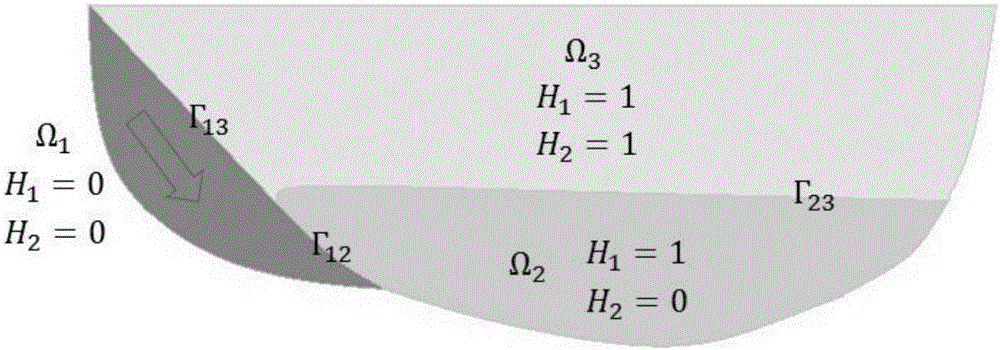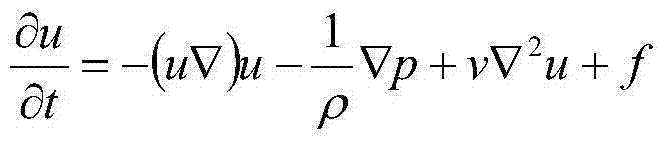Patents
Literature
72 results about "Navier–Stokes equations" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics, the Navier–Stokes equations (/nævˈjeɪ stoʊks/), named after Claude-Louis Navier and George Gabriel Stokes, describe the motion of viscous fluid substances. These balance equations arise from applying Isaac Newton's second law to fluid motion, together with the assumption that the stress in the fluid is the sum of a diffusing viscous term (proportional to the gradient of velocity) and a pressure term—hence describing viscous flow.
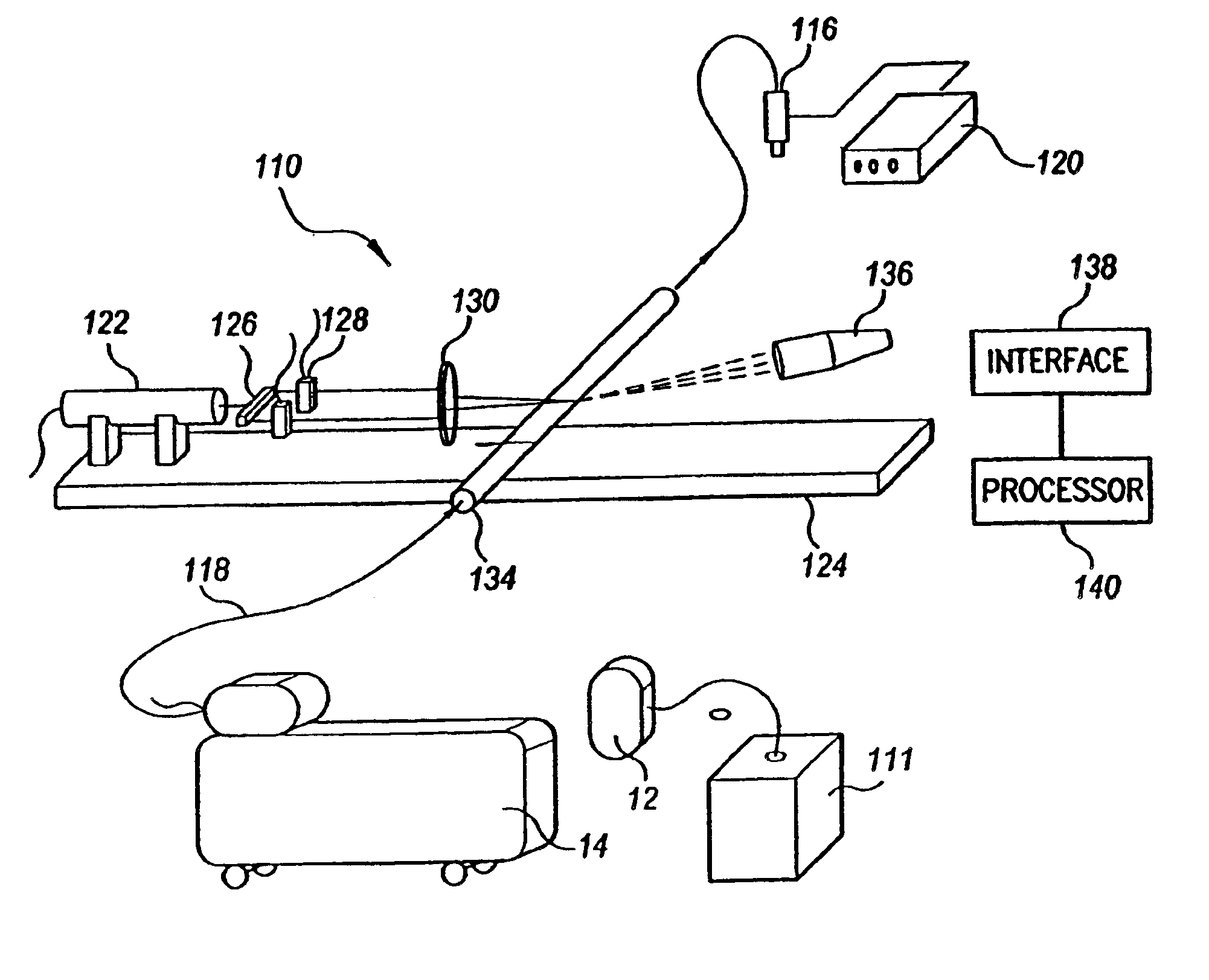
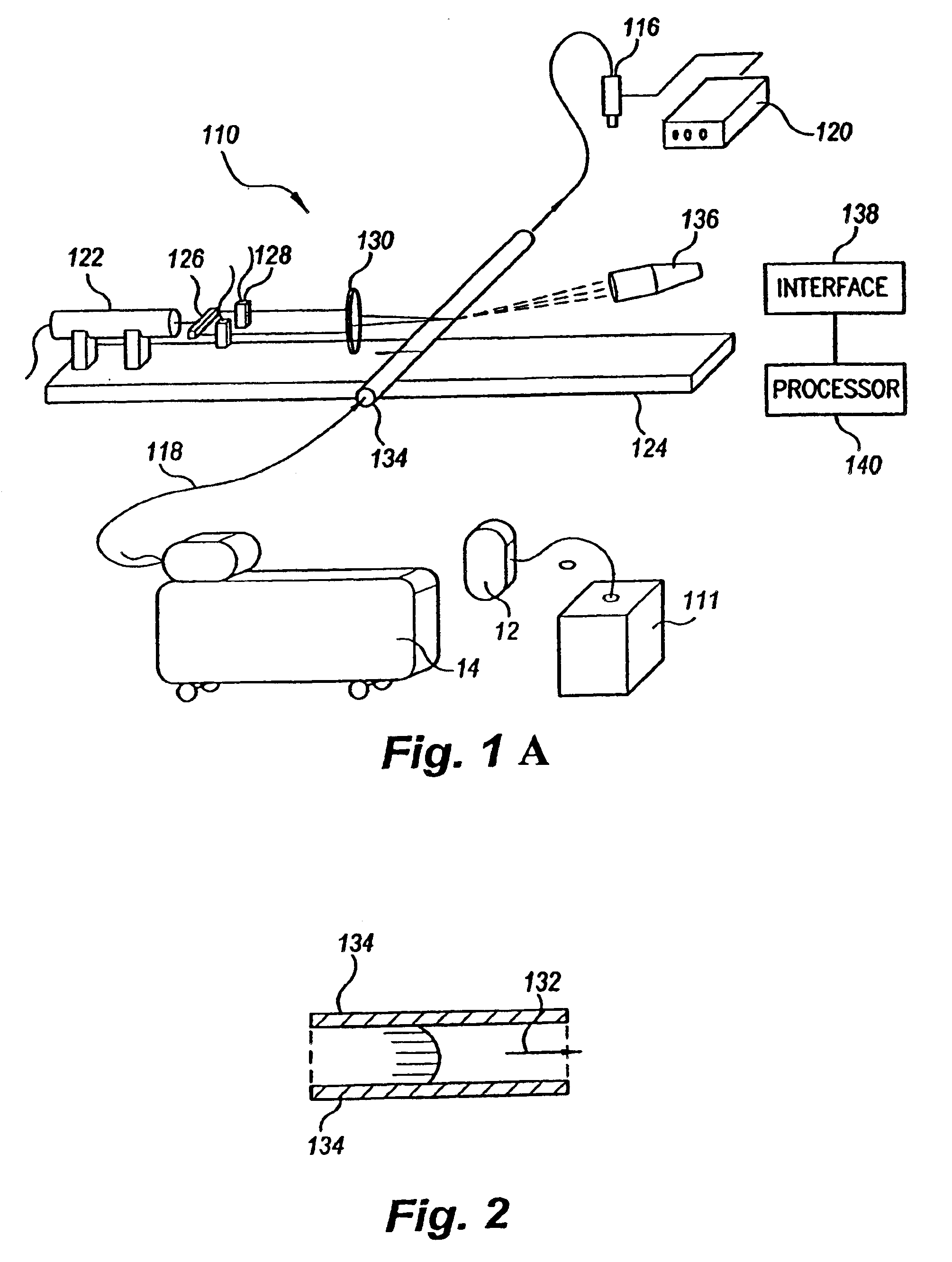
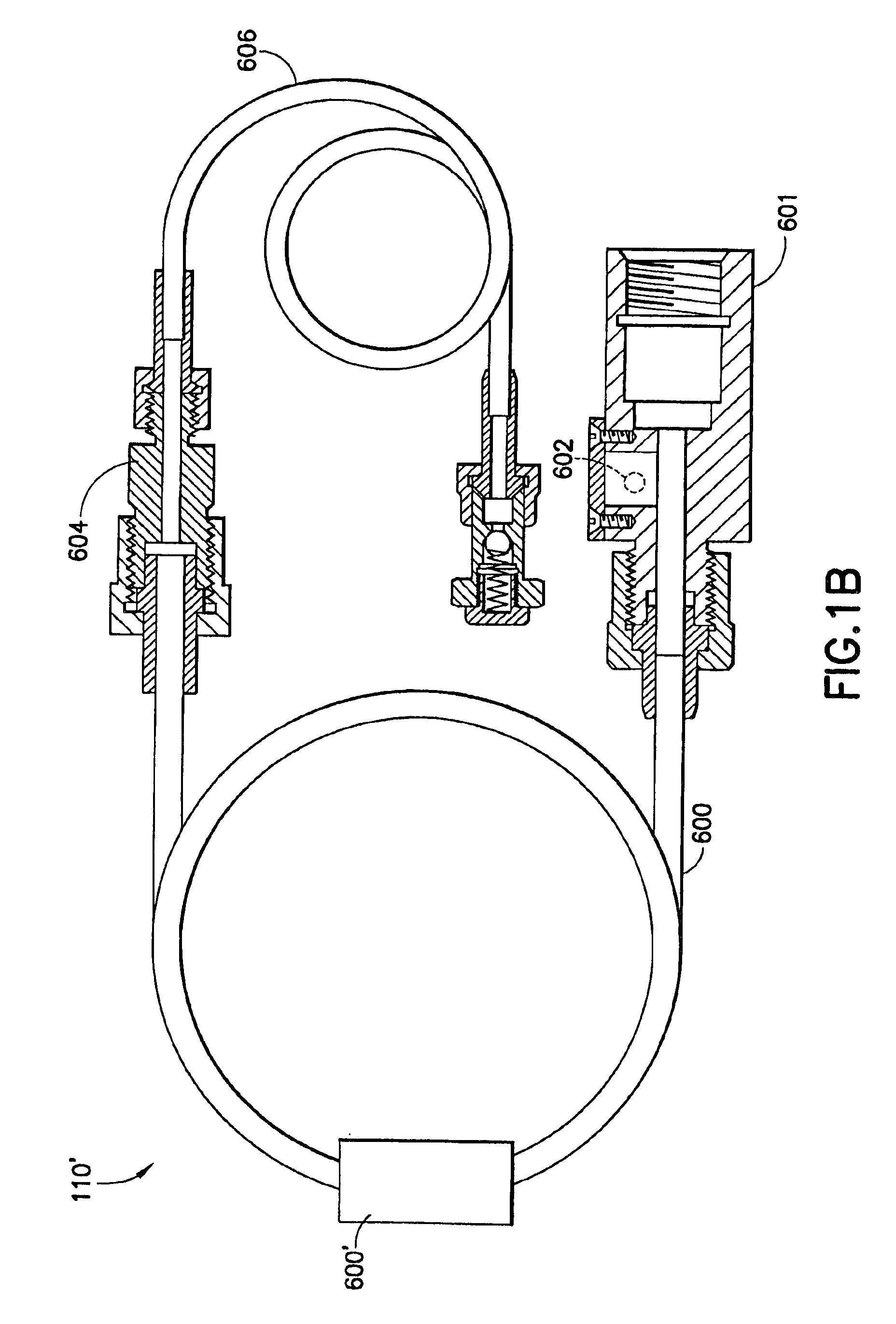
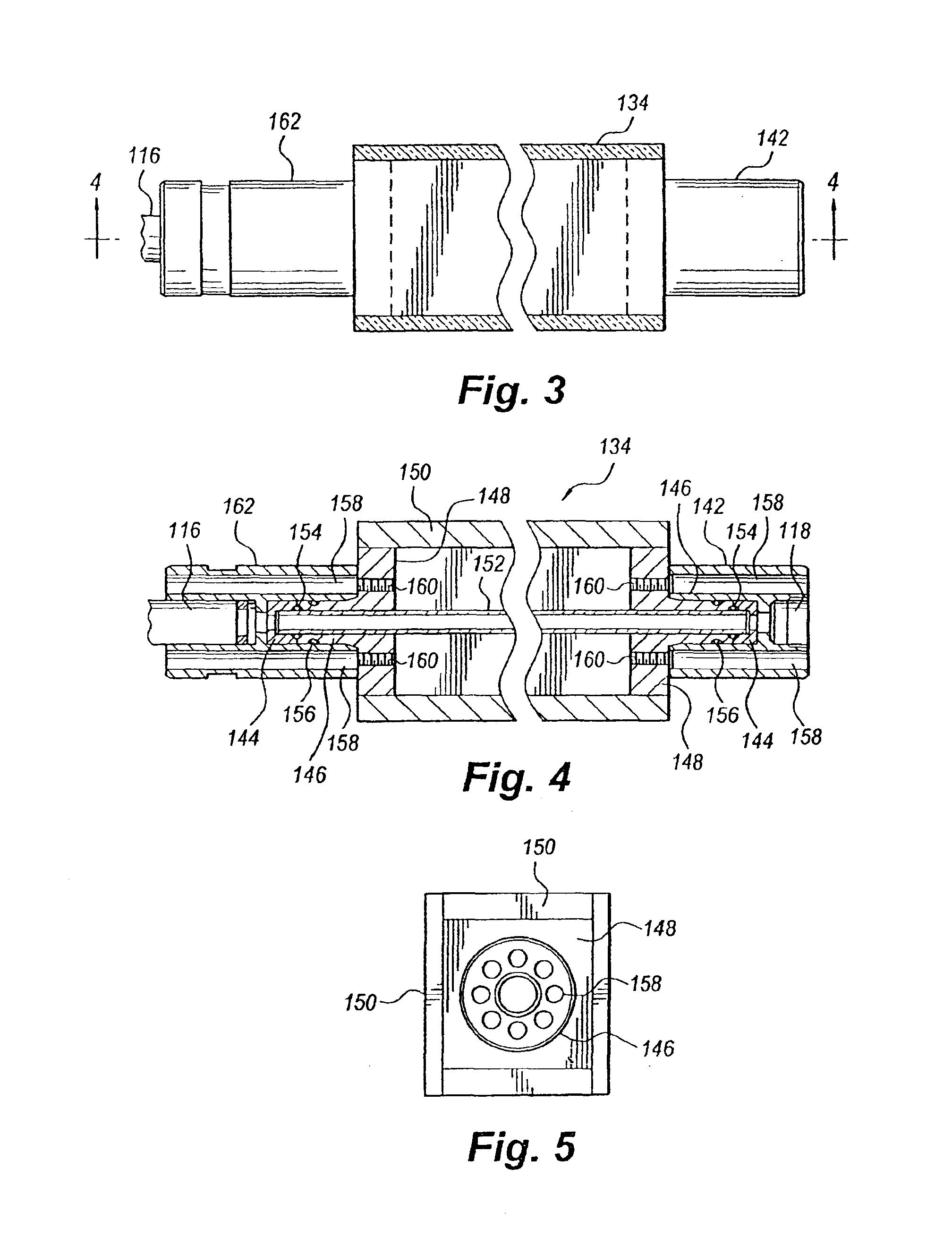
Flow meter
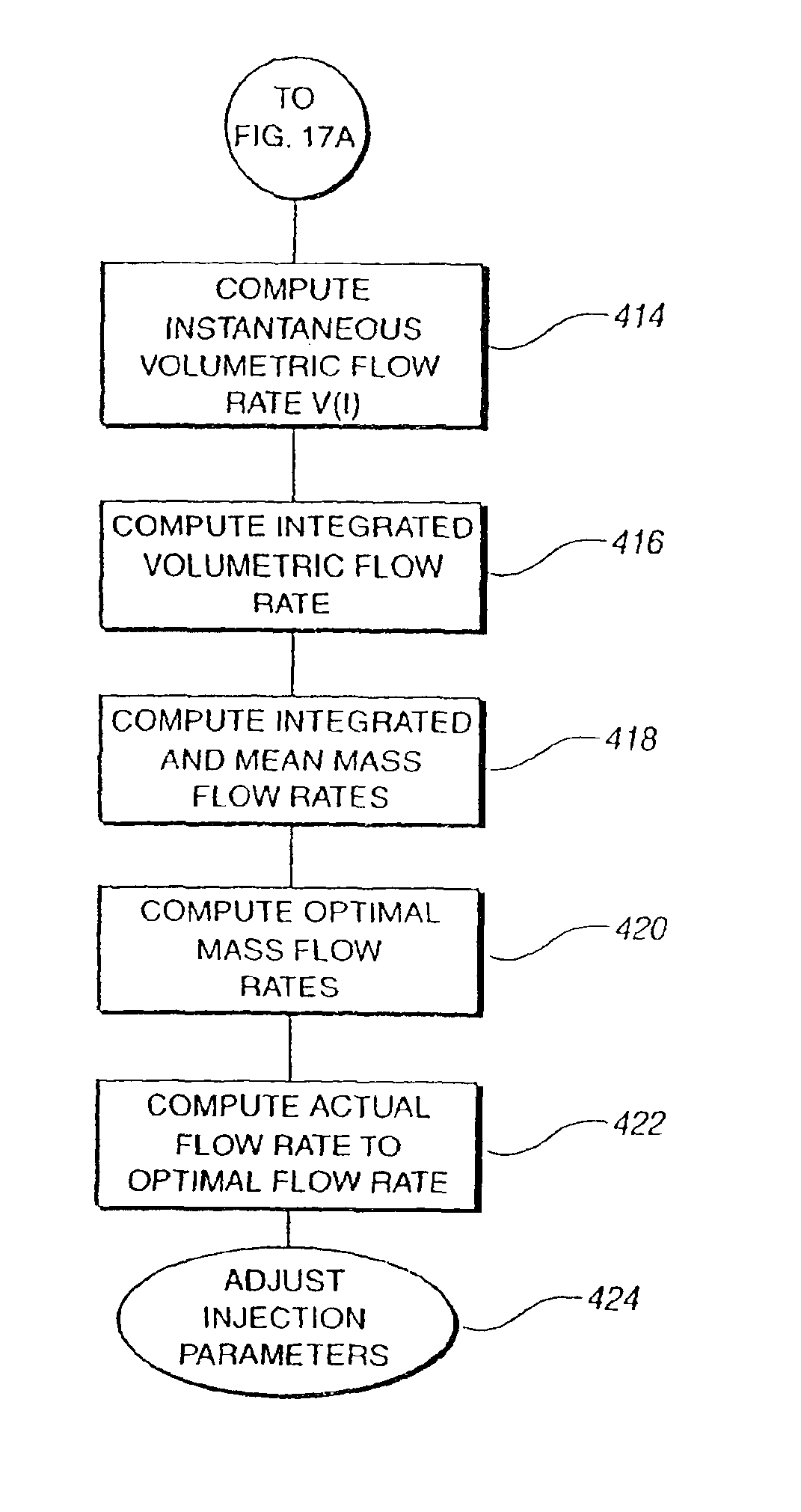
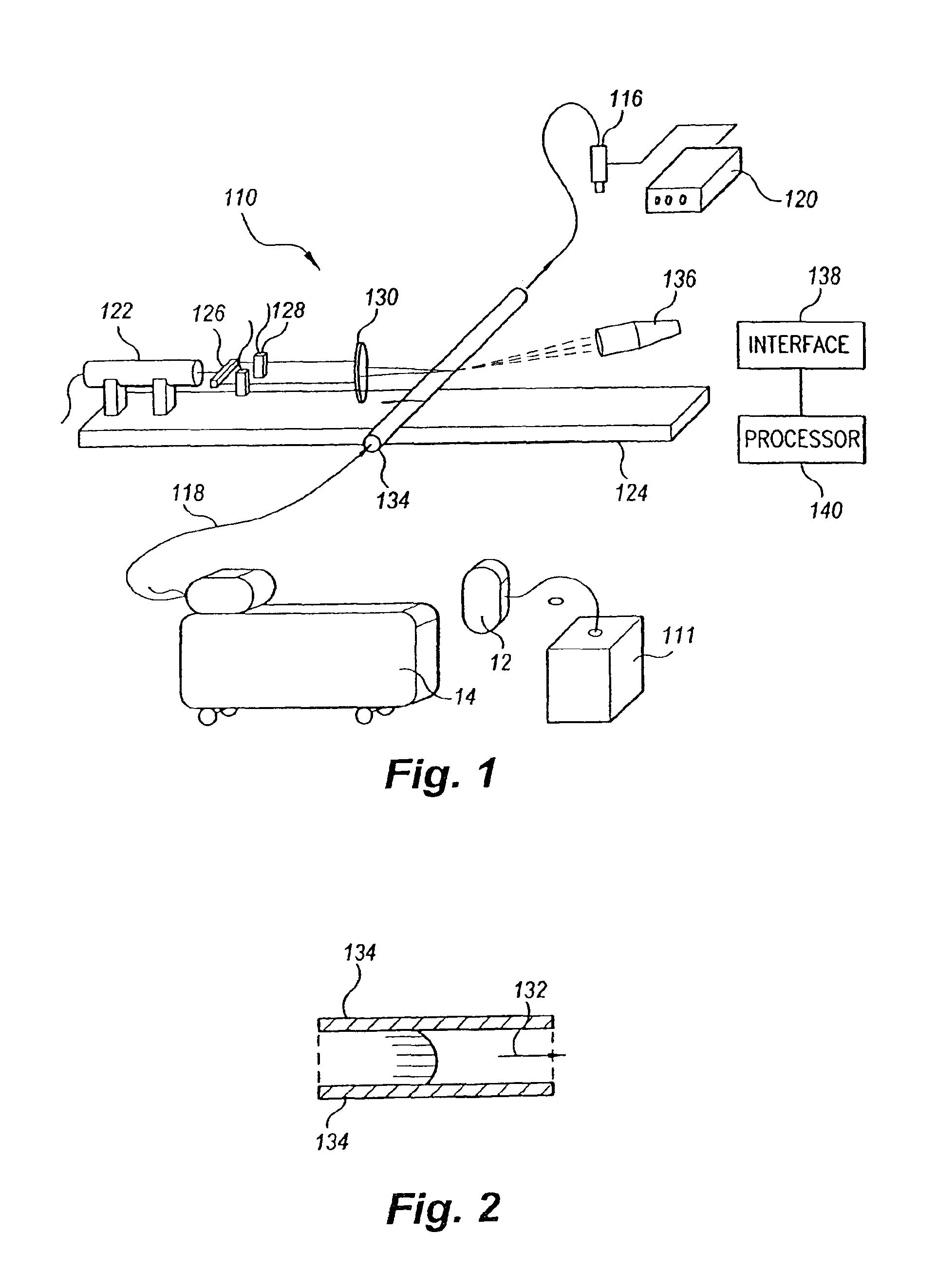
Various embodiments of the present invention provide a flow meter device having a laser Doppler anemometer (LDA) which measures the instantaneous center line velocity of fluid flow in a pipe. The flow meter may process the instantaneous velocity so obtained to compute the volumetric flow rate, mass rate, and / or other flow characteristics (e.g., as instantaneous quantities and / or integrated over a time interval) The flow meter may use an electronic processing method. The electronic processing method may provide essentially an exact solution to the Navier-Stokes equations for any periodically oscillating flow.
Owner:COMBUSTION DYNAMICS
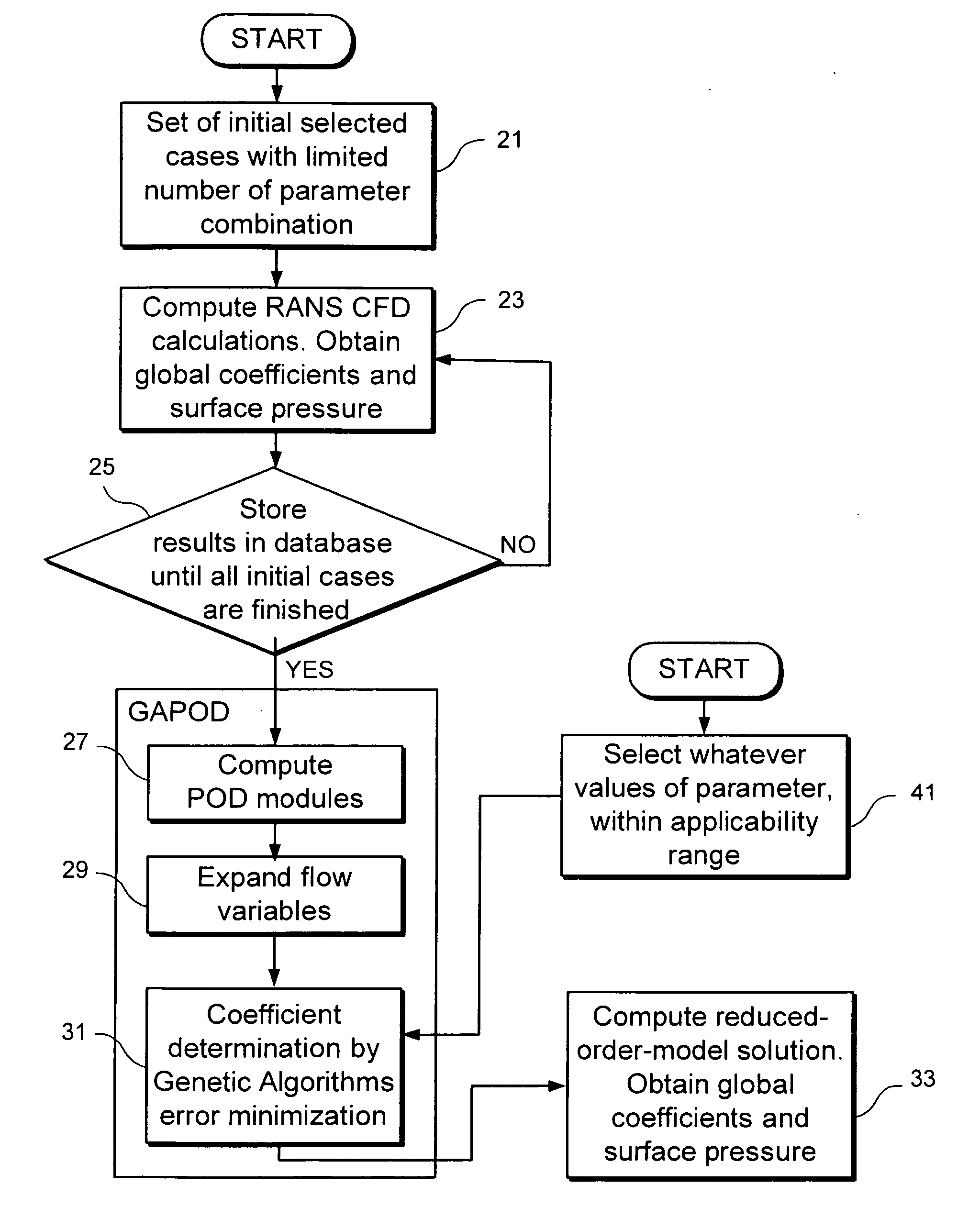
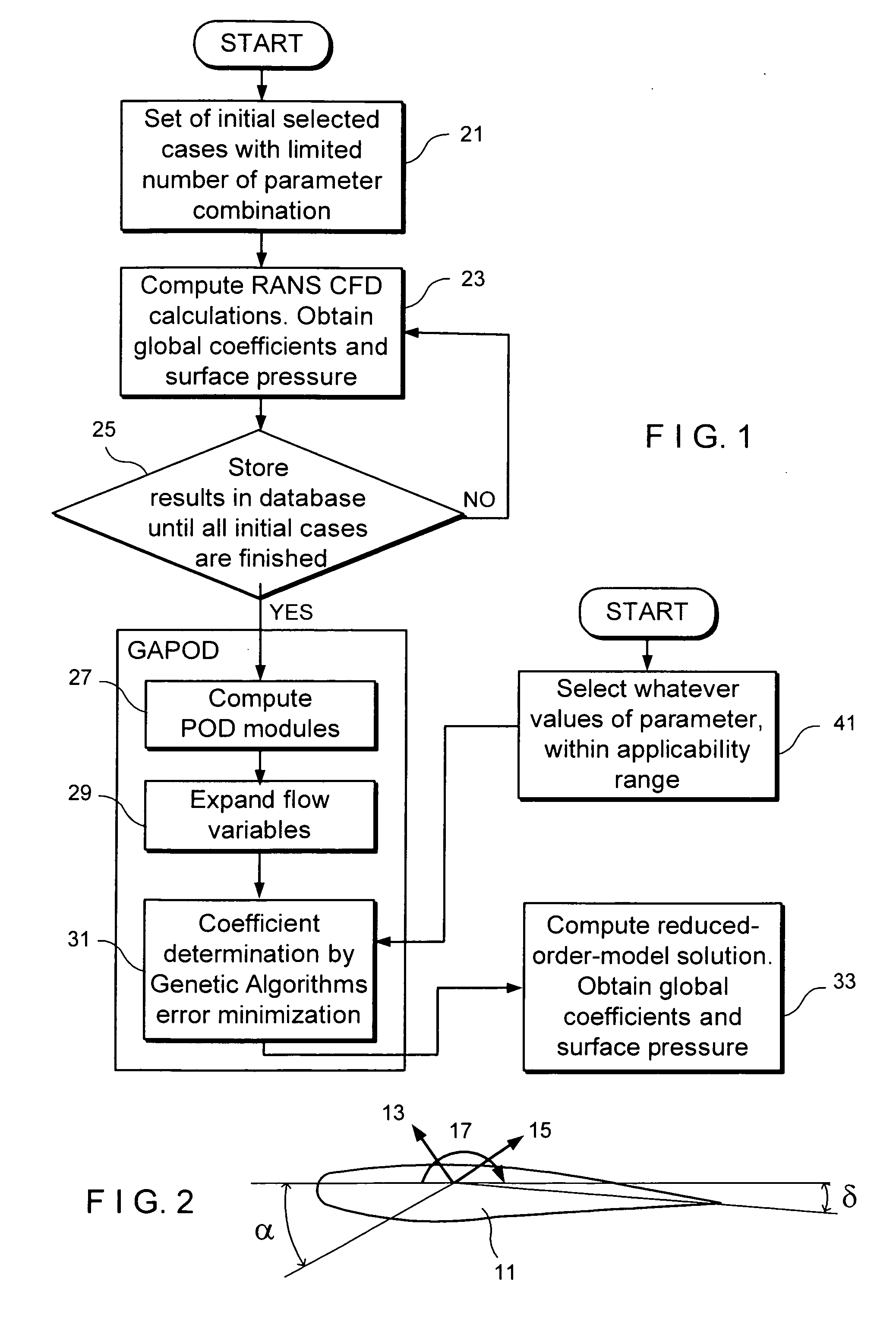
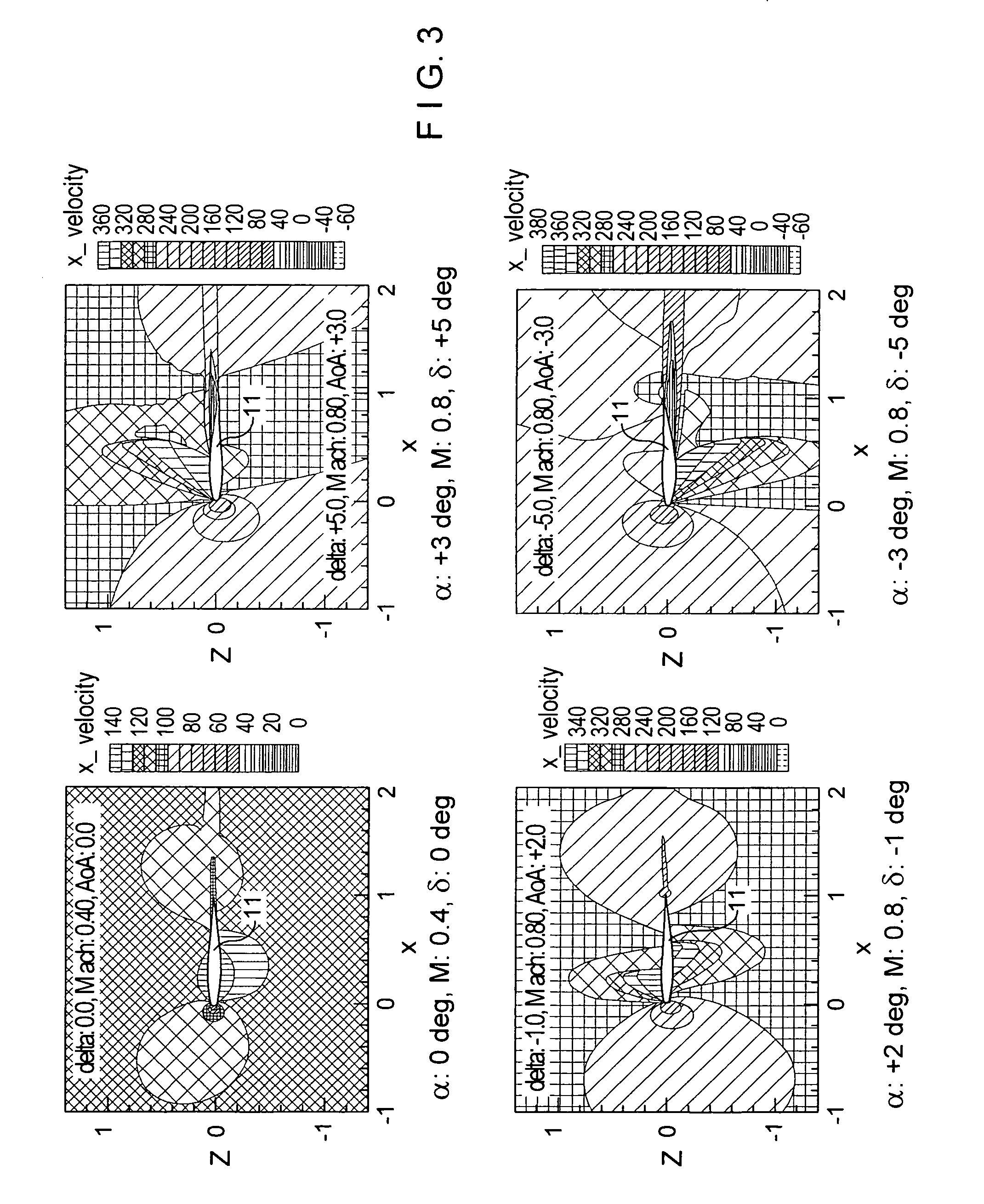
Method and system for a quick calculation of aerodynamic forces on an aircraft
InactiveUS20090157364A1Quick calculationError minimizationGeometric CADSustainable transportationGenetic algorithmComputer-aided
A computer-aided method suitable for assisting in the design of an aircraft by providing the dimensioning aerodynamic forces and other relevant values comprising the following steps: a) Selecting a set of parameters of the aircraft, being said aerodynamic forces and other relevant values dependant of said parameters; b) Performing flow field CFD RANS computations for a number N1 of different combination of values of said parameters; c) Obtaining said aerodynamic forces and other relevant values for whatever combination of values of said parameters through a reduced-order model, generated by computing the POD modes of the flow variables, expanding the flow variables using said POD modes and obtaining the POD coefficients of said expanded flow variables using a genetic algorithm that minimizes the error associated to the expansion of the Navier-Stokes equations. The invention also refers to a system for carrying out said method.
Owner:UNIV MADRID POLITECNICA +1
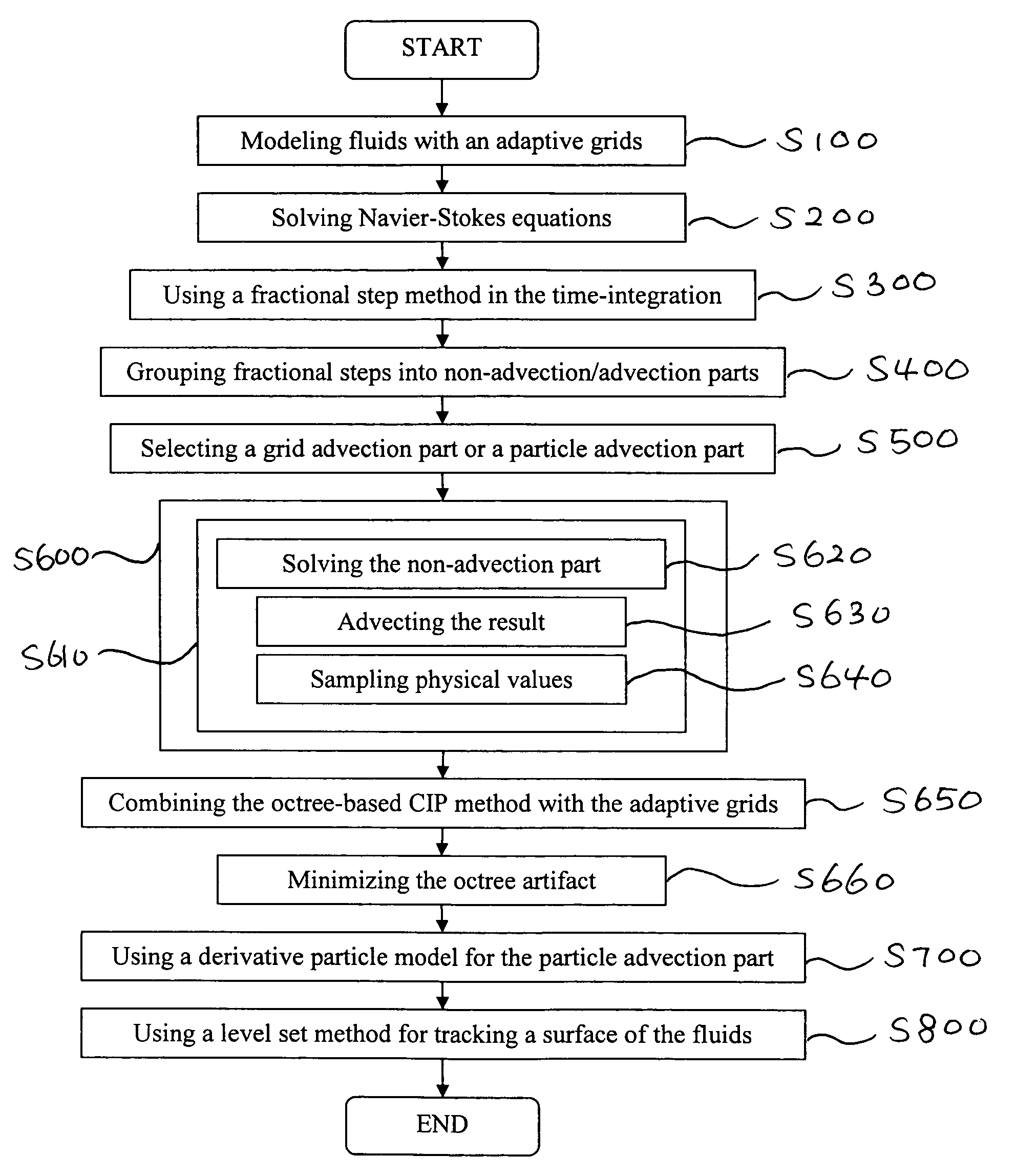
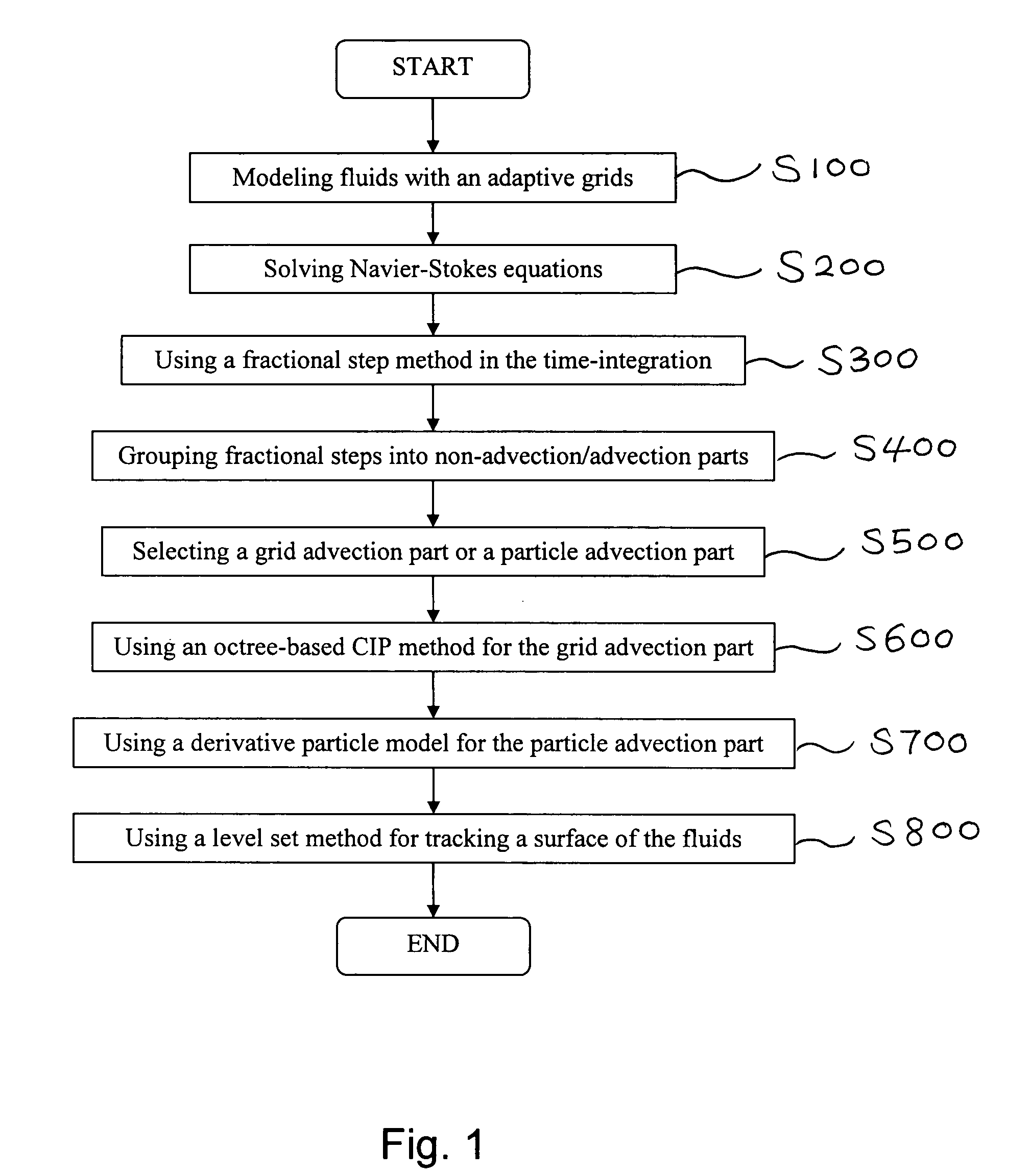
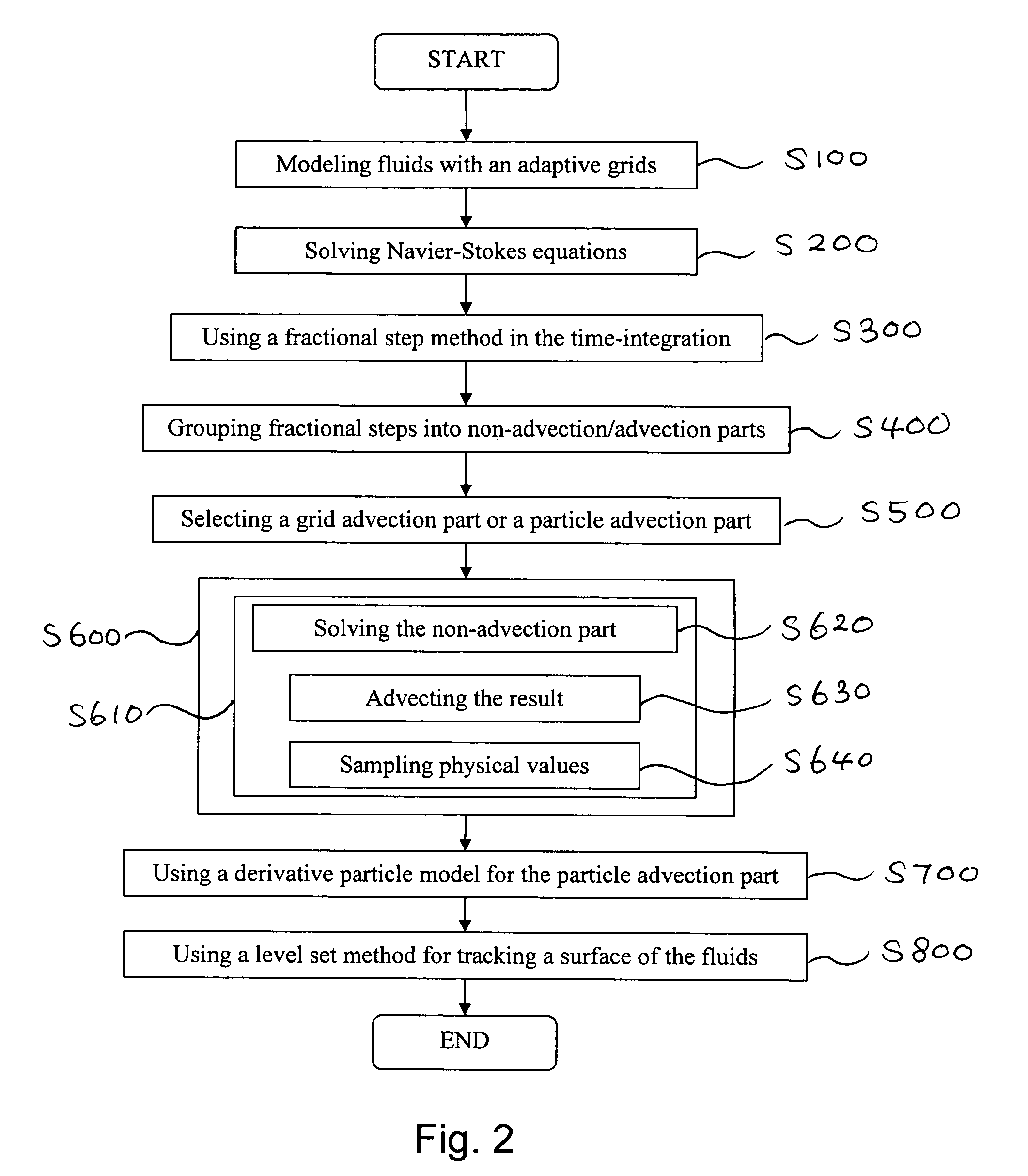
Method of simulating detailed movements of fluids using derivative particles
ActiveUS7565276B2Avoid interventionReduce the total massComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationGrid basedAdvection
The method provides a new fluid simulation technique that significantly reduces the non-physical dissipation of velocity using particles and derivative information. In solving the conventional Navier-Stokes equations, the method replace the advection part with a particle simulation. When swapping between the grid-based and particle-based simulators, the physical quantities such as the level set and velocity must be converted. A novel dissipation-suppressing conversion procedure that utilizes the derivative information stored in the particles as well as in the grid points is developed. Through several experiments, the proposed technique can reproduce the detailed movements of high-Reynolds-number fluids, such as droplets / bubbles, thin water sheets, and whirlpools. The increased accuracy in the advection, which forms the basis of the proposed technique, can also be used to produce better results in larger scale fluid simulations.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
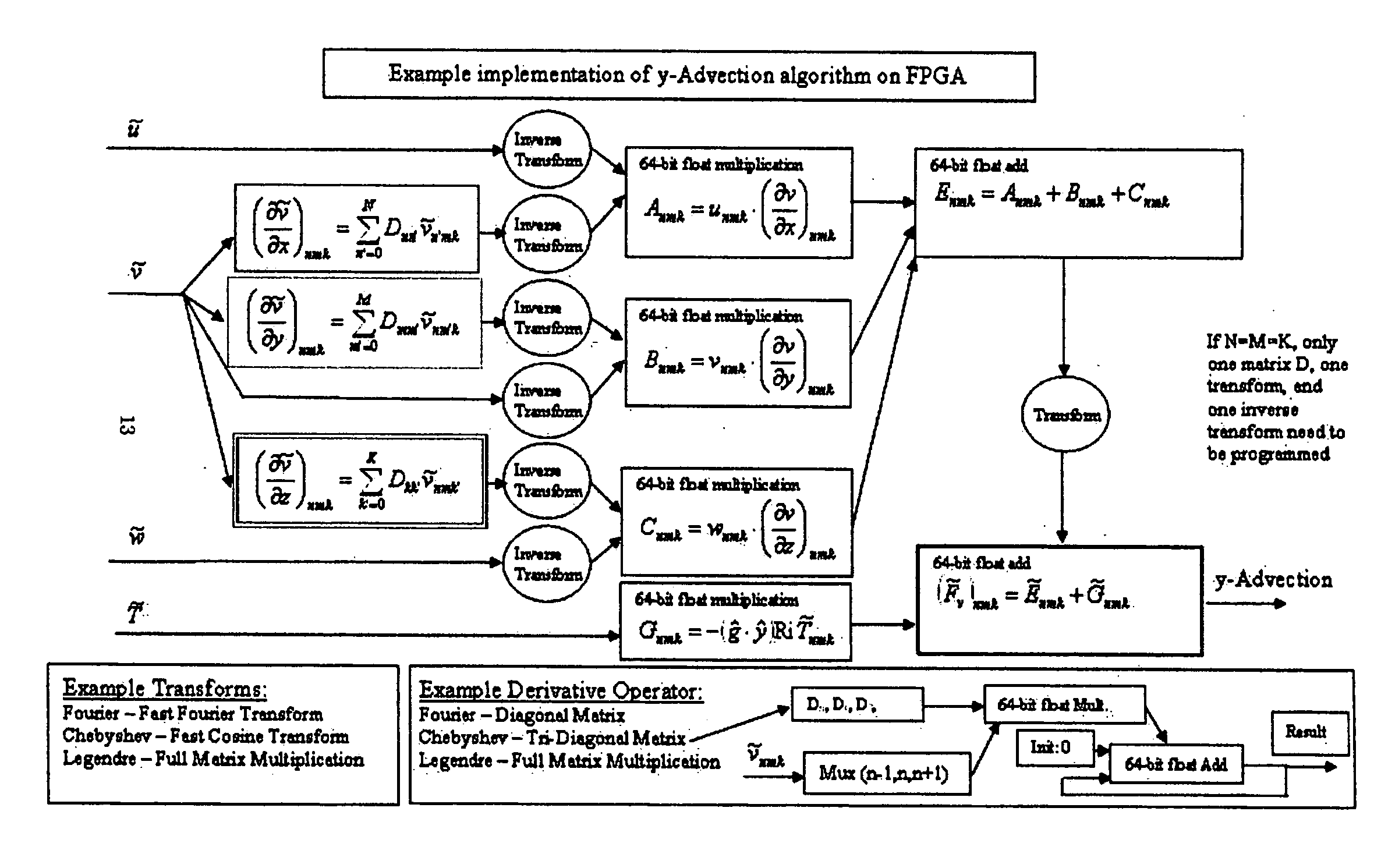
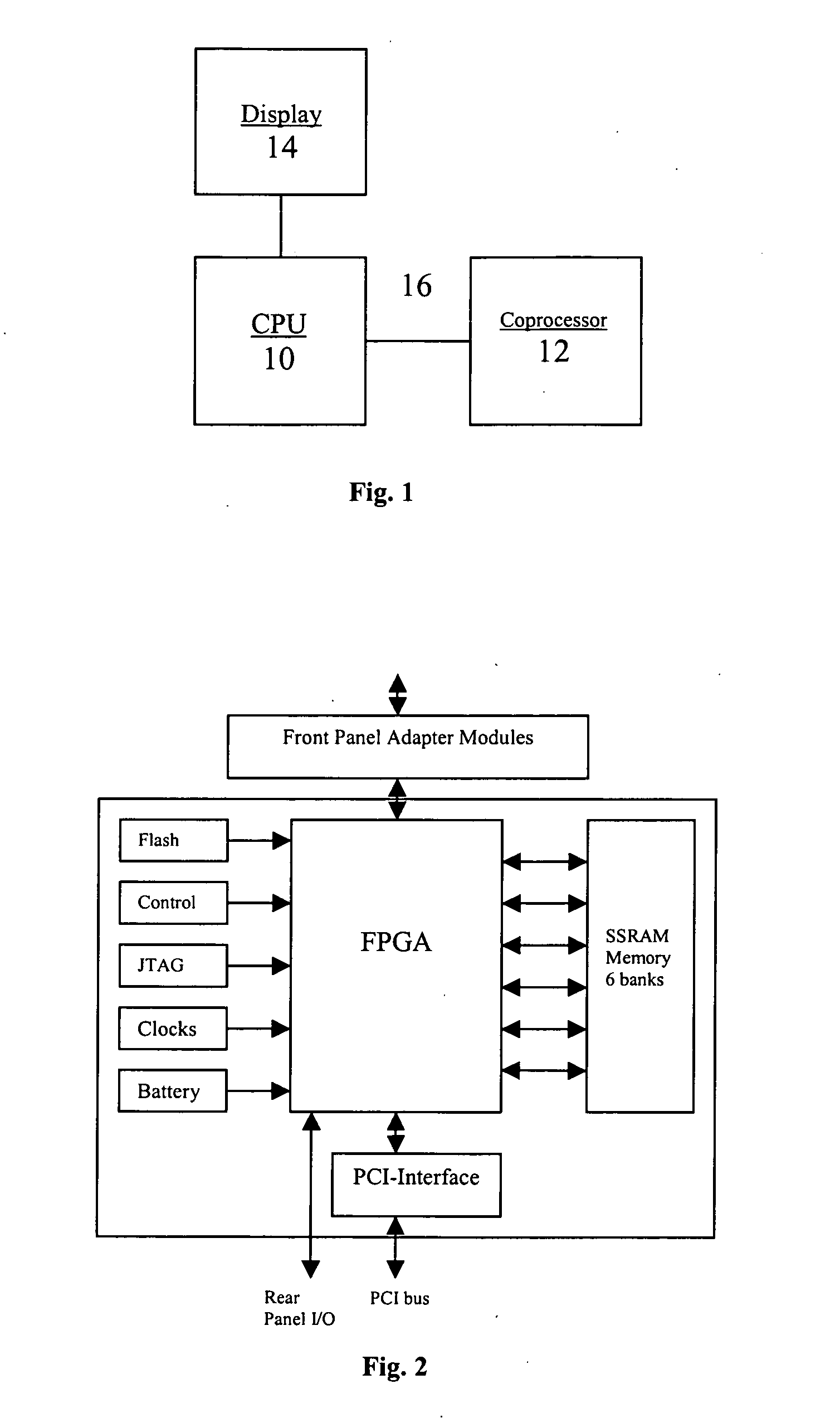
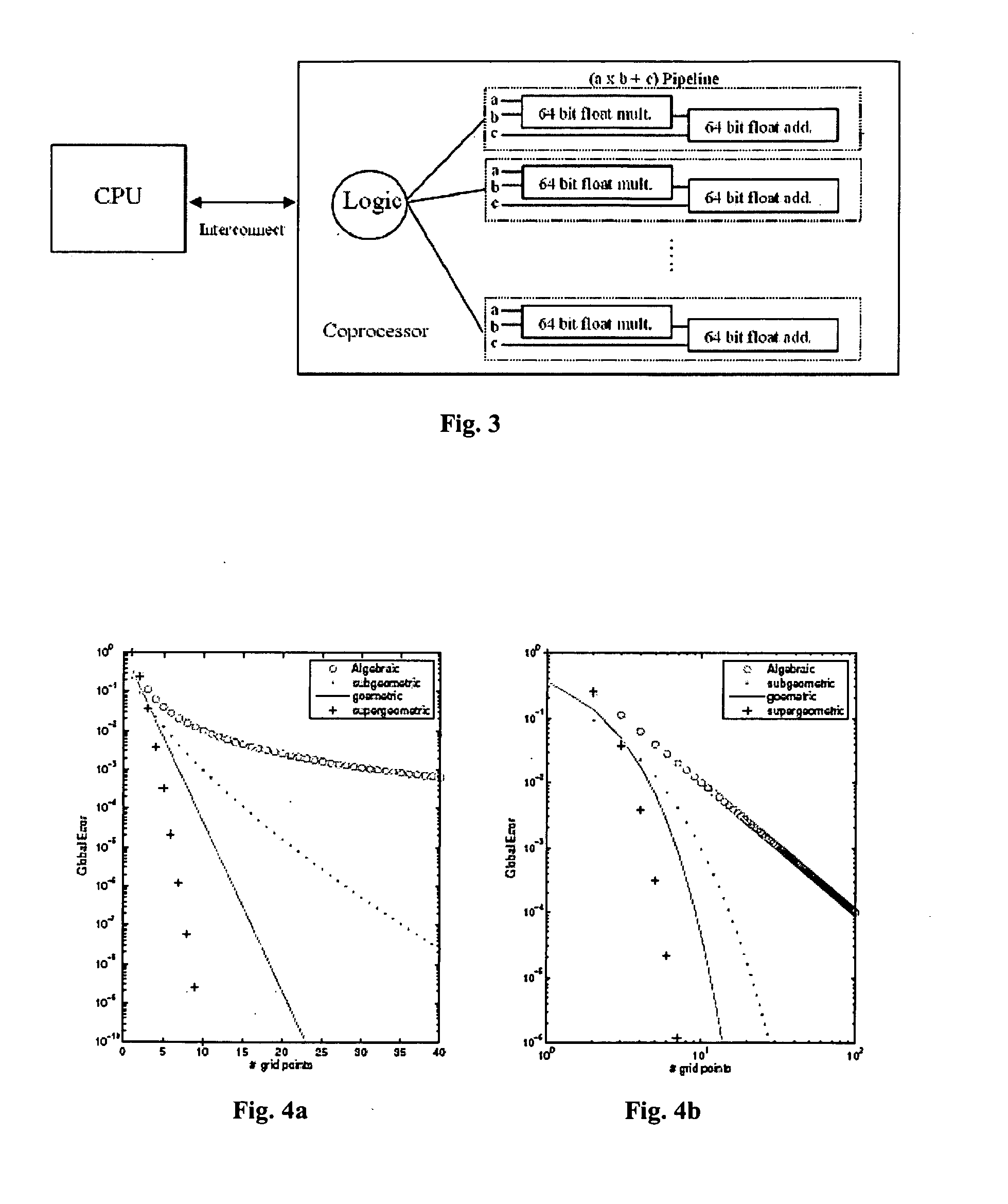
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) coprocessor-enhanced system and method
InactiveUS20070219766A1Cost-effectiveWide variety of usDesign optimisation/simulationProgram controlCoprocessorDisplay device
The present invention provides a system, method and product for porting computationally complex CFD calculations to a coprocessor in order to decrease overall processing time. The system comprises a CPU in communication with a coprocessor over a high speed interconnect. In addition, an optional display may be provided for displaying the calculated flow field. The system and method include porting variables of governing equations from a CPU to a coprocessor; receiving calculated source terms from the coprocessor; and solving the governing equations at the CPU using the calculated source terms. In a further aspect, the CPU compresses the governing equations into combination of higher and / or lower order equations with fewer variables for porting to the coprocessor. The coprocessor receives the variables, iteratively solves for source terms of the equations using a plurality of parallel pipelines, and transfers the results to the CPU. In a further aspect, the coprocessor decompresses the received variables, solves for the source terms, and then compresses the results for transfer to the CPU. The CPU solves the governing equations using the calculated source terms. In a further aspect, the governing equations are compressed and solved using spectral methods. In another aspect, the coprocessor includes a reconfigurable computing device such as a Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA). In yet another aspect, the coprocessor may be used for specific applications such as Navier-Stokes equations or Euler equations and may be configured to more quickly solve non-linear advection terms with efficient pipeline utilization.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Method for simulating stable but non-dissipative water
ActiveUS20070043544A1Decrease dampeningReduce the numberAnalogue computers for chemical processesComputation using non-denominational number representationDiffusionEngineering
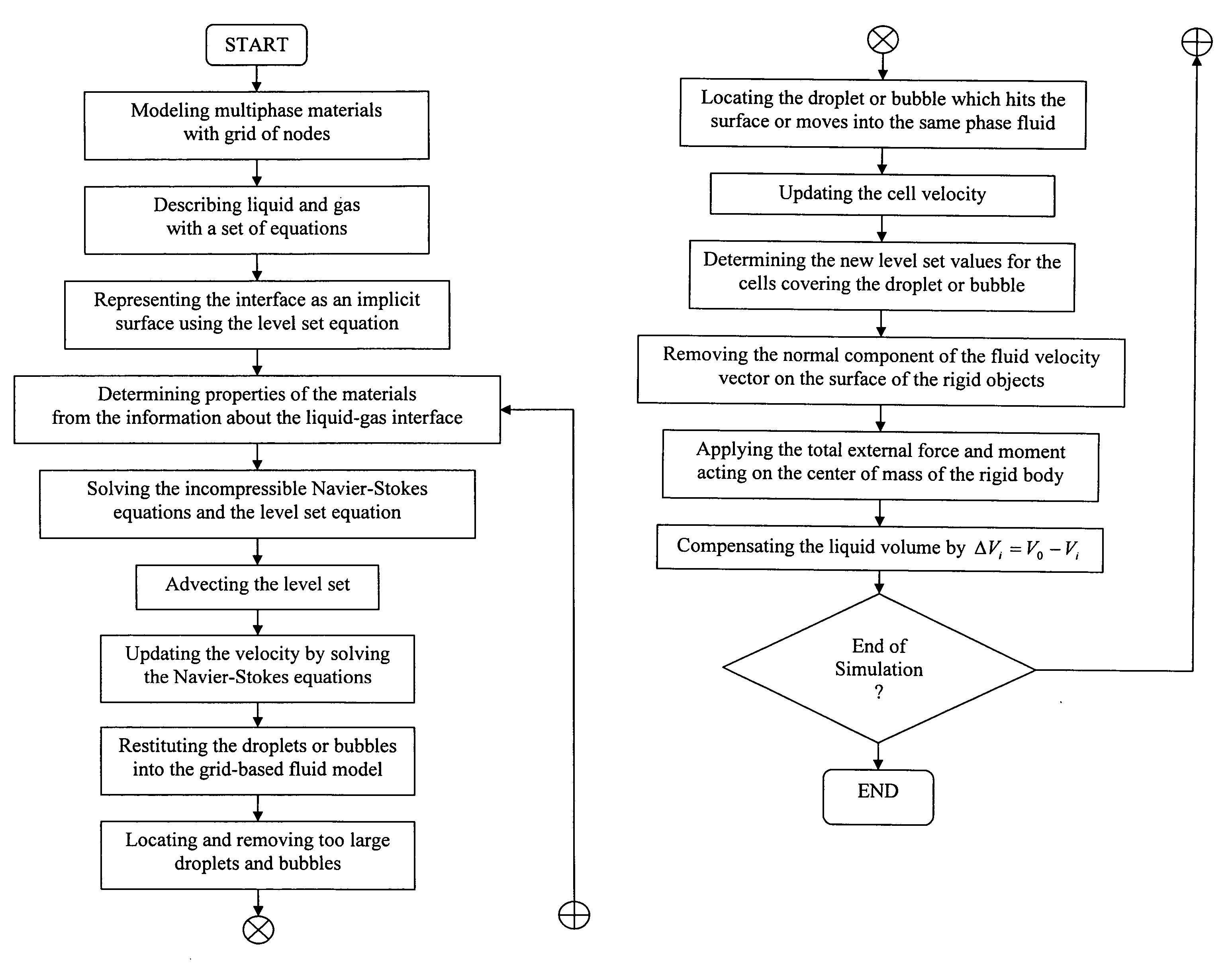
A method for graphically simulating stable but non-dissipative water in real-time includes steps for modeling multiphase materials with grid of nodes, suppressing numerical dissipation for getting rid of loss of mass of material, and suppressing numerical diffusion for reducing dampening of the fluid motion of materials in liquid phase. The step of modeling multiphase materials includes steps of describing liquid and gas with a set of nonlinear partial differential equations, representing the liquid-gas interface as an implicit surface, and determining properties of the materials, from the information about the liquid-gas interface, including the surface curvature and the surface tension. The set of nonlinear partial differential equations includes multiphase incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. The step of representing the liquid-gas interface includes a level set method.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND +1
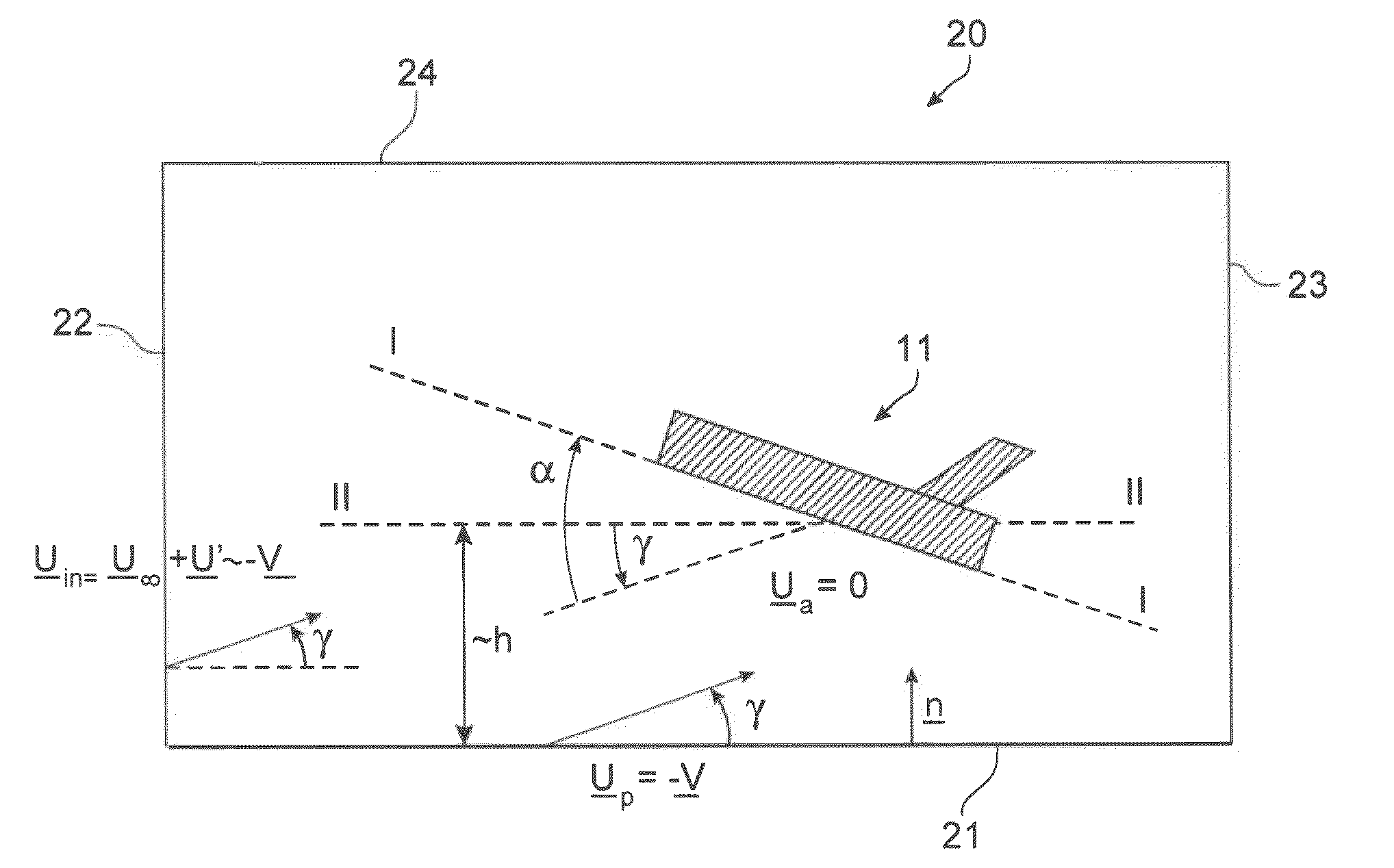
Method and tool for simulation of the aerodynamic behaviour of an aircraft in flight close to the ground
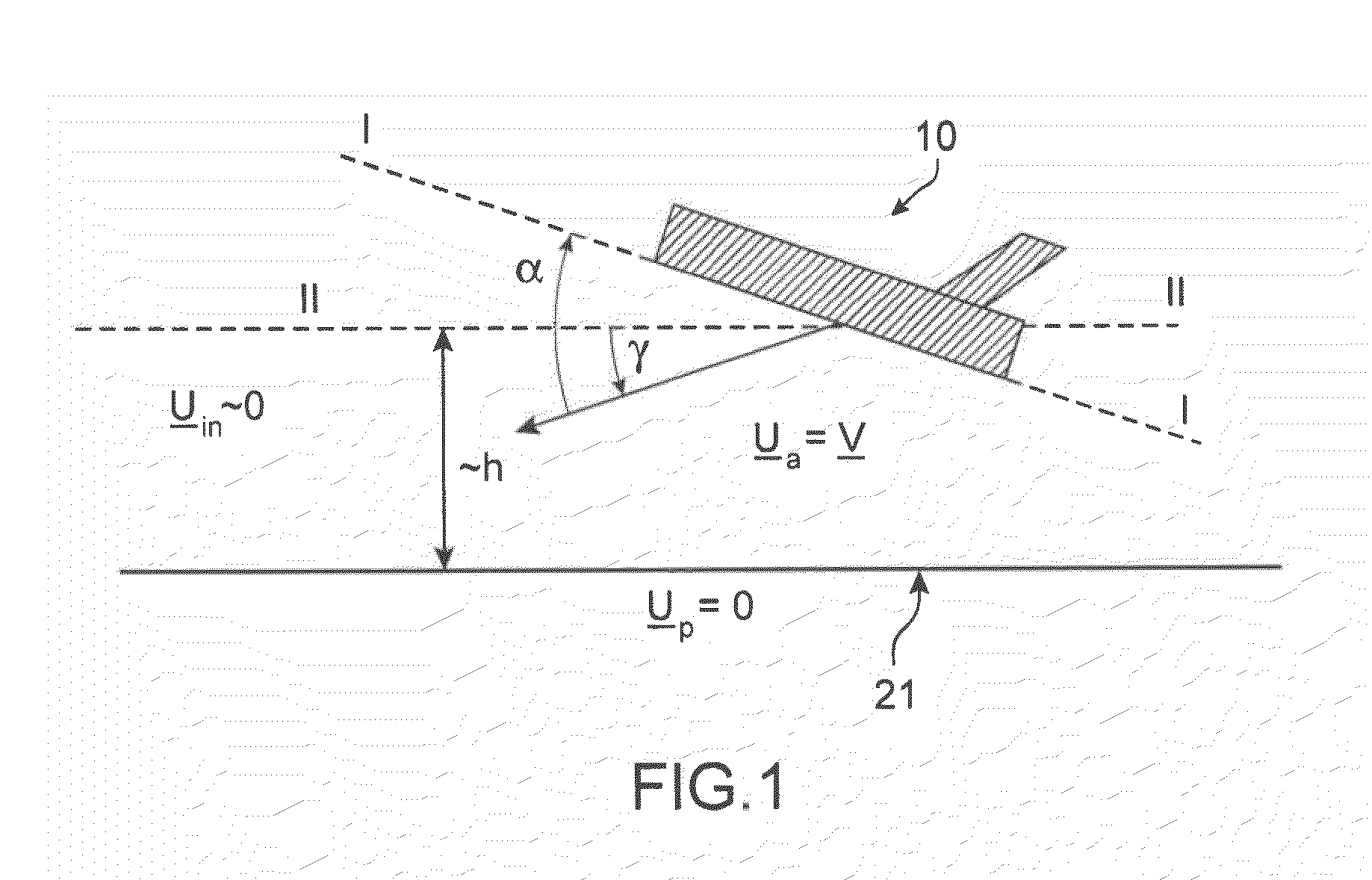
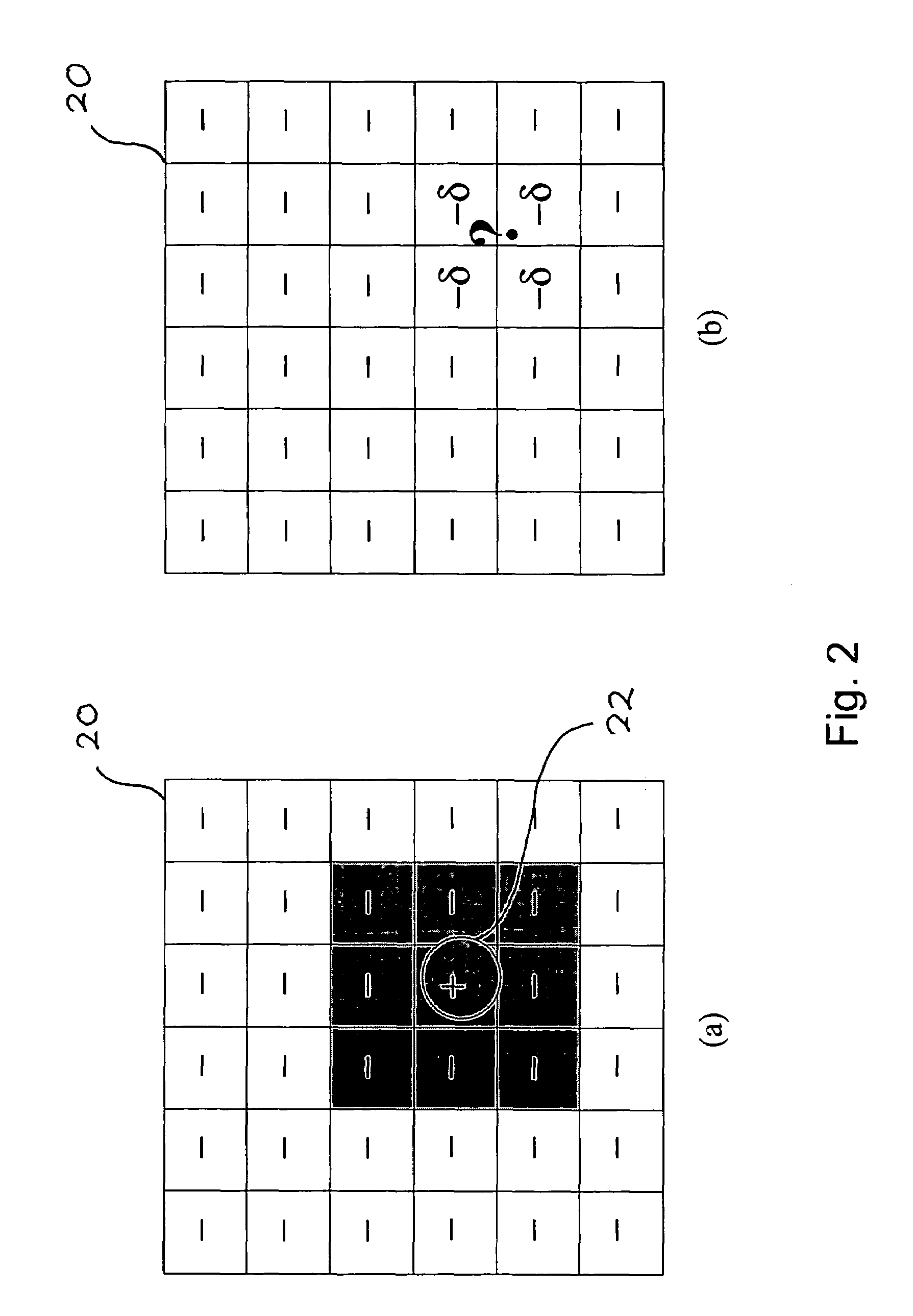
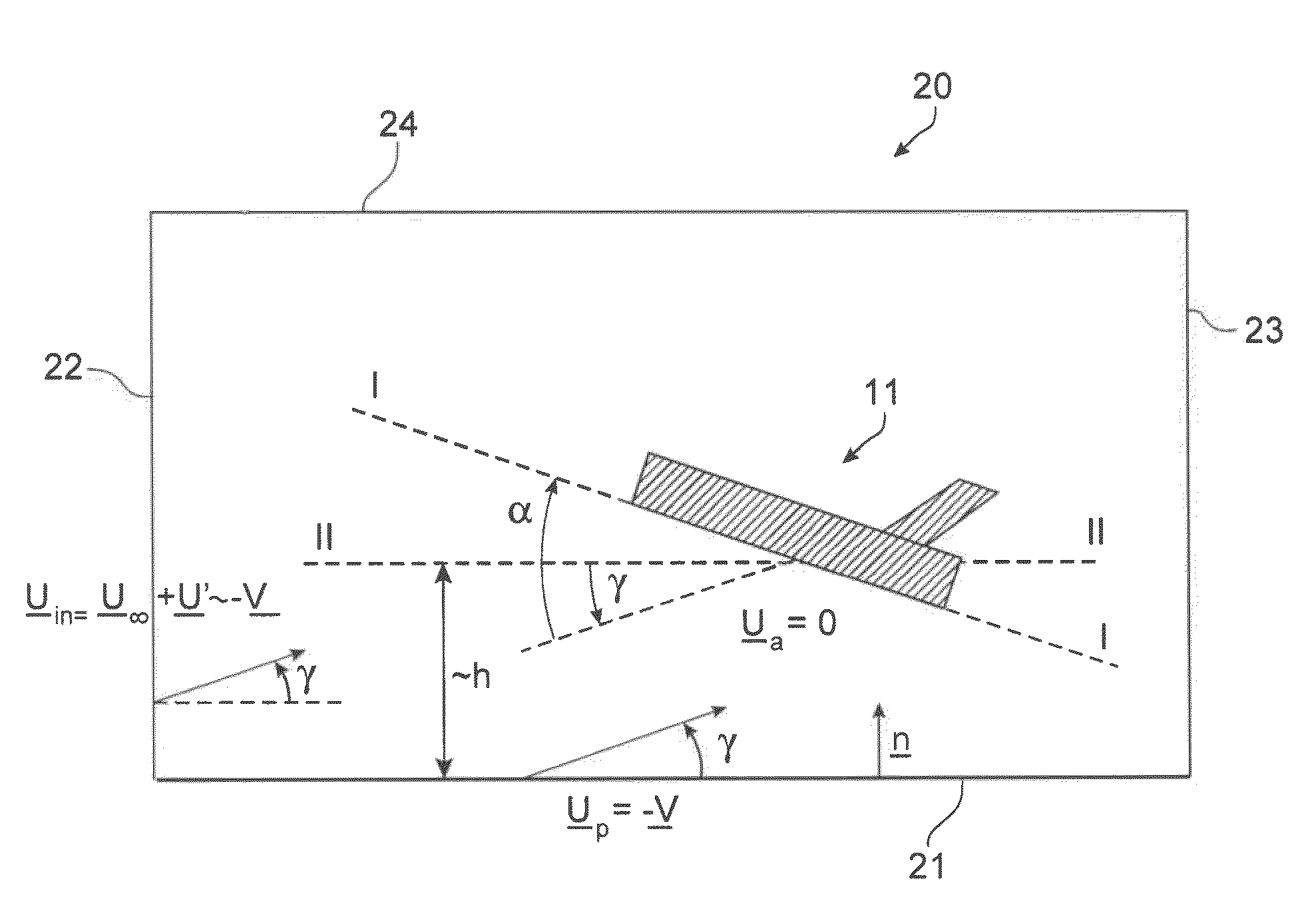
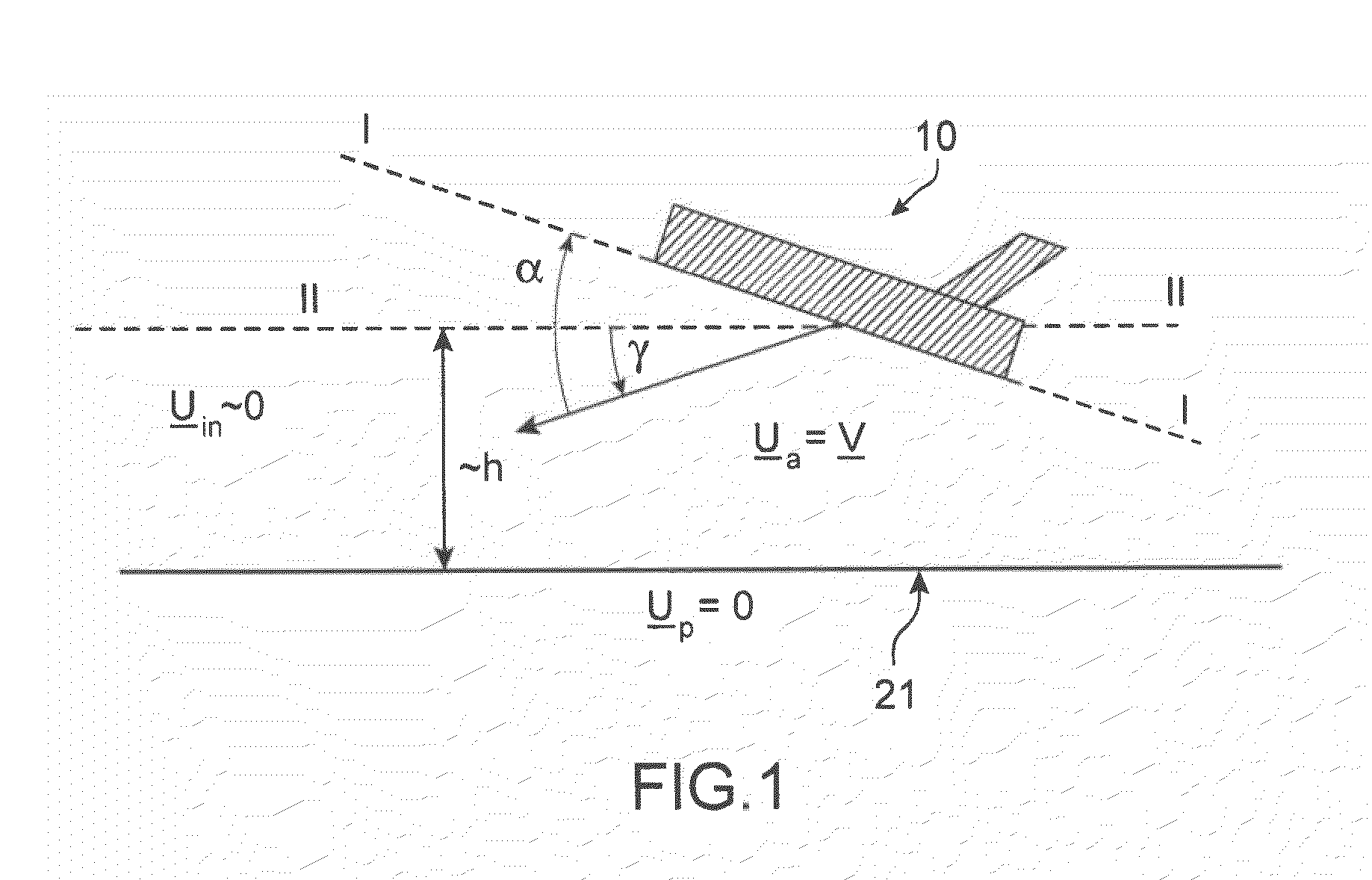
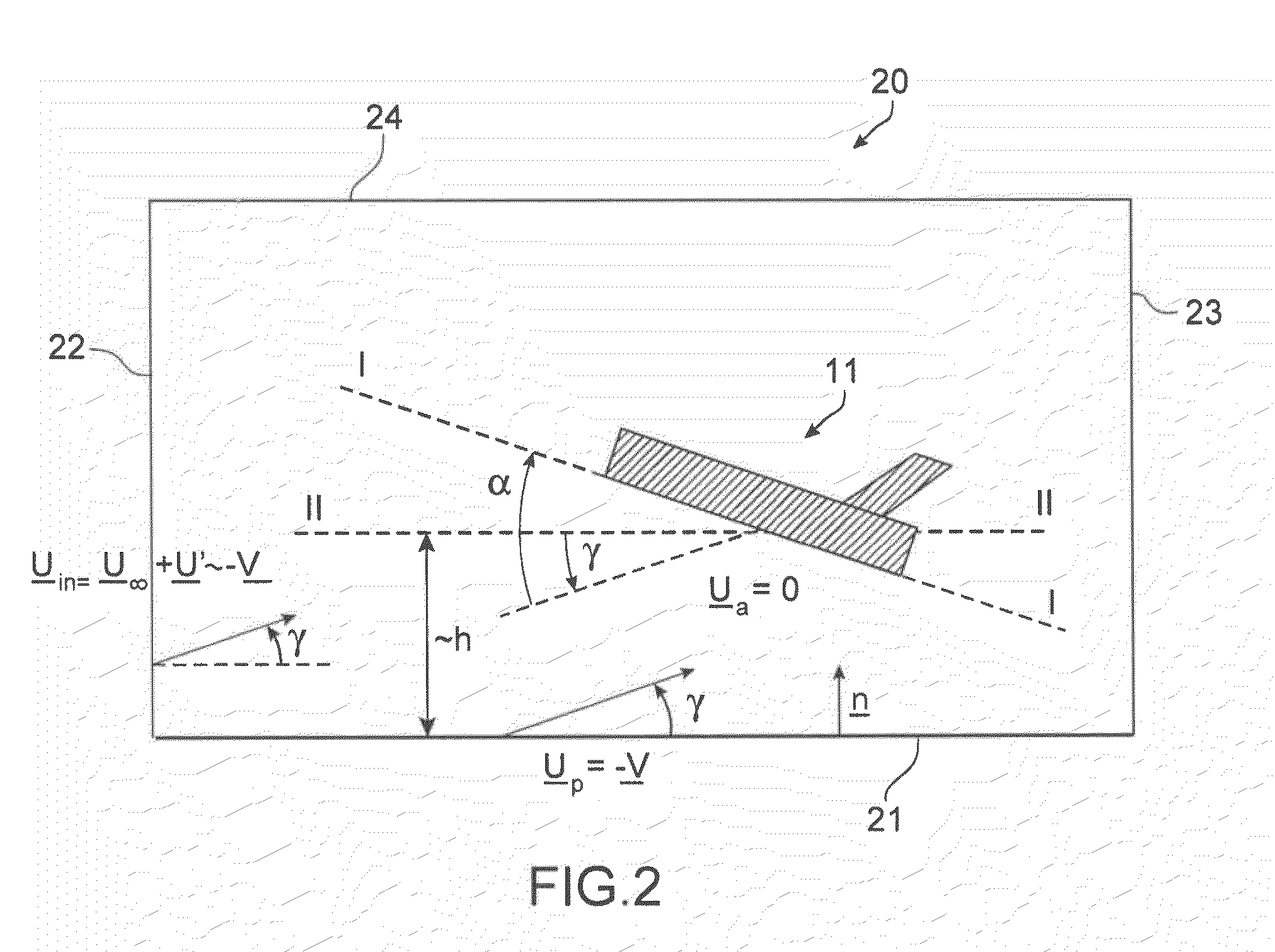
The invention relates to a method of computer simulation of the aerodynamic behaviour of an aircraft (10) in flight close to the ground. This method is used to identify the slope effect relative to the ground effect.To achieve this, a uniform boundary condition comprising a predetermined speed (UP) with a non-zero tangential component and a non-zero normal component is imposed on a plane (21) modelling the ground; and a discrete numerical model of the Navier-Stokes equations is solved by computer on a volume mesh with said boundary condition imposed on said plane (21), so as to obtain a numerical solution for a fluid flow inside a computational domain defined by said mesh.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
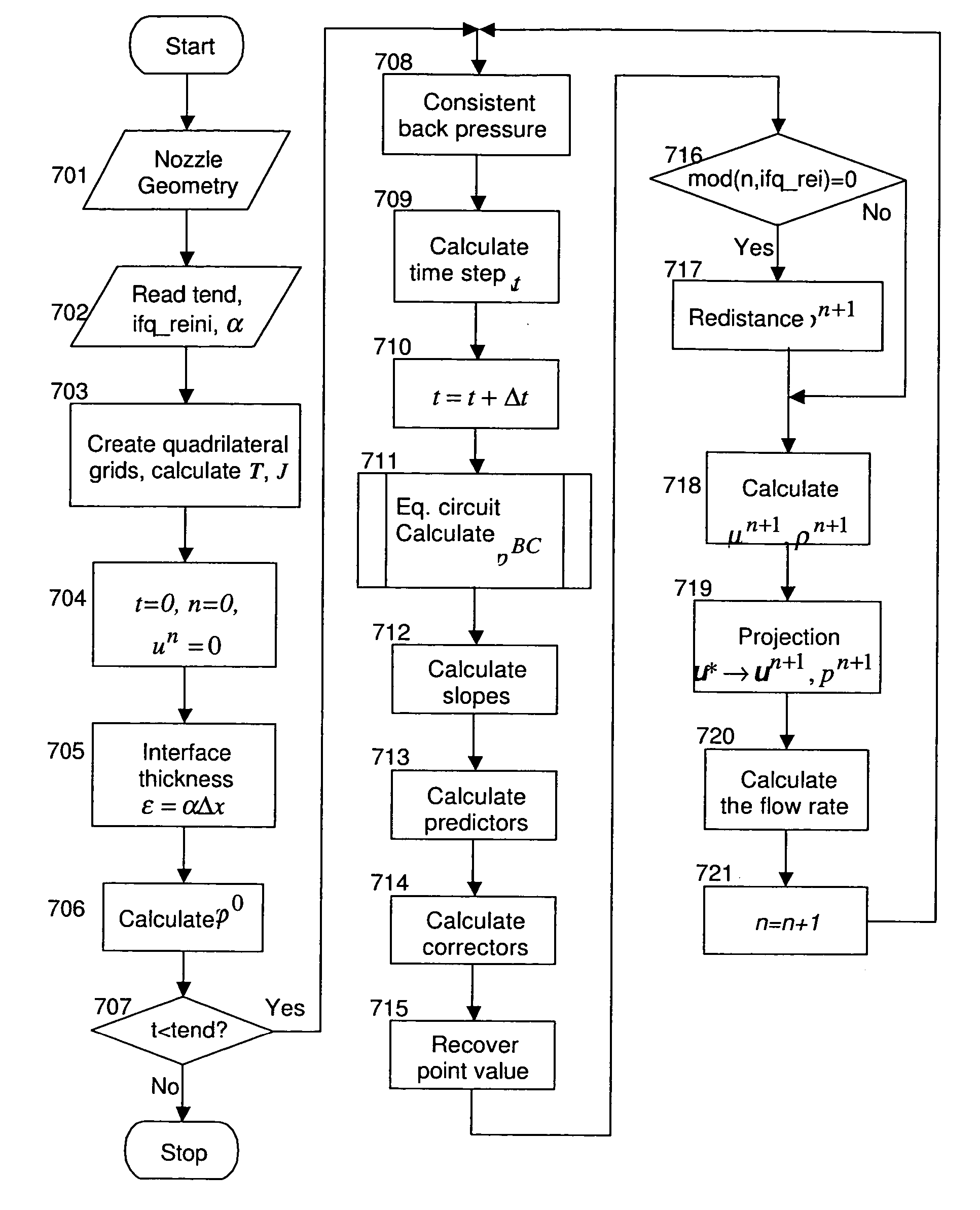
Quadrilateral grid extension of central difference scheme for ink-jet simulations
InactiveUS20070136042A1Design optimisation/simulationOther printing apparatusQuadrilateral gridComputer science
A central difference scheme, on which a coupled level set projection method is based, is extended to quadrilateral grids on axi-symmetric coordinate systems. The level set projection method is incorporated into a finite-difference-based ink-jet simulation algorithm. The extension involves modification of the Navier-Stokes equations and the level set convection equation. Moreover, the velocity and level set correctors in axi-symmetric coordinate systems should be “recovered” to point values before being projected. Numerical differentiation and integration in the central difference scheme are done in the computational space. The inventive algorithm may be embodied in methods, apparatuses, and instruction sets carried on device-readable mediums.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method of evaluation wind flow based on conservation of momentum and variation in terrain
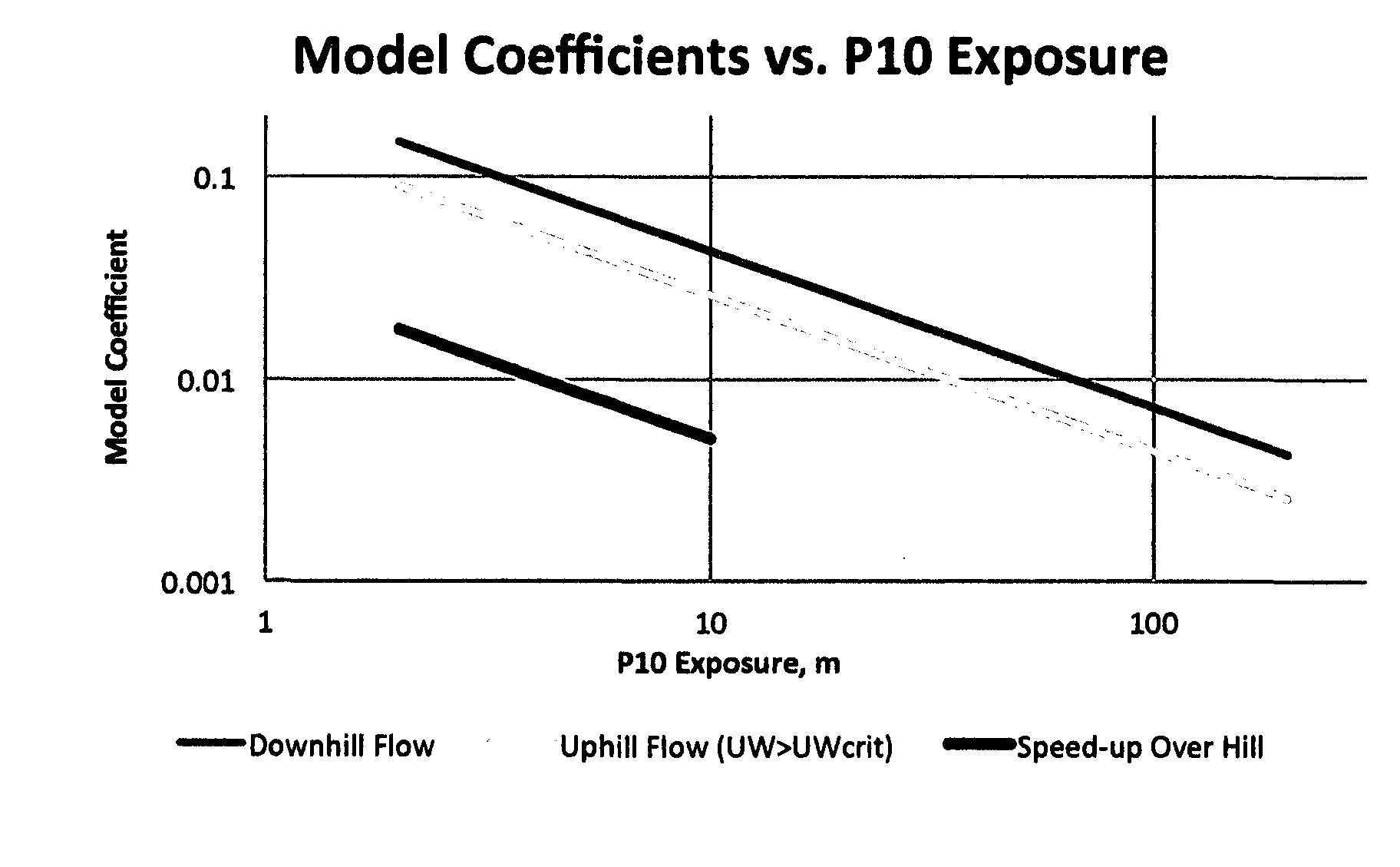
A method of modeling the spatial variation in wind resource at a prospective wind farm site. The method involves a simplified analysis of the Navier-Stokes equation and utilizes data from all of the met sites simultaneously to develop site-calibrated models. The model coefficients, mUW and mDW, describe the sensitivity of the wind speed to changes in the upwind and downwind terrain exposure and are defined for downhill and uphill flow. The coefficients are a function of terrain complexity and, since terrain complexity can change across an area, the estimates are performed in a stepwise fashion where a path of nodes with a gradual change in complexity is found between each pair of sites. Also, coefficients are defined for each wind direction sector and estimates are performed on a sectorwise basis. The site-calibrated models are created by cross-predicting between each pair of met sites and, through a self-learning technique, the model coefficients that yield the minimum met cross-prediction error are found.
Owner:ONE ENERGY ENTERPRISES INC
Simulation analysis method for pressure separation of spacecraft
ActiveCN108388742ASustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationBoltzmann equationContinuous flow
The invention relates to a simulation analysis method for pressure separation of a spacecraft, and belongs to the technical field of spacecraft simulation. The simulation analysis method comprises thefollowing steps: decomposing a pressure compartment into an internal continuous flow field and an external rarefied flow field for computation respectively; building a theoretical model to give the boundary condition of the entrance / exit of a computation domain; computing an internal region flow field by a CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) method, and solving an external region flow field by a DSMC (Direct simulation of Monte Carlo) method; finally determining the disturbing force of the pressure separation on two spacecrafts according to a flow field analysis result. The computed flow fieldcan be divided into two parts: a flow field inside the pressure compartment (continuous flow) and a flow field outside the spacecraft (rarefied flow). The basic governing equation of the continuous flow field in the pressure compartment is a Navier-Stokes equation, which is computed by the CFD method; the basic governing equation of the rarefied flow field outside the spacecraft is a Boltzmann equation, which is simulated by the DSMC method.
Owner:BEIJING SPACE TECH RES & TEST CENT
Simulation method based on potential distribution of corona discharge space
ActiveCN106354925AAccurate and Efficient ComputingConvenient researchDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElectricityCorona discharge
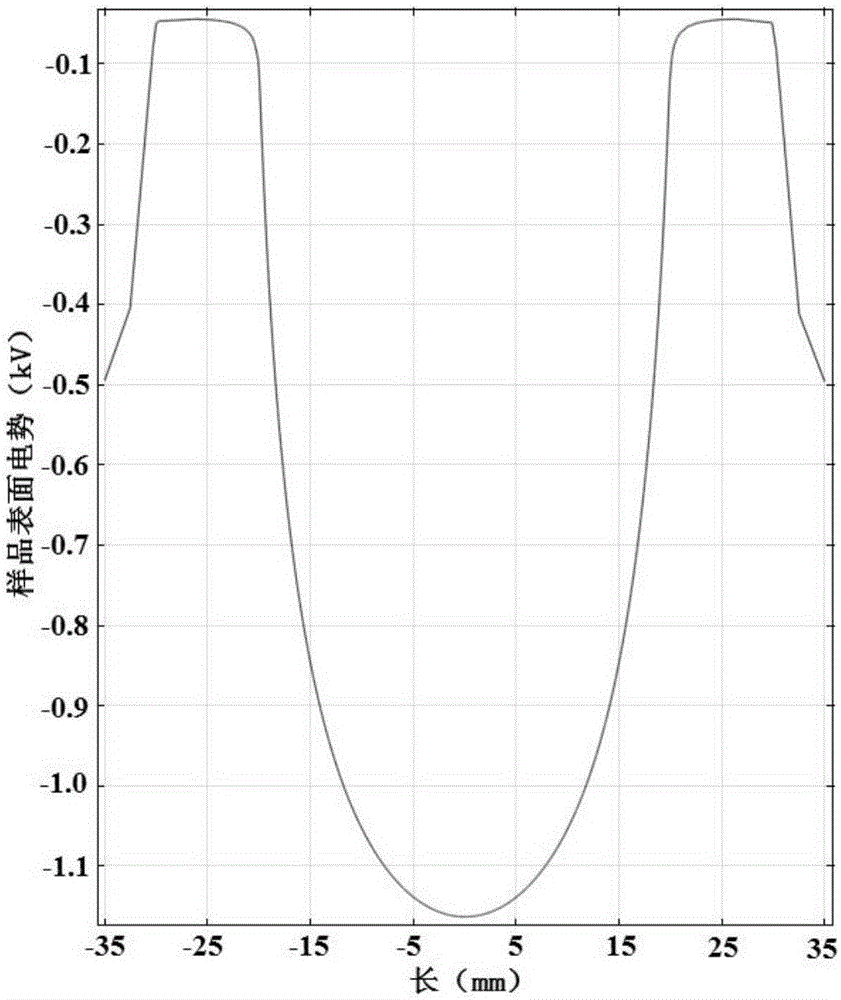
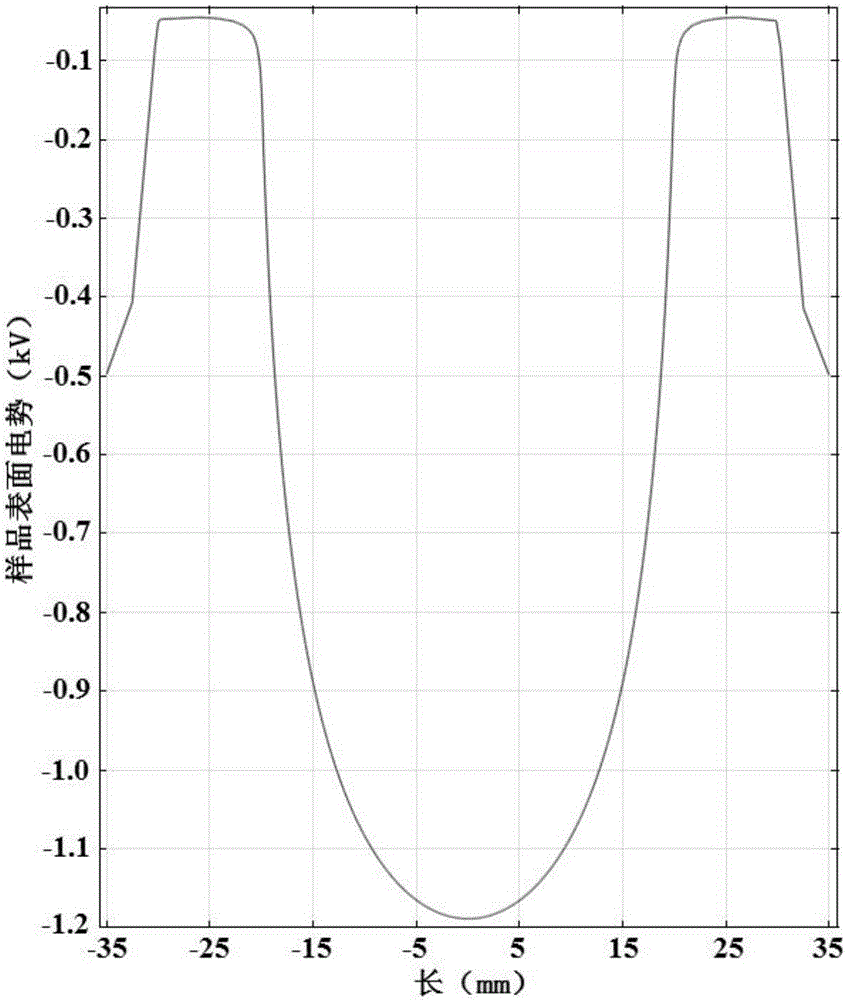
The invention is a simulation method based on potential distribution of corona discharge space. Based on Poisson equation and particle continuity equation, the simulation model adds the Navier-stokes equation which can describe the mobility of particle. The reason is that corona discharge is a process of particle movement and collision, the rapid movement of particle can cause the gas flow in discharge space and can influence the potential distribution in space. Coupling the Navier stokes equation which can describe the mobility of particle with Poisson equation and particle continuity equation, the method gets the potential contribution on the surface of sample through adjusting the parameter of simulation model, then, comparing the potential contribution with the measurement result of potential on the surface of sample to verify the effectiveness of the model. The method can calculate the potential distribution of discharge space rapidly which comprises potential distribution on the surface of sample. The method provides significant theoretical support for studying corona discharge mechanism, microscopic discharge process and simulating the effect of polarization of material.
Owner:榆林市长江送变电工程有限责任公司
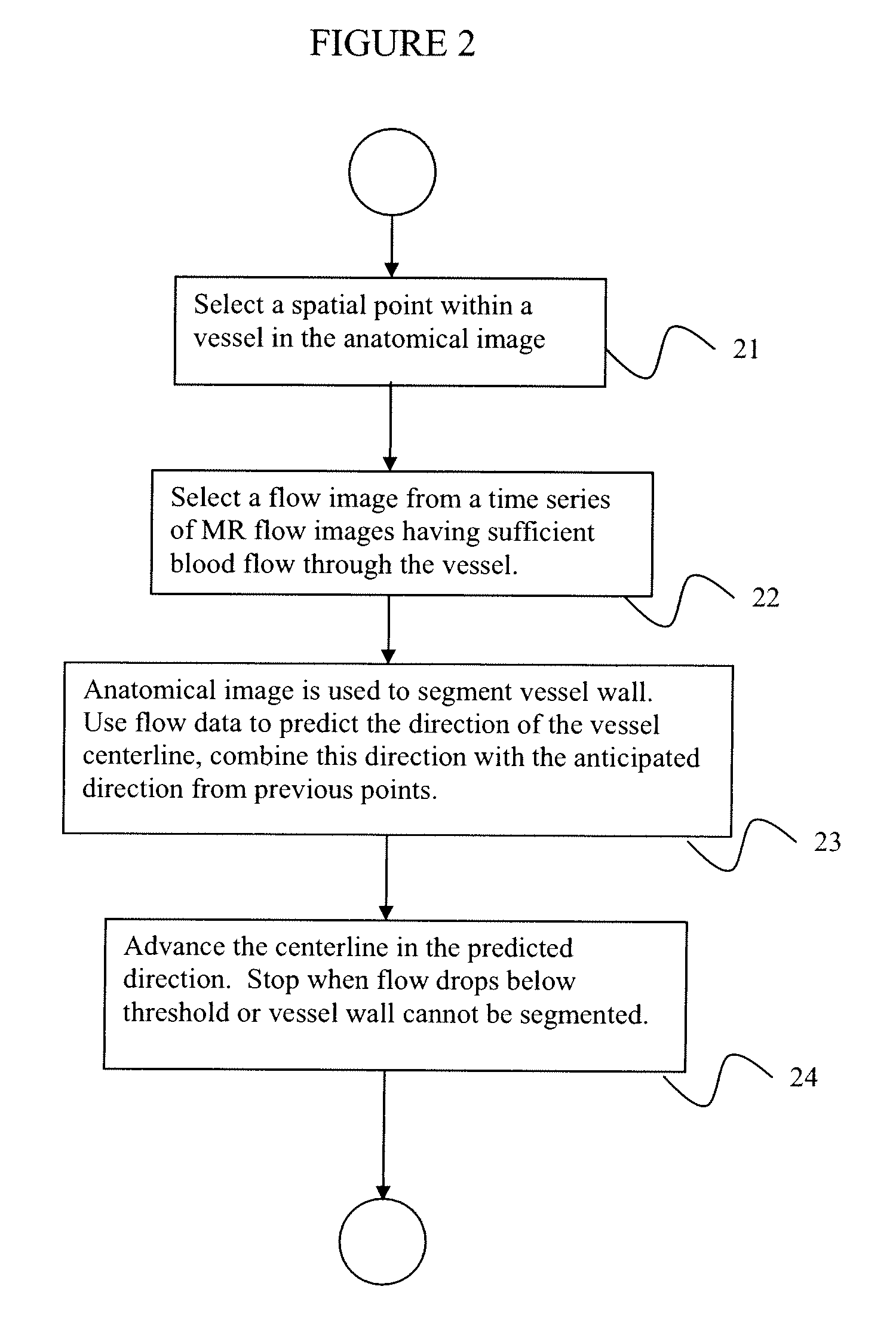
System and method for segmentation of mr flow data using fluid dynamics and tracking
InactiveUS20100014739A1Improve segmentationOptimalImage enhancementImage analysisDiffusion methodsVector field
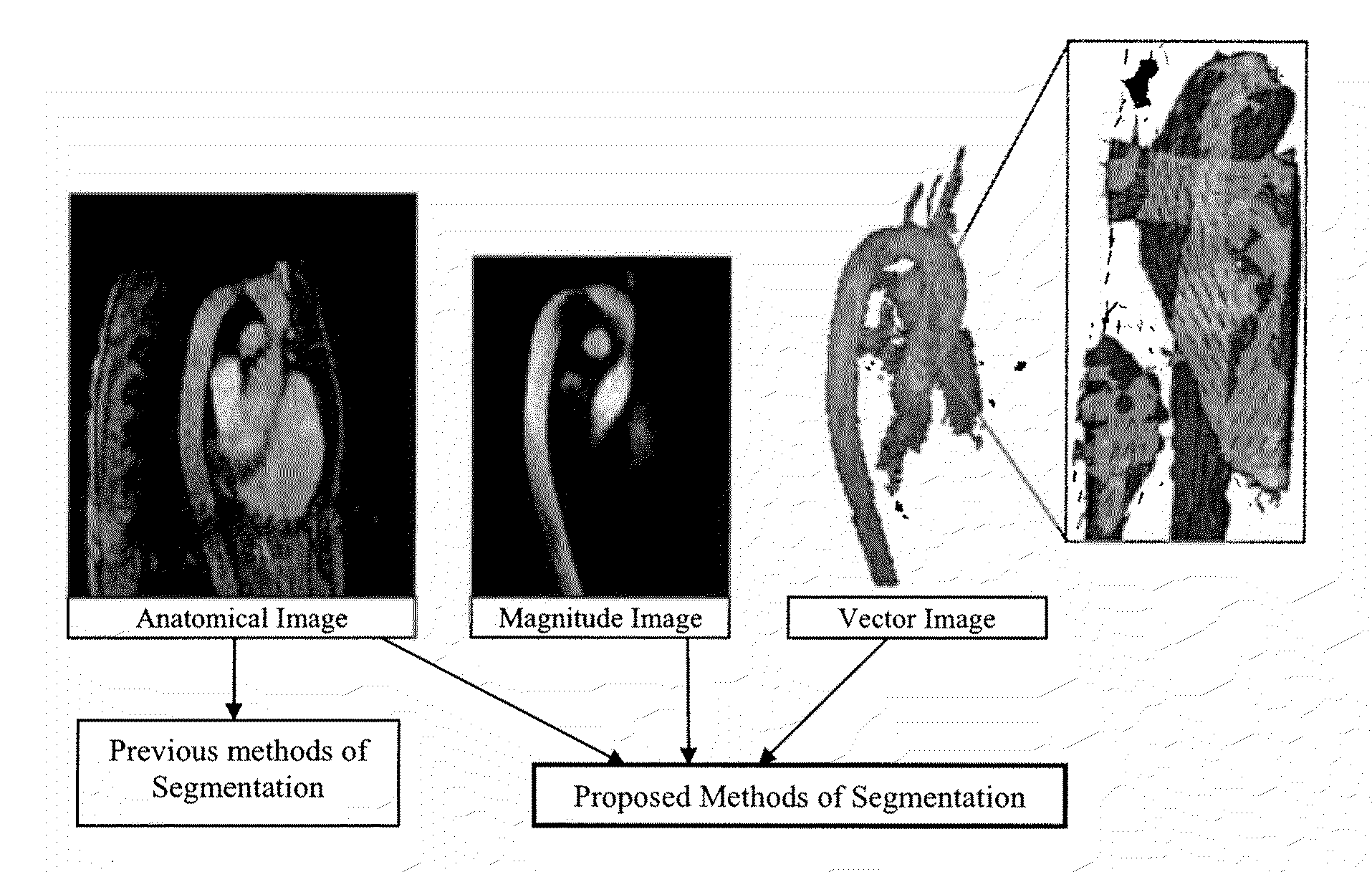
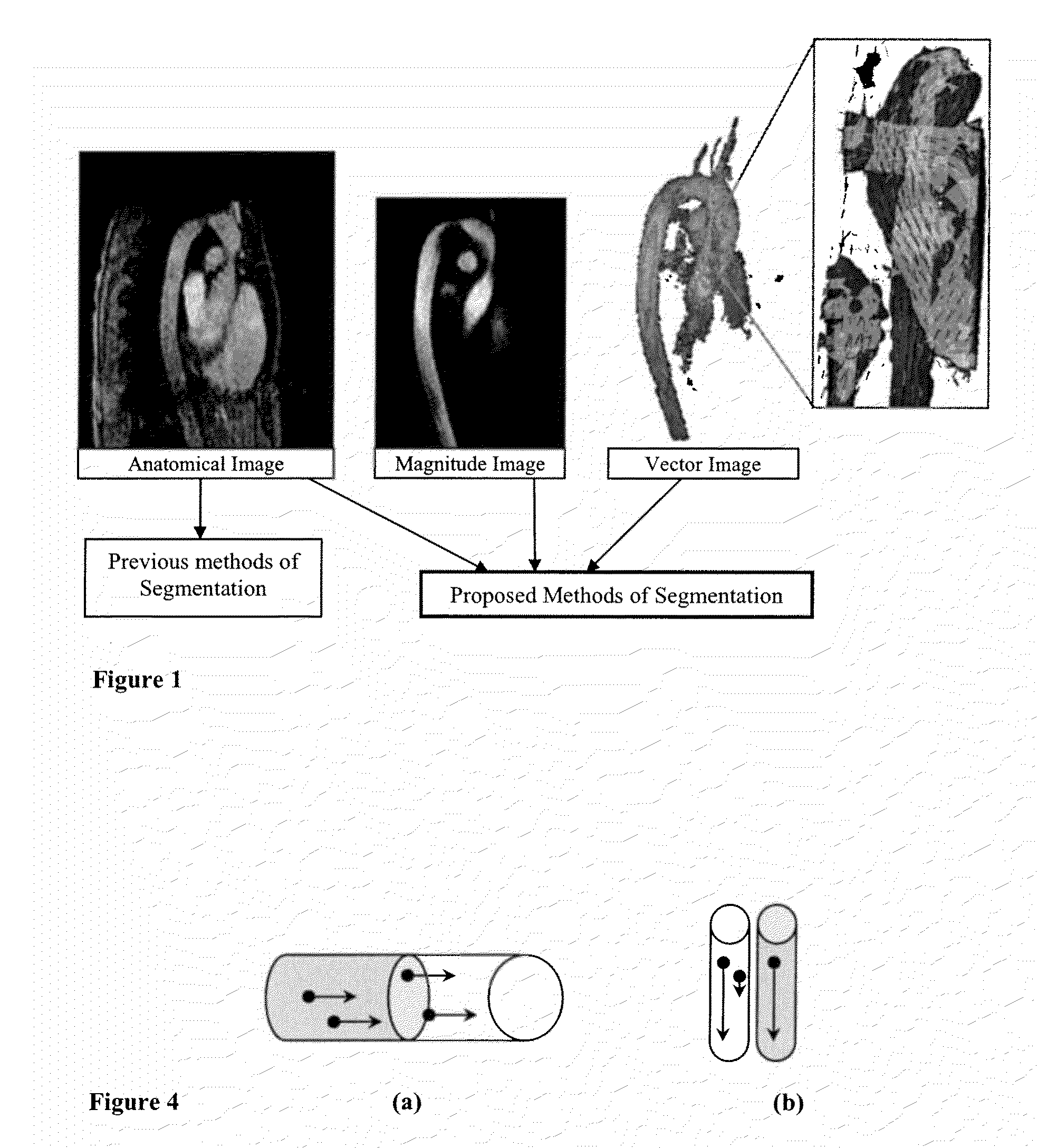
Methods for vessel segmentation and tracking using 7D MRI flow image data incorporate information from the velocity field and the magnitude. A vessel tracking methods selects a time containing sufficient blood flow through a vessel, uses the magnitude image to determine the vessel boundary and uses the velocity image to define the vessel direction. A method for segmenting tubular and circular objects segments the objects into separate vessels and then uses the velocity data to reunite the objects, where touching components are evaluated by the velocity field where they are connected. If vectors point towards the other component, the two components are reconnected. An advection-diffusion method based on fluid dynamics performs a fluid dynamics simulation with image forces according to the Navier-Stokes equations. With the 7D data, the vector field is available from the flow data, from the time point at which maximal flow occurs in the vessel of interest.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
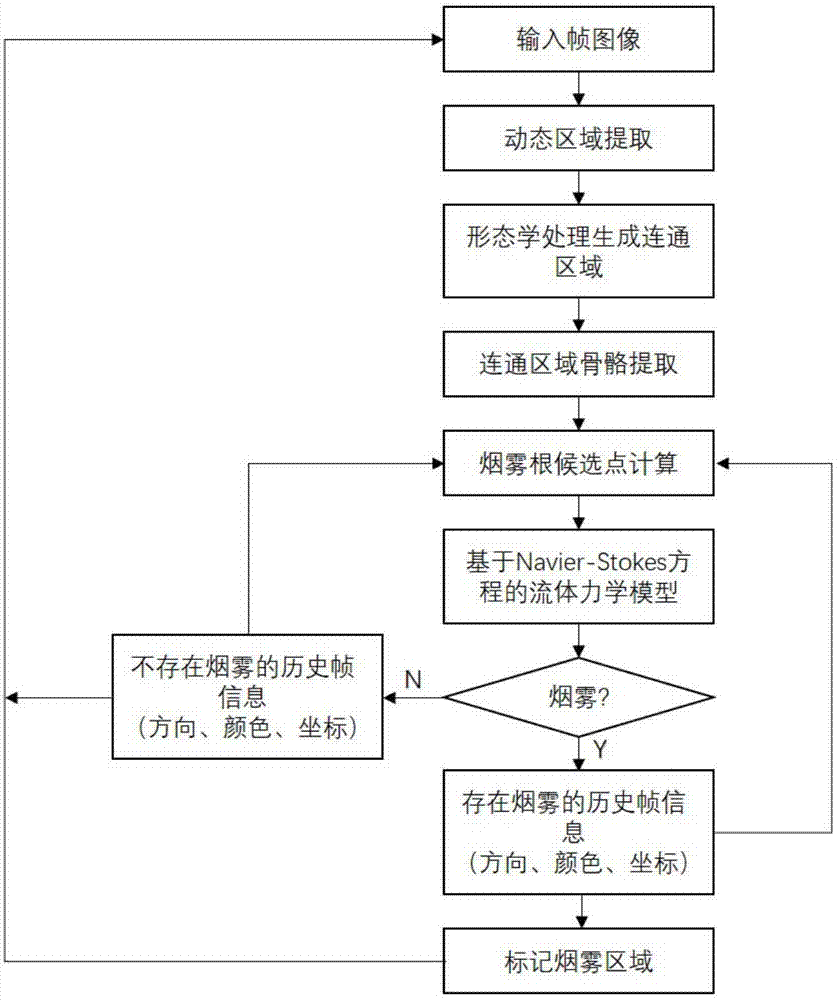
Forest fire smoke video target detection method based on characteristic roots and hydromechanics
ActiveCN108009529AJudgment result is stableAvoid accidental miscalculationCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingCalculation error
The invention discloses a forest fire smoke video target detection method based on characteristic roots and hydromechanics. The method comprises: firstly, extracting a dynamic region from a video by extracting continuous frames of image from the video; secondly, using a morphological algorithm to calculate the connected region skeleton image of the dynamic region; then extracting suspicious smokeroot characteristic candidate points in the endpoints of continuous frames of skeleton image; subjecting the smoke root characteristic candidate points to determination based on a Navier-Stokes equation to obtain the predicted smoke image of the smoke root characteristic; and finally fusing and determining the predicted image and a current actual image to obtain a smoke area. Because the algorithmhas certain predictability and can continuously affect the decision information of continuous frames, a determined result is stable and accidental calculation errors caused by an image processing stage can be avoided.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
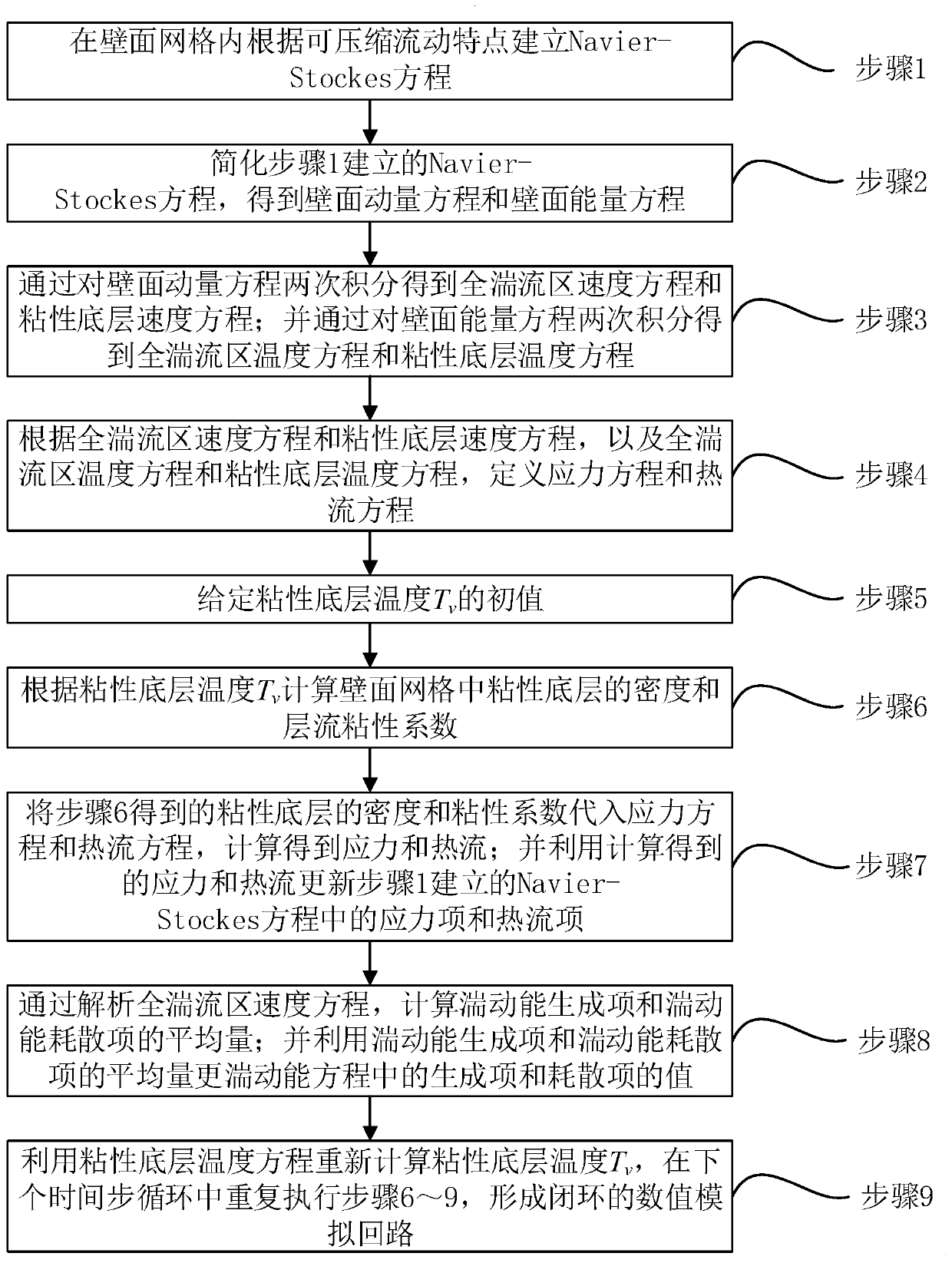
Compressible flow-based numerical simulation method for analyzing wall surface function
ActiveCN110489709ATightly coupledAccurate predictionComplex mathematical operationsSpeed of soundKinetic energy
The invention discloses a numerical simulation method for analyzing a wall surface function based on compressible flow. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a Navier-Stokes equationaccording to compressible flow characteristics, simplifying the Navier-Stokes equation, analyzing the Navier-Stokes equation to obtain a full turbulence zone speed equation, a viscous bottom layer speed equation, a full turbulence zone temperature equation and a viscous bottom layer temperature equation, and further defining a stress equation and a heat flow equation; giving an initial value of the temperature Tv of the viscous bottom layer, and calculating according to the Tv to obtain stress and heat flow; updating a stress item and a heat flow item by utilizing the calculated stress and heat flow; updating the values of a generation item and a dissipation item in the turbulence energy equation by calculating the average quantity of the turbulence energy generation item and the turbulence energy dissipation item; and finally, recalculating Tv by utilizing a viscous bottom layer temperature equation, and repeatedly updating in the next time step cycle. Based on the compressible flow characteristic, the method is particularly suitable for hypersonic flow, and the wall surface heat flow can be predicted more accurately.
Owner:CALCULATION AERODYNAMICS INST CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
Rocket engine tail jet flow simulation method and system
ActiveCN108304684AMake up for the inability to accurately predict supersonic compressible jet flow under large temperature gradientImprove accuracyGeometric CADSustainable transportationJet flowComputational model
The invention relates to a rocket engine tail jet flow simulation method and system. The method includes the steps of (1), establishing a three-dimensional geometric model with the size same as a rocket engine jet pipe; (2), conducting grid partition and encryption on the three-dimensional geometric model to determine boundary conditions; (3), establishing a calculation model to ensure that a tailjet flow process satisfies a viscosity Navier-Stokes equation; (4), conducting iterative solution on a rocket engine tail jet flow model by using a computational model, and completing the simulationprocess of rocket engine tail jet flow. A temperature-corrected SST k-omega turbulence model is adopted for calculating the rocket engine tail jet flow, the defect that existing turbulence models cannot accurately predict supersonic compressible jet flow under a large temperature gradient is remedied, the accuracy of a simulation result is significantly improved, and an error between the simulation result and an experimental result is reduced to 1%.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE PROPULSION INST
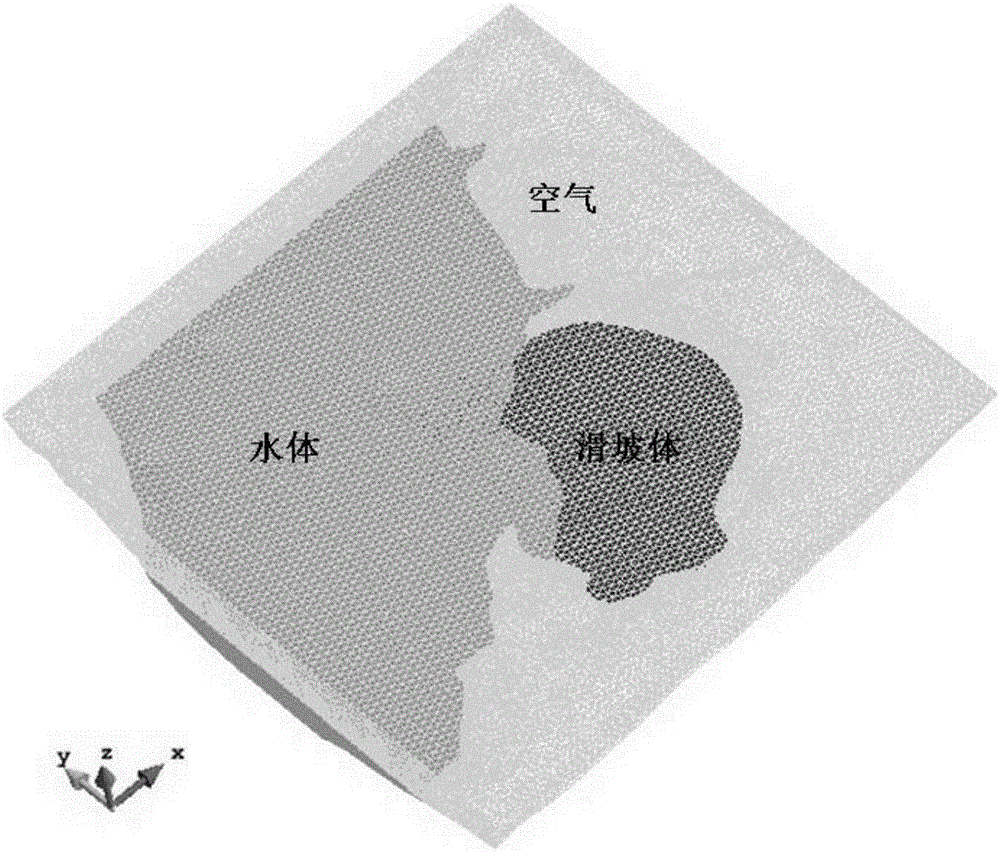
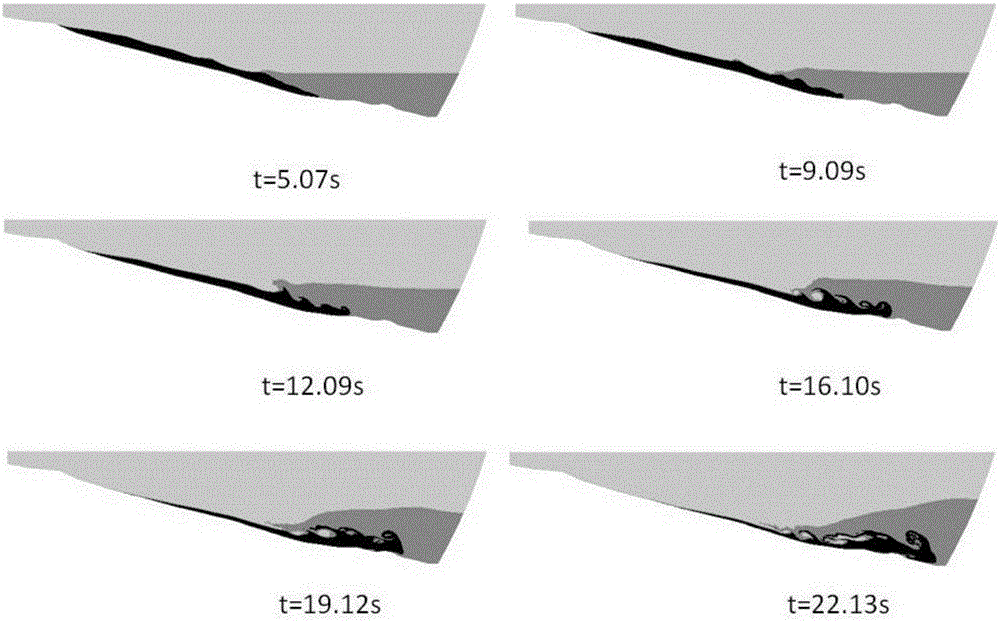
Land slide surge calculation method
The invention relates to a land slide surge calculation method. The process from bank slope slip mass water entry to stages of surge propagation serves as a complete and unified process for analysis and research. The method includes the following steps that firstly, a three-dimensional finite element model is built according to existing terrain, water level and slip mass shape position data; secondly, the interaction of a water body, air and a slip mass is described by means of a Navier-Stokes equation, the free surface of a fluid is accurately captured through an improved conserving scheme Level Set method, the surge generation process is truly simulated, and reasonable preconditions are provided for surge propagation and disaster prediction; thirdly, the surge propagation process is simulated by means of a fluid control equation of an integral along the water depth, numerical forecasting is conducted on a surge motion track and an inundation area, and a surge disaster is assessed. The method has a great theoretical significance and practical value in prediction of bank slope unstable failures and surge secondary disasters, and also has a referential significance in numerical simulation of similar landslide, debris flow, barrier lakes and other geological disasters.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
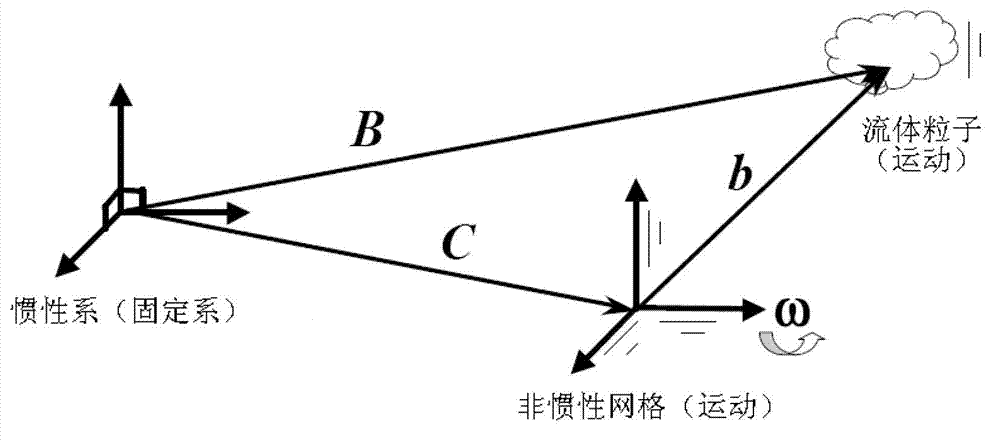
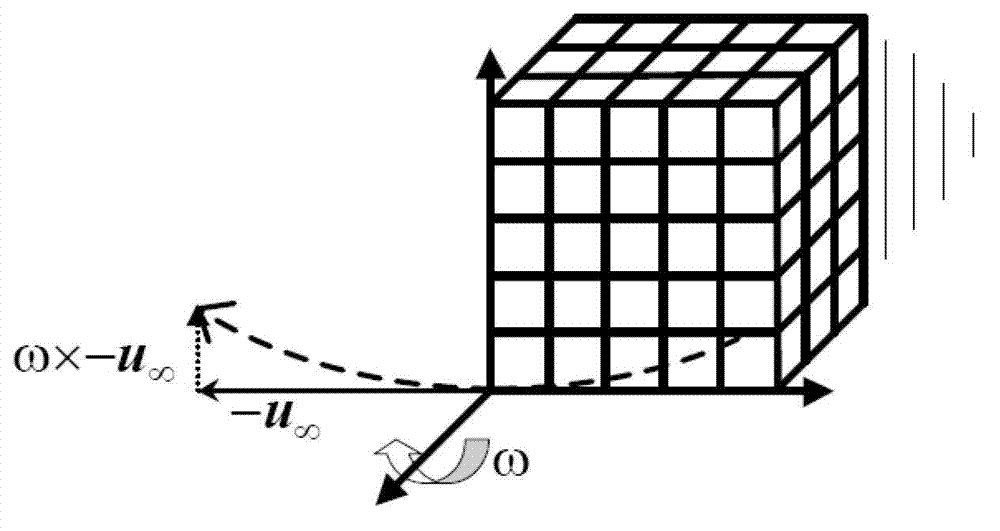
High-reliability method for rapidly forecasting rolling dynamic derivative of aircraft
ActiveCN103400035AQuick forecastIncrease credibilitySpecial data processing applicationsRotation velocityComputer science
The invention discloses a high-reliability method for rapidly forecasting a rolling dynamic derivative of an aircraft. The high-reliability method includes the steps of generation of model surface grids and division of spatial grids, calculation of aerodynamic parameters under a rotating coordination system, and difference calculation of the rolling dynamic derivative. A calculation method for the aerodynamic parameters under the rotating coordination system includes (1), transforming a Navier-Stokes equation under an inertial system to the rotating coordinate system; (2), performing numerical solution on the transformed equation to acquire a flow field of each state; (3), acquiring aerodynamic force through surface integration of object-plane pressure and viscous stress, taking moment from the center of mass through surface force and integrating to acquire aerodynamic moment acting on the center of mass. The difference calculation includes calculating the aerodynamic force and the aerodynamic moment of a model at two different revolving speeds, and acquiring the rolling dynamic derivative of the model by a difference method. The method is high in reliability of calculation results, has a much smaller calculated amount as compared with a non-steady forced vibration method which is time-consuming for accurate solution, and can quickly forecast the rolling dynamic derivative of the aircraft in a highly reliable manner.
Owner:INST OF HIGH SPEED AERODYNAMICS OF CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
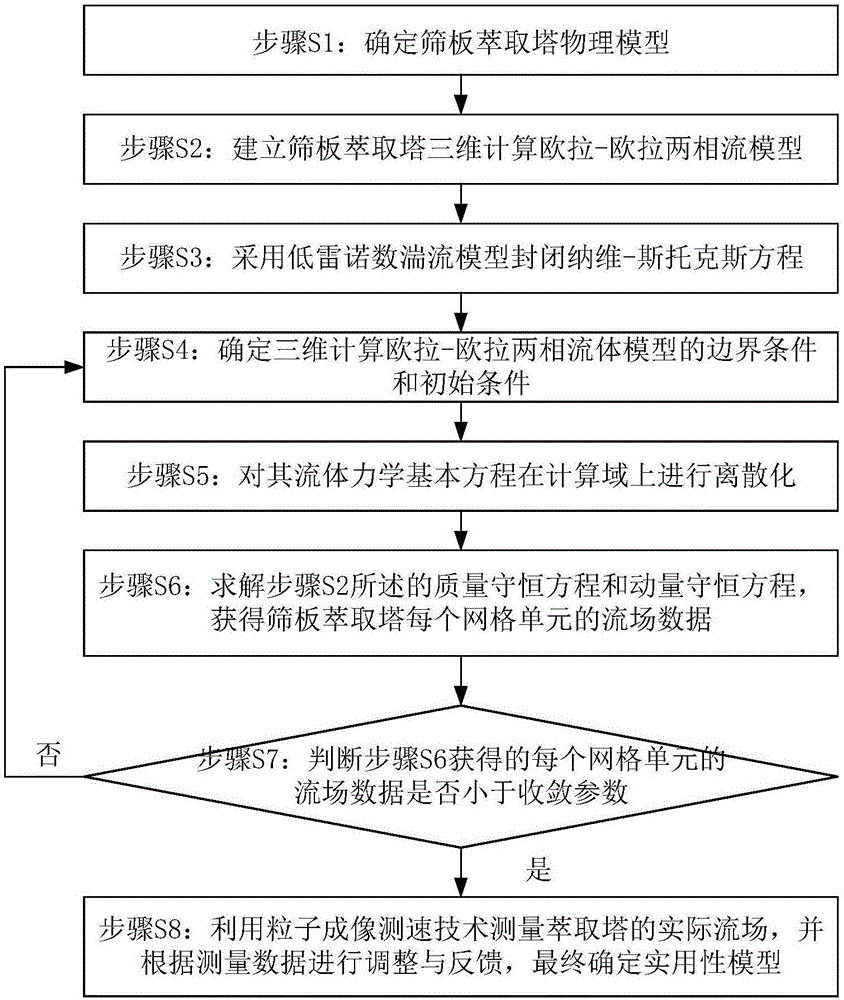
Method for calculating sieve plate extraction tower liquid flow field by using low Reynolds number turbulence model
InactiveCN106682348AAccurate calculation of hydrodynamic informationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsPhysical modelEngineering
The invention discloses a method for calculating a sieve plate extraction tower liquid flow field by using a low Reynolds number turbulence model. The method includes the following steps: (1) determining a sieve plate extraction tower physical model; (2) establishing a sieve plate extraction tower three-dimensional calculation Euler-Euler two-phase flow model; (3) using the low Reynolds number turbulence model to seal a Navier-Stokes equation (N-S equation); (4) determining a boundary condition and an initial condition for solving the three-dimensional calculation Euler-Euler two-phase flow model; (5) performing discretization on a fluid mechanics basic equation in a computational domain; and (6) solving a mass conservation equation and a momentum conservation equation, and acquiring flow field data of each grid unit in the sieve plate extraction tower; and (7) measuring an actual flow field of the extraction tower by using a particle imaging velocity measurement technique, performing adjustment and feedback according to the measured data, and finally determining a practical model. The model method for precisely calculating the sieve plate extraction tower liquid flow field is implemented, and reliable fluid mechanics information for an actual design of the sieve plate extraction tower.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
GPU-accelerated fluid-structure coupling simulation method through immersion boundary and lattice Boltzmann methods
InactiveCN104866695AImprove computing efficiencyThe interaction realization process is simple and straightforwardSpecial data processing applicationsBody shapeMeasurement point
The invention provides a GPU-accelerated fluid-structure coupling simulation method through immersion boundary and lattice Boltzmann methods. The GPU-accelerated fluid-structure coupling simulation method comprises the following steps: 1, establishing a structure body to be detected and an internal fluid immersion boundary body shape in professional pre-processing software, and dividing a boundary lattice for program read; reading boundary body shape data through a program, and setting a boundary condition of a point required to be measured and a program model parameter; calculating the boundary acting force applied to a fluid by using a finite element method according to a structure of the boundary at the current time and a reference structure; diffusing the boundary acting force to surrounding fluids through the Dirac function; solving a Navier-Stokes equation carrying an external force term by using the lattice Boltzmann method; interpolating the fluid speed into the boundary through the Dirac function to obtain a boundary movement speed to further update the boundary position; repeatedly performing the steps 3-6 till the updated boundary position reaches an calculated ending point. According to the GPU-accelerated fluid-structure coupling simulation method, structure bodies in any shapes can be processed, an underlying fluid lattice does not require to be reconstructed in the calculation process, and the calculation efficiency is high.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
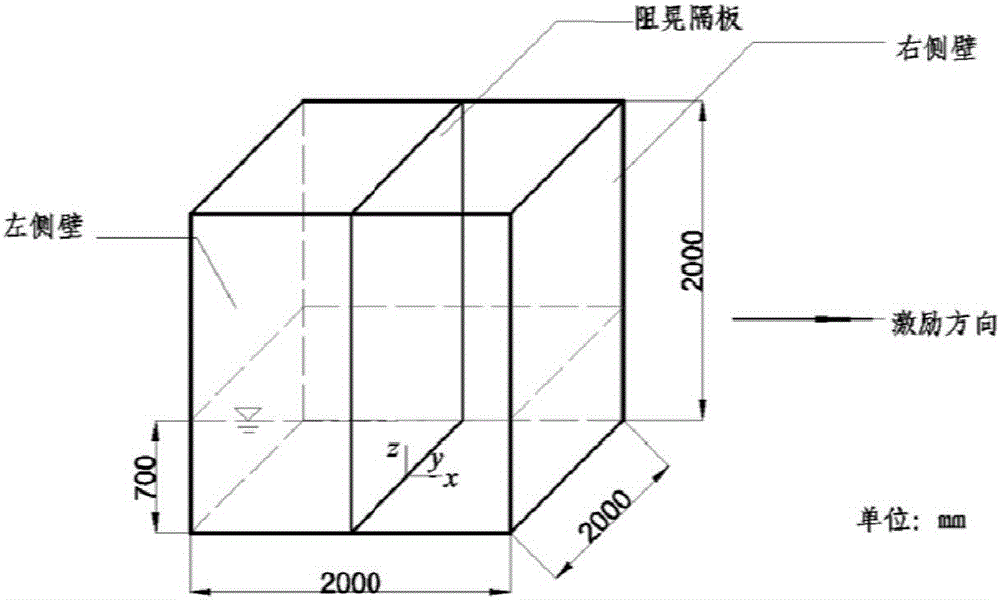
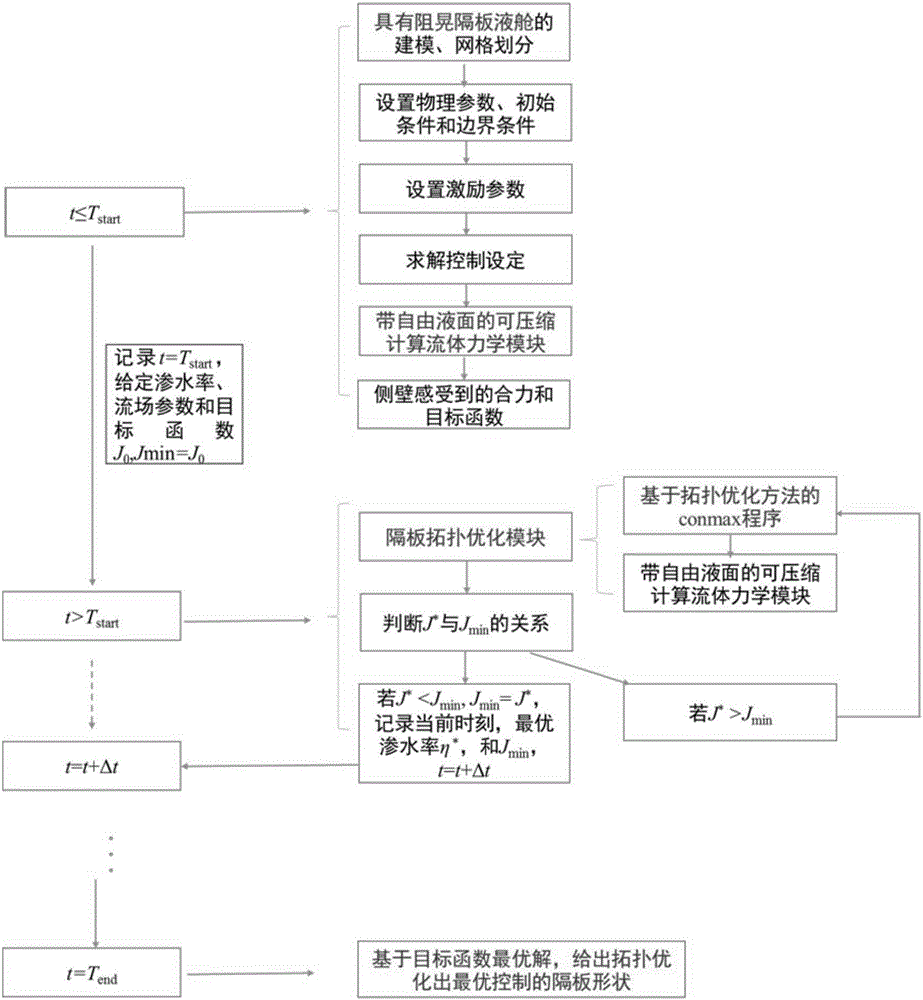
Clapboard optimization method for inhibiting compressible two-phase flow oscillation
ActiveCN106547944AGeometric CADSustainable transportationCompressed fluidCompressible navier stokes equations
The invention provides a clapboard optimization method for inhibiting compressible two-phase flow oscillation. The method comprises the following steps: solving a compressible Navier Stokes equation set based on a finite volume method and in combination with a fluid volume method to obtain a flow velocity of compressible two-phase flow oscillation and a resultant force applied to a side wall of a liquid bin after an anti-oscillation clapboard is added in the liquid bin; performing optimal control on the water permeability of the anti-oscillation clapboard based on a topological optimization method and in combination with a compressible two-phase flow movement algorithm with a free liquid level by using the resultant force as a target function and using the water permeability of the anti-oscillation clapboard as an optimal variable, wherein the water permeability is a ratio of an upper hollowed area of the anti-oscillation clapboard to the total area of the anti-oscillation clapboard; and determining the shape of the anti-oscillation clapboard according to the optimal water permeability. By adoption of the clapboard optimization method provided by the invention, the optimal design of the shape of the clapboard for inhibiting the movement of the compressible fluid in the liquid bin is realized while considering the strenuous movement of the compressible two-phase flow with the free liquid level.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
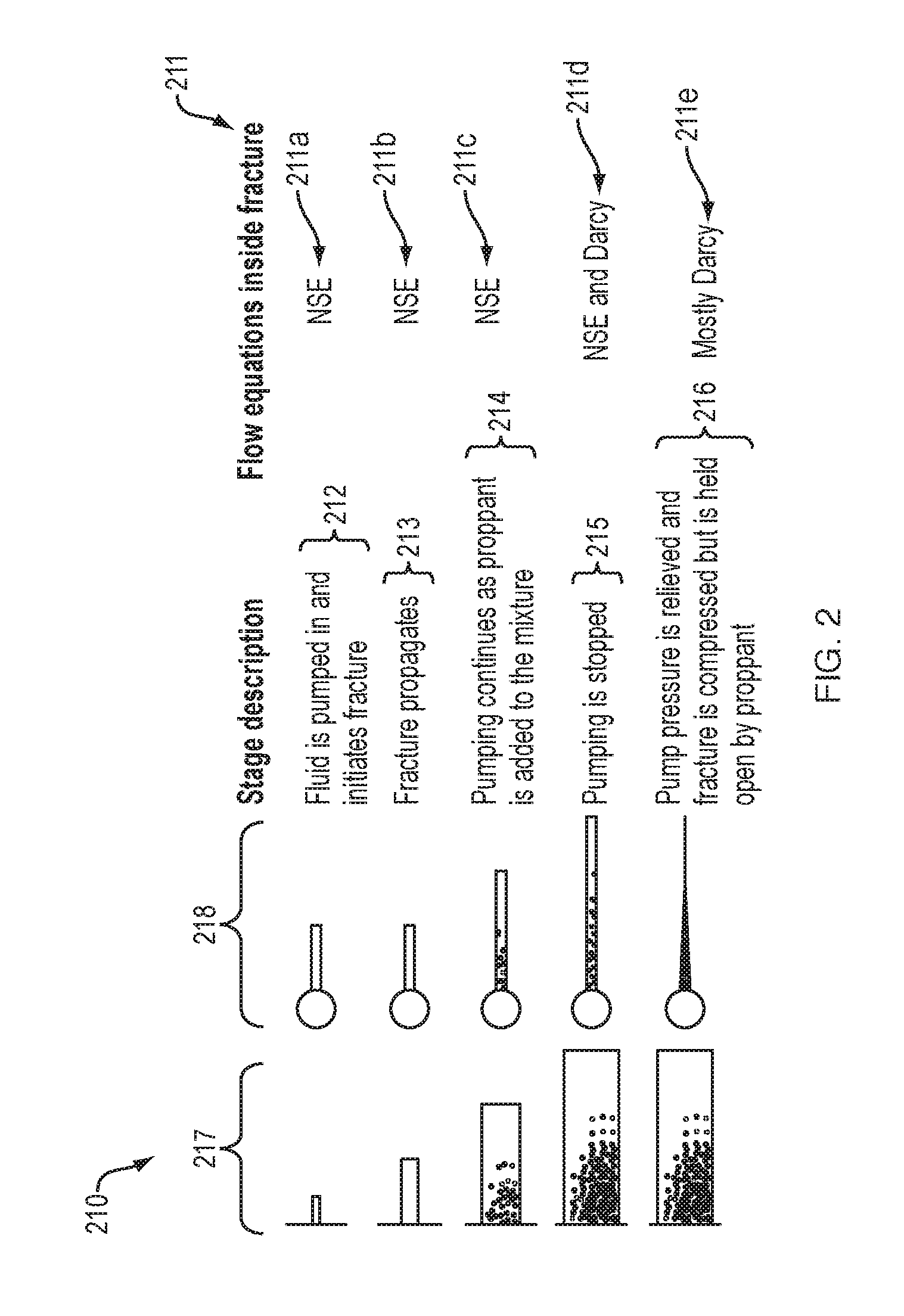
Flow Transition Technology
ActiveUS20160186532A1Improve performanceAcceptable accuracyGeomodellingComputation using non-denominational number representationEngineeringNavier–Stokes equations
Embodiments provide methods and systems for modeling the flow of fluid in variable physical and geological environments using dynamically determined Navier-Stokes equations (NSE), such as Darcy Flow and Poiseuille flow.
Owner:DASSAULT SYSTEMES SIMULIA CORP
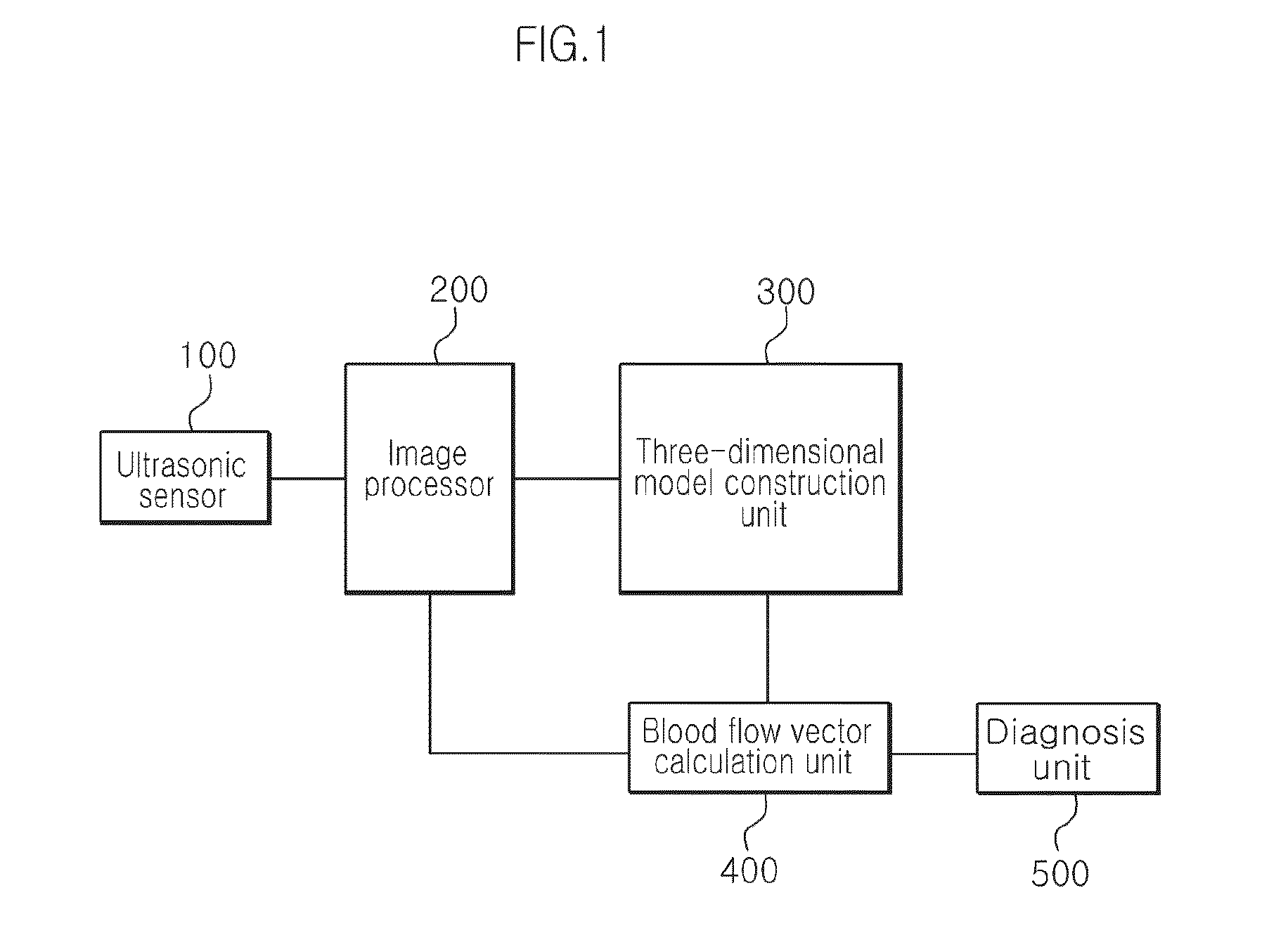
Apparatus and method for processing echocardiogram using navier-stokes equation
InactiveUS20150164468A1Accurate calculationImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisSonificationUltrasonic sensor
An apparatus and method for processing an echocardiogram using the Navier-Stokes equation is provided. The apparatus includes an ultrasonic sensor that transmits ultrasonic waves to the heart in three different directions and receives echoes thereof; an image processor that constructs first to third echocardiograms captured from the three different directions, respectively, based on the received echoes of the ultrasonic waves; a three-dimensional model construction unit that constructs a three-dimensional model of a left ventricle of the heart based on the first to third echocardiograms; and a blood flow vector calculation unit that calculates blood flow vectors within the left ventricle by applying the three-dimensional model of the left ventricle to boundary conditions in the Navier-Stokes equation. In echocardiogram processing, vector components of the blood flow within the left ventricle are calculated using the Navier-Stokes equation, whereby the vector components of the blood flow can be more accurately calculated.
Owner:INST FOR BASIC SCI
Method for modelling mixed material fluid-solid two-phase flow in mixing cylinder of concrete mixer car
InactiveCN1579726AMeet the design parameter requirementsReduce work intensityCement mixing apparatusData simulationHigh volume manufacturing
The invention discloses a method of constructing module to blend material stream and fix up two phase in the mix canister of beater, which is useful in the construction technology industry. This invention concentrate on the complicated density phrase and several phrase system, with the scatter unit method, and enlarge it to the data simulation of 3-D fluid flows and liquid two phrase flow, build group grain and group track soft module, simulate flow continue phrase by Navier-Stokes equation,at the same time, simulate the effect of grain disperse phrase by disperse unit method, the soft module construction of the collision among the grain is built by diverse unit method, to achieve the data simulate of 3-D two phase of blend material, at last optimize the parameter of blend canister. This invention decrease the work intension of the blend canister design, improve the design efficiency, at the same time optimize and improve the capacity of canister. The blend canister which is designed by this method has good capacity, and has been produced in large number, has got good economy and society effects.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for simulating stable but non-dissipative water
ActiveUS7647214B2Decrease dampeningReduce the numberAnalogue computers for chemical processesTypewritersDiffusionDissipative system
A method for graphically simulating stable but non-dissipative water in real-time includes steps for modeling multiphase materials with grid of nodes, suppressing numerical dissipation for getting rid of loss of mass of material, and suppressing numerical diffusion for reducing dampening of the fluid motion of materials in liquid phase. The step of modeling multiphase materials includes steps of describing liquid and gas with a set of nonlinear partial differential equations, representing the liquid-gas interface as an implicit surface, and determining properties of the materials, from the information about the liquid-gas interface, including the surface curvature and the surface tension. The set of nonlinear partial differential equations includes multiphase incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. The step of representing the liquid-gas interface includes a level set method.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND +1
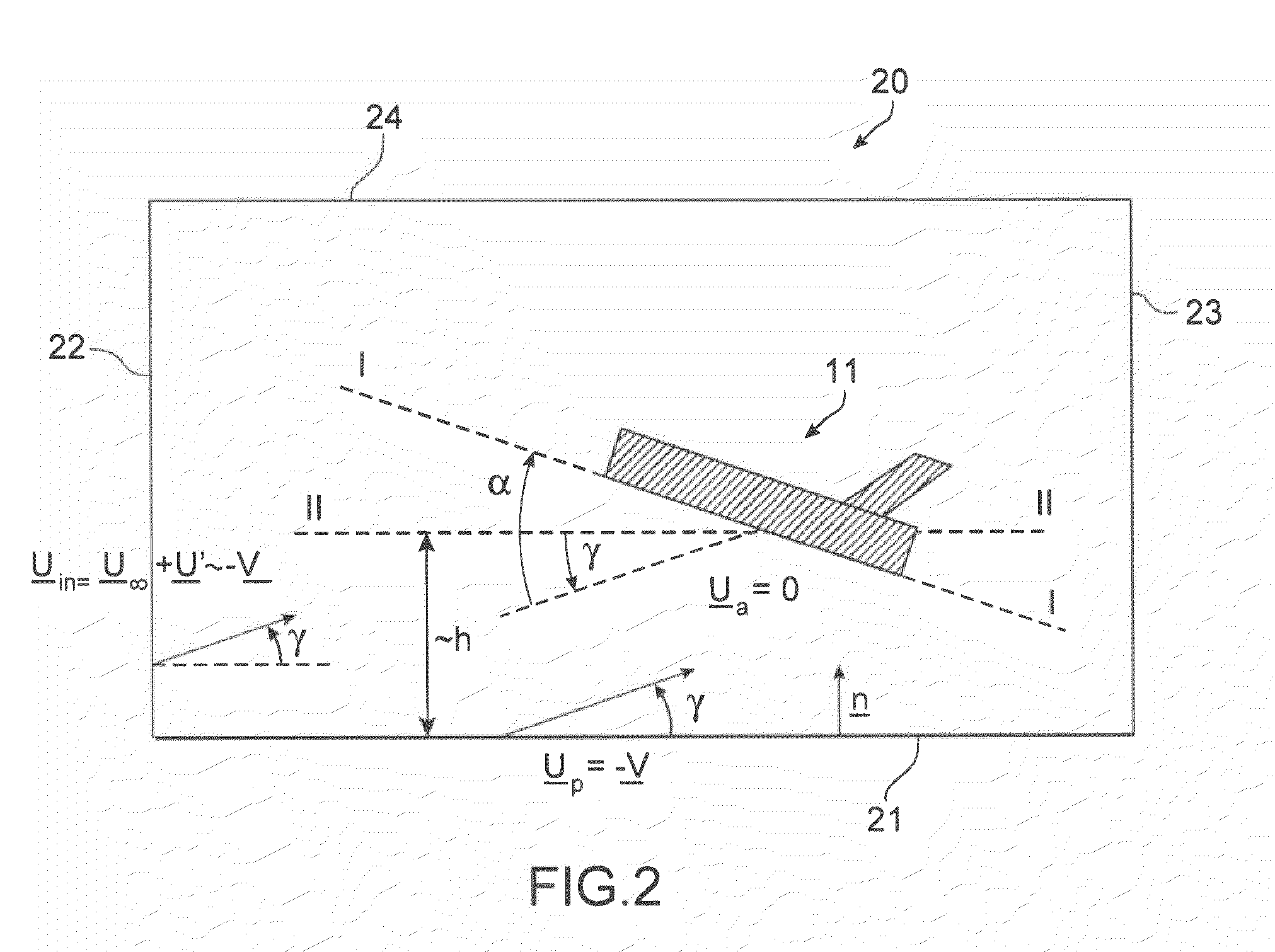
Method and tool for simulation of the aerodynamic behaviour of an aircraft in flight close to the ground
A method of computer simulation of an aerodynamic behavior of an aircraft in flight close to the ground includes generating a volume mesh of a three-dimensional geometric domain. The volume mesh is at least partly delimited by a three-dimensional geometric model of the aircraft and by a plane modelling the ground. The volume mesh defines a computational domain. The method also includes imposing a uniform boundary condition on the plane comprising a predetermined speed vector with a non-zero tangential component and a non-zero normal component, and solving a discrete numerical model of the Navier-Stokes equations by computer on the volume mesh with the uniform boundary condition imposed on the plane to obtain a numerical solution of a fluid flow inside said computational domain.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
Prediction method of leakage rate of contact mechanical seal
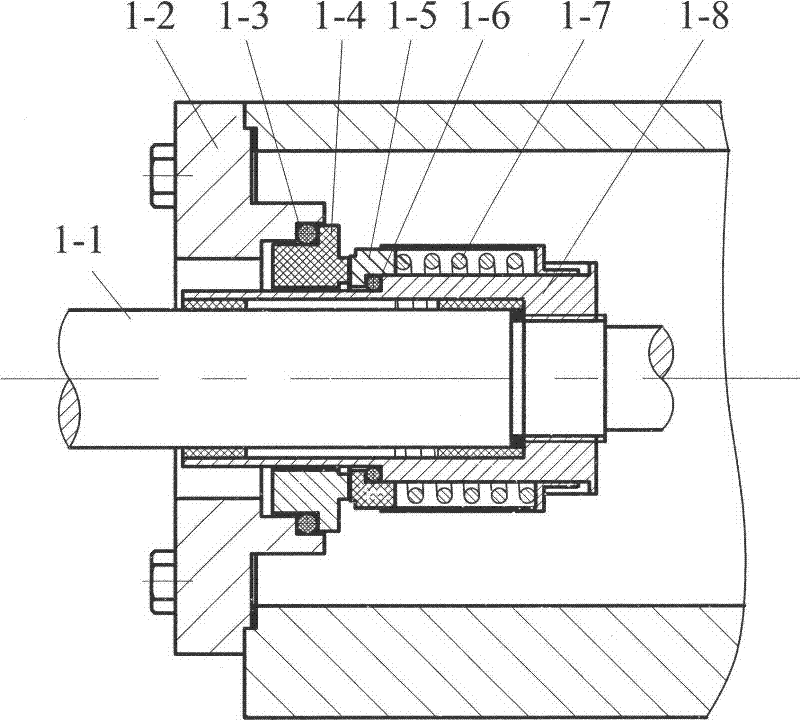
ActiveCN102411669AGuarantee safety and reliabilityLow cost operationSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringStress relaxation
The invention relates to a prediction technology of a leakage rate of an existing contact mechanical seal. By utilizing a seal interface topography evolvement rule in the wear process of a movable ring and a stationary ring, and a contact compression stress variation rule of primary and secondary seal interfaces due to the wear-down of the movable ring and the stationary ring and the stress relaxation of an O-shaped ring, the topography parameters of the seal interfaces and loads on the movable ring and the stationary ring seal interfaces, the O-shaped ring and the internal diameter and external diameter contact interfaces of the O-shaped ring are determined after the mechanical seal runs for a certain time, and the characteristic sizes of percolation channels between the movable ring and the stationary ring seal interfaces and the O-shaped ring and the internal diameter and external diameter contact interfaces of the O-shaped ring are obtained by a percolation theory, a contact mechanics theory and a fractal theory at the moment, the effect of surface tension and centrifugal force of the sealed medium is considered, and then the leakage state of the existing contact mechanical seal is predicated by a Navier-Stokes equation. The method is simple and practical, the accident problems caused by frequent replacement or expiration of the mechanical seal can be effectively solved, and the safety and reliability of equipment are improved.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Flow meter
InactiveUS6938611B2Improve fuel economyIncrease engine powerElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesOn boardEngineering
The flow meter is a device having a laser Doppler anemometer (LDA) which measures the instantaneous center line velocity of fluid flow in a pipe and processes the instantaneous velocity so obtained to compute the volumetric flow rate, mass rate, and other flow characteristics as instantaneous quantities and / or integrated over a time interval using an electronic processing method which provides an exact solution to the Navier-Stokes equations for any periodically oscillating flow. The flow meter is particularly adapted for measuring the flow characteristics of high pressure automotive fuel injection systems. Three embodiments of the flow meter are described, including a stationary stand for off-line bench testing flow rate in a fuel injection system, a portable flow meter for inline testing in a vehicle's fuel line, and an on-board flow meter sensor connected to an engine control module.
Owner:COMBUSTION DYNAMICS
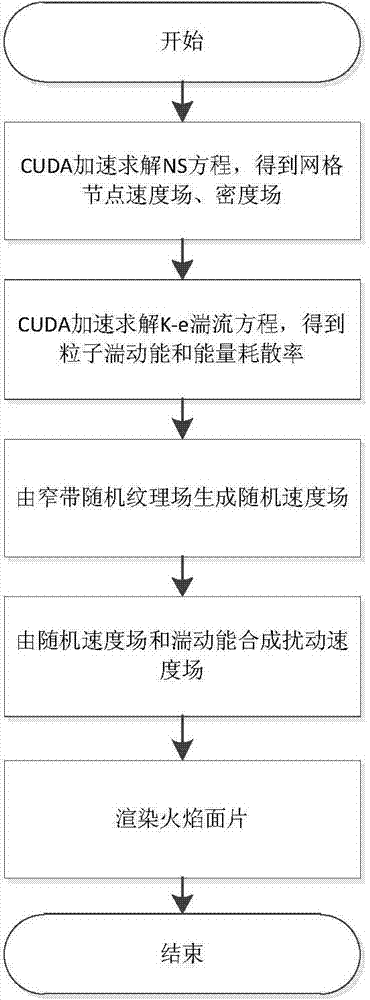
Method for enriching flame simulation details through turbulence equation
InactiveCN103839287AAvoid transmissionImprove computing efficiency3D-image renderingData fieldEulerian method
The invention relates to a method for enriching flame simulation details through a turbulence equation. The method comprises the steps that (1) an Euler method based on a grid is adopted, a Navier-Stokes equation is solved in an accelerated mode through a CUDA, and a speed field of flames, a density field of the flames and a temperature field of the flames are obtained; (2) the standard k-e turbulence equation is simplified by the adoption of the particle method, and the CUDA is used for accelerating solving to obtain the turbulence energy and the energy dissipation rate of a particle; (3) a narrowband random texture field is generated, then the rotation is solved to obtain the speed field, and sampling is conducted in the random speed field according to the position of the particle to obtain the speed of the position where the particle is located; (4) the turbulence speed of the particles is synthesized, then the speed is used for disturbing the speed of the positions of network nodes in a neighborhood of the particle at the Gauss attenuation weight, and the density field and the temperature field are driven to move; (5) the CUDA and mapping of a buffer area of an OpenGL are used for directly rendering a data field worked out by the CUDA, and flame surface patches are obtained.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
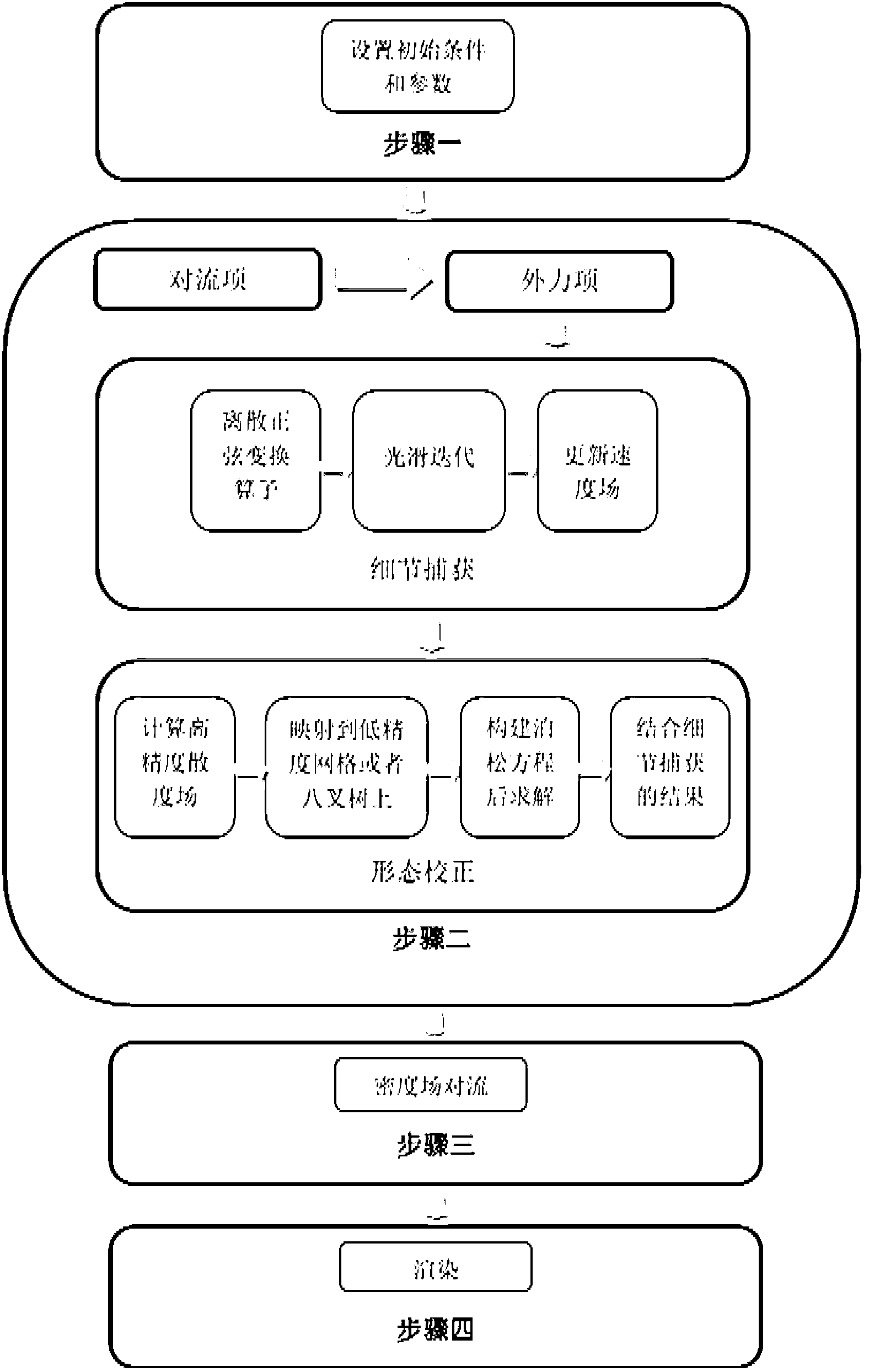
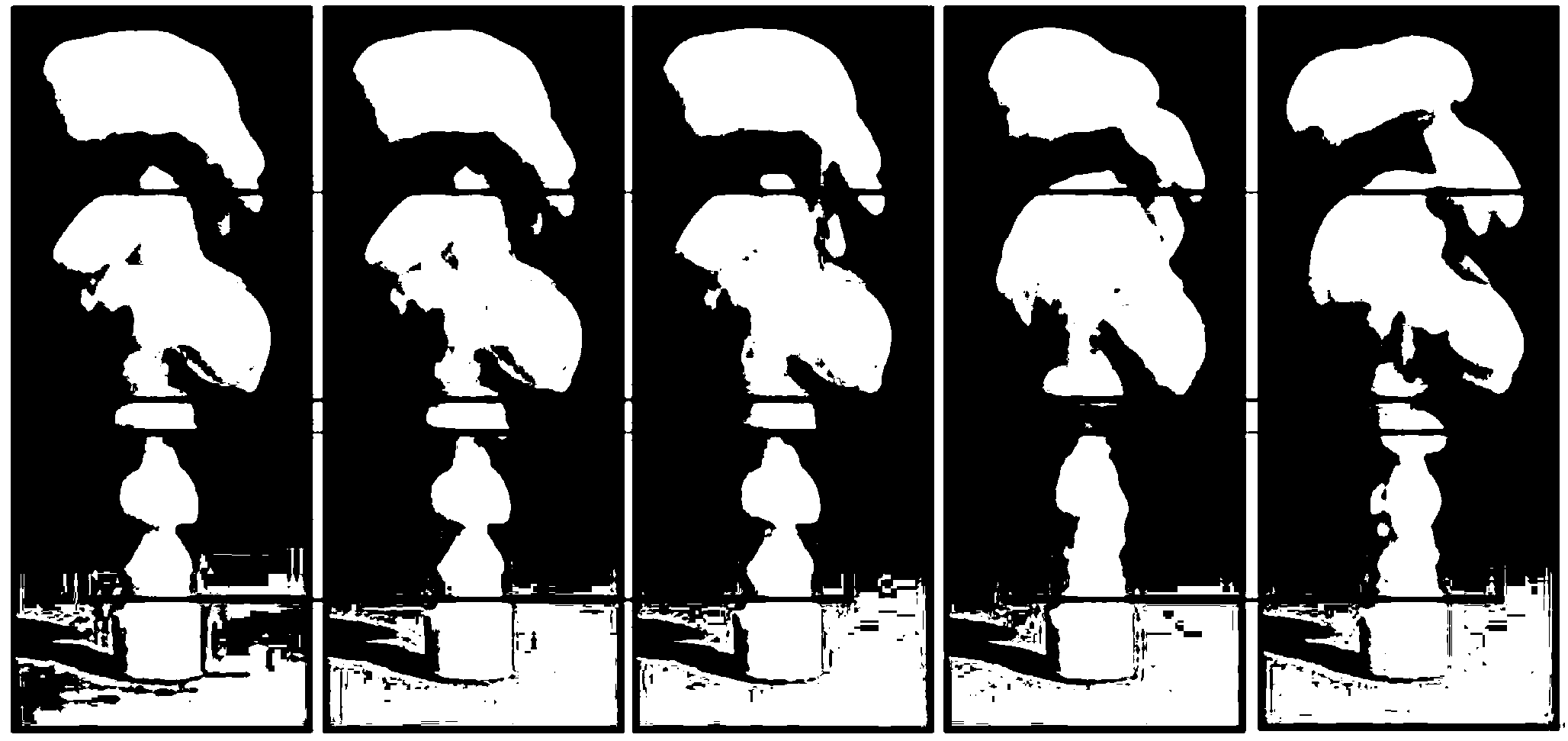
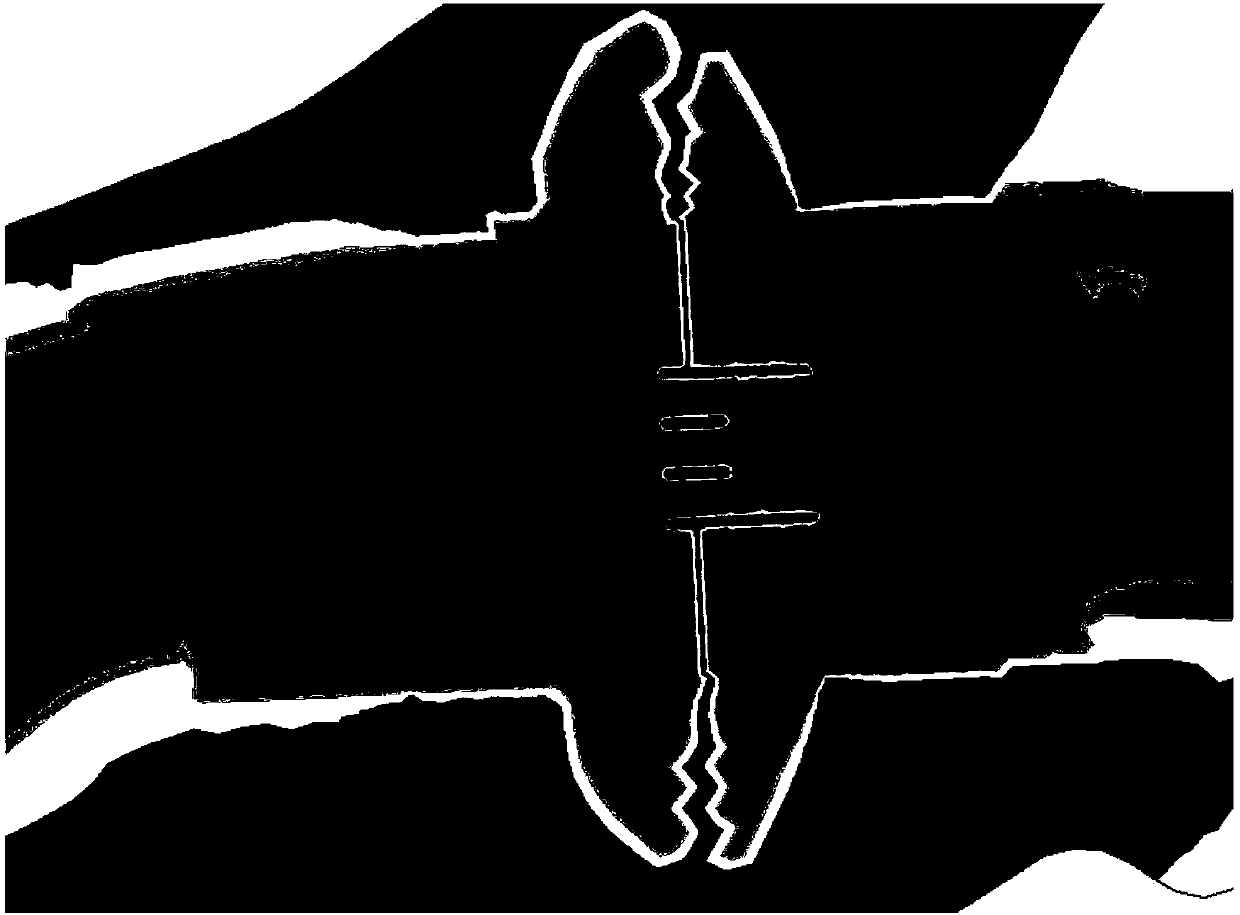
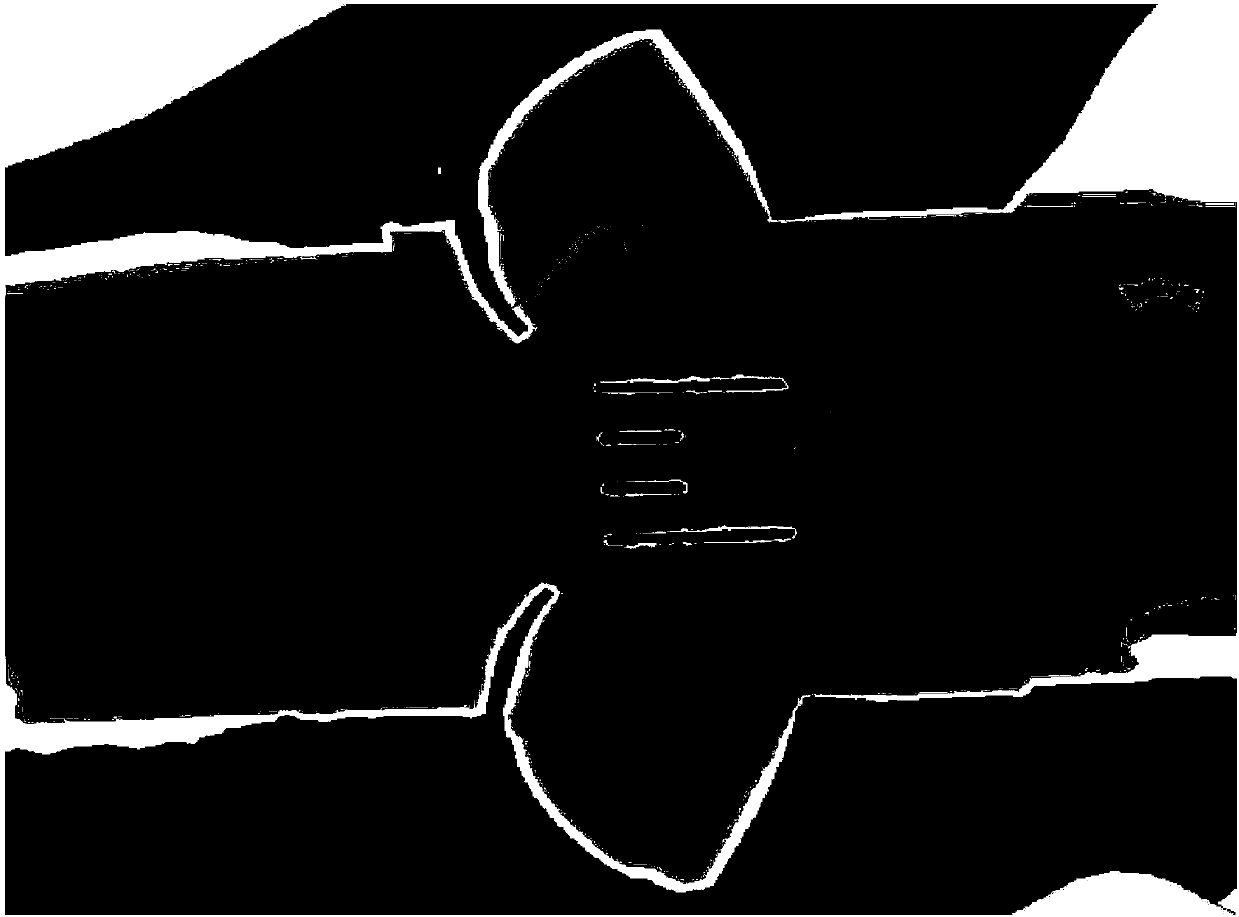
Fluid animation rendering method based on detail capturing and form correcting
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Numerical simulation method for flood drainage and damp-proof operation scheduling of large flat open gate
PendingCN108595799AClimate change adaptationDesign optimisation/simulationMathematical modelPhysical model
The invention discloses a numerical simulation method for flood drainage and damp-proof operation scheduling of a large flat open gate. The simulation method comprises the steps of firstly building atwo-dimensional mathematic model, and calculating flood processes and tidal level processes of all frequencies of a river channel; and secondly verifying actual tidal level process, flow velocity andflow process of the river channel through the two-dimensional mathematic model. The two-dimensional mathematic model comprises a three-direction incompressibility and Reynolds value uniform distribution-based Navier-Stokes equation, and obeys a Boussinesq assumption and a hydrostatic pressure assumption; and dynamic simulation of an opening or closing process of the flat open gate is realized through a method for decomposing the opening degree of the flat open gate stage by stage and correspondingly adjusting initial calculation conditions during simulation of the opening degree of all the stages. The technical problems of result distortion and incapability of directly realizing simulation of the dynamic opening or closing process of the flat open gate temporarily in the two-dimensional mathematic model of the river channel due to a scale effect and the like in realizing opening or closing simulation of the flat open gate by utilizing a river physical model are solved.
Owner:FUJIAN PROVINCIAL INVESTIGATION DESIGN & RES INST OF WATER CONSERVANCY & HYDROPOWER
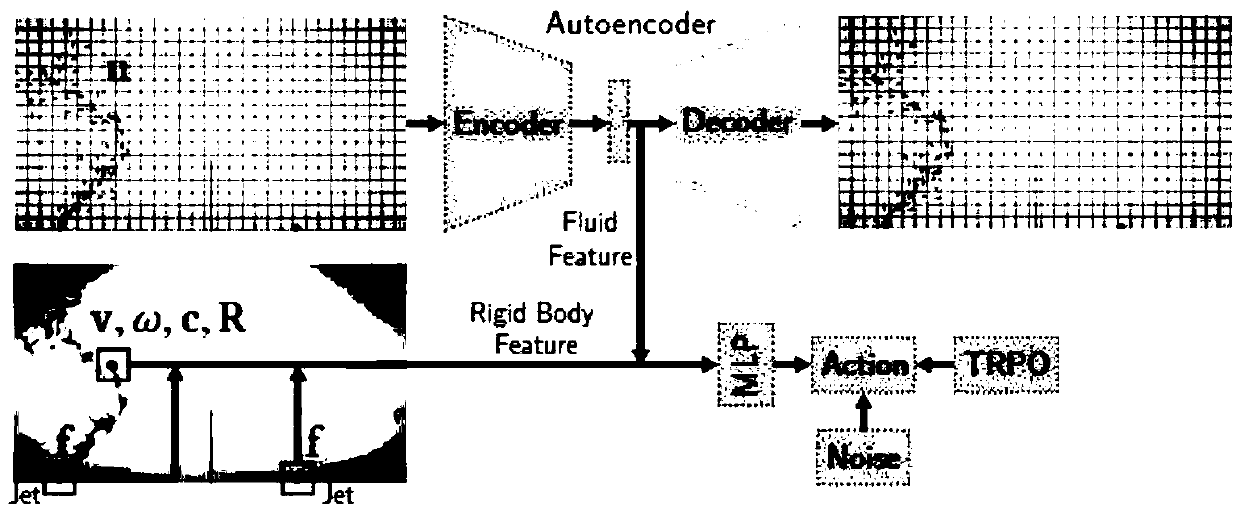
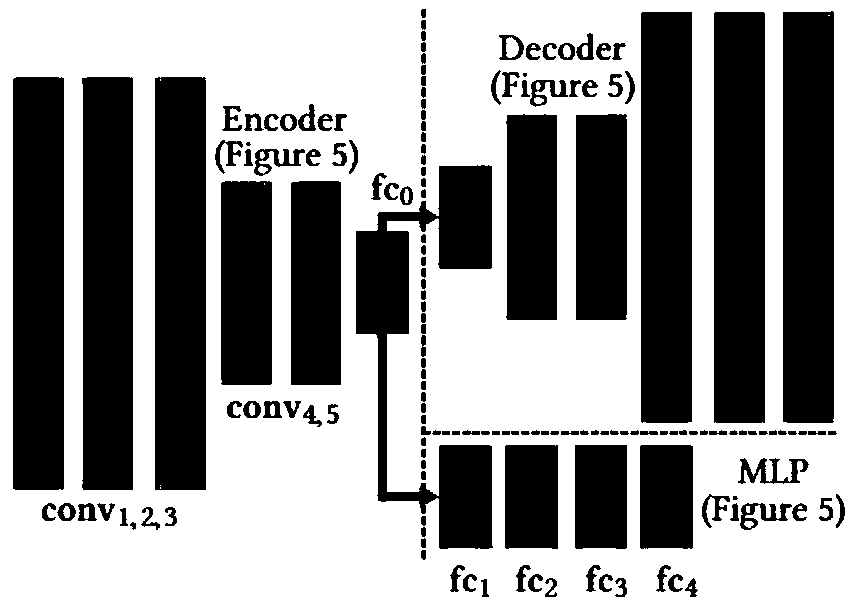
Rigid body control method for fluid guide based on deep reinforcement learning
The invention discloses a rigid body control method for fluid guide based on deep reinforcement learning. In the method, the behavior of a fluid-rigid body simulator is changed by applying a control force only at the boundary of a simulated region, and the fluid is controlled by a Navier-Stokes equation and the rigid body is controlled by a Newton-Euler equation in the simulated region. The controller of the method is a neural network trained by deep reinforcement learning, and through pre-training, a control action can be generated in an online mode. The controller based on the method receives states of the fluid and the rigid body as input, a fluid nozzle is controlled to move at the boundary and injects fluid towards the rigid body in the simulated region, and thus, physical realistic simulation results can be generated, and good effects are obtained in multiple two-dimensional fluid-rigid control tasks. The method can also expanded to a three-dimensional fluid-rigid coupling system, for example, the rigid body can be controlled to accurately move to a specified three-dimensional target point.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com