Patents
Literature
38 results about "HomoloGene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
HomoloGene, a tool of the United States National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), is a system for automated detection of homologs (similarity attributable to descent from a common ancestor) among the annotated genes of several completely sequenced eukaryotic genomes.
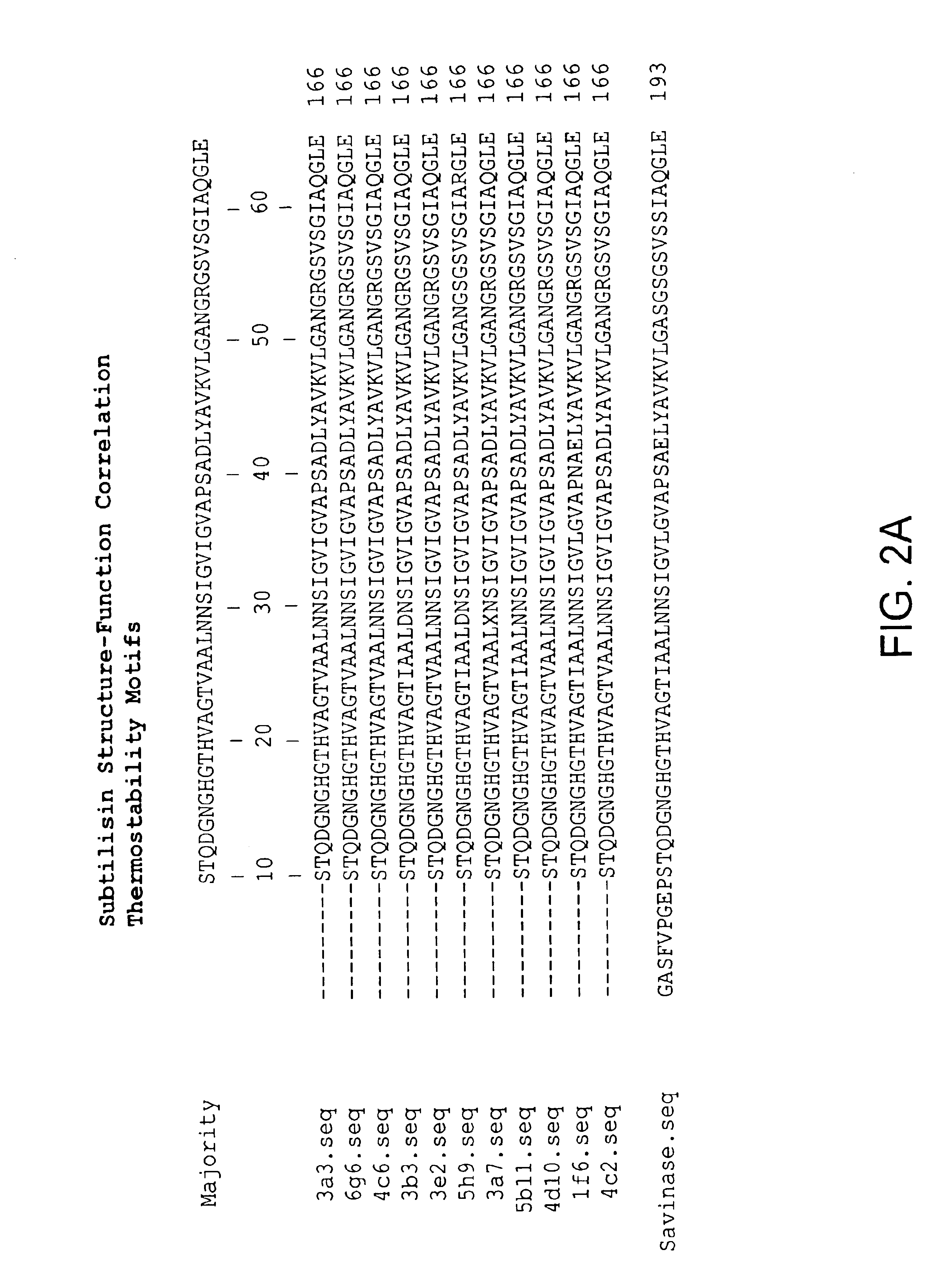
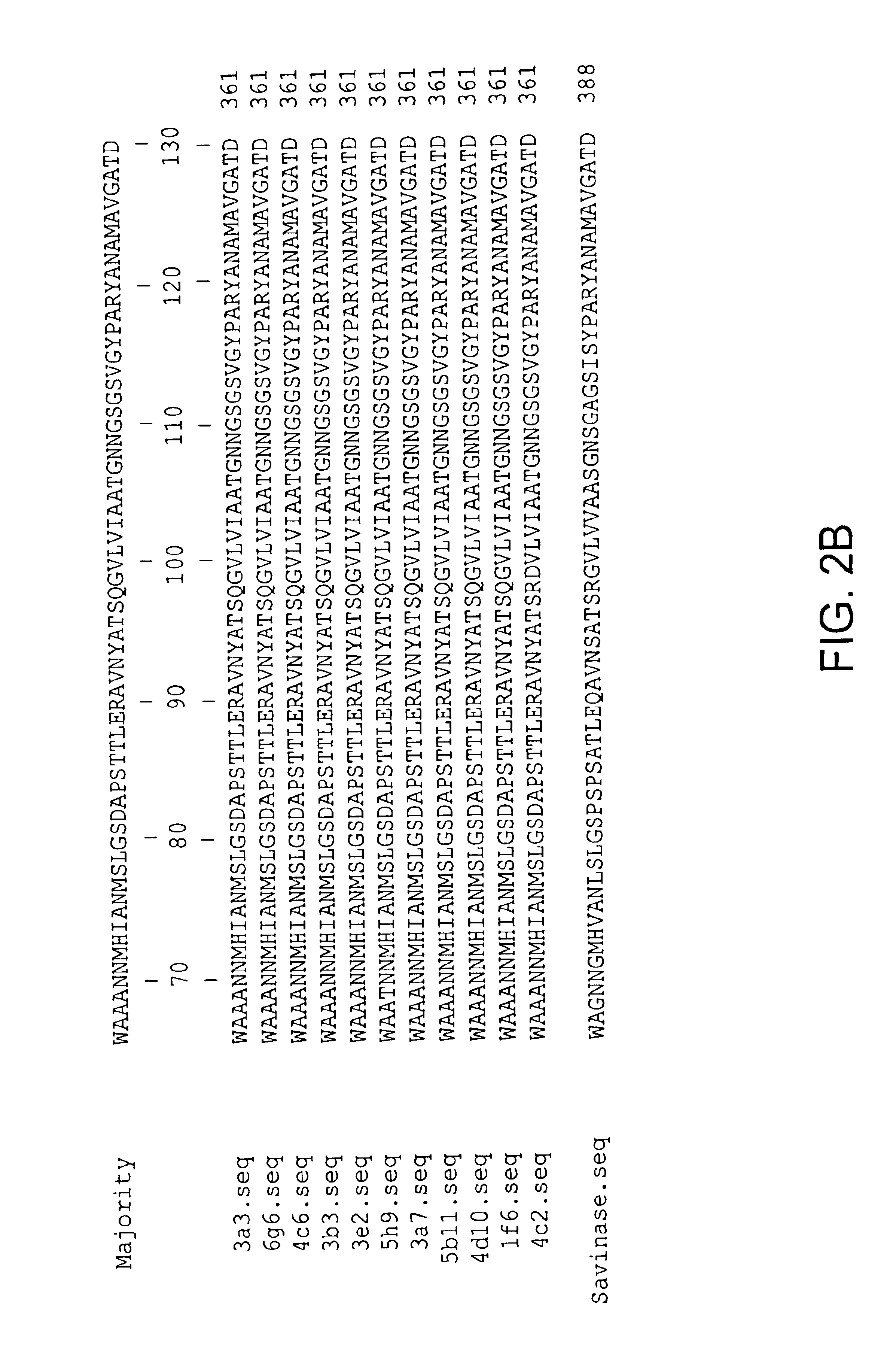
Subtilisin variants
New subtilisin homologues (both nucleic acids and proteins) are provided. Compositions which include these new proteins, recombinant cells, shuffling methods involving the new homologues, antibodies to the new homologues, and methods of using the homologues are also provided.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS +1
Transgenic plants presenting a modified inulin producing profile
A method is disclosed for producing a transgenic plant with a modified inulin producing profile comprising in its genome a combination of one or more expressible 1-SST enzyme encoding genes and one or more expressible 1-FFT enzyme encoding genes, wherein either of these genes or both of them comprise one or more recombinant genes containing one or more 1-SST, respectively 1-FFT, enzyme encoding DNA sequences of plant origin or an expressible homologous sequence thereof. The invention also relates to a method for modifying and controlling the inulin profile of plants and to a method for producing inulin from said transgenic plants. Furthermore, a novel cDNA sequence of a 1-SST enzyme encoding gene of Helianthus tuberosus and a novel cDNA sequence of a 1-FFT enzyme encoding gene of Cichorium intybus are disclosed, novel recombinant DNA constructs and genes derived thereof, as well as novel combinations of expressible 1-SST and 1-FFT enzyme encoding genes. Moreover, the invention also relates to novel polypeptides, homologues thereof and fragments thereof, which have 1-SST activity of 1-FFT activity, and to antibodies capable of specifically binding one or more of them.
Owner:TIENSE SUIKERRAFINADERIJ +1
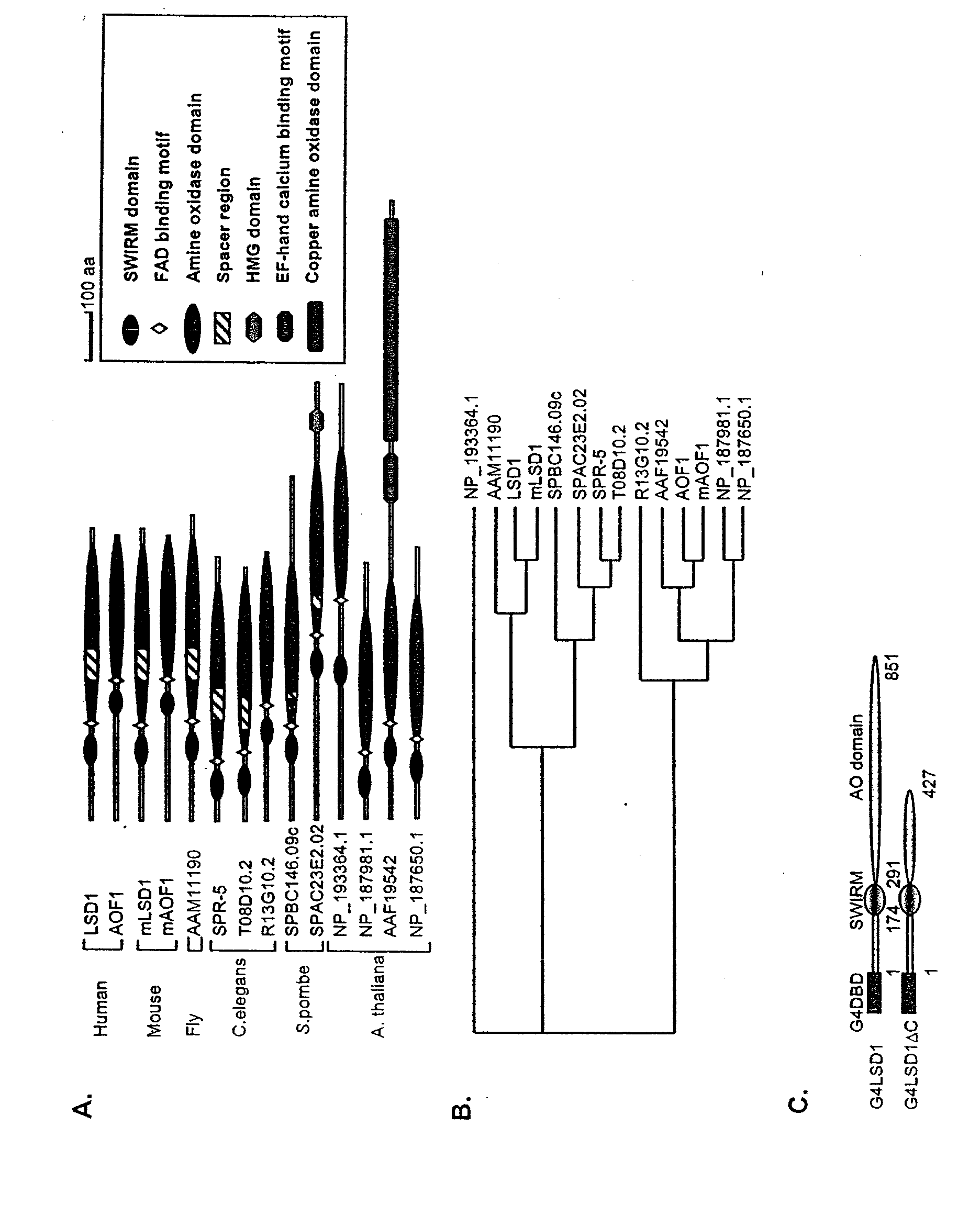
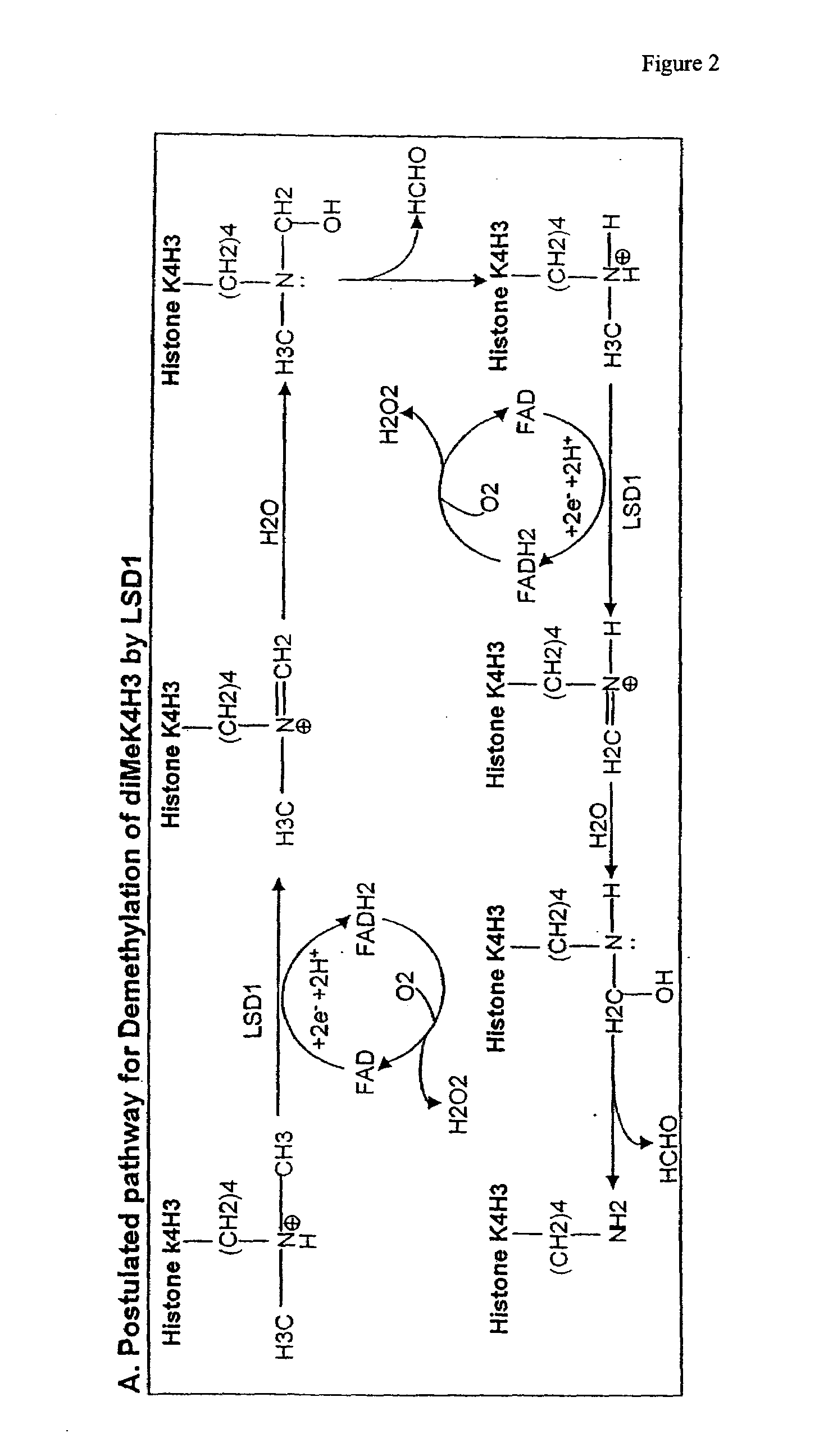
Histone Demethylation Mediated By The Nuclear Amine Oxidase Homolog LSD1
LSD1, a homolog of nuclear amine oxidases, functions as a histone demethylase and transcriptional co-repressor. LSD1 specifically demethylates histone H3 lysine 4, which is linked to active transcription. Lysine demethylation occurs via an oxidation reaction that generates formaldehyde. Importantly, RNAi inhibition of LSD1 causes an increase in H3 lysine 4 methylation and concomitant de-repression of target genes, suggesting that LSD1 represses transcription via histone demethylation. The results thus identify a histone demethylase conserved from S. pombe to human and reveal dynamic regulation of histone methylation by both histone methylases and demethylases.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Immunogenic bacterial vesicles with outer membrane proteins
ActiveUS20100015212A1Good curative effectHighly effective in raisingAntibacterial agentsBiocideLytic transglycosylase activityImmunogenicity
Knockout of the meningococcal mltA homolog gives bacteria that spontaneously release vesicles that are rich in immunogenic outer membrane proteins and that can elicit cross-protective antibody responses with higher bactericidal titres than OMVs prepared by normal production processes. Thus the invention provides a bacterium having a knockout mutation of its mltA gene. The invention also provides a bacterium, wherein the bacterium: (i) has a cell wall that includes peptidoglycan; and (ii) does not express a protein having the lytic transglycosylase activity of MltA protein. The invention also provides compositions comprising vesicles that, during culture of bacteria of the invention, are released into the culture medium.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
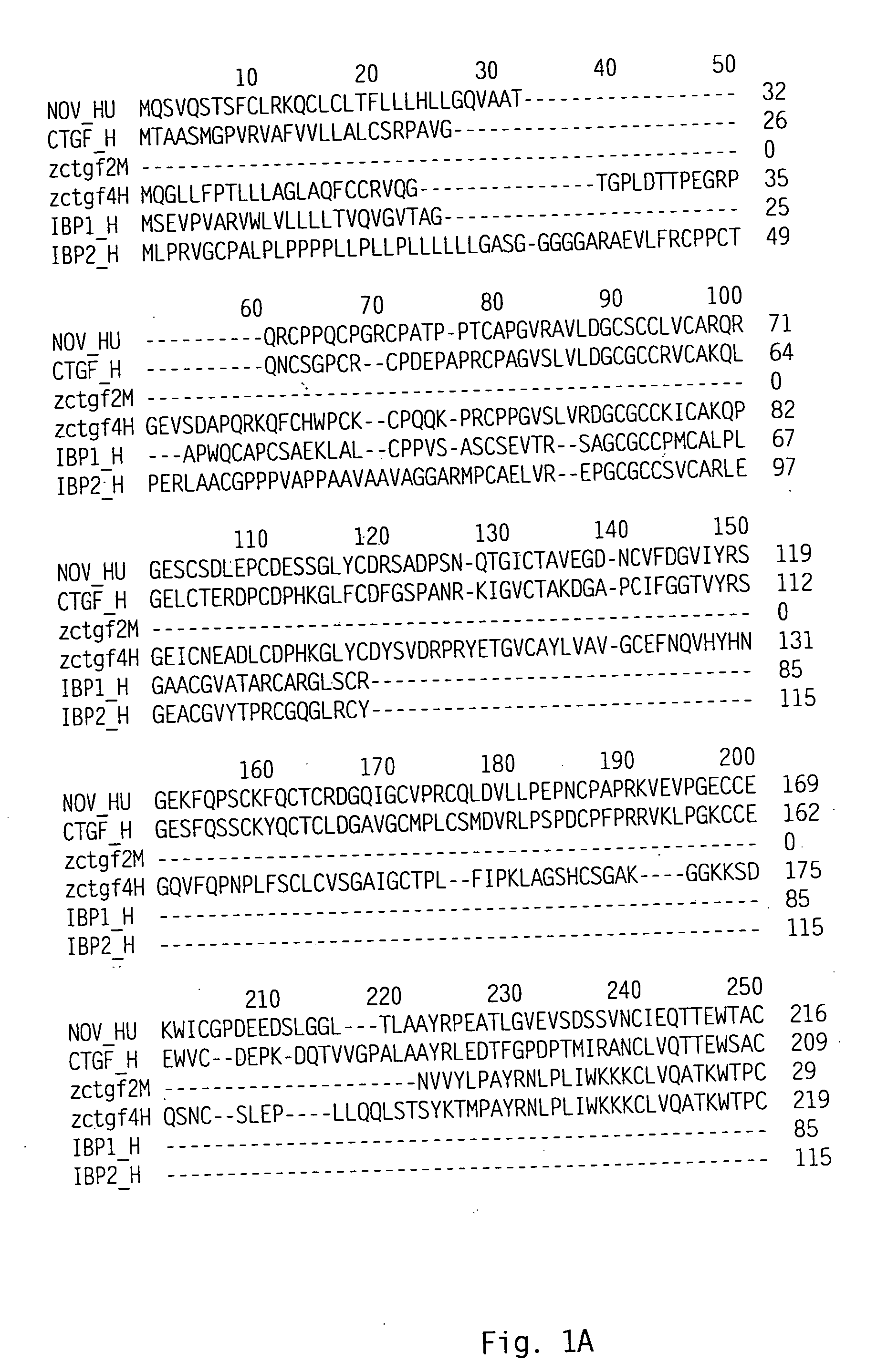
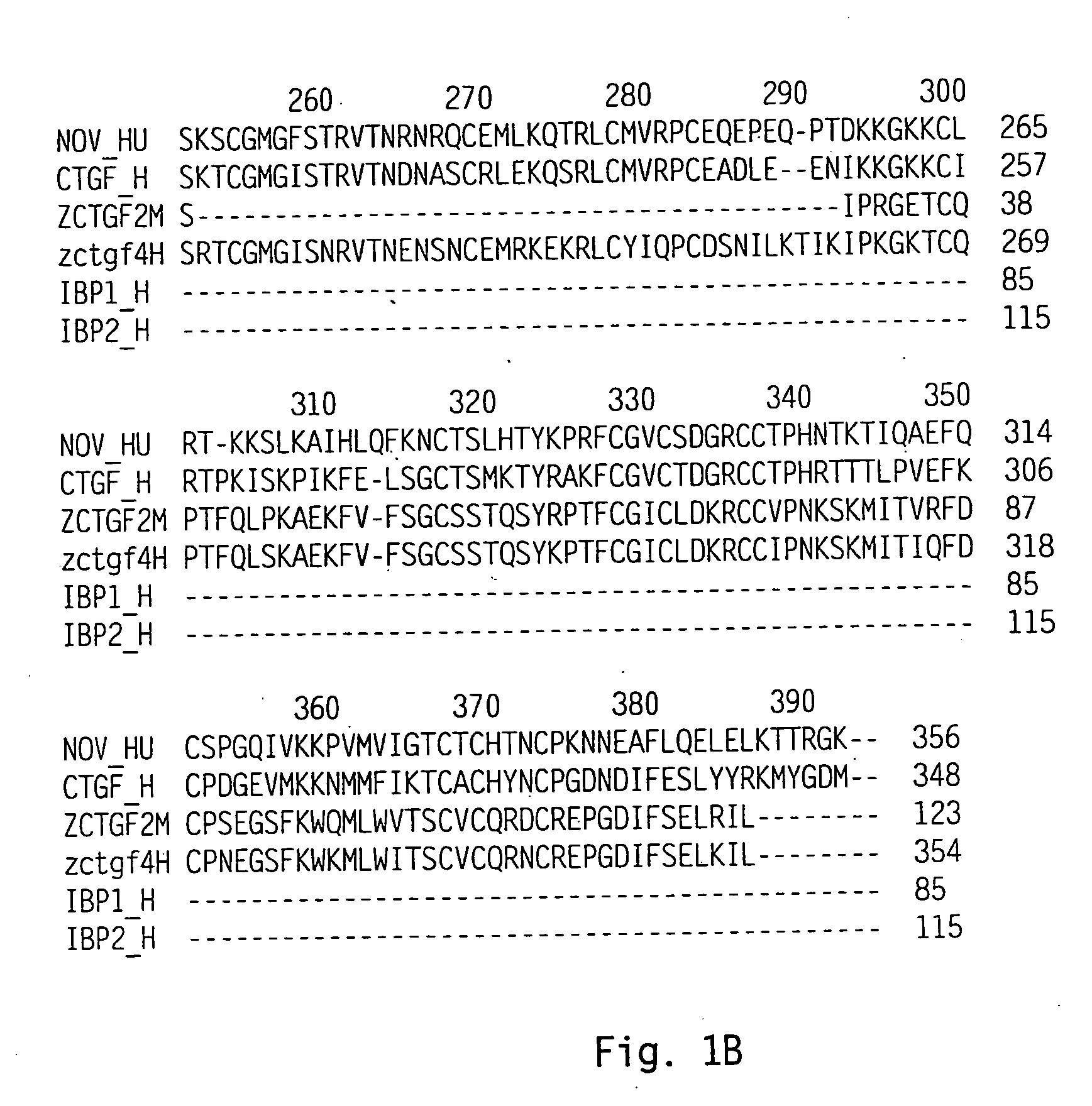
Connective tissue growth factor homologs
InactiveUS20050240014A1Sugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsConnective tissue fiberAntibody expression
This present invention is directed to polypeptide and polynucleotide molecules that encode a new connective tissue growth factor homolog polypeptide. The human polypeptides have been designated zCTGF4 and the mouse orthologs have been designated zCTGF2. The invention also includes antibodies, expression vectors, host cells expressing zCTGF4 and variants. Also included are methods for producing the polypeptides and using the polynucleotides and polypeptides.
Owner:SHEPPARD PAUL +2
Methods for identifying cell cycle regulators
InactiveUS6235467B1Avoid deathAvoid cell deathMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisAntigenProliferating cell nuclear antigen
The present invention relates to a method for identifying a substance capable of disrupting an interaction between (i) a herpes simplex virus (HSV) ICP34.5 polypeptide or a homologue thereof, or a derivative thereof, and (ii) proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) or a homologue thereof, or a derivative thereof. The method comprises: (a) providing an HSV ICP34.5 polypeptide or a homologue thereof, or a derivative thereof, as a first component; (b) providing PCNA, or a homologue thereof, or a derivative thereof, as a second component; (c) contacting the two components with a substance to be tested under conditions that would permit the two components to interact in the absence of the substance; and (d) determining whether the substance disrupts the interaction between the first and second components.
Owner:CRUSADE LAB
Nucleic acid-binding chips for the detection of phosphate deficiency conditions in the framework of bioprocess monitoring
InactiveUS20070281312A1Reliable indicationImprove readabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPhosphoric acidPhosphatase I
The present application relates to nucleic acid-binding chips for monitoring bioprocesses, especially for detecting phosphate deficiency conditions. Said chips support probes for at least three of the following 47 genes: yhcR, tatCD, ctaC, gene for a putative acetoin reductase, spoIIGa, nasE, pstA, spoIIAA, gene for a hypothetical protein, yhbD, cotE, gene for a conserved hypothetical protein, yurl, spoVID, gene for a putative aromatic-specific dioxygenase, yhbE, gene for a putative benzoate transport protein, pstBB, spoIIIAH, gene for a hypothetical protein, spoIIQ, spoIIIAG, yvmA, gene for a putative ribonuclease, dhaS, yrbE, gene for a putative decarboxylase / dehydratase, htpG, yfkH, spoIIAB, spoIIIAF, alsD, gdh, yfkN, pstC, yfmQ, pstBA, dhaS homolog, gene for a putative phosphatase, phy, cypX, alsS, phoD, pstS, phoB, yvnA, yvmC, the total number of phosphate metabolism-specific different probes on the nucleic acid-binding chips not exceeding 100. The present application further relates to the use of corresponding gene probes, in particular on such chips, and to corresponding methods and possible uses.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
Rna interference mediated inhibition of btb and cnc homology 1, basic leucine zipper transcription factor 1 (bach 1) gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (sina) sequence listing
The present invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods for the study, diagnosis, and treatment of traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of Bach1 gene expression and / or activity, and / or modulate a Bach1 gene expression pathway. Specifically, the invention relates to double-stranded nucleic acid molecules including small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules that are capable of mediating or that mediate RNA interference (RNAi) against Bach1 gene expression.
Owner:SCHERING AG
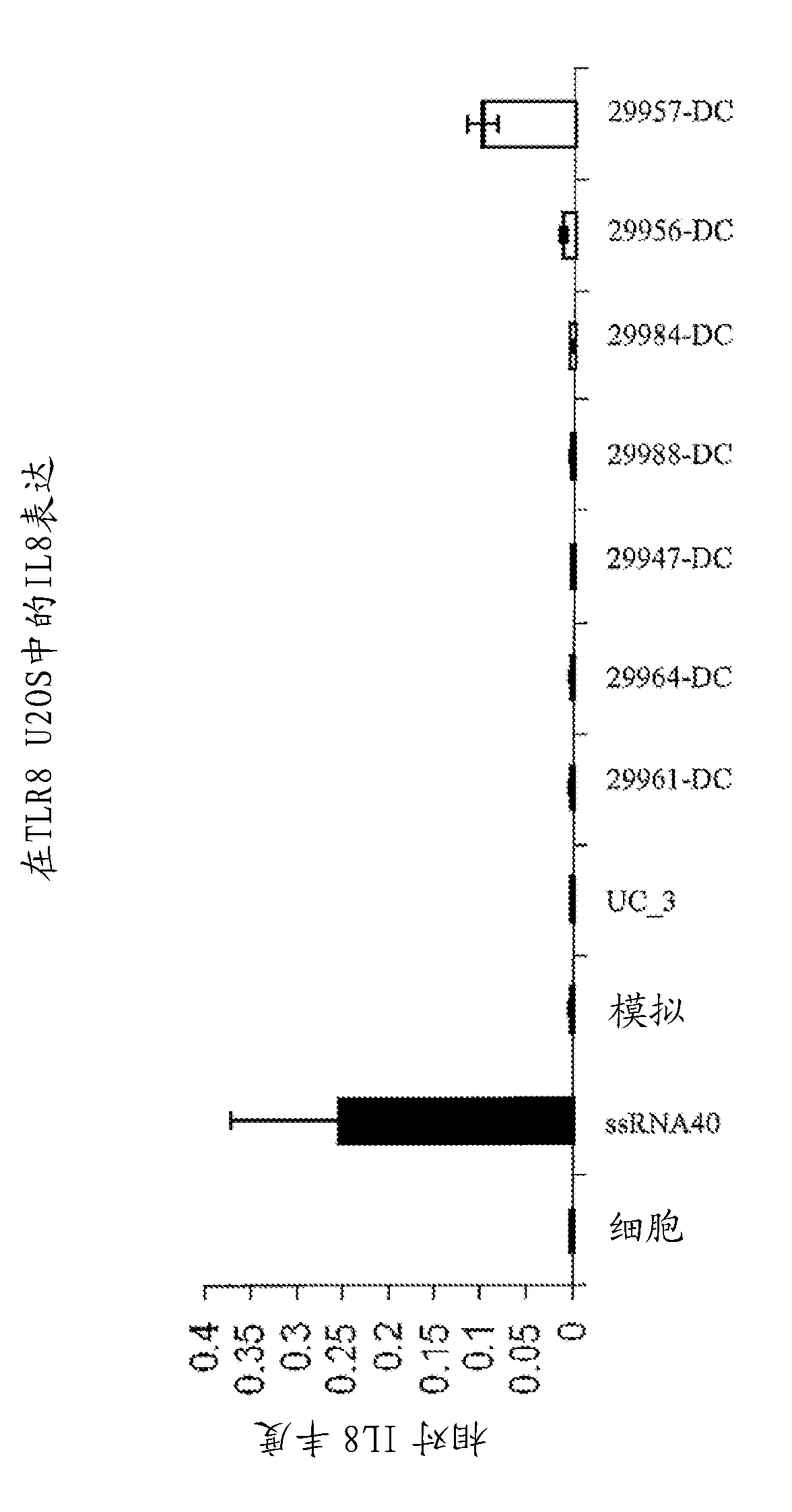
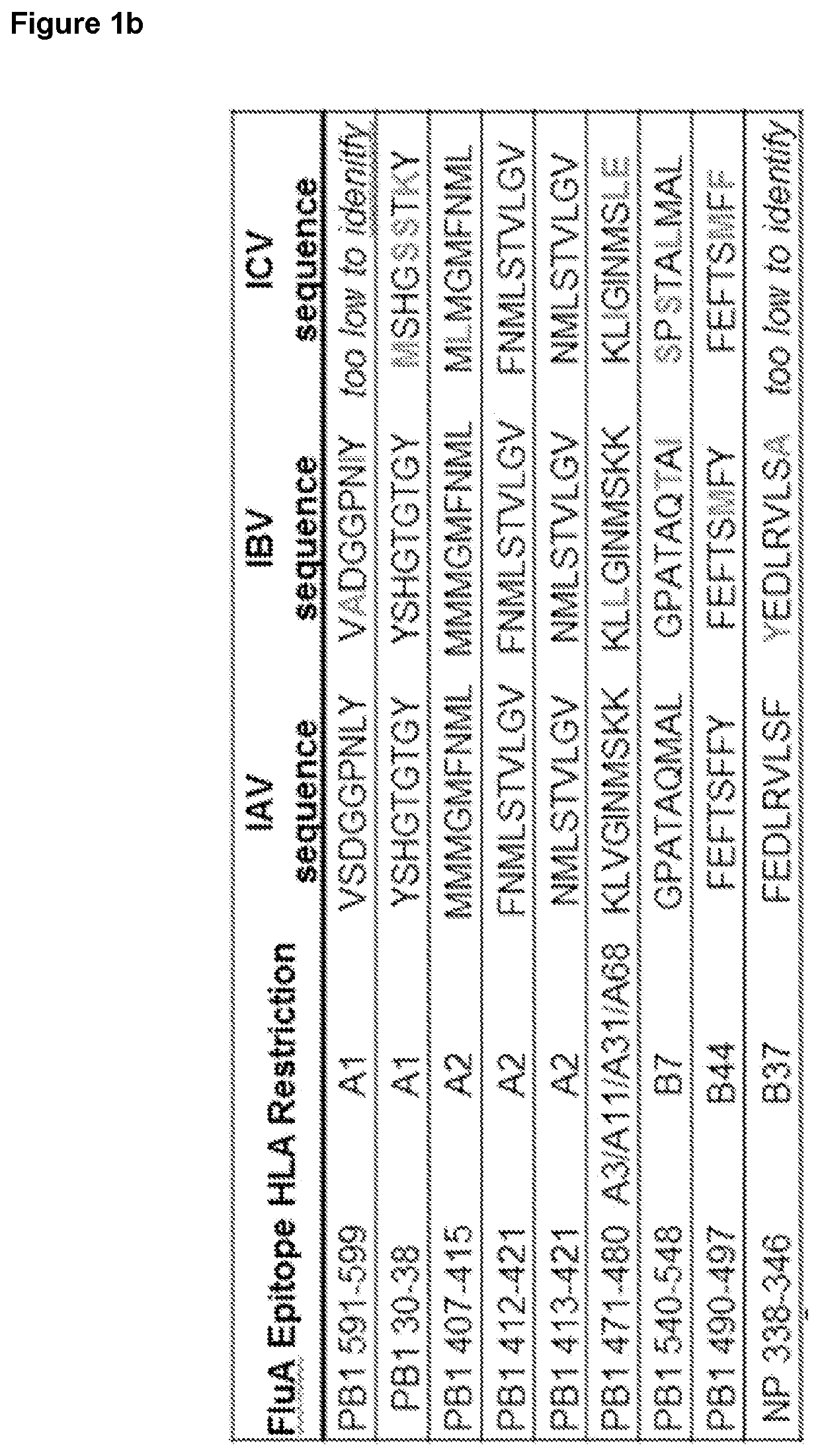
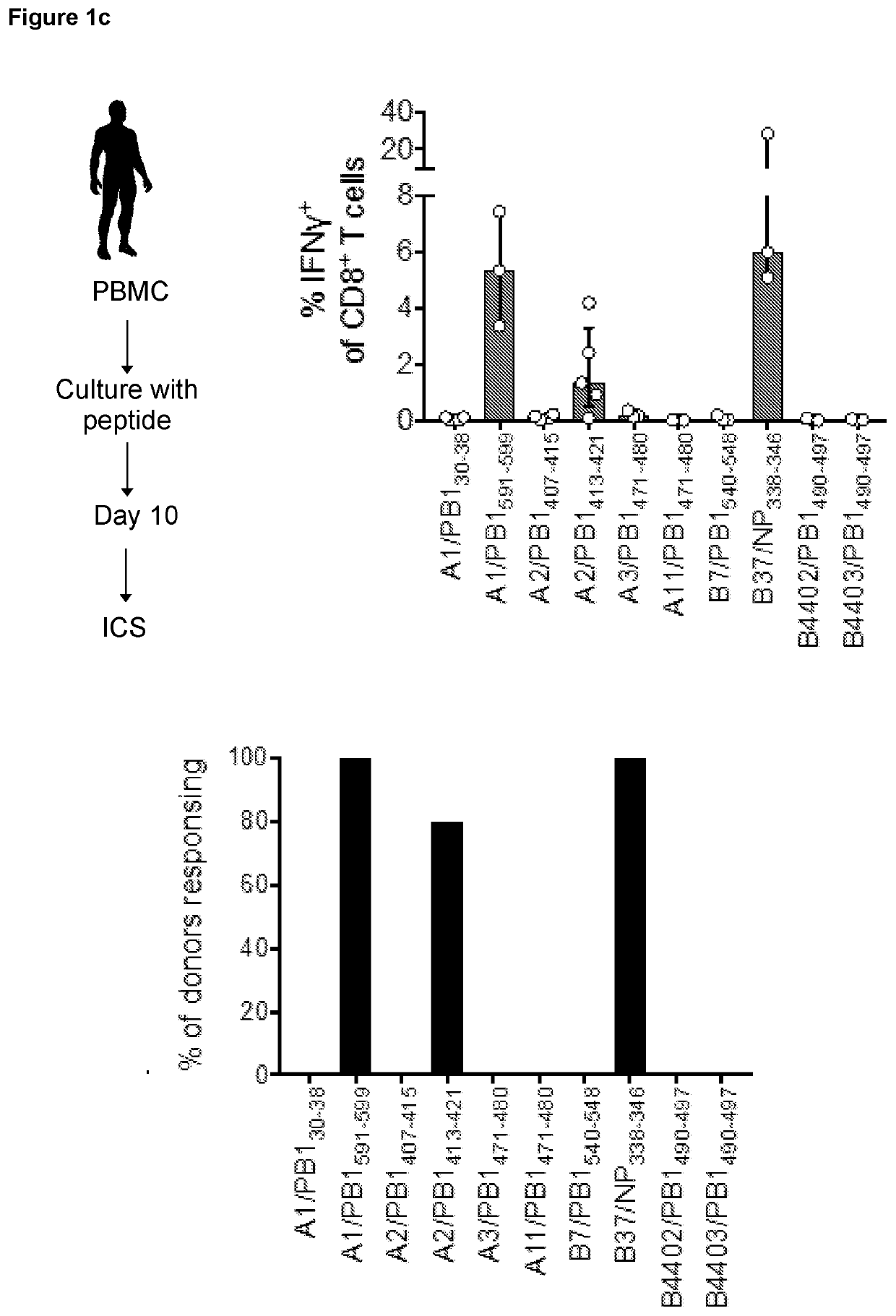
Methods and compositions for preventing influenza infection
ActiveUS20200368345A1SsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsViral infectionInfluenza a
The present invention provides novel methods and compositions for use in preventing infection with at least one type of influenza virus, including the use of peptides or compositions comprising a peptide comprising, consisting or consisting essentially of an amino acid sequence selected from the group of sequences as shown in SEQ ID Nos: 1 to 53, or functional derivatives or homologues thereof.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE
Method for directional accumulation of specific homolog components of antimicrobial lipopeptides of bacilli
InactiveCN105695538AImprove efficacyMicroorganism based processesFermentationSurfactinAnti bacterial
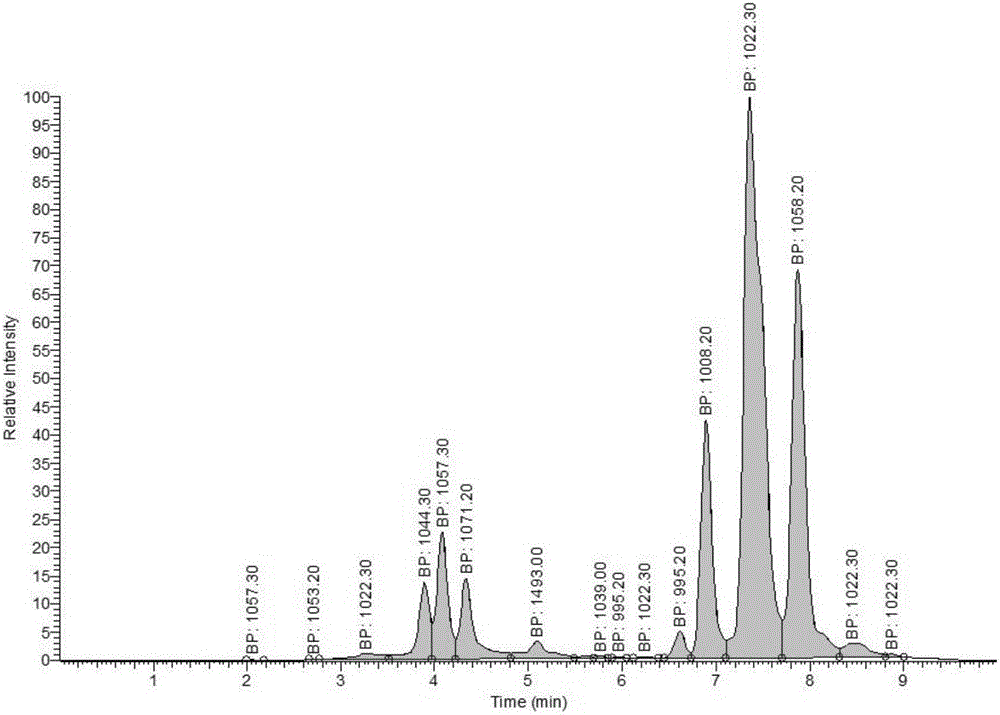
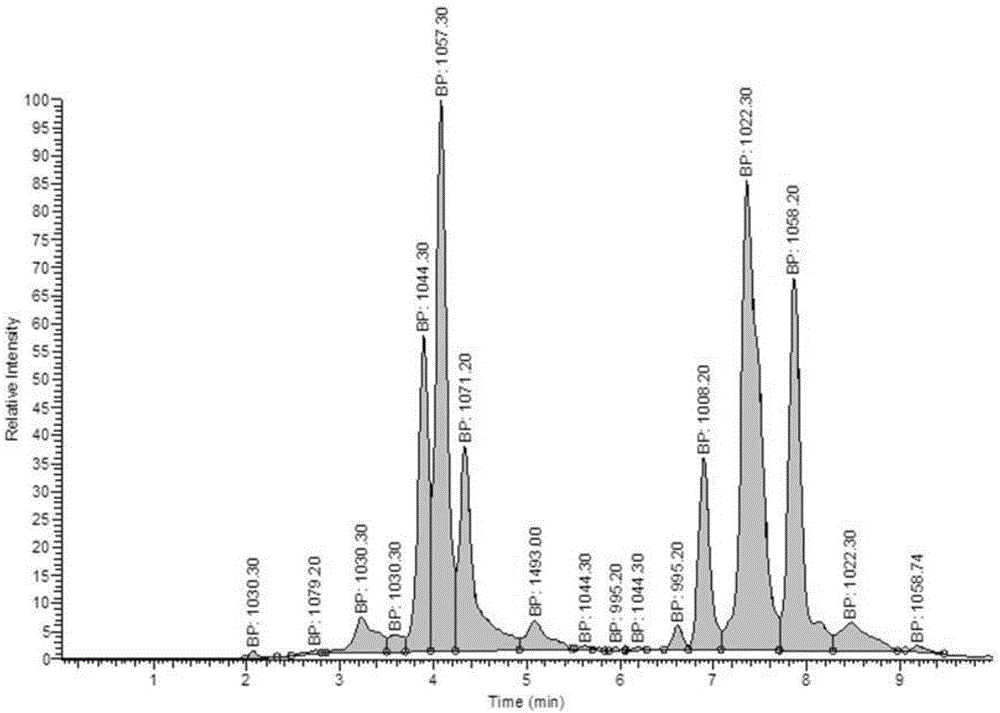
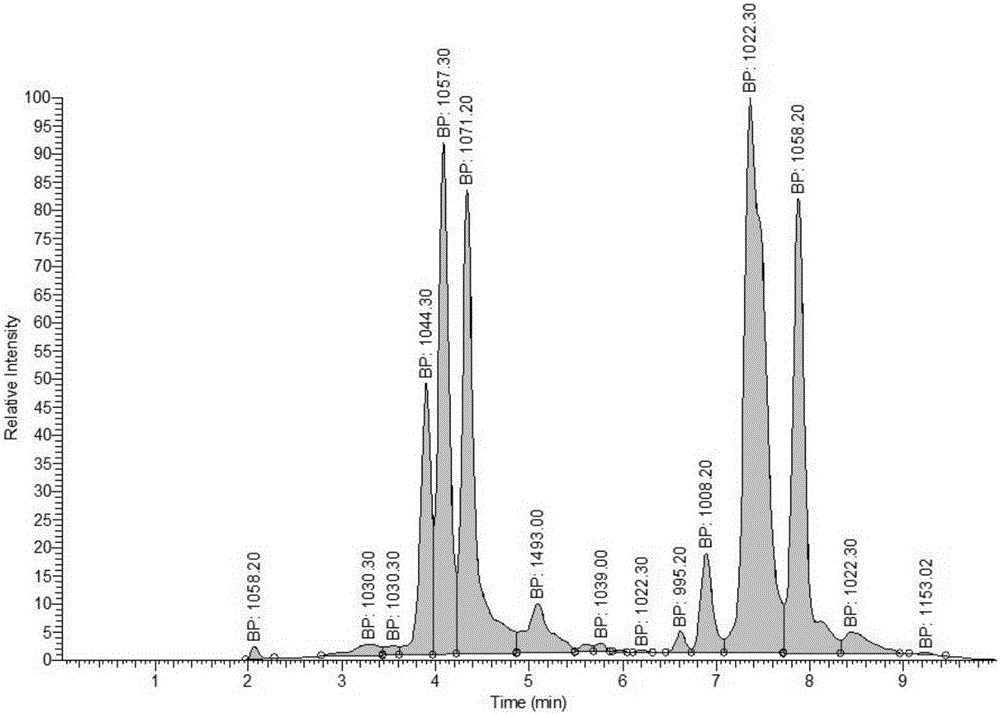
The invention belongs to the technical field of fermentation and discloses a method for directional accumulation of specific homolog components of antimicrobial lipopeptides of bacilli. Bacillus natto NT-6 strains serve as original strains, Landy serves as a culture medium, culture is performed at 28-32 DEG C for 36-48 h under the condition of 160 r / min, and the specific components comprise Iturins containing homologs with cytoplasmic-nuclear ratios being 1044.30, 1057.20 and 1071.20 and Surfactins containing homologs with cytoplasmic-nuclear ratios being 995.20, 1008.20, 1022.30 and 1058.20. With the adoption of the method, directional accumulation can be performed on the specific homolog components of the antimicrobial lipopeptides of the bacilli by controlling the fermentation culture medium and fermentation conditions, lipopeptide products comprising different specific homolog components and having specific ratios of the specific homolog components can be produced, so that effects of the lipopeptide products are improved, and the use range of the lipopeptide products is expanded.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY
Plants With Altered Root Architecture, Related Constructs and Methods Involving Genes Encoding Leucine Rich Repeat Kinase (LLRK) Polypeptides and Homologs Thereof
InactiveUS20090130685A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant rootsLeucine-rich repeat
Isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides and recombinant DNA constructs particularly useful for altering root structure of plants, compositions (such as plants or seeds) comprising these recombinant DNA constructs, and methods utilizing these recombinant DNA constructs. The recombinant DNA construct comprises a polynucleotide operably linked to a promoter functional in a plant, wherein said polynucleotide encodes a polypeptide useful for altering plant root architecture.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO +1
Mus101 and homologue thereof
InactiveUS20030170655A1Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsDrosophila ornatifronsAntiendomysial antibodies
Plynucleotides encoding a novel Drosophila gene product designated mus101 and homologues thereof as well as mus101 polypeptides are provided. Polynucleotide probes derived from the nucleotide sequence of mus101 and antibodies that bind to mus101 protein are also provided as well as assays for identifying substances that regulate mus101 function.
Owner:CYCLACEL
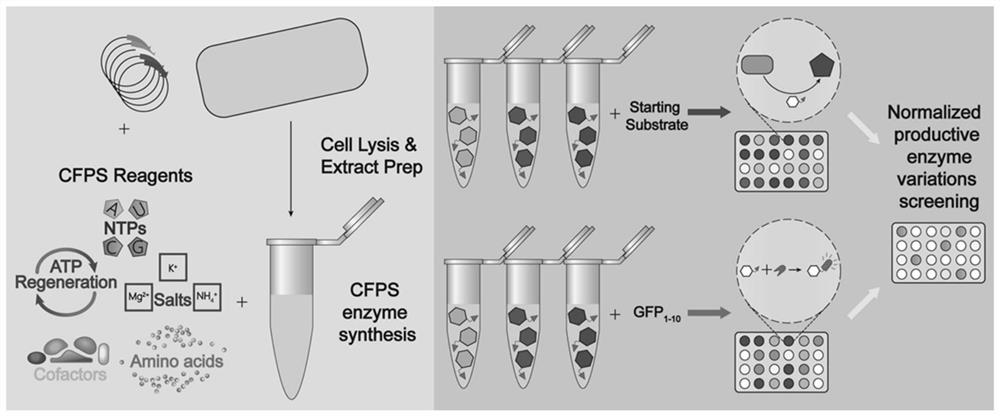
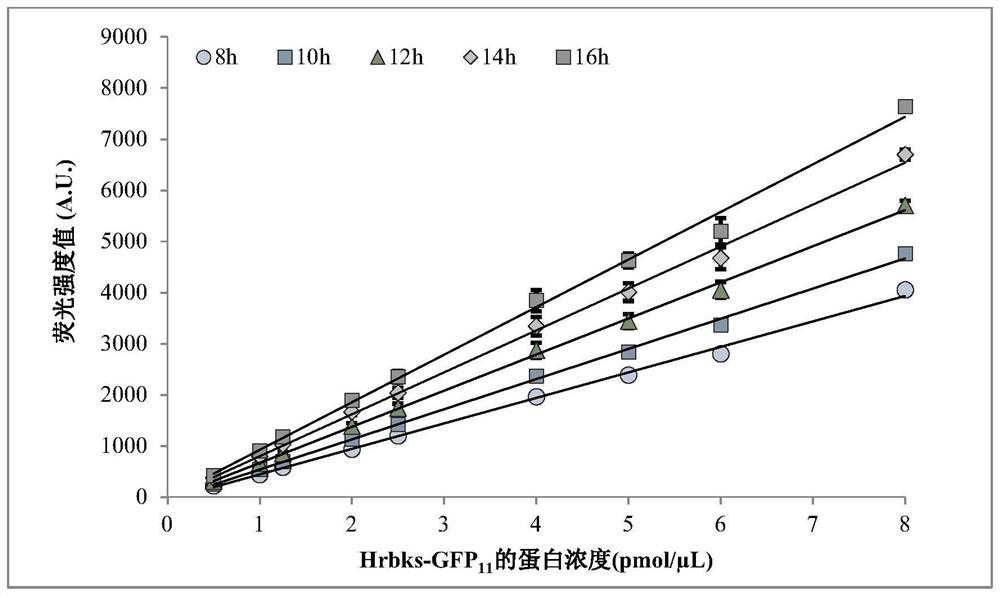
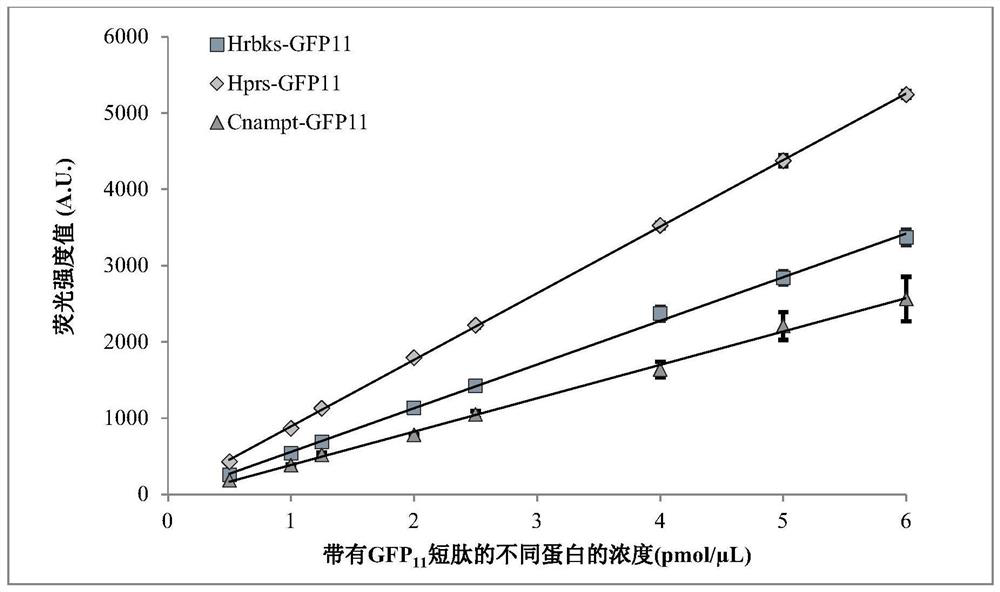
Method for quantitatively detecting target protein yield of cell-free protein synthesis system and method for screening zymoprotein with high catalytic activity
PendingCN114019169AQuick checkNo action requiredBacteriaMicroorganism based processesProtein targetFree protein
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively detecting the target protein yield of a cell-free protein synthesis system and screening zymoprotein with high catalytic activity. According to the method for quantitatively detecting the yield of the target protein in the CFPS system, the expression quantity of the target protein in the CFPS system can be rapidly analyzed by segmenting the intensity value of fluorescence emitted by spontaneous binding of fluorescent protein, and rapid detection of the expression quantity of the target protein in the CFPS system is facilitated; meanwhile, based on the method, the enzyme homologues with high catalytic activity can be quickly screened by calculating the ratio of the quantity of products obtained by catalysis of each enzyme protein to the fluorescence intensity value after spontaneous binding of segmented fluorescent protein, and a conventional large intestine transformation-expression-purification process is not needed, so that the time and the material cost are greatly saved, the screening speed is increased, and moreover, the screening leakage risk of the high-catalytic-activity protein caused by too low protein expression quantity is avoided, and rapid and accurate screening of the high-catalytic-activity zymoprotein is facilitated.
Owner:林影 +1
Disintegrin homologs
The present invention relates to polynucleotide and polypeptide molecules for zdint1, a novel member of the Disintegrin Proteases. The polypeptides, and polynucleotides encoding them, are believed to be cell-cell interaction modulating and may be used for delivery and therapeutics. The present invention also includes antibodies to the zdint1 polypeptides.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
Regulation of gene expression through manipulation of mRNA splicing and its uses
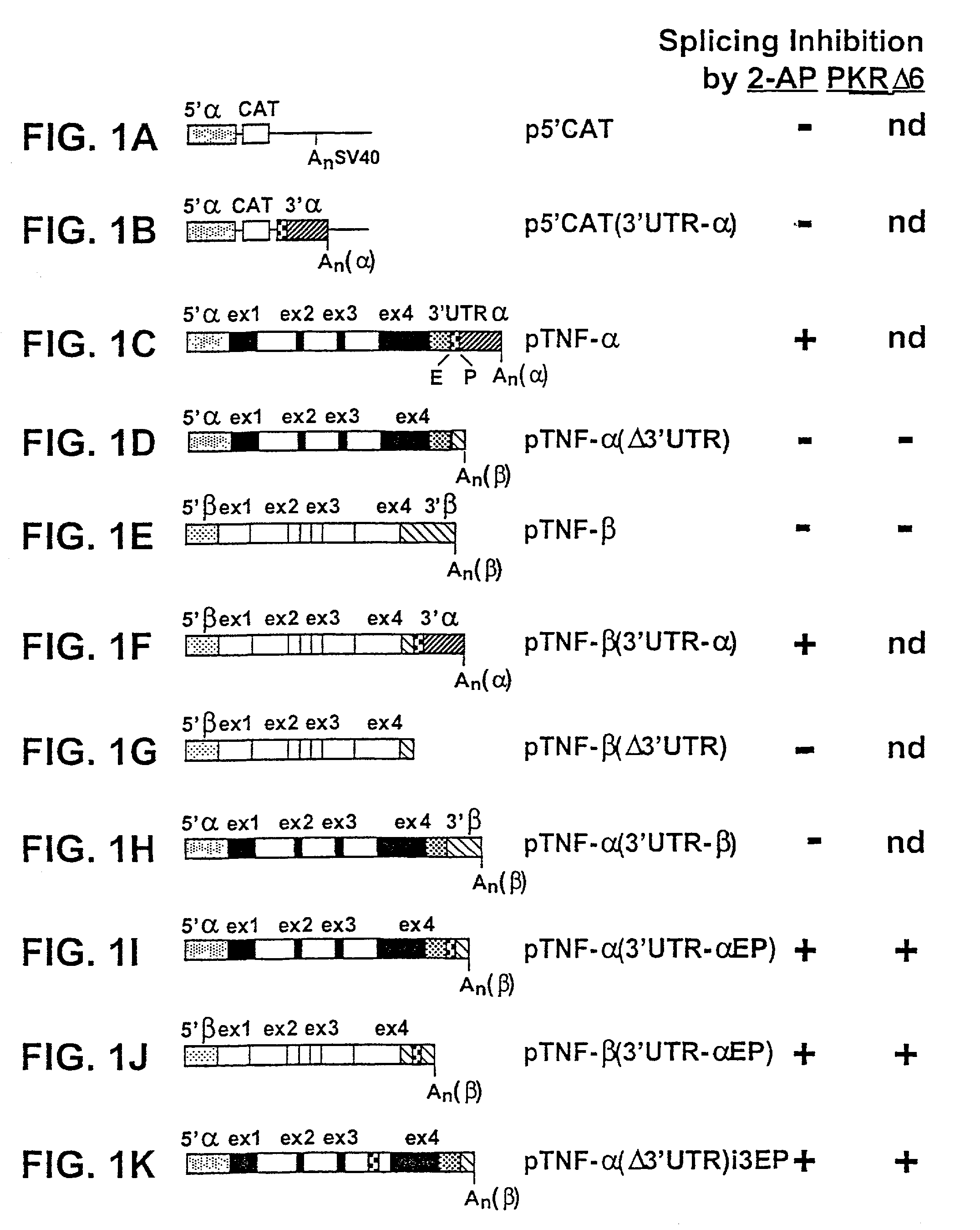
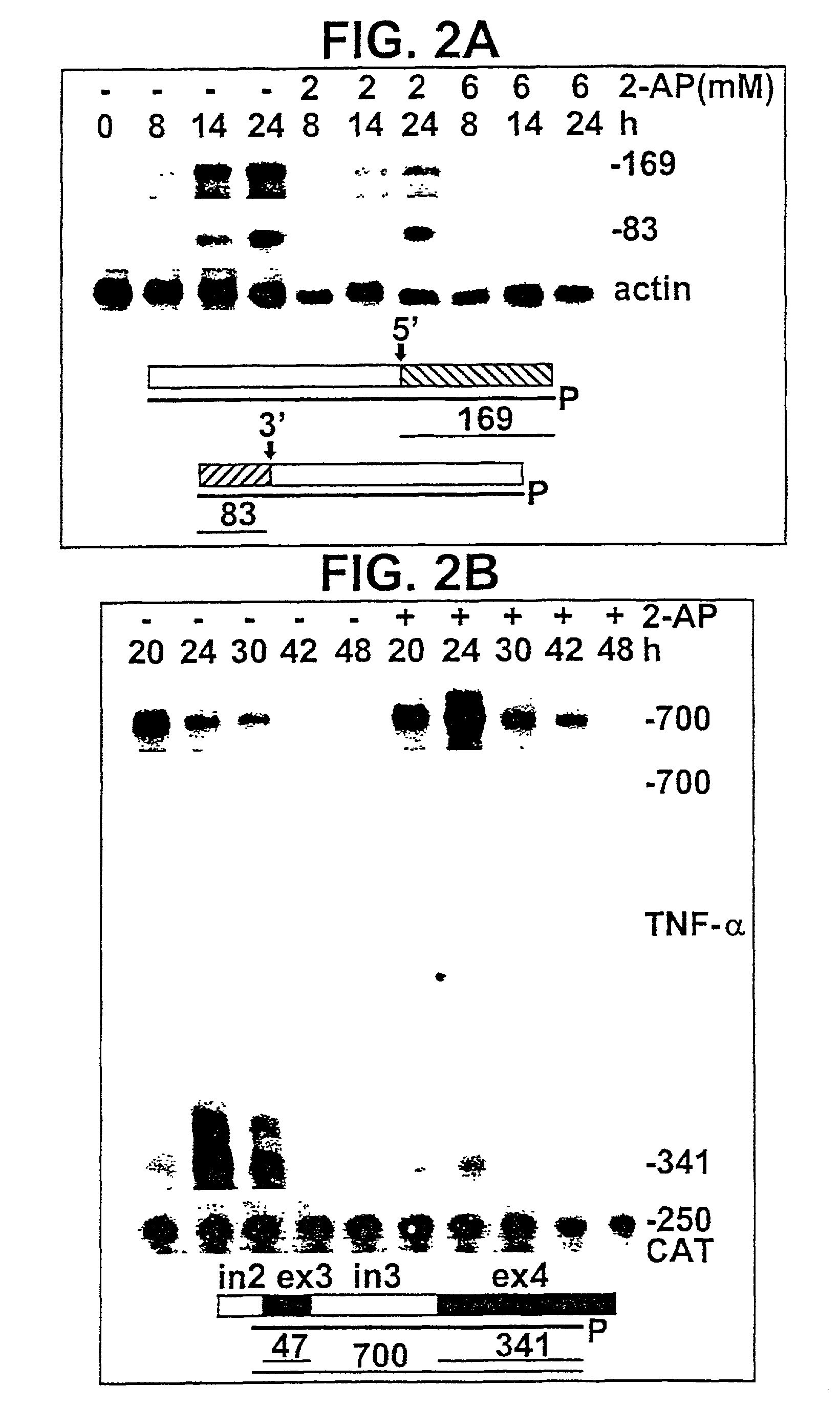
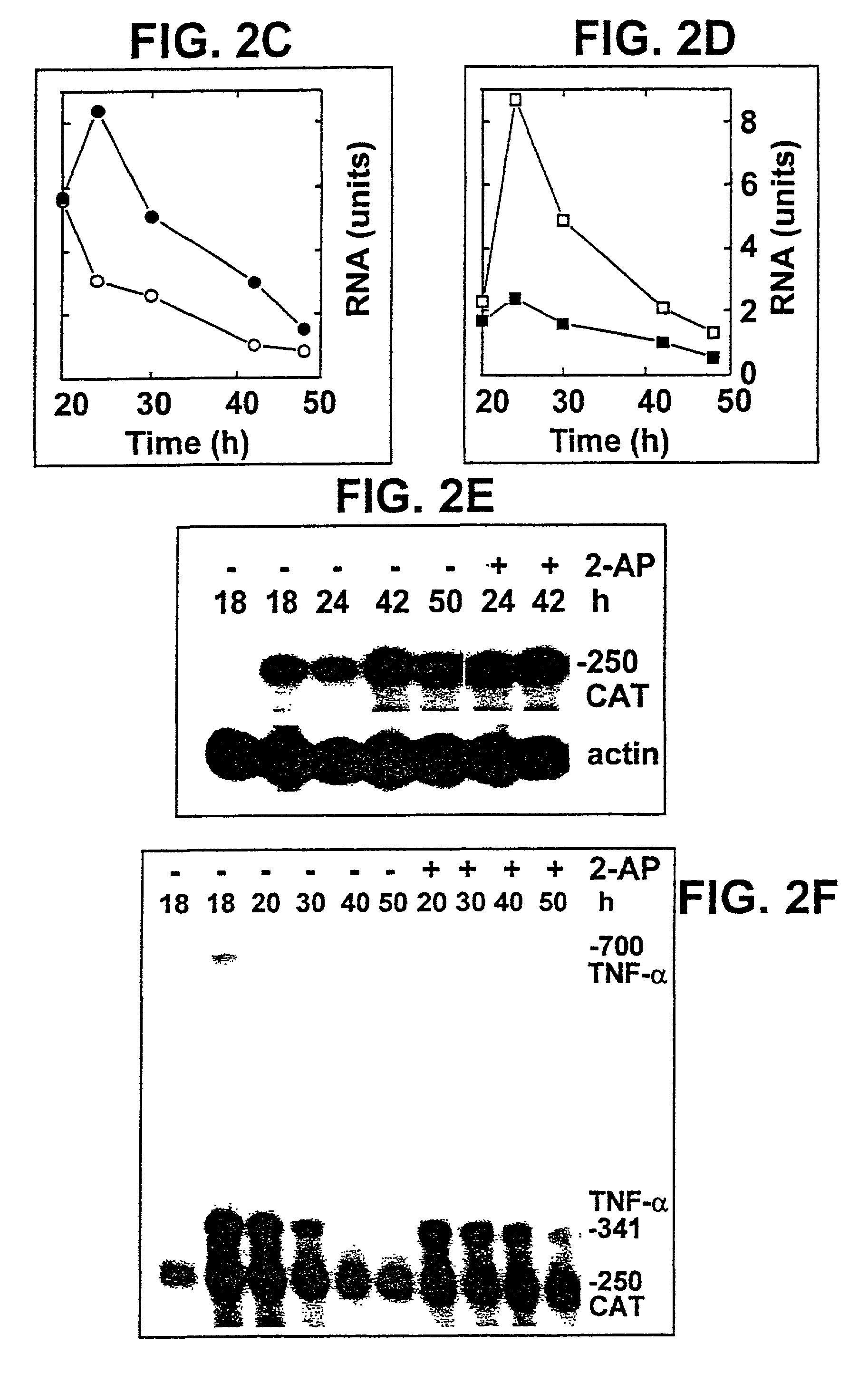
A cis-acting nucleotide sequence which is capable of rendering the removal of introns from a precursor transcript encoded by a gene, which gene harbors at least one such cis-acting nucleotide sequence, occurring during the production of mRNA of a gene, dependent upon activation of a trans-acting factor. The trans-acting factor is an RNA-activated protein kinase which is capable of phosphorylating the α-subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2. The trans-acting factor is preferably, the RNA-activated protein kinase (PKR). The cis-acting nucleotide sequence can be derived from the 3′ untranslated region of the human tumor necrosis factor α gene (TNF-α3′-UTR) and may comprise the nucleotide sequence as denoted by SEQ ID NO:1 or biologically functional fragments, derivatives, mutants and homologues thereof.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREW UNIV OF JERUSALEM LTD
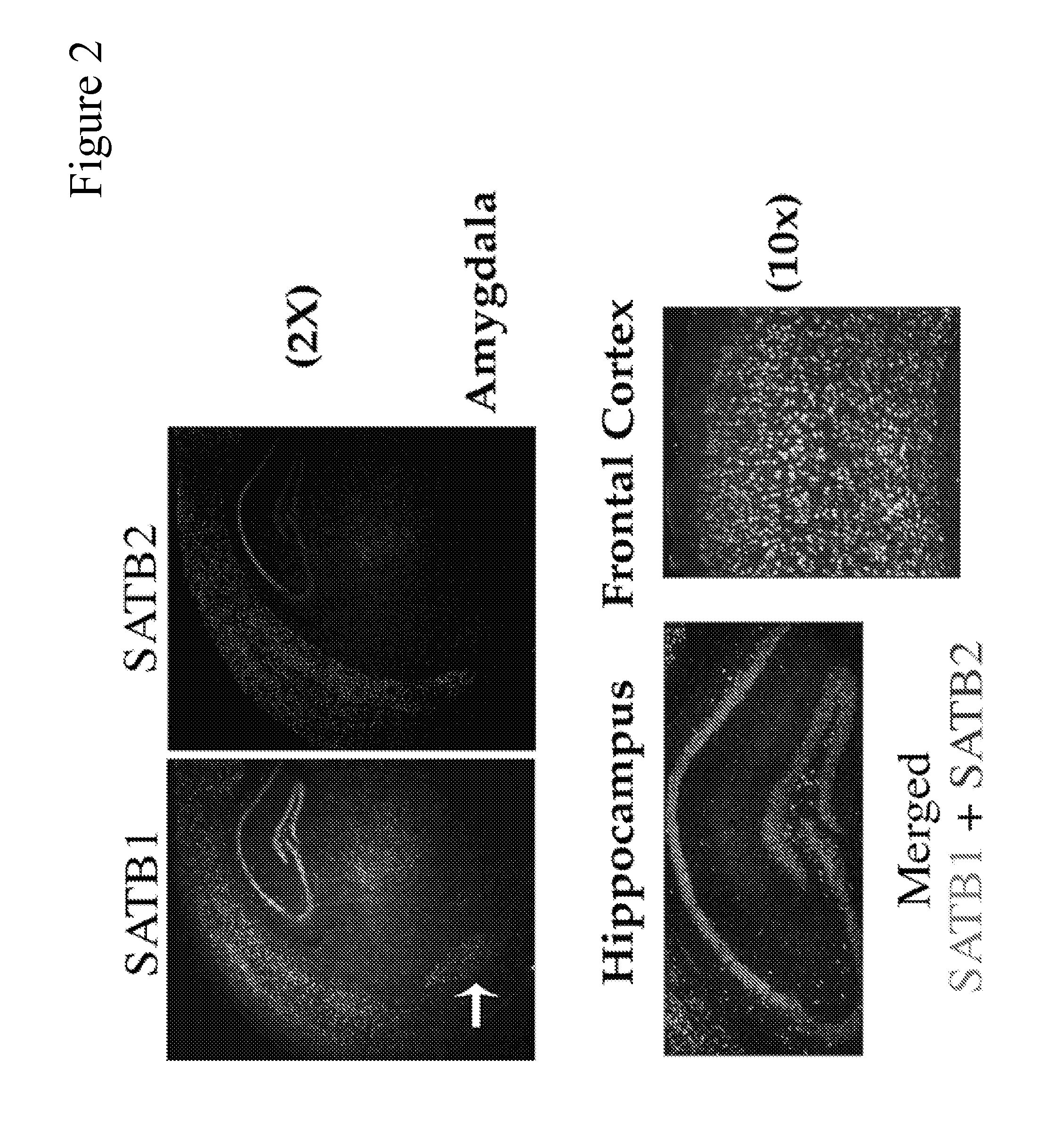
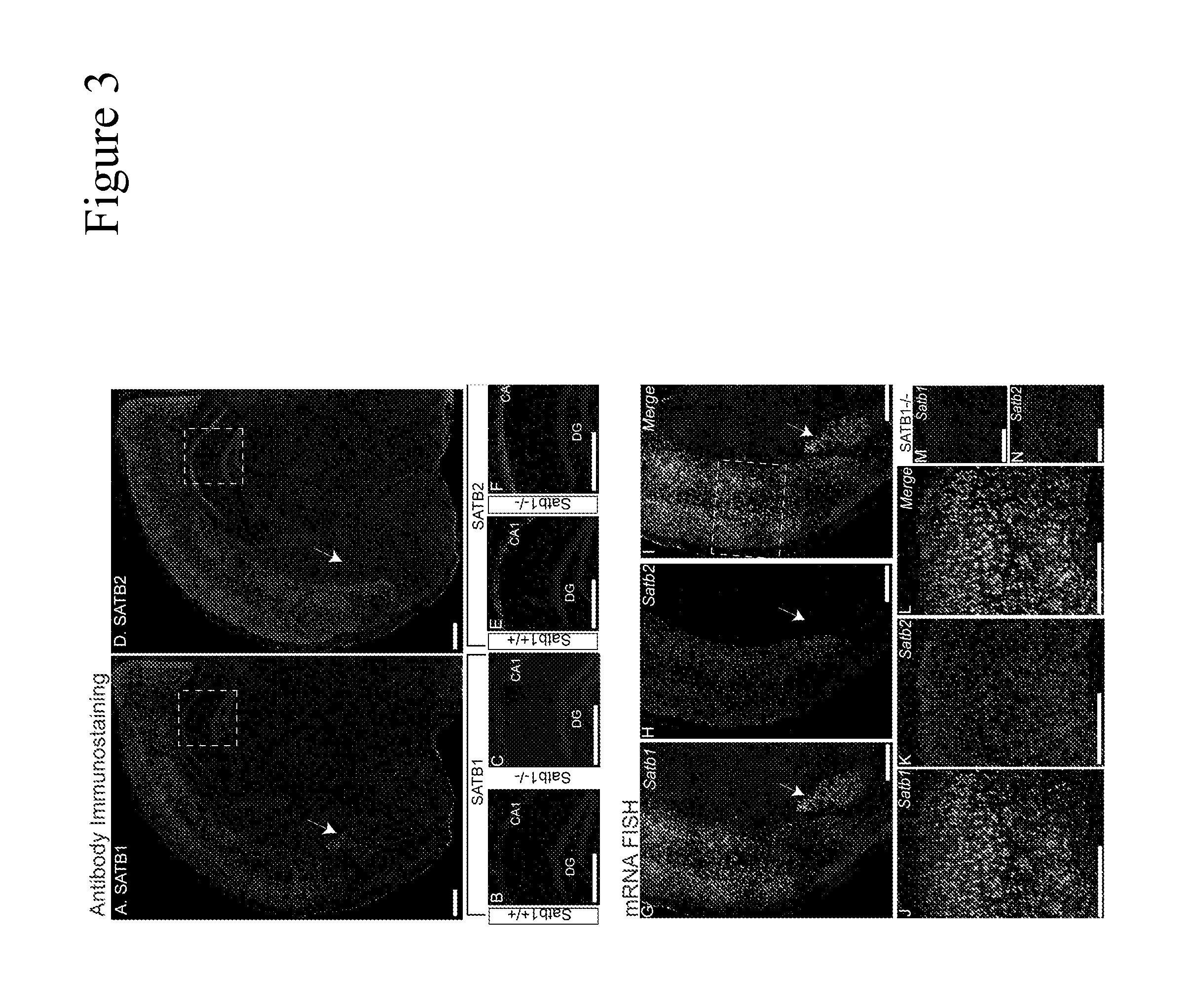
Potential Prognostic Markers and Therapeutic Targets for Neurological Disorders
We recently found that Satb1 is expressed highly by mature neurons in specific regions of the postnatal brain. Satb2, a homolog of Satb1, is expressed at low levels in the postnatal brain. Neurons respond to external stimuli and rapidly and dynamically change their expression. Satb1 has been found to directly regulate a set of genes in the postnatal brain, presumably playing a crucial role as a ‘genome organizer’ for brain function and behaviors. Satb2 may also have a similar function, even though it is expressed at low levels in the postnatal brain. The present invention describes compositions, reagents and tools using wild type and variant SATB1 and SATB2 genes and proteins for use in diagnosis, prognosis and therapeutics in neurological dysfunction and psychiatric disorders.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
OX2 receptor homolog
InactiveCN101255425AAntibacterial agentsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsOX2 RECEPTORAntibody
The present invention provides OX2 receptor homologs. The present invention also provides nucleic acids encoding mammalian, e.g., primate, receptors of OX2, purified proteins and fragments thereof. Antibodies, both polyclonal and monoclonal, are also provided. Method of using the compositions for both diagnostic and therapeutic utilities are described.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL +1
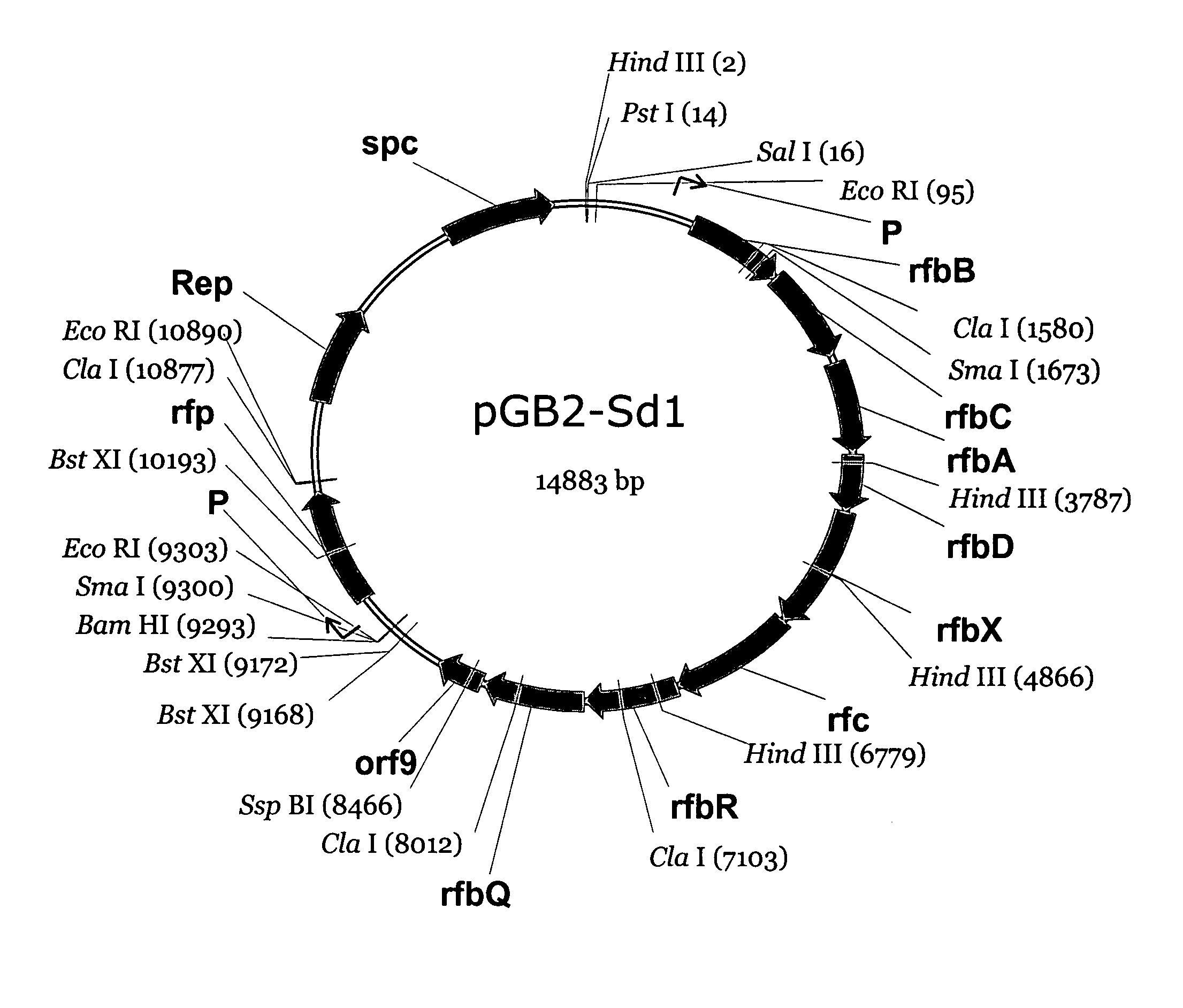
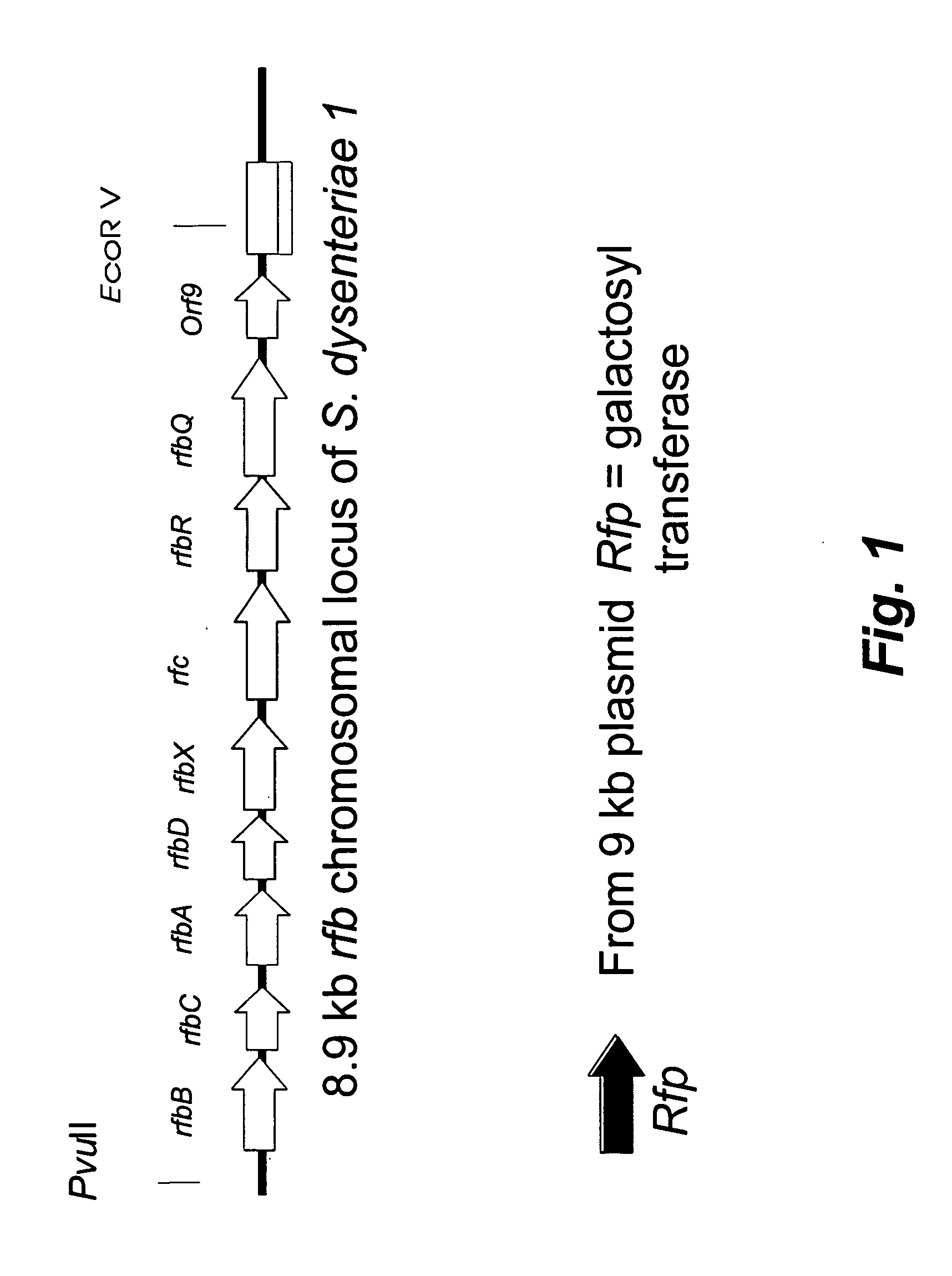
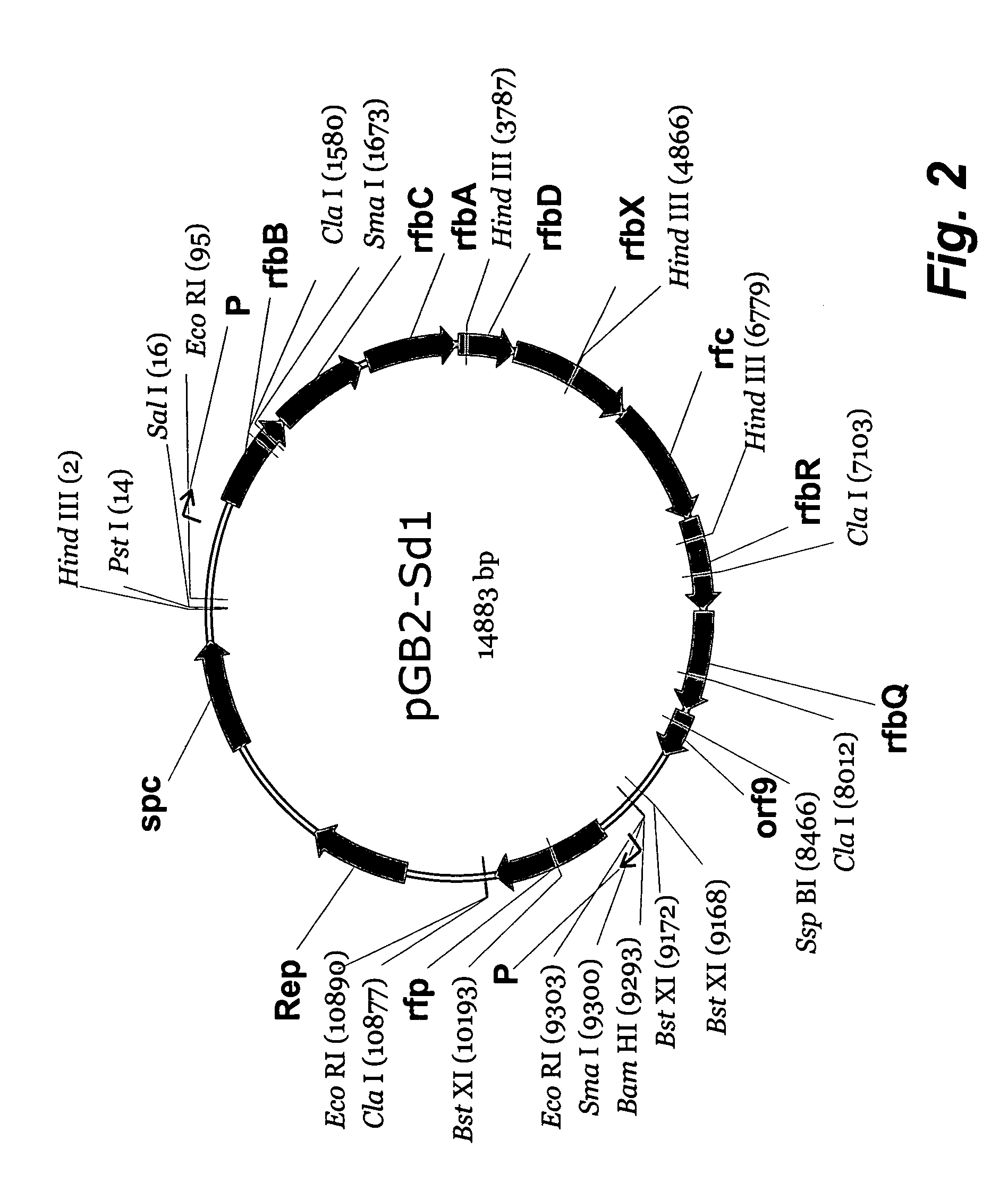
Live, Oral Vaccine for Protection Against Shigella Dysenteriae Serotype 1
The invention relates to Salmonella typhi Ty21a comprising core-linked Shigella dysenteriae type 1 O-specific polysaccharide (O-Ps) and DNA encoding O antigen biosynthesis, said DNA selected from the group consisting of: a) the DNA sequence set out in any one of SEQ ID NOs: 1 and 2 and species homologs thereof; b) DNA encoding S. dysenteriae polypeptides encoded by any one of SEQ ID NOs: 1 and 2, and species homologs thereof; and c) DNA encoding a O antigen biosynthesis gene product that hybridizes under moderately stringent conditions to the DNA of (a) or (b); and related sequences, compositions of matter, vaccines, methods of using, and methods of making.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
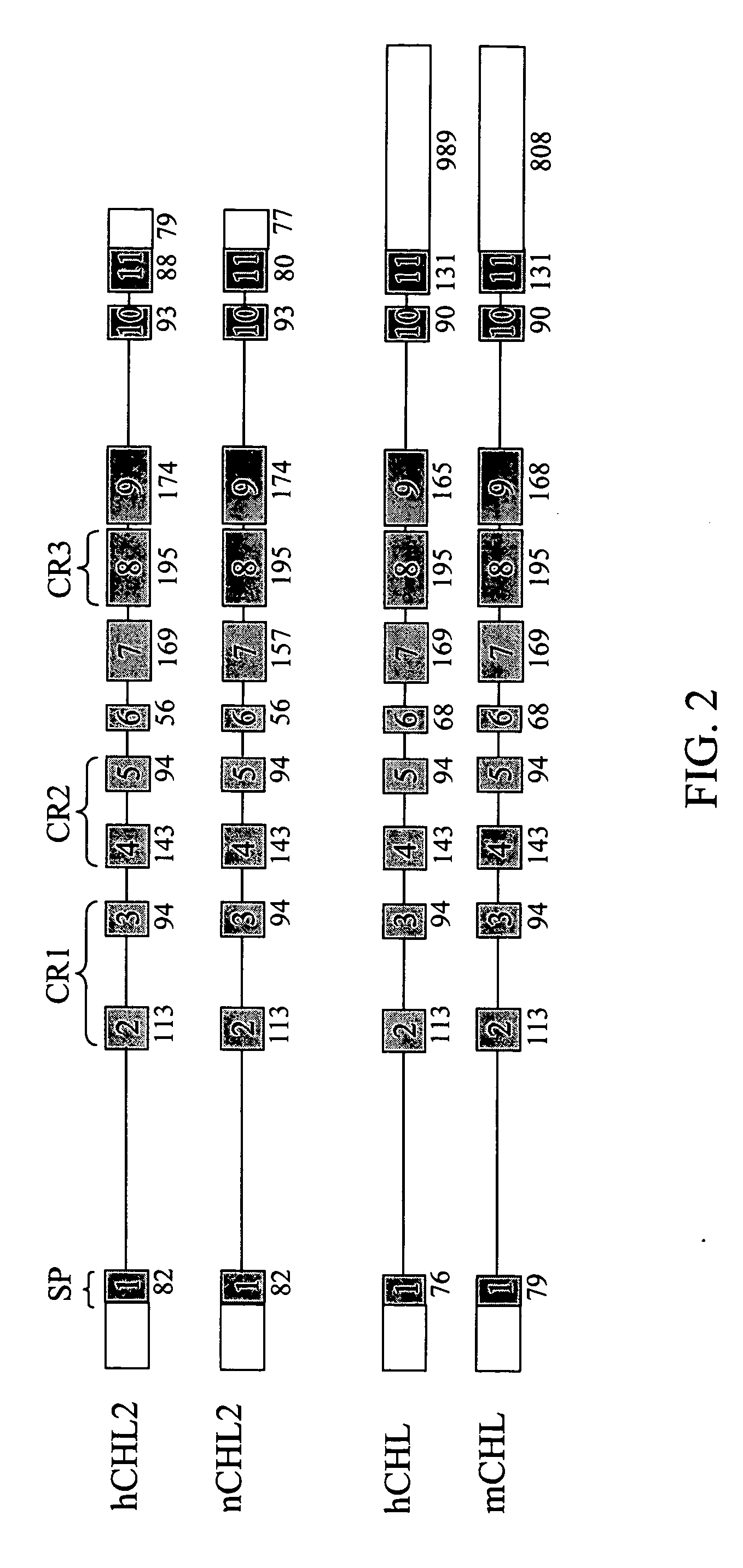
Chordin-like homologs
InactiveUS20050118615A1High degreeImprove the level ofNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention concerns several splice variants of a Chordin like homologues (CHL2) and depicts their nucleic acid and amino acid sequences, vectors and host cells containing said nucleic acid sequences and antibodies reactive with the amino acid sequences. The invention also concerns pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment of a plurality of diseases, comprising nucleic acid sequences, amino acid sequences, expression vectors and antibodies. The invention also concerns methods for detecting the above nucleic acid or amino acid sequences or antibodies in a biological sample.
Owner:COMPUGEN
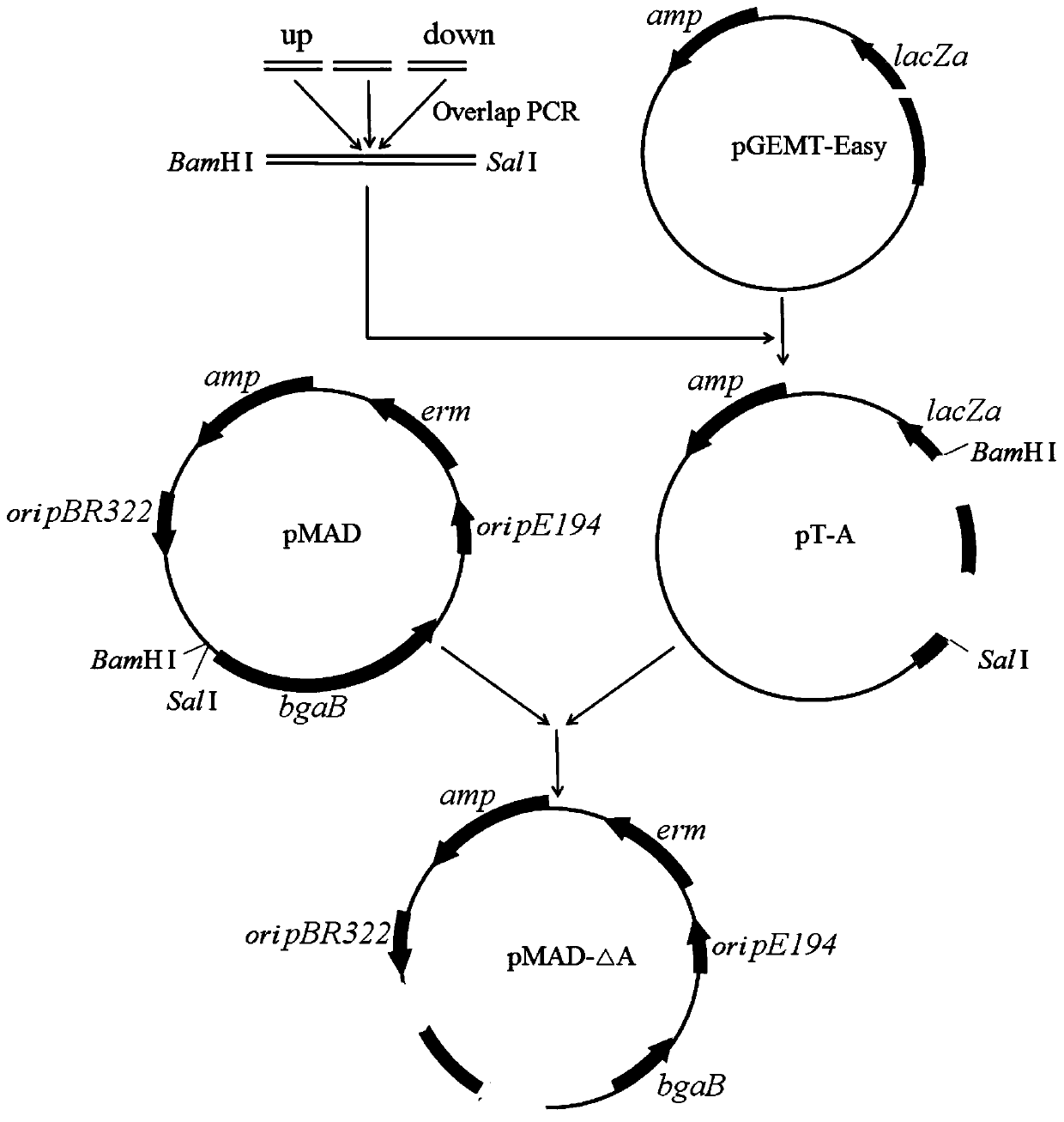
Method for regulating and controlling components of polymyxin B homolog
ActiveCN111041037ARaise the ratioReduce the ratioMicroorganism based processesPolymyxinsBiotechnologyMicrobiology
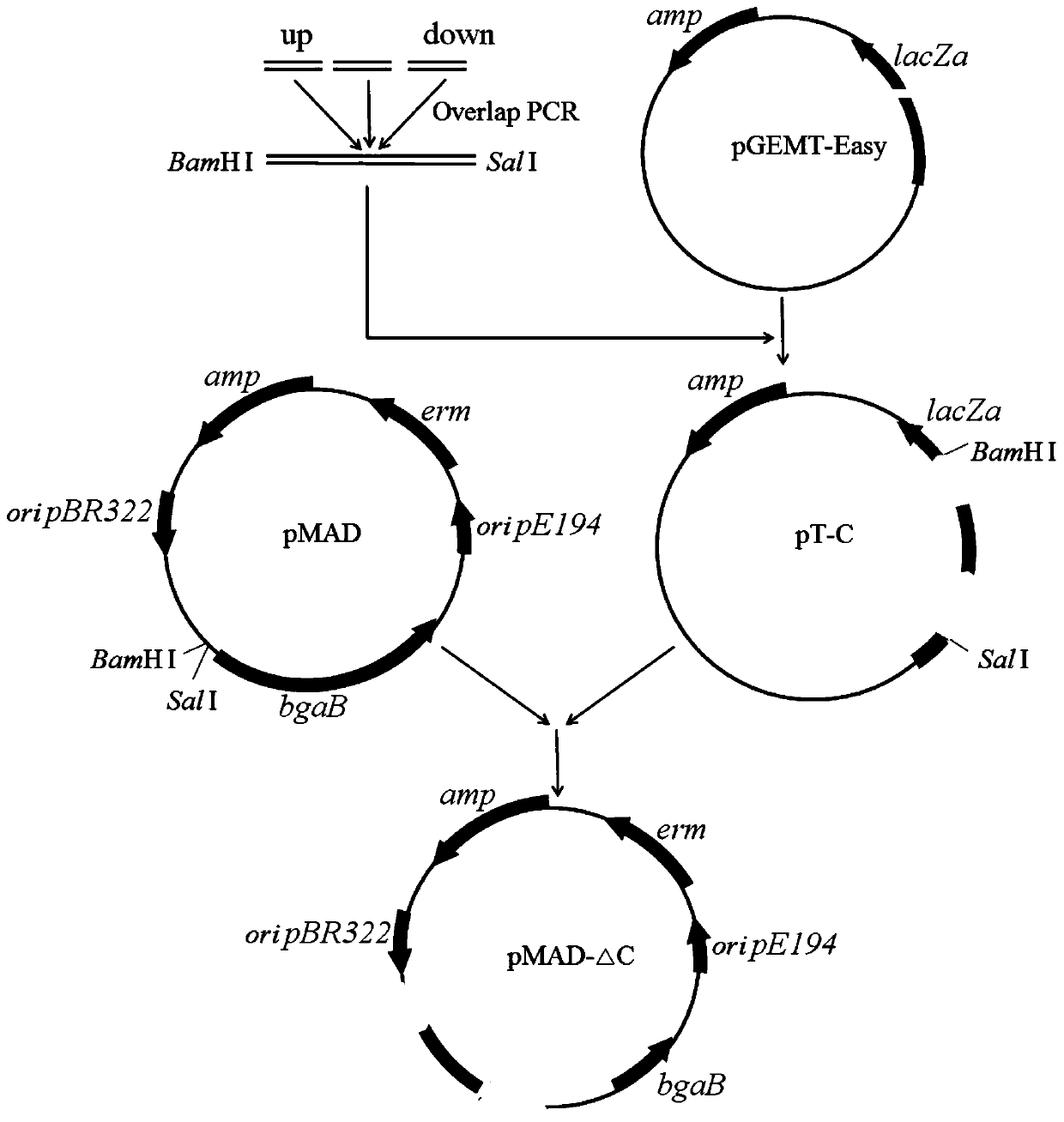
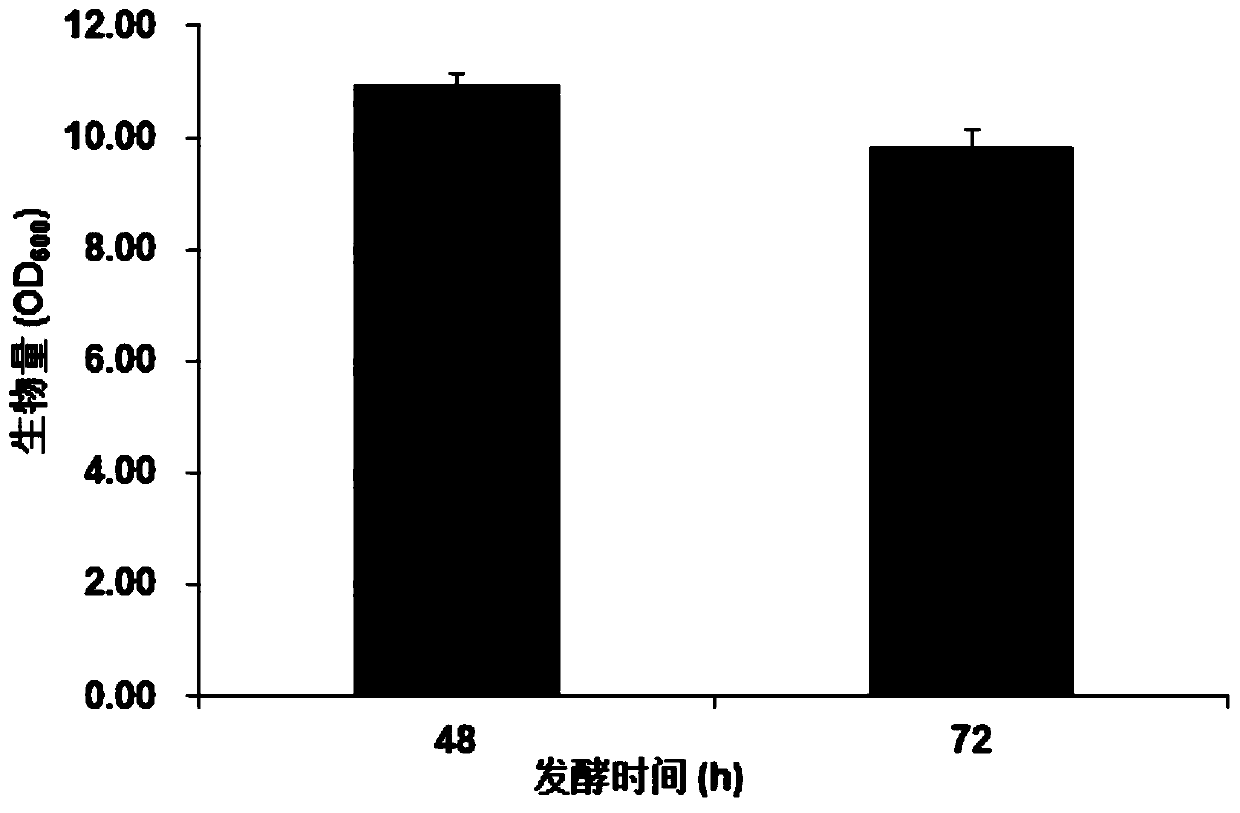
The invention discloses a method for regulating and controlling the components of a polymyxin B homolog. The method comprises the following steps: (1) constructing pMAD-DeltaA and pMAD-DeltaC; (2) transforming pMAD-DeltaA into CJX518 strains, conducting screening to obtain successfully-transformed strains, performing culturing and subculturing to obtain plasmid-lost strains, verifying the plasmid-lost strains as structural domain-replaced strains 518-A through PCR sequencing, transforming pMAD-DeltaC into the CJX518 strains, screening the pMAD-DeltaC transformed strains 518-A, carrying out culturing and subculturing to obtain plasmid-lost strains, and verifying the plasmid-lost strain as structural domain-replaced strains 518-AC through PCR sequencing; (3) carrying out seed culture to obtain secondary seeds; and (4) producing polymyxin B by inoculating the secondary seeds into a fermentation medium, and carrying out fermenting for 72 hours. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the components of the polymyxin B homolog are regulated and controlled, a ratio of B1 to B2 is increased, and a ratio of B3 to B1-1 is reduced.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
A kind of methionine sulfoxide reductase and its coding gene, preparation method and application
ActiveCN111454917BFacilitate the realization of large-scale industrial productionLower acquisition costsSenses disorderNervous disorderGenetic engineeringDrug biological activity
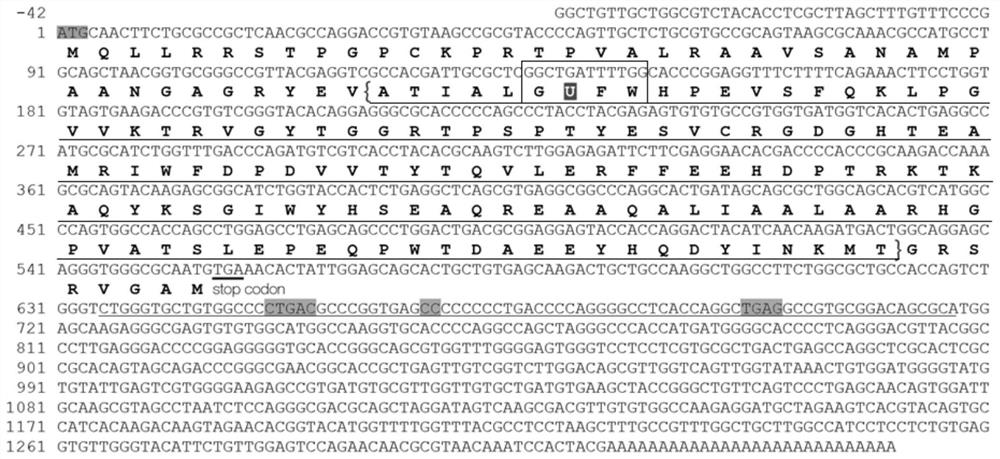
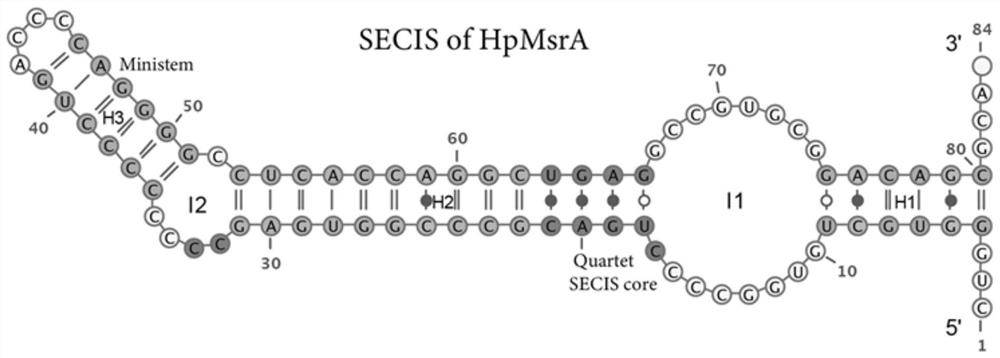
The invention discloses a methionine sulfoxide reductase, which is selected from any one of the following (a1)-(a3): (a1) its amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1; (a2) is the same as SEQ ID Amino acid sequences with at least 85% homology to the amino acid sequence shown in NO.1; (a3) homologues, derivatives, fragments or mutations that do not lose biological activity with the amino acid sequence shown in (a) or (b) body. The invention provides the sequence of the methionine sulfoxide reductase of Haematococcus pluvialis for the first time, lays the foundation for the genetic engineering expression of the selenoprotein MsrA, and is beneficial to realize the large-scale industrial production of the methionine sulfoxide reductase with high catalytic activity. The invention also discloses a gene encoding the above-mentioned methionine sulfoxide reductase, a recombinant expression vector, a recombinant cell line or a recombinant strain, which is beneficial to realizing the genetic engineering expression of MsrA in vitro and reduces the acquisition cost of MsrA.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
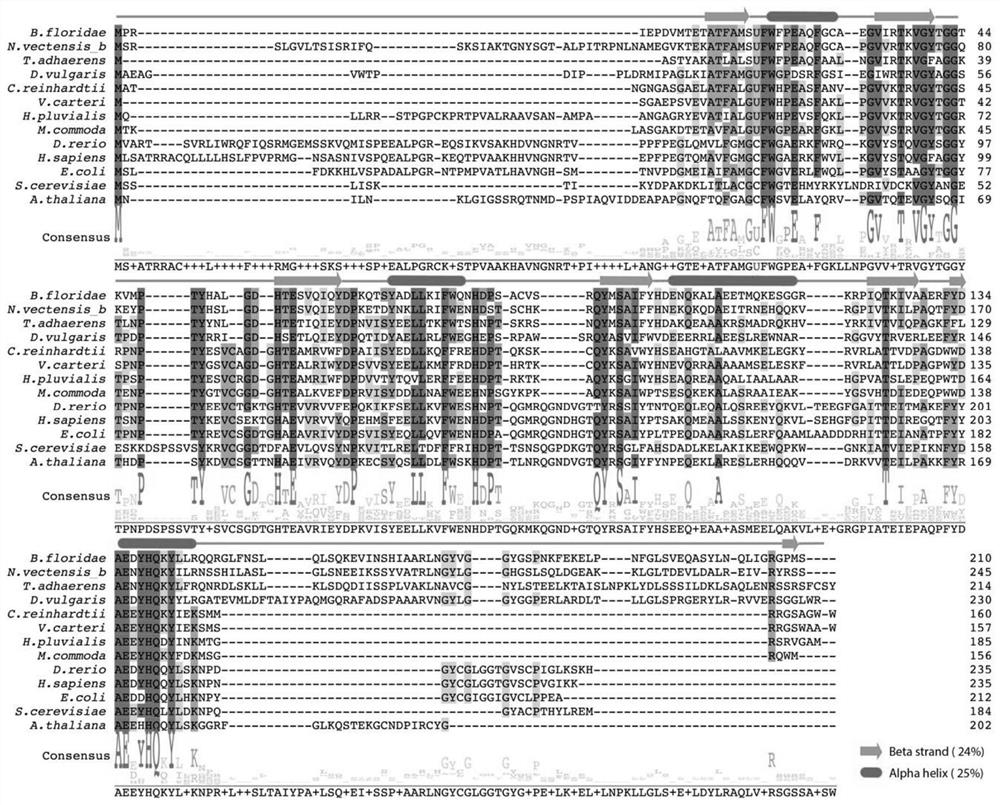
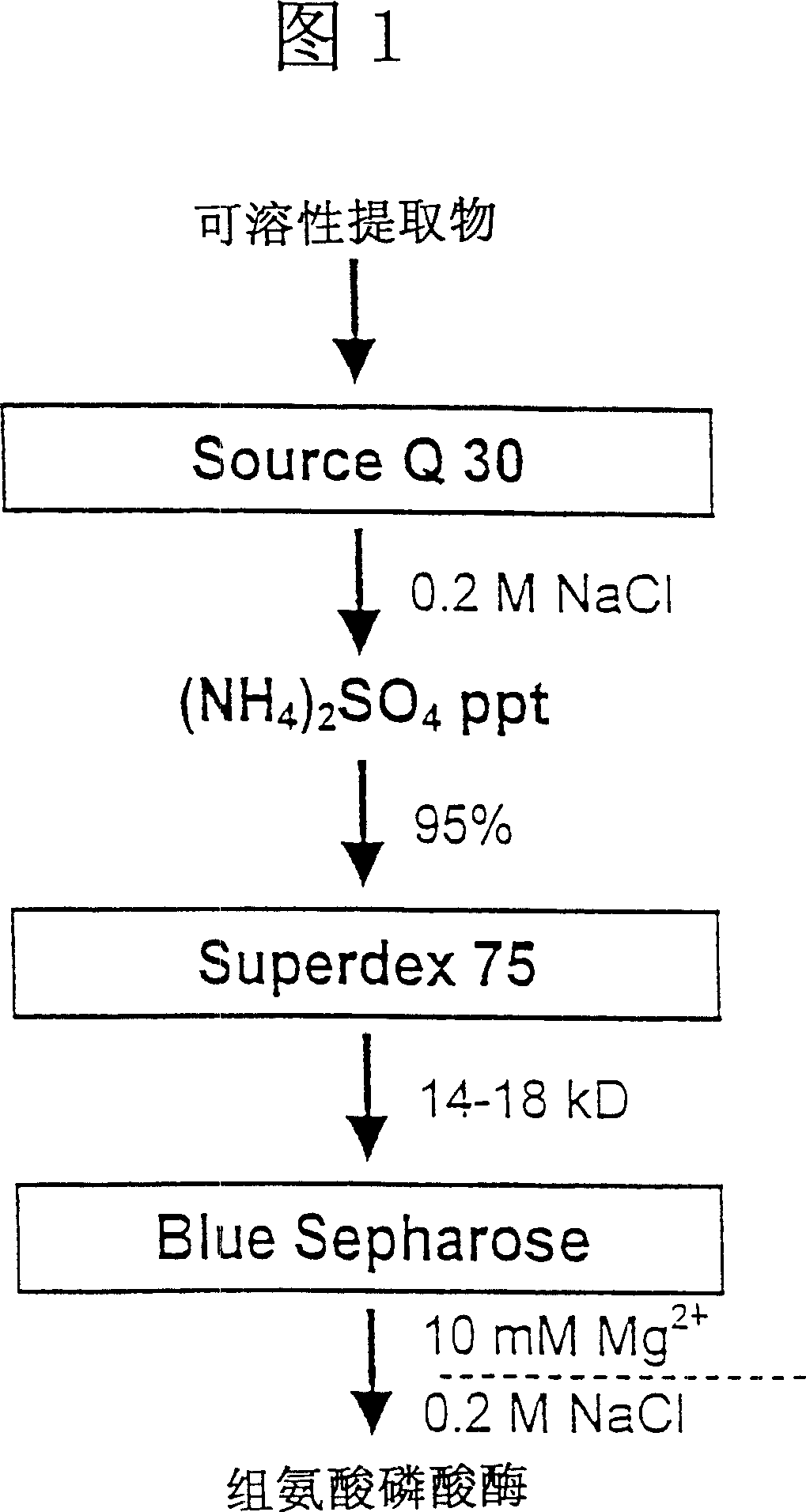
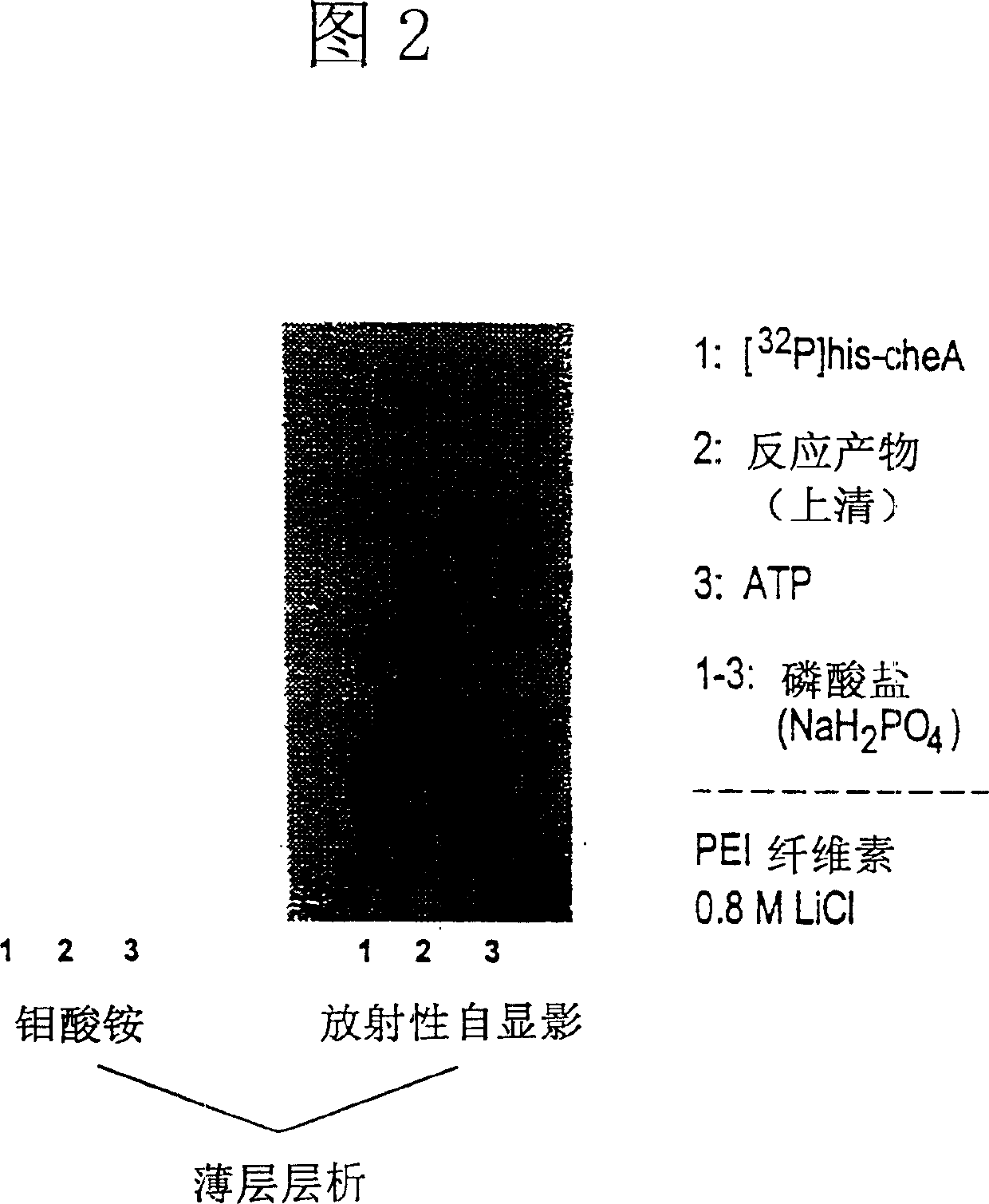
Histidine protein-phosphatase
The present invention relates to a novel mammalian-derived enzyme, histidine protein phosphatase, and homologue variants thereof. The invention also relates to DNA sequences encoding said proteins, methods for preparing said proteins and antibodies against them. This novel phosphatase is useful in the diagnosis of pathological states of cell regulation and cell growth, and as a drug for the treatment of pathological diseases associated with said enzyme disorders.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Method of detecting pathogenic legionella strains
InactiveUS20130237457A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNAPathogenicity
The invention relates to a kit for detecting pathogenic Legionella pneumophila strains by hybridizing genomic DNA of a sample suspected to contain Legionella to two or five specific sequence markers, as identified by MARKER NO. 1 through MARKER NO. 5 or homologues thereof.
Owner:NEDERLANDSE ORG VOOR TOEGEPAST NATUURWETENSCHAPPELIJK ONDERZOEK TNO
Usage of exocyst complex component or sec3 or its homolog in delivery of exogenous molecules in transit
The invention relates to the usage of Exocyst complex component or Sec3 or its homolog as a molecular marker for monitoring an exogenous molecule like nucleic acid in transit and optimizing the delivery of the exogenous molecule to a cell. Delivery of the molecule is monitored by detecting expression of an Exocyst complex component or Sec3 or its homolog in said cell, wherein the expression of the Exocyst complex component or Sec 3 or its homolog indicates that the cell is competent to receive the exogenous molecule. The invention may be used (a) to determine the efficiency of delivery; (b) to control the copy number of DNA delivery; (c) to identify the cells transformed with an exogenous DNA; (d) to identify molecular markers associated with transformation competency of a cell; (e) identifying, characterizing and producing cells competent to receive exogenous nucleic acid.
Owner:PAN SHEN QUAN
Plants with altered root architecture, related constructs and methods involving genes encoding protein phophatase 2c (PP2C) polypeptides and homologs thereof
Isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides and recombinant DNA constructs particularly useful for altering root structure of plants, compositions (such as plants or seeds) comprising these recombinant DNA constructs, and methods utilizing these recombinant DNA constructs. The recombinant DNA construct comprises a polynucleotide operably linked to a promoter functional in a plant, wherein said polynucleotide encodes a polypeptide useful for altering plant root architecture.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO +1
Methods and compositions for detecting protein targets
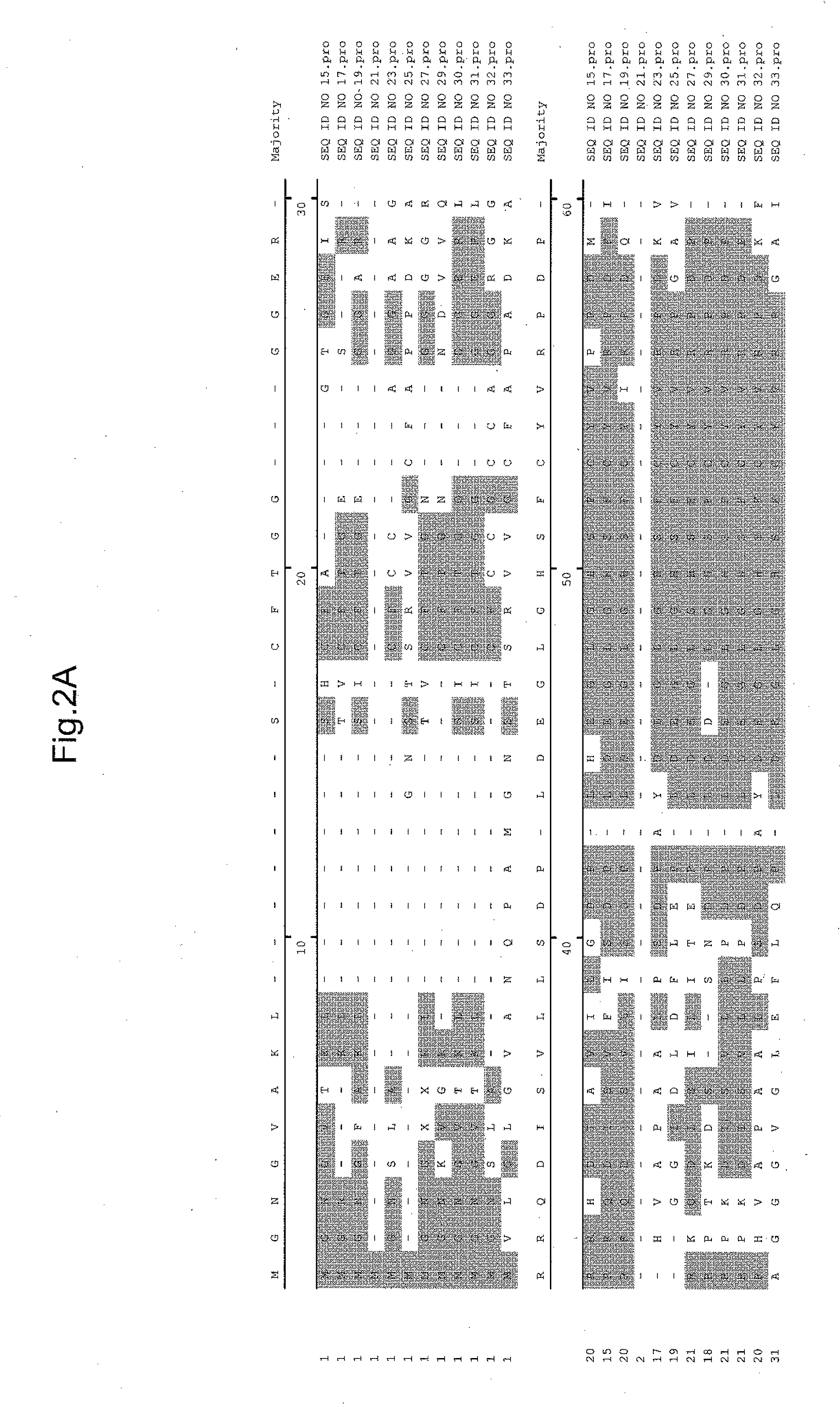
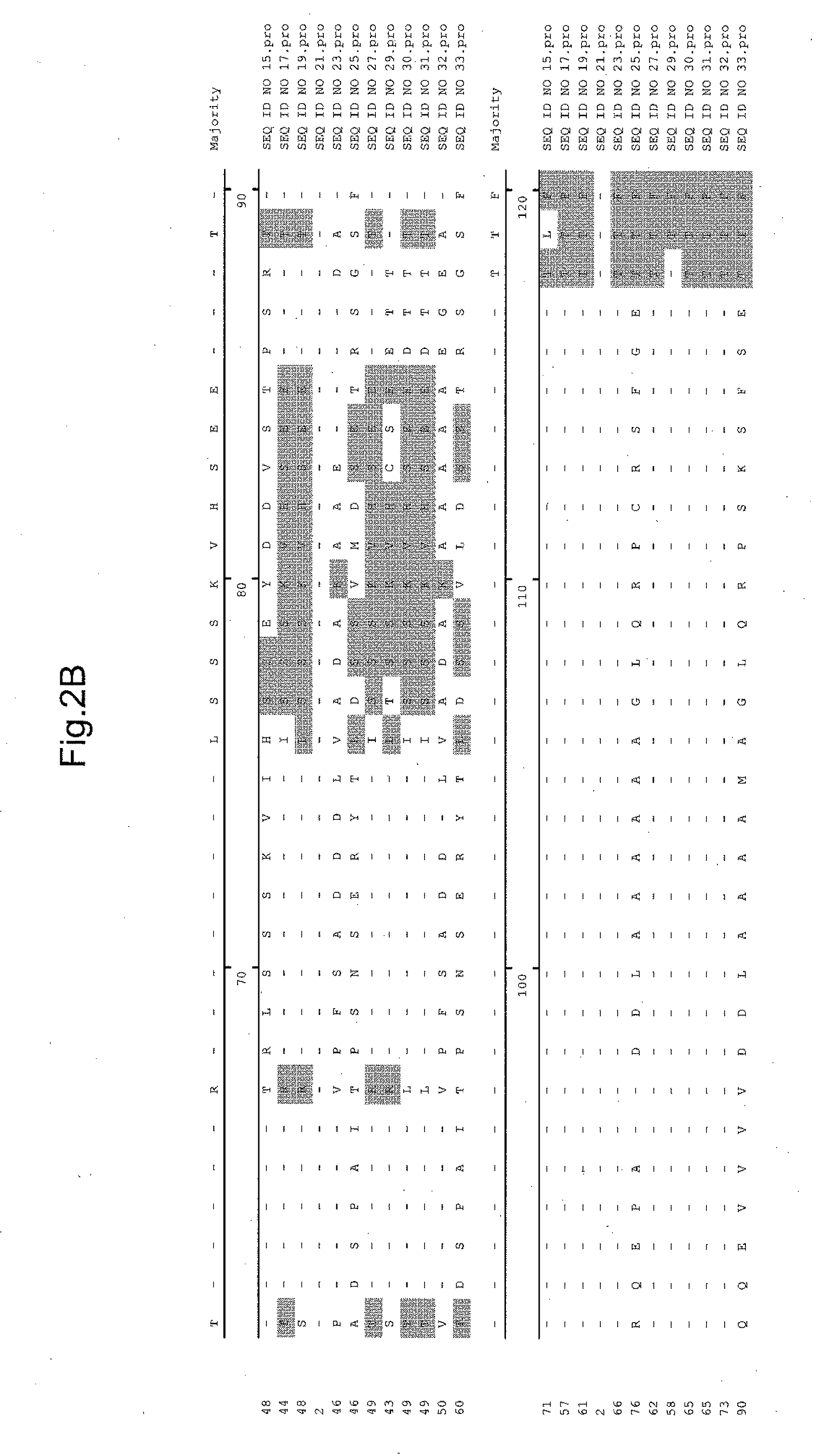
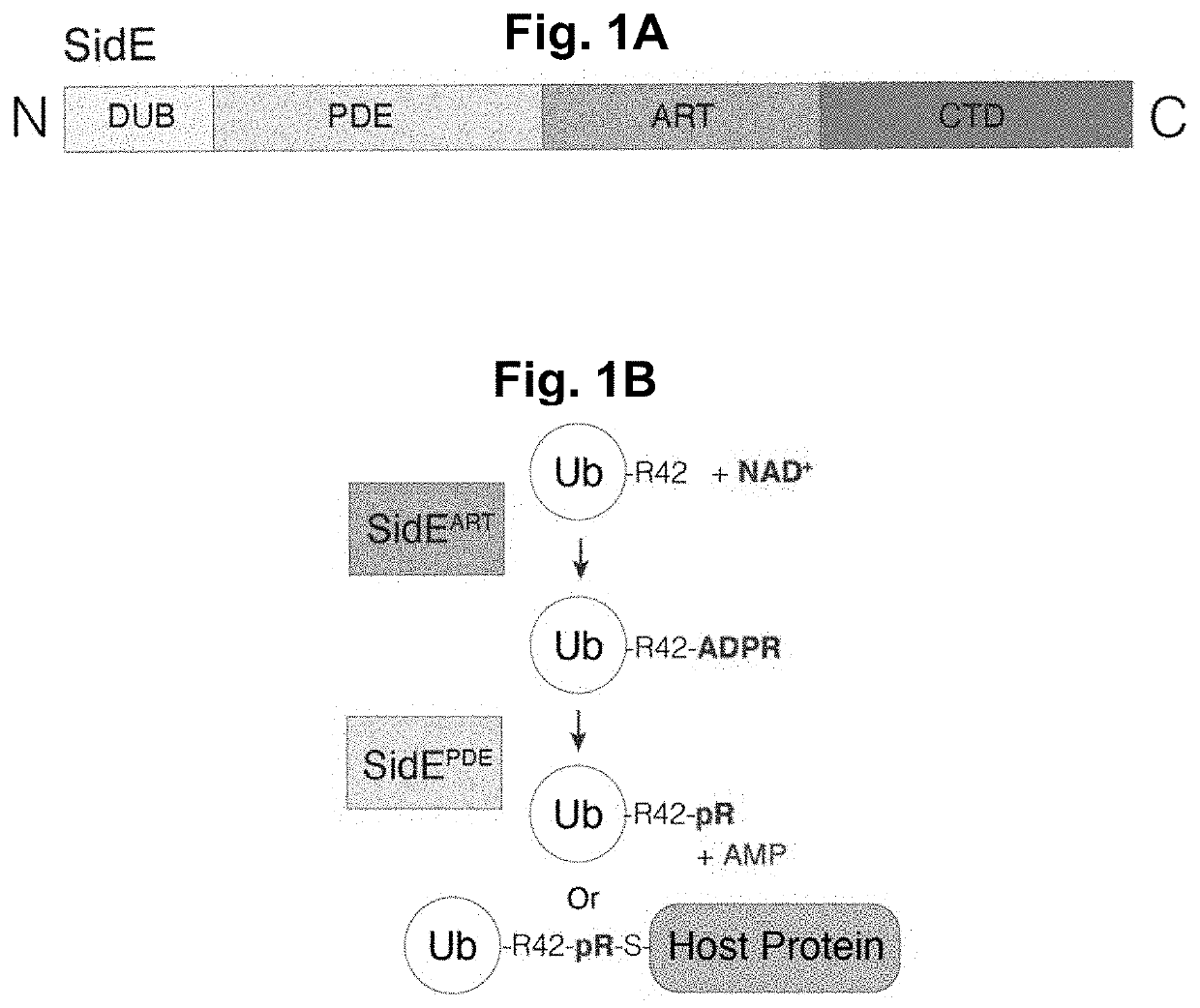
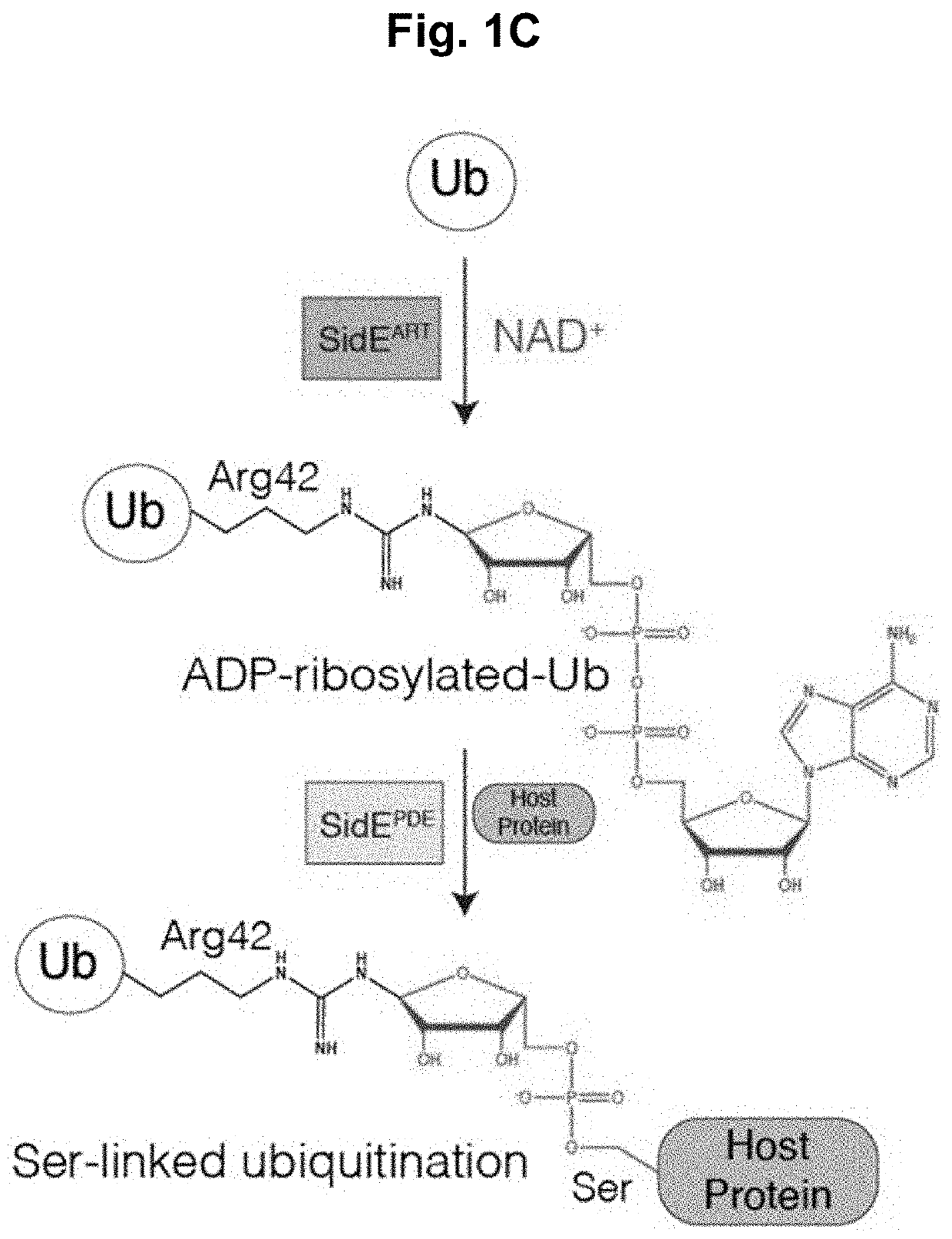
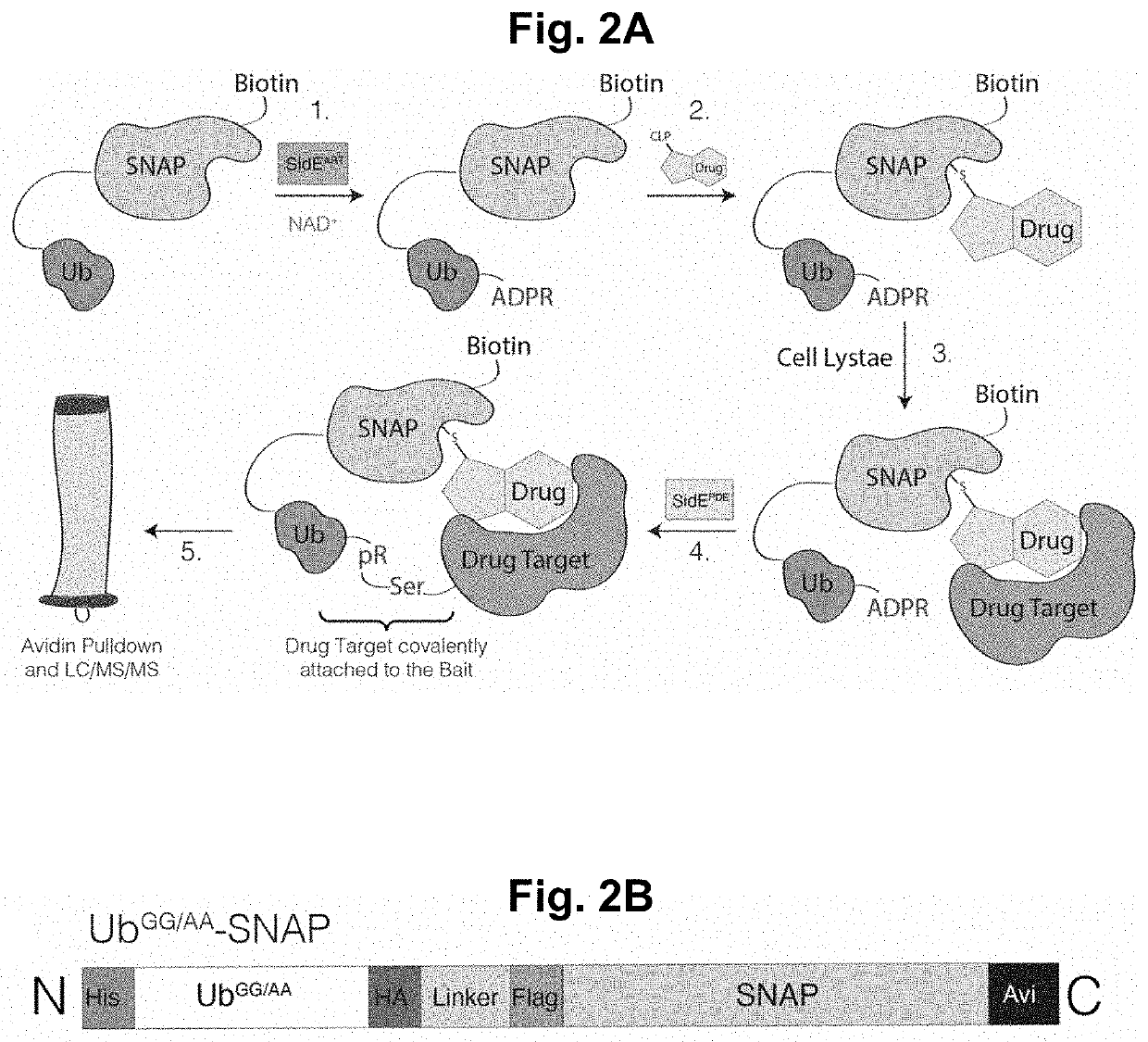
PendingUS20220283179A1Facilitate final target identificationConvenient treatmentBiological testingAssay labelsPhosphodiesteraseBio molecules
Compositions and methods for detection of protein interaction with a target biomolecule are provided. Compositions can include biomolecule sensors having at least a genetically modified ubiquitin peptide; an ADP-Ribosyltransferase (ART) peptide domain of a SidE-ligase protein or a homolog thereof; and a phosphodiesterase (PDE) domain of a SidE-ligase protein or a homolog thereof.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Oncolytic virus for treating brain tumors using recombinant newcastle disease virus into which newcastle disease virus vector-based pten gene is inserted and composition for treating brain tumors using same
ActiveUS20220364112A1Safe and effective brain tumor treatmentInhibit deteriorationSsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsSTD - Sexually transmitted diseaseNewcastle disease virus NDV
Provided are an oncolytic virus for treating brain tumors using a recombinant Newcastle disease virus into which a Newcastle disease virus (NDV) vector-based PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homolog) gene is inserted and a composition for treating brain tumors using the same which can be used for a therapeutic viral agent that can induce reduction of clinical symptoms or partial or complete remission through brain tumor cell death or brain tumor tissue reduction by expressing normal PTEN protein after being infected with brain tumor cells, as a recombinant Newcastle disease virus containing a human PTEN protein gene.
Owner:LIBENTECH CO LTD
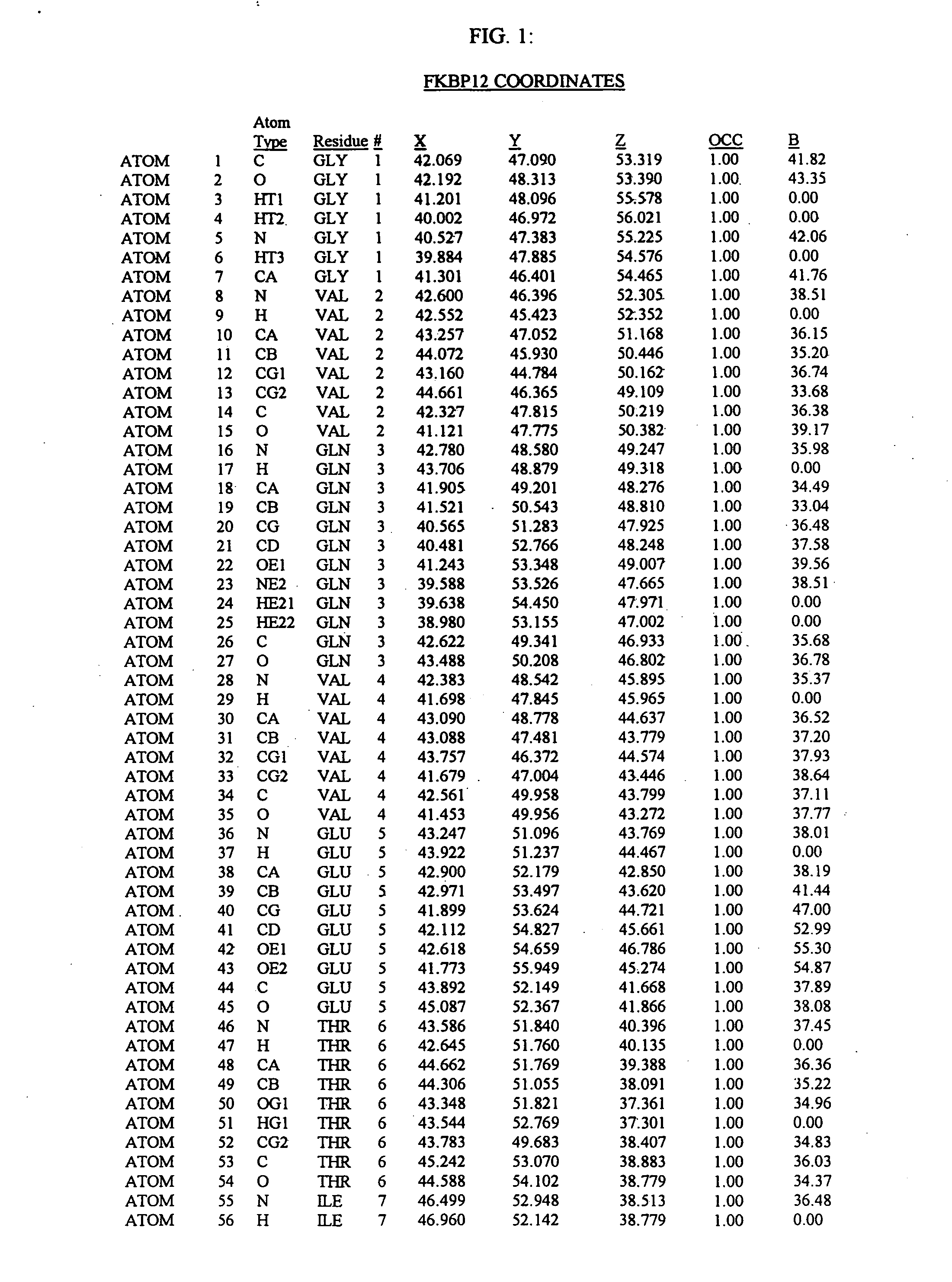
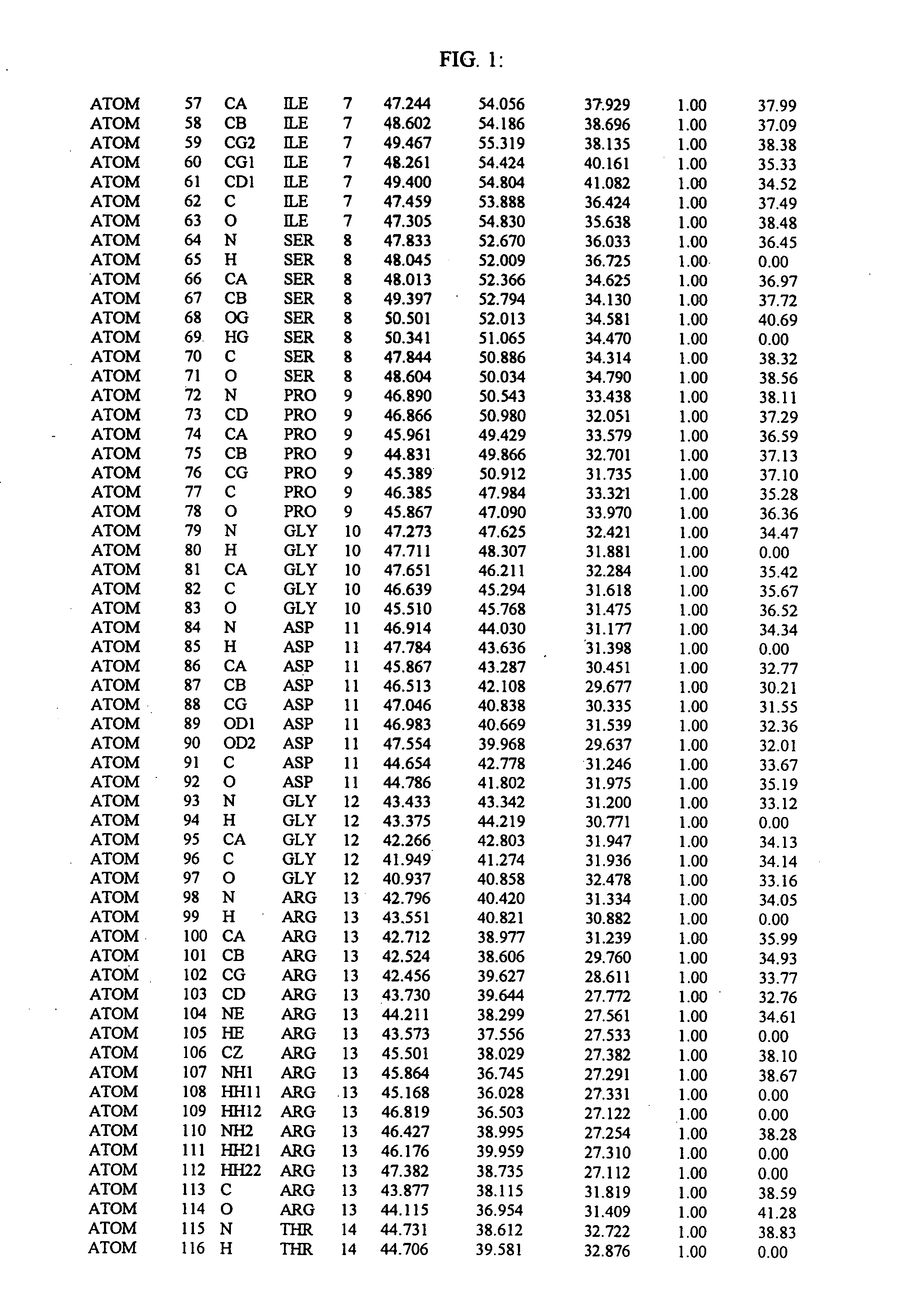
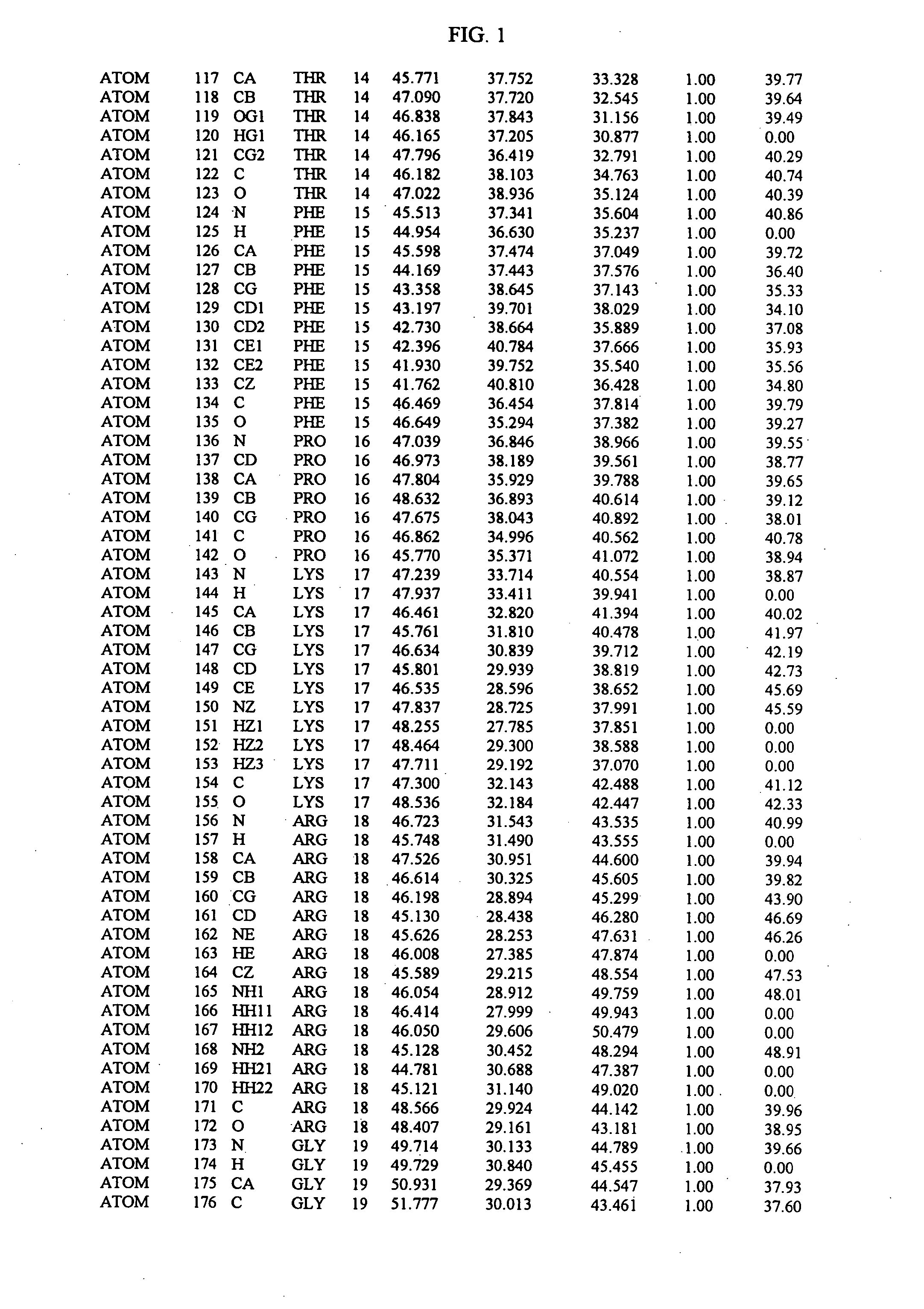
Molecules comprising a calcineurin-like binding pocket and encoded data storage medium capable of graphically displaying them
InactiveUS20070010952A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsHydrolasesCrystallographyGraphics
The present invention relates to crystallized molecules and molecular complexes which comprise the active site binding pocket or the FKBP12 / FK506 binding pocket of calcineurin or close structural homologues to either binding pocket. This invention also relates to a data storage material encoded with the corresponding structure coordinates of those crystallized molecules or molecular complexes. Such data storage material is capable of displaying such molecules and molecular complexes as a graphical three-dimensional representation on a computer screen. In addition, this invention relates to methods of using the structure coordinates of those molecules or molecular complexes to solve the structure of homologous proteins. This invention also relates to methods of using the structure coordinates to screen and design compounds that bind to calcineurin or homologues thereof.
Owner:ARMISTEAD DAVID +8
Monascus purpureus orotic acid-5'-phosphate decarboxylase gene and uses thereof
InactiveCN101497888AEasy reverse selectionEase of genetic transformationMicroorganismsMicroorganism based processesPhosphoric acidEngineered genetic
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
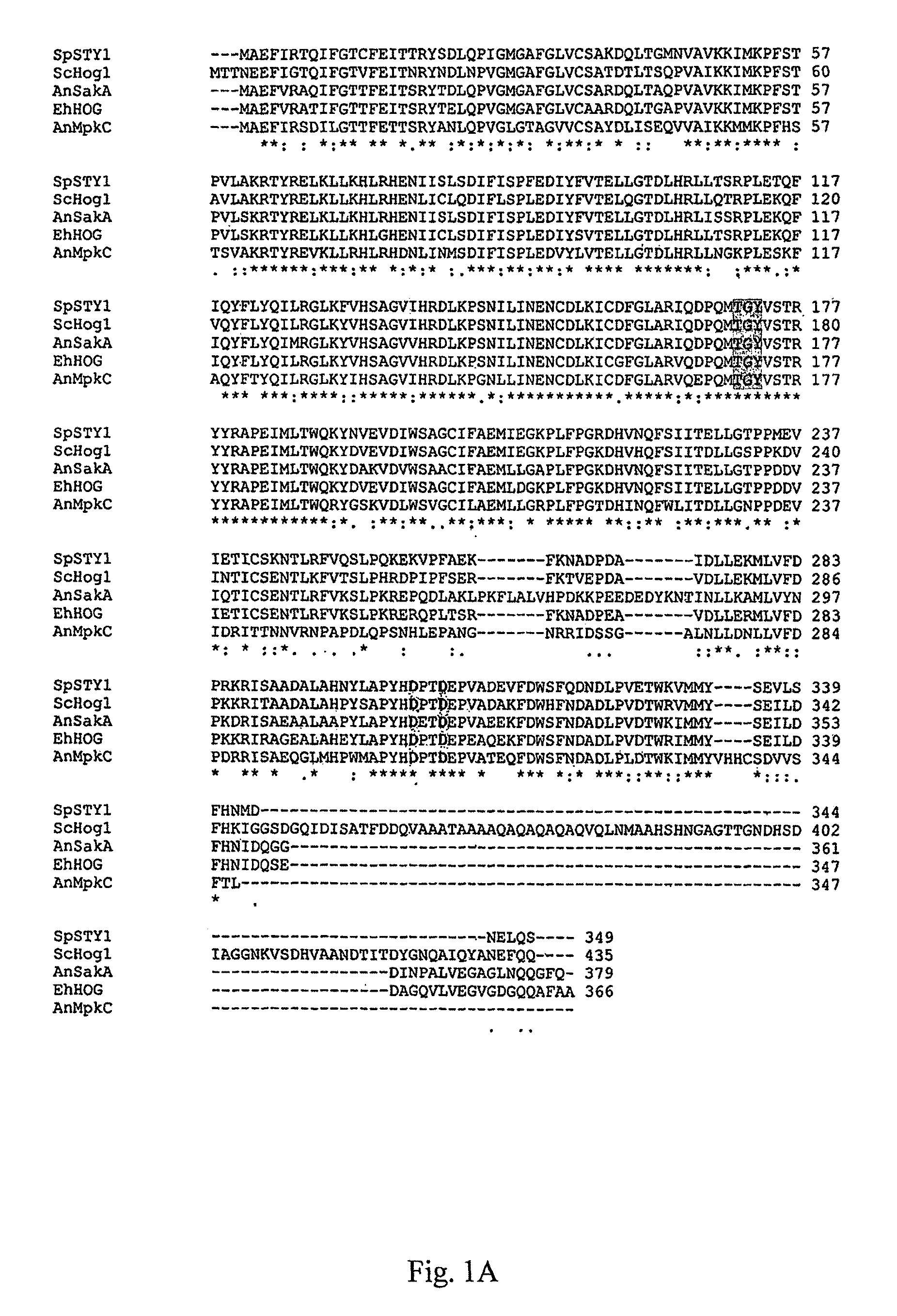
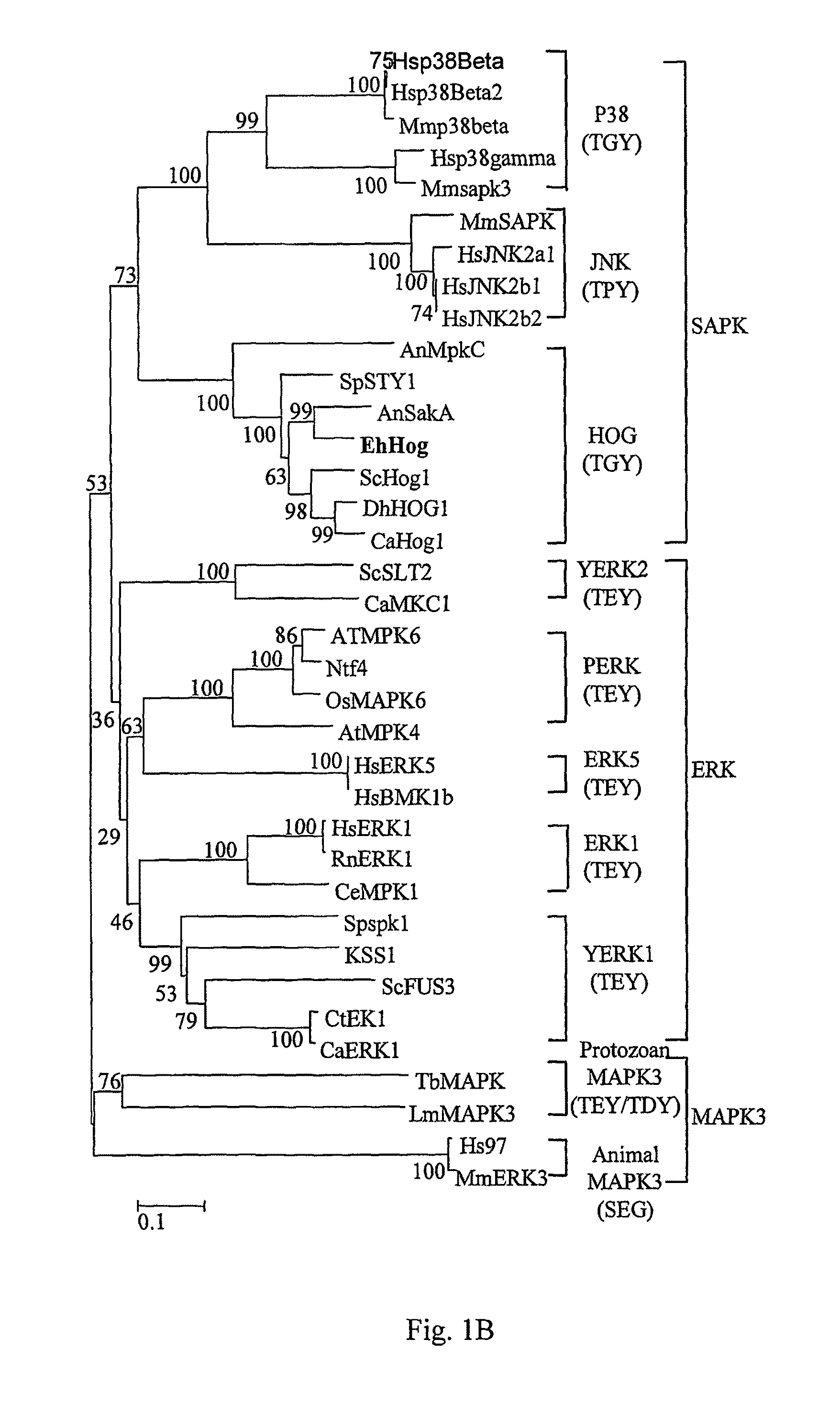
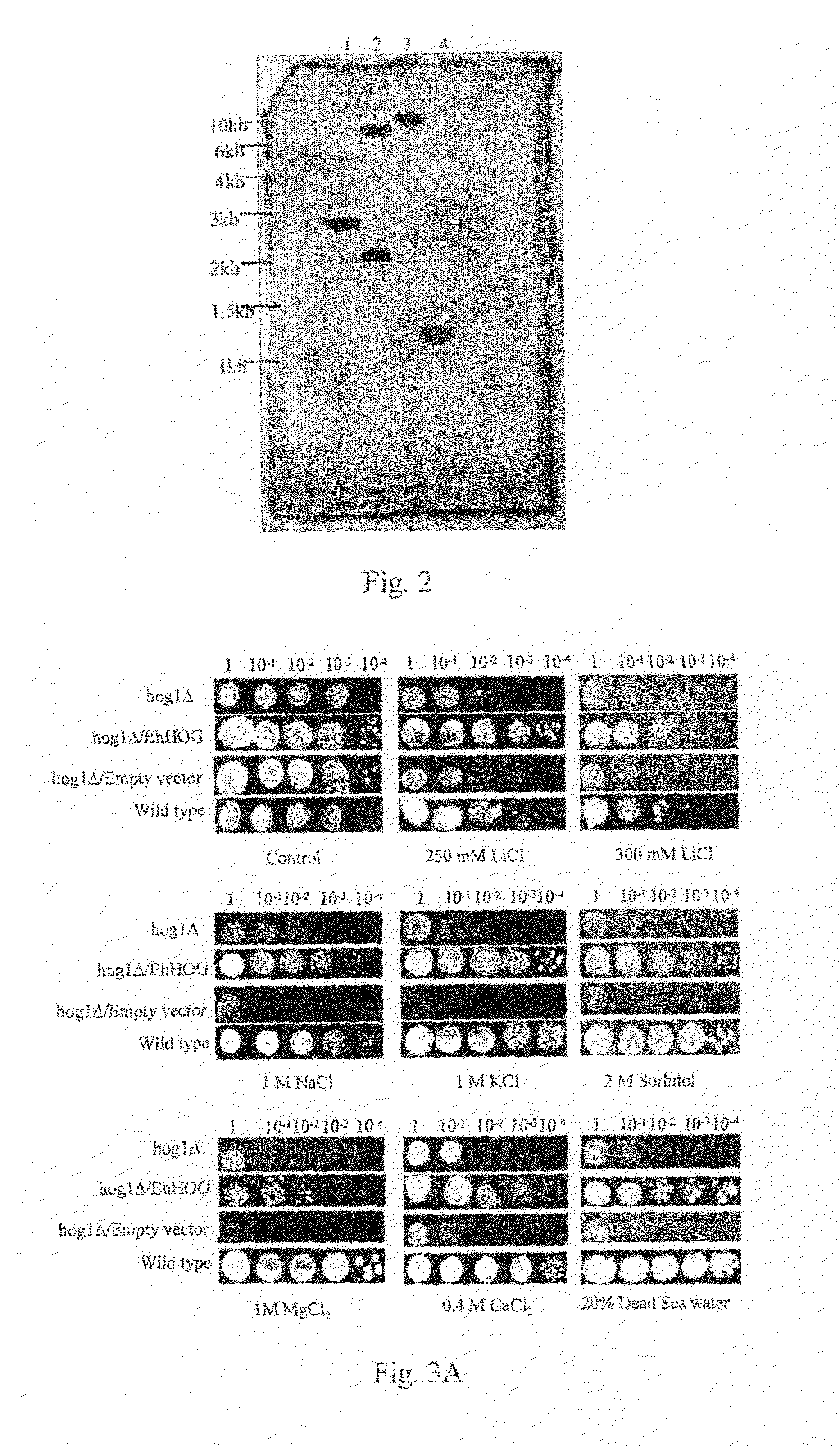
Stress tolerant organisms expressing a map kinase homologue
The present invention provides a MAP kinase homologue gene, designated EhHOG, isolated from Eurotium herbariorum, a common fungal species from the extreme hypersaline environment of the Dead Sea, capable of improving tolerance of plants and other organisms to abiotic stresses such as osmotic, heat, dehydration, freezing-thawing, oxidative and salinity stress.
Owner:SUD CHEM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com