Patents
Literature
79results about "Pulse generation by bulk negative resistance devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Power switching driving apparatus, and power factor correction device and power supply device having the same
InactiveUS20130163289A1Reduce circuit areaIncrease driving speedEfficient power electronics conversionEnergy industryControl signalPower switching
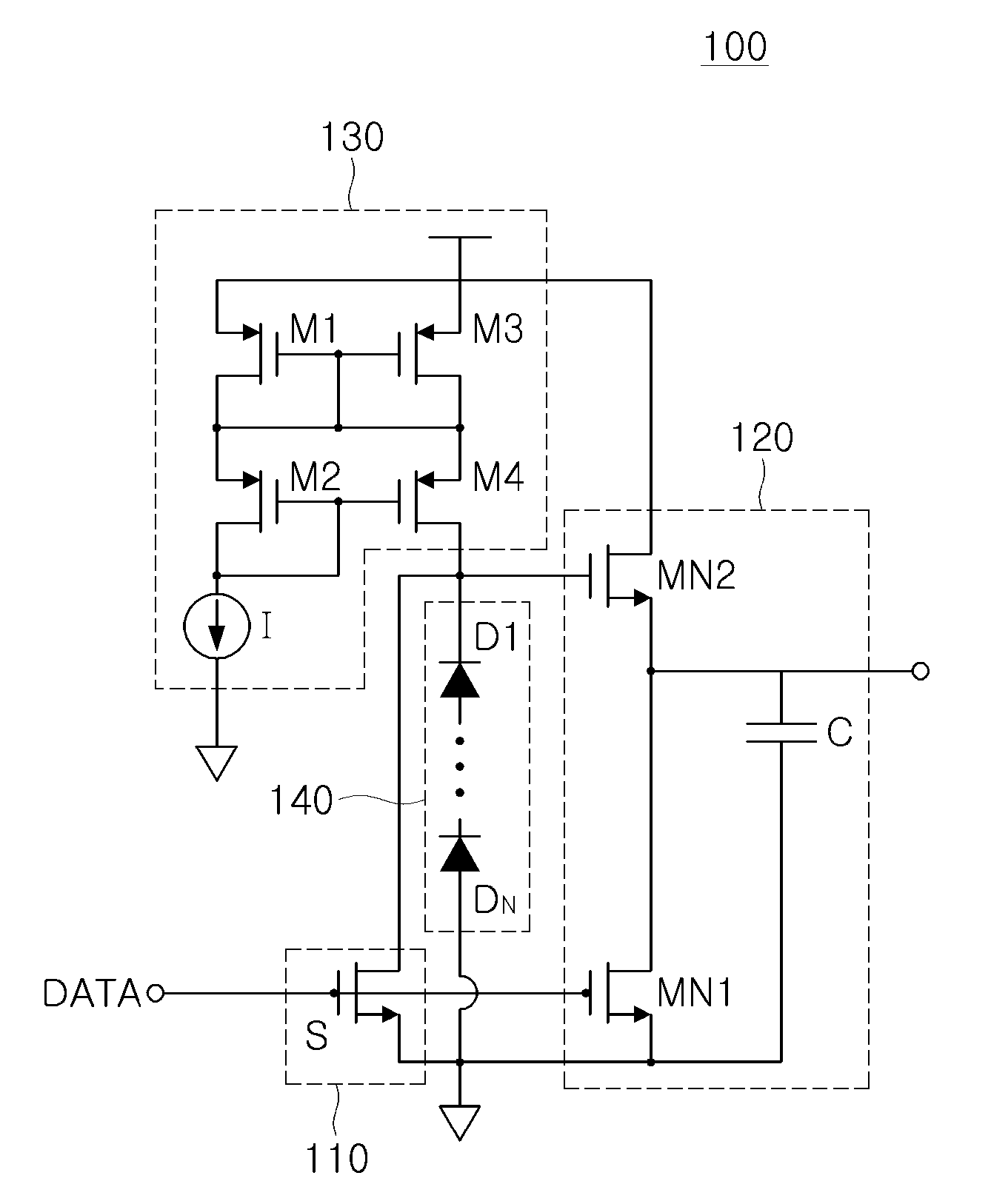
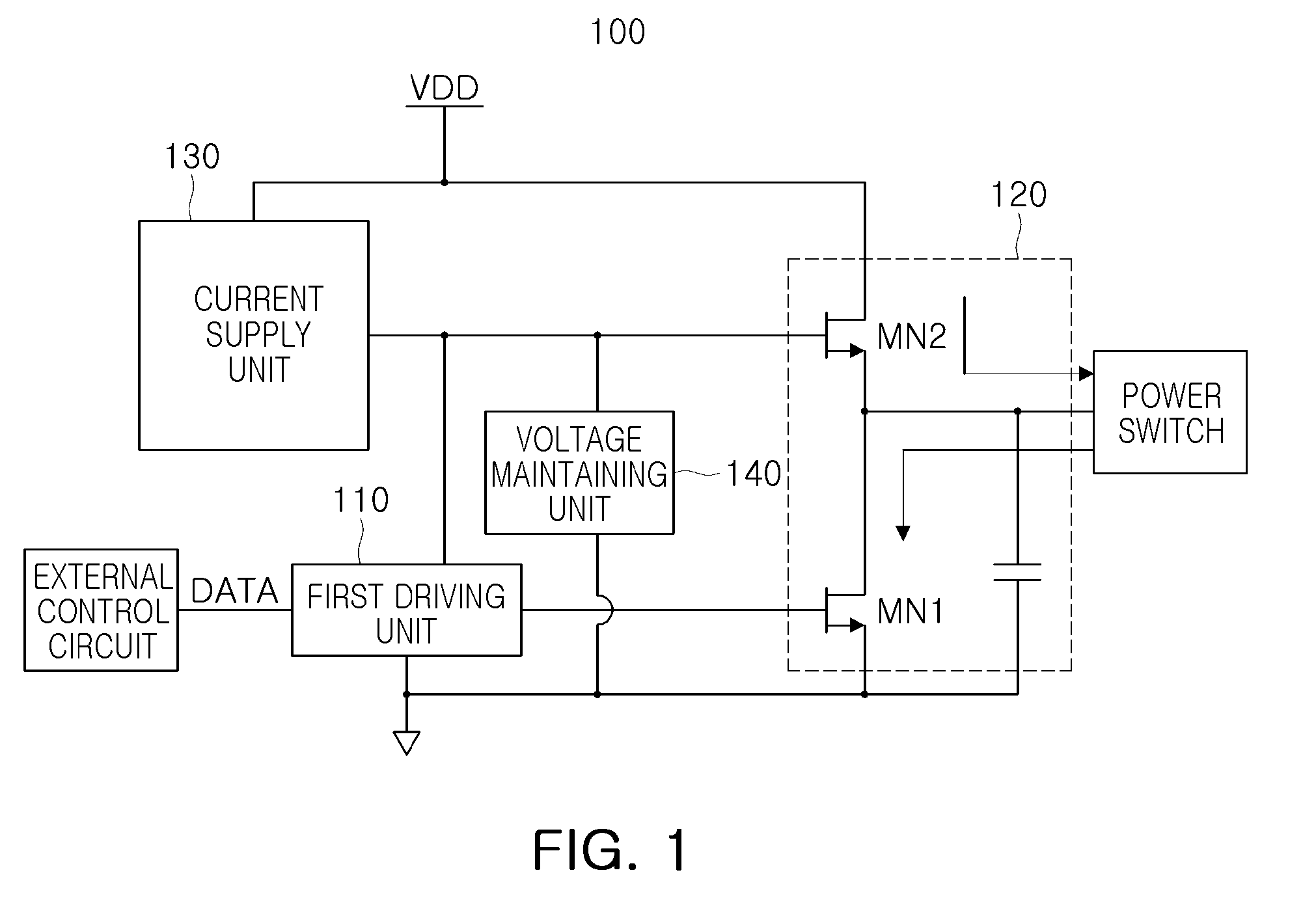
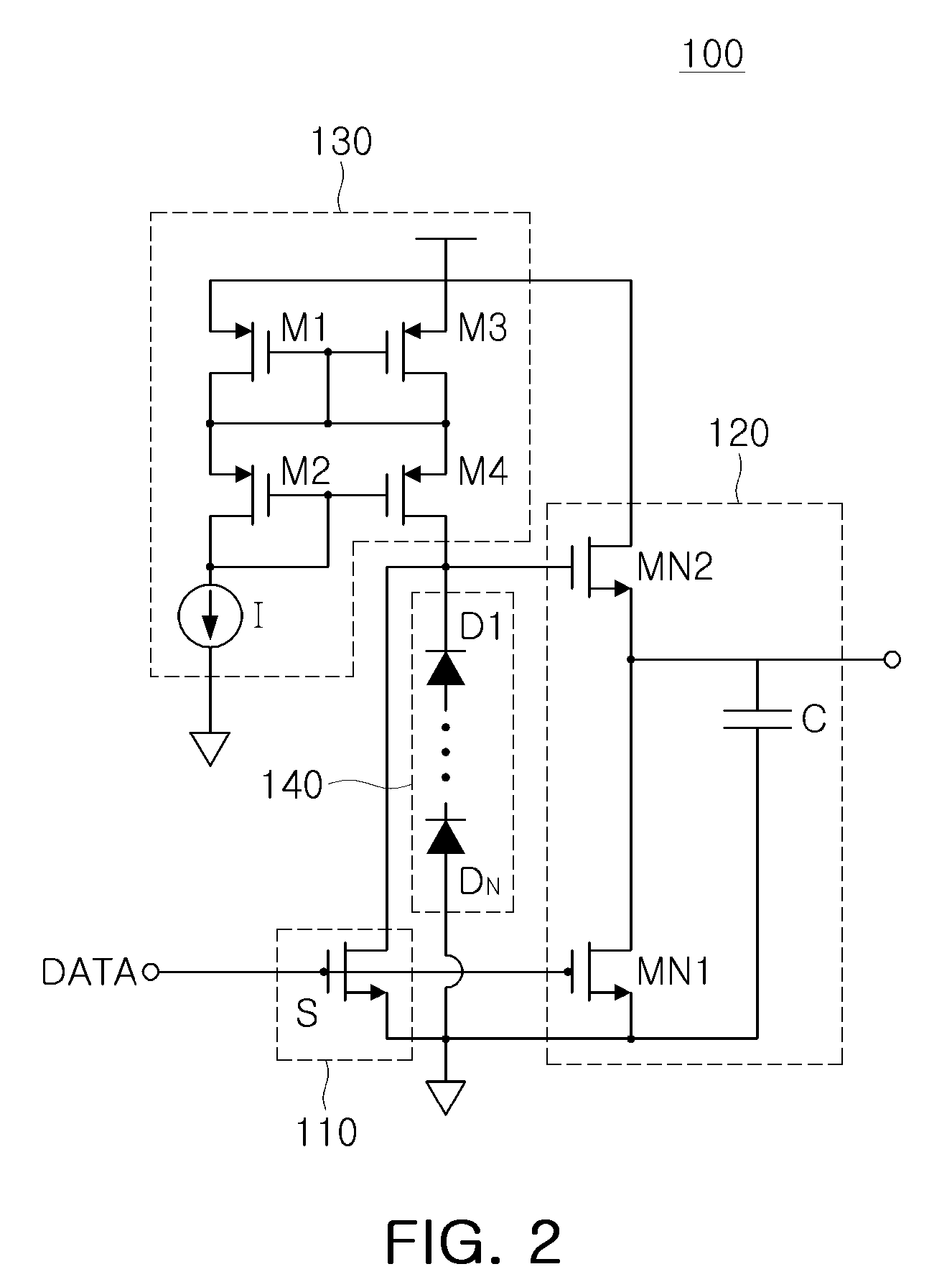
There are provided a power switching driving apparatus able to reduce a circuit area and increase a driving speed, and a power factor correction device and a power supply device having the same. The power switching driving apparatus includes: a first driving unit providing a switching signal in response to a control signal from the outside; a second driving unit including first and second NMOS FETs cascode-connected between an operational power source terminal supplying pre-set operation power and a ground, and performing switching complimentarily in response to the switching signal to provide a switching control signal controlling power switching; a current supply unit supplying a current for driving the second driving unit; and a voltage maintaining unit maintaining a voltage for driving the second driving unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
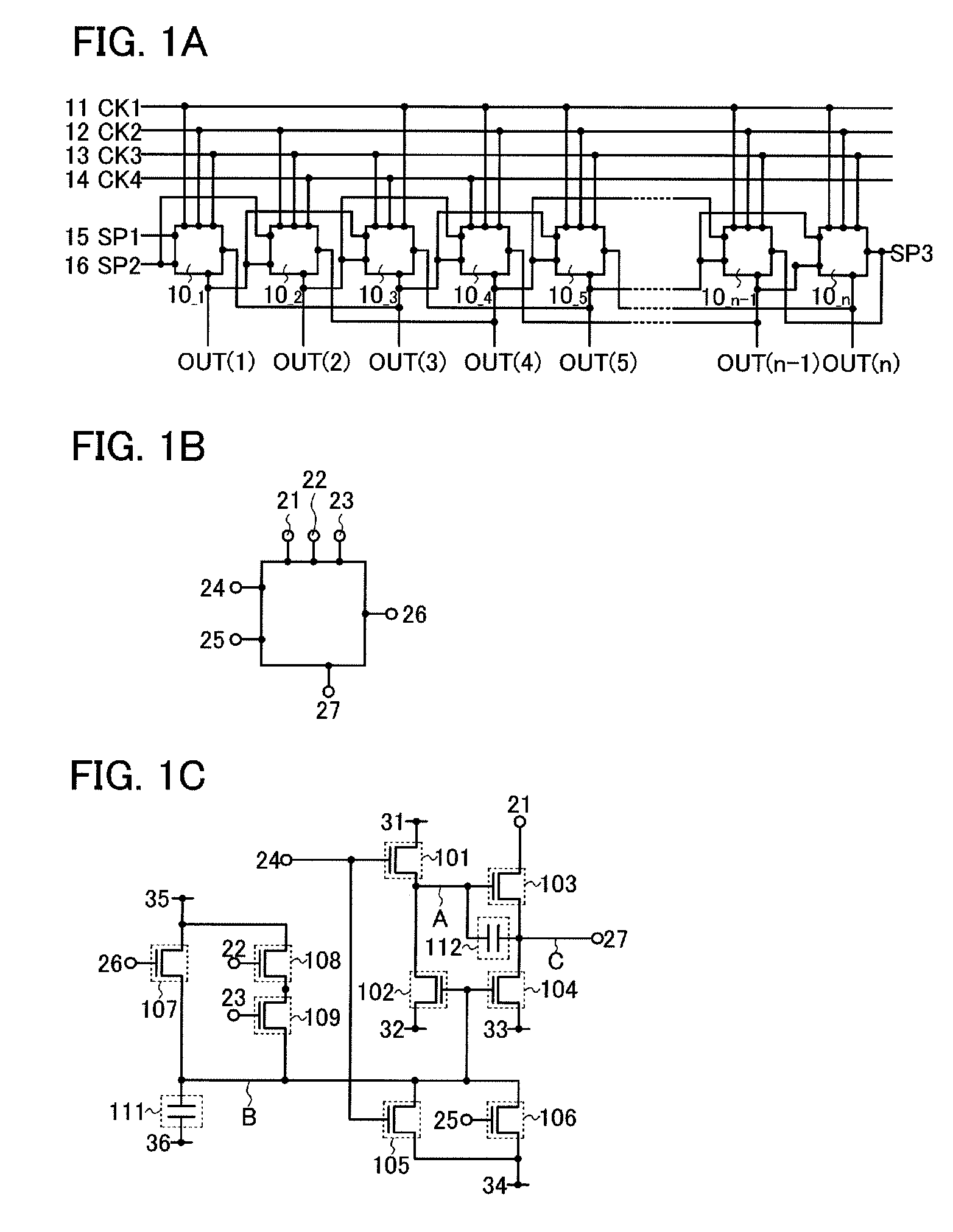
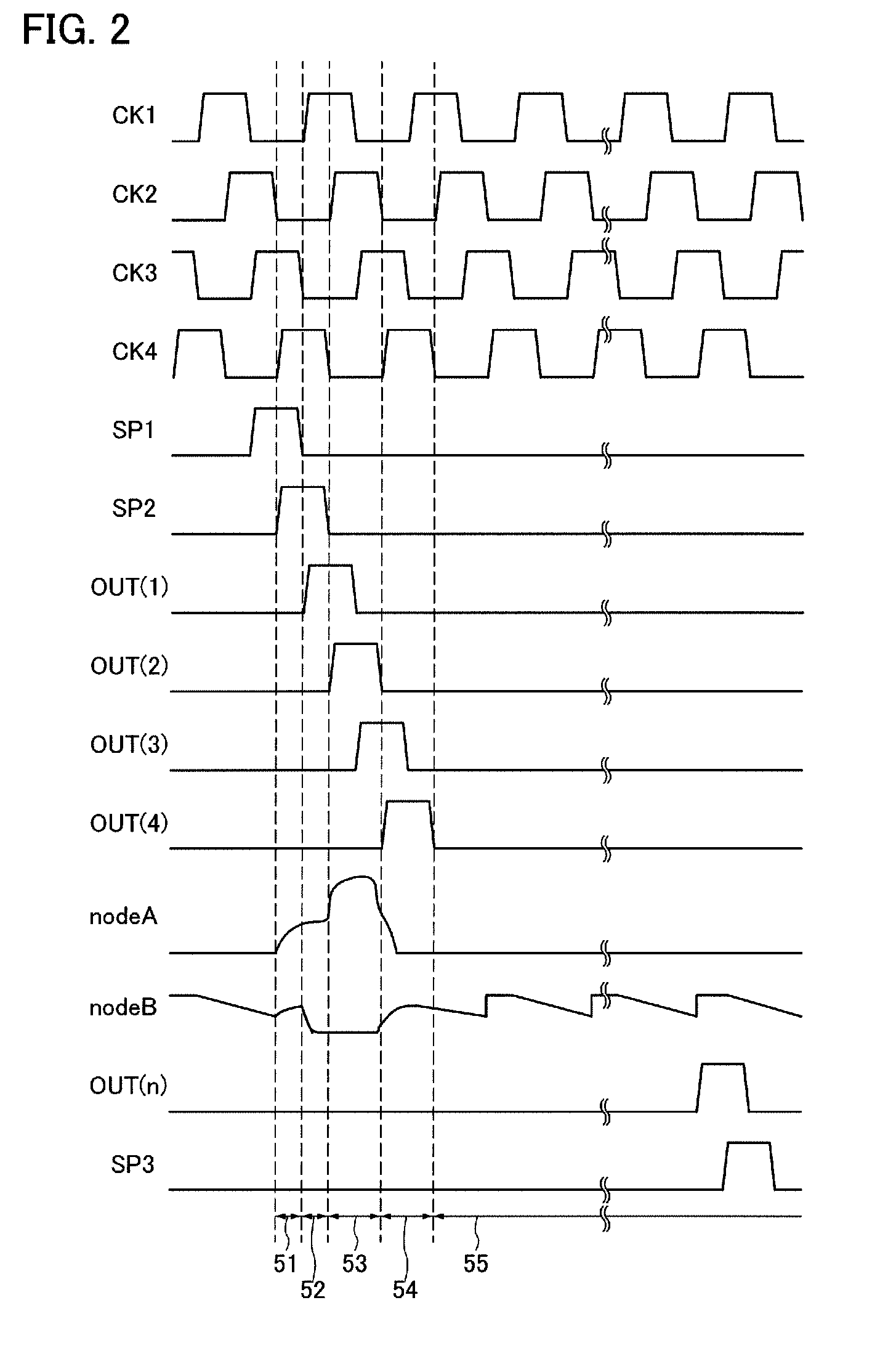
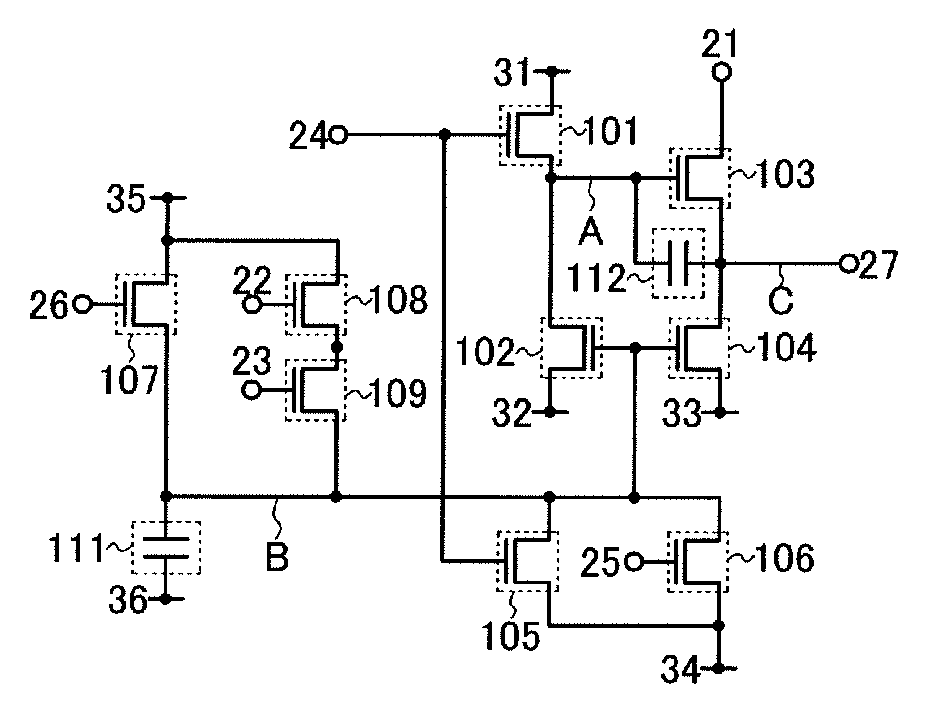
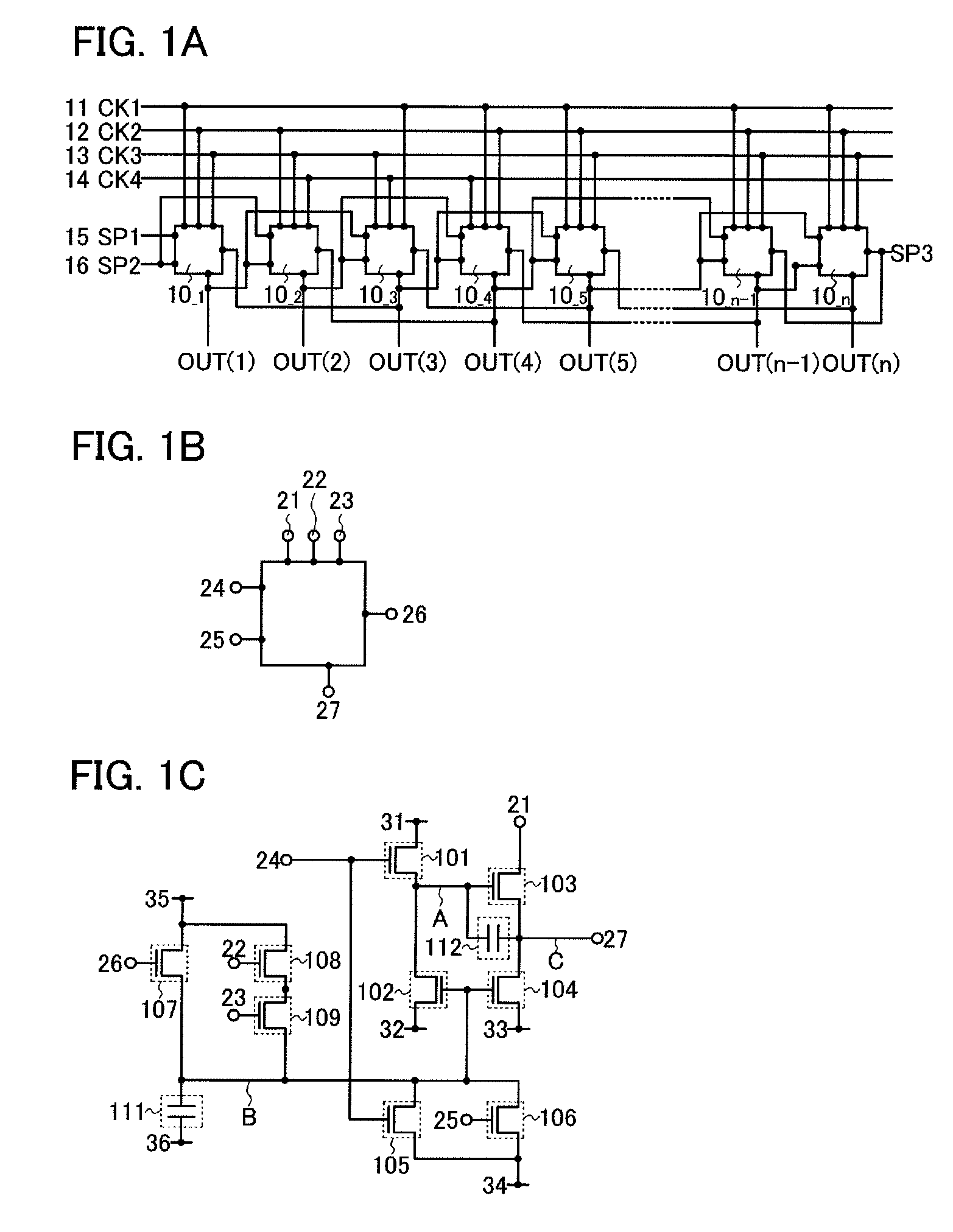
Pulse output circuit, shift register, and display device
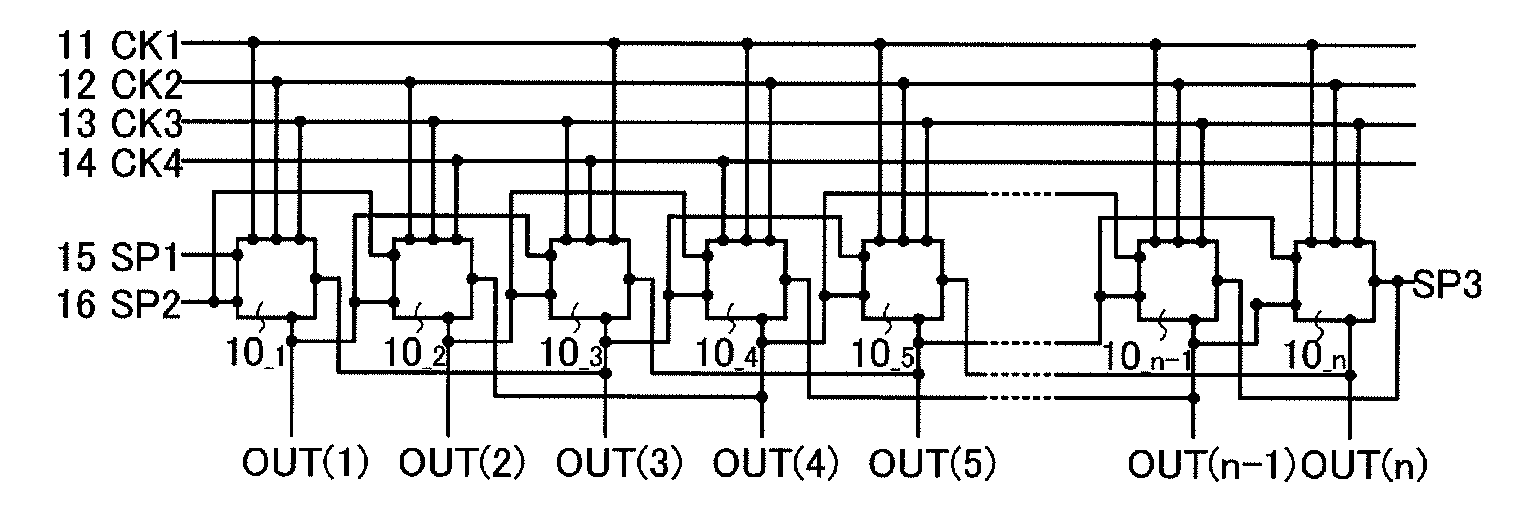
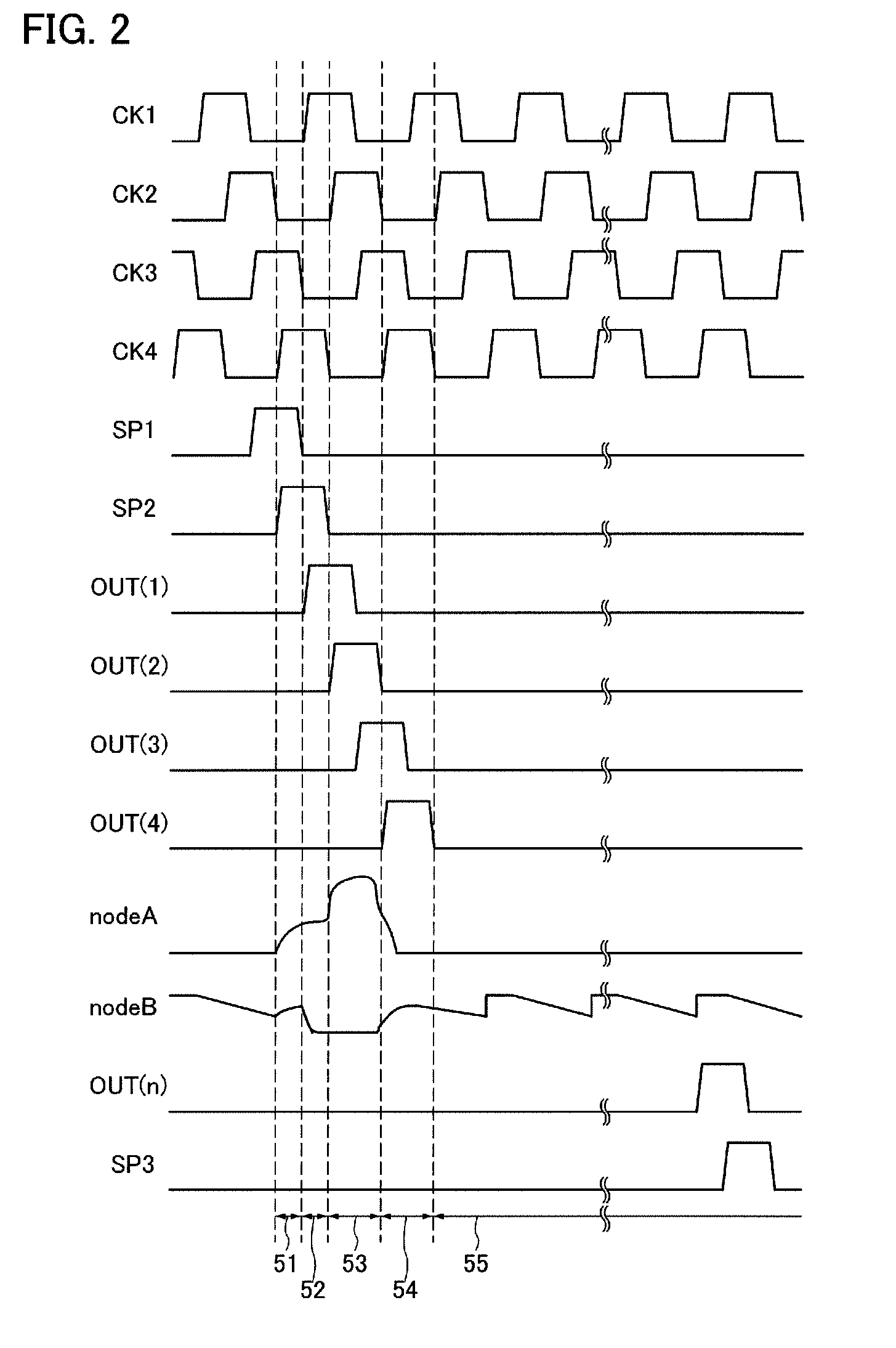
ActiveUS20080258998A1Malfunction can be suppressedWithstand large loadStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesShift registerDisplay device
An object is to suppress change of a threshold voltage of a transistor in a shift register and to prevent the transistor from malfunctioning during a non-selection period. A pulse output circuit provided in the shift register regularly supplies a potential to a gate electrode of a transistor which is in a floating state so that the gate electrode is turned on during a non-selection period when a pulse is not outputted. In addition, supply of a potential to the gate electrode of the transistor is performed by turning on or off another transistor regularly.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Pulse output circuit, shift register, and display device
ActiveUS7932888B2Reduce failureMalfunction can be suppressedStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesShift registerDisplay device
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Digitally Controlled Injection Locked Oscillator
ActiveUS20140266480A1Oscillations generatorsAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionInjection lockedControl signal
An injection locking oscillator (ILO) comprising a tank circuit having a digitally controlled capacitor bank, a cross-coupled differential transistor pair coupled to the tank circuit, at least one signal injection node, and at least one output node configured to provide an injection locked output signal; a digitally controlled injection-ratio circuit having an injection output coupled to the at least one signal injection node, configured to accept an input signal and to generate an adjustable injection signal applied to the at least one injection node; and, an ILO controller connected to the capacitor bank and the injection-ratio circuit configured to apply a control signal to the capacitor bank to adjust a resonant frequency of the tank circuit and to apply a control signal to the injection-ratio circuit to adjust a signal injection ratio.
Owner:INNOPHASE
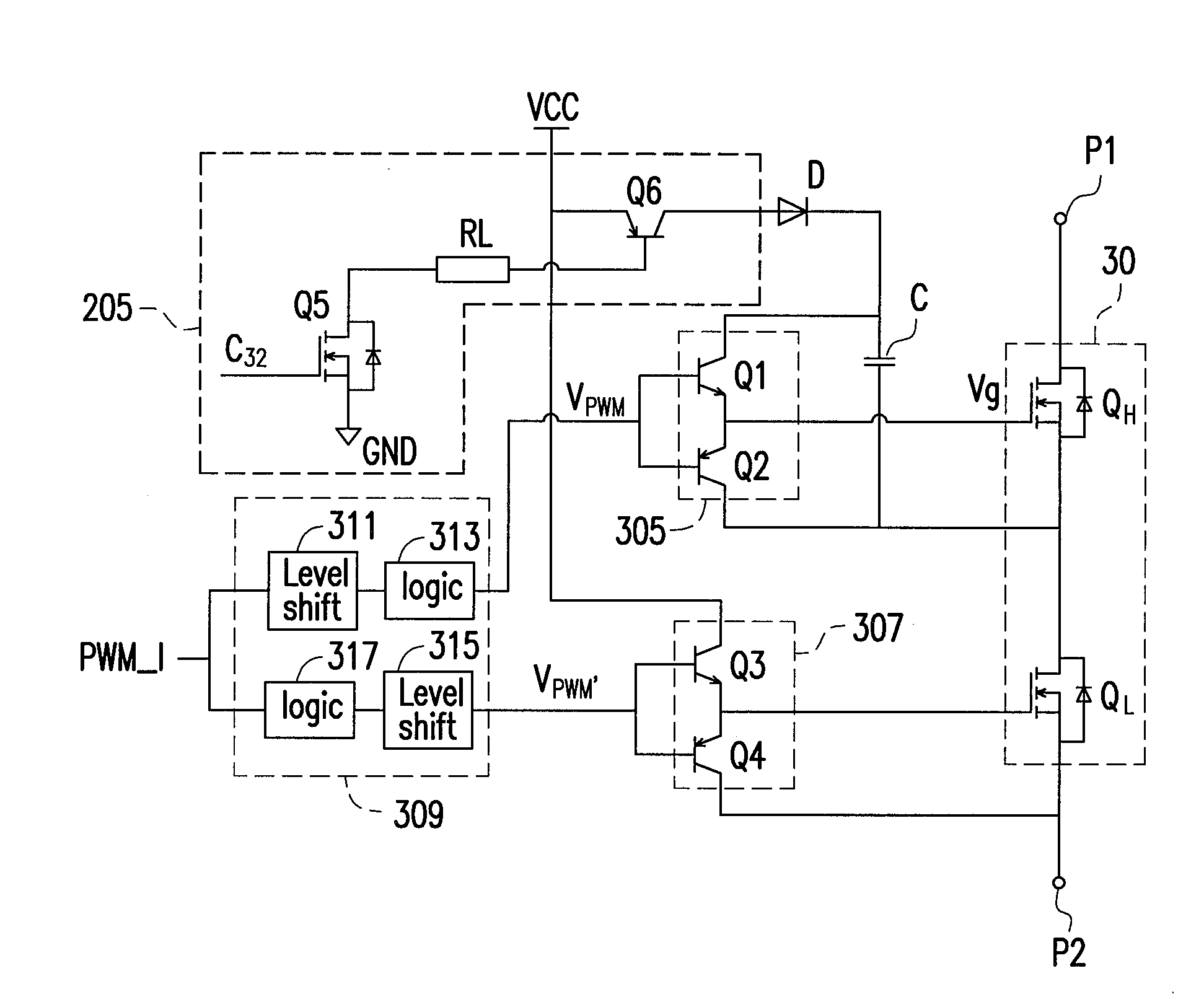
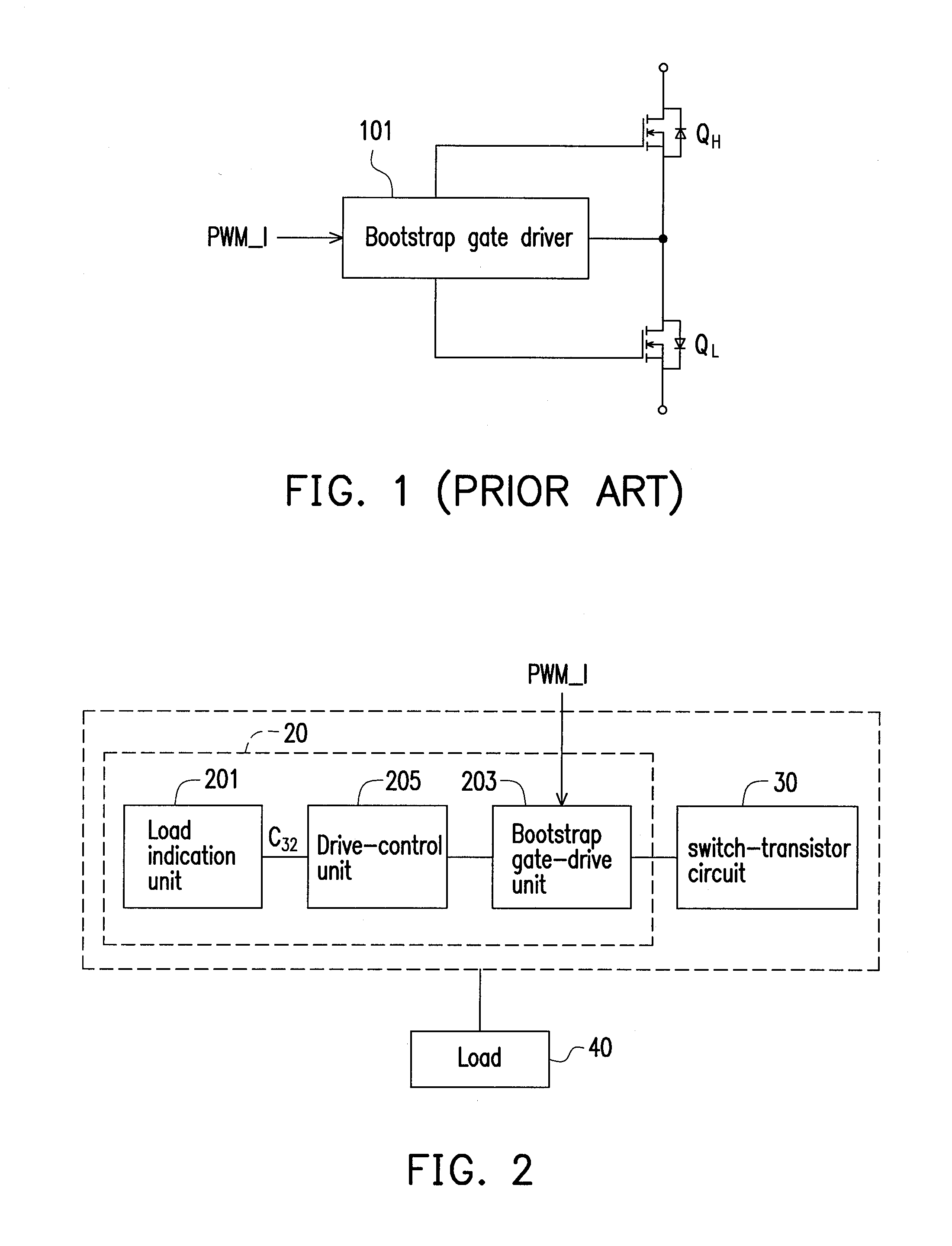
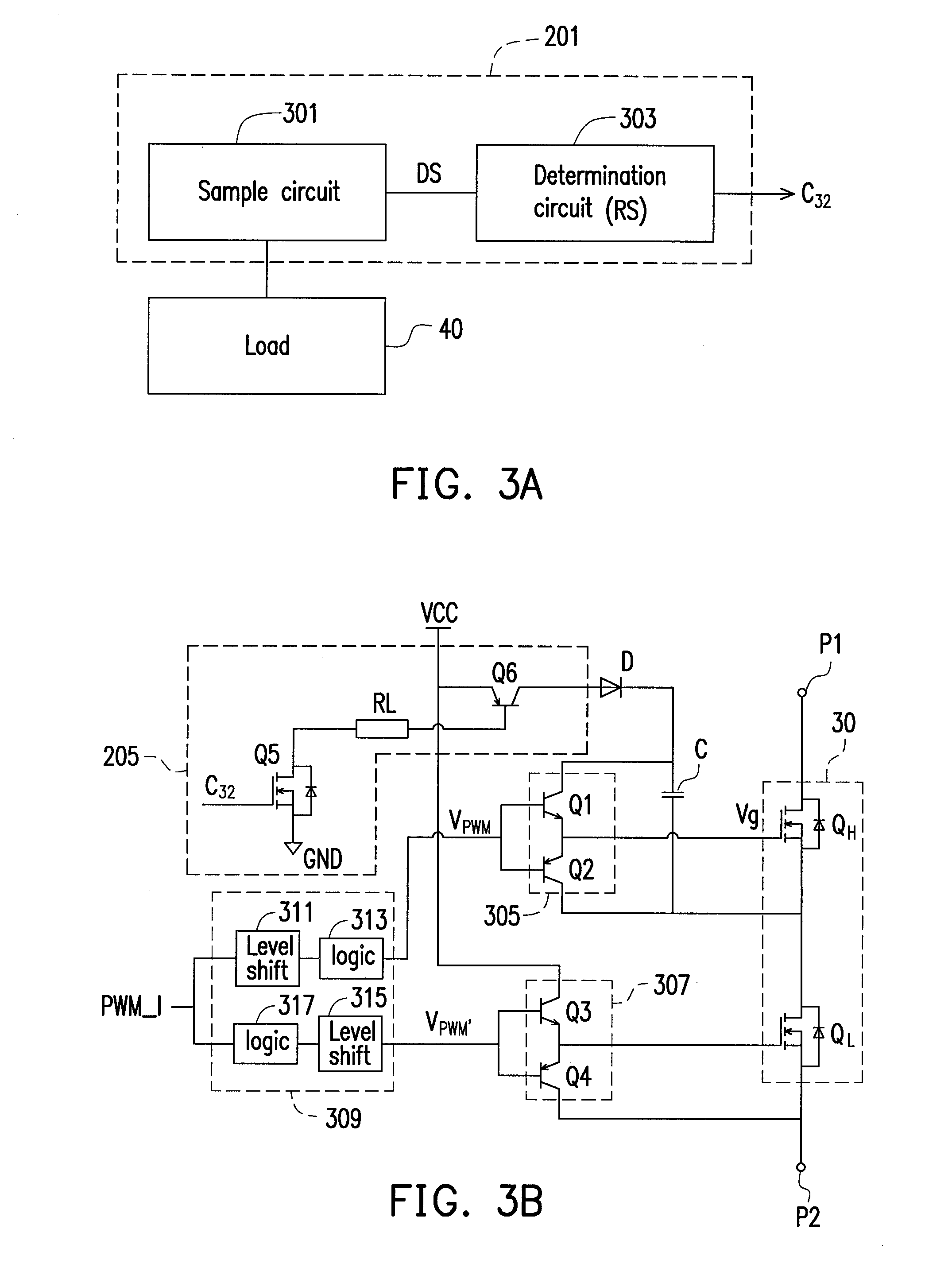
Bootstrap gate driver
ActiveUS20120293219A1Improve efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionTransistor circuitsEngineering
A bootstrap gate driver including a load indication unit, a bootstrap gate-drive unit and a drive-control unit is provided. The load indication unit is configured to generate a load indication signal in response to a state of a load. The bootstrap gate-drive unit is configured to drive a switch-transistor circuit in response to an inputted pulse-width-modulation (PWM) signal, wherein the switch-transistor circuit has a high-side driving path and a low-side driving path. The drive-control unit is coupled to the load indication unit and the bootstrap gate-drive unit, and configured to enable or disable the high-side driving path in response to the load indication signal. In the invention, the operation of the low-side driving path is not affected by enabling or disabling the high-side driving path.
Owner:SPI ELECTRONICS +1
Voltage biased section of non-linear transmission line
InactiveUS6538525B1Reduce stub effectImprove signal integrityTransmission control/equlisationHigh frequency circuit adaptationsCapacitanceEngineering
The principal reason that commercially available 10 gigabits per second electrical interconnect has not previously been available is that such interconnect structures possess too high a level of parasitic inductance, capacitance, resistance and conductance. These result in signal degradation as a result of attenuation, harmonic distortion and dispersion and so sufficiently error-free transmission of data has been virtually impossible for high data rates such as those around 5 gigabits per second and above. By providing compensation mechanisms, signal integrity is improved thus enabling reliable data transmission at data rates of 5 gigabits per second, 10 gigabits per second and above. Non-linear transmission lines are used to form these compensation mechanisms. The non-linear transmission line may take the form of a distributed diode, for example, formed from a layer of N-doped silicon covered on its top surface by a layer of platinum and on its bottom surface by a layer of silicon dioxide. Advantageously, voltage biased sections of NLTL are used to perform compensation for different regions of a signal pulse according to the particular voltage biasing used. A plurality of such voltage biased sections of NLTL may be connected in series in order to obtain improved signal compensation.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Half-bridge driver and power conversion system with such driver
InactiveUS7323912B2Reliable conditionsReducing power consumption and operating temperatureTransistorPulse automatic controlVoltage pulseEngineering
A half-bridge driver includes first and second power switches, connected with their respective current paths in series, a pulse generator for generating a voltage pulse waveform, arranged to drive the first power switch, a first current generator for generating a current pulse for each negative flank of the voltage pulse waveform, a second current generator for generating a current pulse for each positive flank of said voltage pulse waveform, and a differential current receiver circuit. The differential current receiver circuit is connected to the first and second current generators, and is arranged to generate an output signal equal to the difference of the currents flowing through the current generators. The output signal is arranged to drive the second power switch.
Owner:BANG & OLUFSEN ICEPOWER
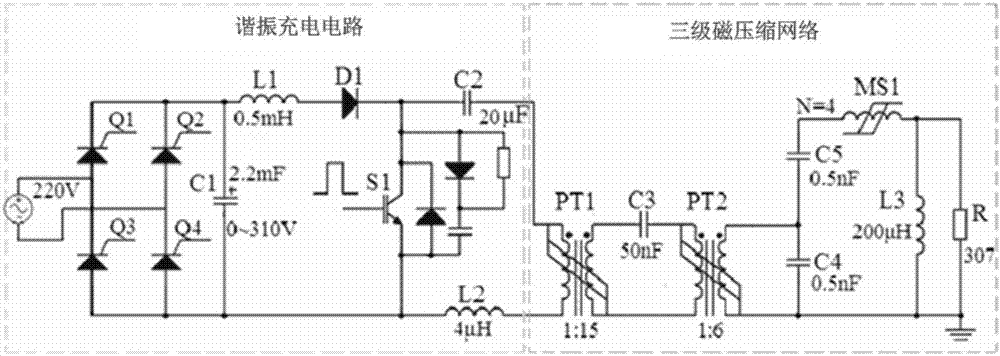
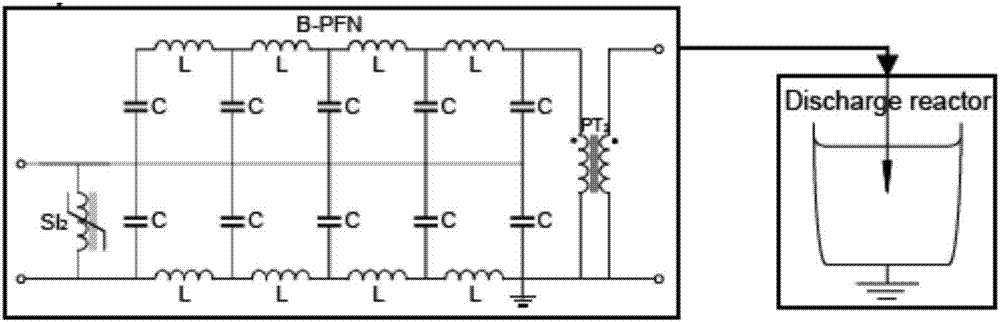
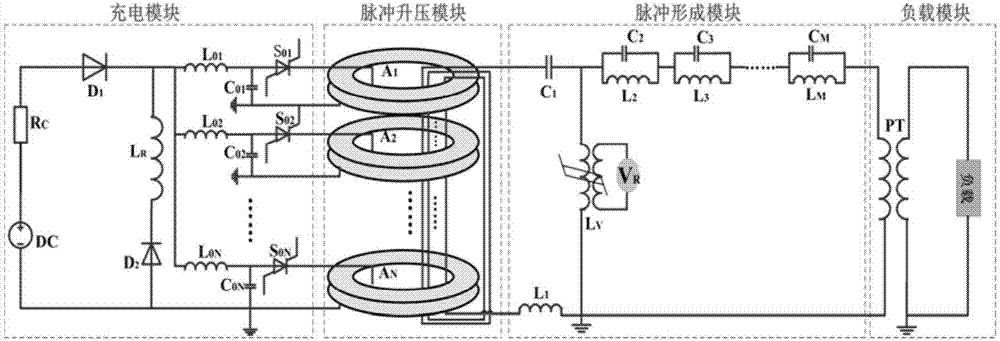
All-solid-state high-voltage microsecond pulse generator based on FRSPT (Fractional-turn Ratio Saturable Pulse Transformer) and anti-resonance network
ActiveCN107040244ACompact integrationAvoid the voltage equalization problem of the working voltagePulse generation by bulk negative resistance devicesAll solid stateMicrowave
The invention relates to a microsecond pulse generator, particularly relates to an all-solid-state high-voltage microsecond pulse generator based on a FRSPT (Fractional-turn Ratio Saturable Pulse Transformer) and an anti-resonance network, and belongs to the field of pulse power. The pulse generator consists of a charging module, a pulse boosting module, a pulse forming module and a load. The charging module is mainly used for charging the pulse generator, and charges the pulse forming module by the pulse boosting module; the pulse boosting module is the FRSPT; in one aspect, the FRSPT is used as a transformer of the pulse boosting module, and in the other aspect, the FRSPT is used as a switch of the pulse forming module; and the pulse forming module is used for forming a quasi-square wave pulse which is reasonable in leading and lagging edge time and good in flat top degree. The pulse generator is long in service life and stable to operate; all-solid-state compact integration of the pulse generator is implemented; an output square wave is high in quality; and the all-solid-state high-voltage microsecond pulse generator can be used for the fields of a high-power microwave source, foods, sterilization and disinfection, wastewater treatment and the like.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
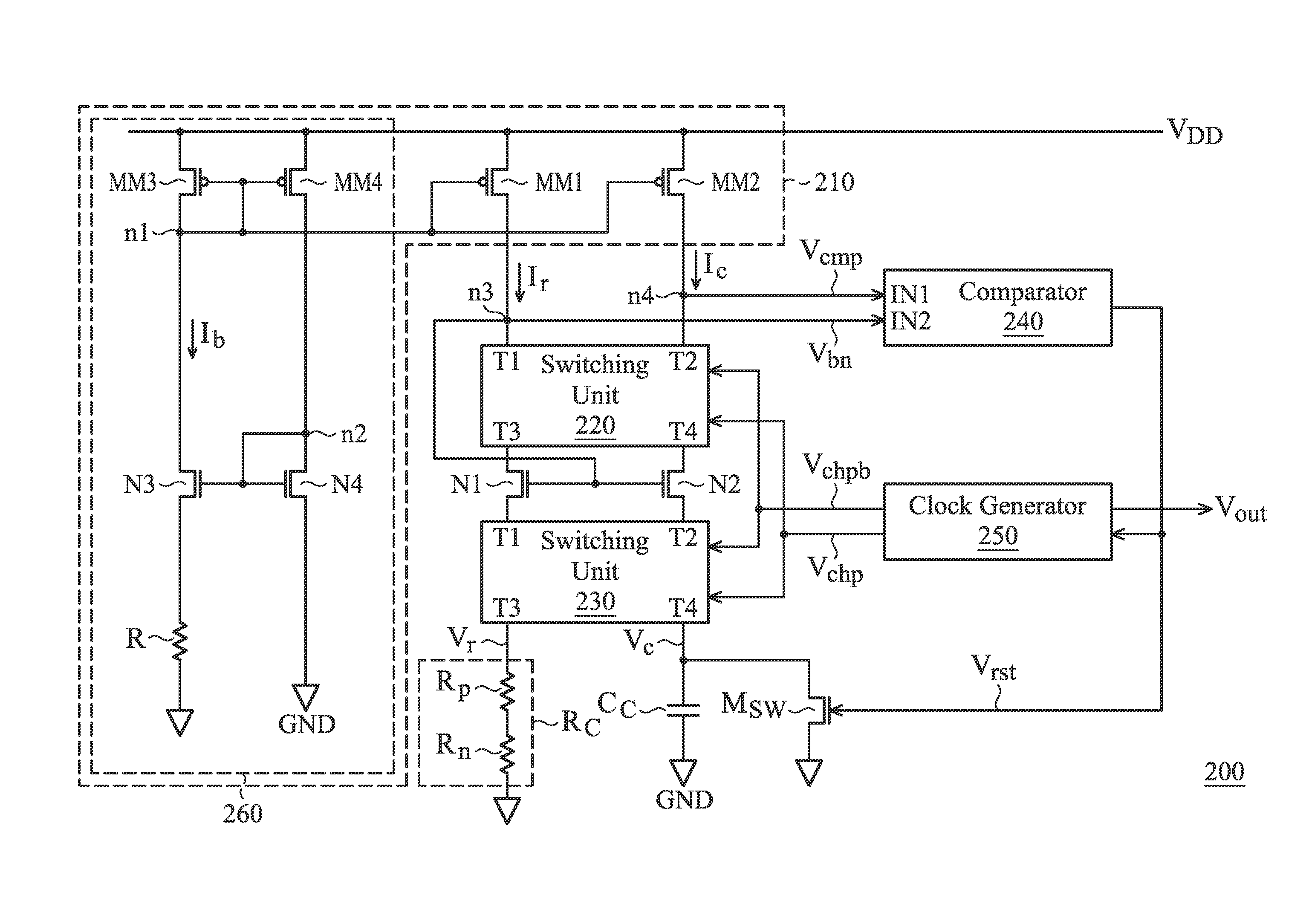
Relaxation oscillator
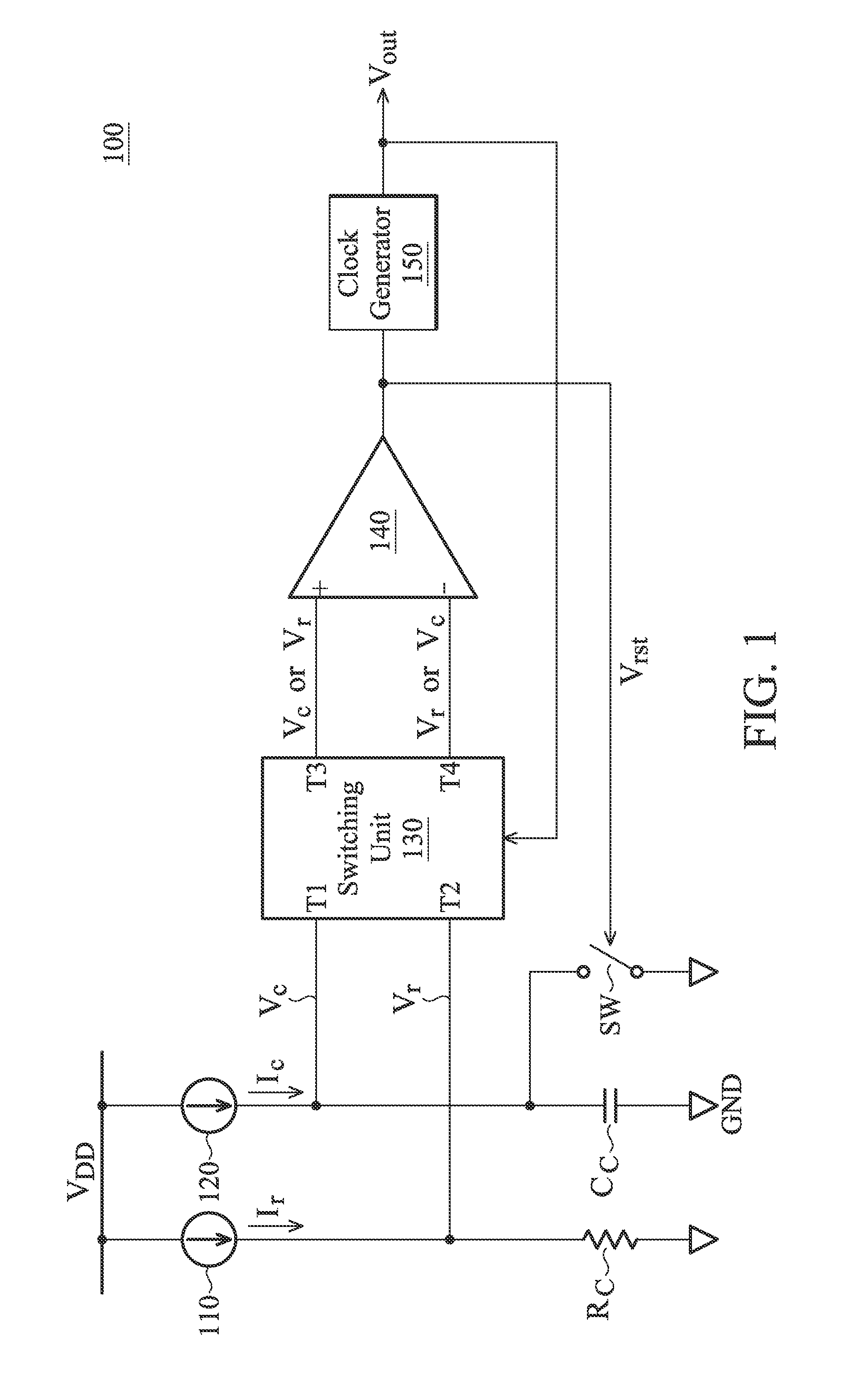
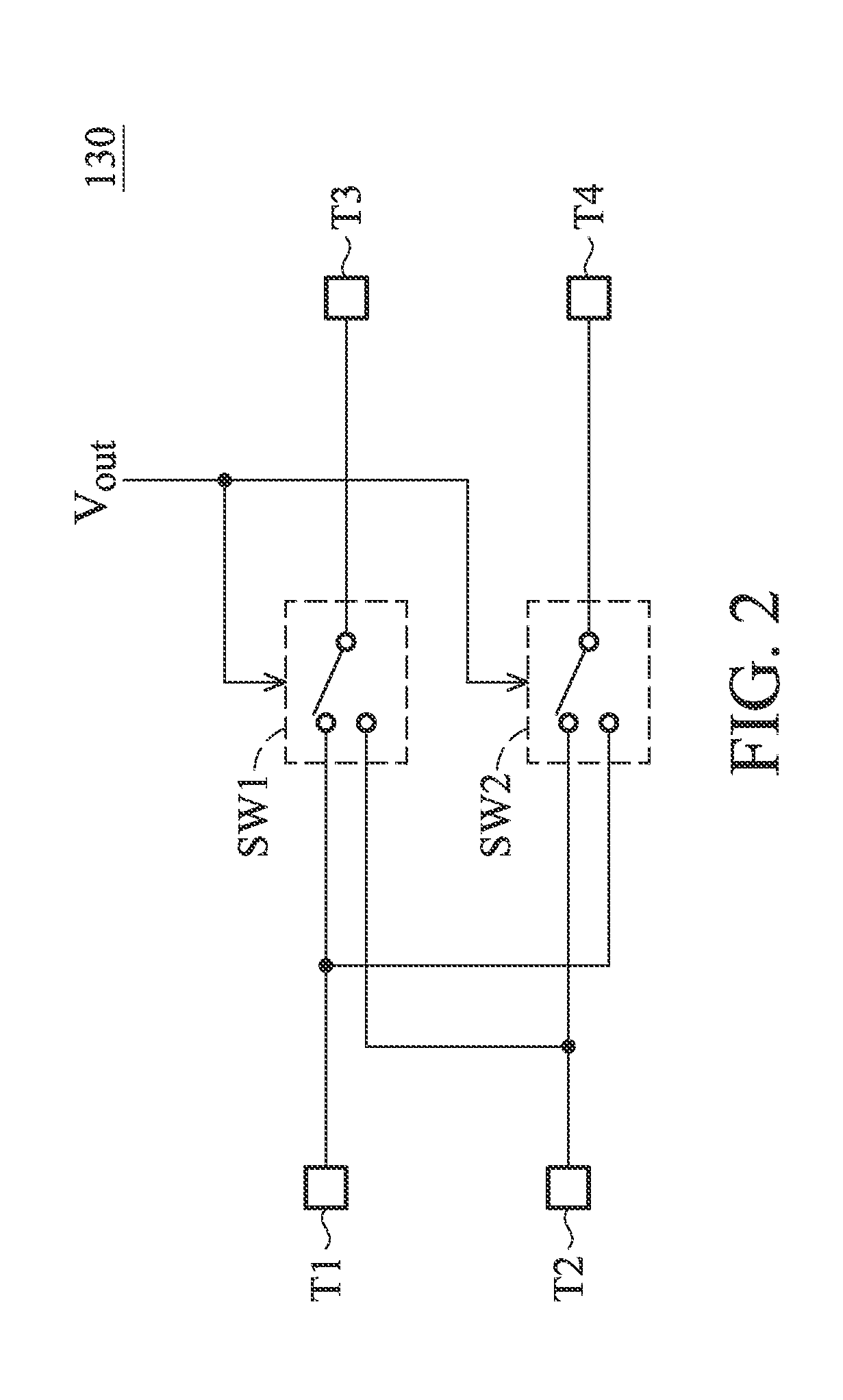
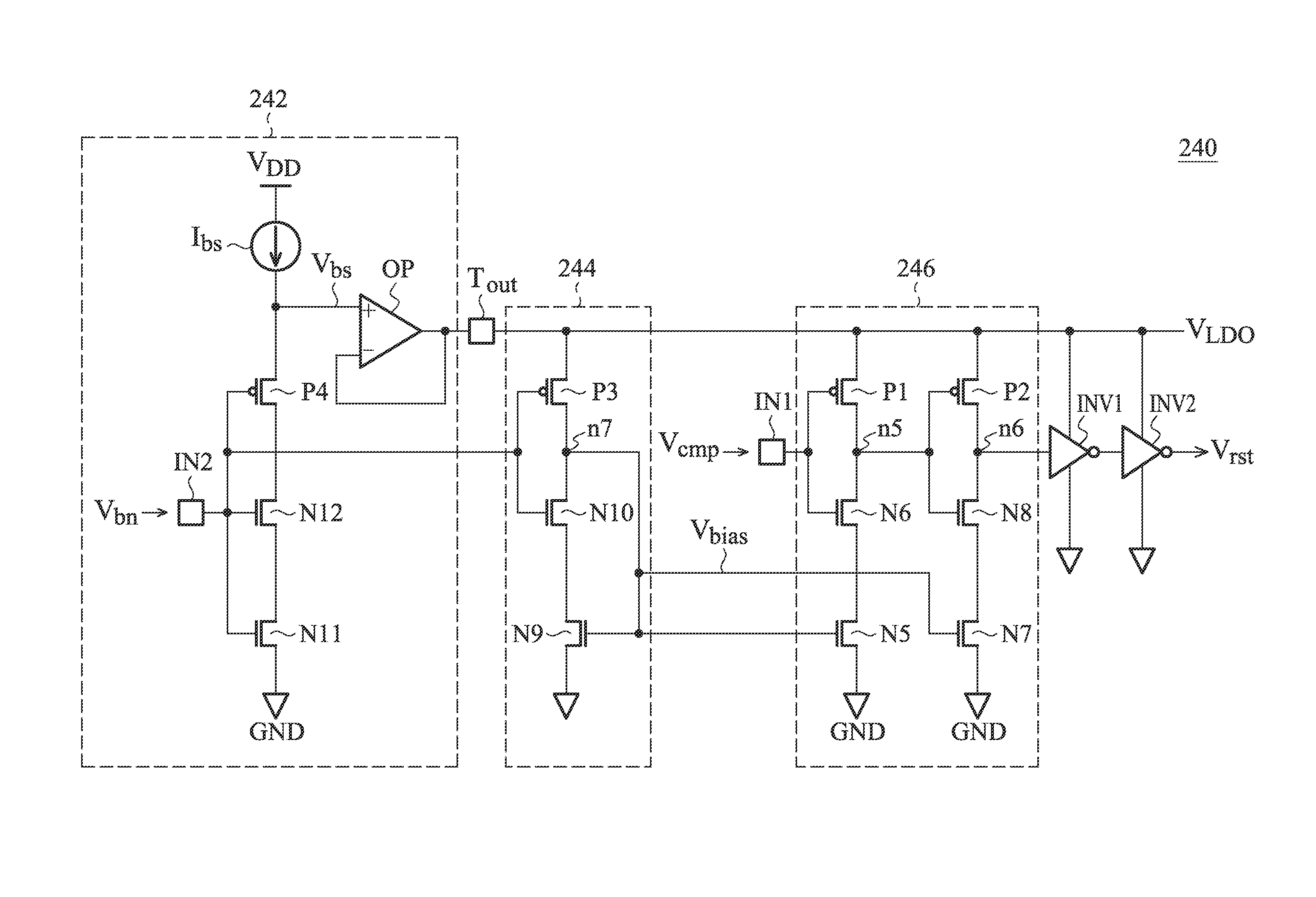
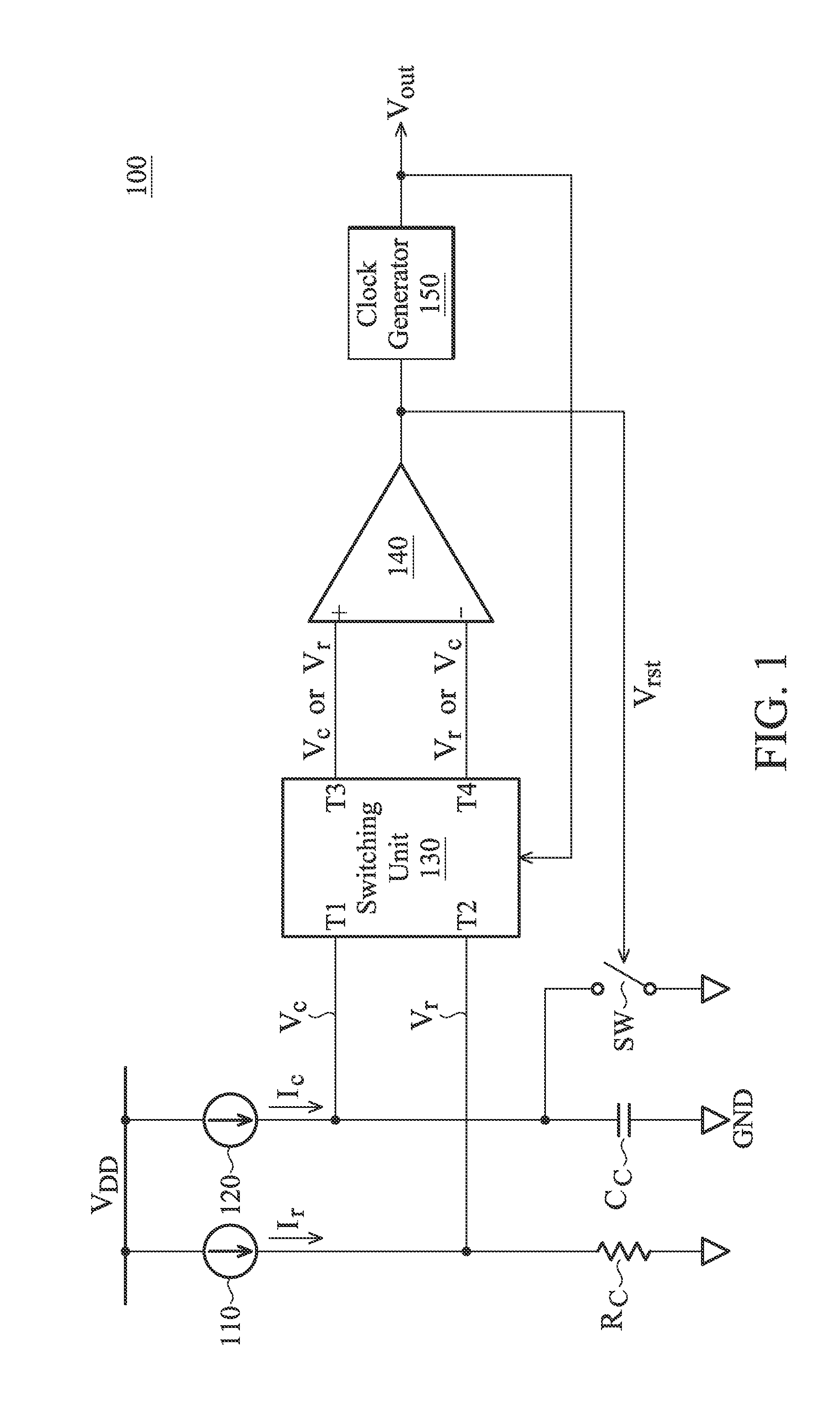
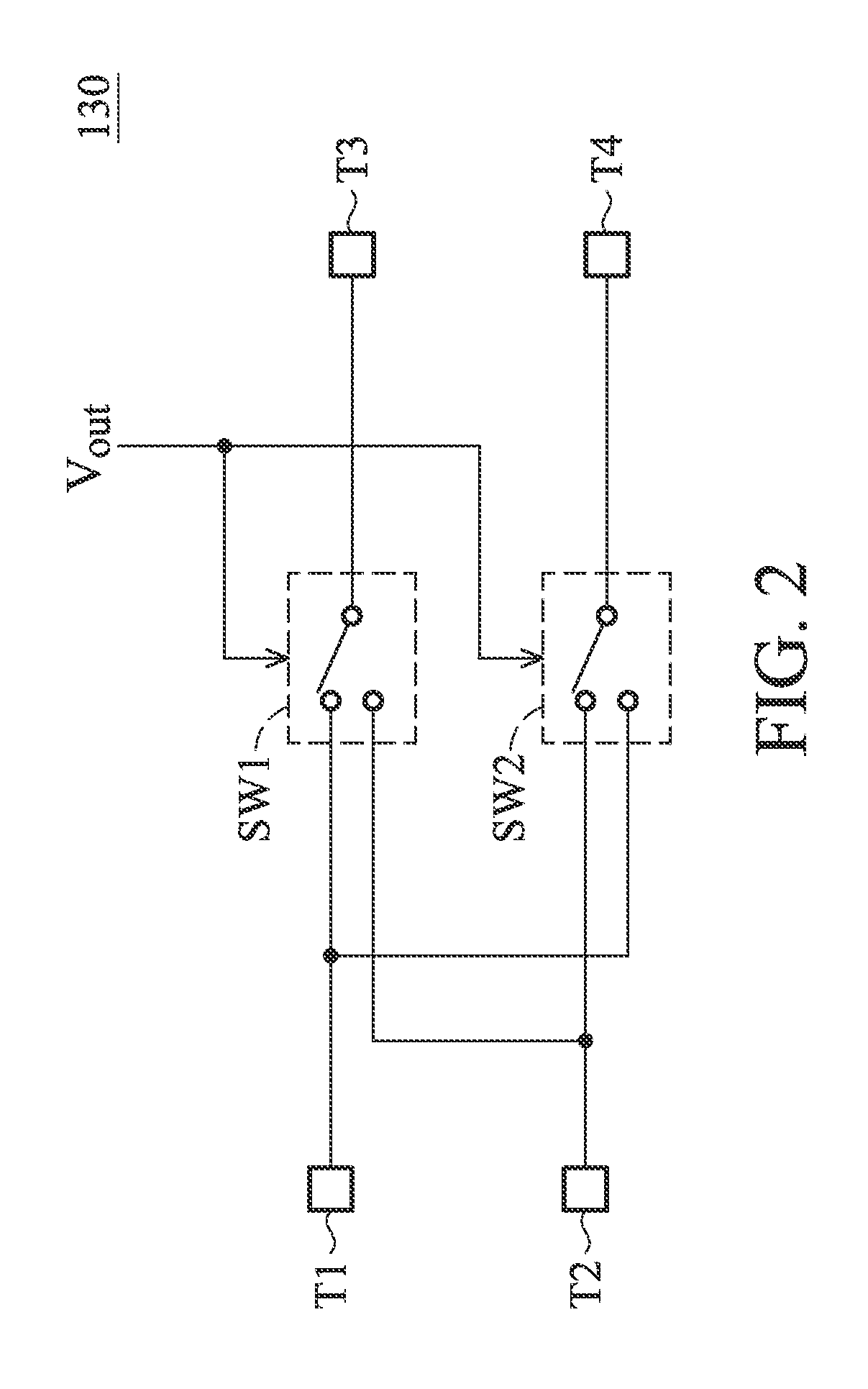
ActiveUS20130200956A1Improve accuracyConvenient to accommodatePulse generation by bipolar transistorsCurrent/voltage measurementCapacitanceOutput compare
A relaxation oscillator is provided. A first current source provides a first current. A second current source provides a second current. A resistive element is coupled between the first current source and a ground. A capacitive element is coupled between the second current source and the ground. A comparator has a non-inverting input terminal, an inverting input terminal and an output terminal for outputting a compare result. A clock generator provides a clock signal according to the compare result. A switching unit alternately couples the non-inverting input terminal and the inverting input terminal of the comparator to the resistive element and the capacitive element according to the clock signal.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
High Current Steering ESD Protection Zener Diode And Method
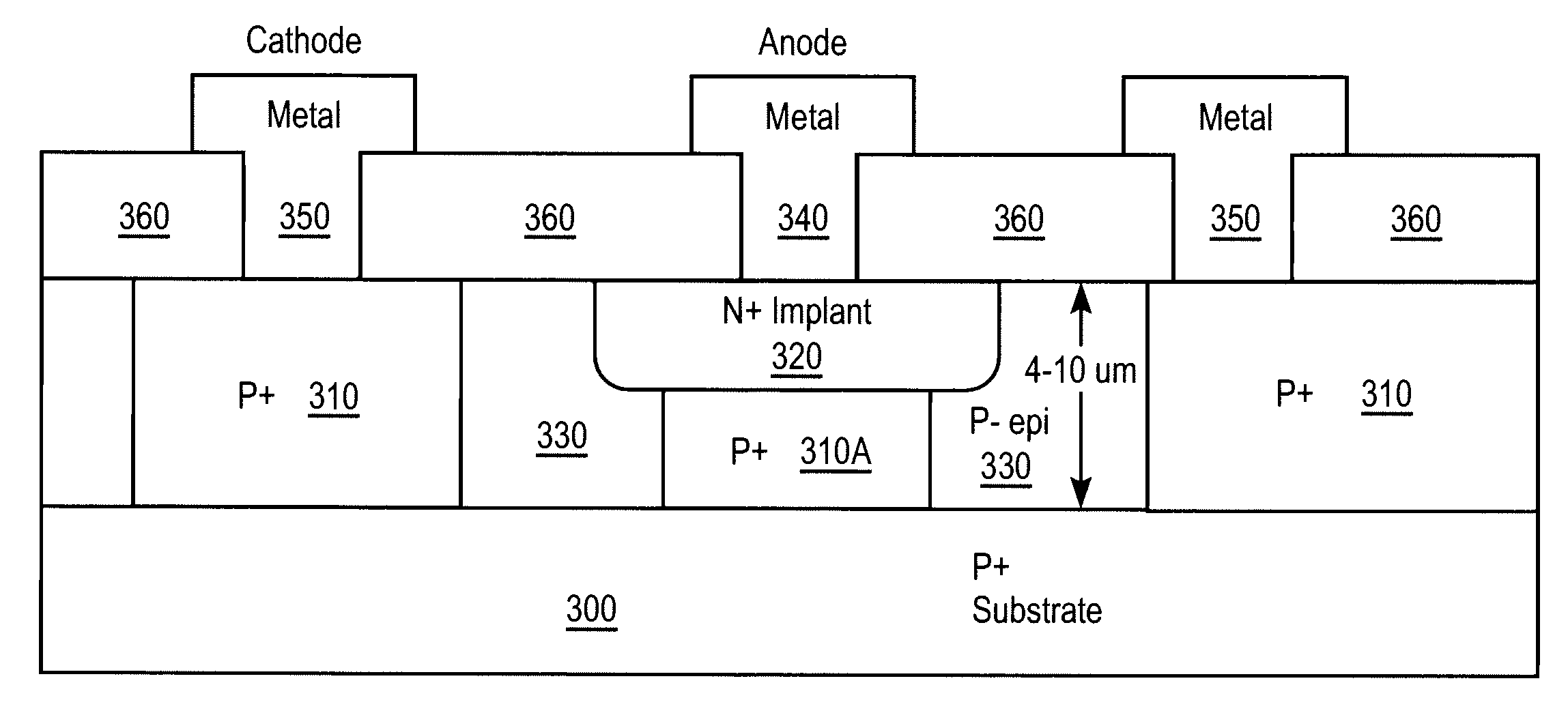
InactiveUS20080258263A1High speedIncreased current handling capabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodeZener diodeHigh current
A method of fabricating a N+ / P+ zener diode where the reverse breakdown occurs in a controlled, and uniform manner leading to improved speed of operation and increase in current handling capability.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Tunable, maximum power output, frequency harmonic comb generator
InactiveUS7193486B2Long delayHigh resolutionTransmission control/equlisationPulse train generatorTime delaysHarmonic
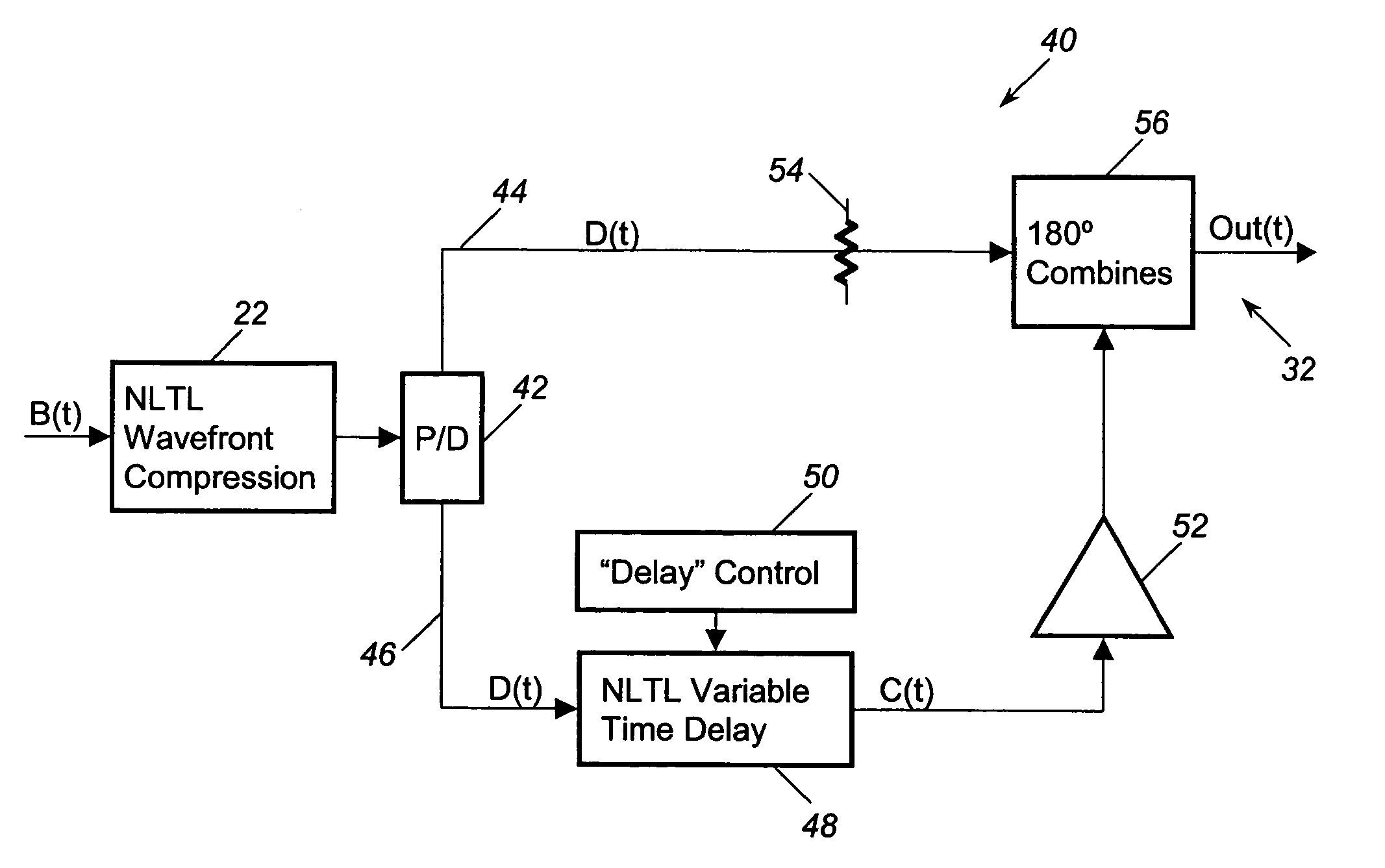
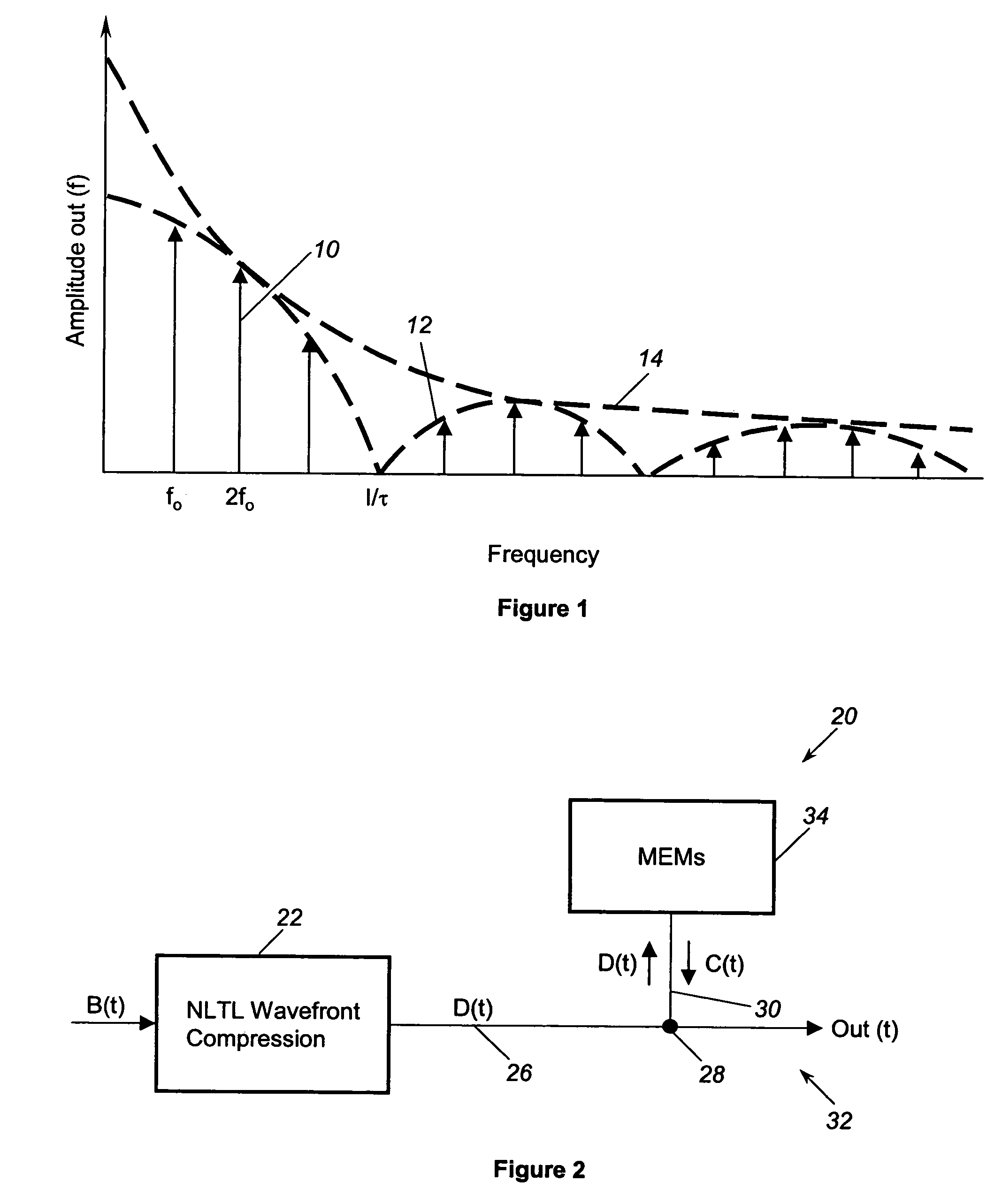
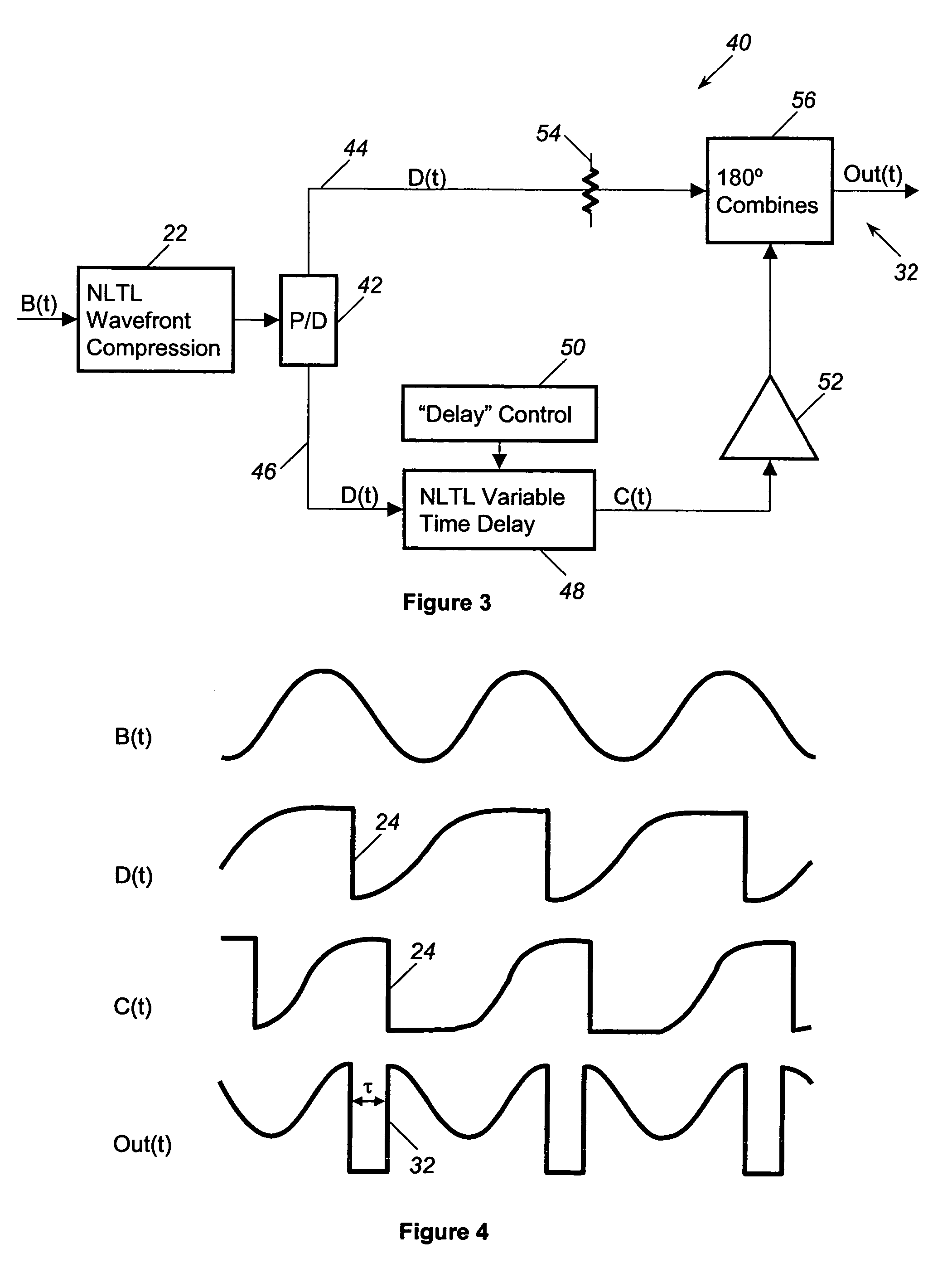
A comb frequency generator that is tunable to vary the width of the pulses in the output signal and achieve a maximum power output at different harmonic frequencies. A wavefront compression device receives a sinusoidal input signal and provides wavefront compression to create a compressed signal having a series of periodic fast edges. A delay device receives the fast-edge compressed signal and delays the fast-edge signal to create a delayed fast-edge signal. A combining device receives the original fast-edge compressed signal and the delayed fast-edge compressed signal to generate an output signal including a series of pulses having a width determined by the delay of the delayed signal. In one embodiment, the delay device is a shorted transmission line stub having a length selectively set by a series of MEM devices. In another embodiment, the delay device is an NLTL variable time delay device that delays the fast-edge signal.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Comparator with transition threshold tracking capability
ActiveUS20130200924A1Improve accuracyConvenient to accommodateMultiple input and output pulse circuitsCurrent/voltage measurementVoltage generatorPower flow
A comparator is provided. The comparator includes a voltage generator, a buffer unit and a threshold control loop. The voltage generator has an output terminal for providing a reference voltage according to a constant current. The buffer unit provides an output signal according to a first input signal and a bias signal. The threshold control loop provides the bias signal to the buffer unit according to a second input signal, so as to regulate a transition threshold of the buffer unit to close to the second input signal. The output signal represents a compare result of the first and second input signals. The buffer unit and the threshold control loop are powered by the reference voltage.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Receiving circuit, LSI chip, and storage medium
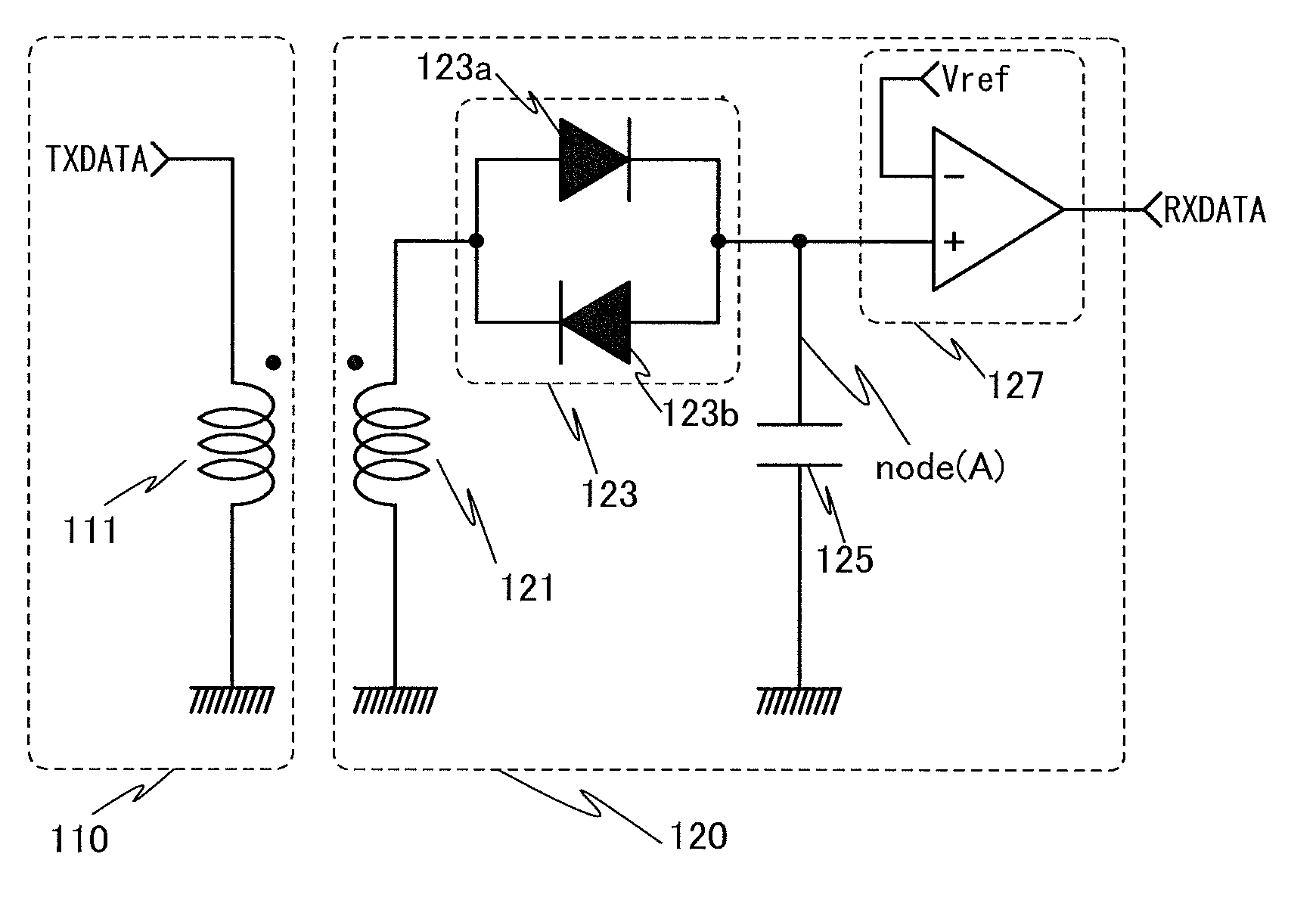
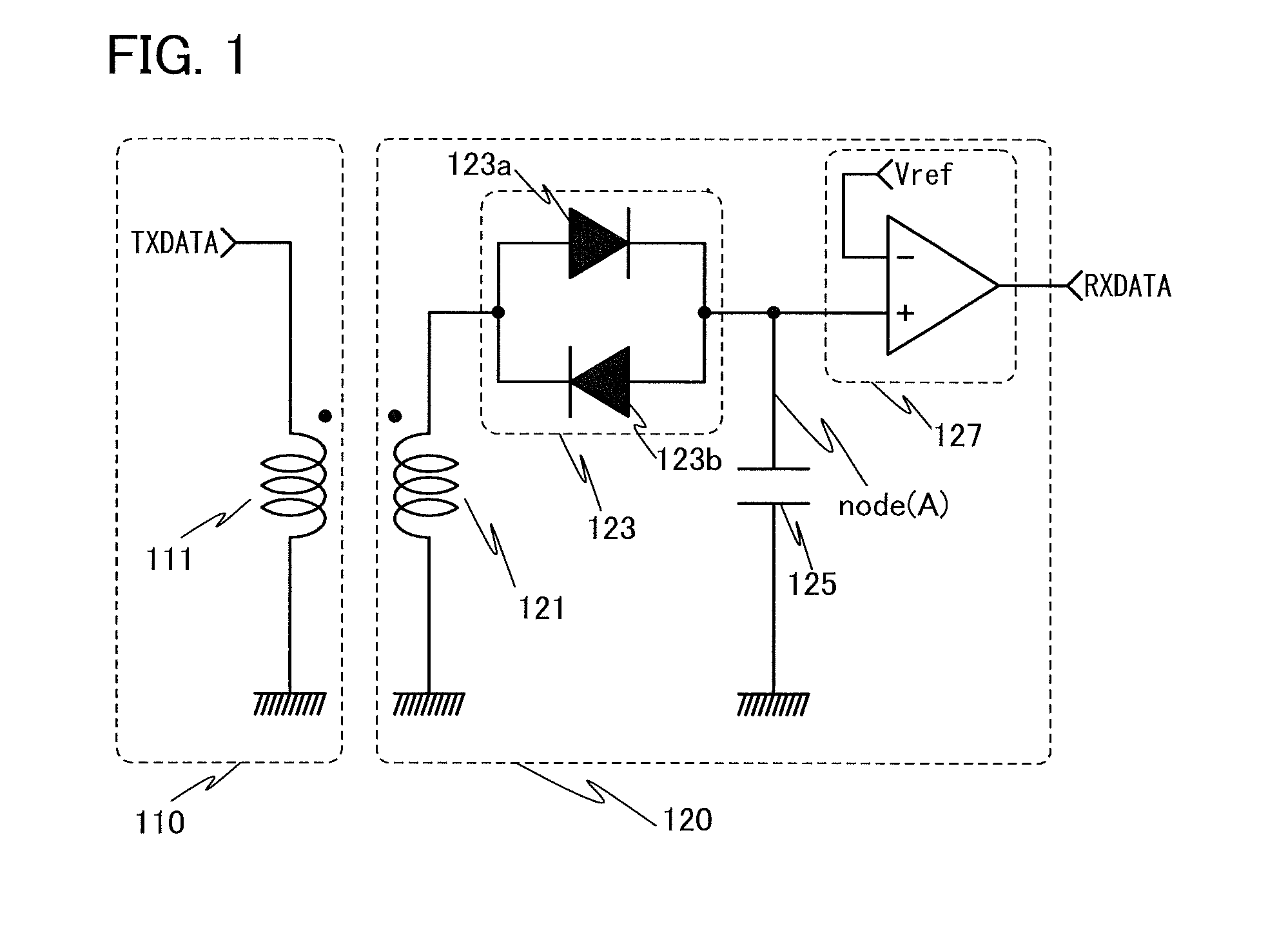
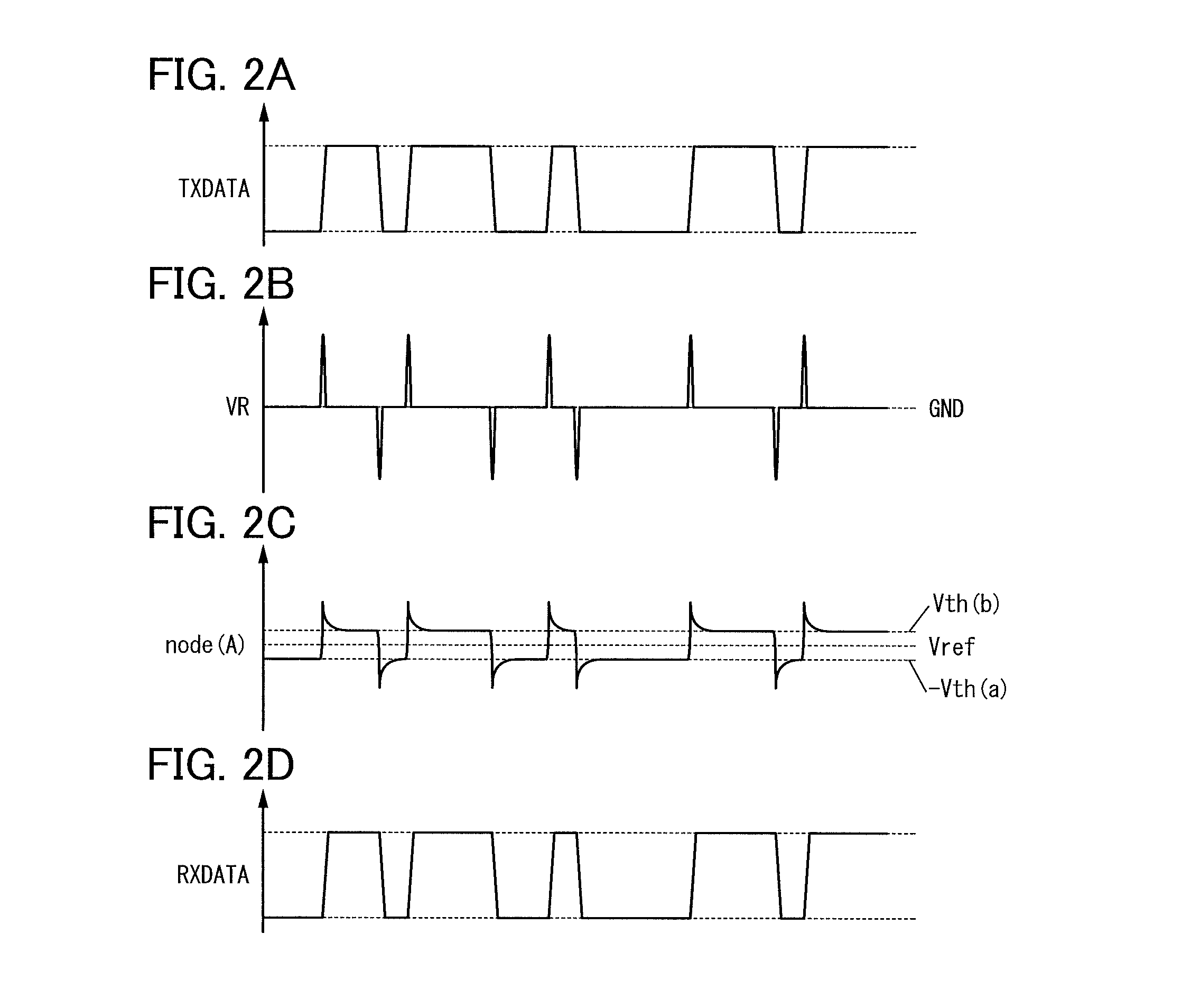
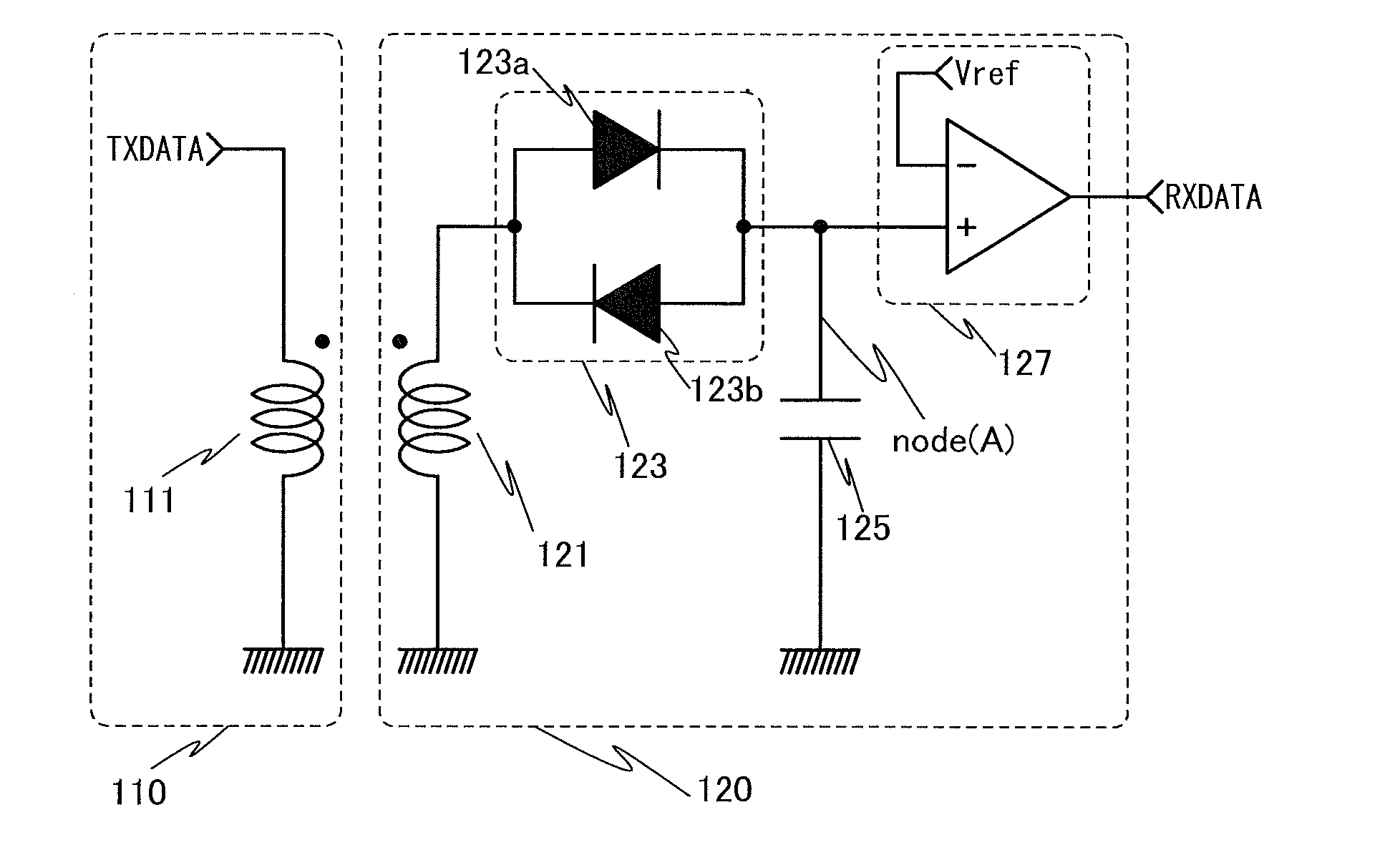
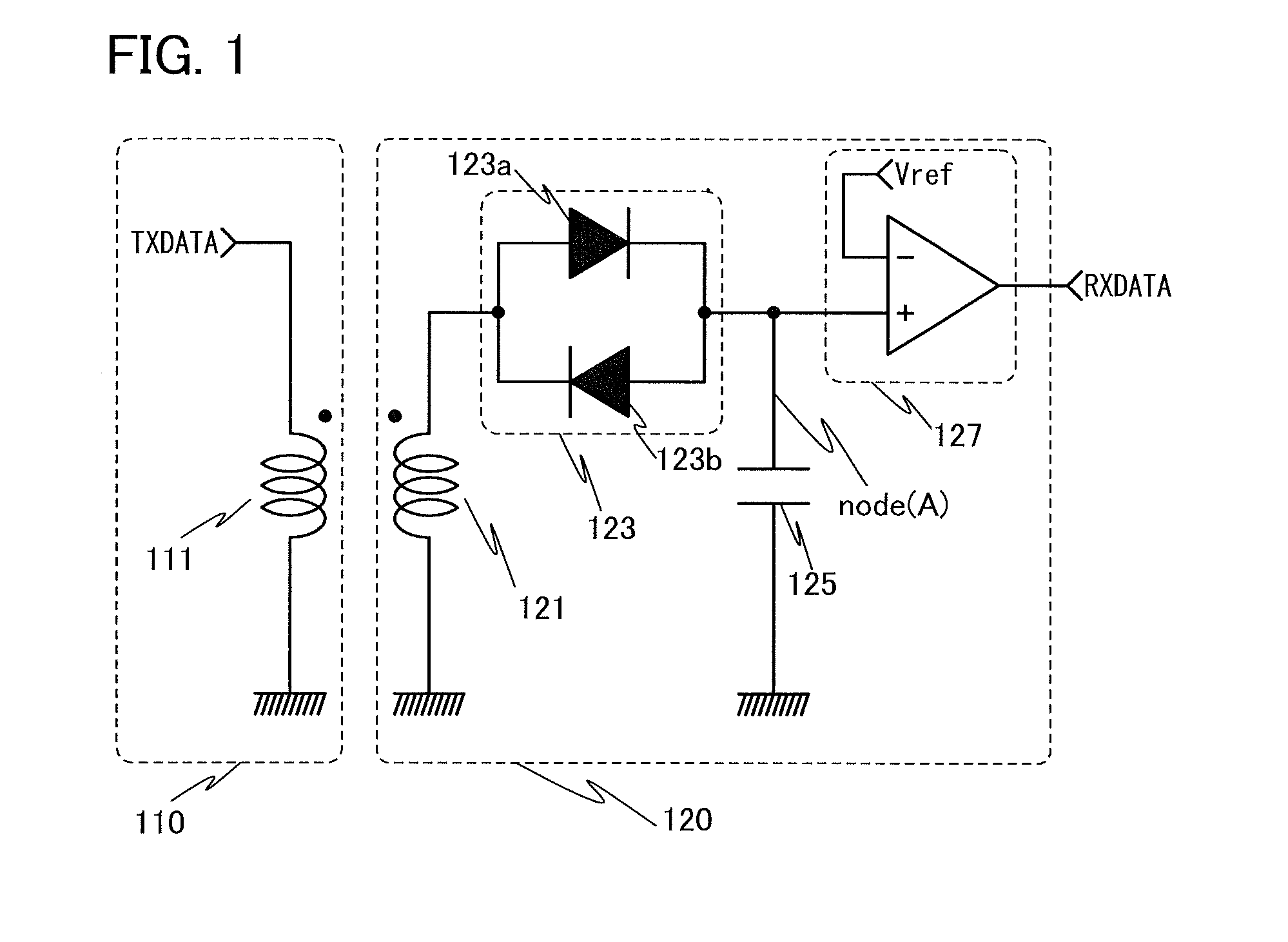
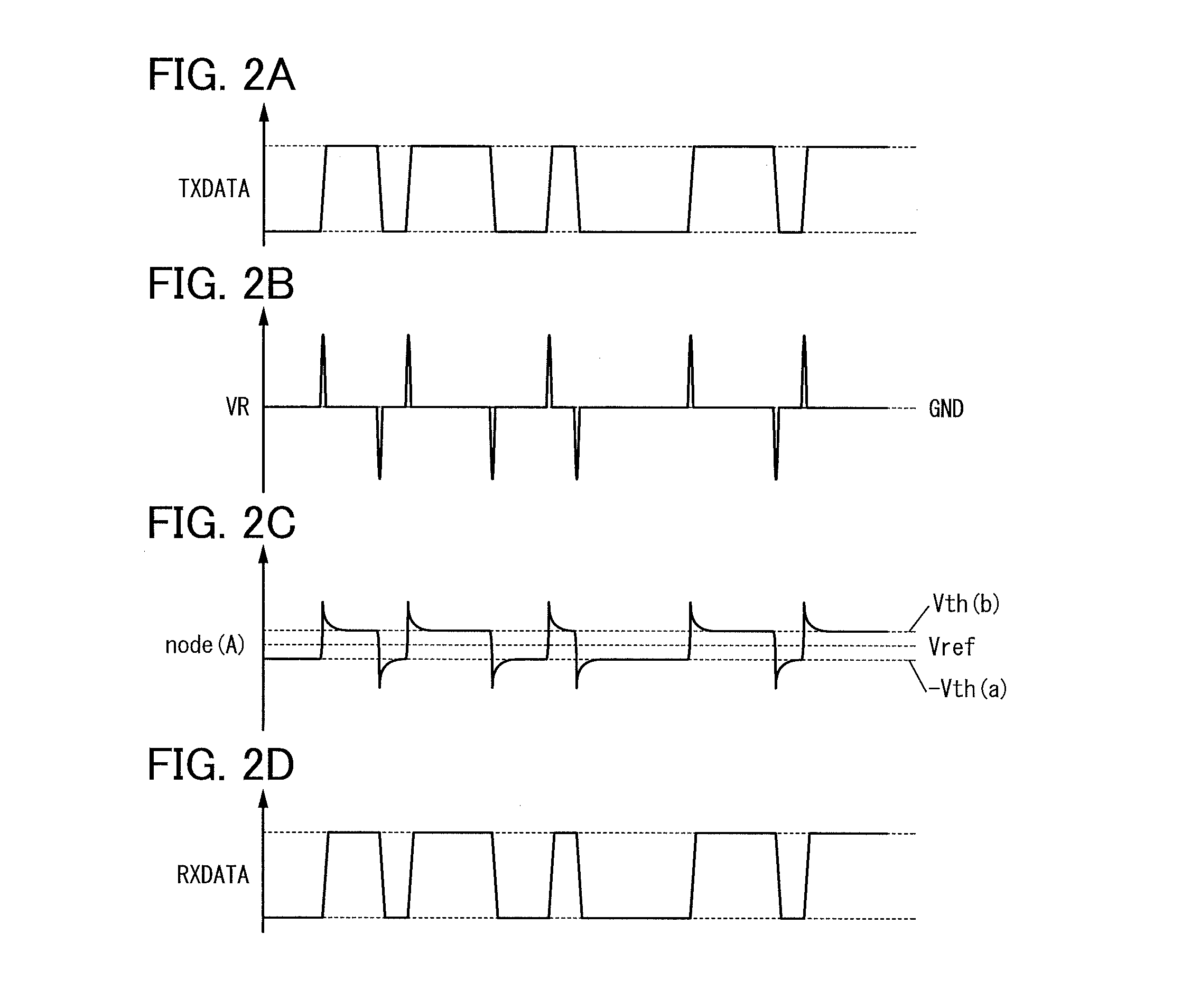
InactiveUS8466740B2Reduce areaReduce storage spaceNear-field transmissionCurrent/voltage measurementEngineeringElectromagnetic induction
A receiving circuit with a simple circuit structure for performing wireless communication utilizing electromagnetic induction is provided. An LSI chip and a storage medium where wireless communication utilizing electromagnetic induction is performed and the circuit scale and circuit size can be reduced are provided. The following receiving circuit may be used: a parallel circuit where two diode elements whose directions are opposite are connected in parallel is used, one end of the parallel circuit is connected to the other end of a coil whose one end is connected to a ground potential line, and a capacitor is connected in series with the other end of the parallel circuit. A transistor whose leakage current is markedly reduced may be used as a diode in the receiving circuit. Such a receiving circuit may be used in an LSI chip or a storage medium.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method, Circuit Configuration and Bridge Circuit
ActiveUS20110116294A1Increase profitIncrease in switching lossAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionMOSFETCapacitance
A method, circuit configuration and bridge circuit for charging a capacitance effective on the main current terminals of a semiconductor switch, in particular an intrinsic capacitance, in particular the drain-source capacitance of a MOSFET semiconductor switch or the collector-emitter capacitance of an IGBT semiconductor switch, the precharging, in particular the at least partial charging, of the effective capacitance being forcibly controlled via a charging current path.
Owner:SEW-EURODRIVE GMBH & CO KG
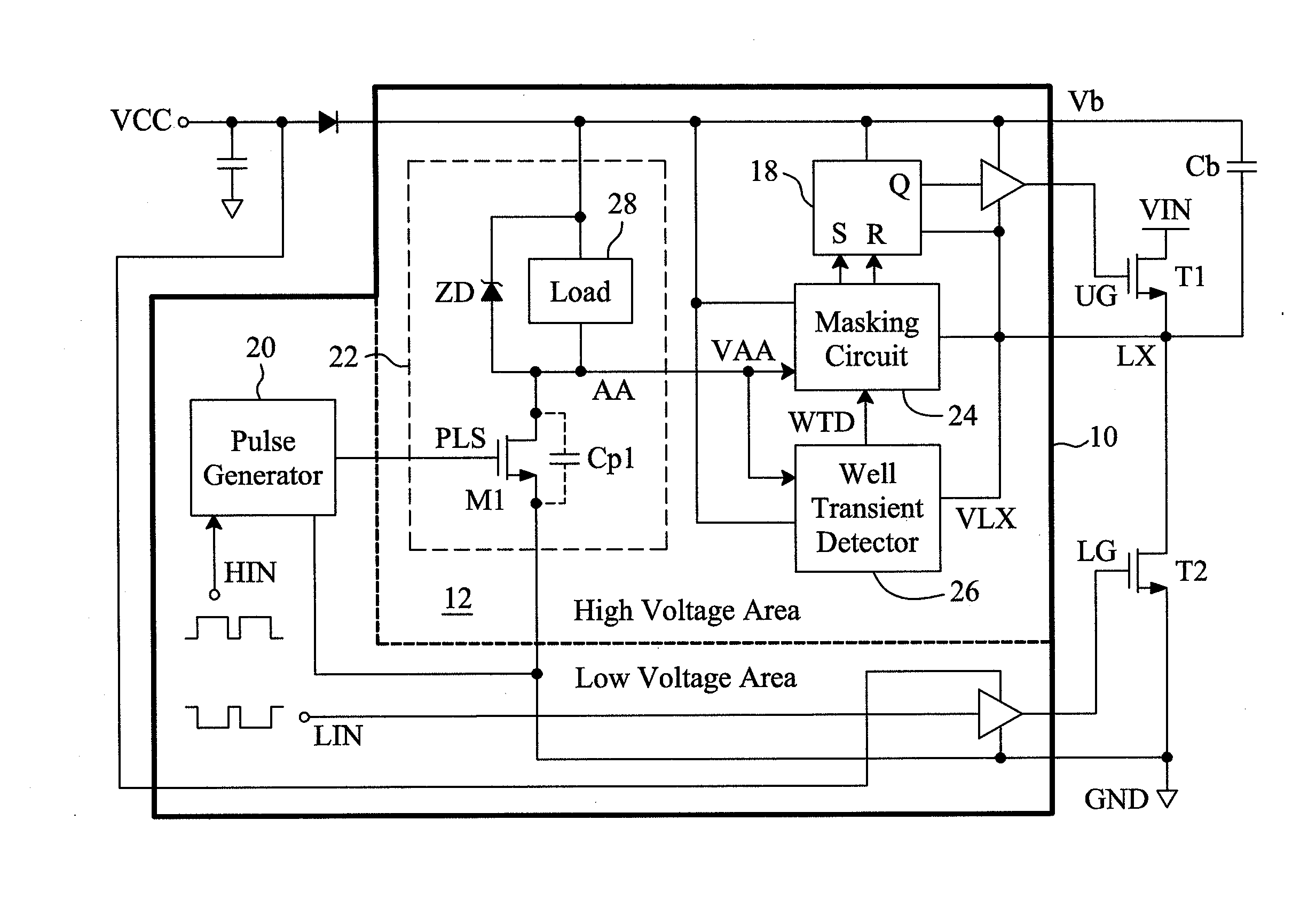
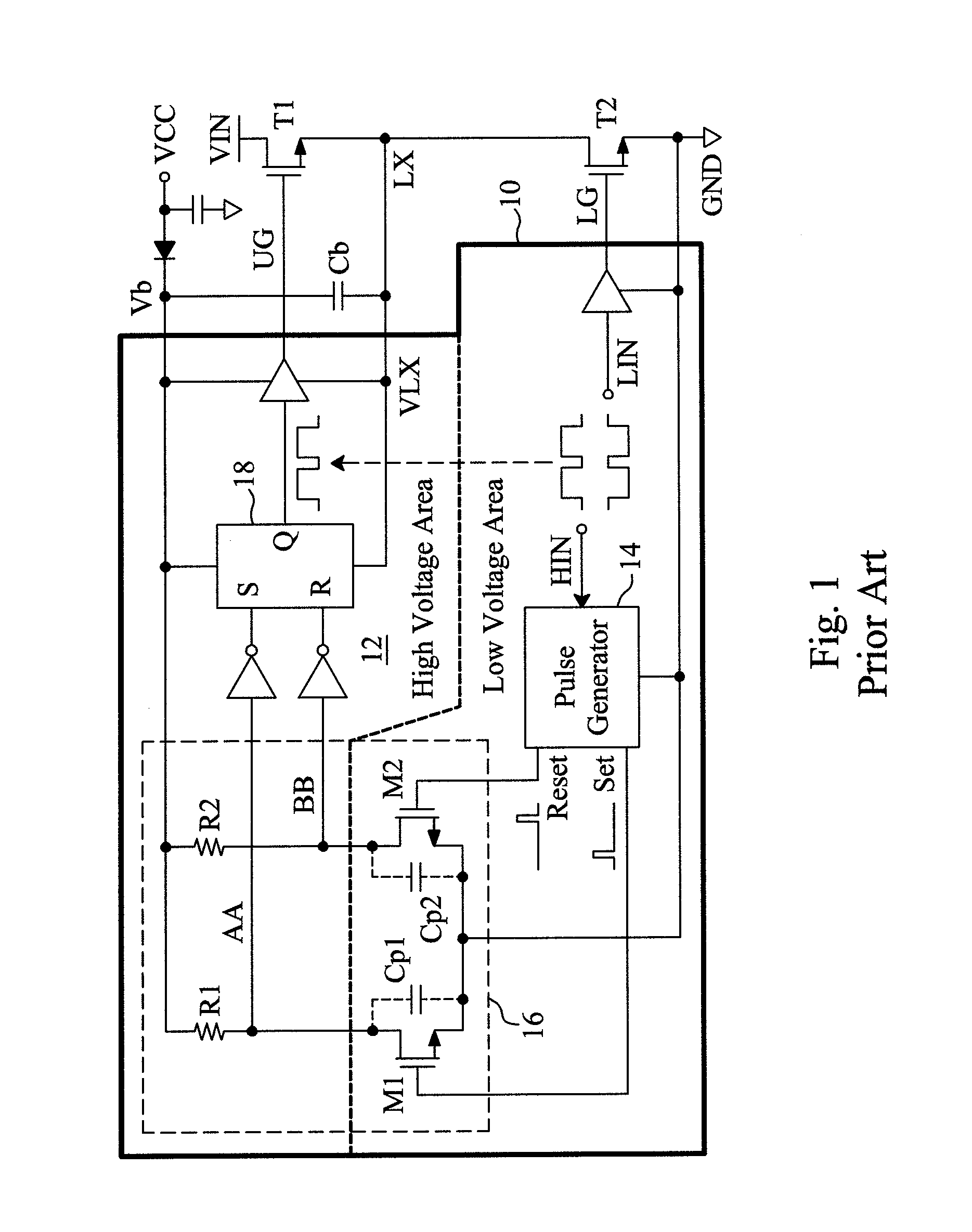
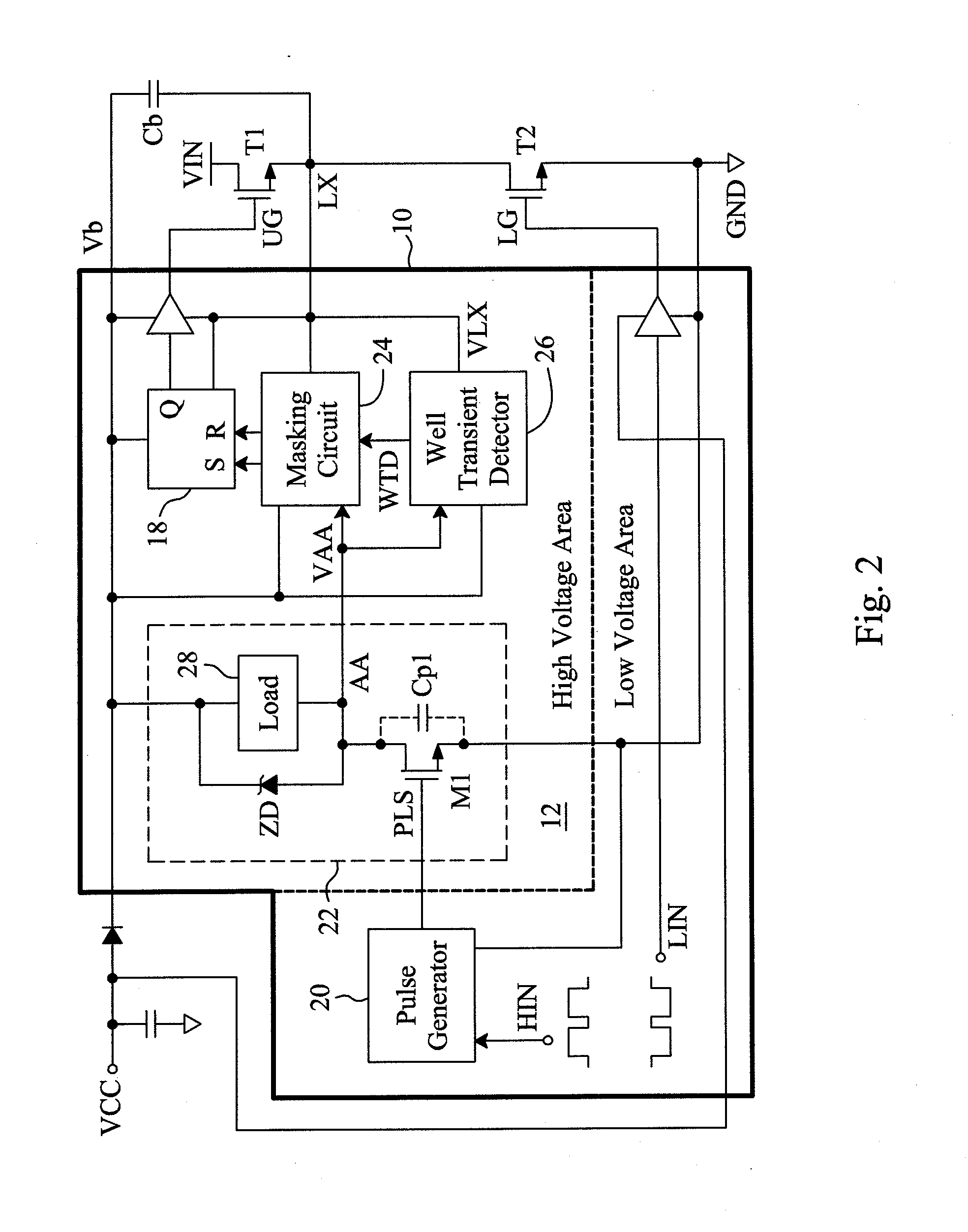
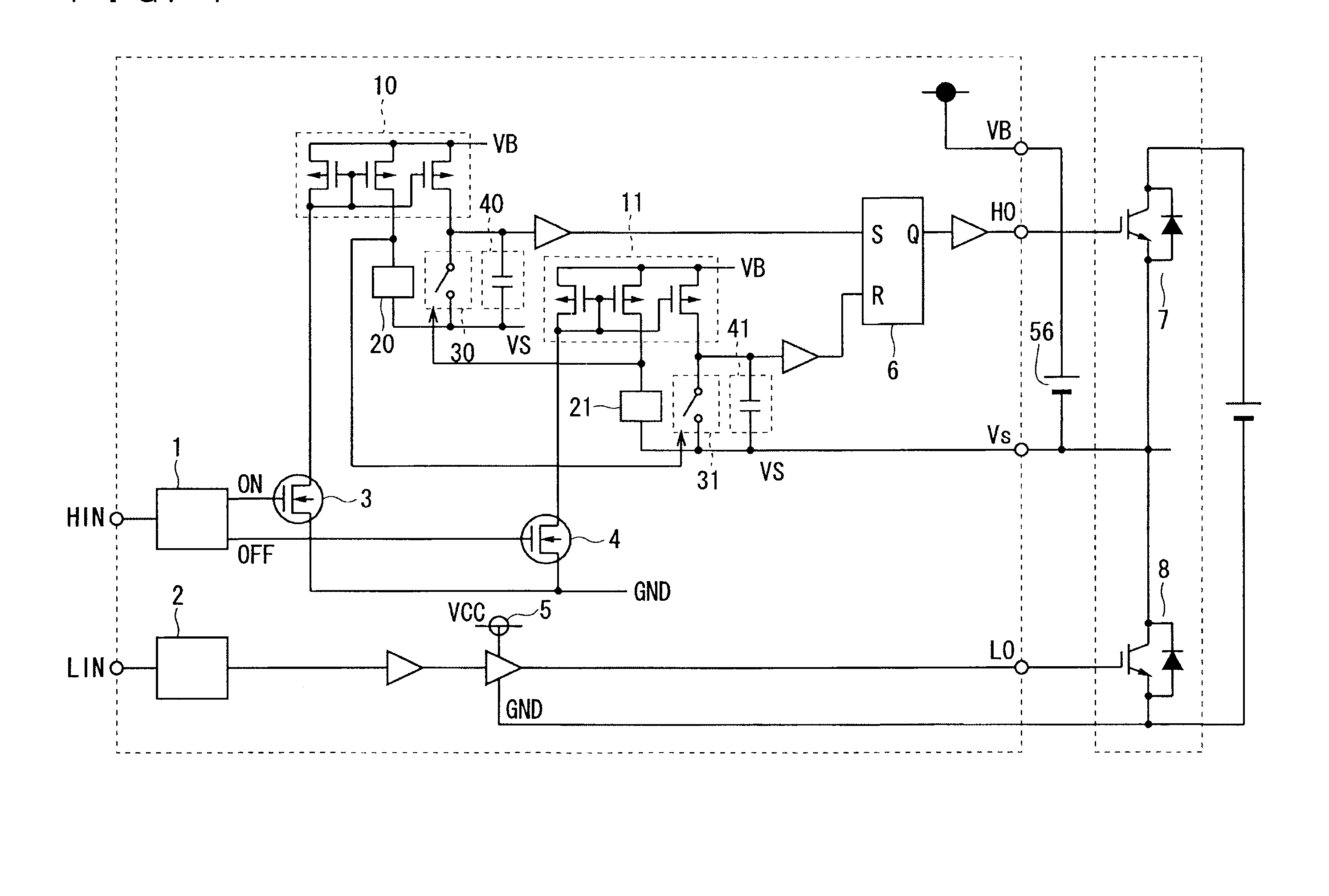
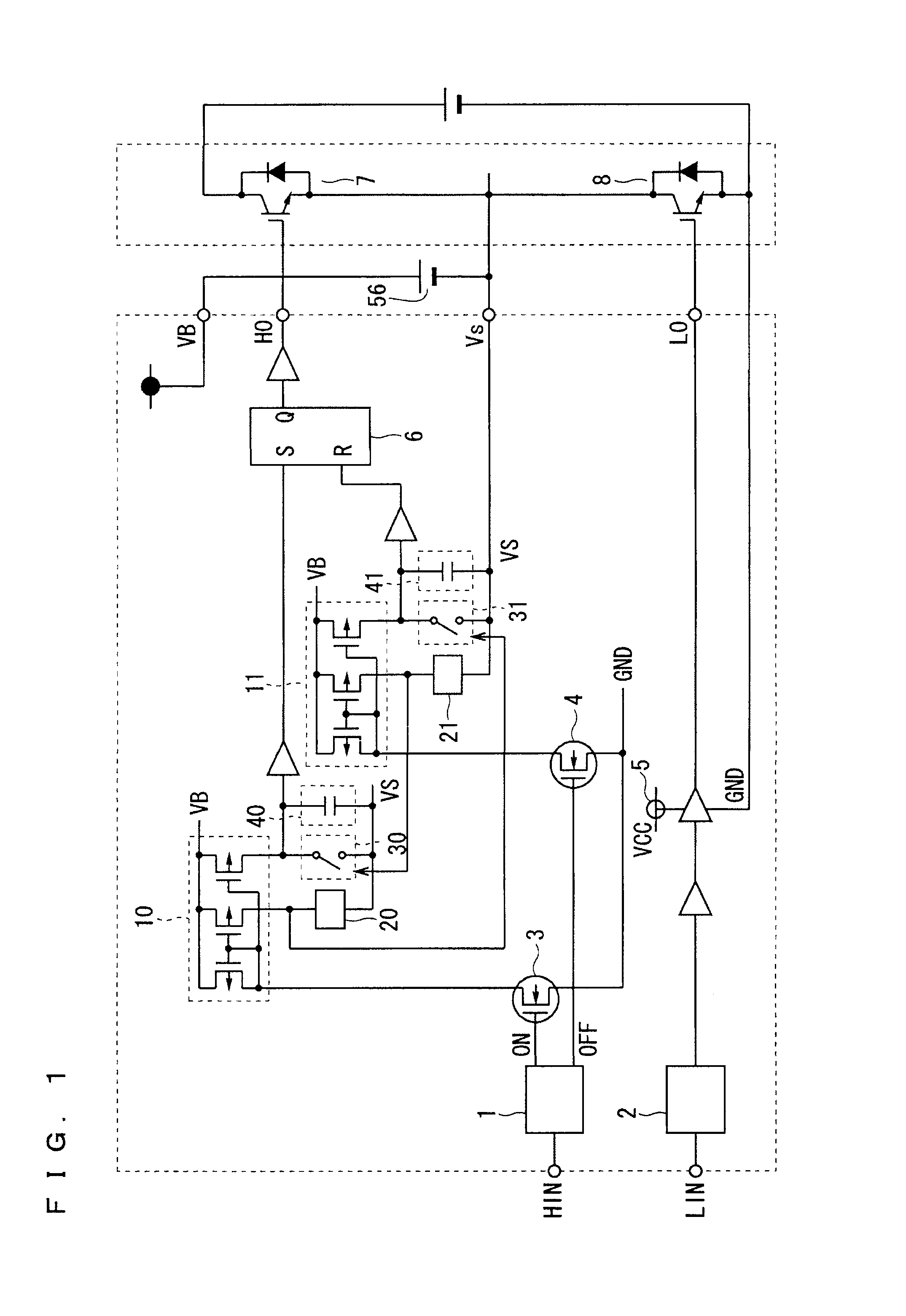
Circuit and method for improving noise immunity of a single-end level shifter in a floating gate driver
ActiveUS20130207704A1Reduce area lossImprove noise immunityPulse automatic controlVoltage/current interference eliminationBistable circuitsSwitching signal
A floating gate driver uses a single-end level shifter to translate a set signal and a reset signal induced by a rising edge and a falling edge of a switch signal to a common output terminal to generate an output voltage for a bistable circuit to generate a level shifted switch signal. Under control of a well transient detect signal asserted by detecting noise in the output voltage, a masking circuit between the single-end level shifter and the bistable circuit masks noise in the output voltage. This configuration has lower area penalty and better noise immunity.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
Dual-trigger low-energy flip-flop circuit
ActiveUS20120212271A1Weaken energyGreat clock signalLogic circuitsPulse generation by bulk negative resistance devicesSwitching frequencyTransistor
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a technique for technique for capturing and storing a level of an input signal using a dual-trigger low-energy flip-flop circuit that is fully-static and insensitive to fabrication process variations. The dual-trigger low-energy flip-flop circuit presents only three transistor gate loads to the clock signal and none of the internal nodes toggle when the input signal remains constant. One of the clock signals may be a low-frequency “keeper clock” that toggles less frequently than the other two clock signal that is input to two transistor gates. The output signal Q is set or reset at the rising clock edge using separate trigger sub-circuits. Either the set or reset may be armed while the clock signal is low, and the set or reset is triggered at the rising edge of the clock.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Oscillator based on a 6T SRAM for measuring the Bias Temperature Instability
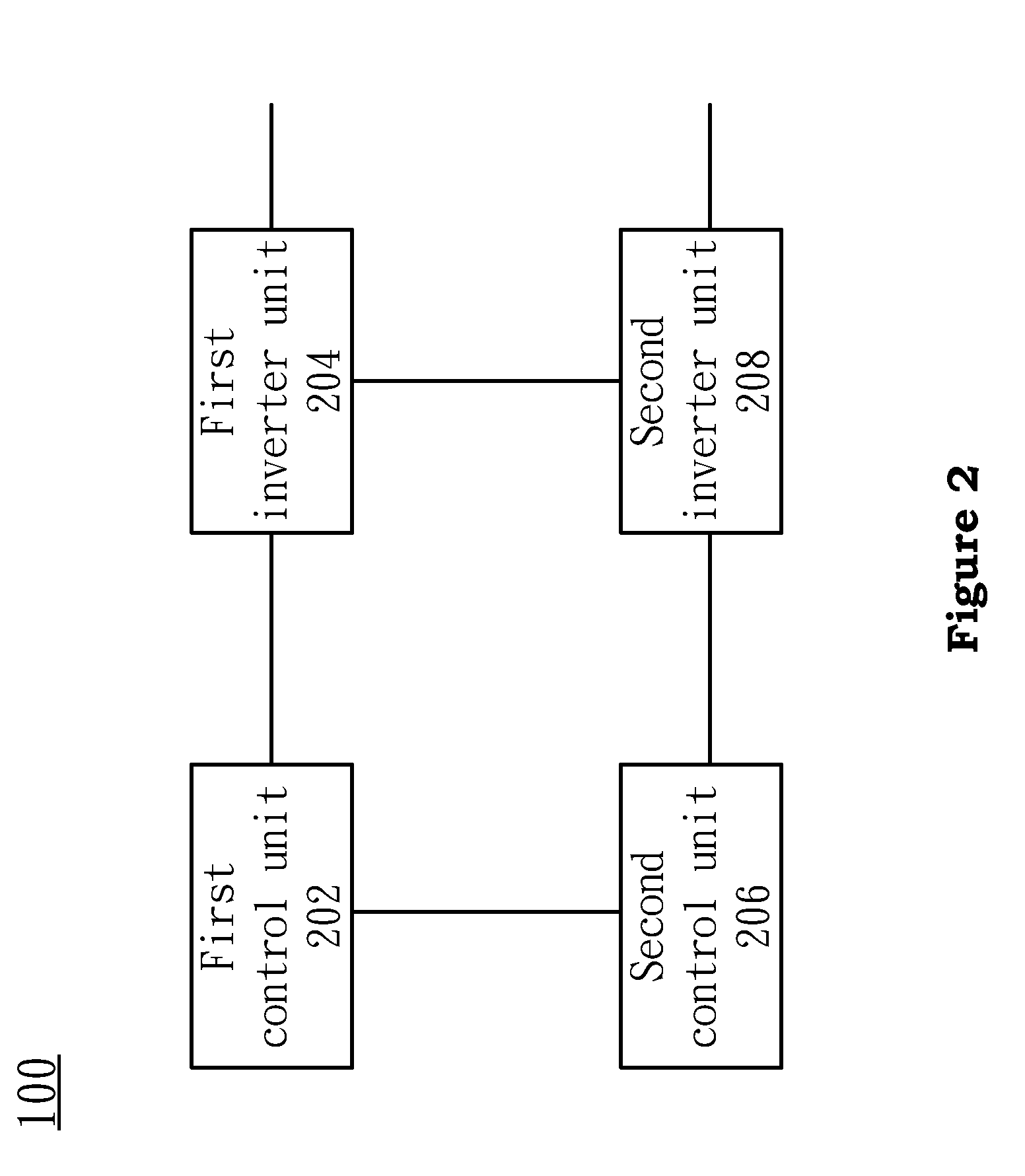
ActiveUS20130222071A1Reliable changePulse generation by logic circuitsDigital storageControl unitElectrical and Electronics engineering
The present invention provides an oscillator which is based on a 6T SRAM for measuring the Bias Temperature Instability. The oscillator includes a first control unit, a first inverter, a second control unit, and a second inverter. The first control unit is coupled with the first inverter. The second control unit is coupled with the second inverter. The first control unit and the second control unit is used to control the first inverter and the second inverter being selected, biased, and connected respectively, so that the NBTI and the PBTI of the SRAM can be measured separately, and the real time stability of the SRAM can be monitored immediately.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
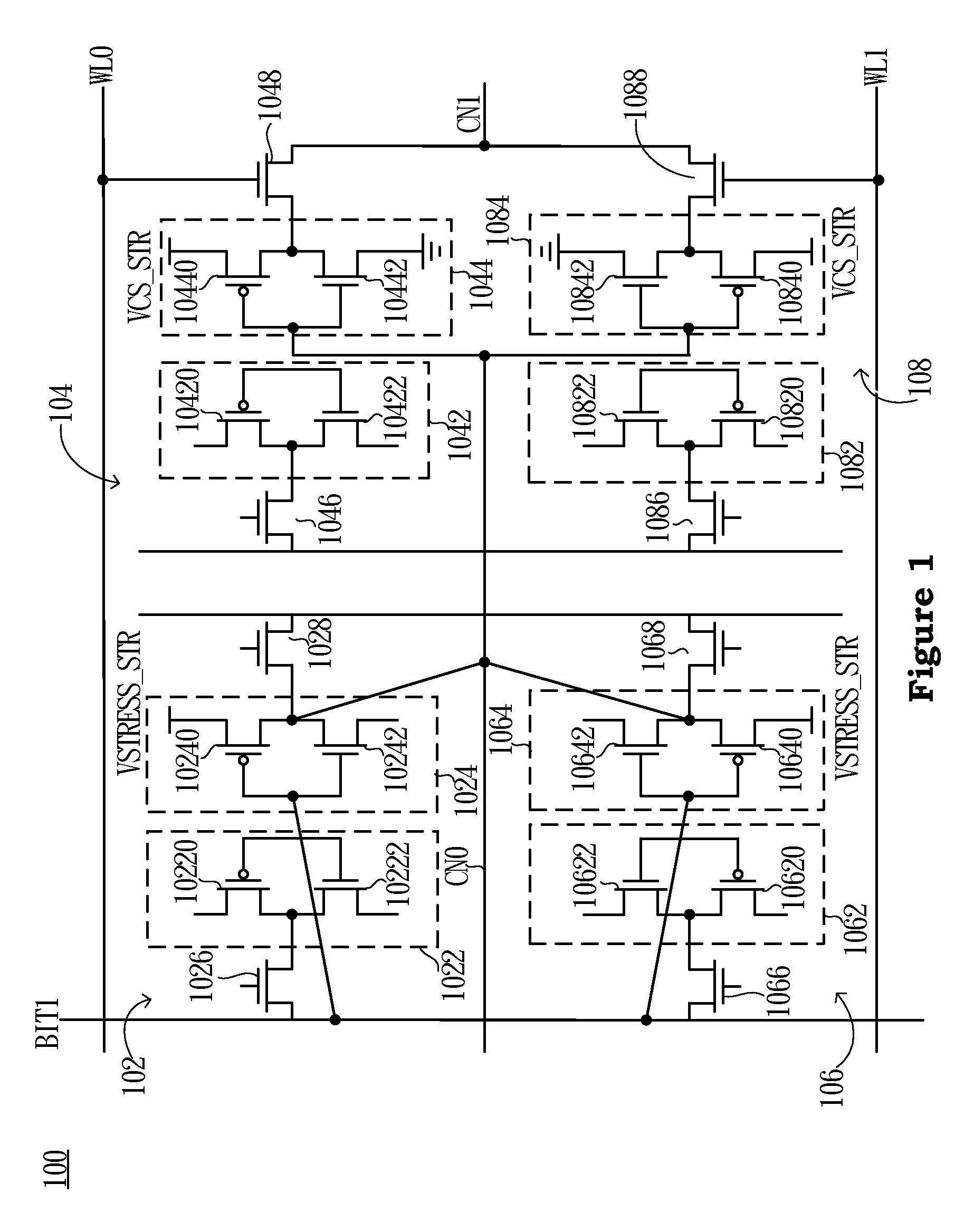
Semiconductor circuit and semiconductor device
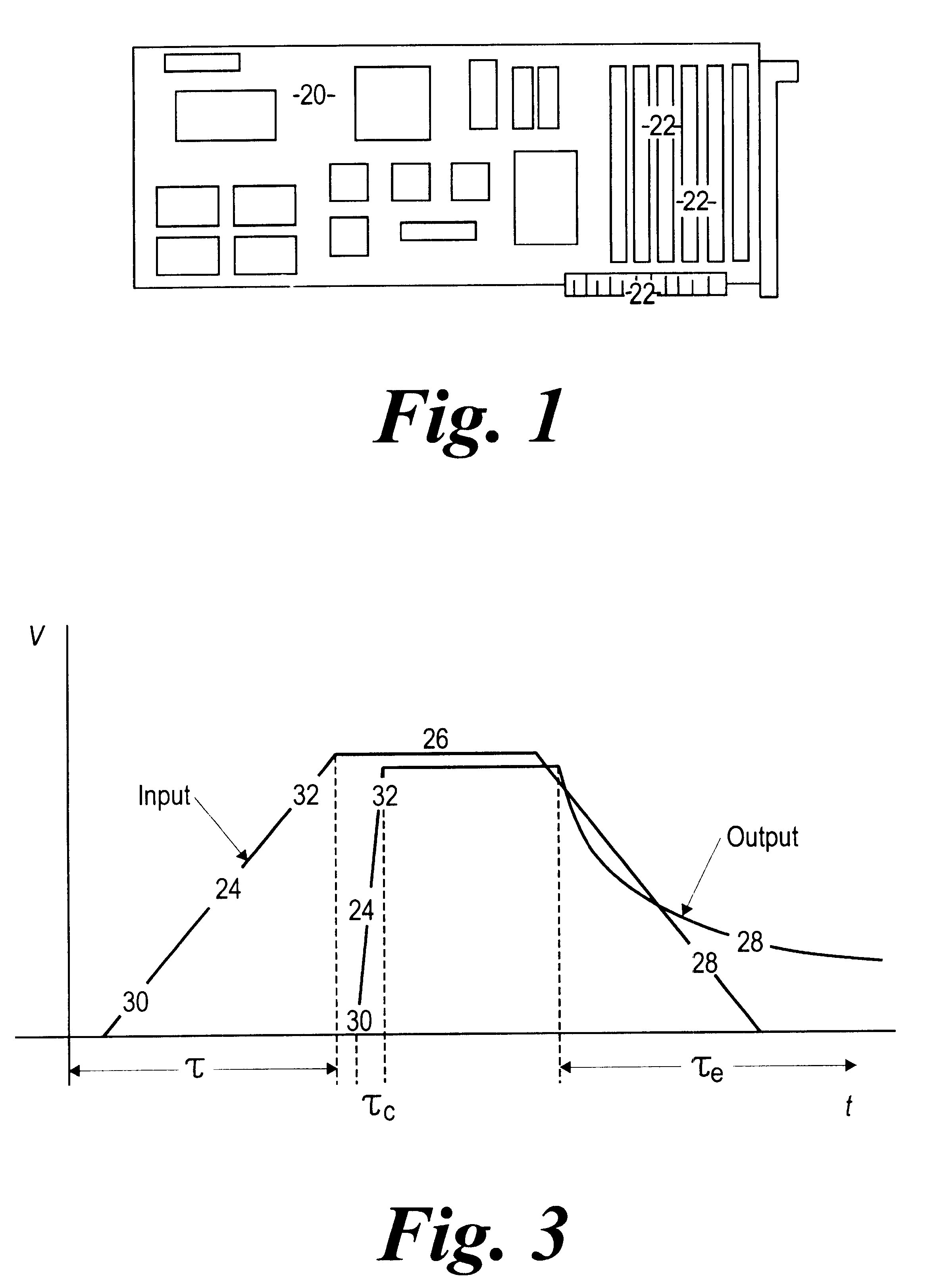
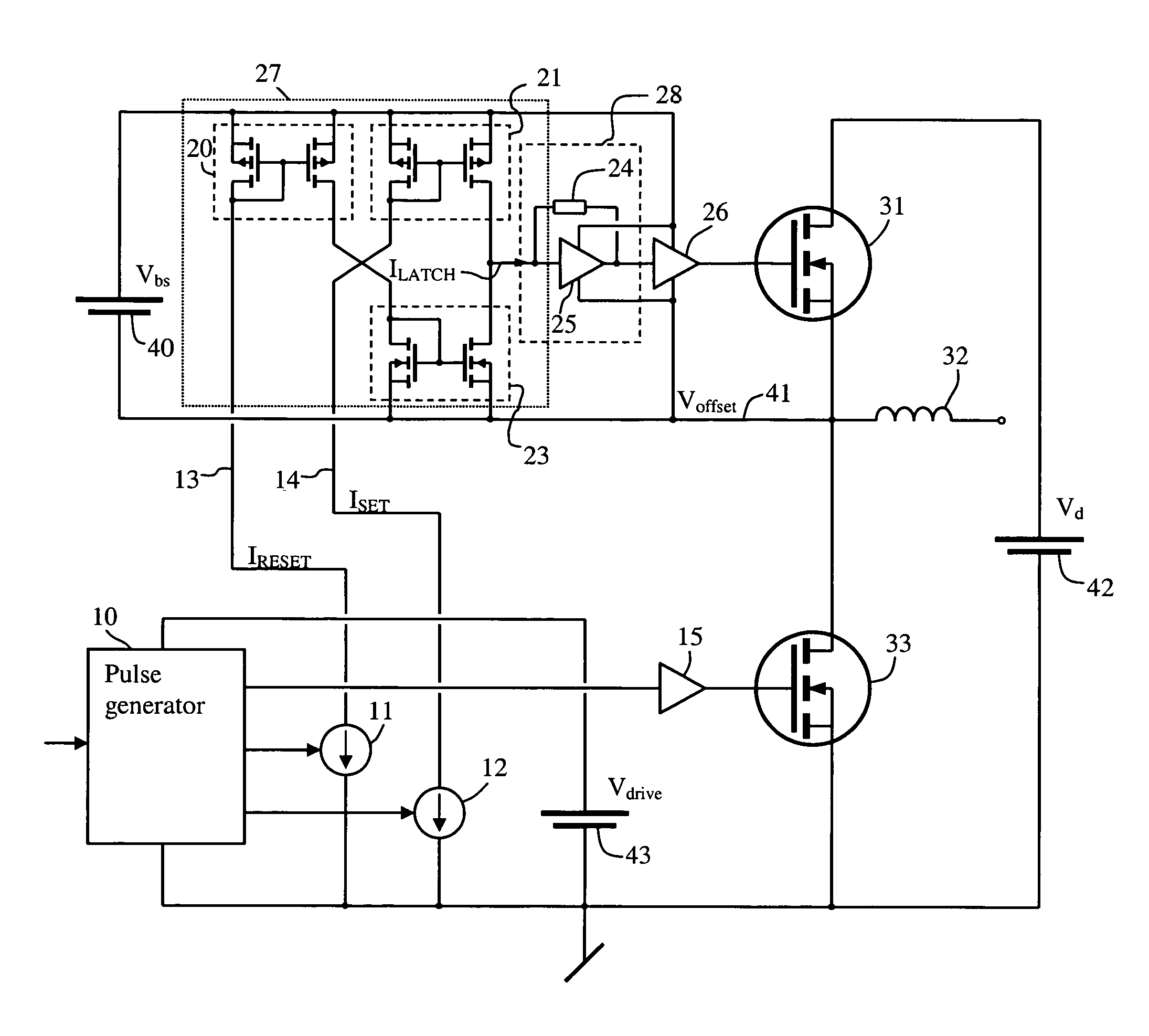
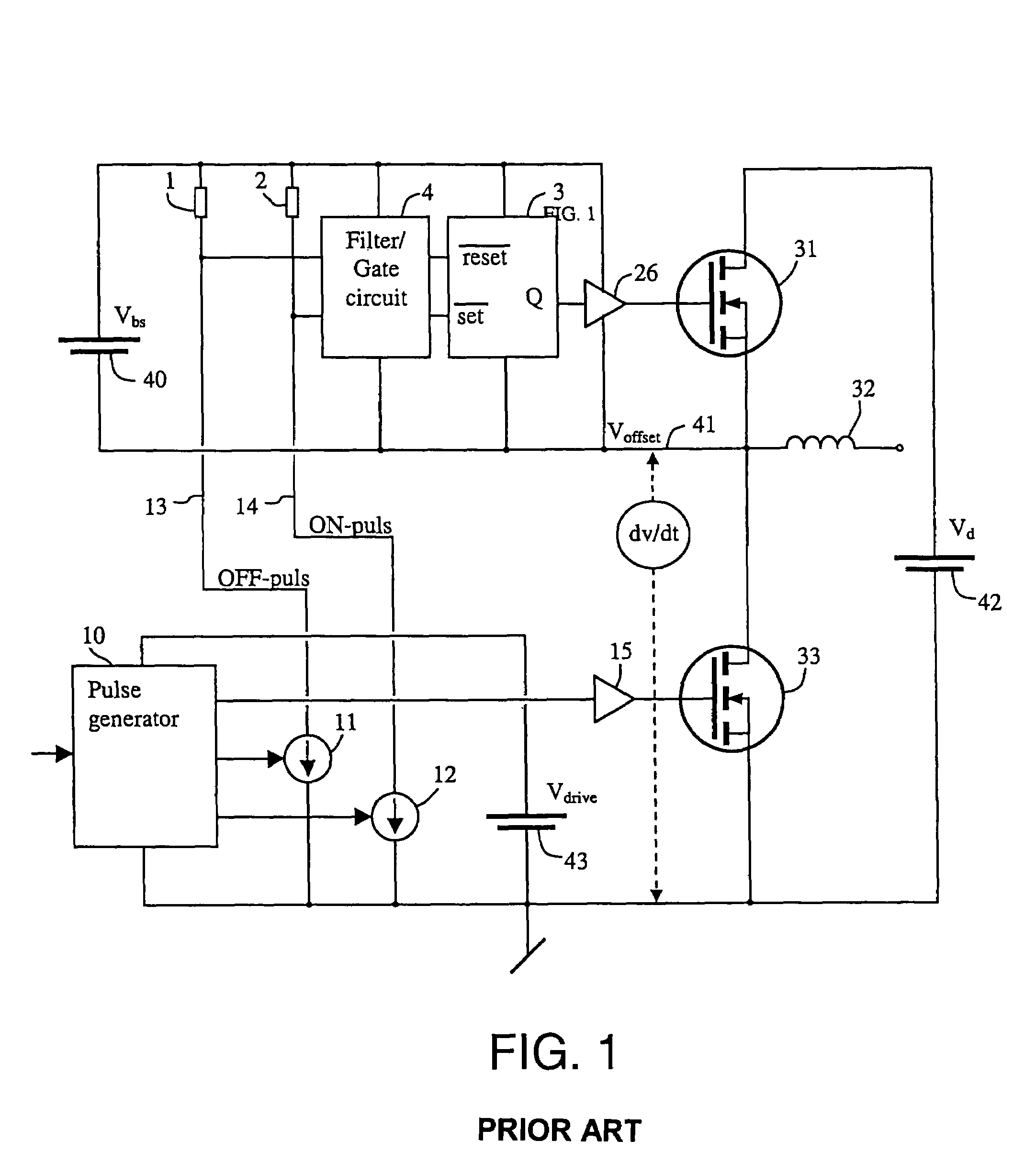
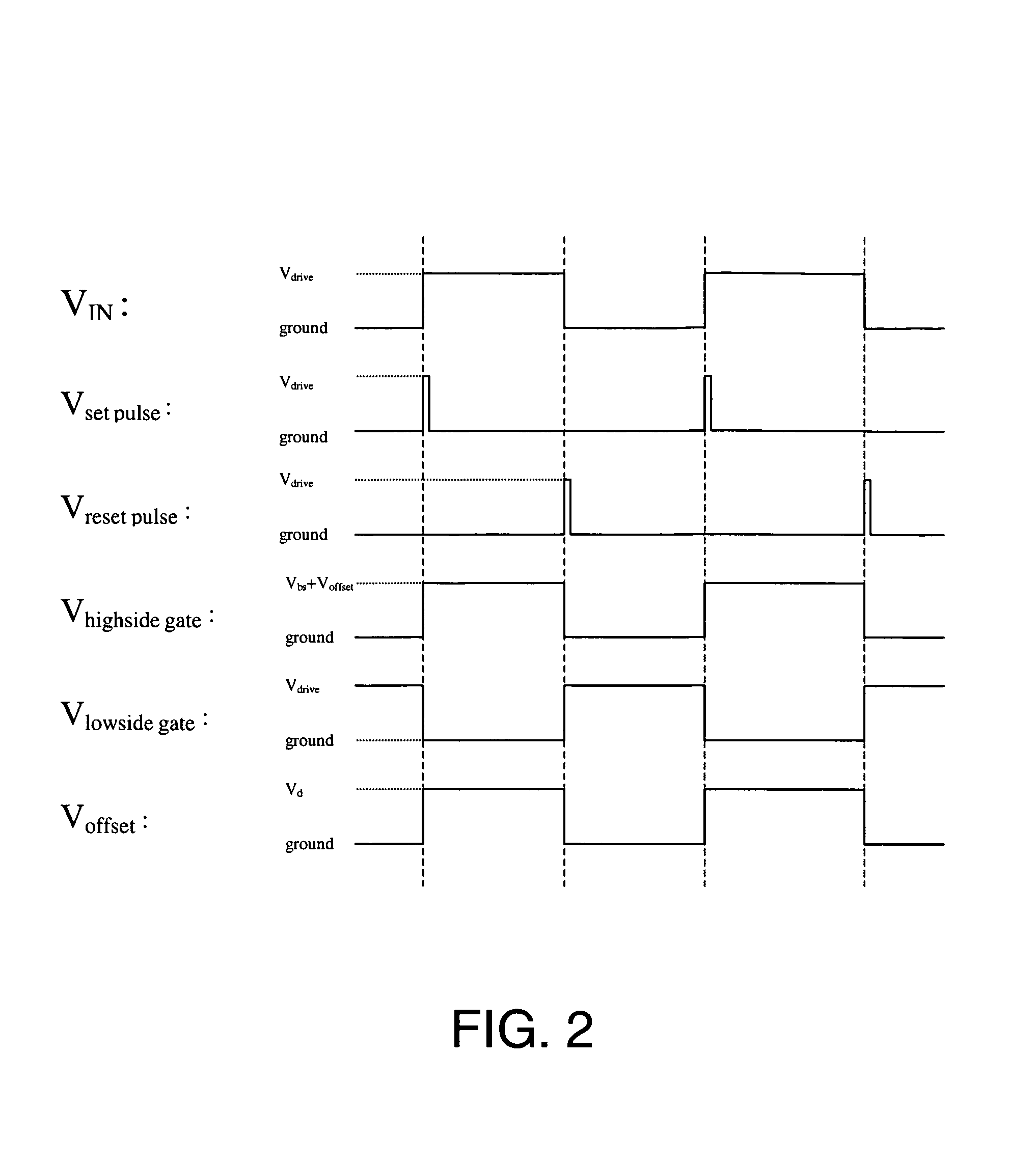
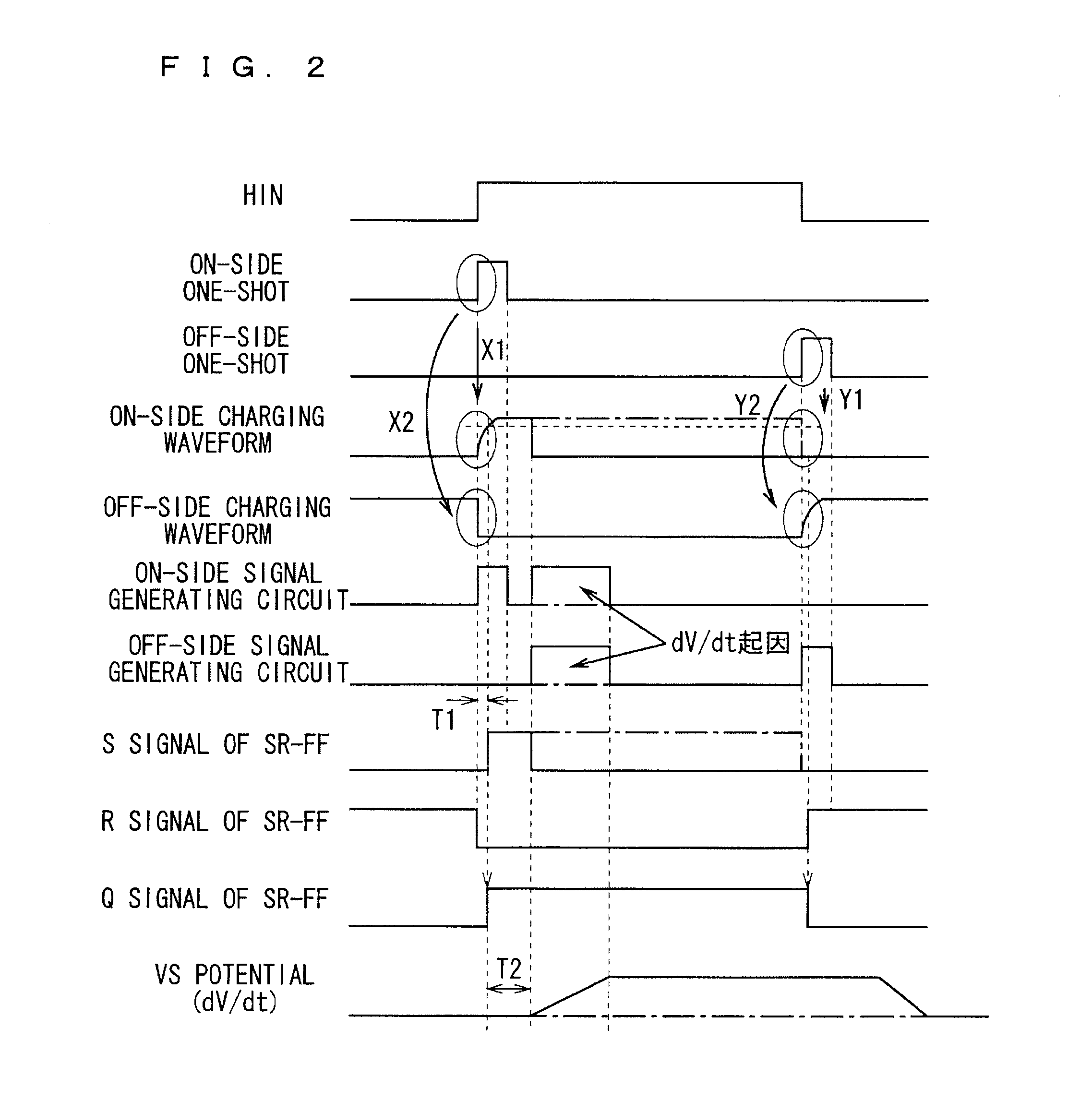
A semiconductor circuit of the present invention comprises a capacitor for charging ON driven electric charges in response to an ON driving signal, a capacitor for charging OFF driven electric charges in response to an OFF driving signal, a signal generating circuit for generating a first trigger signal in response to the ON driving signal, a signal generating circuit for generating a second trigger signal in response to the OFF driving signal, a discharging circuit for discharging the ON driven electric charges in response to the second trigger signal, and a discharging circuit for discharging the OFF driven electric charges in response to the first trigger signal. With this configuration, it is possible to provide a semiconductor circuit and a semiconductor device both of which have a general-purpose malfunction prevention function by which a malfunction due to dV / dt can be prevented without being affected by any external factor.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Dual-trigger low-energy flip-flop circuit
ActiveUS8487681B2Weaken energyGood signalLogic circuitsPulse generation by bulk negative resistance devicesEngineeringSwitching frequency
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a technique for technique for capturing and storing a level of an input signal using a dual-trigger low-energy flip-flop circuit that is fully-static and insensitive to fabrication process variations. The dual-trigger low-energy flip-flop circuit presents only three transistor gate loads to the clock signal and none of the internal nodes toggle when the input signal remains constant. One of the clock signals may be a low-frequency “keeper clock” that toggles less frequently than the other two clock signal that is input to two transistor gates. The output signal Q is set or reset at the rising clock edge using separate trigger sub-circuits. Either the set or reset may be armed while the clock signal is low, and the set or reset is triggered at the rising edge of the clock.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Random Delay Generation for Thin-Film Transistor Based Circuits
InactiveUS20100295661A1Low costReadily apparentSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesEngineeringRandom delay
Circuits and circuit elements configured to generate a random delay, a monostable oscillator, circuits configured to broadcasting repetitive messages wireless systems, and methods for forming such circuits, devices, and systems are disclosed. The present invention advantageously provides relatively low cost delay generating circuitry based on TFT technology in wireless electronics applications, particularly in RFID applications. Such novel, technically simplified, low cost TFT-based delay generating circuitry enables novel wireless circuits, devices and systems, and methods for producing such circuits, devices and systems.
Owner:ENSURGE MICROPOWER ASA
Semiconductor die package and method of producing the package
ActiveCN107785358AReduce package sizeShorten the lengthSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesRedistribution layerElectrical connection
A package including a first die embedded in a reconstructed wafer obtainable by the known FO-WLP or eWLB technologies is disclosed. In one aspect and in addition to the first die, a Through SubstrateVia insert is embedded in the wafer, the TSV insert being a separate element, possibly a silicon die with metal filled vias interconnecting contacts on the front and back sides of the insert. A seconddie is mounted on the back side of the substrate, with contacts on the second die in electrical connection with the TSV insert's contacts on the back side of the substrate. On the front side of the substrate, a lateral connecting device is mounted which interconnects the TSV insert's contacts on the front side of the substrate to contacts on the front side of the first die. The lateral connectingdevice and the TSV insert thereby effectively interconnect the contacts on the first and second dies. In another aspect, the lateral connecting device is mounted on a redistribution layer on the front side of the substrate, as it is known from FO-WLP technology.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
Low Power Direct Conversion Rf Transceiver Architecture and Asic and Systems Including Such
InactiveUS20080100393A1Enhanced feature setReduced Power RequirementsDc network circuit arrangementsPulse automatic controlPhase shiftedEngineering
A direct conversion RF transceiver (2) and ASIC having an on-chip voltage controlled oscillator operating frequency that is half of the transmitter (4) and / or receiver (6) operating frequency, the VCO (20) being comprised of a plurality of synchronized LC oscillators (92A-D) introducing precise phase shifts that eliminate frequency ambiguity. The transceiver incorporates several low power circuits, including on-chip a power converter switchably coupling a capacitor (42) to a power supply (45) and to an electrical load (40), multiple switchable low dropout regulators (60A, B) each coupled to alternate power supplies (62,64) and having electrical components (67A, B) for setting the bandwidth of the respective low dropout regulator. The transceiver also includes a FSK digital modulator utilizing a circuit-implemented polynomial piecewise approximation (71) of a raised cosine signal.
Owner:CUSTOM ONE DESIGN
Oscillator
InactiveUS20120081187A1Reduce phase noiseReduce waveform distortionApparatus using electrochemical resonatorsOscillations generatorsQuartz crystal resonatorCapacitance
An oscillator outputs a sine wave with high purity capable of reducing phase noise. In a Colpitts oscillator circuit using a transistor as an amplifying part, a quartz-crystal resonator for waveform shaping is provided outside or inside an oscillation loop. A quartz-crystal resonator for oscillation and the quartz-crystal resonator for waveform shaping are formed, with an electrode pair and an electrode pair being provided on a common quartz-crystal piece. A separation distance between the electrode of the quartz-crystal resonator and the electrode of the quartz-crystal resonator is set large so that they are not elastically coupled, or even when they are elastically coupled, their coupling degree is weak, and an inductor causing parallel resonance with a parallel capacitance of the quartz-crystal resonator is provided.
Owner:NIHON DEMPA KOGYO CO LTD
Runtime compensated oscillator
Owner:INFINEON TECH AUSTRIA AG
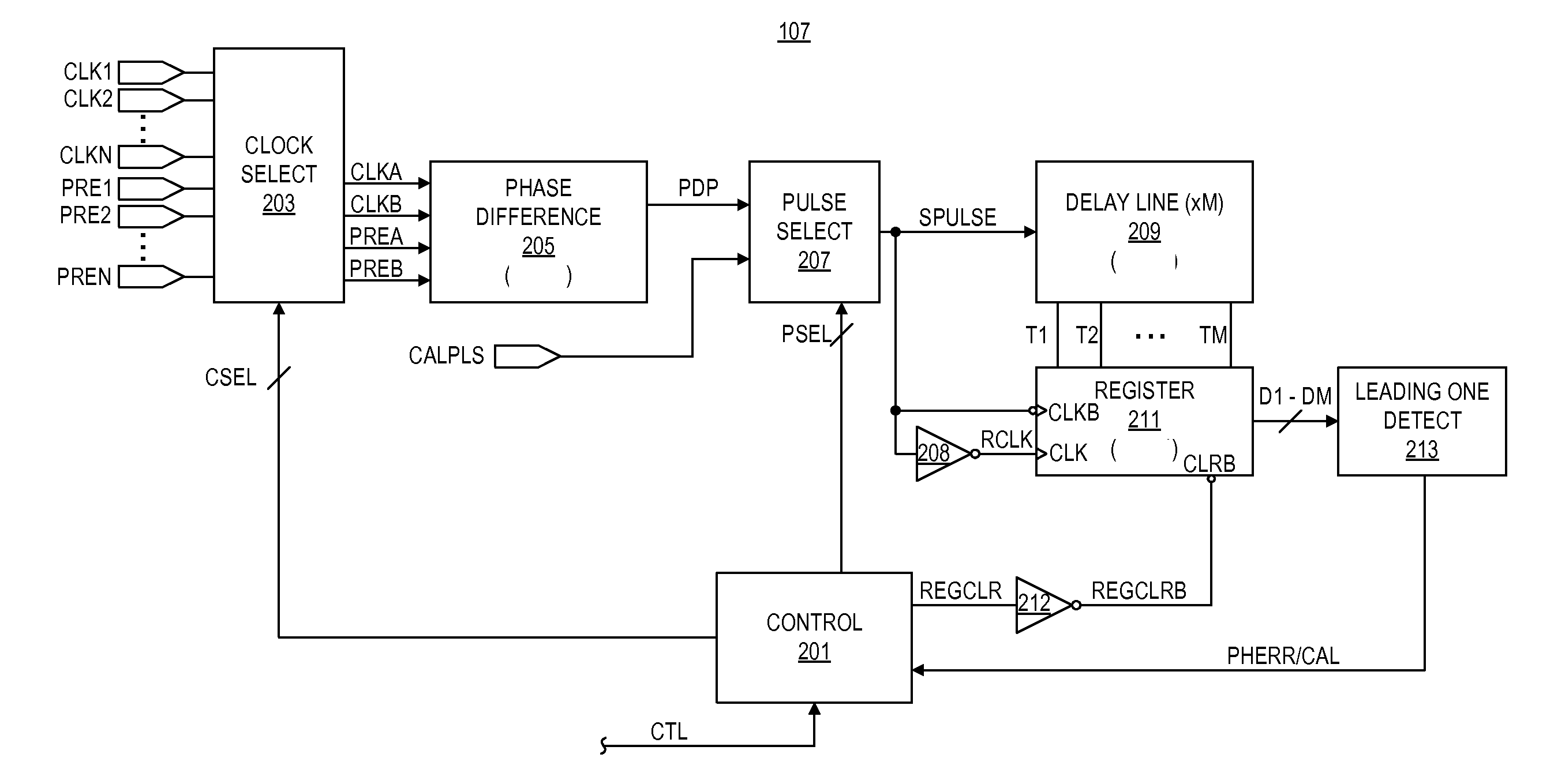
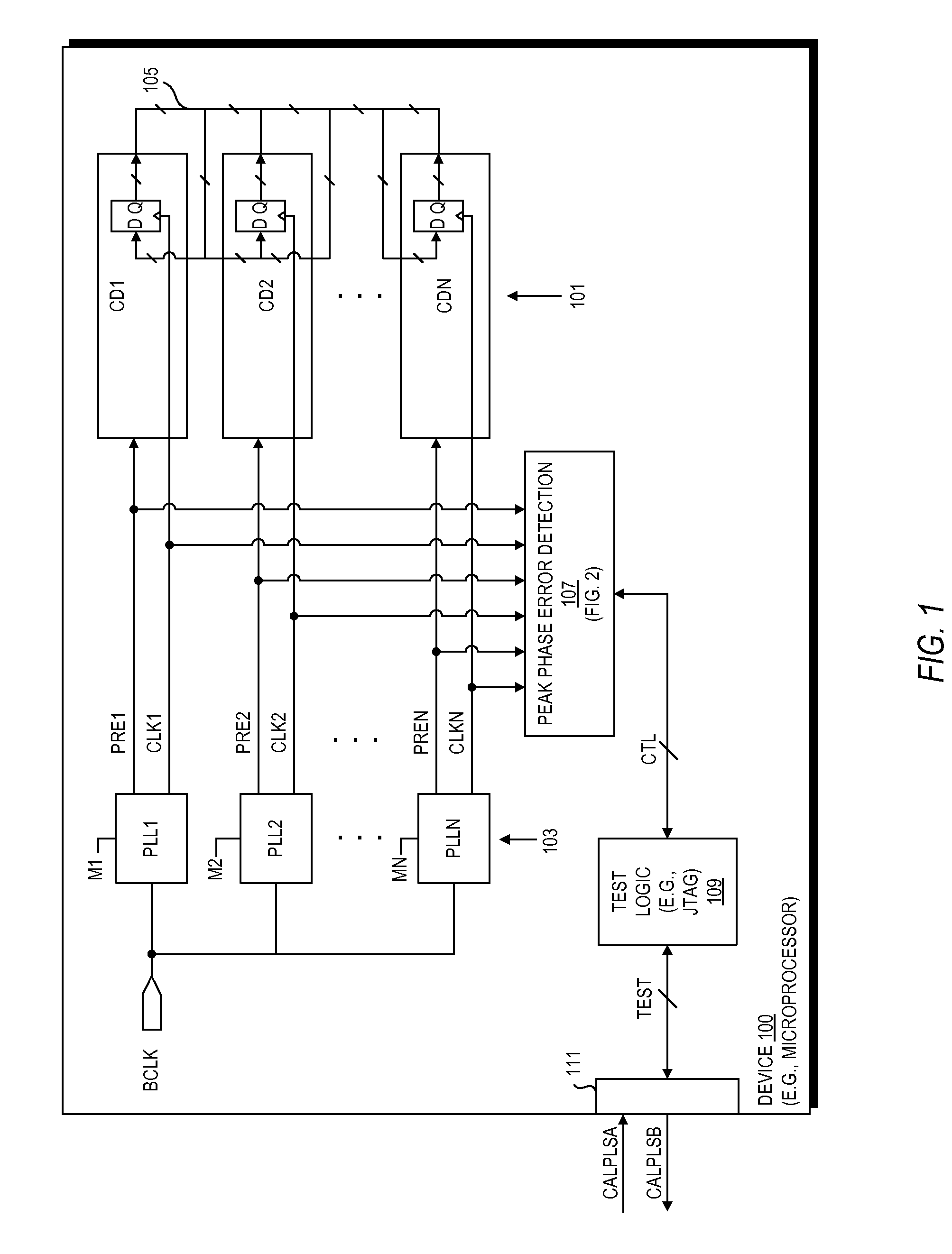
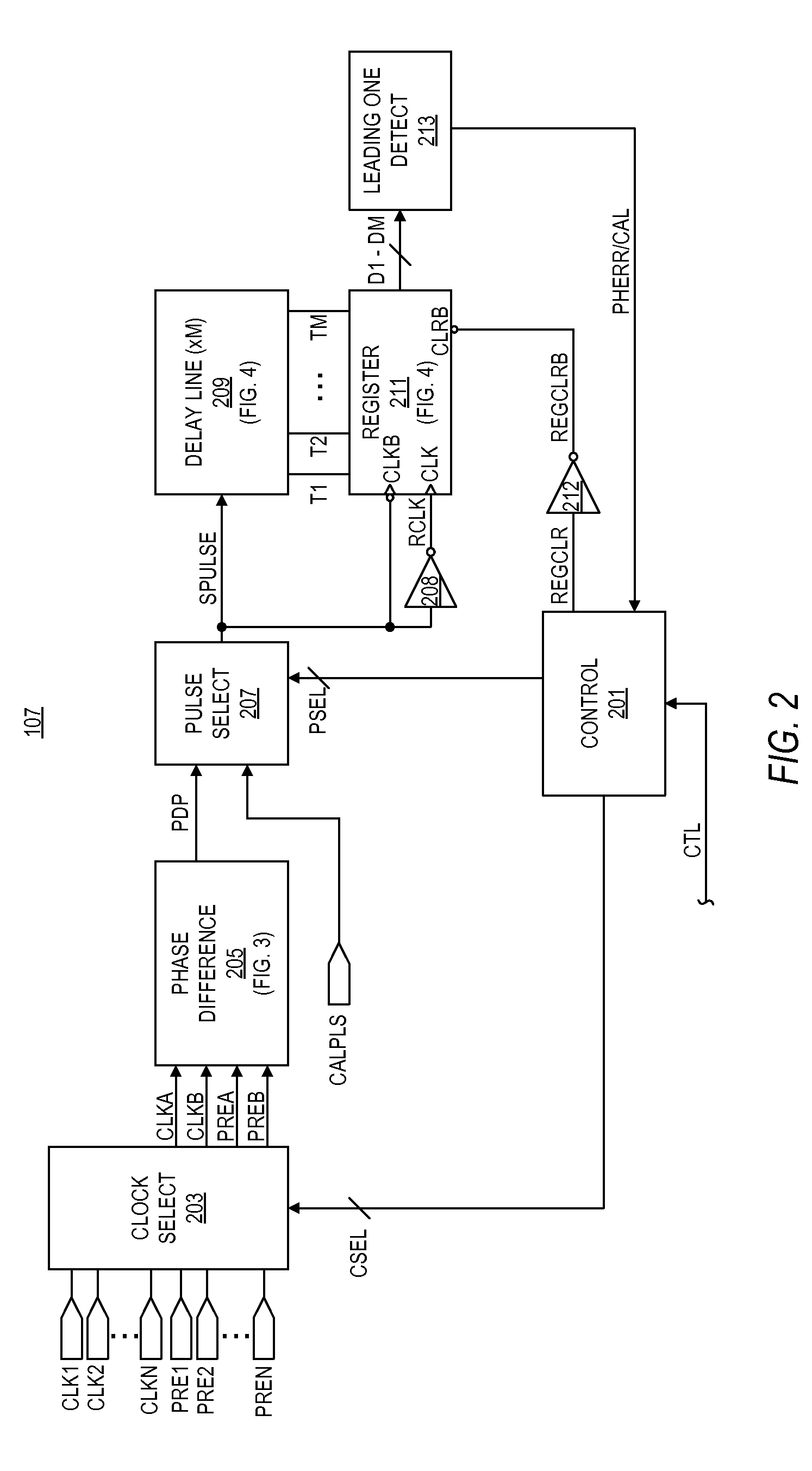
Method and apparatus for determining peak phase error between clock signals
ActiveUS20100264903A1Pulse automatic controlPulse train pattern monitoringProcessor registerPhase difference
A peak phase error circuit including phase difference logic and delay and register logic. The phase difference logic provides a pulse difference signal including at least one difference pulse indicative of a timing difference between selected edges of a pair of clock signals. The delay and register logic receives the pulse difference signal and provides a peak phase error value representing peak phase error between the clock signals. The delay and register logic may include a delay line with multiple delay cells and taps coupled in series in which each tap provides an output state of a delay cell. The register logic registers a state of each tap to provide delay bits in response to each trailing edge of the difference pulses. Each delay bit remains set until reset so that the longest pulse difference signal is registered to provide the peak phase error.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
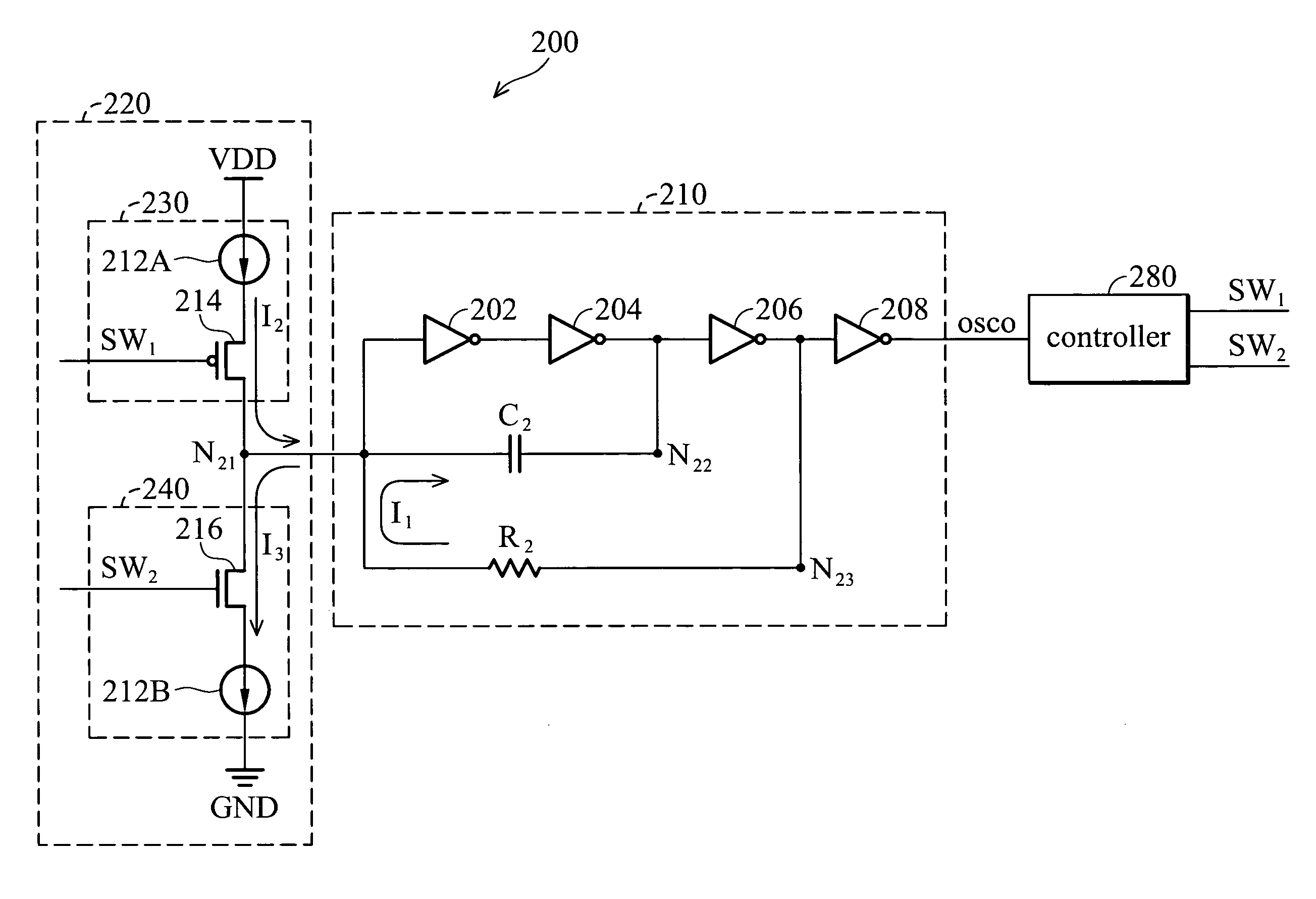
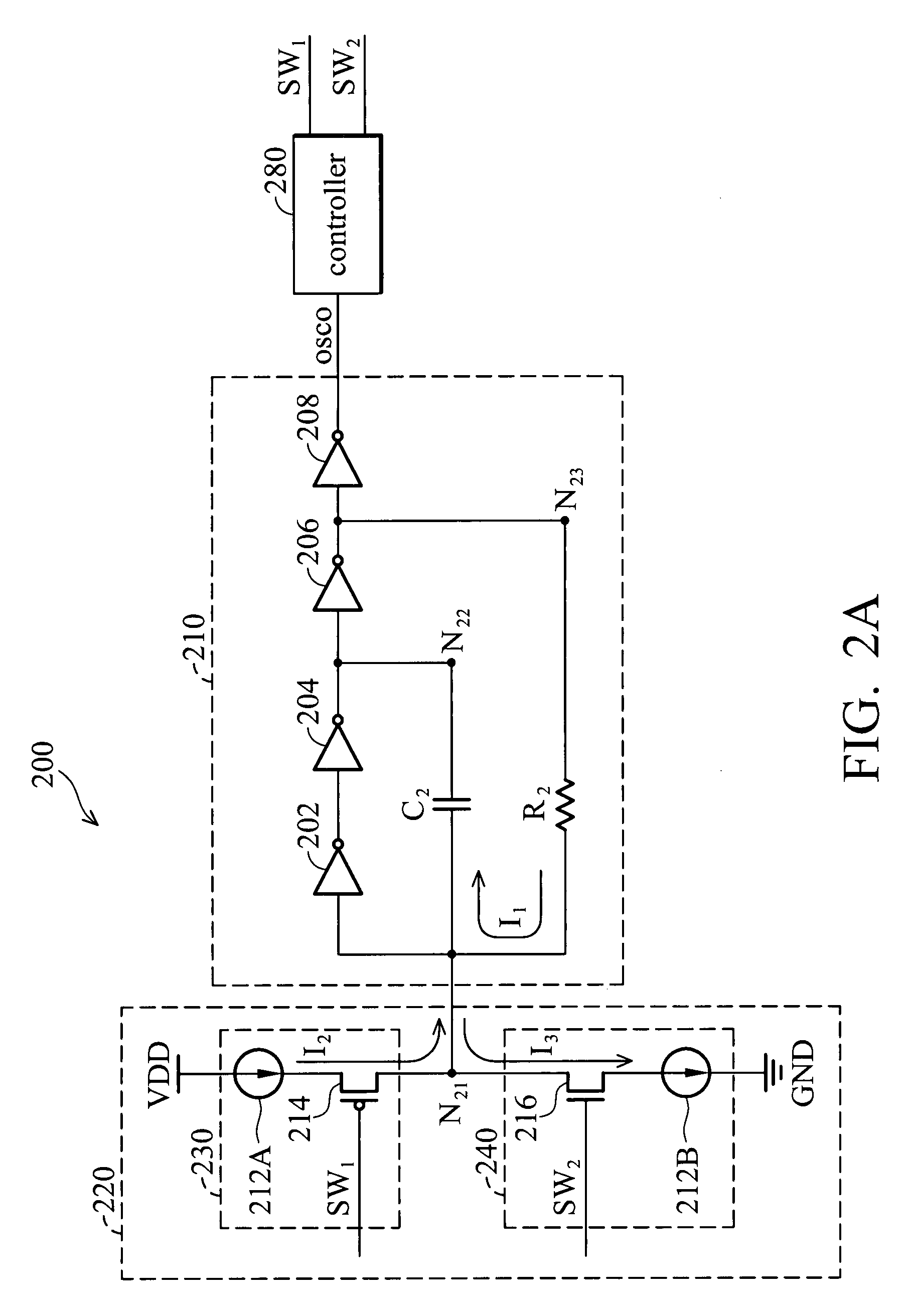
Oscillator
InactiveUS20080024237A1Pulse generation by bipolar transistorsPulse generation by logic circuitsSwitching signalEngineering
An oscillator comprising a compensation circuit, an oscillating module and a controller are disclosed. The compensation circuit comprises a charging circuit and a discharging circuit. The charging circuit comprises a first current source coupled between a voltage source and a second transistor, and the second transistor having a second first terminal coupled to a first current source, a second second terminal coupled to a first node, and a second gate for receiving a first switching signal. The discharging circuit comprises a third transistor having a third first terminal coupled to the first node and a third gate for receiving a second switching signal, and a second current source coupled between the third transistor and ground. The oscillating module couples between the compensation circuit and the controller and generates an output signal. The controller generates the first switching signal and the second switching signal according to the output signal.
Owner:PRINCETON TECHNOLOGY
Oscillation circuit and operating current control method thereof
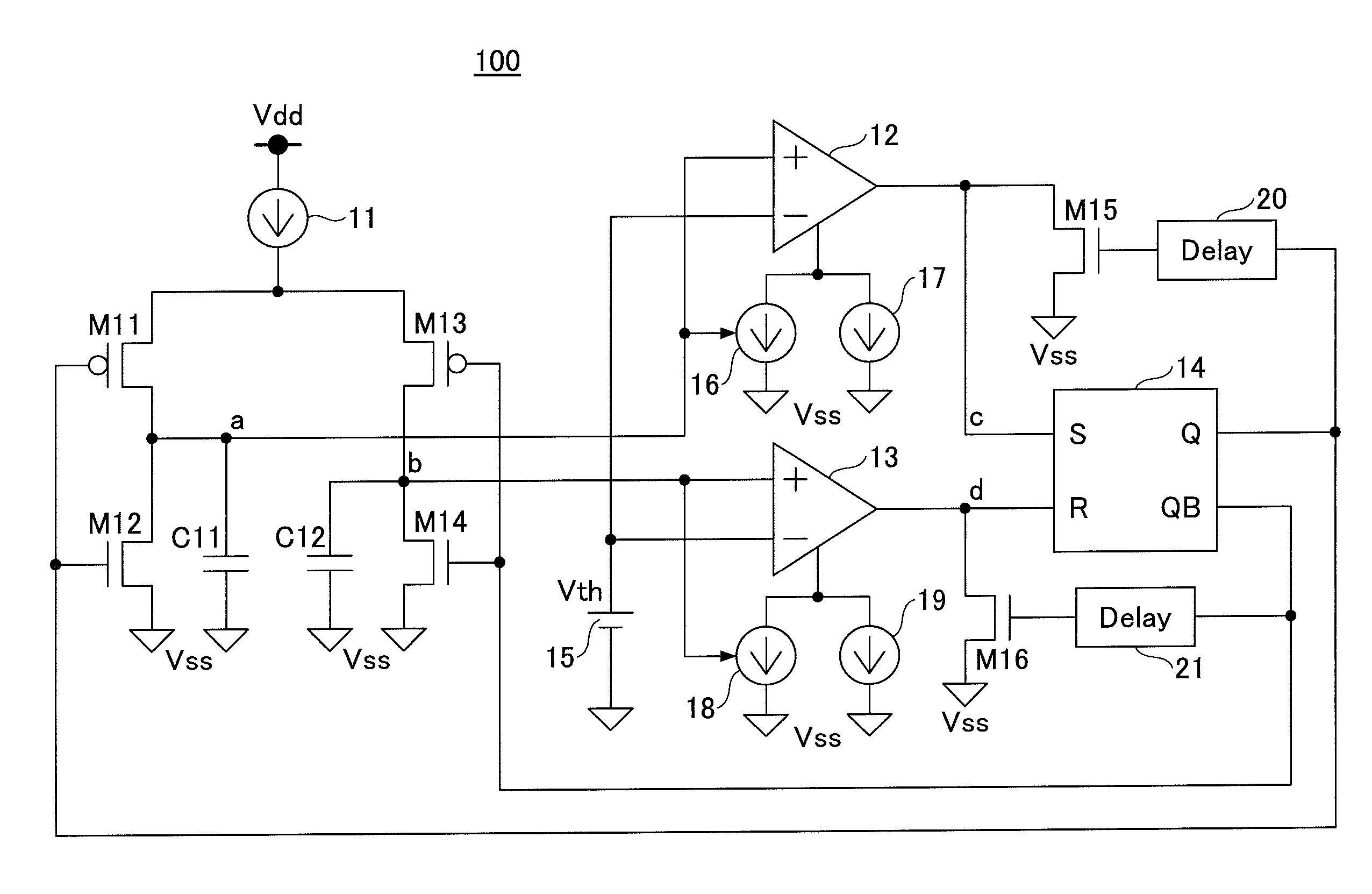
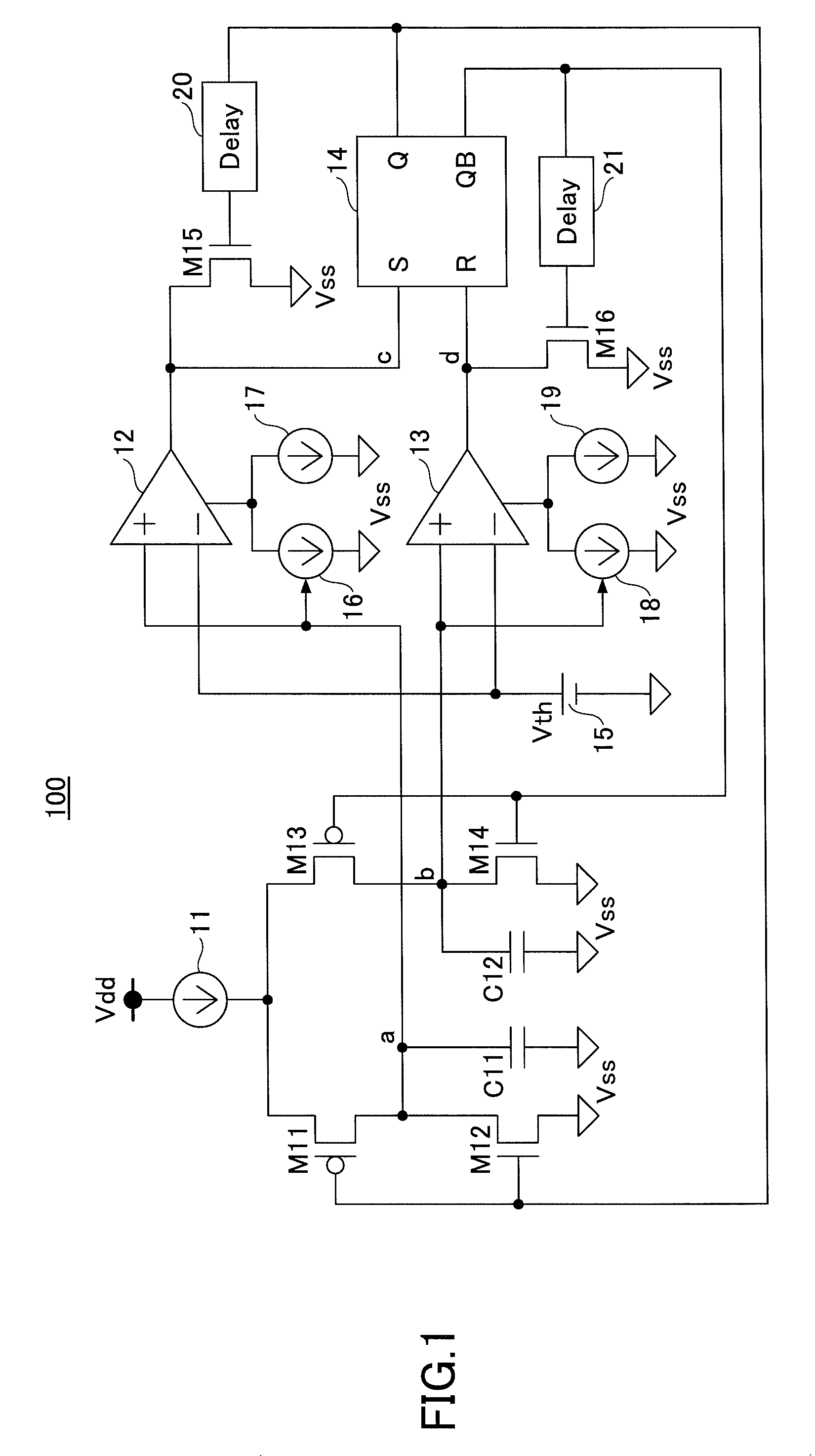
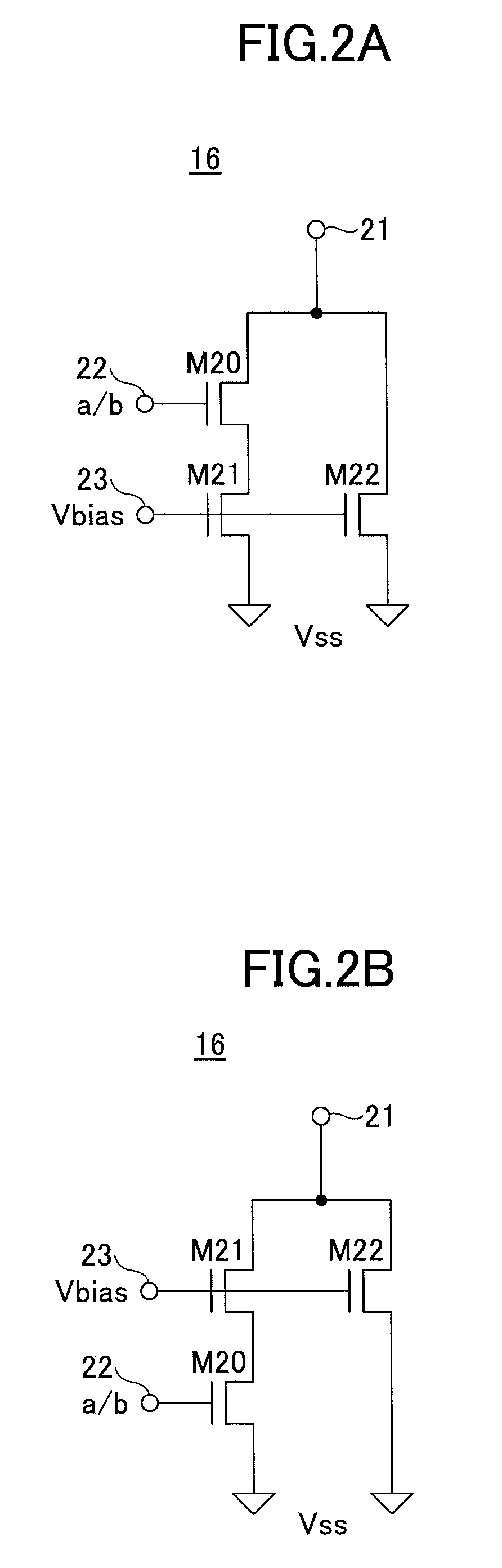
ActiveUS9007137B2Reduce power consumptionPulse generation by bipolar transistorsPulse generation by bulk negative resistance devicesControl signalOutput compare
An oscillation circuit includes a condenser, a charging / discharging part configured to switch between charging and discharging of the condenser according to a control signal, a comparator configured to compare a voltage of the condenser with a reference voltage and output a comparison result signal, a flip-flop configured to be set or reset according to the comparison result signal, supply an output signal as the control signal to the charging / discharging part, and output the output signal as an oscillation signal, and a current control part configured to control an operating current of the comparator in correspondence with the voltage of the condenser.
Owner:MITSUMI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Receiving circuit, LSI chip, and storage medium
InactiveUS20120105130A1Clear positioningReduce areaNear-field transmissionCurrent/voltage measurementCapacitorElectromagnetic induction
A receiving circuit with a simple circuit structure for performing wireless communication utilizing electromagnetic induction is provided. An LSI chip and a storage medium where wireless communication utilizing electromagnetic induction is performed and the circuit scale and circuit size can be reduced are provided. The following receiving circuit may be used: a parallel circuit where two diode elements whose directions are opposite are connected in parallel is used, one end of the parallel circuit is connected to the other end of a coil whose one end is connected to a ground potential line, and a capacitor is connected in series with the other end of the parallel circuit. A transistor whose leakage current is markedly reduced may be used as a diode in the receiving circuit. Such a receiving circuit may be used in an LSI chip or a storage medium.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
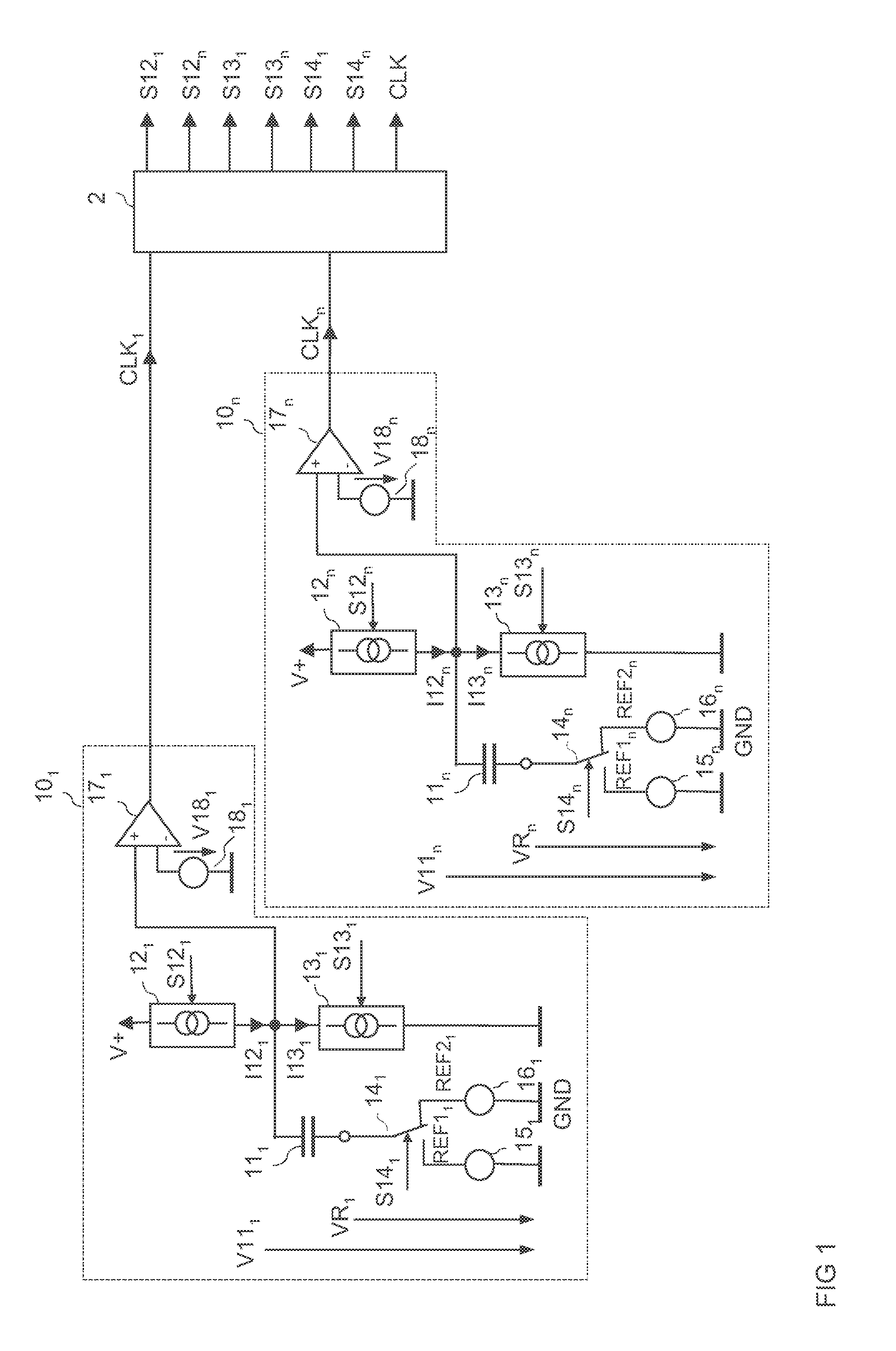
Pulse generating circuit and sampling circuit
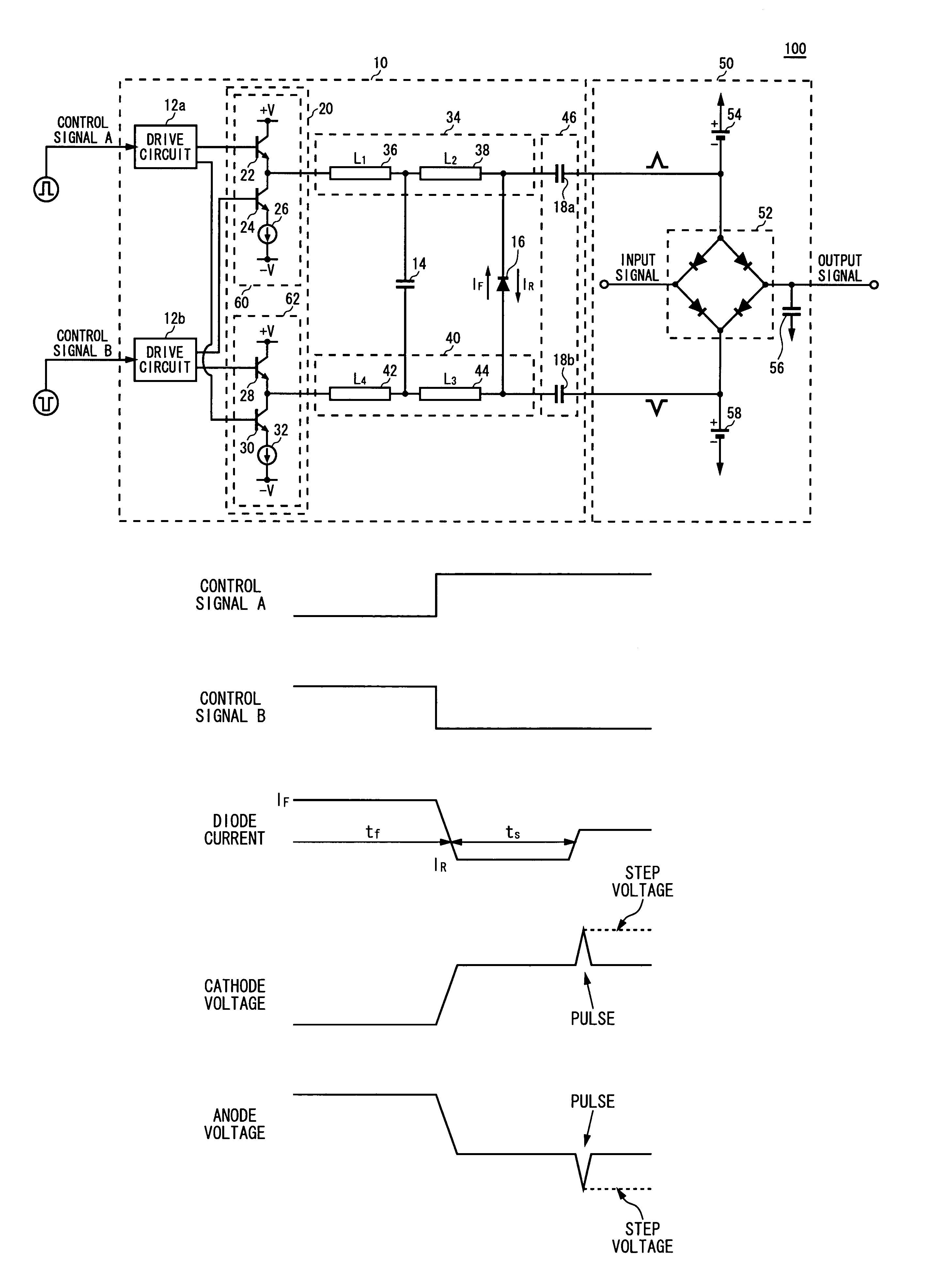
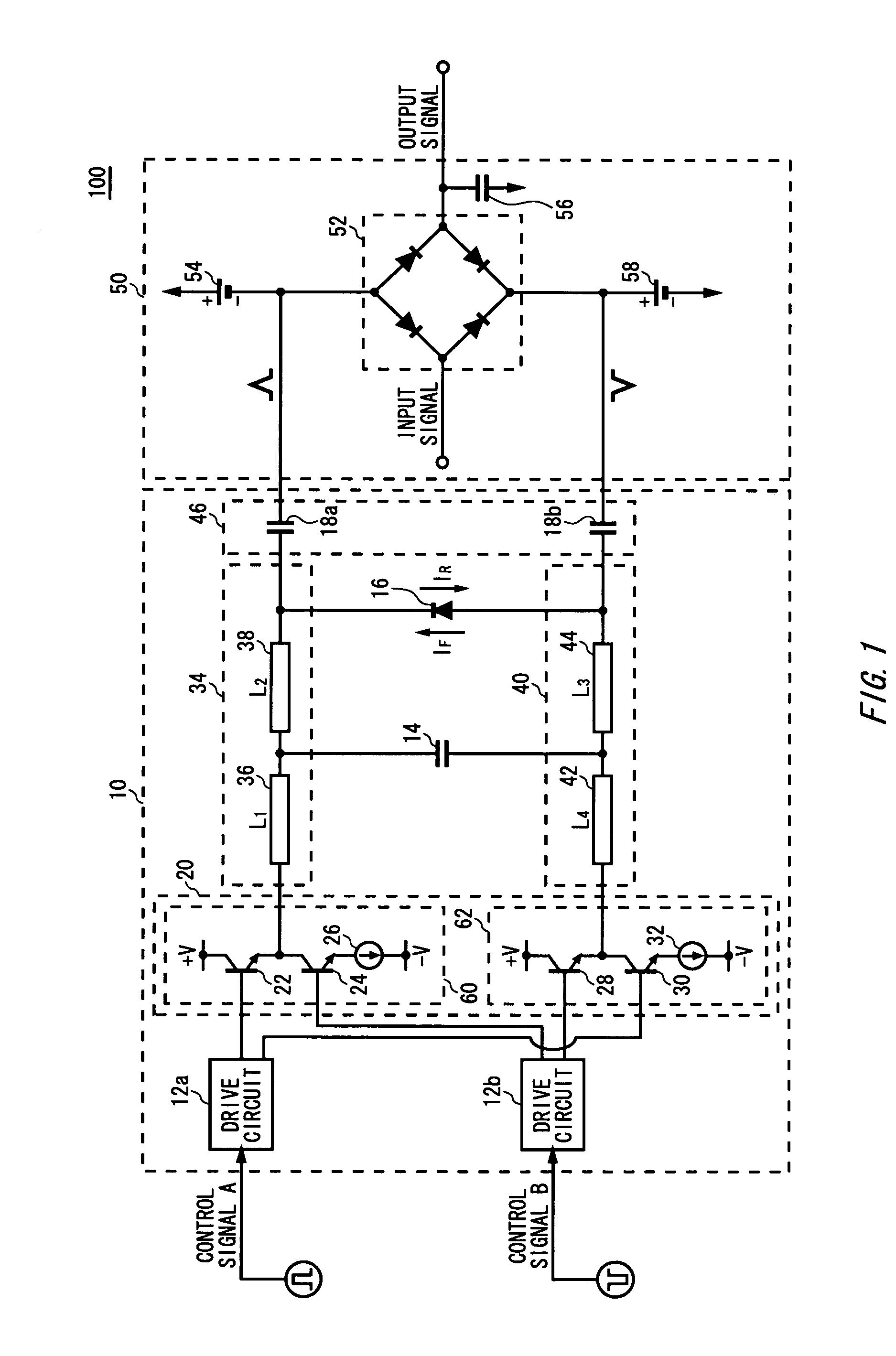
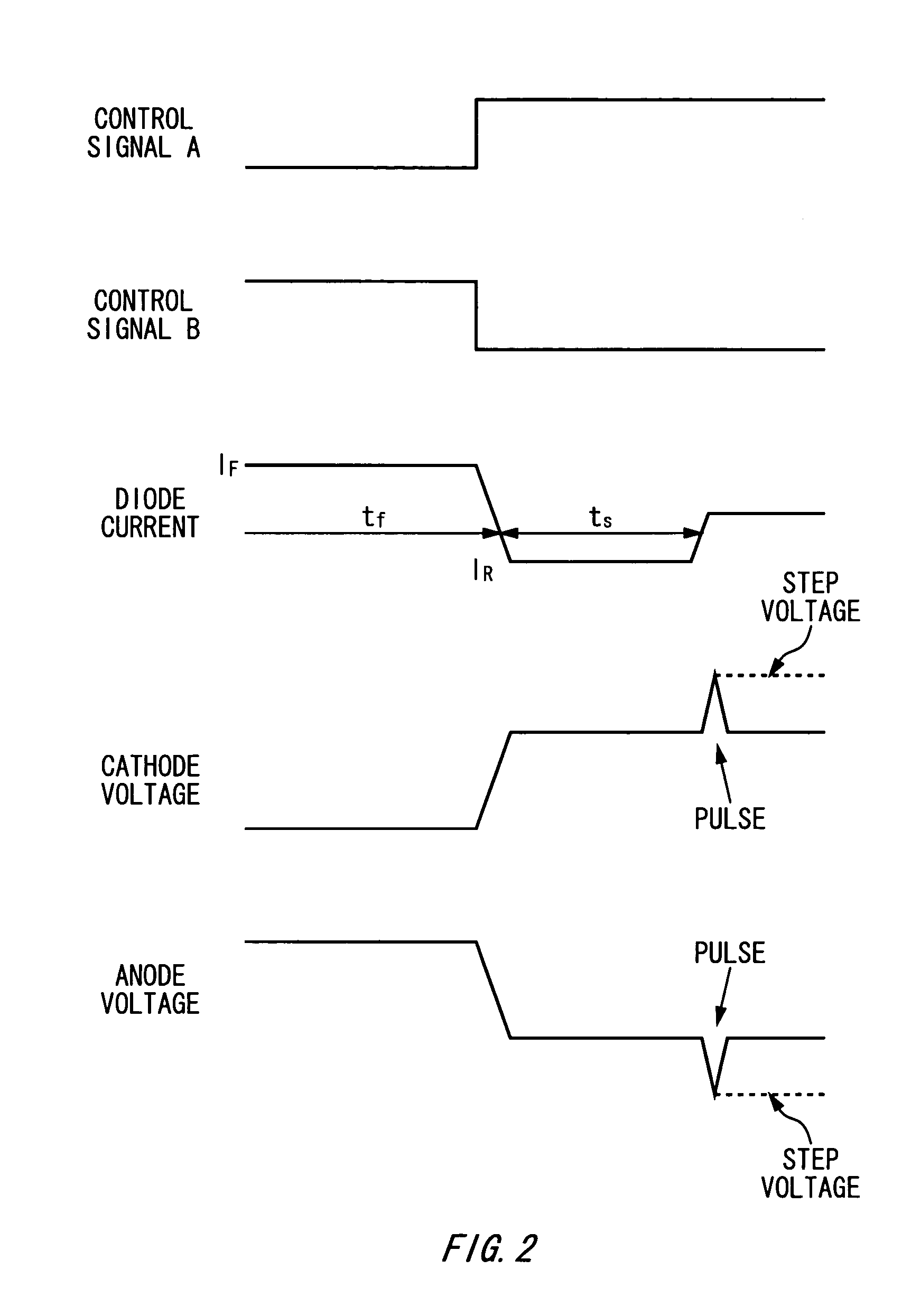
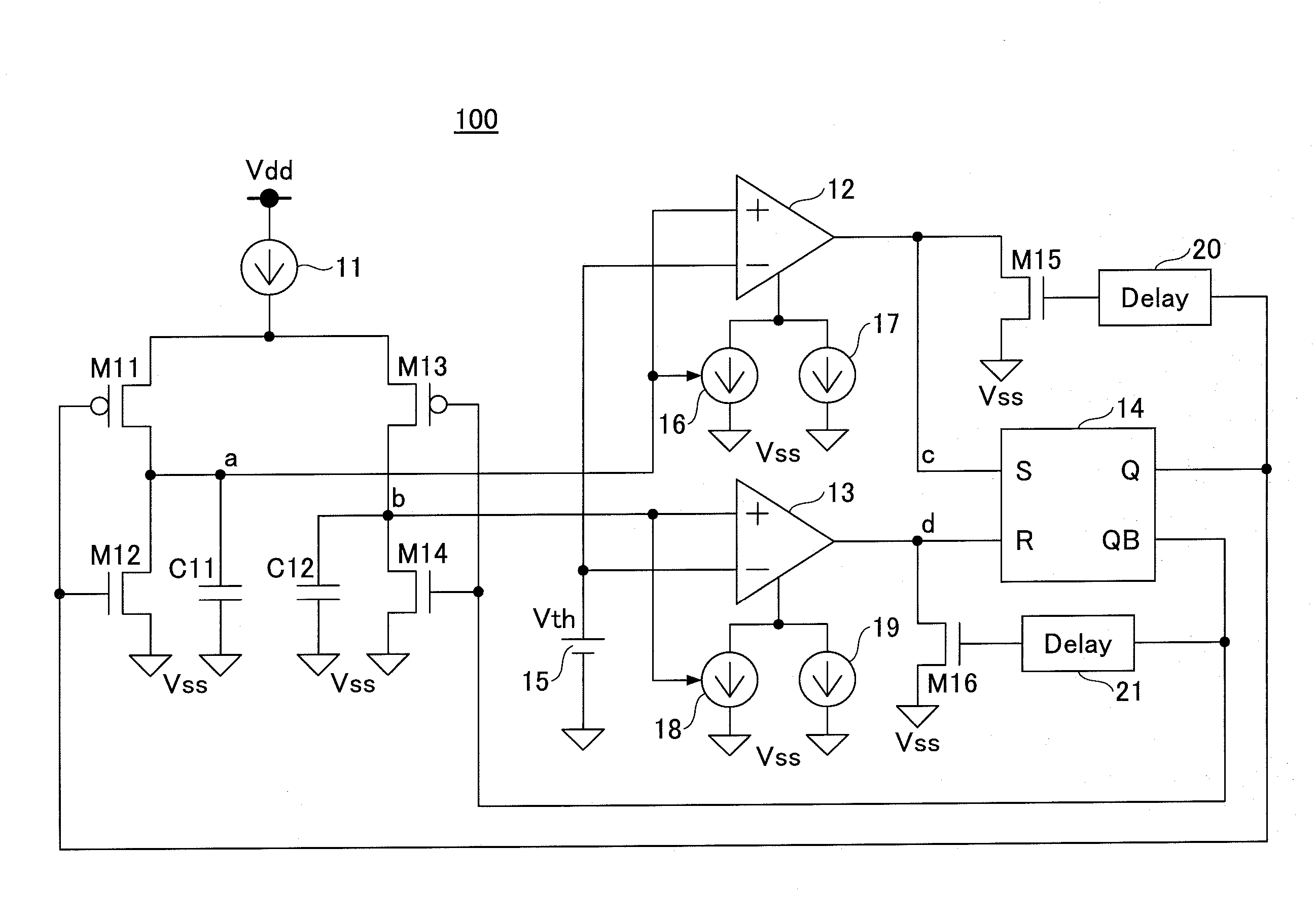
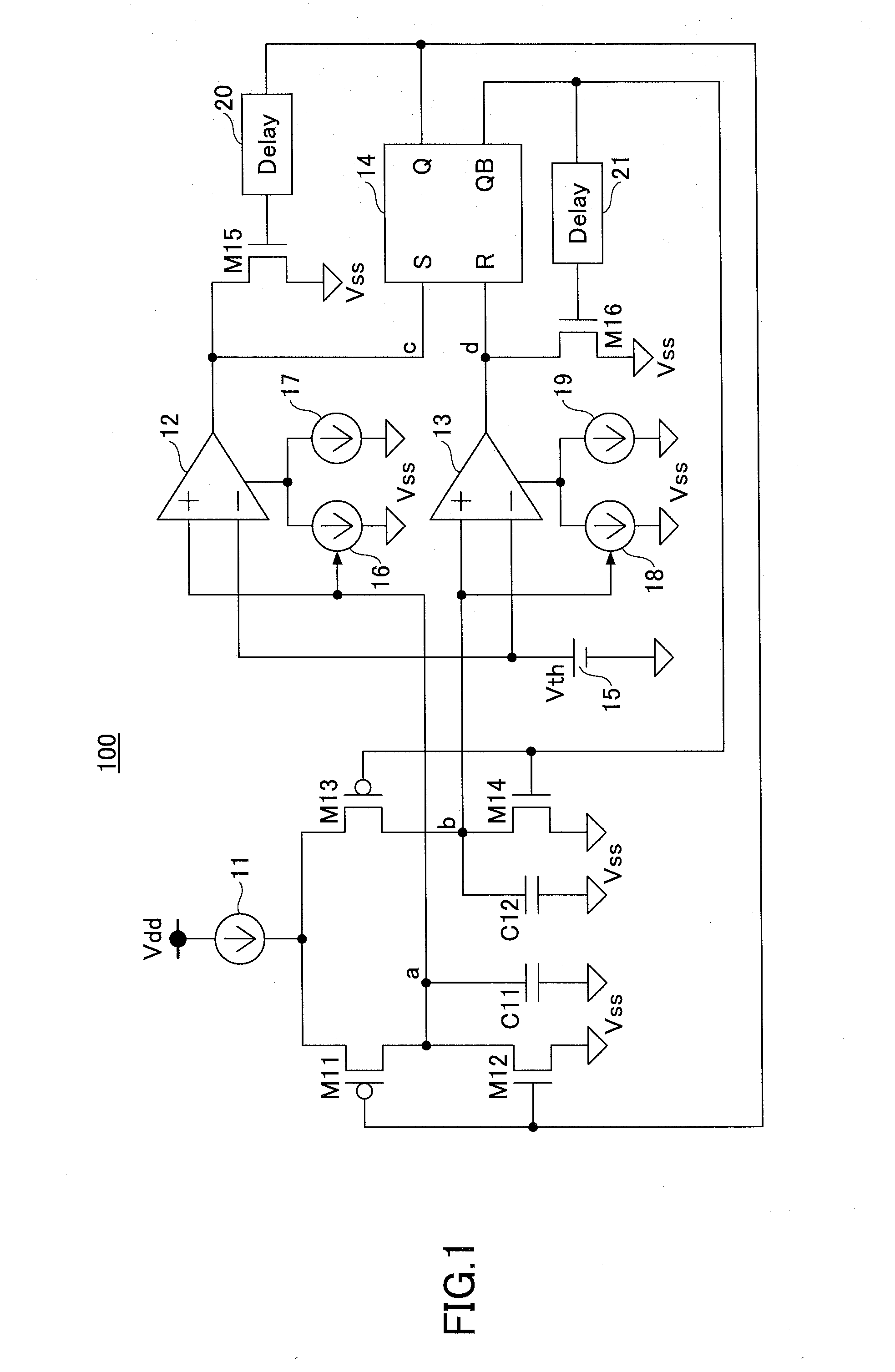
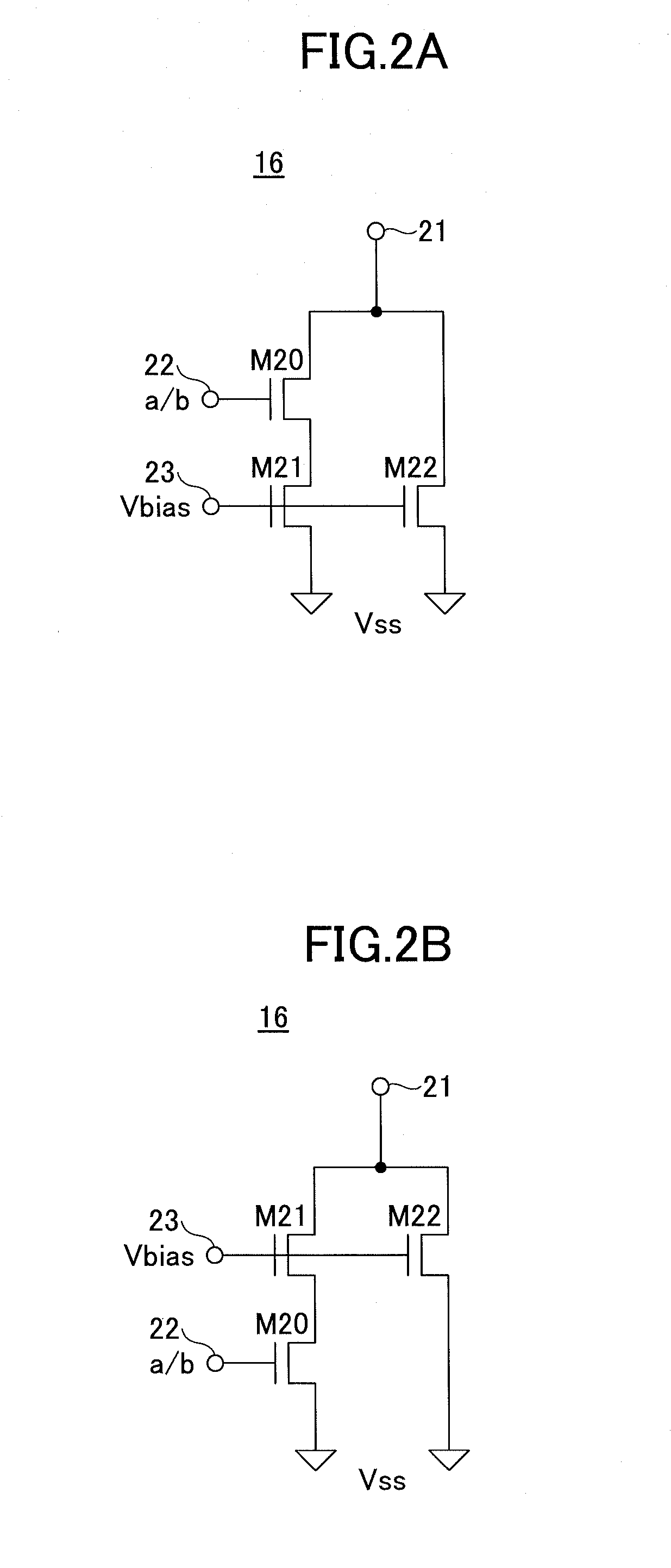
There is provided a pulse generating circuit, which generates two pulses having a sign of amplitude different from each other, including: a step recovery diode of which electric potential of an anode and a cathode is respectively output as the pulses; a bias unit operable to select either a forward bias or a backward bias according to a given control signal and apply the selected bias to the step recovery diode; a forward current source operable to prescribe a forward current to be supplied to the step recovery diode when the forward bias is applied to the step recovery diode; and a backward current source operable to prescribe a backward current to be supplied to the step recovery diode when the backward bias is applied to the step recovery diode.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
Oscillation circuit and operating current control method thereof
ActiveUS20130082789A1Reduce power consumptionPulse generation by bipolar transistorsPulse generation by bulk negative resistance devicesOutput compareControl signal
An oscillation circuit includes a condenser, a charging / discharging part configured to switch between charging and discharging of the condenser according to a control signal, a comparator configured to compare a voltage of the condenser with a reference voltage and output a comparison result signal, a flip-flop configured to be set or reset according to the comparison result signal, supply an output signal as the control signal to the charging / discharging part, and output the output signal as an oscillation signal, and a current control part configured to control an operating current of the comparator in correspondence with the voltage of the condenser.
Owner:MITSUMI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com