Patents
Literature
62 results about "Luminescent Measurements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Techniques used for determining the values of photometric parameters of light resulting from LUMINESCENCE.
Apparatus for measuring in particular luminescent and/or fluorescent radiation
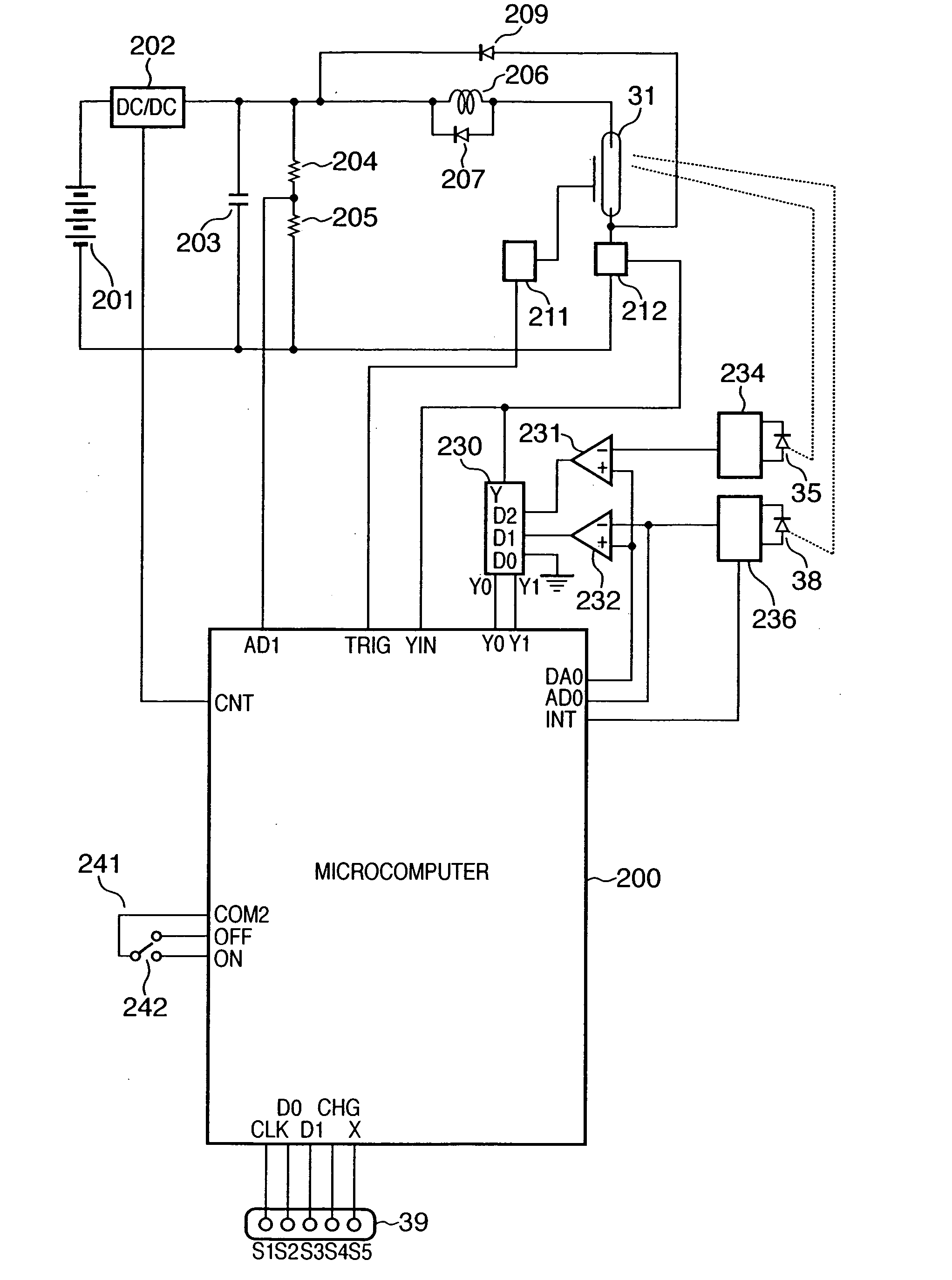
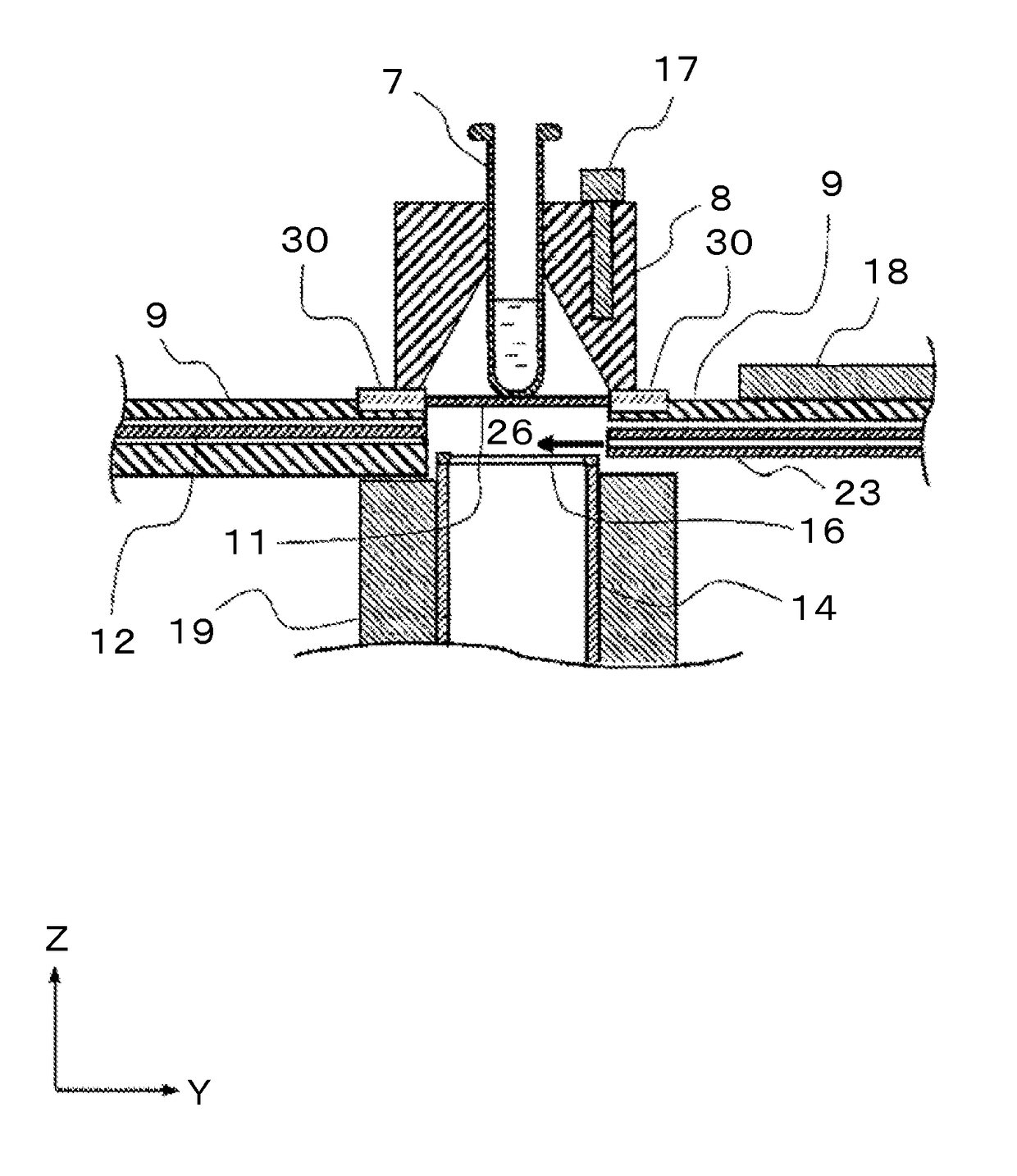
InactiveUS20030042428A1Compact structureBroad spectrumChemiluminescene/bioluminescencePhotometryFluorescent radiationMeasuring instrument
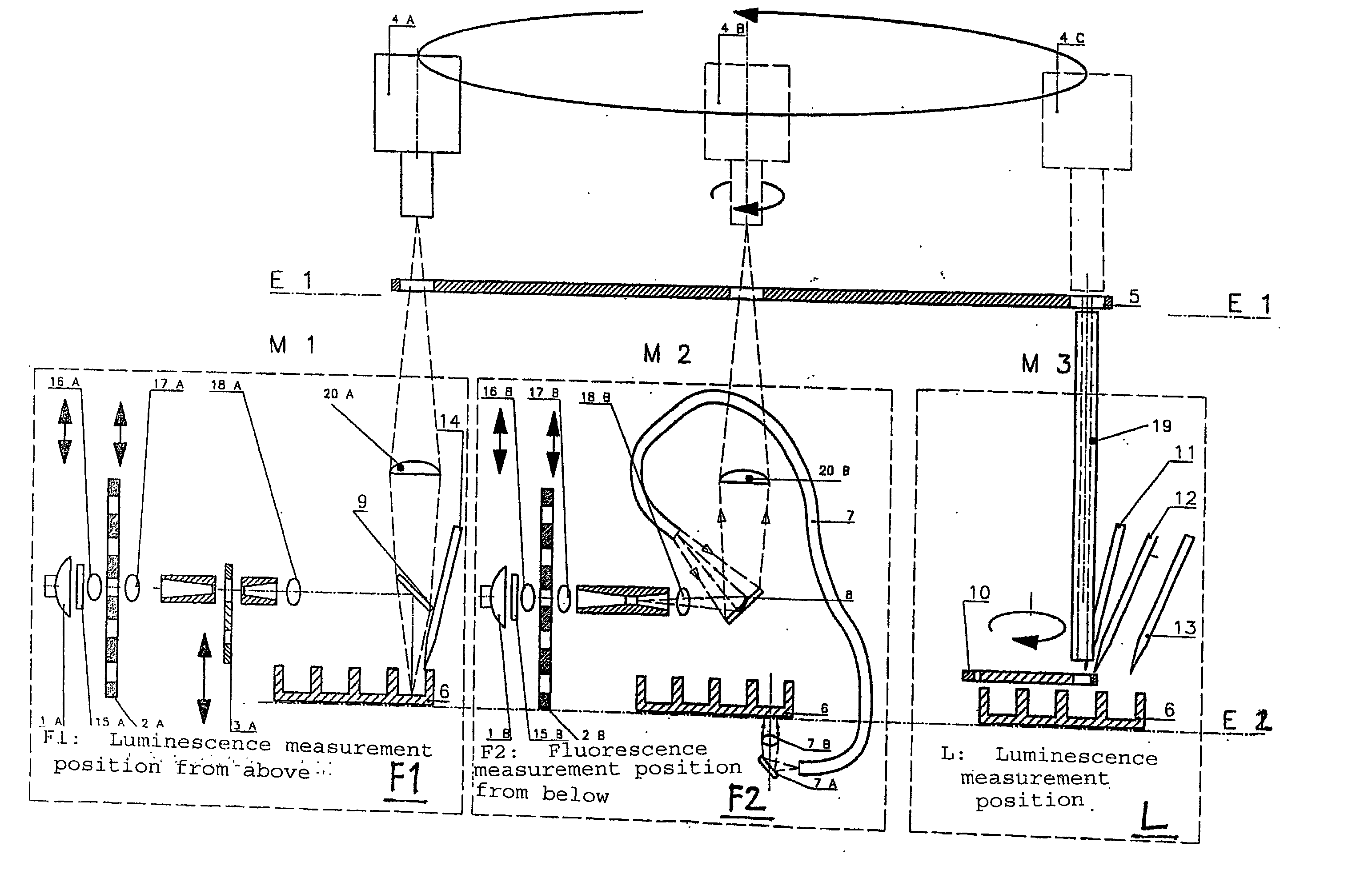
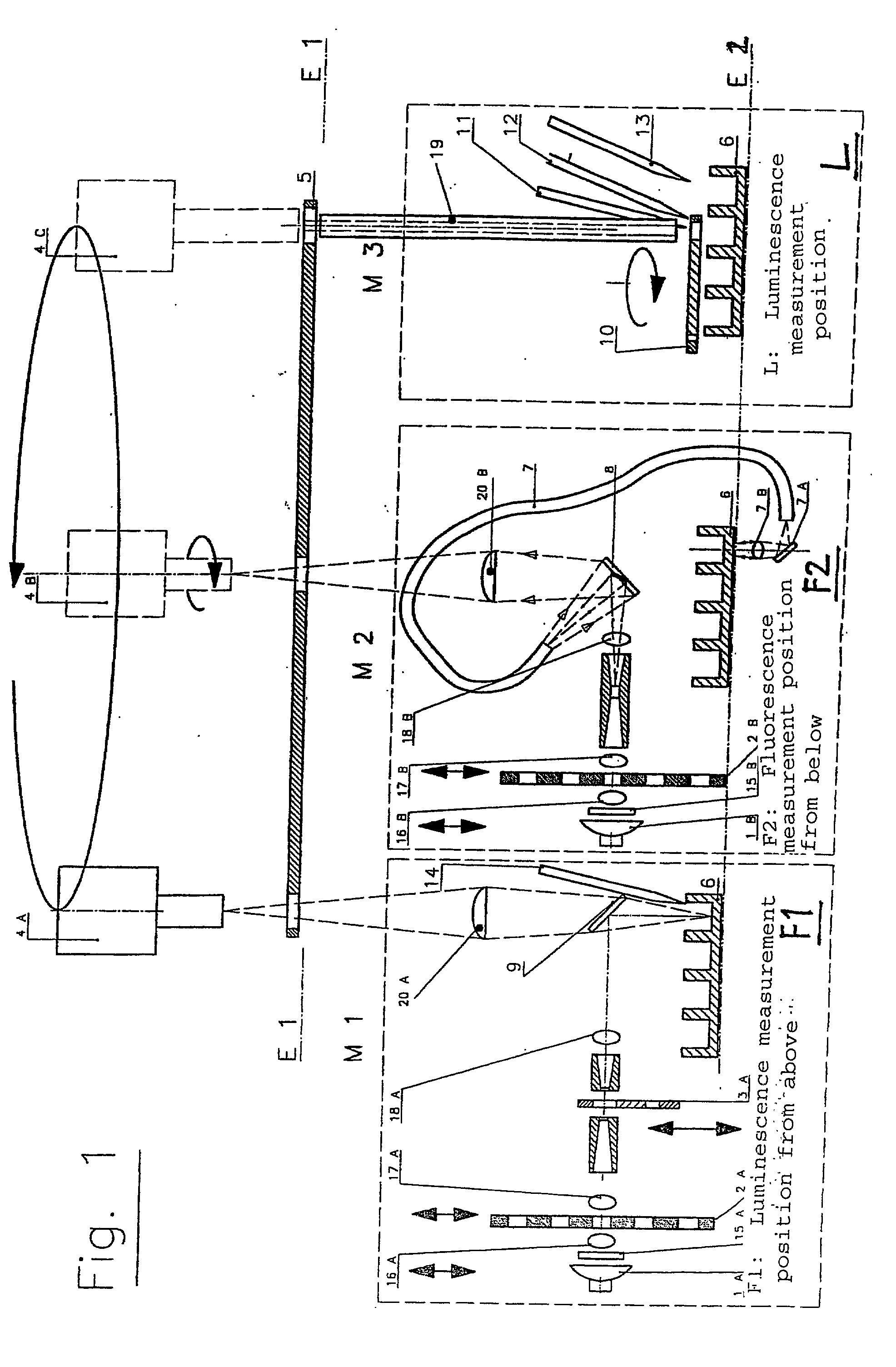
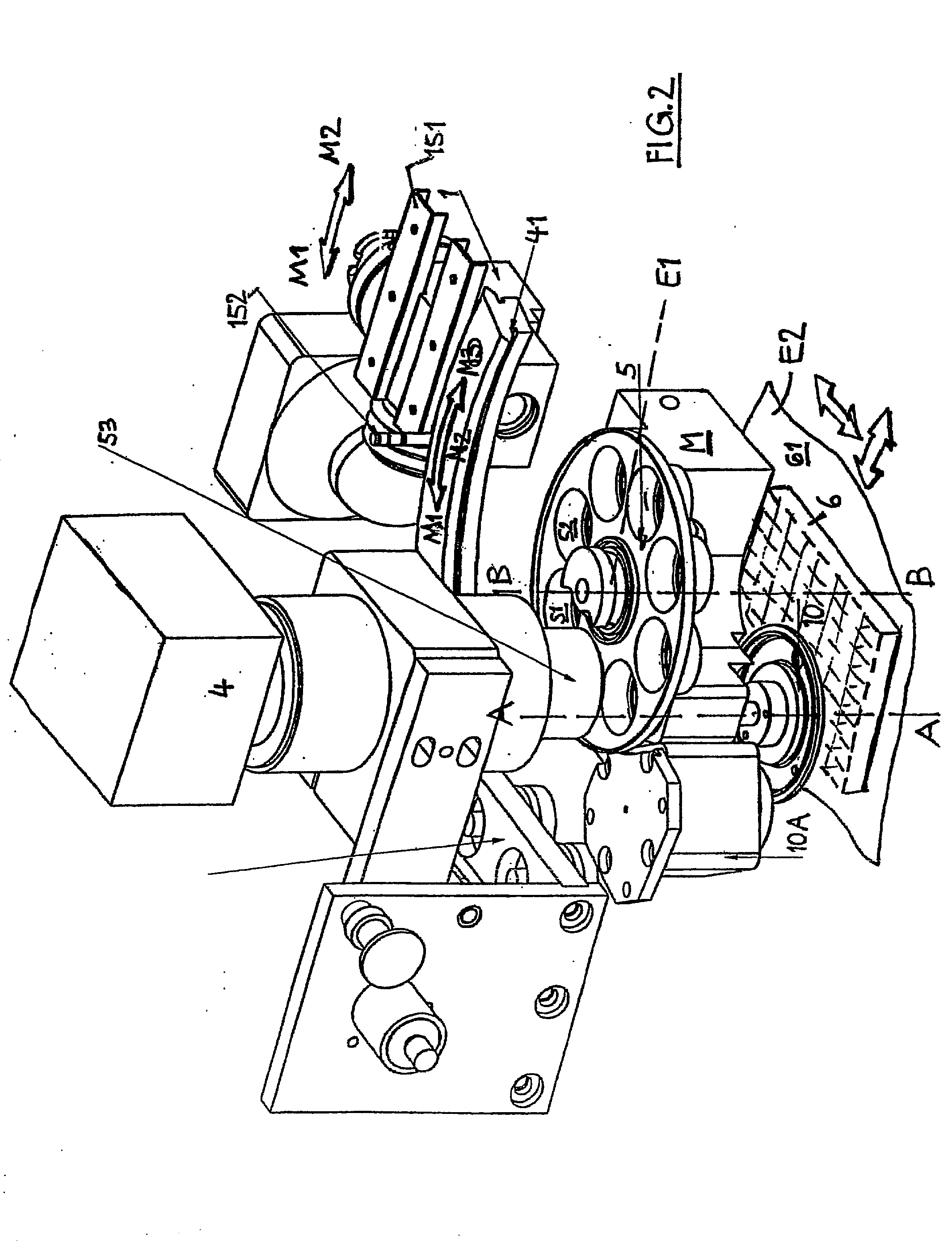
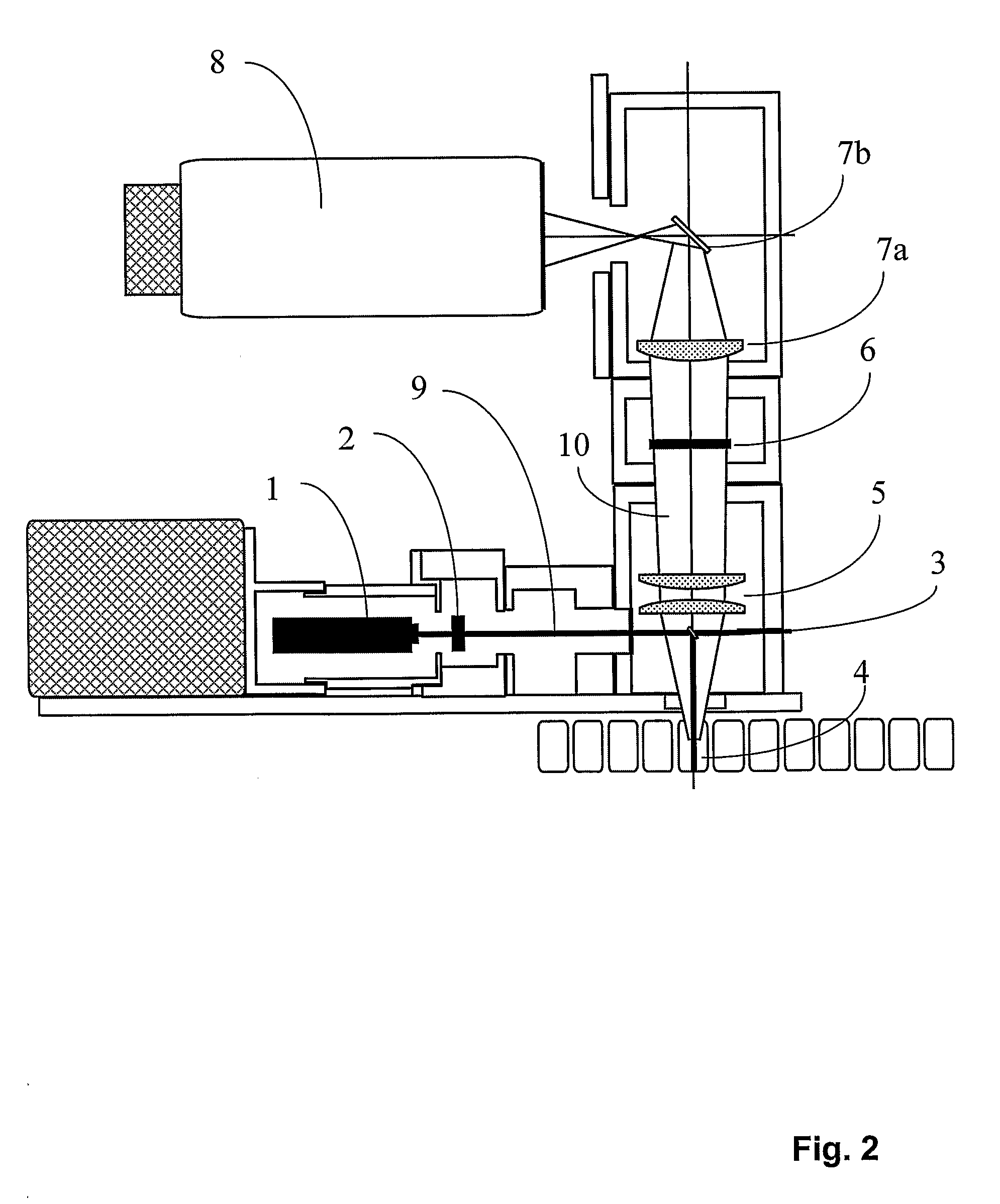
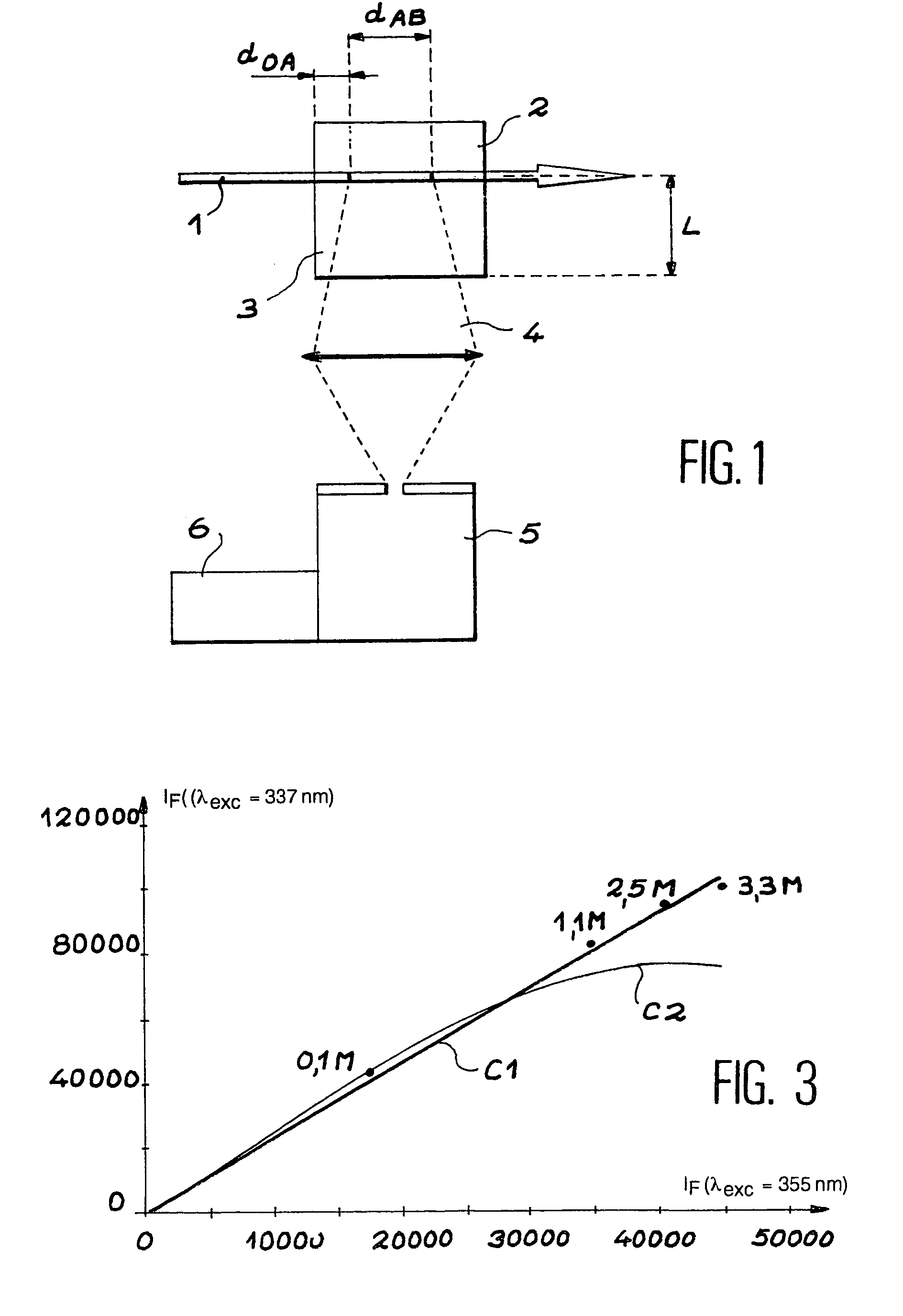
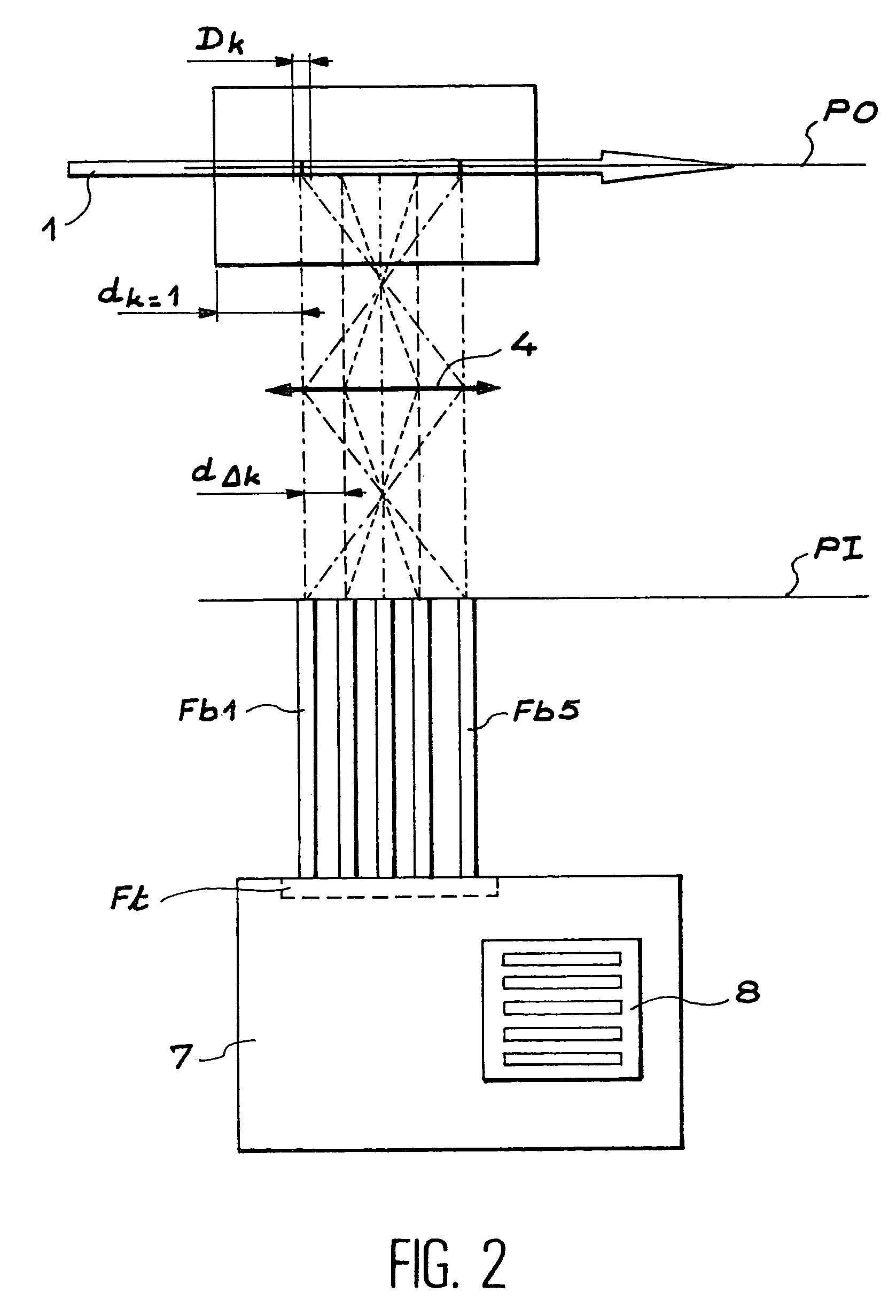
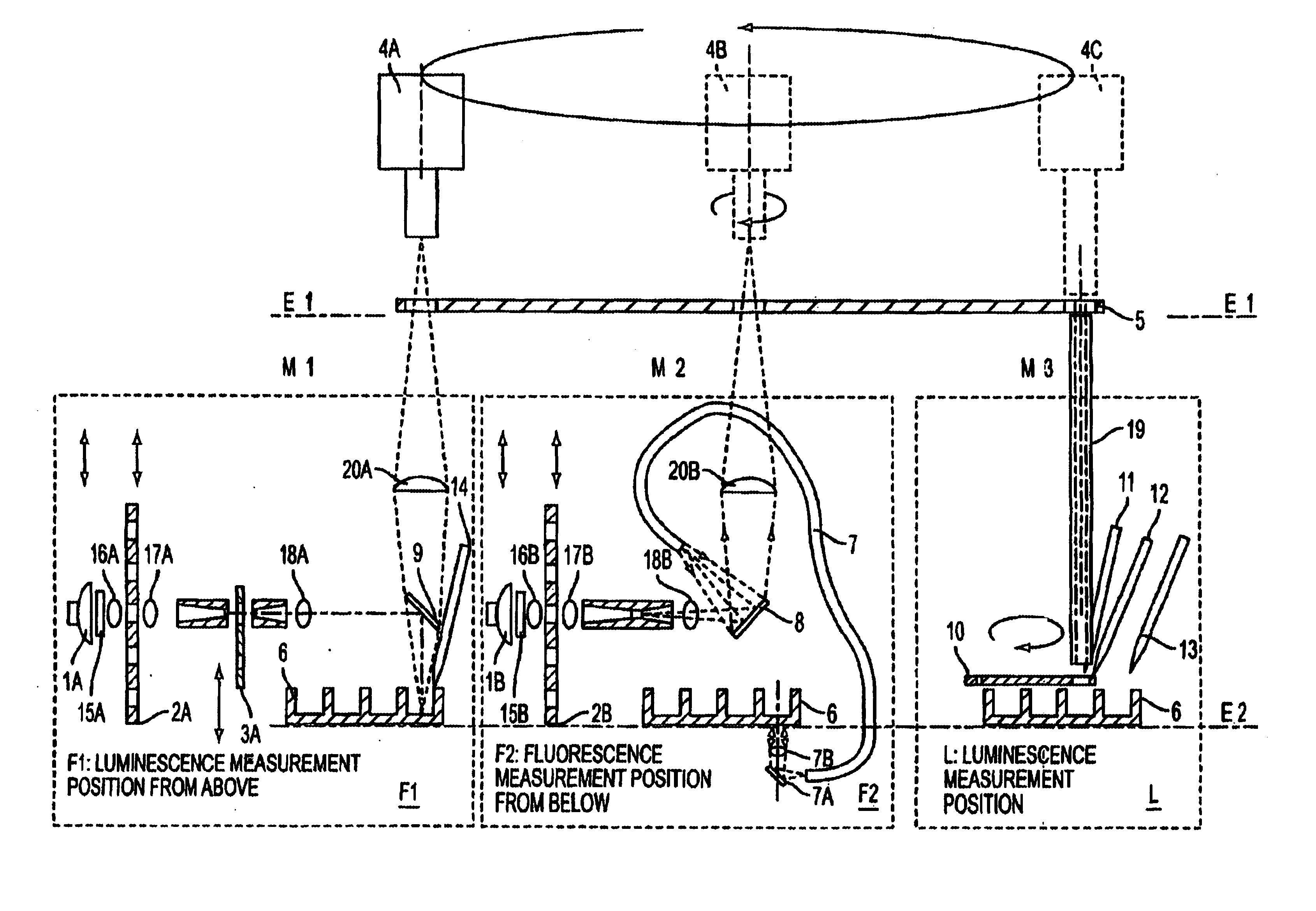
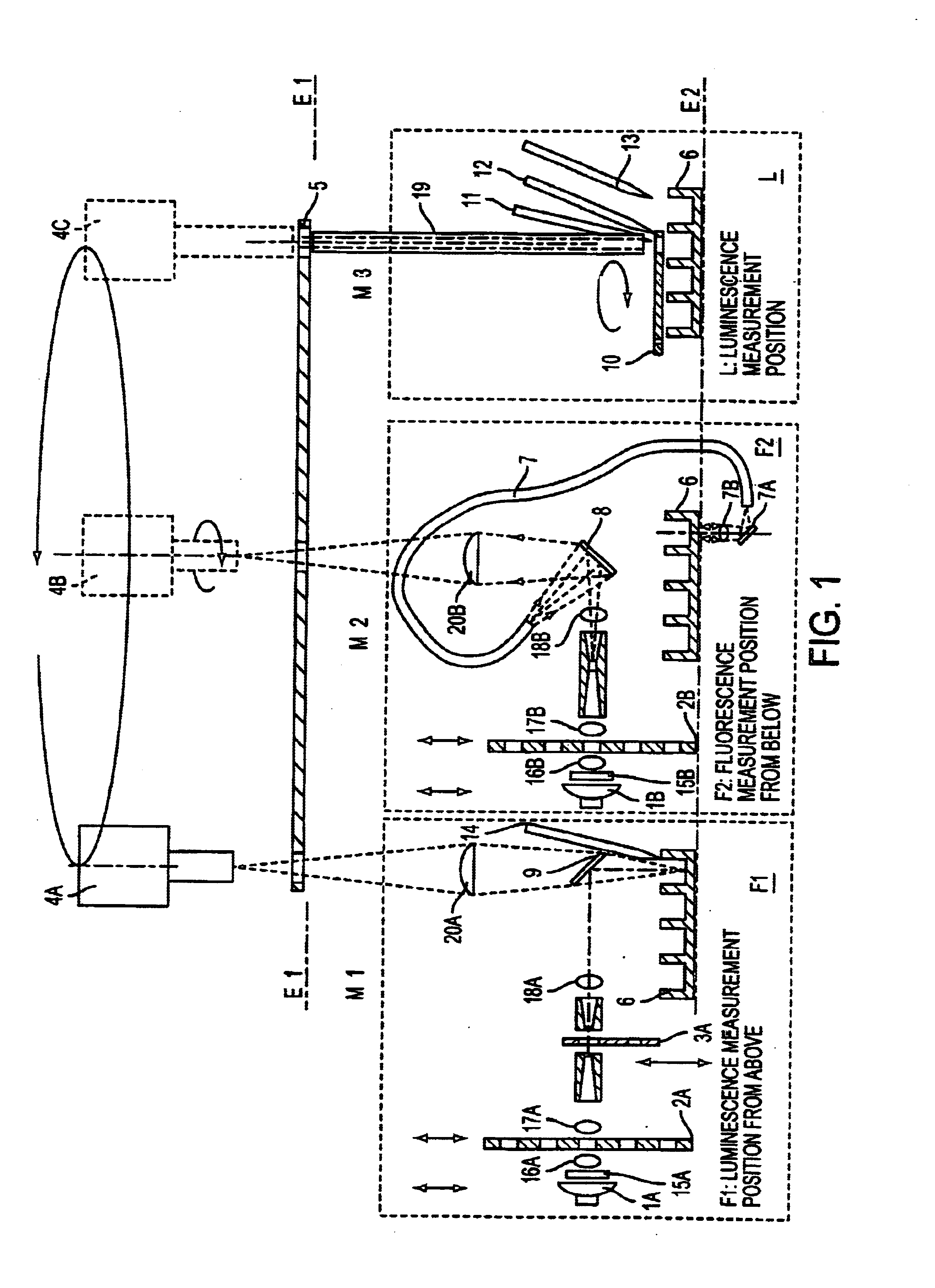
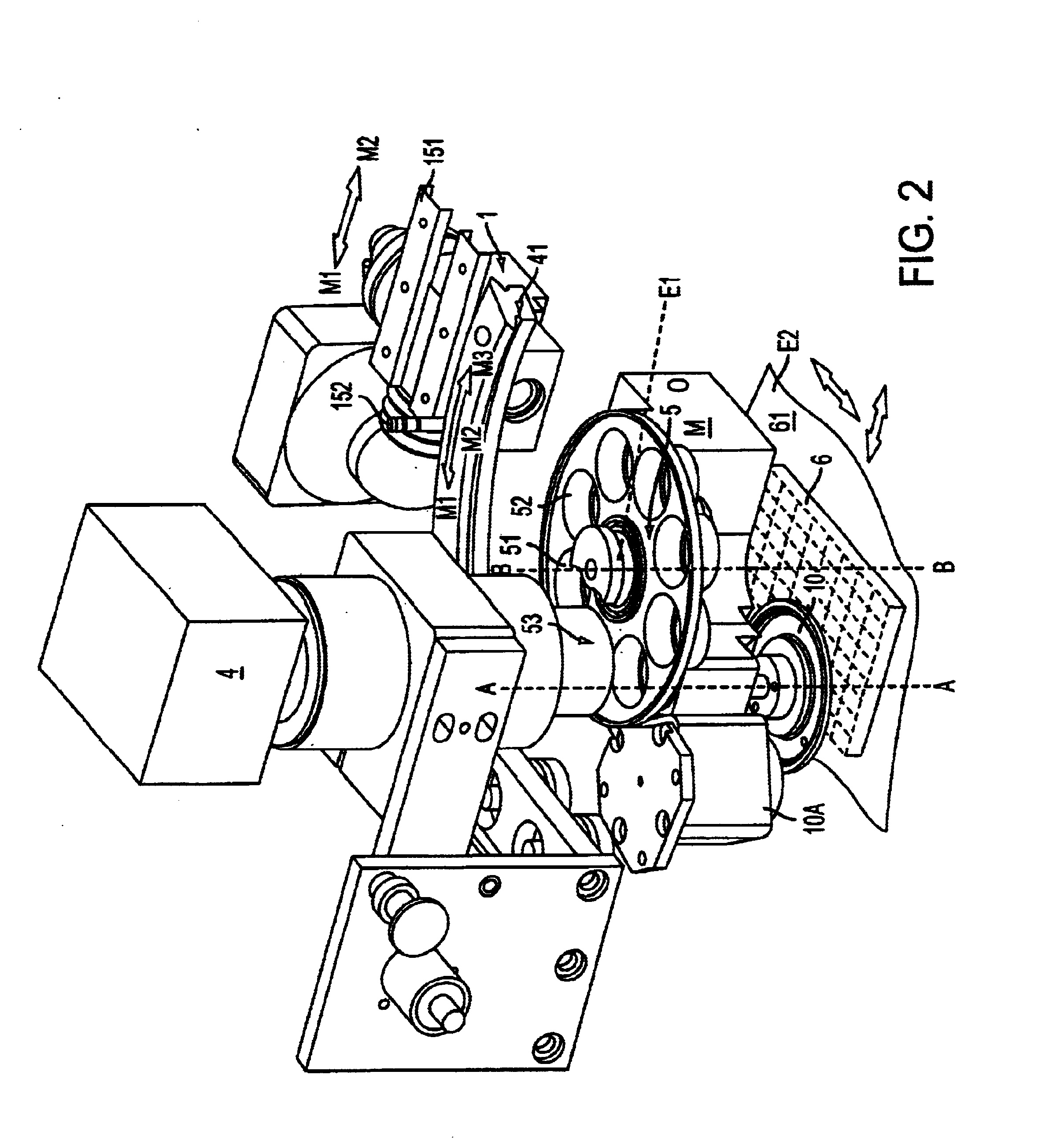
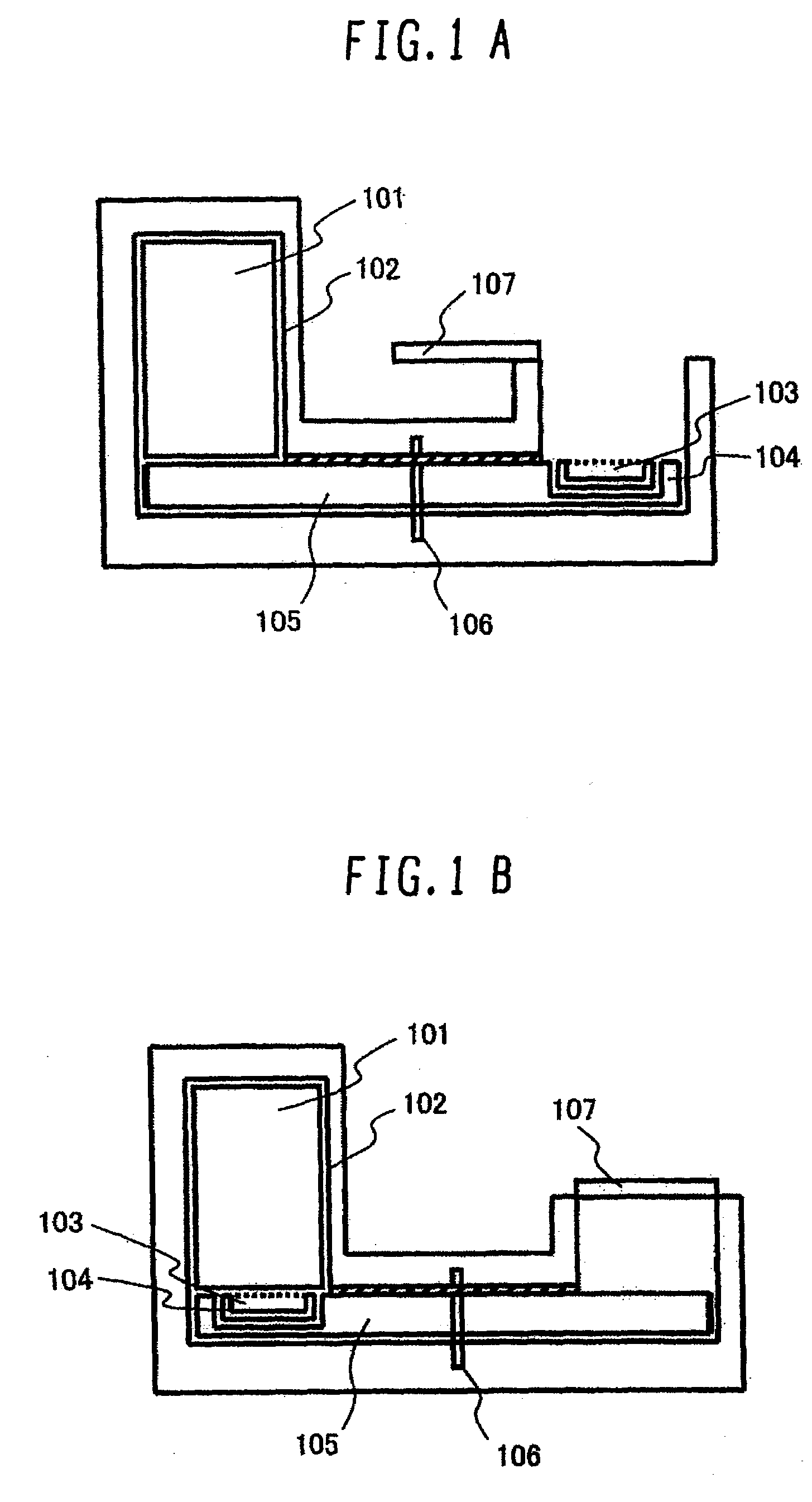
An apparatus for selected measurement of in particular luminescent and / or fluorescent radiation has a plurality of measurement light paths (M1, M2, M3), which each have their own measuring devices optimized for the particular measurement mode. As a common device, a filter holder (5) is used, in which the detector and each of the measuring devices have access to each of the openings of the filter holder, and each of these openings can be equipped with an emissions filter that is expedient for the particular measurement mode involved. The result is an especially compact arrangement of a multipurpose measuring instrument with measurement properties that is largely equivalent to the measurement properties of special individual measuring instruments and that is also suitable in particular as an individual instrument for special luminescence measurements, such as BRET measurements.
Owner:BERTHOLD TECH
Correction Method and Measurement Device For Anti-Stokes Photoluminescence Measurement
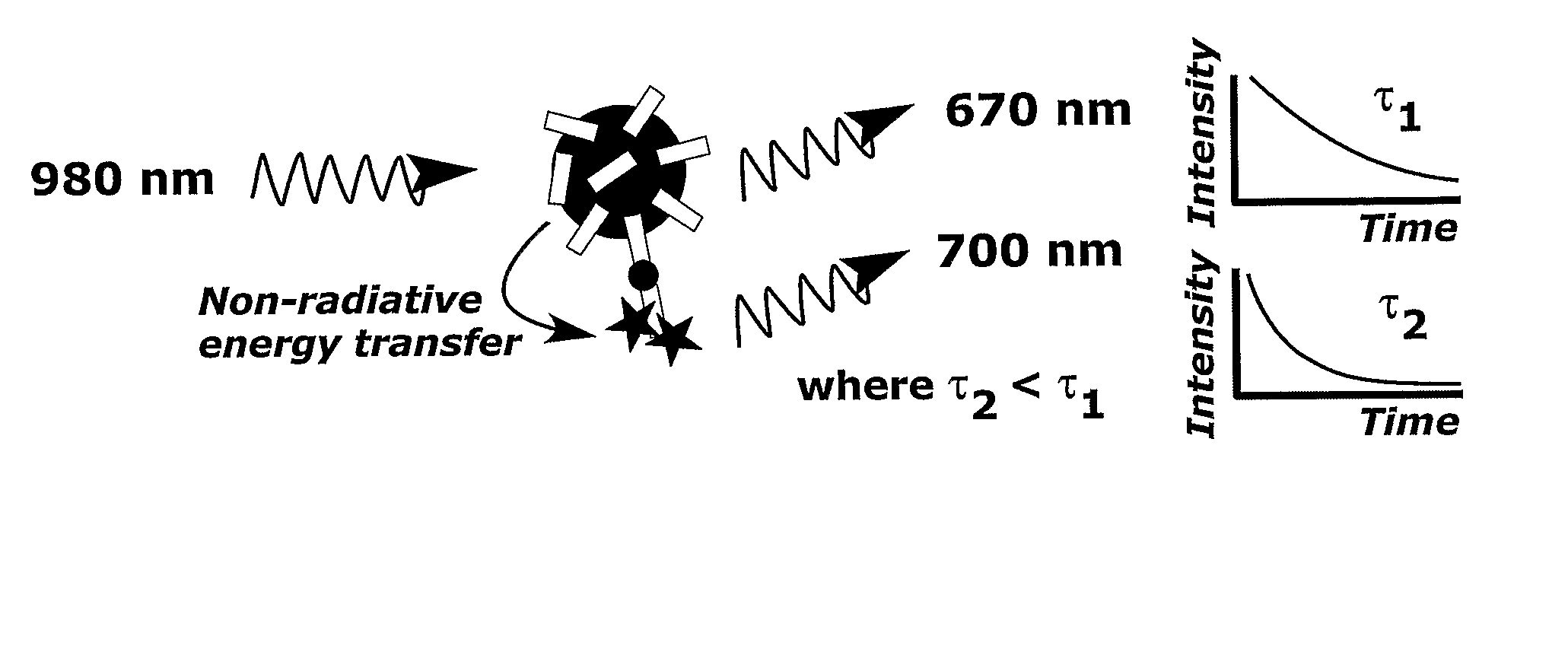
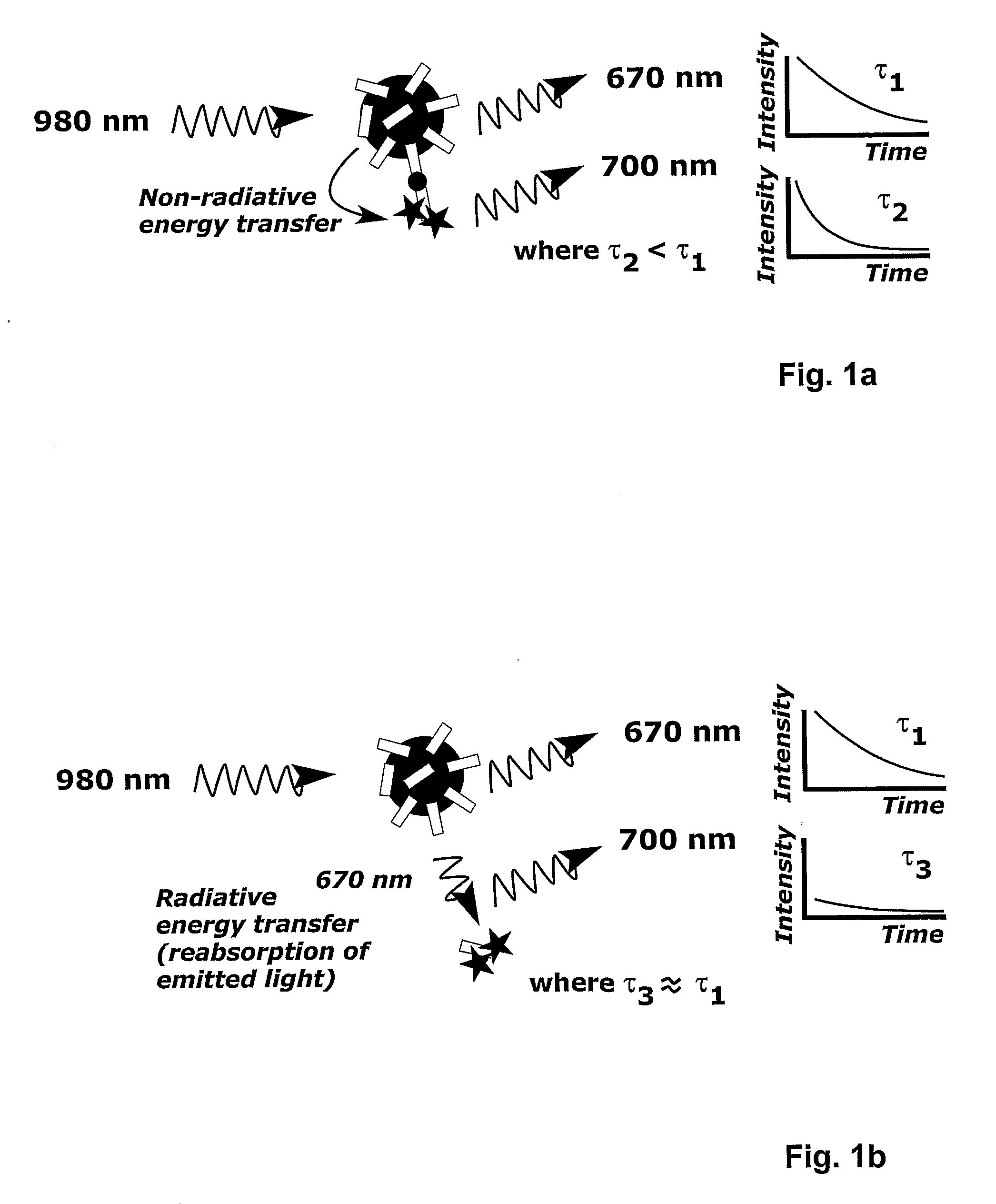
This invention relates to a method to correct for error in an anti-Stokes photoluminescence measurement in a Foerster-type resonance energy-transfer assay. The method comprises the steps of exciting anti-Stokes photoluminescent molecules, ions, phosphors, chelates, or particles, i.e. donors of the assay, with one wavelength or multiple wavelengths of light wherein the wavelength or wavelengths are greater than that of an emission wavelength of acceptor molecules in the assay; measuring emission light signal at a wavelength, which is the emission wavelength of the acceptor molecules in the Foerster-type resonance energy-transfer assay, and which differs from the emission wavelength of the anti-Stokes photoluminescent donor in at least two different time windows; a first time window within the time window defined by the excitation light pulse, i.e. within the time window opening when the excitation light pulse is switched on and closing when the excitation light pulse is switched off, and a second time window to follow the first time window not at all overlapping with the time window defined by the excitation pulse; and correcting the emission light signal measured, comprising signals originating from non-radiative and radiative energy transfer, within the first time window by estimating the ratio of the signals from non-radiative and radiative energy transfer or the signal originating from radiative energy transfer using at least one emission light signal measured in the second time window. This invention also relates to the use of a device according to the method of the invention, a system for carrying out the method and a software product for the system.
Owner:HIDEX
Separation of doping density and minority carrier lifetime in photoluminescence measurements on semiconductor materials
InactiveUS20120181452A1Provide usageSimple methodSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPhotometryBrickSemiconductor materials
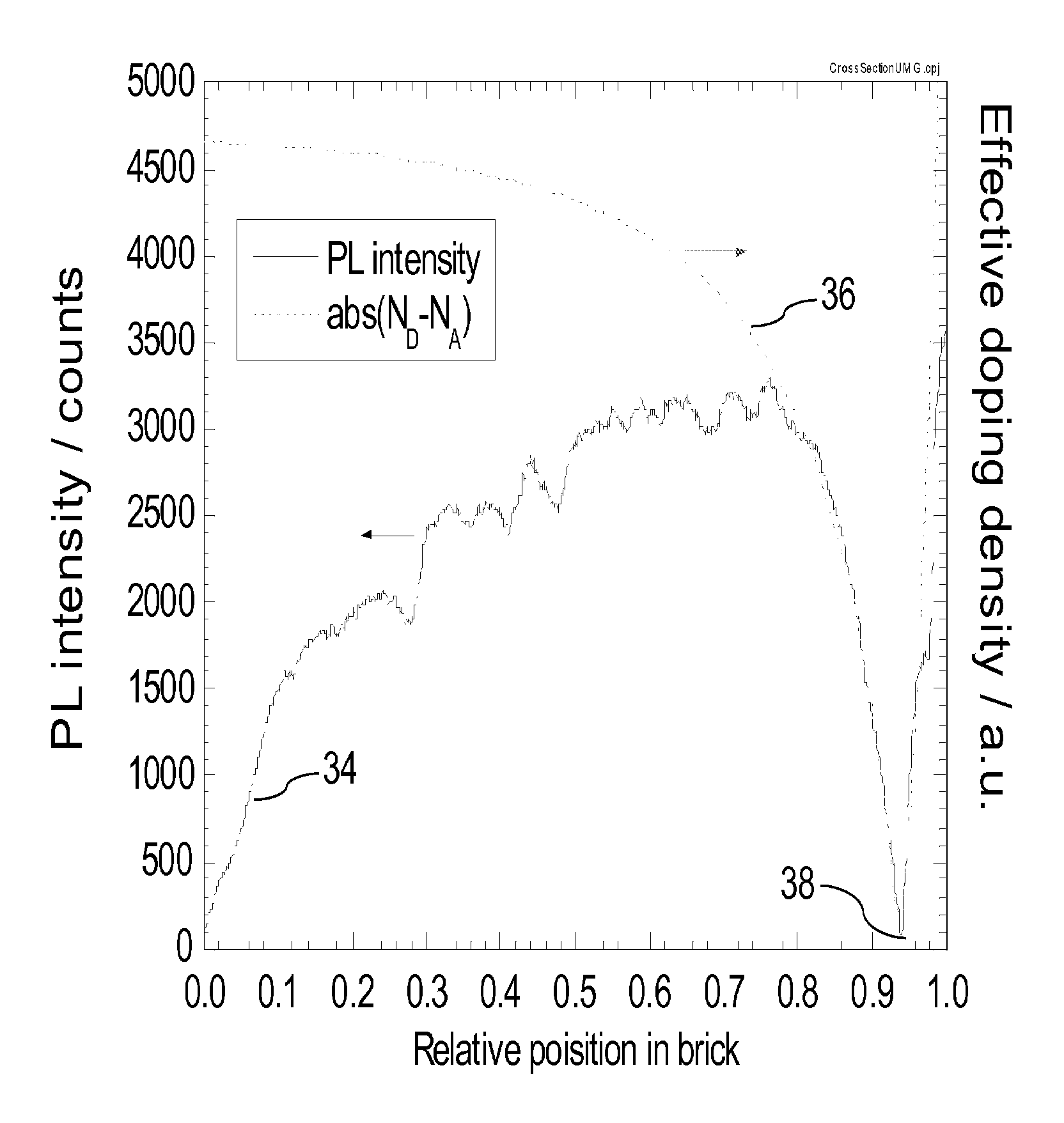
Methods are presented for separating the effects of background doping density and effective minority carrier lifetime on photoluminescence (PL) generated from semiconductor materials. In one embodiment the background doping density is measured by another technique, enabling PL measurements to be analysed in terms of effective minority carrier lifetime. In another embodiment the effective lifetime is measured by another technique, enabling PL measurements to be analysed in terms of background doping density. In yet another embodiment, the effect of background doping density is removed by calculating intensity ratios of two PL measurements obtained in different spectral regions, or generated by different excitation wavelengths. The methods are particularly useful for bulk samples such as bricks or ingots of silicon, where information can be obtained over a much wider range of bulk lifetime values than is possible with thin, surface-limited samples such as silicon wafers. The methods may find application in solar cell manufacturing for improving the manufacture of silicon ingots and bricks, or for providing a cutting guide for wafering.
Owner:BT IMAGING PTY LTD
Fluorescence-optical combined tomography system and measuring method
InactiveCN102920434AHigh sensitivityStable jobDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsOptical tomographyFluorescence
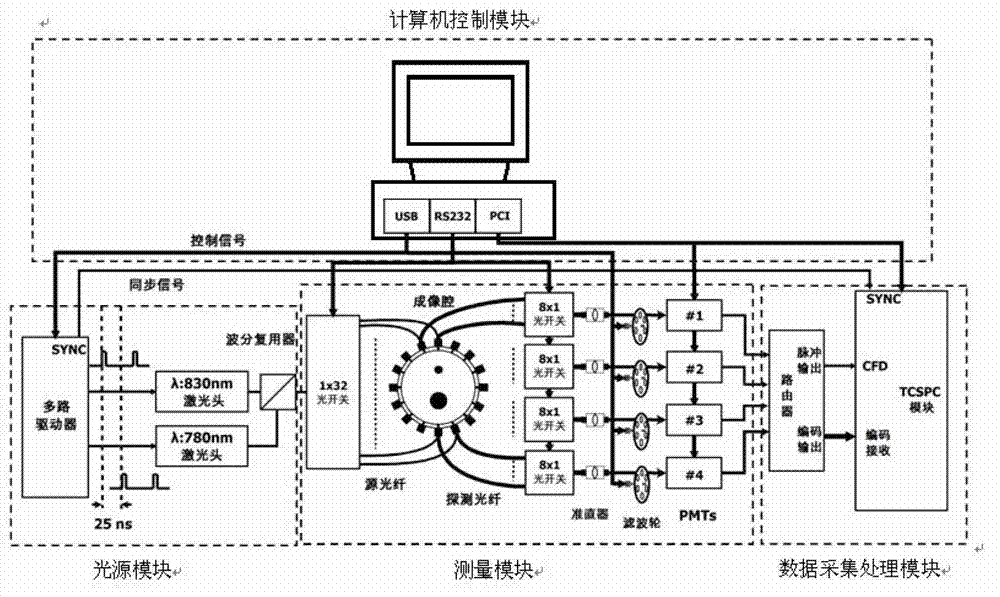
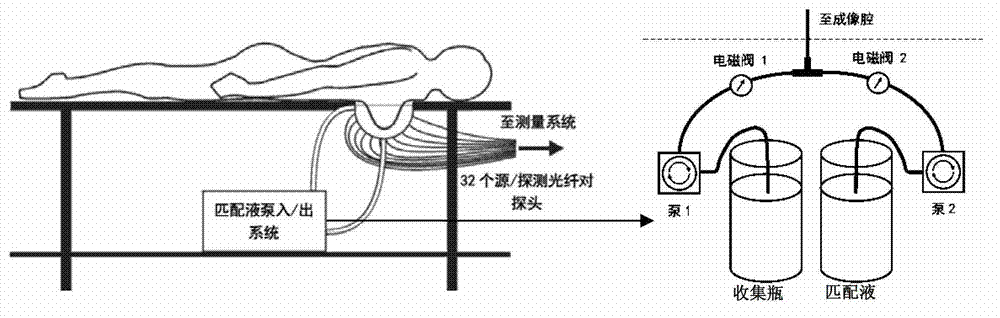
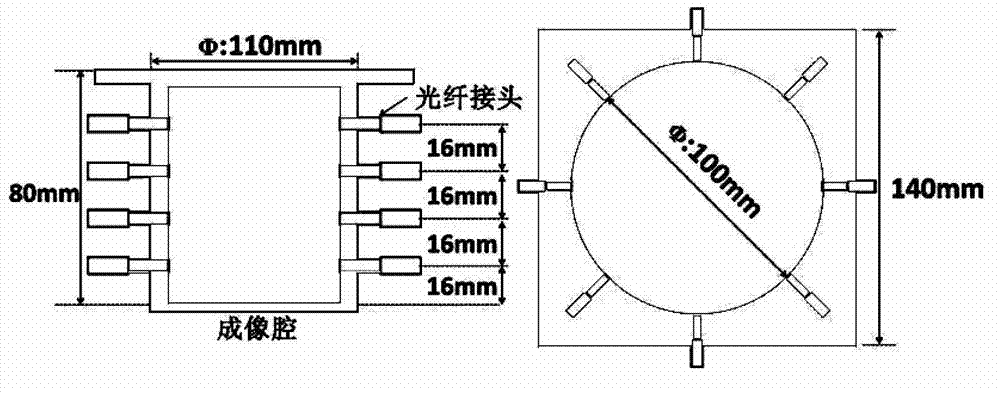
The invention discloses a fluorescence-optical combined tomography system and a measuring method. The fluorescence-optical combined tomography system comprises a light source module, a measuring module, a data acquisition and processing module, and a computer control module, wherein the light source module produces exciting light with different wavelengths and couples the exciting light into composite exciting light; the measuring module is used for placing an imaging target body, receiving the composite exciting light, measuring the imaging target body in a layering mode, realizing fully three-dimensional scanning, scattering a photon signal, and converting the photon signal into a pulse electric signal for output; the data acquisition and processing module receives the pulse electric signal, and performs multi-dimensional photon counting measurement; and the computer control module is used for controlling the modules, and acquiring, analyzing and displaying data. According to the system, fluorescence diffuse optical tomography (FDOT) and diffuse optical tomography (DOT) are fused, so that the simultaneous reconstruction of the fluorescence yield and the fluorescence lifetime in the FDOT is realized, a target in an affected region is extracted, and accurate position information is provided for the reconstruction of an absorption coefficient and a scattering coefficient in the DOT in the next step.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
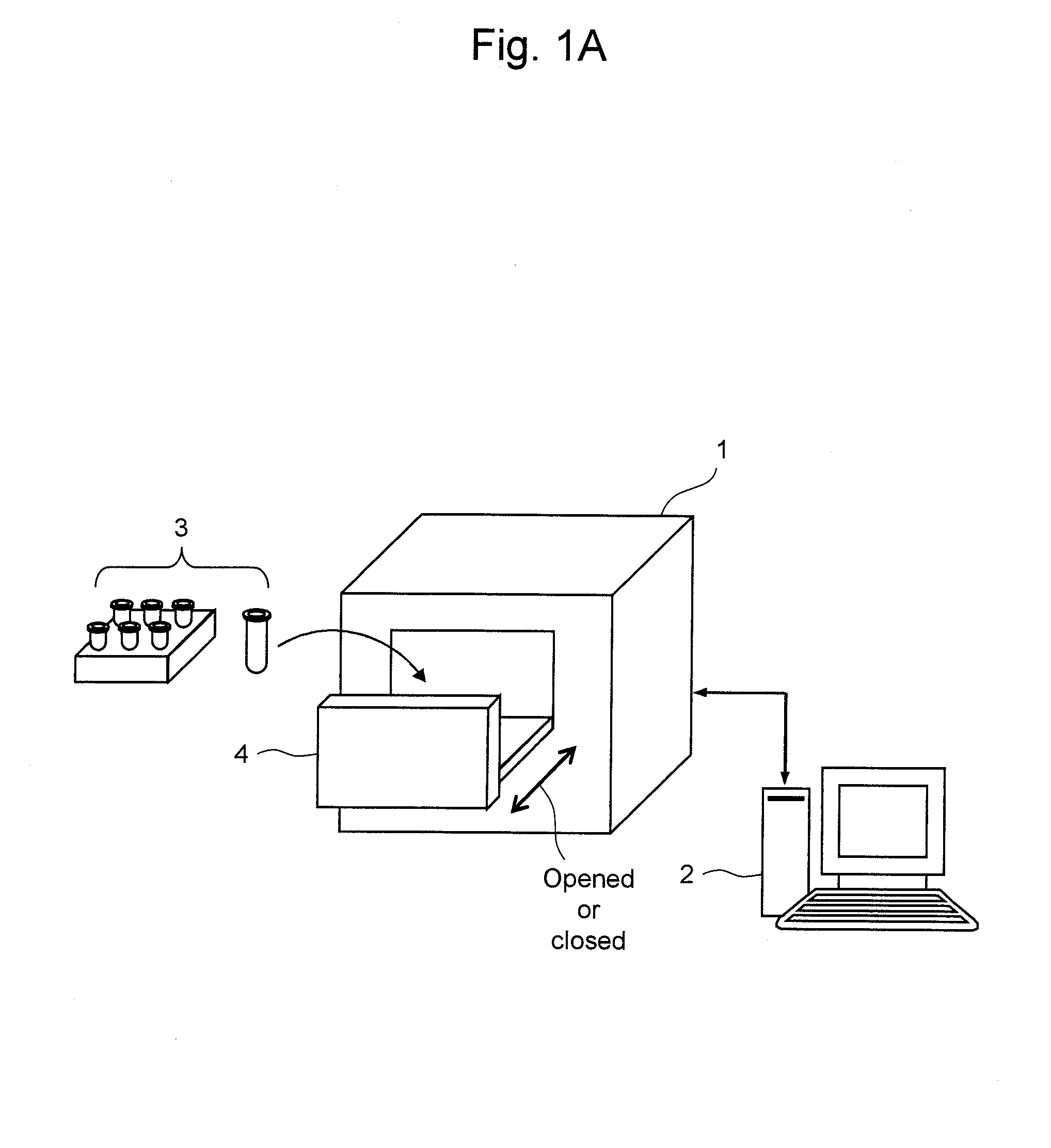
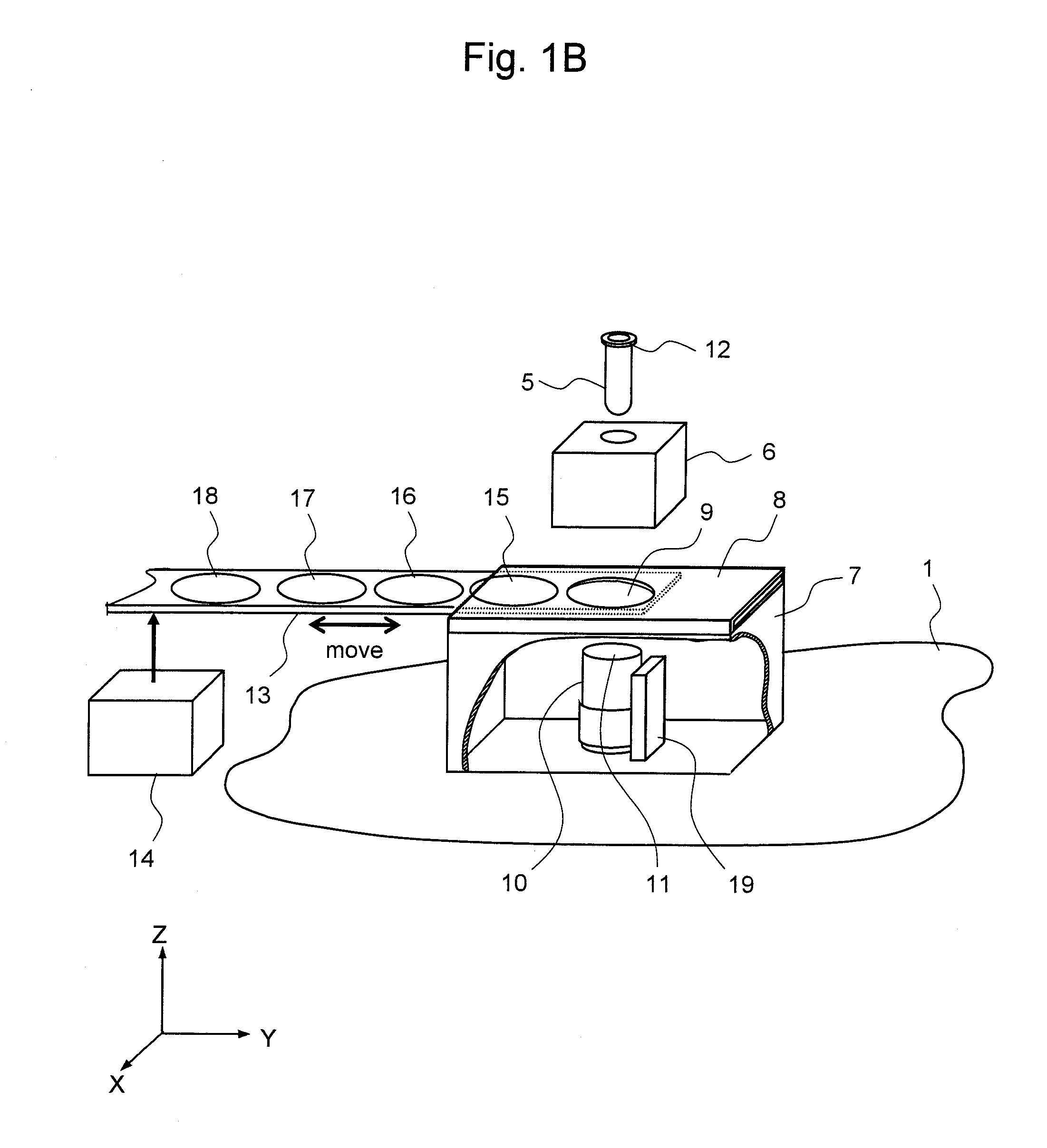
Luminescence measuring apparatus
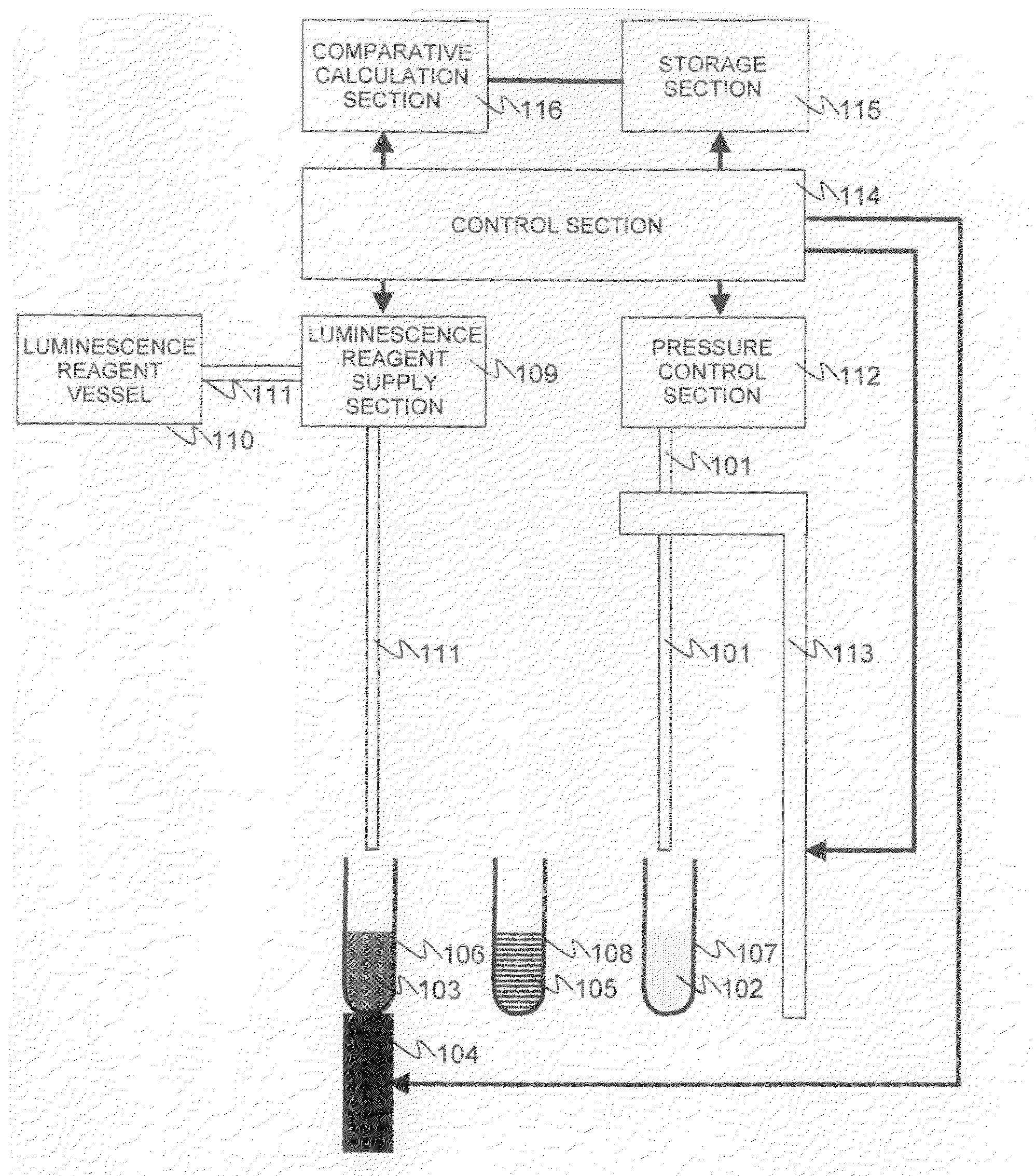
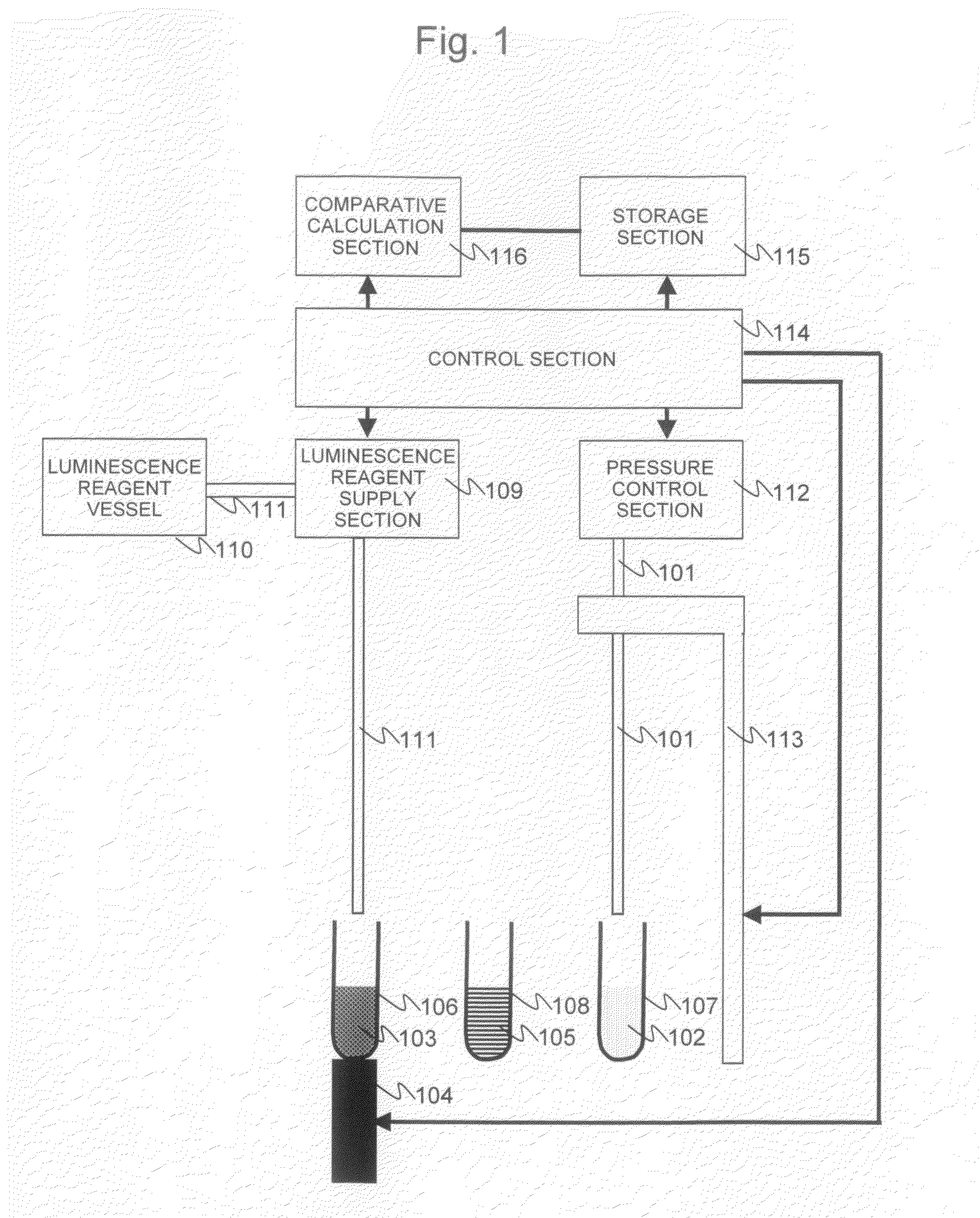
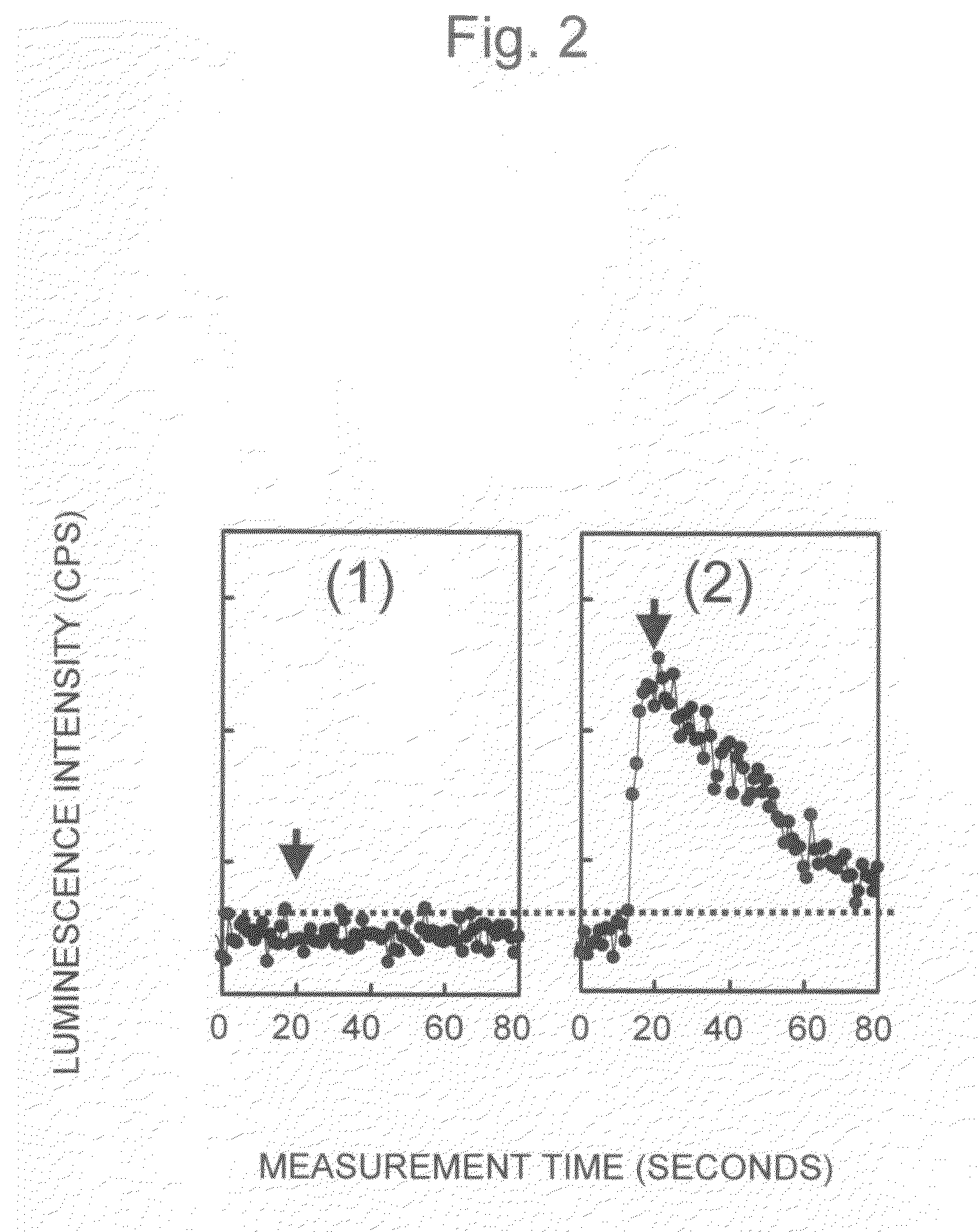
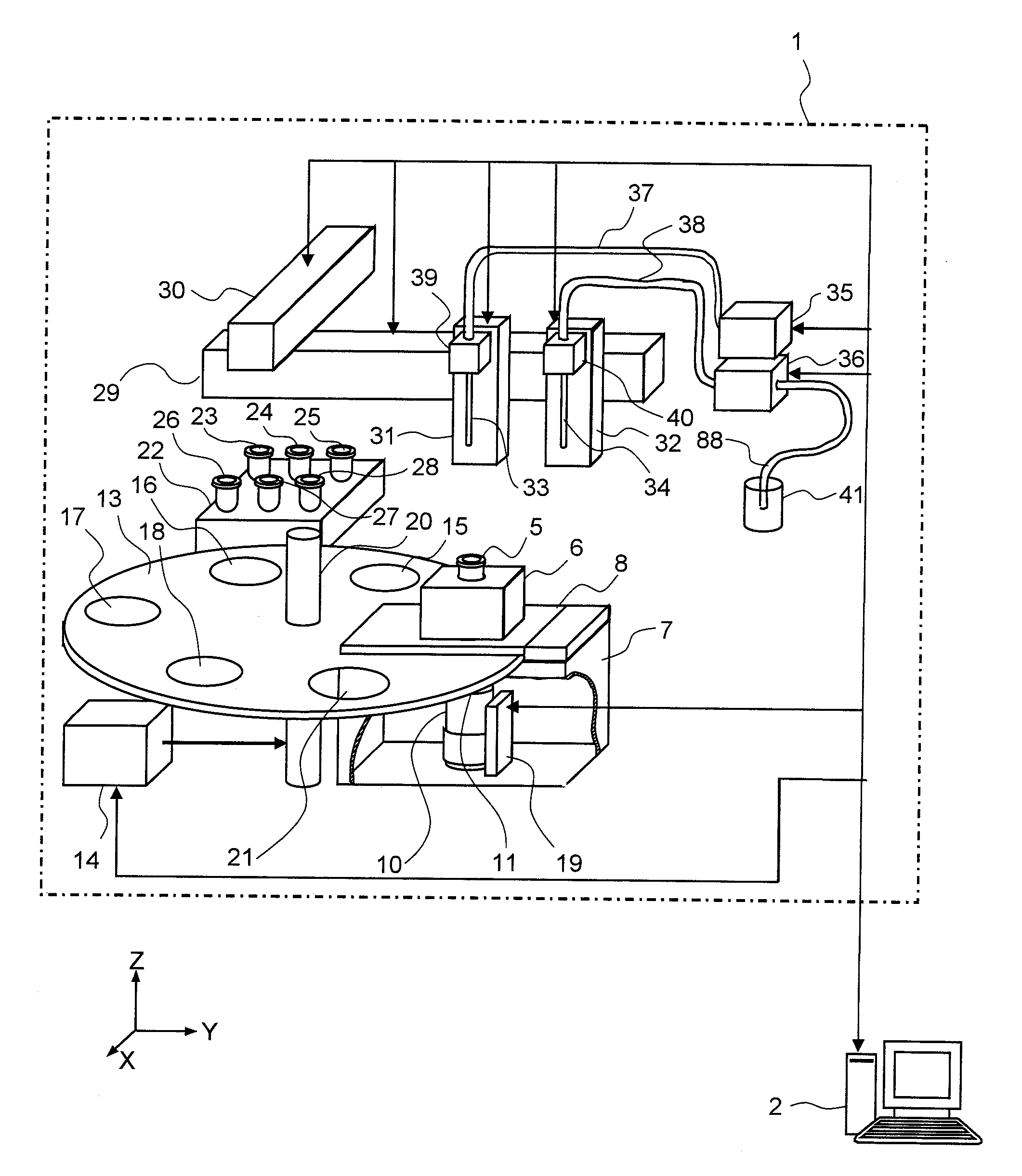
InactiveUS20080241871A1Optimize washing stepQuick and easy measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReagentLuminescent Measurements
The present invention provides a luminescence measuring method that can be accurately and quickly carried out while inhibiting a possible background associated with viable bacteria adhering to a nozzle or Adenosine Tri Phosphate remaining in the nozzle, and an apparatus for the method. The present invention uses a washing apparatus characterized by including a nozzle, a lysys solution, a luminescence reagent solution, and a detection section, as well as a relevant washing method and a relevant luminescence measuring method. To remove viable bacteria adhering to the nozzle, the nozzle is immersed in the lysys solution and then in the luminescence reagent solution. The detection section monitors luminescence occurring during a washing process.
Owner:HITACHI PLANT TECH LTD
Luminescence measuring apparatus and microbe counting apparatus
InactiveUS20120250024A1High sensitivityProductivity fallChemiluminescene/bioluminescencePhotometryPhotodetectorChemiluminescence
The present invention relates to a luminescence measuring apparatus for detecting, at high sensitivity and high accuracy, chemoluminescence and bioluminescence of a substance contained in a sample. Specifically, the present invention provides an apparatus for measuring an amount of luminescence in a sample, comprising: a container for the sample; a photodetector for detecting luminescence from the container; and at least one optical filter inserted between the photodetector and the container, and / or a pH modifier added to the container, wherein the photodetector performs measurement of light emitted from the container at all wavelength regions and spectrometry at a specific wavelength range, and / or measurement of light, the intensity of which is changed by the pH modifier. The present invention also relates to a microbe counting apparatus based on luminescence detection of ATP in a viable microbial cell.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
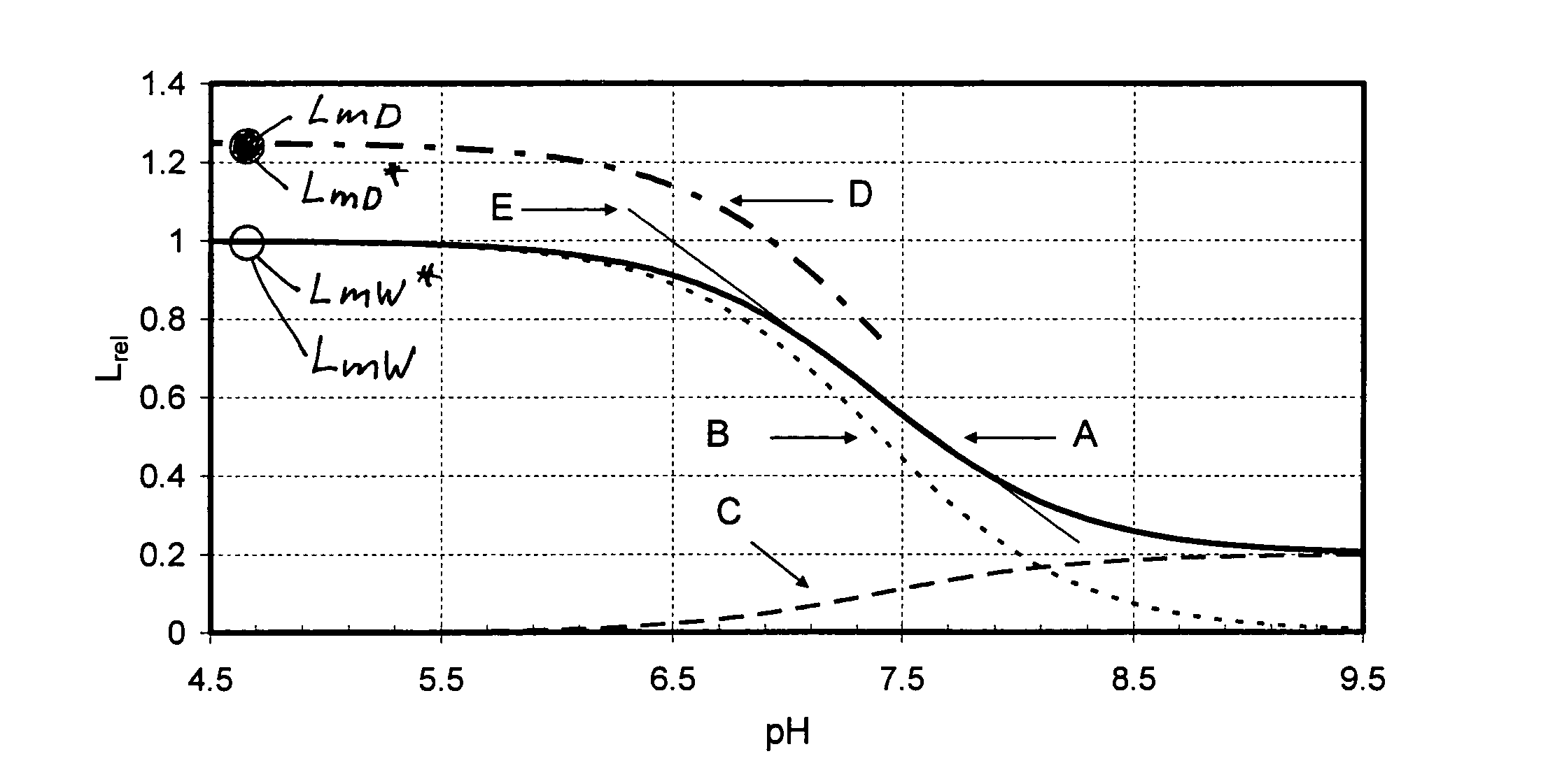
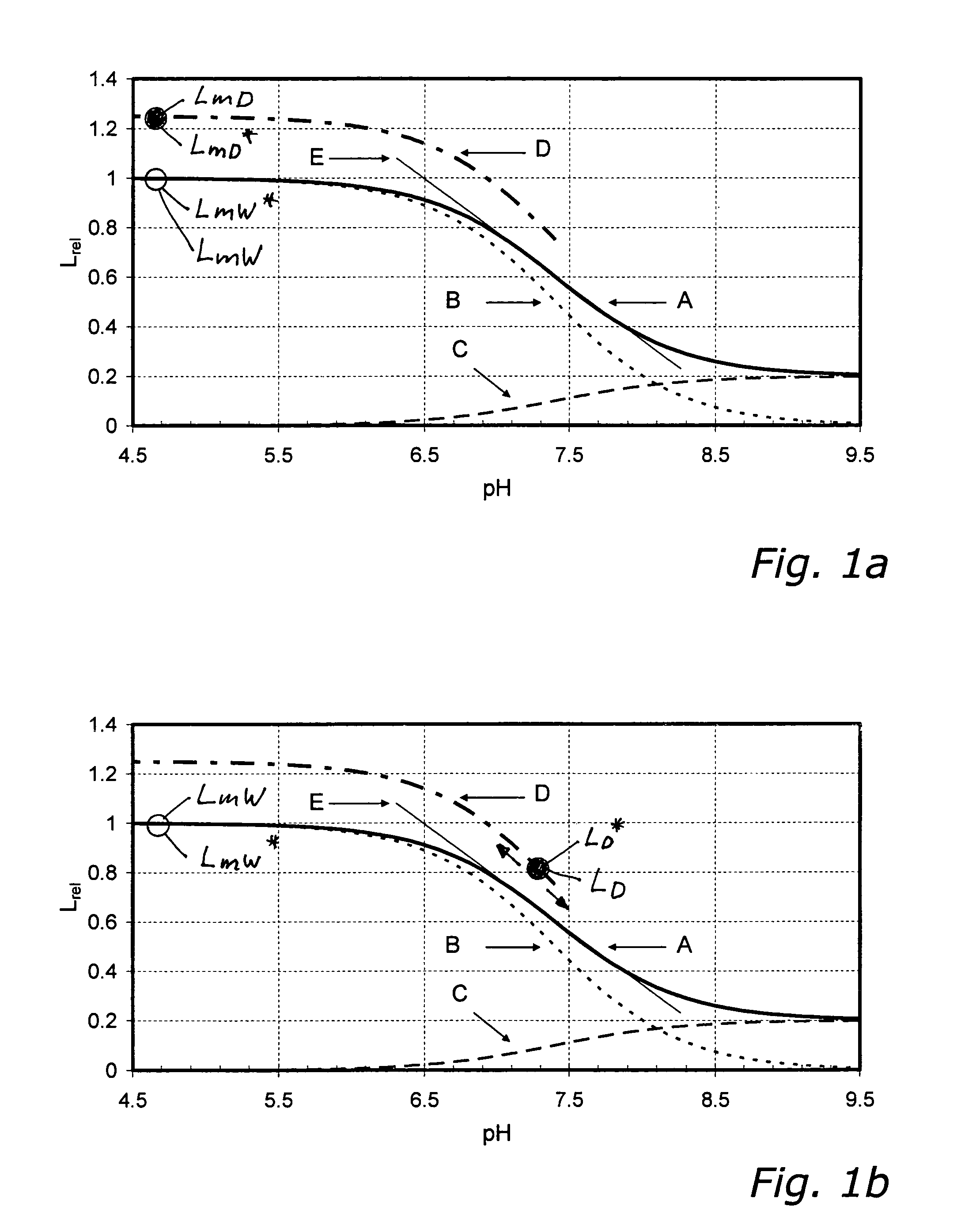
Method for the determination of the concentration of a non-volatile analyte
ActiveUS8158438B2Photometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorAnalyteOptical transducers
The invention relates to a method for the determination of the concentration of a non-volatile analyte in an aqueous sample medium, with the use of an optical sensor which contains a luminescent dye and is calibrated at the user site by means of a single-point-calibration. To enable the user to completely dispense with all calibration media a luminescence measurement value is obtained at the user site with the sensor in contact with the aqueous or bloodlike sample medium, which value is referenced to the relative characteristic obtained at the factory site and to a measured dry calibration value obtained at the user site, the concentration of the non-volatile analyte being deduced from these data.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Single reaction cup luminescent measurement chamber
ActiveCN107167427AGuaranteed service lifeGuaranteed accuracyChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceShutterEngineering
The invention relates to a single reaction cup luminescent measurement chamber. The single reaction cup luminescent measurement chamber comprises: a measuring chamber, a top cover; a photon counter; a shutter structure, which is arranged between the photon counter and the measurement chamber and can close or open a photon via hole. Through the design of the shutter structure, before opening of the top cover, a driving part is rotated to drive the movement of a baffle plate, so that a through hole on the baffle plate and the photon via hole can be staggered, i.e. a lens of the photon counter can be shielded to prevent the incidence of external light into the photon counter, thus ensuring the service life and precision of the photon counter. After close of the top cover, the driving part is rotated to drive the baffle plate to move, so that the through hole on the baffle plate can coincide with the photon via hole, therefore the photon counter can collect the luminescent amount of a substance in a reaction cup.
Owner:SUZHOU HYBIOME BIOMEDICAL ENG CO LTD
Luminescense measuring apparatus and luminescense measuring method
InactiveUS20100227316A1Easy to detectEasy to measureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLuminous intensityGene expression
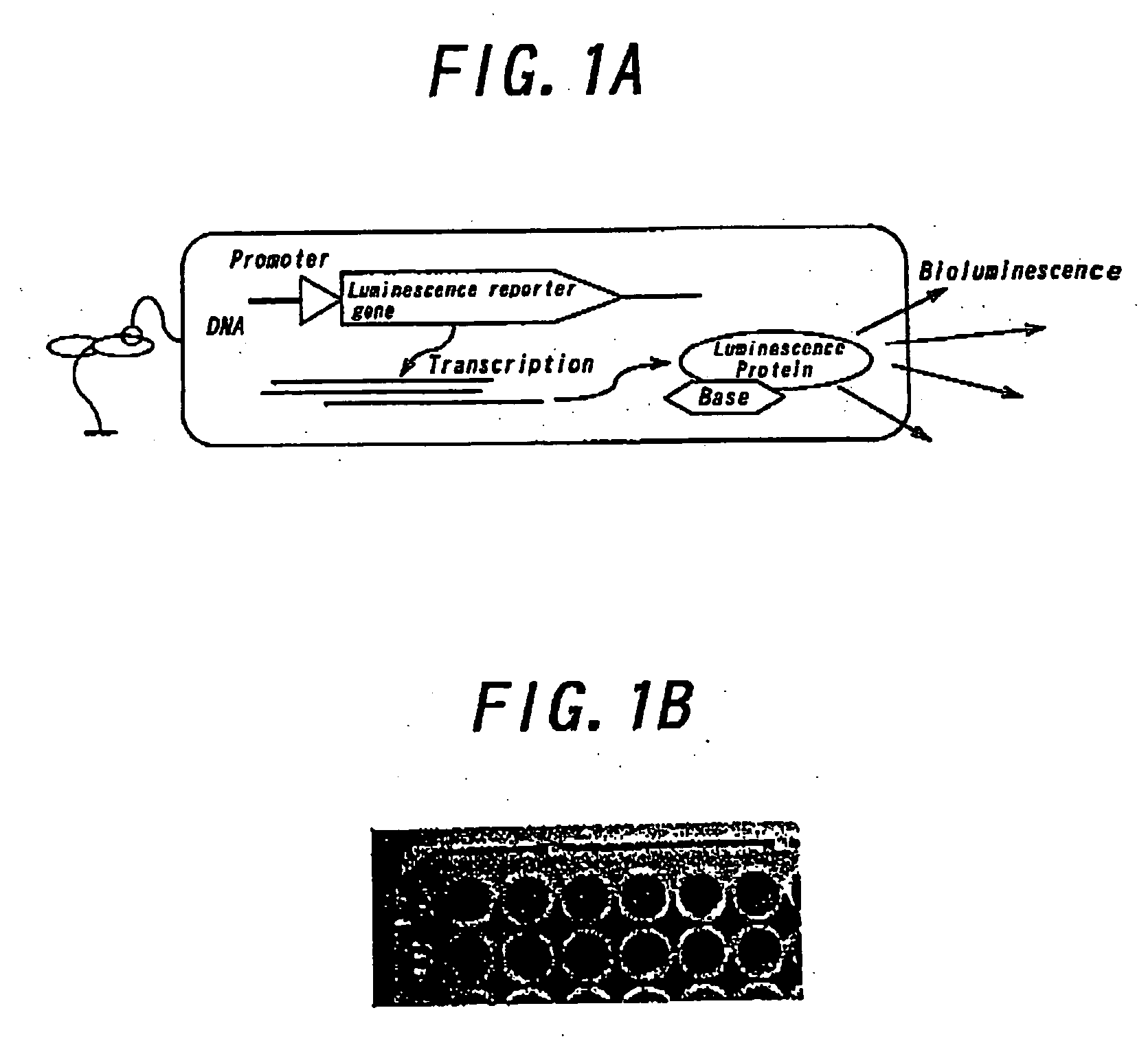
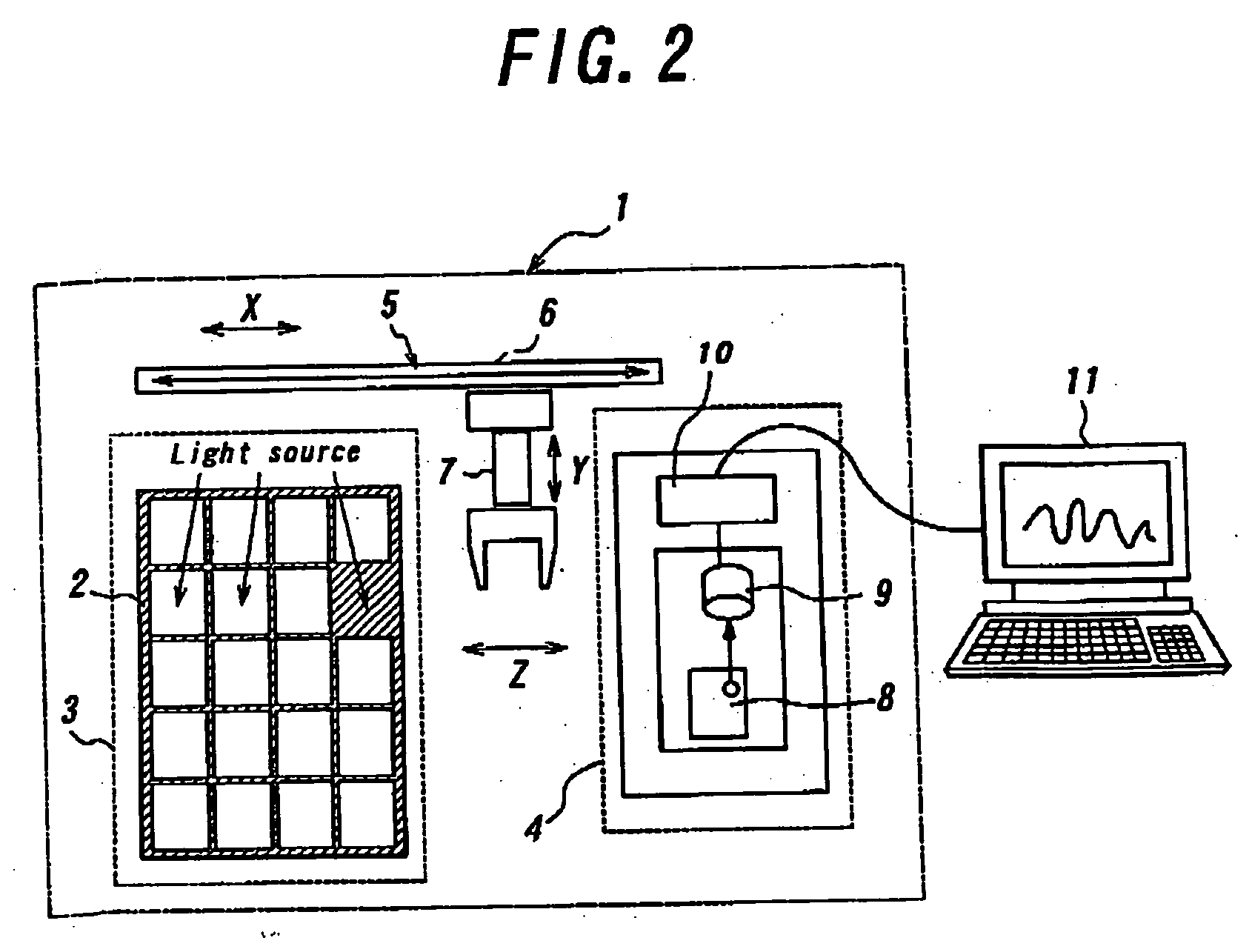
There is provided a novel luminescence measuring apparatus that enables measuring a luminescence amount or a luminescence intensity from plural living biological samples, such as tissues, cells, and biological individuals, into which a gene expressing a luminescent protein has been introduced, individually for the respective biological samples. The inventive luminescence measuring apparatus comprises an image acquisition portion that acquires a luminescence image of biological samples; a measurement region determination portion that determines at least one measurement region in the luminescence image; and a luminescence measurement portion that measures the luminescence amount or luminescence intensity in the determined measurement region; thereby measuring the luminescence amount or luminescence intensity individually by the biological sample(s) included in the measurement region. Irrespective of an efficiency of transfer of a luminescent protein gene into a cell, etc., it becomes possible to execute a luminescence measurement successfully while observing only biological samples having a gene expression.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
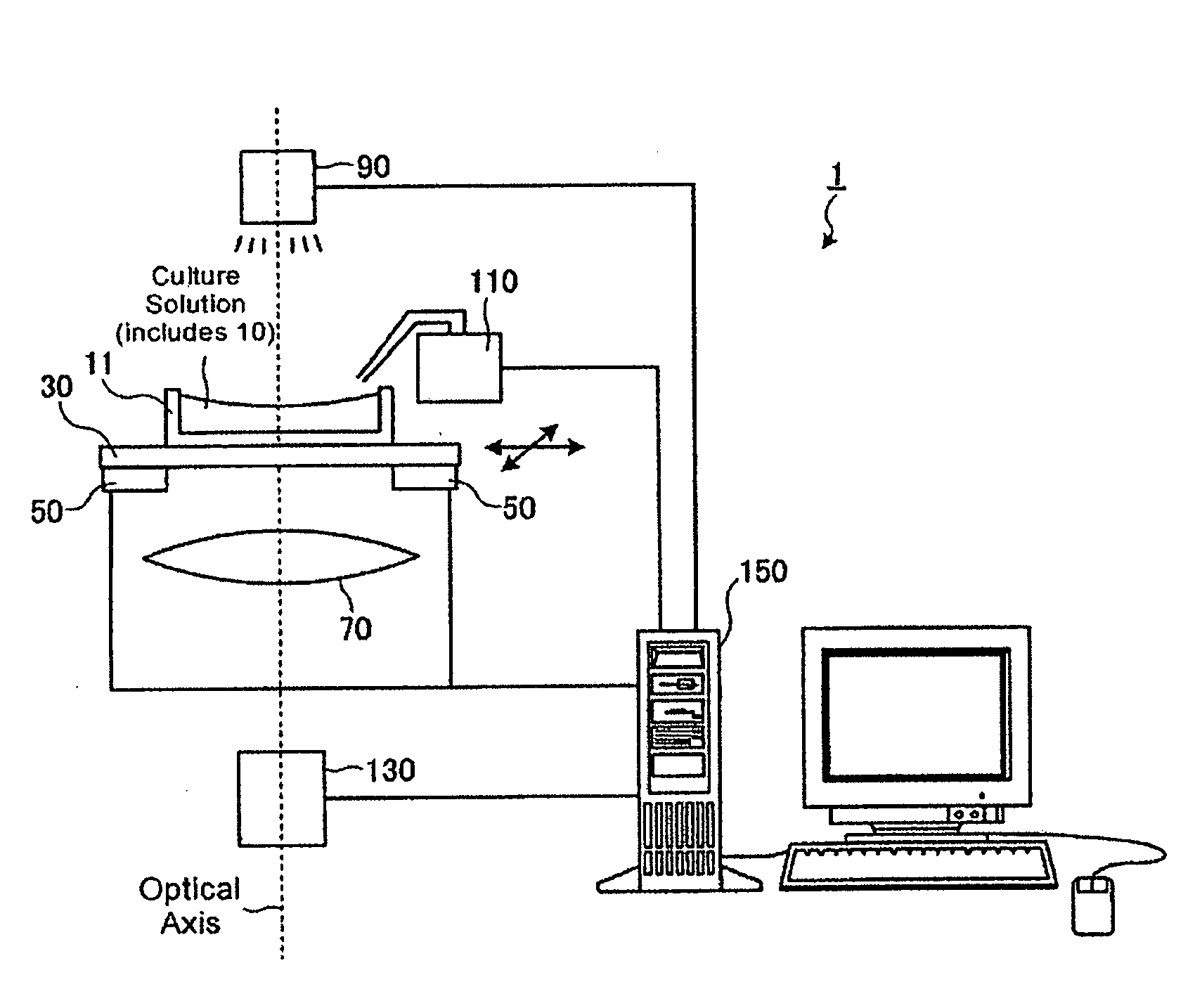
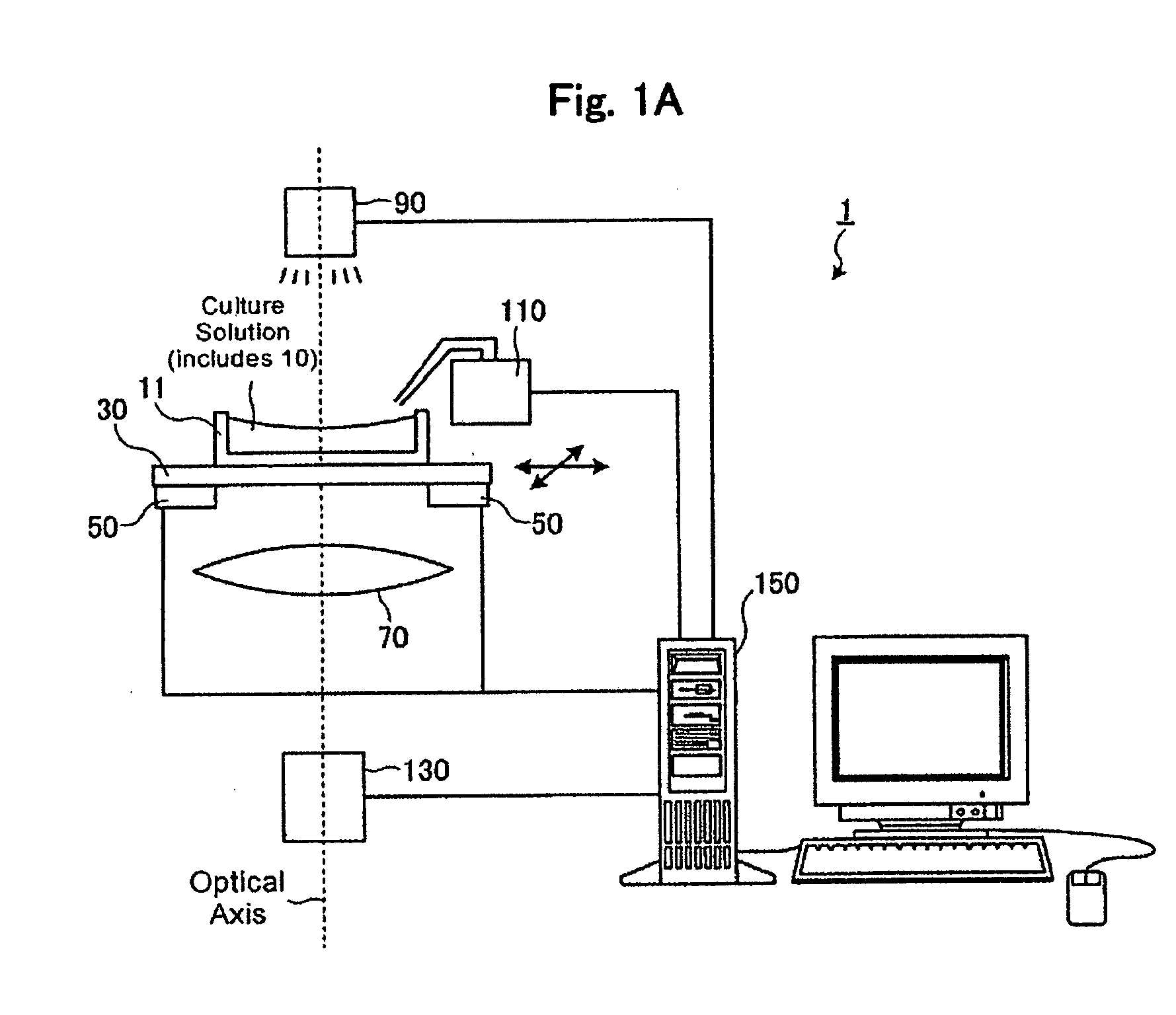
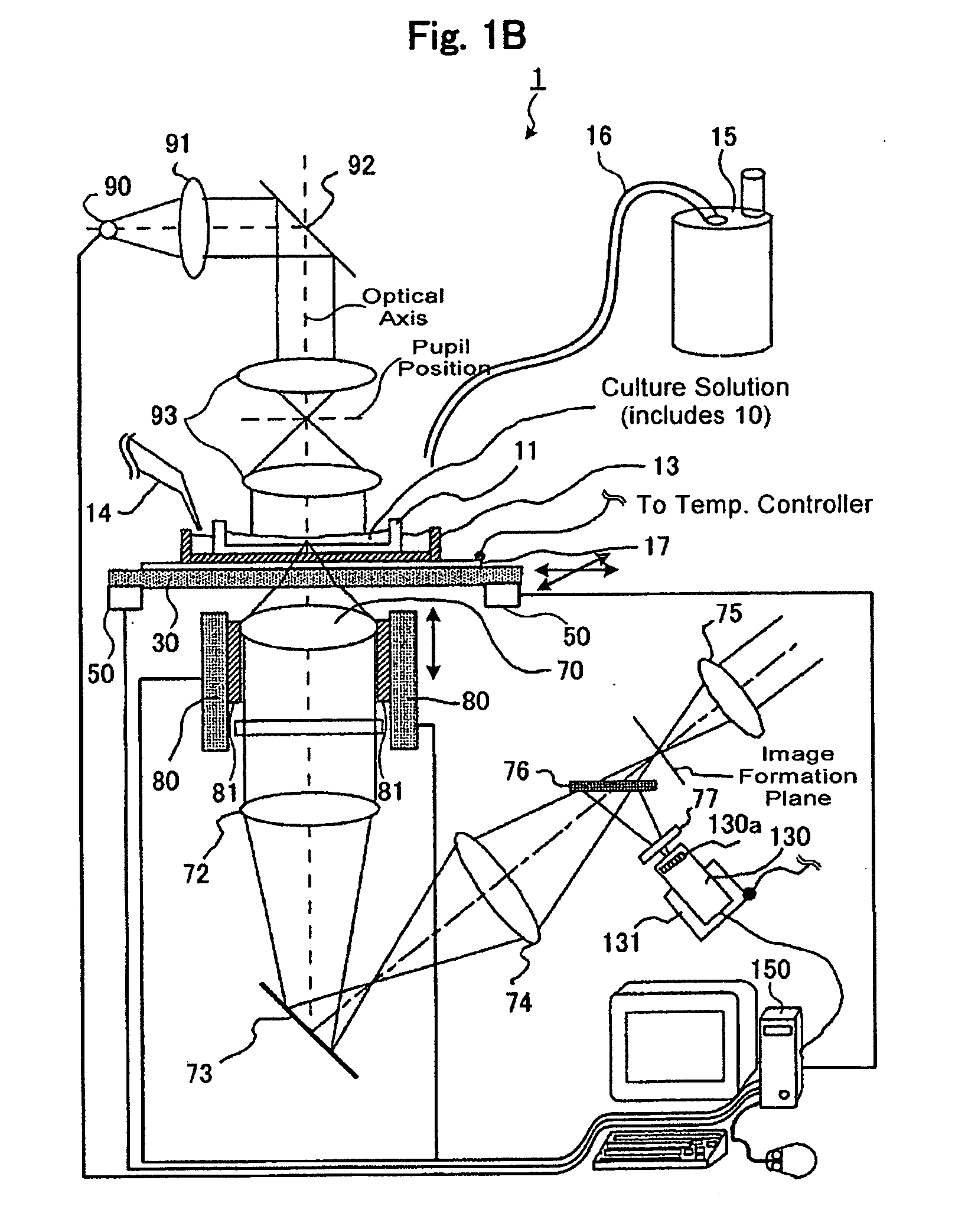
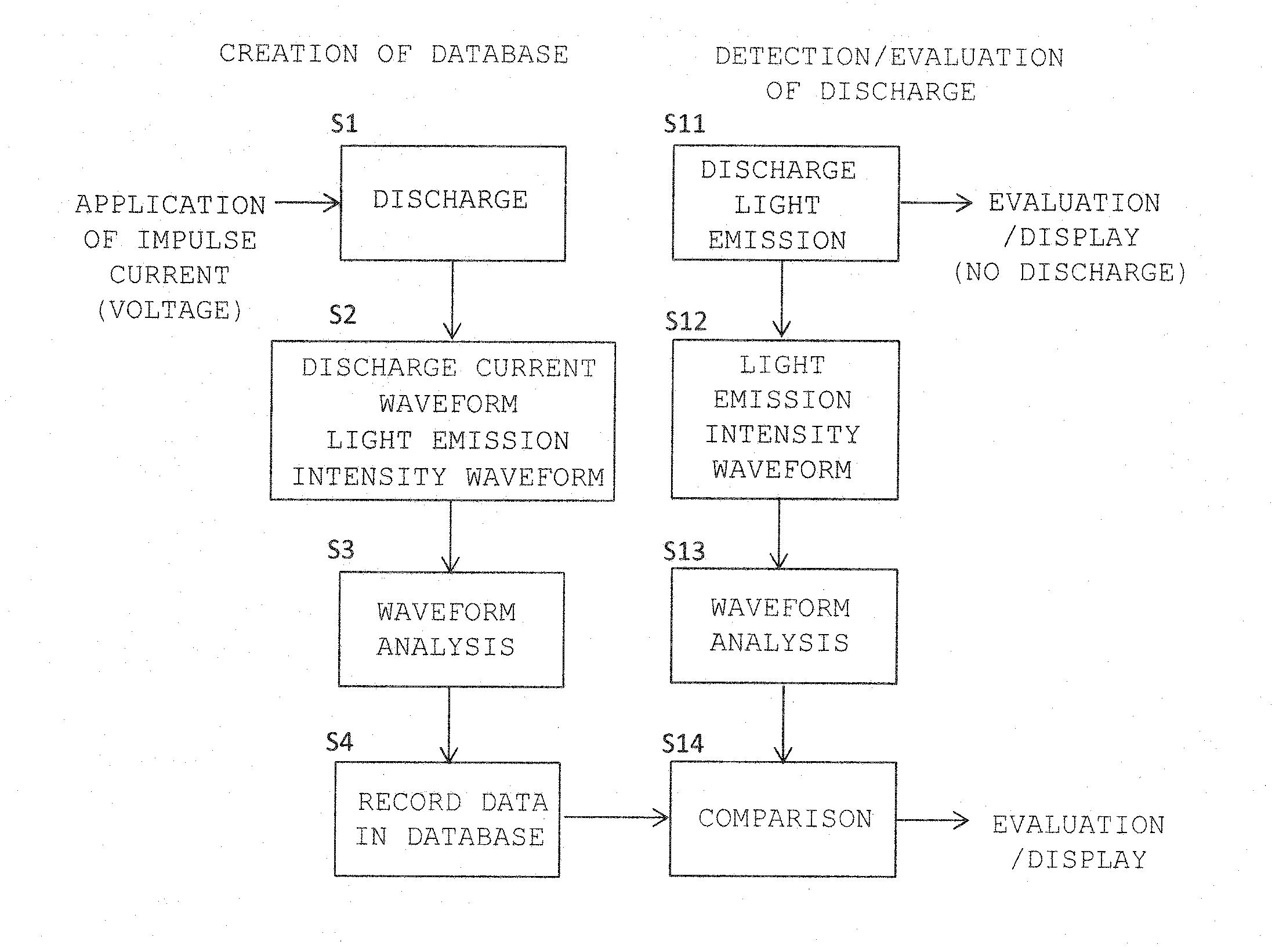
Non-contact discharge test method and device
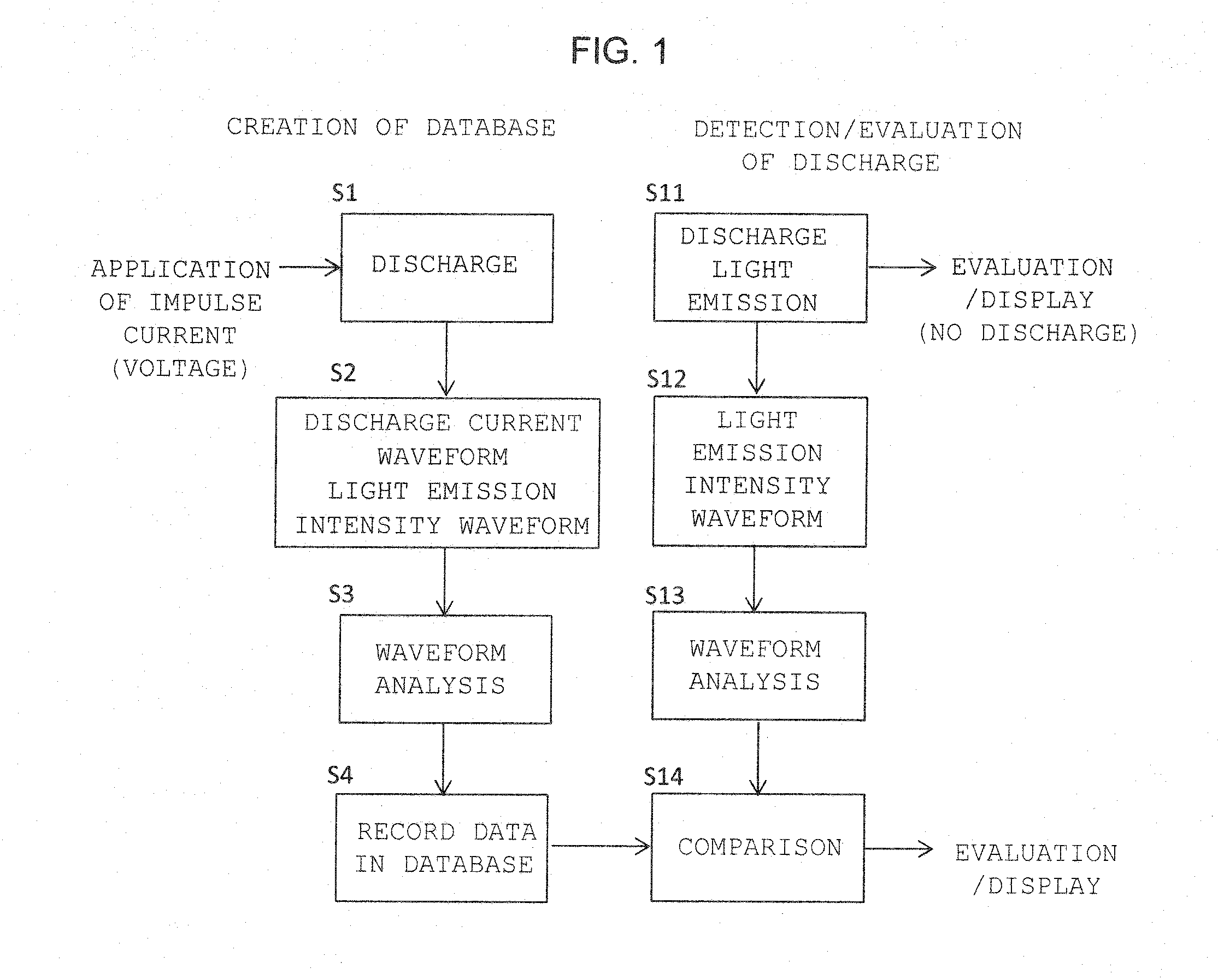
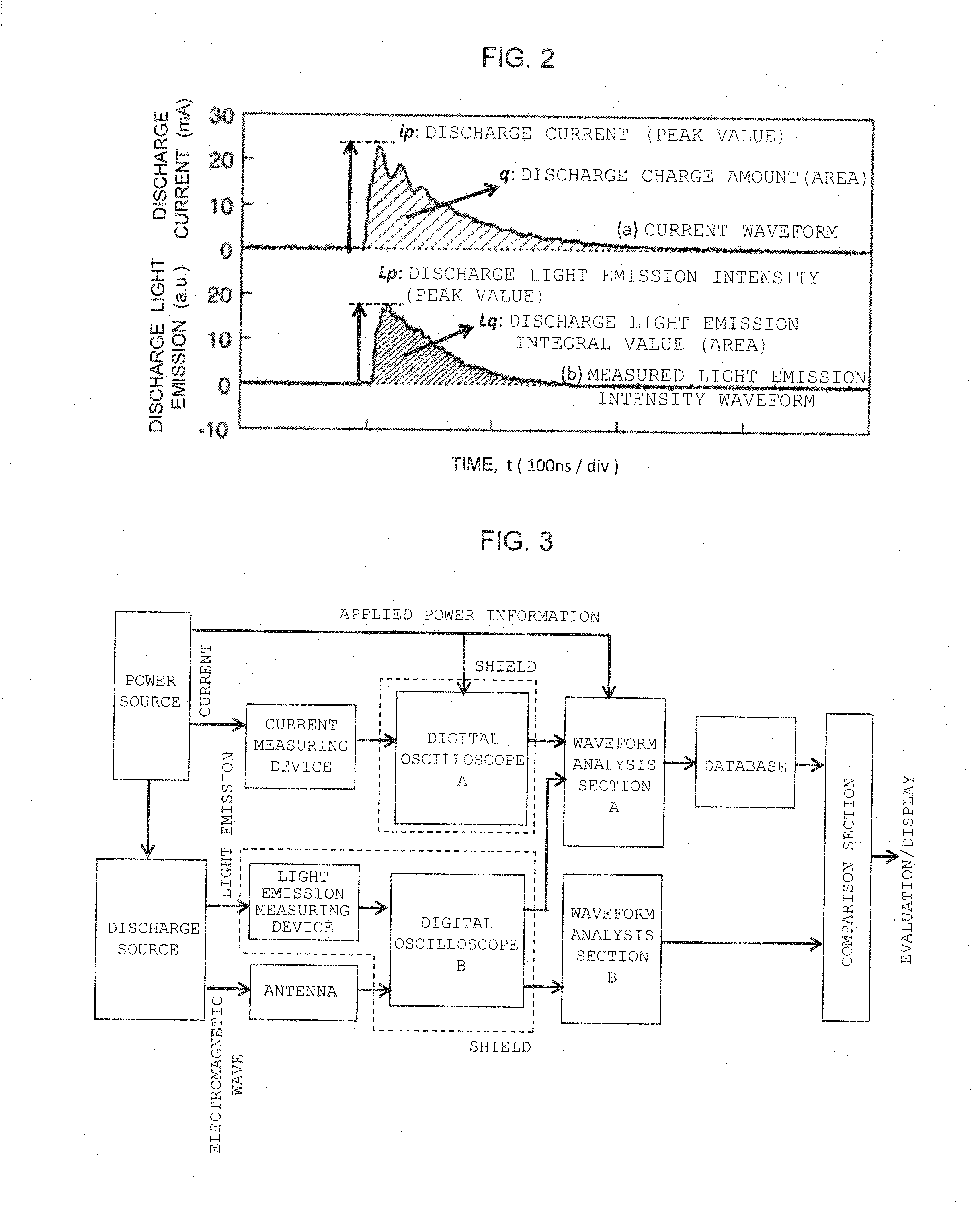
ActiveUS20160018459A1Testing electric installations on transportTesting using optic methodsWaveform analysisLuminous intensity
In a non-contact discharge test performed in a poor electromagnetic noise environment, the energy of discharge is evaluated by detecting weak light emission and processing the intensity waveform of light emission of the discharge. A database is created by measuring the intensity waveform of light emission of discharge generated as a result of application of a voltage or current to a measurement object through use of a light emission measuring device, simultaneously measuring the current waveform of the discharge through use of a current measuring device, and storing in the database the relation between analysis data sets obtained through analysis of the waveforms on the basis of information of the voltage or current applied to the measurement object. The intensity waveform of the light emission of the discharge or spark generated from the measurement object is measured while an electromagnetic wave generated as a result of the discharge of the measurement object is used as a reference. The magnitude of the discharge is estimated as a value by comparing light emission data obtained through analysis of the intensity waveform with the data recorded in the database.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP KYUSHU INST OF TECH (JP)
Chemiluminescence measuring instrument and measuring method of chemical liquid luminescence intensity
ActiveCN102393358AReduce volumeFast measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansMicrowell PlateClinical diagnosis
The invention relates to a chemiluminescence measuring instrument and a measuring method of chemical liquid luminescence intensity. Current chemiluminescence measuring instruments have a large volume and a slow measuring speed. Therefore, the chemiluminescence measuring instrument comprises a micropore plate, a photoelectric sensor, and a micropore plate driving system; the micropore plate driving system can drive the micropore plate to move longitudinally; the chemiluminescence measuring instrument is characterized in that the instrument also comprises an optical fiber; one end of the the optical fiber is fixed on an input end of the photoelectric sensor, and the other end is a movable end, and is equipped with a transverse driving mechanism; the transverse driving mechanism can drive the movable end to move laterally above the micropore plate. For optimization, when the movable end of the optical fiber moves relative to the micropore plate, row-by-row reciprocating motion or column-by-column reciprocating motion is performed. The chemiluminescence measuring instrument of the invention has the advantages of small volume, high measuring speed, and high efficiency, and the measuring method of chemical liquid luminescence intensity of the invention measures during the reciprocating stroke, has a high speed, and high efficiency, and is applicable to the fields of biochemistry and clinical diagnosis.
Owner:ZHUHAI LIVZON DIAGNOSTICS
System and method for ranking bacterial activity leading to tooth and gum disease
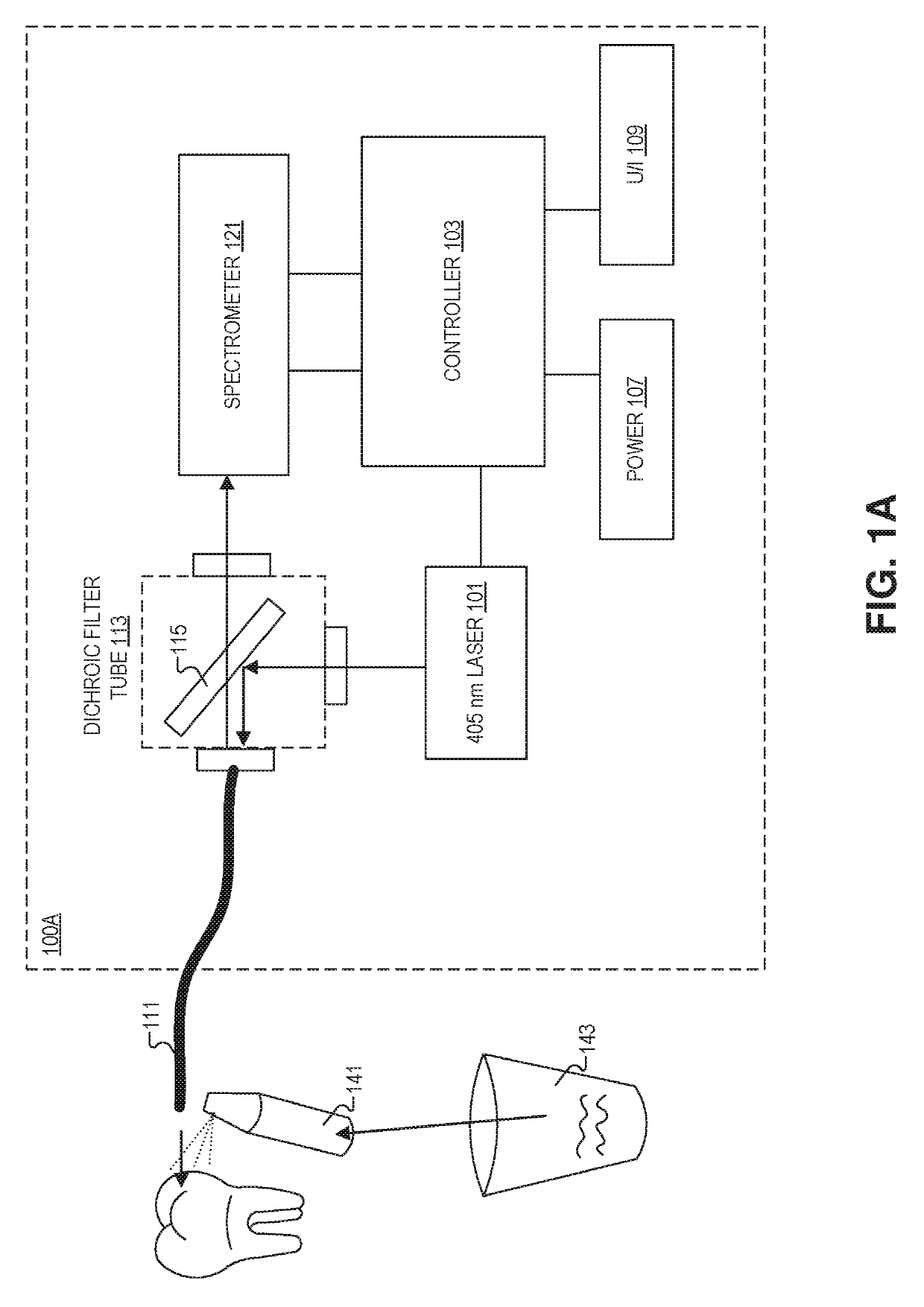
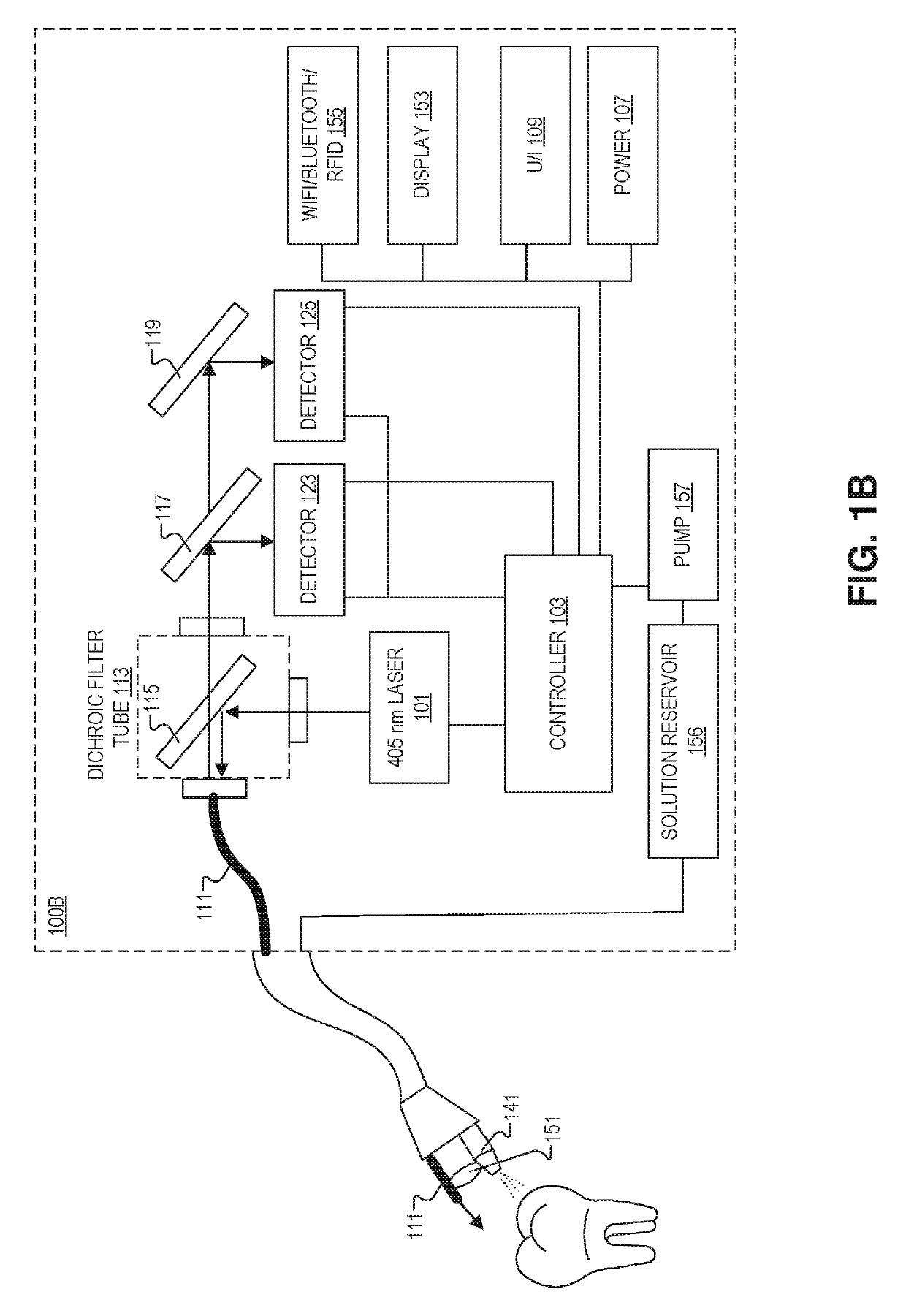
A system for the optical measurement of pH includes a light emitter to emit an excitation light, and a detector coupled to receive florescence light produced by a compound in a mouth of a patient in response to the excitation light. A controller is coupled to the detector, and the controller includes logic that when executed by the controller, causes the system to perform operations. The operations may include emitting the excitation light from the light emitter; measuring an intensity of the florescence light emitted from a surface of individual teeth in a plurality of teeth in the mouth; and determining, based on the intensity of the florescence light, one or more locations on the individual teeth likely to develop demineralization.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Image sensing device and control method thereof
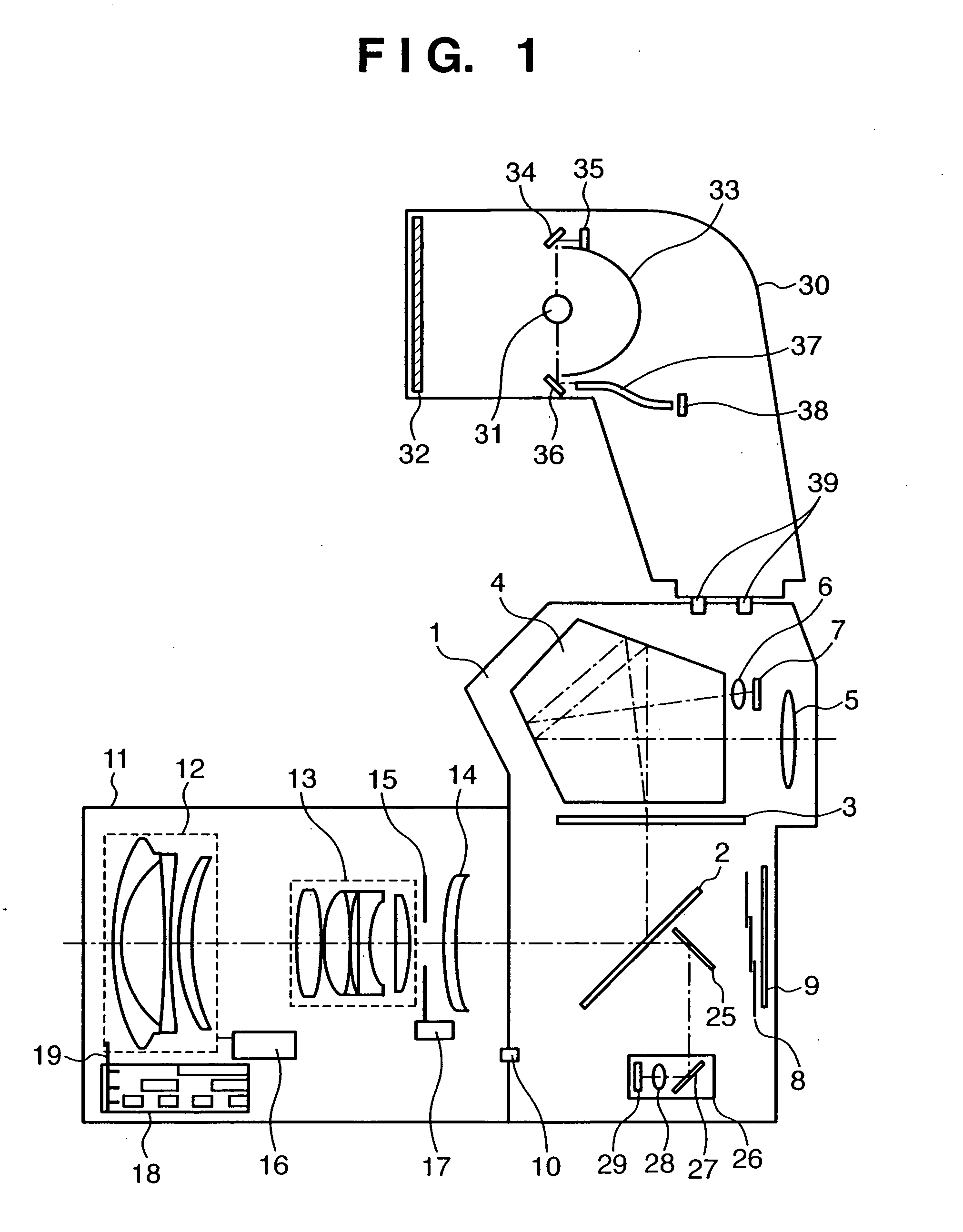
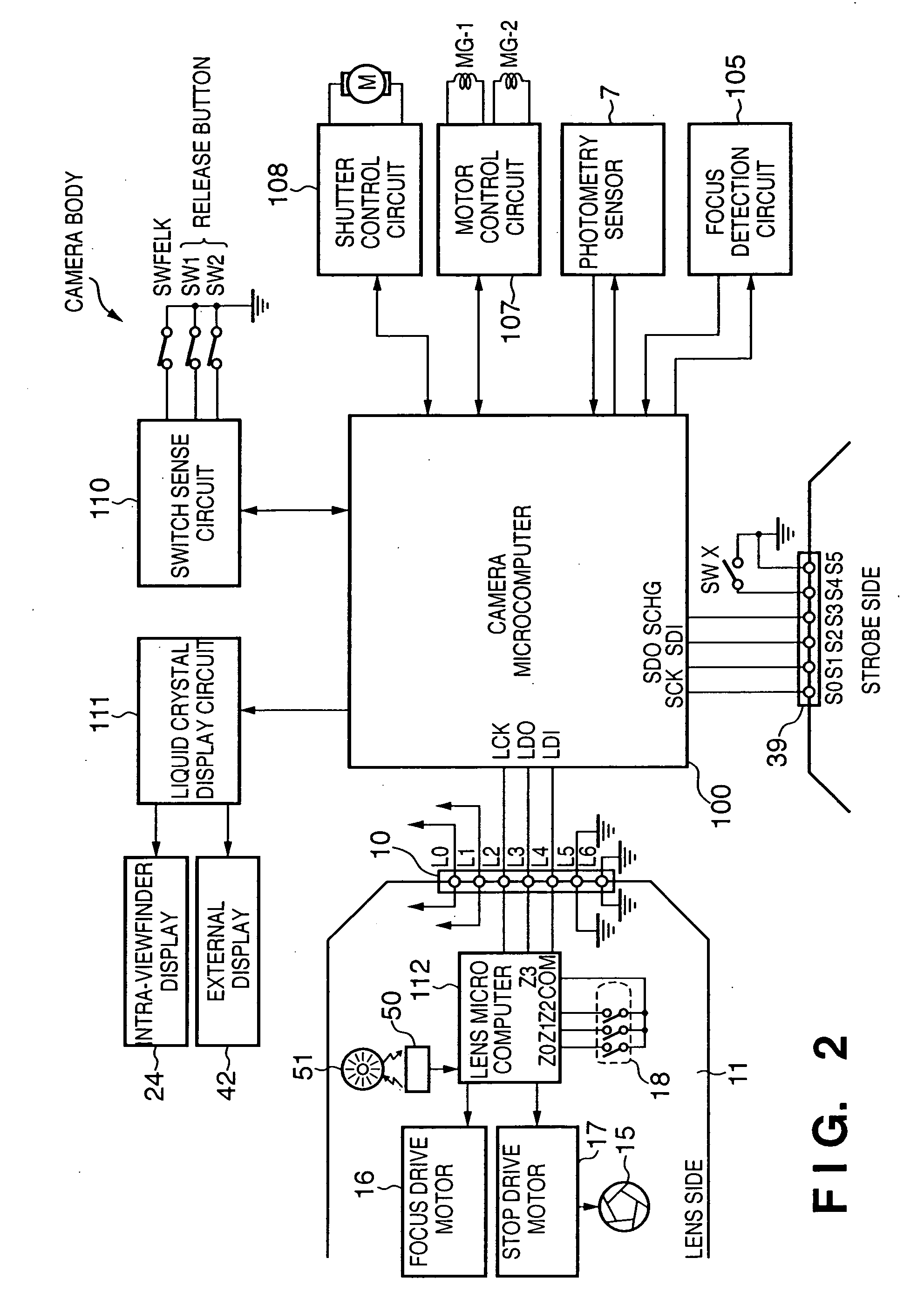
InactiveUS20050244151A1Exclude influenceNot easy to influenceProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementExposure valueAutofocus
This invention allows to shoot an image using correct object distance information and light emitting amount when the main light emitting amount upon shooting an object image is calculated by making the pre-light emission after the auto-focusing process. To this end, when a predetermined button independent of a release button is operated, a focusing process is executed first. Then, photometry is made while inactivating a strobe, i.e., under available light, and an exposure value is determined based on an object distance. Then, pre-light emission is made, light reflected by the object in the pre-light emission is measured, and the photometry result under the available light is subtracted from that in the pre-light emission, so as to obtain a brightness value of object reflected light of only the pre-light emission. This brightness value is corrected to be equal to lower than an allowable maximum value depending on the object distance to compute a main light emitting amount. After that, when the release button is operated, the strobe is driven on the basis of the determined main light emitting amount, and shooting is made using the determined exposure value.
Owner:CANON KK
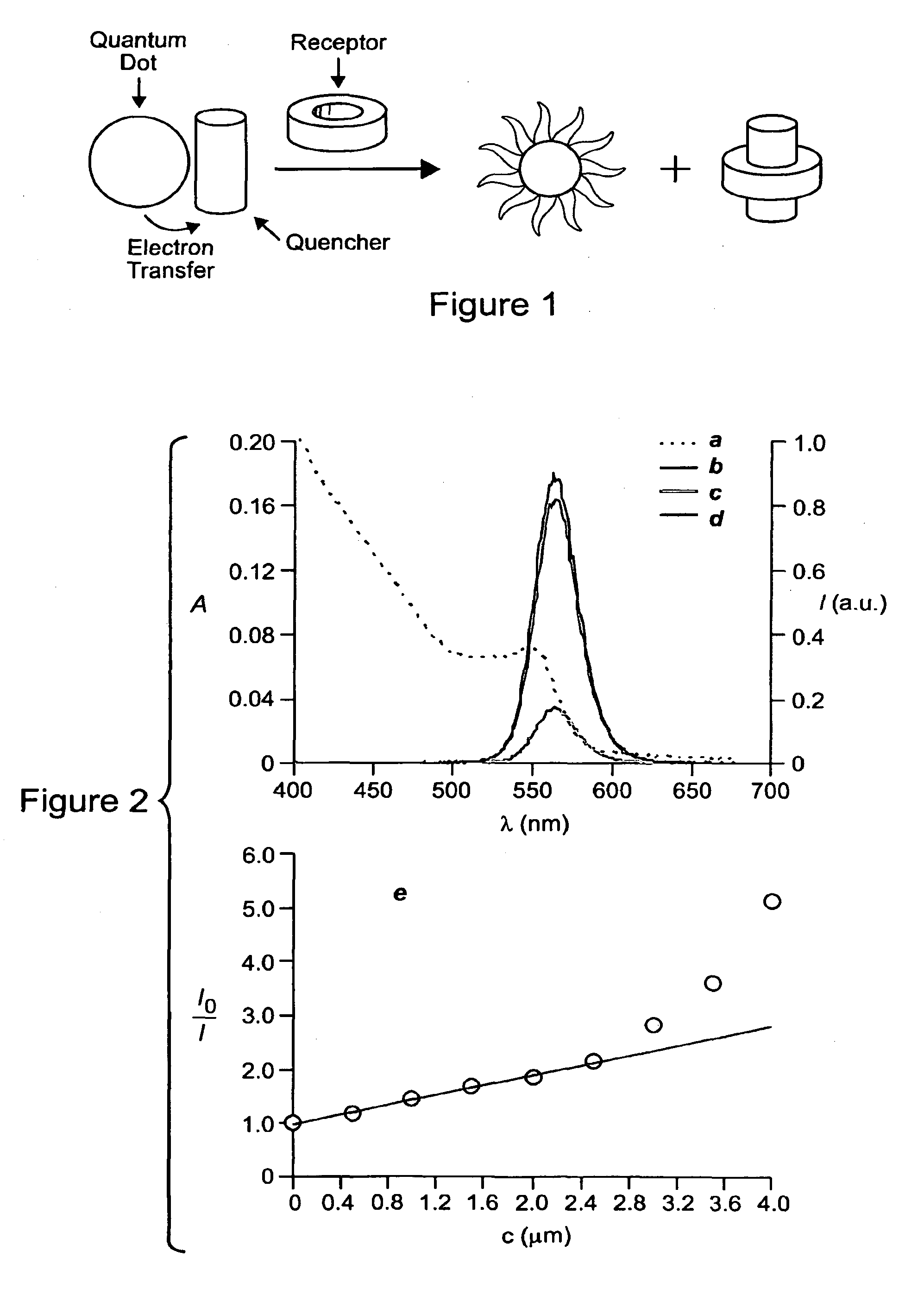
Mechanism to signal receptor-ligand interactions with luminescent quantum dots
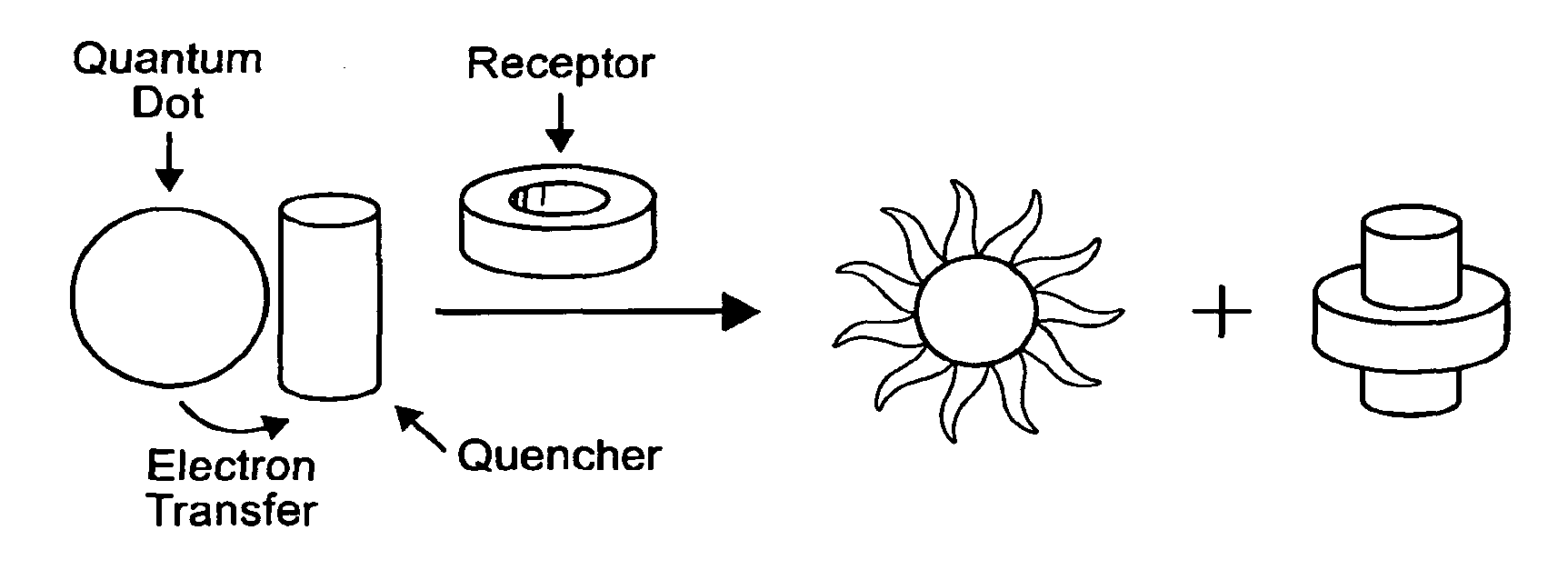
InactiveUS20100112560A1Microbiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceReceptorSemiconductor quantum dots
Semiconductor quantum dots are becoming valuable analytical tools for use in biomedical applications. Indeed, their unique properties offer the opportunity to design luminescent probes for imaging and sensing with unprecedented performance. In this context, we have identified operating principles to transduce supramolecular association of complementary receptor-ligand binding pairs into enhancement or suppression in the luminescence of sensitive quantum dots. Thus, complementary receptor-ligand binding pairs can be identified with luminescence measurements relying on our design logic. In fact, we have demonstrated with a representative example that our protocol can be adapted to signal receptor-ligand binding.
Owner:UNIV OF MIAMI
Luminescence Measuring Device
ActiveUS20150253250A1Easy to measureSuppress noiseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemiluminescenceLuminescent Measurements
The present invention relates to luminescence detection with respect to a substance contained in a sample. In particular, it relates to a weak luminescence detection device adapted to detect chemiluminescence and bioluminescence of the substance contained in the sample with high sensitivity and high precision.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Luminescene measuring device with prefilter effect suppression
InactiveUS20040130716A1Radiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationChemical speciesUltimate tensile strength
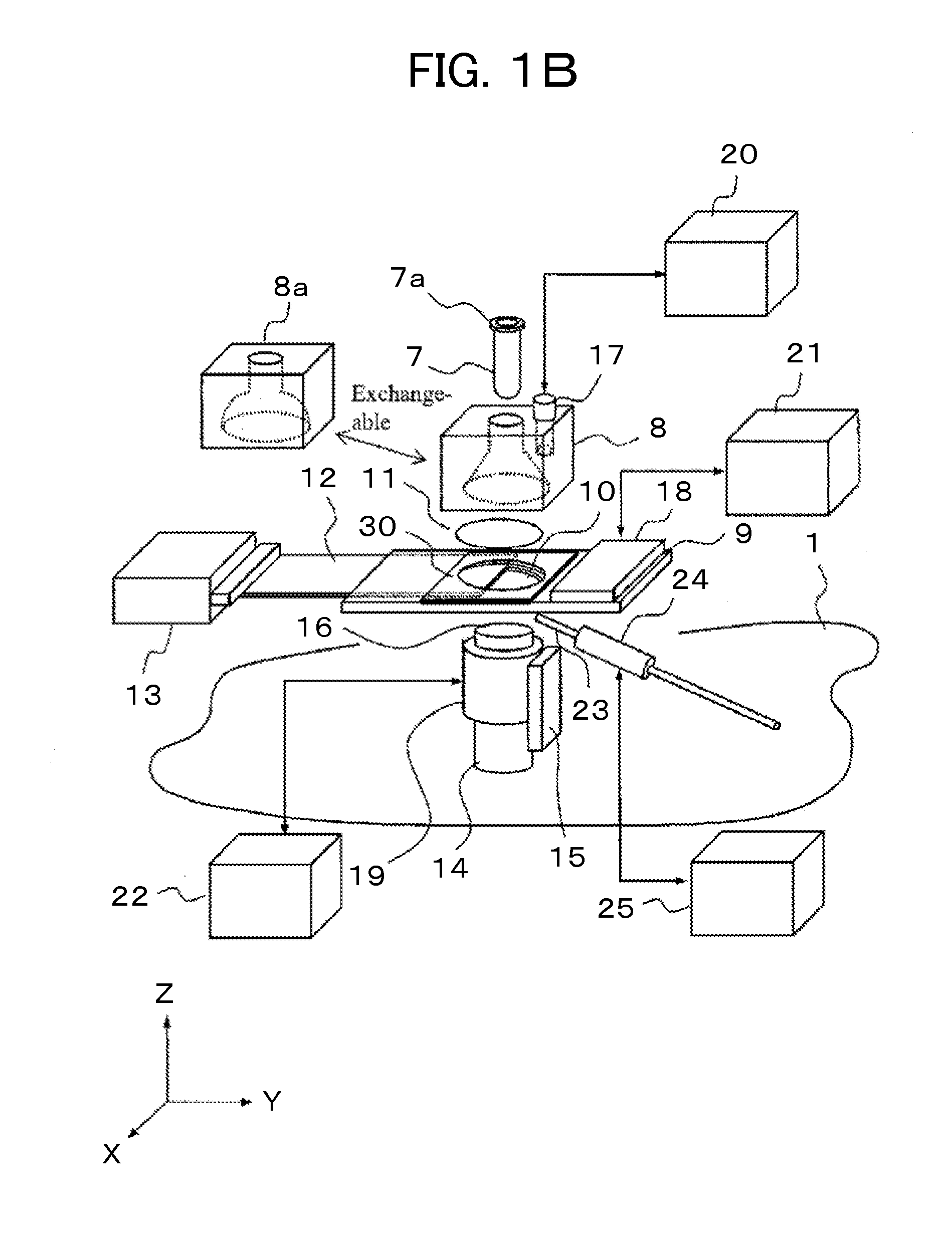
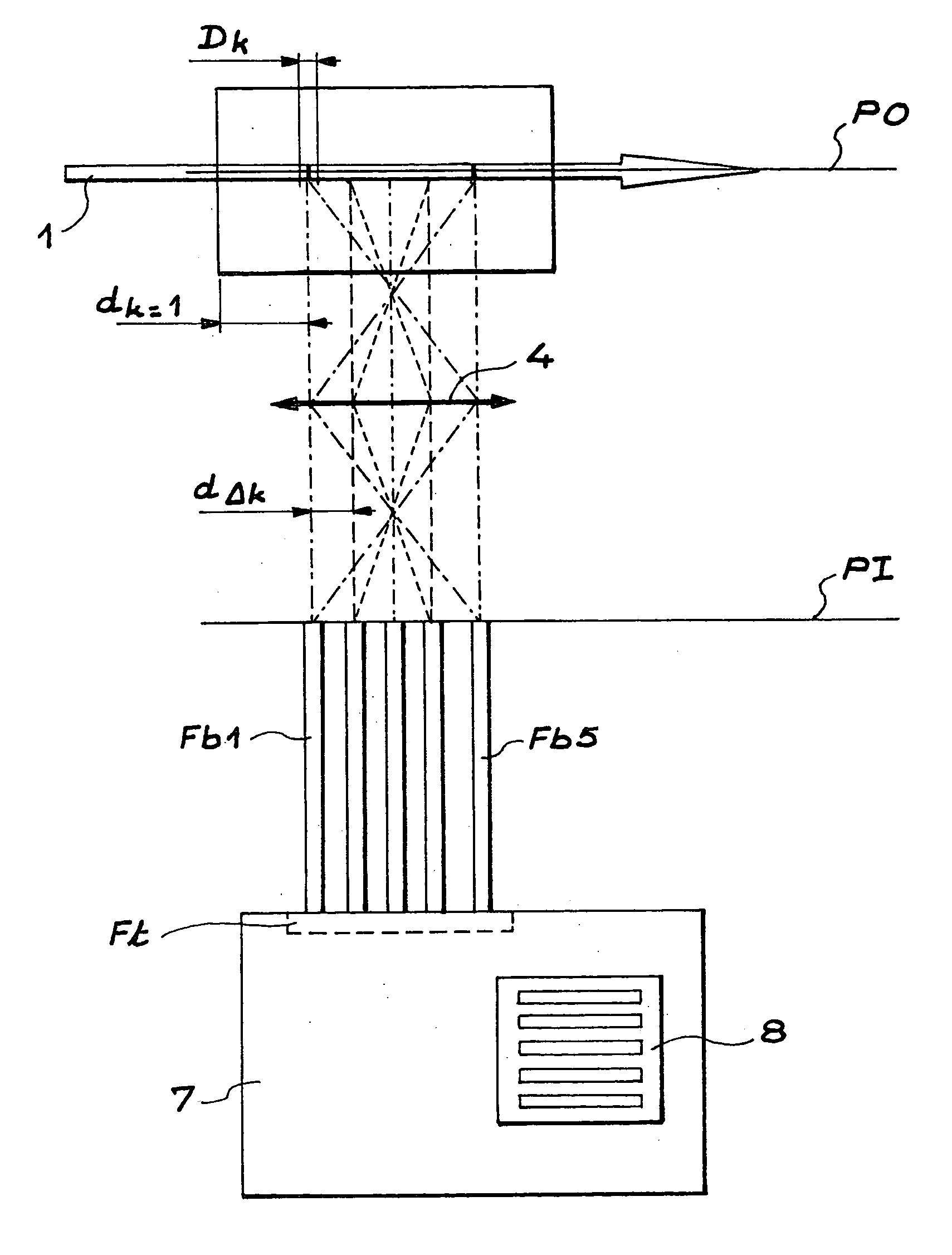
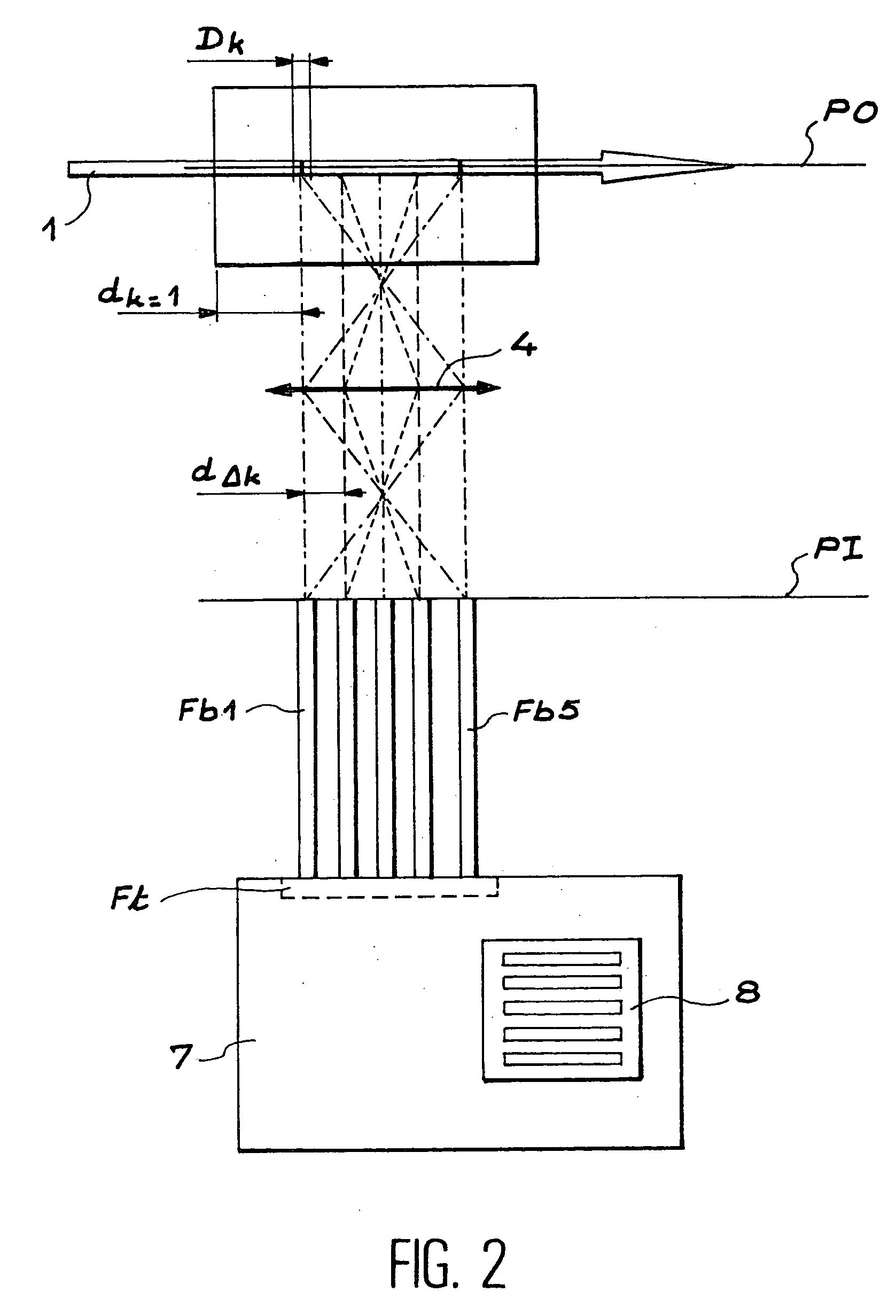
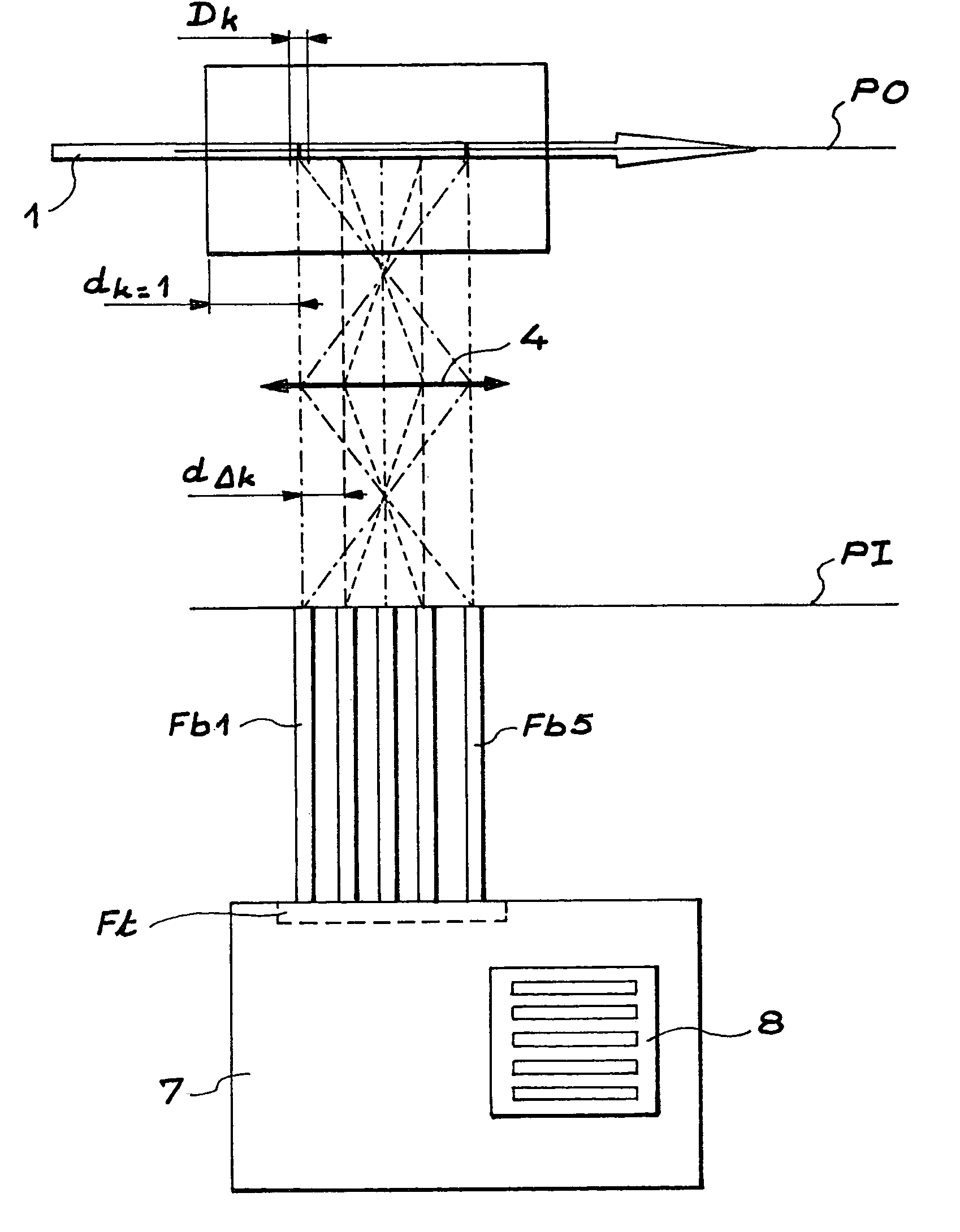
The invention relates to a device for measuring the intensity of a luminescence radiation emitted by at least one chemical species probed, along a trajectory by an excitation radiation. The device comprises n measurement channels, where n is an integer greater than or equal to 2, each measurement channel being used to measure a fraction of the intensity of the luminescence radiation emitted along the trajectory. The invention is also applicable to analytical chemistry to make speciation measurements.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Method for analysing a sample comprising at least a first and a second scale inhibitor
ActiveUS9816927B2The method is simple and reliableMethod is fastMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPreparing sample for investigationLanthanideLength wave
The invention relates to a method for analysing a sample comprising at least a first and a second scale inhibitor, which scale inhibitors are synthetic organic compounds comprising at least one ionised group. The method comprises optionally diluting and / or purifying the sample, and allowing the sample interact with a reagent comprising lanthanide(III) ion. The sample is excited at a first excitation wavelength and a sample signal deriving from the lanthanide(III) ion is detected at a signal wavelength by using time-resolved luminescence measurement. The total concentration of the first and the second scale inhibitor is determined by using the detected sample signal, and the concentration of the first scale inhibitor in the sample is determined. The concentration of the second scale inhibitor is determined mathematically by using the obtained results for the total concentration and for the first scale inhibitor concentration.
Owner:KEMIRA OY
Single-photon counting system for measuring weak luminescence of dielectric medium
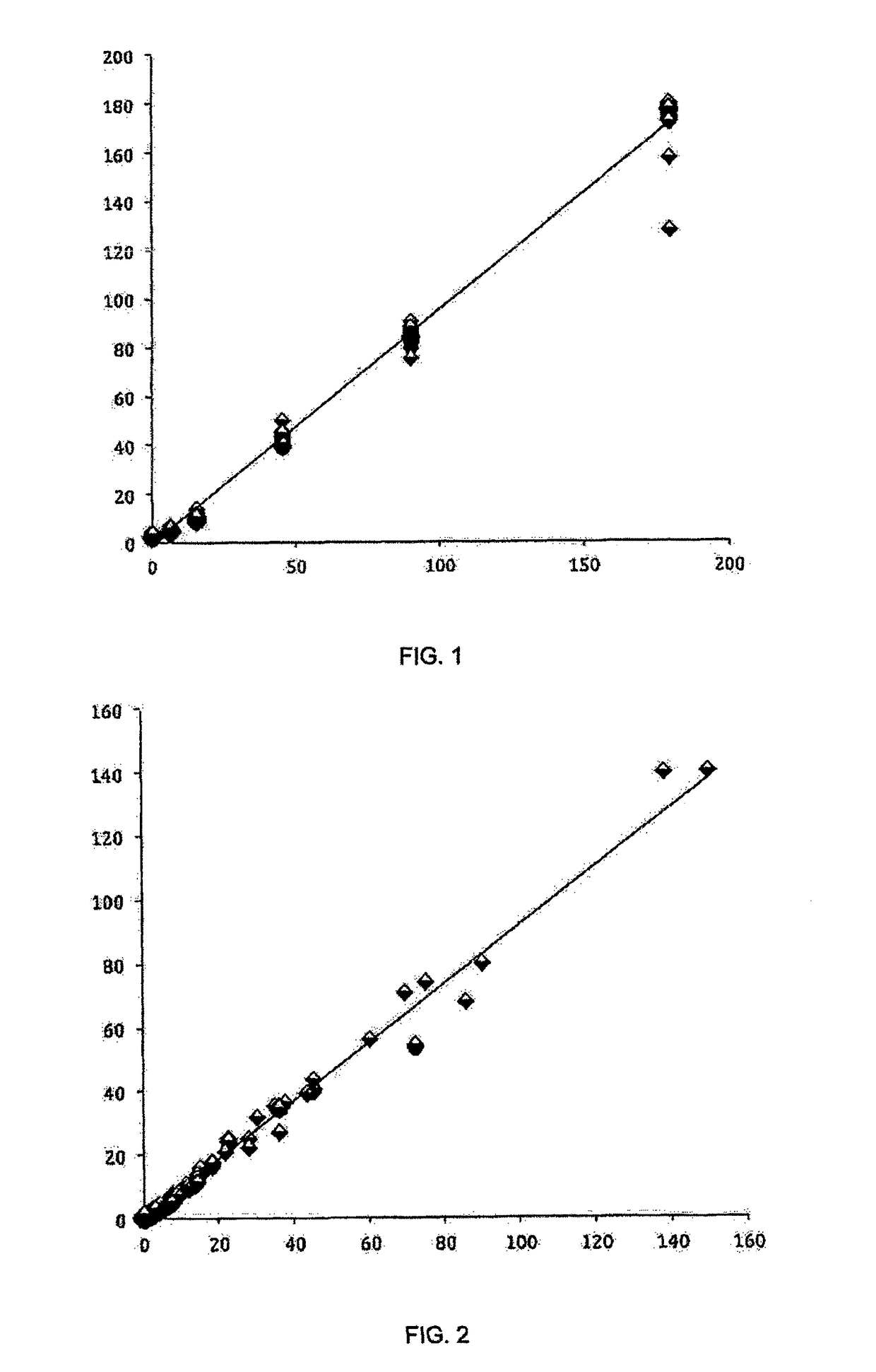
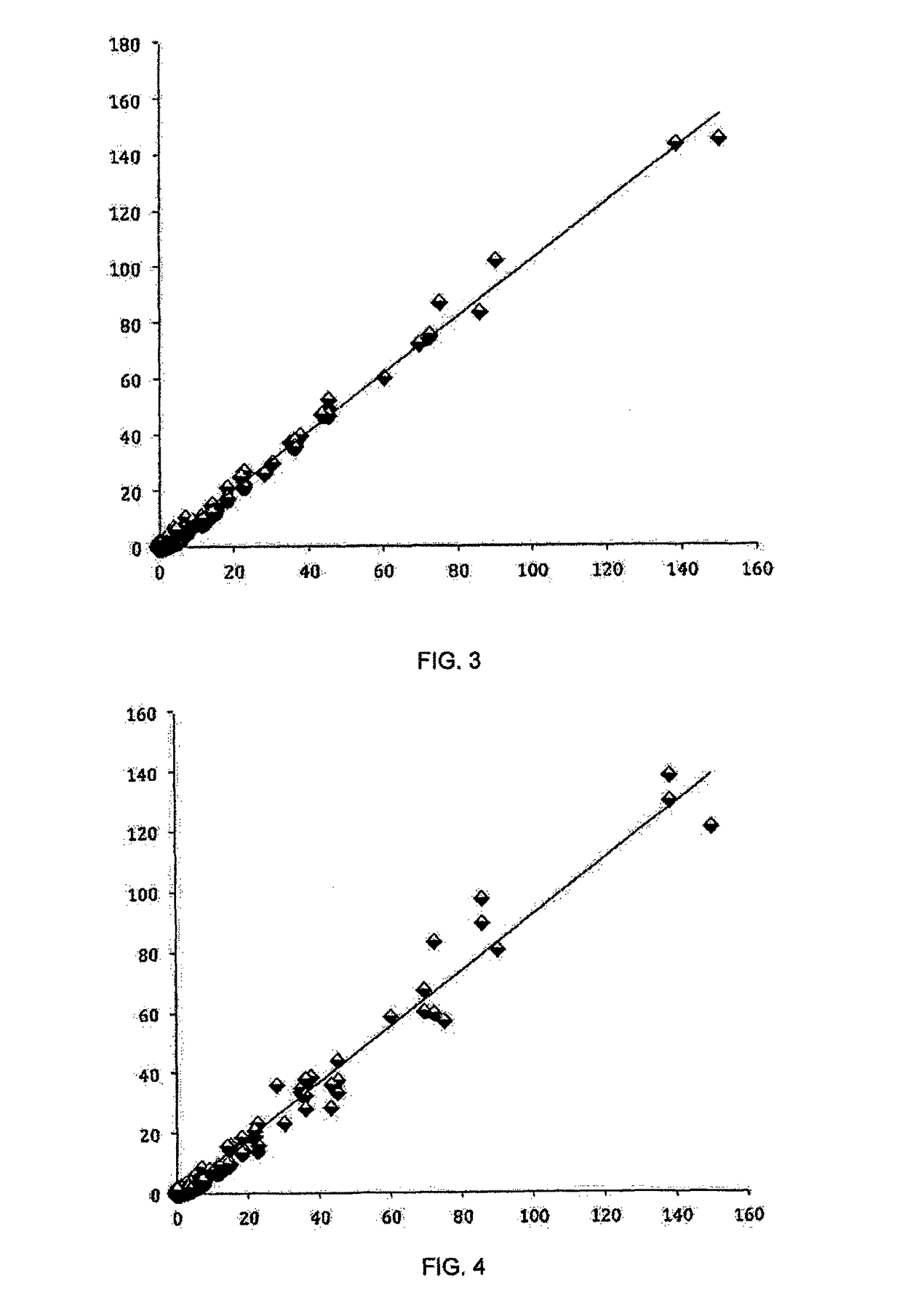
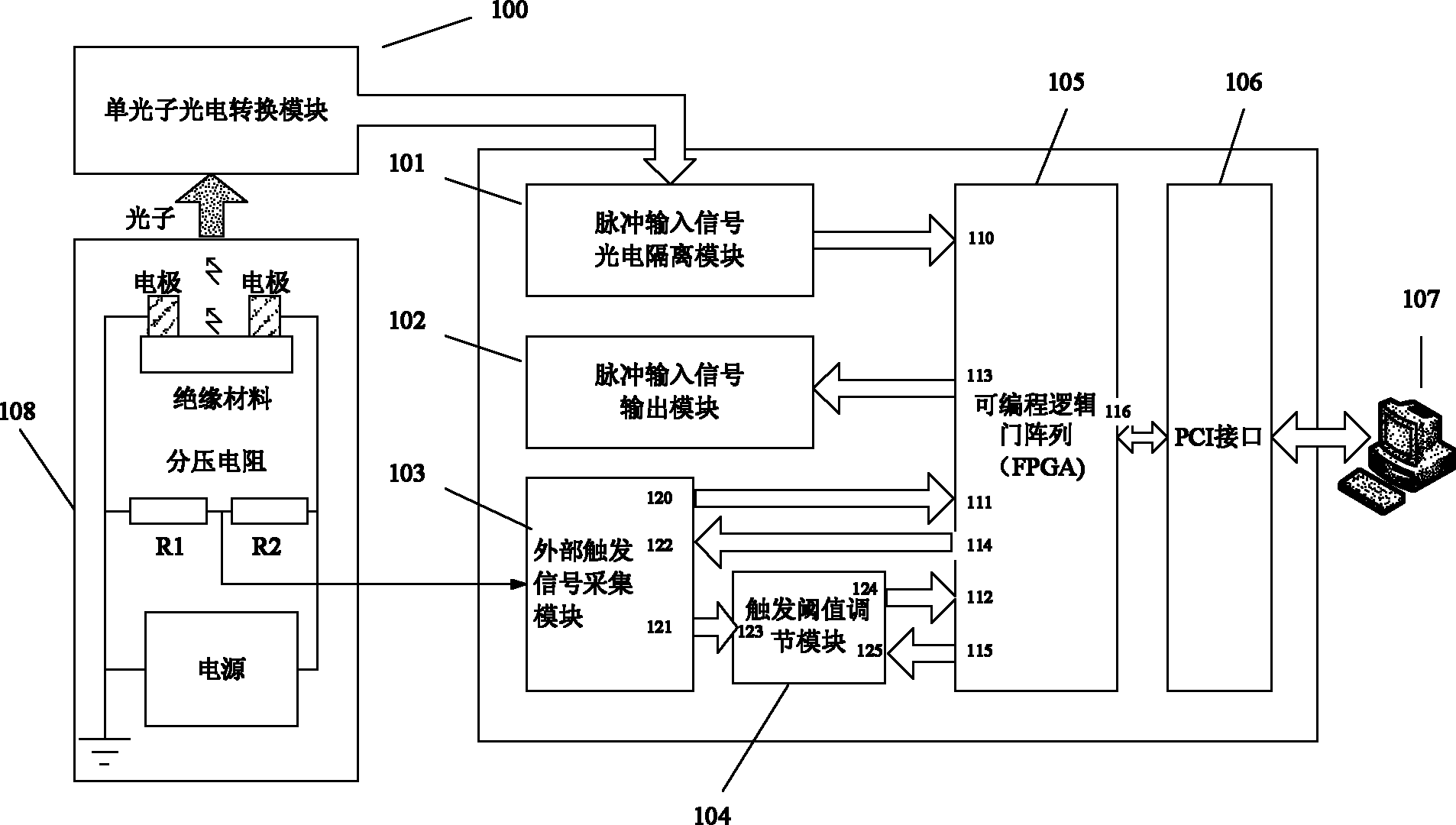
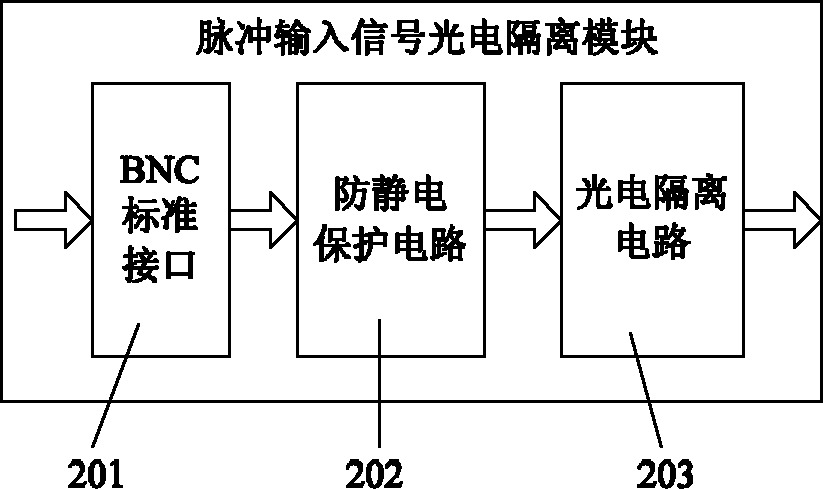
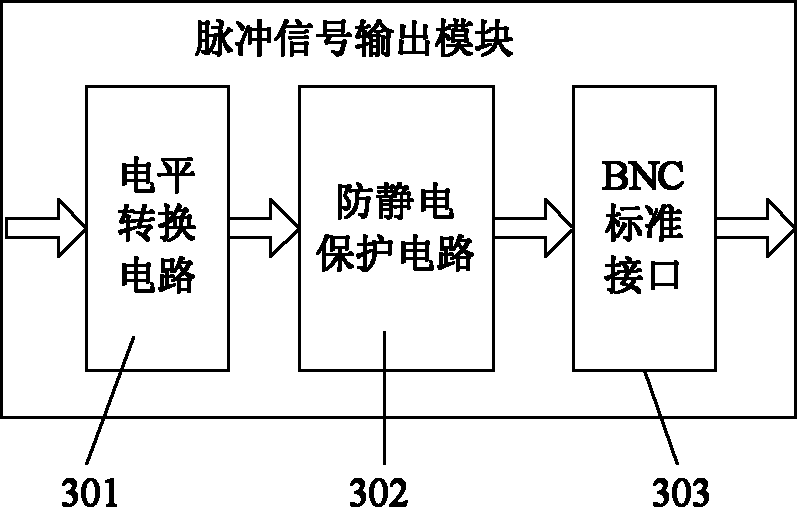
ActiveCN102072774ASimple designMeet the needs of weak luminescence photon measurementPhotometryFluorescence/phosphorescenceEngineeringField-programmable gate array
The invention discloses a single-photon counting system for measuring weak luminescence of a dielectric medium, comprising a single-photon photoelectric converting module, an input signal photoelectric separating module, a pulse signal output module, an external triggering signal collecting module, a triggering threshold adjusting module, a field programmable gate array (FPGA) module and a peripheral component interconnect (PCI) interface module. In the system, theFPGA module is adopted, so that the complex control circuit is mounted in one chip, the volume of the device is reduced and the design of the circuit is simplified, thereby being convenient for producing and debugging; and simultaneously, in the system, the PCI interface and PC (personal computer) are adopted to transfer the data so as to satisfy the requirements for measuring the weak luminescence of polymers by means of the excellent communication speed and interference resistance of the PCI interface.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Separation of doping density and minority carrier lifetime in photoluminescence measurements on semiconductor materials
InactiveUS8742372B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPhotometrySemiconductor materialsBrick
Methods are presented for separating the effects of background doping density and effective minority carrier lifetime on photoluminescence (PL) generated from semiconductor materials. In one embodiment the background doping density is measured by another technique, enabling PL measurements to be analyzed in terms of effective minority carrier lifetime. In another embodiment the effective lifetime is measured by another technique, enabling PL measurements to be analyzed in terms of background doping density. In yet another embodiment, the effect of background doping density is removed by calculating intensity ratios of two PL measurements obtained in different spectral regions, or generated by different excitation wavelengths. The methods are particularly useful for bulk samples such as bricks or ingots of silicon, where information can be obtained over a much wider range of bulk lifetime values than is possible with thin, surface-limited samples such as silicon wafers. The methods may find application in solar cell manufacturing for improving the manufacture of silicon ingots and bricks, or for providing a cutting guide for wafering.
Owner:BT IMAGING PTY LTD
Transient grating time resolved luminescence measurements
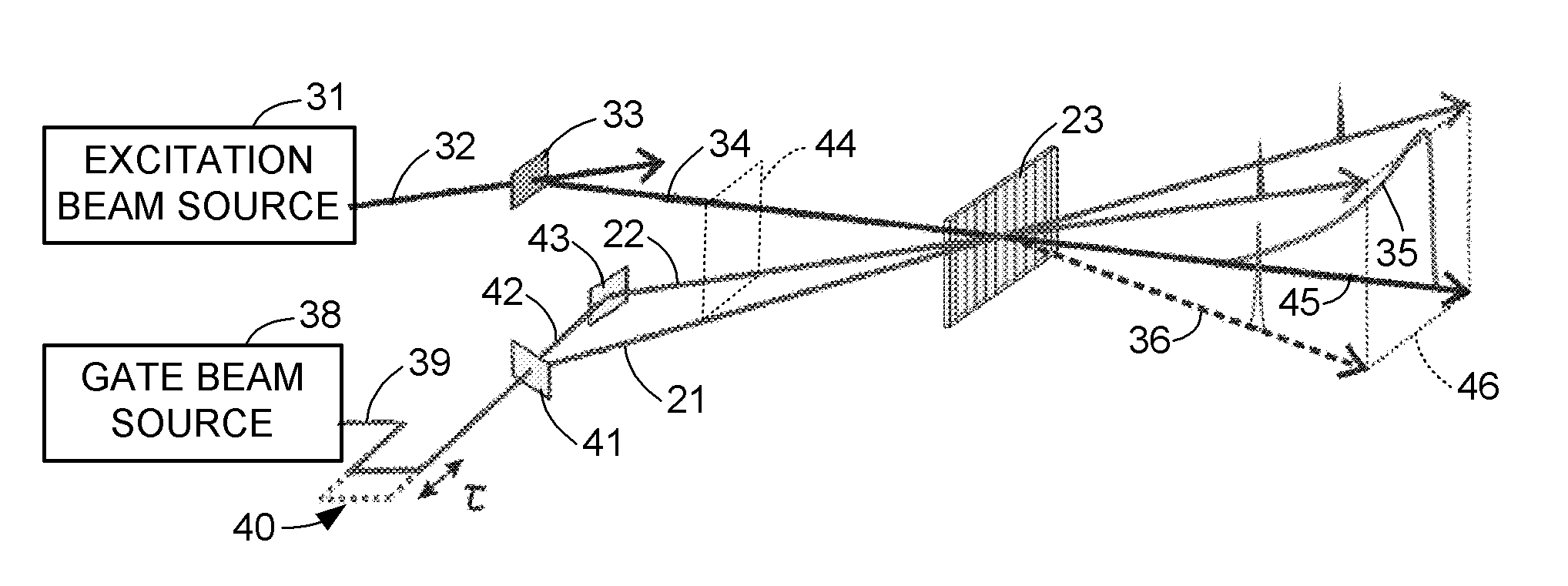
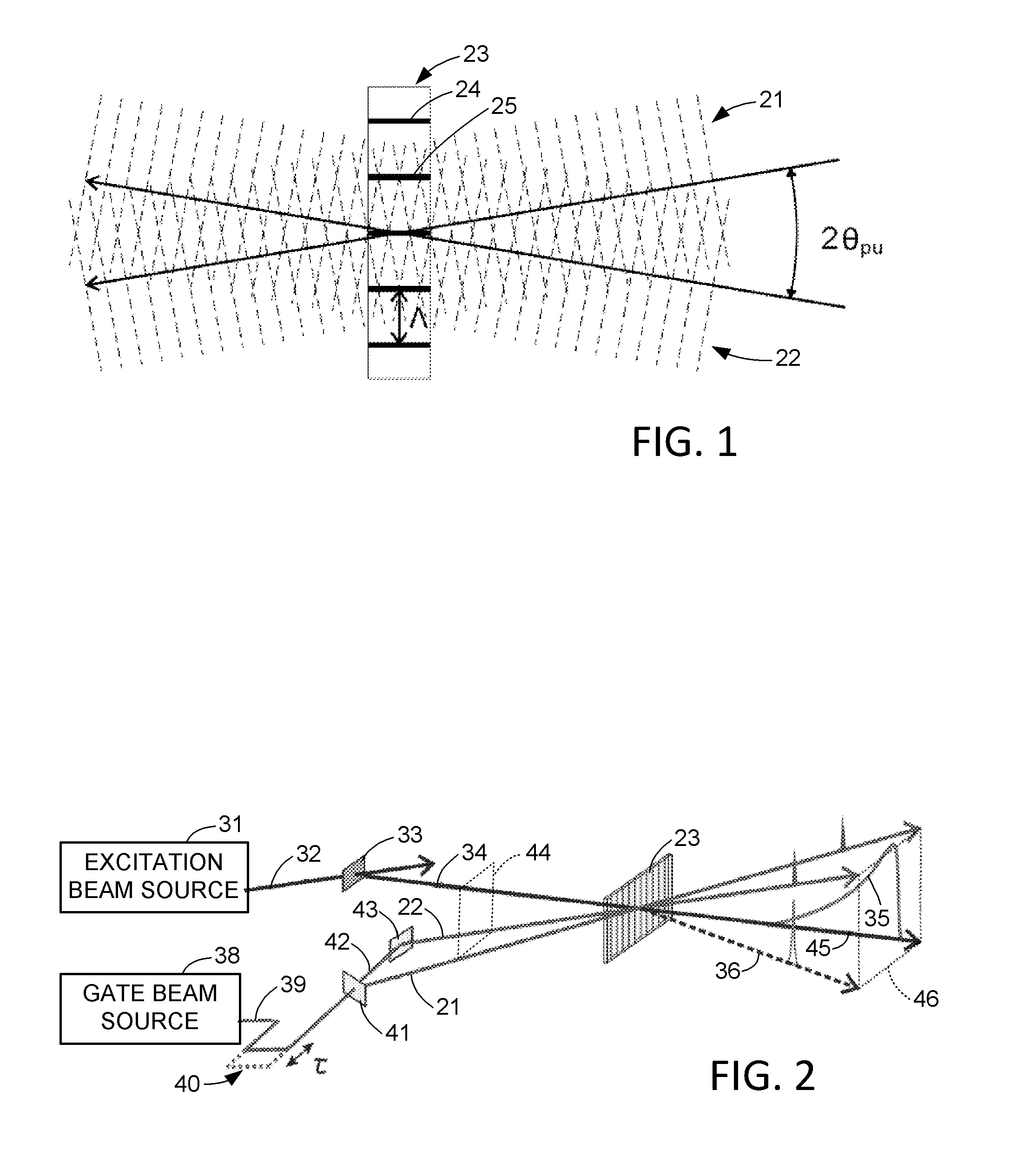
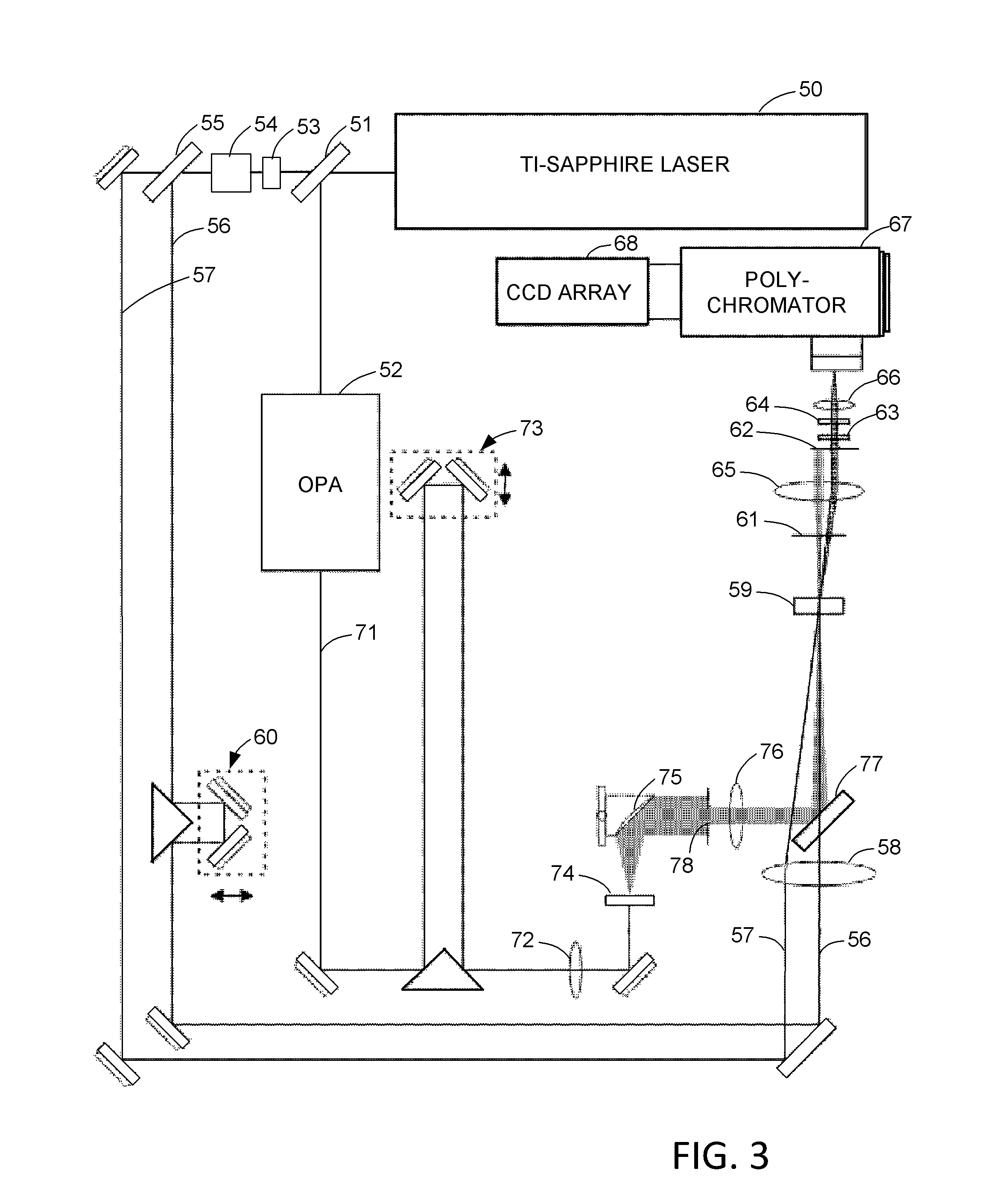
ActiveUS20160356644A1Minimize dispersionHigh numerical aperture opticRaman/scattering spectroscopyRaman scatteringGratingDetector array
A transient grating (TG) is used as an optical gating element with sub-picosecond time resolution for luminescence measurements from a photo-detector array. The transient grating is formed in a gate medium by one or more pulsed gate beams. For photoluminescence measurements such as photoluminescence spectroscopy or imaging, a source is excited by a pulsed excitation beam, and the pulsed gate beams are synchronized to the pulsed excitation beam with an adjustable delay between the excitation of the source and the formation of the TG. Moreover, a source or its spectra can be imaged at two different regions of the photo-detector array at two different times spaced in time by a selected duration of time with sub-picosecond resolution over a range of a nanosecond or more. A beam from the source is deflected to the different regions by changing the frequency or geometry of the pulsed gate beams.
Owner:VICTORIA LINK LTD
Method for measuring and analyzing bioluminescence and device for measuring and analyzing bioluminescence
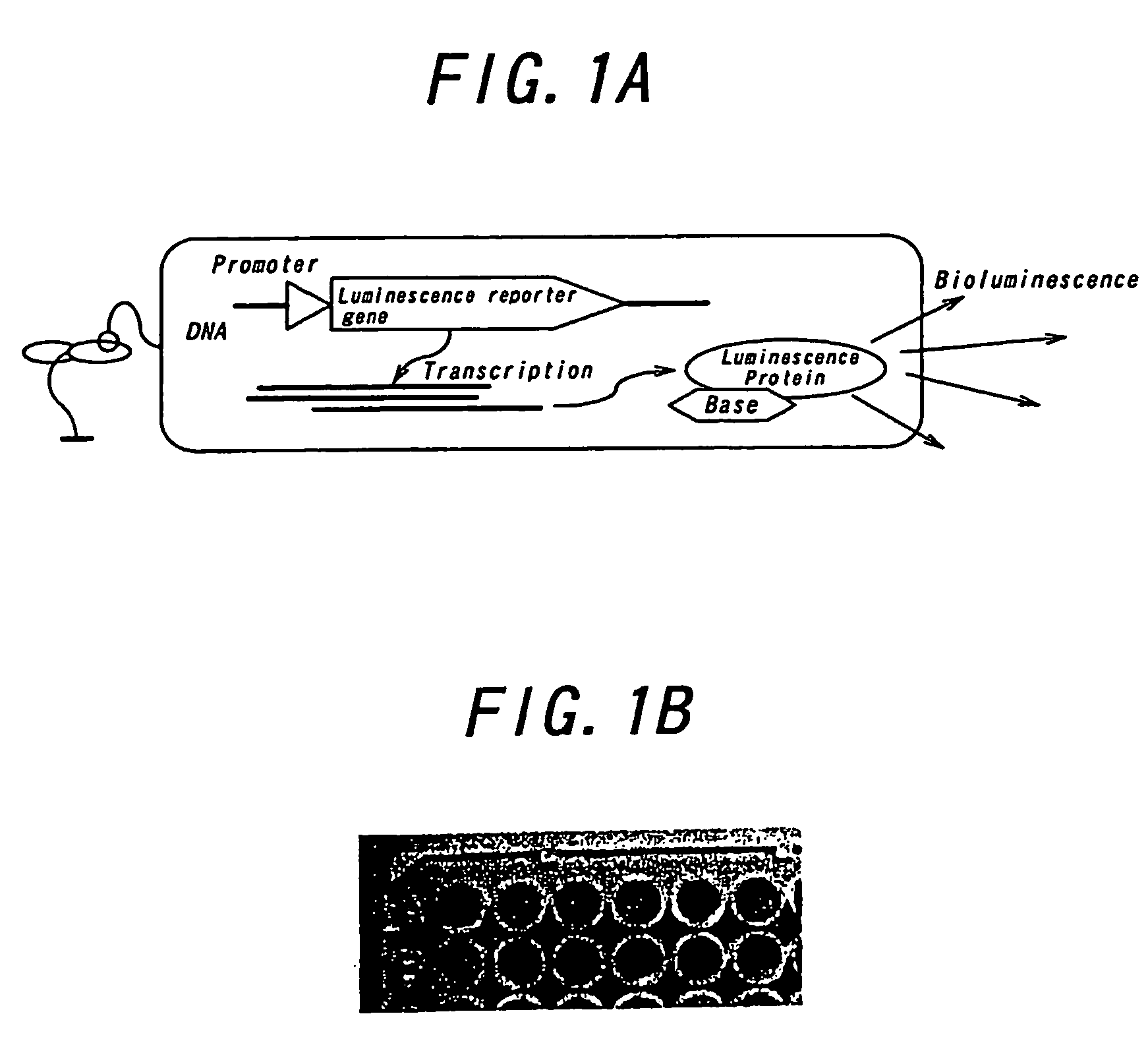
InactiveUS20040232351A1Limiting conditionShorten the time periodMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceLuminescent MeasurementsBioluminescence
A method for measuring and analyzing bioluminescence, including the steps of receiving in real-time a luminescence measurement result group from a creature sample group, displaying and maintaining in real-time the luminescence measurement result group, receiving in real-time another luminescence measurement result group from the creature sample group, and displaying and maintaining in real-time the another luminescence measurement result group, instead of the luminescence measurement result group.
Owner:NAGOYA UNIVERSITY
Light Emission Measuring Apparatus and Light Emission Measuring Method
InactiveUS20070257182A1Many timesComplicated operationRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationMicroscopic imageLight emission
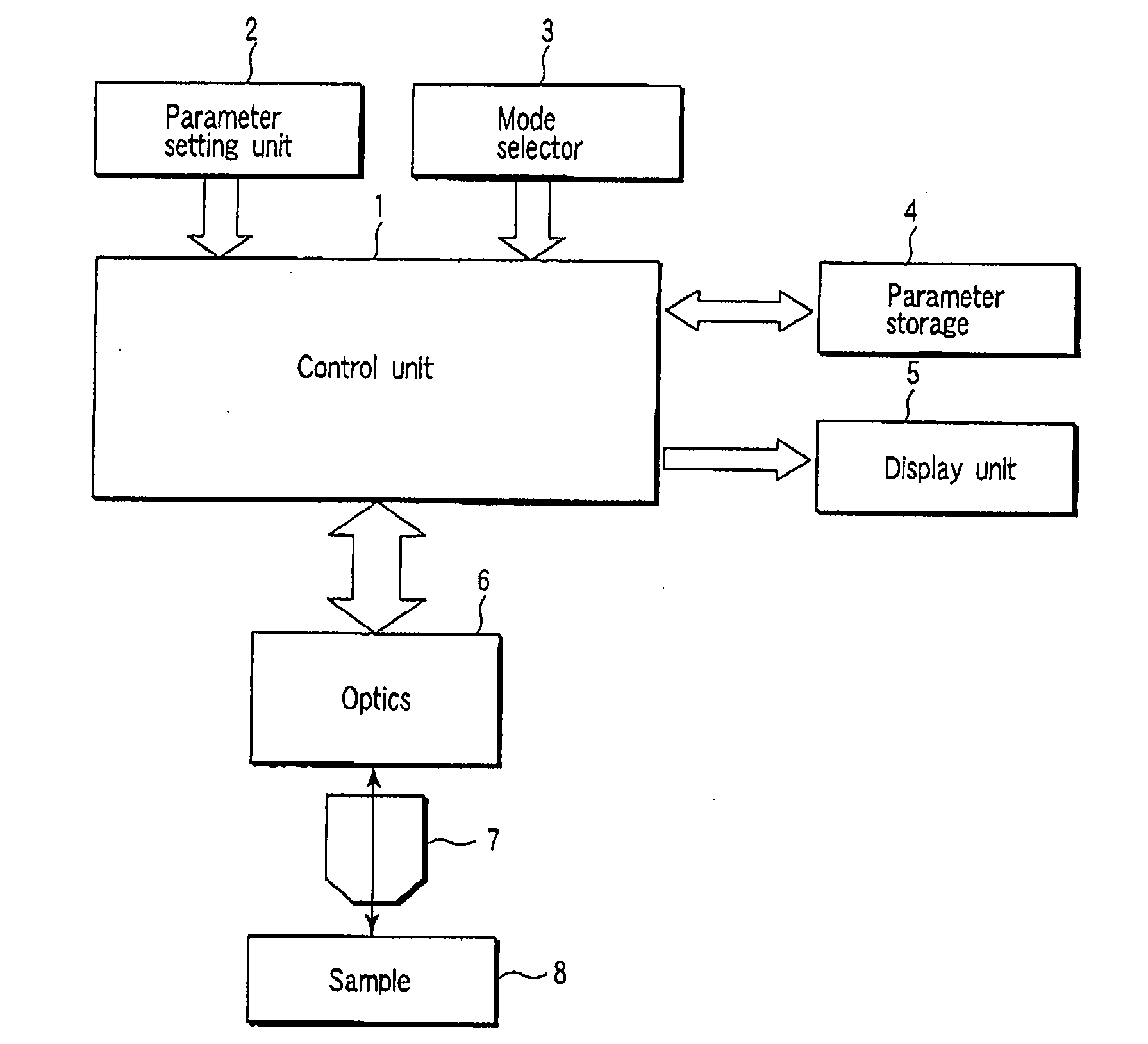
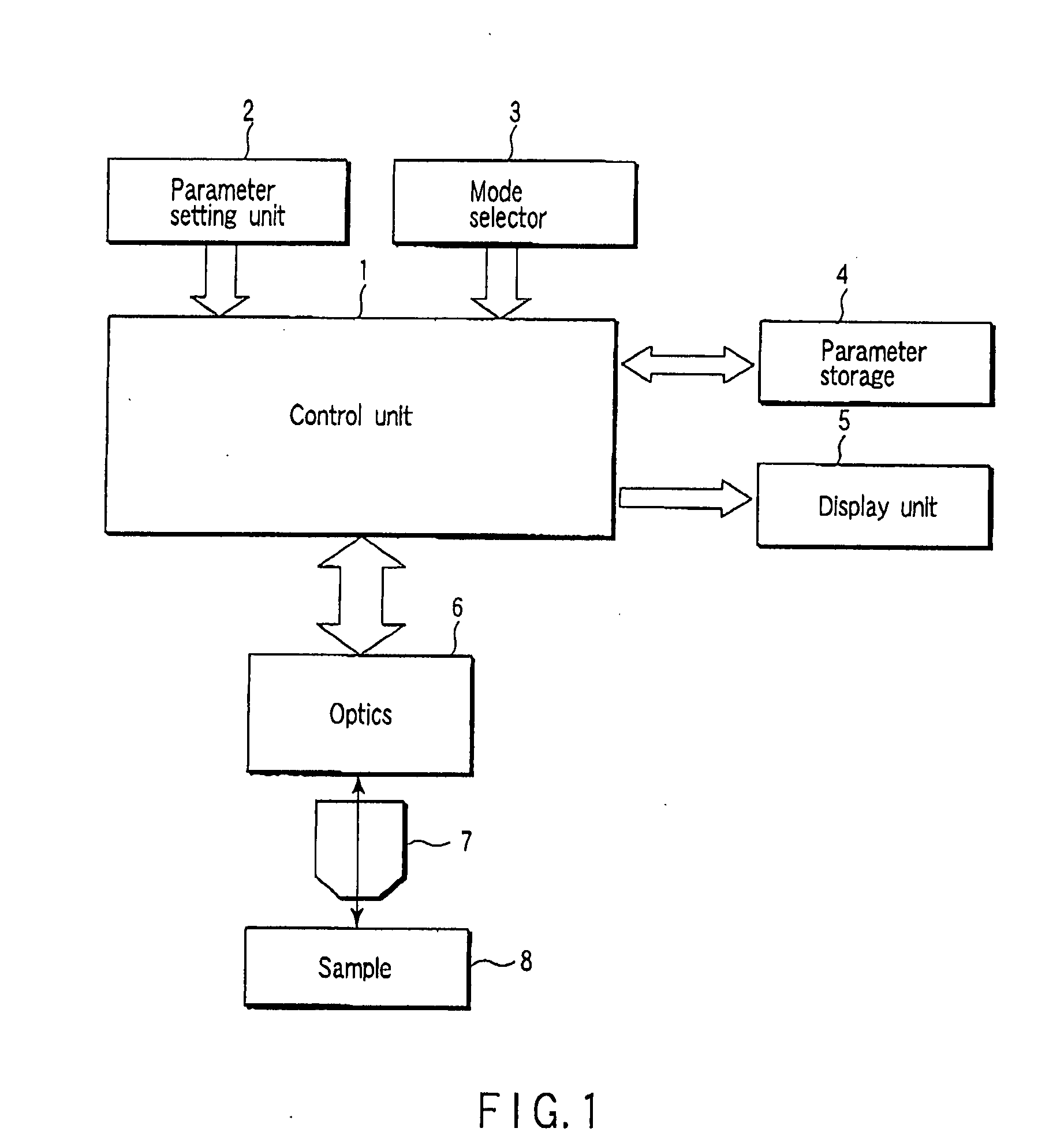
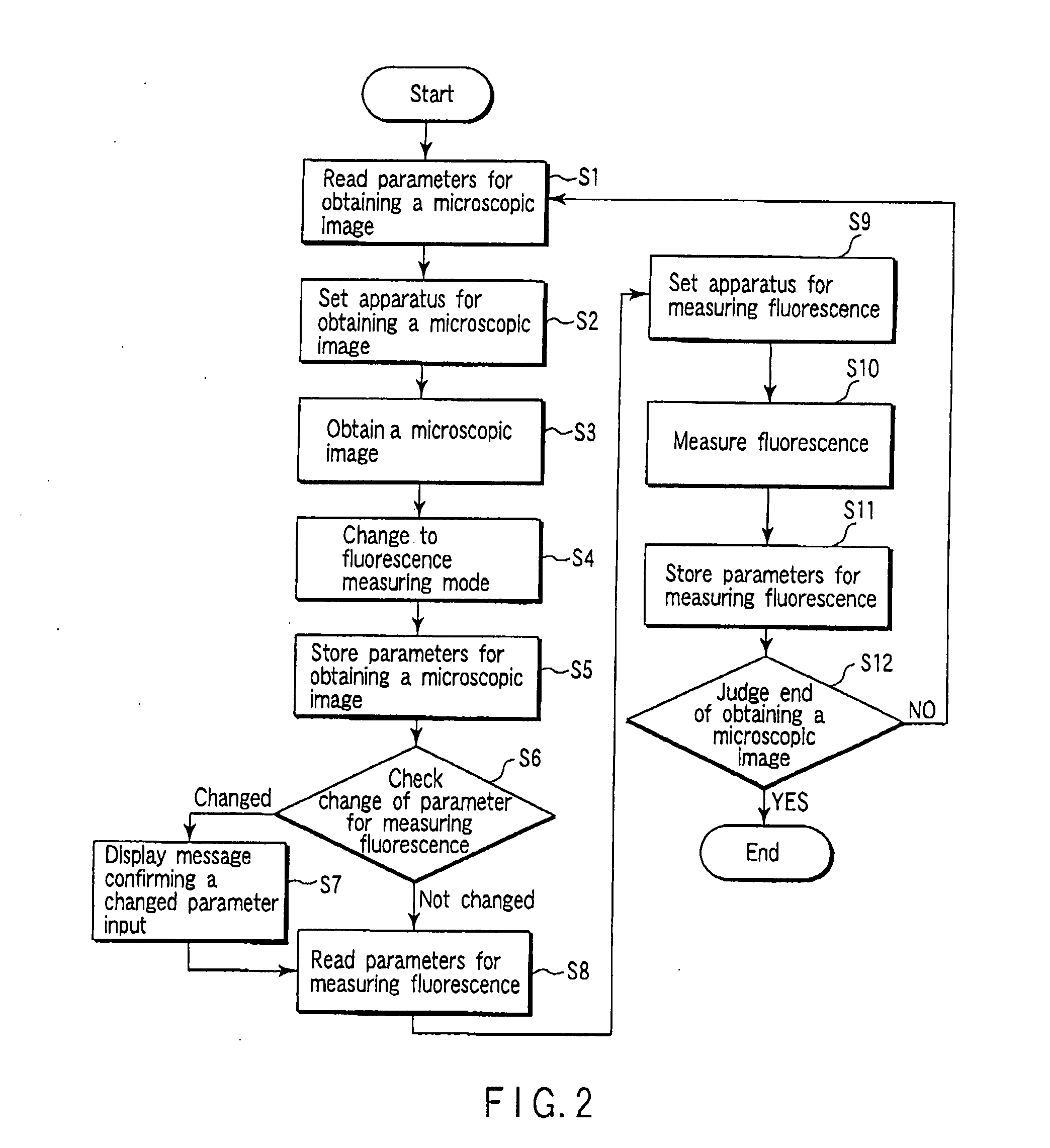
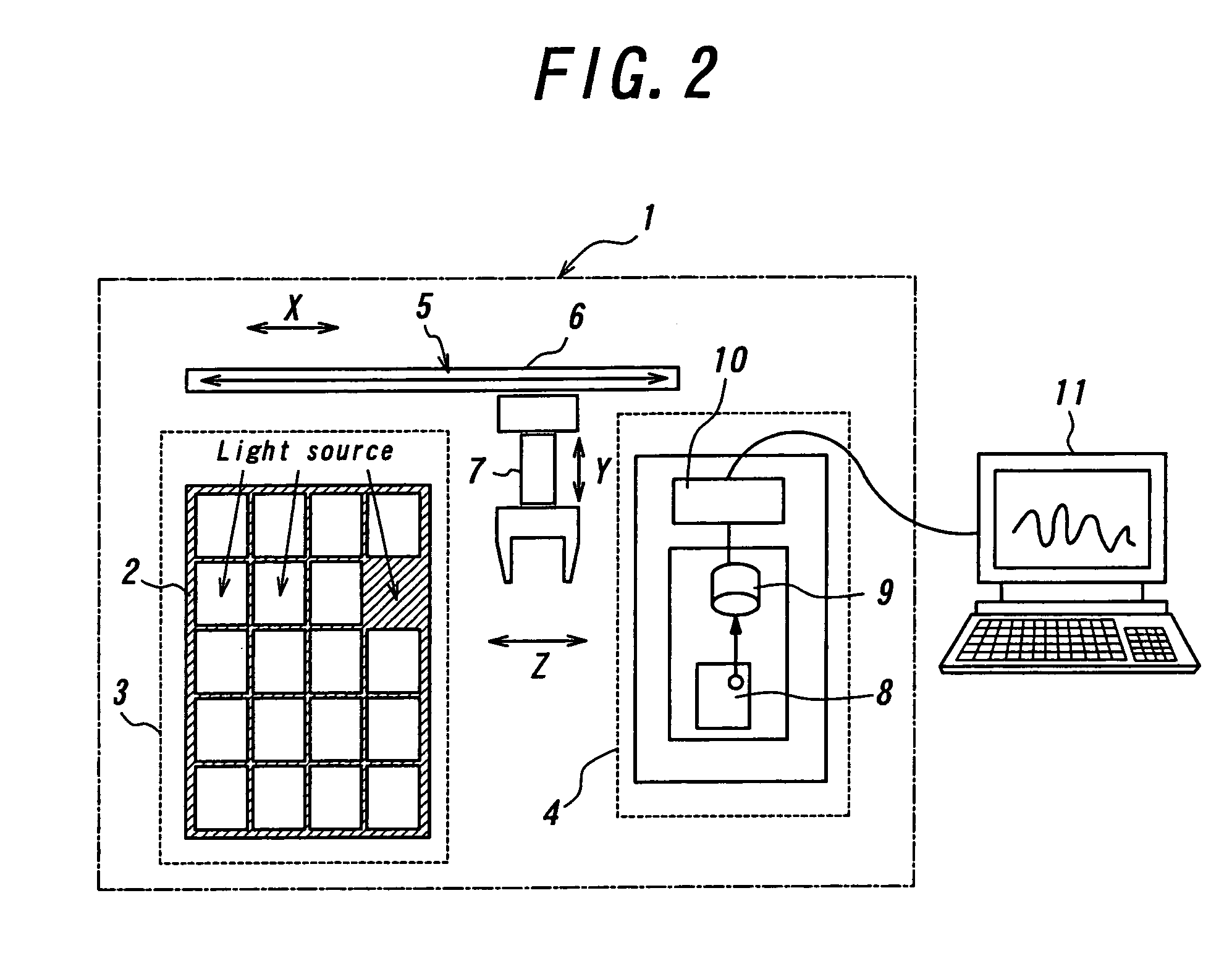
A light fluctuation measuring apparatus, comprising a parameter setting unit 2 which sets parameters of a microscopic image obtaining unit and / or parameters of a light emission measuring unit used for observing light emission in a desired area of a sample in time series, a parameter storage 4 which stores parameters, a mode selector 3 which selects one of a microscopic image obtaining mode for obtaining a microscopic image by a microscopic image obtaining unit, and a light emission measuring mode for observing light emission in a desired area by a light emission measuring unit, and a control unit 1 which reads parameters stored in the storage 4 based on a selected mode, inputs the parameter to a microscopic image obtaining unit or a light emission measuring unit, and controls these units.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Method for measuring and analyzing bioluminescence and device for measuring and analyzing bioluminescence
InactiveUS7199378B2Flexible controlShorten the time periodMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceReal time displayComputer science
A method for measuring and analyzing bioluminescence, including the steps of receiving in real-time a luminescence measurement result group from a creature sample group, displaying and maintaining in real-time the luminescence measurement result group, receiving in real-time another luminescence measurement result group from the creature sample group, and displaying and maintaining in real-time the another luminescence measurement result group, instead of the luminescence measurement result group.
Owner:NAGOYA UNIVERSITY
Single-reaction cup luminescence measurement method
ActiveCN107271433APrevent missing collectionGuaranteed service lifeChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceEngineeringPhoton counter
The invention relates to a single-reaction cup luminescence measurement method, which includes the following steps: (S1) an opening and closing driver is started, so that the opening of a measurement chamber is opened by a top cover, and a reaction cup is put into a containing cavity of the measurement chamber; (S2) the opening and closing driver is started, so that the opening of the measurement chamber is closed by the top cover, a rotation driver is started, so that a through hole in a baffle is superposed with a photon through hole, and a photon counter is started; (S3) an initiating agent and an excitant are added into the reaction cup via a reagent-adding tube; (S4) after a period of time, the rotation driver is started, so that the through hole in the baffle is staggered from the photon through hole; (S5) the opening and closing driver is started, so that the opening of the measurement chamber is opened by the top cover, and the reaction cup is taken away. Since the photon counter is started and the light passage is opened before the initiating agent and the excitant are added, failure to collect photons is prevented, and the collecting precision is increased.
Owner:SUZHOU HYBIOME BIOMEDICAL ENG CO LTD
Method for detecting microalgae content in ship ballast water
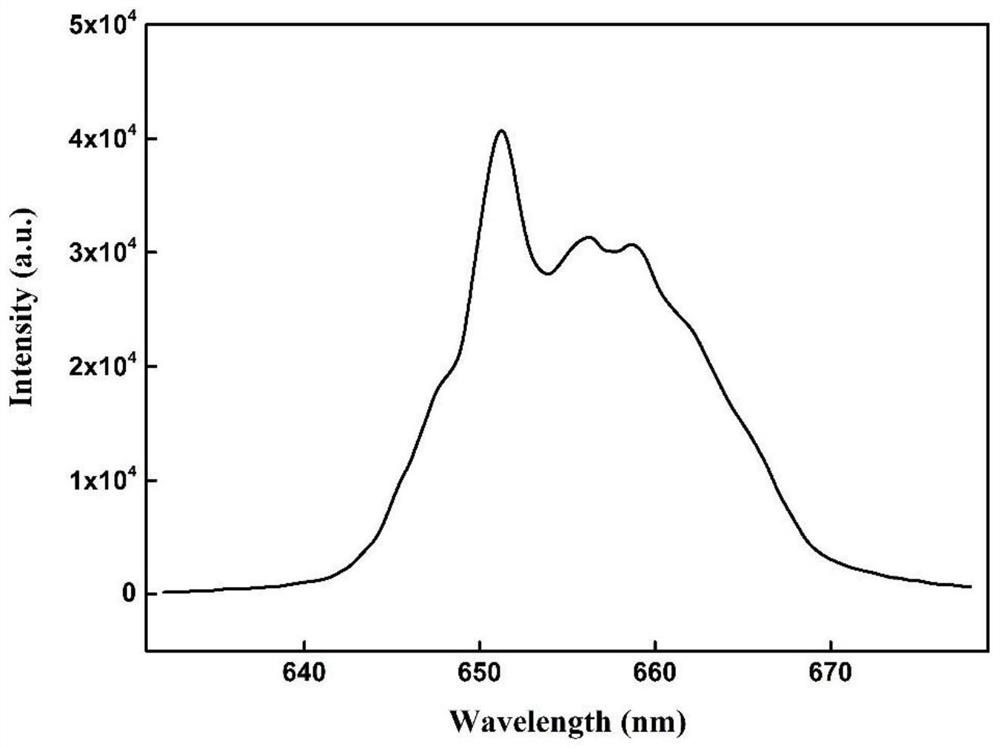
ActiveCN114563362ADoes not cause spontaneous background fluorescenceLight damage is smallColor/spectral properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluoProbesLuminous intensity
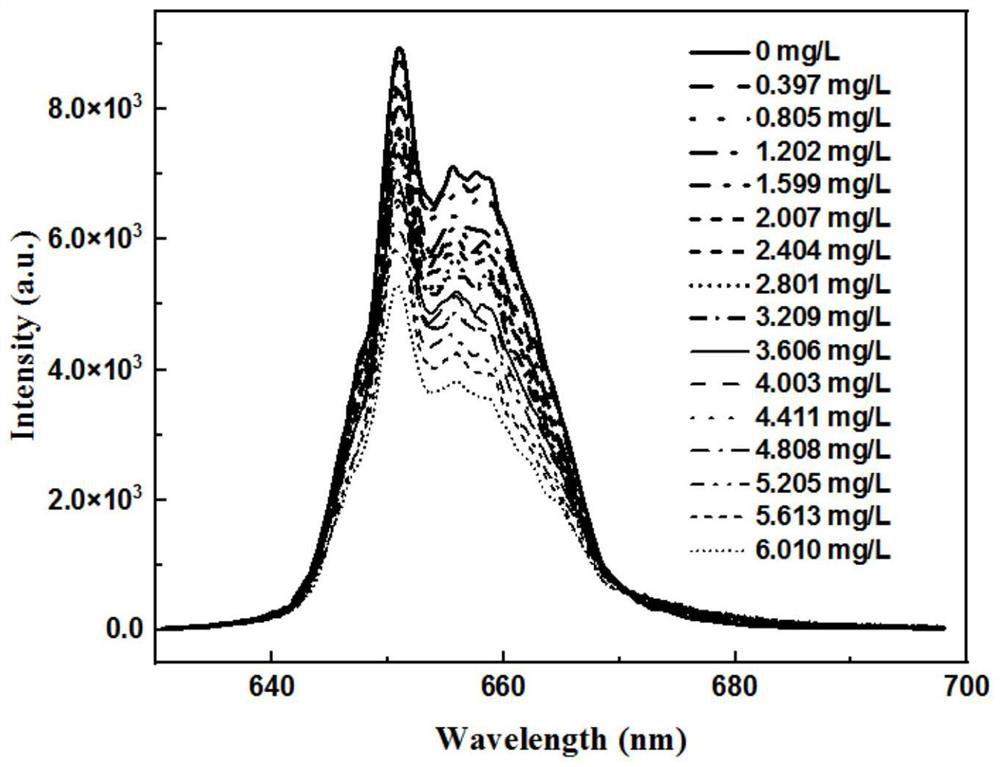
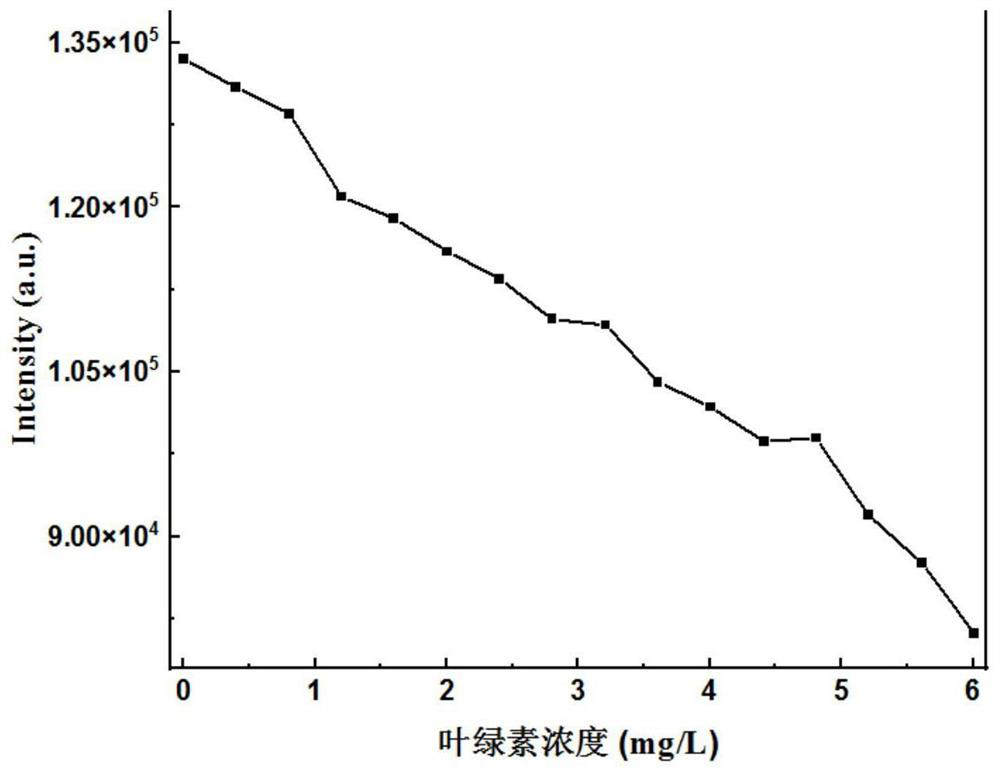
The invention belongs to the technical field of ship ballast water microalgae content detection, and particularly relates to an up-conversion nano fluorescent probe which realizes rapid detection of microalgae content through competitive emission. According to the method, a red up-conversion nano fluorescent probe is adopted, red luminescence of the fluorescent probe is highly overlapped with the maximum absorption peak of ballast water microalgae chlorophyll a under excitation of near-infrared light, a relation curve of luminescence intensity and the content of chlorophyll a is established through competitive luminescence measurement, and the content of the chlorophyll a is determined according to the corresponding relation of the content of the chlorophyll a and the microalgae cell biomass. And establishing a relation model between the luminous intensity and the microalgae cell biomass so as to calculate the microalgae biomass in the ballast water sample. According to the present invention, the rapid detection of the microalgae biomass can be achieved, the operation is simple and convenient, the sensitivity is high, the safe long wavelength near-infrared light is adopted as the excitation source, the light damage to the organism is reduced, the spontaneous background fluorescence of the microalgae cannot be caused, the detection sensitivity can be improved in the order of magnitude, and the method is suitable for promotion and application.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Luminescence measuring device with pre-filter effect suppression
InactiveUS7180589B2Radiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationChemical speciesUltimate tensile strength
A device for measuring the intensity of a luminescence radiation emitted by at least one chemical species probed, along a trajectory by an excitation radiation. The device includes n measurement channels, where n is an integer greater than or equal to 2, each measurement channel being used to measure a fraction of the intensity of the luminescence radiation emitted along the trajectory. The device is also applicable to analytical chemistry to make speciation measurements.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Apparatus for measuring in particular luminescent and/or fluorescent radiation
InactiveUS6949754B2Compact structureBroad spectrumChemiluminescene/bioluminescencePhotometryMeasuring instrumentFluorescent radiation
Owner:BERTHOLD TECH
Luminescence measuring device
ActiveUS9683942B2Easy to measureSuppress noiseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTemperature controlLuminescent Measurements
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Luminescence measuring apparatus
InactiveUS20080225279A1Reduce reflectionHigh measurement sensitivityPhotometryColor/spectral properties measurementsAmount of substanceLuminescent Measurements
To increase the direct light received by the detector and decrease reflections from the detection component support structures, the luminescent substance is placed as close to the detector as possible. More specifically, the apparatus is configured so as to slide out a structure shielding the detector from light and at the same time slide in the vessel containing the luminescent substance therein until the vessel comes right under the detector. The invention can detect trace luminescence from a small-volume sample by maximizing the amount of direct light received from the sample and minimizing the decay of indirect light received from the sample attributable to interactions with the vessel for containing the sample therein, the structure for collecting light, and the structure for supporting other detection components.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Systems and methods for detecting tissue ischemia and evaluating organ function using serum luminescence
Methods for the early sensing of tissue ischemia and / or infarctions within organs using the spectroscopic features of serum luminescence include (i) isolating serum from a blood sample, (ii) directing an excitation light at the serum, (iii) receiving an endogenous serum chromophore emission light from the excited serum, and (iv) determining a presence of an ischemic condition based on the intensity of the endogenous serum chromophore emission light. Methods of detecting organ dysfunction can include transmitting excitation light to luminal contents of a mammalian blood vessel comprising trace amounts of exogenous chromophores administered to the subject mammal via the circulatory system. Transdermal luminescence measurements from the trace amounts of exogenous chromophores can then be used to determine organ dysfunction. Such methods enable routine monitoring of blood luminescence to bridge the diagnosis gap between sensitive symptom diagnosis and specific marker diagnosis, resulting in an effective early screening modality.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MACAU
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com