Patents
Literature
63results about How to "Switching loss increase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
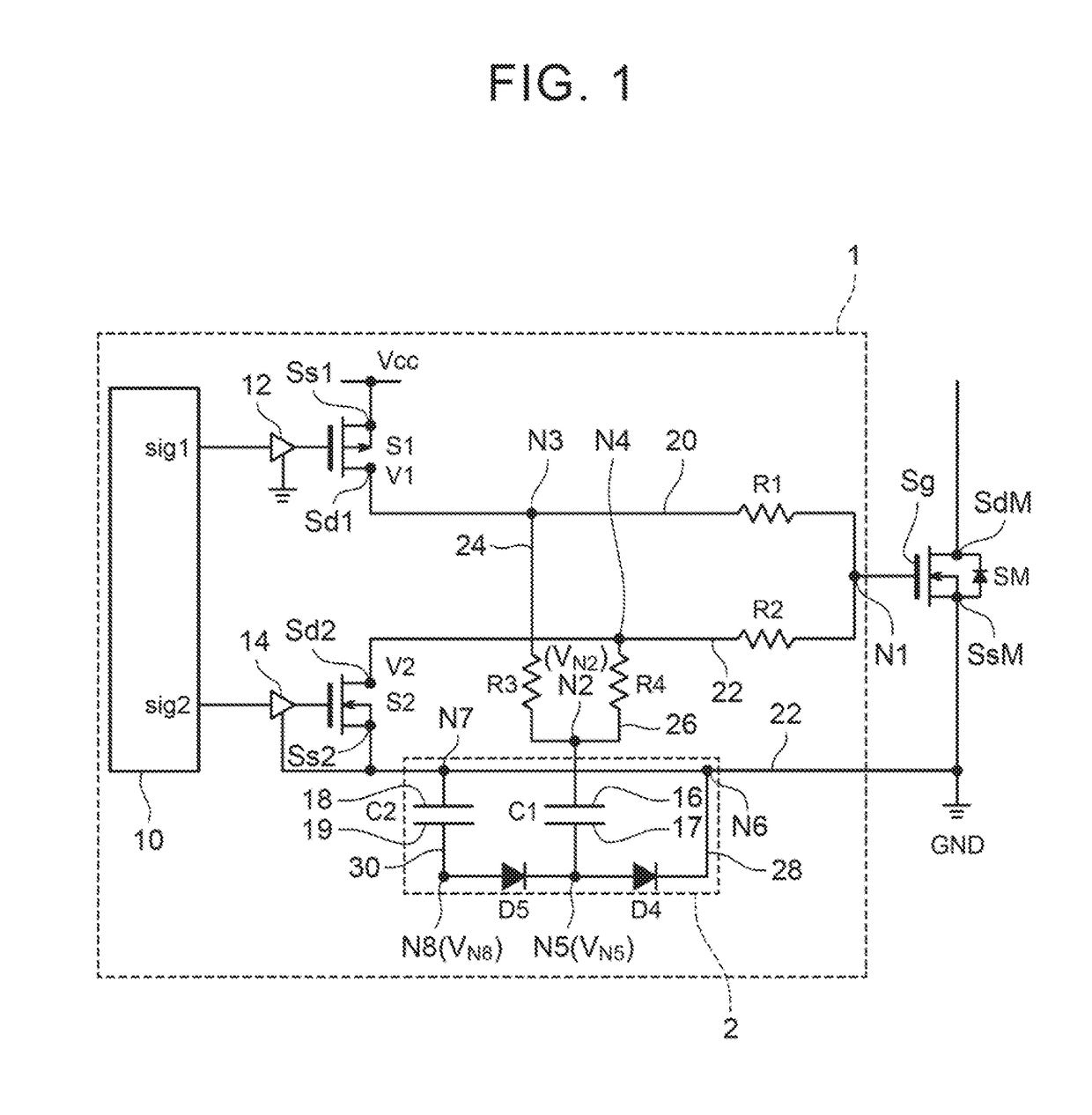
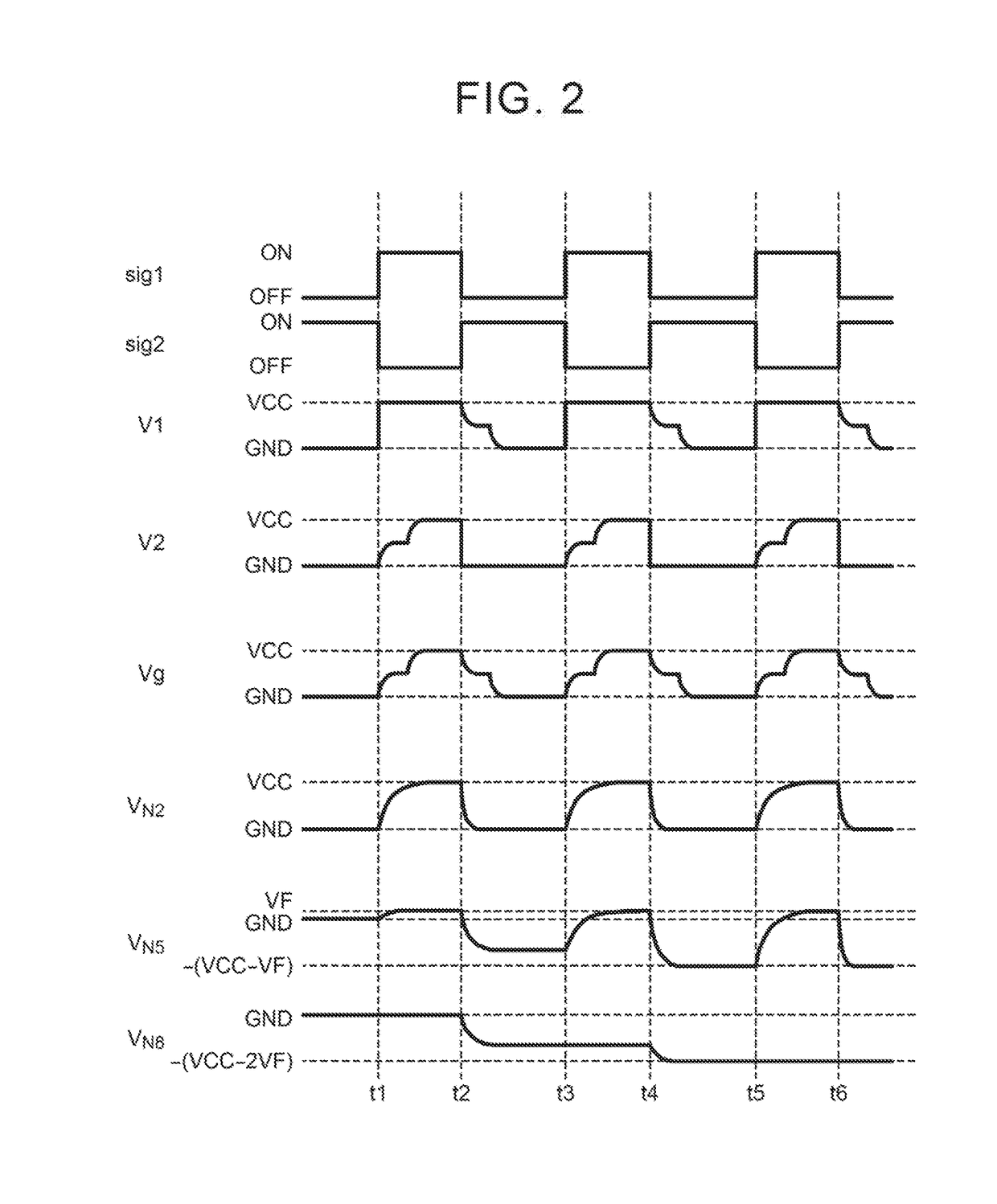
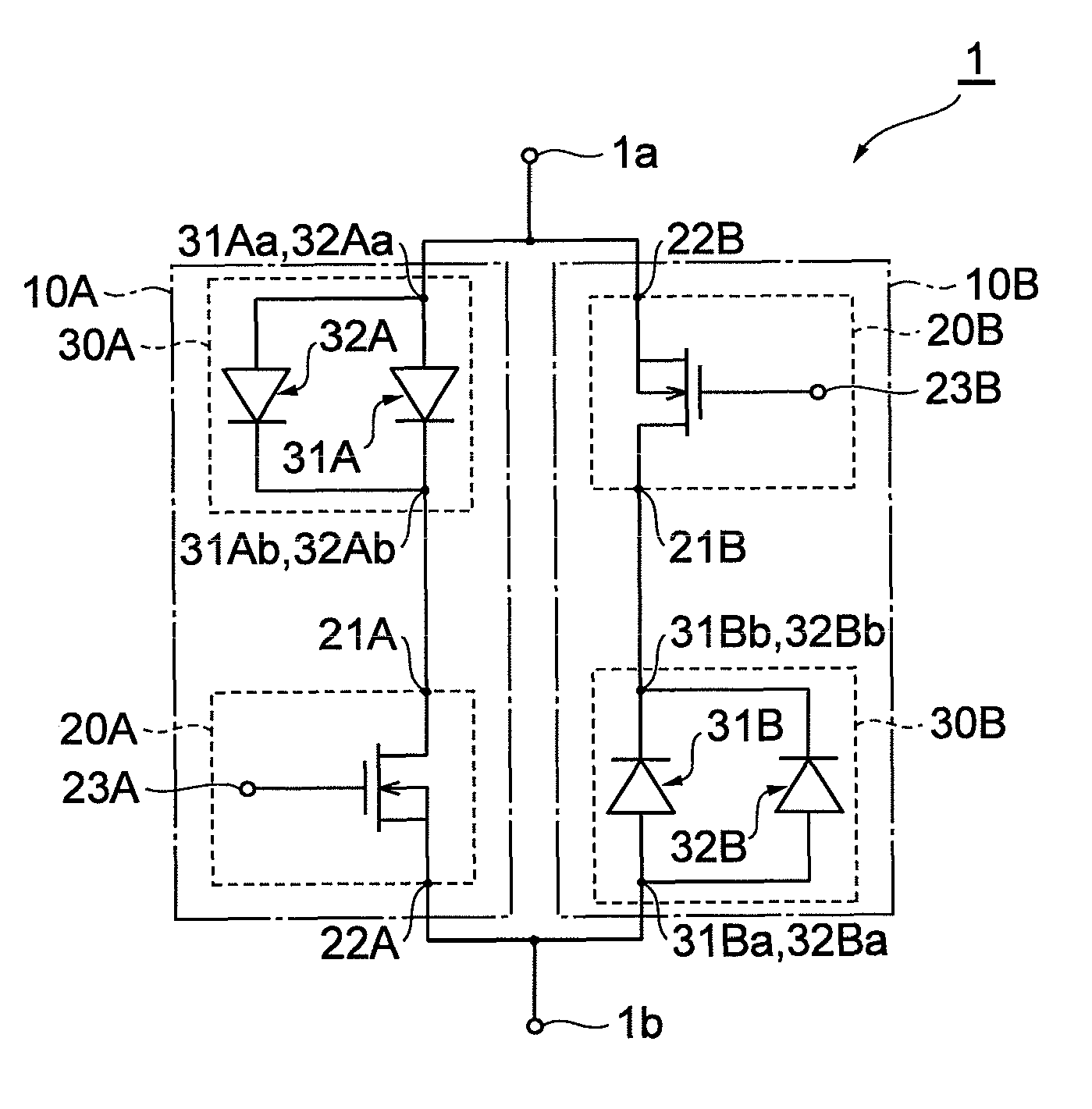
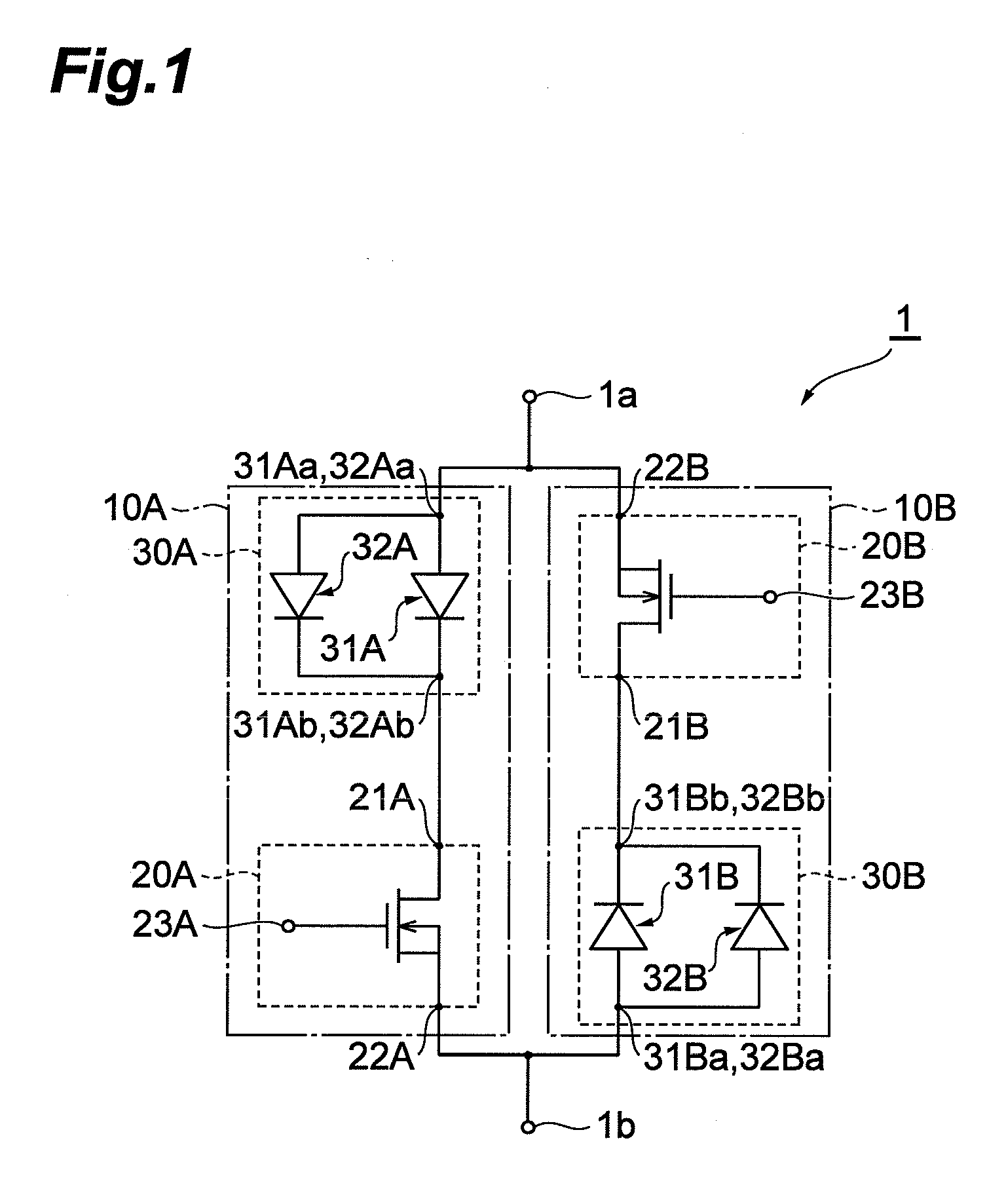
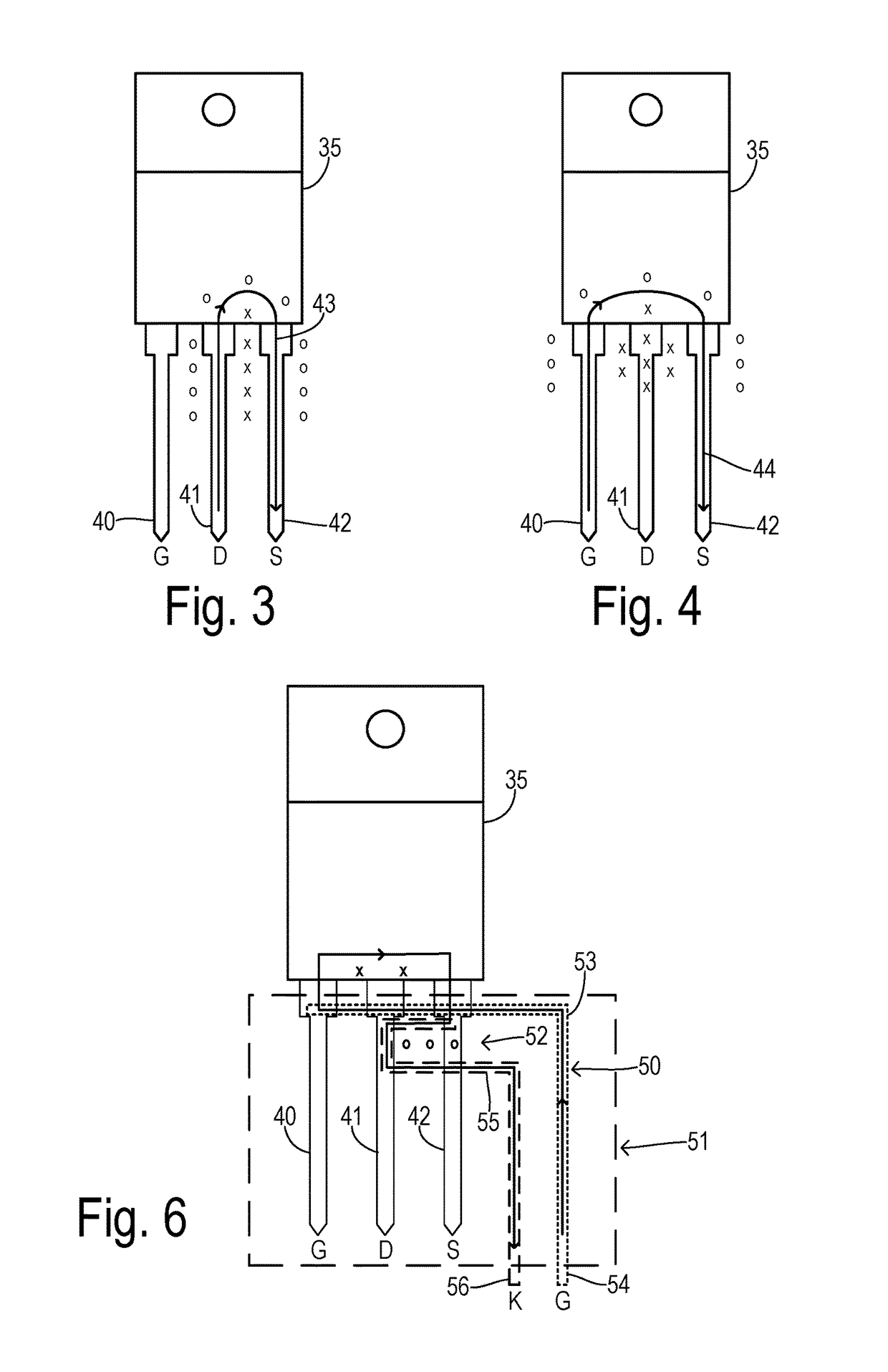
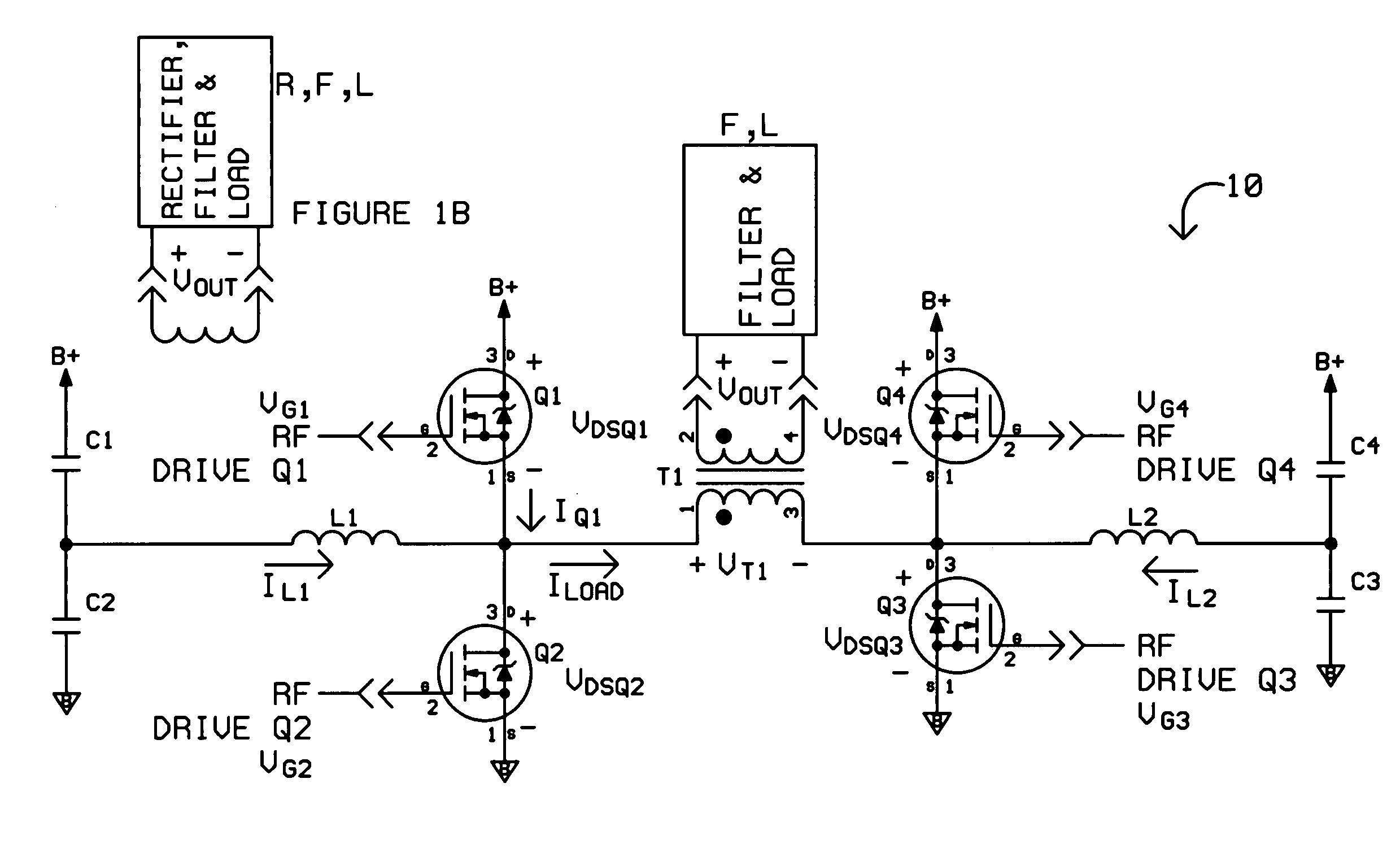
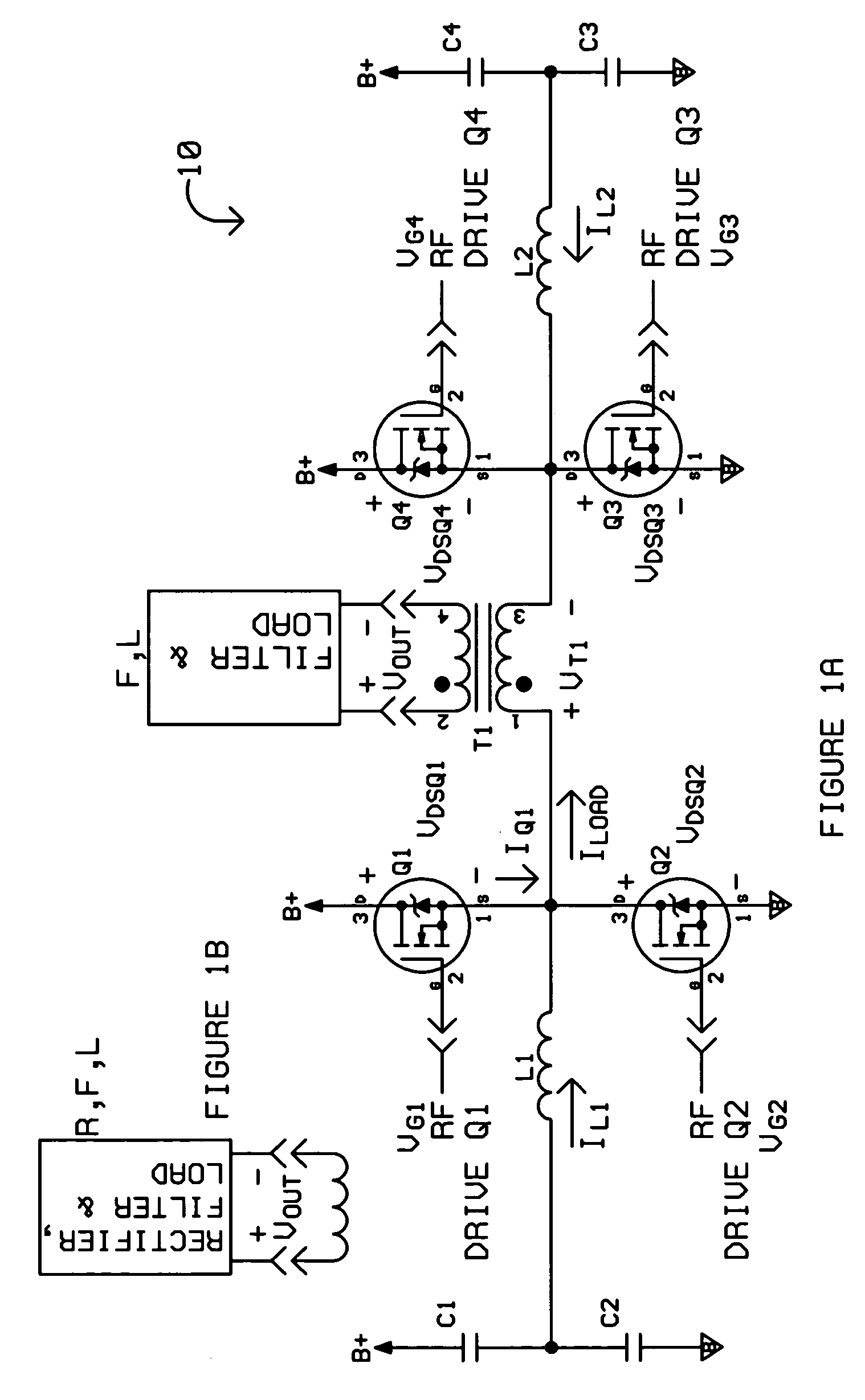
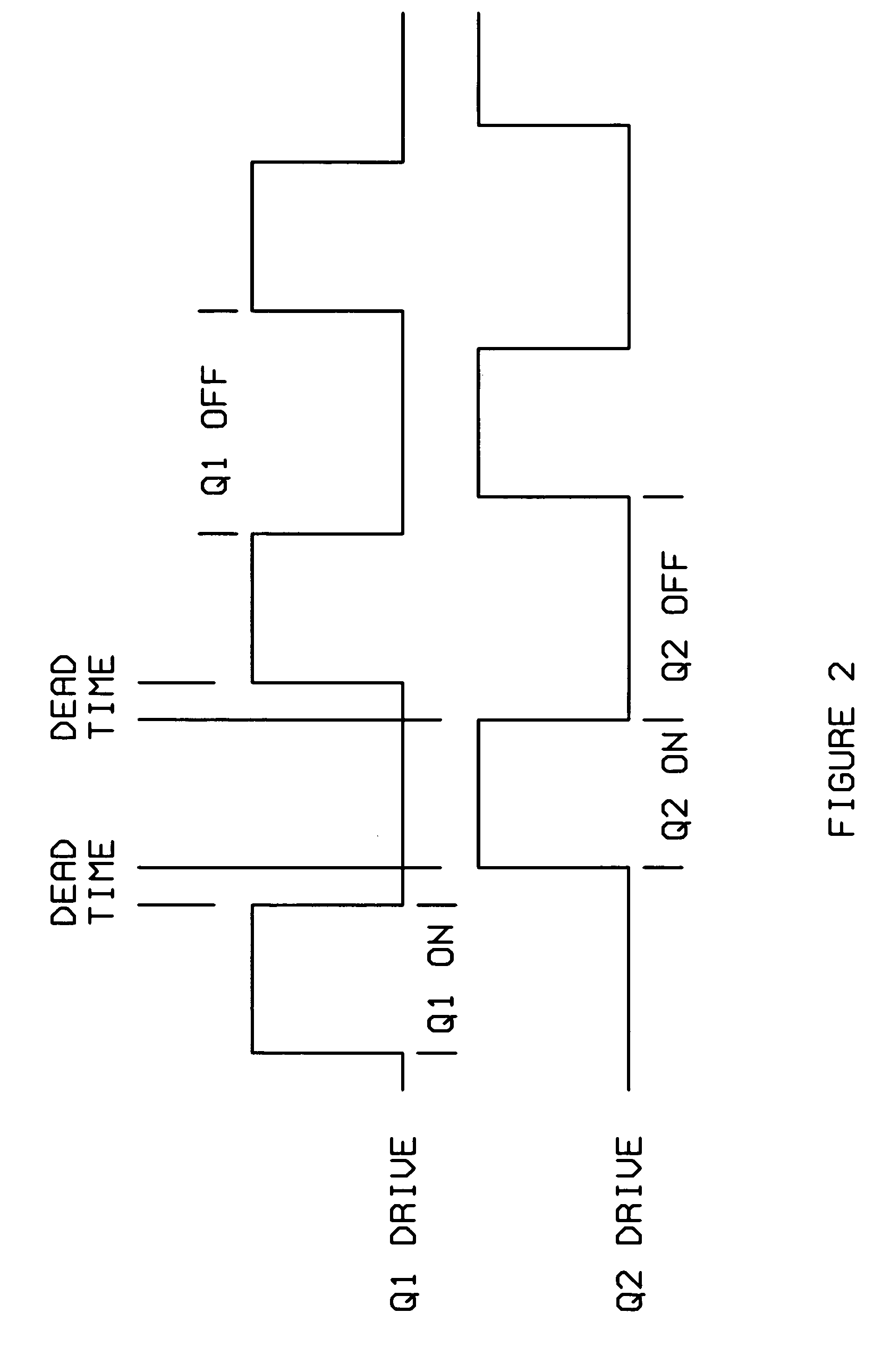
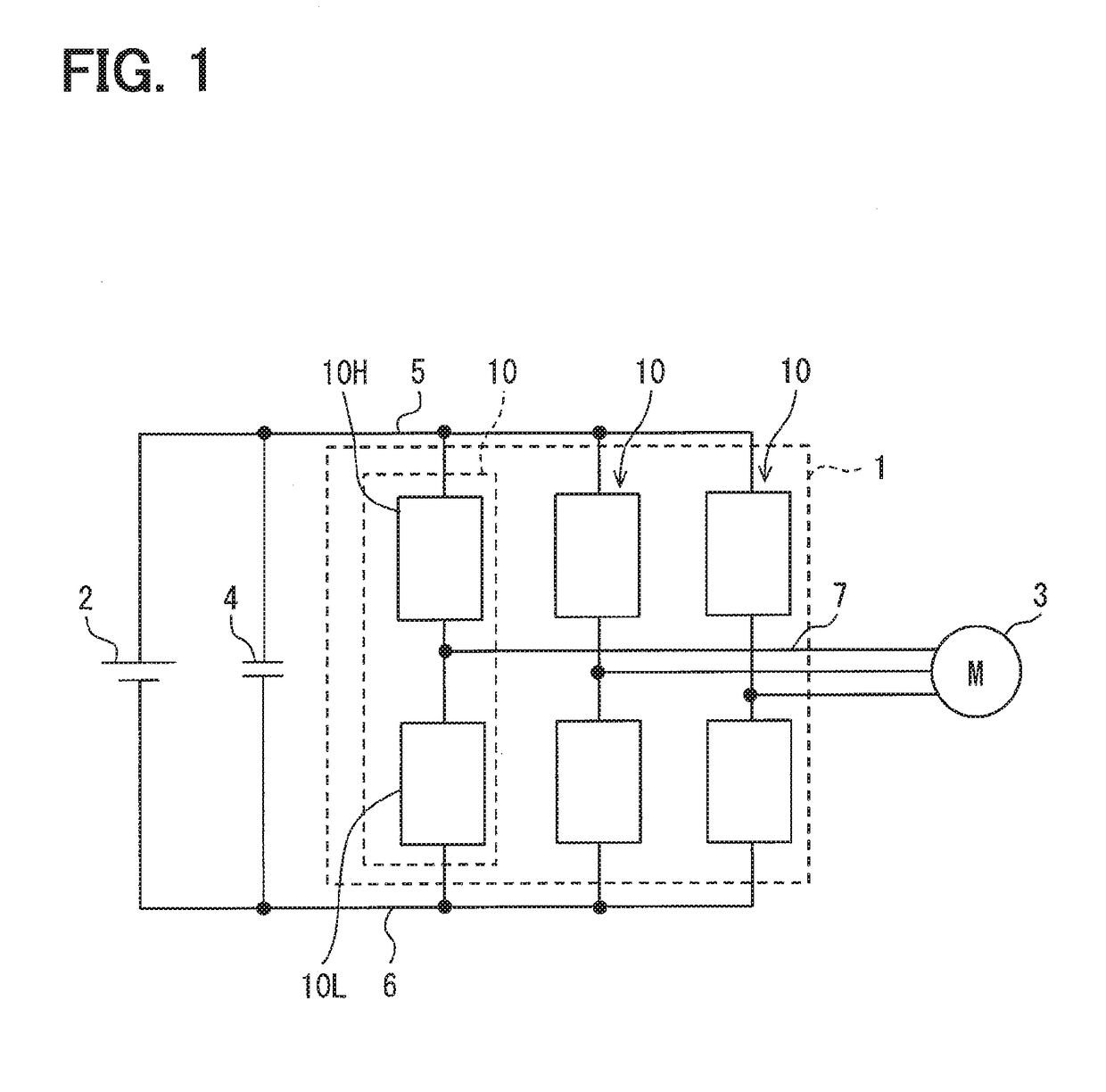
Power circuit
ActiveUS20100171553A1Efficiency can be prevented being reducedSwitching loss increaseHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlPower circuitsLinear amplifier
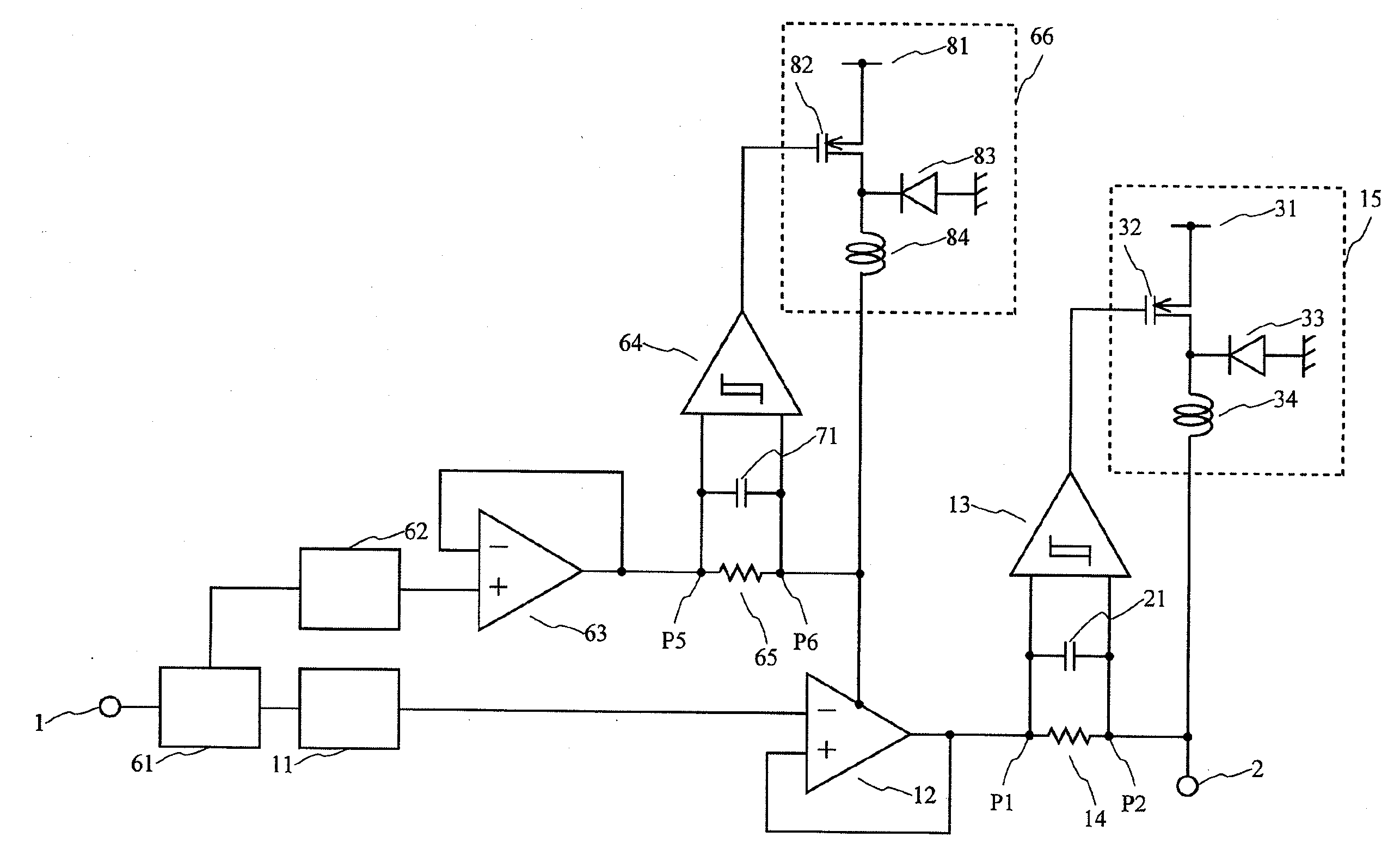
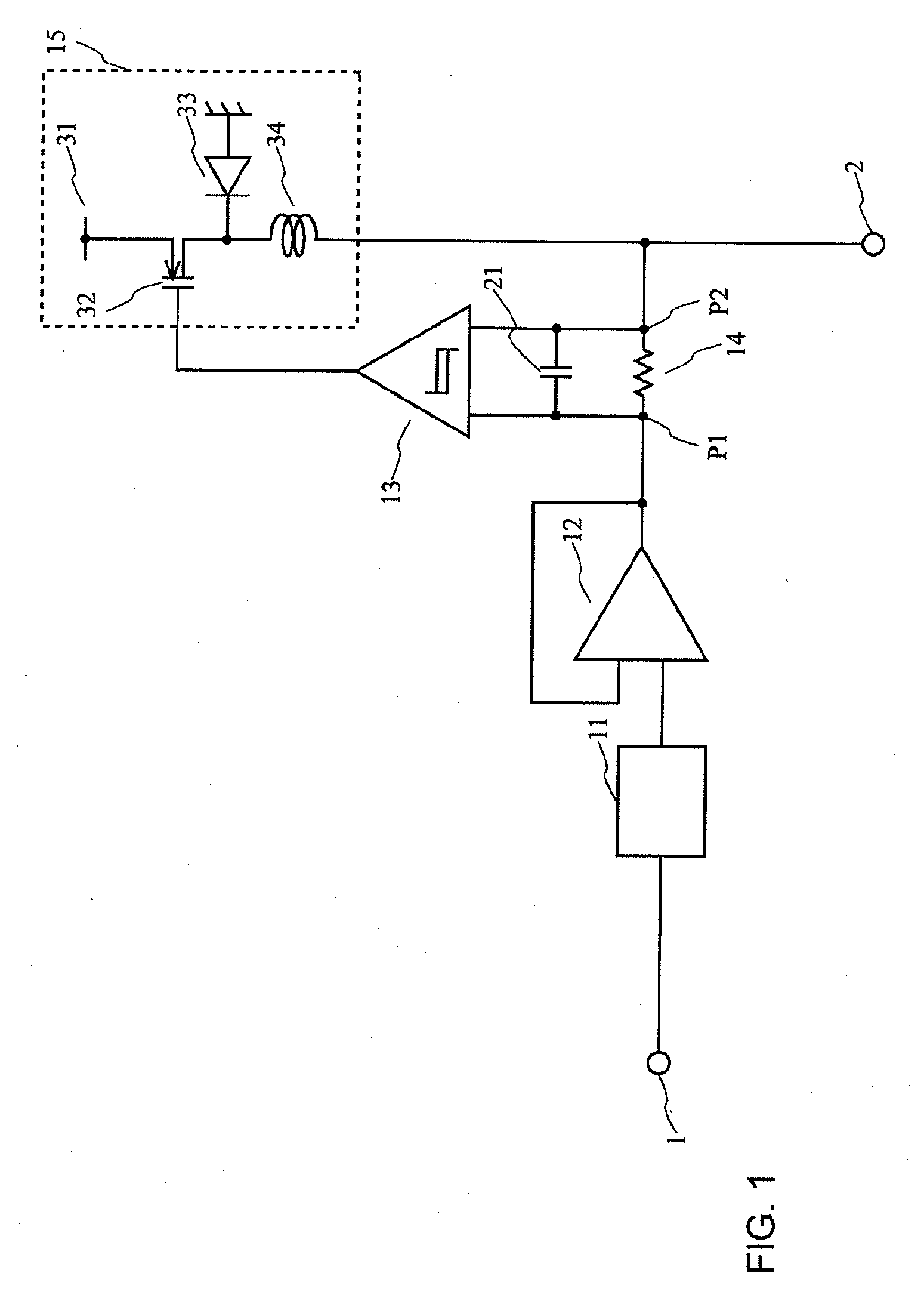
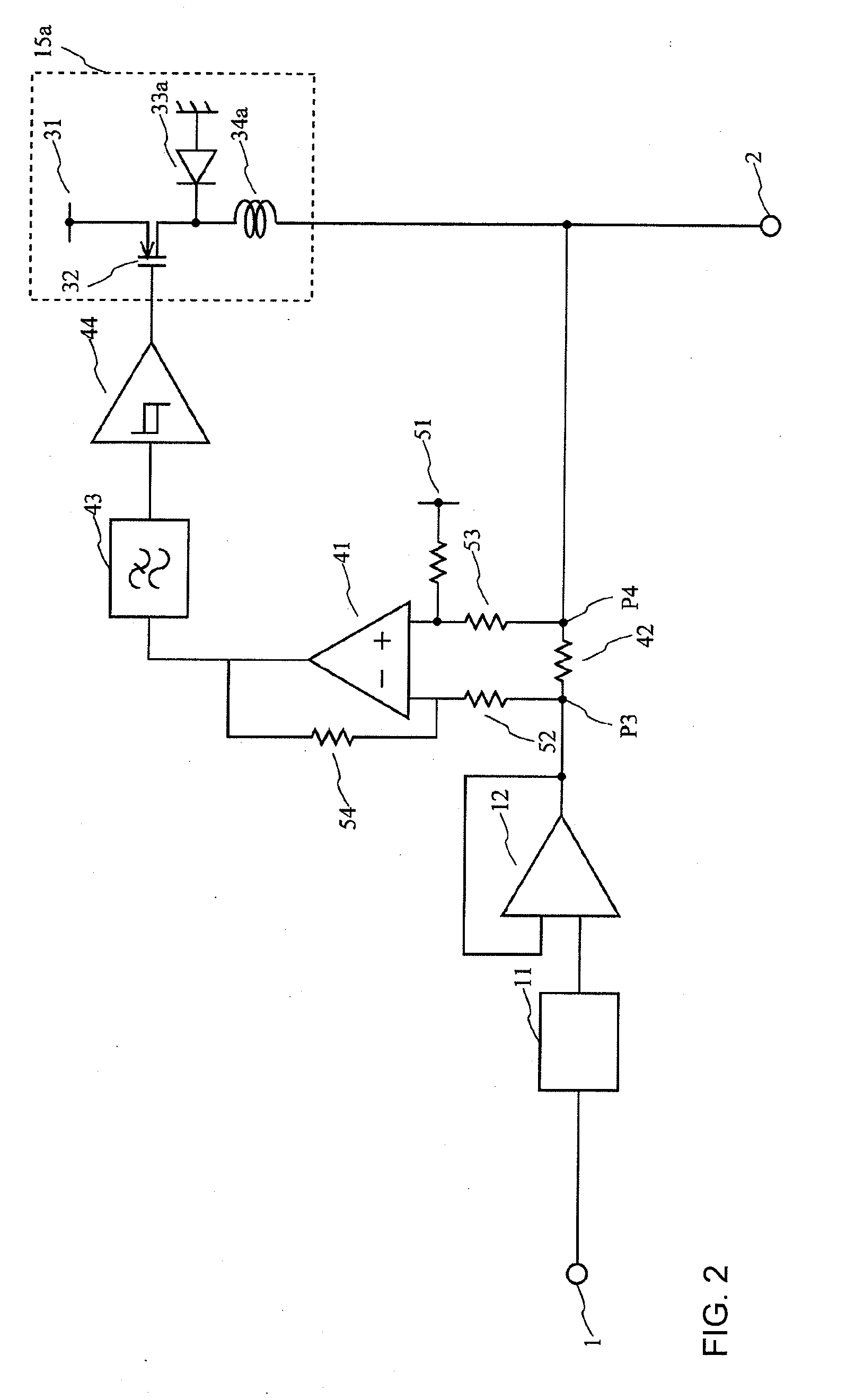
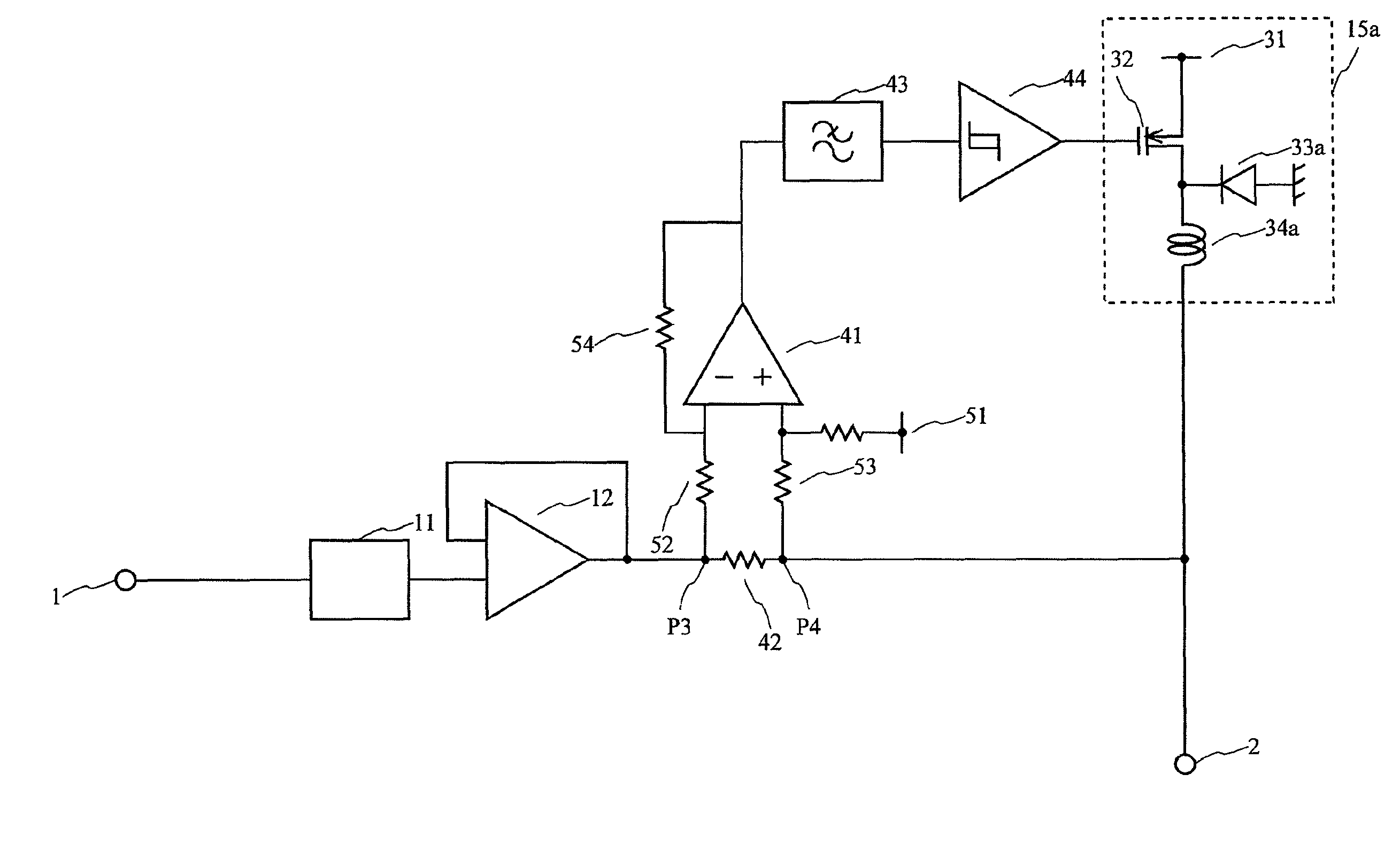
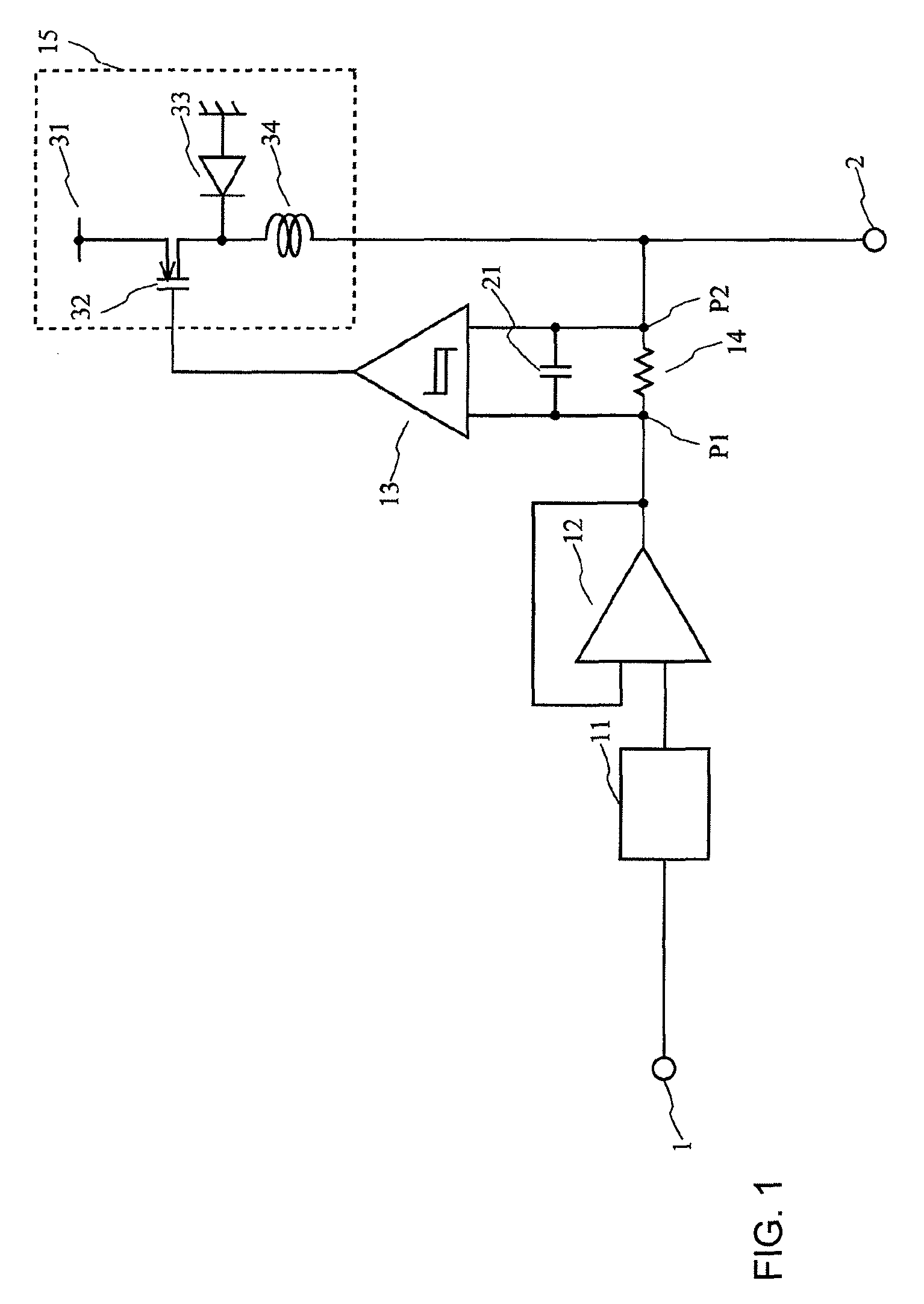
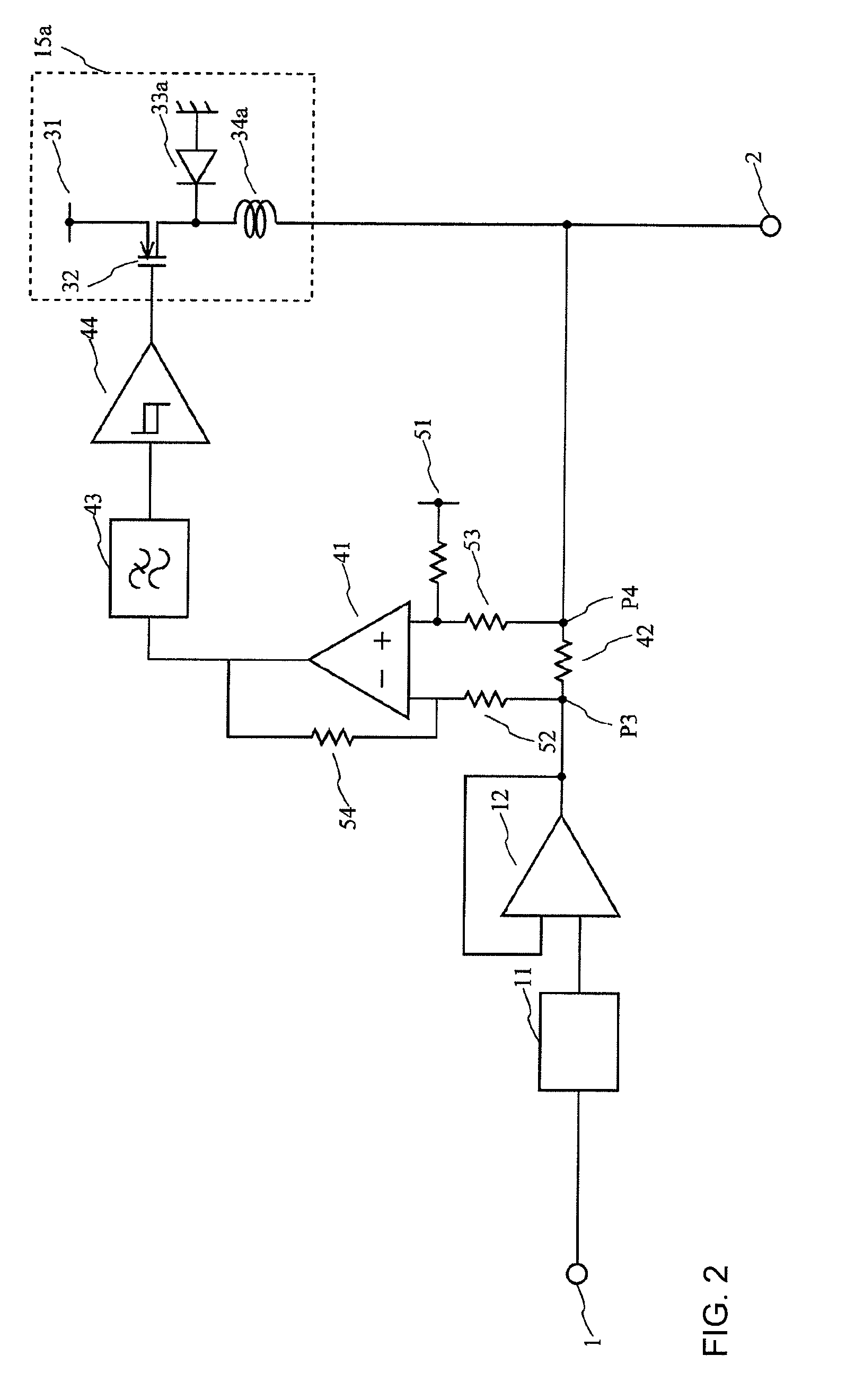
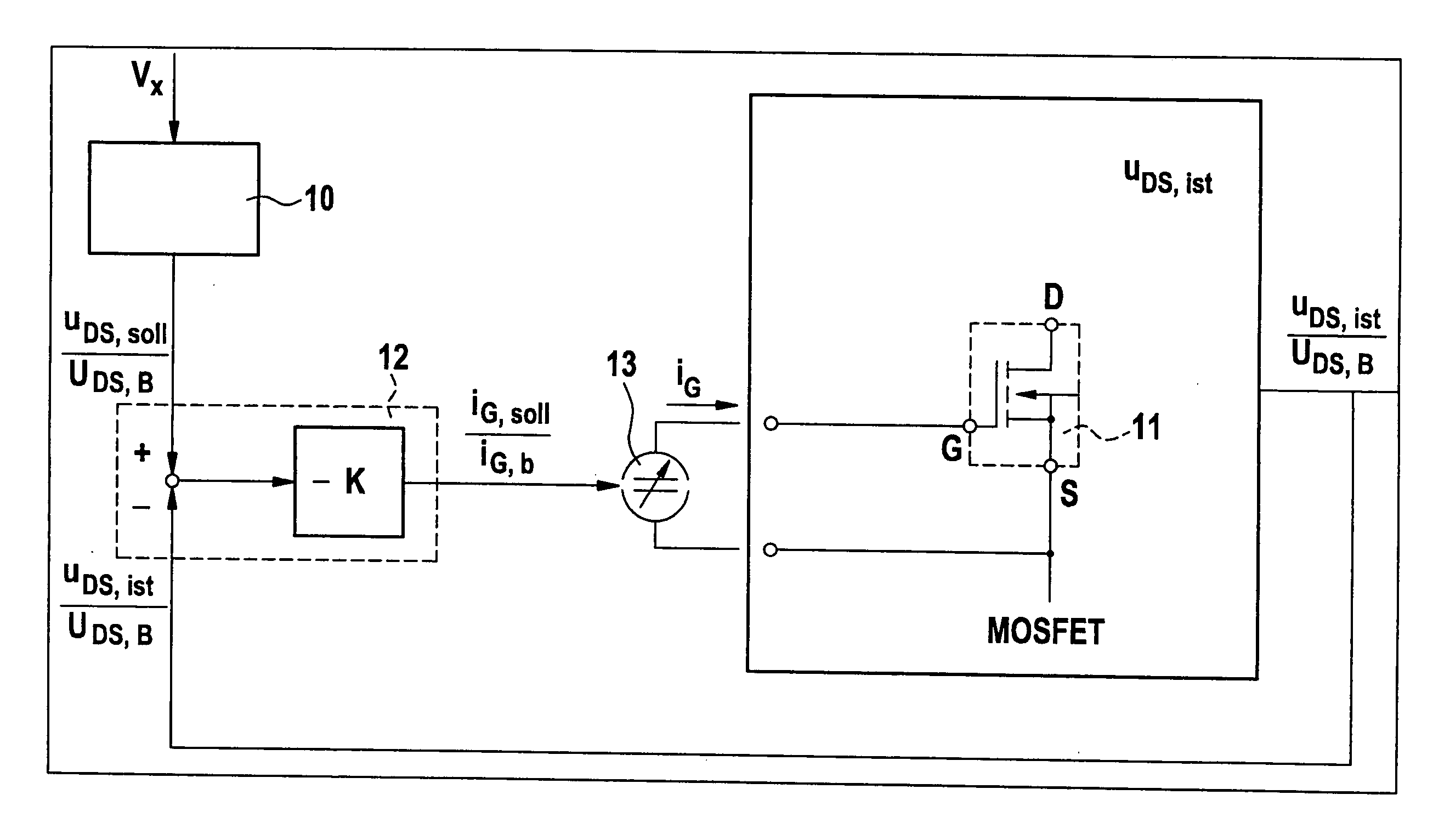
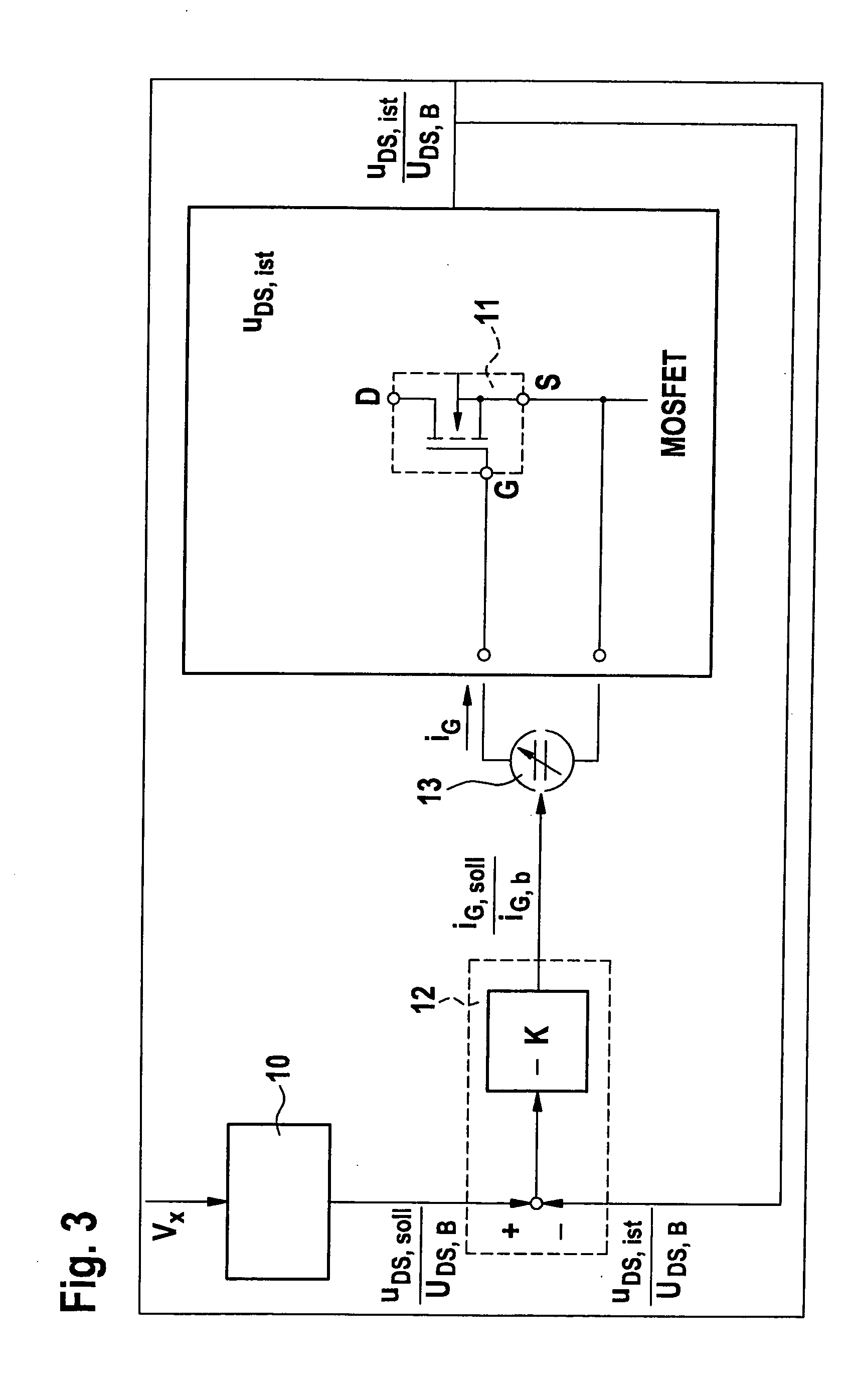
A power circuit used for an amplifier, which includes an amplifier provided with a linear amplifier serving as a voltage source, a DC / DC converter serving as a current source, a hysteresis comparator controlling the DC / DC converter, and a current detector detecting output current from the linear amplifier to output the detected output current to the hysteresis comparator; and a switching restricting means for restricting a switching interval in the DC / DC converter such that the switching interval is not equal to or less than a constant time or is not shorter than the constant time.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Synchronous electric motor drive system
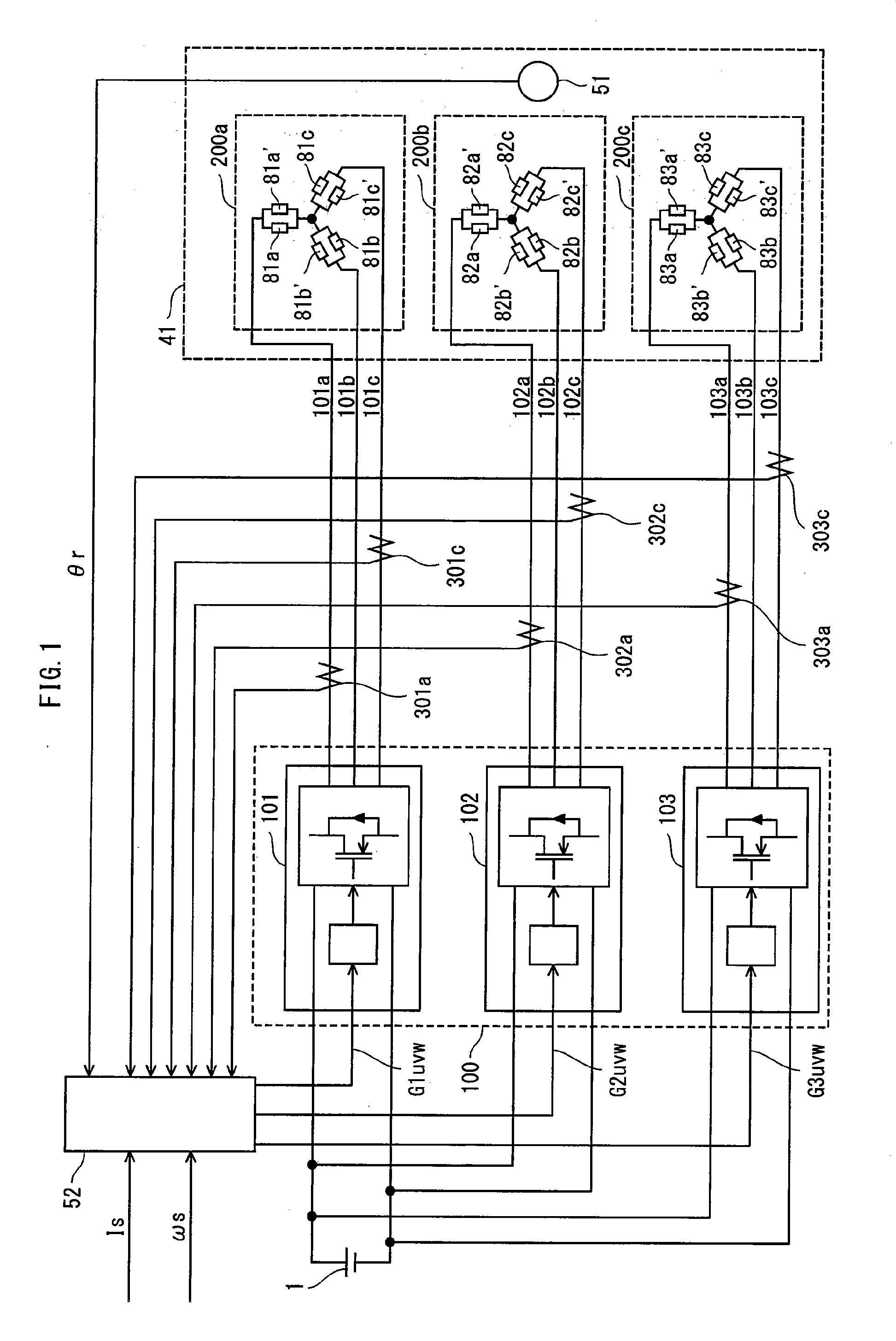
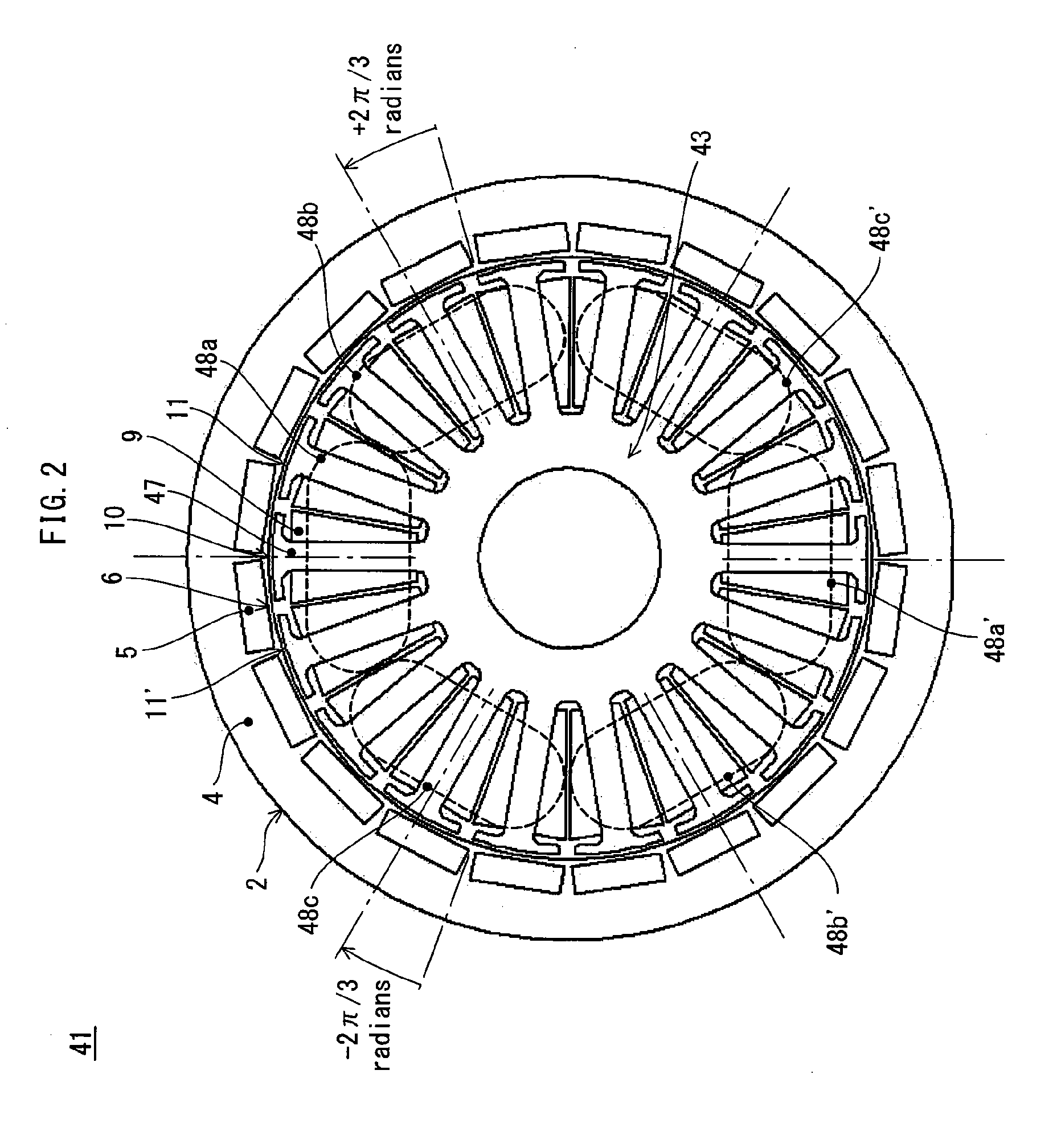
ActiveUS20110057591A1Prevents degradation of inverter efficiencyPrevents an increase of iron lossesTorque ripple controlSynchronous motors startersSynchronous motorDC - Direct current
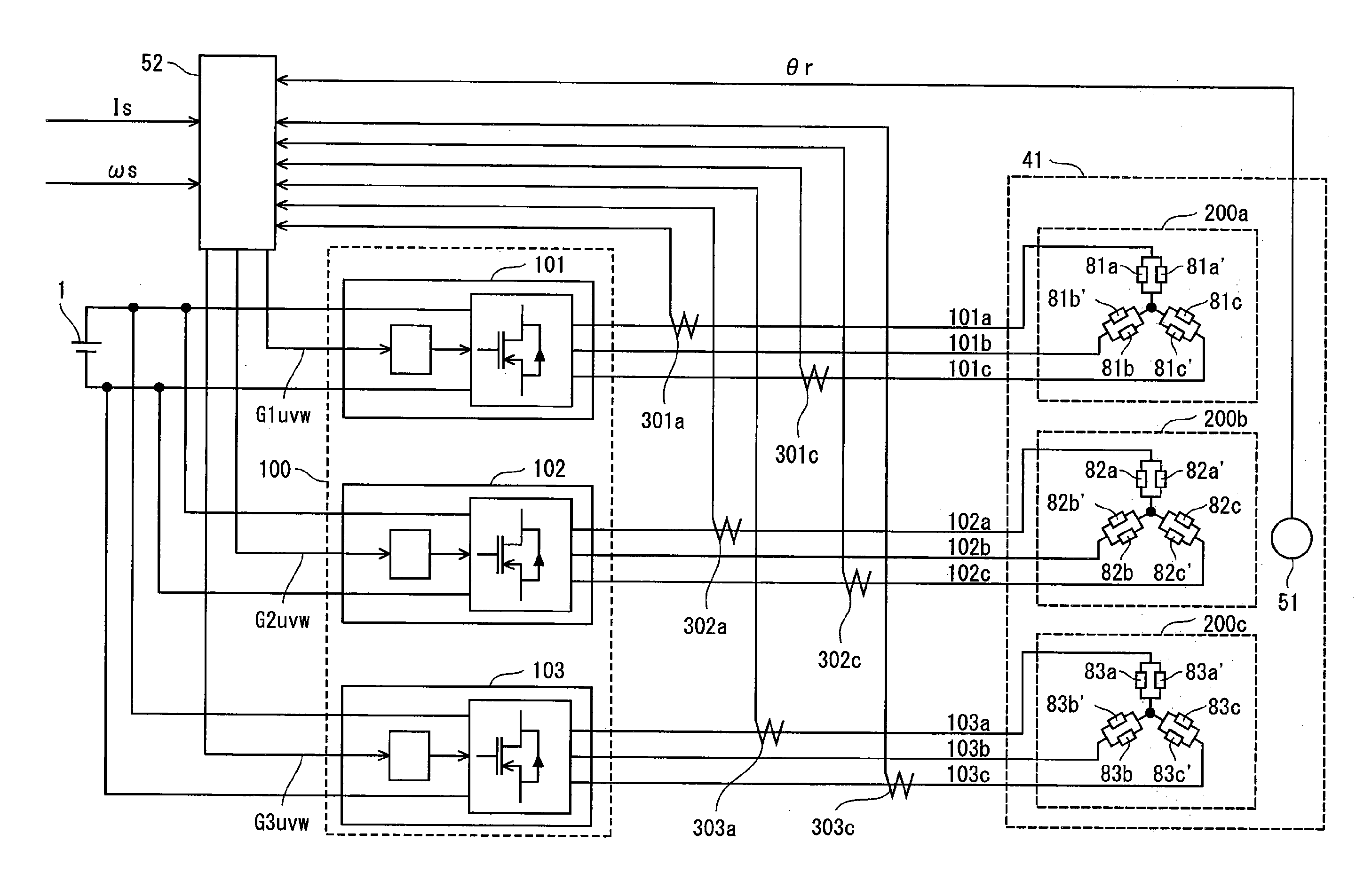
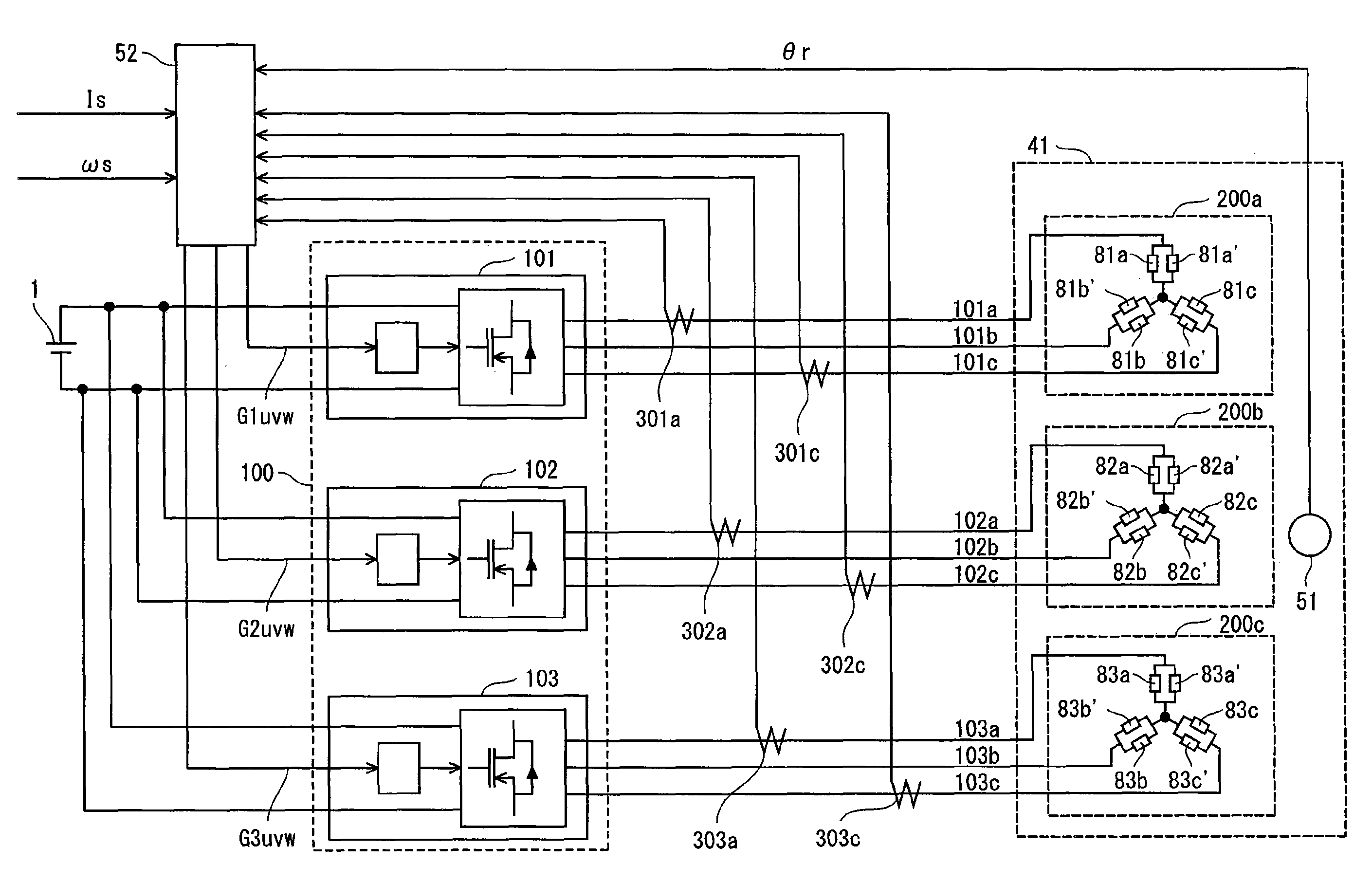
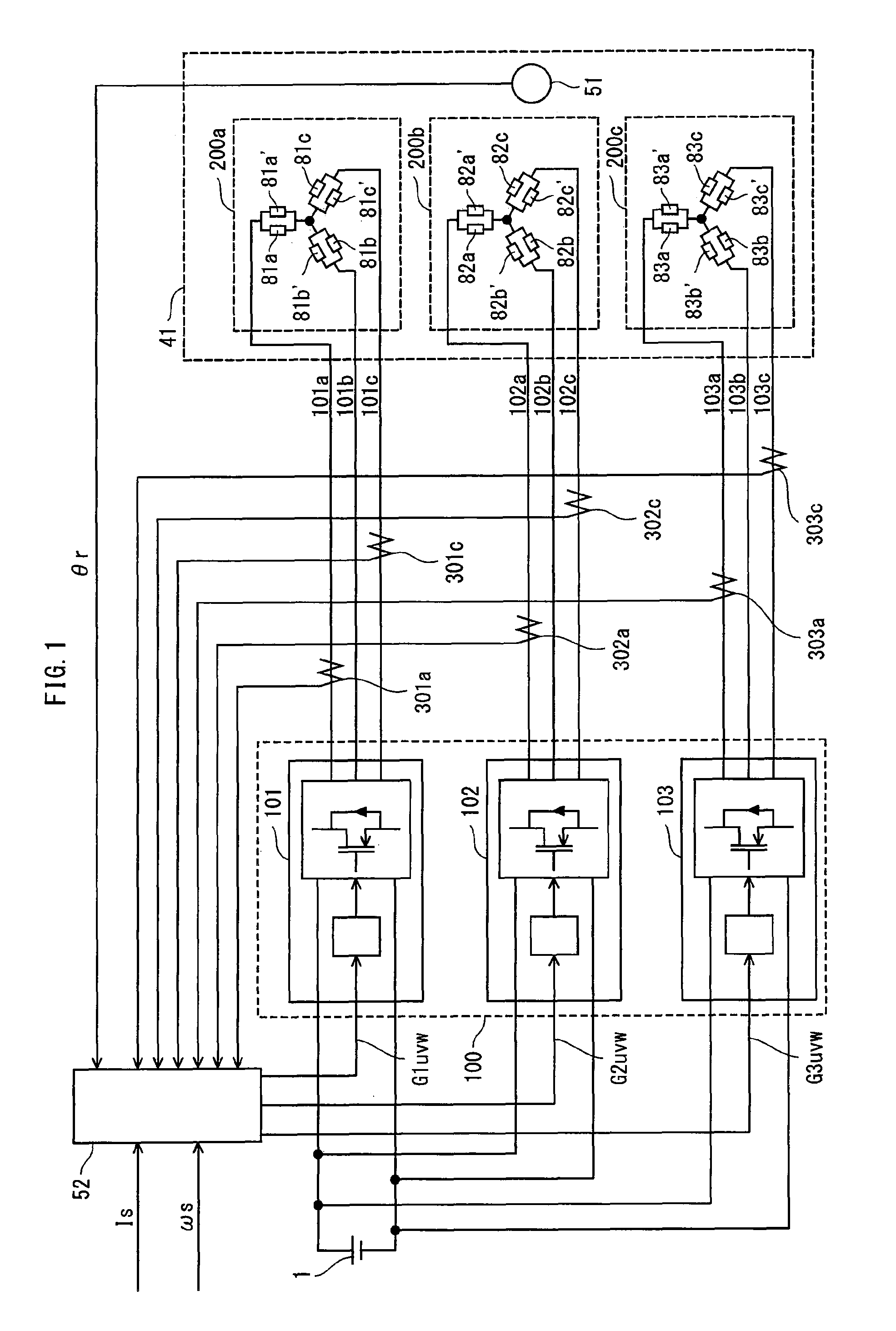
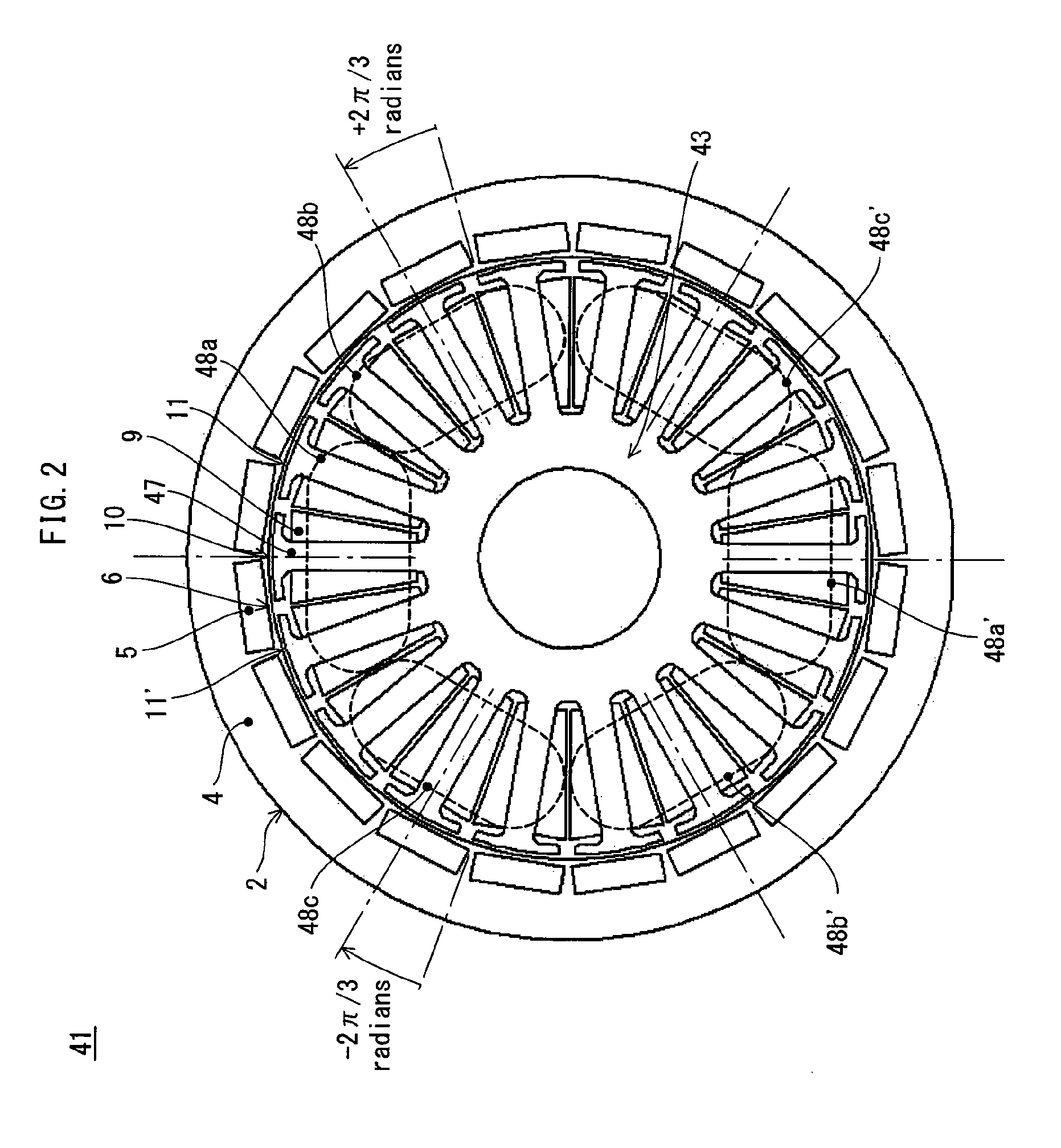
The present invention provides a synchronous motor drive system designed to realize reduced vibration and noise along with high output. The system includes: inverters 101, 102, and 103 for converting a direct current to a three-phase alternating current; a current application control unit 52 that controls operations of the three-phase inverters; and a synchronous motor 41 driven by three-phase alternating currents supplied from the three-phase inverters. The current application control unit 52 determines, for each three-phase inverter, a current phase angle and a current amount of a three-phase alternating current to output, and each inverter supplies a three-phase alternating current having the determined current phase angle and current amount to a different one of three-phase coil groups 200a to 200c.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Motor control device
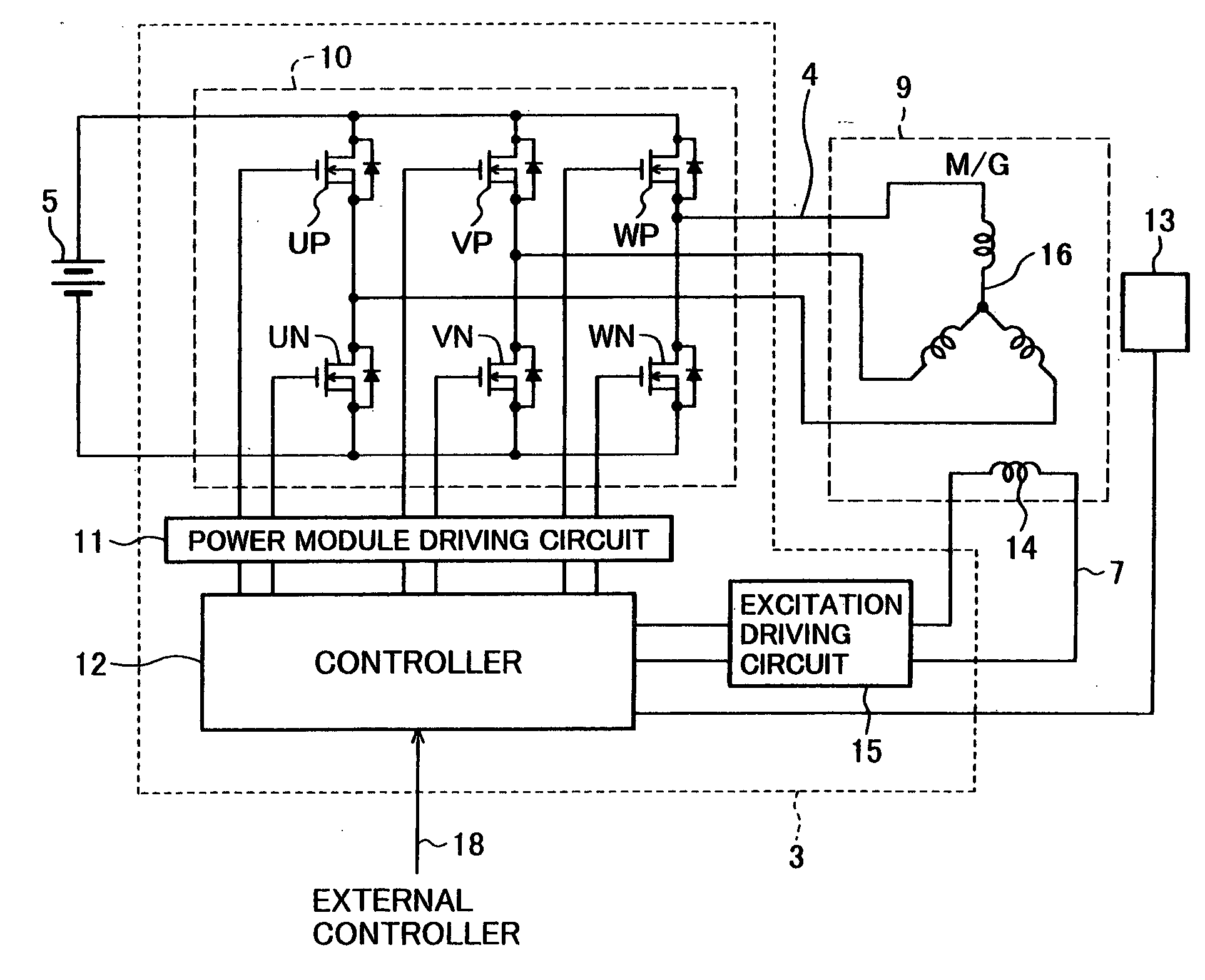
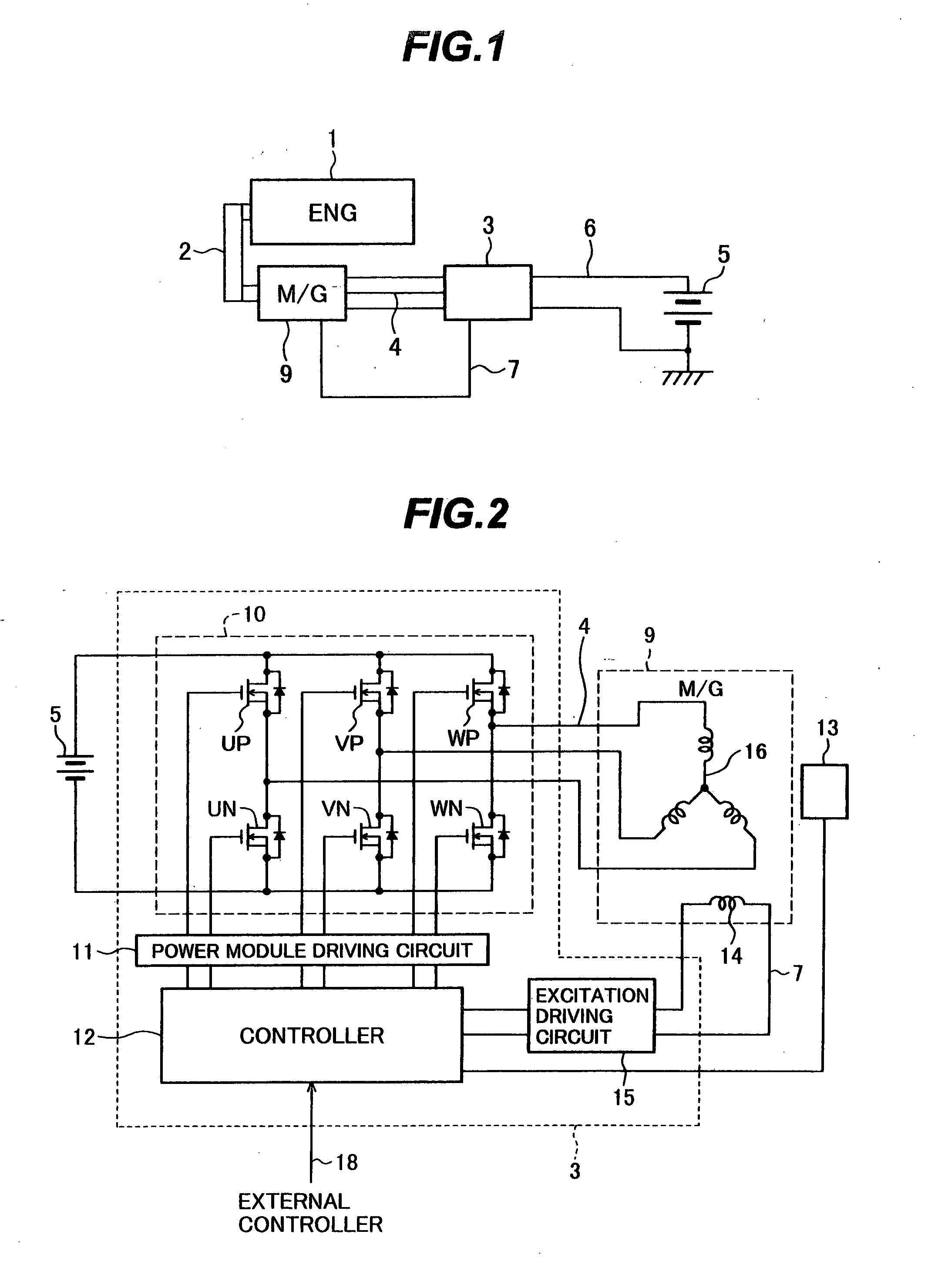
InactiveUS20050001582A1Improve rectification efficiencyImprove efficiencyAC motor controlAc-dc conversionElectric machineEngineering
The invention is intended to provide a control device for a vehicular AC motor, which has higher efficiency of voltage utilization in a power running mode and has higher efficiency of electricity generation in an electricity generation mode. The motor control device comprises rectifying devices and switching devices for three phases, which are connected between a DC power source and armature coils of an AC motor operatively coupled to an internal combustion engine. The motor control device has the inverter function of converting a DC power from the DC power source into an AC power and supplying the AC power to the armature coils, and the converter function of converting an AC power generated by the AC motor into a DC power and supplying the DC power to the DC power source. Rectangular-wave driving control of applying rectangular wave voltages to the armature coils of the AC motor is performed when the AC motor is operated for power running, and synchronous rectification control for making synchronous rectification of the AC power generated by the AC motor is performed when the AC motor is operated for electricity generation.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Power semiconductor device with trench bottom polysilicon and fabrication method thereof
ActiveUS20110298042A1Increased switching lossesReduce input capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceDopant
A power semiconductor device comprising a base, a trench, a heavily doped polysilicon structure, a polysilicon gate, a gate dielectric layer, and a heavily doped region is provided. The trench is formed in the base. The heavily doped polysilicon structure is formed in the lower portion of the trench. At least a side surface of the heavily doped polysilicon structure touches the naked base. The polysilicon gate is located in the upper portion of the trench. The gate dielectric layer is interposed between the polysilicon gate and the heavily doped polysilicon structure. The dopants in the heavily doped polysilicon structure are diffused outward to form a heavily doped region.
Owner:SUPER GROUP SEMICON
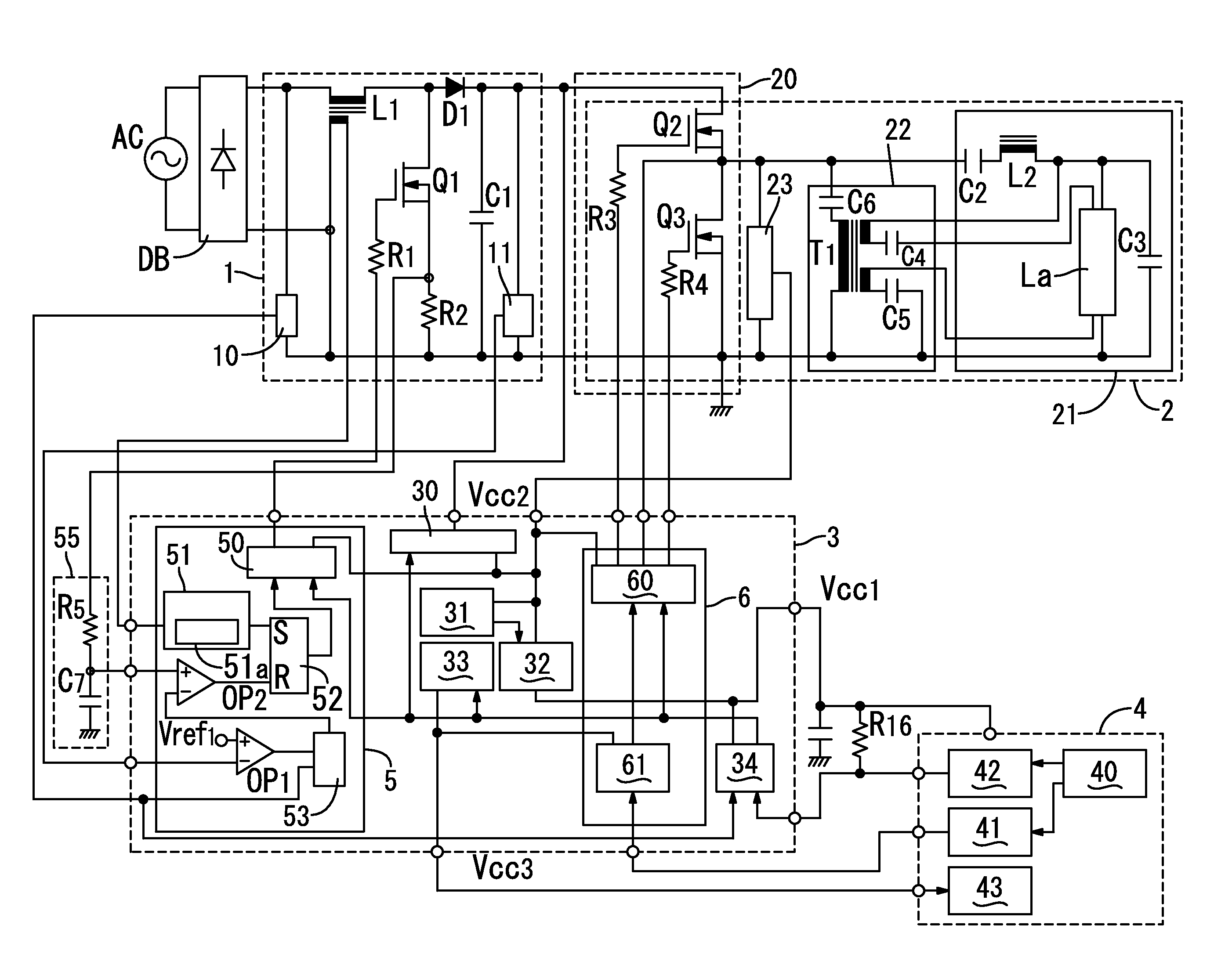
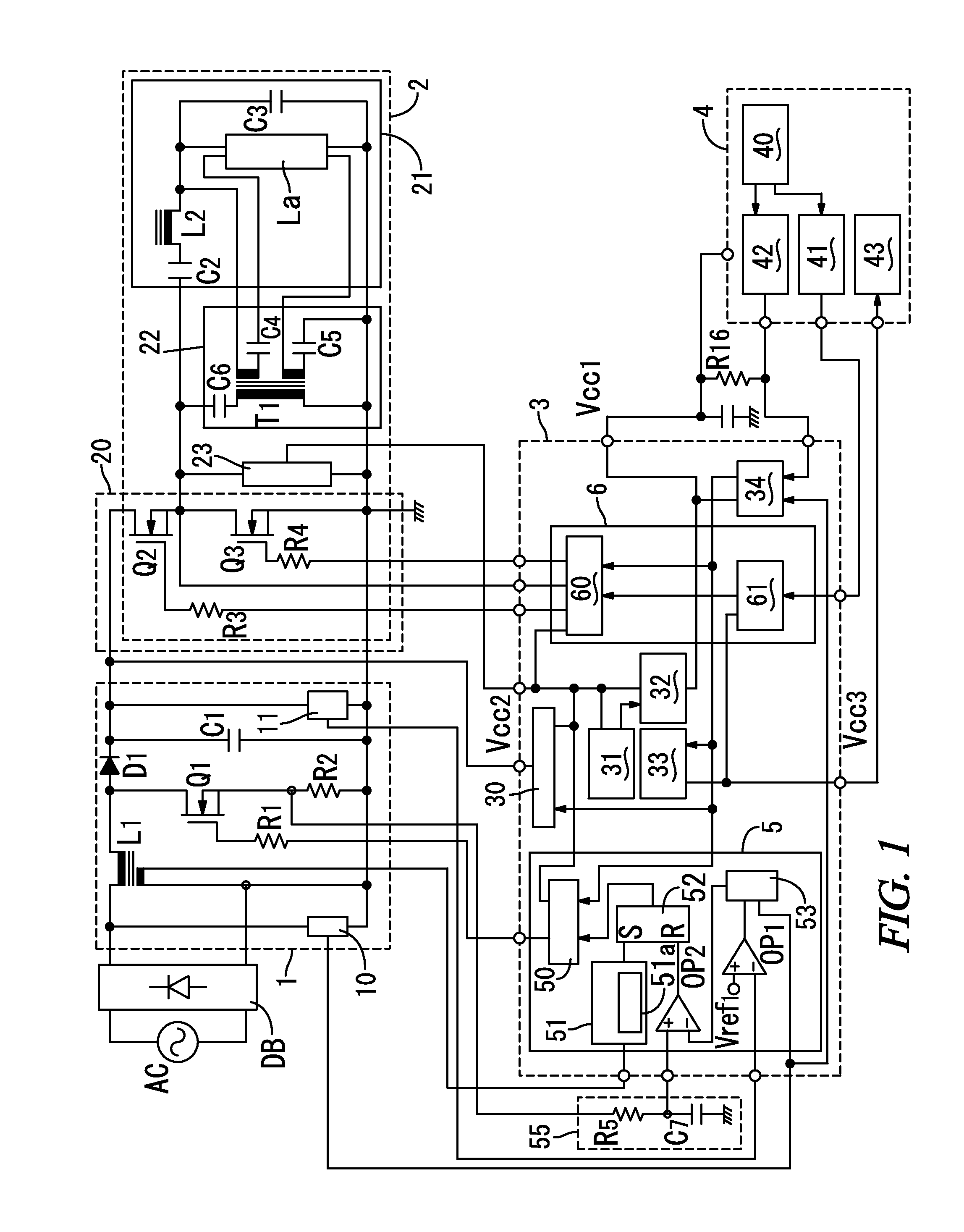
Power factor correction circuit
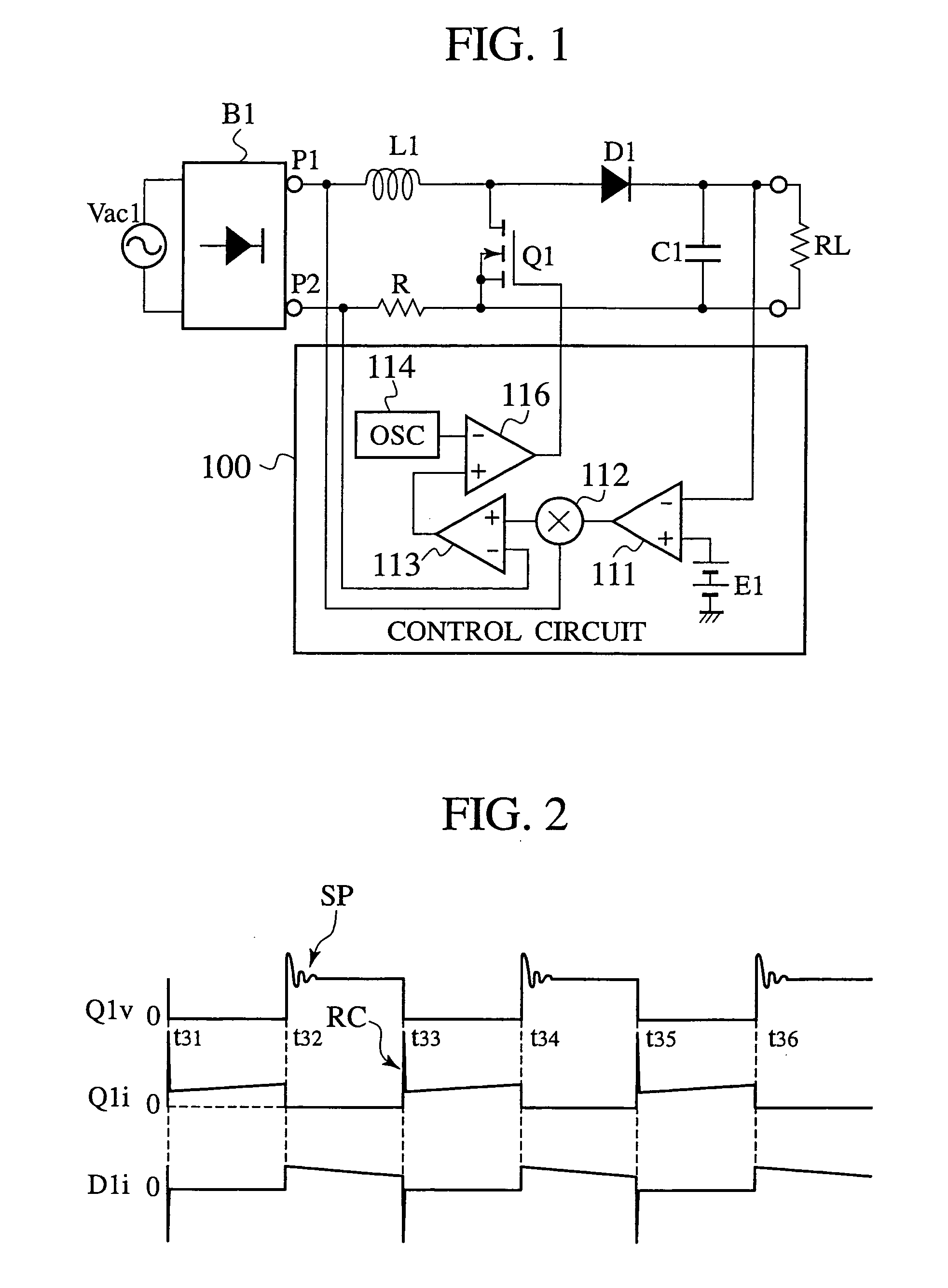
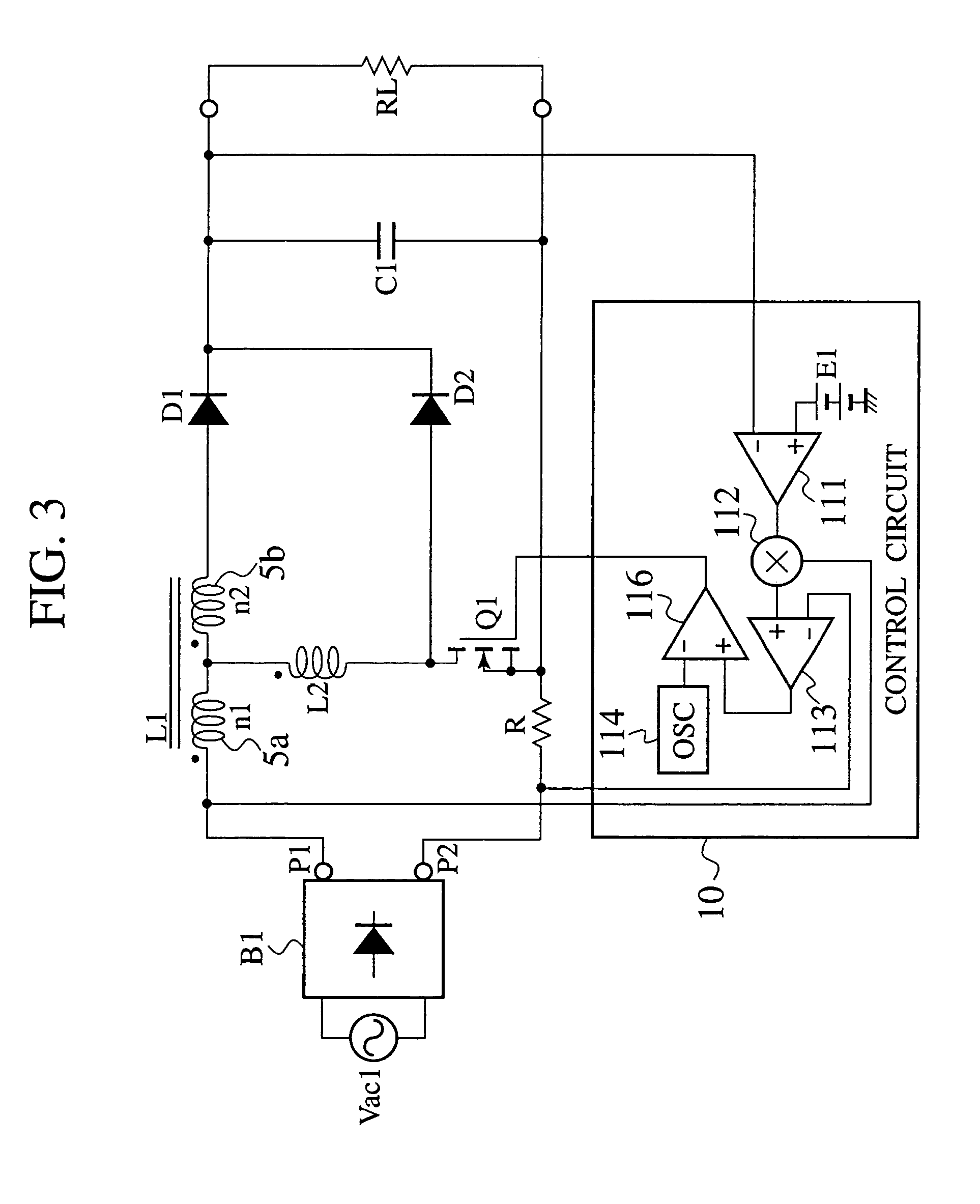
InactiveUS7183753B2Increase lossSwitching loss increaseAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionFull waveAlternating current
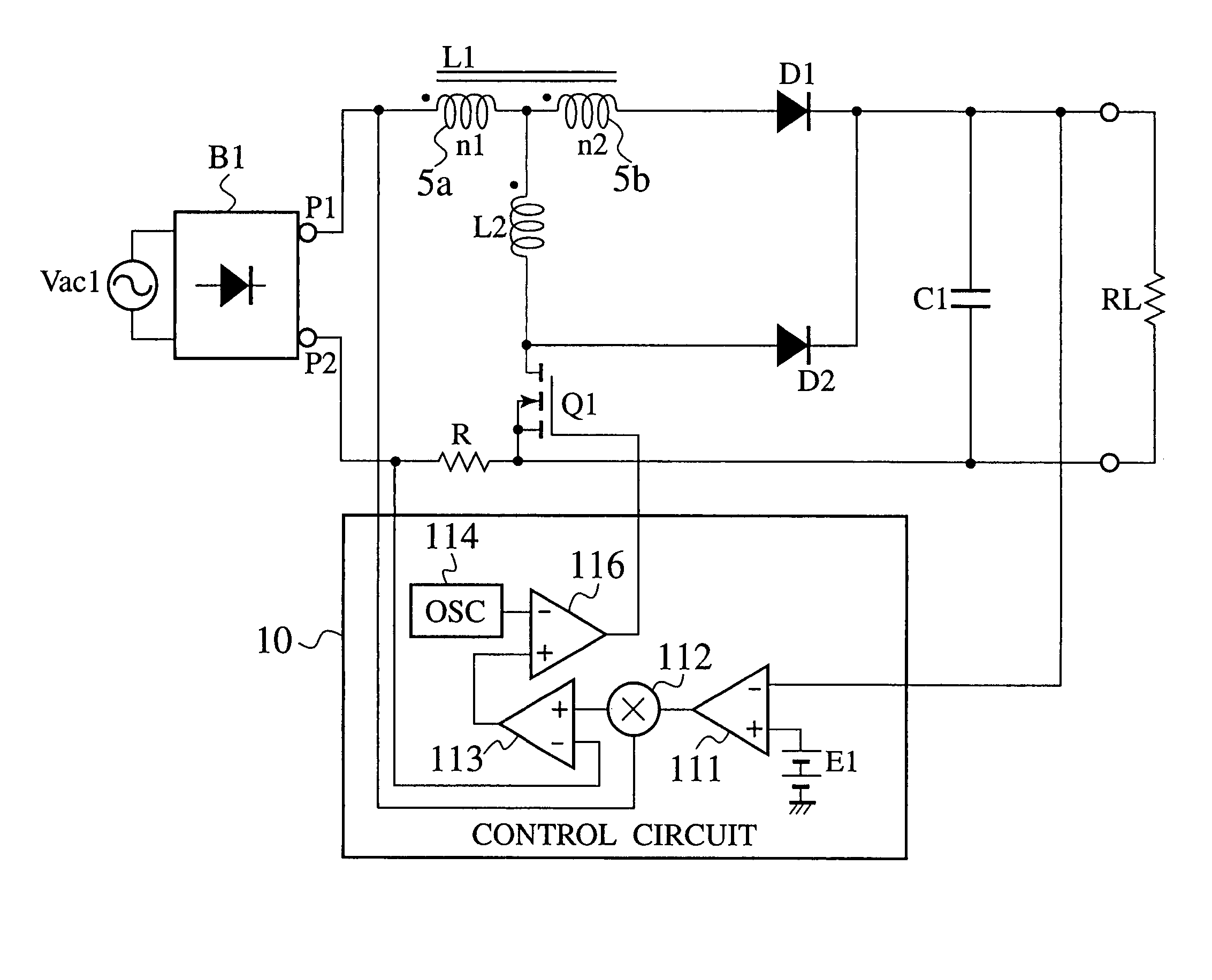
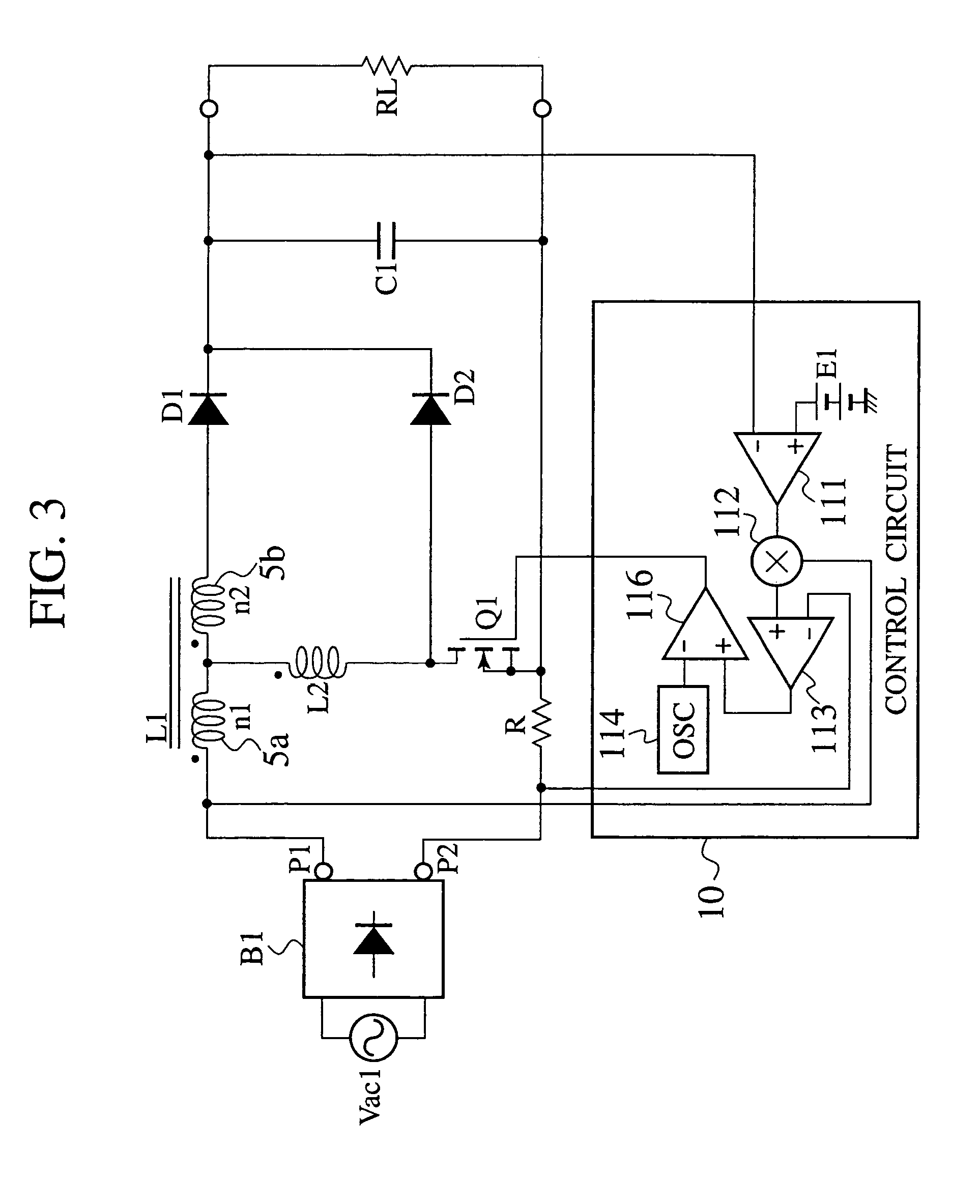
A power factor correction circuit includes; a series circuit connected to a positive-electrode output terminal P1 and negative-electrode output terminal P2 of a full-wave rectifying circuit B1, which rectifies an having current power-supply voltage of an alternating current power-supply Vac1, and including a booster winding 5a and a wind-up winding 5b wound on a booster reactor L1, a diode D1 and a smoothing capacitor C1; a series circuit, connected between the positive-electrode output terminal P1 and the negative-electrode output terminal P2 and having the booster winding 5a, a ZCS reactor L2 and a switch Q1; a diode D2 connected between a junction, between the switch Q1 and the ZCS reactor L2, and the smoothing capacitor C1; and a control circuit 10 that controllably turns the switch Q1 on and off for controlling an output voltage of the smoothing capacitor C1 to a given voltage.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
Power factor impoving circuit
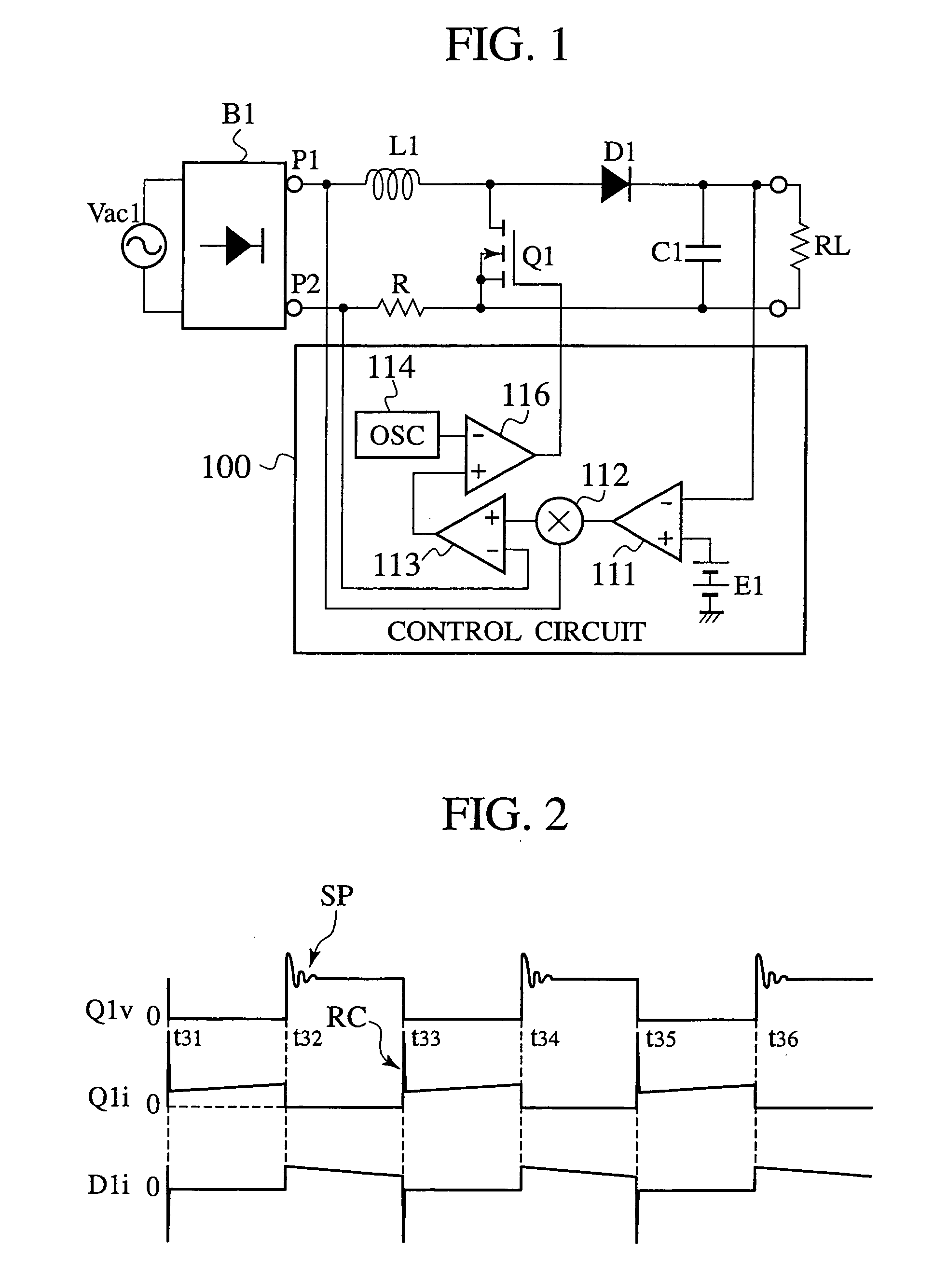
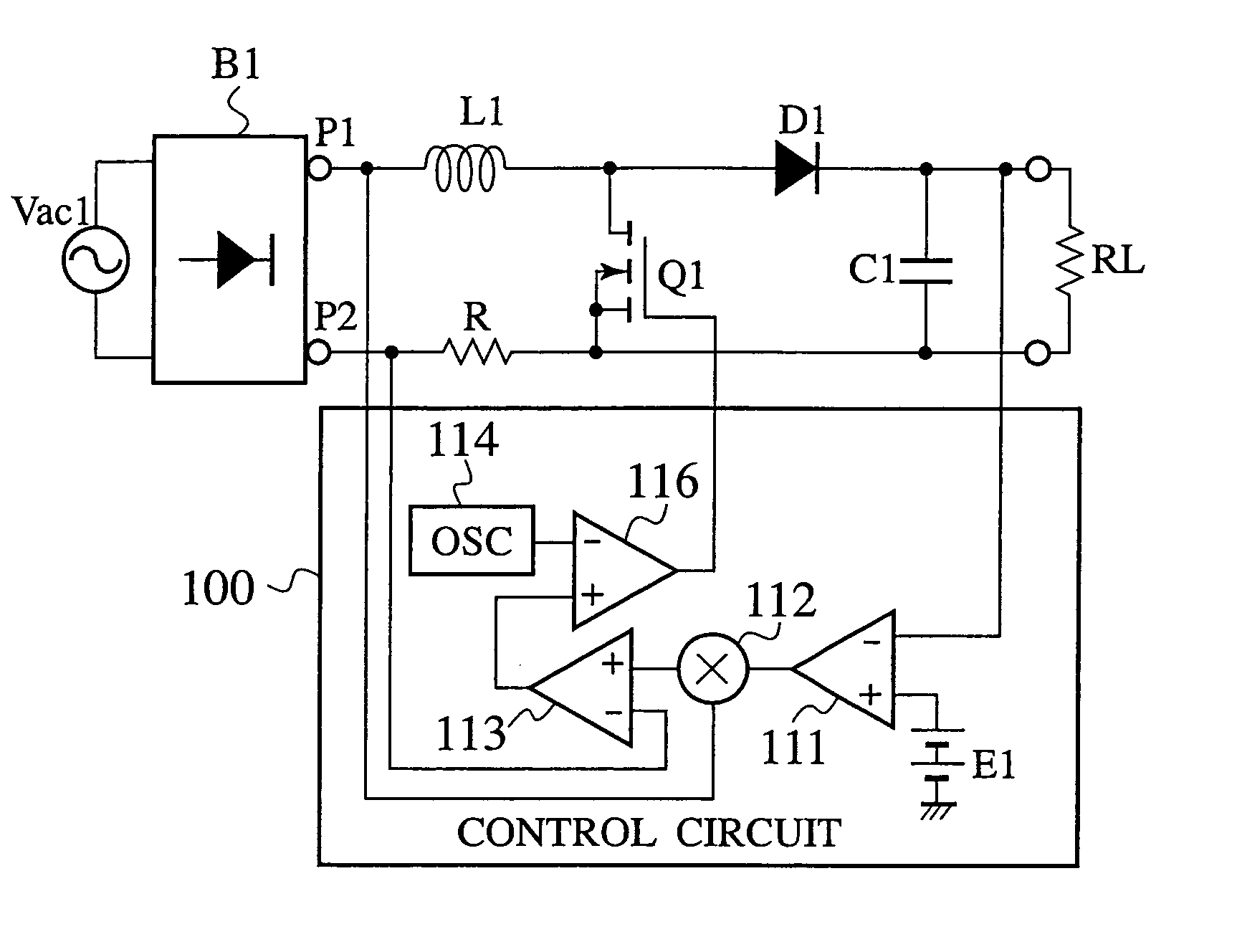
InactiveUS20050226015A1Improve efficiencyReduce noiseAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionFull waveAlternating current
A power factor correction circuit includes; a series circuit connected to a positive-electrode output terminal P1 and negative-electrode output terminal P2 of a full-wave rectifying circuit B1, which rectifies an having current power-supply voltage of an alternating current power-supply Vac1, and including a booster winding 5a and a wind-up winding 5b wound on a booster reactor L1, a diode D1 and a smoothing capacitor C1; a series circuit, connected between the positive-electrode output terminal P1 and the negative-electrode output terminal P2 and having the booster winding 5a, a ZCS reactor L2 and a switch Q1; a diode D2 connected between a junction, between the switch Q1 and the ZCS reactor L2, and the smoothing capacitor C1; and a control circuit 10 that controllably turns the switch Q1 on and off for controlling an output voltage of the smoothing capacitor C1 to a given voltage.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
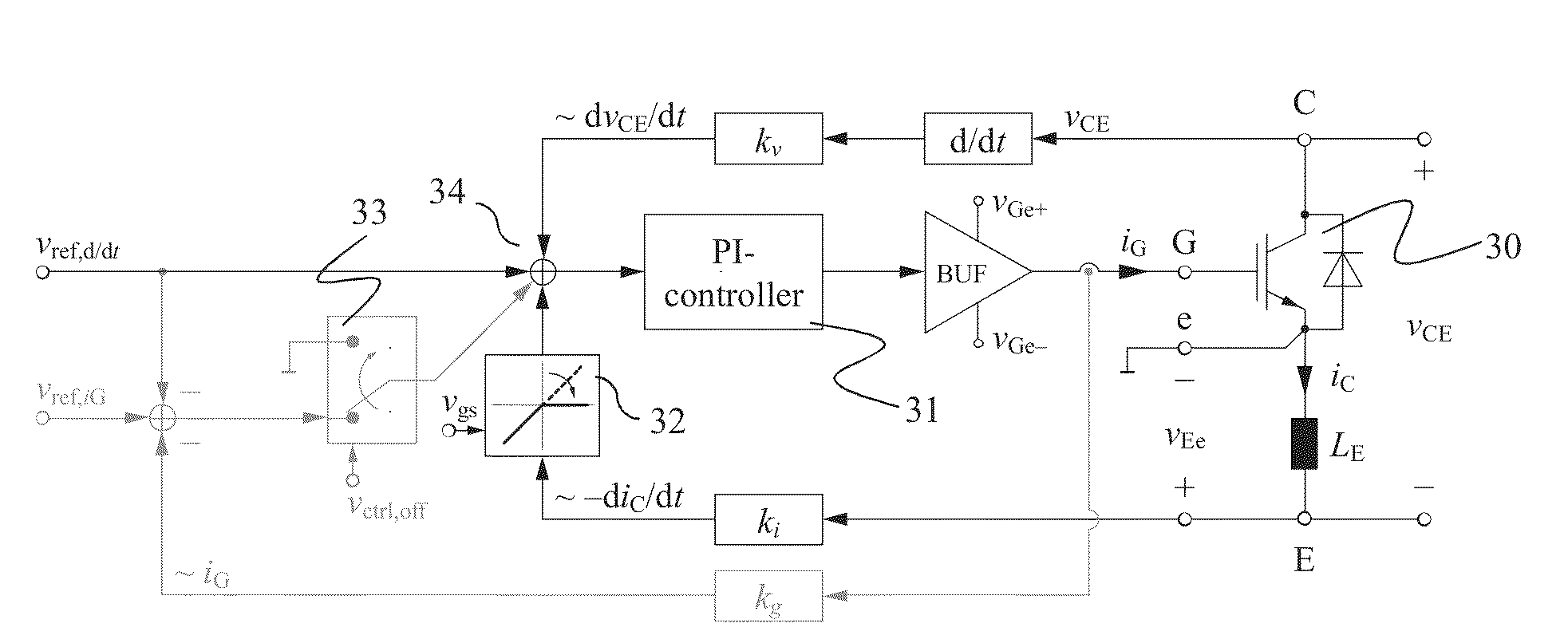
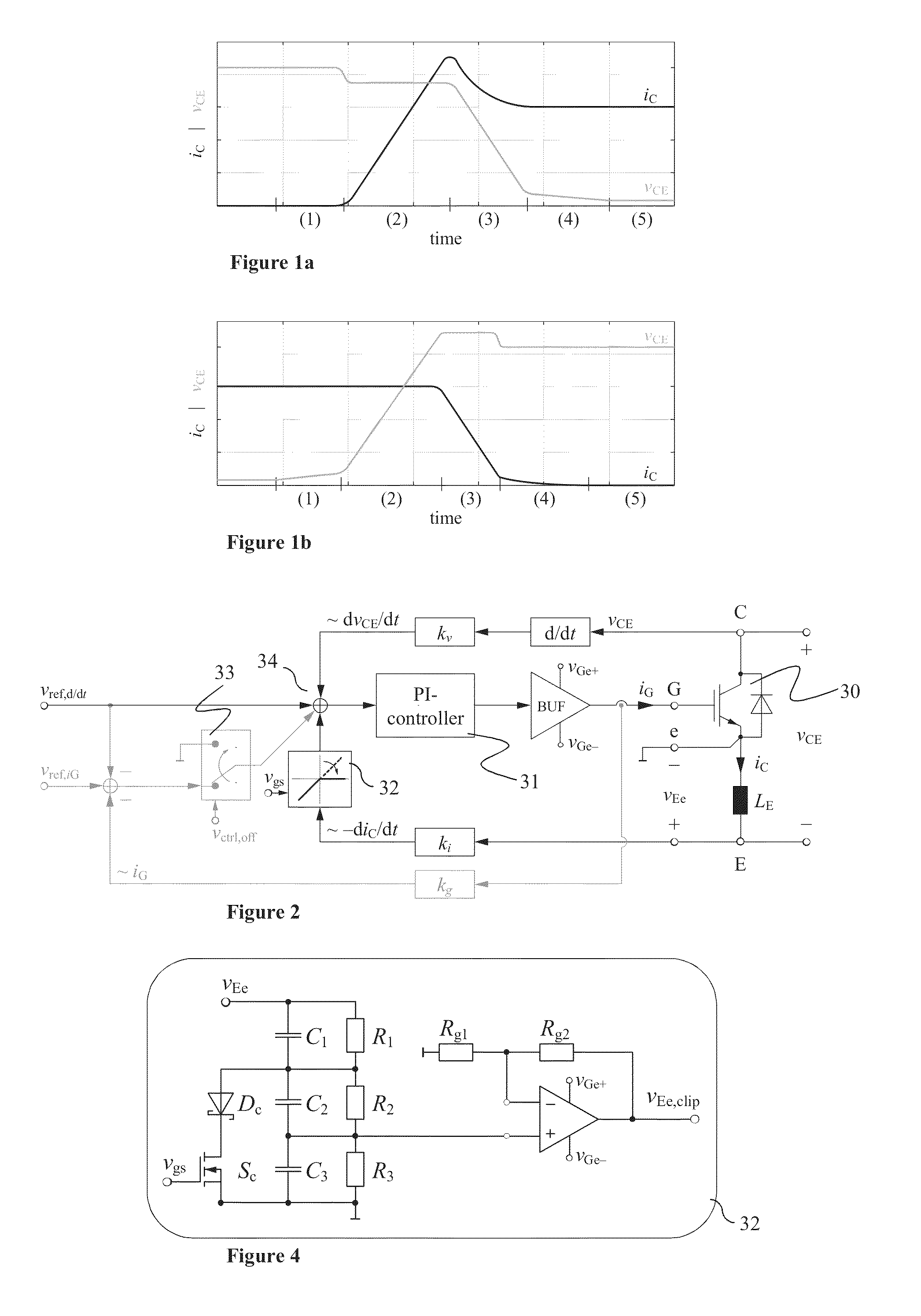
Active gate drive circuit
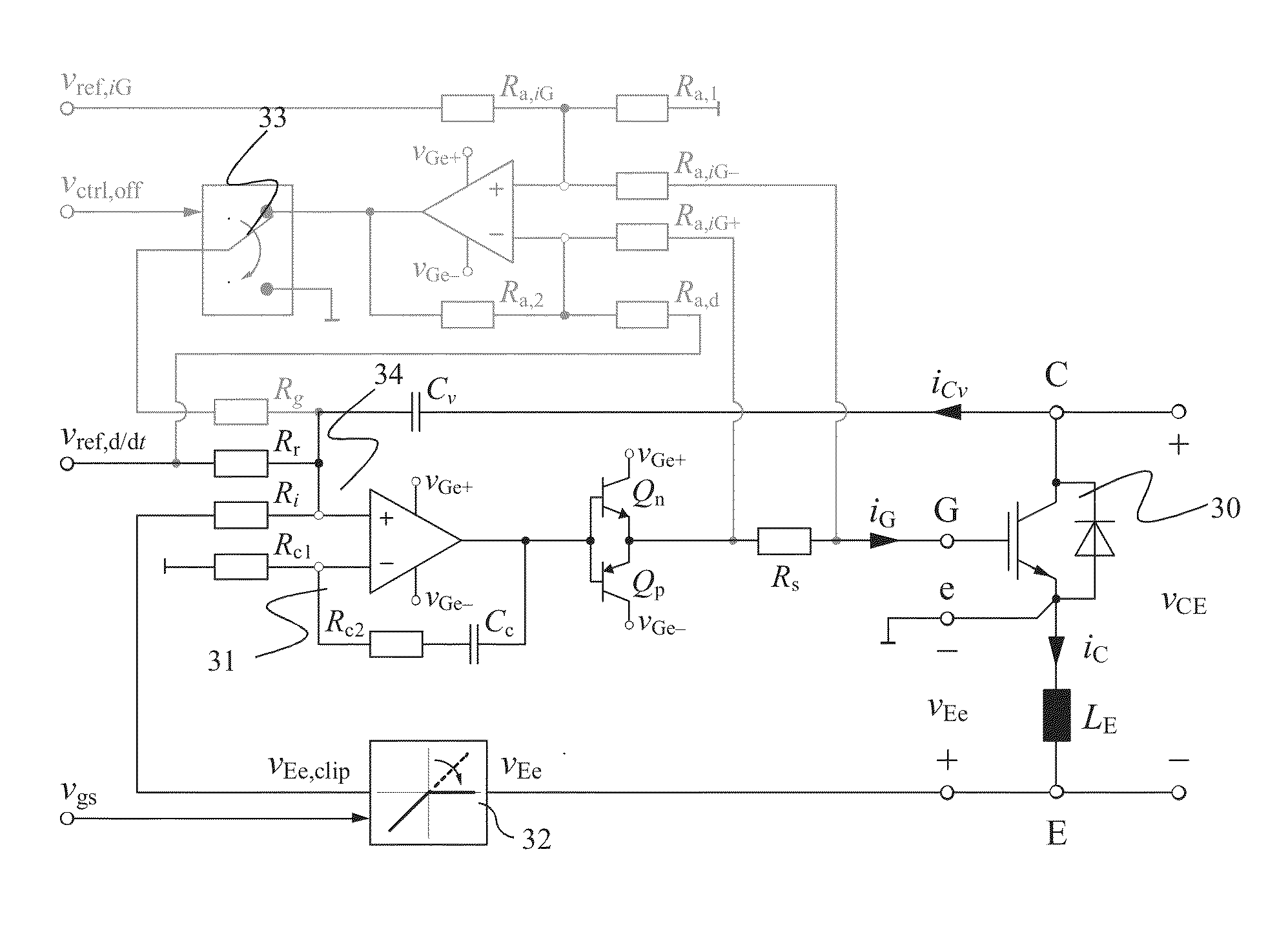
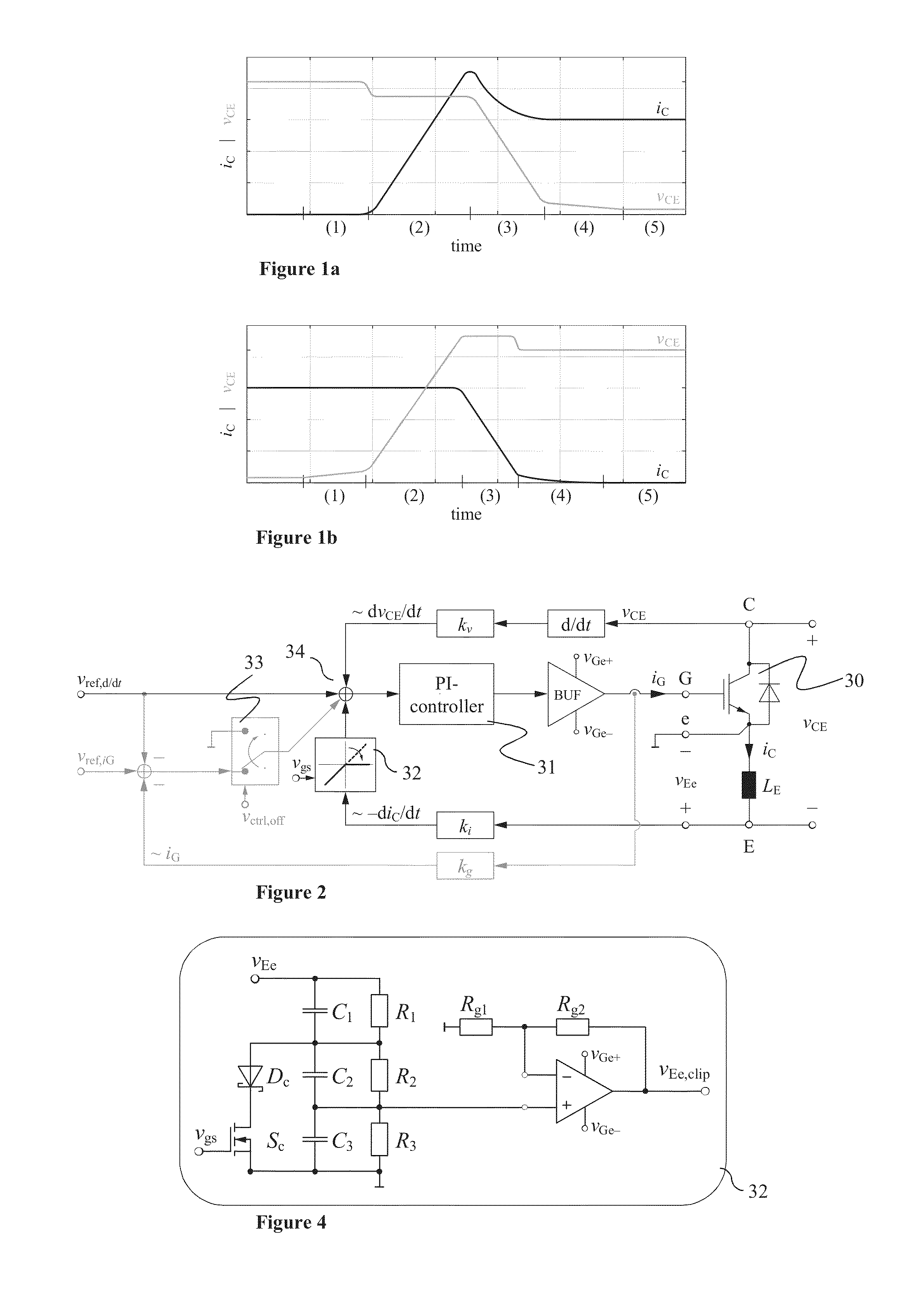
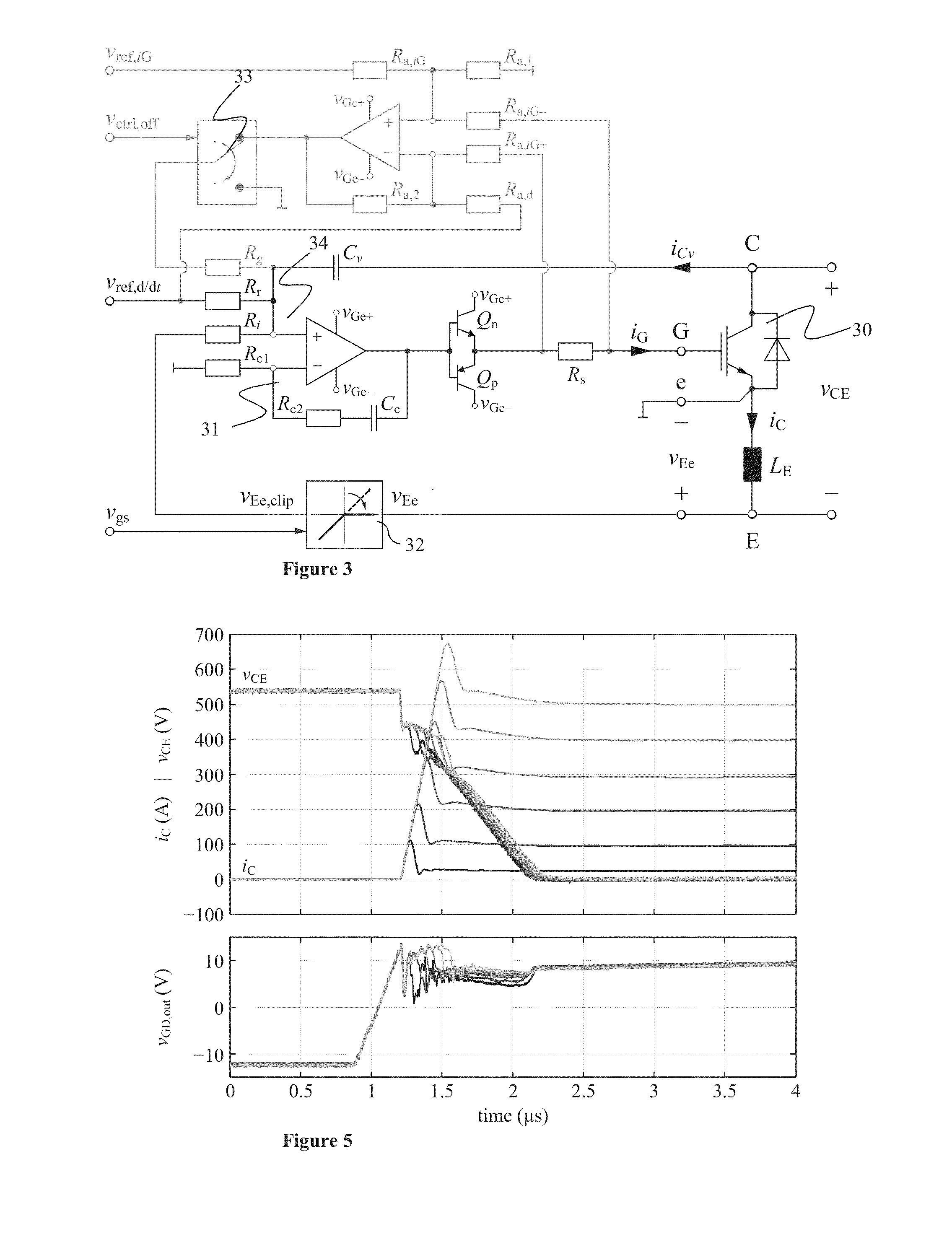
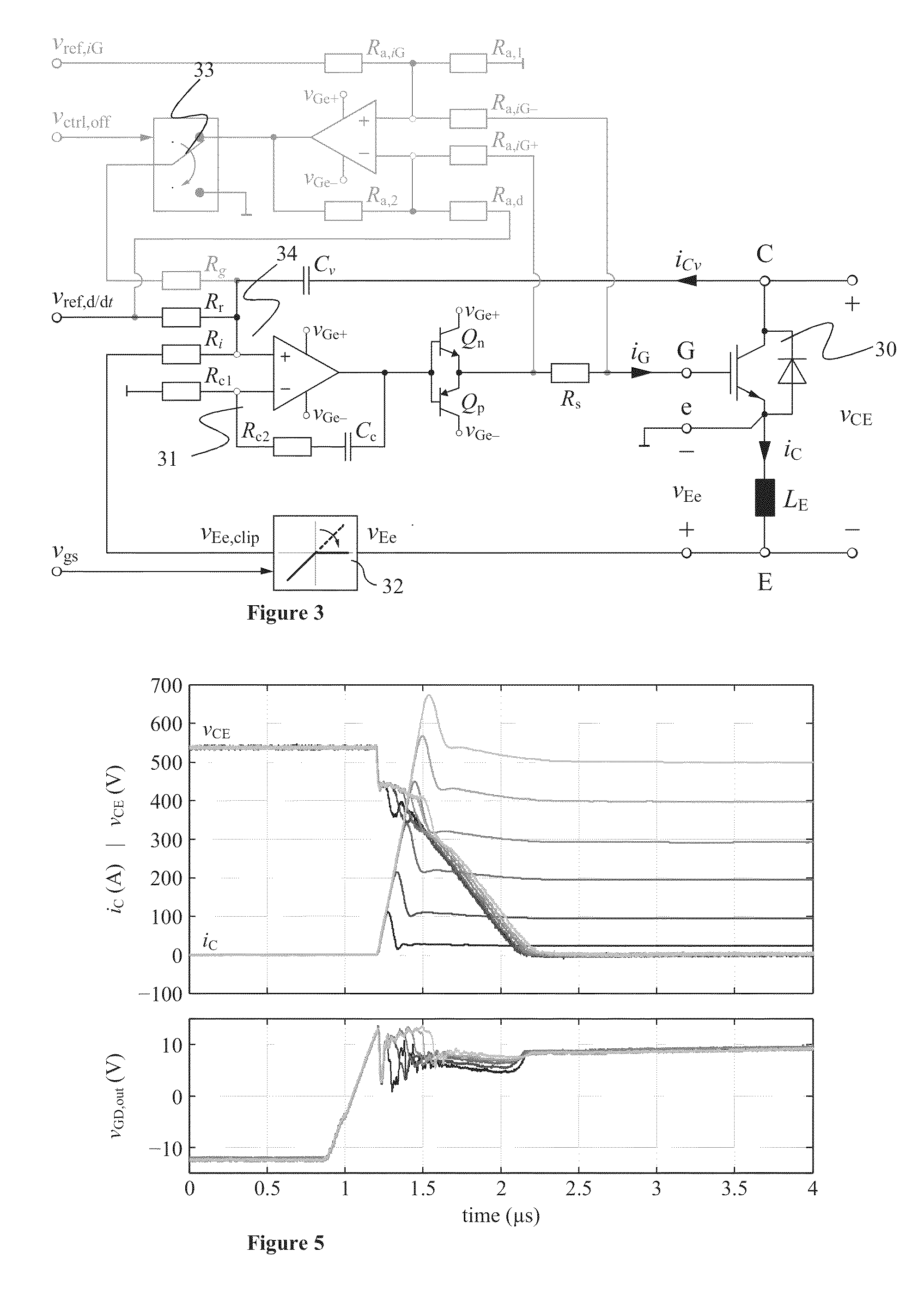
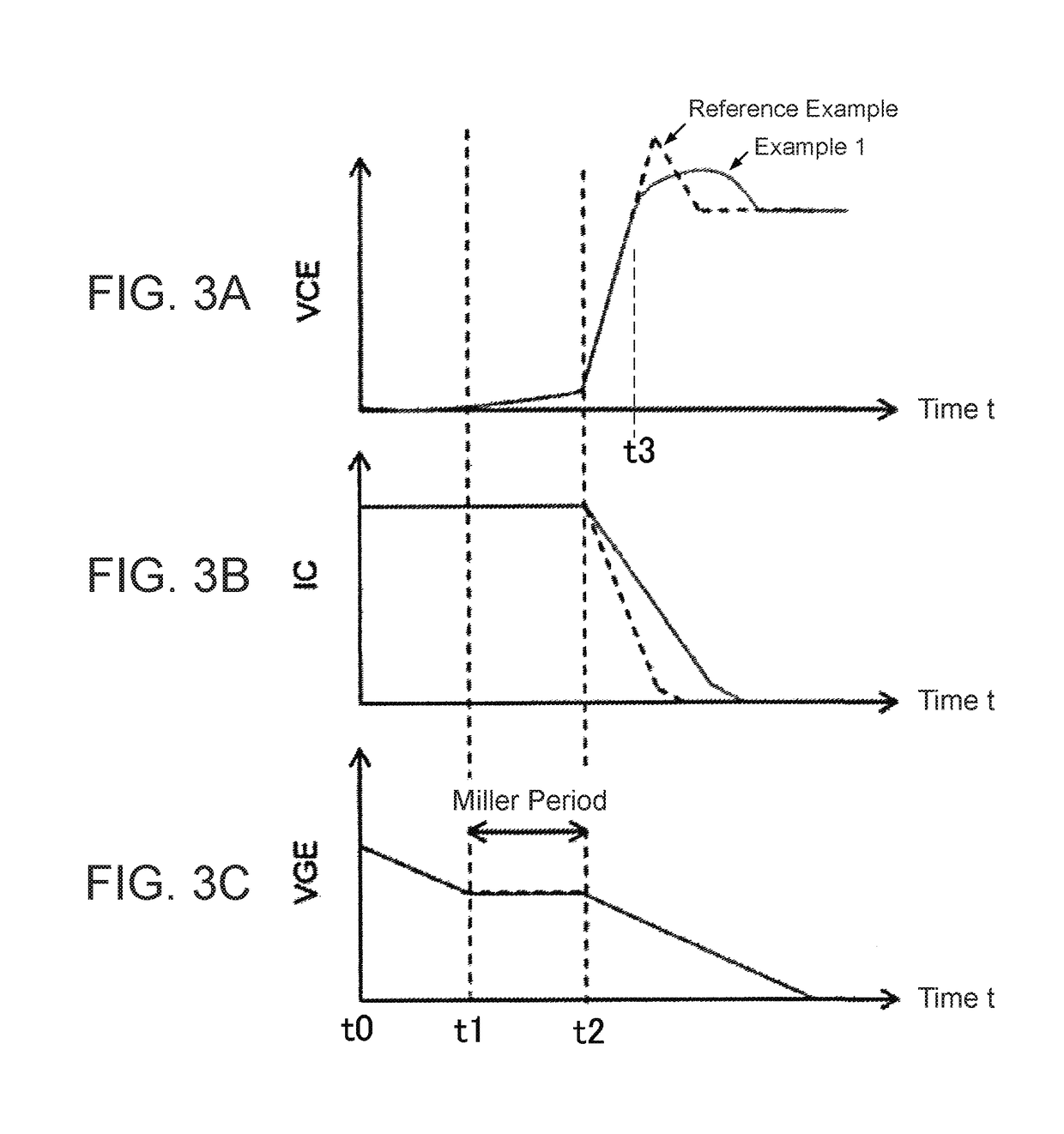
ActiveUS20130181750A1Switching loss increaseAccurate detectionElectronic switchingElectric pulse generatorTime derivativeGate voltage
Exemplary embodiments are directed to a gate drive circuit and a method for controlling a gate-controlled component. The gate drive circuit includes a PI controller that receives an input reference signal (vref,d / dt) controls a gate voltage of the gate-controlled component. The gate drive circuit also includes a first feedback loop for the PI controller adapted to provide feedback from a time derivative of a collector-to-emitter voltage (vCE) of the controlled component. The first feedback loop has a first gain (kv). A second is provided in the gate drive circuit feedback loop for the PI controller that provides feedback from the time derivative of the collector current (iC) of the controlled component. The second feedback loop has second gain (ki) and includes a clipping circuit that modifies the feedback signal in the second feedback loop during turn-on of the controlled component when the time derivative of the collector current is negative.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Package configurations for low EMI circuits
ActiveUS8592974B2Reduce and eliminate capacitanceImprove performance and longevityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHigh pressureElectronic component
An electronic component includes a high voltage switching transistor encased in a package. The high voltage switching transistor comprises a source electrode, a gate electrode, and a drain electrode all on a first side of the high voltage switching transistor. The source electrode is electrically connected to a conducting structural portion of the package. Assemblies using the abovementioned transistor with another transistor can be formed, where the source of one transistor can be electrically connected to a conducting structural portion of a package containing the transistor and a drain of the second transistor is electrically connected to the second conductive structural portion of a package that houses the second transistor. Alternatively, the source of the second transistor is electrically isolated from its conductive structural portion, and the drain of the second transistor is electrically isolated from its conductive structural portion.
Owner:TRANSPHORM INC
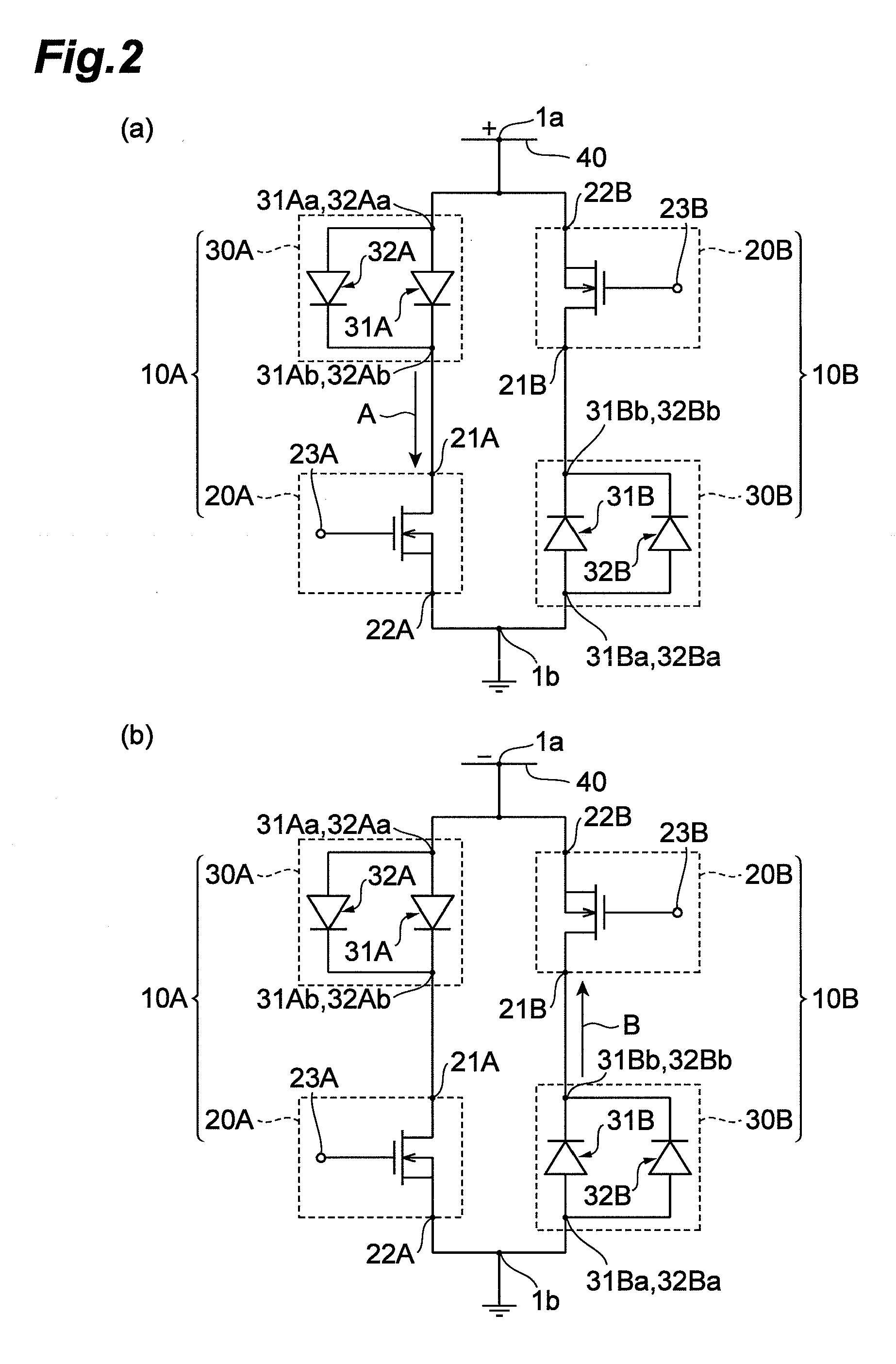
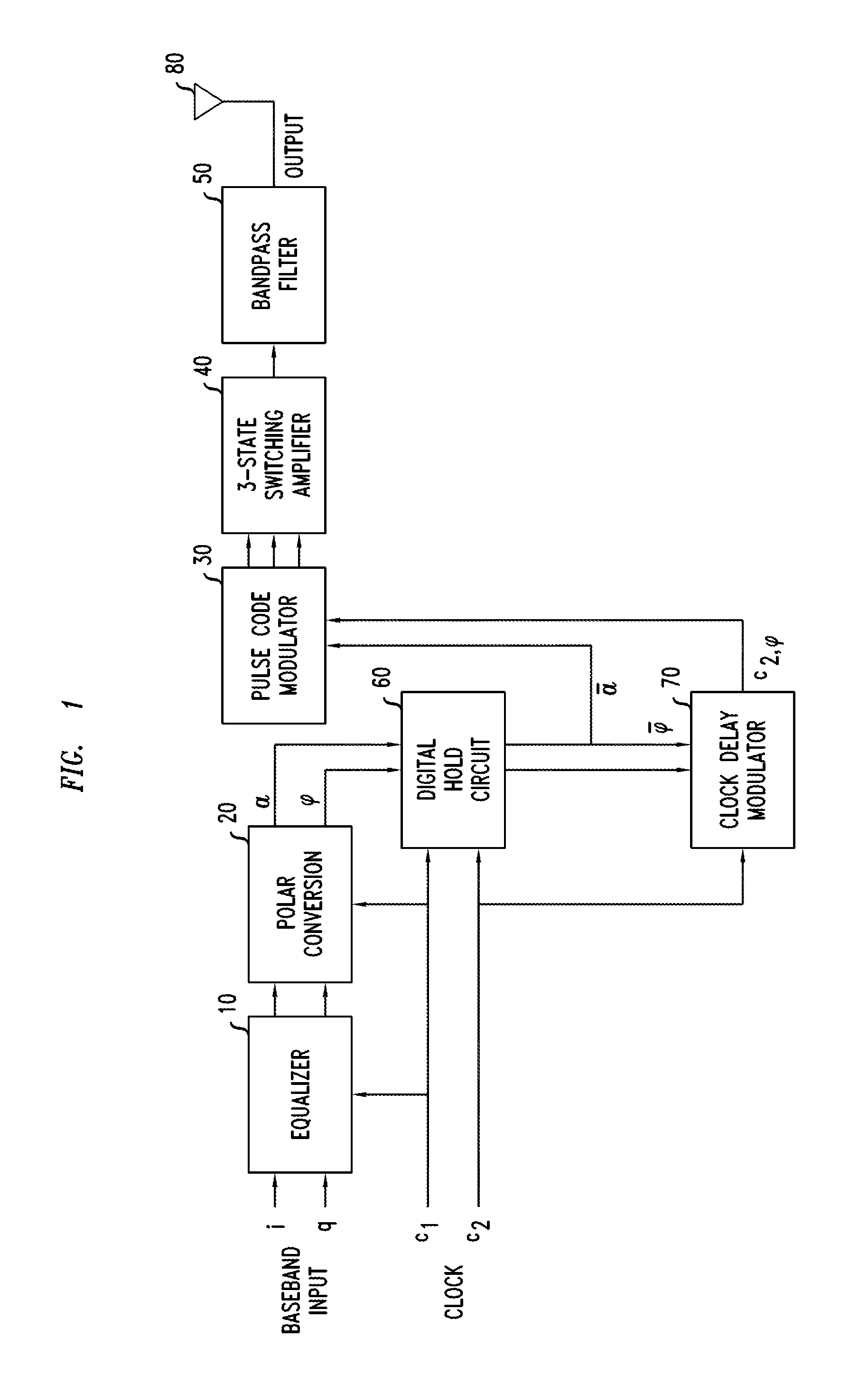
Power circuit used for an amplifier
InactiveUS8030995B2Avoid efficiencySwitching loss increaseHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlAudio power amplifierPower flow
A power circuit used for an amplifier, which includes an amplifier provided with a linear amplifier serving as a voltage source, a DC / DC converter serving as a current source, a hysteresis comparator controlling the DC / DC converter, and a current detector detecting output current from the linear amplifier to output the detected output current to the hysteresis comparator; and a switching restricting device for restricting a switching interval in the DC / DC converter such that the switching interval is not equal to or less than a constant time or is not shorter than the constant time.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
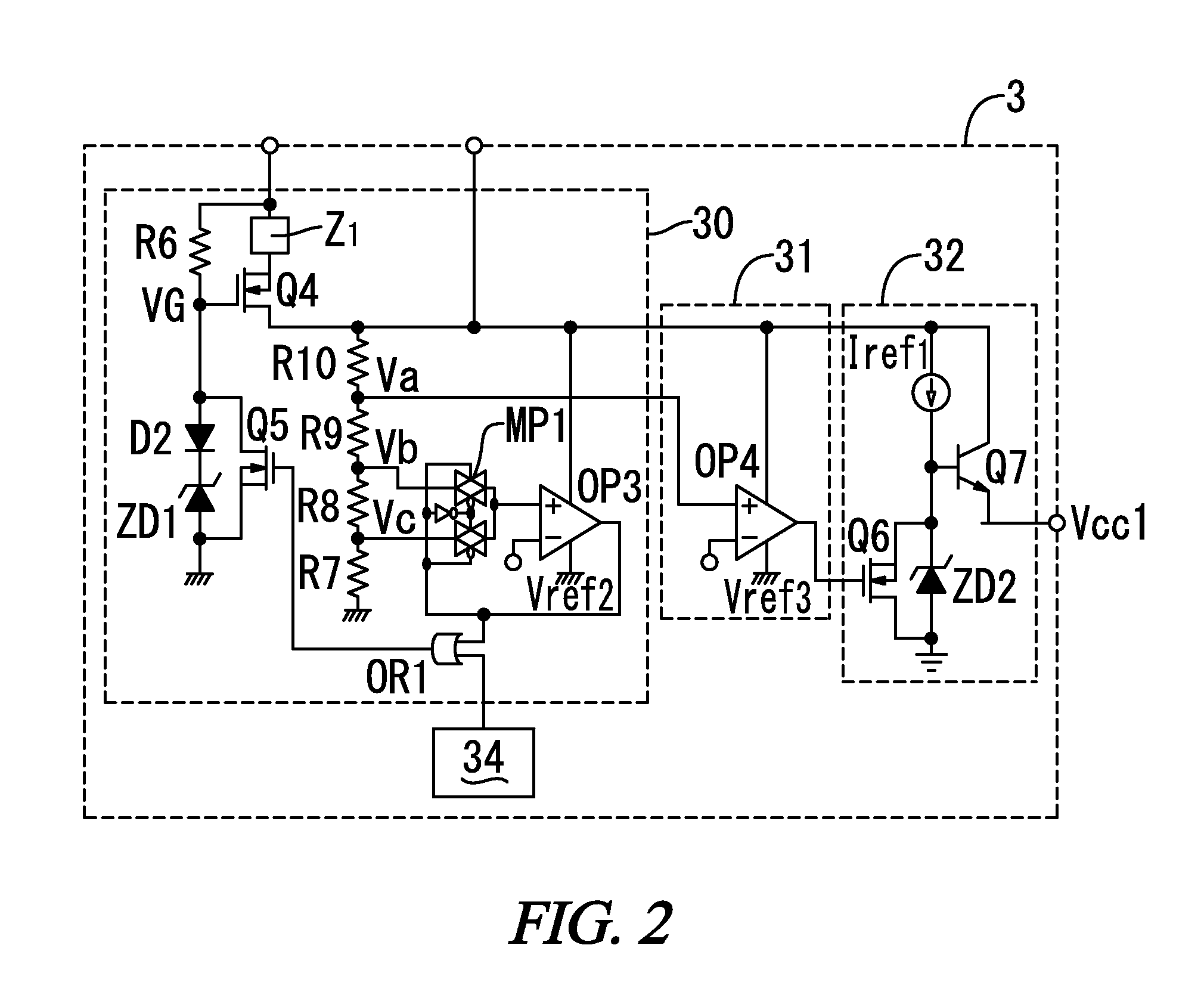
IGBT module
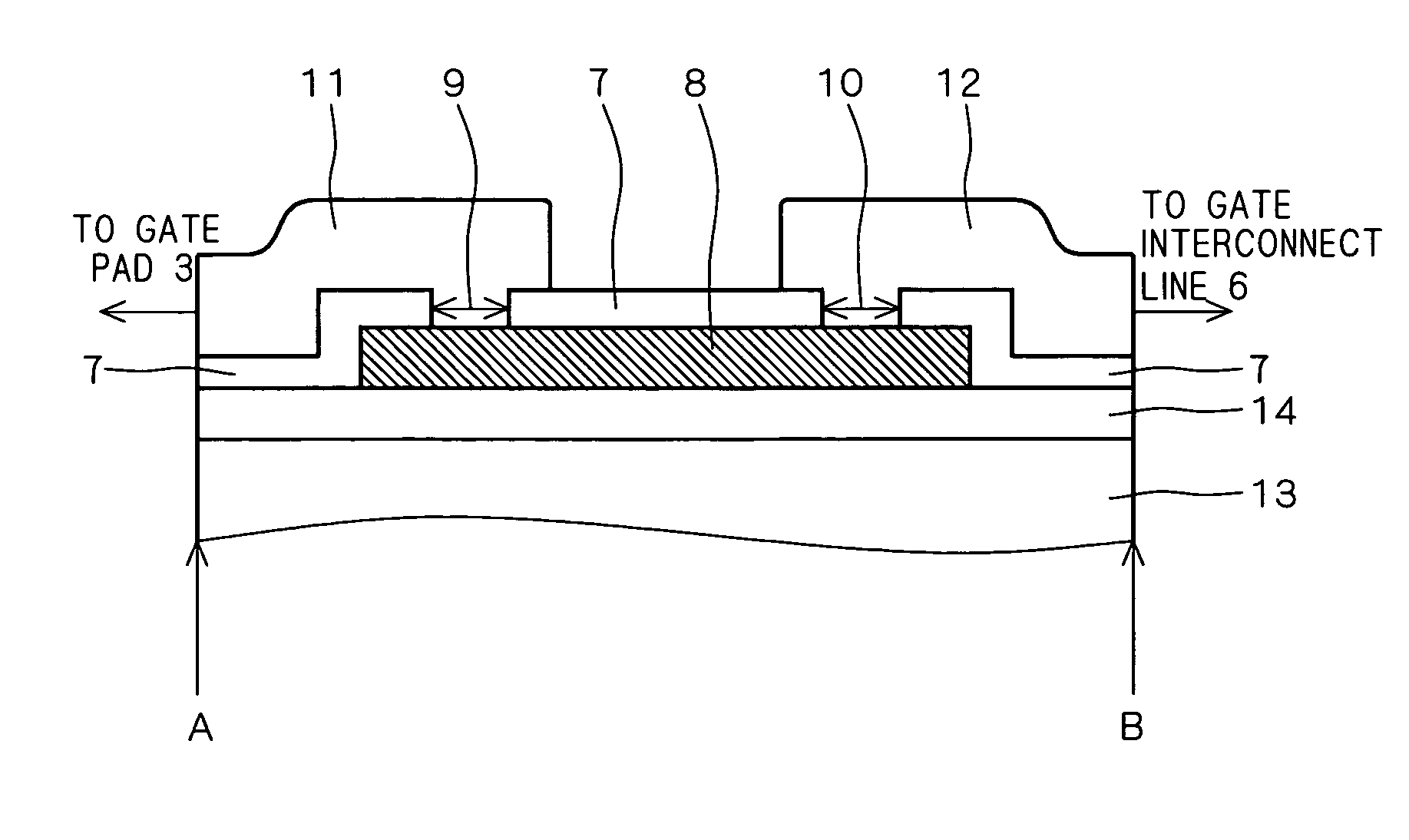
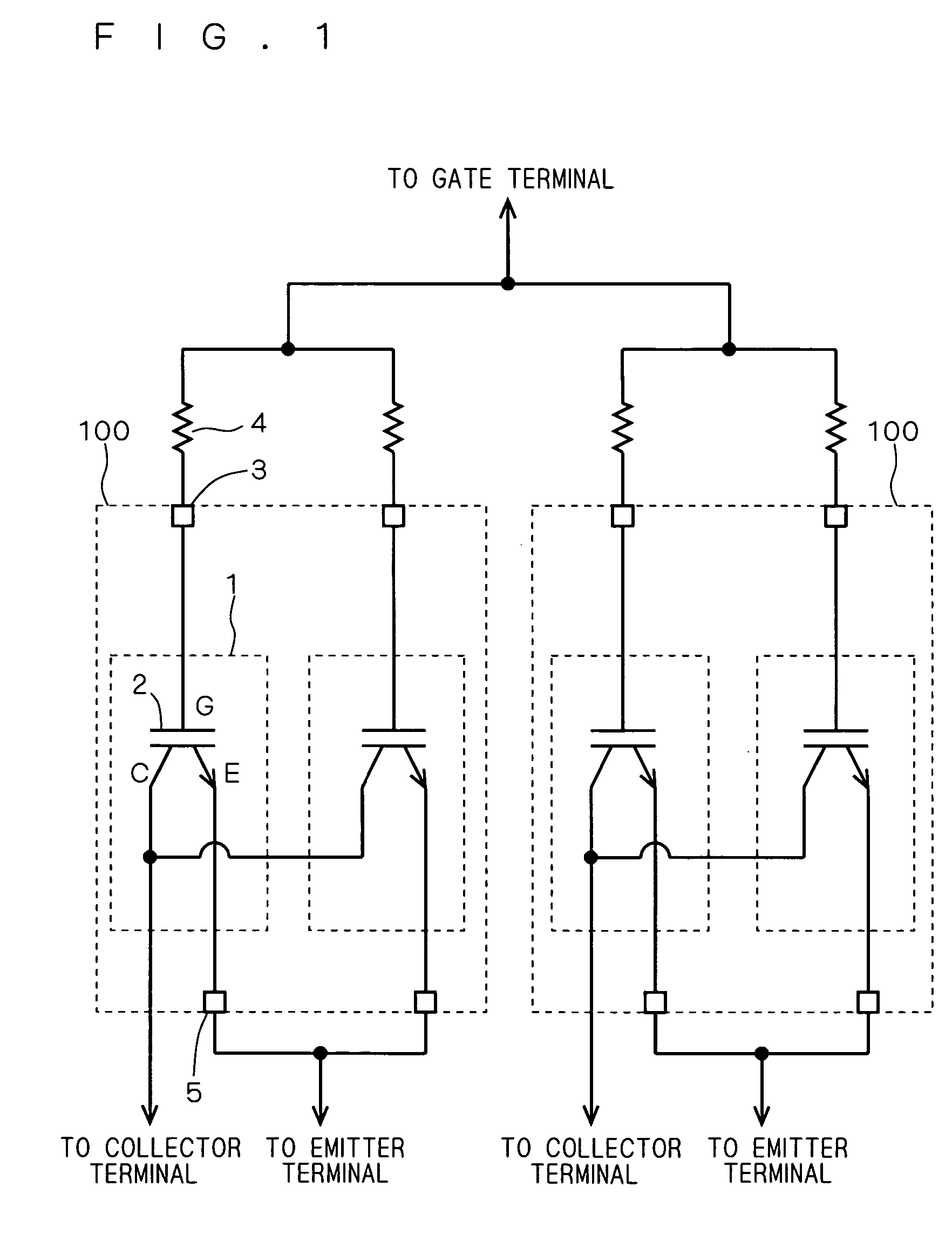
InactiveUS20050194660A1Suppressing gate voltage oscillationIncreased switching lossesTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCommon emitterCommon collector
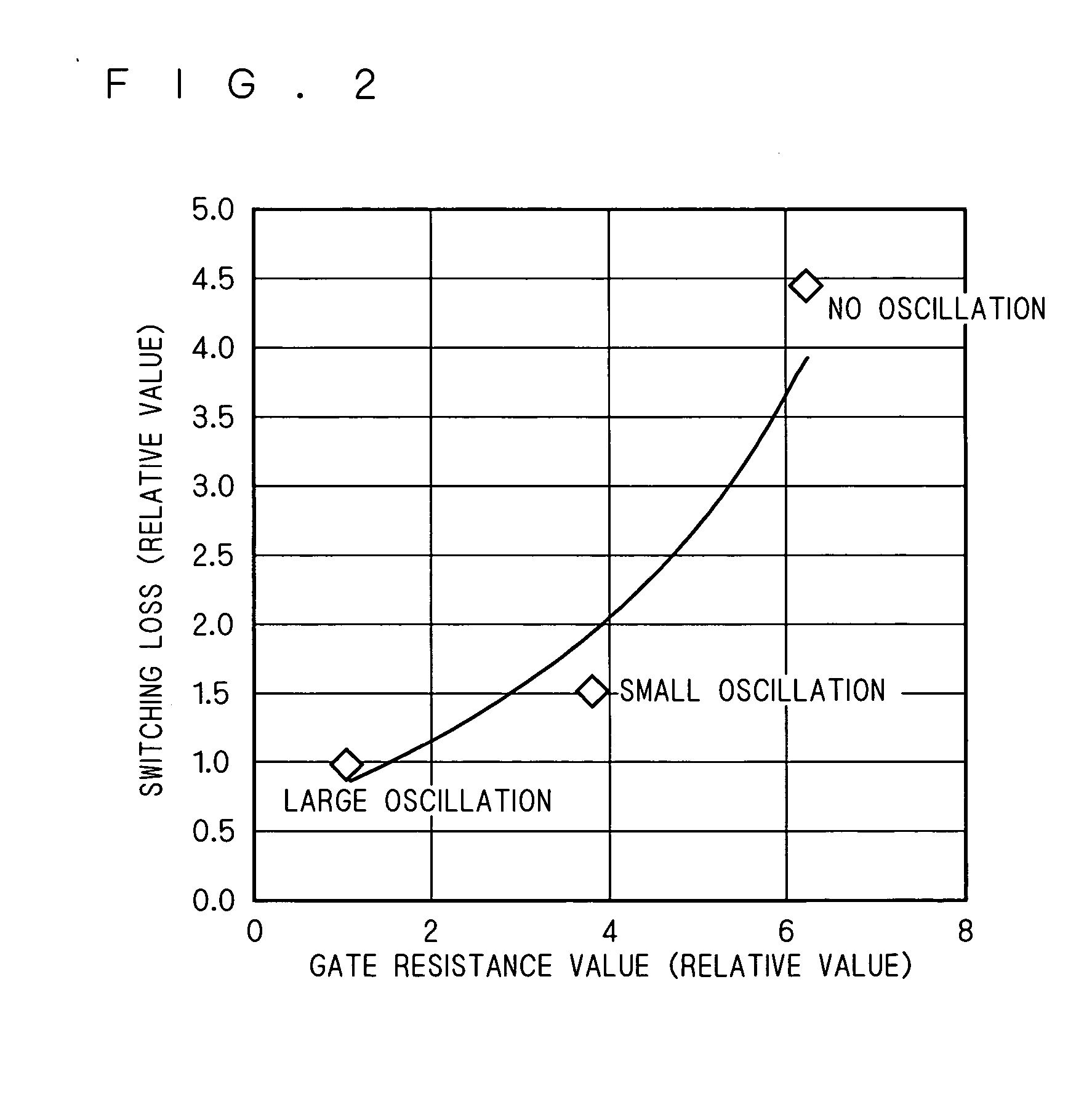
An IGBT module is configured with a plurality of IGBT cells connected to each other. The IGBT chips are each configured a plurality of unit cells connected to each other. The unit cells each include one IGBT element. Gate voltage is applied to the gate of the IGBT element from a common gate terminal through a gate pad and a gate resistor. Emitter voltage is applied to the emitter of the IGBT element from a common emitter terminal through an emitter pad. Collector voltage is applied to the collector of the IGBT element from a common collector terminal. The gate pad, gate transistor and emitter pad are provided for each of the unit cells. Thus obtained is an IGBT module capable of suppressing gate voltage oscillation without significantly increasing switching loss.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Apparatus and method for efficient dc-to-dc conversion through wide voltage swings
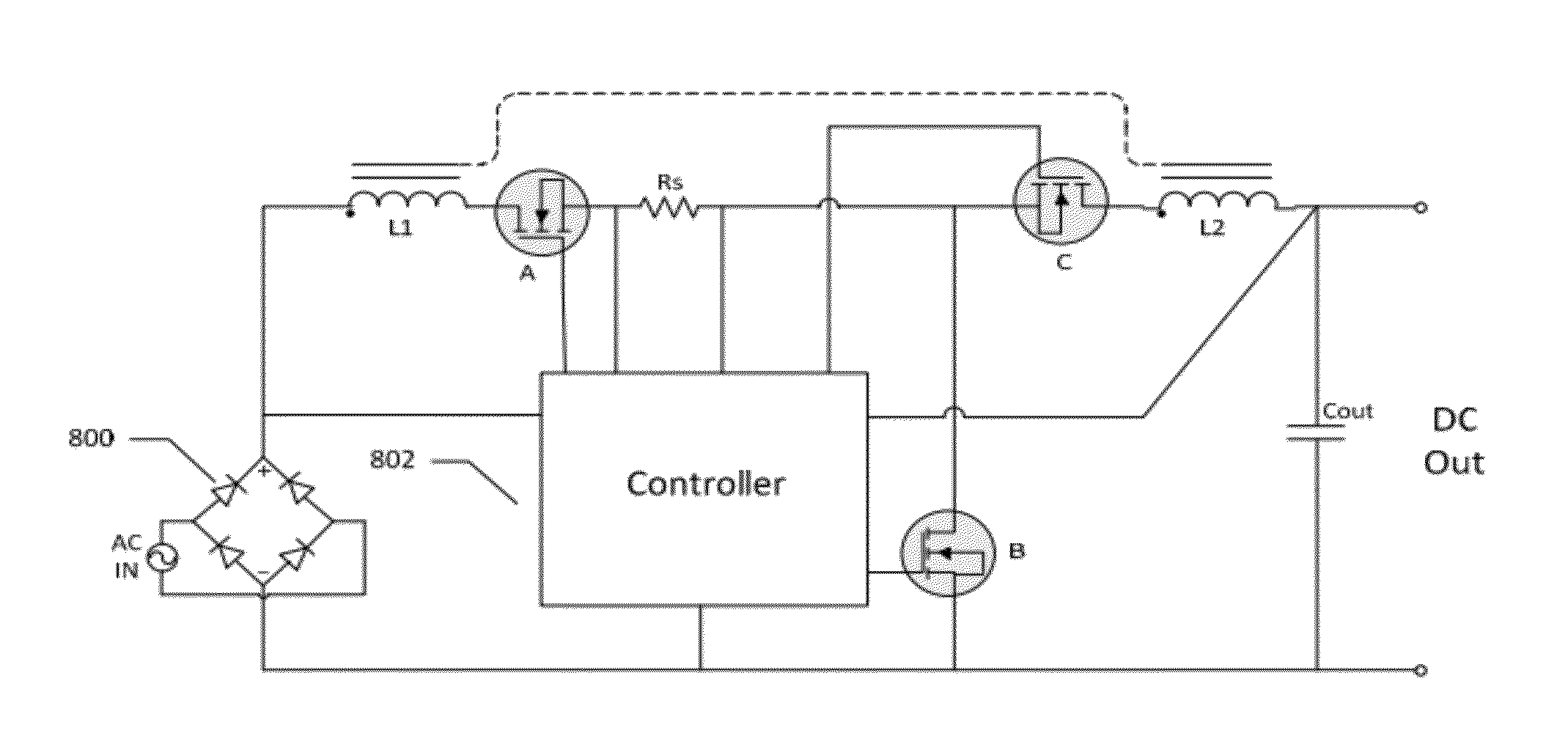
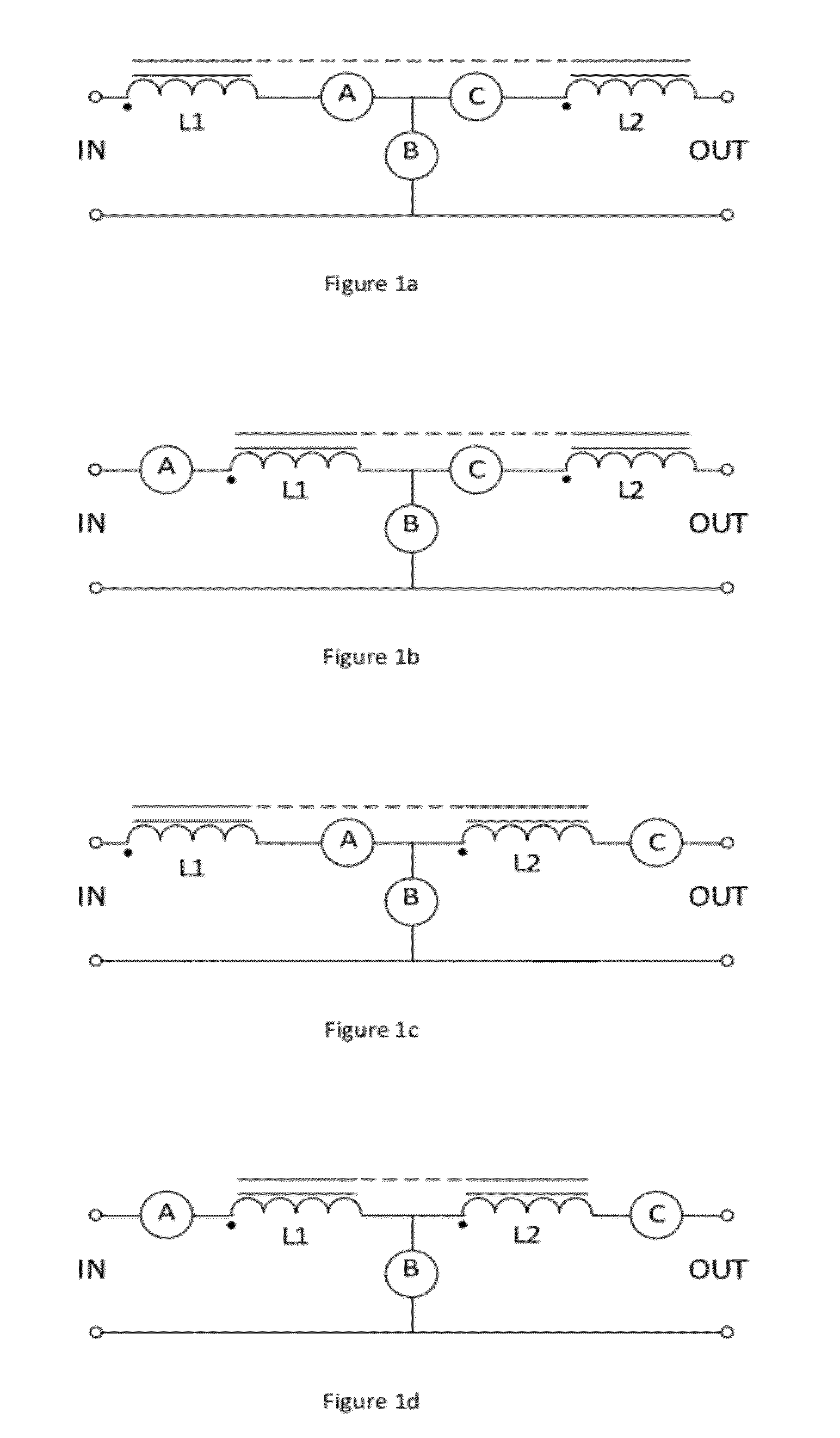
ActiveUS20120243267A1Improve efficiencyReduce switching lossesDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationVoltage swingDC-to-DC converter
A DC-to-DC converter includes two or more inductors coupled to a common core and two or more active switches, where at least one active switch is in an input current path. A controller operates the two or more active switches such that a DC input is driven through one or more of the two or more inductors to implement a power conversion operation.
Owner:LEDILLION TECH
Electronic ballast with input voltage fault control
InactiveUS20100270949A1Avoid damageSwitching loss increaseElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesDriver circuitPeak value
An electronic ballast includes circuitry to prevent a switch from being damaged in the case where an abnormality occurs in an output voltage of an input power supply. A DC power supply control circuit has a zero current detection circuit that, when a current through an inductor becomes equal to or less than a predetermined current value, outputs a zero signal. A peak current detection circuit, when current through a switch the DC power supply circuit becomes equal to or greater than the predetermined current value, outputs a peak signal. A first drive circuit turns on the switch according to the zero signal, and turns off the switch Q1 according to the peak signal. The zero current detection circuit is provided with a mask circuit that stops the zero signal from being outputted to the first drive circuit for a predetermined period after the current through the inductor has become equal to or less than the predetermined current value.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Switching Circuit And Power Conversion Circuit
ActiveUS20170149330A1Reduce switching speedSwitching loss increaseTransistorApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCapacitanceNegative voltage
A first switching element and a gate of a voltage-driven switching element are connected by a gate turn-on wiring through a first resistor. The gate of the voltage-driven switching element and a second switching element are connected by a gate turn-off wiring through a second resistor. A charge pump unit has a first capacitor, and a second capacitor configured to output a negative voltage. A resistor unit is arranged in at least one of a first wiring configured to connect the gate turn-on wiring and the first capacitor and a second wiring configured to connect the gate turn-off wiring and the first capacitor, and is configured to charge the first capacitor through the first wiring when the first switching element is turned on and to discharge the first capacitor through the second wiring when the second switching element is turned on.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
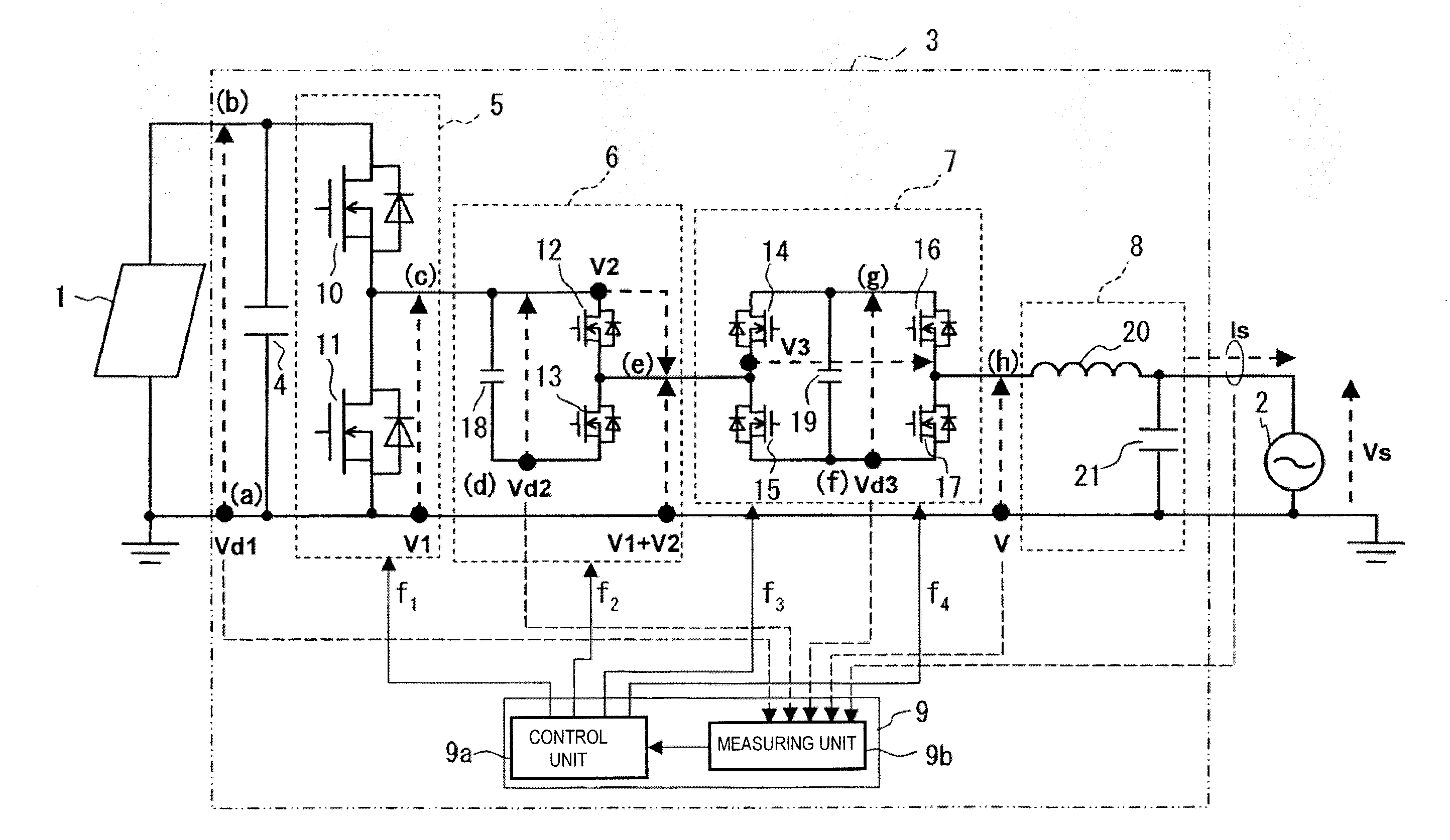
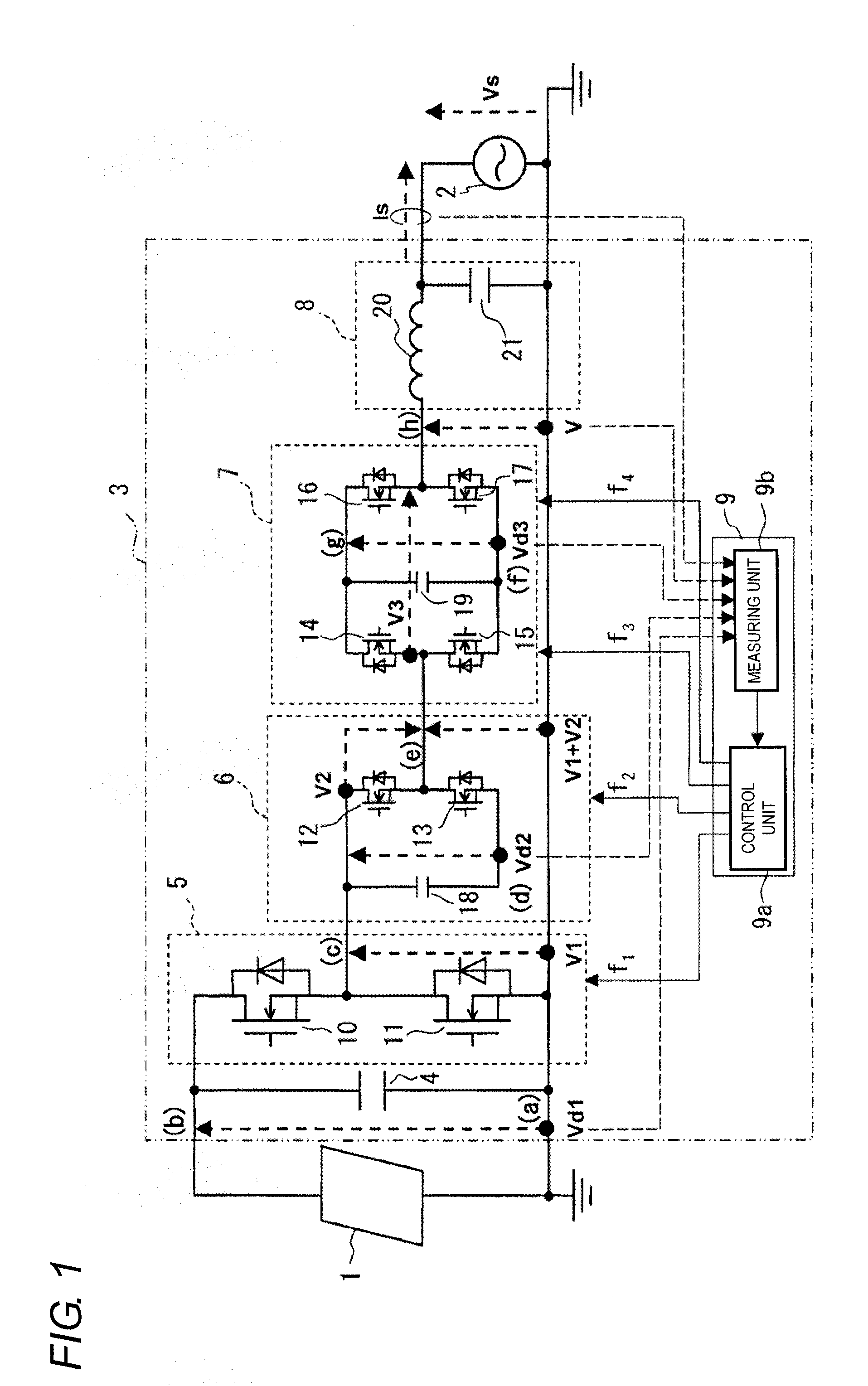
Power converter and power conditioner
ActiveUS20110235384A1Reduce switching lossesReduce conduction lossAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionPower conditionerSquare waveform
A power converter enhances conversion efficiency from DC power to AC power. A first chopper circuit chops DC voltage from a photovoltaic panel at a system frequency producing a first square-wave whose voltage level changes positively. A second chopper circuit chops the first square-wave at a frequency double the system frequency producing a second square-wave whose voltage level changes negatively and adds the first square-wave and the second square-wave to produce a third square-wave that changes positively and negatively in a sine-wave manner. A third chopper circuit charges and discharges by chopping the third square-wave at a third frequency fixed by timing according to a difference between the third square-wave and a sine-wave voltage. PWM control is performed on the charge and discharge outputs such that the difference is corrected, producing a sine-wave voltage that continuously changes positively and negatively. A spike noise of an output voltage is suppressed.
Owner:ORMON CORP
Power unit for electric vehicle
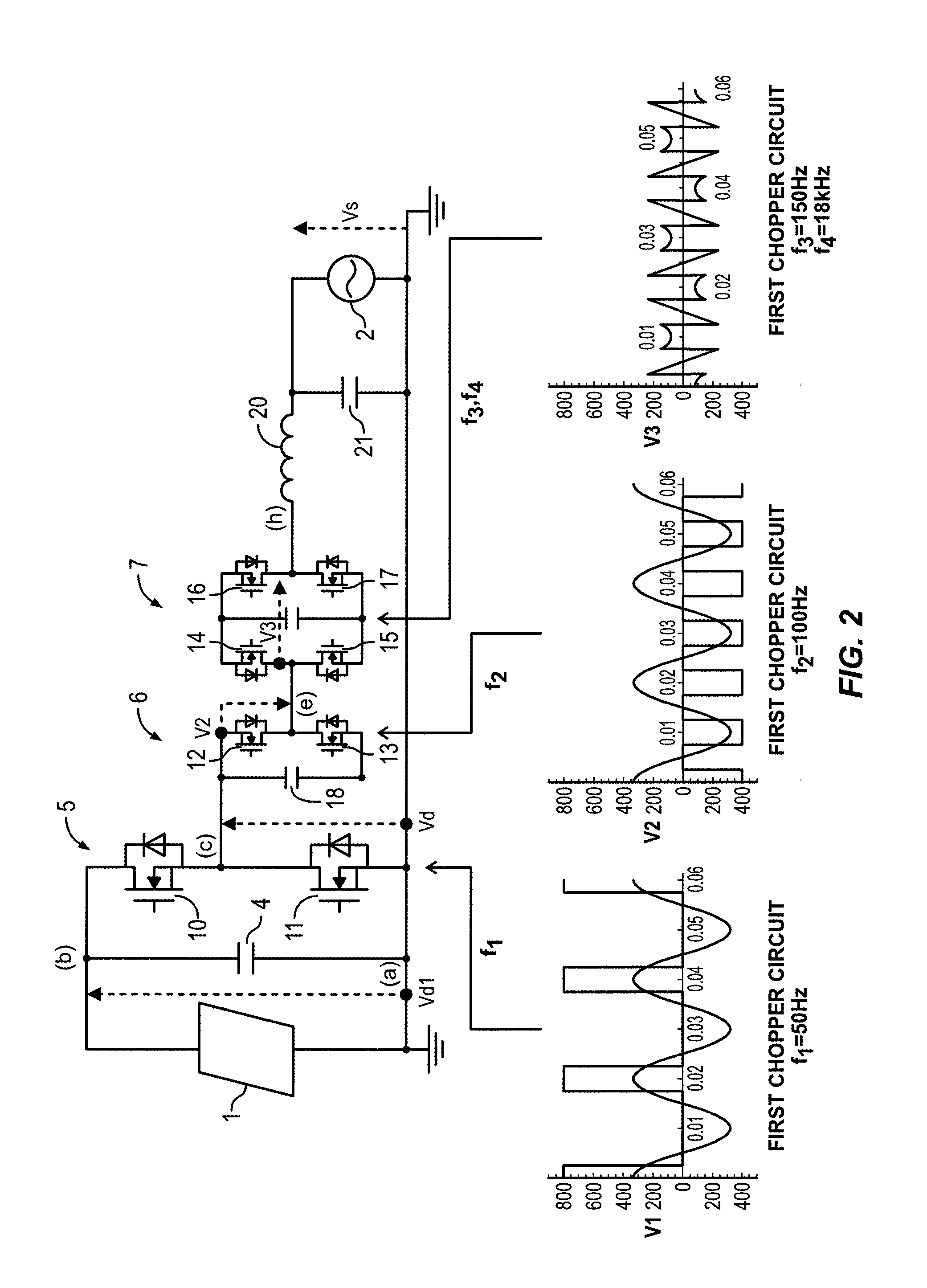
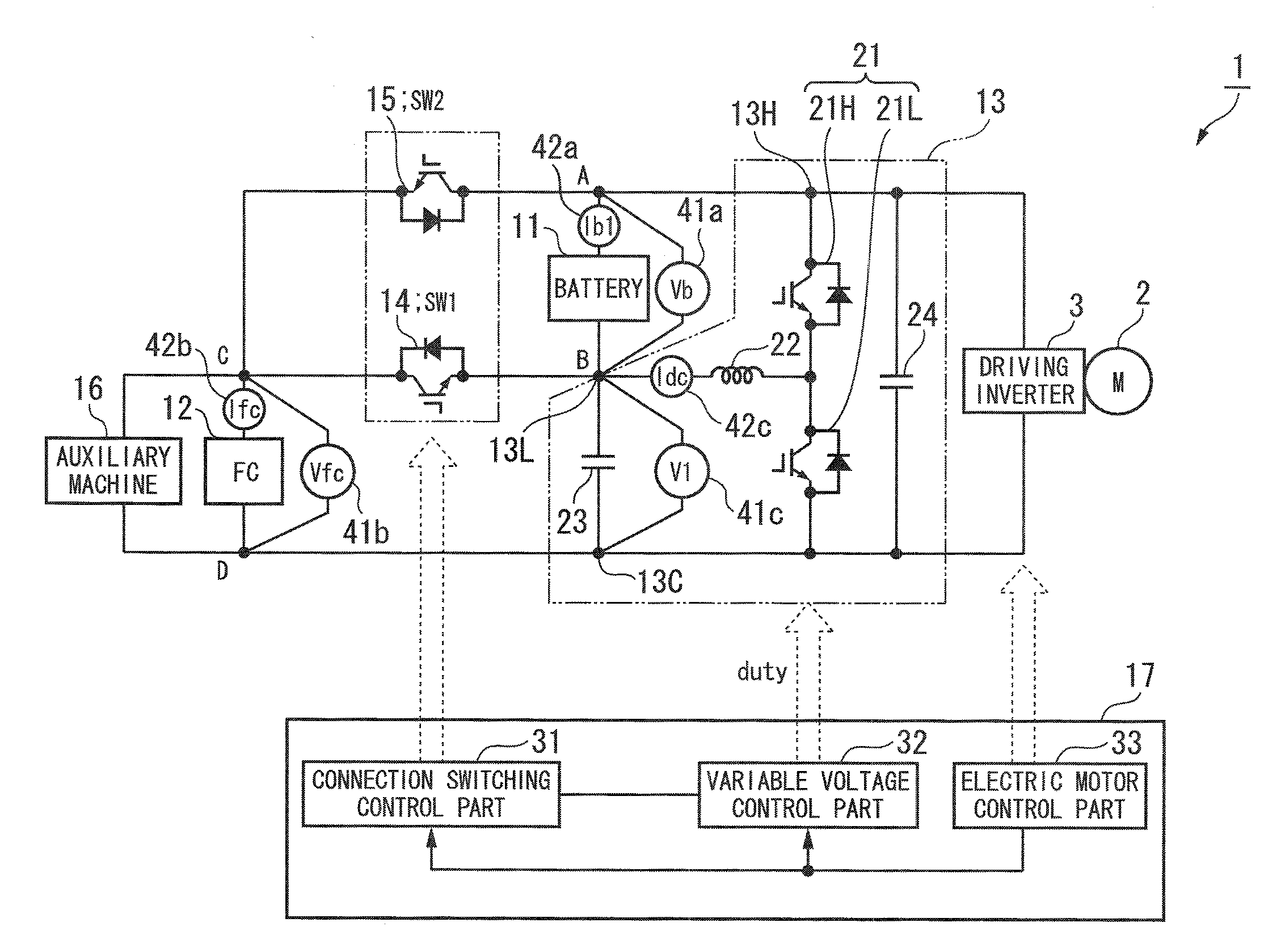
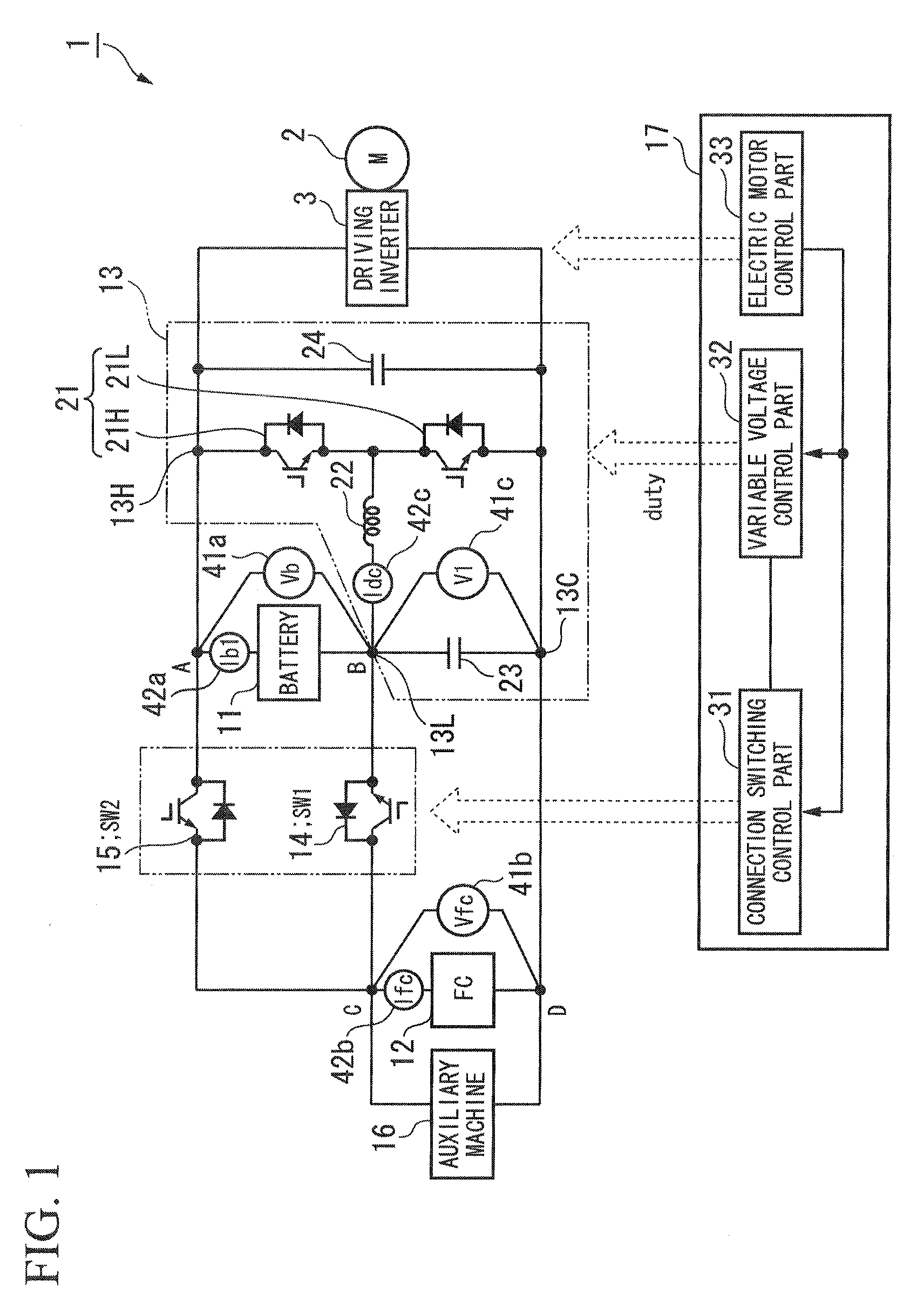
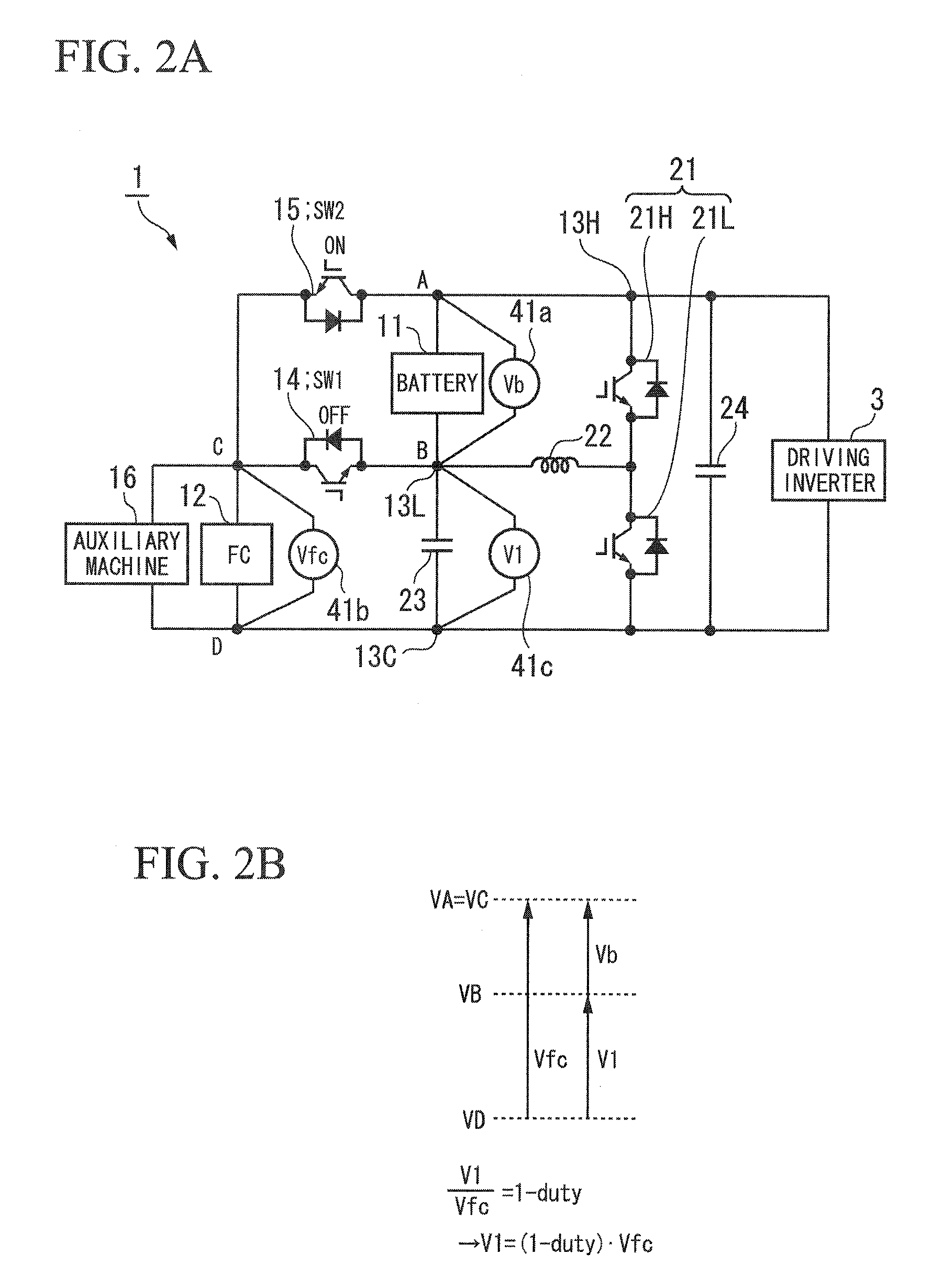
ActiveUS20120187755A1High power outputSwitching loss increaseAC motor controlPower to auxillary motorsDc dc converterFuel cells
A power unit for an electric vehicle includes: a first power source connected between a first node and a second node; a first switch connected between the second node and a third node; a second power source connected between the third node and a fourth node; a second switch connected between the first node and the third node; and a DC-DC converter, wherein the DC-DC converter adjusts an electric potential of the first node by changing an electric potential of the second node by making the first node connectable to the third node, or, by making the second node connectable to the third node; an output electric power obtained from between the first node and the fourth node is supplied to an electric motor; and the first power source or the second power source is a fuel cell stack and an another is a secondary battery.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Synchronous electric motor drive system
ActiveUS8497648B2Prevents degradation of inverter efficiencyPrevents an increase of iron lossesTorque ripple controlAC motor controlElectricitySystems design
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
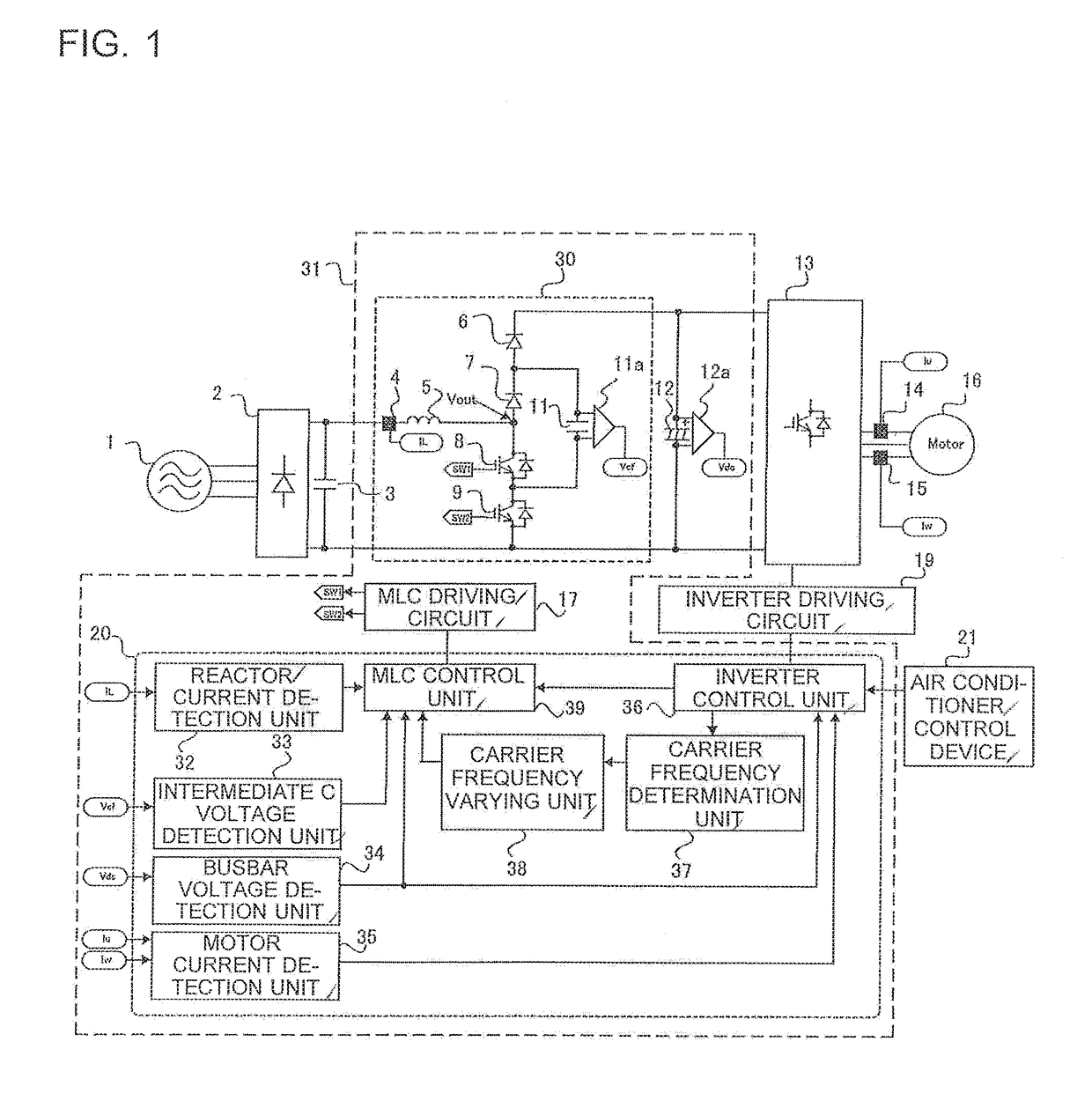
Power conversion device and refrigeration cycle apparatus
ActiveUS20170201186A1Lowered carrier frequencyMinimizeCompressorTorque ripple controlBoost rectifierRefrigeration
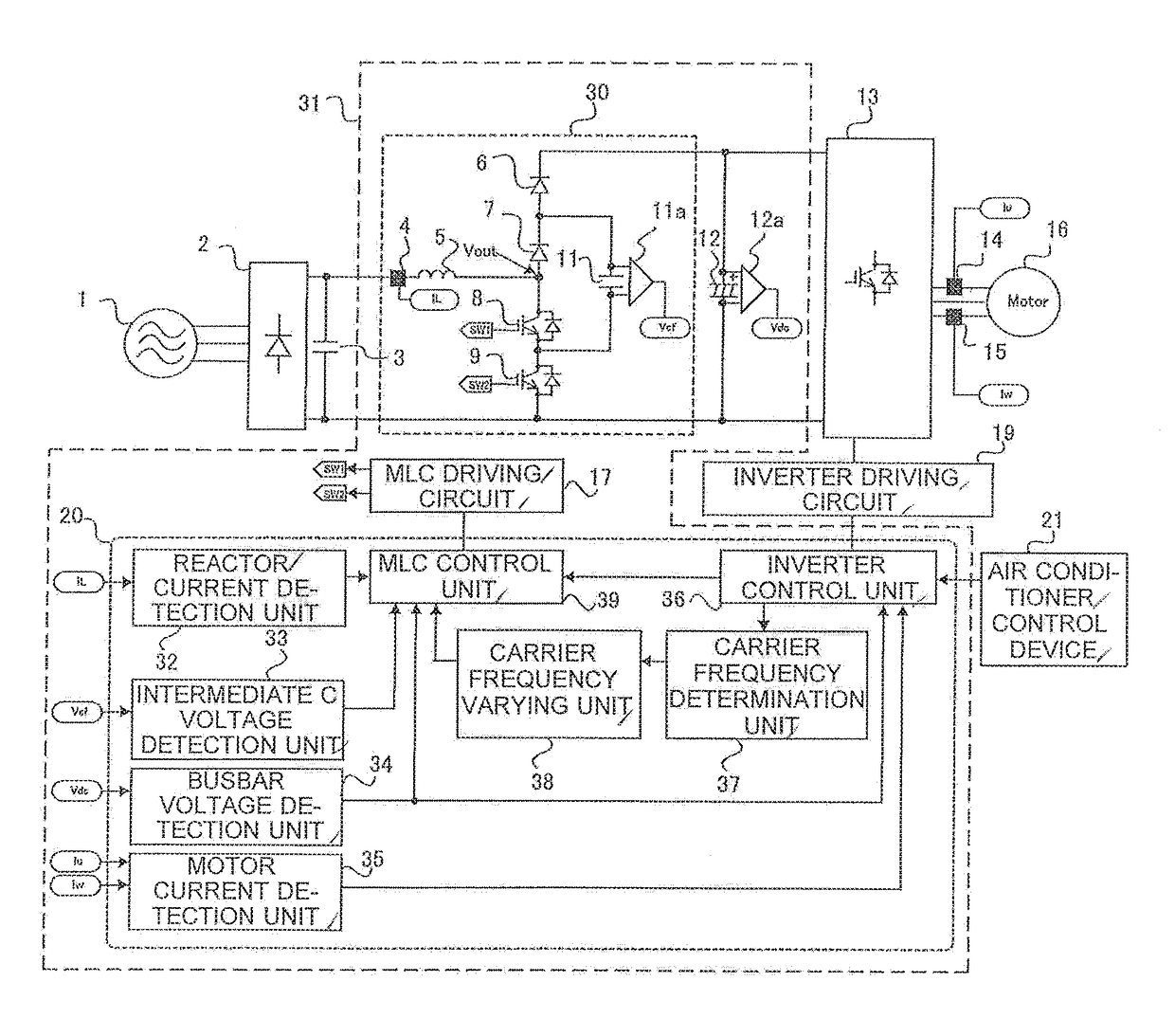
A rectifier, a booster circuit configured to boost an output voltage of the rectifier, a smoothing capacitor configured to smooth an output voltage of the booster circuit, and an inverter circuit configured to convert a DC voltage of the smoothing capacitor to an AC voltage and drive a motor forming a part of a device supplied with the voltage after the conversion, are included. In addition, a reactor, a first backflow prevention element, a second backflow prevention element, a first switching element, a second switching element, an intermediate capacitor, and a controller configured to control the first switching element and the second switching element, are included.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Active gate drive circuit
ActiveUS8710876B2Switching loss increaseAccurate detectionElectronic switchingElectric pulse generatorGate voltageControl theory
Exemplary embodiments are directed to a gate drive circuit and a method for controlling a gate-controlled component. The gate drive circuit includes a PI controller that receives an input reference signal (vref,d / dt) controls a gate voltage of the gate-controlled component. The gate drive circuit also includes a first feedback loop for the PI controller adapted to provide feedback from a time derivative of a collector-to-emitter voltage (vCE) of the controlled component. The first feedback loop has a first gain (kv). A second is provided in the gate drive circuit feedback loop for the PI controller that provides feedback from the time derivative of the collector current (iC) of the controlled component. The second feedback loop has second gain (ki) and includes a clipping circuit that modifies the feedback signal in the second feedback loop during turn-on of the controlled component when the time derivative of the collector current is negative.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Lighting apparatus and luminaire
InactiveUS20160066375A1Increase the switching frequencySuppress noiseElectroluminescent light sourcesDc-dc conversionPower flowLight equipment
Lighting apparatus which supplies a current to solid-state light-emitting device (LED) includes: DC power supply circuit (AC / DC converter); and DC / DC converter that converts an output voltage of DC power supply circuit and applies, to solid-state light-emitting device, the output voltage converted. DC / DC converter includes: switching element; and DC / DC control circuit that performs a control of repeatedly turning ON and OFF switching element in a boundary conduction mode, and DC power supply circuit adjusts the output voltage to make a switching frequency of switching element higher than a first frequency, based on a forward voltage to be applied to solid-state light-emitting device.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Bidirectional switch
InactiveUS20130002336A1High voltageHigh currentElectronic switchingDiodeSemiconductor materialsReverse current
A bidirectional switch according to one embodiment switches bidirectionally the direction of current flowing between a first and a second terminal, and includes: first and second series circuit sections including first and second semiconductor switch elements that do not have a tolerance in a reverse direction, and first and second reverse current blocking diode sections serially connected to the first and second semiconductor switch elements in a forward direction. The first series circuit section and the second series circuit section are connected in parallel between the first and second terminals so that the forward directions of the first and second semiconductor switch elements face opposite to each other. Each of the first and second reverse current blocking diode sections is configured by connecting in parallel a diode containing GaN as a semiconductor material and a diode containing SiC as a semiconductor material.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Circuit for driving power switch, power supply apparatus and method for driving power switch
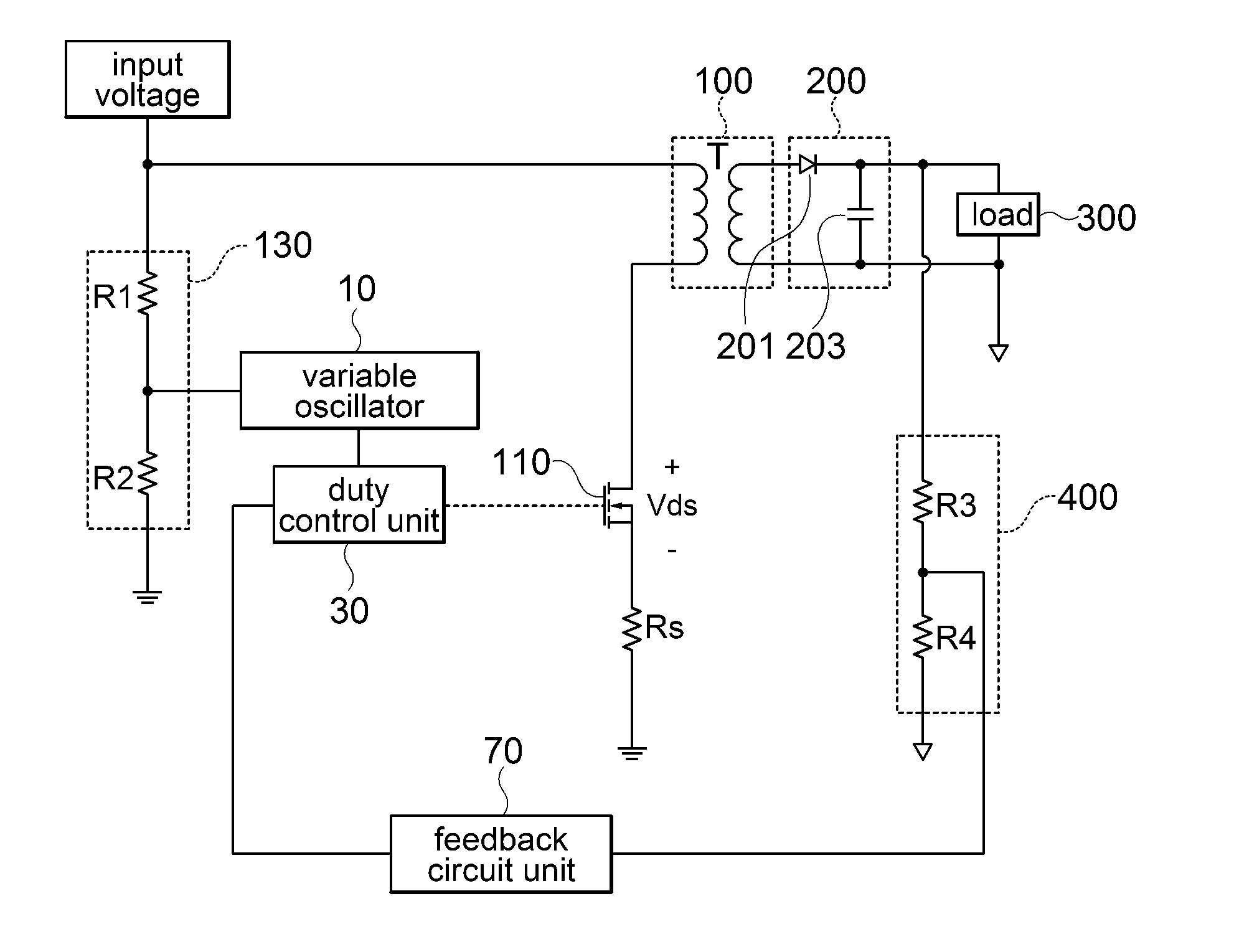
InactiveUS20150043250A1Reduce frequencySwitching loss increaseEfficient power electronics conversionElectronic switchingVoltageSecondary side
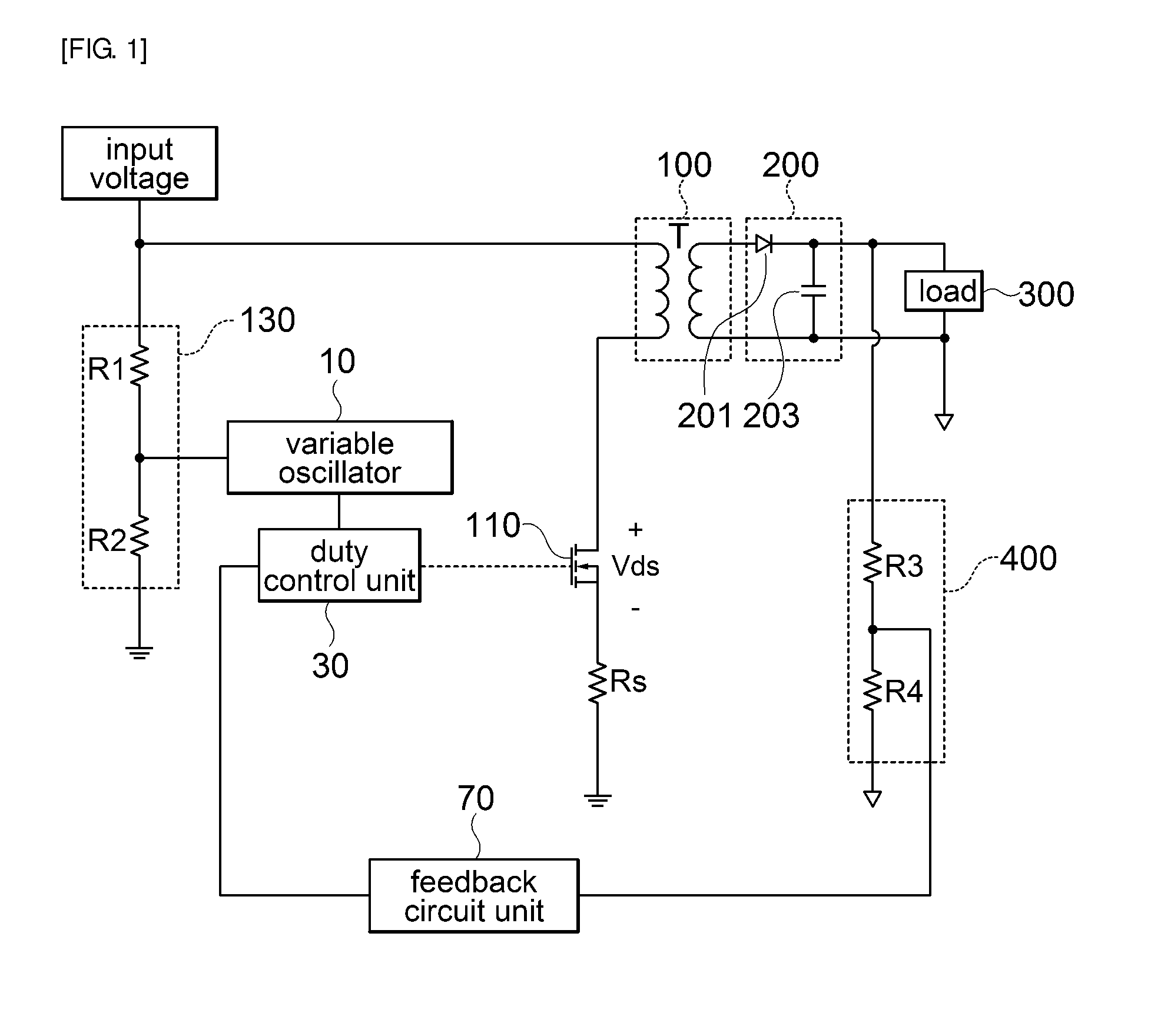
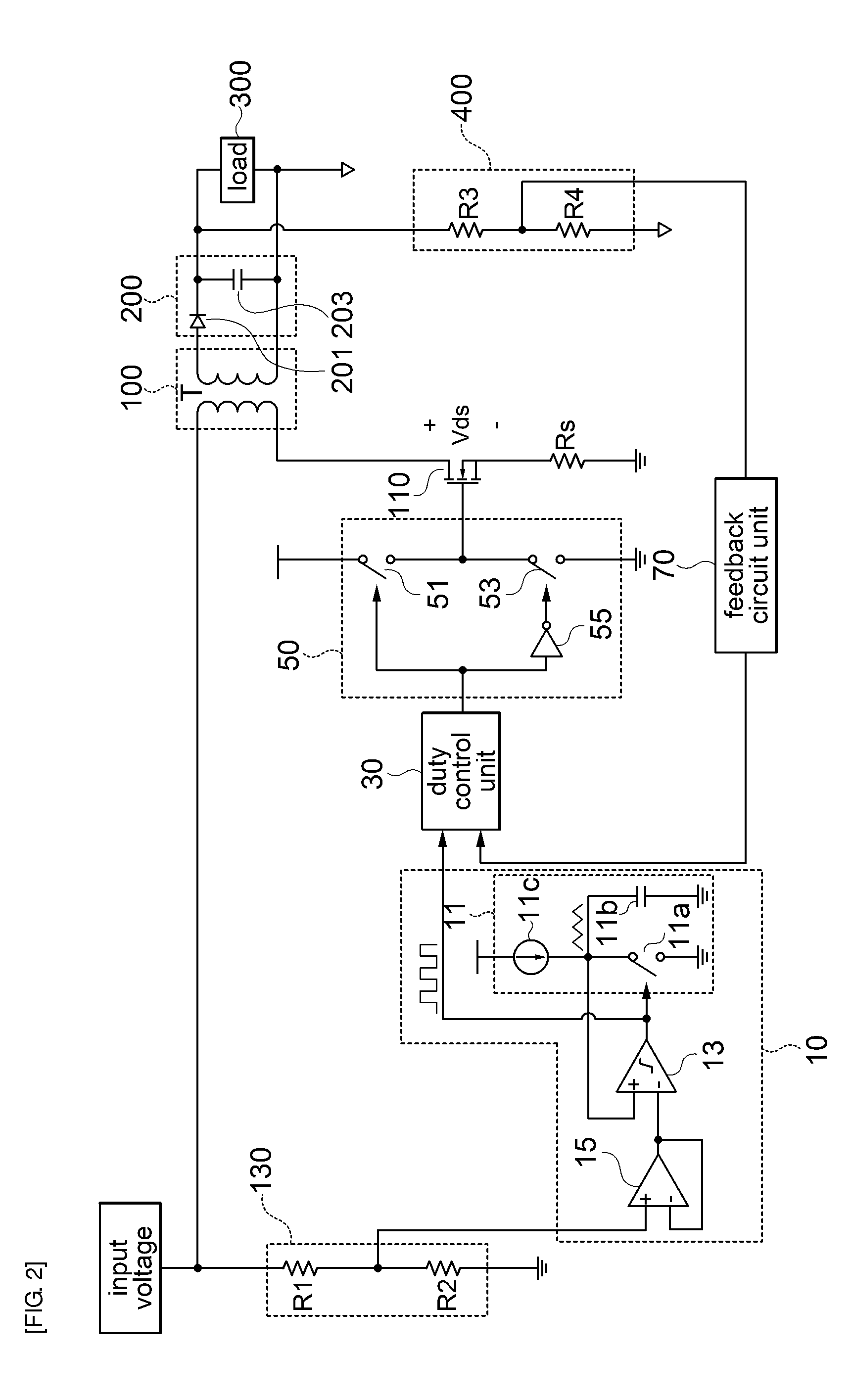
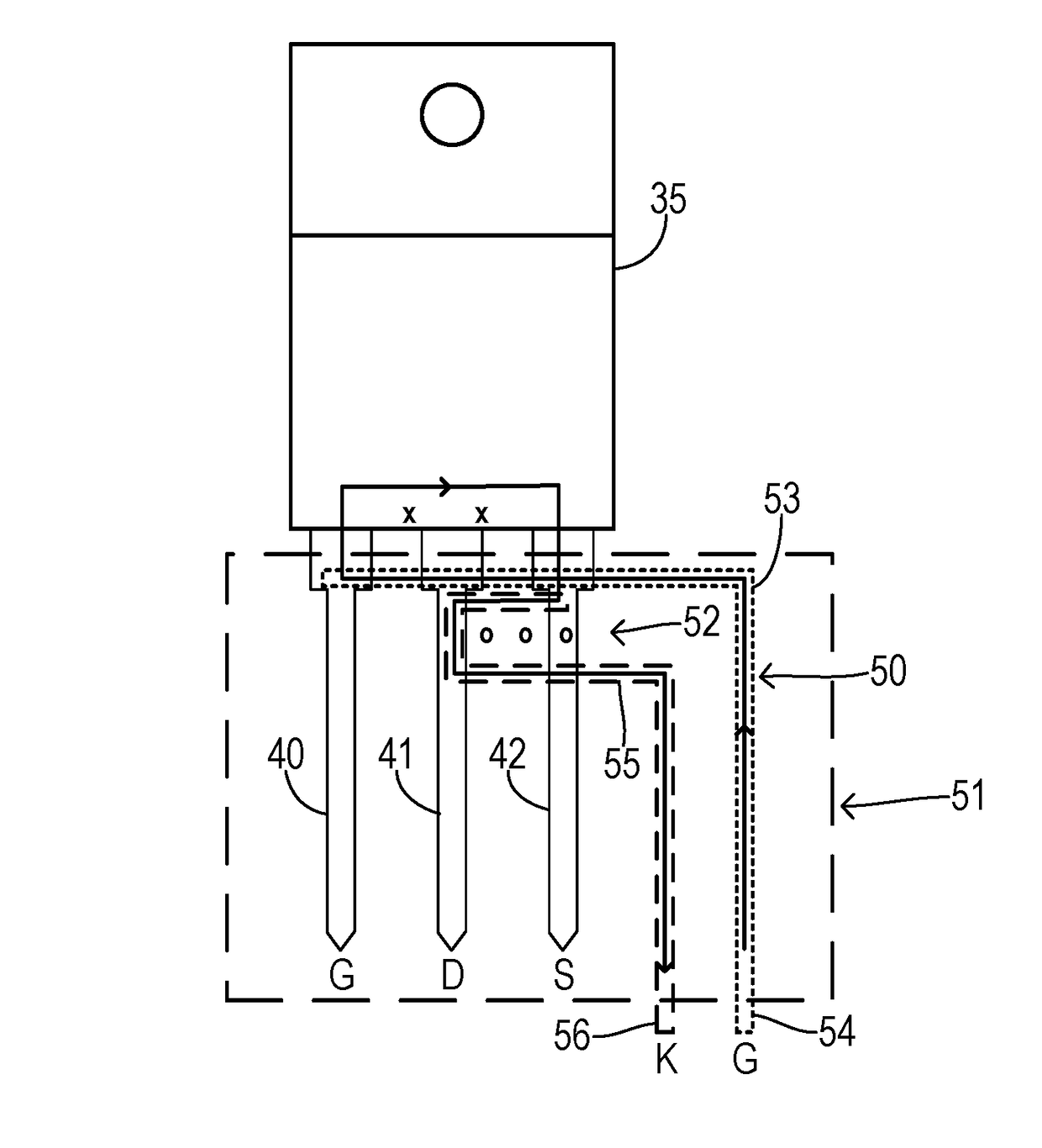
The present invention relates to a circuit for driving power switch, a power supply apparatus, and a method for driving a power switch. According to an embodiment of the present invention, a circuit for driving power switch, which includes a variable oscillator for varying a frequency according to a change in primary side input voltage to output a reference signal for duty control; and a duty control unit for receiving a feedback signal fed back from a secondary side output signal and the reference signal for duty control from the variable oscillator and outputting a duty control signal for driving a power switch, is provided. Further, a power supply apparatus and a method for driving a power switch are provided.
Owner:SOLUM CO LTD
Discrete power switching devices with reduced common source inductance
ActiveUS20170353177A1Increased switching lossesFast switching speedAC motor controlEfficient power electronics conversionPower switchingEngineering
Routing of a gate signal for controlling a discrete power switching device (such as in an inverter for an electric vehicle drive) is configured to compensate for the common source inductance inherent in the switching device as a result of its integrated circuit packaging. The power device has a gate signal path via a gate pin and a power signal path via first and second power pins, wherein the gate signal path and the power signal path have a first mutual inductance. A circuit board apparatus provides a gate wiring loop juxtaposed with the power signal path, wherein the gate wiring loop and the power signal path have a second mutual inductance substantially canceling the first mutual inductance. The resulting reduction in common source inductance avoids the reductions in switching speed and the increased switching losses otherwise introduced by the common source inductance.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Phase to amplitude H-Bridge switching circuit
InactiveUS7092269B1Switch loss increaseSwitching loss increaseConversion with intermediate conversion to dcPower amplifiersWave shapePhase relationship
A high power AM-band transmitter amplifier comprises four switches in an H-Bridge configuration and operates by adjusting the duty cycle of the voltage waveform on a transformer. The duty cycle is adjusted by changing the phase relationship between the diagonal switch pairs. An embodiment of the amplifier operates efficiently by the addition of a current source that may comprise inductor and capacitor circuits to assure zero voltage switching of all the switches. The inventive H-Bridge configuration can also be utilized in a phase modulated power supply.
Owner:BROADCAST ELECTRONICS
Control Circuit for Controlling an Electronic Circuit and Method for This
InactiveUS20080001586A1Improve electronic performanceSwitching loss increaseTransistorPulse generatorTerminal voltageCharge control
A control circuit for controlling an electronic circuit, which has a current path through a semiconductor switch and a line; when the semiconductor switch is switched, the inductance of the line and / or of a component in the current path producing an excess voltage between a first and a second current-carrying terminal of the semiconductor switch; the control circuit having a controllable current source for charging or discharging a charge-controlled gate of the semiconductor switch with the aid of a control current, as well as a control unit; the control unit controlling the current source in such a manner, that in the case of a switching operation, the terminal voltage across the current-carrying terminals of the semiconductor switch does not exceed a predefined setpoint terminal voltage.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Method And Apparatus Of Switched Amplification Having Improved Efficiency
ActiveUS20120300858A1Reduce power lossEasy to seeModulated-carrier systemsAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAudio power amplifierControl signal
A signal coding technique for switching amplifiers includes quantizing the amplitude A(t) of an input signal to produce a time series Â(t) having M levels; modulating a clock signal in response to Â(t), thereby to produce a control signal; switching among at least three different power supply output levels in response to the control signal, thereby to generate an output pulse stream; and filtering the output pulse stream to produce an output signal for transmission.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Shielded gate trench mosfet with ESD diode manufactured using two poly-silicon layers process
ActiveUS20210104510A1Increased switching lossesReduced in gate widthSolid-state devicesDiodeTrench mosfetEngineering
A SGT MOSFET having ESD diode and a method of manufacturing the same are disclosed. The SGT trench MOSFET according to the present invention, has n+ doped shielded electrode in an N channel device and requires only two poly-silicon layers, making the device can be shrunk with reducing shielded gate width for Rds reduction without increasing switching loss and having dynamic switching.
Owner:NAMI MOS CO LTD
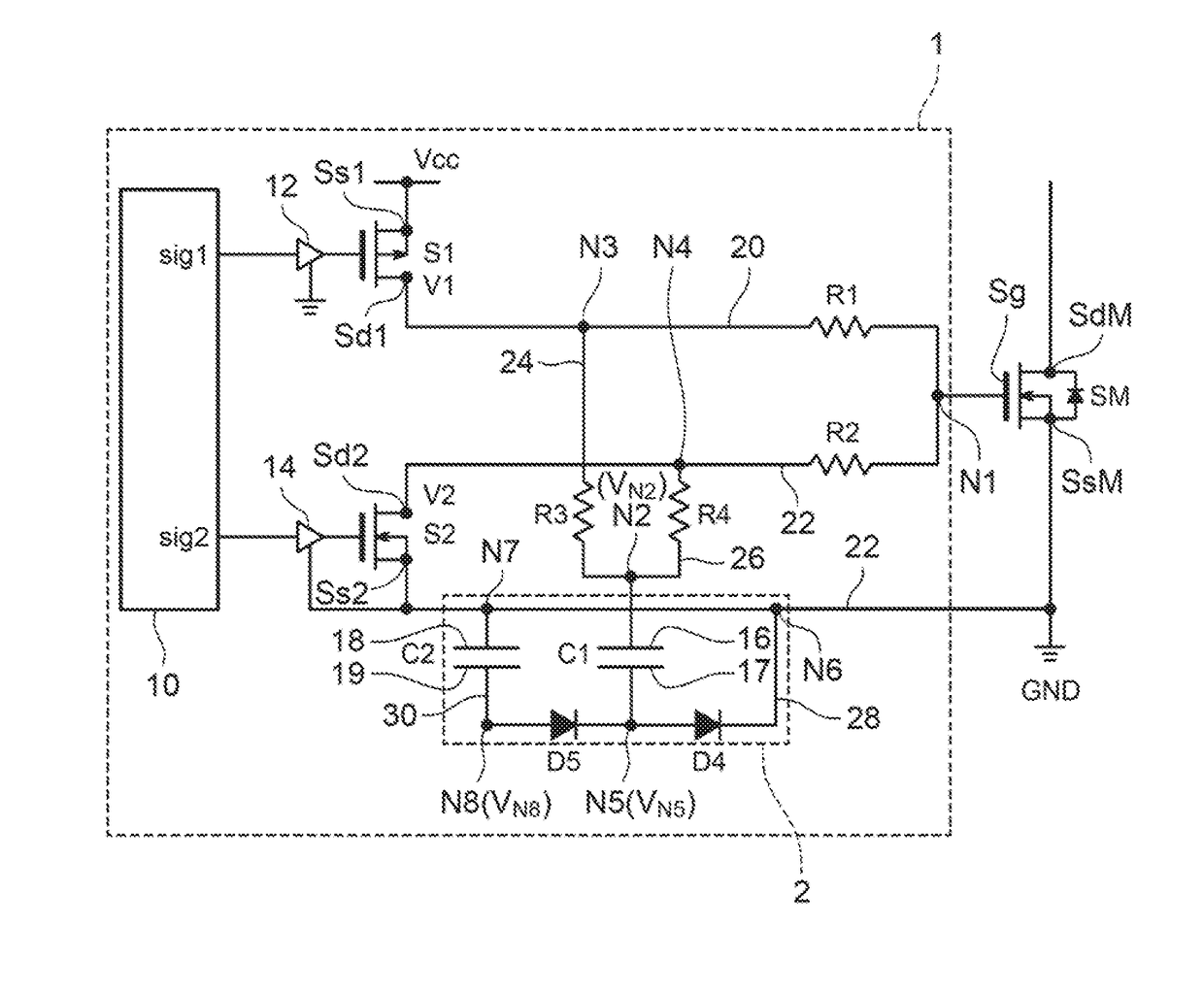
Semiconductor device
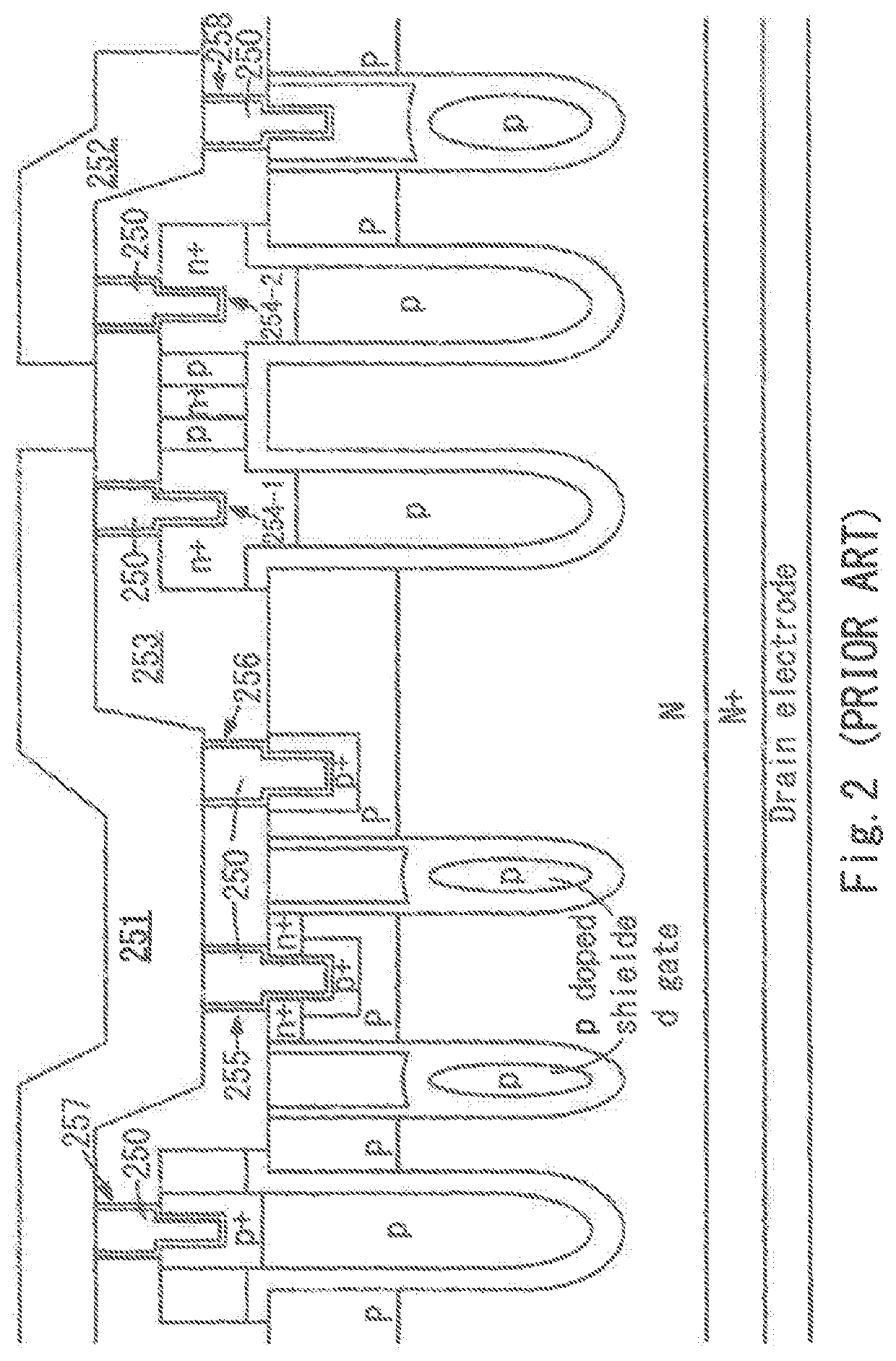
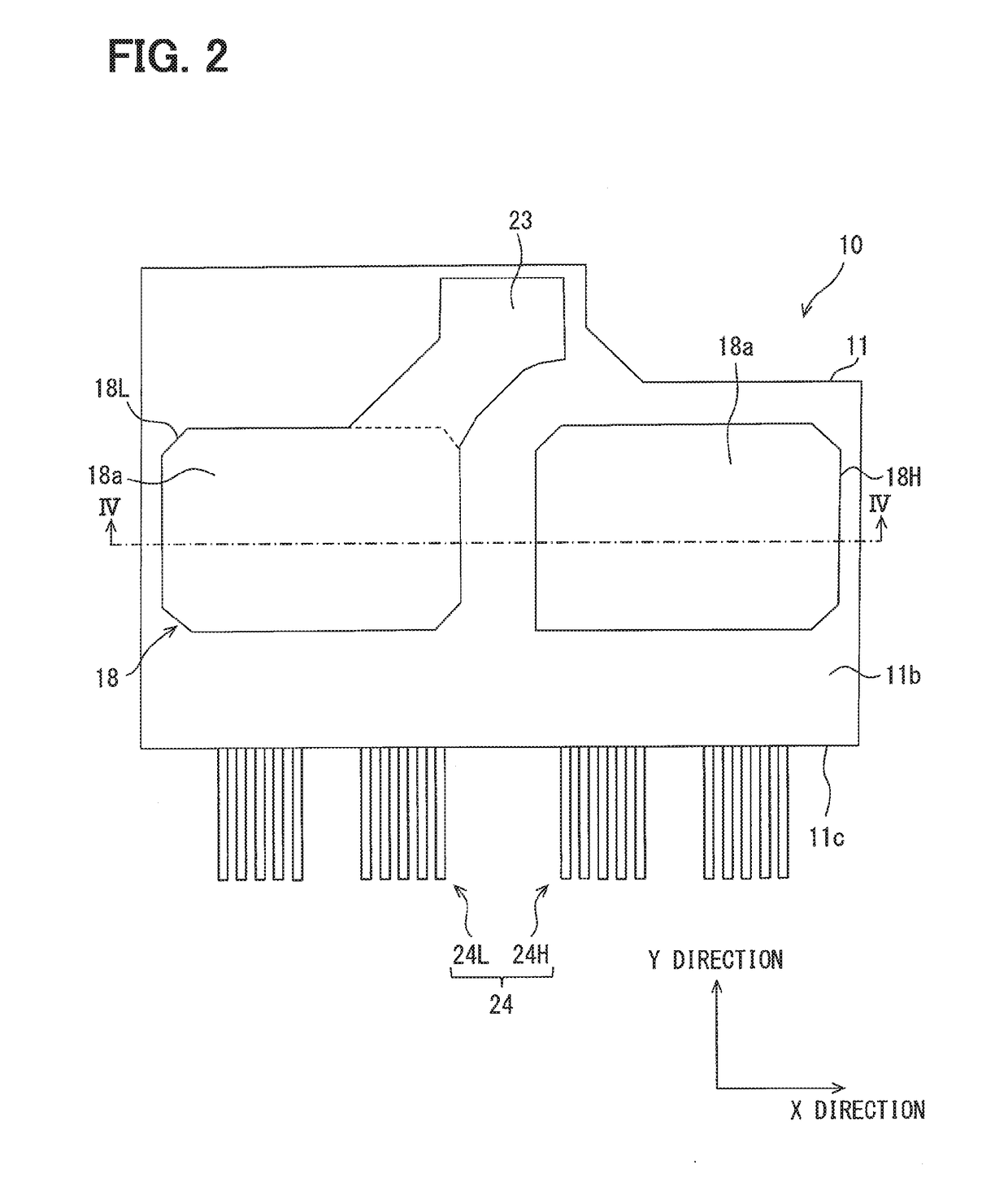
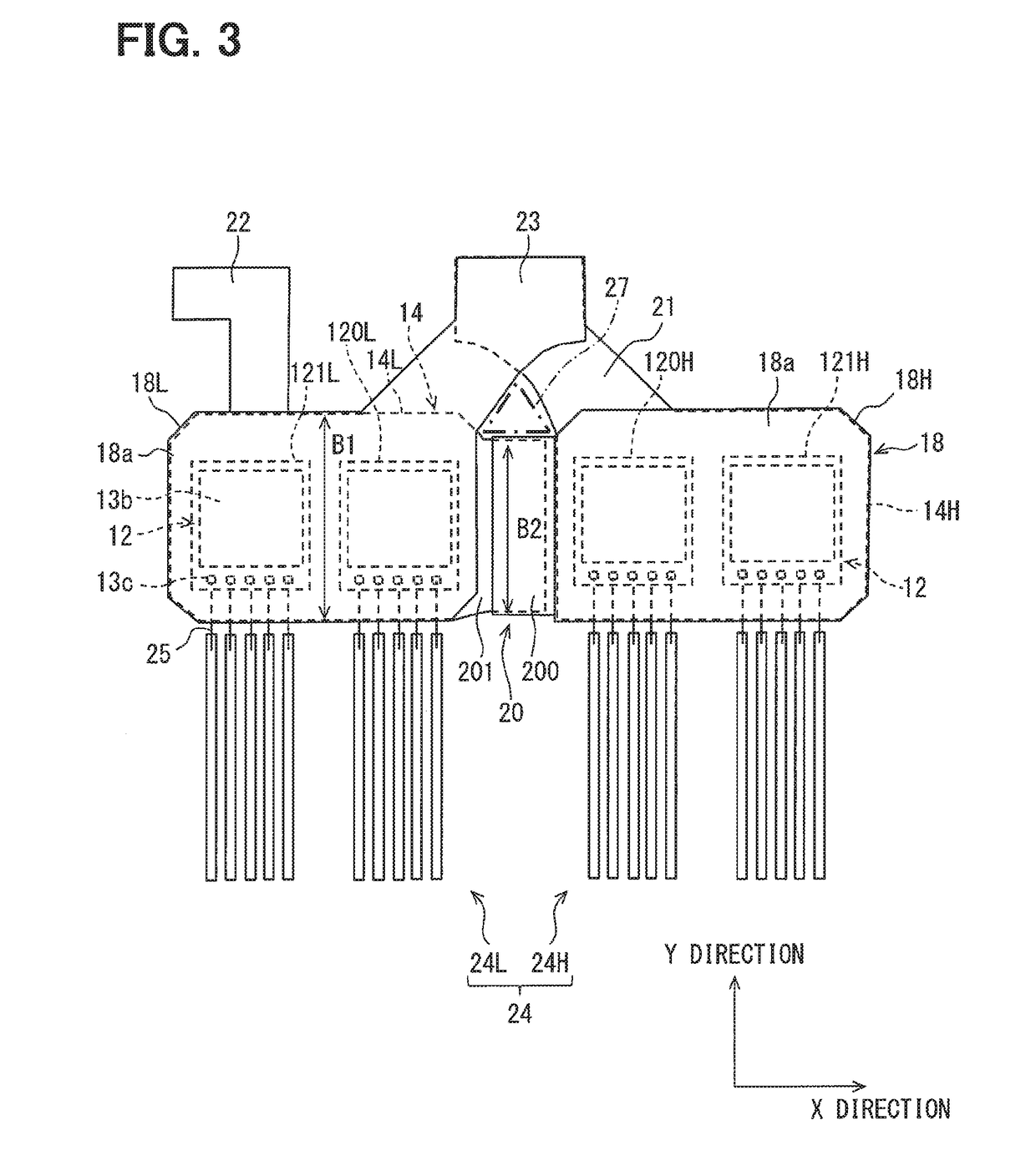
ActiveUS20190088568A1Connection structureAvoid current changesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsConversion constructional detailsPower semiconductor deviceSemiconductor chip
In a semiconductor device, a plurality of semiconductor chips included in an upper-arm circuit are connected in parallel between a pair of upper-arm plates, while a plurality of semiconductor chips included in a lower-arm circuit are connected in parallel between a pair of lower-arm plates. In each of the arm circuits, the plurality of semiconductor chips are arranged in a direction perpendicular to a direction in which emitter electrodes and pads are arranged, the pads are disposed on the same side of the emitter electrodes, and signal terminals extend in the same direction. A series-connecting part between the upper- and lower-arm circuits includes a joint part 20 continued to respective side surfaces of the corresponding upper- and lower-arm plates. Each of inductances of respective parallel-connecting parts of the upper- and lower-arm plates which connect the semiconductor chips in parallel is smaller than an inductance of the series-connecting part.
Owner:DENSO CORP
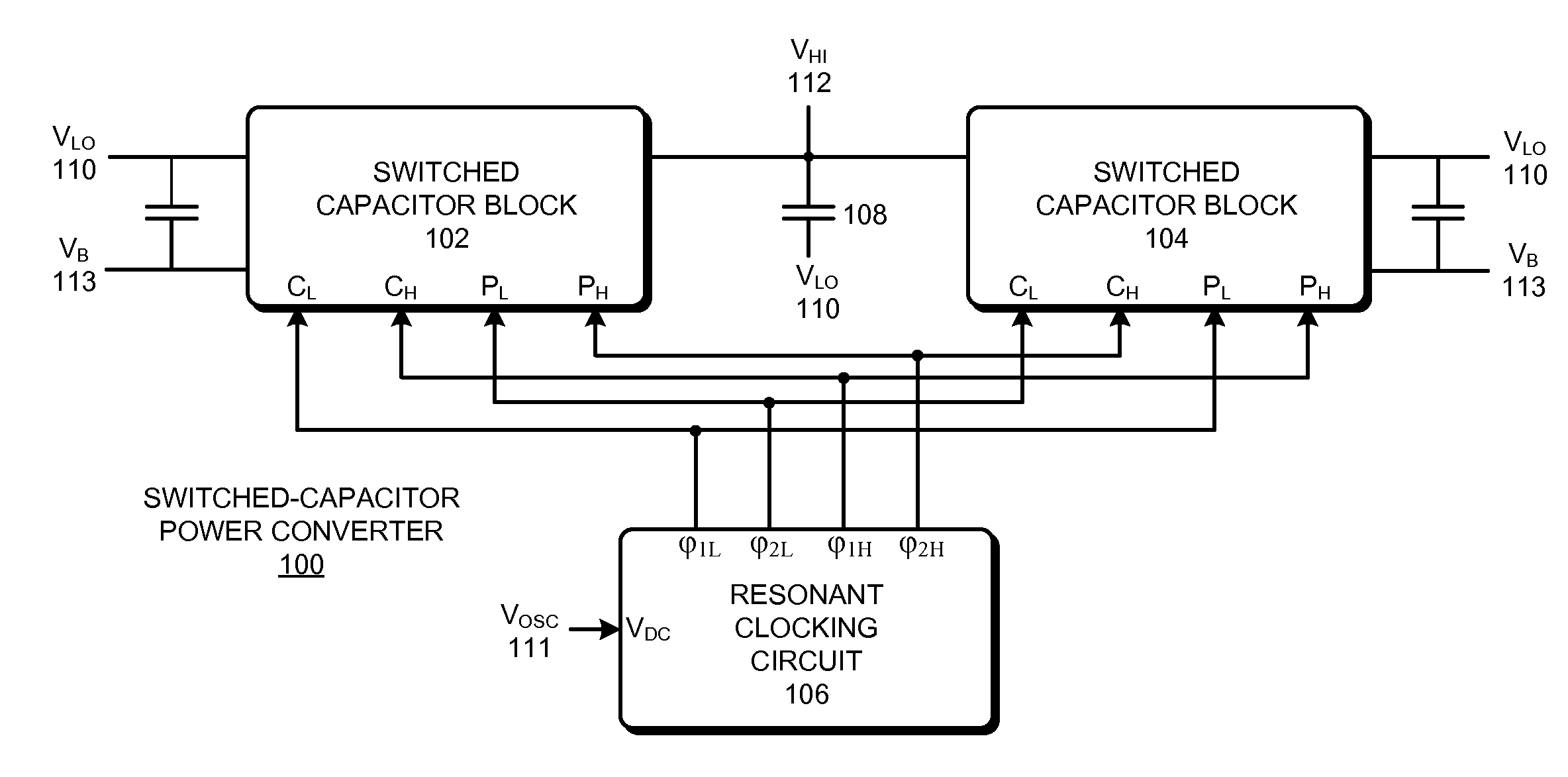
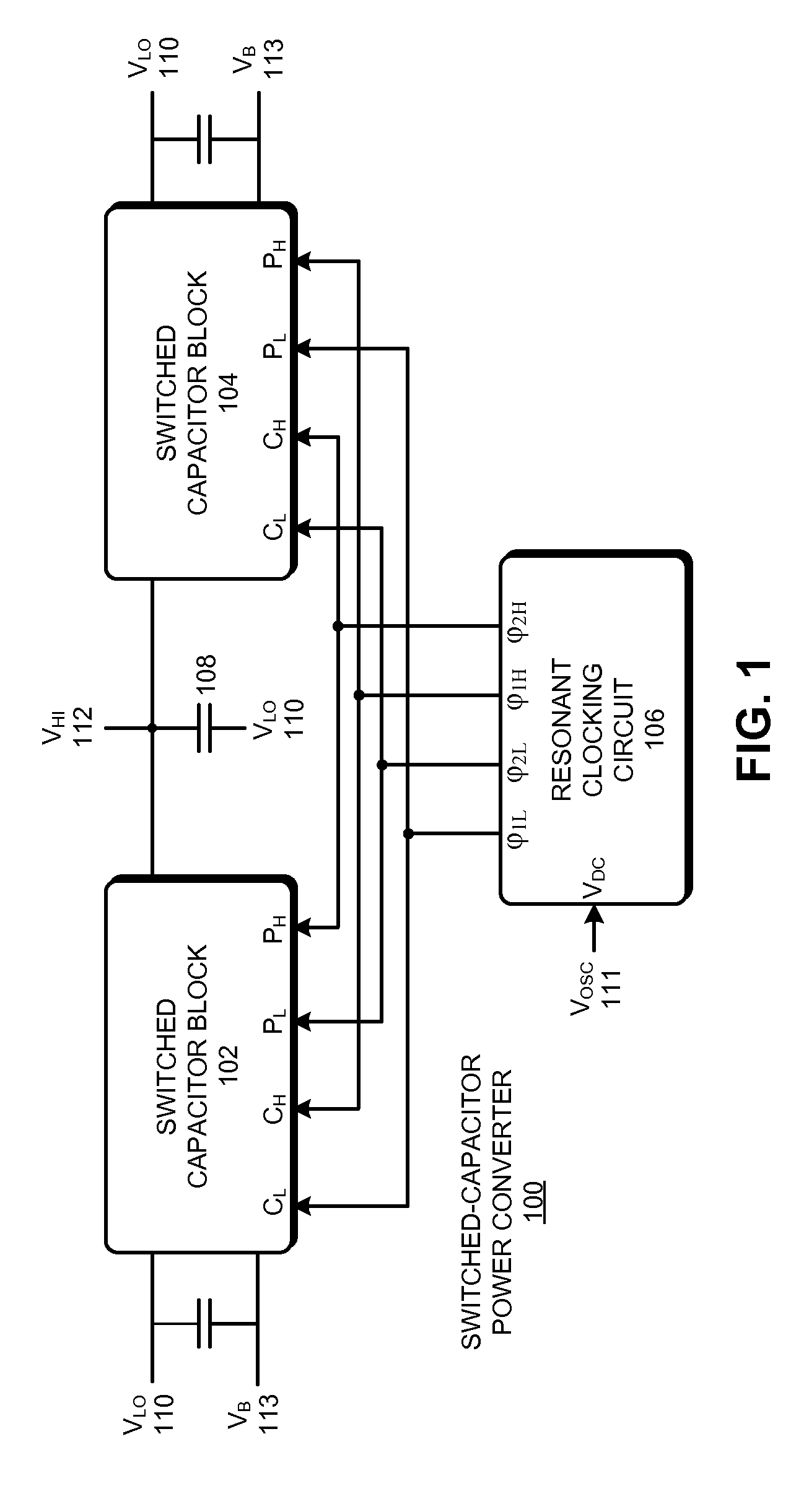
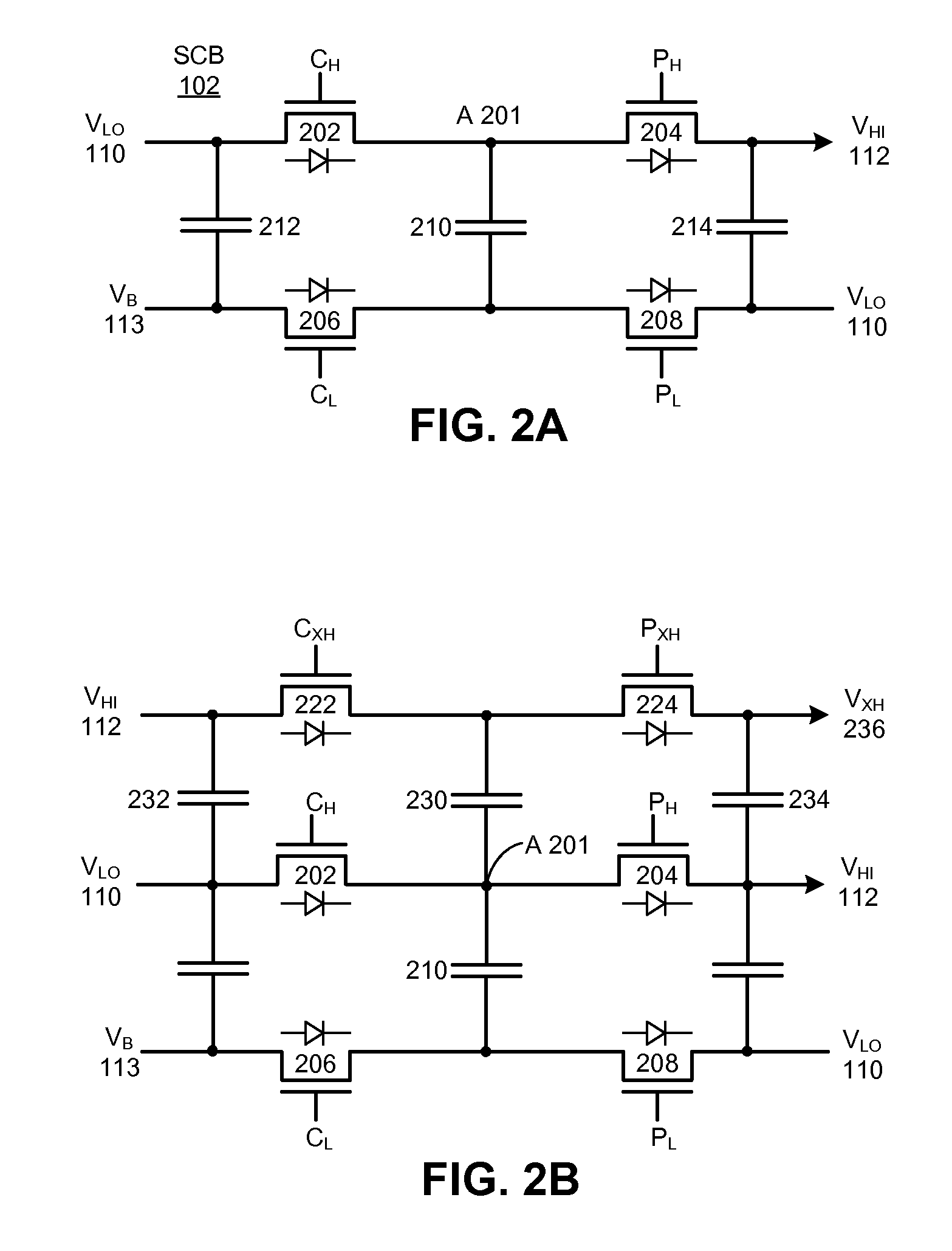
Controlling power loss in a switched-capacitor power converter
ActiveUS8541999B2Power Loss MinimizationReduce conduction lossMultiple-port networksEfficient power electronics conversionControl powerVoltage reference
The disclosed embodiments relate to a system that implements a switched-capacitor power converter which is configured to actively control power loss while converting an input voltage to an output voltage. This system includes one or more switched-capacitor blocks (SCBs), wherein each SCB includes a first capacitor and a set of switching devices configured to couple a constant-potential terminal and a time-varying-potential terminal of the first capacitor between the input voltage, the output voltage and a reference voltage. The system also includes a clocking circuit which produces gate drive signals for switching transistors in the one or more SCBs. The system additionally includes a controller configured to actively control the gate drive signals from the clocking circuit to substantially minimize the power loss for the switched-capacitor power converter.
Owner:APPLE INC
Semiconductor module
ActiveUS20190058468A1Reduce surge voltageSwitch loss increaseTransistorSolid-state devicesVoltage referenceAnode
A semiconductor module includes a high-side switching device and a low-side switching device that respectively form an upper arm and a lower arm, freewheeling diodes that are respectively connected to the switching devices in anti-parallel, and a high-side driver circuit and a low-side driver circuit that respectively switch the high-side switching device and the low-side switching device ON and OFF. In the upper arm, an anode electrode of the freewheeling diode and a reference voltage electrode of the high-side driver circuit are directly connected via a first wiring, and the anode electrode of the freewheeling diode is connected to a reference voltage electrode of the high-side switching device via a second wiring having an inductance.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
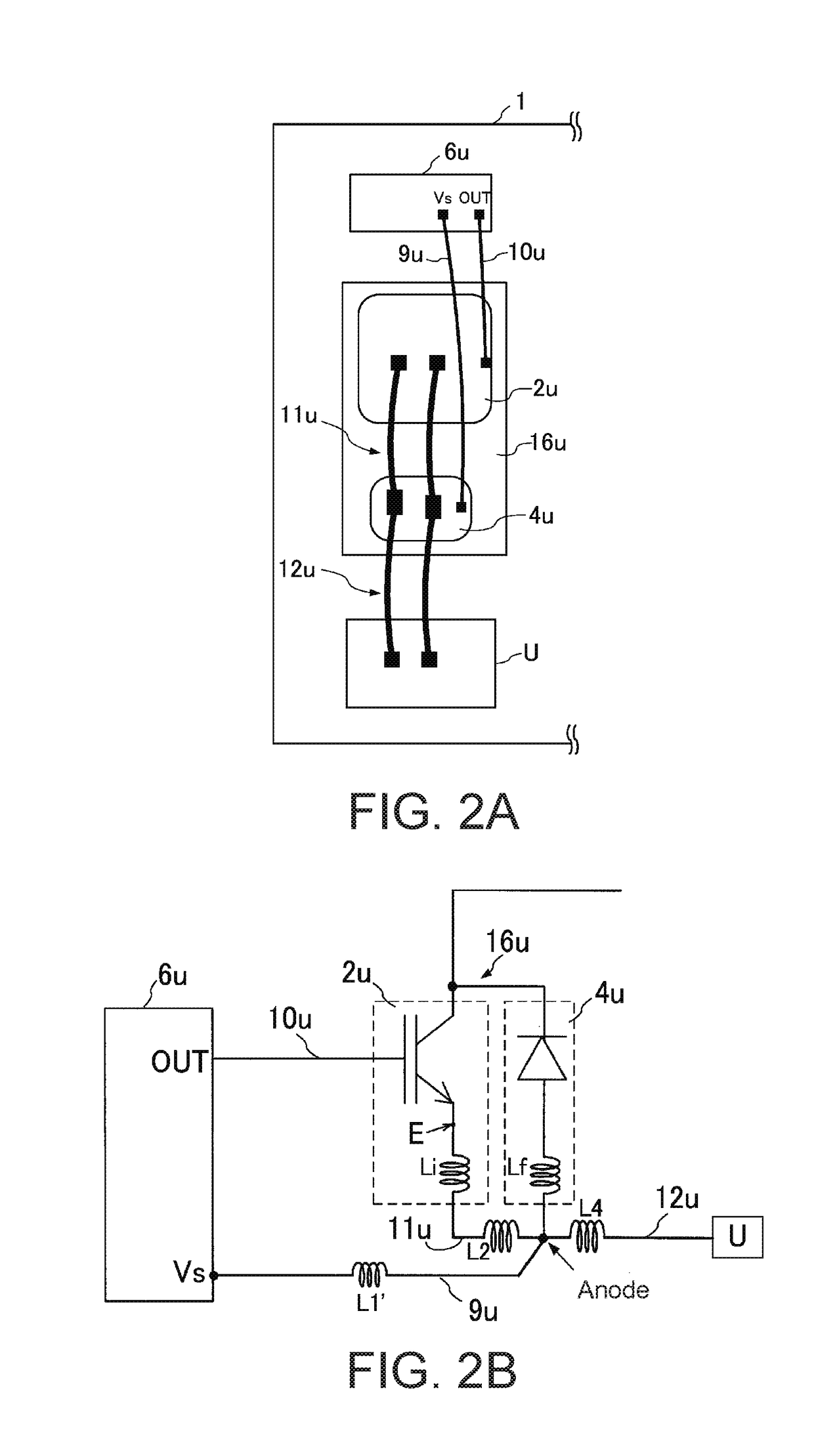
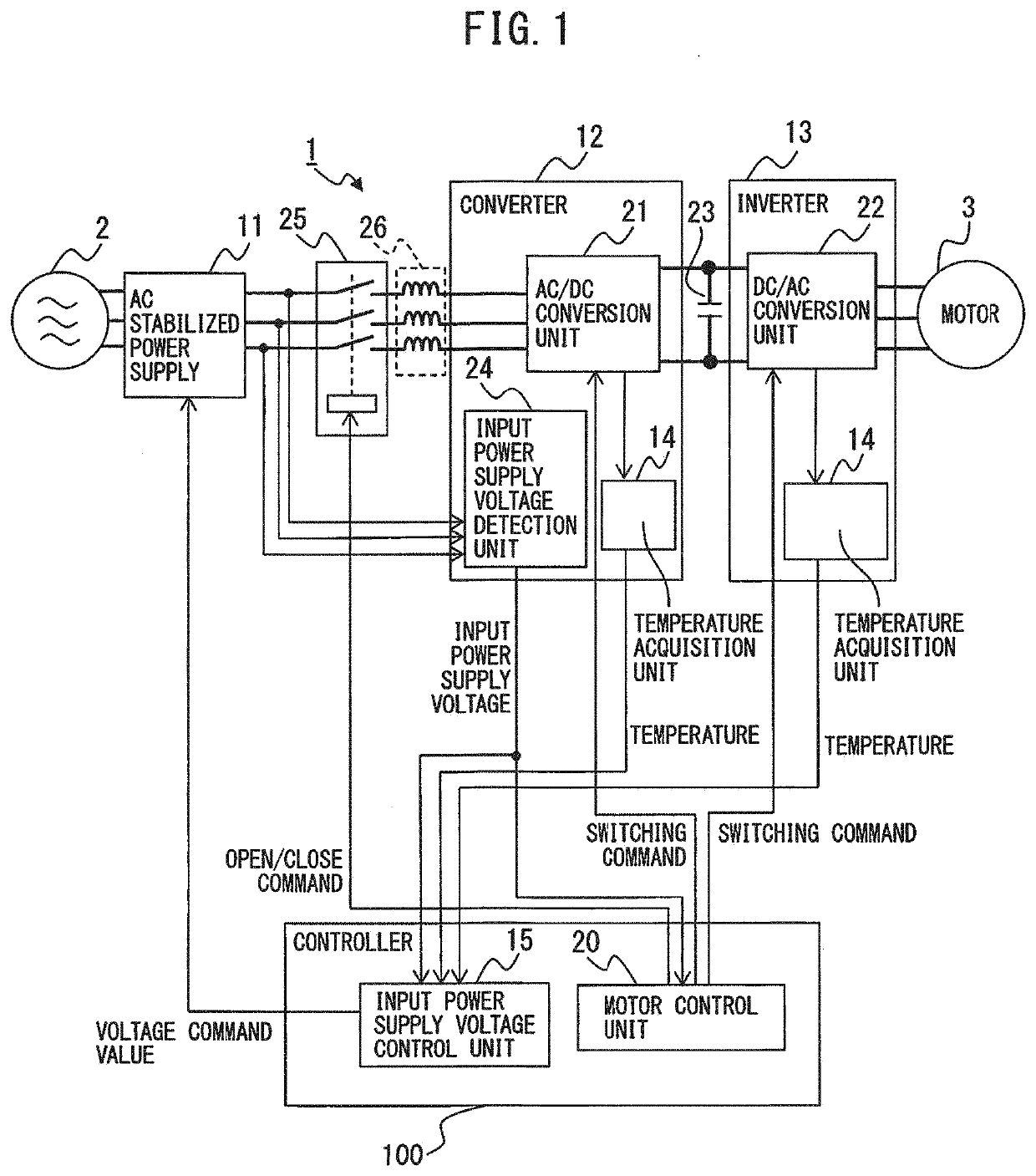
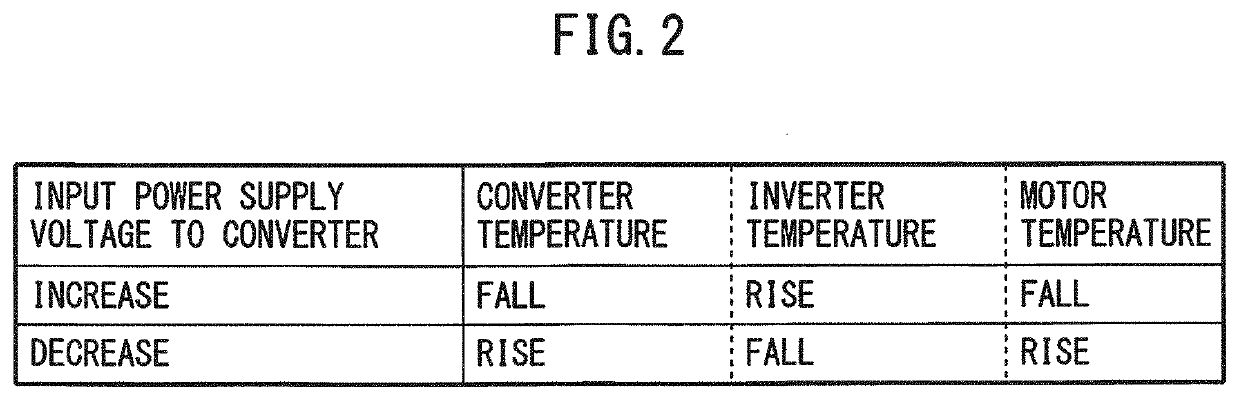
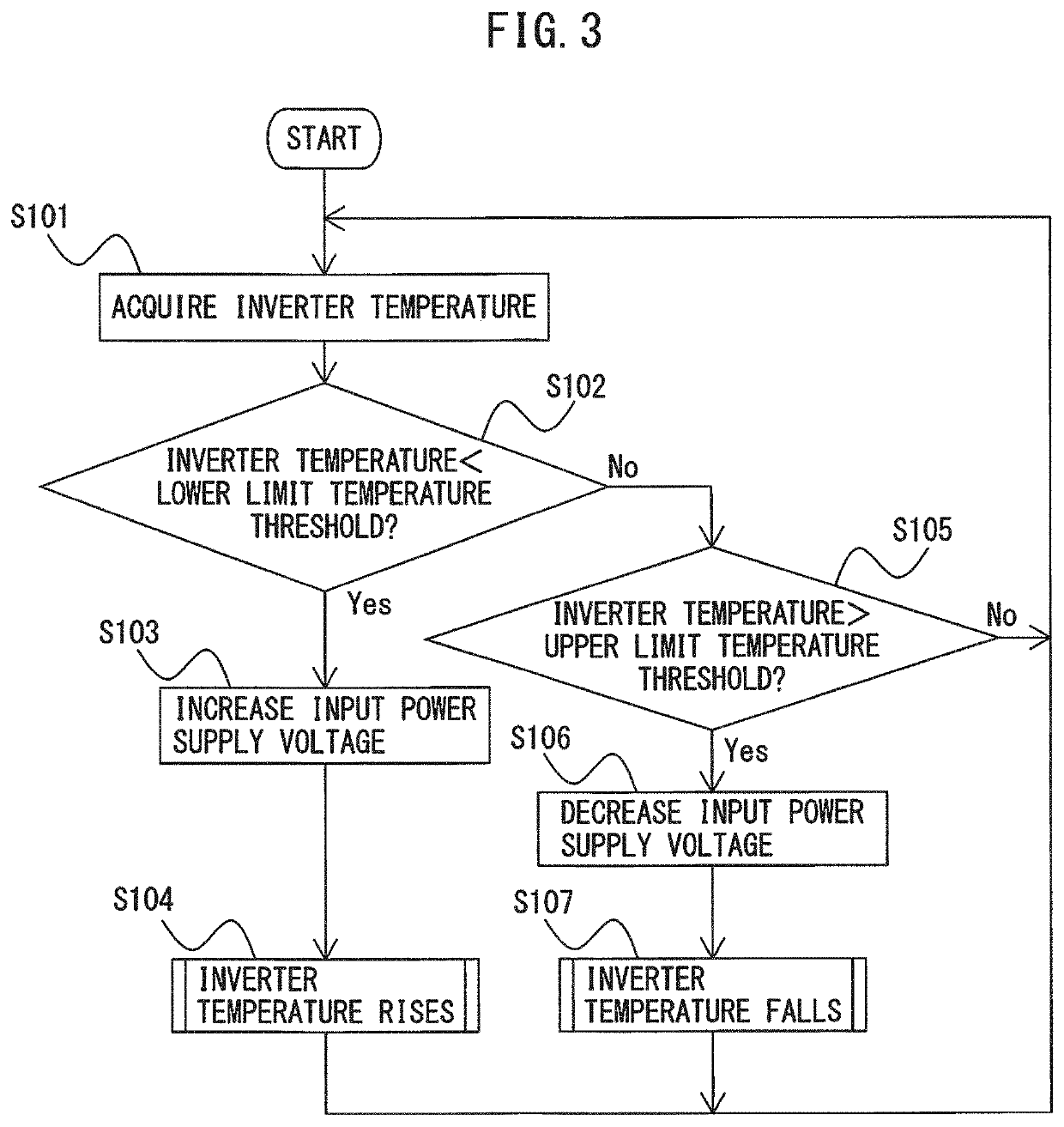
Motor drive apparatus having input power supply voltage adjustment function
ActiveUS20200052642A1Suppress feverSolution to short lifeAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersConvertersElectric machine
A motor drive apparatus includes an AC stabilized power supply configured to convert AC voltage of a commercial AC power source into input power supply voltage according to a received voltage command value and output the input power supply voltage, a converter configured to convert the input power supply voltage into DC voltage and output the DC voltage to a DC link, an inverter configured to convert the DC voltage at the DC link into AC voltage for driving a motor, and an input power supply voltage control unit configured to control the input power supply voltage that is output by the AC stabilized power supply.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com