Patents
Literature
46results about How to "Satisfied with precision" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
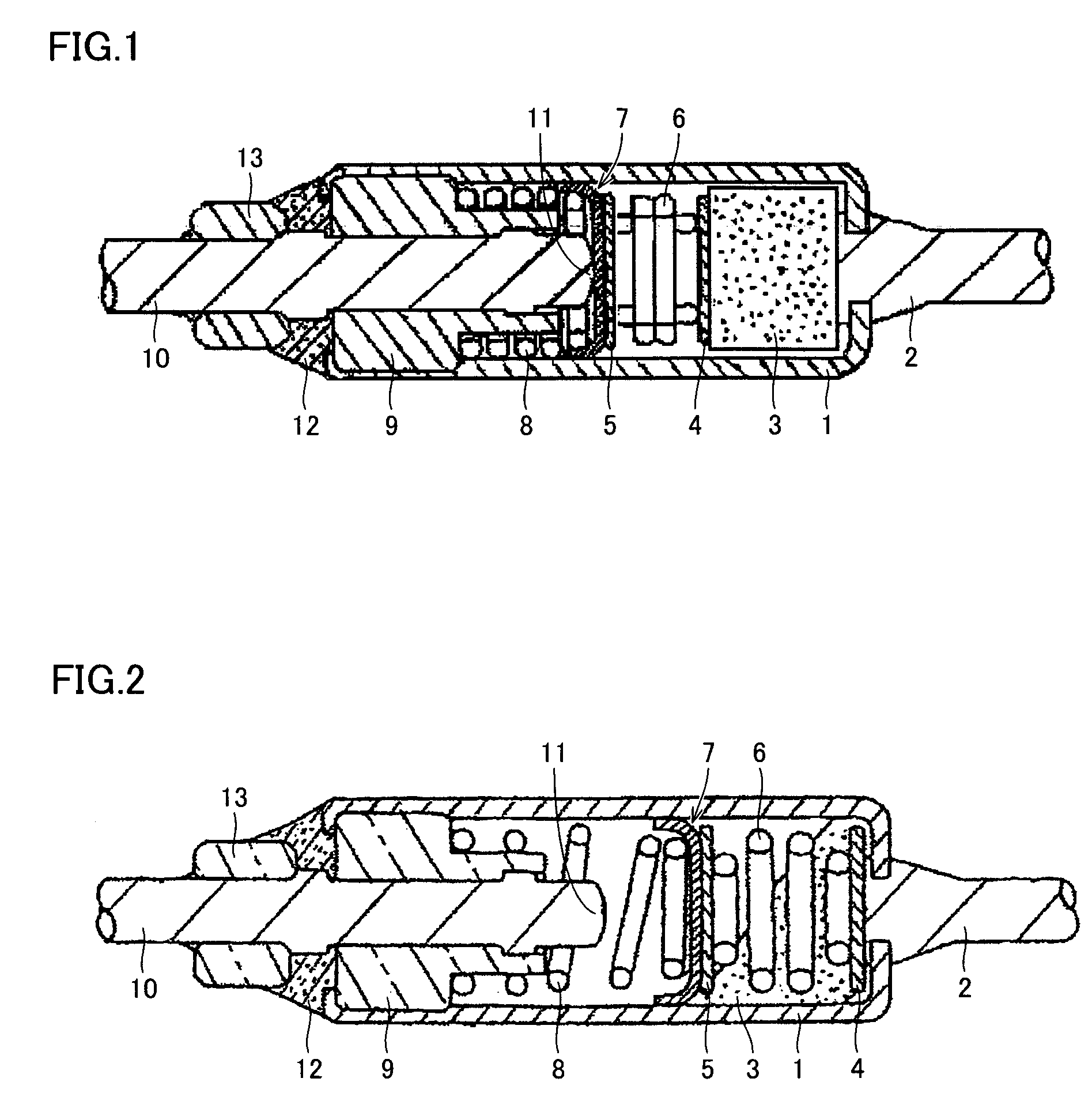
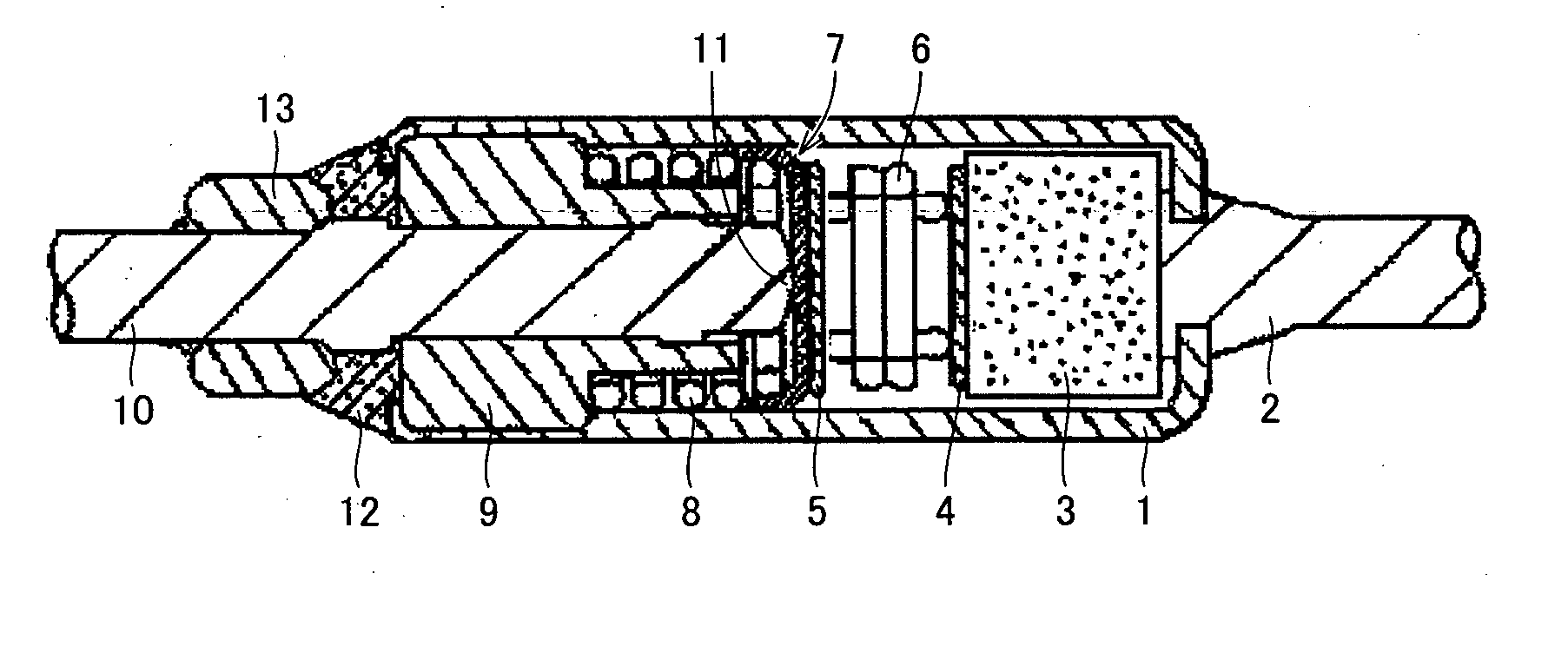
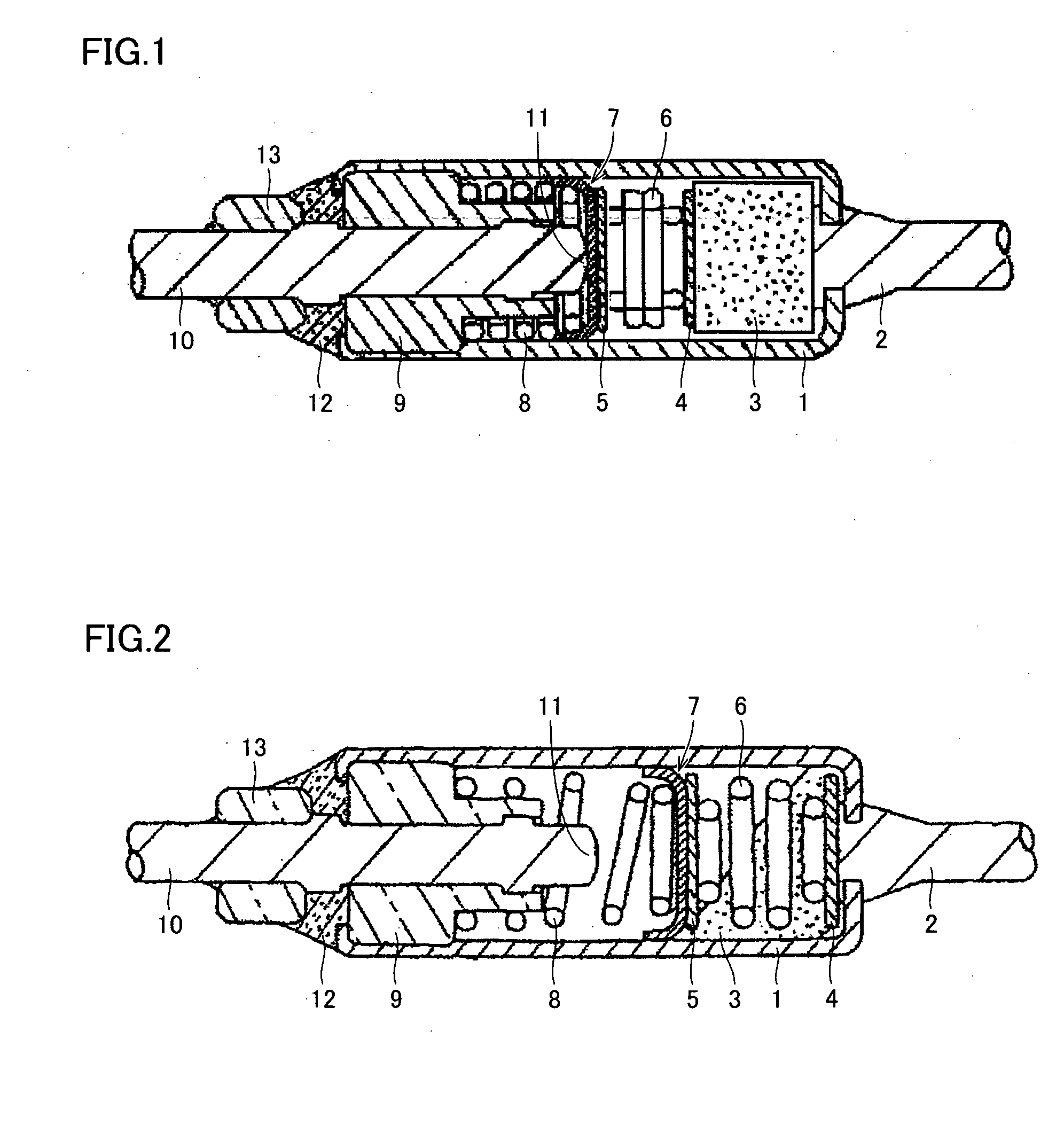
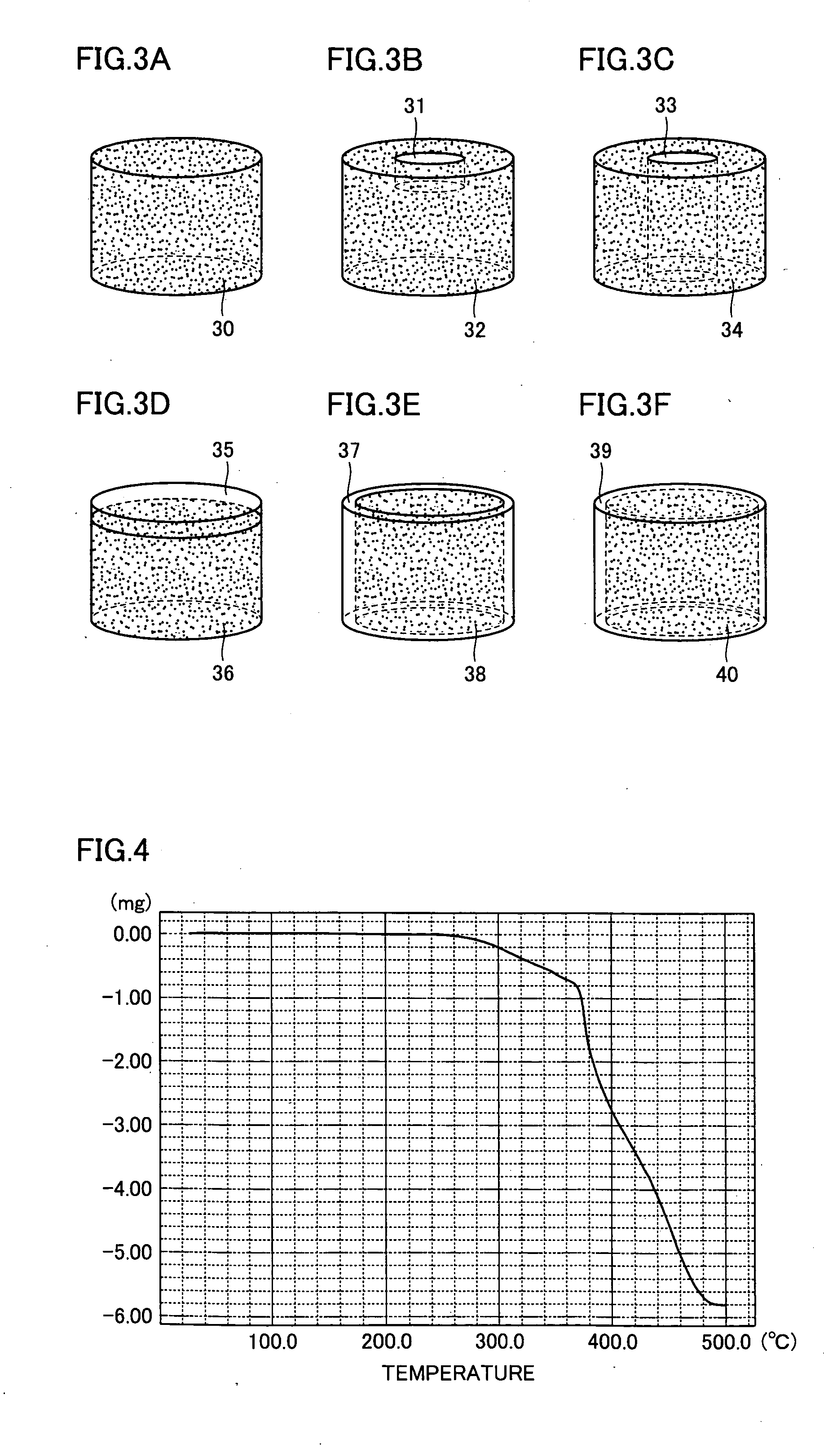
Gas flow rate verification unit
ActiveUS7716993B2Increase flow rateUniform pressureMultiple way valvesPipeline systemsEngineeringGas supply
A gas flow rate verification unit capable of enhancing reliability of gas flow rate verification. The gas flow rate verification unit has a first cutoff valve that is connected to a flow rate control device and to which gas is inputted, a second cutoff valve for discharging the gas, a communication member for allowing the first cutoff valve and the second cutoff valve to communicate with each other, a pressure sensor for detecting the pressure of the gas supplied between the first cutoff valve and the second cutoff valve, a temperature detector for detecting the temperature of the gas supplied between the first cutoff valve and the second cutoff valve, and a control means for verifying the flow of the gas flowing in the flow control device, the verification being performed by using both the result of the pressure detected by the pressure sensor and the result of the temperatures detected by the temperature detector. The volume (Vk) between the valve seat of the first cutoff valve and the valve seat of the second cutoff valve is equal to or less than the volume (Ve) between the outlet of the flow control device and the valve seat of the first cutoff valve.
Owner:CKD
Thermal pellet incorporated thermal fuse and method of producing thermal pellet
ActiveUS7323966B2Improve featuresReduce deliquescenceFuse device manufactureHeating/cooling contact switchesHeat deflection temperatureHot melt
A thermal fuse incorporating a thermal pellet has its operating temperature, or heat distortion temperature, adjusted and the thermosensitive material of the pellet avoids deformation, modification or similar deficiency if it is exposed to a severe external environment. The inexpensive thermal fuse provides a wider range from which an operating temperature can be selected, improved insulation resistance after operation, faster response speed in operation, and enhanced strength of the thermal pellet. The thermosensitive material is formed of a thermoplastic resin corresponding to a high molecular weight substance. The thermal pellet's heat distortion temperature is adjusted by a temperature setting method. An enclosure of the fuse has a metal casing with a spring member's strong and weak compression springs both accommodated therein and hermetically sealed.
Owner:SCHOTT JAPAN CORP
Thermal pellet incorporated thermal fuse and method of producing thermal pellet
ActiveUS20050088272A1Rapid responseLow costFuse device manufactureHeating/cooling contact switchesHeat deflection temperatureHot melt
There is provided a thermosensitive material allowing a thermal pellet incorporated thermal fuse's operating temperature, or heat distortion temperature, to be adjusted and preventing deformation, modification or similar deficiency if it is exposed to severe external environment, and there is provided an inexpensive thermal fuse that provides a wider range from which an operating temperature is selected, improved insulation resistance after operation, faster response speed in operation, and enhanced strength of the thermal pellet. To do so, the thermosensitive material is formed of thermoplastic resin corresponding to a high molecular substance, the thermal pellet's heat distortion temperature is adjusted by a temperature setting method, and an enclosure has a metal casing with a spring member's strong and weak compression springs and both accommodated therein and hermetically sealed.
Owner:SCHOTT JAPAN CORP
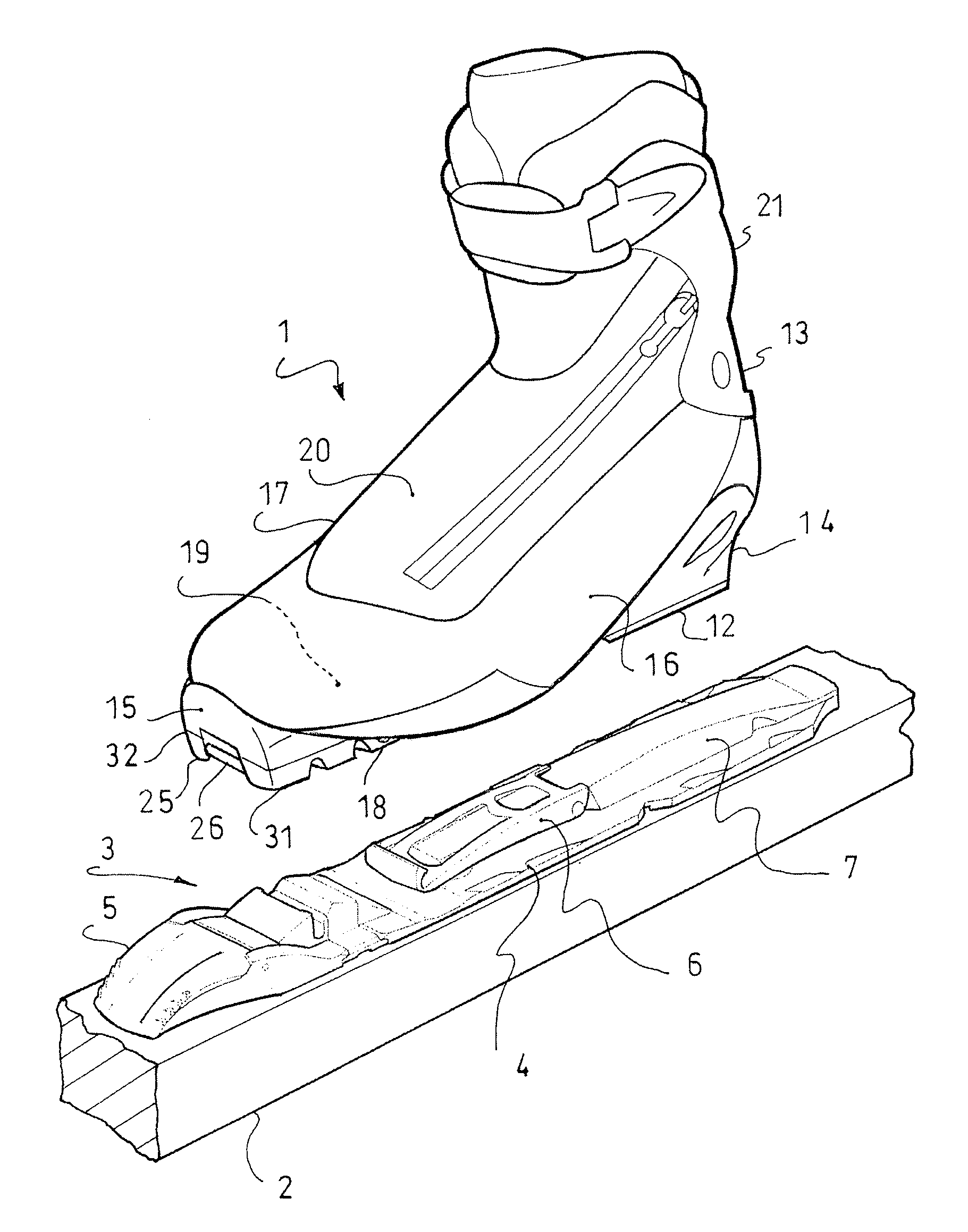
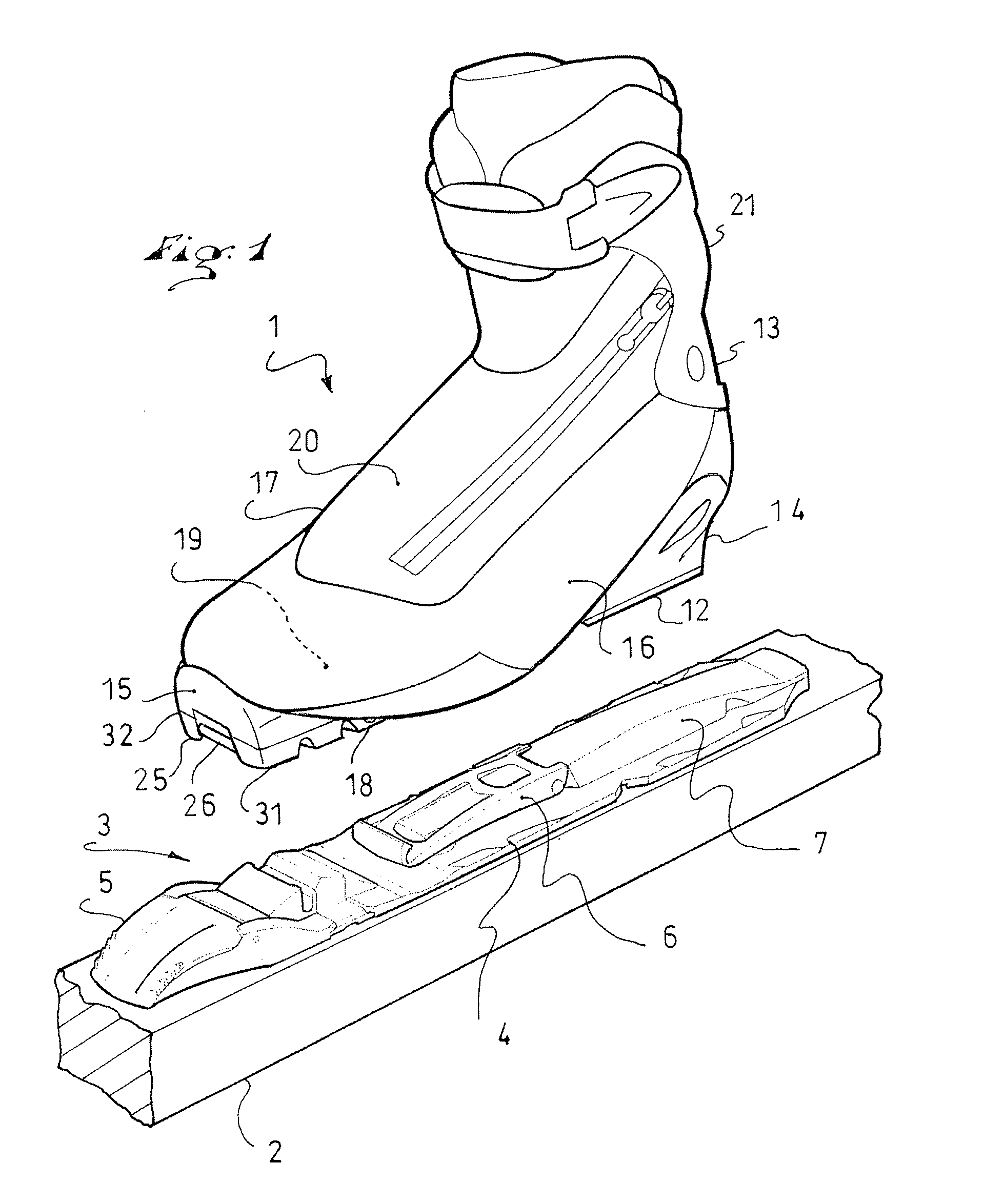
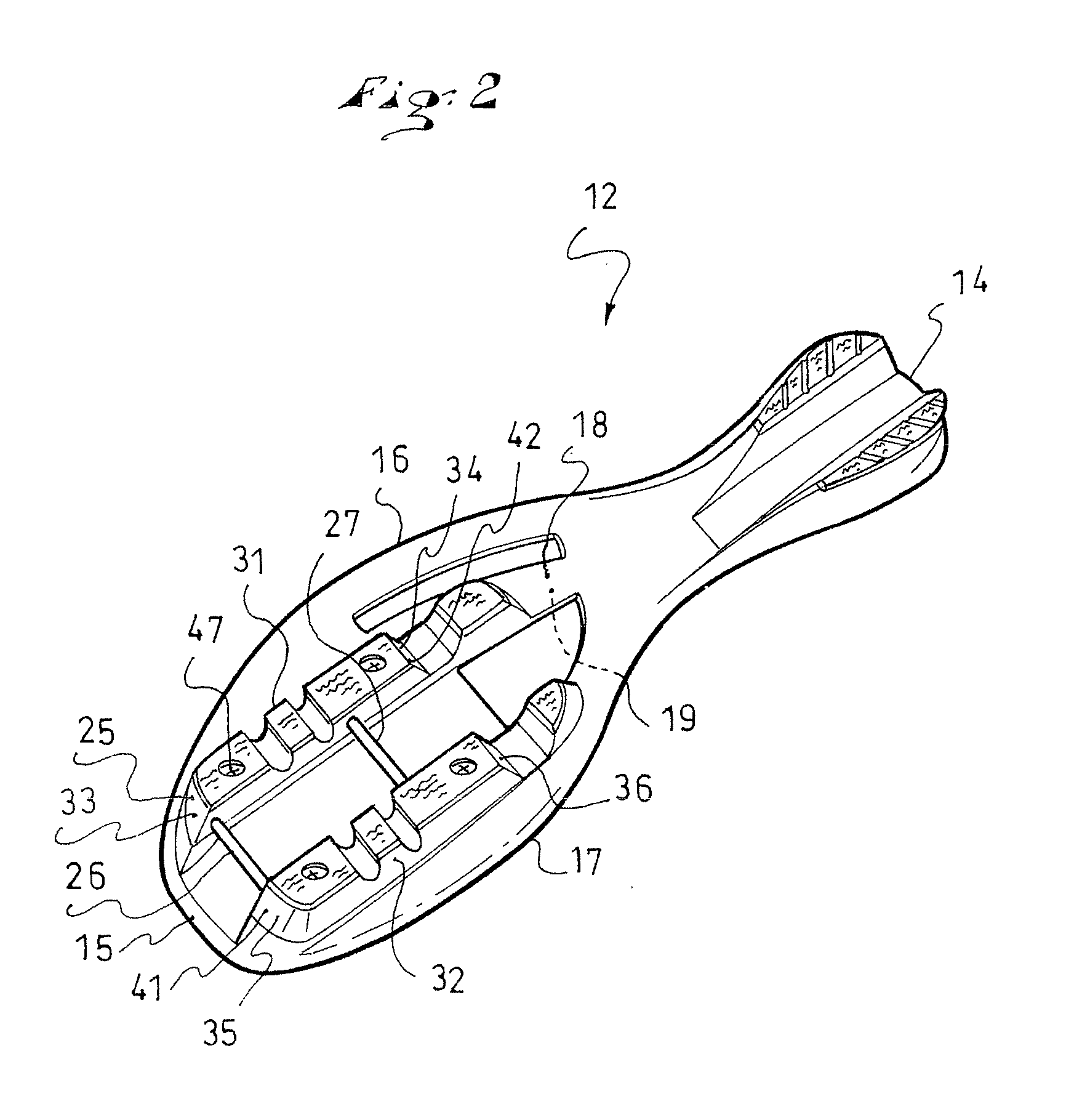
Sports footwear
InactiveUS20120151801A1Satisfactory steering precisionMost efficientFootwearLocking mechanismEngineering
An article of footwear, such as a boot, adapted to be removably retained on a sports apparatus, the boot including an outer sole assembly, an upper and a fastening element, the latter being adapted to cooperate with a locking mechanism, itself adapted to be affixed to the apparatus. The boot includes a connection mechanism adjustable in position, which adjustably connects the fastening element to the outer sole assembly.
Owner:SALOMON SA
Semiconductor manufacturing apparatus and semiconductor manufacturing method using the same
InactiveUS20070137570A1Satisfied with precisionSimple configurationConveyorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingManufactured apparatusEngineering
A semiconductor manufacturing apparatus comprising: a plurality of vacuum chambers corresponding to a plurality of processing sections necessary for manufacturing a semiconductor device; an exhaust device connected to each vacuum chamber; a plate shaped guide plate arranged at the bottom of each vacuum chamber and having a plurality of gas emission holes; and a gas supply source for supplying gas to the gas emission holes, wherein the plurality of vacuum chambers are adjacent to each other by way of a shutter, one of the two adjacent vacuum chambers includes a tray mounted on the guide plate for mounting a substrate to be performed with a predetermined process, a conveying function section having a conveying arm for moving the tray from one vacuum chamber to the other vacuum chamber along the guide plate, and a controlling function section, the controlling function section performing the control so as to open the shutter to communicate the two adjacent vacuum chambers, emit gas from the gas emission holes of the guide plate of the vacuum chambers, and move the tray in one vacuum chamber, which is floated by the emitted gas, from the guide plate of one vacuum chamber to the guide plate of the other vacuum chamber along the guide plate by means of the conveying arm.
Owner:SHARP KK
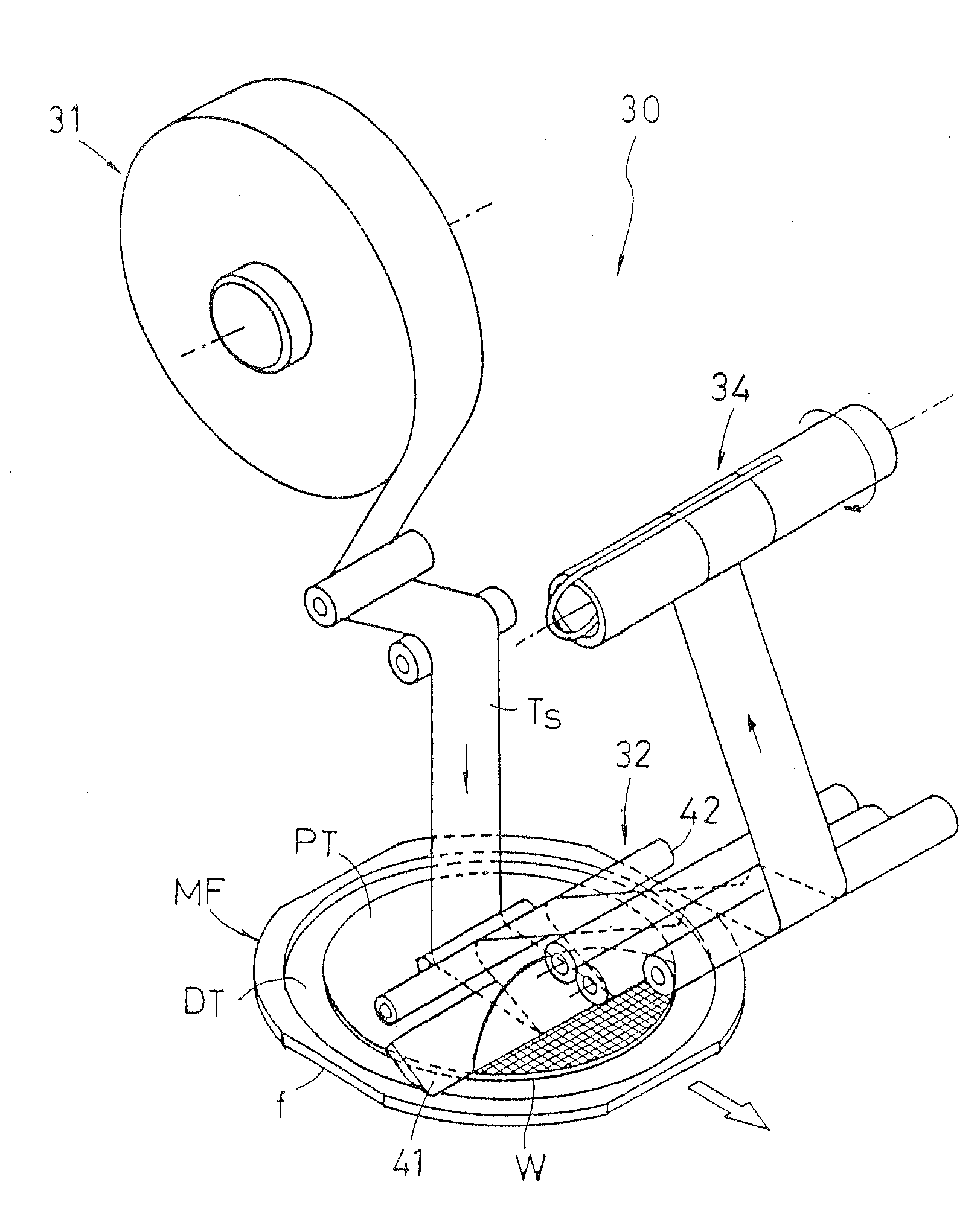
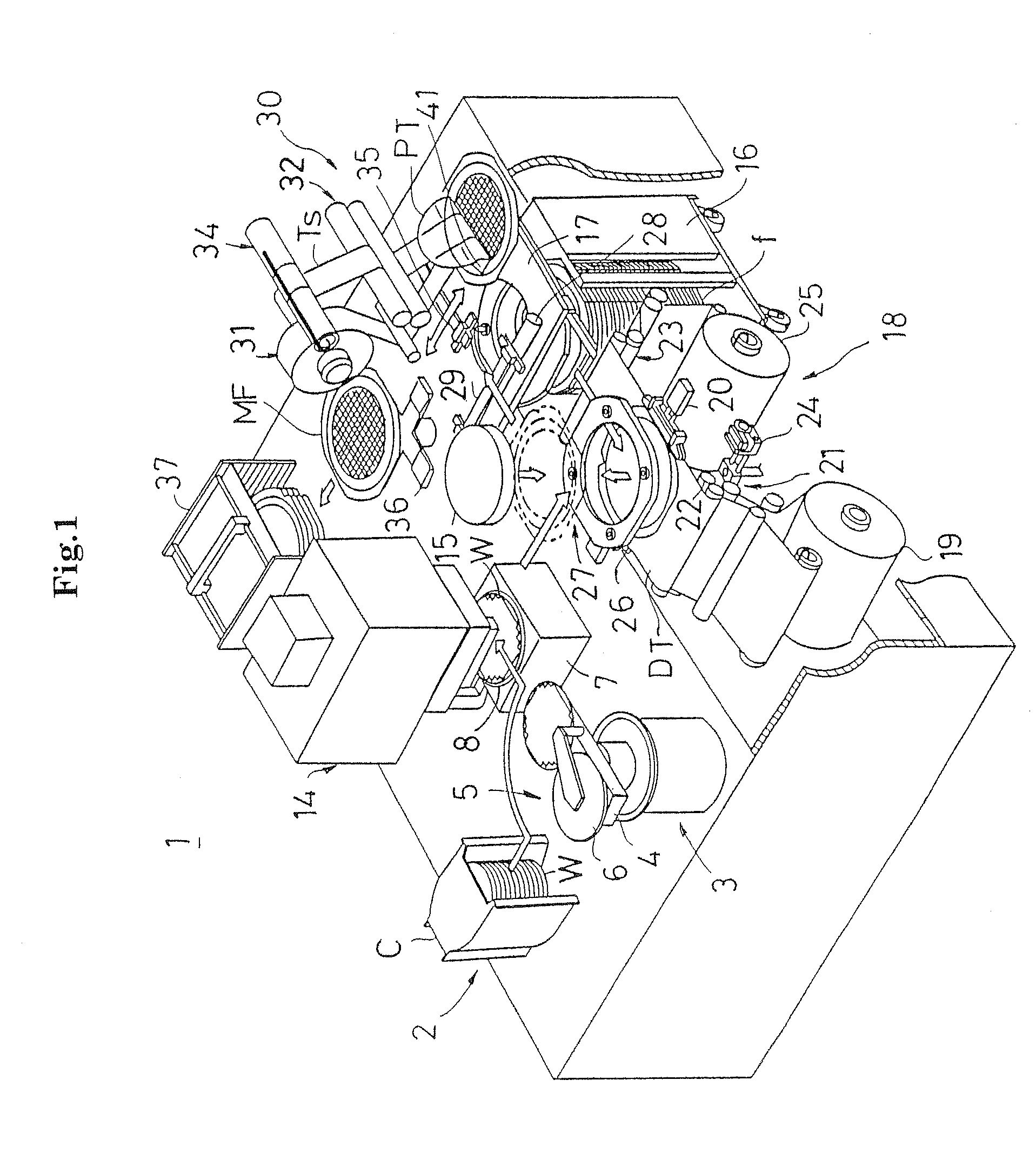
Process for producing spiral membrane element
InactiveUS20040124134A1Process stabilityAvoid damageSemi-permeable membranesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisDistortionMembrane configuration
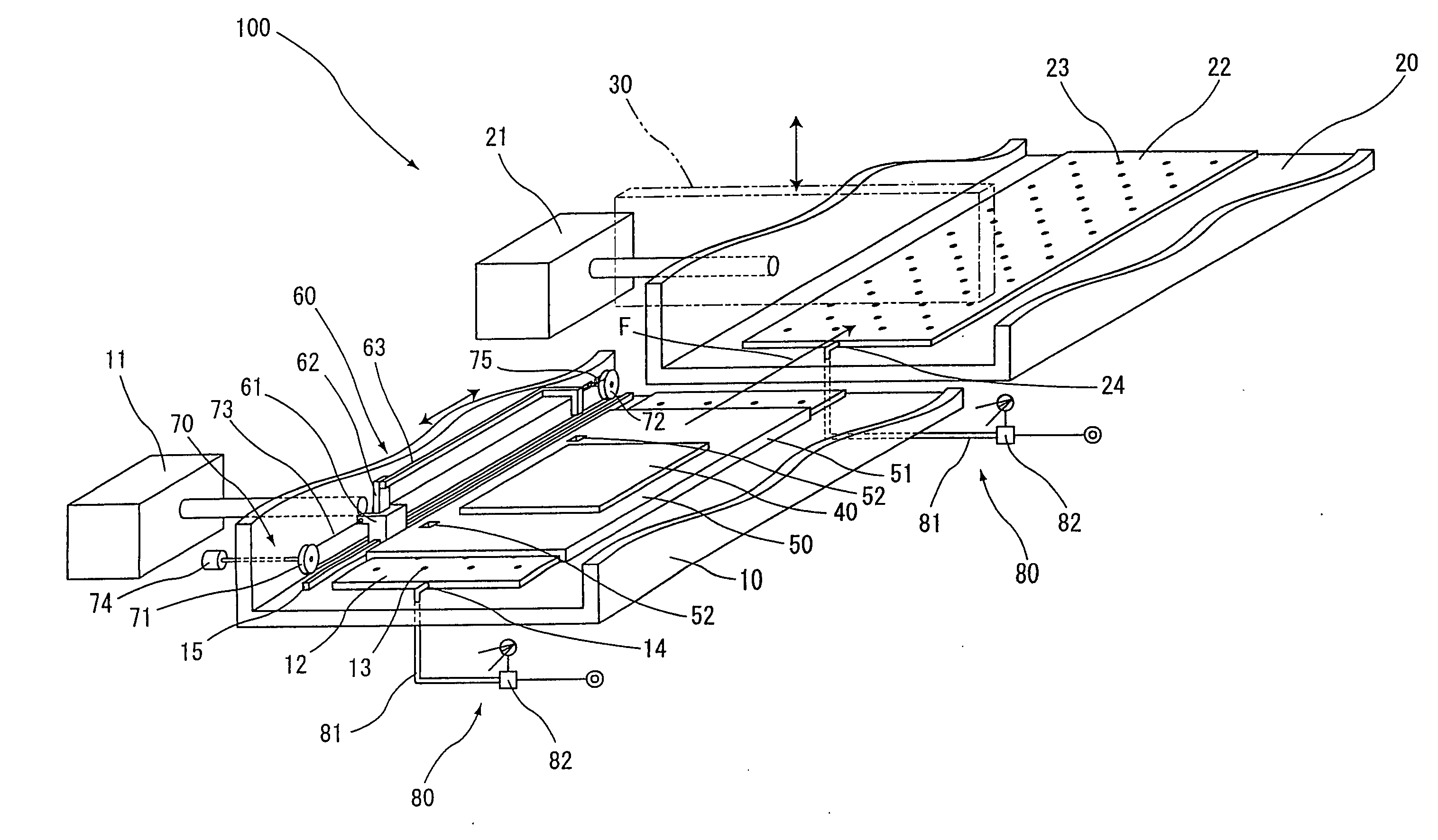
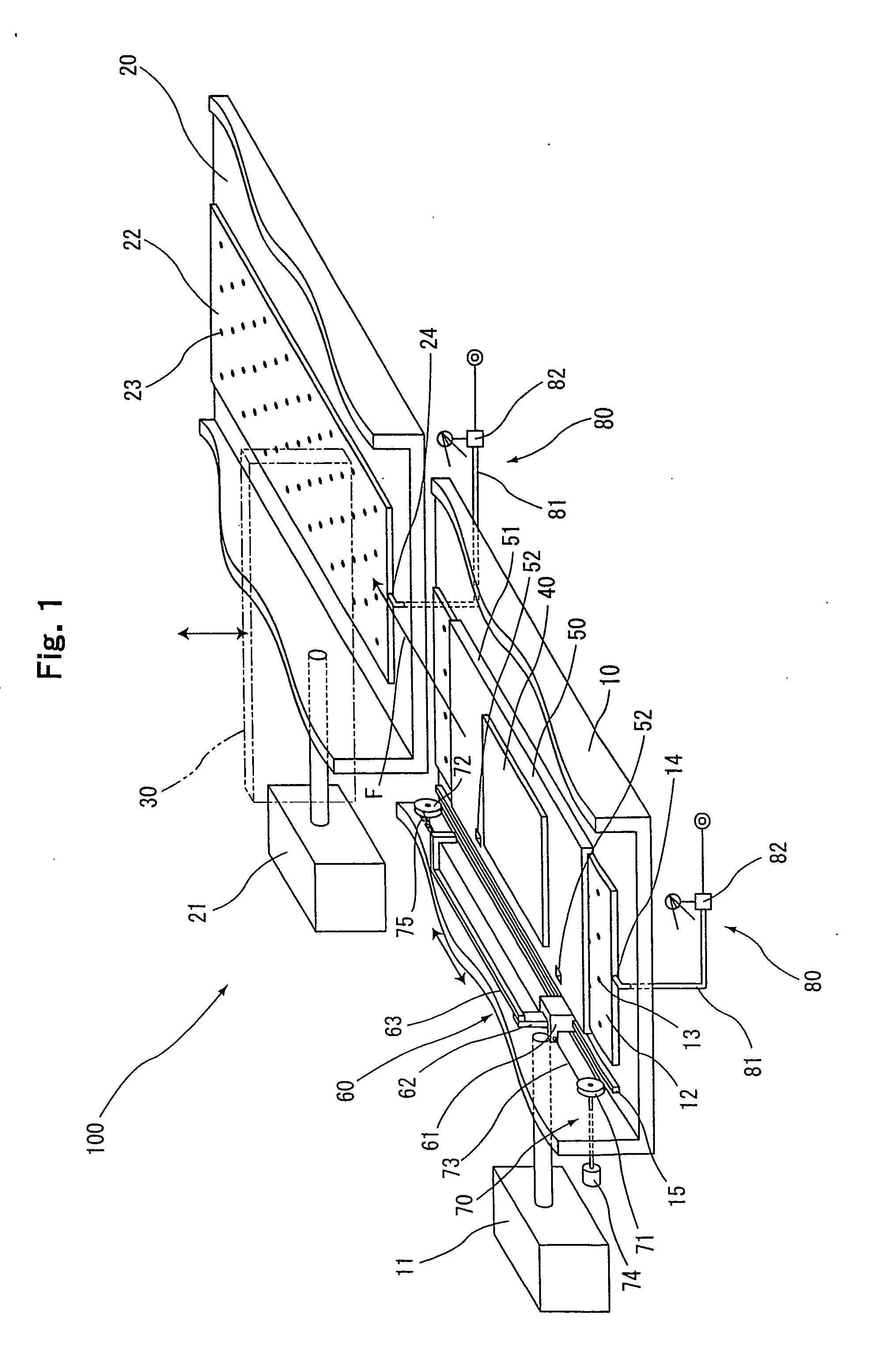
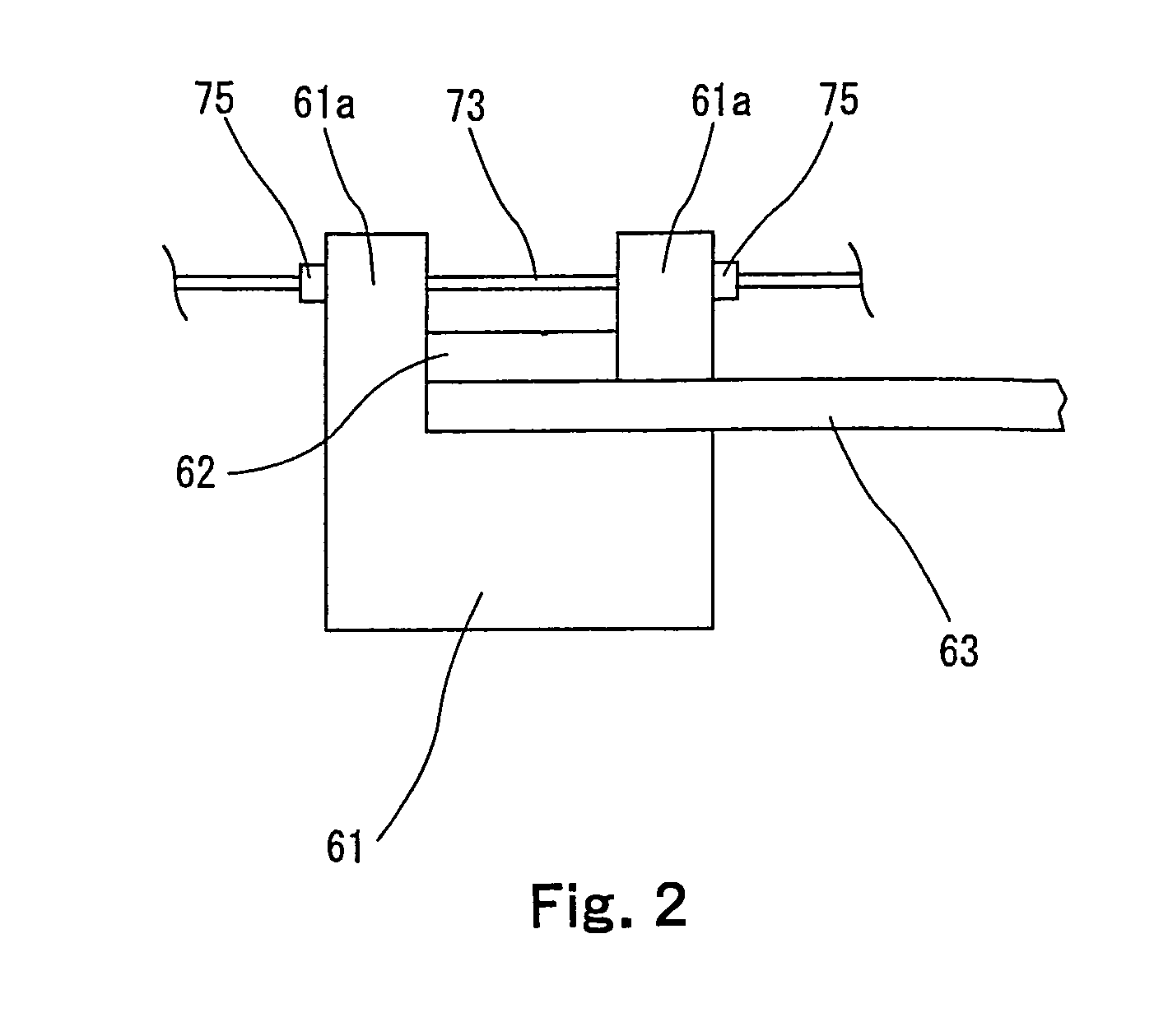
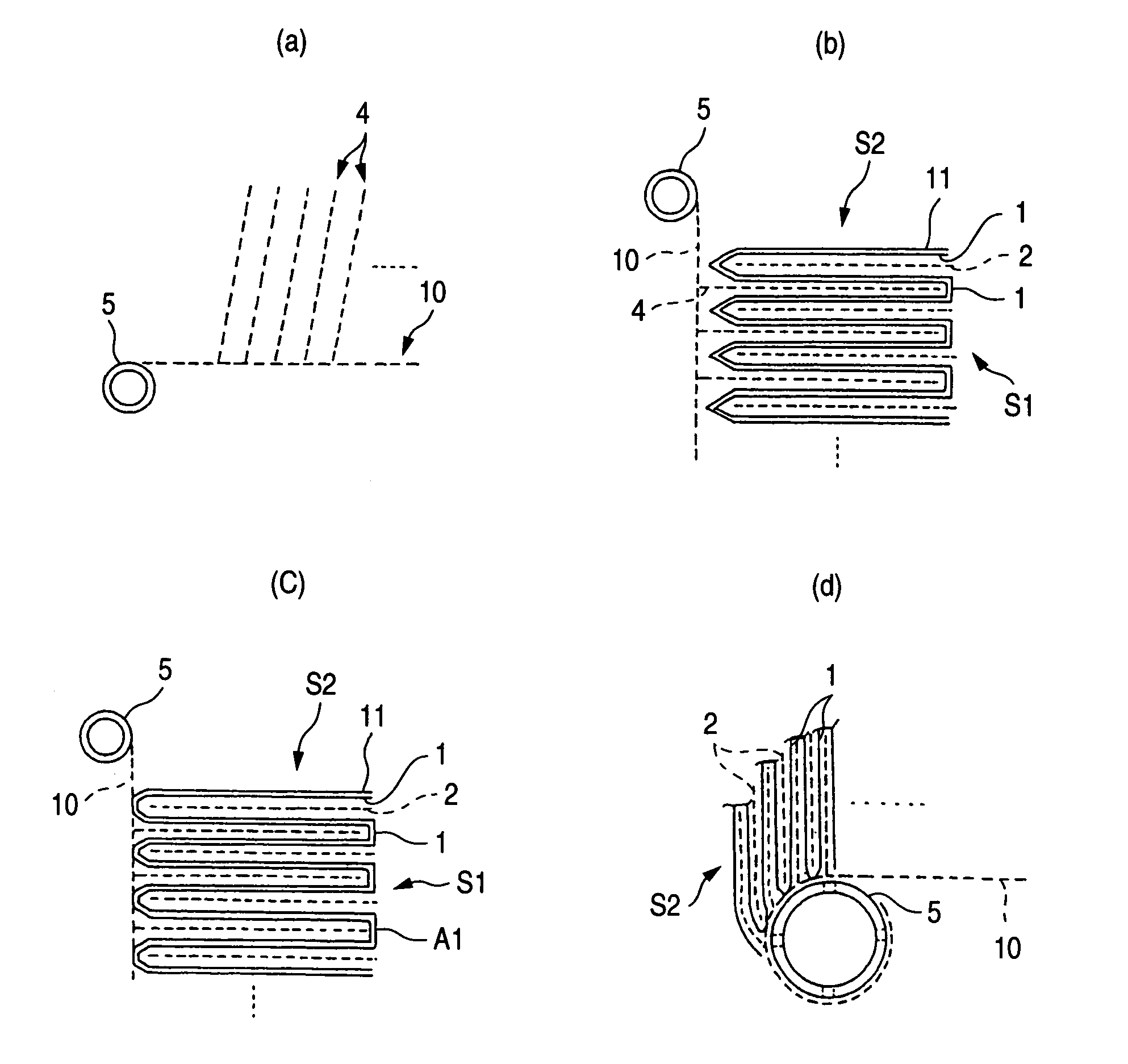
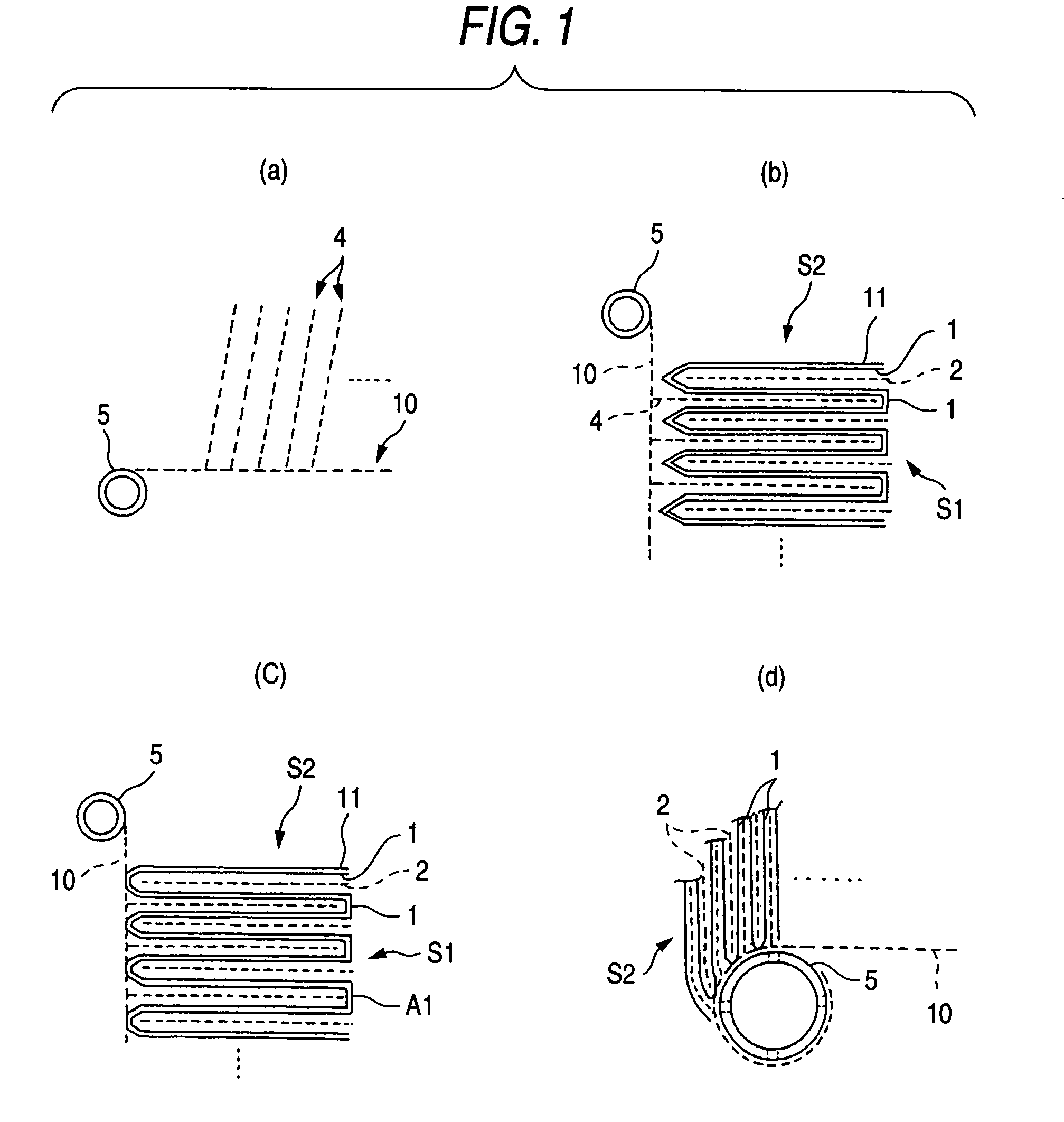
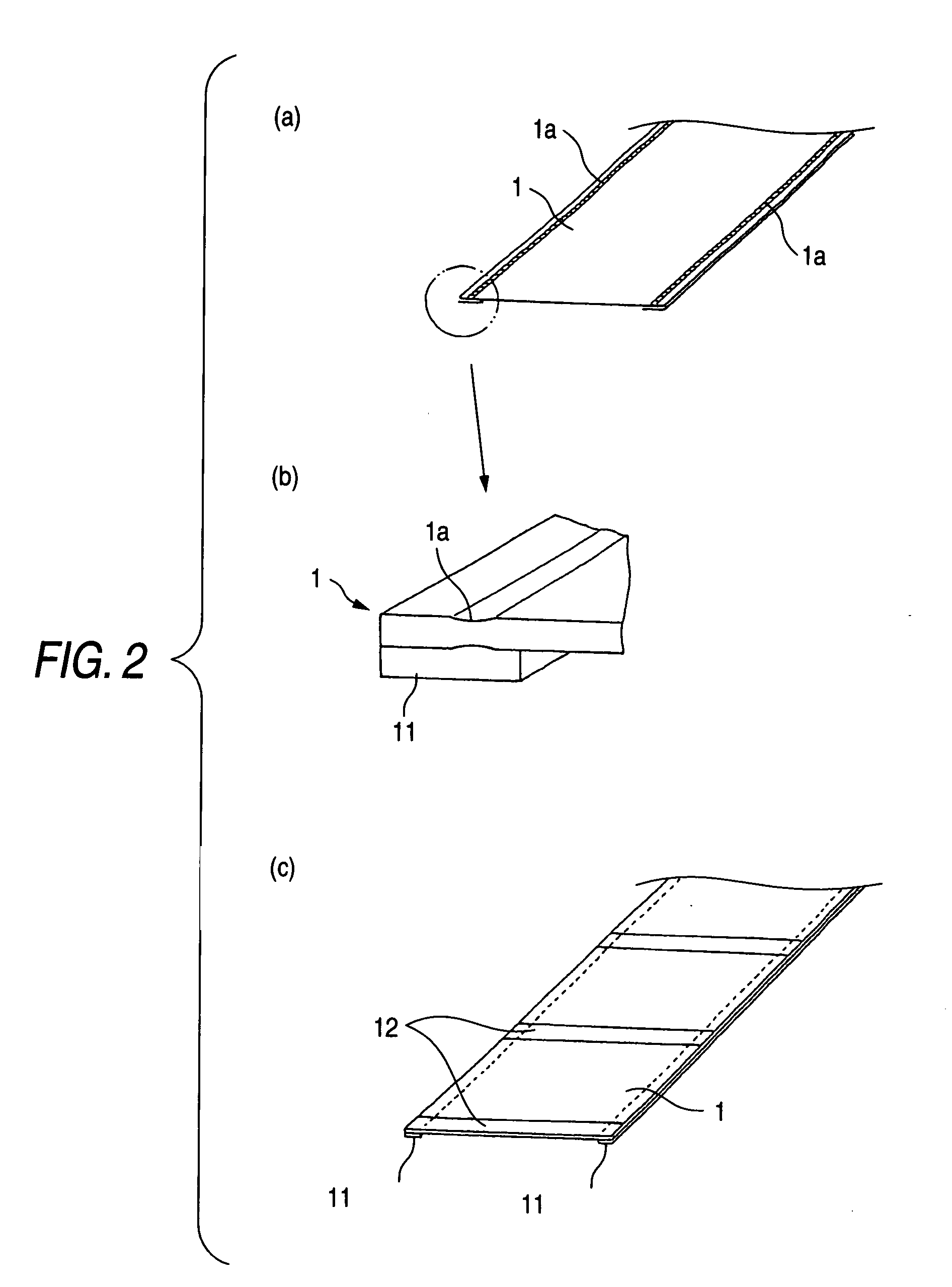
A process for spiral membrane element production is disclosed in which creases are stably and sufficiently formed to thereby enable the later step of winding or the like to be smoothly conducted while eliminating the "wrinkling" or "breakage" caused by the distortion of creased parts. The process comprises the step of forming a multilayer structure S2 comprising a membrane 1 which has been folded, a feed-side passage material disposed on the feed side of the folded membrane 1, and a permeation-side passage material disposed on the permeation side of the folded membrane 1 and the step of spirally winding at least the multilayer structure S2 on a perforated core tube 5, wherein the folded membrane 1 is obtained by forming beforehand in a membrane a folding initiation part L2 reduced in bending resistance along each of folding lines L1 for the membrane, folding the membrane 1 at the folding initiation parts L2, and heating and pressing the membrane 1 during and / or after the folding.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Apparatus and method of performing product-sum operation
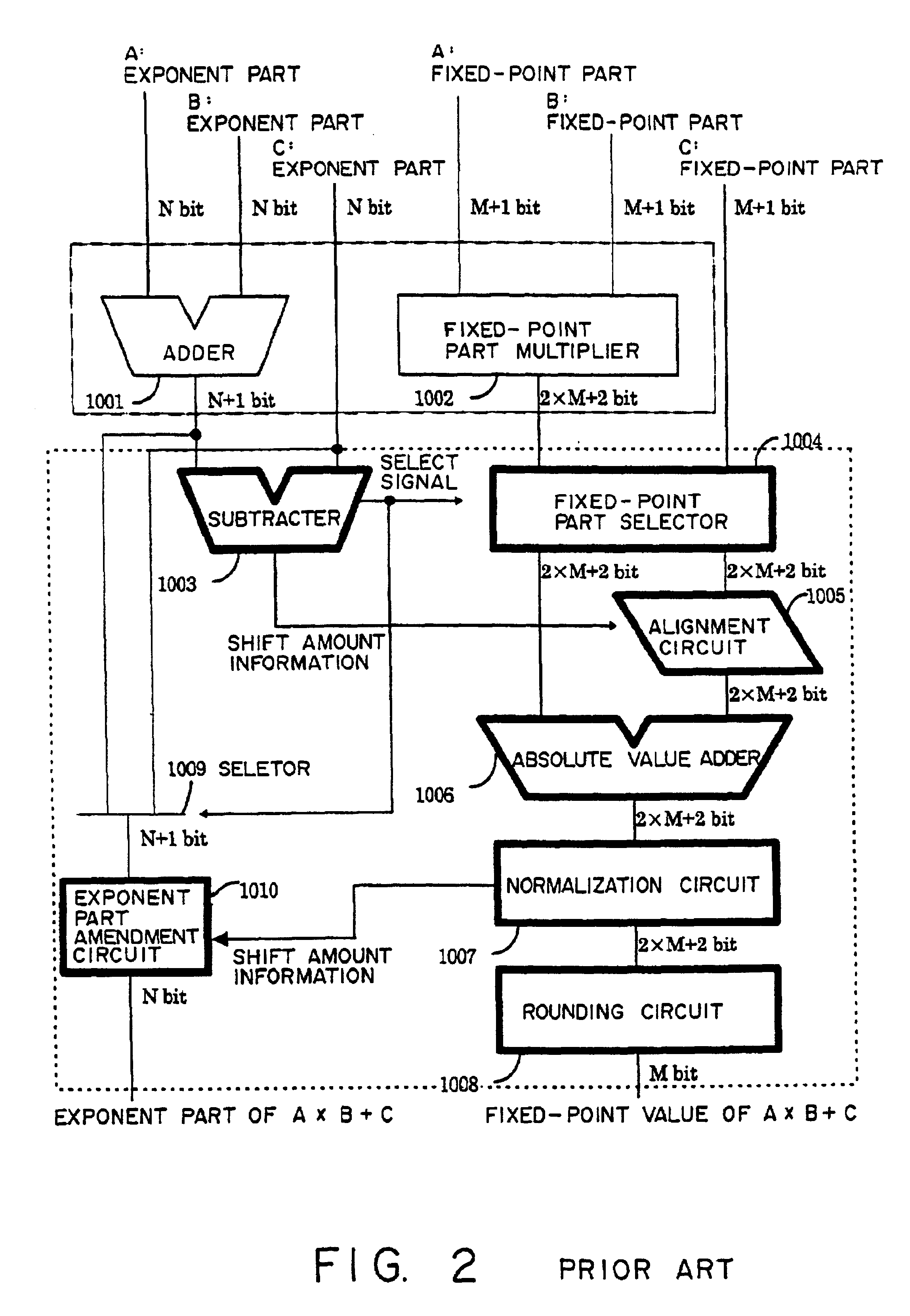
InactiveUS6895423B2Reduce circuit sizeSmall circuitComputation using non-contact making devicesComplex mathematical operationsTheoretical computer scienceFloating point multiplier
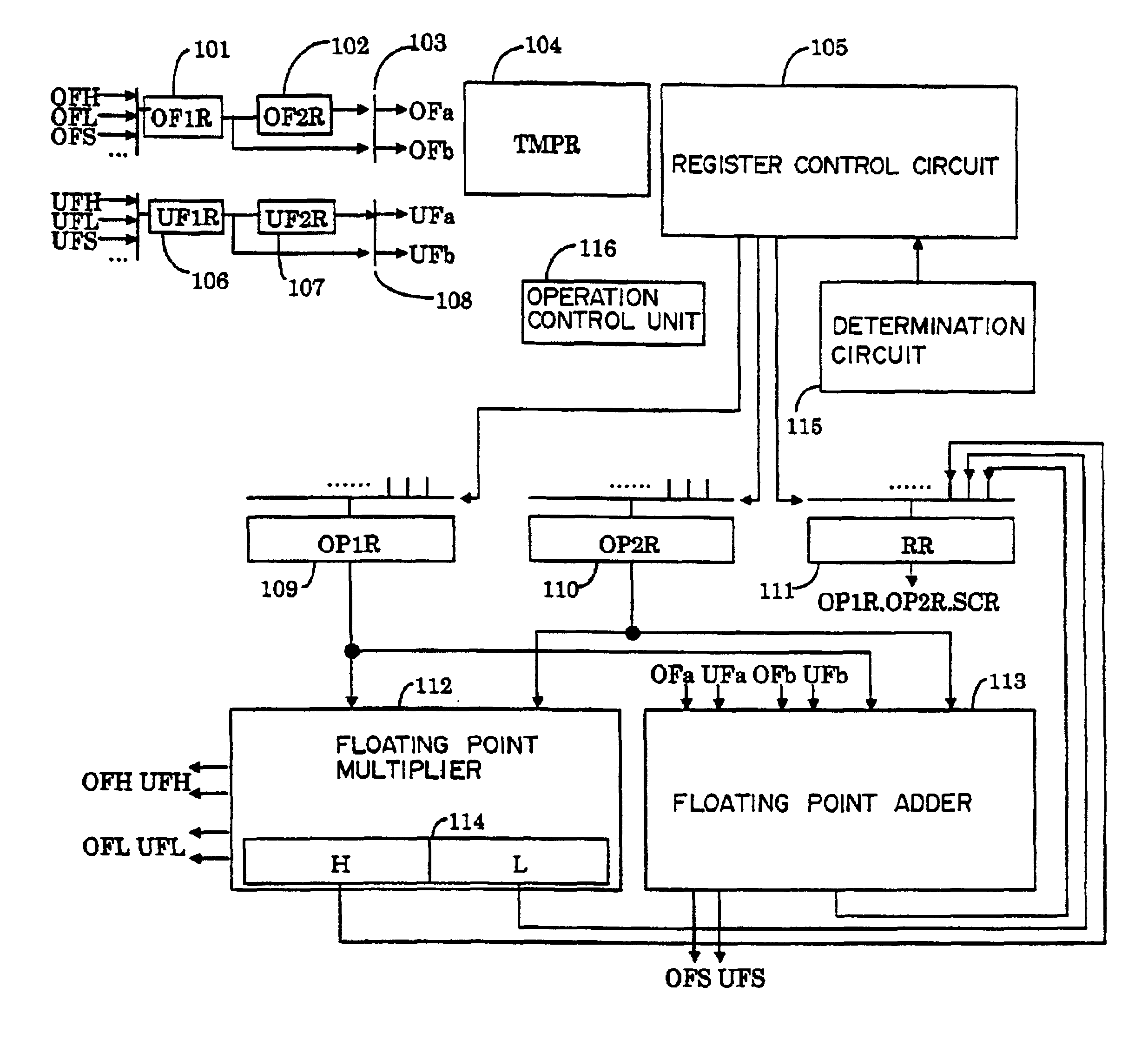
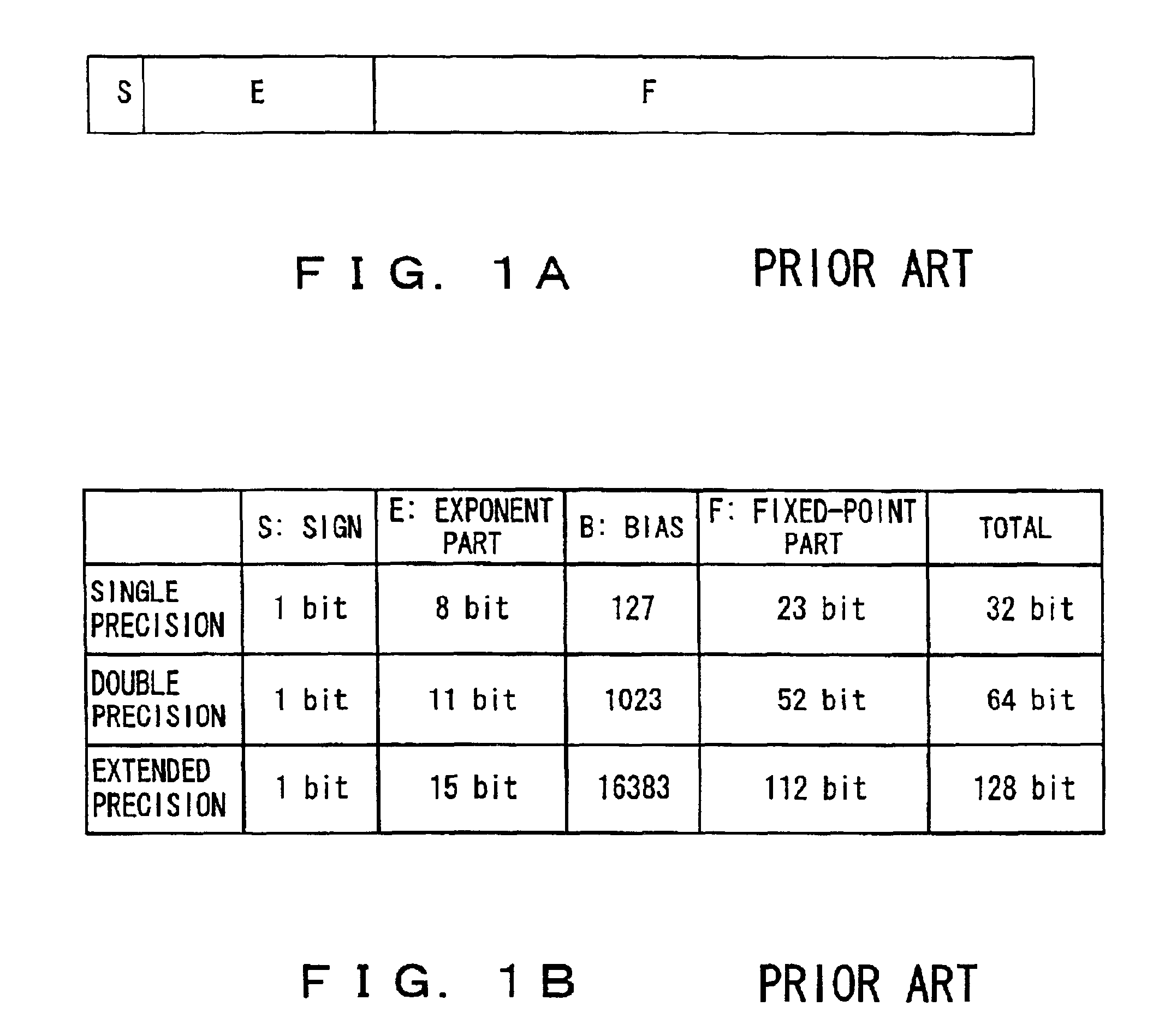
To perform a product-sum operation by adding third data to a product of first data and second data, a floating point multiplier first multiplies the first data by the second data, and a bit string representing a fixed-point part in the multiplication result is divided into a portion representing more significant digits in the fixed-point part and a portion representing less significant digits in the fixed-point part. Then, a floating point adder first adds less significant multiplication result data having a bit string representing the less significant digits as a fixed-point part to the third data, and then adds the addition result to more significant multiplication result data having a bit string representing the more significant digits as a fixed-point part. A rounding process is performed on the two addition results to obtain a result of the product-sum operation.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
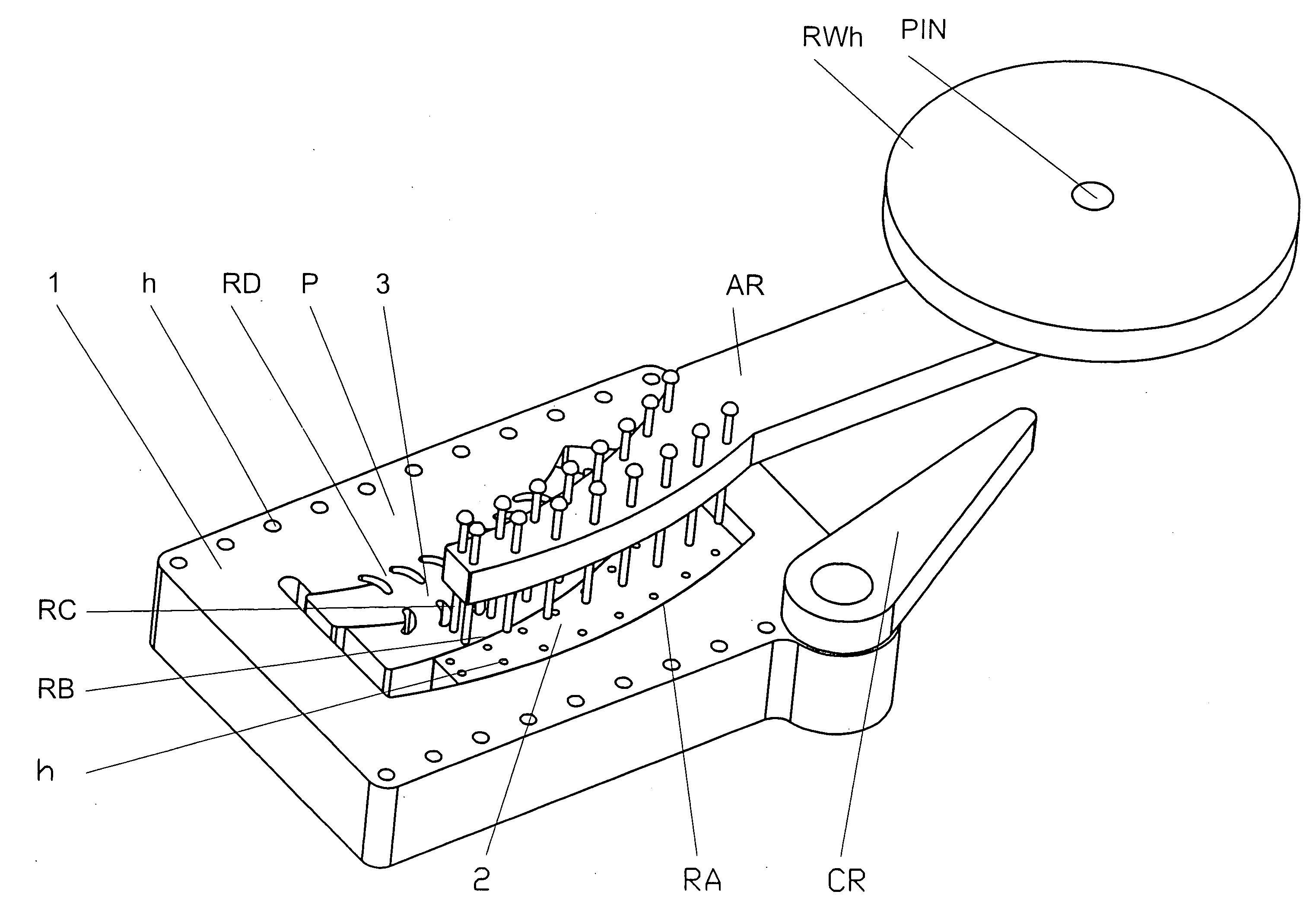
Alpine ski
InactiveUS6499759B2Satisfied with precisionImprove mobilitySki bindingsSki-brakesEngineeringMechanical engineering
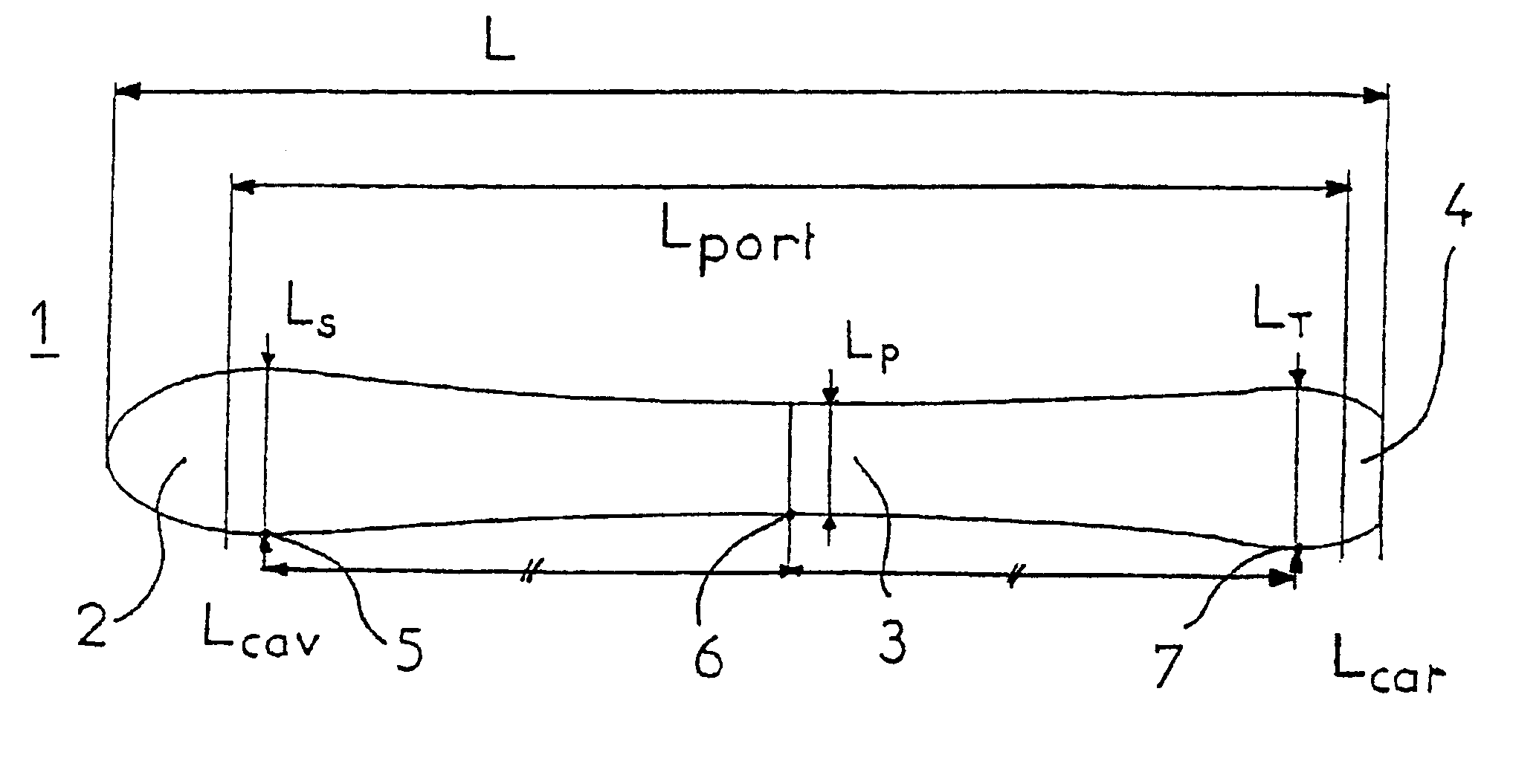
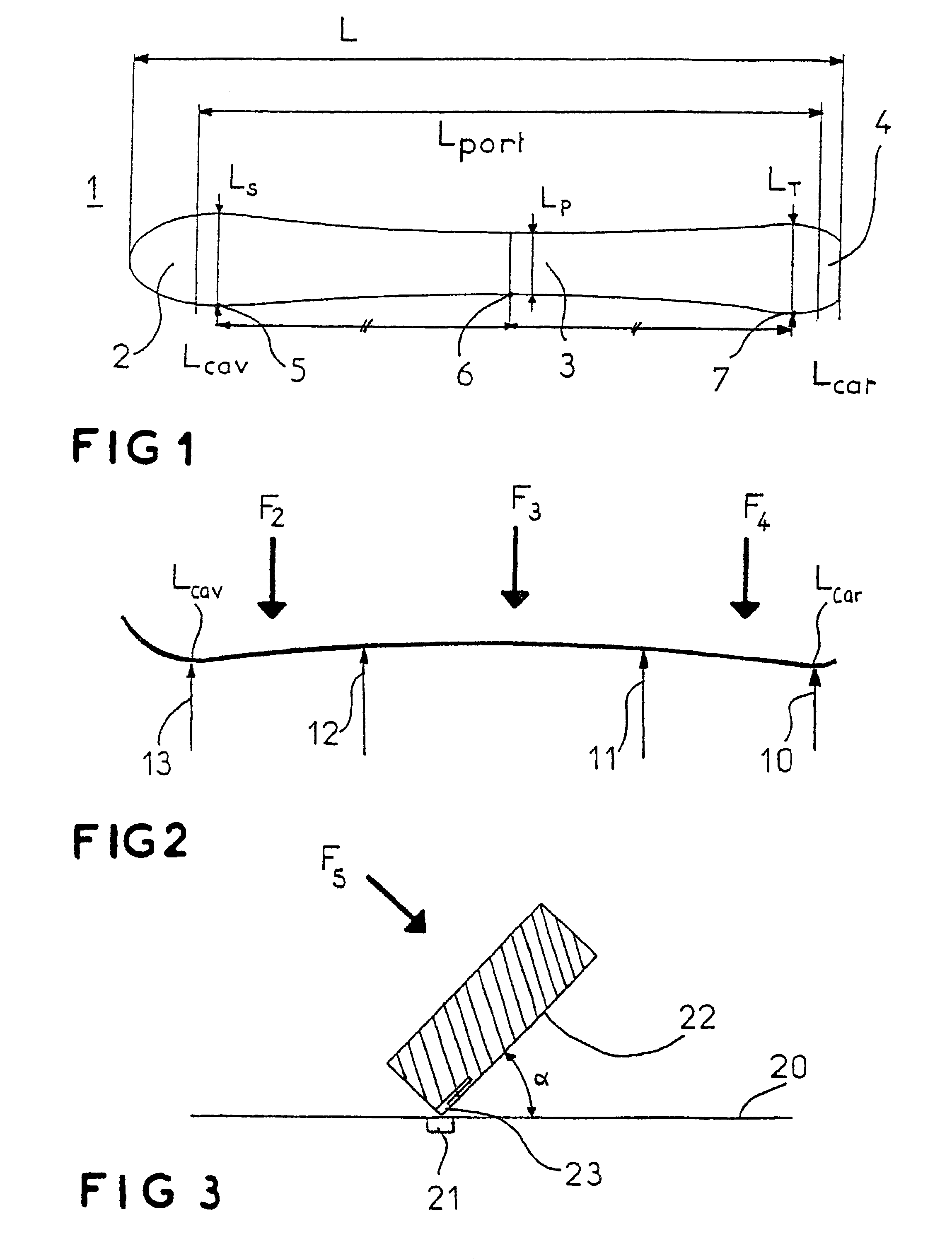
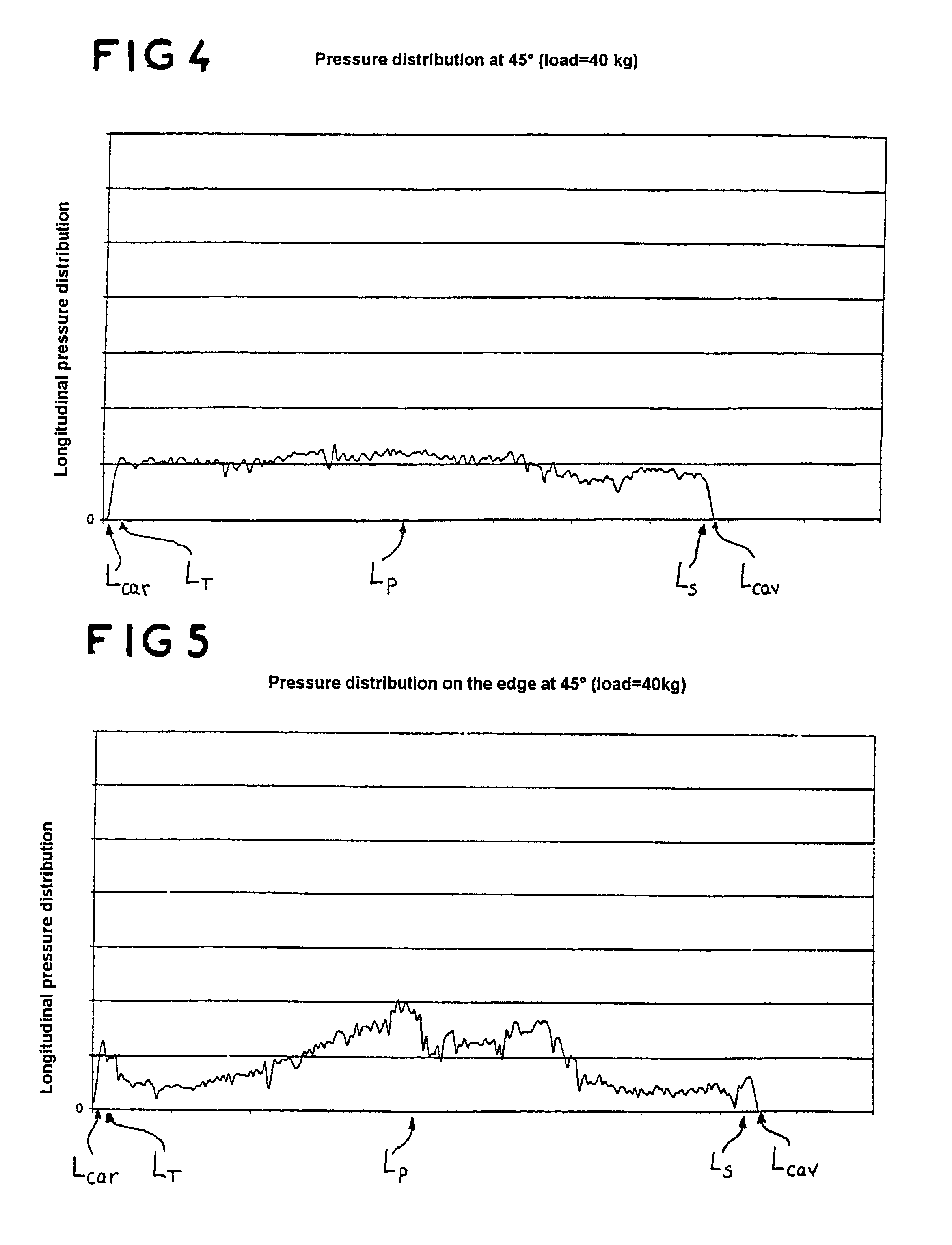
Alpine ski (1) which can be broken down over its length into a tip area (2), a binding area (3) and a heel area (4), in which the side line is such that the binding area (3) has a minimum width level (LP), the tip area (2) has a front maximum width level (LS), and the heel area (4) has a rear maximum width level (LT), characterized in that:the radius of the side line, calculated on the basis of three points (5, 6, 7) on the side line, respectively a first point (5) located at the front maximum width level (LS), a second point (7) located at the rear maximum width level (LT), and a third point (6) located centrally between the levels (LS, LT), is between 7 and 21 meters;the pressure distribution along the side line is such that, when the ski is placed on a flat surface (20) so that its underside (22) forms an angle (alpha) of 45° with the flat surface (20), and when the ski receives, at the location of the center of the boot, a force (F5) of 400 Newtons perpendicularly to its underside (22), the pressures measured along the side line differ by less than 10% from the average value of the three pressures measured respectively at the rear maximum width level (LT), at the minimum width level (LP) and at the front maximum width level (LS).
Owner:SKIS ROSSIGNOL
Wireless communication terminal and wireless communication method
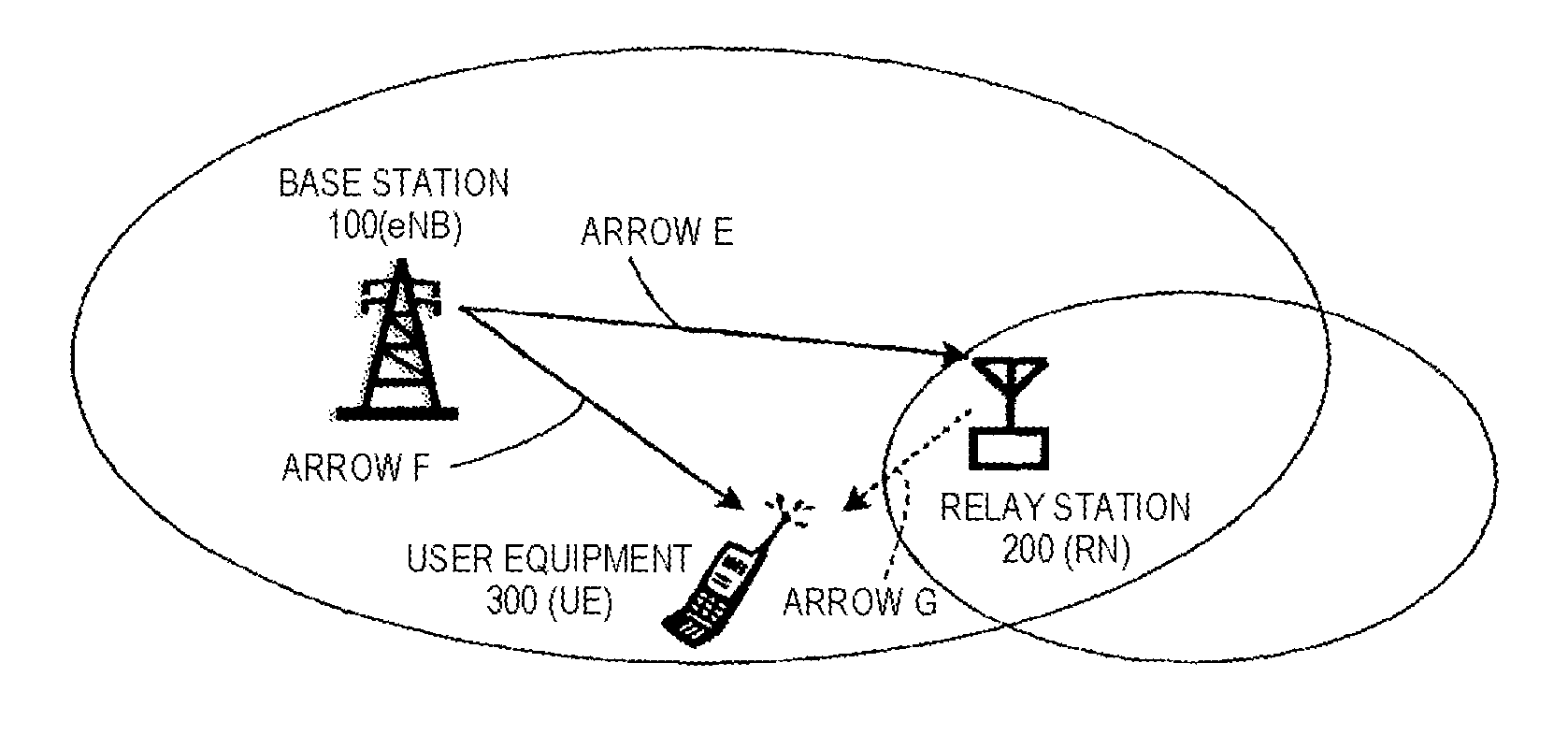
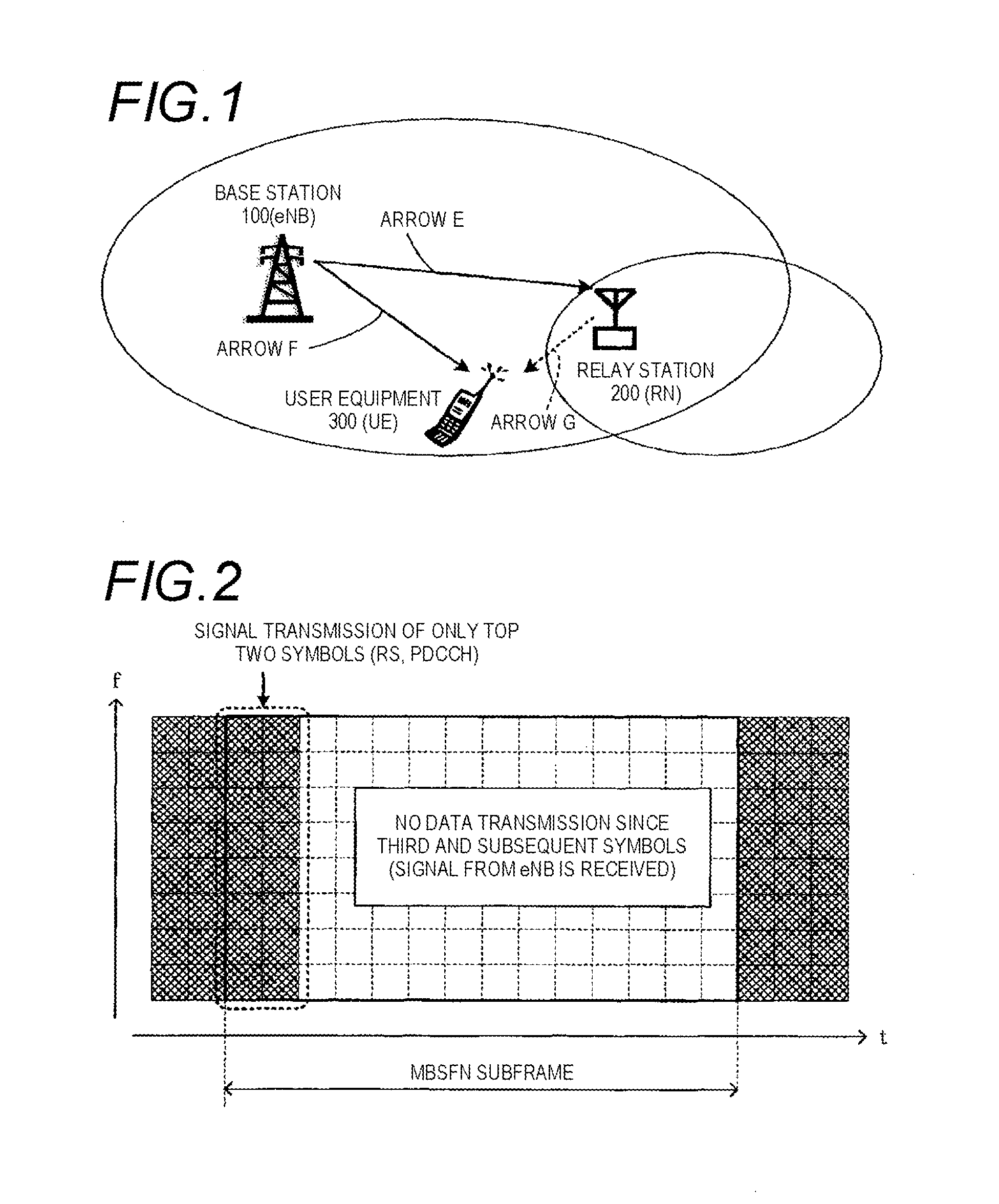
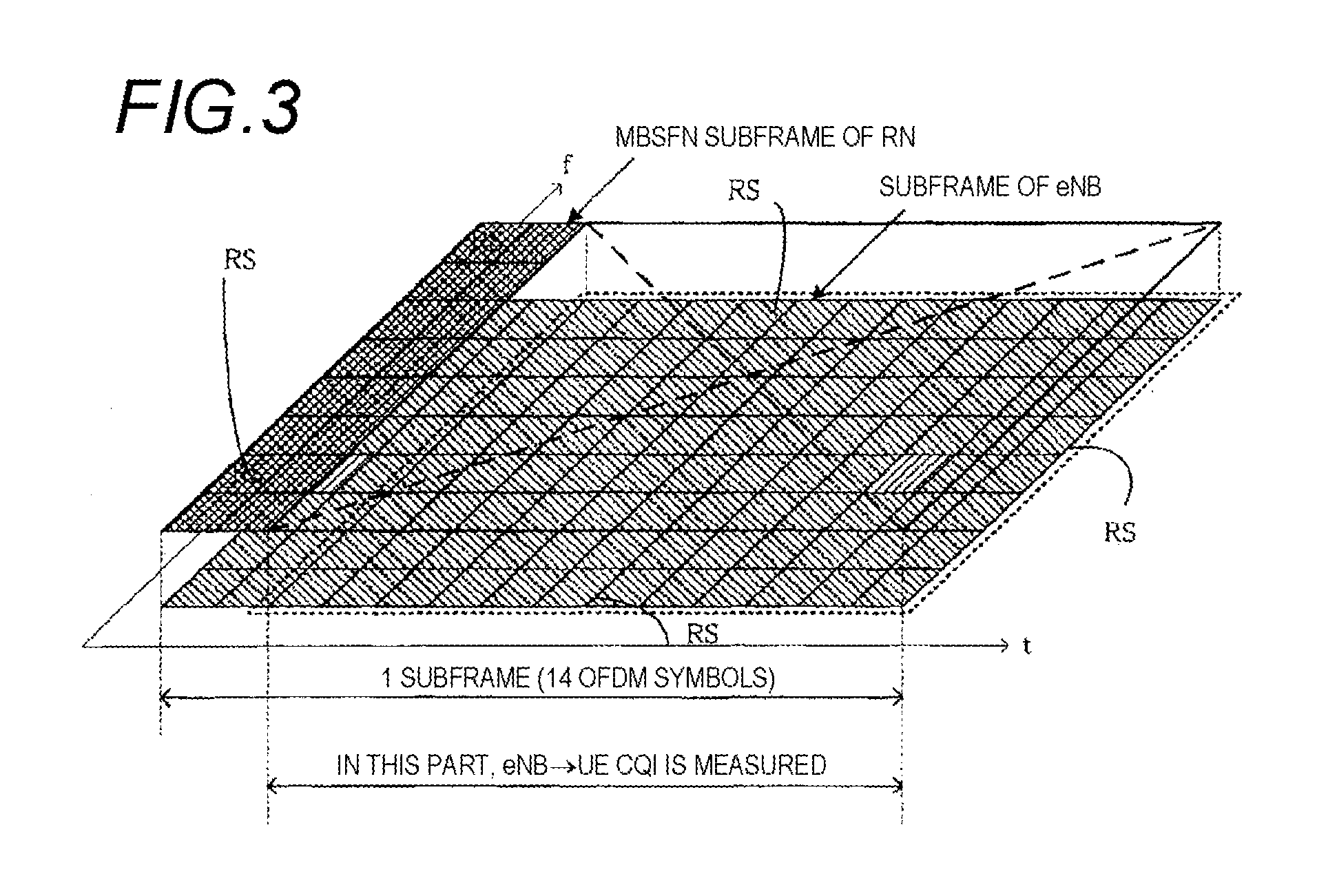
InactiveUS20120051256A1Satisfied with precisionSatisfactory precisionError preventionTransmission systemsCurrent cellInterference (communication)
To measure the channel quality of adjacent cells with satisfactory precision without interference of a current cell. A wireless communication terminal of the invention is connected to a relay station and configured to receive data from at least one of the relay station, a base station, and another relay station different from the relay station. The wireless communication terminal includes a receiver which receives a signal including control information for measuring the channel quality of the non-connected base station or another non-connected relay station from the connected relay station, an extractor which extracts the control information from the signal received by the receiver, a measurement section which measures the channel quality of the non-connected base station or non-connected another relay station in a region, in which the connected relay station does not transmit other signals to the wireless communication terminal, on the basis of the control information, and a transmitter which transmits the measurement result of the channel quality of the non-connected base station or another non-connected relay station measured by the measurement section to the connected relay station.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
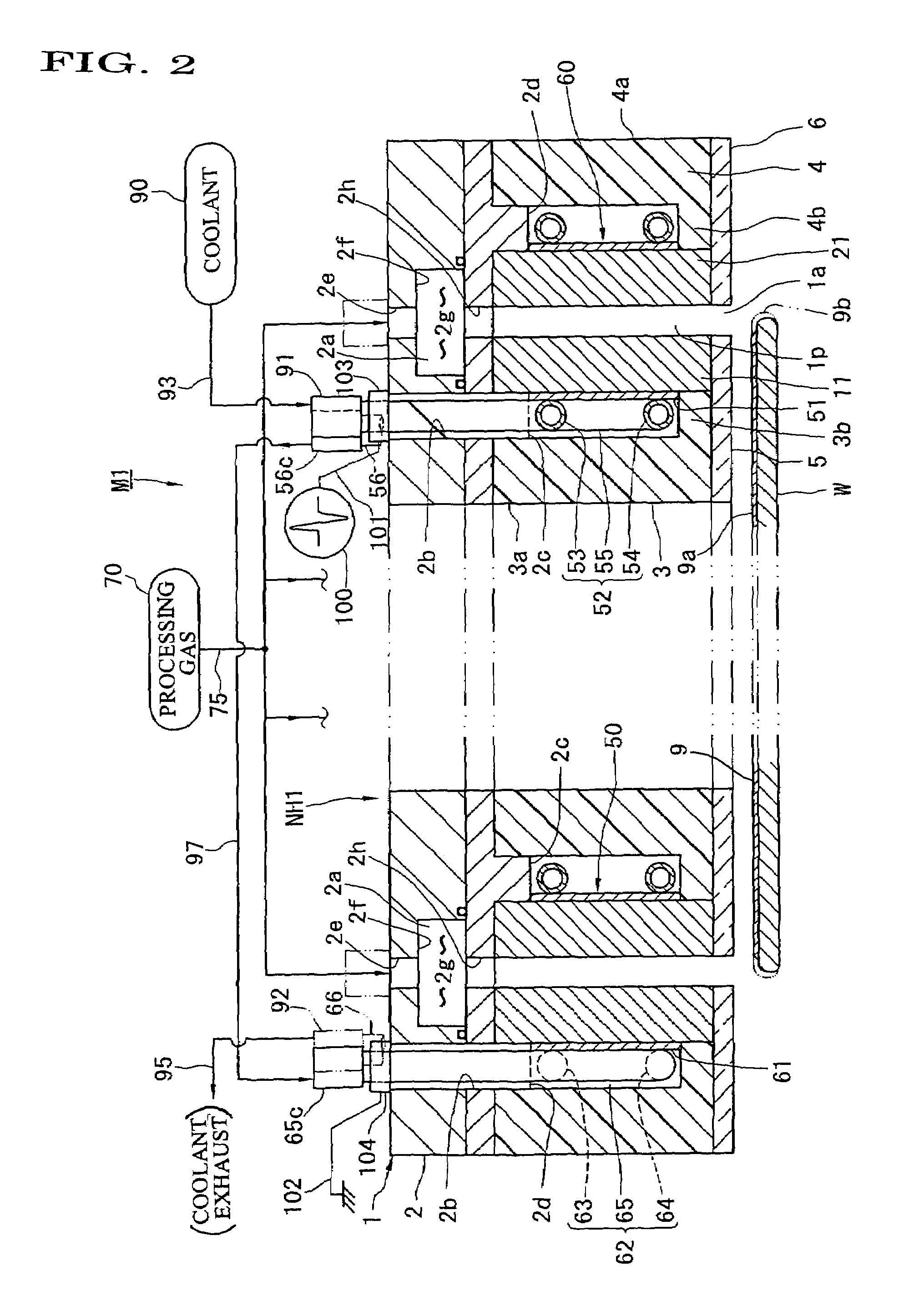
Plasma processing apparatus and method
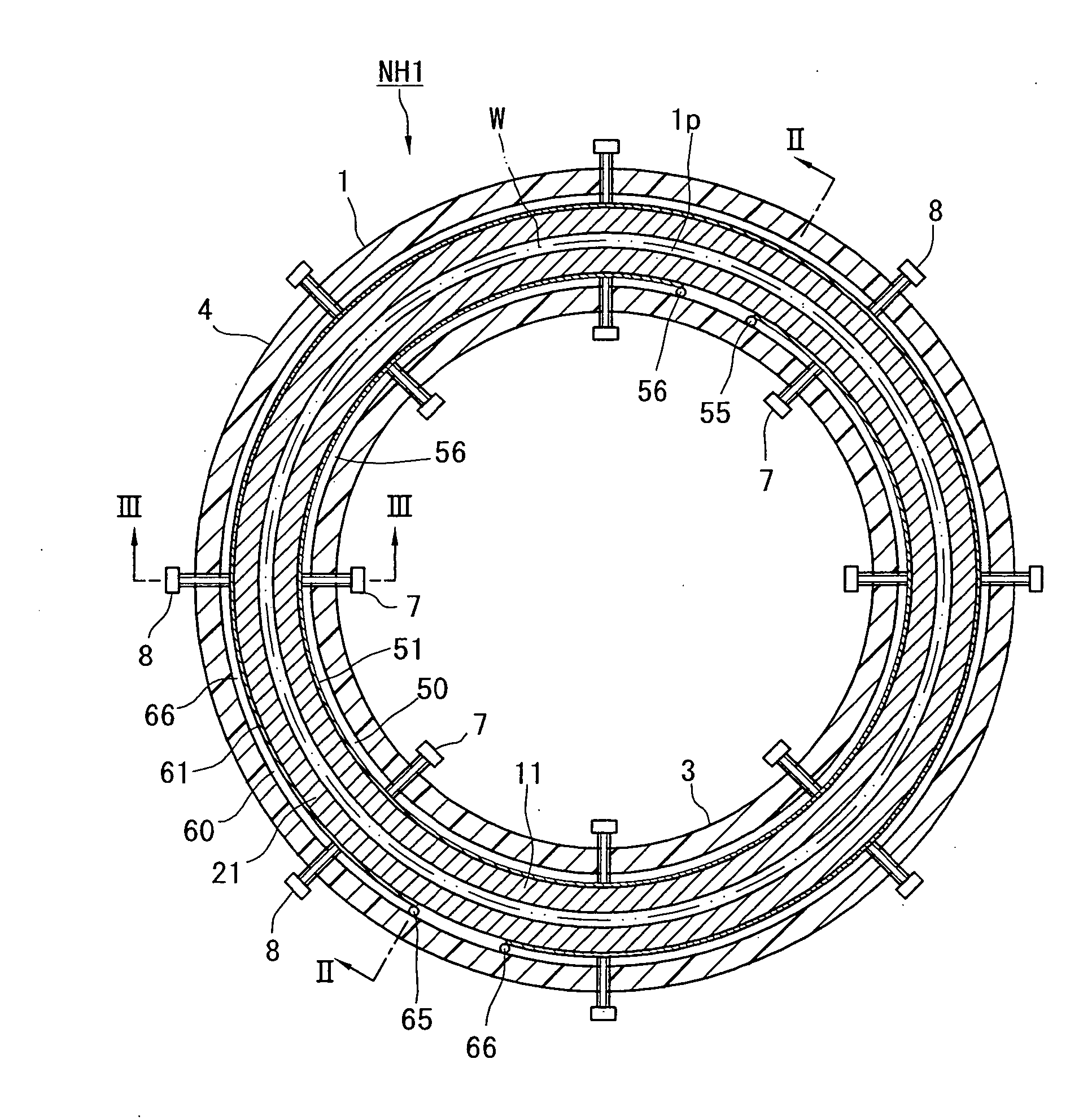
InactiveUS20060260748A1Satisfied with precisionGuaranteed ease of operationLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesEngineeringPlasma processing
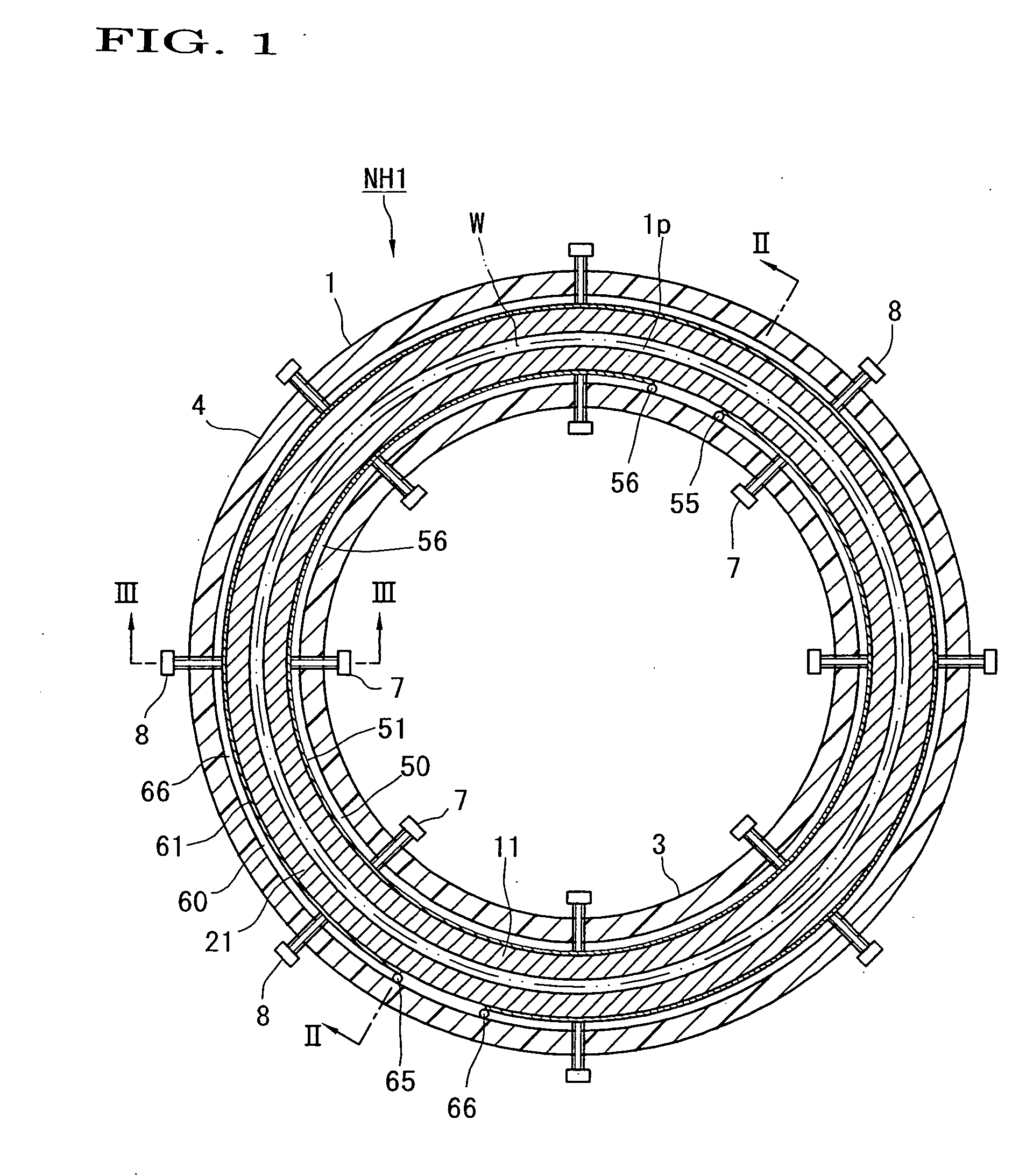
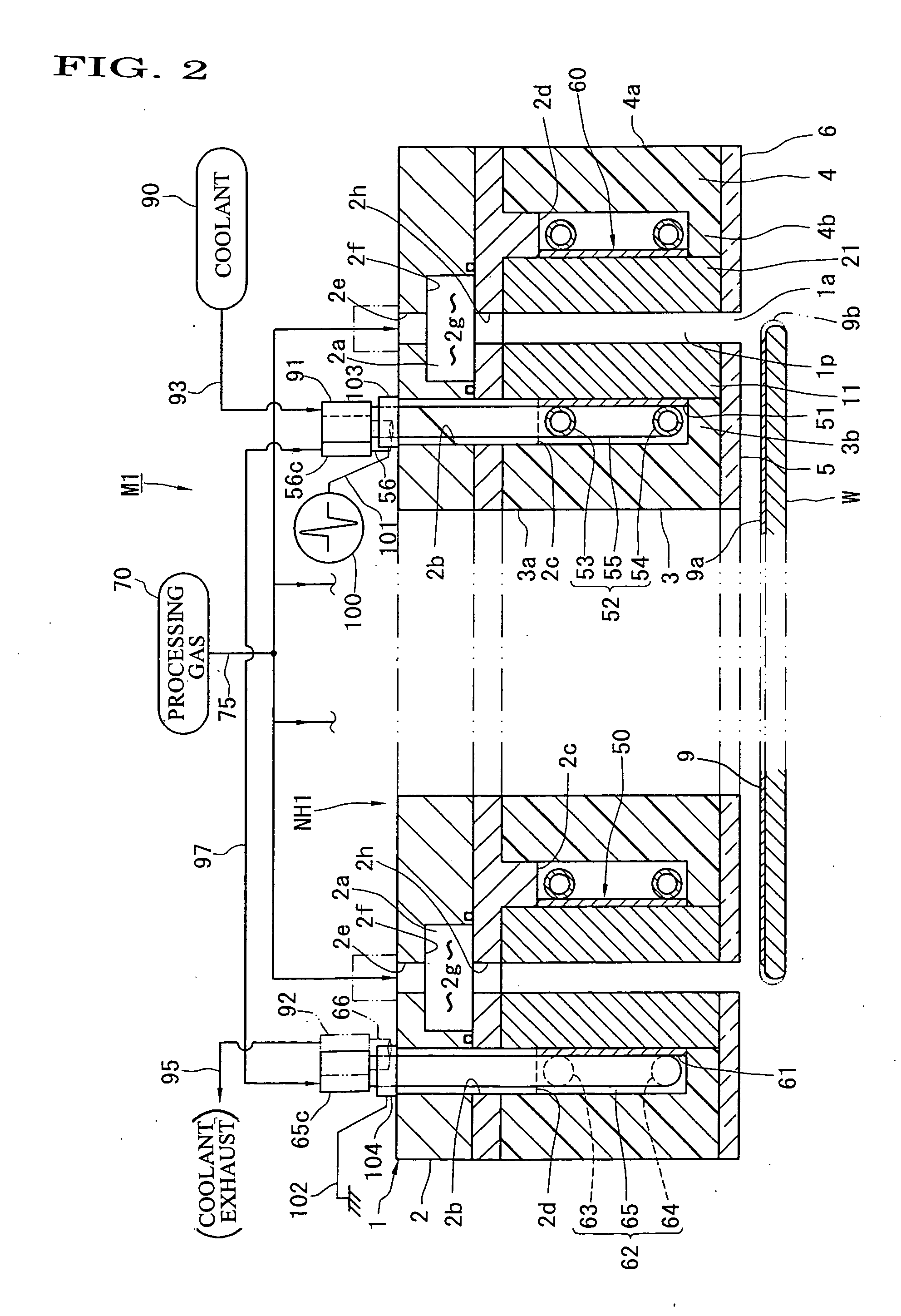
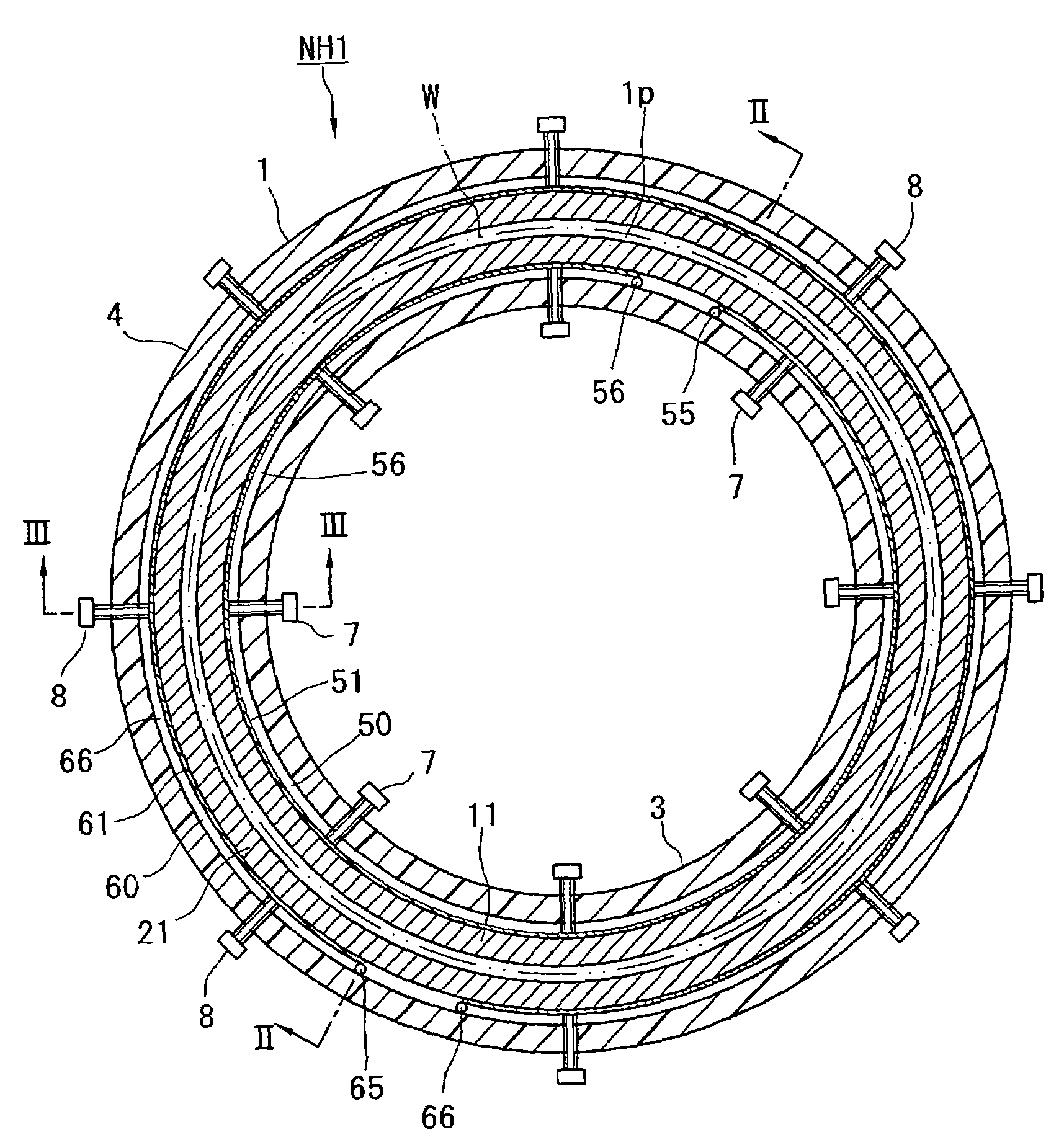
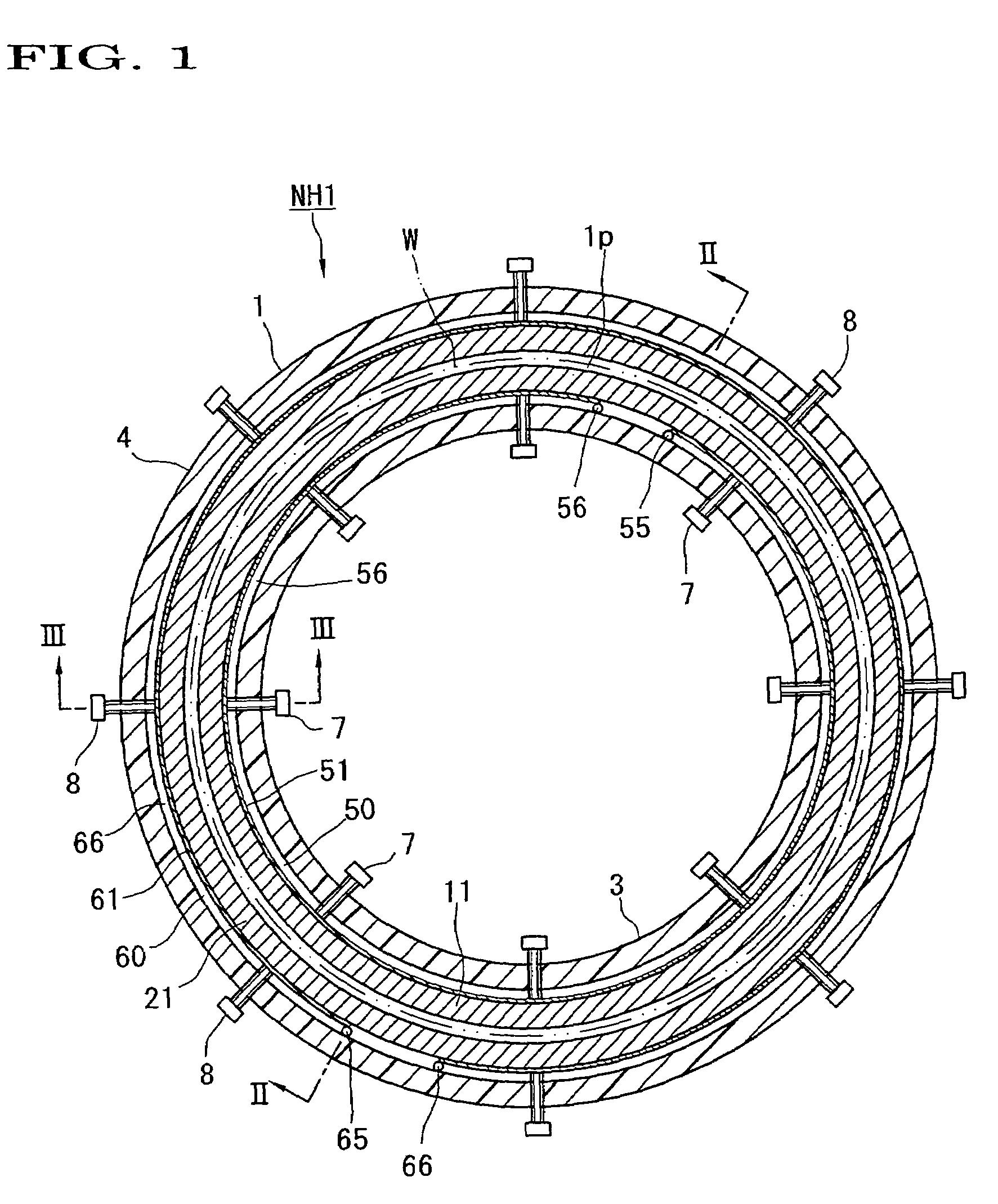
A nozzle head NH of a plasma processing apparatus comprises an annular inner holder 3, an annular inner electrode 11 surrounding this holder 3, an annular outer electrode 21 surrounding this electrode 11, and an annular outer holder 4 surrounding this electrode 21. The inner holder 3 is provided with a plurality of bolts 7 spacedly arranged in the peripheral direction and adapted to push the inner electrode 11 radially outwardly. The outer holder 4 is provided with a plurality of bolts 8 spacedly arranged in the peripheral direction and adapted to push the outer electrode 21 radially inwardly. Owing to this arrangement, the operation for disassembling, assembling and centering the annular electrodes 11, 21 can be carried out with ease.
Owner:SEKISUI CHEM CO LTD
System and method for precision detection of biomarkers
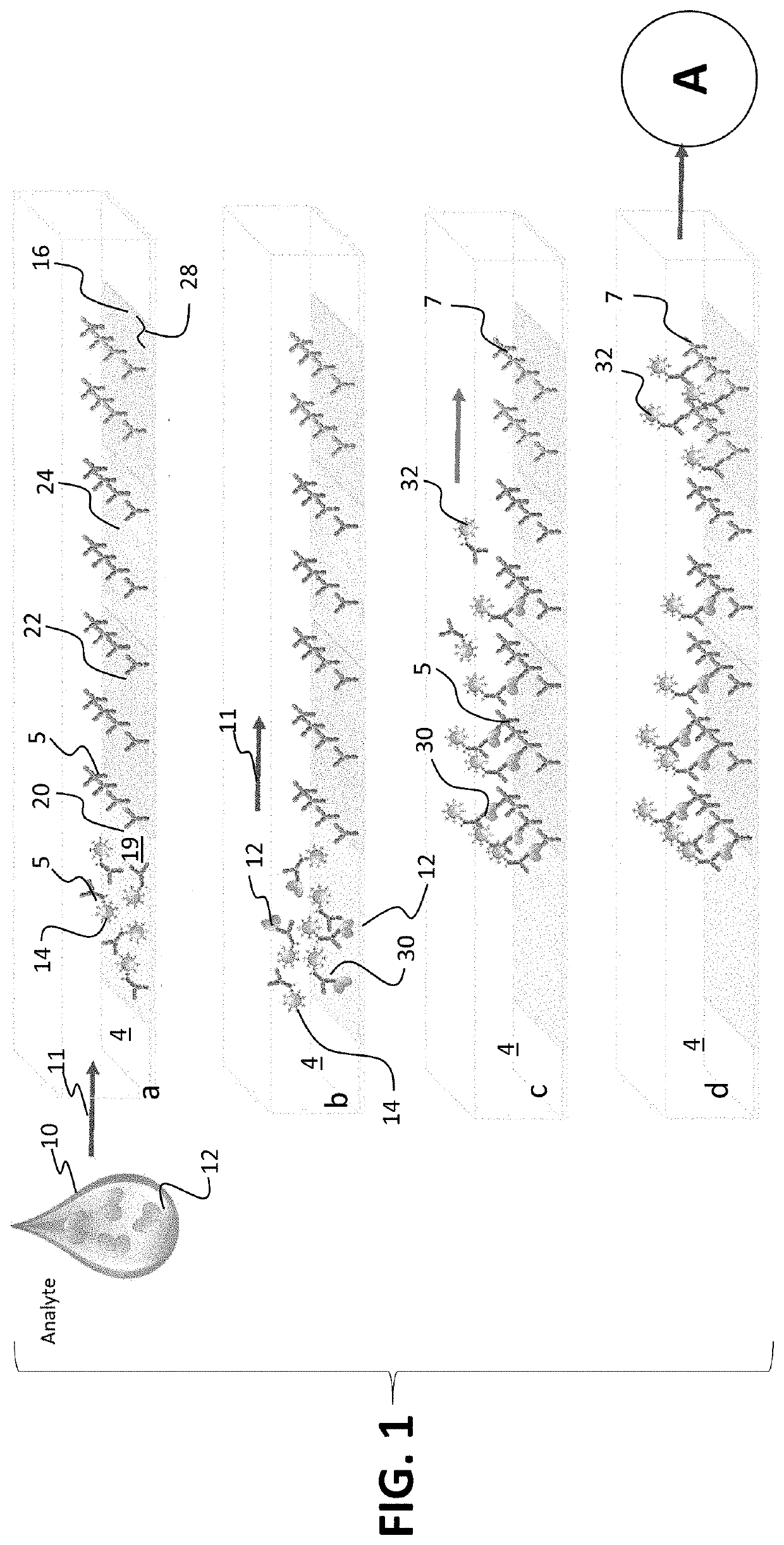
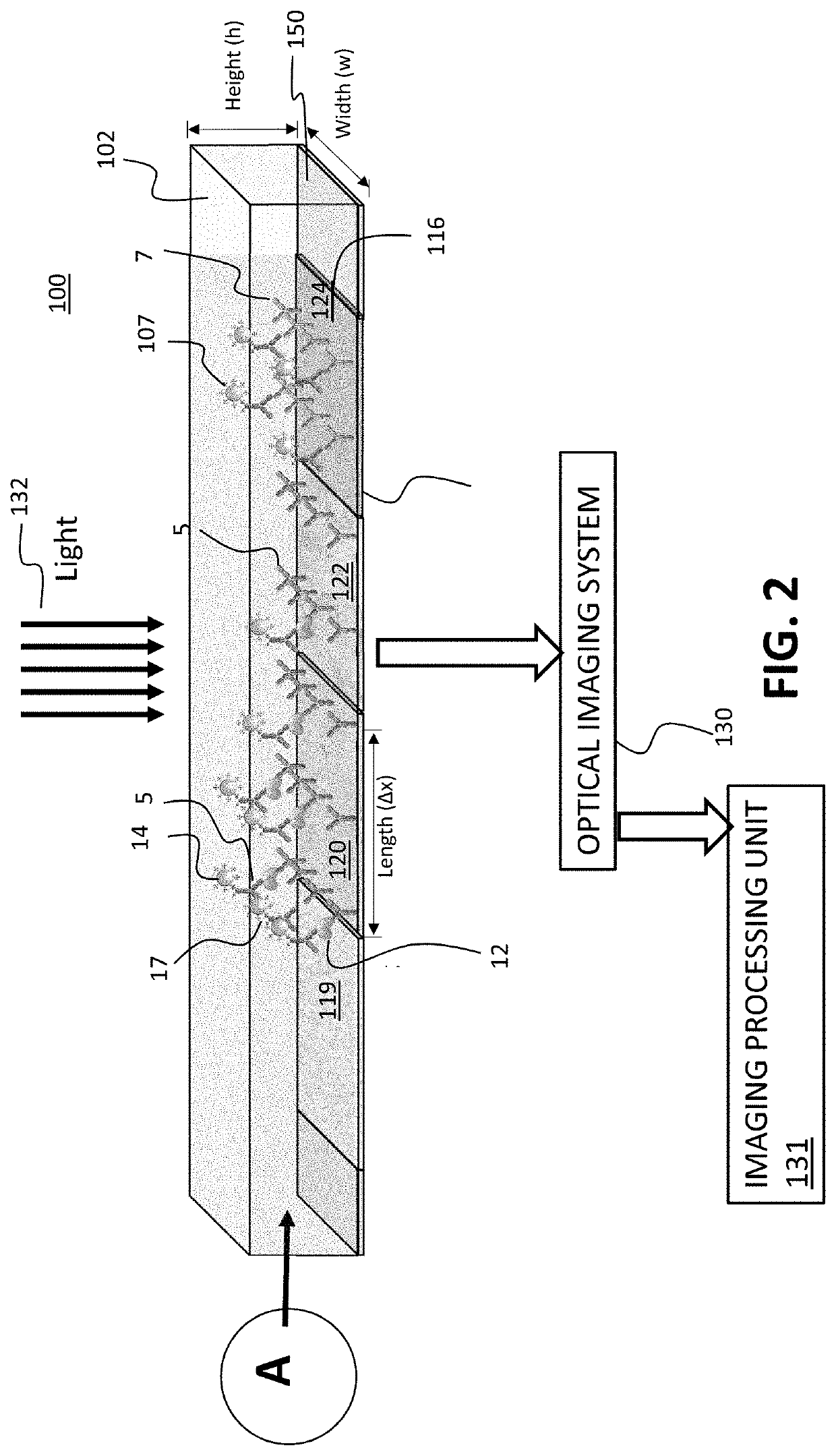
ActiveUS20200156074A1Improve accuracy and precisionOptimizing detection timePreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansPhysicsTested time
A method for detecting biomarkers with shortened test time and maximized precision. A sample from the body fluid is made to flow over a sensor surface coated with a capture antibody to allow binding of a biomarker in the sample to the capture body. An optical method detects and counts the individual binding events along the sensor surface with single molecule resolution, and difference in the binding events along the sensor surface is detected in real time and analyzed to determine the biomarker concentration.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Liquid material discharge method, wiring substrate manufacturing method, color filter manufacturing method, and organic el element manufacturing method
InactiveUS20080286442A1Satisfactory precisionSatisfied with precisionLiquid surface applicatorsElectroluminescent light sourcesEngineeringDischarge rate
A liquid material discharge method includes positioning a substrate and a discharge head having a plurality of nozzles to face each other, discharging droplets of a liquid material including a functional material onto the substrate in synchronization with a primary scanning for moving the discharge head and the substrate in relative manner, and varying one of a discharge timing and a discharge rate for discharging the droplets from at least one of the nozzles based on landing position information of the droplets that are discharged from the nozzles.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
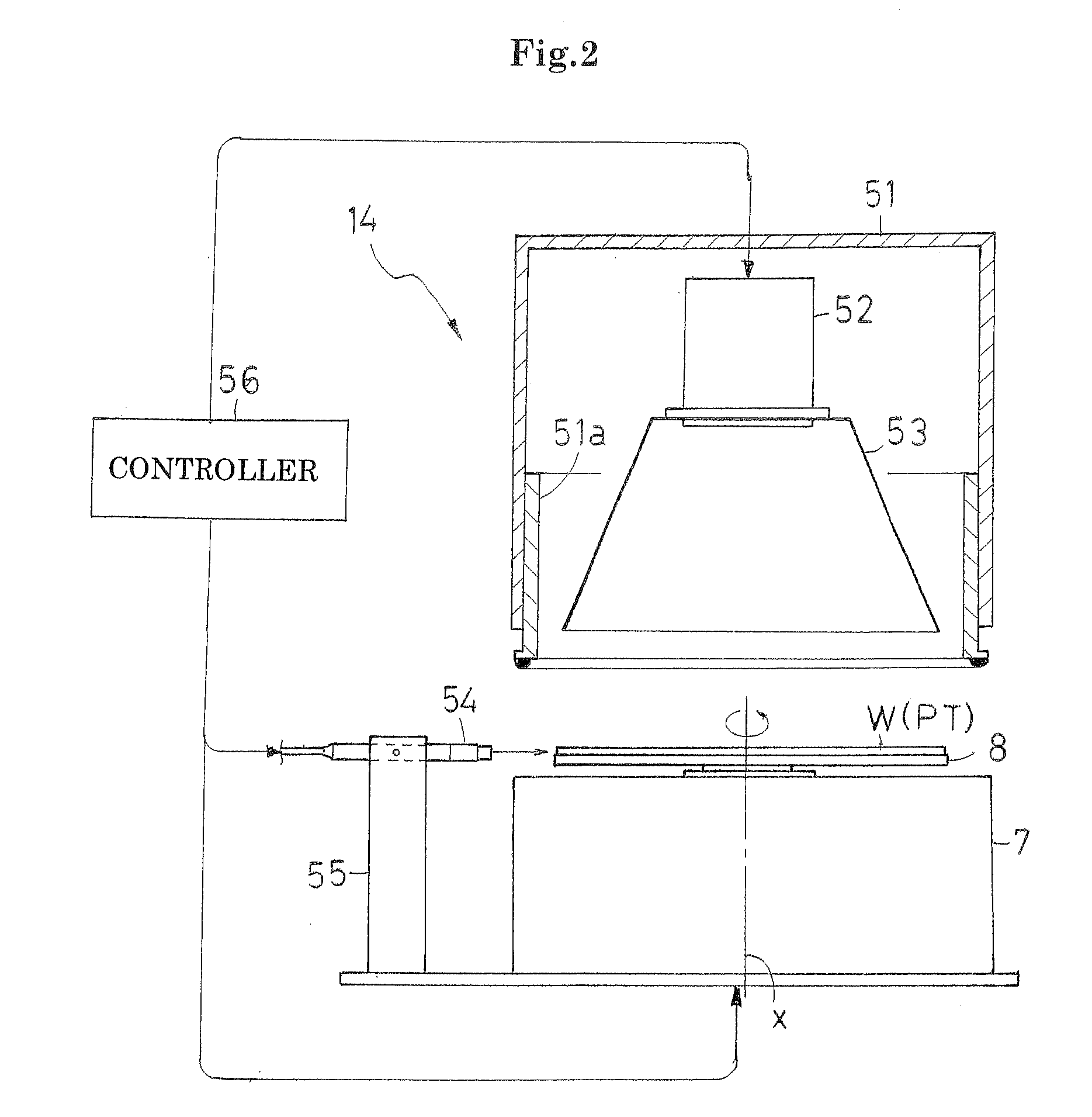
Ultraviolet irradiation method and apparatus using the same
InactiveUS20090095418A1Satisfied with precisionUniform curingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAdhesivesUltravioletUltraviolet irradiation
The ultraviolet ray is applied on the surface of the protective tape from an ultraviolet ray generator. In addition, the ultraviolet ray having intensity higher than that from the ultraviolet ray generator is applied on spot on the wafer edge by an irradiation gun. In this case, the ultraviolet ray intensity and the rotation speed of the holding table are controlled by a controller so that the ultraviolet irradiation amount per unit area of the wafer edge portion becomes equal to that to the joining surface of the protective tape.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Smooth non-linear springs, particularly smooth progressive rate steel springs, progressive rate vehicle suspensions and method
InactiveUS20080093786A1Satisfied with precisionEfficient designLeaf springsSprings/dampers functional characteristicsElastomerEngineering
Owner:OLEDZKI WIESLAW JULIAN
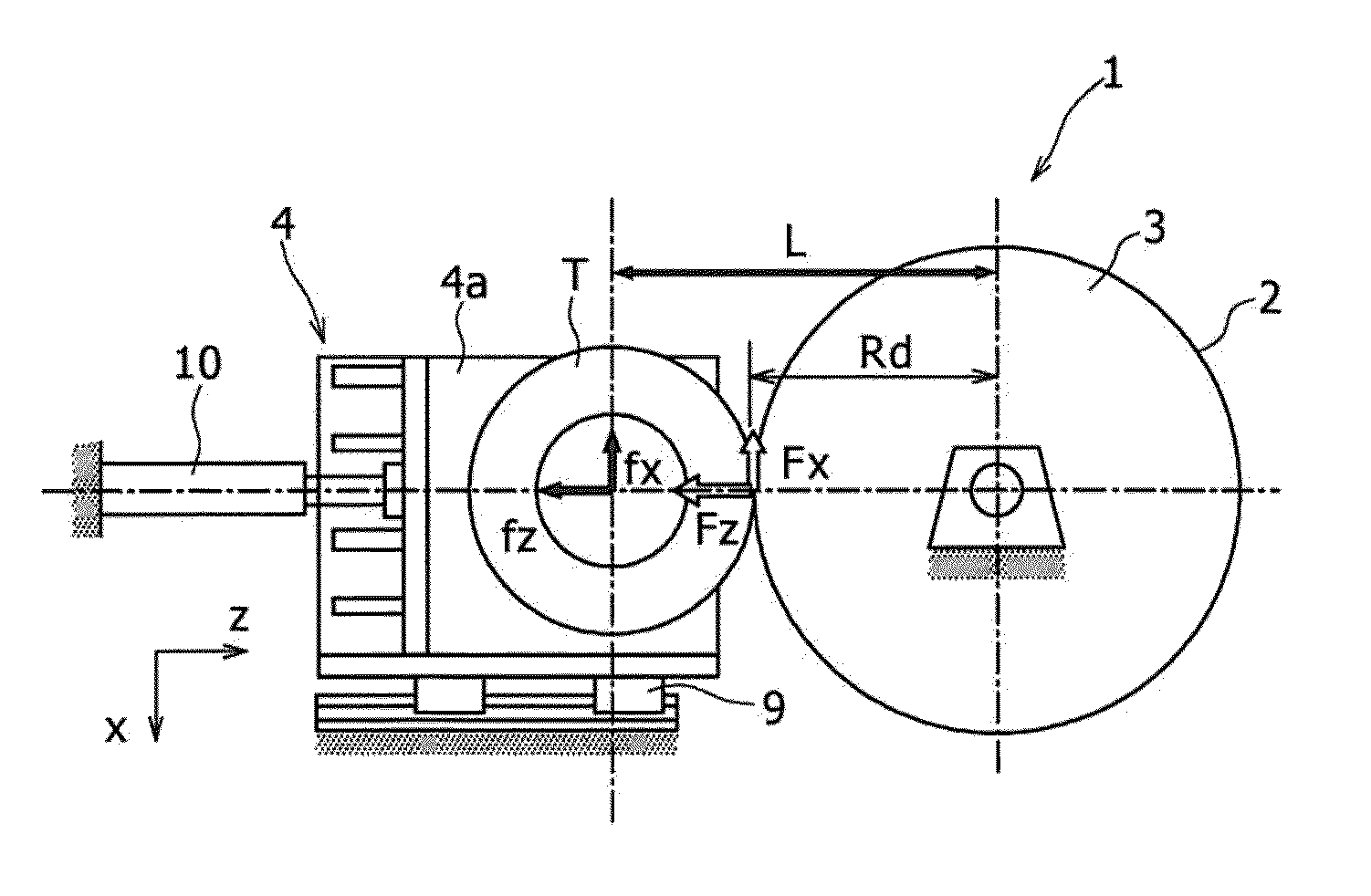
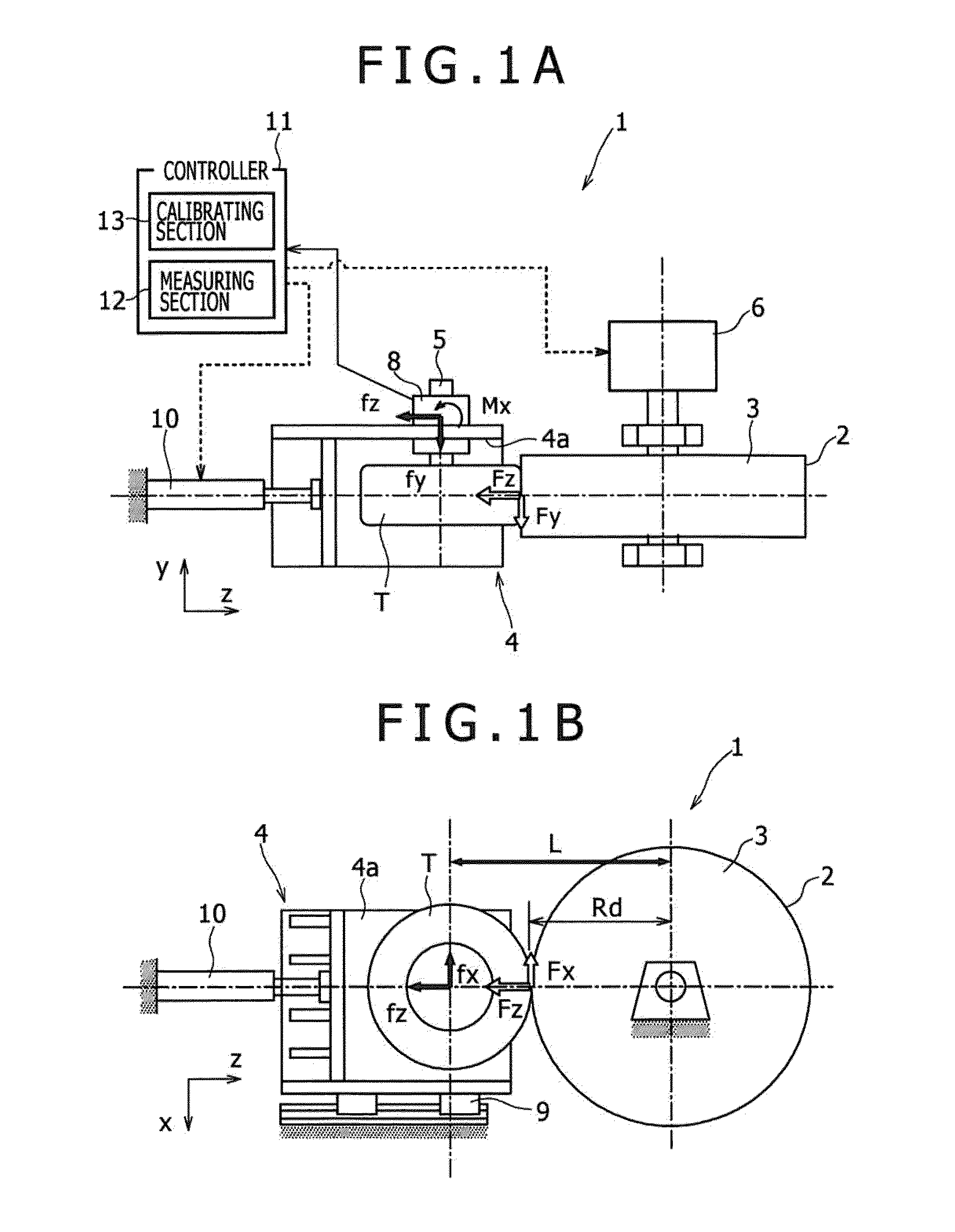
Calibration method for multi-component force detector provided in rolling resistance testing machine
ActiveUS20150143868A1Improve accuracyEasy and highly calibrationWeighing apparatus testing/calibrationForce/torque/work measurement apparatus calibration/testingRolling resistanceRoad surface
The calibration method for a multi-component force detector is a calibration method for a multi-component force detector provided in a rolling resistance testing machine comprising a spindle to which a tire is mounted, and a traveling drum having a simulated traveling road surface against which the tire is pressed, wherein when processing for calculating force acting on the tire from the measurement value of the multi-component force detector using a crosstalk correction factor for correcting the influence of crosstalk occurring in the multi-component force detector is performed, a test is conducted using at least one or more reference tire the rolling resistance value of which is already known, and the crosstalk correction factor is calibrated using “rolling test data” composed of force measured by the multi-component force detector during the test using the reference tire, and the rolling resistance value of the reference tire used for the measurement.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Flow rate measuring method and flowmeter, flow rate measuring section package used for them and flow rate measuring unit using them, and piping leakage inspection device using flowmeter
InactiveUS20050155421A1Satisfied with precisionSatisfactory sensitivityMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsTemperature controlEngineering
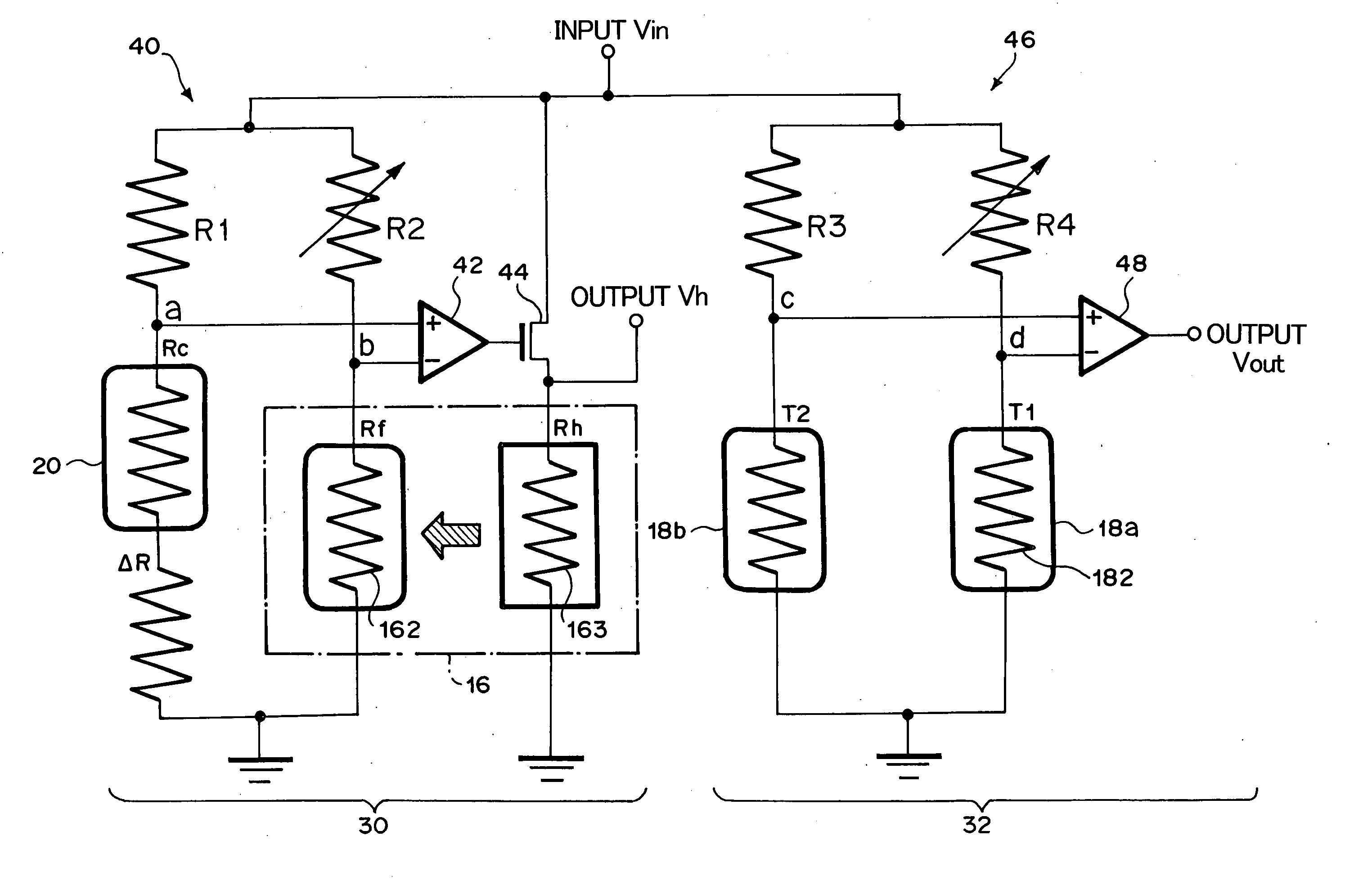
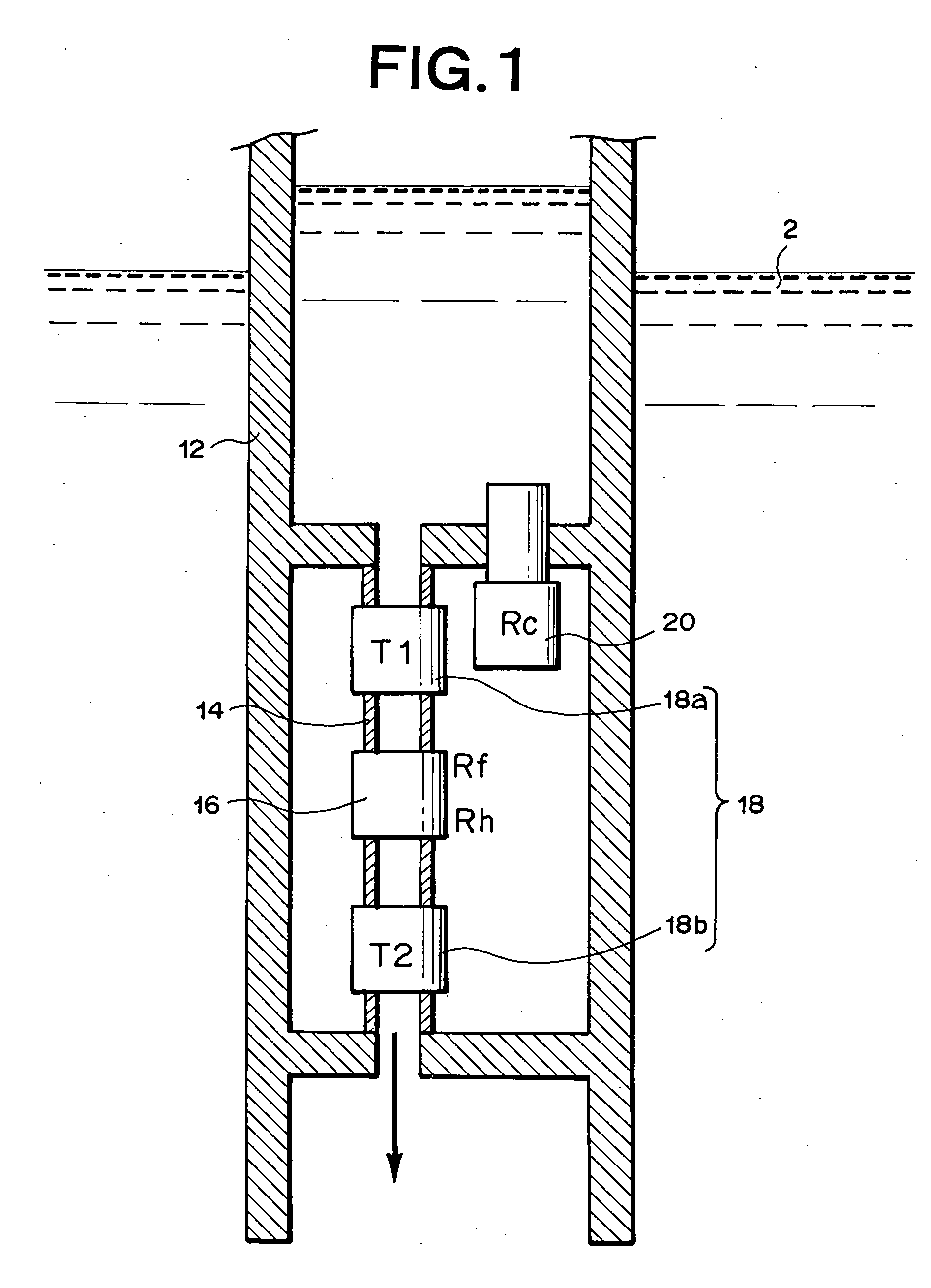
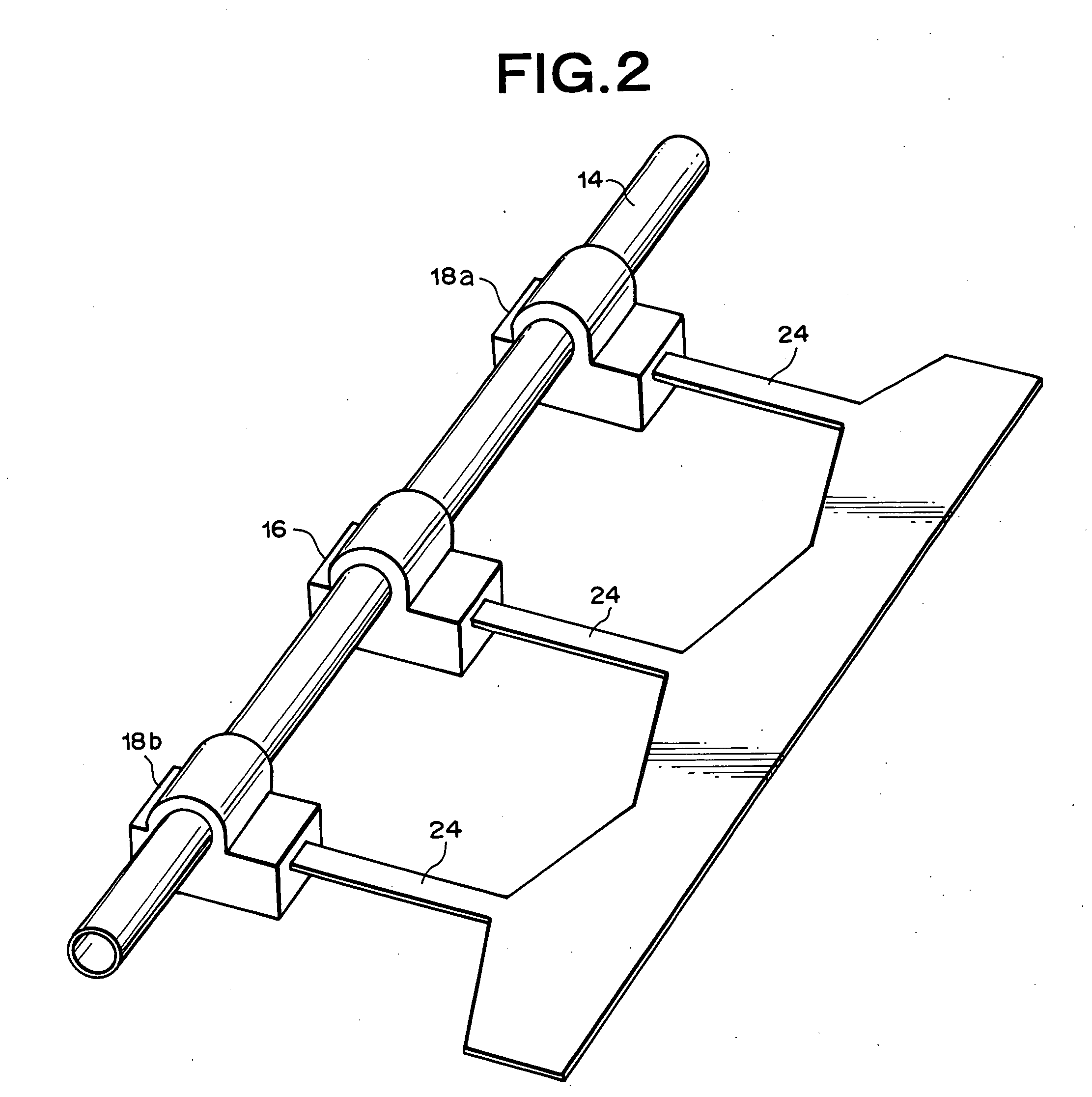
Measurements are obtained by a computing unit based on an output Vh from an indirectly-heated constant-temperature controlling flow rate measuring section (16) and an output Vout from a two-constant-point temperature difference detecting flow rate measuring sections (18a, 18b). In the flow rate measuring section (16), a heating element (163) is feedback-controlled based on a detected temperature by a heat sensing element (162) to obtain an output Vh based on the feedback-controlled condition. An output Vout is obtained from flow rate measuring sections (18a, 18b) based on the detected temperature difference between a heat sensing element (182) disposed on the liquid-flow-direction upstream side of the flow rate measuring section (16) and a temperature sensing element disposed on the downstream side. A computing unit outputs as a measurement a flow rate obtained based on the output Vh in a flow rate region where a flow rate is larger than a predetermined boundary flow rate, and outputs as a measurement a flow rate obtained based on the output Vout in a flow rate region where it is less than a boundary flow rate. Accordingly, a flow rate is measured with good precision and sensitivity over a wide flow rate range from a trace-amount flow rate region to a comparatively large flow rate region.
Owner:SAN-A
Controller
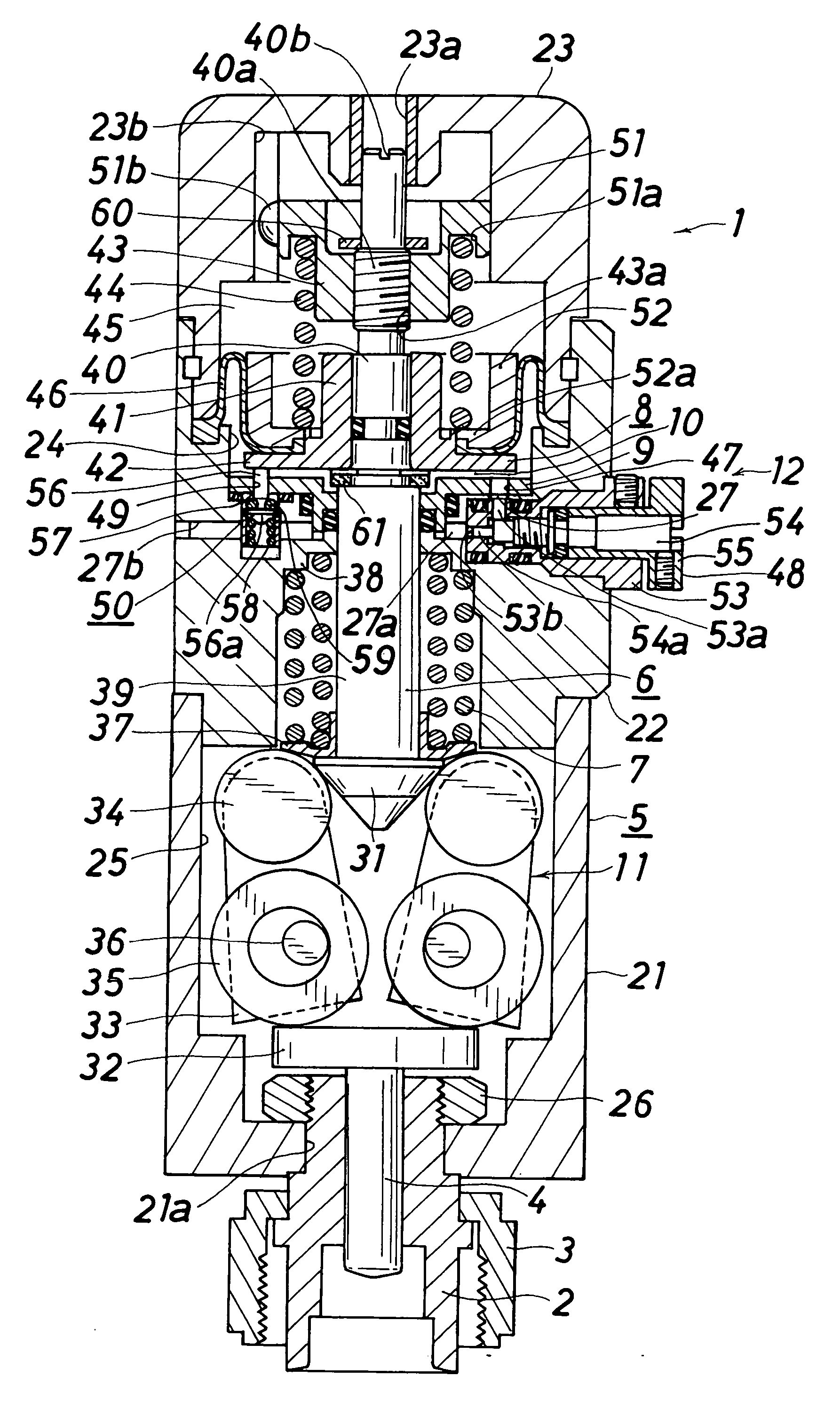
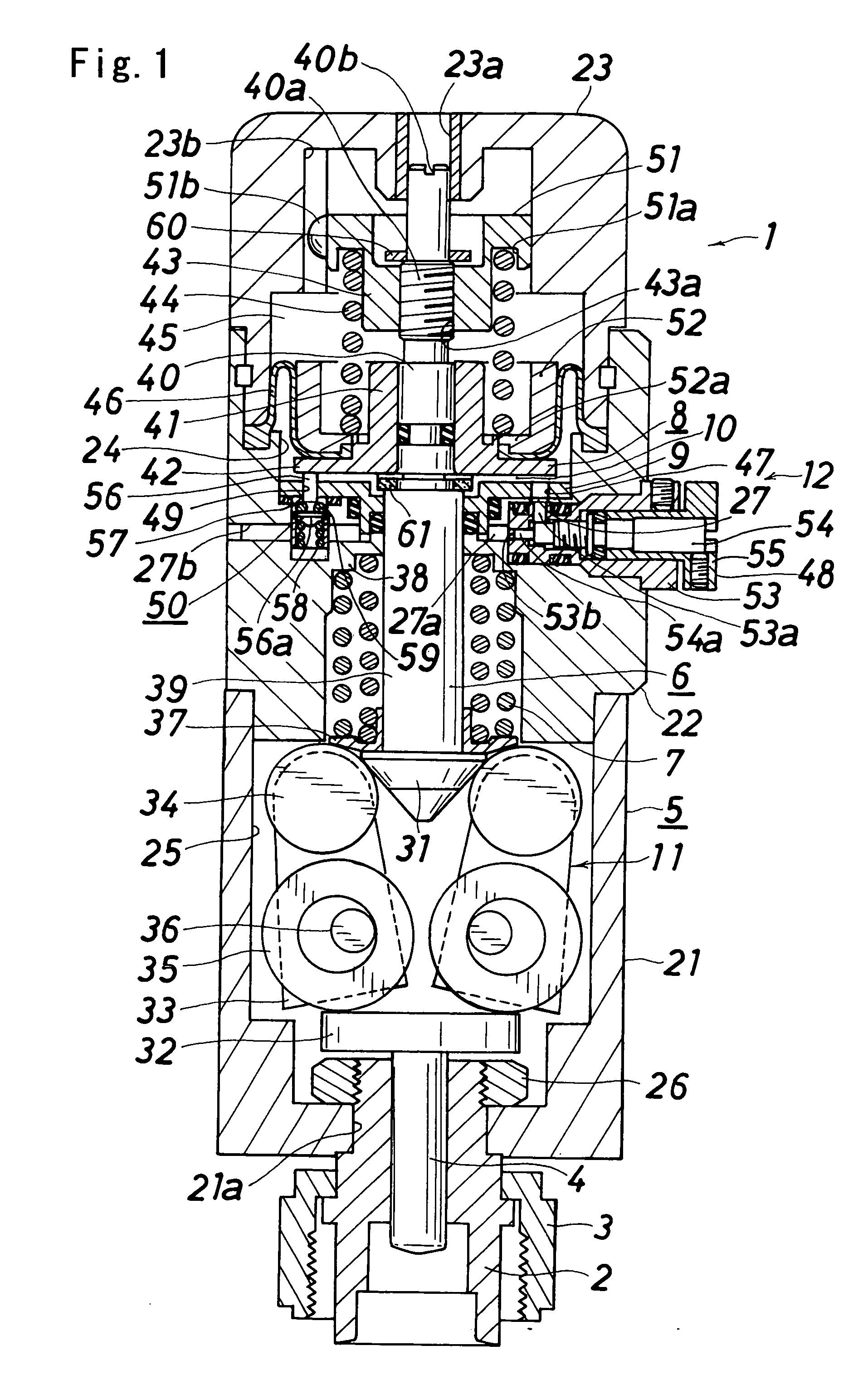
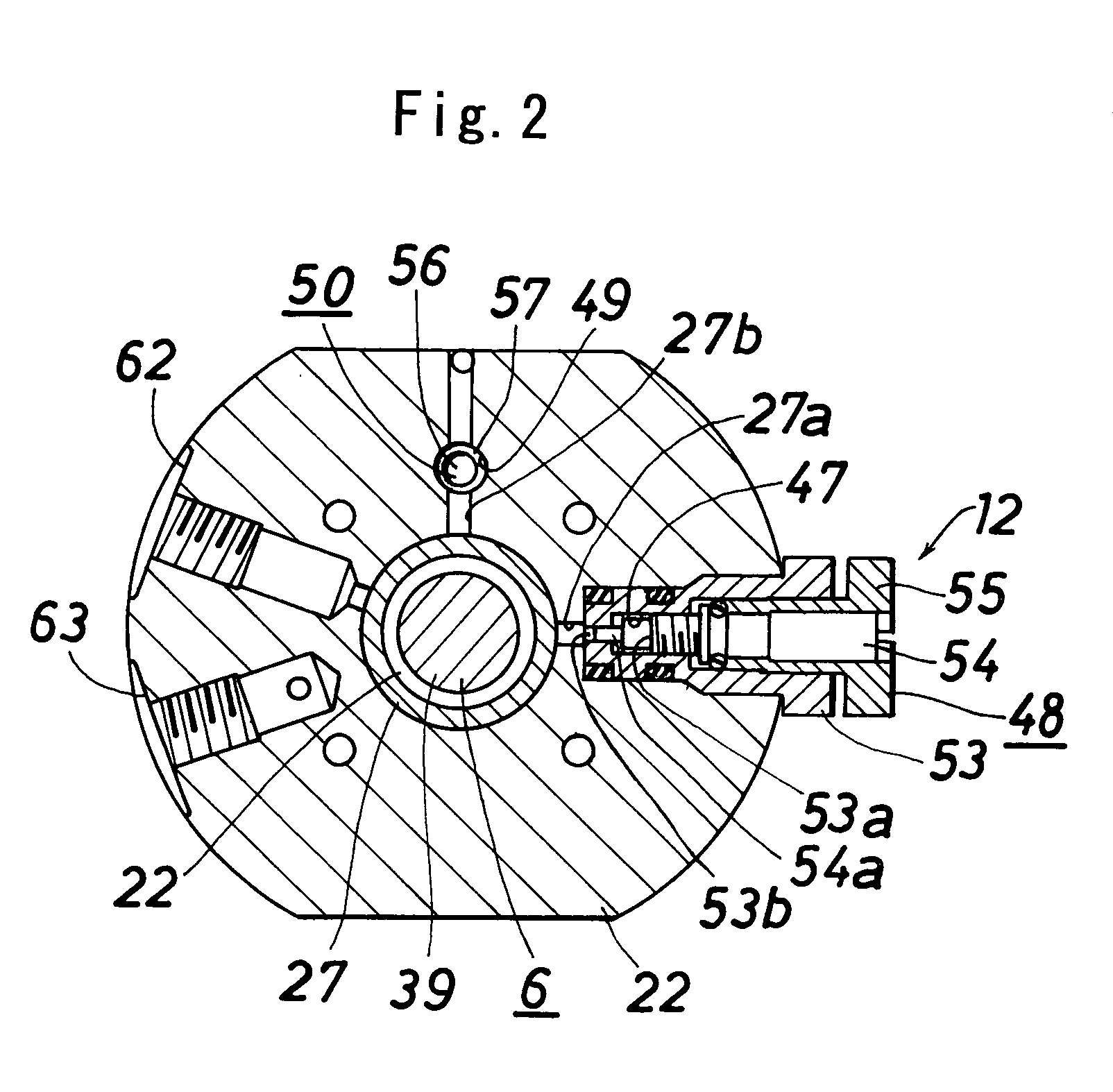
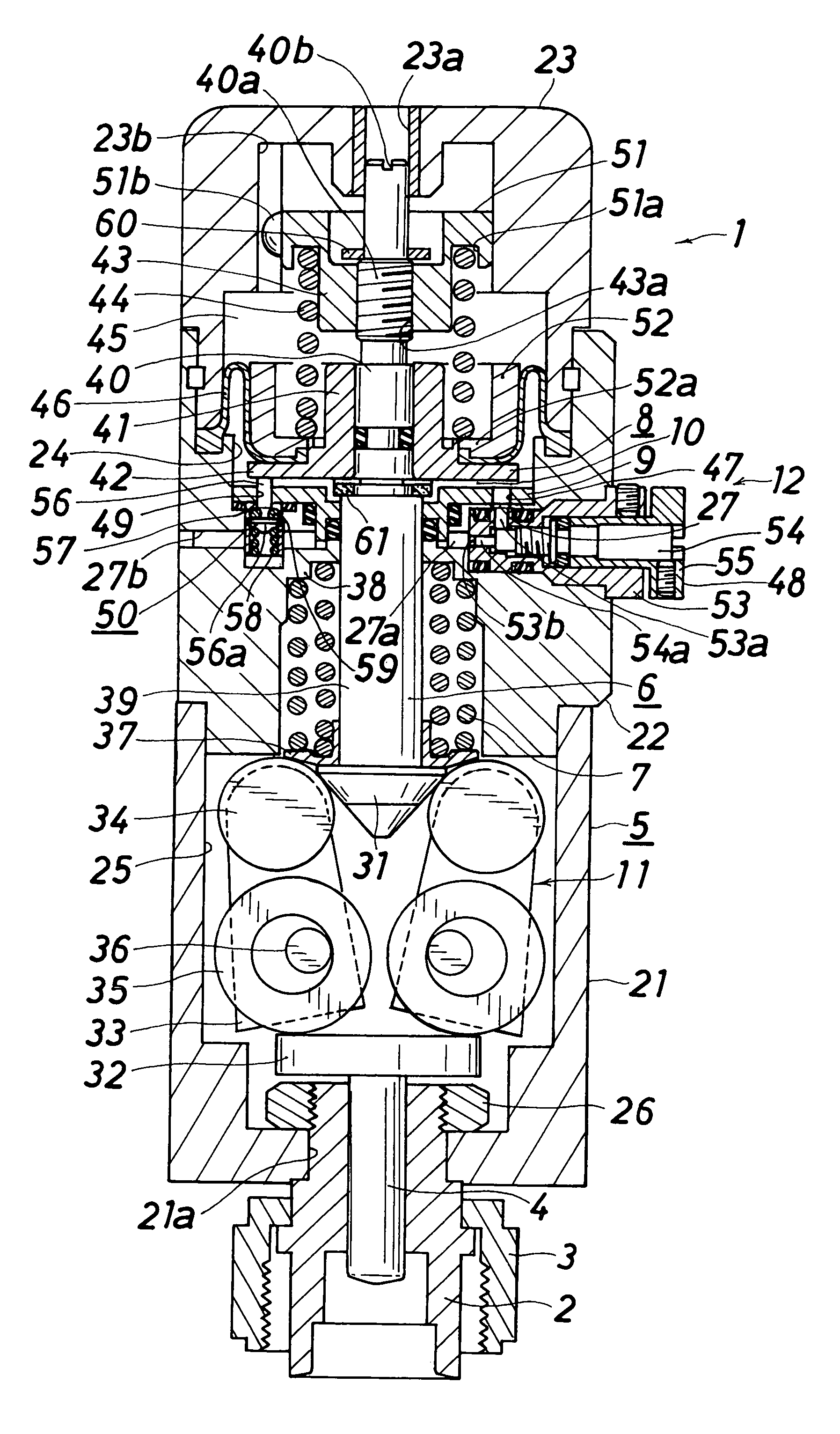
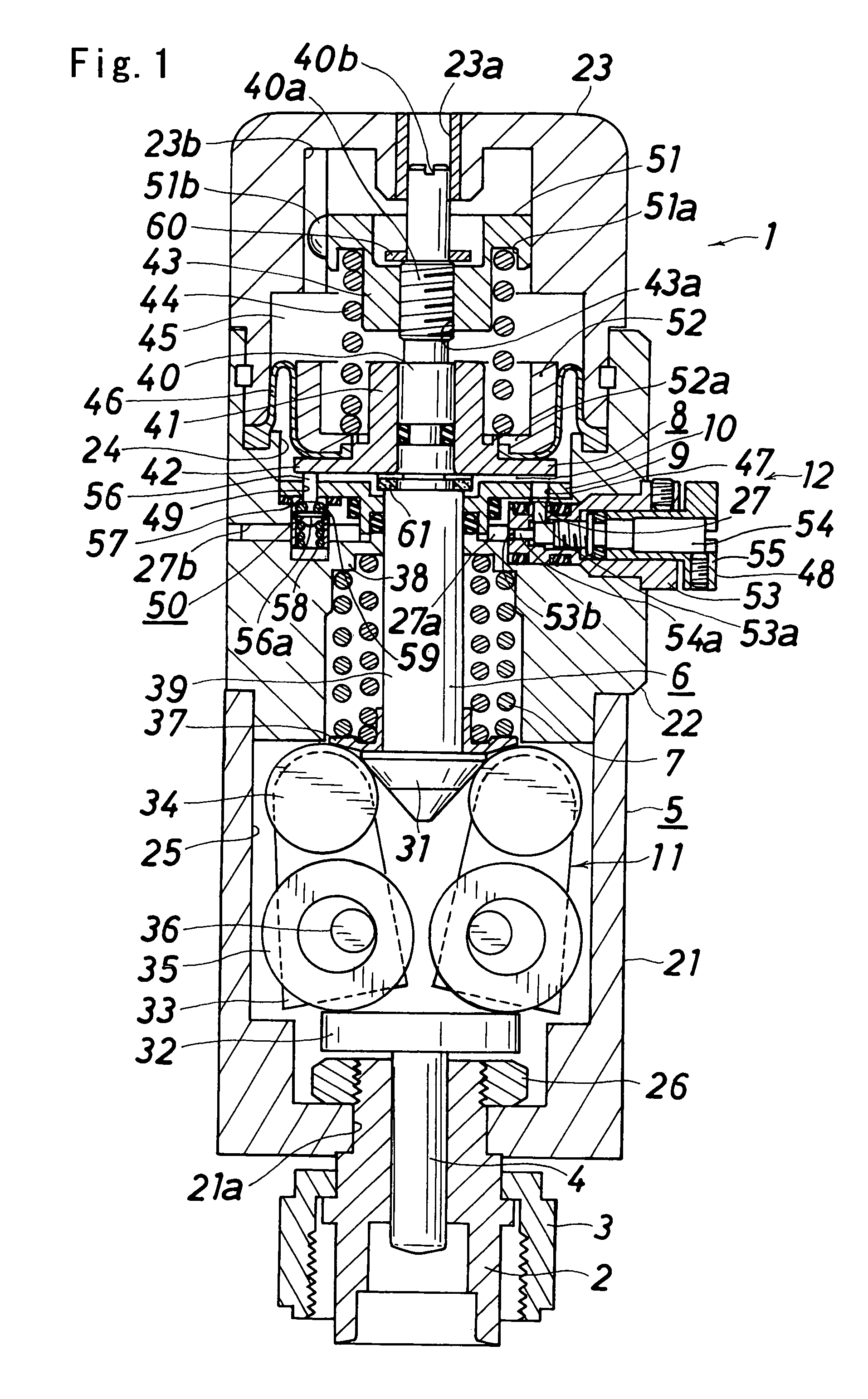
InactiveUS20070120080A1Reduce trafficReduce flow rateOperating means/releasing devices for valvesGearingEngineeringVALVE PORT
A controller comprises power transmitting means (11) for amplifying the force applied on the operating shaft (6) and transmitting to the valve rod (4); and a slow start means (12) for slowly moving the operating shaft (6) upward are arranged. The slow start means (12) includes a piston (8) that moves up and down with respect to the operating shaft (6); a pressure spring (44), arranged between a pressure spring receiver (43) arranged at the operating shaft. (6) and the piston (8); a constantly opened communication passage (47) and an auxiliary communication passage (49) for communicating the pressure chamber (10) and the operation gas introducing chamber (27); a flow adjusting valve (48) provided in the constantly opened communication passage (47); and an open-close valve (50), arranged in the auxiliary communication passage (49), for opening the communication passage (49) when the piston (8) is at the lower most position and closing the communication passage (49) when raised from the lower most position by a predetermined distance and reaching the auxiliary communication shut off position.
Owner:FUJIKIN INC
Multi-beam light scanning optical system and image forming apparatus using same
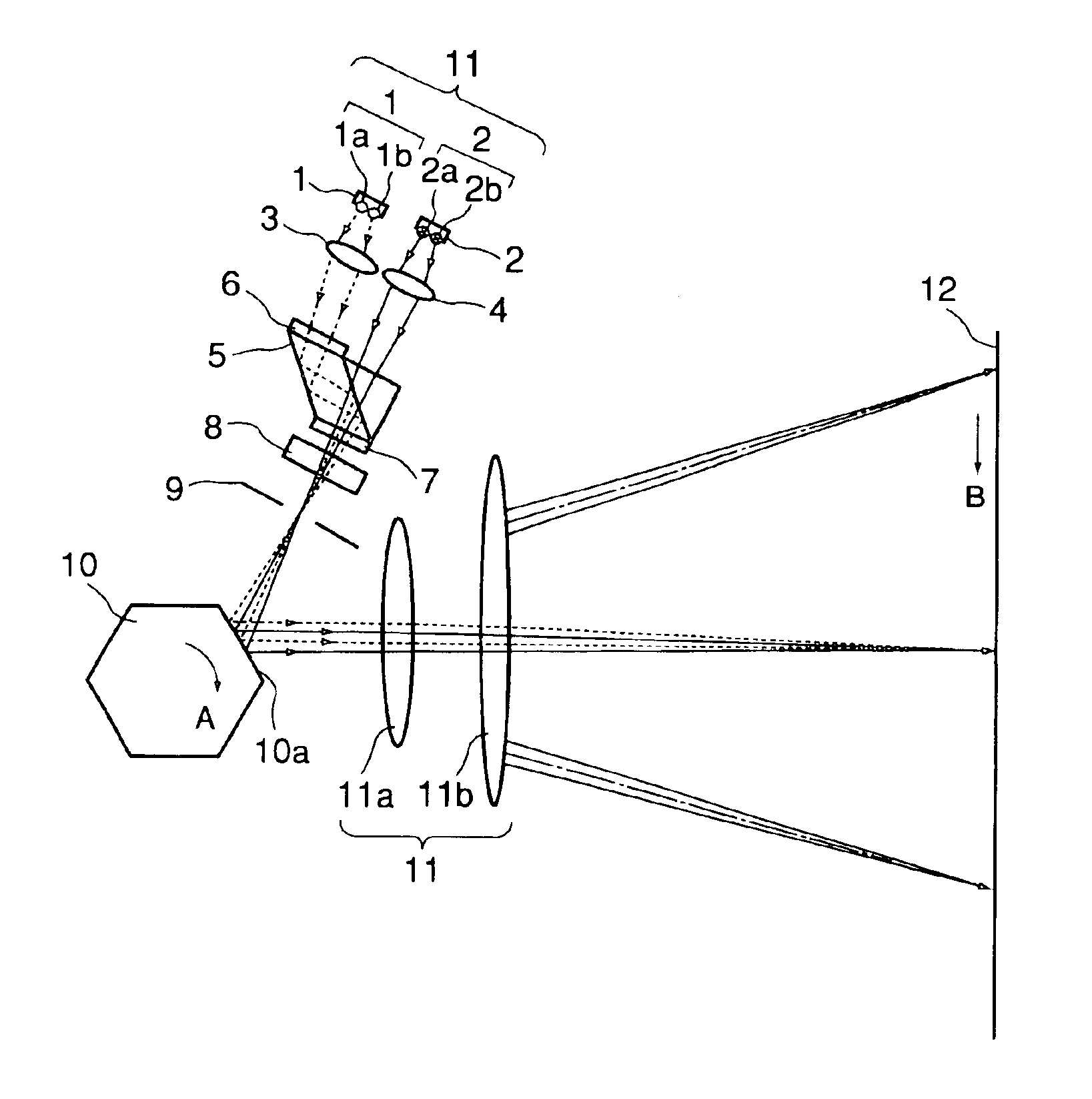
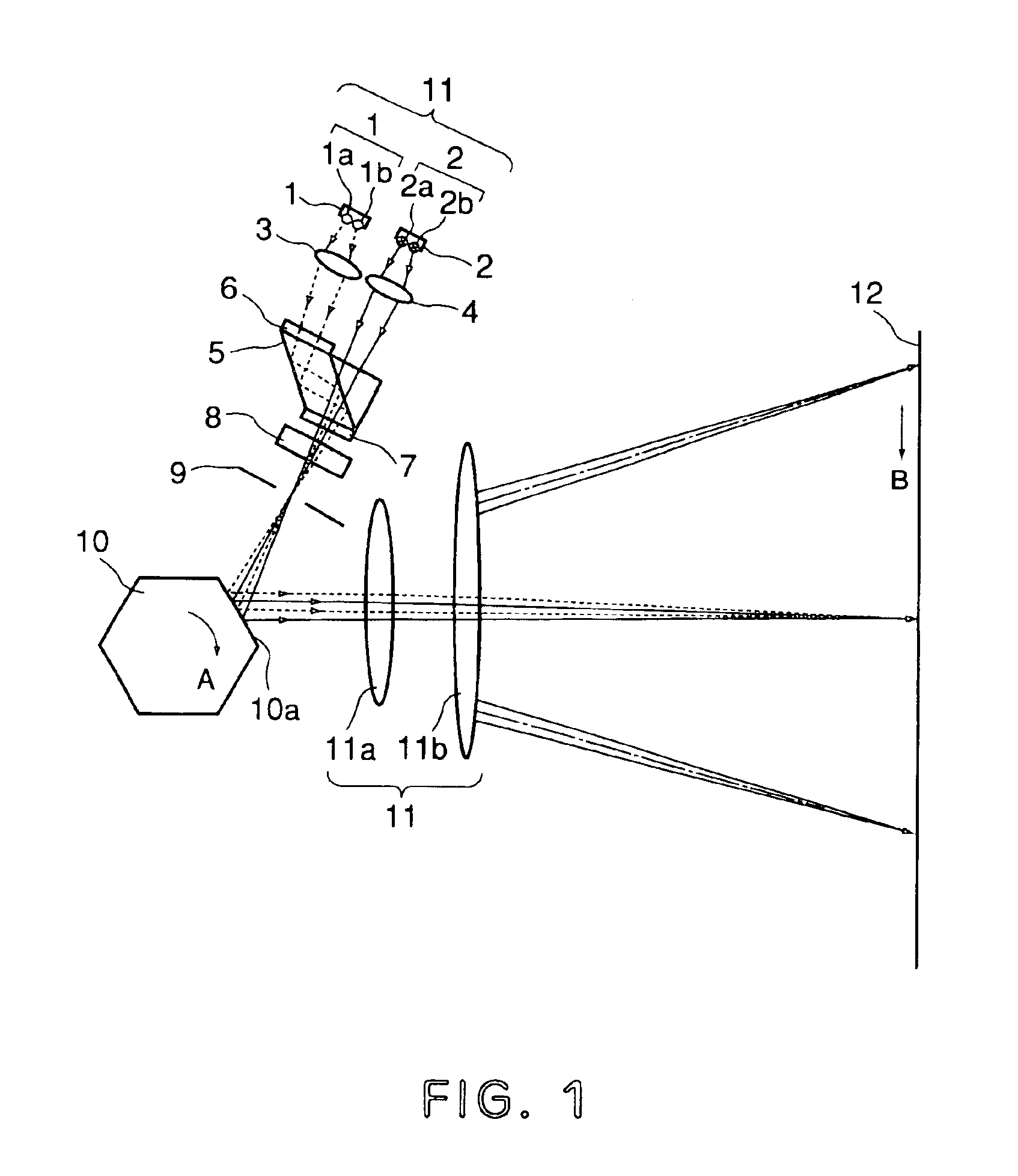
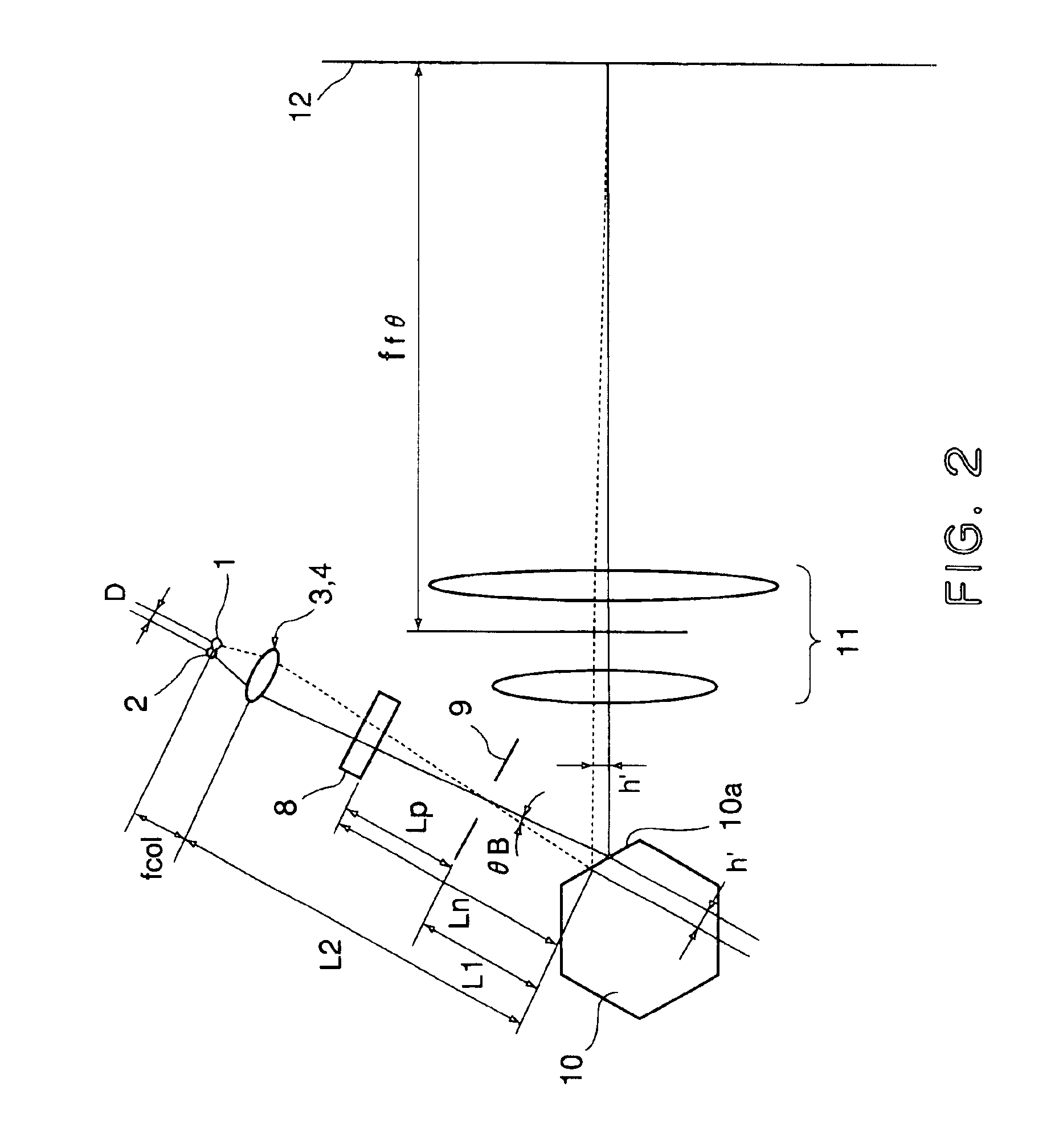
InactiveUS6930812B2Image performanceSatisfactory printing precisionInking apparatusBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsLight beamImage formation
A multi-beam light scanning optical system includes n (n≧2) light source means having m (m≧2) light emitting points; beam synthesizing means for synthesizing n×m light beams emitted by the light source means; deflecting means for deflecting n×m light beams from the beam synthesizing means; an imaging optical system for imaging the n×m light beams from the deflecting means on a surface to be scanned, wherein the surface to be scanned is scanned in a main scan direction with n×m light beams by a deflection scanning operation of the deflecting means; an aperture stop provided between the beam synthesizing means and the deflecting means, wherein principal rays of the n×m light beams are intersected at a position of the aperture stop, and the light beams which are adjacent to each other in a sub-scan direction on the surface to be scanned are the beams emitted from different ones of the light source means.
Owner:CANON KK
Controller
InactiveUS7677528B2Satisfied with precisionReduce trafficOperating means/releasing devices for valvesGearingEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:FUJIKIN INC
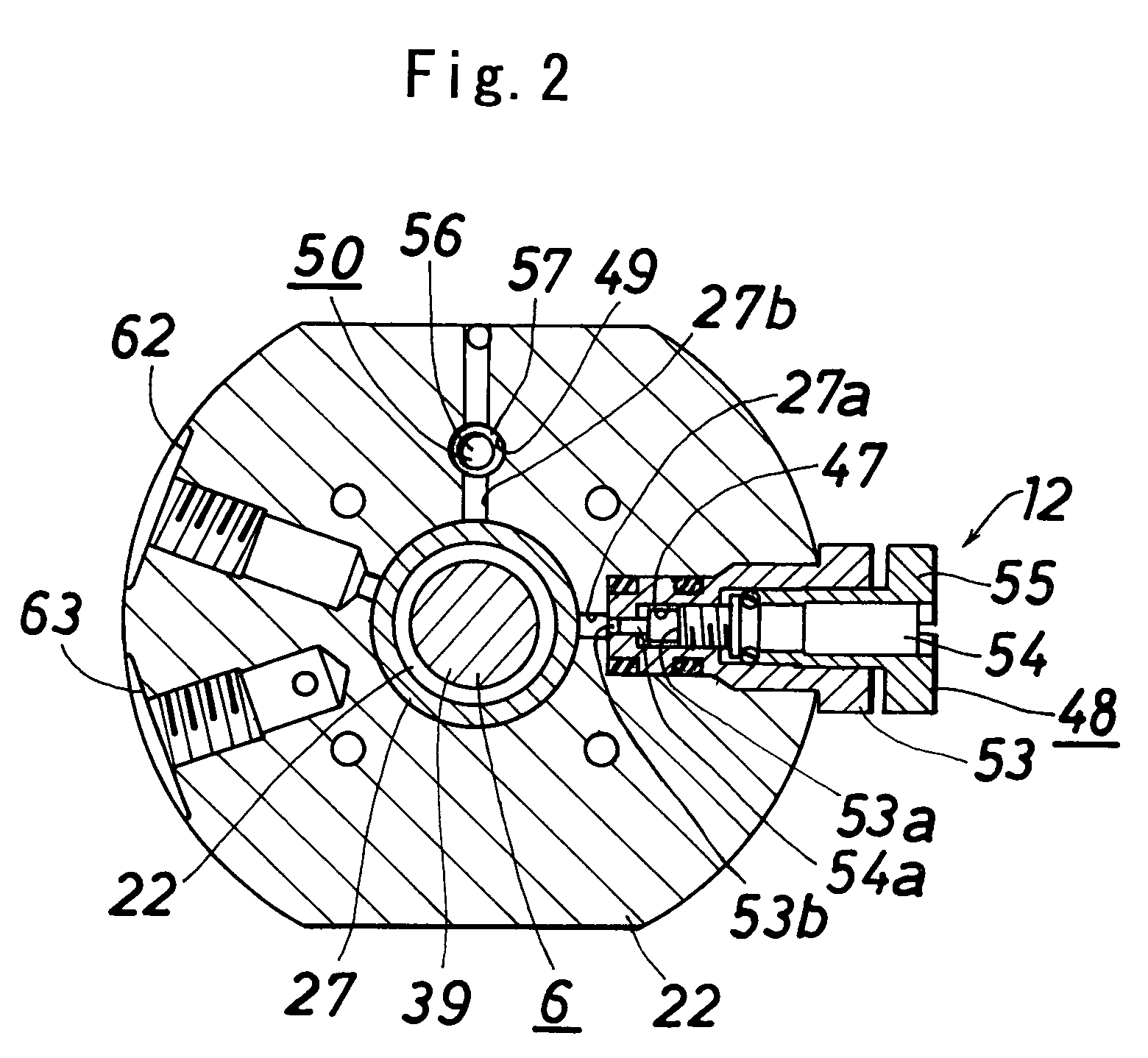
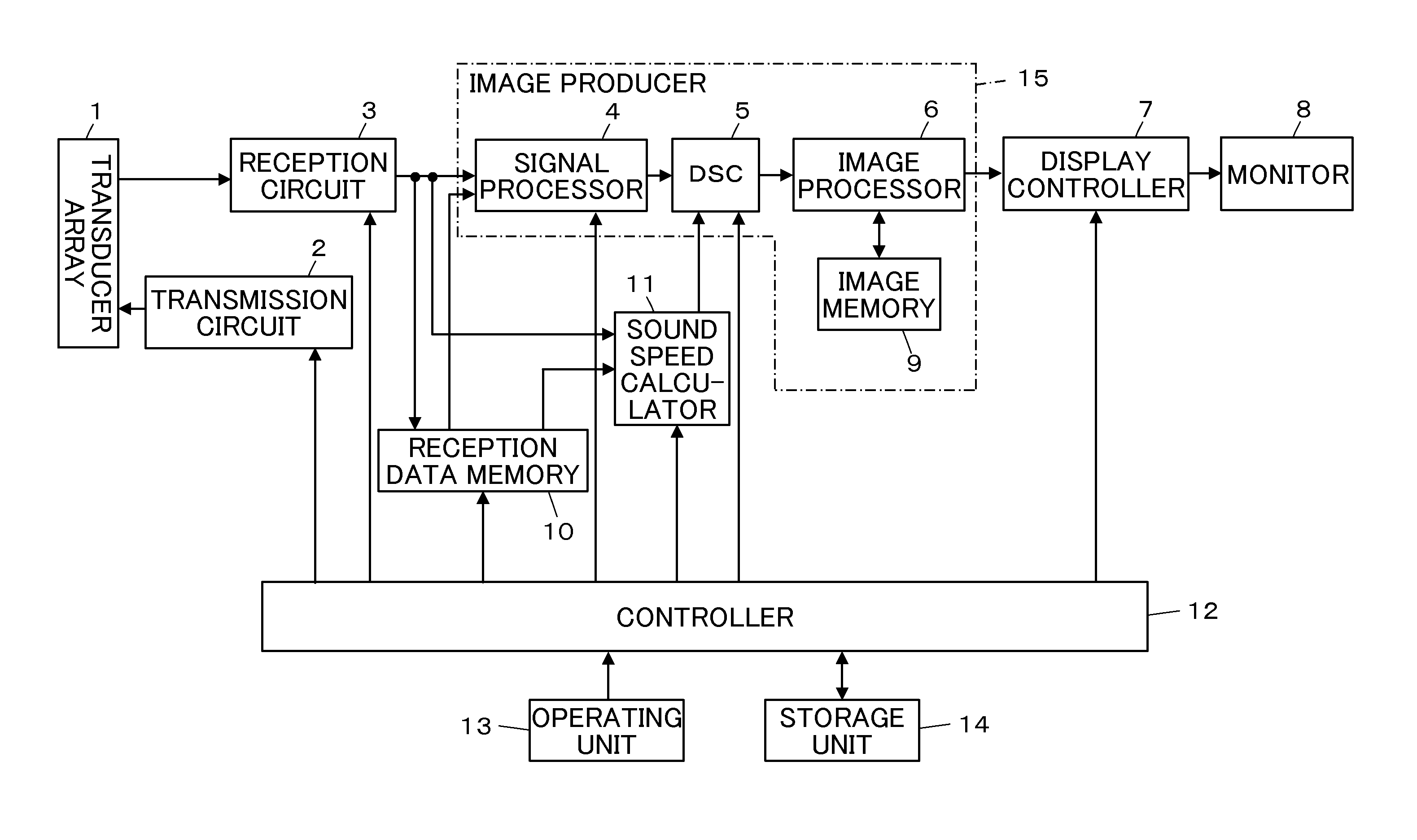
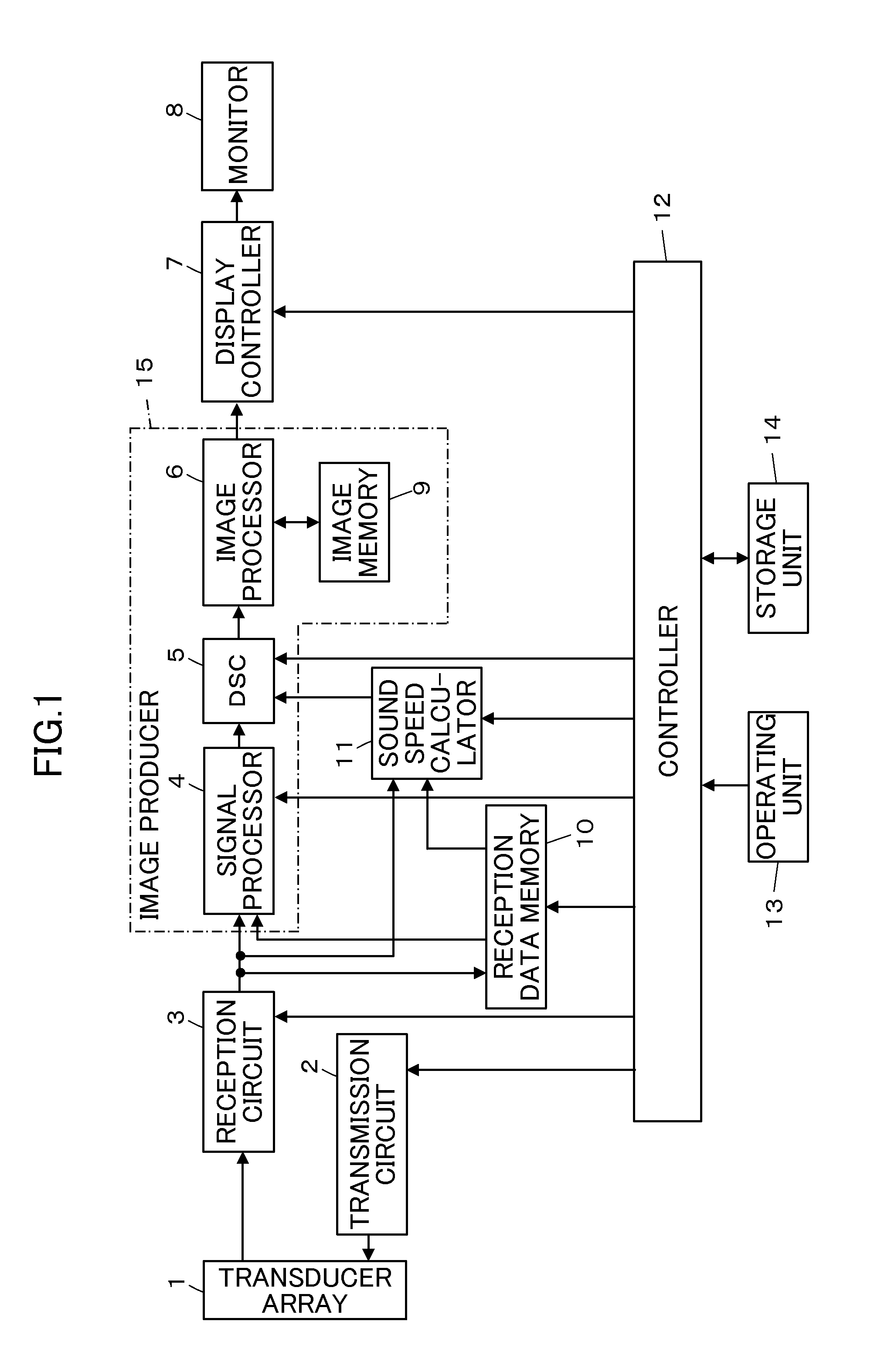
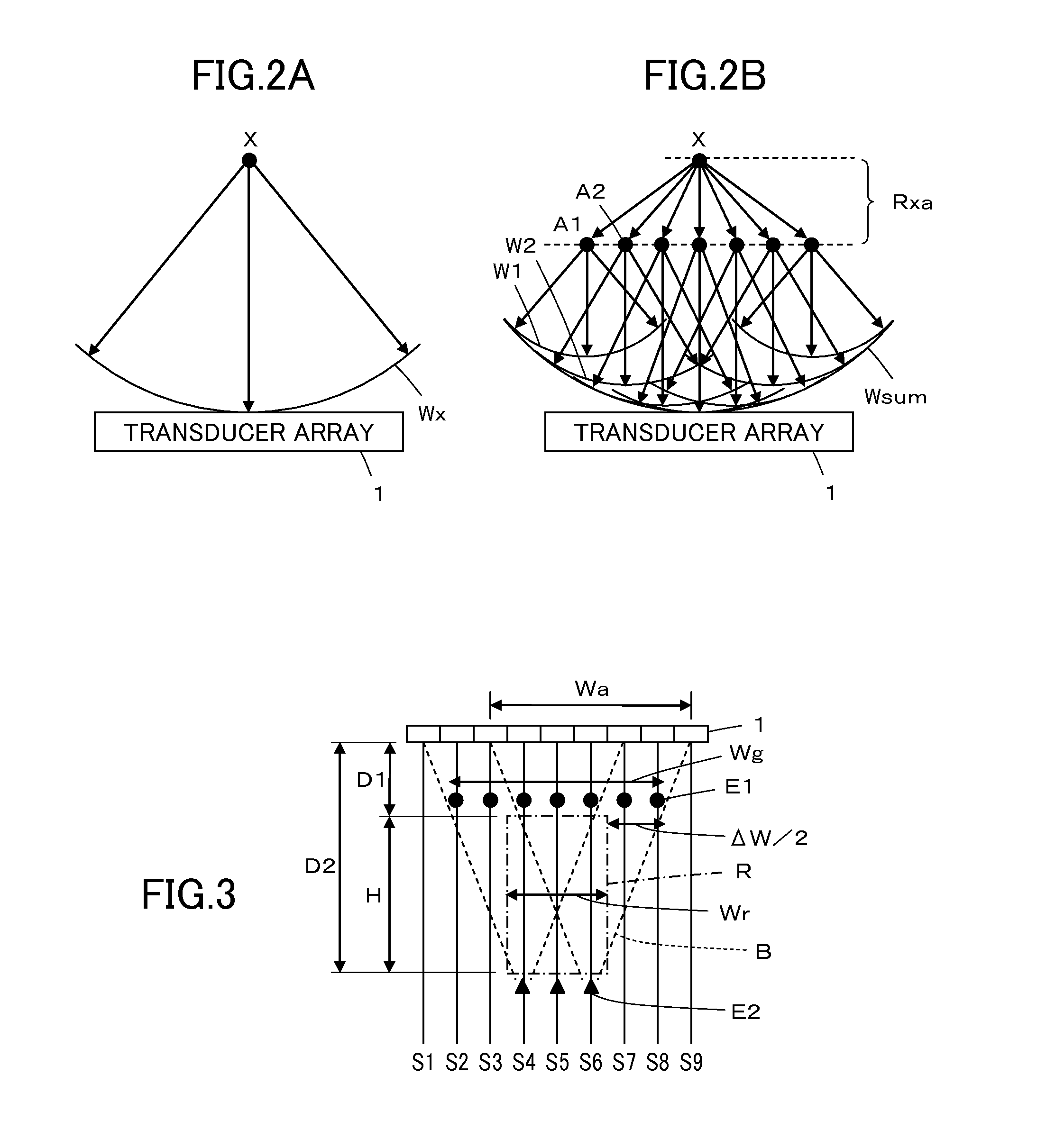
Ultrasound diagnostic apparatus and method of producing ultrasound image
InactiveUS20120245468A1Short timeSatisfied with precisionAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWave based measurement systemsUltrasonic beamSonification
An ultrasound diagnostic apparatus includes a region of interest setter which sets a region of interest on a B-mode image, a controller which performs transmission and reception of ultrasonic beams with forming transmission focuses at a plurality of points set on sound rays at a shallower position and a deeper position than the region of interest to acquire reception data for sound speed measurement, and a sound speed calculator which calculates an average local sound speed value in the region of interest on the basis of reception data for sound speed measurement.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Tracking of a subimage in a sequence of images
InactiveUS20070081736A1Simple and inexpensive in calculation powerSatisfied with precisionTelevision system detailsImage analysisComputer vision
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV +1
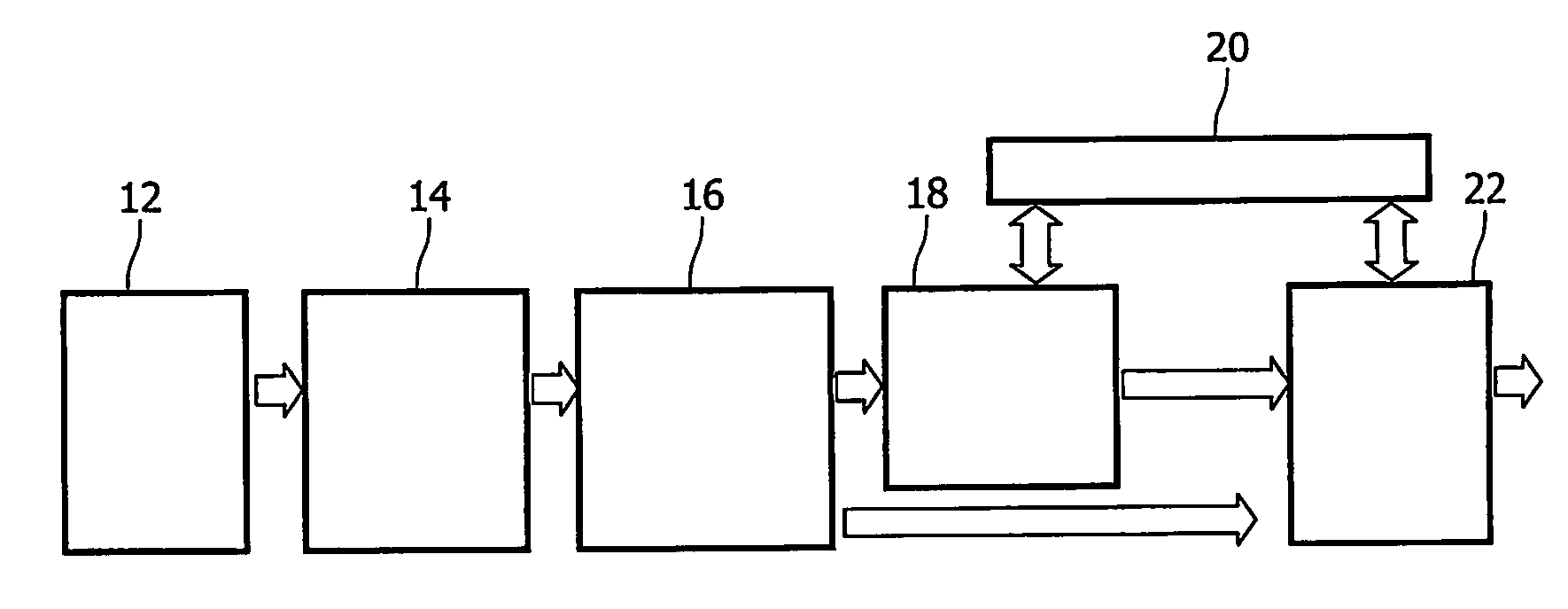
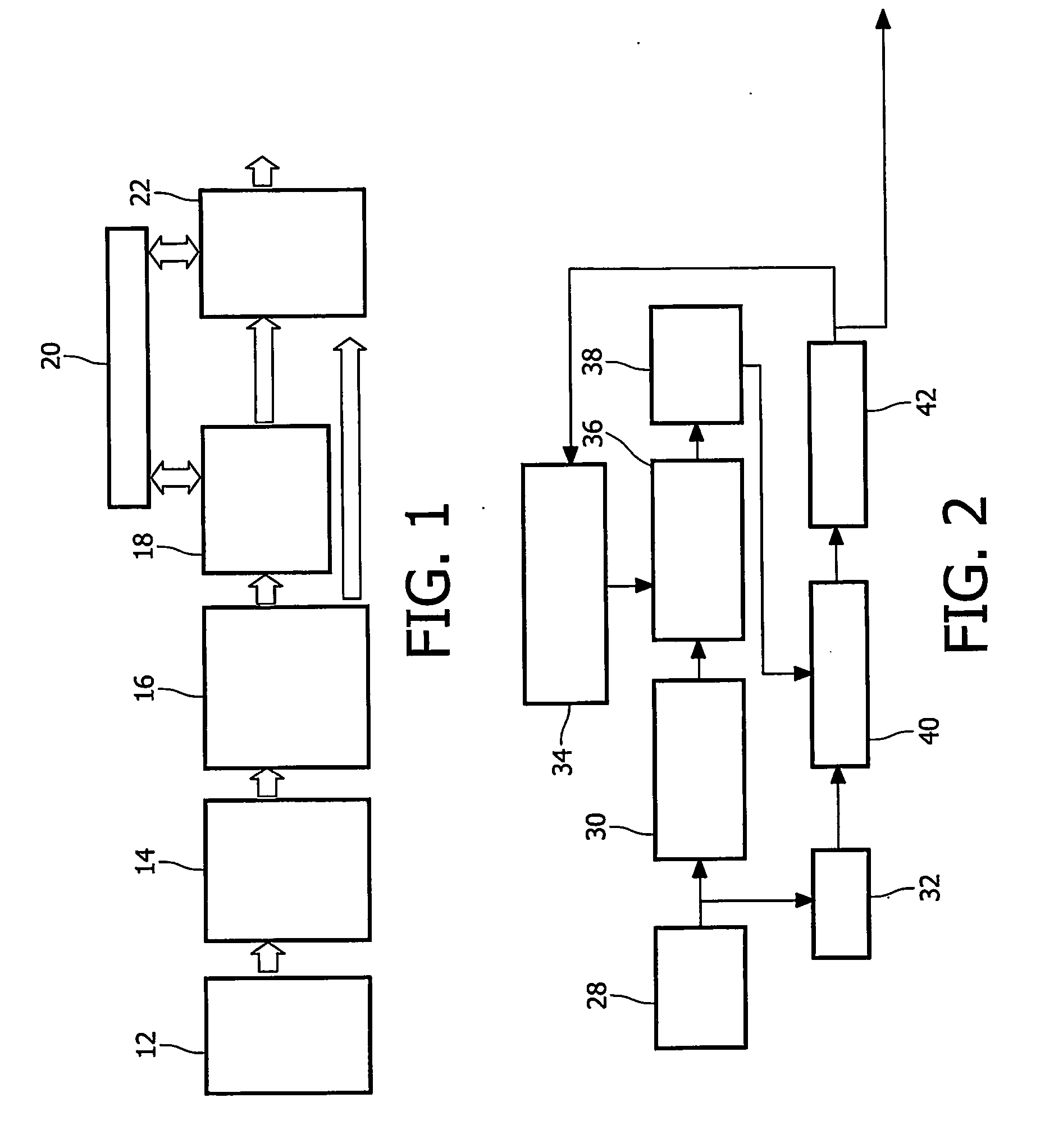
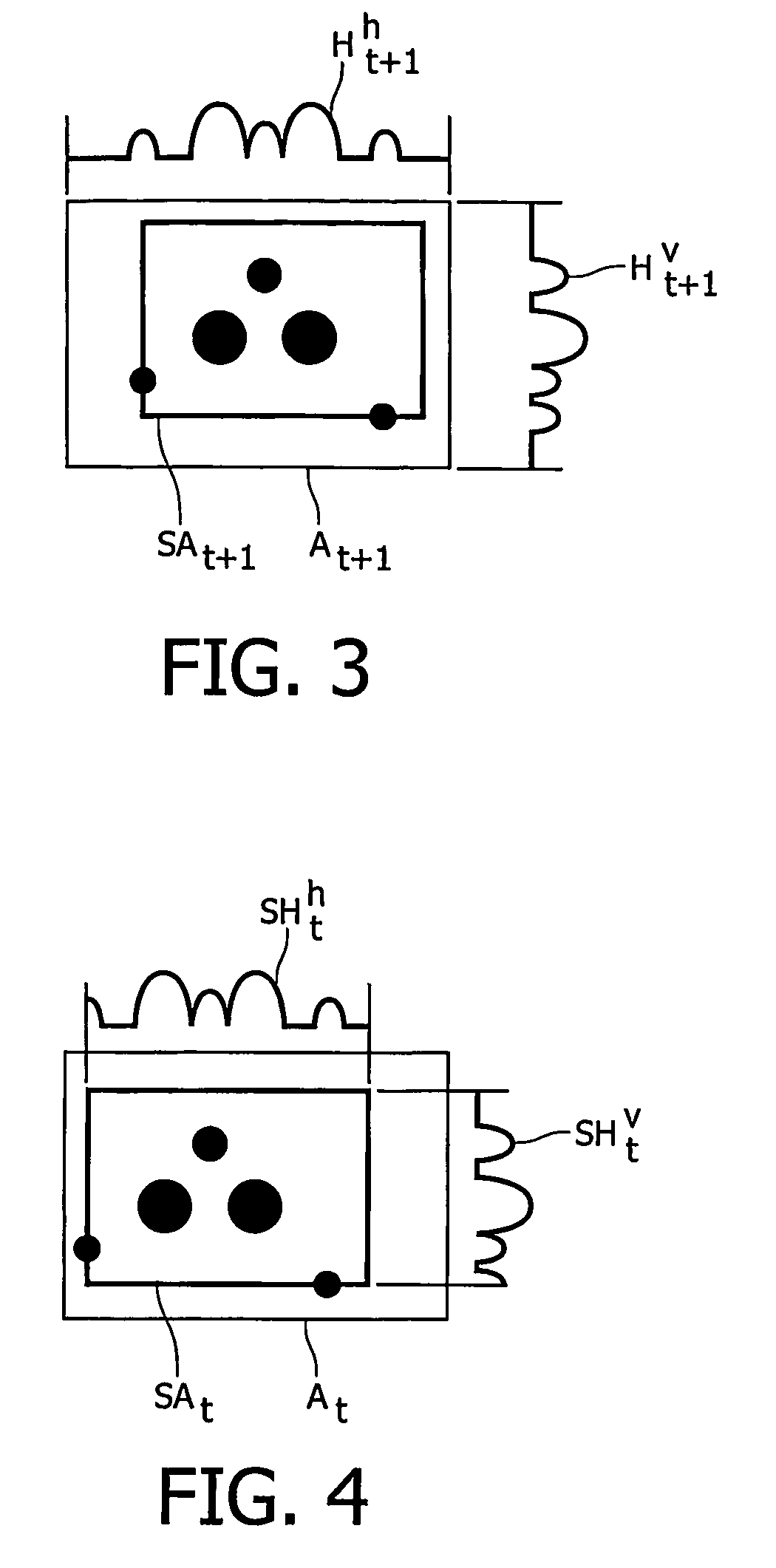
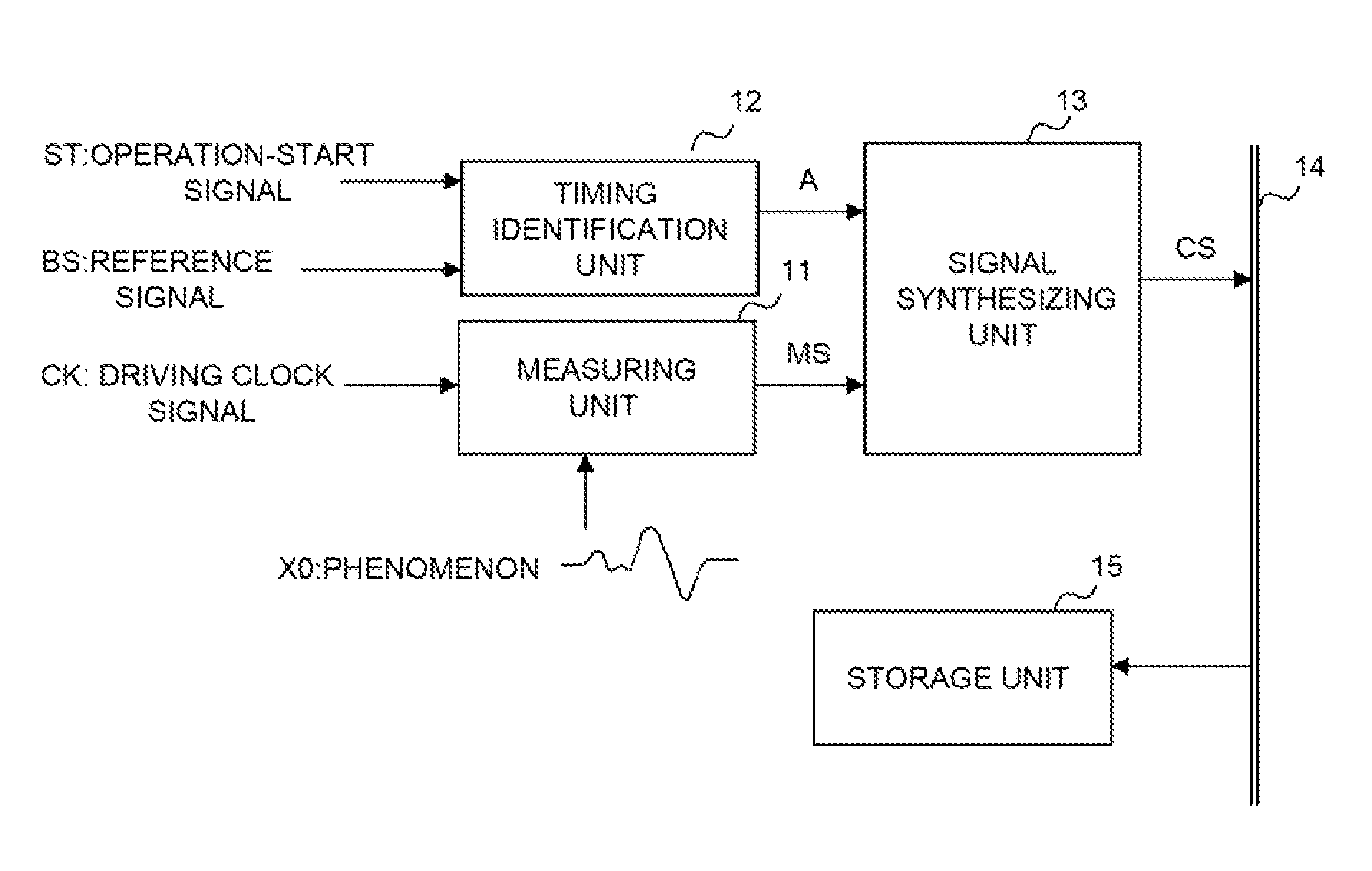
Signal measuring device and signal measuring method
InactiveUS8635040B2Satisfied with precisionEstimate measurement timeDigital variable displayAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceEngineeringVIT signals
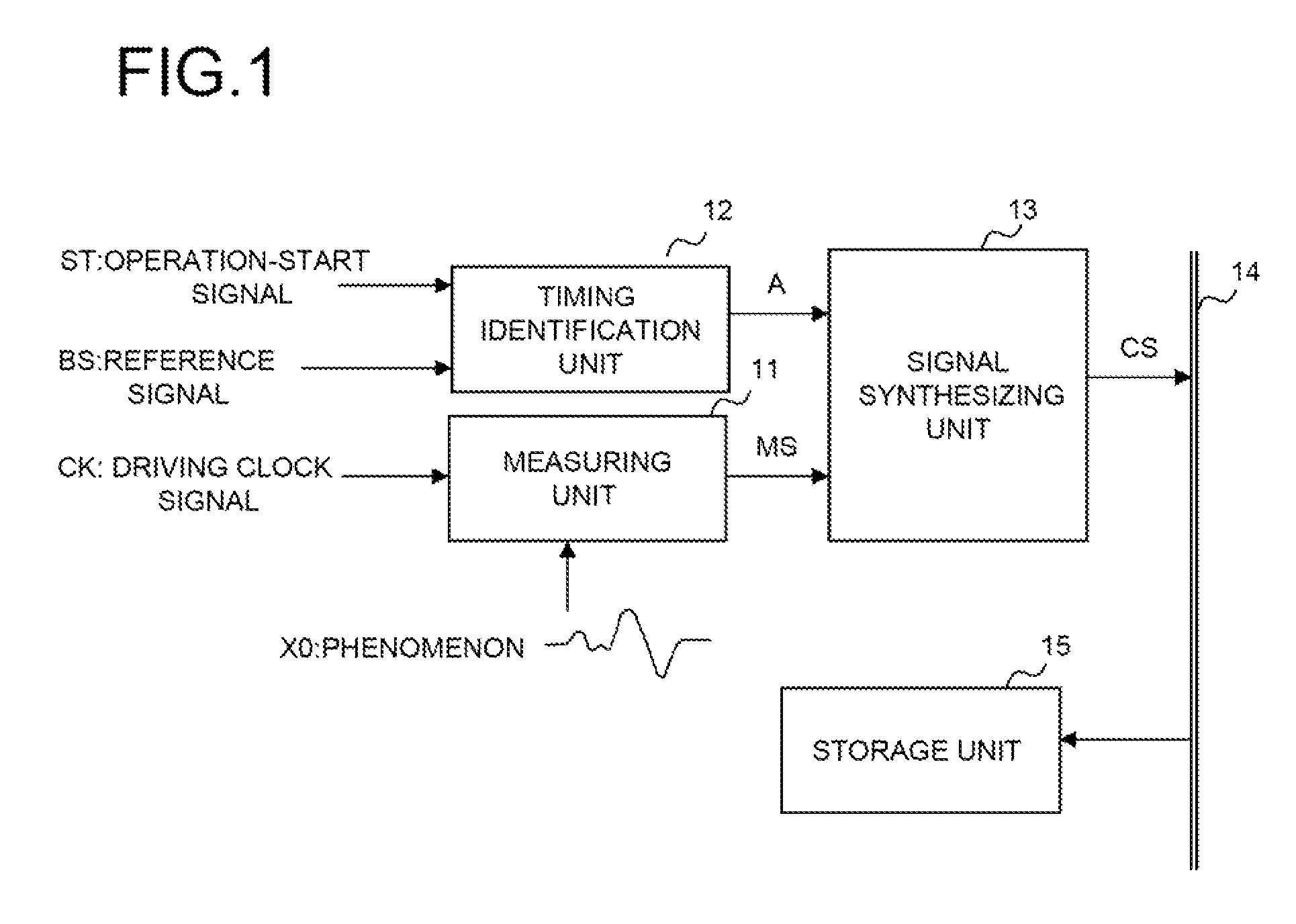
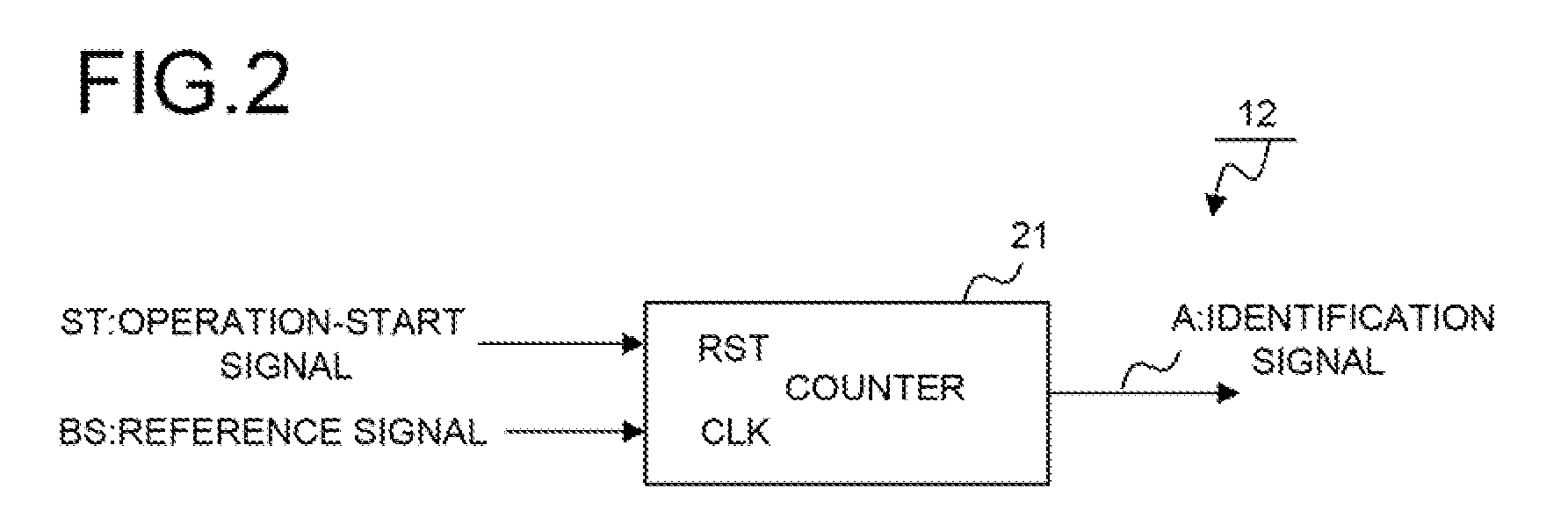
A signal measuring device, comprises one set, or a plurality of sets, of measuring unit(s) measuring an object of measurement in synch with a driving clock signal for measurement and outputting result of measurement as first data, and a timing identification unit which, in accordance with a measurement-start command, outputs a value, which differs every period, as second data in synch with a reference signal having a prescribed period and a speed lower than that of the driving clock signal; and a storage unit collecting and successively storing the first data and the second data as one set in synch with the driving clock signal.
Owner:NEC CORP
Plasma processing apparatus and method thereof
InactiveUS7332039B2Satisfied with precisionGuaranteed ease of operationLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesEngineeringPlasma processing
A nozzle head NH of a plasma processing apparatus comprises an annular inner holder 3, an annular inner electrode 11 surrounding this holder 3, an annular outer electrode 21 surrounding this electrode 11, and an annular outer holder 4 surrounding this electrode 21. The inner holder 3 is provided with a plurality of bolts 7 spacedly arranged in the peripheral direction and adapted to push the inner electrode 11 radially outwardly. The outer holder 4 is provided with a plurality of bolts 8 spacedly arranged in the peripheral direction and adapted to push the outer electrode 21 radially inwardly. Owing to this arrangement, the operation for disassembling, assembling and centering the annular electrodes 11, 21 can be carried out with ease.
Owner:SEKISUI CHEM CO LTD
Manufacturing method of optical devices
InactiveUS7166487B2Avoid it happening againMinimizes processing distortionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCamera filtersMiniaturizationEngineering
A first objective of the present invention is to provide a more productive method of manufacturing optical devices that minimizes processing distortion, maintains optical characteristics satisfactorily, and promotes smallness. A second objective thereof is to provide a method of manufacturing optical devices that prevents the occurrence of fine dust and maintains the optical characteristics satisfactorily. A third objective thereof is to provide a method of manufacturing optical devices of a multi-layer configuration that are obtained by applying a scribing / cutting method. A method of manufacturing optical devices in accordance with the present invention, wherein an optical wafer having surfaces polished to a mirror finish is divided into a plurality of optical chips, is provided with a first step of providing hairline cracks by a diamond blade edge in one main surface of the optical wafer and a third step of applying pressure along the hairline cracks after the first step, to divide the optical wafer into the plurality of optical chips.
Owner:NIHON DEMPA KOGYO CO LTD
Friction welding apparatus
InactiveUS8578992B2Loss in rotational energyLittle energy lossWelding/cutting auxillary devicesTubular articlesClutchElectricity
Disclosed is a friction welding apparatus in which electricity is supplied to a servo motor to rotate a spindle to thereby impart a fixed relative rotational motion to one workpiece and another workpiece, and, while doing so, the one workpiece and the other workpiece are brought into contact with each other and imparted a frictional thrust thereto to soften a bonding interface between the two workpieces. After this, the friction welding apparatus undergoes speed reduction until the RPM of the spindle becomes a phase adjustment RPM; when the RPM of the spindle attains the phase adjustment RPM, a clutch device is engaged with the spindle, and the electricity supply to the servo motor is cut off to stop the rotation of the spindle.
Owner:TOYOTA IND CORP +1
Printing device
ActiveUS20180099513A1Stably carry-outSimple configurationTypewritersOther printing apparatusMechanical engineeringRecording media
Owner:MIMAKI ENG
Axial gap type generator
InactiveUS20130187393A1Satisfied with precisionHigh precisionMagnetic circuit rotating partsMachines/enginesCentre of rotationCrankcase
There is provided an axial gap type generator. The axial gap type generator includes: a stator core fixed to a crank case of an engine; a rotor yoke fixed to a crankshaft of the engine and opposing the stator core across spacing in an axial direction of the crankshaft; a first planar section provided in the crankshaft and formed to have a planar shape that is perpendicular to a rotation center axis; a second planar section provided at a base, at which the rotor yoke is mounted on the crankshaft, and disposed opposing the first planar section; and a shim clamped between the first planar section and the second planar section.
Owner:SUBARU CORP
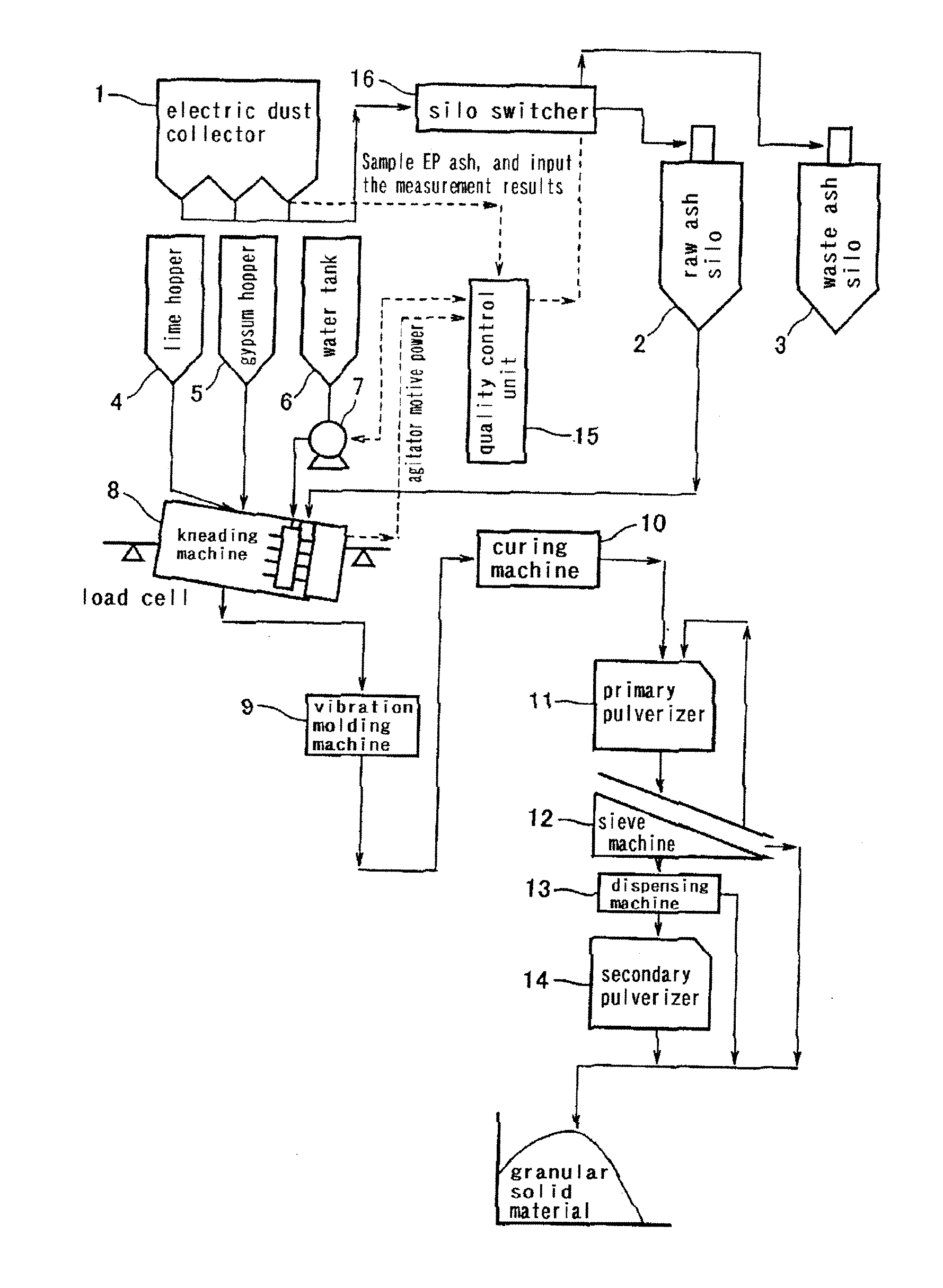
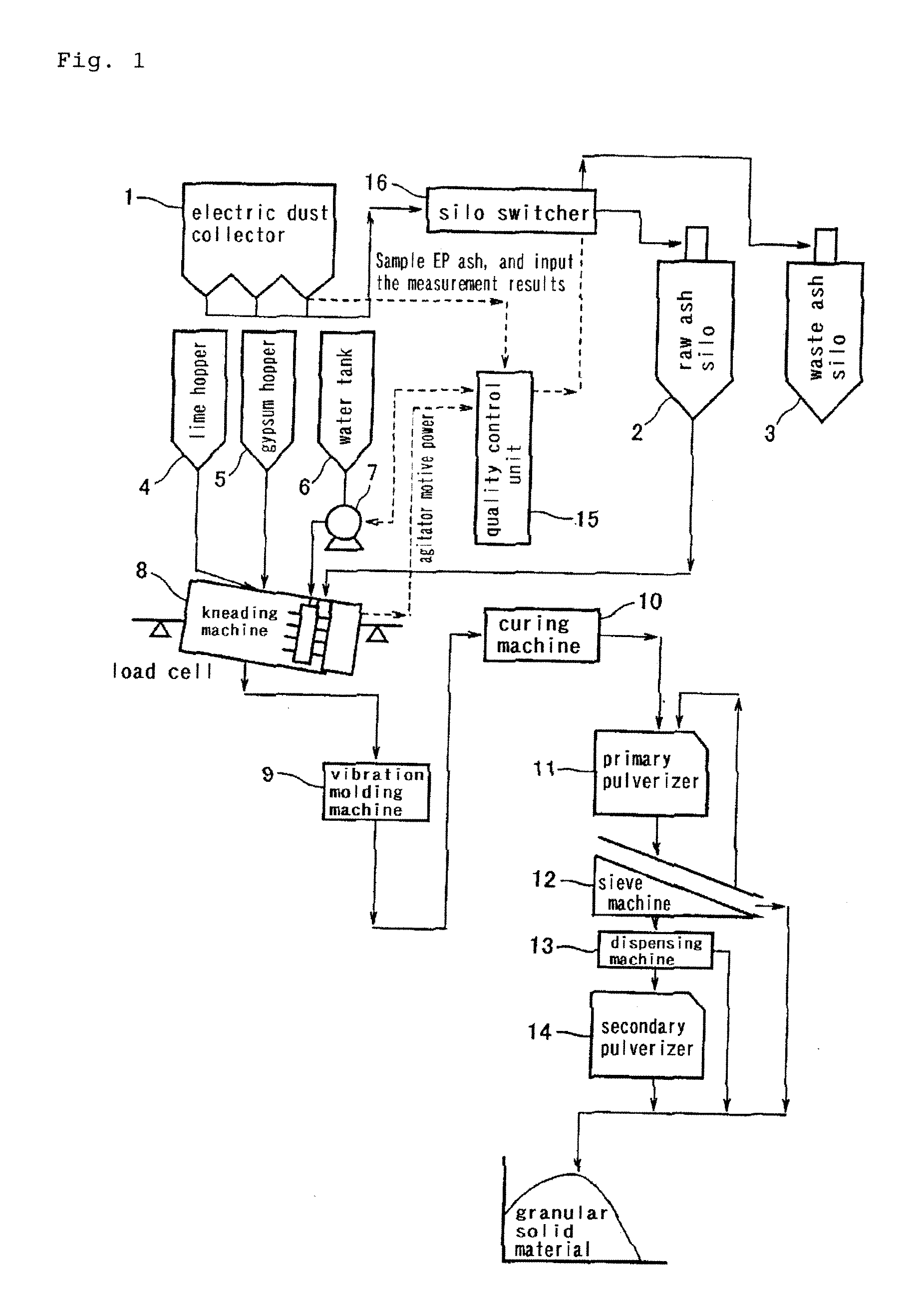
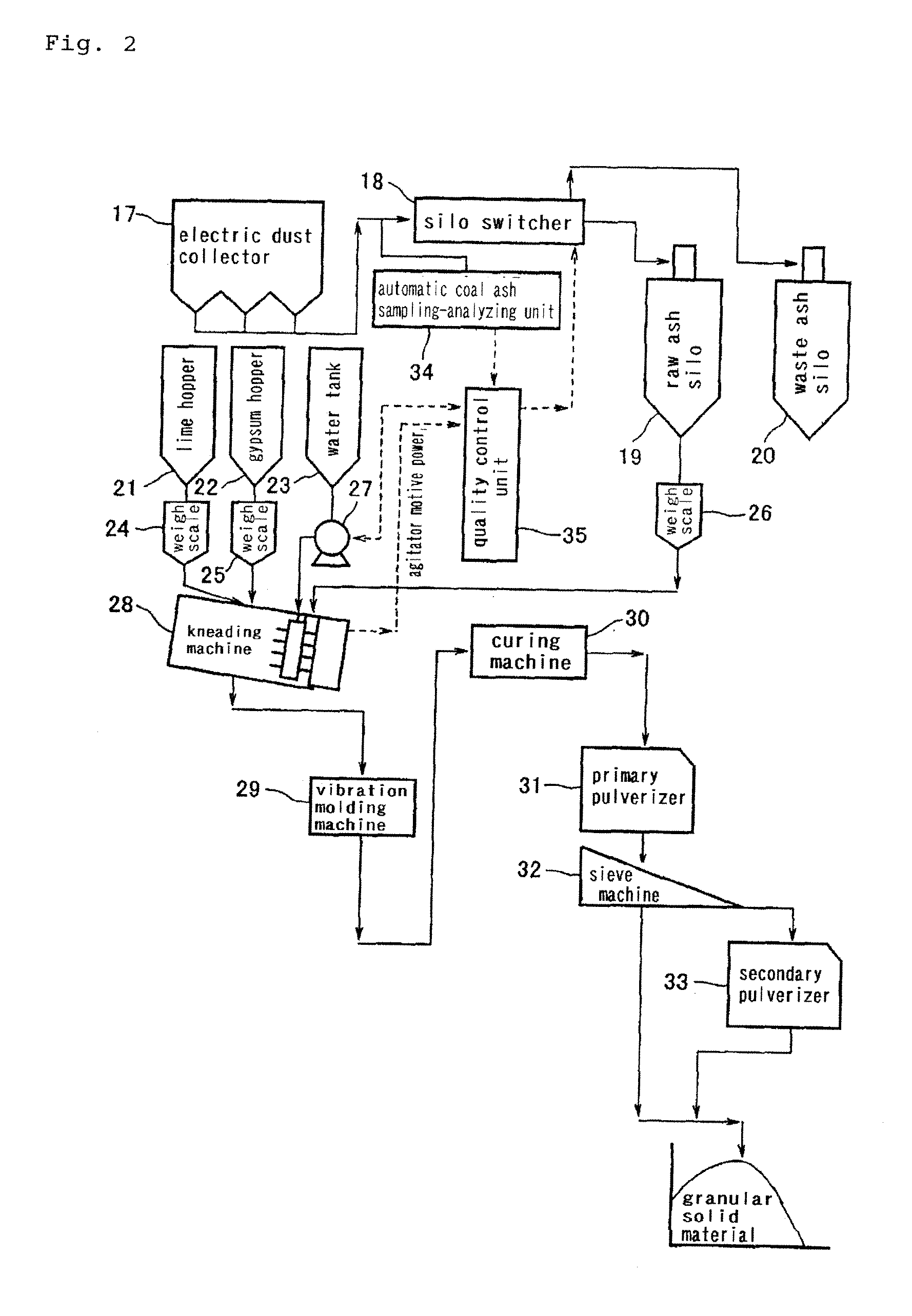
Process for Producing Granular Solid Matter from Coal Ash as Raw Material and Apparatus Therefor
InactiveUS20100108788A1Stable productionHydrating reactivity of a coal ash can be estimatedTransportation and packagingSolid waste disposalPulverized fuel ashSolid matter
A method of estimating the hydration reactivity of coal ash with high precision and determining the amount of milling water for obtaining a milling product in funicular form at the stage of milling; and a molding method being free from the problem of adhesion to a pressurization board at the stage of molding after the milling. When any collected coal ash exhibits a corrected basicity ((CaO+Fe2O3+MgO) / SiO2 (weight ratio)) of 0.1 or higher and a reactivity index (corrected basicity / (R2O / Al2O3) (weight ratio)) of 10 or higher, the coal ash as a raw ash is transferred to raw ash silo (2). Otherwise, the coal ash is transferred to waste ash silo (3). The raw ash within the raw ash silo (2) is poured in mill (8), and lime and gypsum are added and further milling water is charged thereto and milled. The amount of milling water is regulated so that with respect to agitator power per weight of material milled by the mill, the ratio of (average of power during 30 to 40 sec after completion of water charging) / (power at idling) ranges from 3 to 4, and so that with respect to agitator power per weight of material milled during 30 to 90 sec after completion of water charging, the ratio of (width of power fluctuation) / (average of power) ranges from 0.1 to 0.3.
Owner:JAPAN COAL ENERGY CENT +1
Method and apparatus for electron-beam lithography
InactiveUS7342241B2High beam positioning-precisionSatisfactory throughputThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersAtmospheric pressureElectron-beam lithography
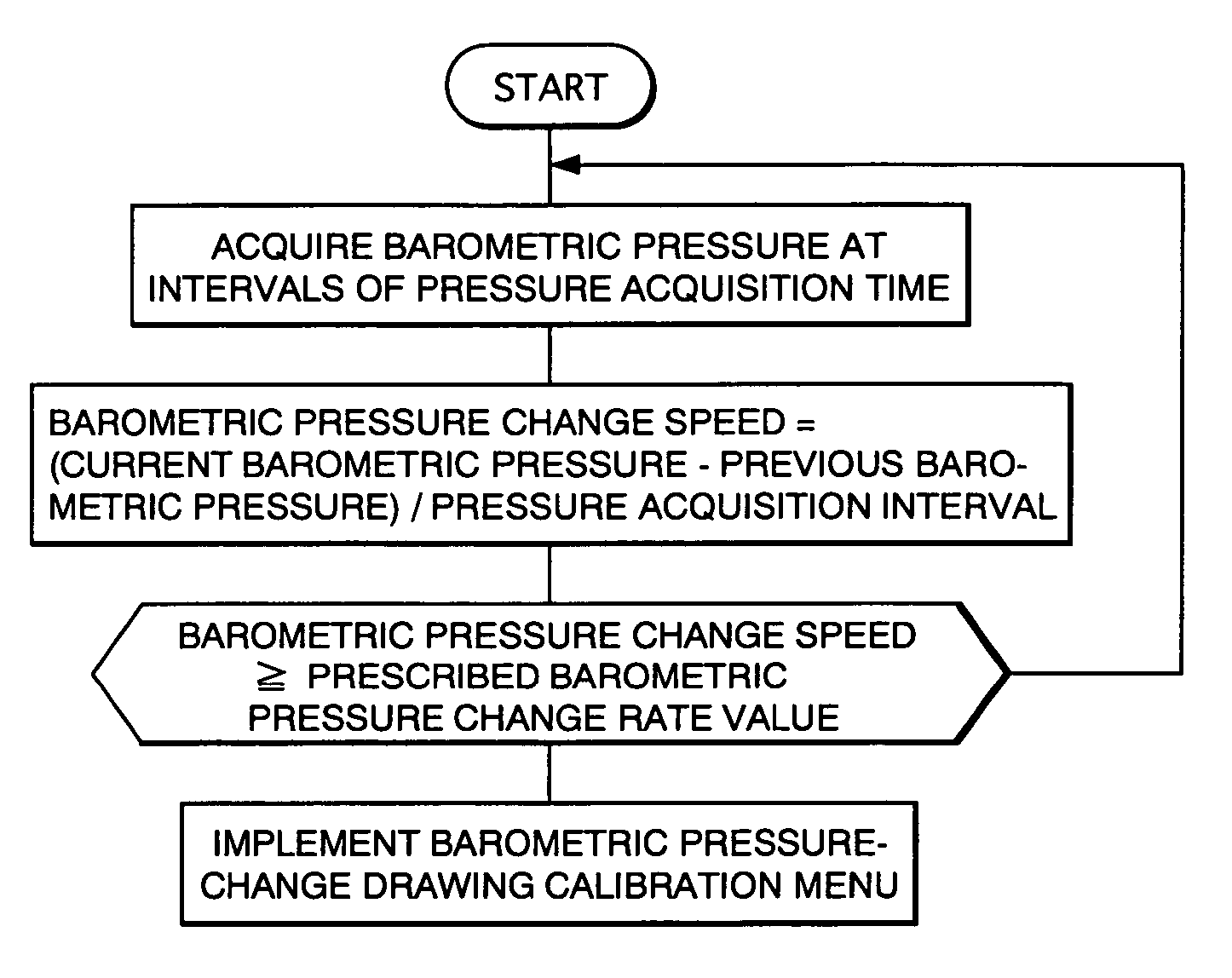
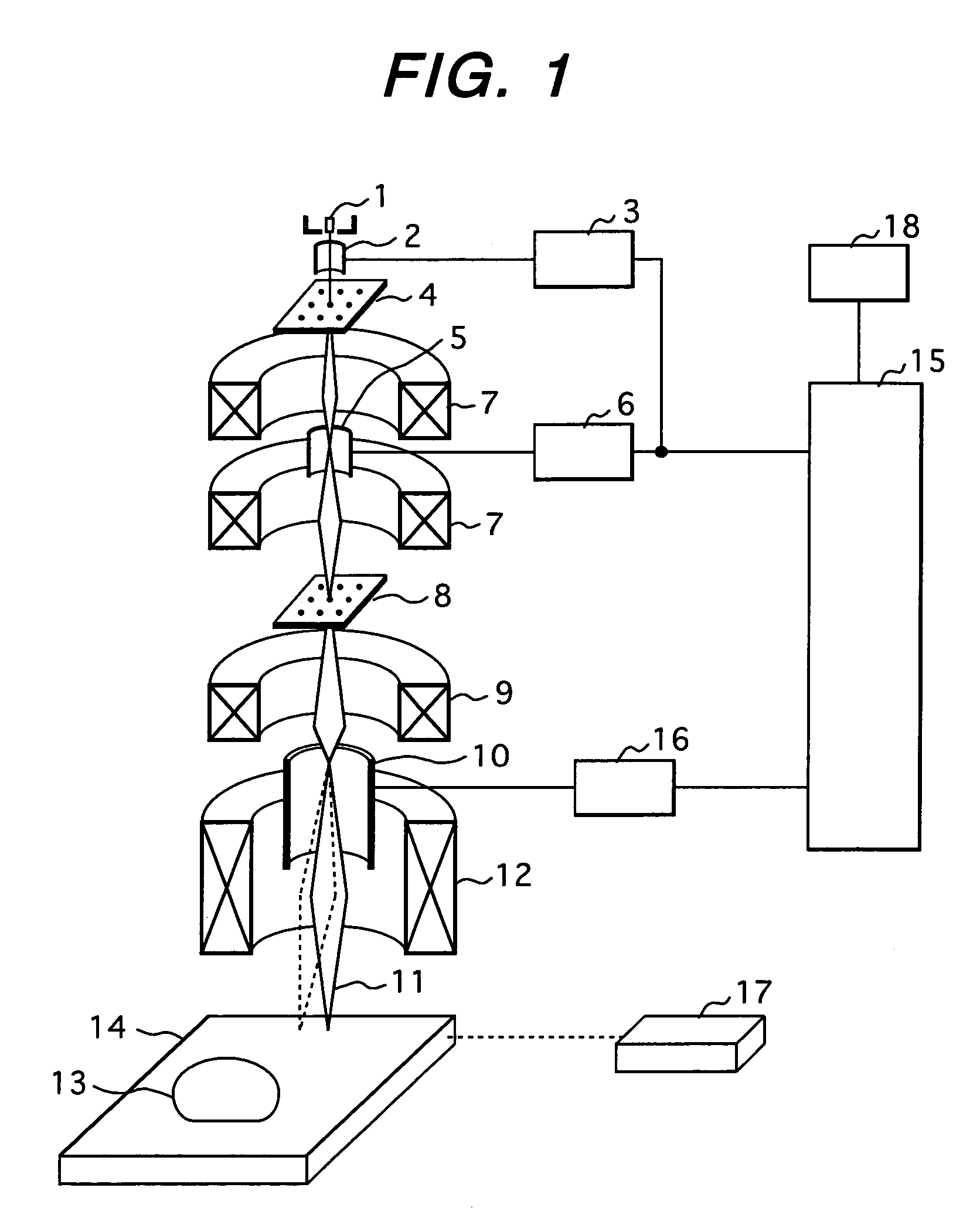
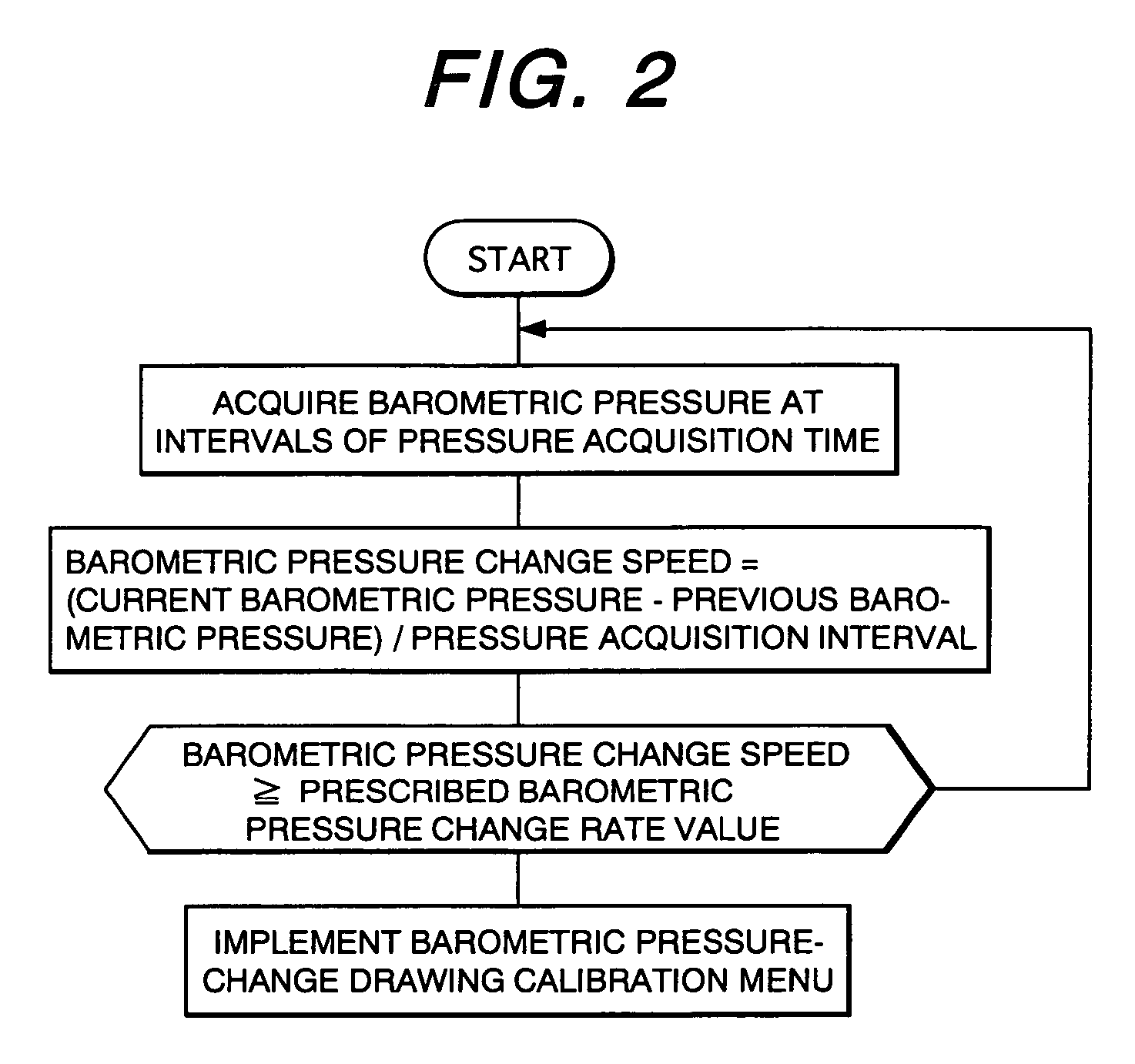
The present invention is to provide an electron-beam lithography method and an electron-beam lithography apparatus that can draw patterns with a high precision despite a change in barometric pressure, can ensure a satisfactory throughput, and are inexpensive. In the electron-beam lithography method that uses an electron beam to draw patterns on a sample, a difference between a current measured barometric pressure and a previous measured barometric pressure, and an elapsed time between their barometric pressure-measurement points in time are determined. When the rate of the difference of their barometric pressures with respect to the elapsed time is equal to or larger than a prescribed barometric pressure change rate value, a drawing precision is calibrated.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
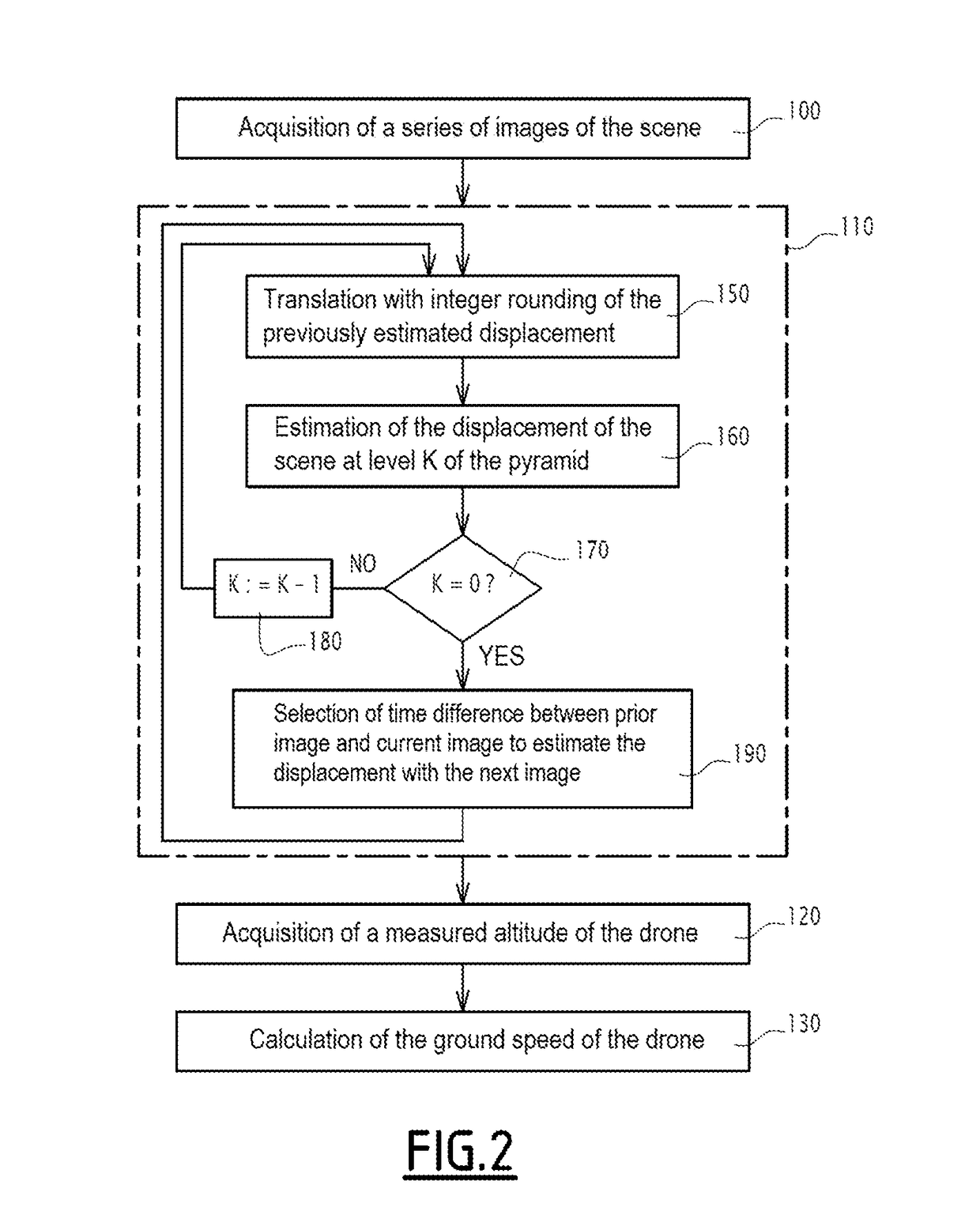
Electronic device and method for estimating a displacement of a scene observed by a drone, electronic apparatus for calculating a ground speed of the drone, related drone and computer program
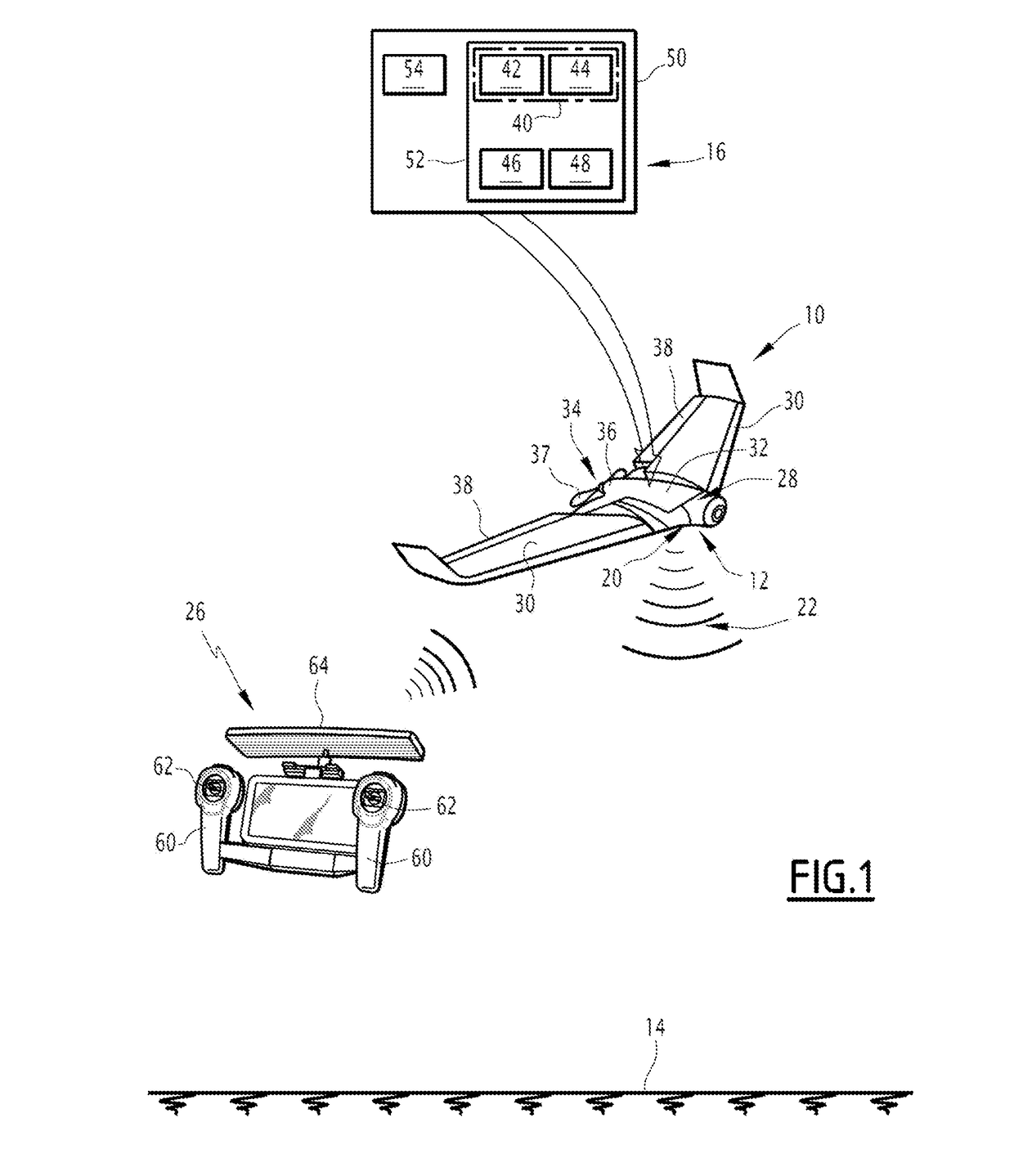
InactiveUS20190033336A1Effective estimateReduce Algorithmic ComplexityImage enhancementImage analysisUncrewed vehicleOptical flow
A electronic device for estimating a displacement of a scene observed by an image sensor equipping a drone comprises a first module for acquiring a series of images of the scene, taken by the image sensor, and a module for estimating, via an optical flow algorithm applied iteratively at several successive levels, a displacement of the scene between an acquired prior image and current image, the level of the image being a sub-sampled image of the image of the following level, the final level being the acquired image. The estimating module calculates at least one estimate of the displacement of the scene at each level, the prior image being translated by an estimated displacement, during the passage from one level to the next. The estimating module is further configured to determine integer rounding of the estimated displacement, the prior image then being translated by the rounded displacement, during the passage from one respective level to the next.
Owner:PARROT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com