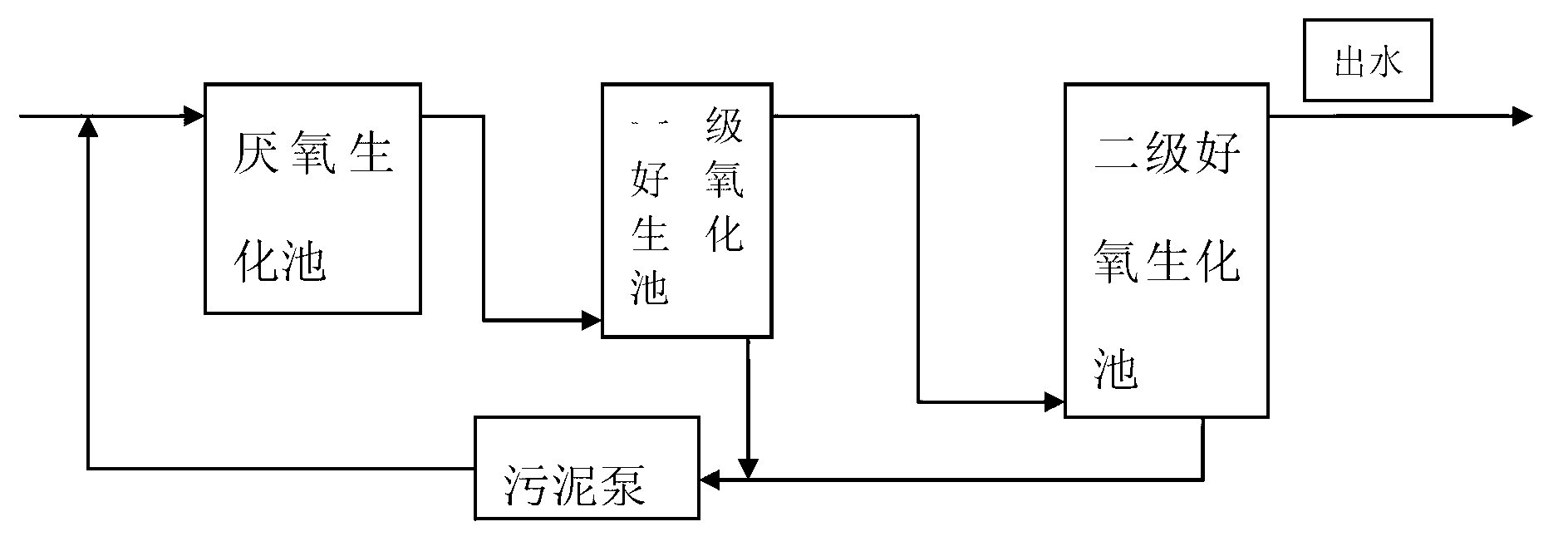
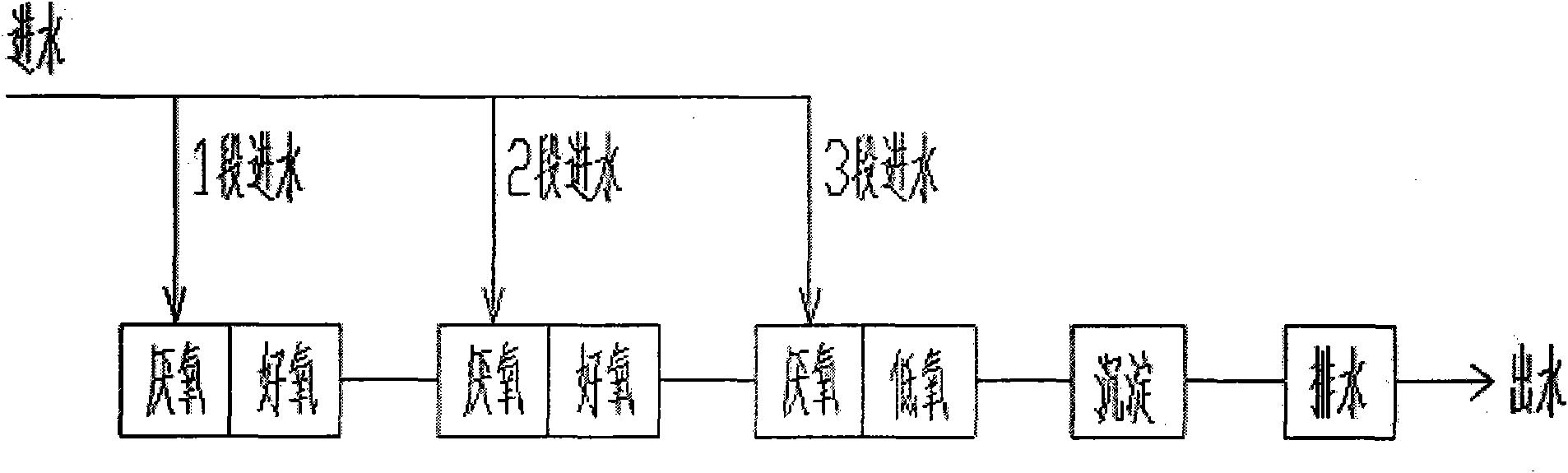
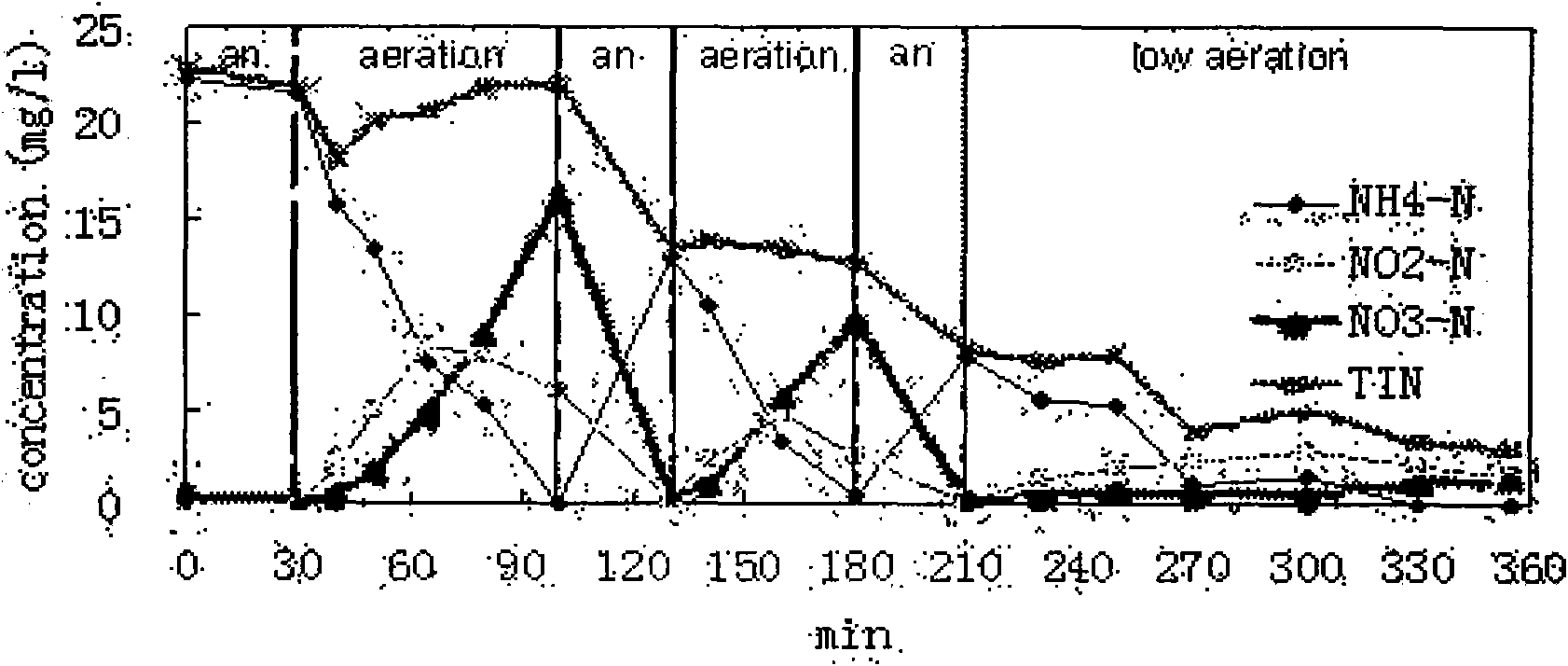
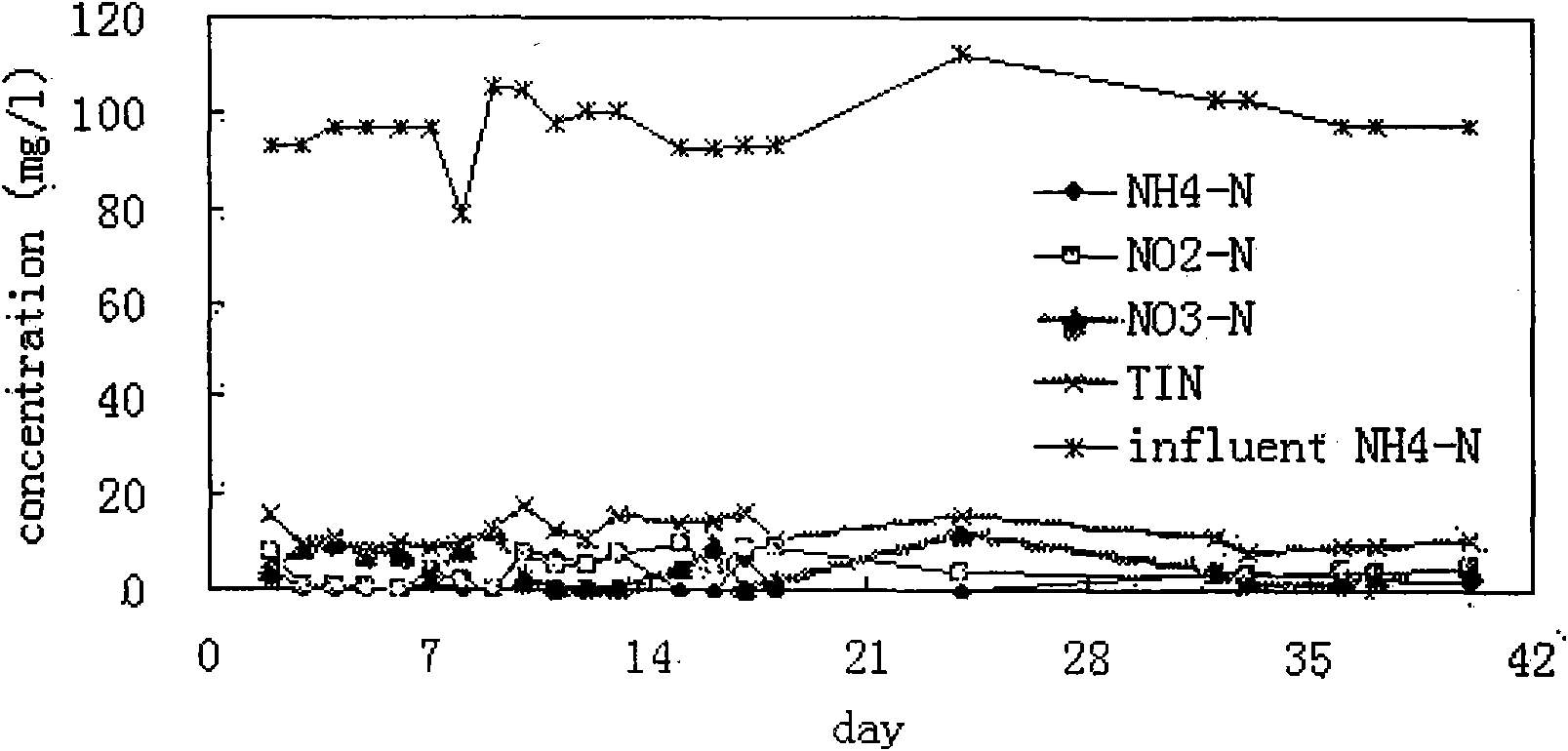
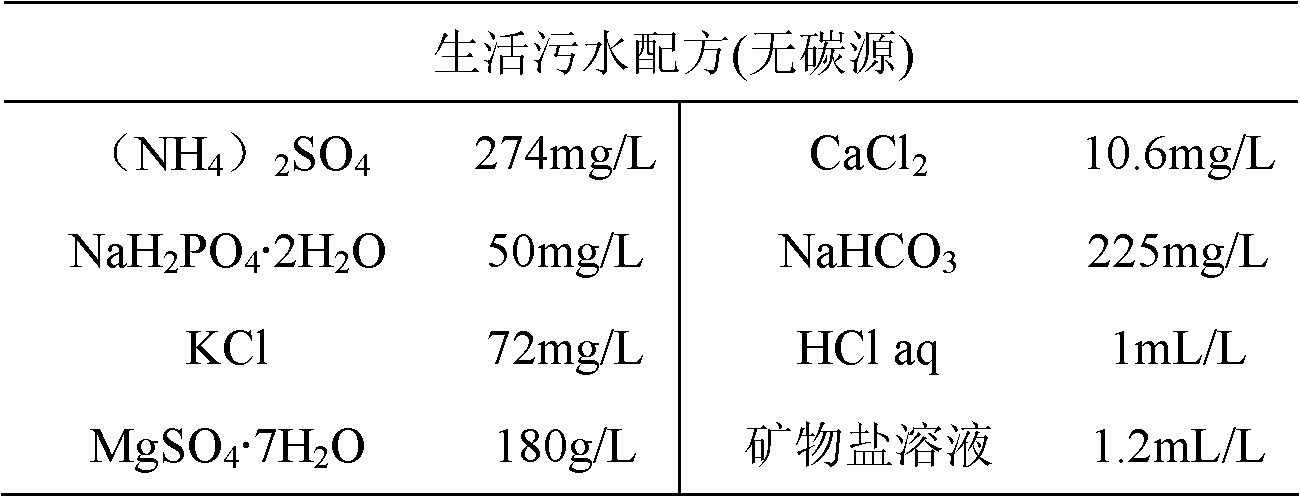
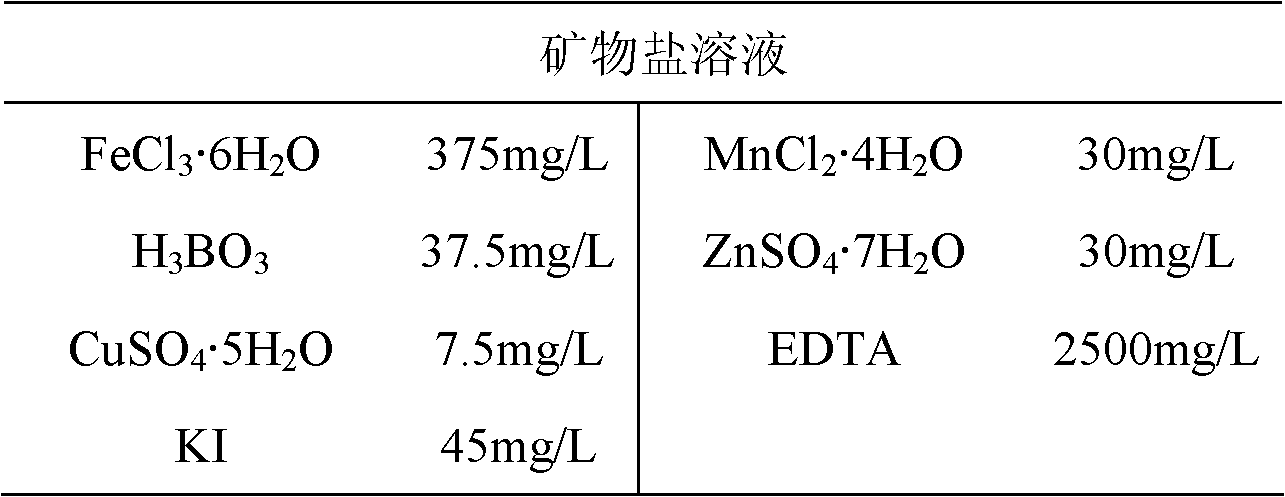
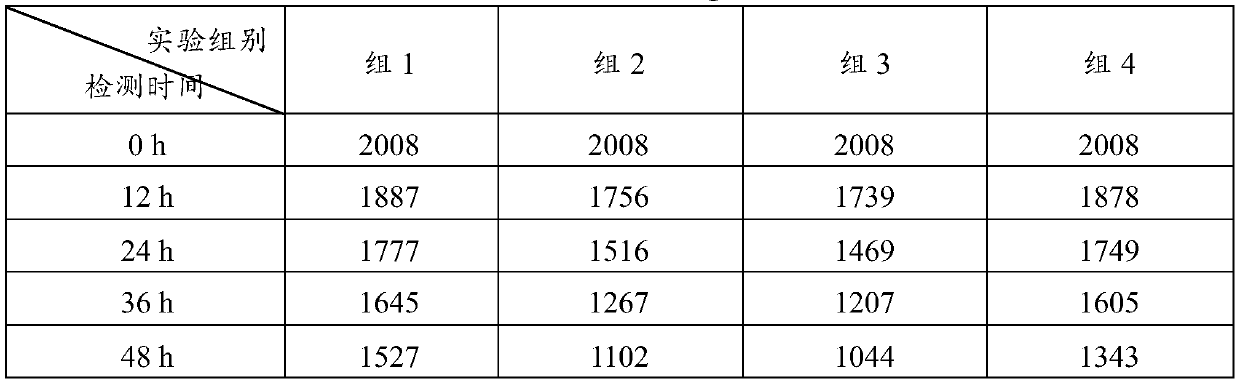
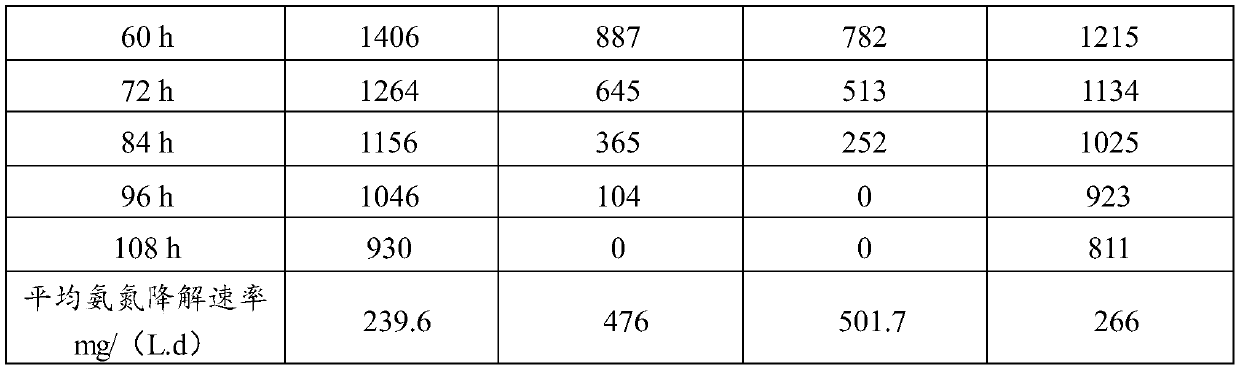
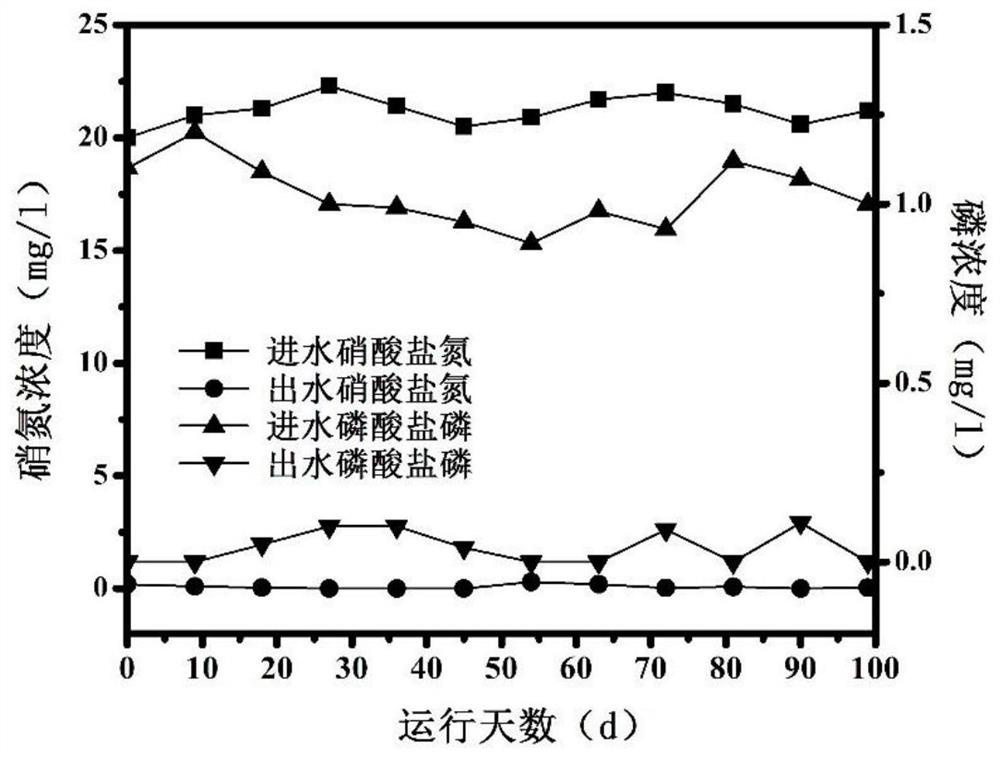
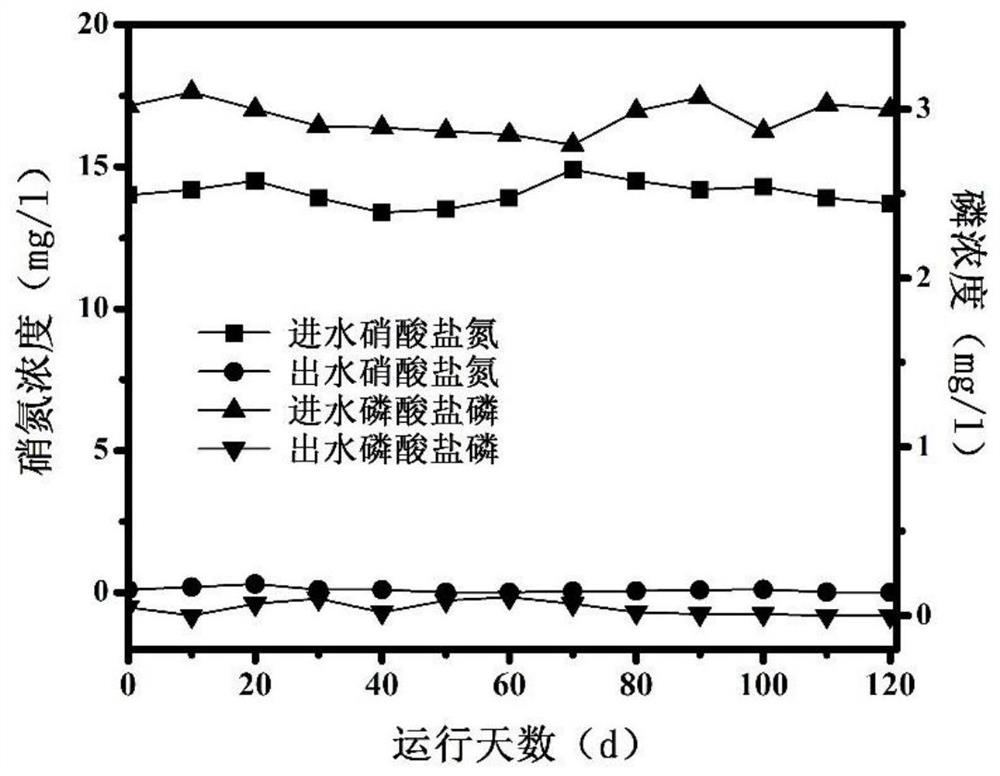
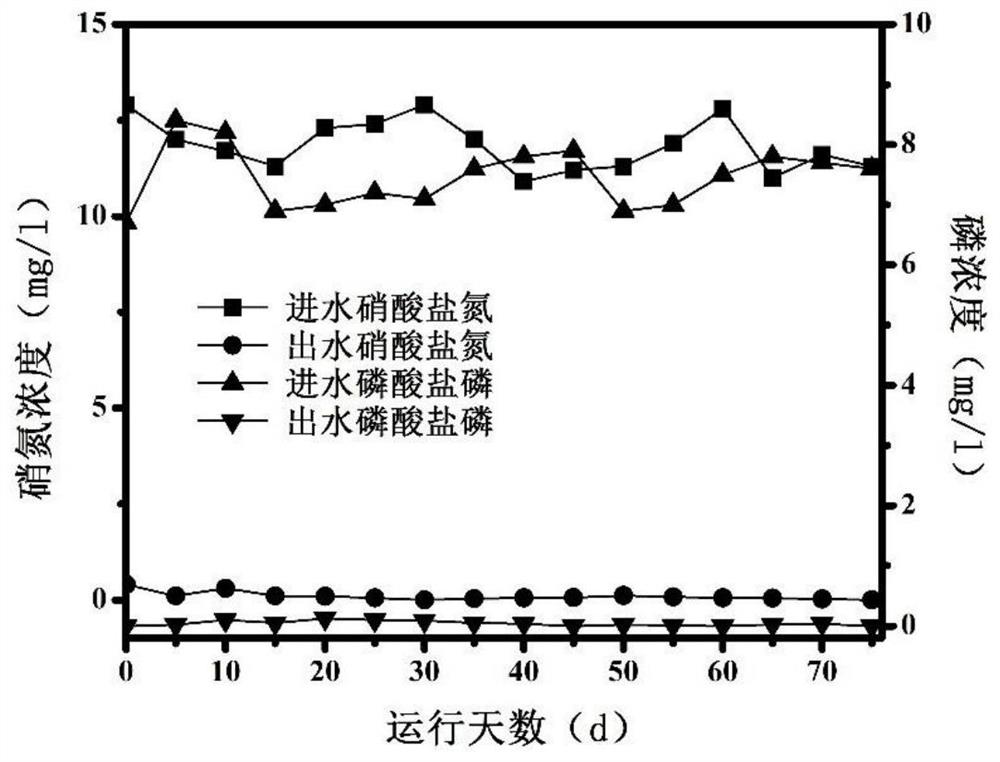
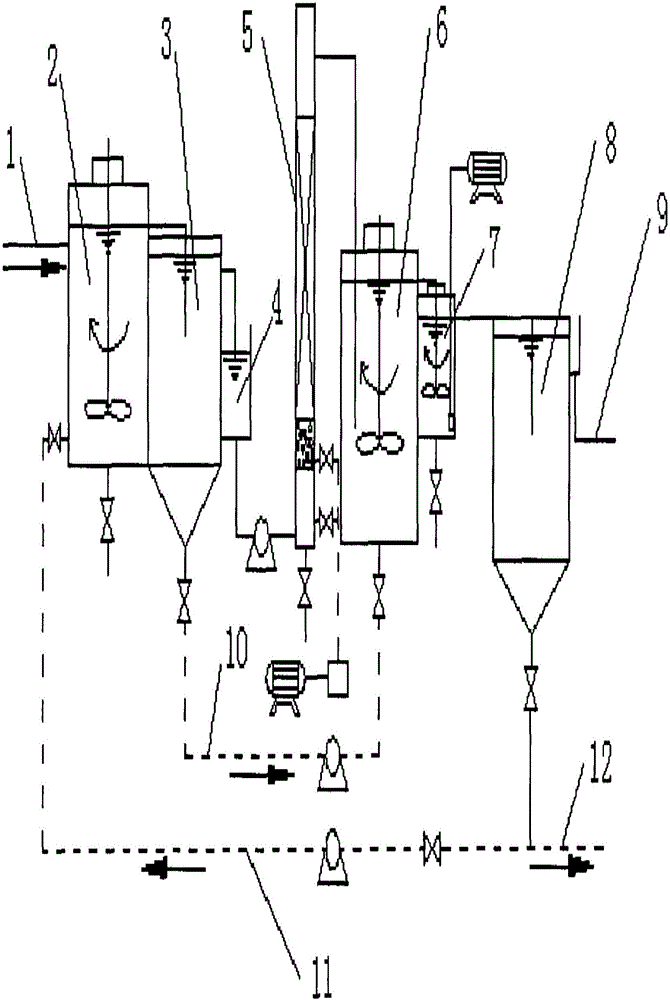
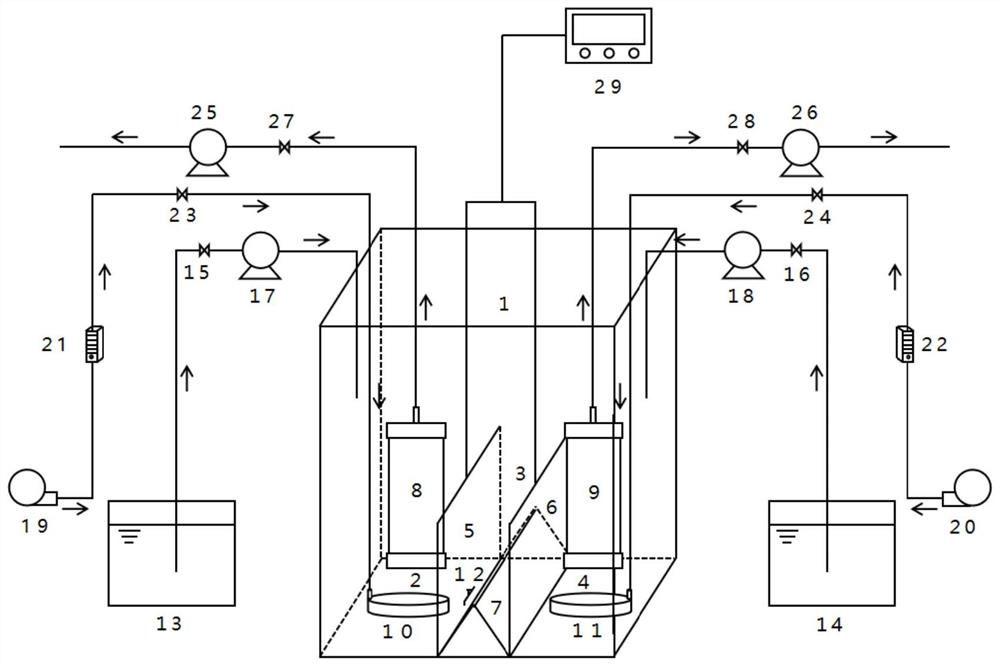
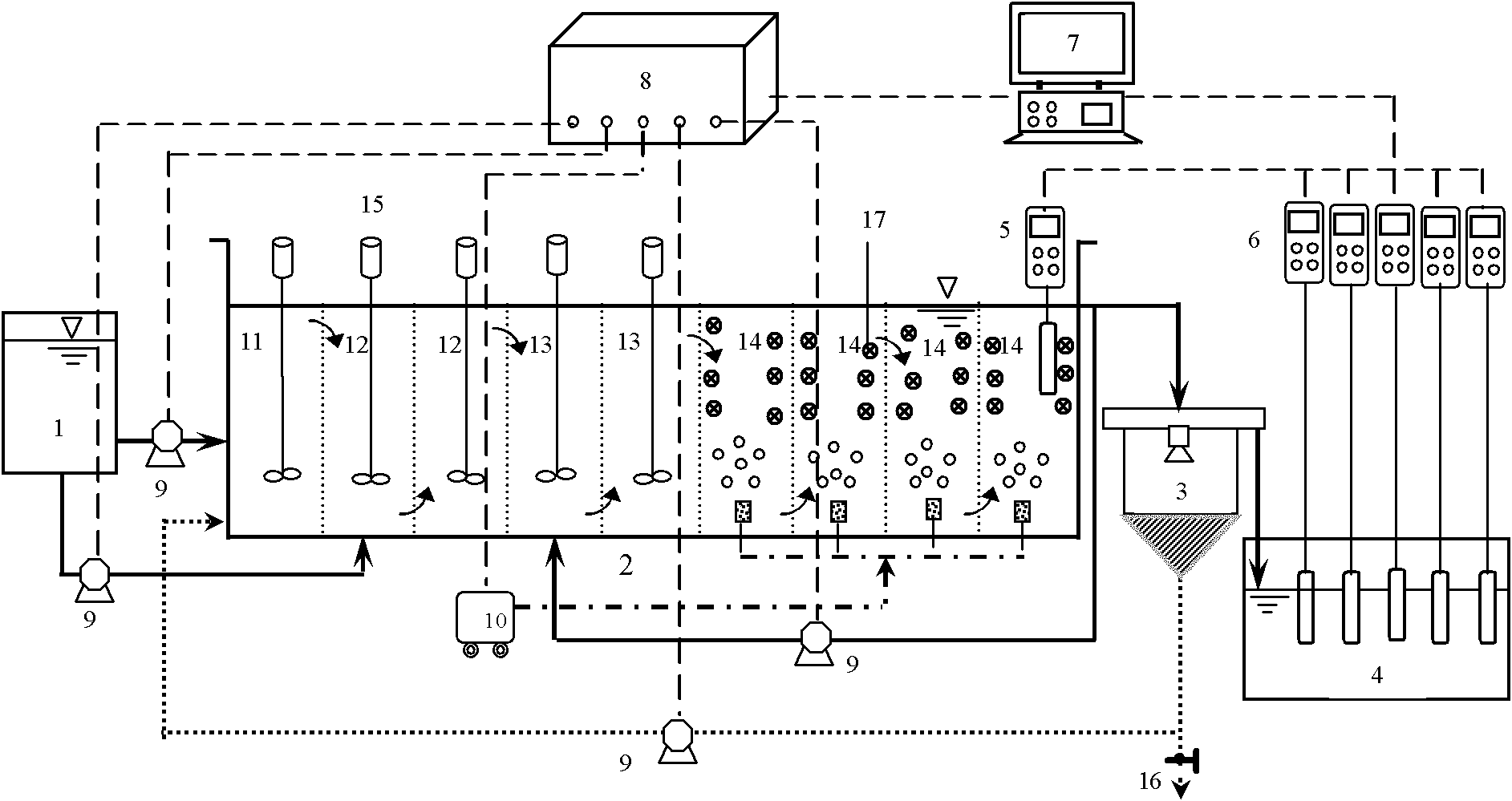
Patents
Literature
36results about How to "Increase nitrification rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
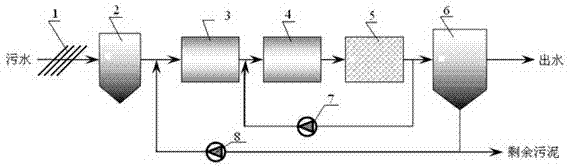
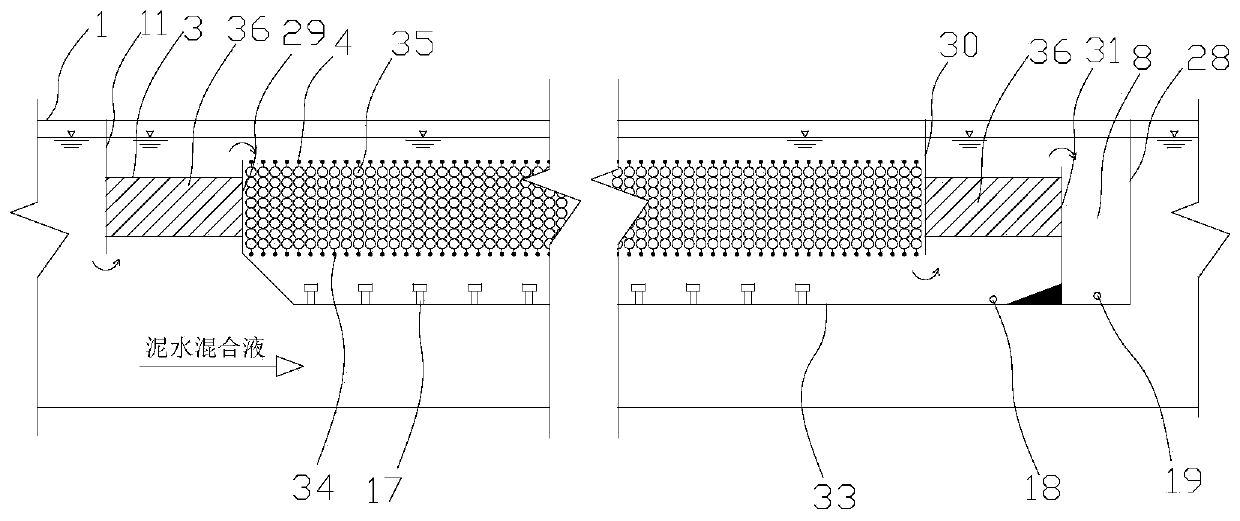
SBR alternant aerobic/anaerobic technology for biological denitrification and real time control device and method thereof
InactiveCN1569690AIncrease speedShort reaction timeTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSludgeTime control
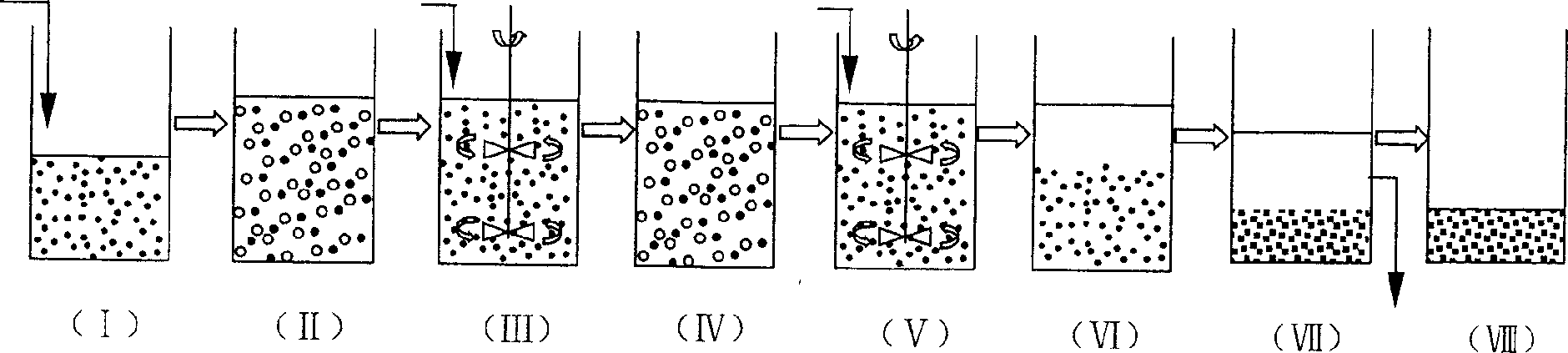
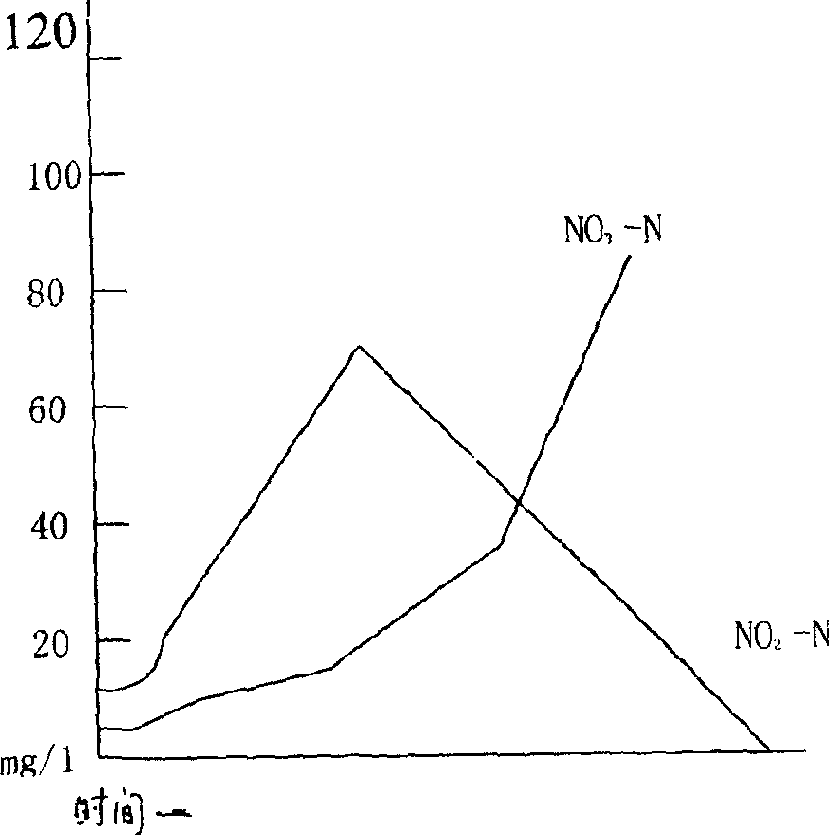
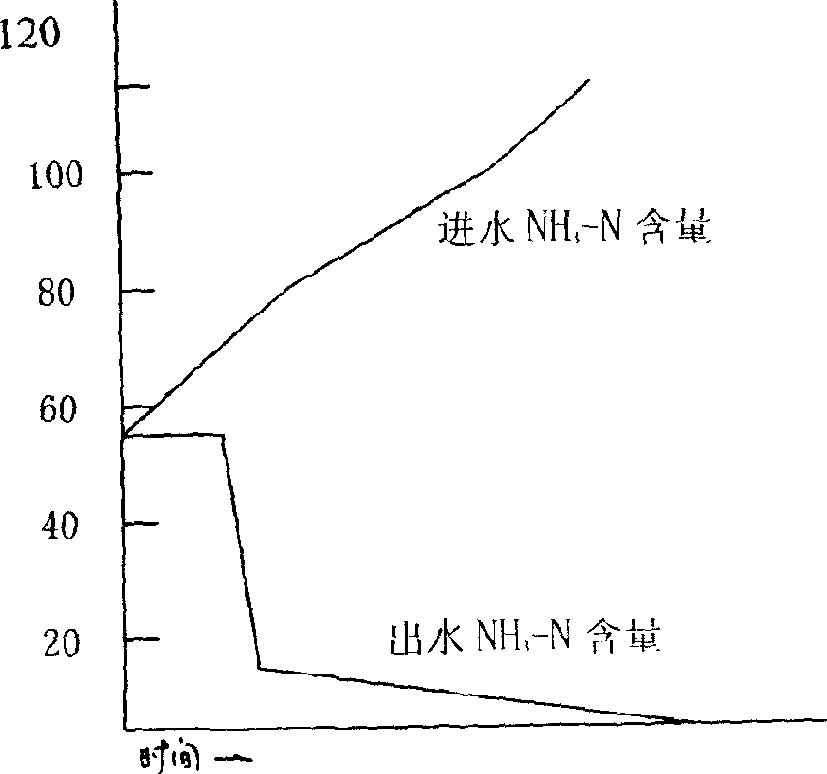
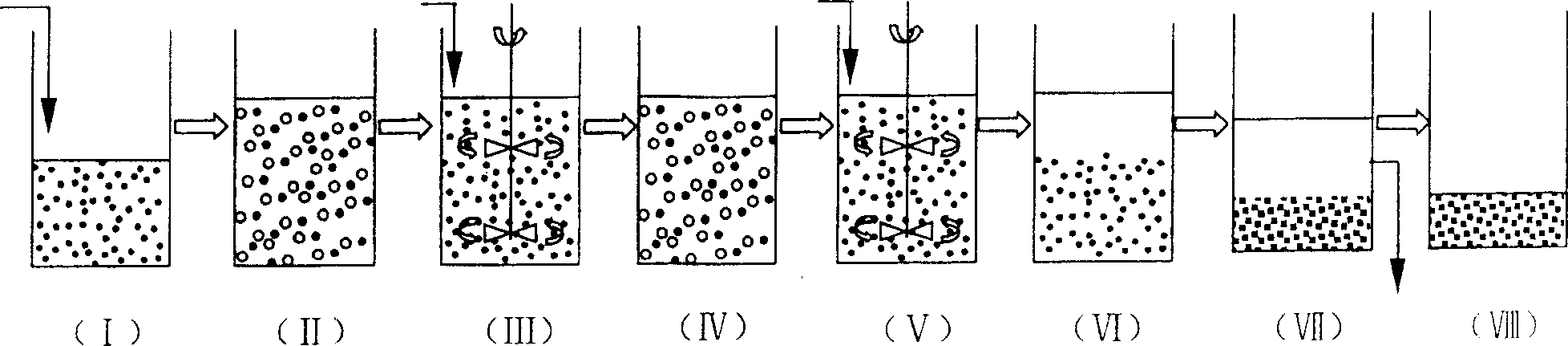
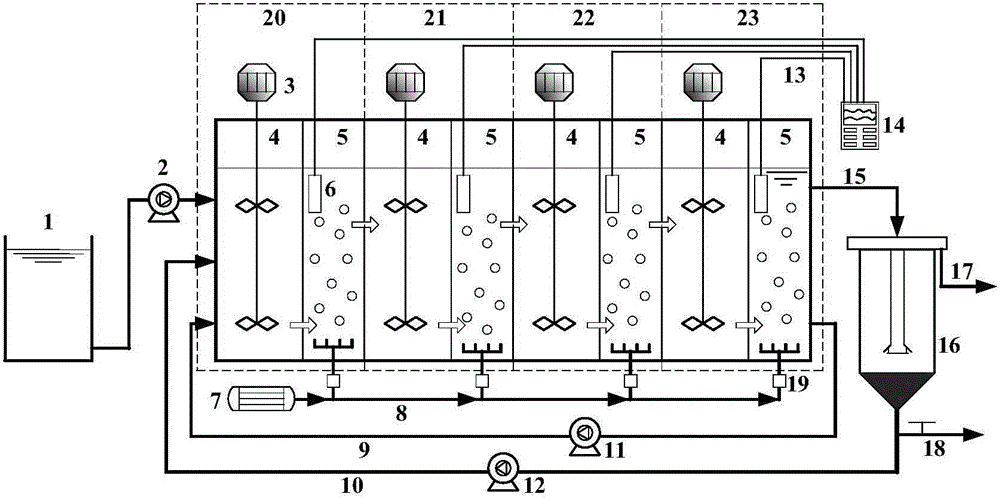
The invention discloses a SBR alternant aerobic / anaerobic technology for biological denitrification and real time control device and method thereof which consists of, dividing the waste water to be treated into three portions, loading each portion into a reactor, alternatively carrying out the operating mode of aerobic aeration and anoxybiotic agitating under real time procedure control, so as to realize the organics degradation and nitrogen-containing compound removal.
Owner:BEIJING TANSI ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECHCO
Coupling filler autotrophic denitrification biofilter and application
ActiveCN109052641ADifficult to dissolveIncrease speedWater treatment compoundsTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesBiofilmSewage
The invention discloses a coupling filler autotrophic denitrification biofilter and application and belongs to the technical field of sewage treatment. Pyrrhotite, sulfur and a carbon source are utilized to be mixed and coupled according to certain proportion; then the materials are put into a reactor, and the autotrophic denitrification biofilter can be formed after inoculating biofilm formation;sewage flows through the biofilter, and nitrogen and phosphorus in the water are removed. The biofilter disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simpleness, easiness, practicability and shortbiofilm formation time; when the biofilter is utilized to treat nitrogen and phosphorus containing sewage, hydraulic retention time is only 0.5 to 3 h, and yielding water can meet a requirement; furthermore, the biofilter has the advantages of excellent nitrogen and phosphorus removal effect, low cost and suitability for engineering application.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Device and method for realizing partial short-range nitrification-anaerobic ammonia oxidation by adding hydroxylamine
ActiveCN106865773AAddress serious problemsNo swellingTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesHydroxylamineAmmonia-oxidizing bacteria
The invention discloses a device and a method for realizing partial short-range nitrification-anaerobic ammonia oxidation by adding hydroxylamine, and belongs to the field of urban domestic sewage biological treatment. For two-stage partial short-range nitrification-anaerobic ammonia oxidation, the stable operation of the short-range nitrification is crucial to a process; the short-range nitrification is very difficult to start and maintain stably only through process parameter control; a very good nitrite accumulating effect can be achieved by adding the hydroxylamine in the patent; partial short-range nitrification reactors can be started and high nitrite accumulation can be maintained within a short time. The hydroxylamine serves as an intermediate product in a nitrifying process, is a reducing agent of ammonia monooxygenase and a stimulating agent of AOB (Ammonia Oxidizing Bacteria) and can improve the cell yield of the AOB; meanwhile, the hydroxylamine is an inhibiting agent of NOB (Nitrite Oxidizing Bacteria) and can elutriate the NOB. Compared with a conventional denitrogenation process, a partial short-range nitrification-anaerobic ammonia oxidation process can save aeration quantity and carbon source, and is particularly suitable for urban domestic sewage with low C / N.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Short distance denitrifying dephosphatation double-sludge technique taking granular sludge as medium and device thereof
ActiveCN101628772ASink fastHigh activityTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSludgeShortest distance
The invention belongs to the field of sewage treatment and provides a short distance denitrifying dephosphatation double-sludge technique taking granular sludge as medium and a device thereof. The device sequentially comprises a raw water pipe, a water inlet tank and a water inlet valve, and is characterized by further sequentially comprising an anaerobic / anoxic SBR reactor and an intermediate water tank which are connected with each other by a pipeline as well as a short distance nitration SBR reactor and a back flow water tank that are also connected with each other by the pipeline; wherein the intermediate water tank is connected with the short distance nitration SBR reactor, and the back flow water tank is connected with the anaerobic / anoxic SBR reactor; the anaerobic / anoxic SBR reactor and the short distance nitration SBR reactor are internally provided with stirring devices, and a drain pipe is arranged on the anaerobic / anoxic SBR reactor; the short distance nitration SBR reactor is internally provided with an aerating apparatus; the granular sludge which is processed by acclimatization and has the function of denitrifying dephosphatation is put into the anaerobic / anoxic SBR reactor, and the granular sludge which is processed by acclimatization and has the function of short distance nitration is put into the short distance nitration SBR reactor. The invention solves the problems of unstable effect of nitrogen and phosphorus removal of sewage, high content of effluent suspended matter and lower pass rate, so as to be used for low C / N waste water treatment.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG BISHUIYUAN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION ENG CO LTD
Method for degrading ammonia nitrogen in high-salinity sewage by microbes
InactiveCN103232145ASolve the problem of ammonia nitrogen degradationShort reaction timeTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentChemical oxygen demandSludge
The invention discloses a method for degrading ammonia nitrogen in high-salinity sewage by microbes, wherein a treatment system in the method comprises an anaerobic biochemical reaction tank, a first-stage aerobic biochemical pool and a second-stage aerobic biochemical pool. Firstly, the sewage and the recirculation water simultaneously flow into the anaerobic biochemical reaction tank to be treated by denitrification and hydrolysis reaction; then, the sewage orderly flows into the first-stage aerobic biochemical pool and the second-stage aerobic biochemical pool to be respectively treated by first-stage aerobic treatment and the second stage aerobic treatment; the active sludge in the first-stage aerobic biochemical pool is the domesticated salt-tolerant bacteria for performing first-stage nitration on the ammonia nitrogen, and besides the domesticated salt-tolerant bacteria, efficient nitrifying bacteria are also added into the second-stage aerobic biochemical pool for performing second-stage high-strength nitration on the ammonia nitrogen=, thus, the effluent ammonia nitrogen and the COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) can reach the emission standard.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
Method for efficiently denitriding aerobic granular sludge by combining stepwise water feeding with alternate anaerobic and aerobic treatment
InactiveCN102417268AImprove nitrogen removal efficiencyImprove performanceTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentSequencing batch reactorAnaerobic aerobic
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological treatment of wastewater, and relates to a method for efficiently denitriding aerobic granular sludge by combining stepwise water feeding with alternate anaerobic and aerobic treatment. In the method for efficiently denitriding aerobic granular sludge, the reaction process is designed into multiple stages on the basis of a sequencing batch reactor, and an anaerobic-aerobic or low-oxygen alternate running mode is adopted at every stage; a water feeding mode for feeding water according to different proportions at multiple sections is designed according to the quality of fed water, and a water feeding point is set at the early anaerobic stage or the entire anaerobic stage of every stage in the reaction process. The method for efficiently denitriding aerobic granular sludge disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high denitriding efficiency, stable granular sludge performance and no need of adding any running cost, and is widely applied in the field of wastewater treatment.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
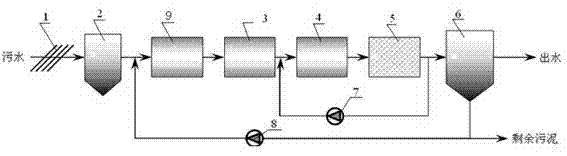
Sewage treatment system and application thereof
InactiveCN102765857AFast nitrification rateIncrease nitrification rateTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentAmmoniacal nitrogenWater discharge
The invention discloses a sewage treatment system which comprises a grating, a grit tank, a preaeration tank, an anaerobic tank, an anoxia tank, an aerobic tank and a secondary sedimentation tank. Sewage enters the grit tank after being treated by the grating, water discharged from the grit tank sequentially enters a biological treatment unit composed of the anaerobic tank, the anoxia tank and the aerobic tank to be treated, obtained mixed liquid enters the secondary sedimentation tank, two outlets are arranged on the secondary sedimentation tank, one outlet is a discharging port of treated sewage, and the other outlet is a discharging port of surplus sludge. A bypass is arranged on the discharging port of the surplus sludge, and one part of the surplus sludge discharged from the secondary sedimentation tank flows back to the preaeration tank through a sewage backflow pump. Simultaneously, one part of the mixed liquid from the aerobic tank flows back to the anoxia tank through a mixed liquid backflow pump on the bypass. The sewage treatment system has the advantages of being high in nitrobacterium activity, high in nitrification rate, high in ammonia nitrogen removing rate and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
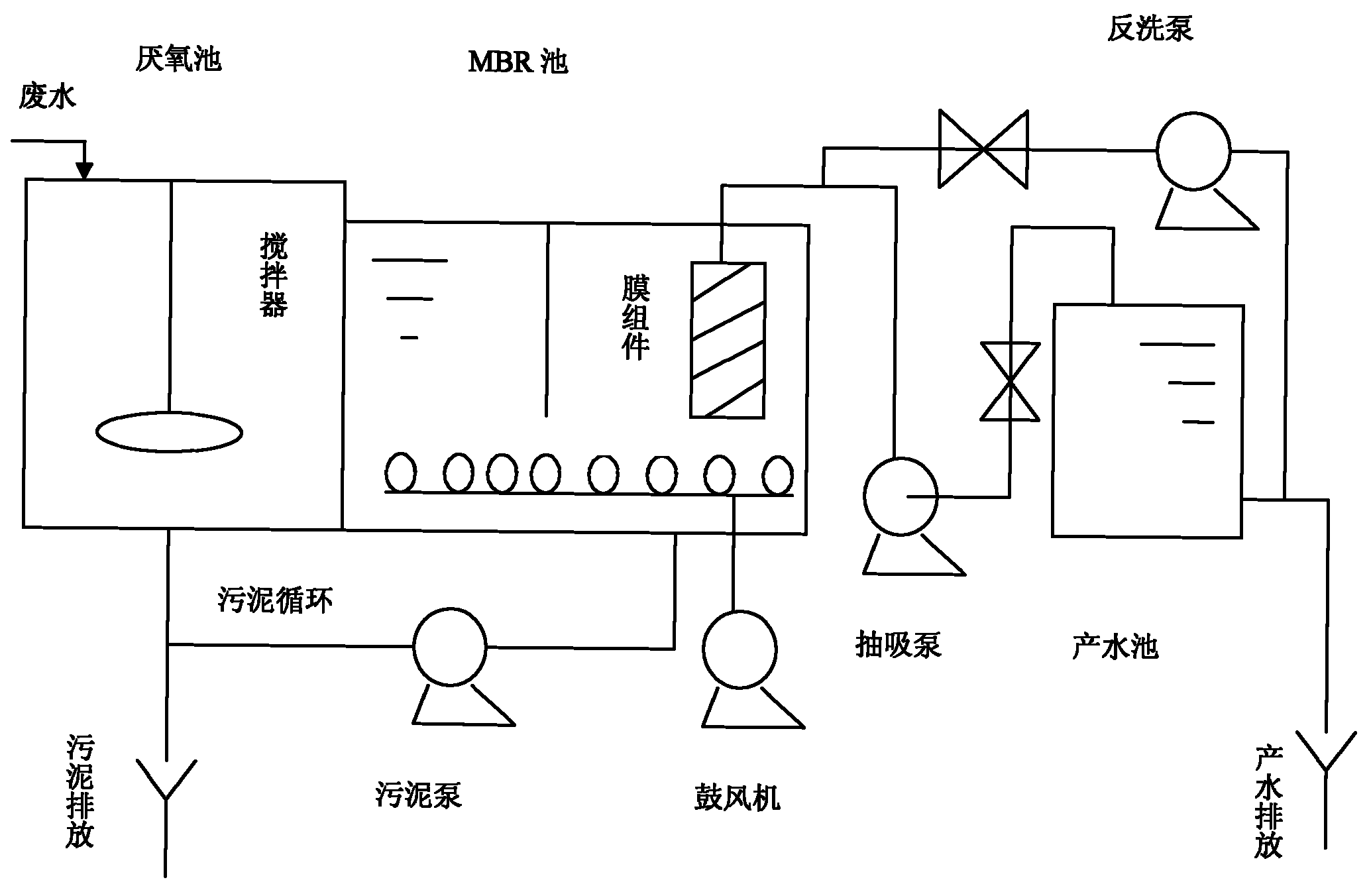
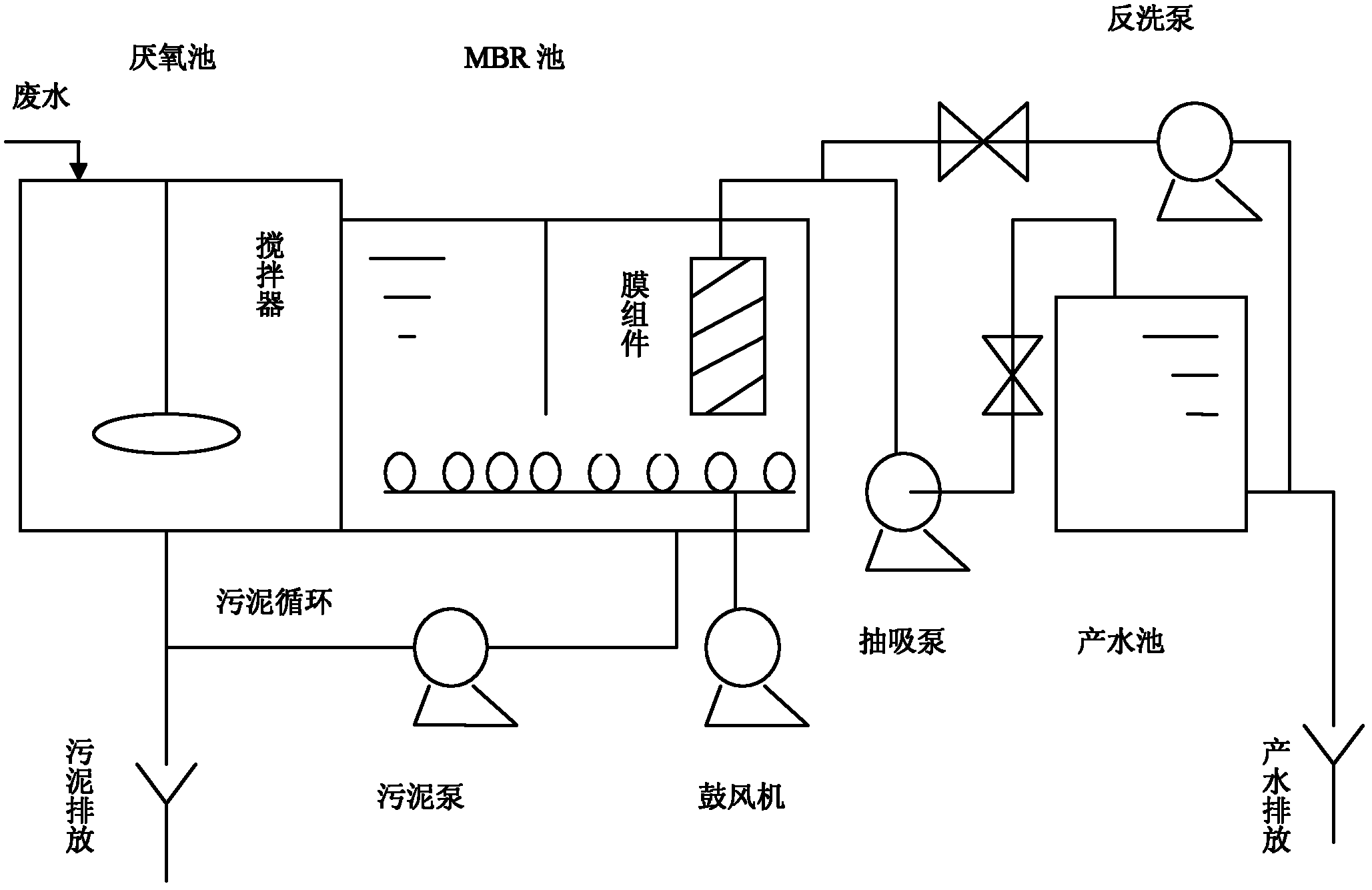
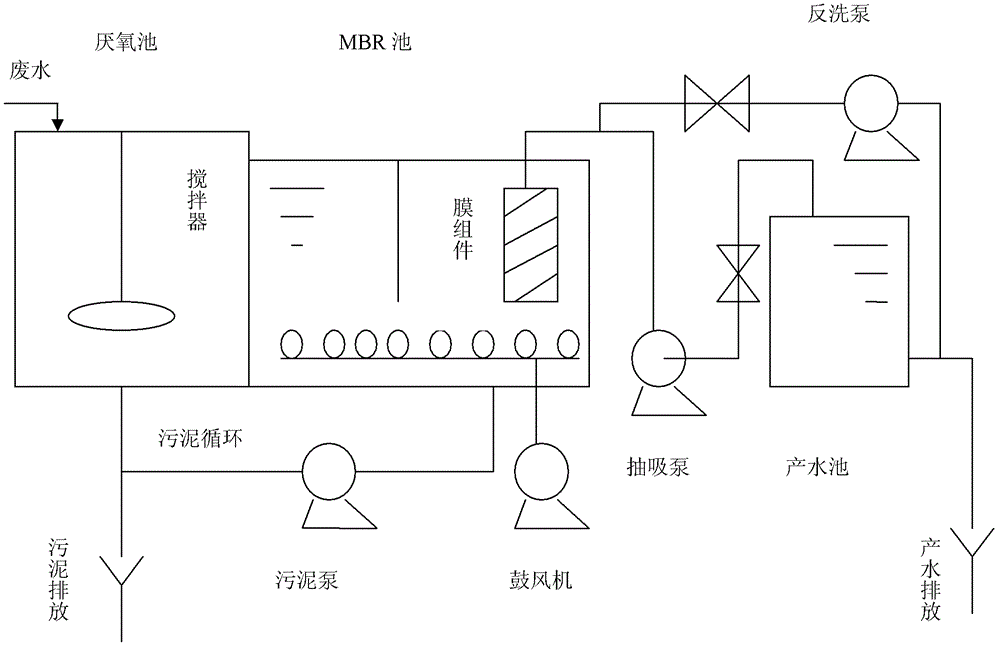
Reinforced-denitrification MBR (membrane bioreactor) sewage treatment method
ActiveCN103030250AReduce demandAchieving dual use of oxygenMultistage water/sewage treatmentNitrogen gasPrecipitation
The invention relates to a reinforced-denitrification MBR (membrane bioreactor) sewage treatment method which comprises steps as follows: (1) pretreated town sewage enters an anoxic tank together with 300-400% of reflux precipitation tank sludge and 200-400% of reflux membrane tank nitrification solution, and denitrifying bacteria reduce nitrate nitrogen carried by reflux into nitrogen by using a carbon source in the sewage; (2) the effluent of the anoxic tank enters a precipitation tank to be subjected to sludge-water separation together with the refluxed membrane tank nitrification solution, part of the precipitated sludge refluxes to the anoxic tank, and the rest of sludge is discharged; and (3) the effluent of the precipitation tank enters a membrane tank to be nitrified so as to oxidize ammonia nitrogen into nitrate nitrogen, a pump extracts water from the membrane tank via the intervals of the membrane, and the effluent water is discharged or reused. The invention sufficiently combines the inherent characteristics of the MBR and MBBR (moving bed biofilm reactor) techniques, reduces the influence of the biological denitrification influencing factor, and has the characteristics of high denitrification efficiency, high denitrification stability, simple process and the like.
Owner:NORTH CHINA MUNICIPAL ENG DESIGN & RES INST
Method for treating carbonized sewage through cultivating and domesticating nitrobacterium and denitrified bacterium
InactiveCN1626464AIncrease nitrification rateReduce domesticationMultistage water/sewage treatmentSewageSewage treatment
A process for treating the coking sewage by culturing and naturalizing the nitrifying bacteria and the denitrifying bacteria is disclosed. The process for culturing and naturalizing the denitrifying bacteria includes filling the mixed liquid from aerobic pool into anaerobic pool, flowing the supernatant from depositing pool back into anaerobic pool, inoculating denitrifying bacteria, culturing and naturalizing. The process for culturing and naturalizing the nitrifying bacteria includes introducing the nitrogen-contained sewage to aerobic pool, culturing naturalizing.
Owner:WUKUN STEEL
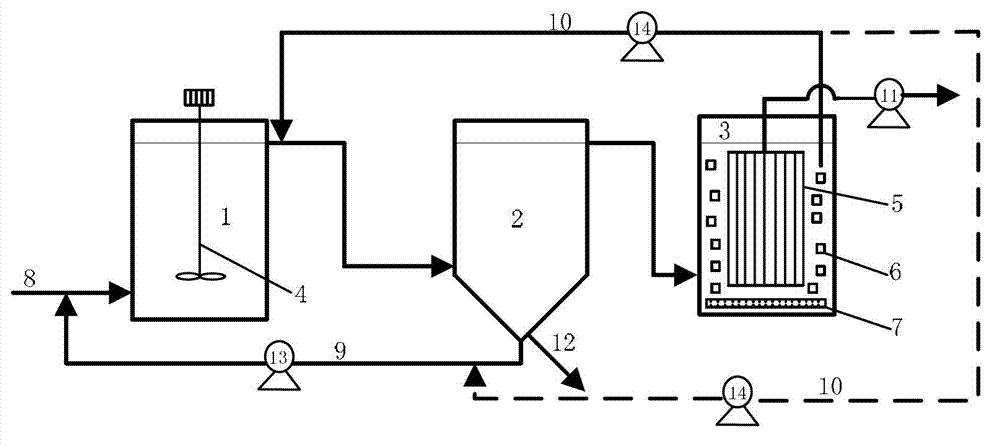
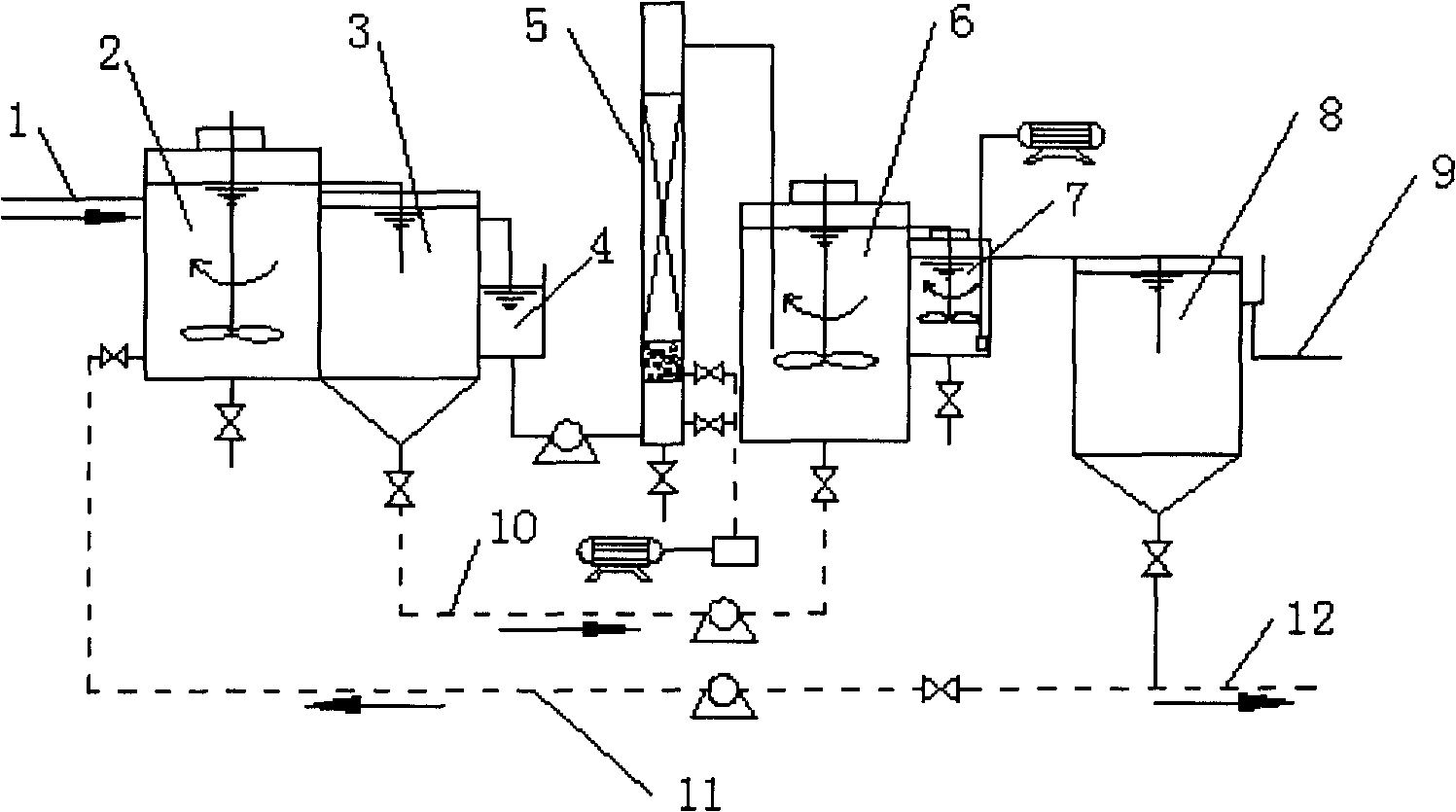
Biological sewage treatment device and method for synchronous nitrogen and phosphorus removal and sludge reduction
InactiveCN101786774AReduce yieldRelieve pressureWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentSludgeWater quality
The invention discloses a biological sewage treatment device and a biological sewage treatment method for synchronous nitrogen and phosphorus removal and sludge reduction. The device comprises a water inlet pipe 1, an anaerobic pond 2, a mid-sedimentation tank 3, an intermediate pool 4, a BAF 5, an anoxic pond 6, a post-aeration tank 7, a secondary sedimentation tank 8, and a water outlet pipe 9 in series connection in order; the treatment process comprises the following steps: mixing raw water and P-rich returned sludge in the anaerobic pond, wherein denitrifying phosphorus accumulating bacteria (DPBs) absorb and store VFA in a body in a form of PHB (poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate) and release a large amount of phosphorus; removing VOD remained in the BAF and nitrating the nitrogen; introducing BAF nitrification liquid and the sludge in the mid-sedimentation tank into the anoxic pond together, wherein the DPBs performs denitrification for absorbing the phosphorous by using the PHB in the body as an energy source and a carbon source and using NO3<-> as an electron acceptor; removing the unnecessary phosphorus contained in the post-aeration tank and blowing off the nitrogen to prevent the sludge from floating upwards; discharging the supernatant in the secondary sedimentation tank, wherein part of the sludge containing a large amount of DPBs is refluxed and the remaining sludge is discharged. The biological sewage treatment device and the biological sewage treatment method for the synchronous nitrogen and the phosphorus removal and the sludge reduction resolves the conflict between the denitrification and the phosphorous removal, and ensures the stable water quality of effluent and low yield of the sludge.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Preparation method and application of semi-dry nitration microbial agent
ActiveCN109486740AEasy to handleImprove stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism separationCulture fluidSludge
The invention belongs to the technical fields of biology and water treatment and provides a preparation method and application of a semi-dry nitration microbial agent. The preparation method comprisesthe specific preparation steps: (1) adding aerobic tank active sludge of a sewage treatment plant in a normal working state as a bacteria source into a special inorganic salt culture medium for nitrifying bacteria, and carrying out enrichment culture; (2) after the enrichment culture is finished, carrying out habituated culture, so as to obtain a culture solution with high nitrifying activity; (3) concentrating the culture solution, adding the culture solution into protecting liquid with a certain concentration, and carrying out culturing for a proper period of time; (4) uniformly mixing themixed liquid obtained in the step (3) with processed carriers, so as to obtain the microbial agent; and (5) putting the microbial agent into a vacuum sealing bag, carrying out vacuum sealing, and putting the vacuum sealing bag in a shade place, and carrying out normal-temperature storage. When the microbial agent is used, a user only needs to disperse the microbial agent with water and adding themicrobial agent into an aerobic biochemical system; the microbial agent has the characteristics of high activity and tolerance, good stability, strong stress resistance and the like and further has the advantages of convenience in transportation and storage, small occupied space and the like; and the microbial agent does not need to be excited and rejuvenated in use.
Owner:山东海景天环保科技股份公司
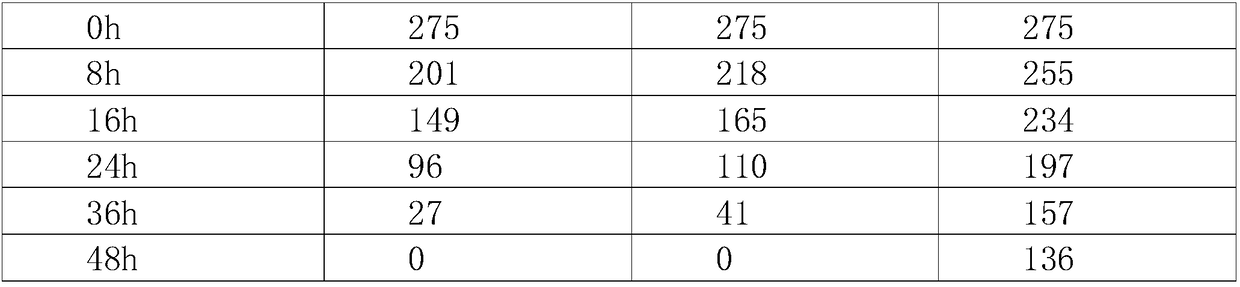
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) mother liquor treatment method based on MBR (Membrane Bioreactor) technique
ActiveCN102557257AGood and stable effluent qualityShort processTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesPolyvinyl alcoholPolyvinyl chloride
The invention discloses a wastewater biochemical treatment method, and specifically discloses a method for treating PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) mother liquor by utilizing MBR (Membrane Bioreactor) technique. The method comprises the following sequential process schemes: carrying out anaerobic reaction treatment on the PVC mother liquor with PVA (Polyvinyl Alcohol)-containing degrading bacteria, wherein the anaerobic reaction temperature is controlled at 20-35 DEG C, the reaction time is controlled at 6-10h, and the dissolved oxygen is controlled at 0.1-0.2mg / L; degrading organic macromolecules into micromolecules so as to improve biodegradability; and then introducing anaerobic reaction effluent to the MBR for aerobic treatment so as to ultimately obtain clean water with COD (Chemical OxygenDemand) not more than 30mg / L, wherein bacilli is contained in the MBR. The method has the advantages that treatment cost is only needed to be invested at one time, and long-term and stable treatment can be realized by expending low maintenance cost and electric cost in the following years; the longer the use time is, the lower the average treatment cost of per ton of wastewater is; and the methodcan be widely applied to sewage treatment enterprises.
Owner:HANGZHOU TIAN CHUANG ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
Local air-water reversing upflow biological aerated filter and sewage treatment method thereof
InactiveCN102583723AImprove space utilizationEvenly distributedSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentWater qualityStreamflow
The invention discloses a local air-water reversing upflow biological aerated filter and a sewage treatment method thereof, and relates to a water treatment device and a water treatment method. According to the biological aerated filter, a needle punched nonwoven filter material is taken as a packing, and a plurality of aeration branch pipes are arranged in the height direction of an aeration main pipe. The water treatment method comprises the following steps of: regulating the pH value of sewage to be treated to be 7.5-8, pumping into the filter, pumping air into the filter, ensuring that the hydraulic retention time is 1 to 2 hours, and directly discharging the obtained supernate. Small-flow aeration of which the aeration direction is opposite to upward water flow, the water flow is disturbed on the water flow section, air and water are uniformly distributed, a mass transfer effect is good, phenomena of short flow and channeling can be reduced, anaerobic areas in a system can be effectively eliminated, a membrane is formed uniformly, a problem of poor nitrification effect during operation of the traditional biological aerated filter is solved to a great extent, and the average ammonia nitrogen concentration of effluent is 8.63mg / L. The invention is used for treating wastewater.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Nitrifying bacterium agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110564619AIncrease nitrification rateTreatment using aerobic processesWaste water treatment from animal processingActivated sludgeNitrifying bacteria
The present invention relates to the technical field of environmental microorganisms and water treatments, and particularly relates to a nitrifying bacterium agent and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the nitrifying bacterium agent comprises: A) activated sludge in an aerobic pond is used as a source of bacteria and enriching and cultivating are conducted by using a nitrifying bacterium inorganic salt culture medium to obtain enriched culture bacterium liquid; the nitrifying bacterium inorganic salt culture medium comprises the following components: ammonium sulfate, sodium carbonate, sodium chloride, magnesium sulfate, ferrous sulfate, trace element mother liquid and water; and the trace element mother liquid comprises the following components of zinc sulfate, cobalt chloride, manganese chloride, boric acid, sodium molybdate and water; B) the enriched culture bacterium liquid is used as a seed and high ammonia nitrogen wastewater is used for gradient domestication culture; and C) after the gradient domestication culture is completed, expanding culture is performed to obtain the nitrifying bacterium agent. The prepared nitrifying bacterium agent has relativestrong tolerance in the high ammonia nitrogen wastewater and high in nitrifying activity.
Owner:山东海景天环保科技股份公司
Sewage treatment method with enhanced denitrification and dephosphorization functions
InactiveCN105601056AGuaranteed stabilityRealize functionTreatment using aerobic processesTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesSludgeSewage
The invention provides a sewage treatment method with enhanced denitrification and dephosphorization functions. The method is implemented by increasing dephosphorization and nitrification techniques on the basis of the anaerobic-anoxic-aerobic technique. The method specifically comprises the following steps: S1: introducing sewage treated by an anaerobic tank into a solid-liquid separation tank; S2: introducing a sludge-water mixture generated by the solid-liquid separation tank into an anoxic tank, introducing part of the generated supernatant into a dephosphorization tank, and introducing the rest of the generated supernatant into a nitrification tank; S3: introducing the mixed solution treated by the dephosphorization tank into a precipitation tank, discharging sludge generated by the precipitation tank, and introducing the generated supernatant into the nitrification tank; and S4: sequentially introducing the nitrification solution treated by the nitrification tank into the anoxic tank and aerobic tank for treatment. According to the method, the dephosphorization tank and the nitrification are separated, so that the dephosphorization and denitrification are not mutually influenced on the premise of implementing the dephosphorization and denitrification functions, thereby keeping the stability of the sewage treatment system.
Owner:SHENZHEN PANGU ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
Efficient denitrification treatment method for kitchen wastewater
InactiveCN112299653AReduce refluxImprove denitrification effectWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsSludgeNitrate nitrogen
The invention discloses an efficient denitrification treatment method for kitchen wastewater. The method comprises the following steps: 1, pretreating the kitchen wastewater; 2, inputting the kitchenwastewater into a first-stage anoxic tank, and mixing the kitchen wastewater with sludge returned by a membrane tank and a mixed solution returned by a first-stage aerobic tank for denitrification reaction; 3, enabling the kitchen wastewater to enter the first-stage aerobic tank, conducting aeration to remove most of organic matter, and achieving a nitration reaction 4, enabling the kitchen wastewater to enter the next-stage anoxic tank, and continuously performing denitrification reaction on the residual nitrate nitrogen; 5, repeatedly executing the step 2 to the step 4, so as to enable the kitchen wastewater to be treated by the multiple stages of anoxic tank treatment and corresponding aerobic tank treatment; 6, enabling the kitchen wastewater to enter the membrane tank, and further degrading residual organic matter; and 7, putting the kitchen wastewater treated by the membrane tank into a clean water pool. The application of the invention can fully ensure the stable operation, highefficiency and reliability of the kitchen wastewater denitrification treatment process.
Owner:SHANGHAI HONESS ENVIRONMENTAL TECH CORP
Blue-green algae mud pressure filtrate treatment method
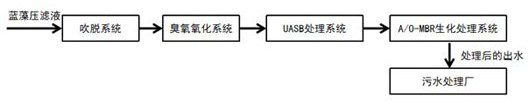
InactiveCN112919728AMitigate distractionsReduce bioinhibitionWater treatment parameter controlSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningEnvironmental chemistryGreen algae
The invention provides a blue-green algae mud pressure filtrate treatment method, which enables a blue-green algae mud pressure filtrate treatment system to be more stable and efficient, and improves the practical application value of a blue-green algae mud pressure filtrate treatment technology. A blue-green algae mud pressure filtrate treatment method is characterized by comprising the following steps: S3, carrying out pressure filtration on blue-green algae mud with the moisture content of 85-95%, carrying out air stripping process treatment on the produced blue-green algae pressure filtrate, and reducing the ammonia nitrogen concentration in the blue-green algae mud pressure filtrate by 20-40%; S4, adding soluble carbonate into the blue-green algae mud pressure filtrate treated by the air stripping process, and precipating calcium ions; S5, introducing ozone into the blue-green algae mud pressure filtrate obtained after calcium ion precipitation treatment for oxidation; S6, treating the blue-green algae mud pressure filtrate subjected to ozone oxidation through an anaerobic bioreactor (such as an up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor) system; and S7, treating the blue-green algae mud pressure filtrate through an aerobic bioreactor system (such as an A / O water treatment process-membrane bioreactor process).
Owner:WUXI GUOLIAN ENVIRONMENTAL SCI & TECH +1
Double sludge oxidation ditch denitrification phosphate-removing apparatus and method thereof
ActiveCN107043163AIncrease nitrification rateLarge biomassTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesPhosphateSewage
The invention discloses a double sludge oxidation ditch denitrification phosphate-removing apparatus and a method thereof. The apparatus comprises an oxidation ditch; an anaerobic zone, an anoxic zone and a water outlet zone which are communicated in order are arranged in the oxidation ditch, an independent nitrification zone is arranged between the anaerobic zone and the anoxic zone along the sewage flowing direction, a pre-anaerobic zone is arranged between the anoxic zone and the anaerobic zone, the independent nitrification zone is separated with the anaerobic zone and the anoxic zone through a first baffle plate and a second baffle plate, a first mud-separation zone, a filling material zone, a second mud-separation zone and a current stabilization zone are arranged in order along the sewage flowing direction, and nitrobacteria is enriched in the filling material zone. The denitrification phosphate-removing method is characterized in that a main channel of the oxidation ditch is always in an anaerobic / anoxic state, so that the denitrifying phosphorus-removing bacteria can be a dominant bacteria, the filling material is employed for hanging a membrane in the independent nitrification zone, so that a stable living environment is provided for nitrobacteria, nitrobacteria biomass in the independent nitrification zone is increased, nitrification rate is increased, and denitrification phosphate-removing effect can be guaranteed.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
A coupling packing autotrophic denitrification biological filter and its application
ActiveCN109052641BDifficult to dissolveIncrease speedWater treatment compoundsTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesBiological filterPyritic sulfur
The invention discloses a coupling filler autotrophic denitrification biofilter and application and belongs to the technical field of sewage treatment. Pyrrhotite, sulfur and a carbon source are utilized to be mixed and coupled according to certain proportion; then the materials are put into a reactor, and the autotrophic denitrification biofilter can be formed after inoculating biofilm formation;sewage flows through the biofilter, and nitrogen and phosphorus in the water are removed. The biofilter disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simpleness, easiness, practicability and shortbiofilm formation time; when the biofilter is utilized to treat nitrogen and phosphorus containing sewage, hydraulic retention time is only 0.5 to 3 h, and yielding water can meet a requirement; furthermore, the biofilter has the advantages of excellent nitrogen and phosphorus removal effect, low cost and suitability for engineering application.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
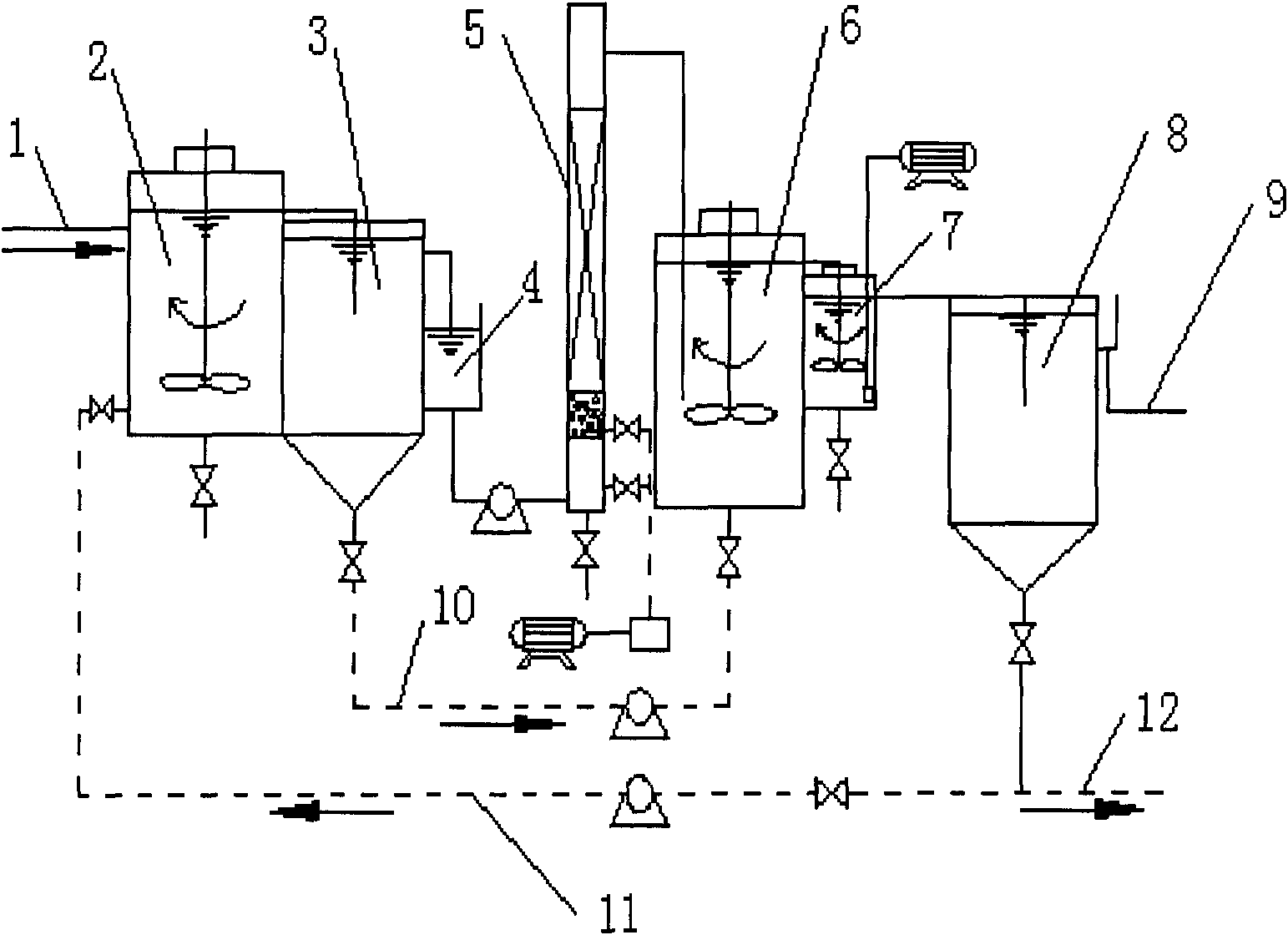
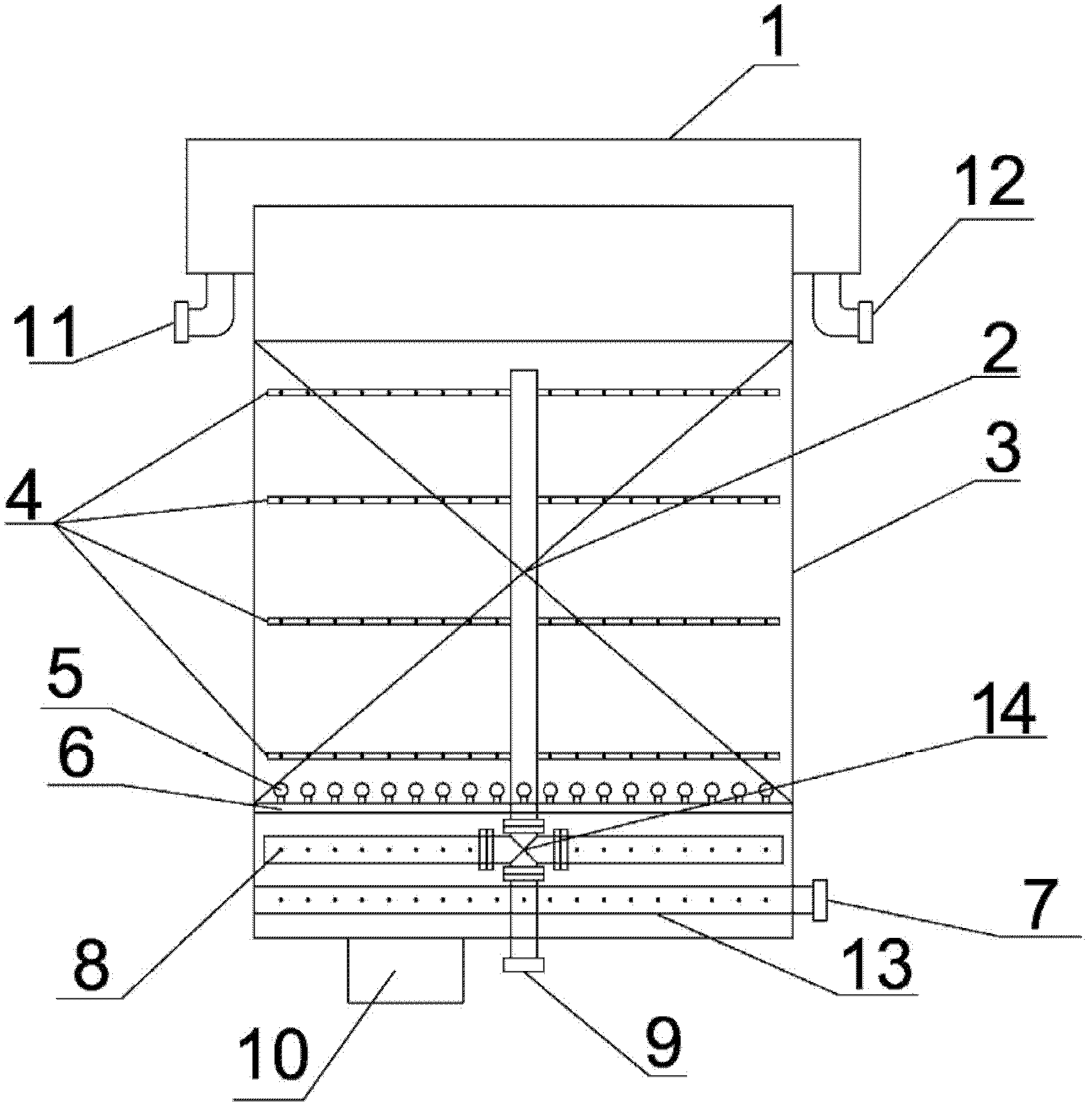
Apparatus and method for biological sewage treatment with effects of nitrogen and phosphorus synchronous removal and sludge reduction
InactiveCN106116059AReduce yieldRelieve pressureWater treatment parameter controlSpecific water treatment objectivesSludgeWater quality
Disclosed are an apparatus and a method for biological sewage treatment with effects of nitrogen and phosphorus synchronous removal and sludge reduction. The apparatus comprises a water inlet pipe 1, an anaerobic tank 2, a median settling tank 3, an intermediate water tank 4, a biological aerated filter (BAF) 5, an anoxic tank 6, a rear aeration tank 7, a secondary settling tank 8 and a water outlet pipe 9 connected in sequence. The method for biological sewage treatment includes mixing raw water and P-enriched returned sludge in the anaerobic tank, utilizing denitrifying phosphorus removing bacteria (DPBs) to absorb volatile organic acid (VFA) and store the same in the form of poly Beta-hydroxybutyric acid (PHB) while releasing a great quantity of phosphorus; carrying out removal of residual COD and nitrification of nitrogen by the BAF, delivering nitrification liquor of the BAF and sludge of the median settling tank into the anoxic tank together, and utilizing the DPBs in the anoxic tank to carry out denitrifying phosphorus-uptake by taking in-vivo PHB as energy source and carbon source and taking NO3<-> as an electron acceptor; removing residue phosphorus and blowing off nitrogen gas to avoid sludge floating in the rear aeration tank, delivering the mixture liquid into the secondary settling tank, discharging supernate, returning a part of sludge containing a great quantity of DPBs and discharging residual sludge. By the method, the problem of conflict between nitrogen removal and phosphorus removal is solved, quality stability of outlet water is guaranteed, and yield of sludge is low.
Owner:天津美能科技有限公司
Integrated denitrification membrane bioreactor and sewage treatment method using bioreactor
ActiveCN114368837AImprove work efficiencyImprove denitrification effectWater treatment parameter controlSpecific water treatment objectivesMicroorganismMembrane bioreactor
The invention provides an integrated denitrification membrane bioreactor and a sewage treatment method using the integrated denitrification membrane bioreactor. The integrated denitrification membrane bioreactor is provided with at least one reaction tank, and the reaction tank comprises a first aerobic unit area, an anoxic unit and a second aerobic unit area; partition plates are respectively arranged between the aerobic unit area I and the anoxic unit and between the anoxic unit and the aerobic unit area II; a convex slope is arranged at the bottom of the anoxic unit. According to the integrated denitrification membrane bioreactor disclosed by the invention, microorganisms can better adapt to an aerobic and anoxic coexistence environment, the problem of poor denitrification effect caused by sludge backflow is avoided, pollutants such as nitrogen and organic matters in domestic sewage are efficiently and stably removed, and the denitrification treatment effect is enhanced.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Carbonate type ammoxidation process and strengthening technology thereof
ActiveCN113213625AAchieve anaerobic nitrificationMeet the needs of different denitrification and denitrification processesWater treatment parameter controlWater contaminantsNitrationNitrifying bacteria
The invention discloses a carbonate type ammoxidation process and a strengthening technology thereof. According to the method, a proper amount of carbonic acid compounds are supplemented into the wastewater to serve as an electron acceptor for ammonia nitrogen autotrophic oxidation and a carbon source for nitrifying bacteria anabolism; nitration of ammonia nitrogen under an anaerobic condition is realized by regulating and controlling environmental factors such as proper temperature and pH value and working conditions such as hydraulic retention time and sludge retention time, and nitrite nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen are stably generated from the ammonia nitrogen; and by supplementing a proper amount of redox mediator in the system, the ammonia nitrogen nitration / oxidation rate can be increased, the nitration degree is more thorough, and the product is mainly nitrate nitrogen. Aeration oxygen supply is not needed in the whole process, and the construction and operation cost of a rear-mounted biological denitrification process based on the nitrification-denitrification process can be greatly reduced.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Real-time control apparatus for floated aerobic biofilm A<2>O system for treating low C/N sewage, and method thereof
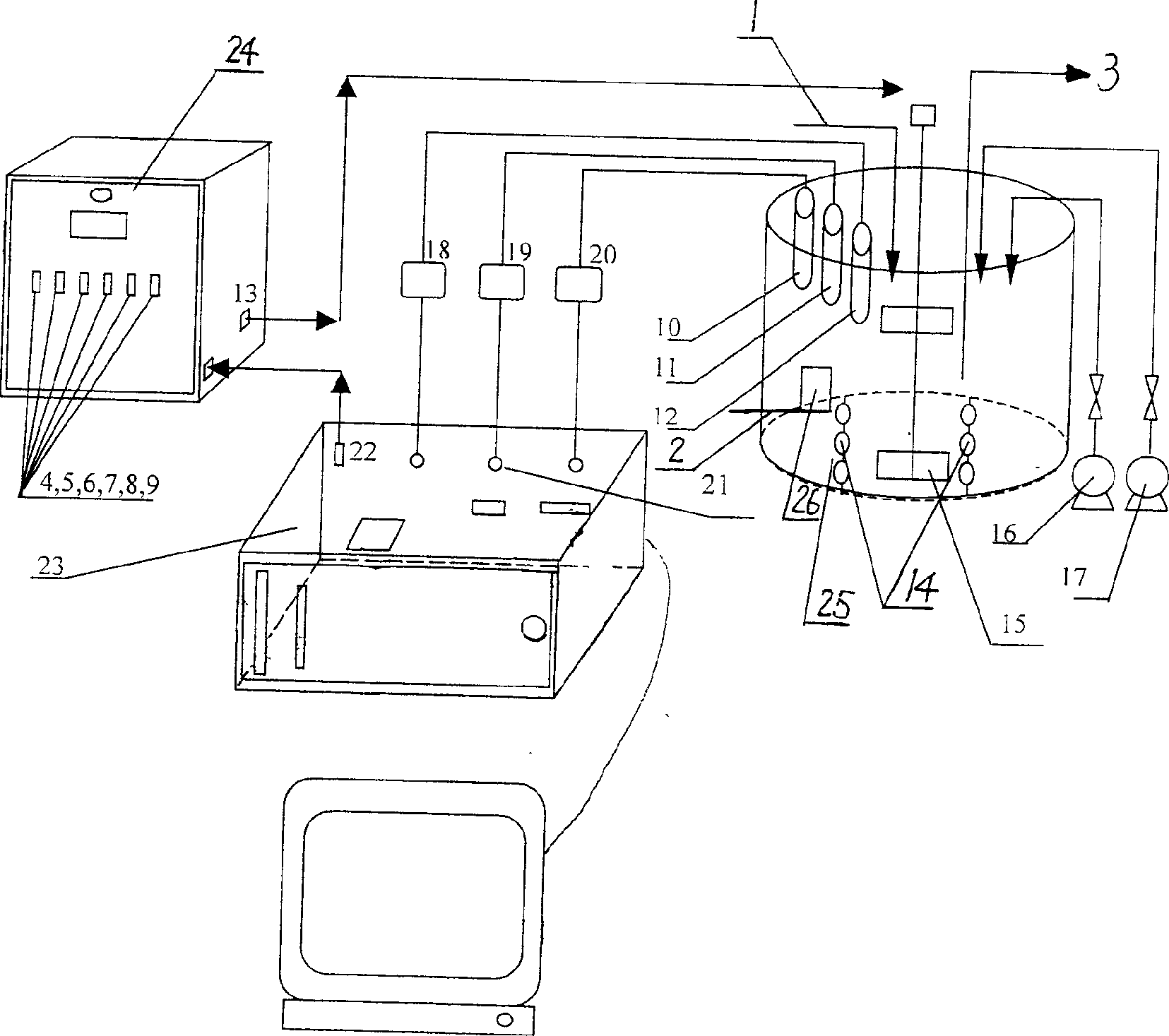
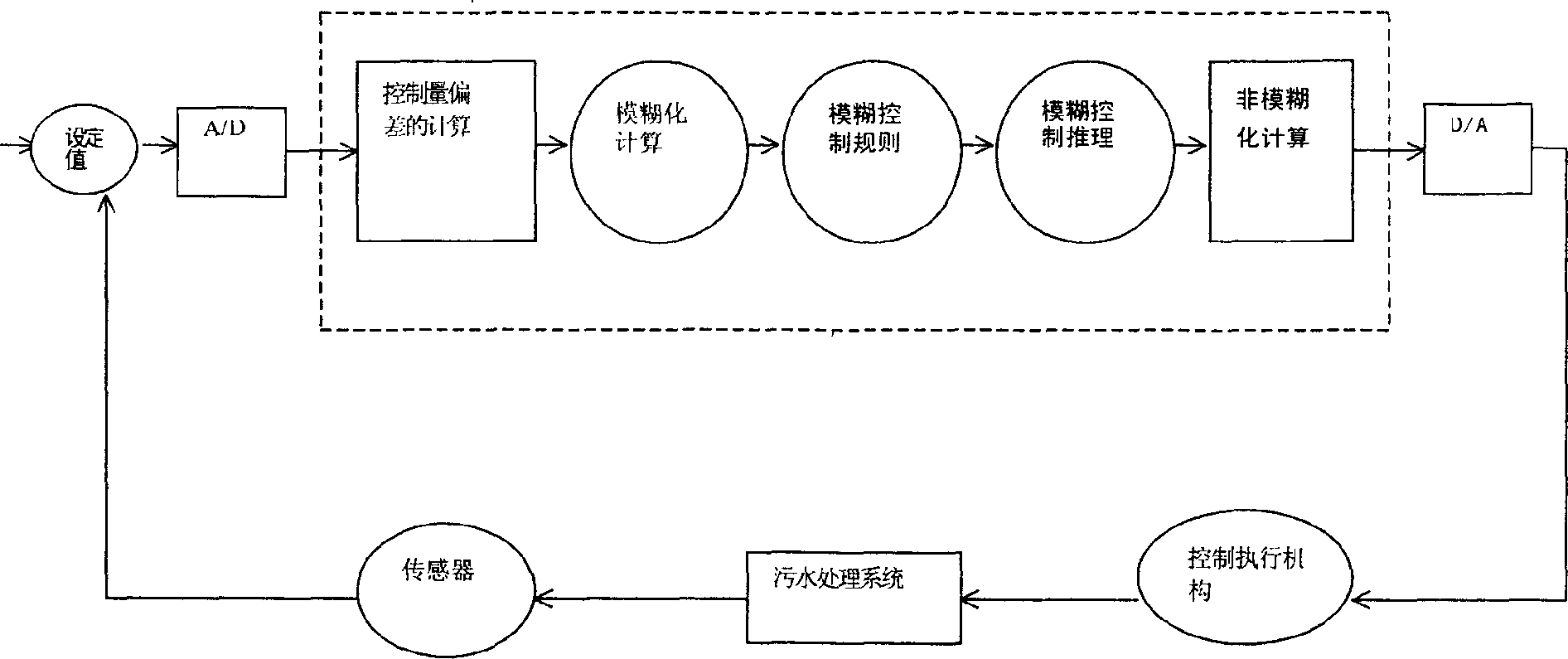
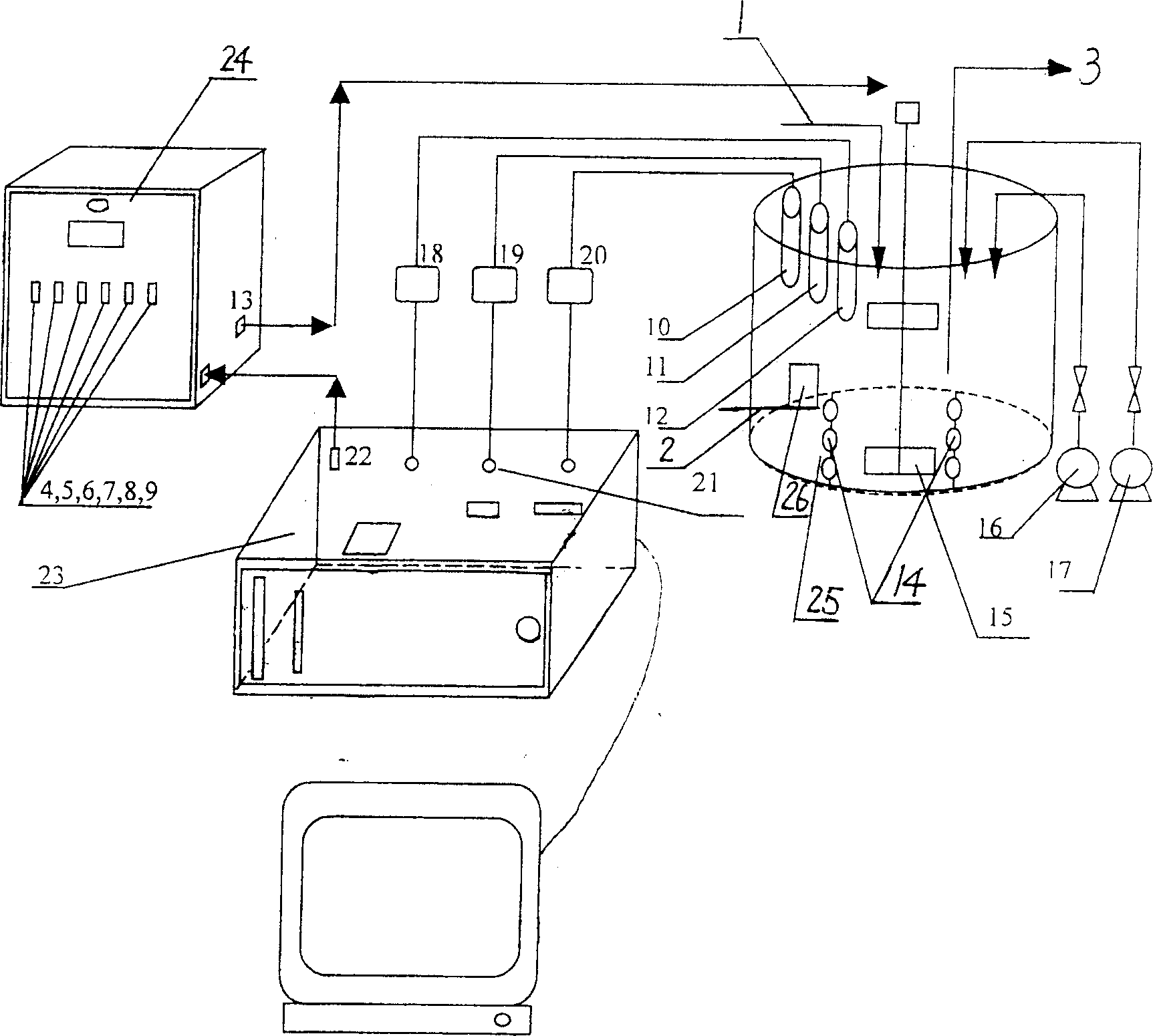
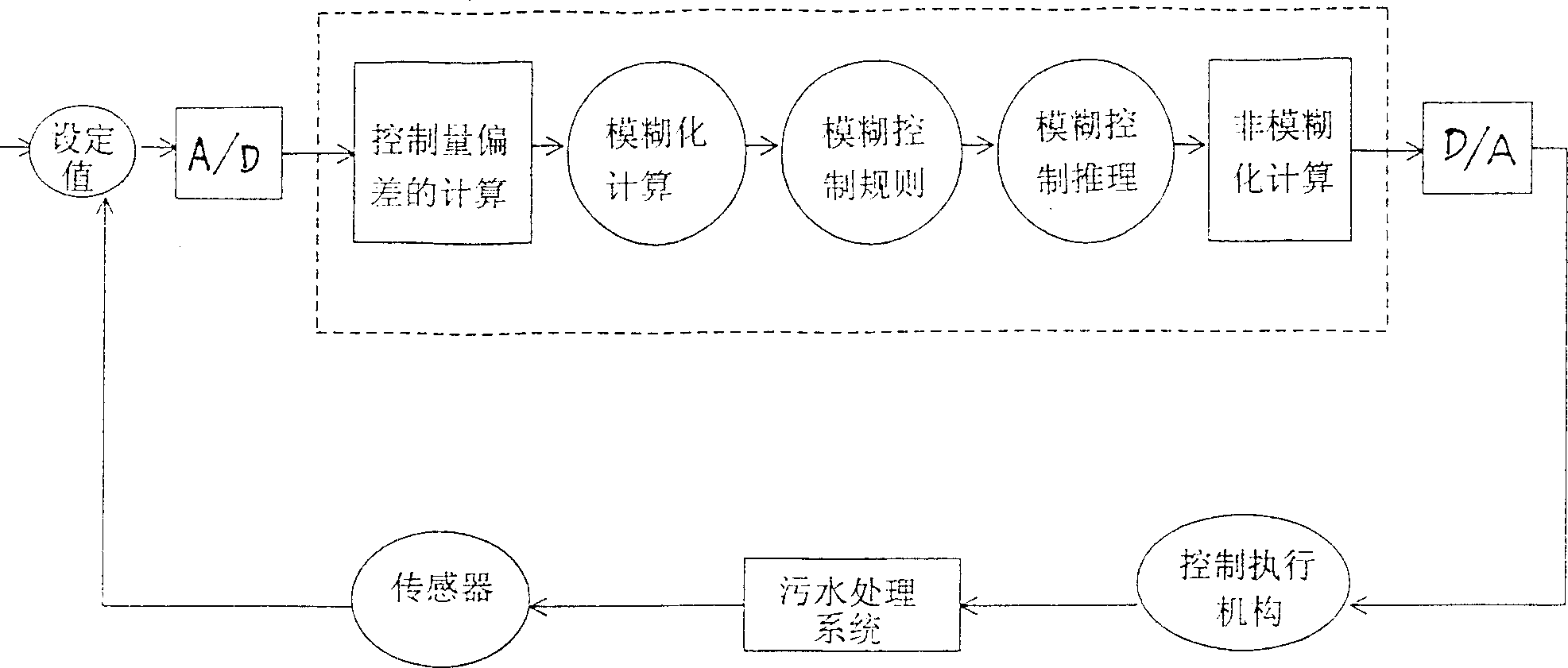
InactiveCN102344198BSolve the contradiction of different sludge age requirementsPromote growthTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesTotal factory controlPeristaltic pumpReal-time Control System
The present invention discloses a real-time control apparatus for a floated aerobic biofilm A<2>O system for treating low C / N sewage, and a method thereof. The real-time control apparatus for the floated aerobic biofilm A<2>O system comprises a raw water tank (1), an aerobic biofilm A<2>O reactor (2), a secondary settling tank (3), a DO meter (5), a on-line tester (6), a computer (7) and a process controller (8). The real-time control method comprises: online collecting ammonia nitrogen concentration in a effluent tank, wherein the real-time control system is adopted to adjust the aeration rate of an air pump; online collecting nitrate nitrogen concentration in the effluent tank, wherein the real-time control system is adopted to adjust the reflux ratio of the nitrified liquid of a peristaltic pump; online collecting the PO4<3->-P concentration in the effluent tank, wherein the real-time control system is adopted to adjust a bypass flow ratio of the peristaltic pump; online collecting the TOC concentration in the effluent tank, wherein the real-time control system is adopted to adjust the aeration rate of the air pump. The method provided by the present invention is one of the most effective methods for treating the low C / N sewage and synchronously denitriding and removing phosphorus. The effluent quality through the apparatus and the method provided by the present invention stably achieve the national one-level (A) standard.
Owner:LANZHOU SHUISEN ELECTRONICS TECH
Two-stage biological selection denitrifying phosphorus and nitrogen removal sewage treatment device and method thereof
ActiveCN101792243BInhibition of reproductionExcellent anaerobic environmentTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesNitrogen removalWastewater
The present invention provides a two-stage biological selection denitrifying phosphorus and nitrogen removal sewage treatment device and a method thereof, relates to a device and a method for sewage treatment, and aims to solve the problem that inner contradiction existing in anaerobic, anoxic, aerobic and other phosphorus and nitrogen removal processes of a sewage treatment plant cannot meet the requirements of 'Discharge standard of pollutants for municipal wastewater treatment plant' (GB 18918-2002) in China. The device adopts a technical scheme that: a second anaerobic biological selector is communicated with a sedimentation tank; and a first anaerobic biological selector is communicated with an anoxic pond. The technical scheme of the method comprises the following steps: 1, pumping raw water into the first anaerobic biological selector; 2, allowing effluent treated by the step 1 to enter the second anaerobic biological selector; 3, allowing the effluent treated by the step 2 to flow to the anoxic pond; 4, allowing the effluent treated by the step 3 to enter a first aerobic pond; 5, allowing the effluent treated by the step 4 to enter a second aerobic pond; and 6, allowing the effluent treated by the step 5 to enter the sedimentation tank, and directly discharging supernatant. The device and the method are used for municipal sewage treatment.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Double sludge oxidation ditch denitrification phosphorus removal device and method
ActiveCN107043163BIncrease nitrification rateLarge biomassTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesPhosphateEngineering
The invention discloses a double sludge oxidation ditch denitrification phosphate-removing apparatus and a method thereof. The apparatus comprises an oxidation ditch; an anaerobic zone, an anoxic zone and a water outlet zone which are communicated in order are arranged in the oxidation ditch, an independent nitrification zone is arranged between the anaerobic zone and the anoxic zone along the sewage flowing direction, a pre-anaerobic zone is arranged between the anoxic zone and the anaerobic zone, the independent nitrification zone is separated with the anaerobic zone and the anoxic zone through a first baffle plate and a second baffle plate, a first mud-separation zone, a filling material zone, a second mud-separation zone and a current stabilization zone are arranged in order along the sewage flowing direction, and nitrobacteria is enriched in the filling material zone. The denitrification phosphate-removing method is characterized in that a main channel of the oxidation ditch is always in an anaerobic / anoxic state, so that the denitrifying phosphorus-removing bacteria can be a dominant bacteria, the filling material is employed for hanging a membrane in the independent nitrification zone, so that a stable living environment is provided for nitrobacteria, nitrobacteria biomass in the independent nitrification zone is increased, nitrification rate is increased, and denitrification phosphate-removing effect can be guaranteed.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
A high-density enrichment method for autotrophic nitrifying bacteria consortia
ActiveCN109055285BRealize automated trainingHigh densityBacteriaBiological water/sewage treatmentCulture mediumsBacterium nitrobacter
Owner:SHENYANG RES INST OF CHEM IND +1
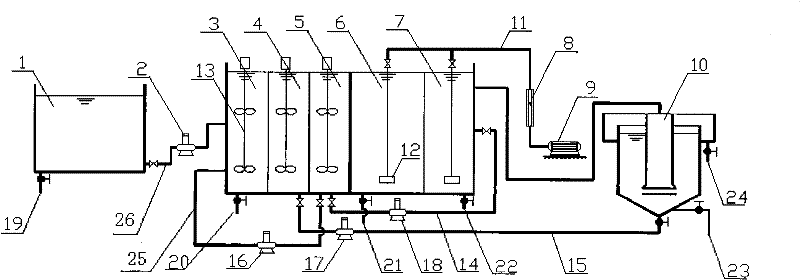
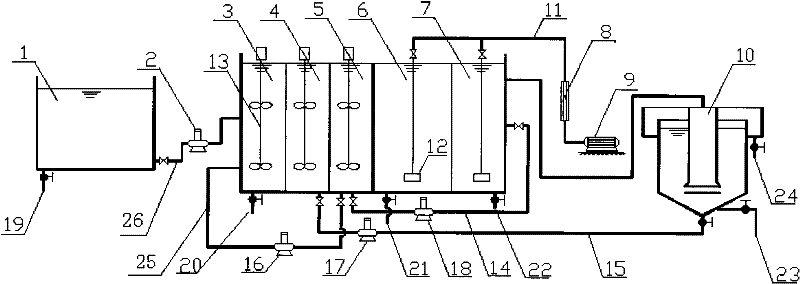
SBR alternant aerobic/anaerobic technology for biological denitrification and real time control device and method thereof
InactiveCN1247470CIncrease throughputIncrease alkalinity dosingTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSludgeTime control
The invention discloses a SBR alternant aerobic / anaerobic technology for biological denitrification and real time control device and method thereof which consists of, dividing the waste water to be treated into three portions, loading each portion into a reactor, alternatively carrying out the operating mode of aerobic aeration and anoxybiotic agitating under real time procedure control, so as to realize the organics degradation and nitrogen-containing compound removal.
Owner:BEIJING TANSI ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECHCO
A kind of preparation method and application of semi-dry nitrifying bacteria agent
ActiveCN109486740BEasy to handleImprove stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism separationBiotechnologyCulture fluid
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and water treatment, and provides a preparation method and application of a semi-dry state nitrifying bacterial agent. (2) After enrichment culture, carry out domestication culture to obtain a culture solution with high nitrification activity; (3) Concentrate the culture solution and place it at a certain concentration (4) Mix (3) the mixed solution with the treated carrier to obtain a bacterial agent; (5) put the bacterial agent into a vacuum-sealed bag, vacuum seal, and place it in a cool place Store at room temperature. The bacterial agent only needs to be dispersed with water, and then added to the aerobic biochemical system. It has the characteristics of high activity, high tolerance, good stability, strong resistance to stress, etc., and is convenient for transportation and storage. , small footprint and other advantages; no activation and rejuvenation are required during application.
Owner:山东海景天环保科技股份公司
Continuous flow operation method for prompting continuous flow sewage treatment system to achieve short range nitration quickly
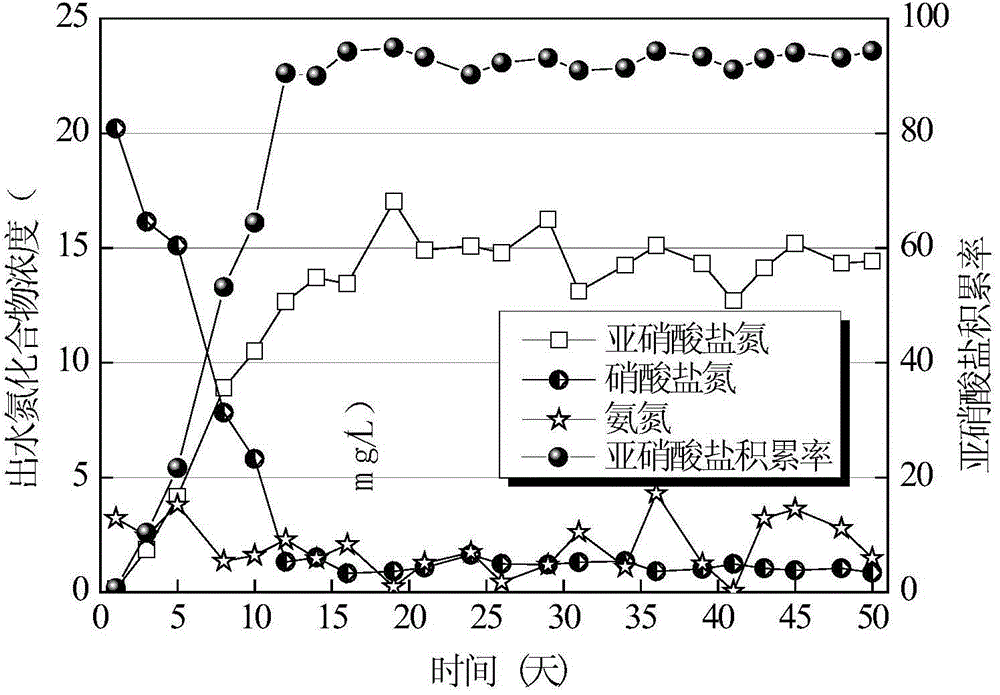
ActiveCN103435160BStable accumulation rateShort startup cycleWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSludgeNitration
A continuous flow operation method for prompting a continuous flow sewage treatment system to achieve short range nitration quickly belongs to the field of sewage treatment by using a biochemical process. According to the invention, by using the characteristics that the activity of nitrite oxidizing bacteria is restrained under an anoxic condition and is slow in recuperate under an aerobic condition, a continuous flow system is modified to be a four-section anoxic-aerobic alternating operation way, and the nitrite accumulation rate is improved stage by stage; the nitrite oxidizing bacteria in the system can be washed through a spoil disposal way, and a stable short range nitration effect is eventually achieved. Practice shows that the nitrite accumulation rate can reach more than 80 percent in about one sludge age after the system is started. Compared with a short range nitrifying method for achieving a continuous flow system by depending on dissolved oxygen, the continuous flow operation method provided by the invention has the advantages of short period, relatively stable short range effect, high nitration rate, capacity of low possibility of sludge expansion and the like, can serve as a quick starting method aiming at short range nitration of the continuous flow system, and is applicable to continuous flow sewage treatment systems with various scales.
Owner:北控水务(中国)投资有限公司
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) mother liquor treatment method based on MBR (Membrane Bioreactor) technique
ActiveCN102557257BGood and stable effluent qualityShort processTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesChemical oxygen demandPolyvinyl alcohol
The invention discloses a wastewater biochemical treatment method, and specifically discloses a method for treating PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) mother liquor by utilizing MBR (Membrane Bioreactor) technique. The method comprises the following sequential process schemes: carrying out anaerobic reaction treatment on the PVC mother liquor with PVA (Polyvinyl Alcohol)-containing degrading bacteria, wherein the anaerobic reaction temperature is controlled at 20-35 DEG C, the reaction time is controlled at 6-10h, and the dissolved oxygen is controlled at 0.1-0.2mg / L; degrading organic macromolecules into micromolecules so as to improve biodegradability; and then introducing anaerobic reaction effluent to the MBR for aerobic treatment so as to ultimately obtain clean water with COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) not more than 30mg / L, wherein bacilli is contained in the MBR. The method has the advantages that treatment cost is only needed to be invested at one time, and long-term and stable treatment can be realized by expending low maintenance cost and electric cost in the following years; the longer the use time is, the lower the average treatment cost of per ton of wastewater is; and the method can be widely applied to sewage treatment enterprises.
Owner:HANGZHOU TIAN CHUANG ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com