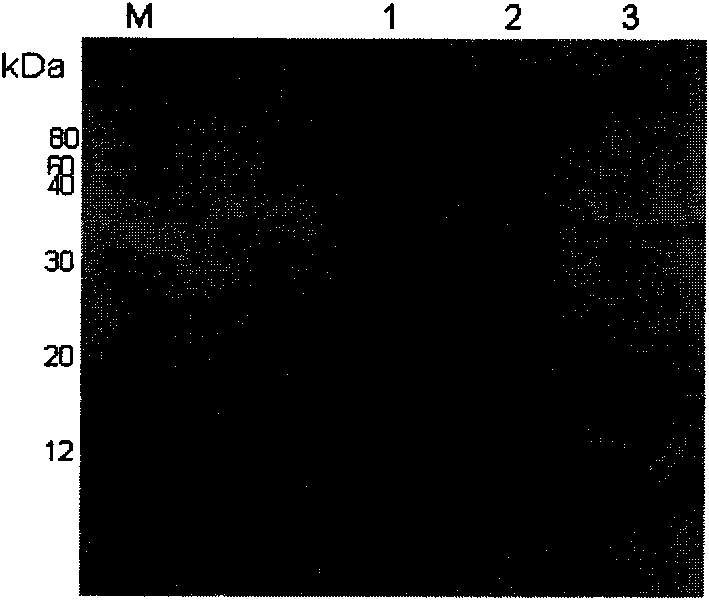
Patents
Literature
41 results about "Genus Shigella" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
See Article History. Shigella, genus of rod-shaped bacteria in the family Enterobacteriaceae, species of which are normal inhabitants of the human intestinal tract and can cause dysentery, or shigellosis. Shigella are microbiologically characterized as gram-negative, non-spore-forming, nonmotile bacteria.
Protein-protein interactions between Shigella flexneri polypeptides and mammalian polypeptides
InactiveUS20030055220A1Treat and prevent bacillary dysenteryMore effective and better targeted therapeutic applicationsPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideADAMTS Proteins
The present invention relates to protein-protein interactions between Shigella polypeptides and mammalian polypeptides. More specifically, the present invention relates to complexes of polypeptides or polynucleotides encoding the polypeptides, fragments of the polypeptides, antibodies to the complexes, Selected Interacting Domains (SID(R)) which are identified due to the protein-protein interactions, methods for screening drugs for agents which modulate the interaction of proteins and pharmaceutical compositions that are capable of modulating the protein-protein interactions.
Owner:HYBRIGENICS SA
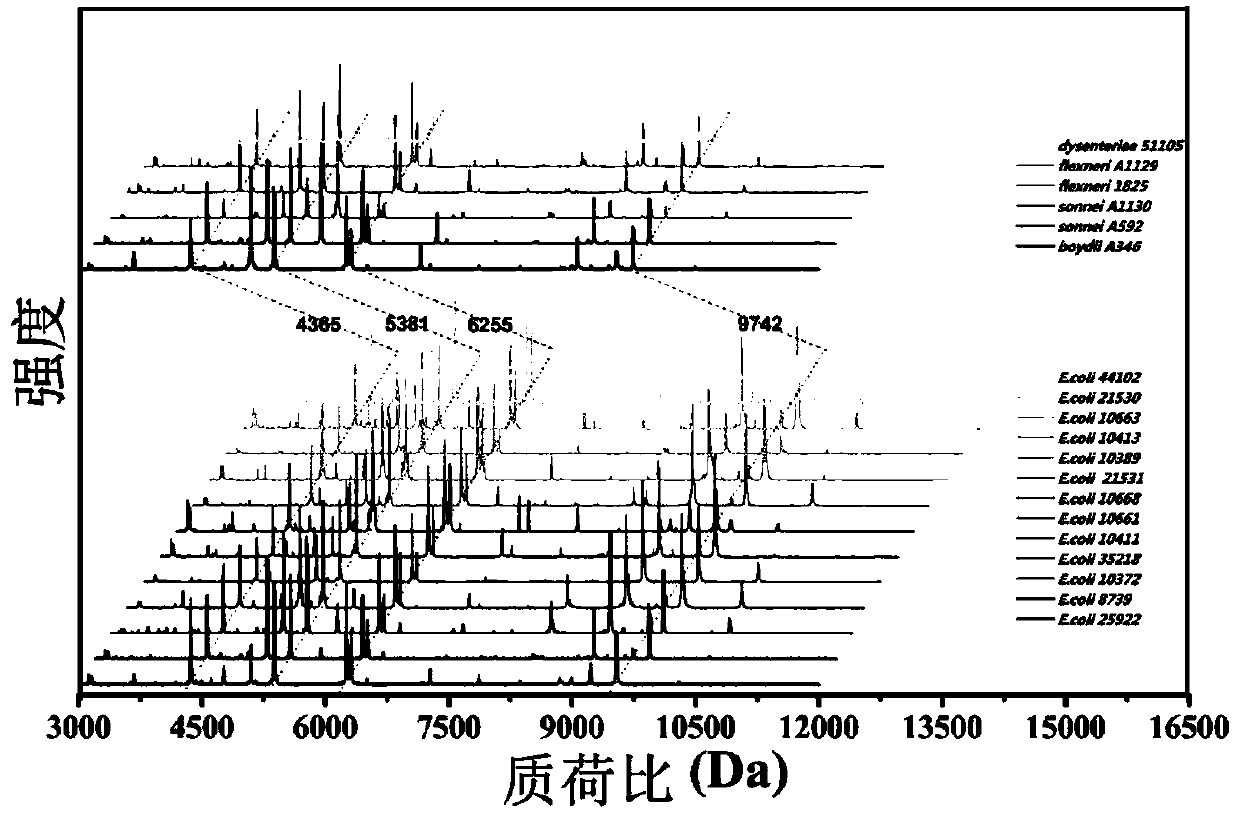
Identification of Shigella sonnei by using MALDI-TOF-MS (matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry)
InactiveCN107085034AMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansShigella sonneiTime-of-flight mass spectrometry
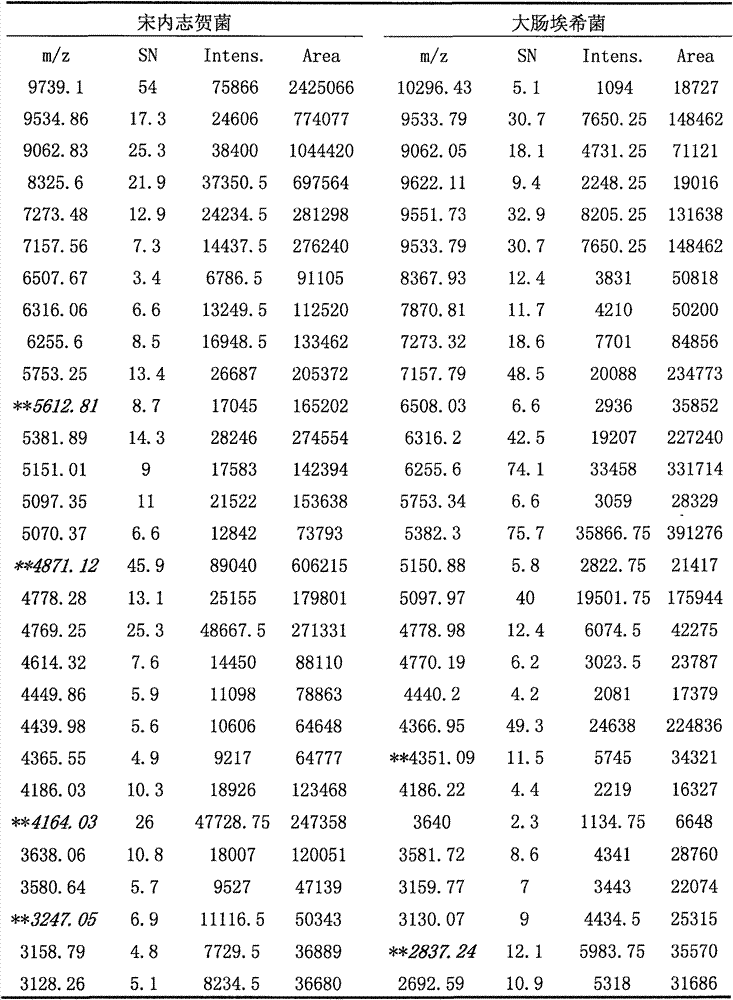
The invention discloses a novel method for identifying Shigella sonnei by using MALDI-TOF-MS. The invention provides an identification method for distinguishing whether a to-be-detected strain is Shigella sonnei or other batacteria. The invention also discloses application of a set consisting of a MALDI-TOF-MS detection instrument, a reagent for the MALDI-TOF-MS detection instrument and a readable carrier. The readable carrier can record the following conditions: if protein peaks obtained after detection of the to-be-detected strain by using MALDI-TOF-MS contains the four characteristic protein peaks with mass-charge ratios of 5612.81 + / - 8.7, 4871.12 + / - 45.9, 4164.03 + / - 26 and 3247.05 + / - 6.9, respectively, the to-be-detected strain is Shigella sonnei or candidate Shigella sonnei. Experimental results prove that MALDI-TOF-MS has good accuracy and specificity in identification of Shigella sonnei and shortens identification time.
Owner:THE FIFTH MEDICAL CENT OF CHINESE PLA GENERAL HOSPITAL
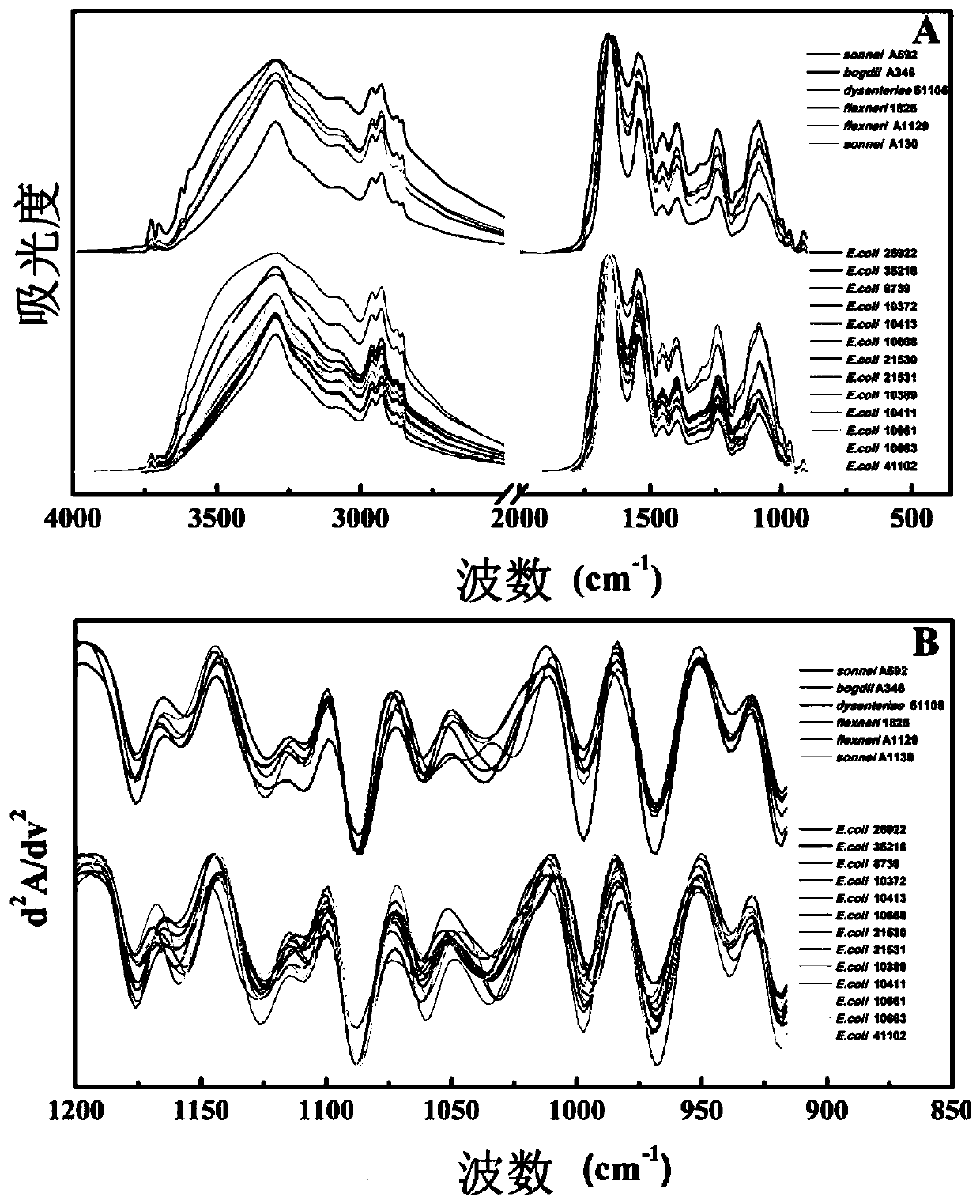
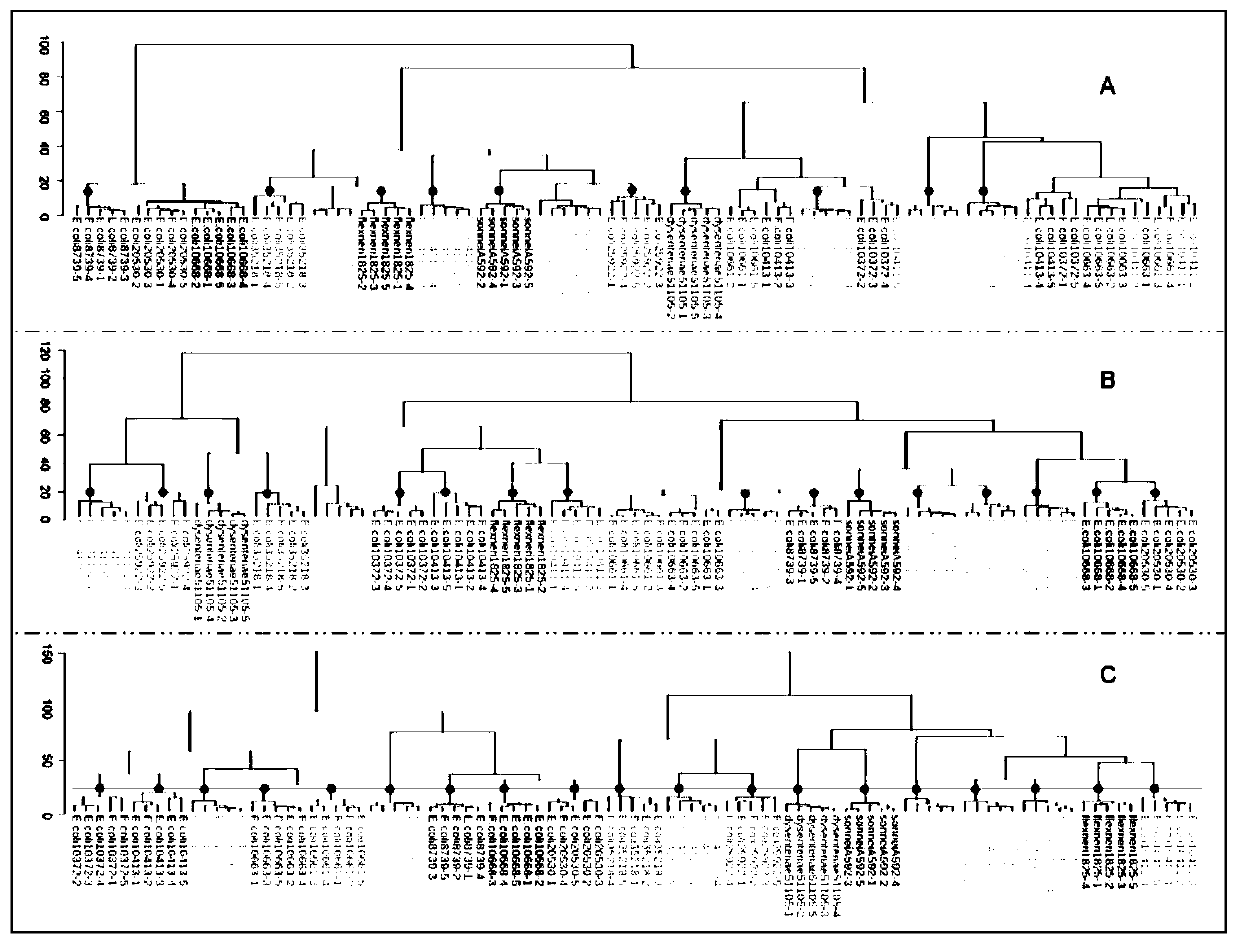
Microorganism identification and typing method in combination with mass spectrums and FTIR spectrums based on matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization flight time
InactiveCN110687191AEasy to distinguishMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEscherichia coliData set
The invention discloses a microorganism identification and typing method in combination with mass spectrums and FTIR spectrums based on matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization flight time. The method comprises the following specific steps: (1) respectively collecting microorganism characteristic mass spectrums and infrared absorption spectrums; (2) preprocessing the collected characteristic mass spectrums and infrared absorption spectrums; (3) performing data fusion on the data of the preprocessed characteristic mass spectrums and infrared absorption spectrums; and (4) carrying out clusteranalysis on the fused data of the mass spectrums and the infrared absorption spectrums to realize identification and typing of microorganisms. A data set used for microbial typing contains more characteristic biological information, and effective distinguishing of extremely similar strains difficult to distinguish by simple means, such as Escherichia coli and Shigella, can be realized.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
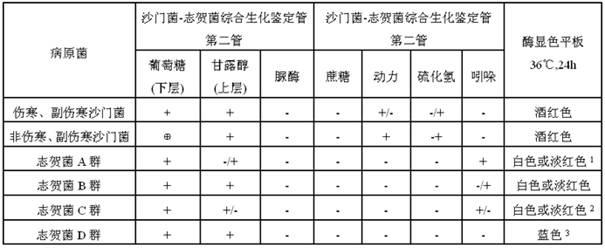
Kit for synchronously separating and identifying salmonella and shigella as well as preparation and application
InactiveCN102031281AImprove timelinessImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBiotechnologyColony morphology
The invention relates to a method for synchronously separating and identifying salmonella and shigella in enteric pathogenic bacteria, which mainly solves the technical problems of high detection-missing rate, complicated identification step, high cost and unintuitive screening result in the existing method for separating the salmonella and the shigella. The kit comprises: 1) a TSB (Trypticase Soy Broth) serving as an universal-type non-selective proliferous liquid; 2) a 10-folds concentrated TSB serving as a 10-folds concentrated universal-type non-selective proliferous liquid; 3) a selenite brilliant green-sulfanilamide proliferous liquid serving as a salmonella proliferous liquid; 4) a shigella proliferous liquid; 5) a xylose lysine deoxycholate agar plate; 6) a salmonella chromogenic agar plate; 7) a salmonella-shigella comprehensive biochemical identification tube comprising a first test tube and a second test tube; 8) a hydrogen sulphide filter paper strip; and 9) an indole filter paper strip. In the invention, typical colonial morphology corresponding to the growth of a selective isolation medium, simple biochemistry and reaction combination test of a specific enzyme and a substrate are adopted to identify two kinds of enteric pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Anti-I type Shiga toxin IgY antibody as well as preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN101570574AInhibition of biological effectsEgg immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaEscherichia coliAntigen
The invention discloses an anti-I type Shiga toxin IgY antibody, and the antibody can be prepared by the following method: non-toxic Shiga toxin immune antigen is prepared by the method of chemical synthesis or gene recombinant expression, egg-laying hens are immunized, eggs are collected, and the biological chemical method is applied in extracting and purifying egg yolk immunoglobulin (IgY antibody). The antibody has the effects of neutralizing Shiga toxin and effectively inhibiting the toxicity of the Shiga toxin, can be used as an oral antitoxin for preventing and treating complications caused by toxin-producing Shigella, entero-hemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157, vibrio cholerae and the like and can be simultaneously applied in the detection and the infection diagnosis of type I Shiga toxin and pathogen thereof.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
Shigella flexneri serotype detection primer, and multiplex amplification using it
ActiveCN103589778AEase of identification and specificityTimely identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMultiplexShigella flexneri
The invention relates to a Shigella flexneri serotype detection primer, and multiplex amplification using it. The primer comprises sequences represented by SEQ ID Nos.2 and 3, SEQ ID Nos.4 and 5, SEQ ID Nos.6 and 7, SEQ ID Nos.8 and 9, SEQ ID Nos.10 and 11, SEQ ID Nos.12 and 13, SEQ ID Nos.14 and 15, SEQ ID Nos.16 and 17, SEQ ID Nos.18 and 19. The primer is specific and has an annealing temperature consistency. The invention also relates to a method for realizing the multiplex amplification by using the primer, and further relates to an application of the Shigella flexneri serotype detection primer in the preparation of a detection agent, and a Shigella flexneri serotype detection kit including the primer.
Owner:ICDC CHINA CDC
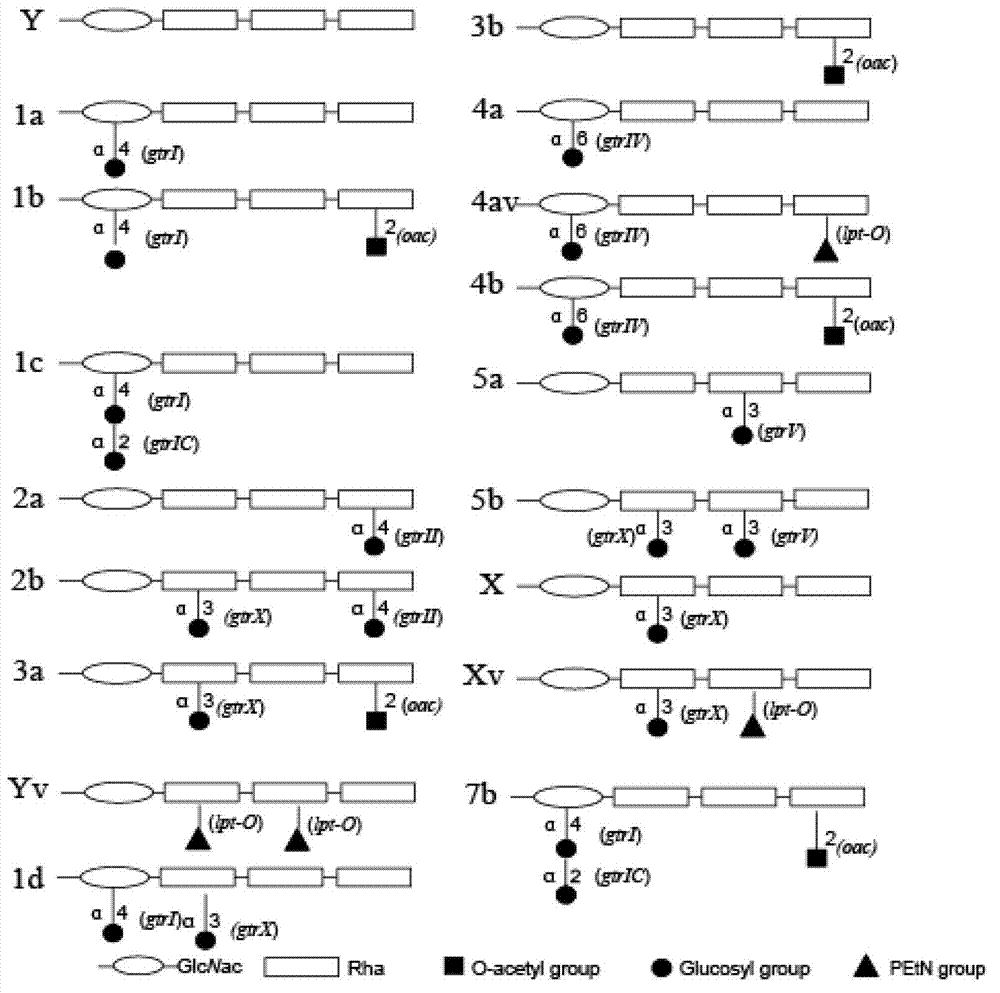
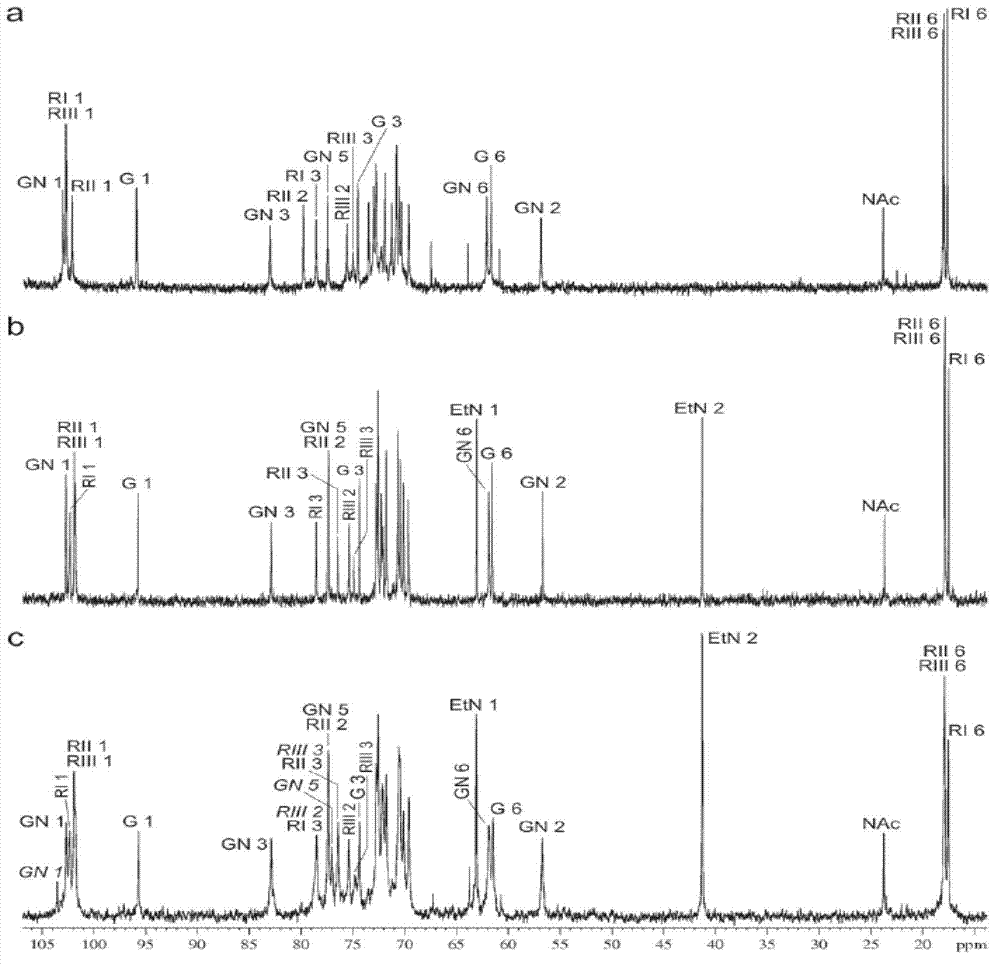
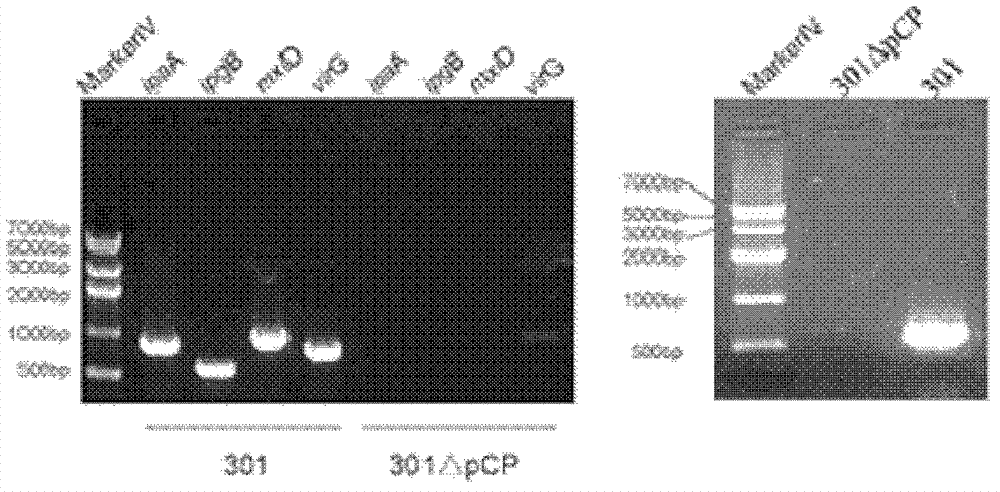
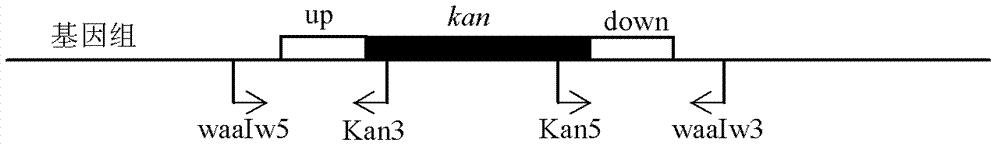
Nontoxic shigella flexneri with lipopolysaccharide synthesis deficiency and construction method thereof
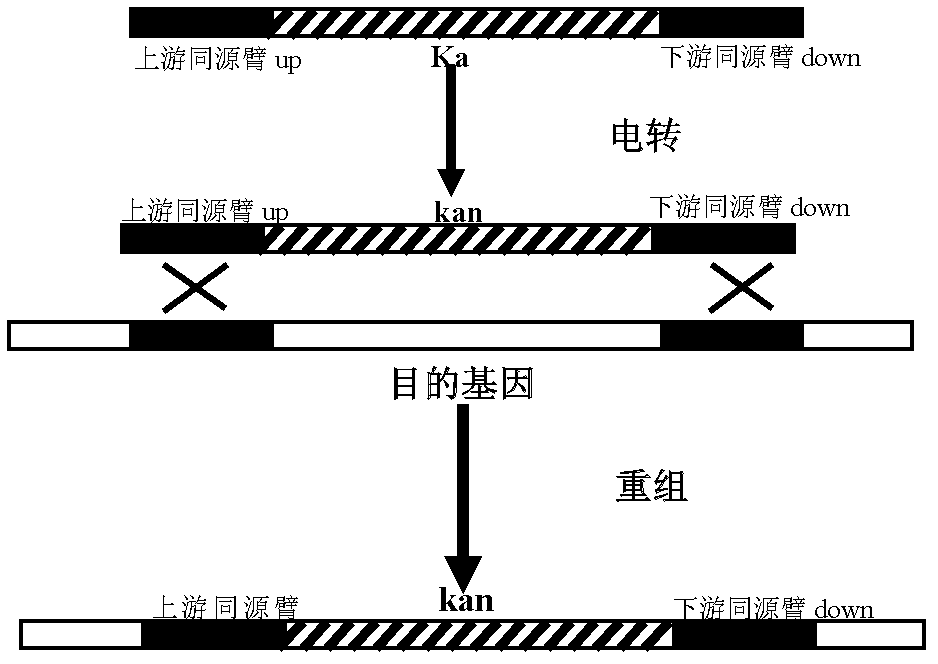
The invention discloses a nontoxic shigella flexneri with lipopolysaccharide synthesis deficiency and a construction method thereof. The invention provides a recombinant bacterium A, which is a recombinant bacterium obtained by removing large virulence plasmid in shigella flexneri 2a and O-antigen ligase coding gene in genome of the shigella flexneri 2a. Experiments show that according to the method of the invention, large virulence plasmid in shigella flexneri 2a 301 is firstly removed based on a plasmid exclusion principle, and a large virulence plasmid traceless deletion mutant 301 delta pCP is constructed, which is the nontoxic shigella flexneri; a target gene is substituted by a resistance gene by using homologous recombination technology based on the action of lambda bacteriophage Red recombinase; then the resistance gene is removed from a host bacterium under the action of transposase, and thus a waaI deletion strain of the nontoxic shigella flexneri is obtained.
Owner:INST OF BIOENG ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE CHINESE
Combined bacteriophage preparation for treating piglet diarrhea
ActiveCN111481574AReduce abundancePrevent diarrheal diseasesAntibacterial agentsViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsEscherichia coliEnterobacter
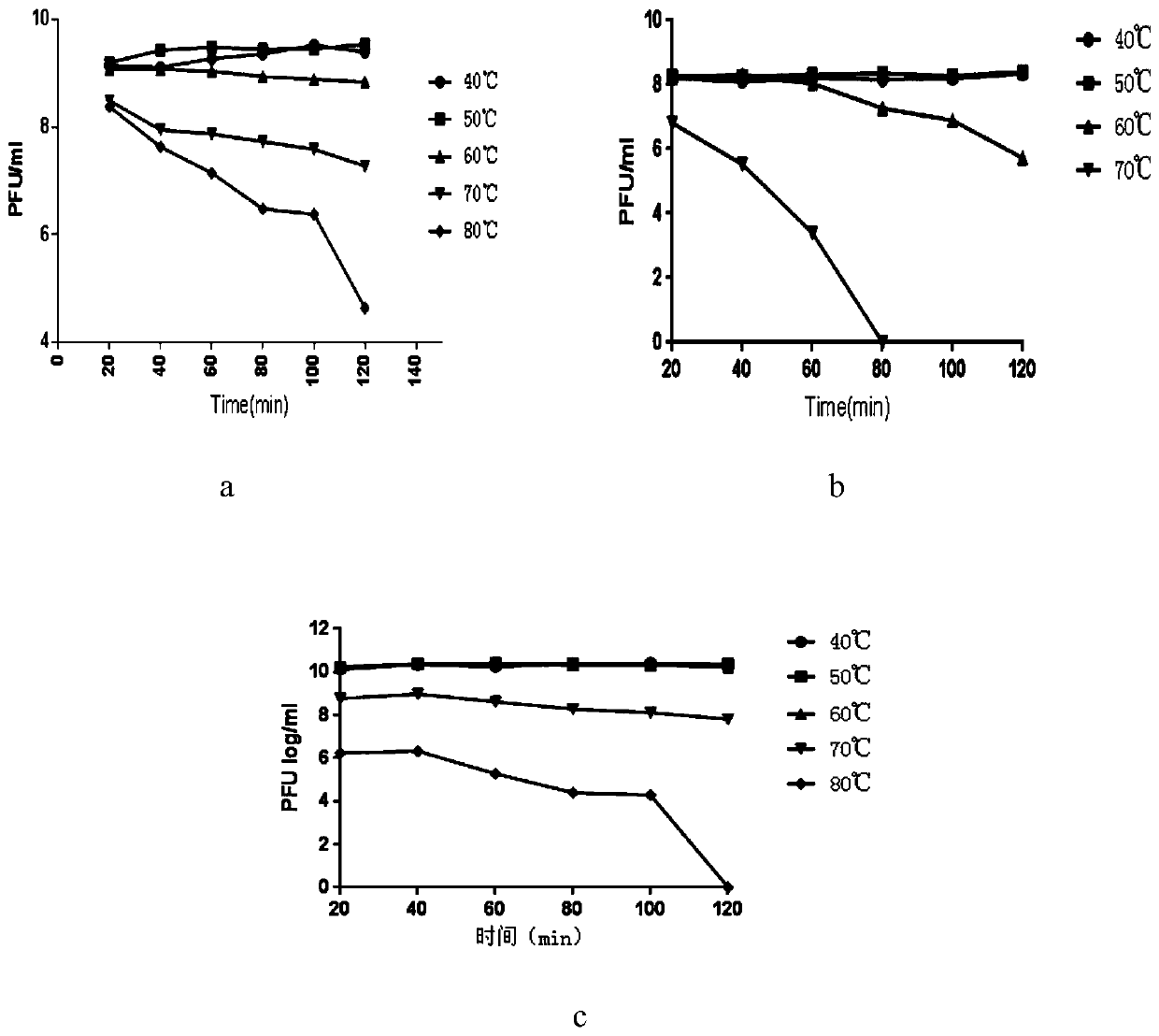
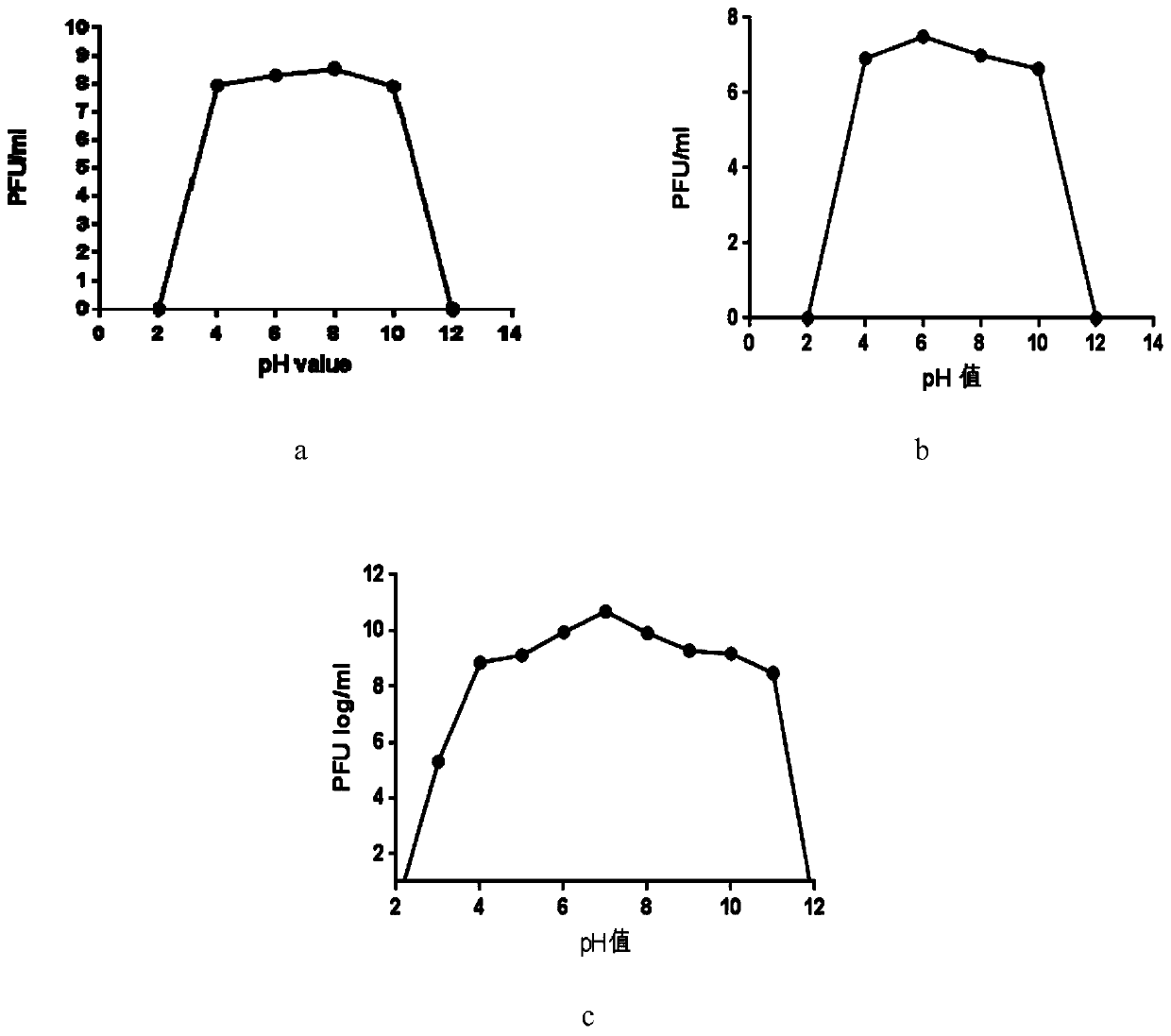
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and particularly relates to a combined bacteriophage preparation for treating piglet diarrhea. The bacteriophage comprises an escherichia colibacteriophage vB _ EcoP _ E21, an escherichia coli bacteriophage vB _ EcoM _ F2 and a shigella bacteriophage vB _ SsoM _ Z31, the preservation number of the escherichia coli bacteriophage vB_EcoP_E21is shown as follows: vB_EcoP_E21; the preservation number of the escherichia coli bacteriophage vB _ EcoM _ F2 is CGMCC 18871, and the preservation number of the shigella bacteriophage vB _ SsoM _ Z31is CGMCC 18870. The combined bacteriophage preparation is applied in a direct drenching mode, the abundance of escherichia coli and shigella can be reduced, diarrhea diseases of piglets in the breeding process are effectively prevented and treated, the survival rate of the piglets is increased, and economic losses are reduced. The combined bacteriophage preparation provided by the invention can replace traditional feed antibiotics, has the characteristics of safety, high efficiency, no residue and the like, and is an ideal antibiotic substitute.
Owner:JILIN ACAD OF AGRI SCI +2
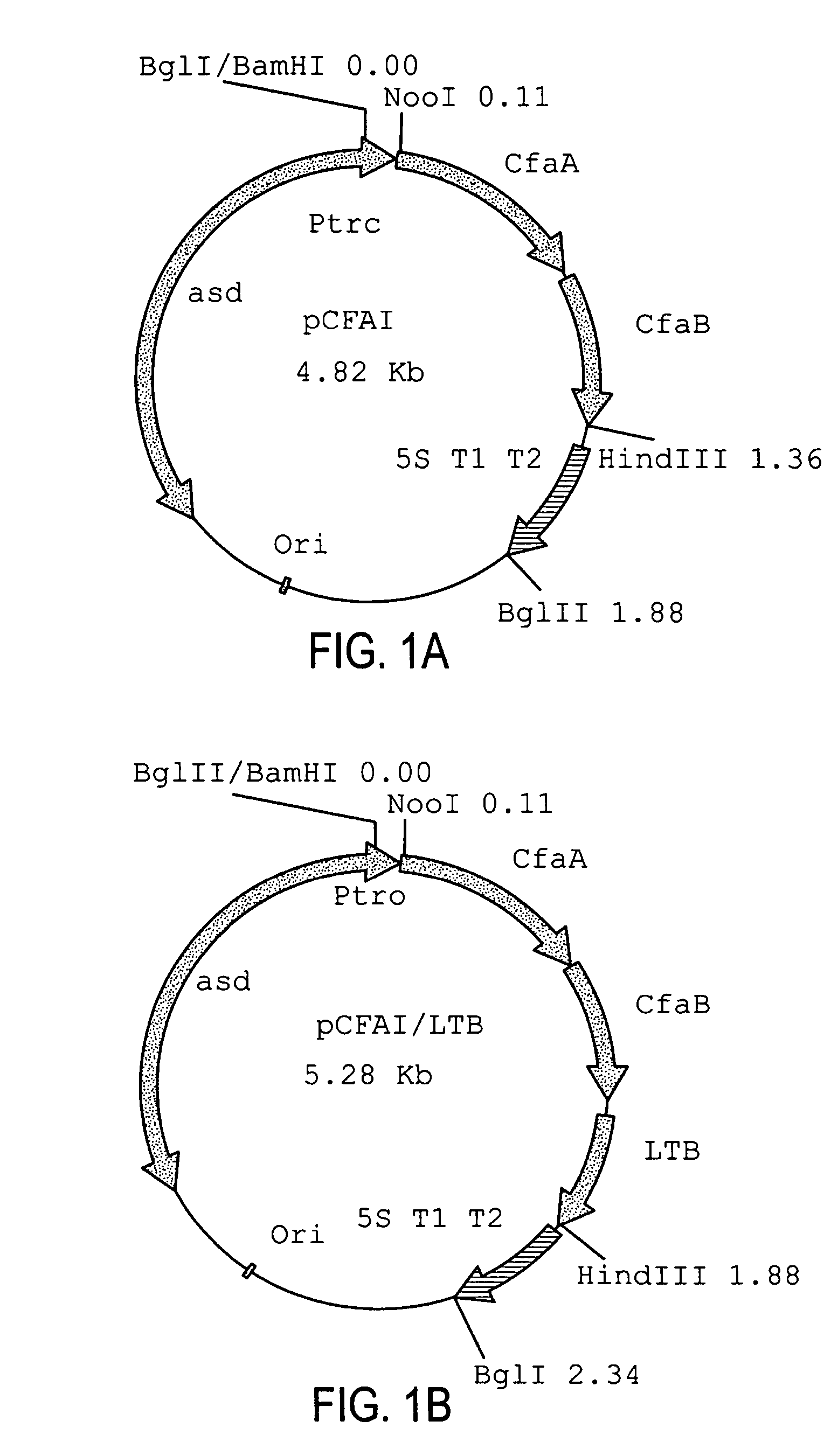
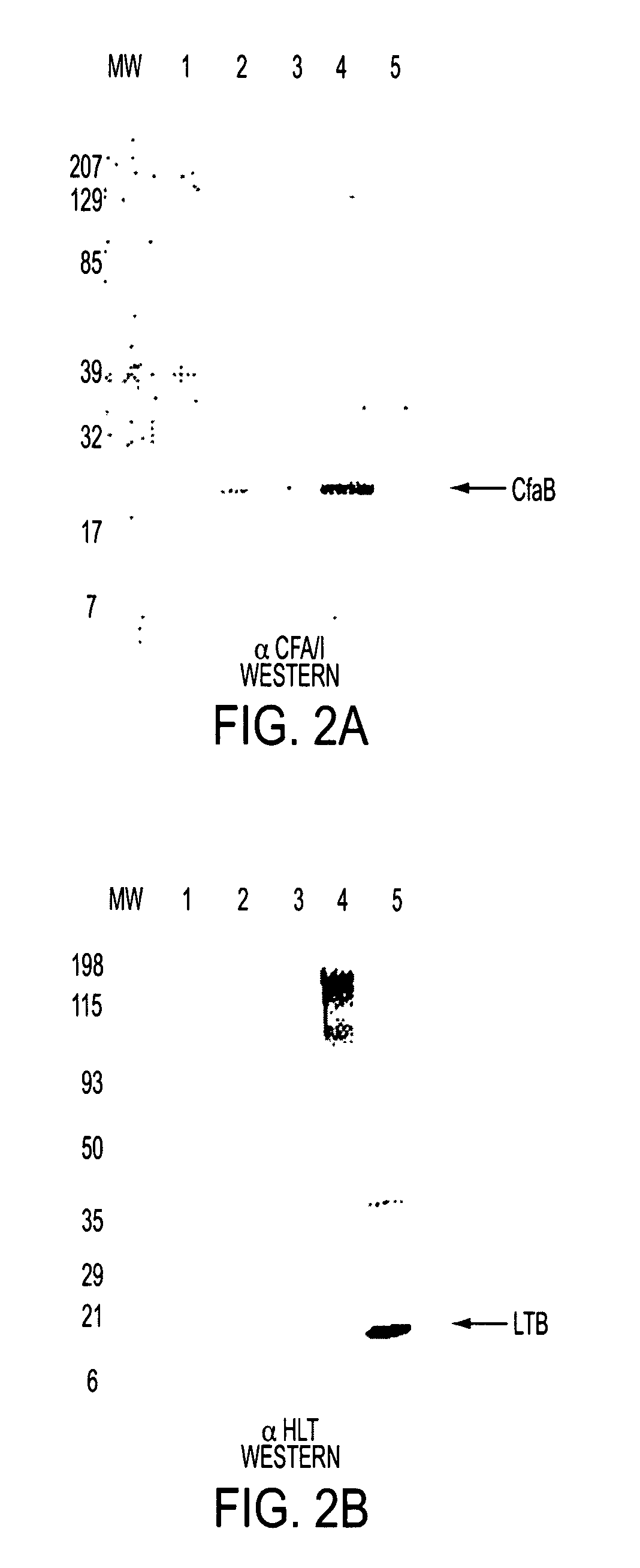
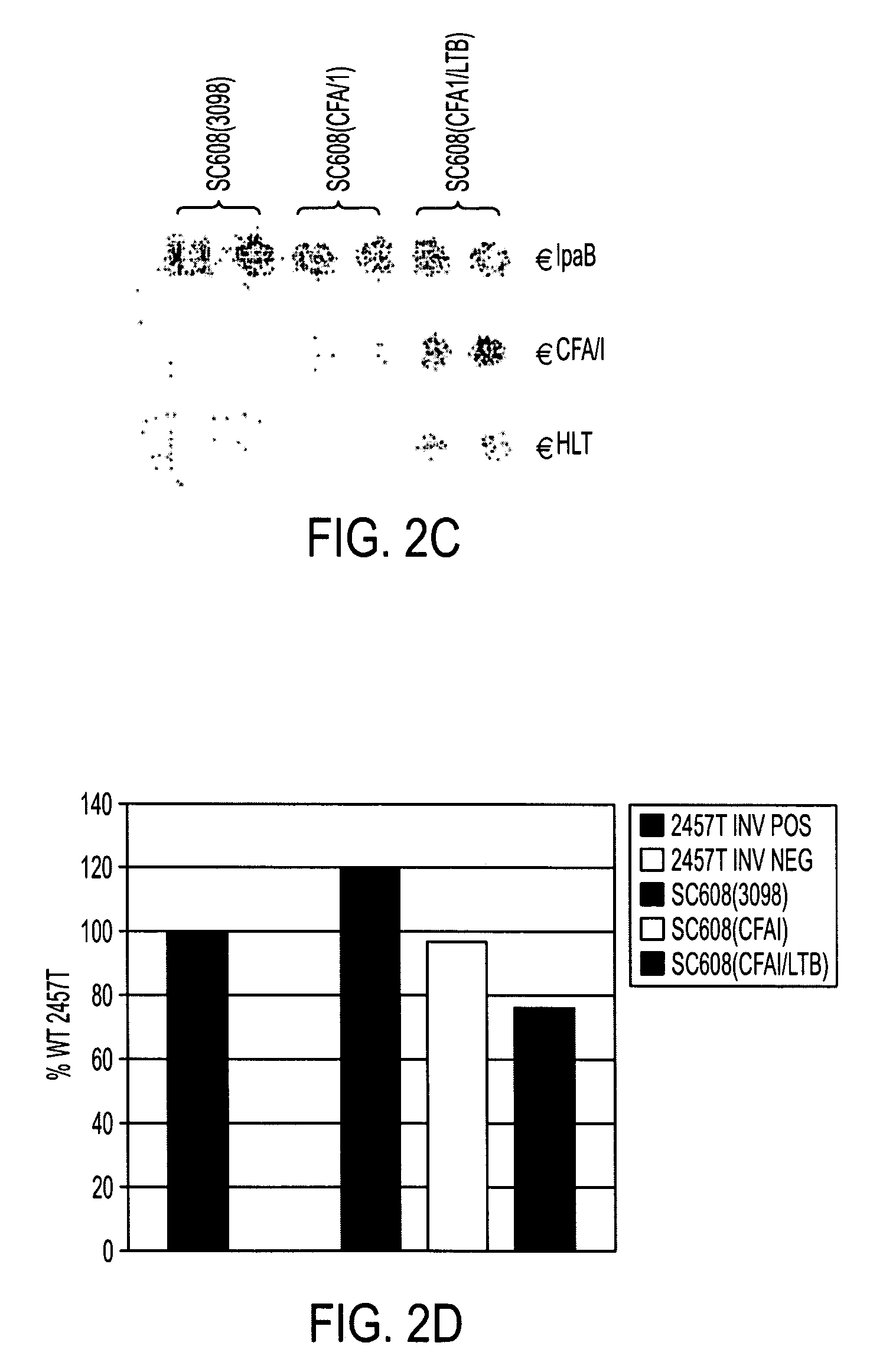
Construction of live attenuated Shigella vaccine strains that express CFA/I antigens (CfaB and CfaE) and the B subunit of heat-labile enterotoxin (LTB) from enterotoxigenic E. coli
ActiveUS7759106B2Reduce intrusionBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaHeterologousMucosal Immune Responses
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
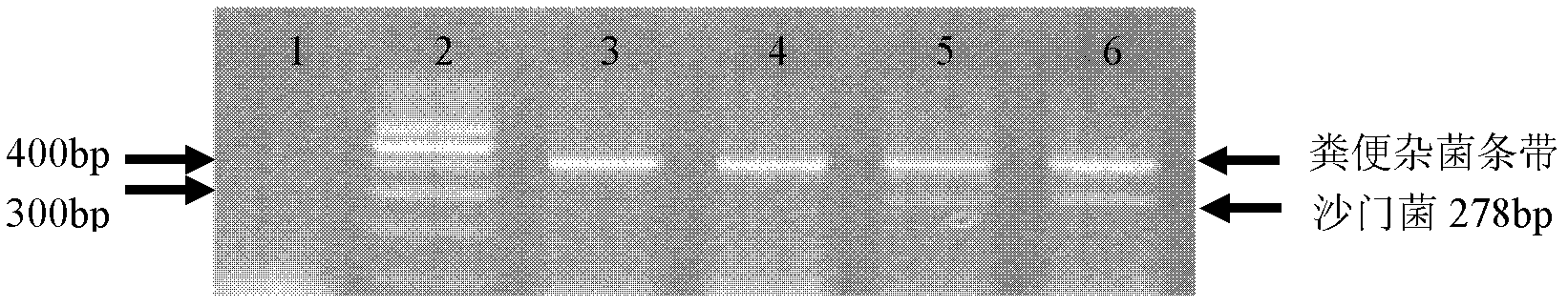
Method for quickly detecting salmonella, shigella and Escherichia coli in faeces
InactiveCN102424839AShort detection timeReduce dosageMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesEscherichia coli
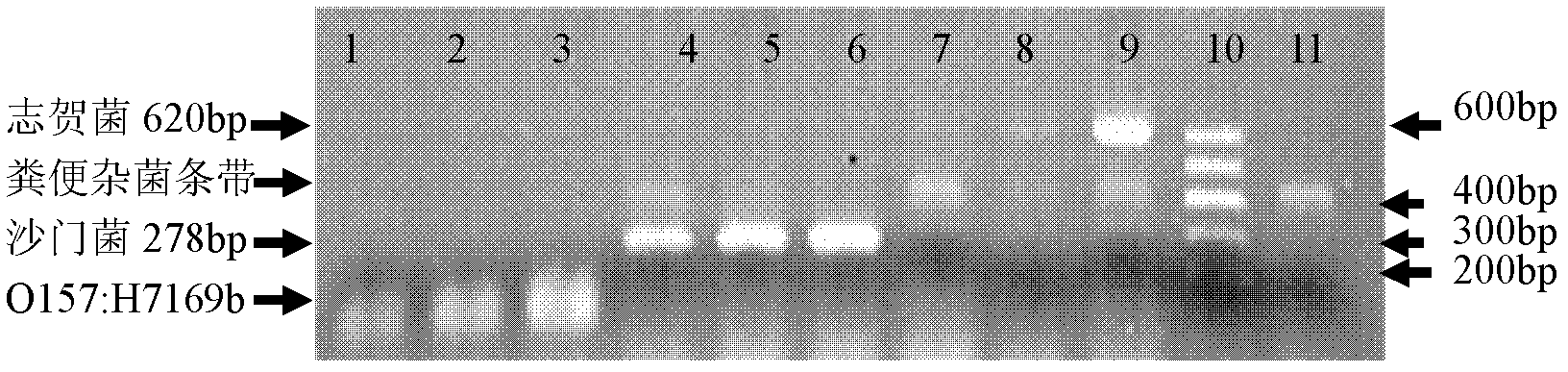
The invention aims to solve the technical problem that salmonella, shigella and Escherichia coli O157:H7 in a faeces sample are difficult to quickly detect and solve in the field of the prior art. In order to solve the technical problem, the technical scheme of the invention provides a multiple PCR (polymerase chain reaction) primer group and quick detection method for detecting the above bacteria among in-vitro bacteria. The multiple PCR primer group for detecting salmonella and shigella in in-vitro faeces contains a primer pair for salmonella invA genes and a primer pair for shigella ipaH genes. The invention also provides a method for carrying out multiple PCR amplification by using the primer group. Compared with the traditional method, the method provided by the invention has the characteristics of high speed, high accuracy, low cost and the like, can finish the detection of salmonella, shigella and Escherichia coli O157:H7 in faeces within 12 hours, and has good application prospects.
Owner:樊学军 +4
Protected tetrasaccharides, their process of preparation and their use as transglucosylase acceptor substrates in chemo-enzymatic synthesis of shigella flexneri specific oligosaccharides
Owner:INST PASTEUR +3
Detection reagent for Shigella flexneri plasmid-carried gene Ipt-O and application thereof
ActiveCN103374612AStrong specificityAvoid subjectivityMicrobiological testing/measurementShigella flexneriSerotype
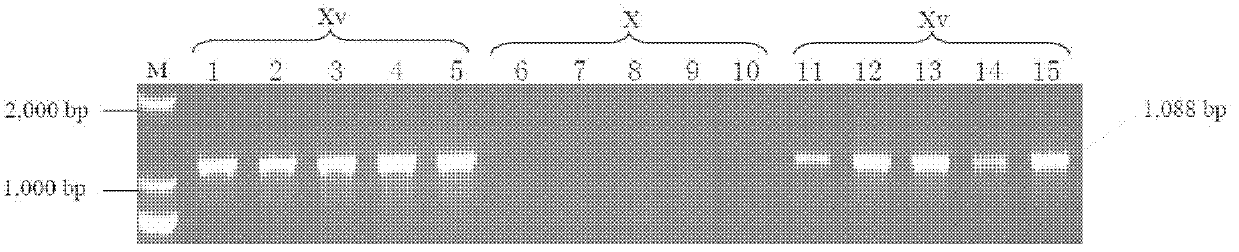
The invention relates to a detection reagent for a Shigella flexneri plasmid-carried gene Ipt-O and an application thereof, and in particular relates to an application of the detection reagent for a Shigella flexneri plasmid-carried gene Ipt-O in preparation of a Shigella flexneri serotype detection agent. The detection agent is used for detecting the Shigella flexneri serotype or detecting the differential diagnosis sample containing Shigella flexneri. The invention also relates to a reagent for Shigella flexneri MASF IV-1 phenotype detection, which is composed of a primer pair of the Shigella flexneri plasmid-carried gene Ipt-O as shown in the SEQ ID No.2 and SEQ ID No.3, and further relates to a method for detecting the Shigella flexneri MASF IV-1 phenotype by using the primer pair, and a method for distinguishing Shigella flexneri Xv serotype and X serotype, 4a serotype and 4av serotype as well as Y serotype and Yv serotype.
Owner:ICDC CHINA CDC
Method for detecting bacterium serotypes
ActiveCN111100862AAchieving Simultaneous DetectionLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesEscherichia coli serotypeVibrio parahemolyticus
The application provides a method for detecting bacterium serotypes. Through the adoption of the method, the existence of various bacterium serotypes (such as escherichia coli O serotypes, escherichiacoli H serotypes, escherichia coli K serotypes, salmonella O serotypes, salmonella H serotypes, vibrio parahaemolyticus O serotypes, vibrio parahaemolyticus K serotypes, shigella O serotypes and vibrio cholerae O serotypes) in samples can be detected at the same time. In addition, the application further provides a probe set and a reagent kit comprising one or more probe sets. The probe sets andthe reagent kit can be used for implementing the method disclosed by the invention. In addition, the application further provides the reagent kit. The existence or the level of a plurality of bacterium serotypes in the samples can be detected at the same time in a round of reactions.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Inhibitors Of Bacterial Type III Secretion System
ActiveUS20120114633A1Effectively clearEfficient killingAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesEnteroinvasive E. coli
Organic compounds showing the ability to inhibit effector toxin secretion or translocation mediated by bacterial type III secretion systems are disclosed. The disclosed type III secretion system inhibitor compounds are useful for combating infections by Gram-negative bacteria such as Salmonella spp., Shigella flexneri, Pseudomonas spp., Yersinia spp., enteropathogenic and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli, and Chlamydia spp. having such type III secretion systems.
Owner:MICROBIOTIX
Quadruple PCR detection primer group and kit for simultaneously detecting shigella, salmonella, clostridium welchii and escherichia coli
PendingCN112725478AGood economic valueHomologous relationship is smallMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliSalmonella kiel
The invention discloses a quadruple PCR detection primer group for simultaneously detecting shigella, salmonella, clostridium welchii and escherichia coli, which comprises four pairs of primers, namely a shigella upstream primer pair and a shigella downstream primer pair which are respectively SEQIDNO: 1 and SEQIDNO: 2; an upstream primer pair and a downstream primer pair of salmonella are respectively SEQ ID NO: 3 and SEQ ID NO: 4; the clostridium welchii A type primer pair is shown as SEQ ID NO: 5 and SEQ ID NO: 6 respectively; and the primer pairs of the escherichia coli are respectively SEQ ID NO: 7 and SEQ ID NO: 8. A multiple detection method is established for common enteropathogenic bacteria in chicken farms, on the basis of high detection accuracy and good specificity, the detection time is shortened, the detection efficiency is improved, and the multiple detection method is more beneficial to application in large-scale breeding production.
Owner:青岛迪诺瓦基因科技有限公司 +2
Substrate combination, detection reagent and detection kit for detecting escherichia coli and/or shigella
ActiveCN112161976AQuick distinctionMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansShigella flexneriShigella dysenteriae
The invention relates to the field of biological detection, and particularly relates to a substrate combination, a detection reagent and a detection kit for detecting escherichia coli and / or shigella.The substrate combination provided by the invention is a detection kit for quickly distinguishing escherichia coli and the shigella based on biochemical and chromogenic principles and a preparation method thereof is provided. By using the kit disclosed by the invention, the escherichia coli, shigella bogdii, shigella sonnei, shigella flexneri and shigella dysenteriae can be quickly distinguishedwithin 1-2 hours by only one step of operation.
Owner:AUTOBIO DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
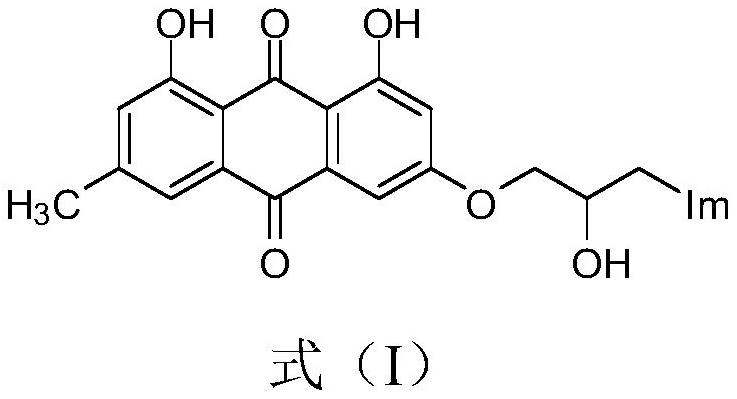
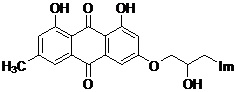
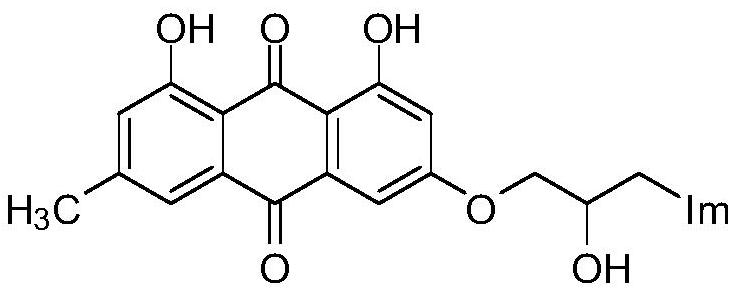
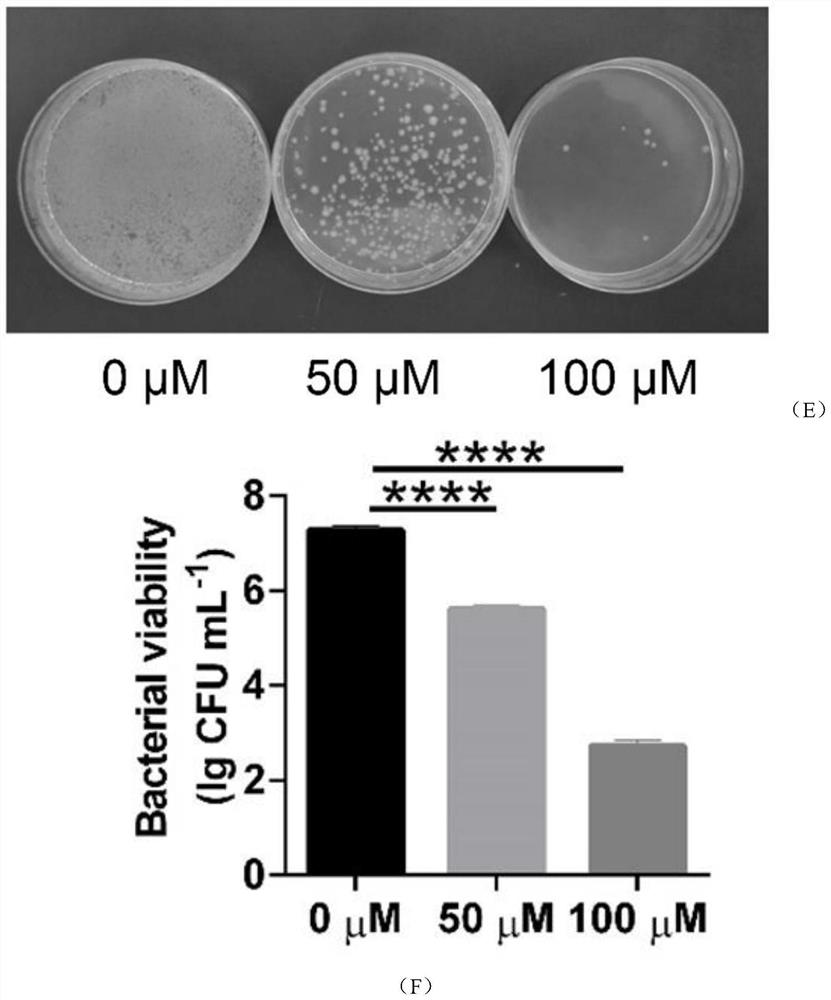
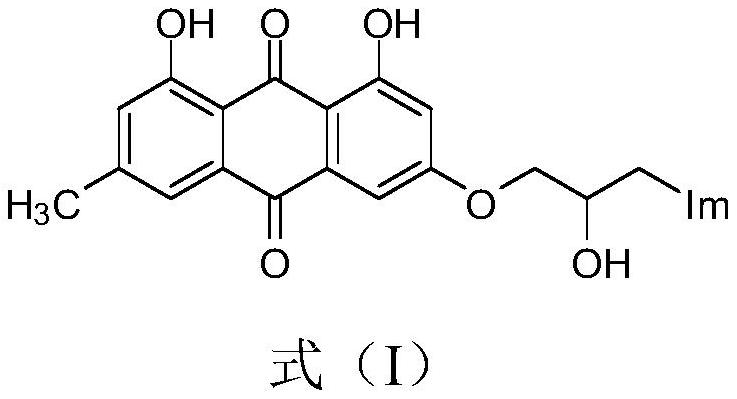
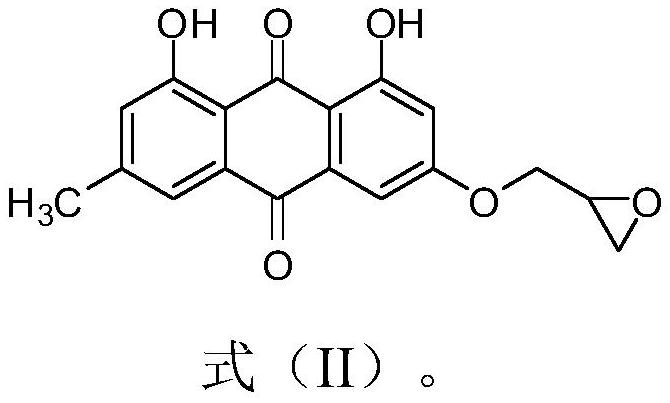
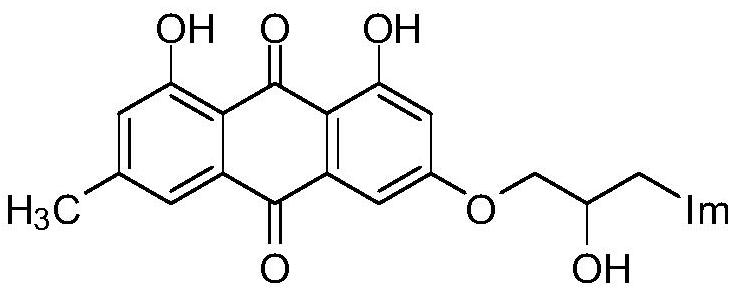
Emodin azole alcohol compound and application thereof
ActiveCN111875553ASimple structureStrong antimicrobial activity in vitroAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBiotechnologyAspergillus flavus
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicinal chemistry, and discloses an emodin azole alcohol compound shown as a formula I. The emodin azole alcohol compound has high in-vitro antimicrobial activity and especially has very high inhibitory activity on staphylococcus aureus, bacillus subtilis, micrococcus luteus, escherichia coli, proteus, pseudomonas aeruginosa, shigella dysenteriae,salmonella typhimurium and other bacteria, and candida utilis, candida albicans, saccharomyces cerevisiae, aspergillus flavus, candida albicans and other fungi. The emodin azole alcohol can be used for preparing antibacterial and / or antifungal drugs, so that more efficient candidate drugs are provided for clinical antimicrobial treatment, and the clinical treatment problems of increasingly seriousdrug resistance, stubborn pathogenic microorganisms, newly appearing harmful microorganisms and the like are solved.
Owner:LINYI UNIVERSITY
Method for rapidly detecting shigella by duplex scorpion primer fluorogenic quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
InactiveCN103436614ASimple methodEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceIdiopathic Pulmonary Arterial HypertensionBiology
The invention discloses a method for rapidly detecting shigella by duplex scorpion primer fluorogenic quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction). The method comprises the following steps: preparing a pMD18-T-ipaH (Polarisation Mode Dispersion 18-T-Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension) standard sample, and rapidly detecting the shigella by adopting fluorogenic quantitative PCR. The method is simple, convenient and easy to operate, has the advantages of high sensitivity and low cost, and lays the foundation in development of a novel pathogen test kit and scientific research application.
Owner:NANTONG ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU OF THE PEOPLES REPUBLIC OF CHINA
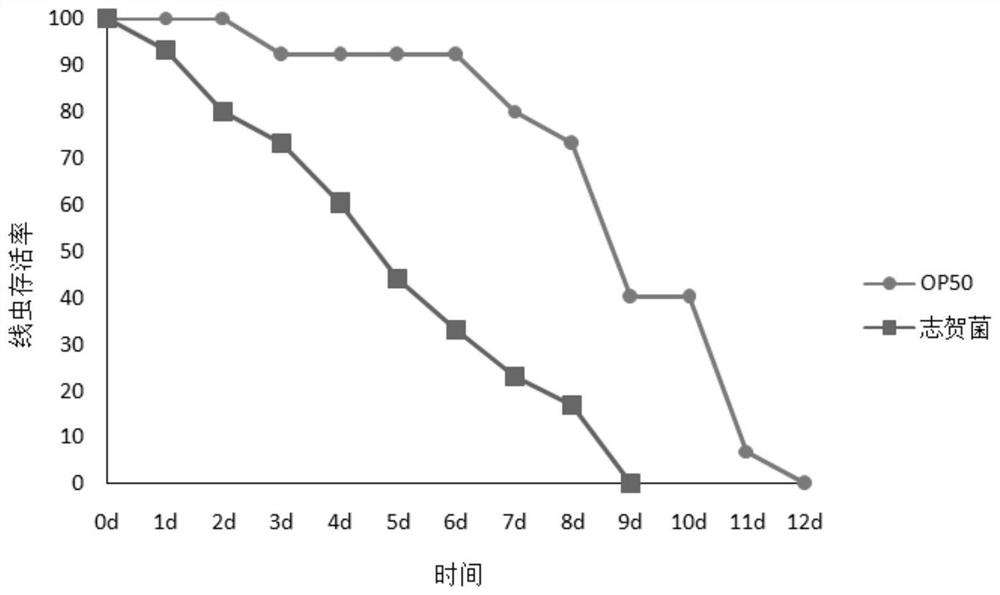
Method for rapidly detecting bovine-derived shigella virulence by using defective caenorhabditis elegans
PendingCN112575055AQuick checkEfficient detectionCompounds screening/testingMicrobiological testing/measurementAntimicrobial drugAnti-infective therapy
The invention discloses a method for rapidly detecting bovine-derived shigella virulence by using defective caenorhabditis elegans, relates to the technical field of biological models, and aims to rapidly and quantitatively detect the bovine-derived shigella virulence by utilizing sek-1, glp-1 gene defective caenorhabditis elegans more sensitive to pathogenic bacteria. The method has higher sensitivity to temperature, pathogenic bacteria and other factors, can efficiently detect the toxicity of shigella with high throughput, and can be used for researching the pathogenic mechanism of pathogenic bacteria and further screening antibacterial drugs, thereby providing a theoretical basis for clinical anti-infection treatment and medication of intestinal shigella.
Owner:GUANGXI VETERINARY RES INST
Detection reagent for Shigella flexneri plasmid-carried gene Ipt-O and application thereof
ActiveCN103374612BTimely identificationAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementShigella flexneriSerotype
Owner:ICDC CHINA CDC
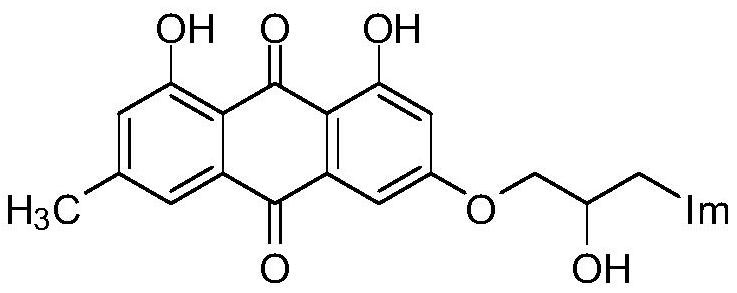
A kind of emodin azole alcohol compound and its application
ActiveCN111875553BSimple structureStrong antimicrobial activity in vitroAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBiotechnologyAspergillus flavus
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicinal chemistry, and discloses an emodin azole alcohol compound as shown in formula I, which has strong antimicrobial activity in vitro, especially against Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis and Micrococcus luteus , Escherichia coli, Proteus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Shigella dysenteriae, Salmonella typhimurium and other bacteria, as well as Candida utilis, Candida albicans, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Aspergillus flavus, Candida, etc. Fungi show high inhibitory activity and can be used to prepare antibacterial and / or antifungal drugs, thereby providing more efficient drug candidates for clinical antimicrobial treatment, and helping to solve the increasingly serious drug resistance, stubborn Clinical treatment issues such as pathogenic microorganisms and emerging harmful microorganisms.
Owner:LINYI UNIVERSITY
Application of Plum Extract in Preparation of Antibacterial Products
ActiveCN112316009BHas antibacterial effectTake advantage ofAntibacterial agentsBiocideBiotechnologyShigella flexneri
The invention discloses the application of Prunus japonica extract in the preparation of antibacterial products. Plum extract has a significant inhibitory effect on Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Shigella flexneri, Proteus, Salmonella typhi, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Escherichia coli, and will be used as an antibacterial agent in the future. There is significant potential in research for the development of drugs and other antimicrobial products.
Owner:NINGXIA MEDICAL UNIV
Escherichia coli and Shigella detection primers, kits and detection methods based on specific sequences
ActiveCN106755423BEasy to operateIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHomologous sequence
The invention discloses escherichia coli and shigella detection primers based on a specific sequence, a kit and a detection method, belonging to the technical field of molecular biology. The primers are designed and synthesized for a specific sequence (as shown in SEQ ID NO. 3) shared by escherichia coli and shigella or a homologous sequence, the homology of which reaches 96% or above. The primers are specifically as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2. The detection method comprises the steps of by taking genomic DNA of a to-be-detected sample or a single colony as a template, performing PCR amplification by means of the primers; judging the amplification primers as suspected positive if the amplification primers have same stripes with positive control; recovering the amplification primers which are suspected positive; performing sequencing and analyzing; and judging the primers which are as same as the sequence as shown in the SEQ ID NO.3 or the homology of which reaches 96% or above, as escherichia coli and shigella positive. According to the detection method, the operation is high, sensitivity and specificity are high, the result is consistent to species results of escherichia coli and shigella, the detection cost is low and the method has good promotion and application prospect.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV +1
Application of nanogold in preparation of medicine for treating shigella infectious enteritis and medicine preparation of nanogold
PendingCN113318124AHigh antibacterial activityReduced antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsInorganic active ingredientsShigella flexneriCell membrane
The invention discloses application of nanogold in preparation of a medicine for treating shigella infectious enteritis and a medicine preparation of the nanogold, and belongs to the field of biological medicine. Experiments show that in vitro, nanogold has relatively strong bacteriostatic activity on various strains, especially clinical drug-resistant bacteria, can obviously destroy the cell structure of shigella and reduce the biofilm activity of shigella; and in addition, the rise of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cells can be induced, and cell membranes are destroyed so as to obviously kill shigella and relieve clinical symptoms of shigella enteritis. In vivo, the nanogold can relieve clinical symptoms of shigella flexneri enteritis, relieve intestinal injury caused by shigella infection and reduce shigella load in excrement. The application field of the nanogold is widened, an experimental basis is provided for clinical application of the nanogold in preparation of the medicine for treating shigella infectious enteritis, and the nanogold has a good application prospect and a huge potential value.
Owner:XUZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Emodin azole alcohol compound and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111961008ASimple structureStrong antimicrobial activity in vitroAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBiotechnologyAspergillus flavus
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicinal chemistry. The invention discloses an emodin azole alcohol compound as shown in a formula I which is described in the specification. The compound has relatively strong in-vitro antimicrobial activity; the compound has very high inhibitory activity on staphylococcus aureus, bacillus subtilis, micrococcus luteus, escherichia coli, proteus, pseudomonas aeruginosa, shigella dysenteriae, salmonella typhimurium and other bacteria, and candida utilis, candida albicans, saccharomyces cerevisiae, aspergillus flavus, candida albicans and other fungi. The compound can be used for preparing antibacterial and / or antifungal drugs, so that more efficient candidate drugs are provided for clinical antimicrobial treatment, and the clinical treatmentproblems of increasingly serious drug resistance, stubborn pathogenic microorganisms, newly appearing harmful microorganisms and the like are solved.
Owner:LINYI UNIVERSITY
Lamp primers and detection methods for the detection of Shigella flexneri serotypes 2a and xv
ActiveCN113403410BEasy to operateHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesAntigenShigella flexneri
The present invention provides a LAMP primer and a detection method for detecting Shigella flexneri 2a and Xv serotypes. The present invention designs LAMP primers according to the type-specific antigenic determinants and group-specific antigenic determinants of the main serotypes 2a and Xv of Shigella flexneri, wherein the 2a serotype is (gtrII and wzx genes are positive, gtrX and opt genes are negative) ), Xv serotype (gtrX, opt and wzx genes positive, gtrII gene negative). The method does not require expensive equipment and instruments, and can rapidly, accurately and specifically detect Shigella flexneri 2a and Xv serotypes.
Owner:ICDC CHINA CDC
Short peptide for inhibiting Shiga toxin and application thereof
ActiveCN101016332BInhibition of biological effectsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntinoxious agentsEscherichia coliDisease
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
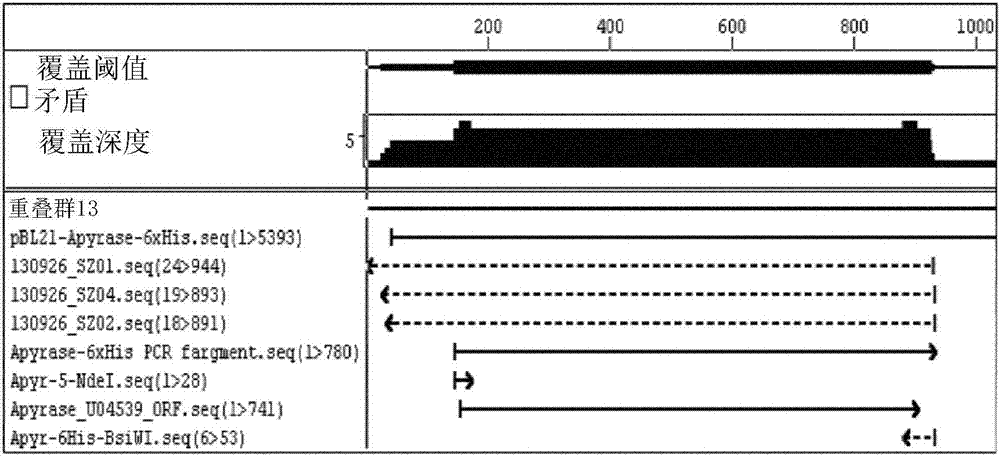
Analytical and diagnostic methods utilizing shigella flexneri apyrase
InactiveCN107075552AHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementShigella flexneriNucleoside diphosphate
A method, comprising the steps of providing a sample containing contaminating nucleoside diphosphates and / or nucleoside triphosphates, such as ATP and / or ATP analogues including deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates;reducing the amount of the contaminating nucleoside diphosphates and / or nucleoside triphosphates in the sample with an apyrase enzyme, wherein said apyrase enzyme is a Shigella flexneriapyrase; andperforming an analysis of the sample, wherein said analysis comprises an assay that would have been affected by the contaminating nucleoside diphosphates and / or nucleoside triphosphates had they not been reduced in the reduction step.
Owner:APIRAYS BIOSCI AB
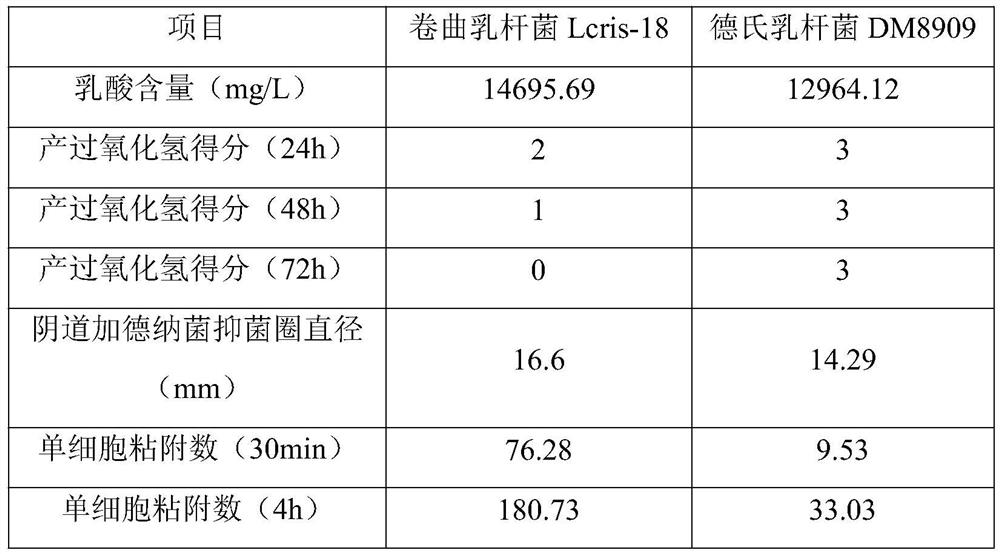
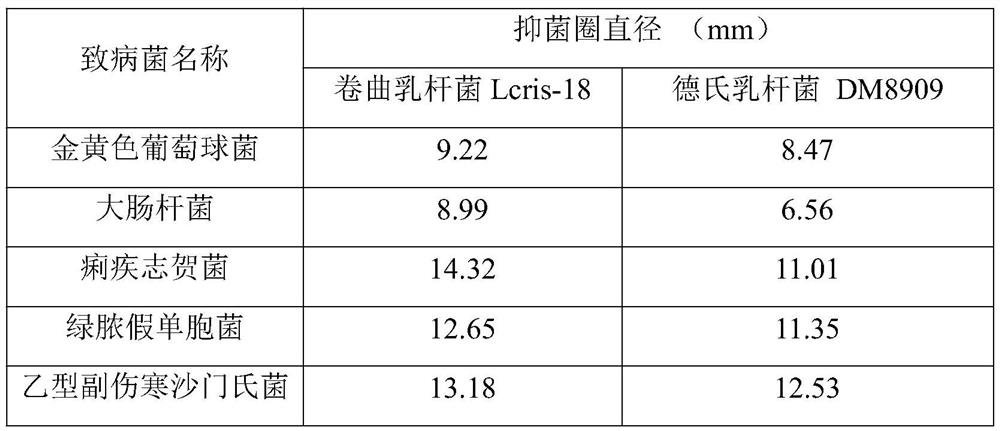
Lactobacillus crispatus and application thereof
PendingCN112708578ASuperior Cell AdhesionInhibition of colonizationAntibacterial agentsBacteriaBiotechnologyCell adhesion
The invention relates to the technical field of microorganisms, and discloses lactobacillus crispatus and application thereof. The lactobacillus crispatus has the advantage of cell adhesion, so that the lactobacillus crispatus can be adhered to vaginal epithelial cells, a micro-ecological barrier is formed, and pathogenic bacteria are prevented from colonizing or competing for epithelial cell receptors; meanwhile, the lactic acid producing capacity is high, the pH can be reduced, and moreover, generated antibacterial substances, such as hydrogen peroxide, lactic acid, bacteriocin and the like, can also inhibit the growth of the various pathogenic bacteria, such as gardnerella vaginalis, staphylococcus aureus, pseudomonas aeruginosa, escherichia coli, salmonella paratyphi B, shigella dysenteriae and the like.
Owner:SICHUAN ANAEROBIC BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Application of cerasus humilis extract in preparation of antibacterial products
ActiveCN112316009AHas antibacterial effectTake advantage ofAntibacterial agentsBiocideBiotechnologyShigella flexneri
The invention discloses application of a cerasus humilis extract in preparation of antibacterial products. The cerasus humilis extract has a remarkable inhibition effect on staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus epidermidis, klebsiella pneumoniae, shigella flexneri, proteus, salmonella typhimurium, pseudomonas aeruginosa and escherichia coli, and has great potential in development and research of antibacterial drugs and other antibacterial products in the future.
Owner:NINGXIA MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com