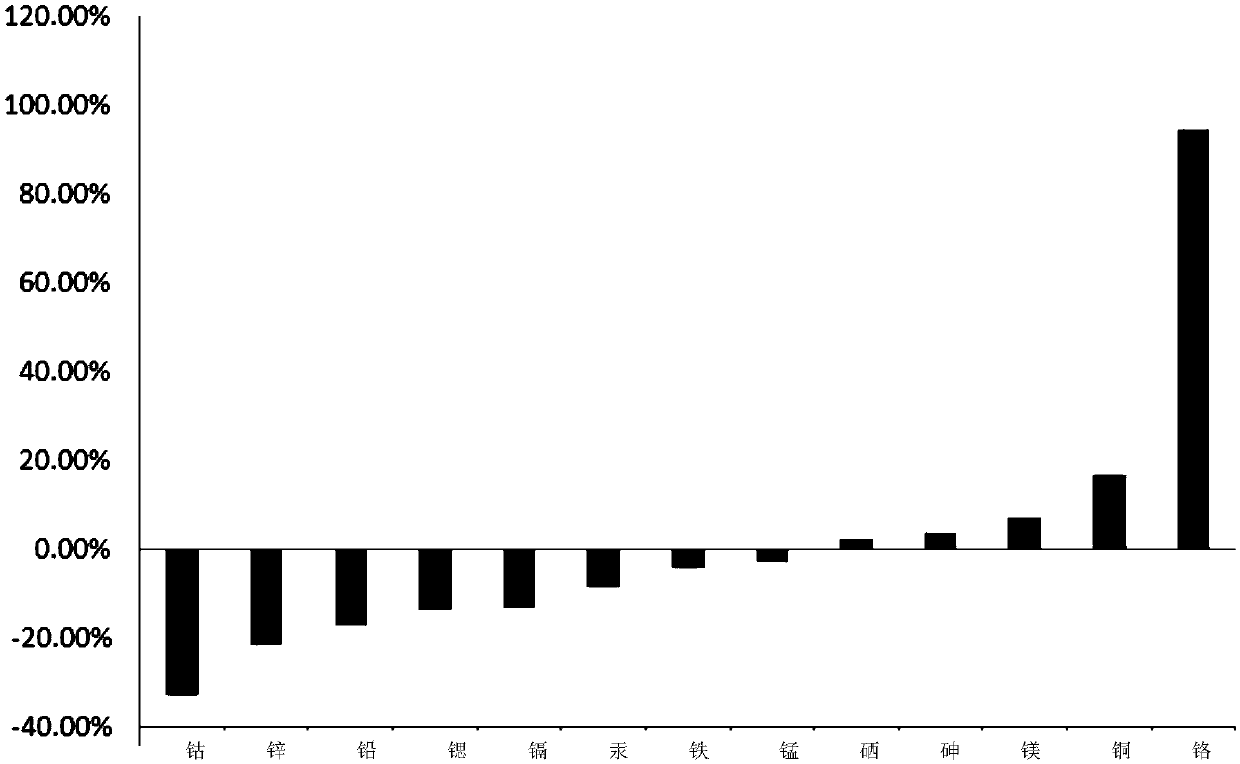
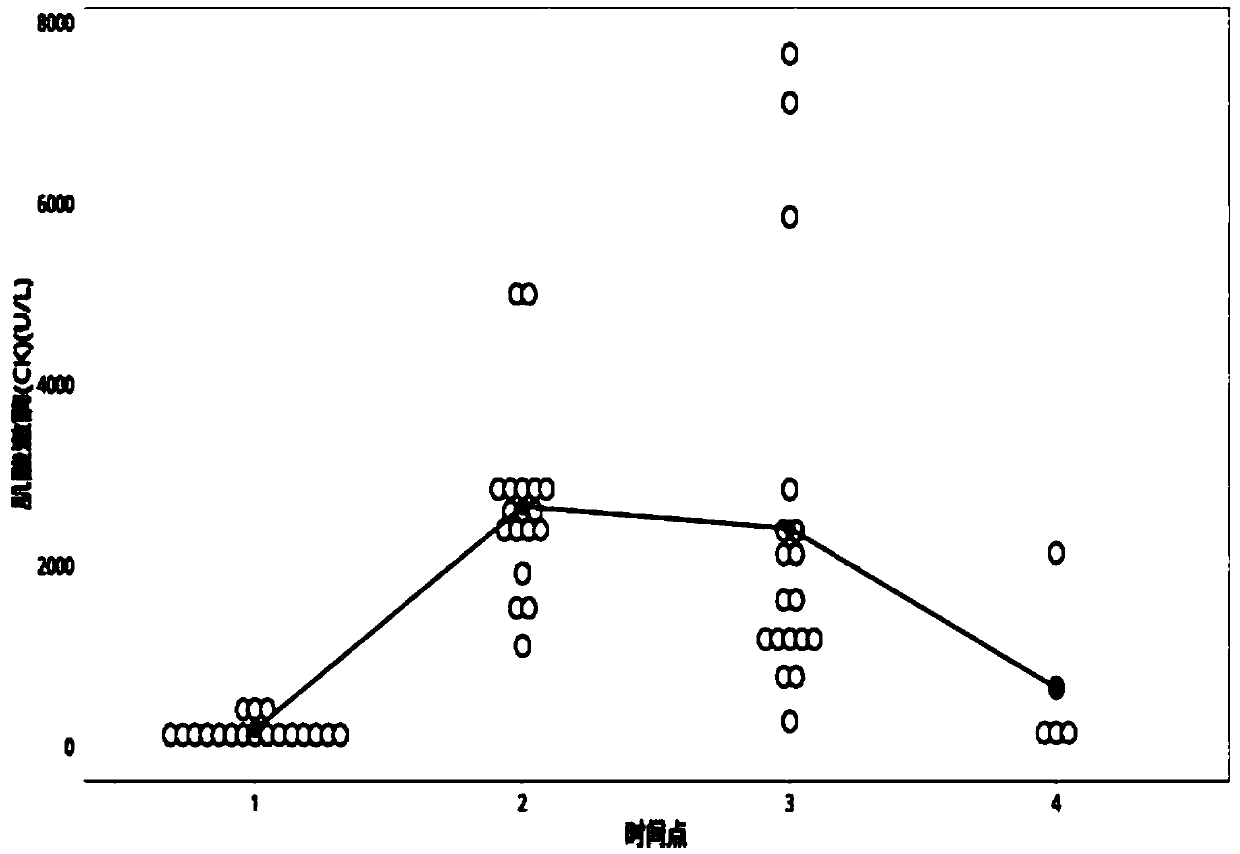
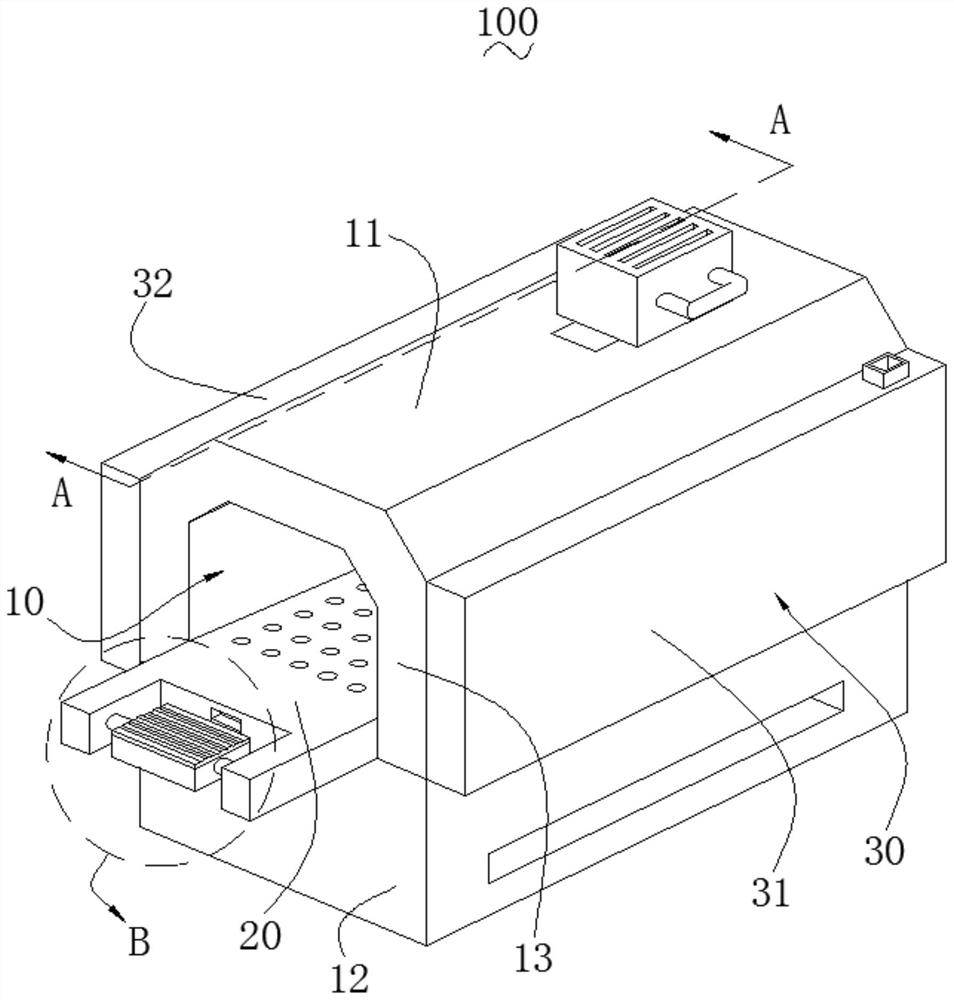
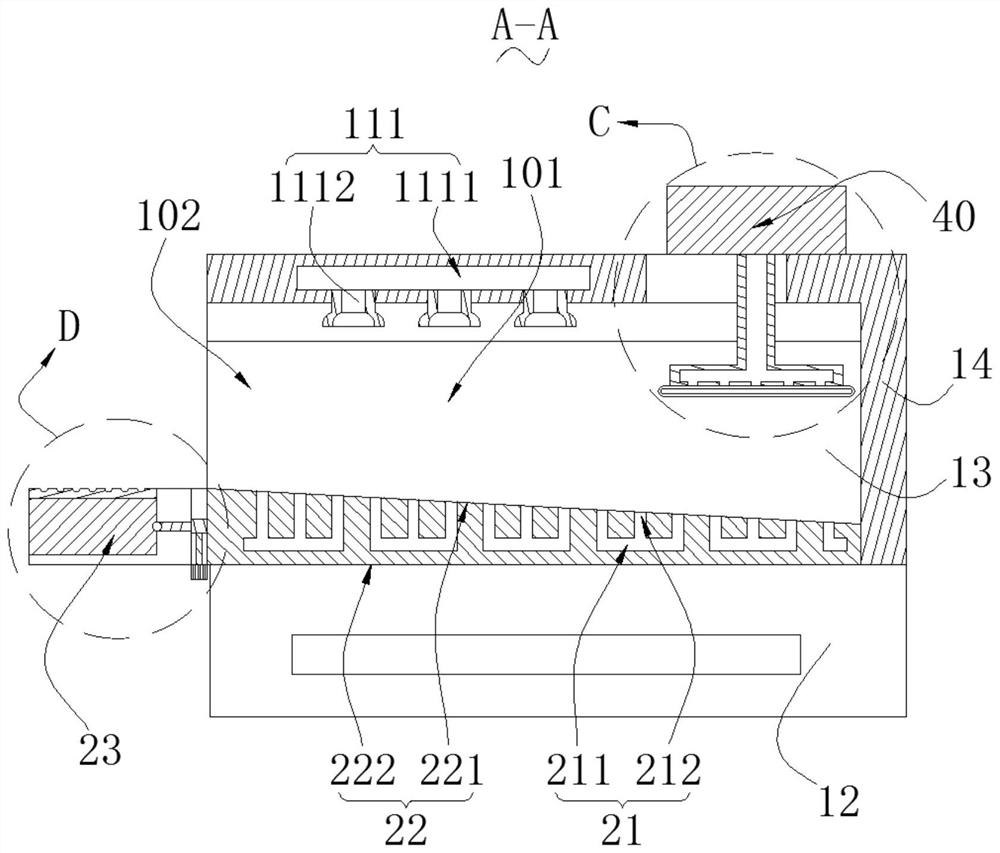
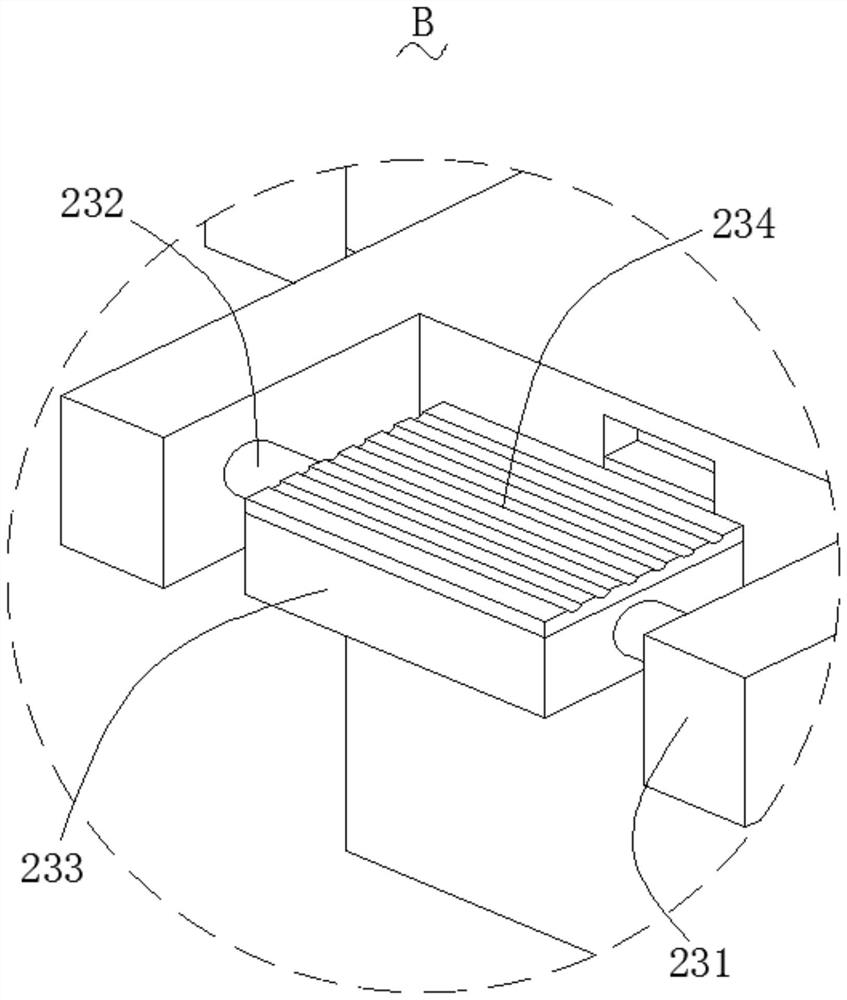
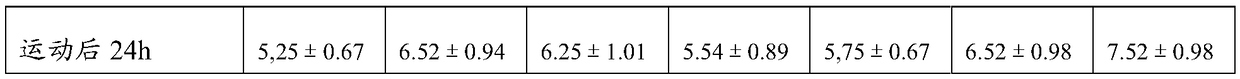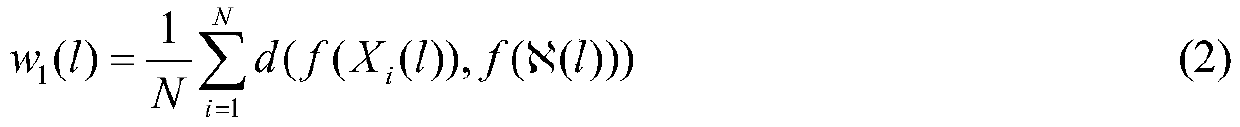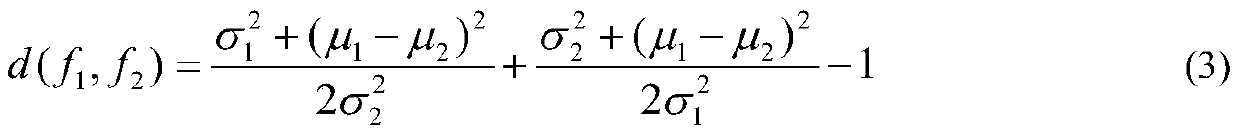Patents
Literature
42 results about "Pre exercise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
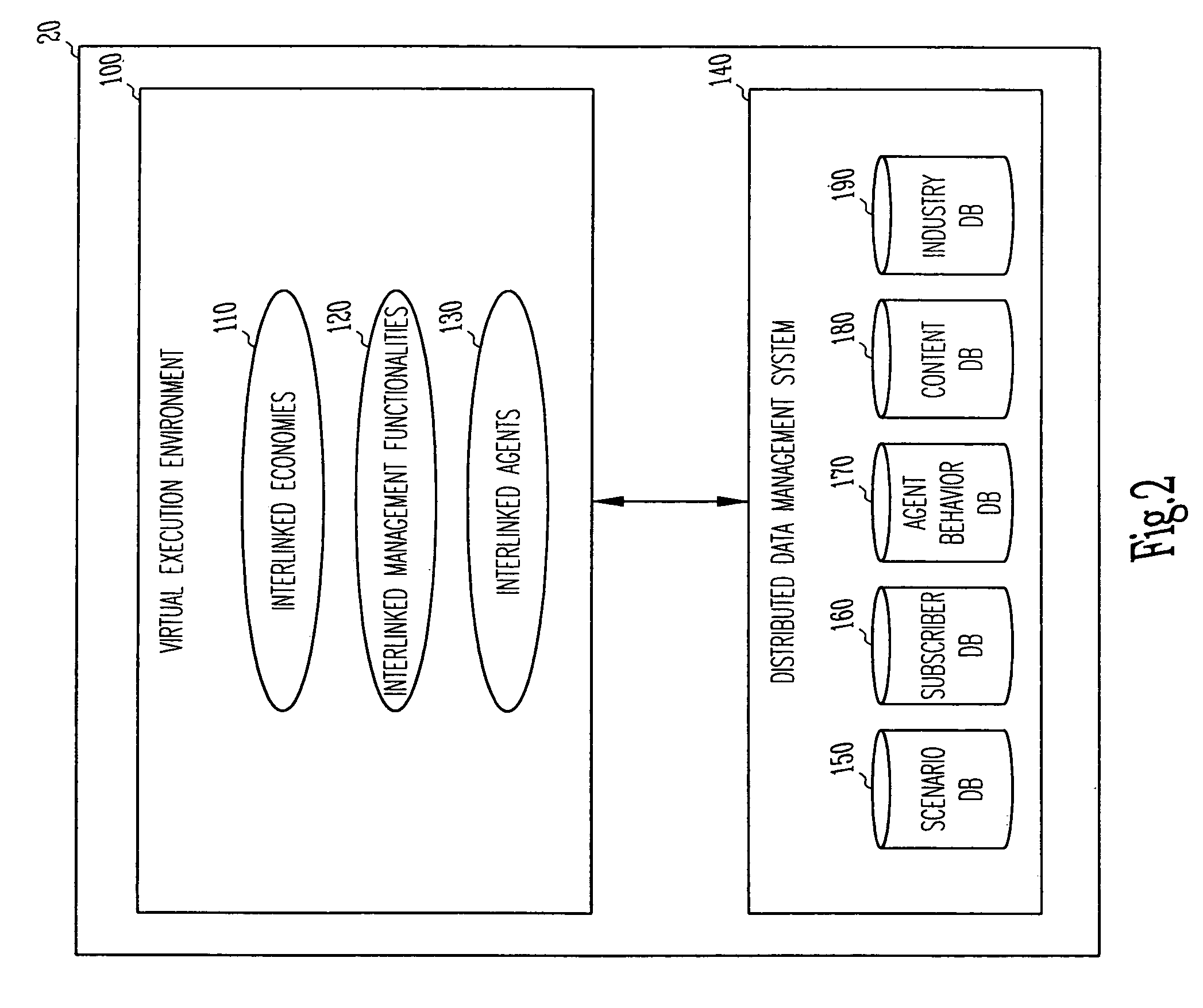
Industry simulation environment
ActiveUS6931365B1Multiprogramming arrangementsResourcesSynthetic Environment for Analysis and SimulationsIndustrial systems
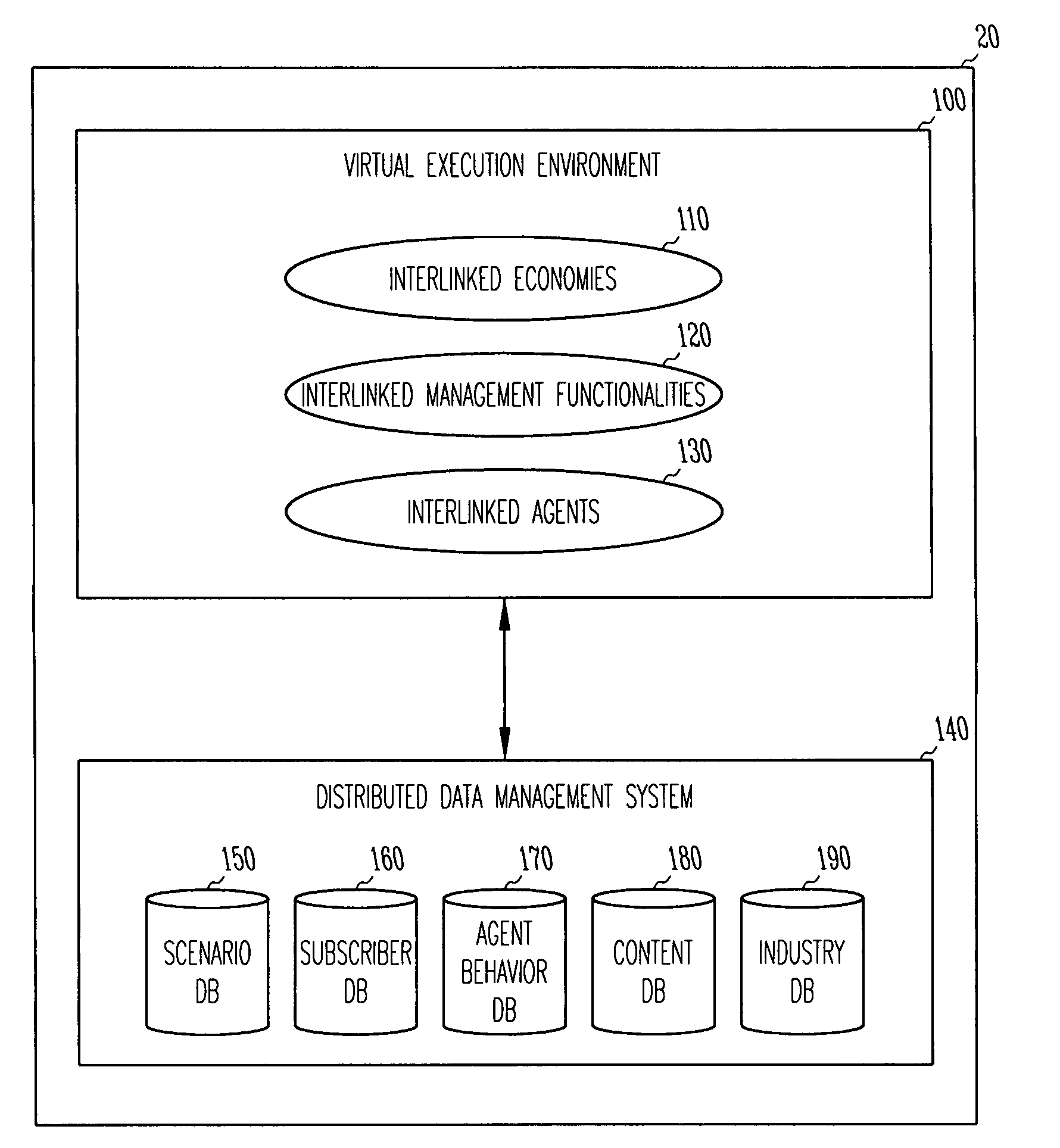
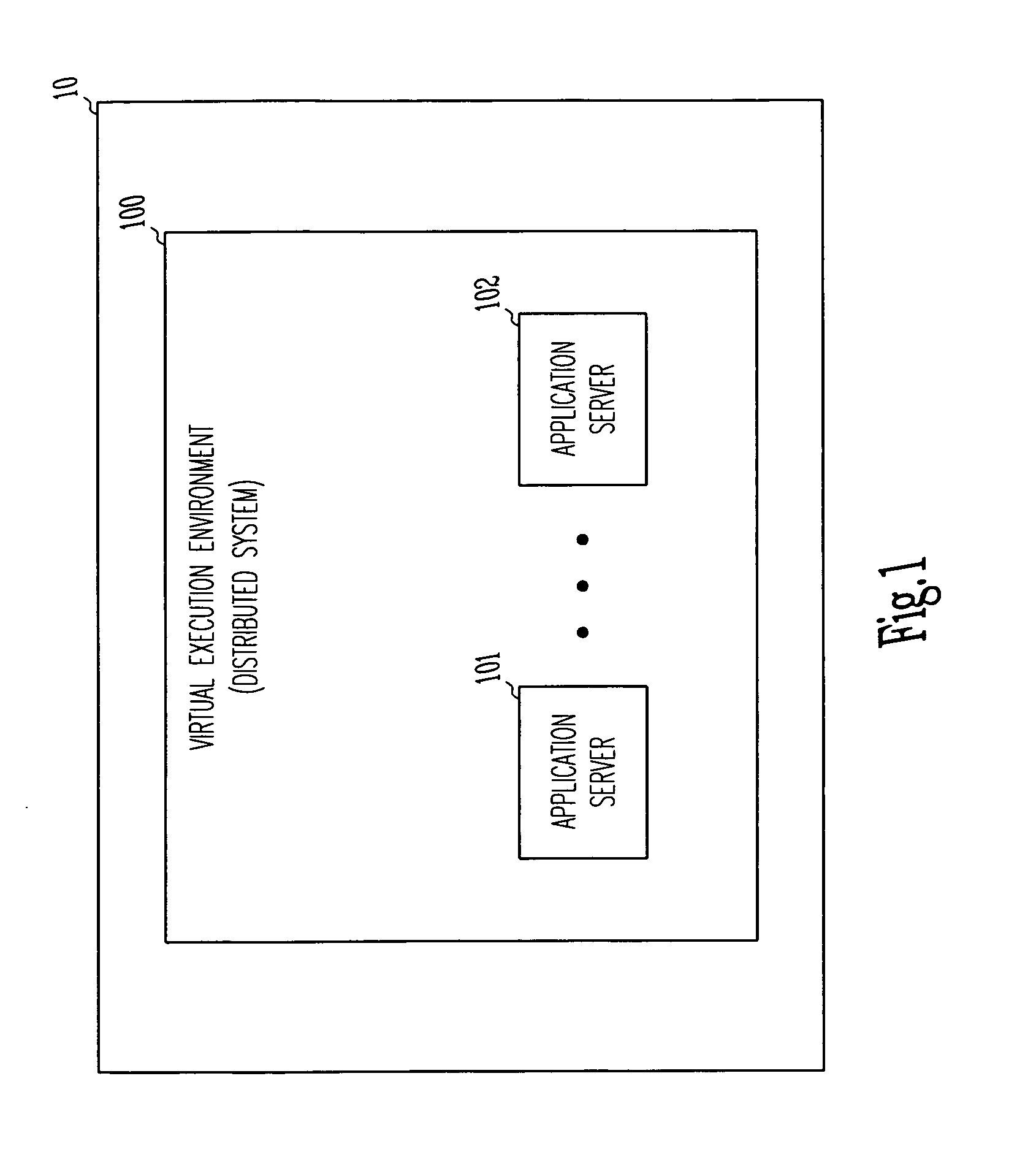
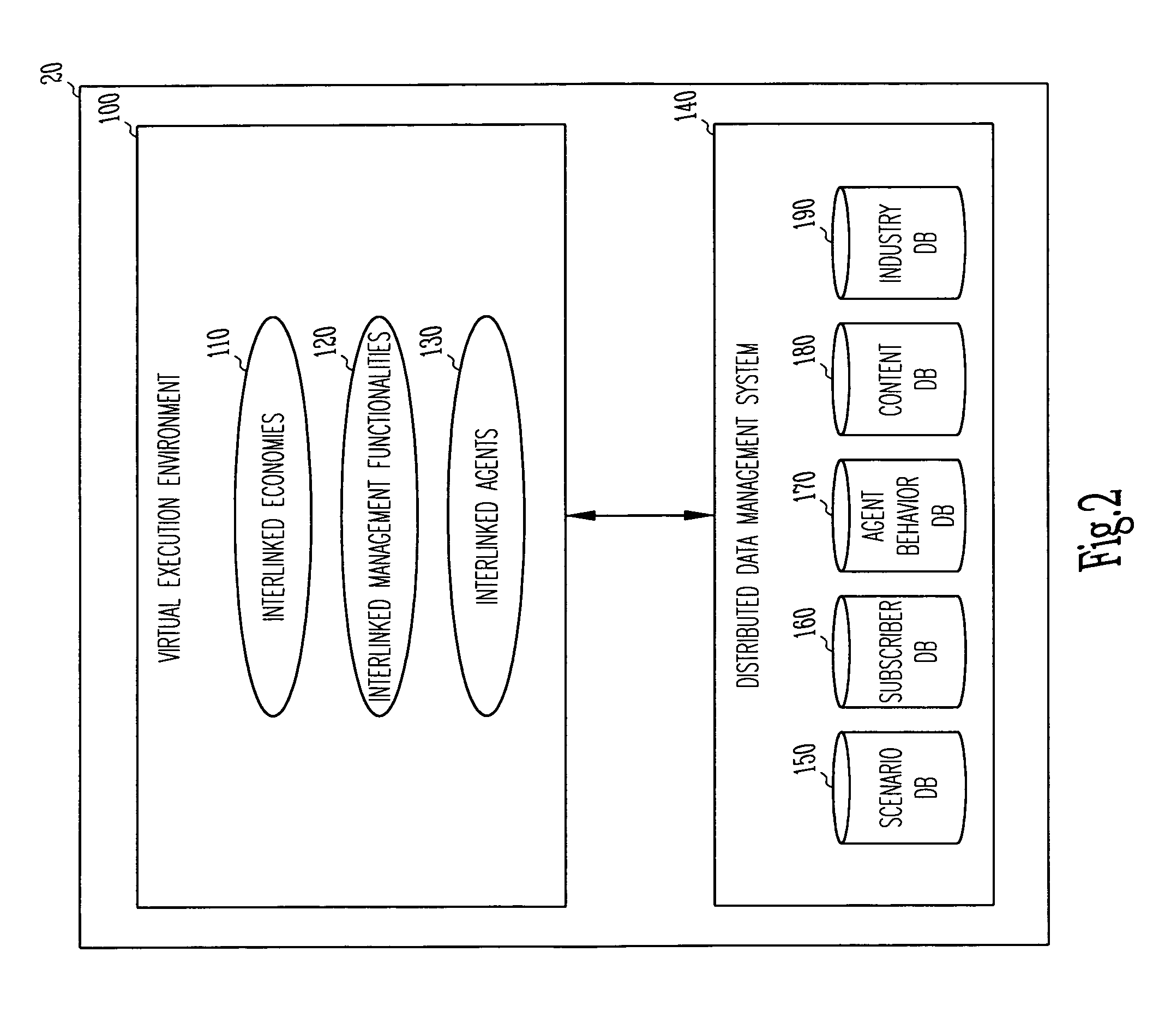
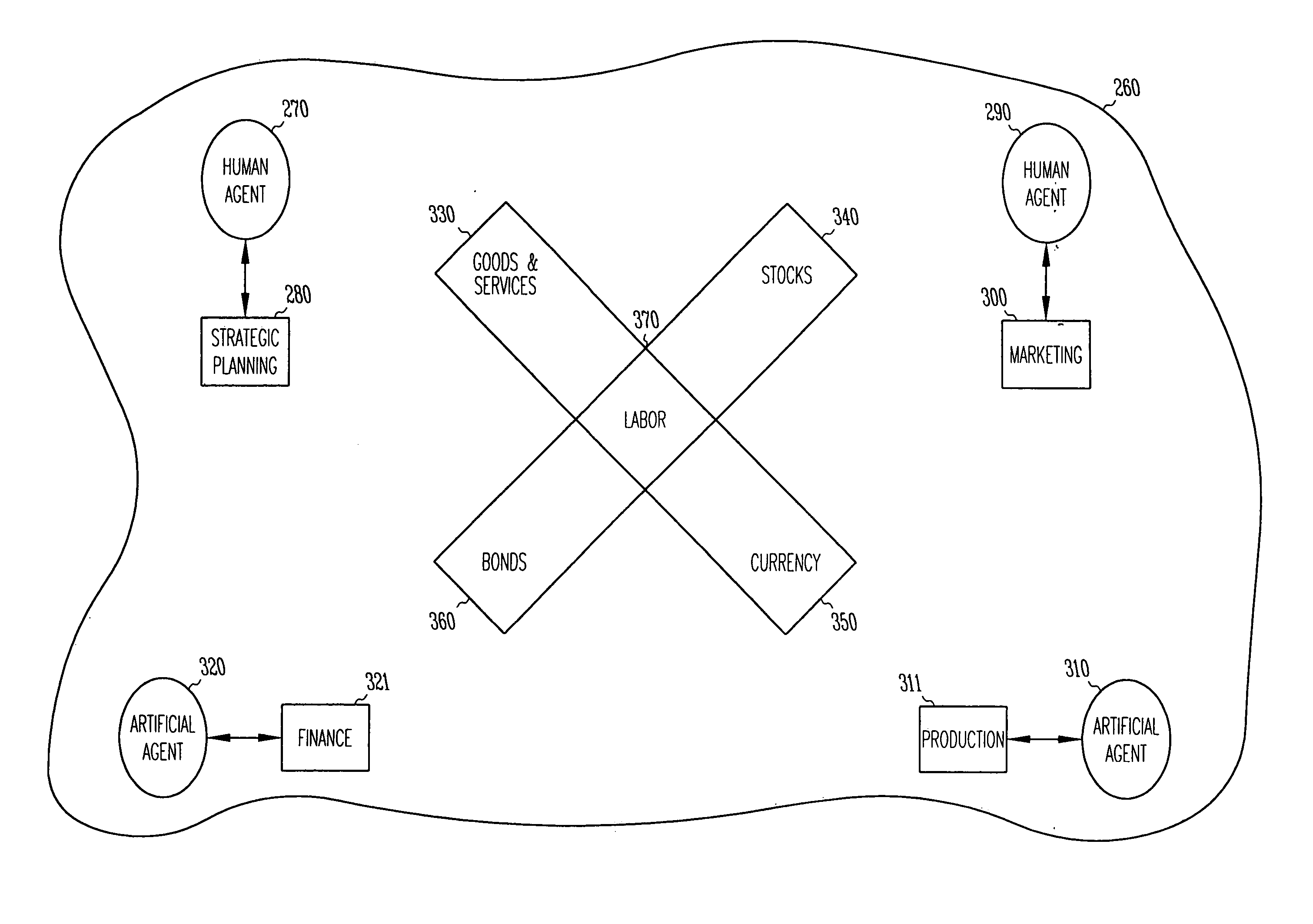
An apparatus and method for simulating a global industrial environment. In one embodiment, the global industrial environment models a global economy as a set of interlinked economies, models a management framework as a set of interlinked management functionalities, and models both individual and organizational behaviors through a use of a set of interlinked agents. In another embodiment, operational data independent from the interlinked economies, interlinked management functionalities, and interlinked agents is customized at run-time. In another embodiment, individuals are electronically trained in a synthetic environment for analysis and simulation of a global industrial system. In this embodiment, the environment includes a virtual execution environment, a pre-exercise briefing, one or more rounds of exercise-time activity, and a post-game analysis.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Method for reducing free radical formation in healthy individuals undergoing hypoxic exercise and medical conditions with increased oxygen free radicals
InactiveUS20030212006A1Increase productionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsFree Radical FormationOxygen
A method of inhibiting the formation of oxygen-containing free radicals and derivatives of them during and following exercise is disclosed. It includes administering an amount of a supplement containing one or more compounds selected from the group consisting of pentose carbohydrates and derivatives thereof in conjunction with said exercise. The supplement is administered as a dose at one or more times selected from prior to, during and after exercise.
Owner:BIONERGY
Abdominal exercise device for inverted abdominal exercises
InactiveUS7063651B2Reduce strainReduce pressureStiltsMuscle exercising devicesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationPre exercise
An exercise device allowing a user to exercise his abdominal region by lying on his back while extending his arms generally upwards is disclosed. The device has a hand-gripping member positioned generally above the user's head for the user to grip while exercising. The hand-gripping member allows for a wide range of motion which may include side-to-side, front-to-back, diagonal, and / or rotational motion. This enables the user can exercise his abdominal region by moving in a variety of different directions, while keeping his arms extended.
Owner:KERRYMAGYARI
Compositions and methods for enhancing exercise performance
ActiveUS9596870B2Good sports performanceImprove bioavailabilityAccessory food factorsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationExercise performance
Compositions and methods are provided for improving canine exercise performance. The compositions are pre-exercise supplements that generally comprise (a) about 35% to about 60% protein or amino acids, comprising one or more structural proteins, one or more bioavailable proteins and one or more branched chain amino acids; (b) about 20% to about 38% fat, comprising at least one source of medium chain triglycerides; and (c) about 5% to about 25% carbohydrate. The methods involve administering the supplement to the animal within about 30-60 minutes before the beginning of the exercise session. The supplements can be administered in conjunction with one or more other exercise performance-enhancing or recovery agents.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
Slimming warm-up oil
InactiveCN102895134APlay a warm-up roleCosmetic preparationsHydroxy compound active ingredientsChemistryPropanolamine
The invention discloses a slimming warm-up oil, which is prepared by mixing 10-20 parts of lecithin,10-20 parts of polyoxyethylene, 10-20 parts of octadecyl hydroxyl betaine, 0.8-1 part of low molecular weight polyacrylamide, 10-15 parts of glycerol, 0.5-1.5 parts of tallow alkyl propanolamine and 30-40 parts of cation water. The slimming warm-up oil provided by the invention can be applied to the body before exercise, and has warm-up effect as well as slimming effect.
Owner:启东市中远机械有限公司
Medical rehabilitation physical training device
PendingCN113521645AMeet training standardsEasy to adjustChiropractic devicesWeightsEngineeringMedical treatment
The invention relates to the technical field of medical rehabilitation exercise, in particular to a training device suitable for postprandial nursing of old people, which comprises a bottom plate, a cushion, a controller, an exercise mechanism, a stretching mechanism and an auxiliary mechanism, the cushion is fixedly arranged at the top of the bottom plate, and the exercise mechanism is arranged at the top of the bottom plate to support training of the old people; the exercise mechanism comprises a supporting frame, a sliding assembly and two counterweight assemblies, the stretching mechanism is arranged below the exercise mechanism to support the old people to do stretching movement, the stretching mechanism comprises a pull ring, a traction assembly, a transmission assembly and an opening assembly, the auxiliary mechanism is arranged on the side of the seat cushion and comprises a backup plate and an adjusting assembly, and the adjusting assembly is electrically connected to the controller. According to the training device suitable for postprandial nursing of the old people, the exercise intensity can be accurately adjusted and controlled according to the physical condition of the old people, meanwhile, stretching can be conducted before and after exercise, injury and muscular soreness are avoided, and the exercise mode is more scientific, efficient and reasonable.
Owner:王林香
Device and method for recognizing free weight training motion and method thereof
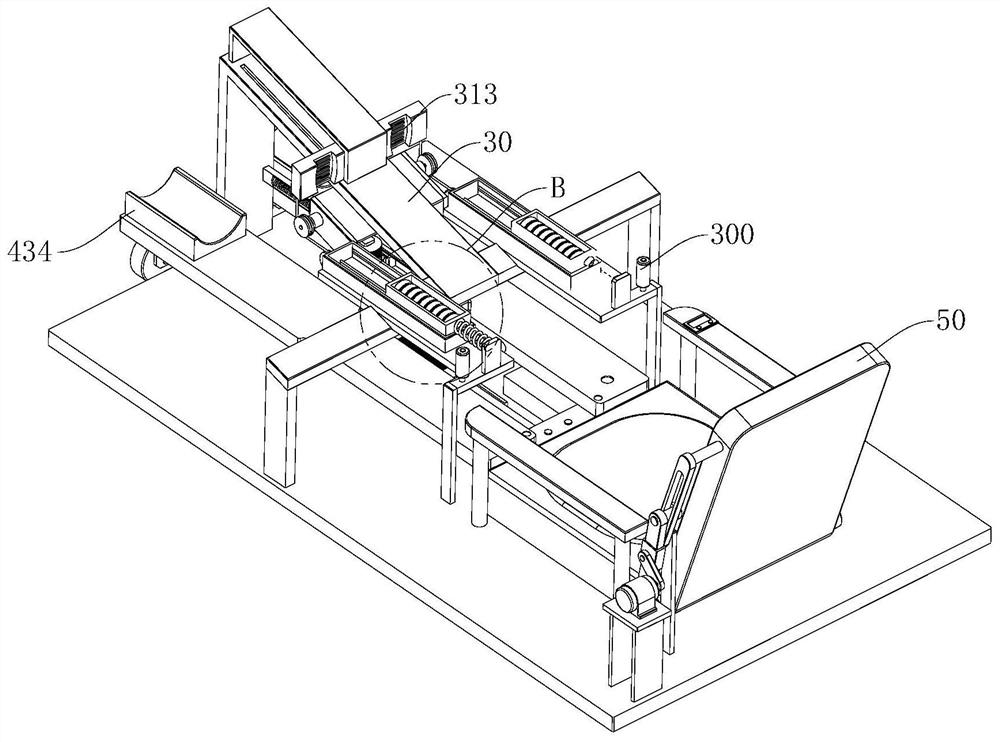
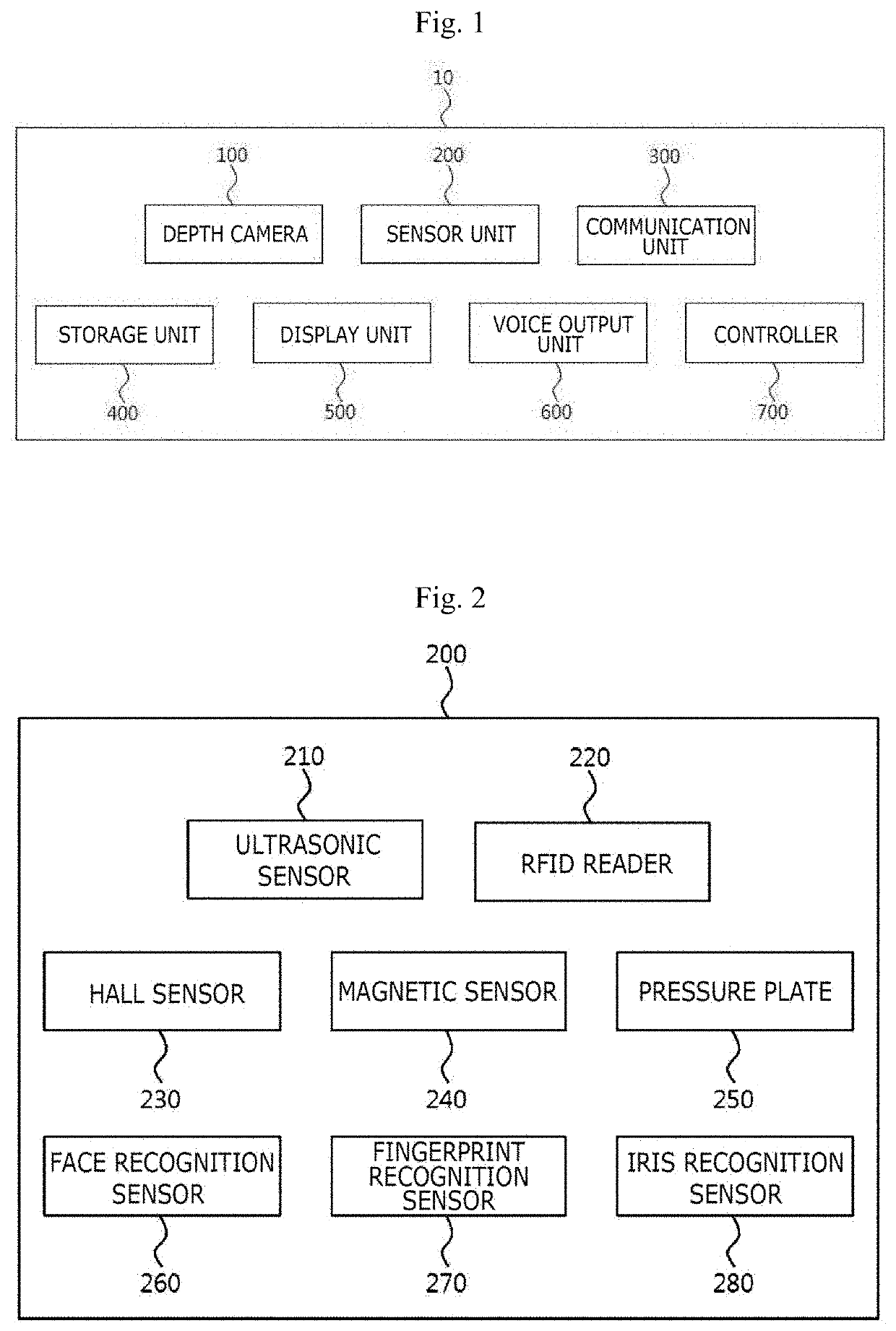
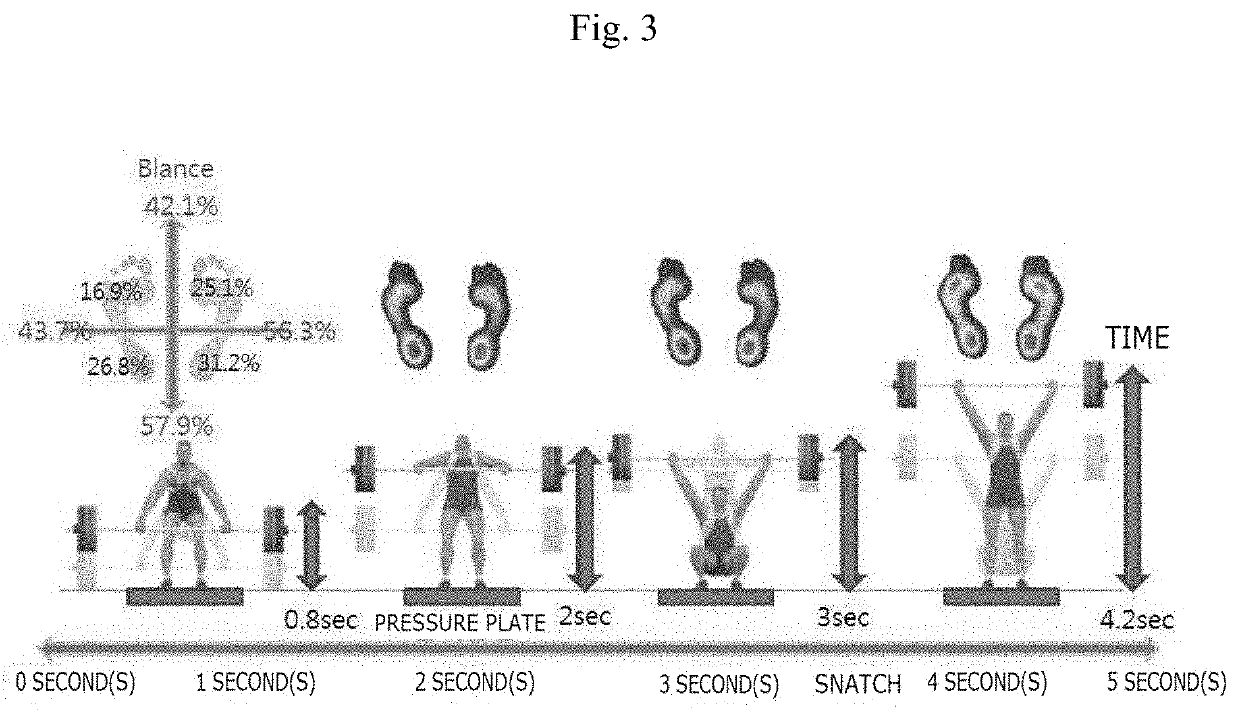
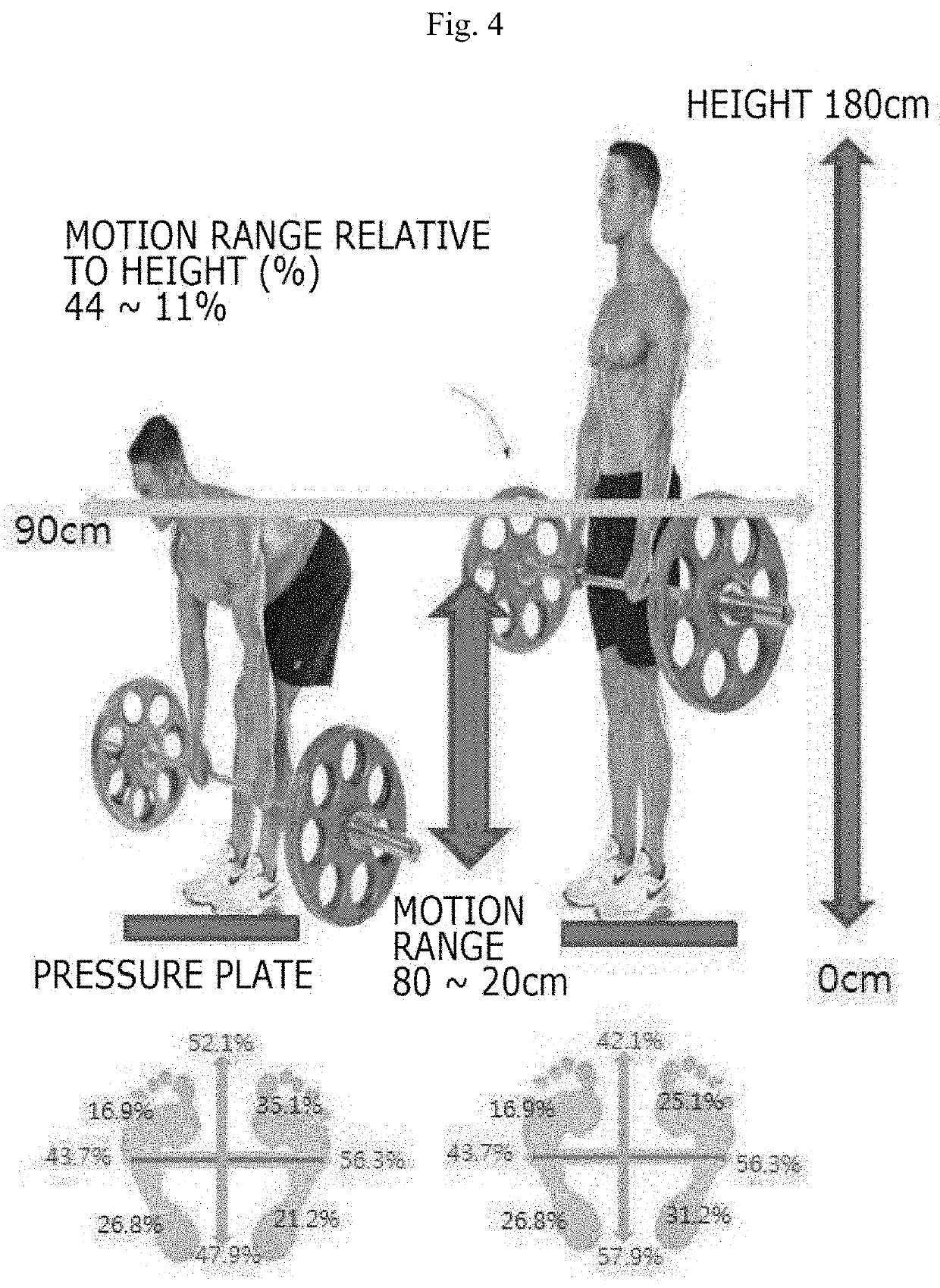
PendingUS20210016150A1Identified easily and convenientlyPhysical therapies and activitiesDumb-bellsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationPre exercise
According to an embodiment, a device for recognizing a free weight training motion comprises a depth camera obtaining image information for measuring a user's body information before exercise and obtaining image information including a unique identifier attached to a piece of exercise equipment and motion of each joint of the user and a variation in body surface due to a motion of the body of the user doing exercise using the piece of exercise equipment, a sensor unit measuring a state of the piece of exercise equipment and recognizing the user, and a controller controlling the depth camera and the sensor unit and processing various pieces of information obtained by the depth camera and the sensor unit.
Owner:JEONG JAE HOON
Soy/whey protein recovery composition
InactiveUS20070190223A1Improve efficiencyTiming impairmentCocoaLipidic food ingredientsDiseaseVegetable oil
A novel soy / milk protein composition is disclosed which can be in drink, powder or gel from which acts as a sports recovery drink restores tissue to its pre-exercise or illness state, reduces muscle glycogen breakdown, and acts to forestalls and prevent the catabolic effects of strenuous exercise. The composition includes soy protein, carbohydrate, water, vegetable oil, and an emulsifier in an appropriate ratio to maximize taste and beneficial effects of the same.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Biological information acquiring system and biological information acquiring method
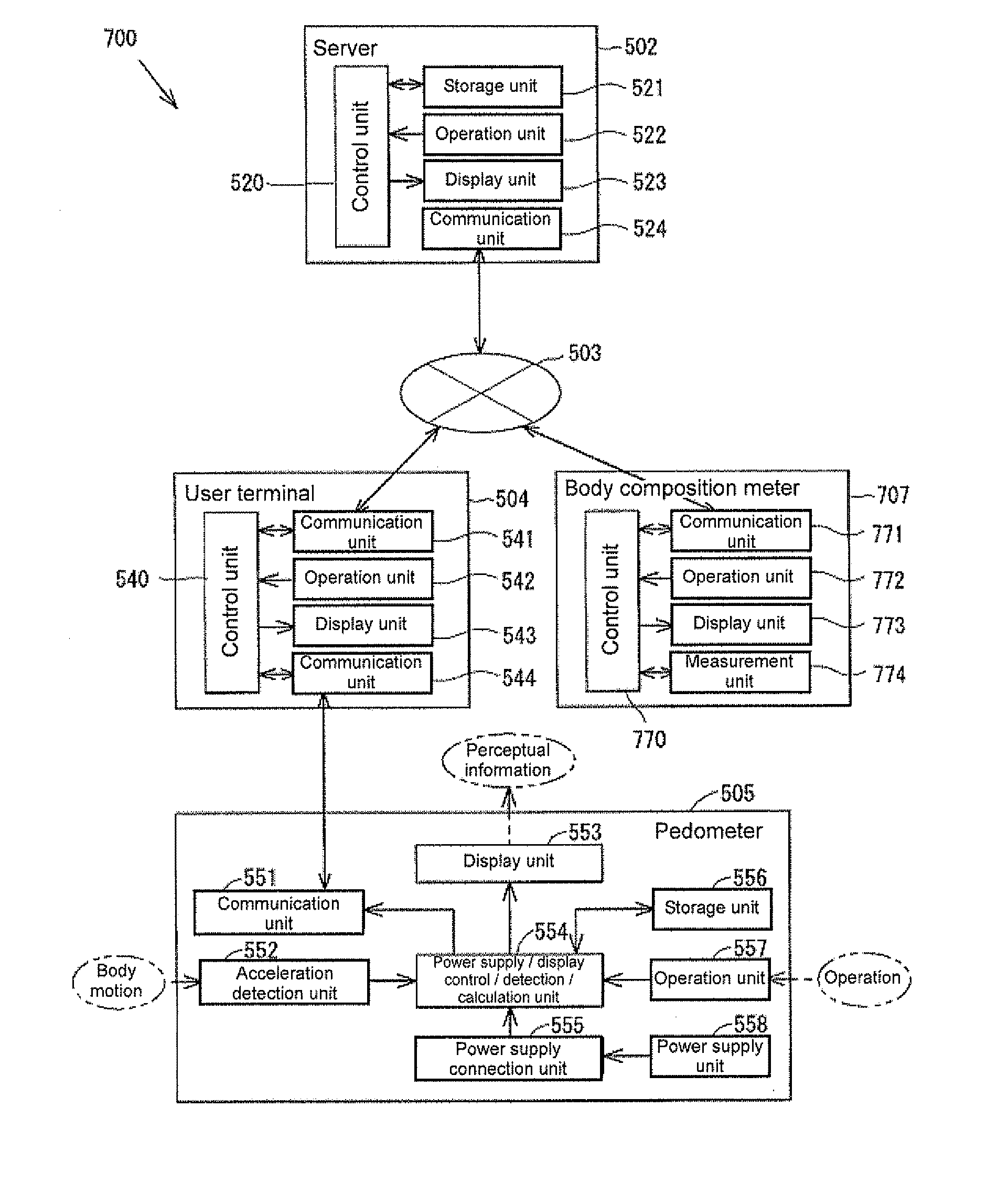
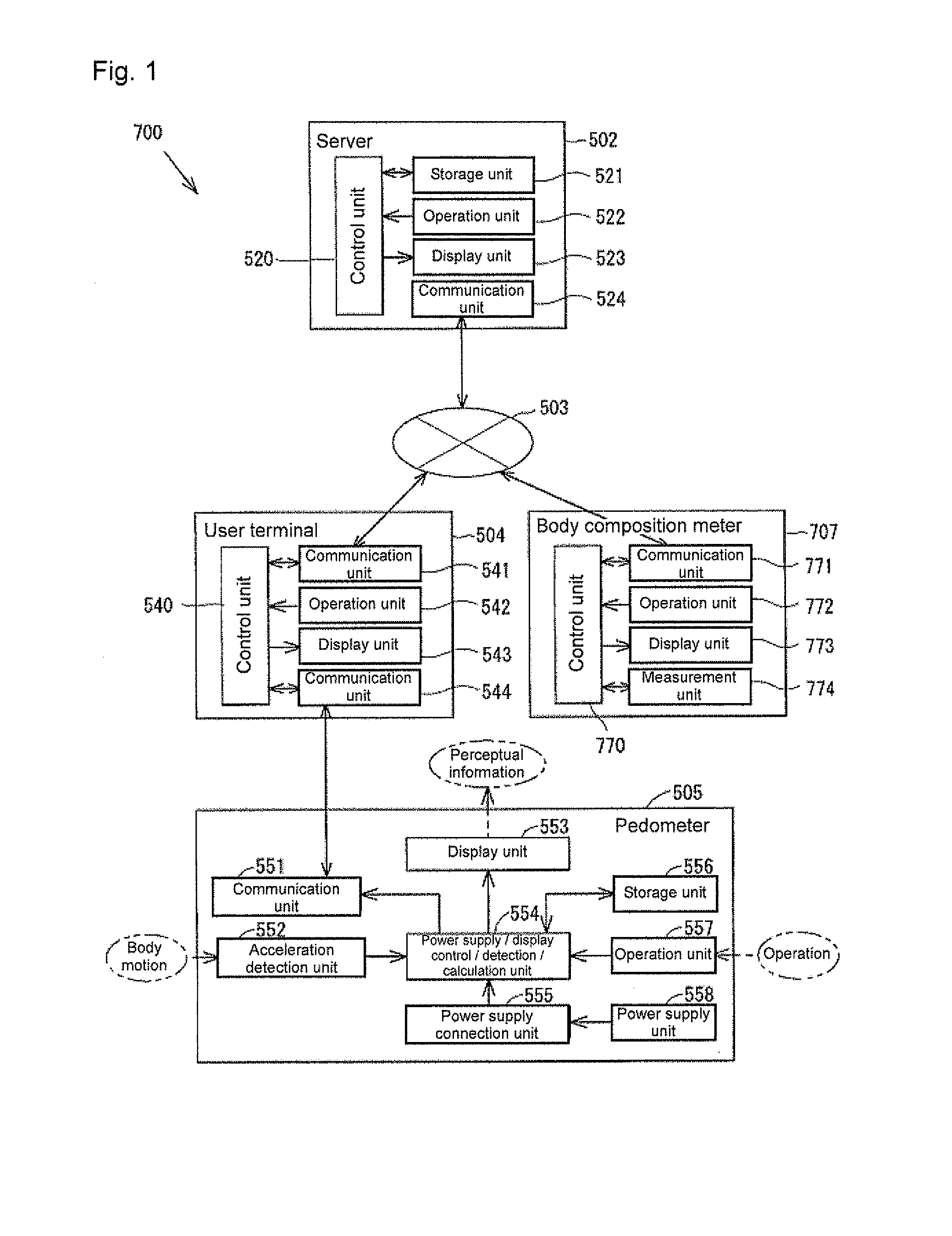
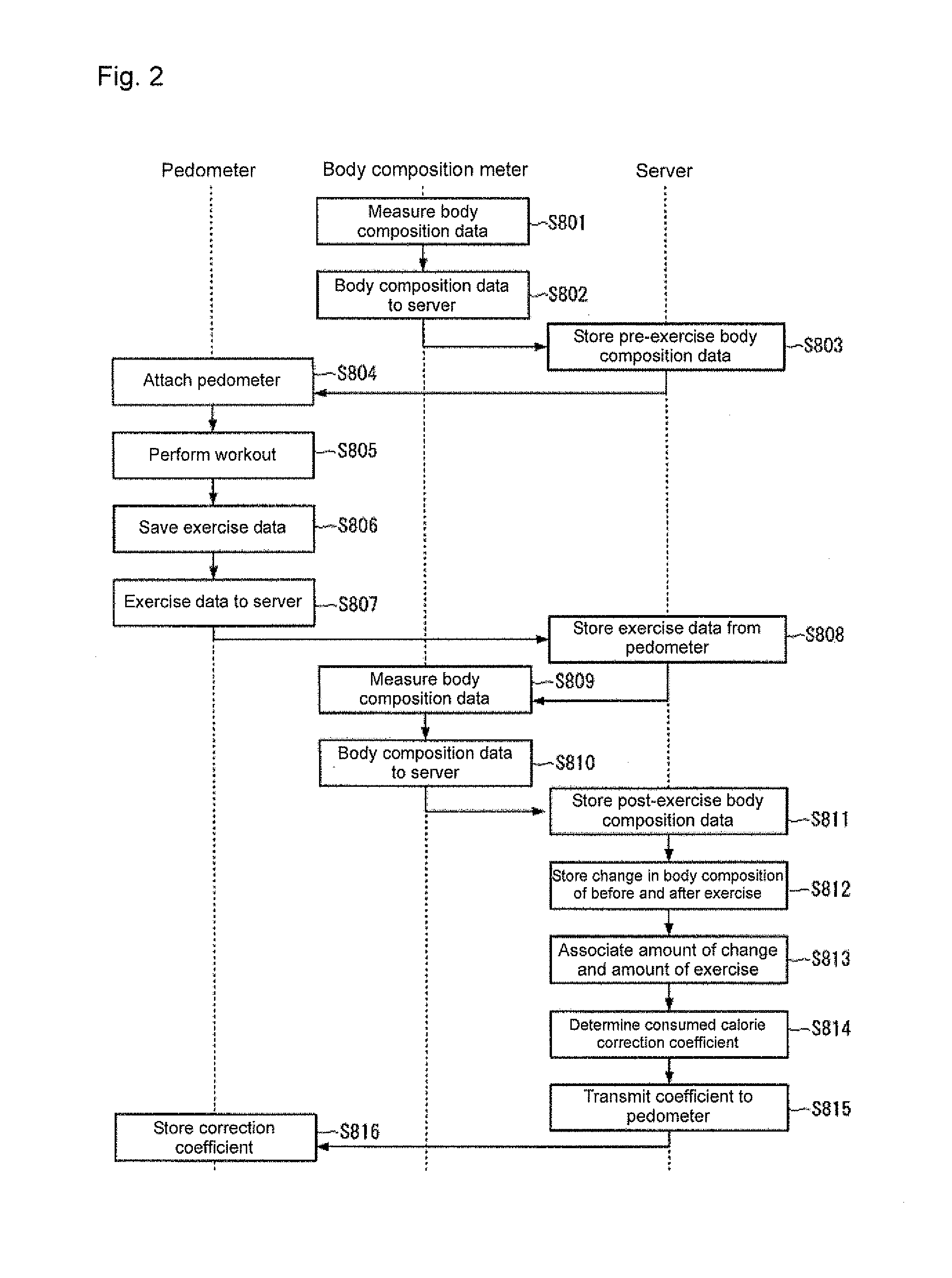
ActiveUS20110238326A1Accurate calculationImprove calculation accuracyBiological testingWeighing auxillary devicesPre exercisePost exercise
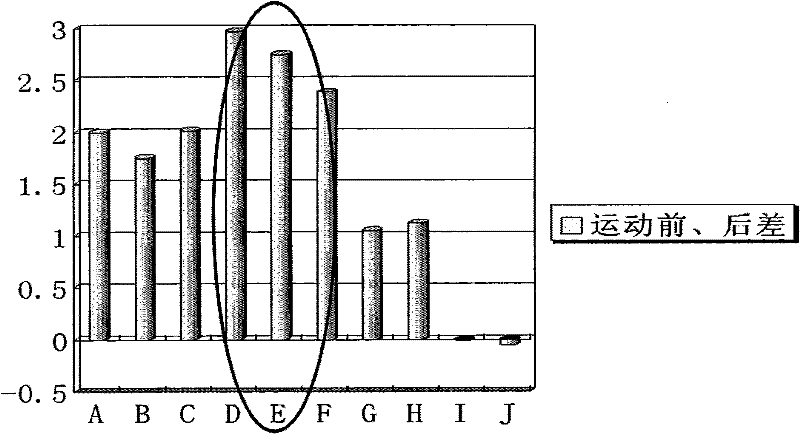
It is an object of the present invention to provide a biological information acquiring system and a biological information acquiring method capable of enhancing the calculation accuracy to more accurately calculate the exercise effect information, and capable of enhancing the satisfaction level of the user.In a biological information acquiring system, a body composition meter is configured to acquire pre-exercise body composition data measured before start of exercise and post-exercise body composition data measured after end of exercise. A pedometer is configured to acquire vibration data during exercise. The consumed calorie of the user can be more accurately calculated by arranging consumed calorie correction coefficient acquiring unit for acquiring a consumed calorie correction coefficient α based on the pre-exercise body composition data, the post-exercise body composition data, and the vibration data; and a consumed calorie calculation unit for calculating the consumed calorie using the consumed calorie correction coefficient α.
Owner:OMRON HEALTHCARE CO LTD
Method for establishing application ratio standard of sportswear ventilate fabric and corresponding clothing
The invention provides a method for establishing a standard for the application ratio of ventilate fabric of sport functional clothing, which comprises the following steps that: multiple measured parts are selected on the surface of a human body; an infrared thermograph is used for measuring the temperature of the multiple measured parts before and after the human body takes exercise; the temperature difference of each measured part before and after the exercise of the human body is calculated; the parts utilizing the ventilate fabric on the sport functional clothing are determined according to the temperature difference; and the percentage of the ventilate fabric in the textile fabric of the sport functional clothing is determined. The invention also provides sport functional clothing which is manufactured through the method.
Owner:LI NING SPORTS SHANGHAI
Treatments for burns using thyroid hormone compound in a human
A topical preparation for treating first and second degree burns includes TriAc. The topical preparation preferably includes less than 10 mg of TriAc per 100 ml of pharmaceutical excipient base. In another embodiment, a topical preparation includes TriAc for decreasing cellulite. In this embodiment, the topical preparation is preferably applied only before exercise. In a preferred embodiment, the preparation is applied only intermittently, preferably no more than three times a week, or in amounts sufficient to not downregulate receptor number and become inefficacious.
Owner:KOO CATHERINE DR
Industry simulation environment
InactiveUS20050256736A1ResourcesComplex mathematical operationsSynthetic Environment for Analysis and SimulationsIndustrial systems
An apparatus and method for simulating a global industrial environment. In one embodiment, the global industrial environment models a global economy as a set of interlinked economies, models a management framework as a set of interlinked management functionalities, and models both individual and organizational behaviors through a use of a set of interlinked agents. In another embodiment, operational data independent from the interlinked economies, interlinked management functionalities, and interlinked agents is customized at run-time. In another embodiment, individuals are electronically trained in a synthetic environment for analysis and simulation of a global industrial system. In this embodiment, the environment includes a virtual execution environment, a pre-exercise briefing, one or more rounds of exercise-time activity, and a post-game analysis.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Food compositions that enhance nitric oxide mediated signalling
InactiveUS20160095341A1Improve exercise performanceImprove post-exercise recoveryAnimal feeding stuffCocoaMuscle tissueNitrate
The invention includes compositions and methods for improving exercise performance or improving recovery of muscle tissue after exercise performance. One method includes administering a composition of a plant-derived nitrate and a cocoa-derived product daily and before exercise. The synergistic combination of nitrate and cocoa polyphenols acts to improve recovery from a strenuous exercise bout.
Owner:THE HERSHEY COMPANY
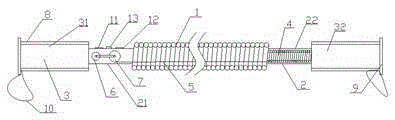
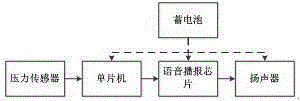
Variable-force arm power exercise apparatus with high safety performance
InactiveCN106730585ARaise the power levelAvoid dangerResilient force resistorsComputer modulePre exercise
The invention discloses a variable-force arm power exercise apparatus with high safety performance. The variable-force arm power exercise apparatus comprises a spring, a connecting rod and handles. The connecting rod is arranged at two ends of the spring, the handles are arranged at two ends of the connecting rod, the connecting rod is divided into a left connecting rod and a right connecting rod, the handles include a left handle and a right handle, pressure sensors are arranged on the handles, a processing module and a loudspeaker are arranged in the left handle, output ends of the pressure sensors are connected with an input end of the processing module, an output end of the processing module is connected with an input end of the loudspeaker, a power device is arranged in the left connecting rod, an inner spring is arranged in the right connecting rod, and the power device is connected with the inner spring by a steel wire. The variable-force arm power exercise apparatus has the advantages that users can be reminded of necessary pre-exercise preparation, and accordingly the exercise safety can be improved; the force level can be upgraded, and accordingly the variable-force arm power exercise apparatus is applicable to the different users and low in cost.
Owner:YANGZHOU YIHE FITNESS EQUIP CO LTD
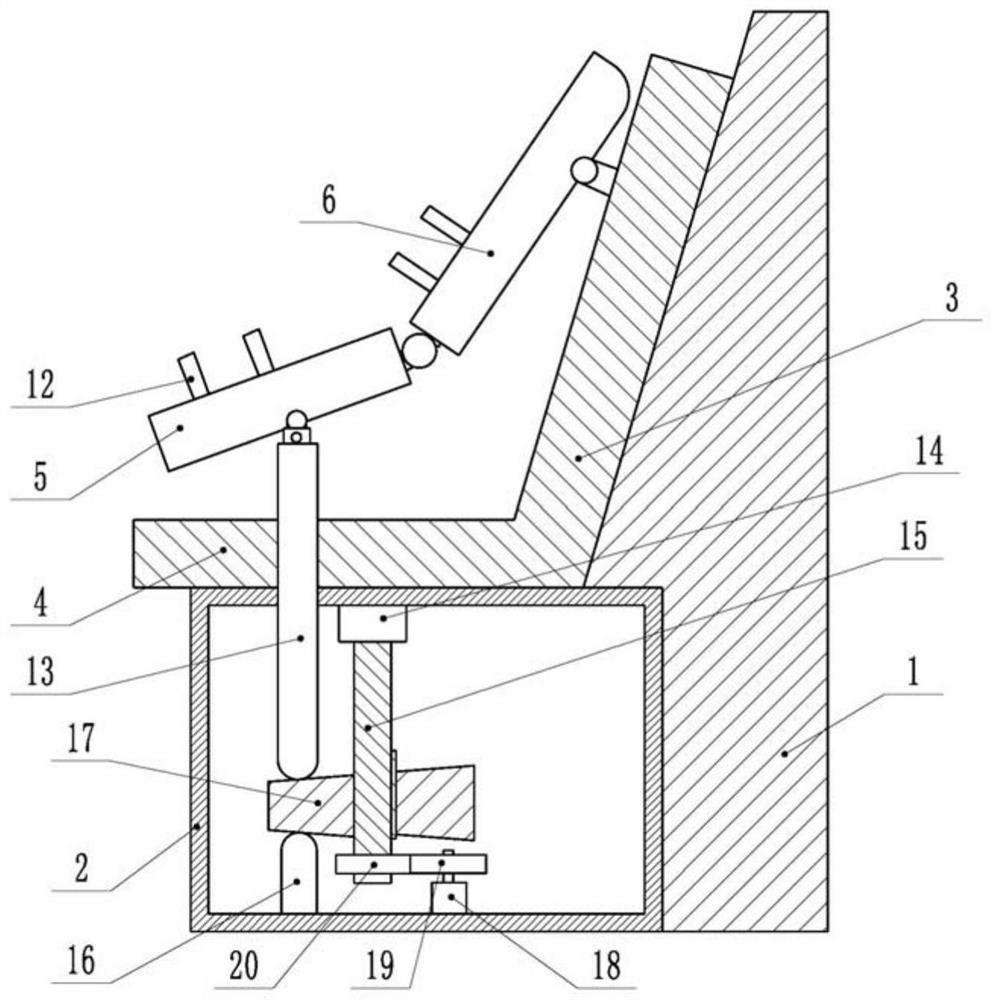
Upper limb assisting and rehabilitation training robot
ActiveCN112618254APlay a role in helpingSmooth recovery exerciseChiropractic devicesMedizinische rehabilitationPre exercise
The invention relates to the field of medical rehabilitation equipment, and discloses an upper limb assisting and rehabilitation training robot which comprises a support, a seat is fixedly connected to the support, two sides of the seat are all provided with an upper limb exercising assembly, each upper limb exercising assembly comprises a forearm fixing plate and an upper arm fixing plate, and the forearm fixing plates are hinged to the upper arm fixing plates. A driving unit for driving the forearm fixing plate to swing up and down is arranged in the support, the driving unit comprises a cam column, a lifting rod and a power piece for driving the cam column to rotate, the lifting rod is in vertical sliding fit with the support, one end of the lifting rod is hinged to the forearm fixing plate, and the other end of the lifting rod penetrates through the support and abuts against the top end of the cam column; the top end of the cam column is an inclined face, the cam column drives the lifting rod to move up and down reciprocally while rotating, and the forearm fixing plate and the upper arm fixing plate are provided with fixing pieces used for fixing the forearm and the upper arm respectively. According to the invention, the upper limbs of a patient can be automatically assisted, so that the upper limbs of the patient can be effectively exercised.
Owner:CHONGQING COLLEGE OF ELECTRONICS ENG
Astaxanthin effervescent tablet for improving athletic ability and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110876440APromote absorptionReduce generationInorganic compound food ingredientsFood ingredient functionsEffervescent tabletMedicine
The invention discloses an astaxanthin effervescent tablet for improving athletic ability and a preparation method thereof. The effervescent tablet comprises the following raw materials (by weight): 1-200 parts of astaxanthin, 1-50 parts of taurine, 5-300 parts of a sodium water soluble compound, 5-300 parts of a potassium water soluble compound, 1-200 parts of a calcium water soluble compound, 1-100 parts of a magnesium water soluble compound, 1-50 parts of vitamin, 5-500 parts of an acid compound, 5-200 parts of a sweetener, 0.1-50 parts of a flavoring agent, and 1-50 parts of an adhesive. The prepared effervescent tablet is dissolved rapidly to uniformly disperse effective components in the formed solution, thus being more beneficial to absorption by human body. The effervescent tabletprepared by the invention can be used before, during and after exercise, and can supplement electrolytes and vitamins, increase fat consumption during exercise, enhance endurance, reduce the occurrence of exercise fatigue and inflammation, and promote recovery after exercise.
Owner:睿藻生物科技(苏州)有限公司
Coenzyme-Q10 vitamin-C sports lozenges
InactiveCN110801018AGuaranteed supplyPrevent dental cariesFood scienceHeart rate accelerationVitamin C
The invention discloses a group of sports energy lozenges which are composed of coenzyme Q10 and fructose as main ingredients, and have very good protective effects on heart rate acceleration, musclefatigue and excessive energy consumption state caused by various kinds of excessive exercises. The sports energy lozenges are characterized by taking the coenzyme Q10 and the fructose as the main rawmaterials, wherein each 100 pieces of the sports energy lozenges contain 1-3 g of the coenzyme Q10 and 10-30 g of the fructose; and the prepared sports energy lozenges can be used for supplementing energy during exercise. According to different stages of sports, the invention further designs three sports formulas, including a speed-type formula before sports, an endurance-type formula during sports and a recovery-type formula after sports, in which different nutritional supplements are added in line with different states of athletes in sports; and the nutritional supplements comprise vitamin C, creatine, taurine and the like. Therefore, different sports nutrients can be provided to different sports groups. The sports energy lozenges are capable of providing power and energy for the heart,as well as resisting oxidation and scavenging free radicals, so that the sports energy lozenges are capable of maintaining good health state in long-term consumption, thereby making the body vigorous,full of vitality and abundant in brainpower.
Owner:GUANGDONG MEDICAL UNIV +1
A foldable auxiliary leg press device for physical training
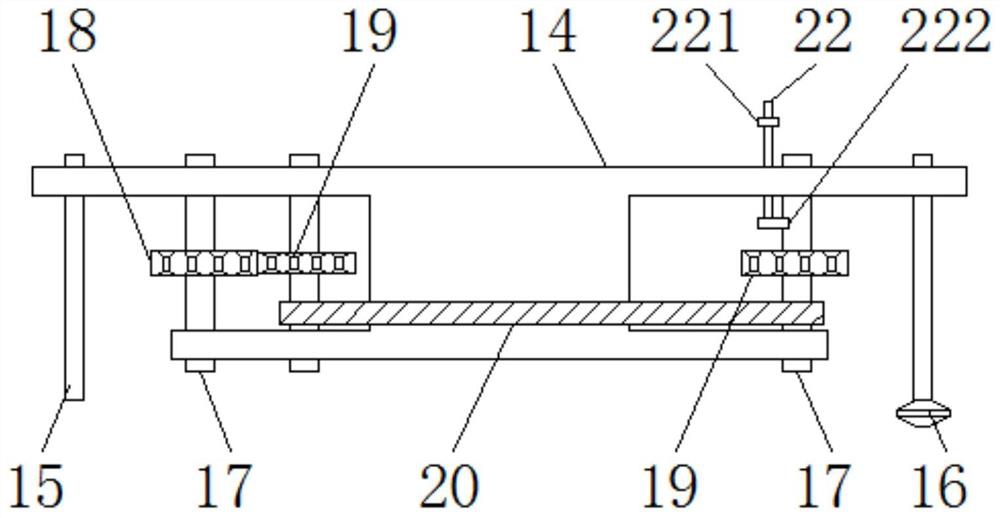
The invention discloses a foldable auxiliary leg pressing device for physical training, which comprises a bottom plate, a fixed block, a storage box and a connecting shaft, a first support seat is arranged on the side of the bottom plate, and the fixed block is arranged on At the bottom, the vertical plate is installed on the upper end surface of the bottom plate, a spring is installed inside the vertical plate, a leg presser is installed on the inner side of the fixed rod, and a rack is connected to the top of the fixed rod, and the storage box is installed On the upper end of the vertical plate, the connecting shaft runs through the storage box, and a first gear is installed on the outside of the connecting shaft, a second gear is arranged on the side of the first gear, and another gear is installed on the other end of the crawler belt. the second gear, and a stopper is arranged above the other second gear. The folding auxiliary leg pressing device for physical training is convenient for the user to stretch the leg ligaments before exercising, avoiding leg muscle strain during exercising, and the design of the device body meets the use requirements of the user.
Owner:温州高伟通工业设计有限公司
Compositions and methods for enhancing exercise performance
ActiveUS20150004279A1Good sports performanceImprove bioavailabilityProtein composition from fishAnimal feeding stuffAnimal scienceExercise performance
Compositions and methods are provided for improving canine exercise performance. The compositions are pre-exercise supplements that generally comprise (a) about 35% to about 60% protein or amino acids, comprising one or more structural proteins, one or more bioavailable proteins and one or more branched chain amino acids; (b) about 20% to about 38% fat, comprising at least one source of medium chain triglycerides; and (c) about 5% to about 25% carbohydrate. The methods involve administering the supplement to the animal within about 30-60 minutes before the beginning of the exercise session. The supplements can be administered in conjunction with one or more other exercise performance-enhancing or recovery agents.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
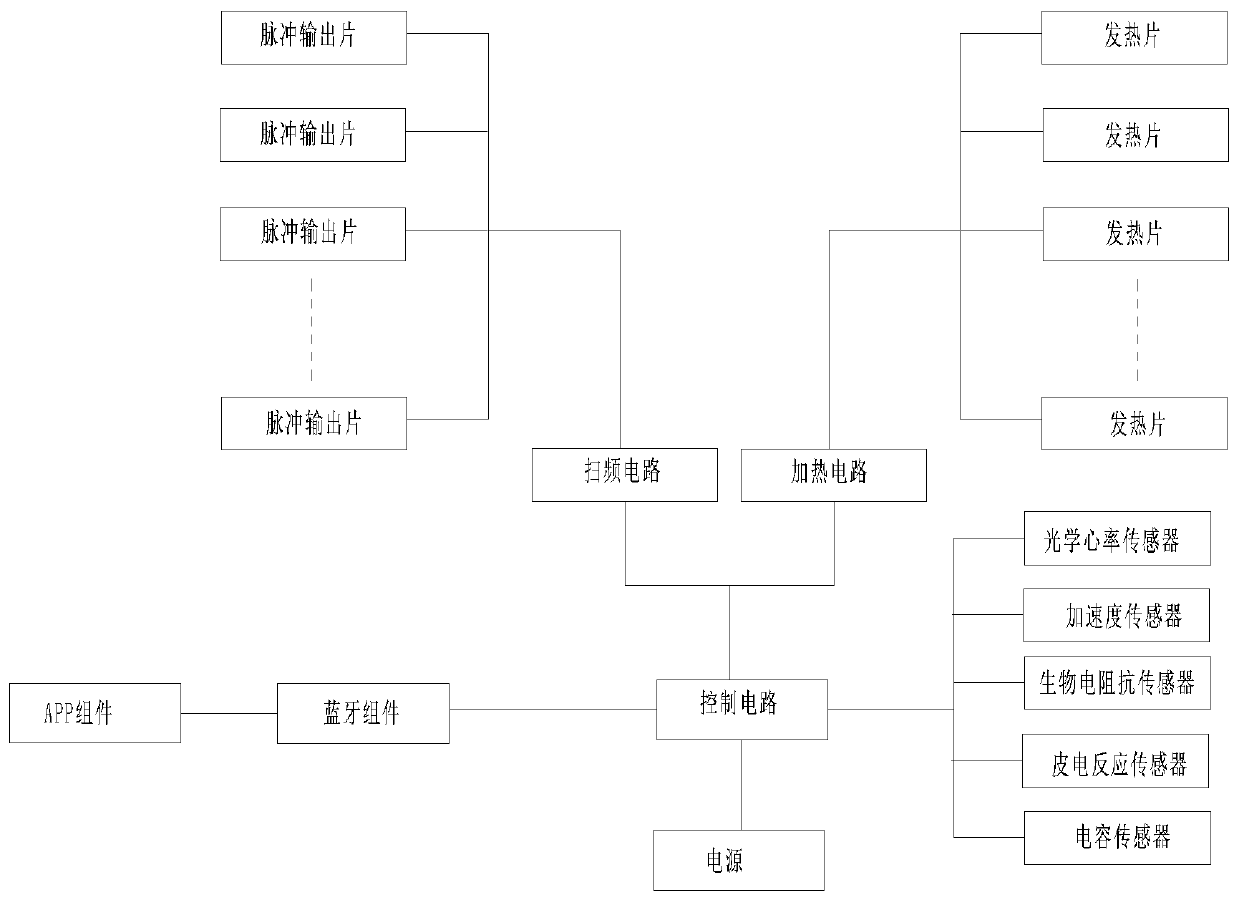
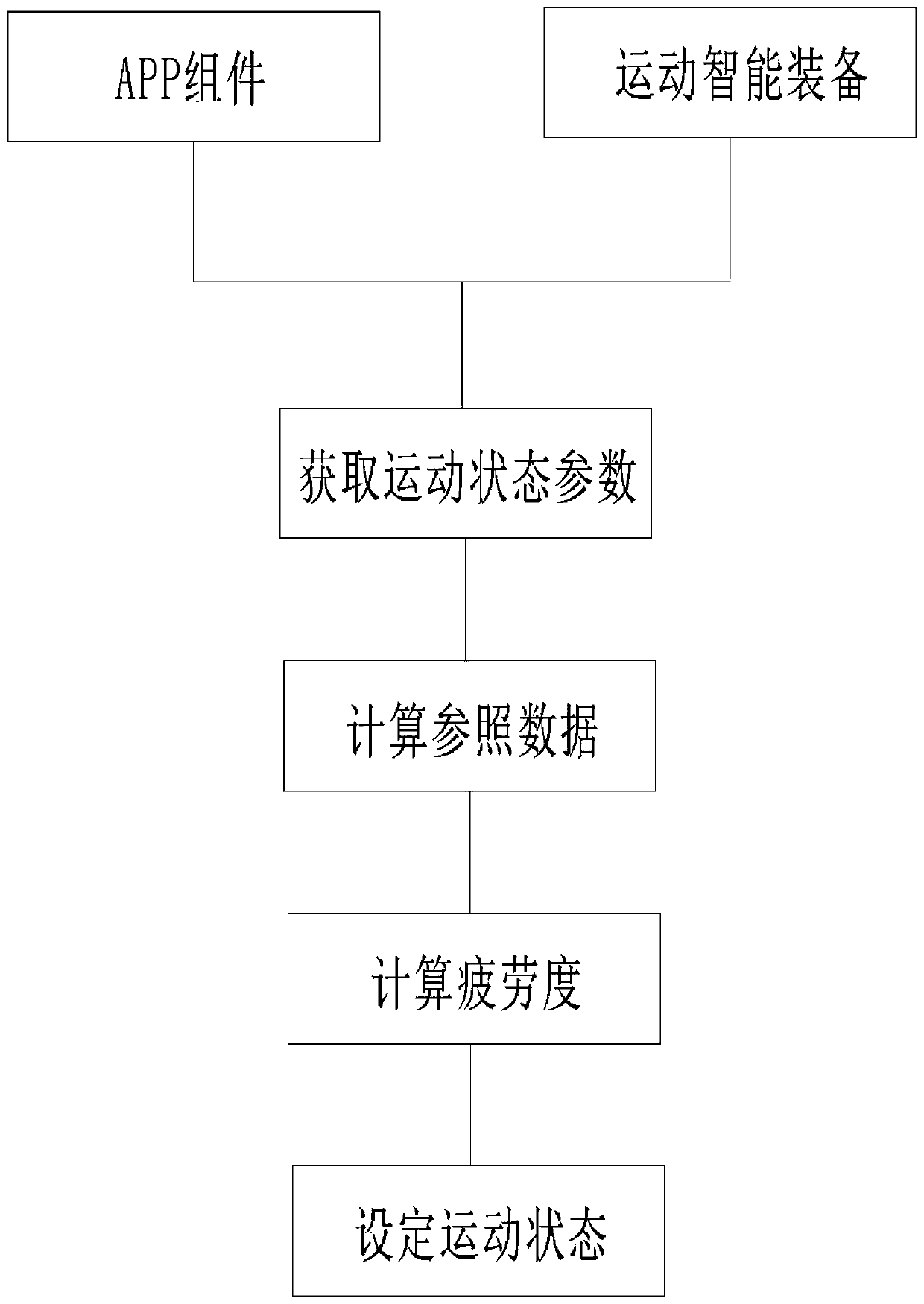
Athletic fitness running method for monitoring athletic states, and intelligent equipment
The invention provides an athletic fitness running method for monitoring athletic states, and intelligent equipment. The athletic fitness running method comprises the steps of testing, athletic statesetting and bioelectricity outputting. The athletic states of users are set according to the athletic fatigue of the user, the corresponding athletic states, including warming up, athletic effect enhancing, relaxing massage after exercising and the like, are guided, warming is conducted before exercising, thus bodies are in a warming-up state, muscles are relaxed, the loading effect is simulated during exercising, the muscle strength after exercise training is enhanced, and the intelligent equipment serves as an auxiliary tool for strength training, and the muscles are massaged after exercising; and the users can also manually control and adjust the matched athletic states to assist in the exercising process.
Owner:天狼联盟材料科技研究(广东)有限公司
All-Natural Drink Composition for Synthesizing and Regenerating Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) in Muscle Cells and Neurons, Repairing Exercise-Induced Muscle Fiber Damage, Repletion of Glycogen Stores in the Muscle and Liver, Enhancing Blood Flow to Tissue during Intense Exercise, and Preventing and Reducing Oxidative Damage to Tissues during Exercise with Minimal Gastrointestinal Disturbances
InactiveUS20200054045A1Improve muscle performanceDelayed gastric emptyingFood scienceWhite blood cellNutrition
The present invention provides for a nutritional composition in a liquid drink form, dry powder form, gel form, or carrier form intended to optimize human physiological performance during intense exercise and subsequently return the body to its healthy, pre-exercise state. The composition comprises a carbohydrate and a protein, and preferably a ratio of the carbohydrate to the protein is greater than about 4.3 parts by weight carbohydrate to 1 part by weight protein. Preferably, the liquid nutritional composition is comprised of: (1) carbohydrate in the range of 3.45-10% by weight of the liquid nutritional composition to allow immediate and long-term energy production by muscle cells and neurons, insulin modulation, and muscle glycogen sparing, the carbohydrate being in the form of monosaccharides or polysaccharides or a combination thereof, and the saccharides preferably comprising 40-95% dextrose by weight of the final volume of saccharides, 5-45% fructose by weight of the final volume of saccharides, and 1-25% glucose polymer by weight of the final volume of saccharides; (2) a protein source that contains all 20 “standard” amino acids, in the range of 0.1-0.8% by weight of the liquid nutritional composition, whose inherent structure plus further chemical modification results in amino acid absorption into the bloodstream rapid enough for initiating and enhancing protein synthesis and subsequent muscle cell repair during the exercise and post-exercise periods; (3) Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAA), leucine, isoleucine, valine, for use by muscle cells for energy thus sparing glycogen stores, for increasing protein synthesis by stimulating insulin and growth hormone release, and for reducing protein degradation; (4) precursors of the signaling molecule nitric oxide, important for increasing blood flow and subsequent nutrient delivery (including those in this composition) to tissue during intense exercise; (5) precursors of creatine, a molecule important for ATP regeneration in muscle and nerve cells and for muscle cell volumizing effects; (6) a mixture of hydrophilic and hydrophobic antioxidants: retinol / Beta-carotene (Vitamin A), ascorbic acid (Vitamin C), and di-alpha-tocopheryl acetate (Vitamin E); ubiquinone (coenzyme Q10 [5-100 mg / 500 ml], which in addition to its antioxidant properties is also important for ATP generation and Vitamin E regeneration; a mixture of 10-100 mg epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) and 25-150 mg polyphenols from green tea extract; 40-250 mg ellagic acid and punicalagin from pomegranate or raspberry extract, at ratios comparable to that found in the whole fruit, which have been shown to have protective effects on blood vessels as well as inhibiting stimulation of the pro-inflammatory protein interleukin-1b (IL-b) which causes degradation and damage to joints (These six antioxidants prevent and eradicate reactive oxygen species and free radicals generated during strenuous exercise, thus preserving muscle integrity.); and (7) the ions Na+, Cl−, K+, Ca+2, Mg+2, and Zn+2, which are important for the muscle fiber contraction and relaxation cycle, for neuronal signal propagation, for repletion of such ions lost in excessive perspiration during exercise, for water absorption in the gastrointestinal tract, and for catalytic action by energy producing and antioxidant enzymes.
Owner:BIOMECHANICAL TECH LLC
Pre-exercise stretching instrument
ActiveCN113521656AStop bendingPrevent rotationGymnastic exercisingVibration suppression adjustmentsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationPre exercise
The invention belongs to the technical field of exercise fitness equipment, and particularly relates to a pre-exercise stretching instrument which comprises a horizontal bottom plate, a support is fixedly mounted on the upper surface of the bottom plate, and a horizontal bearing plate is fixedly mounted at the top of the support. Two rotating mechanisms are installed on the end face of one side of the bearing plate, and a positioning mechanism is installed on the end face of the bearing plate. Buffering mechanisms are installed on the upper surface of the bottom plate. When the instrument is used for stretching legs, it is guaranteed that the legs are always in a straightened state, the other leg is in a horizontal straightened state while one leg is stretched, and therefore the stretching effect is guaranteed. Ligament injury caused by too high leg lifting is avoided, and ligament injury caused by too high speed in the leg putting-down process is avoided.
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF ECONOMIC & TRADE TECH
Pre-exercise functional drink
PendingCN108669391ACreatine kinase levels stabilizedReduce sports injuriesFood ingredient functionsVitamin K2Vitamin C
The invention discloses a pre-exercise functional drink. The composition provided by the invention comprises the following seven effective ingredients: III-1, III-2, III-3, III-4, III-5, III-6 and III-7 that supply vitamin B1, vitamin B2, vitamin B6, vitamin B9, vitamin C, zinc and iron in order, and the ratio of vitamin B1 to vitamin B2 to vitamin B6 to vitamin B9 to vitamin C to zinc to iron is0.2-6:0.2-4:0.2-4:0.05-0.5:10-300:2-12:2-20. The invention also provides a product containing the composition. The composition or product can be used for preparation of a functional drink taken beforeexercise and used as a functional drink taken before exercise. The pre-exercise functional drink provided by the invention fills the blank of precise nutrition supply in domestic extreme endurance events.
Owner:深圳华大运动控股有限责任公司 +1
Pre-workout Effervescent Tablet
This invention relates to a pre-portioned single, multiple, or fractional serving(s) in effervescent tablet form, containing doses of stimulants, amino acids, vitamins, and minerals in unique quantities to enhance performance of exercise related activities. The composition and delivery of these components is unique and solves problems pertaining to the traditional packaging, composition, and delivery methods used for these products. This invention provides a product that can serve as a pre-workout stimulant, energy aid, or exercise related improvement supplement that is delivered in effervescent tablet form.
Owner:PARKER SHANE MATTHEW +3
Physical health promotion evaluation system for pregnant women
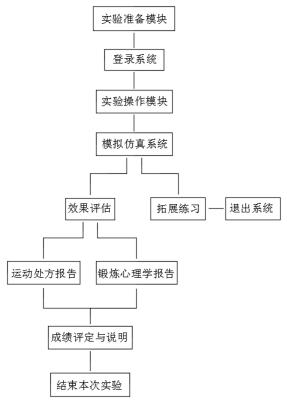
InactiveCN112002387AEasy to learn and summarizeEnhance knowledge applicationPhysical therapies and activitiesHealth-index calculationPregnancyPhysical health
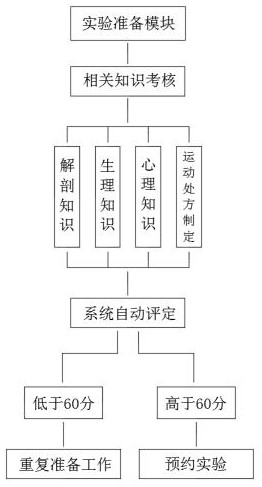
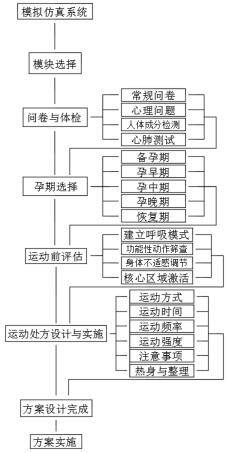
The invention discloses a physical health promotion evaluation system for pregnant women. The physical health promotion evaluation system comprises an experiment preparation module, an experiment operation module and an effect evaluation module. The experiment operation module comprises questionnaire and physical examination, pregnancy selection, pre-exercise evaluation, exercise prescription design and implementation, scheme design completion and scheme implementation; and the effect evaluation module comprises effect grading, report submission and score evaluation and explanation. Accordingto the system, relevant knowledge of pregnant women of students is assessed through the experiment preparation module, so that the students can be familiar with relevant knowledge such as anatomical physiological characteristics of the pregnant women, exercise prescription formulation and exercise psychological intervention; all-around detection and guidance are carried out on pregnant women in different conditions through the experiment operation module, so that an exercise scheme with strong pertinence and a good effect is conveniently formed; experimental results of the students are evaluated through the effect evaluation module, knowledge learning summary of the students is facilitated, knowledge application of the students is enhanced, and teaching quality is improved.
Owner:LINYI UNIVERSITY
Pumping oligosaccharide solid beverage
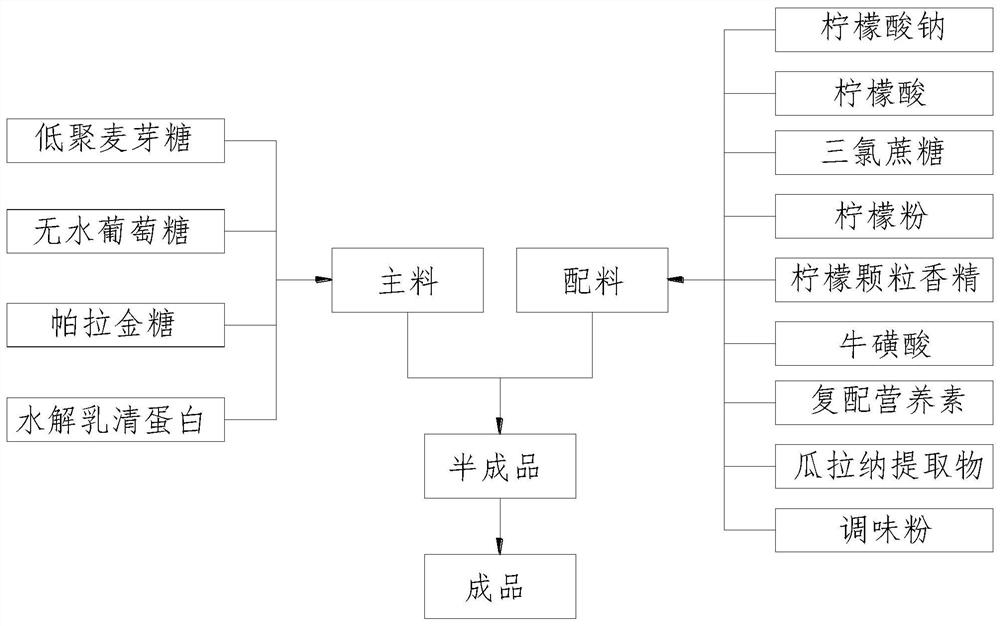
PendingCN112753924AEasy to synthesizeIncrease energy reservesSugar food ingredientsFood ingredient functionsHydrolysateArginine
The invention relates to the field of sports nutrition, and particularly relates to a pumping oligosaccharide solid beverage. The pumping oligosaccharide solid beverage comprises 25% of maltooligosaccharide, 38% of anhydrous glucose, 20% of palatinose, 4% of whey protein hydrolysate, 1.5% of sodium citrate, 5% of citric acid, 0.1% of sucralose, 3% of lemon powder, 0.5% of lemon particle essence, 0.1% of taurine, 0.8% of compound nutrients, 1% of guarana extract and 1% of seasoning powder. The maltooligosaccharide and the palatinose are reasonably proportioned, after an athlete takes the beverage, the energy reserve can be improved before exercise, energy is continuously and stably provided for the body during exercise, meanwhile, the burden of the intestines and stomach can be reduced, the immunity is improved, and the body can be helped to recover quickly after exercise. The whey protein hydrolysate and the guarana extract are added, arginine in the whey protein hydrolysate and the guarana extract can protect the cardiovascular system, promote blood circulation, enhance muscle activity, activate brain excitability and quickly improve the training and competition state.
Owner:广州普瑞米尔生物制品有限公司
Sports drinks with low glycemic index and methods for their preparation and use
ActiveCN105685737BGood effectLow insulin indexSugar food ingredientsFood ingredient functionsLow glucoseFood additive
Owner:BEIJING SPORT UNIV
Food compositions that enhance nitric oxide mediated signalling
ActiveUS10660350B2Speed up the conversion processDecrease in available plasma nitrite levelsCocoaMuscle tissueExercise performance
The invention includes compositions and methods for improving exercise performance or improving recovery of muscle tissue after exercise performance. One method includes administering a composition of a plant-derived nitrate and a cocoa-derived product daily and before exercise. The synergistic combination of nitrate and cocoa polyphenols acts to improve recovery from a strenuous exercise bout.
Owner:THE HERSHEY COMPANY
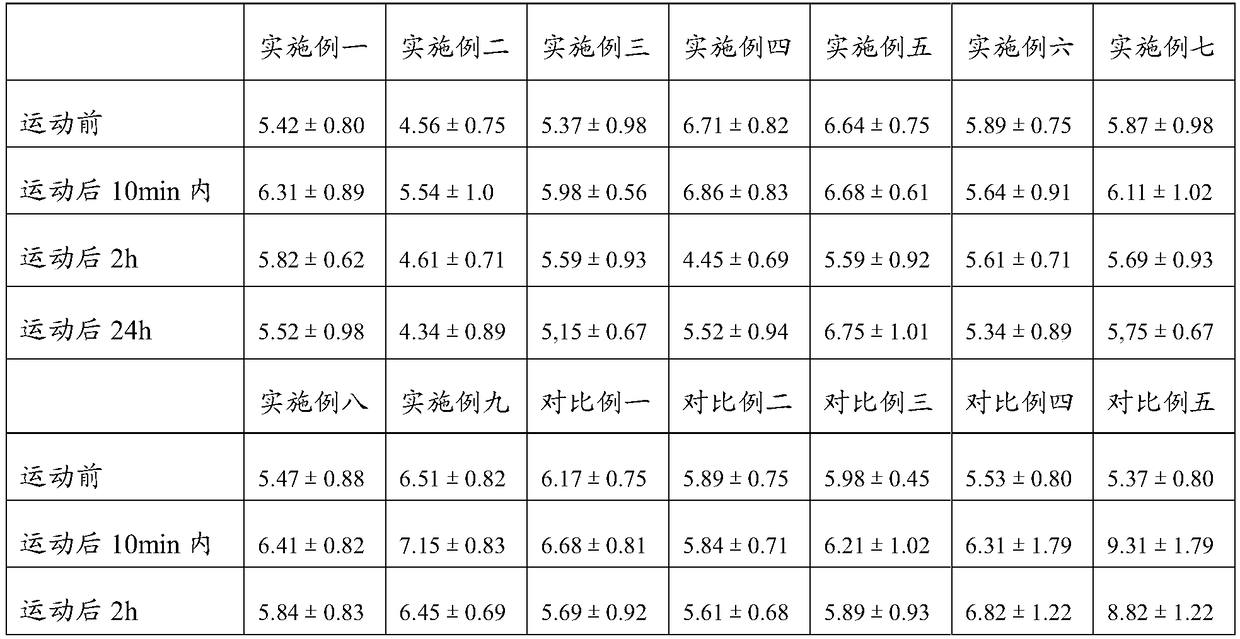
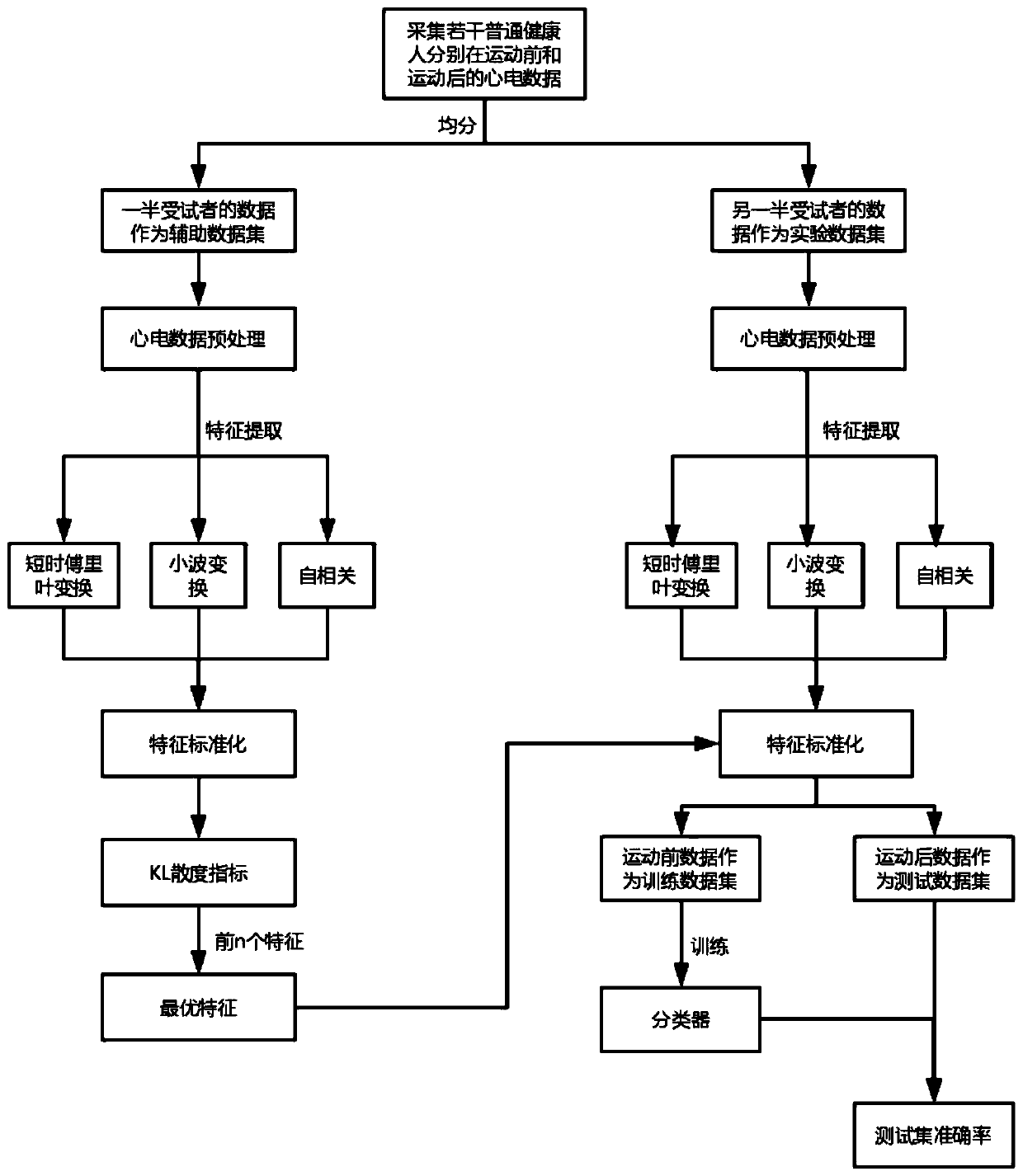
An effective method for identification of ECG signals before and after exercise
The invention discloses an effective method for identification of ECG signals before and after exercise. The method comprises the following steps: collecting ECG signals of several subjects before andafter exercise, using half of the subjects' ECG signal data as an auxiliary data set for selecting optimal features, and the taking other half of the subjects as an experimental data set for verifying the validity of the selected optimal feature; performing various feature extraction on the collected ECG signal data; standardizing the extracted features; using a KL divergence indicator to sort the various features after standardization on the auxiliary data set to find the optimal feature combination; on the experimental data set, using the selected optimal feature combination and ECG signaldata before exercise for training a classifier, classifying and evaluating the ECG signal data after exercise, and verifying the validity of the optimal feature combination; registering the ECG signalof ordinary person before exercise, and performing the ECG signal identification according to the optimal feature combination after exercise.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
Special massage device before and after exercise and use method thereof
PendingCN113081739APromote blood circulationEasy accessPneumatic massageChiropractic devicesStructural engineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a special massage device before and after exercise, which comprises a shell with a massage space, a support pad with a first water flow channel, a water supply mechanism and an inflatable massage mechanism, and is characterized in that the shell comprises a top plate, and a second water flow channel is arranged in the top plate; the water supply mechanism comprises a first water tank, a second water tank, a first water supply pipeline, a second water supply pipeline, a first water supply pipeline and a second water supply pipeline, one end of the second water supply pipeline is connected with the second water tank, and the other end is communicated with the first water flow channel and the second water flow channel. Compared with the prior art, the massage device special for the athletes before and after exercise can effectively adjust the body active degree of the athletes, limb muscle groups of the athletes can quickly enter the exercise state, and the muscle tension state of the athletes after exercise can be effectively relieved. The invention further provides a using method of the special massage device before and after exercise.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com