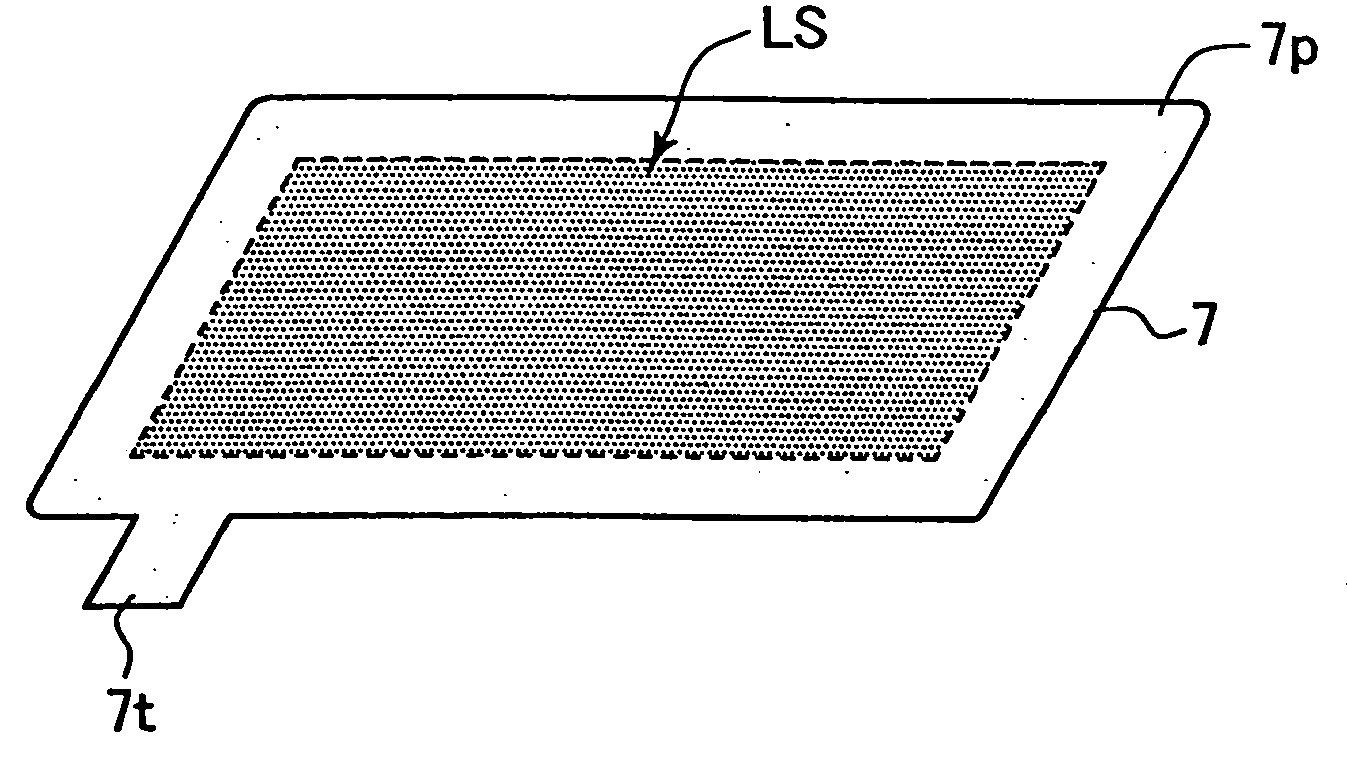
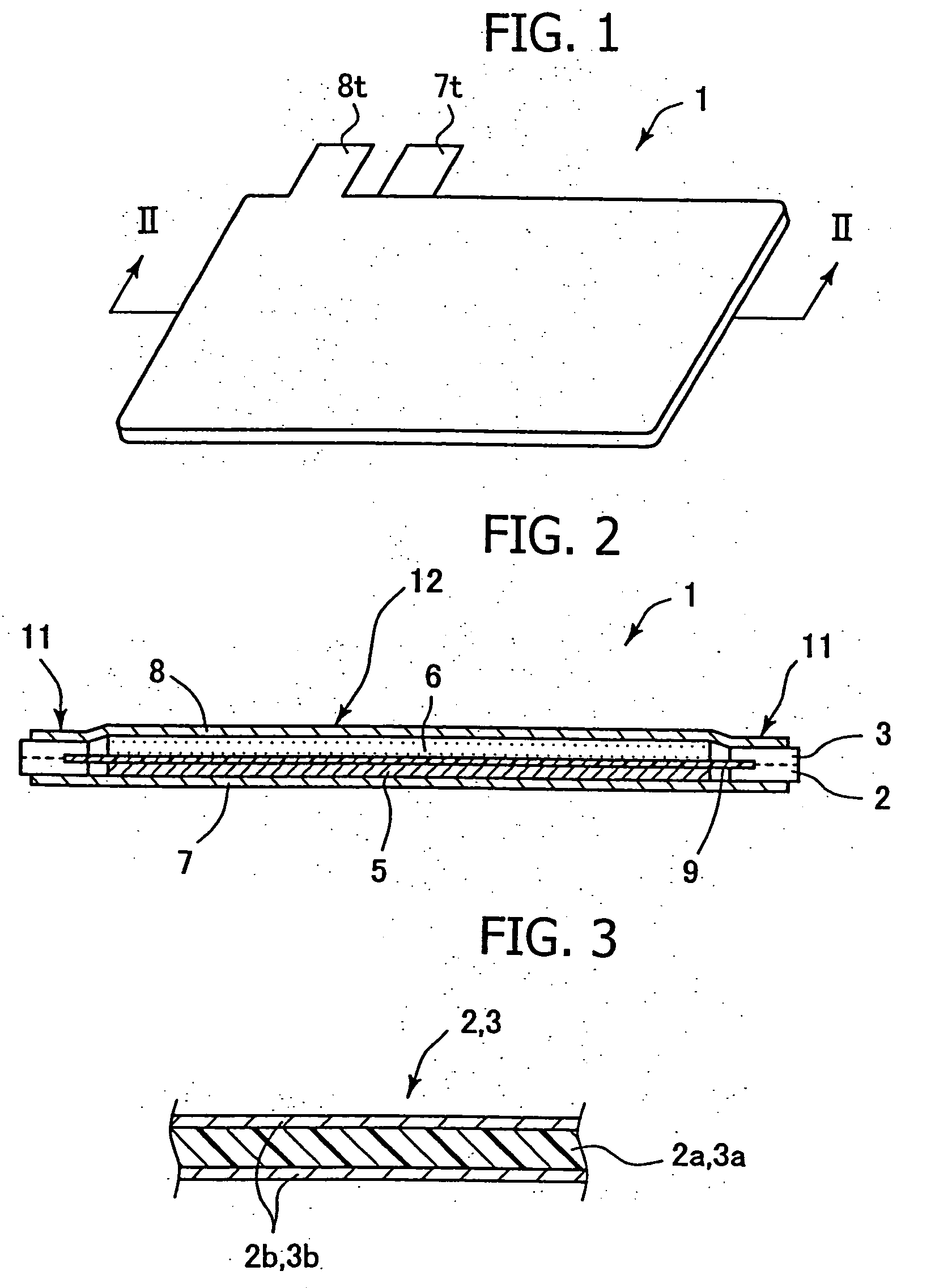
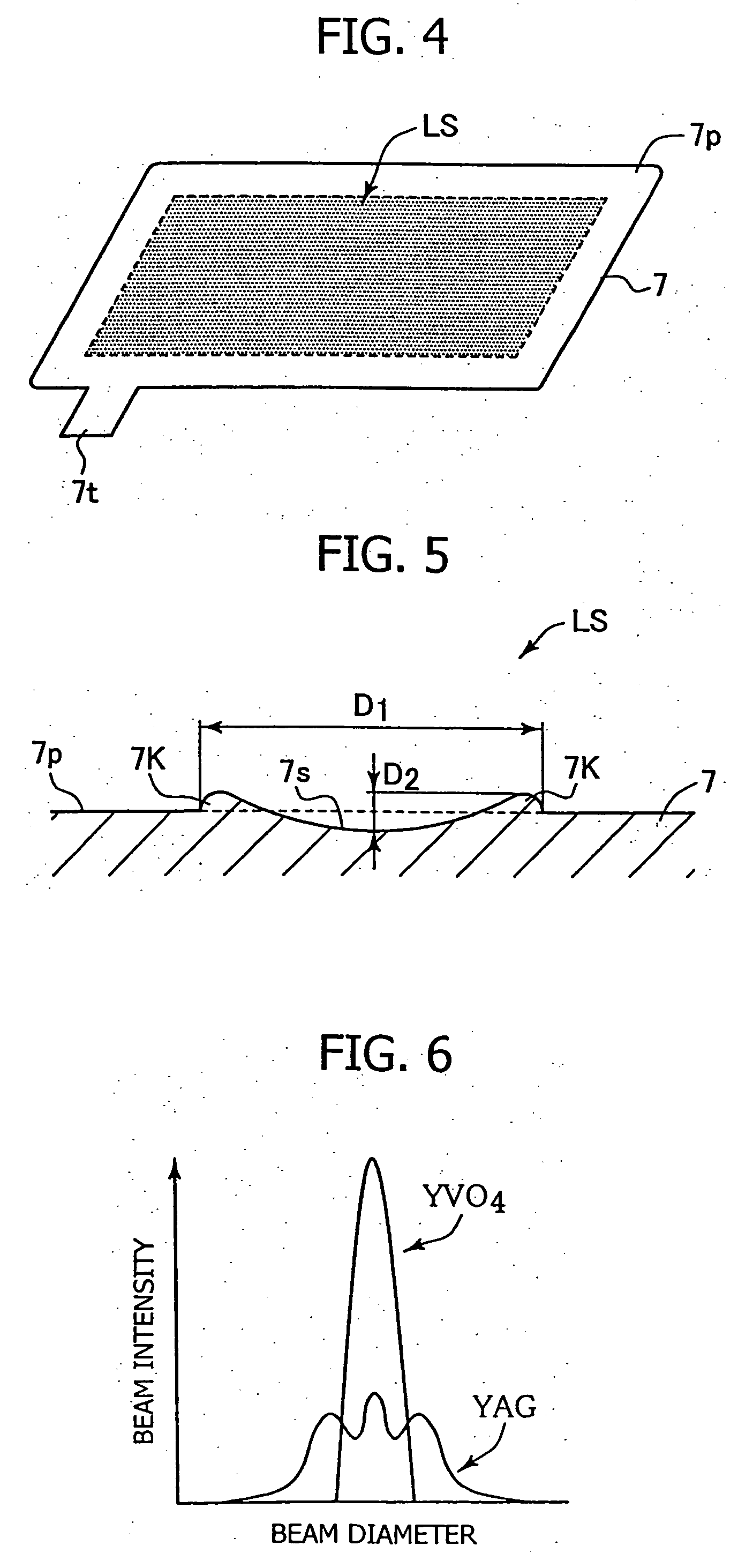
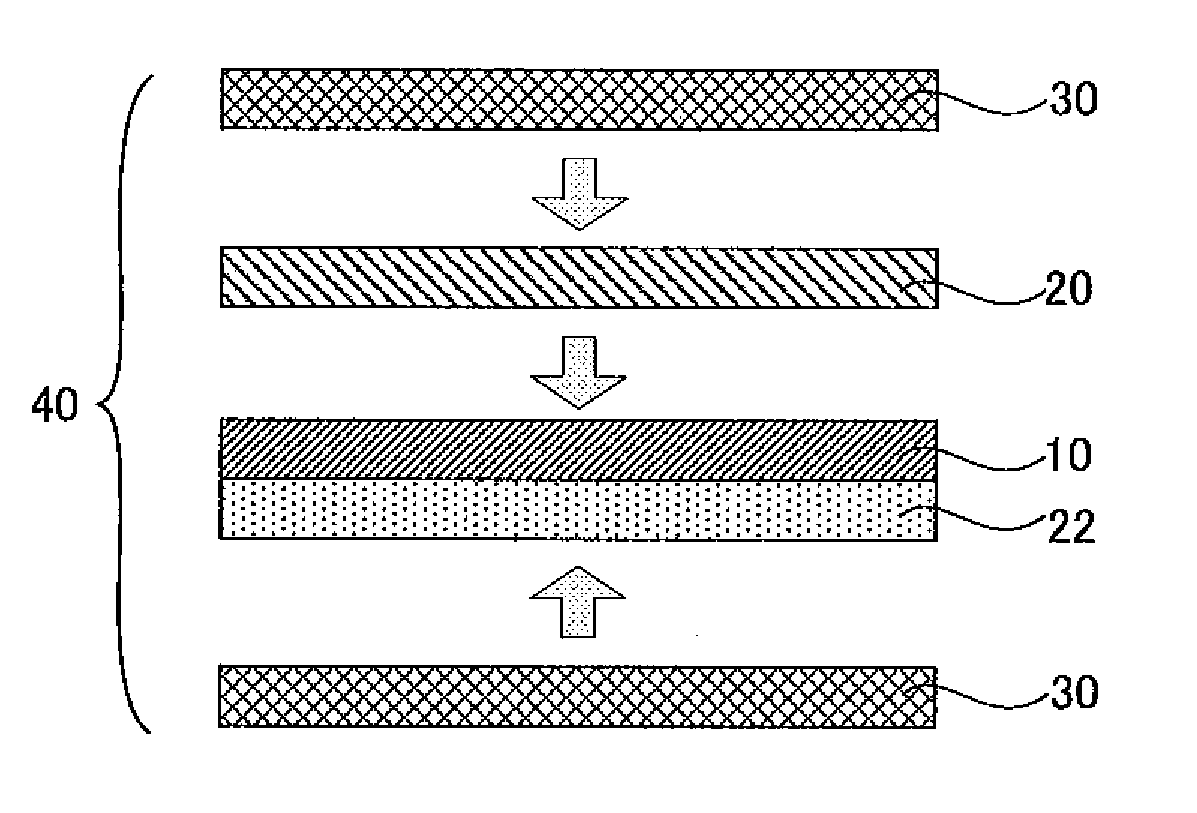
Patents
Literature
60results about How to "Surface roughening" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
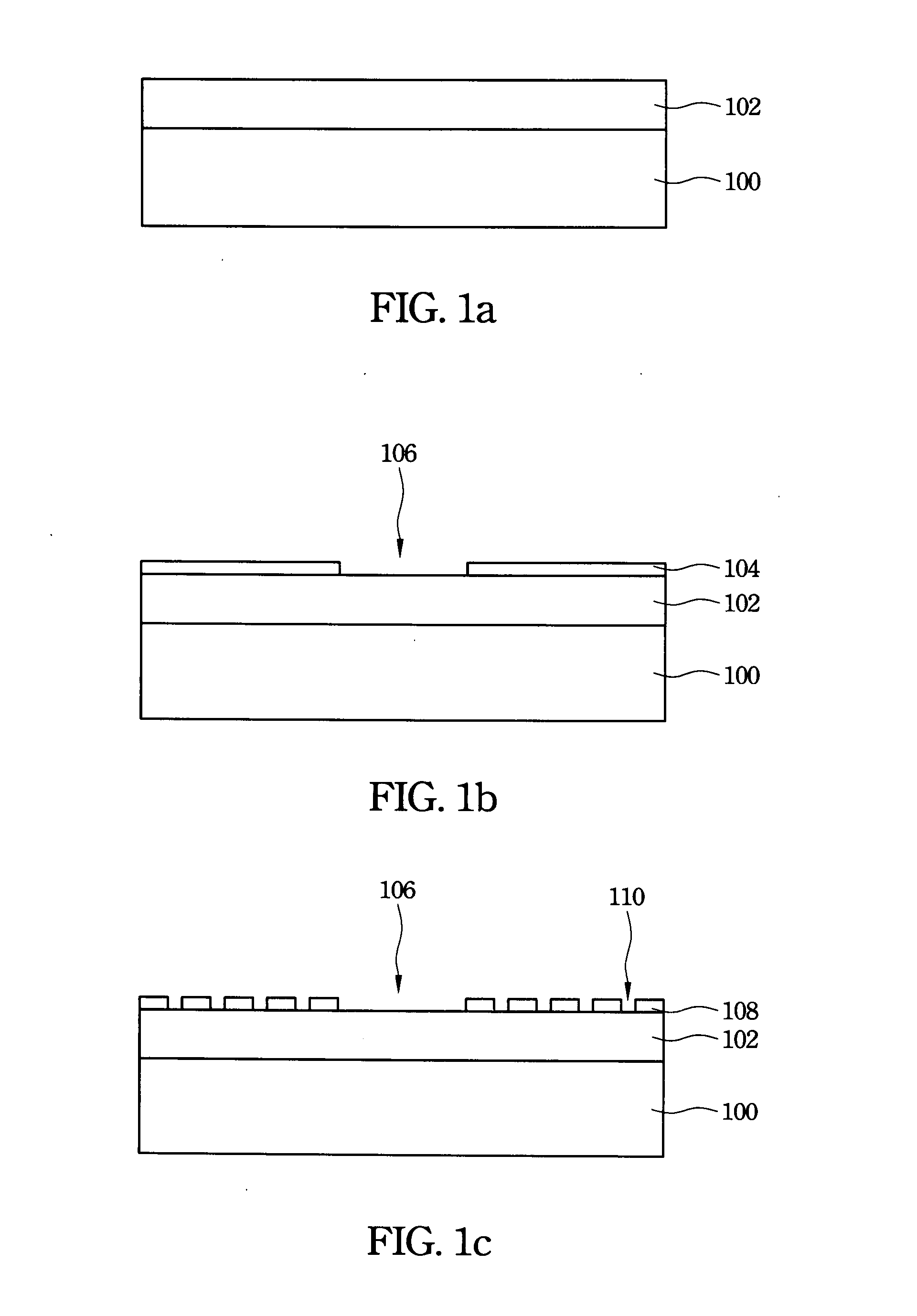
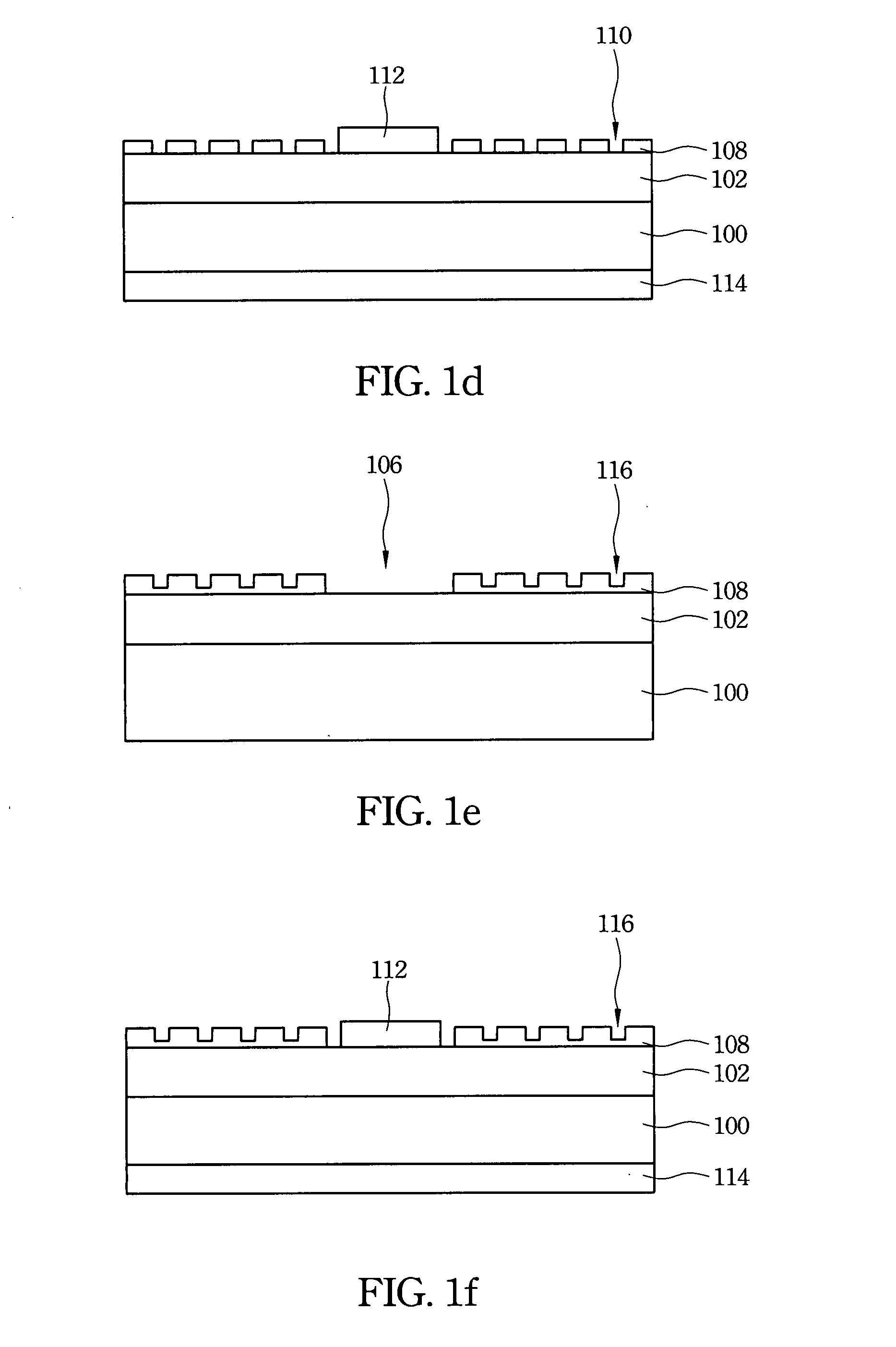
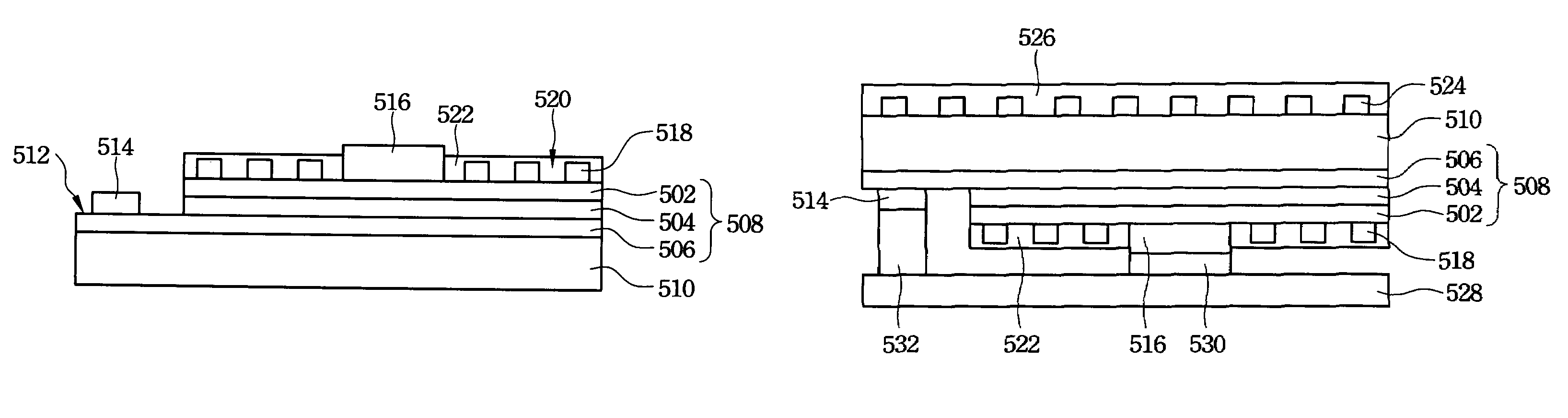
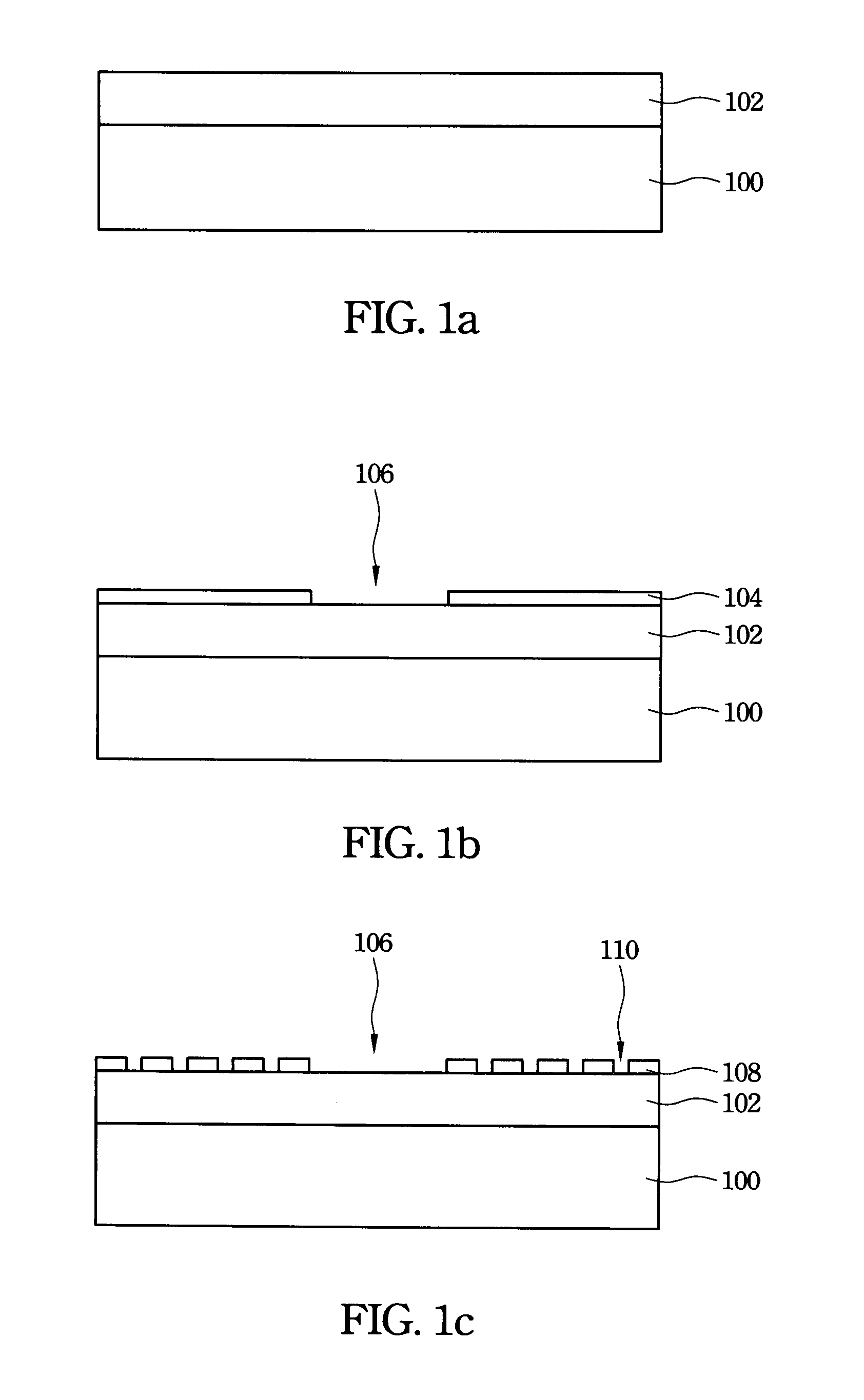
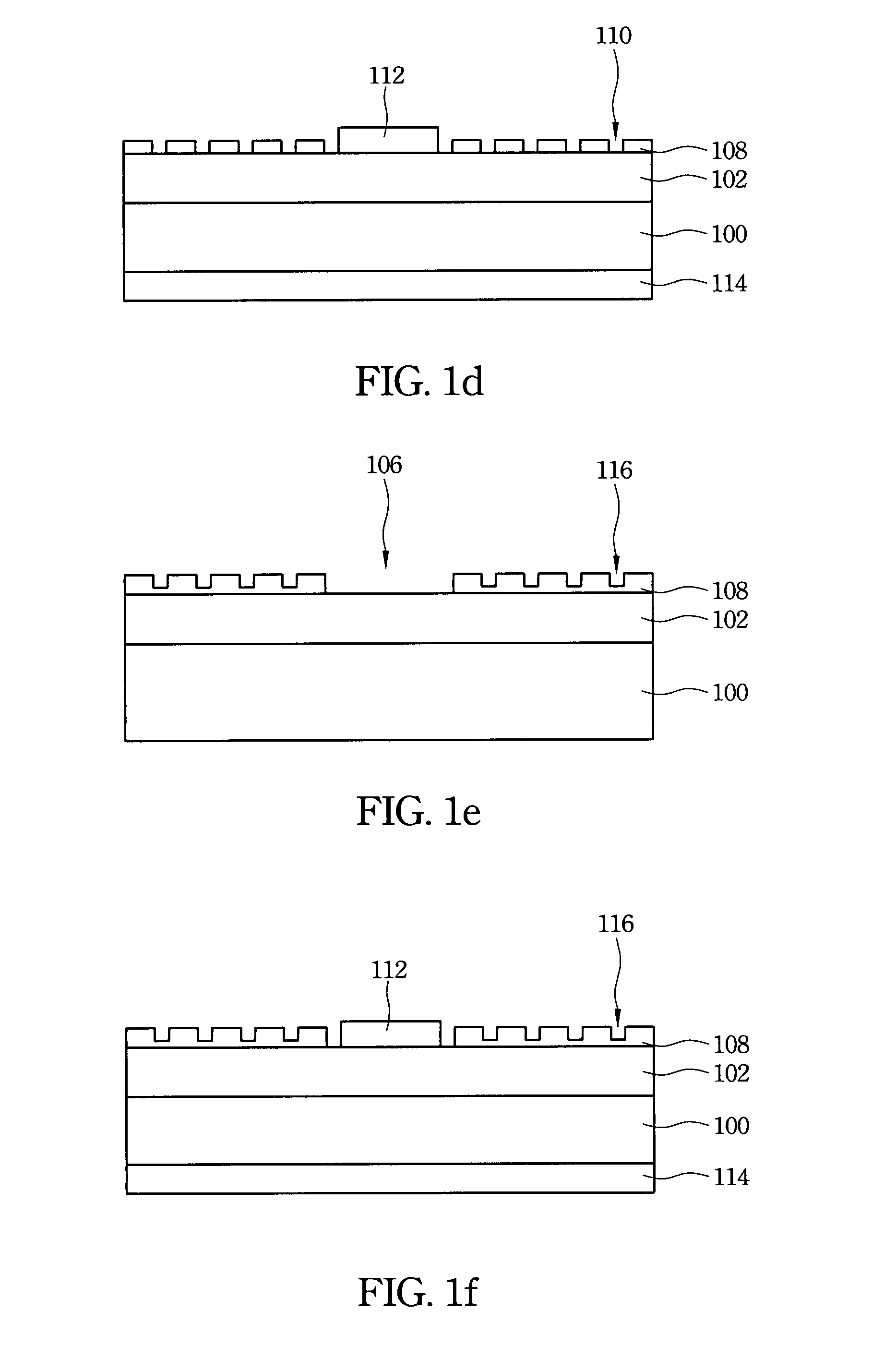
Group III nitride compound semiconductor device and method for producing the same
InactiveUS6982435B2Substrate surface efficientlyEfficiently formedLaser detailsSolid-state devicesNitrideSubstrate surface
A group III nitride compound semiconductor device is produced according to the following manner. A separation layer made of a material which prevents group III nitride compound semiconductors from being grown thereon is formed on a substrate. Group III nitride compound semiconductors is grown on a surface of the substrate uncovered with the separation layer while keeping the uncovered substrate surface separated by the separation layer.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Process for producing magnet
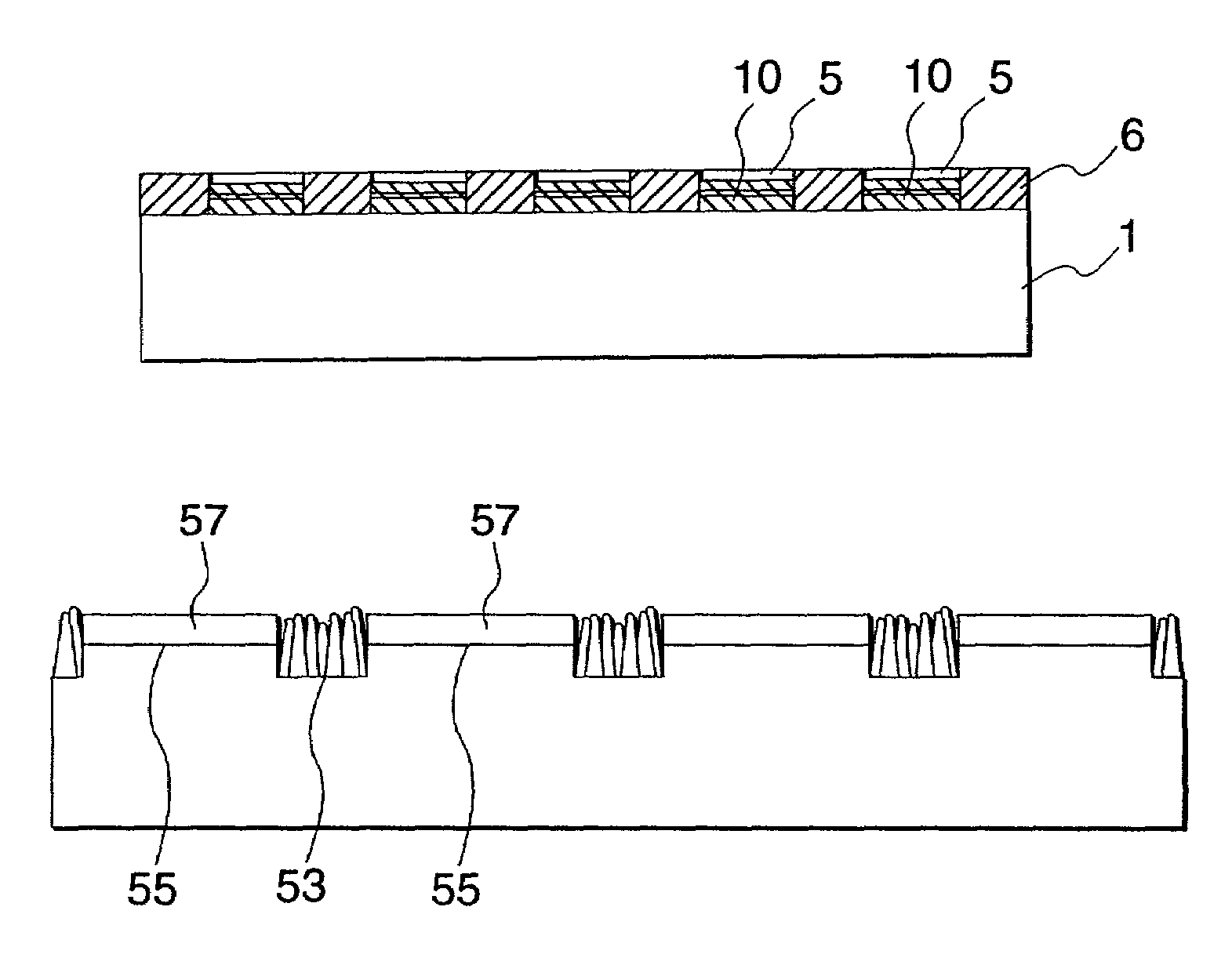
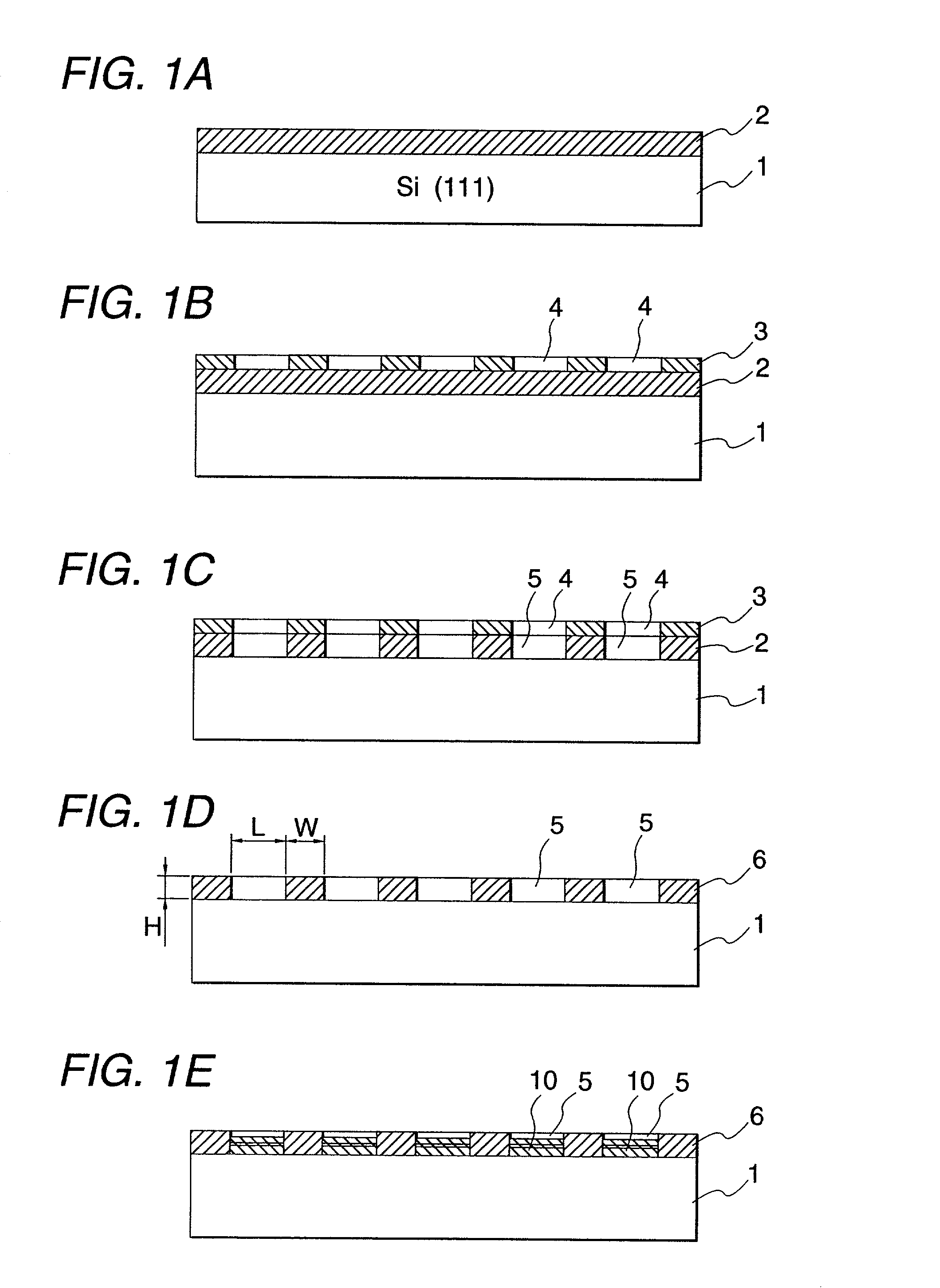
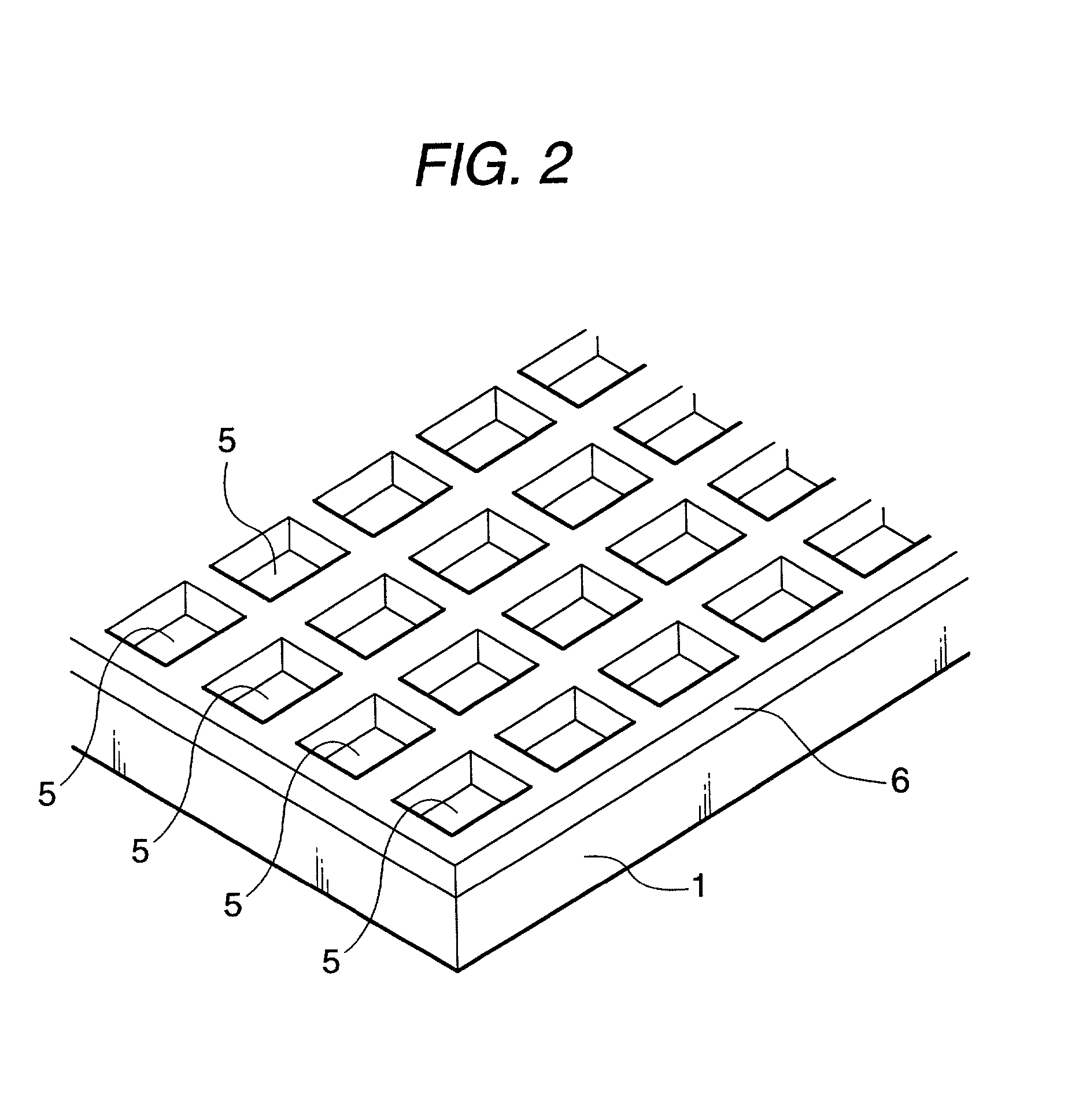
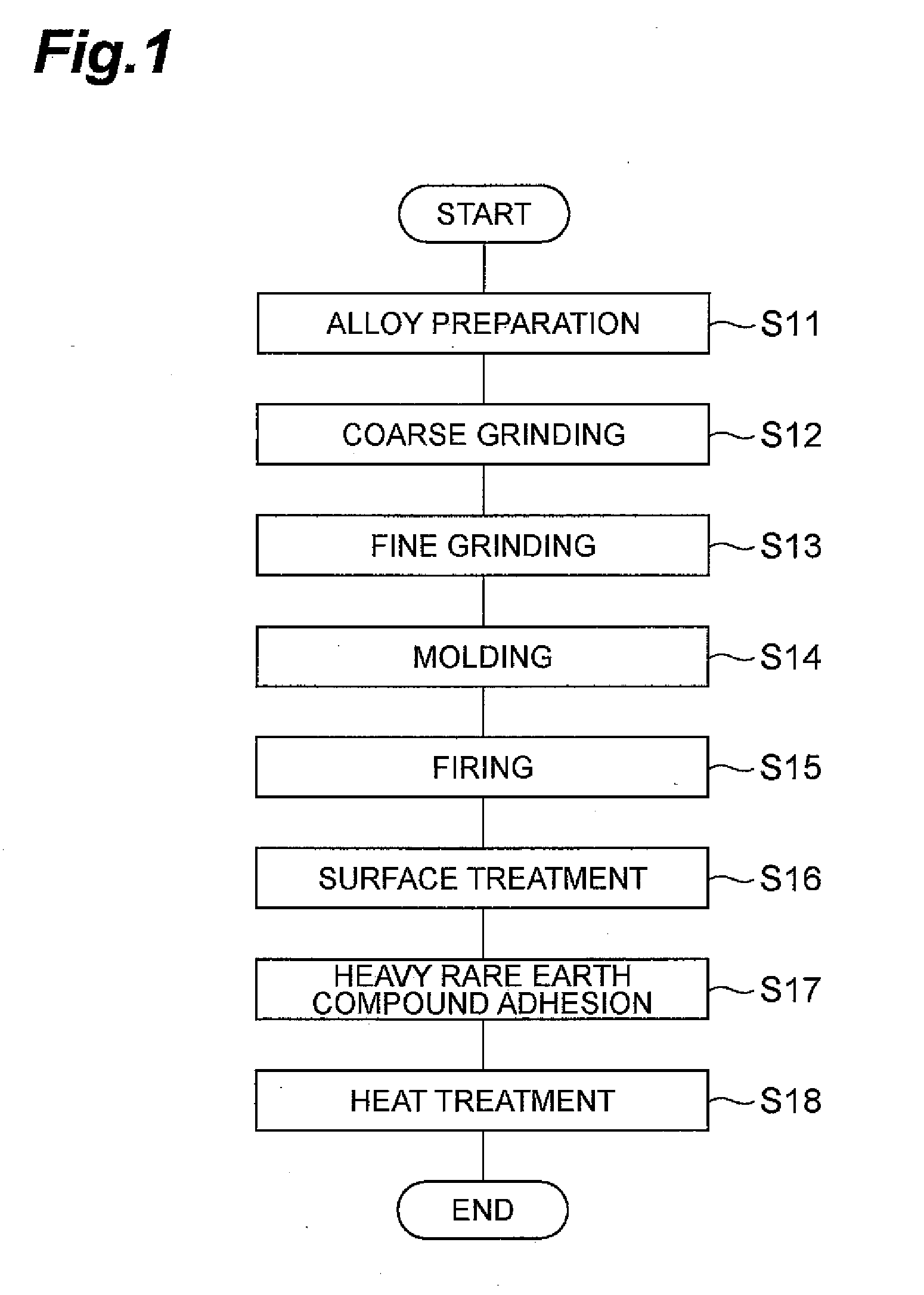
ActiveUS20090297699A1Excellent high magnetic propertyEvenly bondedSpecial surfacesCoatingsRare-earth elementRare-earth magnet
The process for producing a magnet according to the invention is characterized by comprising a first step in which a heavy rare earth compound containing Dy or Th as a heavy rare earth element is adhered onto a sintered compact of a rare earth magnet and a second step in which the heavy rare earth compound-adhered sintered compact is subjected to heat treatment, wherein the heavy rare earth compound is a Dy or Th iron compound.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Method and apparatus for the elimination of interference fringes in an OLED device
InactiveUS20070108900A1Reduced Newton 's ring patternReduce formationDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsNewton's ringsLight emitting device
A technique for reducing the appearance of Newton's rings for a light emitting device is disclosed. The light emitting device comprises a scattering layer positioned contiguous with the inner surface of a cover substrate. Scattering the light reduces or eliminates the opportunity for constructive interference and as a result reduces or eliminates Newton's ring formation.
Owner:CORNING INC
Surface treated metallic implant and blasting material
InactiveUS20040158330A1Improve long-term stabilitySurface rougheningPigmenting treatmentImpression capsApatiteCrystalline materials
The invention relates to a metallic implant, which has vitreous-crystalline bioactive material on the surface thereof. According to the invention, a metallic implant base body arranged on the surface of the particles has a bioactive, vitreous-crystalline material consisting of 15-45 wt. % CaO, 40-45 wt. % P2O5, 10-40 wt. % ZrO2 and 0.7-3.5 wt. % fluoride, having apatite and calcium zirconium phosphate as main crystalline and a glass phase as an auxiliary component. Said vitreous crystalline material contains at least 35 wt. % main crystal phases and at least 5-15 wt. % auxiliary compounds. All of the percentage data is expressed in relation to the total weight of the vitreous crystalline material and the particle size of the vitreous crystalline material is between 60-350 mum.
Owner:HUMBOLDT UNIV BERLIN CHARITE UNIVSKLINIKUM CCM +1
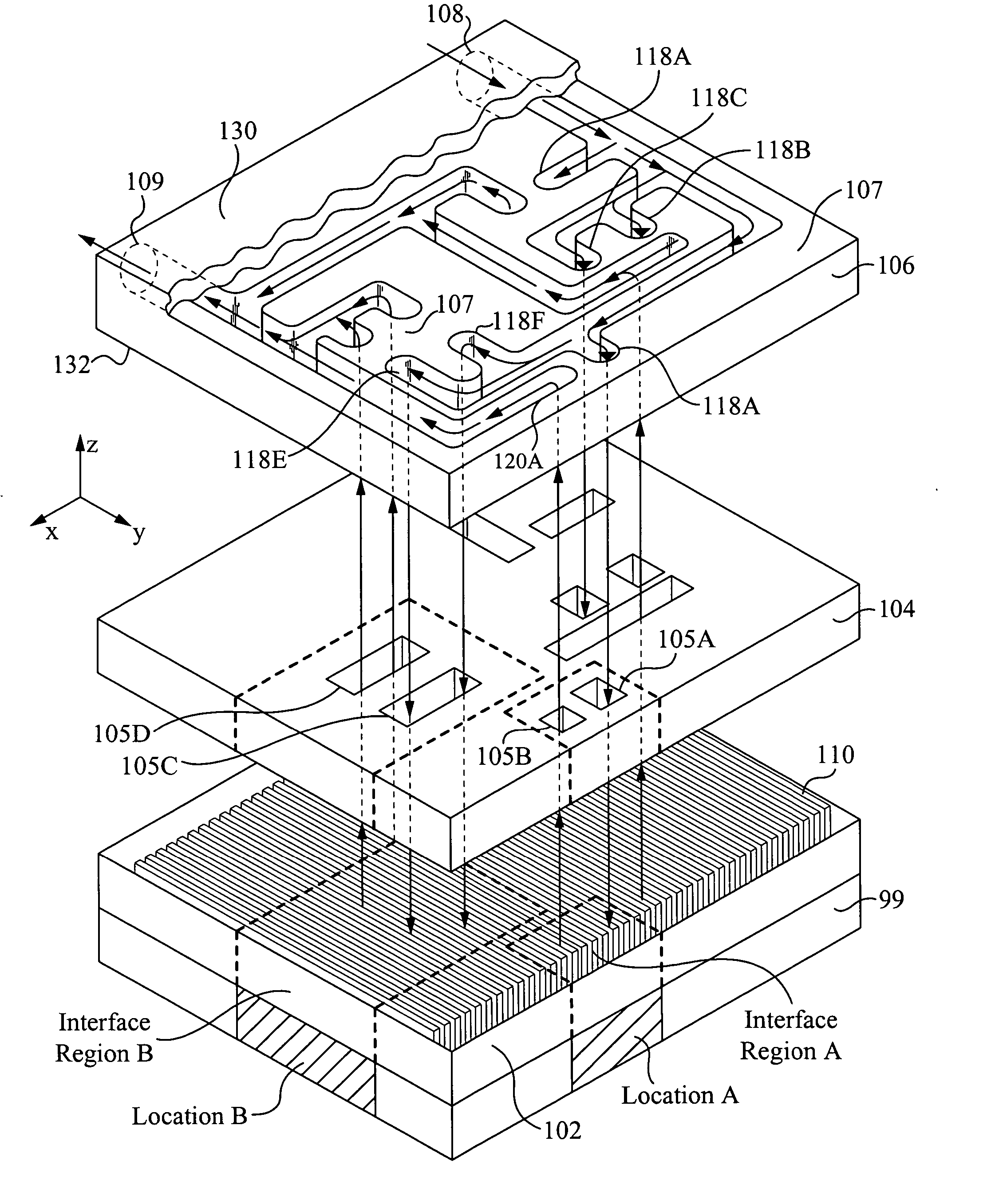
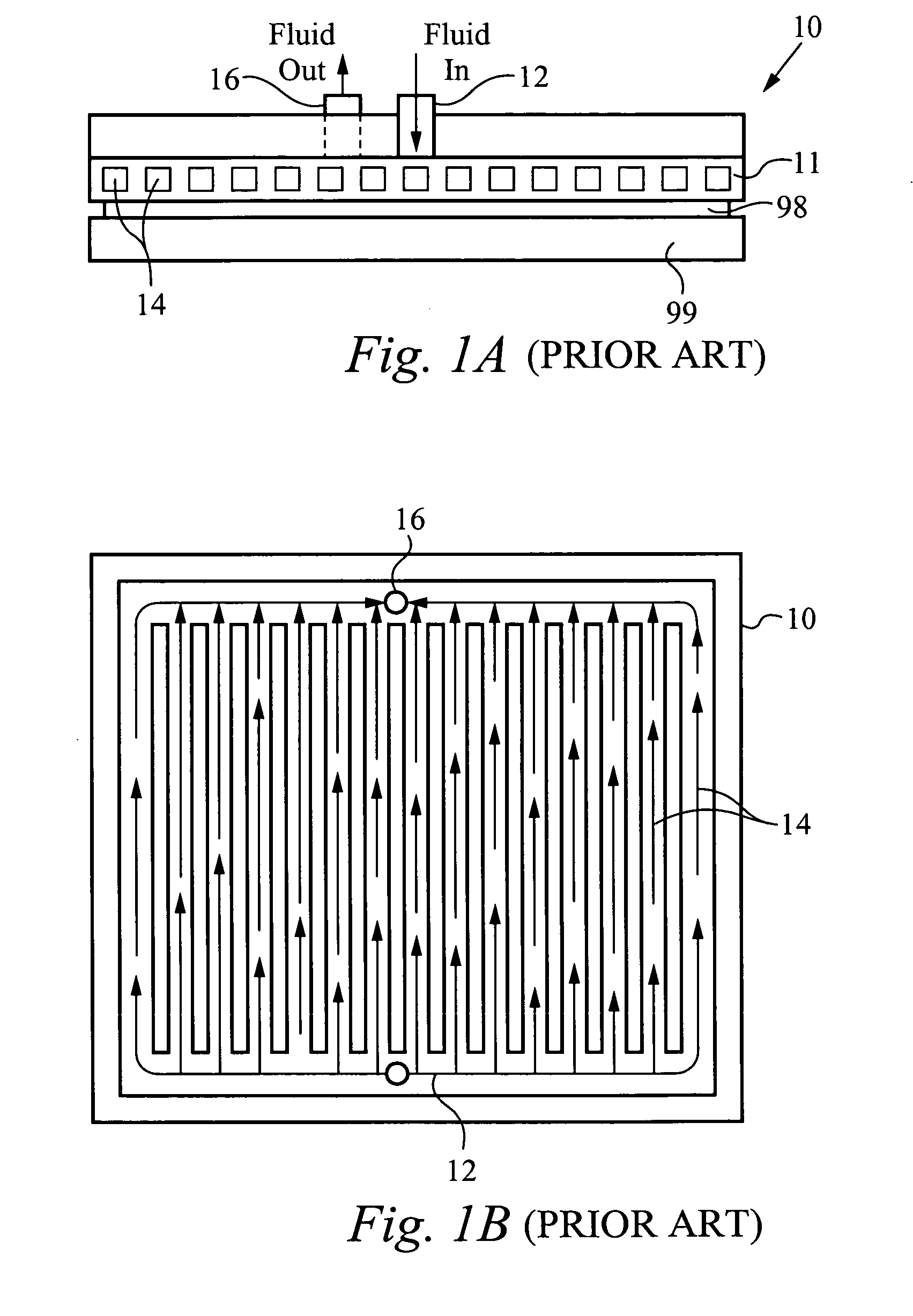
Method and apparatus for flexible fluid delivery for cooling desired hot spots in a heat producing device
InactiveUS20050211427A1Optimize hot spot cooling of heat sourceSurface rougheningTemperatue controlSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsThermal conductivityEngineering
A heat exchanger apparatus and method of manufacturing comprising: an interface layer for cooling a heat source and configured to pass fluid therethrough, the interface layer having an appropriate thermal conductivity and a manifold layer for providing fluid to the interface layer, wherein the manifold layer is configured to achieve temperature uniformity in the heat source preferably by cooling interface hot spot regions. A plurality of fluid ports are configured to the heat exchanger such as an inlet port and outlet port, whereby the fluid ports are configured vertically and horizontally. The manifold layer circulates fluid to a predetermined interface hot spot region in the interface layer, wherein the interface hot spot region is associated with the hot spot. The heat exchanger preferably includes an intermediate layer positioned between the interface and manifold layers and optimally channels fluid to the interface hot spot region.
Owner:COOLIGY INC
Metallic Pigment and Coating Material Containing the Same
InactiveUS20080081864A1Improve corrosion resistanceImprove adhesionPigmenting treatmentChemical recyclingNitrogenDouble bond
Disclosed is a metallic pigment which enables to provide a coating film with very brilliant appearance and excellent corrosion resistance at the same time. Also disclosed is a coating material containing such a metallic pigment. Specifically disclosed is a metallic pigment which is composed of aluminum particles as the base particles whose surfaces are covered with a coating-layer composed of one or more layers. The outermost layer of the coating-layer contains a polymer which is obtained by polymerizing a monomer having a basic group and at least one polymerizable double bond. The monomer may preferably contain nitrogen. The metallic pigment may preferably be provided with a surface modification layer. Also specifically disclosed is a coating material containing such a metallic pigment.
Owner:TOYO ALUMINIUM KK
Surface light source device and light guide used therefor
InactiveUS20050174803A1Reduce power consumptionQuality improvementMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesLight guideOptoelectronics
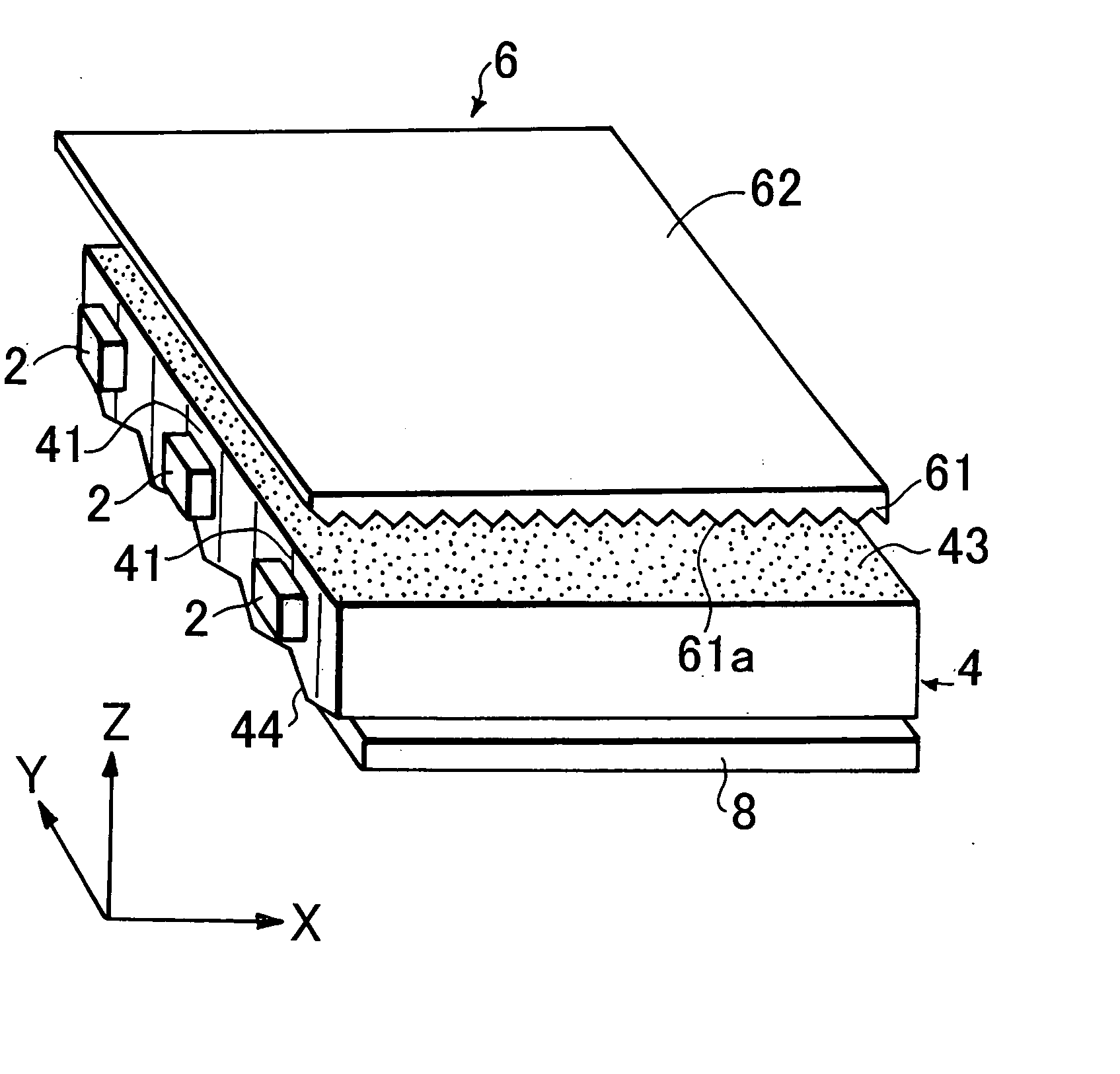
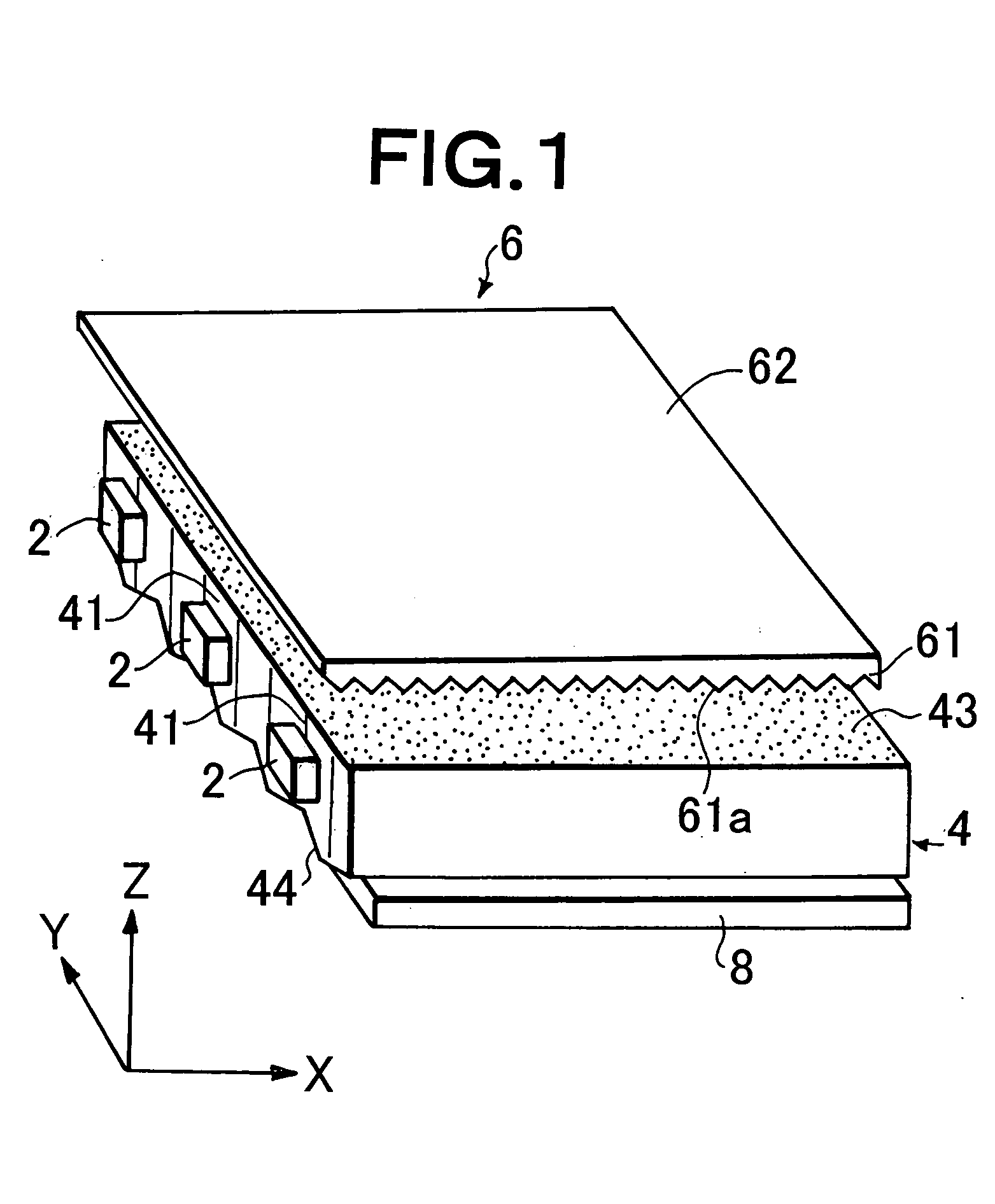
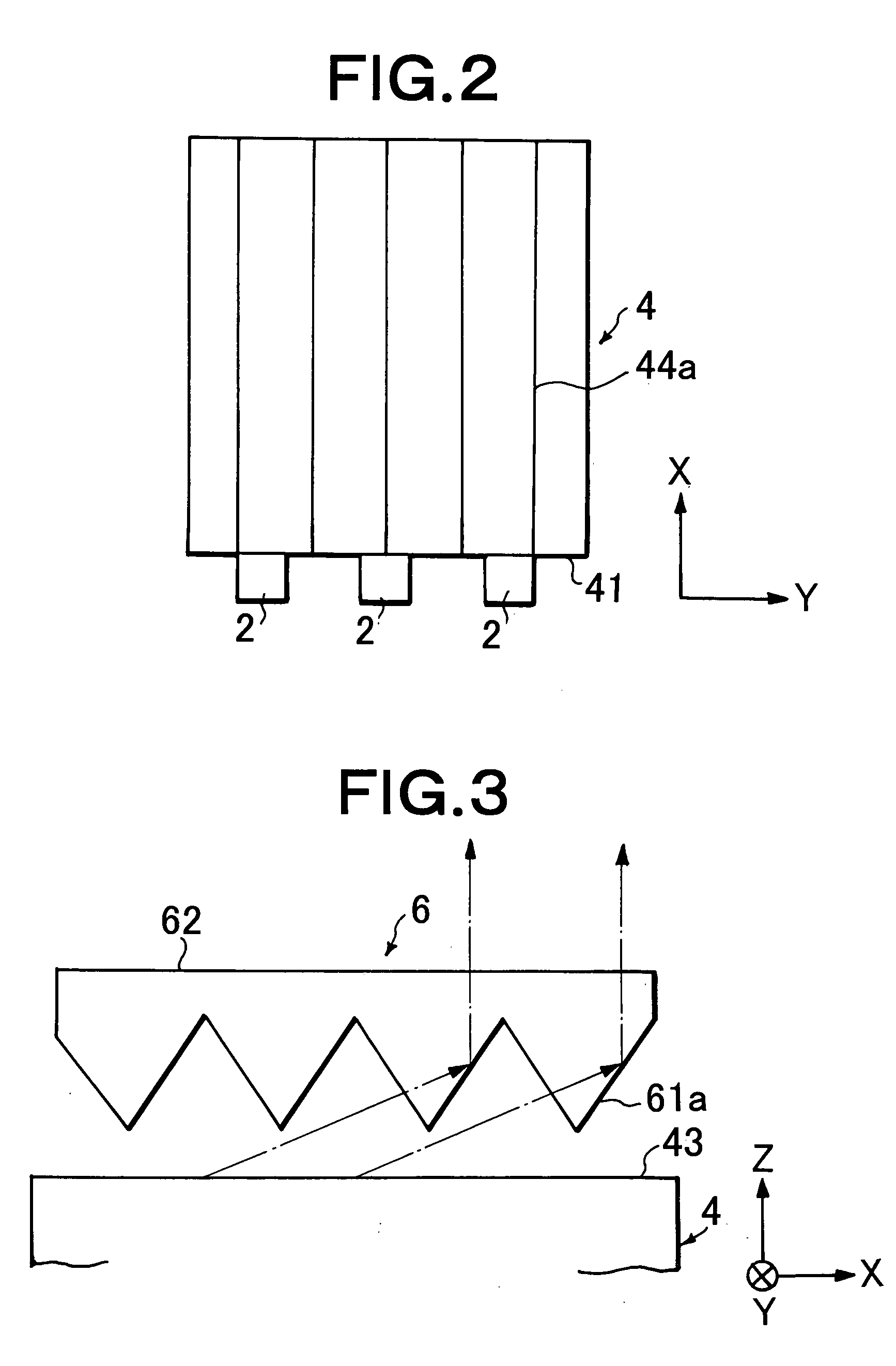
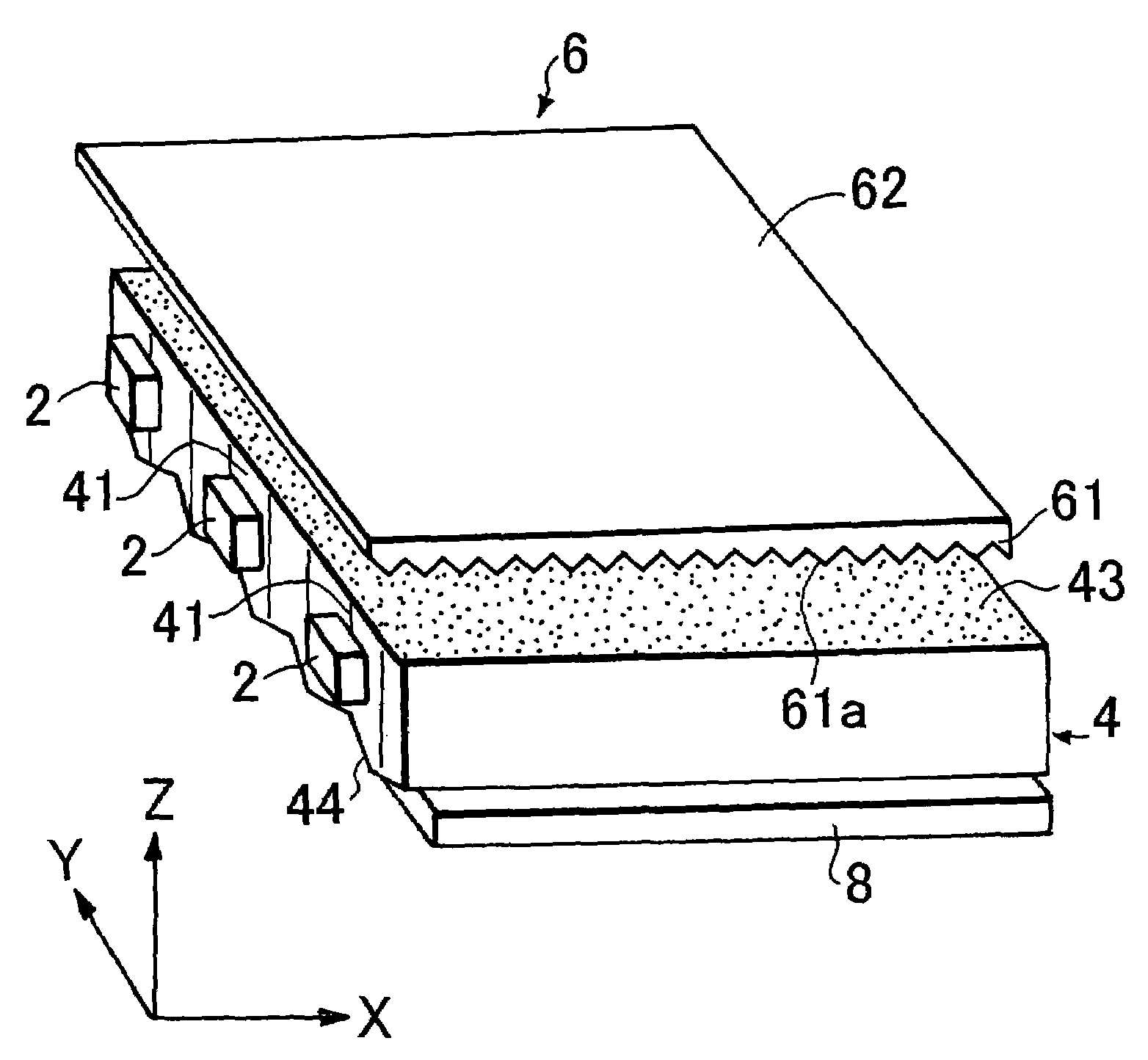
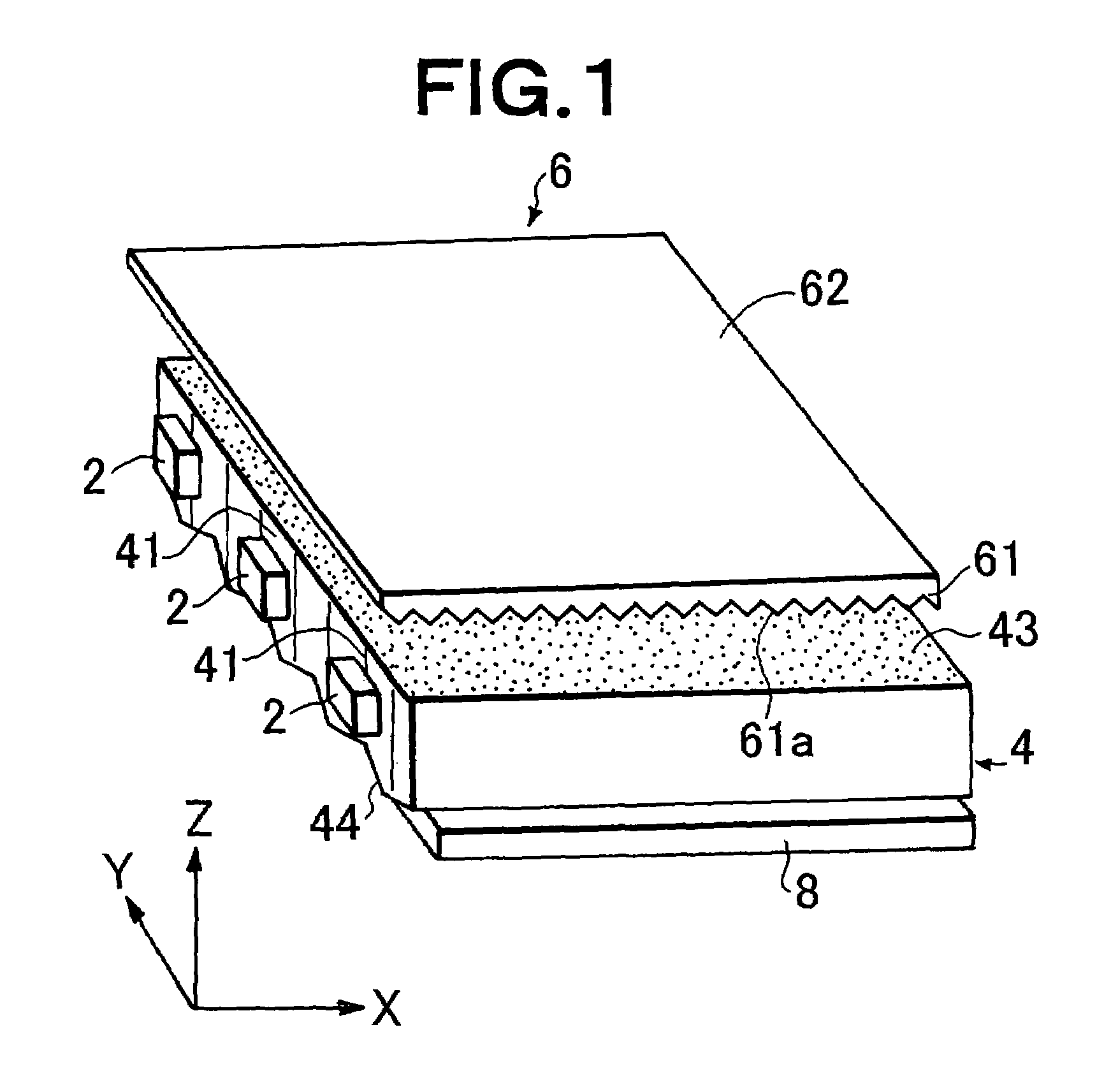
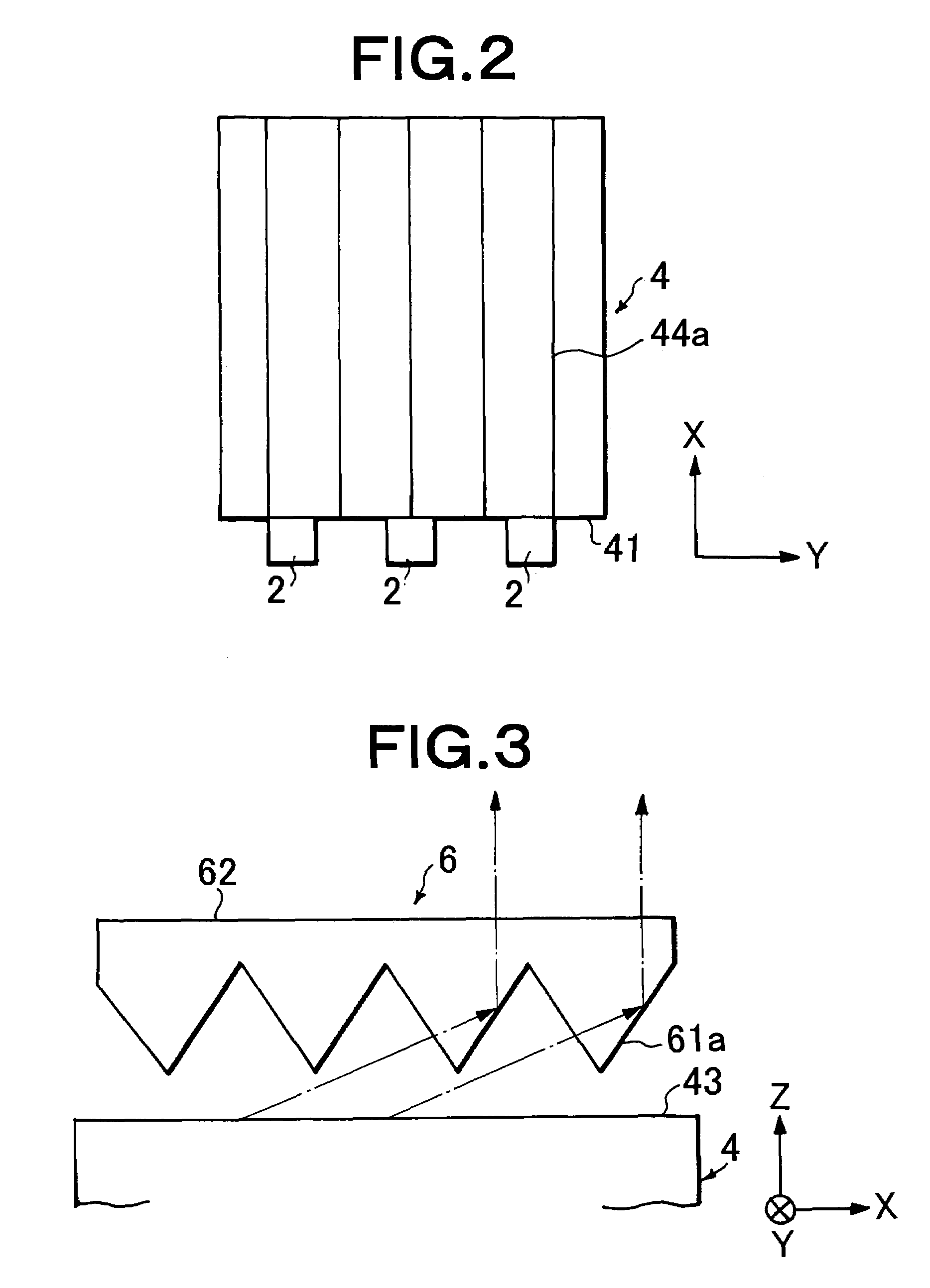
A platy light guide (4) which guides light emitted from an LED (2) and has a light incident end surface (41) for receiving light from the LED (2) and a light outputting surface (43) for outputting a guided light, wherein a plurality of lens rows extending along the directivity direction (X direction) of a light guide incident light in a plane along the light outputting surface (43) and arranged in parallel to each other are formed on a rear surface (44). In the vicinity of the LED (2), the shape of the section perpendicular to their extending directions of the plurality of lens rows is such that the existence proportion of an angle component having an absolute value of at least 20° and up to 50° of an inclination angle formed by a tangent and a lens row forming surface in each fine area is at least 10%. A light deflection element (6) disposed adjacent to the light guide light outputting surface (43) is provided on the light entrance surface (61) thereof with a plurality of lens rows (61a) extending in a direction parallel to the light guide light incident end surface (41) and being parallel to each other. Accordingly, a high-quality surface light source device free from brightness unevenness caused by a fewer LEDs used is provided.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Surface light source device and light guide used therefor
InactiveUS7226197B2Reduce power consumptionQuality improvementMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesLight guideOptoelectronics
A light guide which guides light emitted from an LED includes a light incident end surface for receiving light, a light outputting surface for outputting a guided light, and a lens forming surface that has a plurality of elongated lenses arranged in parallel to each other and formed along the directivity of light incident from the LED, such that a plurality of micro regions are defined over the plurality of elongated lens. In the vicinity of the LED, a distribution of micro regions having an inclination angle between 20° and 50° is at least 10% over all micro regions. A light deflection element disposed adjacent to the light guide light outputting surface includes a light entrance surface having a plurality of lenses formed thereon that are parallel to each other and extend in a direction parallel to the light guide light incident end surface.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Electronic component and method for manufacturing same
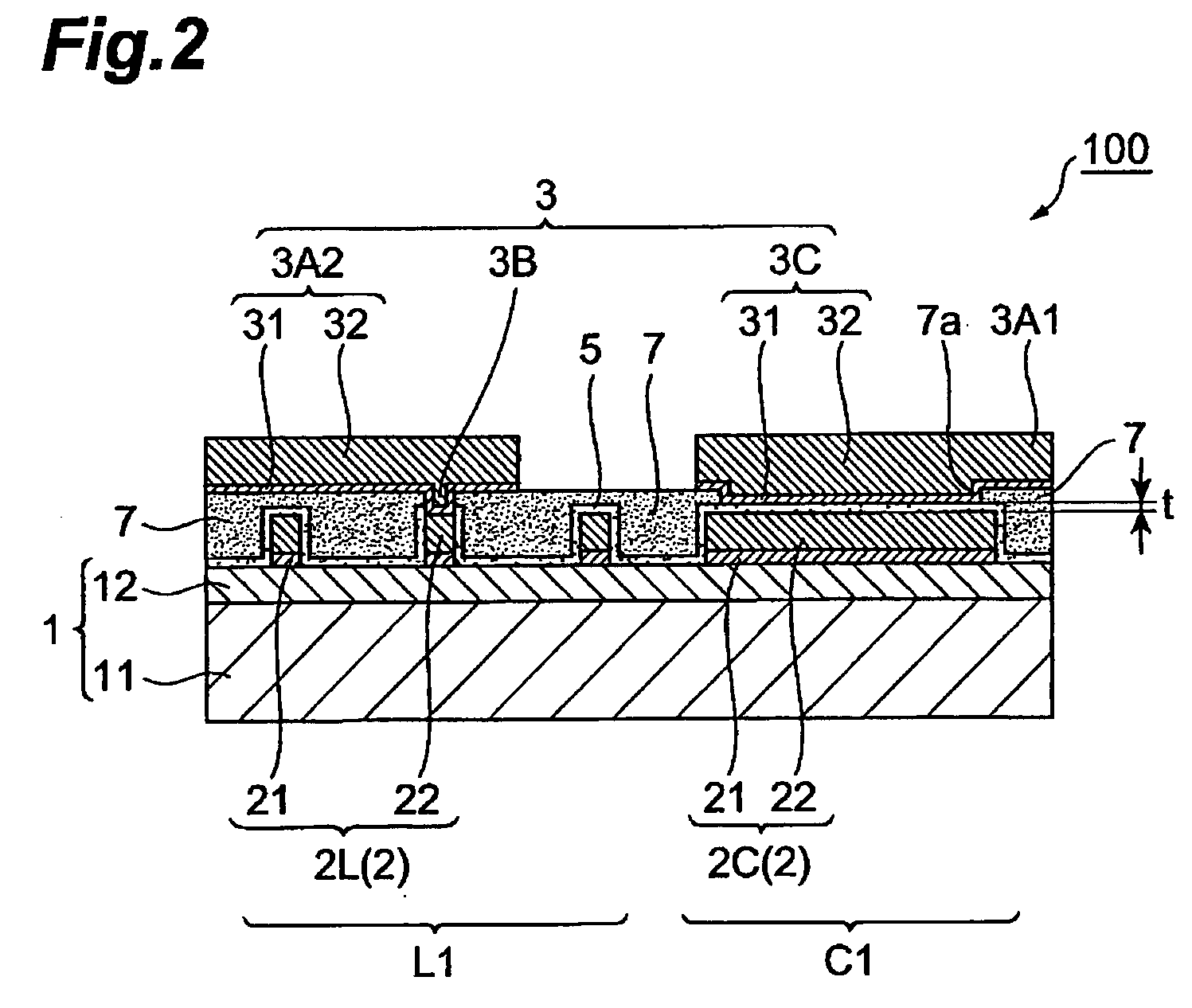
ActiveUS20080023219A1Improve efficiencyLow costMultiple-port networksSolid-state devicesDielectricElectrical conductor
An electronic component having: a substrate, a lower conductor layer provided on the substrate; an inorganic dielectric film that covers the lower conductor layer; and an upper conductor layer having an upper electrode portion provided on the inorganic dielectric film. The lower conductor layer has a lower electrode portion that together with the upper electrode portion and the inorganic dielectric film constitutes a capacitor, and a coil portion that constitutes an inductor. The entire inorganic dielectric film is formed integrally, and the lower conductor layer is in contact only with the substrate, inorganic dielectric film, and upper conductor layer.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Semiconductor substrate, method for fabricating the same, and method for fabricating semiconductor device
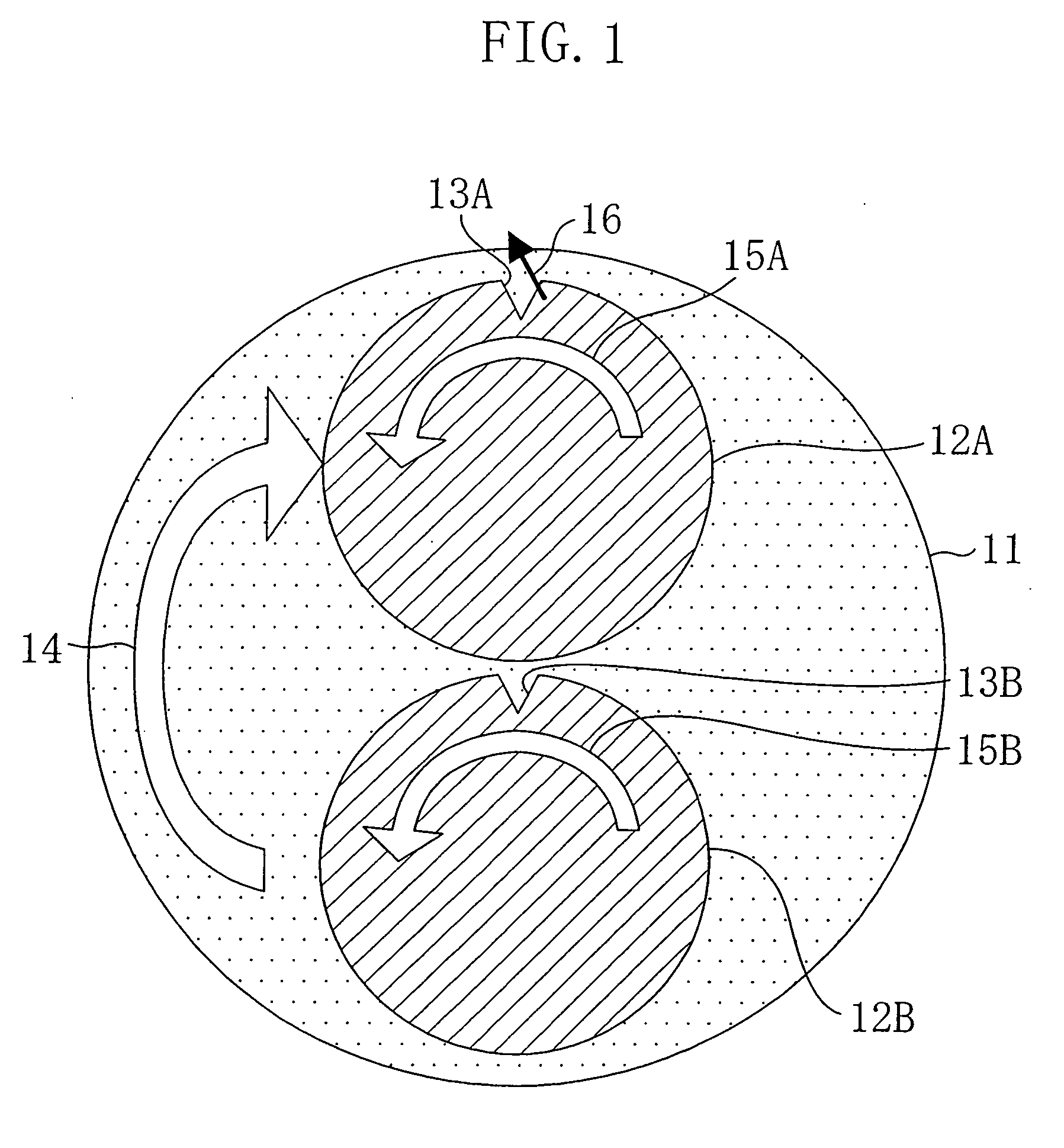
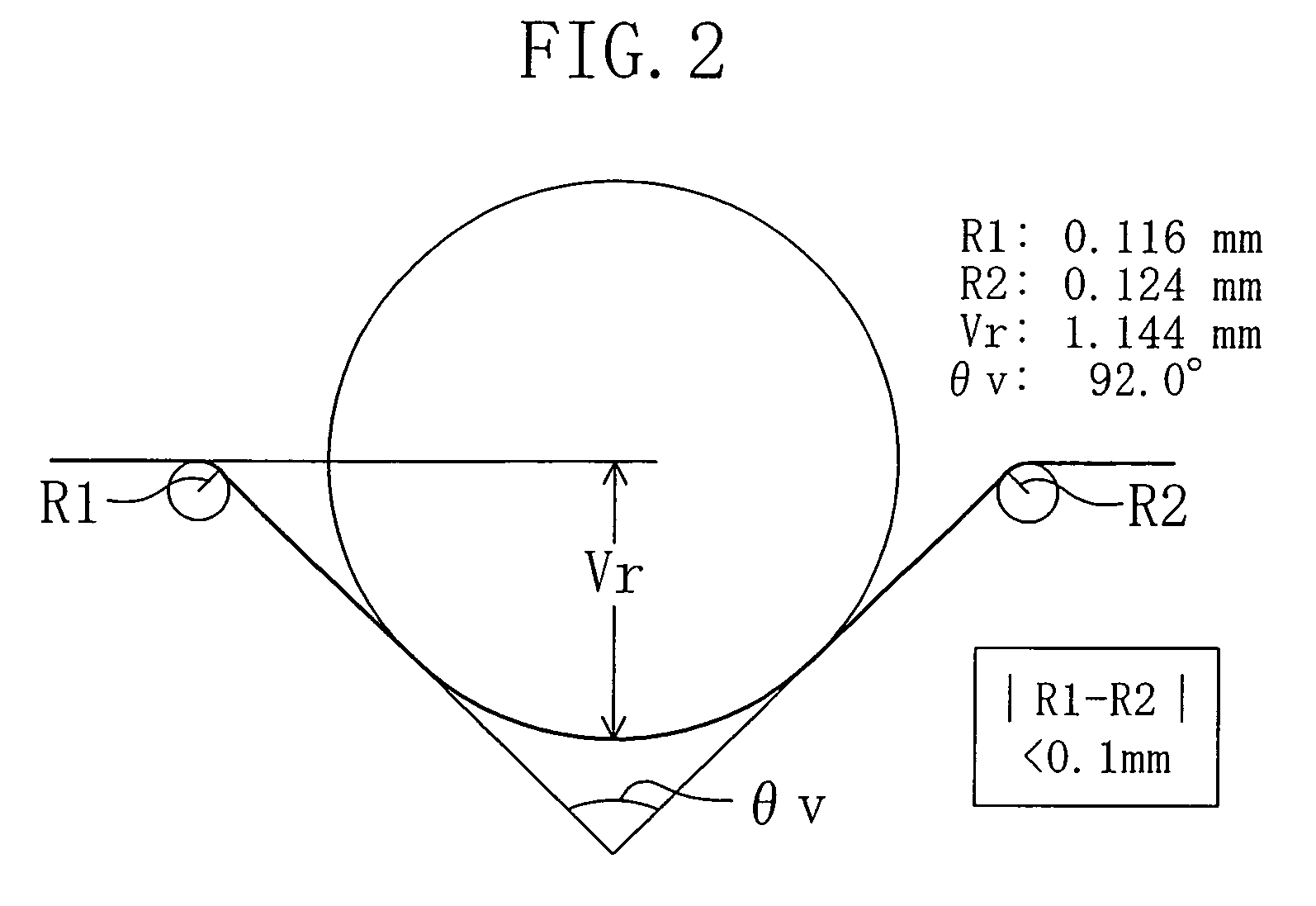
ActiveUS20060270193A1Shorten speedStable polishing speedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMetallurgyDevice material
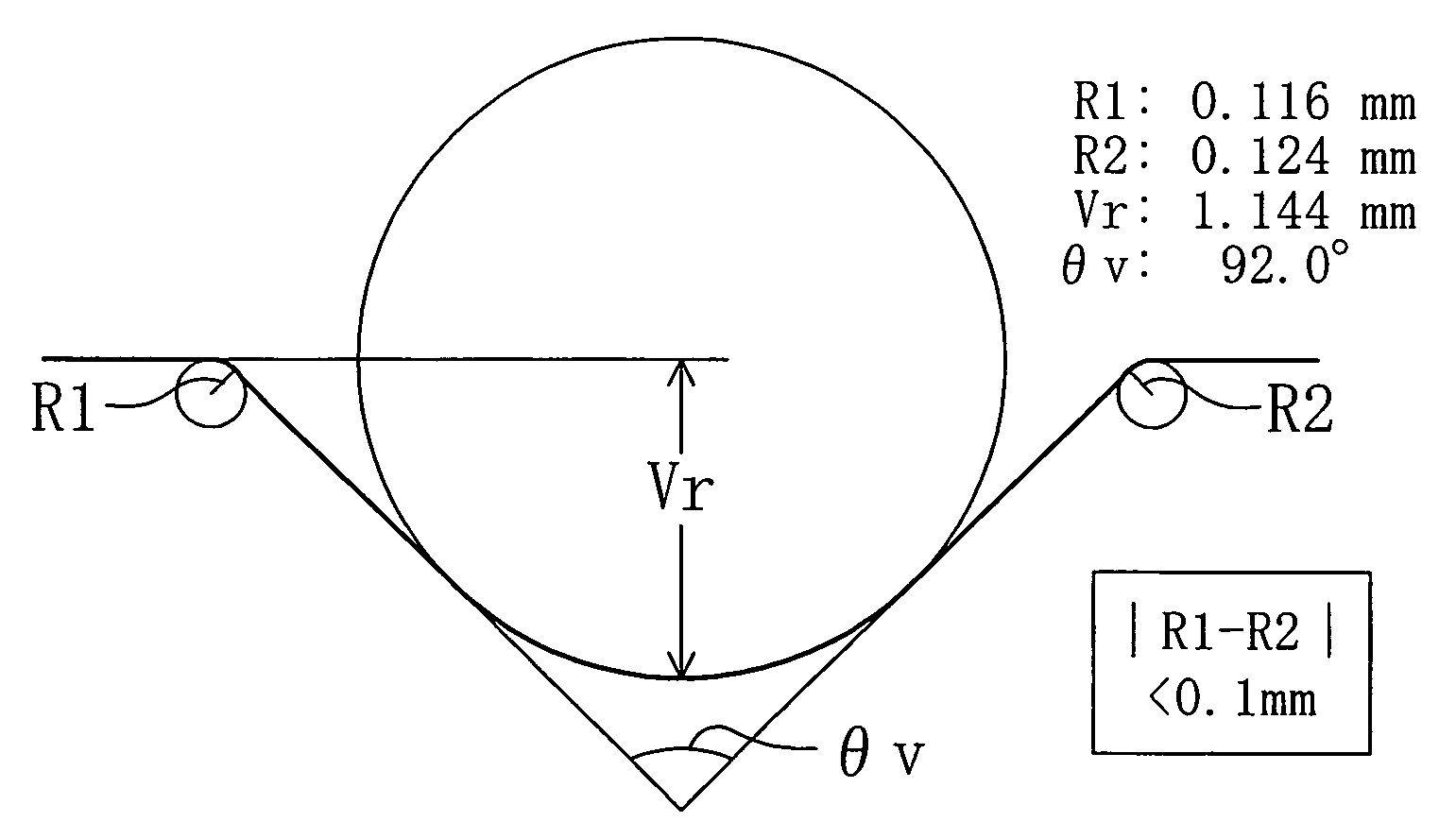
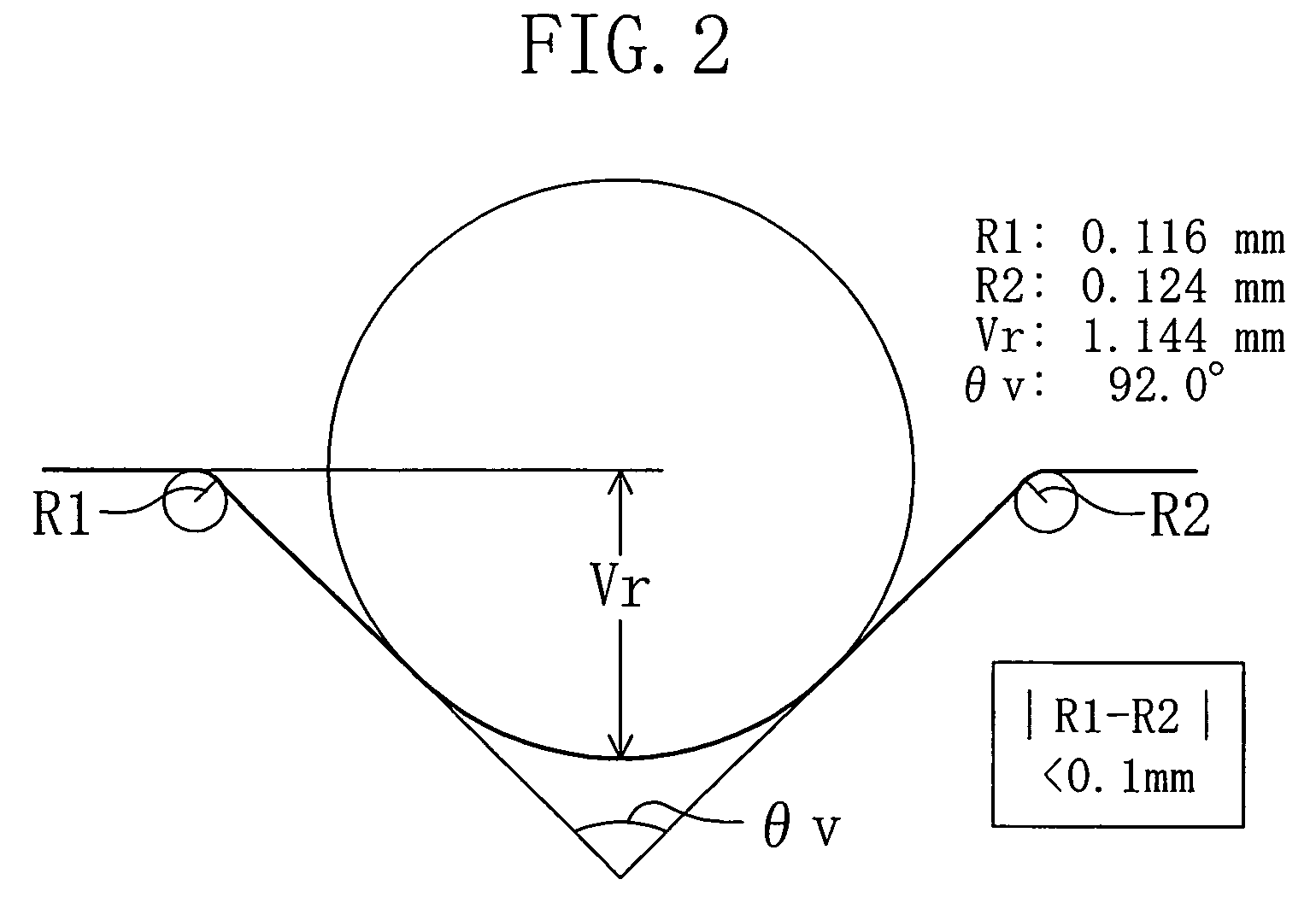
In a semiconductor substrate having a notch in an edge portion thereof, each of the two shoulder portions of the notch is configured as an arc and the difference in curvature between the two shoulder portions of the notch is not less than 0 mm and not more than 0.1 mm.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
Ultraviolet light emitting diode devices and methods for fabricating the same
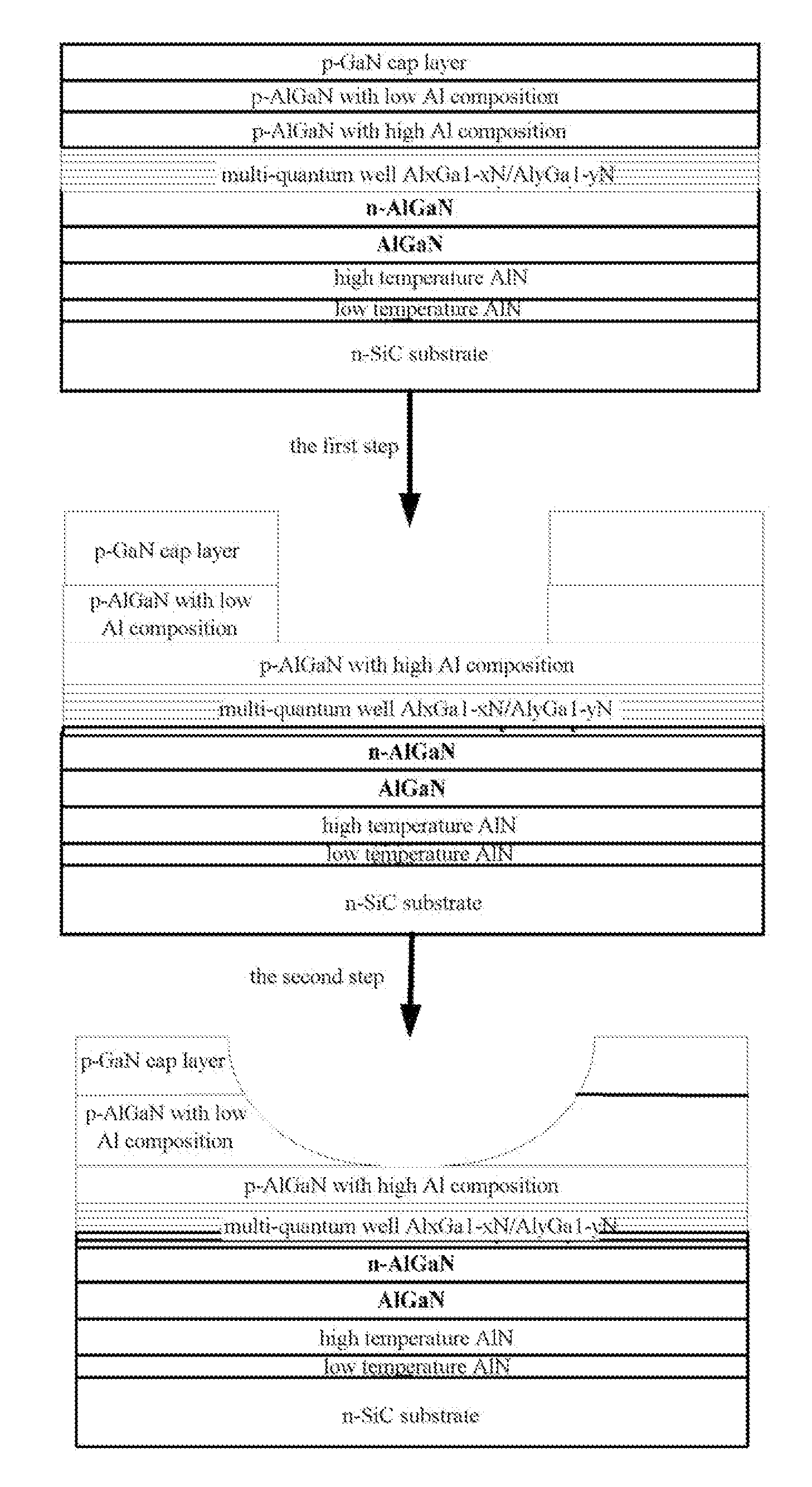
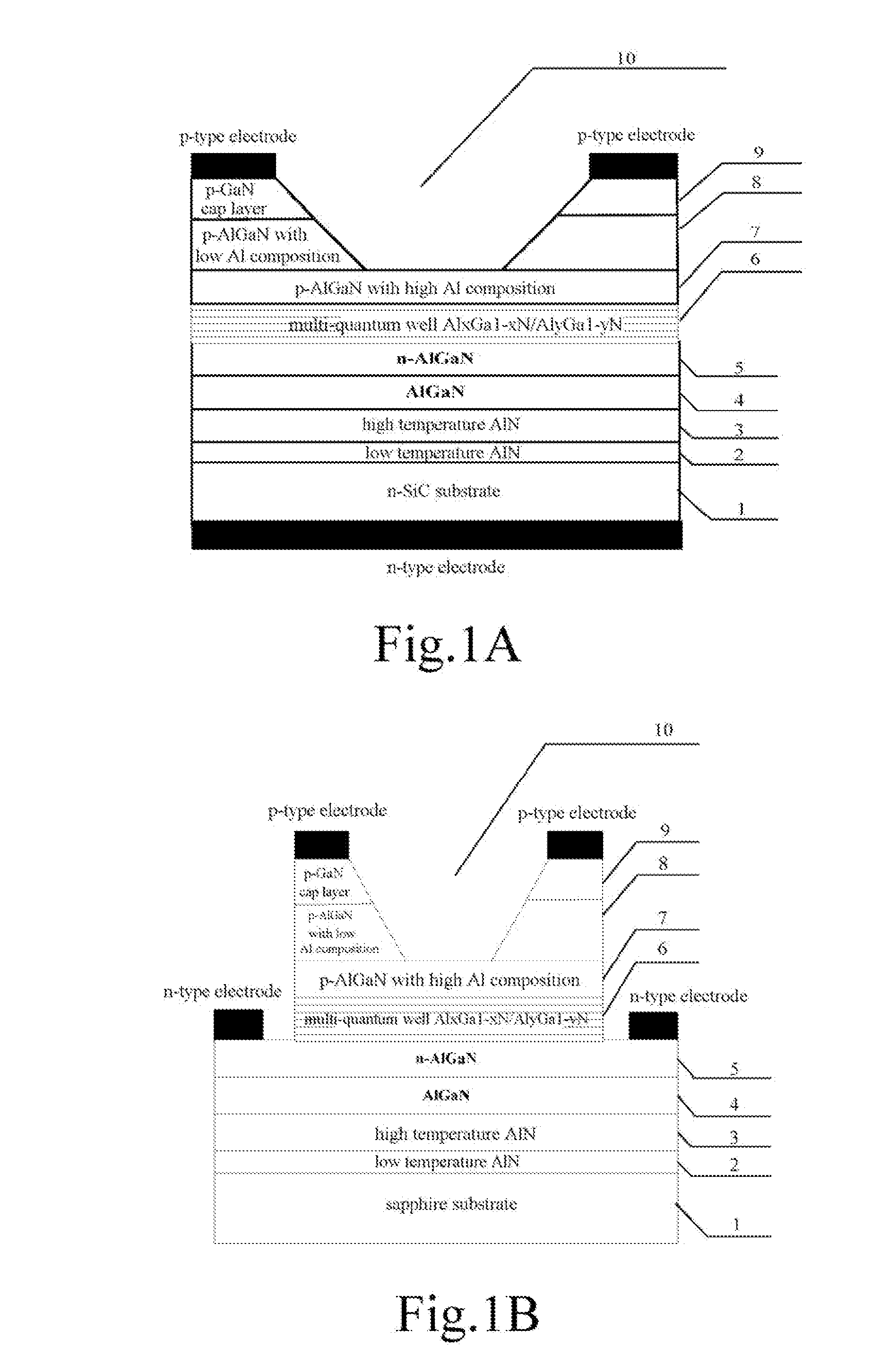
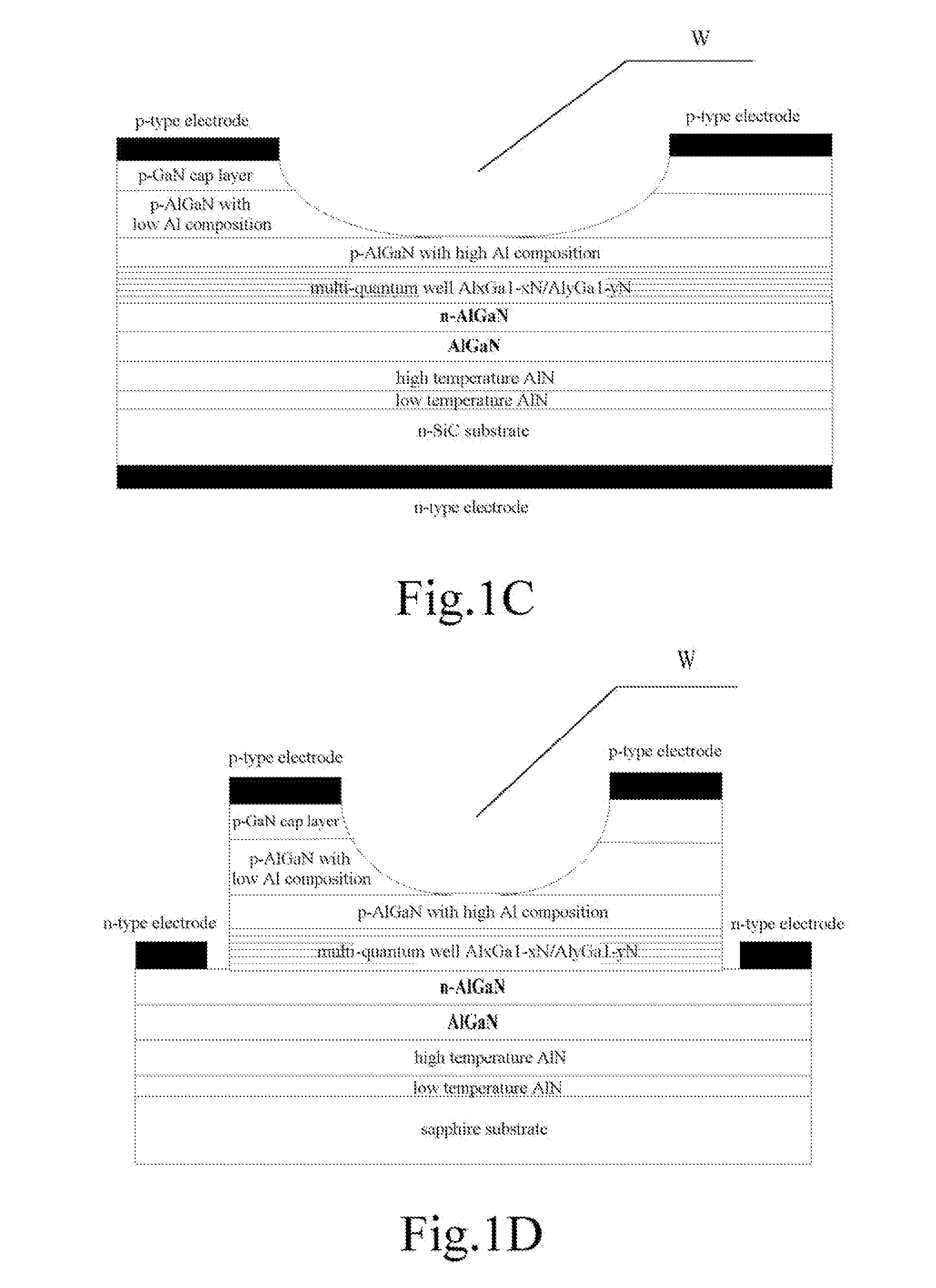
InactiveUS20120018753A1Easy to practiceImproved light emissionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesUltraviolet lightsGallium nitride
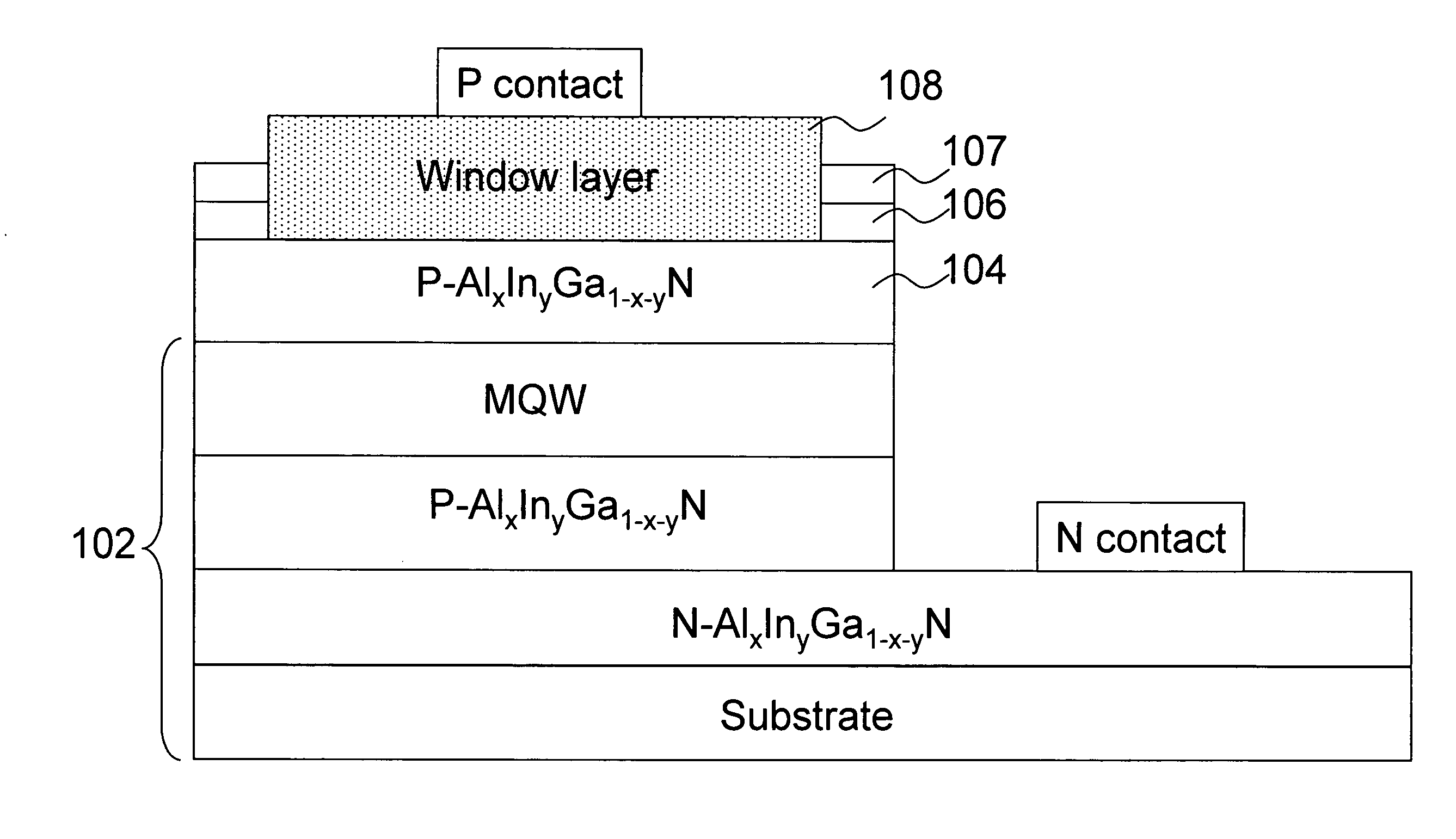
A UV LED device and the method for fabricating the same are provided. The device has aluminum nitride nucleating layers, an intrinsic aluminum gallium nitride epitaxial layer, an n-type aluminum gallium nitride barrier layer, an active region, a first p-type aluminum gallium nitride barrier layer, a second p-type aluminum gallium nitride barrier layer, and a p-type gallium nitride cap layer arranged from bottom to top on a substrate. A window region is etched in the p-type gallium nitride cap layer for emitting the light generated.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
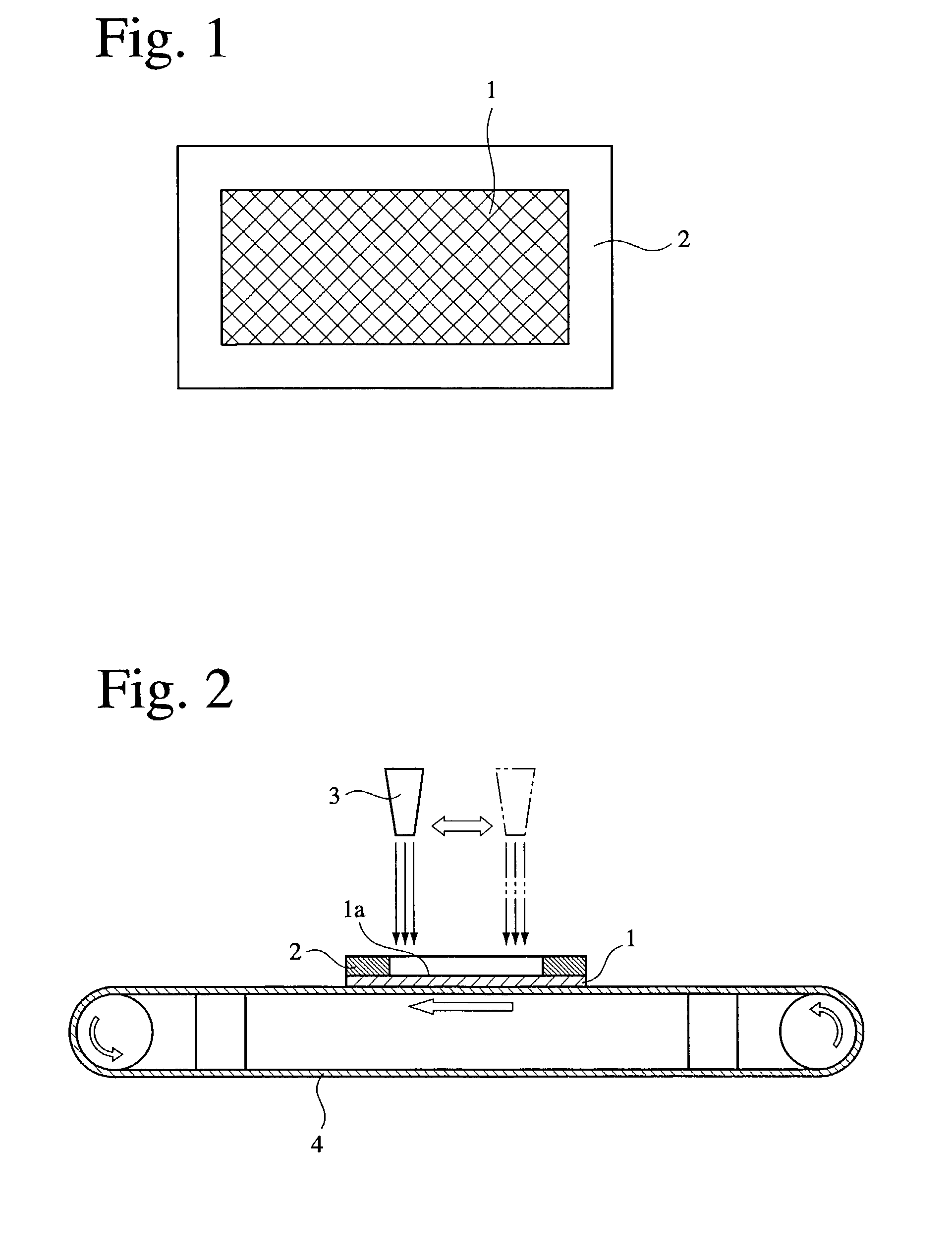
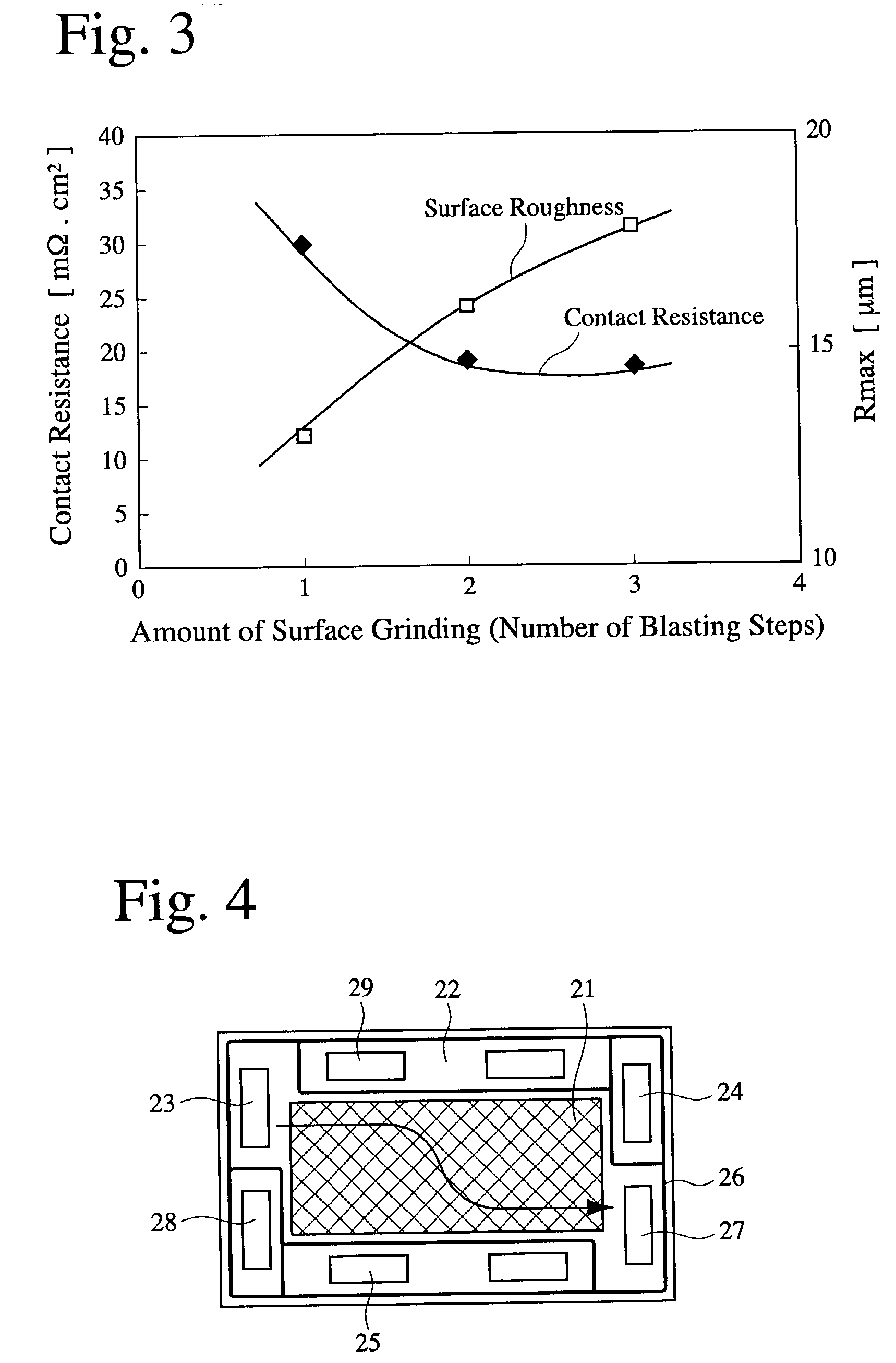
Fuel cell separator plate and method for producting it
ActiveUS20030087143A1Reduce contact resistanceImprove air tightnessFuel cells groupingFinal product manufactureFuel cellsSurface roughness
A fuel cell separator plate comprising a portion in contact with an electrode, and a sealing portion provided around the contact portion, the contact portion having a larger surface roughness (Rmax) than that of the sealing portion. It is preferably a molded separator plate made of a composite carbon material comprising carbon and a thermosetting resin.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
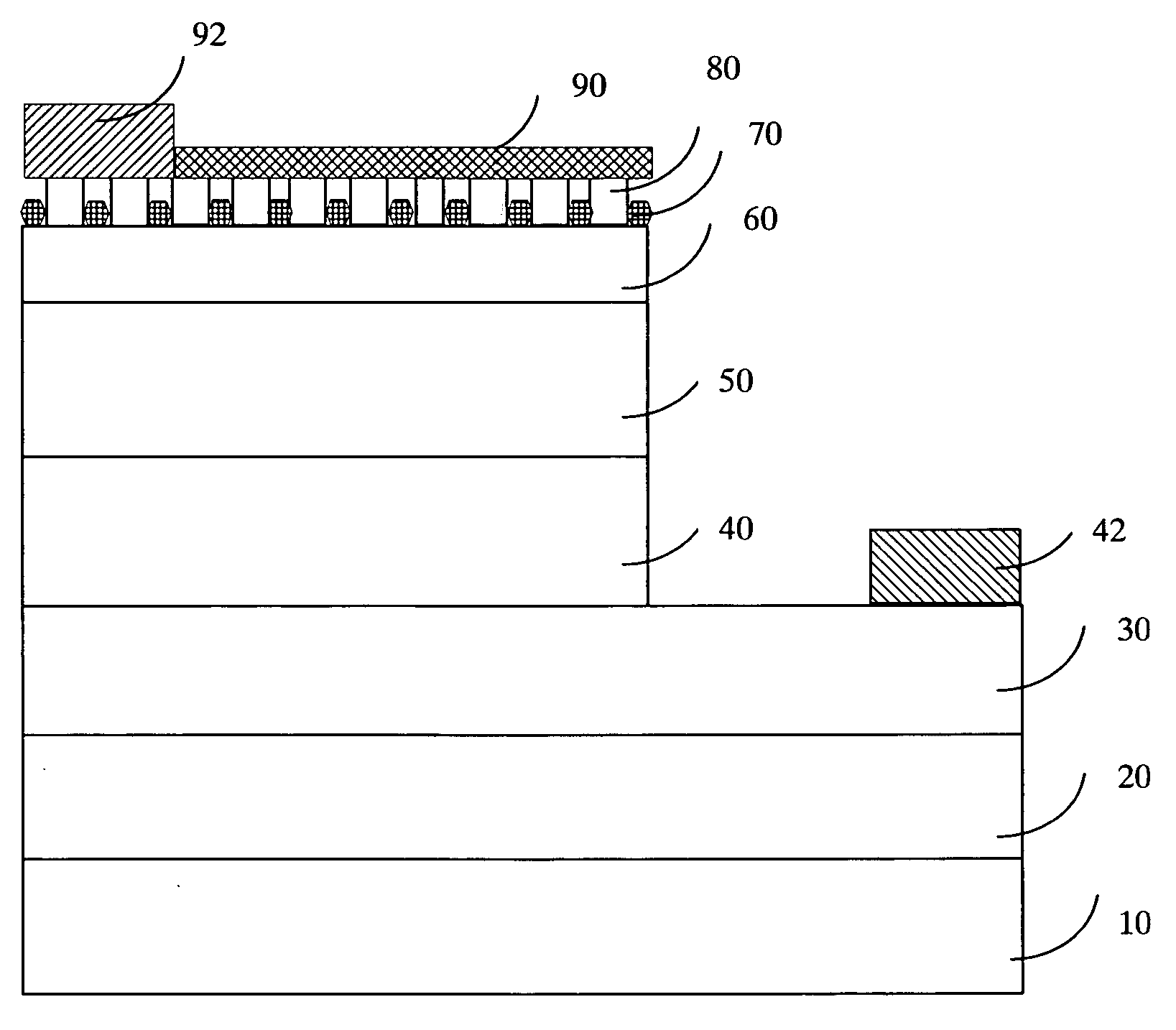
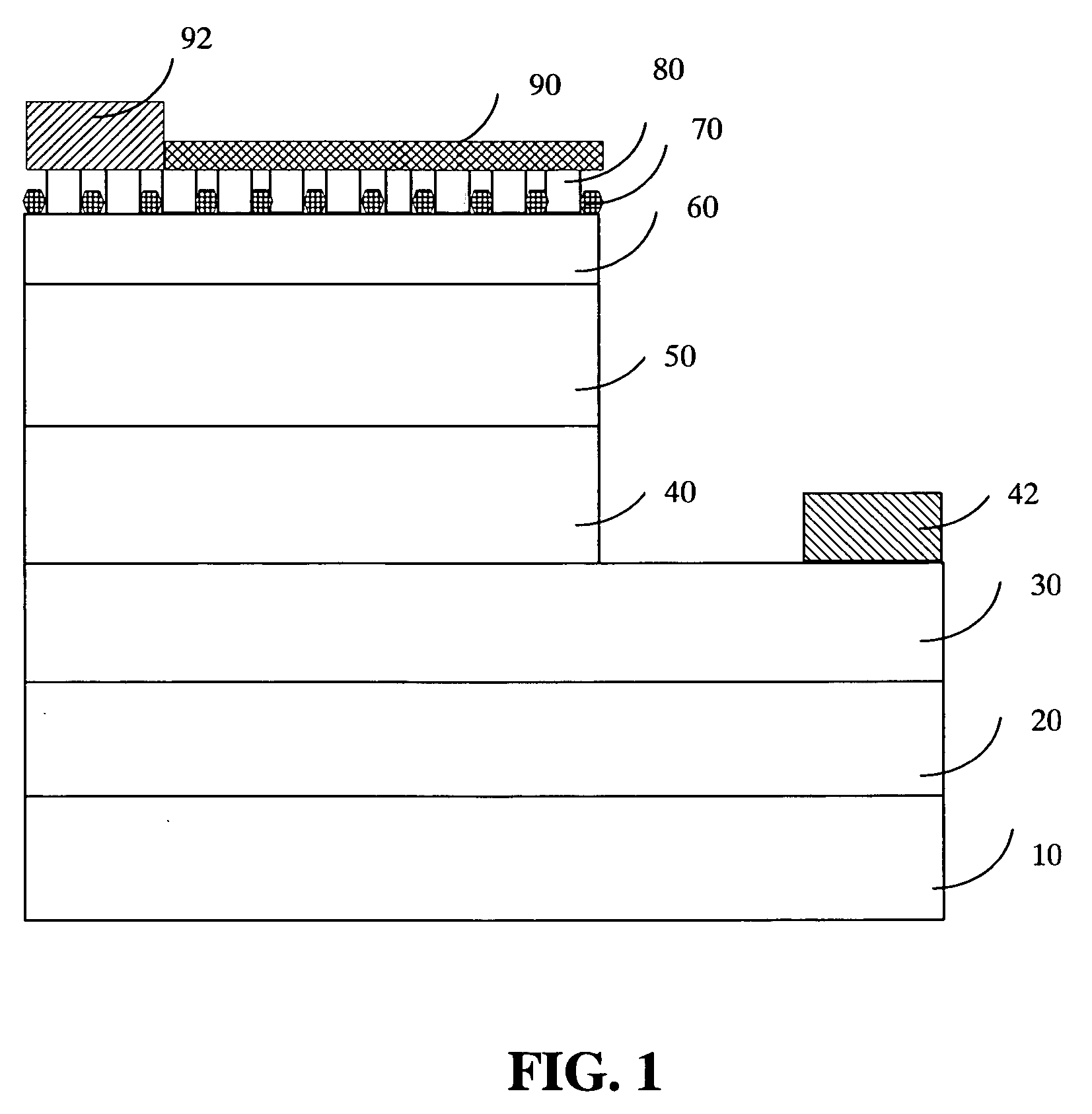
High-brightness gallium-nitride based light emitting diode structure
InactiveUS20060086942A1Improve external quantum efficiency and luminous efficiencySurface rougheningSemiconductor devicesRefractive indexGallium
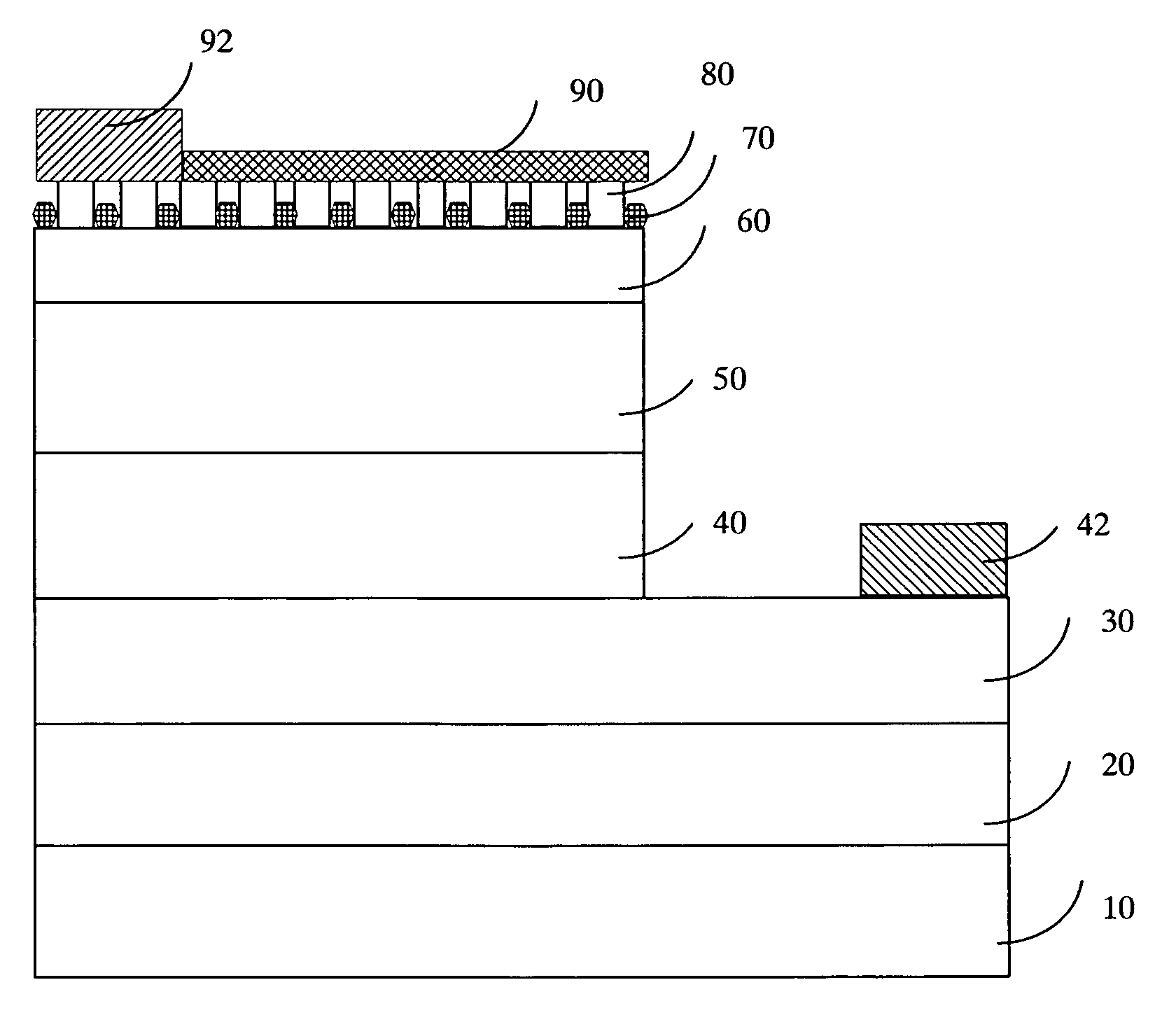
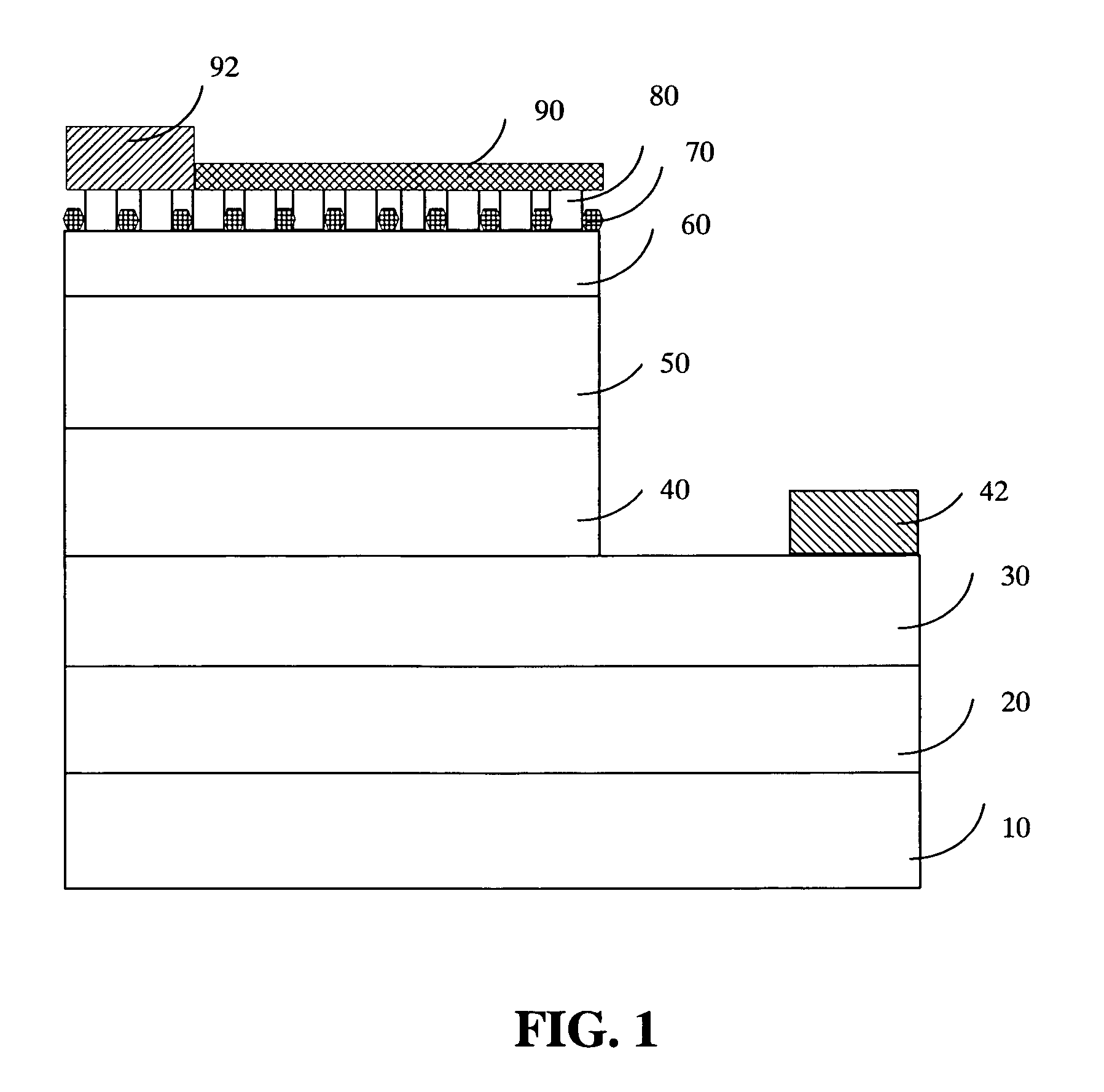
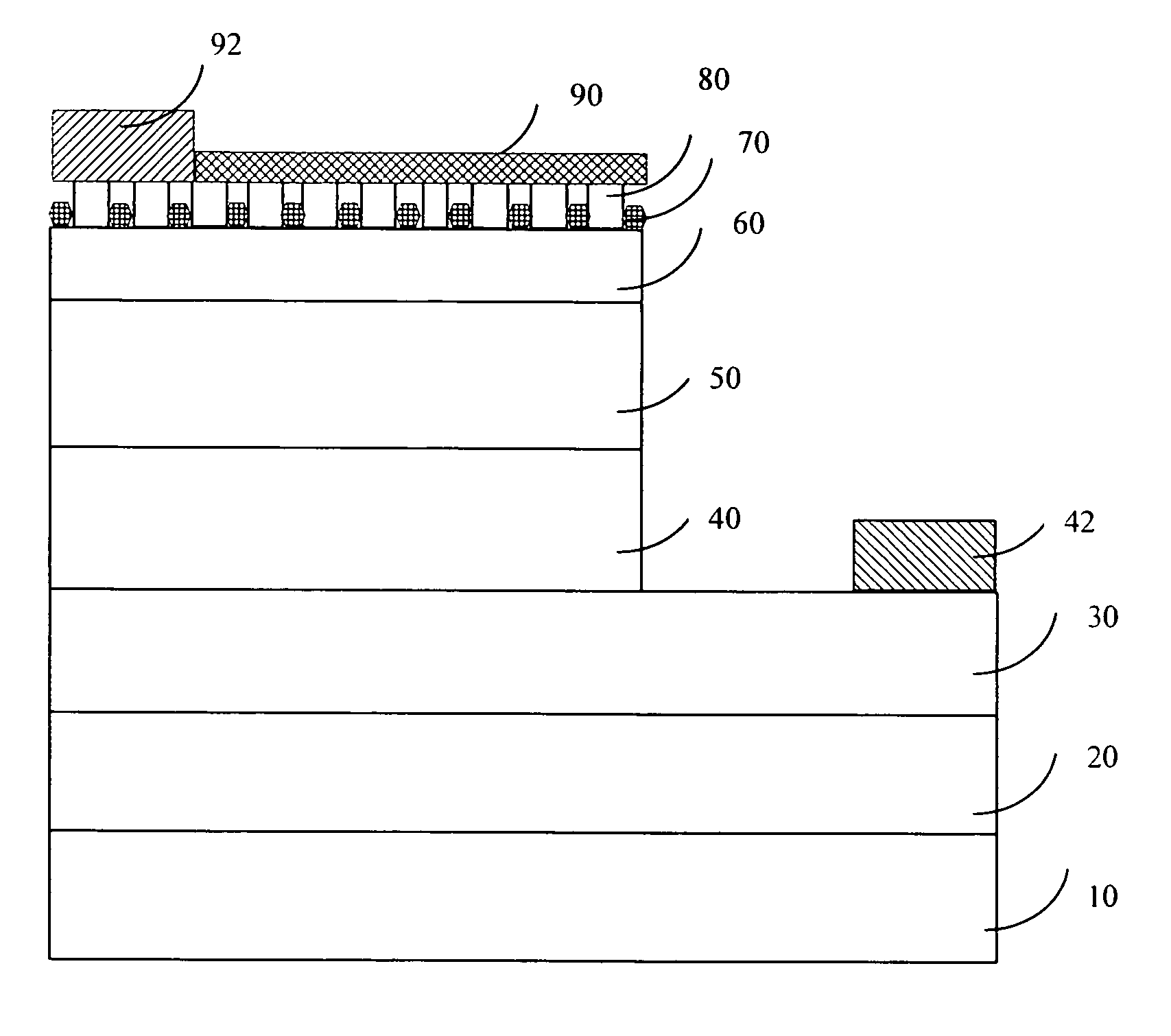
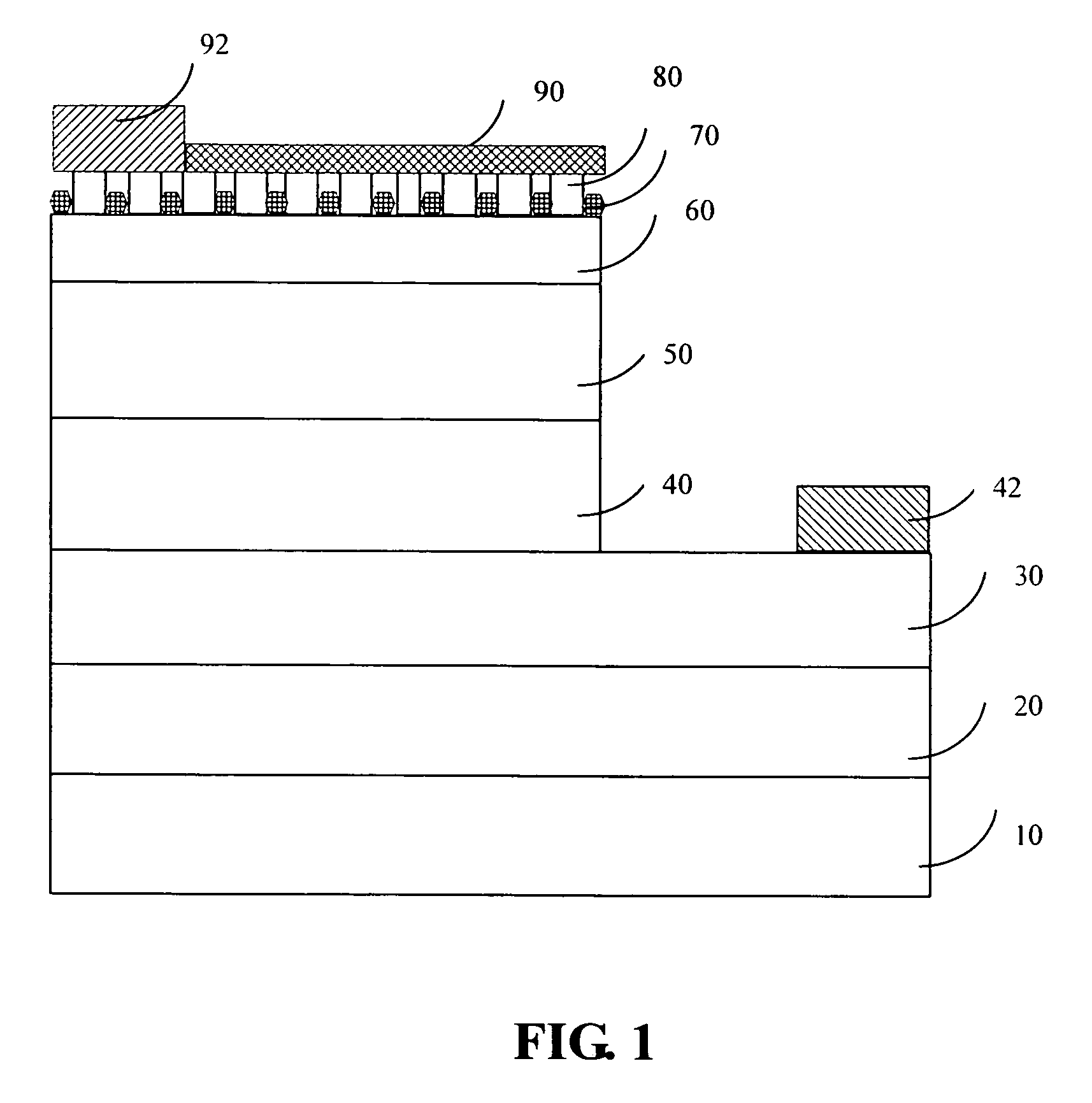
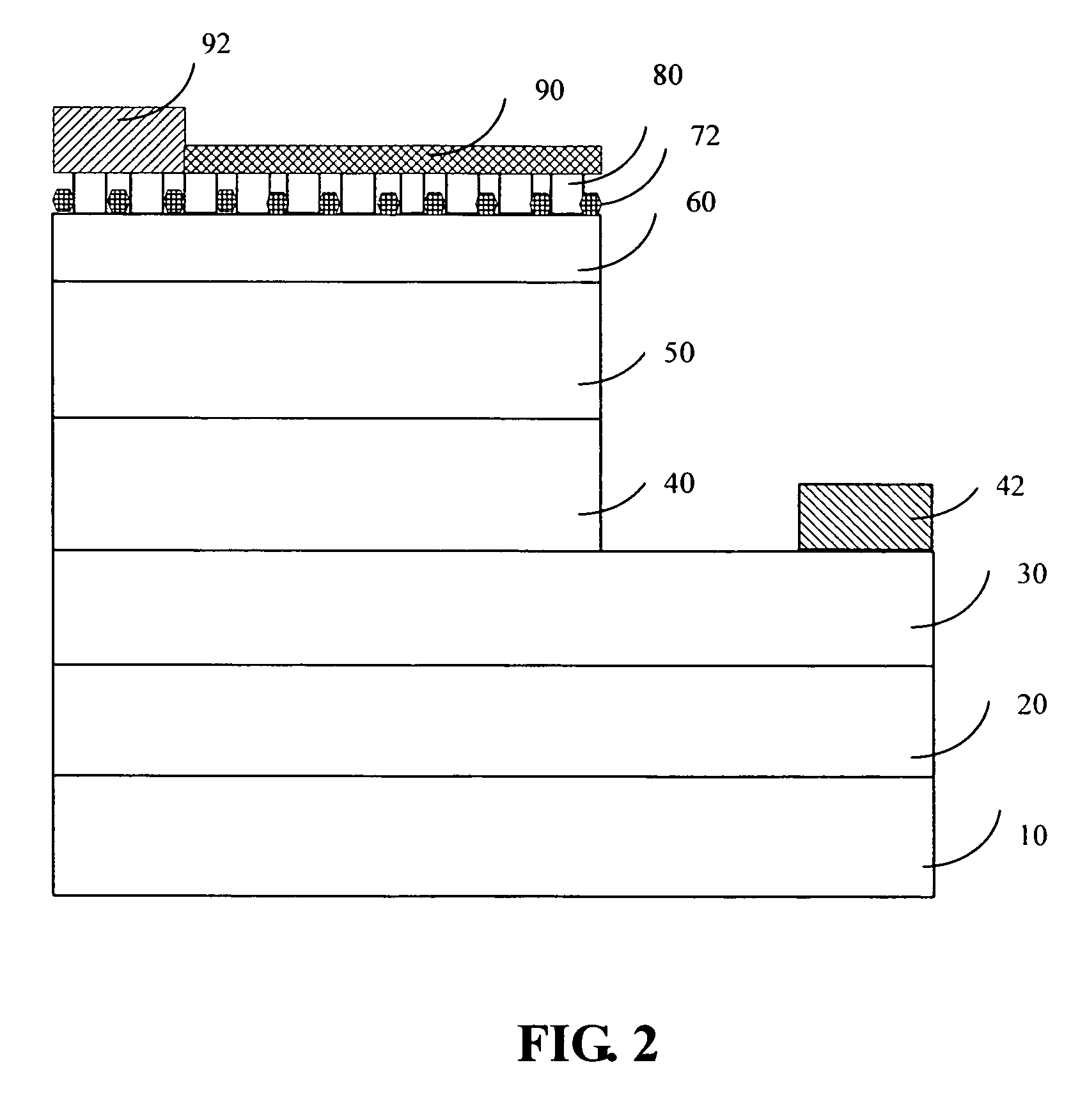
A GaN-based LED structure is provided so that the brightness and luminous efficiency of the GaN-based LED are enhanced effectively. The greatest difference between the GaN-based LEDs according to the invention and the prior arts lies in the addition of a masking buffer layer on top of the p-type contact layer and a p-type roughened contact layer on top of the masking buffer layer. The masking buffer layer could be formed using MOCVD to deposit SixNy (x,y≧1), MgwNz (w,z≧1), or AlsIntGa1-s-tN (0≦s,t<1, s+t≦1) heavily doped with Si and / or Mg. The masking buffer layer is actually a mask containing multiple randomly distributed clusters. Then, on top of the masking buffer layer, a p-type roughened contact layer made of p-type AluInvGa1-u-vN (0≦u,v<1, u+v≦1) is developed. The p-type roughened contact layer does not grow directly on top of the masking buffer layer. Instead, the p-type roughened contact layer starts from the top surface of the underlying p-type contact layer not covered by the masking buffer layer's clusters. The p-type roughened contact layer then grows upward until it passes (but does not cover) the mask of the masking buffer layer for a specific distance. The total internal reflection that could have been resulted from the GaN-based LEDs' higher index of refraction than that of the atmosphere could be avoided. The GaN-based LEDs according to the present invention therefore have superior external quantum efficiency and luminous efficiency.
Owner:FORMOSA EPITAXY INCORPORATION +1
Method for enhancing electrical injection efficiency and light extraction efficiency of light-emitting devices
InactiveUS20110127551A1Improve efficiencyConvenient lightingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysical chemistryEngineering
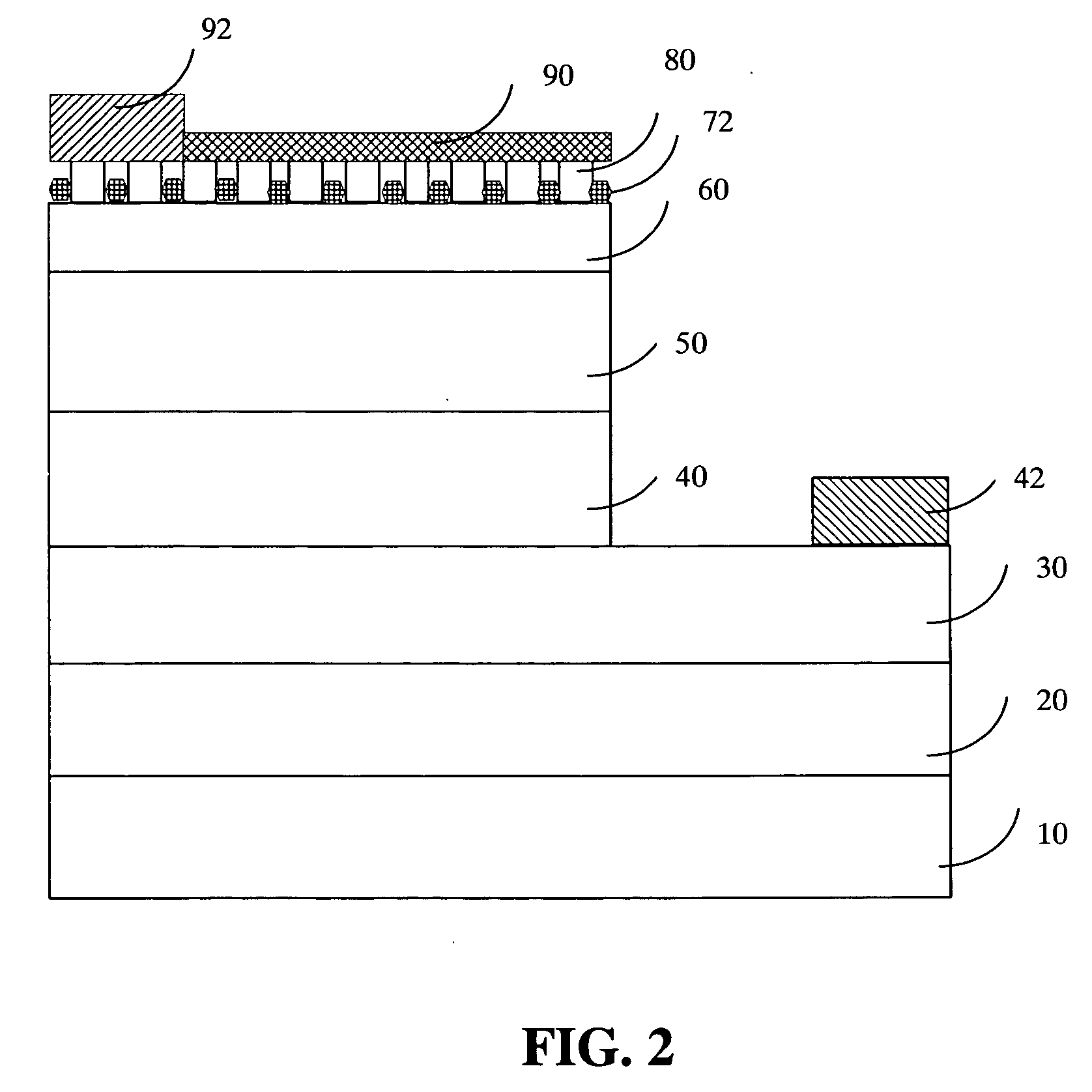
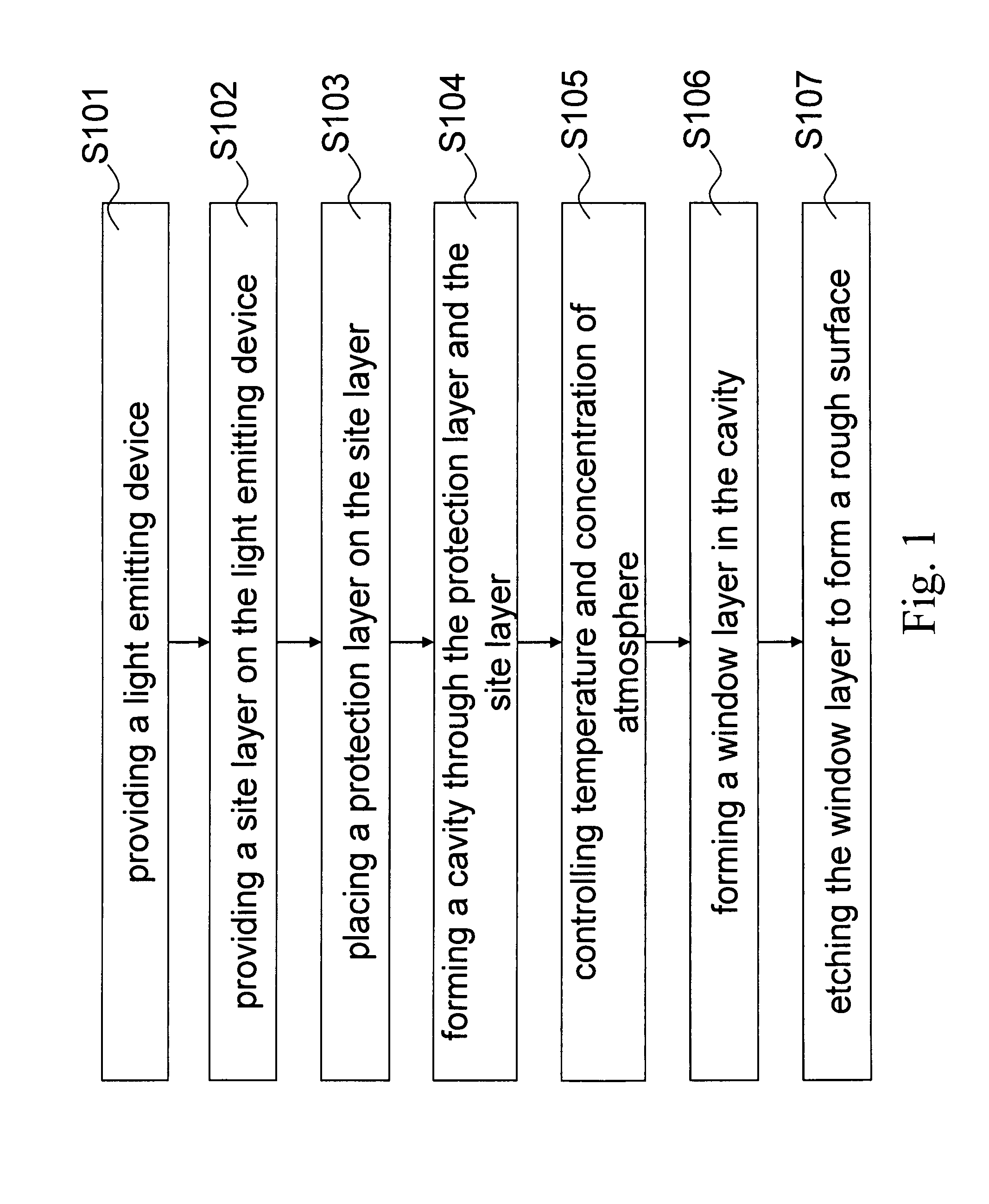
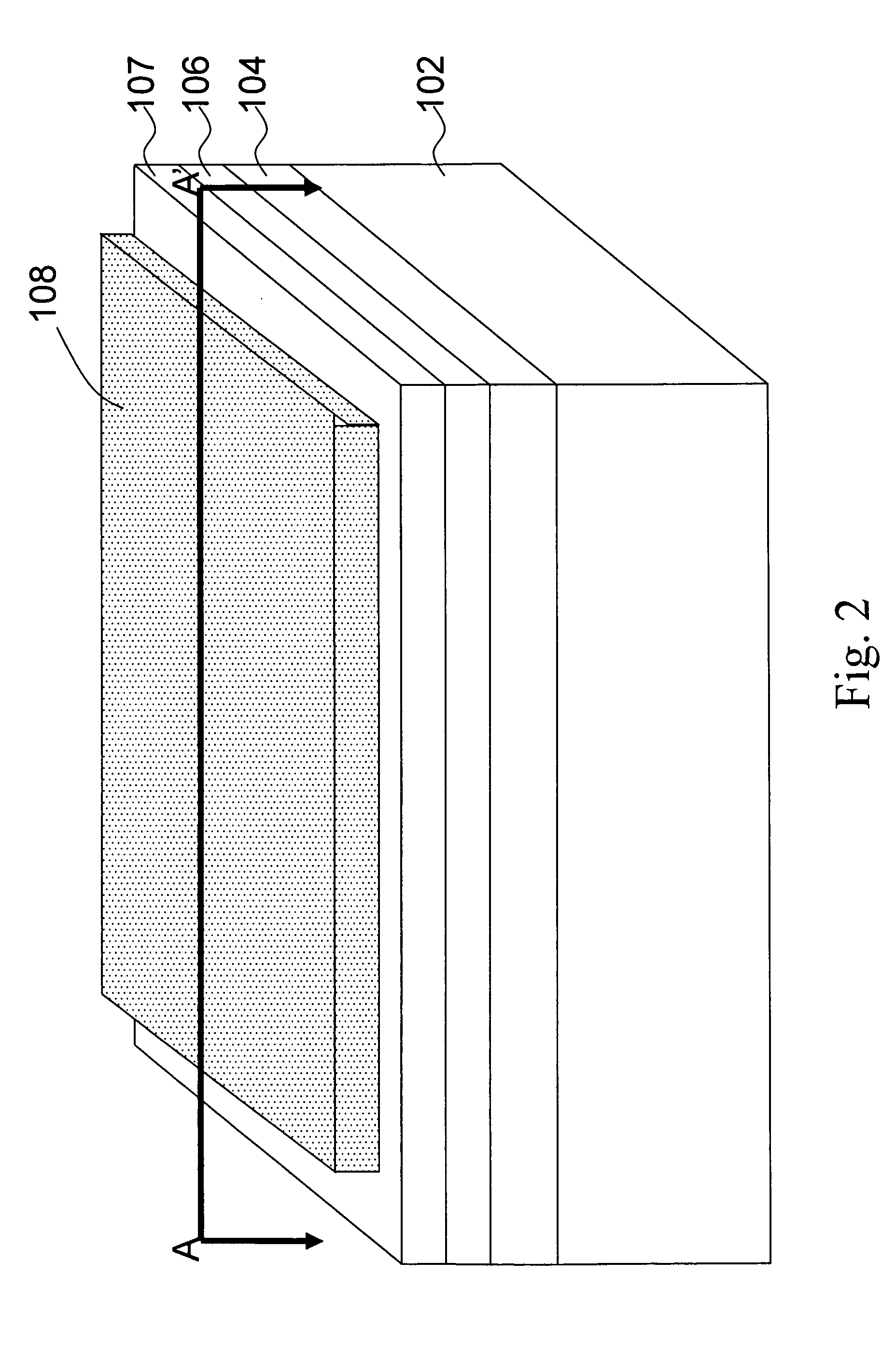
A method for enhancing electrical injection efficiency and light extraction efficiency of a light-emitting device is disclosed. The method includes the steps of: providing a site layer on the light-emitting device; placing a protection layer on the site layer; forming a cavity through the protection layer and the site layer; and growing a window layer in the cavity. The shape of the window layer can be well controlled by adjusting reactive temperature, reactive time, and N2 / H2 concentration ratio of atmosphere such that light escape angle of the window layer can be changed.
Owner:WALSIN LIHWA
High-brightness gallium-nitride based light emitting diode structure
InactiveUS7049638B2Improve external quantum efficiency and luminous efficiencySurface rougheningSemiconductor devicesRefractive indexContact layer
Owner:FORMOSA EPITAXY INCORPORATION +1
Light-emitting diode and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20070221927A1The implementation process is simpleHigh yieldSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxideMetal
A light-emitting diode (LED) and a method for manufacturing the same are described. The method for manufacturing the LED comprises the following steps. An illuminant epitaxial structure is provided, in which the illuminant epitaxial structure has a first surface and a second surface on opposite sides, and a substrate is deposed on the first surface of the illuminant epitaxial structure. A metal layer is formed on the second surface of the illuminant epitaxial structure. An anodic oxidization step is performed to oxidize the metal layer, so as to form a metal oxide layer. An etching step is performed to remove a portion of the metal oxide layer, so as to form a plurality of holes in the metal oxide layer.
Owner:EPISTAR CORP
Light-emitting diode and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7439091B2Effectively enhancing light extractionSurface rougheningSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight-emitting diodeMetal
A light-emitting diode (LED) and a method for manufacturing the same are described. The method for manufacturing the LED comprises the following steps. An illuminant epitaxial structure is provided, in which the illuminant epitaxial structure has a first surface and a second surface on opposite sides, and a substrate is deposed on the first surface of the illuminant epitaxial structure. A metal layer is formed on the second surface of the illuminant epitaxial structure. An anodic oxidization step is performed to oxidize the metal layer, so as to form a metal oxide layer. An etching step is performed to remove a portion of the metal oxide layer, so as to form a plurality of holes in the metal oxide layer.
Owner:EPISTAR CORP
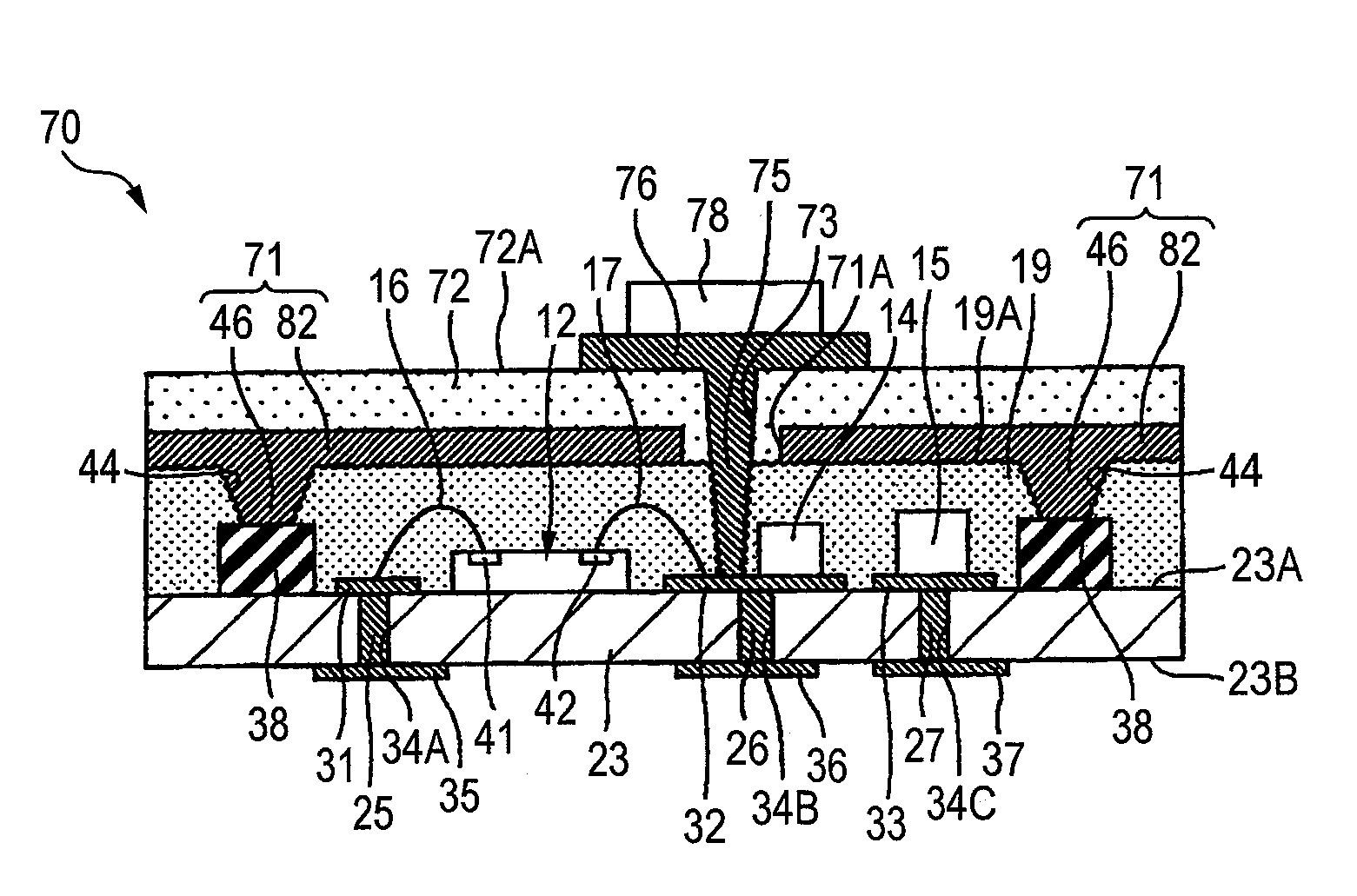
Method of manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20090029506A1Low costSurface rougheningSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCross-talk/noise/interference reductionHydrogen fluorideDevice material
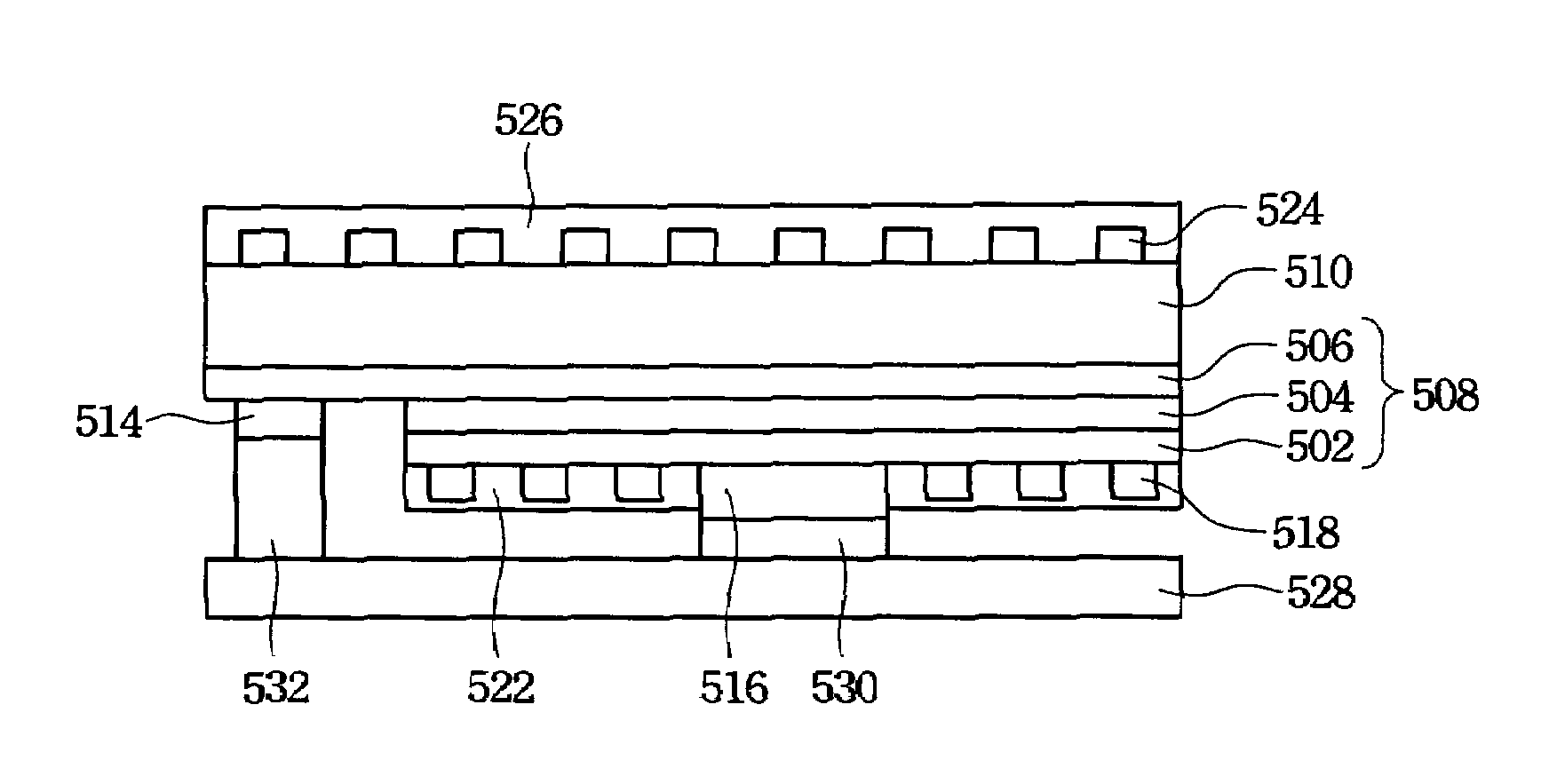
In a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device 10 including a wiring board 11 having a ground terminal 38, a semiconductor chip 12 and passive components 14 and 15 which are electronic components mounted on the wiring board 11, and a sealing resin 19 containing a silica filler for sealing the semiconductor chip 12 and the passive components 14 and 15, the silica filler present on a surface of the sealing resin 19 is dissolved with a hydrogen fluoride solution, and a shield layer 21 which is electrically connected to the ground terminal 38 is then formed on the surface of the sealing resin 19 by a plating method.
Owner:SHINKO ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Semiconductor substrate, method for fabricating the same, and method for fabricating semiconductor device
InactiveUS7102206B2Stable polishing speedReduced polishing speedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMetallurgySemiconductor
In a semiconductor substrate having a notch in an edge portion thereof, each of the two shoulder portions of the notch is configured as an arc and the difference in curvature between the two shoulder portions of the notch is not less than 0 mm and not more than 0.1 mm.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for processing a surface of a component
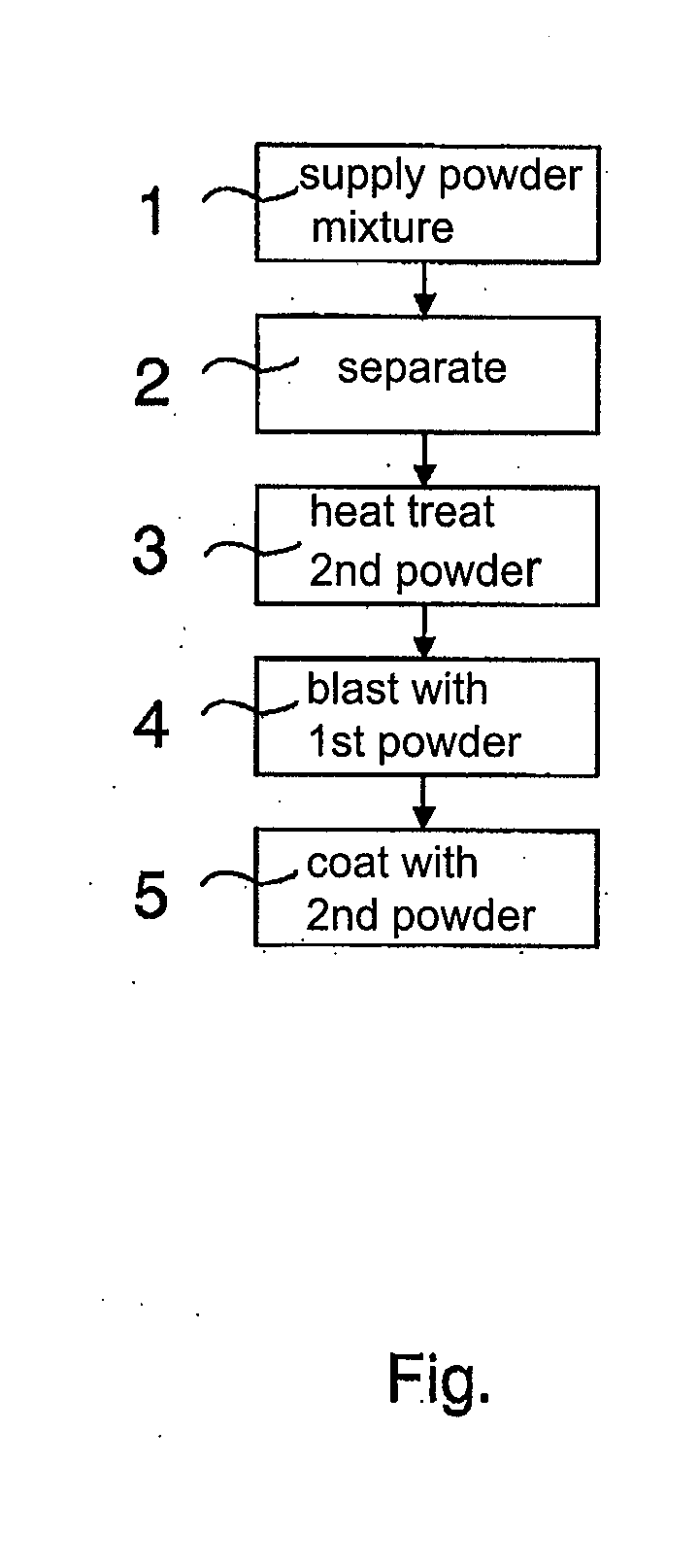
InactiveUS20130034661A1Reduce disadvantagesImprove adhesionMolten spray coatingPretreated surfacesChemical compositionMetallurgy
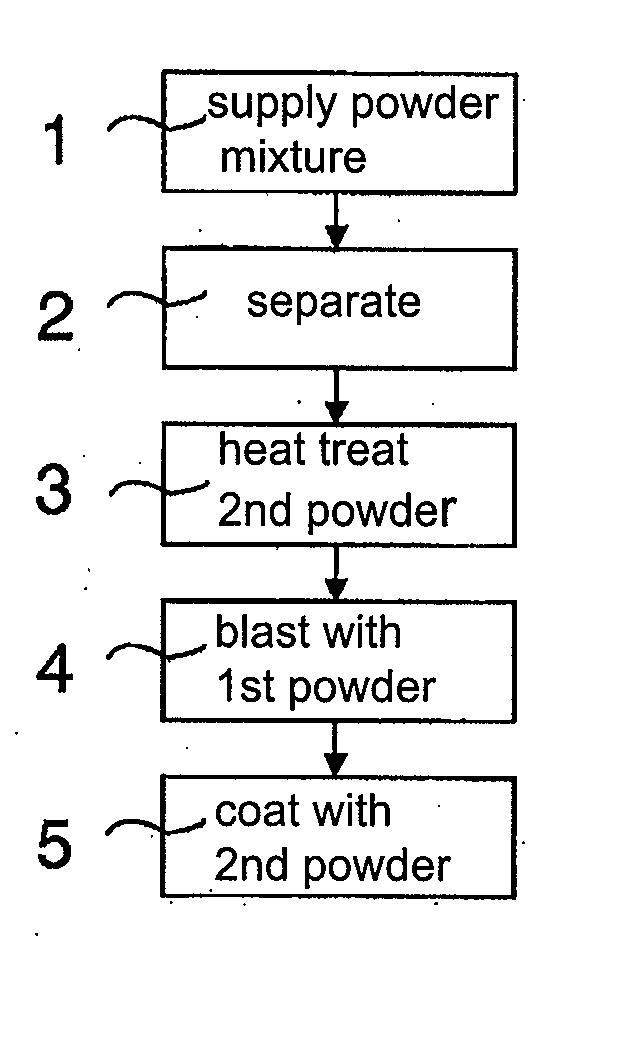
A method for processing a surface of a component, in particular in the aviation sector, including the following steps: spraying the component with a first powder and coating the component with a second powder, the first powder having the same chemical composition as the second powder.
Owner:MTU AERO ENGINES GMBH
Mask blank, transfer mask, method of manufacturing a transfer mask, and method of manufacturing a semiconductor device
ActiveUS20120156596A1Small biasSuppress surface reflectionLayered productsPhotomechanical apparatusSurface layerRefractive index
A mask blank for use in the manufacture of a transfer mask adapted to be applied with ArF excimer laser exposure light is disclosed. The mask blank has, on a transparent substrate, a light-shielding film for forming a transfer pattern. The light-shielding film has an at least two-layer structure including a lower layer and an upper layer from the transparent substrate side. The lower layer is made of a material composed of a transition metal, silicon, and nitrogen and having a nitrogen content of 21 at % or more and a refractive index n of 1.9 or less. The upper layer is made of a material composed of a transition metal, silicon, and nitrogen and having a refractive index n of 2.1 or less. A surface layer of the upper layer contains oxygen and has a nitrogen content of 14 at % or more.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Lithium cell and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050112469A1Good adherent contactImprove adhesionElectrode manufacturing processesFinal product manufactureAlloyMachining
Owner:NGK SPARK PLUG CO LTD
Magnetic sheet and production method thereof
ActiveUS20090324982A1Preventing electromagnetic disorderIncrease surface lubricityMagnetic/electric field screeningParticle applicationPolyresinMaterials science
A magnetic sheet, which contains: a magnetic layer including a magnetic powder and a resin composition containing the magnetic powder therein; and a convex-concave forming layer, in which the convex-concave forming layer has Bekk smoothness of 70 sec / mL or less. A method for producing a magnetic sheet, which contains: adding a magnetic powder to a resin composition to prepare a magnetic composition, and giving the magnetic composition a shape to form a magnetic layer; and placing and stacking a convex-concave forming layer and a pattern transferring material on a surface of the magnetic layer in this order, and hot pressing the stacked layers so as to bond the convex-concave forming layer with the magnetic layer to form a laminate, as well as to transfer a surface configuration of the pattern transferring material to a surface of the laminate of the convex-concave forming layer and the magnetic layer.
Owner:DEXERIALS CORP
Process for producing nitrile rubber-metal laminate
InactiveUS20100190018A1Prevent peelingEffectively used as seal materialPretreated surfacesSuperimposed coating processPolymer scienceNitrile rubber
A nitrile rubber solution prepared by dissolving and dispersing into an organic solvent a nitrile rubber composition comprising 100 parts by weight of nitrile rubber, 40 parts by weight or more of carbon black having a DBP oil absorption amount of 30-100 ml / 100 g (according to ASTM D1765-91), 15-100 parts by weight of silica having particle sizes of 0.01-0.1 μm, 0-40 parts by weight of other inorganic filler than the carbon black and silica, and 5-20 parts by weight of an organic peroxide, and preferably further containing 2-10 parts by weight of a silane coupling agent is applied to an adhesive layer on one side or both sides of a metallic sheet, followed by vulcanizing the coated layer, thereby forming a rubber layer.
Owner:NOK CORP
Process for Separating Disk-Shaped Substrates with the Use of Adhesive Powers
InactiveUS20080286947A1No risk damage and impairmentPulled off reliablySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFine working devicesAdhesion forcePhotovoltaic industry
The present invention relates to a device and a method for dividing up substrates (2) in wafer form (e.g. wafers), which is used in the semiconductor industry, MST (microstructure technology) industry and photovoltaic industry, whereby improved reliability of the process and lower reject rates are accomplished. This object is achieved according to the invention by using adhesion forces that act between the substrates in wafer form and the devices (1) thereby used.
Owner:COENEN WOLFGANG +1
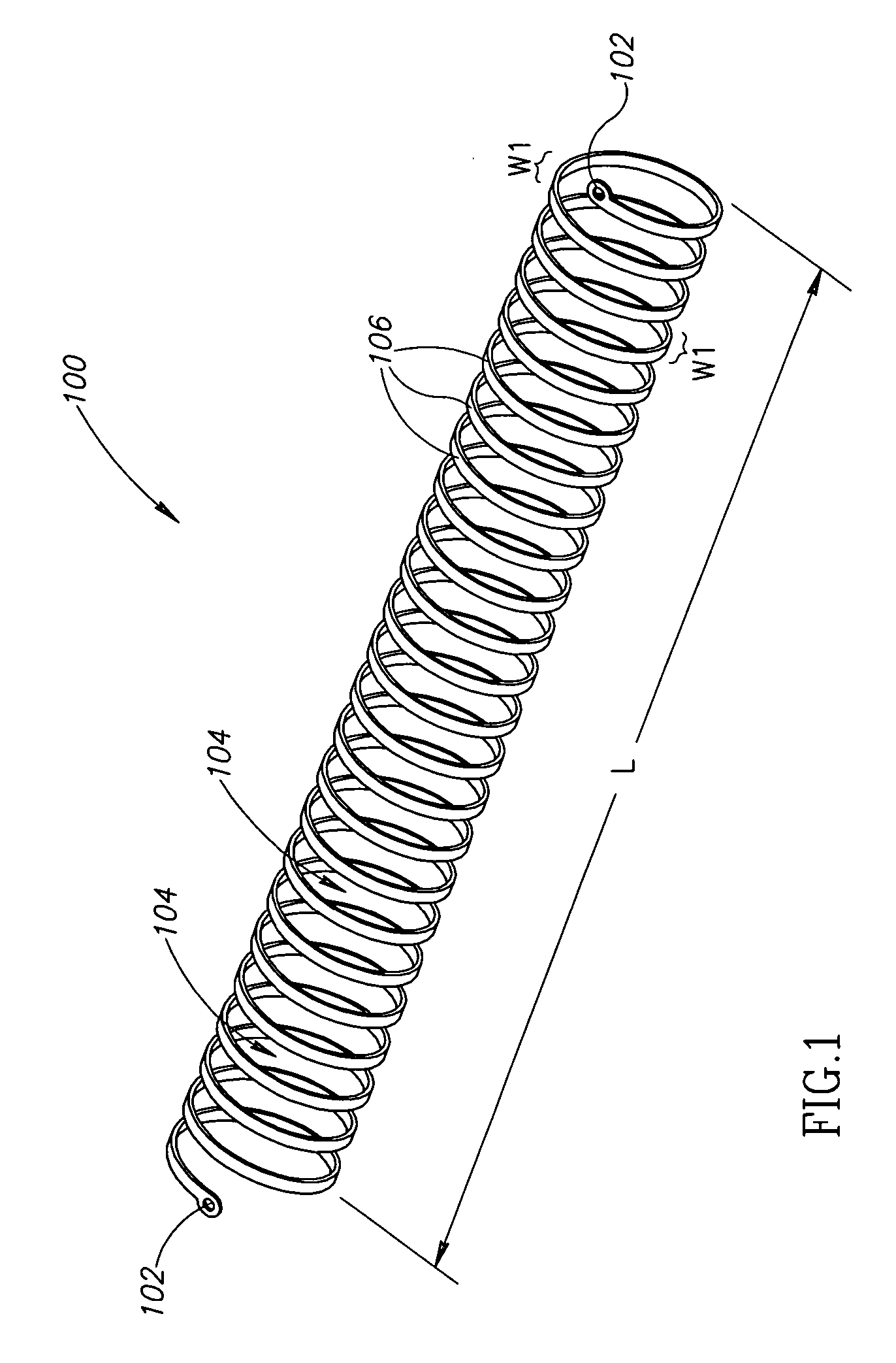
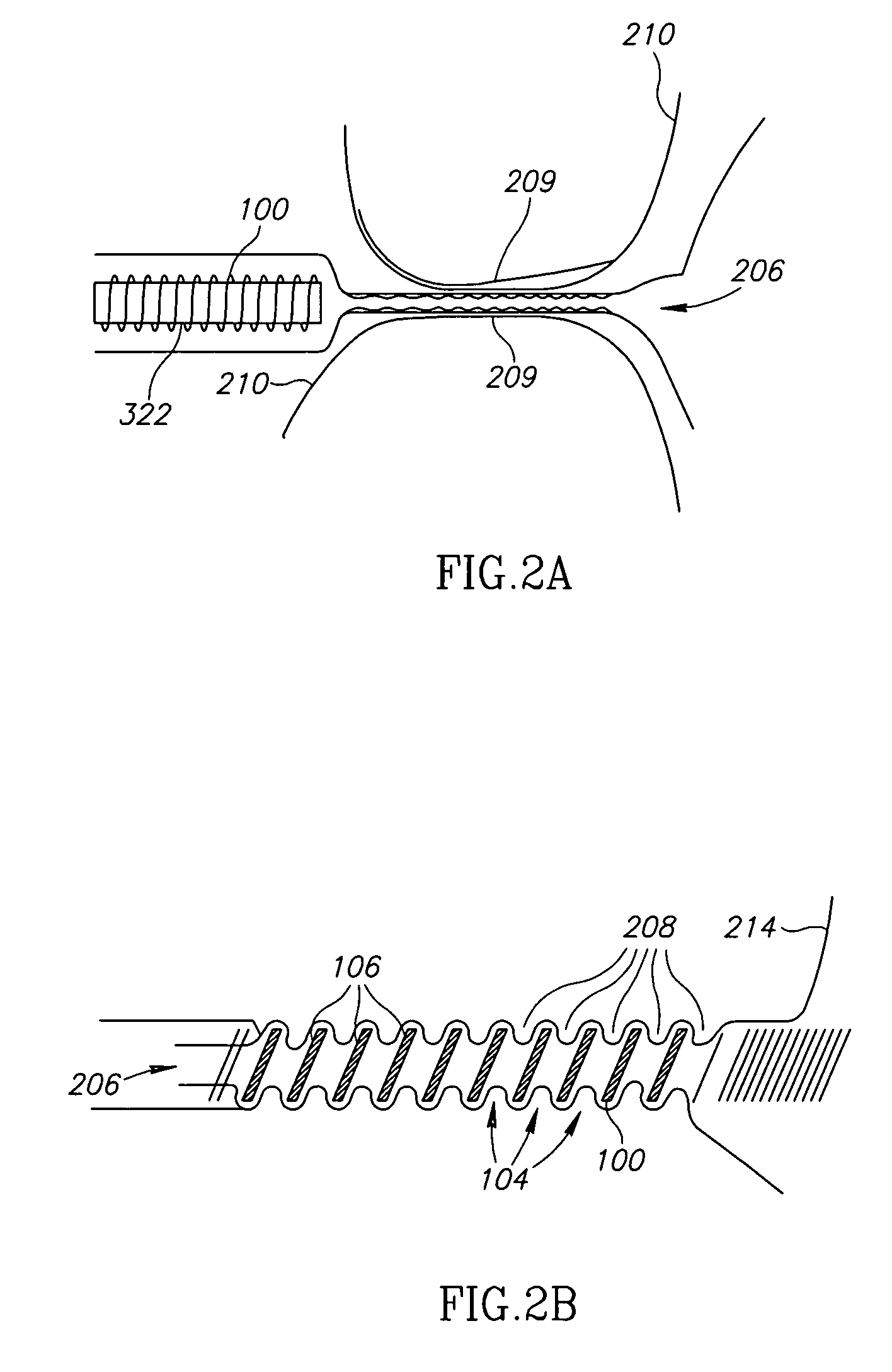
Tube and steerable introduction element comprising the tube
ActiveUS20150282693A1Convenient and accurateHigh positioning accuracyConfectionerySurgeryMiniaturizationAlloy
The invention relates to a tube (2) and a steerable introduction element like a catheter, an endoscope or a sheath comprising the tube. The tube comprises a composite material including a shape memory alloy material (12) and a non-shape-memory polymer material (22). The tube is used for making the introduction element steerable in a relatively easy way by modifying the temperature of the tube as required for achieving a preferred bending of the introduction element. By using this steering mechanism the introduction element can be positioned relatively accurately, because the composite material includes a non-shape-memory polymer material, which is more stable than, for instance, a shape-memory polymer material and which may be optimized for other properties like hardness, stiffness, et cetera. Furthermore, using the tube for steering an introduction element can lead to cost reductions and can enable miniaturization.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
High-brightness gallium-nitride based light emitting diode structure
InactiveUS20060145179A1Improve external quantum efficiency and luminous efficiencySurface rougheningSemiconductor devicesRefractive indexGallium
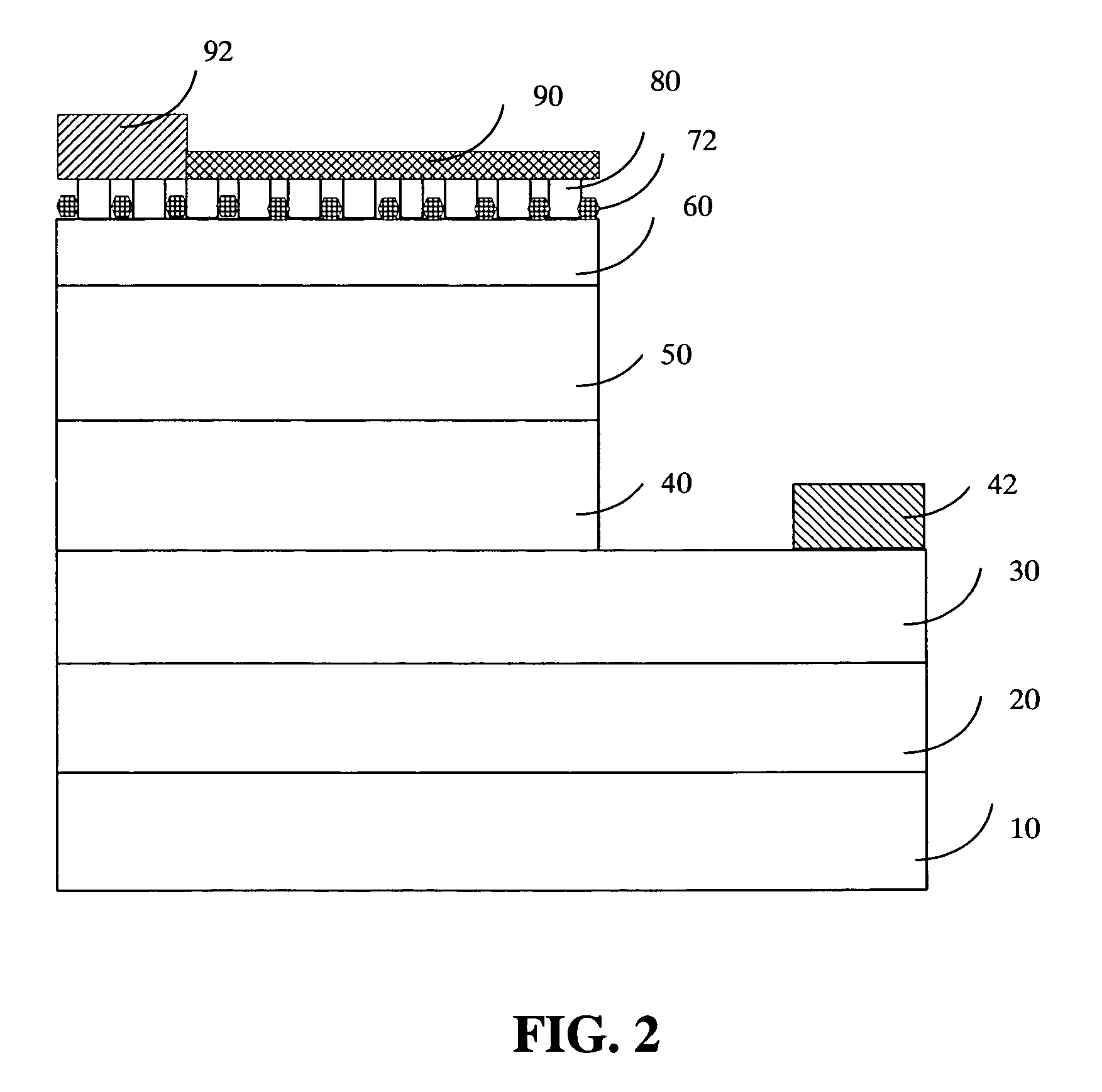
A GaN-based LED structure is provided so that the brightness and luminous efficiency of the GaN-based LED are enhanced effectively. The greatest difference between the GaN-based LEDs according to the invention and the prior arts lies in the addition of a masking buffer layer and a roughened contact layer on top of the masking buffer layer. The masking buffer layer contains randomly distributed clusters made of a group-IV nitride SixNy (x,y≧1), a group-II nitride MgwNz (w,z≧1), or a group-III nitride AlsIntGa1-s-tN (0≦s,t<1, s+t≦1) heavily doped with at least a group-II and group-IV element such as Mg and Si. The roughened contact layer, made of AluInvGa1-u-vN (0≦u,v<1, u+v≦1), starts from the top surface of an underlying second contact layer not covered by the masking buffer layer's clusters, and then grows upward until it passes (but does not cover) the clusters of the masking buffer layer for an appropriate distance. The total internal reflection that could have been resulted from the GaN-based LEDs' higher index of refraction than that of the atmosphere could be avoided.
Owner:FORMOSA EPITAXY INCORPORATION +1
High-brightness gallium-nitride based light emitting diode structure
InactiveUS7345321B2Improve external quantum efficiency and luminous efficiencySurface rougheningSemiconductor devicesRefractive indexContact layer
A GaN-based LED structure is provided so that the brightness and luminous efficiency of the GaN-based LED are enhanced effectively. The greatest difference between the GaN-based LEDs according to the invention and the prior arts lies in the addition of a masking buffer layer and a roughened contact layer on top of the masking buffer layer. The masking buffer layer contains randomly distributed clusters made of a group-IV nitride SixNy (x,y≧1), a group-II nitride MgwNz (w,z≧1), or a group-III nitride AlsIntGa1−s−tN (0≦s,t<1, s+t≦1) heavily doped with at least a group-II and group-IV element such as Mg and Si. The roughened contact layer, made of AluInvGa1−u−vN (0≦u,v<1, u+v≦1), starts from the top surface of an underlying second contact layer not covered by the masking buffer layer's clusters, and then grows upward until it passes (but does not cover) the clusters of the masking buffer layer for an appropriate distance. The total internal reflection that could have been resulted from the GaN-based LEDs' higher index of refraction than that of the atmosphere could be avoided.
Owner:FORMOSA EPITAXY INCORPORATION +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com