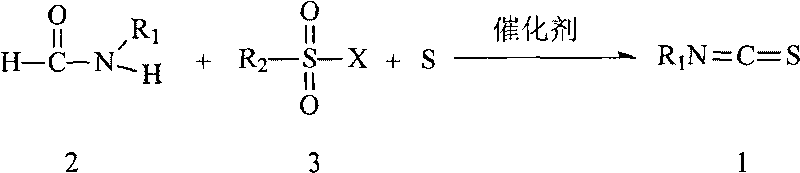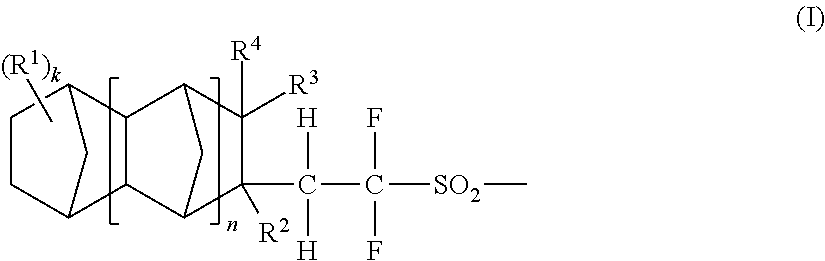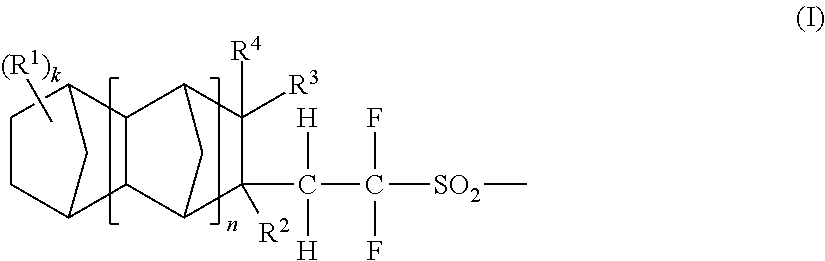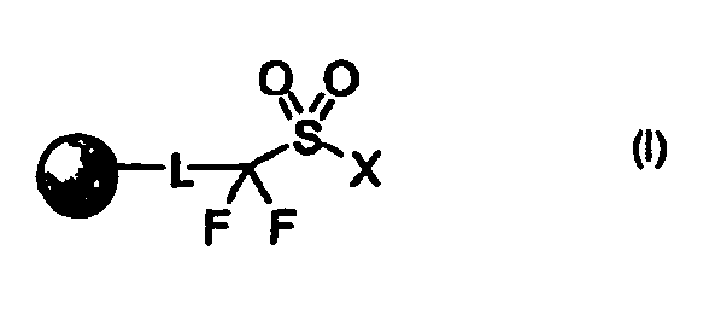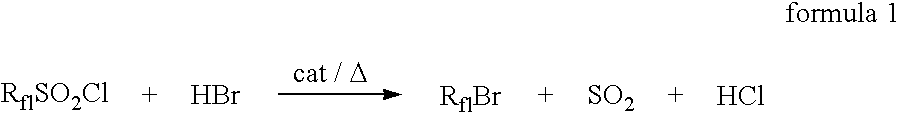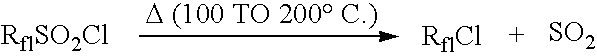Patents
Literature
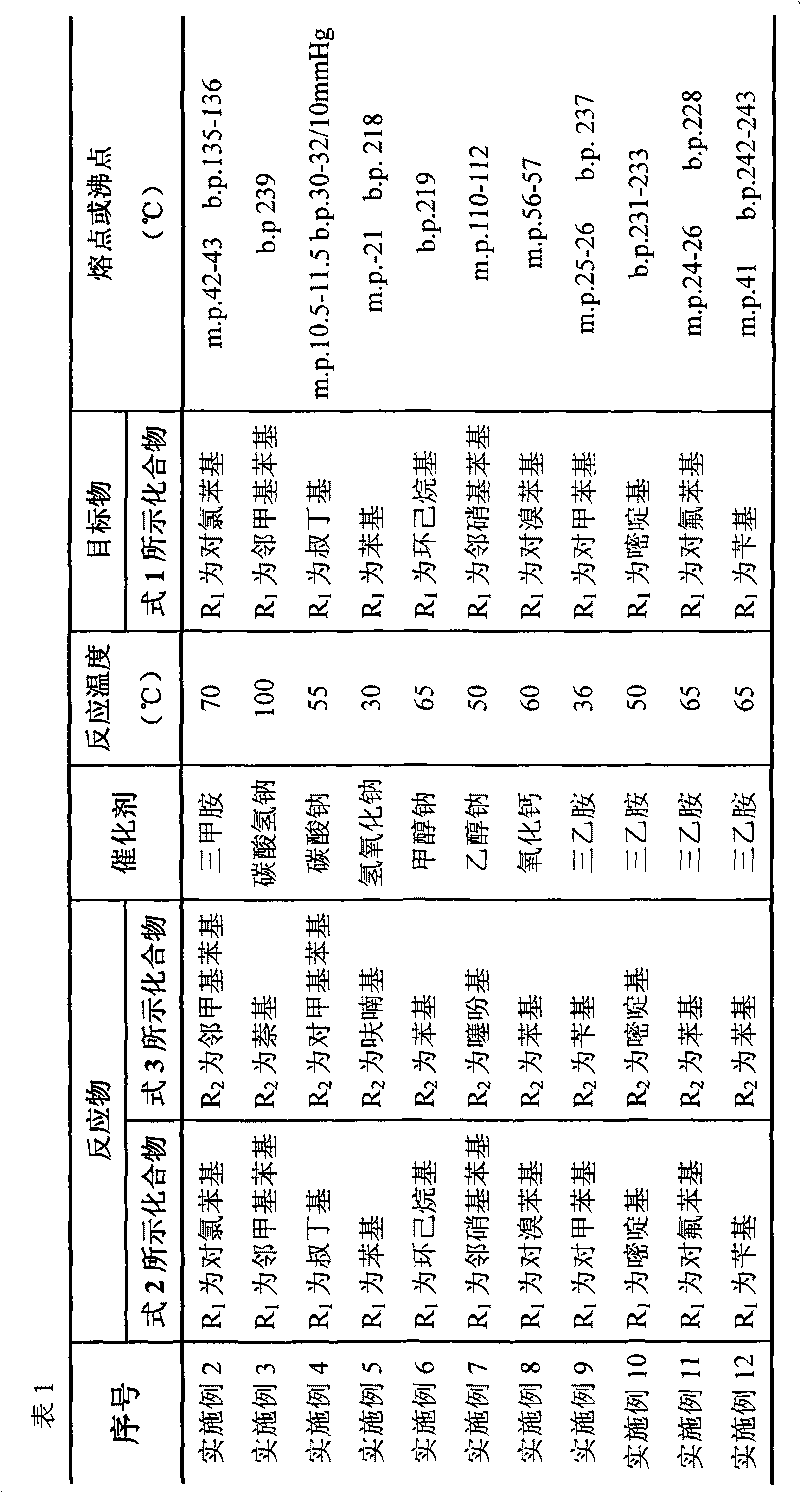
99 results about "Sulfonyl halide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
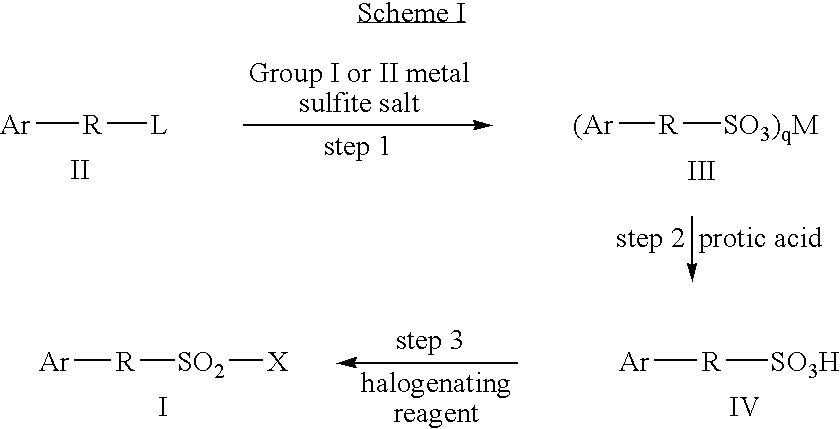
Sulfonyl halide groups occur when a sulfonyl functional group is singly bonded to a halogen atom. They have the general formula RSO₂X where X is a halogen. The stability of sulfonyl halides decreases in the order fluorides > chlorides > bromides > iodides, all four types being well known. The sulfonyl chlorides are of dominant importance in this series.
Reverse osmosis composite membranes for boron removal
InactiveUS20110049055A1Semi-permeable membranesGeneral water supply conservationSulfonyl halidePolyamide
Improved methods for reducing boron concentration in seawater or brackish water, while simultaneously maintaining or improving the salt rejection of membrane and flow performance of polyamide reverse osmosis (RO) membranes include contacting the water with a composite membrane comprising moieties derived from an aromatic sulfonyl halide, a heteroaromatic sulfonyl halide, a sulfinyl halide; a sulfenyl halide; a sulfuryl halide; a phosphoryl halide; a phosphonyl halide; a phosphinyl halide; a thiophosphoryl halide; a thiophosphonyl halide, an isocyanate, a urea, a cyanate, an aromatic carbonyl halide, an epoxide or a mixture thereof.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for reducing NOx during combustion of coal in a burner
InactiveUS20060228282A1Reduce outputEasy to oxidizeNitrogen compoundsTobacco treatmentNano catalystSulfonyl halide
An organically complexed nanocatalyst composition is applied to or mixed with coal prior to or upon introducing the coal into a coal burner in order to catalyze the removal of coal nitrogen from the coal and its conversion into nitrogen gas prior to combustion of the coal. This leads to reduced NOx production during coal combustion. The nanocatalyst compositions include a nanoparticle catalyst that is made using a dispersing agent. The dispersing agent includes at least one functional group such as a hydroxyl, a carboxyl, a carbonyl, an amine, an amide, a nitrile, a nitrogen having a free lone pair of electrons, an amino acid, a thiol, a sulfonic acid, a sulfonyl halide, and an. acyl halide. The dispersing agent forms stable, dispersed, nano-sized catalyst particles. The catalyst composition can be formed as a stable suspension to facilitate storage, transportation and application of the catalyst nanoparticles to a coal material. The catalyst composition can be applied before or after pulverizing the coal material or it may be injected directly into the coal burner together with pulverized coal.
Owner:HEADWATERS TECH INNOVATION GRP
Additive for non-aqueous electrolyte and secondary battery using the same
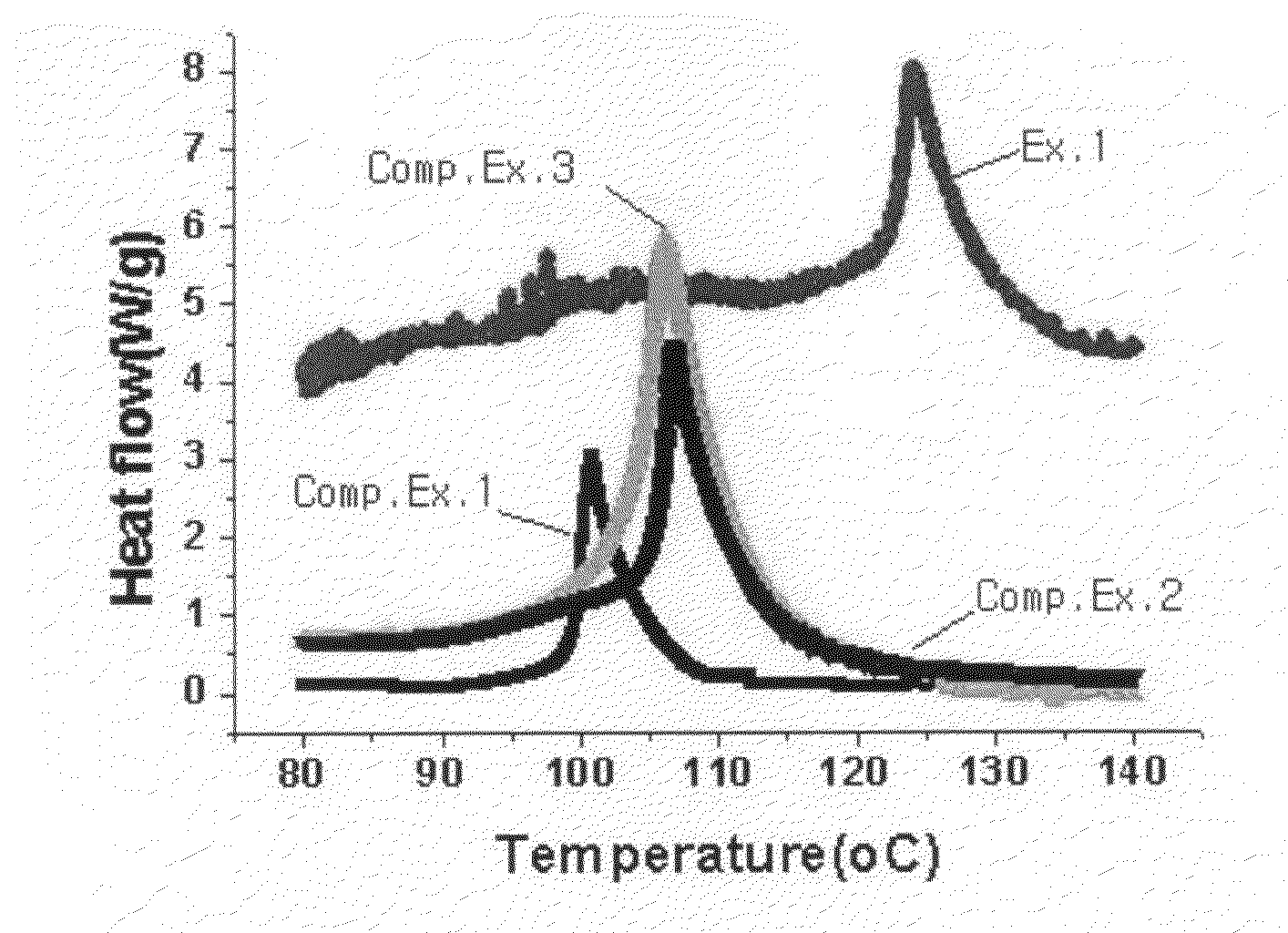
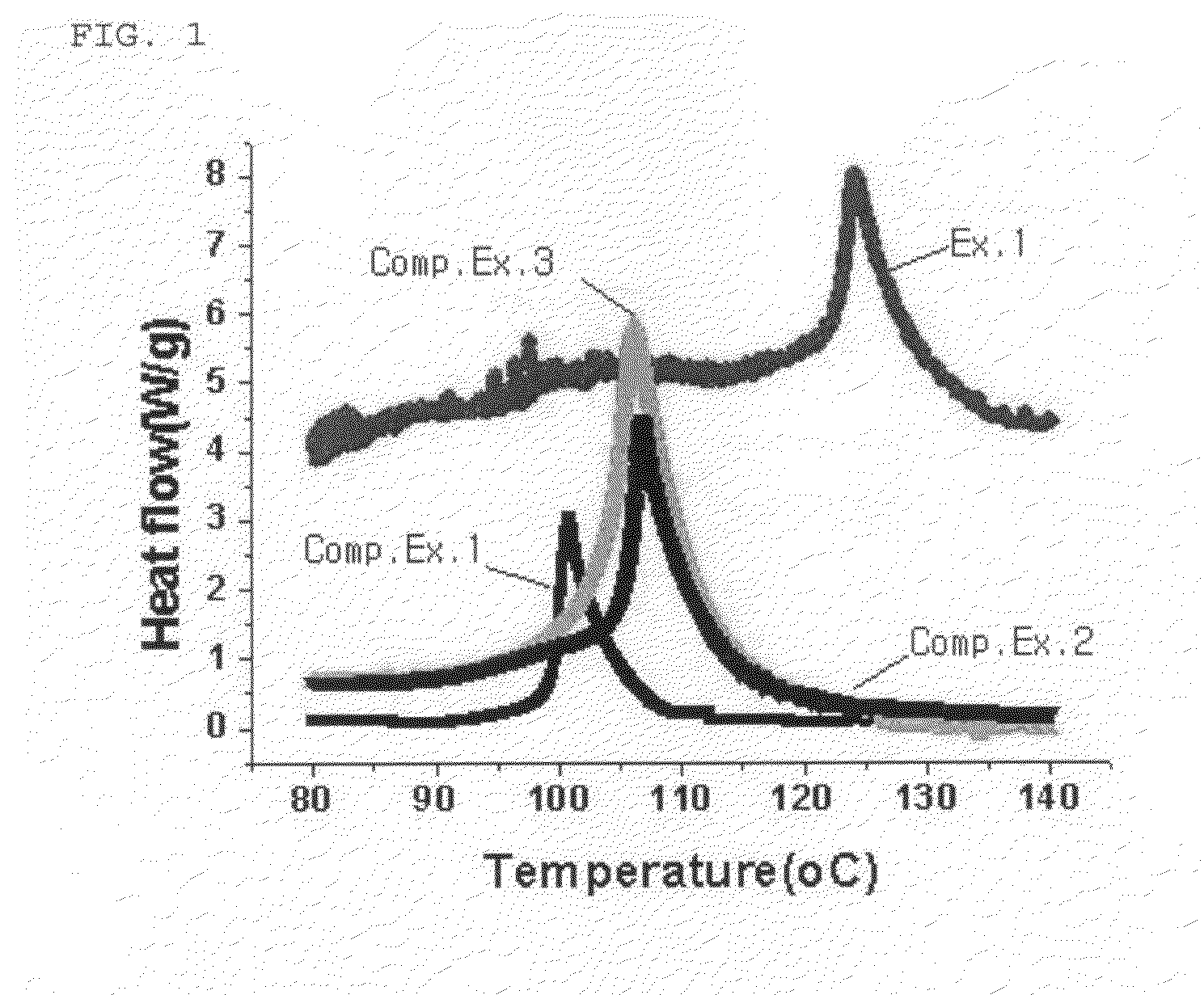
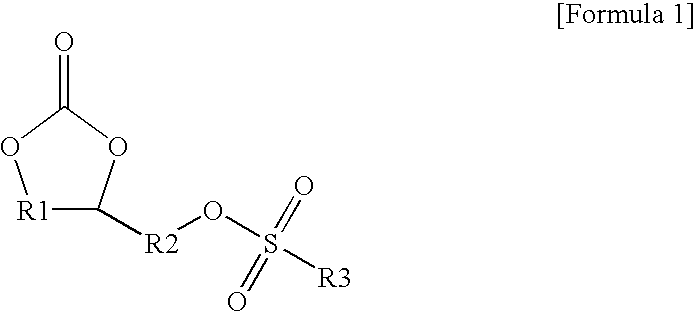
ActiveUS20090280414A1Excellent characteristicsExtend the lifespanOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationHydrogen atomSulfonyl halide
Disclosed is an electrolyte comprising a compound having both a sulfonate group and a cyclic carbonate group. The electrolyte forms a more stable and dense SEI layer on the surface of an anode, and thus improves the capacity maintenance characteristics and lifespan characteristics of a battery. Also, disclosed is a compound represented by the following Formula 1, and a method for preparing the same by reacting 4-(hydroxyalkyl)-1,3-dioxolan-2-one with a sulfonyl halide compound:wherein each of R1 and R2 independently represents a C1˜C6 alkylene group optionally containing a C1˜C6 alkyl group or C2˜C6 alkenyl group introduced thereto; R3 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom, C1˜C20 alkyl group, C3˜C8 cyclic alkyl group, C2˜C6 alkenyl group, halo-substituted alkyl group, phenyl group and benzyl group.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
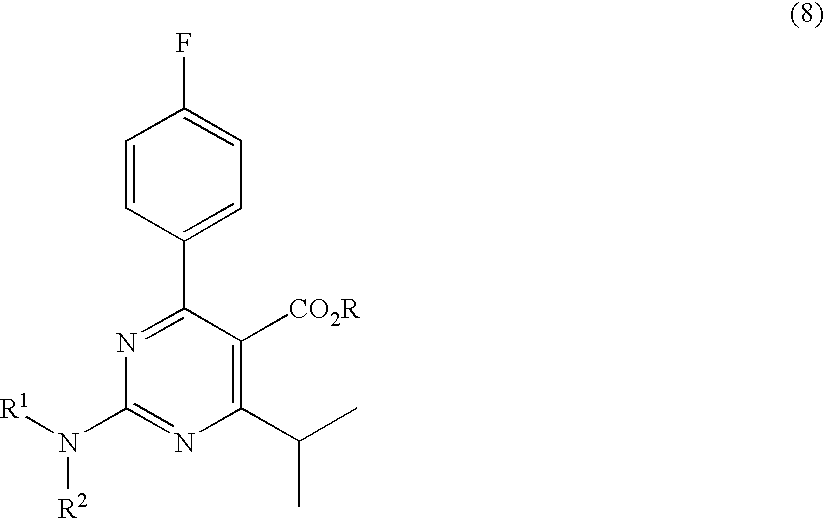
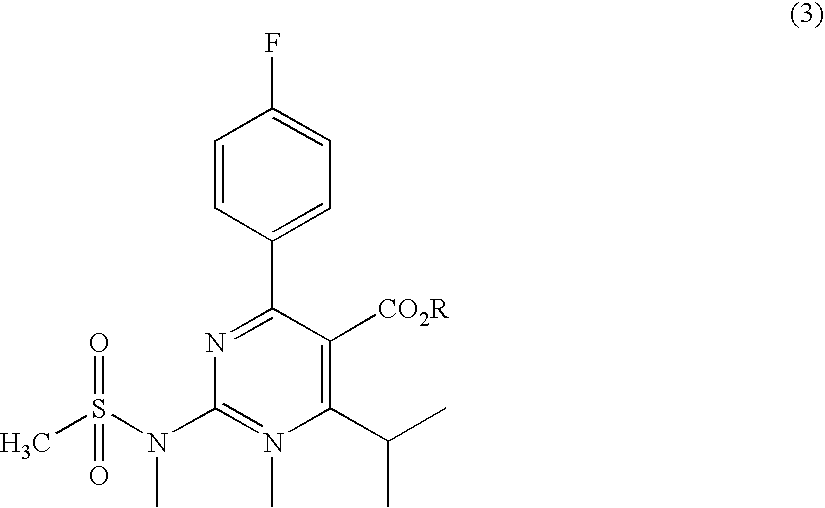
Preparation of aminopyrimidine compounds
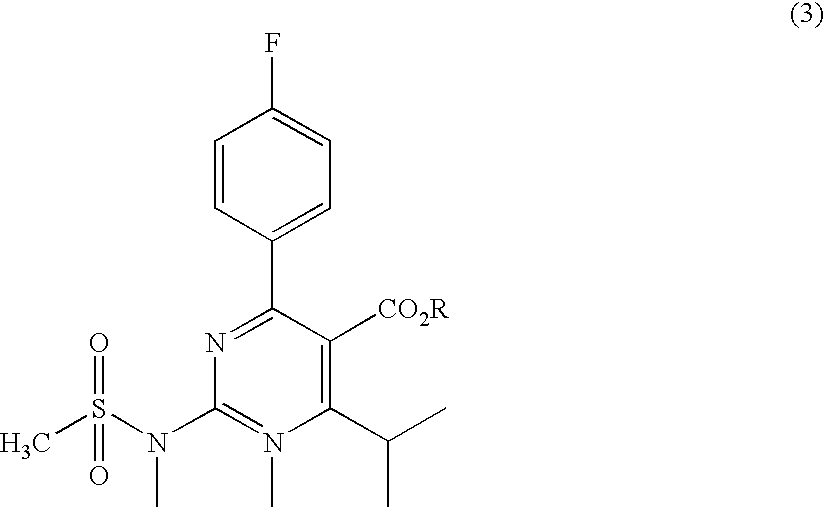
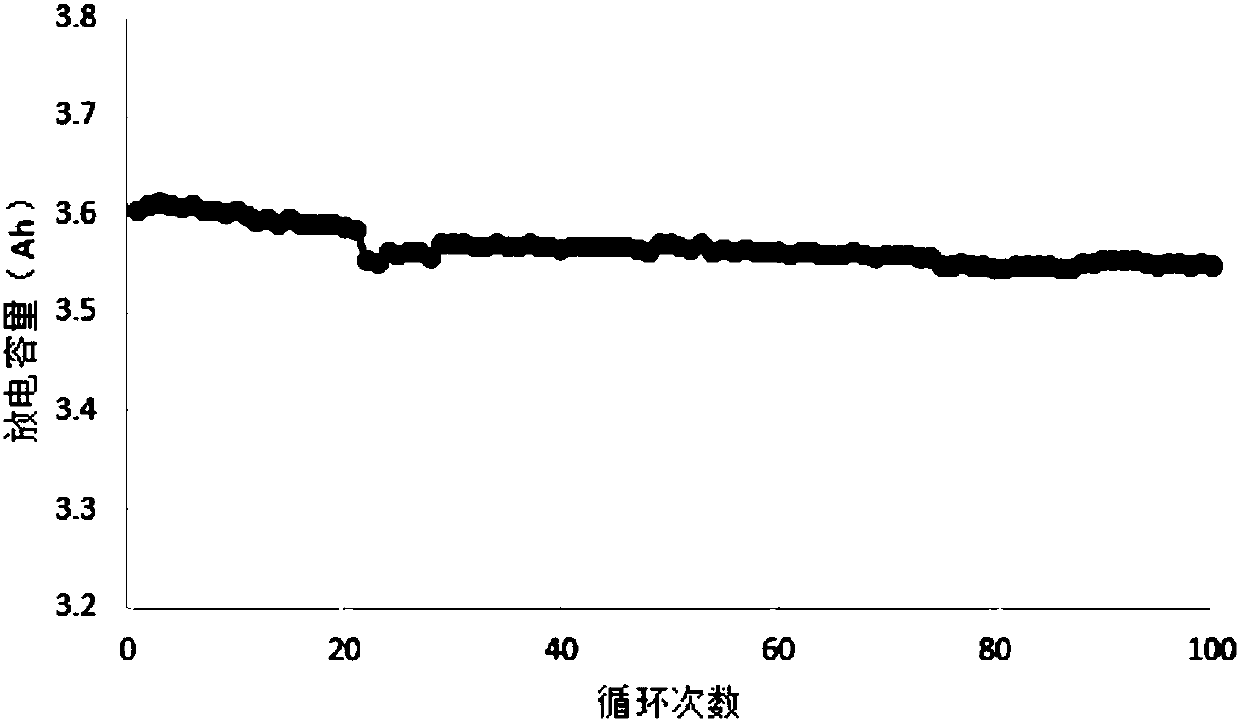
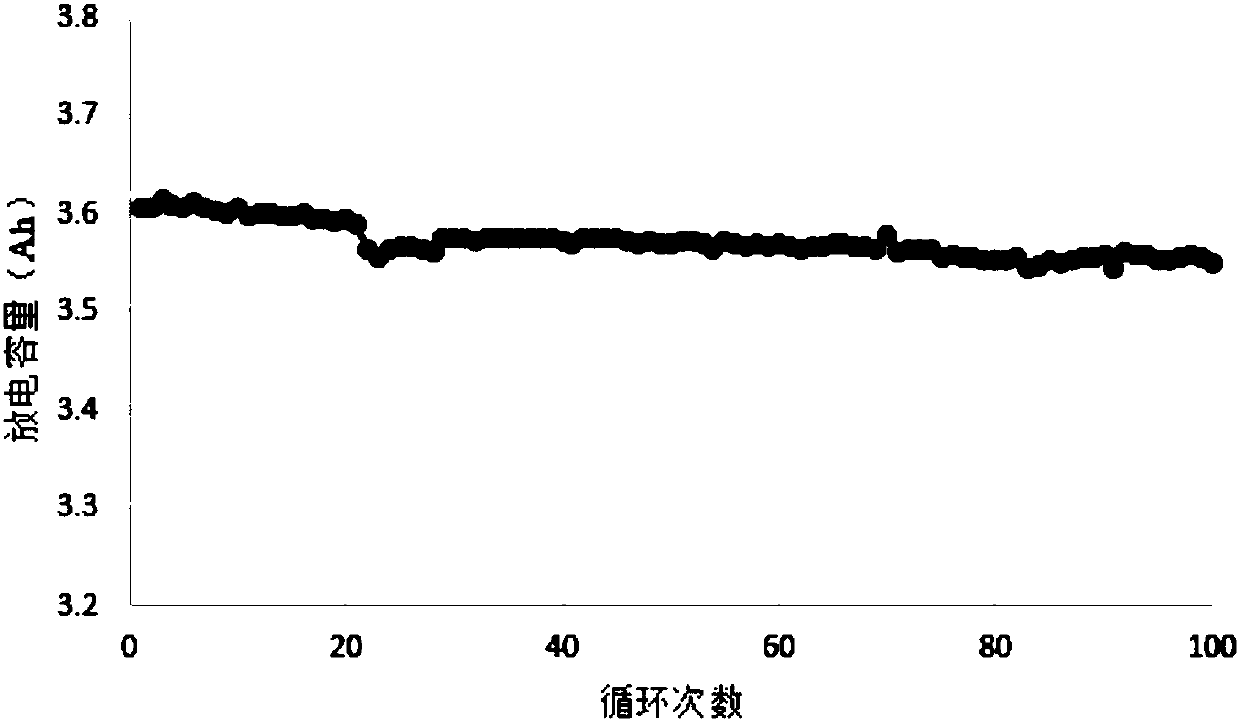
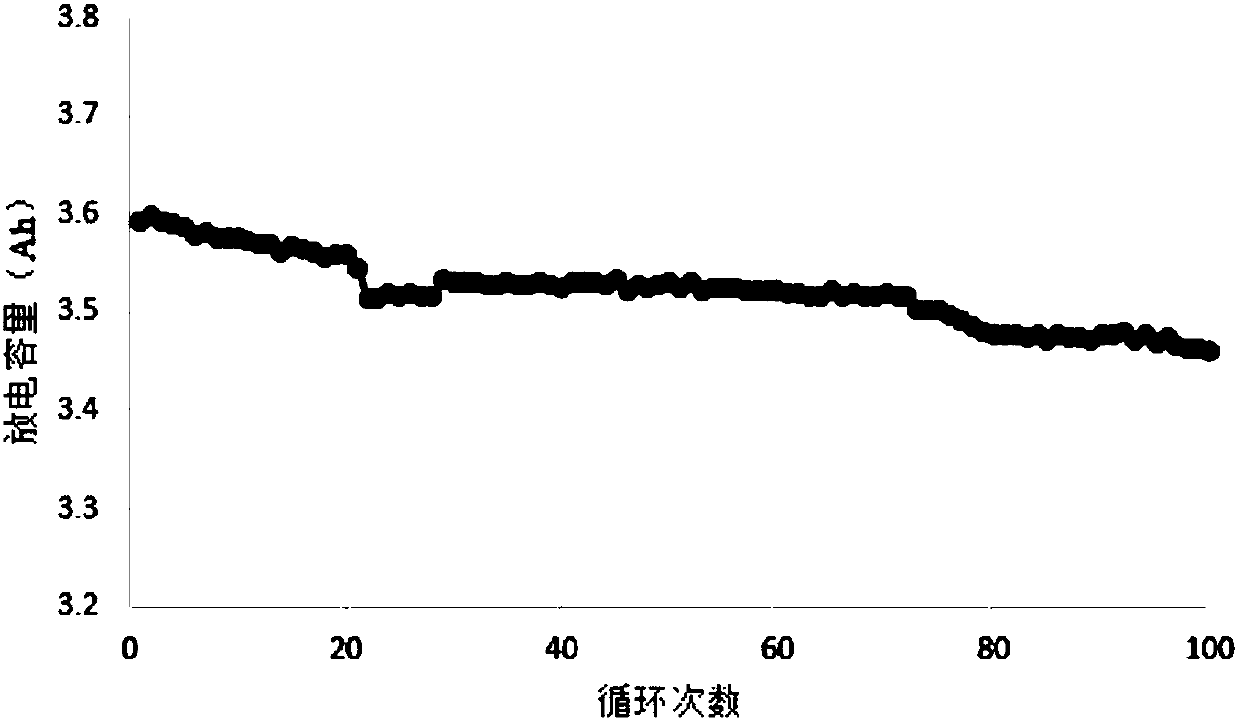
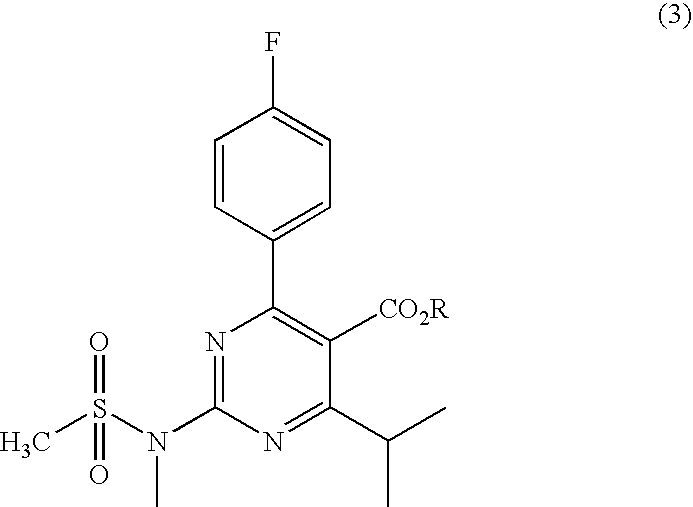
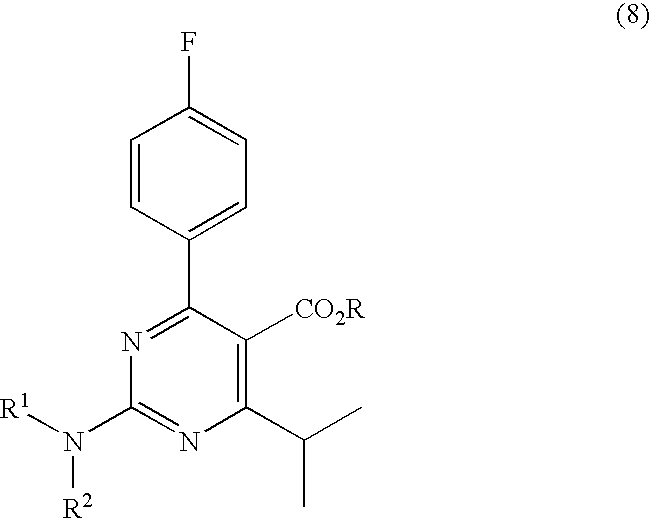
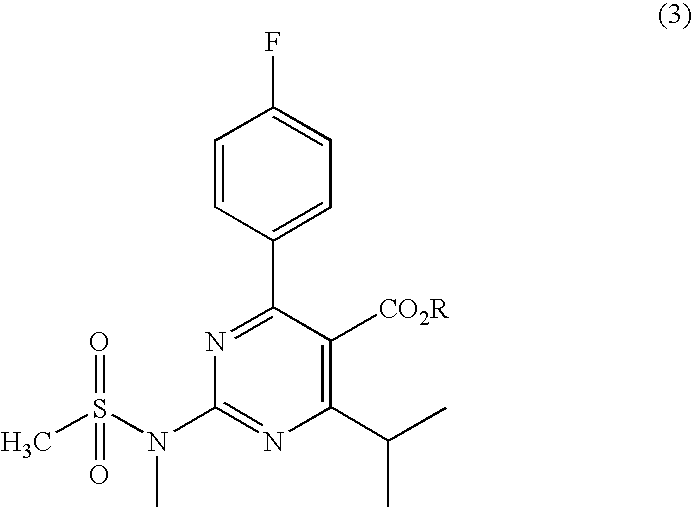
A 2-(N-methyl-N-methanesulfonylamino)pyrimidine compound of the formula (3): [R is a hydrocarbyl group], is prepared by the steps of: (I) reacting an isobutyrylacetate ester with 4-fluorobenzaldehyde and urea in the presence of a protonic compound and a metal salt; (II) oxidizing the reaction product of the step (I); (III) reacting the oxidation product of the step (II) with an organic sulfonyl halide or an organic sulfonyl anhydride; and (IV) reacting the reaction product of the step (III) with N-methyl-N-methanesulfonamide.
Owner:ASTRAZENCA UK LTD
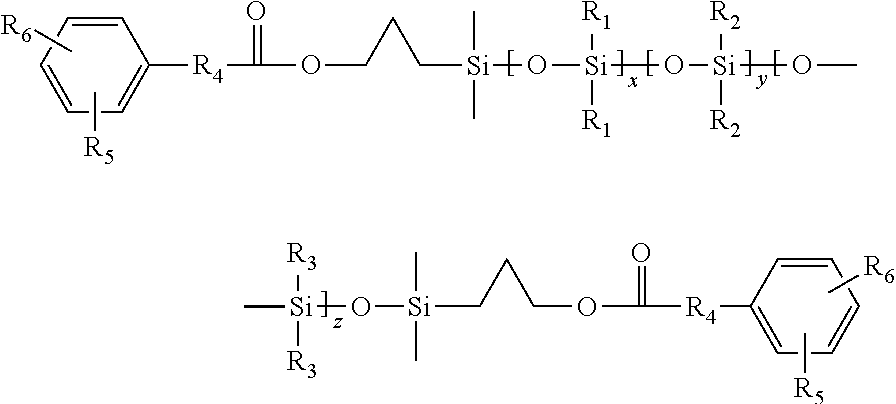
Ester-functional polysiloxanes and copolymers made therefrom
There is described a polysiloxane having the structure:wherein R1, R2, and R3 are independently a hydrocarbon radical, an unsaturated radical, an alkoxy radical, an aryl radical or an alkenyloxy radical, R4 is independently a direct bond or hydrocarbon radical optionally substituted with oxygen and nitrogen, R5 is independently a hydrogen, a halogen, an aliphatic group having from 1 to 6 carbon atoms, an aromatic group having 6 to 8 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having from 1 to 6 carbon atoms, or an aryloxy group, R6 is independently a hydroxyl group, an amine group, an acid chloride group, or a sulfonyl halide group, x is from 1 to 300; y is from 0 to 50; and z is from 0 to 50. The polysiloxane is used to make various copolymers and polymer blends. A variety of articles can be made using the polysiloxane described as a polymer blend or copolymer.
Owner:MOMENTIVE PERFORMANCE MATERIALS INC
Heat treatment of anchored nanocatalysts in a non-zero oxidation state and catalysts made by such method
InactiveUS20060160695A1High activityImprove stabilityMaterial nanotechnologyMolecular sieve catalystsNano catalystSulfonyl halide
A catalyst manufacturing process includes heat treating an intermediate catalyst composition that includes catalyst nanoparticles having catalyst atoms in a non-zero oxidation state bonded to a dispersing / anchoring agent. The catalyst nanoparticles are formed using a dispersing agent having at least one functional group selected from the group of a hydroxyl, a carboxyl, a carbonyl, an amide, an amine, a thiol, a sulfonic acid, sulfonyl halide, an acyl halide, an organometallic complex, and combinations of these. The dispersing agent can be used to form single- or multicomponent supported nanocatalysts. The dispersing agent also acts as an anchoring agent to firmly bond the nanocatalyst to a support. Performing the heat treating process in an inert or oxidative environment to maintain the catalyst atoms in a non-zero oxidation helps maintains a stronger bonding interaction between the dispersing agent and the catalyst atoms. This, in turn, increases the dispersion and / or distribution of catalyst components throughout the supported catalyst.
Owner:HEADWATERS TECH INNOVATION GRP
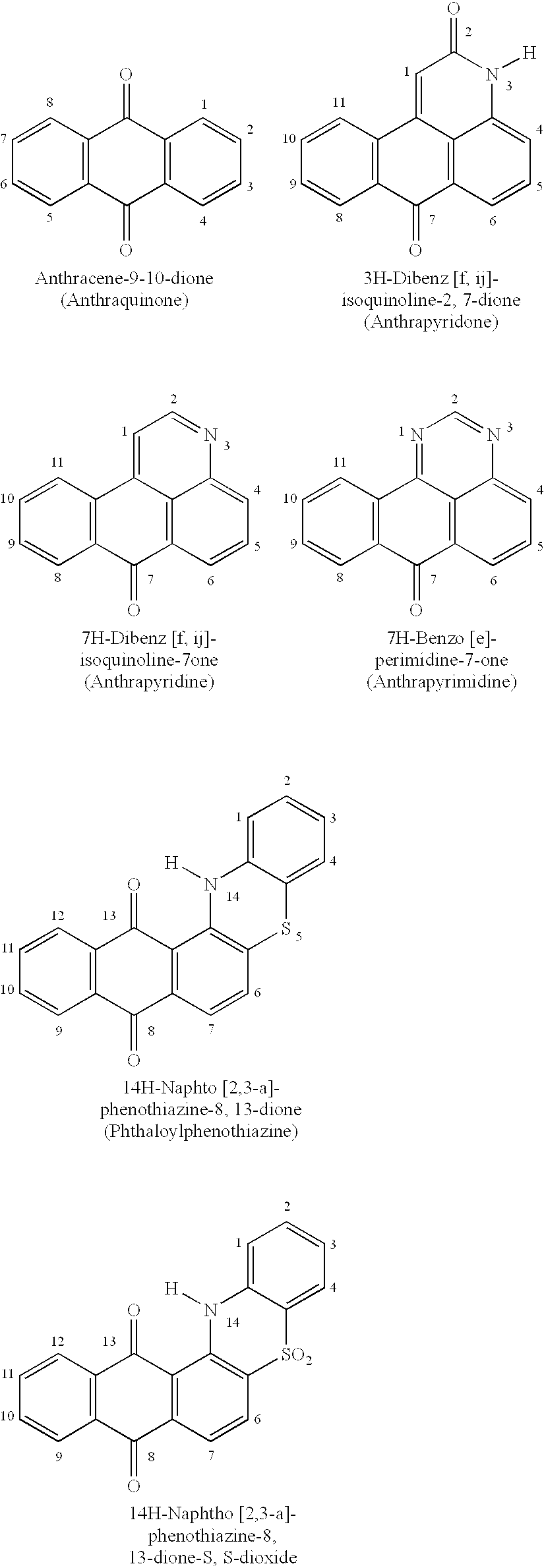
Anthraquinone and condensed anthraquinone colorants having sulfonamido linked poly (oxyalkylene) moieties and their preparation
The process for chemically modifying metal-free, colored anthraquinone or condensed anthraquinone compounds or the compounds prepared by said process for improving one or more properties thereof such as water dispersibility, compatibility with other organics, or increased chemical reactivity, wherein the process includes providing material with from 1-6 sulfonylhalide groups or sulfonate ester groups or mixtures thereof, and contacting the material under sulfonamido forming conditions with one or more reactants containing one or more poly(oxyalkylene) moieties, each of the reactants having from 1 to 4 functional amino groups, and each of the poly(oxyalkylene) moieties being comprised of from about 4 to about 200 epoxide reactant residues at least about 50 mole percent of which residues contain 2-4 carbons and wherein the total of said epoxide reactant residues is from about 4 to about 600.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Acid generators, sulfonic acids, sulfonyl halides, and radiation sensitive resin compositions
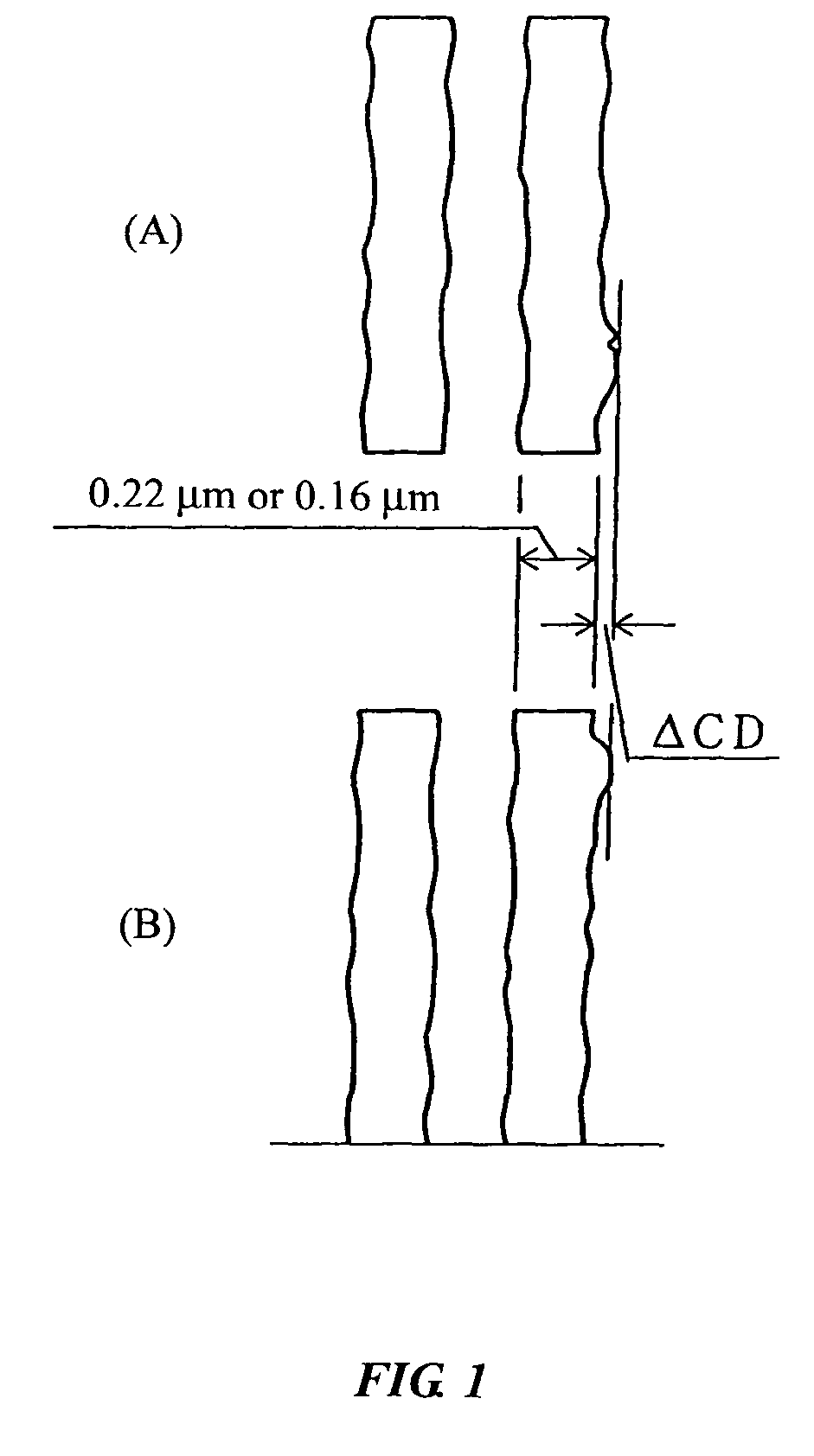
ActiveUS20070054214A1Reduce probabilityInduce meanderingOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationPolymer scienceSulfonyl halide
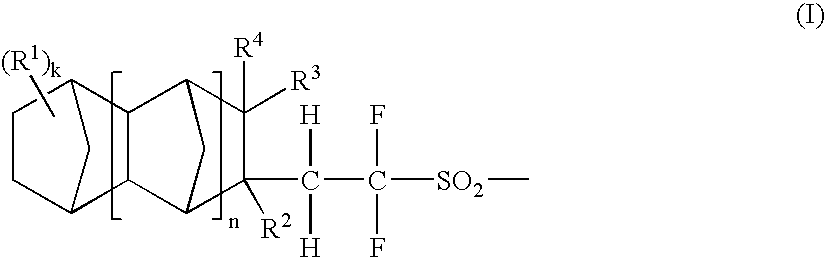
The invention provides novel acid generators which are unproblematic in combustibility and accumulation inside the human body and can generate acids having high acidities and high boiling points and exhibiting properly short diffusion lengths in resist coating films and which permit the formation of resist patterns excellent smoothness with little dependence on the denseness of a mask pattern; sulfonic acids generated from the acid generators; sulfonyl halides useful as raw material in the synthesis of the acid generators; and radiation-sensitive resin compositions containing the acid generators. The acid generators have structures represented by the general formula (I), wherein R1 is a monovalent substituent such as alkoxycarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, or alkoxysulfonyl, R2 to R4 are each hydrogen or alkyl; k is an integer of 0 or above; and n is an integer of 0 to 5. Among the radiation-sensitive resin compositions, a positive one contains a resin having acid-dissociable groups in addition to the above acid generator, while a negative one contains an alkali-soluble resin and a crosslinking agent in addition to the acid generator.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Crosslinked phenolic compound, method of forming, and polymer composition containing the same
A method of forming a crosslinked polyphenol, the method comprising: reacting a bio-based phenolic compound comprising at least one phenolic hydroxyl group, with a crosslinking agent comprising at least two functional groups reactive with the phenolic hydroxyl group, wherein the at least two functional groups are each independently a halogen group, acid halide group, sulfonyl halide group, glycidyl group, anhydride group, or a combination comprising at least one of the foregoing, to provide the crosslinked polyphenol.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS +1
Solid flame retardant polymer, electrode slice, diaphragm and lithium secondary battery
ActiveCN109970981AImprove securityCycle performance is not affectedNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesLi-accumulatorsLithiumImide
The embodiment of the invention provides a solid flame retardant polymer. The solid flame retardant polymer includes a repetitive unit containing a cyclotriphosphazene structure, the repetitive unit is formed by graft polymerization of monomers containing the cyclotriphosphazene structure, and the general formula is shown as formula (I) or formula (II), X is selected from alkylidene, alkylidene halide, alkyleneoxy, alkyleneoxy halide, alkenylene, alkenylene halide, alkenyleneoxy, alkenyleneoxy halide, arylene, arylene halide, aryleneoxy, aryleneoxy halide, substituted phosphite, substituted imido or substituted sulfonylimido; and Y is selected from oxygen, sulfur, alkylene, alkylene halides, alkylene halides, arylene halides, arylene halides, arylene halides, arylene halides, arylene halides, sulfonyl halides or sulfonyl imides; Y is selected from oxygen, sulfur, alkylidene, alkylidene halide, alkyleneoxy, alkyleneoxy halide, alkenylene, alkenylene halide, alkenyleneoxy, alkenyleneoxyhalide, arylene, arylene halide, aryleneoxy, aryleneoxy halide, substituted phosphite, substituted imido or substituted sulfonylimido. The invention also provides a lithium secondary battery electrodeslice, a diaphragm and a lithium secondary battery.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Preparation of Aminopyrimidine Compounds
A 2-(N-methyl-N-methanesulfonylamino)pyrimidine compound of the formula (3): [R is a hydrocarbyl group], is prepared by the steps of: (I) reacting an isobutyrylacetate ester with 4-fluorobenzaldehyde and urea in the presence of a protonic compound and a metal salt; (II) oxidizing the reaction product of the step (I); (III) reacting the oxidation product of the step (II) with an organic sulfonyl halide or an organic sulfonyl anhydride; and (IV) reacting the reaction product of the step (III) with N-methyl-N-methanesulfonamide.
Owner:ASTRAZENCA UK LTD
Preparation method of isothiocyanate
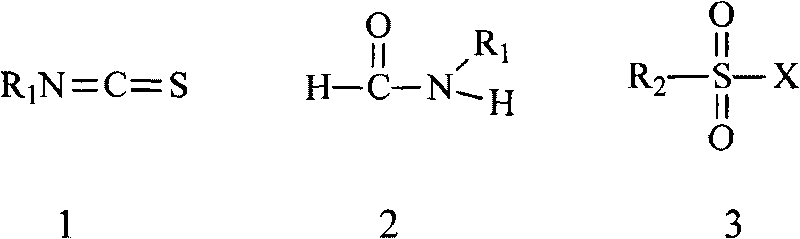
The invention relates to a preparation method of isothiocyanate, which comprises the main step that in the presence of elemental sulfur and a catalyst, replaced formamide reacts with aryl sulfonyl halide at the temperature of 30 to 100 DEG C to obtain a target compound. The invention avoids using (thio) phosgene, derivatives (such as triphosgene) thereof and carbon disulfide, is operated safely and is environment-friendly. In addition, the synthetic route of the preparation method is simple (only one step of reaction), the preparation condition is mild, and with the method, the scale commercial preparation of the isothiocyanate is easy.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Processes for the preparation of aryl-and heteroaryl-alkylsulfonyl halides
InactiveUS20050187408A1Increase productionAvoiding sulfur dioxide lossSulfonic acids salts preparationSulfonic acid preparationArylSulfonyl halide
Owner:WYETH LLC
Carboxylated polysaccharides 6-substituted
InactiveUS6482941B1Easily substitutedObtain the necessary reactivity of the polysaccharideSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationArylOrganic solvent
A new class of polysaccharides containing carboxylic groups selectively substituted with halogens on the carbon atom on position 6 of the glicopyranosidic residue and the procedure to obtain these derivatives is therein described. The procedure entails the halogenation of carboxylated polysaccharides with alkyl aryl sulfonyl-halides in organic solvent. The products of this invention can be used as substrates in synthesis where the reactive site is the carbon that binds the halogen. Moreover, they can be used in the medical-diagnostic field.
Owner:EURAND PHAMACEUTICALS LTD +1
Heat treatment of anchored nanocatalysts in a non-zero oxidation state and catalysts made by such method
InactiveUS7449423B2Increases stability and activity and distributionGood adhesionMaterial nanotechnologyMolecular sieve catalystsNano catalystSulfonyl halide
A catalyst manufacturing process includes heat treating an intermediate catalyst composition that includes catalyst nanoparticles having catalyst atoms in a non-zero oxidation state bonded to a dispersing / anchoring agent. The catalyst nanoparticles are formed using a dispersing agent having at least one functional group selected from the group of a hydroxyl, a carboxyl, a carbonyl, an amide, an amine, a thiol, a sulfonic acid, sulfonyl halide, an acyl halide, an organometallic complex, and combinations of these. The dispersing agent can be used to form single- or multicomponent supported nanocatalysts. The dispersing agent also acts as an anchoring agent to firmly bond the nanocatalyst to a support. Performing the heat treating process in an inert or oxidative environment to maintain the catalyst atoms in a non-zero oxidation helps maintains a stronger bonding interaction between the dispersing agent and the catalyst atoms. This, in turn, increases the dispersion and / or distribution of catalyst components throughout the supported catalyst.
Owner:HEADWATERS TECH INNOVATION GRP
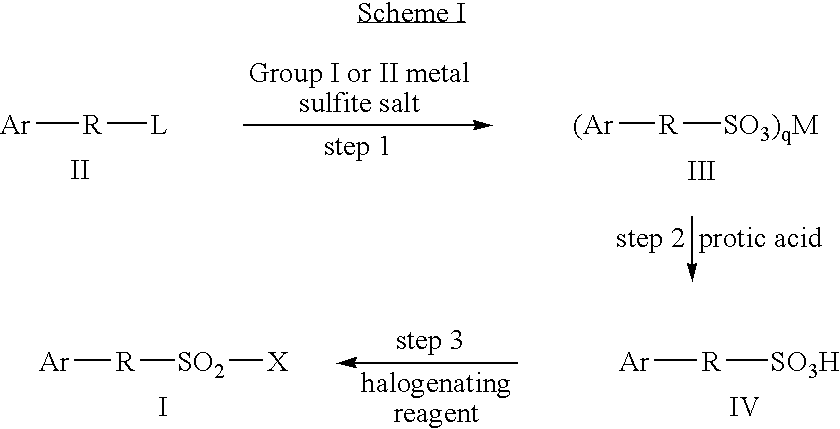
Process for the production of sulfonic esters
InactiveUS20030162966A1High reaction yieldImprove purification effectOrganic compound preparationSulfonic acid esters preparationSulfonateOrganic solvent
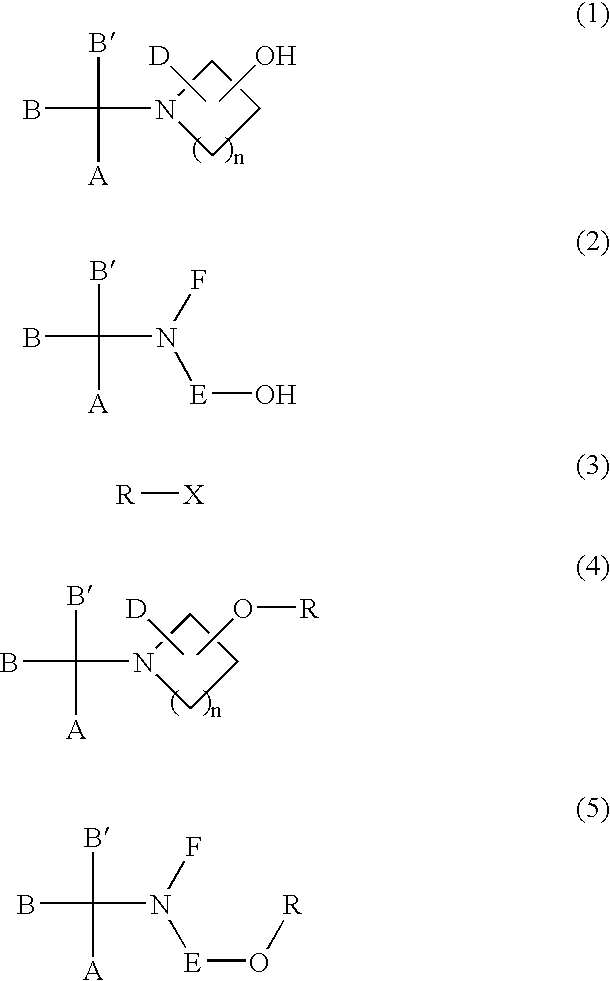
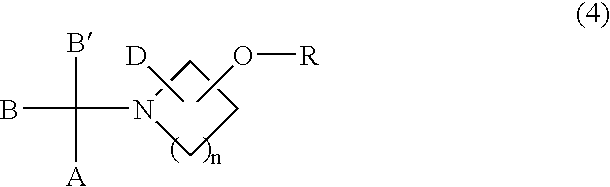
Sulfonic acid ester derivatives represented by the general formula (4) or (5) are produced by reacting an amino alcohol derivative represented by the general formula (1) or (2) with an organic sulfonyl halide represented by the general formula (3), in a mixed solvent composed of an aprotic organic solvent and water in the presence of a non-water-prohibiting inorganic base. This procedure can be carried out in a simple, easy, safe and economical manner while reducing the load on the environment. Wherein n represents an integer of 0 to 5, A represents a phenyl group, which may be substituted, R represents a methanesulfonyl, ethanesulfonyl, p-toluenesulfonyl or p-nitrobenzenesulfonyl group and X represents a chloride, bromine or iodine atom.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
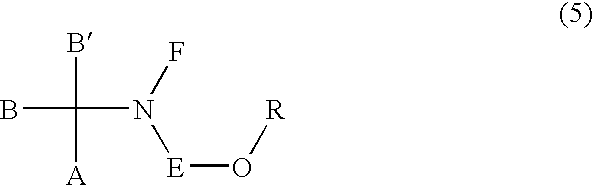
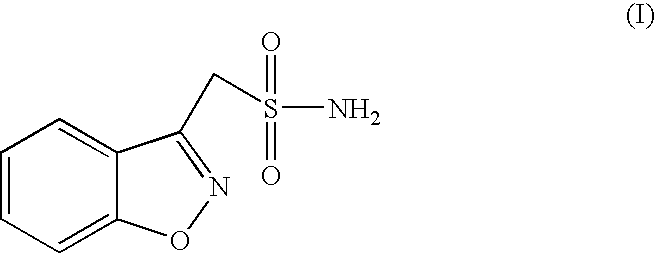
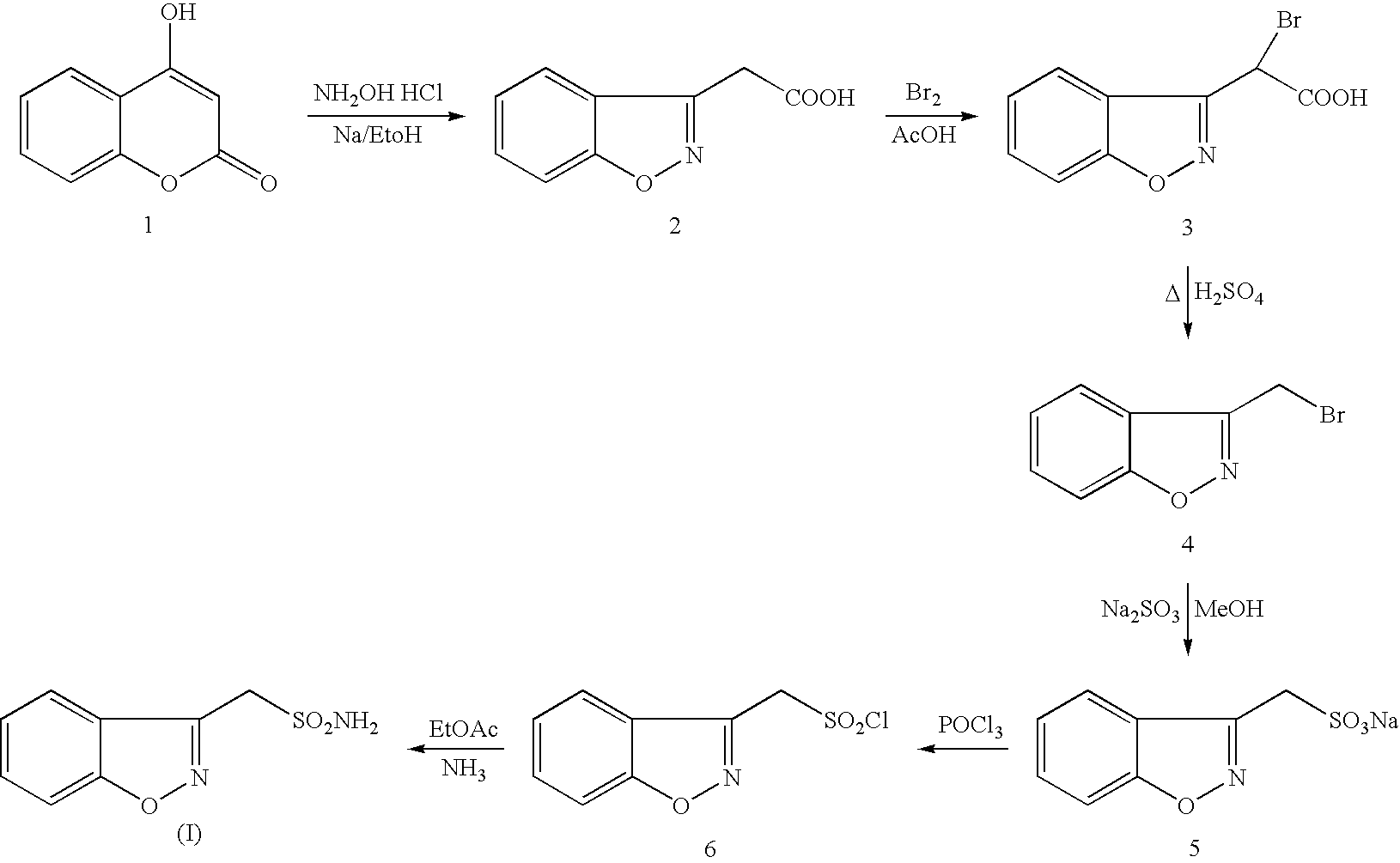
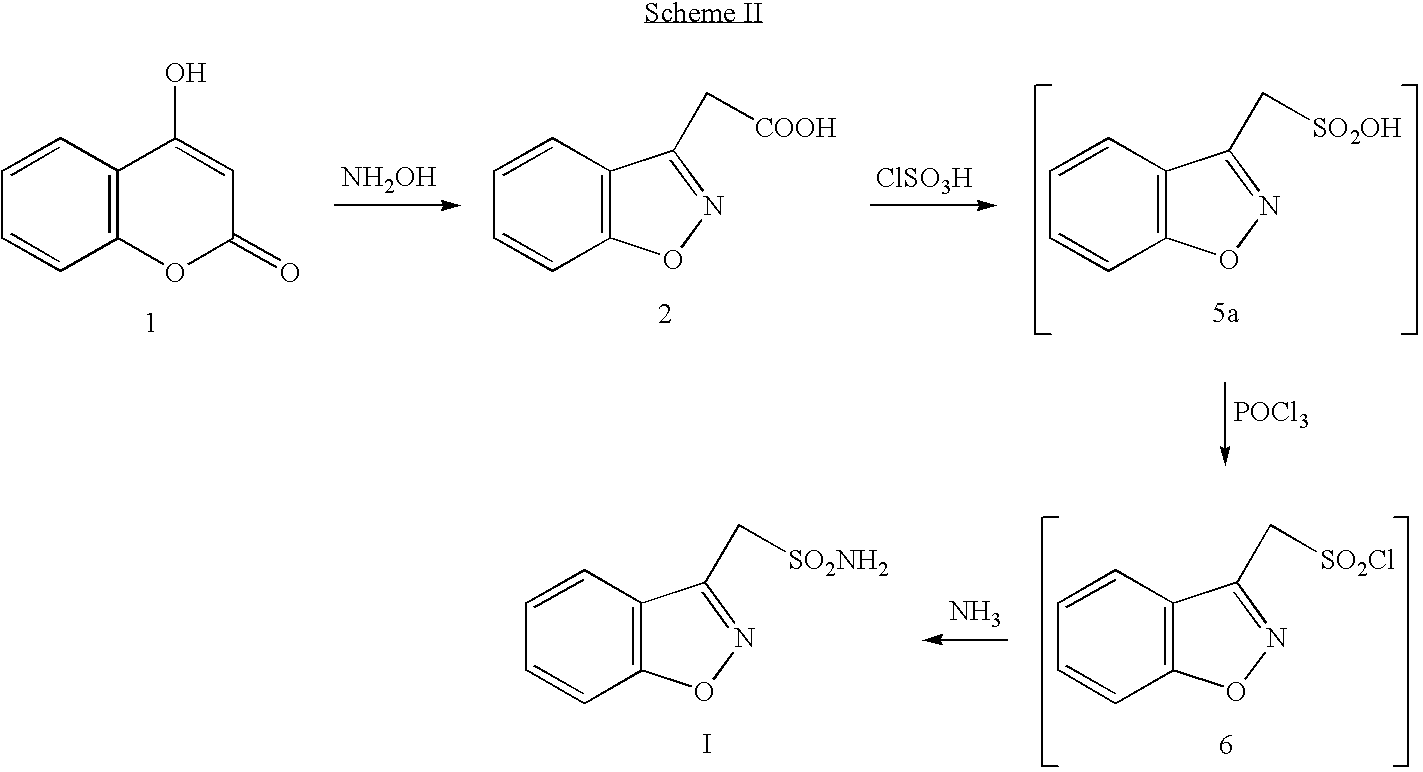
Process for the preparation of zonisamide
InactiveUS20060084814A1Good lookingAvoid isolationOrganic chemistryMethane sulfonic acidOrganic solvent
The present invention provides an improved process for the preparation of zonisamide or a derivative thereof comprising (a) reacting 1,2-benzisoxazole-3-methane-sulfonic acid with a halogenating agent in a first organic solvent to provide benzisoxazole methane sulfonyl halide; and, (b) reacting benzisoxazole methane sulfonyl halide with an amine in a second organic solvent to form zonisamide or a derivative thereof.
Owner:GLENMARK PHARMACEUTICALS LIMITED
Acid generators, sulfonic acids, sulfonyl halides, and radiation sensitive resin compositions
ActiveUS8043786B2Strong electron drawingDifficult to sublimateOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationResistHydrogen
The invention provides novel acid generators which are unproblematic in combustibility and accumulation inside the human body and can generate acids having high acidities and high boiling points and exhibiting properly short diffusion lengths in resist coating films and which permit the formation of resist patterns excellent smoothness with little dependence on the denseness of a mask pattern; sulfonic acids generated from the acid generators; sulfonyl halides useful as raw material in the synthesis of the acid generators; and radiation-sensitive resin compositions containing the acid generators. The acid generators have structures represented by the general formula (I),wherein R1 is a monovalent substituent such as alkoxycarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, or alkoxysulfonyl; R2 to R4 are each hydrogen or alkyl; k is an integer of 0 or above; and n is an integer of 0 to 5. Among the radiation-sensitive resin compositions, a positive one contains a resin having acid-dissociable groups in addition to the above acid generator, while a negative one contains an alkali-soluble resin and a crosslinking agent in addition to the acid generator.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Process to prepare fluoropolymer dispersions and membranes
Described is a process to prepare fluoropolymer organic-liquid dispersions containing a homogeneous mixture of reacted and unreacted sulfonyl halide groups. The dispersions are useful in the preparation of crosslinked membranes.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Perfluoro sulfonyl halides and related species as polymer support modifiers
Activated Supports, support-bound activators, strongly acidic supports, and silylating supports are provided; the activated support having the formula (I): wherein L is a linking group component; X is F, Cl, OH, and trisubstituted silyloxy; and the shaded circle represents a solid or semi-solid support. Methods of using the activated supports in solid phase organic synthesis are also provided.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
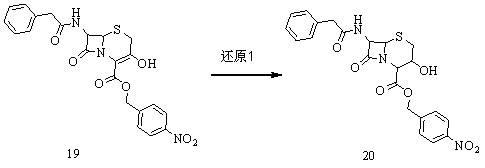
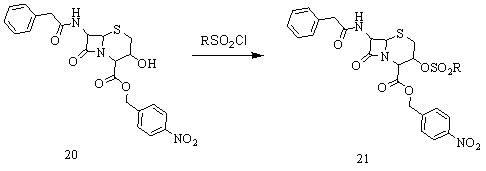
Method for preparing 7-amino-3-nor-3-cephalo-4-carboxylic acid
The invention provides a method for preparing 7-amino-3-nor-3-cephalo-4-carboxylic acid (7-ANCA for short). In the method, 7-phenylacetyl amide-3-hydroxy-3-cephalo-4-carboxylic acid-para-nitrobenzyl ester is taken as a raw material, and the method comprises the following steps of: firstly, reducing a double bond between a 3 position and a 4 position of a parent nucleus by using metal borohydride; secondly, esterifying a 3-position hydroxyl group by using sulfonyl halide; thirdly, removing 3-position methyl sulfonate group by using alkali to restore the double bond between the 3 position and the 4 position; and finally, removing a protective group on a 4-position carboxyl group of the parent nucleus by a catalytic hydrogenation method, and removing a protective group on 7-position amino group of the parent nucleus by an enzymatic method to obtain the 7-ANCA. In the method, the integral process is simple and practicable, the quality of the product is improved, the production cost is reduced, and environmental pollution is reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG APELOA TOSPO PHARMA +1
Diazaphosphacycles
A diazaphosphacycle may be synthesized by reacting a phosphine with a diimine and optionally one or more equivalents of an acid halide, a sulfonyl halide, a phosphoryl halide, or an acid anhydride in the substantial absence of O2 to form the diazaphosphacycle. The phosphine has the formula R1—PH2 where R1 is a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkyl group, or a substituted or unsubstituted ferrocenyl group.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Synthesis of diazaphosphacycles
ActiveUS7355073B2Rhodium organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsArylDiimine
A diazaphosphacycle may be synthesized by reacting a phosphine with a diimine and optionally one or more equivalents of an acid halide, a sulfonyl halide, a phosphoryl halide, or an acid anhydride in the substantial absence of O2 to form the diazaphosphacycle. The phosphine has the formula R1—PH2 where R1 is a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkyl group, or a substituted or unsubstituted ferrocenyl group.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
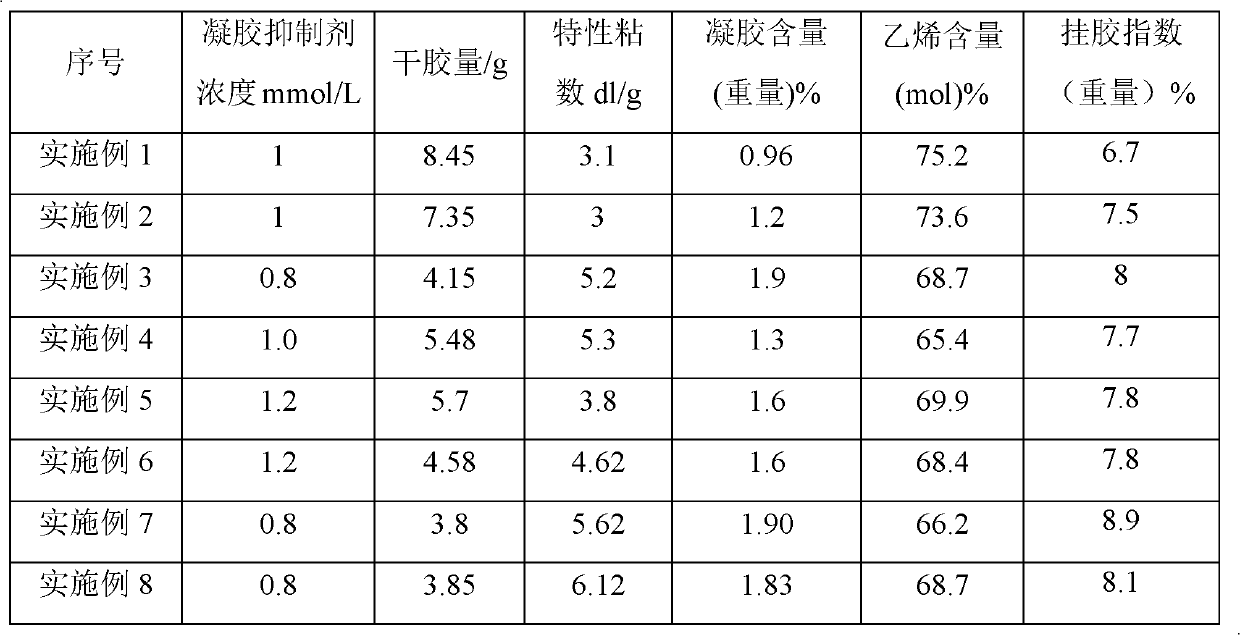
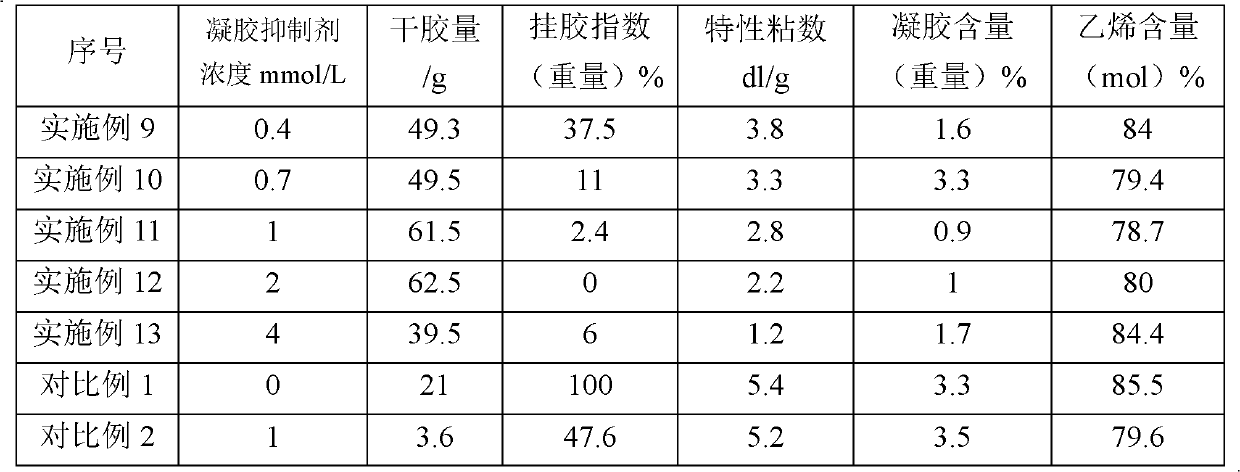
Ethylene-alpha olefin copolymer and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an ethylene-alpha olefin copolymer and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following step of: enabling ethylene and alpha olefin to be in contact with a catalyst under the condition of olefin solution polymerization in the presence of a solvent and a gel inhibitor to obtain the ethylene-alpha olefin copolymer, wherein the catalyst contains an organic aluminum and vanadium compound, and the gel inhibitor is selected from one or more of 1,1,2,3,3,3-hexachloro-1-propene, hexachlorocyclopentadiene, aryl sulfonyl halide, halogenated fatty acid ester with at least two halogen atoms and aryl halide with at least three halogen atoms. By using the method provided by the invention, gel generated in the copolymerization process can be reduced.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for producing fluorine-containing halide
ActiveUS20070185355A1High yieldLow costOrganic compound preparationHalogenated hydrocarbon preparationSulfonyl halideIodide
The present invention provides a method for producing a fluorine-containing halide, comprising reacting a fluorine-containing sulfonyl halide or fluorine-containing disulfonyl chloride with a metal halide or metal component in the present or absence of a solvent. In accordance with the present invention, a fluorine-containing bromide, fluorine-containing iodide or fluorine-containing chloride can be readily produced in high yield at low cost, using an industrially advantageous process.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
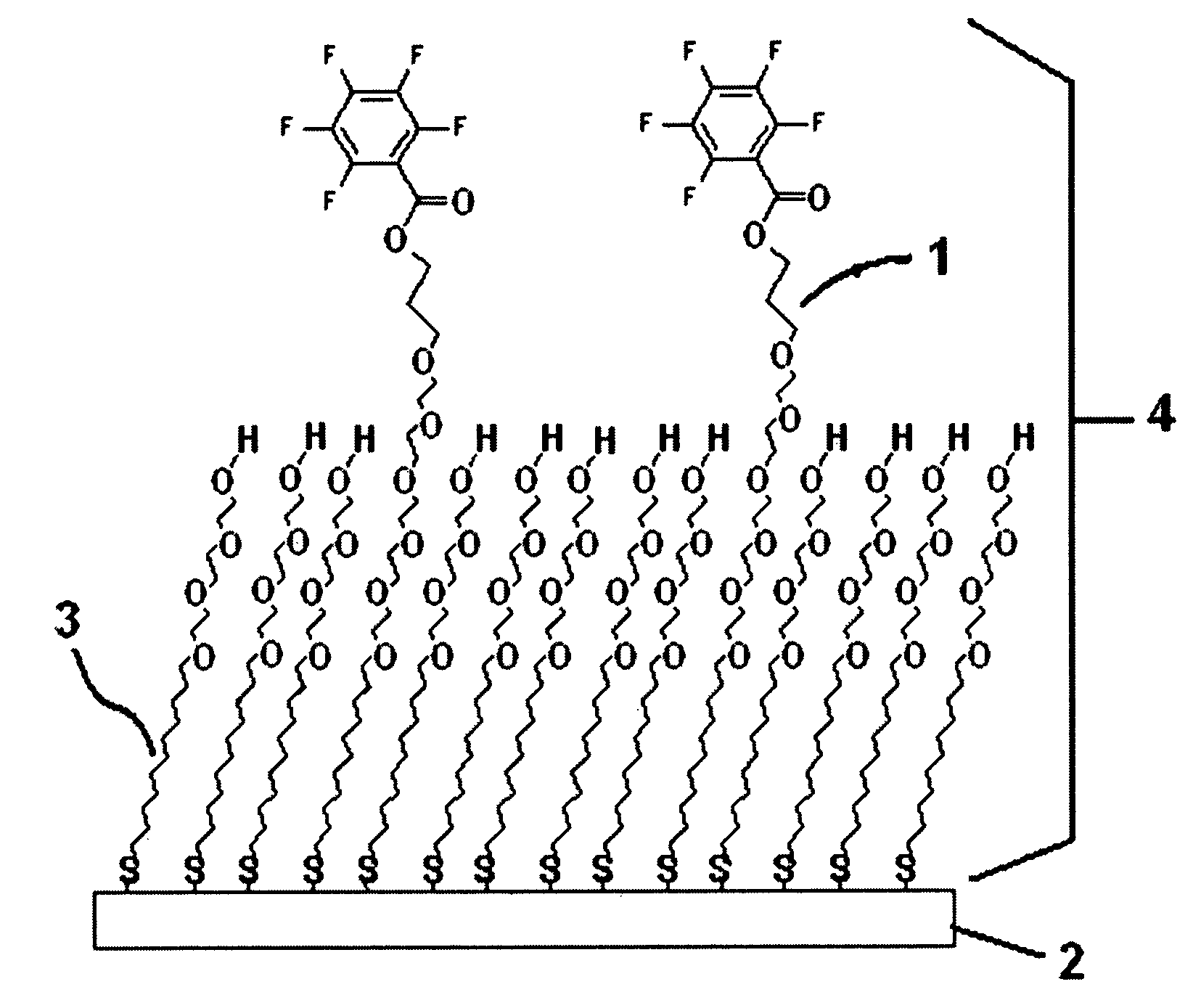
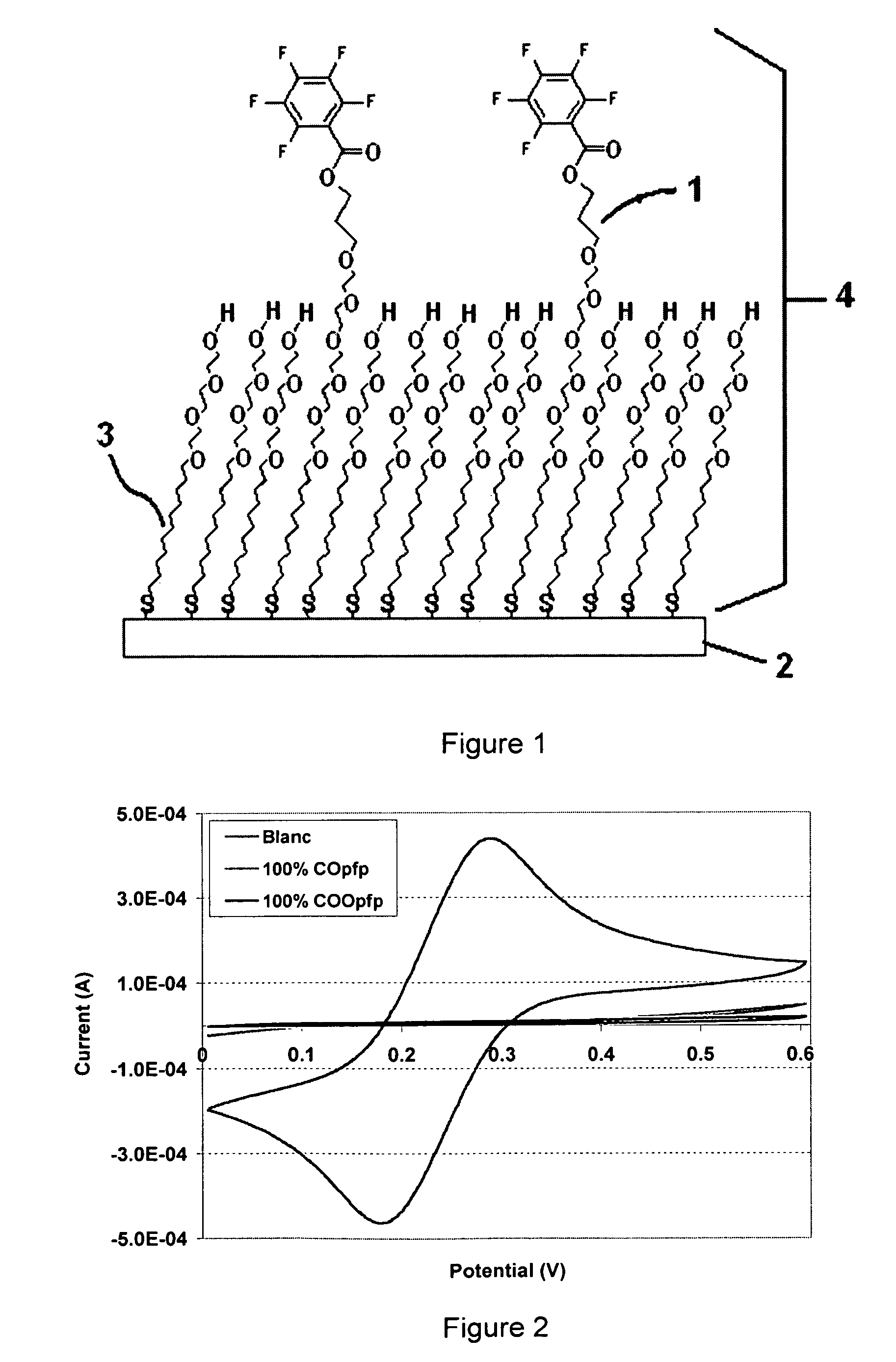
Thiol or disulfide molecules having poly(ethylene oxide) groups for use in a self assembled monolayer bound to a metal layer for covalently immobilizing biomolecules in a biosensor
ActiveUS7770437B2High selectivityImprove stabilityMaterial nanotechnologyIsocyanic acid derivatives preparationSelf-assembled monolayerSulfonyl halide
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
Processes for the preparation of aryl- and heteroaryl-alkylsulfonyl halides
InactiveUS7321061B2Increase productionAvoiding sulfur dioxide lossSulfonic acids salts preparationSulfonic acid preparationArylSulfonyl halide
Owner:WYETH LLC
Hydroxylamine synthesis method
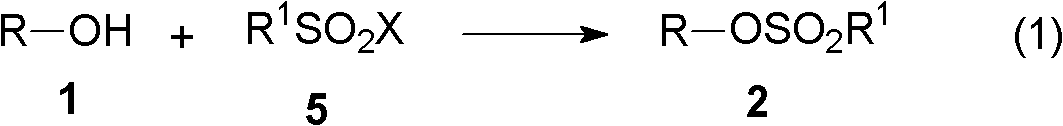
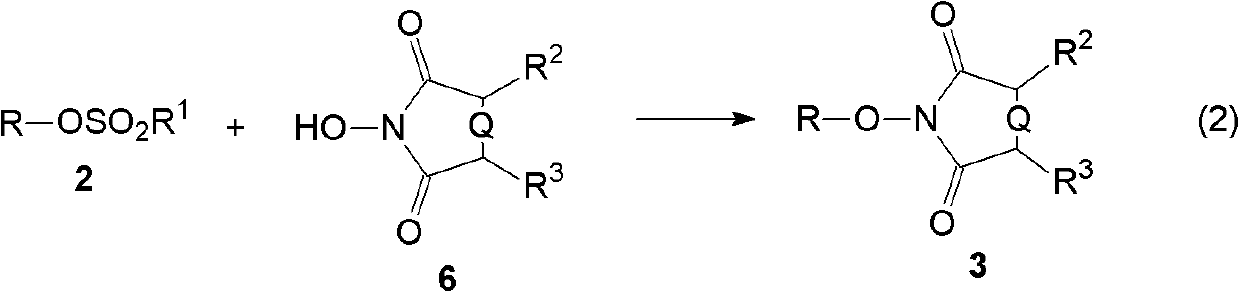
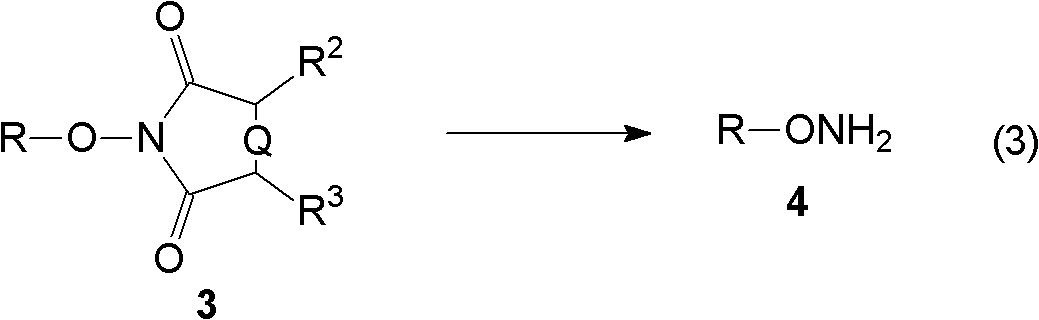
The invention relates to a hydroxylamine synthesis method. The hydroxylamine synthesis method comprises the following steps: (A) enabling alcohol to react with alkyl sulfonyl halide in the presence of an acid-binding agent to obtain sulphonate; (B) enabling the obtained sulphonate in the step (A) to react with N-hydroxycyclodiimide in the presence of alkali to generate alkylate of the N-hydroxycyclodiimide; and (C) enabling the alkylate obtained in the step (B) to react with an aminolysis reagent or a hydrazinolysis reagent to obtain the hydroxylamine. The method is high in yield and suitable for large-scale industrial hydroxylamine synthesis.
Owner:乐威医药(天津)有限公司
Preparation method of trifluoromethyl sulfinyl halide
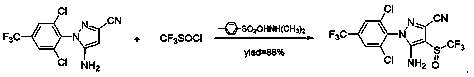
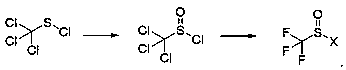
InactiveCN111004155AAvoid low boiling pointReduce manufacturing costOrganic compound preparationSulfonic acid preparationFipronilSulfonyl halide
The present invention relates to a process for the preparation of a trifluoromethyl sulfinyl halide (Formula F<3>CSOX). The trifluoromethyl sulfinyl halide (Formula F<3>CSOX) is used for the preparation of insecticides, pharmaceuticals and fine chemicals, in particular for the preparation of insecticide fipronil. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) reacting trichloromethyl sulfur chloride, namely Cl<3>CSCl, with an oxidizing agent to obtain trichloromethyl sulfinyl chloride, namely Cl<3>CSOCl; and (2) enabling trichloromethyl sulfinyl chloride (Cl<3>CSOCl) to react with afluoride to obtain the trifluoromethyl sulfinyl halide, namely F<3>CSOX. The preparation method has the advantages that firstly, the preparation of trifluoromethyl sulfinyl halide avoids low-boiling-point and highly-toxic raw materials and intermediates, namely trifluoromethyl thionyl chloride and di (trifluoromethyl) disulfide, and has the advantages of simplicity, high efficiency, safety, convenience and the like; and 2, the cheap and easily available raw material trichloromethyl sulfur chloride or a mixture thereof is adopted, so that the manufacturing cost is reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG AVILIVE CHEM CO LTD +1
Fluoropolymer dispersions and membranes
InactiveCN101460554AElectrolyte holding meansSolid electrolyte fuel cellsSulfonyl halideOrganic liquids
The invention is directed to fluoropolymer organic-liquid dispersions and membranes containing a homogeneous mixture of reacted and unreacted sulfonyl halide groups. The dispersions are useful in the preparation of crosslinked membranes.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com