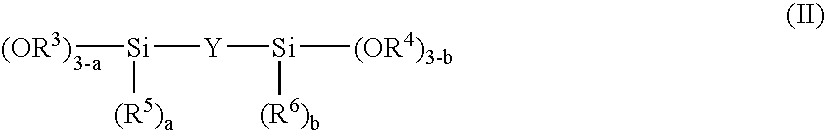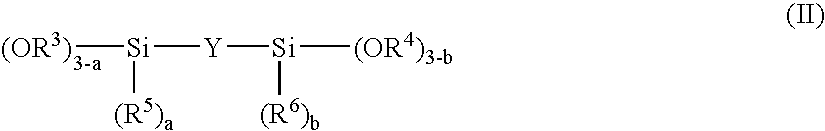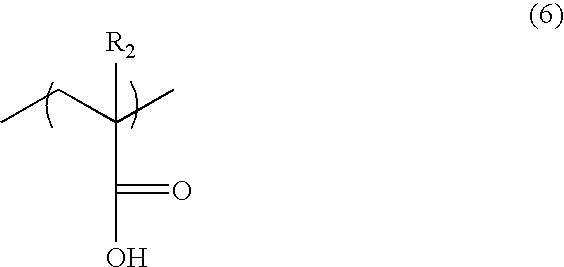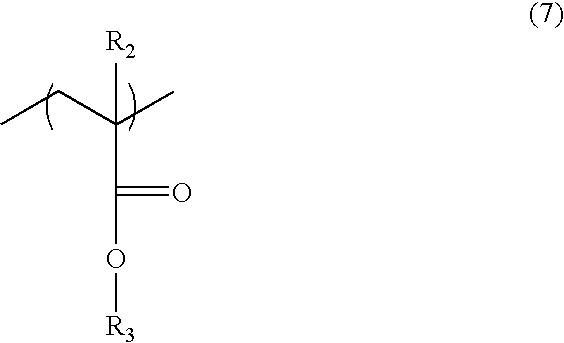Patents
Literature
45results about How to "Great index of refraction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
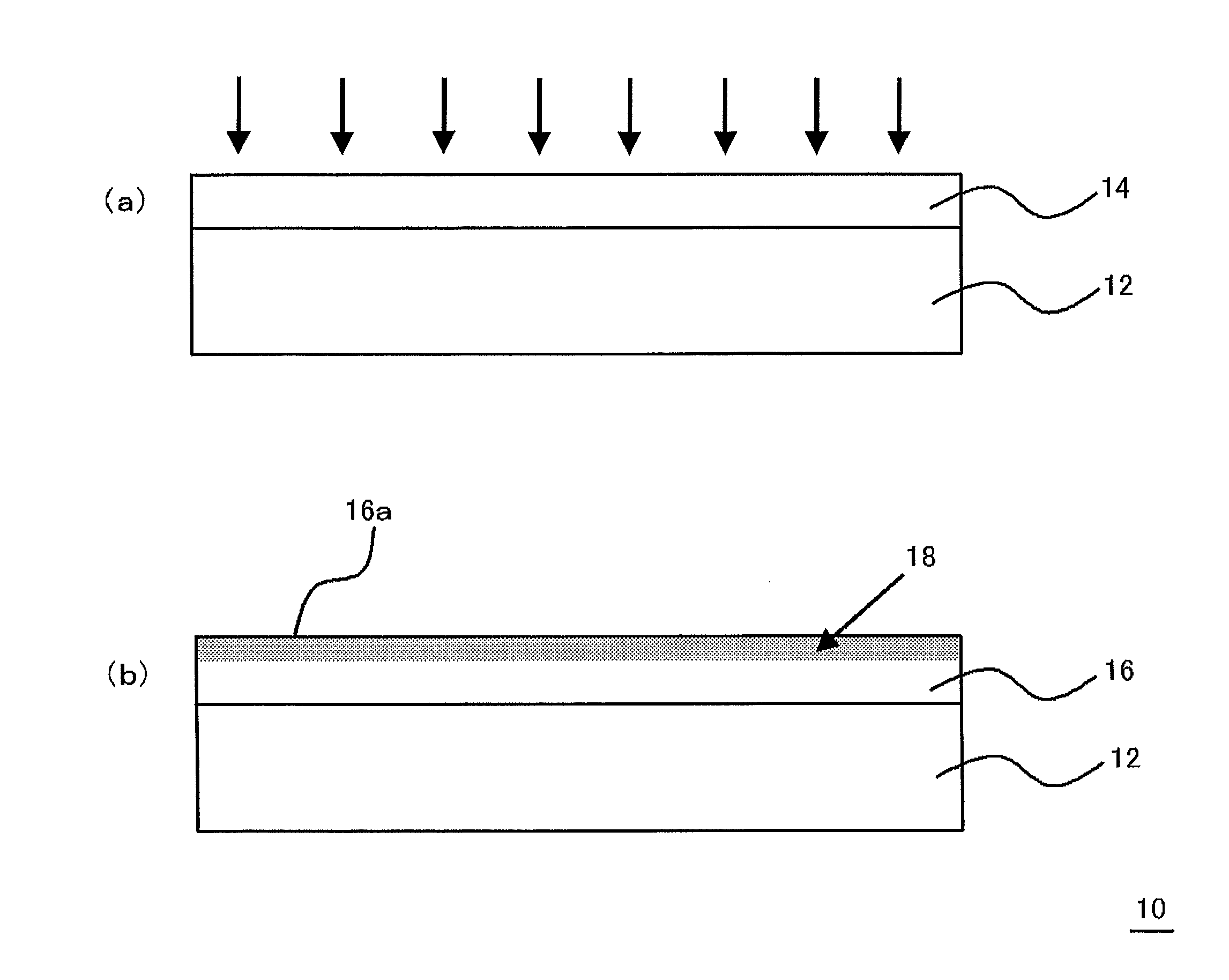
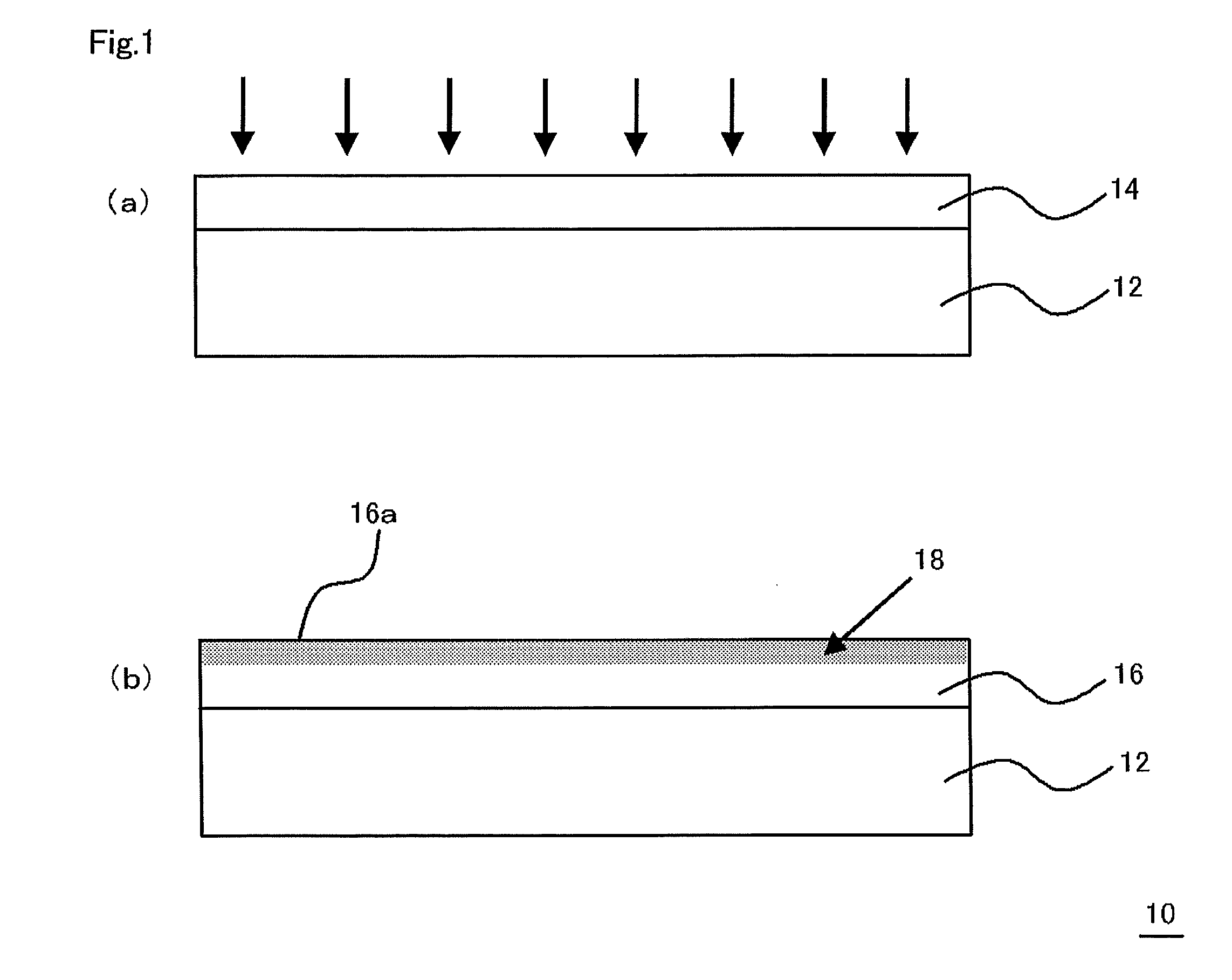
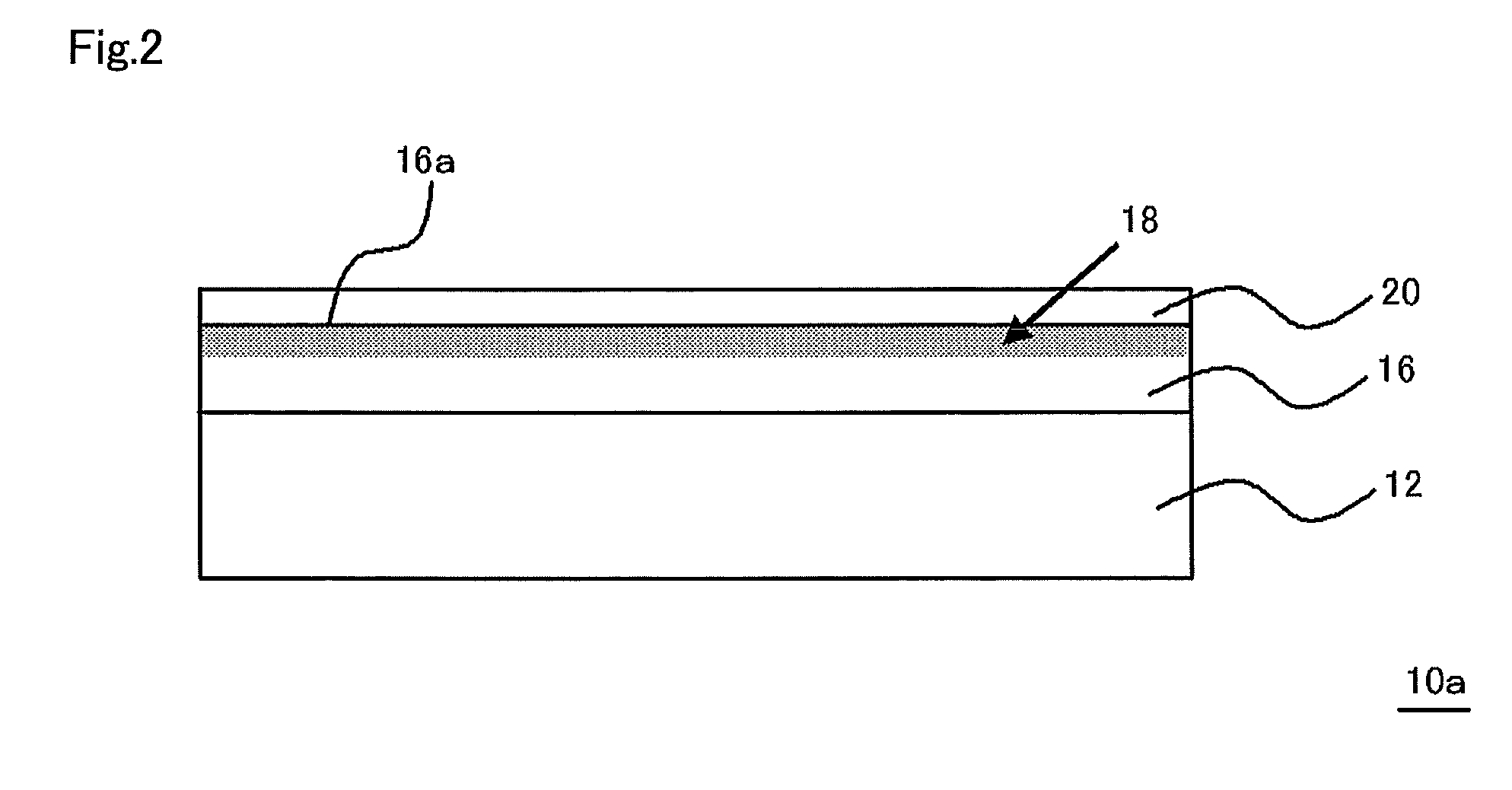
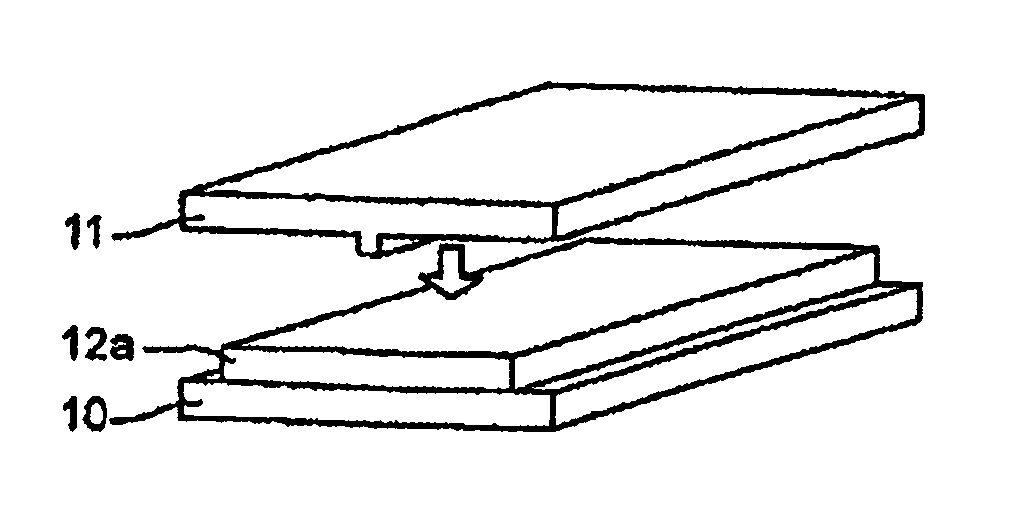
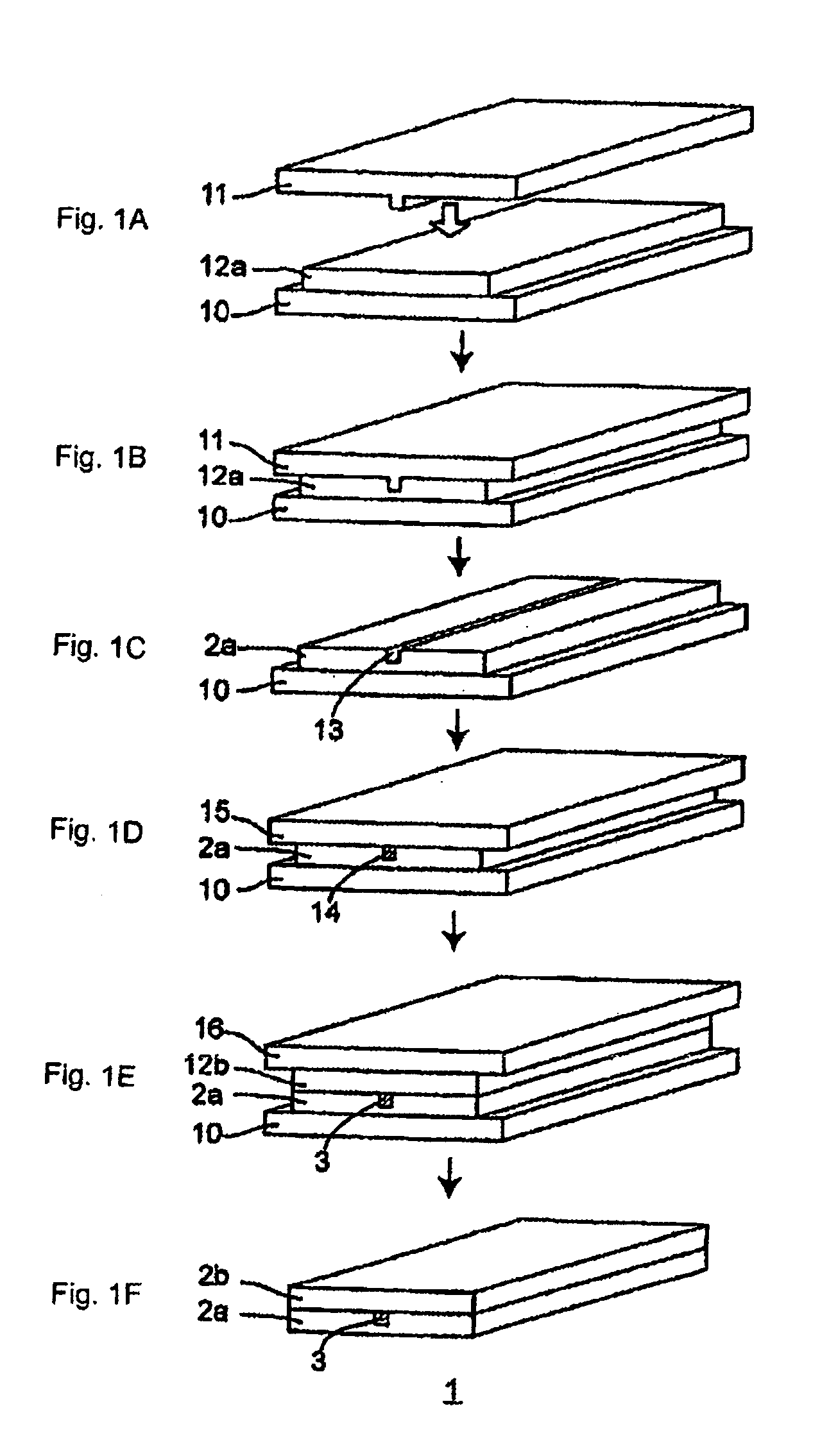
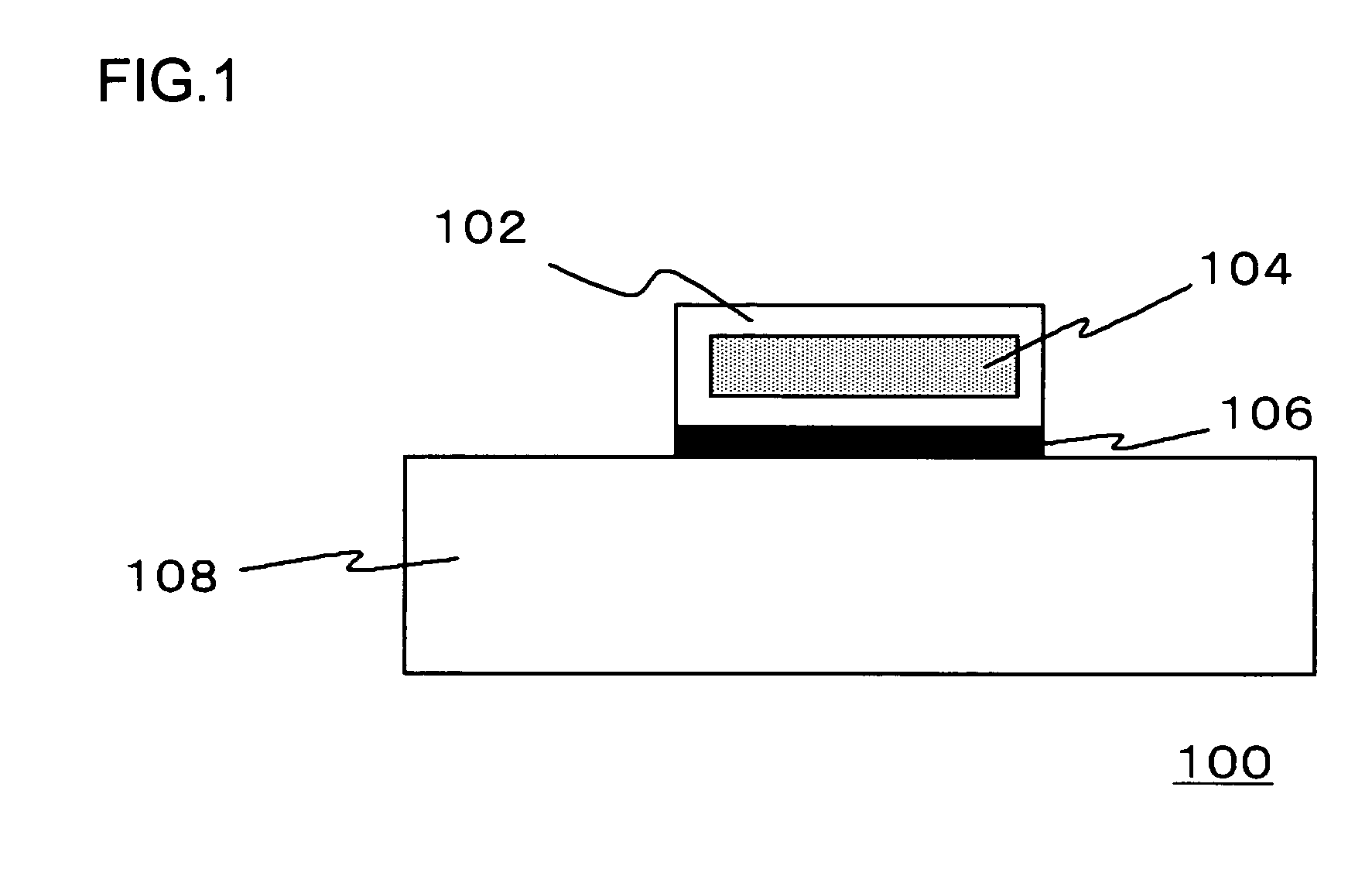
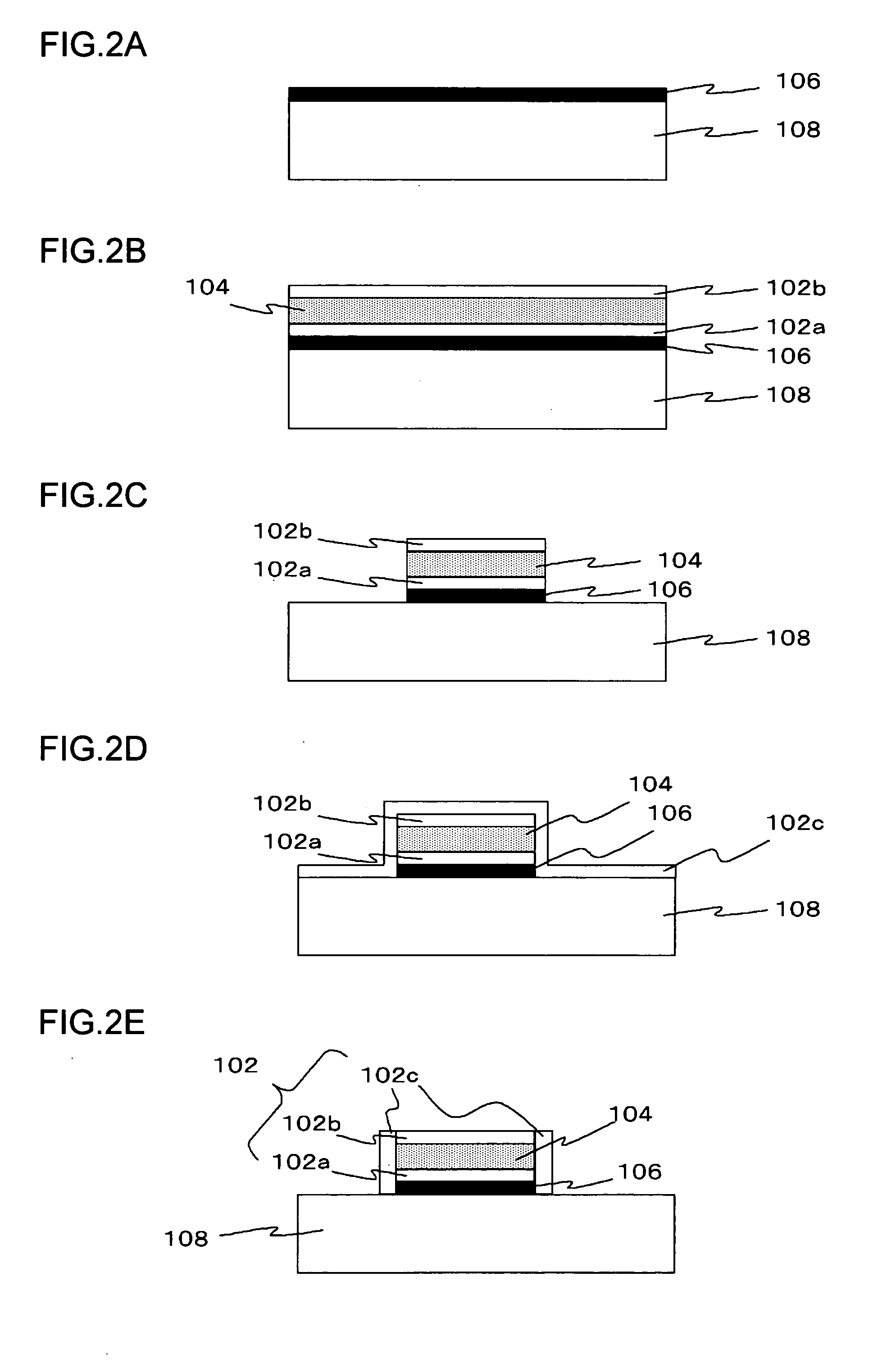
Multilayered material and method of producing the same
InactiveUS20120107607A1Reduce the impactIncrease production capacityRadiation applicationsPretreated surfacesWater vaporPolysilazane
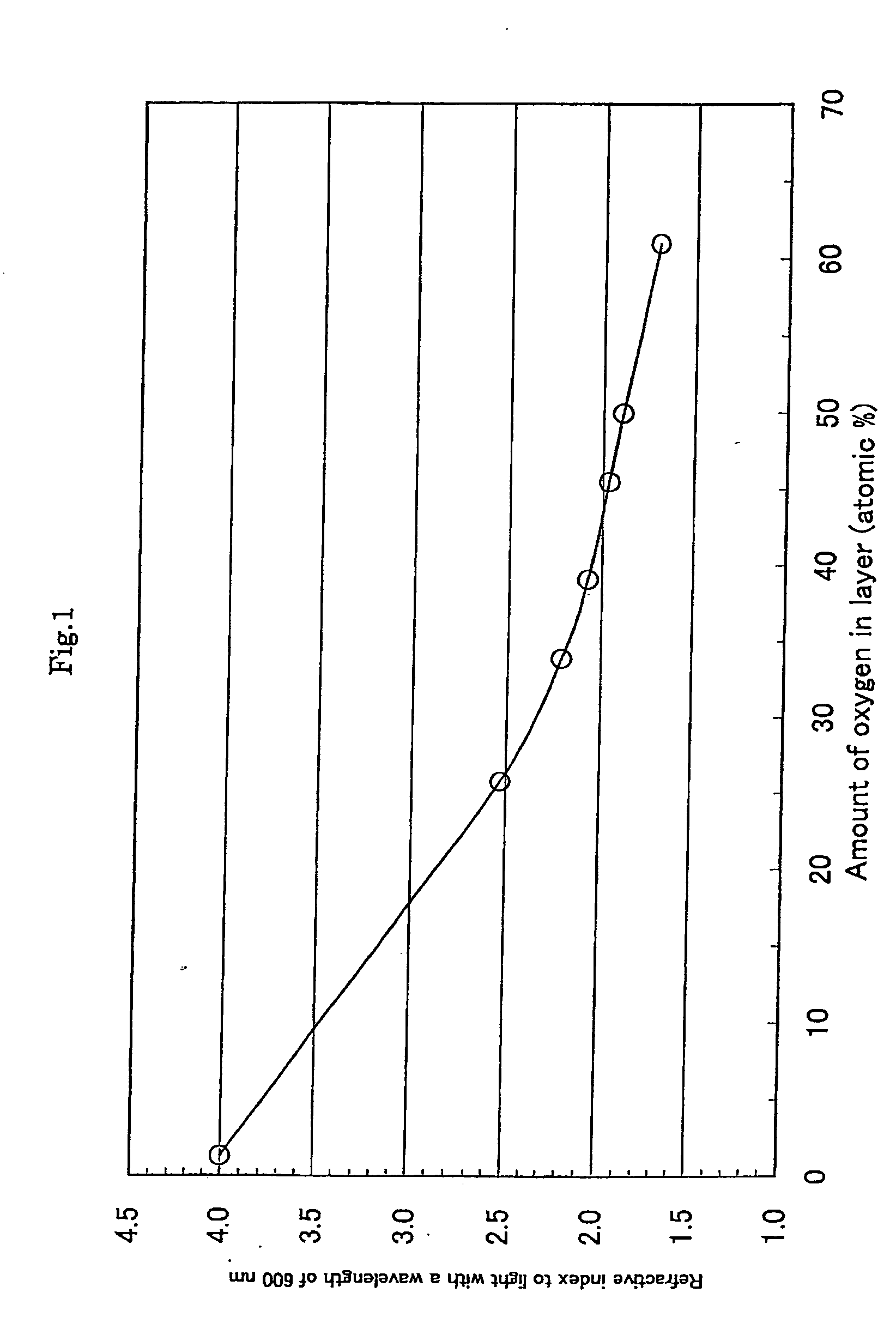
A multilayered material is provided which includes a substrate and a silicon-containing film formed on the substrate, wherein the silicon-containing film has a nitrogen-rich area including silicon atoms and nitrogen atoms, or silicon atoms, nitrogen atoms, and an oxygen atoms and the nitrogen-rich area is formed by irradiating a polysilazane film formed on the substrate with an energy beam in an atmosphere not substantially including oxygen or water vapor and denaturing at least a part of the polysilazane film. A method of producing the multilayered material is also provided.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Depth fused display
ActiveUS20050206582A1Remarkable effectImprove usabilityCathode-ray tube indicatorsSteroscopic systemsDisplay deviceParallel imaging
A method of displaying an image with variable perceived depth using a display (1) including one or more at least partially transparent, substantially parallel imaging screens (3) located in front of, and overlapping with, a rear imaging screen (4), characterised in that a physical image is formed on two or more imaging screens (3,4), each image being of substantially identical configuration and being sized and aligned such that like portions of each image are coterminous to a viewer observing the display, wherein at least two of said coterminous images are displayed with different luminance.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Depth fused display
InactiveUS7619585B2Increasing acceptable viewing angleImprove usabilityCathode-ray tube indicatorsColor television detailsParallel imagingDisplay device
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Silicon based thin film solar cell
InactiveUS20060174935A1Low costSufficient light trapping effectPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceTrapping
According to the present invention, sufficient light trapping effect can be exhibited and series resistance can be kept small, by sequentially forming a silicon based low refractive index layer and a thin silicon based interface layer on a backside of a photoelectric conversion layer observed from a light incident side, and as a result a silicon based thin film solar cell may be provided efficiently and at low cost.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Very high transmittance, back-illuminated, silicon-on-sapphire semiconductor wafer substrate for high quantum efficiency and high resolution, solid-state, imaging focal plane arrays
InactiveUS20120193636A1High light transmittanceImprove quantum efficiencyLaser detailsSolid-state devicesSingle crystalRefractive index matching
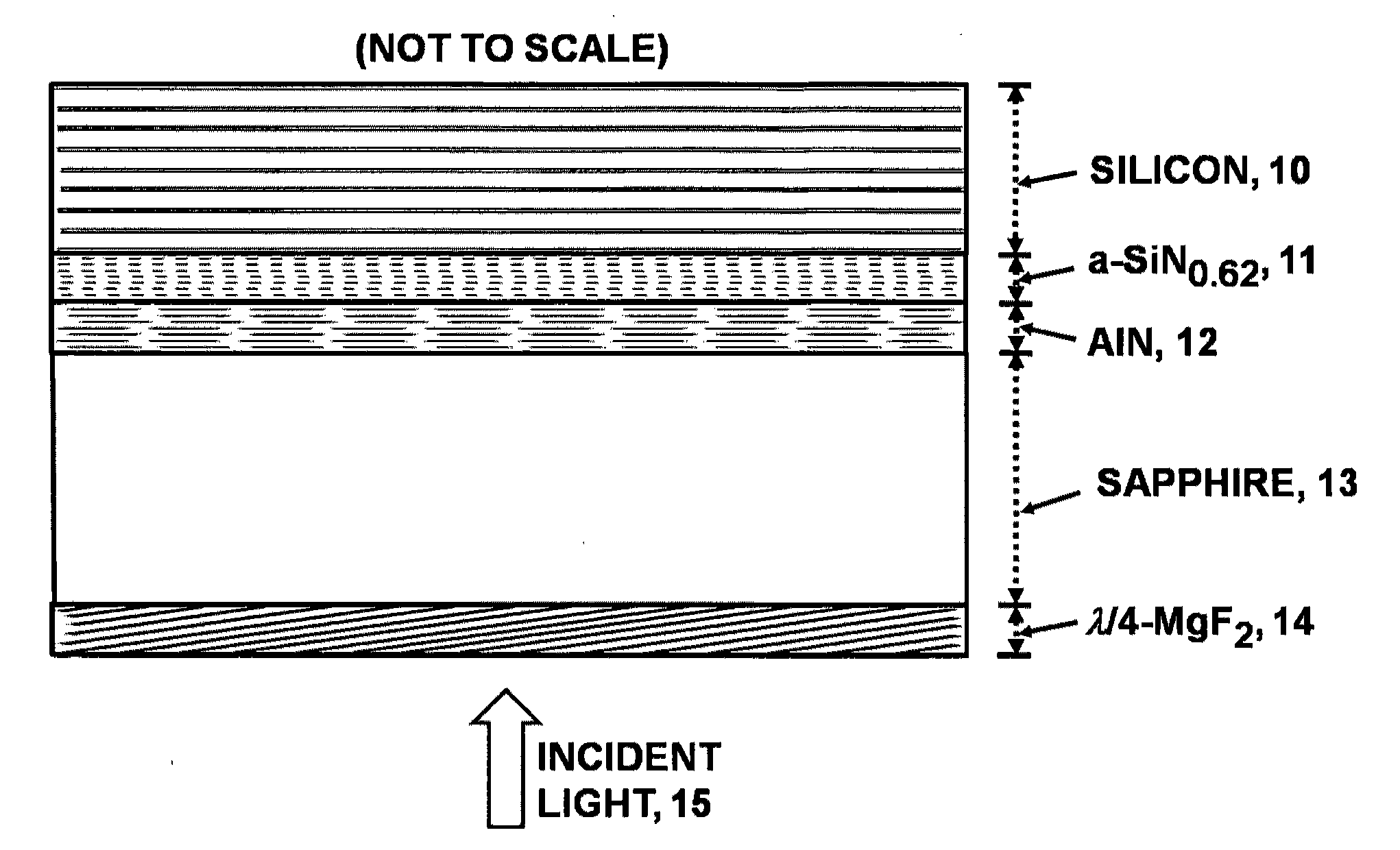
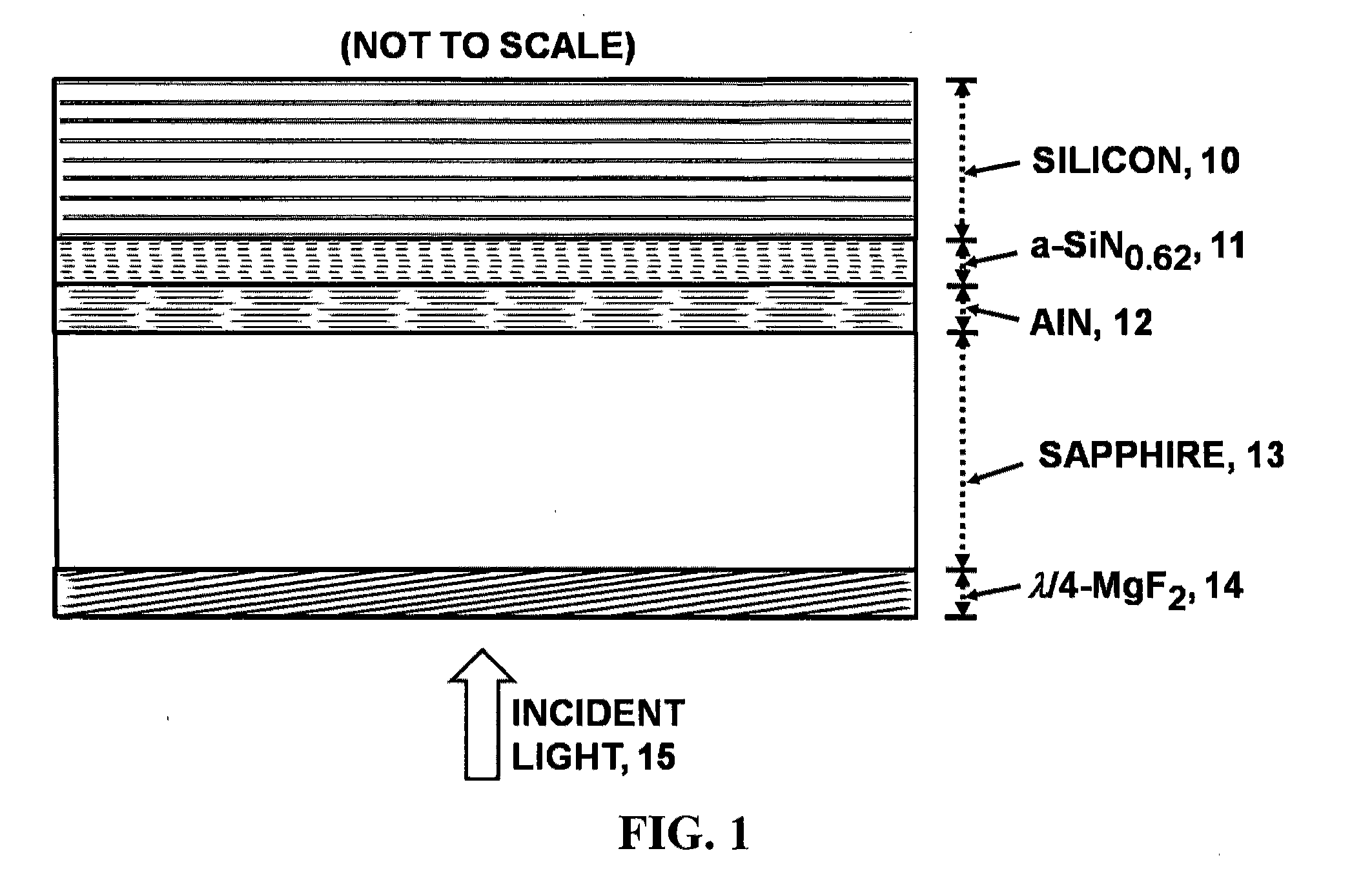
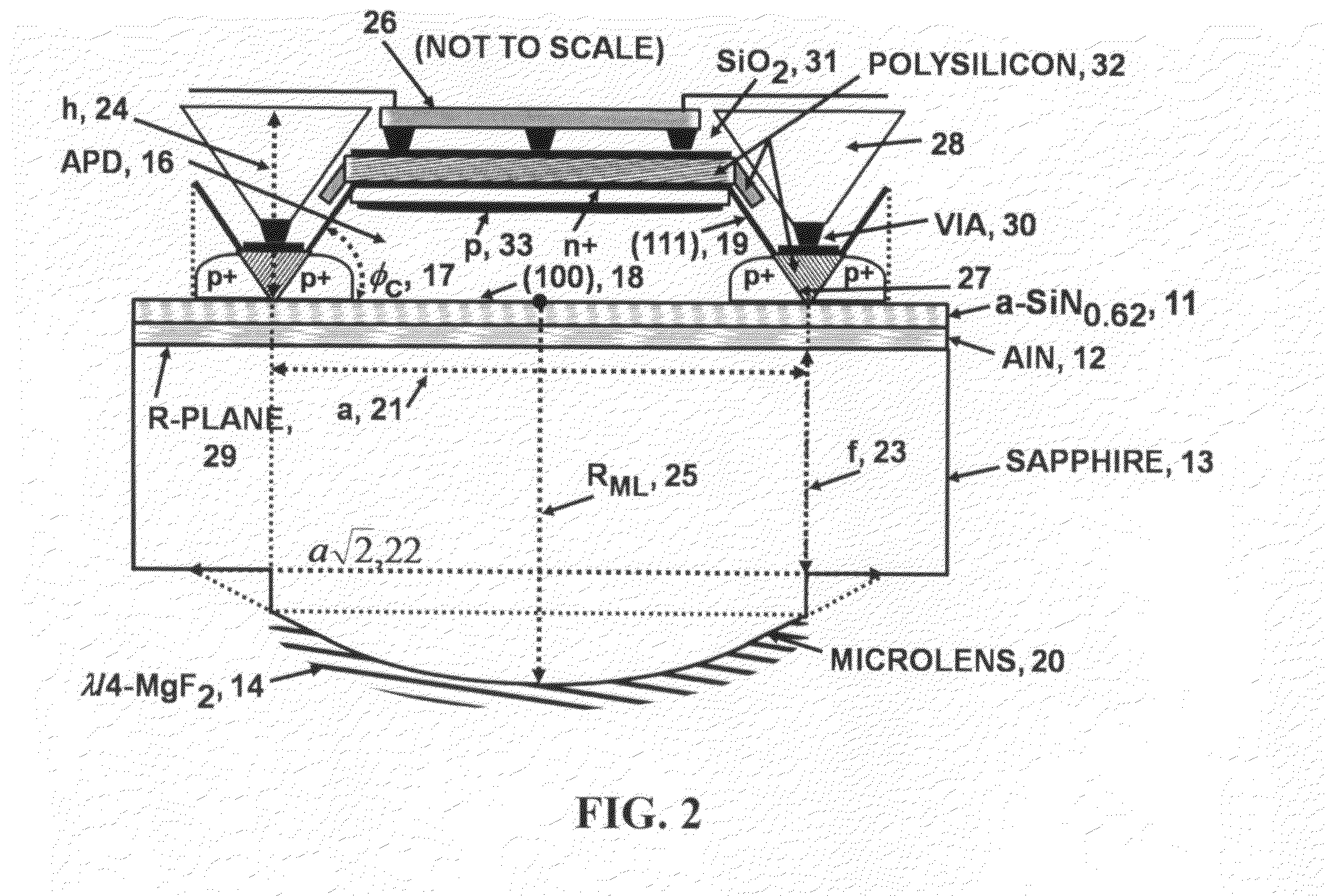
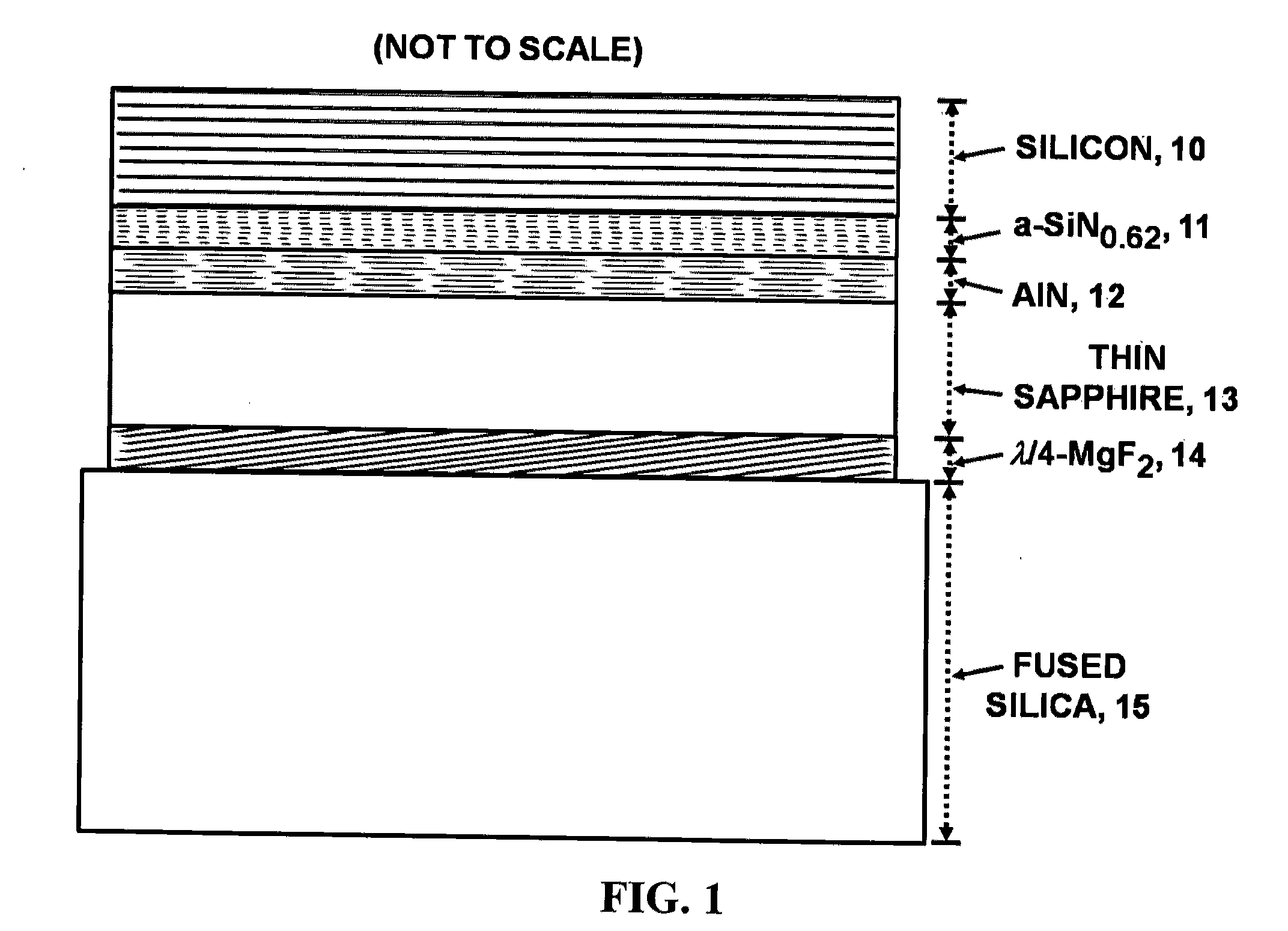
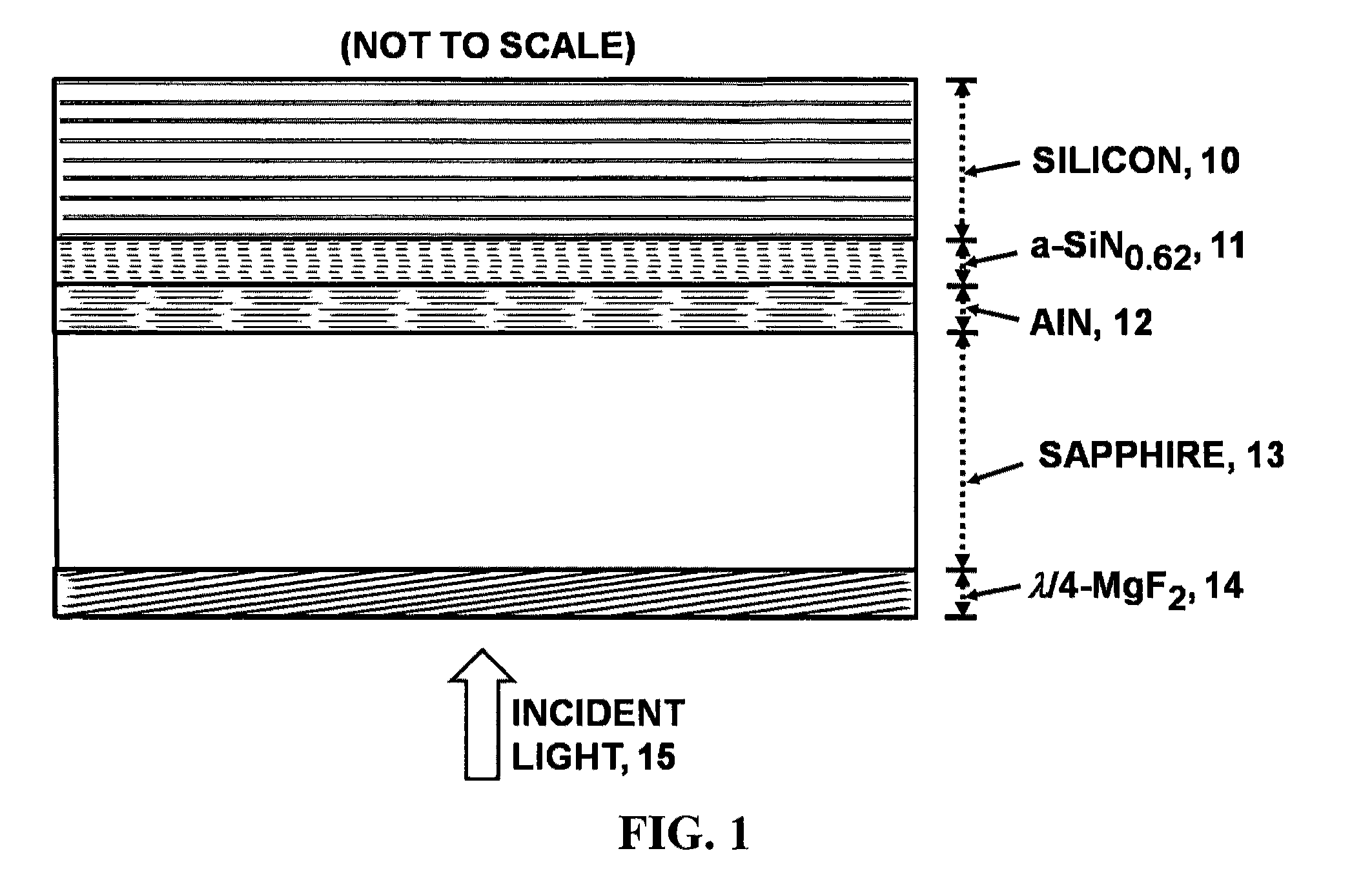
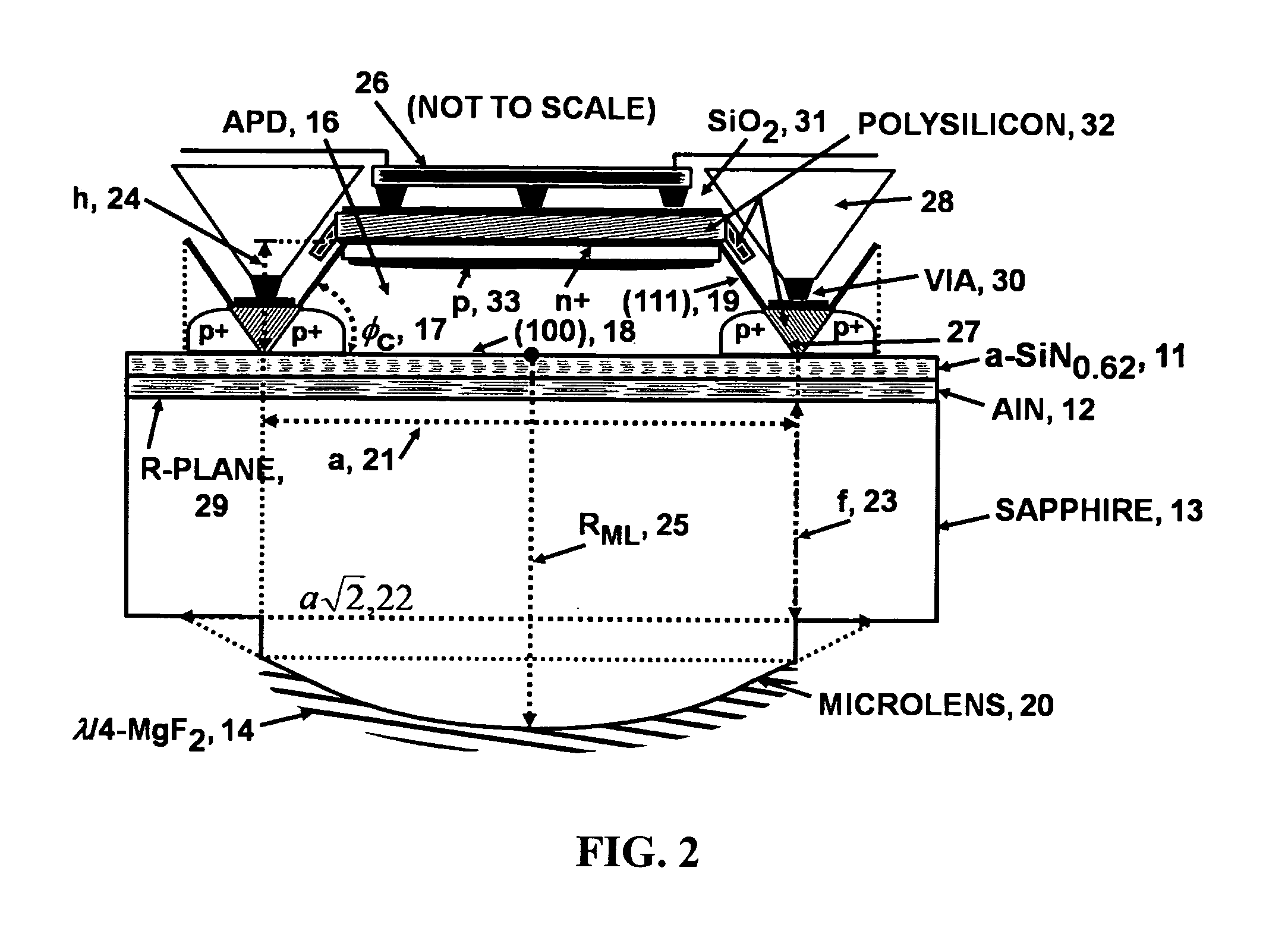
An advanced, very high transmittance, back-illuminated, silicon-on-sapphire wafer substrate design is presented for enabling high quantum efficiency and high resolution, silicon or silicon-germanium avalanche photodiode detector arrays. The wafer substrate incorporates a stacked antireflective bilayer between the sapphire and silicon layers, comprised of single crystal aluminum nitride (AlN) and non-stoichiometric, silicon rich, amorphous silicon nitride (a-SiNX<1.33), that provides optimal refractive index matching between sapphire and silicon. A one quarter wavelength, magnesium fluoride (λ / 4-MgF2) antireflective layer deposited on the back surface of the thinned sapphire provides refractive index matching at the air-sapphire interface. Selecting a composition of x=0.62 for a-SiNX, tunes an optimal refractive index for the layer. Selecting design thicknesses of 52 nm for single crystal AlN, 30 nm for a-SiN0.62, and 120 nm for λ / 4-MgF2 yields a back-illuminated optical transmittance T>50% for 250-300 nm, T>70% for 300-400 nm and T>90% for 400-1100 nm.
Owner:STERN ALVIN GABRIEL
Thin, very high transmittance, back-illuminated, silicon-on-saphire semiconductor substrates bonded to fused silica
InactiveUS20120299143A1High light transmittanceSuppression problemSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSingle crystalSilicon dioxide
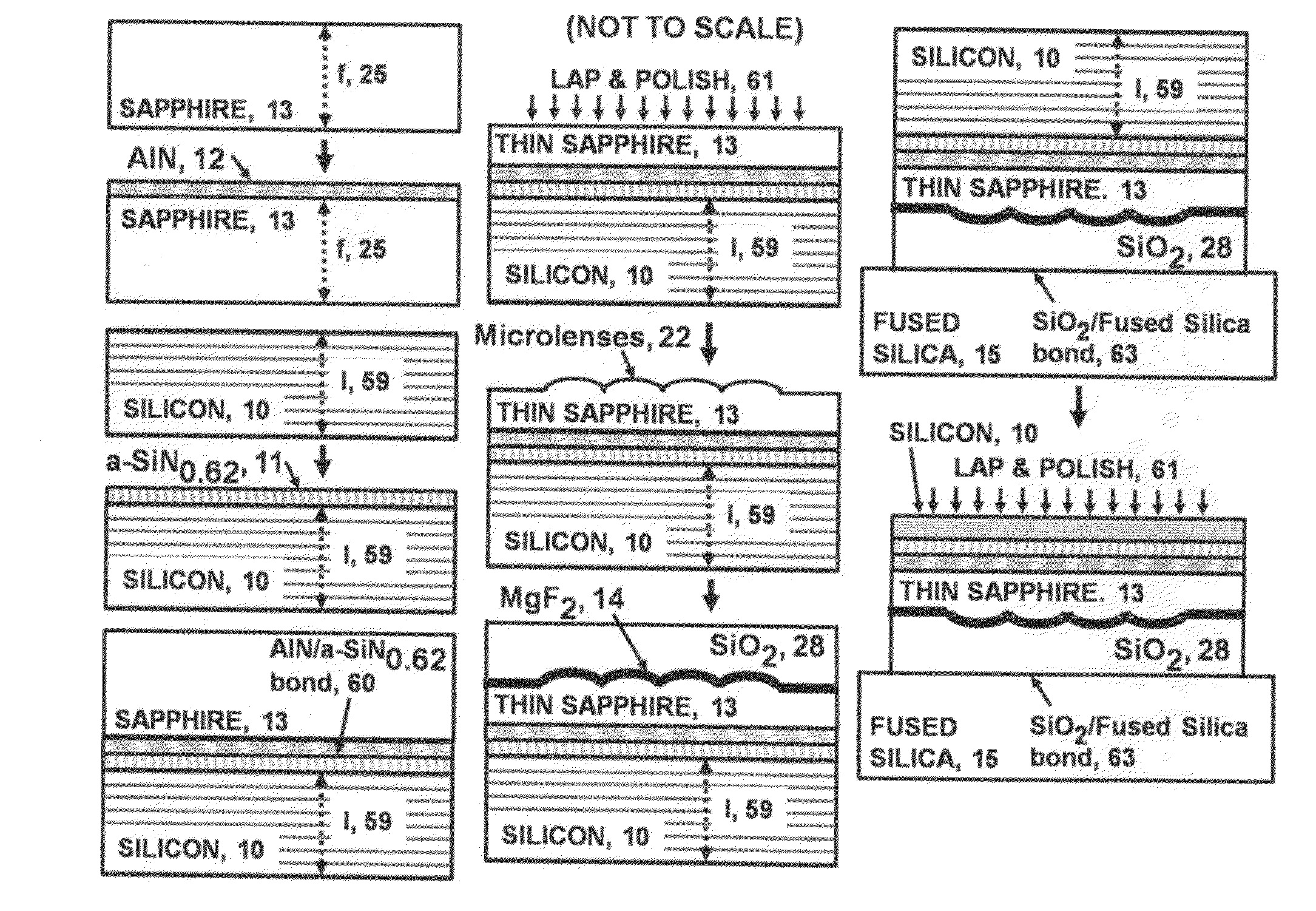
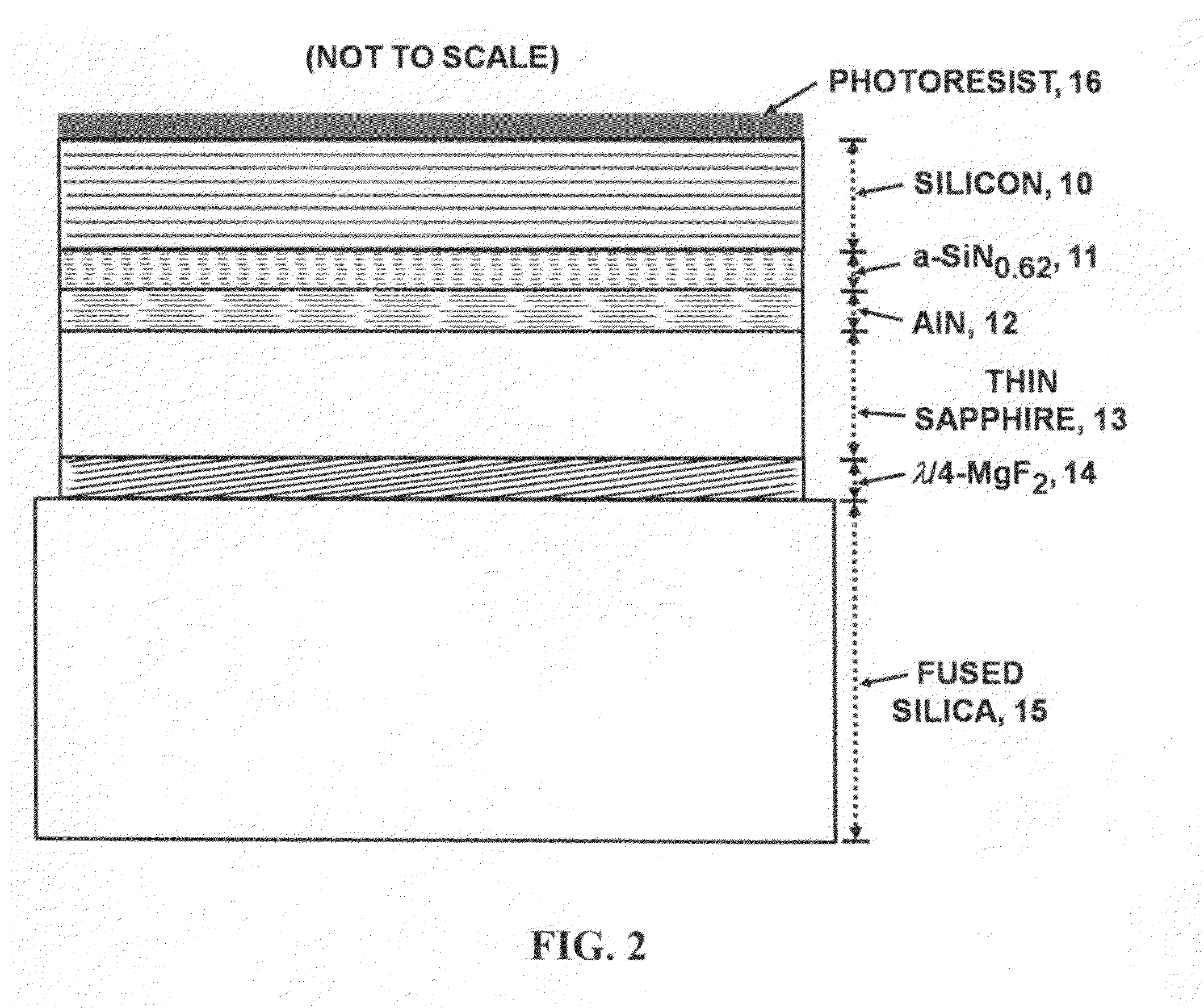
A very high transmittance, back-illuminated, silicon-on-thin sapphire-on-fused silica wafer substrate design is presented for enabling high quantum efficiency and high resolution, silicon or silicon-germanium avalanche photodiode detector arrays with improved indirect optical crosstalk suppression. The wafer substrate incorporates a stacked antireflective bilayer between the sapphire and silicon, comprised of single crystal aluminum nitride (AlN) and non-stoichiometric, silicon rich, amorphous silicon nitride (a-SiNX<1.33), as well as a one quarter wavelength, magnesium fluoride (λ / 4-MgF2) back-side antireflective layer which is bonded to a fused silica wafer. The fused silica provides mechanical support, allowing the sapphire to be thinned to optimal thickness below 50 μm, for improved optical transmittance and in conjunction with monolithic sapphire microlenses, suppression of indirect optical crosstalk from multiple reflections of APD emitted light. After solid-state device fabrication, the silicon can be coated with photoresist and the fused silica dissolved in buffered hydrogen fluoride (HF) to recover the thin Si—(AlN / a-SiNX<1.33)-sapphire-(MgF2).
Owner:STERN ALVIN GABRIEL
Very high transmittance, back-illuminated, silicon-on-sapphire semiconductor wafer substrate for high quantum efficiency and high resolution, solid-state, imaging focal plane arrays
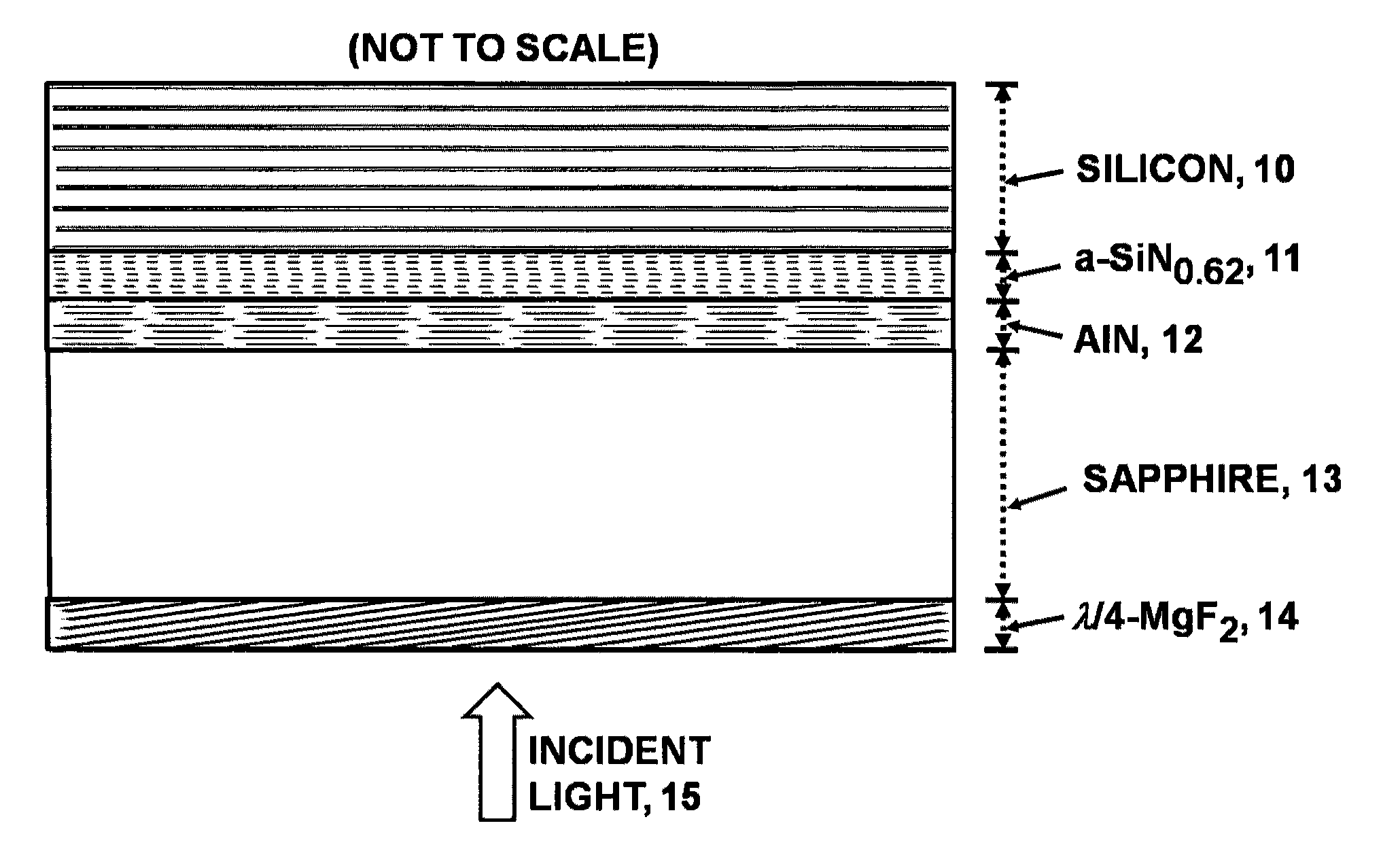
InactiveUS8354282B2High light transmittanceGreat index of refractionLaser detailsSolid-state devicesSingle crystalRefractive index matching
An advanced, very high transmittance, back-illuminated, silicon-on-sapphire wafer substrate design is presented for enabling high quantum efficiency and high resolution, silicon or silicon-germanium avalanche photodiode detector arrays. The wafer substrate incorporates a stacked antireflective bilayer between the sapphire and silicon layers, comprised of single crystal aluminum nitride (AlN) and non-stoichiometric, silicon rich, amorphous silicon nitride (a-SiNX<1.33), that provides optimal refractive index matching between sapphire and silicon. A one quarter wavelength, magnesium fluoride (λ / 4-MgF2) antireflective layer deposited on the back surface of the thinned sapphire provides refractive index matching at the air-sapphire interface. Selecting a composition of x=0.62 for a-SiNX, tunes an optimal refractive index for the layer. Selecting design thicknesses of 52 nm for single crystal AlN, 30 nm for a-SiN0.62, and 120 nm for λ / 4-MgF2 yields a back-illuminated optical transmittance T>50% for 250-300 nm, T>70% for 300-400 nm and T>90% for 400-1100 nm.
Owner:STERN ALVIN GABRIEL
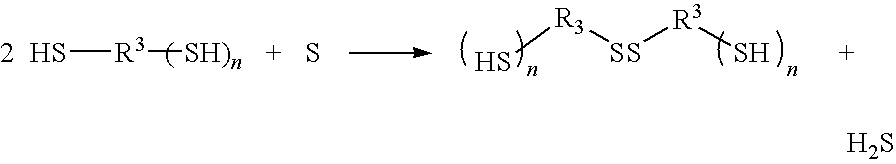
Method for producing polythiourethane resin
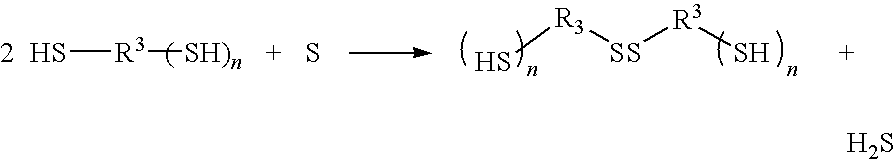
A process for producing a polythiourethane resin which comprises (A) a step of synthesizing a polythiol oligomer having disulfide bond by reaction of a polythiol compound having a functionality of two or greater and sulfur and (B) a step of bringing the polythiol oligomer obtained in step (A) and a compound having poly(thio)isocyanate groups into reaction with each other, wherein step (A) is conducted in the absence of solvents using no catalysts or a catalyst substantially inert to the compound having poly(thio)isocyanate groups. A polythiol oligomer exhibiting a greater refractive index than that of the polythiol compound having a functionality of two or greater used as the starting material is produced at a low cost, and a process for producing a practically useful polythiourethane resin exhibiting a stable great refractive index and a great Abbe number is provided.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Coating composition containing high-refractive-index metal oxide fine particles, and curable coating film obtained by applying the coating composition onto base
ActiveUS20110257298A1High refractive indexPossibility of deteriorationMaterial nanotechnologyInorganic pigment treatmentComposite oxideTitanium
The present invention relates to a coating composition containing metal oxide particles with a high refractive index and low photocatalytic activity and a coating film obtained by applying the coating composition onto a substrate. The coating composition contains metal oxide particles with a high refractive index obtained by coating the specific fine particles of the titanium-based oxide on their surfaces with at least a silica-based oxide or a silica-based composite oxide, and the coating film is obtained by applying the coating composition onto a substrate. The metal oxide particles with not only a high refractive index but also low photocatalytic activity, and therefore a coating film with excellent weathering resistance and light resistance can be formed on a substrate.
Owner:JGC CATALYSTS & CHEM LTD
Bismuth borate glass encapsulant for LED phosphors
ActiveUS20130256598A1Improve stabilityBackscatter can be reducedSolid-state devicesGlass shaping apparatusChemistryBismuth borate
Owner:CORNING INC
Curable resin composition, optical component and optical waveguide
InactiveUS7295749B2Great index of refractionReduce light lossOptical waveguide light guideRefractive indexAlicyclic Hydrocarbons
The present invention is to provide a curable resin composition that is desirably used for manufacturing an optical part, in particular, an optical waveguide, that is superior in heat-resistant properties such as a heat-resistant decomposing property and a coloring-resistant property, and has its refractive index precisely controlled.The present invention provides a curable resin composition, comprising:(A) a monomer that contains a polycyclic alicyclic hydrocarbon skeleton and two or more terminal radical polymerizable groups,(B) a monomer that contains a perfluoroalkylene skeleton and two or more terminal radical polymerizable groups, and(C) a photopolymerization initiator and / or a thermal polymerization initiator.The present also provides an optical part, in particular, an optical waveguide, formed by photo-and / or thermo-curing the above curable resin composition.
Owner:ORMON CORP
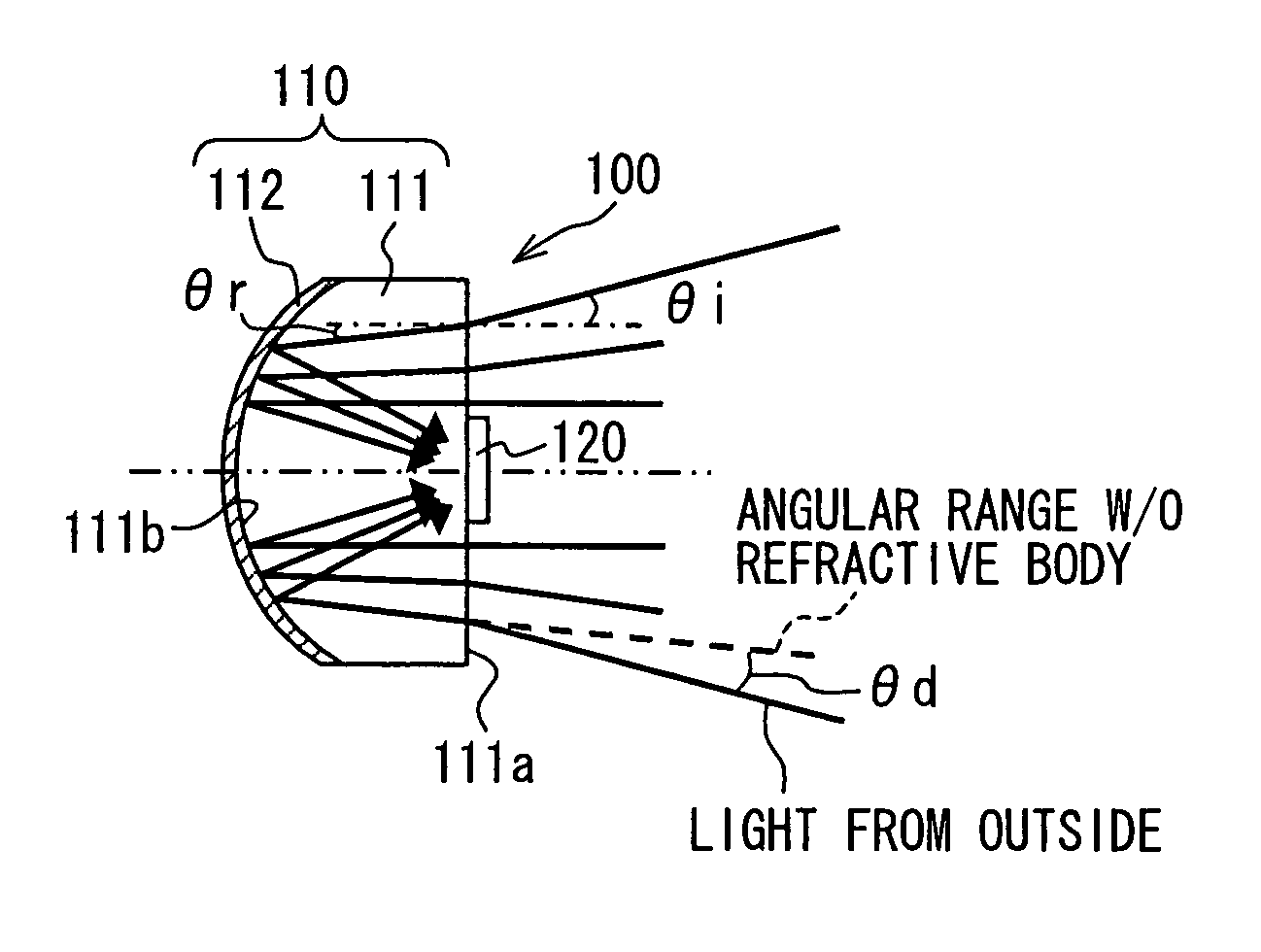
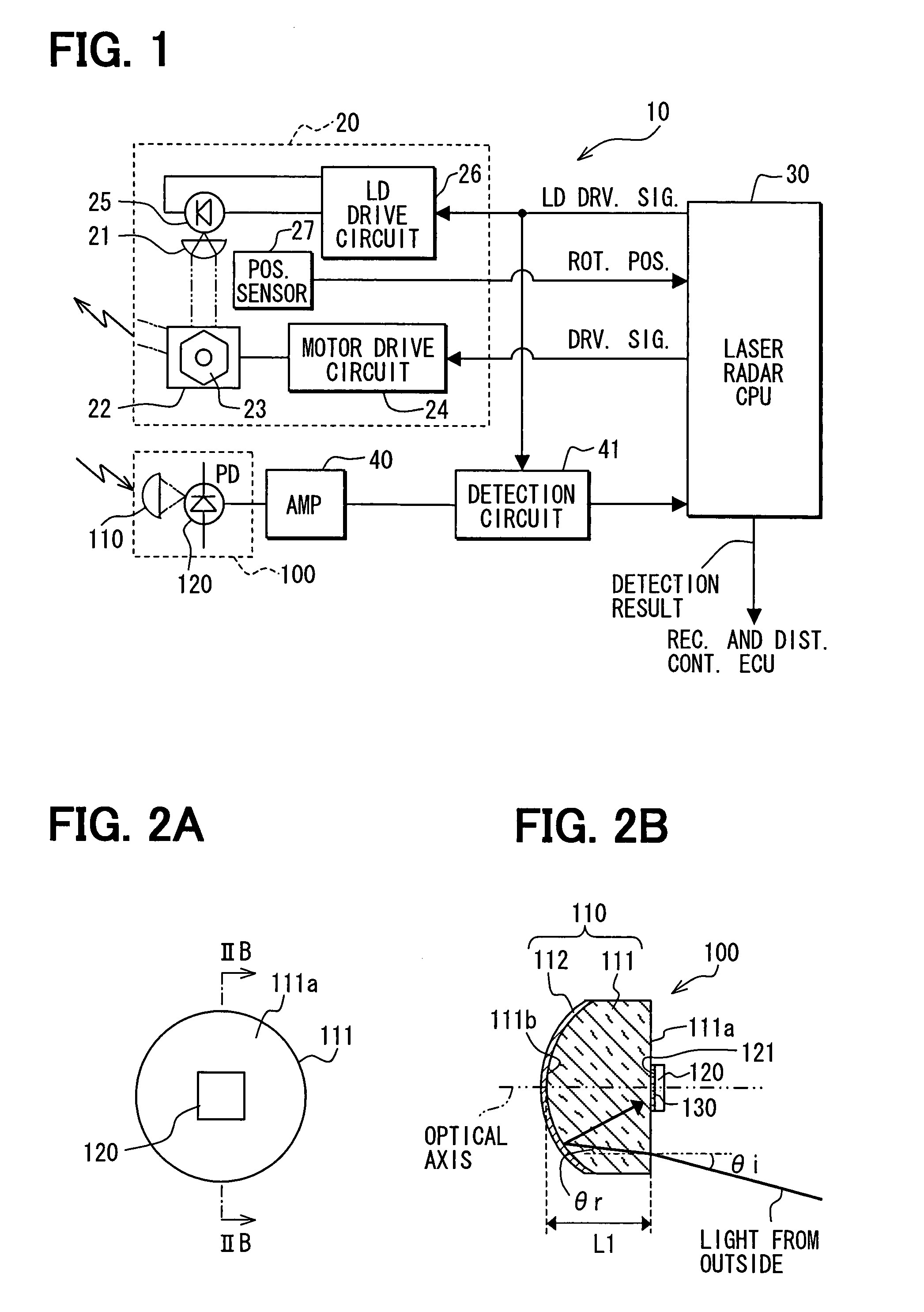
Radar apparatus and optical receiver thereof
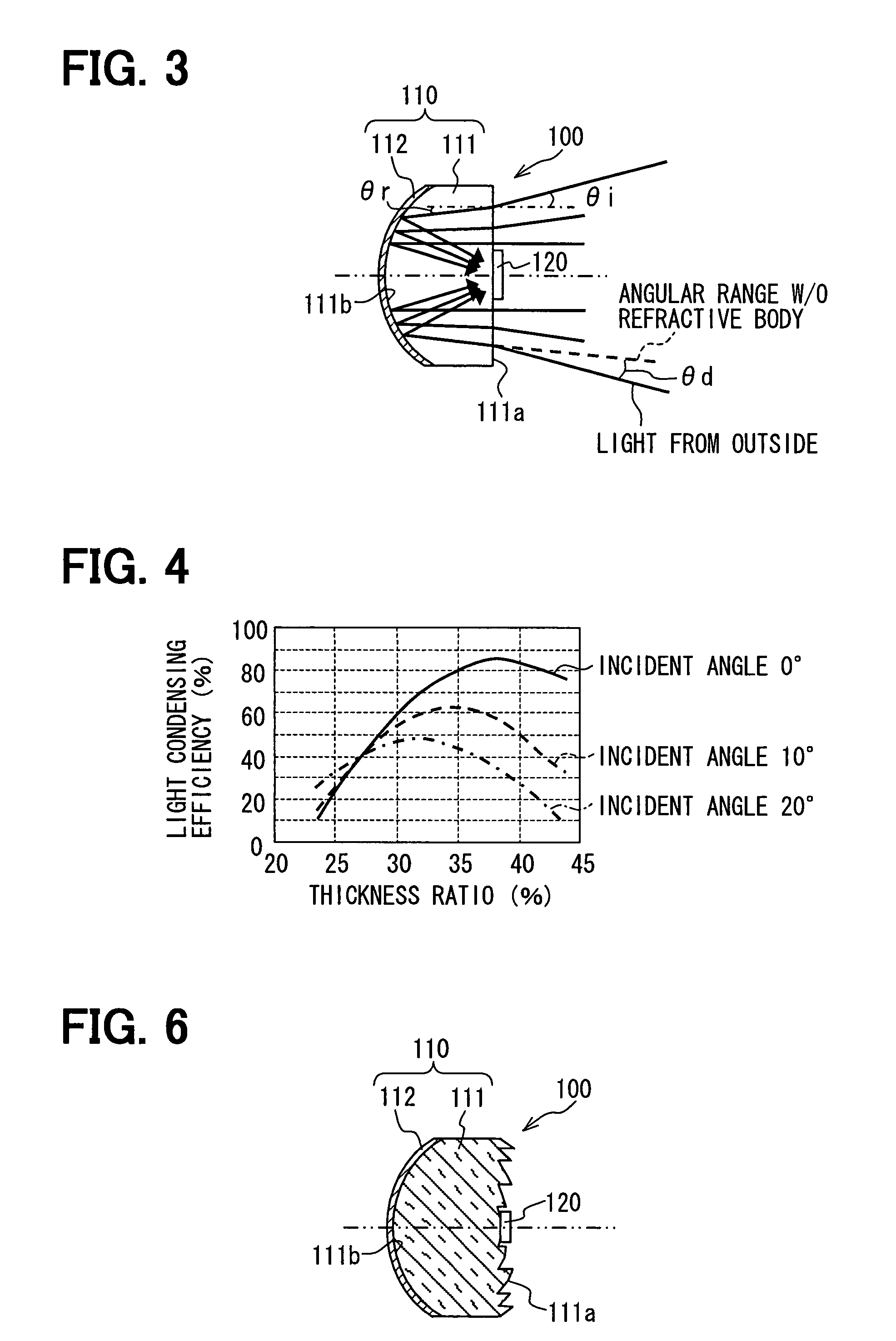
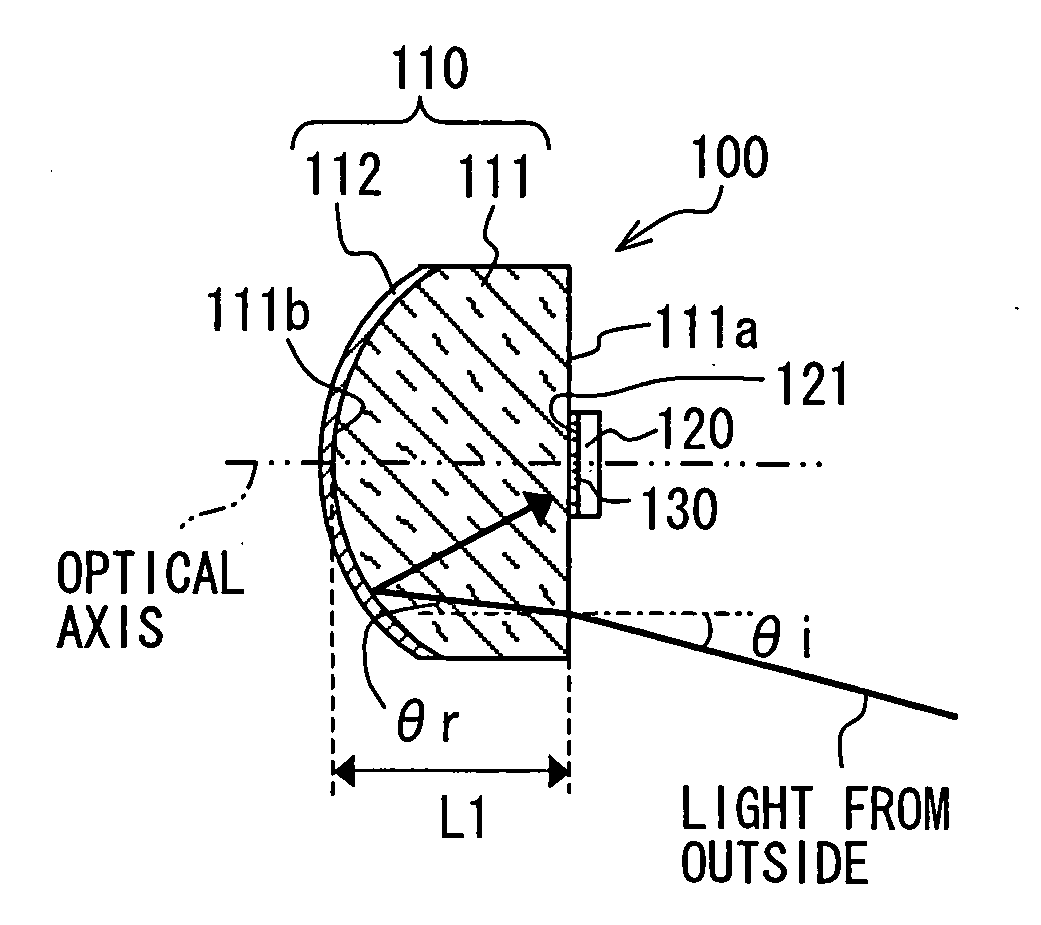
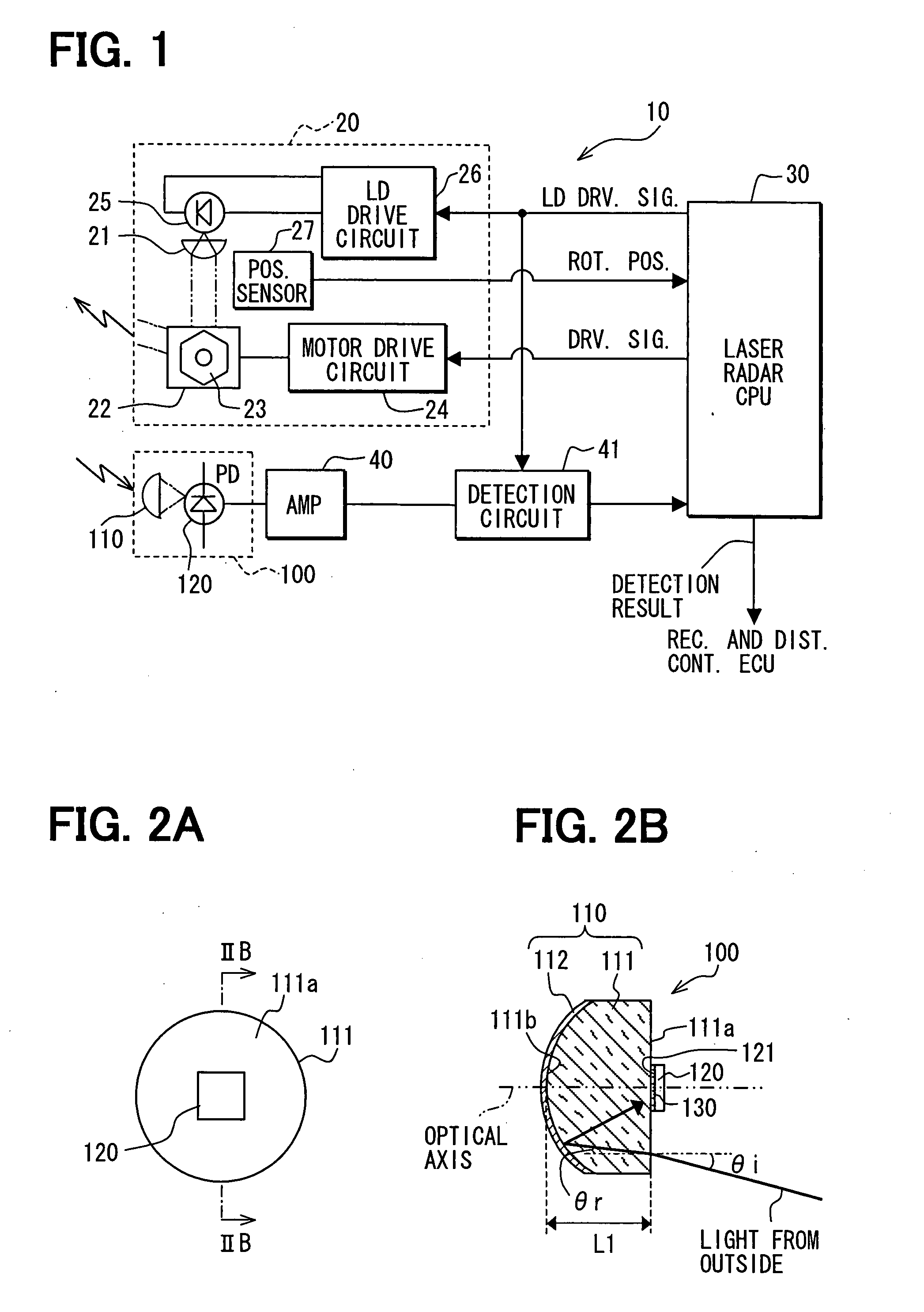
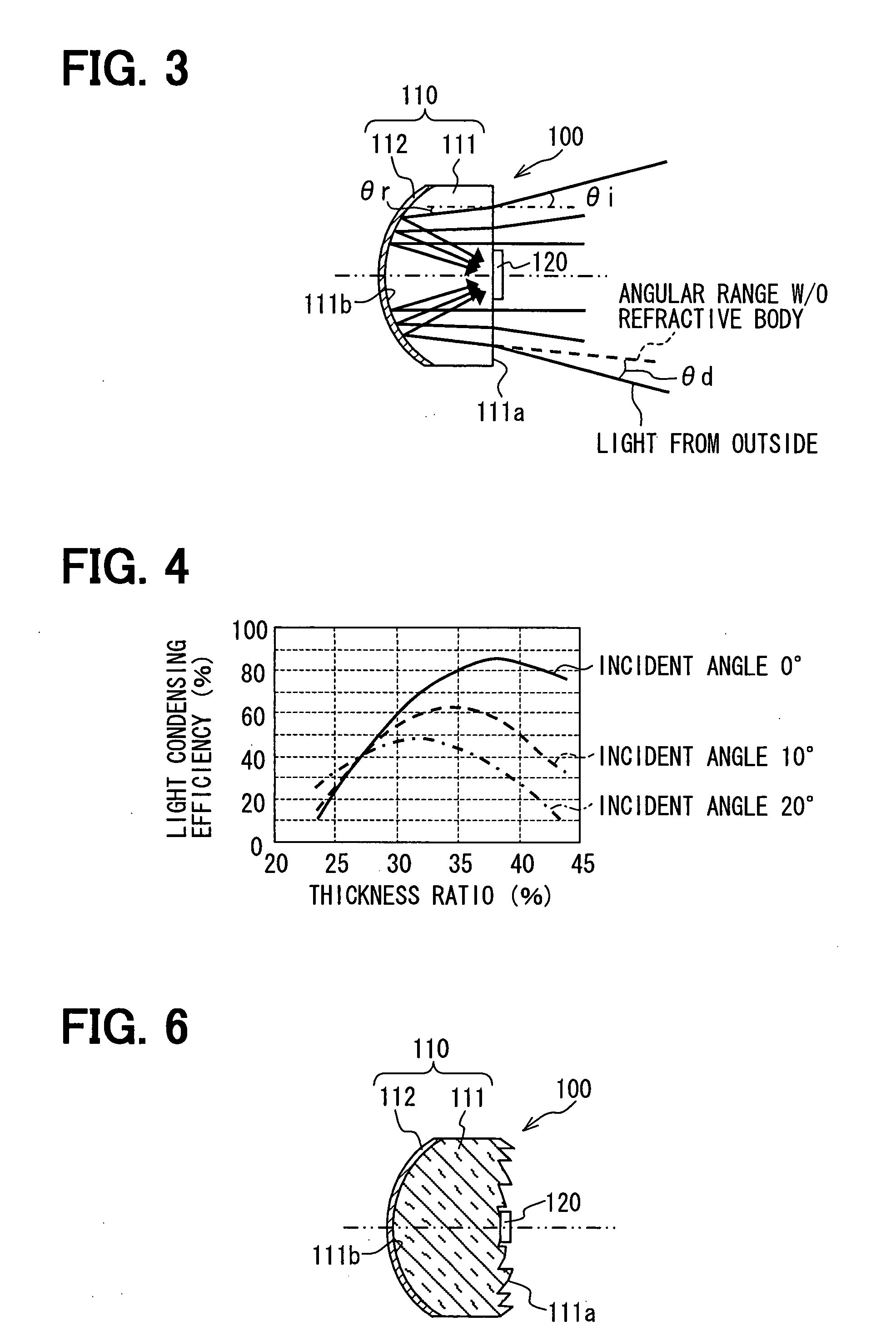
A radar apparatus has a light receiver that includes a refractive body and a mirror on an opposite surface of the refractive body relative to an incidence surface of the refractive body for receiving an incident light from an outside of the radar apparatus. The refractive angle of the refractive body is configured to be smaller than an incident angle of the incident light, and the mirror is configured to reflect at least a portion of the incident light toward a first light receiving element that is disposed on the incidence surface with its light receiving face facing the incidence surface of the refractive body.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Optical waveguide structure
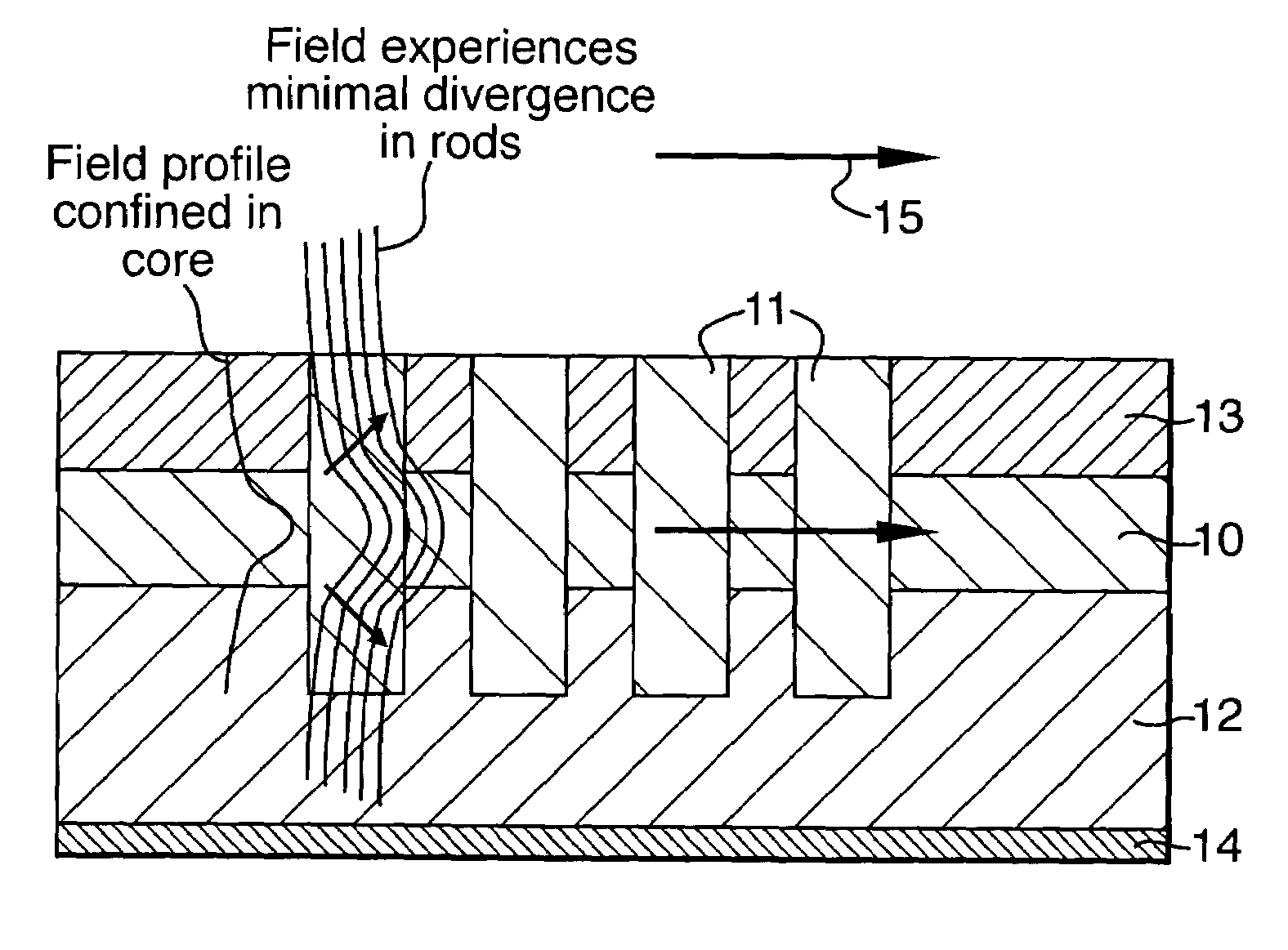
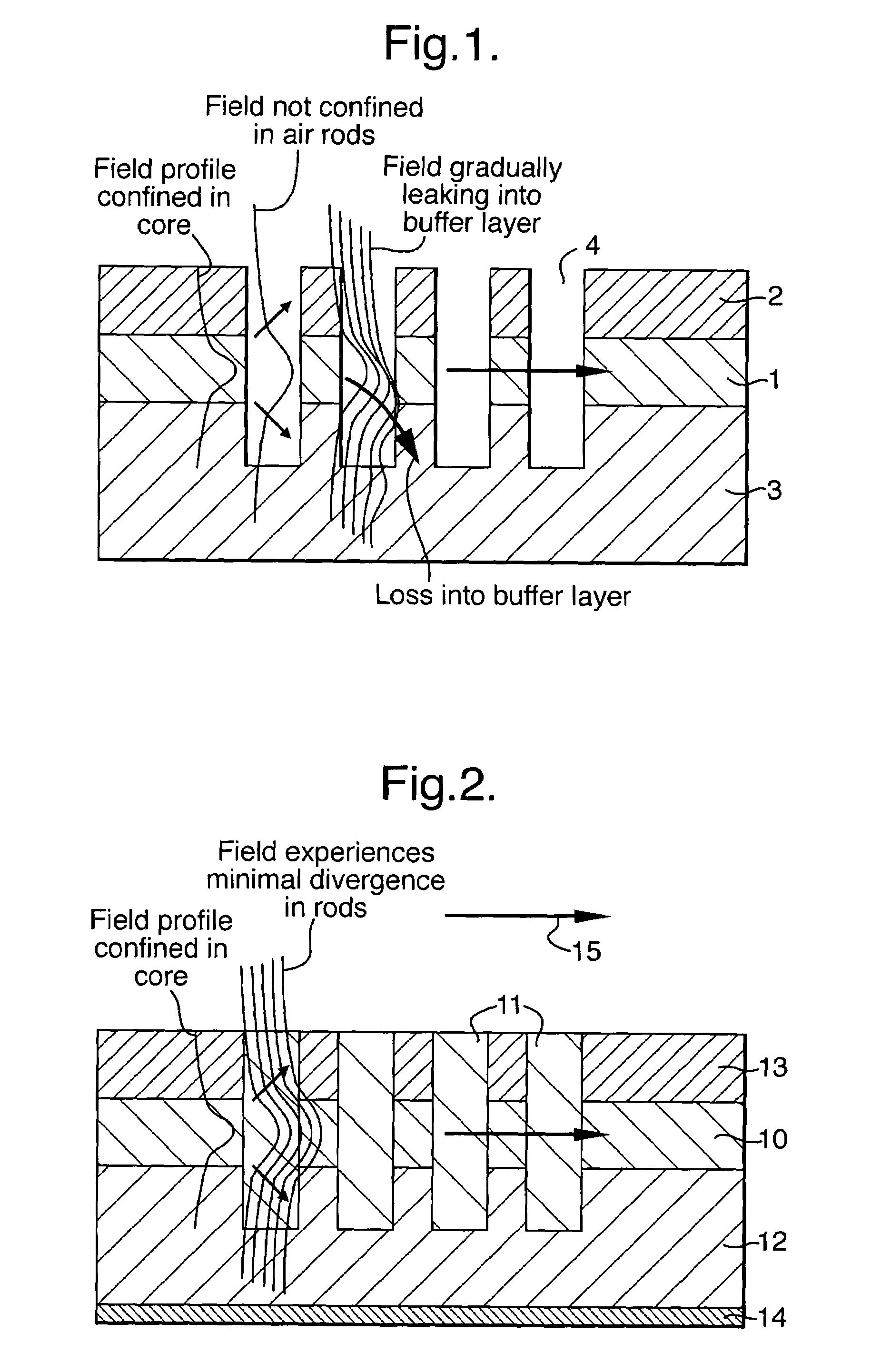
InactiveUS7162132B2Great vertical confinement of lightEnhanced couplingNanoopticsOptical waveguide light guideFiberRefractive index contrast
A waveguide structure according to the invention comprises a core layer (10), having a refractive index ncore, and an array of rods (11) in the core layer having a refractive index nrods. The refractive indices satisfy the inequality: nrods>ncore. In a planar waveguide structure buffer (12) and cladding (13) layers are included, having a refractive index nbuffer and ncladding respectively. The refractive indices then satisfy the inequality: nrods>ncore>ncladding and nbuffer. This condition provides greater vertical confinement of the E-field of an optical signal passing through the waveguide. Furthermore, it allows waveguides to be formed of a glassy material having a similar refractive index and core dimensions to that of a fiber. A high refractive index contrast within the photonic crystal region is used while totally eliminating the need for mode conversion to launch light in and out of the waveguide.
Owner:QUANTUM NIL LTD +1
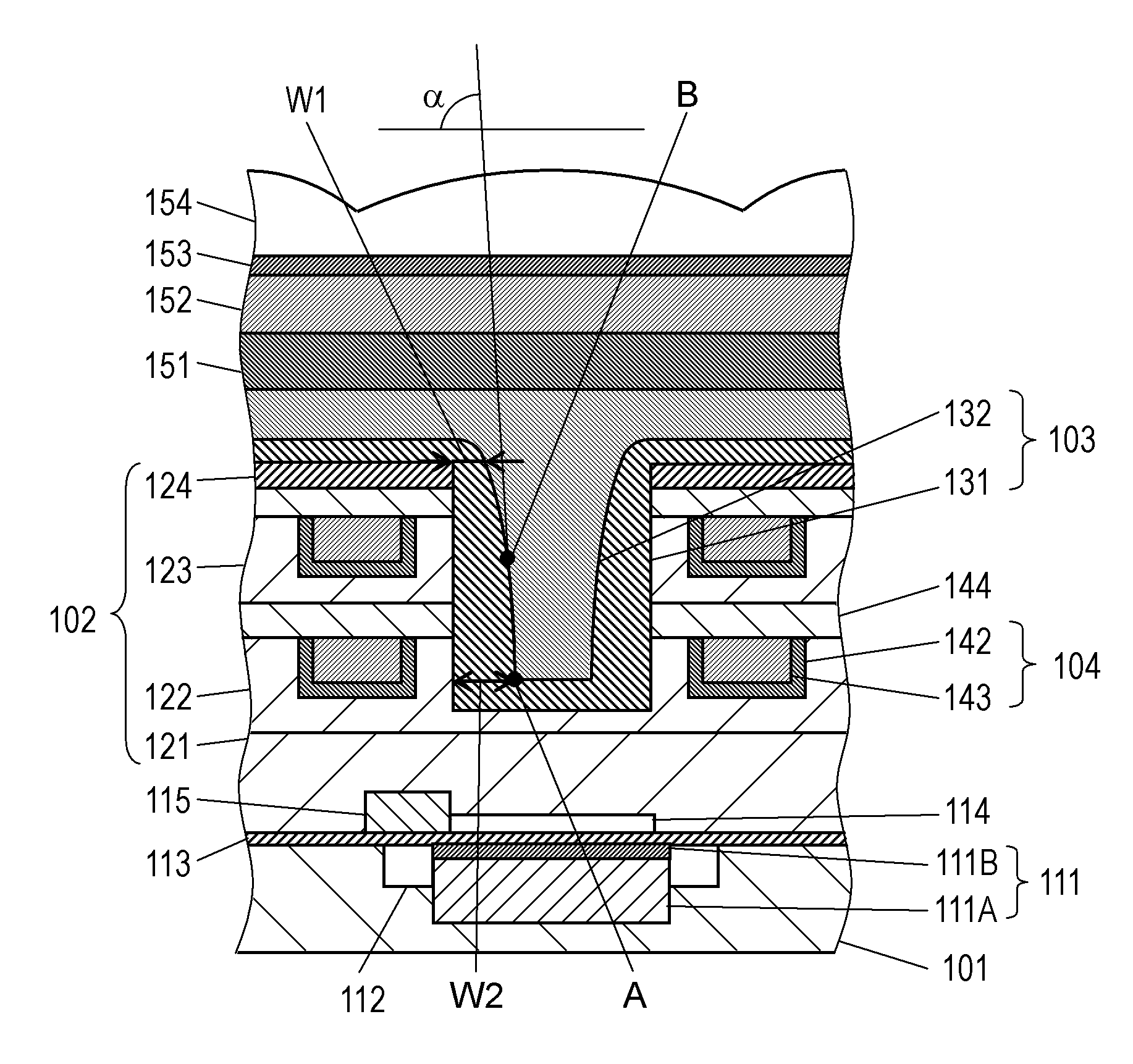
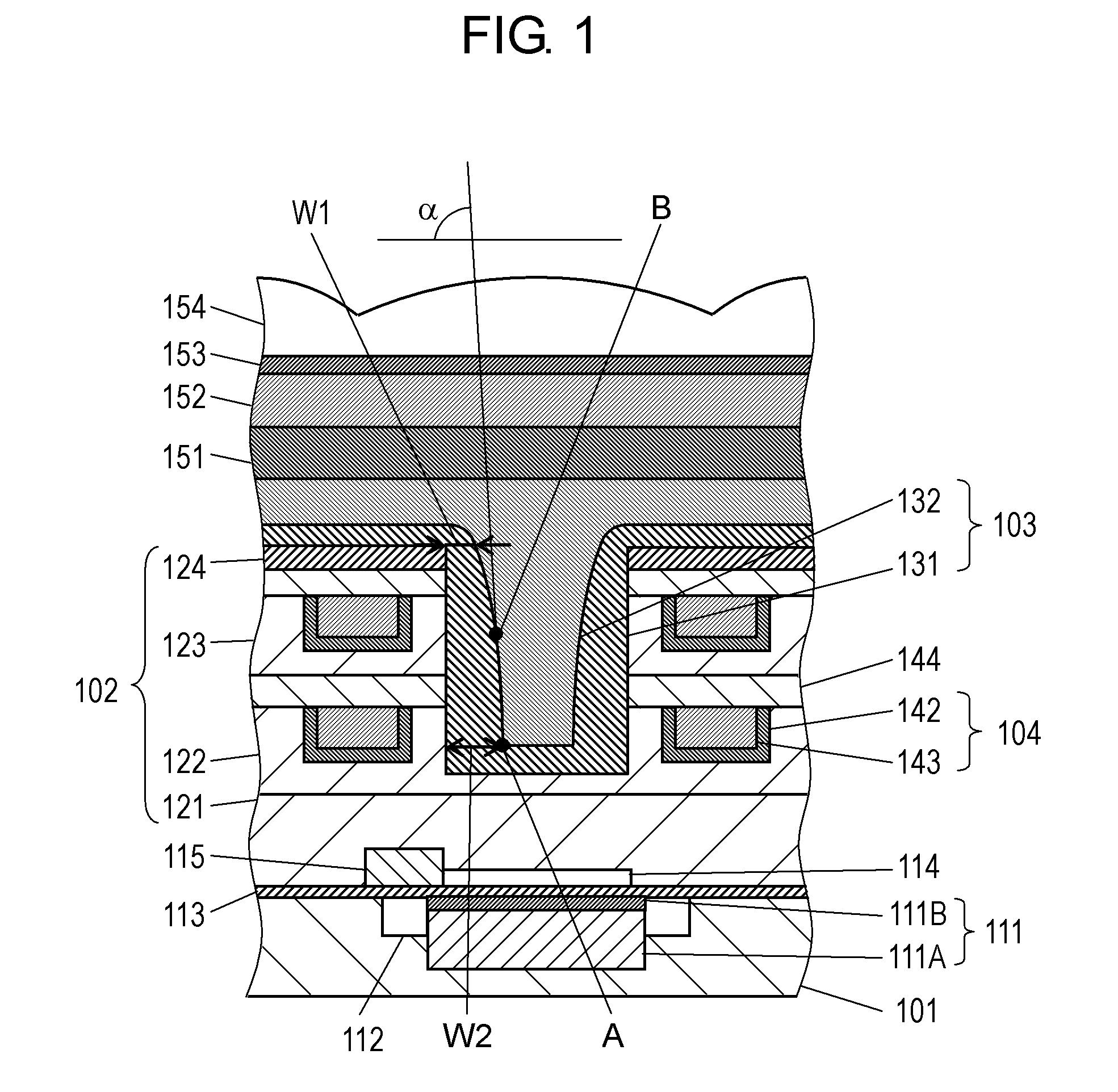
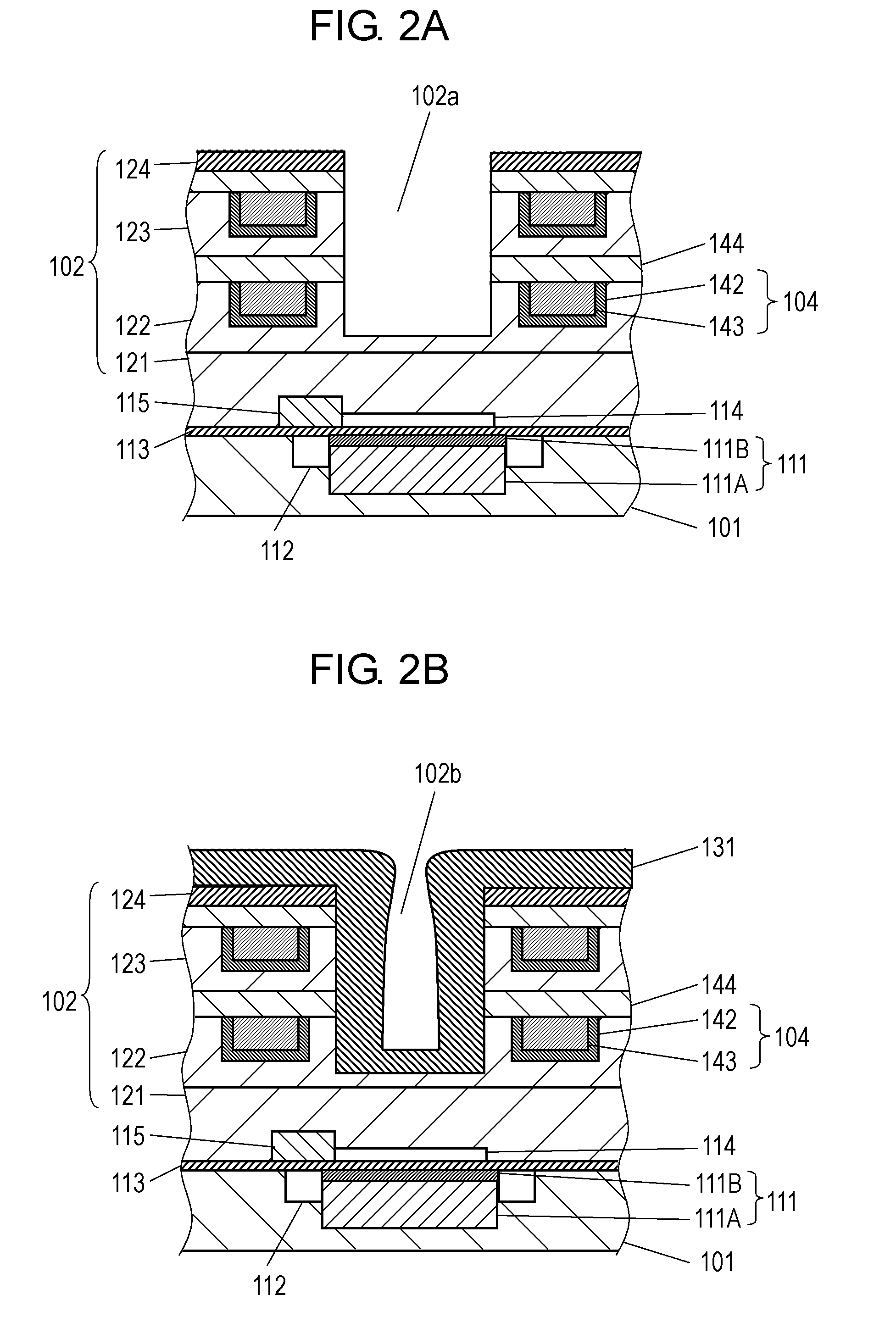
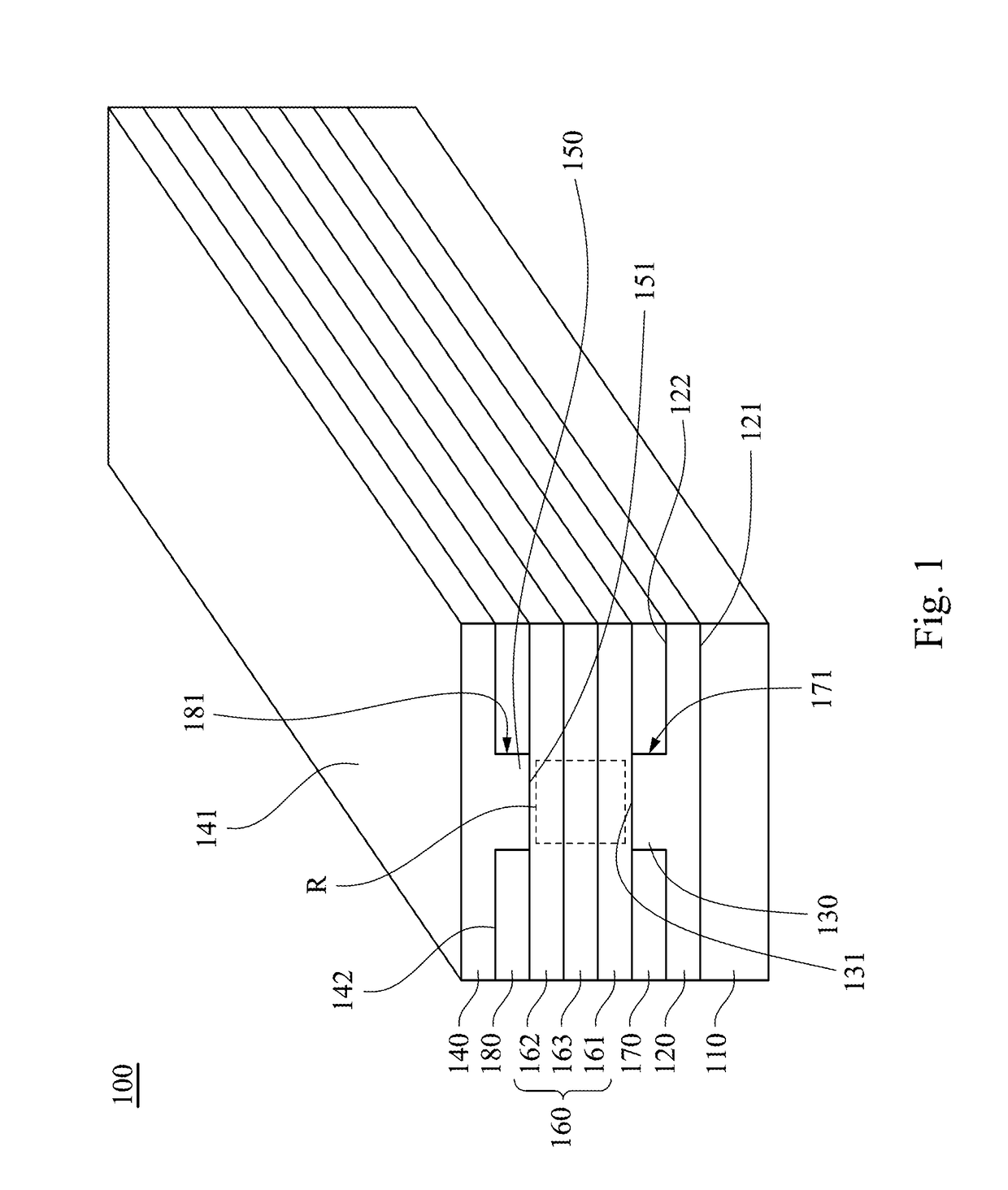
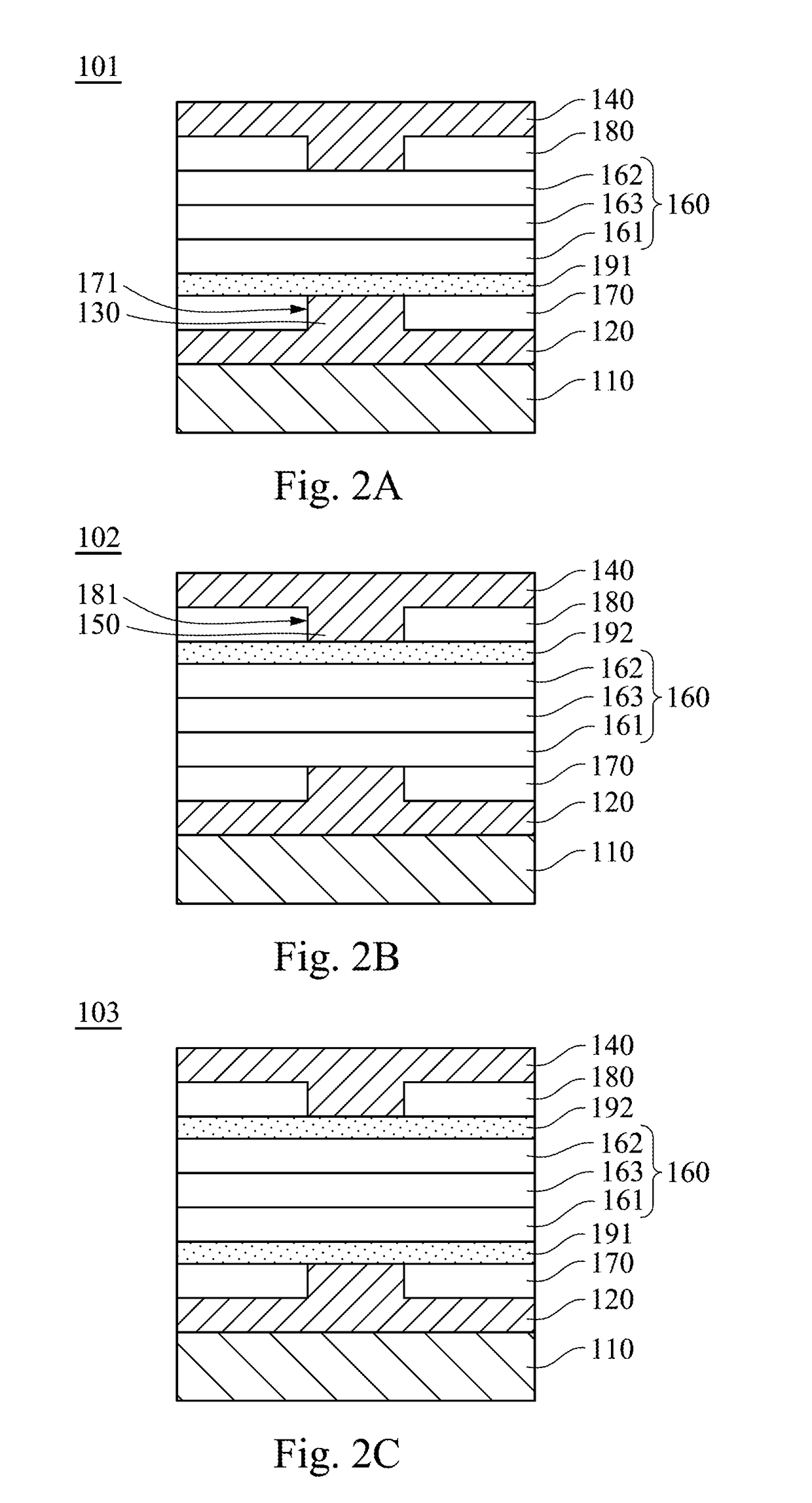
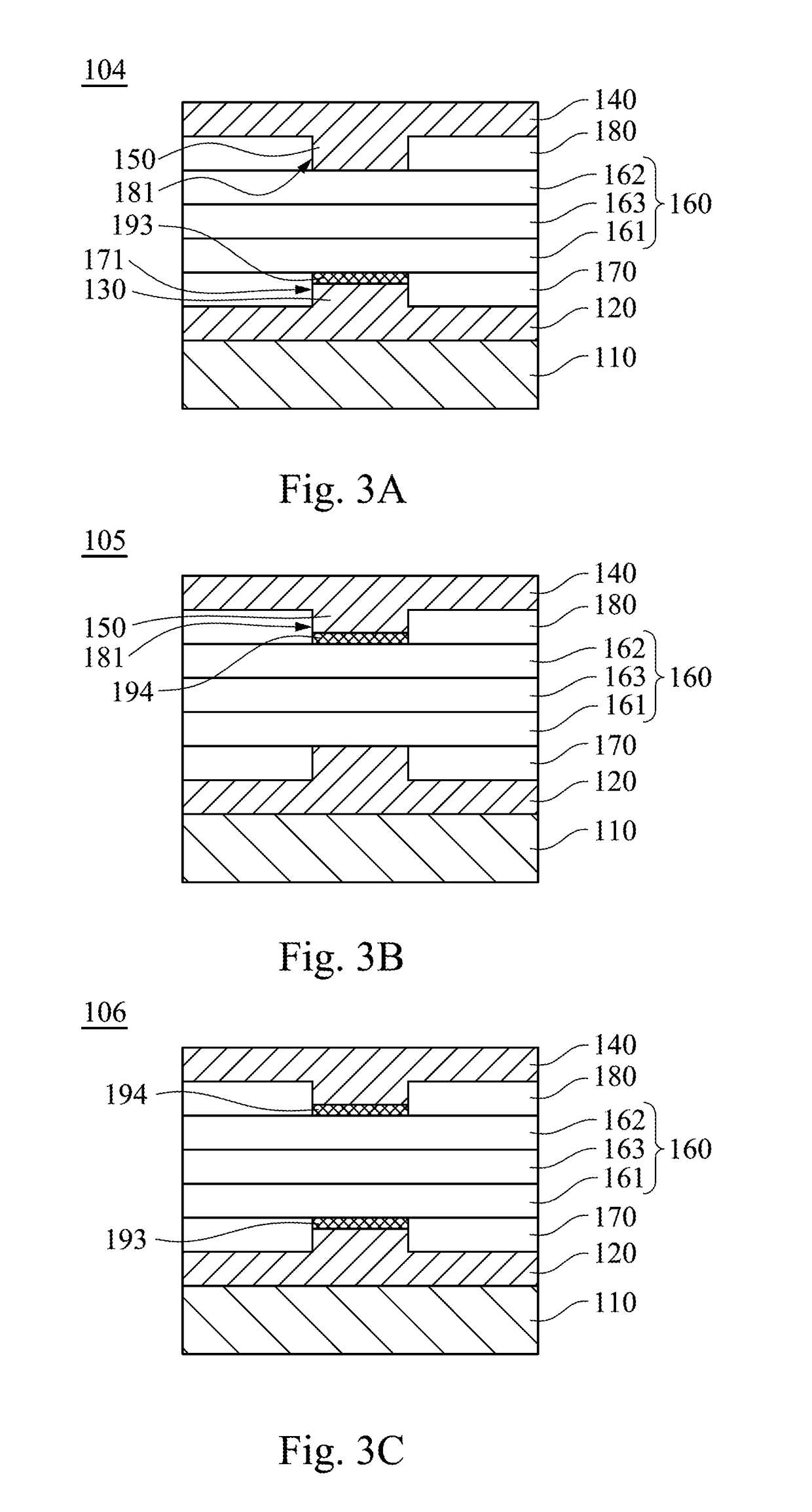
Solid-state imaging device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20120267741A1High refractive indexImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringWaveguide
A solid-state imaging device includes: a light receiving portion formed on a semiconductor substrate; a multilayer structure formed on the semiconductor substrate, that includes an interlayer insulating film and a first concave portion at a position corresponding to the light receiving portion; and an optical waveguide formed in the first concave portion. The optical waveguide includes a first film and a second film formed sequentially from a side of the multilayer structure. The first film covers a side face and a bottom face of the first concave portion and includes a second concave portion. The second film is in contact with the first film and fills up the second concave portion. The thickness of the first film formed on the side face of the first concave portion is thinner at a top portion of the first concave portion than at the bottom portion thereof.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for producing plastic lens
InactiveUS20070196567A1Improve scratch resistanceGreat index of refractionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpecial surfacesRefractive indexUltraviolet lights
The method for producing a plastic lens of the present invention comprises forming a hard coat film by coating a plastic substrate with a coating composition comprising (A) modified colloid particles of a stannic oxide-zirconium oxide composite having diameters of 4.5 to 60 nm which are formed by coating the surface of nuclei with colloid particles of a tungsten oxide-stannic oxide-silicon dioxide composite having diameters of 2 to 7 nm, a ratio of amounts by weight of WO3 / SnO2 of 0.1 to 100 and a ratio of amounts by weight of SiO2 / SnO2 of 0.1 to 100 using as the nuclei colloid particles of a stannic oxide-zirconium oxide composite having diameters of 4 to 50 nm and a structure formed by bonding colloid particles of stannic oxide obtained by reaction of metallic tin, an organic acid and hydrogen peroxide and colloid particles of zirconium oxide to each other in amounts such that a ratio of amounts by weight of the oxides of ZrO2 / SnO2 is 0.02 to 1.0 and (B) an organosilicon compound. The method provides a plastic lens having a hard coat film exhibiting improved scratch resistance and a great refractive index without adverse effects on various properties such as the property of preventing yellowing under irradiation with ultraviolet light and adhesion.
Owner:HOYA CORP
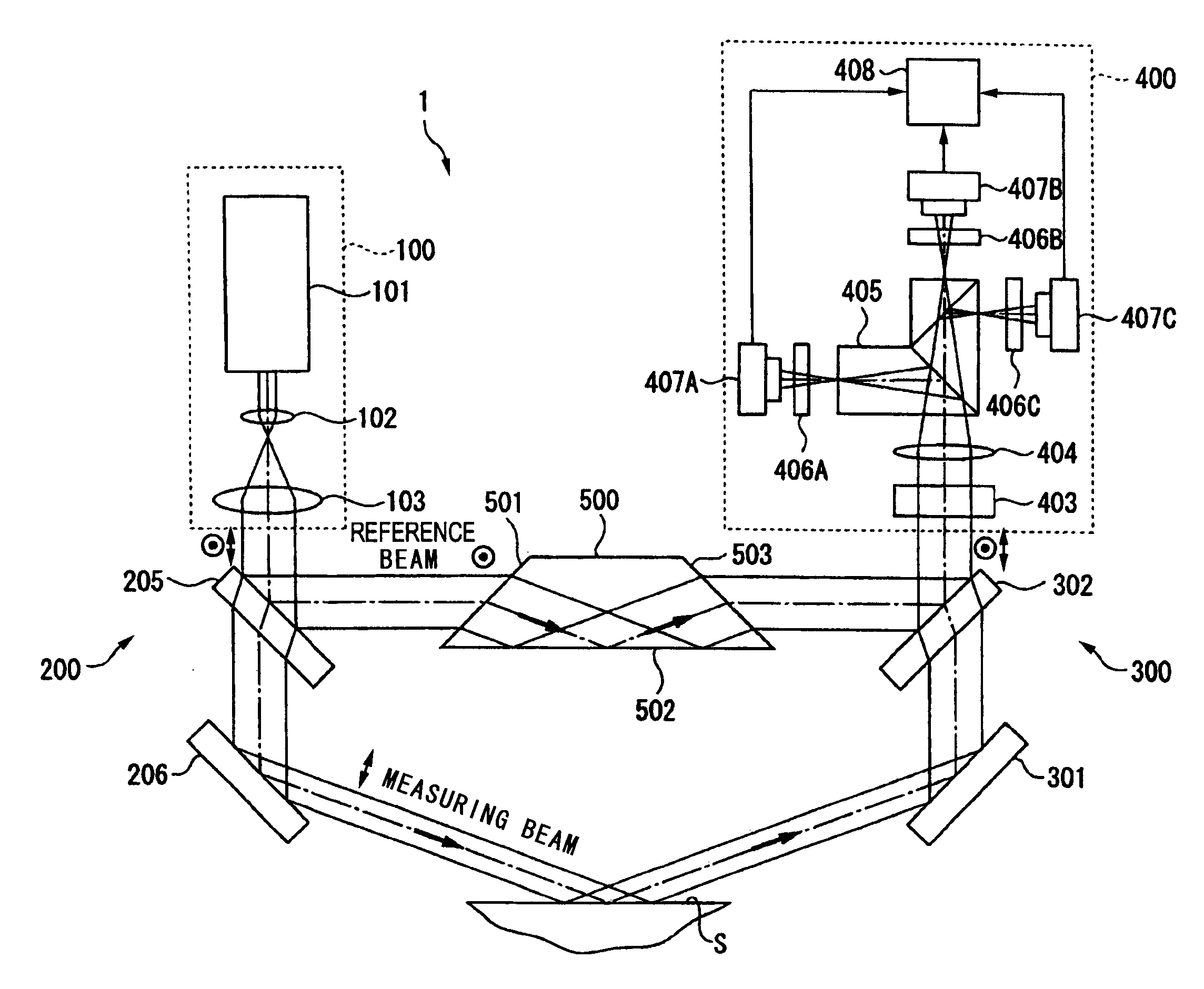
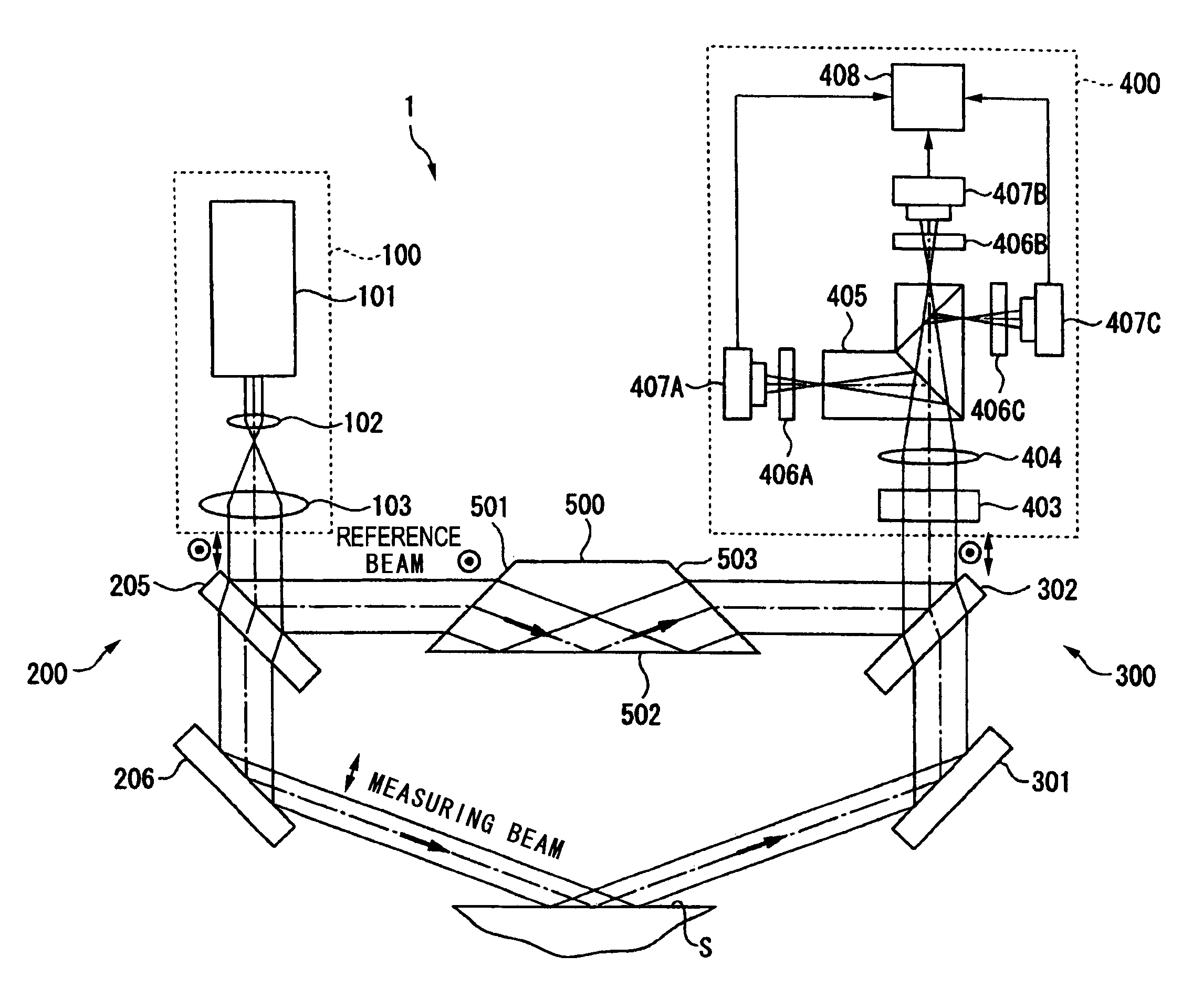
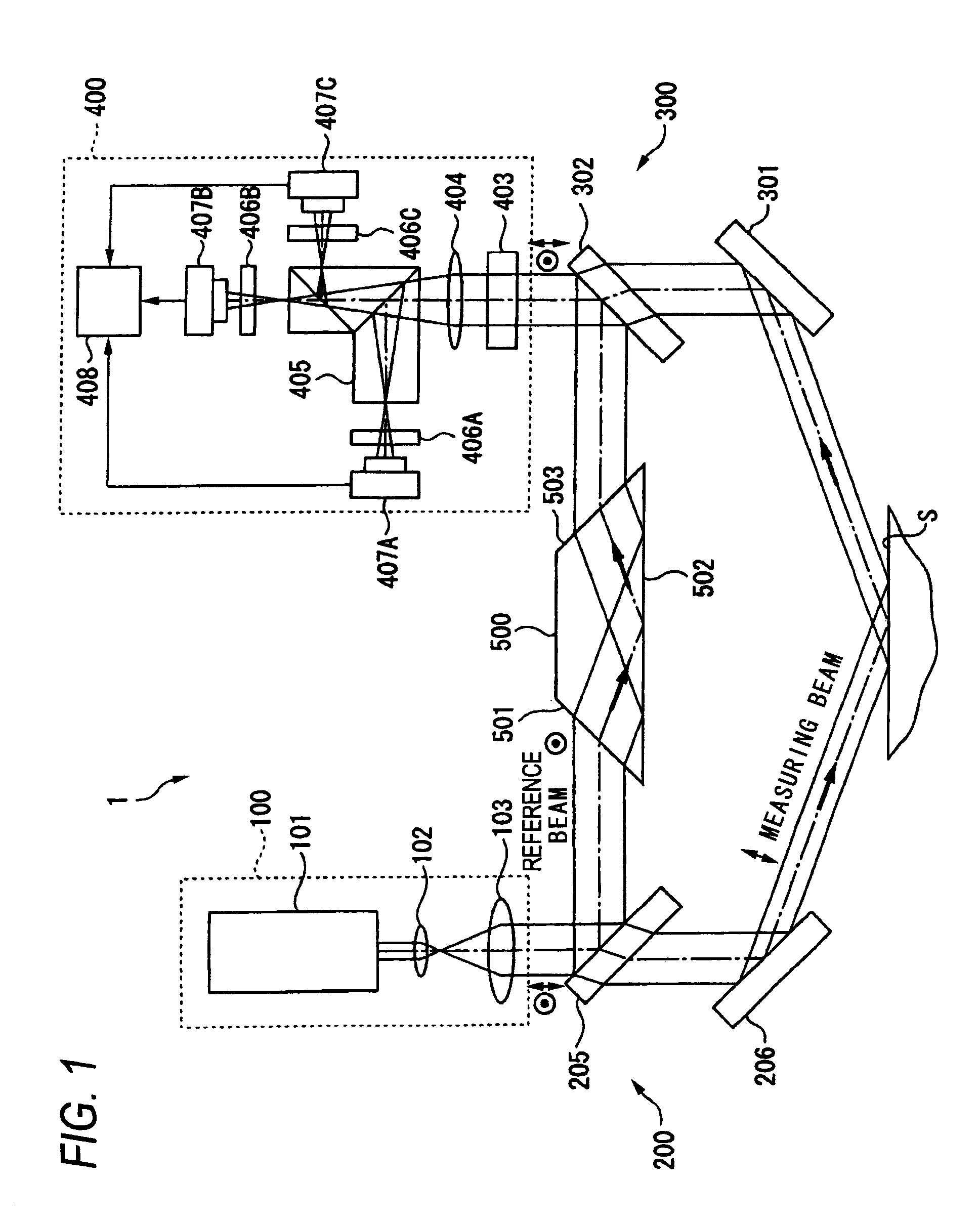
Grazing incidence interferometer
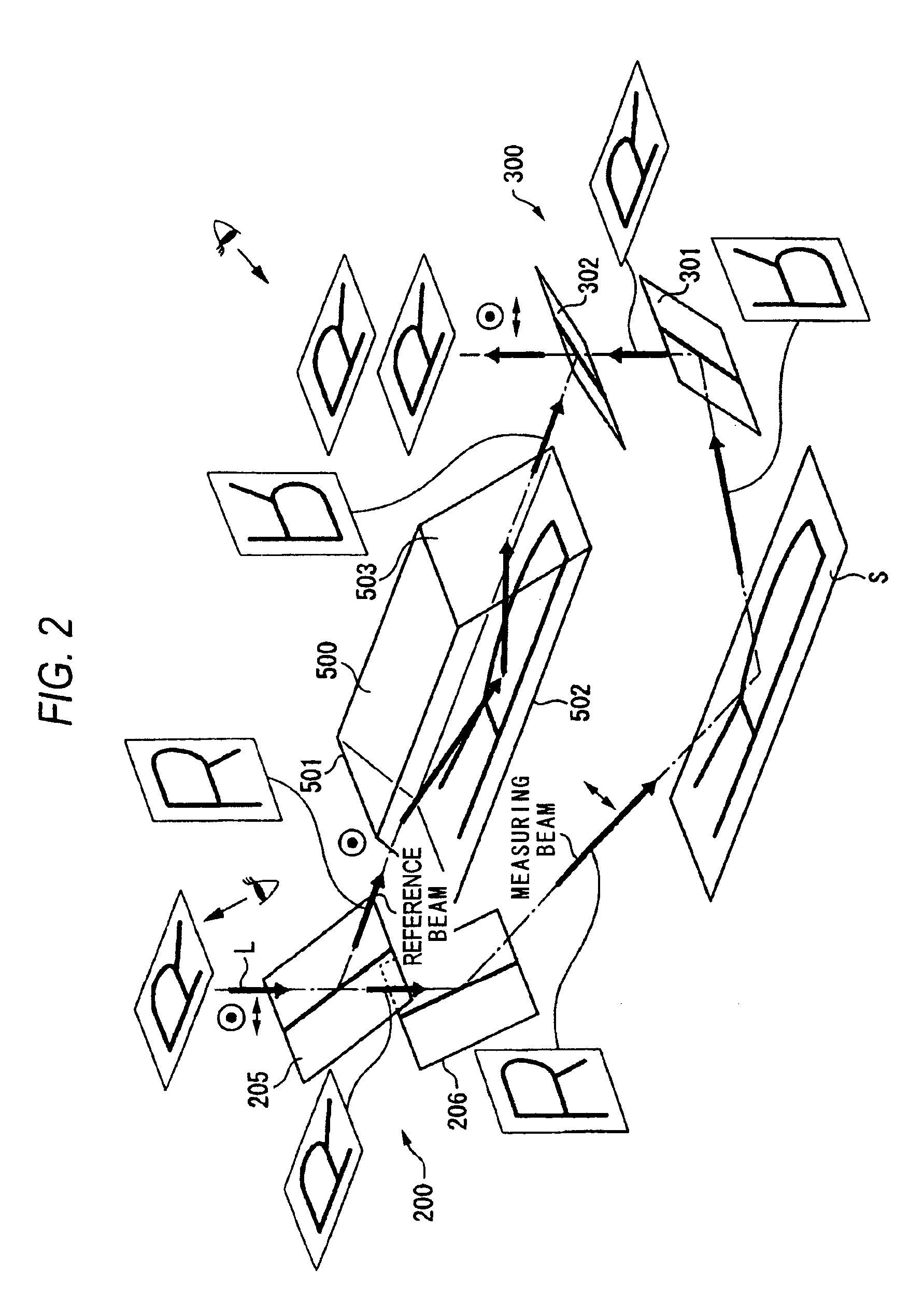
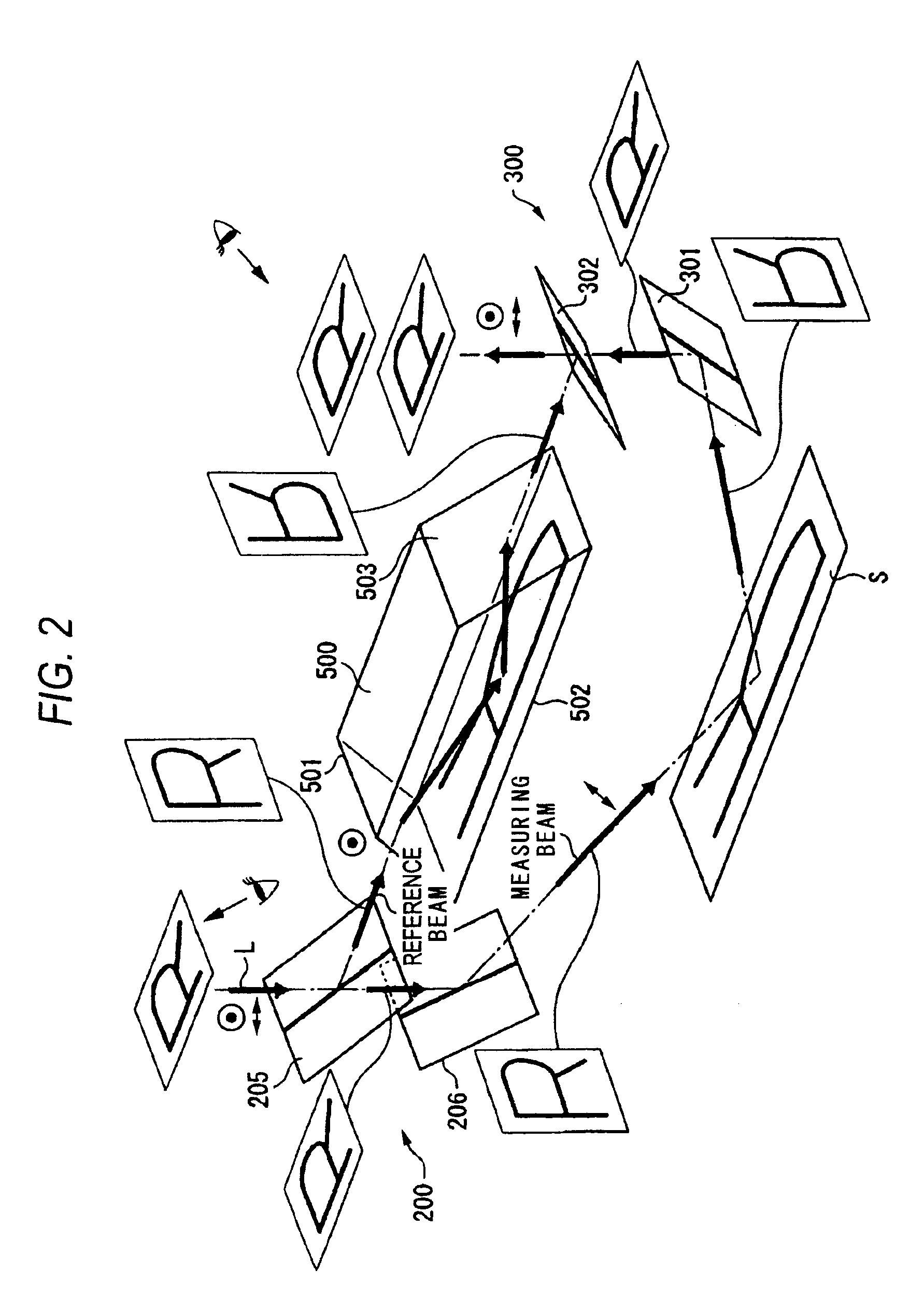
ActiveUS20110032536A1Easy to changeExcellent ease of useInterferometersUsing optical meansBeam splittingBeam source
A grazing incidence interferometer includes: a beam splitting section configured to split a beam from a beam source section into a measuring beam emergent to a measurement surface and a reference beam serving as a measurement reference, and configured to cause the measuring beam to emerge obliquely to the measurement surface; a beam combining part configured to combine the reference beam and the measuring beam reflected at the measurement surface, to obtain a combined beam; a detecting section configured to detect a profile of the measurement surface based on an interference fringe formed by the combined beam; and an image inverting part configured to invert an orientation of a wave front of the measuring beam or the reference beam, the image inverting part being provided in an optical path of the measuring beam or the reference beam leading from the beam splitting section to the beam combining section.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Bismuth borate glass encapsulant for LED phosphors
InactiveUS9011720B2Great index of refractionReducing efficiency-robbing backscatterSolid-state devicesGlass shaping apparatusFritPhosphor
Owner:CORNING INC
Optical film
ActiveUS20060171034A1Easy to getReduce necessityCathode-ray/electron-beam tube vessels/containersOptical articlesFilm (photographic)Aspect ratio
A film for optical applications which effectively prevents reflection of light on the surface of image display devices such as PDP, CRT and LCD, exhibits excellent scratch resistance and transmission of light, provides excellent adhesion between layers and can be produced at a low cost is disclosed. The film comprises (A) a high refractivity hard coat layer (the refractive index: 1.60 to 1.75, the thickness: 2 to 20 μm) comprising (a) an antimony-doped tin oxide having a needle shape (the average particle diameter along the major axis: 0.05 to 10 μm, the average aspect ratio: 3 to 100), (b) at least one other metal oxide and (c) a material cured with an ionizing radiation and (B) a low refractivity layer (the refractive index: 1.30 to 1.45, the thickness: 40 to 200 nm), which are successively laminated at least on one face of a substrate film.
Owner:LINTEC CORP
Radar apparatus and optical receiver thereof
ActiveUS20080130138A1Wide angleImprove reliabilityOptical rangefindersPhotometryRadarRefractive index
A radar apparatus has a light receiver that includes a refractive body and a mirror on an opposite surface of the refractive body relative to an incidence surface of the refractive body for receiving an incident light from an outside of the radar apparatus. The refractive angle of the refractive body is configured to be smaller than an incident angle of the incident light, and the mirror is configured to reflect at least a portion of the incident light toward a first light receiving element that is disposed on the incidence surface with its light receiving face facing the incidence surface of the refractive body.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Silicon based thin film solar cell
InactiveUS7847186B2Sufficient light trapping effectLow costPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceTrapping
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Material for protective film formation and method of forming resist pattern therewith
InactiveUS20090053646A1Improve featuresEasy to handlePhotosensitive materialsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusTectorial membraneResist
A material for protective film formation that is used to form an upper-layer protective film for a resist film and that contains at least a polymer component soluble in water or alkali and an alcohol containing a fluorine atom; and a method of forming a resist pattern with the use of the same. Consequently, not only can the degeneration of resist film during liquid immersion exposure by various liquids for liquid immersion exposure, for example, water and the degeneration of liquid immersion exposure liquids per se be simultaneously prevented in the liquid immersion exposure process, but also without inviting an increase of the number of processing steps, the resistance to post exposure delay of the resist film can be enhanced.
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD
Method for producing a highly refractive composite gemstone, and product
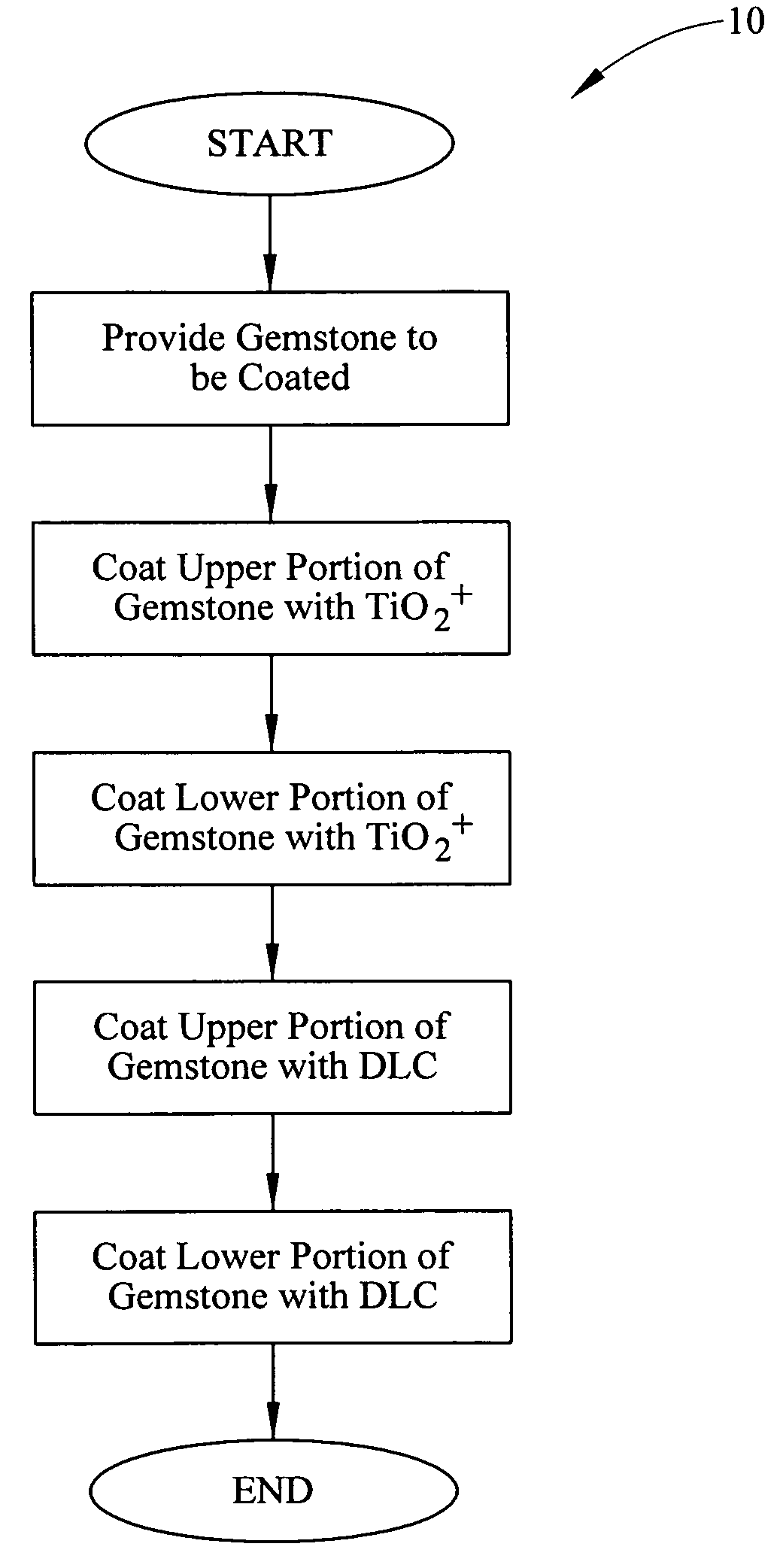
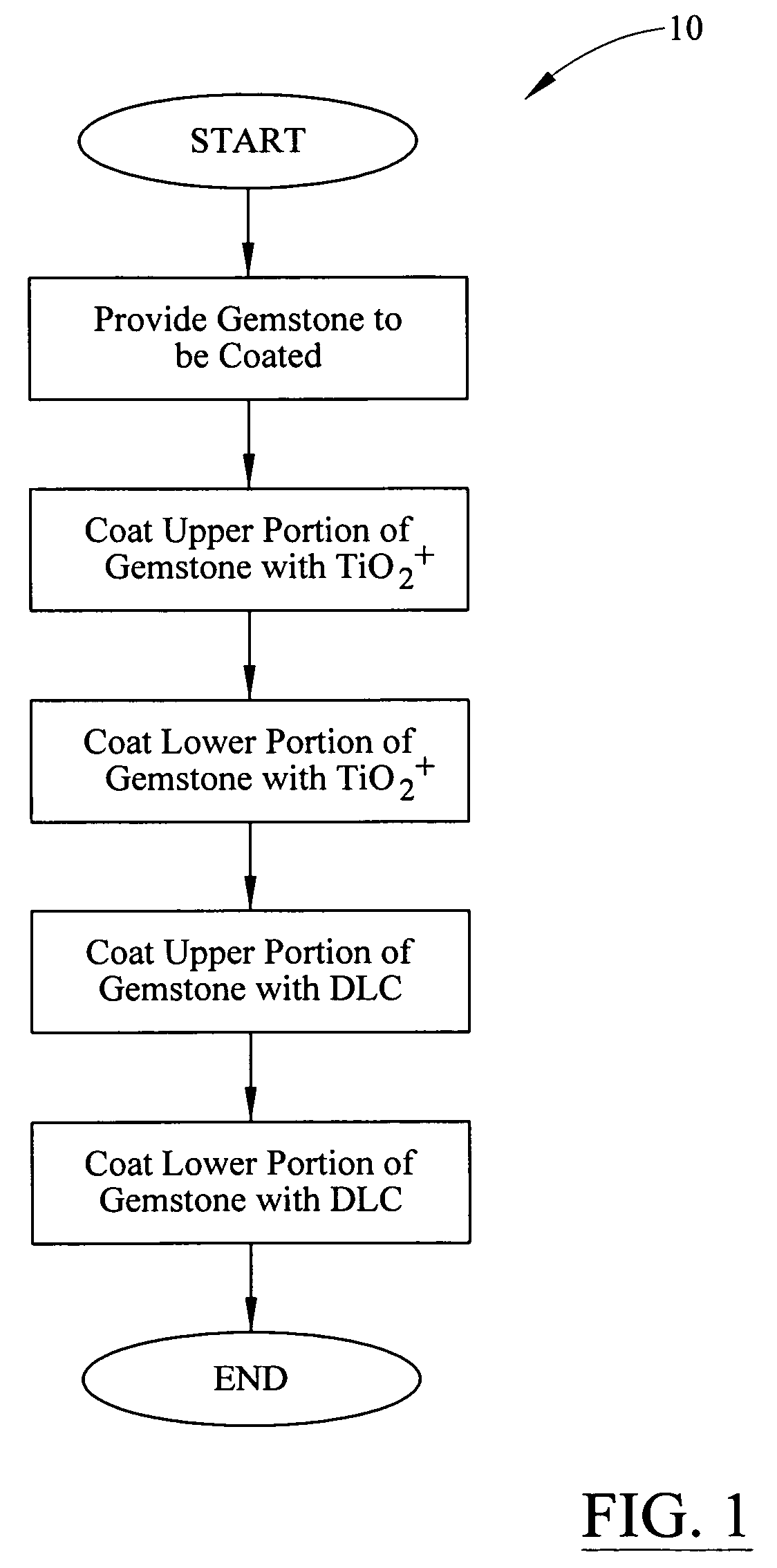
InactiveUS8056363B1Improve optical qualityGreat index of refractionHair accessoriesToupeesDiamond-like carbonGemstone
A method for providing a protective coating and enhanced optical qualities to a gemstone. The method includes coating a first portion and a second portion of a gemstone with TiO2 doped with calcium oxide (TiO2+). The TiO2+ coated gemstone is next coated with a diamond like carbon (DLC) coating. The gemstone may be synthetic or natural. The composite gemstone, having been coated with both TiO2 and DLC, exhibits high refractivity and enhanced wear resistance and color.
Owner:BETTERTHANDIAMOND
Side-view light emitting laser element
ActiveUS10211598B2Guaranteed lighting lifeLight performancesOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsElectrical conductorRefractive index
A side-view light emitting laser element includes a support substrate, a first electrode layer, a second electrode layer, and a light emitting multilayer unit sandwiched between the first electrode layer and the second electrode layer. The first electrode layer is disposed on the support substrate. The second electrode layer is disposed on the first electrode layer. The light emitting multilayer unit includes a first semiconductor layer, a second semiconductor layer and an activating layer sandwiched between the first semiconductor layer and the second semiconductor layer. A first refractive index of the first electrode layer and a second refractive index of the second electrode layer are between 1 and 0, respectively.
Owner:LEXTAR ELECTRONICS CORP
Optical film, method for producing same, and polymer liquid crystal particle
InactiveUS20070183052A1Suppress color mixingReduce light scatterLiquid crystal compositionsDiffusing elementsCompound (substance)Materials science
The present invention provides an optical film that can be suitably used for antiglare treatment to suppress blurry image and reduced contrast, as well as a method of producing such optical film. The optical film proposed by the present invention has a transparent base and a coating layer which is provided on at least one side of the transparent base and where transparent fine particles of 0.5 to 10 μm in average particle size are dispersed in a transparent resin phase, and one of the transparent resin phase or transparent fine particle contains a molecule-oriented high-molecular liquid crystal compound while the other is made of an optical isotropic resin.
Owner:TOMOEGAWA PAPER CO LTD
Solid state imaging device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20050200711A1Increase costSuppresses irregularity in widthTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesDielectricEngineering
A solid state imaging device includes photoelectric conversion portions for performing photoelectric conversion, and transfer portions for transferring signal charge occurring at the photoelectric conversion portions. Each transfer portion includes a transfer electrode formed of polysilicon film or the like, and an insulating coating film formed of a material such as a silicon nitride film and so forth, which has a higher relative dielectric constant than that of the silicon oxide, for coating the bottom face, the upper face, and both side faces, of the transfer electrode. The silicon nitride film is formed with a film thickness which is greater than 0 nm and smaller than 60 nm, on both sides of the transfer electrode.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Coating composition containing high-refractive-index metal oxide fine particles, and curable coating film obtained by applying the coating composition onto base
ActiveUS8974592B2High refractive indexReduced activityMaterial nanotechnologyInorganic pigment treatmentRefractive indexTitanium
The present invention relates to a coating composition containing metal oxide particles with a high refractive index and low photocatalytic activity and a coating film obtained by applying the coating composition onto a substrate. The coating composition contains metal oxide particles with a high refractive index obtained by coating the specific fine particles of the titanium-based oxide on their surfaces with at least a silica-based oxide or a silica-based composite oxide, and the coating film is obtained by applying the coating composition onto a substrate. The metal oxide particles with not only a high refractive index but also low photocatalytic activity, and therefore a coating film with excellent weathering resistance and light resistance can be formed on a substrate.
Owner:JGC CATALYSTS & CHEM LTD
Method for producing polythiourethane resin
Owner:HOYA CORP
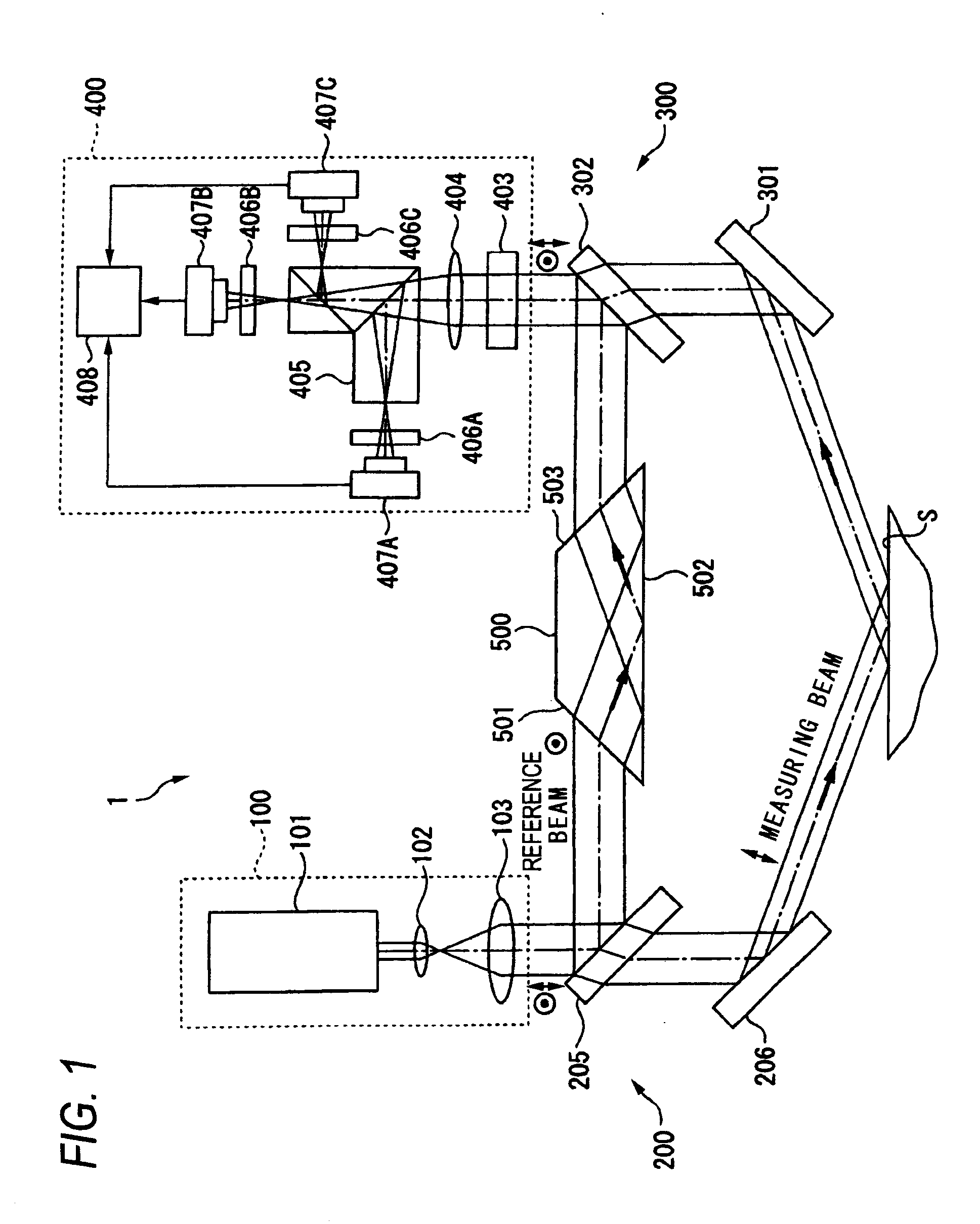
Grazing incidence interferometer
ActiveUS8441650B2Excellent ease of useGuaranteed Error AccuracyInterferometersUsing optical meansBeam sourceBeam splitting
A grazing incidence interferometer includes: a beam splitting section configured to split a beam from a beam source section into a measuring beam emergent to a measurement surface and a reference beam serving as a measurement reference, and configured to cause the measuring beam to emerge obliquely to the measurement surface; a beam combining part configured to combine the reference beam and the measuring beam reflected at the measurement surface, to obtain a combined beam; a detecting section configured to detect a profile of the measurement surface based on an interference fringe formed by the combined beam; and an image inverting part configured to invert an orientation of a wave front of the measuring beam or the reference beam, the image inverting part being provided in an optical path of the measuring beam or the reference beam leading from the beam splitting section to the beam combining section.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Curable resin composition, optical component and optical waveguide
InactiveUS20070025679A1Good refractive indexReduce light lossOptical waveguide light guideHeat resistanceRefractive index
The present invention is to provide a curable resin composition that is desirably used for manufacturing an optical part, in particular, an optical waveguide, that is superior in heat-resistant properties such as a heat-resistant decomposing property and a coloring-resistant property, and has its refractive index precisely controlled. The present invention provides a curable resin composition, comprising: (A) a monomer that contains a polycyclic alicyclic hydrocarbon skeleton and two or more terminal radical polymerizable groups, (B) a monomer that contains a perfluoroalkylene skeleton and two or more terminal radical polymerizable groups, and (C) a photopolymerization initiator and / or a thermal polymerization initiator. The present also provides an optical part, in particular, an optical waveguide, formed by photo-and / or thermo-curing the above curable resin composition.
Owner:ORMON CORP
Arrangement comprising two elements which can be rotatably displaced in respect of one another
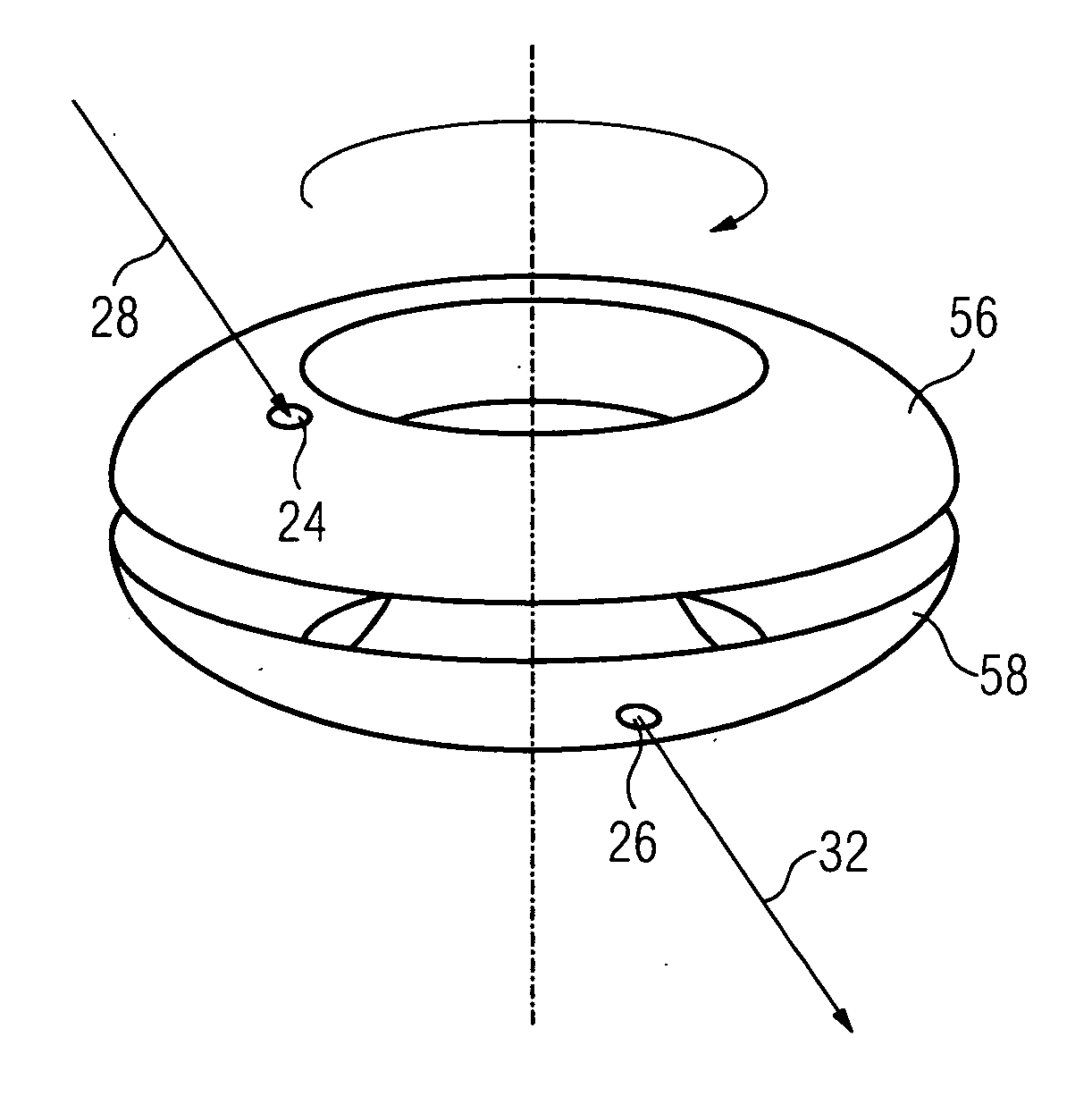
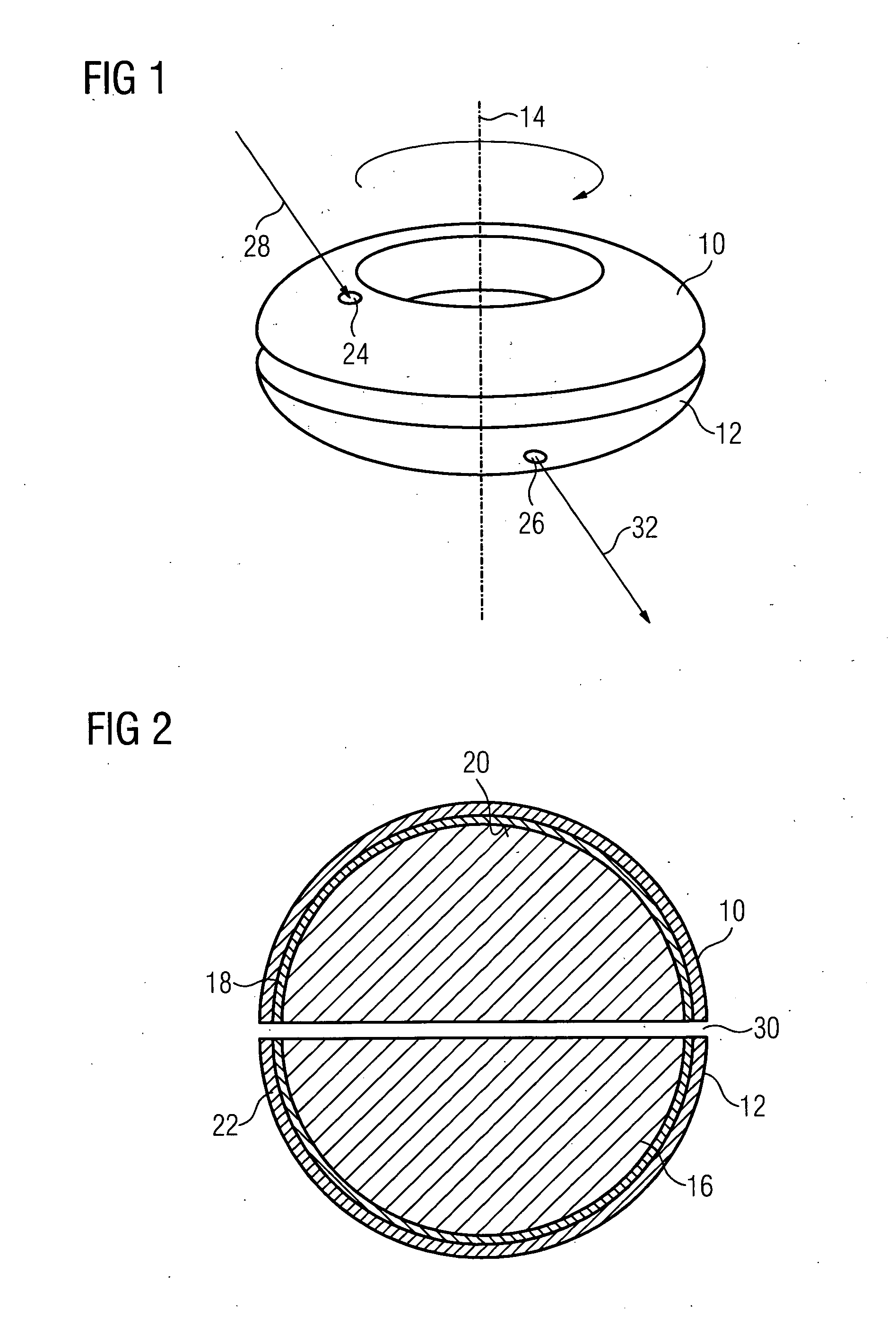
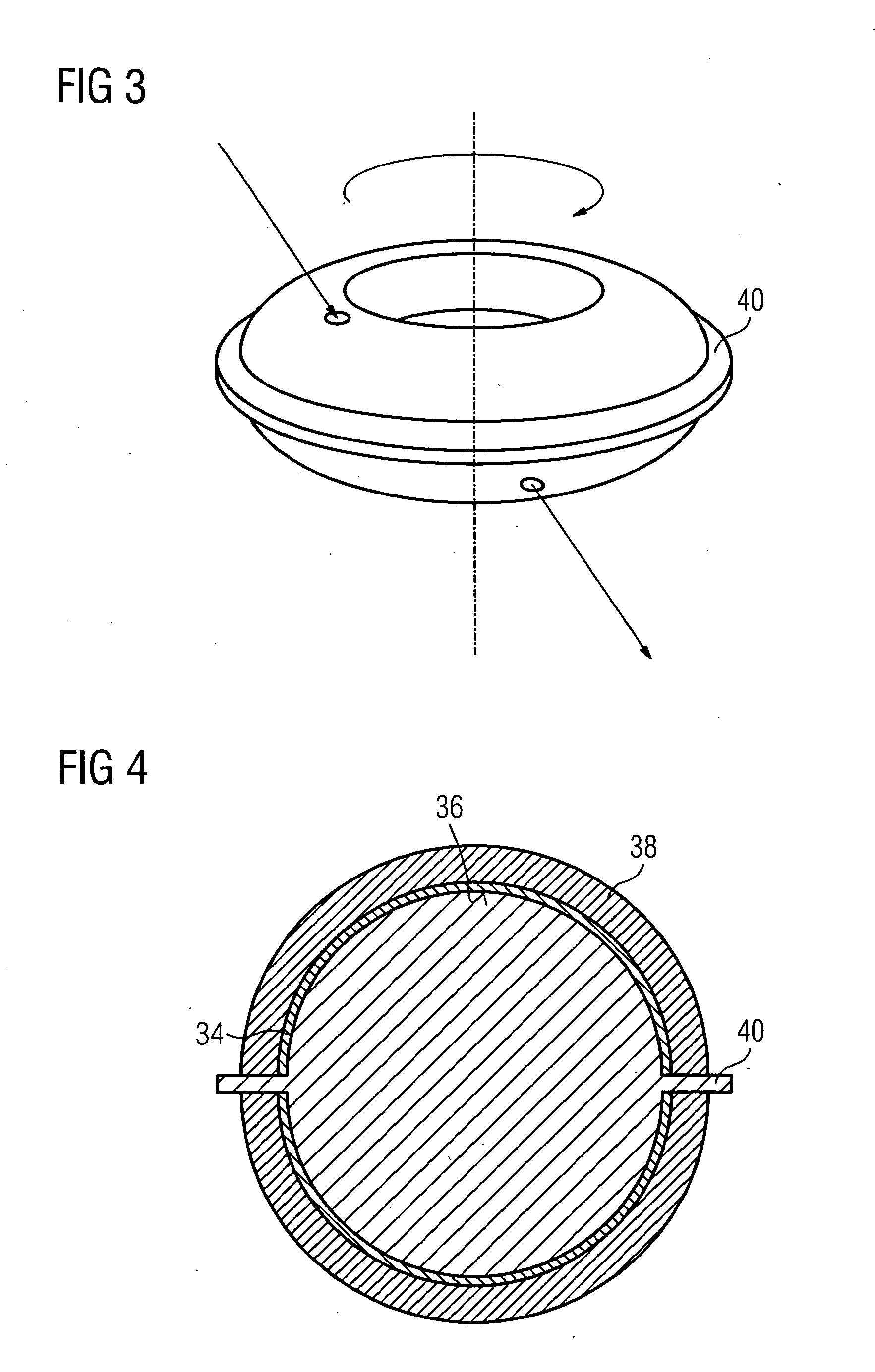
InactiveUS20090152478A1Simple producibilitySmall toleranceRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringHollow core
Data is to be exchanged between a rotating element and a further element, with the rotating element being rotated by way of a hollow shaft. Light is coupled into torus halves and is reflected into a torus half and onto torus inner walls so often by way of a small opening until it exits at an opening of the other torus half. In a first embodiment, a torus-shaped optical fiber is divided into two torus halves. In another embodiment, hollow tori are used, which are filled with a fluid, namely either with a liquid or with air.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com