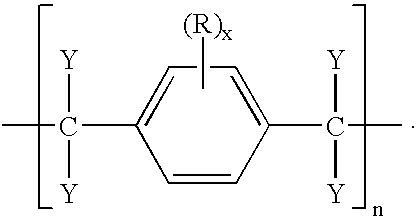
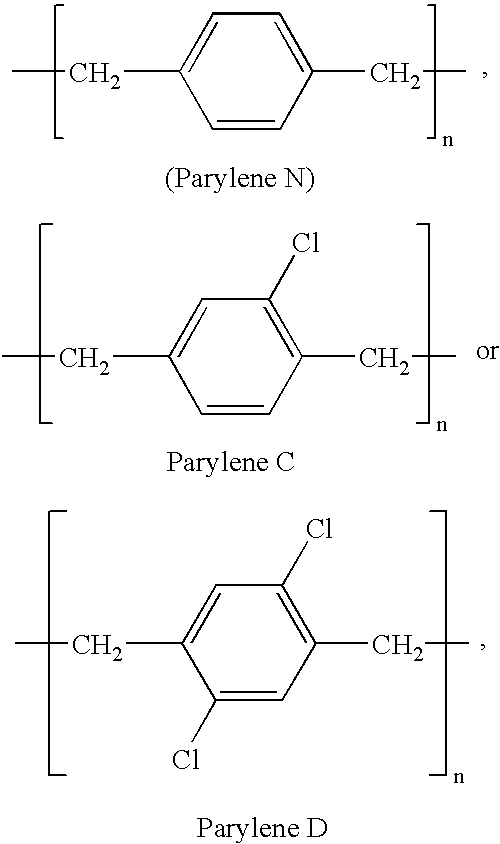
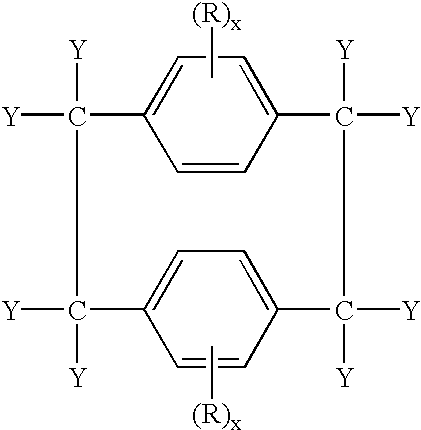
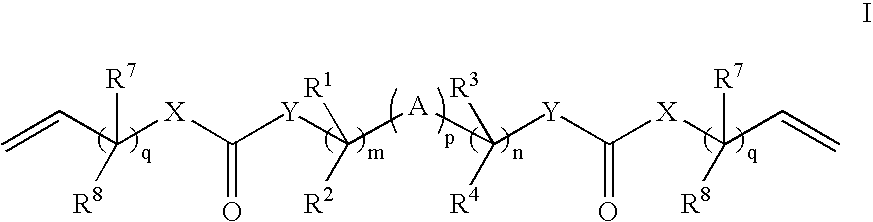
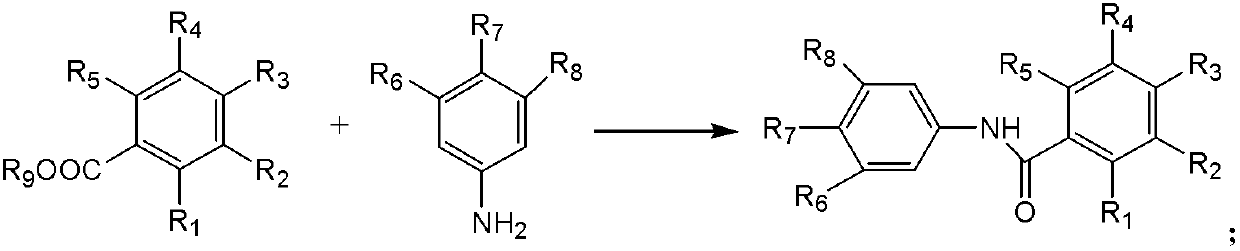
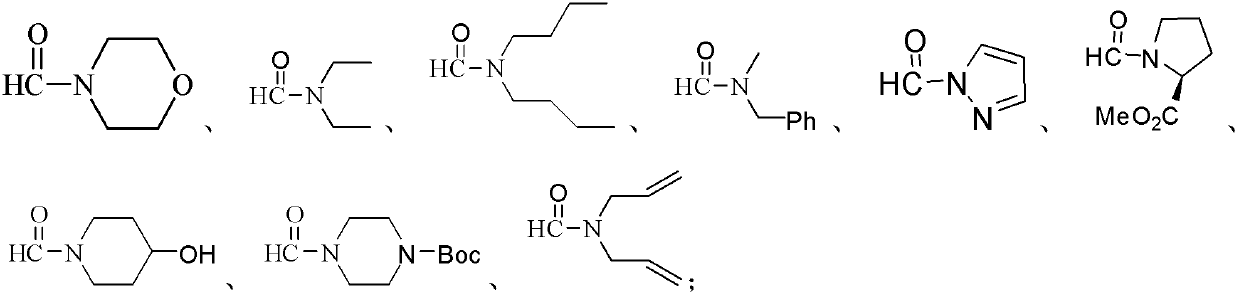
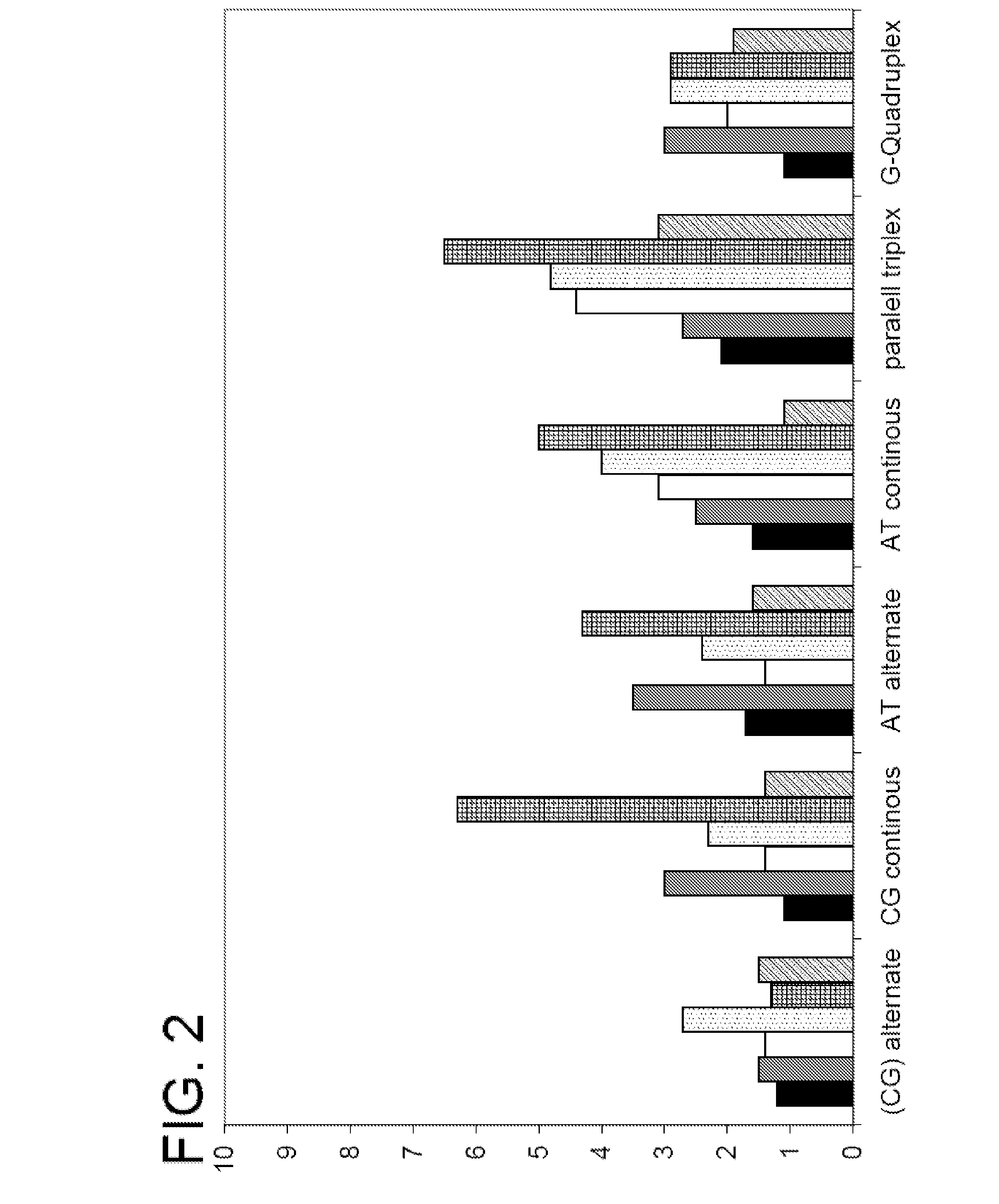
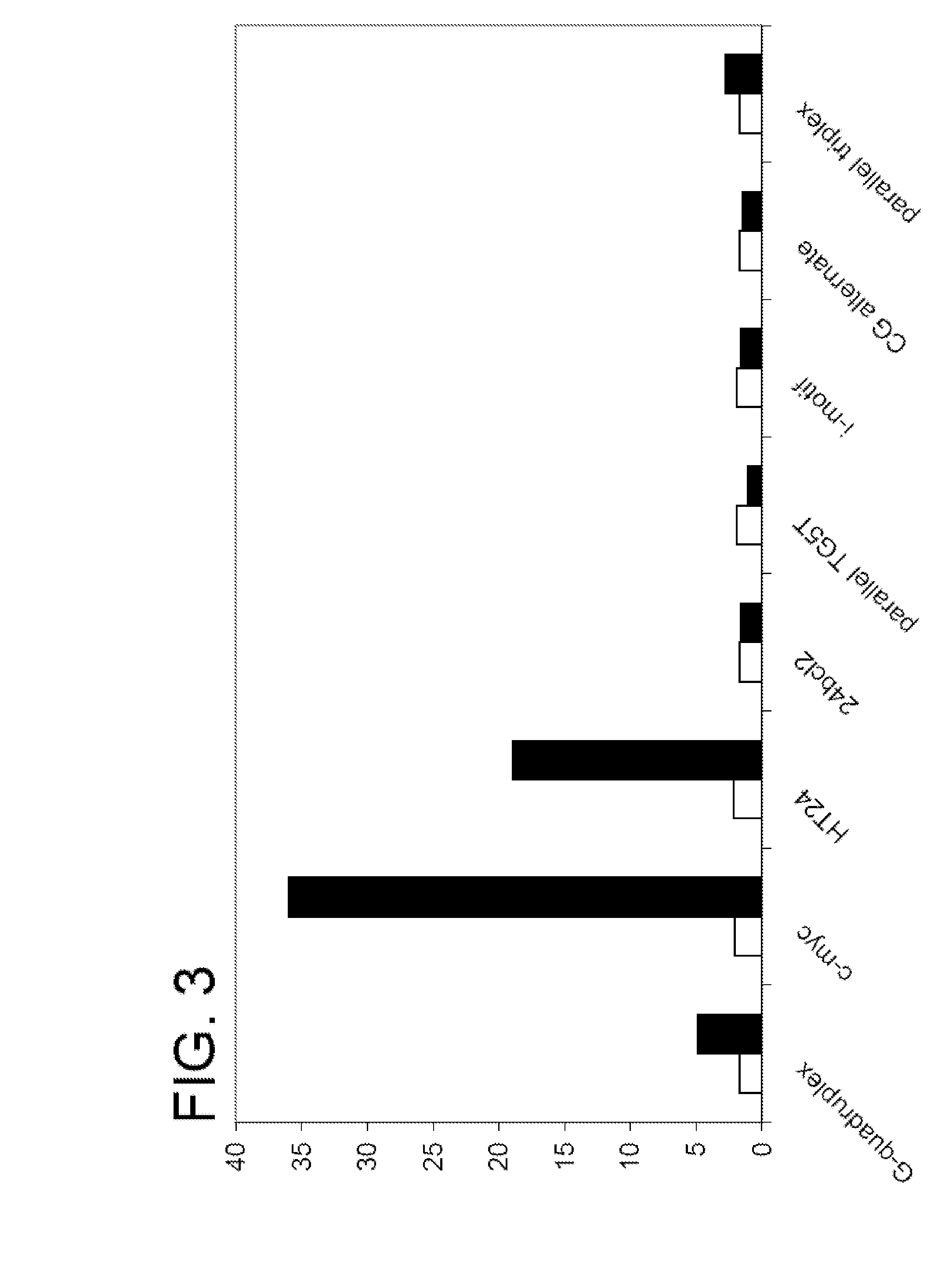
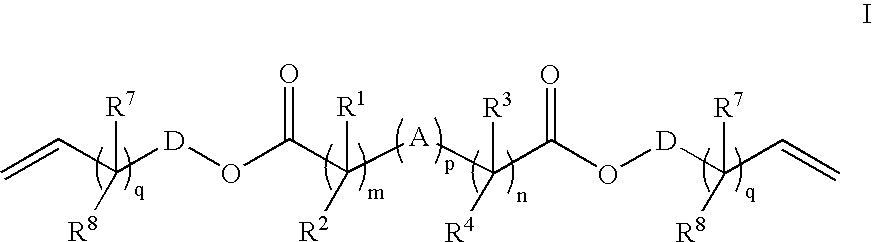
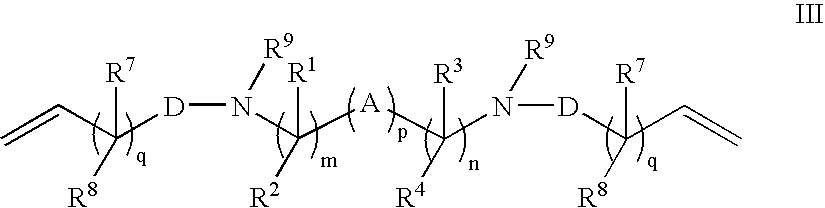
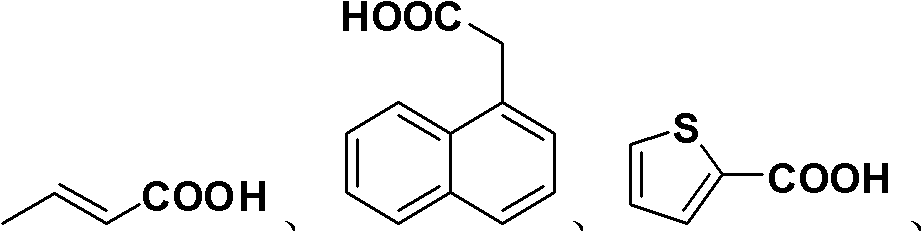
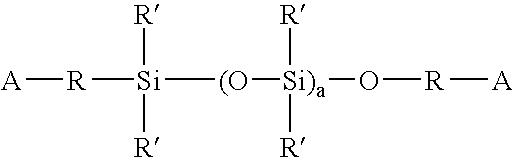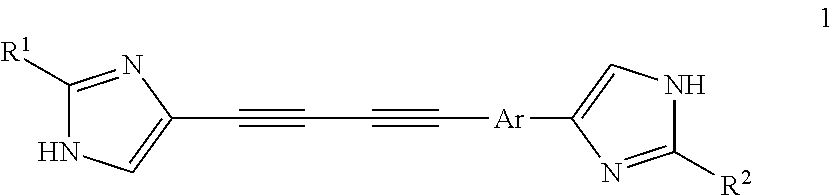Patents
Literature
44 results about "Diradical" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A diradical in organic chemistry is a molecular species with two electrons occupying degenerate molecular orbitals (MO). The term "diradical" is mainly used to describe organic compounds, where most diradical are extremely reactive and in fact rarely isolated. Diradicals are even-electron molecules but have one fewer bond than the number permitted by the octet rule.
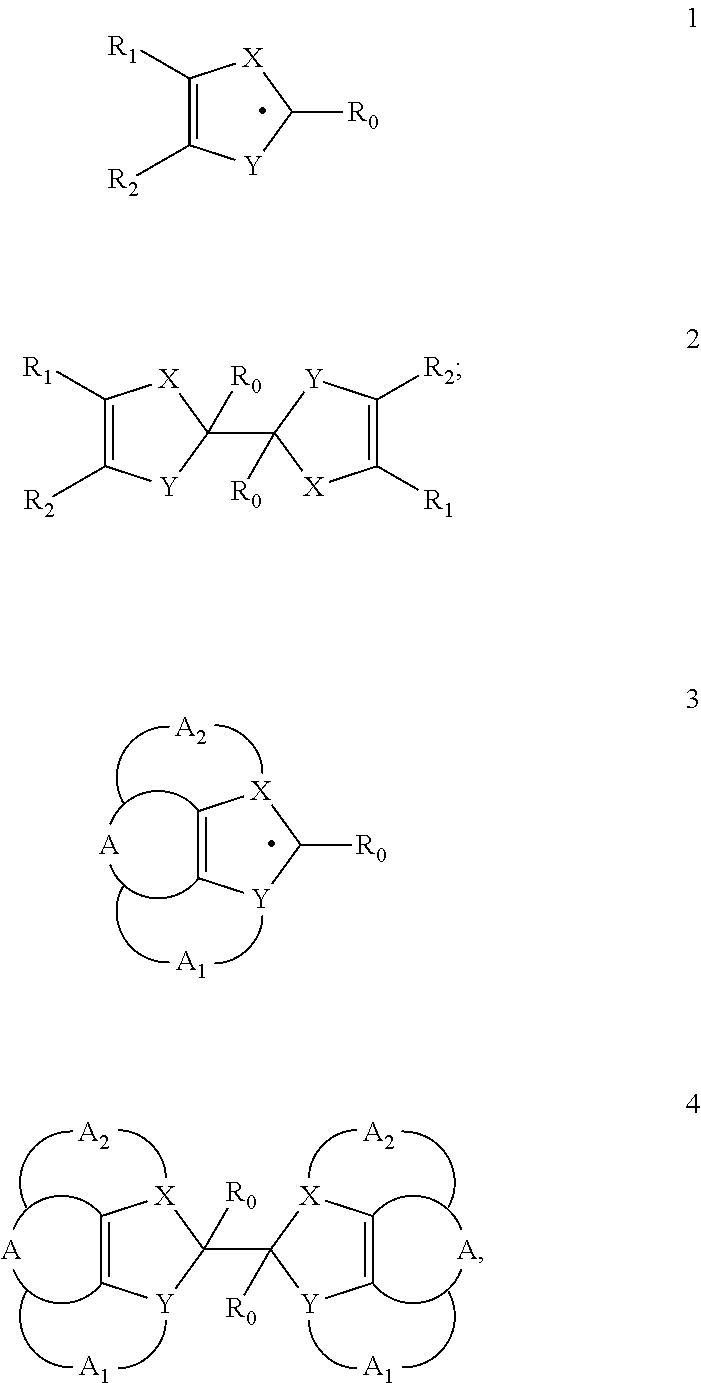
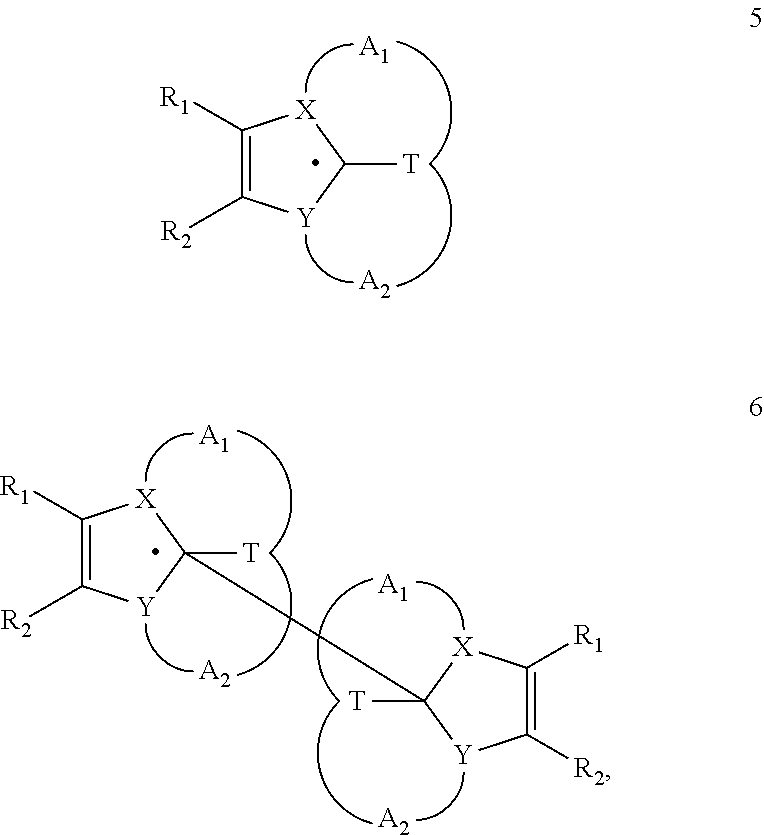
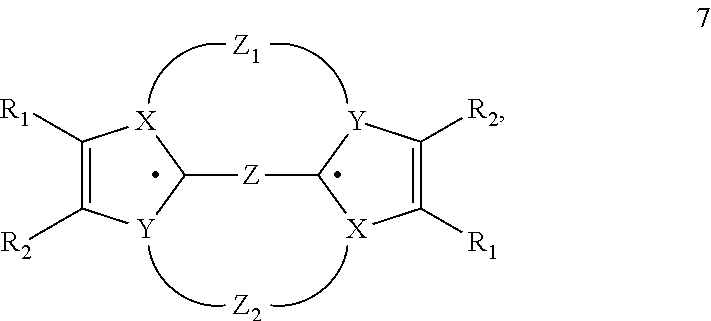
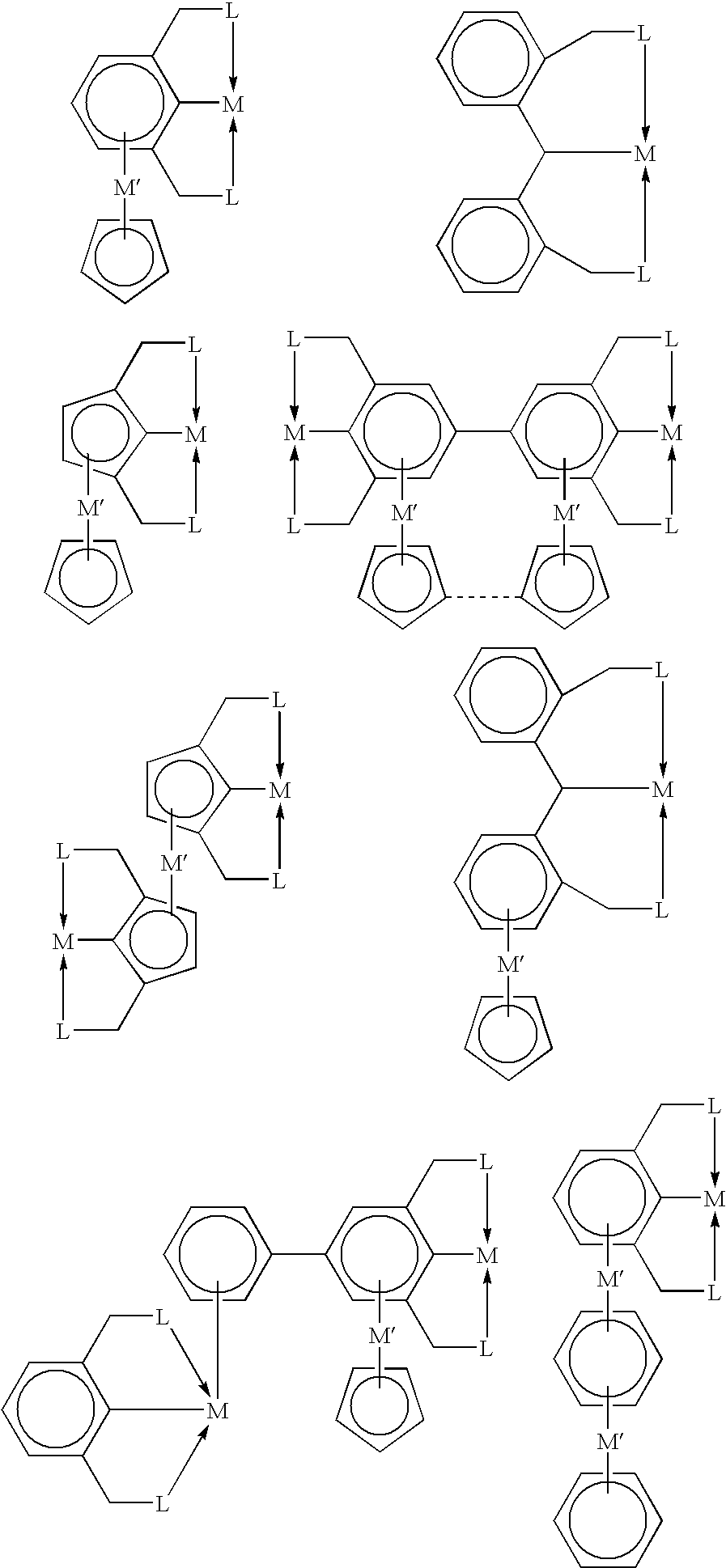
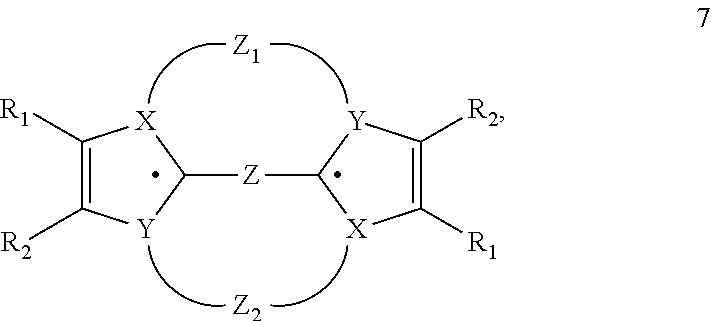
Heterocyclic Radical or Diradical, The Dimers, Oligomers, Polymers, Dispiro Compounds and Polycycles Thereof, the Use Thereof, Organic Semiconductive Material and Electronic or Optoelectronic Component
ActiveUS20120146012A1Improve stabilityOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesOligomerOrganic semiconductor
Owner:NOVALED GMBH
Alkane and alkane group dehydrogenation with organometallic catalysts
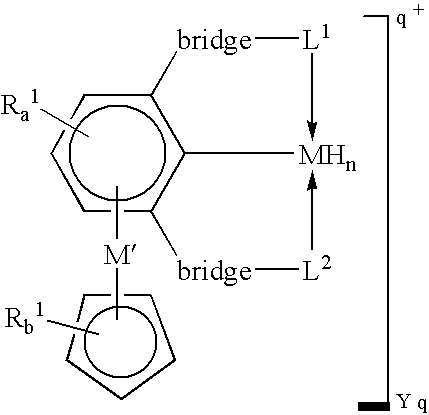
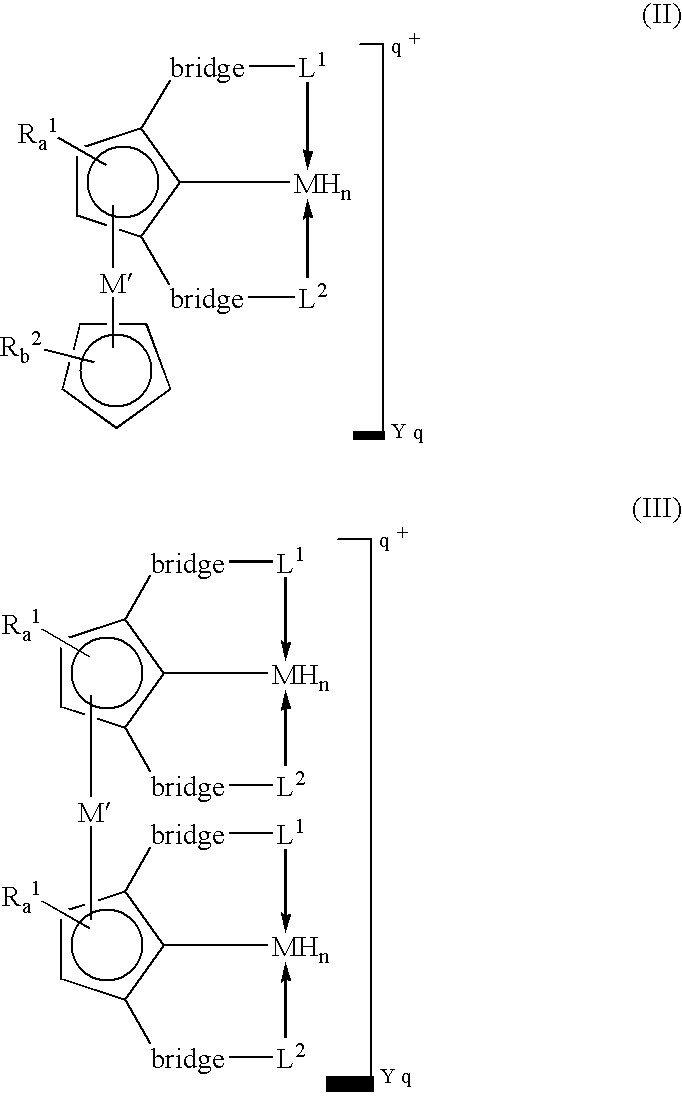
Novel polynuclear organometallic complexes useful as catalysts for the reversible deshydrogenation of alkanes and alkane group are disclosed. The novel compounds comprise a first transition, a second transition metal p-bonded to an ?5-aromatic ligand, and a pincer ligand. The pincer ligand comprises a 6p-electron aromatic ring having at least 2 ring atoms in an 1, 3 relationship bonded each to a neutral Lewis base through a bridge, the bridge being a diradical. The pincer ligand binds the first transition metal through each of the Lewis bases and through the ring atom adjacent to both Lewis bases and p-coordinates the second transition metal through all aromatic ring atoms. The first transition metal may also bond to 2 or 4 hydrogen atoms.
Owner:POWERNOVA TECH
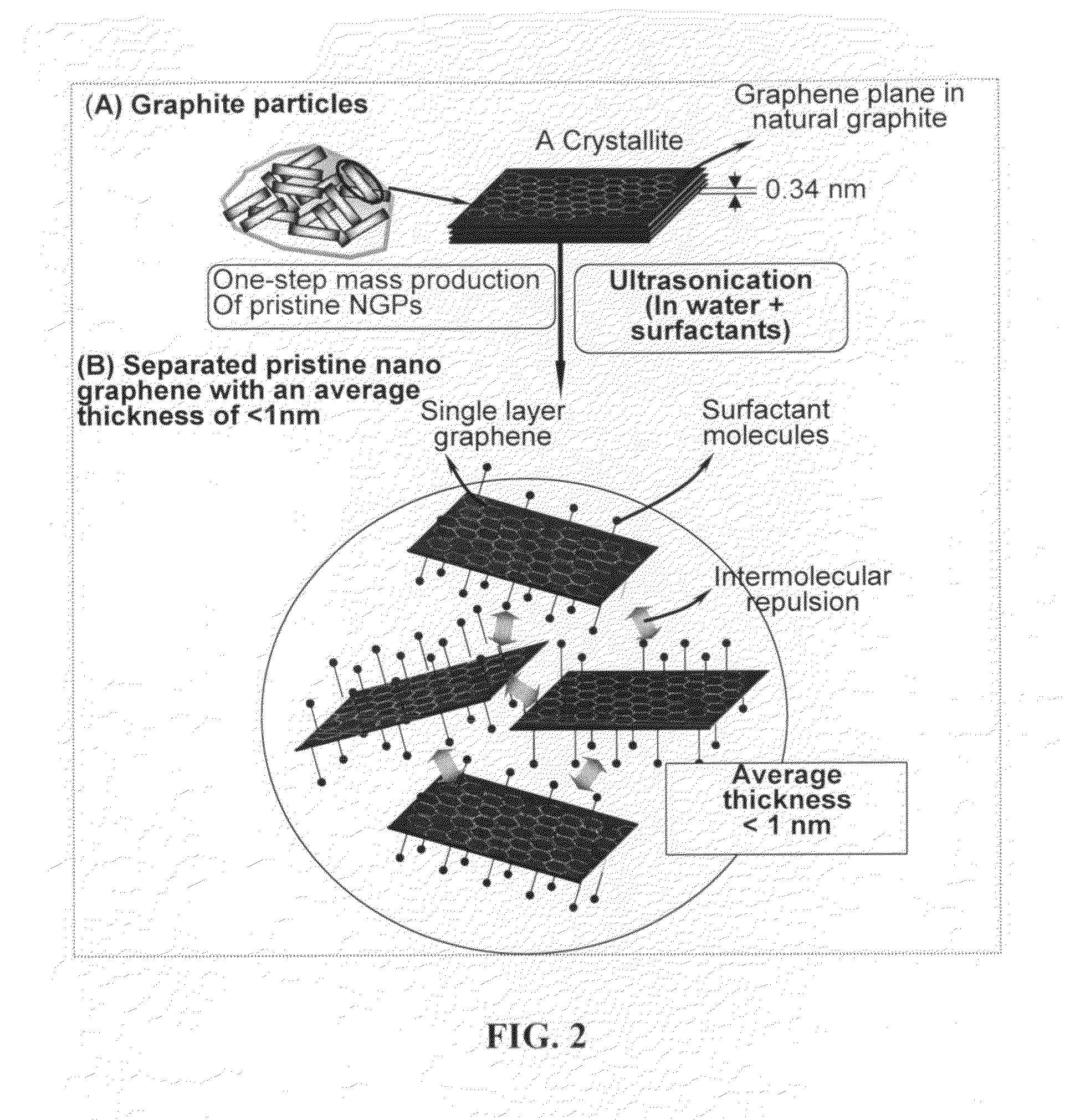
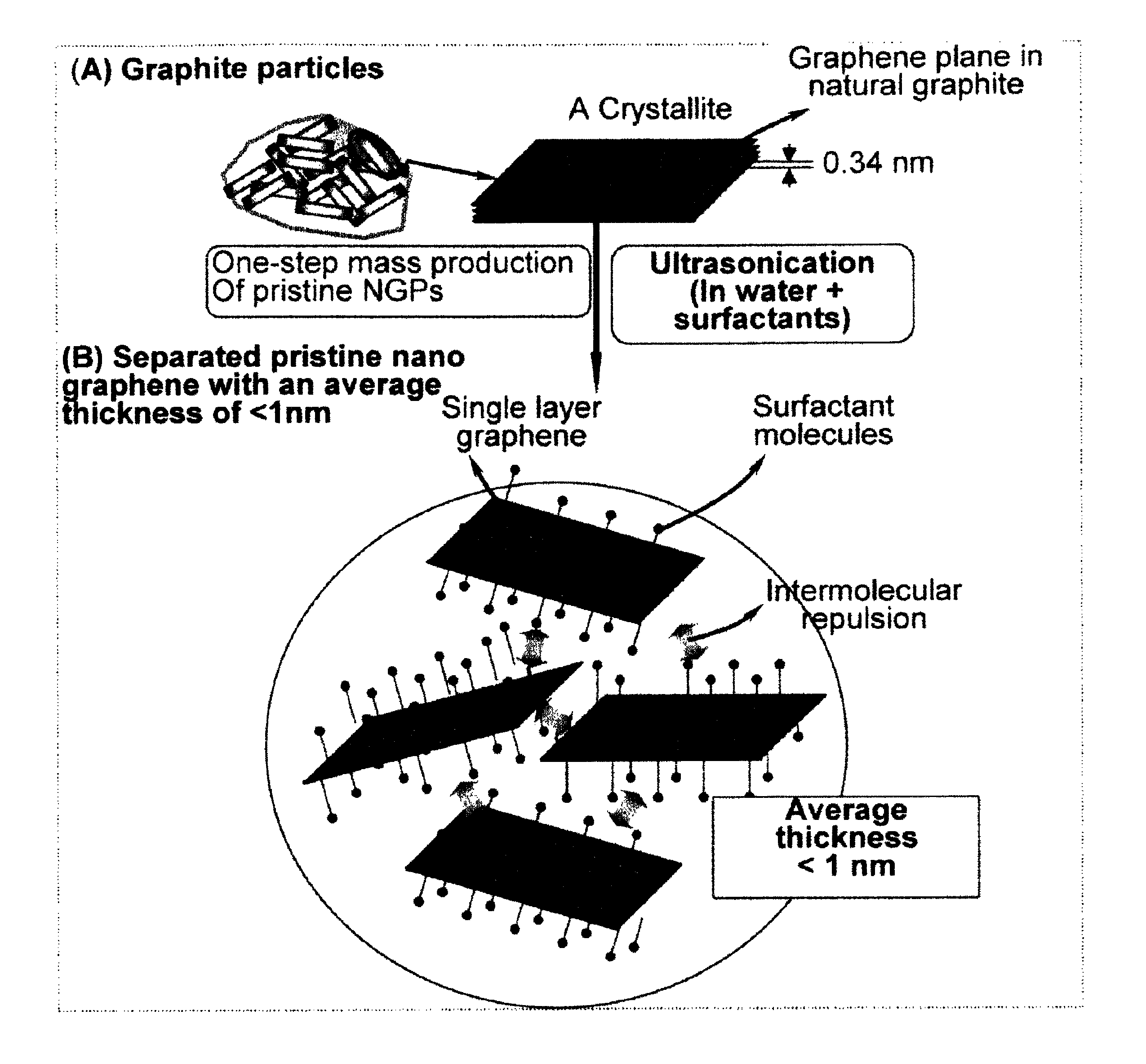
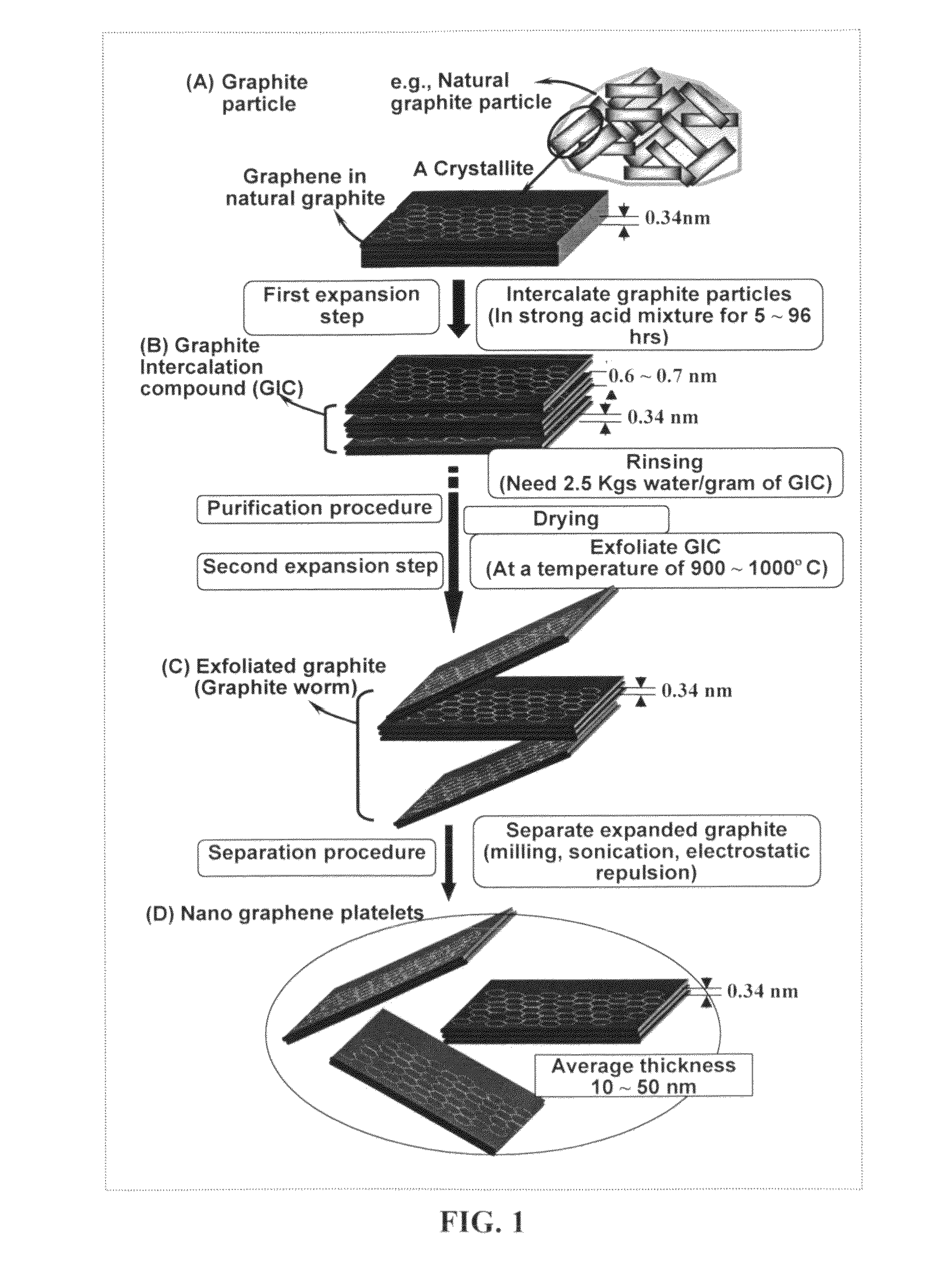
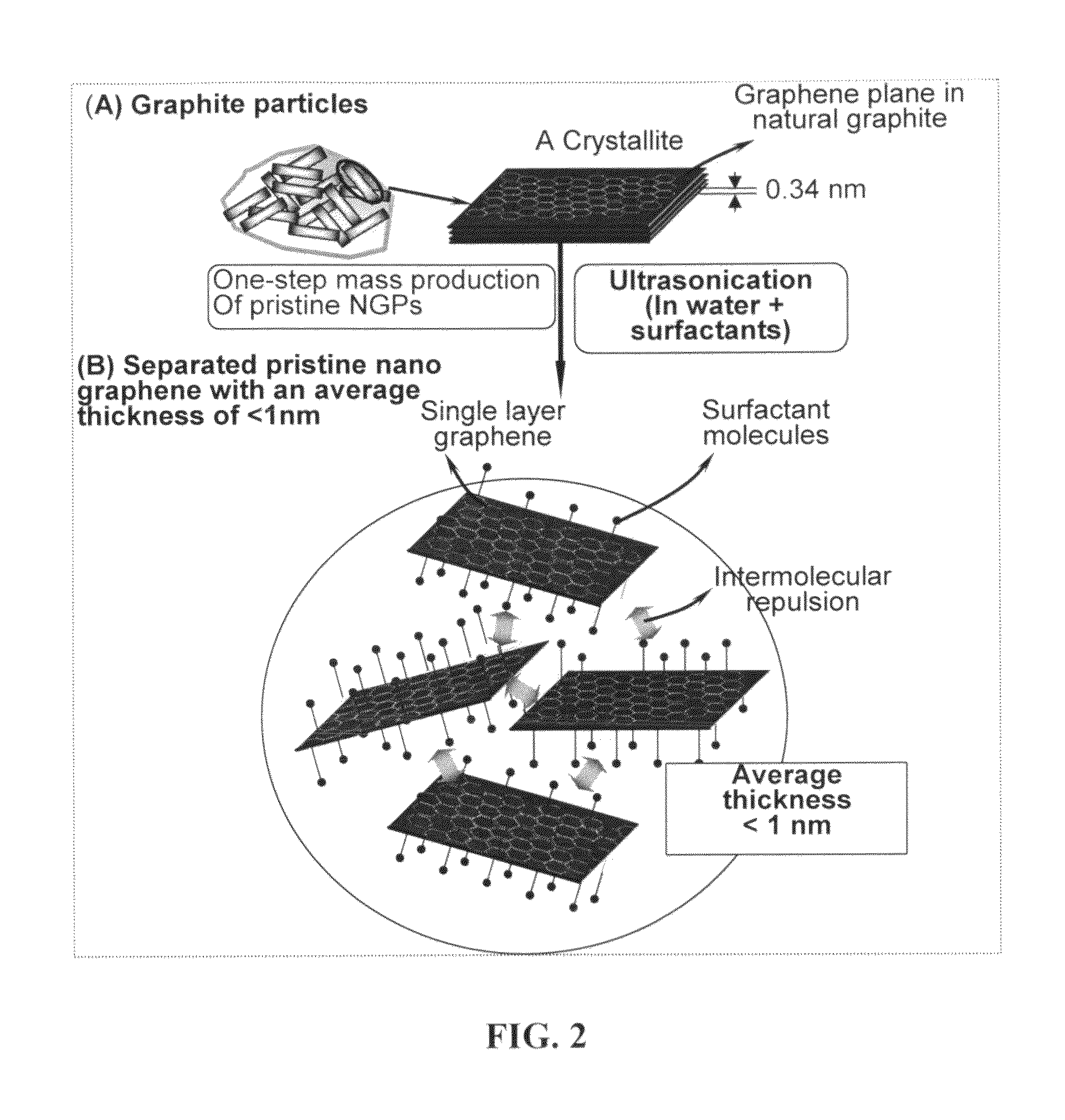
Production of chemically functionalized nano graphene materials
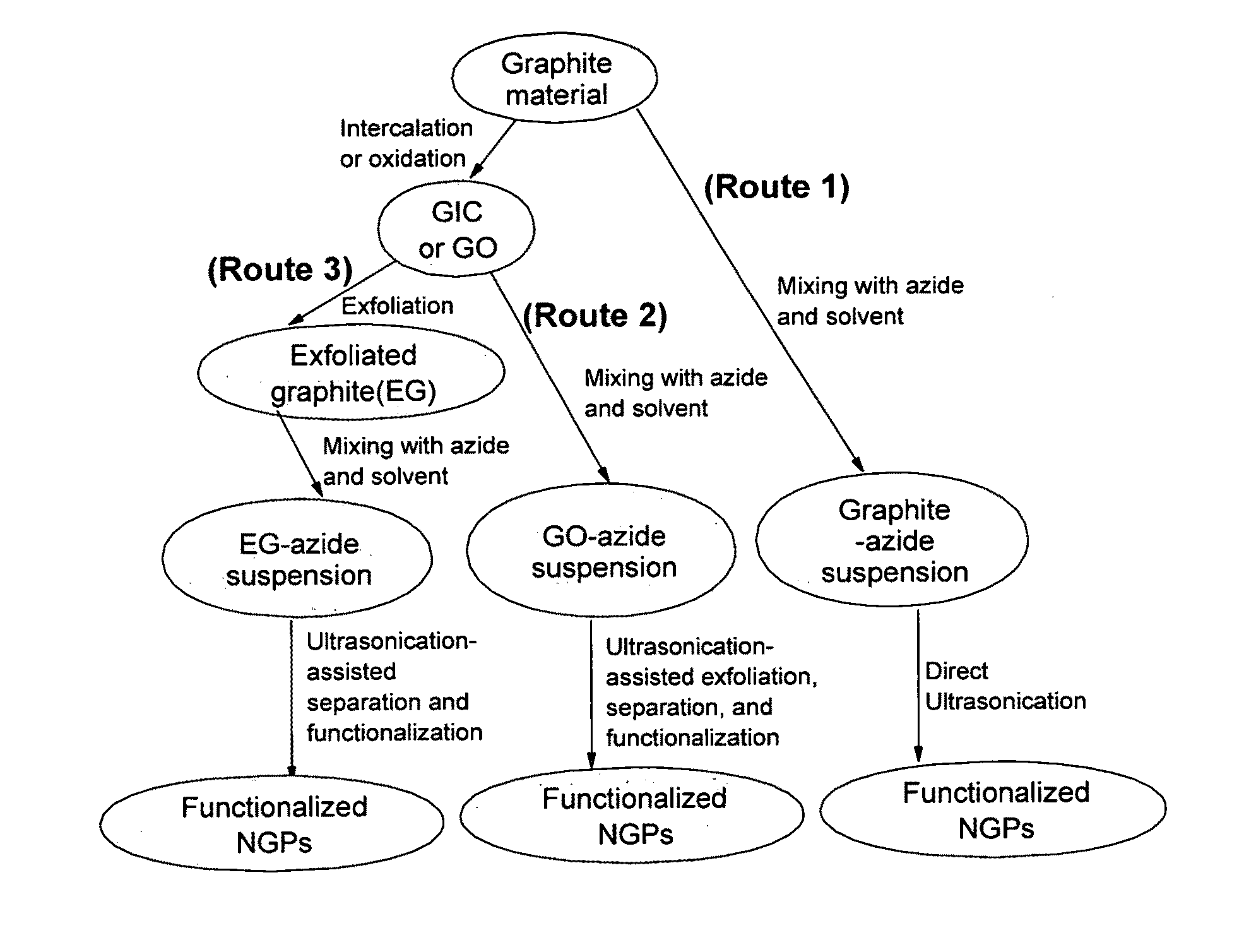
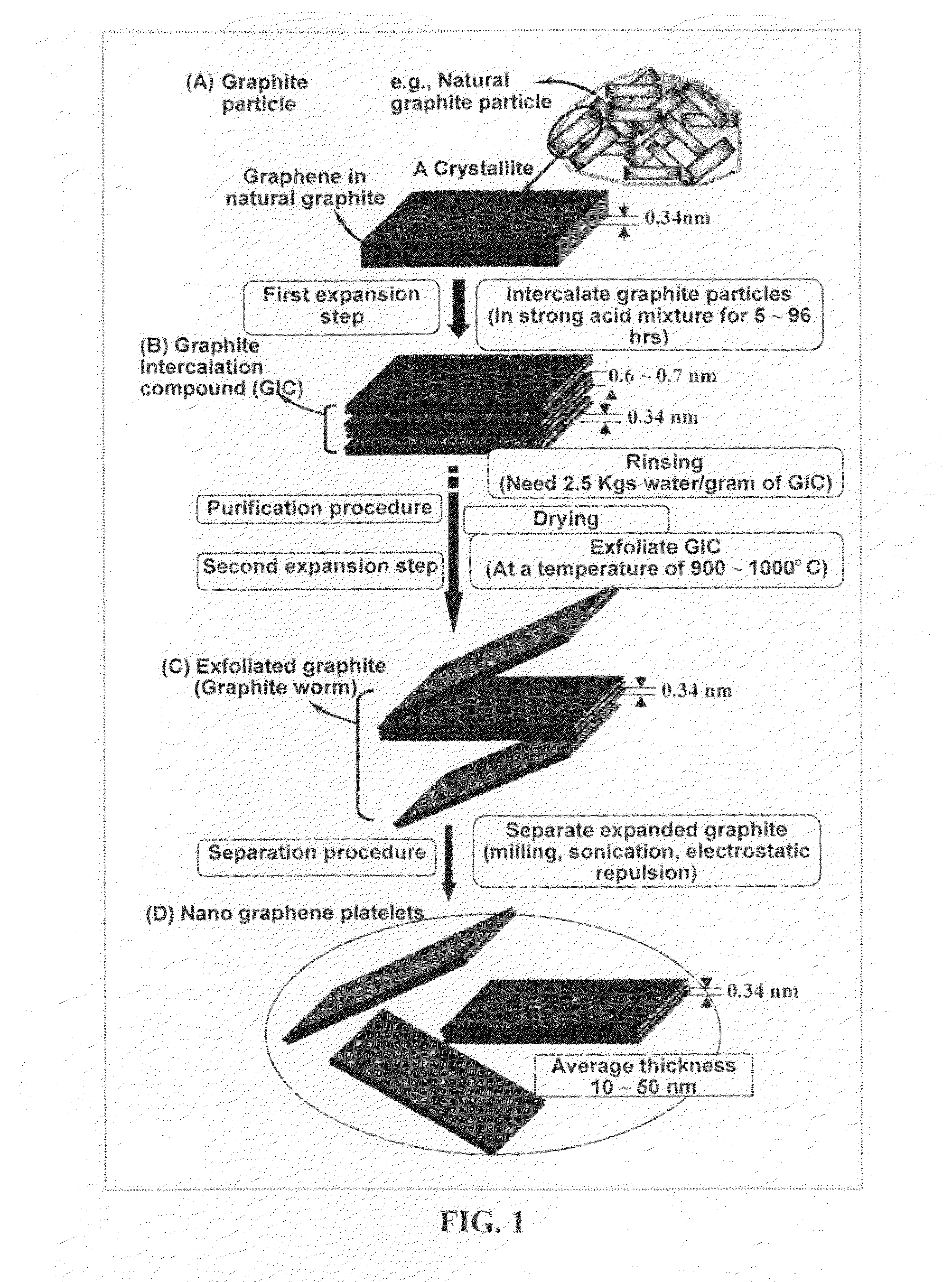
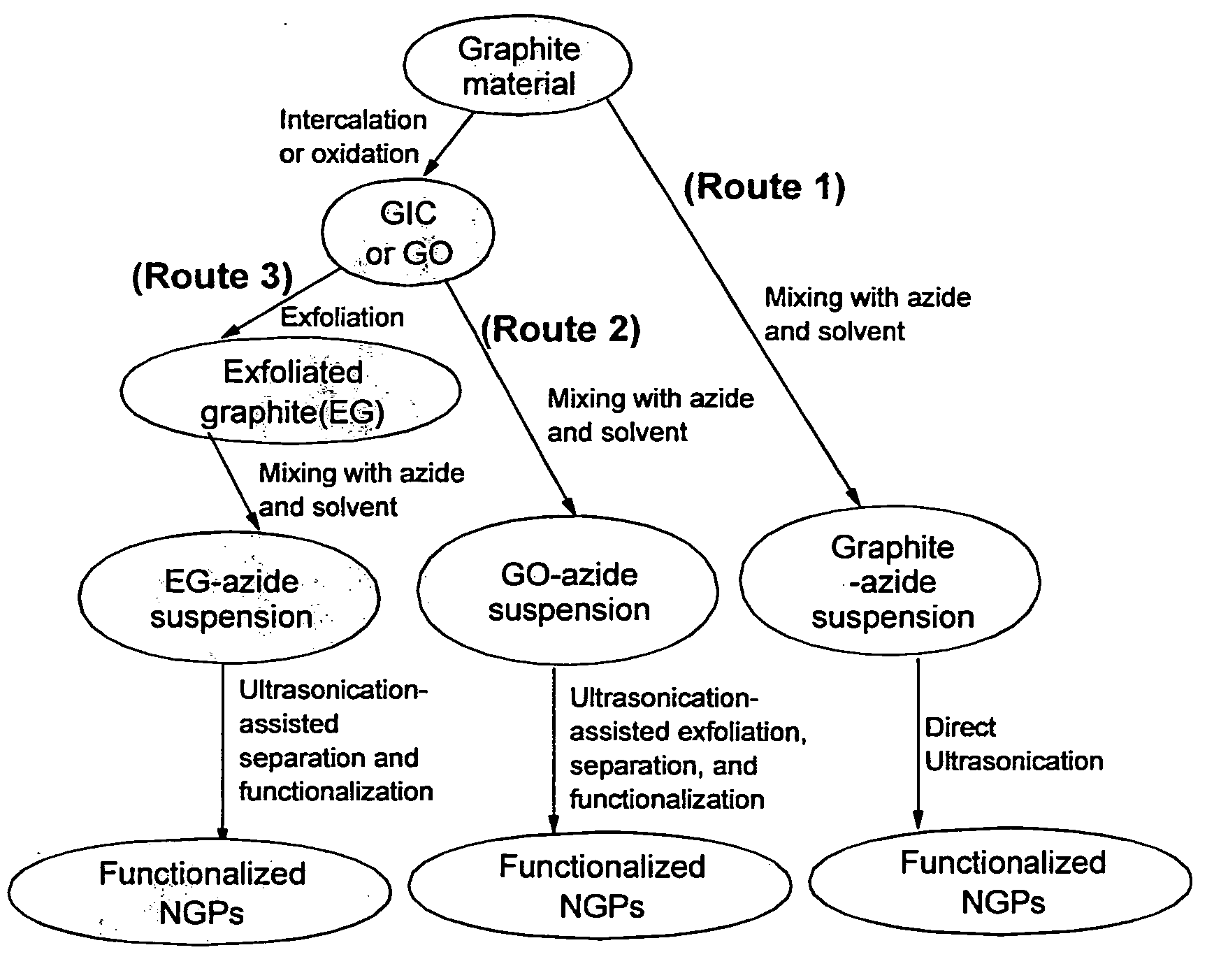
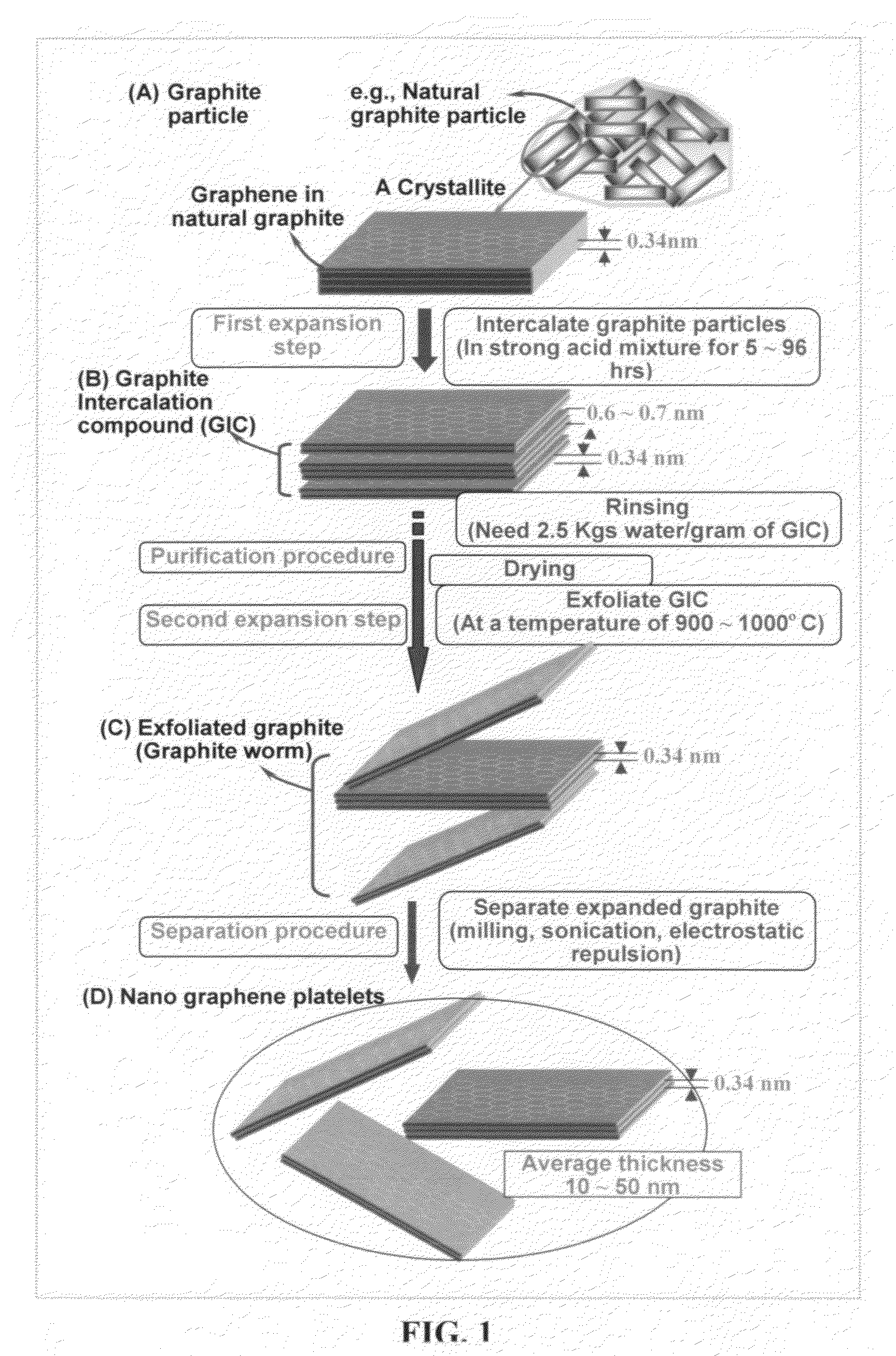
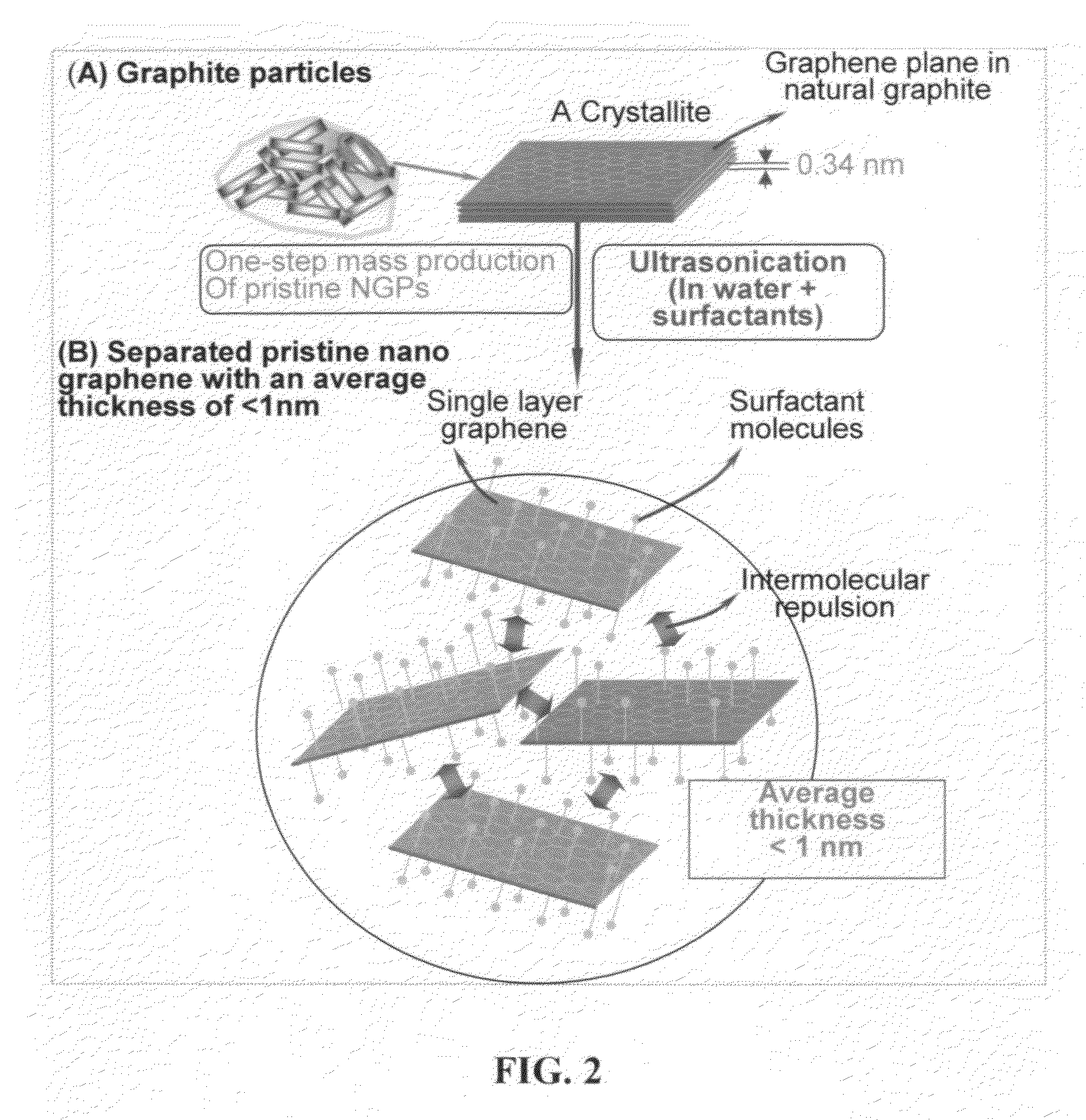
Provided in this invention is a process for producing chemically functionalized nano graphene materials, known as nano graphene platelets (NGPs), graphene nano sheets, or graphene nano ribbons. Subsequently, a polymer can be grafted to a functional group of the resulting functionalized NGPs. In one preferred embodiment, the process comprises (A) dispersing a pristine graphite material and an azide or bi-radical compound in a liquid medium comprising to form a suspension; and (B) subjecting the suspension to direct ultrasonication with to ultrasonic waves of a desired intensity or power level for a length of time sufficient to produce nano graphene platelets and to enable a chemical reaction to occur between the nano graphene platelets and the azide or bi-radical compound to produce the functionalized nano graphene material. Concurrent production and functionalization of NGPs directly from pristine graphitic materials can be achieved in one step and in the same reactor.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Polysiloxane prepolymers for biomedical devices
InactiveUS20060142526A1Low viscosityEasy to processTissue regenerationWater-setting substance layered productDiolPrepolymer
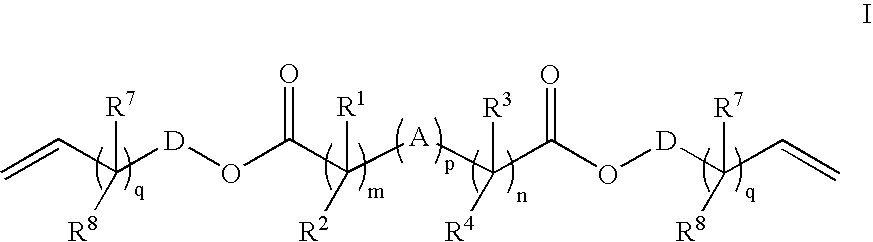
A polysiloxane prepolymer that is useful for forming biomedical devices has the formula: M(*Dii*PS)x*Dii*M (I) wherein: each M is independently a polymerizable ethylenically unsaturated radical; each Dii is independently a diradical residue of a diisocyanate; each PS is independently a diradical residue of a polysiloxane-diol or a polysiloxane-diamine; each * is independently —NH—CO—NH—, —NH—COO— or —OCO—NH—; and x is at least 2.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Vapor deposition process for producing a stent-graft and a stent-graft produced therefrom
A stent-graft endoprosthesis is provided. The graft is a non-textile graft made from biocompatible polymers. The biocompatible compatible polymers include poly-para-xylylene polymeric material. The stent is also coated with a poly-para-xylylene polymeric material. The graft is formed by vacuum vapor deposition of diradicals forming the poly-para-xylylene material. The stent is also coated with the poly-para-xylylene material by vacuum vapor deposition.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Crosslink Agents and Dual Radical Cure Polymer
ActiveUS20090018233A1Carbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationHydrophilic monomerEye lens
A synthetic route to polymers comprised of at least two monomers each with a very different reactivity ratio by using a corresponding crosslink agent for each monomer. Novel crosslink agents are described that provide for the copolymerization of at least one hydrophilic monomer with at least one lens monomer typically used to prepare materials for ophthalmic lenses. The new crosslink agents have a relatively high selectivity for the hydrophilic monomer and limited reactivity with the crosslink agent used to polymerize the lens monomer.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Preparation of amino-functional organopolysiloxanes
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
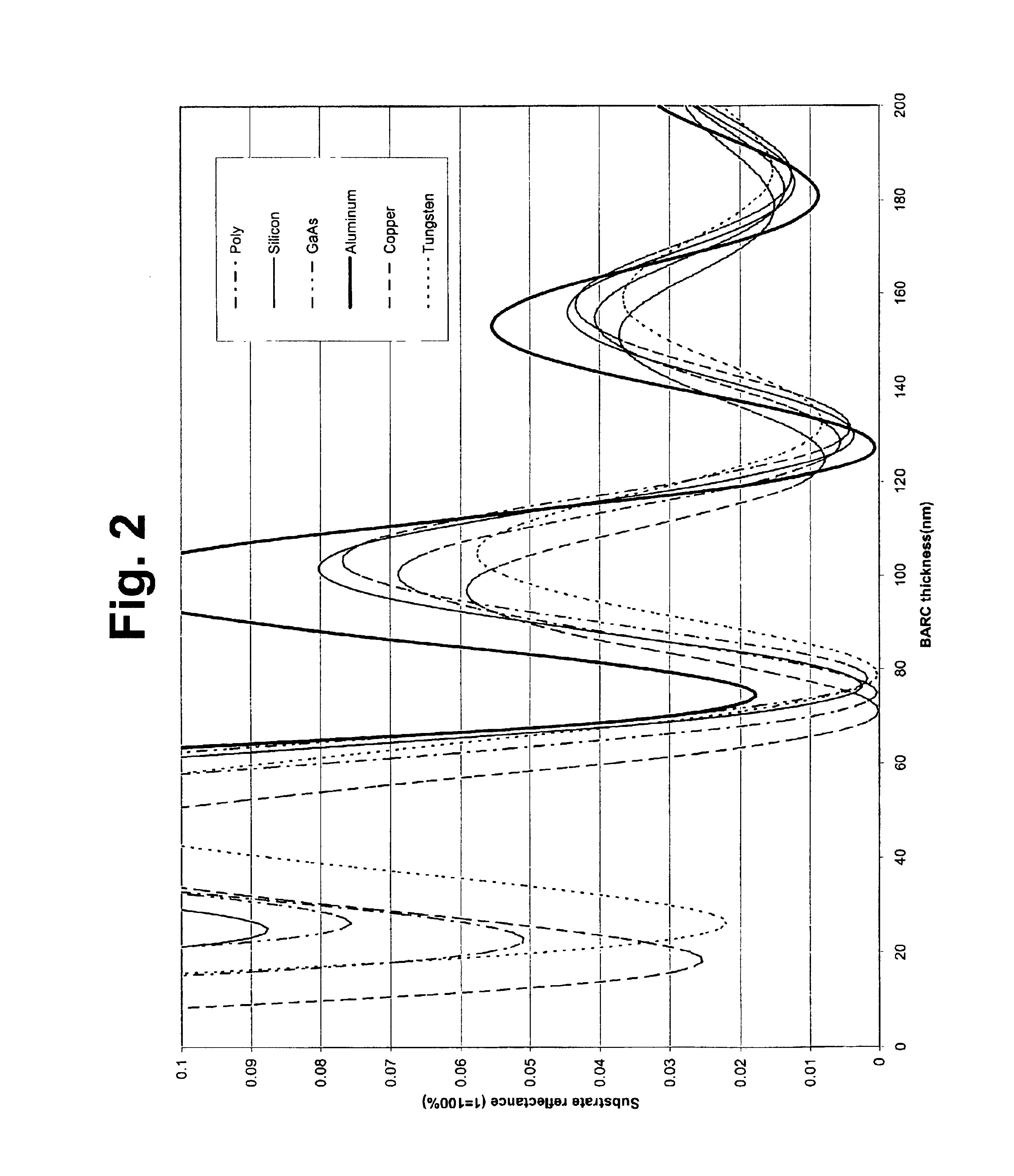
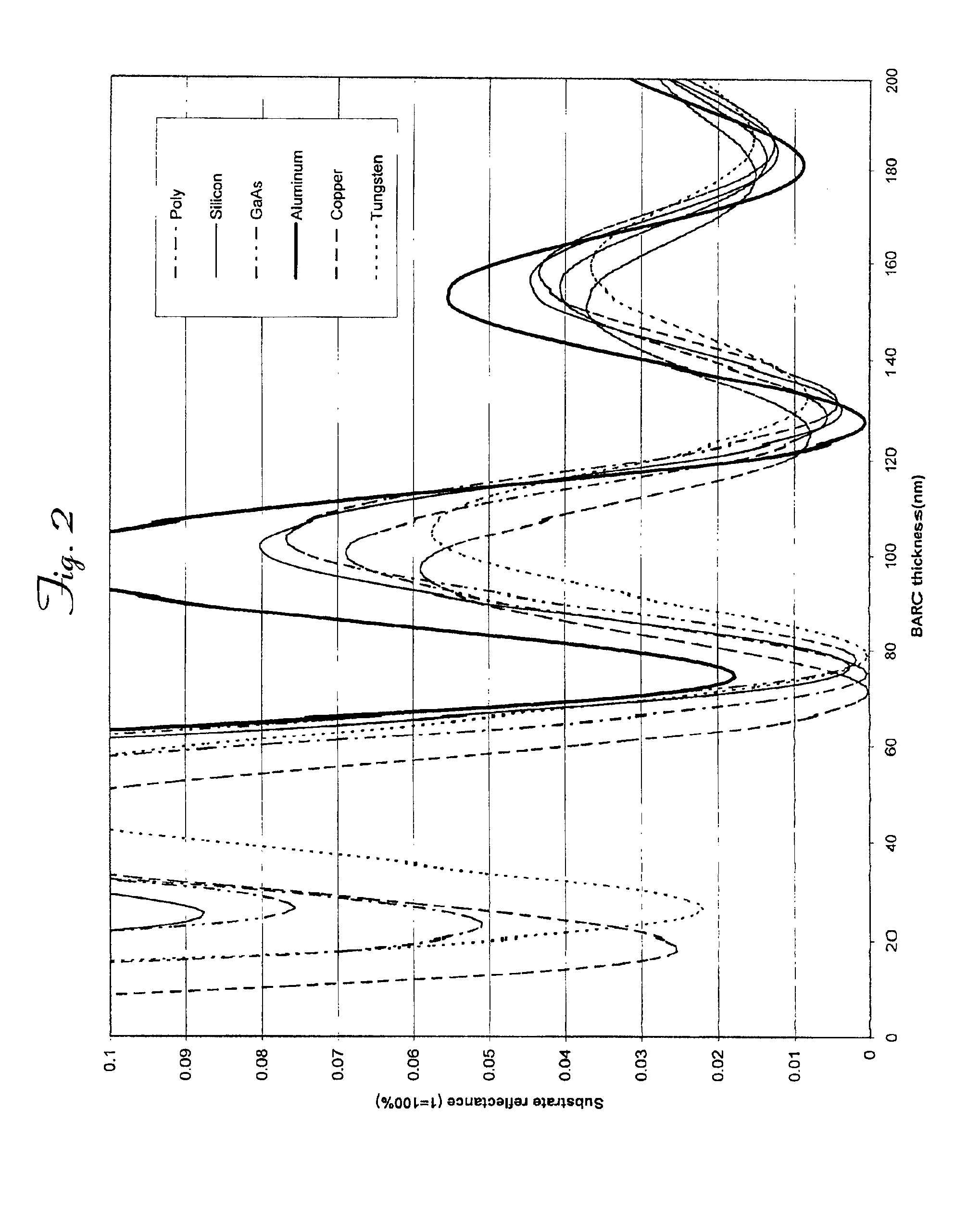
Organic polymeric antireflective coatings deposited by chemical vapor deposition
InactiveUS6869747B2Negative effectReduce wasteDispersed particle filtrationPhotosensitive materialsGas phaseStrain energy
An improved method for applying organic antireflective coatings to substrate surfaces and the resulting precursor structures are provided. Broadly, the methods comprise chemical vapor depositing (CVD) an antireflective compound on the substrate surface. In one embodiment, the compound is highly strained (e.g., having a strain energy of at least about 10 kcal / mol) and comprises two cyclic moieties joined to one another via a linkage group. The most preferred monomers are [2.2](1,4)-naphthalenophane and [2.2](9,10)-anthracenophane. The CVD processes comprise heating the antireflective compound so as to vaporize it, and then pyrolizing the vaporized compound to form stable diradicals which are subsequently polymerized on a substrate surface in a deposition chamber. The inventive methods are useful for providing highly conformal antireflective coatings on large substrate surfaces having super submicron (0.25 μm or smaller) features.
Owner:BREWER SCI
Preparation method of amide
ActiveCN102584509AReact SafeMild reaction conditionsCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationTetramethylammonium iodideSodium iodide
The invention discloses a preparation method of amide. With an aldehyde derivative and a formamide derivative as a reaction substrate, iodide as catalyst and tert-butanol hydrogen peroxide as an oxidizing agent, the amide is prepared through decarbonylation double free radical cross-coupling reaction, wherein the chemical structural formula of the aldehyde derivative is shown in the description, R1 is selected from a naphthyl, a heterlcyclic ring, an alkylene or a mono-substituted aryl; and the iodide is one selected from sodium iodide, potassium iodide, cuprous iodide, lithium iodate, an iodine elementary substance, tetrabutyl ammonium iodide, tetraheptylammonium iodide, tetramethylammonium iodide and benzyltrimethylammonium iodide. According to the invention, because the amide is prepared by using the iodide as the catalyst and using the double free radical cross-coupling method, the use of the traditional metal catalyst with expensive price and larger toxicity as well as a complicated experiment method is avoided so that the reaction is simpler, more convenient, easier, safer, greener and more economic; moreover, the preparation method of the amide disclosed by the invention has the advantages of quite moderate reaction condition, simpler post-treatment and potential industrial application value.
Owner:铜陵市官作文化有限公司
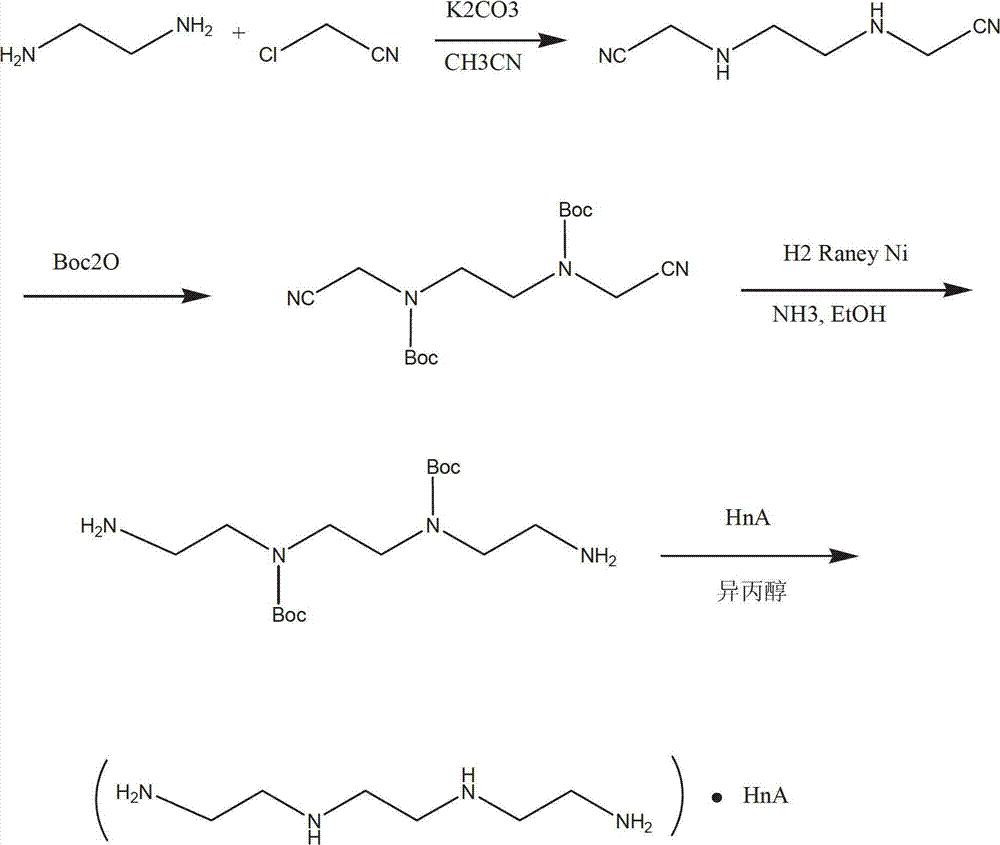
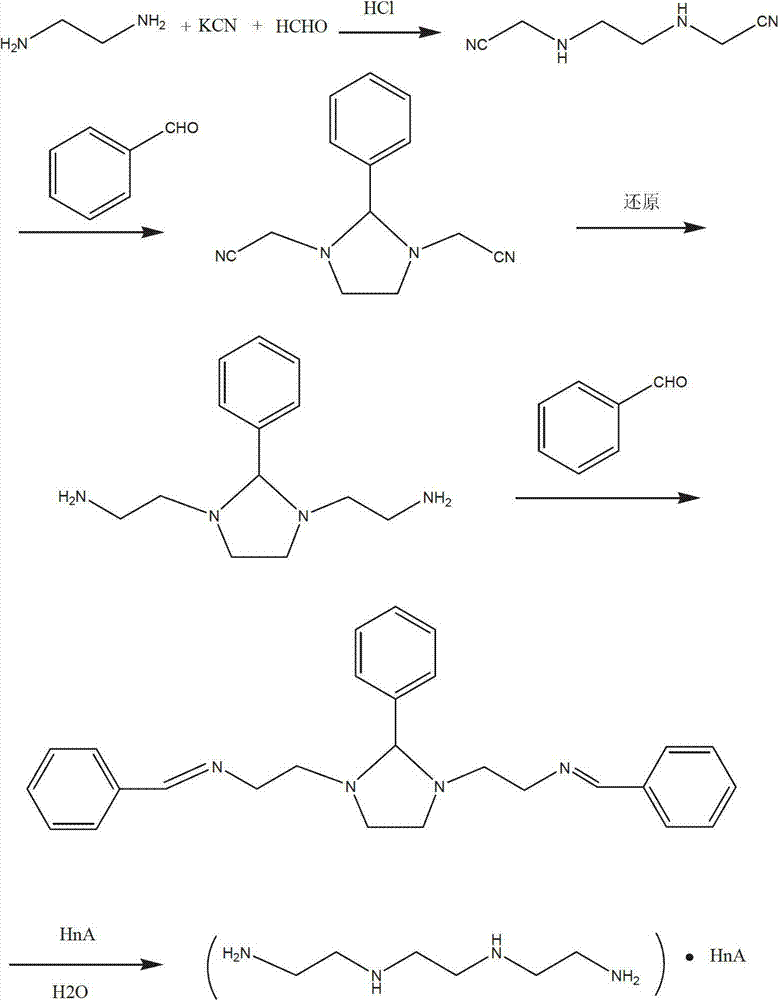
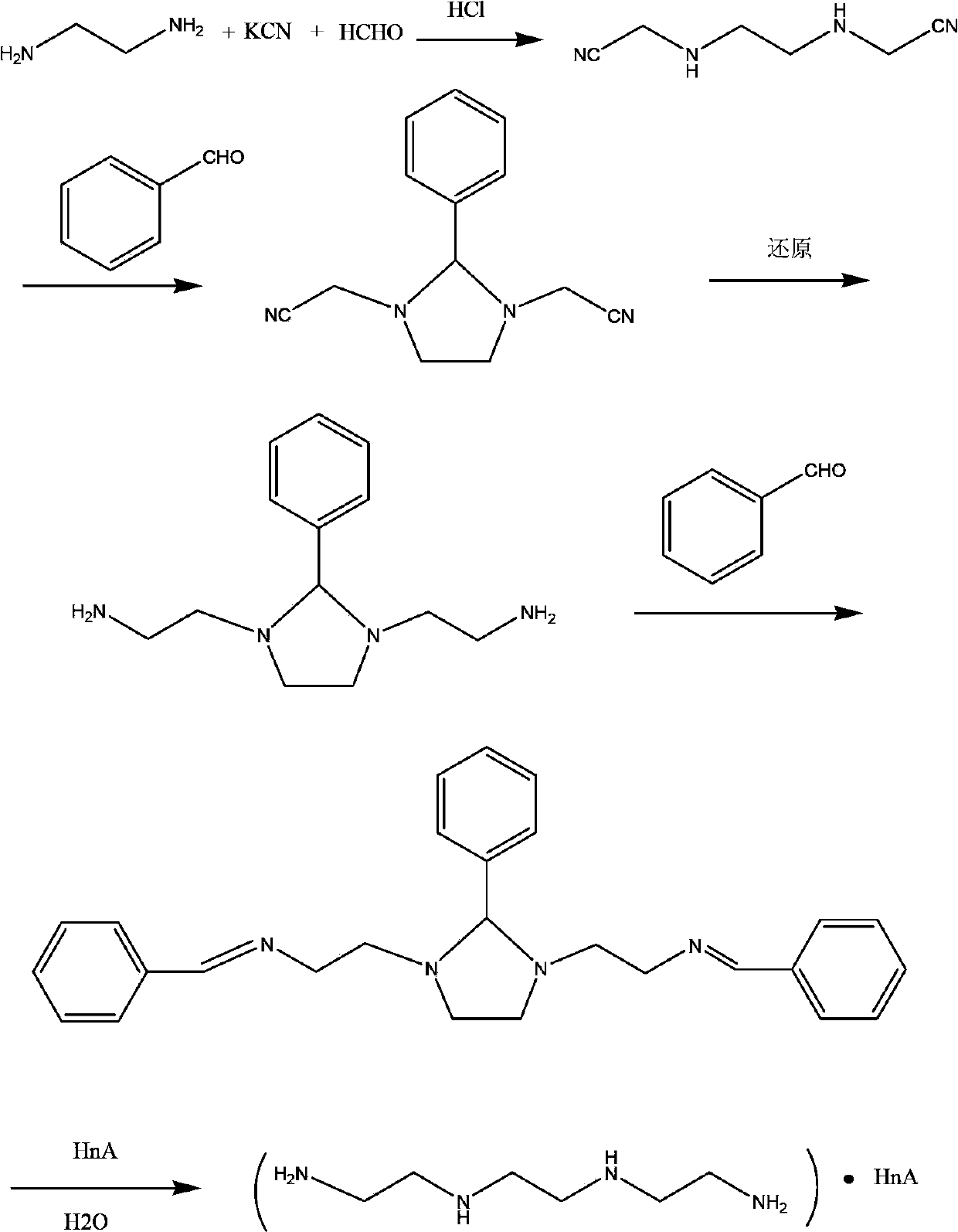
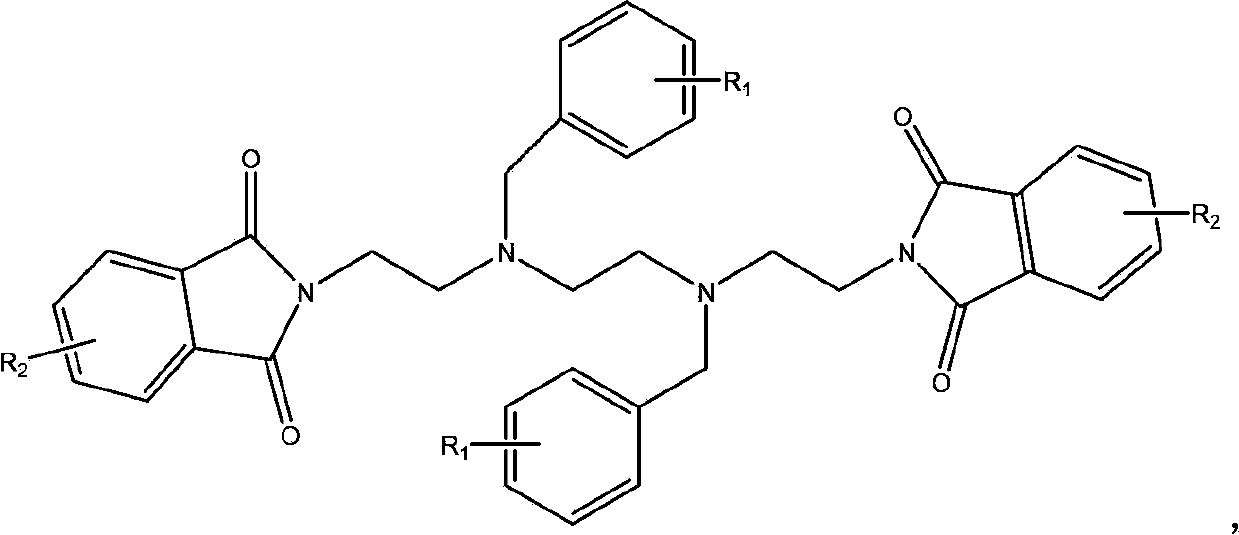
Synthetic process of hydrochloric acid trientine
InactiveCN102924289AReduce usageReduce pollutionOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationPotassium cyanideKetone
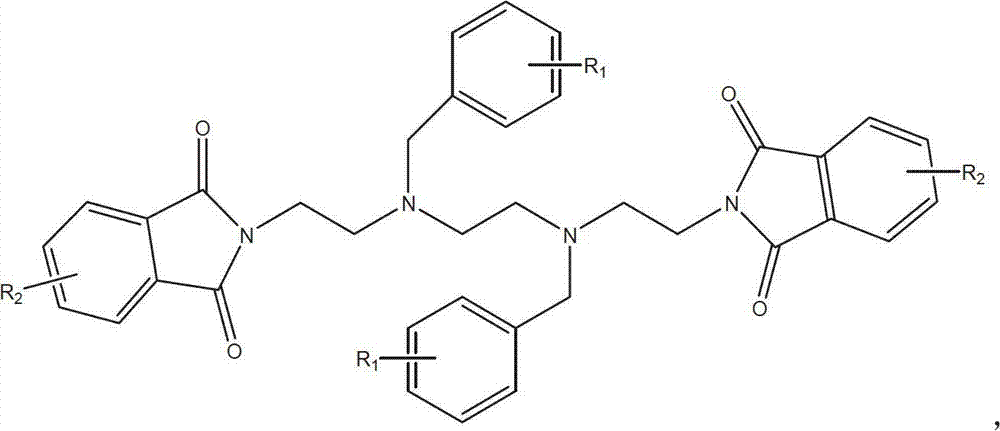
The invention discloses a novel synthetic process of hydrochloric acid trientine, and aims at providing the synthetic method of the hydrochloric acid trientine. The synthetic process can avoid using a highly-toxic material, namely potassium cyanide, and is temperate in reaction condition. A compound 2,2'-(2,2'-(ethane-1,2-diradical-bibenzyl-di (ethane-2,1-double radical)) bi isoindole-1,3-diketone is used as an initiator, after hydrazinolysis, an intermediate N1, N1'-(ethane-1,2-diradical) di(N1-nethyl ethane-1,2-diamine) is obtained. Through carbobenzoxy protection (Cbz protection), salt is generated,and dibenzyl 2,2'-(ethane-1,2-diradical-di (benzylamine-diradical)) di (ethane-2,1-diradical) dioctyl phthalatic acid aster hydrochloride is obtained so as to crystallize in ethanol through pressing catalytic hydrogenation deprotection to directly obtain the hydrochloric acid trientine. The synthetic process belongs to the organic synthetic technical field.
Owner:GUANGDONG AOERCHENG PHARMA
Vapor deposition process for producing a stent-graft and a stent-graft produced therefrom
A stent-graft endoprosthesis is provided. The graft is a non-textile graft made from biocompatible polymers. The biocompatible compatible polymers include poly-para-xylylene polymeric material. The stent is also coated with a poly-para-xylylene polymeric material. The graft is formed by vacuum vapor deposition of diradicals forming the poly-para-xylylene material. The stent is also coated with the poly-para-xylylene material by vacuum vapor deposition.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Production of chemically functionalized nano graphene materials
Provided in this invention is a process for producing chemically functionalized nano graphene materials, known as nano graphene platelets (NGPs), graphene nano sheets, or graphene nano ribbons. Subsequently, a polymer can be grafted to a functional group of the resulting functionalized NGPs. In one preferred embodiment, the process comprises (A) dispersing a pristine graphite material and an azide or bi-radical compound in a liquid medium comprising to form a suspension; and (B) subjecting the suspension to direct ultrasonication with to ultrasonic waves of a desired intensity or power level for a length of time sufficient to produce nano graphene platelets and to enable a chemical reaction to occur between the nano graphene platelets and the azide or bi-radical compound to produce the functionalized nano graphene material. Concurrent production and functionalization of NGPs directly from pristine graphitic materials can be achieved in one step and in the same reactor.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Substituted azoles, antiviral active component, pharmaceutical composition, method for preparation and use thereof
Owner:IVACHTCHENKO ALEXANDRE VASILIEVICH DR +3
Organic polymeric antireflective coatings deposited by chemical vapor deposition
InactiveUS6900000B2Stable diradicalsReduce wasteRadiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseStrain energy
An improved method for applying organic antireflective coatings to substrate surfaces and the resulting precursor structures are provided. Broadly, the methods comprise chemical vapor depositing (CVD) an antireflective compound on the substrate surface. In one embodiment, the compound is highly strained (e.g., having a strain energy of at least about 10 kcal / mol) and comprises two cyclic moieties joined to one another via a linkage group. The most preferred monomers are [2.2](1,4)-naphthalenophane and [2.2](9,10)-anthracenophane. The CVD processes comprise heating the antireflective compound so as to vaporize it, and then pyrolizing the vaporized compound to form stable diradicals which are subsequently polymerized on a substrate surface in a deposition chamber. The inventive methods are useful for providing highly conformal antireflective coatings on large substrate surfaces having super submicron (0.25 μm or smaller) features.
Owner:BREWER SCI
Cyanoguanidine prodrugs
The invention relates to compounds of formula (I), wherein X1 and X2 independently represent a bond; a straight, branched and / or cyclic hydrocarb on diradical, optionally substituted with one or more hydroxy, halogen, nitro, amino, cyano, aminosulfonyl, alkylsulfonylamino, alkylcarbonyl, formyl, aminocarbonyl or alkylcarbonylamino; a heteroarylene or non-aromatic heterocyclic hydrocarbon diradical, all of which are optionally substituted with one or more straight, branched and / or cyclic non-aromatic hycrocarbon radical, hydroxyl, halogen, amino, nitro, cyano, aminosulfonyl, alkylsulfonylamino, alkylcarbonyl, formyl, aminocarbonyl or alkylcarbonylamino; Y1 and Y2 independently represent a bond, an ether diradical (R'-O-R''), an amine diradical (R'-N-R''), O, S, S(O), S(O)2, C(O) , NH-CO, CO-NH, SO2-N(R'), methylene or N(R')-SO2 wherein R' et R'' independently represent straight or branched hydrocarbon diradicals containi ng up to 4 carbon atoms; Y3 represents O, O-C(O), C(O)-O, N(R8), R8 being hydrogen or C1-4alkyl; R1 represents hydrogen or straight, branched and / or cyclic alkyl, optionally substituted with phenyl; or an aromatic hydrocarbon radical; R2 represents aryl, heteroaryl or a non-aromatic heterocyclic hydrocarbon radical, all of which are optionally substituted; tetrahydropyranyloxy, di-(C1-4 alkoxy)phosphinoyloxy or C1-4 alkoxycarbonylamino; R3 represents hydrogen; a straight, branched and / or cyclic hydrocarbon radical, optionally substituted with one or more amino, hydroxy, carboxy, halogen, nitro, cyano, alcoxy, aminocarbonyl, C1- 4alkoxycarbonyl, C1-4alkoxycarbonylamino, sulfo, hydroxysulfonyloxy, dihydroxyphosphinoyloxy, phosphono, sulfamino, aminosulfonyl, aminoacylamino or dialkoxyphosphinoyl; heteroaryl or a non-aromatic heterocyclic hydrocarbo n radical, all of which are optionally substituted by one or more group.
Owner:LEO PHARMA AS
Process for producing chemically functionalized nano graphene materials
Provided in this invention is a process for producing chemically functionalized nano graphene materials, known as nano graphene platelets (NGPs), graphene nano sheets, or graphene nano ribbons. Subsequently, a polymer can be grafted to a functional group of the resulting functionalized graphene. In one preferred embodiment, the process comprises a step of mixing a starting nano graphene material having edges and two primary graphene surfaces, an azide or bi-radical compound, and an organic solvent in a reactor, and allowing a chemical reaction between the nano graphene material and the azide compound to proceed at a temperature for a length of time sufficient to produce the functionalized nano graphene material.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Polymers and their use as fluorescent labels
InactiveUS20100129800A1Avoid inconvenienceHigh selectivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHydrogenSide chain
The present invention relates to a polymer composed by two to ten monomers of formula (I) as well as to a process for its preparation and its use as fluorophore wherein: X is a radical of formula (II) wherein —R5 is an electron pair or a (C1-C3)-alkyl radical; —Ra and —Rb are radicals independently selected from the group consisting of H, (C1-C4)-alKyI, (C1-C4)-alkoxy, (C1-C4)-alkylamino, phenyl, F, Cl, Br, amino, hydroxy, and nitro or —Ra and —Rb are fused forming with the carbon atoms to which they are attached a ring of formula (III) with the condition that (I) when —R5 is an electron pair, a is a N═C double bond, and Ra and Rb are fused forming the ring (III), said ring being a biradical selected from (IIIa) and (IIIb), thus, radical (II) is (IIa) or (IIb) respectively (II) when —R5 is a (C1-C3)-alkyl radical, a is a N—C single bond and Ra and Rb are fused forming the ring (III), said ring being a biradical (a), thus, the radical (II) is (IIc) R1-R4 and R7-R18 represent radicals, same or different, selected for the group consisting of H1 (C1-C4)-alkyl, (C1-C4)-alky-lamiπo, phenyl, F, Cl, Br, amino, hydroxy, and nitro; p is an integer from 0 to 1; R6 is a biradical selected from the group consisting of —CO—; —CONH(CH2)mCO—; and —CO[NHCHR″CO]m—, wherein —R″ are side chains radicals, same or different, corresponding to natural aminoacids; and m is an integer from 1 to 3; Z is a triradical of formula (IV) wherein r is an integer from 0 to 1; v is an integer from O to 1; Z′ is a triradical selected from —CH2— and nitrogen; Z″ is H, with the proviso that: (a) when Z′ is nitrogen, forming an amide bound with R6, then is hydrogen and v is an integer from O to 1, and (b) when Z″ is —NH—, forming an amide group with R6, then Z1 is —CH2 and v=O or of formula (V) wherein Z″ is selected from —CH3 and —CH2NH—, Z1v is selected from H and NH, Zv is selected from S and O atom, W is an integer from 0 to 1, with the proviso that (c) when R6 is bound to Z′″ then Z′″ is —CH2NH—, Z1v is hydrogen and w is 0; and (d) when Z1v is —NH— forming an amide bound with R6, Z′″ is —CH3 and w is 1; and and wherein the monomers of formula (I) are linked through the triradical Z, forming an amide or phosphate bound.
Owner:AYMAMI BOFARULL JUAN +6
Crosslink Agents and Dual Radical Cure Polymer
Crosslink agents used to copolymerize at least one hydrophilic monomer with at least one lens monomer typically used to prepare polymeric materials for ophthalmic lenses. The crosslink agents have a relatively high selectivity for the hydrophilic monomer and limited reactivity with the crosslink agent used to polymerize the lens monomer. Accordingly, the invention is also directed to a hydrophilic crosslinked polymer that comprises at least two monomeric units and at least two different crosslink units. The use of the dual crosslink system provides an improved means to control the final chemical, physical and structural characteristics of the resulting polymer.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
4,4-di(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl imidazoline-3-oxidation-1-oxy radical) phenyl ether and preparation method thereof
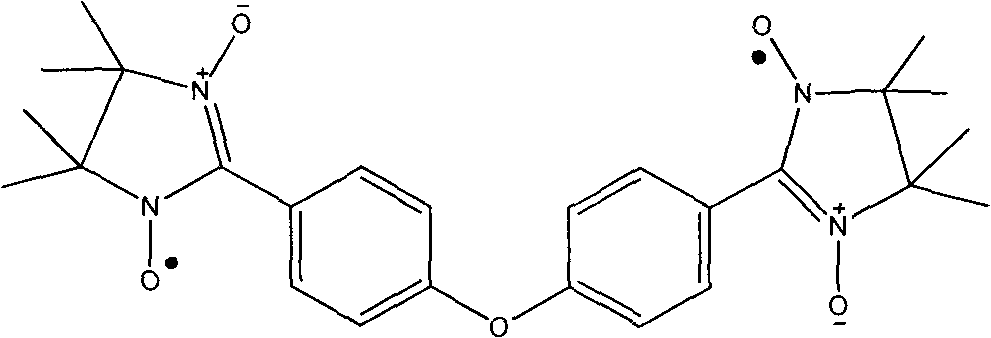
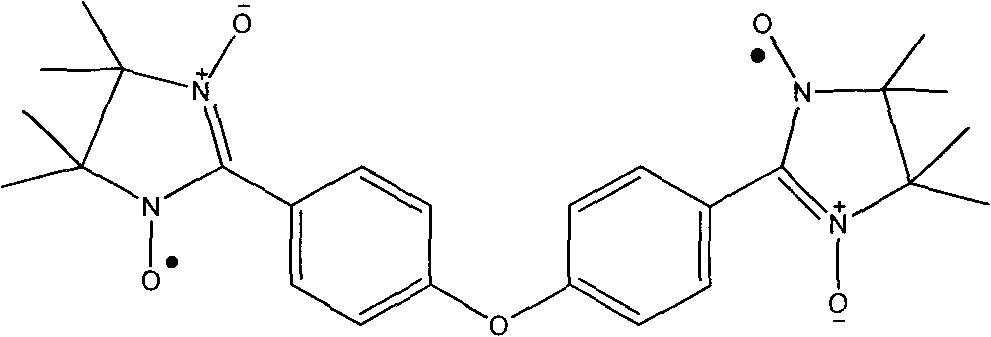
The invention relates to 4,4-di(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl imidazoline-3-oxidation-1-oxy radical) phenyl ether and a preparation method thereof. The structural formula of the ether is shown in the specification of the invention. The ether is a diradical with potential application value and can form a chain-type structure which is similar to [Co(hfac)2(NITp-PhOMe)]n when combined with the hexafluoroacetyl acetonate of the transition metal Co(II), which provides an important way for the radical to be synthesized into a molecular ferromagnet, and the biradical also has the characteristics of relatively few synthesizing steps, simple operation and high yield.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
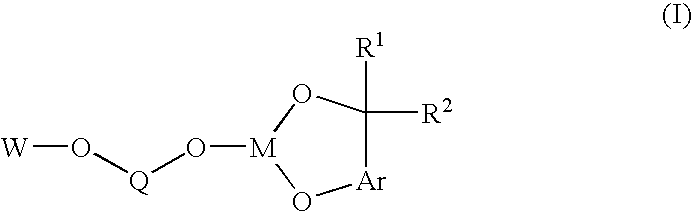
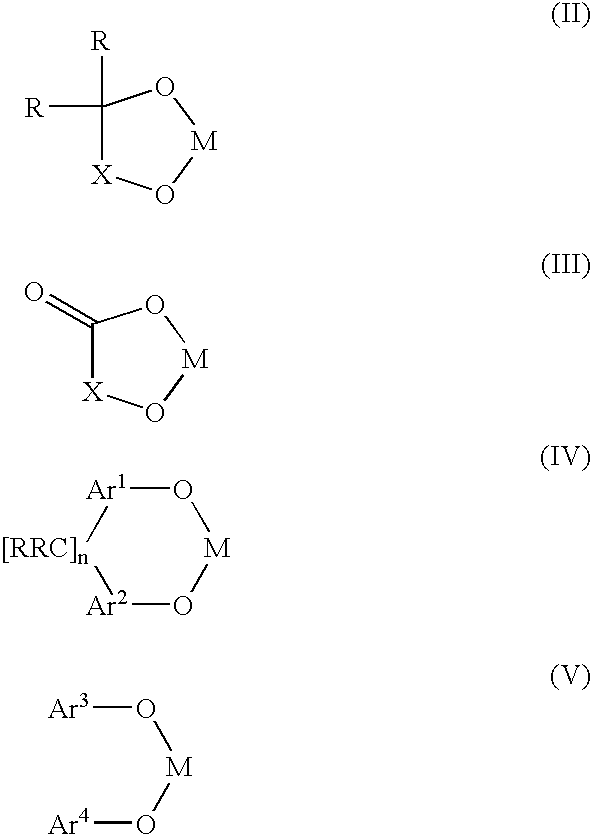
Bis-chelating ligand and use thereof in carbonylation processes
ActiveUS7294729B2High activityImprove stabilitySilicon organic compoundsRhodium organic compoundsHydrogenCarbonylation
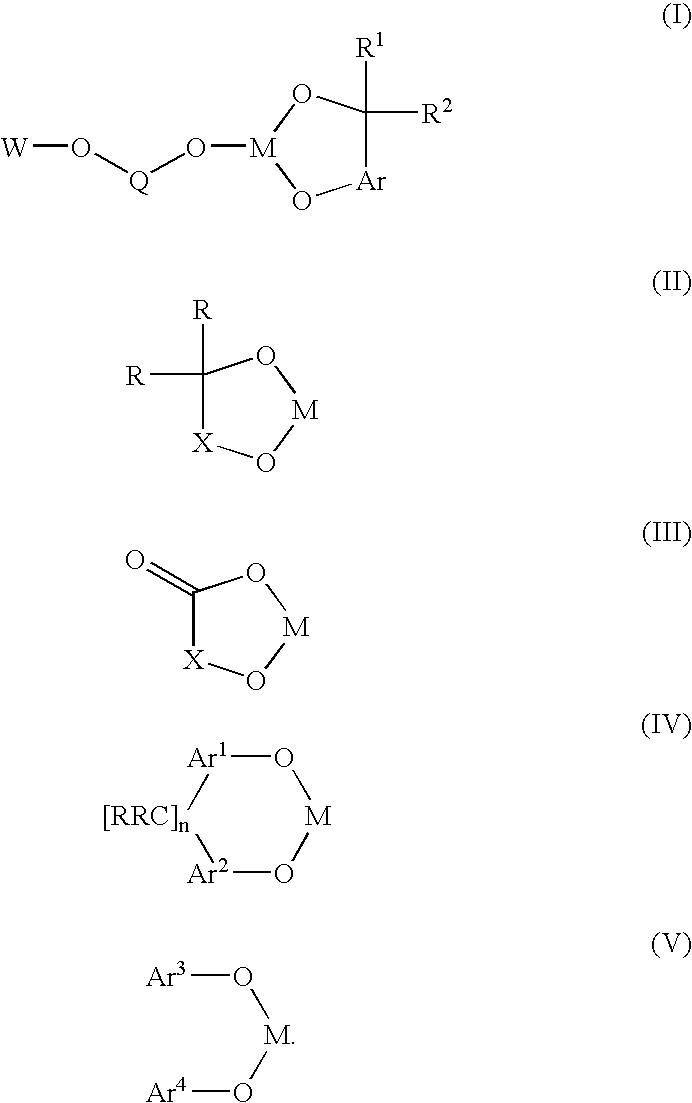
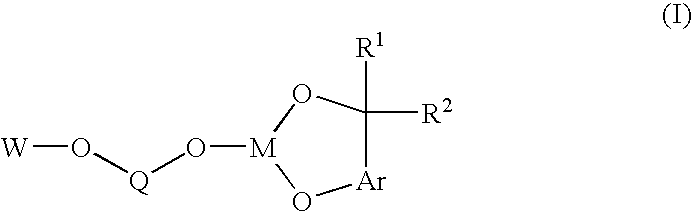
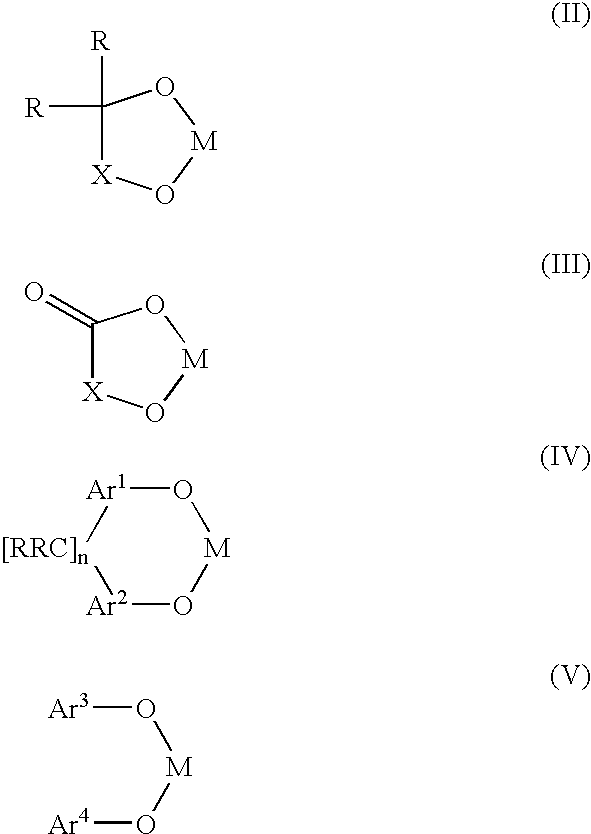
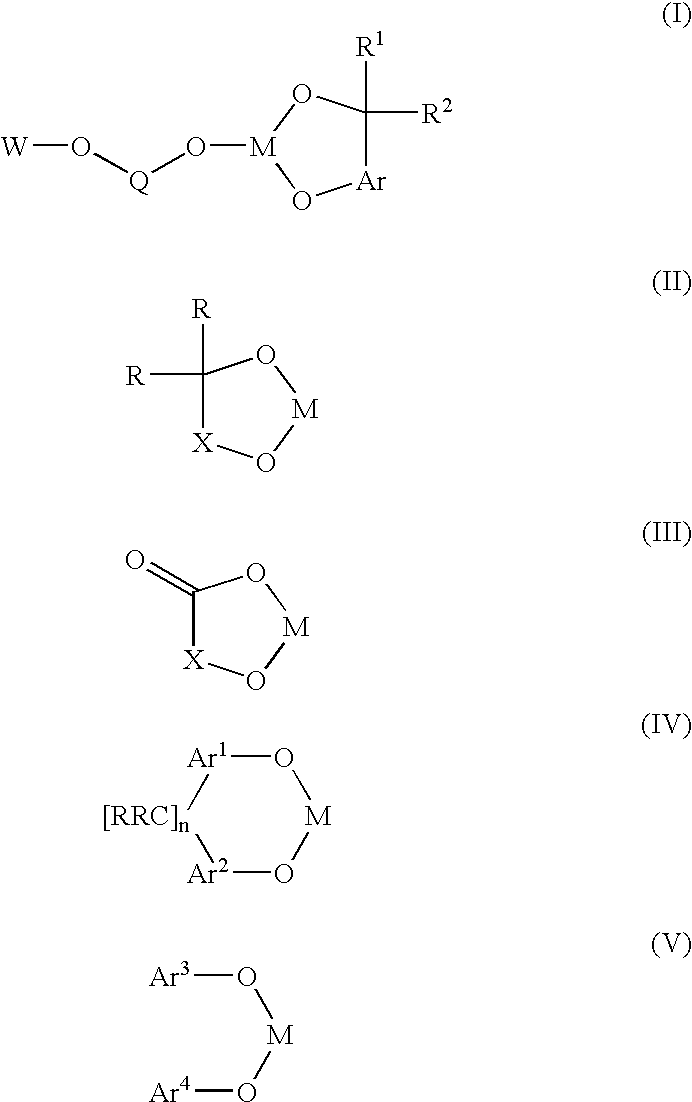
A novel bis-chelating composition characterized by formula I: wherein M is a Group VB element; R1 and R2 are each independently selected from hydrogen and monovalent hydrocarbyl radicals; or R1 and R2 are bonded together to form a diradical; or one of R1 or R2 is hydrogen or a monovalent hydrocarbyl radical, while the other of R1 or R2 is a hydrocarbyl radical bonded to an atom in Ar; wherein Ar is selected from 1,2-arylenes; Q is selected from 1,2-arylenes, 2,2′-bisarylenes and alkyl diradicals; and W is selected from II, III, IV, or V: wherein M is as defined hereinbefore; each R is independently selected from hydrogen and monovalent hydrocarbyl radicals; X is selected from alkyl and aryl diradicals; Ar1 and Ar2 are each independently selected from 1,2-arylenes;Ar3 and Ar4 are each independently selected from monovalent aryl radicals; and n in formula IV is 0 or 1. The composition finds utility as a ligand in catalysts for carbonylation processes
Owner:DOW TECH INVESTMENTS
Bis-chelating ligand and use thereof in carbonylation processes
ActiveUS20060058557A1High activityImprove stabilitySilicon organic compoundsRhodium organic compoundsHydrogenCarbonylation
A novel bis-chelating composition characterized by formula I: wherein M is a Group VB element; RI and R2 are each independently selected from hydrogen and monovalent hydrocarbyl radicals; or R1 and R2 are bonded together to form a diradical; or one of RI or R2 is hydrogen or a monovalent hydrocarbyl radical, while the other of R1 or R2 is a hydrocarbyl radical bonded to an atom in Ar; wherein Ar is selected from 1,2-arylenes; Q is selected from 1,2-arylenes, 2,2′-bisarylenes and alkyl diradicals; and W is selected from II, III, IV, or V: wherein M is as defined hereinbefore; each R is independently selected from hydrogen and monovalent hydrocarbyl radicals; X is selected from alkyl and aryl diradicals; Ar1 and Ar2 are each independently selected from 1,2-arylenes; Ar3 and Ar4 are each independently selected from monovalent aryl radicals; and n in formula IV is 0 or 1. The composition finds utility as a ligand in catalysts for carbonylation processes.
Owner:DOW TECH INVESTMENTS
Organic polymeric antireflective coatings deposited by chemical vapor deposition
InactiveUS6936405B2Negative effectReduce wastePhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsGas phaseStrain energy
An improved method for applying organic antireflective coatings to substrate surfaces and the resulting precursor structures are provided. Broadly, the methods comprise chemical vapor depositing (CVD) an antireflective compound on the substrate surface. In one embodiment, the compound is highly strained (e.g., having a strain energy of at least about 10 kcal / mol) and comprises two cyclic moieties joined to one another via a linkage group. The most preferred monomers are [2.2](1,4)-naphthalenophane and [2.2](9,10)-anthracenophane. The CVD processes comprise heating the antireflective compound so as to vaporize it, and then pyrolizing the vaporized compound to form stable diradicals which are subsequently polymerized on a substrate surface in a deposition chamber. The inventive methods are useful for providing highly conformal antireflective coatings on large substrate surfaces having super submicron (0.25 μm or smaller) features.
Owner:BREWER SCI
Diazoacetate-ethoxycarbonyl carbene copolymer and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a diazoacetate-ethoxycarbonyl carbene copolymer and a synthesis method of the copolymer. The main chain of the polymer comprises carbon atoms and nitrogen atoms, wherein the carbon atoms are prepared by carbene polymerization reaction, and the nitrogen atoms are added into the main chain of the polymer by double-free-radical polymerization. The invention also provides a preparation method of the copolymer, which takes diazoacetate as raw material, and comprises the following steps: putting the diazoacetate into a microwave oven, and carrying out microwave irradiation on the diazoacetate for a period of time under the protection of argon; and finally, carrying out reprecipitation and vacuum drying to obtain the product. The method does not use catalyst and solvent, and is simple and convenient in steps as well as simple in reaction and aftertreatment; and the prepared polyester with the novel structure can be applied to the wide fields such as optical study and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
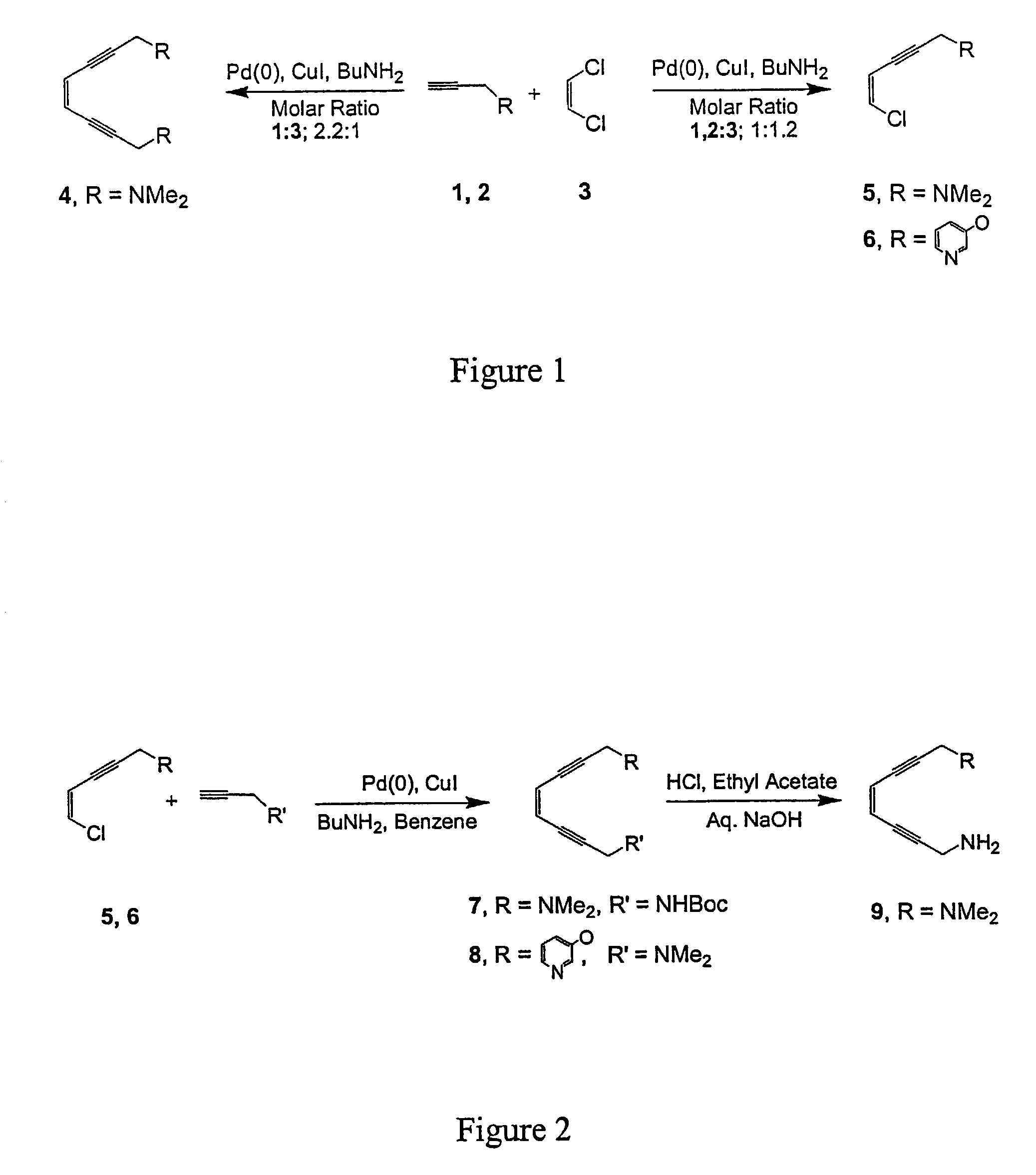
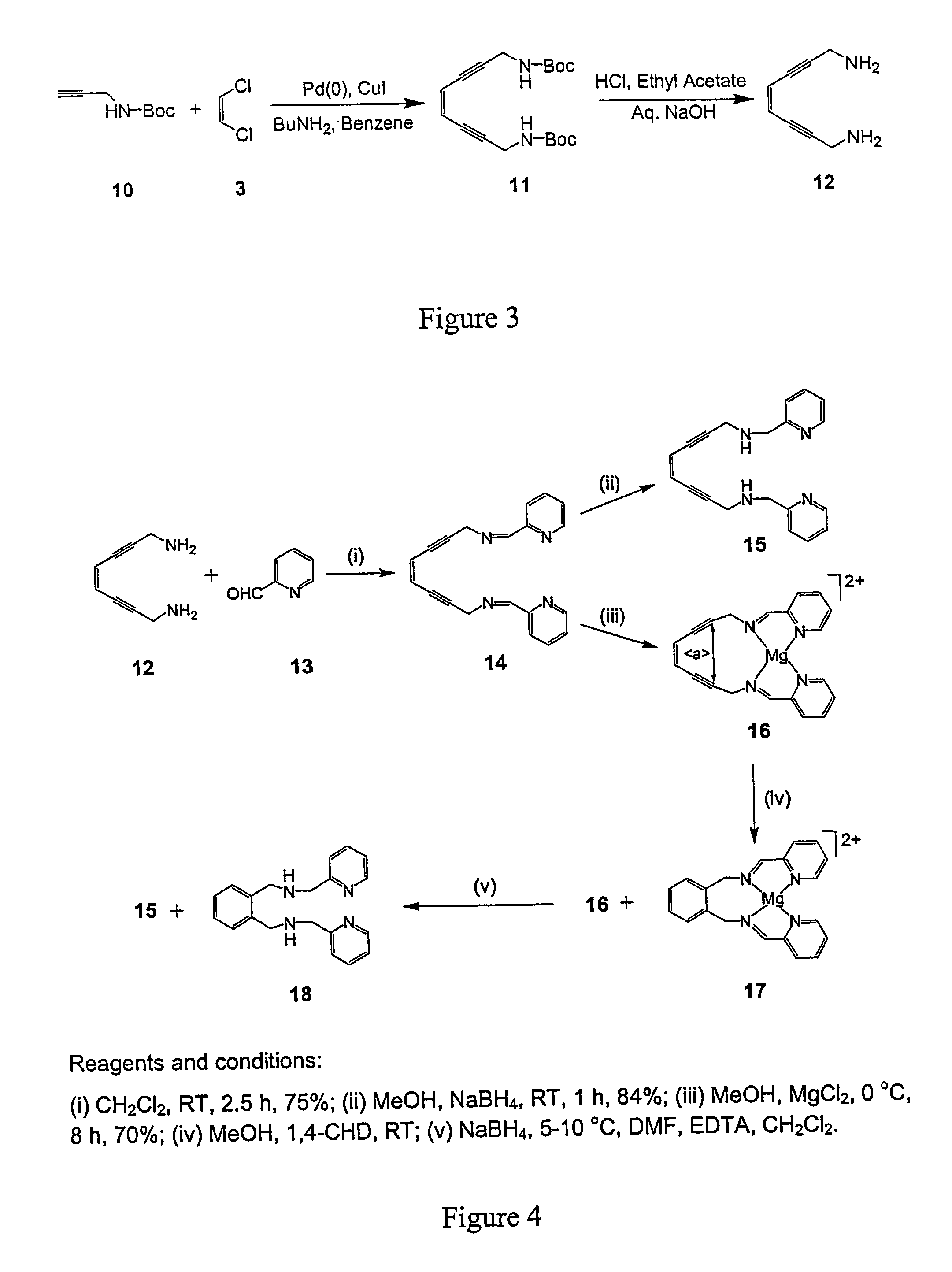
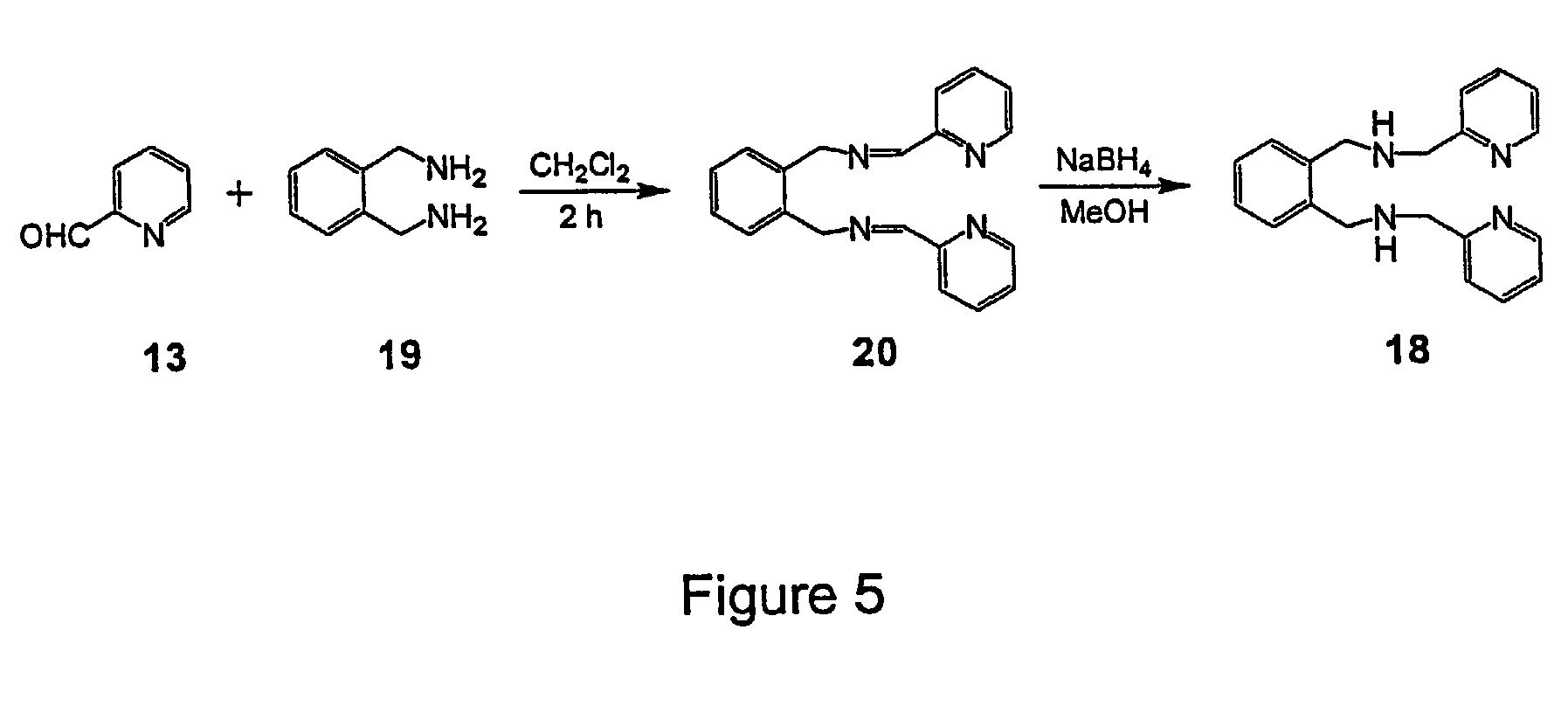
Enediyne compounds and methods related thereto
The invention provides novel tetradentate enediyne ligands that are themselves thermally stable, yet react at about room temperature or slightly higher upon addition of metal ions or under photothermal conditions. In another aspect of the invention, a method of treating a disorder in a mammal comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound or composition is provided. In addition, the free ligand can be delivered to the mammal prior to complexation to metals, such that the ligand is exposed to a metal in the body and forms a metal complex in vivo. Furthermore, a metal complex of the invention can be administered to the mammal such that the complex exchanges the first metal center with another endogenous metal in order to form a second metal complex in vivo. The second metal complex is capable of forming a benzenoid diradical under physiological conditions and / or under photothermal conditions.
Owner:ADVANCED RES TECH INST
Cyanated benzoxanthene and benzothioxanthene compounds
InactiveUS20180065980A1High fluorescence quantum yieldProvide goodOrganic chemistryNaphthalimide/phthalimide dyesArylAlkoxy group
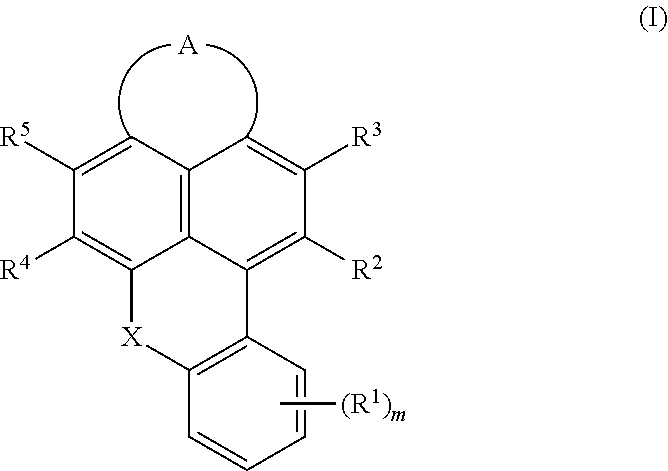
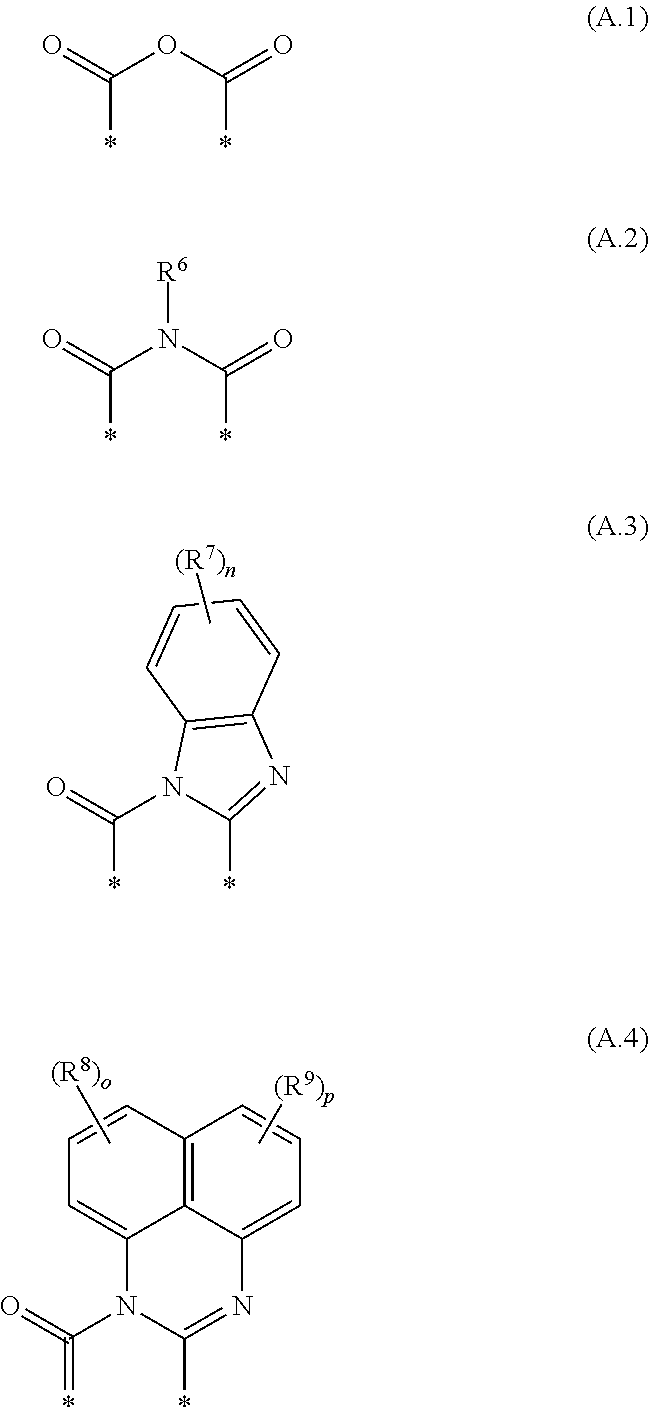
Disclosed herein are cyanated compounds of the formula (I) wherein at least one of the radicals R2, R3, R4 and R5 is CN, and the remaining radicals are selected from hydrogen, chlorine and bromine; X is O, S, SO or SO2; m is 0, 1, 2, 3 or 4; 10 is selected from bromine, chlorine, cyano, —NRaRb, C1-C24-alkyl, C1-C24-haloalkyl, C1-C24-alkoxy, C1-C24-haloalkoxy, C3-C24-cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, heteroaryl, C6-C24-aryl, C6-C24-aryloxy, C6-C24-aryl-C1-C10-alkylene, etc.; A is a diradical selected from diradicals of the general formulae (A.1), (A.2), (A.3), and (A.4) wherein R6, (R7)n, (R8)o and (R9)p are as defined in the claims and in the description. Also disclosed are color converters containing at least one polymer as a matrix material and at least one cyanated compound of formula (I) or mixtures thereof as a fluorescent dye, the use of the color converters, and lighting devices containing an LED and at least one color converter.
Owner:BASF AG
Preparation method of allyl esters
InactiveCN102603523ASimple and reliable process stepsHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationTetramethylammonium iodideAcid derivative
The invention discloses a preparation method of allyl esters, which comprises the following steps: using acid derivative and olefin as reaction substrates; using iodide as a catalyst, using tert-butyl hydroperoxide as an oxidizing agent; reacting through biradical cross coupling reaction to obtain allyl esters. The iodide selects from cuprous iodide, tetramethyl-ammonium iodide, tetraethylammonium iodide, tetrabutyl ammonium iodide or tetraheptylammonium iodide. The invention discloses a new preparation method of allyl esters, the allyl esters can be manufactured directly by means of biradical cross-coupling, therefore, the process step is simple and reliable, the yield ratio is higher, and the better effect is achieved.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Bi-radical compound composed of triaryl methyl radical and nitroxide radical and salt thereof and preparation method and application of bi-radical compound composed of triaryl methyl radical and nitroxide radical and salt thereof
ActiveCN108794510AExcellent frequency matchingHigh CE efficiencyOrganic chemistryWater resource assessmentMagic angle spinningSolubility
The invention provides a bi-radical compound composed of a triaryl methyl radical and a nitroxide radical and salt thereof and a preparation method and application of the bi-radical compound composedof the triaryl methyl radical and the nitroxide radical and the salt thereof. A structural formula of the bi-radical compound is as shown in the formula 1; the formula is shown in the description; thepreparation method comprises the steps that a compound A1 and a compound A2 are subjected to acid amide condensation reaction to obtain a compound A3; the compound A3 and a compound A4 are subjectedto acid amide condensation reaction to obtain the bi-radical compound and the salt thereof. The portion, provided with both the nitroxide radical and the triaryl methyl radical, of a bi-radical polarization agent has the following advantages that the frequency matching ability is better, and the CE efficiency is higher; under a magic angle spinning condition, a depolarization effect does not exist, and a high field DNP enhancing effect is better; exchange interaction is stronger; the water solubility is good, so that the DNP enhancing multiple is high; by modifying R1, R2, R3, R4, R5 and R6 groups, exchange interaction can be improved moderately, bi-radical relaxation time can be prolonged moderately, and the bi-radical water solubility can be improved moderately, so that the DNP propertyof the polarization agent is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
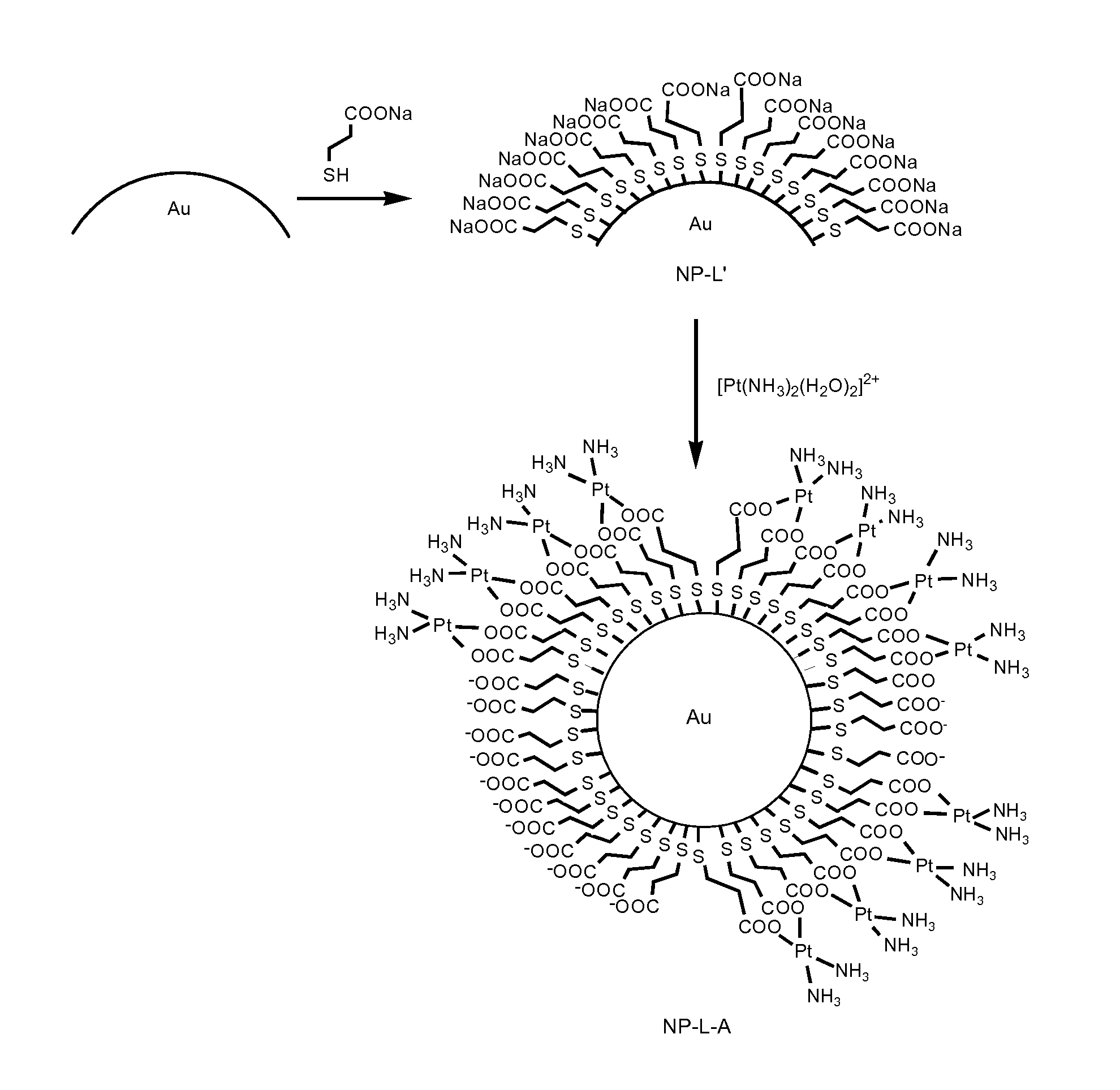
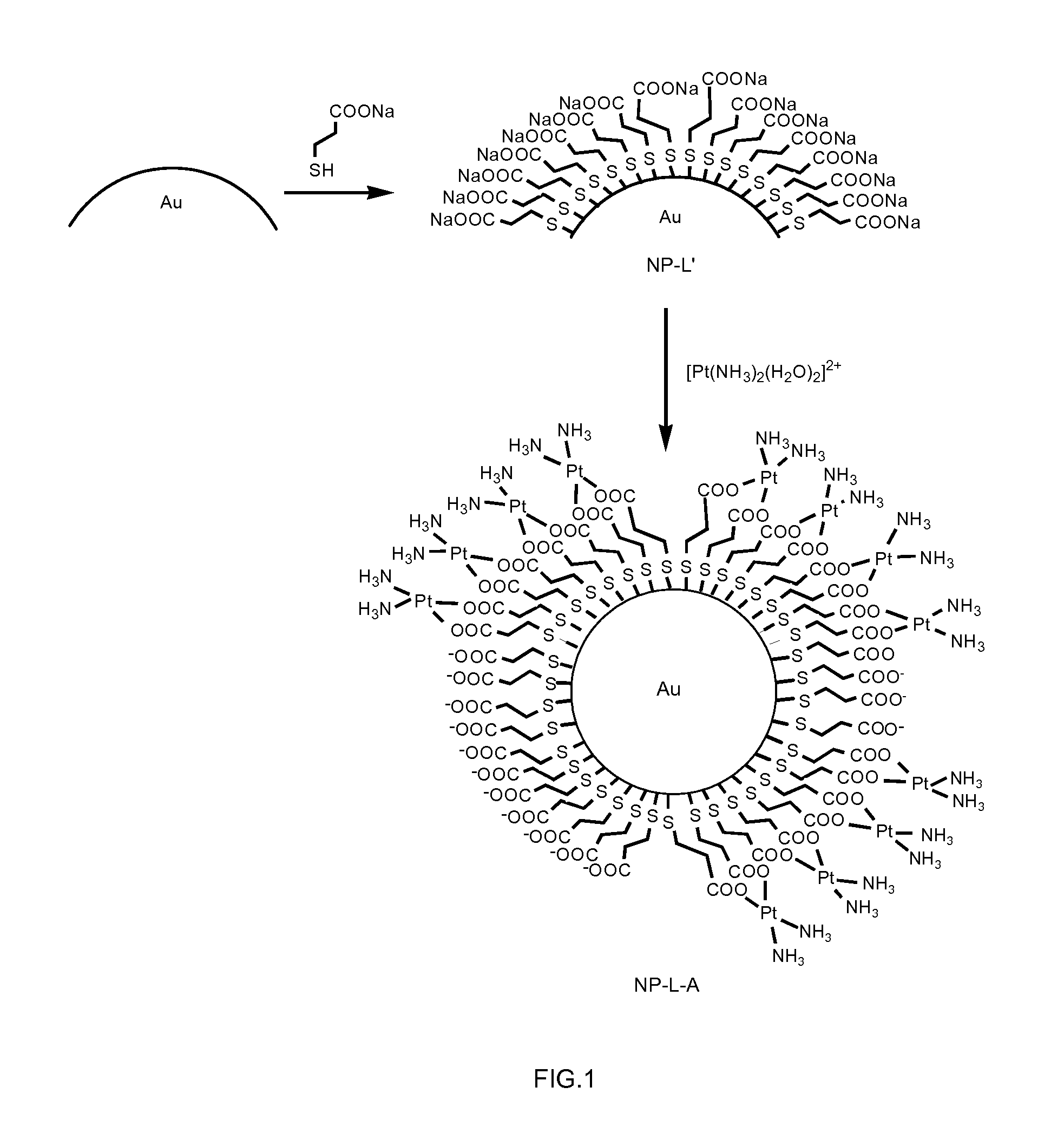
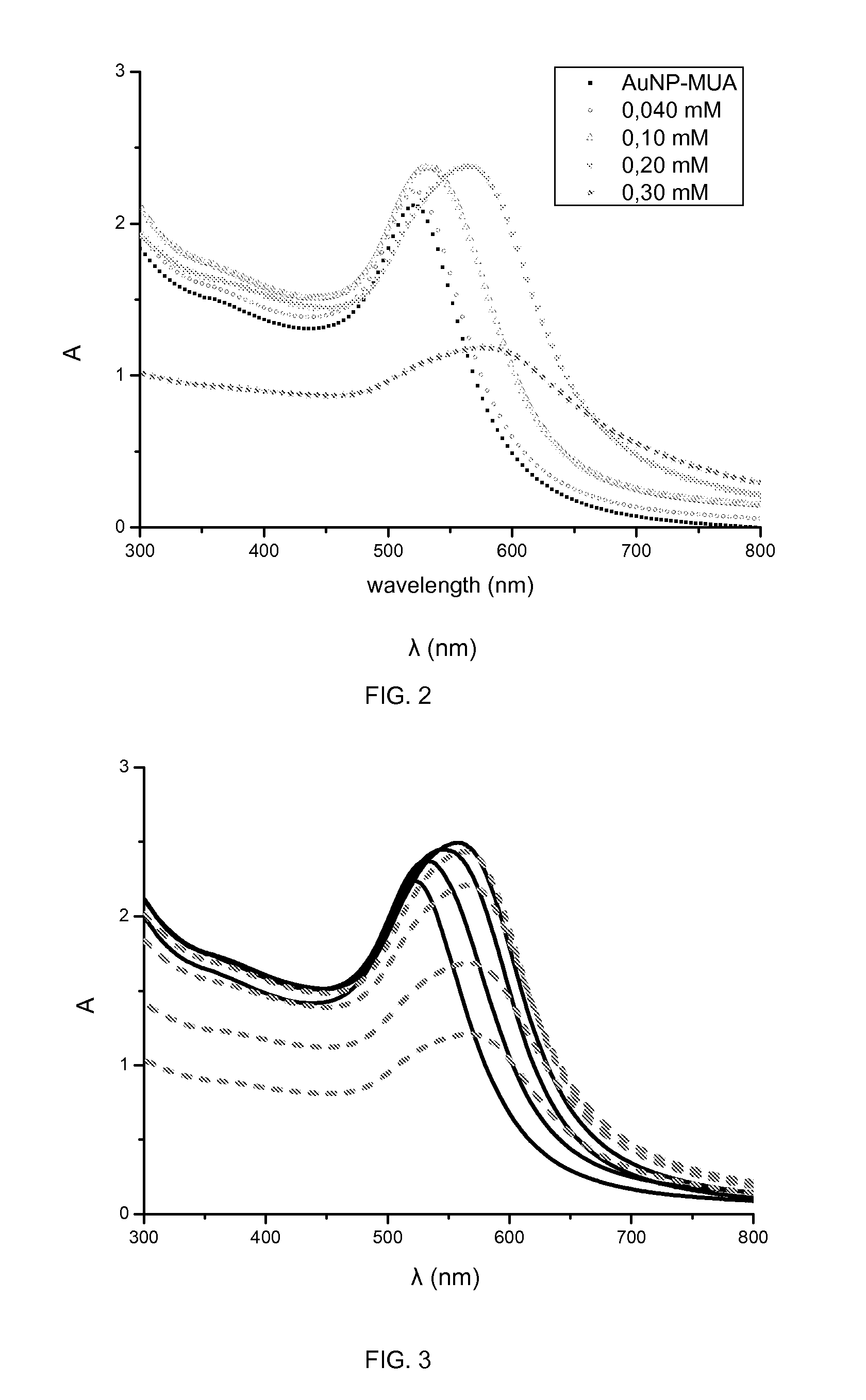
Conjugates comprising nanoparticles coated with platinum containing compounds
The present invention relates to conjugates of formula (I) having colloidal stability in a medium, wherein NP is a gold, silver or platinum nanoparticle; L is a linker selected from the group consisting of formula (II), formula (III), and a stereoisomer of any of the formulas (II) and (III), which is attached to the nanoparticle NP through sulfur atoms; wherein the meanings of X, n, p, Y and s are further specified in the description; and A is a platinum (II) biradical selected from the group consisting of formula (IV), formula (V) and formula (VI) including any of the stereoisomers of all of them, wherein the biradical is optionally in the form of a salt and is attached to the linker L through the single bonded oxygen atoms of the carboxyl groups. It also relates to a process for the preparation of the conjugates of formula (I) and to pharmaceutical compositions containing them. The conjugates of the invention are used for the treatment of cancer.
Owner:FUNDACIO PRIVADA INST CATALA DE NANOTECNOLOGIA +4
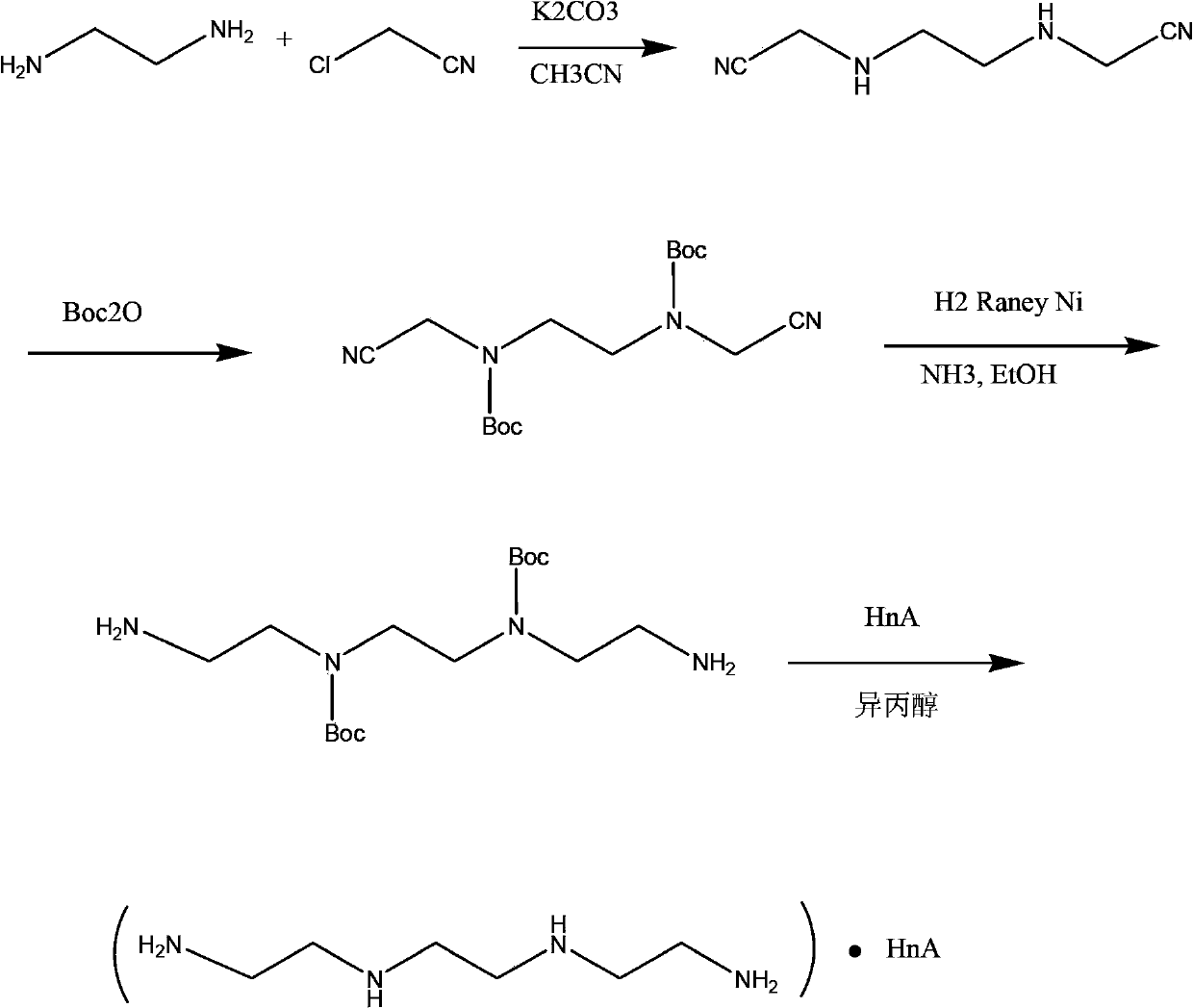
Synthetic process of hydrochloric acid trientine
InactiveCN102924289BReduce usageReduce pollutionOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationPotassium cyanideKetone
The invention discloses a novel synthetic process of hydrochloric acid trientine, and aims at providing the synthetic method of the hydrochloric acid trientine. The synthetic process can avoid using a highly-toxic material, namely potassium cyanide, and is temperate in reaction condition. A compound 2,2'-(2,2'-(ethane-1,2-diradical-bibenzyl-di (ethane-2,1-double radical)) bi isoindole-1,3-diketone is used as an initiator, after hydrazinolysis, an intermediate N1, N1'-(ethane-1,2-diradical) di(N1-nethyl ethane-1,2-diamine) is obtained. Through carbobenzoxy protection (Cbz protection), salt is generated,and dibenzyl 2,2'-(ethane-1,2-diradical-di (benzylamine-diradical)) di (ethane-2,1-diradical) dioctyl phthalatic acid aster hydrochloride is obtained so as to crystallize in ethanol through pressing catalytic hydrogenation deprotection to directly obtain the hydrochloric acid trientine. The synthetic process belongs to the organic synthetic technical field.
Owner:GUANGDONG AOERCHENG PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com