Patents
Literature
30results about How to "Reduce detection background" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
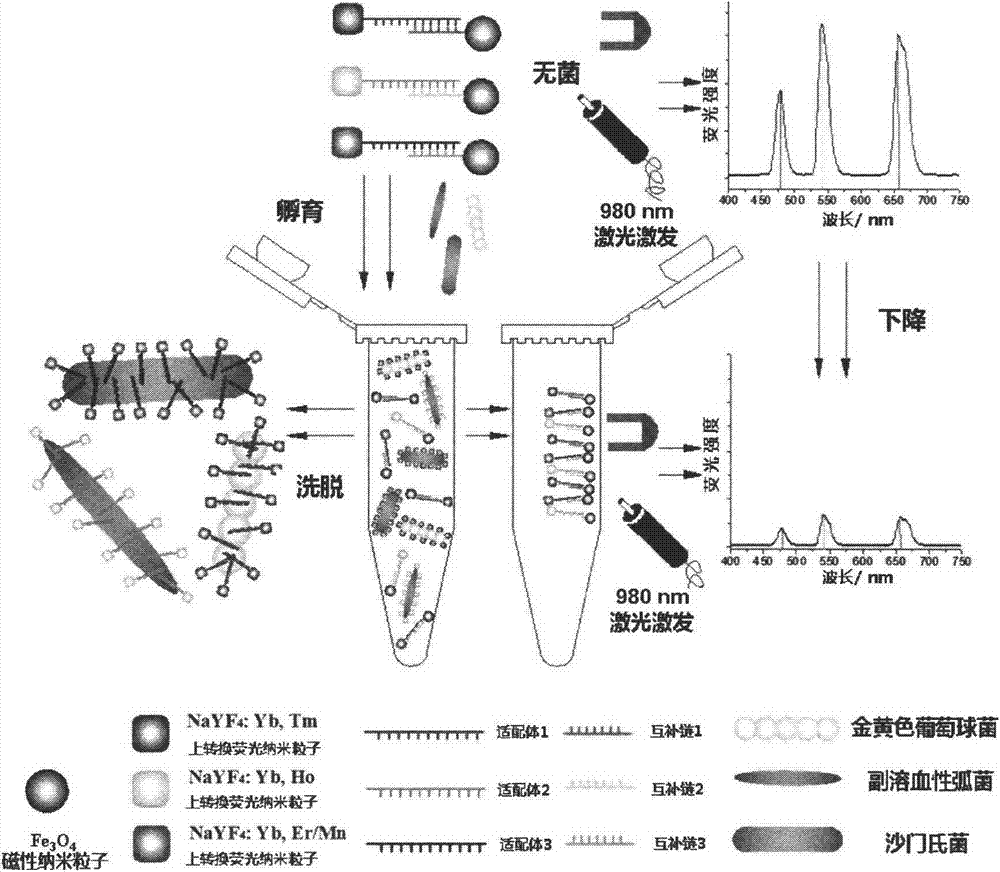
Method used for simultaneous detection of three food-borne pathogenic bacteria based on multicolor upconversion fluorescence labeling
ActiveCN103940792AImprove accuracy and stabilityHigh sensitivityFluorescence/phosphorescencePathogenic bacteriaFluorescence spectrometry
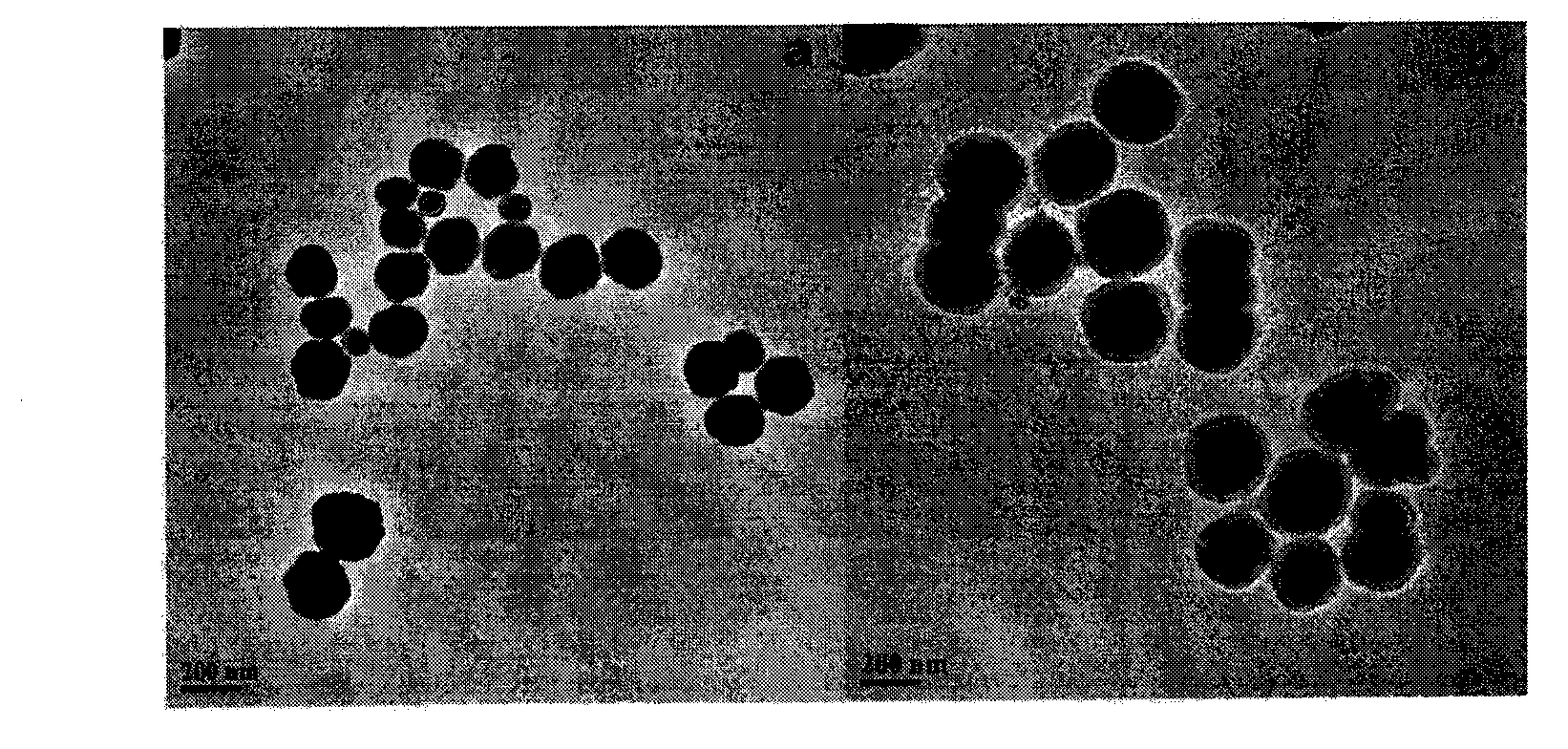
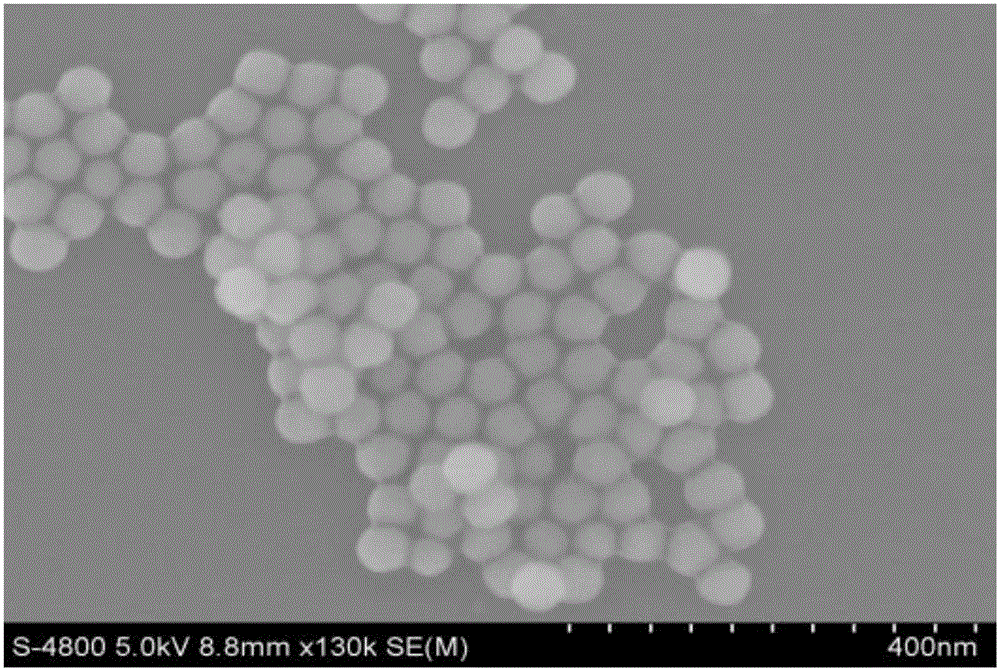
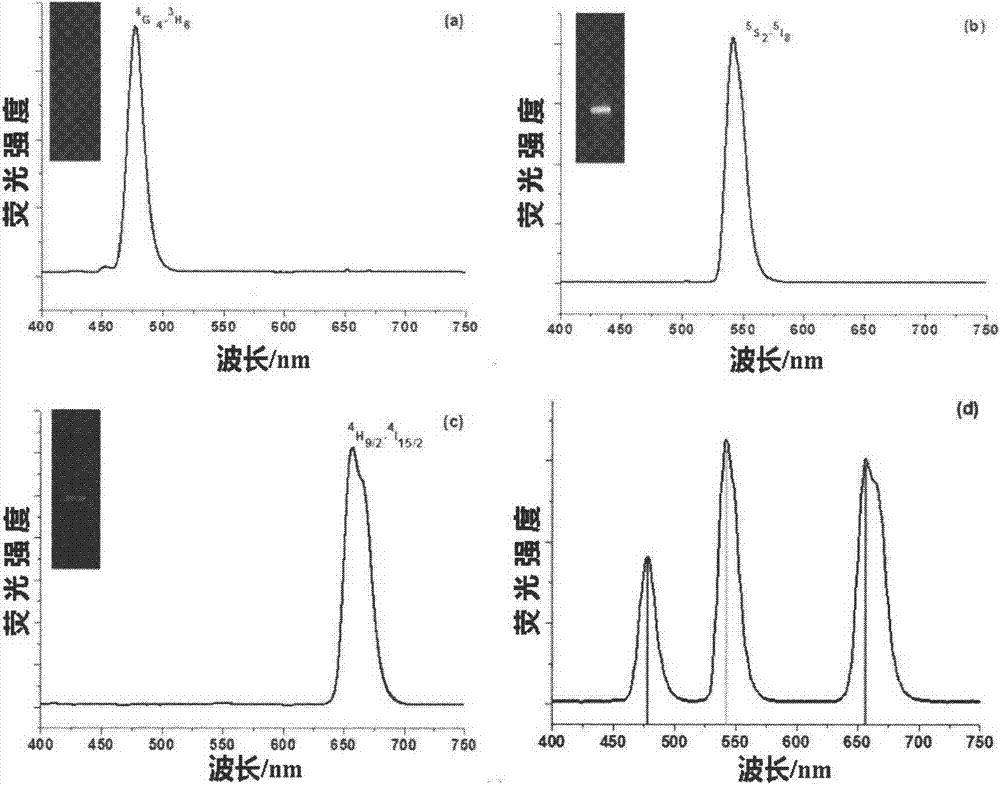
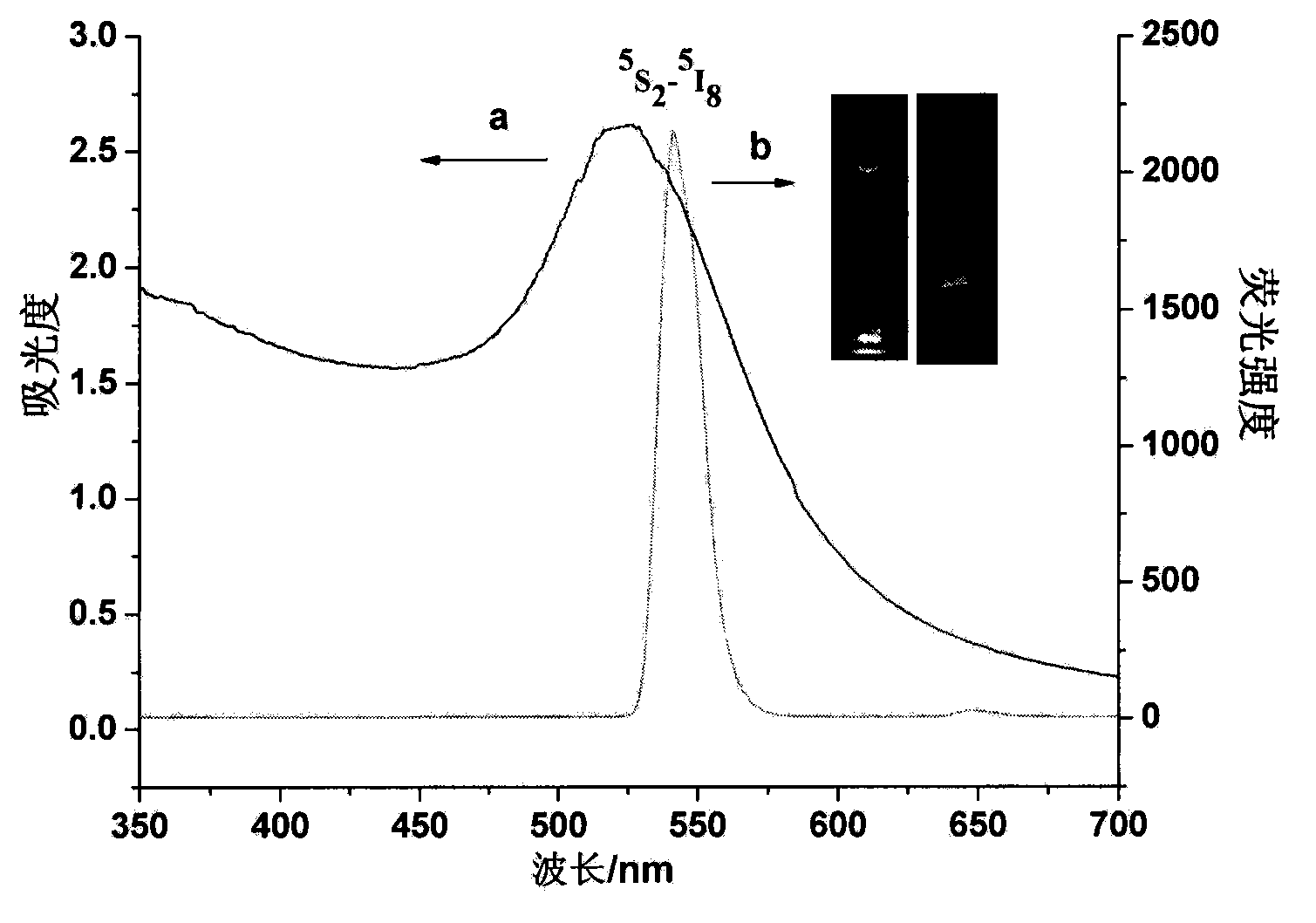
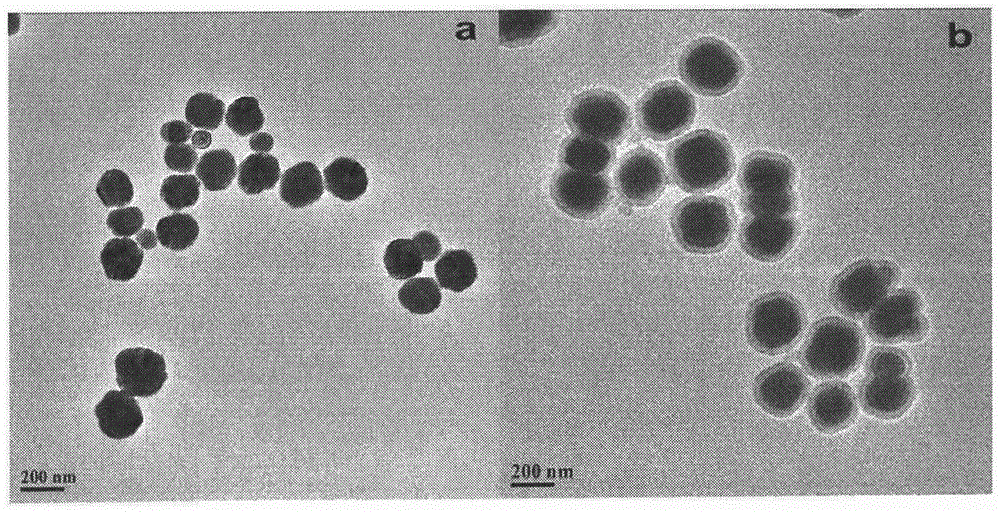
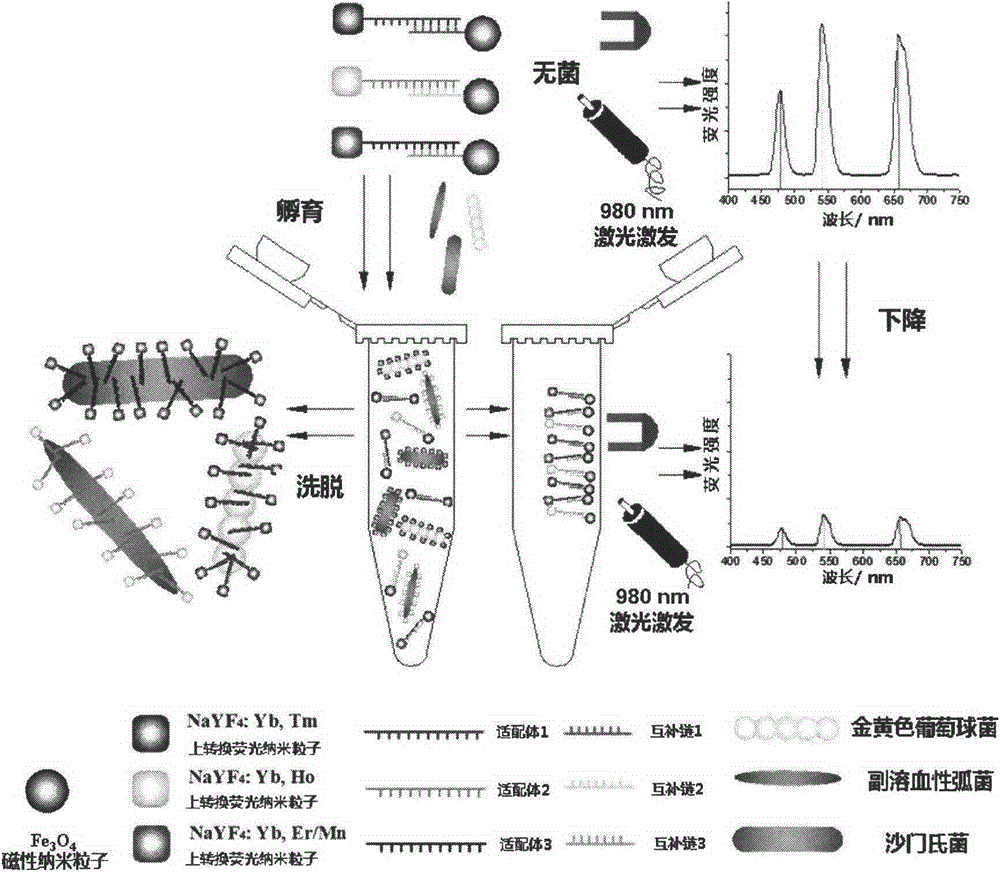
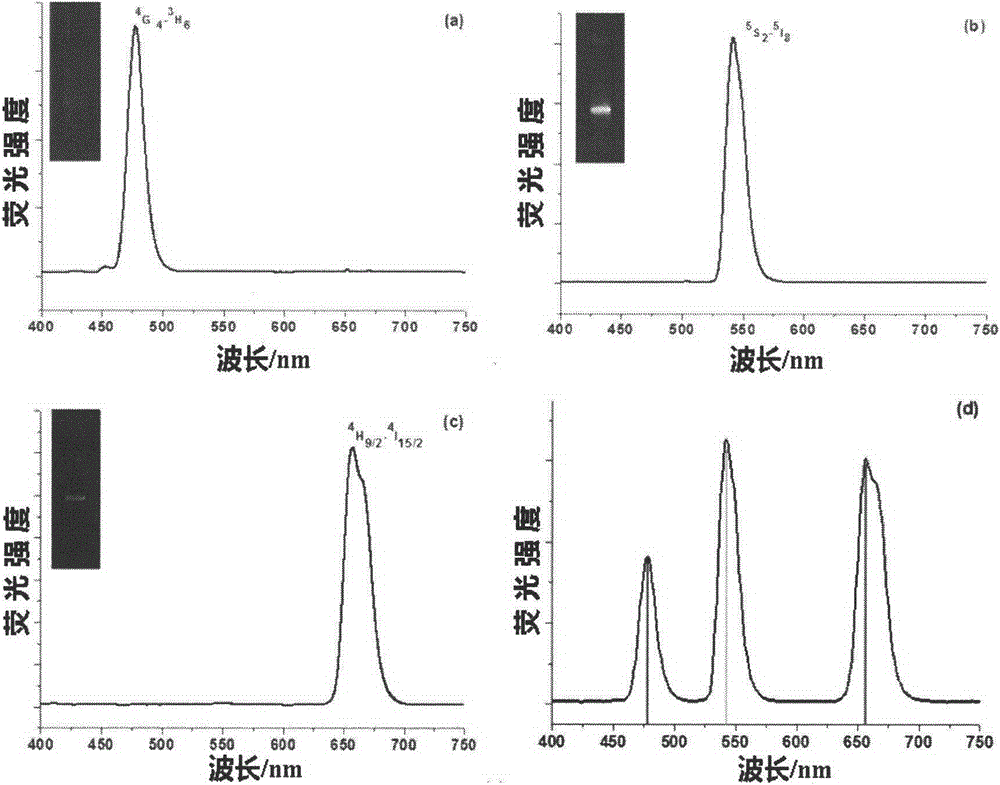
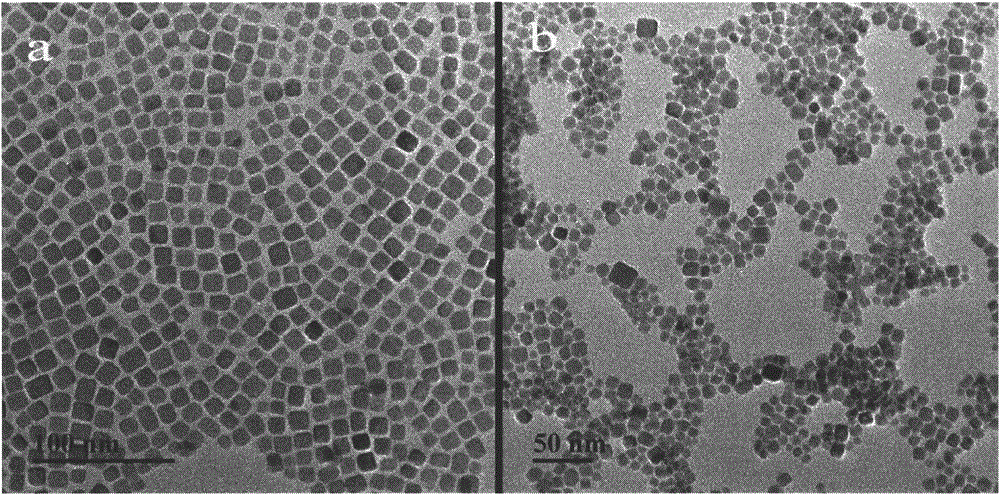
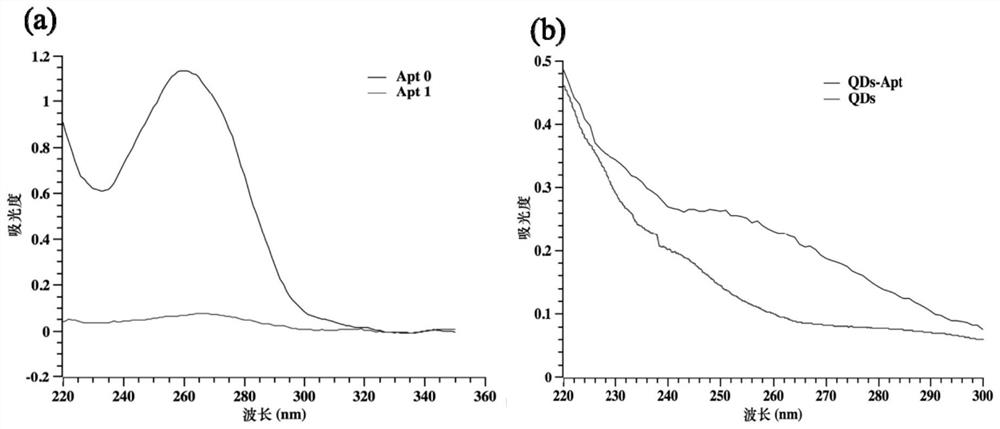
The invention provides a method used for simultaneous detection of three food-borne pathogenic bacteria based on multicolor upconversion fluorescence labeling. According to the method, three upconversion materials with differentiable fluorescence spectrums are used for forming multicolor upconversion fluorescent nanoprobes via respective connection with aptamers of staphylococcus aureus, vibrio parahaemolyticus, and salmonella, and complementary oligonucleotide single chains of the aptamers are connected with magnetic nanoparticles so as to form nano-composites. When bacteria to be tested are in a detection system, double chain unwinding is realized because of specific binding of the pathogenic bacteria with corresponding aptamers; it is possible to realize simultaneous quantitative determination of staphylococcus aureus, vibrio parahaemolyticus, and salmonella by monitoring upconversion fluorescence signal strength at 477nm, 550nm, and 660nm, detection linear range ranges from 50 to 1000000cfu / ml, and detection limits are 25cfu / ml, 10cfu / ml, and 15cfu / ml respectively. The method is used for detection of pathogenic bacteria, is high in sensitivity, is rapid and convenient, and can be used for detection of the three pathogenic bacteria in food such as milk and shrimp meat; and results are accurate and reliable.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
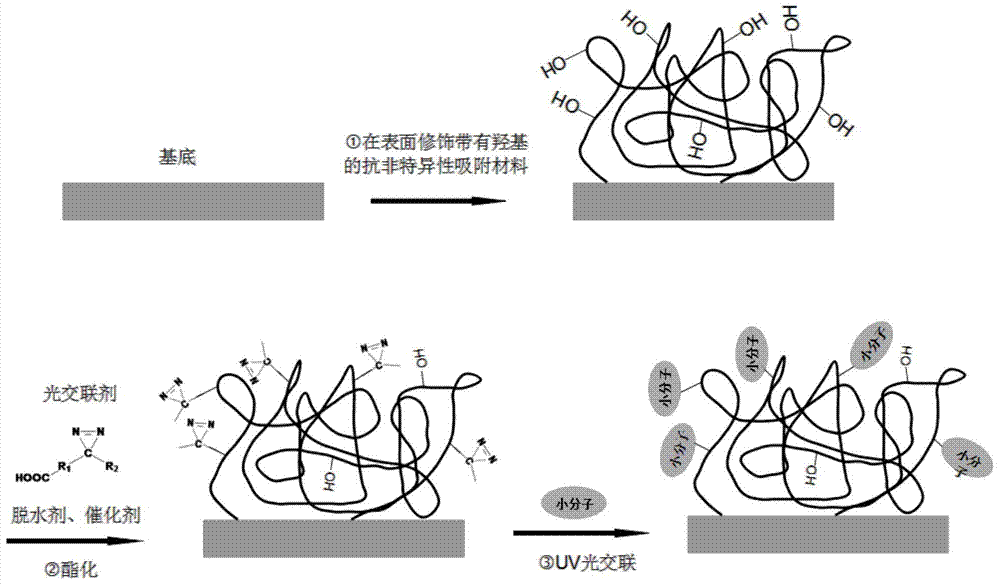
Small-molecule microarray and preparation method thereof
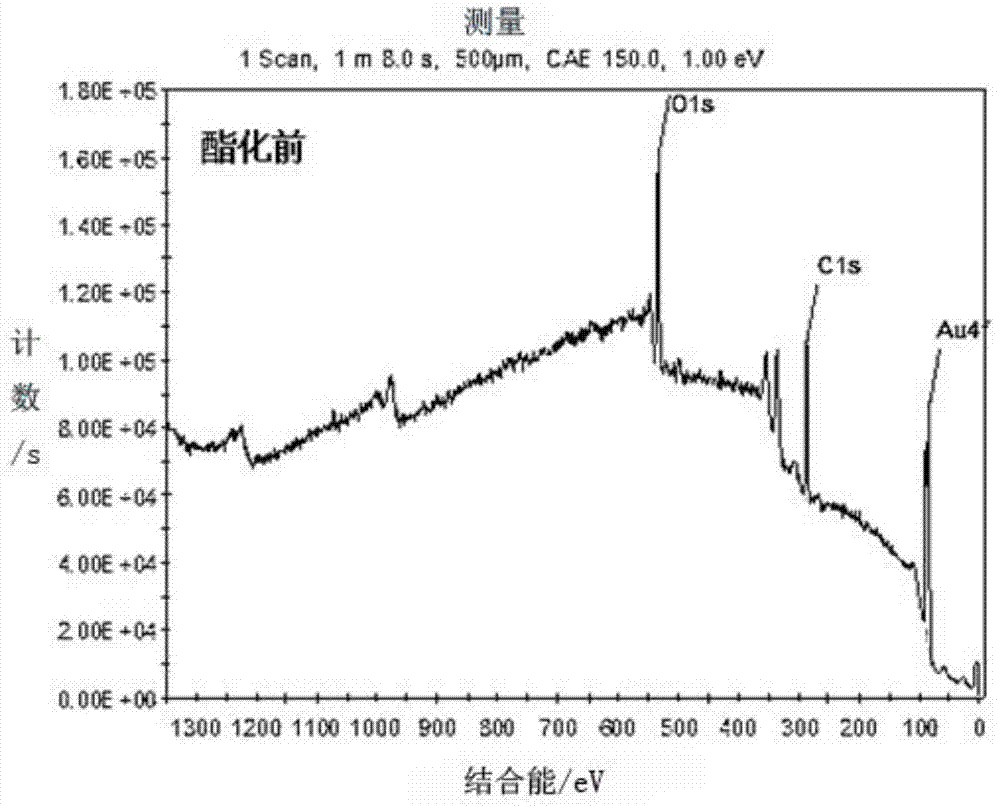
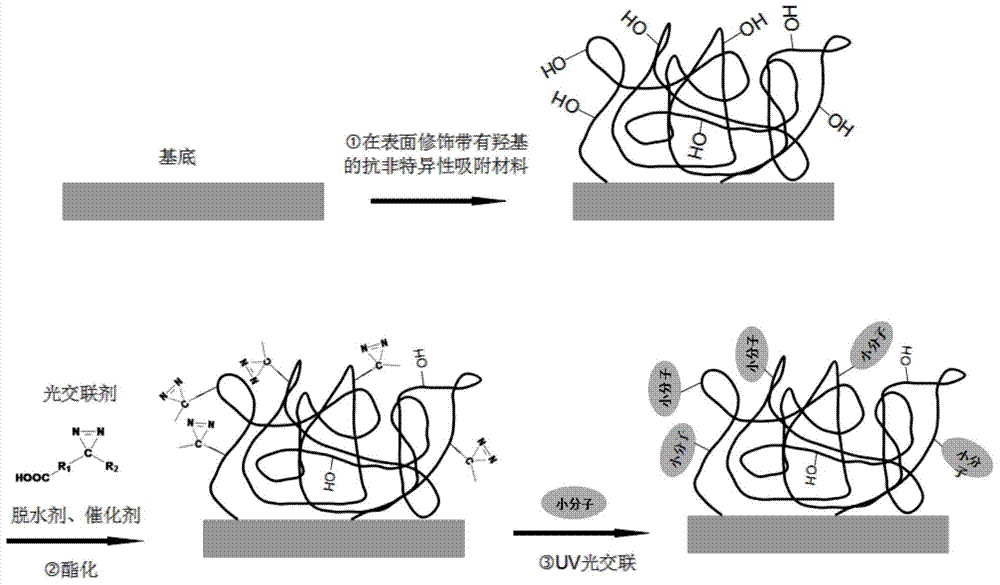
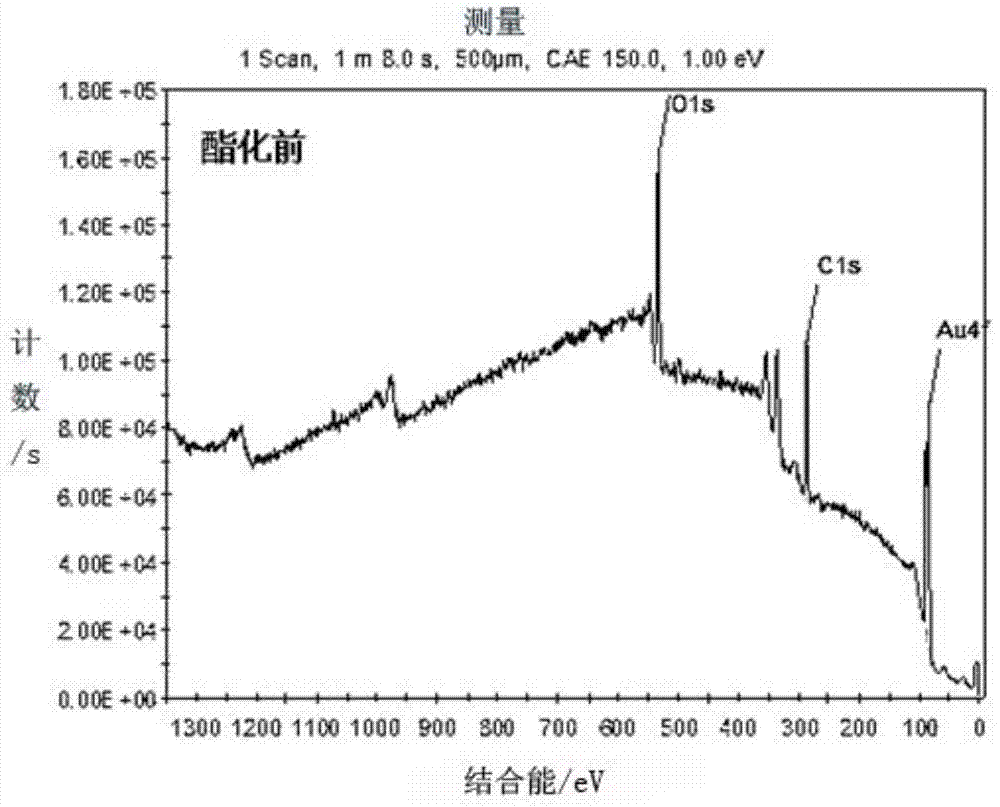
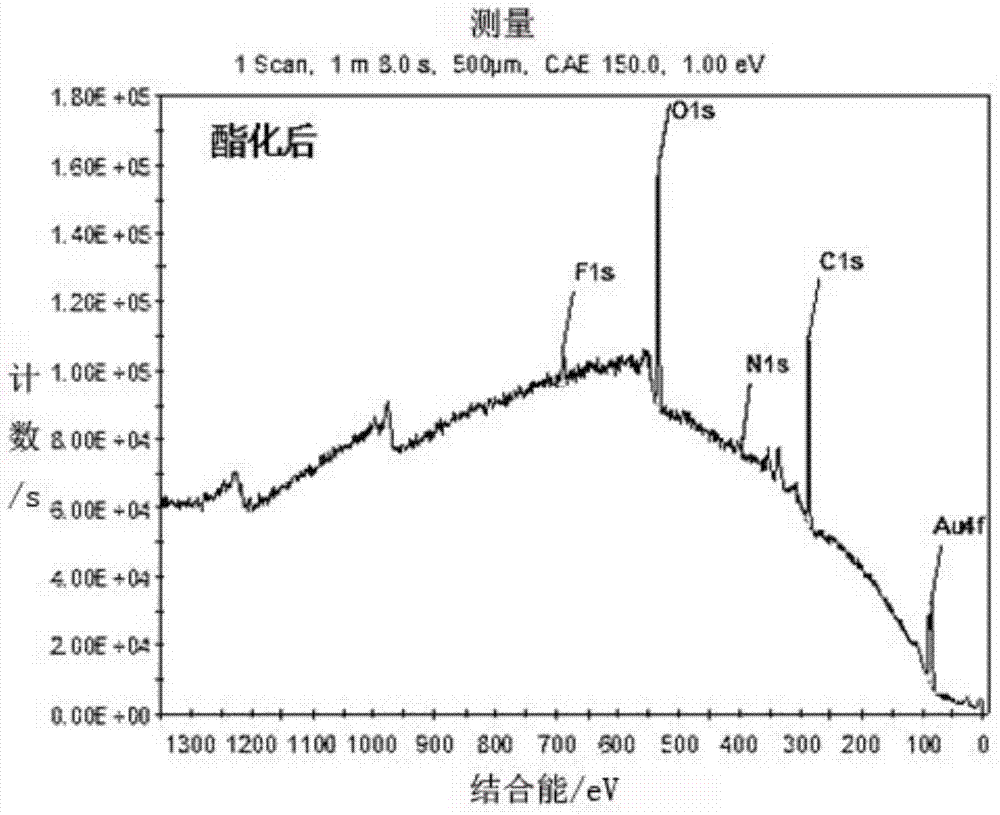
ActiveCN103792345AHigh resistance to non-specific adsorptionThe modification process is simple and convenientLaboratory glasswaresBiological testingHigh fluxEsterification reaction
The invention discloses a preparation method for a small-molecule microarray. The preparation method comprises the steps of bonding the hydroxyl terminal of a nonspecific adsorption resistance material modified on a chip substrate with the hydroxyl terminal of a small-molecule light crosslinking agent through an esterification reaction, and randomly fixing small molecules on the hydroxyl terminals through light crosslinking. By the adoption of a direct esterification mode, the small-molecule light crosslinking agent is quickly and efficiently coupled to the surface of the nonspecific adsorption resistance material; a chip modification process is simple and convenient and can be implemented under a normal temperature condition; therefore, the modification cost is reduced, and the modification efficiency is improved; a high detection signal is guaranteed; a non-reacted group still keeps high nonspecific adsorption resistance capacity, so that a background signal is reduced; the prepared small-molecule microarray is high in detection signal and low in background signal and can be used for mutual action between high-flux screened small-molecule medicaments and targets.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
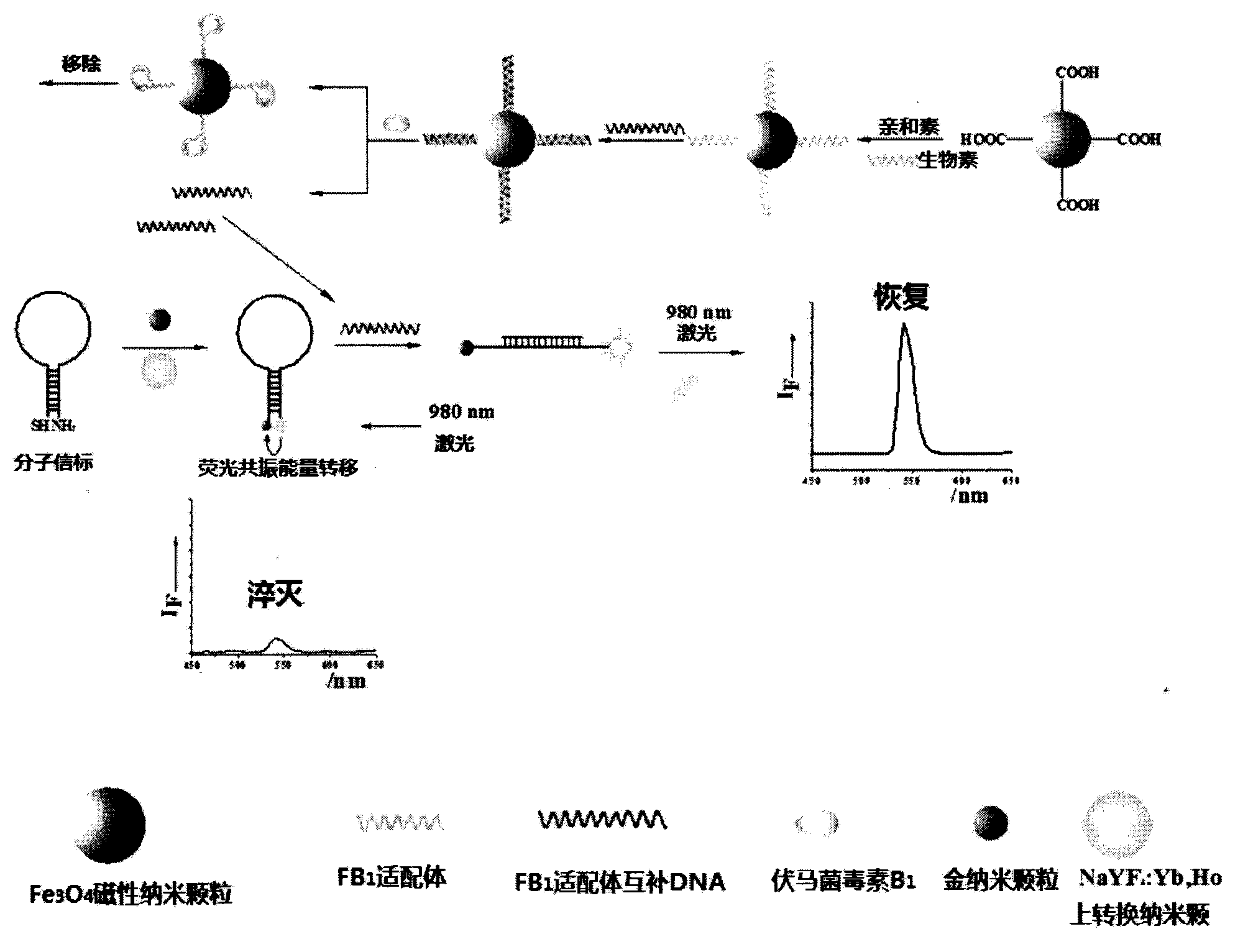
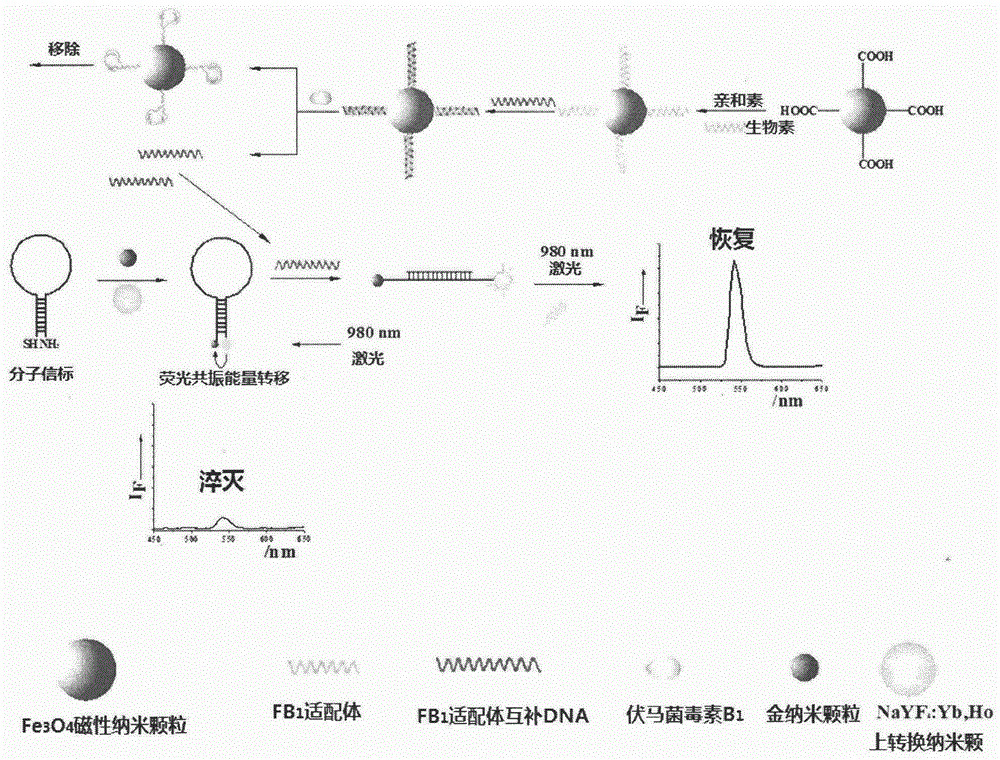
Method for detecting fumonisin B1 based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer
ActiveCN103901000AImprove accuracyImprove stabilityFluorescence/phosphorescenceEnergy transfer upconversionMagnetite Nanoparticles
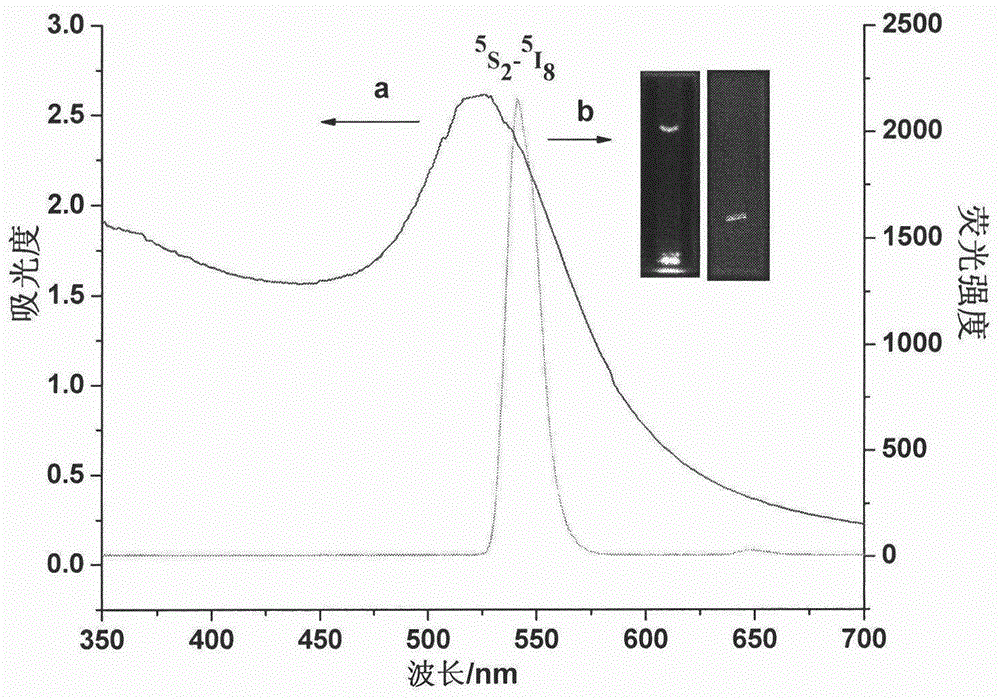
The present invention provides a method for detecting fumonisin B1 based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer. The method comprises that: NaYF4:Yb,Ho upconversion fluorescence nanoparticles and gold nanoparticles are respectively and covalently bound to both ends of the stem-like part of the specific molecular beacon, wherein the fluorescence resonance energy transfer upconversion fluorescence can be quenched by the gold nanoparticles; and a fumonisin B1 aptamer and a complementary strand thereof are subjected to hybridization immobilization on the surface of magnetic nanoparticles, an analyte fumonisin B1 is added and is specifically bound with the aptamer so as to make the complementary strand be separated from the magnetic nanoparticles, and the separated complementary strand and the molecular beacon are subjected to hybridization so as to open the ring-like part of the molecular beacon, such that the fluorescence resonance energy transfer system is broken, the fluorescence signal is restored, and the fumonisin B1 content can be determined by detecting the fluorescence signal intensity, wherein the detection limitation of the method achieves 0.01 ng.mL<-1>. According to the present invention, the fumonisin B1 content in the food sample can be rapidly, accurately e and sensitively detected.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Nanometer-material-photothermal-effect-based cell detection method and cell detection device
ActiveCN104655594AThe detection method is simpleNo complicated steps requiredAnalysis by material excitationPhosphateTreated cell
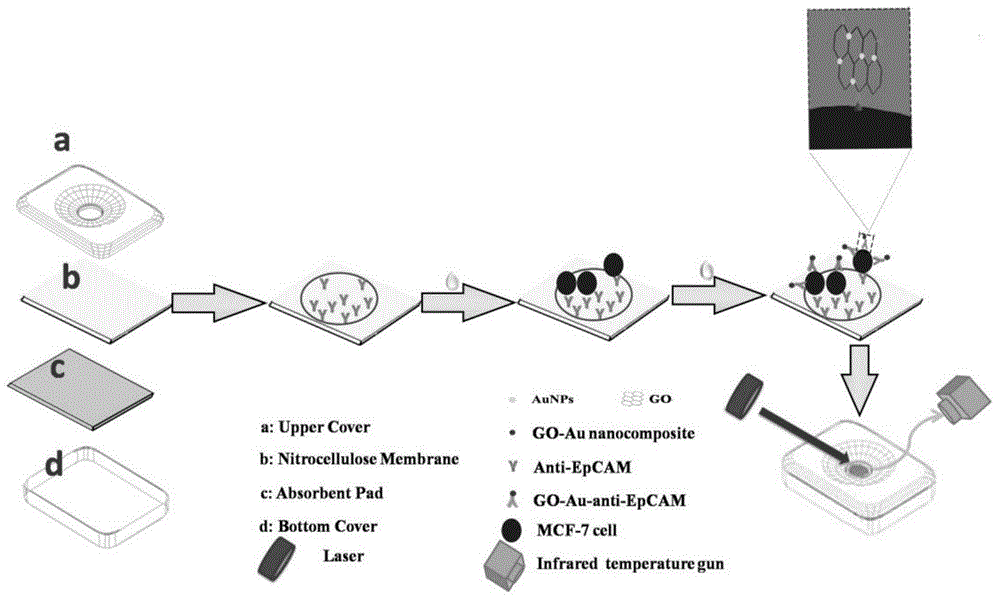
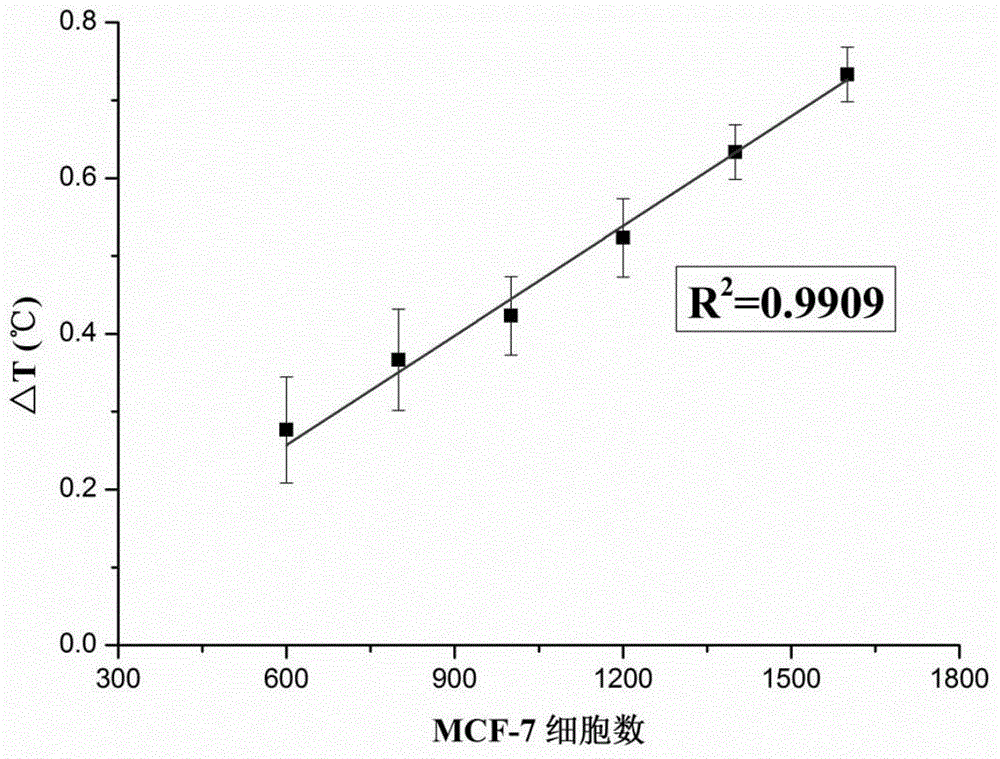
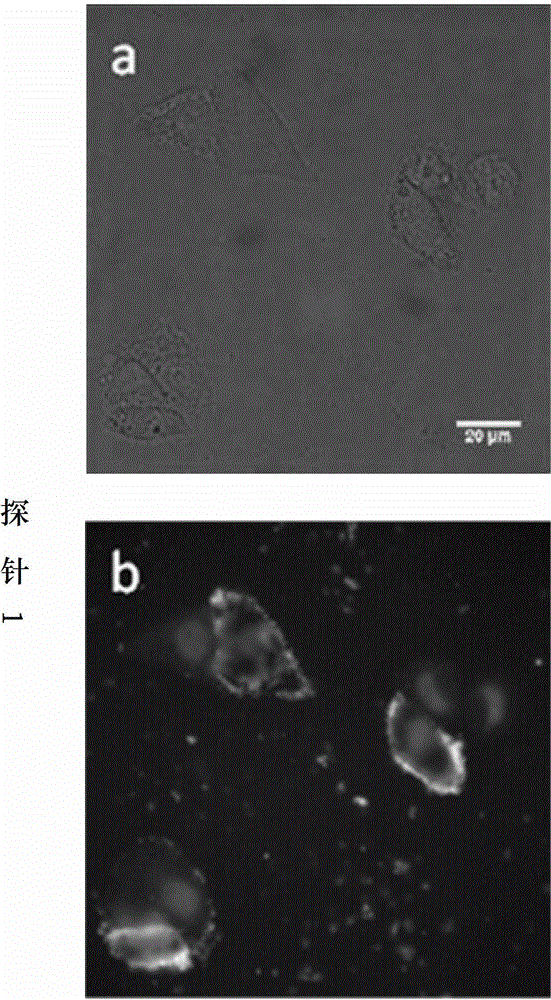
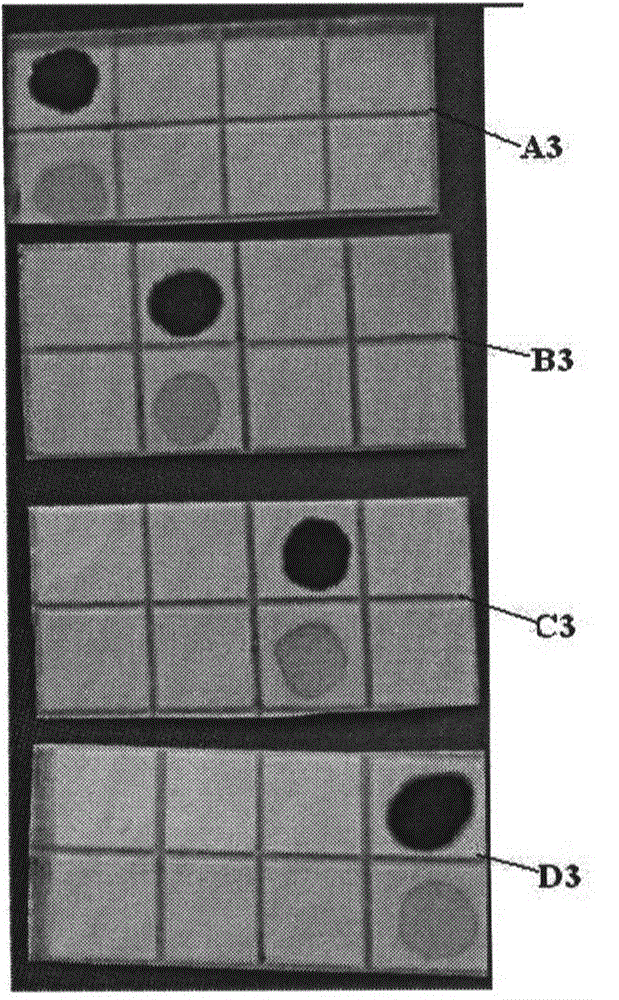
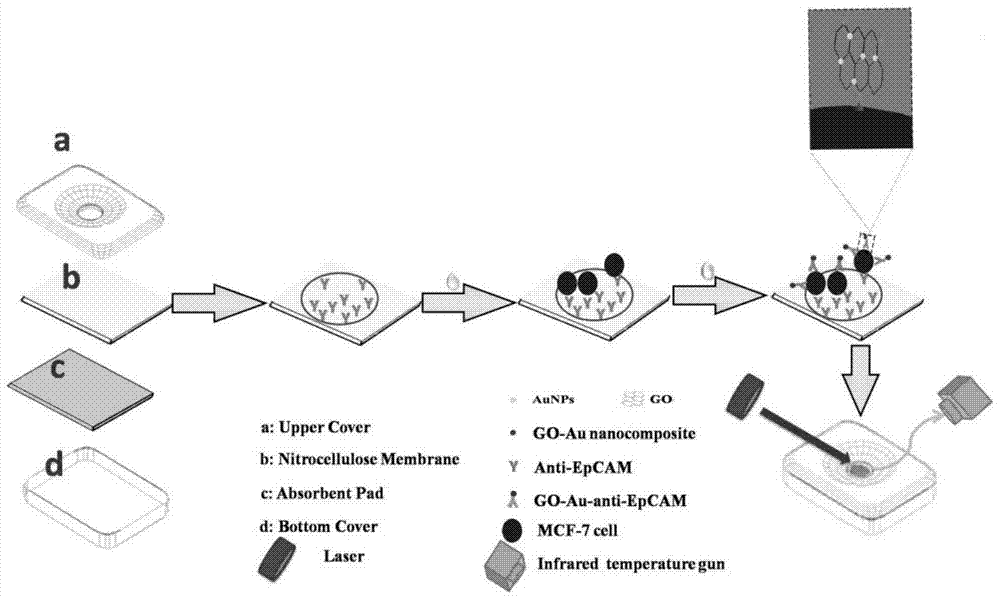
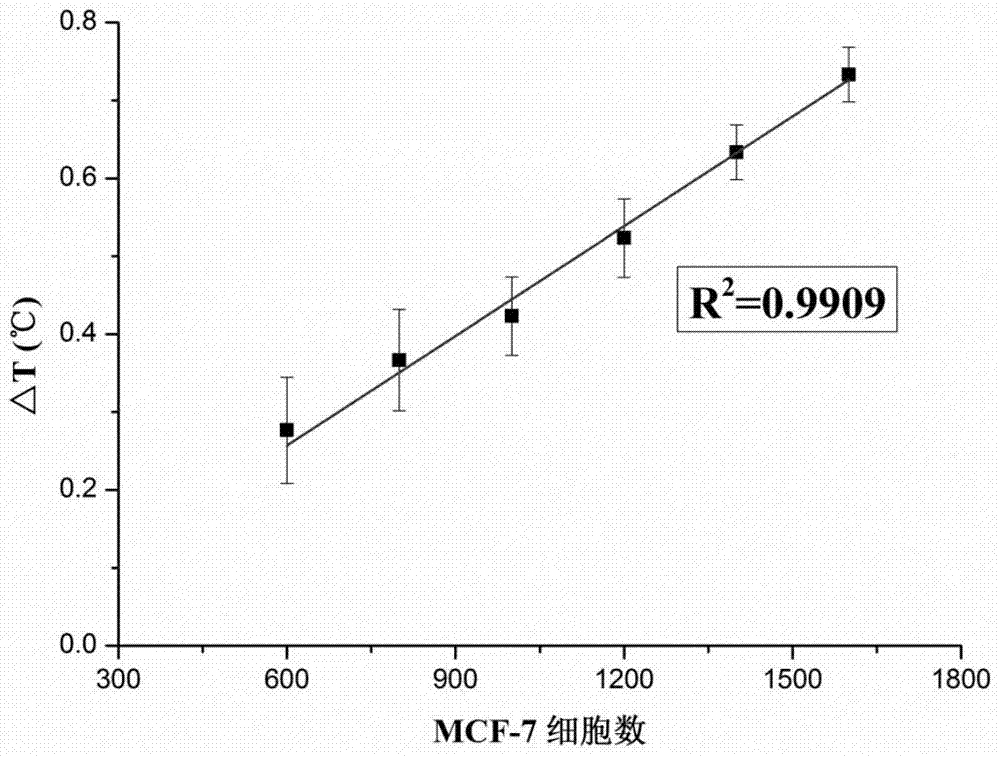
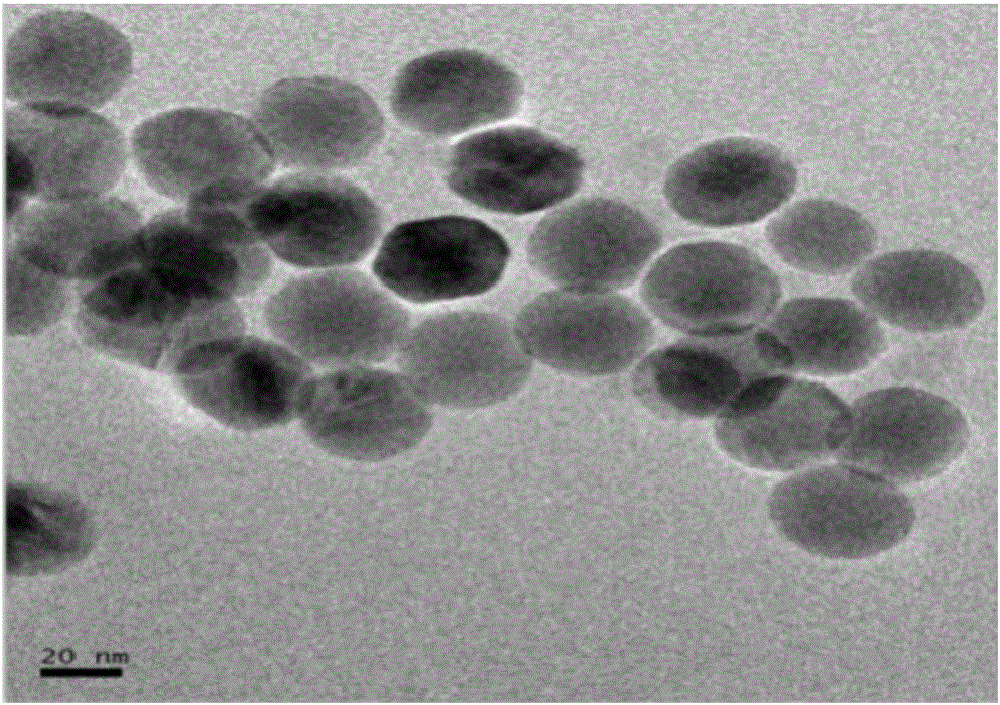
The invention discloses a nanometer-material-photothermal-effect-based cell detection method and a cell detection device. The method comprises the following detecting steps: (1) centrifuging cell solution to be detected, discharging supernatant, redissolving with PBS (Phosphate buffer solution) and centrifuging again, repeating the operations, discharging supernatant, and dissolving centrifuged precipitates with 10mul of PBS buffer solution; (2) dropwise adding the treated cell sample onto a sample adding area of an infiltration test strip, and washing for three times with PBST (Phosphate buffer solution-tween) solution; (3) adding with 5-20muL of grapheme-gold-antibody compound into the sample adding area of the infiltration test strip, washing for three times with PBST solution and airing; and (4) radiating the sample adding area of the detection device with laser with the excitation wavelength of 808nm for 10-90s, recording the temperature before and after radiation, calculating the temperature difference, and drawing a calibration curve by use of the cell number as an x-coordinate and the temperature difference as a y-coordinate, wherien when one sample is detected, the temperature difference of the sample is detected and is substituted into the calibration curve to calculate the cell number. The detection device and the detection method have the advantages that the detection method is simple, the detection time is short, the detection sensitivity is high and the like.
Owner:山东师大瑞柏生物科技有限公司
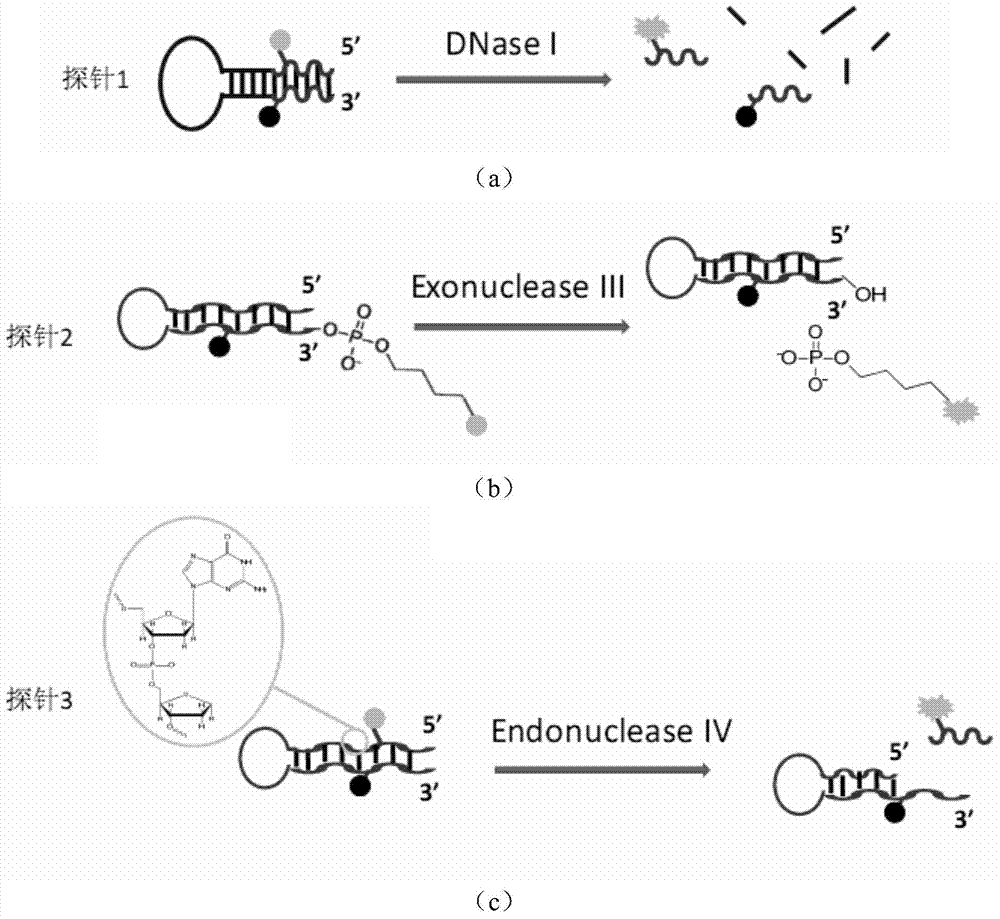
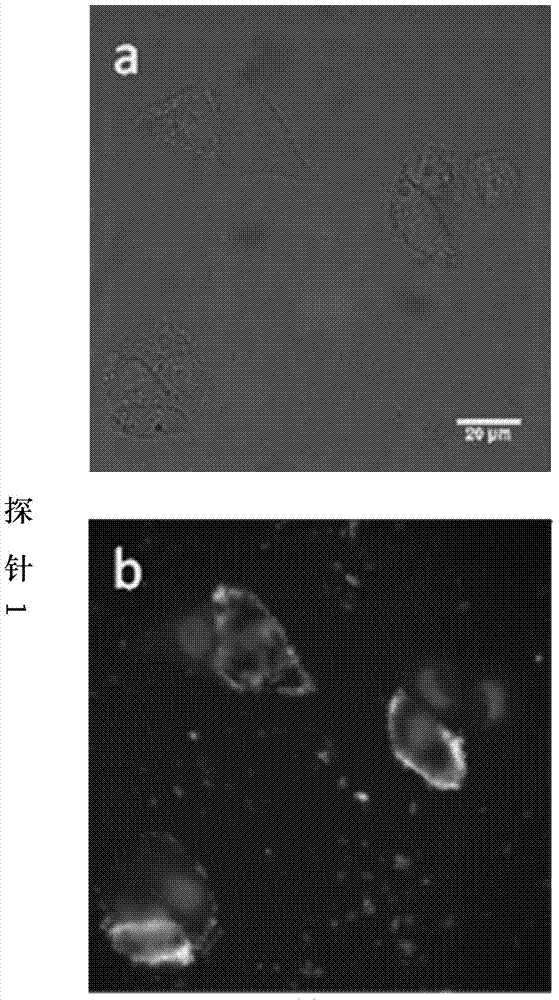
Phosphorthioate-modified oligonucleotide fluorescence probe and application thereof in detection of nuclease
ActiveCN103333888AAccurate analysisHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescenceLyase
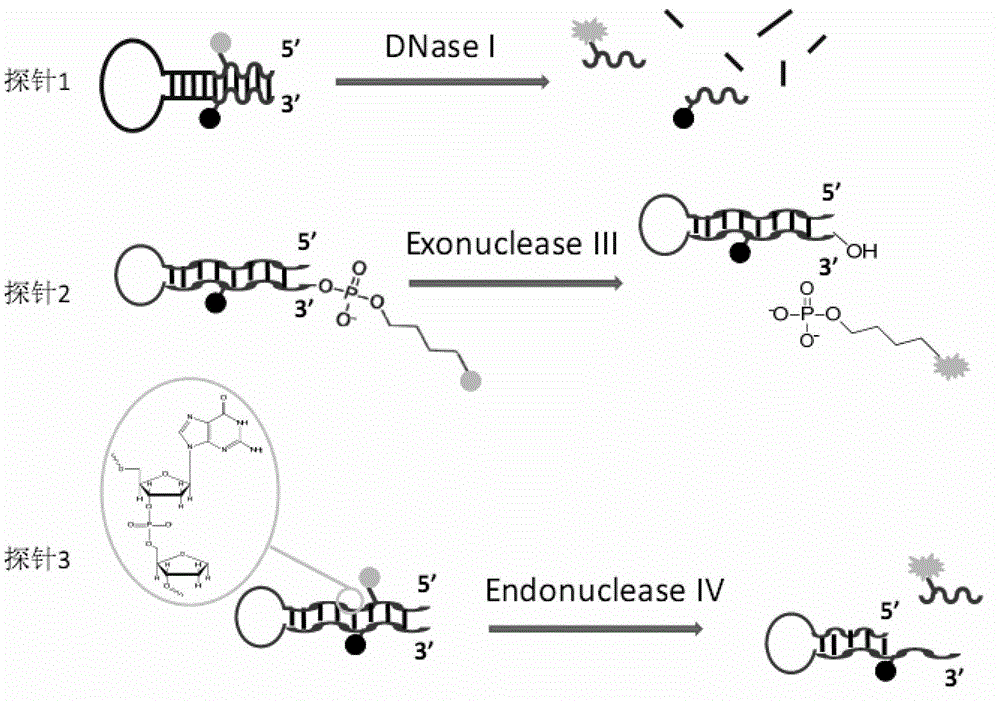
The invention discloses a phosphorthioate-modified oligonucleotide fluorescence probe and an application thereof in the detection of nuclease. The phosphorthioate-modified oligonucleotide fluorescence probe is provided with a stem-and-loop structure, the ring part of the phosphorthioate-modified oligonucleotide fluorescence probe is of a single-stranded structure and comprises 4-8 nucleotide residues, the stem part of the phosphorthioate-modified oligonucleotide fluorescence probe comprises 8-15 pairs of nucleotide residues, O- in part of phosphate diester bond of a probe is replaced by S-, and the probe is divided into a non-restriction endonuclease probe, an exonuclease probes and a depurination / depyrimidination site lyase probes according to the activity function of the nuclease to be detected. The phosphorthioate-modified oligonucleotide fluorescence probe is an accurate and reliable analytic method which can be used for detecting the activity of the nuclease in real time, has strong selectivity and high sensitivity and is fast in speed and low in cost, so that lots of limitations in the prior art are overcome.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for detecting glucose by paper-based colorimetric assay
InactiveCN104374769AReduce experiment costEasy to operateMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorWaxPaper based
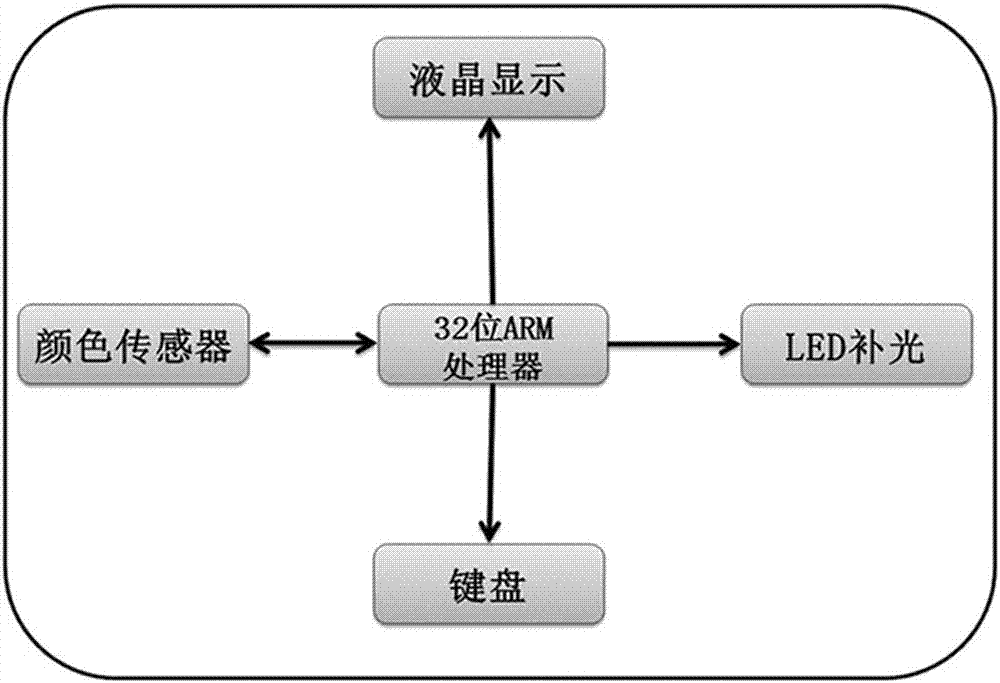
The invention discloses a method for detecting glucose by paper-based colorimetric assay. The method comprises the following steps: manufacturing a homemade colorimeter; designing a hydrophobic wax printing pattern; cutting a piece of filter paper; printing the hydrophobic wax printing pattern onto the filter paper; molding by dewaxing; preparing ZnFe2O4; preparing a mixed solution; dropwise adding the mixed solution into a detection pool; dropwise adding a solution to be tested; folding the paper in half; and detecting by the homemade colorimeter. The method for detecting the glucose is simple to operate, can be operated by unprofessional people, and is high in detection speed, low in cost, simple in aftertreatment and free from pollution.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Method and reagent kit for simultaneously detecting resistance site of three nucleotide analogues of hepatitis B virus
InactiveCN101812537AAchieve accuracyAchieve reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMulti siteNucleotide
The invention provides a method and a reagent kit for simultaneously detecting the resistance sites of the three nucleotide analogues of a hepatitis B virus (HBV). Based on the genotype sequence of the HBV, four nested amplification primers and twenty-seven wild resistance-detection oligonucleotides probes aiming at ten resistance sites are designed in an HBV polymerase area, digoxin-labeled oligonucleotides universal primers are used for conducting nested PRC reaction to amplify a target DNA segment, a target DNA amplification product to be labeled is used for hybridizing with specific oligonucleotide probes on matrix, and the existence of the resistance of the HBV to the three nucleotide analogues is judged through enzymatic color development reaction link-coupled by hybridization conjugates. The method improves the accuracy, the reliability and the sensitivity and can simultaneously detect the ten resistance sites of the three nucleotide analogues, thereby realizing the high-throughput, multi-site, economic and rapid detection and fitting to clinical needs in a better way. The method is of great significance to the realization of early detection and the proper guide of clinical personalized medication.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Cell model for quick screening of histone deacetylase inhibitor
InactiveCN101008009ASensitive detectionEfficient exclusionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDrug developmentLuciferases
The invention discloses a cell sifting moudle for fast sifting of antineoplastic- histone precursor histone deacetylase inhibitor compound from compound storage during new drug development. The moudle makes use of speciality that the precursor histone deacetylase inhibitor can activate some starting subsequence, constructs te oexpression vector containing special starting factor and firefly luciferase reporting gene, and builds cos- 7 clone that stably expresses said vector. The cell contains starting subsequence with different degree of activity for luciferase, the starting factor can be acitvated by histone precursor histone deacetylase inhibitor and then the expression of luciferase reporting gene is intensified, and so the detection for histone precursor histone deacetylase inhibitor activity in sample through detection of luciferase activity change can be finished in a short time. The cell sifting moudle can be used for fast and high- flux sifting of new antineoplastic and histone precursor histone deacetylase inhibitor compound from compound storage during new drug development.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA
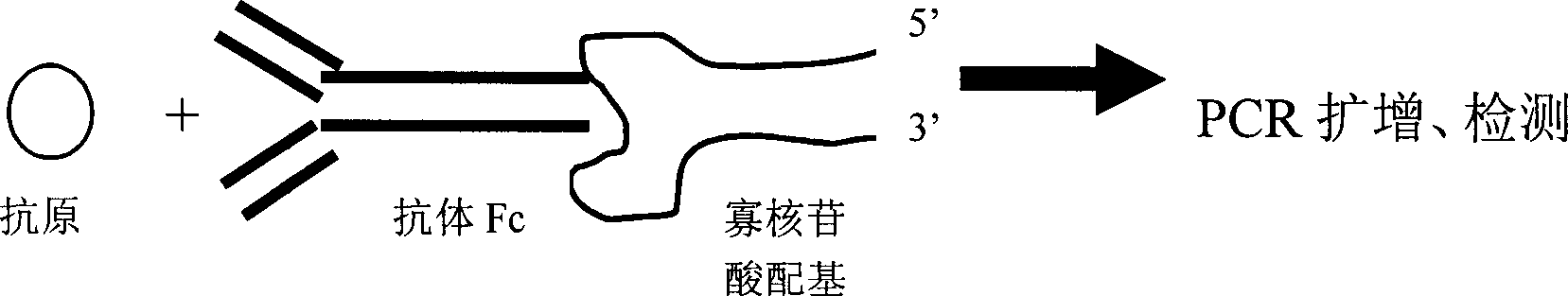
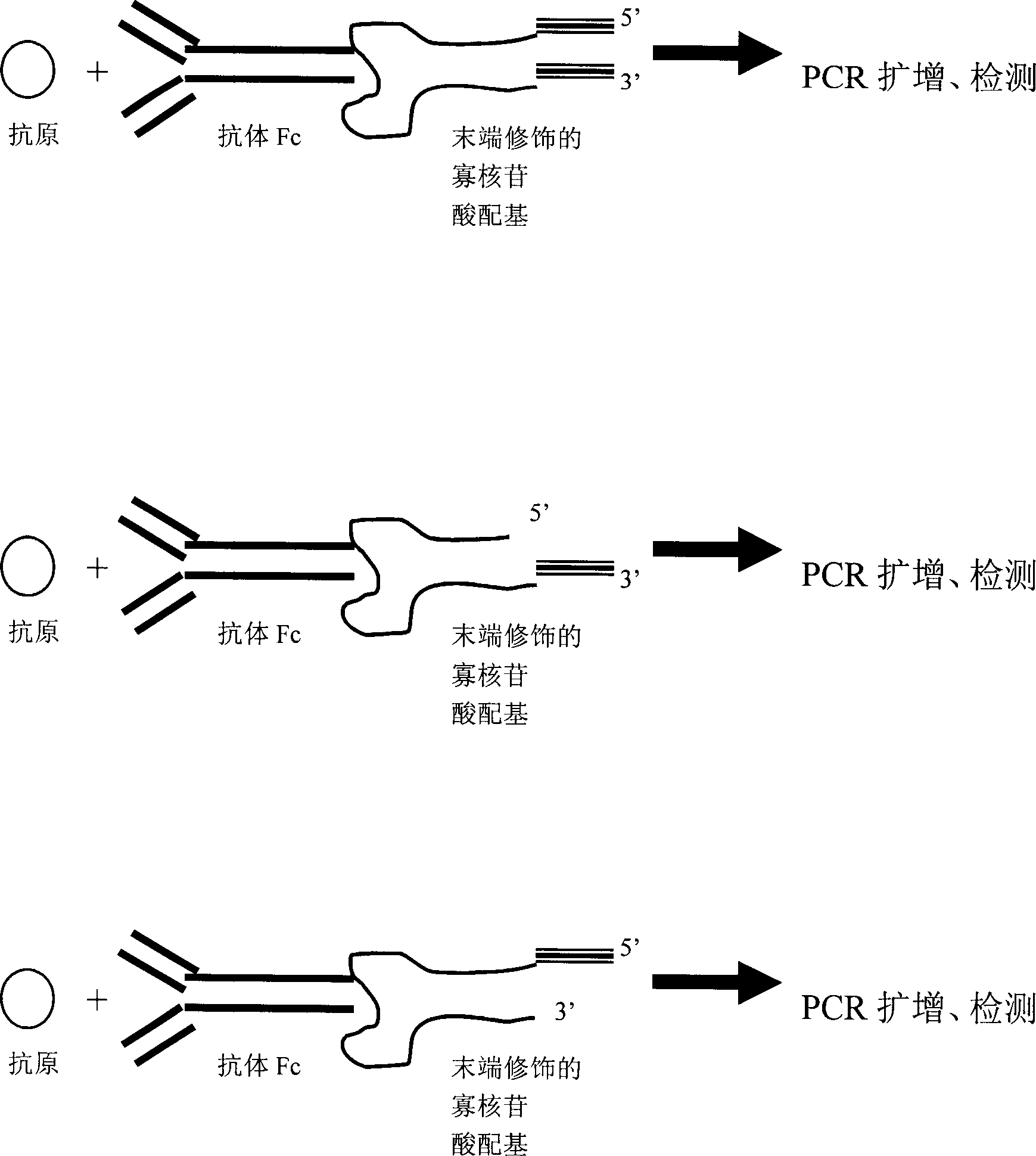
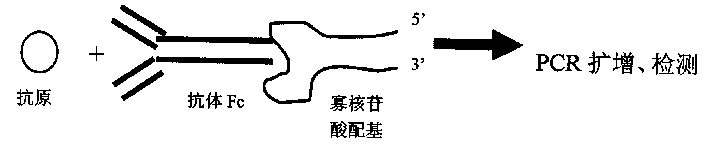
Antigen detection method and detection device made up by using said method
The present invention relates to a new type antigen detection method. Said method utilizes the direct combination of antibody Fc fragment specific oligonucleotide ligand and antibody, and converts the antibody signal into nucleic acid signal, then utilizes PCR amplification technique to detect antigen. The utilization of said method can form the detection kit or develop practical protein ship or other biological chip for detecting other various antigens.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA +1
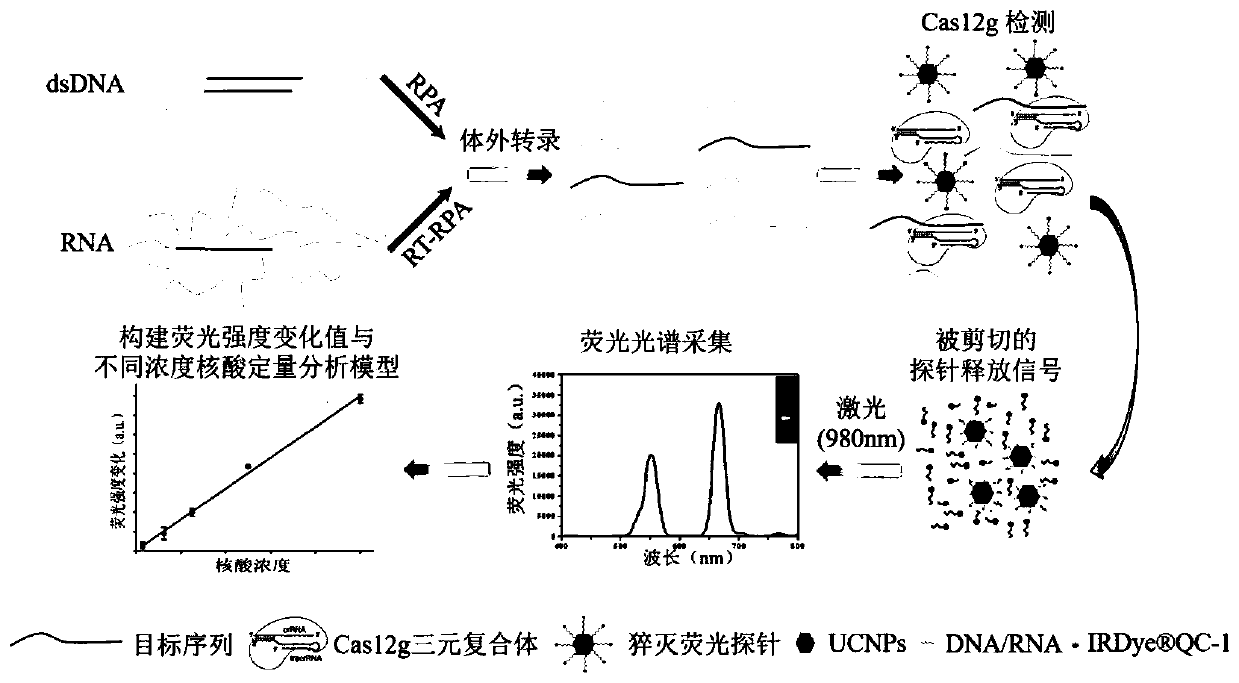
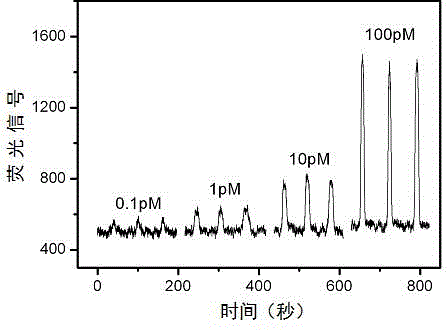
Rapid detection method for nanometer fluorescent trace of specific nucleic acid fragment on basis of CRISPR-Cas12g
PendingCN111378722ARealize quantitative detectionThe detection process is fastMicrobiological testing/measurementFluoProbesFluorescence spectra
The invention discloses a rapid detection method for nanometer fluorescent trace of specific nucleic acid fragment on the basis of CRISPR-Cas12g. The rapid detection method comprises the following steps: with the specific nucleic acid fragment in a biological sample as a research object, preparing a nucleic acid target, a quenching fluorescence probe and a Cas12g ternary complex of the biologicalsample; mixing the Cas12g ternary complex, the nucleic acid target, the quenching fluorescent probe, background RNA and an RNA enzyme inhibitor in a nuclease buffer solution for incubation, after theCas12g ternary complex is recognized and matched with the nucleic acid target, shearing the nucleic acid target in accompany with non-specific trans-shearing of the quenching fluorescent probe so as to obtain detectable fluorescence; and collecting fluorescence spectrum data, and constructing a quantitative detection model of an up-conversion nanometer fluorescence intensity change value and nucleic acid targets with different concentrations so as to realize rapid detection of the nanometer fluorescence trace of the nucleic acid target in the biological sample. The rapid detection method provided by the invention is applicable to rapid, specific and sensitive detection of the specific nucleic acid fragment in the biological sample.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Thio probe for detecting nuclease with 3'-5' exo activity
ActiveCN104293917AAccurate analysisHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationThio-Phosphate
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Drug-resistant heterogeneous circulating tumor cell capture and gene analysis reagent, device and method
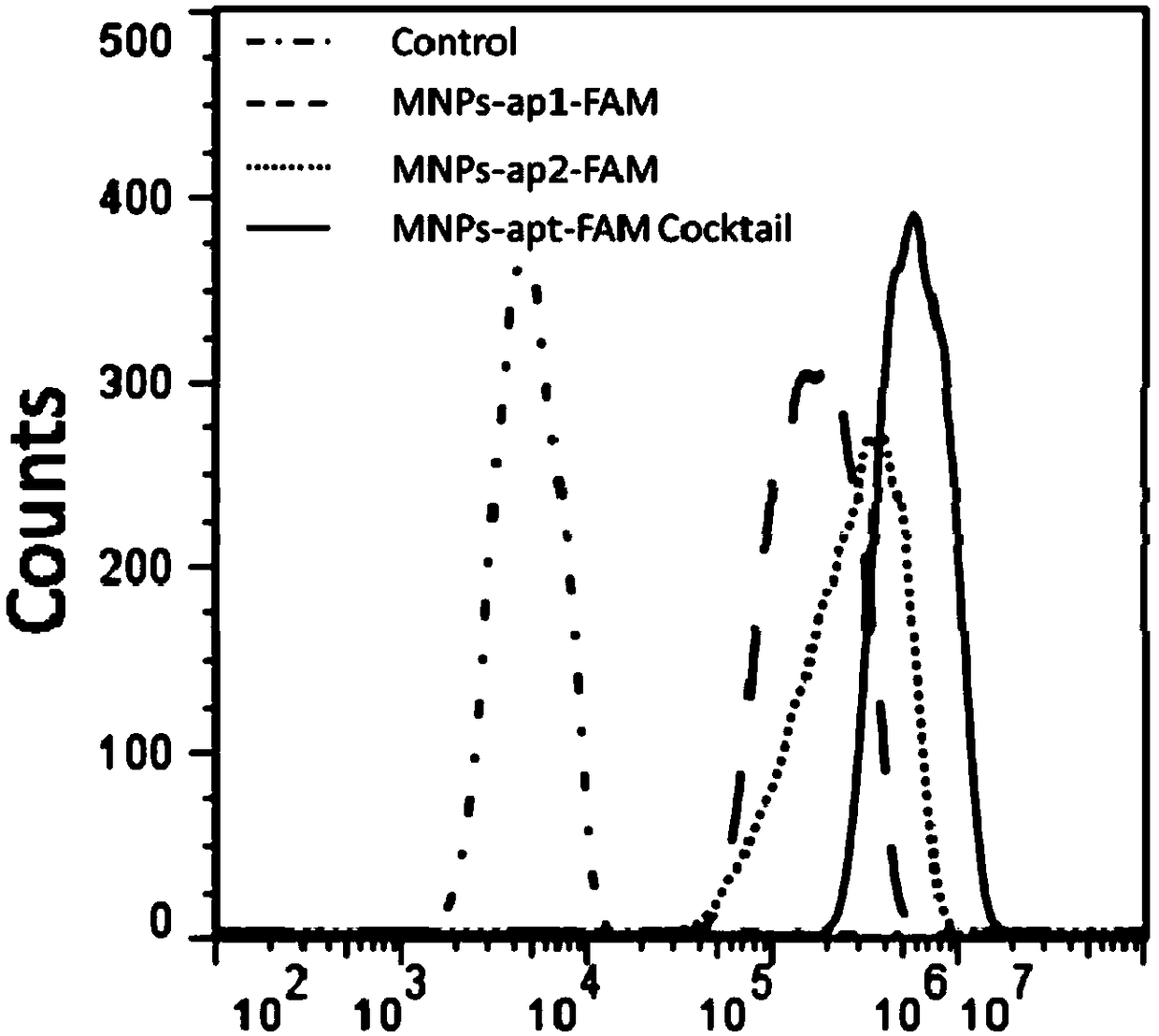
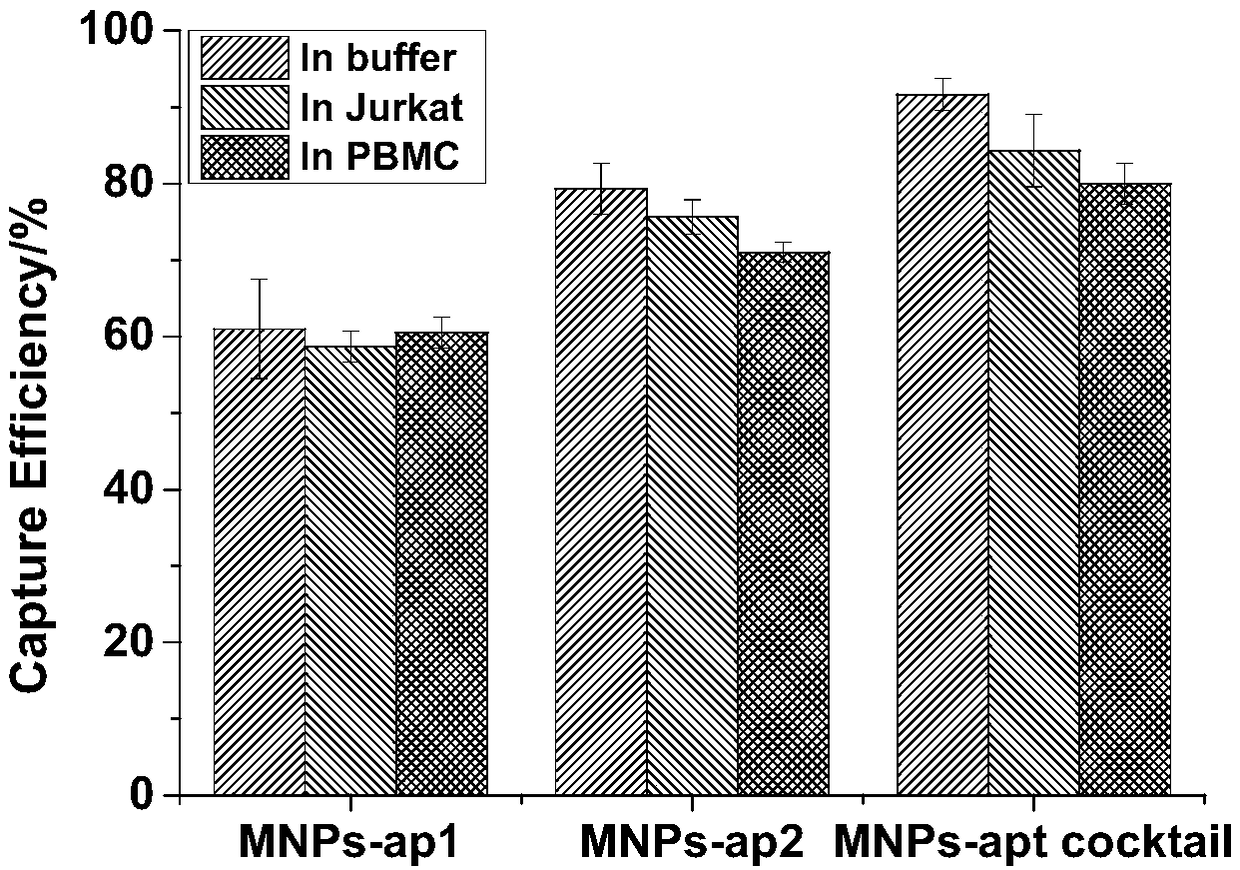
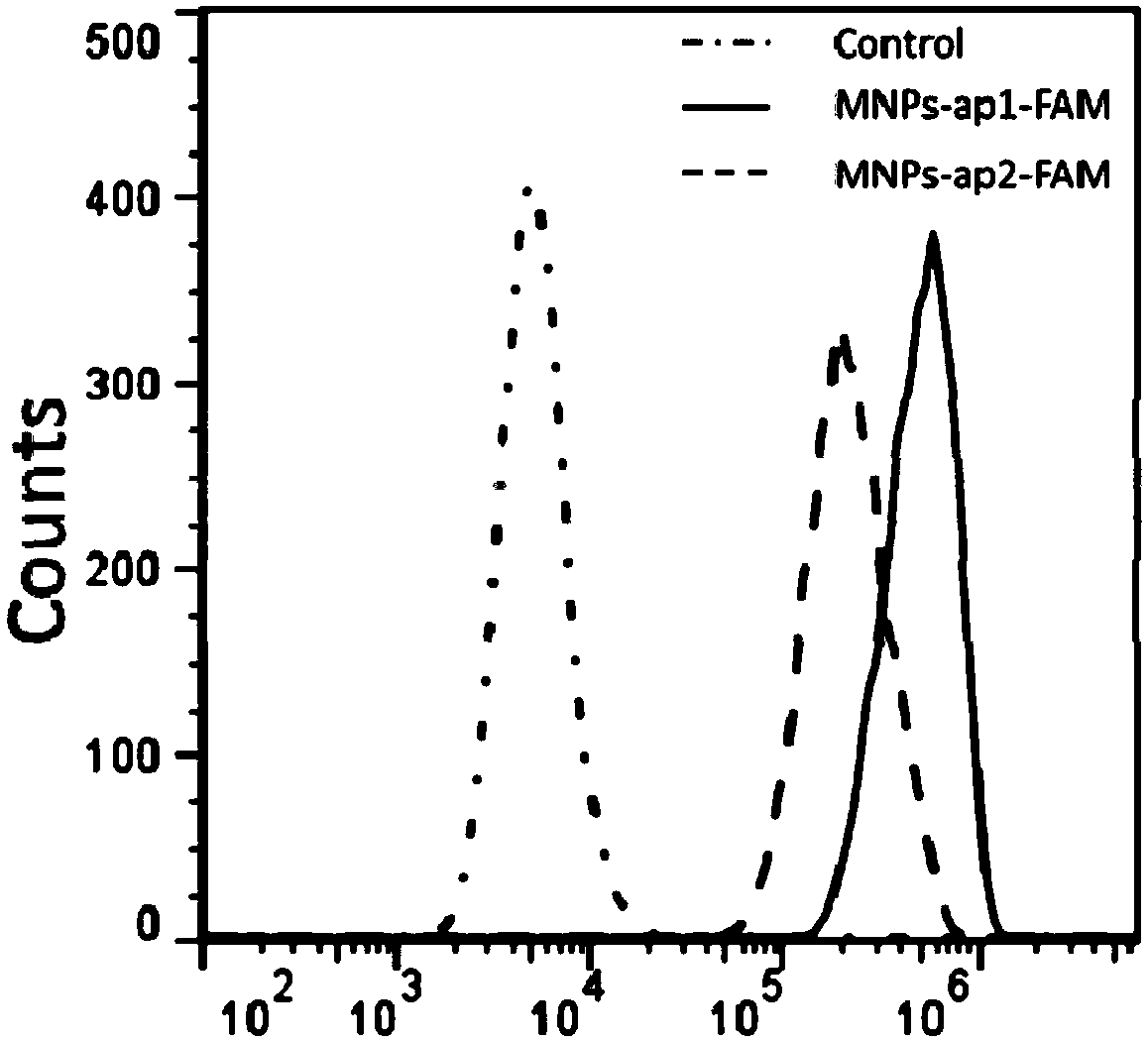
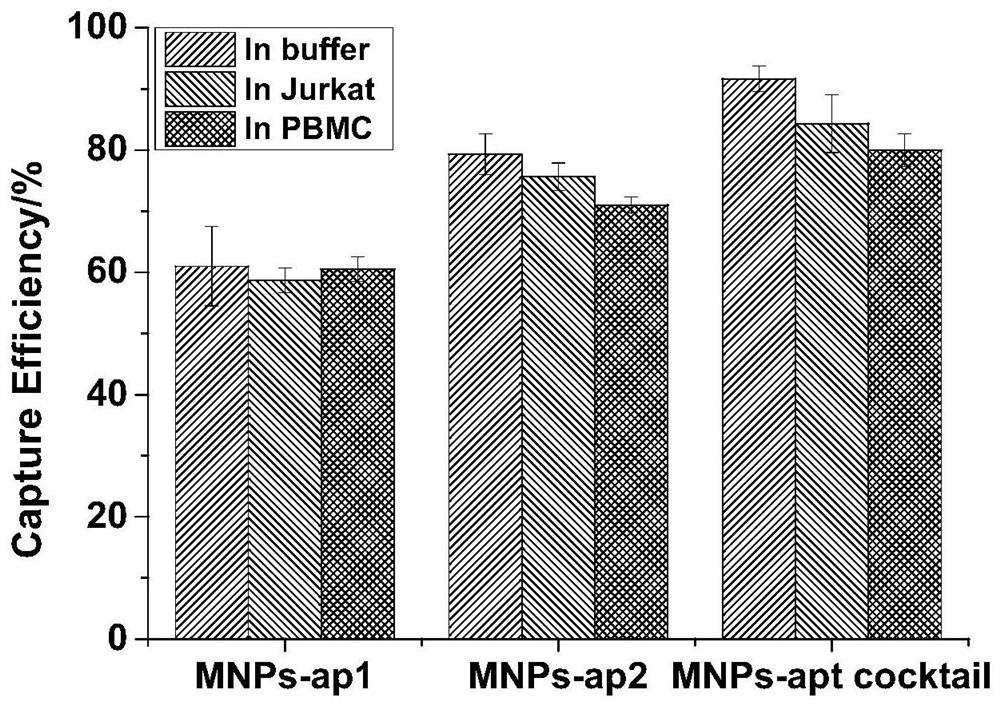
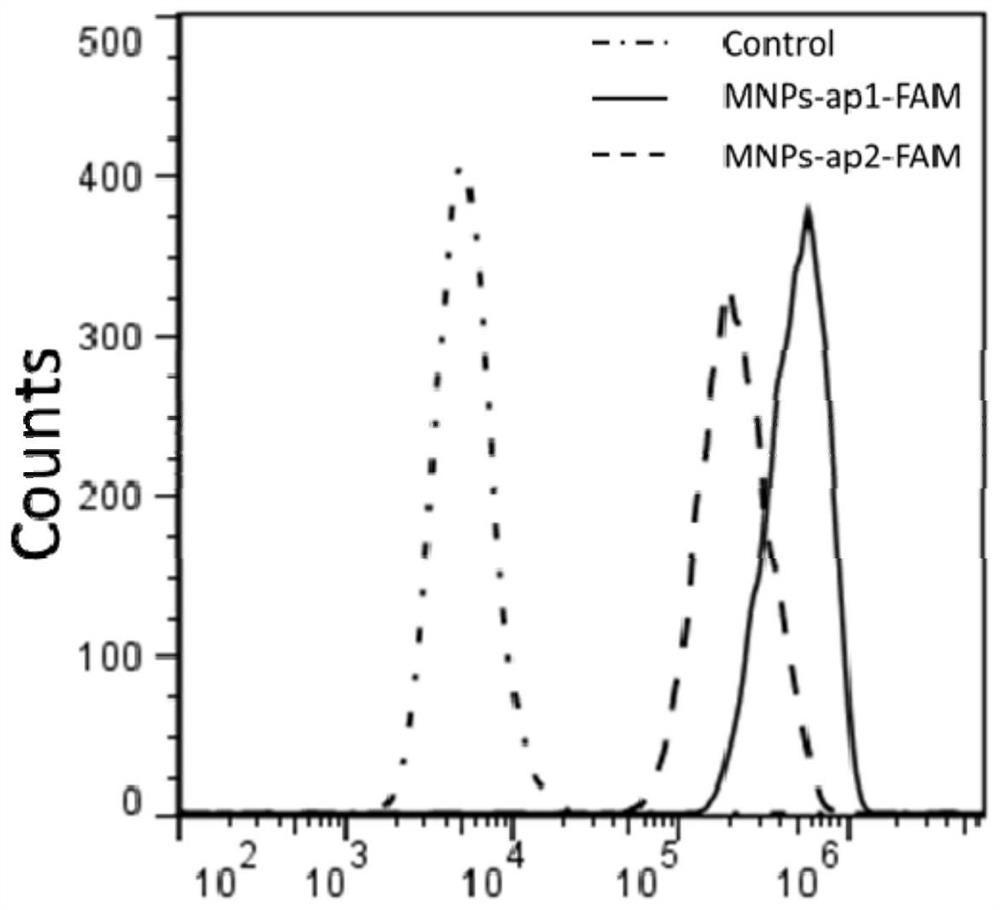
ActiveCN109266653AHigh affinityLow affinityCell dissociation methodsMicrobiological testing/measurementAptamerMagnetic bead
The invention relates to a nucleic acid aptamer with high affinity for cisplatin-resistant circulating tumor cells and magnetic beads modified by the nucleic acid aptamer. The nucleic acid aptamer ormagnetic bead of the invention are combined with other nucleic acid aptamers or magnetic beads known in the prior art, the capture efficiency of circulate tumor cells can be improved, and further, thepurity of circulating tumor cells can be improved by utilizing a microporous chip for secondary purification, so as to meet the requirements of gene analysis. A method and a reagent for efficiently capture circulating tumor cell of drug-resistant heterogeneous non-small cell lung cancer for gene analysis are particularly provided.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Micro-fluidic chip capable of removing bubbles
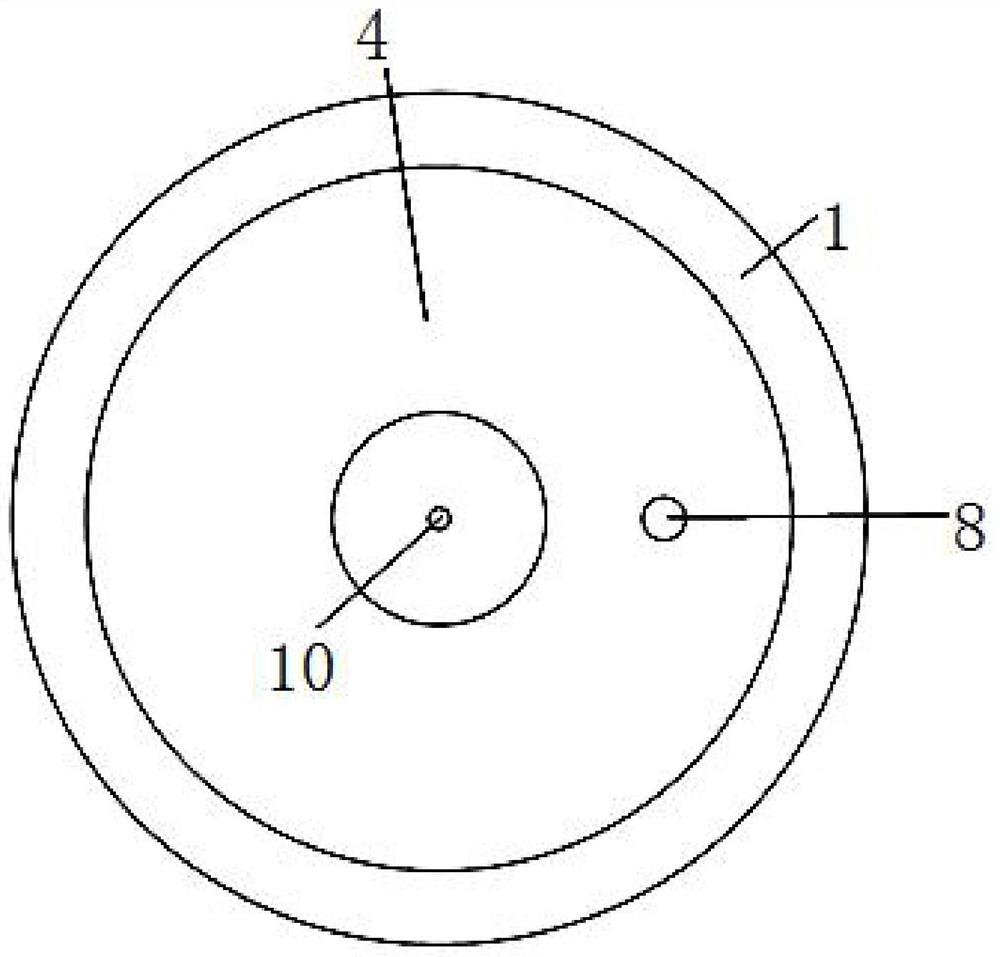
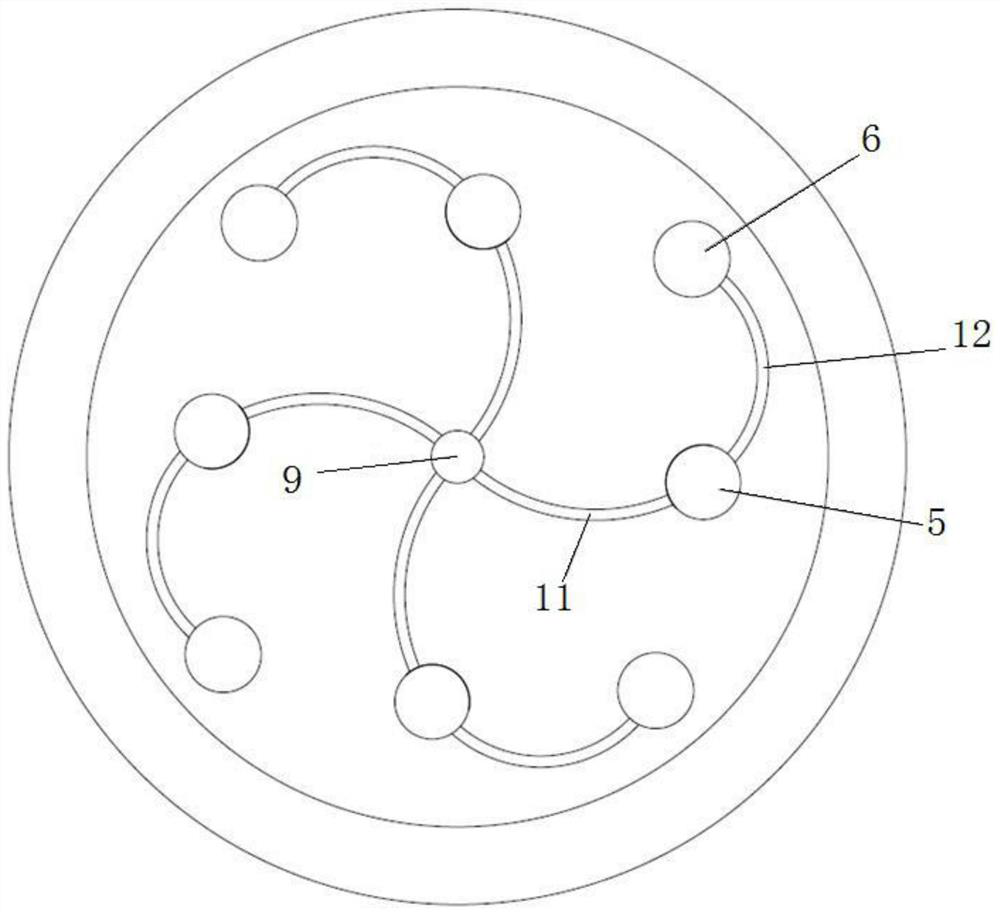
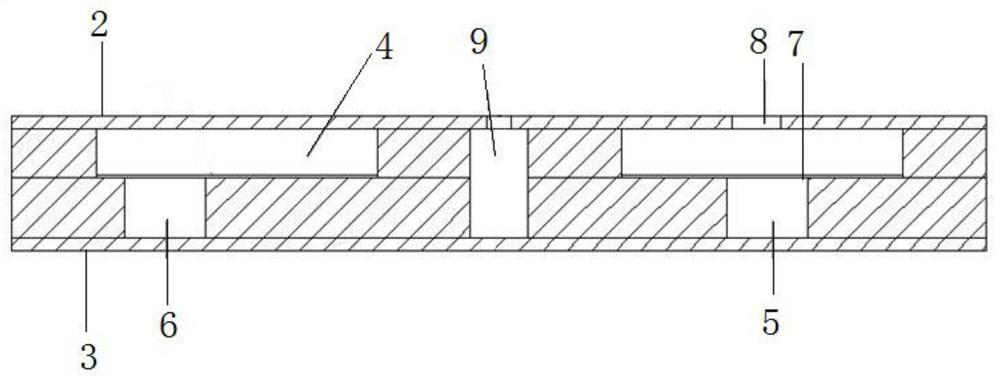
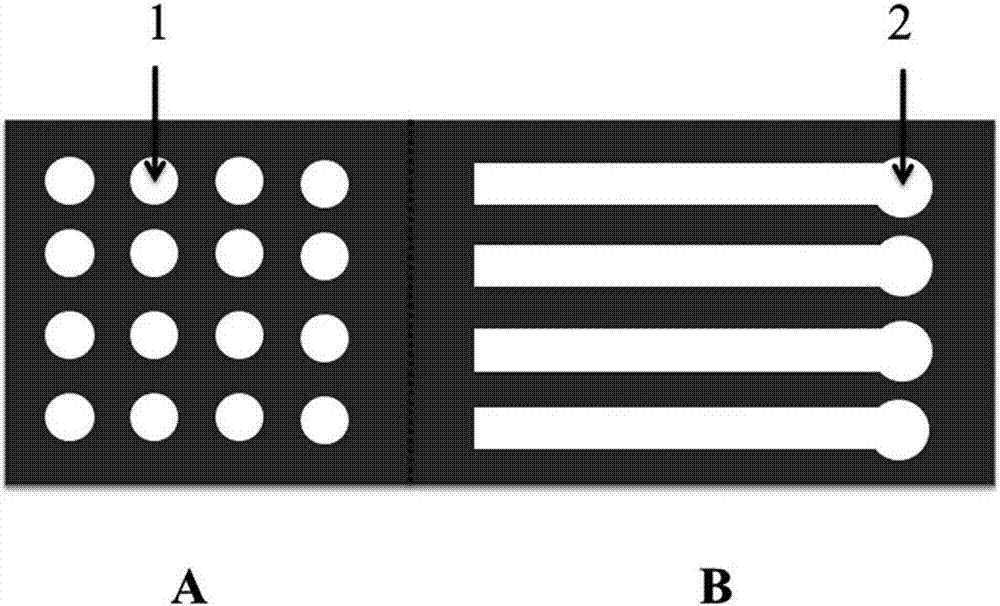
PendingCN113134400AReduce distractionsReduce detection backgroundLaboratory glasswaresPhysicsMicrofluidic chip
The invention discloses a micro-fluidic chip capable of removing bubbles; the top of a chip body is provided with an annular gas communication pool, the inner bottom of the gas communication pool is provided with a concave gas filtering pool and a reaction pool, the inner bottom of the gas communication pool is covered with a hydrophobic filter membrane, and the gas communication pool and the gas filtering pool as well as the gas communication pool and the reaction pool are separated by the hydrophobic filter membrane; a gas hole communicated with the gas communication pool is formed in the area, corresponding to the gas communication pool, of the upper cover plate; a sample adding pool is formed in the center of the chip body; a sample adding hole communicated with the sample adding pool is formed in the position, corresponding to the sample adding pool, of the upper cover plate; the bottom of the sample adding pool is communicated with the gas filtering pool through a first channel; and the bottom of the gas filtering pool is communicated with the reaction pool through a second channel. The influence of bubbles on the detection result in the sample detection process can be avoided, so that the accuracy of the detection result is improved. The chip is small in size, does not need mechanical driving force for sample adding, is convenient to use, and is suitable for various POCT scenes.
Owner:HANGZHOU TINKER BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Fluorescence resonance energy transfer-based detection of fumonisin b 1 Methods
ActiveCN103901000BImprove accuracyImprove stabilityFluorescence/phosphorescenceEnergy transfer upconversionMagnetite Nanoparticles
The present invention provides a method for detecting fumonisin B1 based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer. The method comprises that: NaYF4:Yb,Ho upconversion fluorescence nanoparticles and gold nanoparticles are respectively and covalently bound to both ends of the stem-like part of the specific molecular beacon, wherein the fluorescence resonance energy transfer upconversion fluorescence can be quenched by the gold nanoparticles; and a fumonisin B1 aptamer and a complementary strand thereof are subjected to hybridization immobilization on the surface of magnetic nanoparticles, an analyte fumonisin B1 is added and is specifically bound with the aptamer so as to make the complementary strand be separated from the magnetic nanoparticles, and the separated complementary strand and the molecular beacon are subjected to hybridization so as to open the ring-like part of the molecular beacon, such that the fluorescence resonance energy transfer system is broken, the fluorescence signal is restored, and the fumonisin B1 content can be determined by detecting the fluorescence signal intensity, wherein the detection limitation of the method achieves 0.01 ng.mL<-1>. According to the present invention, the fumonisin B1 content in the food sample can be rapidly, accurately e and sensitively detected.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A Method for Simultaneous Detection of Three Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria Based on Multicolor Upconversion Fluorescent Labeling
ActiveCN103940792BImprove accuracyImprove stabilityFluorescence/phosphorescenceNano compositesFood borne
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A paper-based colorimetric method for detecting glucose
InactiveCN104374769BReduce experiment costEasy to operateMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorProcess engineeringFilter paper
The invention discloses a method for detecting glucose by paper-based colorimetry, which comprises the following steps: making a self-made colorimeter; designing a hydrophobic wax printing pattern; cutting filter paper; printing the hydrophobic wax printing pattern on the filter paper; melting wax into shape; preparing ZnFe 2 o 4 ; Prepare mixed solution; Add the mixed solution dropwise to the detection pool; Add the measured solution dropwise; The method for detecting glucose of the present invention is simple to operate, can be operated without professional technicians, has high detection speed, low cost, and simple post-treatment without pollution.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
A detection method of an eccentric focusing laser-induced fluorescence detection device suitable for detection on a capillary column
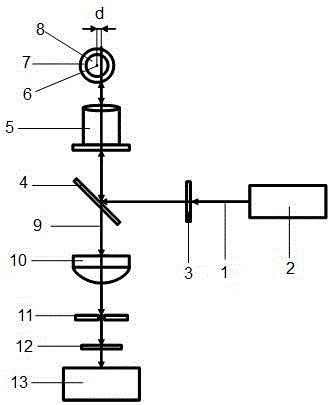
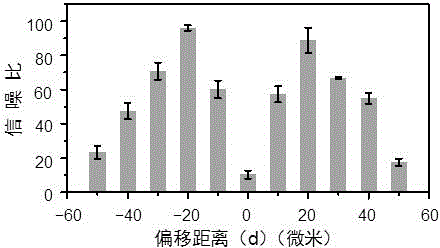
InactiveCN103245651BSimple structureEasy to analyzeFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicro columnLaser light
The invention relates to the field of analytical instrument research, and particularly relates to a detection method of a high-sensitivity laser-induced fluorescence detection device suitable for detection on a capillary column. The high-sensitivity laser-induced fluorescence detection device is characterized in that laser light is emitted from a laser, is filtered by a laser light filter, reflected by a dichroscope placed at a 45-degree angle relative to a horizontal plane and focused by an objective lens and finally enters a channel of a circular capillary tube from a position horizontally deviating from the center of the capillary tube by a certain distance so as to excite a component to be tested in the channel to generate fluorescence, and the fluorescence generated by excitation is collected by the objective lens, passes through the dichroscope, a focusing lens, a spatial filtering micropore and a fluorescence light filter respectively and finally enters a photoelectric detection device. The detection method not only is suitable for micro-column separation systems of capillary electrophoresis, capillary chromatography, capillary electrochromatography and the like, but also can be applied to analytic systems for flow injection analysis, sequence injection analysis, microfluidic liquid drop analysis, flow cytometry and the like based on circular capillary flow cells.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
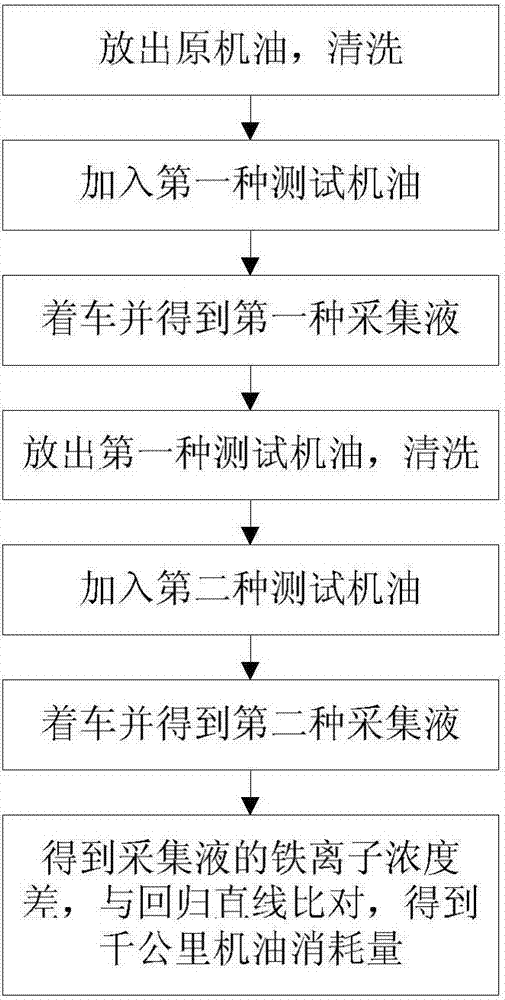
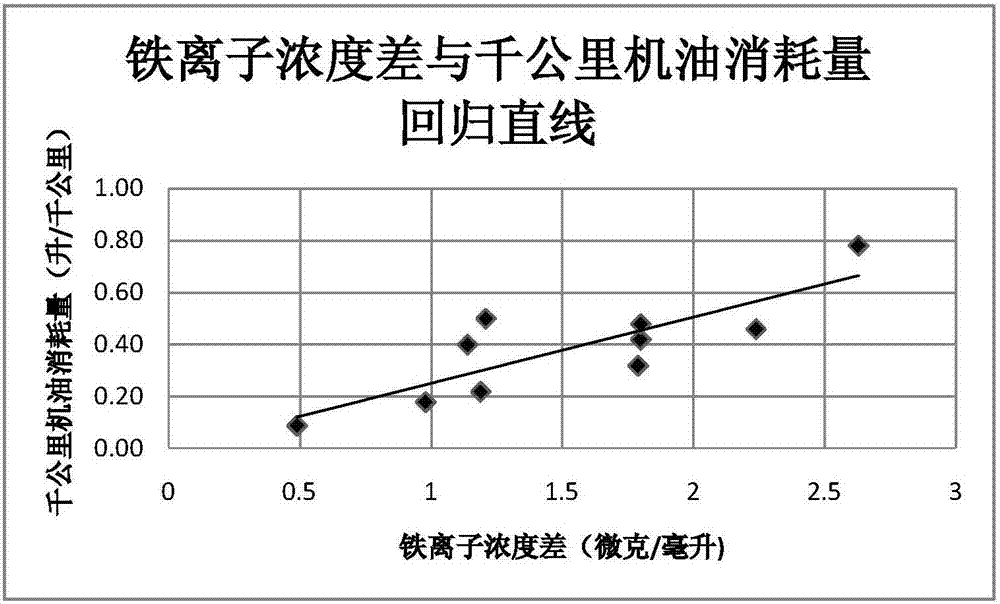
A rapid detection method for automobile engine oil consumption
ActiveCN106197589BConsumption in timeReduce detection backgroundRelative volume flow measurementsChemical compoundAutomotive engine
The invention discloses a method for quickly detecting the oil consumption of an automobile. In the present invention, the oil tank is first cleaned to reduce the detection background, and then the test engine oil without iron and organic ligand compounds and the test engine oil with iron and organic ligand compounds are added to the oil tank successively. , respectively measure the iron ion concentration in the exhaust gas after the combustion of the two test engine oils, and obtain the iron ion concentration difference. According to the regression line between the iron ion concentration difference and the oil consumption per thousand kilometers, the oil consumption per thousand kilometers of the vehicle is obtained, and then the vehicle is judged The degree of "burning engine oil"; the method of the present invention can accurately and timely detect engine oil consumption, has the advantages of short test time, simple equipment structure and strong practicability, and can be used as a basis to establish an accurate result of automobile engine oil consumption The test method can accurately judge the degree of "burning engine oil" of the car.
Owner:BEIJING HUA AO AUTOMOBILE SERVICE CO LTD
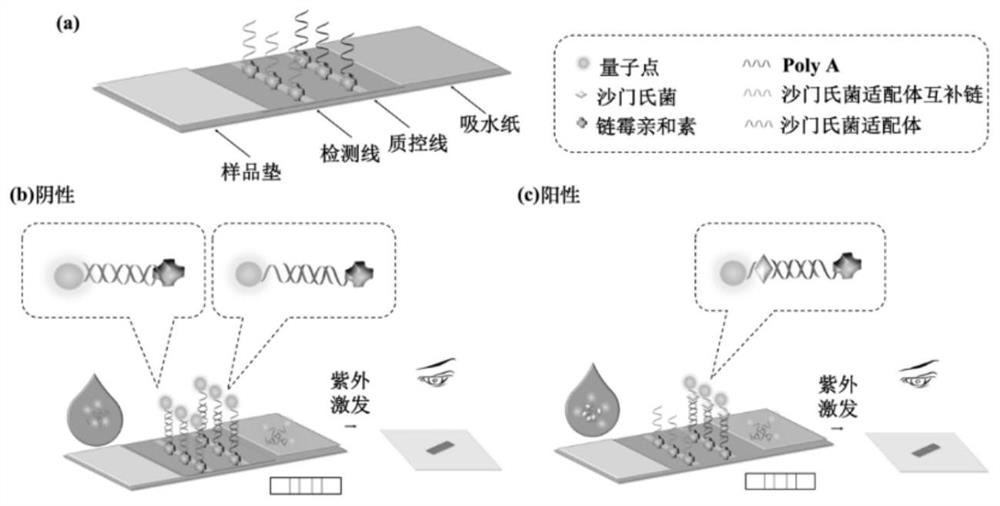
Detection test strip based on quantum dot labeling as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN112114142ASimple and fast operationSimple processBiological material analysisBiological testingAptamerCellulose
The invention discloses a salmonella detection test strip based on quantum dot labeling and a preparation method of the salmonella detection test strip and belongs to the field of food safety detection. A ZnS:Mn quantum dot is connected with a salmonella aptamer to serve as a signal probe, and the salmonella is detected by utilizing a test strip chromatography principle. The test strip is composedof a sample pad, a nitrocellulose membrane (NC film), absorbent paper and a back plate. the aptamer complementary sequence connected with streptavidin and Poly A is sprayed and fixed on a NC film byusing a BioDot three-dimensional spray point instrument to form a detection line T line and a quality control line C line. The quantum dots and the salmonella aptamer (the aptamer contains a Poly T sequence) are coupled to serve as a signal probe, and when the signal probe and a sample solution are mixed and then dropwise added to a sample pad, due to the capillary force effect caused by absorbentpaper, the signal probe migrates from the sample pad to the absorbent paper through the NC film. The salmonella is detected according to the fluorescence intensity ratio of the T line to the C line.
Owner:中华人民共和国太仓海关
A cleaning head for a porous plate
The invention discloses a cleaning head for a porous plate and relates to cleaning equipment for a porous plate and a porous biological chip. It includes a row of water suction pipes, a row of water injection pipes, water injection interface, water outlet interface, main part, side plate, side plate rubber pad, porous partition, and the main part, side plate rubber pad and porous partition. The formed water injection chamber, water outlet chamber, water injection buffer chamber and water outlet buffer chamber. The water injection interface is connected to the water injection pipe through the water injection buffer chamber, the holes in the porous partition and the water injection chamber, and the water outlet interface is connected to the water suction pipe through the water outlet buffer chamber, the holes in the porous partition and the water outlet chamber. The side plate and the side plate rubber pad are fixed on the main part in a detachable manner by screws or slots on both sides of the main part, so as to facilitate cleaning and maintenance of the chambers, partitions and pipelines. The invention has the advantages of good uniformity, convenient cleaning, maintenance and use, flexible cleaning methods, suitable for experiments of various scales, and good operability.
Owner:上海裕隆生物科技有限公司
A kind of small molecule microarray and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103792345BHigh resistance to non-specific adsorptionThe modification process is simple and convenientLaboratory glasswaresBiological testingHigh fluxEsterification reaction
The invention discloses a preparation method for a small-molecule microarray. The preparation method comprises the steps of bonding the hydroxyl terminal of a nonspecific adsorption resistance material modified on a chip substrate with the hydroxyl terminal of a small-molecule light crosslinking agent through an esterification reaction, and randomly fixing small molecules on the hydroxyl terminals through light crosslinking. By the adoption of a direct esterification mode, the small-molecule light crosslinking agent is quickly and efficiently coupled to the surface of the nonspecific adsorption resistance material; a chip modification process is simple and convenient and can be implemented under a normal temperature condition; therefore, the modification cost is reduced, and the modification efficiency is improved; a high detection signal is guaranteed; a non-reacted group still keeps high nonspecific adsorption resistance capacity, so that a background signal is reduced; the prepared small-molecule microarray is high in detection signal and low in background signal and can be used for mutual action between high-flux screened small-molecule medicaments and targets.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Reagent, device and method for drug-resistant heterogeneous circulating tumor cell capture and gene analysis
ActiveCN109266653BHigh affinityLow affinityCell dissociation methodsMicrobiological testing/measurementSCLC - Small cell lung cancerCirculating cancer cell
The invention relates to a nucleic acid aptamer with high affinity for cisplatin-resistant circulating tumor cells and magnetic beads modified by the nucleic acid aptamer. The nucleic acid aptamer or magnetic beads of the present invention can be used in combination with other nucleic acid aptamers or magnetic beads known in the prior art to improve the capture efficiency of circulating tumor cells, and further use of microporous chips for secondary purification can improve the purity of circulating tumor cells , to meet the requirements of genetic analysis. It also particularly provides a method and reagents for efficiently capturing drug-resistant heterogeneous non-small cell lung cancer circulating tumor cells and performing gene analysis.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method for high specificity detection of target DNA in sample, and application thereof
InactiveCN105368919AImprove detection efficiencyAvoid false positivesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSustenanceHybridization reaction
The invention discloses a method for high specificity detection of target DNA in a sample. The method comprises the steps of pretreatment, preliminary treatment, a one-step reaction, post-treatment, and a color development reaction. Traditional molecular hybridization methods are substantially improved, nucleic acid hybridization and enzyme linking reactions are carried out in a combined manner, and synergistic cooperation treatment of solid sustenance surfaces before and after the hybridization reaction are carried out through pretreatment, preliminary treatment and post-treatment, so the detection efficiency of the target DNA in the sample and the solid sustenance surface DNA molecule hybridization specificity are improved, and the false positivity of a detection result is effectively avoided.
Owner:BEIJING BIOLKEY BIOLOGICAL TECH
A cell detection method and device based on the photothermal effect of nanomaterials
ActiveCN104655594BThe detection method is simpleNo complicated steps requiredAnalysis by material excitationPhosphateTreated cell
The invention discloses a nanometer-material-photothermal-effect-based cell detection method and a cell detection device. The method comprises the following detecting steps: (1) centrifuging cell solution to be detected, discharging supernatant, redissolving with PBS (Phosphate buffer solution) and centrifuging again, repeating the operations, discharging supernatant, and dissolving centrifuged precipitates with 10mul of PBS buffer solution; (2) dropwise adding the treated cell sample onto a sample adding area of an infiltration test strip, and washing for three times with PBST (Phosphate buffer solution-tween) solution; (3) adding with 5-20muL of grapheme-gold-antibody compound into the sample adding area of the infiltration test strip, washing for three times with PBST solution and airing; and (4) radiating the sample adding area of the detection device with laser with the excitation wavelength of 808nm for 10-90s, recording the temperature before and after radiation, calculating the temperature difference, and drawing a calibration curve by use of the cell number as an x-coordinate and the temperature difference as a y-coordinate, wherien when one sample is detected, the temperature difference of the sample is detected and is substituted into the calibration curve to calculate the cell number. The detection device and the detection method have the advantages that the detection method is simple, the detection time is short, the detection sensitivity is high and the like.
Owner:山东师大瑞柏生物科技有限公司
Multispectral up-conversion nanoparticle-based immunochromatographic test paper for rapidly detecting multiple pesticide residues and preparation method for immunochromatographic test paper
InactiveCN106018797ALow toxicityGood chemical stabilityBiological material analysisBiological testingAntigenNanoparticle
The invention relates to multispectral up-conversion nanoparticle-based immunochromatographic test paper for rapidly detecting multiple pesticide residues and a preparation method for the immunochromatographic test paper, and belongs to the technical field of chemical analysis. The pesticide test paper comprises a test paper board, a sample dropwise-addition unit, a detection unit and a sample recovery unit, wherein the sample dropwise-addition unit, the detection unit and the sample recovery unit are all connected to the test paper board; the detection unit is positioned in middle of the test paper board, and comprises an antigen coating buffer and confining liquid. The immunochromatographic test paper and the preparation method for the same have the beneficial effects that the test paper has the characteristics of rapidness, convenience, specificity, sensitivity and low cost, particularly has the characteristics of rapidness and convenience, is particularly suitable for grassroots units, field operating personnel, large-batch short-time detection and large-scale general survey and the like, has great development potential and broad application prospect, is considered as one of the most promising novel technologies for food safety detection, and becomes the main development trend of food safety detection.
Owner:DALIAN NATIONALITIES UNIVERSITY
Probe and kit for improving pathogenic microorganism antigen detection sensitivity
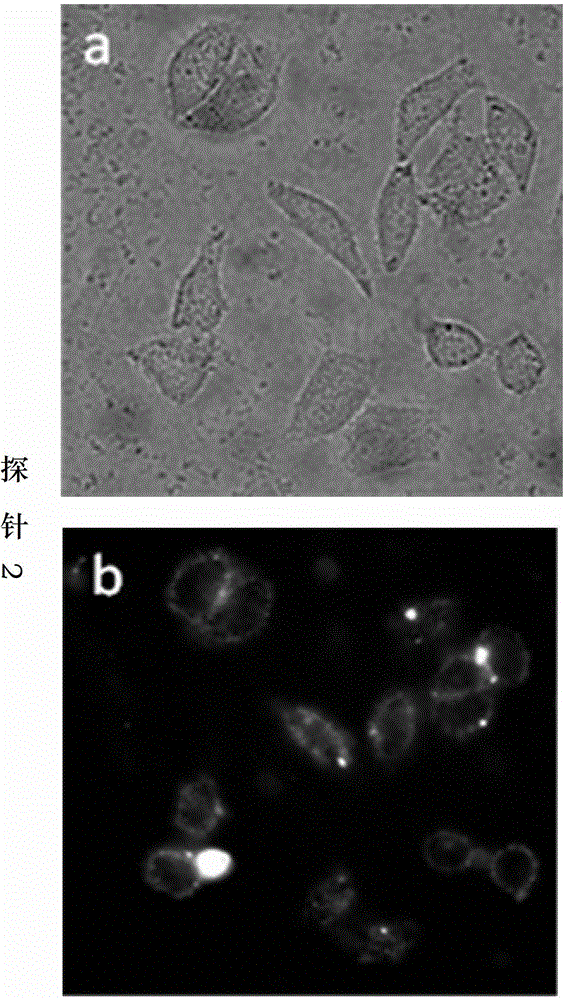
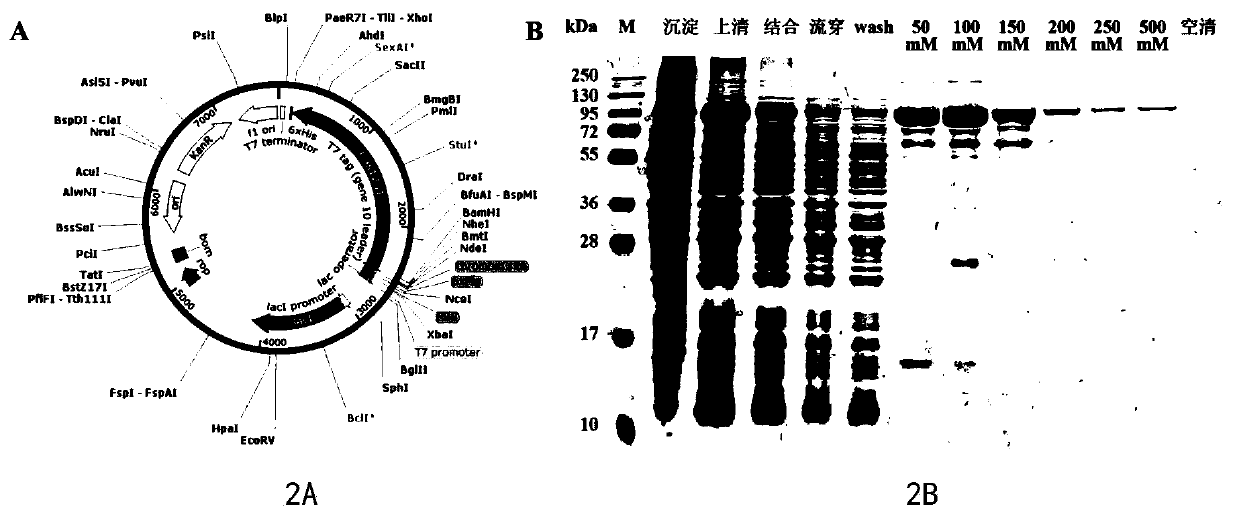
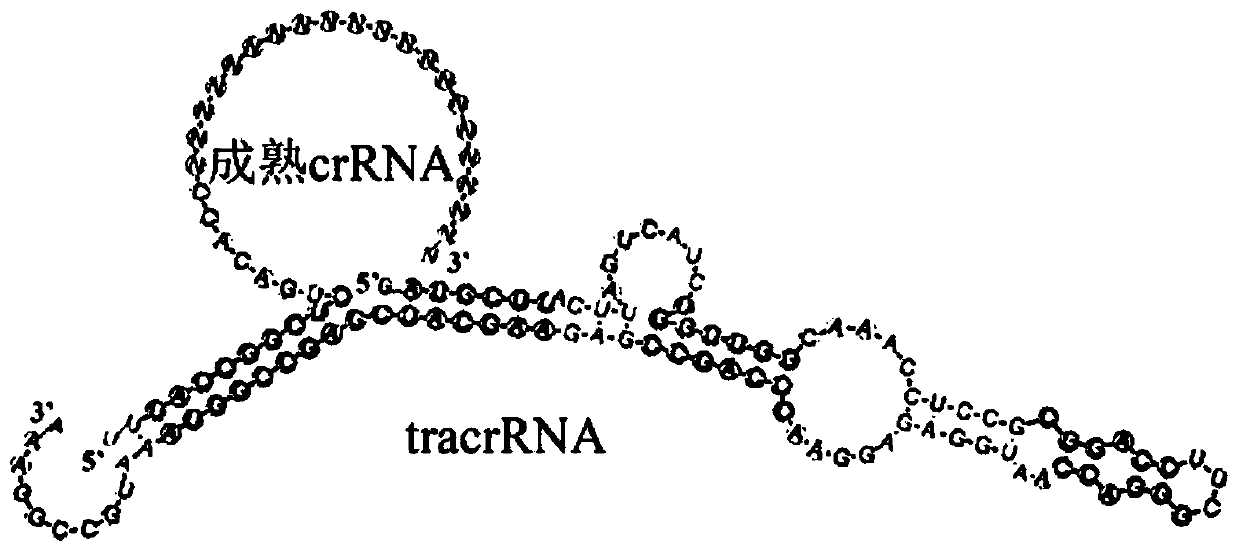
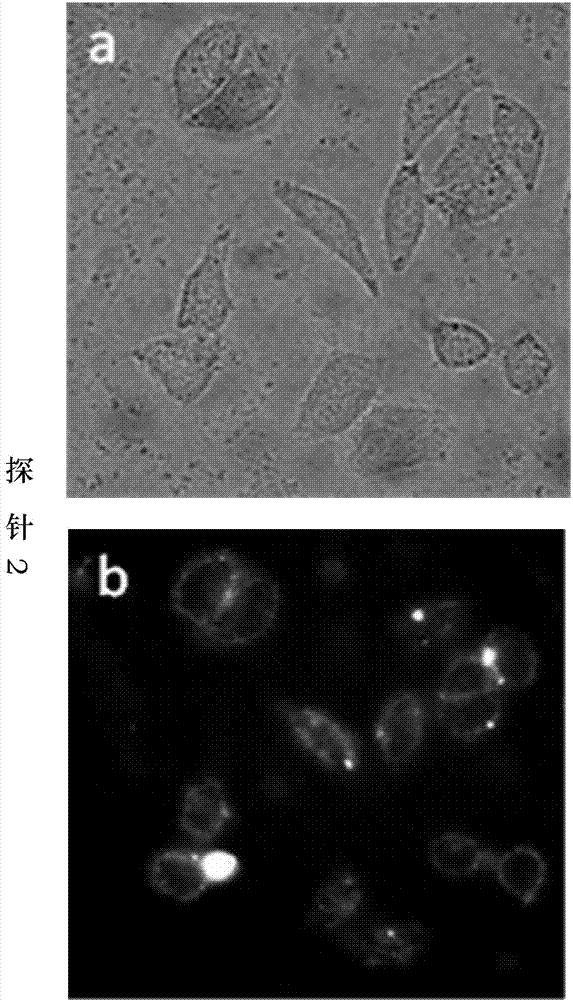
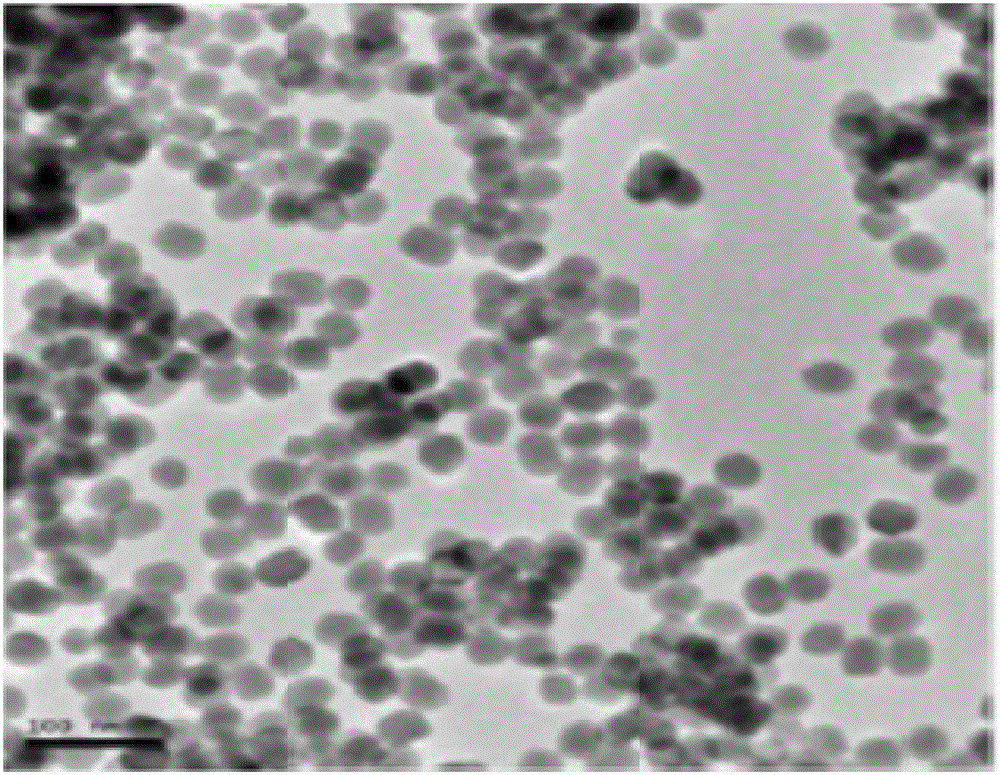
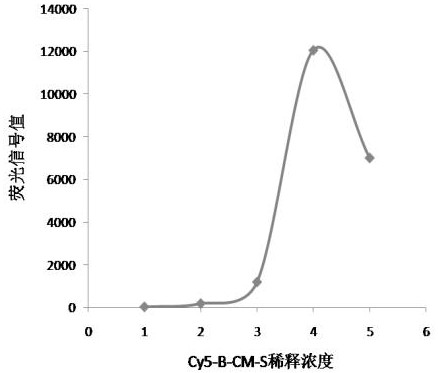
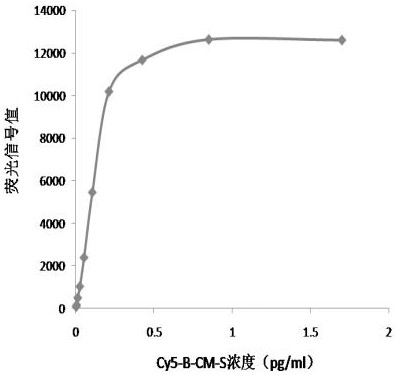
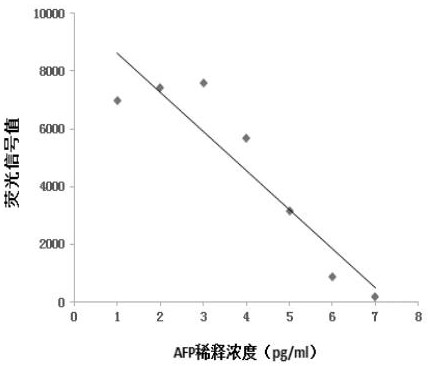
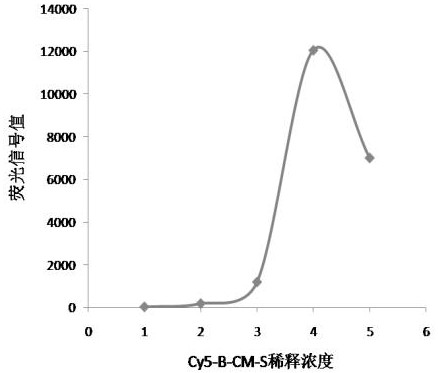
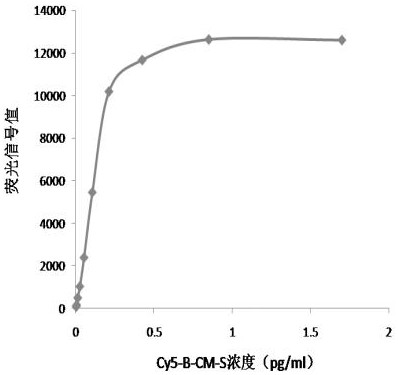
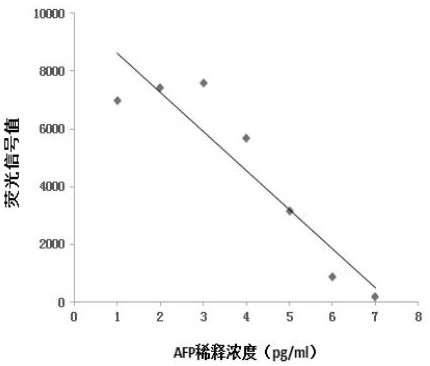
ActiveCN113252892AReduce detection backgroundHigh detection sensitivityBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceAntigenPathogenic microorganism
The invention discloses a probe for improving antigen detection sensitivity of pathogenic microorganisms and a kit containing the probe. The probe is double-stranded DNA which contains a fluorescence label and is provided with a restriction enzyme site, and the double-stranded DNA consists of Cy5-B-CM-S and NH2-B-CM-AS; wherein the Cy5-B-CM-S is as shown in SEQ ID No. 1, and the NH2-B-CM-AS is as shown in SEQ ID No. 2. The probe is combined with a detection antibody of a to-be-detected antigen, so that the detection background can be greatly reduced, the detection sensitivity of the pathogenic microorganism antigen is improved, and a foundation is laid for research and development of a single-molecule diagnostic reagent of the pathogenic microorganism antigen. Meanwhile, the probe restriction enzyme design can realize rapid detection of antigens.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF HEPATOLOGY
Probe and kit for improving detection sensitivity of pathogenic microorganism antigen
ActiveCN113252892BHigh detection sensitivityReduce detection backgroundBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescencePathogenic microorganismMicrobiology
The invention discloses a probe for improving the detection sensitivity of pathogenic microorganism antigen and a kit containing the probe. The probe is a double-stranded DNA containing a fluorescently labeled restriction endonuclease site, and the double-stranded DNA is composed of Cy5-B-CM-S and NH2-B-CM-AS; the Cy5-B-CM ‑S is shown in SEQ ID No.1, and the NH2‑B‑CM‑AS is shown in SEQ ID No.2. Combining the probe with the detection antibody of the antigen to be tested can greatly reduce the detection background, improve the detection sensitivity of the pathogenic microorganism antigen, and lay a foundation for the development of single-molecule diagnostic reagents for the pathogenic microorganism antigen. At the same time, the restriction endonuclease design of the probe can realize the rapid detection of the antigen.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF HEPATOLOGY
Method and reagent kit for simultaneously detecting resistance site of three nucleotide analogues of hepatitis B virus
InactiveCN101812537BAchieve accuracyAchieve reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMulti siteNucleotide
The invention provides a method and a reagent kit for simultaneously detecting the resistance sites of the three nucleotide analogues of a hepatitis B virus (HBV). Based on the genotype sequence of the HBV, four nested amplification primers and twenty-seven wild resistance-detection oligonucleotides probes aiming at ten resistance sites are designed in an HBV polymerase area, digoxin-labeled oligonucleotides universal primers are used for conducting nested PRC reaction to amplify a target DNA segment, a target DNA amplification product to be labeled is used for hybridizing with specific oligonucleotide probes on matrix, and the existence of the resistance of the HBV to the three nucleotide analogues is judged through enzymatic color development reaction link-coupled by hybridization conjugates. The method improves the accuracy, the reliability and the sensitivity and can simultaneously detect the ten resistance sites of the three nucleotide analogues, thereby realizing the high-throughput, multi-site, economic and rapid detection and fitting to clinical needs in a better way. The method is of great significance to the realization of early detection and the proper guide of clinicalpersonalized medication.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Exonuclease III-driven three-dimensional DNA nanomachines and their applications
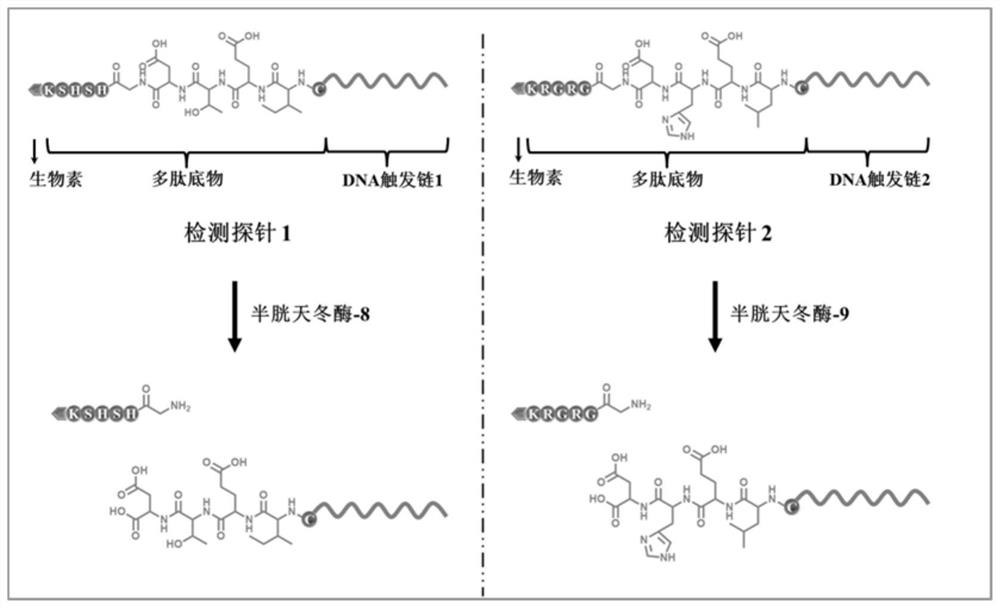
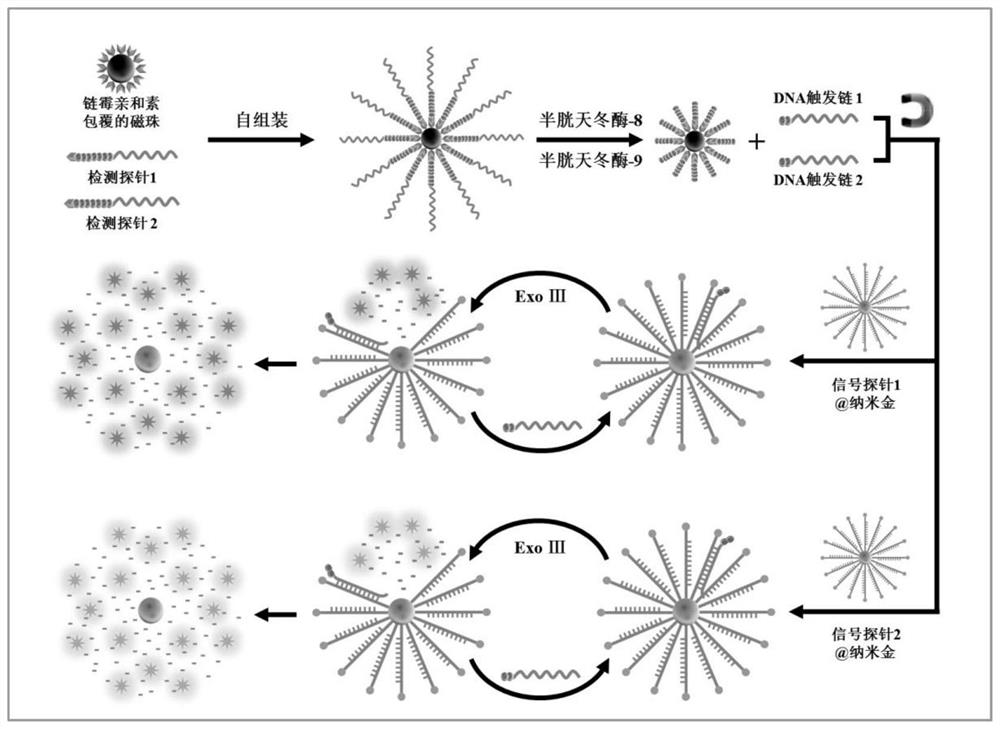
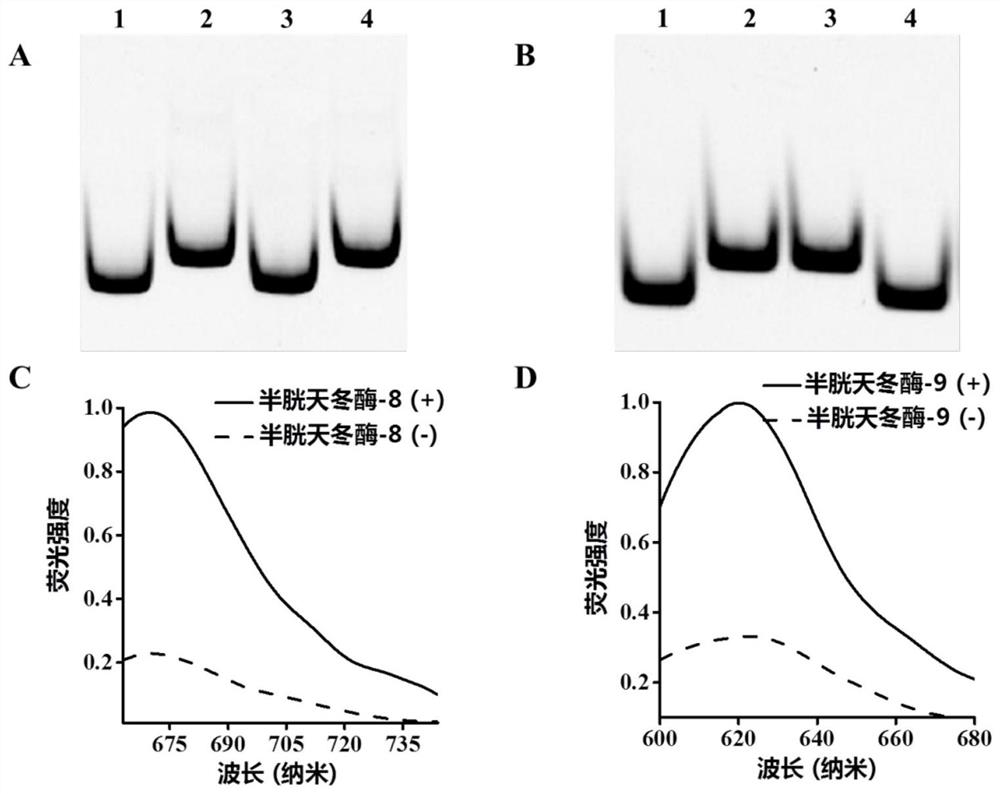
ActiveCN113106147BAchieving Sensitive DetectionReduce background signalMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCaspase inhibitorsExonuclease III
The present application provides an exonuclease III-driven three-dimensional DNA nanomachine and its application. The three-dimensional DNA nanomachine includes a signal probe@nano-gold structure and a detection probe, and the signal probe includes a signal probe sequence and a fluorescence Molecules, the detection probe contains a caspase recognition site and a DNA trigger strand, and the DNA trigger strand is complementary to the signal probe sequence; the detection probe is cleaved in the presence of caspase to release the DNA trigger strand containing the DNA trigger strand. structure, the DNA trigger strand in this structure hybridizes with the signal probe to form double-stranded DNA, the double-stranded DNA can be recognized and digested by exonuclease III, and the fluorescent molecules in the signal probe are released. Continue to hybridize with other signaling probes to achieve cyclic release of fluorescent molecules. The invention can realize the simultaneous detection of multiple caspase activities with high detection sensitivity, and can also be used for screening caspase inhibitors.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Cell model for quick screening of histone deacetylase inhibitor
InactiveCN101008009BSensitive detectionEfficient exclusionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDrug developmentLuciferases
The invention discloses a cell sifting moudle for fast sifting of antineoplastic- histone precursor histone deacetylase inhibitor compound from compound storage during new drug development. The moudlemakes use of speciality that the precursor histone deacetylase inhibitor can activate some starting subsequence, constructs te oexpression vector containing special starting factor and firefly luciferase reporting gene, and builds cos- 7 clone that stably expresses said vector. The cell contains starting subsequence with different degree of activity for luciferase, the starting factor can be acitvated by histone precursor histone deacetylase inhibitor and then the expression of luciferase reporting gene is intensified, and so the detection for histone precursor histone deacetylase inhibitor activity in sample through detection of luciferase activity change can be finished in a short time. The cell sifting moudle can be used for fast and high- flux sifting of new antineoplastic and histoneprecursor histone deacetylase inhibitor compound from compound storage during new drug development.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com