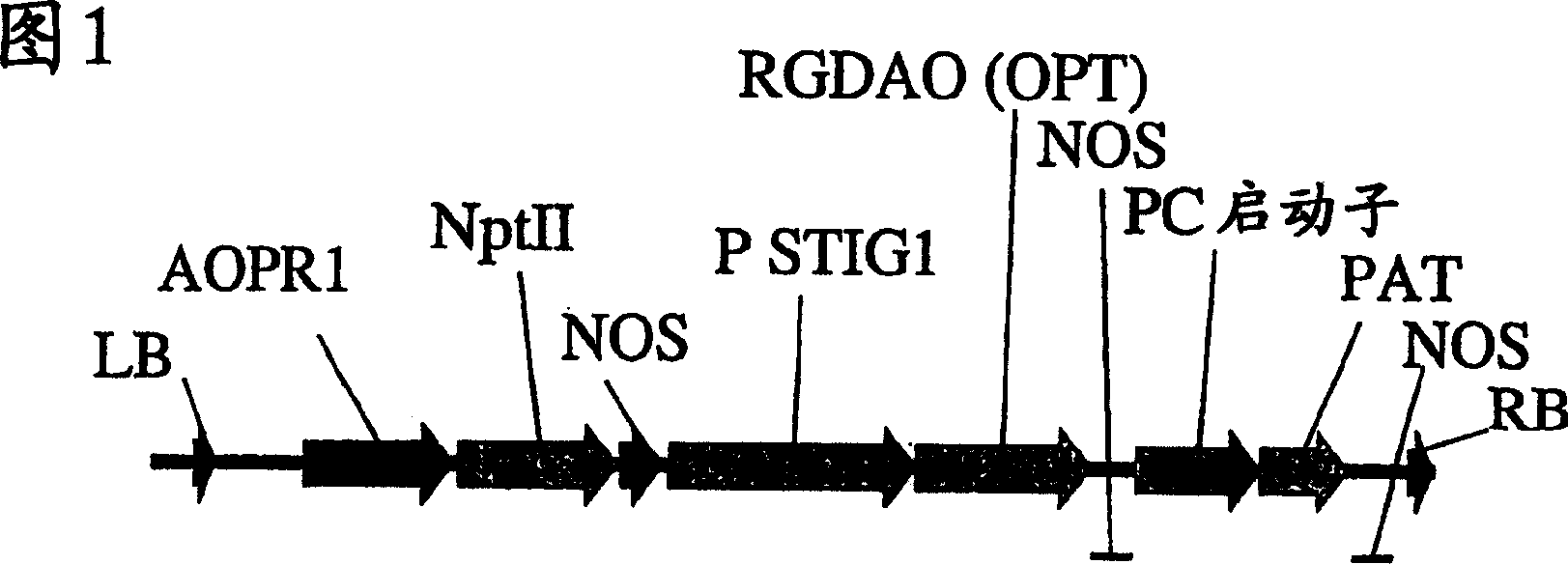
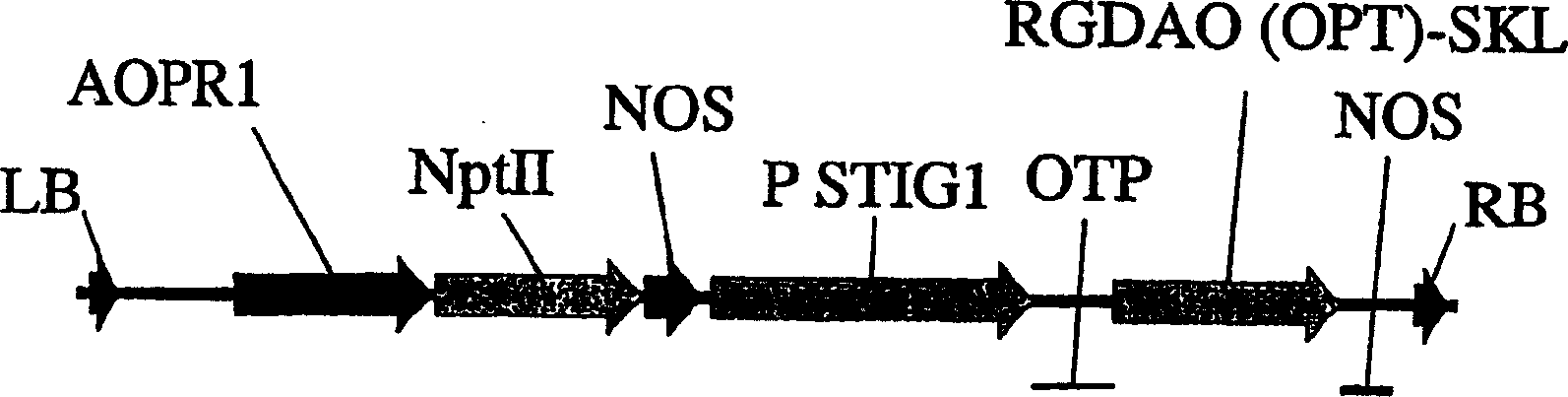
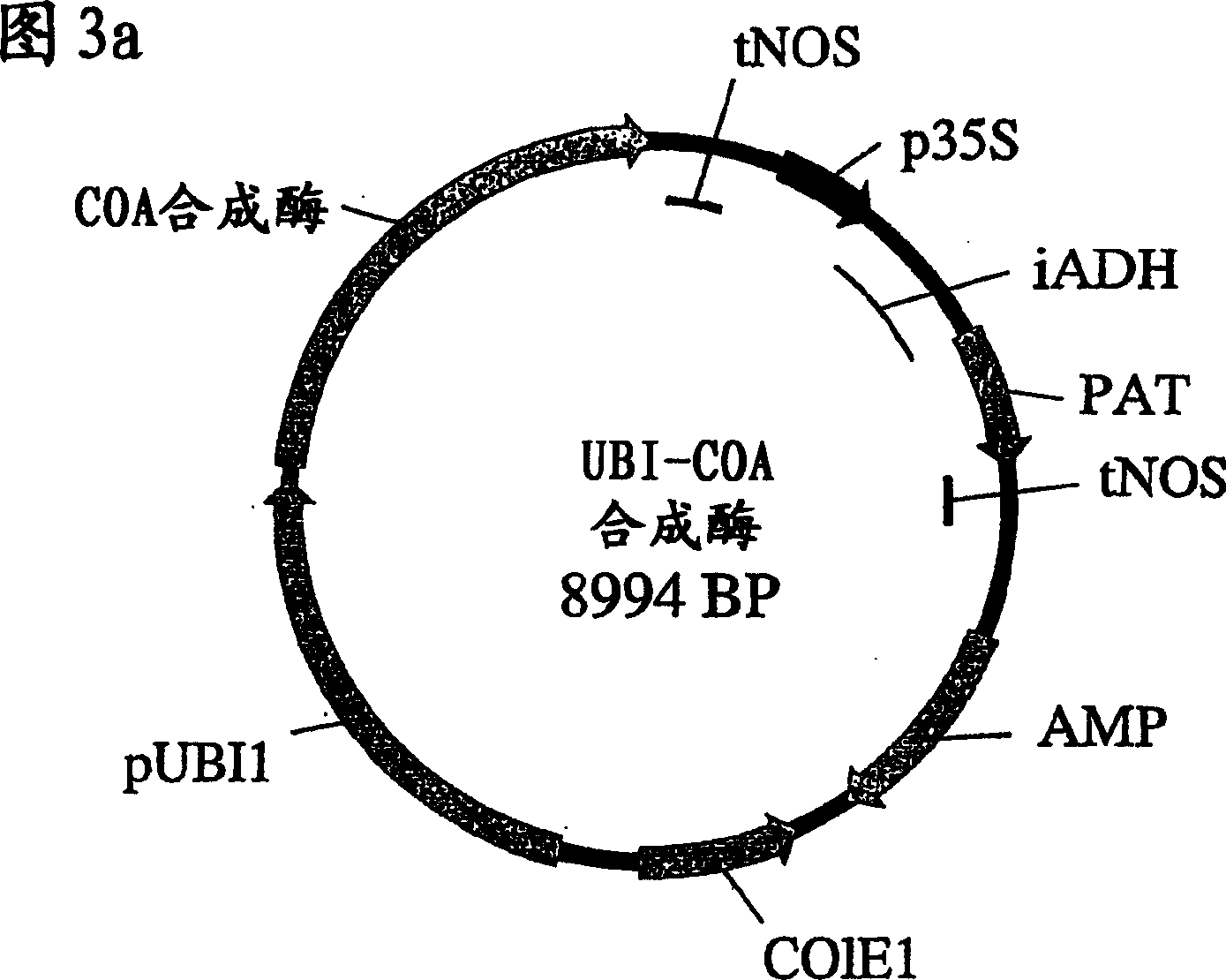
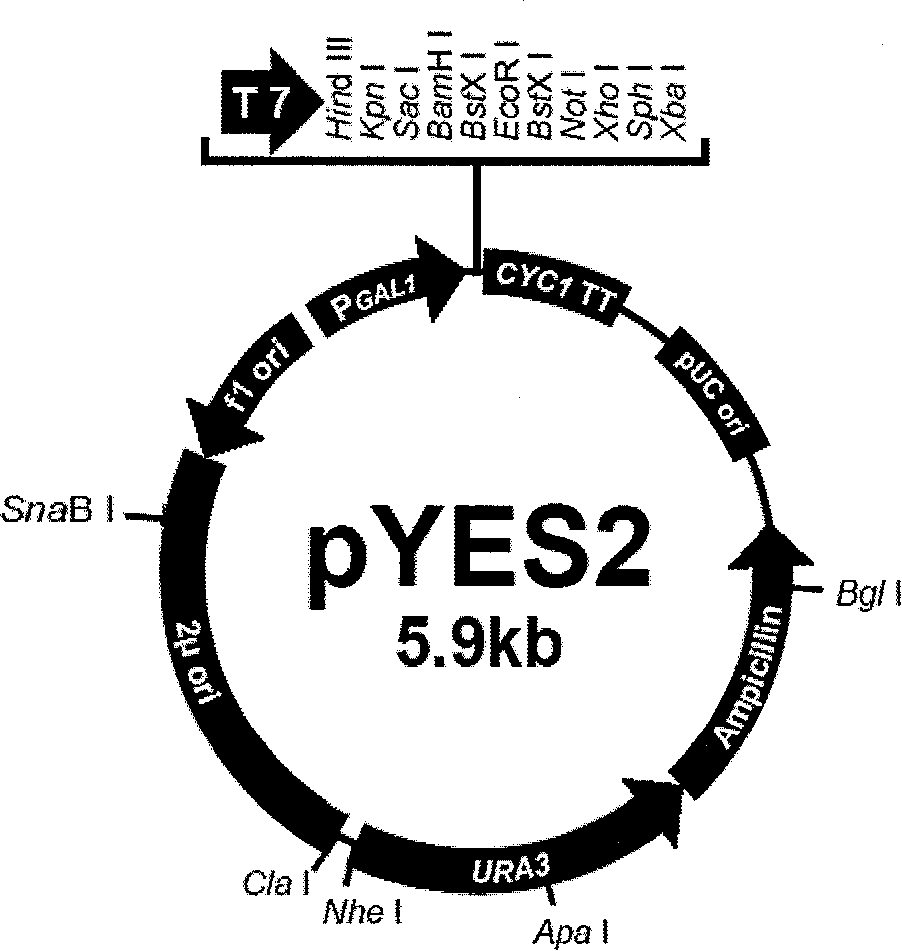
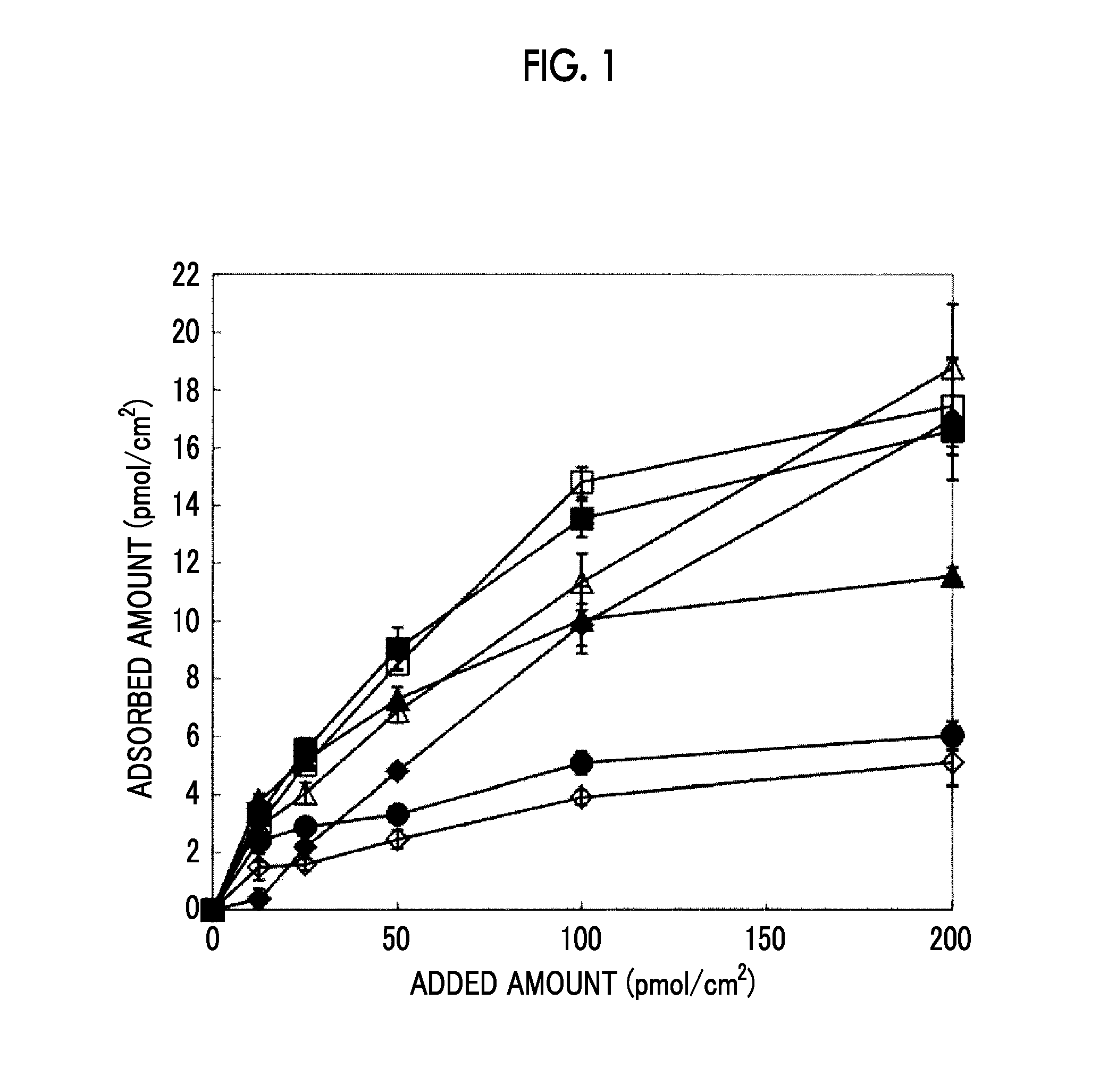
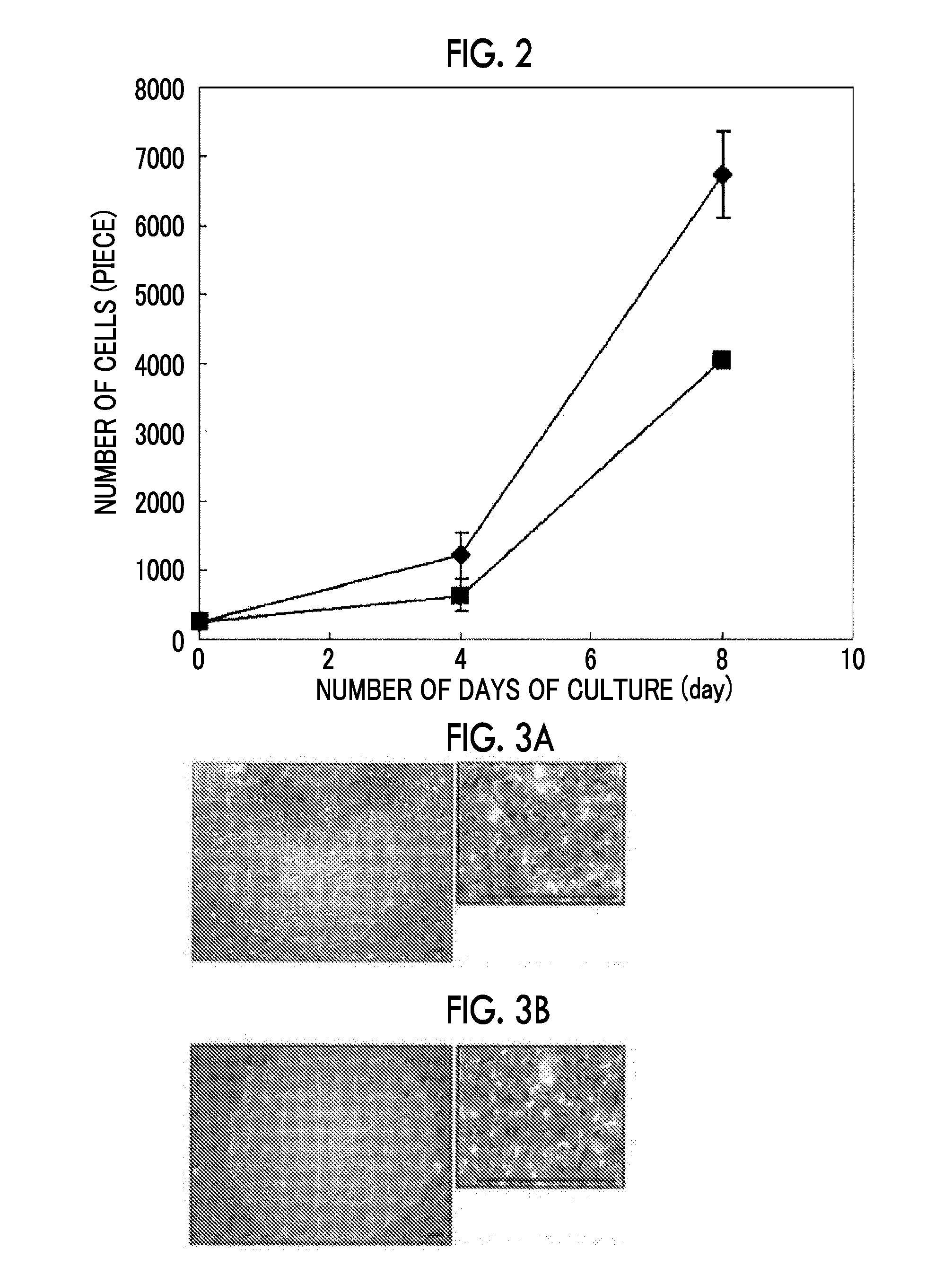
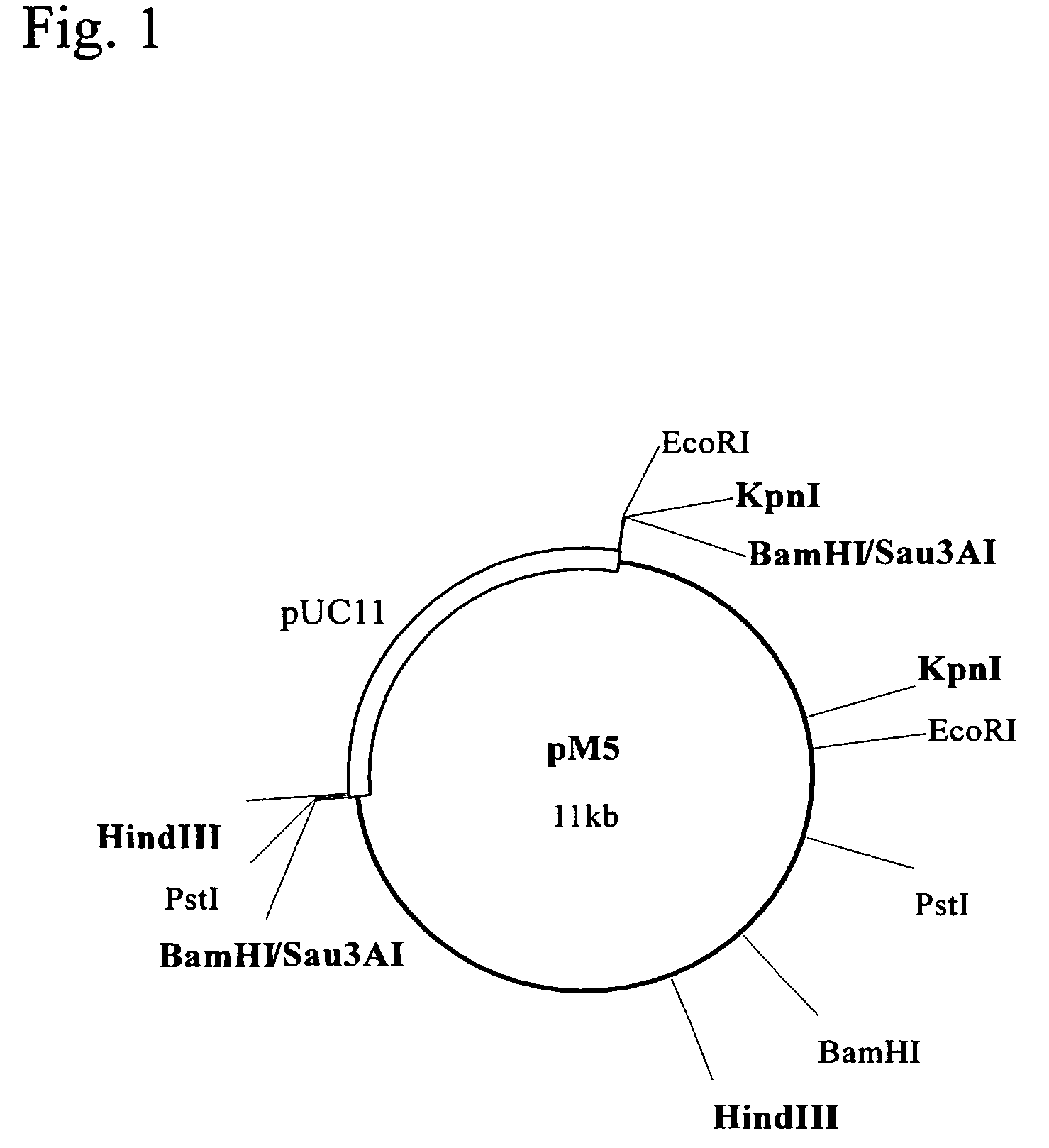
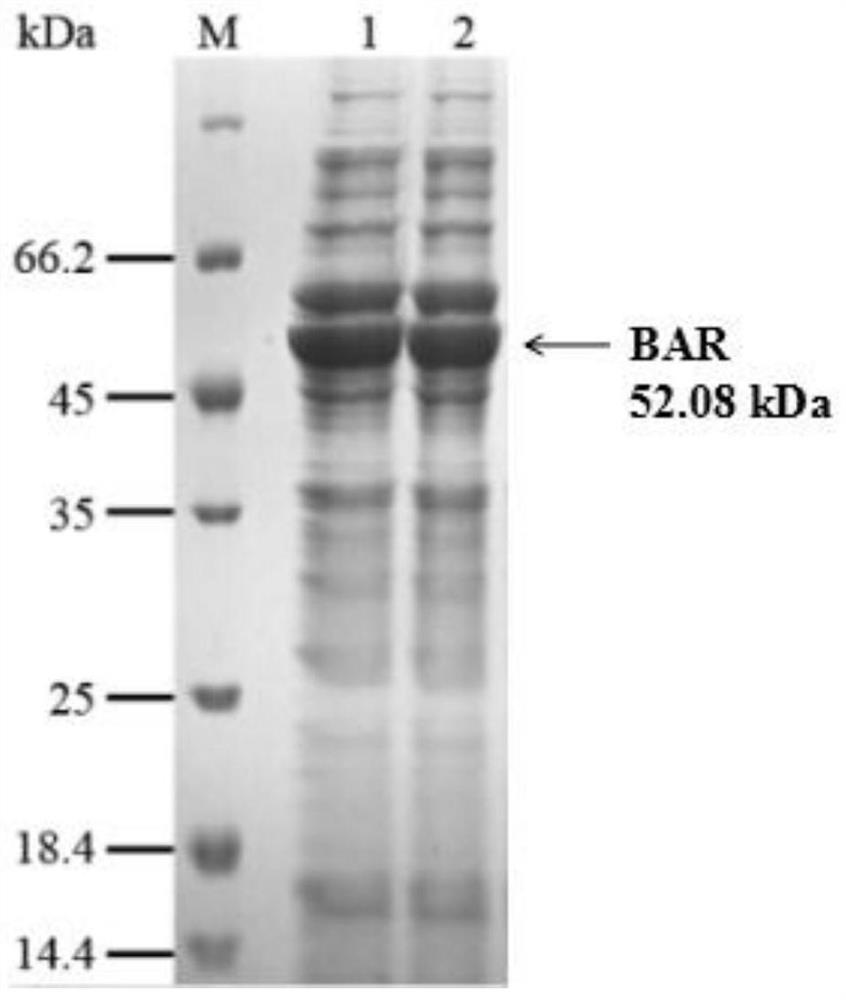
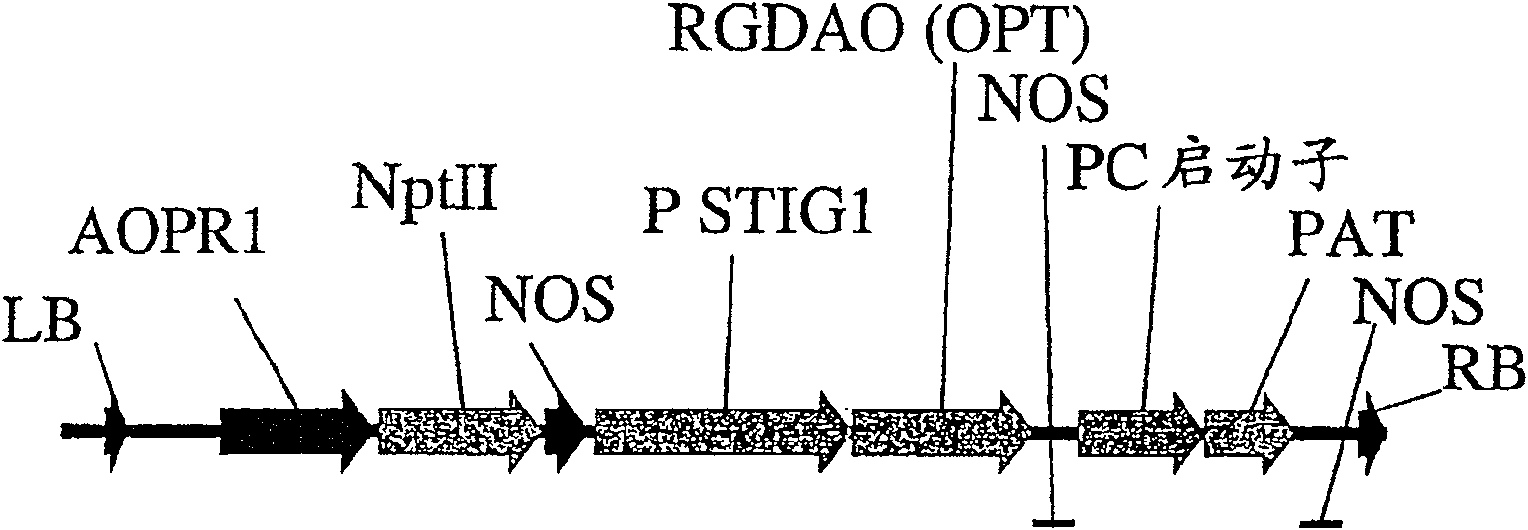
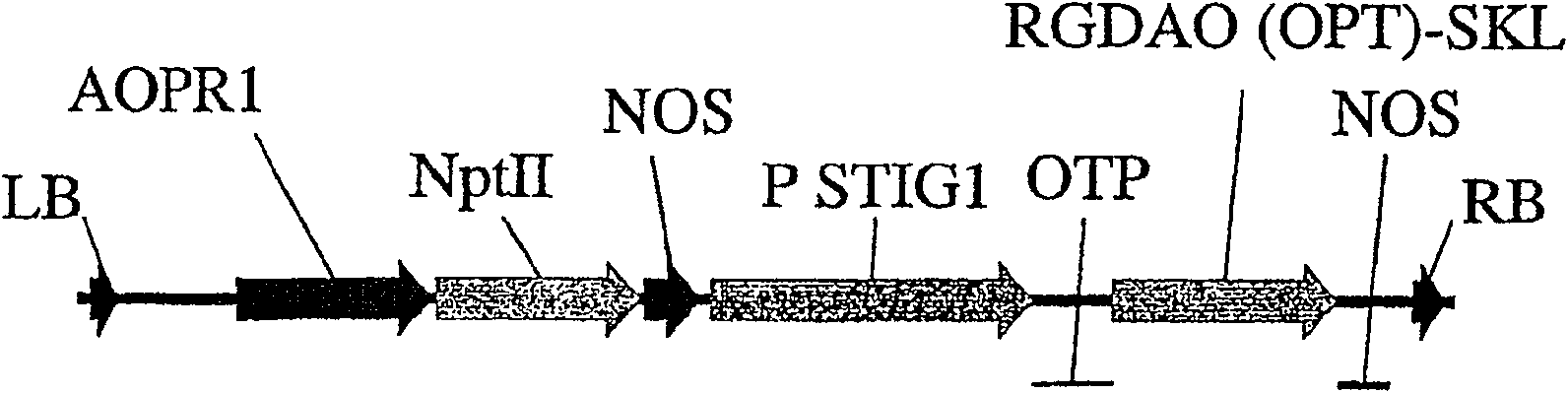
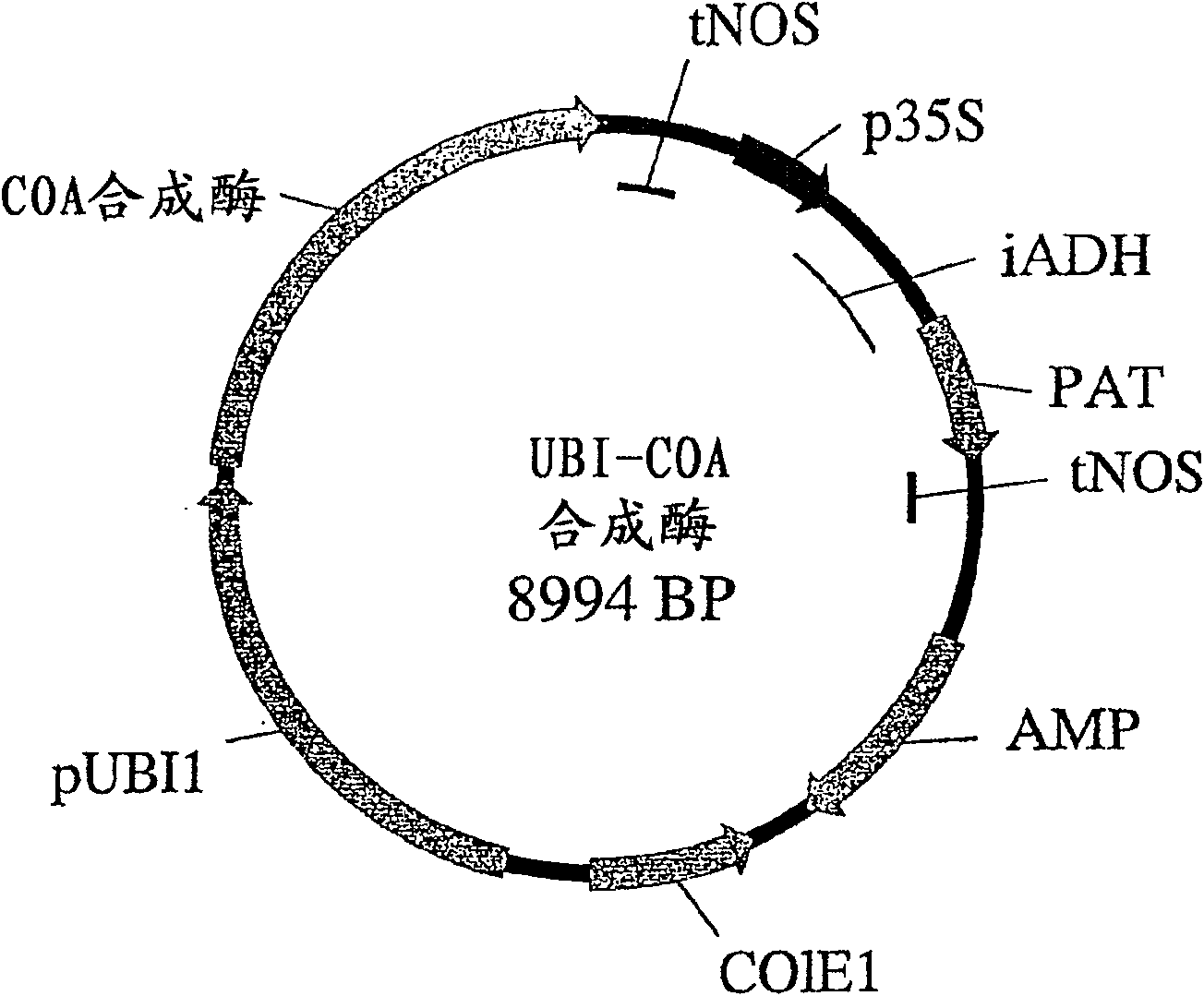
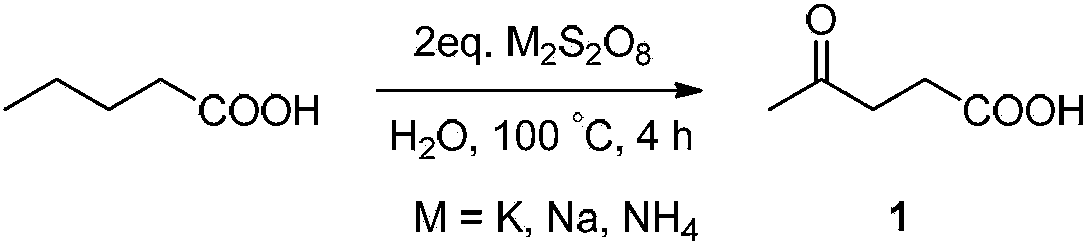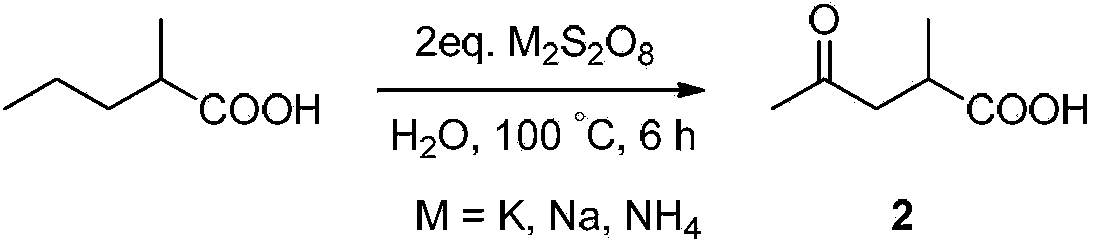Patents
Literature
37 results about "Amino-acid racemase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In enzymology, an amino-acid racemase (EC 5.1.1.10) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction an L-amino acid ⇌ a D-amino acid Hence, this enzyme has one substrate, L-amino acid, and one product, D-amino acid. This enzyme belongs to the family of isomerases, specifically those racemases and epimerases acting on amino acids and derivatives. The systematic name of this enzyme class is amino-acid racemase.
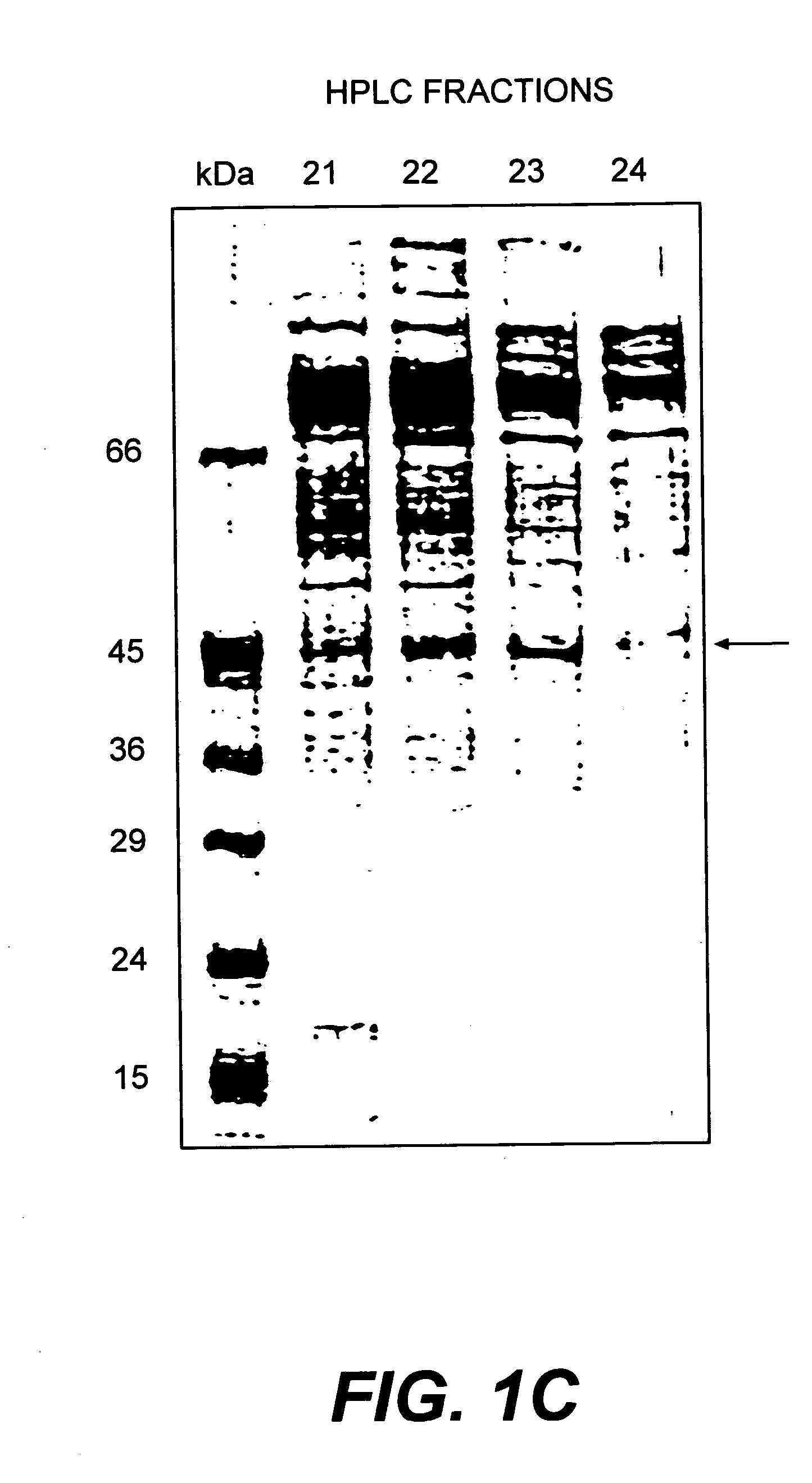
Fructose amino acid oxidase, preparation method and glycatedalbumin detection kit comprising oxidase
ActiveCN103695380AReduce performanceGood dilution linearityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisD-amino acid oxidaseGlutamic acid
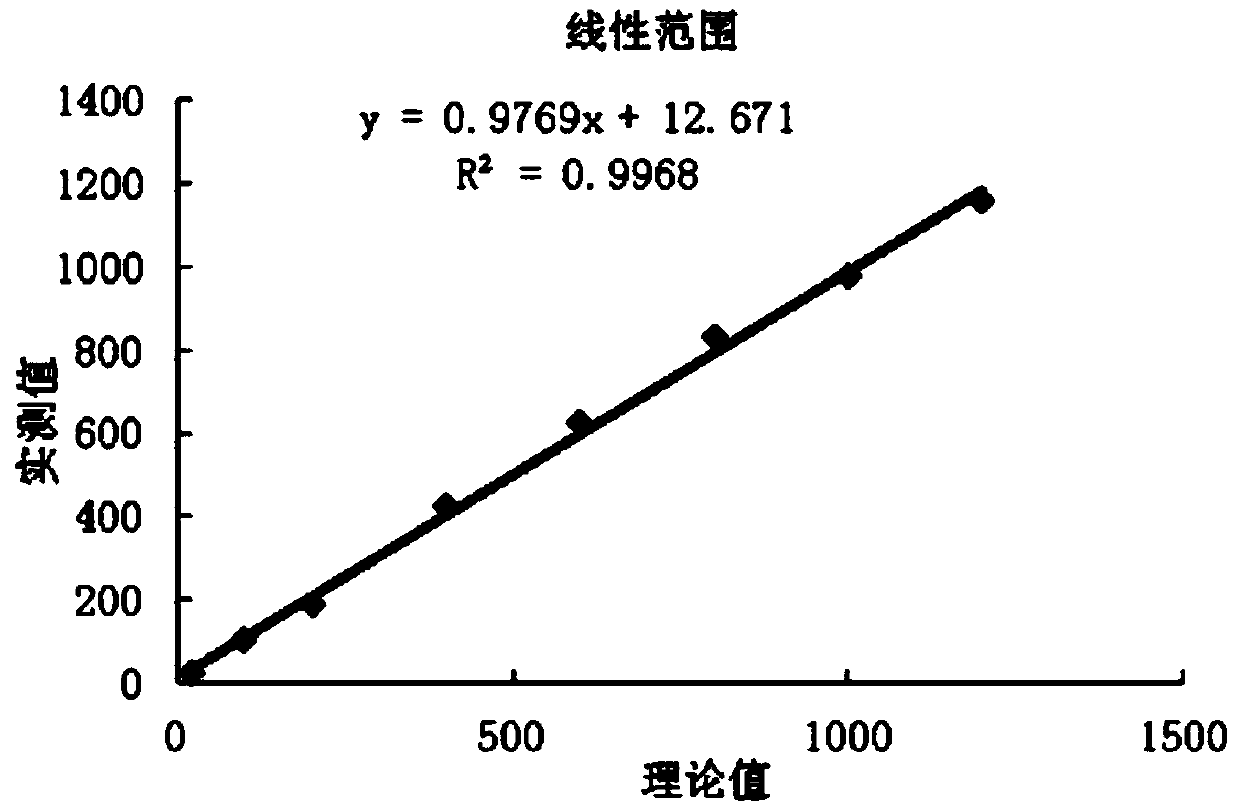
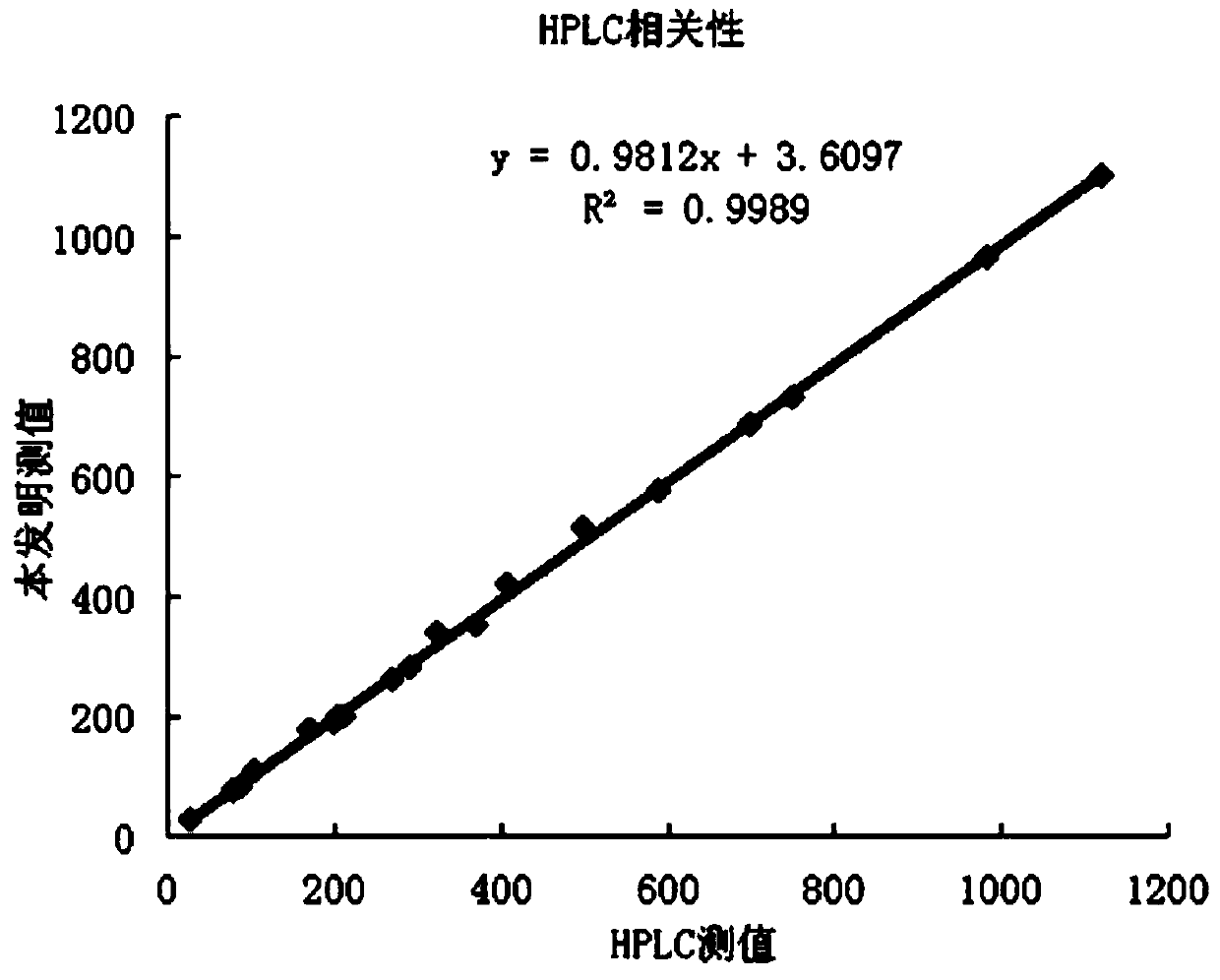
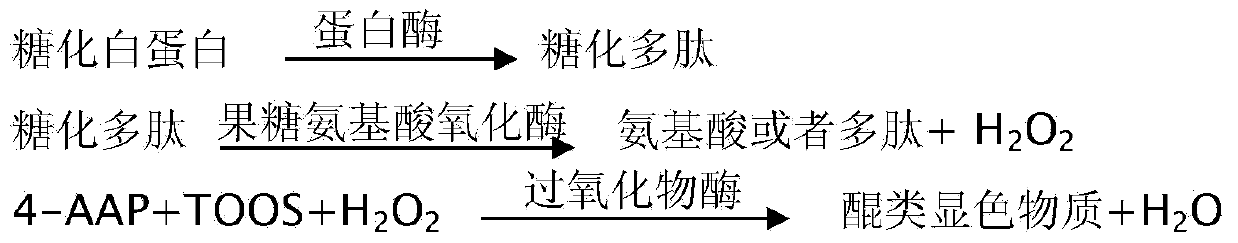
The invention discloses fructose amino acid oxidase which has an amino acid sequence shown as SEQID.No.1 (sequence identifier number 1) or has above 80% homology with the amino acid sequence. One or more amino acid residues in corresponding positions of amino acid selected from (a) to (f) are substituted. The obtained fructose amino acid oxidase has higher thermostability: (a) 59-site glutamic acid, (b) 98-site glutamic acid, (c) 225-site glycine, (d) 277-site lysine, (e) 283-site glutamic acid and (f) 355-site aspartic acid. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the oxidase and a kit comprising the oxidase and used for determining glycatedalbumin. The kit has higher thermostability and can accurately determine the glycatedalbumin.
Owner:NINGBO MEDICAL SYSTEM BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Method for preparing L-tertiary leucine compound by two enzyme system
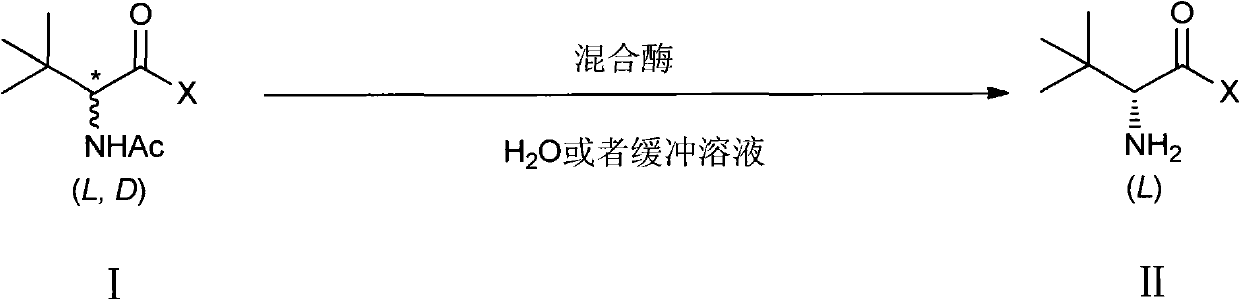
The invention relates to a method for preparing a chiral compound based on splitting by adopting a biological enzyme preparation, in particular to a method for preparing an L-tertiary leucine compound by a two enzyme system. The method prepares the chiral L-tertiary leucine compound of the formula III by using the reaction of an N-acylating tertiary leucine compound of the formula II in water or a buffer solvent at 15 to 60 DEG C in the presence of the two enzyme system. The biological enzyme is a mixed enzyme of an acylating amino acid racemase (alanine racemase) and a hydrolase; and the preparation reaction equation is as follows, wherein X is any group of OH, NH2, NR1R2 and OR3 (wherein R1, R2, R3 are a C1-C5 straight chain, a branch chain and a one, two or three-halogen substituted alkane respectively). The invention can be implemented at room temperature and ensures simple operation and no pollution, while remarkably lowering the production cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A method of selectively producing male or female sterile plants
A method of producing male or female sterile plants comprising the steps of transforming plant material with a polynucleotide which encodes at least one enzyme which reacts with a non-phytotoxic substance to produce a phytotoxic one, and regenerating the thus transformed material into a plant, wherein the said non-phytotoxic substance is applied to the plant up to the time of male or female gamete formation and / or maturation, so that the non-phytotoxic substance provides for the production of a phytotoxic one which selectively prevents the formation of or otherwise renders the said gametes non-functional, wherein the enzyme is expressed preferentially in either male or female reproductive structures, characterised in that (i) the non-phytotoxic substance is selected from the group consisting of ester derivatives of non-phosphonate herbicides which herbicides are directly phytotoxic to non-green tissue, D-alpha amino acids, peptide derivatives of non-protein D-alpha amino acids, S-enantiomers of aryloxyphenoxypropionates and S-enantiomers of ester derivatives of aryloxyphcnoxypropionatcs and (ii) the enzyme is selected from the group consisting of carboxylesterases, D-amino acid oxidases, D-amino acid dehydrogenases, D-amino acid racemases, 2-arylpropionyl-CoA epimerases, alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemases, thioesterases and acyl-CoA synthetases.
Owner:SYNGENTA BIO TECH CHINA
Ocean micro-alga delta5 aliphatic acid desaturase and application thereof
InactiveCN101210234AStrong specificityIncrease enzyme activityUnicellular algaeEnzymesFatty acidAmino-acid racemase
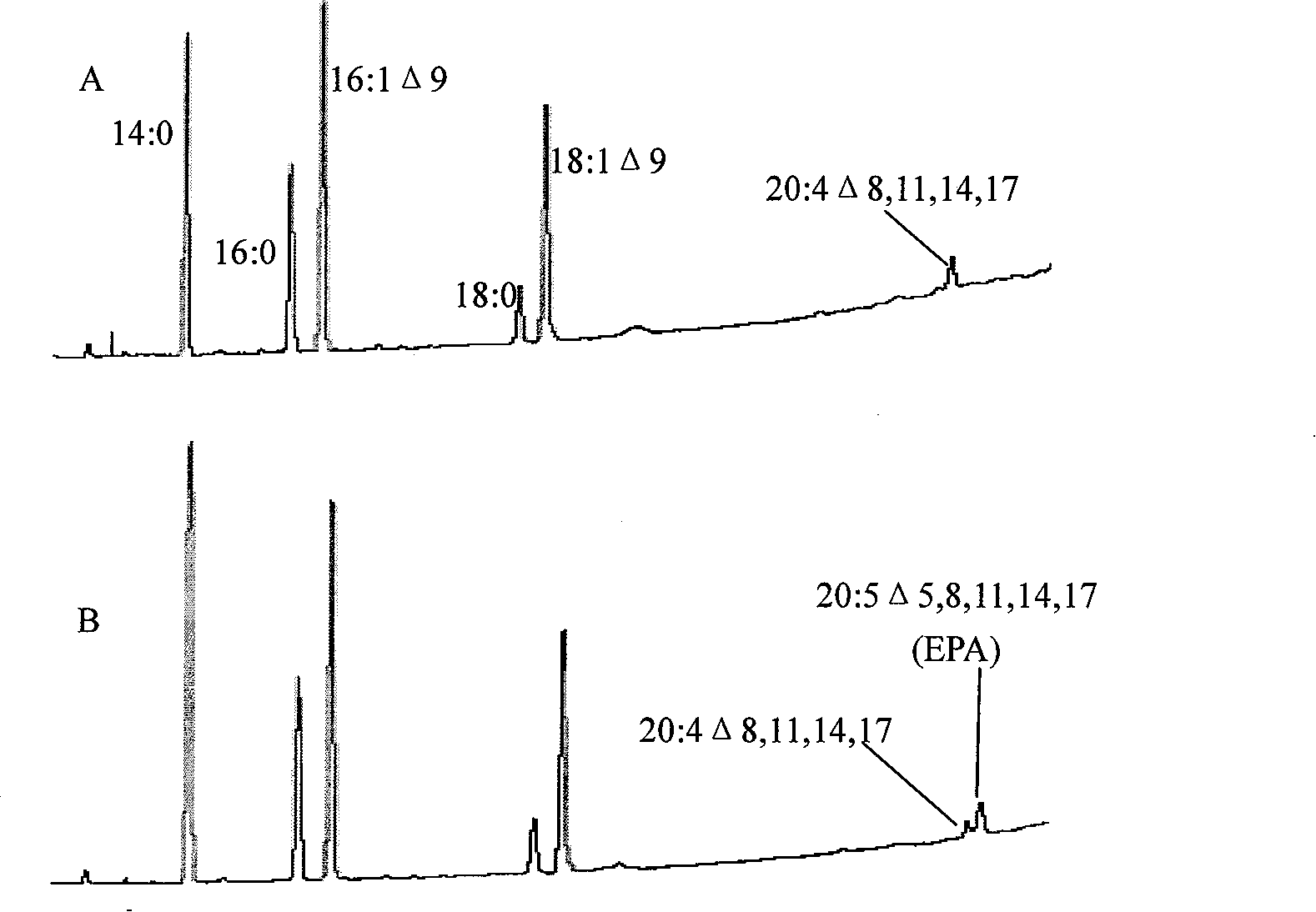
The invention provides a Delta 5 fatty acid desaturase from ocean microalgae, and coding gene and an application thereof. The inventive Delta 5 fatty acid desaturase has amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2 or amino acid subjected to substitution, deletion or addition of one or more amino acid residues of the amino acid sequence and having the same functions. The inventive Delta 5 fatty acid desaturase can effectively catalyze the conversion of ETA(20:4 Delta 8,11,14,17) to EPA(20:5 Delta 5,8,11,14,17), and has the advantages of high specificity of substrate and high enzyme activity.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Cloning, sequencing and expression of a gene encoding an eukaryotic amino acid racemase, and diagnostic, therapeutic, and vaccination applications of parasite and viral mitogens
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
Three alpha-conus polypeptides and use thereof
InactiveCN102304171AStrong analgesic activityIncreased pain thresholdPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticConusAmino-acid racemase
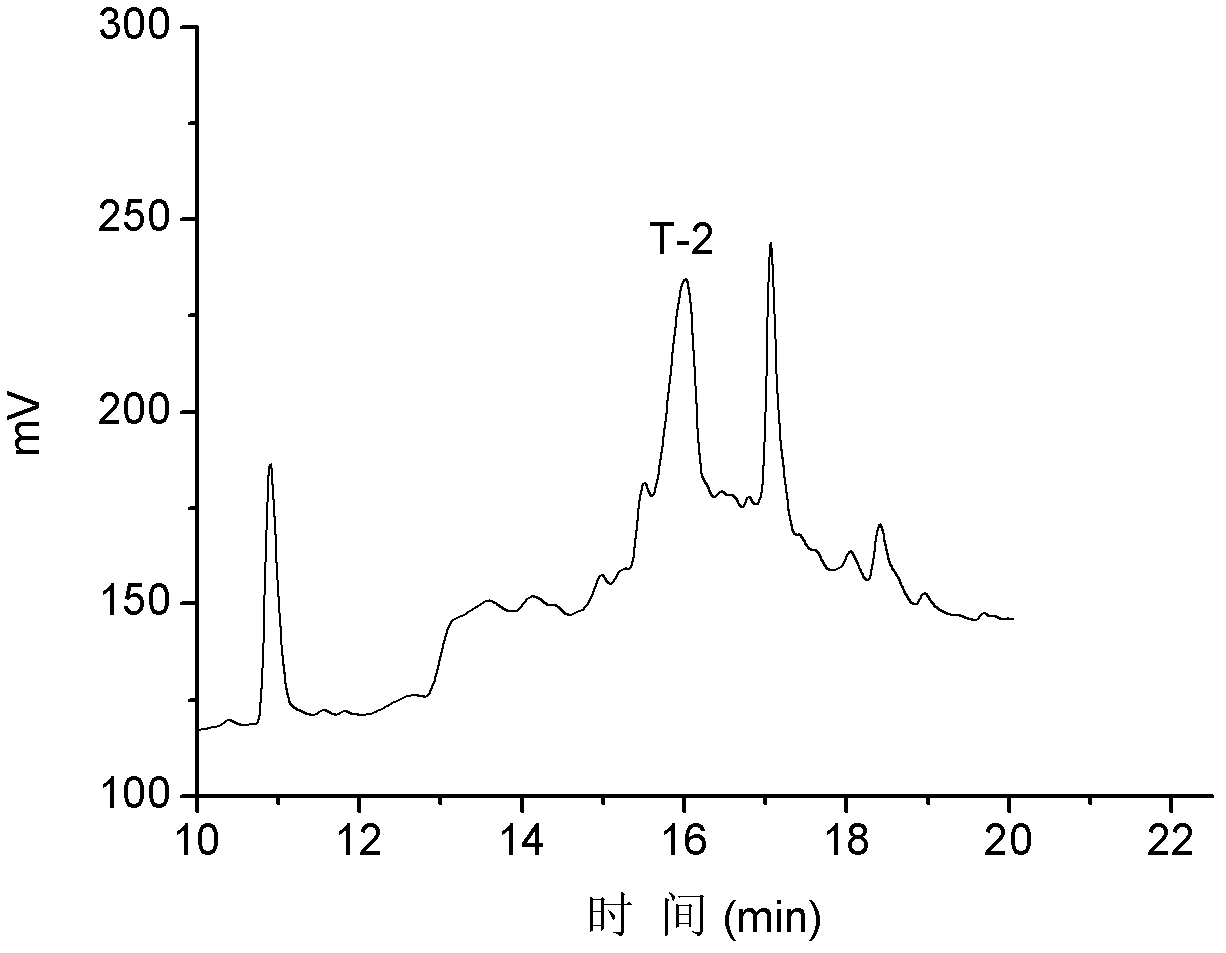
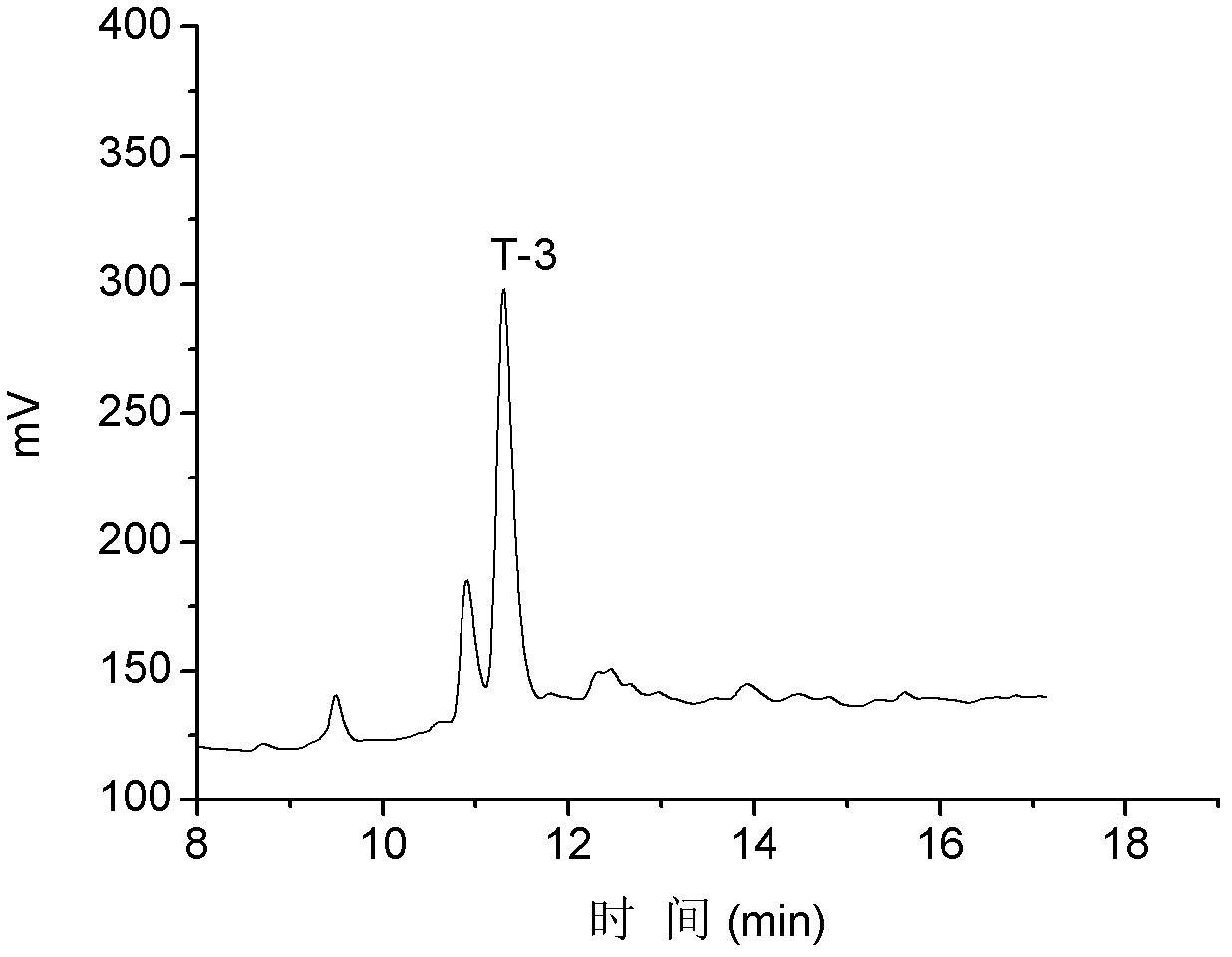
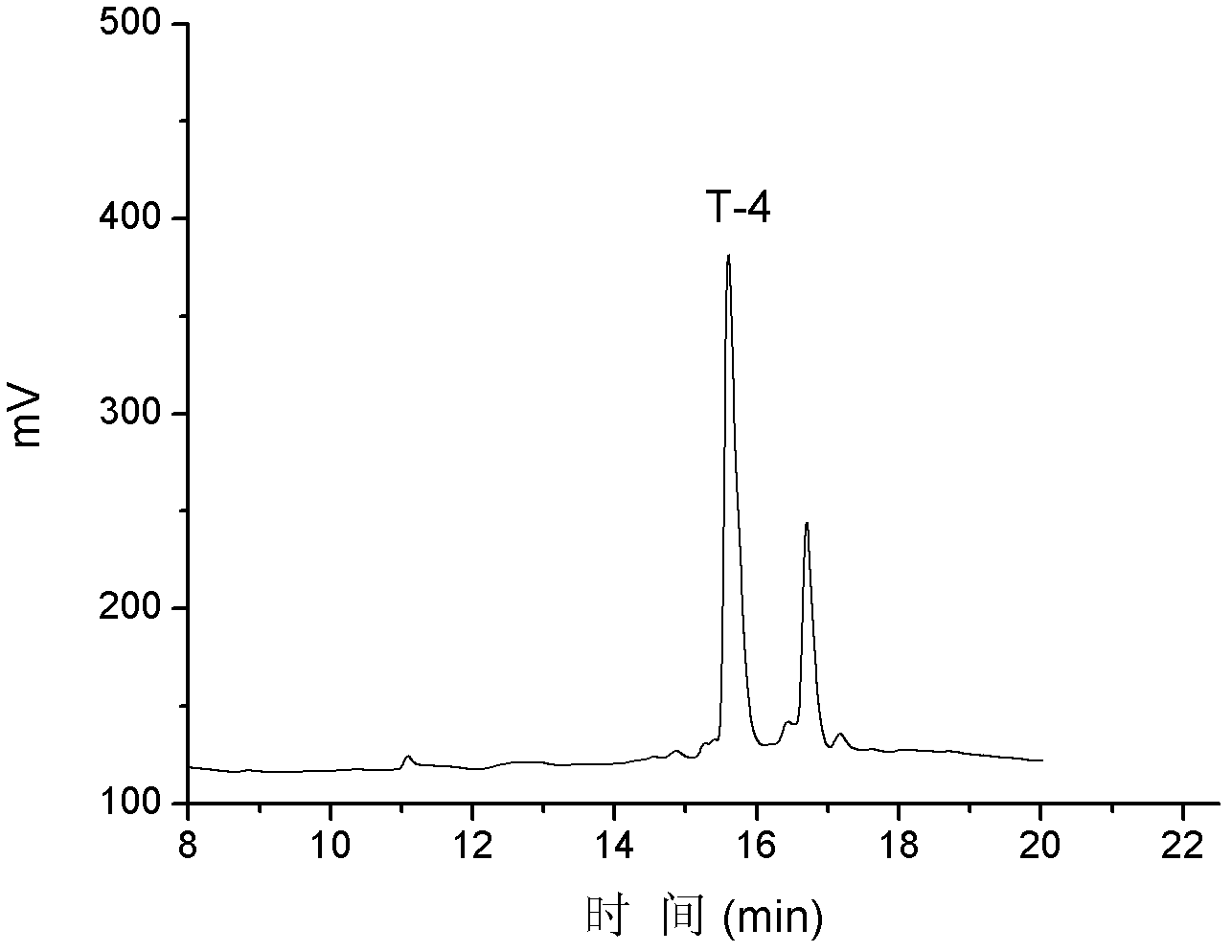
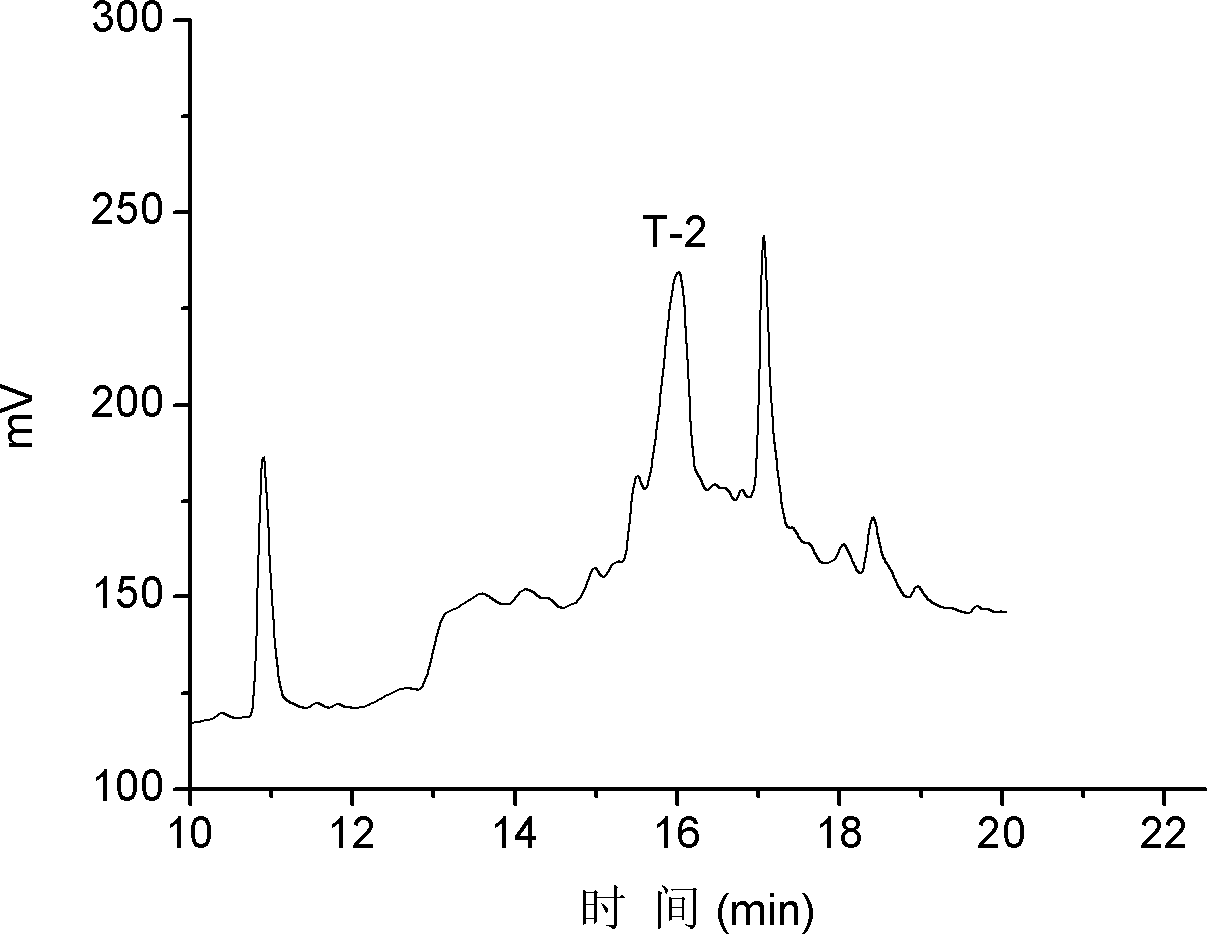
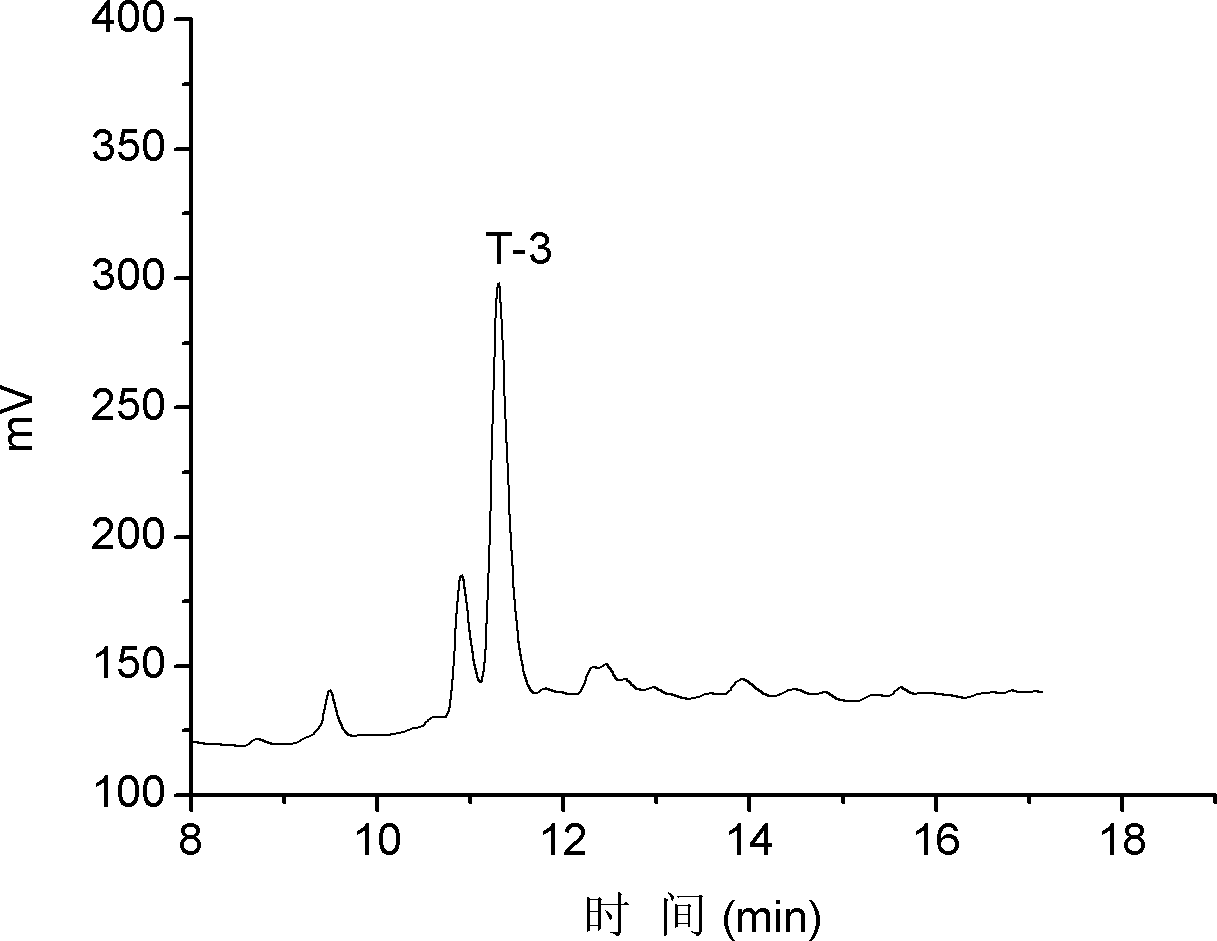
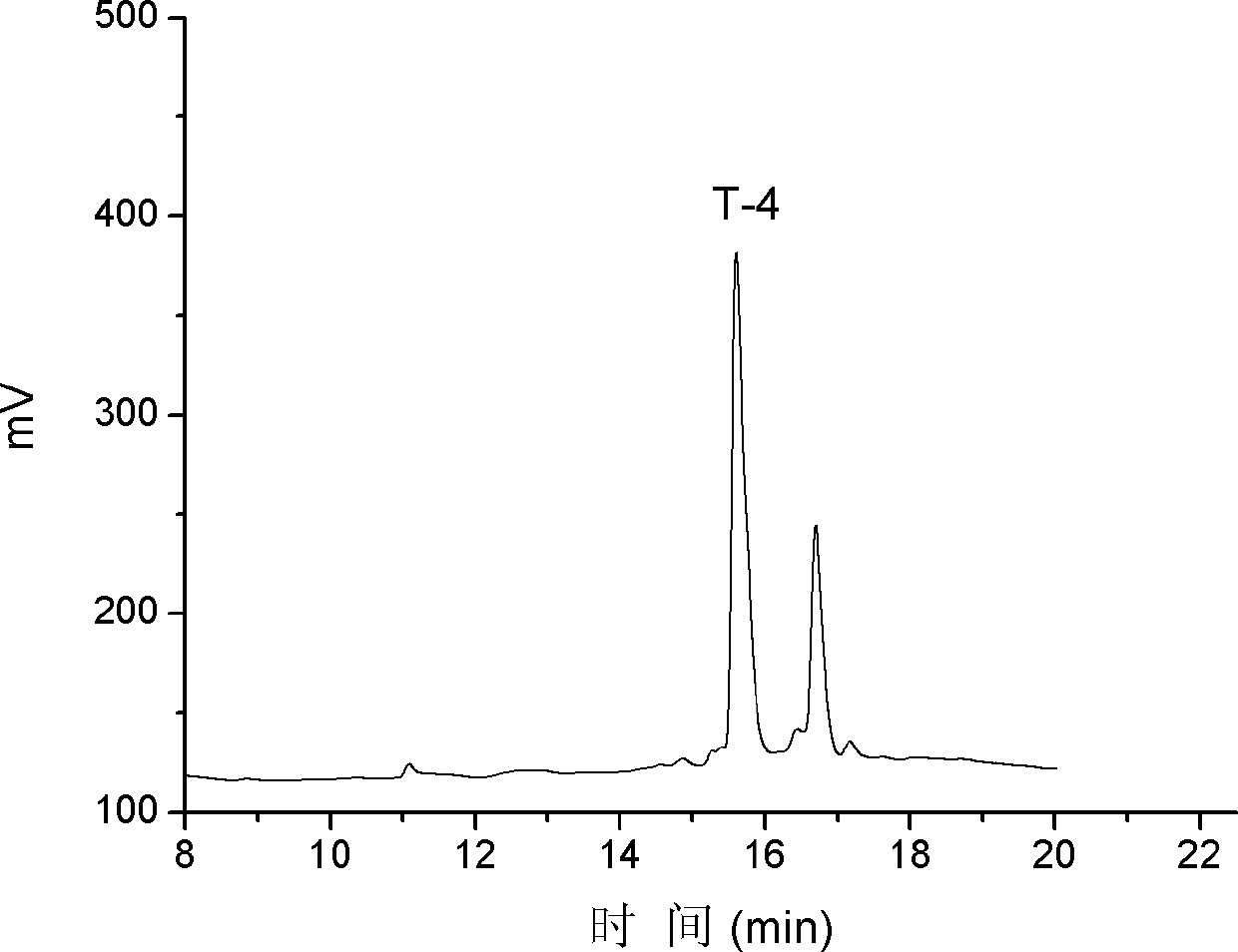
The invention discloses alpha-conus polypeptides and use thereof. The invention provides seven polypeptides: a polypeptide I of which the amino acid sequence is represented by a sequence 7 in a sequence table and in which the last amino acid residue is amidated; a polypeptide II of which the amino acid sequence is represented by a sequence 8 in the sequence table and in which the last amino acid residue is amidated; a polypeptide III of which the amino acid sequence is represented by a sequence 9 in the sequence table and in which the last amino acid residue is amidated; a polypeptide IV of which the amino acid sequence is represented by a sequence 10 in the sequence table and in which the last amino acid residue is amidated; a polypeptide V of which the amino acid sequence is representedby a sequence 11 in the sequence table and in which the last amino acid residue is amidated; a polypeptide vI of which the amino acid sequence is represented by a sequence 12in the sequence table andin which the last amino acid residue is amidated; and a polypeptide VII of which the amino acid sequence is represented by a sequence 13 in the sequence table and in which the last amino acid residueis amidated. The result of activity tests, the seven polypeptides of the general formula (I) have pain relieving effect, alpha-conus polypeptides T-1, T-2, T-3 and T-4 have obvious pain-relieving activity, and the alpha-conus polypeptides T-5, T-6 and T-7 also have obvious pain-relieving effect, and the alpha-conus polypeptides have application values in pain-reliving aspect.
Owner:INST OF BIOENG ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE CHINESE
Mutant glutamine synthetase and method for producing amino acids
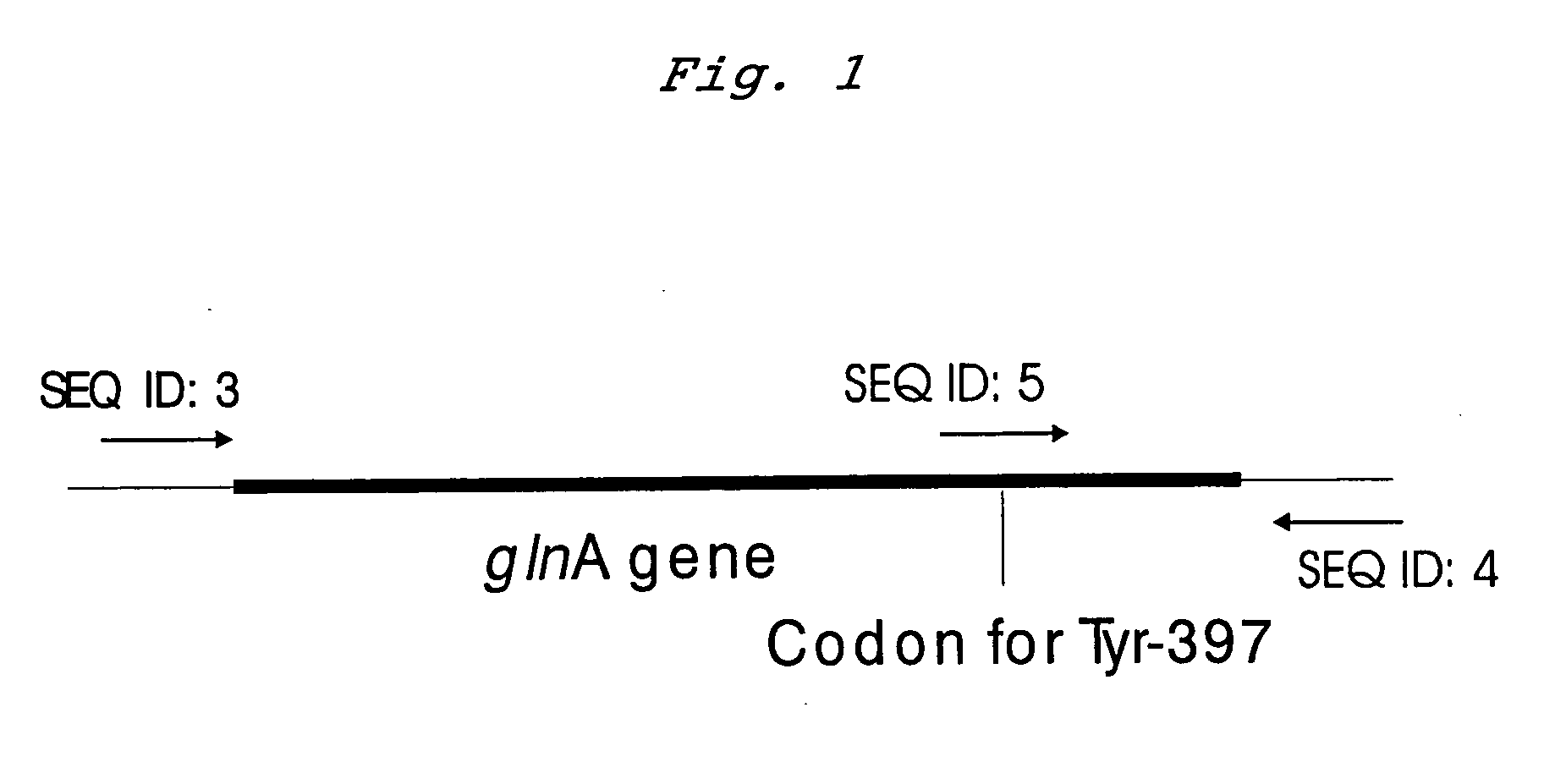
Amino acids, such as L-glutamine, L-arginine, L-tryptophan, L-histidine and L-glutamate are produced using a bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia harboring a mutant glutamine synthetase in which the tyrosine amino acid residue corresponding to position 397 in a wild type glutamine synthetase is replaced with any of amino acid residues, preferably with phenylalanine.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Formaldehyde absorption board
InactiveCN105797566AImprove cleanlinessIncrease contact areaGas treatmentDispersed particle separationSodium BentoniteThreonine
The invention relates to a formaldehyde absorption board.The formaldehyde absorption board comprises a water-containing layer, wherein the aqueous solution of amino acid infiltrates the water-containing layer, a porous layer wraps the water-containing layer, a breathable waterproof layer wraps the porous layer, the porous layer is made of bentonite or activated carbon, the water-containing layer is made of cotton and sponges, and the aqueous solution of the amino acid is the aqueous solution of one or more of glycine, alanine, valine, leucine, tryptophan, methionine, proline, tyrosine, cysteine amino acid, asparagine, threonine, serine and glutamic acid.The formaldehyde absorption board has the advantages that the aqueous solution of the amino acid infiltrates the water-containing layer, the aqueous solution of the amino acid can outwardly infiltrate to enter the pores of the porous layer and contact with air, and the amino acid reacts with the formaldehyde so as to remove the formaldehyde; the formaldehyde absorption board is of a board shape, the contact area with the air can be increased, and the formaldehyde removing effect is increased.
Owner:BAOHUSAN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION SCI & TECH CHENGDU
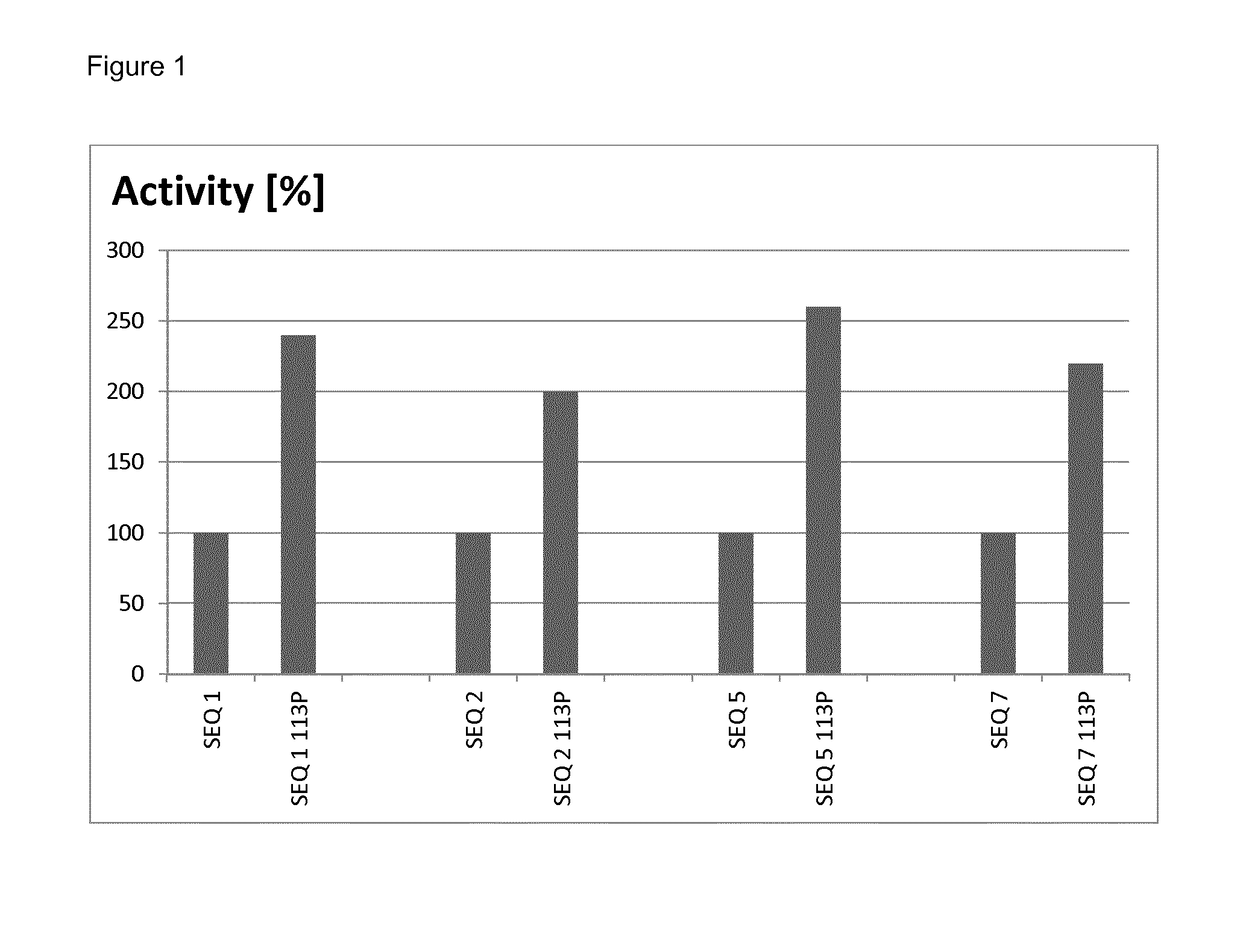
Laccase variants with improved properties
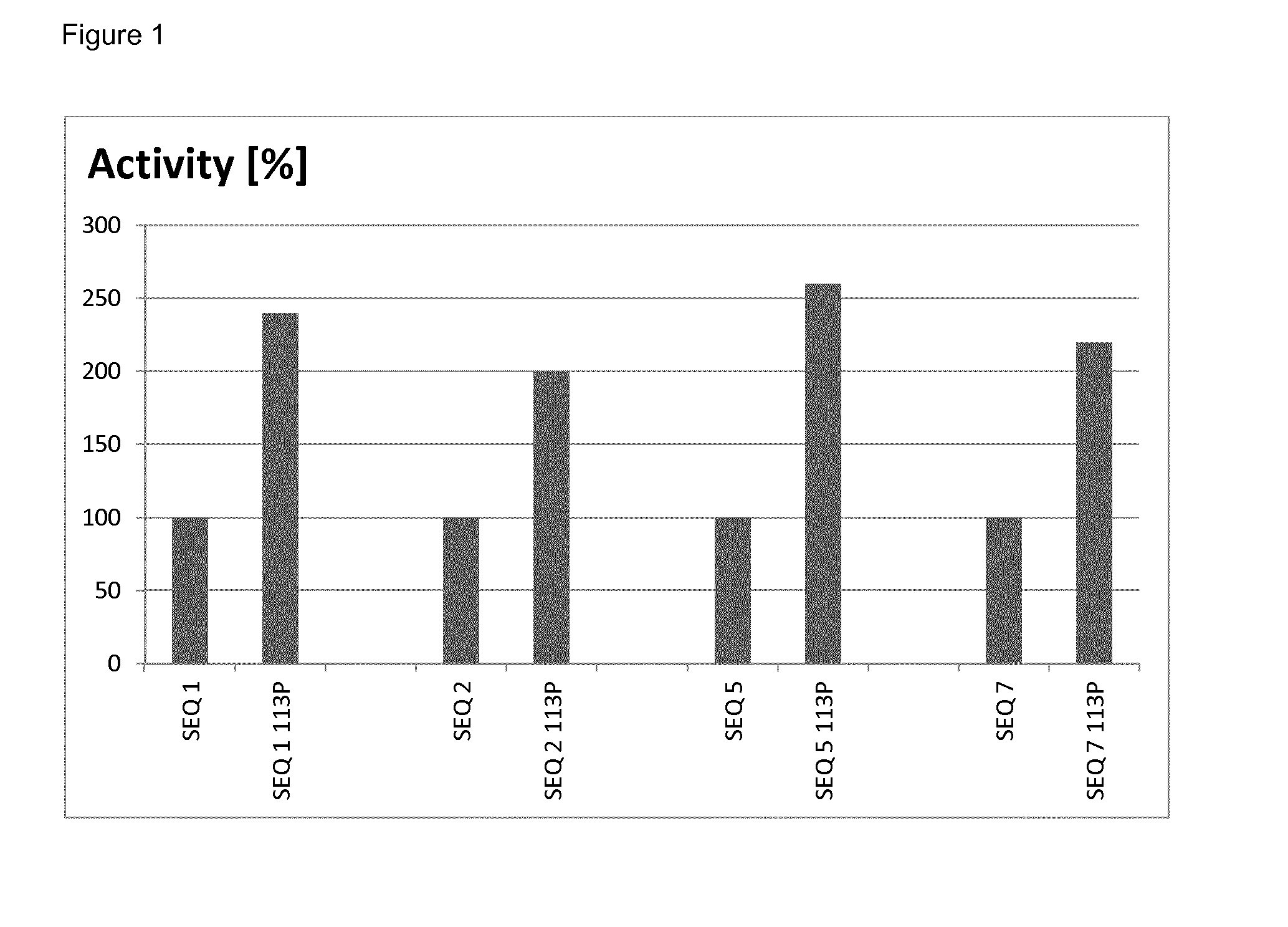
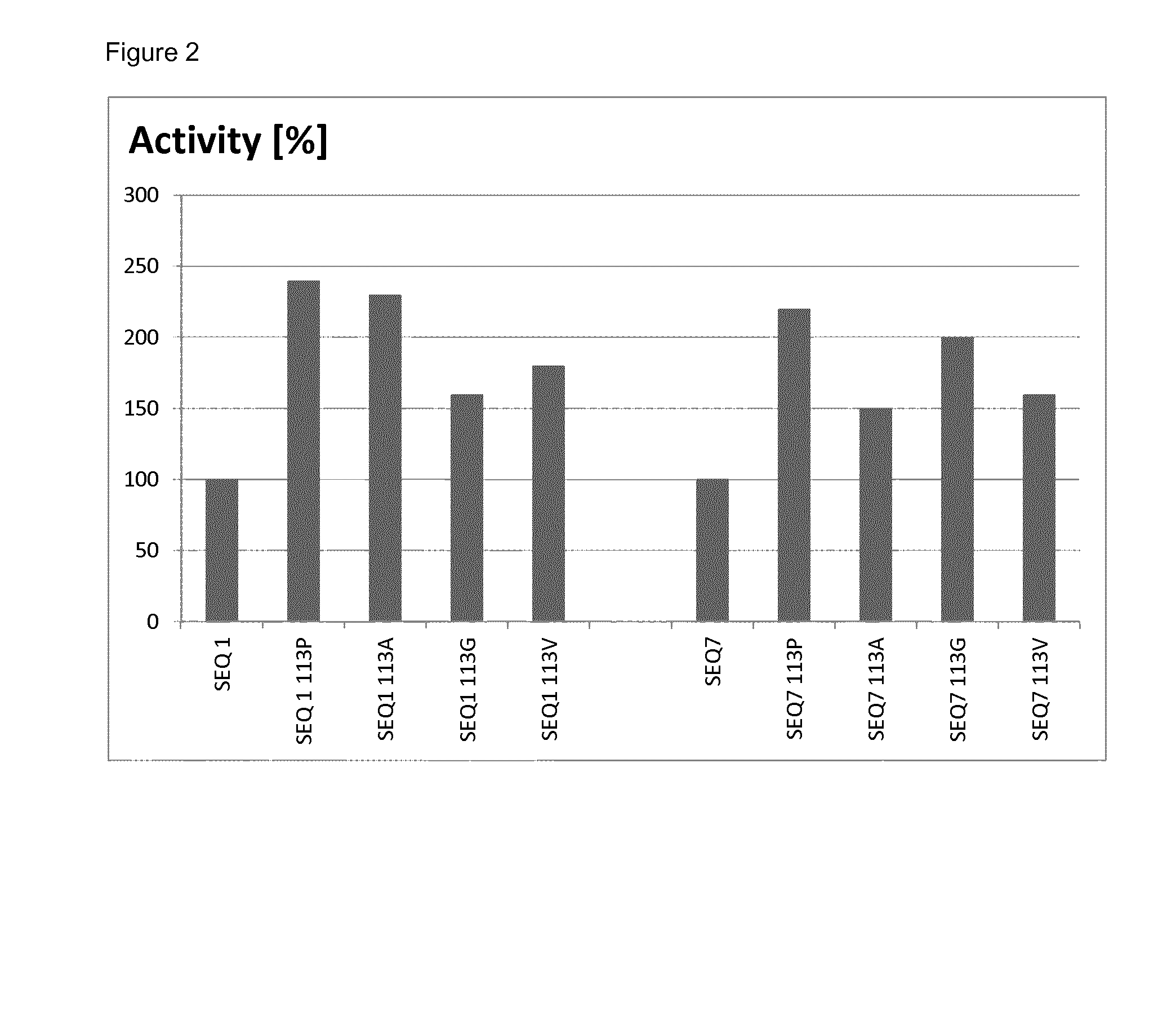
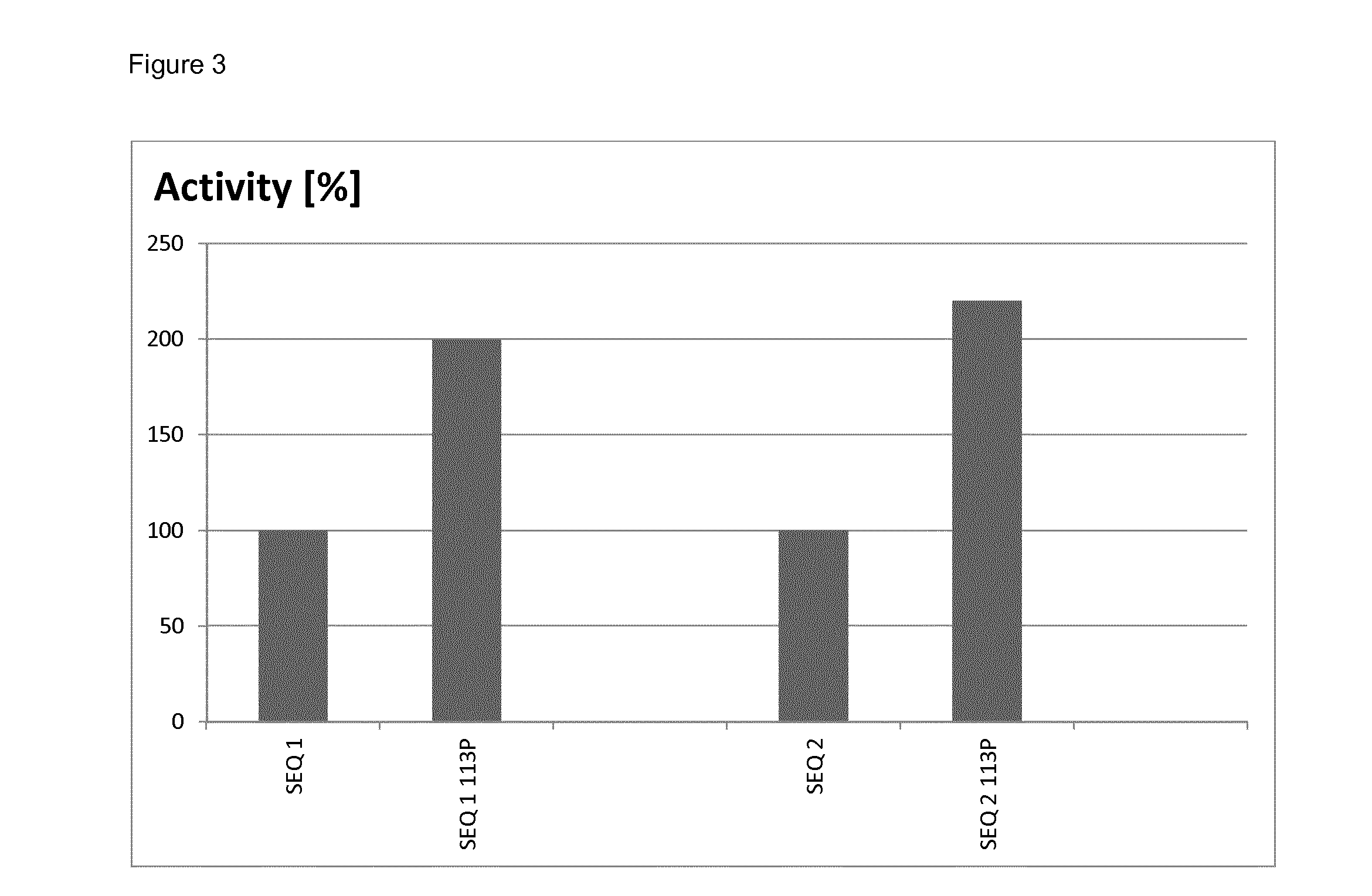
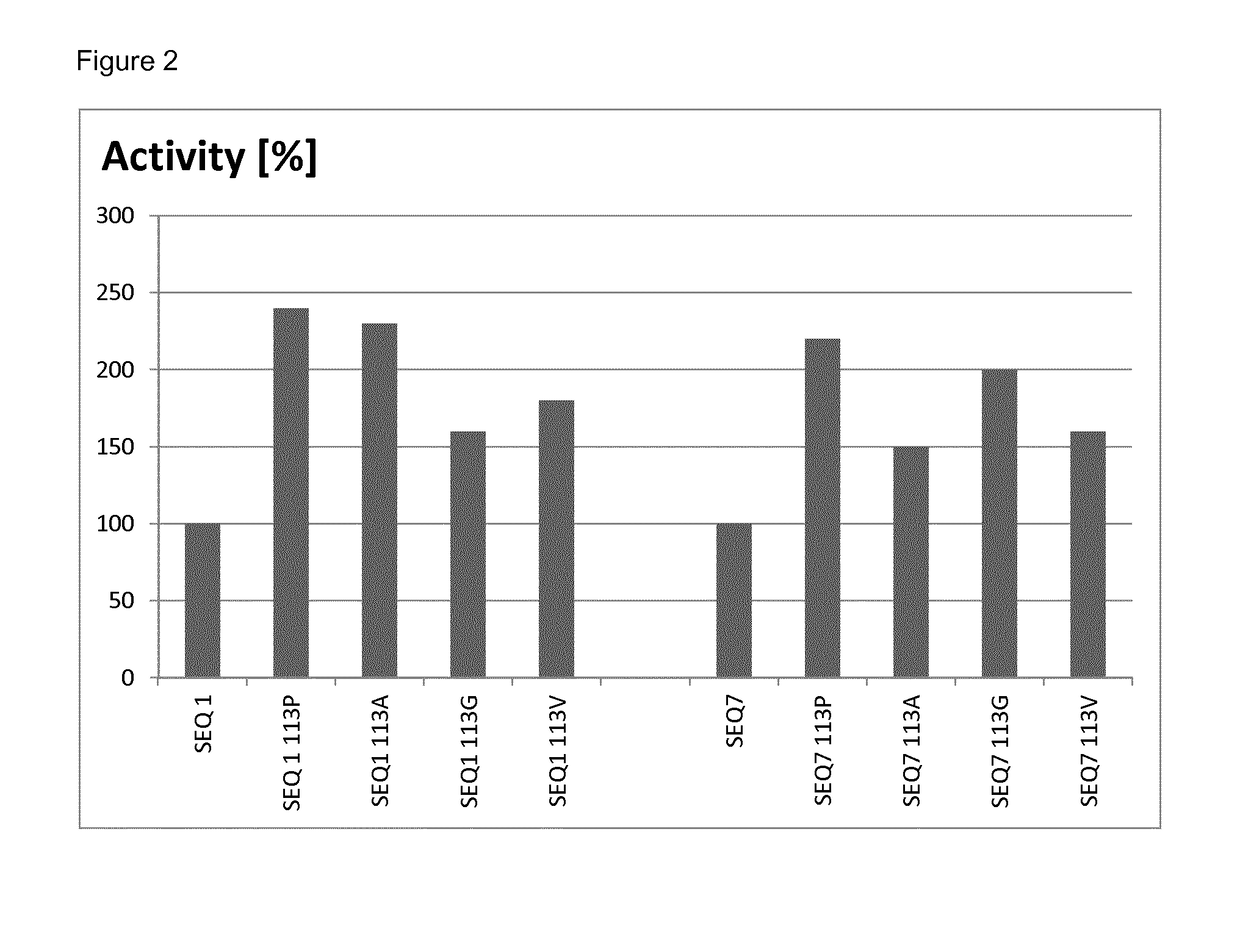
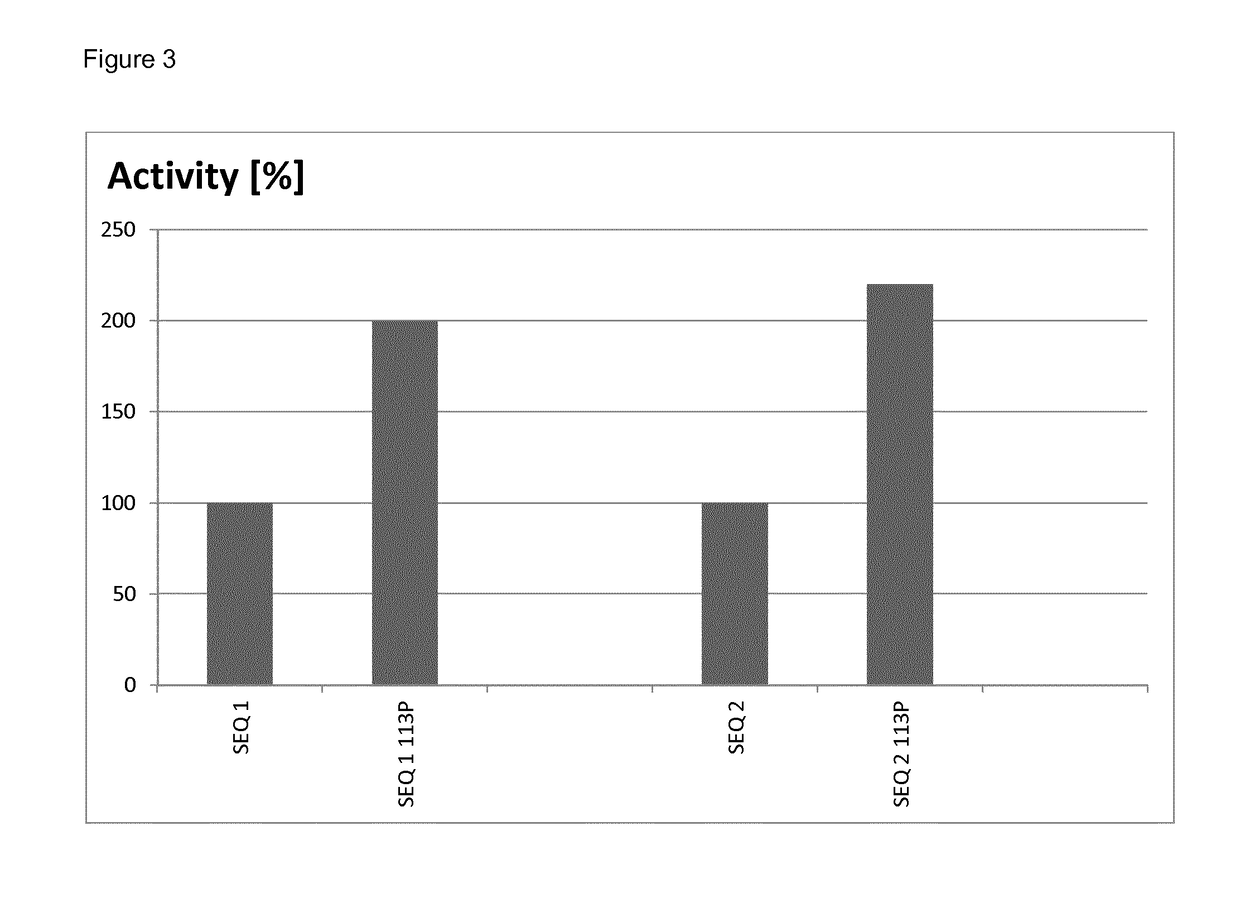
This application relates to laccase variants and uses thereof as eco-friendly biocatalysts in various industrial processes. More in particular, the disclosure relates to a polypeptide with laccase activity comprising an amino acid sequence that is more than 80% identical to the amino acid sequence according to SEQ ID NO: 1, wherein the polypeptide comprises a non-polar amino acid, preferably an amino acid residue selected from the group consisting of proline, alanine, glycine and valine at a position corresponding to amino acid 113 of SEQ ID NO: 1.
Owner:METGEN
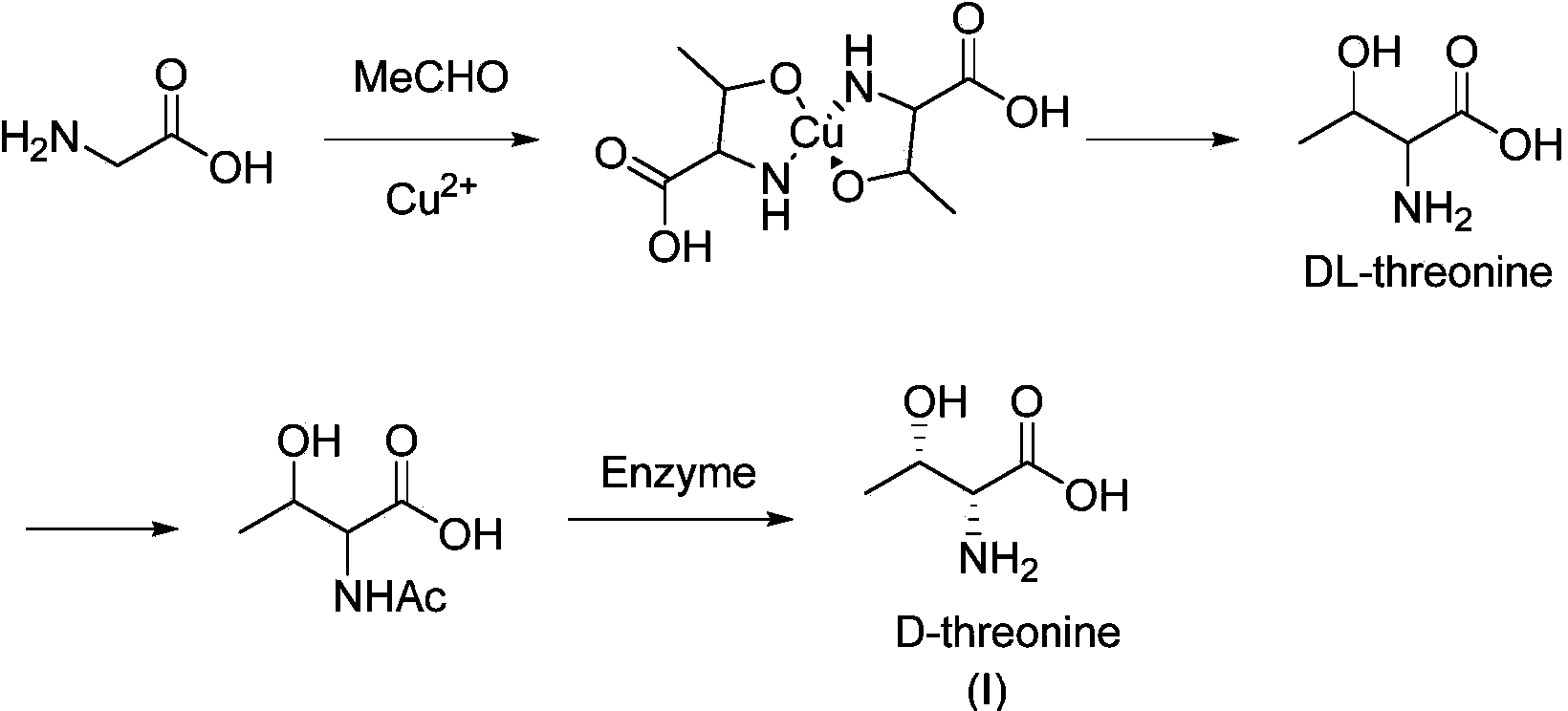
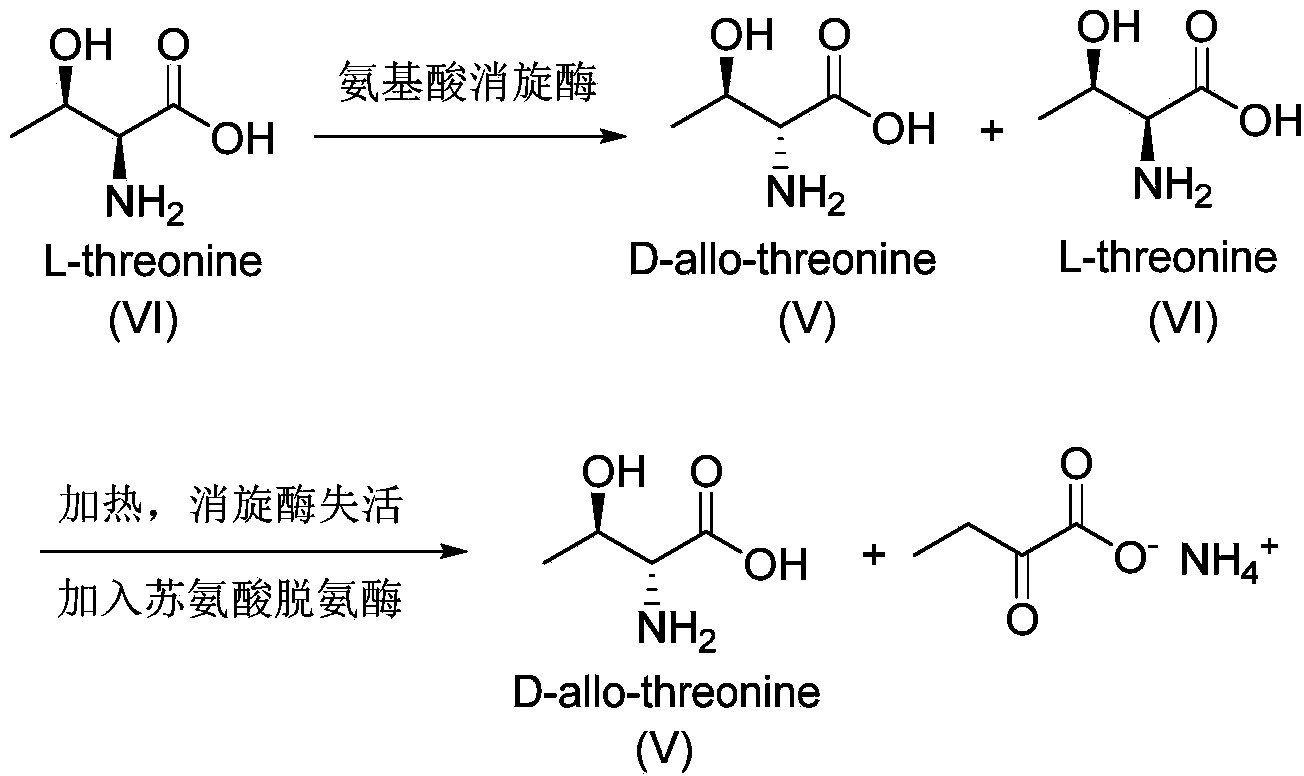
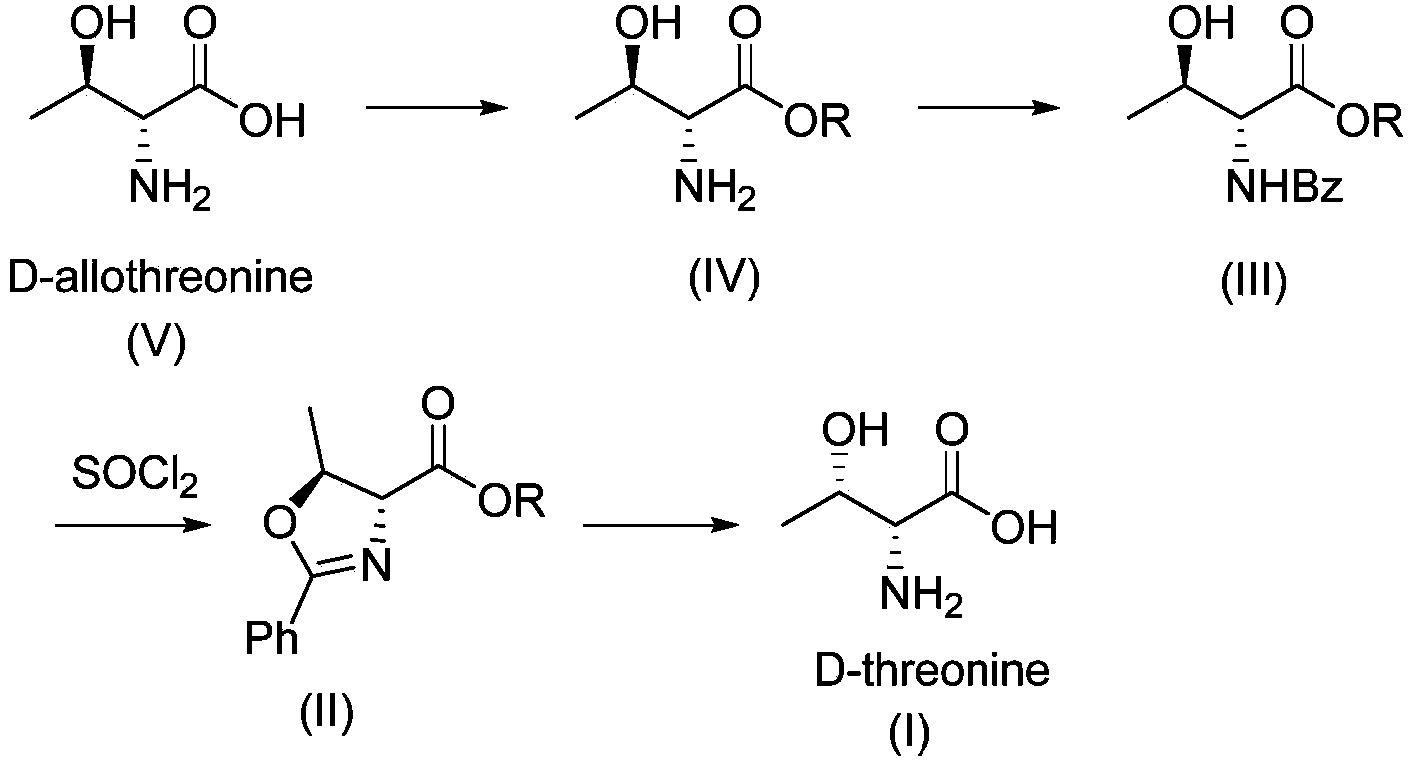
Synthesis method of D-threonine
InactiveCN103450040AReduce fermentation costsLow priceOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationSynthesis methodsThreonine
The invention relates to a synthesis method of D-threonine (I). The method comprises the following steps: preparing D-allothreonine (V) from L-threonine (VI) serving as a raw material through racemization of amino acid racemase, action of L-threonine deaminase and purification sequentially; performing esterification on D-allothreonine (V) serving as a starting material to obtain an intermediate (IV); protecting amino by using benzoyl to obtain a compound of a formula (III); performing intramolecular cyclization on the compound of the formula (III) in the presence of sulfoxide chloride and turning over the spatial configuration of hydroxyl to obtain an oxazoline intermediate (II); performing ring opening on the intermediate (II) under the action of acid and removing a protecting group to obtain D-threonine (I). The synthesis method of D-threonine (I) is smart in design, the starting materials are cheap and readily available, the process flow is simple and practical, and a new method is provided for producing D-threonine on a large scale.
Owner:SHANGHAI PUYI CHEM CO LTD
Preparation method of D-amino acid
The invention relates to a preparation method of D-amino acid. The method comprises the steps of 1, the constructing of recombinant bacteria: an N-acetyl-D-aminoacylase gene is cloned, and the gene isconnected to a pET series carrier or a pKK 223-3 carrier and transformed to BL21 (DE3) host bacteria to construct D acylase recombinant bacteria (NLase); an N-acetyl-amino acid racemase gene is cloned, the gene is connected to the pET series carrier of the pKK223-3 carrier, transformed to the BL21(DE3) host bacteria to construct N-acetylamino acid racemase recombinant bacteria (NAAR); 2, recombinant bacteria fermentation; 3, immobilized enzyme preparation; 4, immobilized enzyme transforming combining with membrane separation; 5, product crystallization. By means of the method, the cost of theenzyme is reduced, the inhibition on the racemase of byproduct acetic acid is reduced, meanwhile, the transformation solution has little impurity, the separation and purification are simple, the yield is high, the product quality is good, the e.e. value of the obtained D-amino acid reaches 99.9% or above, the content is 99% or above, and the mole yield reaches 85% or above.
Owner:浙江正硕生物科技有限公司
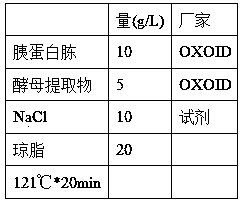
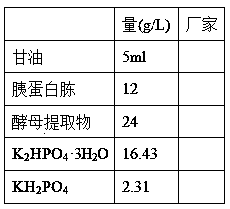
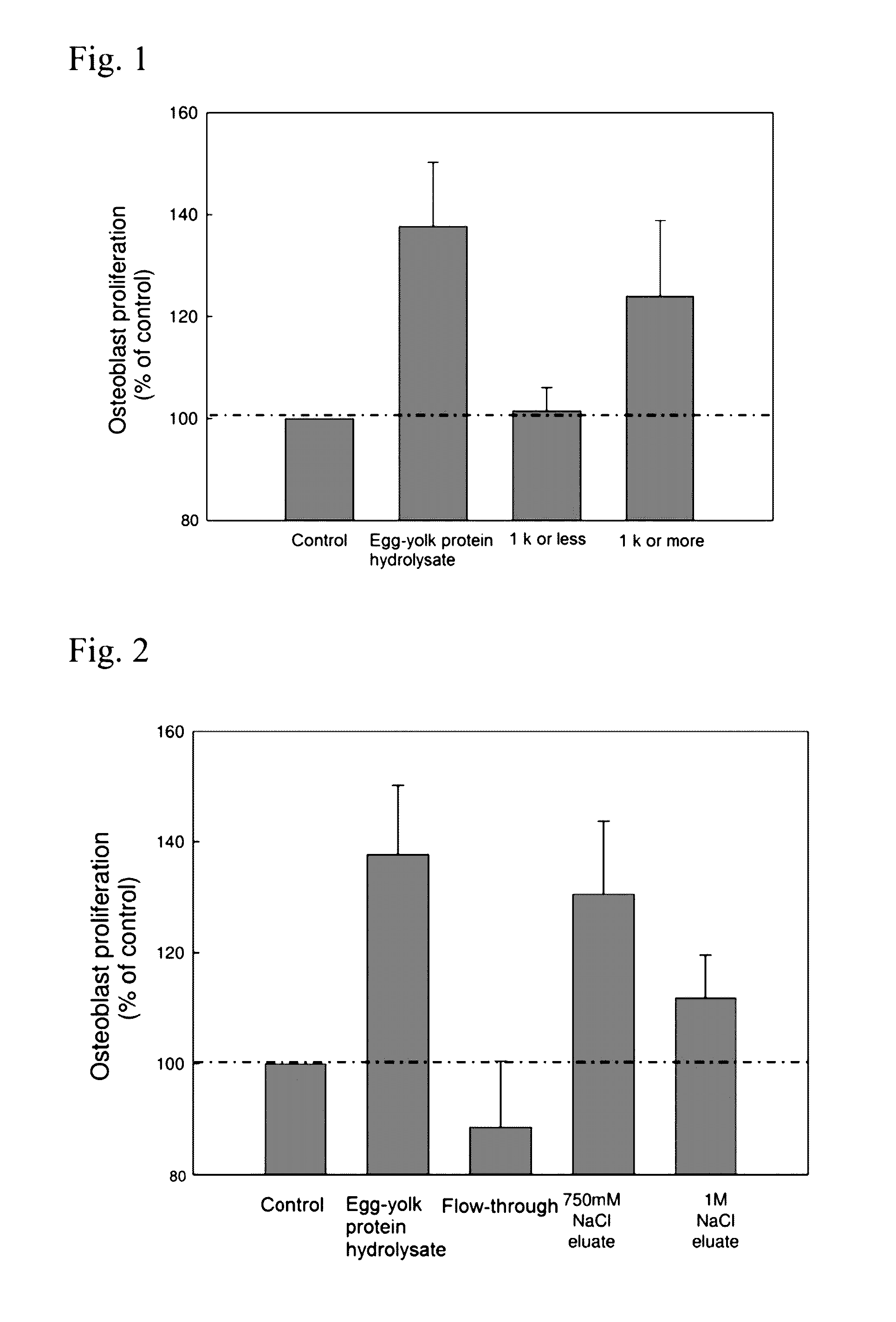
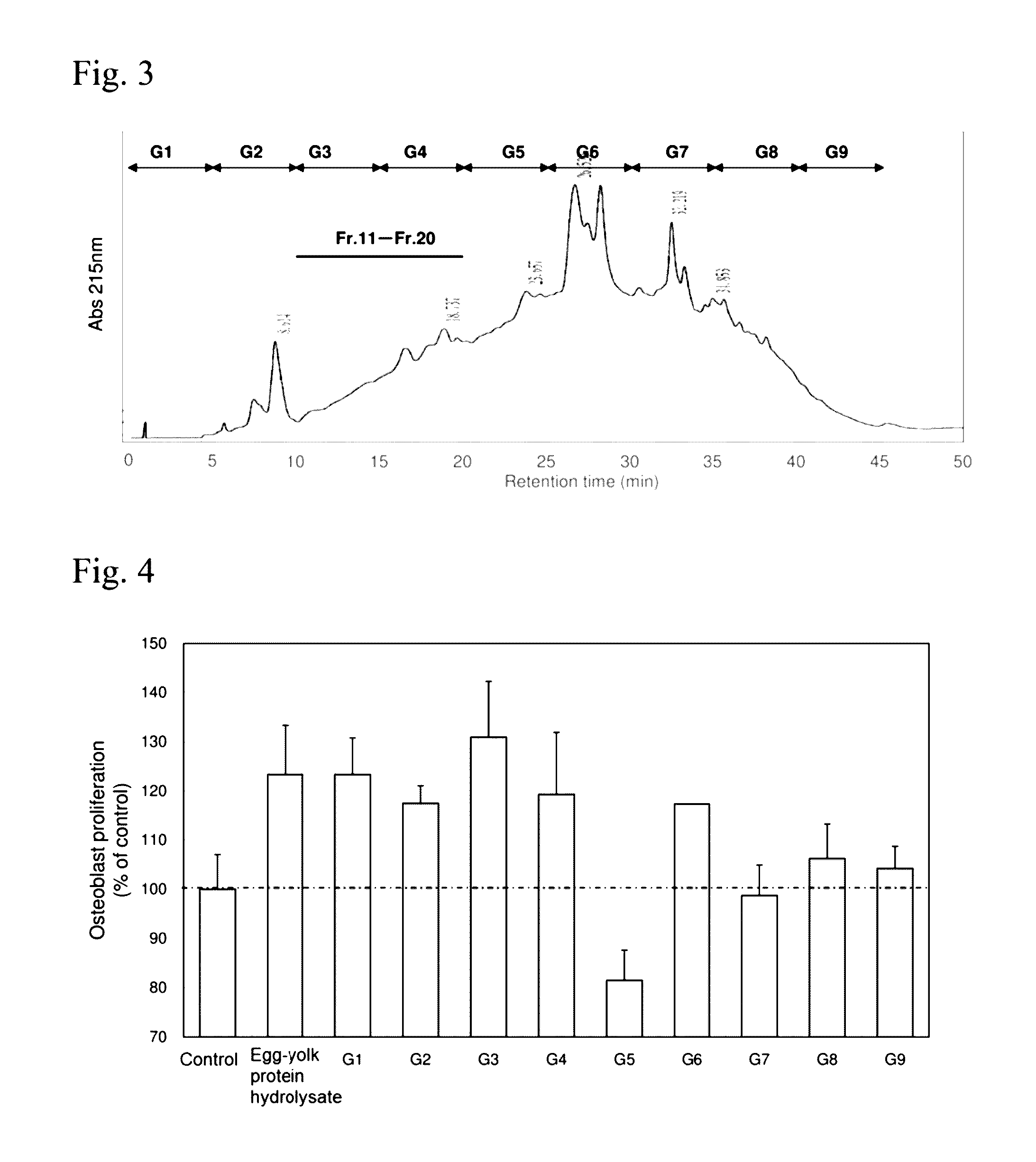
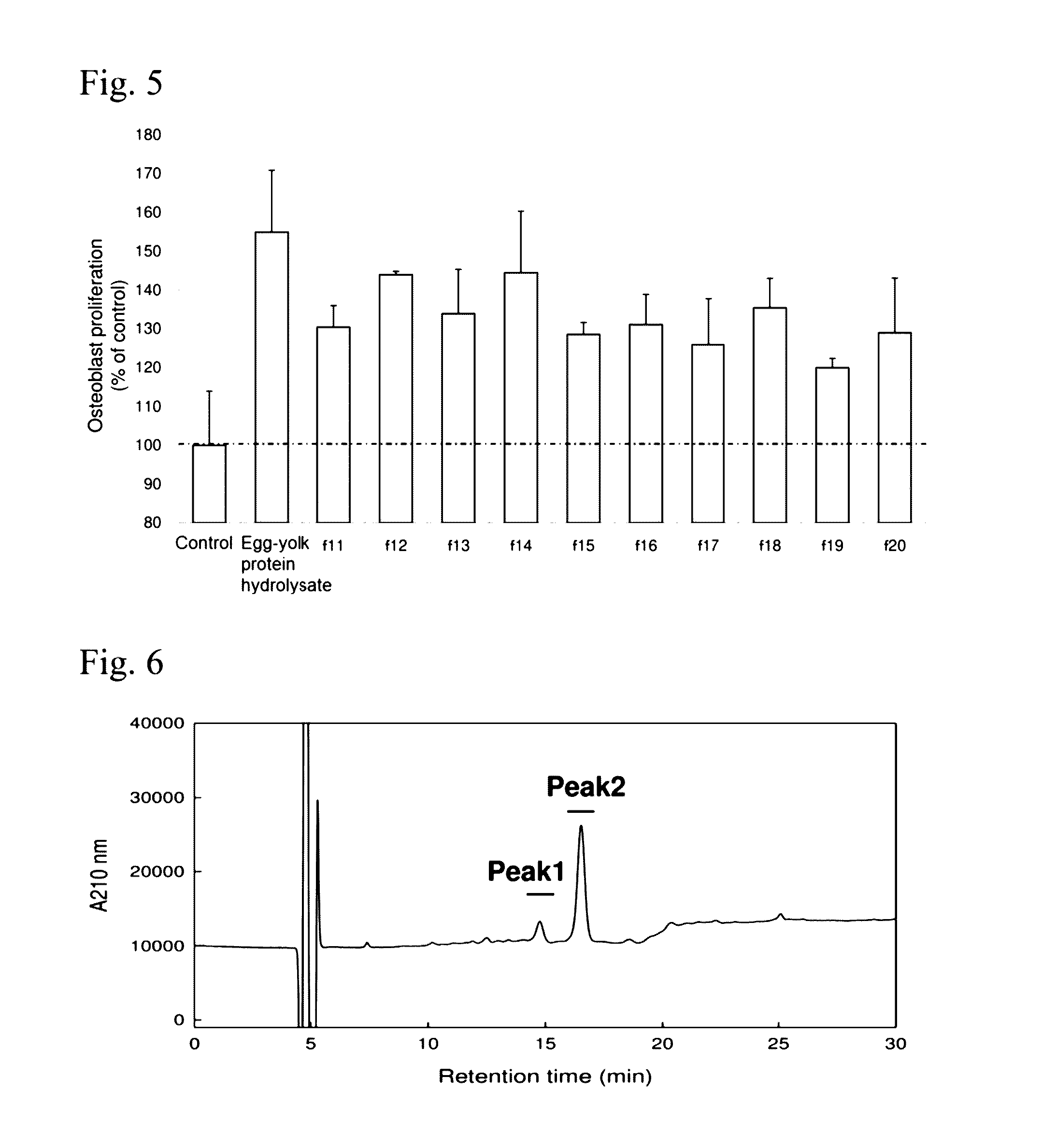
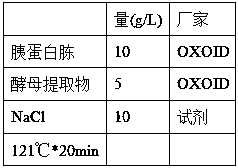
Peptides having osteoblast growth-promoting activity and use thereof
ActiveUS20160362466A1Promotes bone formationPreventing or alleviating a cartilage disorder or joint painCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsOsteoblastBone formation
The present invention provides a novel peptide having bone formation-promoting effect and chondrocyte growth-promoting effect, in particular, a peptide having osteoblast growth-promoting activity, having 100 amino acid residues or less comprising an amino acid sequence selected from(a) Val-Asn-Pro-Glu-Ser-Glu-Glu-Glu-Asp-Glu-Ser-Ser-Pro-Tyr-Glu (SEQ ID NO: 1),(b) an amino acid sequence derived from the amino acid sequence (a) by conservative substitution or deletion of 1 to 3 amino acids, and(c) an amino acid sequence consisting of at least four contiguous amino acids of the amino acid sequence (a) or (b), ora derivative thereof or a salt thereof.
Owner:PHARMA FOODS INT CO LTD
Method for preparing D-amino acid and alpha keto acid
InactiveCN109097409AHas economic valueImprove product qualityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEnzyme catalysis
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and relates to a method for preparing D-amino acid and alpha keto acid. The method includes the first step of recombinant construction: conductingwhole gene synthesis to obtain an L-amino acid deaminase gene LAAD and connecting an expression vector to be transformed into an expression strain to construct a recombinant PMLAAD; conducting whole gene synthesis to obtain an amino acid racemase gene AAR and connecting the expression vector to be transformed into the expression strain to construct a recombinant AAR; the second step of fermentation; the third step of enzyme catalysis; the fourth step of isolation and purification. The alpha-keto acid calcium and the D-amino acid are produced by enzyme catalysis, and both products have economicvalue and high product quality, so that the production cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:浙江正硕生物科技有限公司
Engineering bacteria for producing D-tryptophan and construction method and purpose of producing D-tryptophan
InactiveCN108359695AIncreased acyl hydrolysis activityIncrease productionBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliBacterial strain
The invention discloses engineering bacteria for producing D-tryptophan and a construction method and a purpose of producing D-tryptophan. The construction method comprises the following steps: transferring an acylated amino acid racemase mutant gene and a N-acetyl-D-amino acid acyl hydrolase mutant gene in escherichia coli, and constructing the engineering bacteria for producing D-tryptophan. Theconstruction method optimizes the N-acetyl-D-amino acid acyl hydrolase mutant gene and the acylated amino acid racemase mutant gene, the acyl hydrolysis activity of the N-acetyl-D-tryptophan by the N-acetyl-D-amino acid acyl hydrolase and the racemization activity of the N-acetyl-L tryptophan by the acylated amino acid racemase are increased, and the output and the product quality of the D-tryptophan are increased. Two types of enzymes can be expressed by the same engineering bacterial strain, the fermentation cost is saved, and the production technology is simplified.
Owner:天津博瑞威生物医药科技有限公司
Dipeptides as feed additives
The invention relates to feed additives containing dipeptides or salts thereof, in which one amino acid residue of the dipeptide is a DL-methionyl residue and the other amino acid residue of the dipeptide is an amino acid in the L-configuration selected from lysine, threonine, tryptophan, histidine, valine, leucine, isoleucine, phenylalanine, arginine, cysteine and cystine; feed mixtures containing these additives and method of producing the dipeptides.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Cloning, sequencing and expression of a gene encoding an eukaryotic amino acid racemase, and diagnostic, therapeutic, and vaccination applications of parasite and viral mitogens
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECH SCI (C N R S) +2
Laccase variants with improved properties
This application relates to laccase variants and uses thereof as eco-friendly biocatalysts in various industrial processes. More in particular, the disclosure relates to a polypeptide with laccase activity comprising an amino acid sequence that is more than 80% identical to the amino acid sequence according to SEQ ID NO: 1, wherein the polypeptide comprises a non-polar amino acid, preferably an amino acid residue selected from the group consisting of proline, alanine, glycine and valine at a position corresponding to amino acid 113 of SEQ ID NO: 1.
Owner:METGEN
Method for producing DL-tyrosine by enzyme, and broad-spectrum amino acid racemase and use thereof
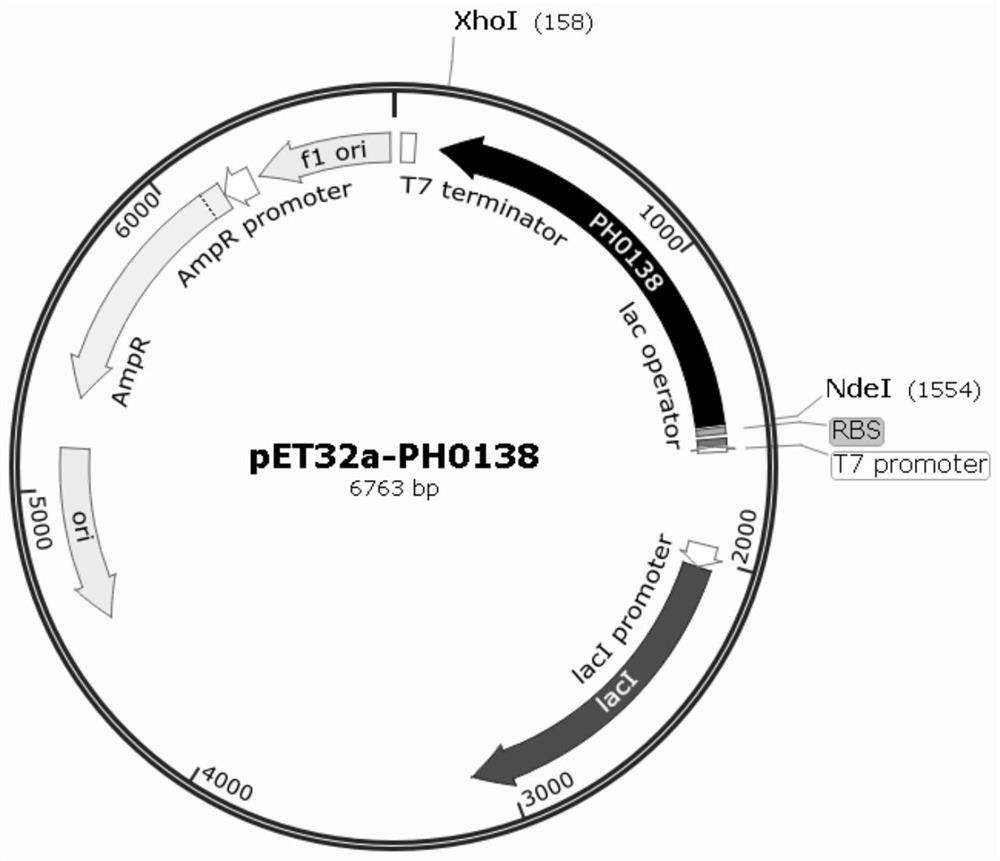
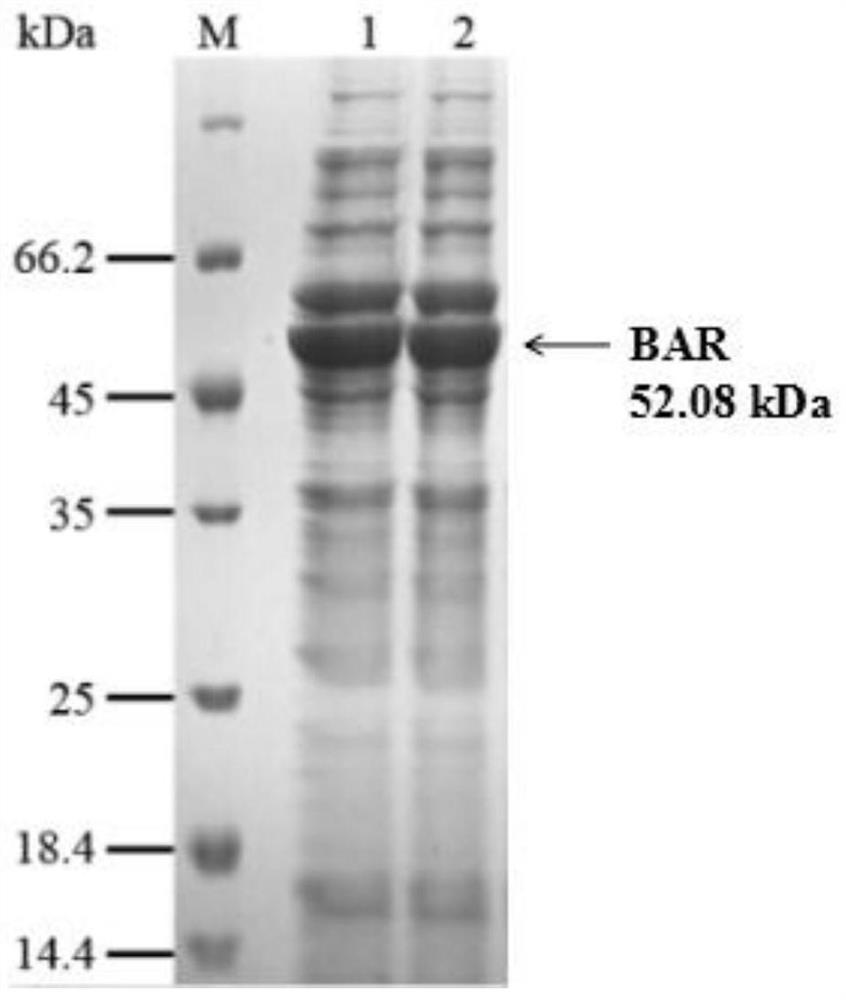
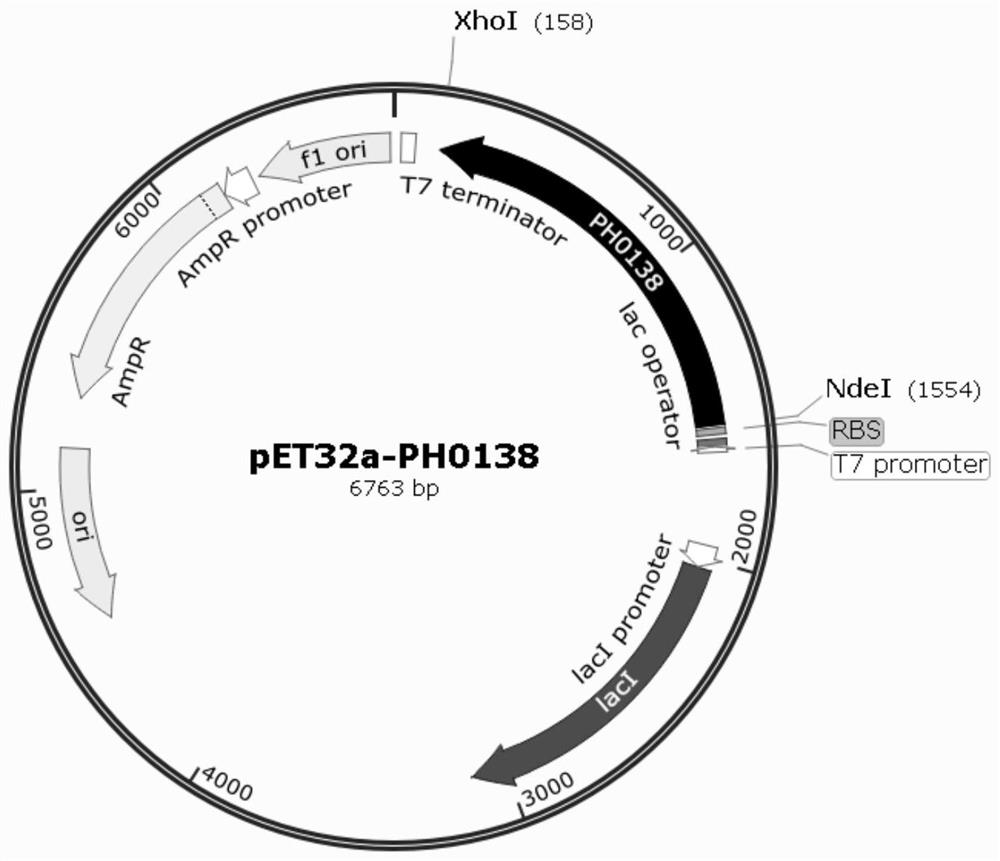
The invention discloses a method for producing DL-tyrosine by an enzyme, and a broad-spectrum amino acid racemase and use thereof. The method for producing DL-tyrosine by the enzyme comprises the following steps: S1, constructing a recombinant expression vector pET32a-PH0138 and transforming the recombinant expression vector into escherichia coli BL21(DE3) / pG-KJE8 to obtain a recombinant engineering bacteria BBAR; S2, fermenting the recombinant engineering bacteria BBAR expressing a BAR enzyme to obtain wet bacteria body; S3, suspending the wet bacteria body and crushing the bacteria with a crushing solution containing crude enzyme liquid of a broad-spectrum amino acid racemase; and S4, adding L-tyrosine and PLP into the crude enzyme liquid obtained in step S3, conducting stirring and converting until specific rotation is 0 degree and terminating the reaction to obtain a DL-tyrosine aqueous solution. The method has advantages of low raw material price, high conversion rate, simple post-treatment and high product quality, and is suitable for industrial mass production.
Owner:绵阳晟氏健康科技有限公司
Method for synthesizing dipeptide with glutamic acid as first amino acid residue
InactiveCN104151398AHigh purityRaw materials are easy to getPeptide preparation methodsDipeptideN-Hydroxysuccinimide
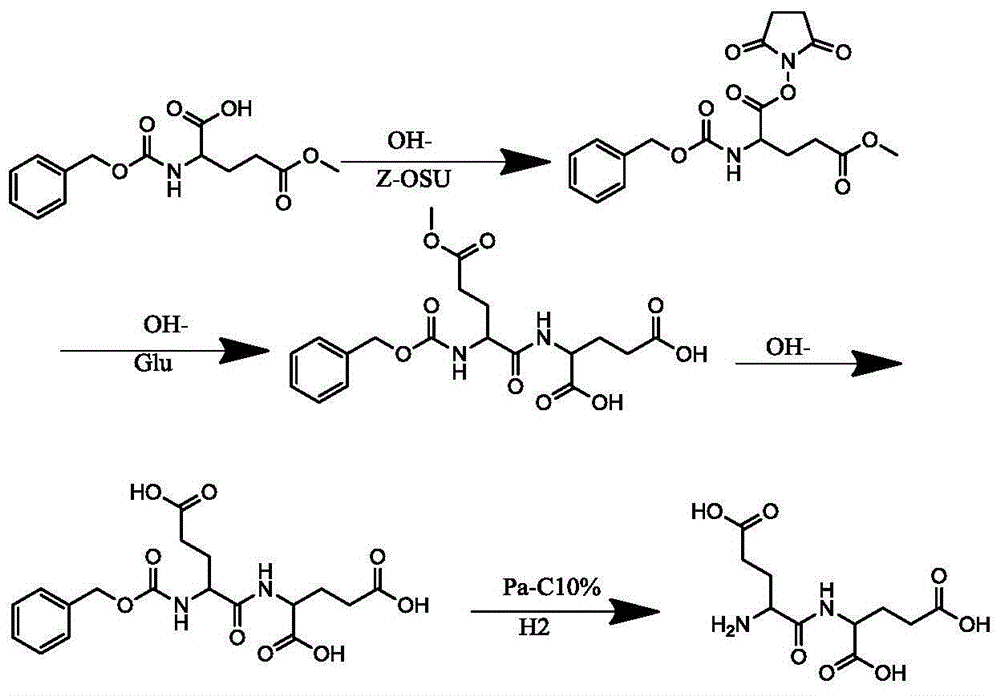
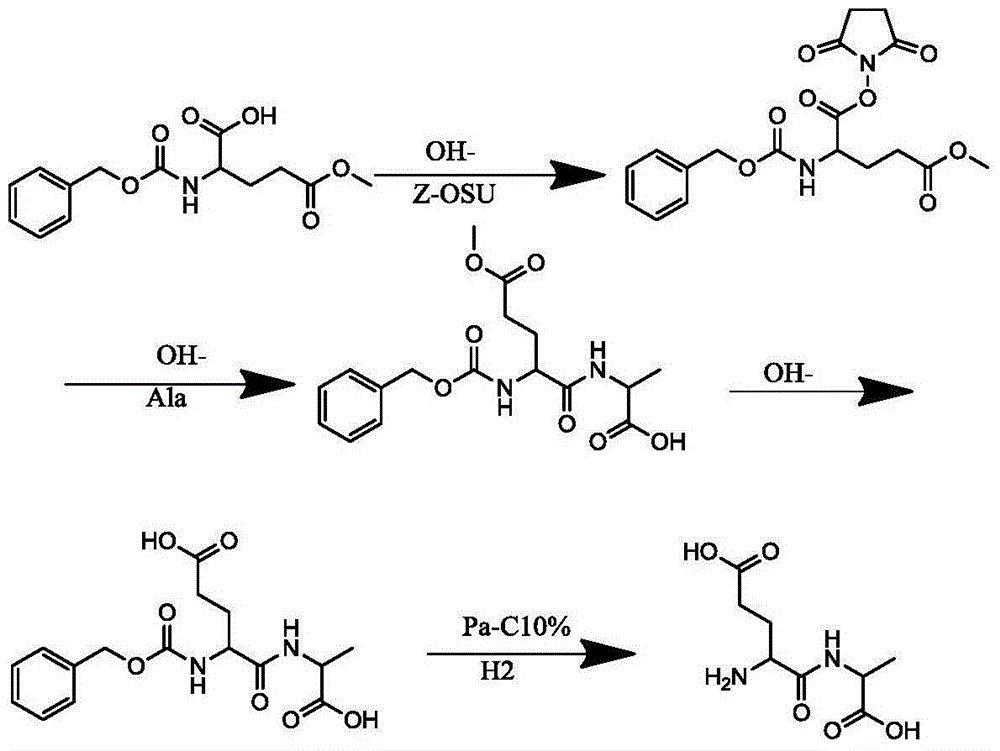
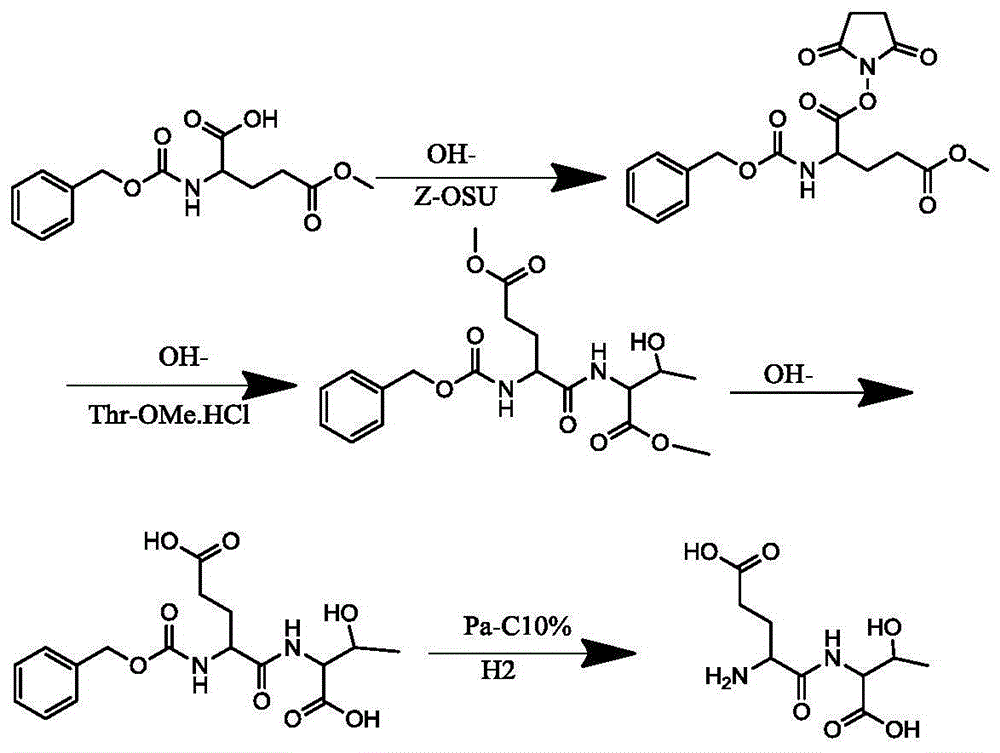
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing dipeptide with glutamic acid as the first amino acid residue. The method comprises the following steps: protecting the amino group of glutamic acid-5 methyl ester serving as an initial raw material by using carbobenzoxy; reacting with dicyclohexyl carbodiimide and N-hydroxy succinimide to prepare a high-purity midbody; further reacting with another group of amino acid under the alkali condition to obtain protected dipeptide; finally hydrogenating to obtain high-purity dipeptide which takes glutamic acid as the first amino acid residue. The method is environment-friendly, simple to operate, nearly free of waste discharge and beneficial to industrial production.
Owner:SICHUAN TONGSHENG AMINO ACID CO LTD
Culture method for pluripotent stem cells, culture kit, and medium for pluripotent stem cell culture
ActiveUS20160251613A1High activityConnective tissue peptidesCulture process2-MercaptoethanolStem cell culture
A culture method for pluripotent stem cells includes culturing pluripotent stem cells on a cell culture surface of a support by using a medium in which the concentration of 2-mercaptoethano is equal to or less than 10 μM in the presence of a polypeptide consisting of 40 to 450 amino acid residues, in which the polypeptide includes (1) a first domain including at least one amino acid sequence selected from the group consisting of an amino acid sequence represented by CSYYQSC (SEQ ID NO: 1) and an amino acid sequence represented by RGD and (2) a second domain including (2-i) an amino acid sequence which is represented by PRPSLAKKQRFRHRNRKGYRSQRGHSRGRNQN (SEQ ID NO: 2), (2-ii) an amino acid sequence which shares sequence identity of equal to or higher than 50% with the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 2 and exhibits adsorbability with respect to the cell culture surface of the support, or (2-iii) an amino acid sequence which is formed by the addition, substitution, or deletion of 1 to 30 amino acids in the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 2 and exhibits adsorbability with respect to the cell culture surface of the support.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Polynucleotide encoding a thermostable amide hydrolase and methods for producing an L-α-amino acid
InactiveUS7977073B2Efficient productionImprove thermal stabilitySugar derivativesBacteriaNucleotideEnzyme protein
The present invention relates to an amide hydrolase which is with excellent thermostability and stereoselectively hydrolyzes an α-amino acid amide; a gene encoding the enzyme protein; a novel recombinant vector containing the gene; a transformant containing the recombinant vector; and a process for producing an L-α-amino acid using the transformant.
Owner:MITSUBISHI RAYON CO LTD
Method for enzymatically producing dl-tyrosine, broad-spectrum amino acid racemase, and application
ActiveCN112899320BImprove securityLow priceRacemaces/epimerasesIsomerasesEscherichia coliAmino-acid racemase
The invention discloses a method for enzymatically producing DL-tyrosine and a broad-spectrum amino acid racemase and its application. The method for enzymatically producing DL-tyrosine comprises the following steps: S1, constructing a recombinant expression vector pET32a-PH0138, Transform into Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) / pG‑KJE8 to obtain the recombinant engineered bacteria BBAR; S2, ferment the recombinant engineered bacteria BBAR expressing BAR enzyme to obtain wet cells; S3, suspend the wet cells and perform crushing treatment, crush The solution is a crude enzyme solution containing a broad-spectrum amino acid racemase; S4, adding L-tyrosine and PLP to the crude enzyme solution obtained in step S3, stirring and converting, until the specific rotation is 0°, the reaction is terminated, and the obtained DL‑Tyrosine in water. The method has the advantages of low raw material price, high conversion rate, simple post-treatment, high product quality, and is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:绵阳晟氏健康科技有限公司
A method of selectively producing male or female sterile plants
A method of producing male or female sterile plants comprising the steps of transforming plant material with a polynucleotide which encodes at least one enzyme which reacts with a non-phytotoxic substance to produce a phytotoxic one, and regenerating the thus transformed material into a plant, wherein the said non-phytotoxic substance is applied to the plant up to the time of male or female gamete formation and / or maturation, so that the non-phytotoxic substance provides for the production of a phytotoxic one which selectively prevents the formation of or otherwise renders the said gametes non-functional, wherein the enzyme is expressed preferentially in either male or female reproductive structures, characterised in that (i) the non-phytotoxic substance is selected from the group consisting of ester derivatives of non-phosphonate herbicides which herbicides are directly phytotoxic to non-green tissue, D-alpha amino acids, peptide derivatives of non-protein D-alpha amino acids, S-enantiomers of aryloxyphenoxypropionates and S-enantiomers of ester derivatives of aryloxyphcnoxypropionatcs and (ii) the enzyme is selected from the group consisting of carboxylesterases, D-amino acid oxidases, D-amino acid dehydrogenases, D-amino acid racemases, 2-arylpropionyl-CoA epimerases, alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemases, thioesterases and acyl-CoA synthetases.
Owner:SYNGENTA BIO TECH CHINA
Heat-resistant isoamylase
InactiveUS10017751B2Improve heat resistanceHigh purityFermentationGlycosylasesHeat resistanceMethionine biosynthesis
An isoamylase having improved heat resistance and an industrial method for producing maltose from starch.The isoamylase is an isoamylase consisting of the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1 or an isoamylase resulting from deletion, substitution, or insertion of one to several amino acid residues in the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1, wherein at least valine at amino acid number 515 and methionine at amino acid number 570 are mutated to other amino acids.
Owner:GODO SHUSEI
A kind of amino acid racemase and its application
ActiveCN111321192BRacemic activityThermally stableRacemaces/epimerasesIsomerasesEnzyme catalysisBiology
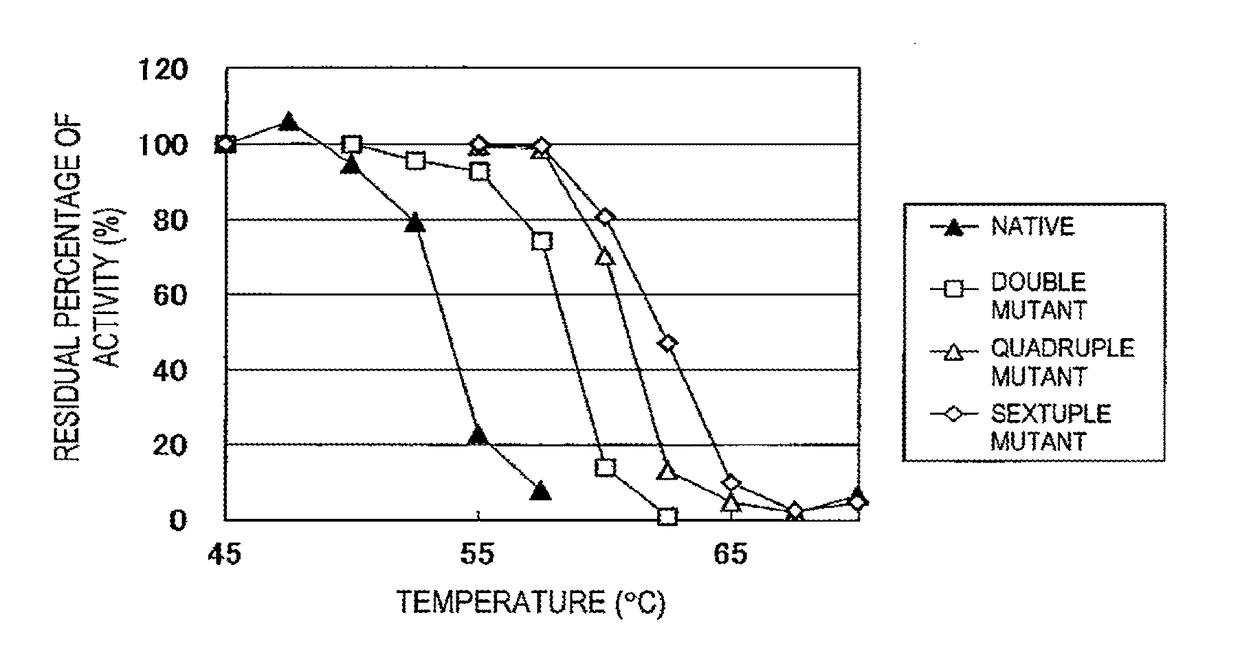
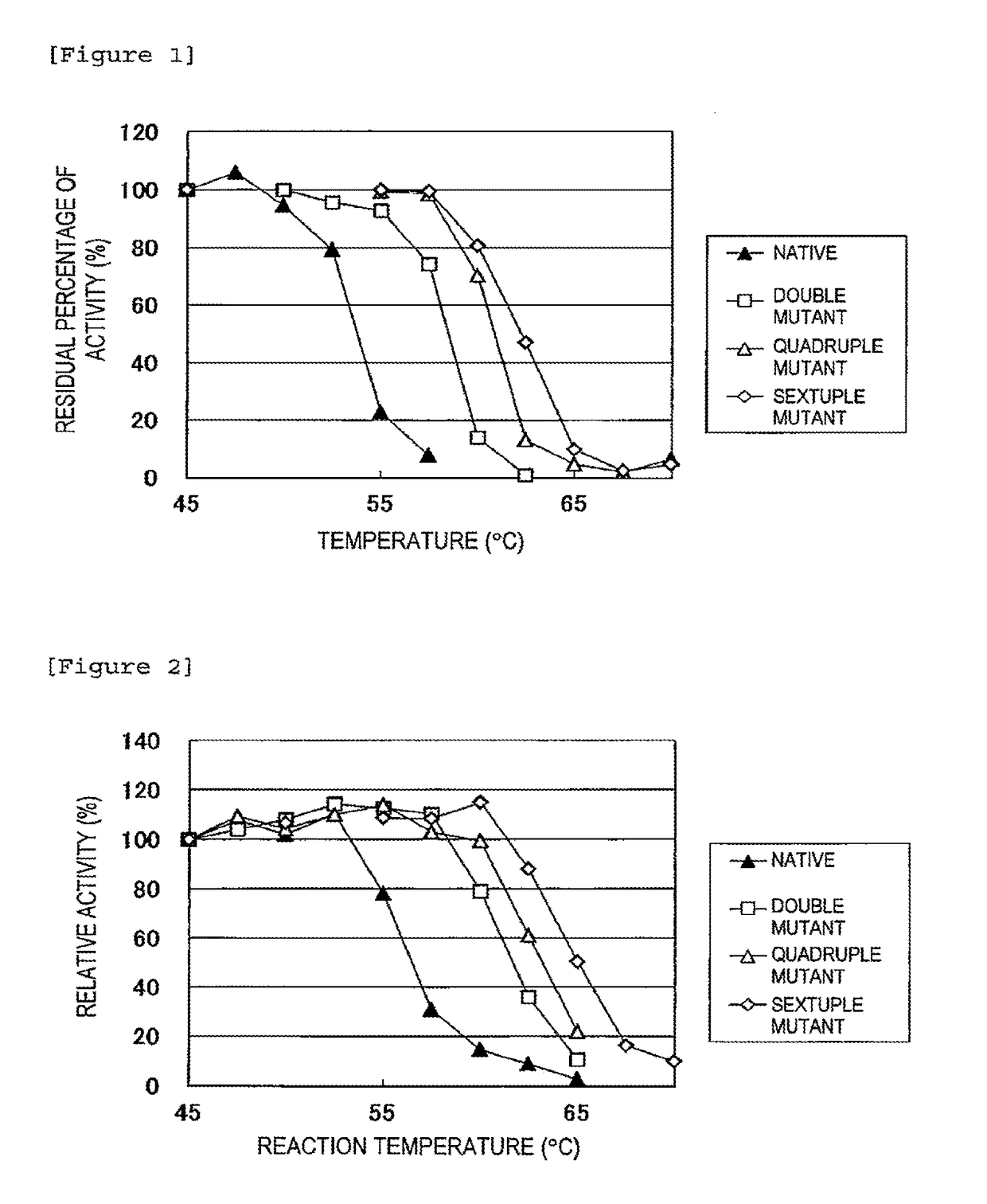
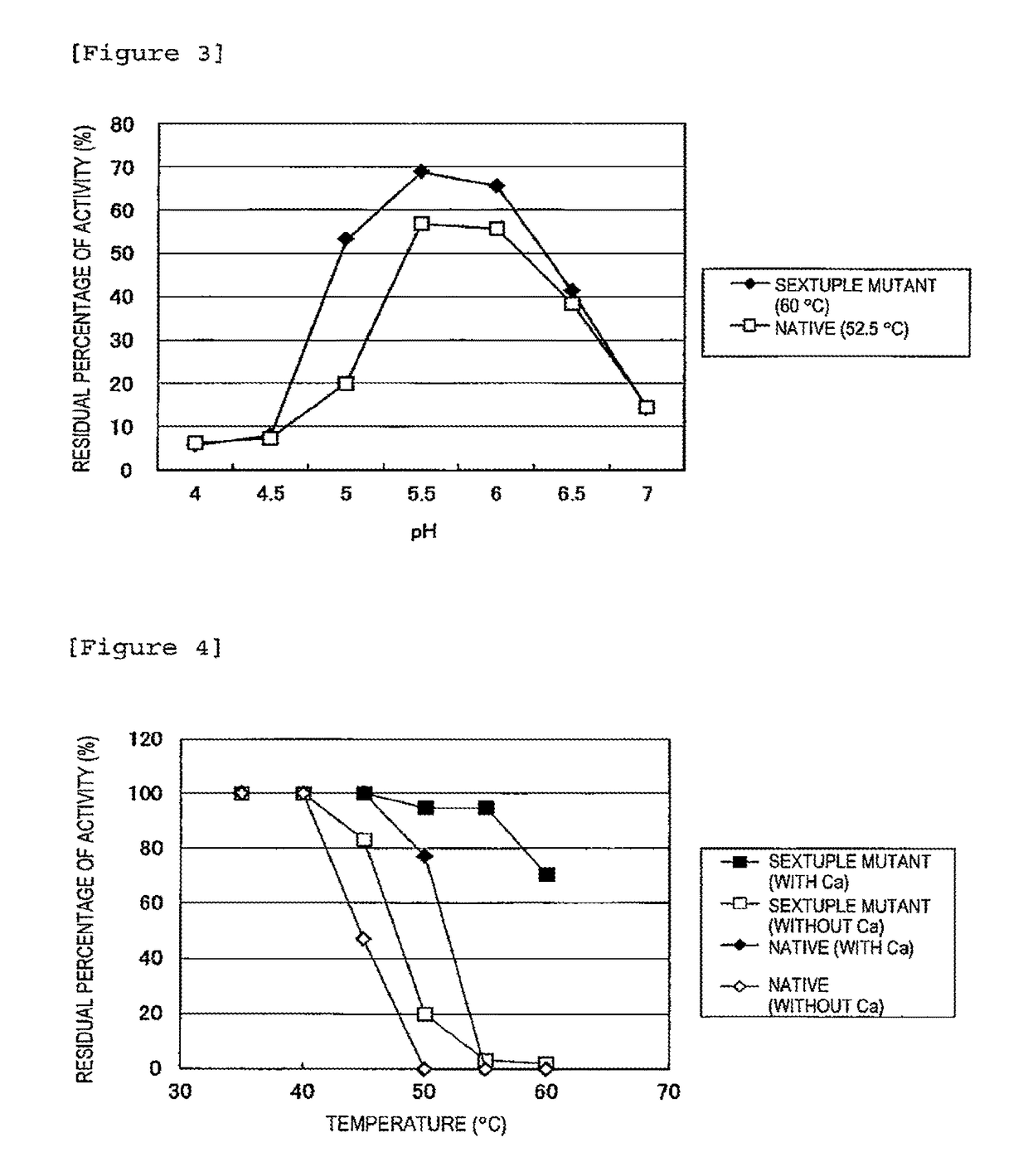
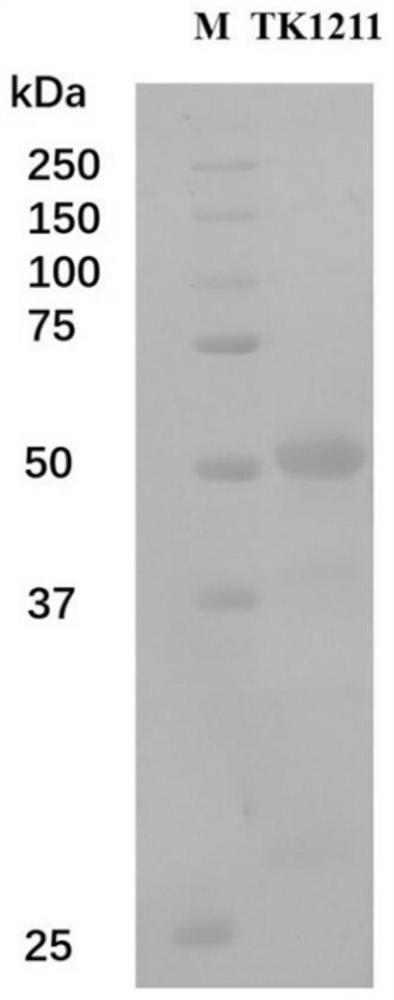
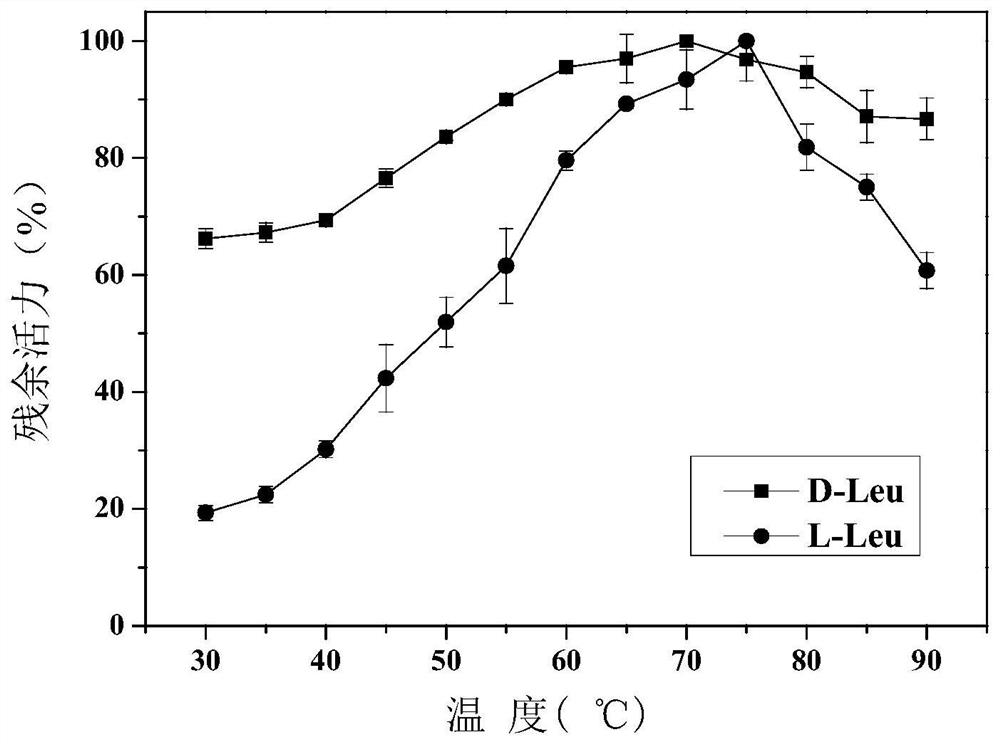
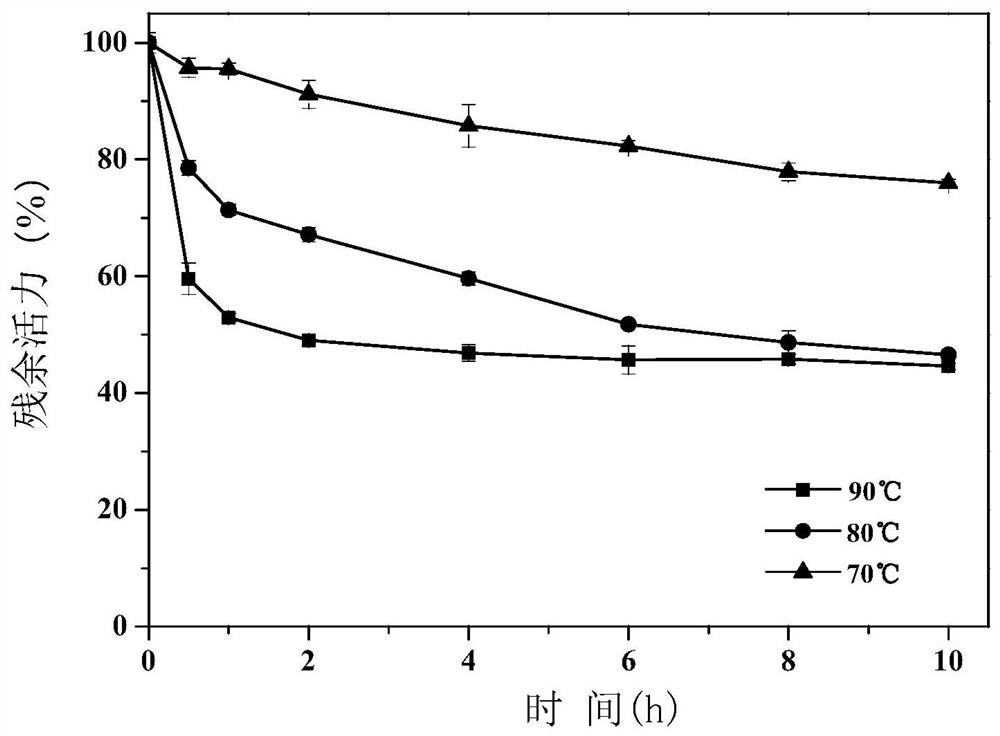
The invention discloses an amino acid racemase and its application in catalyzing the racemization of amino acids, belonging to the field of biotechnology. The amino acid racemase is a polypeptide I having an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 or a polypeptide II having at least 70% identity with the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and having the function of catalyzing amino acid racemization. Amino acid racemase has racemization activity for various amino acid isomers such as Leu and Met, and is thermostable, so it can be applied to enzyme-catalyzed digestion of L-Leu / D-Leu, L-Met / D-Met Rotation is of great significance for the mutual transformation of amino acid enantiomers.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Heat-resistant isoamylase
InactiveUS20170362581A1Improve heat resistanceHigh purityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHeat resistanceMethionine biosynthesis
An isoamylase having improved heat resistance and an industrial method for producing maltose from starch.The isoamylase is an isoamylase consisting of the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1 or an isoamylase resulting from deletion, substitution, or insertion of one to several amino acid residues in the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1, wherein at least valine at amino acid number 515 and methionine at amino acid number 570 are mutated to other amino acids.
Owner:GODO SHUSEI
Deinococcus N-acylamino acid racemase and use of preparing L-amino acid
The present invention relates to a novel thermostable N-acylamino acid racemase (NAAAR) isolated from Deinococcus radiodurans NCHU1003, the coding sequence and the preparation thereof. The present invention also discloses the process for preparing highly optically pure L-amino acids, such as L-homophenylalanine (L-HPA) and the derivatives thereof, from N-protected amino acid by using the novel NAAAR combined with L-N-carbamoylase.
Owner:NATIONAL CHUNG HSING UNIVERSITY
Three alpha-conus polypeptides and use thereof
InactiveCN102304171BStrong analgesic activityIncreased pain thresholdPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticConusAmino-acid racemase
The invention discloses alpha-conus polypeptides and use thereof. The invention provides seven polypeptides: a polypeptide I of which the amino acid sequence is represented by a sequence 7 in a sequence table and in which the last amino acid residue is amidated; a polypeptide II of which the amino acid sequence is represented by a sequence 8 in the sequence table and in which the last amino acid residue is amidated; a polypeptide III of which the amino acid sequence is represented by a sequence 9 in the sequence table and in which the last amino acid residue is amidated; a polypeptide IV of which the amino acid sequence is represented by a sequence 10 in the sequence table and in which the last amino acid residue is amidated; a polypeptide V of which the amino acid sequence is representedby a sequence 11 in the sequence table and in which the last amino acid residue is amidated; a polypeptide vI of which the amino acid sequence is represented by a sequence 12in the sequence table andin which the last amino acid residue is amidated; and a polypeptide VII of which the amino acid sequence is represented by a sequence 13 in the sequence table and in which the last amino acid residueis amidated. The result of activity tests, the seven polypeptides of the general formula (I) have pain relieving effect, alpha-conus polypeptides T-1, T-2, T-3 and T-4 have obvious pain-relieving activity, and the alpha-conus polypeptides T-5, T-6 and T-7 also have obvious pain-relieving effect, and the alpha-conus polypeptides have application values in pain-reliving aspect.
Owner:INST OF BIOENG ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE CHINESE
Method for preparing gamma-carbonyl carboxylic acid, amino acid, amino acid ester and amide compounds
ActiveCN104276938AHigh regional selectivityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationHydrogenPersulfate
The invention discloses a method for preparing gamma-carbonyl carboxylic acid, amino acid, amino acid ester and amide compounds. The method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing a methylene-containing compound, an oxidizing agent and water to perform selective methylene carbon-hydrogen bond oxidation, so as to obtain at least one of gamma-carbonyl carboxylic acid, gamma-carbonyl amino acid and gamma-carbonyl amide compounds after the reaction is finished. The method is a methylene selective oxidation reaction which does not need a catalyst for catalysis and employs a persulfate as an oxidizing agent, and the reaction is successfully applied to oxidation of methylene carbon-hydrogen bonds of carboxylic acids, amino acids and amide compounds, excellent selectivity is obtained, and the method has important application value.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
A kind of preparation method of d-amino acid
ActiveCN109136298BLow costReduce inhibitionImmobilised enzymesHydrolasesAcetic acidAmino-acid racemase
The present invention relates to a preparation method of D-amino acid, comprising the following steps: 1. Construction of recombinant bacteria: cloning N-acetyl-D-aminoacylase gene, connecting the gene into pET series vector or pKK223-3 vector, and transforming it into BL21 (DE3) host bacteria, construct D-acylase recombinant bacteria (NLase); clone N-acetyl-amino acid racemase gene, connect the gene into pET series vector or pKK223-3 vector, transform into BL21(DE3) host bacteria, construct N-acetylamino acid racemase recombinant bacteria (NAAR); 2. Fermentation of recombinant bacteria; 3. Preparation of immobilized enzyme; 4. Transformation of immobilized enzyme combined with membrane separation; 5. Product crystallization. The invention reduces the cost of the enzyme and reduces the inhibition of the by-product acetic acid on the racemase. At the same time, because the conversion liquid has few impurities, the separation and purification are simple, the yield is high, and the product quality is good. The obtained D-amino acid has an e.e. value of more than 99.9%, a content of more than 99%, and a molar yield of more than 85%.
Owner:浙江正硕生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com