Patents
Literature
43 results about "Beta-Xylosidase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of preparing heat-proof xylanase, heat-proof beta-xylosidase or heat-proof beta-glucosidase
The invention discloses a making method of heat-proof xylanase, heat-proof beta-xylosidase or heat-proof beta-glucosidase, which comprises the following steps: adopting agricultural waste as carbon source; fermenting Paecilomyces thermophila J18 at 40-60 deg.c to obtain the ferment liquid with heat-proof xylanase, heat-proof beta-xylosidase or heat-proof beta-glucosidase; purifying; obtaining electrophoretic grade product.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Beta-xylosidase for conversion of plant cell wall carbohydrates to simple sugars
InactiveUS20090280541A1High activity and stabilityModerately high-temperaturesSugar derivativesBiofuelsHydrolysatePlant cell
Xylose-containing plant material may be hydrolyzed to xylose using a β-D-xylosidase which exhibits unexpectedly high activity. The enzyme has a kcat value for catalysis of approximately 185 sec−1 for 1,4-β-D-xylobiose (X2) when measured at a pH of 5.3 and a temperature of 25° C.; this is at least 10-fold greater than reported for other xylosidases at 25° C. and their optimal pH. The enzyme also has an isoelectric point of approximately 4.4. When reacted at a pH between about 4.5 and about 7.7, the β-D-xylosidase exhibits surprisingly high activity for hydrolyzing xylose-containing plant materials to xylose. The xylose released from plant materials may then be converted to other secondary products such as ethanol by fermentation or other reaction. This β-D-xylosidase may be used alone or in combination with other hydrolytic or xylanolytic enzymes for treatment of lignocellulosic or hemicellulosic plant materials or plant material hydrolysates or xylooligosaccharides.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
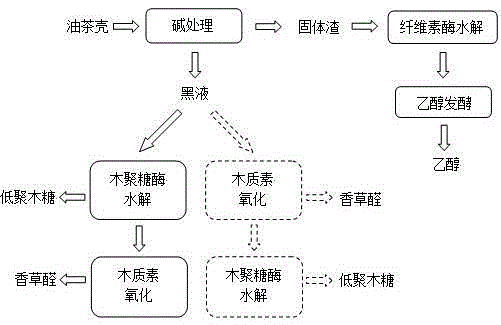
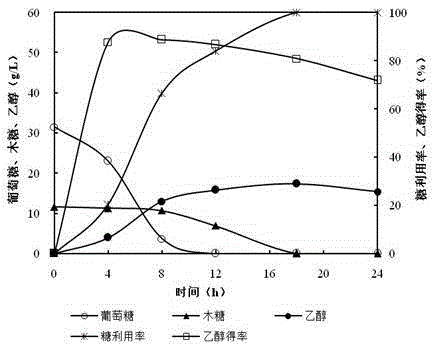
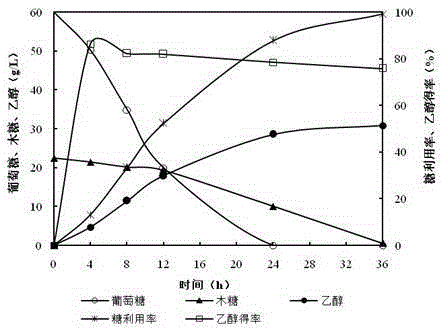
Comprehensive utilization method of oil-tea camellia shells
ActiveCN103320477ARelieve pressureBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationCamellia oleifera
The invention discloses a comprehensive utilization method of oil-tea camellia shells. The method comprises the following steps: crushing oil-tea camellia shells, performing alkaline pretreatment, and performing solid-liquid separation to obtain black liquor and solid residues; performing enzymolysis on the solid residues through cellulase to prepare monosaccharide and performing alcohol fermentation, and preparing ethanol; regulating pH of the black liquor, and performing solid-liquid separation to obtain residues and a vanillic aldehyde solution; and performing enzymolysis on the residues through xylanase to prepare an xylooligosaccharide solution and residues, and oxidizing the residues to prepare the vanillic aldehyde. According to the comprehensive utilization method, the solid residues obtained by solid-liquid separation are hydrolyzed by cellulase and further fermented to prepare fuel ethanol by using the condition that the oil-tea camellia shells are pretreated by sodium hydroxide; the black liquor obtained by solid-liquid separation is neutralized to the pH of 6, wherein the supernatant obtained by solid-liquid separation contains high-concentration vanillic aldehyde (lignin oxidization is not required), enzyme hydrolysis is carried out on the precipitation to prepare xylooligosaccharide by employing xylanase containing a small amount of beta-xylosidase, and further the residues obtained by enzymolysis are further oxidized to prepare the vanillic aldehyde. Therefore, according to research of the process, the biomass can be totally utilized for preparing the fuel ethanol, xylooligosaccharide and vanillic aldehyde finally.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Biological compound enzyme preparation and dark green tea making process using same for improvement of tea quality
ActiveCN102747050AIncrease enzyme activityContinuous and stable enzymatic hydrolysisPre-extraction tea treatmentEnzymesAlgluceraseGlucanase
The invention discloses a biological compound enzyme preparation and a dark green tea making process using the same for improvement of tea quality, belonging to the field of tea making processes. The compound enzyme preparation contains pectin hydrolase, beta-glucanase, beta-glucosidase, beta-xylosidase and the like; when applied in the dark green tea making process, the compound enzyme preparation can both increase the fragrance of tea and greatly improve the quality of dark green tea, so the compound enzyme preparation has good popularization and application values.
Owner:山东东兴生物科技股份有限公司
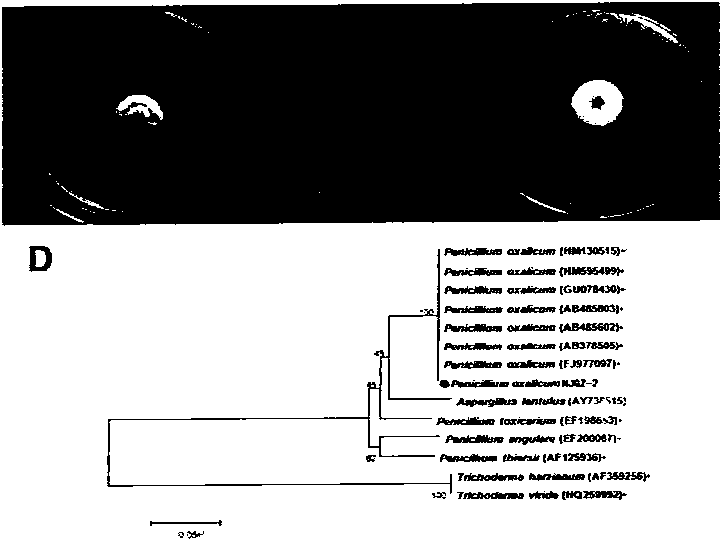
Agricultural straw degrading fungus penicillium oxalicum NJGZ-2 and fungal agent thereof
The invention relates to a normal-temperature fungus NJGZ-2 capable of degrading agricultural waste straw, belonging to the agricultural waste resource utilization technology. The class of the strain NJGZ-2 is named penicillium oxalicum, and the culture is collected in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), with collection number CGMCC No.7527. Tests indicate that after the rice straw is inoculated with a spore suspension (1% 10<7> spores / mL), the weight loss ratio of the rice straw is 59.7% after 7 days of 170r / min liquid fermentation culture at 30 DEG C. In the fermentation crude enzyme extraction liquid, the activities of incision enzyme, beta-glucosidase, xylanase, beta-xylosidase and total cellulose are 113.3U / gds, 11.6U / gds, 1,439.7U / gds, 2.0U / gds and 13.8U / gds respectively. The crude enzyme liquid can hydrolyze low-concentration alkali-treated corncob to generate high-concentration reducing sugar (962.2mg of reducing sugar / gram of substrate). According to the invention, the agricultural waste straw is degraded by the microbial fermentation technology and is converted into organic fertilizer, therefore, the waste can be turned into wealth to protect the environment, and application prospects are broad.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
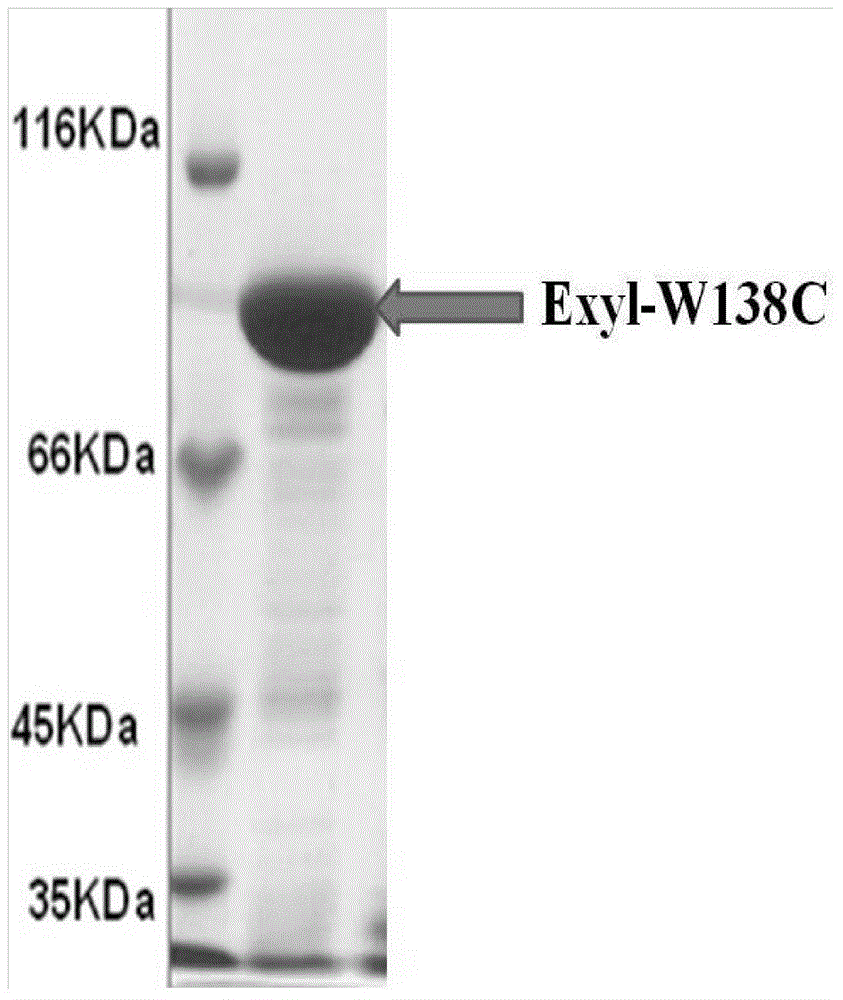
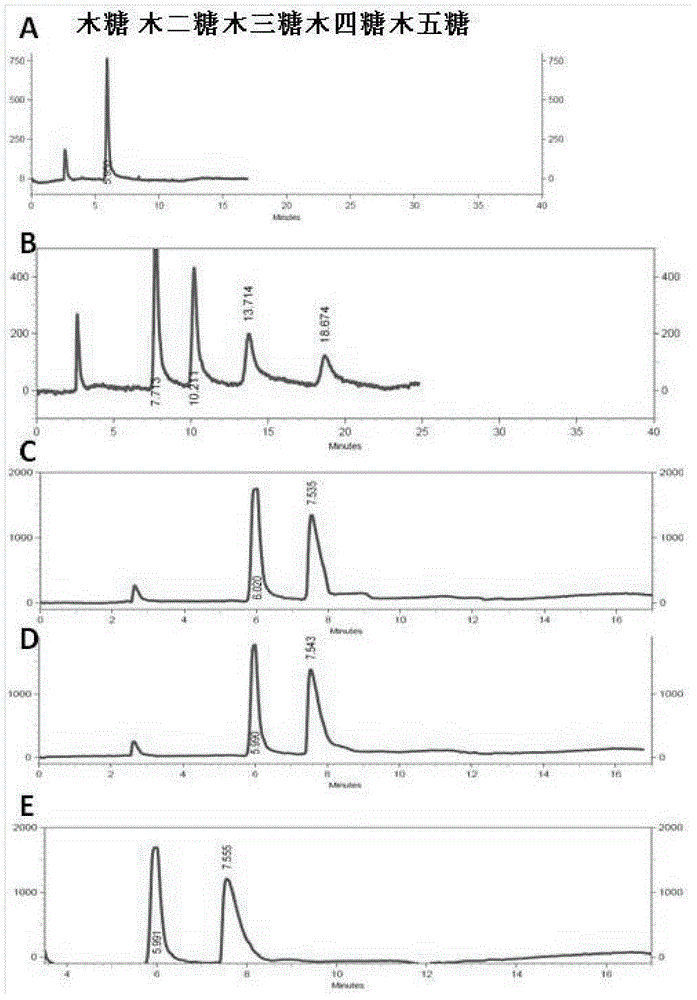
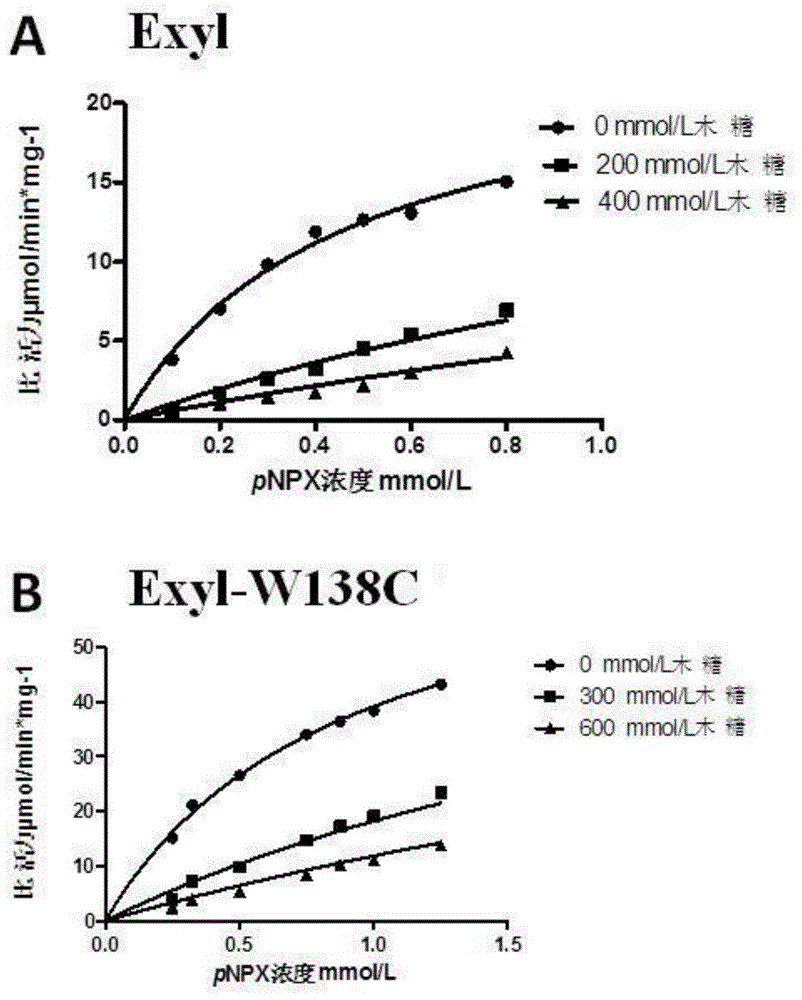
Beta-xylosidase mutant and use thereof
The invention discloses a beta-xylosidase mutant and a use thereof. The beta-xylosidase mutant has an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The mutant enzyme has high xylose and glucose tolerance compared with non-mutated beta-xylosidase, and has wide use in degradation of xylo-oligosaccharide.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Beta-xylosidase and encoding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN101724615AEasy to purifyHigh recovery rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBiology
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Beta-xylosidase and application thereof
ActiveCN107189994AUnique toleranceOmit steps to removeFermentationGlycosylasesBiotechnologyHigh concentration
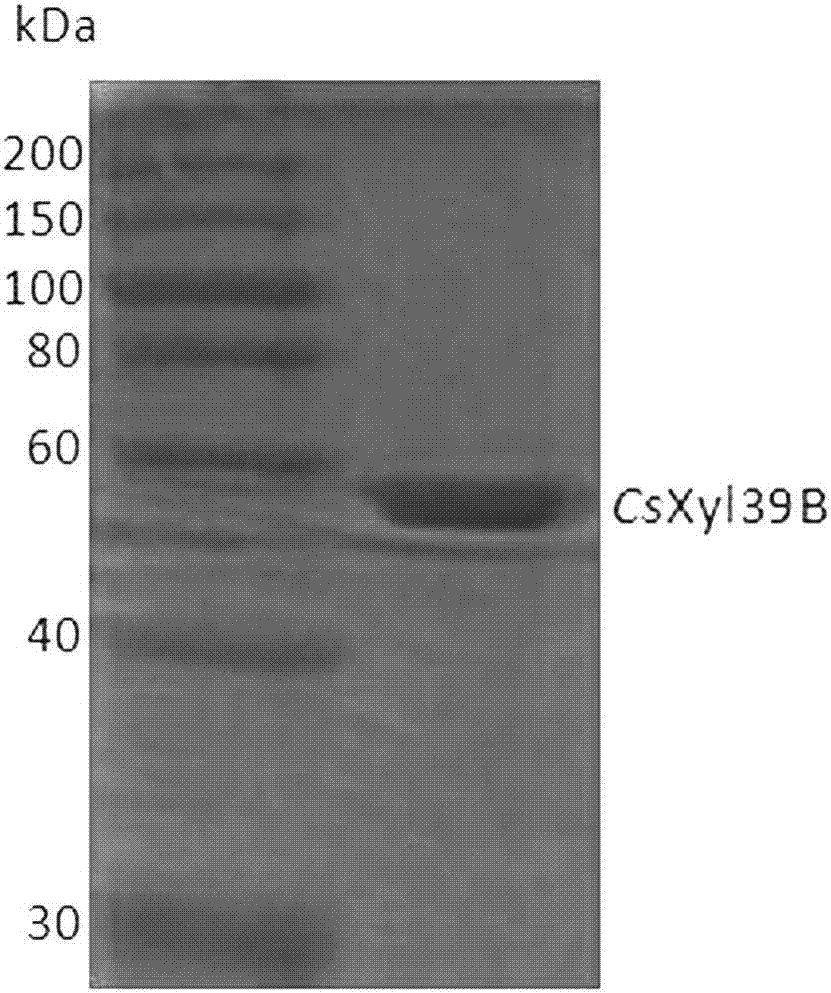
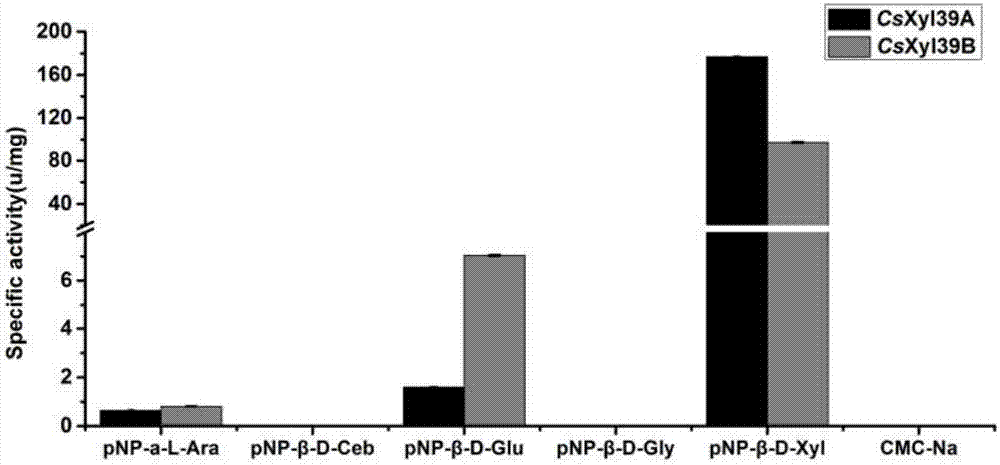
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to two types of beta-xylosidase from caldicellulosiruptor saccharolyticus and application thereof in biological conversion of natural compounds containing xylosyl modification. Beta-1,4-xylosidase is beta-xylosidase CsXy139A and beta-xylosidase CsXy139B from the same gene cluster of the caldicellulosiruptor saccharolyticus. The beta-xylosidase has the advantages that proved by experiment, the CsXy139A can resist the organic solvent, and the natural compound containing the xylosyltaxol can be hydrolyzed in an organic solvent water solution with higher concentration; meanwhile, the CsXy139A is suitable for the enzyme immobilizing technique; CsXy139B has a good tolerance ability on the hydrolysis products of xylose and glucose, and the heat stability is relatively good; and the two types of beta-xylosidase can perform high-efficiency biological catalyzing on natural drugs containing xylosyl modification.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Chromogenic medium for separating and detecting enterobacter cloacae
ActiveCN103820373AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesMicroorganism
The invention relates to a chromogenic medium for separating and detecting enterobacter cloacae, and in particular relates to a medium and method for specifically separating and detecting enterobacter cloacae by using beta-xylosidase and a corresponding substrate. The beta-xylosidase chromogenic substrate is decomposed in the presence of a bacterial enzyme to free chromogenic groups out, and colonies present the color of the chromogenic groups, so that the enterobacter cloacae is distinguished from other enterobacteriaceae bacteria. The medium for separating and detecting the enterobacter cloacae, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages of strong specificity, high sensitivity, easiness in operation, simplicity in result judgment and the like, and is applicable in the fields of medical clinical microbial examination, food safety microbial detection, environmental protection and the like.
Owner:BEIJING JUNLIKANG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
High-temperature-resistant compound enzyme and applications thereof
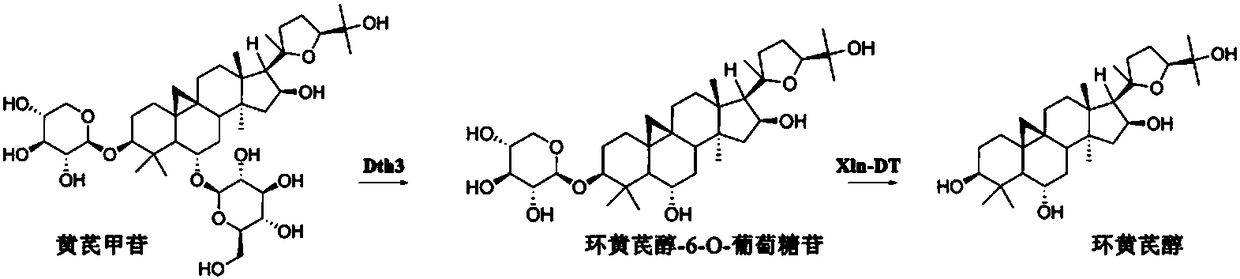
ActiveCN108384769AImprove heat resistanceImprove temperature stabilityFermentationGlycosylasesAstragalosideAlglucerase
The invention provides a high-temperature-resistant compound enzyme and applications of the high-temperature-resistant compound enzyme. The high-temperature-resistant compound enzyme is composed of beta-glucosidase and beta-xylosidase. The compound enzyme provided by the invention is strong in specificity, and can completely convert astragaloside, so that the conversion recovery rate of cycloastragenol is improved. The whole process is completed within 3h, the preparation process of cycloastragenol is greatly shortened, and the production efficiency is improved; in the reaction process, the reagents including strong reducing agents, oxidizing agents, strong acid and the like do not need to be added, so that the environmental pollution is reduced; self-making of the two enzymes can be realized, thus the production cost is greatly reduced, and the process is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
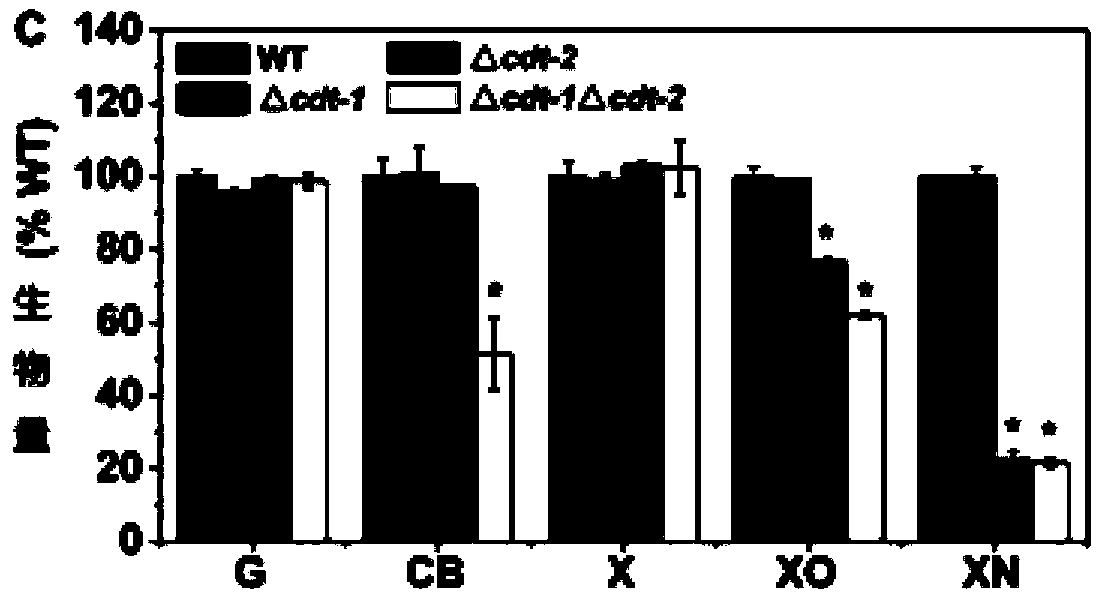
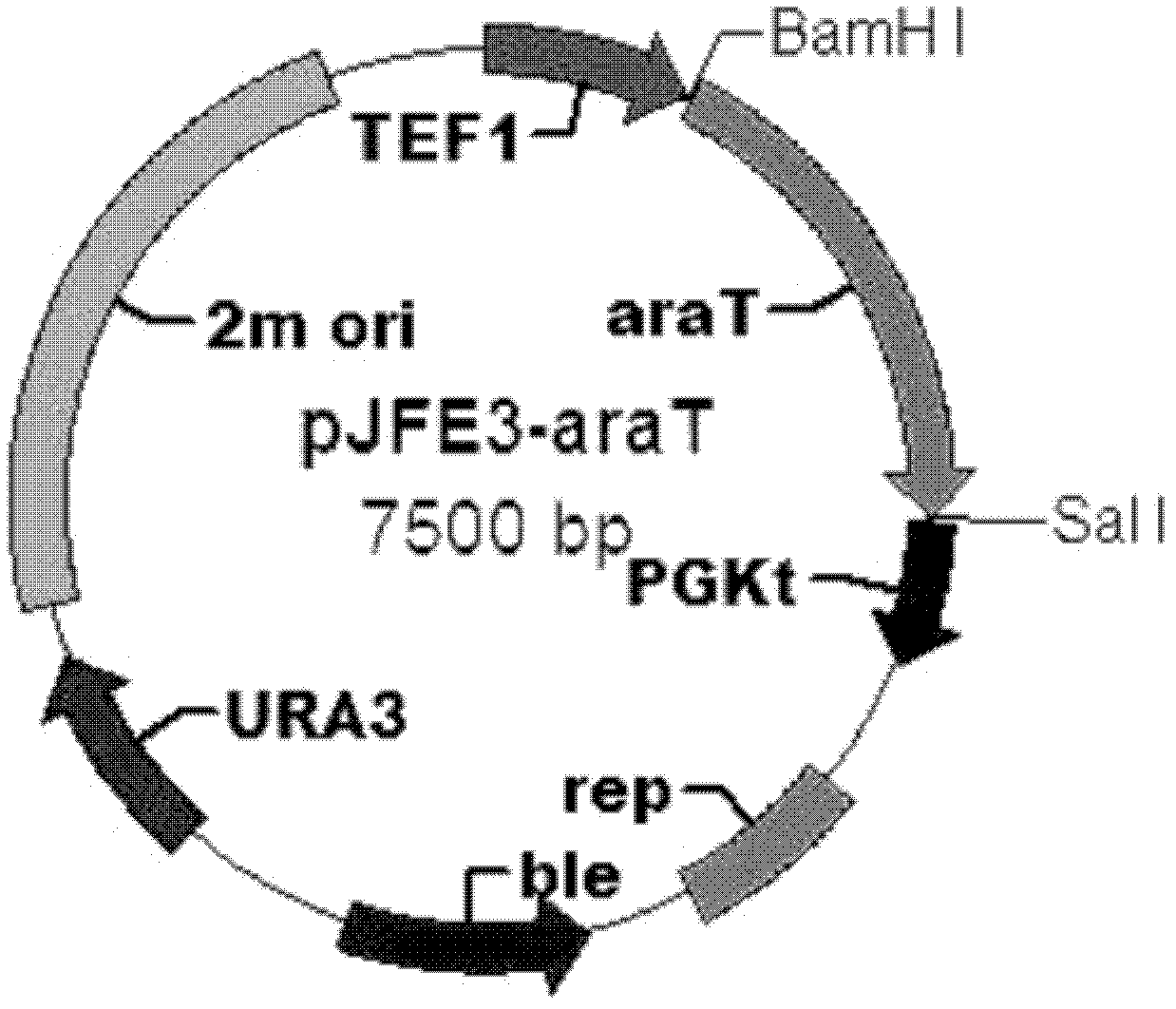
CDT (carbohydrate deficient transferrin)-2 new use and method using CDT-2 to promote microbial cells to transport xylo-oligosaccharides and application thereof
The invention discloses a method for promoting microbial cells to transport and / or hydrolyze xylo oligosaccharides and application thereof. Experiments prove that cello-oligosaccharide transport protein CDT-2 also has xylo-oligosaccharide transport capacity, beta xylosidase GH43-2 has hydrolysis effect on the xylo-oligosaccharides, according to the method, cdt-2 gene and / or gh43-2 gene are / is introduced into a microbial strain to obtain a recombinant microbial strain, and compared with a starting strain, the recombinant microbial strain acquires or improves the capability for transporting the xylo-oligosaccharides from extracellular to intracellular and / or hydrolyzing the xylo-oligosaccharides into xylose. By discovery of the xylo-oligosaccharide transport protein CDT-2 and application of the beta xylosidase GH43-2, an idea using modified yeast to directly use the xylo-oligosaccharides derived from hemicellulose degradation for producing biological chemicals is provided, co-fermentation of glucose, xylose, cello-oligosaccharide and xylo-oligosaccharide mixed sugar can be realized by co expression of cdt-2 and gh43-2 and cdt-1 and gh43-1 in brewer's yeast containing xylose metabolic pathway to produce the biological chemicals, and the production cost is greatly saved.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Expression of Recombinant Beta-Xylosidase Enzymes
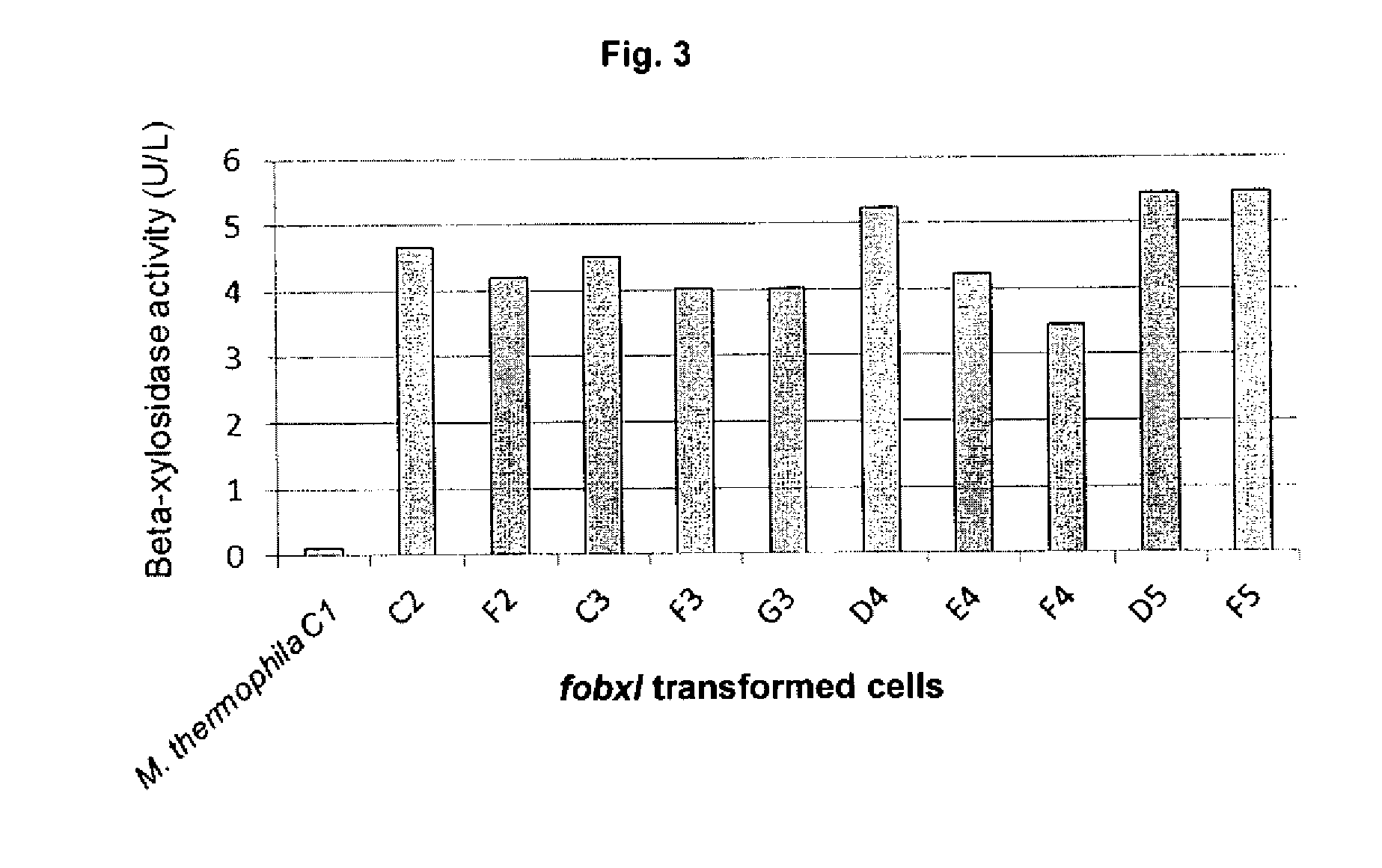
InactiveUS20160272956A1Improve hydrolysis efficiencyIncrease productionBiofuelsFermentationBioproductsMyceliophthora thermophila
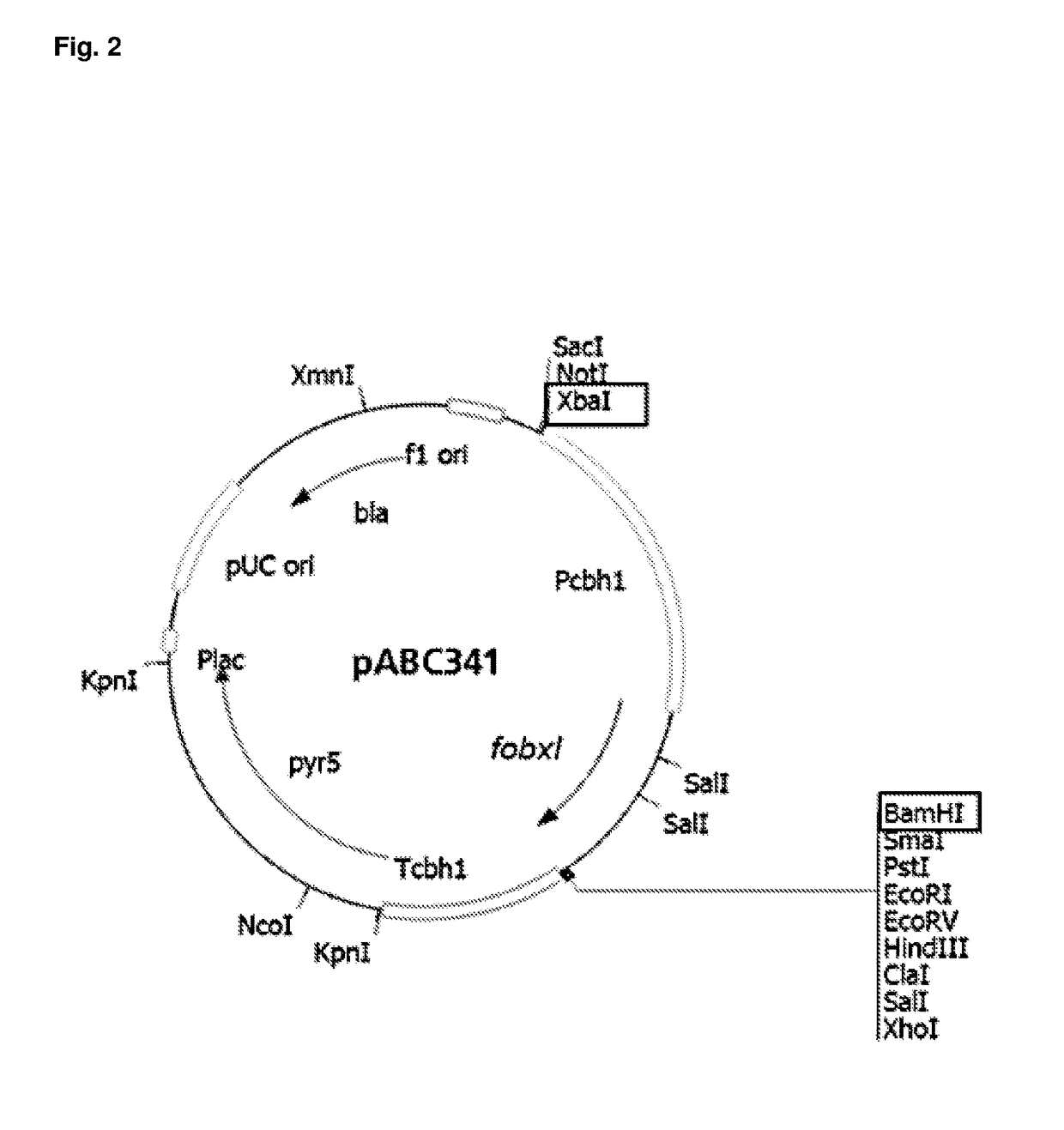
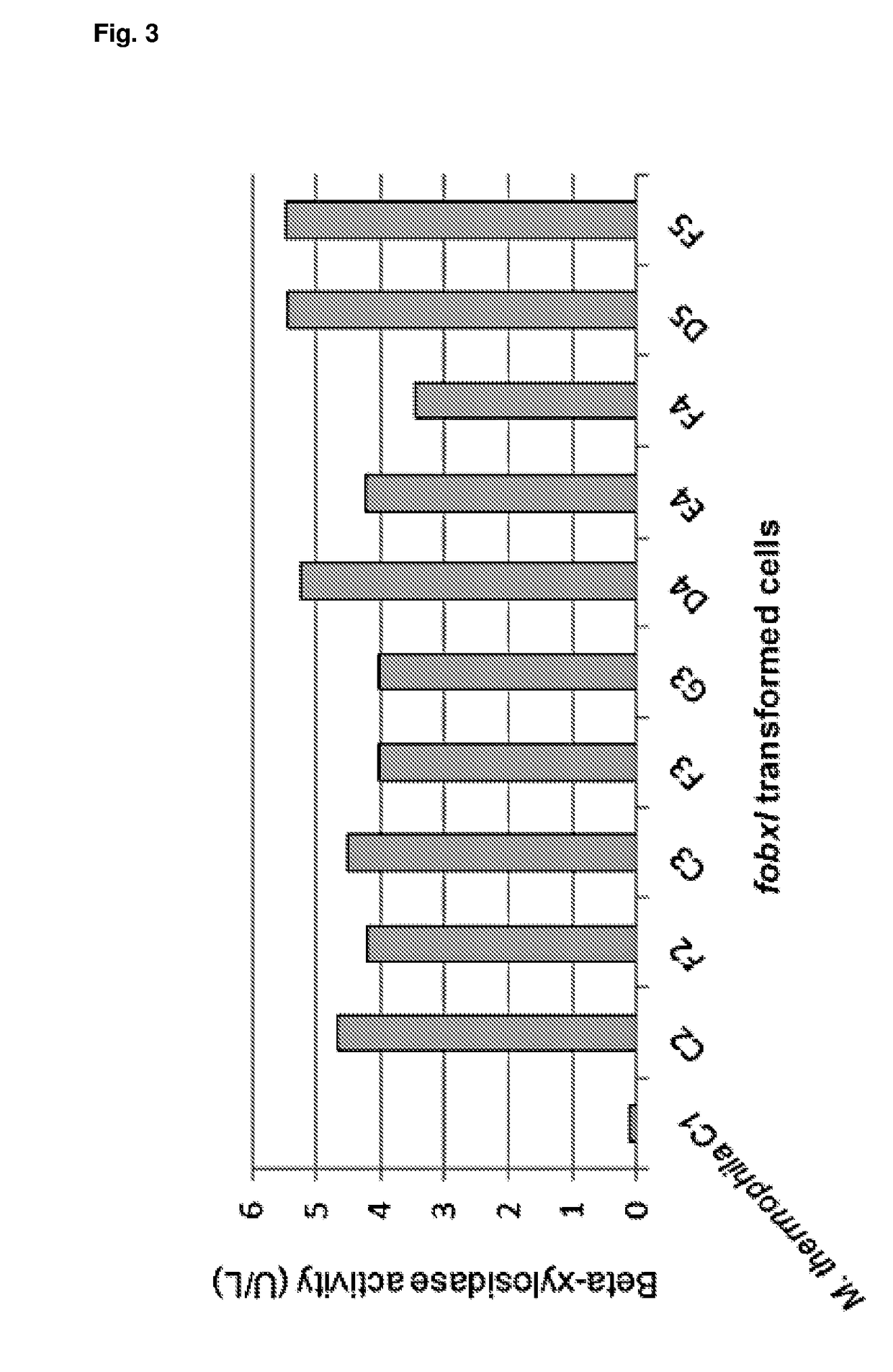
The present invention relates to a host cell, preferably Myceliophthora thermophila cell, which expresses recombinant enzymes with beta-xylosidase activity, an enzymatic composition comprising said cell and / or the recombinant enzyme with beta-xylosidase activity expressed by said cell, the use of this host cell, the recombinant enzyme with beta-xylosidase activity expressed by said cell or the composition for the degradation of biomass and a method of producing bioproducts, preferably bioethanol, which comprises the use of said host cell, the recombinant enzyme with beta-xylosidase activity expressed by said cell or said composition.
Owner:ABENGOA BIOENERGIA NUEVAS TECHAS
Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and method for selecting saccharomyces cerevisiae strains expressing activated xylose translocator
ActiveCN102492636ALoose requirementsAvoid False Positive SituationsFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismYeast strain
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
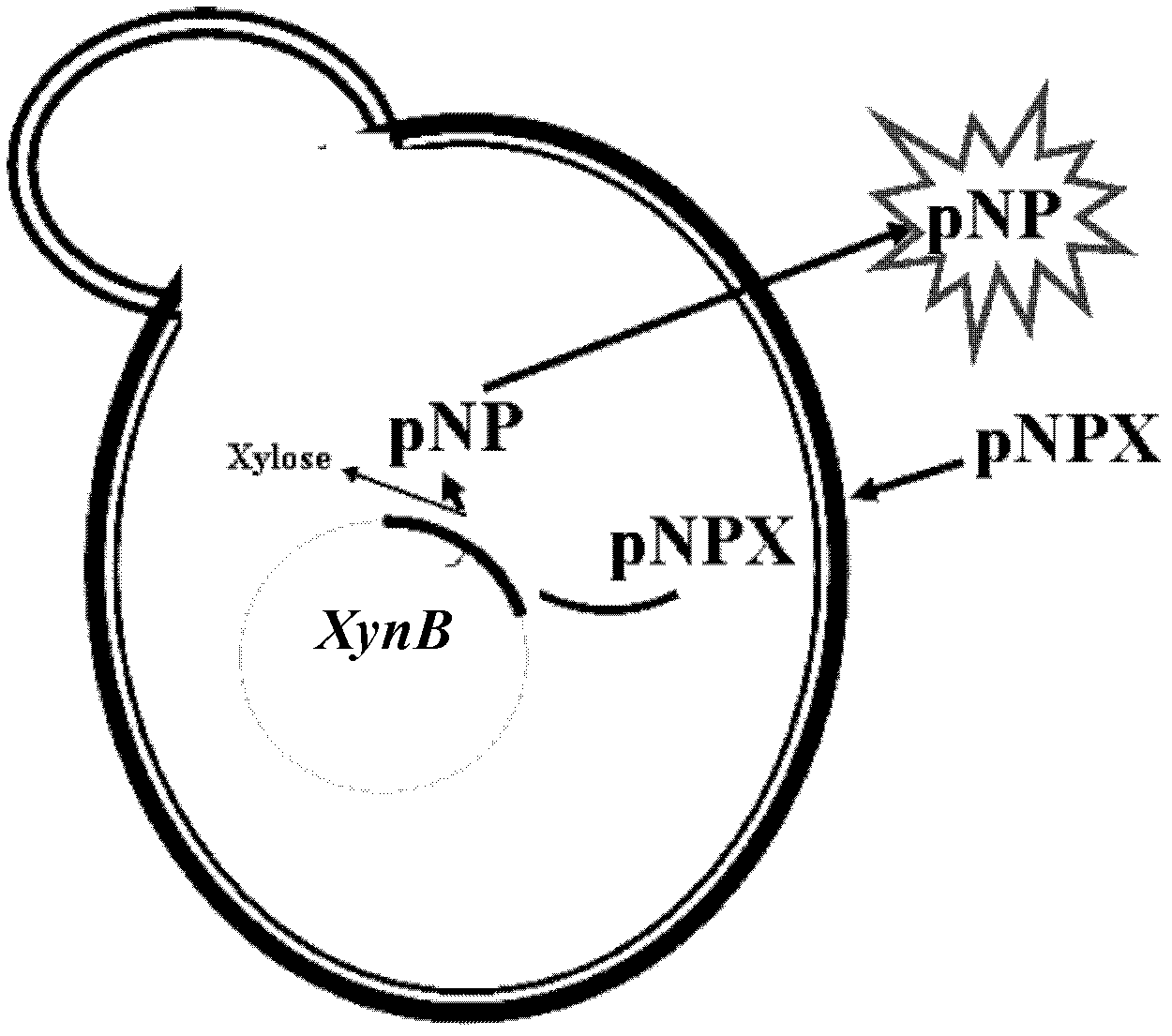
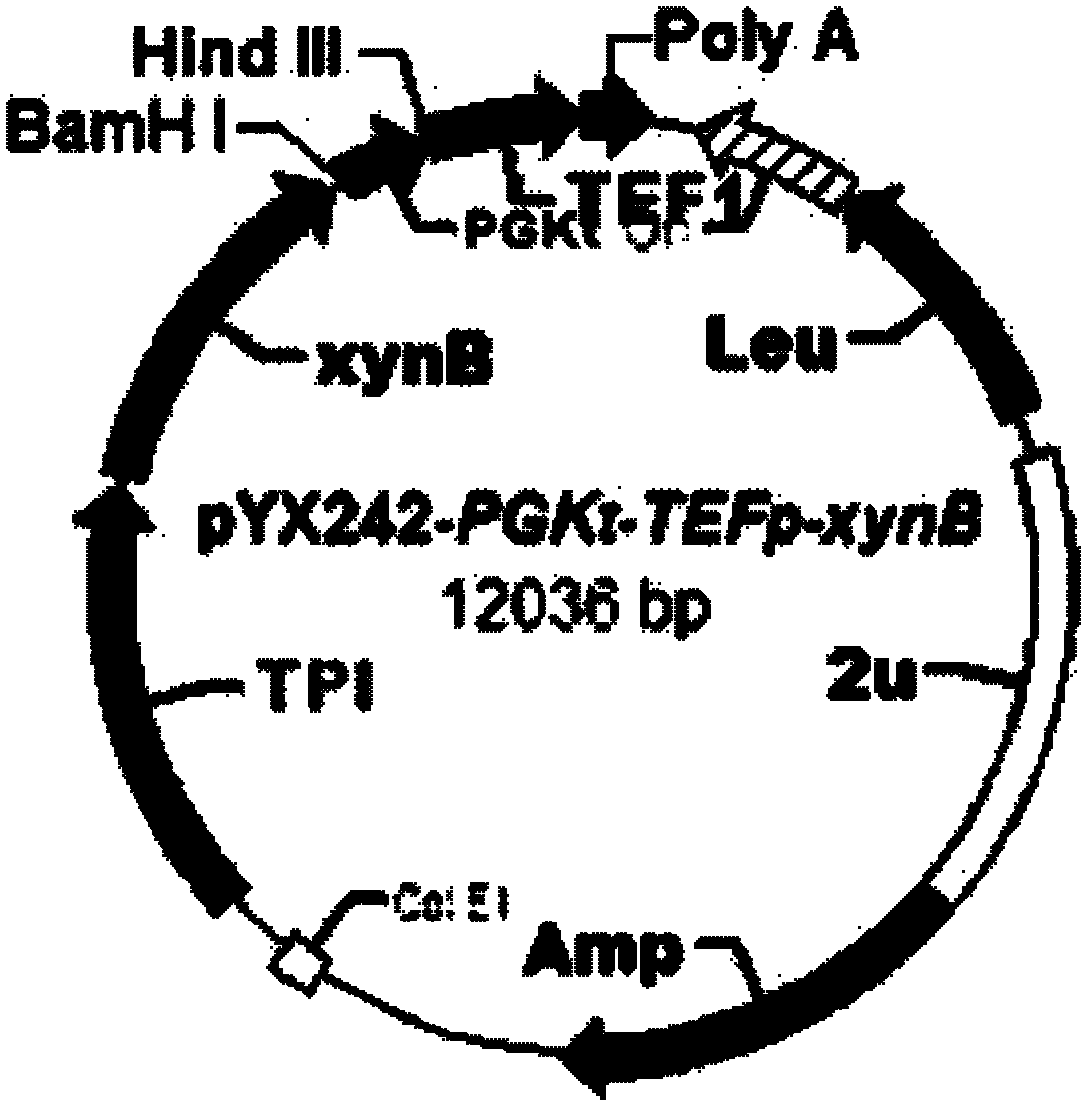
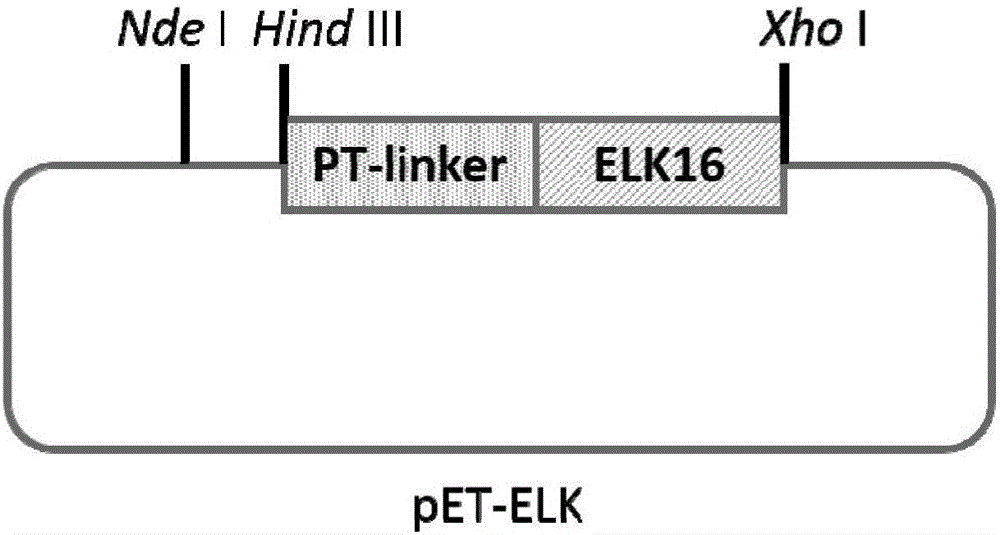
Beta-xylosidase in vivo enzyme aggregate and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106520733AImprove mechanical stabilityHigh purityGlycosylasesVector-based foreign material introductionActive enzymeFiltration
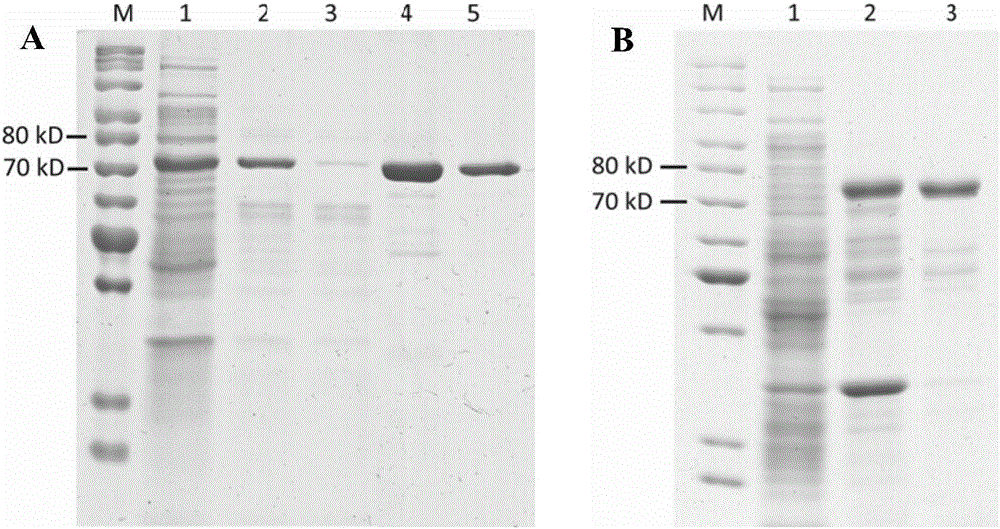
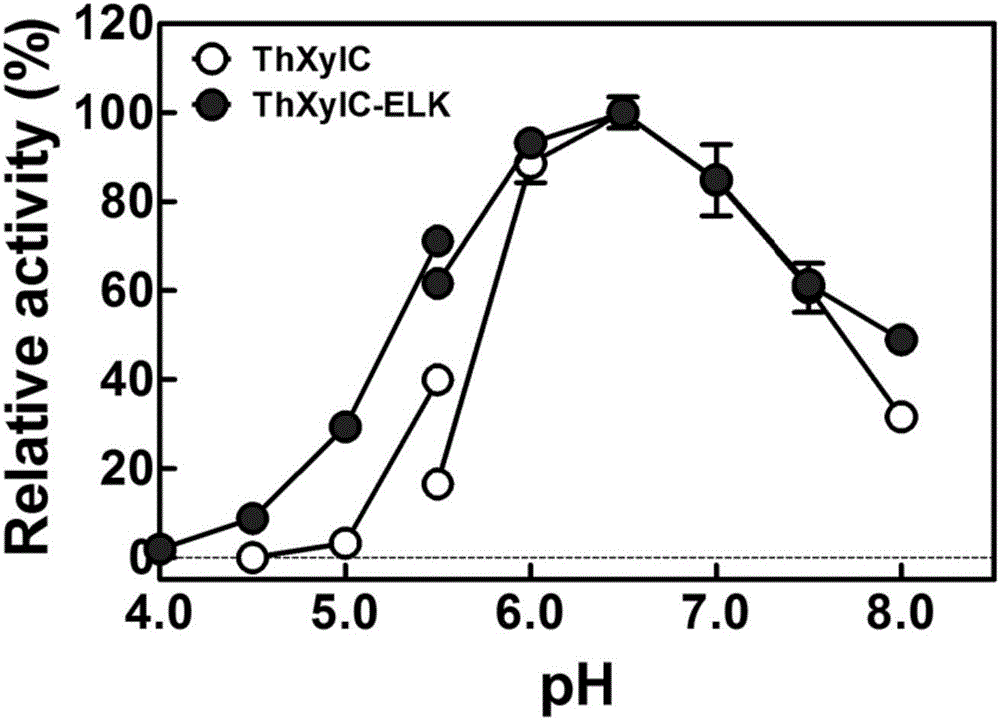
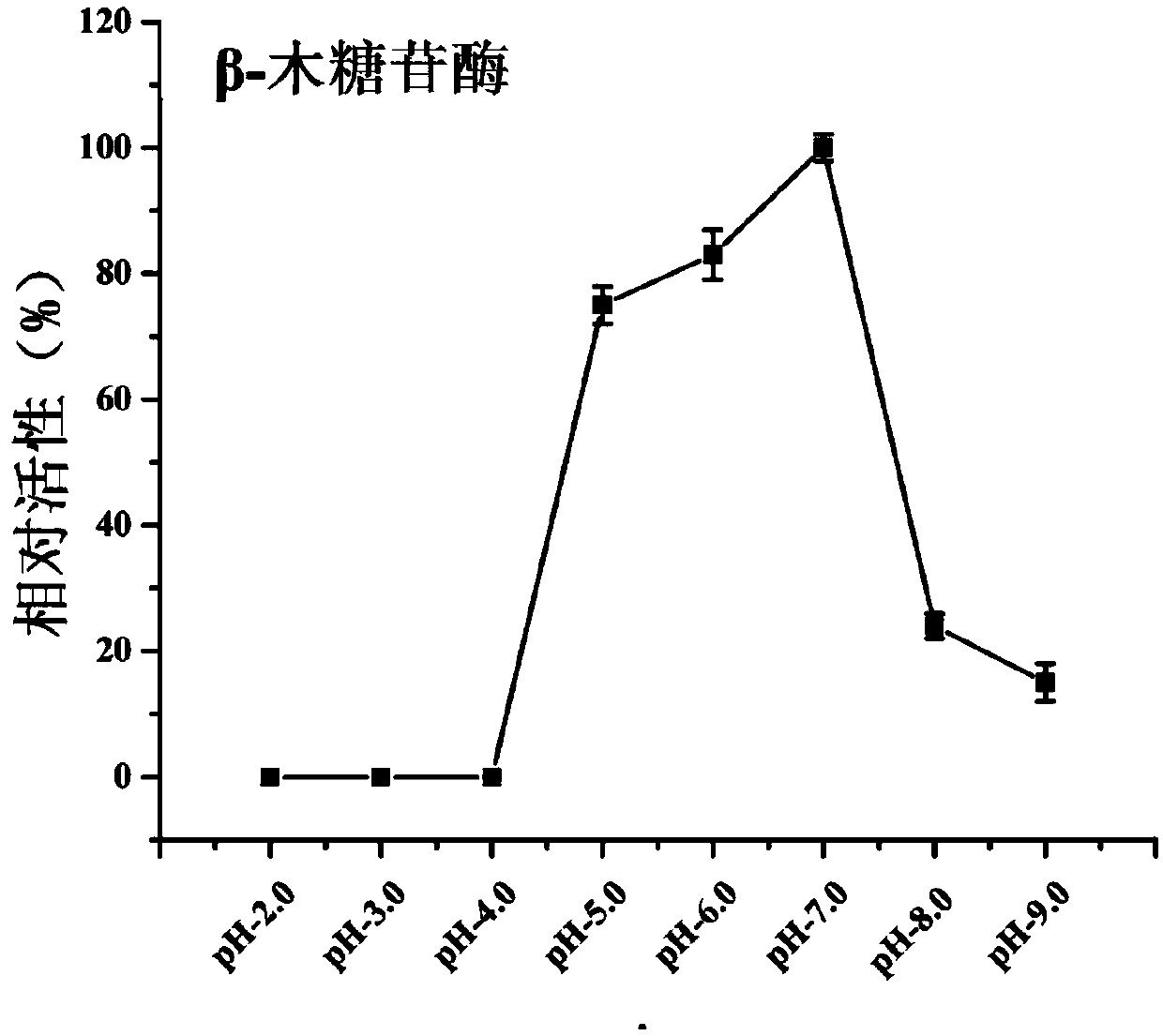
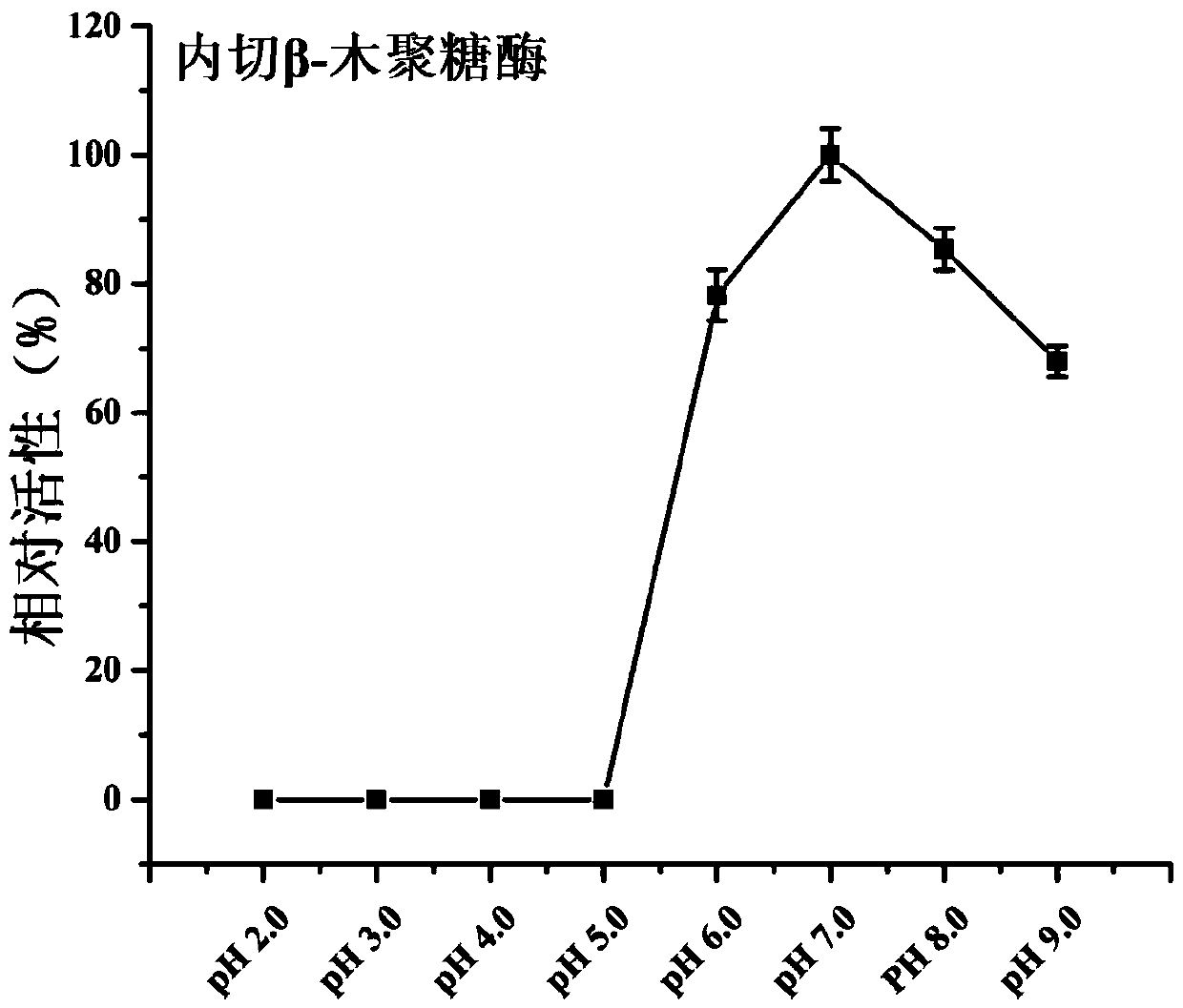
The invention discloses a preparation method of a beta-xylosidase in vivo enzyme aggregate. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) splicing a connecting peptide to a biparental short peptide to construct an expression vector, wherein the biparental short peptide is ELK16; (2) connecting a beta-xylosidase coded gene to the expression vector and transforming the mixture to a recipient bacterium to obtain an engineering bacterium which can express beta- xylosidase-short peptide fused protein; and (3) performing induced expression on the engineering bacterium, breaking the walls of the cells, and performing centrifugalization and / or filtration to obtain a precipitate to obtain the beta-xylosidase in vivo enzyme aggregate. Compared with conventionally expressed ThXylC, the ThXylC-ELK16 active enzyme aggregate obtained by the invention is improved in specific activity and catalytic efficiency, and the heat resistance thereof is further remarkably improved. The method has a huge potential of popularization and application in production.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Milling Process
InactiveUS20150299752A1Enhance the wet milling benefit of one or more enzymesFermentationMedicineBeta-Xylosidase
Process for treating crop kernels, comprising the steps of: a) soaking kernels in water to produce soaked kernels; b) grinding the soaked kernels; c) treating the soaked kernels in the presence of an effective amount of a beta-xylosidase, wherein step c) is performed before, during or after step b).
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Composite enzyme preparation for ramie boiling degumming and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106047841AImprove adsorption efficiencyImprove efficiencyOxidoreductasesGlycosylasesFiberPectinase
The present invention provides a composite enzyme preparation for ramie boiling degumming and a preparation method thereof, wherein the composite enzyme preparation is a mixture of alpha-amylase, low-temperature amylase, alkaline pectinase, endo-beta-1,4-dextranase, neutral protease, oxidase, hemicellulase, beta-xylosidase, papain, keratinase, sorbitol, sodium hydroxide, tetraethyl orthosilicate, sodium metaaluminate and a nanometer desulfurization molecular sieve. According to the present invention, the one-step pickling in the traditional method is eliminated, the one-step alkaline boiling in the traditional process is replaced, a lot of the acid and alkali raw materials are saved, the advantages of mild treatment conditions, low cost, good fiber quality, low environmental pollution and the like are provided, and the efficiency is high compared to the traditional enzyme preparation.
Owner:安徽省华龙麻业有限公司
Encoding gene of glycoside hydrolase for rapid hydrolysizing xylan to generate single xylose, and application of encoding gene
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering, in particular to an encoding gene of glycoside hydrolase for rapid hydrolysizing xylan to generate single xylose, and application of the encoding gene. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. The nucleic acid, which is provided by the invention and is shown in the SEQ ID NO. 2, can be expressed in a large amount in yeast, so that a large amount of the glycoside hydrolase Ttxy43 can be obtained; the glycoside hydrolase Ttxy43 has the activities of beta-xylosidase, endo-beta-xylanase and alpha-L-arabinofuranosidease atthe same time; in addition, the glycoside hydrolase Ttxy43 can directly degrade birch xylan so as to produce a single product xylose; compared with commercial combination of endo-beta xylanase and beta-xylosidase, the glycoside hydrolase Ttxy43 is higher in xylose yield and has a higher commercial application value.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
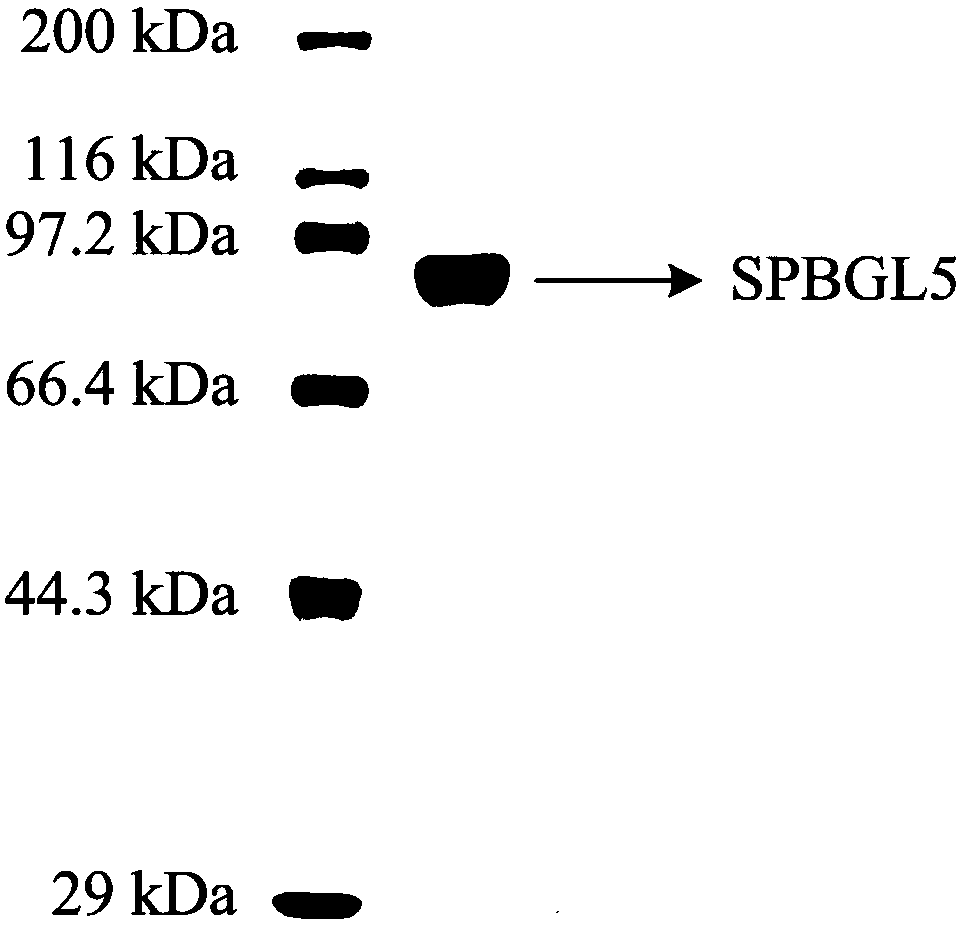
Applications of beta-glucosidase SPBGL5 in hydrolysis of xylan polysaccharide substances
ActiveCN107699551AGreat application potentialFermentationGlycosylasesEscherichia coliSphingomonas sp.
The invention belongs to the technical field of enzymology engineering, and particularly relates to applications of beta-glucosidase SPBGL5 in hydrolysis of xylan polysaccharide substances. Accordingto the present invention, a recombinant Escherichia coli strain containing a beta-glucosidase gene spbgl5 from Sphingomonas sp. ATCC 31461 is constructed, wherein the gene is subjected to induced expression and nickel affinity chromatography purification in Escherichia coli to obtain an expression product beta-glucosidase SPBGL5; and the obtained beta-glucosidase SPBGL5 has the activities of beta-glucosidase, further has the activities of beta-xylosidase and beta-arabinosidase, can separately hydrolyze beech xylan, birch xylan, oat xylan, corncob xylan, wheat araboxylan and lichenin, and has great application potential in degradation of various xylan polysaccharide substances.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
Novel glycosyl hydrolase with beta-xylosidase and beta-glucosidase activities and uses thereof
ActiveUS20130130330A1Improve propertiesMass productionDough treatmentBacteriaSilane compoundsBeta-glucosidase activity
A novel glycosyl hydrolase with activities of beta-xylosidase and beta-glucosidase is provided. Said glycosyl hydrolase can convert 7-xylosyltaxane compounds to 7-hydroxyltaxane compounds.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA AN INST OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Thermostable beta-xylosidase belonging to GH family 3
ActiveUS20160032265A1Suitable for productionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifAnimal cellsMicrobiologyIdopyranose
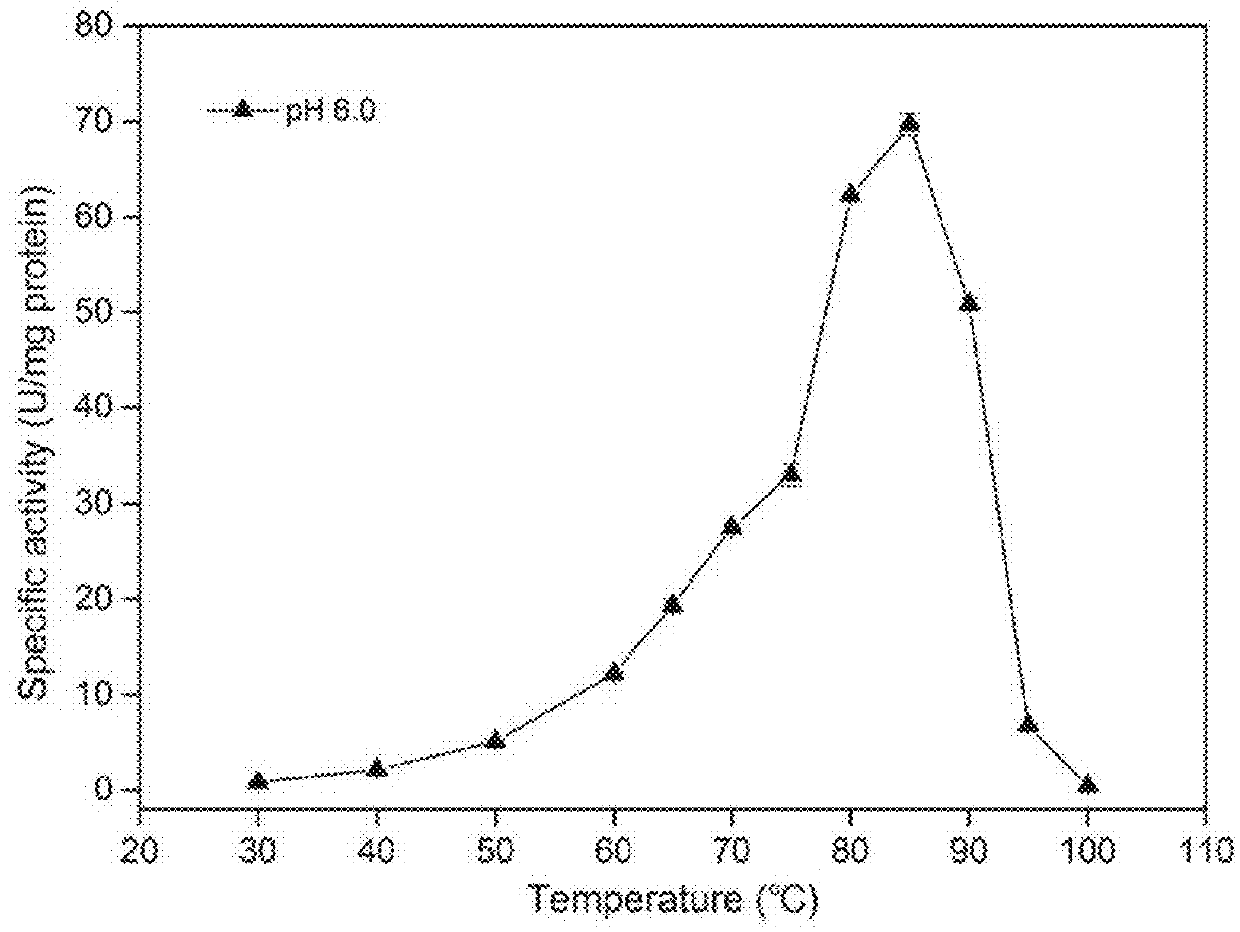
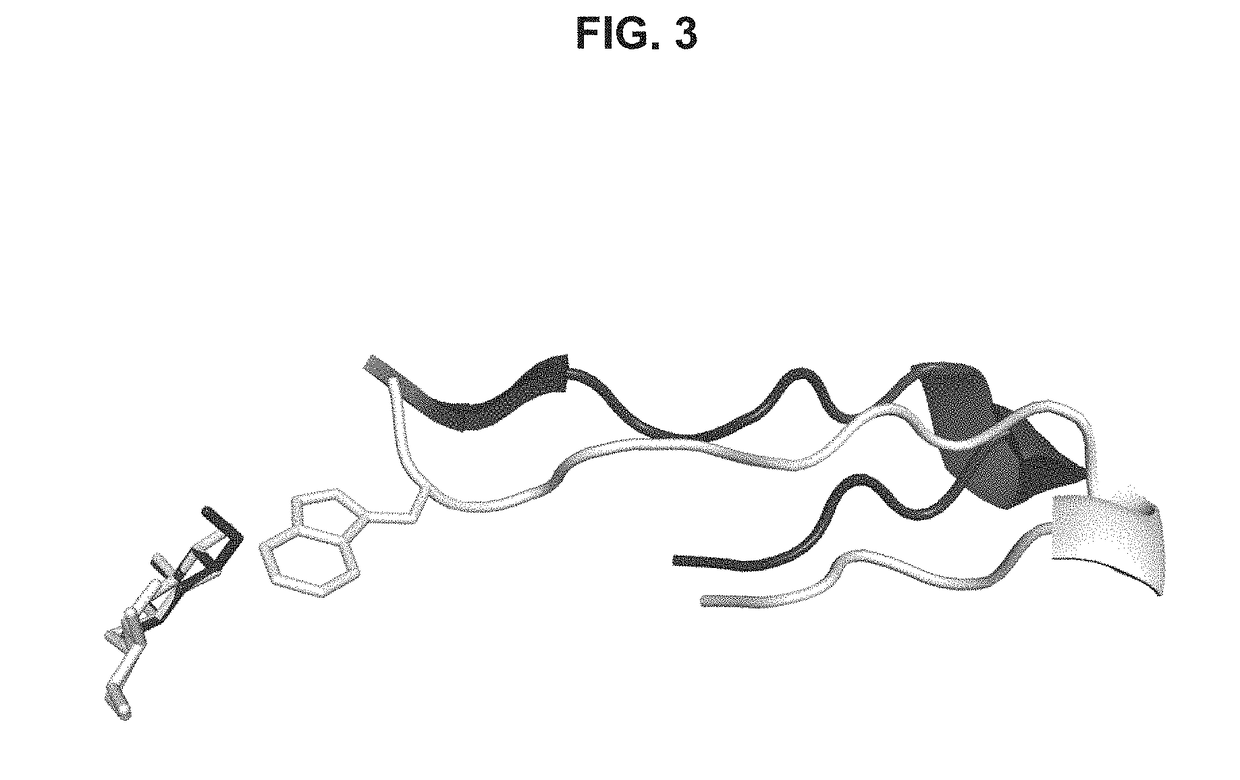
A thermostable β-xylosidase including a β-xylosidase catalytic domain, the β-xylosidase catalytic domain including:(A) a polypeptide including an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1;(B) a polypeptide including an amino acid sequence in which at least one amino acid is deleted, substituted, or added in the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1, and having hydrolytic activity using p-nitrophenyl-β-D-xylopyranoside as a substrate at least under conditions of a temperature of 85° C. and a pH of 6.0; or(C) a polypeptide including an amino acid sequence having at least 80% sequence identity with the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1, and having hydrolytic activity using p-nitrophenyl-β-D-xylopyranoside as a substrate at least under conditions of a temperature of 85° C. and a pH of 6.0.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Beta-xylosidase for conversion of plant cell wall carbohydrates to simple sugars
InactiveUS7993884B2High activity and stabilityModerately high-temperaturesSugar derivativesBiofuelsHydrolysatePlant cell
Xylose-containing plant material may be hydrolyzed to xylose using a β-D-xylosidase which exhibits unexpectedly high activity. The enzyme has a kcat value for catalysis of approximately 185 sec−1 for 1,4-β-D-xylobiose (X2) when measured at a pH of 5.3 and a temperature of 25° C.; this is at least 10-fold greater than reported for other xylosidases at 25° C. and their optimal pH. The enzyme also has an isoelectric point of approximately 4.4. When reacted at a pH between about 4.5 and about 7.7, the β-D-xylosidase exhibits surprisingly high activity for hydrolyzing xylose-containing plant materials to xylose. The xylose released from plant materials may then be converted to other secondary products such as ethanol by fermentation or other reaction. This β-D-xylosidase may be used alone or in combination with other hydrolytic or xylanolytic enzymes for treatment of lignocellulosic or hemicellulosic plant materials or plant material hydrolysates or xylooligosaccharides.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Methods for improving efficiency of simultaneous saccharification and fermentation reactions
The present disclosure is directed, in a first aspect, to the use of inverting beta-xylosidase enzymes to reduce byproduct formation and increase the yield of fermentation products, as well as, in a second aspect, to the use of retaining beta-xylosidase enzymes to improve production of alkyl-beta-xylopyranoside compounds, in a simultaneous saccharification and fermentation reactions.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Expression of recombinant beta-xylosidase enzymes
InactiveUS20180230446A1Improve hydrolysis efficiencyIncrease productionFungiBiofuelsNucleotideMyceliophthora thermophila
The present invention relates to a Myceliophthora thermophila cell, which expresses a nucleotide sequence that codifies a recombinant beta-xylosidase enzyme comprising an amino-acid sequence having at least 70% identity with SEQ ID NO: 1, an enzymatic composition comprising said cell and / or the recombinant enzyme with beta-xylosidase activity expressed by said cell, the use of this host cell, the recombinant enzyme with beta-xylosidase activity expressed by said cell or the composition for the degradation of biomass, and a method of producing biological products, preferably bioethanol, comprising the use of said host cell, the recombinant enzyme with the beta-xylosidase activity expressed by said cell or said composition.
Owner:ABENGOA BIOENERGIA NUEVAS TECHAS
Method of preparing heat-proof xylanase, heat-proof beta-xylosidase or heat-proof beta-glucosidase
InactiveCN100575483CImprove thermal stabilityExcellent hydrolysis performanceBacteriaHydrolasesAlgluceraseXylanase
The invention discloses a making method of heat-proof xylanase, heat-proof beta-xylosidase or heat-proof beta-glucosidase, which comprises the following steps: adopting agricultural waste as carbon source; fermenting Paecilomyces thermophila J18 at 40-60 deg.c to obtain the ferment liquid with heat-proof xylanase, heat-proof beta-xylosidase or heat-proof beta-glucosidase; purifying; obtaining electrophoretic grade product.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Glycosyl hydrolase with beta-xylosidase and beta-glucosidase activities and uses thereof
ActiveUS9206405B2Novel and effectiveMass productionFungiBacteriaSilane compoundsBeta-glucosidase activity
A novel glycosyl hydrolase with activities of beta-xylosidase and beta-glucosidase is provided. Said glycosyl hydrolase can convert 7-xylosyltaxane compounds to 7-hydroxyltaxane compounds.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Milling Process
InactiveUS20170275664A1Enhance the wet milling benefit of one or more enzymesFermentationMedicineBeta-Xylosidase
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Engineered multifunctional enzymes and methods of use
InactiveUS20180002683A1Improved biomass hydrolysis performanceSame levelFermentationGlycosylasesBeta-glucosidase activityMultifunctional Enzymes
Provided are certain glycosyl hydrolase family 3 (GH3) beta-xylosidases engineered to acquire beta-glucosidase activities. Provided also are compositions comprising such multi-functional GH3 enzymes and methods of use or industrial applications thereof.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
A kind of comprehensive utilization method of camellia oleifera shell
ActiveCN103320477BRelieve pressureBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationCamellia oleifera
The invention discloses a comprehensive utilization method of oil-tea camellia shells. The method comprises the following steps: crushing oil-tea camellia shells, performing alkaline pretreatment, and performing solid-liquid separation to obtain black liquor and solid residues; performing enzymolysis on the solid residues through cellulase to prepare monosaccharide and performing alcohol fermentation, and preparing ethanol; regulating pH of the black liquor, and performing solid-liquid separation to obtain residues and a vanillic aldehyde solution; and performing enzymolysis on the residues through xylanase to prepare an xylooligosaccharide solution and residues, and oxidizing the residues to prepare the vanillic aldehyde. According to the comprehensive utilization method, the solid residues obtained by solid-liquid separation are hydrolyzed by cellulase and further fermented to prepare fuel ethanol by using the condition that the oil-tea camellia shells are pretreated by sodium hydroxide; the black liquor obtained by solid-liquid separation is neutralized to the pH of 6, wherein the supernatant obtained by solid-liquid separation contains high-concentration vanillic aldehyde (lignin oxidization is not required), enzyme hydrolysis is carried out on the precipitation to prepare xylooligosaccharide by employing xylanase containing a small amount of beta-xylosidase, and further the residues obtained by enzymolysis are further oxidized to prepare the vanillic aldehyde. Therefore, according to research of the process, the biomass can be totally utilized for preparing the fuel ethanol, xylooligosaccharide and vanillic aldehyde finally.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
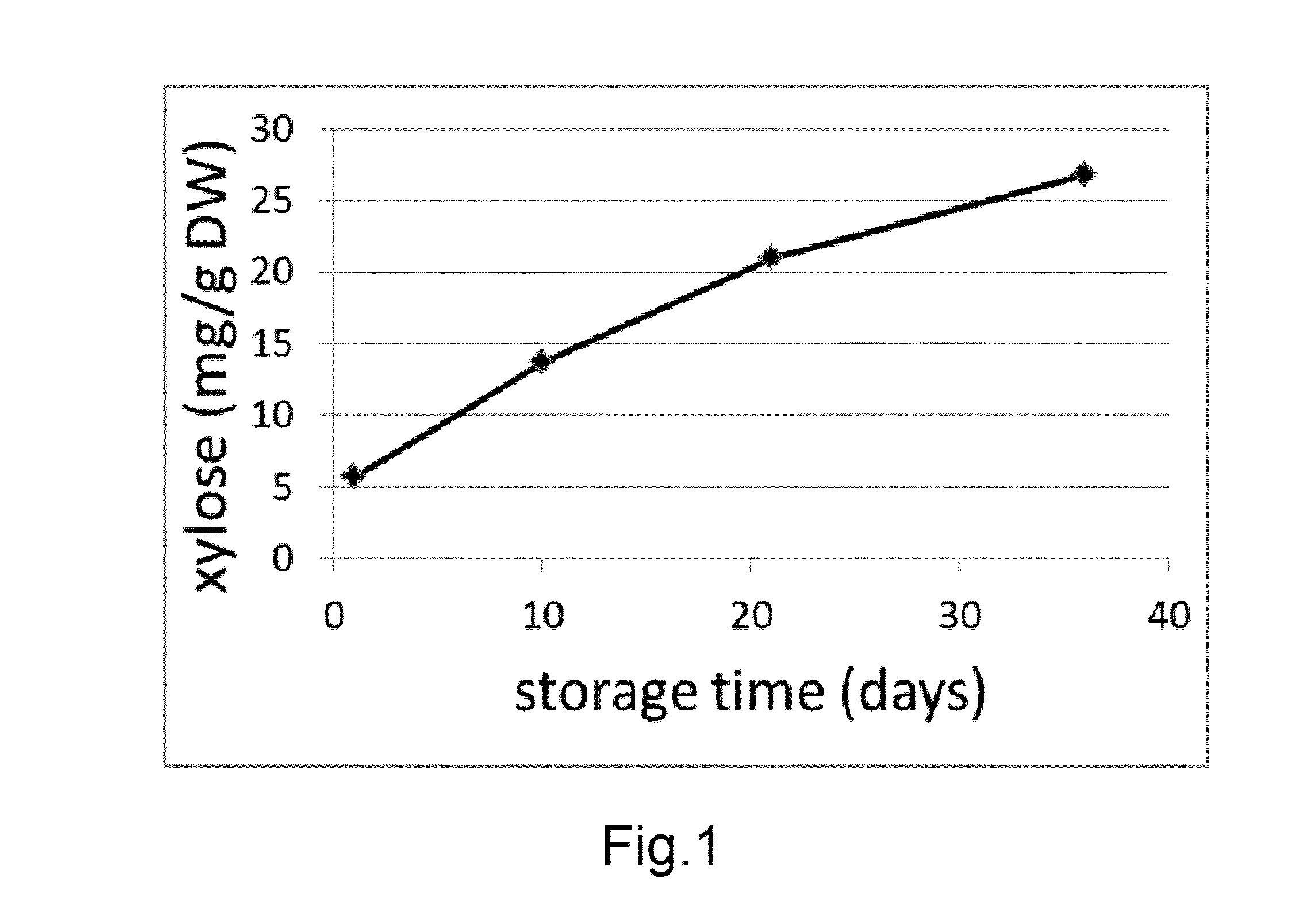
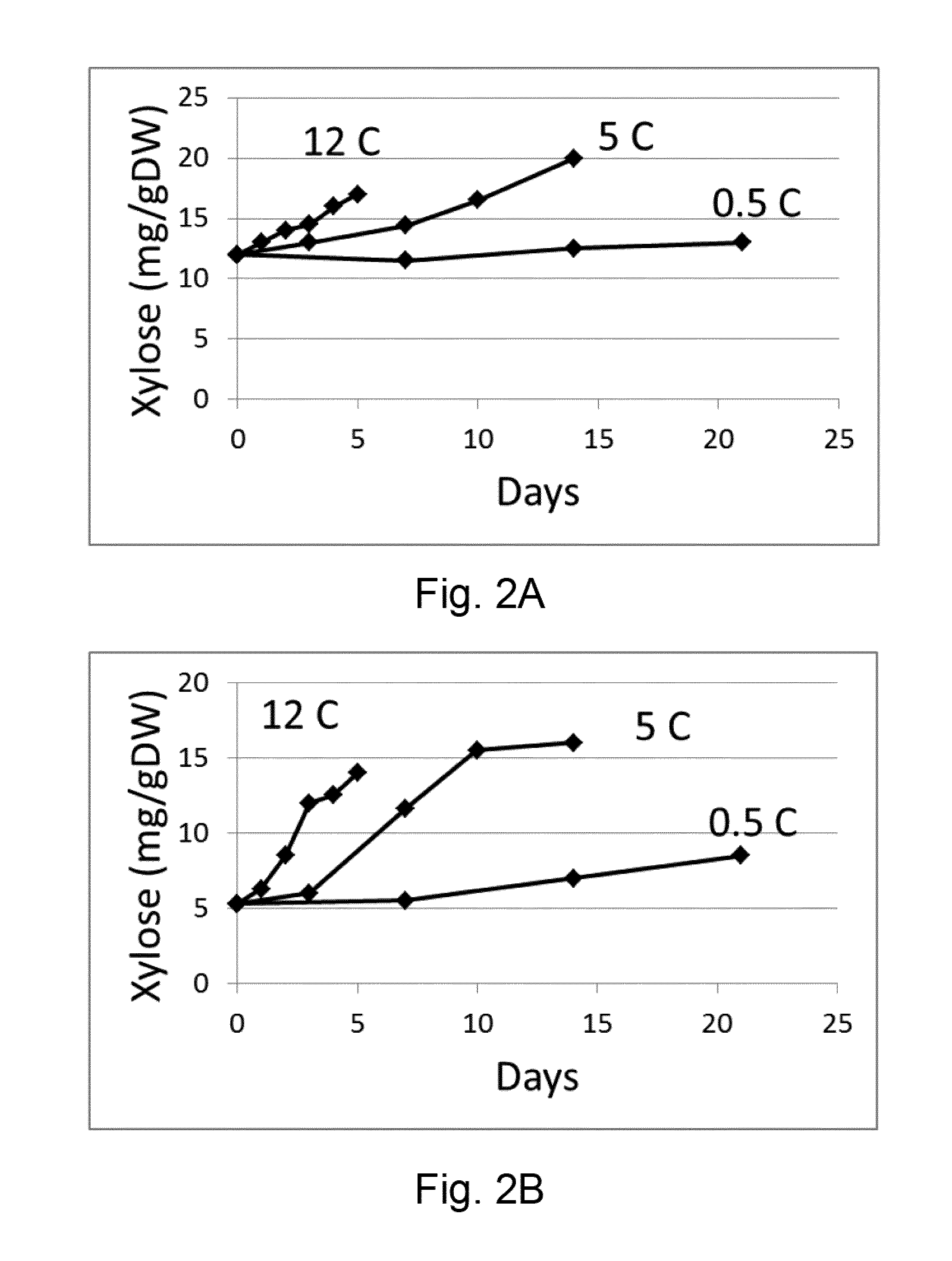
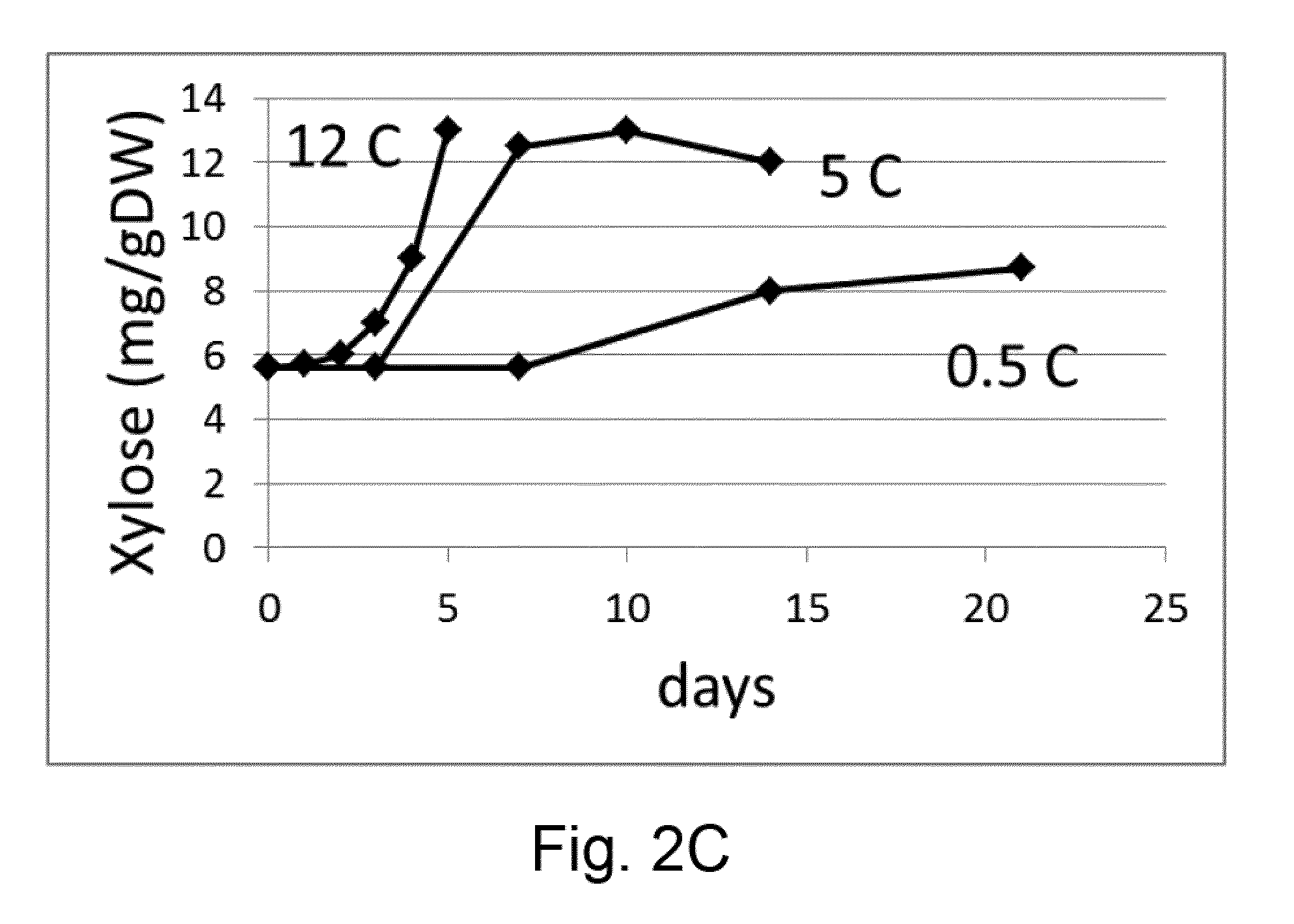
A Method for Determining the Vase Life or Storage History of One or More Cut Flowers, Wherein the Method Comprises Assaying Xylose Concentration or Beta-Xylosidase Expression/Activity
InactiveUS20160145697A1Improve the level ofExtended storage timeMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationTest sampleBiology
A method for determining the vase life or storage history of one or more cut flowers, wherein the method comprises assaying a test sample obtained from the one or more cut flowers for one or more of: (a) an indicator representative of xylose concentration; (b) an indicator representative of β-xylosidase expression; and (c) an indicator representative of β-xylosidase activity; to determine a value for (each of) the one or more indicators in the test sample.
Owner:STICHTING WAGENINGEN RES
Expression of recombinant beta-xylosidase enzymes
InactiveUS9834763B2Improve hydrolysis efficiencyIncrease productionBacteriaBiofuelsFusarium oxysporumBioproducts
The present invention relates to a Myceliophthora thermophila host cell which expresses a recombinant enzymes from Fusarium oxysporum with beta-xylosidase activity. The invention also refers to an enzymatic composition comprising the host cell of the invention and / or the recombinant enzyme with beta-xylosidase activity expressed by the host cell of the invention. The invention further relates to the use of the host cell of the invention, the recombinant enzyme with beta-xylosidase activity expressed by the host cell of the invention or the composition of the invention for the degradation of biomass and to a method of producing bioproducts, preferably bioethanol, which comprises the use of the host cell of the invention, the recombinant enzyme with beta-xylosidase activity expressed by the host cell of the invention or the composition of the invention.
Owner:ABENGOA BIOENERGIA NUEVAS TECHAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com