Patents
Literature
65results about How to "Avoid misinterpretation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and device for visual masking of defects in matrix displays by using characteristics of the human vision system
ActiveUS20070126657A1Avoid wrong image interpretationLess visibleCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceComputer vision
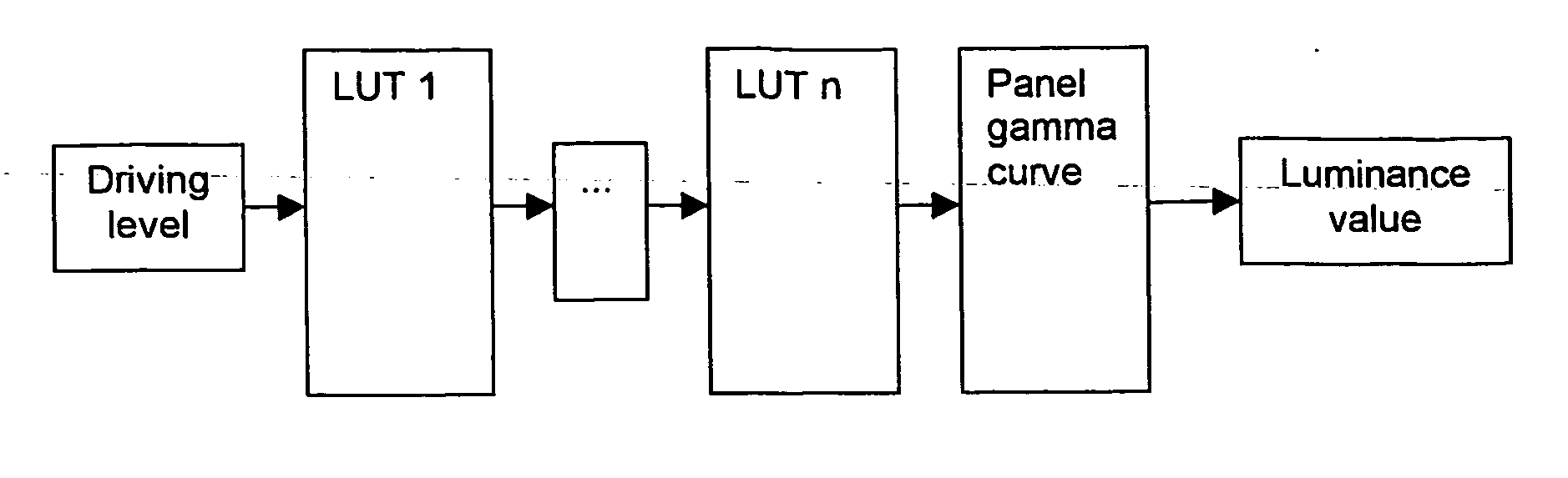
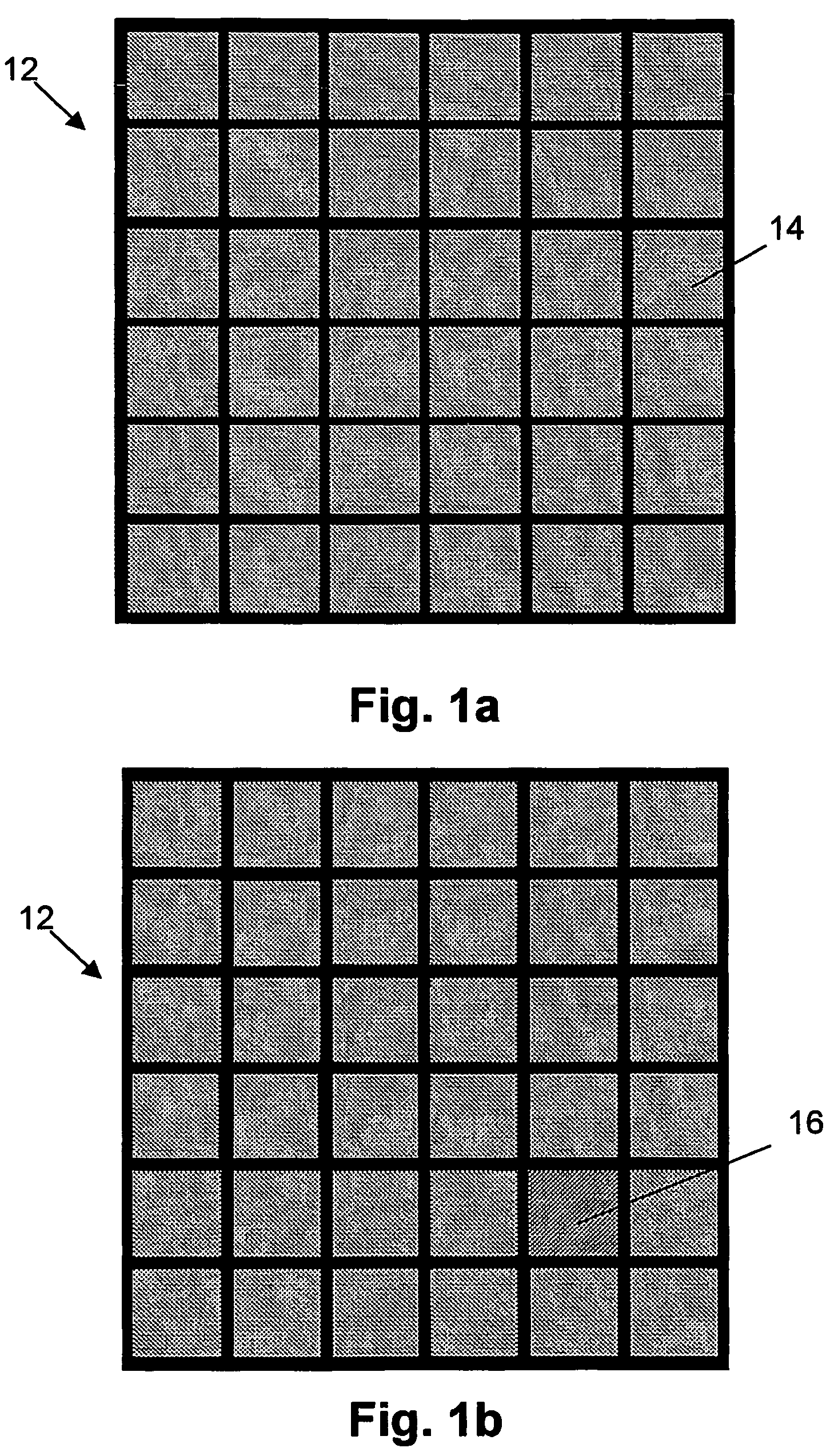
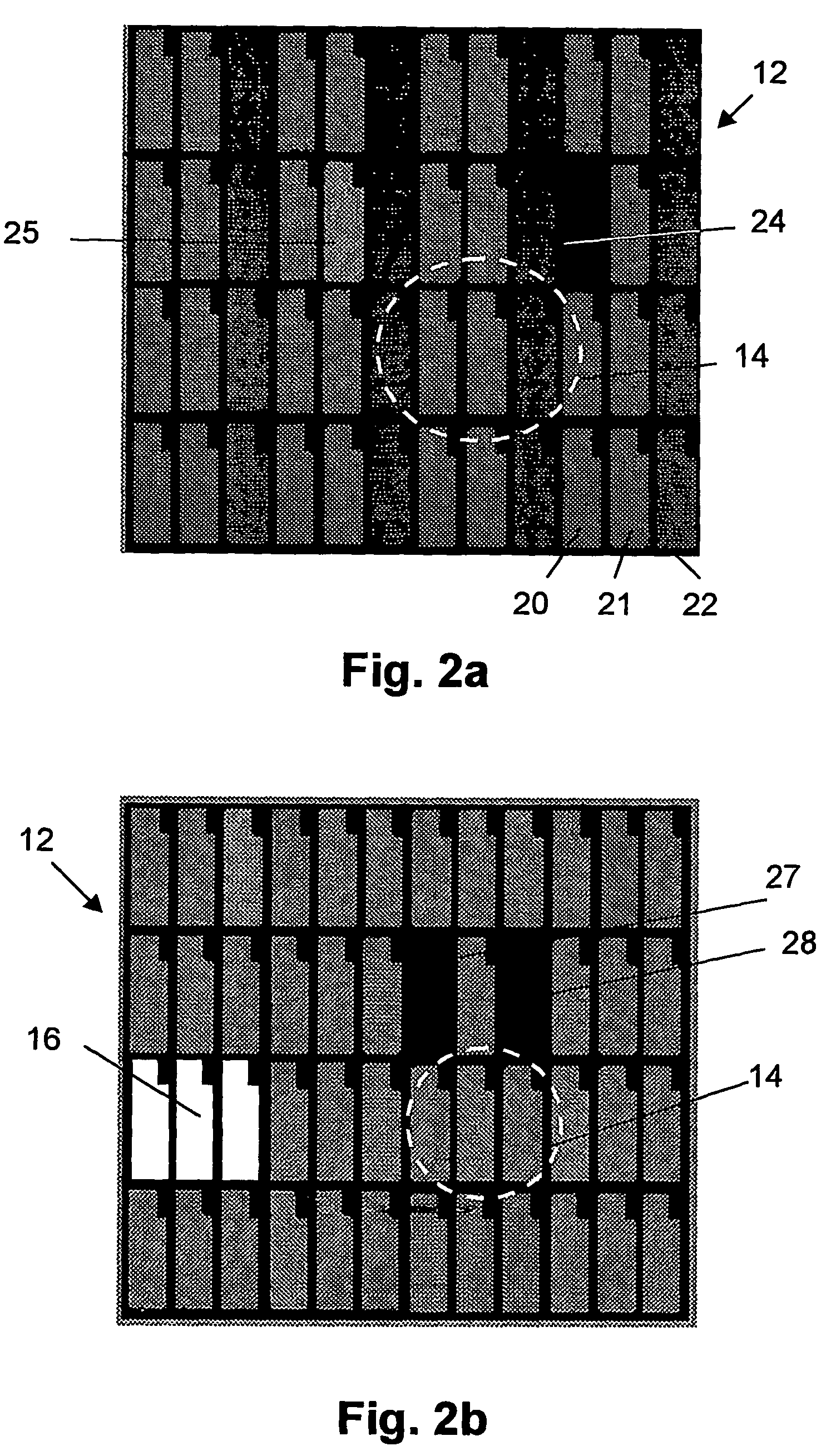
The present invention provides a method for reducing the visual impact of defects present in a matrix display comprising a plurality of pixels, said pixels comprising at least three sub-pixels, each sub-pixel intended for generating a sub-pixel colour which cannot be obtained by a linear combination of the sub-pixel colours of the other sub-pixels of the pixel, the method comprising: providing a representation of a human vision system, characterizing at least one defect sub-pixel present in the display, the defect sub-pixel intended for generating a first sub-pixel colour, the defect sub-pixel being surrounded by a plurality of non-defective sub-pixels, deriving drive signals for at least some of the plurality of non-defective sub pixels in accordance with the representation of the human vision system and the characterizing of the at least one defect sub-pixel, to thereby minimize an expected response of the human vision system to the defect sub-pixel, and driving at lease some of the plurality of non-defective sub-pixels with the derived drive signals, wherein minimizing the response of the human vision system to the defect sub-pixel comprises changing the light output value of at least one non-defective sub-pixel for generating another sub-pixel colour, said another sub-pixel colour differing from said first sub-pixel colour. The present invention also provides a corresponding system for reducing the visual impact of defects present in a matrix display, and a matrix display with reduced visual impact of defects present in the display.
Owner:BARCO NV
Integrated circuit testing method
ActiveCN102866349ASpeed up testingAvoid misinterpretationElectrical testingTest platformAutomatic testing
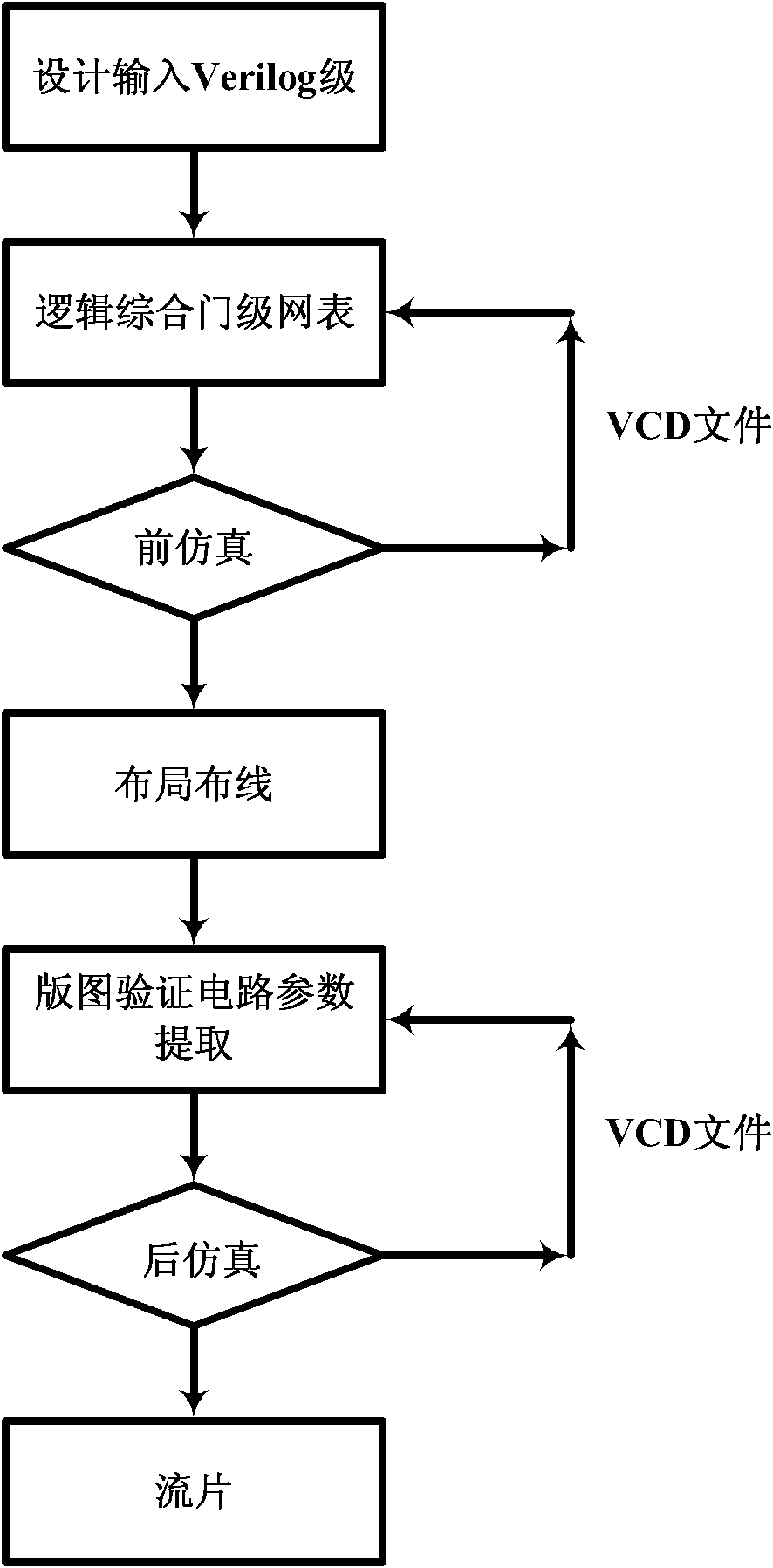
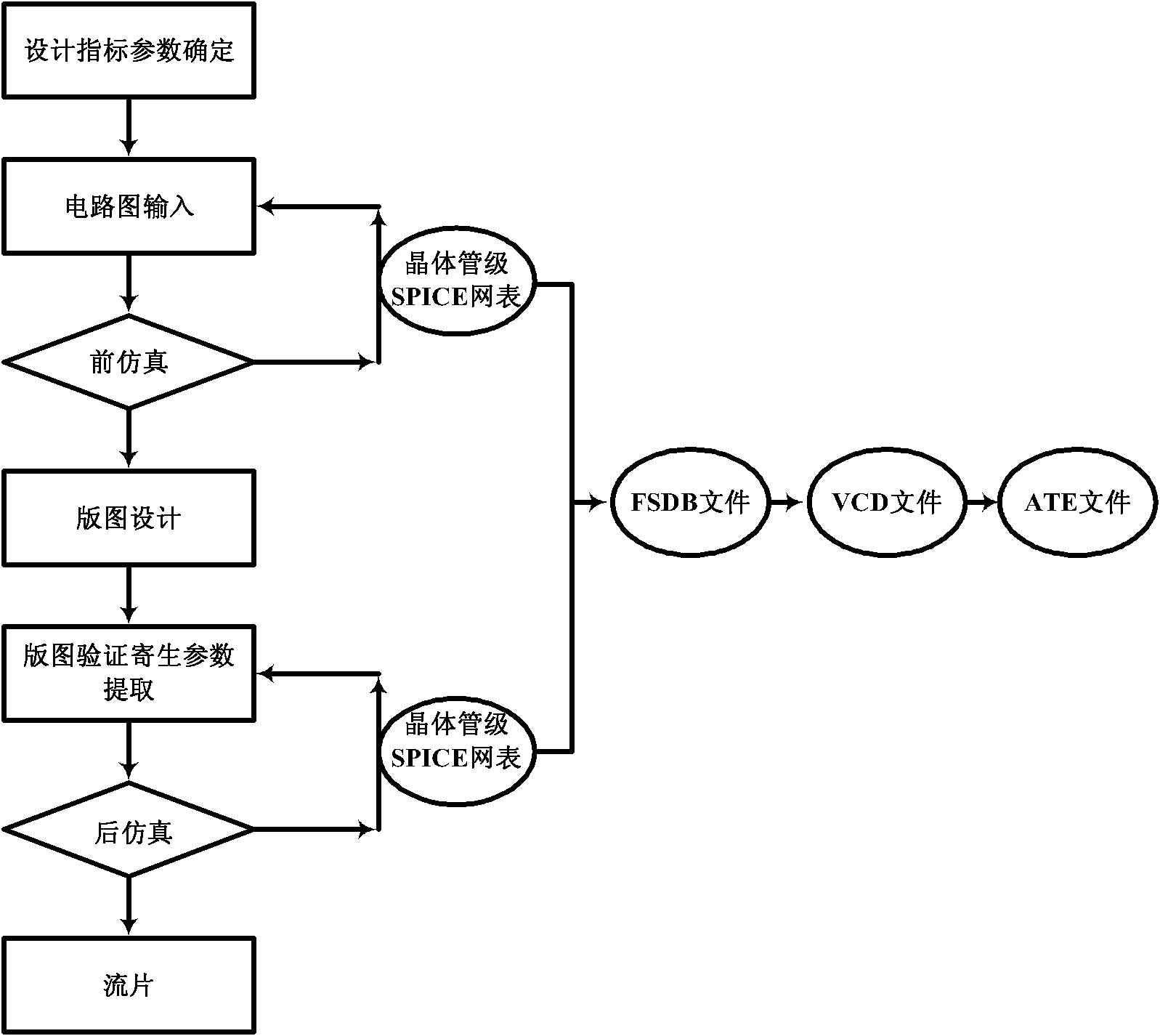
The invention provides an integrated circuit testing method, which comprises the steps of design index parameter determination, circuit diagram input, pre-simulation, layout design, layout verification and parasitic parameter extraction, post-simulation and tape-out. The integrated circuit testing method is characterized in that both the pre-simulation and the post-simulation use a transistor-level SPICE netlist, which can be converted to documents required for an automatic testing platform. The testing method provided by the invention can be used to greatly shorten the original test vector writing time for chip testing personnel, speed up the progress of the test, avoid understanding deviation between designers and testers and achieve seamless butting.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Brushless DC electronic water pump controller with fault diagnosis function and diagnosis method
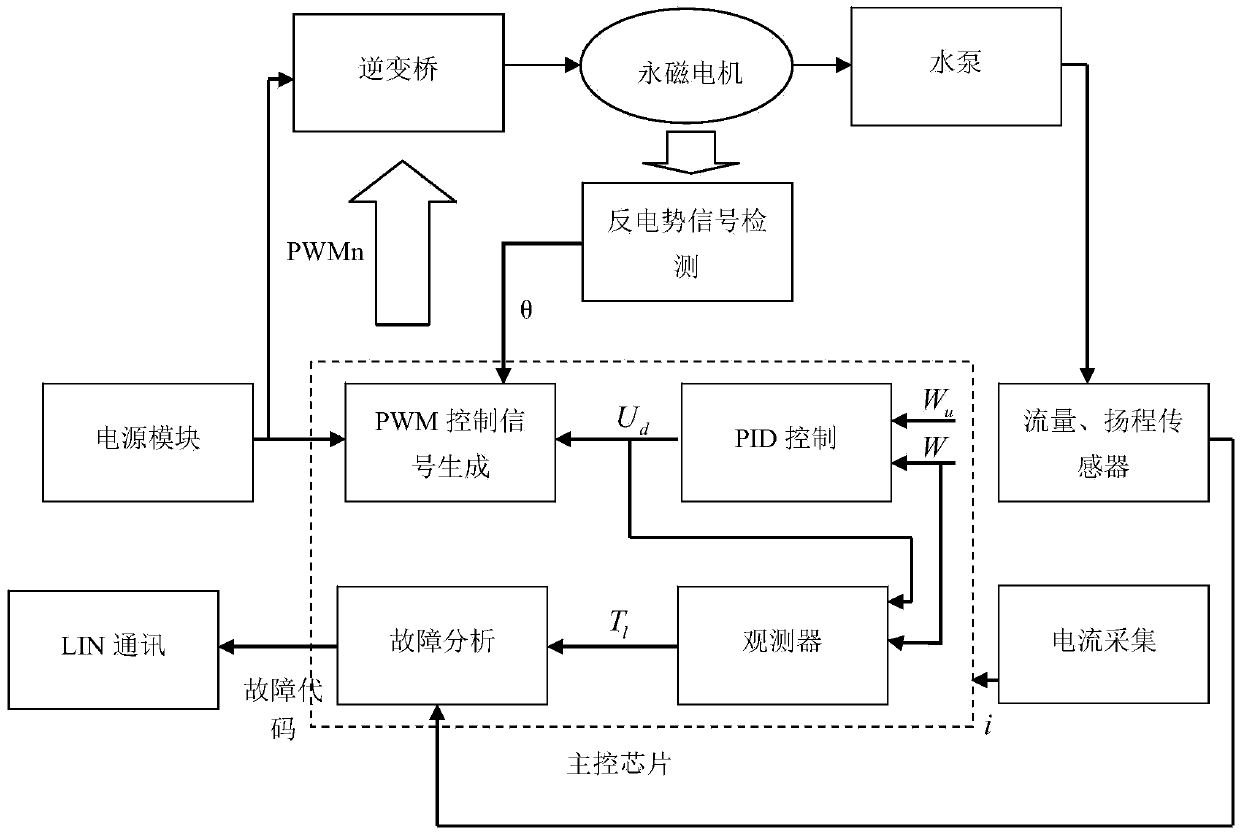
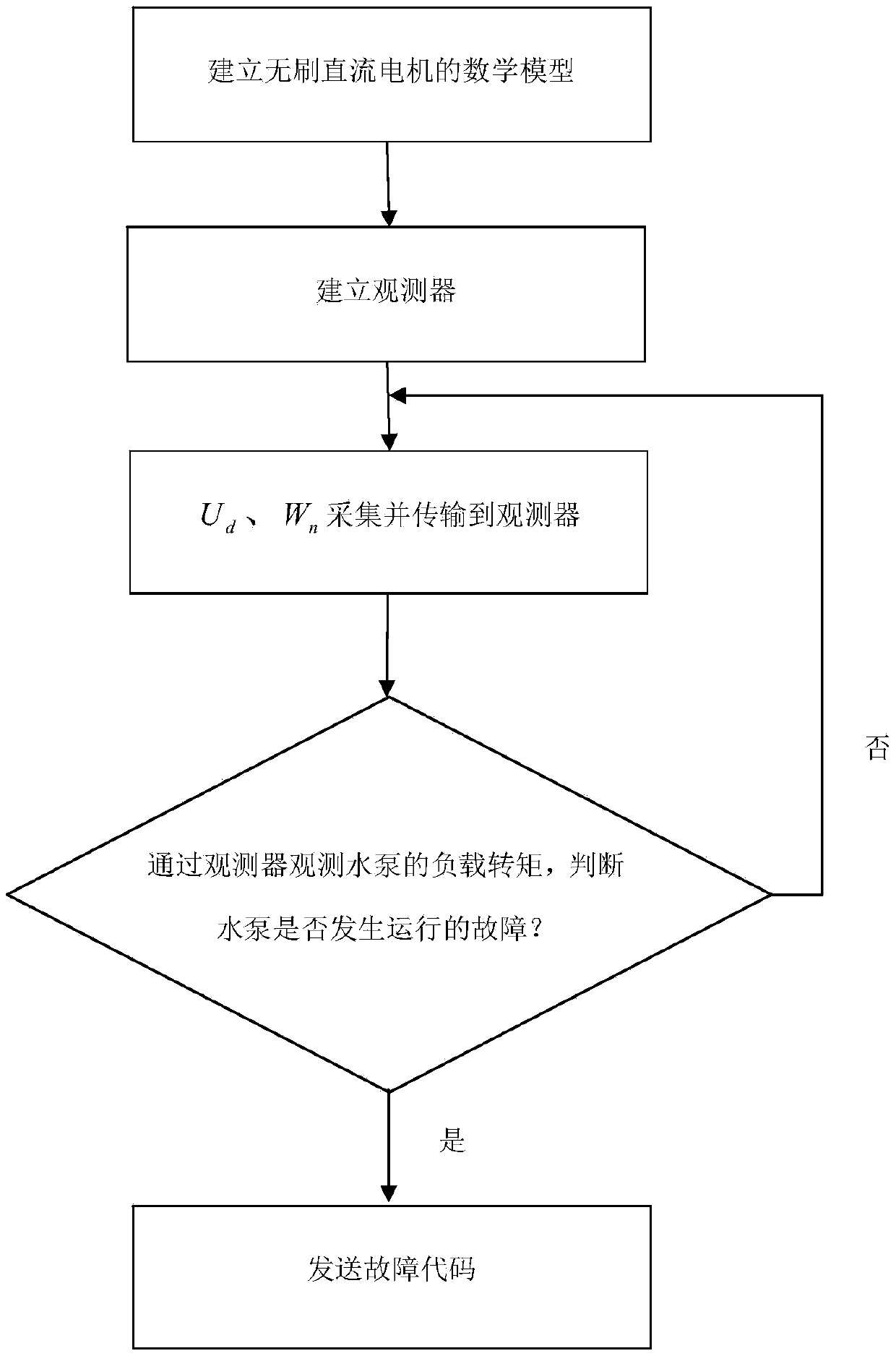
The invention provides a brushless DC electronic water pump fault diagnosis system, which comprises an observer and a fault analysis module, wherein the observer inputs a motor angular velocity and control voltage, and a load torque observation value is obtained; the motor angular velocity is actually measured through a sensor, and the control voltage is obtained through an original brushless DC electronic water pump control system; the fault analysis module comprises a water pump operation fault analysis module; the water pump operation fault analysis module is used for comparing the load torque observation value obtained by the observer and a set load torque range, when the obtained load torque observation value is not in the load torque range, fault is judged to happen to operation of the water pump, and a plurality of load torque observation values are acquired in the case of normal water pump operation, an arithmetic mean value and a standard deviation are calculated, appropriate multiples are selected, and thus the load torque range is obtained. Detection output of the sensor is only used for data calibration, an observer model is built, and fault diagnosis is carried out on the water pump.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
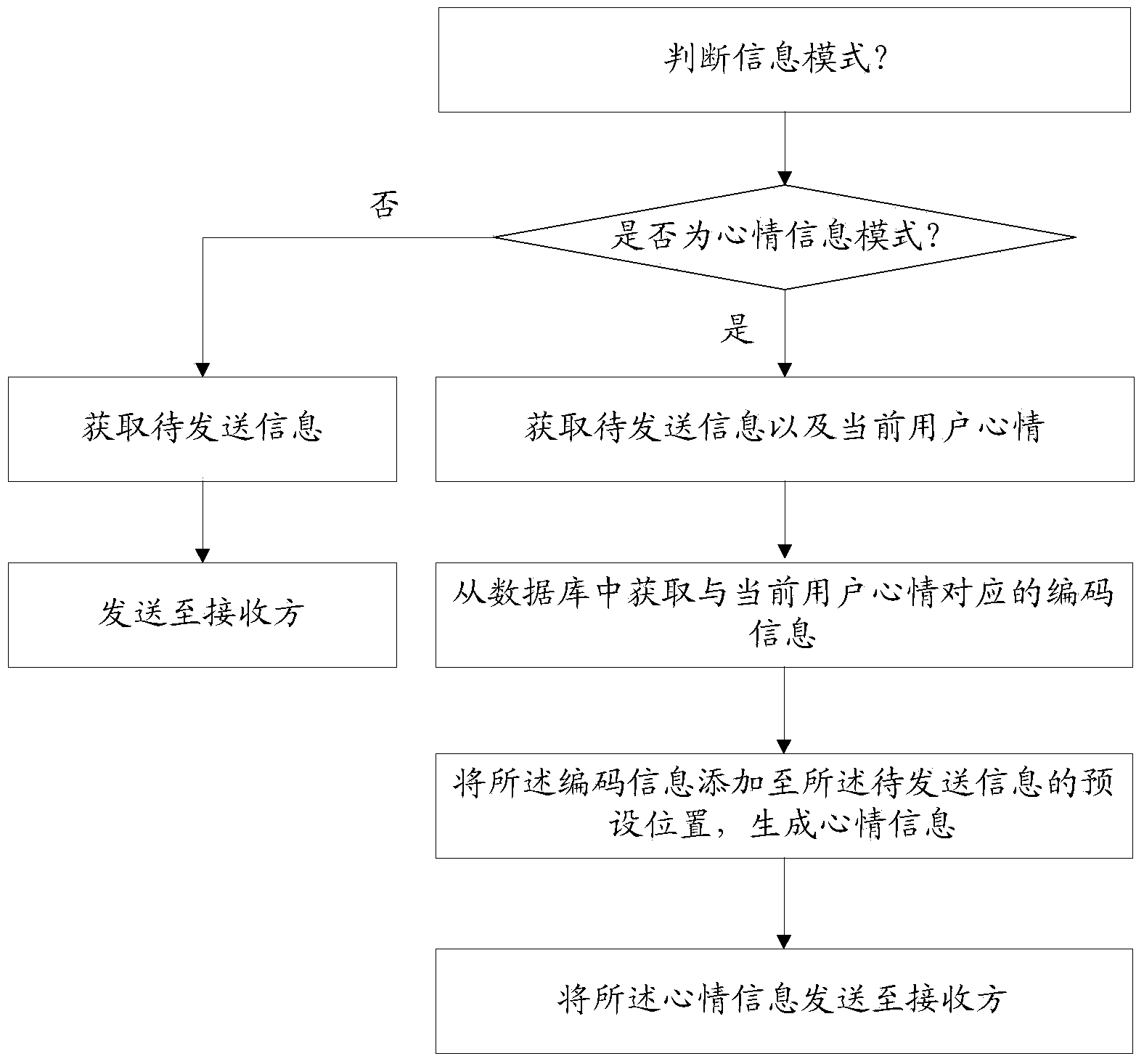
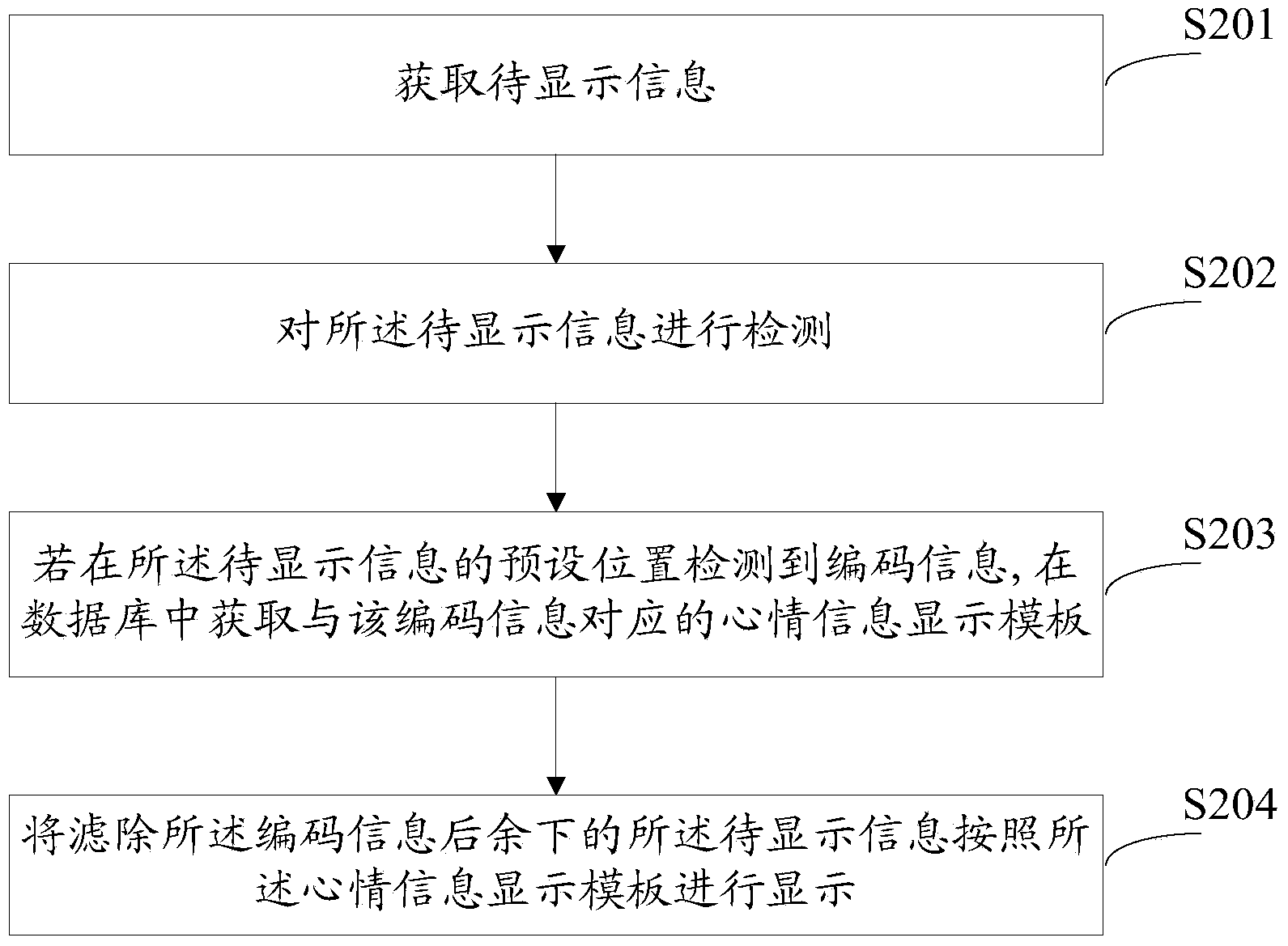
Mood information implementation method and system
InactiveCN104239515AImprove fullnessSolve the problem of content ambiguitySpecial data processing applicationsAmbiguityDependability
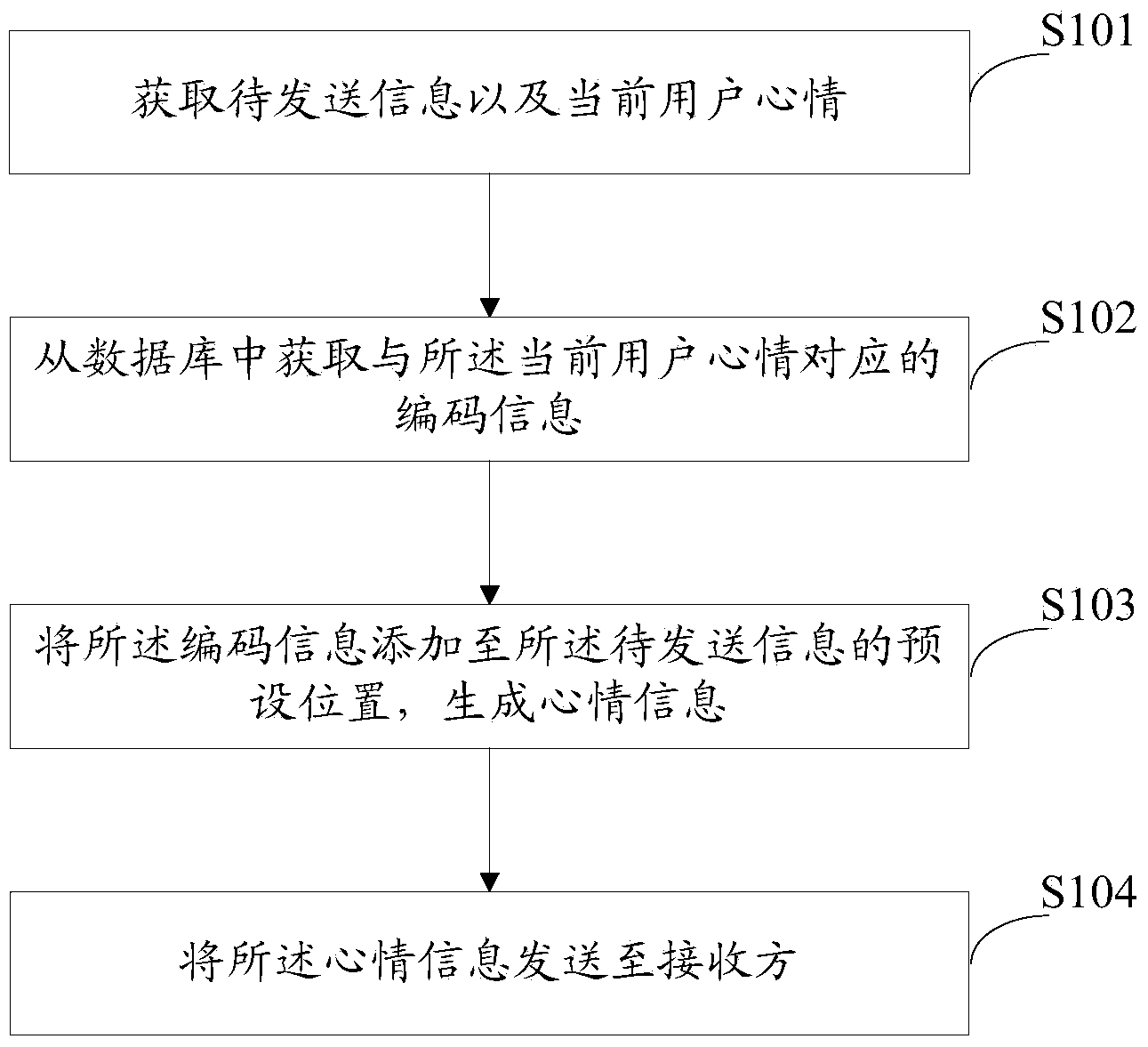
The invention discloses a mood information implementation method and system. A method for transmitting mood information comprises the following steps: acquiring information to be transmitted, and acquiring encoding information which corresponds to the current mood of a user from a database; adding the encoding information into a preset position of the information to be transmitted to generate mood information, and transmitting the mood information to a receiving party. According to the mood information transmitting method provided by the invention, the mood of the user is embedded into the information to be transmitted through an encoding way, and ordinary information becomes mood information with the mood state of the user, so that the fullness of information and the ideographical expression accuracy are effectively increased. The invention further provides a mood information displaying method. After the mood information is received, the mood information is displayed through a stored mood information display template, so that the problem of information content ambiguity is solved, and information interpretation error is avoided effectively. By adopting the mood information implementation method, the reliability of information interaction is realized, and better experience can be brought to the user; the mood information implementation method is wide in application prospect.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Electric connector
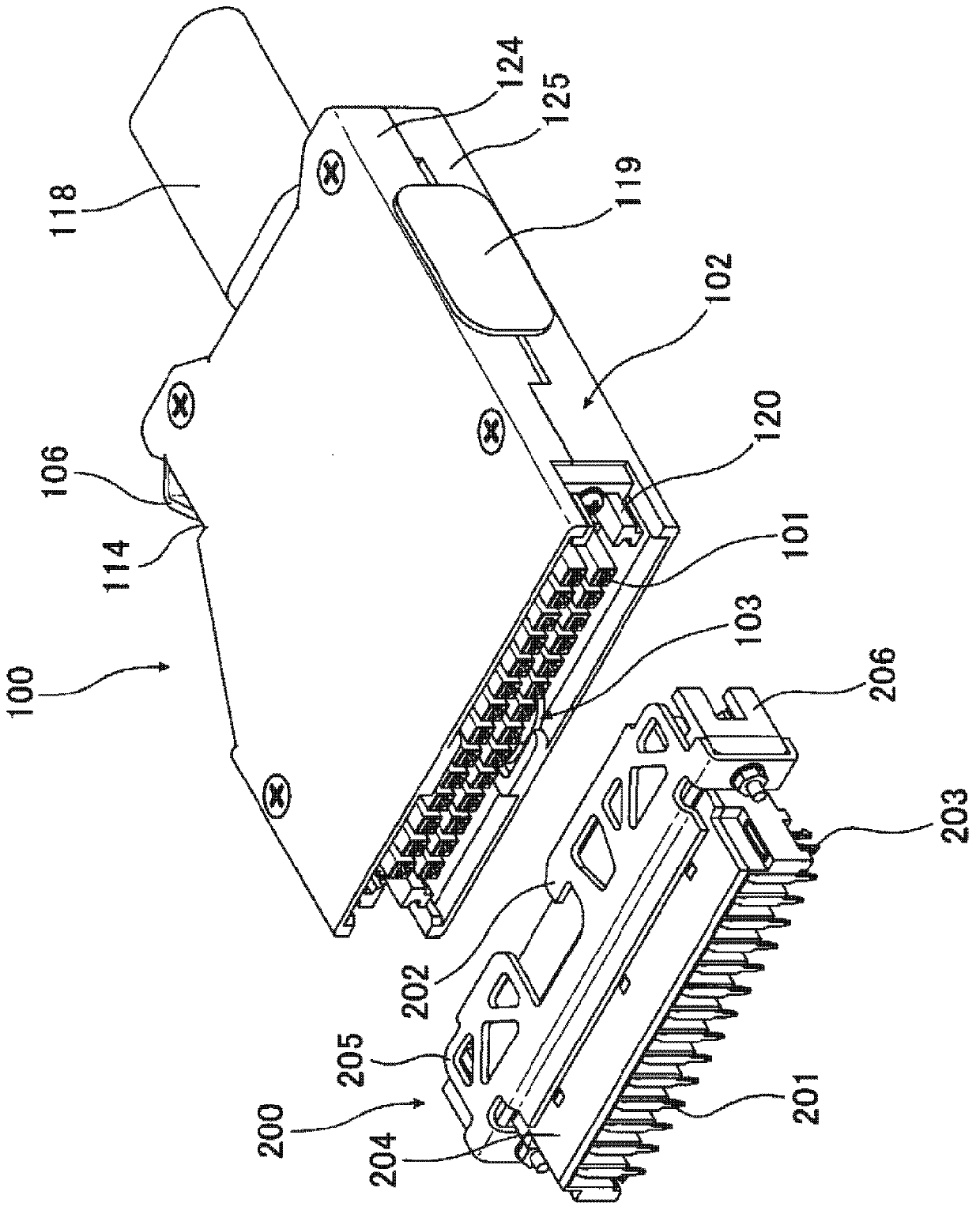
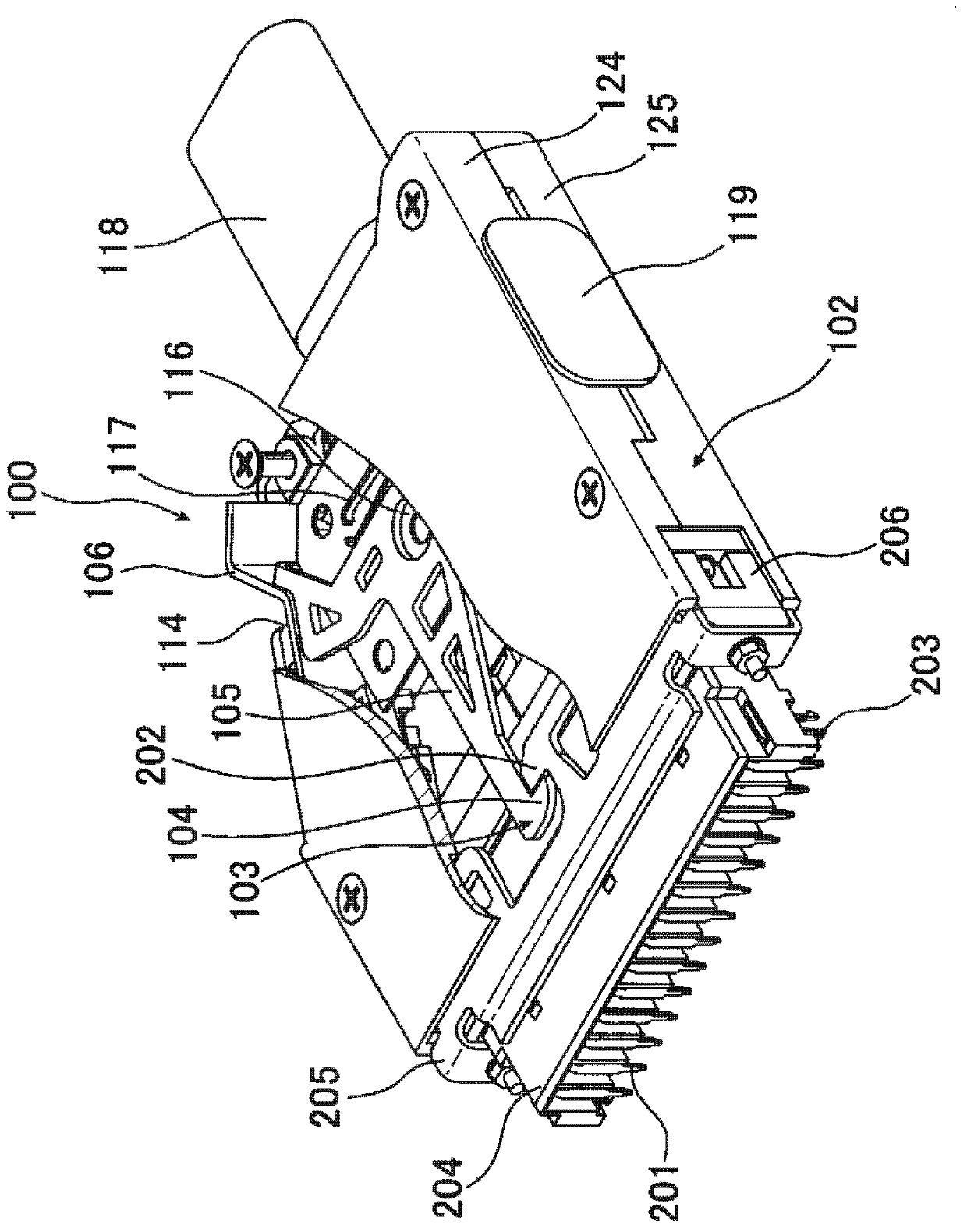
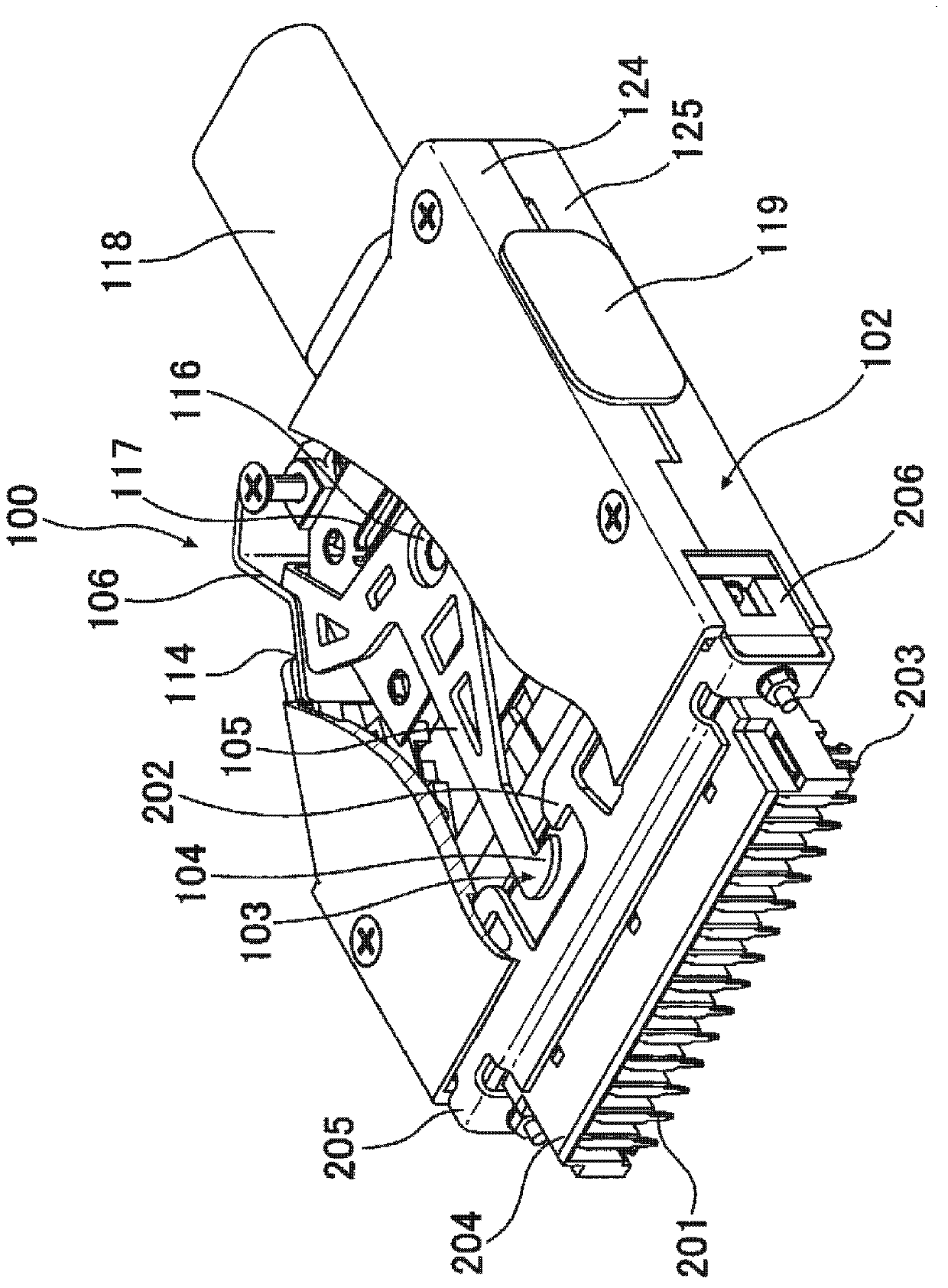
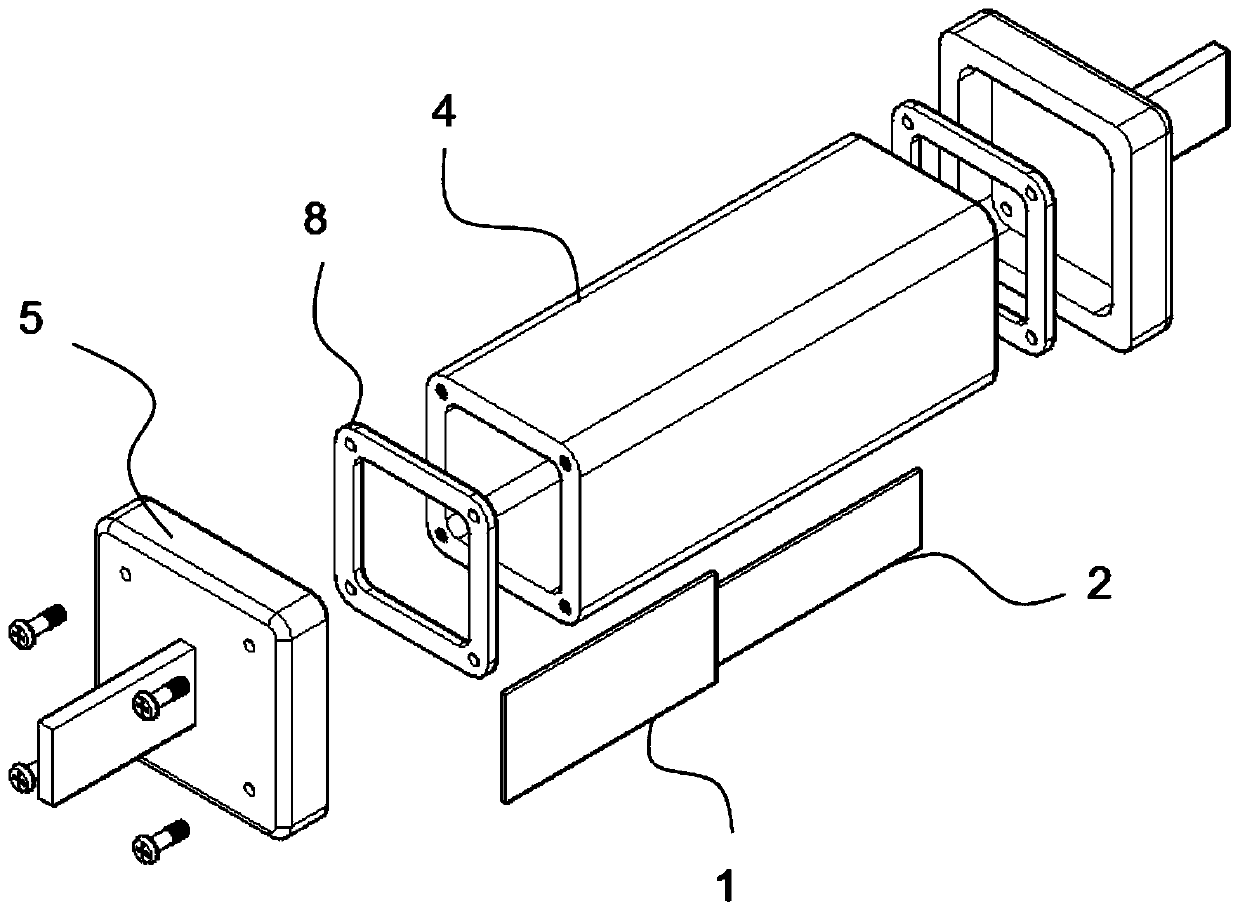
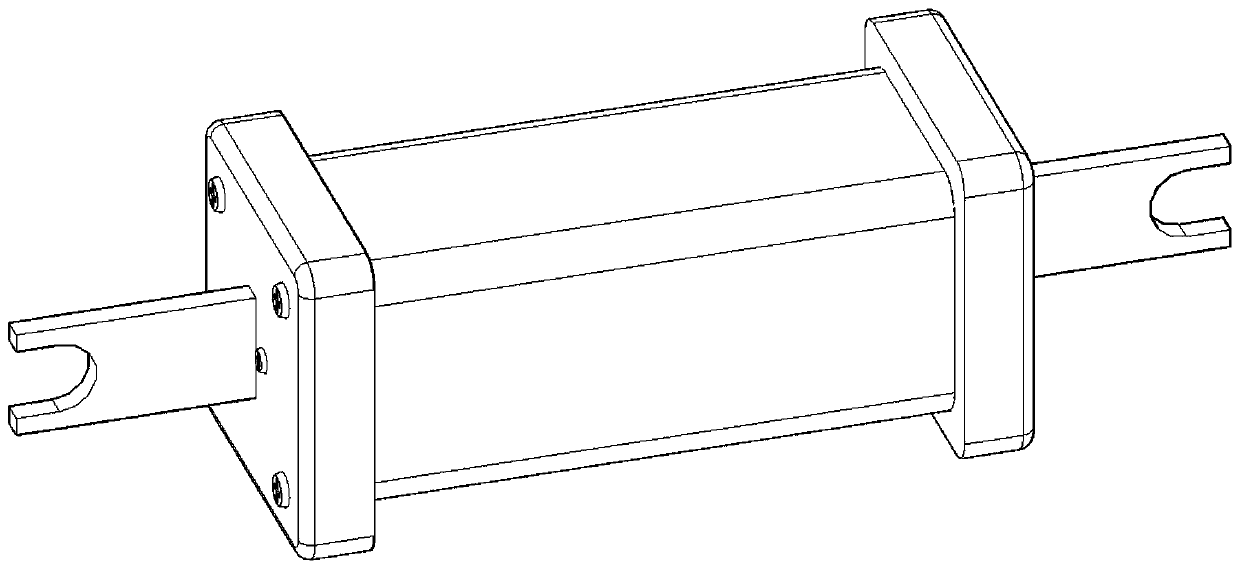
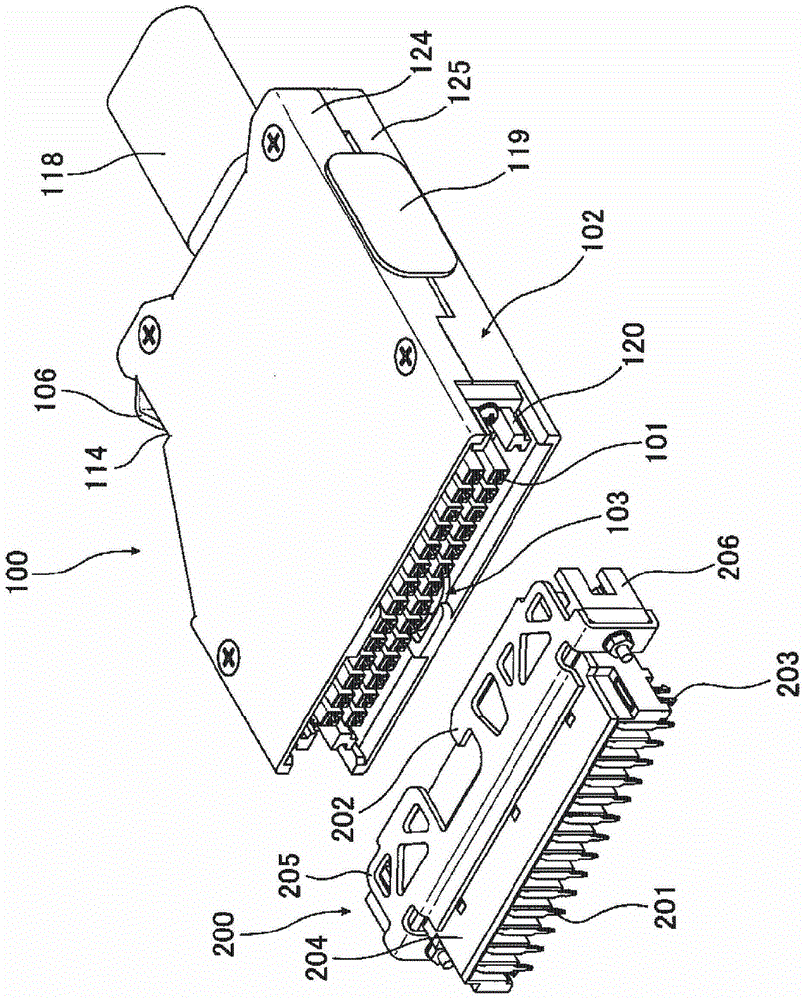
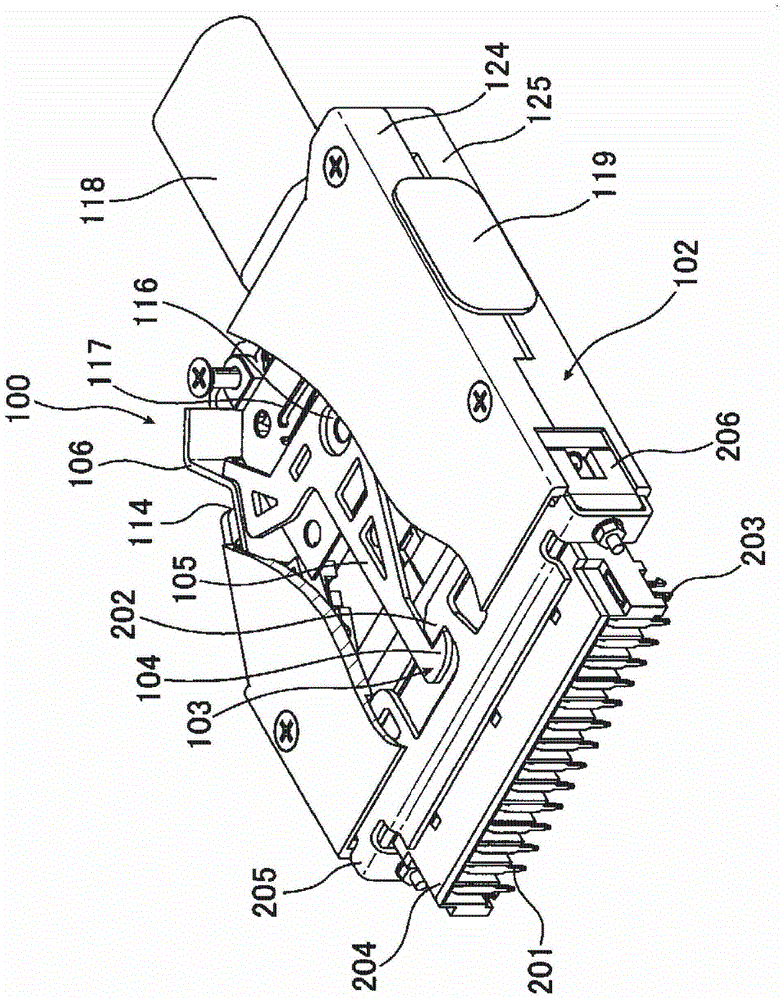
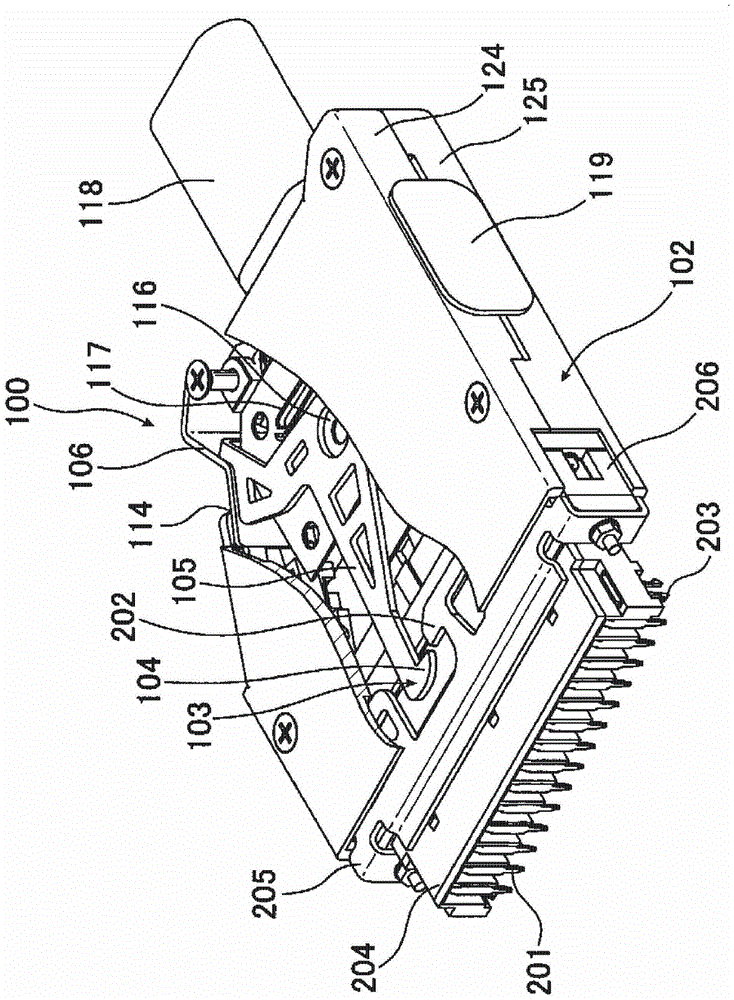
ActiveCN103311739APrevent misinterpretationAvoid misinterpretationCoupling device detailsElectrical connectionStructural engineering
The invention provides a technology for solving a problem that an electric connector having a locking mechanism unlocks accidentally because of vibration and surge. The connector comprises a locking unit (103) for preventing the electric connector from detaching when being fitted with a side connector of an opposite side. The locking unit (103) possess a first snap part (104) snapping with a part of the side connector of the opposite side when the electric connector is fitted with the side connector of an opposite side, a main body part (105) for connecting with the first snap part (104), a first operation part (106) for connecting with the main body part (105) and performing position switch on the first snap part (104). Furthermore, a first position limitation member (107 ) (double lock) for the position that the first operation part switch to which can be selectively moved to a limited part or an unlimited part, and the limitation member (triple lock)for the position of the first position limitation part which can be selectively moved to a limited part or an unlimited part are comprised. In virtue of above arrangement, the electric connector can prevent fault unlocking.
Owner:HIROSE ELECTRIC GROUP
Metagenome or macrotranscriptome sequencing data automatic analysis method and system
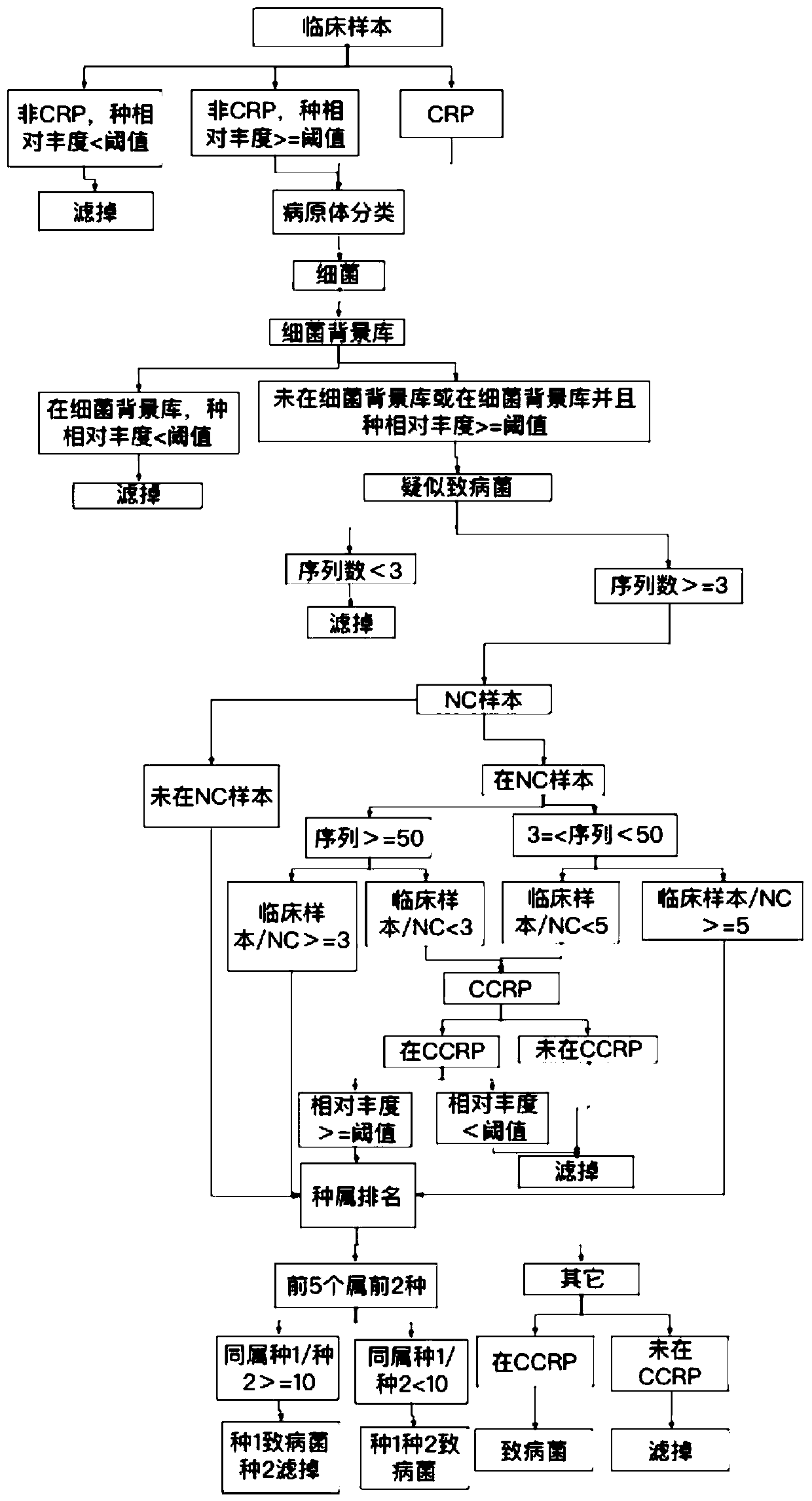
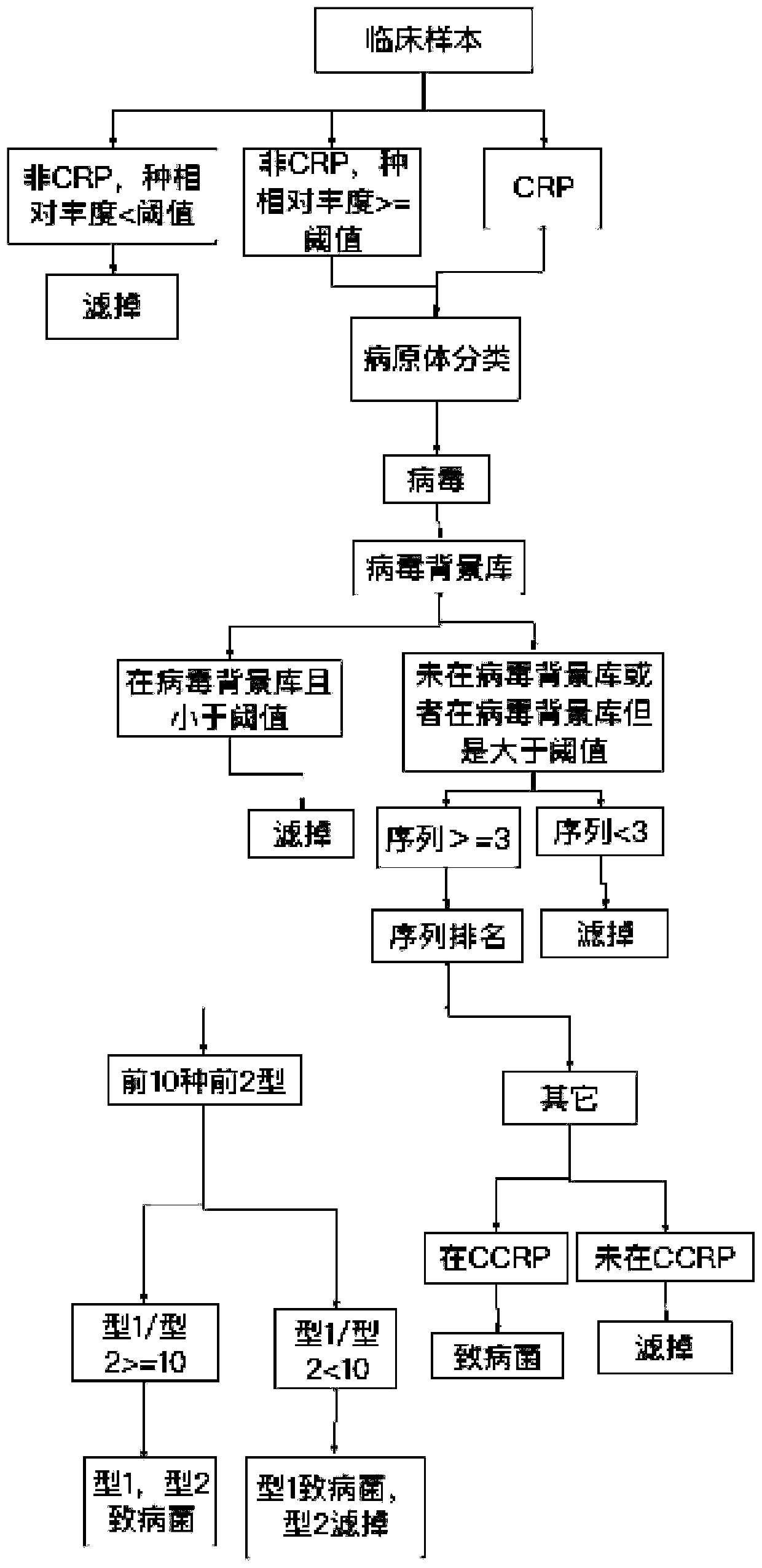
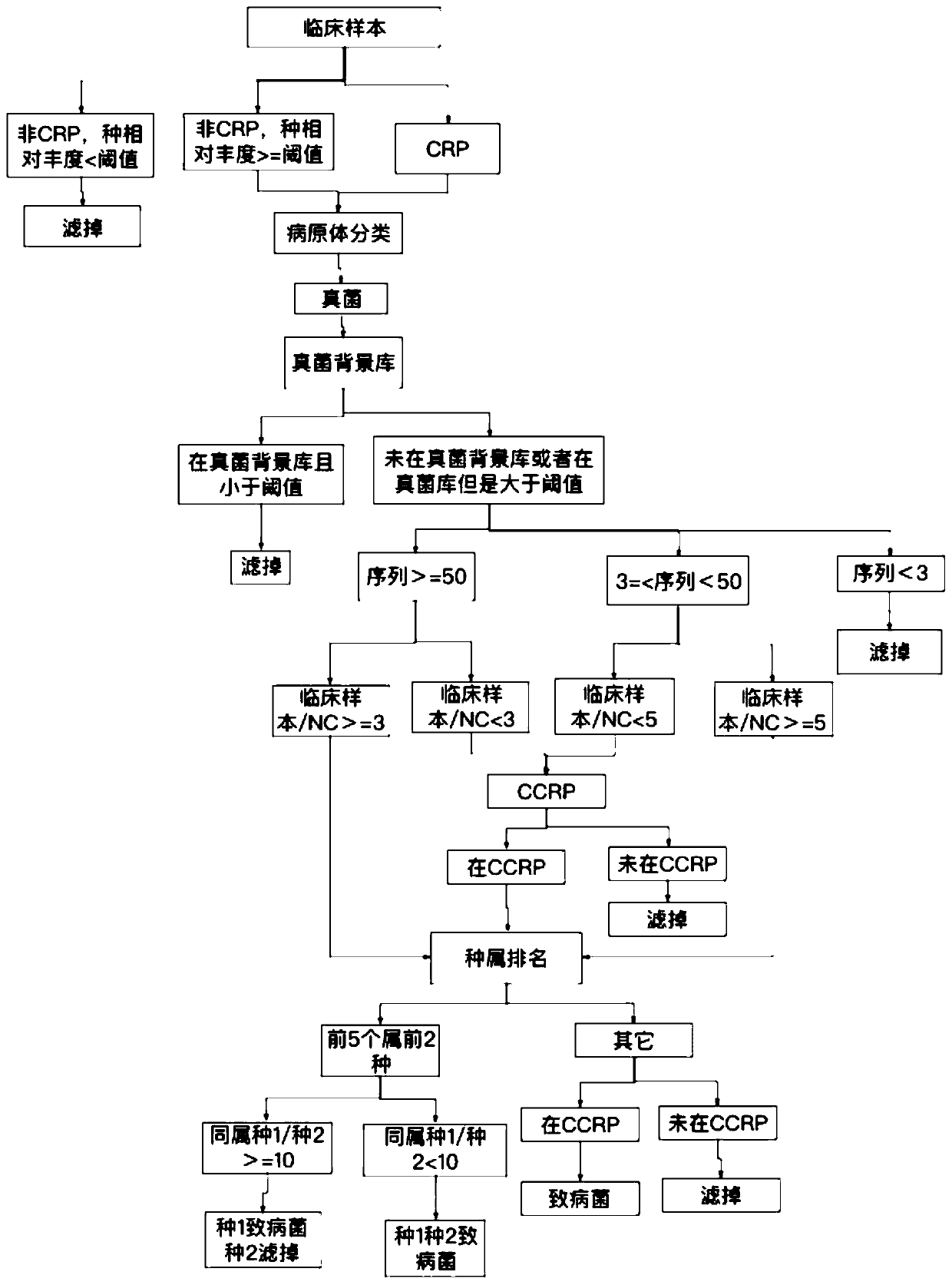
ActiveCN110751984AHigh speedImprove accuracySequence analysisInstrumentsTranscriptome SequencingData mining
The invention relates to a metagenome or macrotranscriptome sequencing data automatic analysis method and system and belongs to the technical field of data gene detection. According to the method, a CRP (clinically reported pathogen) database and a background library are compared with differences of negative control samples to remove redundant information; a report strain is selected through ranking of strains in the genus; and finally, based on a CCRP database, the strains are screened and filtered again to prevent leakage, the report strain is obtained, and a report is automatically generated. According to the method and system, the manual interpretation process is automated, the interpretation speed and accuracy are improved, and meanwhile, backtracking of historical information is brought into the interpretation process, so that the interpretation accuracy and reliability are improved.
Owner:广州微远医疗器械有限公司 +4
Package body capable of realizing signal emission function by power generation device
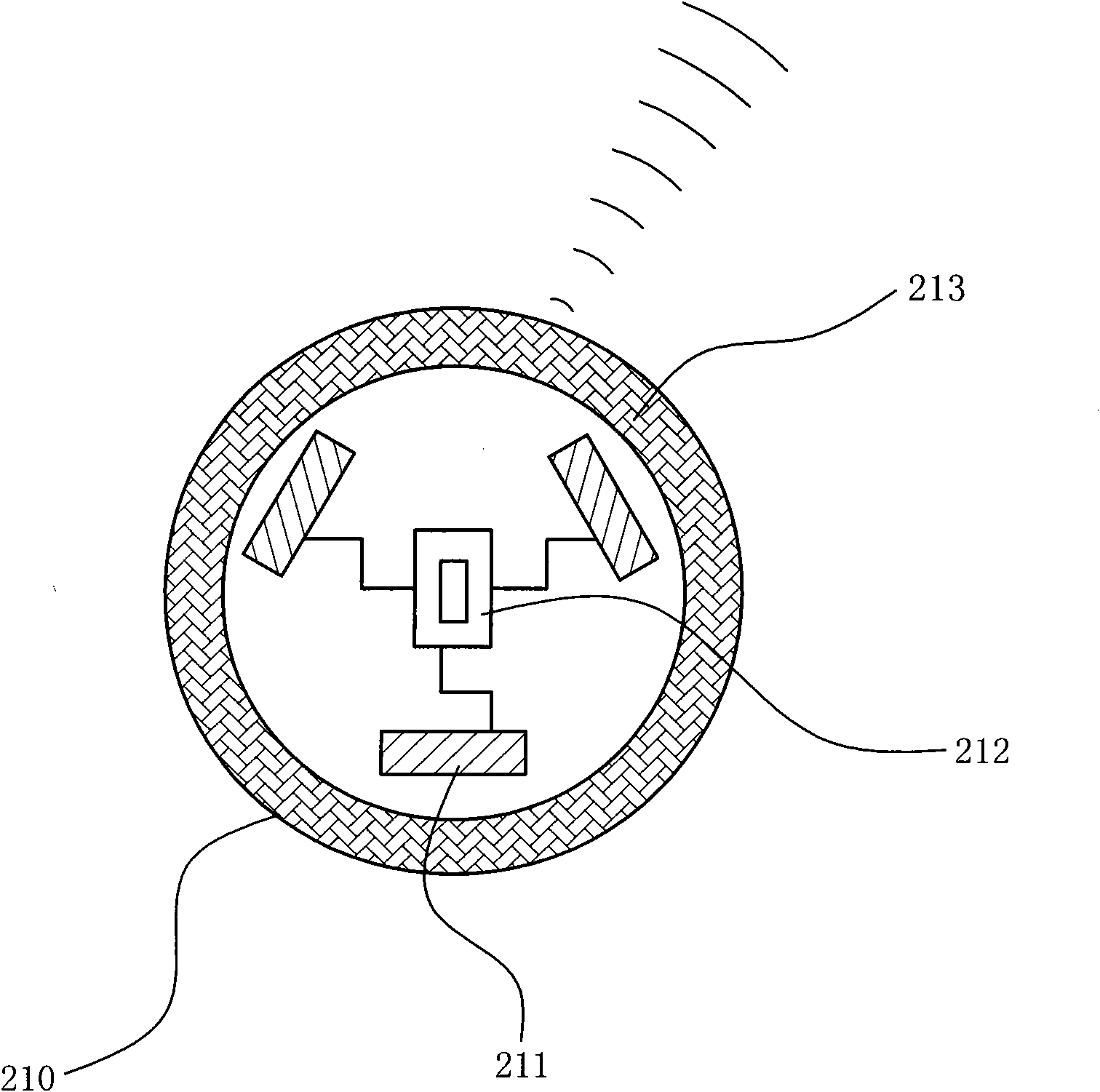
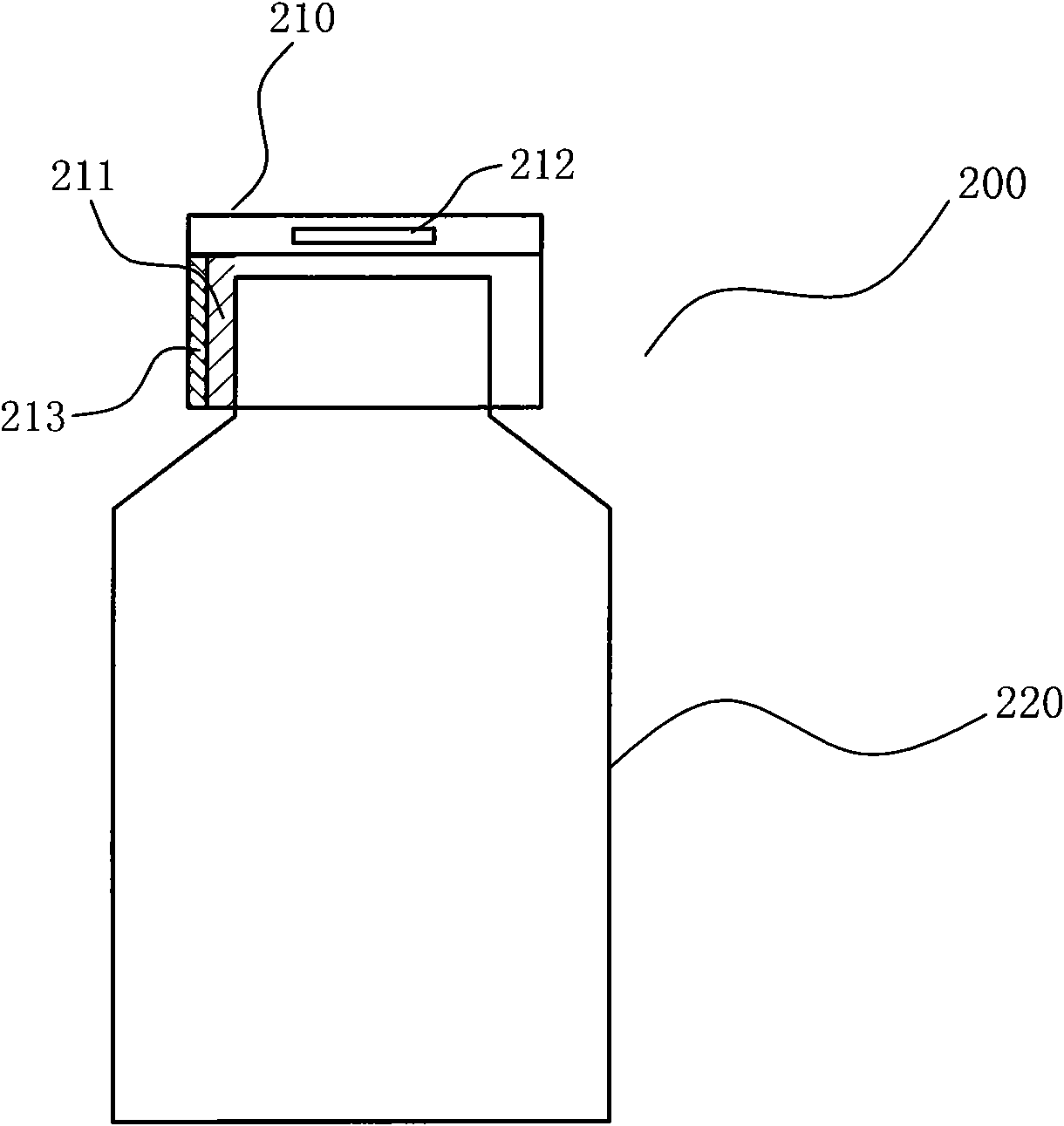
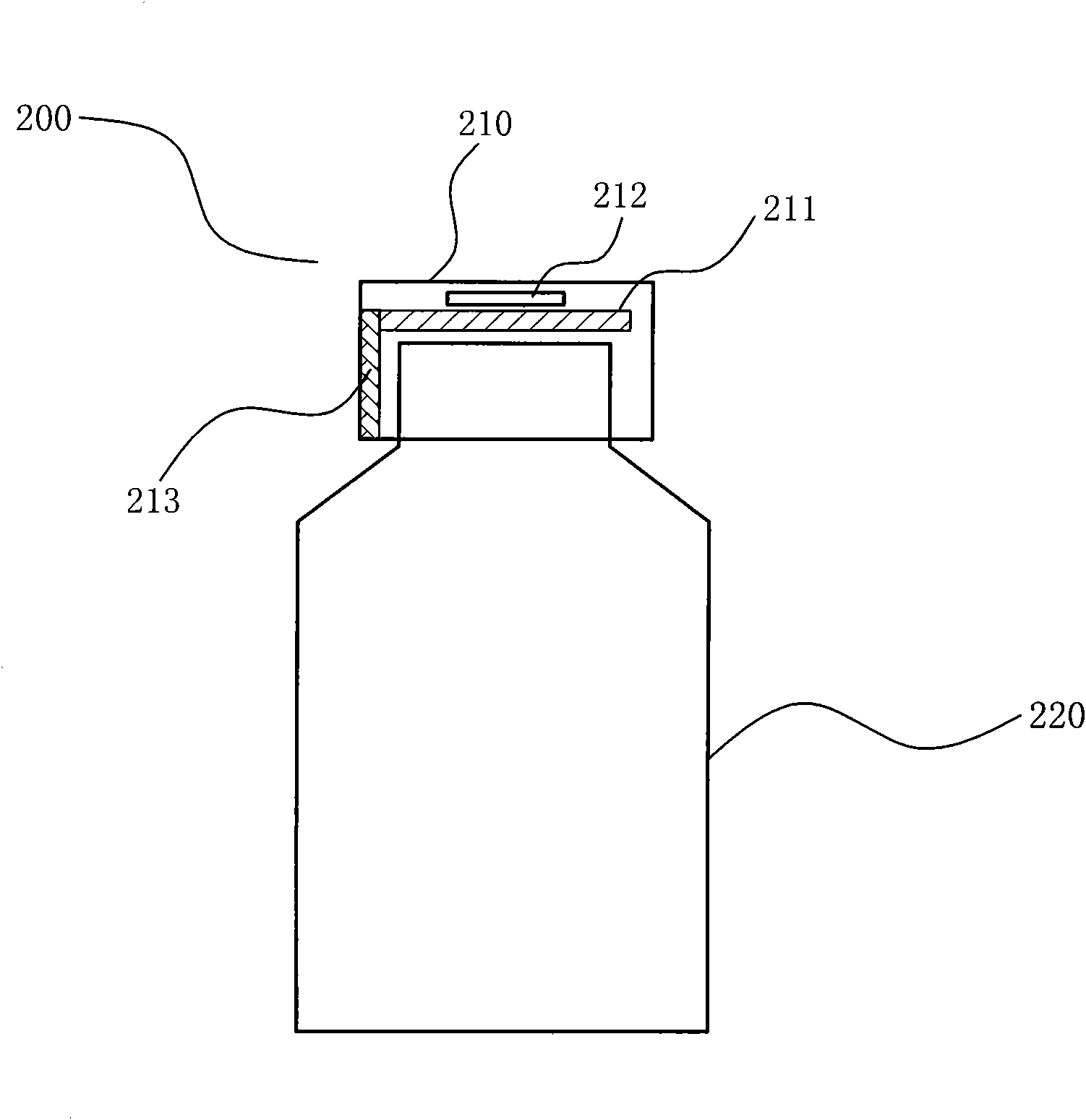
ActiveCN102113962ASelf-activationAvoid misinterpretationOral administration deviceRecord carriers used with machinesComputer moduleApplication areas
The invention provides a package body capable of realizing a signal emission function by a power generation device, belonging to the field of electronic technology application, relating to the application technology on the aspect of radio frequency identification. The package body is provided with a power generation device, and the package body is provided with a signal emission module by corresponding to the power generation device. The signal emission device self is activated by arranging the power generation device on the package body. Because the package body is provided with the signal emission device, such as an RFID (Radio Frequency Identification Devices) chip, medicine is tracked and detected, and related issues, such as date, time, types, amount, flow, matters need attentions and the like for users to take medicines are reminded and guided in time so as to protect people from negligence because people are busy and prevent people from misreading the using method of the medicine.
Owner:马宇尘
Device for monitoring a pump
ActiveCN103249952ACharacteristics clearly definedInhibit deteriorationSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionPump controlEngineeringAcoustic wave
A device and a method for monitoring rotating components in centrifugal pumps or systems which comprise centrifugal pumps is provided. The device includes a first unit which is located on or in the component to be monitored having at least one component property sensor, a sensor signal evaluation unit, a transmitting unit for transmitting analysis results to a receiver arranged spatially separate from the monitored component, and a source for supplying power. The device further includes a second unit having a receiver unit, a transmitted signal evaluation unit, and a sensed component property display and / or information communication element. The analysis result transmission from the first unit to the second unit is acoustic.
Owner:KSB AG
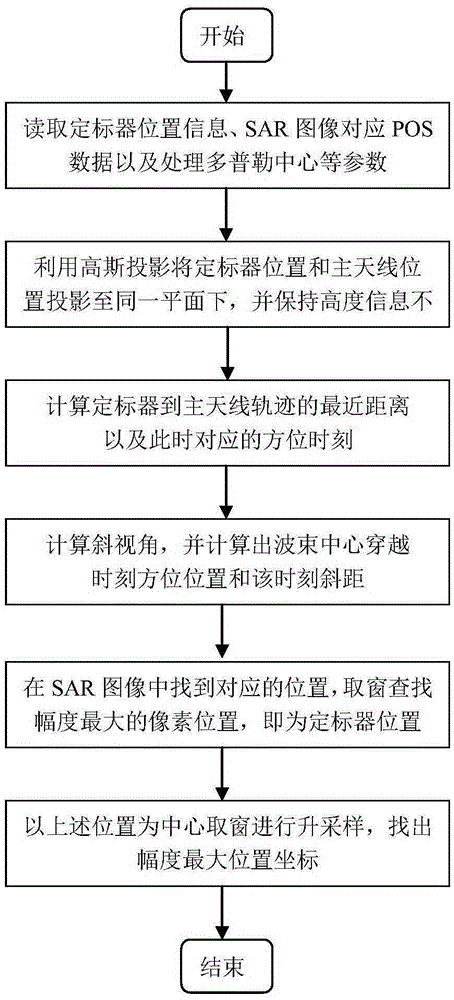
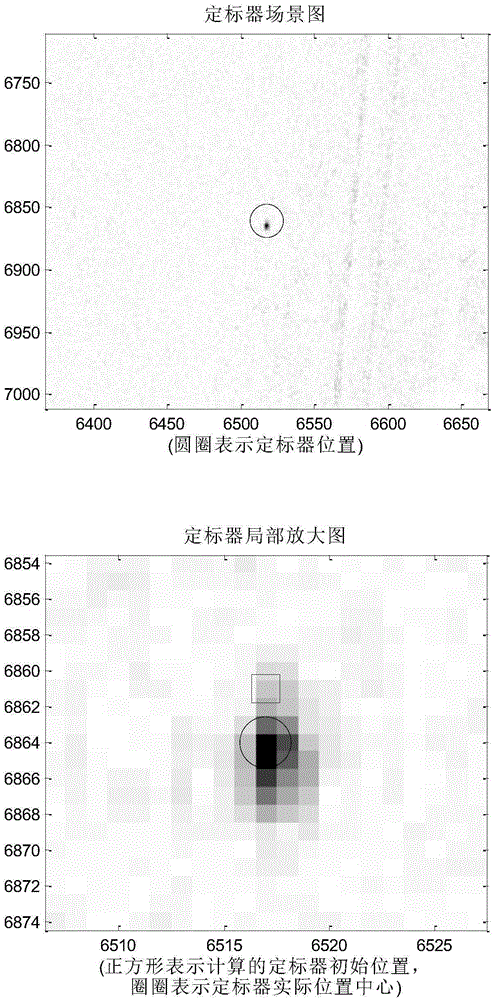
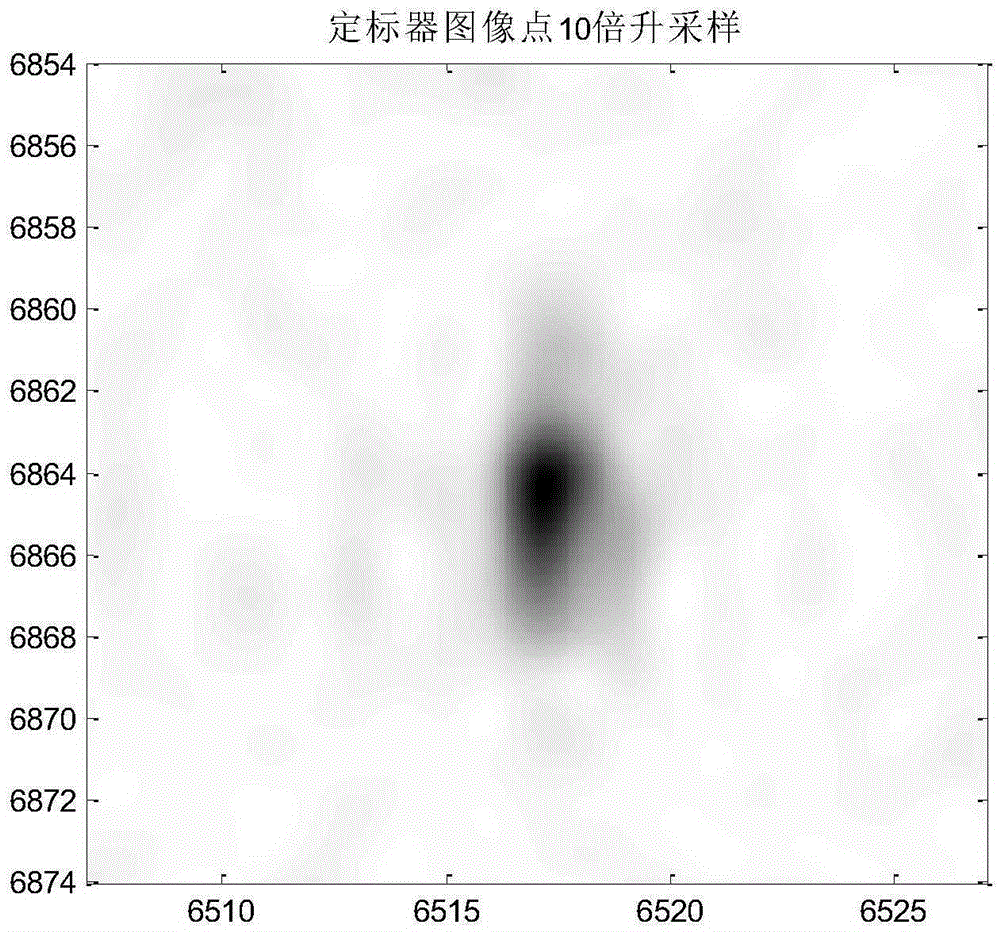
Automatic extraction method for airborne SAR scaler image position
ActiveCN105403886AFully automatedSave human effortRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImaging processingShortest distance
Disclosed in the invention is an automatic extraction method for an airborne SAR scaler image position. With the method, a scaler can be searched automatically in an SAR image rapidly and accurately; and the positioning precision is high. Position information of a scaler and an SAR main antenna as well as an SAR image processing Doppler central frequency is extracted; longitude and latitude information of the scaler and the SAR main antenna are projected to the same plane, and the height information is not changed; a shortest distance between the position of the scaler and the movement locus of the main antenna is calculated and a nearest slant range and a zero Doppler time are obtained; a slant range of the scaler at a wavebeam center passing-through time as well as an azimuth position of the main antenna at the wavebeam center passing-through time is determined based on strabismus geometry; the slant range and the azimuth positio are used as an initial distance position and an initial azimuth positio of the scaler in the SAR image; and then a searching window is taken by using the initial position as a center and the position of a pixel point with the highest intensity in the searching window is the position of the scaler in the SAR image.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and device for visual masking of defects in matrix displays by using characteristics of the human vision system
ActiveUS7714881B2Less visibleAvoid misinterpretationCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceHuman eye
The present invention provides a method for reducing the visual impact of defects present in a matrix display comprising a plurality of pixels, said pixels comprising at least three sub-pixels, each sub-pixel intended for generating a sub-pixel color which cannot be obtained by a linear combination of the sub-pixel colors of the other sub-pixels of the pixel, the method comprising: providing a representation of a human vision system, characterizing at least one defect sub-pixel present in the display, the defect sub-pixel intended for generating a first sub-pixel color, the defect sub-pixel being surrounded by a plurality of non-defective sub-pixels, deriving drive signals for at least some of the plurality of non-defective sub pixels in accordance with the representation of the human vision system and the characterizing of the at least one defect sub-pixel, to thereby minimize an expected response of the human vision system to the defect sub-pixel, and driving at least some of the plurality of non-defective sub-pixels with the derived drive signals, wherein minimizing the response of the human vision system to the defect sub-pixel comprises changing the light output value of at least one non-defective sub-pixel for generating another sub-pixel color, said another sub-pixel color differing from said first sub-pixel color. The present invention also provides a corresponding system for reducing the visual impact of defects present in a matrix display, and a matrix display with reduced visual impact of defects present in the display.
Owner:BARCO NV
Framing method and device for DL/T645 protocol message based on XML
ActiveCN110830466AAchieving a unified descriptionAvoid misinterpretationTransmissionComputer networkDatabase
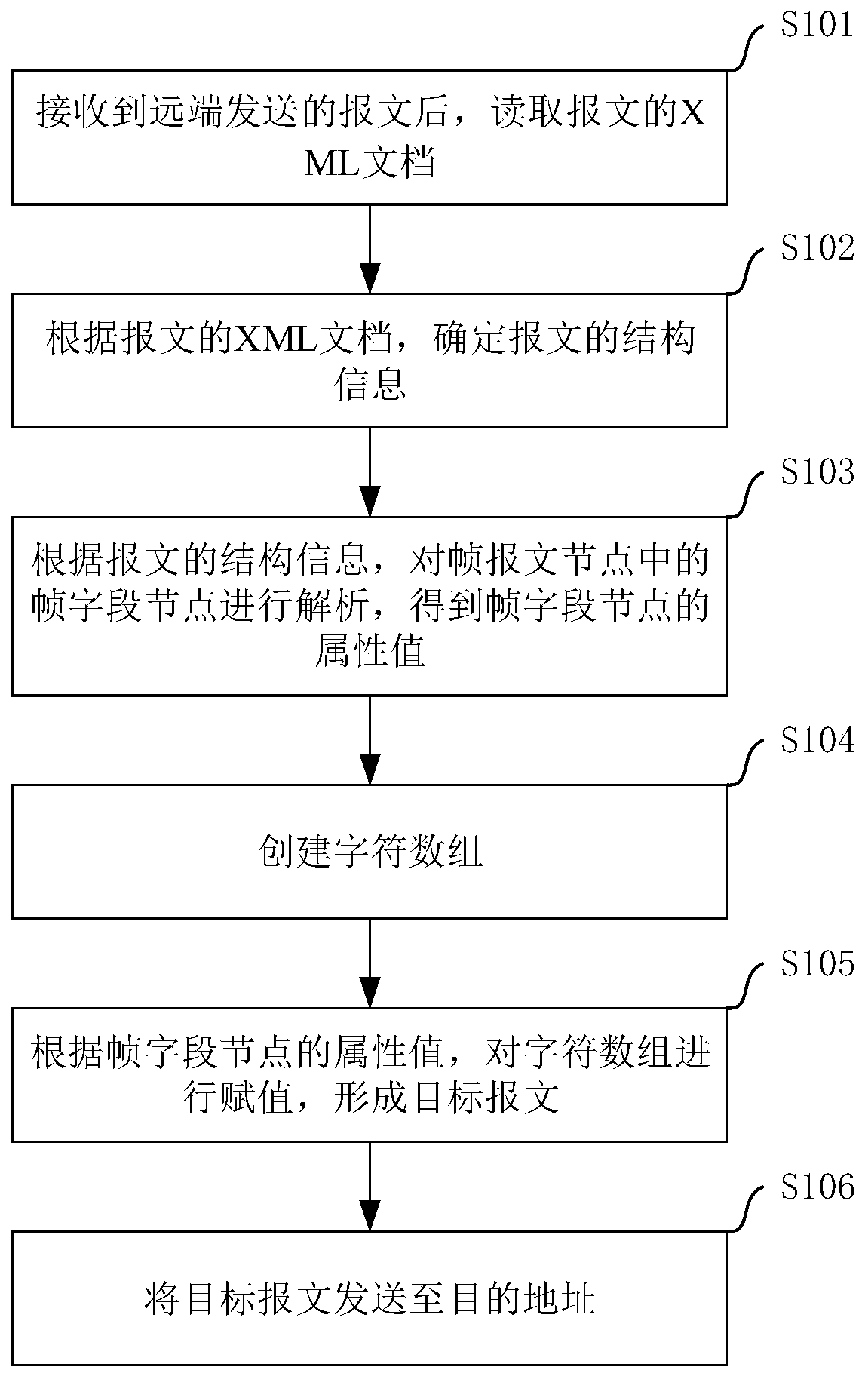
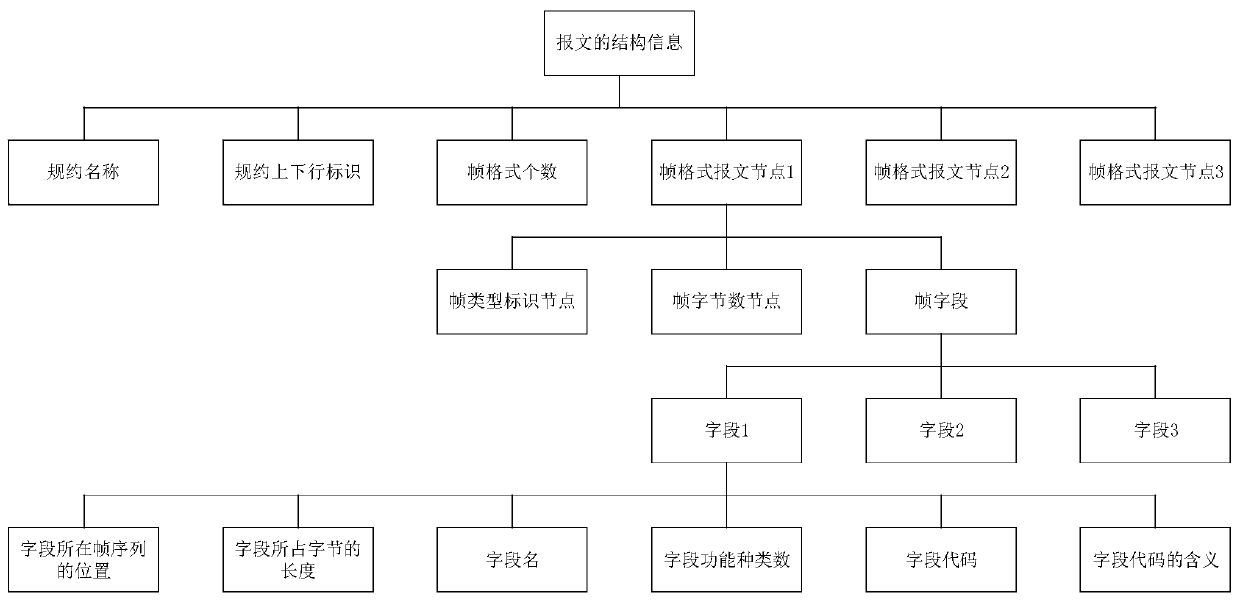
The invention provides a framing method and device for a DL / T645 protocol message based on XML. The method comprises the steps of reading an XML document of a message after the message sent by a far end is received, and determining structure information of the message according to the XML document of the message; analyzing a frame field node in the frame message node according to the structure information of the message to obtain an attribute value of the frame field node; and then creating a character array, assigning the character array according to the attribute value of the frame field node to form a target message, and sending the target message to a destination address. Thus, no matter whether the DL / T645 protocol message is self-defined by a manufacturer or not, the DL / T645 protocolmessage can be framed, so that the structure of the DL / T645 protocol message is described in a unified manner, and deviation of understanding of partial content of the DL / T645 protocol is avoided.
Owner:YUNNAN POWER GRID CO LTD ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
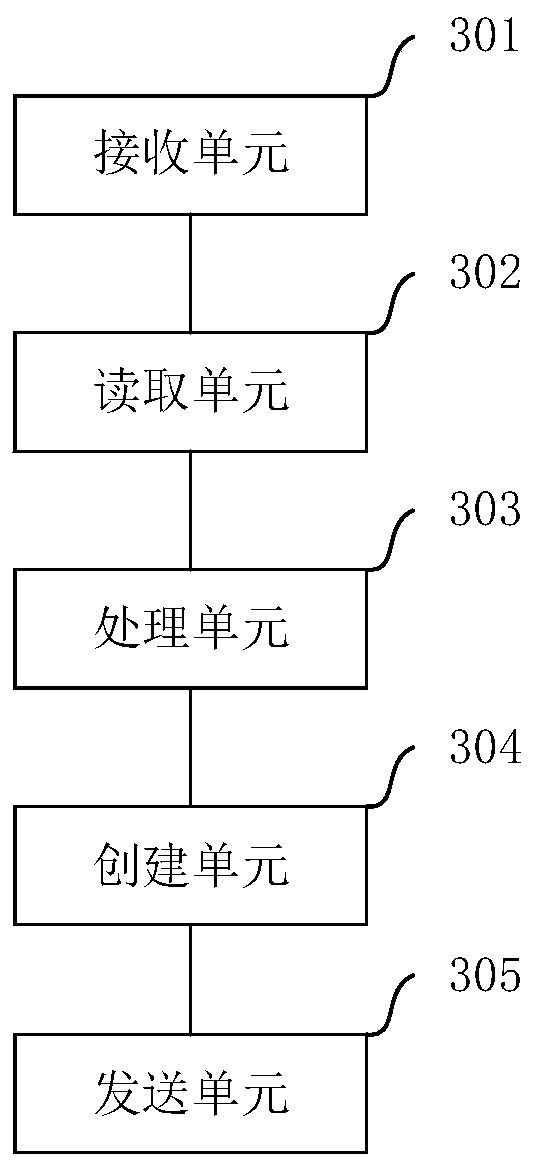
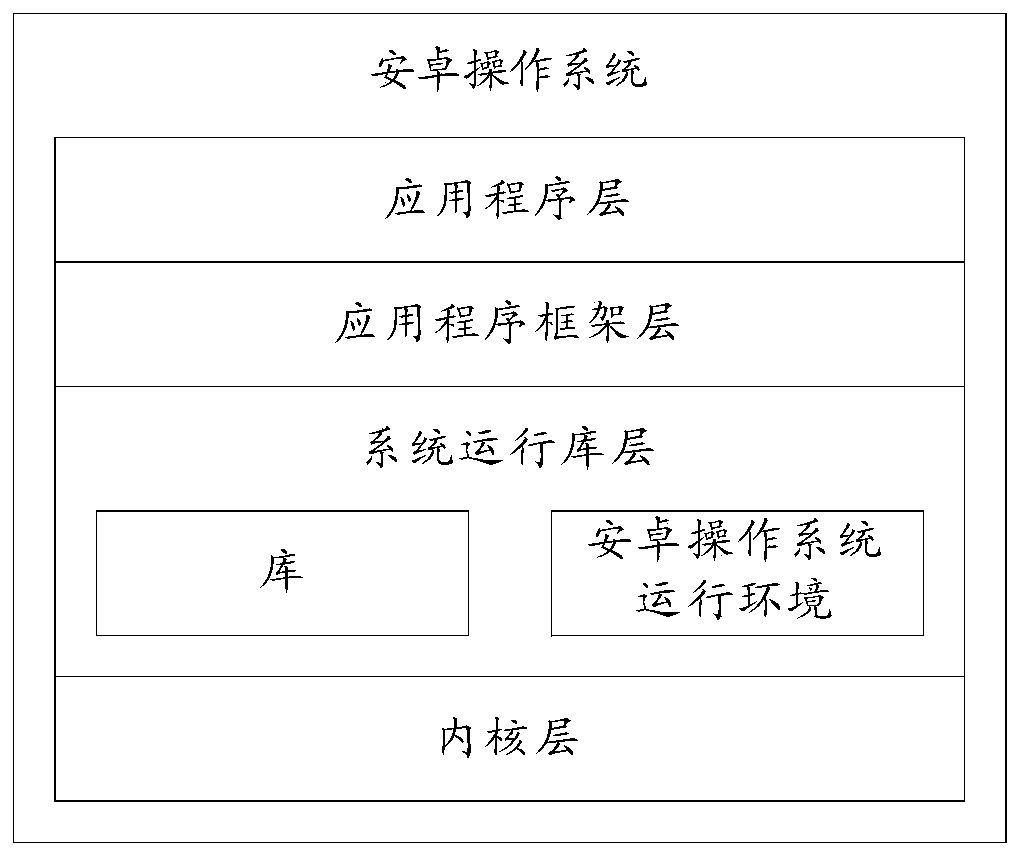
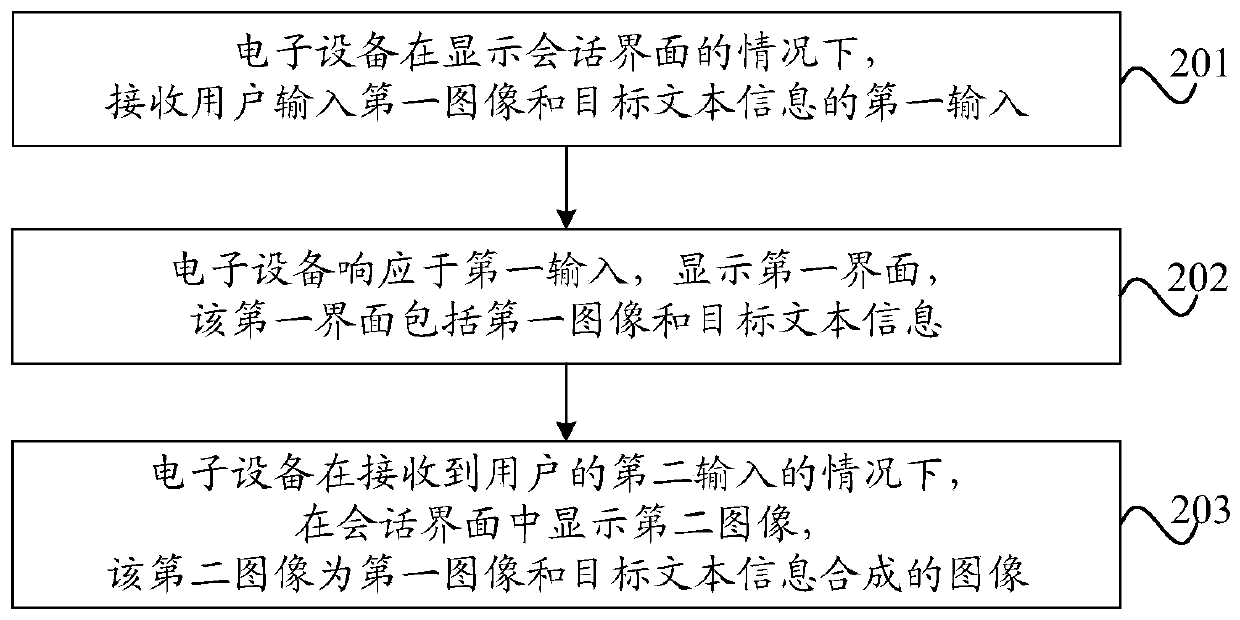
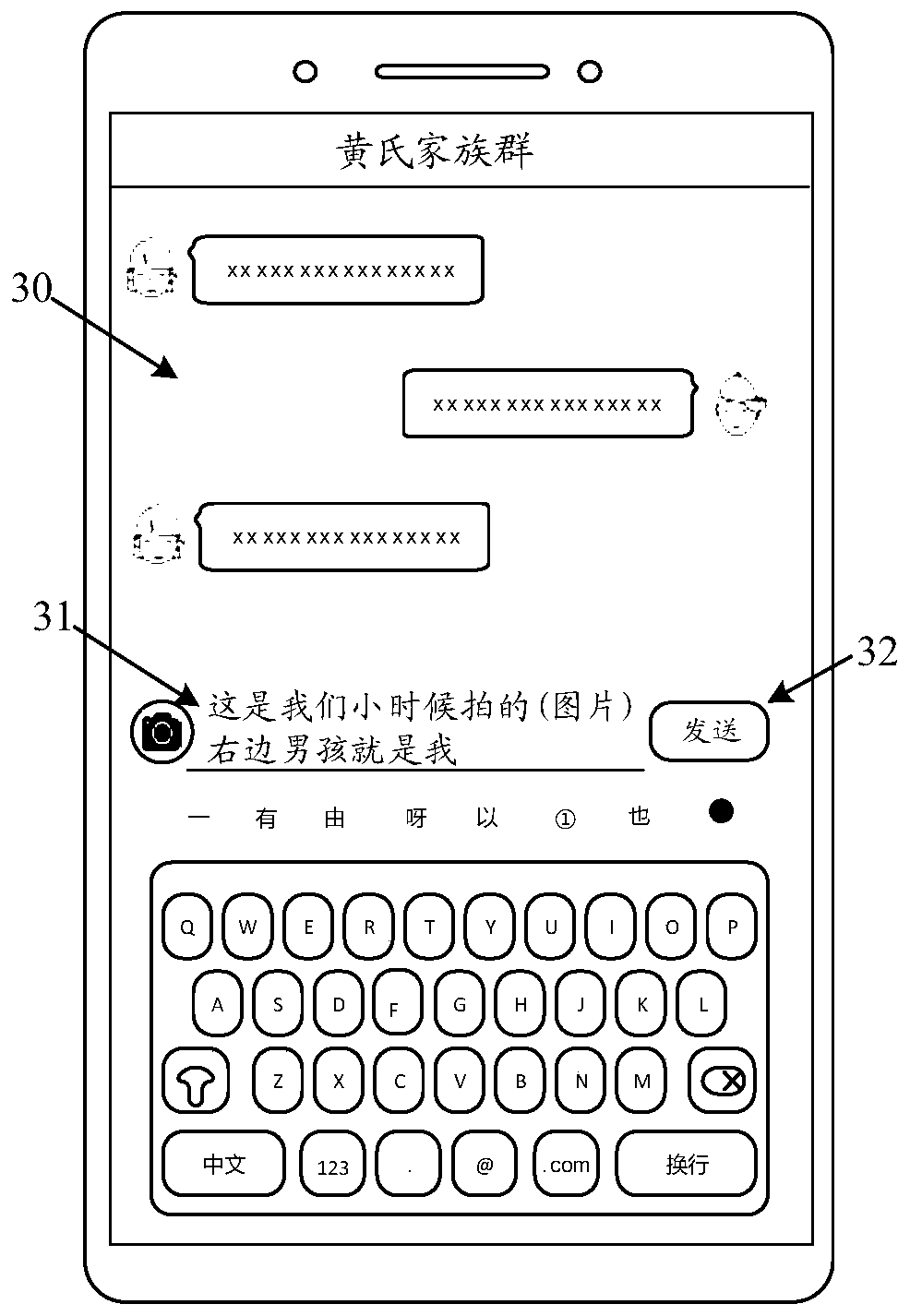
Information processing method and electronic equipment
PendingCN111158817AImprove experienceAvoid misinterpretationExecution for user interfacesData switching networksInformation processingEngineering
The embodiment of the invention provides an information processing method and electronic equipment, relates to the technical field of communication, and aims to solve the problem of poor message display effect of the existing electronic equipment in a chat interface. The method comprises the following steps: receiving a first input of inputting a first image and target text information by a user under the condition of displaying a session interface; displaying a first interface in response to the first input, the first interface comprising a first image and target text information; and under the condition of receiving a second input of the user, displaying a second image in the session interface, the second image being an image synthesized from the first image and the target text information. The method can be applied to the scene that the electronic equipment displays the graphic and text information in the session interface.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
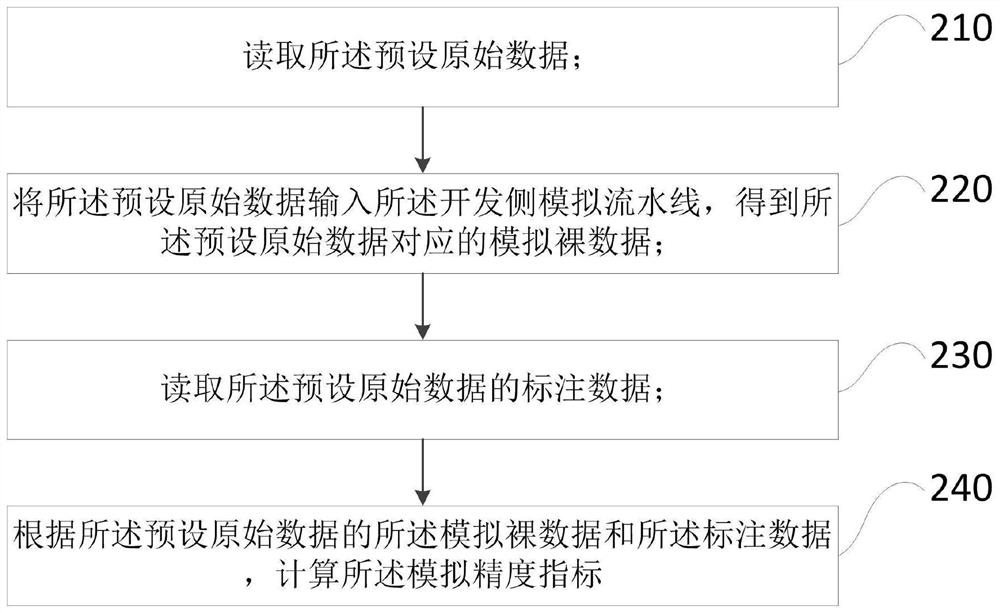
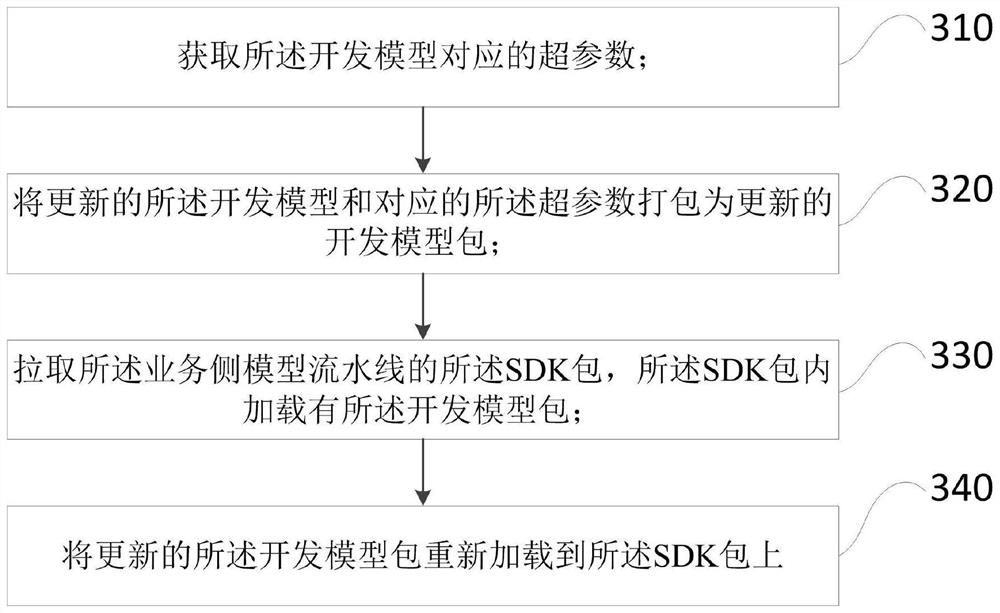
Embedded model SDK development method and development platform
ActiveCN112612472AAvoid misinterpretationReduce manual operationsSoftware testing/debuggingSoftware deploymentProgramming languageComputer engineering
The invention provides an embedded model SDK development method and development platform, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining simulation bare data and simulation precision indexes of preset original data according to an updated development side simulation assembly line after the updating of a development model is detected; pulling an SDK of a business side model assembly line to obtain model bare data and model precision indexes of the preset original data; carrying out bisecting; after detecting that the SDK code is updated, updating the SDK package and conducting a smoking test; and after a version fixing request is detected, carrying out full-quantity testing, and delivering after passing the full-quantity testing. Thus, for personnel of the two parties, understanding deviation does not exist in the aspect of understanding the assembly line on the side, and the link or the position of the problem is judged through the bare data in one-to-one correspondence; and besides, the development model of the new version can be directly tested each time, so that the problems are dispersed, and the personnel of the two parties can search the problems conveniently.
Owner:BEIJING KUANGSHI TECH
Message merging method and device, equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN110620846AImprove message display effectAvoid user understanding biasSubstation equipmentMessaging/mailboxes/announcementsDistributed computing
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
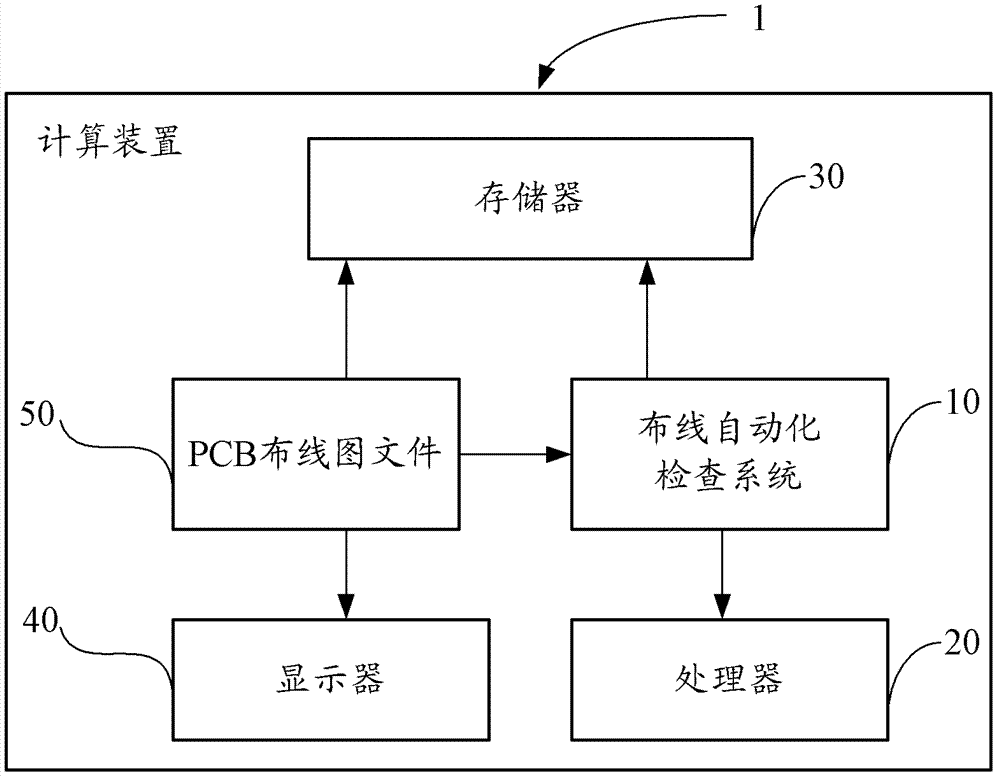
Wiring automatic check system and method
InactiveCN103116662AQuick filterPrecise screeningSpecial data processing applicationsWiring diagramComputer science
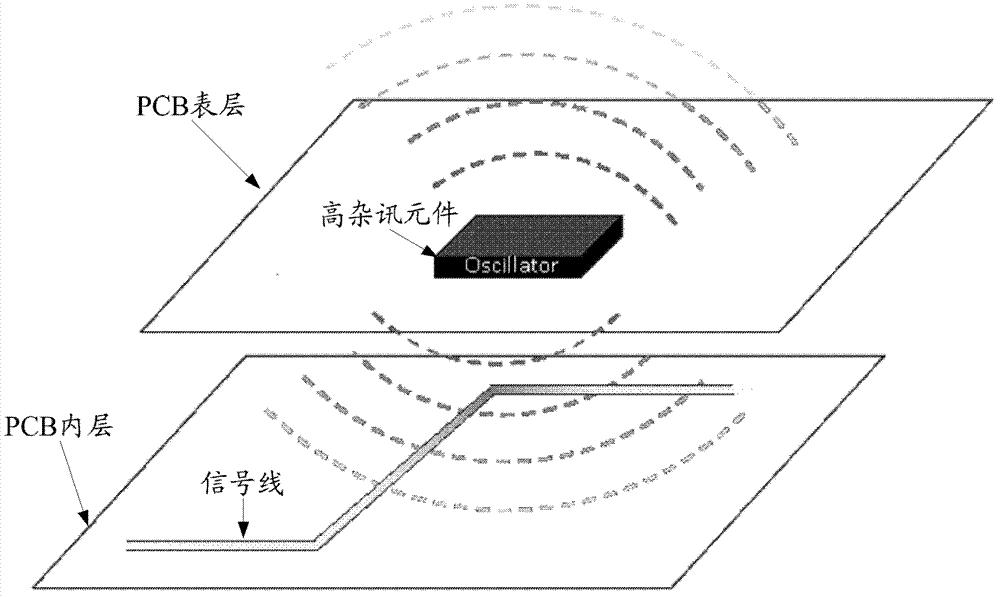
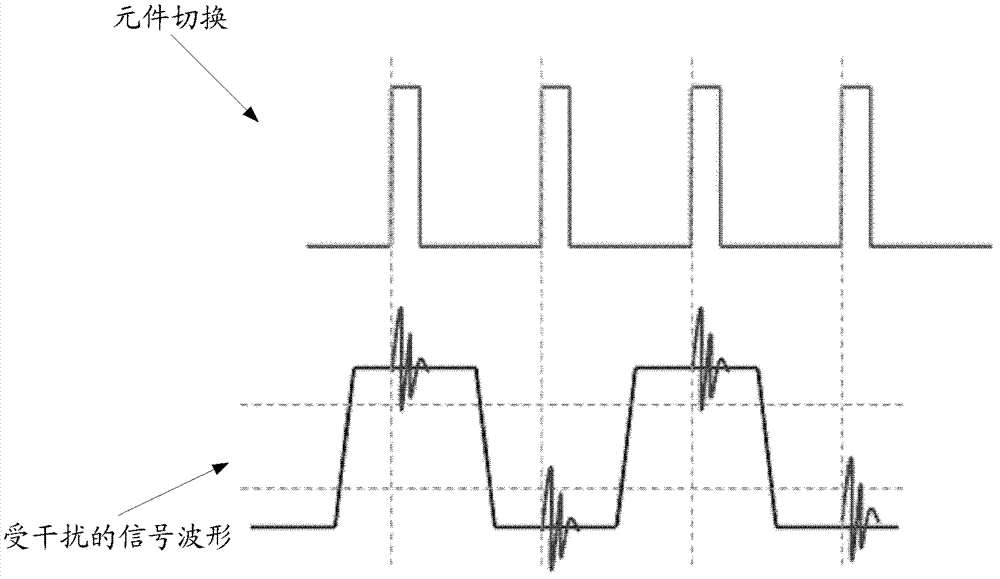
The invention provides a wiring automatic check system. The wiring automatic check system is applied to a calculation device. Component names are screened out from a printed circuit board (PCB) wiring diagram file through inputted keywords of names and are displayed in a first list. The periphery frame of the chosen components in the first list is calculated, according to the periphery frame and presupposed check range distance D, a search range is calculated. All signal lines which are in the PCB wiring diagram file and have intersection with the search range are searched. The fundamental information of the signal lines which have intersection with the search range is displayed in a second list. The invention further provides a wiring automatic check method. With the wiring automatic check system and the method, the signal lines which are disturbed by high noise components can be screened out quickly and accurately.
Owner:SCIENBIZIP CONSULTINGSHENZHENCO
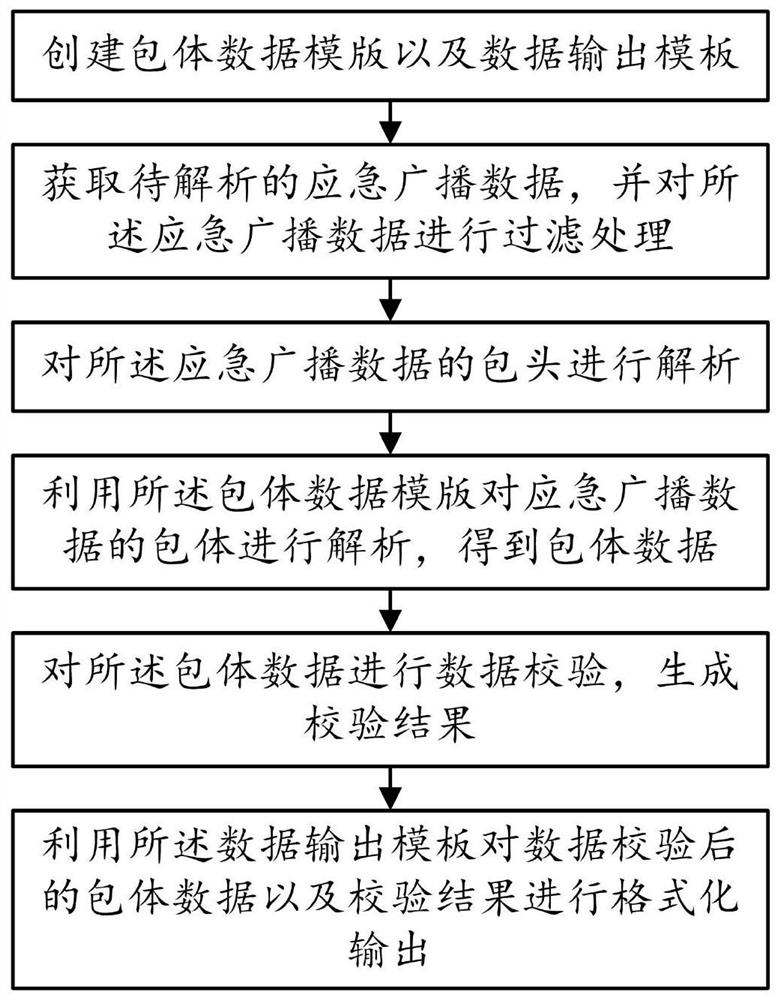
Emergency broadcast data analysis method
ActiveCN112235236AImprove analysis efficiencyImprove normativeSpecial service provision for substationUser identity/authority verificationComputer networkSource Data Verification
The invention provides an emergency broadcast data analysis method in the technical field of emergency broadcast. The emergency broadcast data analysis method comprises the following steps: S10, creating a packet body data template and a data output template; S20, acquiring emergency broadcast data to be analyzed, and filtering the emergency broadcast data; S30, analyzing a packet header of the emergency broadcast data; S40, analyzing the packet body of the emergency broadcast data by using the packet body data template to obtain packet body data; S50, performing data verification on the packet body data to generate a verification result; S60, performing formatted output on the packet body data after data verification and a verification result by utilizing the data output template. The method has the advantage that the standardization and readability of emergency broadcast data analysis are greatly improved.
Owner:FUJIAN NEWLAND COMM SCI TECH
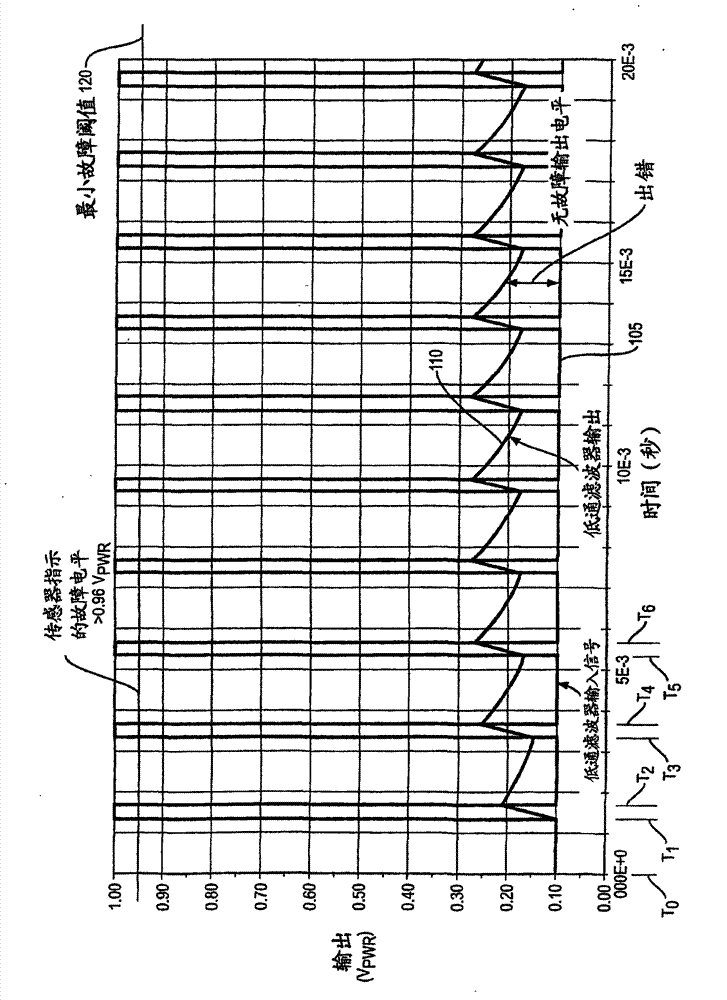
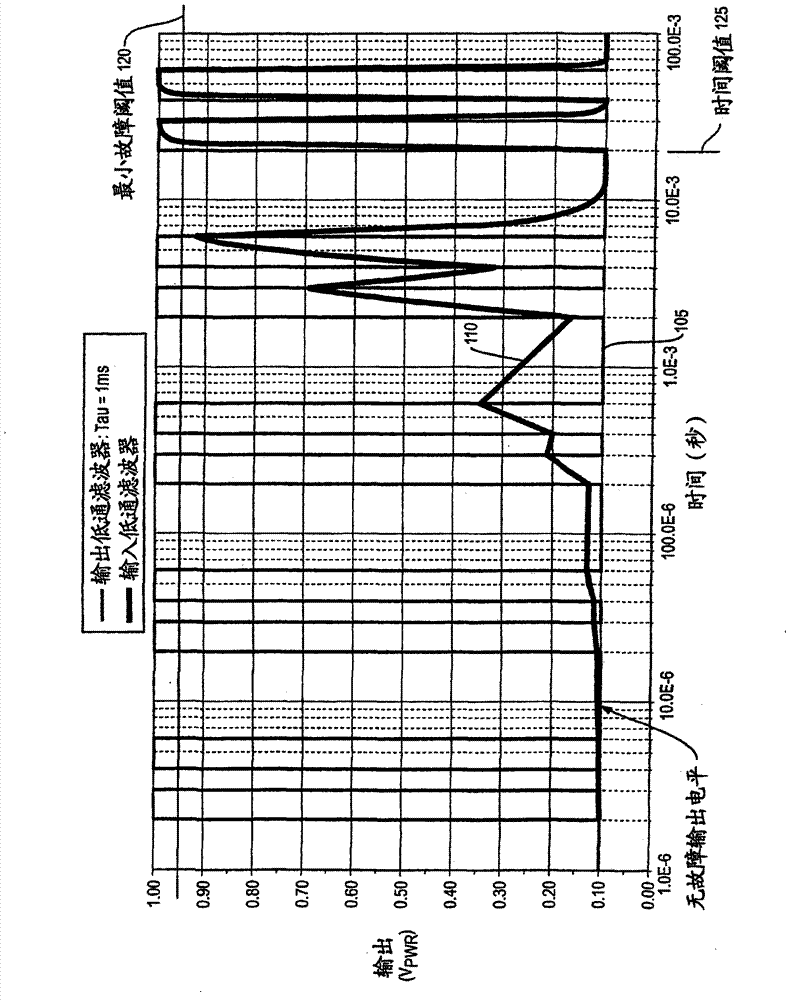
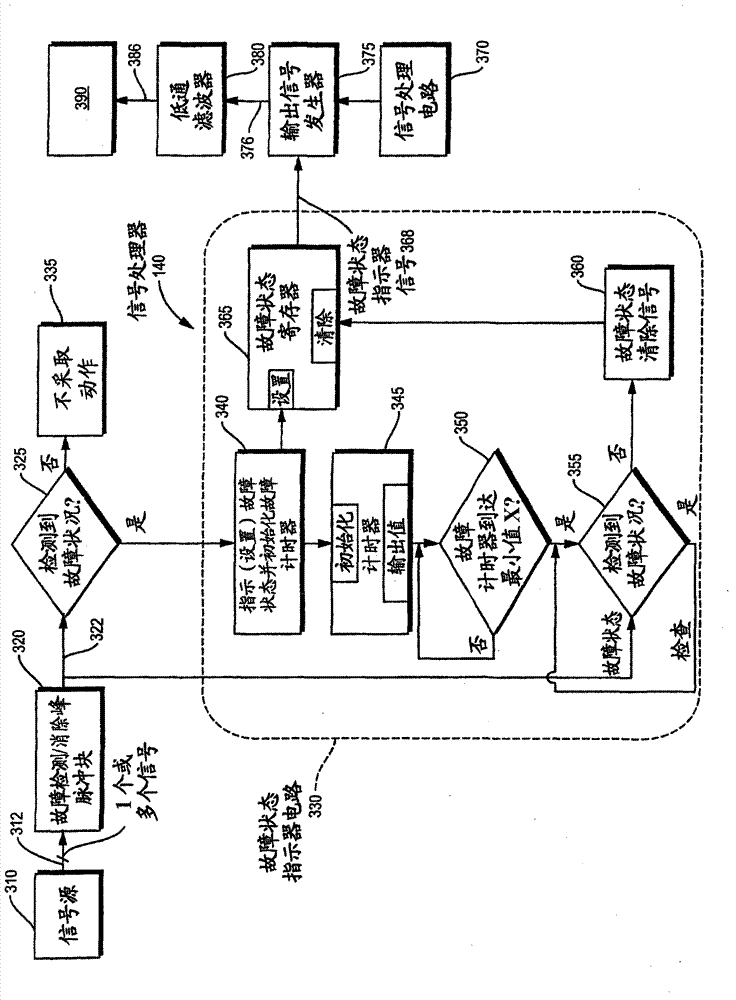
Signal processing during fault conditions
InactiveCN103017810AAvoid misinterpretationFluid pressure measurementProvision for safeguarding apparatusFault indicatorEngineering
The invention relates to signal processing during fault conditions. A system is configured to monitor a received signal. In response to detecting a fault condition associated with the received signal, the system sets a fault status indicator to indicate occurrence of the detected fault condition. The system sets a state of the fault status indicator for at least a predetermined amount of time to indicate occurrence of the detected fault condition. Subsequent to setting the fault status indicator for at least the predetermined amount of time to indicate the occurrence of the detected fault condition, the system monitors integrity of the signal again. After the predetermined amount of time, in response to detecting that there is no longer a fault associated with the monitored signal, the system modifies the fault status indicator to indicate absence of the fault condition.
Owner:SENSATA TECHNOLOGIES INC
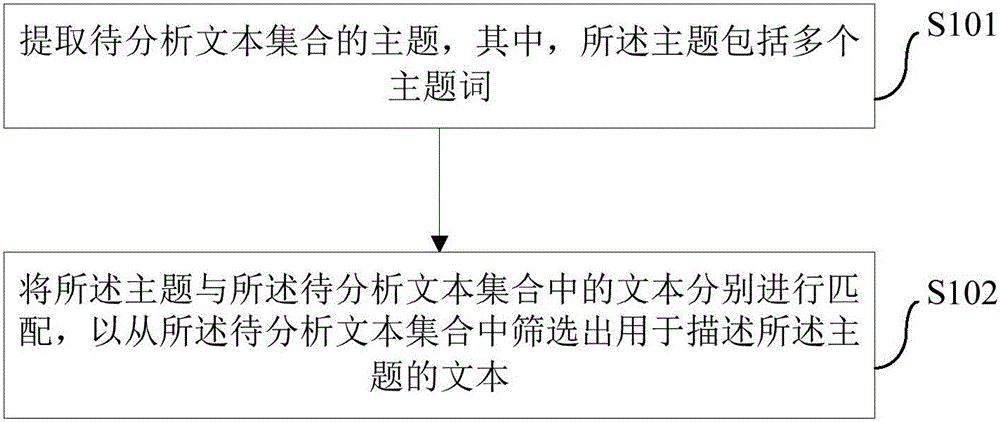
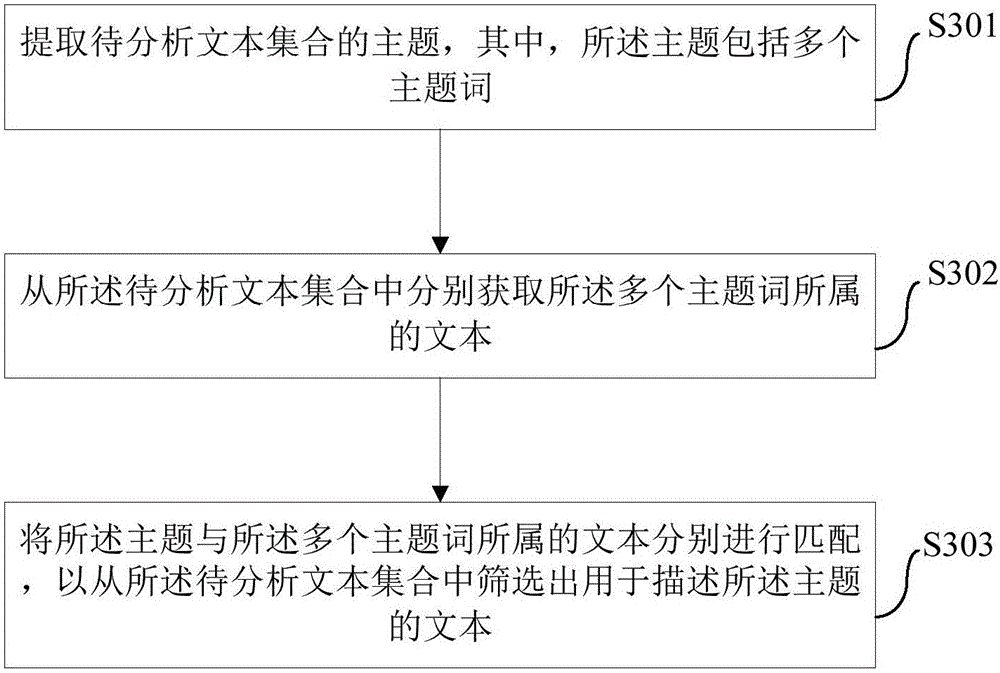
Method and device for acquiring theme information and electronic equipment
ActiveCN106202050AAvoid misinterpretationImprove acquisition efficiency and accuracySemantic analysisSpecial data processing applicationsInformation retrievalData science
The invention provides a method and a device for acquiring theme information and electronic equipment. The method includes: extracting a theme a text set to be analyzed, wherein the theme includes multiple keywords; respectively matching the theme with tests in the text set to be analyzed to screen out the text used for describing the theme from the text set to be analyzed. With the method for acquiring the theme information, acquisition efficiency and accuracy of the theme information can be improved.
Owner:NEUSOFT CORP
Hydropower station equipment fault remote diagnosis system and method
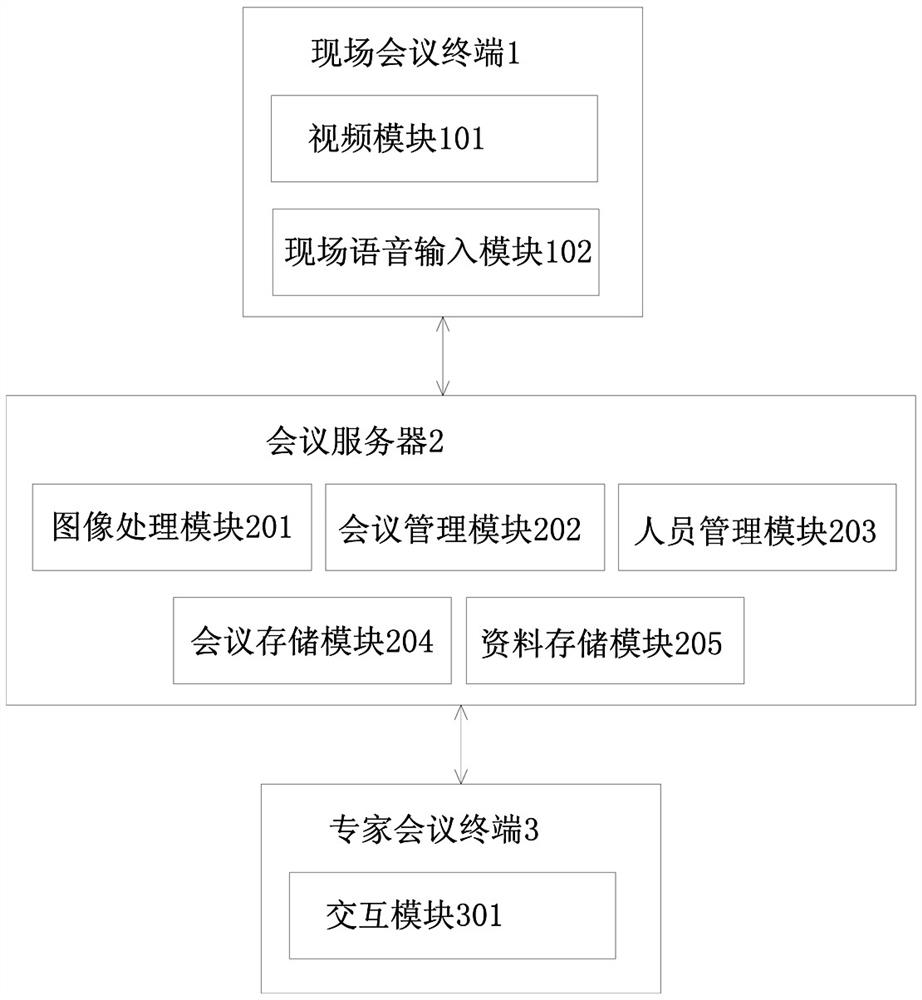
PendingCN111683219AReduce troubleshooting timeImprove troubleshooting efficiencyTelevision conference systemsDetails involving 3D image dataImaging processingImage manipulation
The invention relates to a hydropower station equipment fault remote diagnosis system and method. The invention aims to provide an accurate and efficient hydropower station equipment fault remote diagnosis system and method. According to the technical scheme, the system comprises a field conference terminal, a conference server and a plurality of expert conference terminals, the field conference terminal is in communication connection with the conference server, and the conference server is in communication connection with the expert conference terminals; the on-site conference terminal is provided with a video module and an on-site voice input module; the conference server is provided with an image processing module and a conference management module; the expert conference terminal is provided with an interaction module. The system and the method are suitable for the hydropower station equipment fault diagnosis field.
Owner:POWERCHINA HUADONG ENG COPORATION LTD
Two-stage lightning current withstanding fusing structure and fuse adopting same
PendingCN110047718AReduce false positivesAvoid misinterpretationEmergency protective devicesElectrical conductorSecondary stage
The invention discloses a two-stage lightning current withstanding fusing structure, which is arranged in a fuse, is used for fusing to protect the circuit when the current exceeds a rated value, andcomprises a first-stage conductor connected with an electrode and a second-stage conductor connected with the other electrode, and the first-stage conductor is connected with the second-stage conductor in series; the melting point of the first-stage conductor is higher than that of the second-stage conductor, and the first-stage conductor is electrified and heated and is transmitted to the second-stage conductor, and when the temperature is higher than that of the second-stage conductor, the second-stage conductor is fused and disconnected. The fuse wire temperature diffusion technology, the fuse wire material step combination technology and the fuse wire inductance step offset technology are used, and the characteristics that the fusing structure can withstand large lightning current impact without fusing and the fusing structure can be fused under small power frequency current are achieved.
Owner:XIAMEN TAIHANG TECH
electrical connector
The invention provides a technology for solving a problem that an electric connector having a locking mechanism unlocks accidentally because of vibration and surge. The connector comprises a locking unit (103) for preventing the electric connector from detaching when being fitted with a side connector of an opposite side. The locking unit (103) possess a first snap part (104) snapping with a part of the side connector of the opposite side when the electric connector is fitted with the side connector of an opposite side, a main body part (105) for connecting with the first snap part (104), a first operation part (106) for connecting with the main body part (105) and performing position switch on the first snap part (104). Furthermore, a first position limitation member (107 ) (double lock) for the position that the first operation part switch to which can be selectively moved to a limited part or an unlimited part, and the limitation member (triple lock)for the position of the first position limitation part which can be selectively moved to a limited part or an unlimited part are comprised. In virtue of above arrangement, the electric connector can prevent fault unlocking.
Owner:HIROSE ELECTRIC GROUP
Test piece and manufacturing method thereof
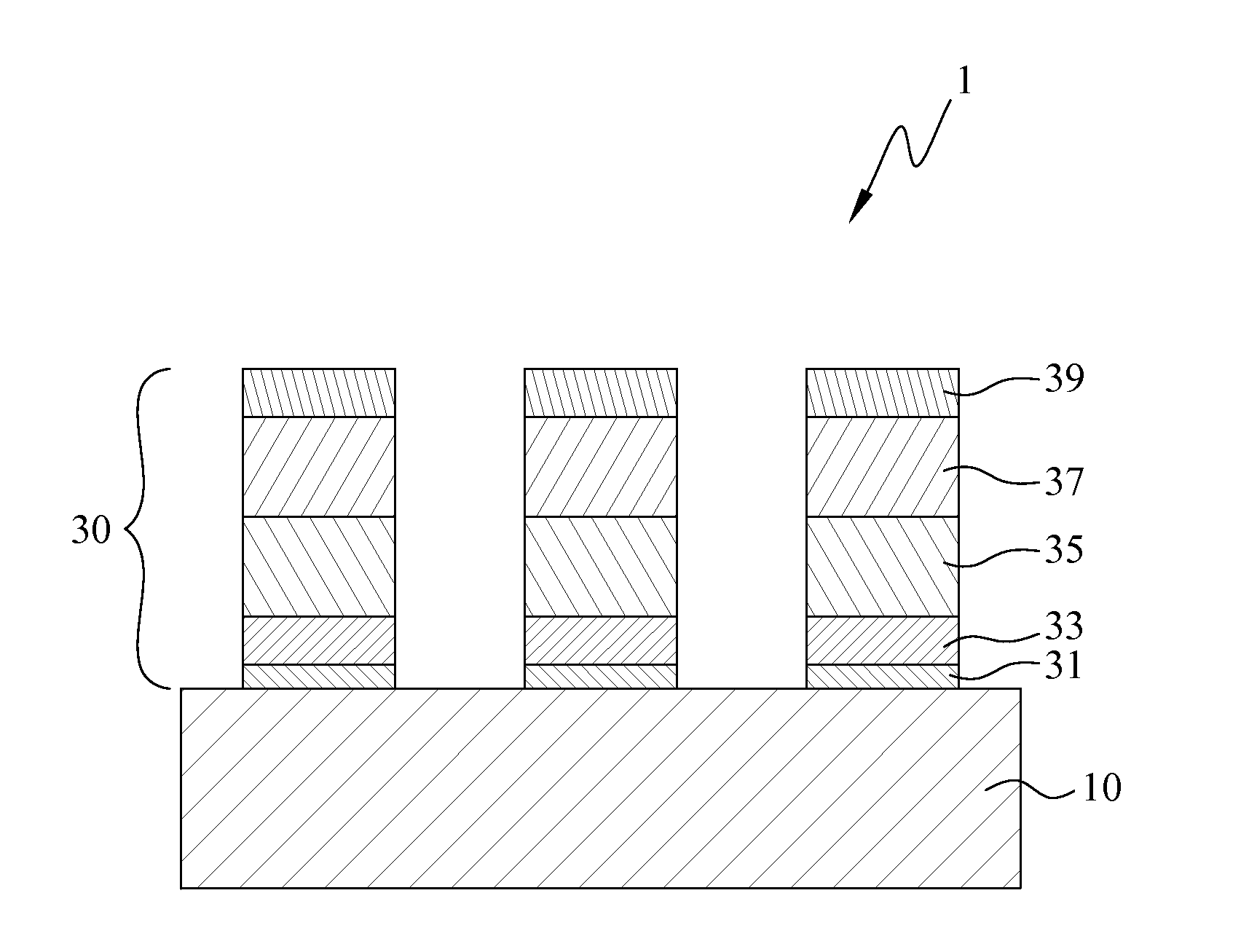
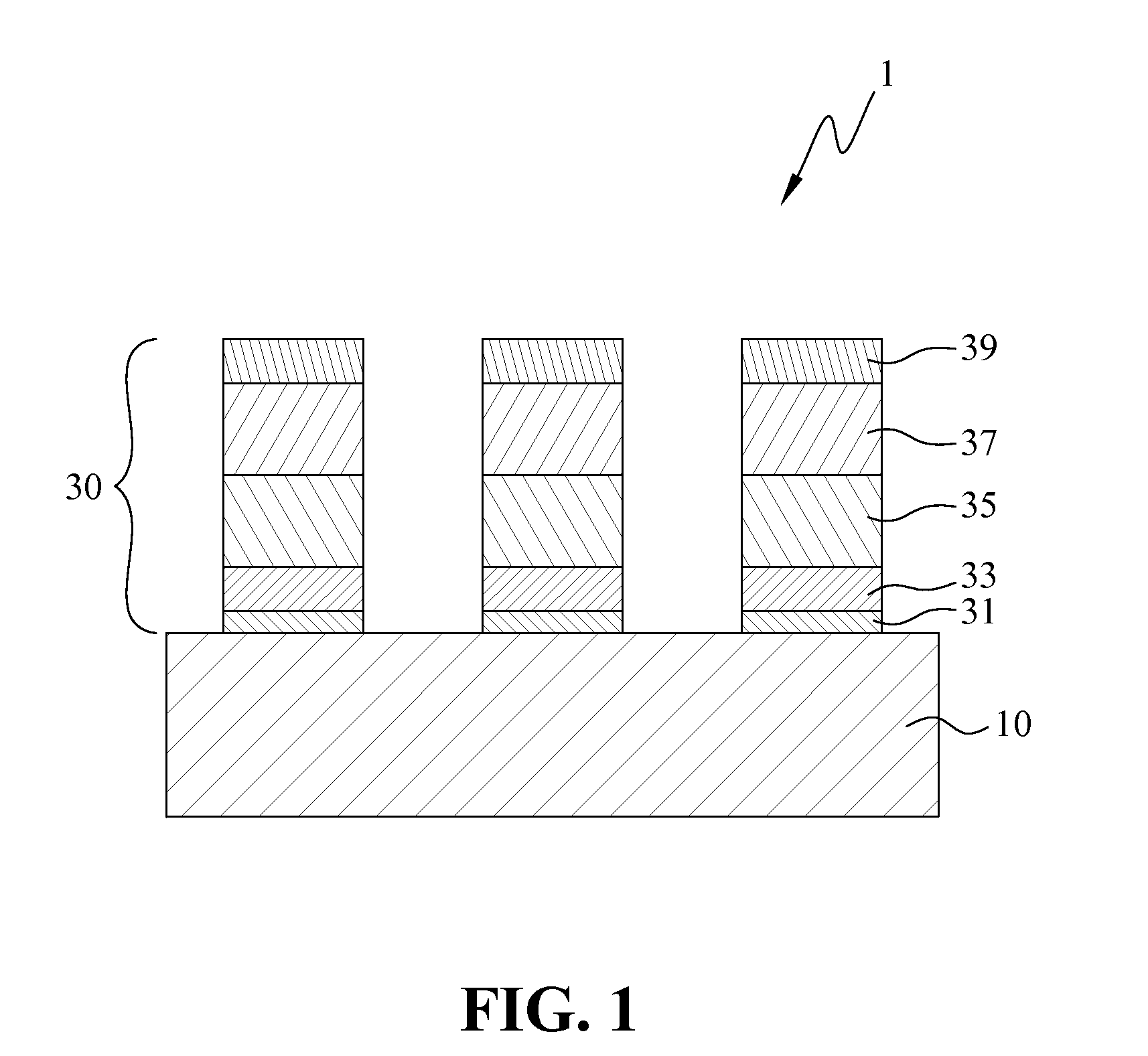
InactiveUS20130240255A1Good film uniformityLower resistancePrinted electric component incorporationPrinted circuit aspectsTest efficiencyPower flow
Disclosed are a test piece and the manufacturing method thereof The test piece includes an insulating substrate and a circuit pattern structure formed on the insulating substrate, wherein circuit pattern structure includes a first metal pattern layer, a second metal pattern layer, a third metal pattern layer, a fourth metal pattern layer, and a fifth metal pattern layer. The first metal pattern layer, the second metal pattern layer, the third metal pattern layer, the fourth metal pattern layer, and the fifth metal pattern layer have same pattern shapes and positions thereof are overlapping in a plane. The first metal pattern layer and the second metal pattern layer are nano-metal films formed by vacuum coating, therefore, the test piece has excellent uniformity of film and low resistance to provide a stable test current to prevent the judging mistakes and to improve the test efficiency.
Owner:CHIANG HUI PING +2
Underground total field magnetic measurement device and temperature drift suppression method
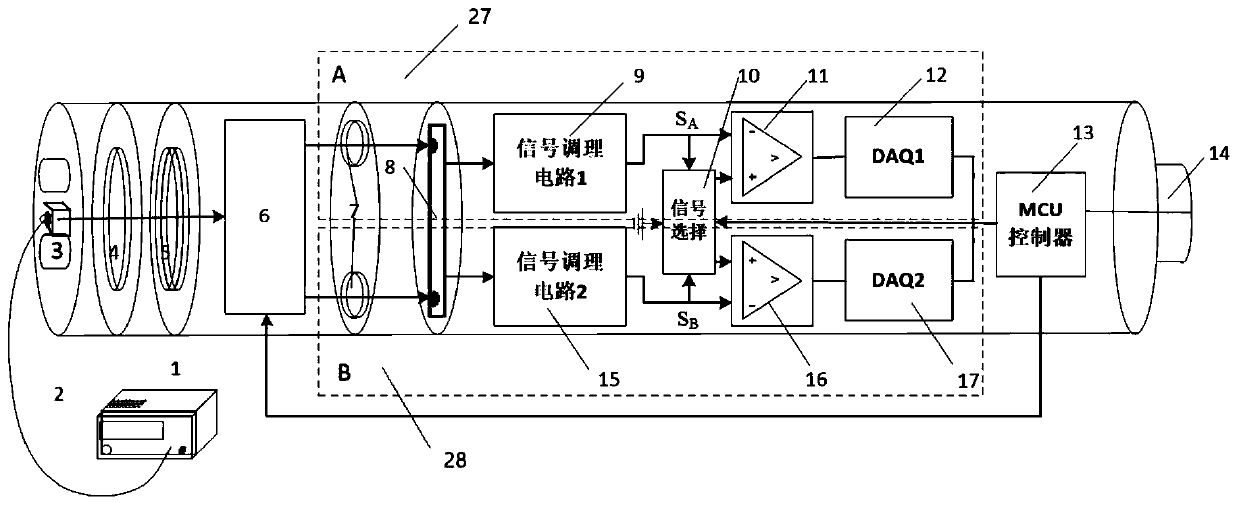
ActiveCN111538072AExtended service lifeSolve the problem of blind spotsEarthquake measurementSeismologyMagnetic measurementsGlass chip
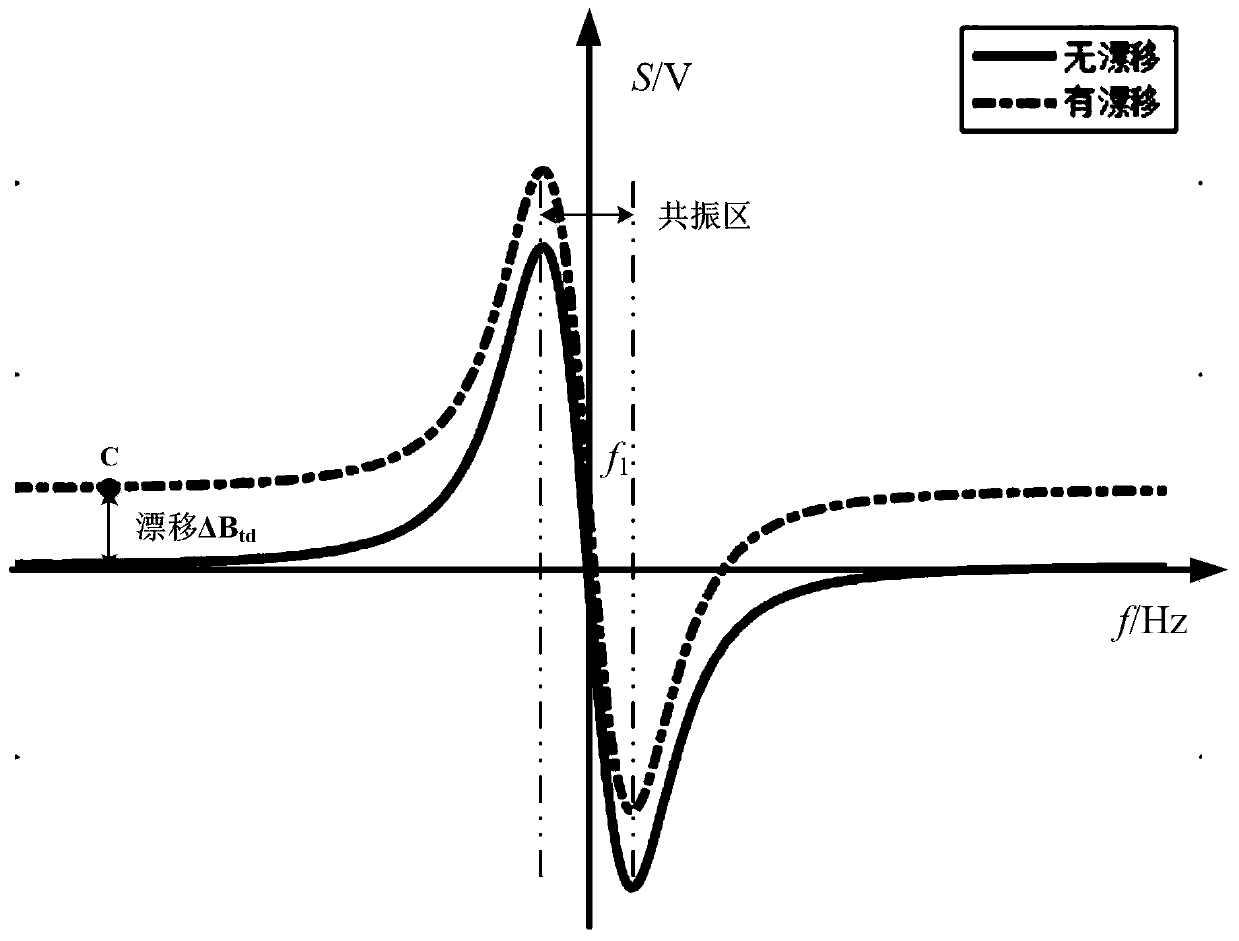
The invention provides an underground total field magnetic measurement device and a temperature drift suppression method. An omnidirectional structure fixed double-air-chamber and accessory device isarranged behind a glass sheet assembly; a laser is connected with an optical fiber coupling head through an optical fiber; incident light sequentially passes through a polarizing film, the glass sheetassembly and the omnidirectional structure fixed double-air-chamber and accessory device ; and the omnidirectional structure fixed double-air-chamber and accessory device is connected with an MCU controller through the photoelectric signal processing A and the photoelectric signal processing B. The service life of an instrument can be prolonged, magnetic measurement parameters are increased, a magnetic measurement blind area is avoided, and magnetic measurement data temperature drift can be inhibited.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
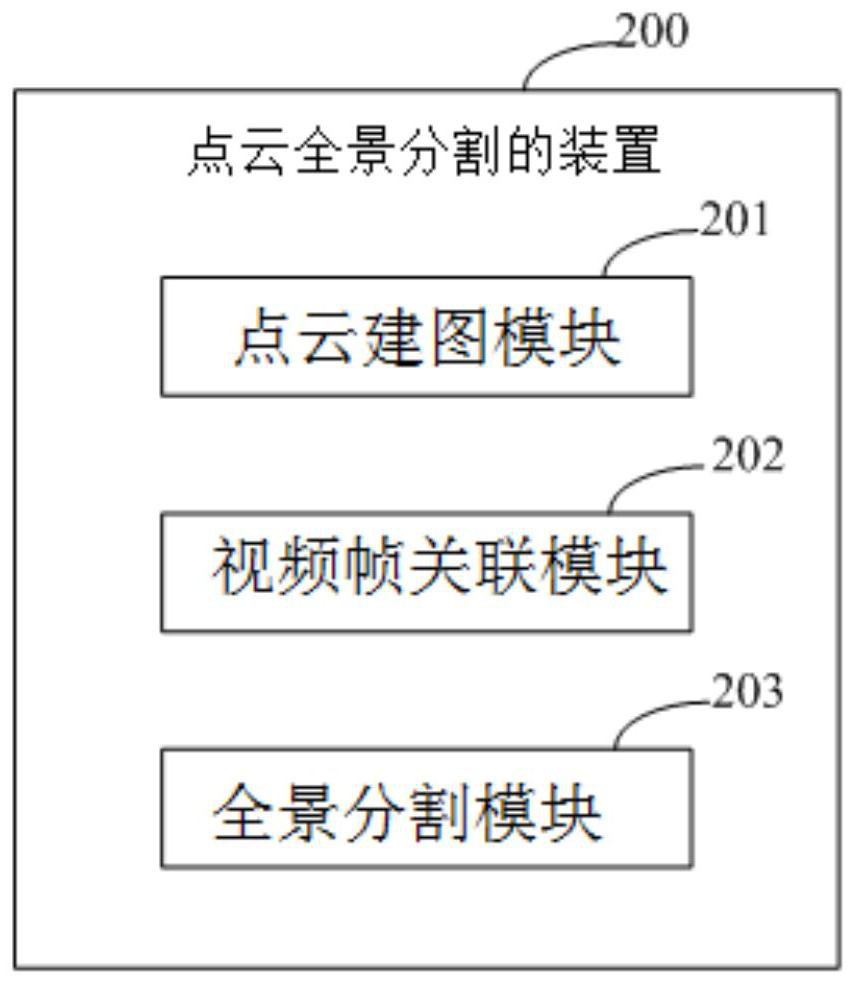
Point cloud panoramic segmentation method and device
PendingCN113379748ASpatiotemporal consistencyAvoid misinterpretationImage enhancementImage analysisInertial navigation systemComputer graphics (images)
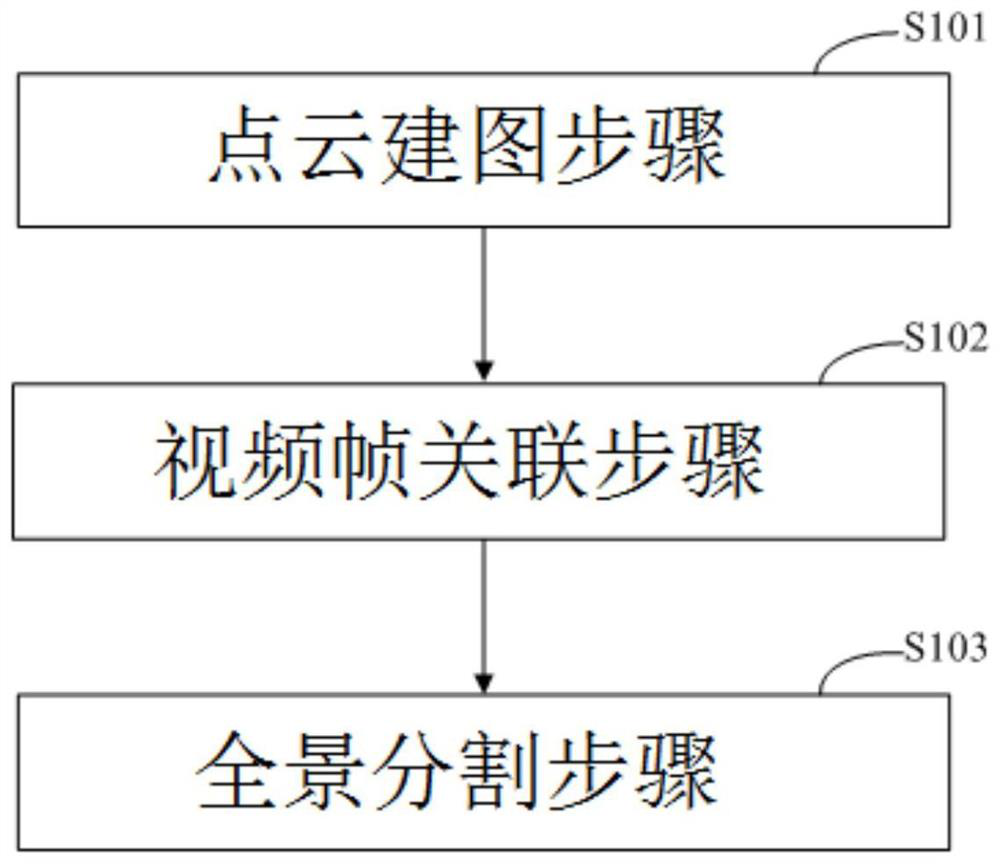
The invention provides a point cloud panoramic segmentation method and device. The method comprises the steps: a point cloud mapping step: projecting a collected point cloud to a world coordinate system, so as to obtain a mapping point cloud; and a video frame association step: projecting each point cloud point in the mapping point cloud to a projectable video frame, and a panoramic segmentation step: carrying out panoramic segmentation on the projectable video frame so as to carry out unified numbering on the semantic recognition probability of each point cloud point. The invention provides a point cloud panorama segmentation method with time-space consistency while mapping by means of a laser radar, a camera and / or a combined inertial navigation system, and provides a point cloud panorama segmentation method with time-space consistency.
Owner:BEIJING JINGDONG QIANSHITECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Method for operating a wireless sensor network, and sensor node
InactiveCN101978402AAvoid misinterpretationInterference free communicationPower managementMeasurement devicesWireless mesh networkWireless sensor networking
The invention relates to a method for operating a wireless sensor network (1) having a plurality of sensor nodes (2-4) which are suitably set up for data transmission by means of non-directional radio transmission, in which a selection set containing at least one sensor node (2) can be selectively changed from a first operating state to a second operating state by means of a spatially delimited first operating state control signal (17), wherein the sensor nodes (2-4) cannot receive or at least cannot process control data by means of non-directional radio transmission in the first operating state and can receive and process control data by means of non-directional radio transmission in the second operating state. The invention also relates to a sensor node which is suitably set up to carry out the method.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
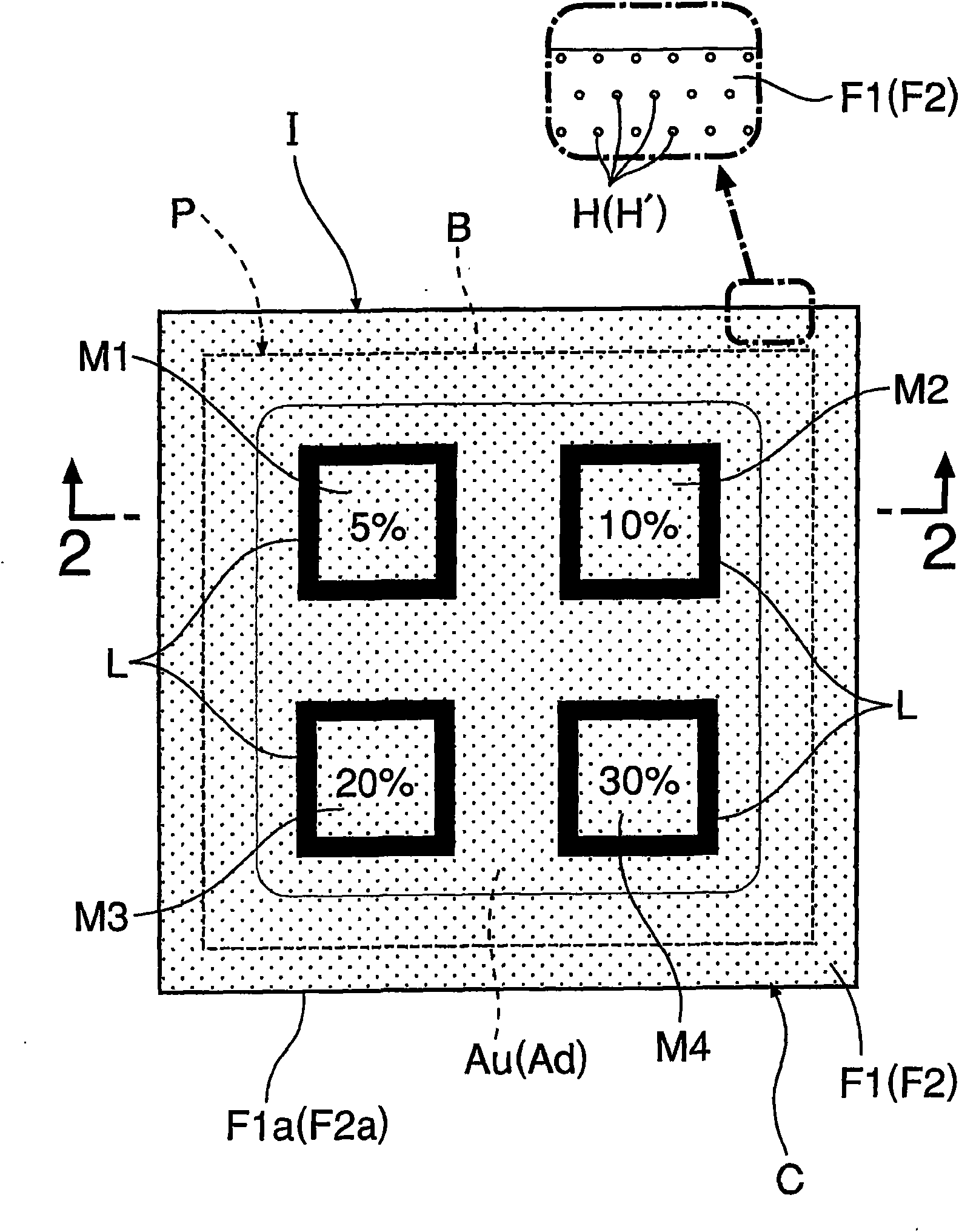
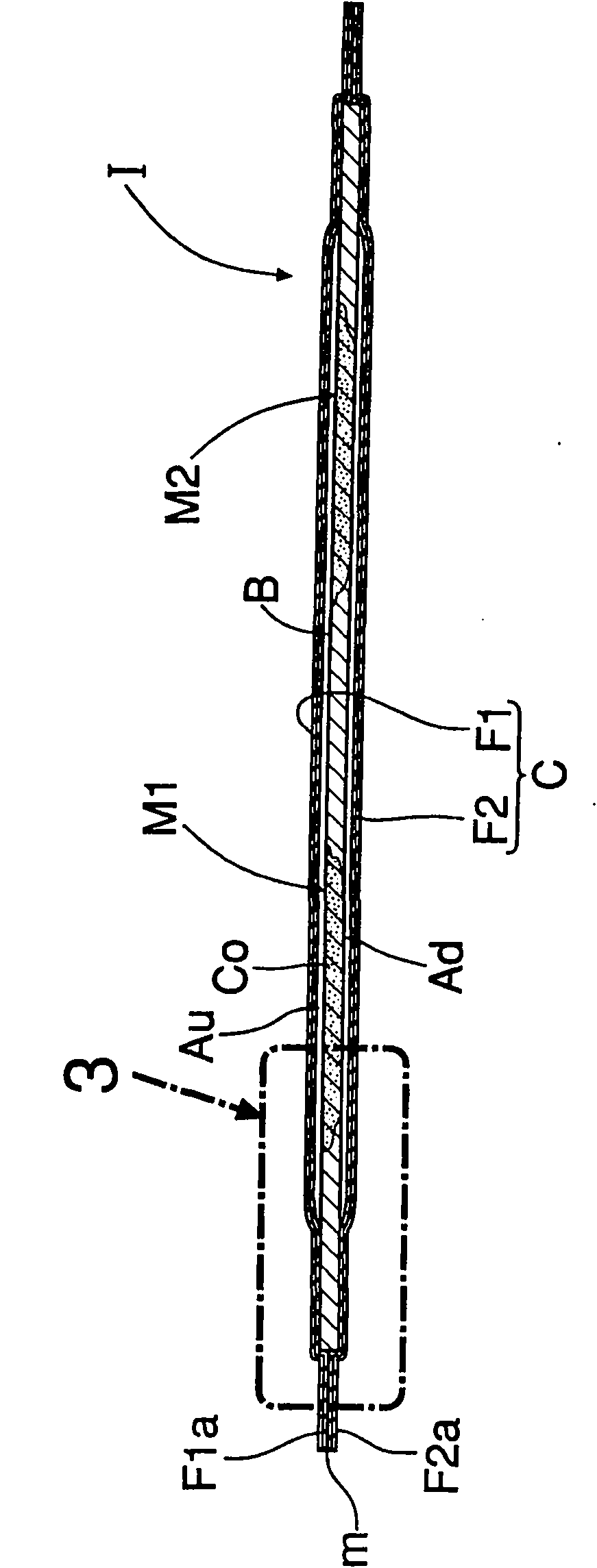
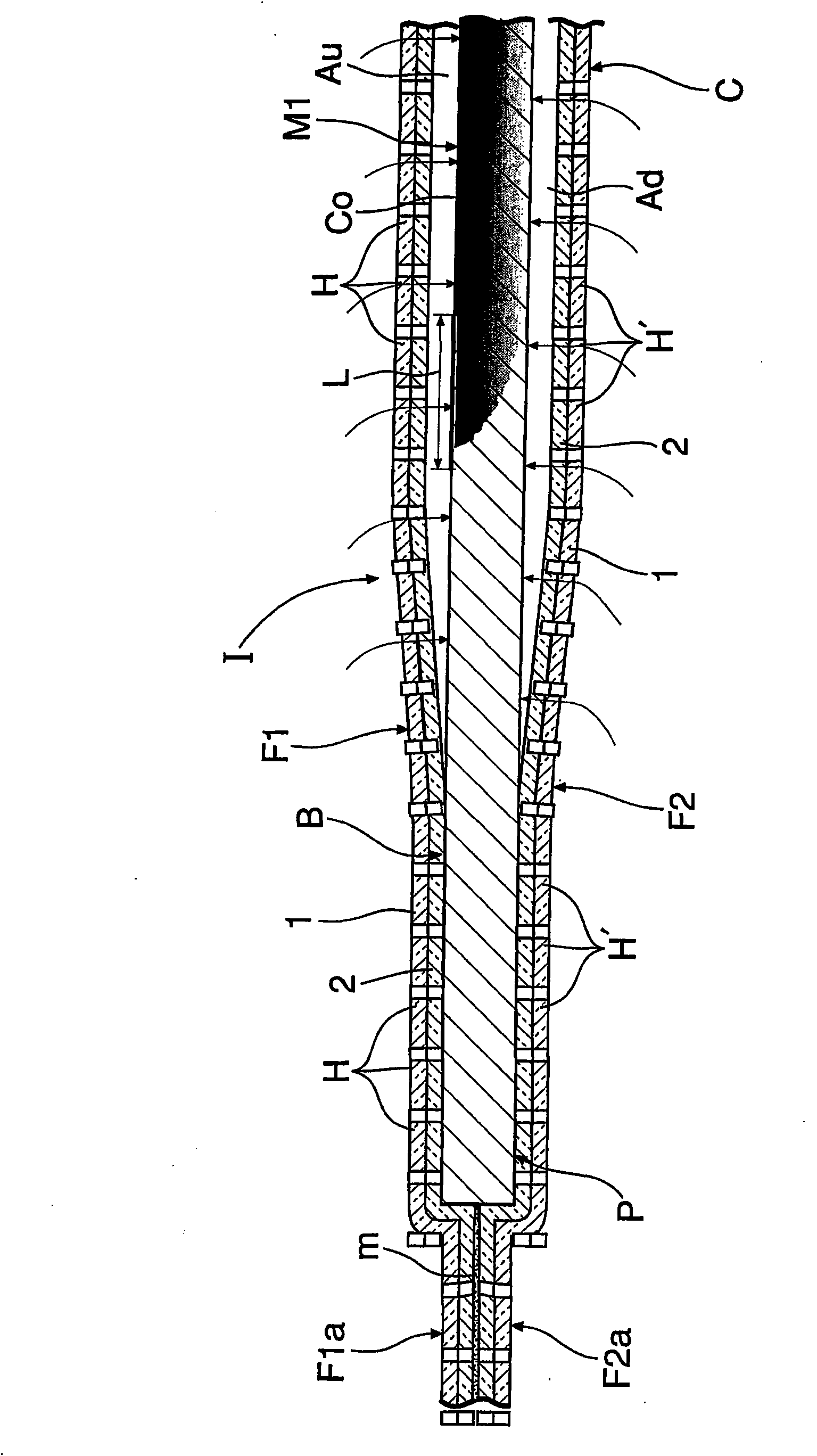
Humidity indicator
InactiveCN101949860APrevent intrusionAvoid misinterpretationMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorInvestigating moisture contentEngineeringColor changes
The invention provides a humidity indicator, which is provided with humidity determining surfaces (M1-M4) on the surface of a paper humidity determining plate (P) and determines humidity according to color change of humidity determining surfaces (M1-M4). The humidity indicator has a first film (F1) covering the surface of a humidity determination plate (B) and a second film (F2) covering the back surface of the plate (B). At least between the first film (F1) and the surface of the humidity determination plate (B) is formed a flat air layer (Au) on which the entire surfaces of humidity determination surfaces (M1-M4) exposing cobalt chloride (Co) are faced, and small holes (H) allowing the air layer (Au) to directly communicate with the atmosphere are formed with intervals in the first film (F1). First and second films (F1, F2) extend from outer periphery of the humidity determining surface plate, are directly engaged (m) on outer peripheral portions (F1a, F2a) and pressed on the humidity determining plate (P) to enclose area corresponding to the air layer.
Owner:山川洋一
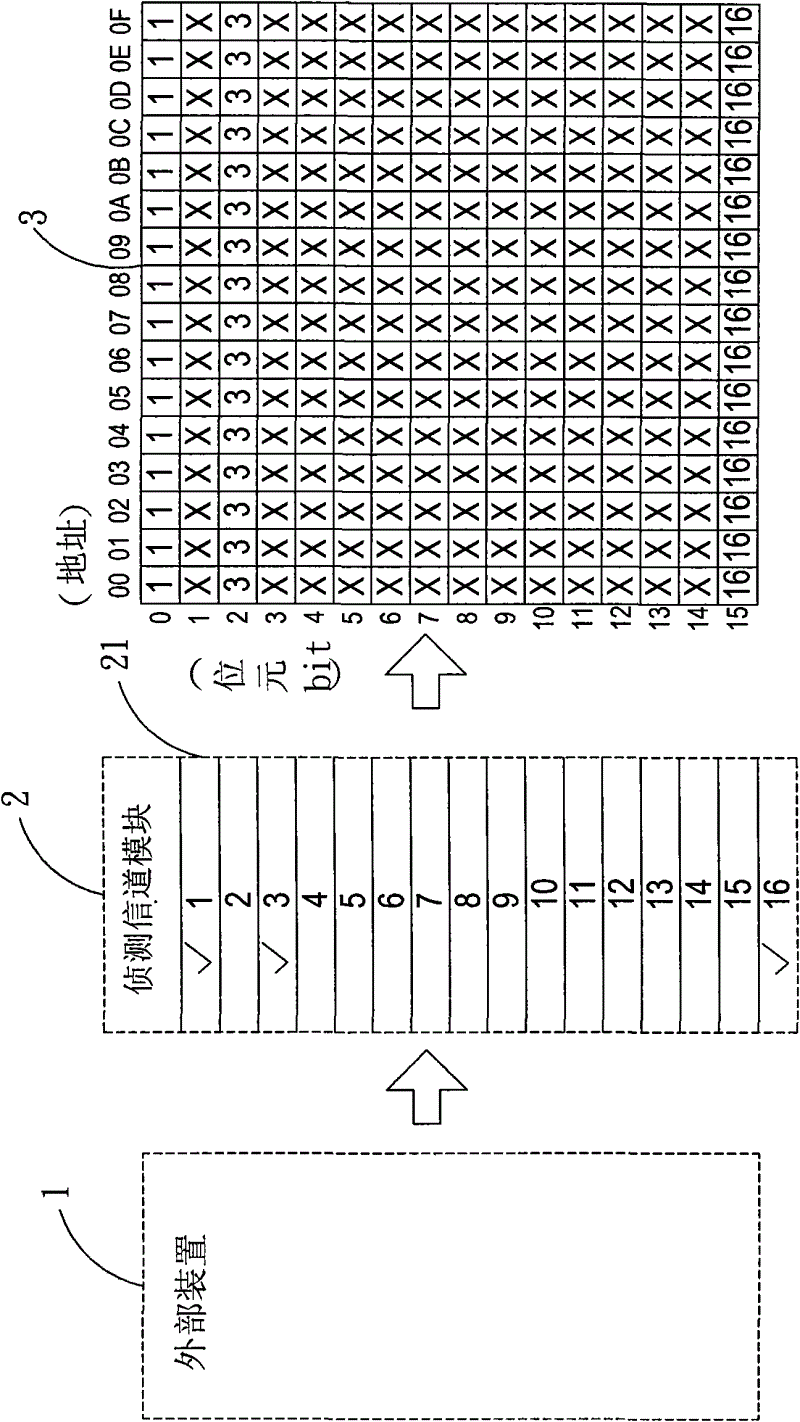
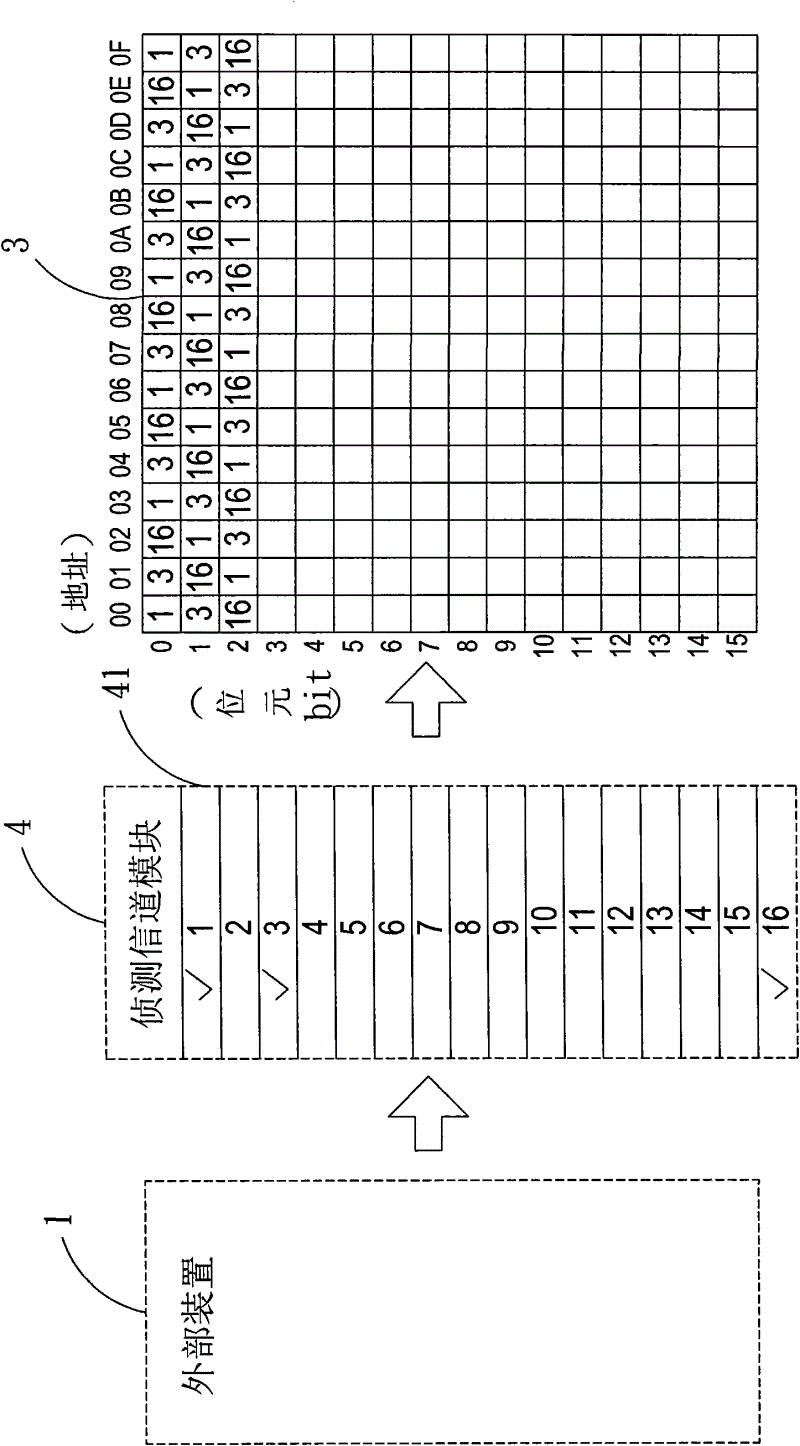
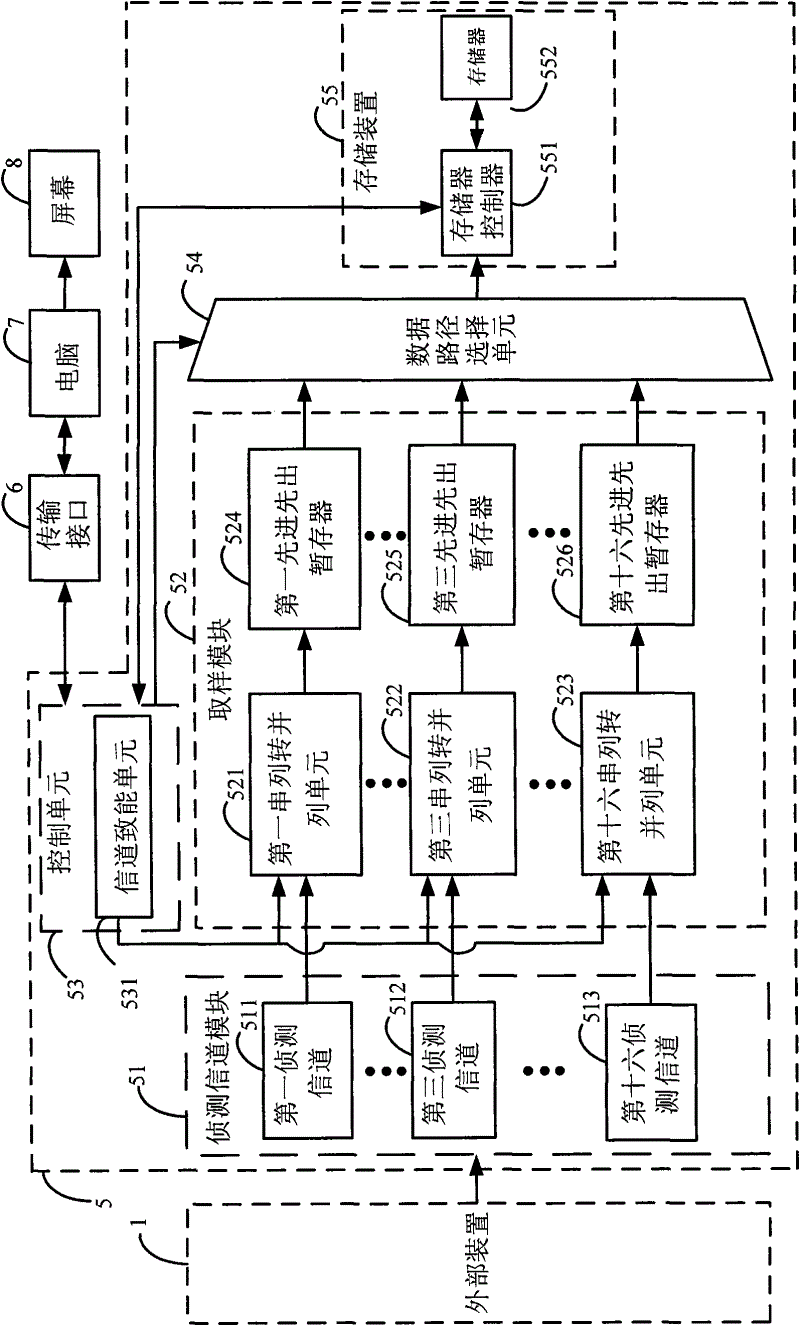
Electronic measuring device and method of converting serial data to parallel data for storage using the same
InactiveCN102621364ASave spaceSave storage spaceMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital variable/waveform displayComputer moduleDatapath
The invention relates to an electronic measuring device and a method of converting serial data to parallel data for storage using the same. The electronic measuring device includes a detection channel module, a sampling module, a control unit, a data path selector and a memory device. A user will be able to selectively enable the desired detection channels, set open or close of each detection channel, and store only data collected from enabled channels. The data collected from the detection channels are in serial data form. The device utilizes a serial-parallel shifter in its sampling module to convert the serial data to parallel data bytes. The innovative data conversion and storage methods of this invention will significantly conserve memory space that otherwise will be occupied by data from the disabled channels, solve waste problem of memory storage space, and through disposing of storage space indications, allow accurate and efficient reading of the stored data.
Owner:ZEROPLUS TECH CO LTD
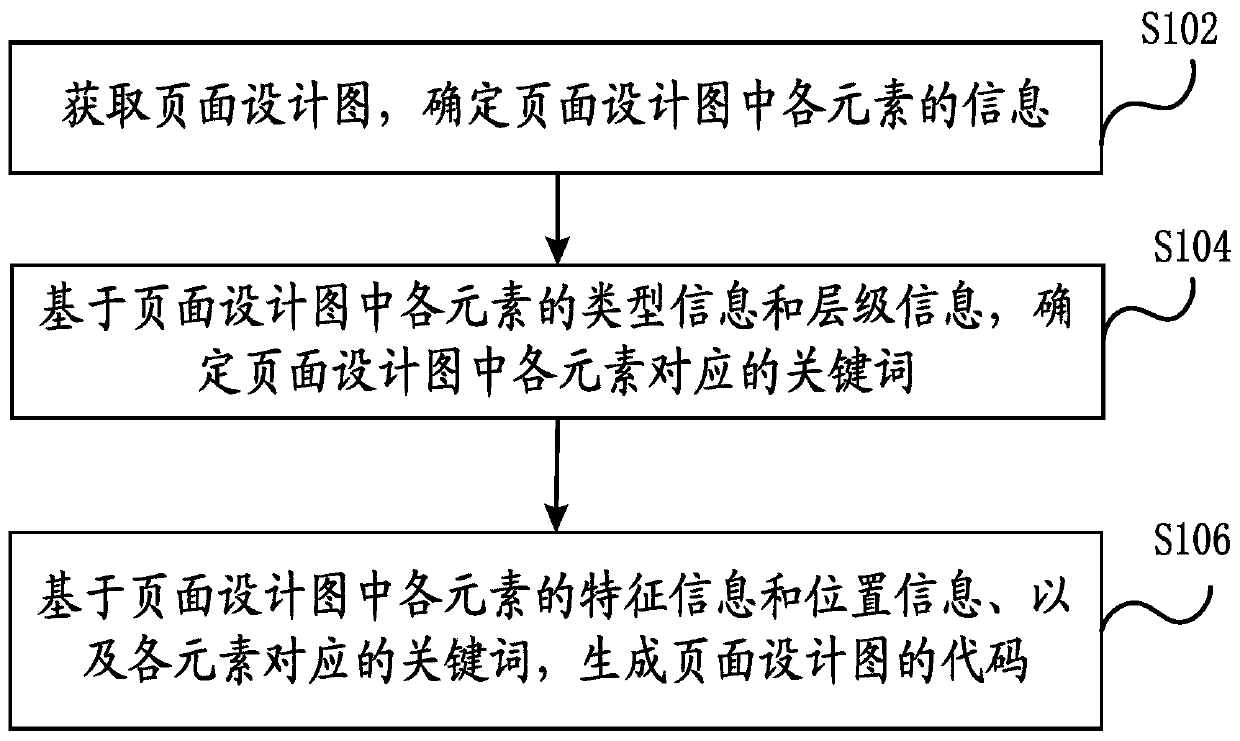
Page code generation method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
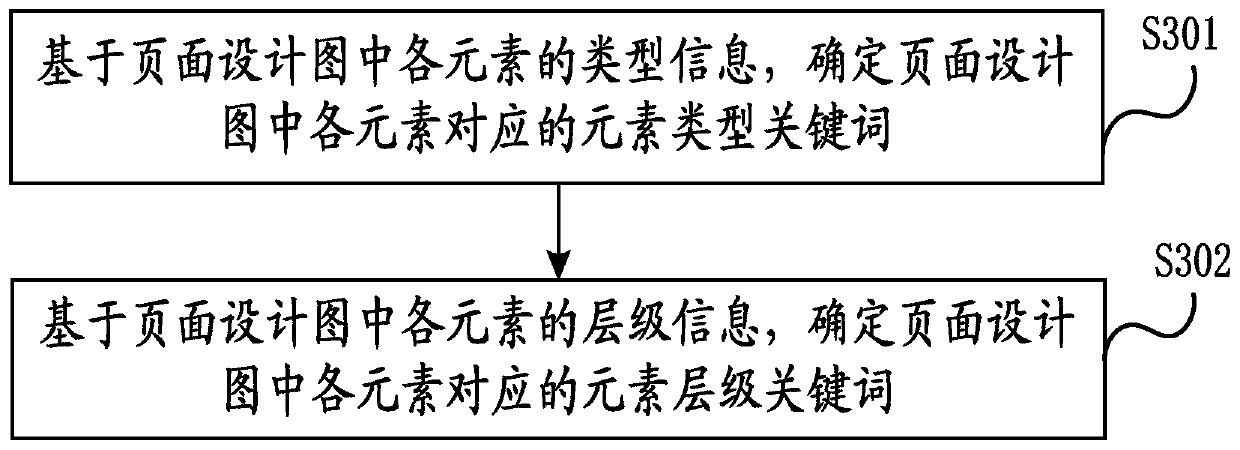
PendingCN111475156AGenerate accuratelyAvoid misinterpretationVisual/graphical programmingProgramming languageSoftware engineering
An embodiment of the invention discloses a page code generation method, a page code generation device, electronic equipment and a storage medium. The page code generation method comprises the steps of: acquiring a page design drawing, and determining information of all elements in the page design drawing; based on the type information and level information of each element in the page design drawing, determining a keyword corresponding to each element in the page design drawing; and generating a code of the page design drawing based on feature information and position information of each element in the page design drawing and the keyword corresponding to each element. Therefore, by adopting the page code generation method and the page code generation device of the invention, the code for generating the page design drawing can be quickly and accurately determined, annotation information in the page design drawing is omitted, and understanding deviation of designers and developers is avoided.
Owner:BEIJING JINTI TECH CO LTD
Water quality detection batched sampling equipment
ActiveCN110806336AEasy to collectAvoid misinterpretationWithdrawing sample devicesWater qualityEnvironmental engineering
The invention relates to sampling equipment, in particular to water quality detection batched sampling equipment. Aiming at the technical problem how to provide the water quality detection batched sampling equipment capable of automatically acquiring water quality samples and transmitting the acquired water quality samples in a batch way, the water quality detection batched sampling equipment comprises an installation plate, a first support rod and a second support rod, wherein the first support rod is arranged at one side of the installation plate, and the second support rod is arranged at the other side of the installation plate. By coordination of a sampling vessel and a device on the sampling vessel, the effect of automatic water taking in a batch way is achieved, various river water detection samples are conveniently collected, the problem of excessively high pollution degree of river water detection due to simple sampling error to cause mis-understanding of a tester is prevented,and the river water quality detection accuracy is ensured; and by a filtering plate, the river water sample acquired in the sampling vessel can be filtered, relatively large impurity is prevented from flowing to a sample collection position with river water, and the effect of initially processing the river water sample is achieved.
Owner:山东深信节能环保科技有限公司
Detection card for forward and reverse ABO blood typing and RhD blood typing
The invention discloses a detection card for forward and reverse ABO blood typing and RhD blood typing, belonging to the field of blood typing. The detection card of the invention comprises 8 micro-columns. A preparation method for the detection card comprises the following steps: (1) preparing an antibody diluent and a reverse typing solution; (2) respectively diluting an anti-A antibody, an anti-B antibody and an anti-D antibody with the antibody diluent into an anti-A antibody solution, an anti-B antibody solution and an anti-D antibody solution with titer of 1: 64 to 1: 256; (3) sequentially add 15-25 microliters of the anti-A antibody solution, the anti-B antibody, the anti-D antibody solution and the antibody dilutent into the micro-columns No. 1 to No. 4 and separately adding the reverse typing solution into the micro-columns No. 5 to No. 8; (4) separately adding glass beads into the 8 micro-columns; (5) and heating aluminum foils to seal the micro-columns. The detection card ofthe invention has good stability in agglutination reactions, is highly objective and accurate in result determination, and effectively prevents the phenomenon of misjudgement; and the effective timeof result interpretation may be a plurality of hours, which effectively prevents interpretation errors caused by improper control of operation time.
Owner:河北鑫辉生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com