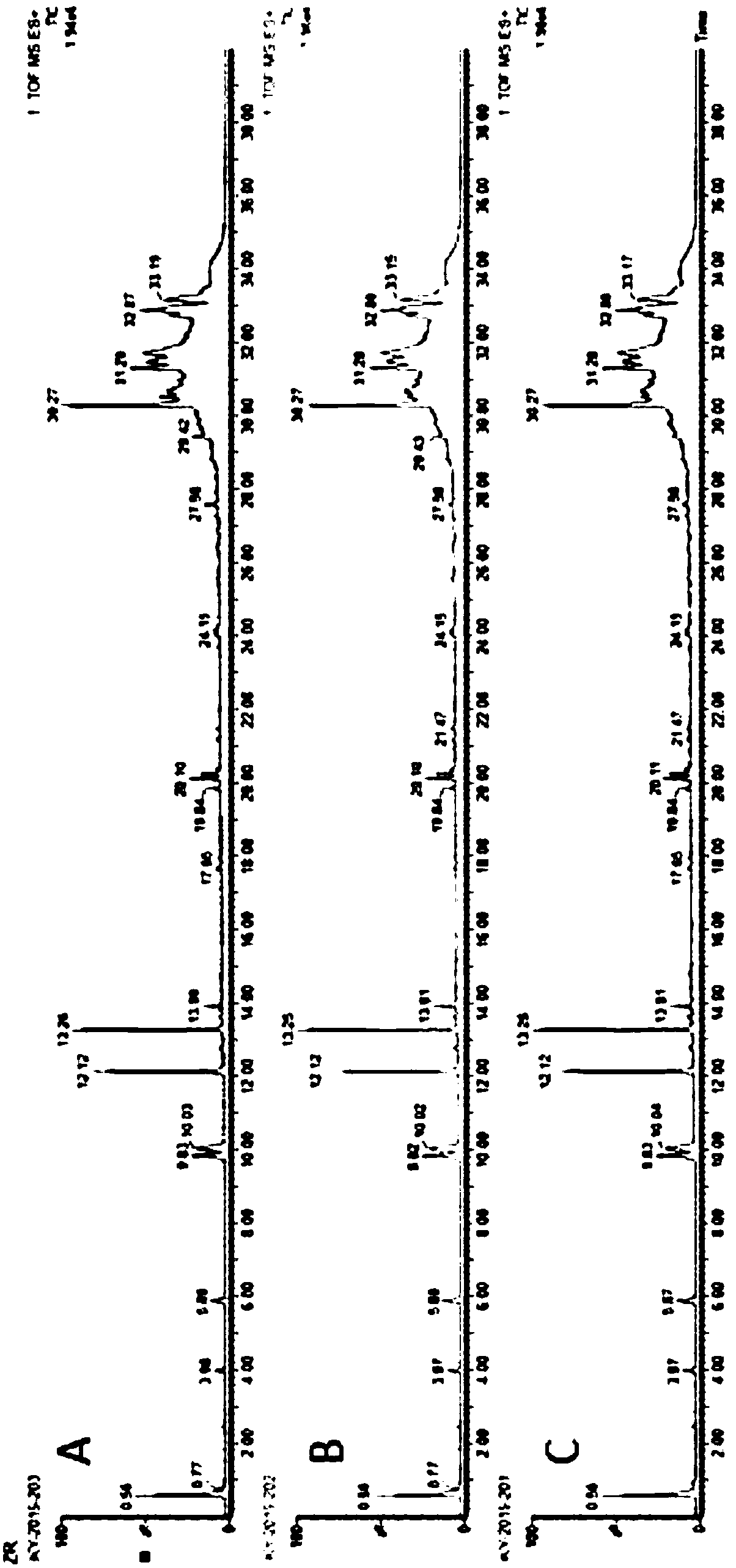
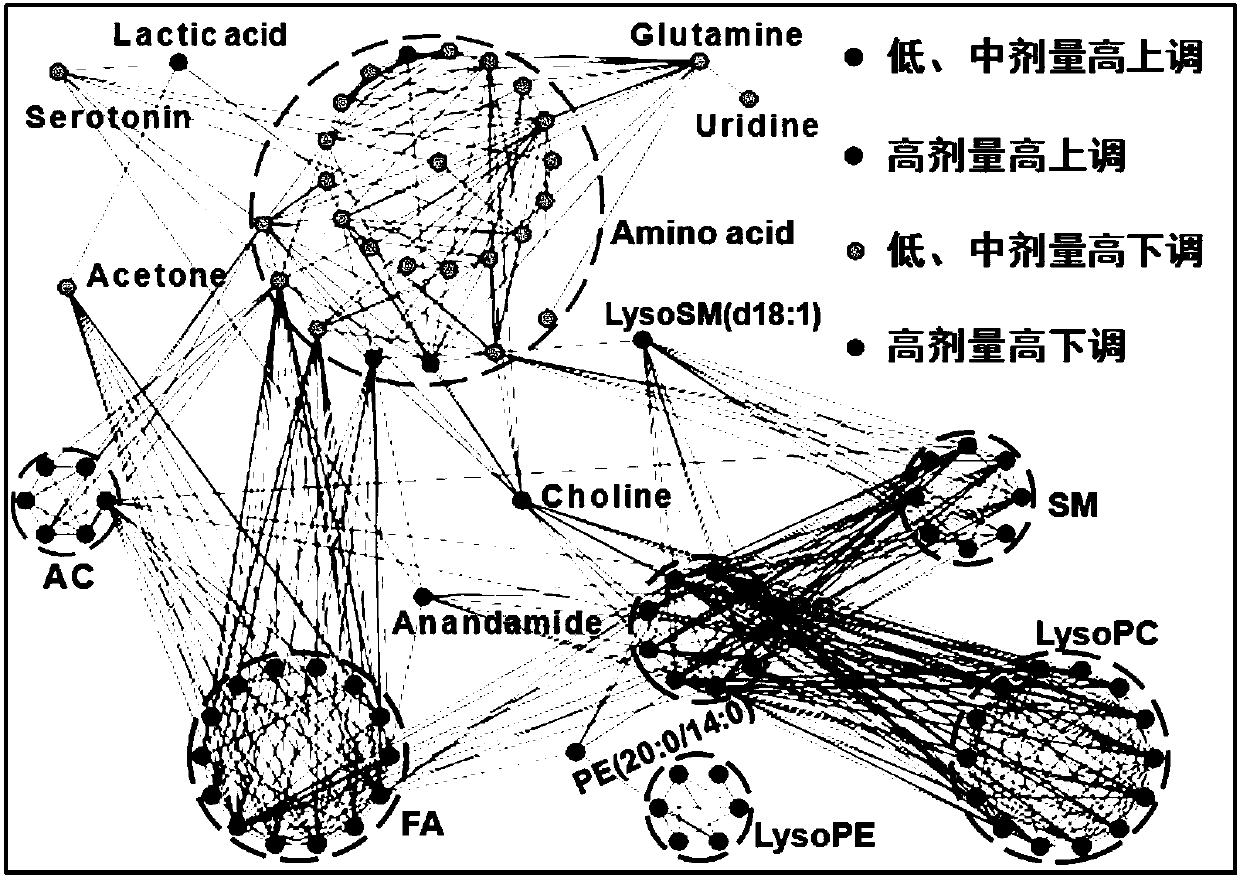
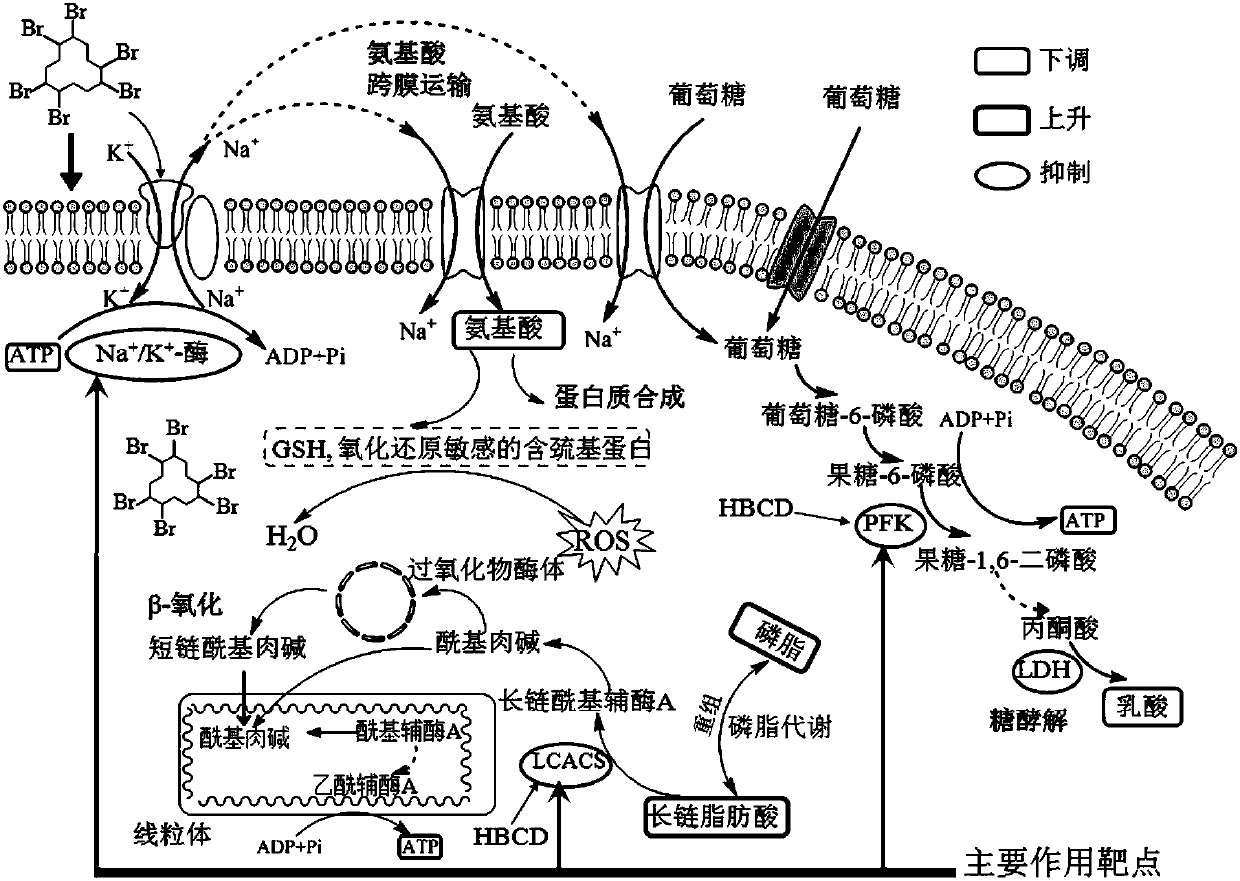
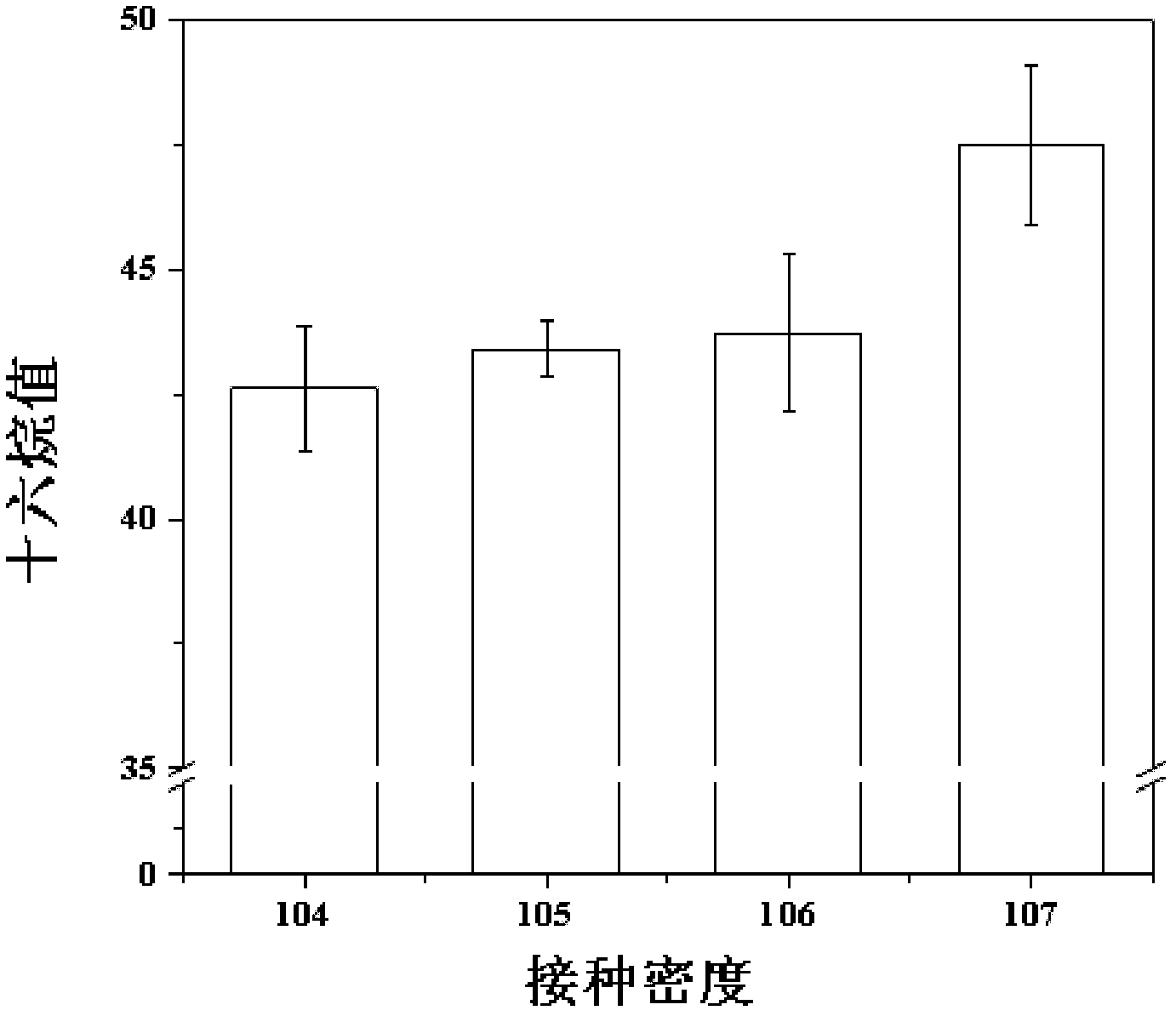
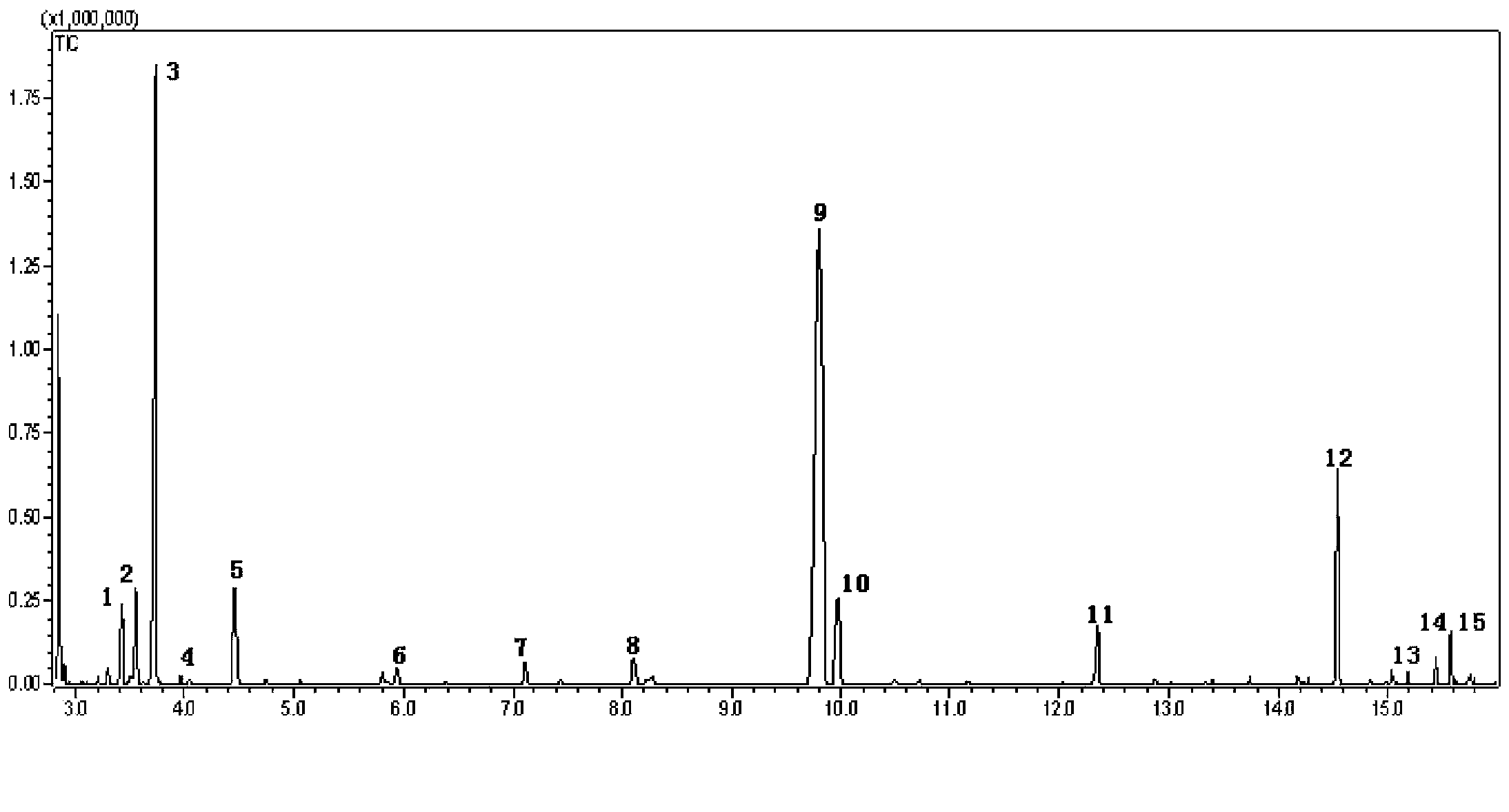
Patents
Literature
66 results about "Intracellular metabolite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Intracellular metabolic flux analysis method using substrate labeled with isotope
InactiveUS20050175982A1Low costMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingDrug metabolismTime course
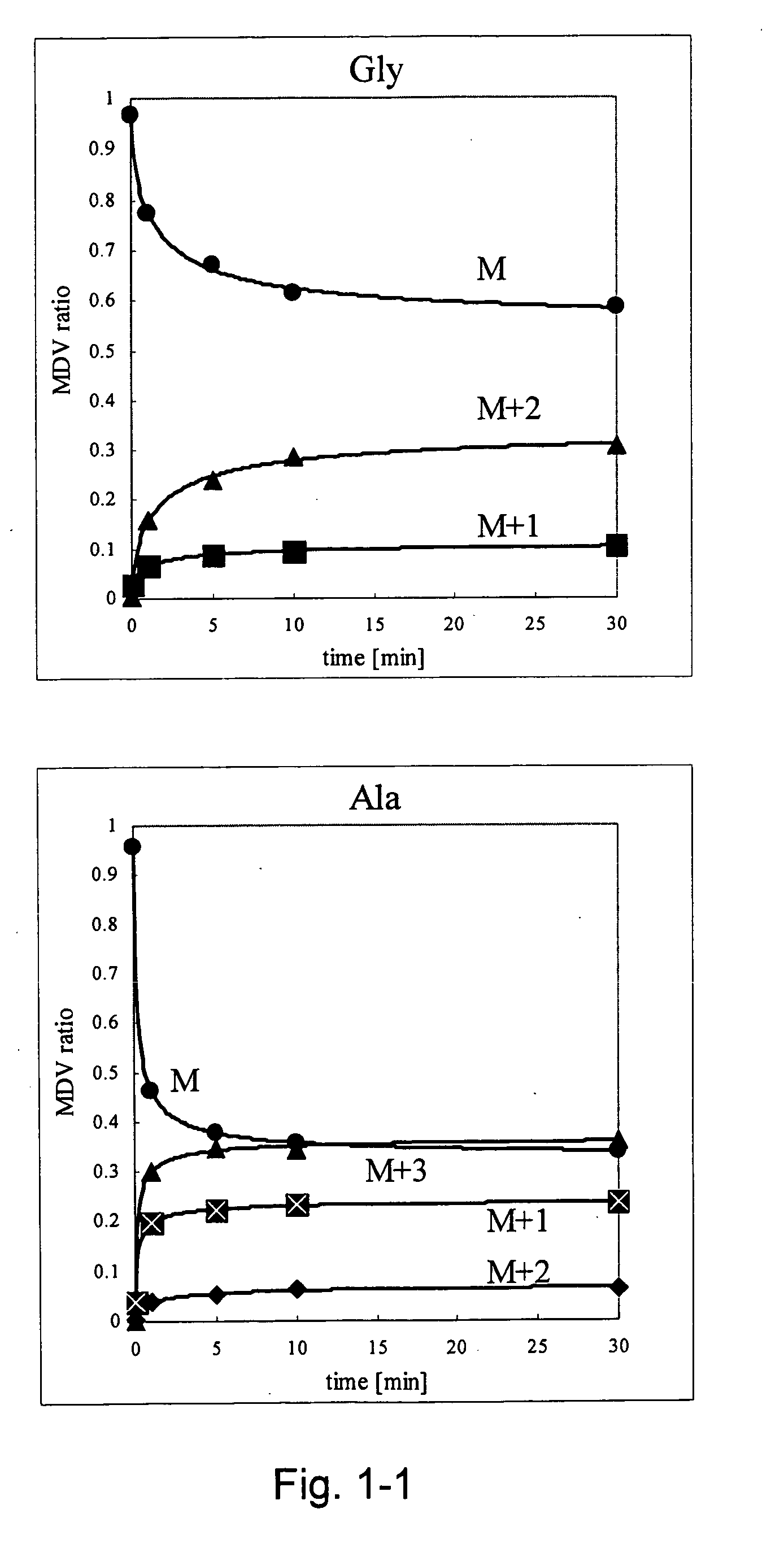
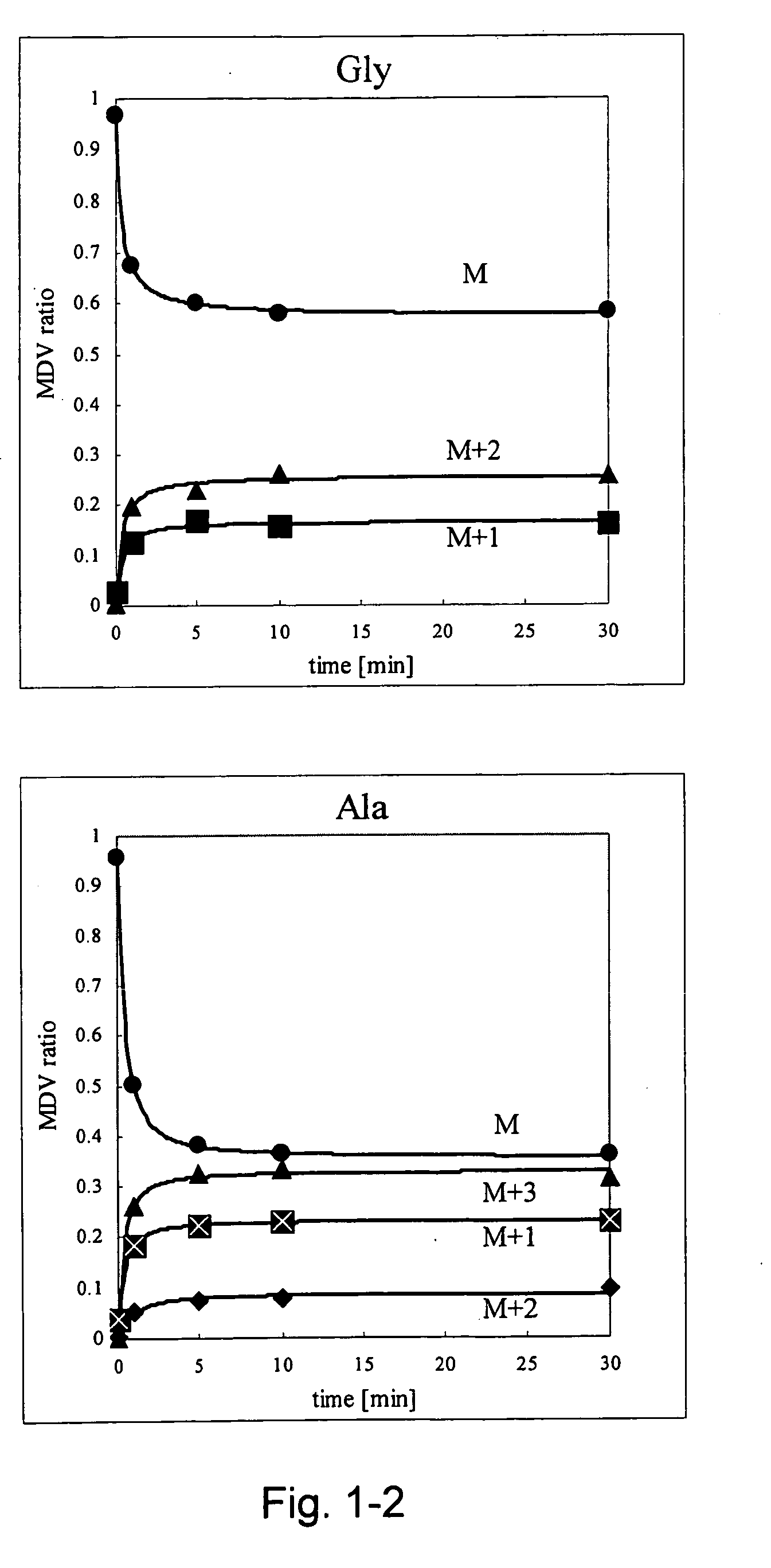
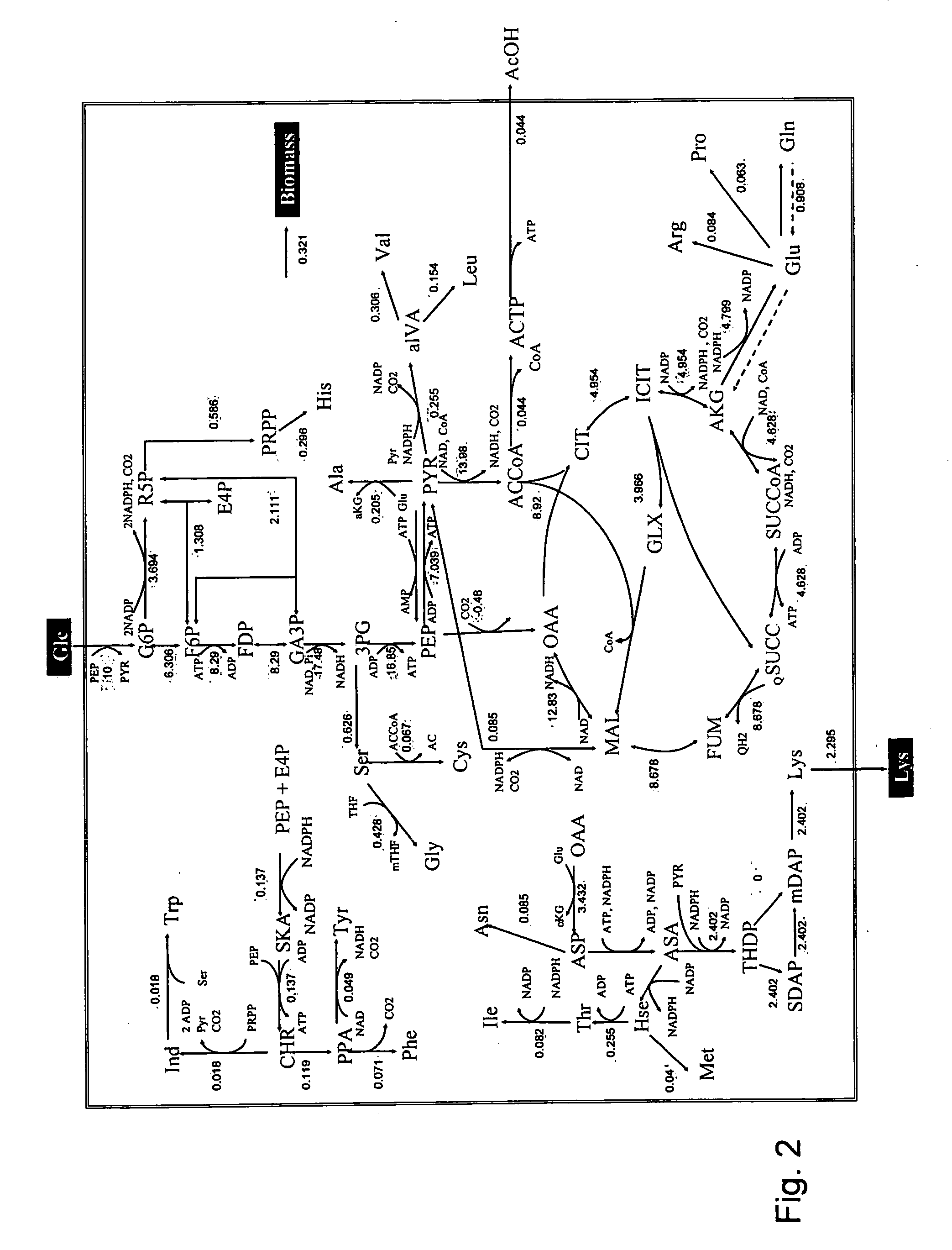
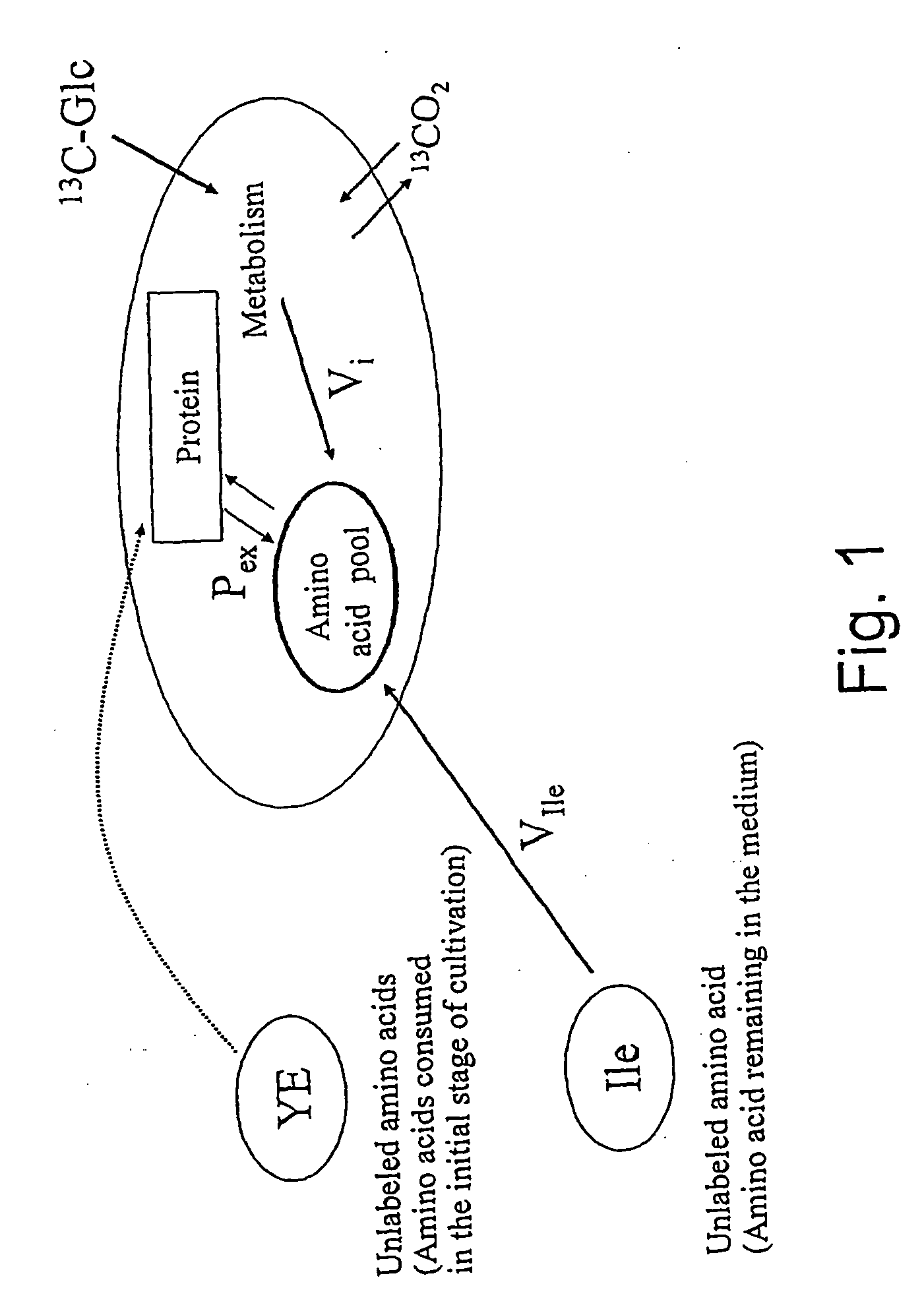
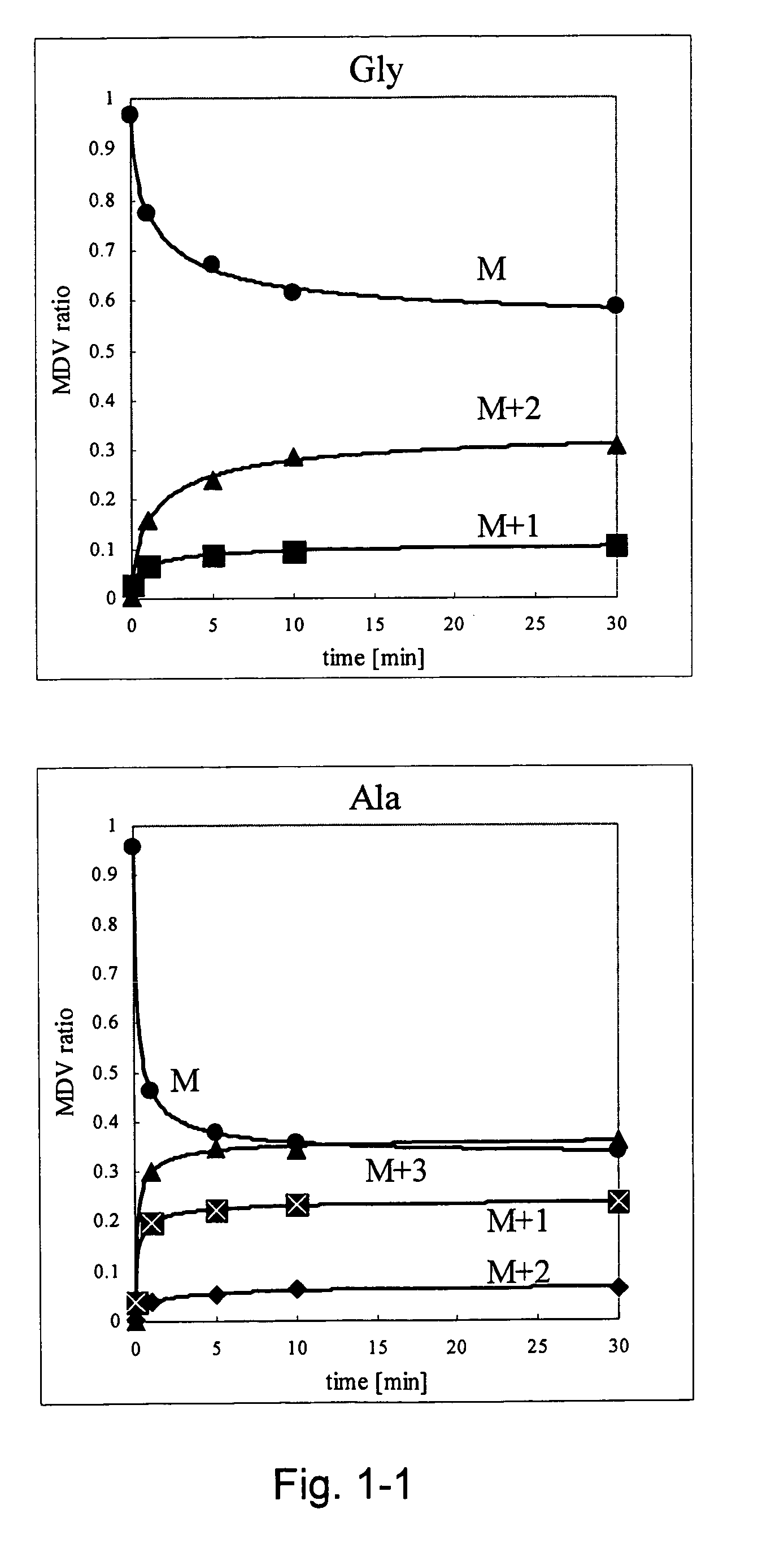
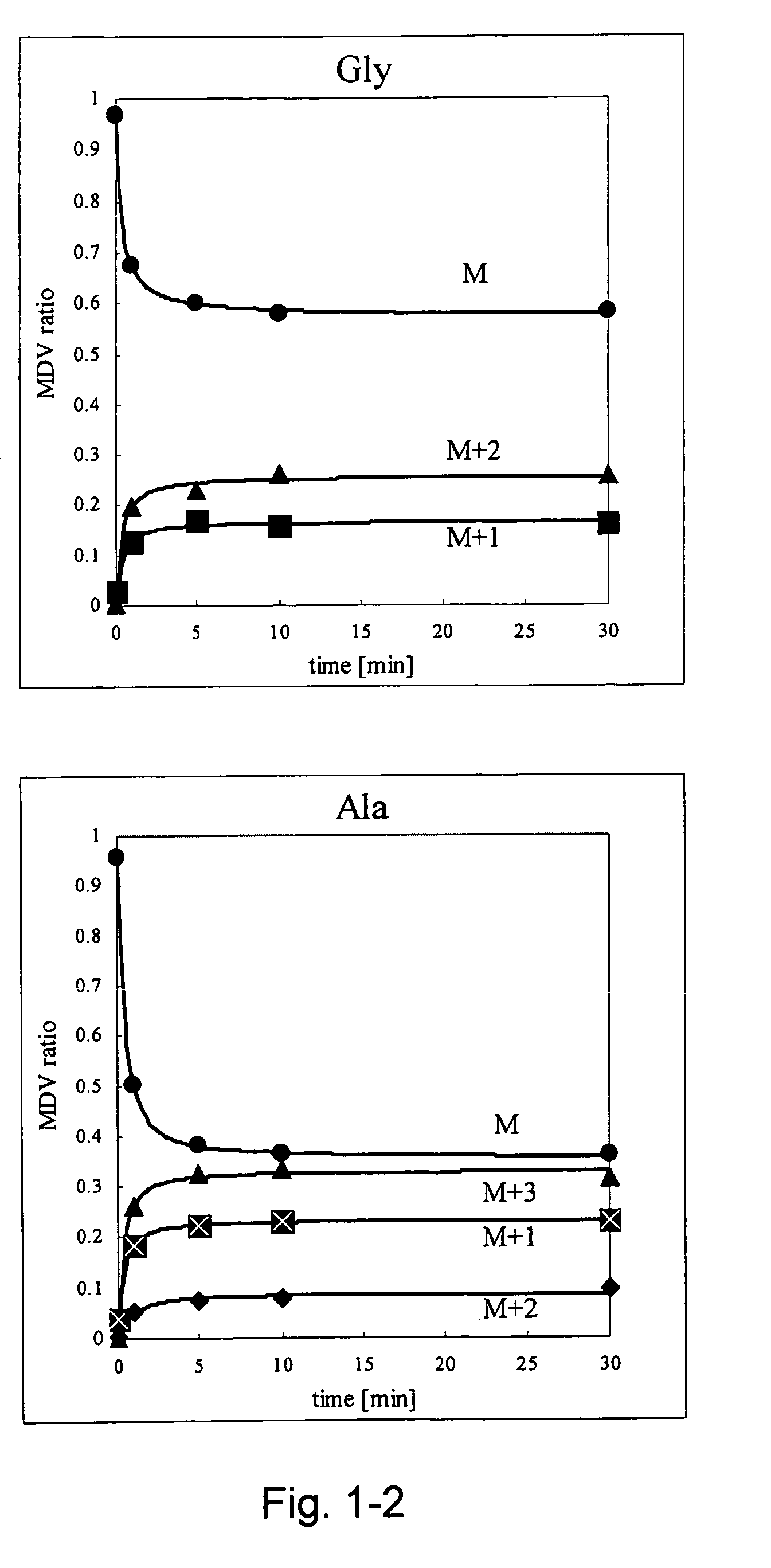
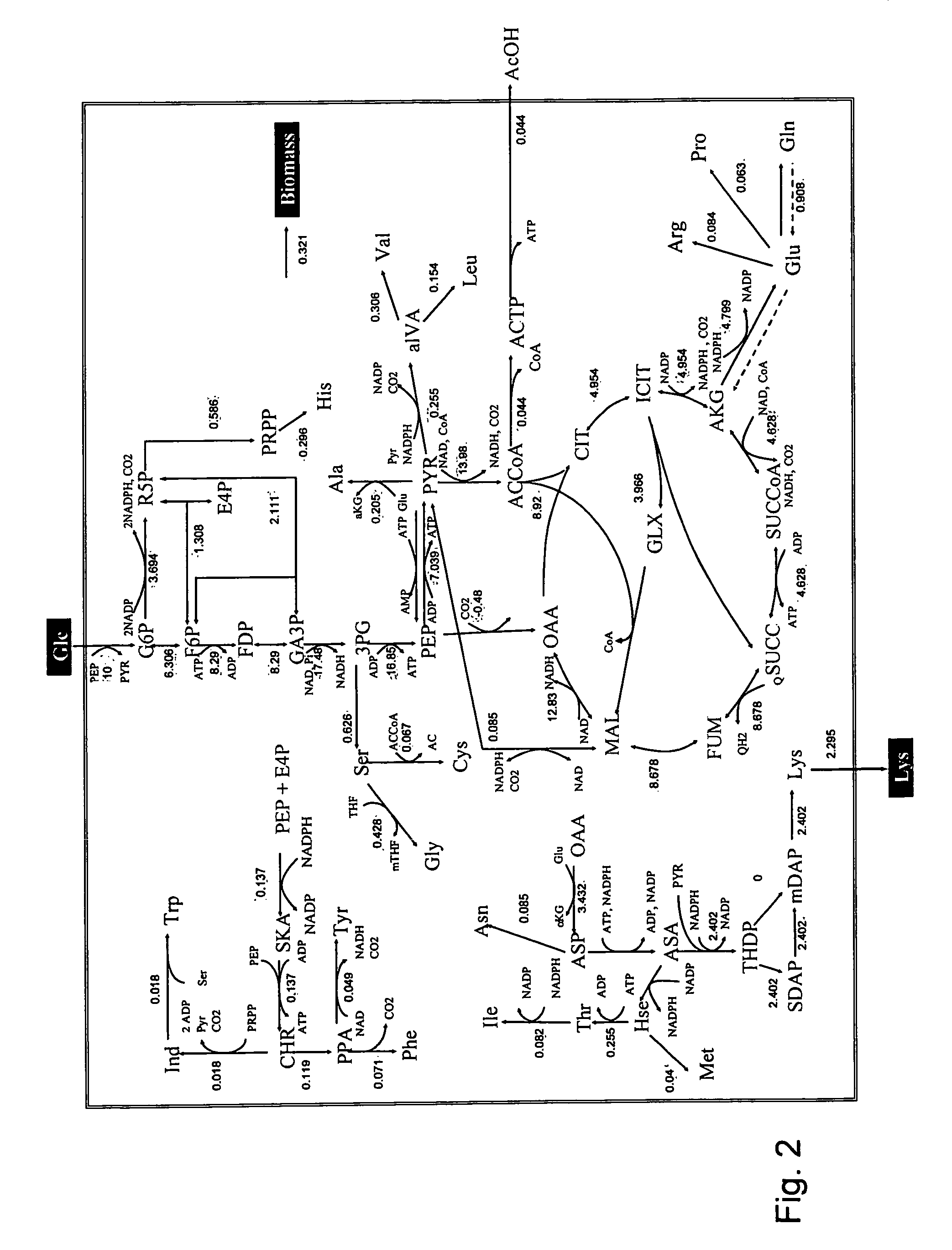
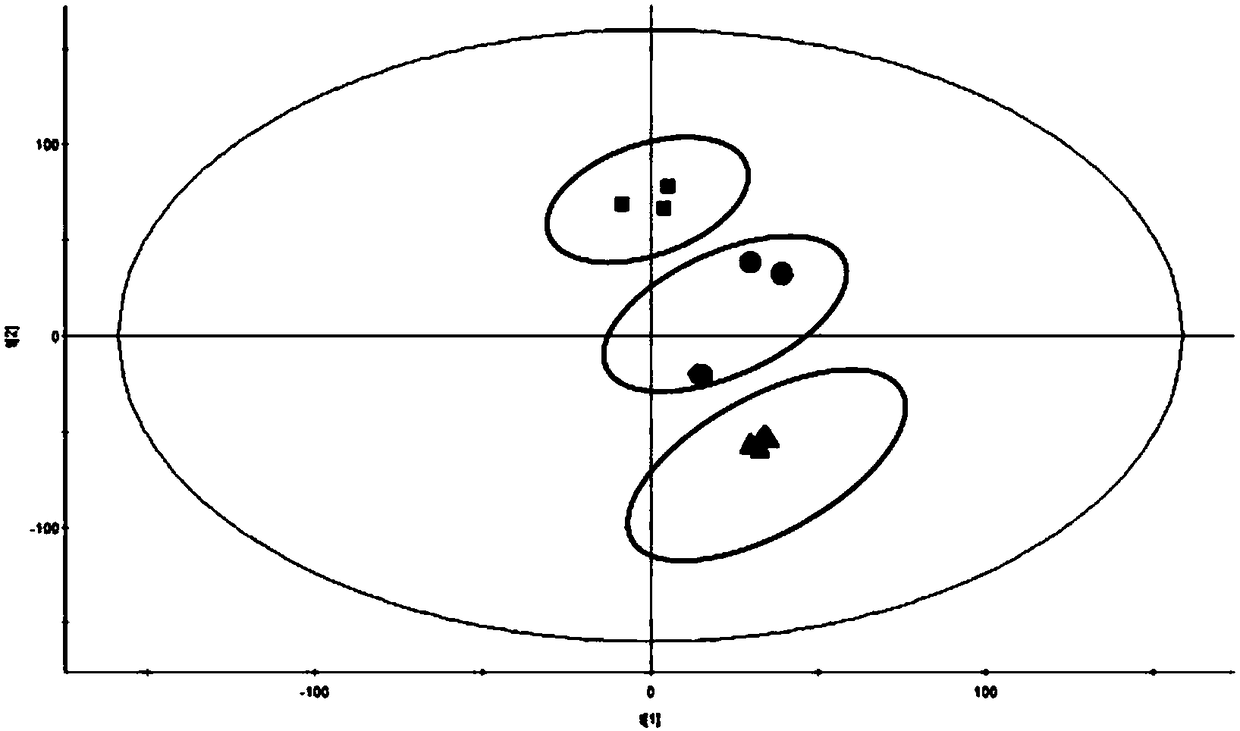
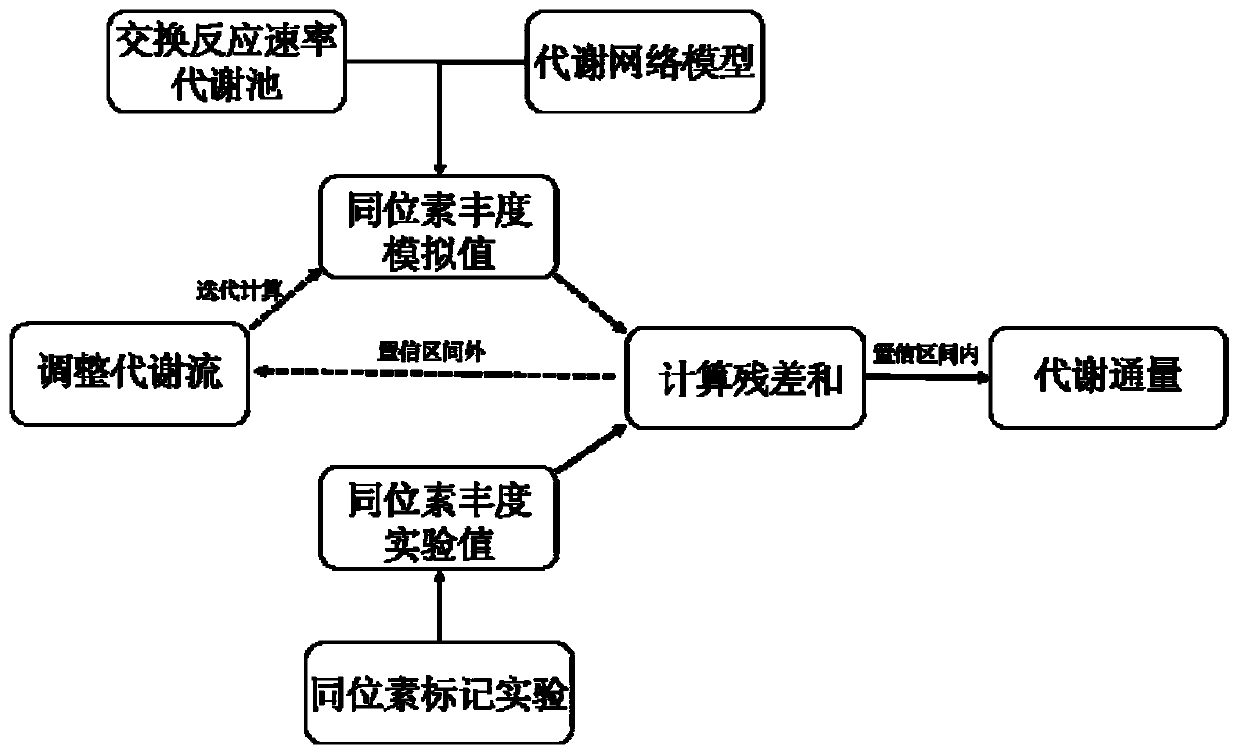
A method for intracellular metabolic flux analysis comprising (a) culturing cells in a medium not containing any isotope-labeled substrate to a target phase of the metabolic flux analysis, (b) adding an isotope-labeled substrate to the medium, and continuing culture and collecting samples from the medium in time course, (c) measuring isotope distribution in an intracellular metabolite contained in the samples collected in time course, (d) performing a regression analysis for measured data and calculating an isotope distribution ratio in a steady state, and (e) analyzing a metabolic flux of the cultured cells by using the calculated isotope distribution ratio.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Intracellular metabolic flux analysis method using substrate labeled with isotope
InactiveUS20060105322A1Reduce analysis errorReduce errorsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingIsotopic labelingIsotope
A method for analyzing an intracellular metabolic flux comprising determining the intracellular metabolic flux from analytical values of cells cultured in a medium containing an isotope-labeled substrate as a carbon source on the basis of an intracellular metabolic flux model constructed for the intracellular metabolic flux to be analyzed, wherein (a) influence of an exchange reaction between an intracellular metabolite and a cell component produced by integration of the intracellular metabolite is considered, (b) uptake of a compound in a medium into cells, which compound is identical to an intracellular metabolite and unlabeled with an isotope, is considered, or (c) carbon dioxide used in a fixation reaction is assumed as carbon dioxide produced in a production reaction.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method of increasing yield of spinosad by improving fermentation condition of saccharopolyspora spinosa based on metabonomics
InactiveCN104450834AImprove fermentation yieldComponent separationMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a method of increasing the yield of spinosad by improving the fermentation condition of saccharopolyspora spinosa based on metabonomics. The method comprises the following steps: (1) determining intracellular metabolite of the saccharopolyspora spinosa; (2) analyzing the capability of the saccharopolyspora spinosa of producing the spinosad; (3) carrying out PLS analysis; and (4) carrying out process analysis. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the metabolite change law in the process of producing the spinosad by virtue of fermentation of the saccharopolyspora spinosa is revealed by utilizing the metabonomics means and combining multivariate statistics, and a metabolic change mechanism related to production of the spinosad is further explained; by analyzing the spinosad production capability and the metabolic level of the saccharopolyspora spinosa in different growth environments, the metabolin related to the production of the spinosad is found, thus providing a direction for optimizing the culture process of the saccharopolyspora spinosa and increasing the fermentation yield of the spinosad. The invention also provides new thinking and method for study in other culture technological processes of producing macrolides microorganisms.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for reinforcing coacervation algae removal and controlling release of intracellular substances
ActiveCN102344190AEasy to handleSimple methodWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationWater/sewage treatment by oxidationEutrophicationFiltration
The invention which belongs to the technical field of drinking water treatment especially relates to a method for reinforcing the coacervation algae removal and controlling the release of intracellular substances in the process of high algae water treatment. The invention which aims at the eutrophication pollution of surface water sources of lakes, reservoirs and the like provides a method for improving the algae cell removal effect of technologies of coagulation, deposition and filtration of a water work with the combined action of potassium permanganate and a ferric salt, wherein the appropriate oxidation effect of potassium permanganate inactivates and inhibits the activity of algae cells and controls the release of intracellular metabolites, and In situ MnO2 which is in situ generatedthrough a reduction reaction of potassium permanganate deposits on the surface of the algae cells to improve the settlement performance of the algae cells; and the electrical neutralization of the ferric salt allows the potential of the surface of the algae cells to be improved, and In situ Fe(OH)3 which is in situ generated through a hydrolysis reaction of the ferric salt deposits on the surfaceof the algae cells to improve the potential and the settlement performance of the surface of the algae cells. The method of the invention which is mainly applied to the purification in the drinking water work can also be applied to landscape water treatment which aims at the landscape water reuse and the water source pretreatment of the eutrophication water to inhibit the growth of the algae cells.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for analyzing microalgae metabolome
ActiveCN102495152AFacilitating Metabolic ResearchComponent separationQuantitative ResultDerivatization
The invention discloses a method for analyzing a microalgae metabolome, comprising the following steps: collecting and quenching microalgae cells, extracting metabolites in the cells, carrying out derivatization on the metabolites, and finally analyzing a sample through GC-MS to obtain a metabolome result. According to the invention, the method relates to the termination of metabolic reaction, the extraction of the metabolites, and the analysis of the metabolites, thus qualitative and quantitative results of the microalgae metabolites under different cultural conditions are acquired. The method has important meanings for promoting the research of microalgae metabolism.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Identification method and equipment for sensibility of bacteria on antibiotic
InactiveCN103725747AShorten the timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms and particularly relates to an identification method and equipment for sensibility of bacteria on antibiotic. The method comprises the following steps: respectively carrying out antibiotic induction on known sensitive bacteria, intermediate sensitive bacteria and drug-resisting bacteria; extracting intracellular metabolites; carrying out mass spectrometry on the intracellular metabolites to obtain a mass spectrum pattern; converting all information of the mass spectrum pattern into a characteristic peak form and carrying out a clustering analysis on a corresponding metabolite wave peak value to respectively obtain clustering patterns of strains which are sensitive, intermediately sensitive and drug-resisting; removing wrongly-classified strains and storing in a database; treating bacteria to be detected by the same steps and combining the metabolite wave peak values of the bacteria to be detected with the obtained database; and reclassifying to obtain the positions of the bacteria to be detected in the clustering patterns, so as to obtain the antibiotic sensibility of the bacteria to be detected. According to the identification method and equipment for the sensibility of the bacteria on the antibiotic, the time for identifying is shortened.
Owner:佟雪梅
Intracellular metabolic flux analysis method using substrate labeled with isotope
InactiveUS8510054B2Low costMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingTime courseCulture cell
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Cell-metabonomics-based difference metabolite metabolic pathway of rubusoside lipotoxicity resistance and research method
InactiveCN108414635AComprehensive evaluationEffective evaluationComponent separationStudy methodsInsulin secreting adenoma
The invention discloses a cell-metabonomics-based difference metabolite metabolic pathway of rubusoside lipotoxicity resistance and a research method, relates to research methods of natural plant drugeffective component action mechanisms, and aims to solve the problem that an existing single pharmacology method cannot systematically and comprehensively evaluate the natural plant drug effective component action mechanisms. The method includes the steps of firstly, using ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrum technology to detect and analyze palmitic acid induced rateinsulin oncocyte and rubusoside intervened intracellular metabolites; secondly, screening 12 potential lipotoxicity related difference metabolites, and identifying; thirdly, screening four metabolic pathways of the rubusoside lipotoxicity resistance and related enzymes and genes on the pathways, and analyzing. The method can comprehensively, efficiently and fast evaluate the rubusoside lipotoxicity resistance action mechanism from cell level in a bias-free manner, and a demonstrative basis is provided for natural plant drug effective component cell metabonomics and action mechanism illustration.
Owner:GUANGXI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for identifying intracellular small molecule metabolites
InactiveCN109870498AWide linear rangeEasy to operateMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMass numberSmall molecule metabolism
The invention provides a method for identifying intracellular small molecule metabolites. The qualitative analysis of the metabolites is performed according to an exact mass number and chromatogram matching, and the metabolite is relatively quantified according to an abundance of the chromatogram. The procedure of the analysis method is as follows: washing cultured adherent cells with PBS quicklyand then quenched with liquid nitrogen; then adding an extract liquor to extract all metabolites in the cells; searching KEGG and METLIN databases to obtain parameters of the metabolic pathway main metabolites such as the ion pair and collision energy and the like, and establishing a detection and analysis method of the small molecule metabolites; and performing qualitative and quantitative analysis on the intracellular metabolites by using tandem quadrupole linear ion trap high performance mass spectrometry (Q-Trap) combined with quadrupole-time of flight mass spectrometry (Q-TOF). The methodfor identifying the intracellular small molecule metabolites can be used for qualitative and quantitative analysis of metabolites in cell samples; the range of the identified metabolites detected bythe method is wider; and the linear range of the metabolites is wider; therefore, the problem that the qualitative analysis of the metabolites in the prior art is difficult and the analysis requires alarge number of standards for comparison is effectively solved.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for evaluating influence of GFP gene transfection on hPMSCs metabonomics based on CILLC-MS
ActiveCN107703219AFully brokenRelease fullyComponent separationMesenchymal stem cellIntracellular metabolite
The present invention relates to a placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell metabolite extraction and detection technology. A purpose of the present invention is to provide a method for evaluating the influence of GFP gene transfection on hPMSCs metabonomics based on CILLC-MS. According to the present invention, the differential metabolites and the differential metabolic pathways before and after transfection are further analyzed by extracting and by detecting and quantitating the intracellular metabolites of hPMSCs before and after GFP gene transfection, and the biological safety of green fluorescent protein in labeling and tracking of mesenchymal stem cells is evaluated from the perspective of metabonomics; the analysis process for comparing the metabonomics difference between hPMSCs and GFP-hPMSCs is firstly created, and the two sample preparation methods are combined for the extraction of the stem cell metabolites, such that the intracellular metabolites are completely released; by combining the CIL LC-MS in the detection of the stem cell intracellular metabolites, the precise quantitative analysis of intracellular metabolites is achieved, and the identification type of metabolites is substantially increased; and with the method, the sensitivity, the reliability and the repeatability of the results are substantially improved, and the operation-induced non-parallelism and theoperation-induced contingency are avoided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Full-automatic accurate-timing quantitative quick-sampling equipment capable of in-place inactivation
InactiveCN103243025AGuaranteed to reflect the truthAvoid conversionMicroorganism based processesBiological material testing proceduresSingle sampleDrive shaft
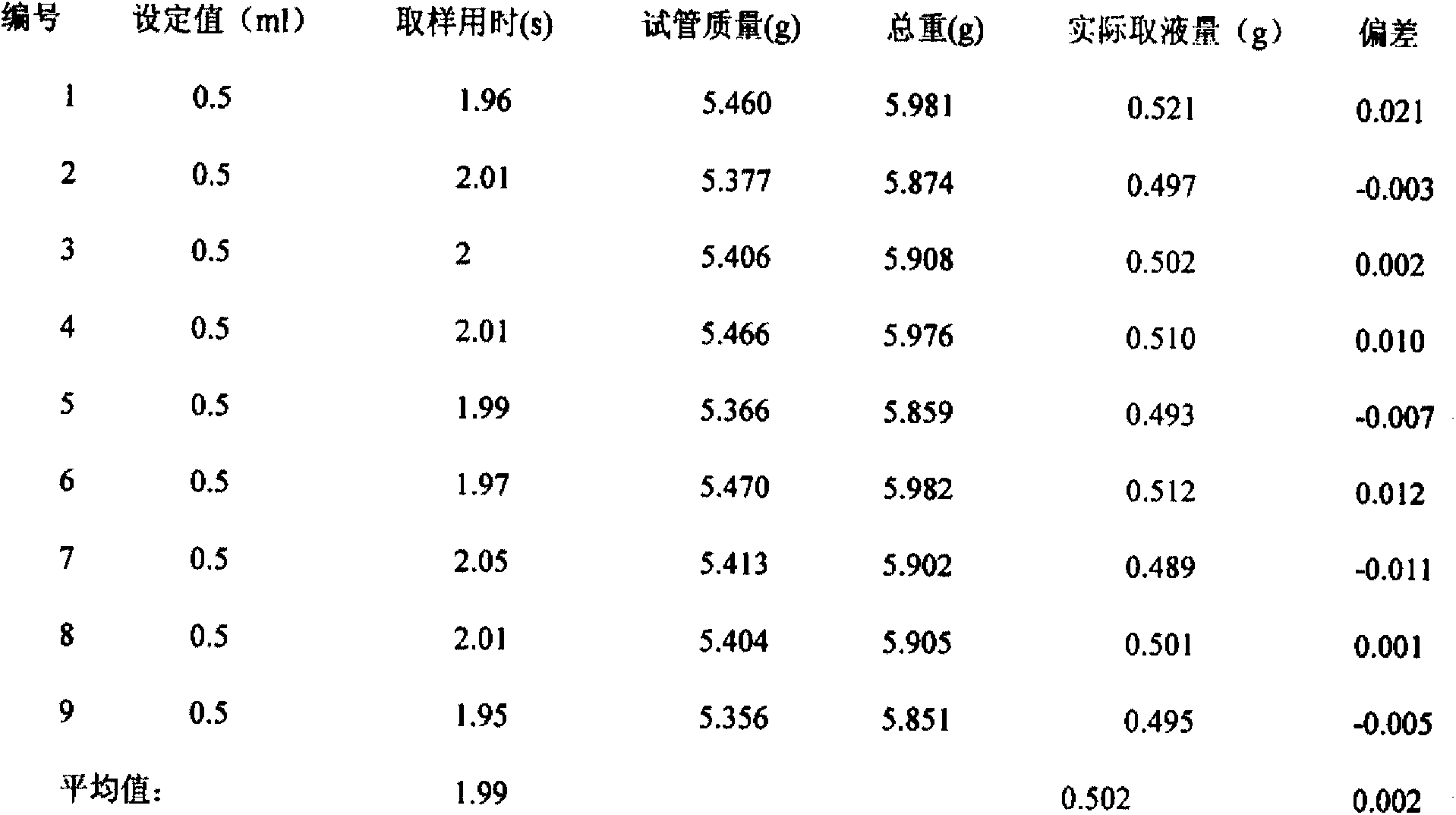
The invention relates to full automatic accurate-timing quantitative quick-sampling equipment capable of in-place inactivation. The equipment comprises a mechanical transmission device, a sampling device and a control device, wherein the control device is used for controlling the sampling device and the mechanical transmission device in a linkage manner; the mechanical transmission device comprises an electric motor, a transmission shaft, a sampling turntable and a liquid storage tank; the electric motor is used for driving the rotation of the sampling turntable through the transmission shaft; a plurality of positioning sampling holes for placing sampling pipes are formed in the sampling turntable; the liquid storage tank is arranged below the sampling turntable; and the control device is used for firstly positioning the positions of the positioning sampling holes in the sampling turntable and then controlling the sampling device to quantitatively sample during sampling. Compared with the prior art, the device has the advantages that the whole process of quick, quantitative, continuous and timing sampling and quenching is completed in a few seconds, full automatization can be realized during the whole process, and a single sample is once sampled within one second, so that the true situation of cells can be really reflected by cytozoic metabolites after quenching, and the cytozoic metabolites are effectively prevented from being transformed and degraded.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
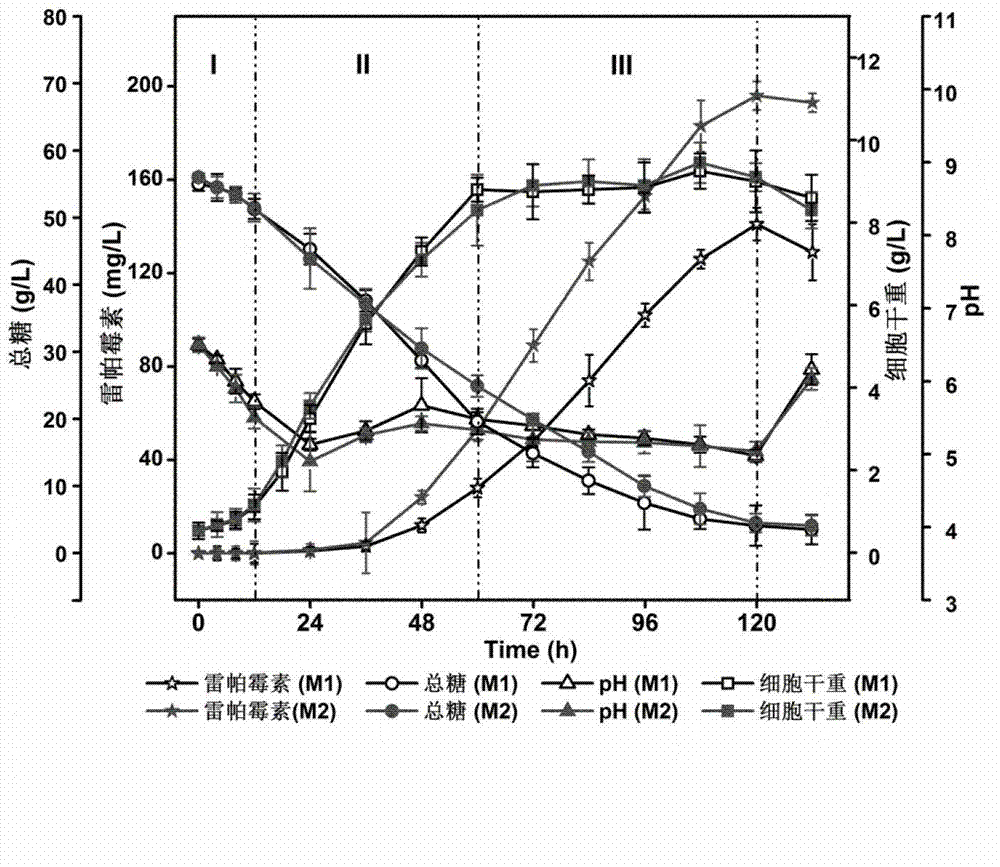
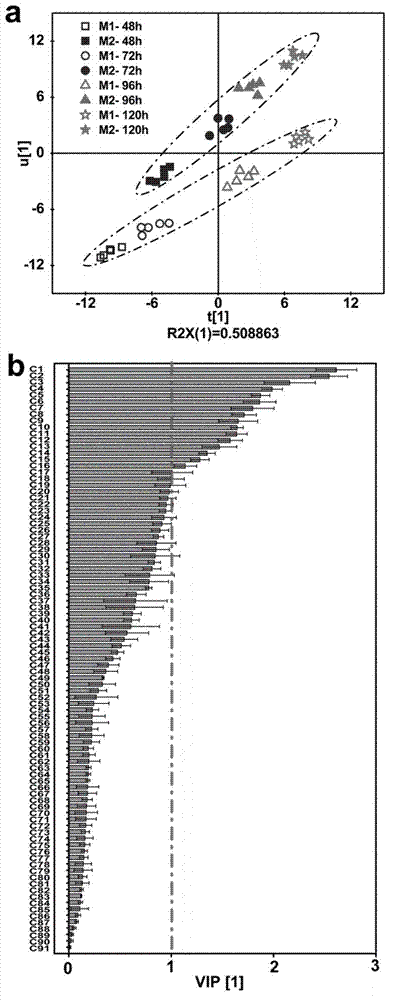
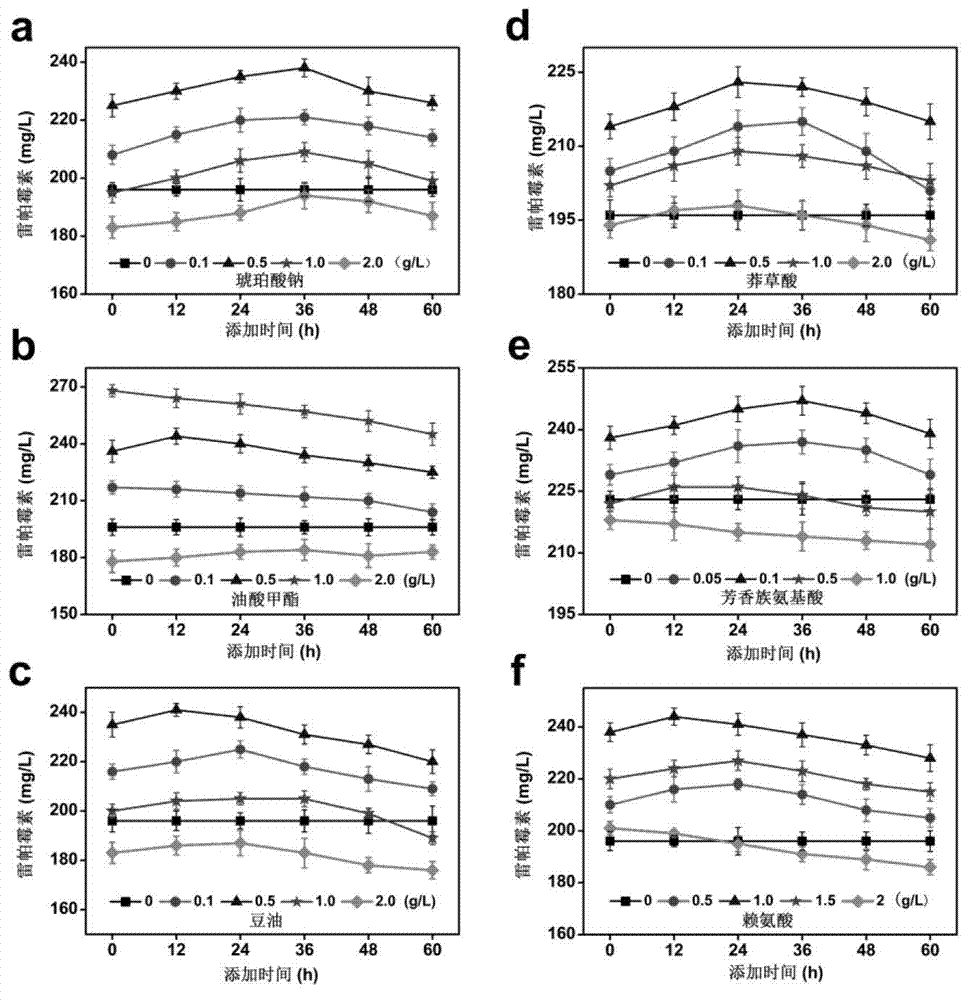
Method for optimizing fermentation medium by improving rapamycin production by using metabolic profiling analysis
InactiveCN103088104AIncrease productionComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementPrimary metabolismMetabolic profile
The invention provides a method for optimizing a fermentation medium by improving rapamycin production by using metabolic profiling analysis, which researches dynamic changes and differences of bacteria intracellular metabolites under the culture conditions of initial fermentation medium and optimized fermentation medium by using the methods of dynamic detection and metabolic profiling analysis. The analysis result of partial least squares indicates that the bacteria primary metabolite profile and the rapamycin production have correlation and a further dynamic adding measure is provided to the medium by analyzing the dynamic changes of the key compounds combining related processes. Due to the research of S.hygroscopicus U1-6E7 fermentation medium, the rapamycin production is improved from 196mg / L to 307mg / L and is improved by 56.6%, which indicates that rational guidance of optimization of fermentation mediums by dynamic detection combining the metabolite profile analysis method is capable of successfully improving fermentation level of antibiotic and providing a new idea for optimization of fermentation mediums.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Metabonomics technology-based persistent organic pollutant cytotoxicity action mechanism research method
InactiveCN107643390ARich varietyGood quantitative effectComponent separationBiological testingStatistical analysisCytotoxicity
The present invention discloses a metabonomics technology-based persistent organic pollutant cytotoxicity action mechanism research method. According to the method, HepG2 cells are exposed to organicpollutants, the intracellular and extracellular culture liquid metabolites can be effectively analyzed by using UHPLC / Q-Trap MS, the influence of the organic pollutants on the cell metabolism pathwaycan be intuitively reflected by combining statistical analysis and metabolic pathway analysis, and by using a biological detection method, the activity of rate-limiting enzyme related to the metabolicpathway is further rapidly analyzed. According to the present invention, the organic pollutant cytotoxicity action mechanism is clarified according to the intracellular metabolite content change andthe activity change of the rate-limiting enzyme in the metabolic pathway, and the pollutant toxicity action mechanism evaluation method is constructed based on molecular biology, and the metabonomicstechnology-based persistent organic pollutant cytotoxicity action mechanism research method has advantages of easy operation, rapid detection, high sensitivity, strong selectivity, good repeatability,comprehensive information acquisition and the like.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Extraction and analysis method for metabolites in tribonema cells
InactiveCN107860857AEasy to operateHigh sensitivityComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationWater bathsN-methyl-N-(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide
The invention belongs to the technical field of analysis of microalgae metabolite components, and particularly relates to an extraction and analysis method for metabolites in tribonema cells. The extraction and analysis method comprises the following steps: extracting pretreated tribonema cells in an excessive solvent, centrifugally collecting supernatant after extraction, adding a pyridine solution of methoxylamine hydrochloride into the supernatant, uniformly mixing the supernatant and the pyridine solution, and putting the mixture into a thermostatic water bath at the temperature of 30 to 40 DEG C for 80 to 90 minutes; after the water bath reaction is finished, adding N-methyl-N-trimethylsilyl trifluoroacetamide (MSTFA) into a reaction system for uniform mixing, and then incubating themixture in a thermostatic water bath at the temperature of 37 to 40 DEG C for 30 to 80 minutes, thus obtaining a tribonema metabolite derived sample; carrying out metabolite detection on the sample byusing a gas chromatograph-mass spectrometer so as to qualitatively determine effective components. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that small molecule intracellular metabolites can be extracted from the tribonema cells, the yield is high, and a reference can be provided for extracting active substances from the tribonema cells; in addition, the extraction and analysis operation is simple.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for detecting amino acid in intracellular and extracellular fluids by gas chromatography-mass spectrum
The invention relates to a method for detecting amino acid in intracellular and extracellular fluids by gas chromatography-mass spectrum, belonging to a biochemistrical examination and determination technology field. The detection method comprises the following steps of: (1) high-speed centrifuging fermentation broth, and respectively collecting cells and the extracellular liquid; (2) preparing metabolin sample of the cell, cleaning the collected thallus with normal saline, ultrasonically breaking thallus after the thallus is dissolved by a cold methanol, extracting under a low temperature, centrifugally collecting an extracted supernatant, adding an internal standard substance, and vacuum-drying under a low temperature; (3) preparing a extracellular liquid sample, removing protein in the extracellular liquid by acetonitrile, vortex-oscillating, then centrifugally collecting a supernatant, adding an internal standard substance, and vacuum-drying under a low temperature; (4) deriving the sample, adding a sugar derivating agent and an amino acid derivating agent; and (5) analyzing by gas chromatography-mass spectrum, and acquiring data. The method provided by the invention has advantages of simple sample treatment, simple operation, short detection time, high sensitivity, and high detection result repeatability, and can implement preparation of a plurality of samples.
Owner:陈东
Method for selecting patients responsive for cancer treatments
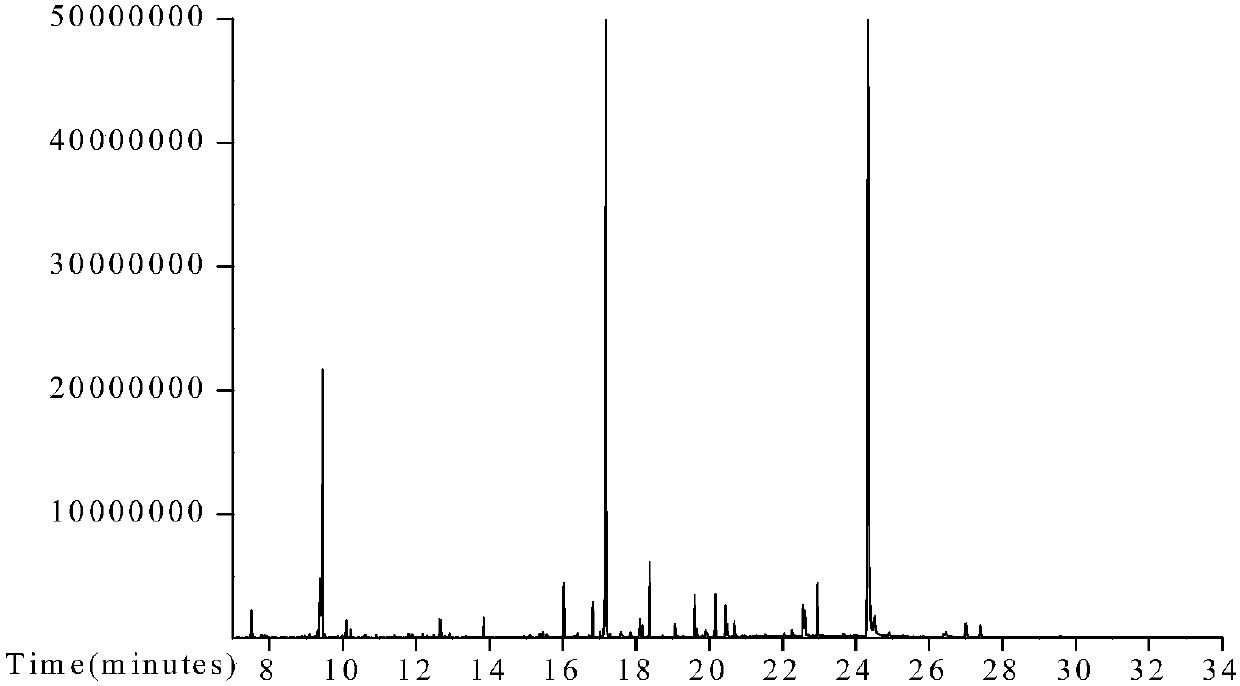
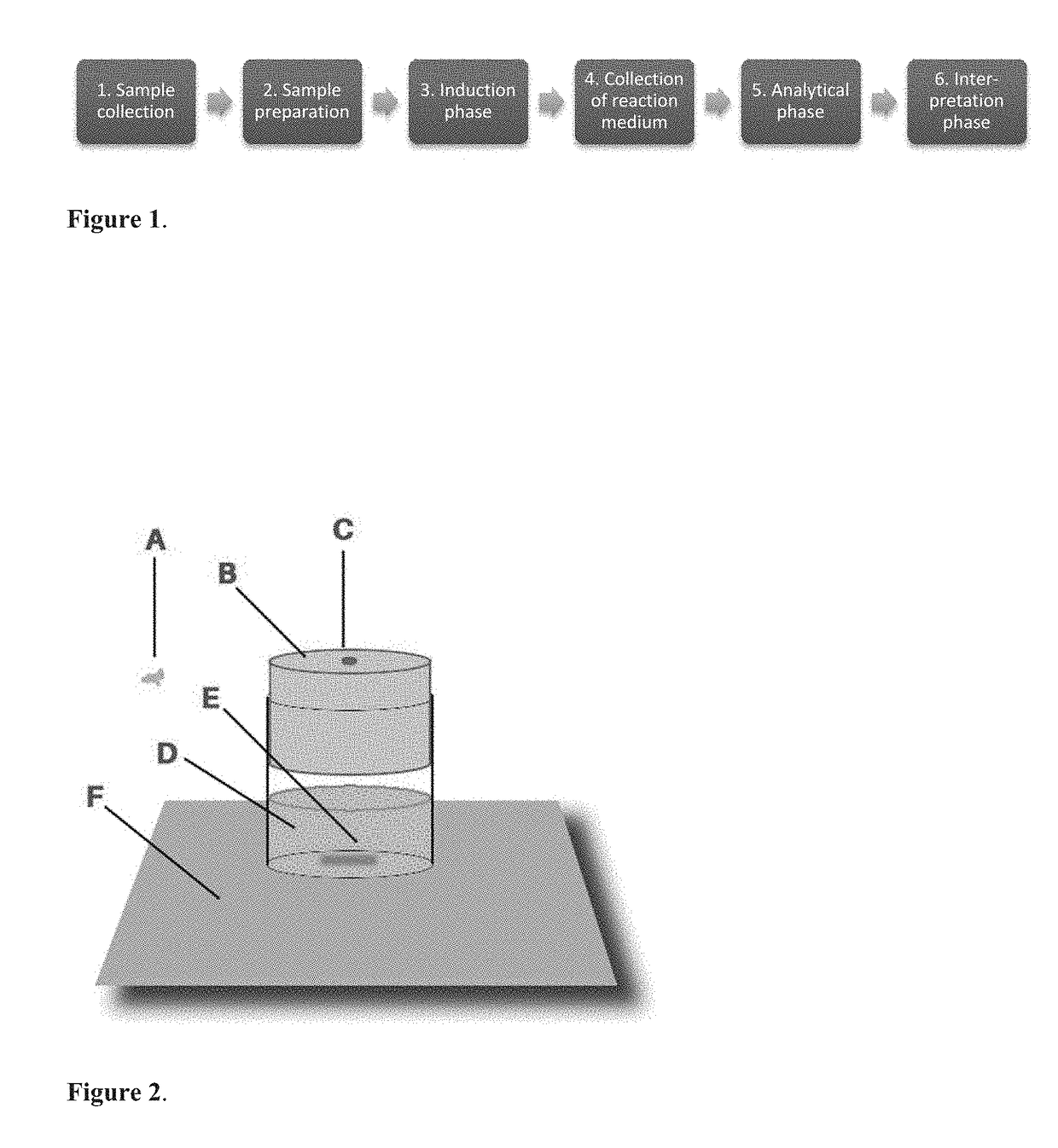
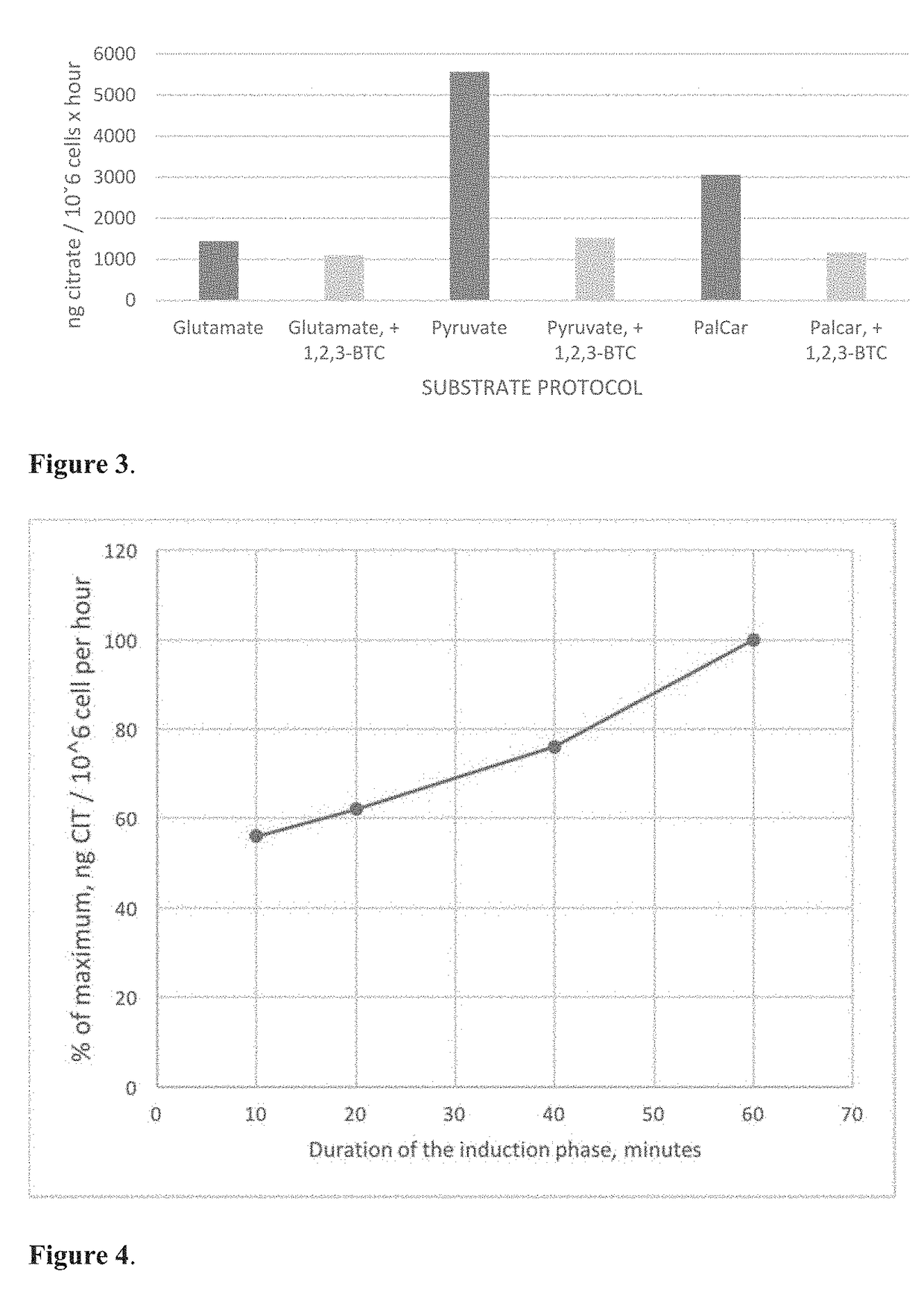
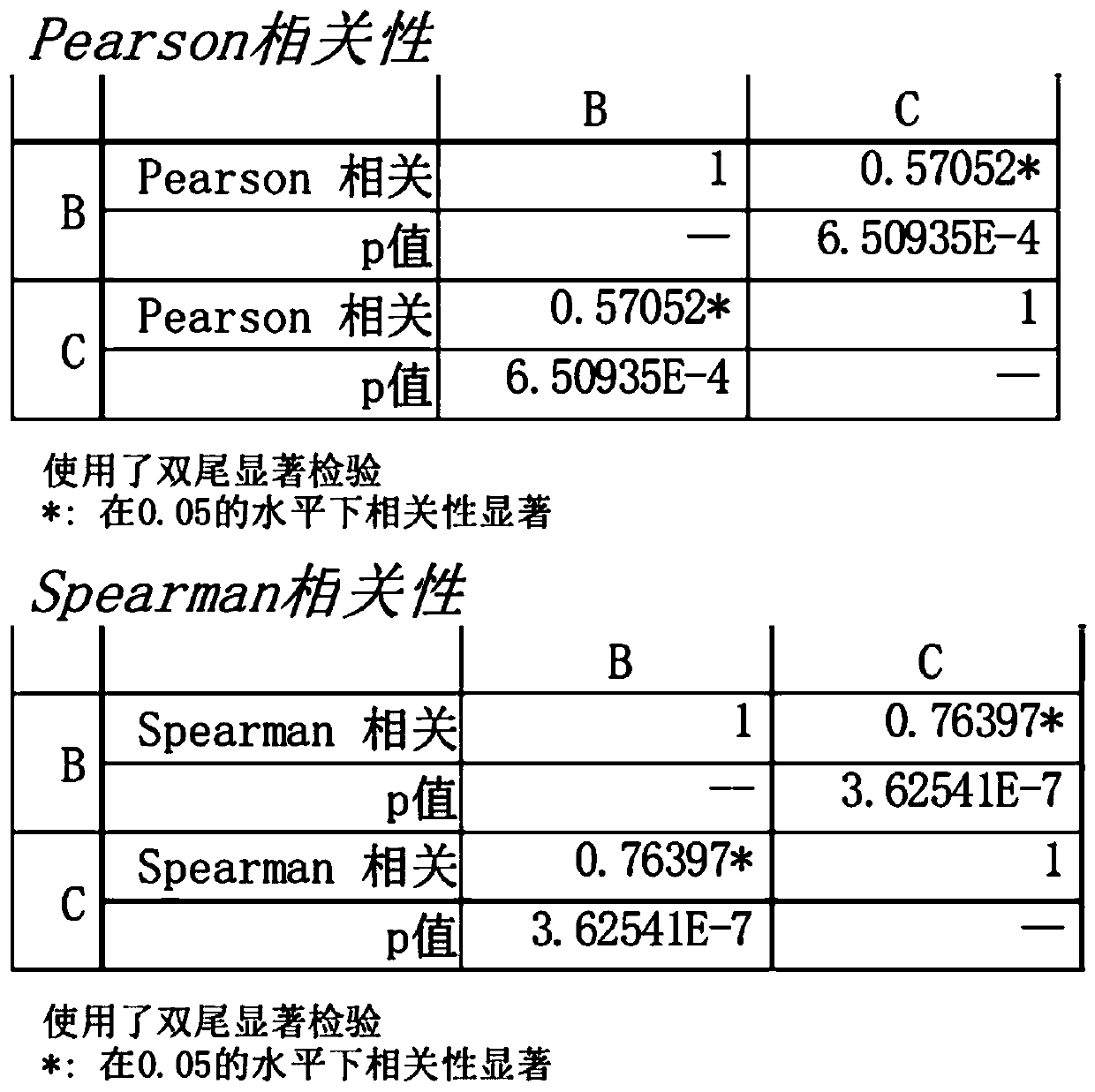
The present invention is directed to a method of quantifying intracellular metabolite effluxes in permeabilized cancer cells for selecting cancer patients responsive for a cancer treatment, the method comprising the steps of: a) providing a sample of cancer cells taken from a patient; b) permeabilizing said cancer cells; c) incubating said permeabilized cancer cells in a reaction medium for a period of time allowing biological activity of intracellular organelles and accumulation of metabolites produced by said activity into the reaction medium in the presence of a substrate or substrates relating to a metabolite efflux or effluxes of interest, wherein said substrates used are at least glutamine and pyruvate; d) determining the quantity of metabolites relating to said metabolite efflux or effluxes of interest accumulated in the reaction medium during step c); and e) comparing the amounts of metabolites determined in step d) to equal measurements performed on control samples of the same tissue type and assessing the aggressiveness of the cancer cells or the treatment response of the cancer cells to a drug affecting a metabolic pathway or pathways relating to said metabolite efflux or effluxes of interest.
Owner:MITOGRO OU
Method for obtaining metabolic flux of intracellular central carbon metabolic pathway in unsteady state of metabolic steady-state isotopes
PendingCN111575336AAccurate Abundance DataAccurate speedComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementIsotopic labelingCarbon metabolism
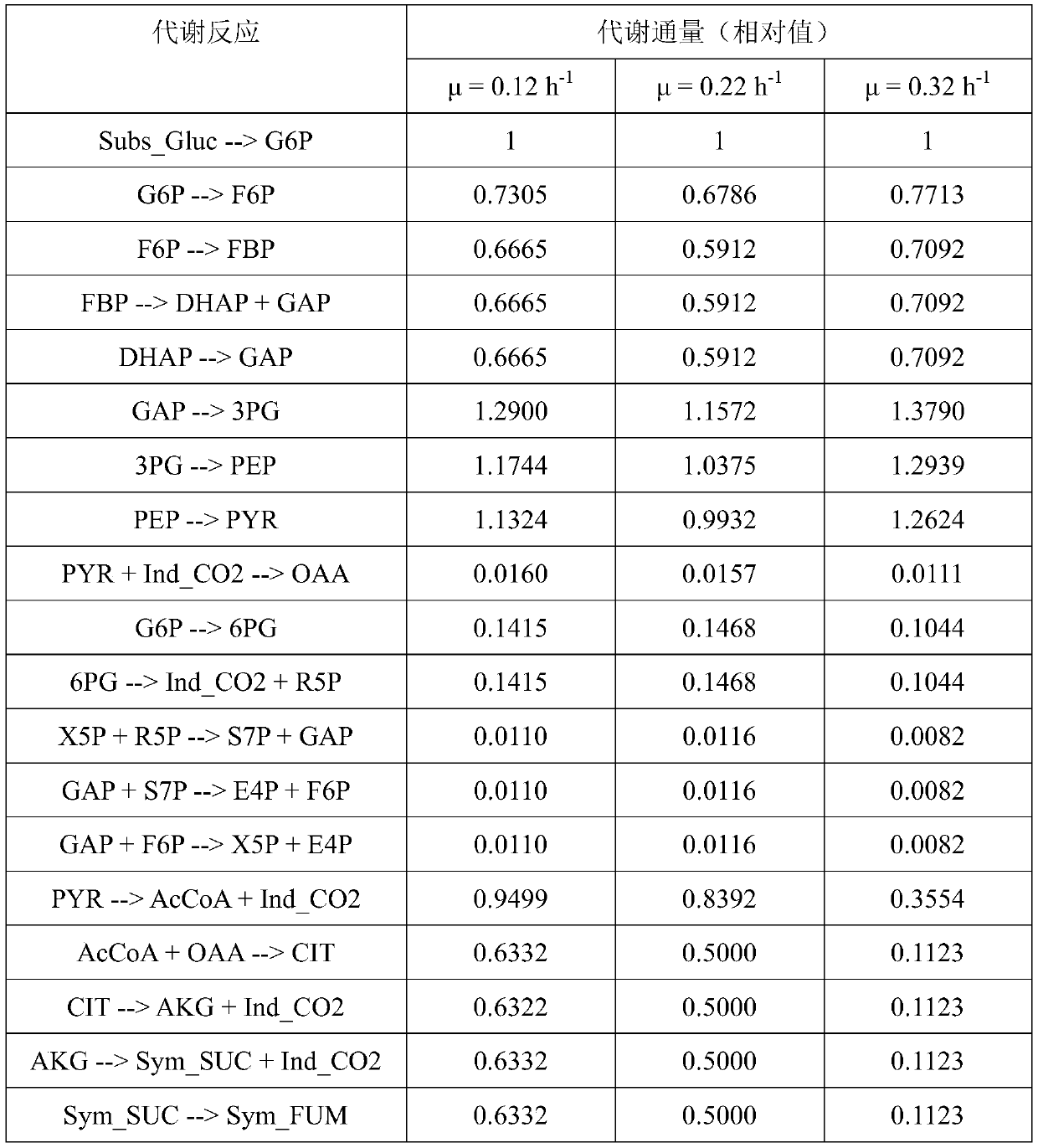
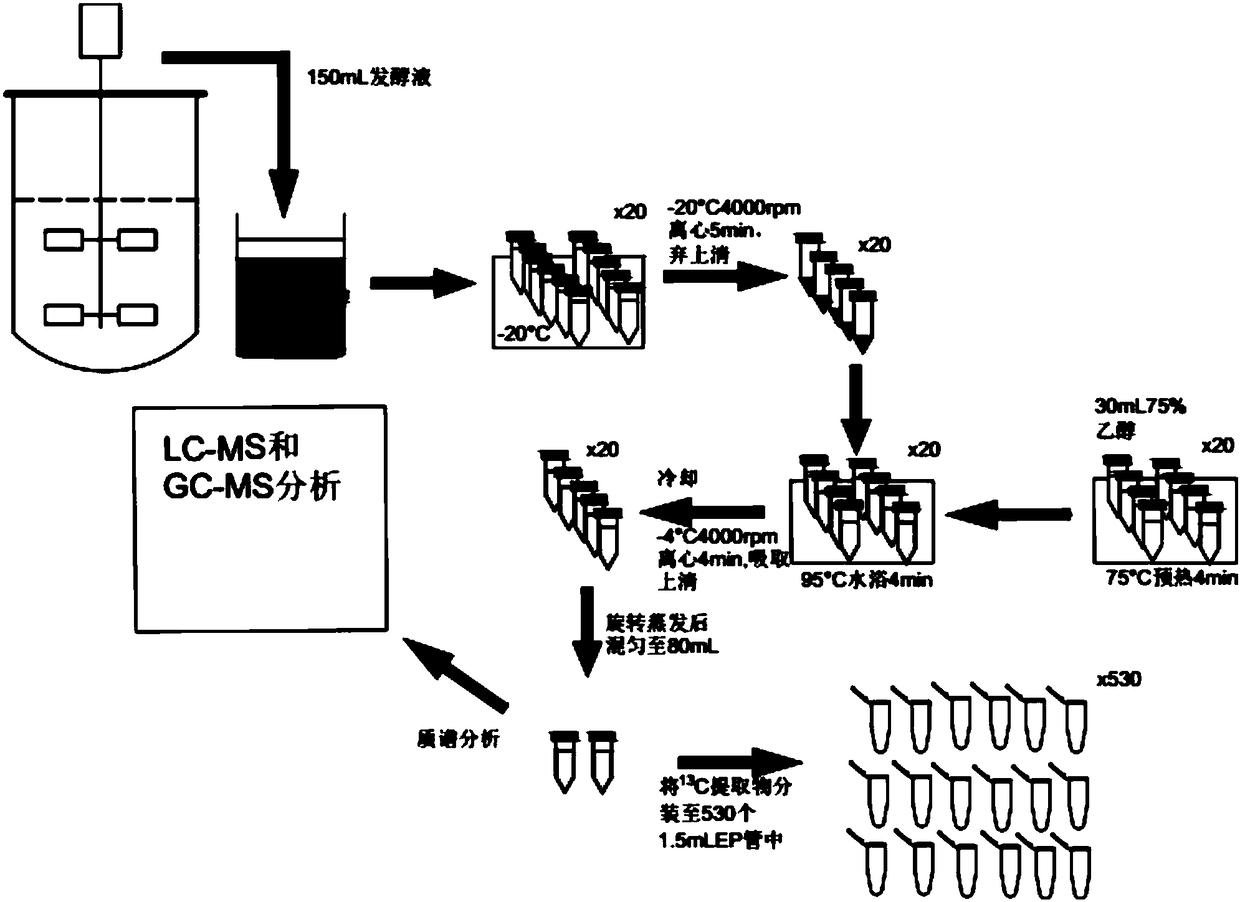
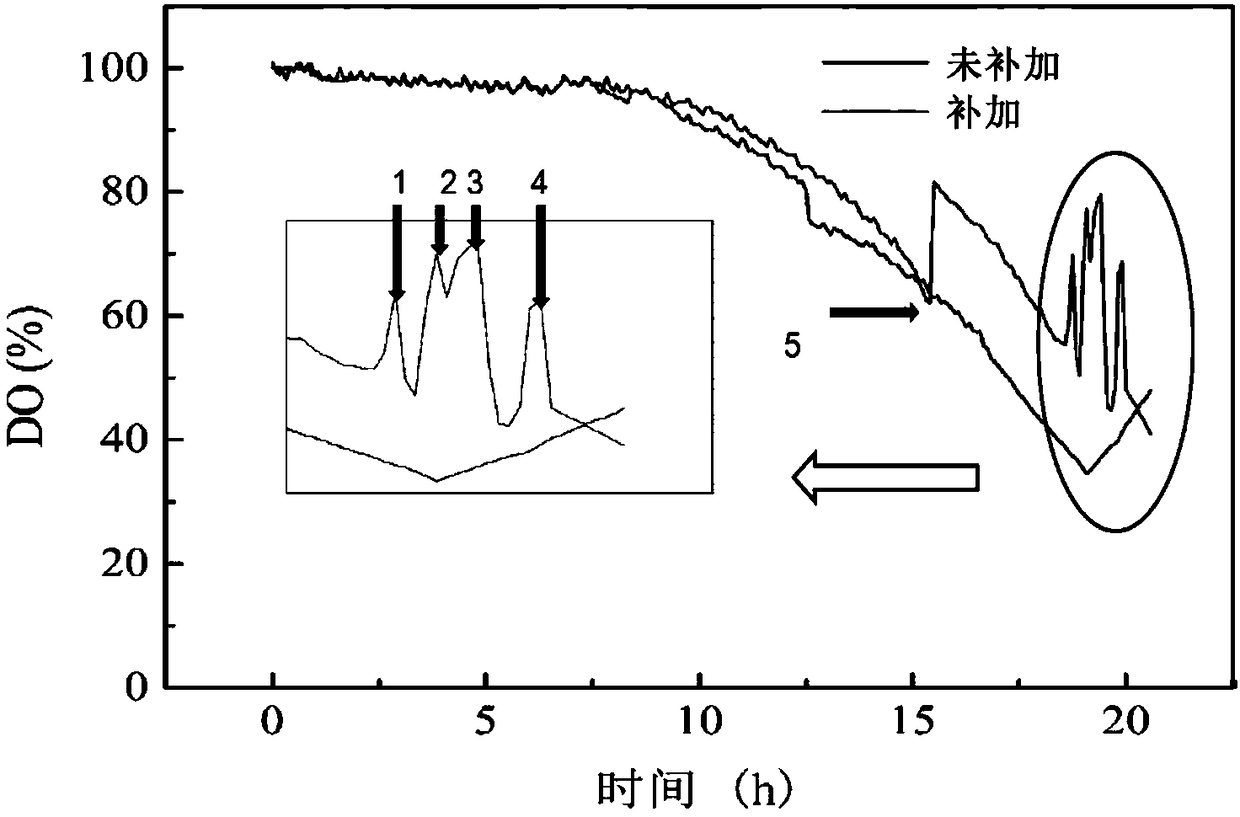
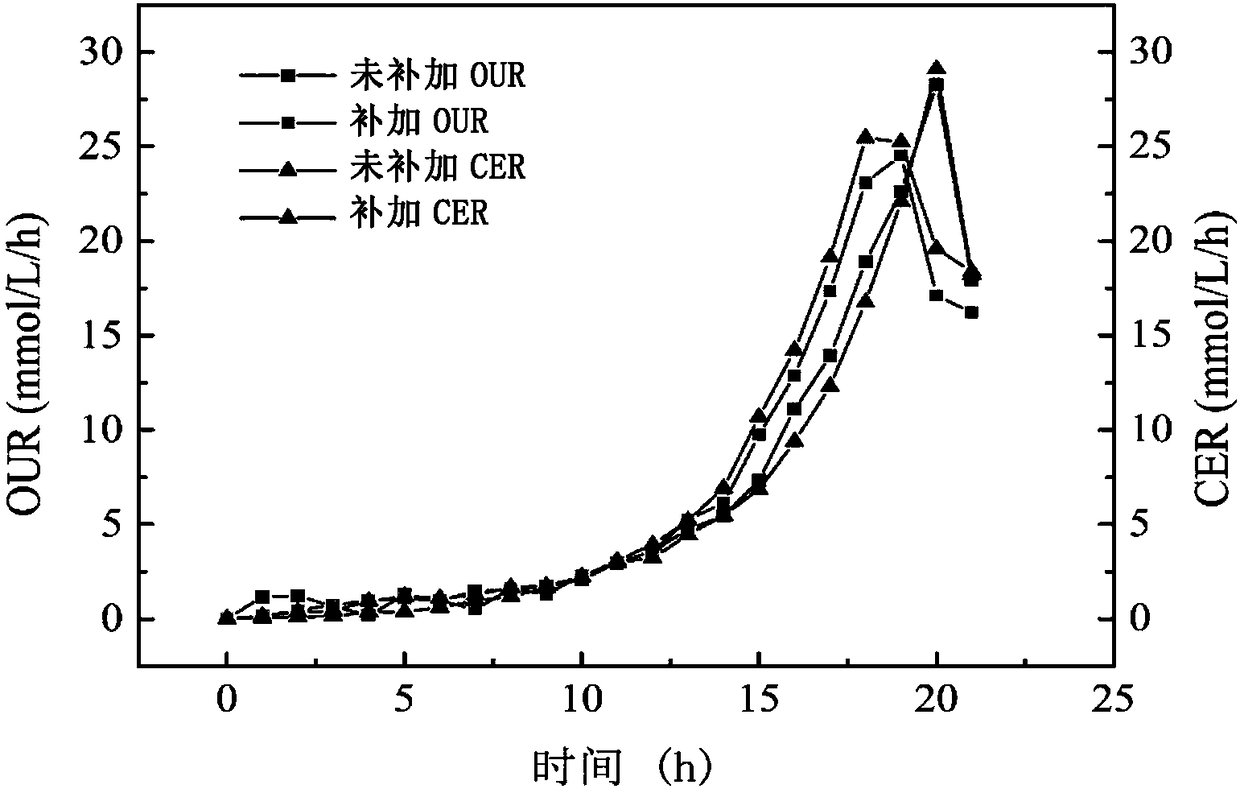
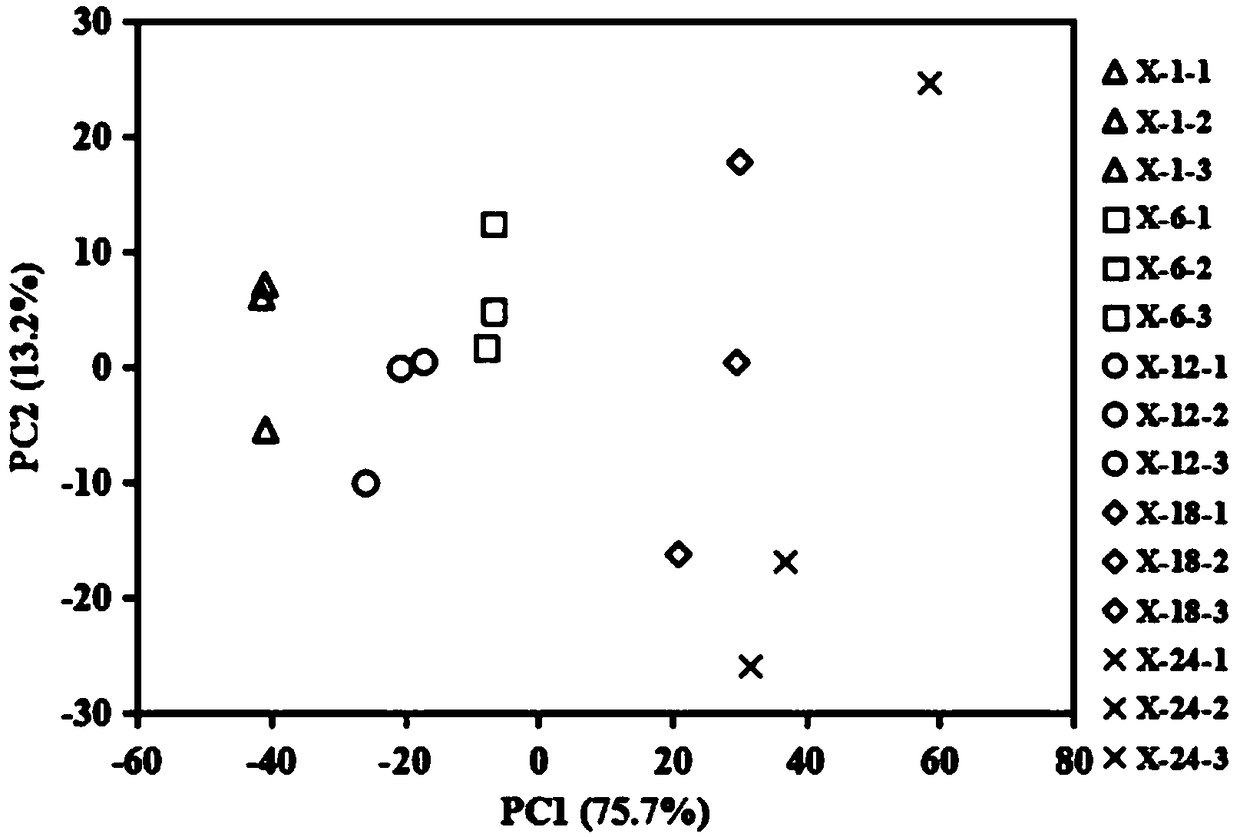
The invention discloses a method for obtaining metabolic flux of an intracellular central carbon metabolic pathway in an unsteady state of metabolic steady-state isotopes. The method adopts a batch culture module, a constant culture module, a sampling module and a sample processing and analyzing module. When the OUR and the CER in the batch culture module decline at the same time, culture is performed in the constant culture module. The constant culture module specifically adopts a process of feeding a nutrient solution containing no isotope labeling substrate, starting waste discharge at thesame time, carrying out constant culture, until the microbial cells are in a metabolic steady state, feeding a nutrient solution containing the isotope labeling substrate, and keeping culture conditions unchanged; and when the isotope labeling substrate flows into a reactor, starting rapid and continuous sampling, and entering the sampling module at the same time. According to the method, a seriesof fermentation liquor samples are obtained in a short time, and then the samples are processed and analyzed to obtain accurate intracellular metabolite isotope abundance data; and the method plays acrucial role in calculating the metabolic flux.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry detection method for intracellular carbohydrates and organic acids
InactiveCN103675129AEasy to analyzeShorten the timeComponent separationGas phaseGas chromatography–mass spectrometry
The invention relates to a gas chromatography-mass spectrometry detection method for intracellular carbohydrates and organic acids, and belongs to the technical field of biochemical detection and testing. The gas chromatography-mass spectrometry detection method comprises the following steps: (1) taking a fermentation liquid for high speed centrifugation, and respectively collecting cells and an extracellular fluid; (2) preparing an intracellular metabolite sample, to be more specific, using normal saline to clean collected bacterium, dissolving in cold methyl alcohol for ultrasonication and low temperature extraction, collecting an extraction supernatant by centrifugation, adding an internal standard, and performing vacuum drying; (3) performing sample derivatization, to be more specific, adding a carbohydrate derivatization agent and an amino acid derivatization agent; and (4) performing gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis and data acquisition. The gas chromatography-mass spectrometry detection method has the advantages of simple sample treatment, convenient operation, short carbohydrate and organic acid detection time, high sensitivity, high test result repeatability, multiple-sample preparation and the like.
Owner:LIUZHOU LIANHAI TECH
Detection method for sugar in intracellular and extracellular fluids through gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
The invention relates to a detection method for sugar in intracellular and extracellular fluids through gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, and belongs to the technical field of biochemistry examination and determination. The detection method comprises steps: first, a fermentation solution is taken and centrifuged at a high speed, and cells and an extracellular fluid are collected respectively; second, intracellular metabolite samples are prepared, the collected thalli are washed in normal saline, dissolved in cold methanol, and subjected to ultrasonication, low temperature extraction, and centrifugation collection, the supernate is extracted, internal standard substances are added, and vacuum drying is carried out at a low temperature; third, extracellular fluid samples are prepared, proteins in the extracellular fluid are removed with acetonitrile, vortex oscillation is carried out, then centrifugation is carried out, the supernate is collected, internal standard substances are added, and vacuum drying is carried out at a low temperature; fourth, sample derivatization is performed, and sugar derivative agents and amino acid derivative agents are added; fifth, gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis and data collection are carried out. The method has advantages of simple sample processing, easy and simple operation, short detection time, high sensitivity, high repeatability of detection results, realization of preparation of multiple samples and the like.
Owner:LIUZHOU LIANHAI TECH
Extraction and analysis method for free amino acid and fatty acid in adherent cells
The invention discloses an extraction and analysis method for free amino acid and fatty acid in adherent cells. The method mainly comprises the steps of: subjecting adherent cells to adherent culture in a culture tray, then subjecting a sample to rapid washing and conducting liquid nitrogen quenching, adding a small amount of water to perform ultrasonication, carrying out lyophilization, then adding MTBE for extraction, then adding water to carry out centrifugation and taking the supernatant, performing blow-drying with nitrogen, then using acetonitrile to make the volume to a constant level, and then carrying out liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS) analysis on the fatty acid component, extracting the remaining part and further adding MTBE and methanol to conduct extraction, performing centrifugation, and taking the lower layer amino acid component to perform LC-MS analysis directly. The method provided by the invention adopts LC-MS to analyze free amino acid and fatty acid components, and utilizes a small sample size to realize simultaneous extraction of amino acid and fatty acid components. Compared with the conventional fatty acid GC-MS analysis method, the method has no need of derivatization, greatly simplifies the sample pretreatment process, and at the same time provides a reference method for extraction of adherent intracellular metabolites. The analysis method can be applied to analysis of free amino acid and fatty acid in other media.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for increasing amount of metabolites in fermentation cells and preparing IDMS standard
ActiveCN108624516AIncrease the amount of metabolitesFungiPreparing sample for investigationBatch fermentationPhases of clinical research
The invention relates to a method for increasing the amount of metabolites in fermentation cells and preparing an IDMS standard. According to the invention, a manner of supplementing a substrate at appropriate time on the basis of batch fermentation is employed for instantaneous supplementation of the substrate in multiple batches, so intracellular metabolites present dynamic response, and the concentrations of a part of the intracellular metabolite are increased; and the fermentation cells are collected at the stage, so a metabolite standard with a <13>C label is efficiently prepared, and theconcentration of the standard is greatly increased.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for reinforcing coacervation algae removal and controlling release of intracellular substances
ActiveCN102344190BEasy to handleSimple methodWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationWater/sewage treatment by oxidationEutrophicationFiltration
The invention which belongs to the technical field of drinking water treatment especially relates to a method for reinforcing the coacervation algae removal and controlling the release of intracellular substances in the process of high algae water treatment. The invention which aims at the eutrophication pollution of surface water sources of lakes, reservoirs and the like provides a method for improving the algae cell removal effect of technologies of coagulation, deposition and filtration of a water work with the combined action of potassium permanganate and a ferric salt, wherein the appropriate oxidation effect of potassium permanganate inactivates and inhibits the activity of algae cells and controls the release of intracellular metabolites, and In situ MnO2 which is in situ generatedthrough a reduction reaction of potassium permanganate deposits on the surface of the algae cells to improve the settlement performance of the algae cells; and the electrical neutralization of the ferric salt allows the potential of the surface of the algae cells to be improved, and In situ Fe(OH)3 which is in situ generated through a hydrolysis reaction of the ferric salt deposits on the surfaceof the algae cells to improve the potential and the settlement performance of the surface of the algae cells. The method of the invention which is mainly applied to the purification in the drinking water work can also be applied to landscape water treatment which aims at the landscape water reuse and the water source pretreatment of the eutrophication water to inhibit the growth of the algae cells.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
An analysis method for a Corynebacterium glutamicum metabolome
InactiveCN108776186AFacilitating Metabolic ResearchComponent separationMultivariate statisticsStatistical analysis
An analysis method for a Corynebacterium glutamicum metabolome is provided. The method includes Corynebacterium glutamicum cell collection and quenching; intracellular metabolite extraction; metabolite derivatization; and sample analysis through GC-Ms and multivariate statistics to obtain a metabolome result finally. Analysis measures for the Corynebacterium glutamicum metabolome relate to metabolic reaction terminating, metabolite extraction, metabolite identification and quantitative and statistical analysis, thus obtaining qualitative and quantitative results of metabolites in different stages in a Corynebacterium glutamicum fermentation process, and providing a way for analysis of the Corynebacterium glutamicum metabolome. The method is of great significance for promoting metabonomic and metabolic engineering researches of Corynebacterium glutamicum.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for detecting organic acid in intracellular fluid and extracellular fluid through gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
InactiveCN103698449AEasy to analyzeShorten the timeComponent separationGas phaseGas liquid chromatographic
The invention relates to a method for detecting organic acid in intracellular fluid and extracellular fluid through gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, which belongs to the technical field of biochemical test and measurement. The detecting method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: (1) high speed centrifuging fermentation liquor, and respectively collecting intracellular fluid and extracellular fluid; (2) preparing an intracellular metabolin sample, cleaning the collected thallus through normal saline, dissolving the thallus in cold methanol, ultrasonic crushing, low temperature extracting, centrifuging to collect extract supernatant, adding internal standard substance, and vacuum drying at a low temperature; (3) preparing an extracellular fluid sample, removing protein in the extracellular fluid through acetonitrile, vortex oscillating, centrifuging to collect supernatant, adding internal standard substance, and vacuum drying at a low temperature; (4) deriving the sample, and adding a sugar derivating agent and an amino acid derivating agent; and (5) carrying out gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis and collecting data. The detecting method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple sample treatment, simple and convenient operation, short detection time, high sensitivity, high repeatability of test results, capability of preparing a plurality of samples, and the like.
Owner:陈东
Method for improving microalgae cultivation condition by using metabonomics so as to improve oil-producing capacity
ActiveCN102517349BIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a method for improving a microalgae cultivation condition by using metabonomics so as to improve the oil-producing capacity. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) detecting intracellular metabolites in microalgae; (2) analyzing the oil-producing capacity of the microalgae; (3) performing partial least squares (PLS) analysis; and (4) process analysis. The oil-producing process of the microalgae, an intracellular metabolism change rule and important metabolites in the oil-producing process can be researched wholly by the method, and the change rule of the metabolism levels lays a base for the internal mechanism of the oil-producing process, so a theoretical base is laid for further optimizing a microalgae cultivation process and improving the grease yield. A new concept and a new method are provided for the research on other oil-producing microorganism cultivation processes.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Pre-treatment method for detecting bacterial metabolomics through gas chromatography-mass spectrometer (GC-MS)
InactiveCN109576172AThe result is validGood energyBacteriaComponent separationGas chromatography mass spectrometerIntracellular metabolite
The invention discloses a pre-treatment method for detecting bacterial metabolomics through a gas chromatography-mass spectrometer (GC-MS), and belongs to the field of chemical analysis and detection.The pre-treatment method comprises the steps: culture of bacteria, quenching of bacterial liquid and extraction of intracellular metabolites; and a bacterial liquid sample is quenched through a mixture of methanol and aseptic water, the intracellular metabolites are extracted through a mixture of acetonitrile, isopropyl alcohol and aseptic water, cells are crushed and extracted repeatedly throughcombination of a tissue crusher and a low-temperature ultrasonic phase to obtain a pre-treatment sample, and detected substances can achieve full coverage and quantity maximization. The pre-treatmentmethod can be used for studying or solving key scientific problems such as bacterial toxin production mechanisms, and drug resistance generation and control, and application prospects are wide.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A method of extracting a microalga intracellular metabolite sample
A method of extracting a microalga intracellular metabolite sample is disclosed. The method includes rapidly deactivating intracellular enzymes by adopting an ice bath manner, performing ultrasonic disintegration with dichloromethane or chloroform, rapidly separating polar compounds, non-polar compounds, insoluble saccharides and protein, for subsequent metabonomical analysis, by adopting a dichloromethane (or chloroform)-methanol-water three-phase system. The method has characteristics of few operation steps, and capability of simultaneously measuring polar and non-polar intracellular components.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for detecting intracellular organic acid through gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
InactiveCN103698450AEasy to analyzeShorten the timeComponent separationGas chromatography–mass spectrometryGas phase
The invention relates to a method for detecting intracellular organic acid through gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, which belongs to the technical field of biochemical test and measurement. The detecting method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: (1) high speed centrifuging fermentation liquor, and respectively collecting cells and extracellular fluid; (2) preparing an intracellular metabolin sample, cleaning the collected thallus through normal saline, dissolving the thallus in cold methanol, ultrasonic crushing, low temperature extracting, centrifuging to collect extract supernatant, adding internal standard substance, and vacuum drying at a low temperature; (3) deriving the sample, and adding a sugar derivating agent and an amino acid derivating agent; and (4) carrying out gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis and collecting data. The detecting method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple sample treatment, simple and convenient operation, short organic acid detection time, high sensitivity, high repeatability of test results, capability of preparing a plurality of samples, and the like.
Owner:LIUZHOU LIANHAI TECH
Method for detecting amino acids, saccharides and organic acids in cells through gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
ActiveCN103675132AEasy to analyzeShorten the timeComponent separationGas phaseGas chromatography–mass spectrometry
The present invention relates to a method for detecting amino acids, saccharides and organic acids in cells through gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, and belongs to the technical field of biochemical analysis determination. The detection method comprises: (1) taking a fermentation broth, carrying out high-speed centrifugation, and respectively collecting cells and extracellular fluid; (2) preparing an intra-cellular metabolite sample, wherein the collected bacteria are washed by using physiological saline, dissolving is performed with cold methanol, ultrasound crushing and low temperature extraction are sequentially performed, centrifugation is performed to collect the supernatant, an internal standard substance is added, and vacuum drying is performed at a low temperature; (3) carrying out sample derivatization, wherein a saccharide derivatization agent and an amino acid derivatization agent are added; and (4) carrying out gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis and data acquisition. The method has advantages of simple sample treatment, easy operation, short amino acid, saccharide and organic acid detection time, high sensitivity, high reproducibility of the detection result, multiple sample preparation achievement and the like.
Owner:神州医疗科技股份有限公司 +1
Method for extracting micromolecular intracellular metabolite from nori
ActiveCN105817051AReduce pollutionHigh yieldOrganic compounds purification/separation/stabilisationSugar derivativesActive matterLiquid nitrogen
The invention discloses a method for extracting micromolecular intracellular metabolite from nori. The method includes the following steps that 1, nori is ground into powder with liquid nitrogen; 2, the powder is added into an extracting solution for extraction, and supernatant liquor is obtained; the supernatant liquor is extracted, a water phase is taken, and the micromolecular intracellular metabolite is obtained. By means of the method, the micromolecular intracellular metabolite can be extracted from nori, and the micromolecular intracellular metabolite is small in pigment pollution, high in yield and capable of serving as a reference for extracting active matter from nori; besides, the extracting method is simple and easy to implement.
Owner:南通中国科学院海洋研究所海洋科学与技术研究发展中心 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com