Patents
Literature
30 results about "Corynebacterium pekinense" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Characterization of Aspartate Kinase from Corynebacterium pekinense and the Critical Site of Arg169. Weihong Min, 1, 2, * Huiying Li, 1, 2 Hongmei Li, 1, 2 Chunlei Liu, 1, 2 and Jingsheng Liu 1, 2. ... The genomic DNA of C. pekinense was isolated with a genomic DNA extraction kit.
Alleles of the zwf gene from coryneform bacteria
The invention relates to mutants and alleles of the zwf gene of coryneform bacteria, which encode variants of the Zwf subunit of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (EC: 1.1.1.49), and to processes for preparing amino acids, in particular L-lysine and L-tryptophan, by using bacteria which harbor said alleles.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Method for producing xanthosine-5'-monophosphate by fermentation using mutant strains of Coryneform bacteria
InactiveUS20020098552A1Increase enzyme activitySuperior in pointBacteriaFermentationBacteroidesCorynebacterium efficiens
Xanthosine-5'-monophosphate is produced by cultivating the bacterium which has a resistance to growth inhibition by an inhibitor selected from the group consisting of inhibitors of cell membrane biosynthesis and / or functioning, phosphorylation inhibitors, uncoupling agents, RNA-polymerase inhibitors and methionine analogs, and has an ability to produce xanthosine-5'-monophosphate according to produce and accumulate xanthosine-5'-monophosphate in the culture, and recovering the xanthosine-5'-monophosphate therefrom.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
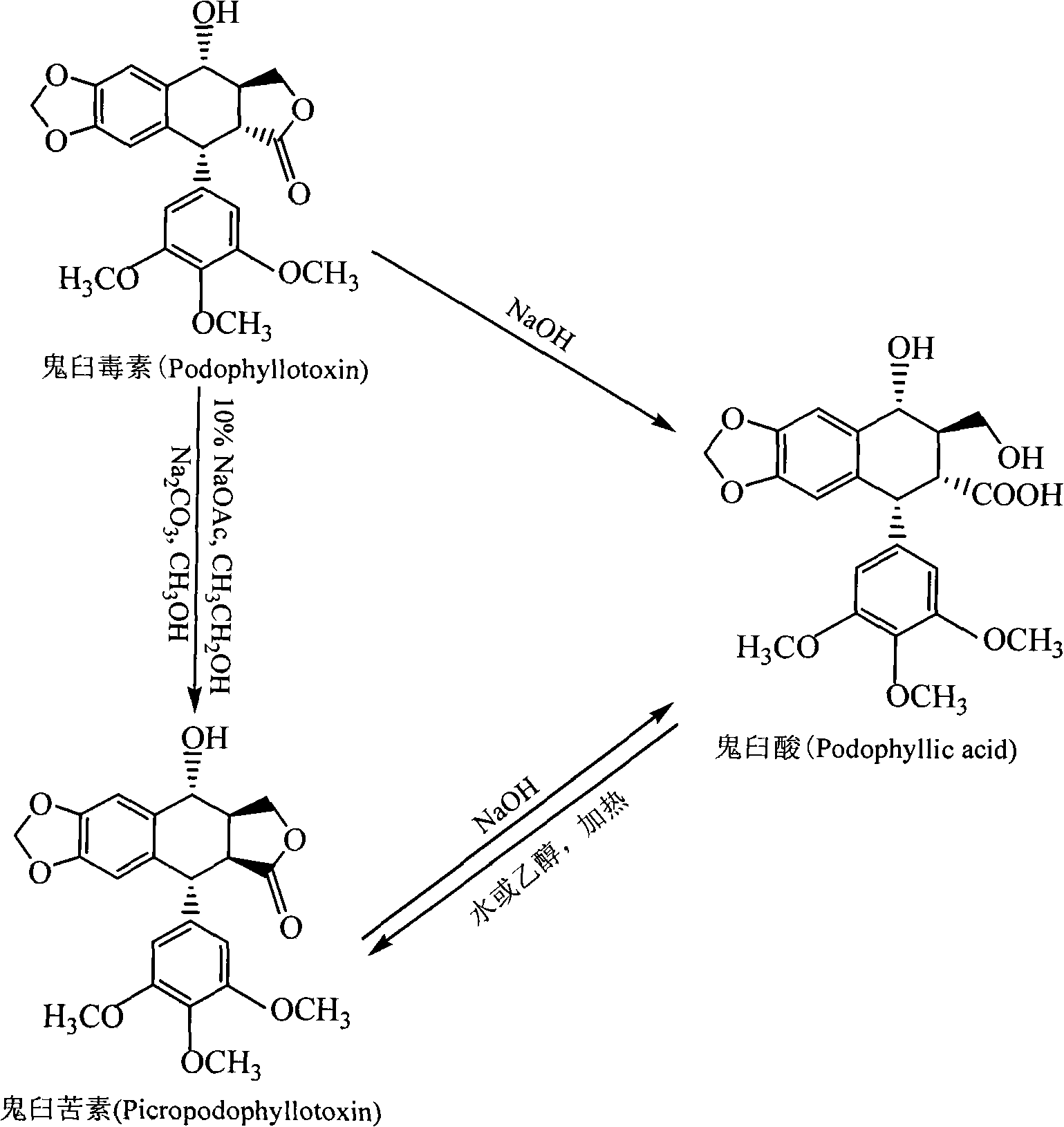
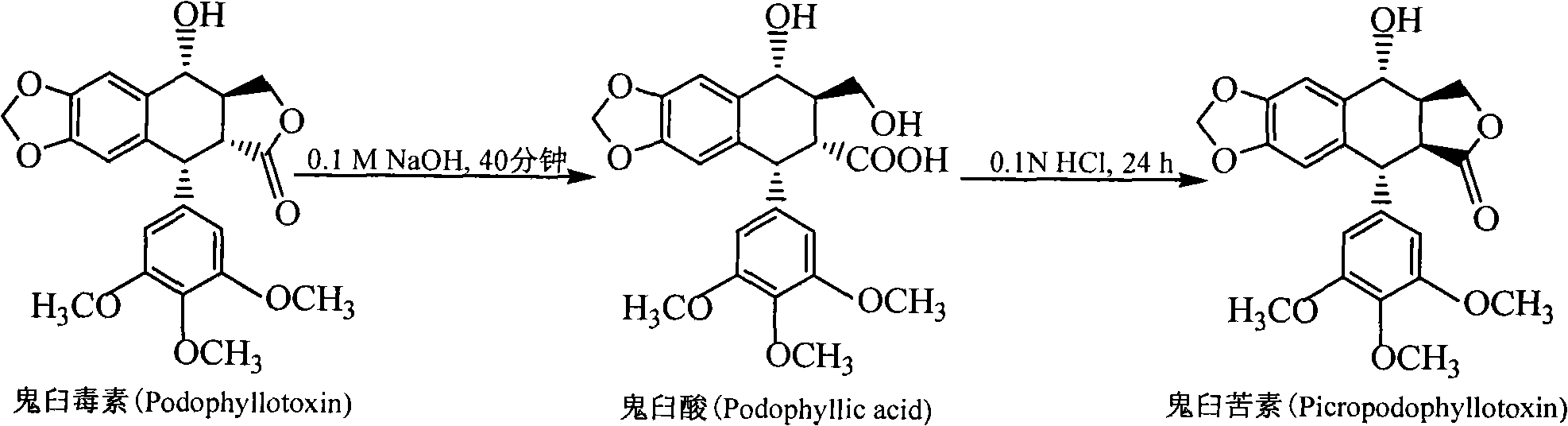
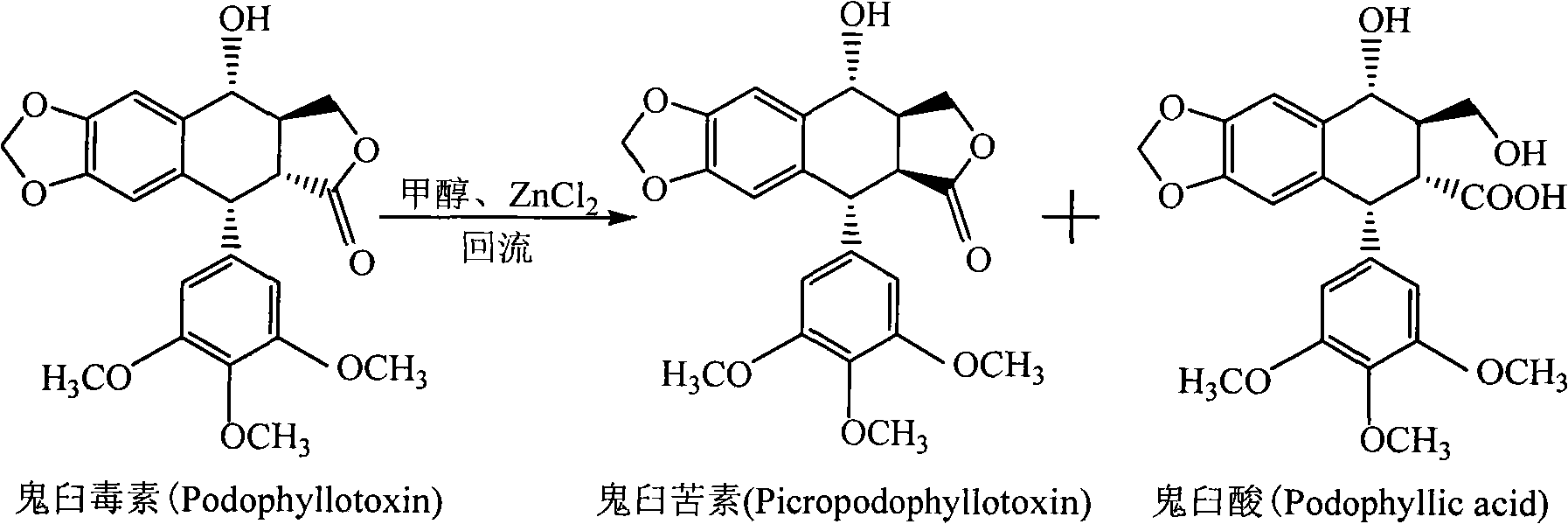
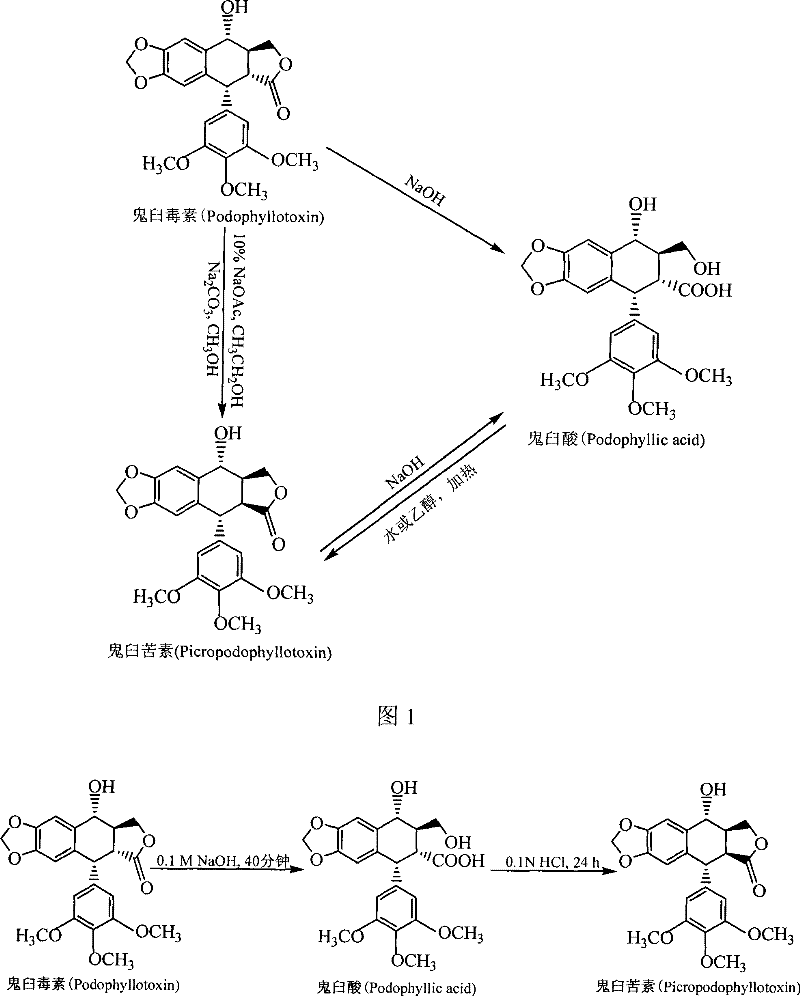
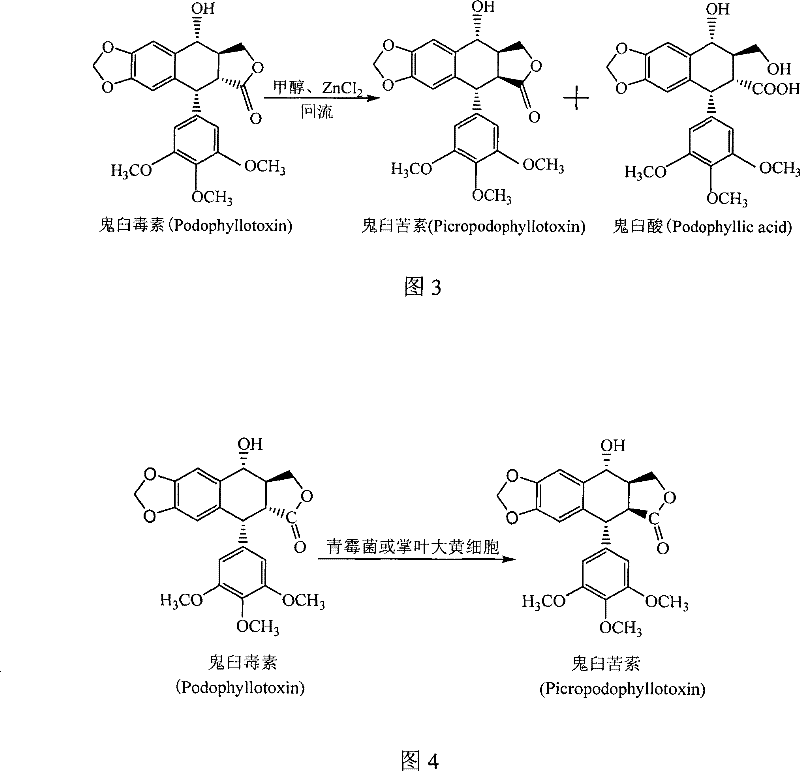
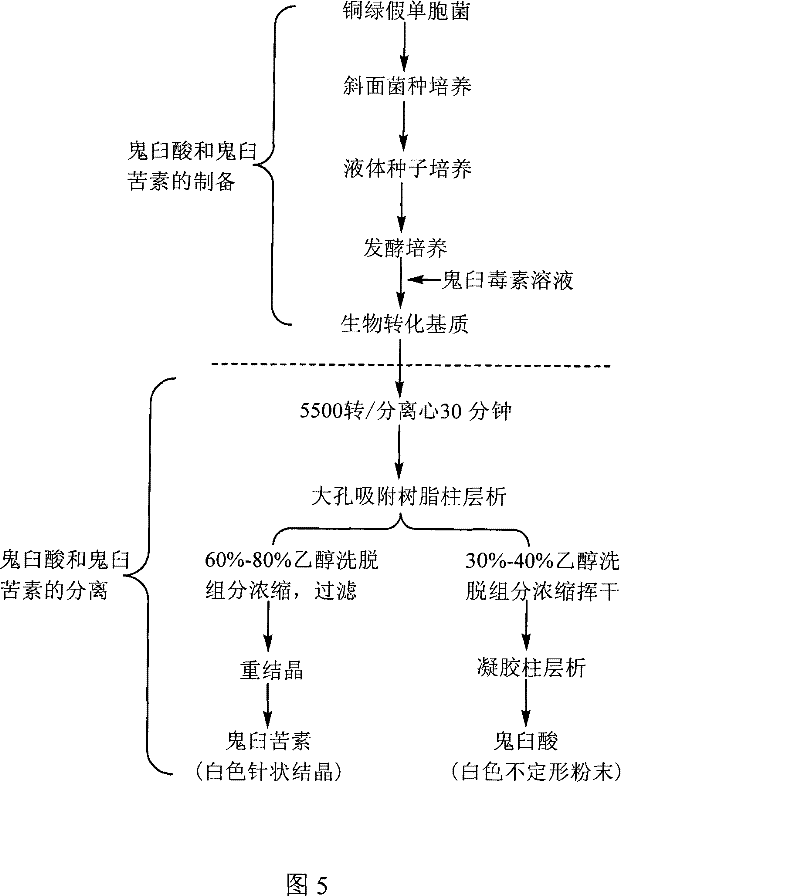
Method for converting podophyllinic acid lactone into podophyllic acid and picropodophyllin
InactiveCN101492704AHigh yieldMild reaction conditionsOrganic chemistryMicroorganism based processesErwinia uredovoraPodophyllic acid
The invention discloses a method for converting podophyllotoxin to podophyllic acid and picropodophyllin, comprising the following steps: the substrate podophyllotoxin solution is added during the fermentation process of microorganism pseudomonas aeruginosa, bacillus, rhodococcus erythropolis, clostridium, corynebacterium pekinense, hay bacillus, erwinia uredovora or bending pseudomonas for carrying out biotransformation reaction, thus obtaining biotransformation matrix with the podophyllic acid and picropodophyllin. The invention also discloses a method for separating the podophyllic acid and picropodophyllin from the obtained biotransformation matrix, comprising the following steps: the macroporous absorbent resin column is adopted to carry out initial separation on the biotransformation matrix and gel column chromatography is adopted to carry out fine separation, thus respectively obtaining the picropodophyllin and the podophyllic acid. In the invention, modification is carried out on the picropodophyllin structure by microbiological transformation, thus obtaining the picropodophyllin and the podophyllic acid, in addition, the conversion rate of the substrate is high, the operation is easy, the reaction conditions are moderate, the generated waste is little, the separation process is simple and the yield is high.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
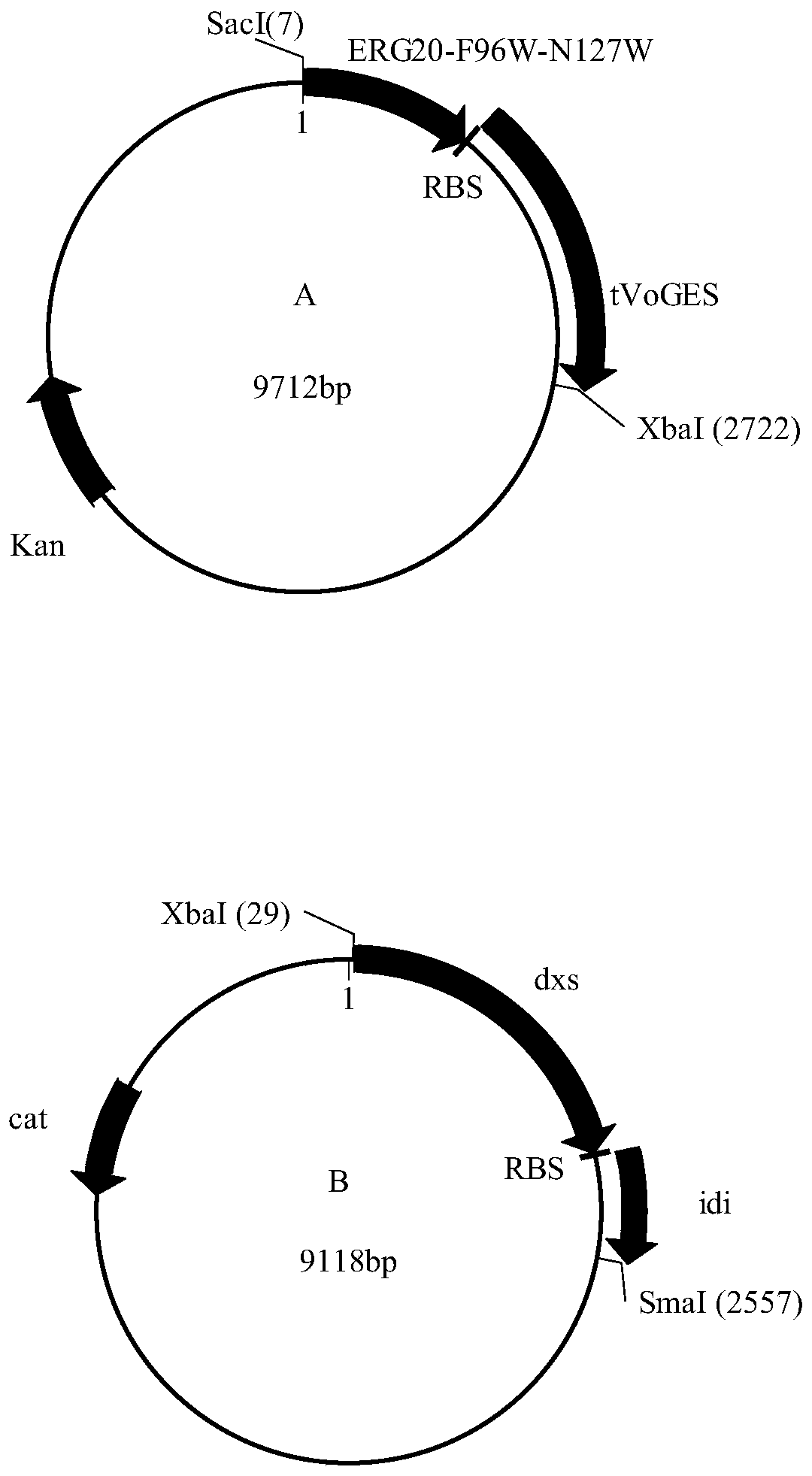
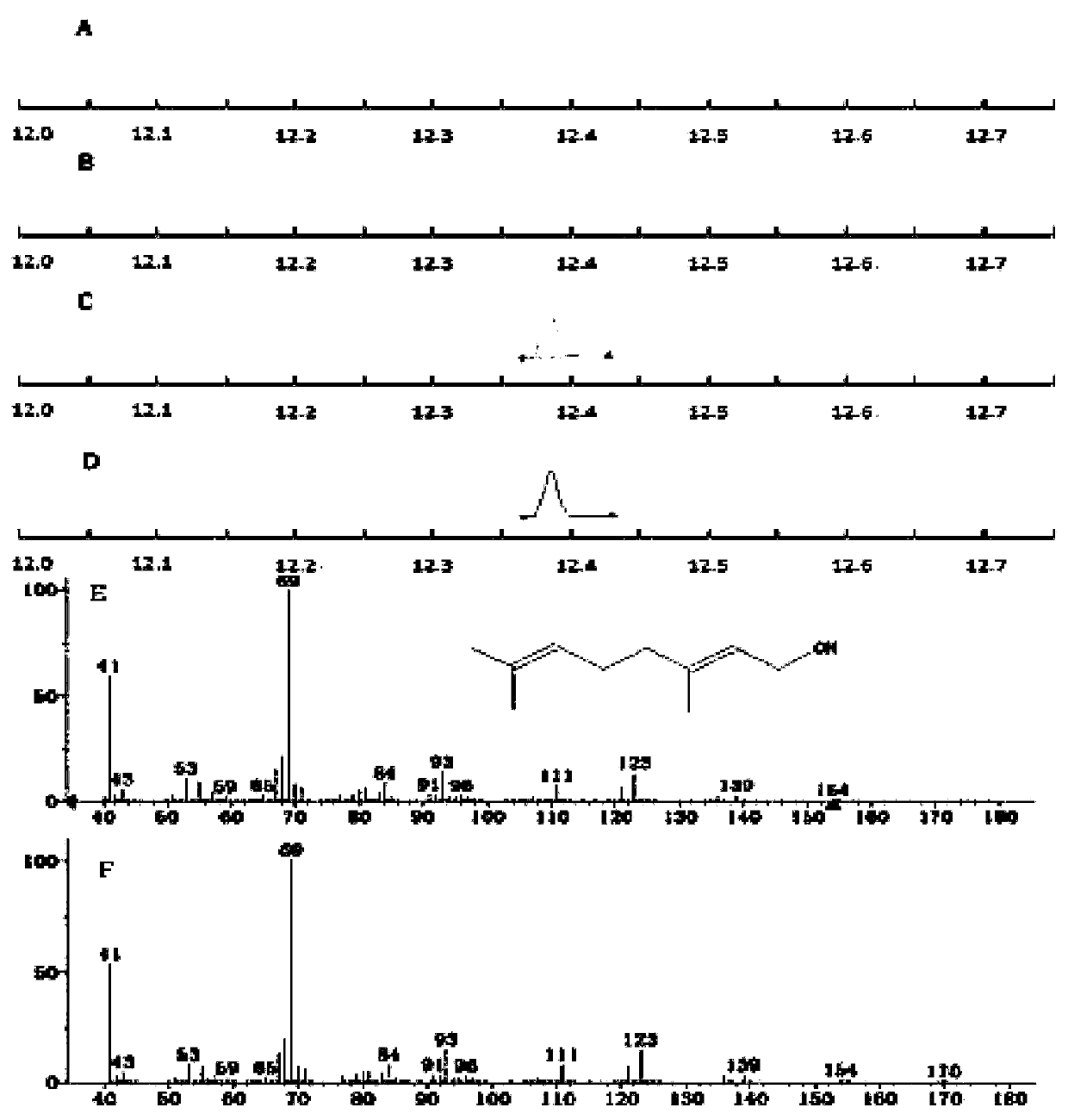
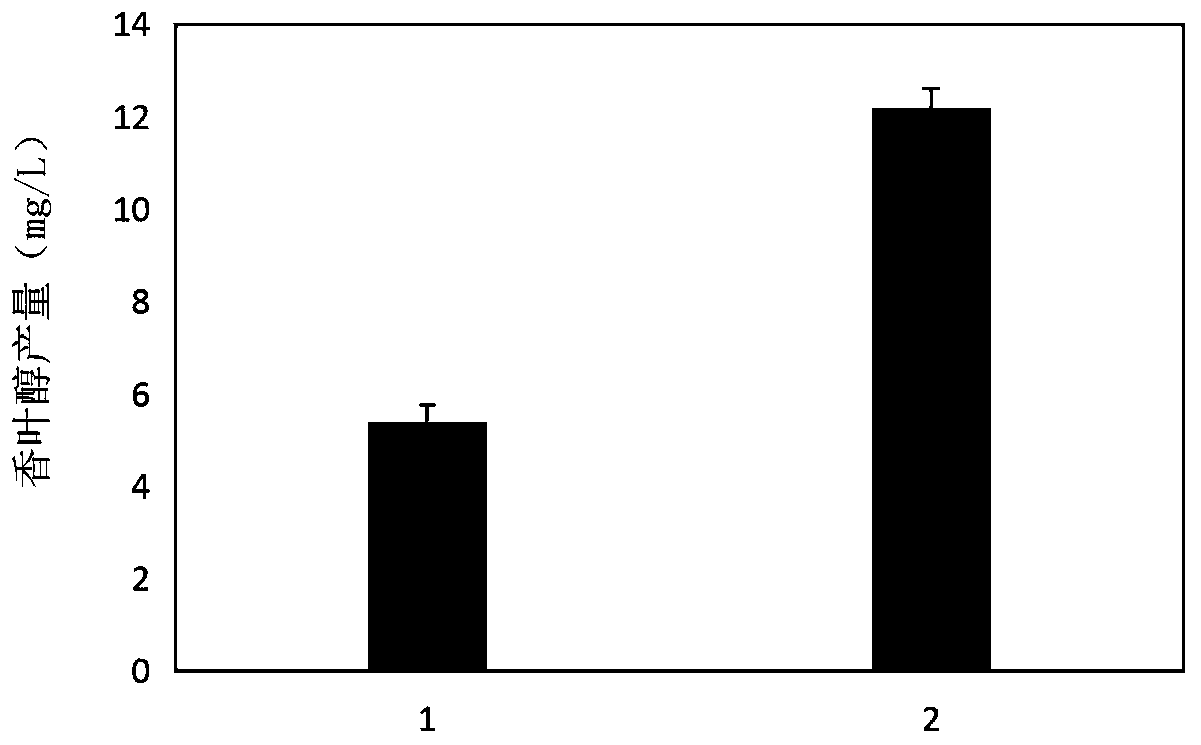
Corynebacterium glutamate for synthesizing geraniol and construction method and application of corynebacterium glutamate
InactiveCN110438145AShort fermentation timeBacteriaTransferasesCorynebacterium efficiensBinding site
The present invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamate for synthesizing geraniol and a construction method and application of corynebacterium glutamate. The construction method of corynebacteriumglutamate comprises the following steps: connecting a saccharomyces cerevisiae-derived mutant geranyl pyrophosphate synthase gene ERG20<F96W-N127W> and a valerian-derived geranol synthase gene tVoGEStruncated through cutting off of C-terminal 53 amino acid residues by fusion PCR, adding a ribosome binding site sequence to a homologous region, inserting SacI and XbaI enzyme cutting sites of a corynebacterium glutamate expression plasmid pEC-XK99E to obtain a plasmid 1; converting the plasmid 1 into corynebacterium glutamate to obtain corynebacterium glutamate 1 for synthesizing geraniol. Theconstruction method provides more precursors and short fermentation time (42 to 48 hours) for the synthesis of geraniol, and corresponding by-products are not detected out by GC-MS detection.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
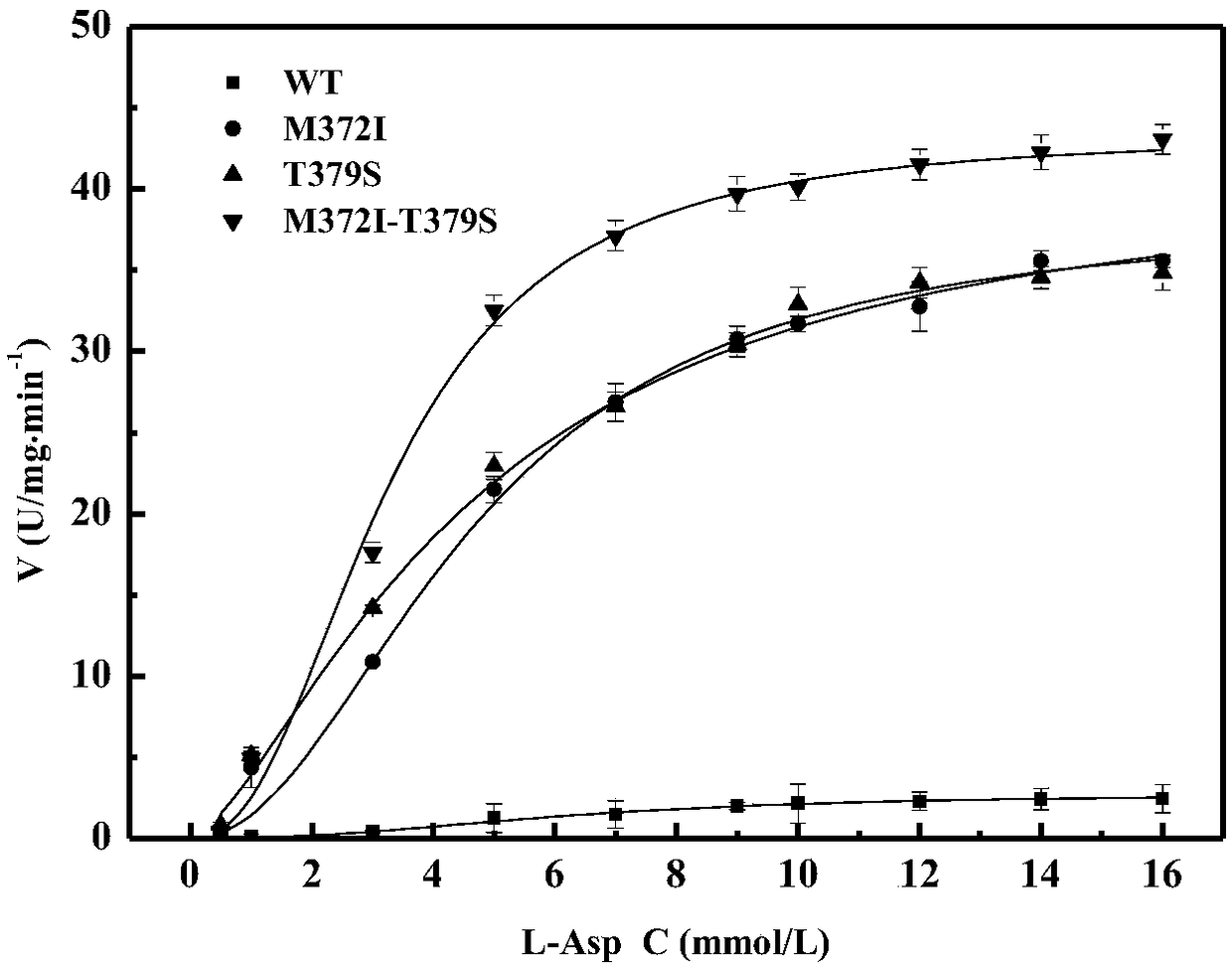
High enzyme activity aspartokinase mutant, engineering bacterial strain and preparation method of mutant
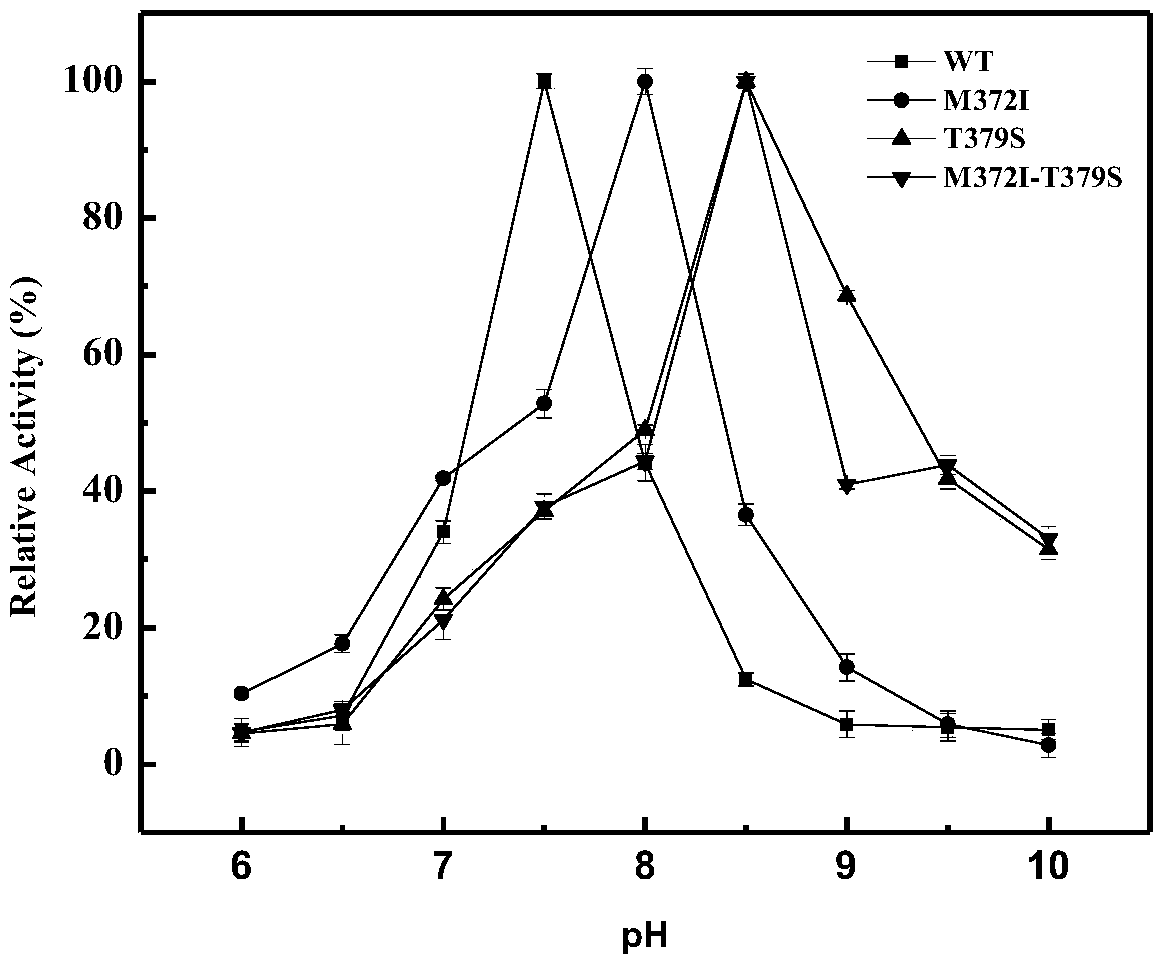
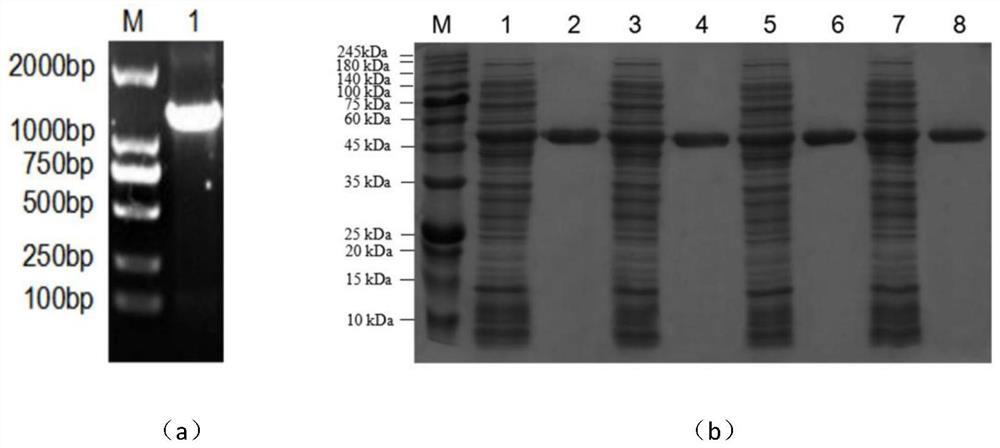
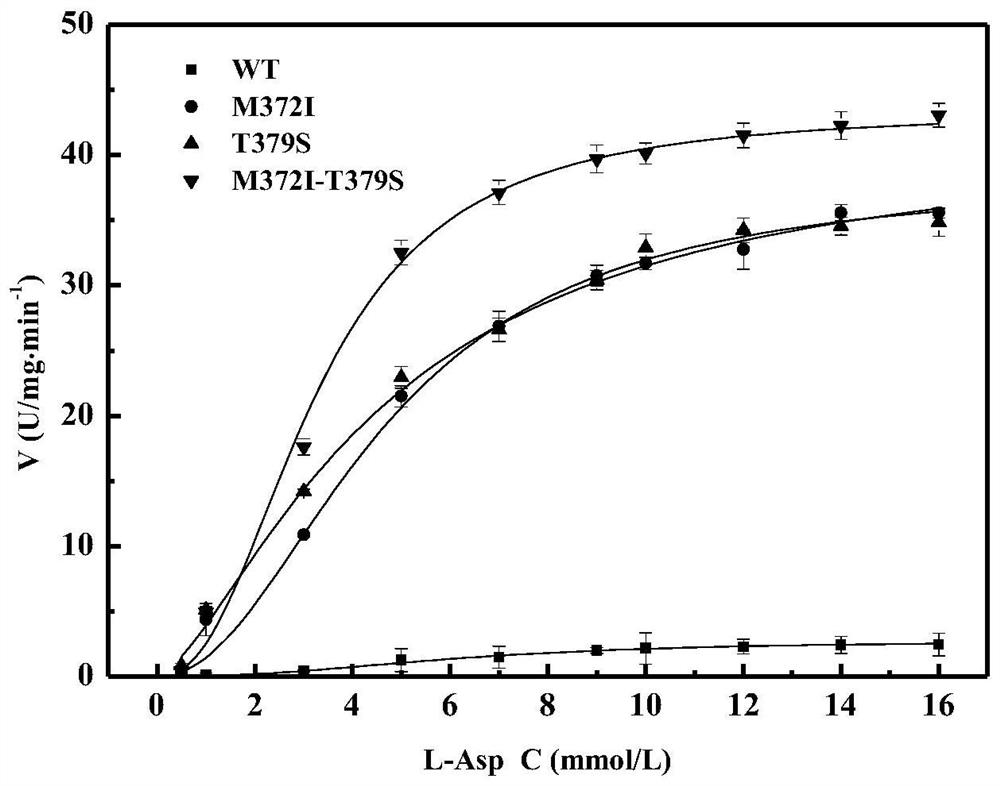
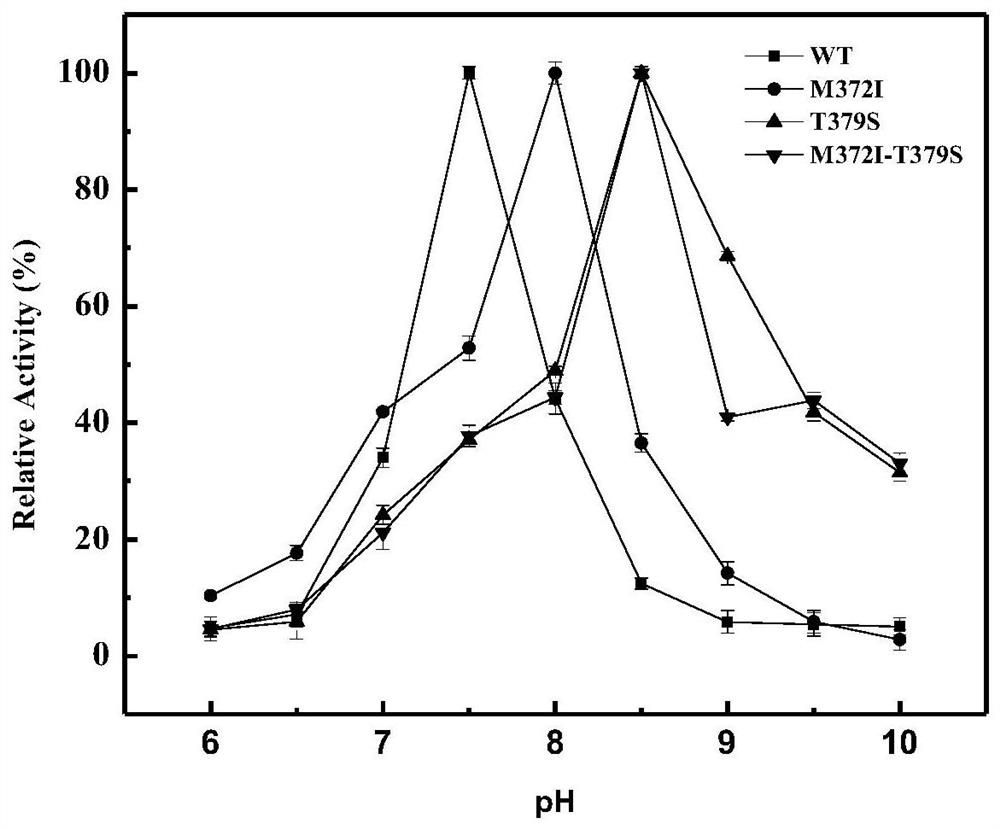
Belonging to the technical field of bioengineering, the invention relates to an aspartokinase mutant, an engineering bacterial strain and a preparation method of the mutant. The high enzyme activity aspartokinase mutant has an amino acid sequence formed by substitution, deletion or addition of 2-10, further 2-6, and even further 2-3 amino acid residues to an exogenous aspartokinase with an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:2, and has the functions of aspartokinase. Preferably, the sequence is formed by substitution, deletion or addition of 2 amino acid residues. In particular, preferably,site-specific saturation mutation is carried out to the 372nd and 379th amino acids in the amino acid sequence, and a high throughput screening method is utilized to select the high enzyme activity aspartokinase mutant. The invention further utilizes the electrotransformation method to transfer a pEC-AK recombinant shuttle expression vector of the aspartokinase mutant that has high enzyme activity and can relieve or weaken Lys feedback inhibition effect into Corynebacterium pekinense, finally the recombinant Corynebacterium pekinense M372I-T379S engineering bacterial strain can be obtained, and fermentation product analysis is conducted on the engineering bacterial strain.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Method for producing l-lysine using corynebacterium sp. that has obtained the activity of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase derived from an alien species
InactiveUS20120208245A1Improve productivityBacteriaFermentationCorynebacterium efficiensGlyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
The present invention relates to a Corynebacterium sp. strain having an activity of NADP-dependent glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and an improved productivity of L-lysine, and a method for producing L-lysine using the same. According to the Corynebacterium sp. strain of the present invention and the method for producing L-lysine using the same, L-lysine can be produced in a high yield.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Method for efficiently producing L-isoleucine
ActiveCN108841884AImprove acid production performanceMeet the needs of industrial productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismBrevibacillus borstelensis
The invention discloses a method for efficiently producing L-isoleucine, and belongs to the technical field of microbial fermentation. In the method provided by the invention, brevibacterium lactofermentation is taken as a production strain of L-isoleucine, and the brevibacterium lactofermentation and corynebacterium pekinense are co-cultured, so that the acid production capacity of the brevibacterium lactofermentation is significantly improved from 13g / L to 21g / L, which can meet the needs of industrial production.
Owner:WUXI JINGHAI AMINO ACID
Corynebacterium pekinense and application thereof
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms and discloses a corynebacterium pekinense, wherein the collection number thereof is CGMCC No.5361. The corynebacterium pekinense with the collection number of CGMCC No.5361 takes a wild corynebacterium pekinense with the collection number of CICC No.21721 as a parent strain, and is prepared by performing chemical mutagenesis and screening through a culture medium containing neomycin; and the capability of generating L-lysine through fermentation is obviously higher than that of the wild corynebacterium pekinense, and the yield of the L-lysine is increased by 14.7 percent, so that the corynebacterium pekinense with the collection number of CGMCC No.5361 is widely applied to the fermentation of the L-lysine.
Owner:新疆梅花氨基酸有限责任公司
Alleles of the zwf gene from coryneform bacteria
The invention relates to mutants and alleles of the zwf gene of coryneform bacteria, which encode variants of the Zwf subunit of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (EC: 1.1.1.49), and to processes for preparing amino acids, in particular L-lysine and L-tryptophan, by using bacteria which harbor said alleles.
Owner:DEGUSSA AG
Synergistic agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103011991AIncrease profitPollution controlFertilizer mixturesCopper sulfateAmmonium Hydrogen Carbonate
The invention discloses a synergistic agent and a preparation method thereof, wherein the synergistic agent comprises the following raw materials according to proportion by weight: 70.8-87.5 parts of stone potassium, 3-8 parts of polyaspartic acid, 3-8 parts of maleic anhydride, 0.3-0.5 parts of azone, 5-10 parts of urea or ammonium hydrogen carbonate, 0.4-0.7 parts of d bacteria liquid, 0.3-0.8 parts of EDTA (Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid) and 0.2-0.5 parts of n-butyl alcohol. The preparation method of the stone potassium comprises the following steps: respectively crashing 50 parts of zeolite ore, 20 parts of phosphorite and 30 parts of leopoldite into 100-200 meshes and then uniformly mixing so as to obtain a mixture; taking 73.5-87.3 parts of mixture, 2-4 parts of urea, 2-5 parts of phosphorus pentoxide, 1-2 parts of potassium sulfate, 0.2-0.5 parts of ammonium molybdate or sodium molybdate, 1-2 parts of manganous sulfate, 3-6 parts of ferrous sulfate, 1-2 parts of zinc sulfate, 1-2 parts of sodium borate, 0.5-1 parts of copper sulfate and 1-2 parts of fulvic acid; and stirring and sealing up for keeping standby. The preparation method of the bacteria liquid comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing colon bacillus, Fusarium moniliforme, Corynebacterium pekinense, Streptomyces jingyangensis, Bacillus megatherium, Bacillus mucilaginosus and Streptomyces according to a proportion of 0.5%: 0.5%: 0.5%: 0.5%: 0.5%: 0.5%: 0.5%. The synergistic agent is multipurpose, nutritious, low in cost, non-toxic, nuisanceless and free of residue.
Owner:冷登书
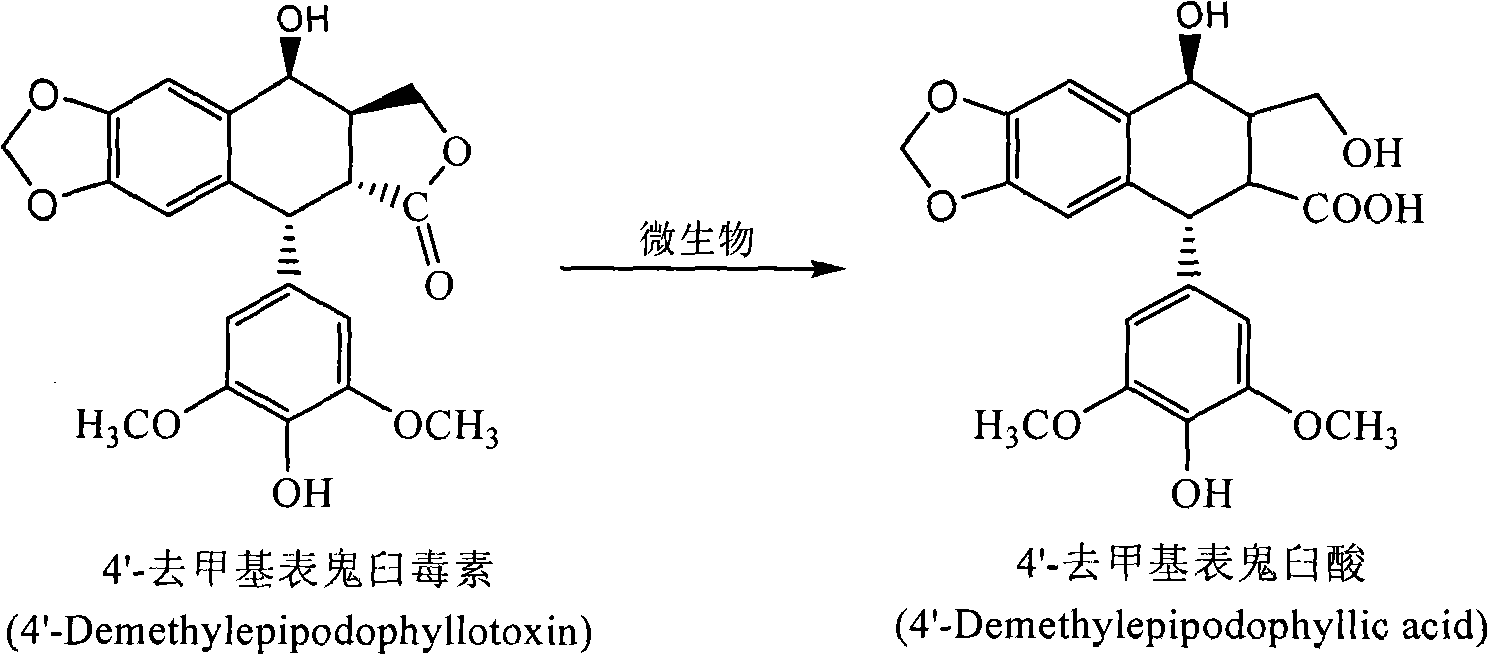
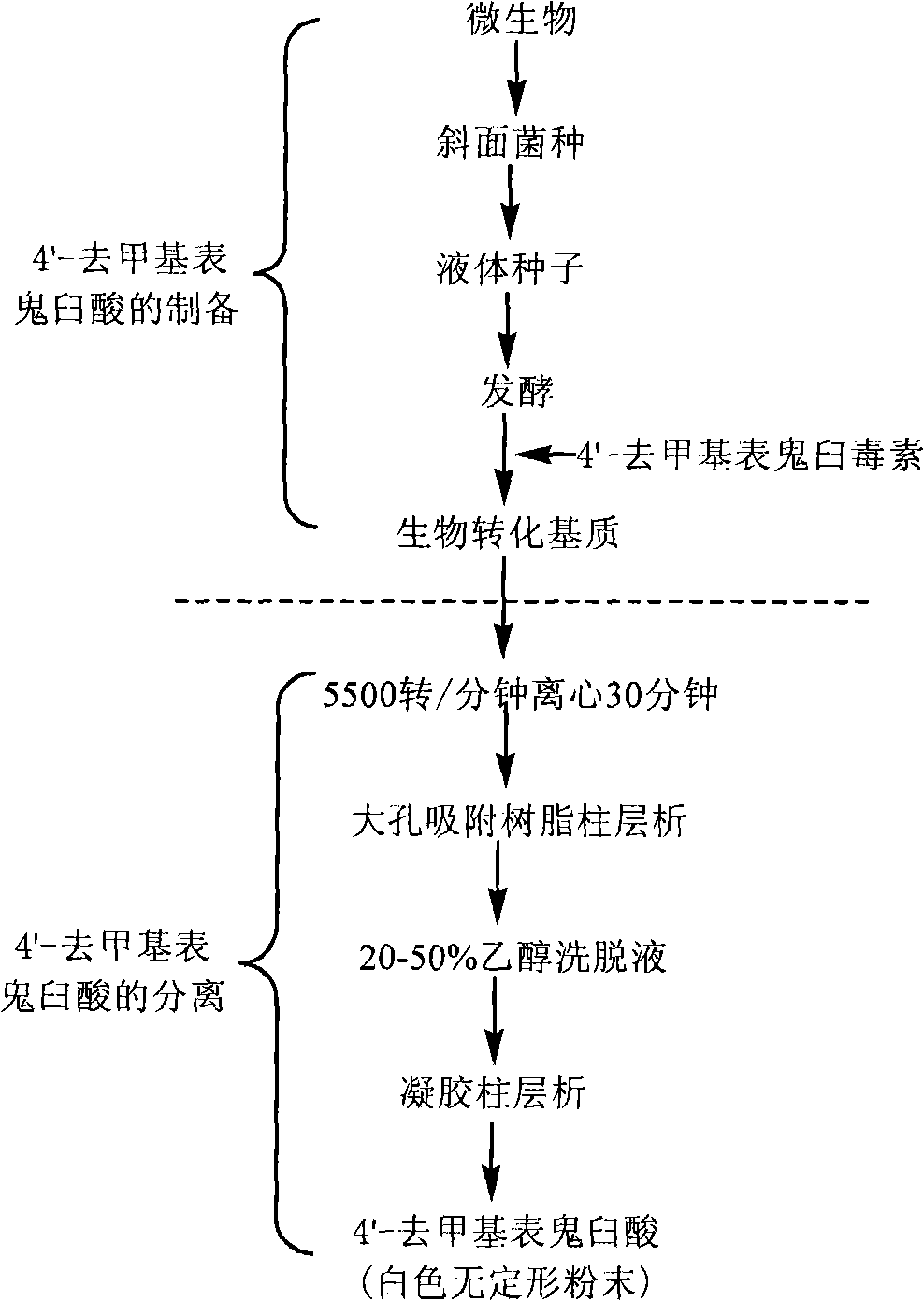
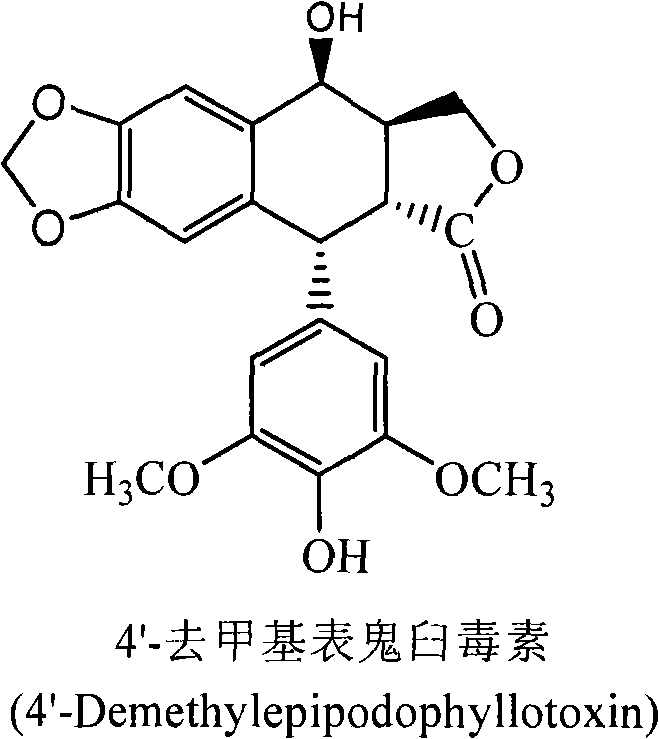
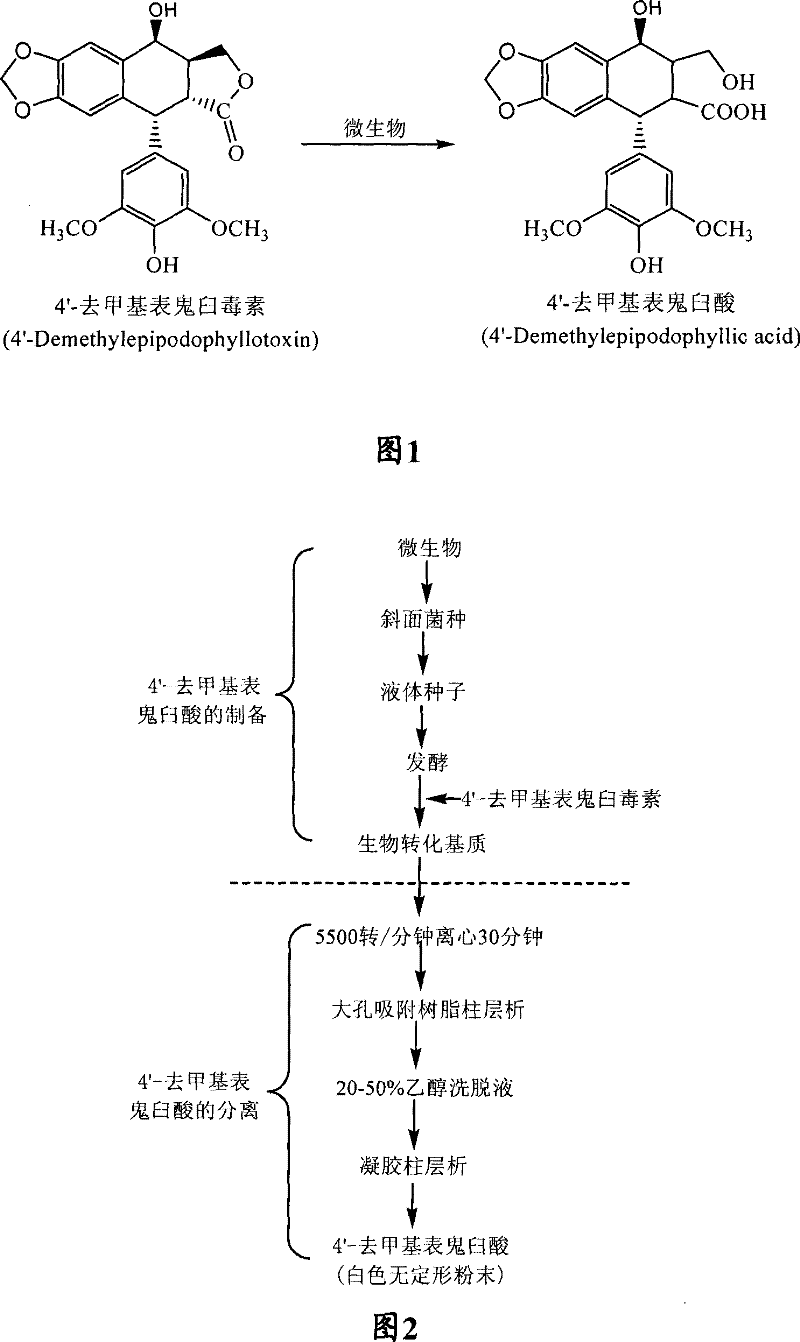
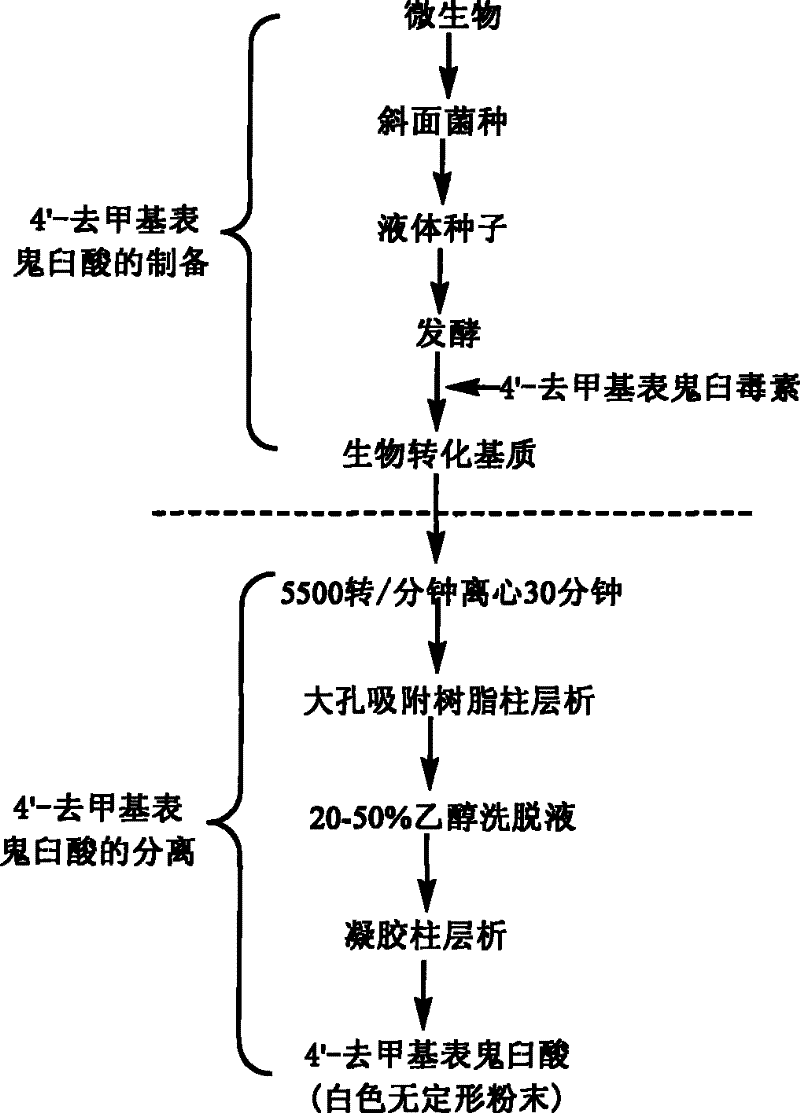
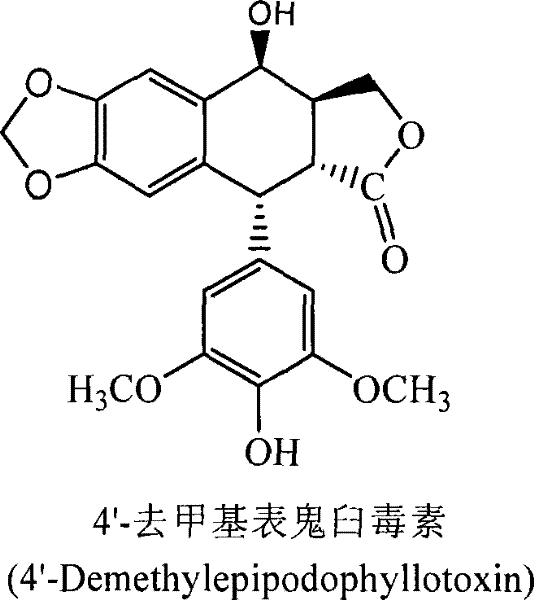
Process for the separation and preparation of 4'-demethyl podophyllic acid
InactiveCN101492703AHigh yieldMild reaction conditionsOrganic chemistryMicroorganism based processesPodophyllic acidErwinia uredovora
The invention discloses a method for converting 4'- demethylpodophyllotoxin to 4'- demethylation epipodophyllic acid, comprising the following steps: the 4'- demethylpodophyllotoxin solution is added during the fermentation process of microorganism clostridium, pseudomonas aeruginosa, rhodococcus erythropolis, corynebacterium pekinense, hay bacillus, erwinia uredovora, bacillus or bending pseudomonas for carrying out biotransformation reaction, thus obtaining biotransformation matrix with the 4'-demethylation epipodophyllic acid. The invention also discloses a method for separating the 4'-demethylation epipodophyllic acid from the biotransformation matrix, comprising the following steps: the macroporous absorbent resin column is adopted to carry out initial separation on the biotransformation matrix and gel column chromatography is adopted to carry out fine separation, thus obtaining 4'-demethylation epipodophyllic acid. In the invention, modification is carried out on the 4'- demethylpodophyllotoxin structure by biotransformation, thus obtaining 4'-demethylation epipodophyllic acid, in addition, the reaction selectivity is high, the operation is easy, the reaction conditions are moderate, the generated waste is little, the separation process is simple and the yield is high.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Phosphoserine phosphatase gene of coryneform bacteria
The present invention provides a DNA coding for a protein defined in the following (A) or (B) is obtained from Brevibacterium flavum chromosomal DNA library by cloning a DNA fragment that complicates serB deficiency of Escherichia coli as a open reading frame in the DNA fragment.(A) A protein which comprises an amino acid sequence of SEQ ID: 2 in Sequence Listing; or(B) A protein which comprises an amino acid sequence including substitution, deletion, insertion, addition or inversion of one or several amino acids in the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 2 in Sequence Listing, and which has phosphoserine phosphatase activity.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
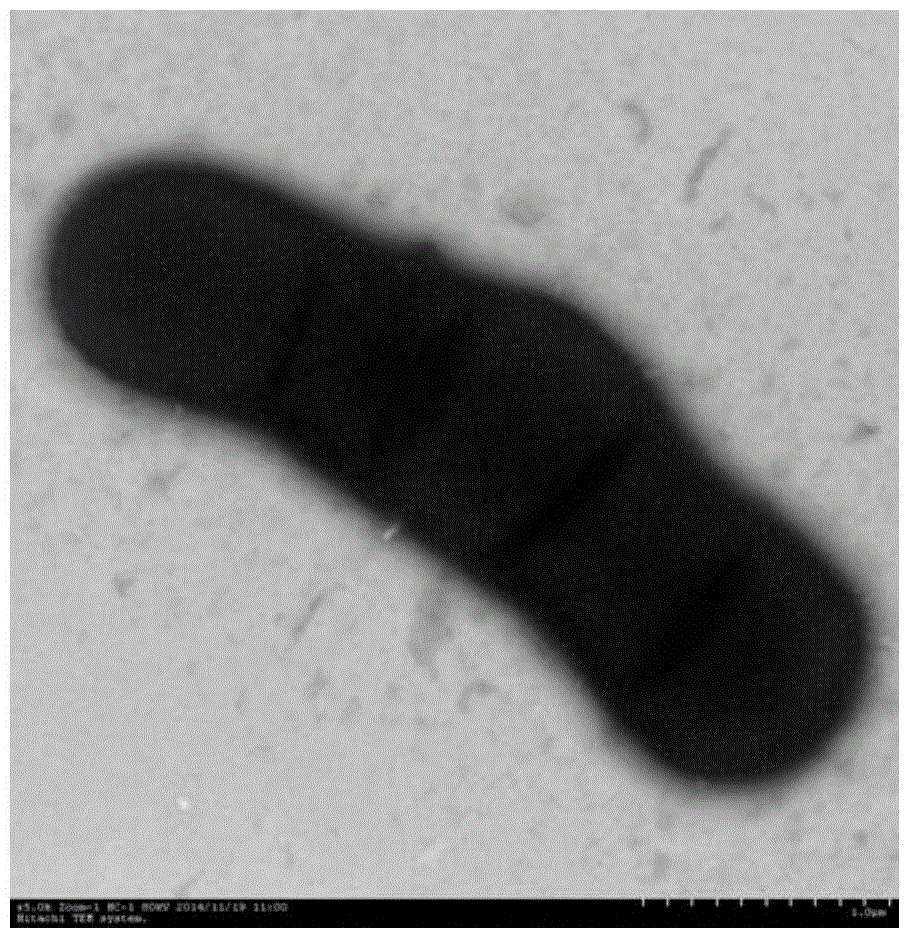
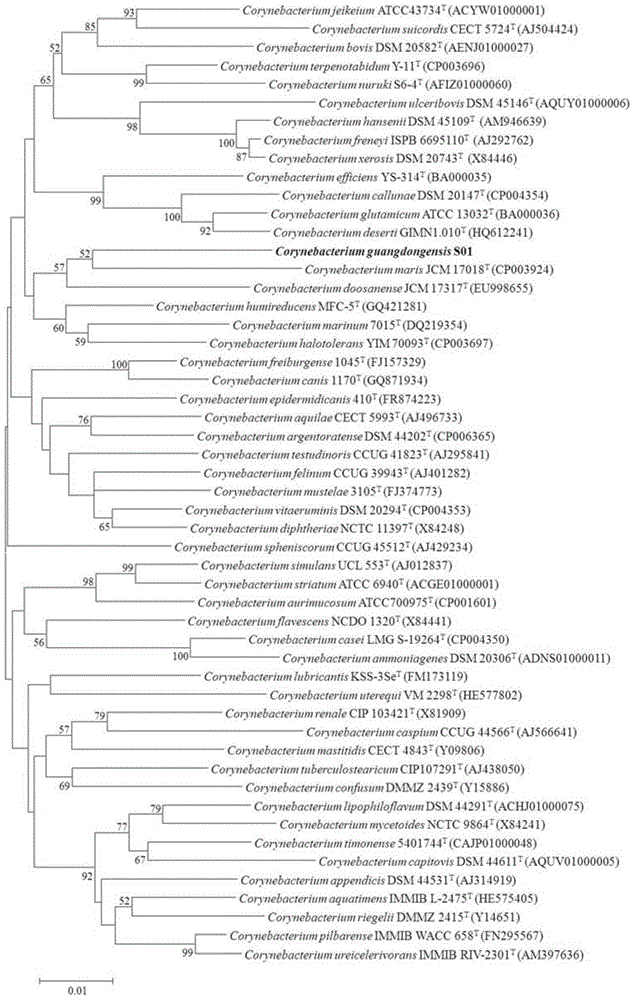
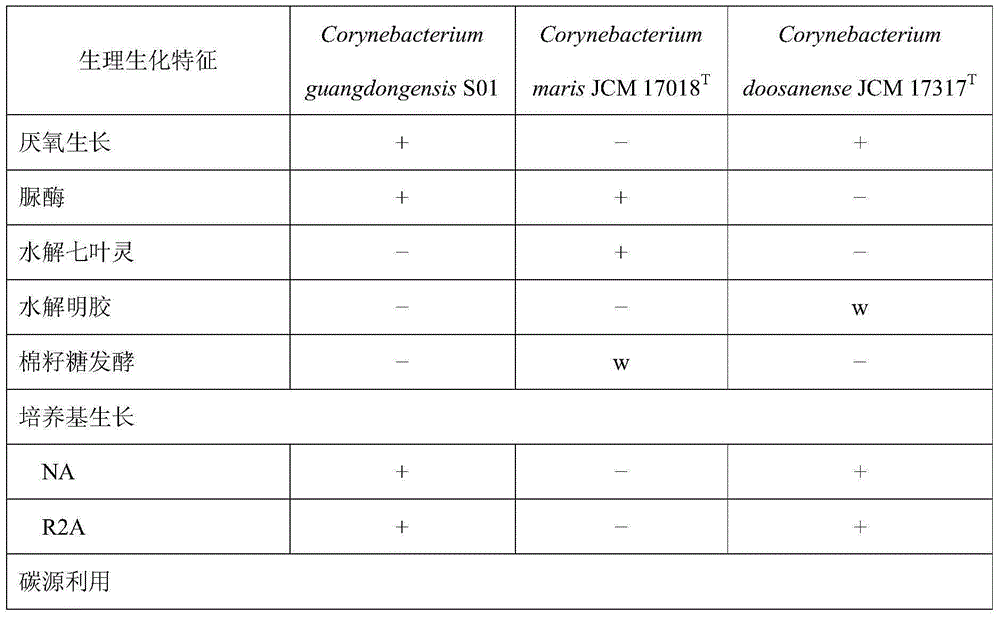
Corynebacterium guangdongensis producing various amino acids and application of Corynebacterium guangdongensis
The invention discloses Corynebacterium guangdongensis and application of the Corynebacterium guangdongensis. Corynebacterium guangdongensis is collected at China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), in the Institute of Microbiology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Chaoyang District of Beijing, China and under number of CGMCC No:11162. Corynebacterium guangdongensis S01 can produce 15 amino acids including aspartic acid, threonine, glutamic acid, glycine, alanine, cystine, valine, methionine, isoleucine, leucine, tyrosine, phenylalanine, lysine, histidine and arginine, thereby having important application value in developing amino acid products.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
Corynebacterium pekinense microbe adsorption agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104069823ASave raw materialsEasy to operateOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionPlastic materialsMicrobiology
The invention discloses a corynebacterium pekinense microbe adsorption agent for heavy metal treatment and a preparation method of the corynebacterium pekinense microbe adsorption agent. The adsorption agent is boned and formed with urethane foam plastic as a carrier, fermented corynebacterium pekinense remains as an adsorption agent and poval as a bonding agent. As the corynebacterium pekinense has good selective adsorptivity to Cd2+, the urethane foam plastic materials is used as a carrier material of the adsorption agent and the poval is used for bonding the urethane foam and microbe. Compared with the adsorption effect of direct microbe adsorption, the maximum adsorption amount for cadmium ions by the adsorption agent can reach 114mg / g; the microbe load effect is good and the adsorption agent can be directly used for heavy metal adsorption treatment; according to the preparation method, the technical process simple and operation is convenient; the microbe adsorption agent aiming at heavy metal ions treatment, particularly cadmium ions treatment, can be obtained and the adsorption agent and the preparation method have certain application prospects and market values.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Coryneform bacterium transformant and process for producing isobutanol using the same
ActiveUS8871478B2Improve efficiencyEasy to collectBacteriaBiofuelsIsobutanolCorynebacterium efficiens
A Corynebacterium glutamicum transformant having the capability of producing isobutanol and the following genes (1) to (5):(1) a gene which encodes an enzyme having acetohydroxy acid synthase activity;(2) a gene which encodes an enzyme having acetohydroxy acid isomeroreductase activity;(3) a gene which encodes an enzyme having dihydroxy acid dehydratase activity;(4) a gene which encodes an enzyme having 2-keto acid decarboxylase activity; and(5) a gene which encodes an enzyme having alcohol dehydrogenase activity,at least one of the genes being endogenous, and at least one of the genes being exogenous, efficiently produces isobutanol.
Owner:RES INST OF INNOVATIVE TECH FOR THE EARTH
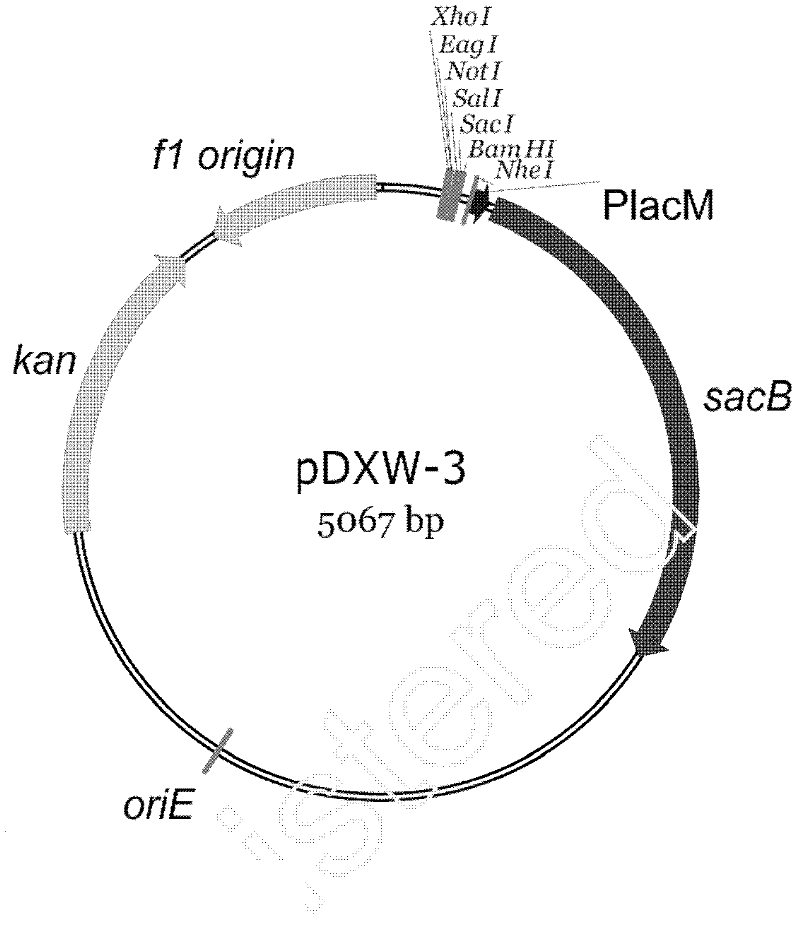
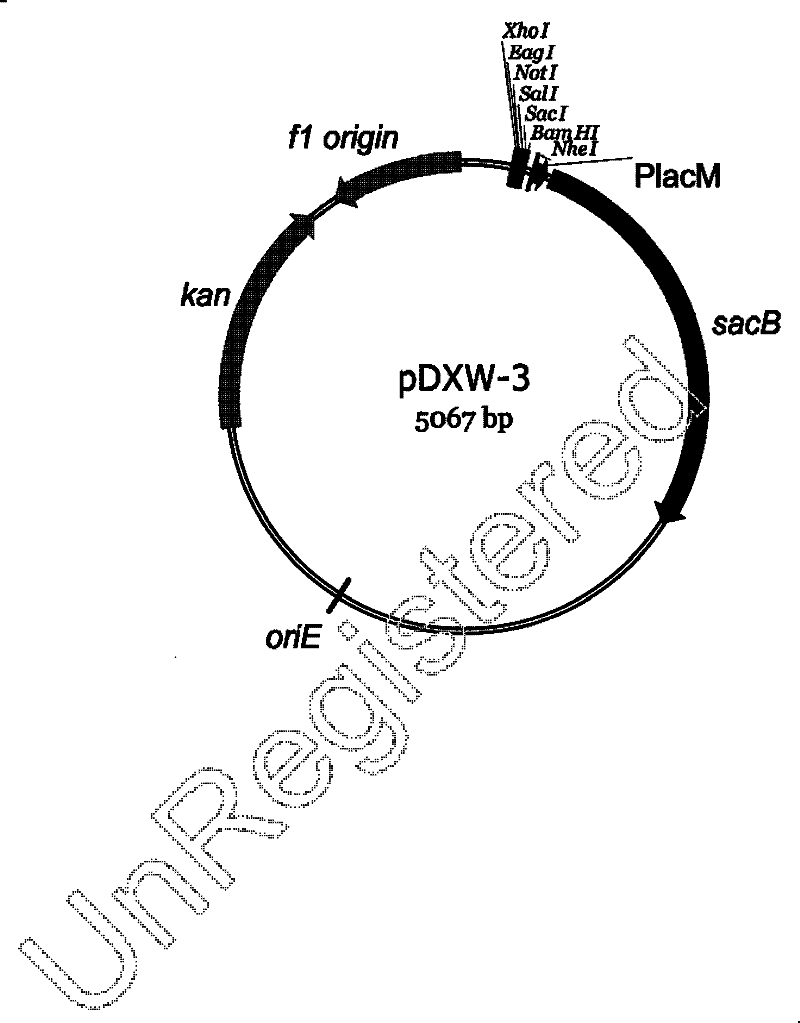
Modified sacB gene and derived integrated vector thereof
InactiveCN102329808AEfficient expressionReduce troubleMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliCorynebacterium efficiens
The invention discloses a modified sacB gene and a derived integrated vector thereof, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. The integrated vector contains a gene sacB, a resistance marker kanamycin marked resistance gene and a multi-cloning site (MCS), wherein the gene sacB is artificially synthesized and promoted by a strong promoter PlacM, can be well transcribed and expressed in corynebacteria and has conditional lethal function; and the resistance marker kanamycin marked resistance gene is used for corynebacteria transformant selection. The sacB has better expression under the strong promoter PlacM and the optimized SD; and moreover, because the promoter and sacR and SD sequences of the sacB are removed, colonies of sucrose resistance and antibiotic resistance are nearly not produced in application, and unnecessary trouble in application is greatly reduced. The vector can be duplicated and stabilized in escherichia coli, cannot be duplicated in the corynebacteria, and is suitable for knockout and substitution of corynebacteria chromogenes.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
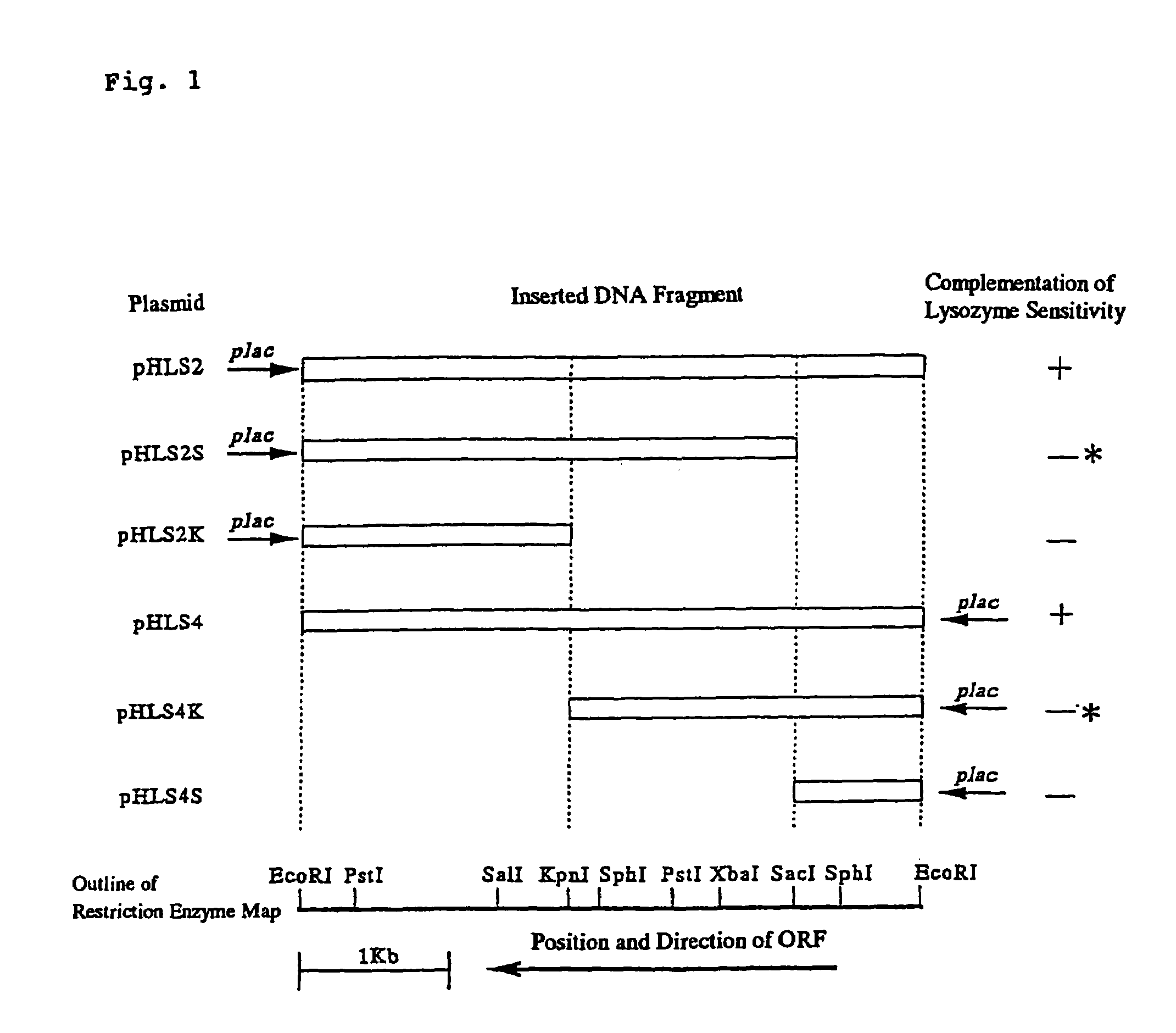
Gene conferring lysozyme insensitivity to Corynebacterium
InactiveUS7223587B2Improve productivityAvoid difficult choicesBacteriaDepsipeptidesBacteroidesCorynebacterium efficiens
The present invention relates to a protein having an activity of giving a lysozyme insensitivity to a lysozyme-sensitive microorganism belonging to Corynebacterium glutamicum; DNA which codes for the protein; a recombinant vector containing the DNA; a transformant obtained by introducing the recombinant vector into a host cell; a bacterium having a lysozyme sensitivity in which the activity of the protein is inactivated; and a method for producing an amino acid using the bacterium.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO BIO CO LTD
Corynebacterium pekinense and application thereof
Owner:新疆梅花氨基酸有限责任公司
High enzyme activity aspartokinase mutant, engineering bacteria and preparation method of the mutant
An aspartokinase mutant, an engineering bacterium and a preparation method of the mutant belong to the technical field of bioengineering. The high-enzyme activity aspartokinase mutant of the present invention is an exogenous aspartokinase whose amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 2 after 2-10, further 2-6, and further 2 A sequence formed by substitution, deletion or addition of ~3 amino acid residues, and has the function of aspartokinase. A sequence formed by substitution, deletion or addition of two amino acid residues is preferred, and it is particularly preferred to perform site-directed saturation mutations on amino acids at positions 372 and 379 in the amino acid sequence, and use a high-throughput screening method Selection of high enzymatic activity aspartokinase mutants. The present invention further utilizes the electroporation method to transfer the pEC-AK recombinant shuttle expression vector of the aspartokinase mutant with high enzyme activity and release or weaken Lys feedback inhibition into Corynebacterium Beijing, and finally obtain the recombinant Corynebacterium Beijing M372I ‑T379S engineering bacteria, and its fermentation product analysis.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Process for the separation and preparation of 4'-demethyl podophyllic acid
InactiveCN101492703BHigh yieldLow toxicityOrganic chemistryMicroorganism based processesErwinia uredovoraPodophyllic acid
The invention discloses a method for converting 4'- demethylpodophyllotoxin to 4'- demethylation epipodophyllic acid, comprising the following steps: the 4'- demethylpodophyllotoxin solution is added during the fermentation process of microorganism clostridium, pseudomonas aeruginosa, rhodococcus erythropolis, corynebacterium pekinense, hay bacillus, erwinia uredovora, bacillus or bending pseudomonas for carrying out biotransformation reaction, thus obtaining biotransformation matrix with the 4'-demethylation epipodophyllic acid. The invention also discloses a method for separating the 4'-demethylation epipodophyllic acid from the biotransformation matrix, comprising the following steps: the macroporous absorbent resin column is adopted to carry out initial separation on the biotransformation matrix and gel column chromatography is adopted to carry out fine separation, thus obtaining 4'-demethylation epipodophyllic acid. In the invention, modification is carried out on the 4'- demethylpodophyllotoxin structure by biotransformation, thus obtaining 4'-demethylation epipodophyllic acid, in addition, the reaction selectivity is high, the operation is easy, the reaction conditions are moderate, the generated waste is little, the separation process is simple and the yield is high.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Corynebacterium for producing l-lysine by fermentation
A method for producing L-lysine by fermentation, comprising modifying a gene for coding an NCBI reference sequence NP_601029.1 and / or NP_599350.1 on a Corynebacterium bacterial chromosome to enable the activity and / or expression quantity of NP_601029.1 and / or NP_599350.1 to be reduced; replacing a promoter of one or more genes on the Corynebacterium bacterial chromosome with a EP5 promoter, and fermenting bacteria obtained by modification to produce L-lysine. Also provided are methods and applications derived from the method, and bacteria and promoter that can used in the methods and the applications.
Owner:NINGXIA EPPEN BIOTECH
Genes for heat resistant enzymes of amino acid biosynthetic pathway derived from thermophilic coryneform bacteria
InactiveUS20050176127A1Improve productivityIncrease volumeSugar derivativesBacteriaCorynebacterium efficiensCorynebacterium crenatum
A plurality of primer sets are designed based on a region where conservation at the amino acid level is observed among various microorganisms for known gene sequences corresponding to a gene coding for an enzyme of the L-amino acid biosynthetic pathway derived from Corynebacterium thermoaminogenes, preferably an enzyme that functions at a higher temperature compared with that of Corynebacterium glutamicum. PCR is performed by using the primers and chromosomal DNA of Corynebacterium thermoaminogenes as a template. The primers with which an amplification fragment has been obtained are used as primers for screening to select a clone containing a target DNA fragment from a plasmid library of chromosomal DNA of Corynebacterium thermoaminogenes.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
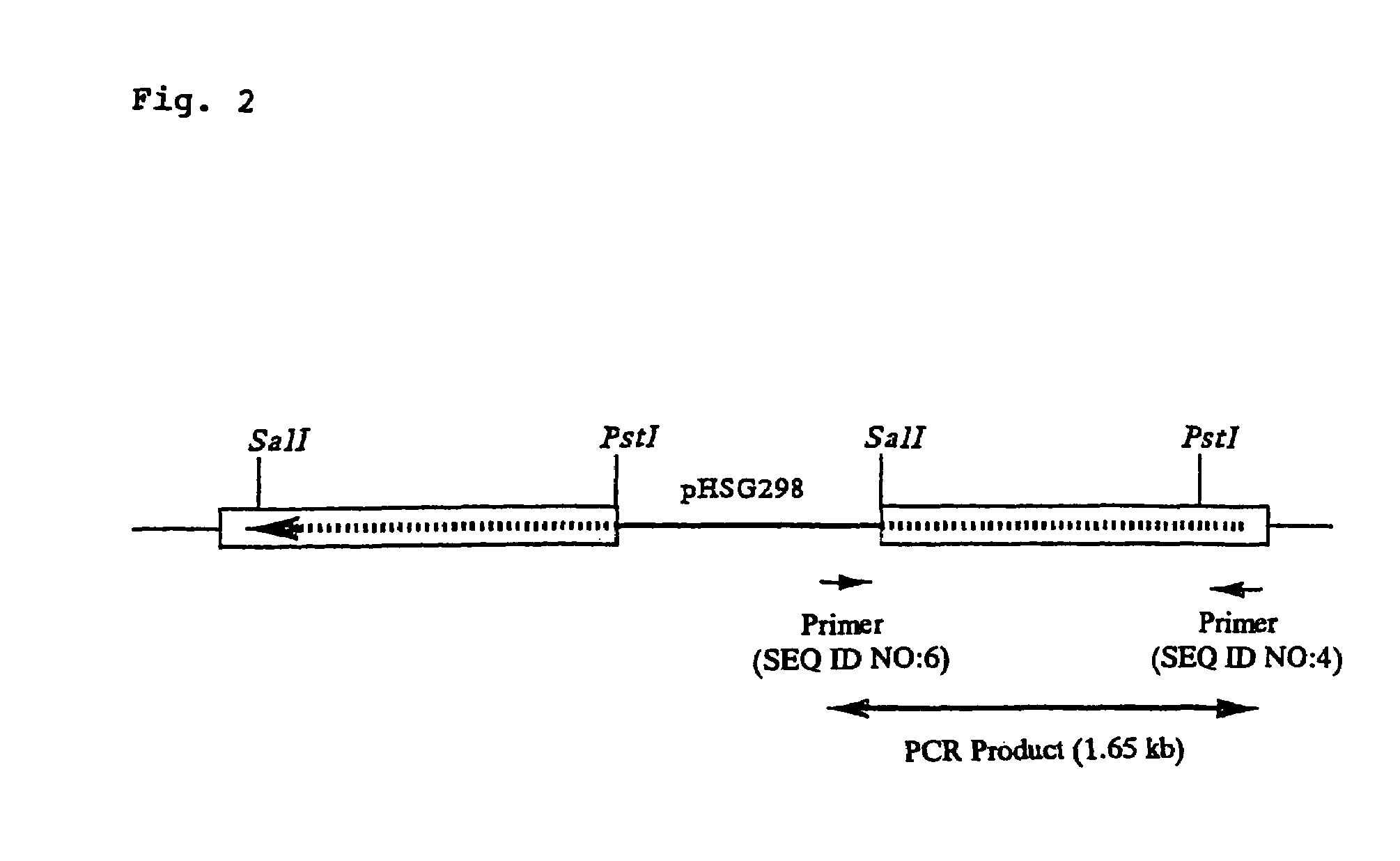
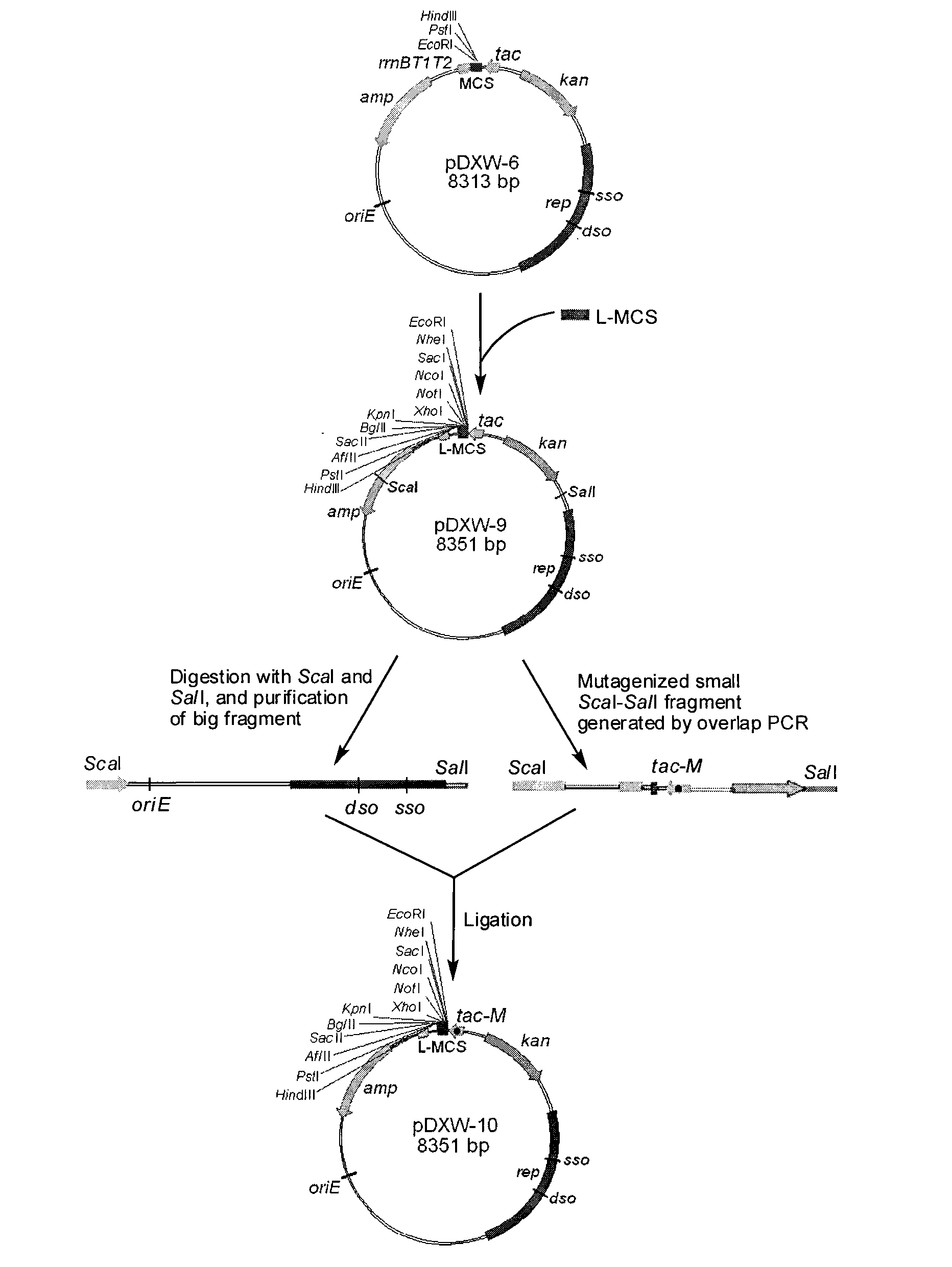
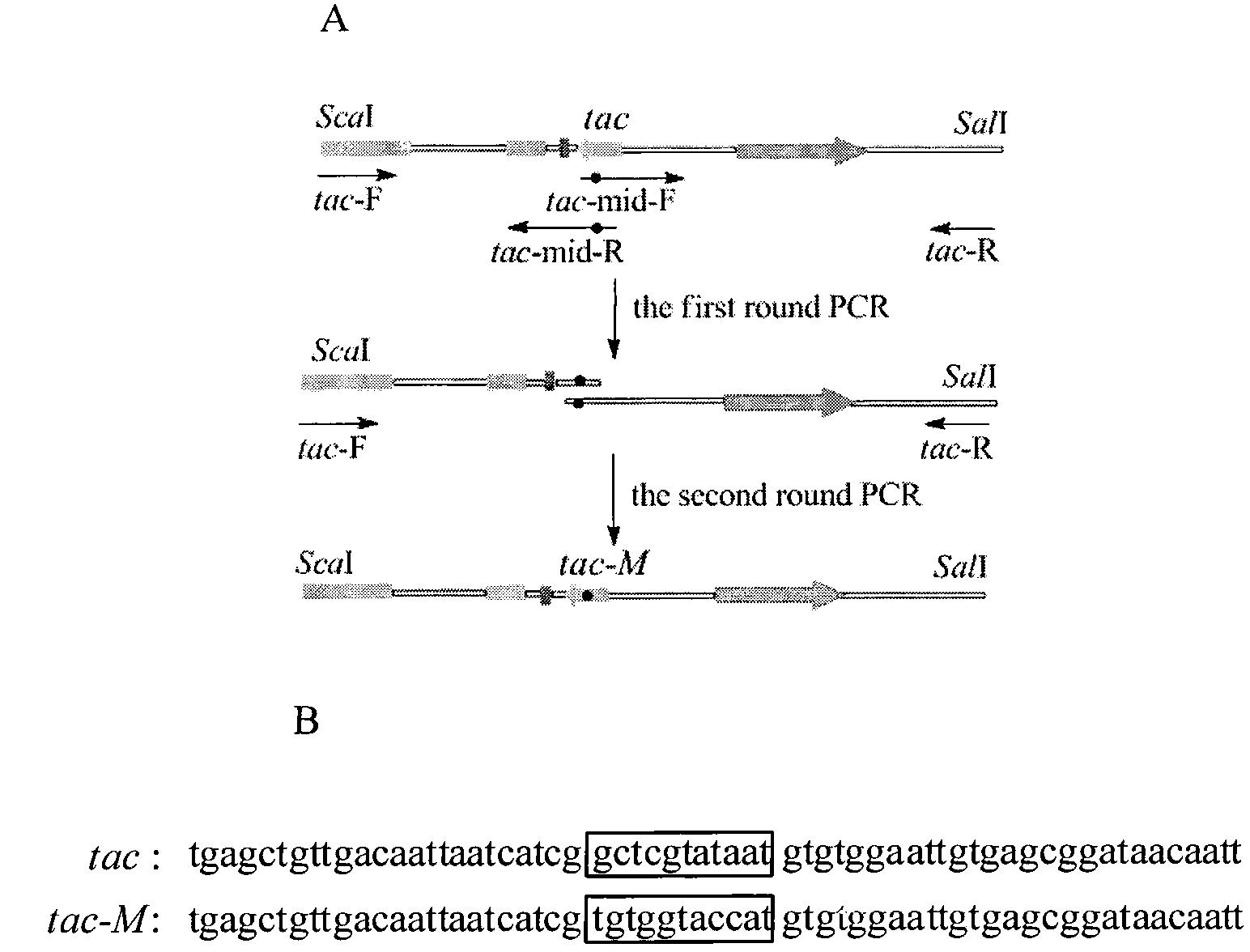
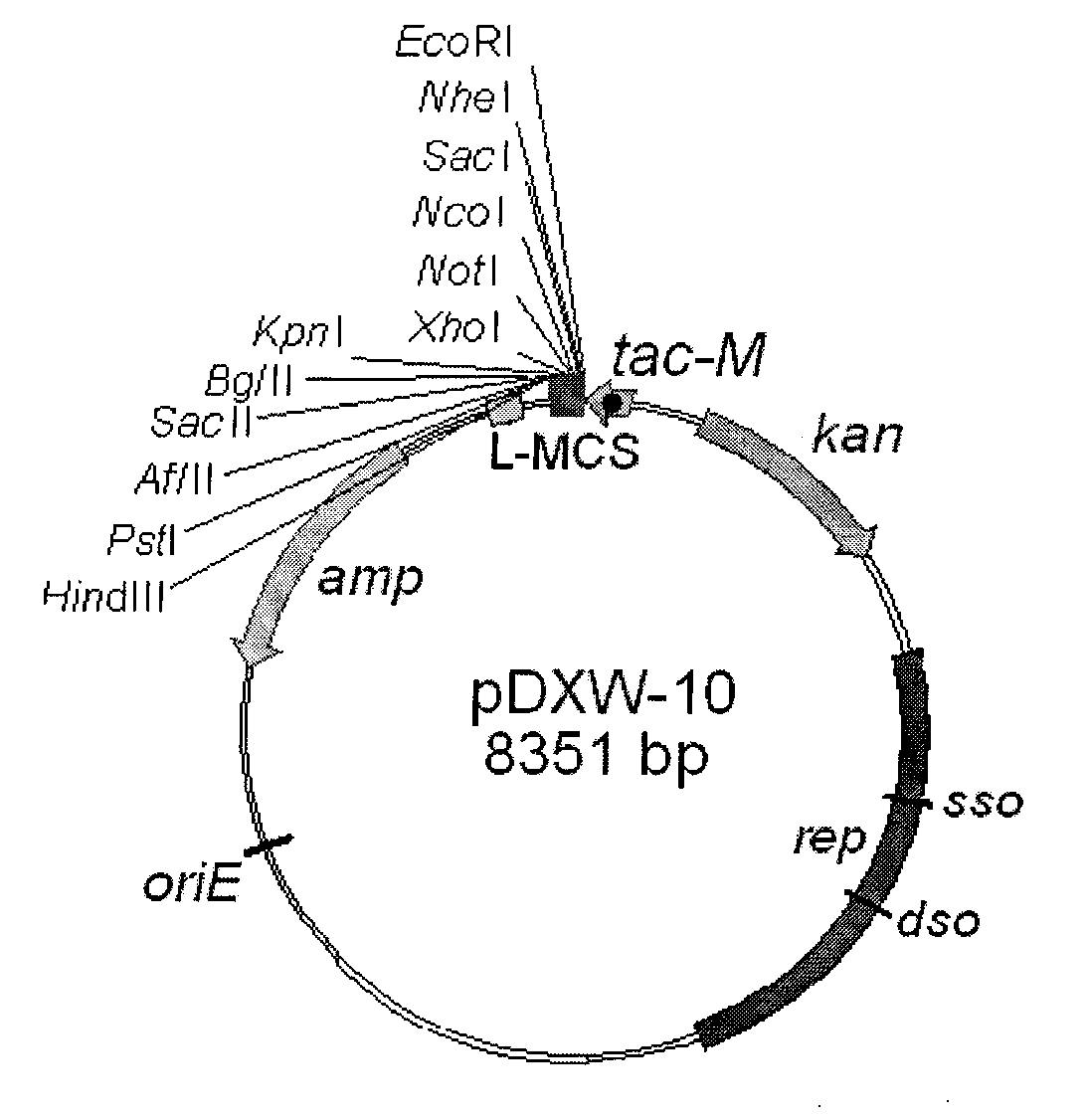
Colibacillus-corynebacterium shuttle constitutive expression carrier and construction method thereof
ActiveCN101838663BEffective cloningVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliKanamycin
The invention relates to a colibacillus-corynebacterium shuttle constitutive expression carrier and a construction method thereof, which belong to the technical field of gene engineering. In the invention, the expression carrier pDXW-10 can be reproduced in colibacillus and corynebacterium, exists in the colibacillus and the corynebacterium stably and contains a tac-M promoter with a transcription initiation function and a terminator rrnBT1T2 with a transcription termination function in both the colibacillus and the corynebacterium; the expression carrier pDXW-10 contains a resistance gene for marking resistance marking kanamycin used for selecting a corynebacterium transformant; and the expression carrier pDXW-10 contains multiple cloning sites L-MCS containing 11 single restriction enzyme tangent points. In the corynebacterium, the carrier has moderate level for expressing foreign proteins and is especially suitable for the research of the metabolic engineering of the corynebacterium.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Corynebacterium pekinense and application thereof
Owner:新疆梅花氨基酸有限责任公司
A method for producing l-isoleucine
ActiveCN108841884BImprove acid production performanceMeet the needs of industrial productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyMicrobiology
The invention discloses a method for producing L-isoleucine, which belongs to the technical field of microbial fermentation. The present invention uses Brevibacterium lactose fermentum ( Brevibacterium lactofermentation ) as an L‑isoleucine producing strain, Brevibacterium lactofermentum ( Brevibacterium lactofermentation ) and Corynebacterium Beijing ( Corynebacterium pekinense ) for co-cultivation, making Brevibacterium lactose fermenterum ( Brevibacterium lactofermentation )’s acid production ability has been significantly improved from 13g / L to 21g / L, which can meet the needs of industrial production.
Owner:WUXI JINGHAI AMINO ACID
A kind of Corynebacterium beijing microbial adsorbent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104069823BImprove the phenomenon of a small amount of peelingEfficient separationOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a Beijing corynebacterium microbial adsorbent for heavy metal treatment and a preparation method thereof. Polyurethane foam is used as the carrier, the fermented Corynebacterium Beijing residue is used as the adsorbent, and polyvinyl alcohol is used as the binder to bond and form. Corynebacterium Beijing has good selective adsorption to Cd2+, polyurethane foam is used as the adsorbent carrier material, and polyvinyl alcohol is used to bond polyurethane foam and microorganisms. Compared with the direct use of microorganisms, the adsorbent can adsorb cadmium ions The highest value reaches 114mg / g, and the microbial loading effect is good, so it can be directly used for heavy metal adsorption treatment. The technical process of the invention is simple, the operation is simple and convenient, and the available microbial adsorbent for treating heavy metal ions, especially cadmium ions, has certain application prospects and market value.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Synergistic agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103011991BIncrease profitPollution controlFertilizer mixturesCopper sulfateAmmonium Hydrogen Carbonate
The invention discloses a synergistic agent and a preparation method thereof, wherein the synergistic agent comprises the following raw materials according to proportion by weight: 70.8-87.5 parts of stone potassium, 3-8 parts of polyaspartic acid, 3-8 parts of maleic anhydride, 0.3-0.5 parts of azone, 5-10 parts of urea or ammonium hydrogen carbonate, 0.4-0.7 parts of d bacteria liquid, 0.3-0.8 parts of EDTA (Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid) and 0.2-0.5 parts of n-butyl alcohol. The preparation method of the stone potassium comprises the following steps: respectively crashing 50 parts of zeolite ore, 20 parts of phosphorite and 30 parts of leopoldite into 100-200 meshes and then uniformly mixing so as to obtain a mixture; taking 73.5-87.3 parts of mixture, 2-4 parts of urea, 2-5 parts of phosphorus pentoxide, 1-2 parts of potassium sulfate, 0.2-0.5 parts of ammonium molybdate or sodium molybdate, 1-2 parts of manganous sulfate, 3-6 parts of ferrous sulfate, 1-2 parts of zinc sulfate, 1-2 parts of sodium borate, 0.5-1 parts of copper sulfate and 1-2 parts of fulvic acid; and stirring and sealing up for keeping standby. The preparation method of the bacteria liquid comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing colon bacillus, Fusarium moniliforme, Corynebacterium pekinense, Streptomyces jingyangensis, Bacillus megatherium, Bacillus mucilaginosus and Streptomyces according to a proportion of 0.5%: 0.5%: 0.5%: 0.5%: 0.5%: 0.5%: 0.5%. The synergistic agent is multipurpose, nutritious, low in cost, non-toxic, nuisanceless and free of residue.
Owner:冷登书
Method for converting podophyllinic acid lactone into podophyllic acid and picropodophyllin
InactiveCN101492704BHigh yieldLow toxicityOrganic chemistryMicroorganism based processesErwinia uredovoraPodophyllic acid
The invention discloses a method for converting podophyllotoxin to podophyllic acid and picropodophyllin, comprising the following steps: the substrate podophyllotoxin solution is added during the fermentation process of microorganism pseudomonas aeruginosa, bacillus, rhodococcus erythropolis, clostridium, corynebacterium pekinense, hay bacillus, erwinia uredovora or bending pseudomonas for carrying out biotransformation reaction, thus obtaining biotransformation matrix with the podophyllic acid and picropodophyllin. The invention also discloses a method for separating the podophyllic acid and picropodophyllin from the obtained biotransformation matrix, comprising the following steps: the macroporous absorbent resin column is adopted to carry out initial separation on the biotransformation matrix and gel column chromatography is adopted to carry out fine separation, thus respectively obtaining the picropodophyllin and the podophyllic acid. In the invention, modification is carried outon the picropodophyllin structure by microbiological transformation, thus obtaining the picropodophyllin and the podophyllic acid, in addition, the conversion rate of the substrate is high, the operation is easy, the reaction conditions are moderate, the generated waste is little, the separation process is simple and the yield is high.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Corynebacterium pekinense and application thereof
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms and discloses Corynebacterium pekinense with the preservation number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.5924. The Corynebacterium pekinense MHZ-0911 with the preservation number of CGMCC No.5924 takes wild type Corynebacterium pekinense CICC (China Center of Industrial Culture Collection) 21721 as an initial strain and is obtained by inducing through a chemical mutagen and screening through a culture medium containing streptomycin. According to the Corynebacterium pekinense, the yield of lactic acid in the fermentation process can be greatly reduced, in particular in the fermentation process of L-lysine, and thus the inhibition of the lactic acid is improved and the generation of final metabolite is facilitated. Therefore, the Corynebacterium pekinense with the preservation number of CGMCC No.5924 can be widely applied to the reduction of the generation of the lactic acid in the fermentation process.
Owner:吉林梅花氨基酸有限责任公司
Corynebacterium pekinense and application thereof
Owner:吉林梅花氨基酸有限责任公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com