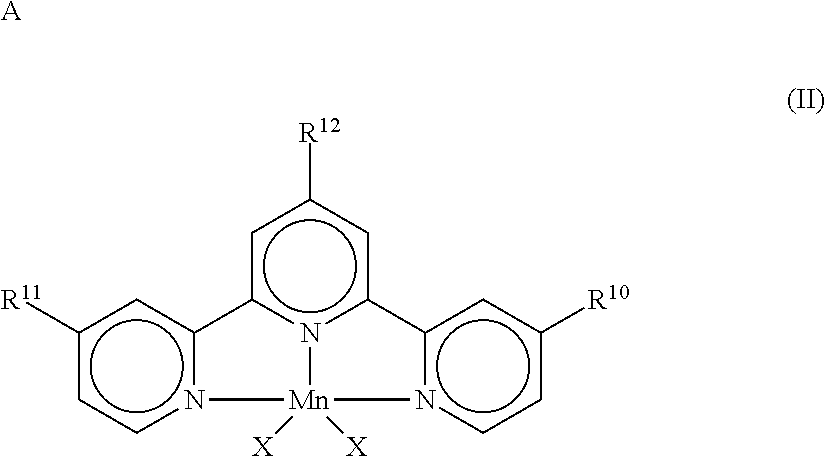
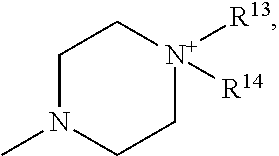
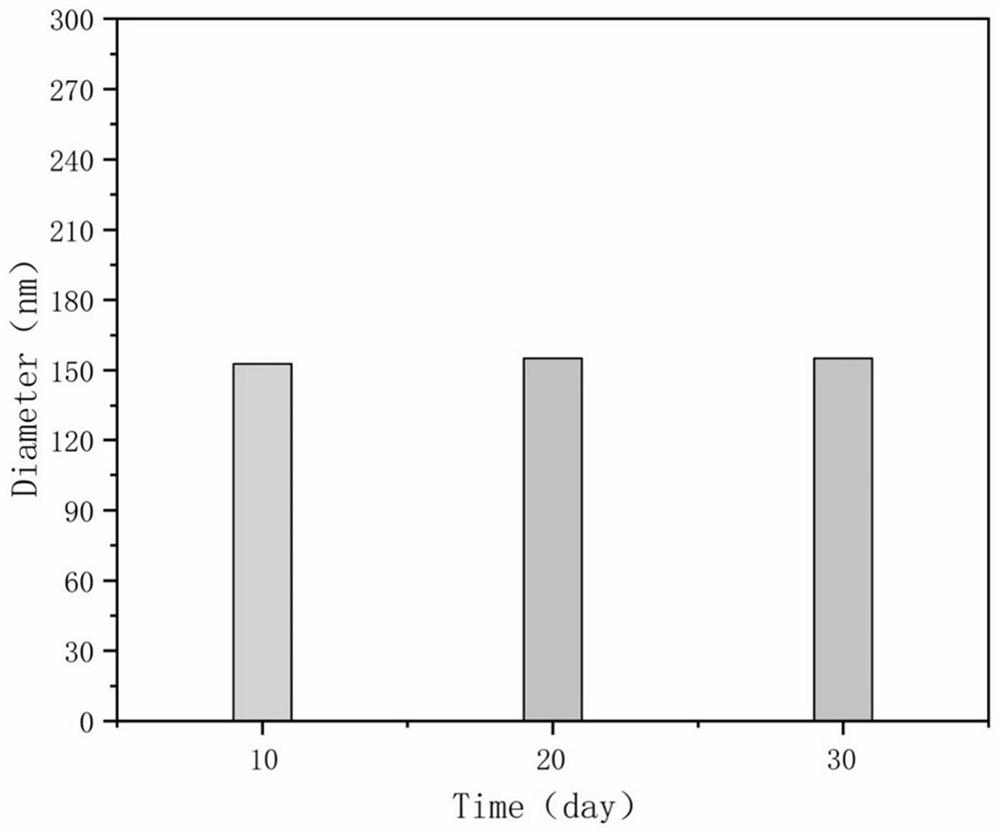
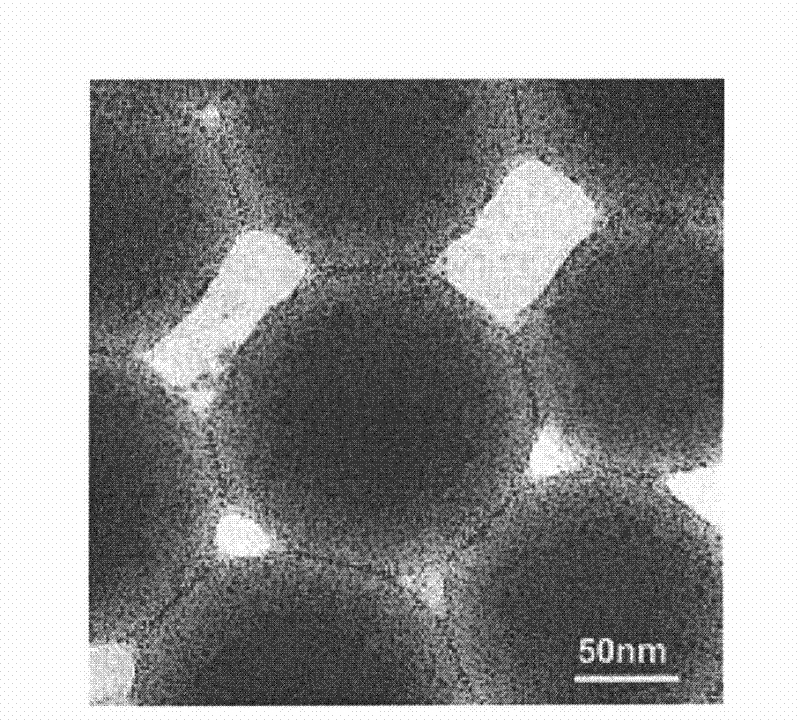
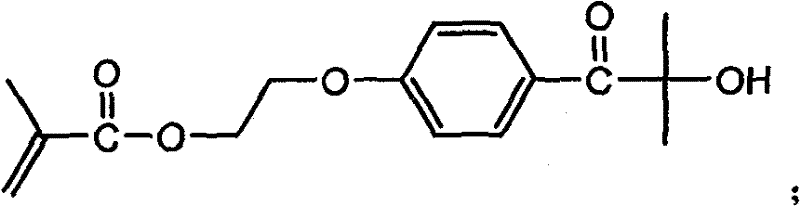
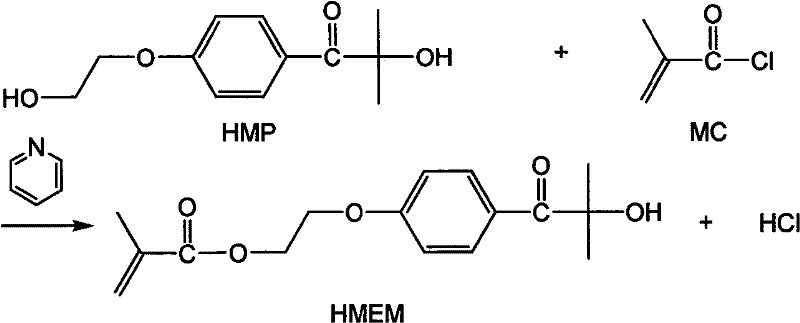
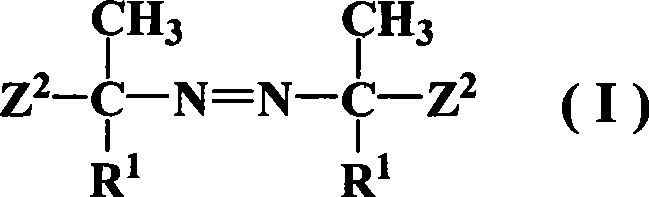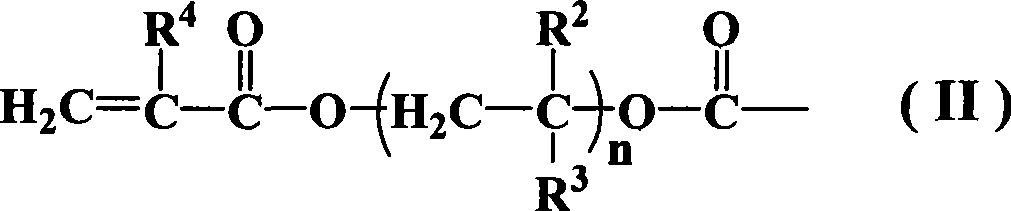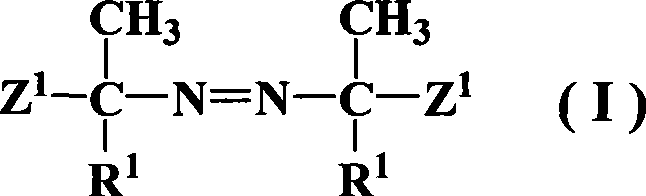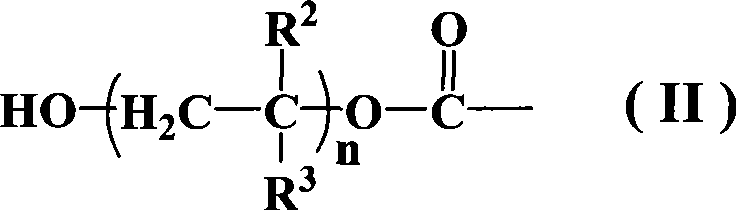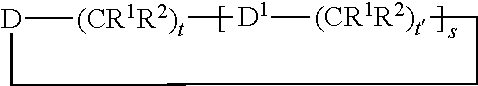Patents
Literature
32 results about "Polyelectrolyte brushes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for preparing nanometer spherical polyelectrolyte brush with magnetic kernel
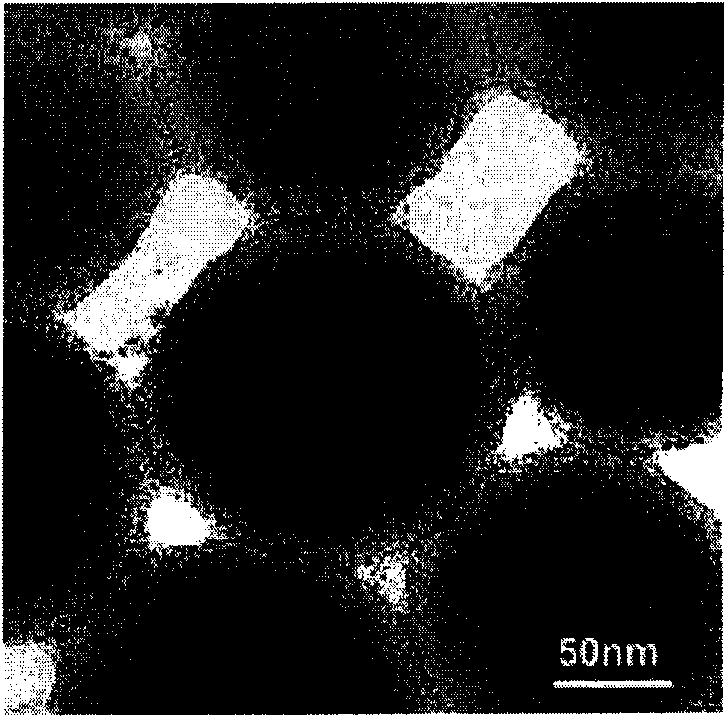
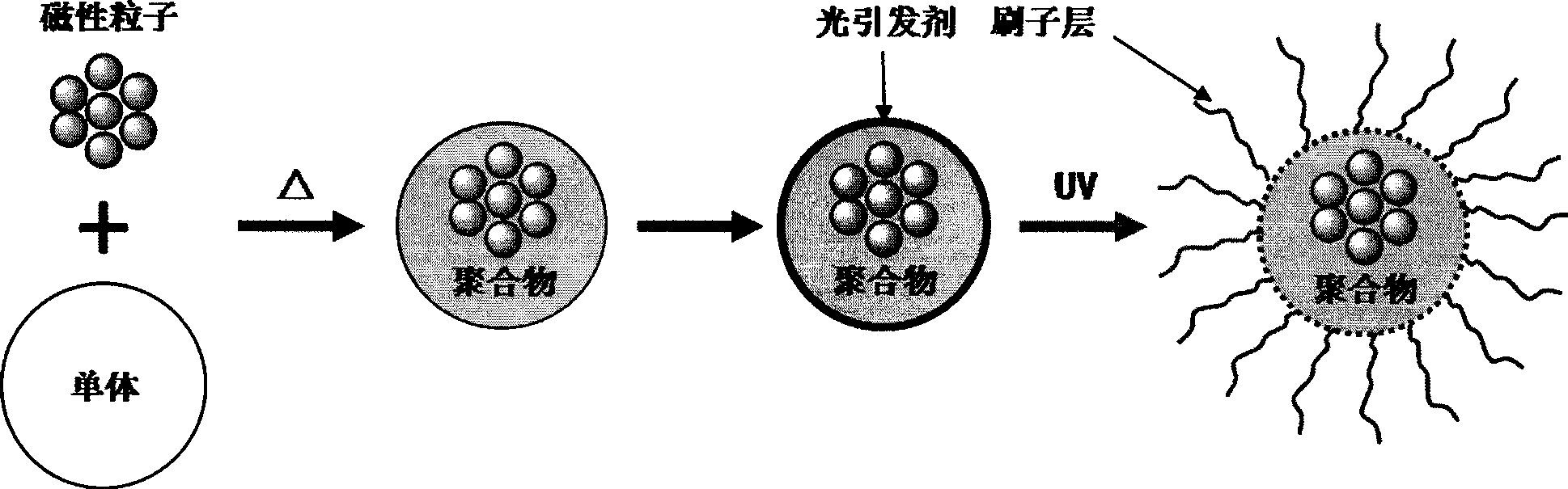
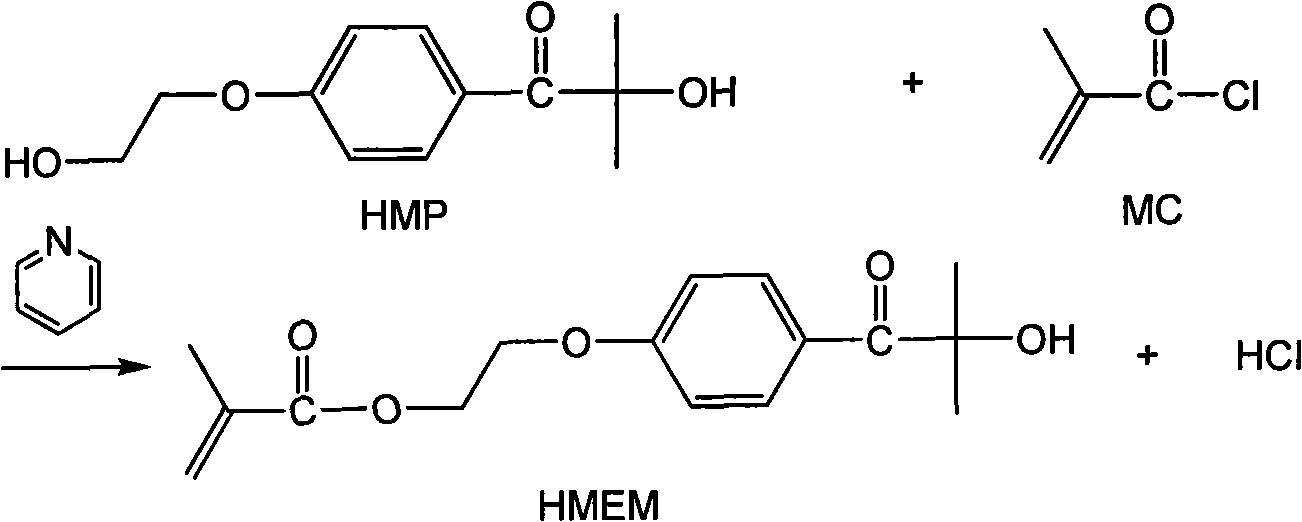
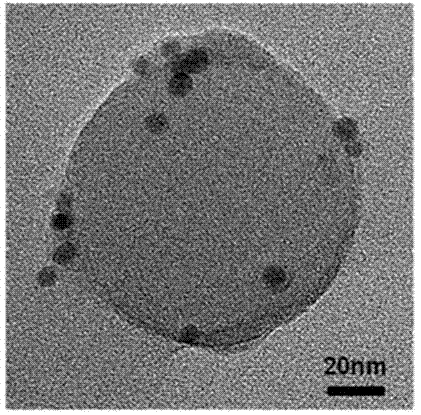
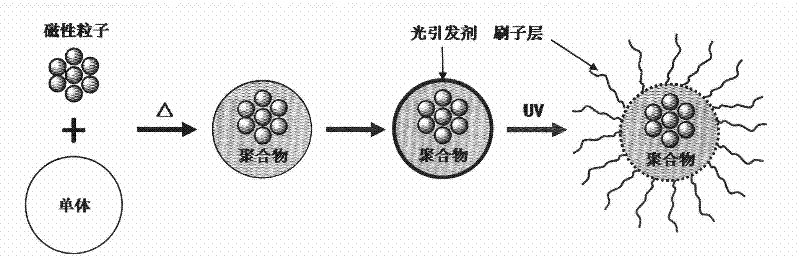
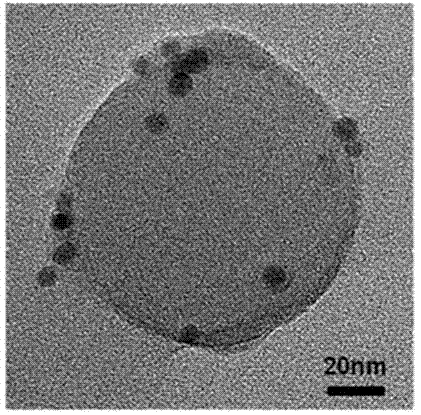
The invention relates to a method for preparing a nanometer spherical polyelectrolyte brush with a magnetic kernel. The whole preparation process is completed by four steps as follows: firstly, preparing ferroferric oxide nanometer magnetic nanoparticles under an alkali condition by a coprecipitation method; secondly, dispersing the magnetic nanoparticles in a styrene monomer, and obtaining polystyrene (PS) microspheres with particle diameter of between 100 and 250 nm by miniemulsion polymerization; thirdly, adding a photoinitiator in the end stage of the miniemulsion polymerization to ensure that the photoinitiator can be coated on the surface of the PS microspheres by chemical bonds to form a photoinitiator layer; and fourthly, adding an electrolyte monomer, and initiating polymerization by illumination of an ultraviolet lamp to obtain the nanometer spherical polyelectrolyte brush with the magnetic kernel, which has the particle diameter of between 180 and 350 nm. The nanometer spherical polyelectrolyte brush with the magnetic kernel can realize quick reclamation and recycle by a magnetic field after the nanometer spherical polyelectrolyte brush is adsorbed on a noble metal ion and subjected to wastewater treatment, and also can be used in targeted dosage treatment under the navigation of the magnetic field.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of spherical polyelectrolyte brush and use thereof
InactiveCN101381435AOvercoming technical deficienciesWater/sewage treatmentIonPolyelectrolyte brushes
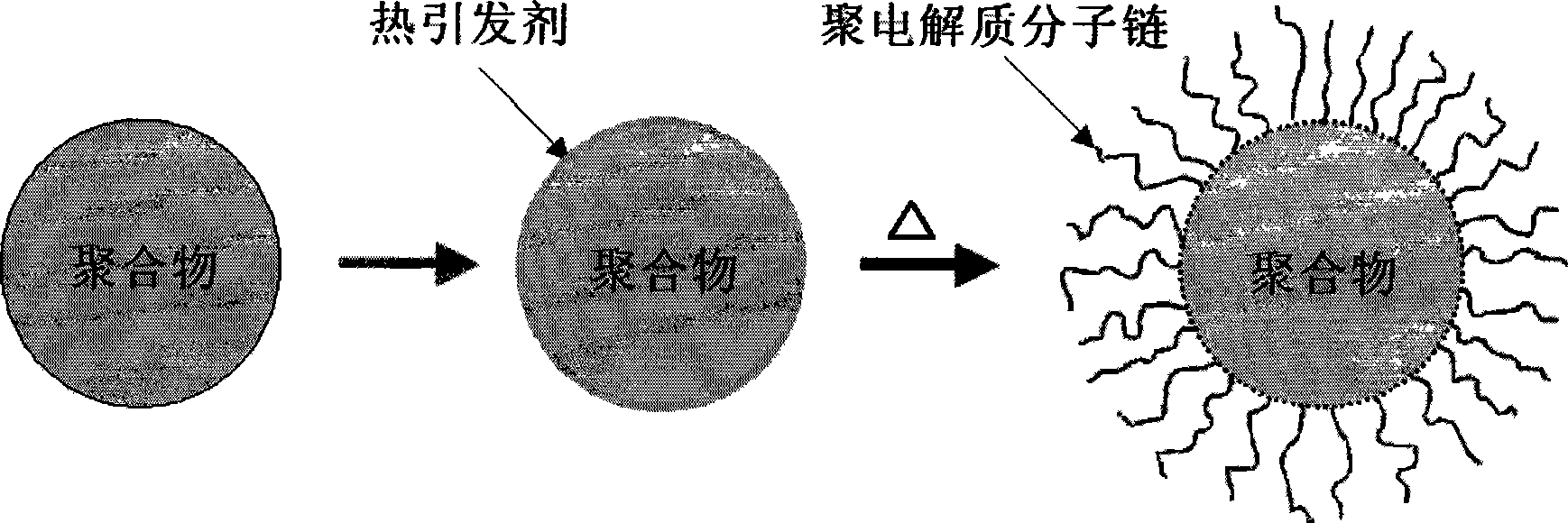
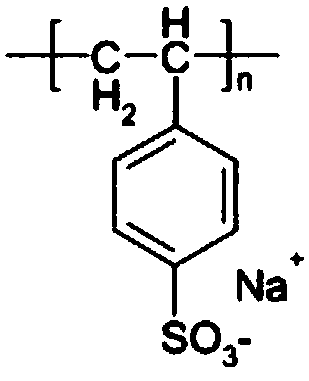
The invention relates to a novel method for preparing a nano spherical polyelectrolyte brush by utilizing a thermal initiator and application thereof. Firstly, styrene and other substances are used as a monomer, and are subjected to oxidation reduction emulsion polymerization at normal temperature to obtain a micro milk globule of polystyrene(PS) with the grain diameter of between 50 and 90 millimeters; secondly, at the final stage of the polyreaction, an azo thermal initiator is added, because a C=C double bond of the end group of the thermal initiator and a surface residual monomer of the micro milk globule are subjected to copolymerization, the thermal initiator is fixed on the surface of the micro milk globule through the covalent bond; and finally, an electrolyte monomer such as acrylic acid, sodium styrene sulfonate and the like is added to initiate the polymerization at certain temperature, and the nano spherical polyelectrolyte brush with the grain diameter of between 100 and 200 millimeters is prepared. The polyelectrolyte brush can be widely applied to fields such as the removal of harmful metallic ions in water, the recovery of precious metal ions, the preparation of nano metal composite catalysts and biological enzyme reactor, the medical diagnosis.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Azos thermal initiator, synthetic method and application thereof
InactiveCN101381421AHigh grafting rateTrigger conditions are simpleOrganic chemistryPolyelectrolyte brushesIn situ polymerization
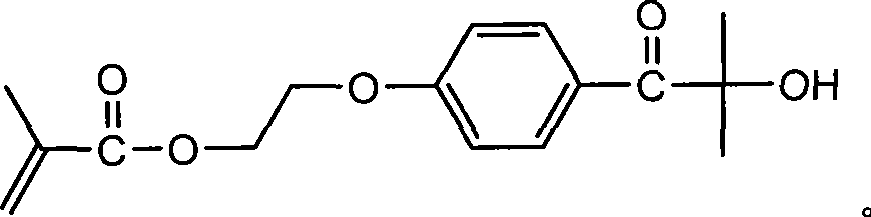
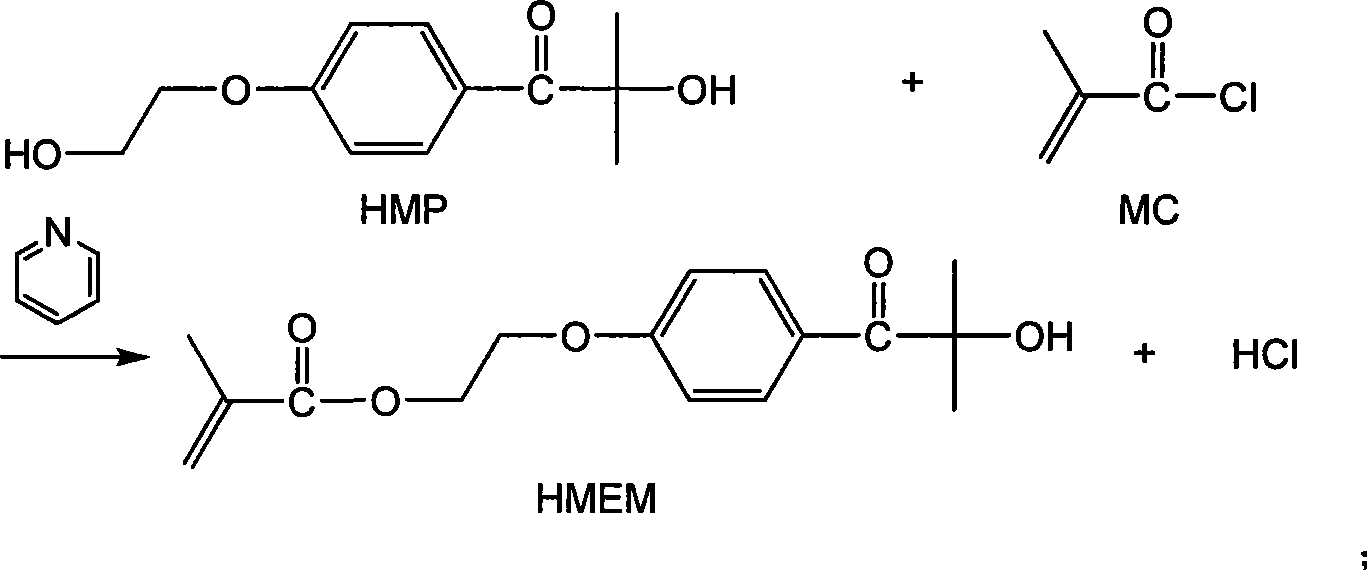
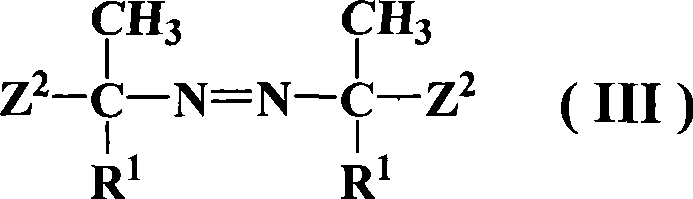
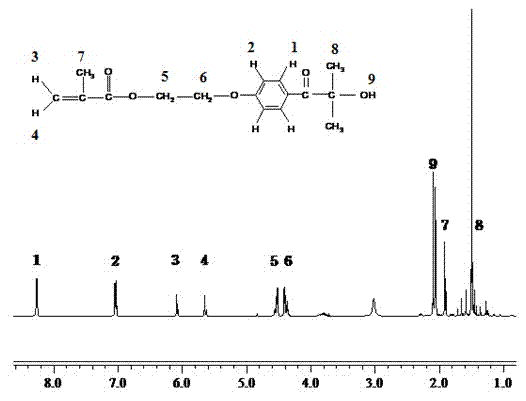
The invention relates to an azo thermal initiator for use in preparation of a nano-sized spherical polyelectrolyte brush, a synthesis method and an application thereof. Firstly, azodiiso-alkylnitrile and diol are taken as raw materials to synthesize an intermediate azodiisoacid diol ester; and then the intermediate reacts with alkyl acrylyl chloride to obtain the novel azo thermal initiator with a C=C double bond as a terminal group. A novel azo thermal initiator both ends of which contain C=C double bonds can be obtained through the separation by a certain method. The thermal initiator can initiate the in-situ polymerization of monomers such as acrylic acid, 4-ethenyl-benzenesulfonic acid sodium salt and so on, on the surfaces of polystyrene milk globules to prepare the nano-sized spherical polyelectrolyte brush with controllable polyelectrolyte length and grafting density.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing nano cationic spherical polyelectrolyte brush
The invention discloses a method for preparing a nano cationic spherical polyelectrolyte brush. The method sequentially comprises the following steps of: 1, preparing monodisperse nano silicon dioxide microspheres; 2, preparing silicon dioxide microspheres of which the surfaces are provided with unsaturated double bonds; and 3, preparing the nano cationic spherical polyelectrolyte brush by adopting a dispersion polymerization method. The method is simple and easy to operate, the process is easy to control and the method is suitable for industrial production; and the cationic spherical polyelectrolyte brush prepared by the method has the grafting ratio of 2.4-17.9 percent, the weight-average molecular weight of 3.23*10<2>-7.173*10<4>g / mol and the grafting density of 3.345*10<-7>-5.54*10<-4>mol / g. The product prepared by the method has high grafting density.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method for fixing egg white by utilizing polyelectrolyte
ActiveCN103467603ACarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesOn/in organic carrierPolyelectrolyte brushesChemistry
The invention discloses a method for fixing egg white by utilizing polyelectrolyte. According to the method, a polyelectrolyte brush with a 3D structure is adopted to serve as a carrier, the polyelectrolyte brush can adsorb a large amount of egg white under the condition benefiting the egg white physical adsorption of the polyelectrolyte brush, and then the egg white is stably bonded to the polyelectrolyte brush carrier through chemical bonds in a coupling chemistry mode. By means of the method, the combining quantity of the egg white is greatly improved, the purpose of stably combining the egg white through the polyelectrolyte brush is achieved, and the method can be effectively and efficiently applied to various downstream biotechnologies.
Owner:SHANGHAI MAG GENE NANOTECH CO LTD
Ionic ball polyelectrolyte brush employing micro-nano carbon sphere as kernel and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an ionic ball polyelectrolyte brush employing a micro-nano carbon sphere as a kernel and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of a nano composite material. The kernel of the ionic ball polyelectrolyte brush is the micro-nano carbon sphere, and an outer brush is an ionic monomer. The preparation method comprises the following steps: loading synthetic azo acyl chloride on the surface of the micro-nano carbon sphere, and synthesizing the ionic ball polyelectrolyte brush employing the micro-nano carbon sphere as the kernel by free radical polymerization. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple and feasible. The product prepared by the method takes the micro-nano carbon sphere as the kernel, and is novel in structure, green and environment-friendly, low in cost, and different molecular weights and different grafting densities of ionic ball polyelectrolyte brushes can be prepared by controlling the reaction time and the density of the monomer. The product can be used as a conductive polymer dopant, a morphology control agent, a deflocculating agent, a papermaking wet-end additive and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Magnetic particles preparation method by using nanometer spherical polyelectrolyte brush as micro-reactor
InactiveCN101630555ARetain propertiesGood dispersionMagnetic materialsPolyelectrolyte brushesMicrosphere
The invention relates a magnetic particles preparation method by using nanometer spherical polyelectrolyte brush as micro-reactor, comprising the following four steps: step 1, obtaining 80-200nm of polymer microspheres by miniemulsion polymerization method; step 2, adding a photoinitiator in the final phase of miniemulsion polymerization to coat the surface of polymer microspheres and form a photoinitiator layer; step 3, initiating polyelectrolyte monomer polymerization with a ultraviolet lamp in a light reactor to obtain 100-350nm of spherical polyelectrolyte brush; step 4, adding ferrous salt and ferric salt in the spherical polyelectrolyte brush emulsion system to react in situ and prepare magnetic particles under the action of coprecipitator and finally obtaining 3-5nm of magnetic nanoparticles evenly distributed inside the spherical polyelectrolyte brush. The nanometer magnetic composite microspheres can have wide application in the fields of high effective catalyst, water purification, biomedicine and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing nano nickel by taking nano spherical polyelectrolyte brush as reactor and application of nano nickel
InactiveCN102240816AGood dispersionImprove catalytic performanceMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic compound preparationPolyelectrolyte brushesNano catalyst
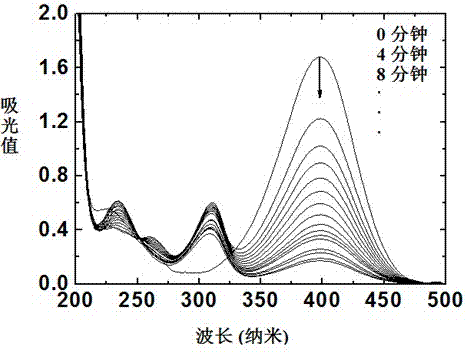
The invention discloses a method for preparing nano nickel by taking a nano spherical polyelectrolyte brush as a microreactor and an application of the nano nickel. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing polymer microspheres with the particle size of 80-140nm by adopting emulsion polymerization initiated by an oxidation-reduction system; adding a photoinitiator in the terminal stage of the emulsion polymerization, coating the photoinitiator on the surfaces of the polymer microspheres to form a photoinitiator layer, then utilizing an ultraviolet lamp to initiate polyelectrolytemonomers to be polymerized so as to obtain a spherical electrolyte brush with the particle size of 10-400nm; then adding sodium hydroxide to dissociate carboxyl on an electrolyte chain; treating the dissociated spherical polyelectrolyte brush by use of a nickel chloride aqueous solution, thus nickel ions exchange sodium ions and enters into the polyelectrolyte brush; and adding sodium borohydrideto reduce the nickel ions into nano nickel in situ, thus finally obtaining controllable nano nickel which are uniformly distributed inside the nano spherical polyelectrolyte brush and have the particle size of 1-14nm. The nano nickel loaded on the spherical polyelectrolyte brush is an ideal efficient nano catalyst.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing nano zinc oxide by taking nano spherical polyelectrolyte brush as microreactor and application of nano zinc oxide
InactiveCN102976391AMassive and uniform adsorptionGood dispersionMaterial nanotechnologyZinc oxides/hydroxidesPolyelectrolyte brushesNano size
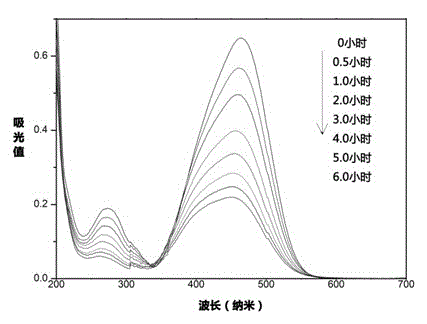
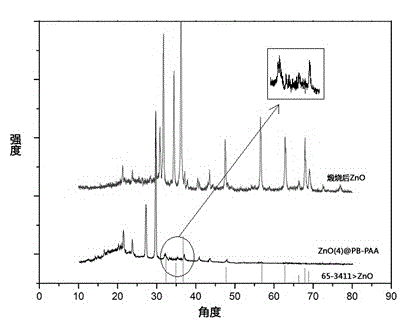
The invention discloses a method for preparing nano zinc oxide by taking a nano spherical polyelectrolyte brush as a microreactor and an application of the nano zinc oxide. The method comprises the following steps of: with 100-140nm polymeric microspheres as raw materials, initiating graft polymerization of monomers on the surfaces of the polymeric microspheres by adopting a thermal-control emulsion polymerization method to obtain a spherical polyelectrolyte brush with the particle diameter of 140-300nm; after adding a divalent zinc salt water solution, making divalent zinc ions enter into the polyelectrolyte brush under the electrostatic interaction, and carrying out in-situ reaction under the action of a precipitant to obtain nano zinc oxide particles uniformly distributed inside the nano spherical polyelectrolyte brush; and calcining the nano spherical polyelectrolyte brush system loaded with the zinc oxide particles to remove the polyelectrolyte brush to obtain the nano-scale pure zinc oxide particles. The nano zinc oxide particles which are synthesized by taking the spherical polyelectrolyte brush as the microreactor are smaller in particle diameter and uniform to distribute, are an ideal high-efficient nano photocatalyst and can be widely applied in the field of water purification and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
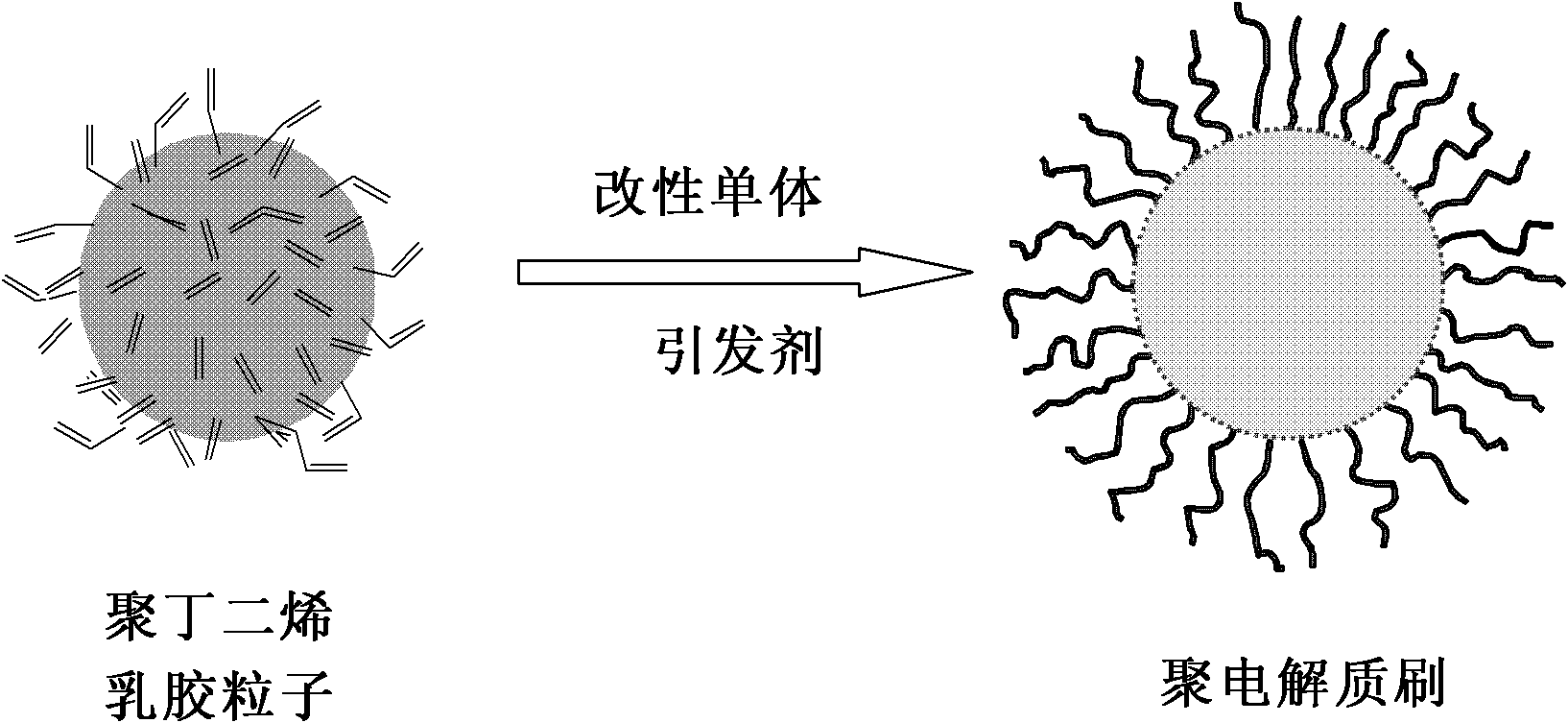
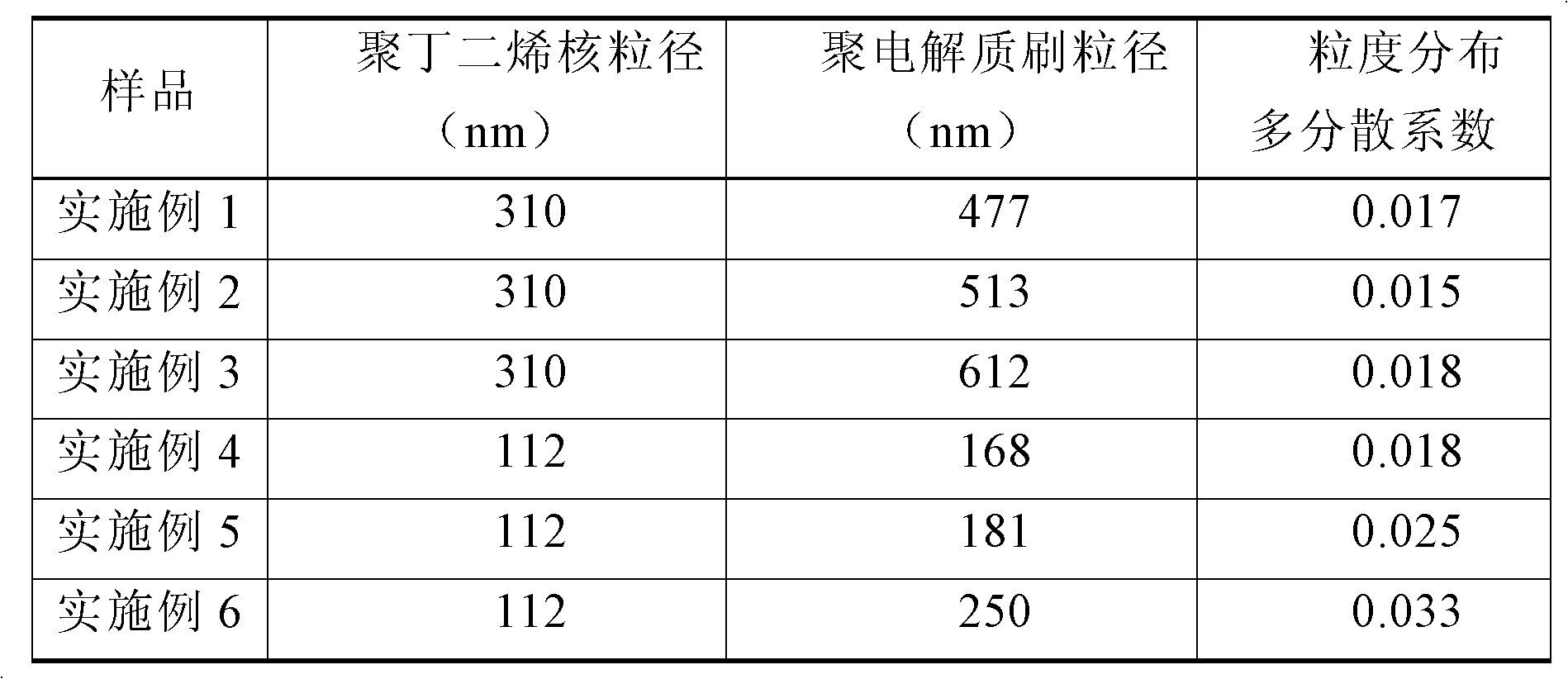
Method for preparing nano spherical polyelectrolyte brush
InactiveCN102516463AOvercoming technical defects that are not easy to industrializePeptide preparation methodsOn/in organic carrierPolyelectrolyte brushesMetal particle
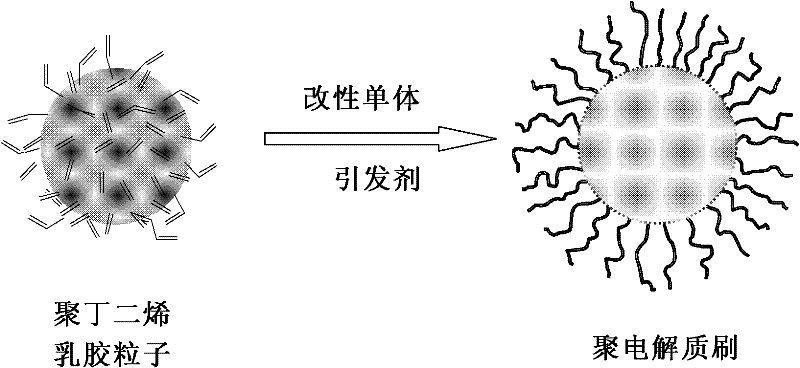
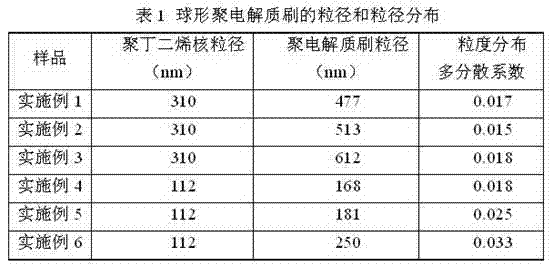
The invention relates to a novel method for preparing a nano spherical polyelectrolyte brush. The method can be used for preparing the spherical polyelectrolyte brush with the particle size of 200 to 600 nanometers by using polybutadiene emulsion particles with the particle sizes of 110 to 320 nanometers as cores and utilizing rich double bonds on the surfaces of the polybutadiene emulsion particles through carrying out copolymerization on the polybutadiene emulsion particles and added electrolyte monomers such as acrylic acid, sodium styrene sulfonate and the like under the initiation of an initiator. The polyelectrolyte brush can be applied to the fields of concentration and adsorption of metal ions with positive electricity and counter ions with negative electricity in water, preparation of nano metal particles by the in-situ reduction reaction, immobilization of a biological enzyme, separation of proteins and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of spherical polyelectrolyte brush and use thereof
InactiveCN101381435BOvercoming technical deficienciesWater/sewage treatmentPolyelectrolyte brushesEnd-group
The invention relates to a novel method for preparing a nano spherical polyelectrolyte brush by utilizing a thermal initiator and application thereof. Firstly, styrene and other substances are used as a monomer, and are subjected to oxidation reduction emulsion polymerization at normal temperature to obtain a micro milk globule of polystyrene(PS) with the grain diameter of between 50 and 90 millimeters; secondly, at the final stage of the polyreaction, an azo thermal initiator is added, because a C=C double bond of the end group of the thermal initiator and a surface residual monomer of the micro milk globule are subjected to copolymerization, the thermal initiator is fixed on the surface of the micro milk globule through the covalent bond; and finally, an electrolyte monomer such as acrylic acid, sodium styrene sulfonate and the like is added to initiate the polymerization at certain temperature, and the nano spherical polyelectrolyte brush with the grain diameter of between 100 and 200 millimeters is prepared. The polyelectrolyte brush can be widely applied to fields such as the removal of harmful metallic ions in water, the recovery of precious metal ions, the preparation of nano metal composite catalysts and biological enzyme reactor, the medical diagnosis.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method for spherical polyelectrolyte brush doped conductive polymer
The invention relates to a preparation method for a spherical polyelectrolyte brush doped conductive polymer nanocomposite material. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a spherical polyelectrolyte brush by surface-initiated polymerization, then introducing to a polymerization system, using an in-situ chemical oxidative polymerization to obtain the spherical polyelectrolyte brush doped nano conductive composite material. The prepared nano conductive composite material has the characteristics of high conductivity, good treatment performance, and simple and convenient operation process.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method for preparing nanometer spherical polyelectrolyte brush with magnetic kernel
The invention relates to a method for preparing a nanometer spherical polyelectrolyte brush with a magnetic kernel. The whole preparation process is completed by four steps as follows: firstly, preparing ferroferric oxide nanometer magnetic nanoparticles under an alkali condition by a coprecipitation method; secondly, dispersing the magnetic nanoparticles in a styrene monomer, and obtaining polystyrene (PS) microspheres with particle diameter of between 100 and 250 nm by miniemulsion polymerization; thirdly, adding a photoinitiator in the end stage of the miniemulsion polymerization to ensurethat the photoinitiator can be coated on the surface of the PS microspheres by chemical bonds to form a photoinitiator layer; and fourthly, adding an electrolyte monomer, and initiating polymerization by illumination of an ultraviolet lamp to obtain the nanometer spherical polyelectrolyte brush with the magnetic kernel, which has the particle diameter of between 180 and 350 nm. The nanometer spherical polyelectrolyte brush with the magnetic kernel can realize quick reclamation and recycle by a magnetic field after the nanometer spherical polyelectrolyte brush is adsorbed on a noble metal ion and subjected to wastewater treatment, and also can be used in targeted dosage treatment under the navigation of the magnetic field.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Spherical polyelectrolyte brush loaded organic conductive composite micro-nano particle and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a spherical polyelectrolyte brush loaded organic conductive composite micro-nano particle and a preparation method thereof. The composite micro-nano particle is composited by a spherical polyelectrolyte brush and an aniline-pyrrole copolymerization conductive polymer. The preparation method comprises the steps of introducing the nano-spherical polyelectrolyte brush into a composite polymeric system, and obtaining the spherical polyelectrolyte brush loaded organic conductive composite micro-nano particle by an in-situ chemical oxidative polymerization method. The preparation method is simple and convenient in operational course; the prepared spherical polyelectrolyte brush loaded organic conductive composite micro-nano particle has the characteristics of high conductivity, controllable particle size and good processing property; the conductive composite micro-nano material with the excellent conductivity can be obtained by controlling a molecular structure of the added spherical polyelectrolyte brush and polymerization reaction condition parameters; and the operational course is simple and convenient.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
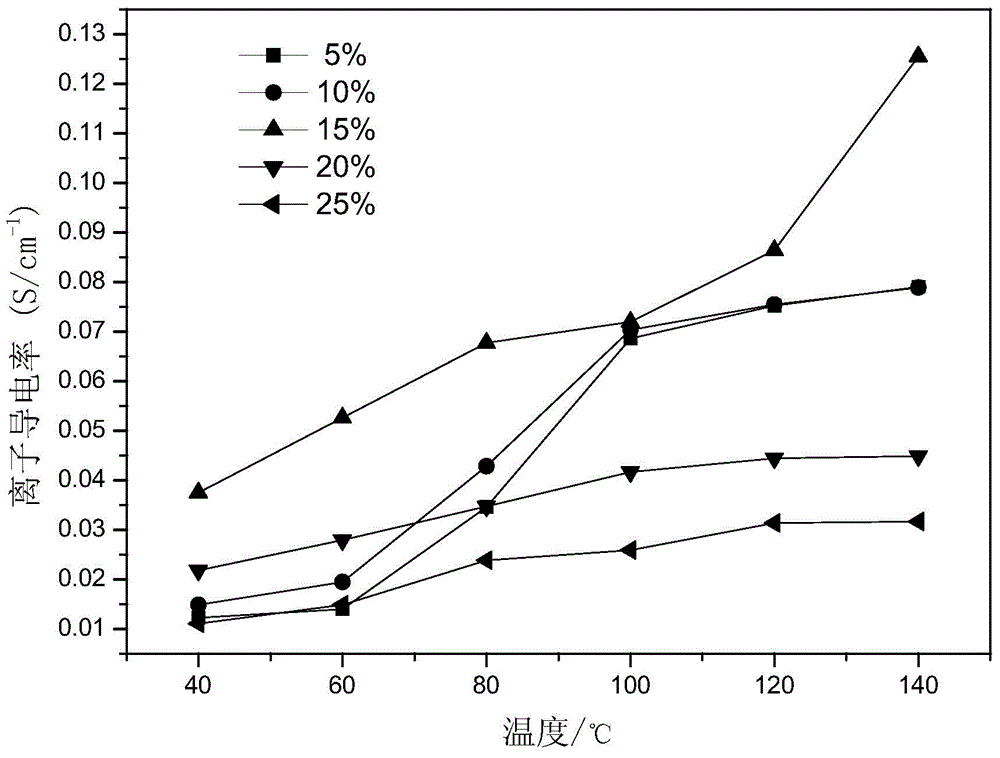
Method for preparing ordered ion conductor based on polyelectrolyte brush
ActiveCN105132987AImprove conduction efficiencyGood ion conductivitySurface reaction electrolytic coatingPolyelectrolyte brushesAnodizing
The invention discloses a method for preparing an ordered ion conductor based on a polyelectrolyte brush. The method includes the following steps that 1, an ordered ion conductor substrate material is prepared, wherein a highly-ordered double-through type titanium dioxide nano tube array is prepared through a two-time anodizing method; 2, a functional azo type initiator is anchored; and 3, the polyelectrolyte brush is grafted, wherein tubes in the titanium dioxide nano tube array are filled with monomer electrolytes through vacuum negative pressure, and free radical polymerization is conducted on the anchored initiator through in-situ initiation; and post-processing is conducted on a product obtained after a reaction, and a final product is obtained. The polyelectrolyte brush in the ion conductor is high in grafting density and of a one-dimensional ordered structure and performs higher ionic conduction efficiency.
Owner:广东南海普锐斯科技有限公司
Method for preparing nano spherical polyelectrolyte brush
InactiveCN102516463BOvercoming technical defects that are not easy to industrializePeptide preparation methodsOn/in organic carrierPolyelectrolyte brushesMetal particle
The invention relates to a novel method for preparing a nano spherical polyelectrolyte brush. The method can be used for preparing the spherical polyelectrolyte brush with the particle size of 200 to 600 nanometers by using polybutadiene emulsion particles with the particle sizes of 110 to 320 nanometers as cores and utilizing rich double bonds on the surfaces of the polybutadiene emulsion particles through carrying out copolymerization on the polybutadiene emulsion particles and added electrolyte monomers such as acrylic acid, sodium styrene sulfonate and the like under the initiation of an initiator. The polyelectrolyte brush can be applied to the fields of concentration and adsorption of metal ions with positive electricity and counter ions with negative electricity in water, preparation of nano metal particles by the in-situ reduction reaction, immobilization of a biological enzyme, separation of proteins and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
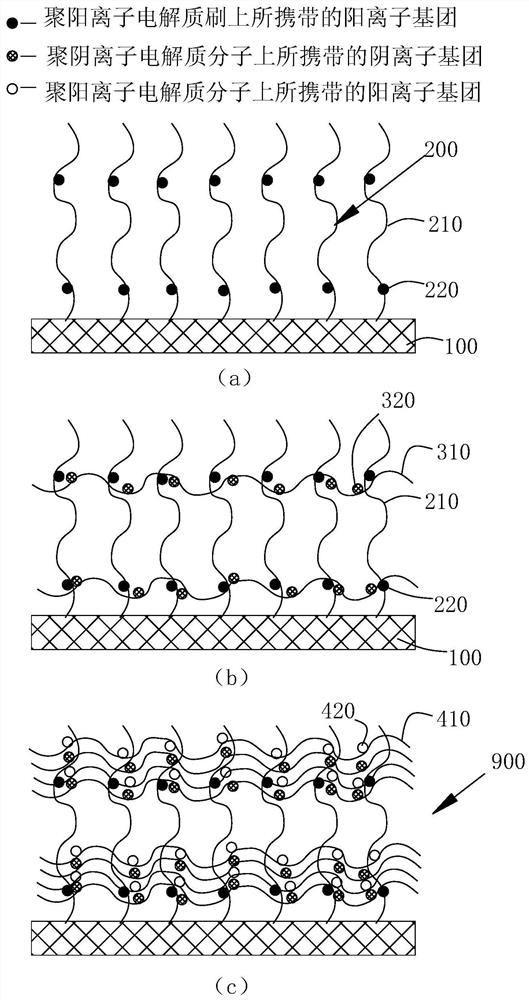
Artificial joint with durable lubricating surface layer and preparation method of artificial joint
PendingCN112546293AIncrease the number of cross-linking sitesImprove shear resistanceMetallic material coating processesTissue regenerationPolyelectrolyte brushesPolymer science
The invention discloses an artificial joint with a durable lubricating surface layer. The artificial joint is composed of a substrate and a cross-linked polyelectrolyte brush layer prepared on the surface of the substrate, and the cross-linked polyelectrolyte brush layer comprises a polyelectrolyte brush layer formed on the substrate and polyelectrolyte molecules cross-linked on the polyelectrolyte brush layer. The preparation method of the joint comprises the following steps of (1) coating the surface of the substrate with an ultraviolet initiator, soaking the substrate into a grafted electrolyte monomer solution, and forming the polyelectrolyte brush layer under ultraviolet light; and (2) repeatedly and sequentially carrying out impregnation and cleaning of a first polyion electrolyte solution and impregnation and cleaning of a second polyion electrolyte solution on the substrate to form the cross-linked polyelectrolyte brush layer of which electrolyte molecules and polyelectrolyte brush molecules penetrate through each other, namely the durable lubricating surface layer. The artificial joint has a good durable lubricating effect, the lubricating service life of the polyelectrolyte brush is prolonged, the polyelectrolyte brush can still keep good tribological performance under the condition of long-term frictional wear, and the service life is prolonged.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Gentle bleaching agent
InactiveUS20120077726A1Cellulosic pulp after-treatmentOther chemical processesCellulosePolyelectrolyte brushes
The aim of the invention is to reduce the damage to cellulosic material during the bleaching treatment of cellulosic material by using catalysts with bleaching activity, without significantly impacting the bleaching performance in the process. This was achieved largely by way of a method for bleaching cellulosic material in the presence of a peroxygen-containing bleaching agent and a bleach-boosting transition metal complex, which is carried out in the presence of spherical polyelectrolyte brushes. The spherical polyelectrolyte brushes preferably contain the transition metal complex in a colloidally bound manner.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
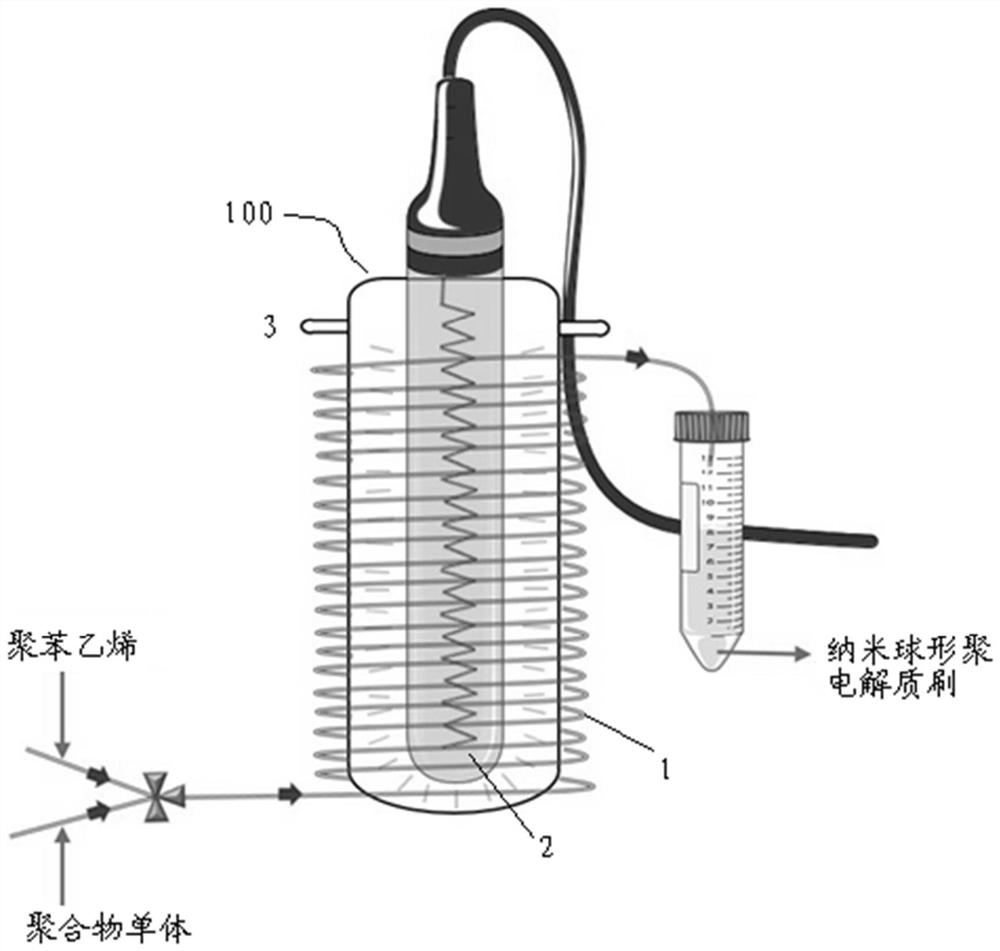
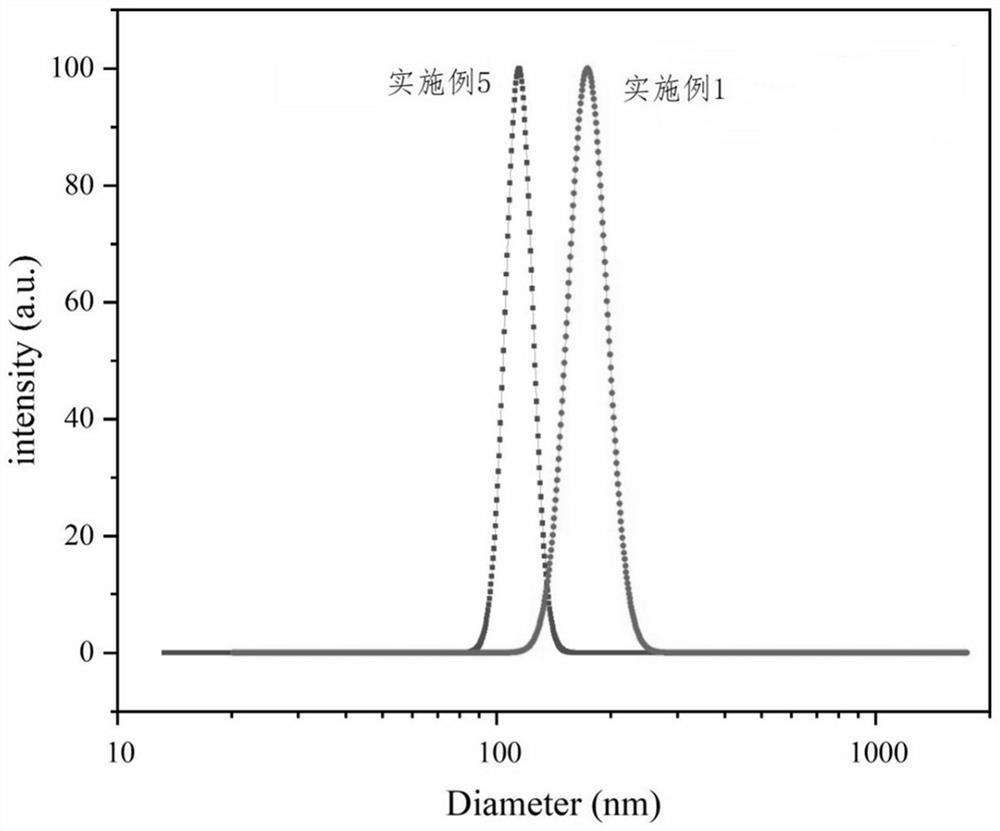
A kind of preparation method of nanometer spherical polyelectrolyte brush
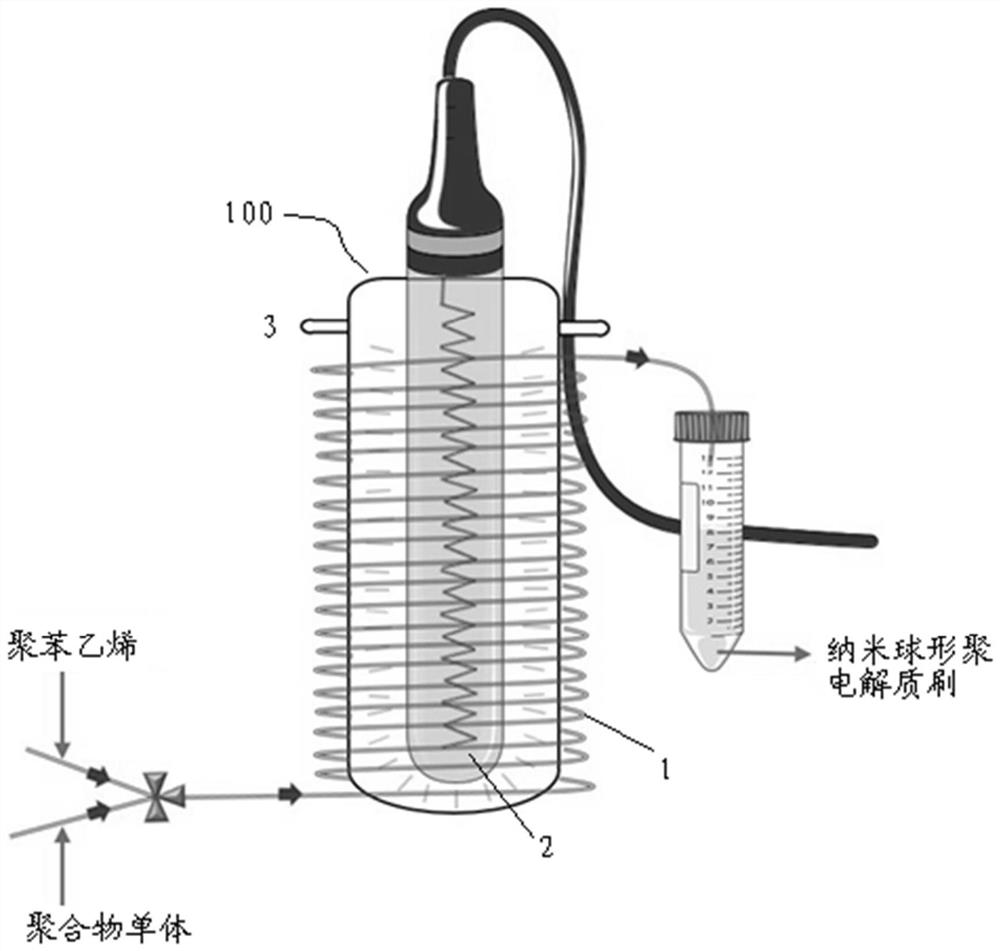
ActiveCN112679665BImprove responseAchieve preparationEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesFeed devicesPolyelectrolyte brushesPolymer science
The invention provides a method for preparing a nano-spherical polyelectrolyte brush, which comprises the following steps: dialyzing a polystyrene core emulsion with ultrapure water to remove impurities, adding the dialysis-purified polystyrene core emulsion into a flask to pump nitrogen, and using The polystyrene core emulsion is drawn out by a syringe, the water-soluble polymer monomer is diluted and then added to the flask to be filled with nitrogen, and the water-soluble polymer monomer is drawn out with a syringe; The syringe of the reactor is fixed on the syringe pump; a channel is set near the high-pressure ultraviolet lamp, and a cooling device is set at the accessories of the channel; the syringe is connected to the channel, and the ultraviolet lamp is turned on. Nano-spherical polyelectrolyte brushes were purified by dialysis. The invention can realize the continuous reaction and preparation of the polyelectrolyte brush, can effectively overcome the problems caused by the batch preparation and the amplification effect, and greatly improve the production efficiency.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
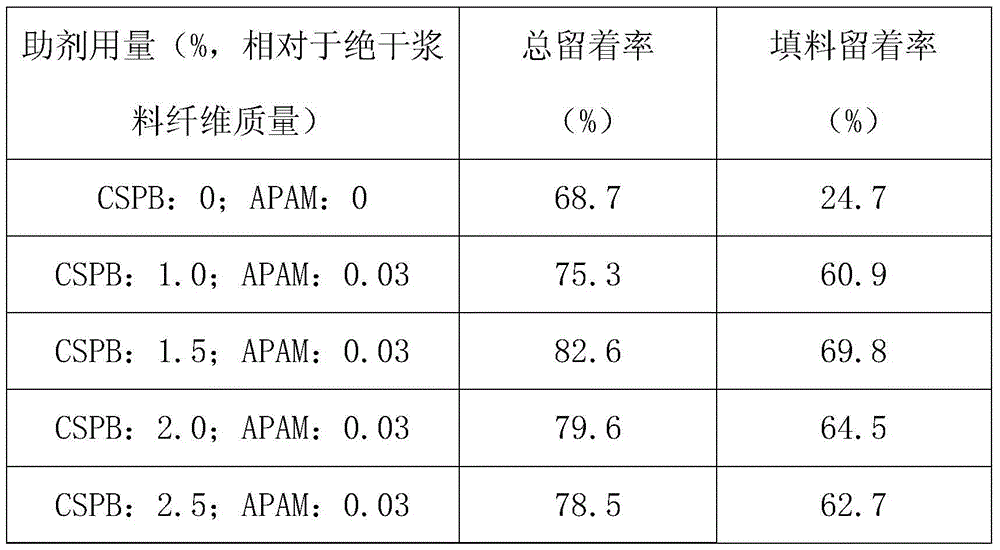
A spherical polyelectrolyte brush dual-element retention aid system and method for improving pulp retention
InactiveCN105088859BSimple structureStrong shear resistanceRetention agents additionPolyelectrolyte brushesPapermaking
The invention provides a binary retention system for a spherical polyelectrolyte brush for improving the retention rate of paper pulp. The binary retention system is composed of a cationic spherical polyelectrolyte brush and anionic polyacrylamide, wherein the cationic spherical polyelectrolyte brush regards SiO2 as an inner core and a copolymer of acrylamide and methacryloyloxyethyl trimethyl ammonium chloride as an outer brush. The invention further provides a method for improving the retention rate by using the binary retention system. The method comprises: sequentially adding the binary retention system composed of the cationic spherical polyelectrolyte brush and anionic polyacrylamide into scattered paper pulp to improve the retention rate of the slurry. The cationic spherical polyelectrolyte brush provided by the invention has high symmetric or quasi-symmetric structures, so that the anti-shear ability is relatively strong. The system has both the characteristics of a highly branched structure and high charge density and is easily to induce flocculation in high speed papermaking so as to improve the retention performance of a modern papermaking system. The binary system adopted by the invention remarkably improves the retention rate of the paper pulp and is simple and convenient to operate and less in use level of auxiliaries.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
A kind of preparation method of nano cationic spherical polyelectrolyte brush
The invention discloses a method for preparing a nano cationic spherical polyelectrolyte brush. The method sequentially comprises the following steps of: 1, preparing monodisperse nano silicon dioxide microspheres; 2, preparing silicon dioxide microspheres of which the surfaces are provided with unsaturated double bonds; and 3, preparing the nano cationic spherical polyelectrolyte brush by adopting a dispersion polymerization method. The method is simple and easy to operate, the process is easy to control and the method is suitable for industrial production; and the cationic spherical polyelectrolyte brush prepared by the method has the grafting ratio of 2.4-17.9 percent, the weight-average molecular weight of 3.23*10<2>-7.173*10<4>g / mol and the grafting density of 3.345*10<-7>-5.54*10<-4>mol / g. The product prepared by the method has high grafting density.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Preparation method of nano spherical polyelectrolyte brush
ActiveCN112679665AImprove responseAchieve preparationEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesFeed devicesPolyelectrolyte brushesPolymer science
The invention provides a preparation method of a nano spherical polyelectrolyte brush, which comprises the following steps: dialyzing polystyrene core emulsion by using ultrapure water to remove impurities, adding the dialyzed and purified polystyrene core emulsion into a flask, pumping nitrogen, pumping out the polystyrene core emulsion by using an injector, diluting the water-soluble polymer monomer, adding the diluted water-soluble polymer monomer into a flask, pumping nitrogen, and pumping out the water-soluble polymer monomer by using an injector; fixing an injector filled with the polystyrene core emulsion and a water-soluble polymer monomer to an injection pump; arranging a channel near the high-voltage ultraviolet lamp, and arranging a cooling device near the channel; and connecting the injector with the channel, turning on the ultraviolet lamp, receiving a product at a connector after the interior of the reactor is stable, and dialyzing and purifying by virtue of a dialysis bag, so as to obtain the nano spherical polyelectrolyte brush. According to the invention, continuous reaction and preparation of the polyelectrolyte brush can be realized, the problems caused by intermittent preparation and amplification effect can be effectively overcome, and the production efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Ionic spherical polyelectrolyte brush with micro-nano carbon sphere as inner core and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an ionic ball polyelectrolyte brush employing a micro-nano carbon sphere as a kernel and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of a nano composite material. The kernel of the ionic ball polyelectrolyte brush is the micro-nano carbon sphere, and an outer brush is an ionic monomer. The preparation method comprises the following steps: loading synthetic azo acyl chloride on the surface of the micro-nano carbon sphere, and synthesizing the ionic ball polyelectrolyte brush employing the micro-nano carbon sphere as the kernel by free radical polymerization. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple and feasible. The product prepared by the method takes the micro-nano carbon sphere as the kernel, and is novel in structure, green and environment-friendly, low in cost, and different molecular weights and different grafting densities of ionic ball polyelectrolyte brushes can be prepared by controlling the reaction time and the density of the monomer. The product can be used as a conductive polymer dopant, a morphology control agent, a deflocculating agent, a papermaking wet-end additive and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Magnetic particles preparation method by using nanometer spherical polyelectrolyte brush as micro-reactor
InactiveCN101630555BRetain propertiesGood dispersionMagnetic materialsPolyelectrolyte brushesFerrous salts
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
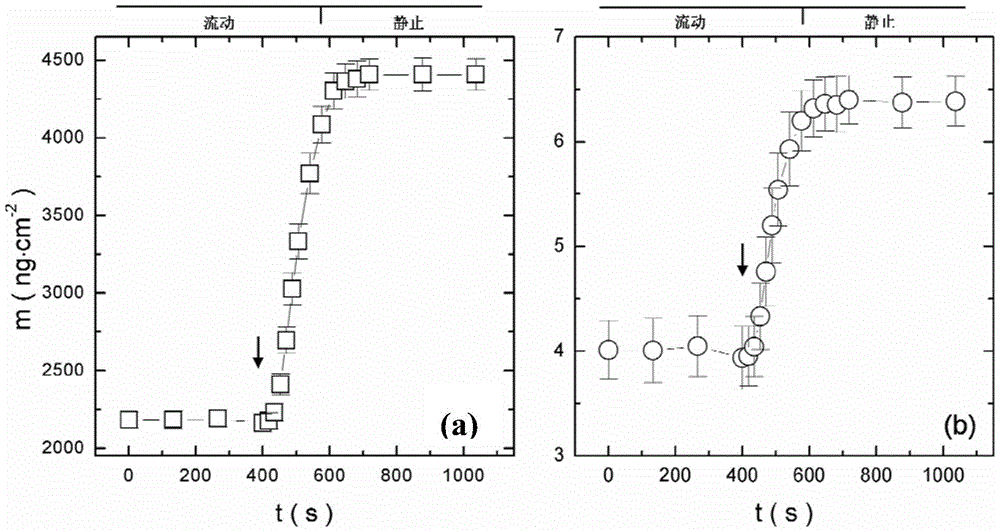
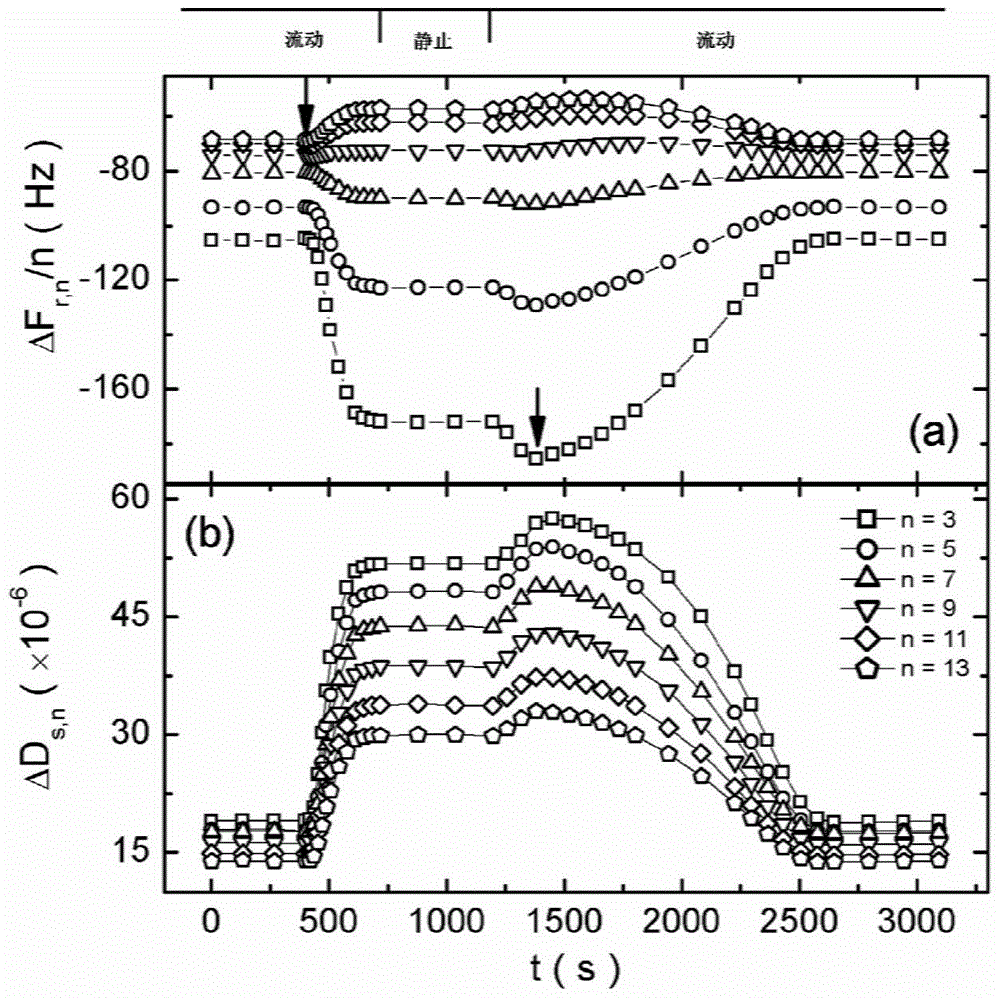
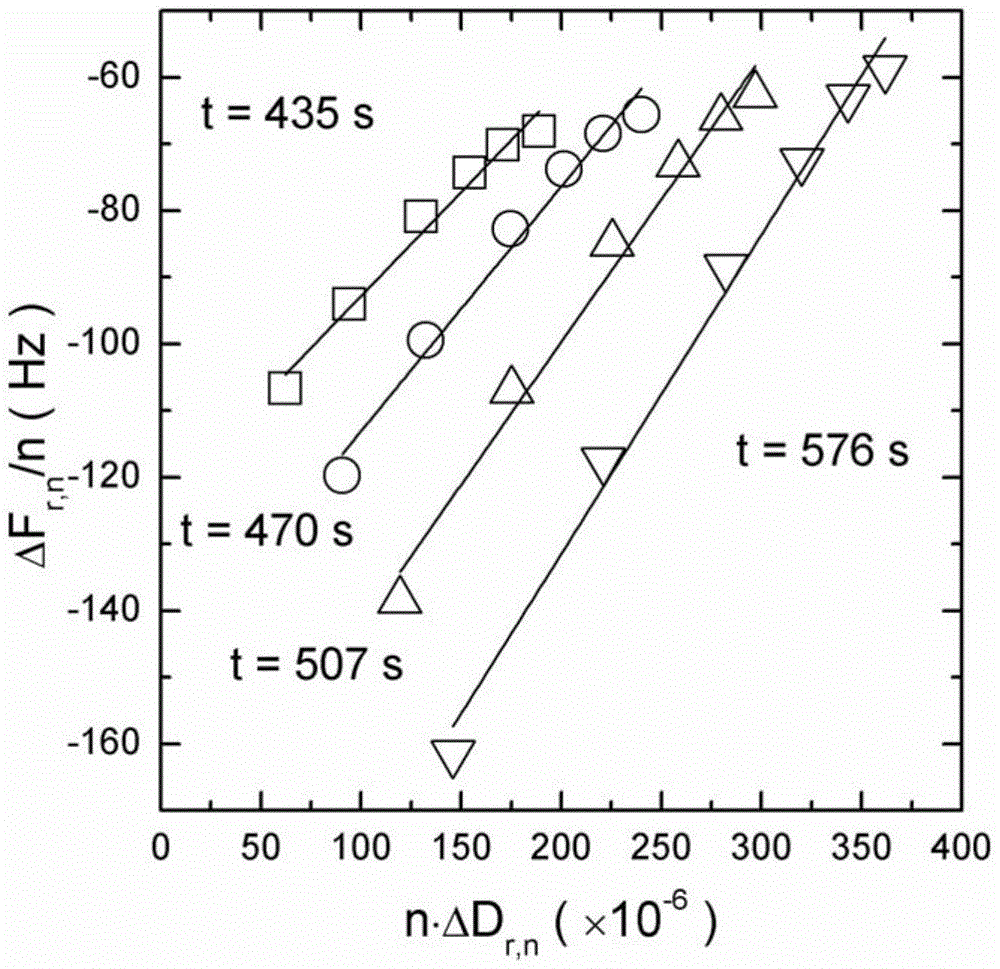
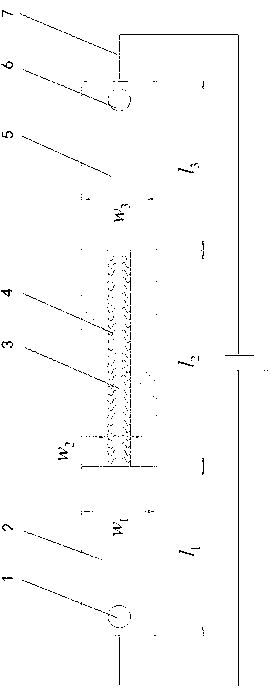
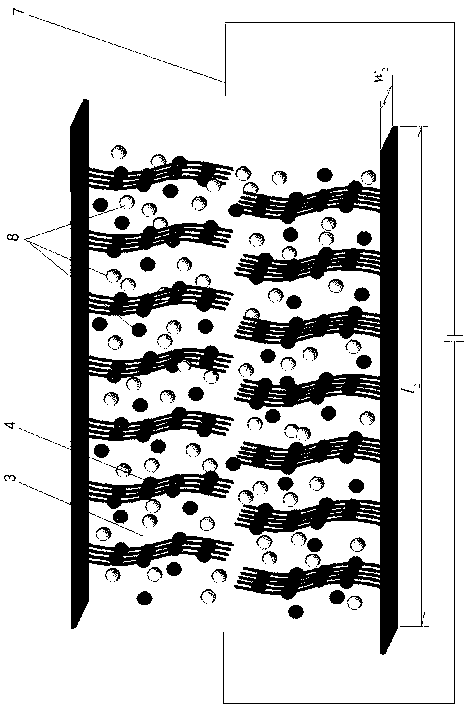
Method for measuring relaxation behaviors of counter ion pairs in polyelectrolyte brush
The invention discloses a method for measuring relaxation behaviors of counter ion pairs in a polyelectrolyte brush. The method comprises the following steps: bonding an initiator to a gold chip by chemical reaction; chemically grafting a monomer onto the gold chip by a radical polymerization method to obtain a gold chip with a polyelectrolyte brush; putting the gold chip with the polyelectrolytebrush in a sample cell and soakng it with a solution; obtaining the relaxation frequency of the counter ion pairs inside the polyelectrolyte brush in the solution by cooperatively using an electrochemical workstation and a quartz crystal microbalance electrochemical module. By adopting the method of cooperatively using the electrochemical workstation and the quartz crystal microbalance electrochemical module and by grafting the polyelectrolyte brush on the gold chip, on one hand, a quartz crystal microbalance can be utilized to measure the mass and viscoelasticity changes of polyelectrolyte brush films in different sodium chloride solutions in real time; on the other hand, the electrochemical workstation can also be utilized to simultaneously measure the relaxation behaviors of the counterion pairs inside the polyelectrolyte brush in the different solutions.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
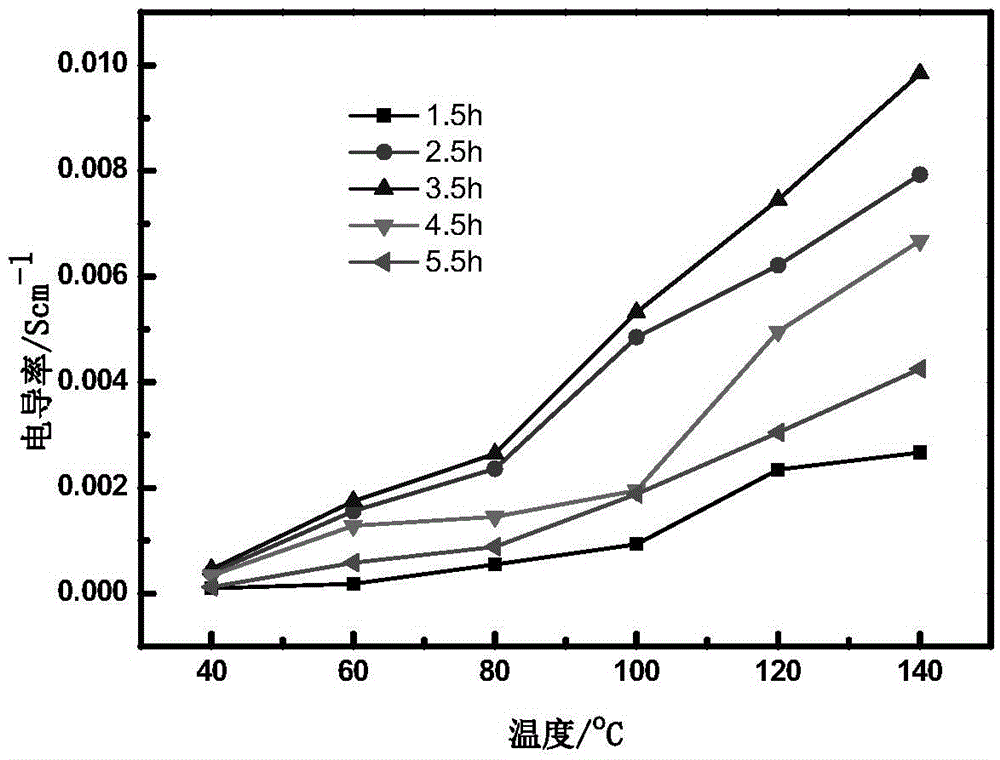
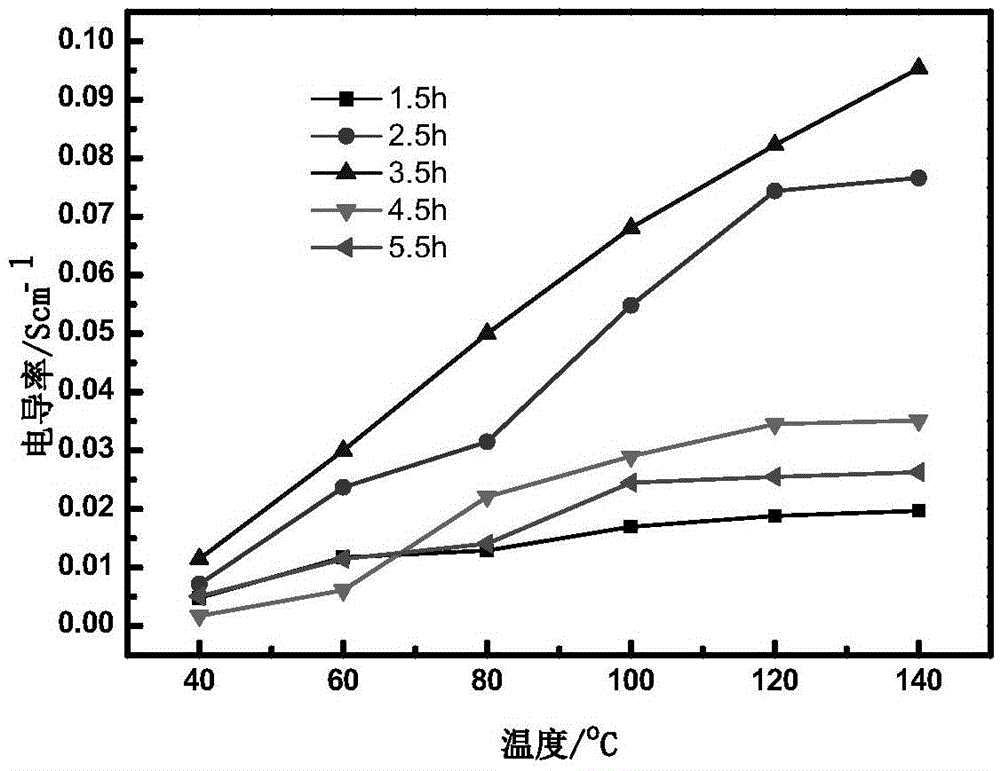
A kind of preparation method of proton conductor based on grafted titanium dioxide nanotube polyelectrolyte brush
InactiveCN103833943BImprove proton conductivityImprove water retentionFuel cellsPolyelectrolyte brushesElectrical conductor
The invention provides a preparation method of a proton conductor based on a grafted titanium dioxide nanotube polyelectrolyte brush. The method comprises the following steps: 1) adding a TiO2 nano tube to a reaction container, adding triethylamine to the reaction container, adding an azo initiator solution under protection of N2, agitating under the condition at room temperature, and then transferring the reacted product to a centrifuge tube, washing, finally baking the lower layer of sediments in the centrifuge tube after transferring, and taking the dried product as an initiator to anchor the product on the surface of the TiO2 nano tube; 2) adding the TiO2 nano tube-initiator product to the reaction container, then adding an electrolyte monomer containing carbon-carbon double bonds, removing the inside air by adopting a mode of freezing-unfreezing for a plurality of times in cycle, carrying out radical polymerization on a mixed solution from which the air is removed, and carrying out post-treatment on the reacted product, so as to obtain the final product. The polyelectrolyte brush has more ion groups in the unit volume, is good in water-retaining property of a membrane, and shows high proton conductivity at low humidity.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
A method for real-time in situ quantitative determination of solution quality and its viscoelasticity in polymer films
ActiveCN104390878BGet it in real timeEasy and accurateFlow propertiesWeighing by absorbing componentPolyelectrolyte brushesLiquid state
The invention relates to a method for measuring the mass of a solution in a thin polymer film and the viscoelasticity of the thin polymer film. The method comprises the steps that (1) in a quartz crystal microbalance, frequency and dissipation change values of a standard chip caused by a solution and frequency and dissipation change values of a standard chip covered by the thin polymer film caused by the solution are recorded in real time, and are subtracted to obtain the frequency and dissipation change values of the solution in the thin polymer film; (2) a product of a frequency multiplying number and the dissipation change value of the solution in the thin polymer film is taken as an X-coordinate, and the ratio of the frequency change value of the solution in the thin polymer film to the frequency multiplying number is taken as a Y-coordinate to make a linear regression equation, so that the intercept of the linear regression equation on a Y-axis is the mass of the solution in the thin polymer film, and the slope of the linear regression equation is the retardation time of the thin polymer film. The method can be used for measuring the mass of the solution in the thin film and the viscoelasticity of the thin film in real time simply and accurately in a liquid environment. The method is particularly suitable for measuring a high-viscoelasticity polyelectrolyte brush brought by highly hydrated swelling.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Micro-fluidic chip for inhibiting electroosmotic flows through grafting polyelectrolyte brush on surface of micro-channel
InactiveCN103212457AHigh control precisionReduce complexityLaboratory glasswaresPolyelectrolyte brushesEngineering
The invention relates to a micro-fluidic chip for inhibiting electroosmotic flows through grafting a polyelectrolyte brush on the surface of a micro-channel, belonging to the field of microfluidics. The micro-fluidic chip comprises a sample feeding pool, an inlet channel, a slit channel, an outlet channel and a waste liquid pool which are sequentially communicated, wherein a polyelectrolyte brush with cations is grafted on the channel surface of the inside of the slit channel, and an uniform electric field is applied parallel to the direction of the channel so as to drive fluid to flow. Under the action of the uniform electric field, the polyelectrolyte brush grafted on the surface of the micro-channel extends along the direction of the electric field, and the fluid in the micro-channel is under the action of the viscous friction and electrostatic attraction of the polyelectrolyte brush, so that surface charges in the channel are balanced, reduced or inhibited; and due to the attraction action among solvent particles and the polyelectrolyte brush, the solvent particles are impregnated into a polyelectrolyte brush layer, thereby achieving the purpose of inhibiting electroosmotic flows. The micro-fluidic chip disclosed by the invention can improve the separation precision of proteins and DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecules, and has the advantages of wide applicability, strong controllability and the like.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Spherical polyelectrolyte brush loaded organic conductive composite micro-nano particle and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a spherical polyelectrolyte brush loaded organic conductive composite micro-nano particle and a preparation method thereof. The composite micro-nano particle is composited by a spherical polyelectrolyte brush and an aniline-pyrrole copolymerization conductive polymer. The preparation method comprises the steps of introducing the nano-spherical polyelectrolyte brush into a composite polymeric system, and obtaining the spherical polyelectrolyte brush loaded organic conductive composite micro-nano particle by an in-situ chemical oxidative polymerization method. The preparation method is simple and convenient in operational course; the prepared spherical polyelectrolyte brush loaded organic conductive composite micro-nano particle has the characteristics of high conductivity, controllable particle size and good processing property; the conductive composite micro-nano material with the excellent conductivity can be obtained by controlling a molecular structure of the added spherical polyelectrolyte brush and polymerization reaction condition parameters; and the operational course is simple and convenient.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method for preparing nano nickel by taking nano spherical polyelectrolyte brush as reactor and application of nano nickel
InactiveCN102240816BGood dispersionImprove catalytic performanceMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic compound preparationPolyelectrolyte brushesNano catalyst
The invention discloses a method for preparing nano nickel by taking a nano spherical polyelectrolyte brush as a microreactor and an application of the nano nickel. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing polymer microspheres with the particle size of 80-140nm by adopting emulsion polymerization initiated by an oxidation-reduction system; adding a photoinitiator in the terminal stage of the emulsion polymerization, coating the photoinitiator on the surfaces of the polymer microspheres to form a photoinitiator layer, then utilizing an ultraviolet lamp to initiate polyelectrolytemonomers to be polymerized so as to obtain a spherical electrolyte brush with the particle size of 10-400nm; then adding sodium hydroxide to dissociate carboxyl on an electrolyte chain; treating the dissociated spherical polyelectrolyte brush by use of a nickel chloride aqueous solution, thus nickel ions exchange sodium ions and enters into the polyelectrolyte brush; and adding sodium borohydrideto reduce the nickel ions into nano nickel in situ, thus finally obtaining controllable nano nickel which are uniformly distributed inside the nano spherical polyelectrolyte brush and have the particle size of 1-14nm. The nano nickel loaded on the spherical polyelectrolyte brush is an ideal efficient nano catalyst.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com