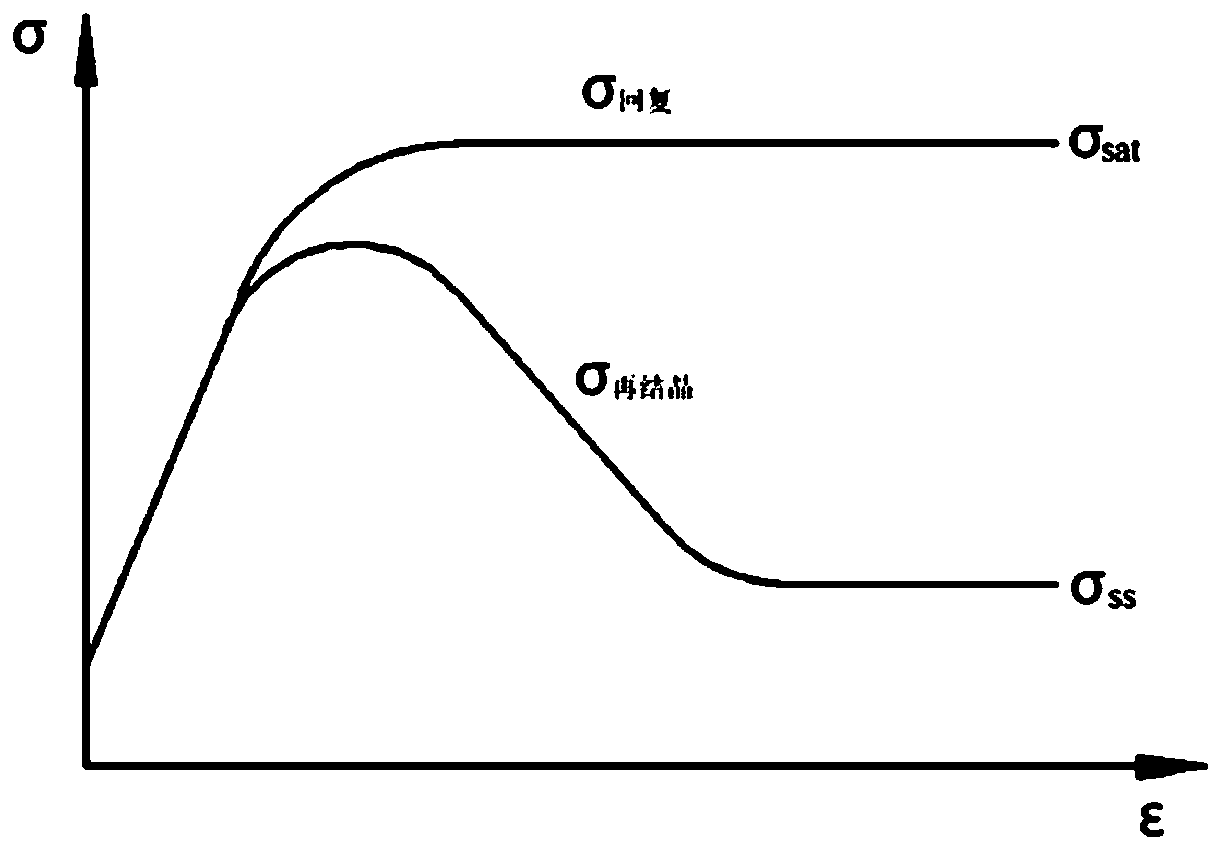
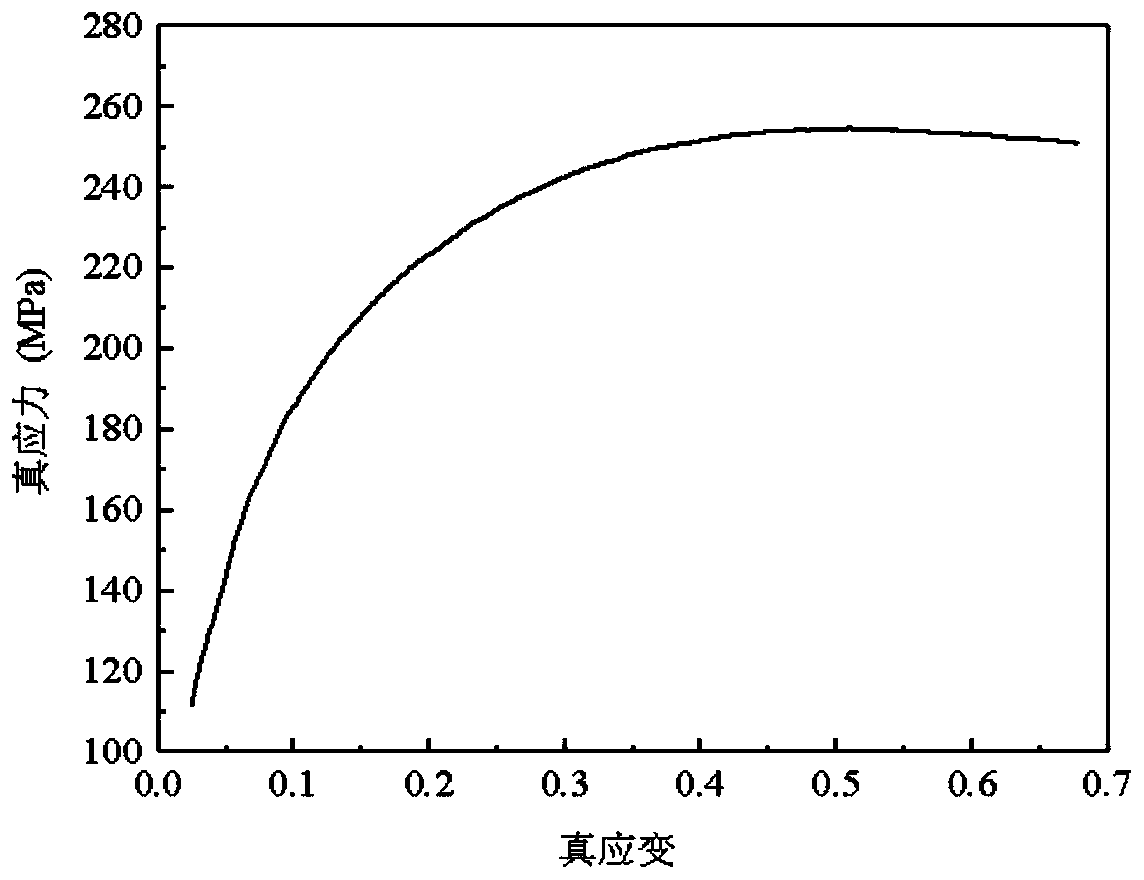
The invention provides a method for determining an Avrami mathematical model coefficient of a metal dynamic recrystallization volume fraction, and the method comprises the following steps: 1, obtaining a stress-strain curve of a material, carrying out water quenching treatment on a sample after the sample is deformed, observing a metallographic structure in the sample, and measuring the recrystallization volume fraction; 2, determining critical strain epsilon c of dynamic recrystallization; 3, determining a return curve; 4, calculating a curve of the volume fraction of the dynamic recrystallization along with the strain; and 5, solving coefficients m and epsilon * of the Avrami mathematical model according to the curve obtained in the step 4. According to the method, only the recrystallization volume fraction in the sample after deformation is measured, the recrystallization volume fraction of the sample in the deformation process is not needed, an equation is directly used for obtaining the curve of the recrystallization volume fraction changing along with strain, and steady-state stress epsilon ss does not need to participate in calculation; compared with the existing method, the method provided by the invention has the advantages of less parameters required in the calculation process, low workload and less sample consumption, and is suitable for popularization.
Owner:BENGANG STEEL PLATES
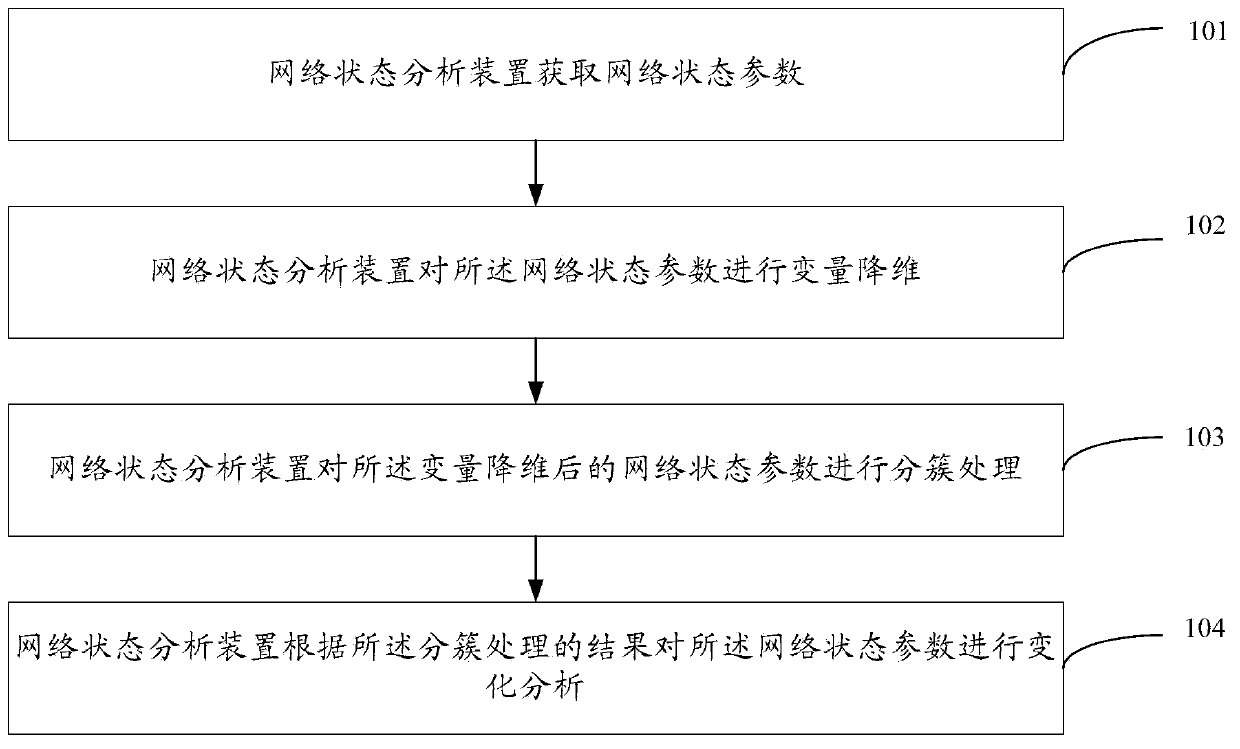
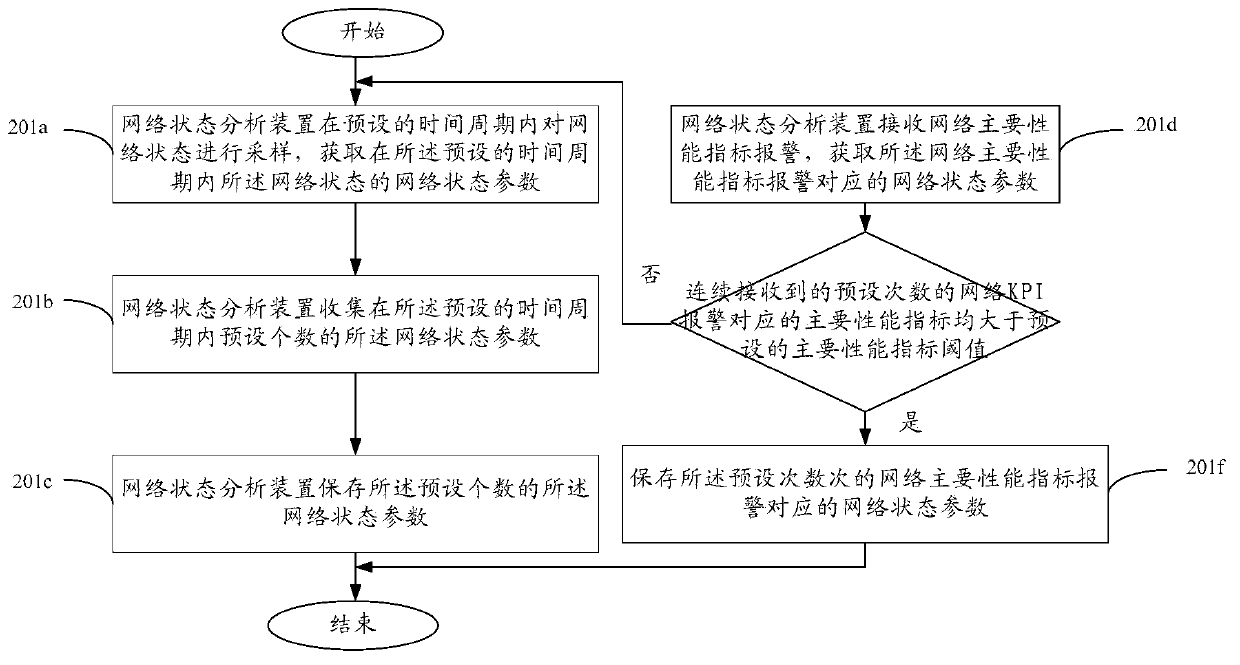
Network state partition method based on SON, device and network system
ActiveCN103731854AReduce maintenance costsImprove solution efficiencyWireless communicationState parameterDimensionality reduction
An embodiment of the invention provides a network state partition method based on an SON, a device and a network system, and relates to the communication field. Maintenance cost for network problems can be reduced, and efficiency of solving the network problems can be improved. The method comprises the steps that network state parameters are obtained, wherein the network state parameters comprise network KPIs, cell measurement values and control parameters; variable dimensionality reduction is conducted on the network state parameters; the network state parameters with the variably reduced dimensionality are clustered; change analysis is conducted on the network state parameters according to clustering results.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
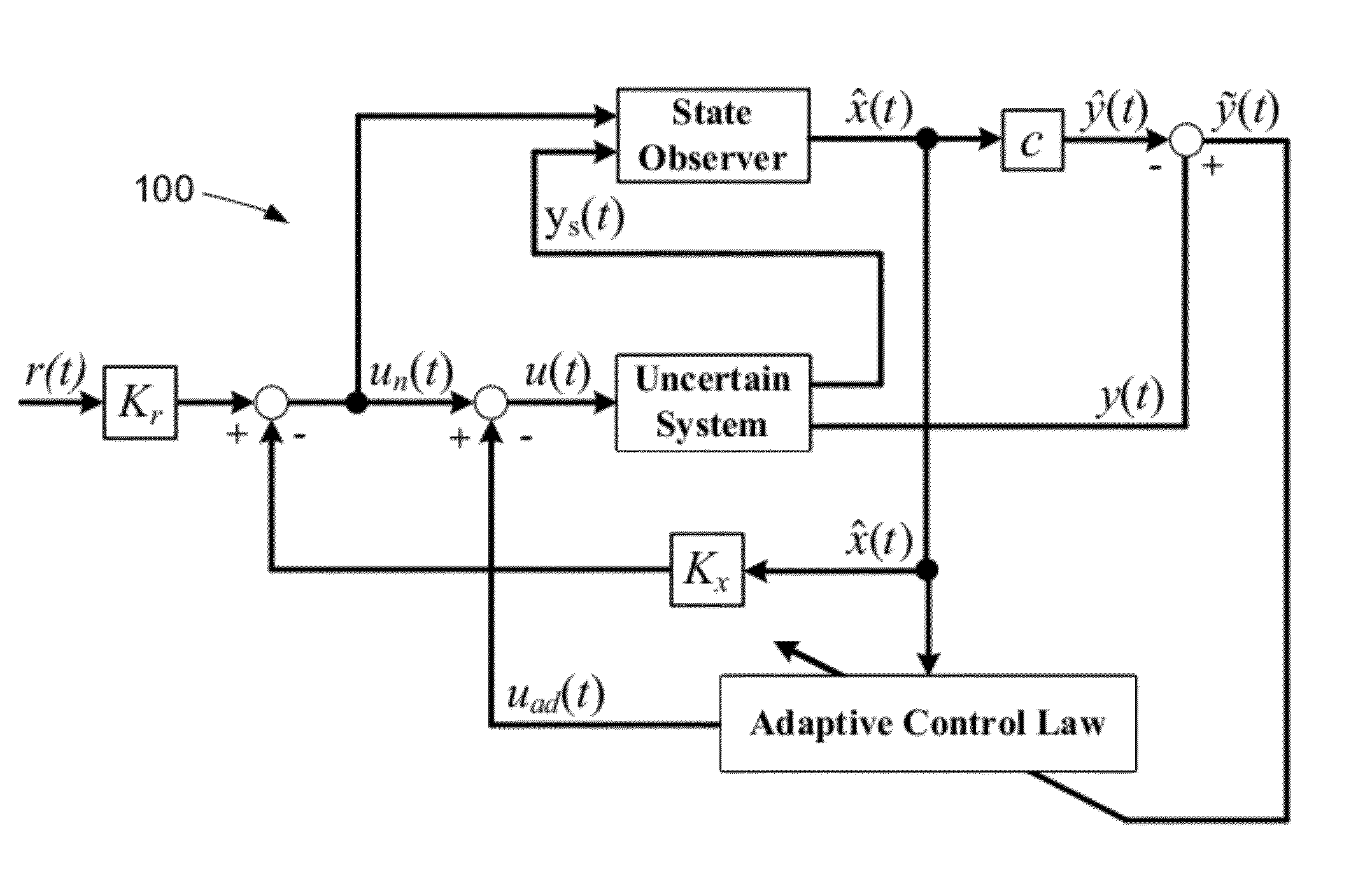
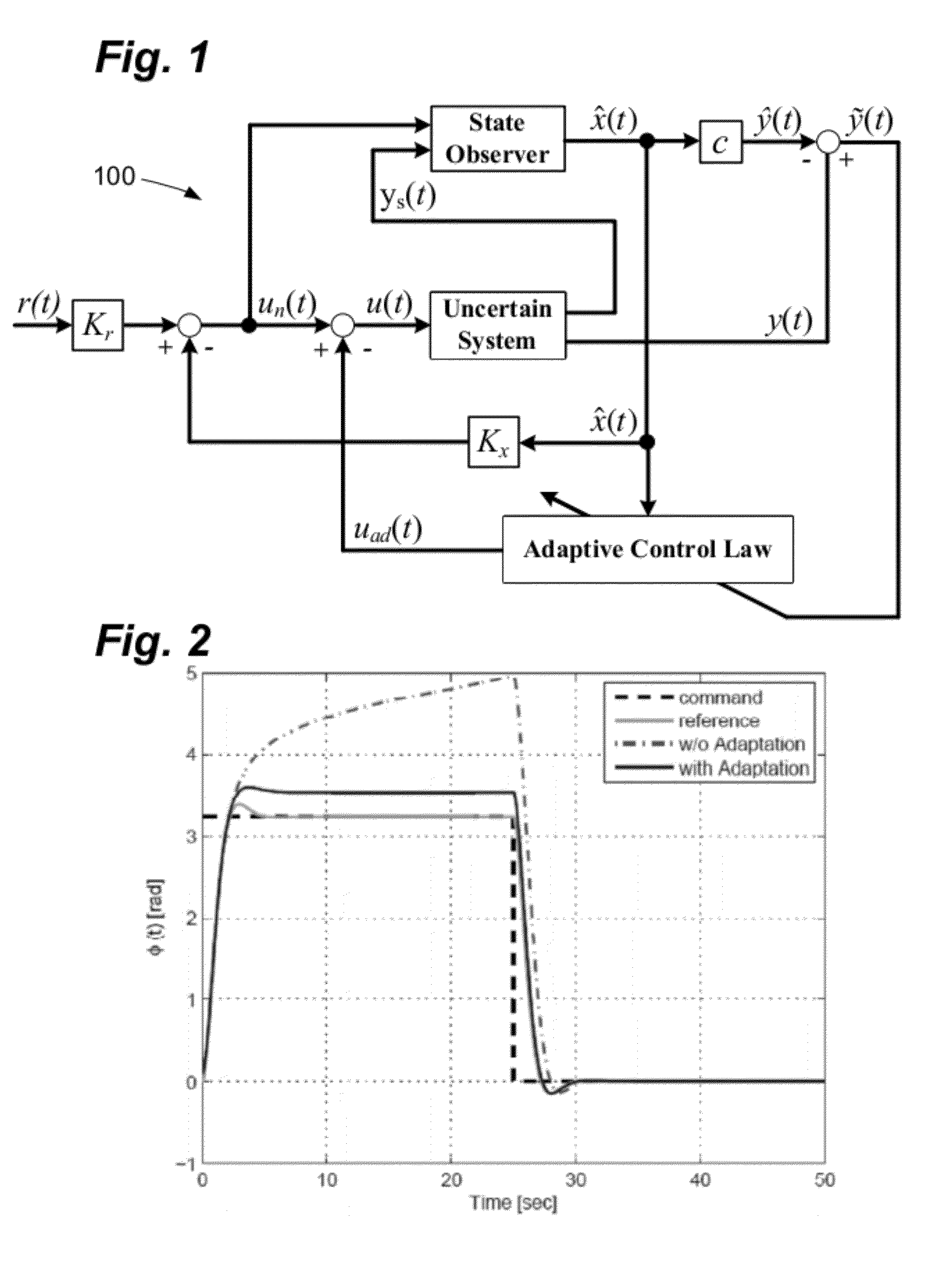
Systems and methods for parameter dependent riccati equation approaches to adaptive control
InactiveUS20120277888A1Minimize complexityRaise the potentialAdaptive controlRiccati equationControl system
Systems and methods for adaptive control are disclosed. The systems and methods can control uncertain dynamic systems. The control system can comprise a controller that employs a parameter dependent Riccati equation. The controller can produce a response that causes the state of the system to remain bounded. The control system can control both minimum phase and non-minimum phase systems. The control system can augment an existing, non-adaptive control design without modifying the gains employed in that design. The control system can also avoid the use of high gains in both the observer design and the adaptive control law.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Method and apparatus for designing a gathering and transporting pipeline network
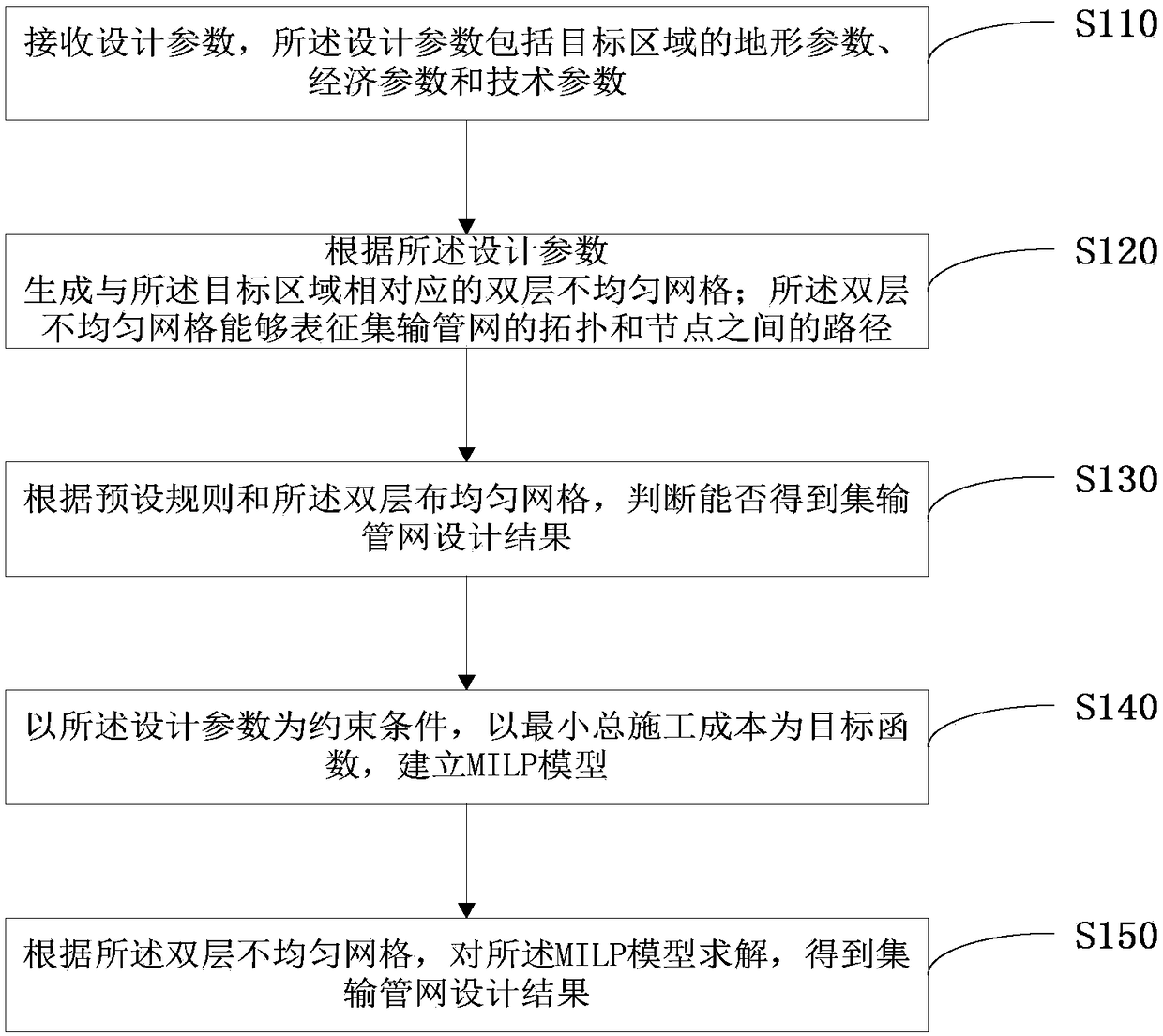
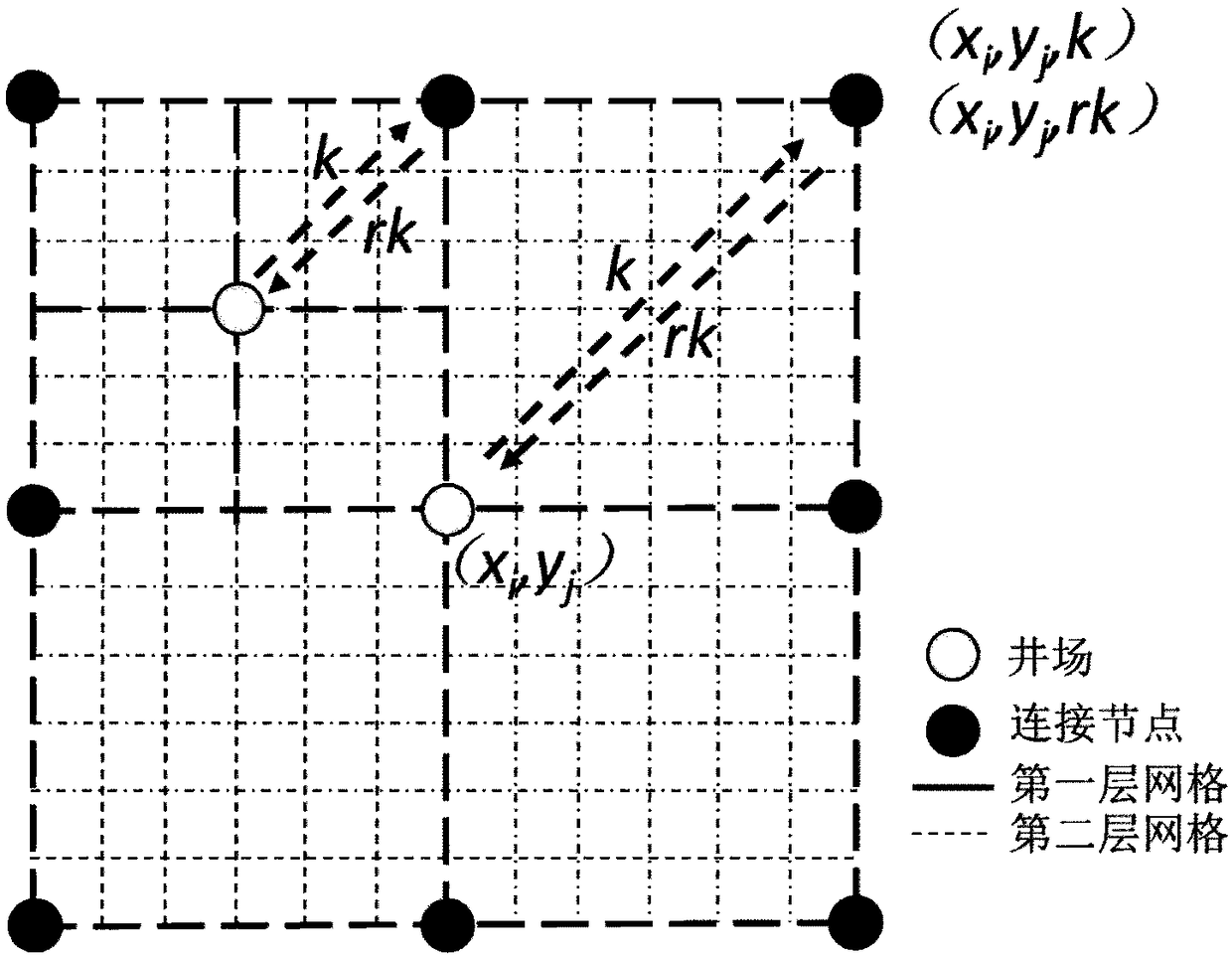
ActiveCN109344555ASimple designGuide engineering constructionGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationTransport systemEconomic parameters
A method and apparatus for designing a gathering and transporting pipeline network include receiving design parameters, wherein that design parameters include topographic parameters, economic parameters and technical parameters; Generating a two-layer non-uniform mesh according to the design parameters, wherein the two-layer non-uniform mesh can characterize and determine the topology of a gathering pipeline network and the path between nodes; Judging whether the design result of the gathering and transporting pipeline network can be realized or not according to the preset rule and the two-layer uneven mesh; establishing A MILP model by taking that design parameter as a constraint condition and taking the minimum total construction cost as an objective function; solving The MILP model according to the two-layer non-uniform mesh to obtain the design result of the gathering and transporting pipeline network. The above method and device take into account the hydraulic calculation and economic flow rate, and can reflect the actual situation of the actual gathering and transporting system. Through the topographic parameters, economic parameters and technical parameters, the optimal gathering and transporting pipeline network design scheme can be obtained, which can guide the engineering construction of the oil and gas field and reduce the cost and increase the efficiency.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING) +1
Systems and methods for constraining representation format parameters for a parameter set
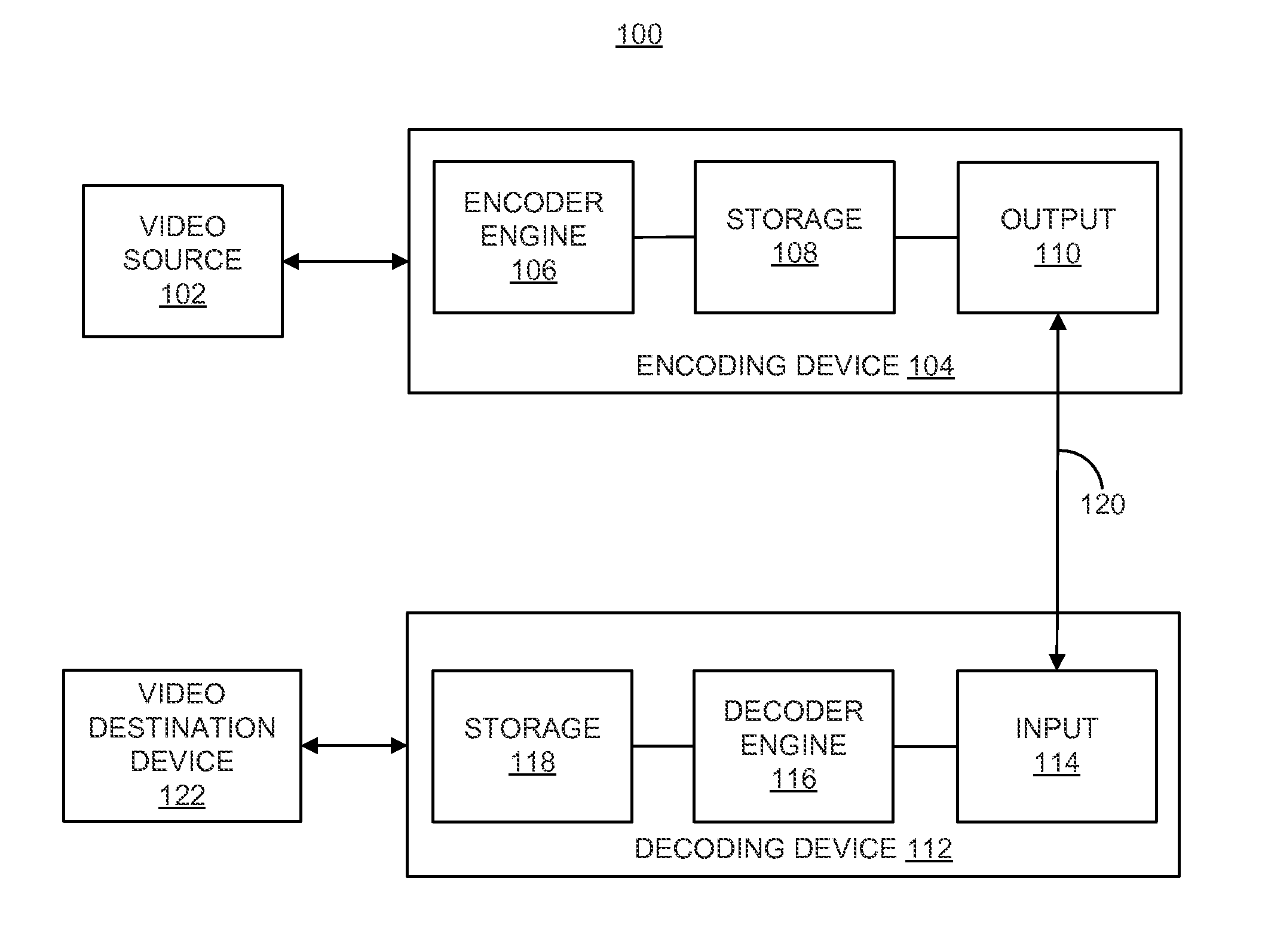
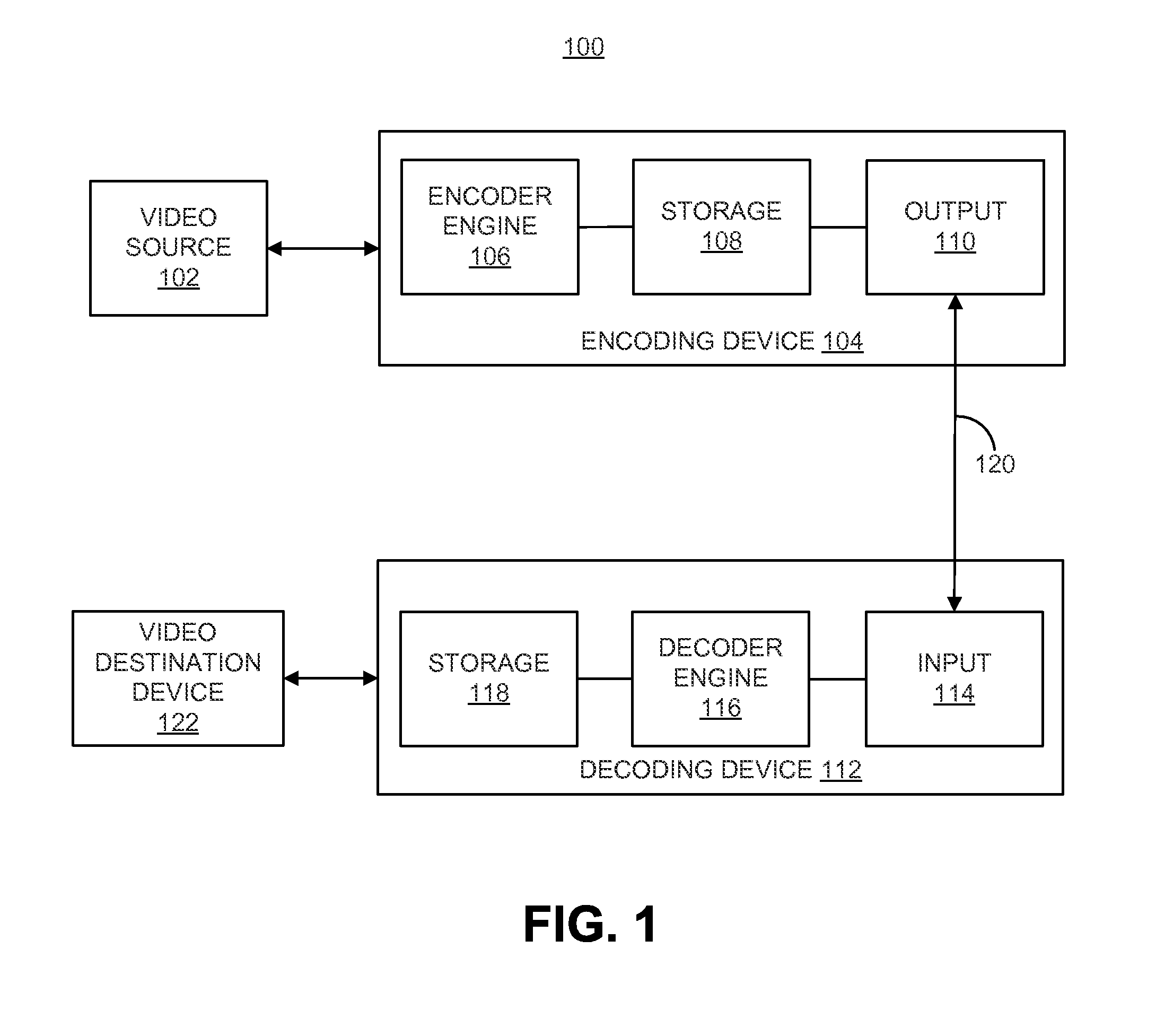
ActiveUS20150373344A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo bitstreamLimit value
Techniques and systems are provided for encoding video data. For example, a method of encoding video data includes generating an encoded video bitstream comprising multiple layers. The encoded video bitstream includes one or more sequence parameter sets and a video parameter set. The method further includes generating, according to a constraint, one or more representation format parameters for a sequence parameter set assigned to a base layer of the encoded video bitstream. The constraint limits values of the one or more representation format parameters in the sequence parameter set to be less than or equal to values of corresponding representation format parameters that are assigned to the base layer in the video parameter set.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
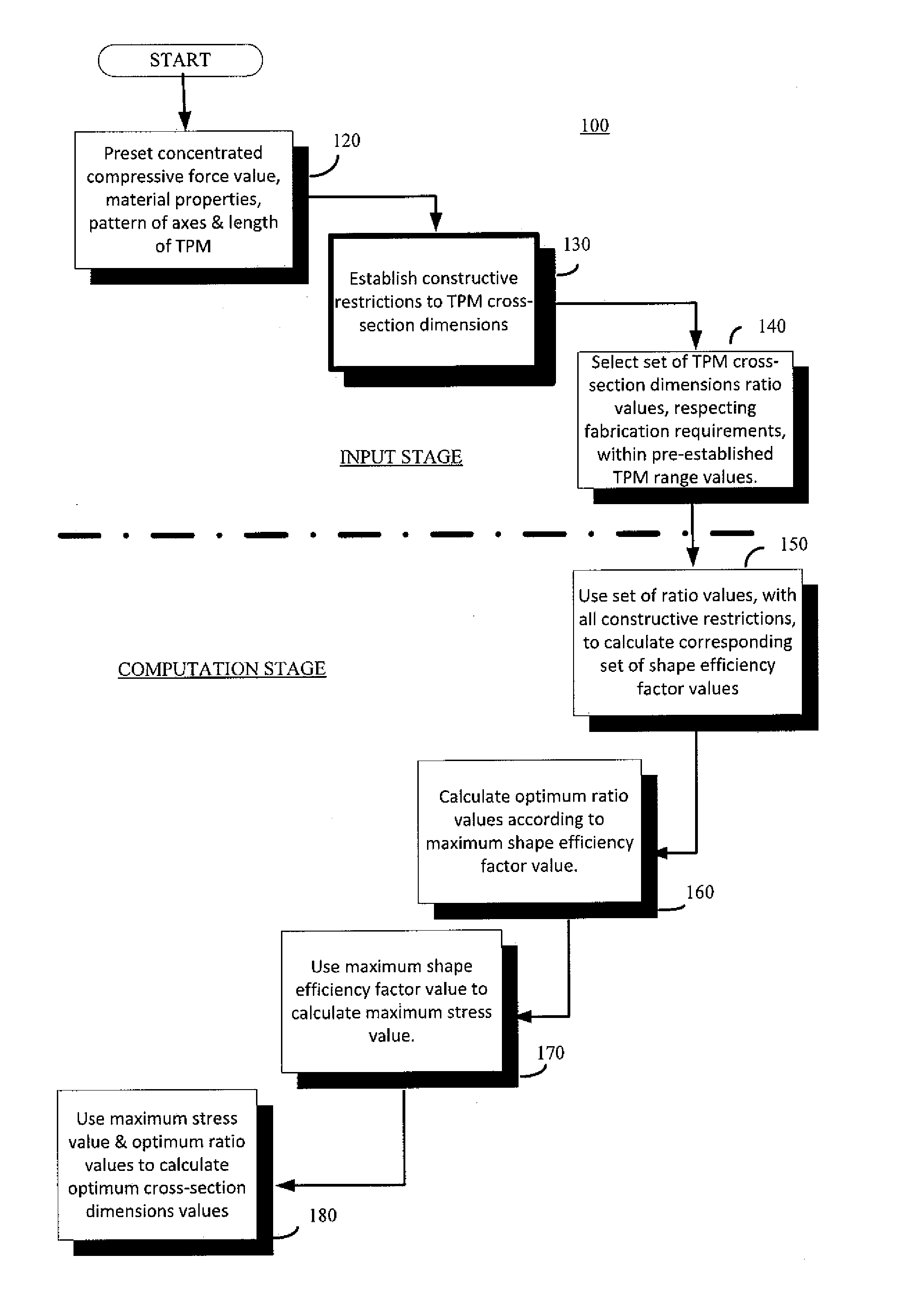
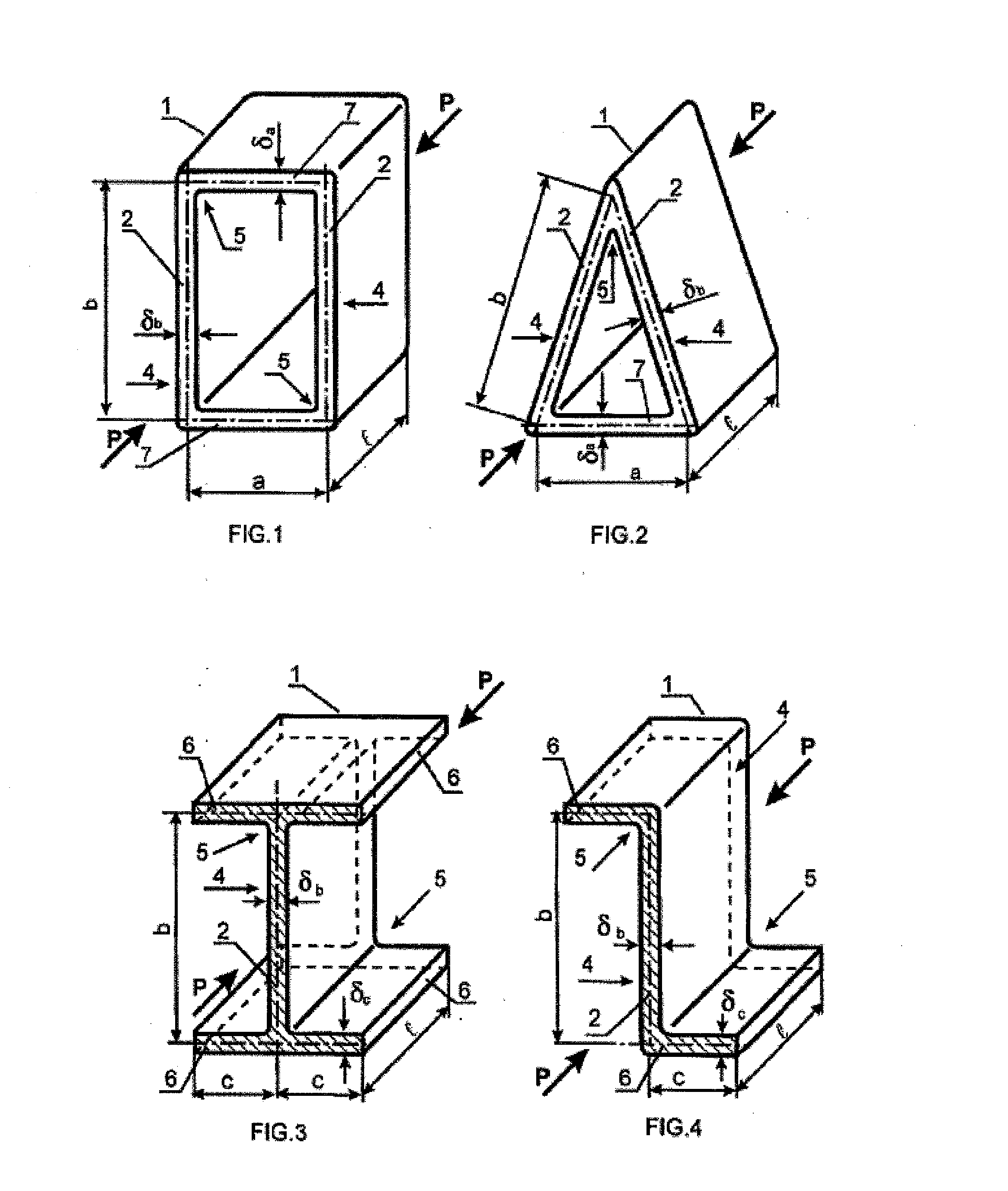
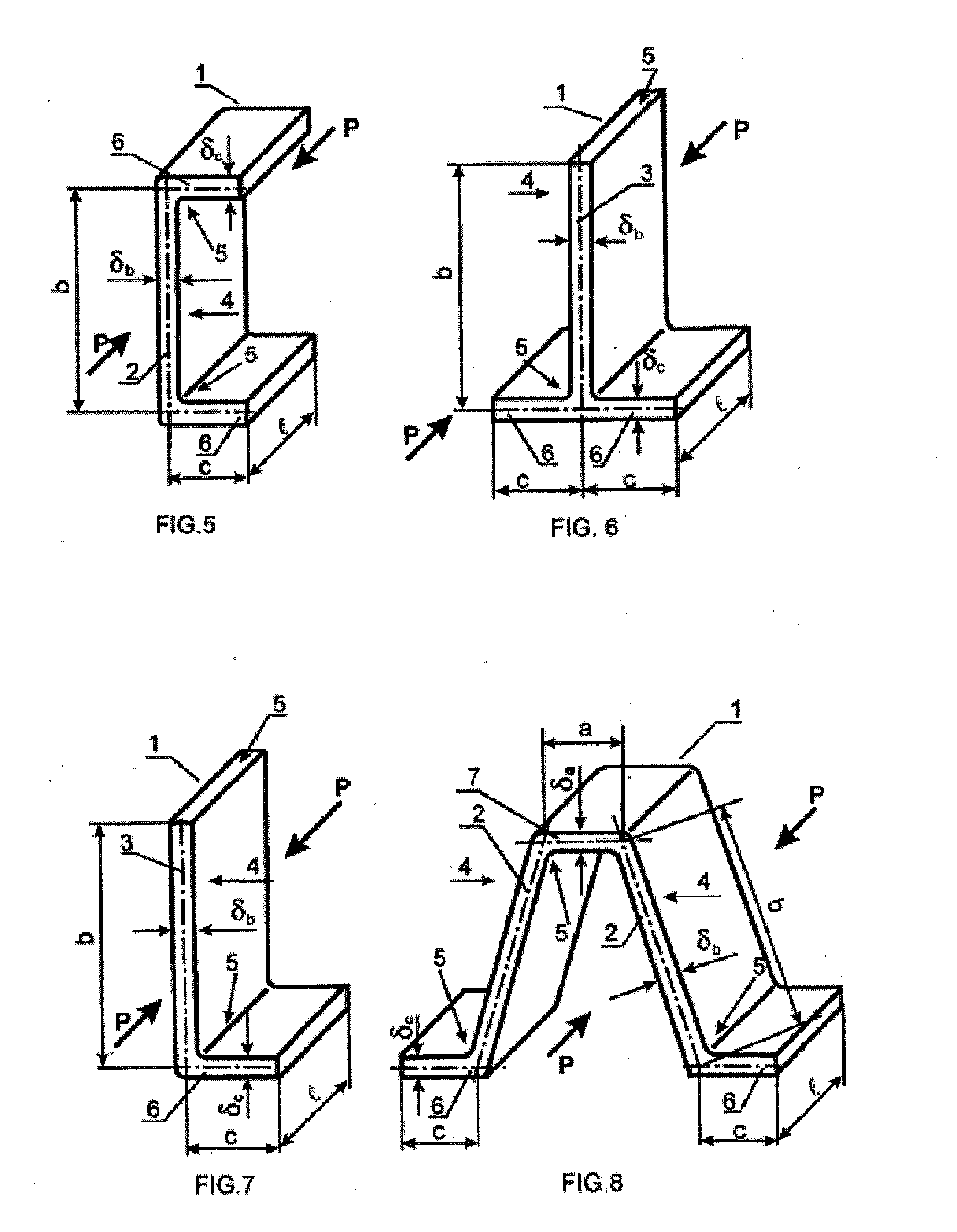
Tool for optimized thin wall profile member (TPM) and tpm-panel design and selection
The present disclosure describes tools and associated computational analysis methodologies employed therein for improved minimum weight design of thin wall profile members (TPMs). The tools draw on inter-dependent parameters relating to TPM cross-section dimensions ratio values and established constructive restrictions to calculate, using appropriate algorithmic computational analysis, the optimum cross-section dimensions values of a given TPM. A design selection saves as a blueprint for the next stage, which is the actual fabrication or manufacturing of the component. For a given set of constructive restrictions, the final product is based on optimum configurations selected from a fixed set of TPMs with varied cross-sectional shapes.
Owner:FAIR SRL
Method And Apparatus For For Monitoring Physical Properties
InactiveUS20140049268A1Increase rangeExpand the measurement rangeThermometer detailsResistance/reactance/impedenceMicrowave cavityPhysical property
This invention relates to methods and apparatus for measuring physical properties using microwave cavity sensors. In operation, a number of microwave cavity sensors are interrogated by a remote wireless unit in order to determine the current resonant frequency for the sensor. The current values for various parameters measured by the sensors, such as temperature, stress / stain, or the like, are determined by comparing the current resonant frequency to a first resonant frequency of the sensor, and thus, detect any change in the value of the selected parameter. In particular, the present invention is directed toward extending the range over which such measurements may be performed, using these types of sensors.
Owner:SMART AUTONOMOUS SOLUTIONS
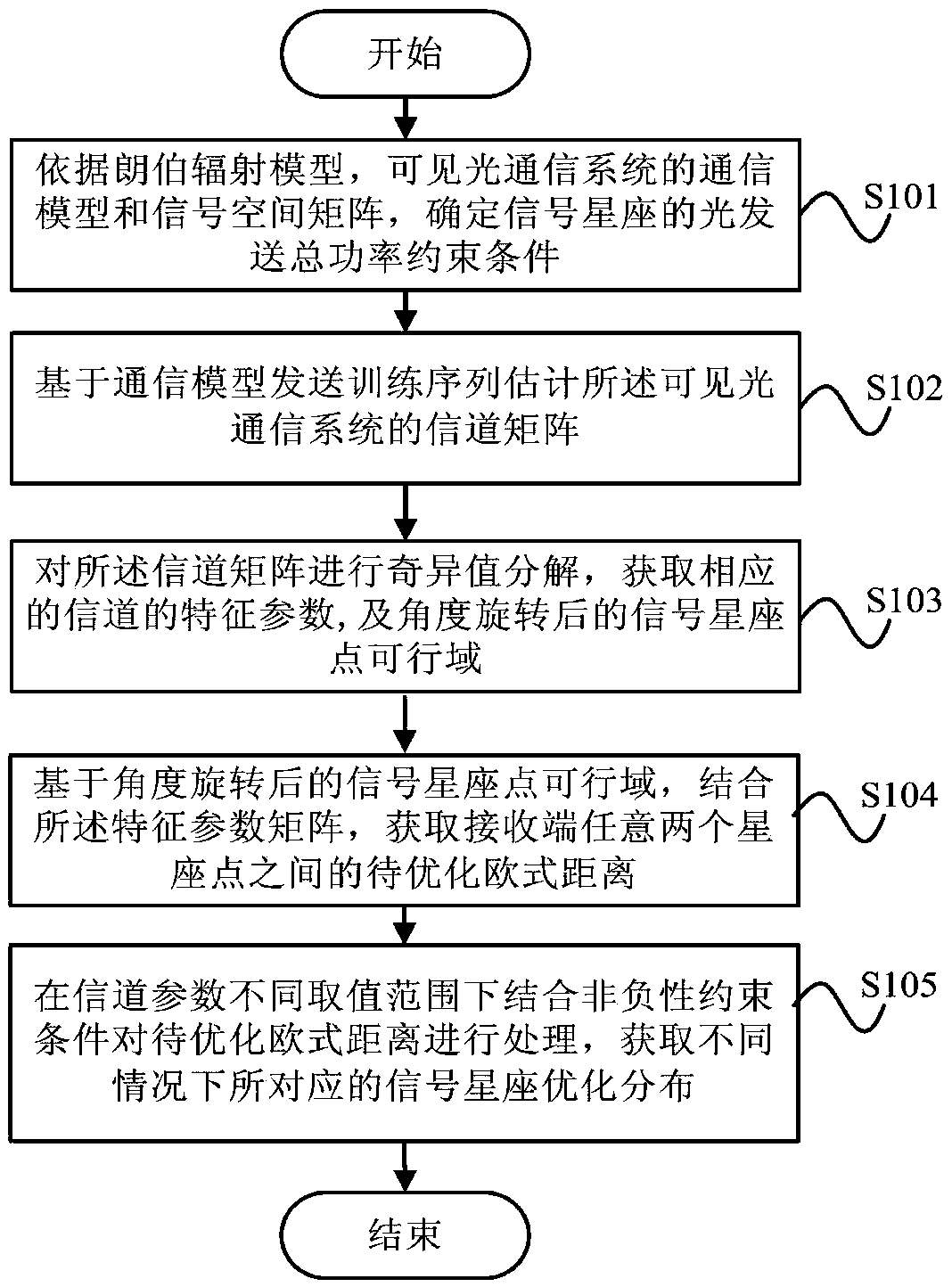
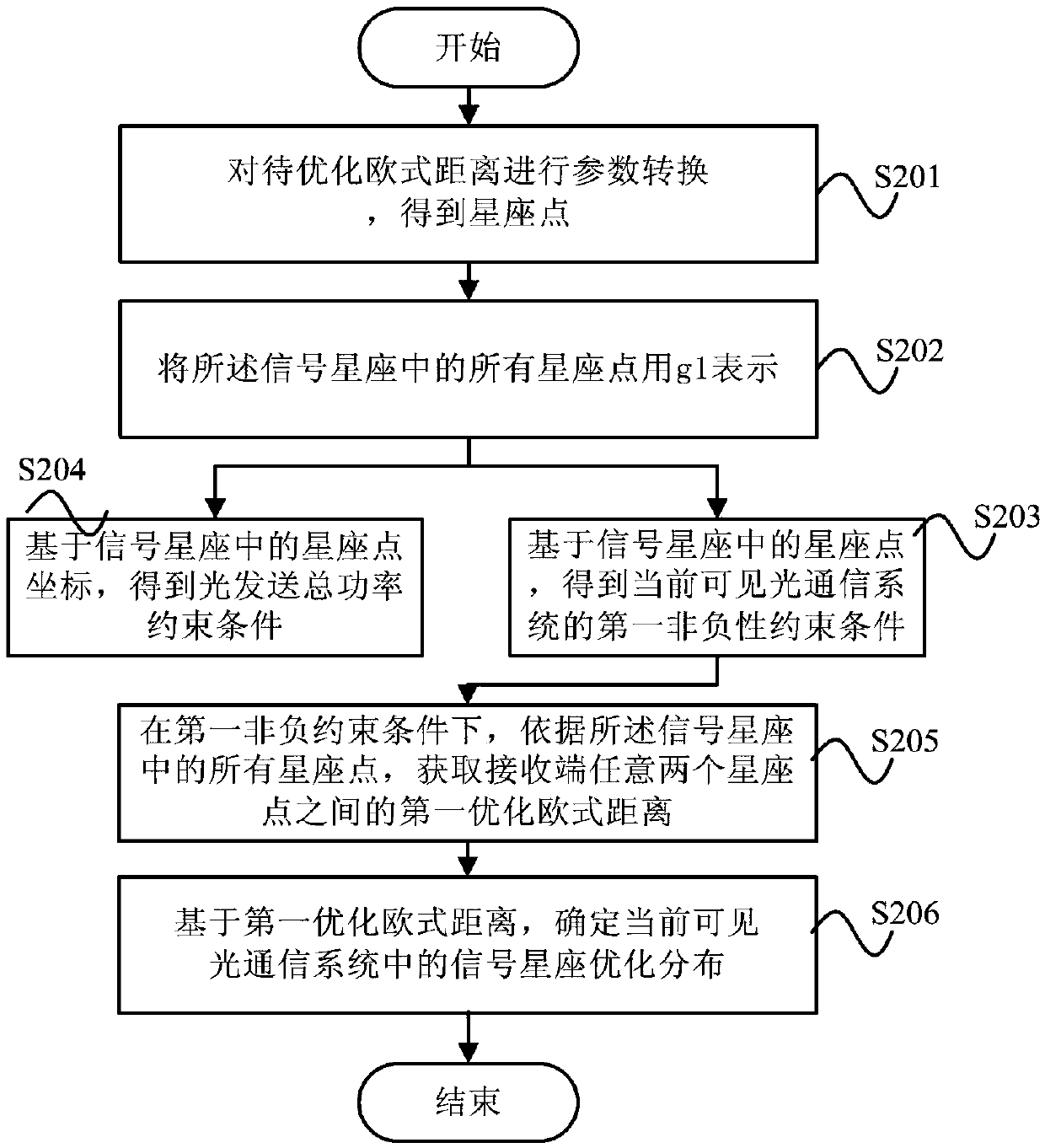
Visible light communication signal constellation design method, device and system
ActiveCN105553554AClose-range type systemsElectromagnetic transmittersSingular value decompositionFeature parameter
The invention discloses a visible light communication signal constellation design method, device and system. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a communication model and a signal space matrix of a visible light communication signal based on a Lambertian radiation model, and determining total light sending power of a signal constellation; sending a training sequence estimation channel matrix based on the communication model, and carrying out singular value decomposition on the channel matrix to obtain channel characteristic parameter matrixes ^ and V, wherein the influence of the channel characteristic parameter matrix V is represented by rotating a signal constellation point for an angle to further obtain channel characteristic parameters lambda 1, lambda 2 and (the formula is as shown in the specification), obtaining an Euclidean distance to be optimized between any two constellation points of a receiving end based on the signal constellation space matrix after angle rotation in combination with the channel characteristic parameter matrix ^, processing the Euclidean distance to be optimized under different value ranges of the channel characteristic parameters lambda 1, lambda 2 and (the formula is as shown in the specification) in combination with a non negative constraint condition to obtain corresponding optimized signal constellation distribution under different conditions, so as to realize the optimal communication performance of the visible light communication system.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
Method and system for processing acoustic waveforms
InactiveUS20160334530A1Quality improvementSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingDispersion curveGoverning equation
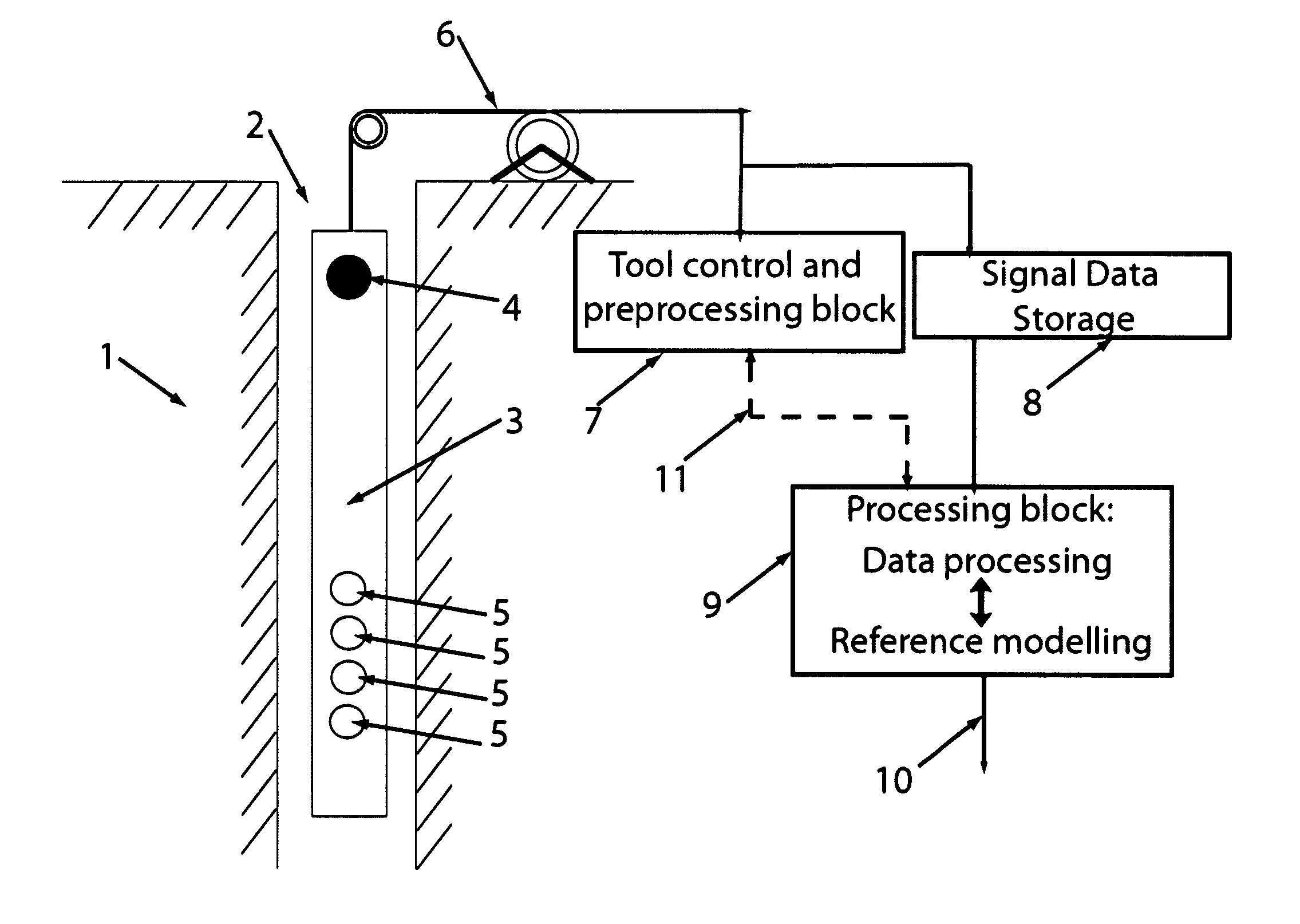
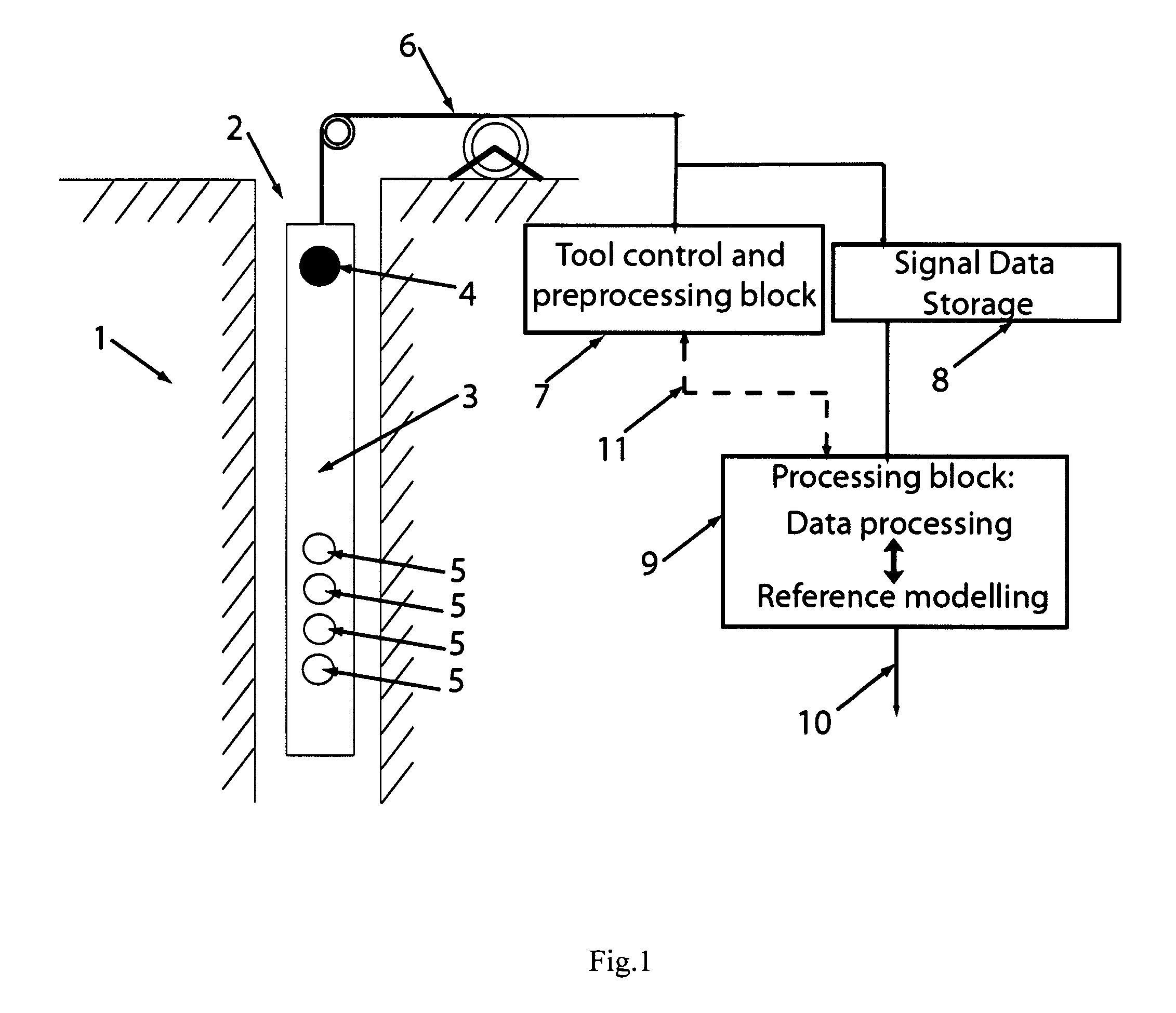
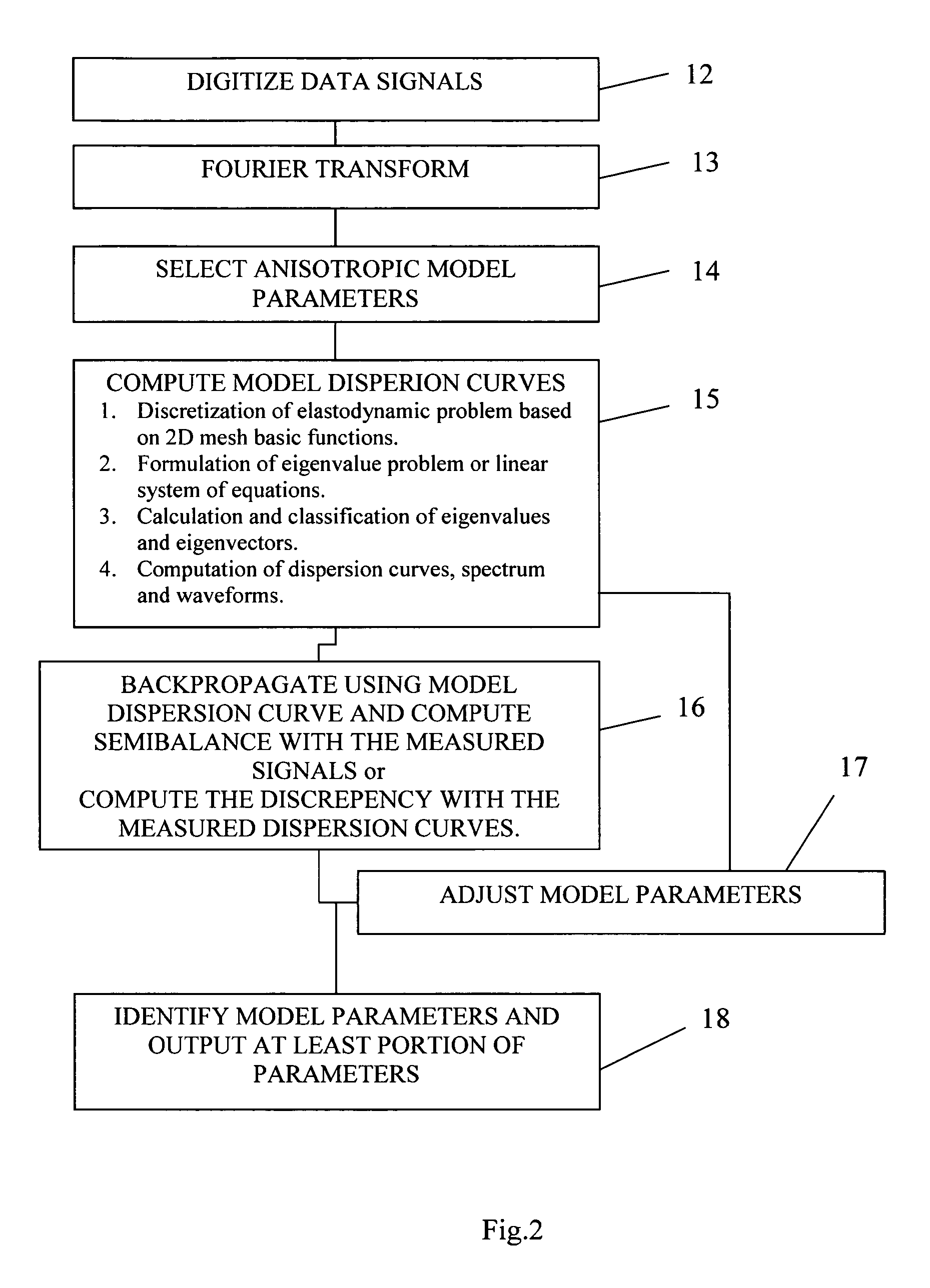
Method for processing acoustic waveforms comprises acquiring acoustic waveforms in a borehole traversing a subterranean formation and transforming at least a portion of the acoustic waveforms to produce frequency domain signals. Then model dispersion curves, modes spectrum or waveforms are generated based on an anisotropic borehole-formation model having a set of anisotropic and geometrical borehole-formation parameters and by specifying governing equations and computational mesh based functional basis. The frequency-domain signals are back-propagating using the model dispersion curves to correct dispersiveness of the signals and coherence of the back-propagated signals is calculated. Alternatively the difference between the measured and the model dispersion curves is determined. Model parameters are iteratively adjusted until the coherence reaches a maximum or exceeds a selected value, or alternatively until the difference between the measured and the model dispersion curves becomes minimal or is reduced to below a selected value. Then at least a portion of the set of anisotropic and geometrical borehole-formation parameters is obtained.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Circuit life prediction method based on accelerated degradation path
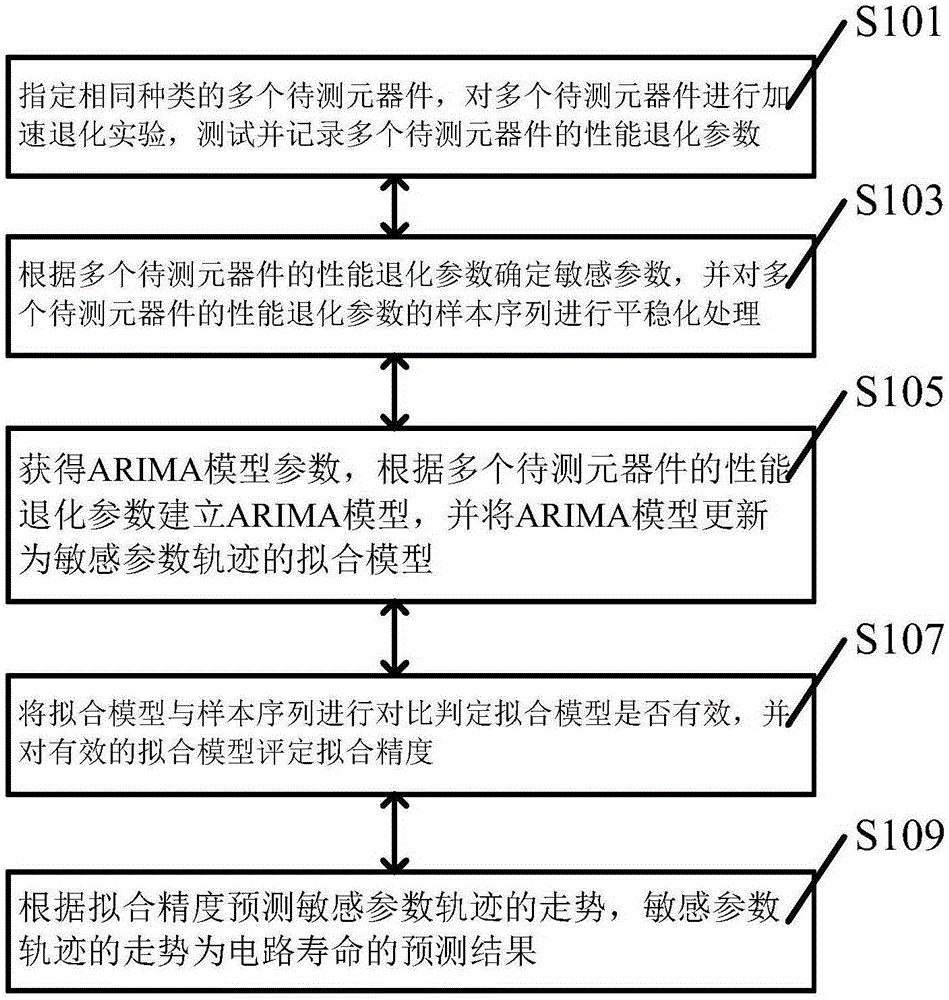
ActiveCN105182218AImprove reliabilityAccurate evaluationElectronic circuit testingSample sequenceModel parameters
The invention discloses a circuit life prediction method based on an accelerated degradation path. The method comprises the following steps: providing a plurality of components to be tested, which are of the same kind, carrying out accelerated degradation experiment on the plurality of components to be tested, and testing and recording performance degradation parameters of the plurality of components to be tested; determining sensitive parameters according to the performance degradation parameters of the plurality of components to be tested, and carrying out stationary processing on sample sequences of the performance degradation parameters of the plurality of components to be tested; obtaining ARIMA model parameters, establishing an ARIMA model according to the performance degradation parameters of the plurality of components to be tested, and updating the ARIMA model into a fitting model of a sensitive parameter path; comparing the fitting model with the sample sequences and judging whether the fitting model is effective, and evaluating fitting precision of the effective fitting model; and predicating the trend of the sensitive parameter path according to the fitting precision, the trend of the sensitive parameter path being predicated result of the circuit life.
Owner:CASIC DEFENSE TECH RES & TEST CENT
Tuning a Mass Spectrometer Using Optimization
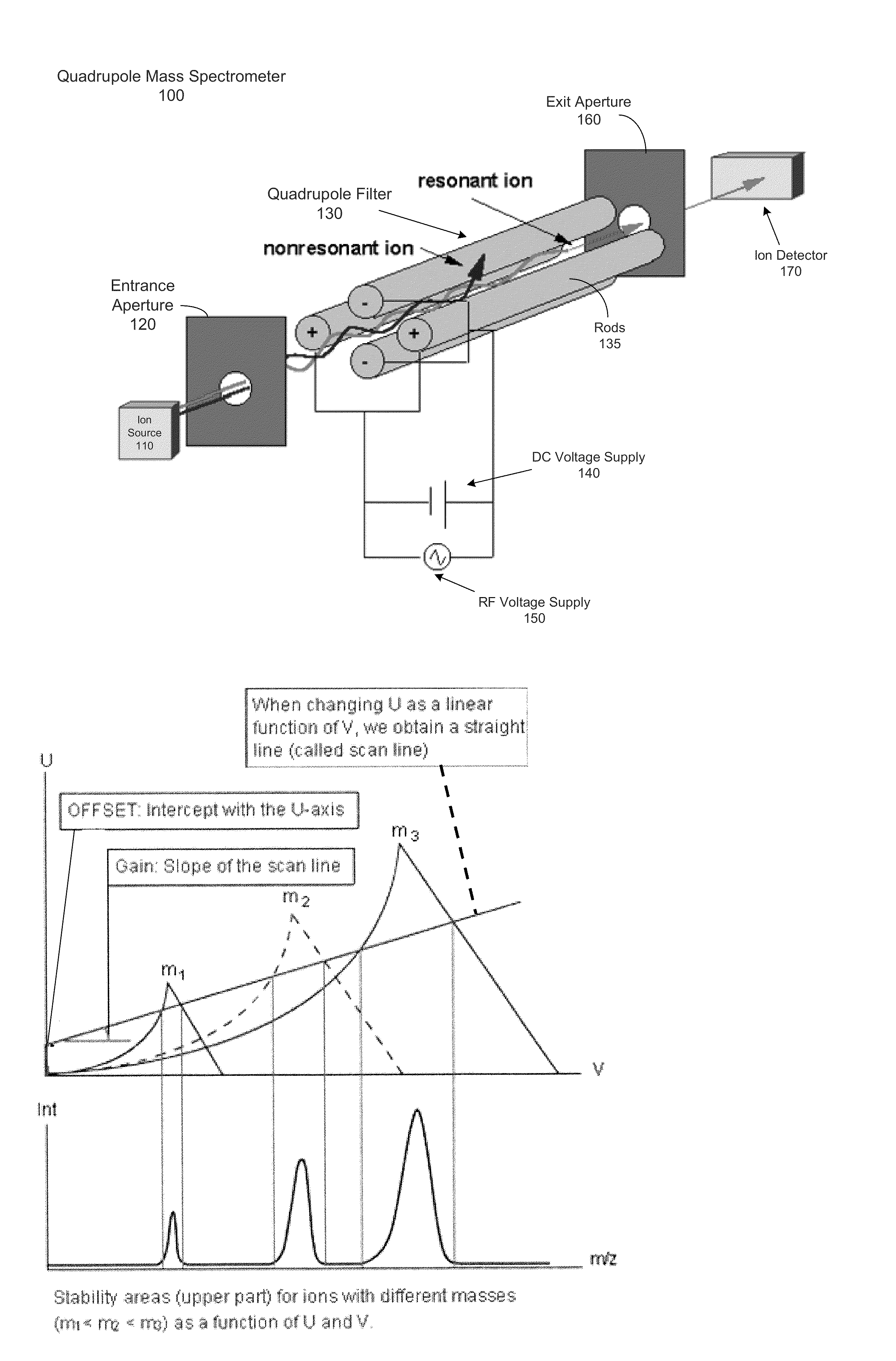
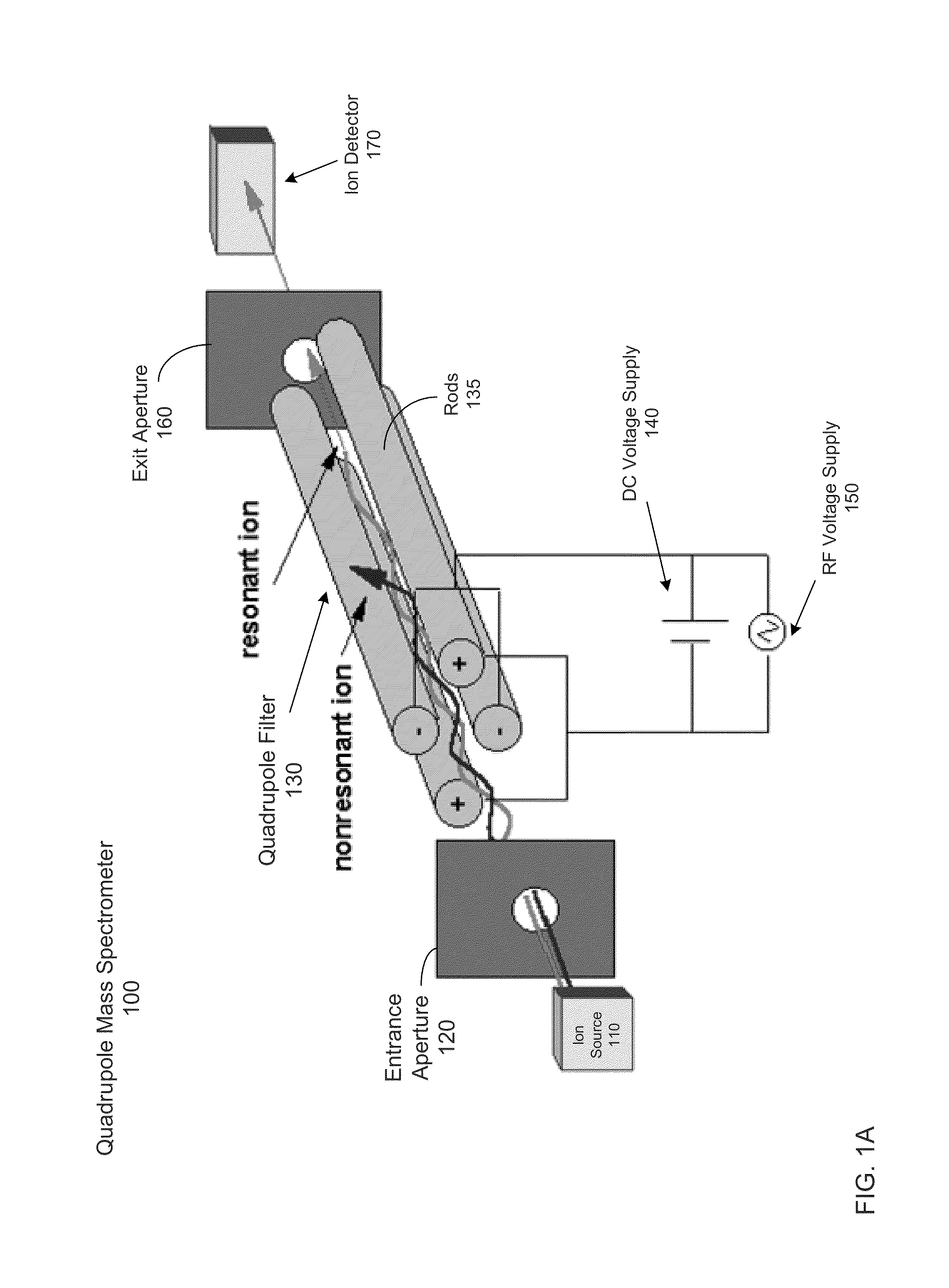
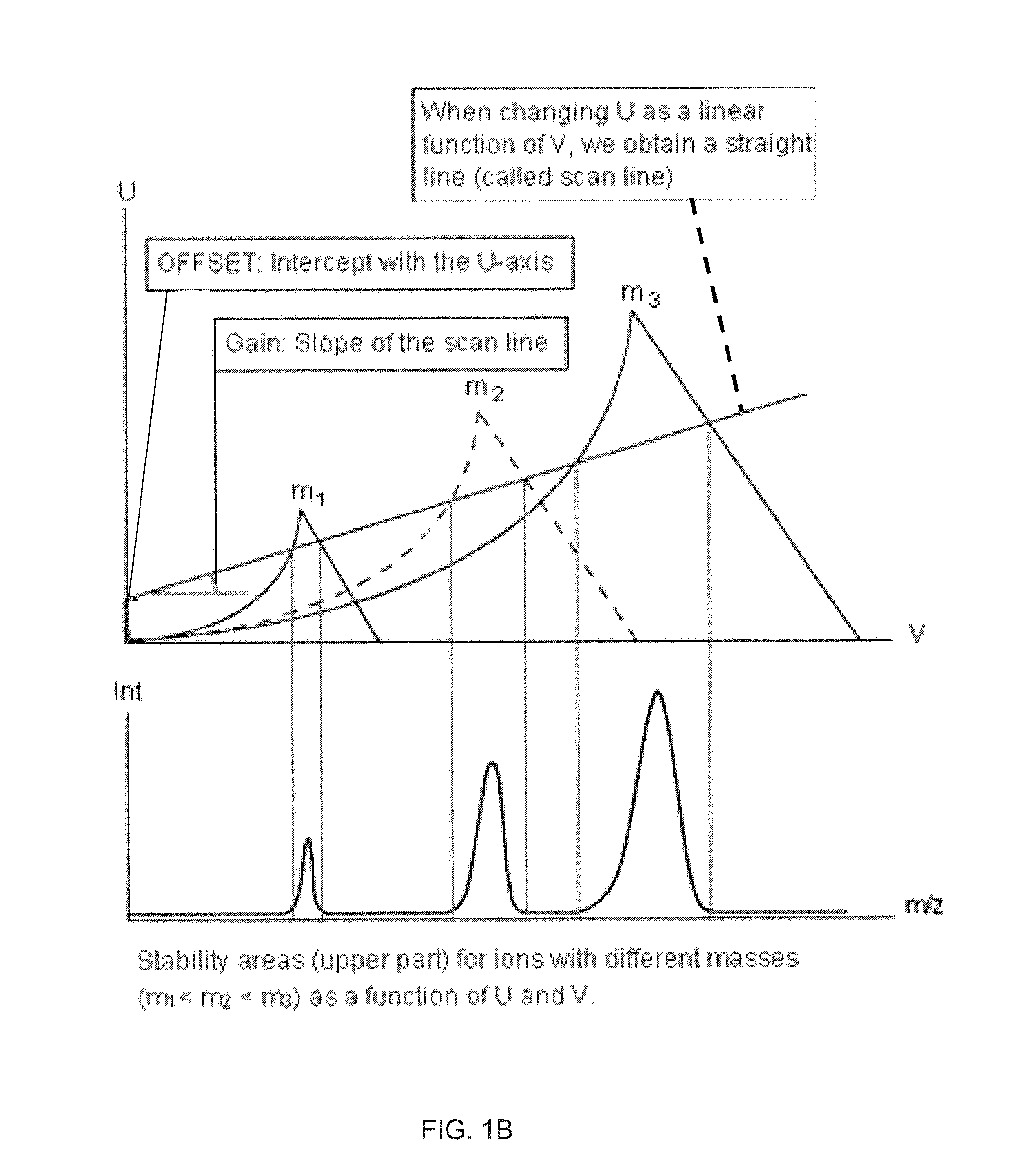
InactiveUS20160181076A1Stability-of-path spectrometersTesting/calibration apparatusMass analyzerQuadrupole
Systems, methods, and apparatuses are provided for tuning a mass spectrometer. An optimization process can be performed to determine optimal parameters for various physical parameters of elements of the mass spectrometer. A cost function (metric) can be defined for optimizing a measured signal output from the spectrometer. The metric can include an intensity term and a rectangularity term. The rectangularity term can provide a quantification of an extent that a measured signal corresponding to a first mass-to-charge ratio approximates a rectangle. The parameter values can be adjusted to find an optimal cost value of the cost function. Techniques may particularly useful when a quadrupole is operated in a broad-stability mode.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
Method and apparatus for encoding/decoding a scalar integer into a parameter representative of a pivot points of a piece-wise linear function
InactiveUS20190132600A1Optimize the numberAvoid pollutionDigital video signal modificationComplex mathematical operationsAlgorithmLeast significant bit
A method for encoding and decoding, a scalar integer into at least one parameter representative of a pivot point comprised in a set of pivot points representative of a piece-wise linear function, said scalar integer being used when modifying pixel values of a picture, and corresponding apparatus, are disclosed. Said encoding method comprises:—a step E1 of selecting a subset of pivot points from the set of pivot points, according to a criterion, said subset comprising a number M of pivot points less than the number N of pivot points of said set of pivot points, —at least one step of coding E2 one bit of a binary representation of said scalar integer in a least significant bit of a component of a pivot point comprised into said subset.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL VC HLDG INC
Singular value decomposition-based method for optimal estimation of turbofan engine thrust and other unmeasurable parameters
InactiveUS7860635B2Vehicle testingAnalogue computers for vehiclesSingular value decompositionKaiman filter
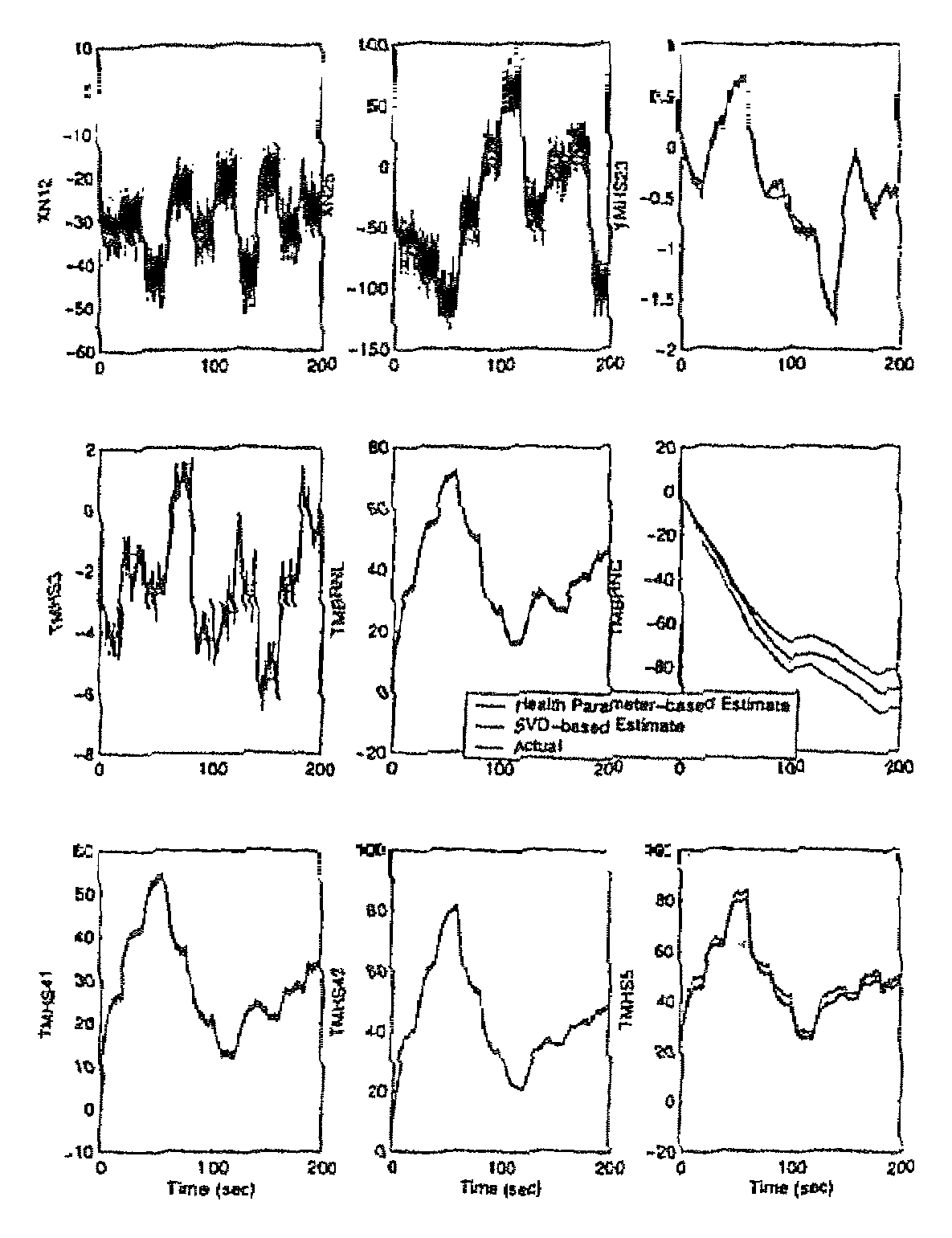
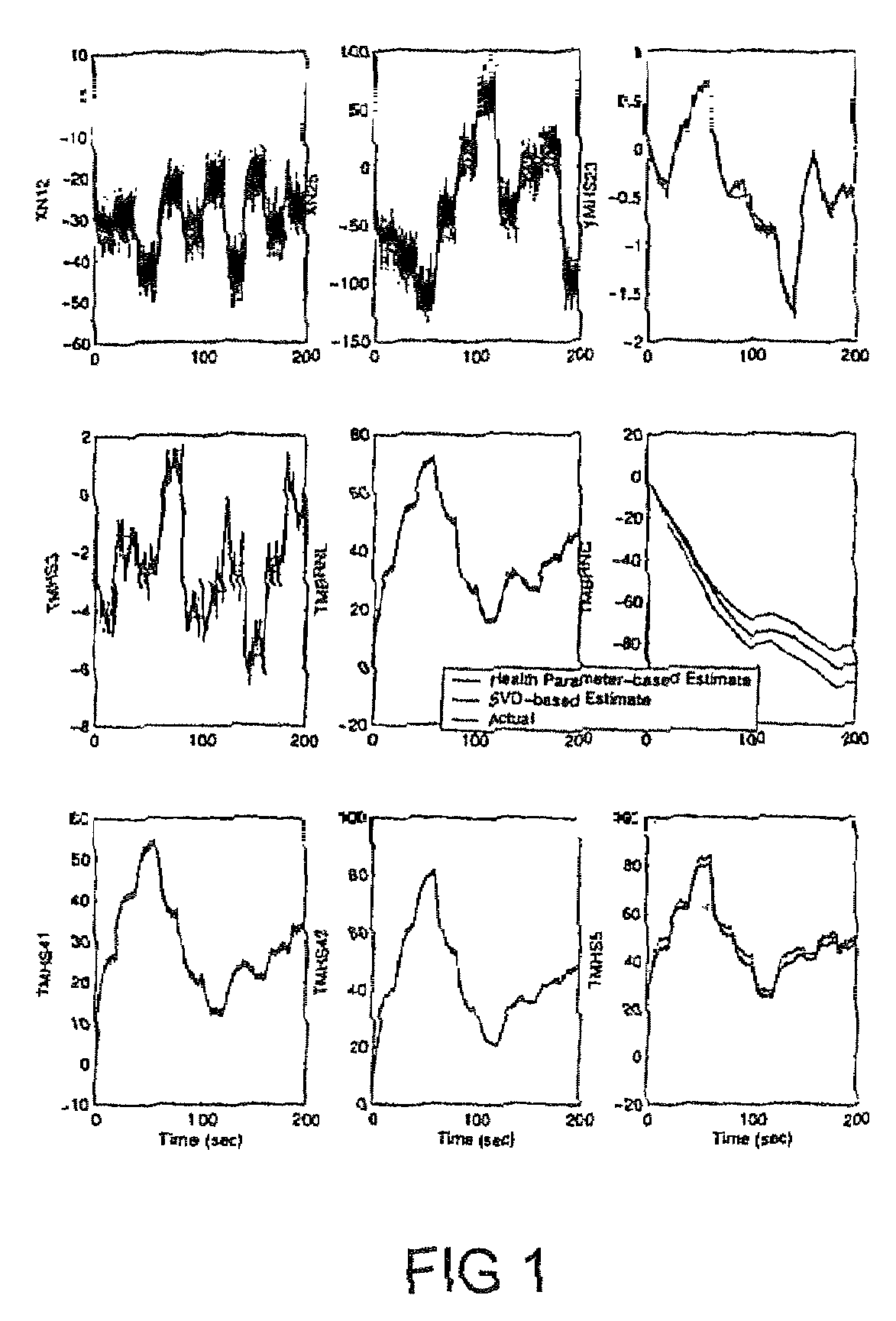
A new linear point design technique is presented for the determination of tuning parameters that enable the optimal estimation of unmeasured engine outputs such as thrust. The engine's performance is affected by its level of degradation, generally described in terms of unmeasurable health parameters related to each major engine component. Accurate thrust reconstruction depends upon knowledge of these health parameters, but there are usually too few sensors to be able to estimate their values. In this new technique, a set of tuning parameters is determined which accounts for degradation by representing the overall effect of the larger set of health parameters as closely as possible in a least squares sense. The technique takes advantage of the properties of the singular value decomposition of a matrix to generate a tuning parameter vector of low enough dimension that it can be estimated by a Kalman filter. A concise design procedure to generate a tuning vector that specifically takes into account the variables of interest is presented. An example demonstrates the tuning parameters' ability to facilitate matching of both measured and unmeasured engine outputs, as well as state variables. Additional properties of the formulation are shown to lend themselves well to diagnostics.
Owner:ARMY US SEC THE
Voice-based mouth shape and/or expression simulation method and device
ActiveCN108538308AReduce analysisSmall amount of calculationSpeech analysisAnimationFrequency spectrumSimulation
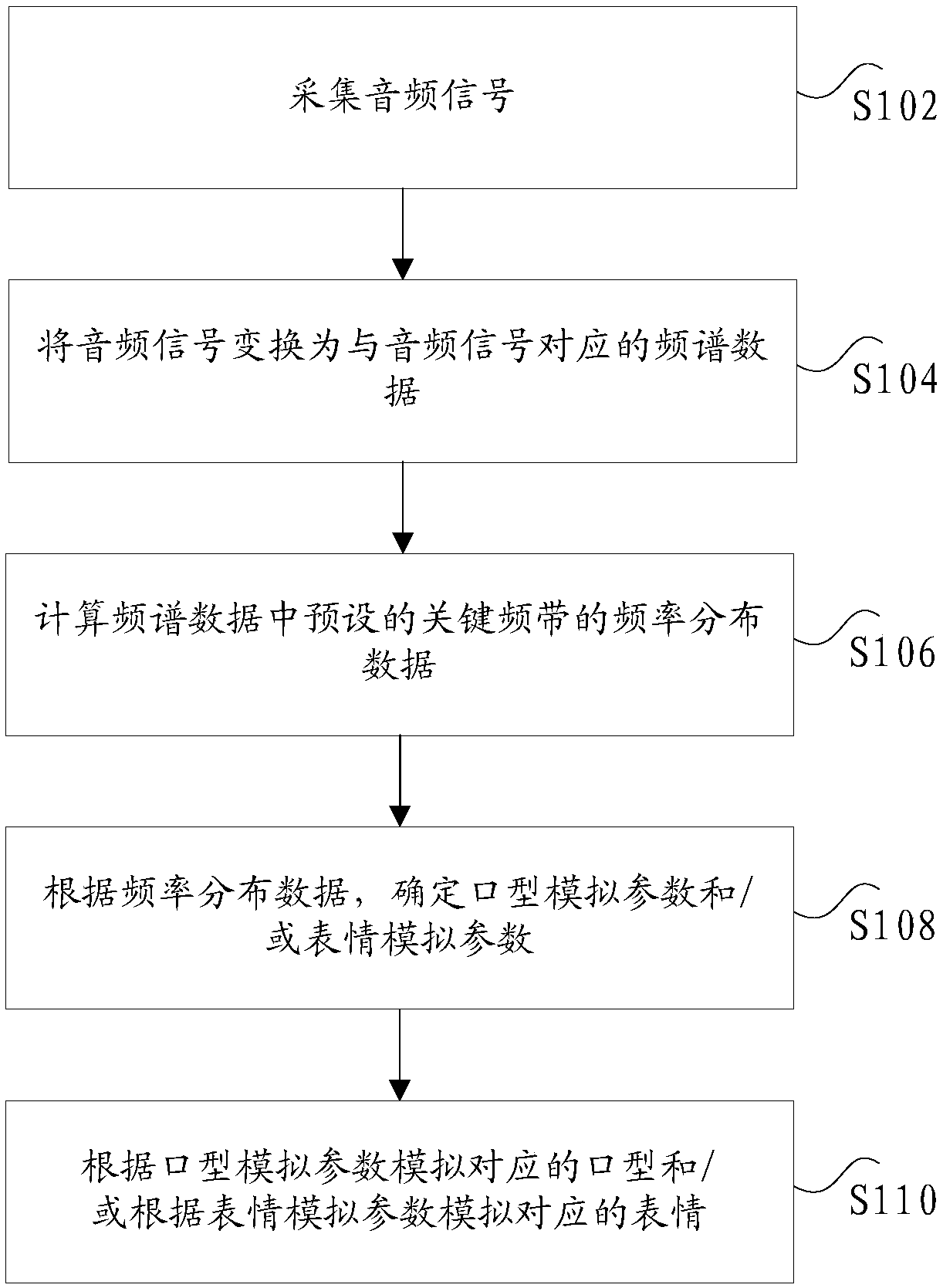
The invention discloses a voice-based mouth shape and / or expression simulation method and device. The method comprises the steps that audio signals are acquired; the audio signals are converted into the spectrum data corresponding to the audio signals; the frequency distribution data are determined according to the spectrum data; the mouth shape simulation parameter and / or the expression simulation parameter are / is determined according to the frequency distribution data; and the corresponding mouth shape is simulated according to the mouth shape simulation parameter and / or the corresponding expression is simulated according to the expression simulation parameter. The technical problems of high workload of mouth shape or expression simulation in the virtual reality application in the related technology can be solved.
Owner:NETEASE (HANGZHOU) NETWORK CO LTD
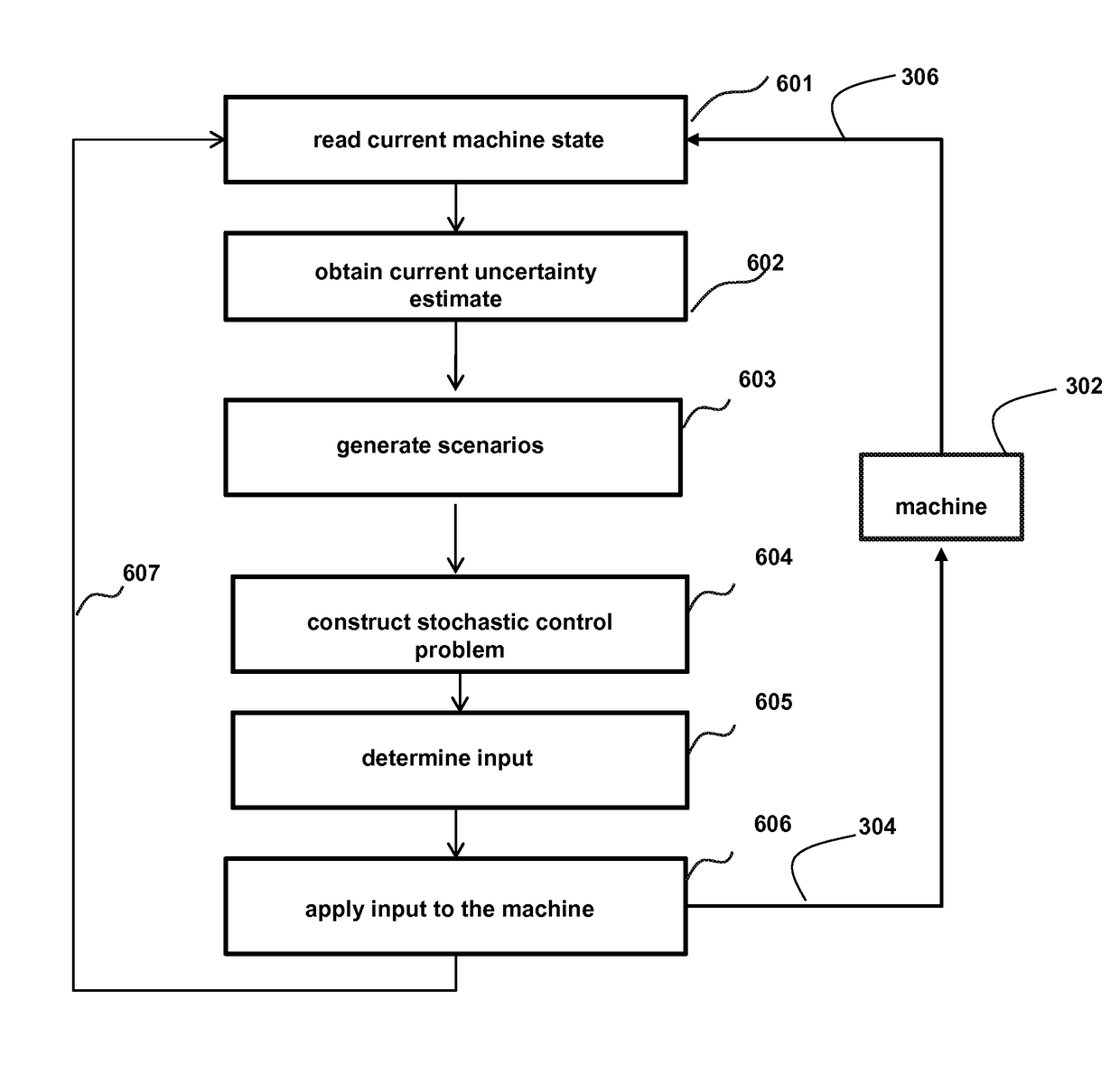
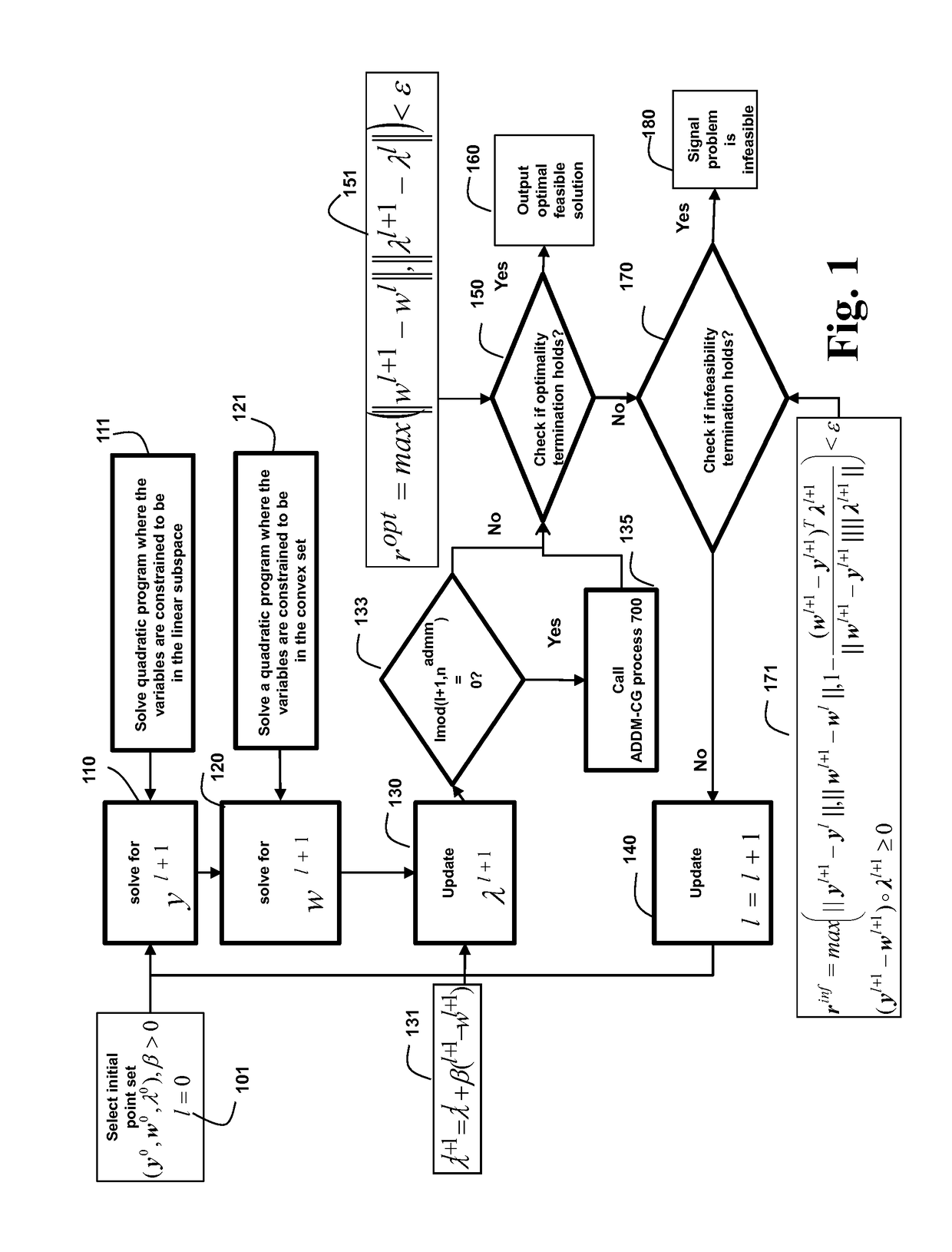
Optimal parameter selection and acceleration in ADMM for multi-stage stochastic convex quadratic programs
ActiveUS9760534B2Minimizes numberSignificant rateComputation using non-denominational number representationComputer aided designAlgorithmComputer science
A method solves a stochastic quadratic program (StQP) for a convex set with a set of general linear equalities and inequalities by an alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM). The method determines an optimal solution, or certifies that no solution exists. The method optimizes a step size β for the ADMM. The method is accelerated using a conjugate gradient (CG) method. The StMPC problem is decomposed into two blocks. The first block corresponds to an equality constrained QP, and the second block corresponds to a projection onto the StMPC inequalities and anticipativity constraints. The StMPC problem can be decomposed into a set of time step problems, and then iterated between the time step problems to solve the decoupled problems until convergence.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
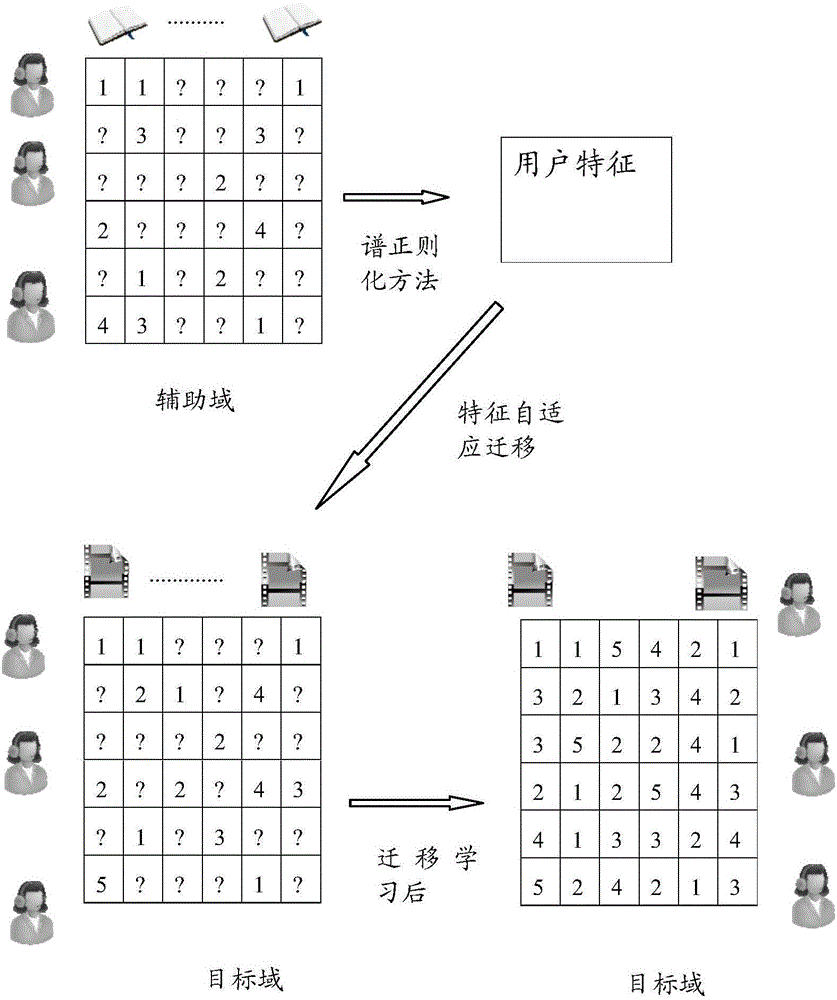
Collaborative filtering method based on domain correlation self-adaption
InactiveCN106227767AStrong correlationScore Prediction Adequate and EffectiveSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmThe Internet
A collaborative filtering method based on domain correlation self-adaption comprises the following steps that 1,the difference of an auxiliary domain and a target domain serves as a regularization term and is introduced into a traditional model to obtain a new model (shown in the description), wherein T is a rating matrix having a partially deleted item in the target domain, Z and T have the same rating item; the equation shown in the description represents an index set representing the target domain, wherein the equation is shown in the description; | | . | | F represents a Frobenius norm, wherein the equation is shown in the description; | | . | | * represents a nuclear norm,| | Z | | *represents the sum of all singular values of a matrix Z; gamma is a regularization parameter, eta < (0, 1) represents the similarity of the auxiliary domain and the target domain; 2,a regular optimization solution Z* = Z of the new model is calculated by using a fixed-point iteration algorithm. The collaborative filtering method can be applied to an Internet recommendation system, introduces the system to a prediction model of the target domain through self-adaptive estimation of their correlation, accordingly achieves knowledge migration effectively and improves the recommendation precision of the target domain.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus for measuring a structure on a substrate, computer program products for implementing such methods and apparatus
ActiveUS9977340B2Degree of freedom is loweredReduce in quantityAnalogue computers for electric apparatusMaterial analysis by optical meansAlgorithmUser input
Diffraction models and scatterometry are used to reconstruct a model of a microscopic structure on a substrate. A plurality of candidate structures are defined, each represented by a plurality of parameters (p1, p2, etc.)). A plurality of model diffraction signals are calculated by simulating illumination of each of the candidate structures. The structure is reconstructed by fitting one or more of the model diffraction signals to a signal detected from the structure. In the generation of the candidate structures, a model recipe is used in which parameters are designated as either fixed or variable. Among the variable parameters, certain parameters are constrained to vary together in accordance with certain constraints, such as linear constraints. An optimized set of constraints, and therefore an optimized model recipe, is determined by reference to a user input designating one or more parameters of interest for a measurement, and by simulating the reconstruction process reconstruction. The optimized model recipe can be determined automatically by a parameter advisor process that simulates reconstruction of a set of reference structures, using a plurality of candidate model recipes. In the generation of the reference structures, restrictions can be applied to exclude unrealistic parameter combinations.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
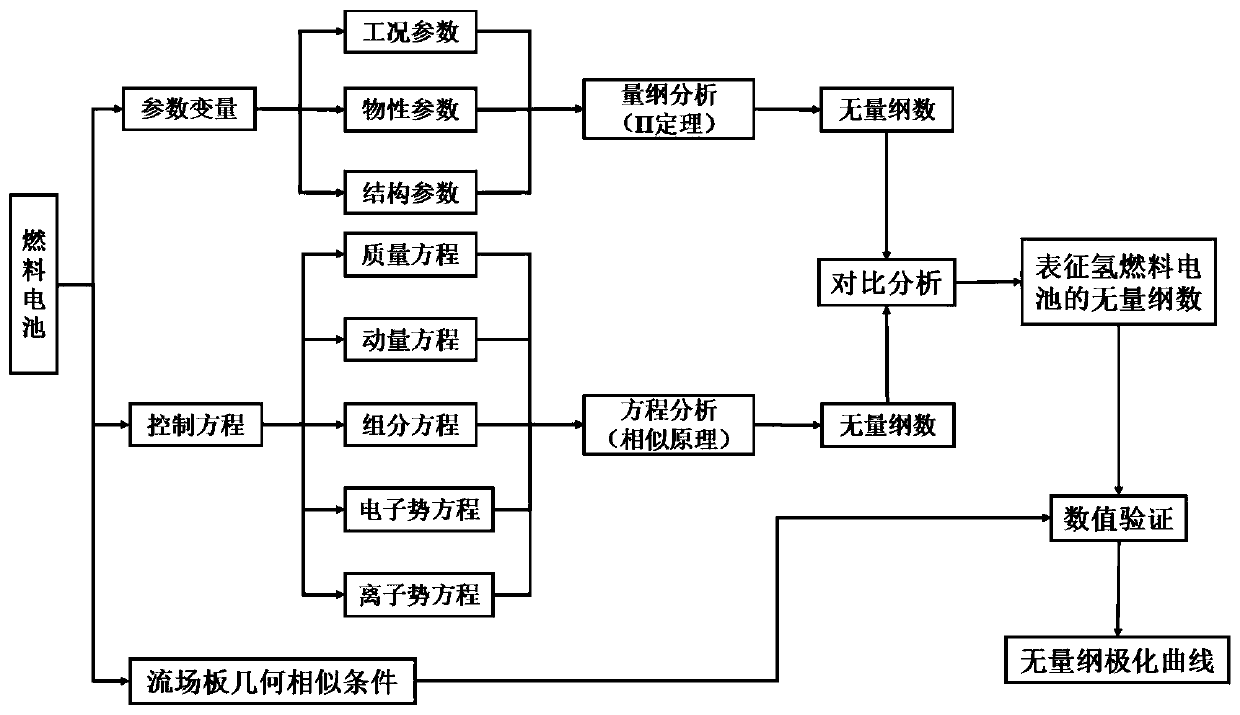
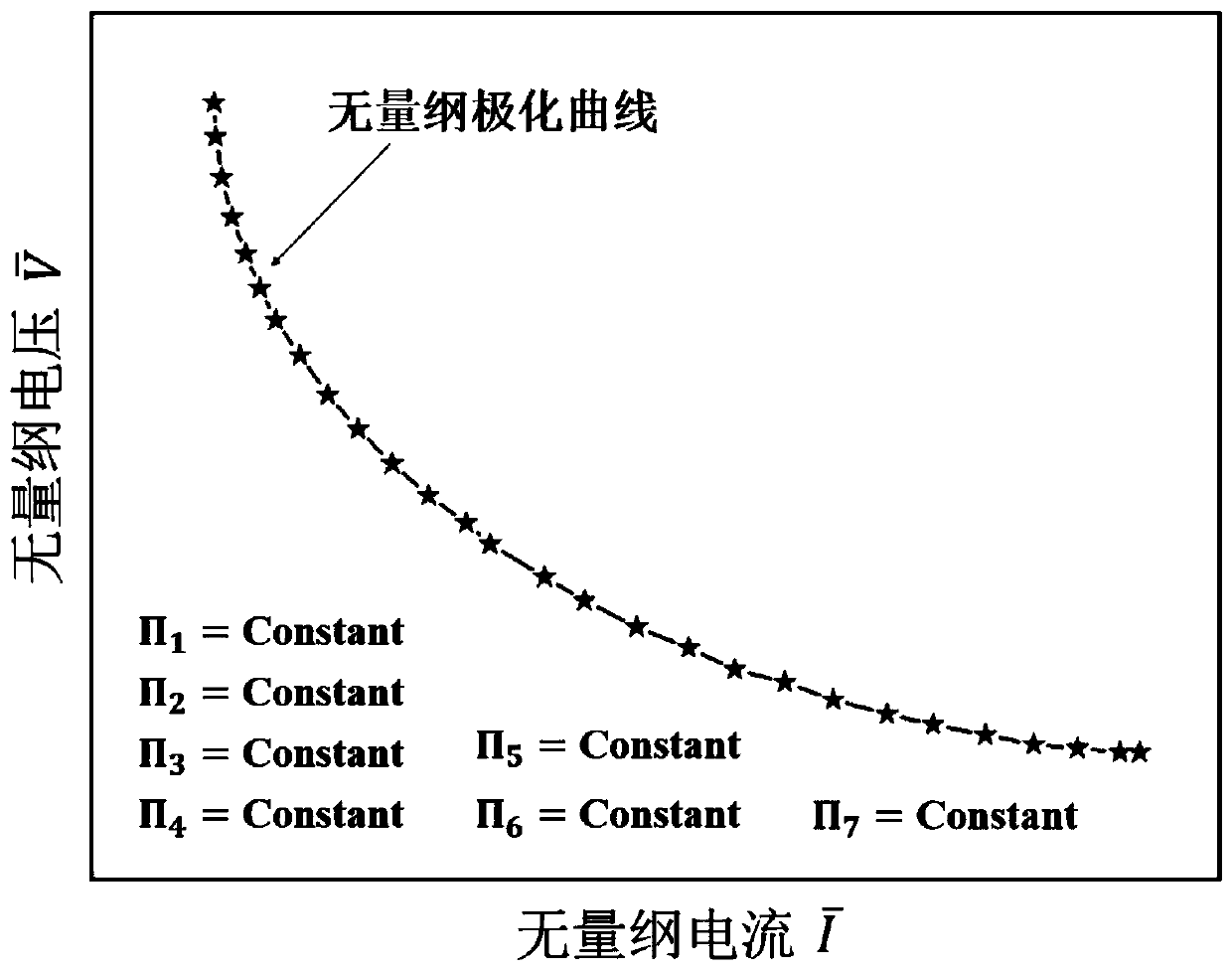
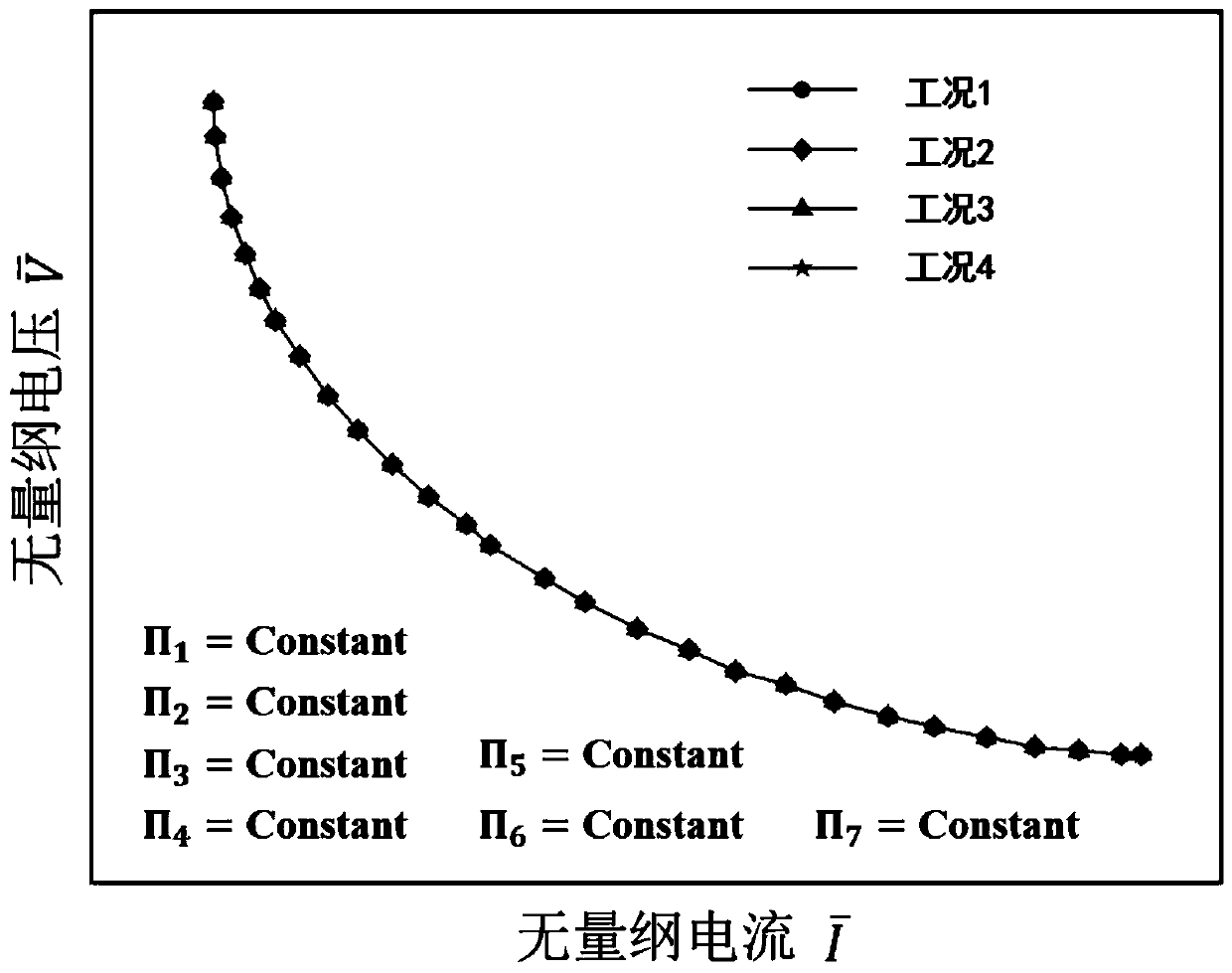
Similarity principle analysis method for input and output characteristics of fuel cell
ActiveCN110413941ASimplified experimental design conditionsReduce the number of experimentsGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationHydrogen fuel cellEngineering
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com