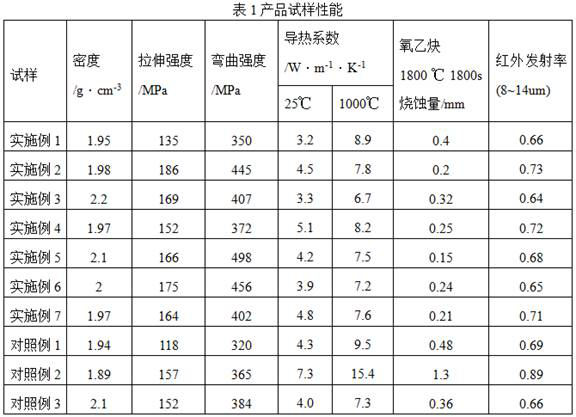
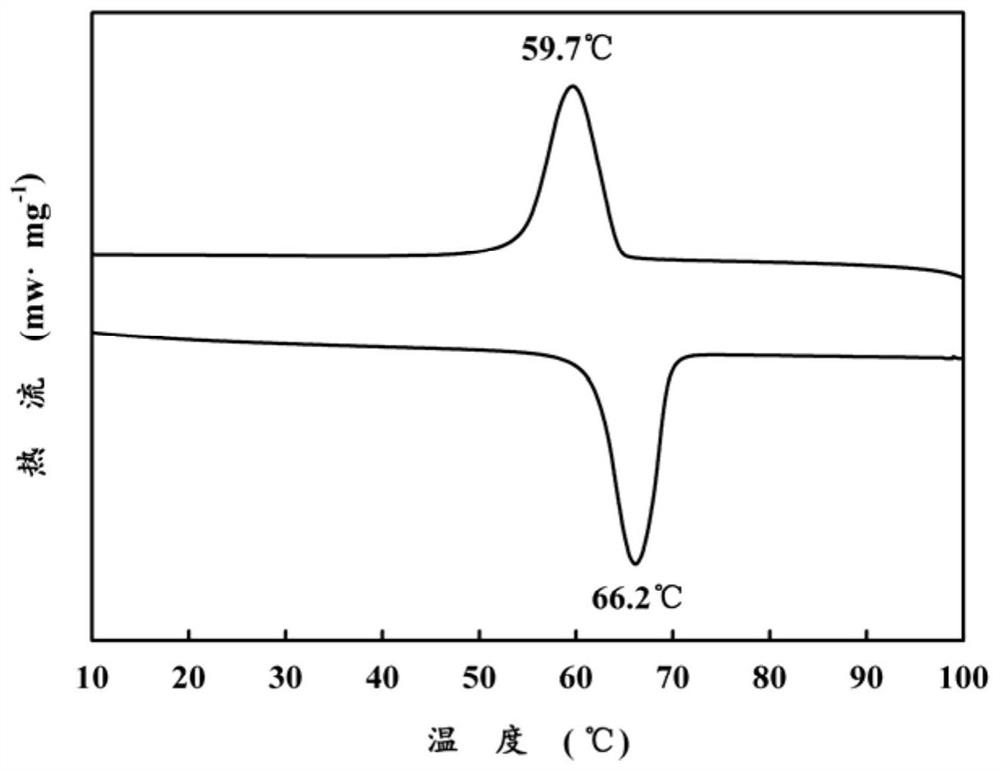
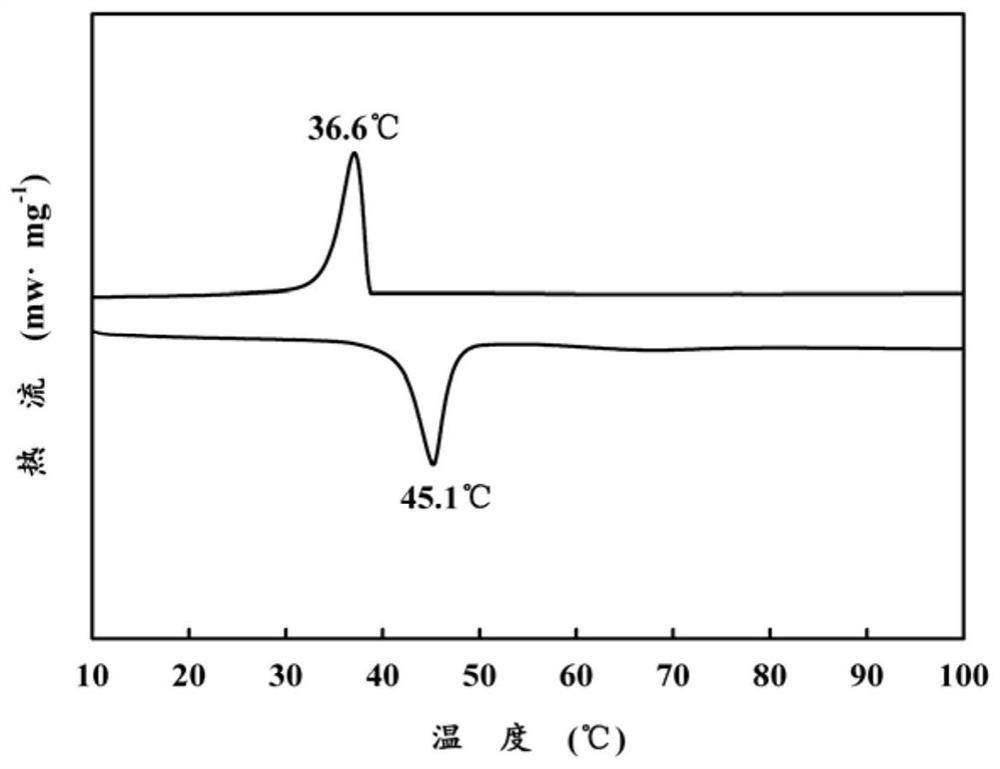
Patents
Literature
42 results about "Low emittance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
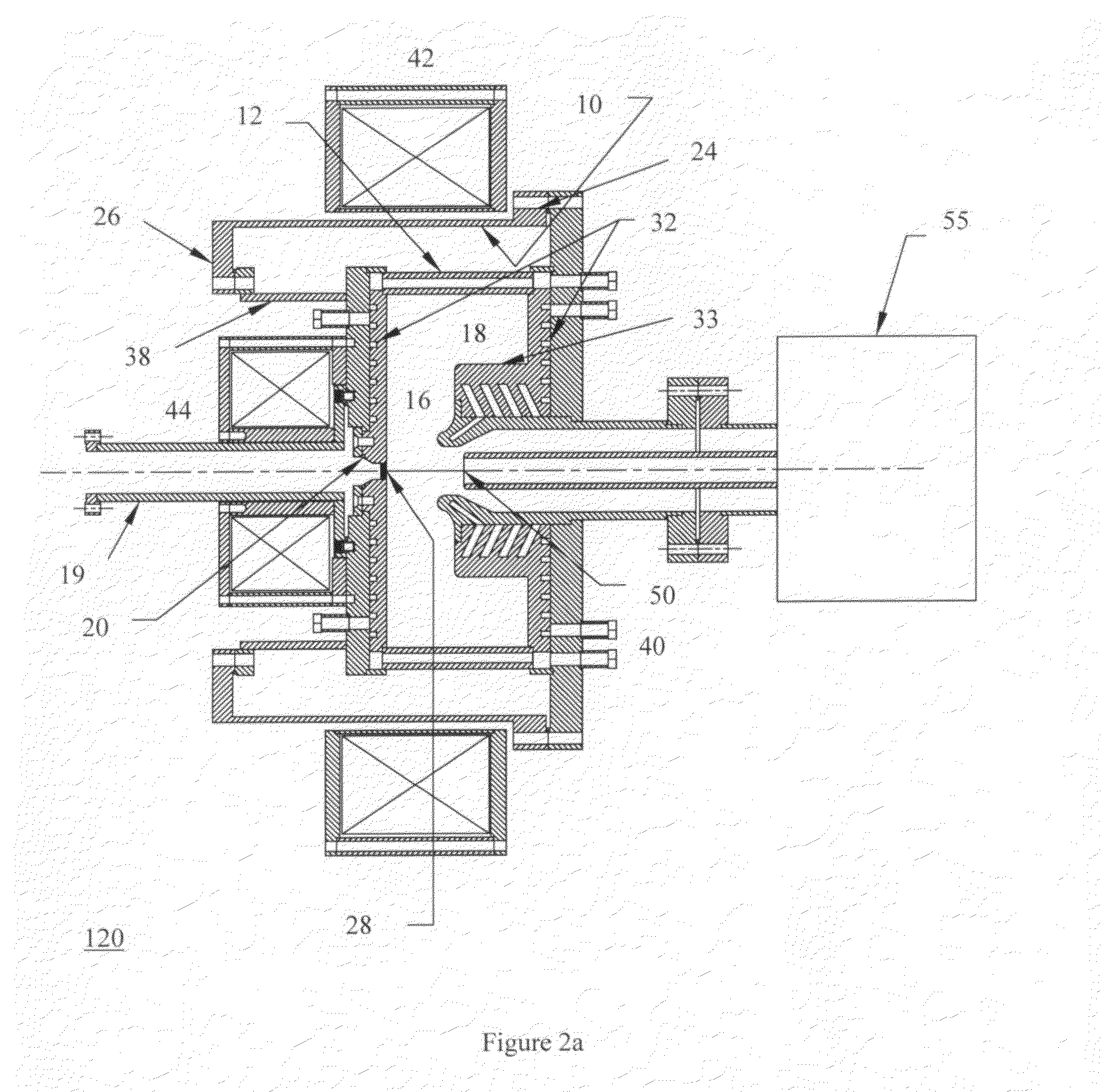
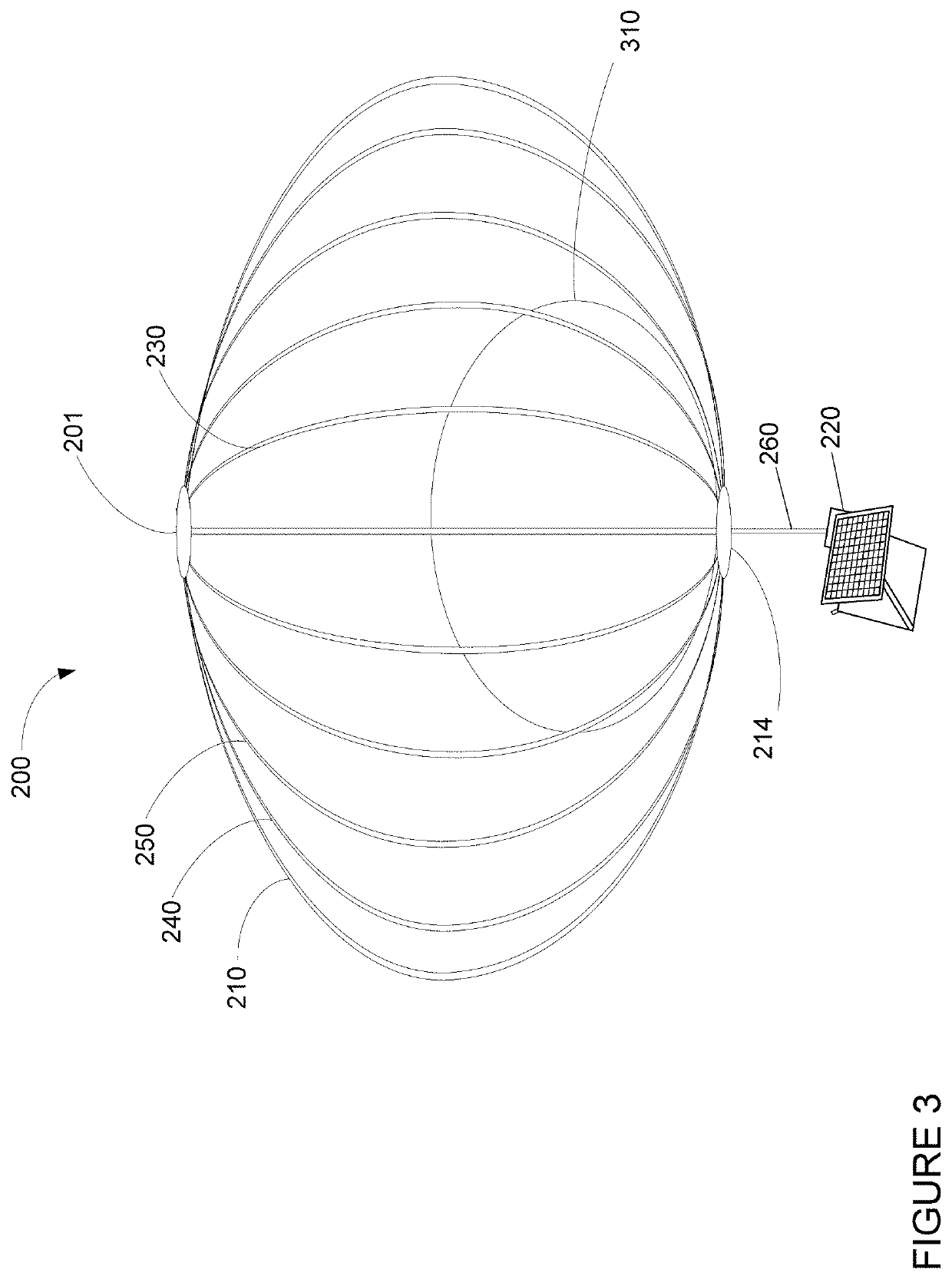
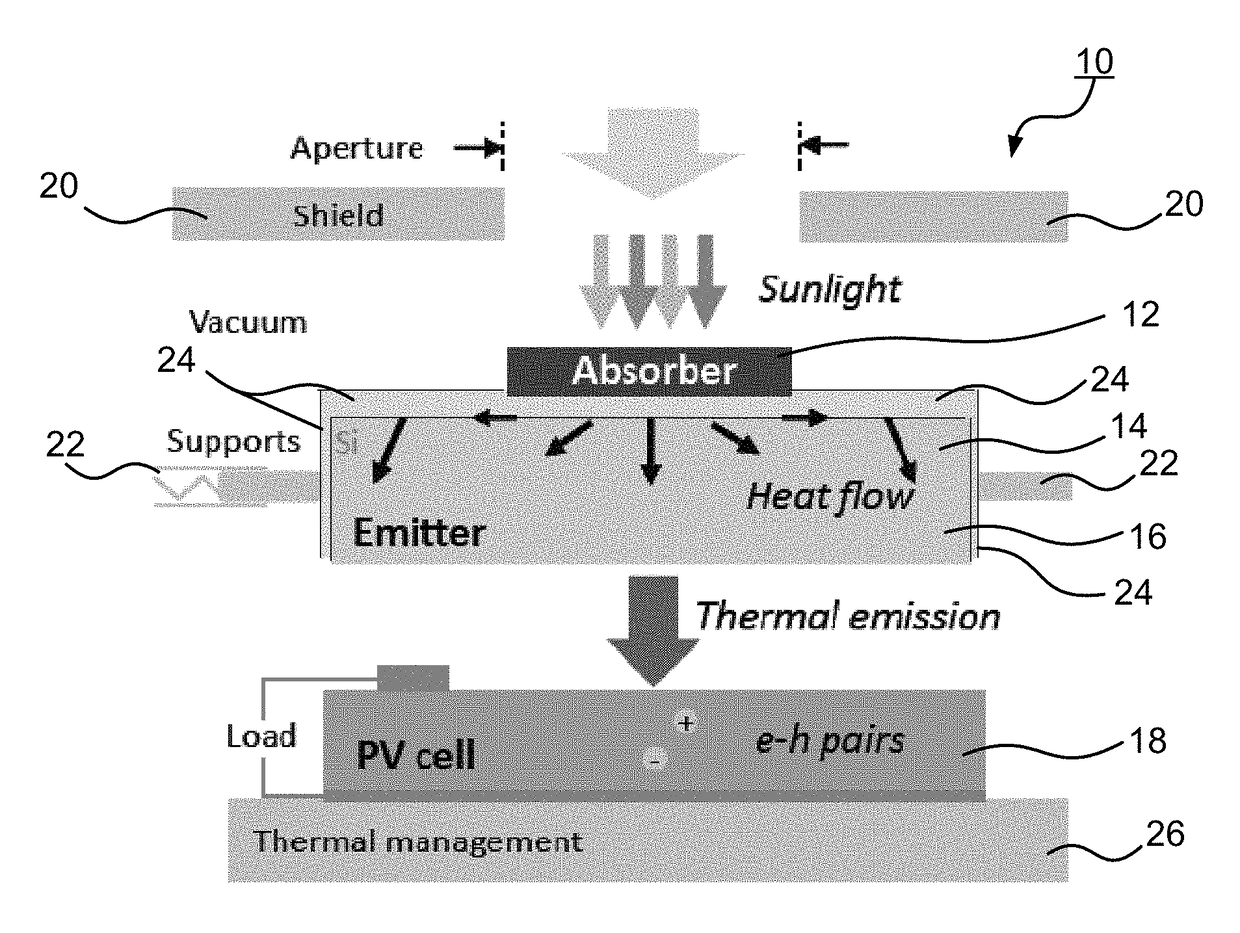
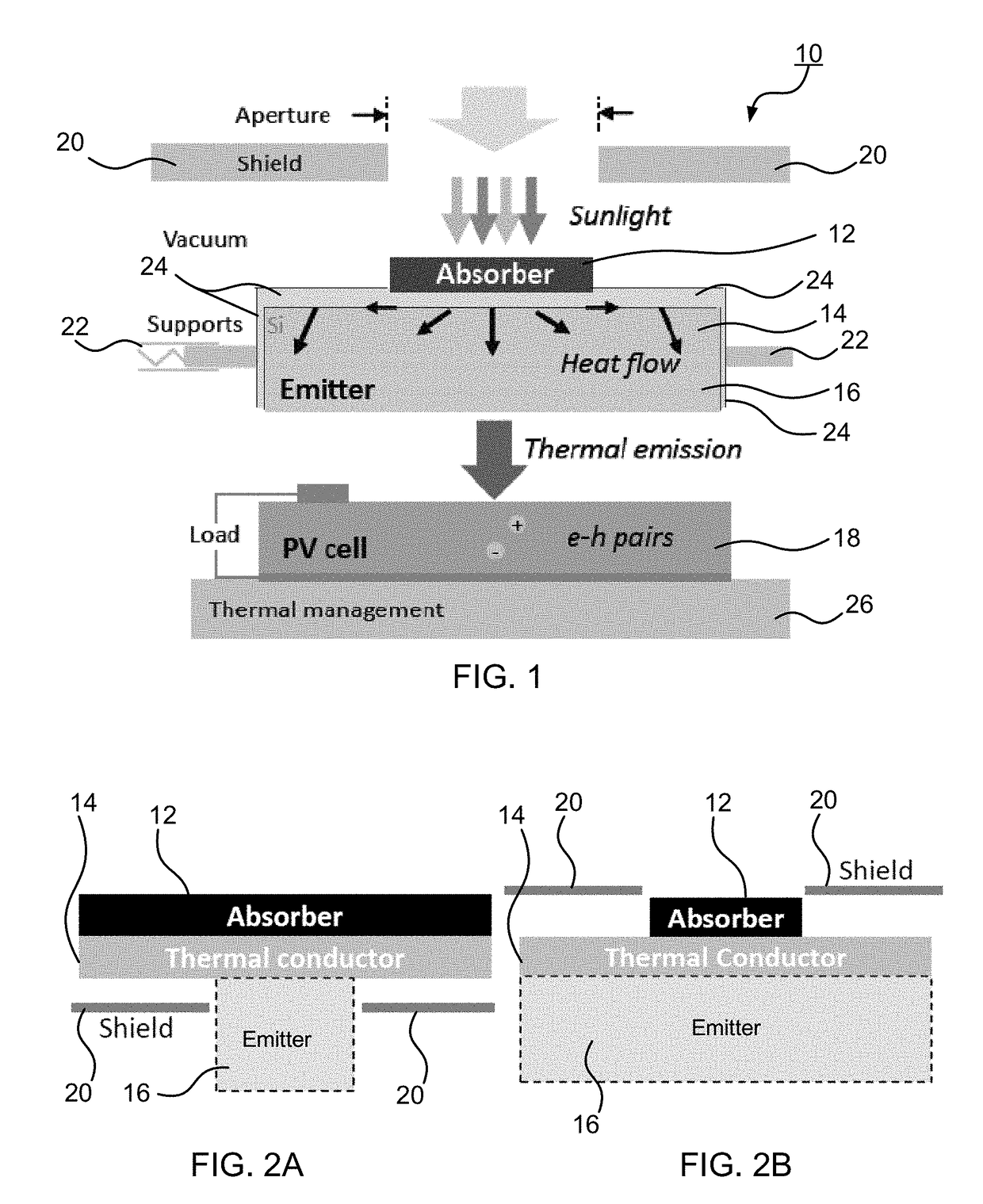
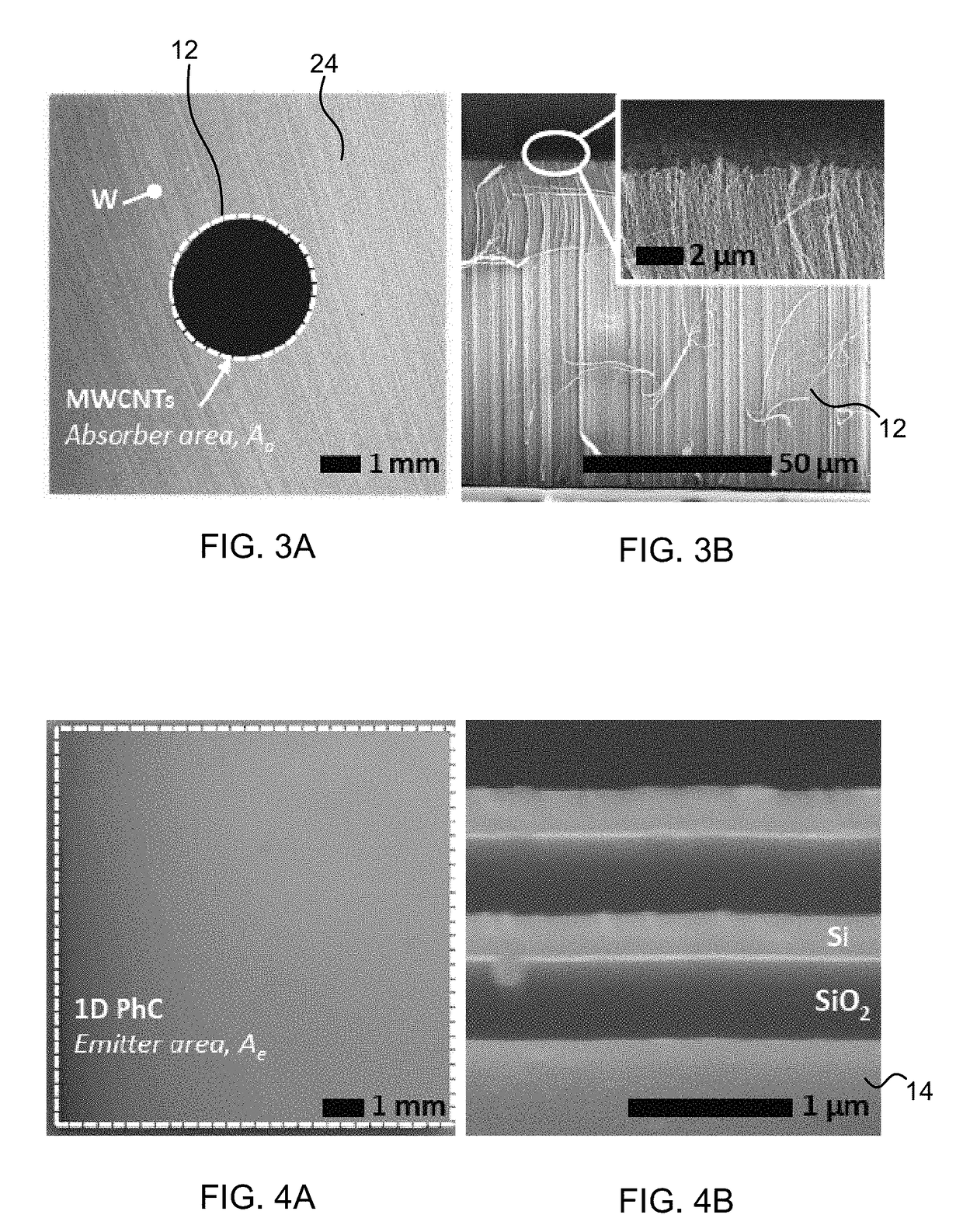
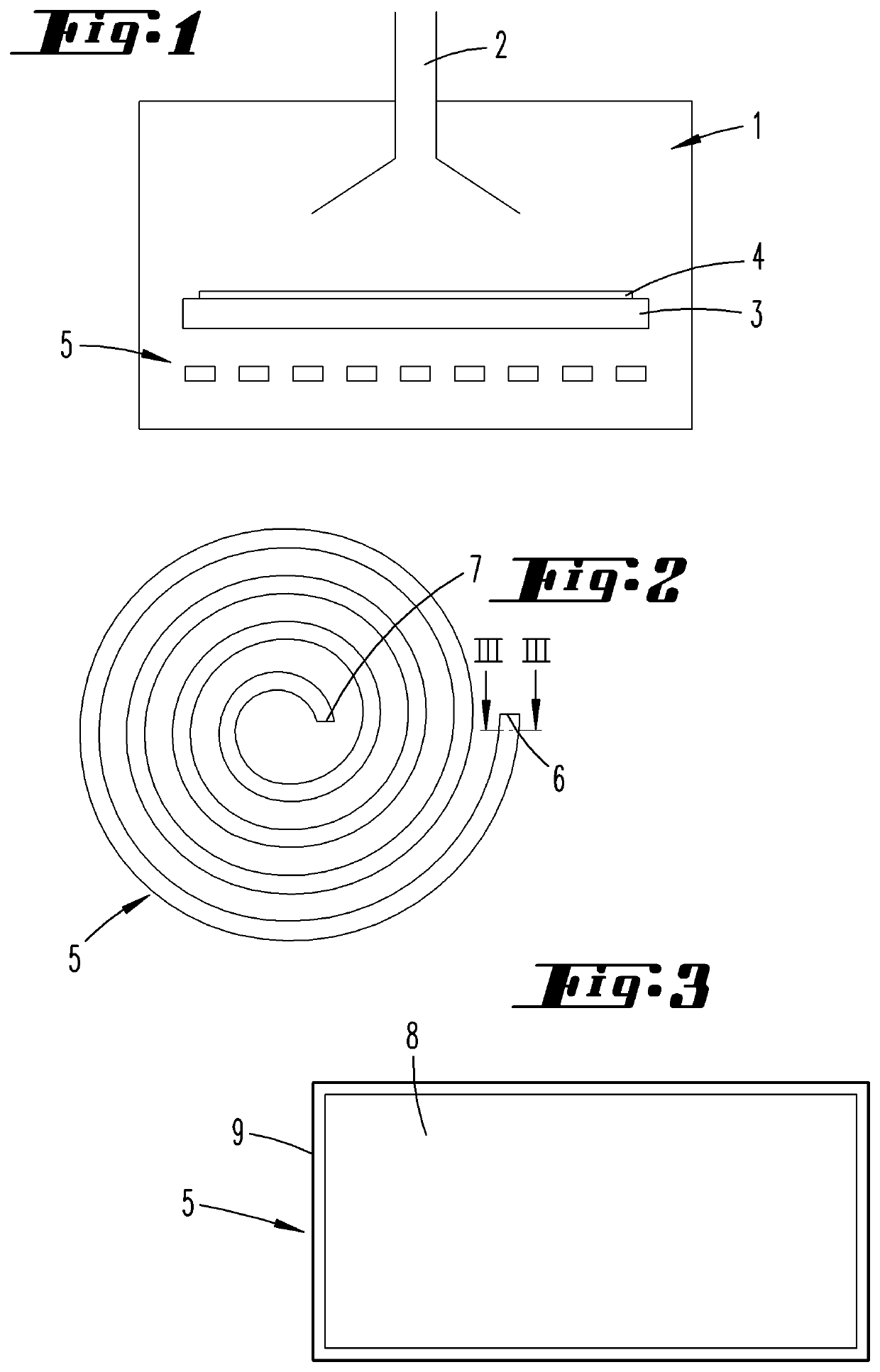
Spectrally-Engineered Solar Thermal Photovoltaic Devices
InactiveUS20160164451A1Reduce parasitic radiationMinimize heat conducted awayPV power plantsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLow emittanceEmissivity
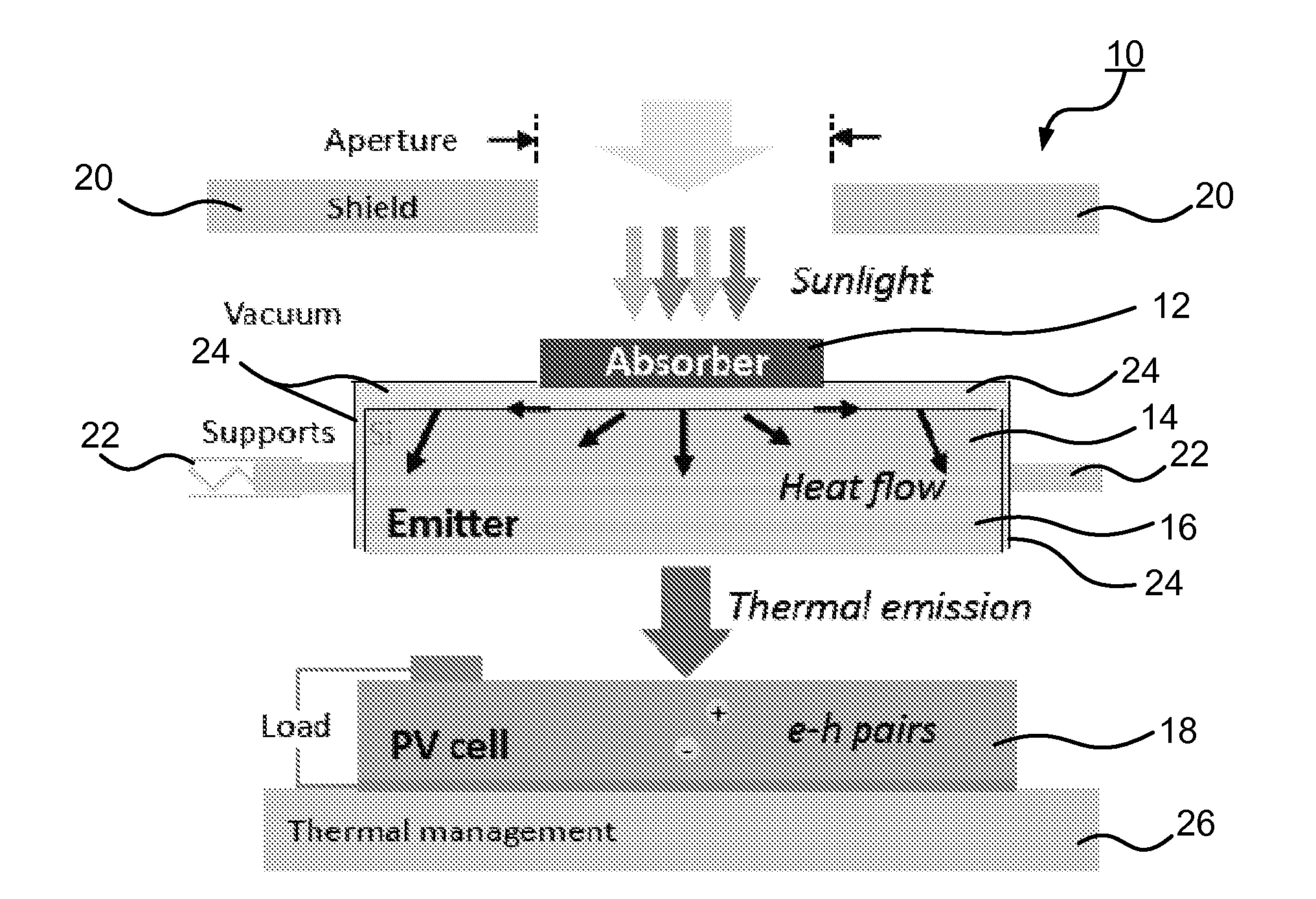
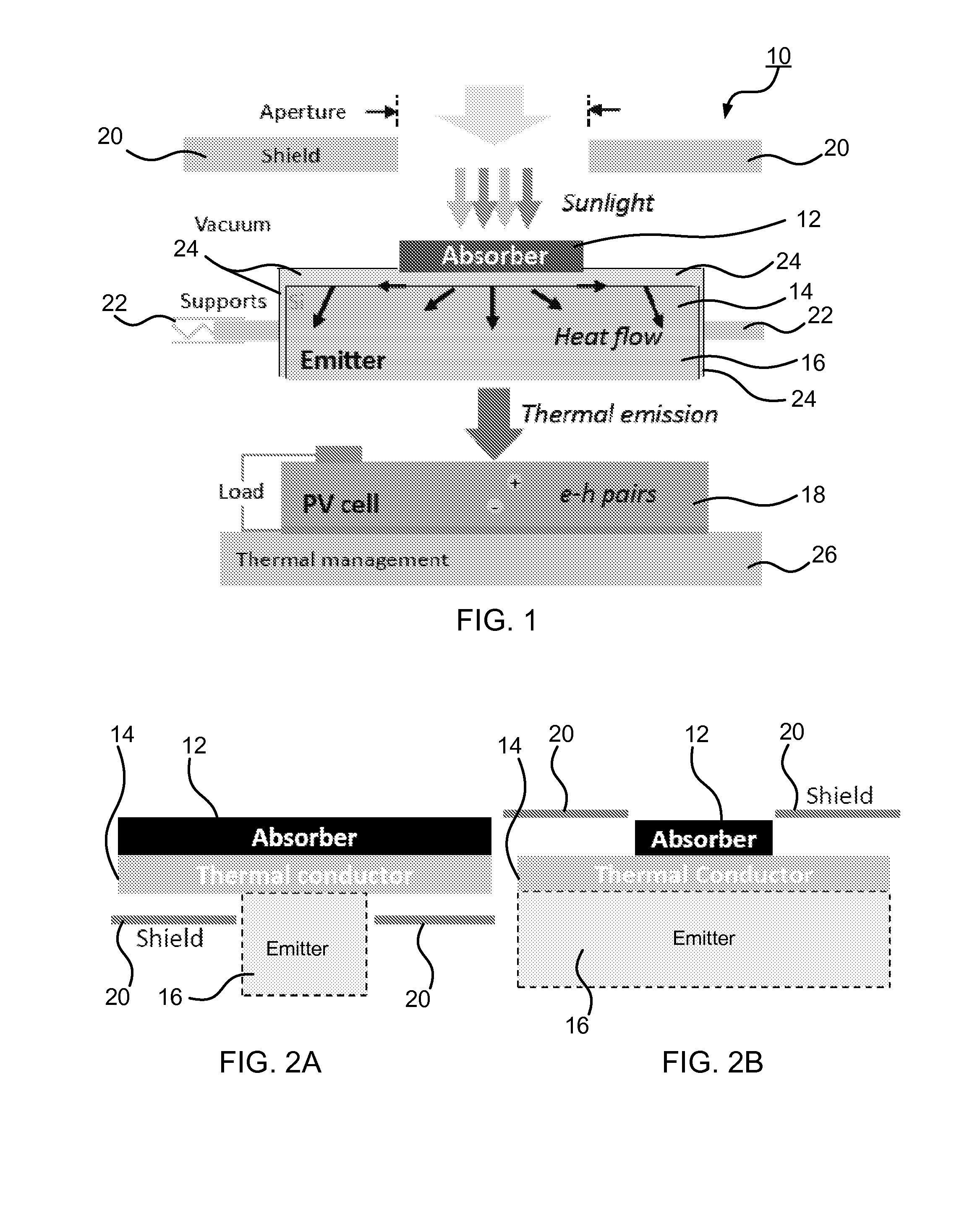
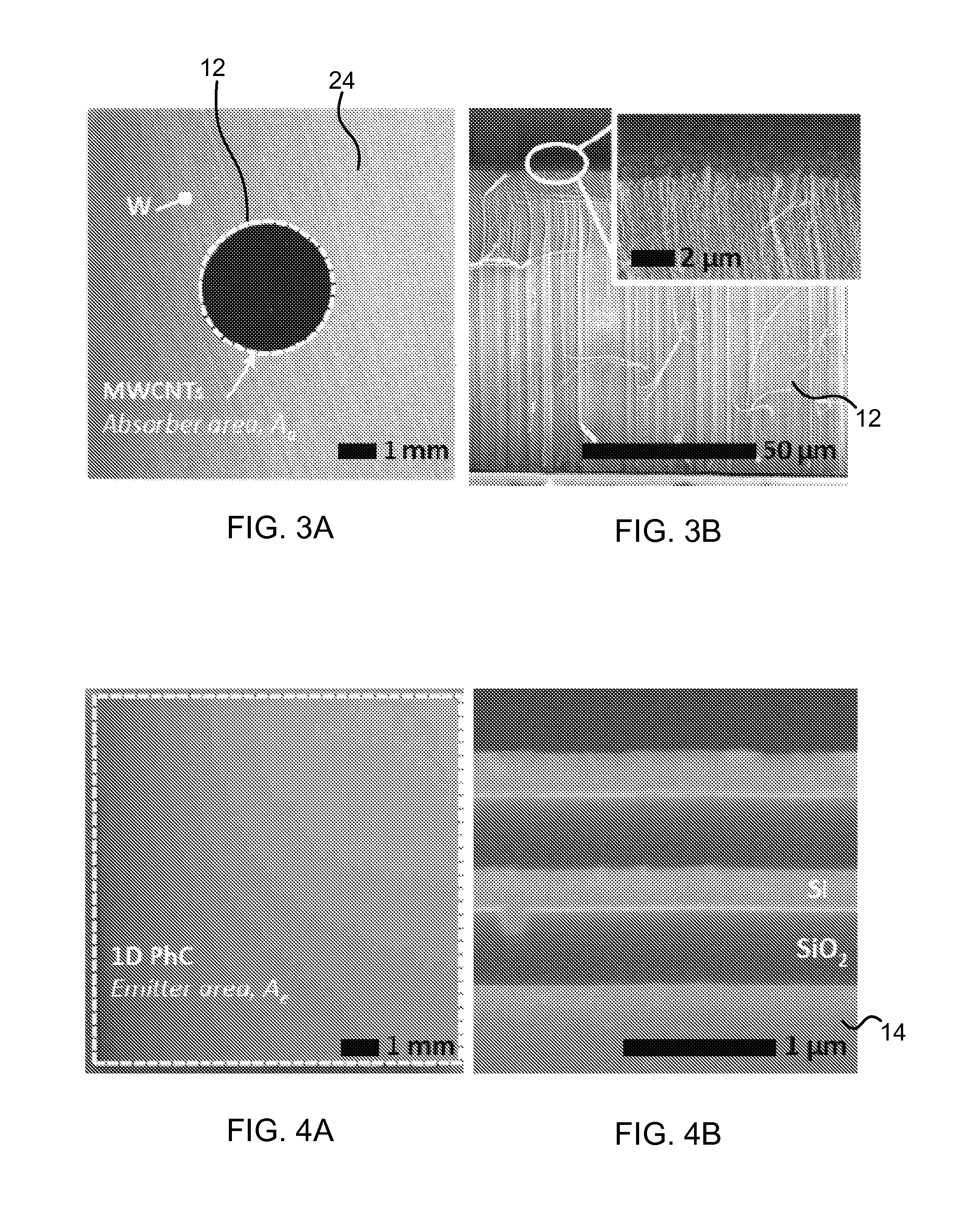
A solar thermal photovoltaic device, and method of forming same, includes a solar absorber and a spectrally selective emitter formed on either side of a thermally conductive substrate. The solar absorber is configured to absorb incident solar radiation. The solar absorber and the spectrally selective emitter are configured with an optimized emitter-to-absorber area ratio. The solar thermal photovoltaic device also includes a photovoltaic cell in thermal communication with the spectrally selective emitter. The spectrally selective emitter is configured to permit high emittance for energies above a bandgap of the photovoltaic cell and configured to permit low emittance for energies below the bandgap.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
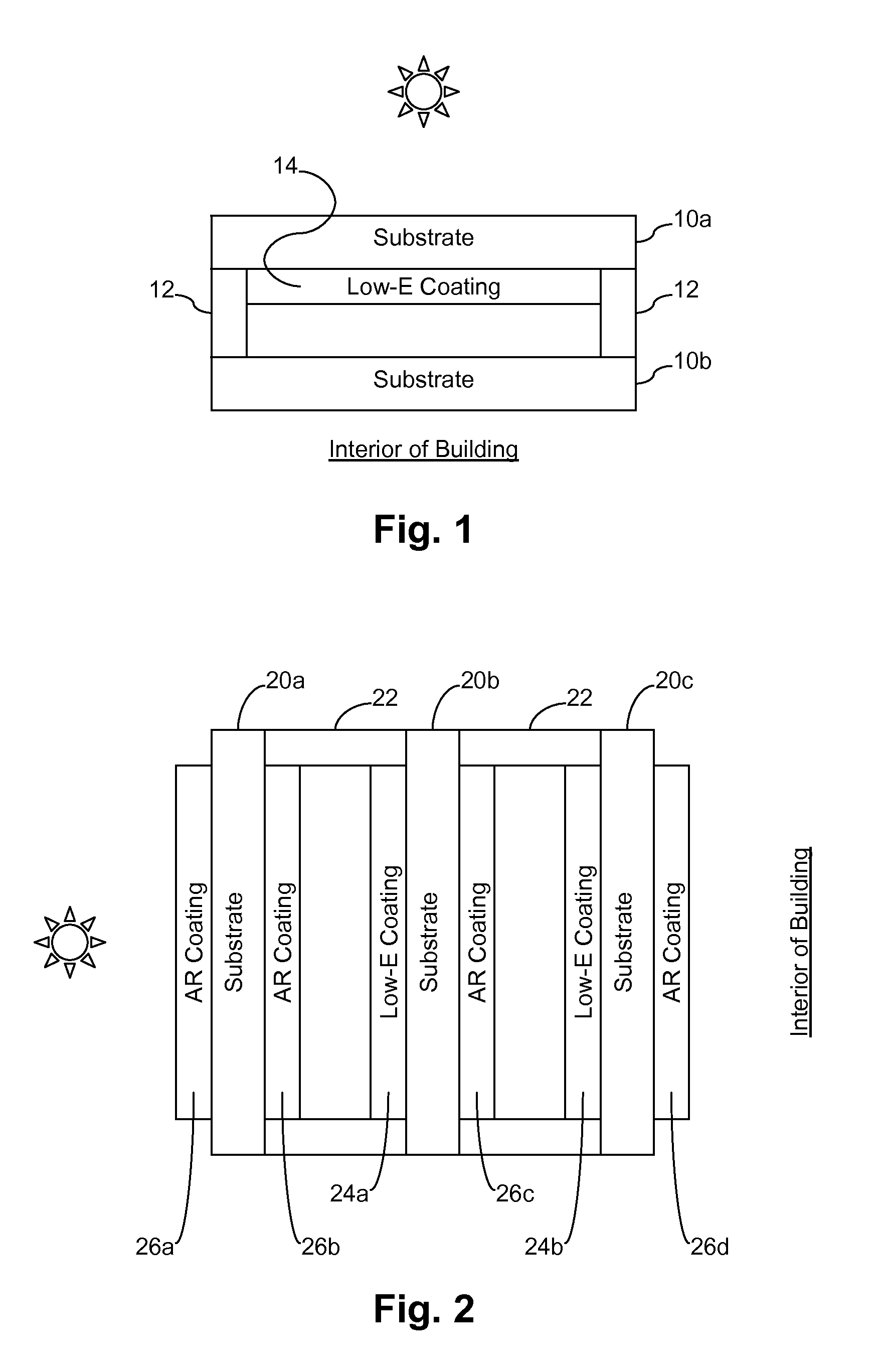
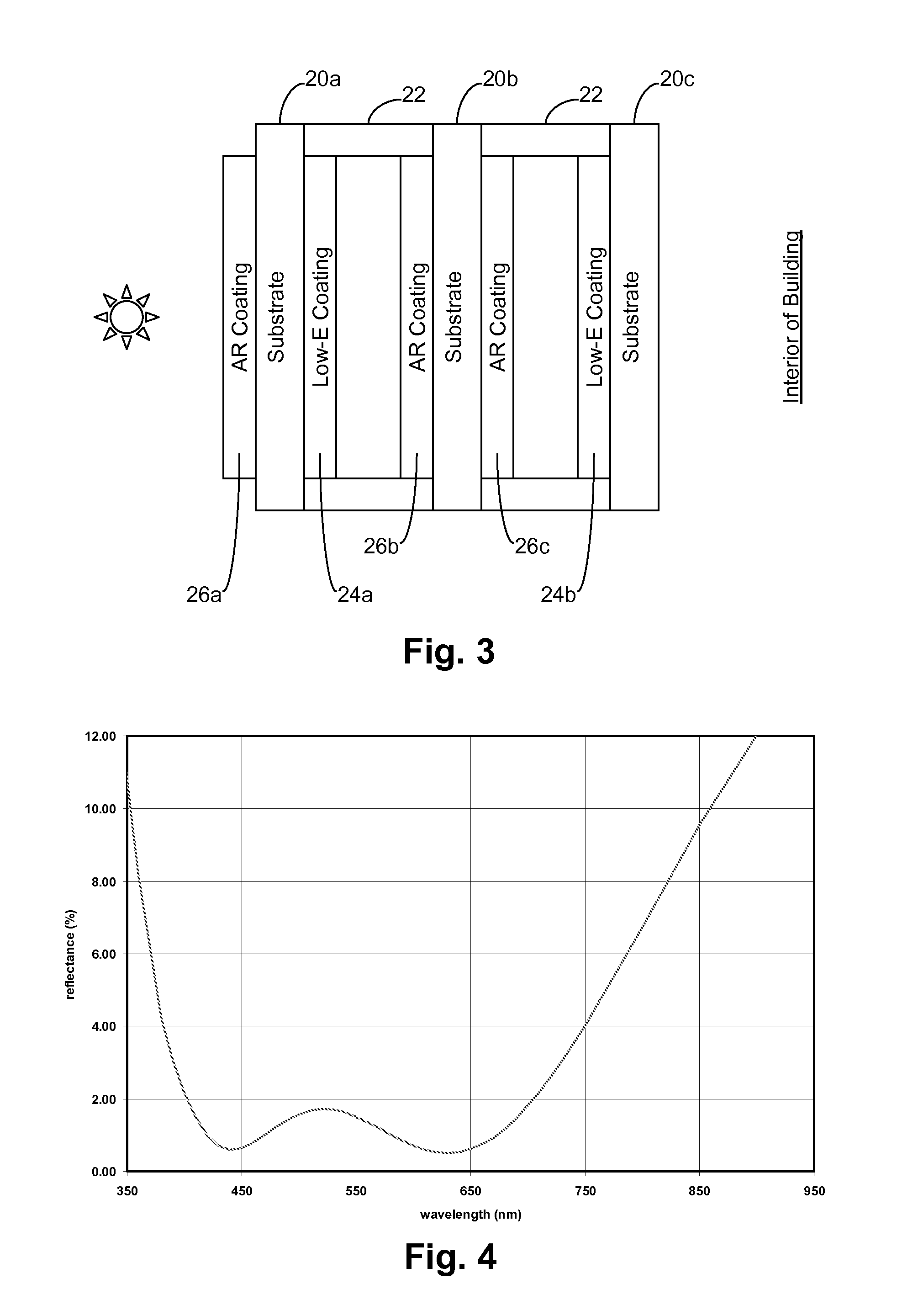
Insulating glass units with low-e and antireflective coatings, and/or methods of making the same
ActiveUS20130149473A1Reduce heat transferMore energy efficientPretreated surfacesWindows/door improvementInsulated glazingLow emissivity
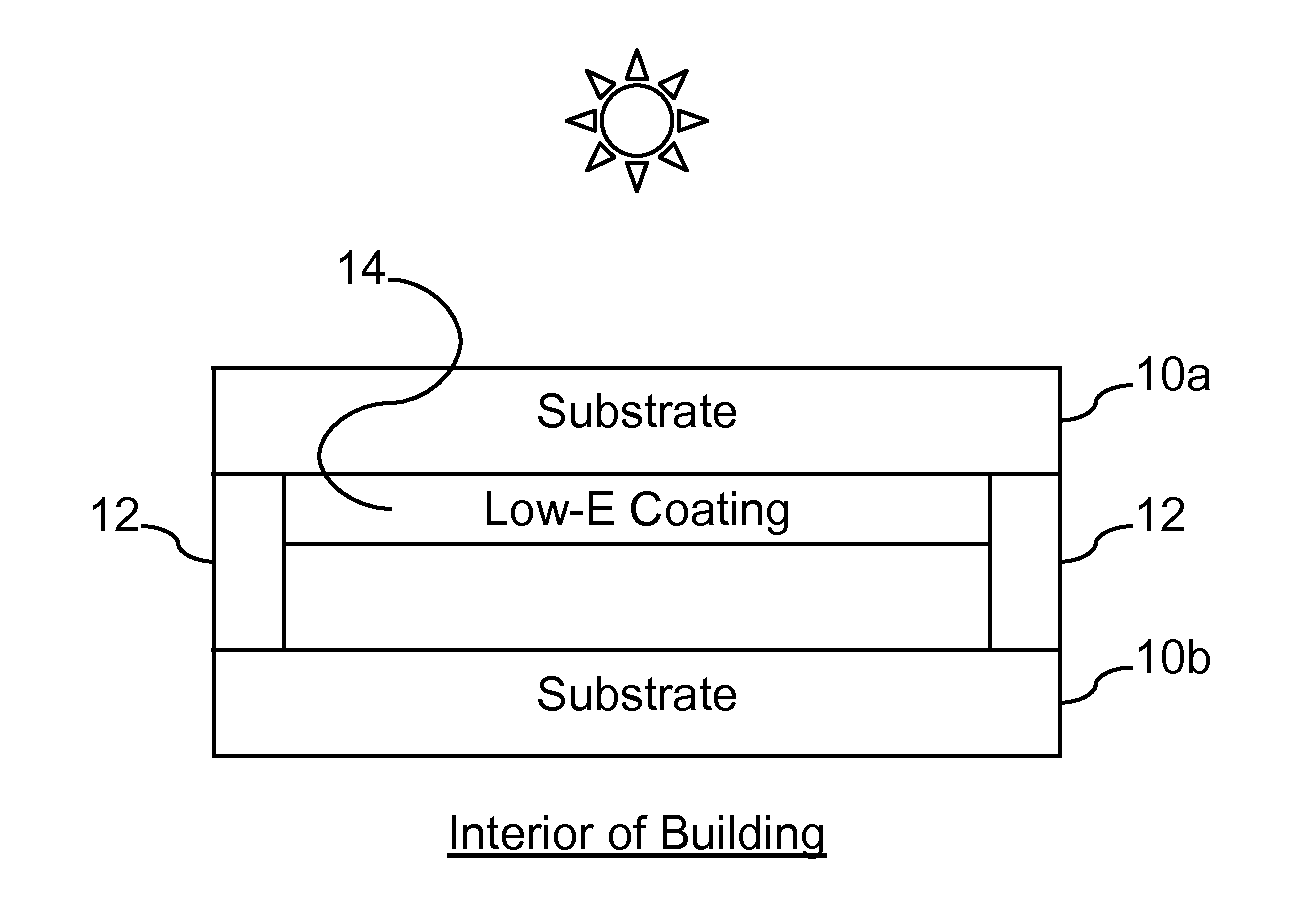
Certain example embodiments of this invention relate to insulating glass (IG) units including three substantially parallel spaced apart glass substrates, wherein at least two of the surfaces include low-emissivity (low-E) coatings and at least some of the non-low E coated surfaces have antireflective (AR) coatings disposed thereon. In certain example embodiments, low-E coatings are provided on the second and fifth surfaces of the IG unit, and each internal surface of the IG unit that does not support a low-E coating does support an AR coating. Additional AR coatings may be provided on one or both of the outermost surfaces in certain example embodiments. In some cases, the center substrate need not be heat treated because of the reduced absorption enabled by providing the low-E coatings on the two outermost substrates, as well as the reduced heat accumulation in the center lite itself and in the two adjacent spacers.
Owner:GUARDIAN EURO S A R L +1
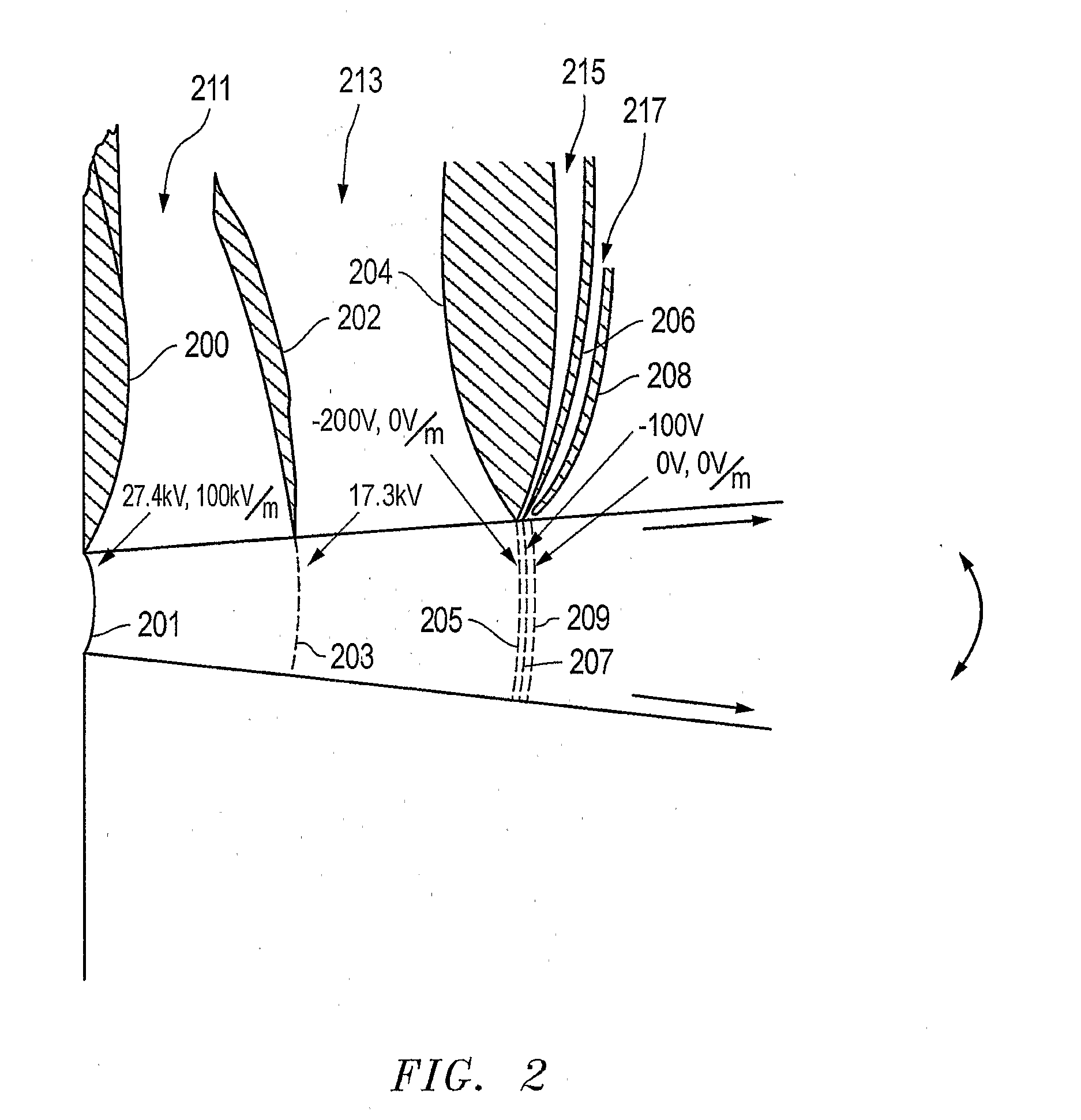
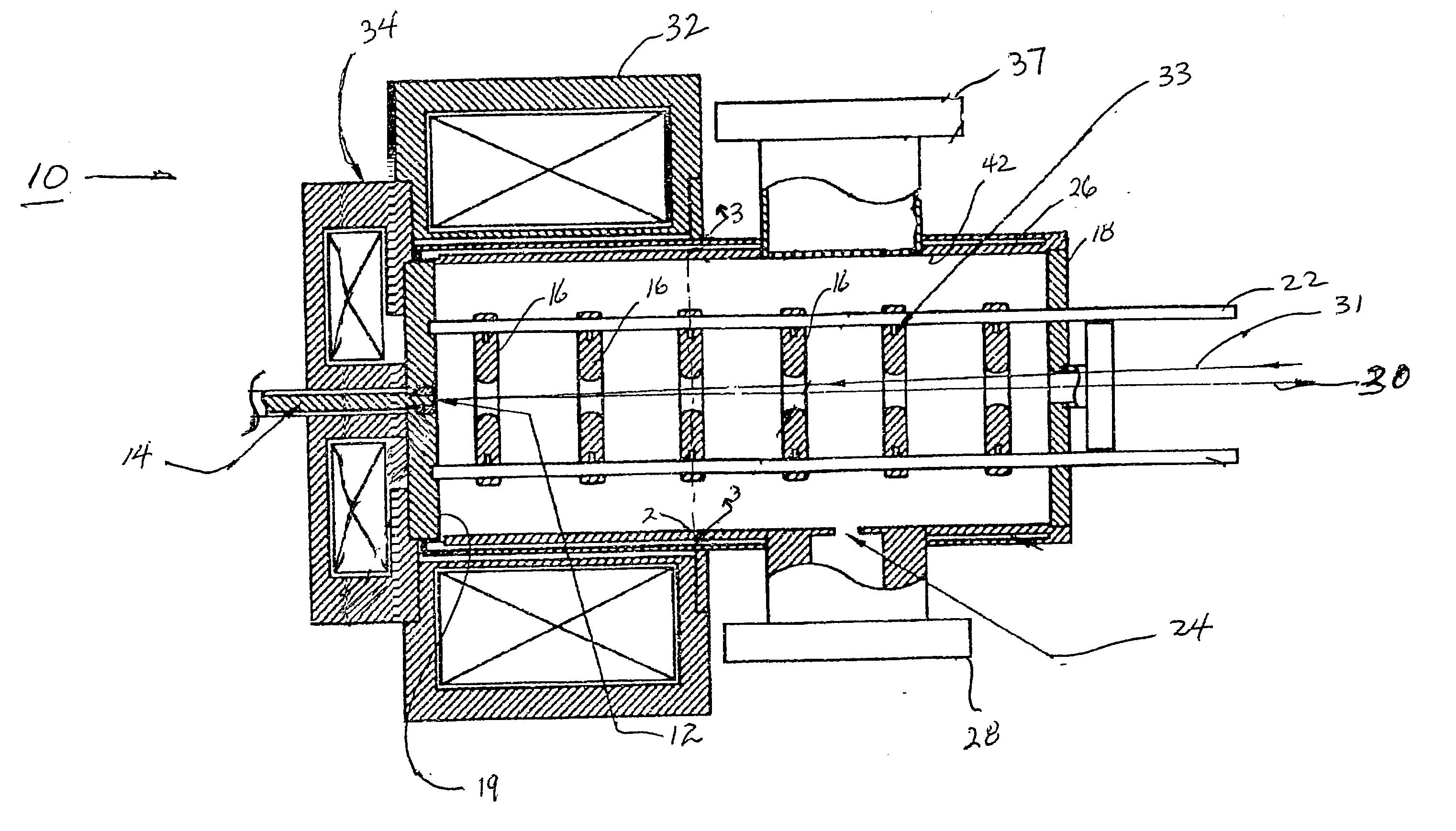
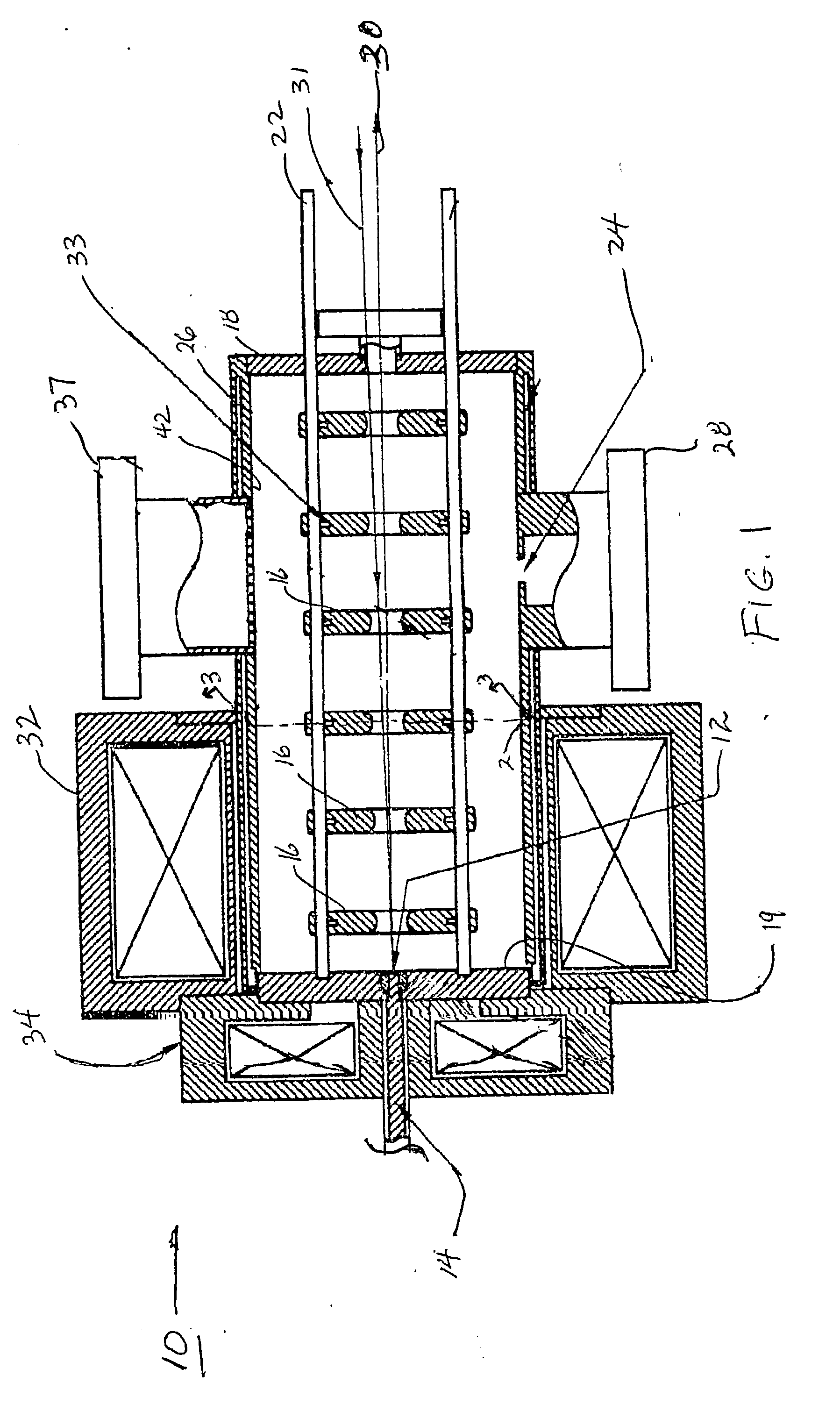
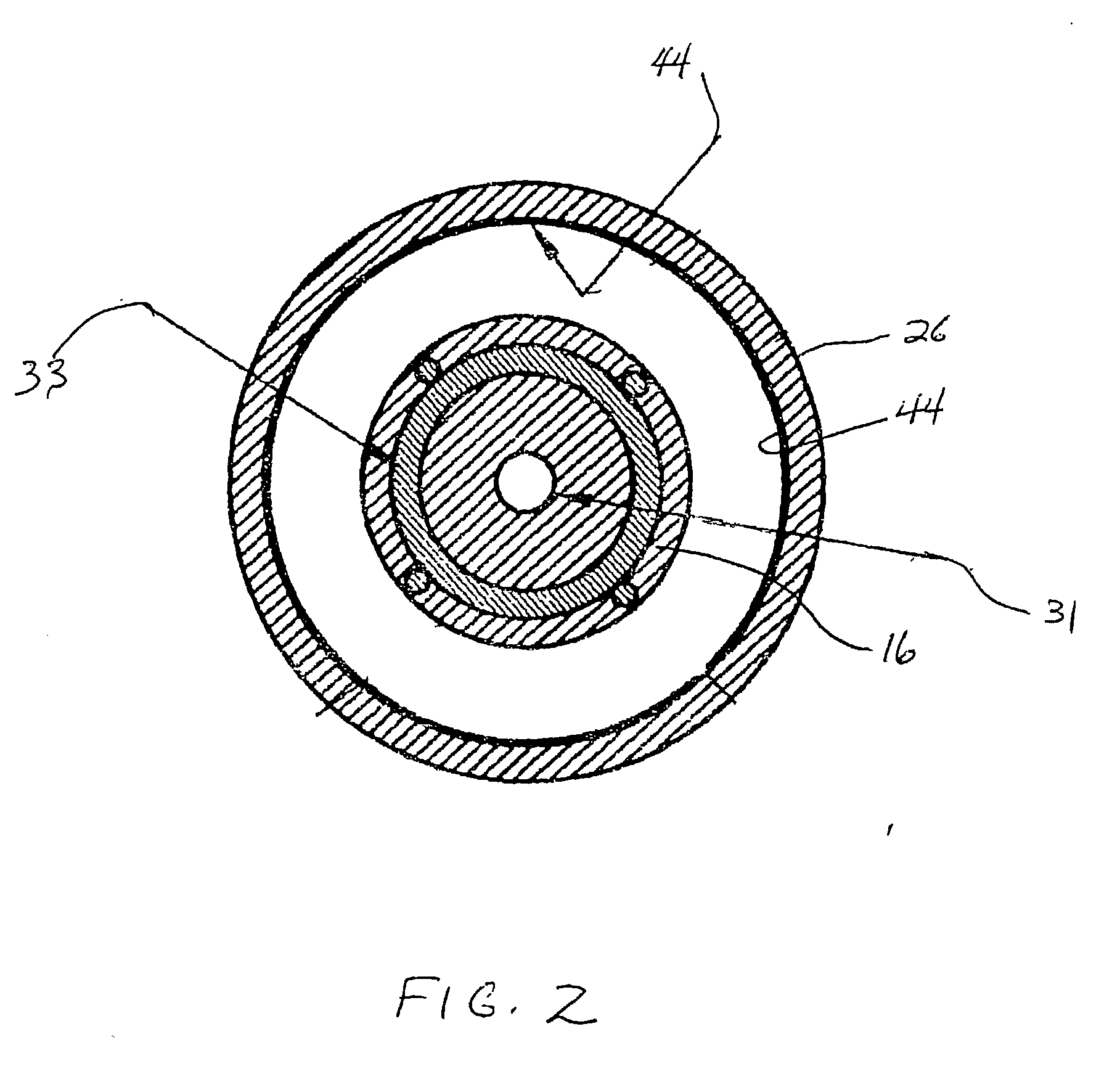
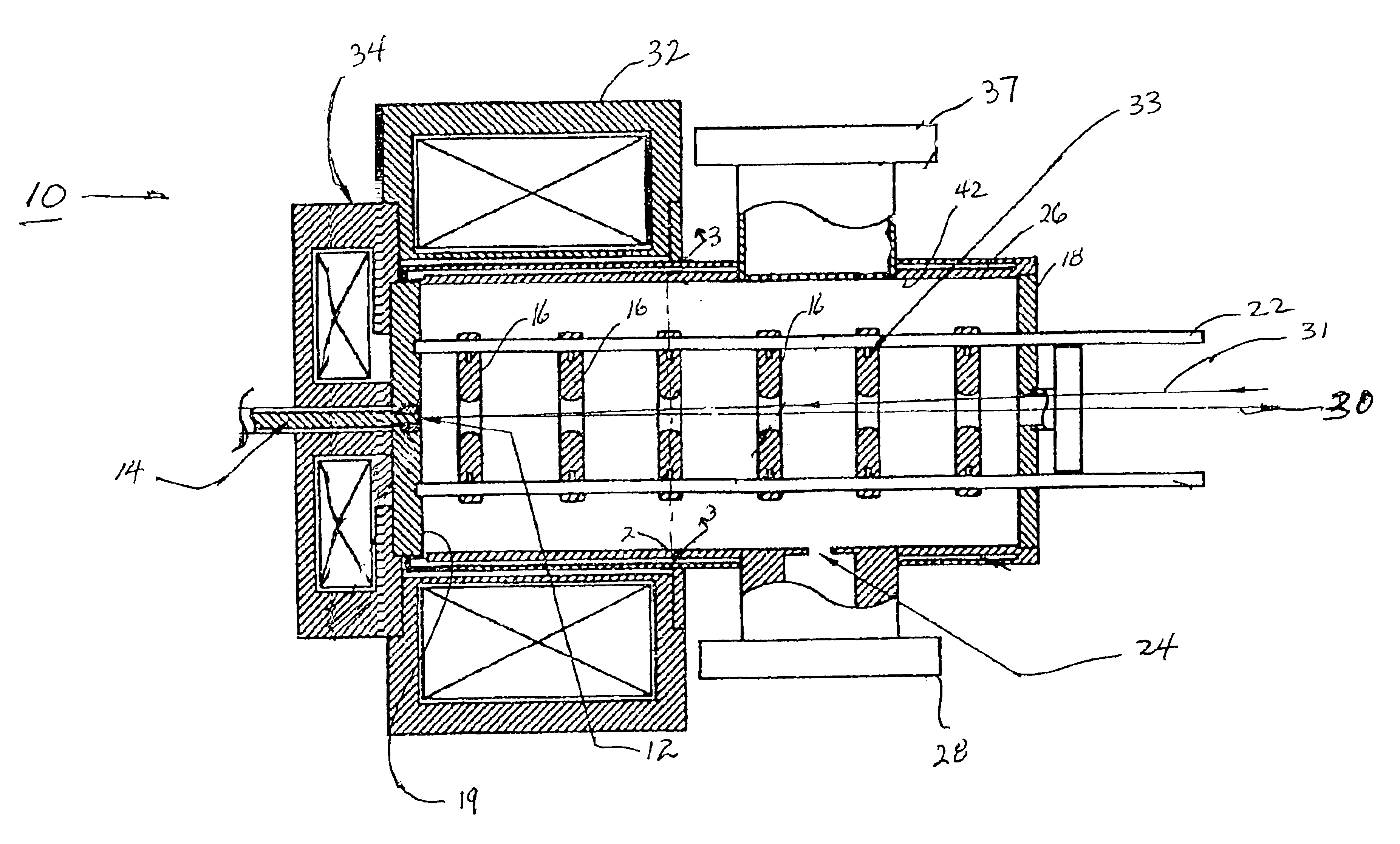
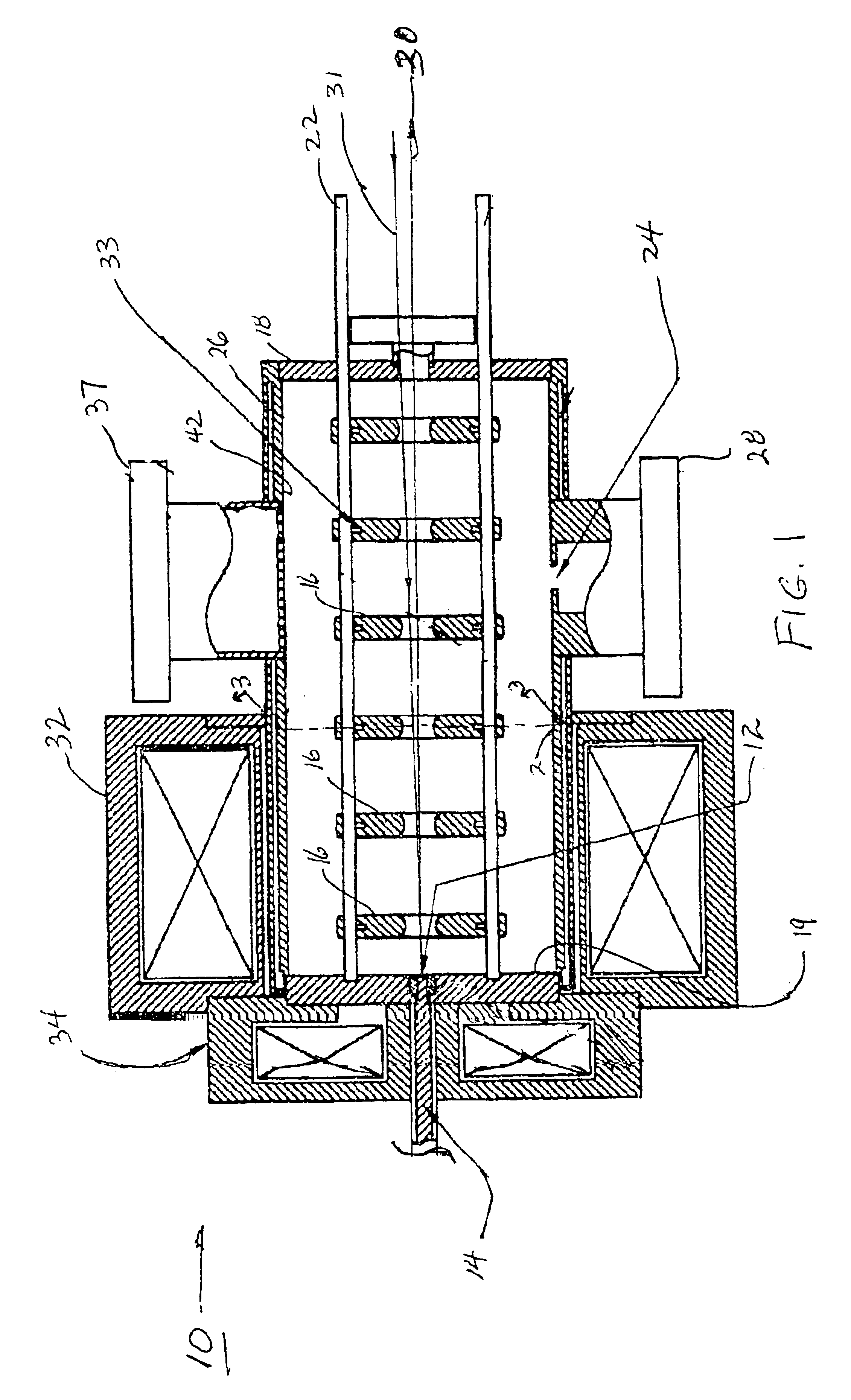
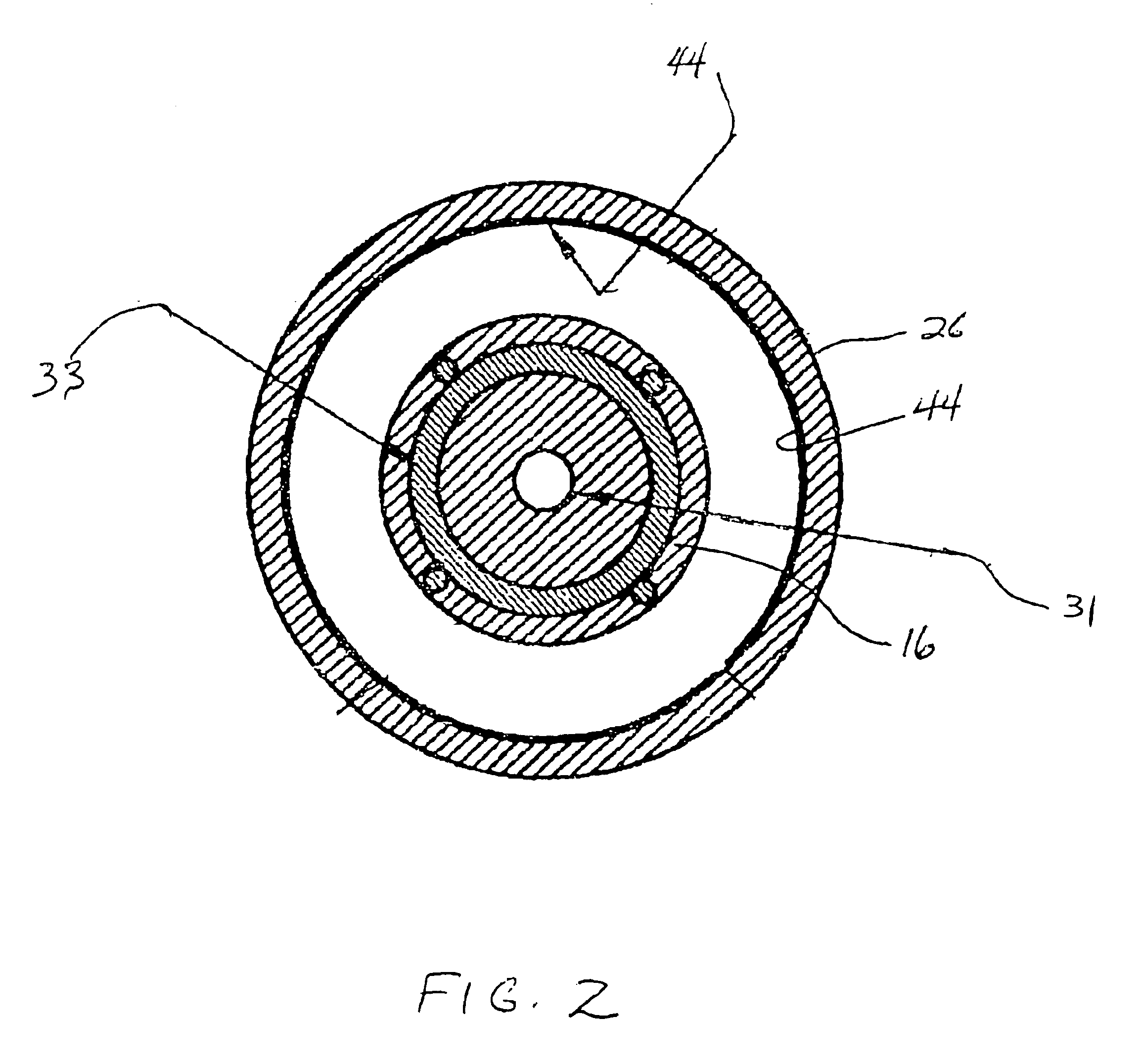
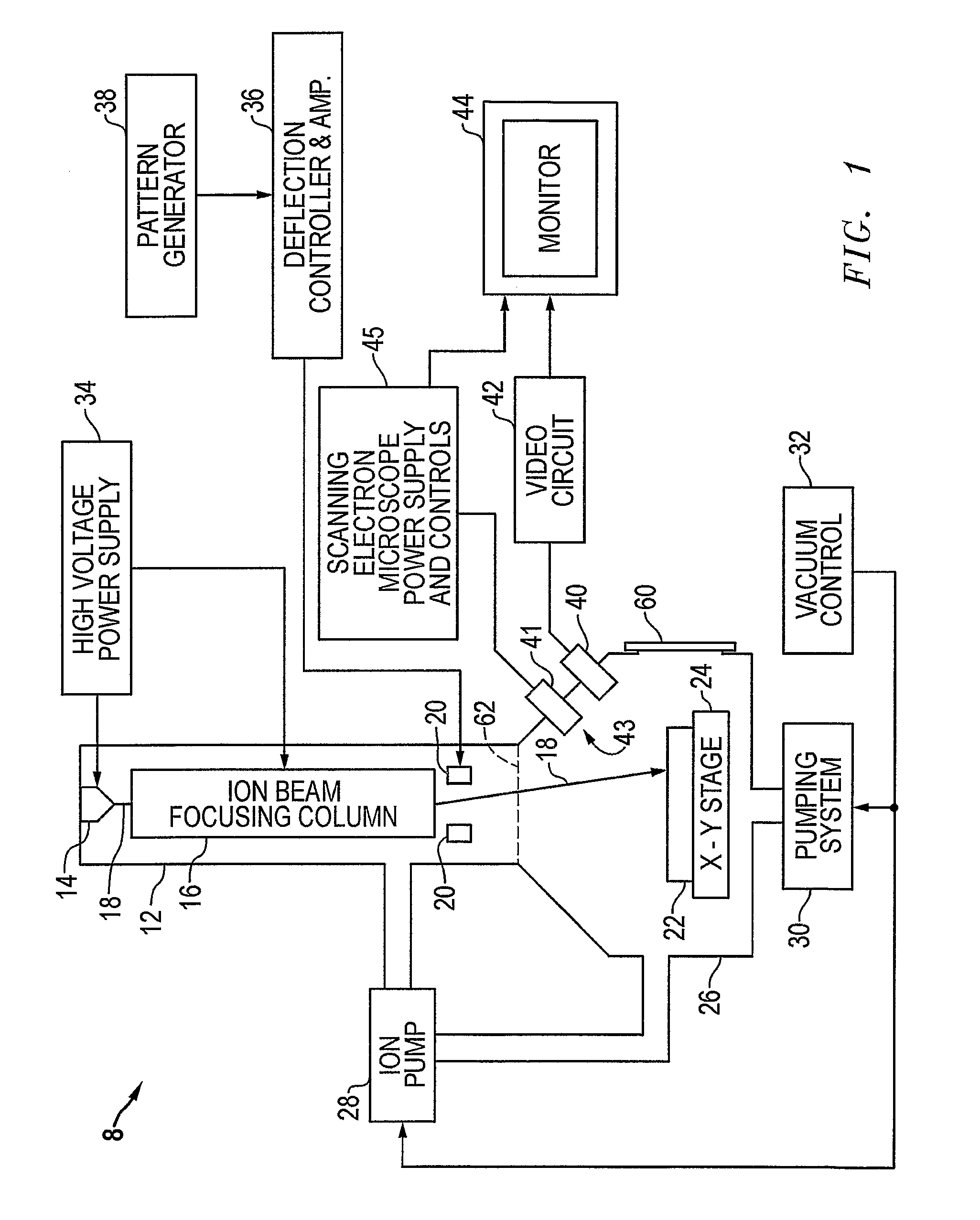
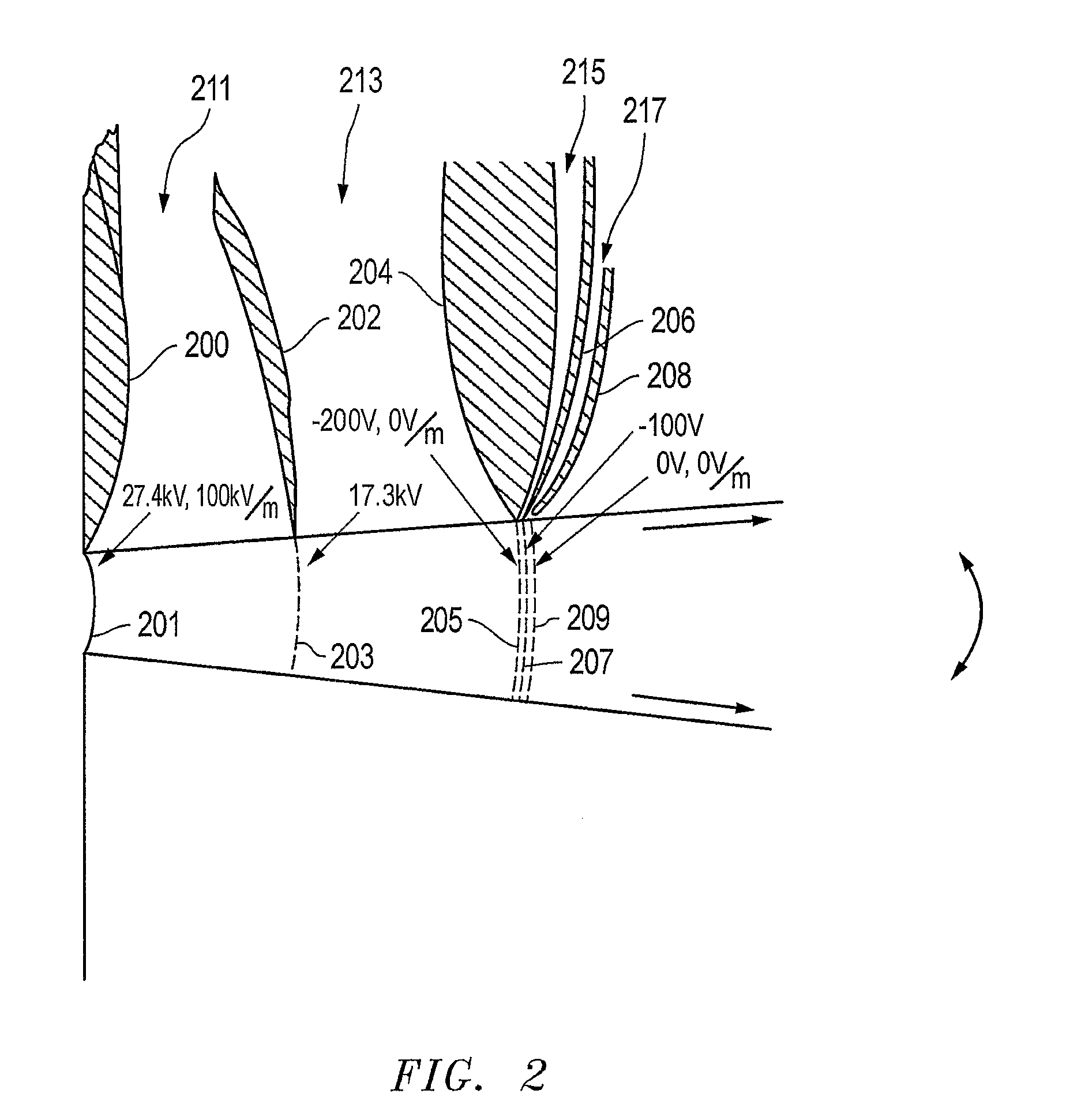
Charged Particle Extraction Device and Method of Design There For
ActiveUS20100044580A1Increase brightnessElectric arc lampsMaterial analysis by optical meansLow emittanceEmissivity
The present invention provides a method for extracting a charged particle beam from a charged particle source. A set of electrodes is provided at the output of the source. The potentials applied to the electrodes produce a low-emittance growth beam with substantially zero electric field at the output of the electrodes.
Owner:FEI CO
Glass article having a solar control coating
InactiveUS6858306B1High degreeReduce the amount requiredMirrorsOptical filtersLow emittanceEmissivity
A glass article having a solar control coating is disclosed for use in producing heat reducing glass especially for use in architectural windows. The coated article includes a glass substrate, a coating of an antimony doped tin oxide deposited on and adhering to the glass substrate and a coating of fluorine doped tin oxide deposited on and adhering to the surface of the coating of antimony doped tin oxide. The low emittance of the coated glass article, when combined with the surprisingly selective solar absorption of the multilayer stack provides improved heat rejection in summer and heat retention in winter, while permitting the transmittance of a relatively high degree of visible light.
Owner:PILKINGTON NORTH AMERICA INC +1
Variable emittance thermochromic material and satellite system
ActiveUS7761053B2Easy to operateKeep the distanceOther chemical processesRadio transmissionElectricityThermochromism
The emittance value is a measure of an amount of energy expelled from a given surface area relative to a black-body reference. Depending on the specific coating a change in the emittance value is actively or passively effected. There are known active variable emittance thermal control coatings. However, such coatings are actually panels housing a mixture of both high and low emissivity materials that are electrically manipulated to control the emittance value of the panel. These “coatings” are classified as either electrochromic or electrophorectic. Both electrochromic and electrophorectic coatings require an applied voltage to cause a change in the emittance value of the coating. By contrast, aspects of the present invention do not include active variable emittance thermal control coatings. Aspects of the present invention do include passive variable emittance thermal control coatings and materials. In accordance with aspects of the present invention “passive” means that the variable emittance value changes in response to changes in the environment without active control (e.g. neither a voltage nor a current is applied). More specifically, in accordance with one aspect of the invention a passive variable emittance thermochromic material is provided that has a relatively low emittance value at low temperatures and a relatively high emittance value at high temperatures.
Owner:MPB COMM
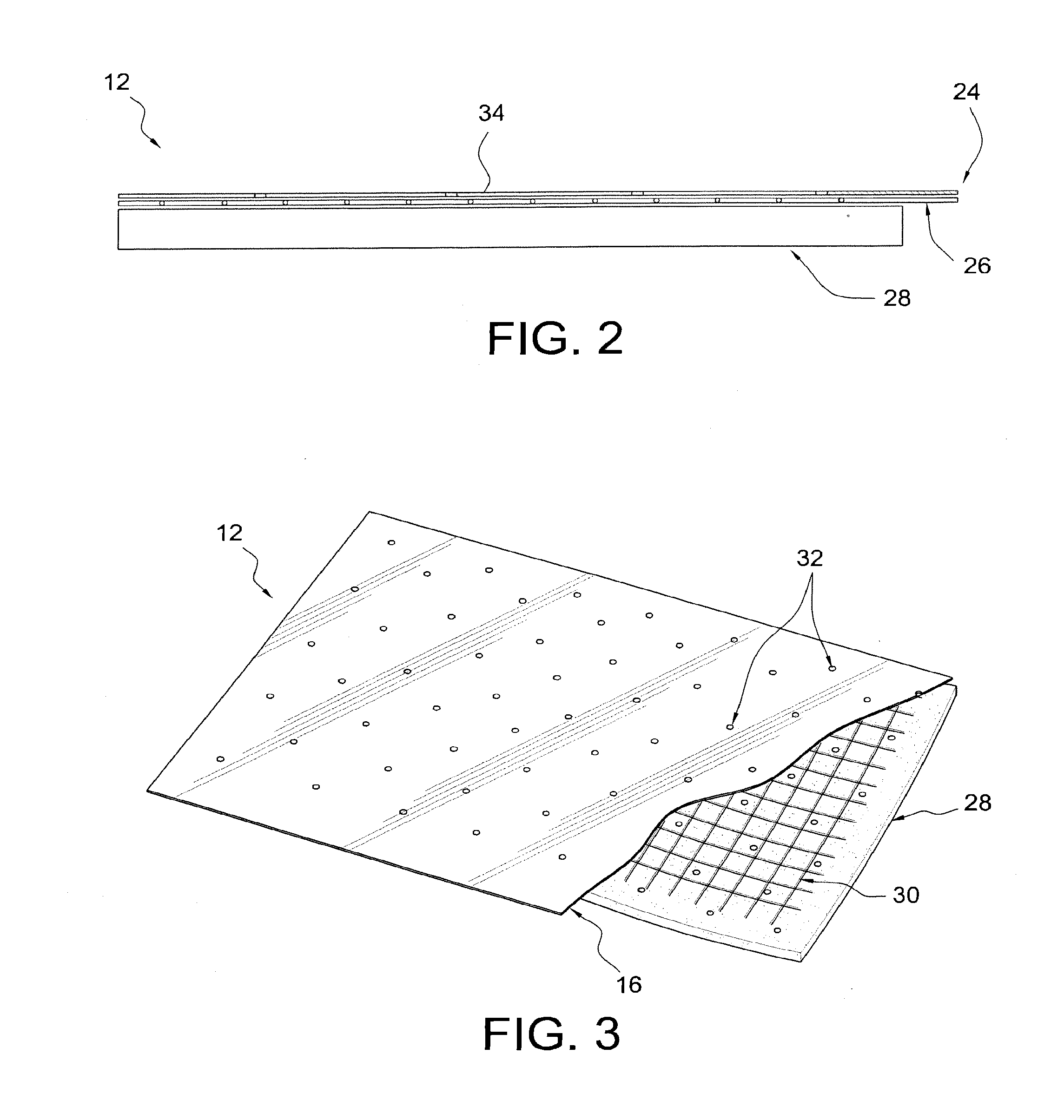
Light-weight strengthened, low-emittance vacuum-insulated glass (VIG) windows
InactiveUS20140186557A1Glass reforming apparatusThin material handlingLow emittanceInsulated glazing
Vacuum-insulated glass windows include two or more glass panes, and glass-bump spacers formed in a surface of one of the panes. The glass-bump spacers consist of the glass material from the body portion of the glass pane. At least one of the glass panes comprises chemically-strengthened glass. Methods of forming VIG windows include forming the glass-bump spacers by irradiating a glass pane with a focused beam from a laser. Heating effects in the glass cause the glass to locally expand, thereby forming a glass-bump spacer. In embodiments where the glass-bump spacers are formed in a chemically-strengthened glass pane, the glass-bump spacers may be formed before or after the chemical strengthening. A second glass pane is brought into contact with the glass-bump spacers, and the edges sealed. The resulting sealed interior region is evacuated to a pressure of less than one atmosphere.
Owner:CORNING INC
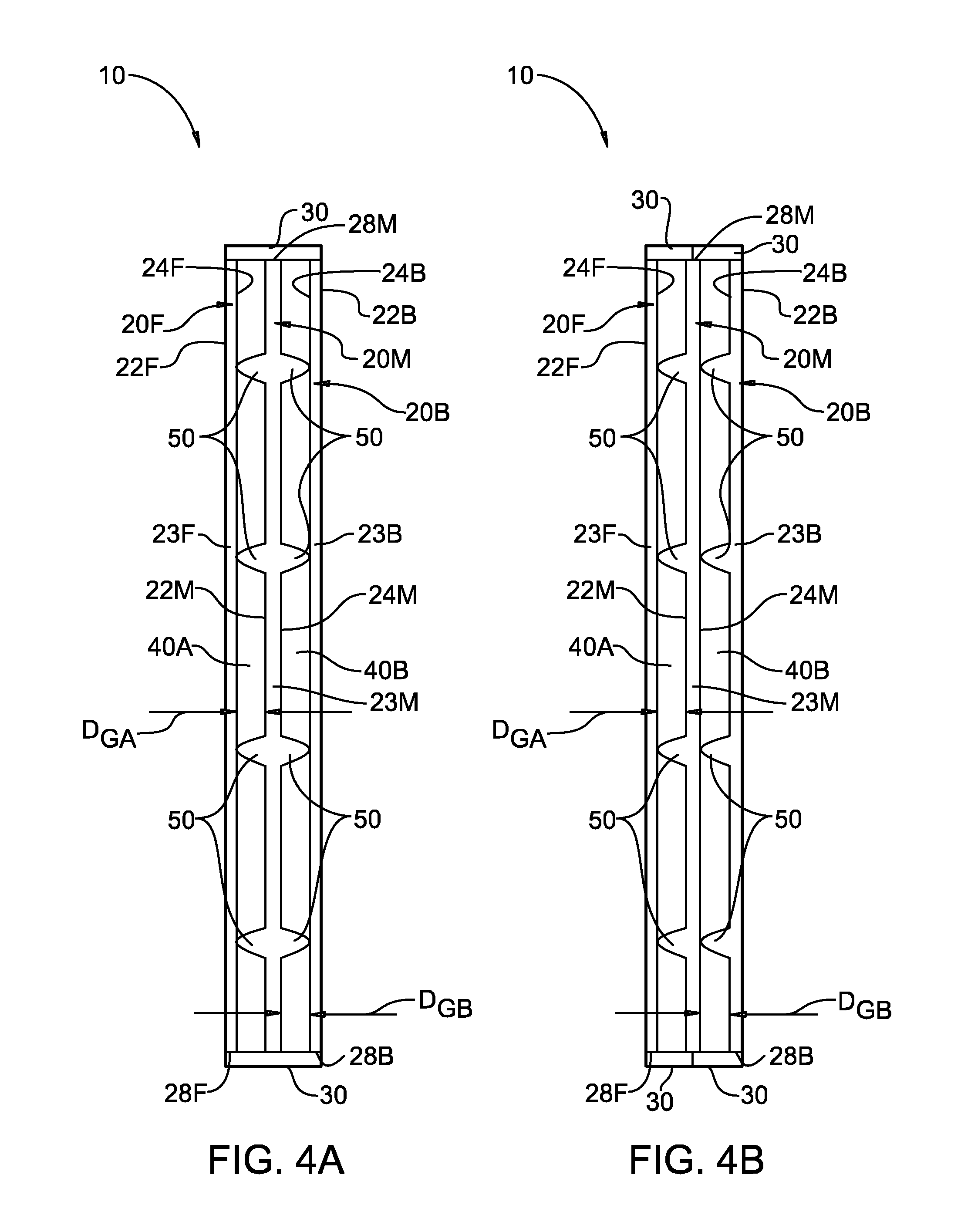
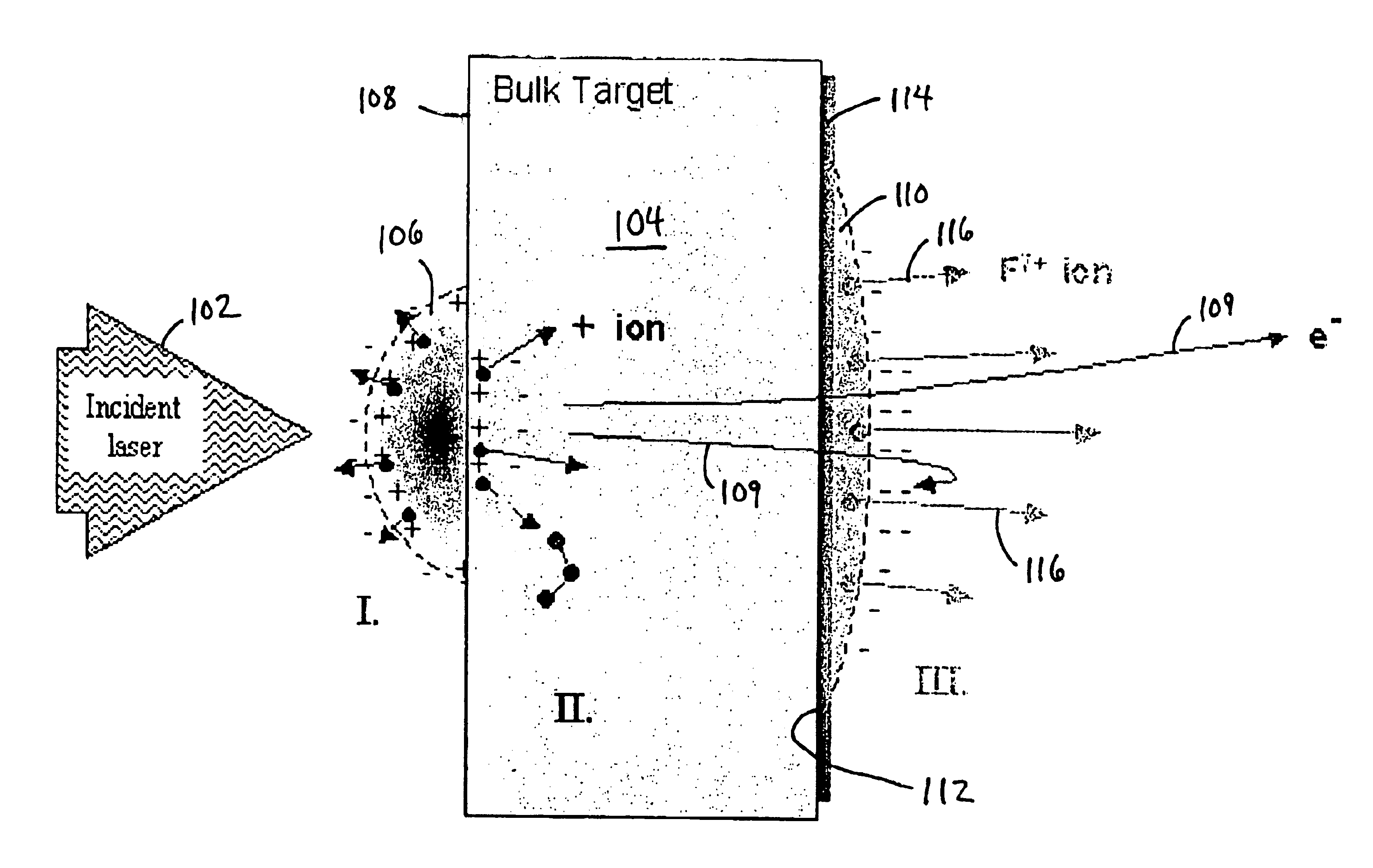
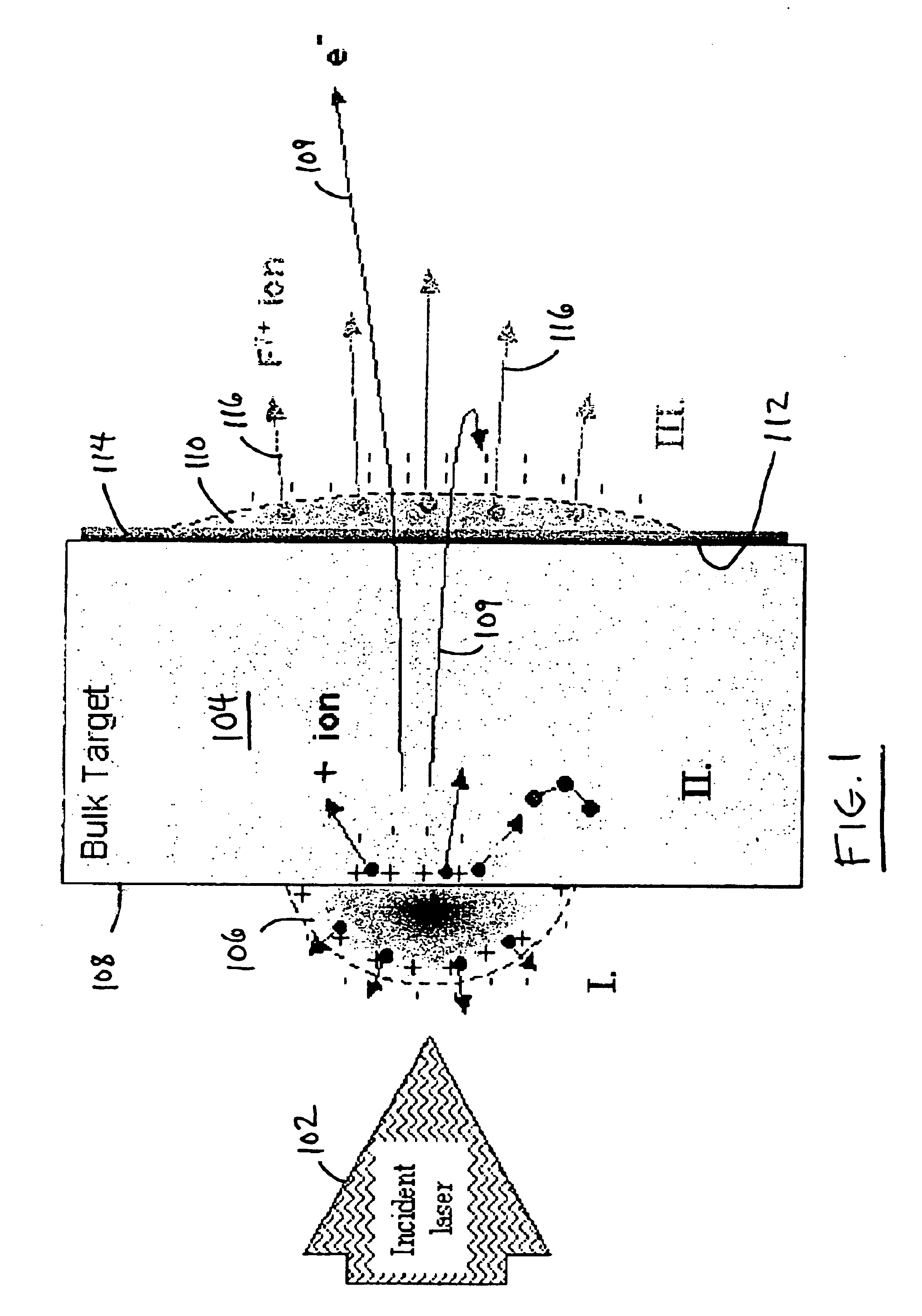
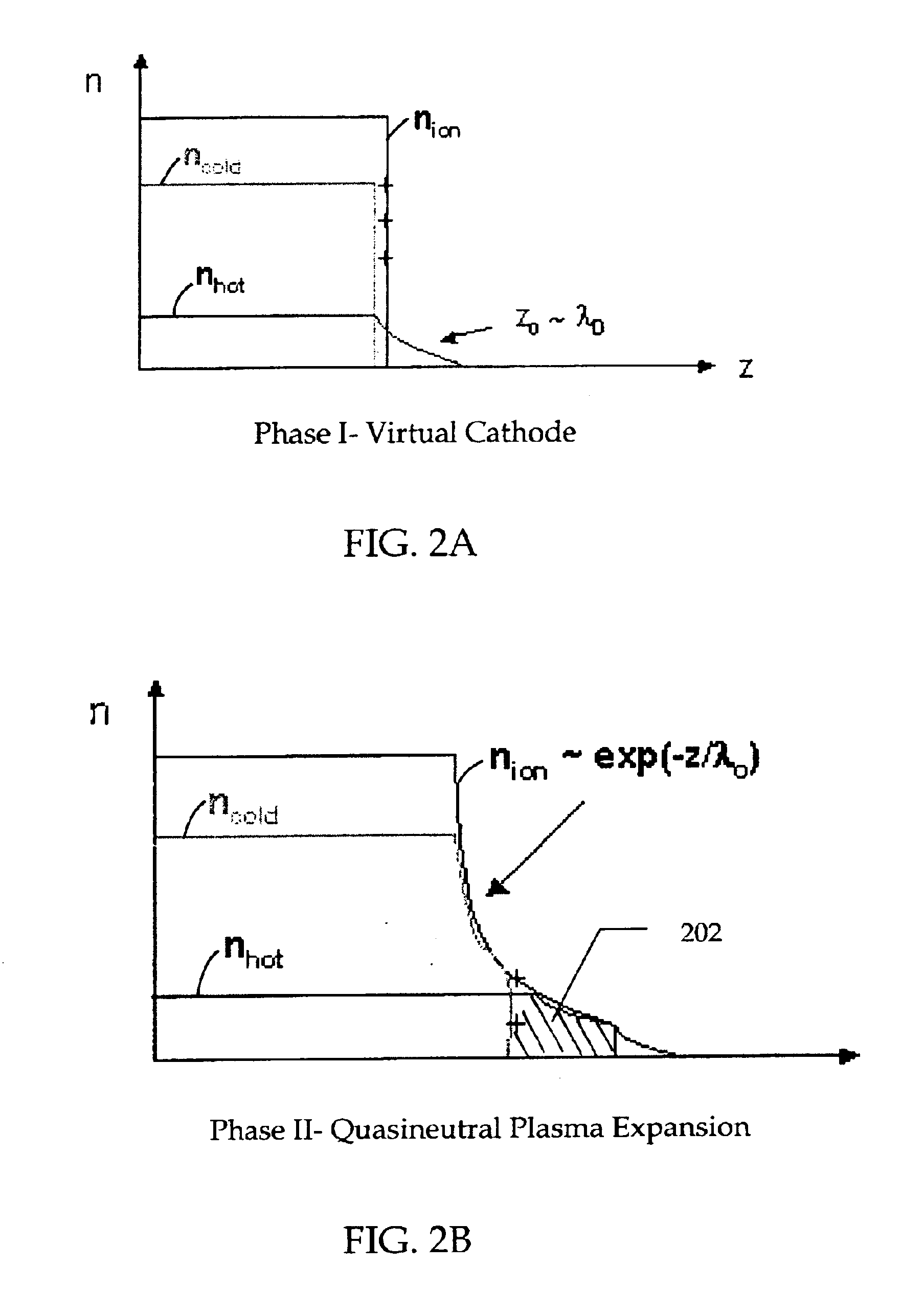
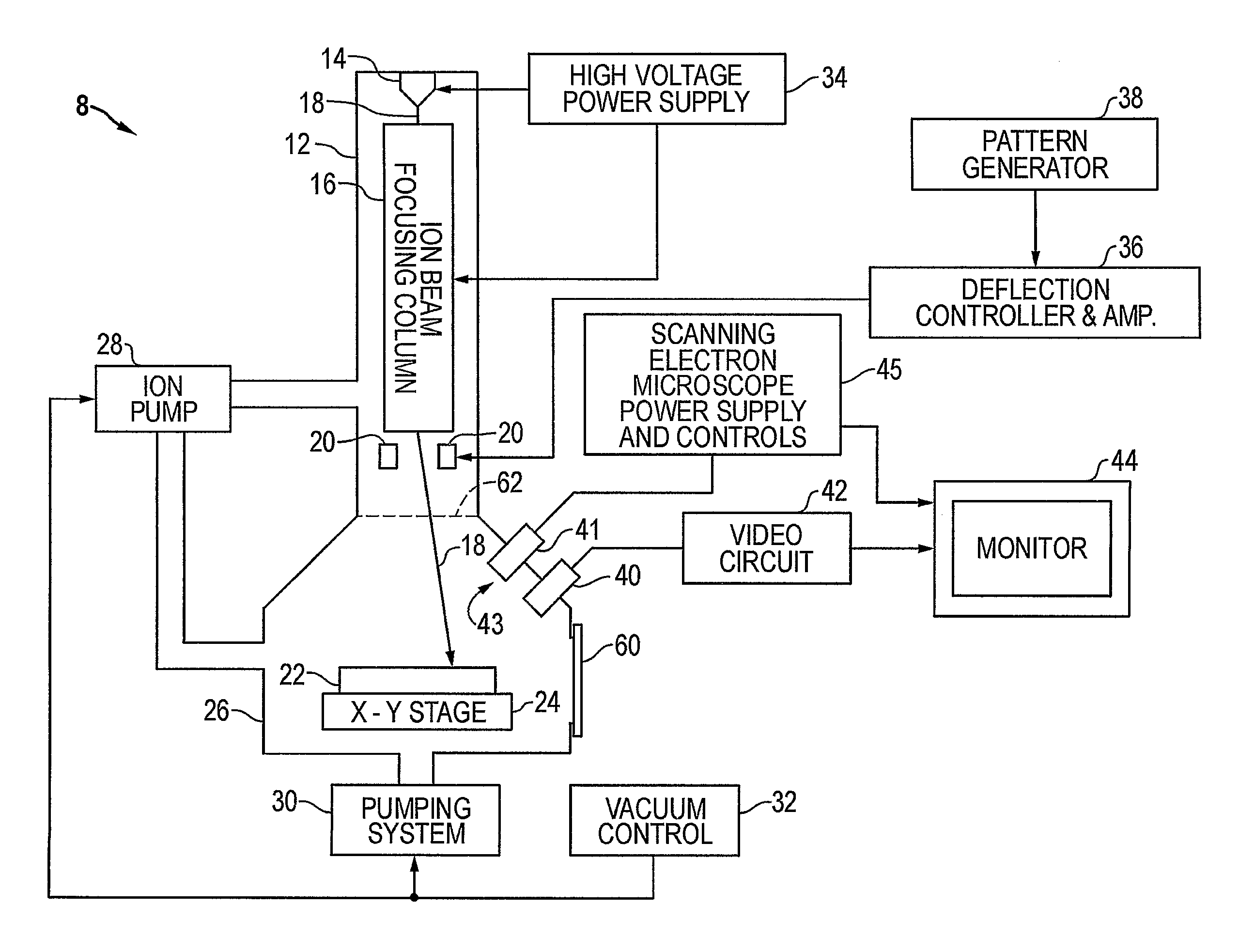
Method and apparatus for nanometer-scale focusing and patterning of ultra-low emittance, multi-MeV proton and ion beams from a laser ion diode
InactiveUS6852985B2Stability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsLow emittanceGrating
Methods and apparatus for focusing proton and ion beams within the profile of the beam envelope of an ultra-low emittance, charge neutralized emission to create a pattern without focusing the entire beam envelope or rastering. In one implementation, a method for use with laser accelerated ion beams comprises the steps: irradiating a surface of a target with pulsed laser irradiation to produce an electron plasma emission on a non-irradiated surface of the target, the electron plasma emission producing an ion beam emission on the non-irradiated surface, the ion beam emission having a beam envelope; and focusing ions of the ion beam emission into a plurality of component beams within the beam envelope as a result of the shape of the non-irradiated surface of the target.
Owner:GENERAL ATOMICS
Major structure of dual-mode superconductive photocathode injector
InactiveCN101888737AReduce repetition rateLow emissivity and high repetition rateDirect voltage acceleratorsLow emittanceDual frequency
The invention relates to a major structure of a dual-mode superconductive photocathode injector, belonging to the technical field of accelerators. In the major structure, the QWR superconductor cavity of a low-frequency TEM mode and the high beta ellipsoidal superconductor cavity of a high frequency TM mode forms a dual-mode dual-frequency superconductor cavity, the QWR superconductor cavity and the high beta ellipsoidal superconductor cavity are connected through a beam tube, the QWR superconductor cavity is used for leading out a low-energy electron beam, the high beta ellipsoidal superconductor cavity is used for bunching and energizing the electron beam, and the frequencies of the two cavities are in frequency multiplication and synchronization relation. The electron beam produced by the invention has the advantages of ultra-short pulse, ultra-low emittance and high average current.
Owner:赵夔
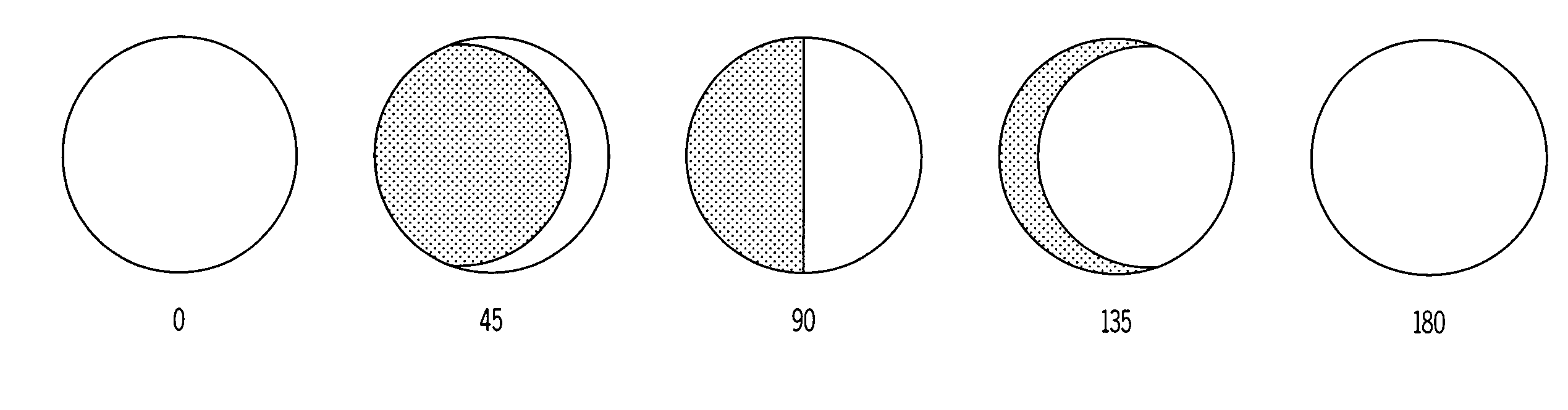
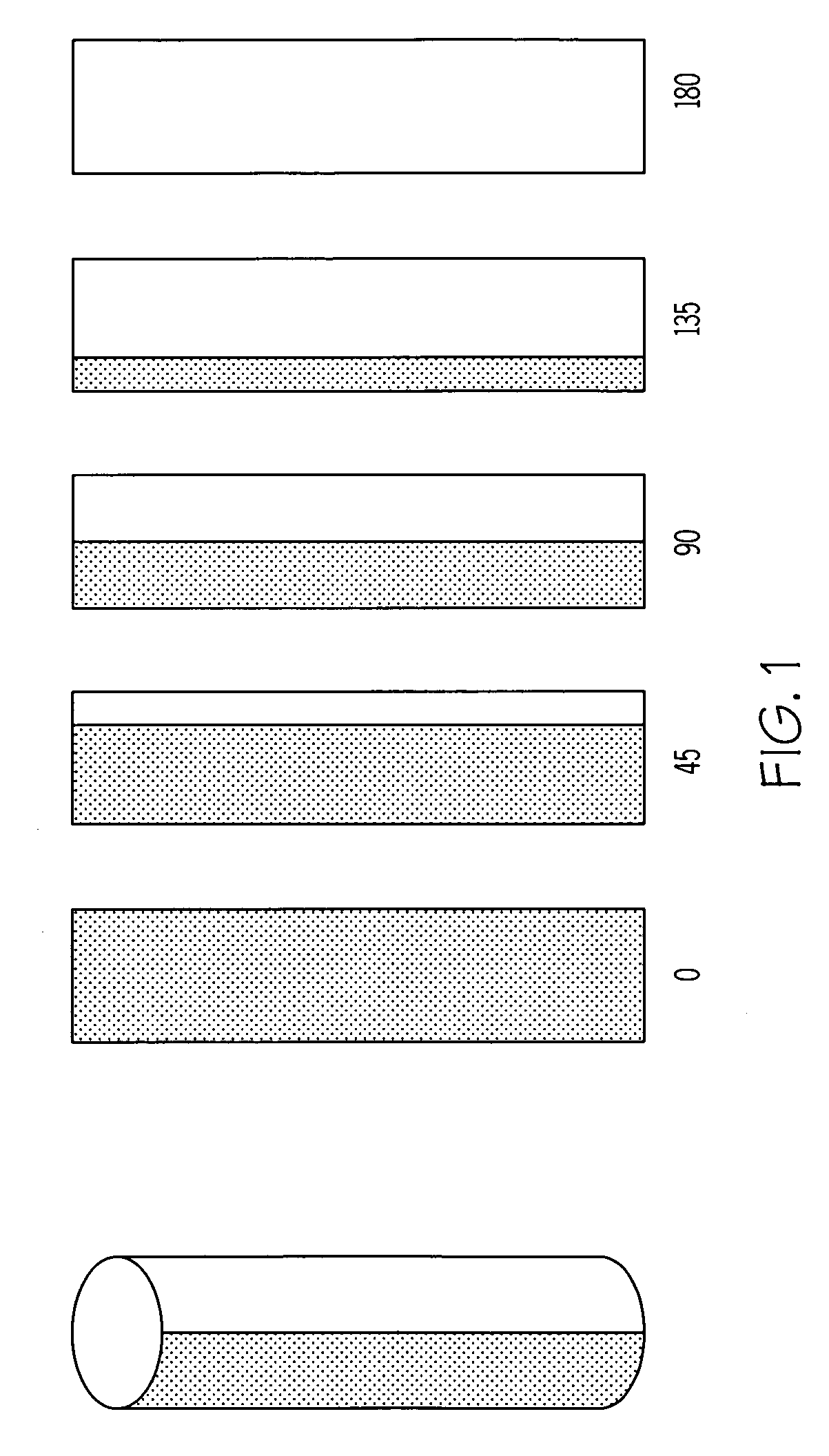
Variable emittance surfaces
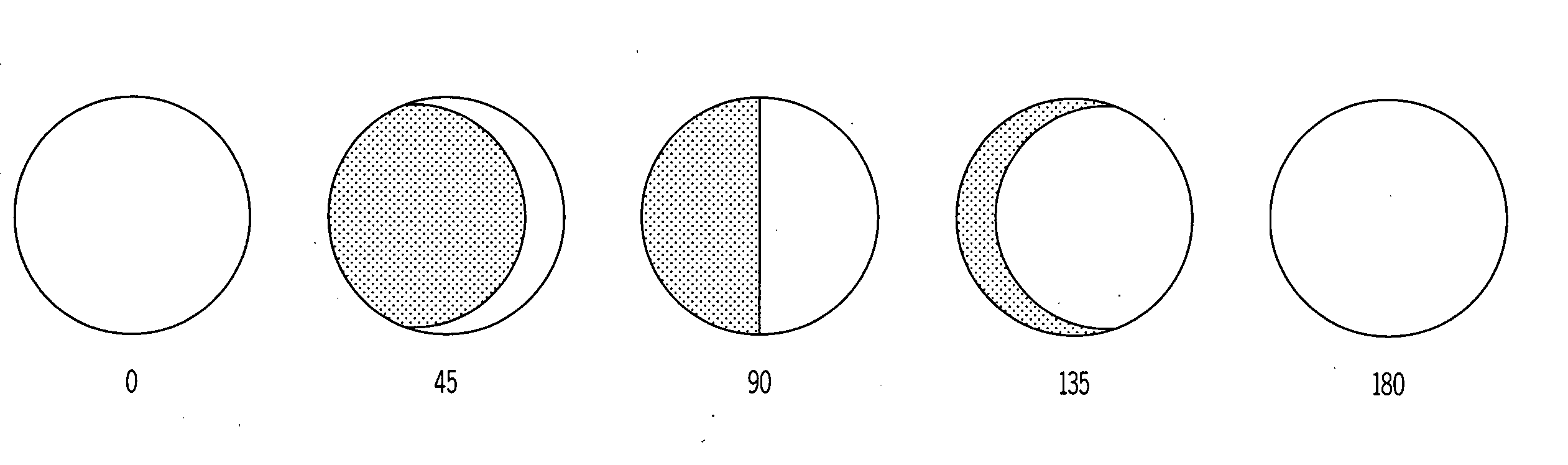
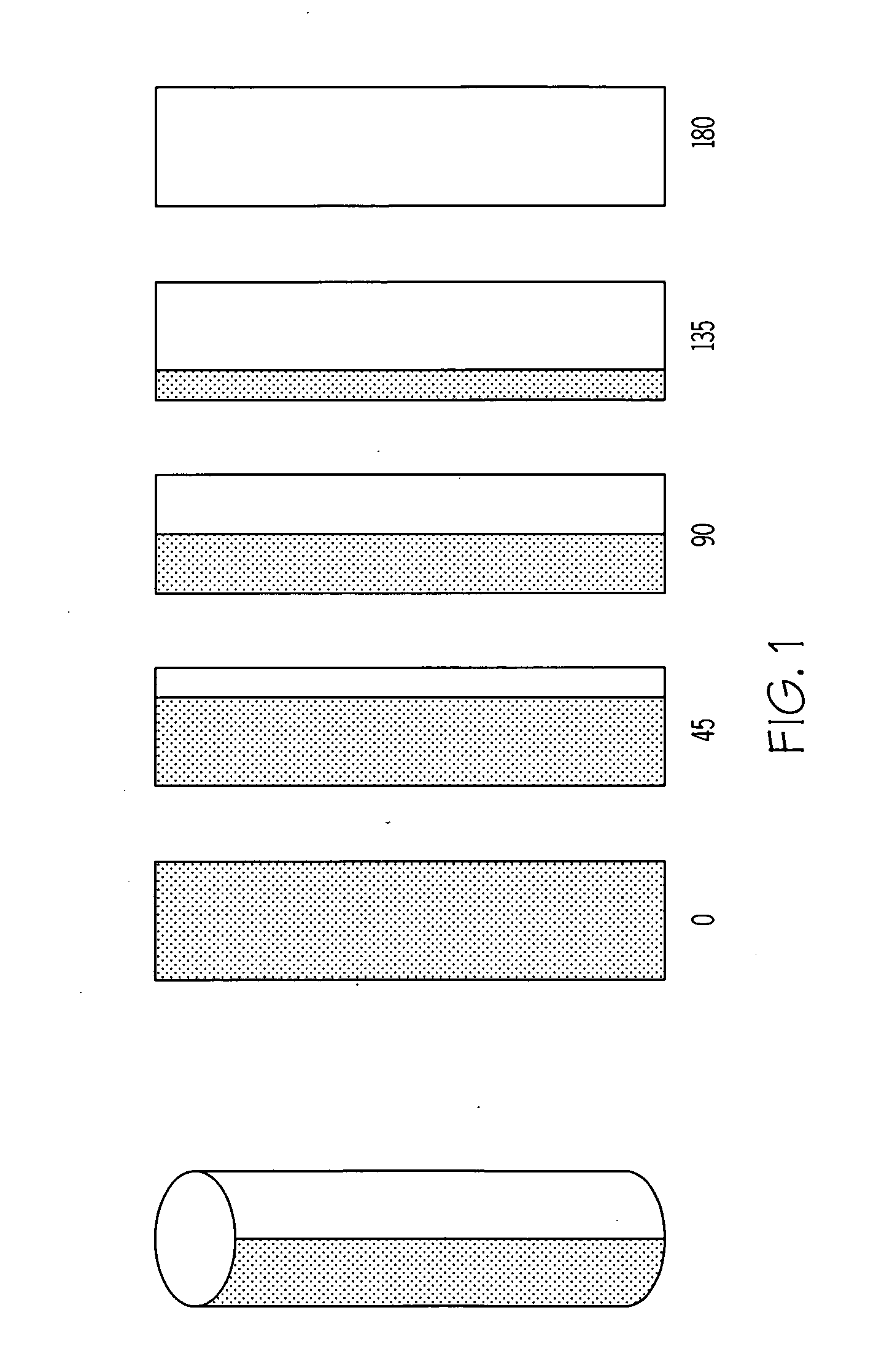
Designs for constructing a surface with variable emittance are described. This is achieved by making a surface where the emissivity varies on a scale smaller than the resolution of a thermal imager viewing the surface. One design utilizes many cylindrical surfaces with their axis parallel and their surfaces nearly in contact. Individual cylinders have the property that when rotated to zero degrees they show a surface with an emissivity of one and when rotated to 180 degrees display a surface with an emissivity of zero. At intermediate angles of rotation a sensor that could resolve individual cylinders would see alternate lines with high and low emittance but a sensor unable to resolve individual cylinders sees a surface with an emittance that depends on the angle the cylinders are rotated. Variable emittance surfaces are expected to be useful for controlling target signature and for making spectral reflectivity measurements using a hyper-spectral radiometer.
Owner:ARMY UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY DEPT OF THE
Temperature induced emissivity reversibly variable material
InactiveCN1544390AReduced heat dissipationIncreased heat dissipationThermosensitive paintsLow emittanceThermal transpiration
The invention relates to a reversibly changing material with temperature emittance used for air-conditioning type construction materials, which is prepared from La2O3, SrCO3, Mn3O4, Na2O, K2O and CaO of a finite weigh proportion through burning, first in 850-1100 deg. C air for 5-15 hrs, and in 1150-1250 deg. C air for 10-20 hrs, the material exhibits low emittance property at low-temperature, thus diminishing thermal transpiration on the object surface, when temperature arises, it exhibits high emissivity property, thus increasing thermal transpiration on the object surface, the two different properties can vary reversibly with the temperature.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
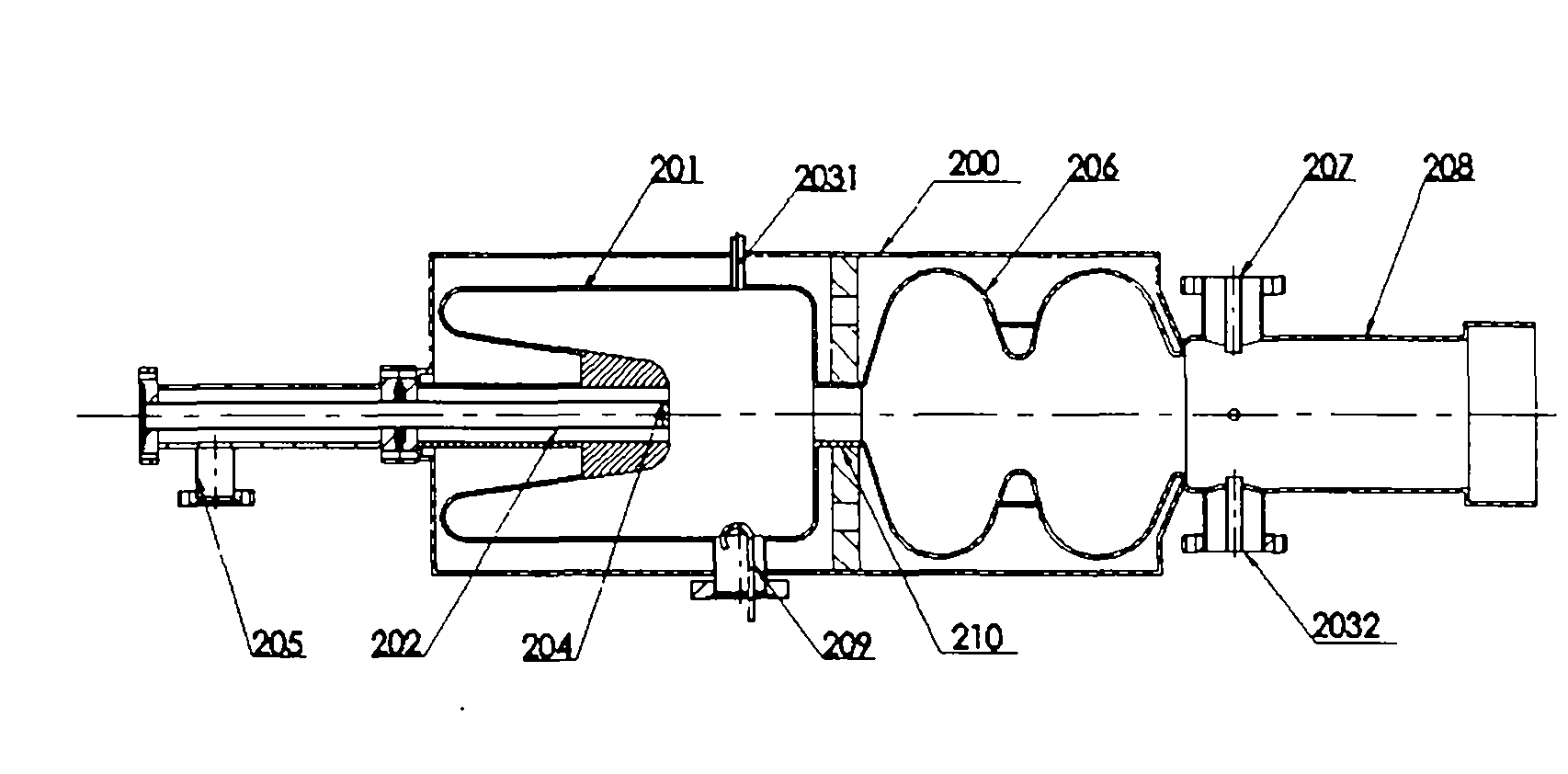
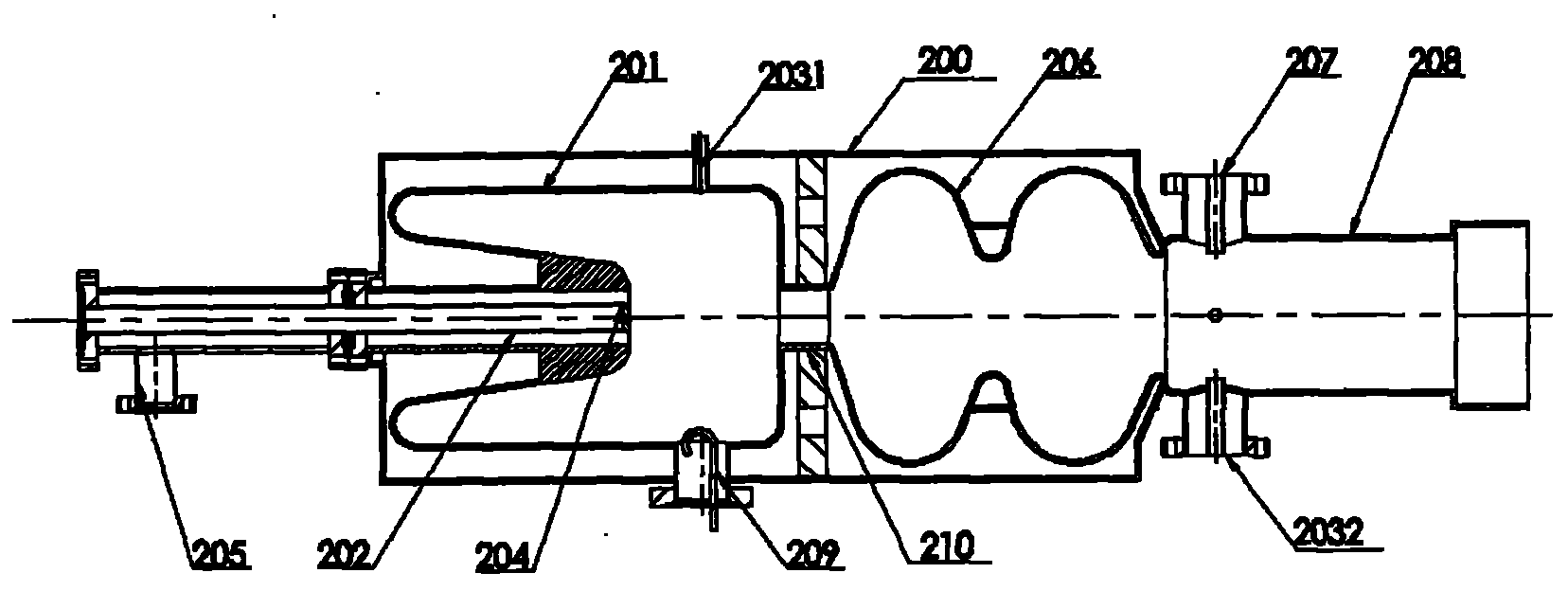
Photoelectron linear accelerator for producing a low emittance polarized electron beam
InactiveUS20040061456A1Improve quantum efficiencyLong lastingElectric discharge tubesLinear acceleratorsLow emittanceEmissivity
A photoelectron linear accelerator for producing a low emittance polarized electron beam. The linear accelerator includes a tube having an inner wall, the inner tube wall being coated by a getter material. A portable, or demountable, cathode plug is mounted within said tube, the surface of said cathode having a semiconductor material formed thereon.
Owner:DULY RES
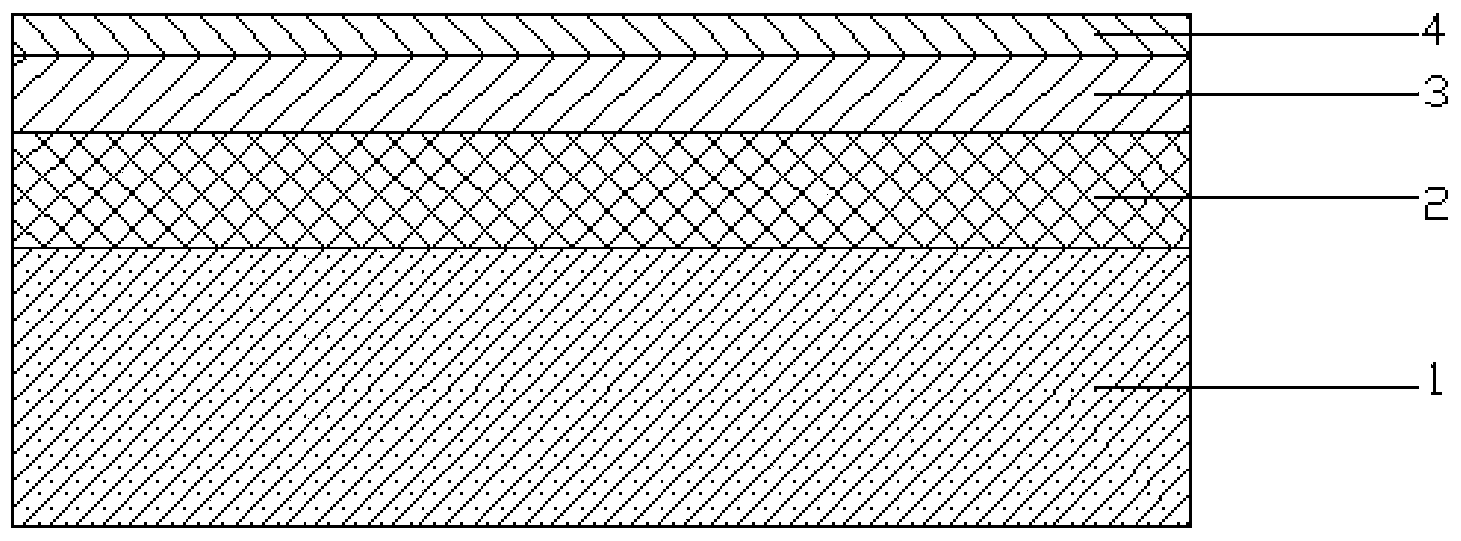
High temperature-resistant low-infrared emittance composite coating and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103924205AIncrease temperatureImprove high temperature stabilityLiquid surface applicatorsVacuum evaporation coatingLow emittanceEmissivity
The invention discloses a high temperature-resistant low-infrared emittance composite coating capable of being coated on stainless steel or an alloy. The high temperature-resistant low-infrared emittance composite coating contains three-layer structures, wherein the three-layer structures sequentially include a dispersion barrier layer, a low emittance functional layer and an MgO protective film from inside to outside; the dispersion barrier layer is formed from a ZnO-Al2O3-SiO2 microcrystalline glass coating, and the low emittance functional layer is formed from an Au film. A preparation method of the high temperature-resistant low-infrared emittance composite coating comprises the following steps: firstly uniformly mixing raw material powder, placing into a crucible, then smelting at high temperature, quenching, carrying out ball milling on obtained glass residues, drying, and screening to obtain glass powder; mixing the glass powder and an organic carrier, and carrying out ball milling dispersion to obtain a dispersion barrier layer coating; and uniformly brushing the dispersion barrier layer coating on a substrate material by adopting a brushing method, preparing the Au film on the prepared dispersion barrier layer by adopting a magnetron sputtering method, and then preparing the MgO film to obtain the high temperature-resistant low-infrared emittance composite coating. The high temperature-resistant low-infrared emittance composite coating disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple preparation process, easiness for operation, excellent product property and low cost.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Photoelectron linear accelerator for producing a low emittance polarized electron beam
InactiveUS6744226B2Improve quantum efficiencyLong lastingElectric discharge tubesLinear acceleratorsLow emittanceEmissivity
Owner:DULY RES
Charged particle extraction device and method of design there for
ActiveUS7872242B2Stability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsLow emittanceEmissivity
The present invention provides a method for extracting a charged particle beam from a charged particle source. A set of electrodes is provided at the output of the source. The potentials applied to the electrodes produce a low-emittance growth beam with substantially zero electric field at the output of the electrodes.
Owner:FEI CO
Ultra-high vacuum photoelectron linear accelerator
InactiveUS20120229053A1Easy to operateImprove cooling effectLinear acceleratorsLow emittanceEmissivity
A photoelectron linear accelerator for producing a low emittance polarized electron beam. The linear accelerator includes a tube having a cylindrical wall, said wall being perforated to allow gas to flow to a pressure chamber containing ultra high vacuum pumps located outside the accelerator. The RF accelerator cavity comprises of two concentric cylindrical regions having different outside diameters and different lengths.
Owner:DULY RES
Energy-efficient fenestration assemblies
InactiveUS20130008101A1Reduce probabilityMore energyRoof covering using slabs/sheetsConstruction materialLow emittanceEmissivity
A fenestration assembly is described. The fenestration assembly includes: (1) a layer of film; (2) a frame having a first surface and a second surface, which is opposite to the first surface, the first surface substantially surrounding and having secured thereon the film and the frame having a thickness such that when the second side is fitted onto a window or a window frame, the thickness of the frame defines a space between the film and the window; and (3) wherein said film is a low-emittance film having an emissivity equal to or less than 0.35.
Owner:SPRING E FRAME LLC
Method for improving bonding strength of low-emissivity coating and carbon fiber base material
ActiveCN112779768ASolve the problem of reduced mechanical propertiesImprove adhesionCarbon fibresFiberLow emittance
The invention relates to a method for improving the bonding strength of a low-emissivity coating and a carbon fiber base material, and solves the problem that the mechanical properties of the coating and the carbon fiber base material are reduced due to high-temperature failure of an organic resin binder on the surface of the carbon fiber base material compared with a traditional direct spraying method. By means of high-temperature pretreatment and preparation of an organic silicon resin middle layer, the binding force of the coating and the surface of the base material is increased, an obtained sample has the advantages of being resistant to high temperature, low in emissivity, high in adhesive force and the like, good infrared performance and good mechanical performance can be achieved, the adhesive force of the sample is about 5.0 + / -0.4 Mpa after the sample is subjected to high-temperature heat treatment for 30 min at the temperature of 500 DEG C, and the requirements of various fields on good binding force of the high-temperature-resistant low-emissivity coating and the polyimide carbon fiber base material are met.
Owner:四川智溢实业有限公司 +1
Preparation method for high-temperature-resistant infrared low-emittance coating
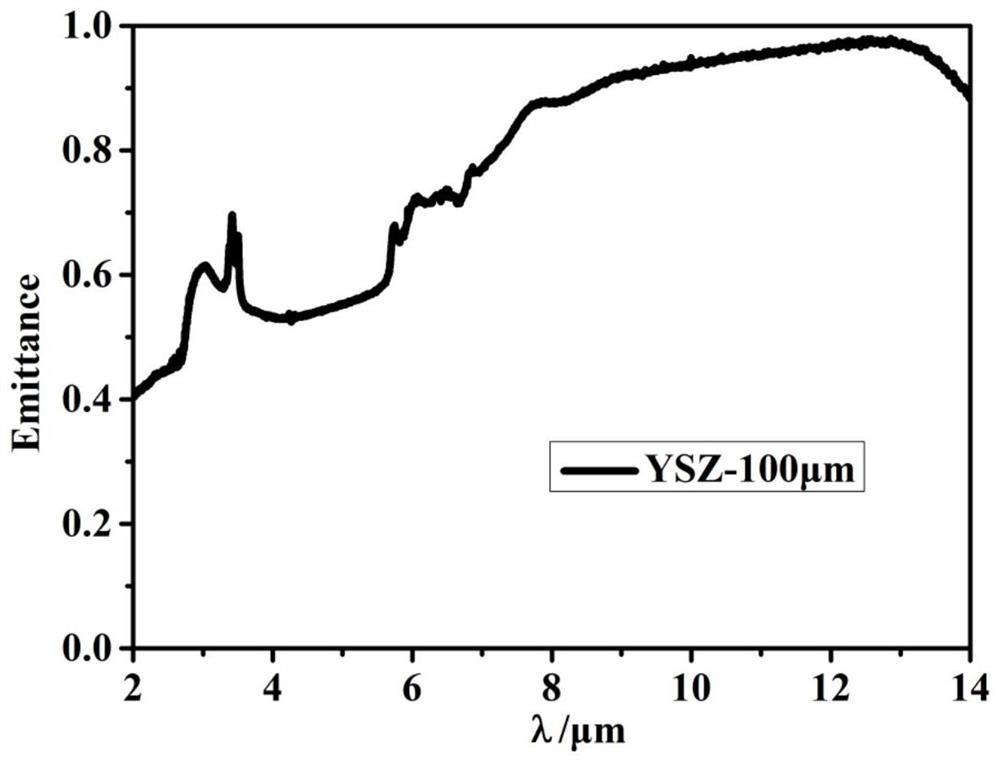
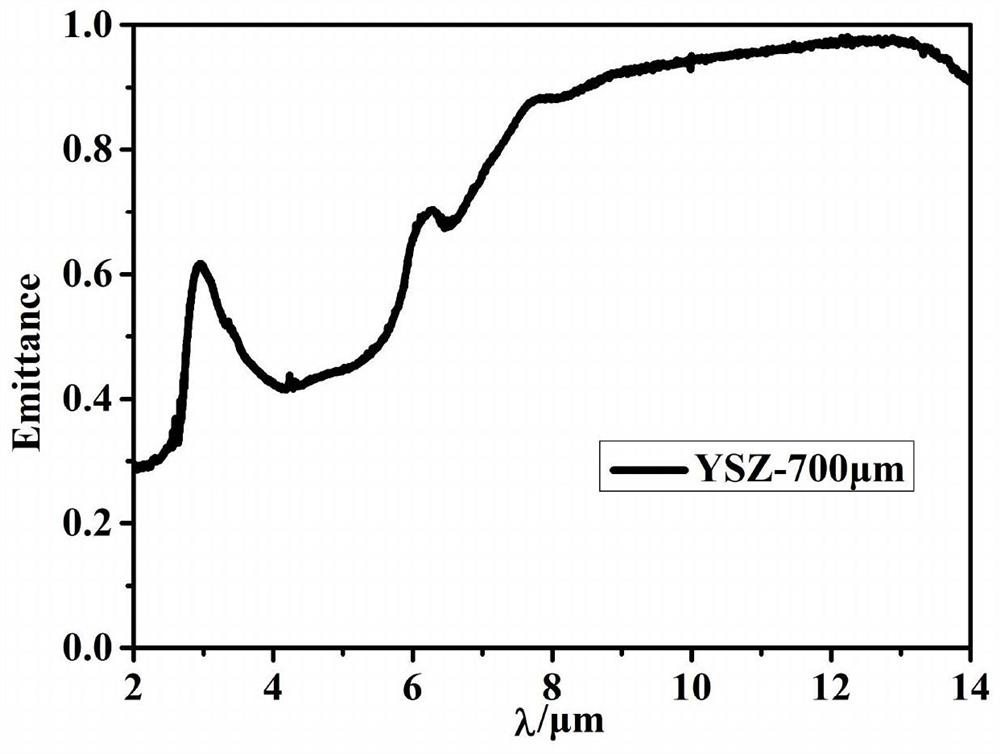
ActiveCN112095067AGood heat insulationReduce the temperatureMolten spray coatingLow emittanceTarget surface
The invention belongs to the technical field of infrared stealth, and particularly relates to a preparation method for a high-temperature-resistant infrared low-emittance coating. According to the method provided by the invention, the coating does not need to be added with an adhesive, so the emittance is not increased at a high temperature; and moreover, the prepared coating is non-transparent inthe normal direction of 2 microns to 14 microns, and the coating provides benefits to an infrared stealth technology. Besides, a YSZ material is relatively good in heat insulation performance. Therefore, when the YSZ material is applied to preparation of a low-emittance coating, reduction of the temperature of a target surface is facilitated. In this way, the effect of reducing the infrared radiation intensity of an aircraft is doubled. Furthermore, in order to make sure that a YSZ coating is non-transparent in other directions, a YSZ / NiCoCrAIY composite coating is sprayed on a graphite substrate in advance, and then preparation of the YSZ coating and stripping of the graphite substrate are carried out on the surface of the composite coating.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
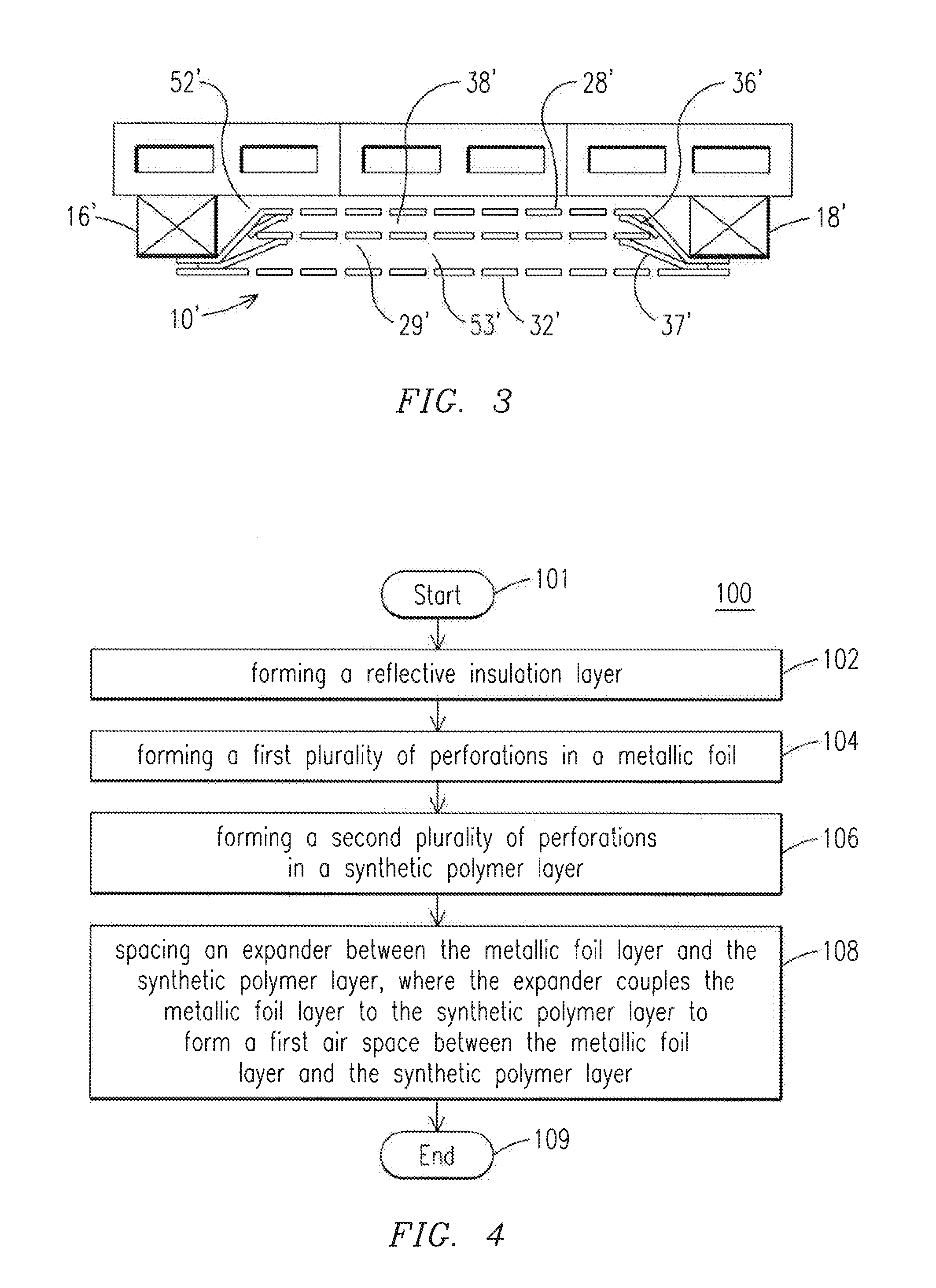
System and method for providing a reflective insulation layer
A reflective insulation layer is provided for a structure. The structure includes a wall and spaced-apart strips which extend along the wall from a top portion of the wall to a bottom portion of the wall. The reflective insulation layer includes a low emittance layer having first perforations, an intermediate low emittance layer having first perforations and an outer synthetic polymer layer having second perforations. Additionally, the reflective insulation layer includes a first expander spaced between the low emittance layer and the intermediate low emittance layer, to couple the low emittance layer to the intermediate low emittance layer and form a first air space. Additionally, the reflective insulation layer includes a second expander spaced between the intermediate low emittance layer and the outer synthetic polymer layer, to couple the intermediate low emittance layer to the outer synthetic polymer layer and form a second air space.
Owner:FI FOIL
Glass panel
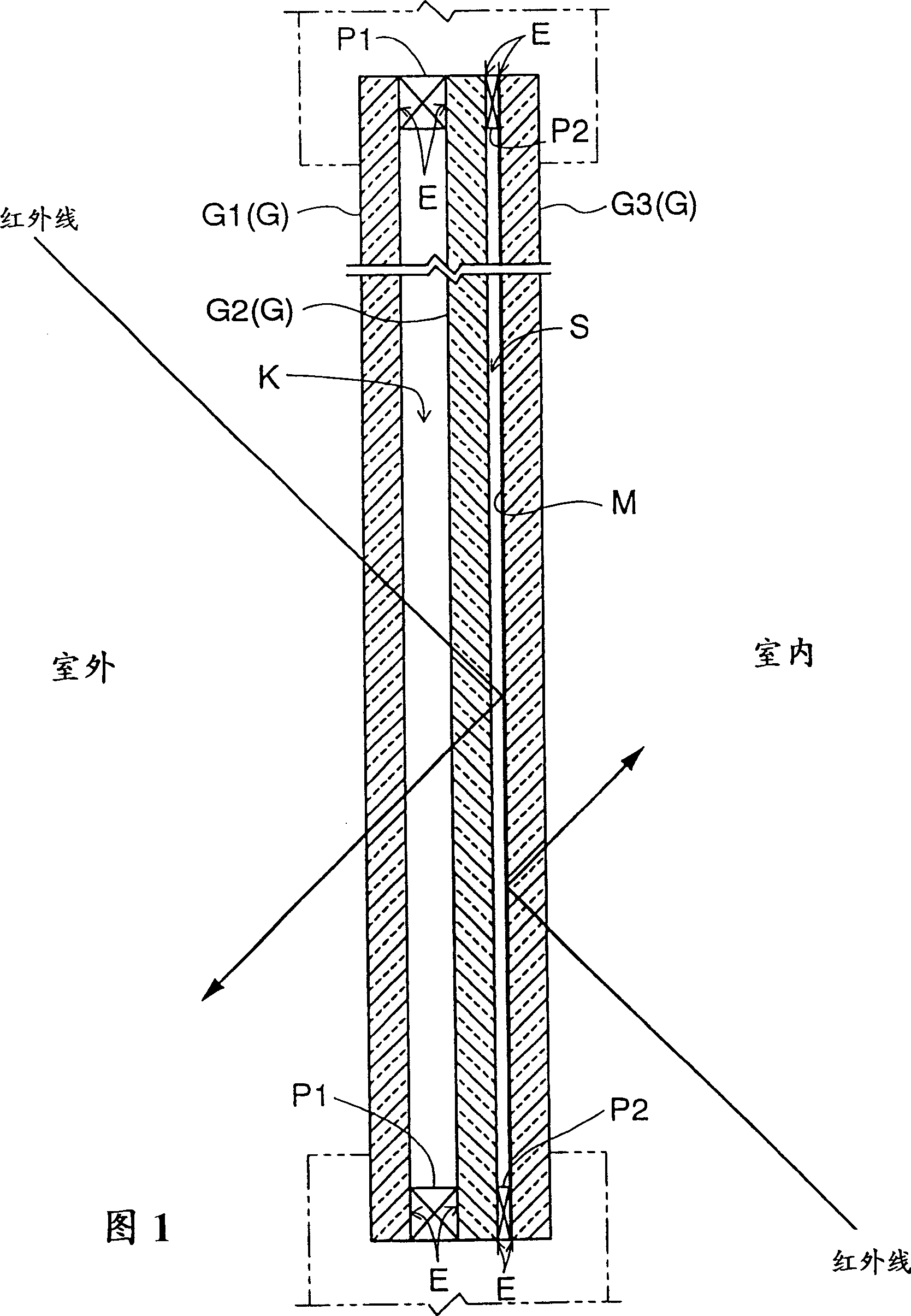
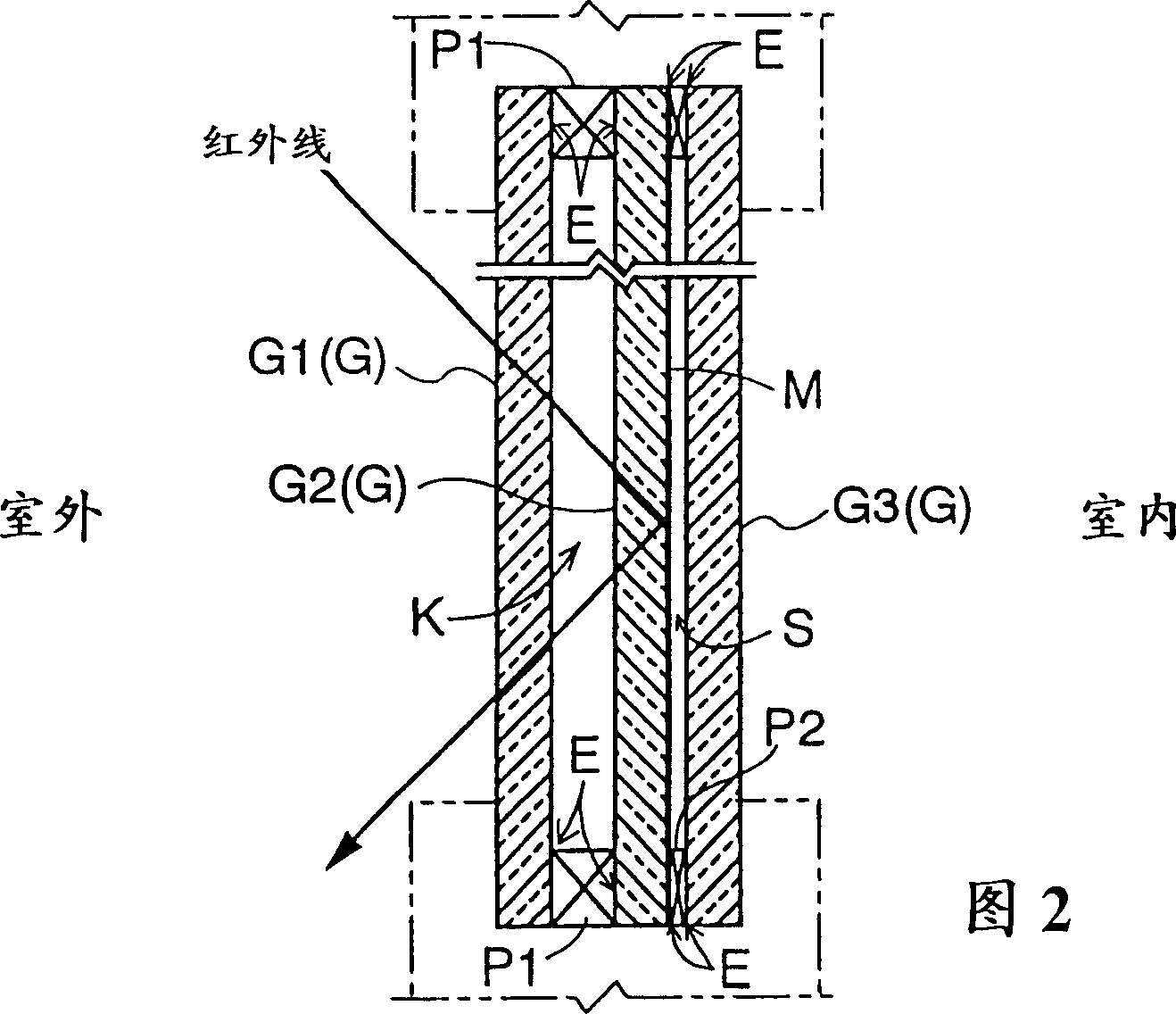
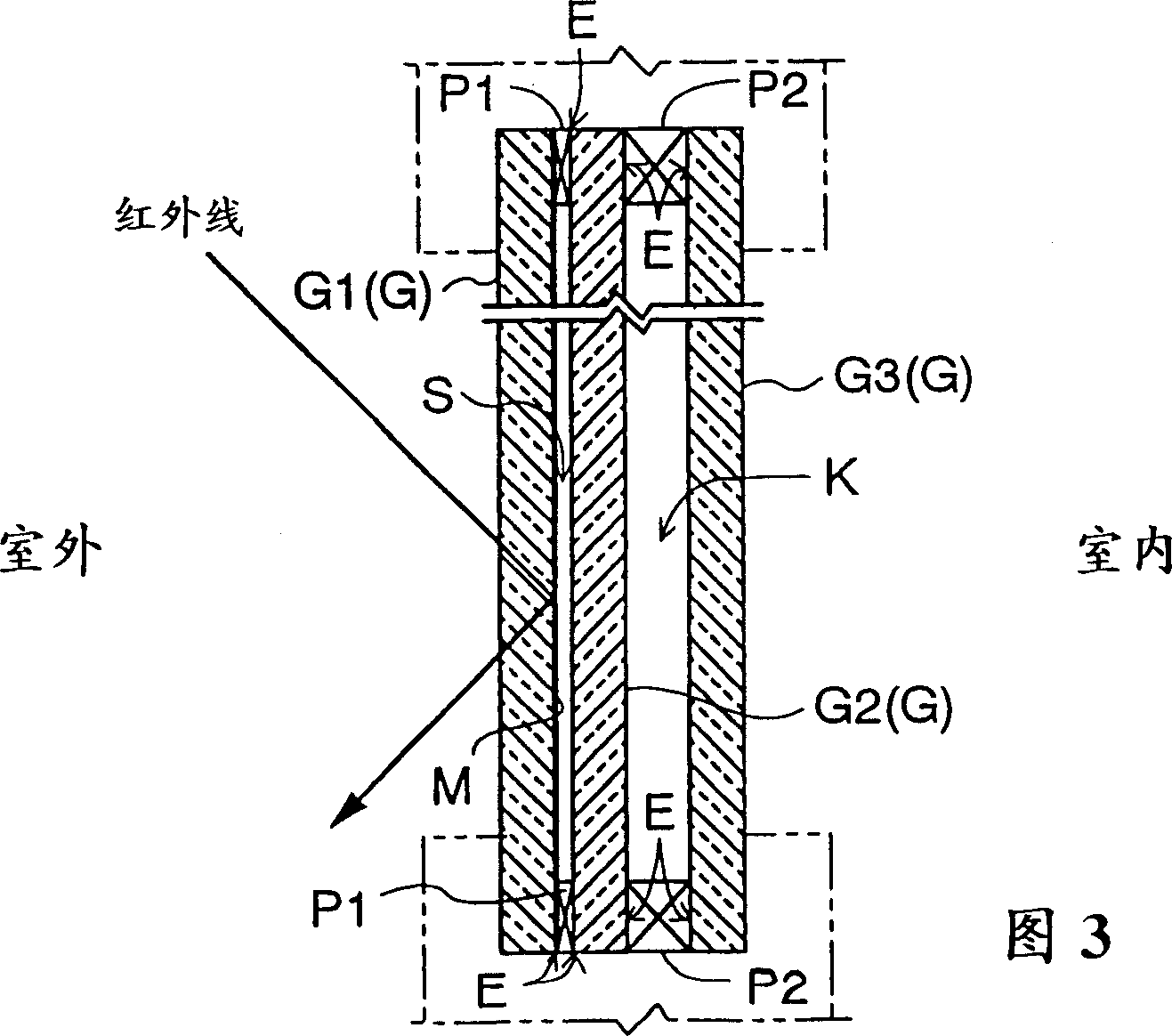
InactiveCN1240925CAvoid emissionsGood insulation performanceClimate change adaptationWindows/door improvementLow emittanceFlat glass
In a glass panel includes at least three glass sheets for forming an air layer (K) and a vacuum layer (S) side by side and for partitioning between outdoor space and indoor space, at least either an outdoor-side glass sheet contacting the outdoor space or an indoor-side glass sheet contacting the indoor space of the glass sheets (G) contacts the vacuum layer (S) and includes a low-emittance film layer (M) formed on a face thereof contacting the vacuum layer (S).
Owner:NIPPON SHEET GLASS CO LTD
Variable emittance surfaces
Designs for constructing a surface with variable emittance are described. This is achieved by making a surface where the emissivity varies on a scale smaller than the resolution of a thermal imager viewing the surface. One design utilizes many cylindrical surfaces with their axis parallel and their surfaces nearly in contact. Individual cylinders have the property that when rotated to zero degrees they show a surface with an emissivity of one and when rotated to 180 degrees display a surface with an emissivity of zero. At intermediate angles of rotation a sensor that could resolve individual cylinders would see alternate lines with high and low emittance but a sensor unable to resolve individual cylinders sees a surface with an emittance that depends on the angle the cylinders are rotated. Variable emittance surfaces are expected to be useful for controlling target signature and for making spectral reflectivity measurements using a hyper-spectral radiometer.
Owner:ARMY UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY DEPT OF THE
Solar heat transfer unit
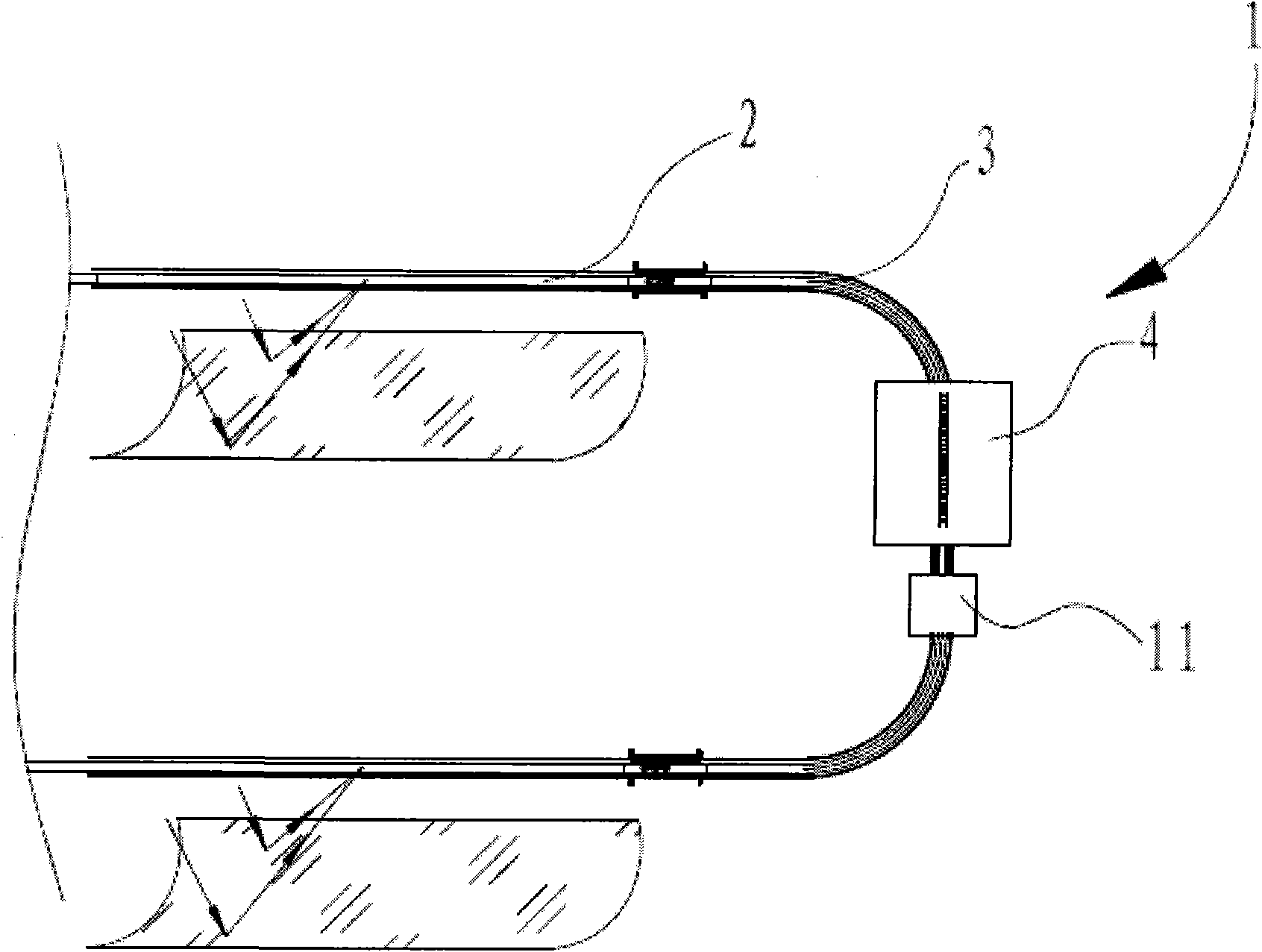
InactiveCN102338476AImprove thermal conductivityImprove heat transfer efficiencySolar heat devicesSolar thermal energy generationLow emittanceHigh absorption
The invention discloses a solar heat transfer unit (1). The solar heat transfer unit (1) comprises a heat-absorbing area (2), a heat-releasing area (4), a fixed-shape heat-transfer medium and a driving device (11), wherein the interiors of the heat-absorbing area (2) and the heat-releasing area (4) are provided with inner-layer metal tubes, and the fixed-shape heat-transfer medium penetrates through the inner-layer metal tubes; the heat-absorbing area (2) is arranged at the position capable of receiving solar energy rays, a coating with high absorption rate and low emittance is coated on the external surface of the part of the heat-absorbing area by the inner-layer metal tube; and the driving device (11) can drive the fixed-shape heat-transfer medium to run in the solar heat transfer unit (1). The invention has the following advantages: the unit can be subjected to mass production and installation in a large size; a sphere metal or sphere ceramic (5) of the fixed-shape heat-transfer medium has high coefficient of heat conductivity, thus the heat transfer efficiency is high, no leak danger exists and an environmentally-friendly goal can be realized; the unit has the ultra-high temperature heat-transfer capacity; the unit has low cost, stable performance and long service life and is easy to manufacture.
Owner:BEIJING TERASOLAR PHOTOTHERMAL TECH CO LTD
Battery for use in the stratosphere
InactiveUS20210104787A1Batteries circuit arrangementsCell temperature controlLow emittanceThermodynamics
Aspects of the disclosure relate to batteries for use in the stratosphere, such as those employed on aerial vehicles. The battery may include an outer case structure, a thermal insulator such as foam arranged within the outer case structure, a battery management unit and a plurality of battery cells both arranged within the thermal insulator, and a heater arranged within the thermal insulator and around the battery cells. In some instances, the battery may also include a thermal reflector arranged between the heater and the thermal insulator, wherein a surface of the thermal reflector is arranged to reflect heat back towards ones of the plurality of battery cells. In some instances, the thermal insulator may include overlapping baffles to reduce an amount of air passing from the outer case and through the thermal insulator. In some instances, the outer case may include a plastic layer with a low emissivity coating.
Owner:LOON LLC
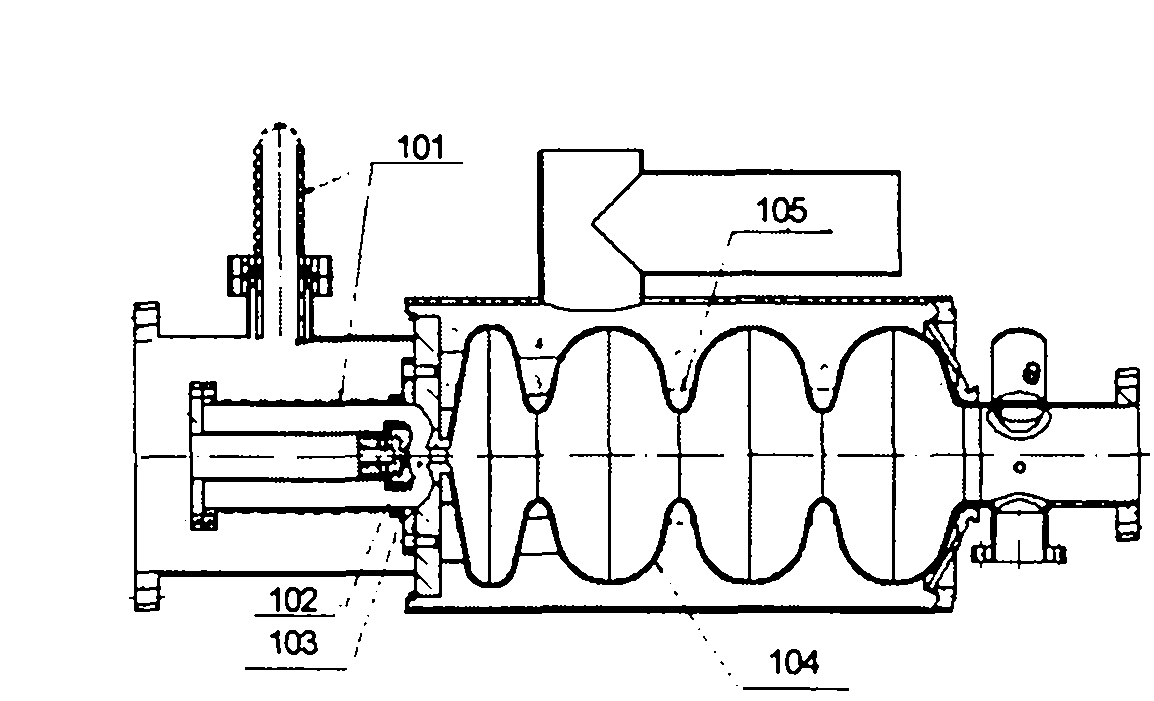
Spectrally-engineered solar thermal photovoltaic devices
A solar thermal photovoltaic device, and method of forming same, includes a solar absorber and a spectrally selective emitter formed on either side of a thermally conductive substrate. The solar absorber is configured to absorb incident solar radiation. The solar absorber and the spectrally selective emitter are configured with an optimized emitter-to-absorber area ratio. The solar thermal photovoltaic device also includes a photovoltaic cell in thermal communication with the spectrally selective emitter. The spectrally selective emitter is configured to permit high emittance for energies above a bandgap of the photovoltaic cell and configured to permit low emittance for energies below the bandgap.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Preparation method of heat-resisting plate for bias plate
ActiveCN112661526ALow thermal conductivityReduce weightNoise reduction installationsFiberLow emittance
The invention belongs to the technical field of bias plates, and discloses a preparation method of a heat-resisting plate for a bias plate. The method comprises the following steps: (1) processing a carbon fiber preform according to the structure of a heat-resistant plate; (2) preparing a pyrolytic carbon interface layer on the surface of the carbon fiber preform by a CVI method; (3) repeating the steps of dipping, curing and low-temperature cracking for 2-4 times; (4) repeating the steps of dipping, curing and high-temperature cracking for 1-3 times; (5) carrying out mechanical rough machining; (6) repeating the steps of dipping, curing and low-temperature cracking for 2-4 times; (7) repeating the steps of dipping, curing and high-temperature cracking for 1-3 times; (8) carrying out mechanical finish machining; and (9) depositing a SiC coating by using a CVD method to obtain the heat-resistant plate for the bias plate. The method is short in preparation period, and the prepared heat-resisting plate is high in density, small in density gradient, extremely low in ablation rate, low in emissivity, good in oxidation resistance and scouring resistance and excellent in mechanical property.
Owner:GONG YI VAN-RES INNOVATION COMPOSITE MATERIAL CO LTD
A kind of adaptive thermal camouflage coating and preparation method thereof
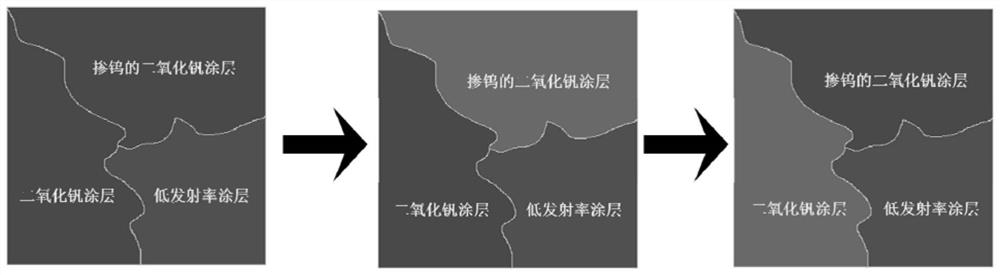
ActiveCN107189552BImprove infrared camouflage effectIncrease adaptive camouflage abilityInksLow emittanceVanadium dioxide
The invention discloses a self-adaptive thermal camouflage coating, which is located on a substrate, and is mainly formed by a vanadium dioxide coating, a tungsten-doped vanadium dioxide coating and a low-emissivity coating. A preparation method of the self-adaptive thermal camouflage coating provided by the invention comprises the steps of (1) preparing vanadium dioxide ink, tungsten-doped vanadium dioxide ink and low emissivity ink; (2) depositing the vanadium dioxide ink, the tungsten-doped vanadium dioxide ink and the low emissivity ink on the surface of the substrate through a spray ink printing method according to designed camouflage patterns, and obtaining a layer of self-adaptive thermal camouflage coating on the surface of the substrate. According to the self-adaptive thermal camouflage coating provided by the invention, the self-adaptive thermal camouflage coating is prepared by adopting vanadium dioxide nano-powder with a thermotropic infrared emittance characteristic, tungsten-doped vanadium dioxide nano-powder and low emissivity silver powder, so that the camouflage patterns can be changed with the temperature change accordingly, and an infrared camouflage effect is greatly improved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Coating device having coated transmitter coil
PendingUS20200123657A1Low optical emissivityHigh light reflectivityElectric discharge tubesLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingTransmitter coilLow emittance
A device, for depositing a layer on a substrate by supplying one or more process gases to a process chamber, includes a susceptor and one or more transmitter coils. The susceptor bearing the substrate can be heated to a process temperature by means of an electromagnetic alternating field generated by the one or more transmitter coils. The one or more transmitter coils have a coating that consists of tin and nickel in order to provide a corrosion-resistant coating, which simultaneously has low emissivity and is therefore effective in the presence of chlorine compounds and moisture.
Owner:AIXTRON AG
SrZrO3 preparation method and SrZrO3 ceramic
ActiveCN110818409AHigh coefficient of thermal expansionLow thermal conductivityLow emittanceTemperature resistance
The invention provides an SrZrO3 preparation method. The preparation method comprises the steps that SrCO3 and ZrO2 are mixed and pressed into a blank, then the blank is placed in a microwave environment to be treated, and the treatment comprises powder treatment or block treatment, wherein the powder treatment comprises the steps: heating the blank to 1100-1400 DEG C, carrying out heat preservation for not less than 30 min, and thus obtaining SrZrO3 powder; and the block treatment comprises the steps: adding powder, burying and sintering, heating to 1200-1650 DEG C at the rate of 5-25 DEG C / min, sintering, and carrying out heat preservation for not less than 30 min to obtain an SrZrO3 block. The prepared SrZrO3 block has the excellent characteristics of good chemical stability, mechanicalstrength, high-temperature sintering resistance and the like, and can be used as an infrared stealth skin material for military weapons such as aircraft, tanks and the like with low emissivity, low thermal conductivity, high expansion coefficient and high temperature resistance. Meanwhile, the invention also provides the SrZrO3 ceramic prepared by the method.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF TECH
High thermal resistance and permeance insulation material
ActiveUS20150233109A1Increasing wall profileAdhesive articlesPassive housesLow emittanceResistive barrier
A low-emittance material having improved energy efficiency protection against air infiltration and moisture build-up in buildings is disclosed. The aforementioned low-emittance material utilizes existing framing openings or without increasing the wall profile of a building. The present invention provides a low-emittance material which may be implemented on traditional 2×4 framing having R-15 mass insulation material within existing or newly constructed framing cavities. The material of the present invention also meets requirements for serving as a water resistive barrier as defined by ICC AC38.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTALLY SAFE SYST
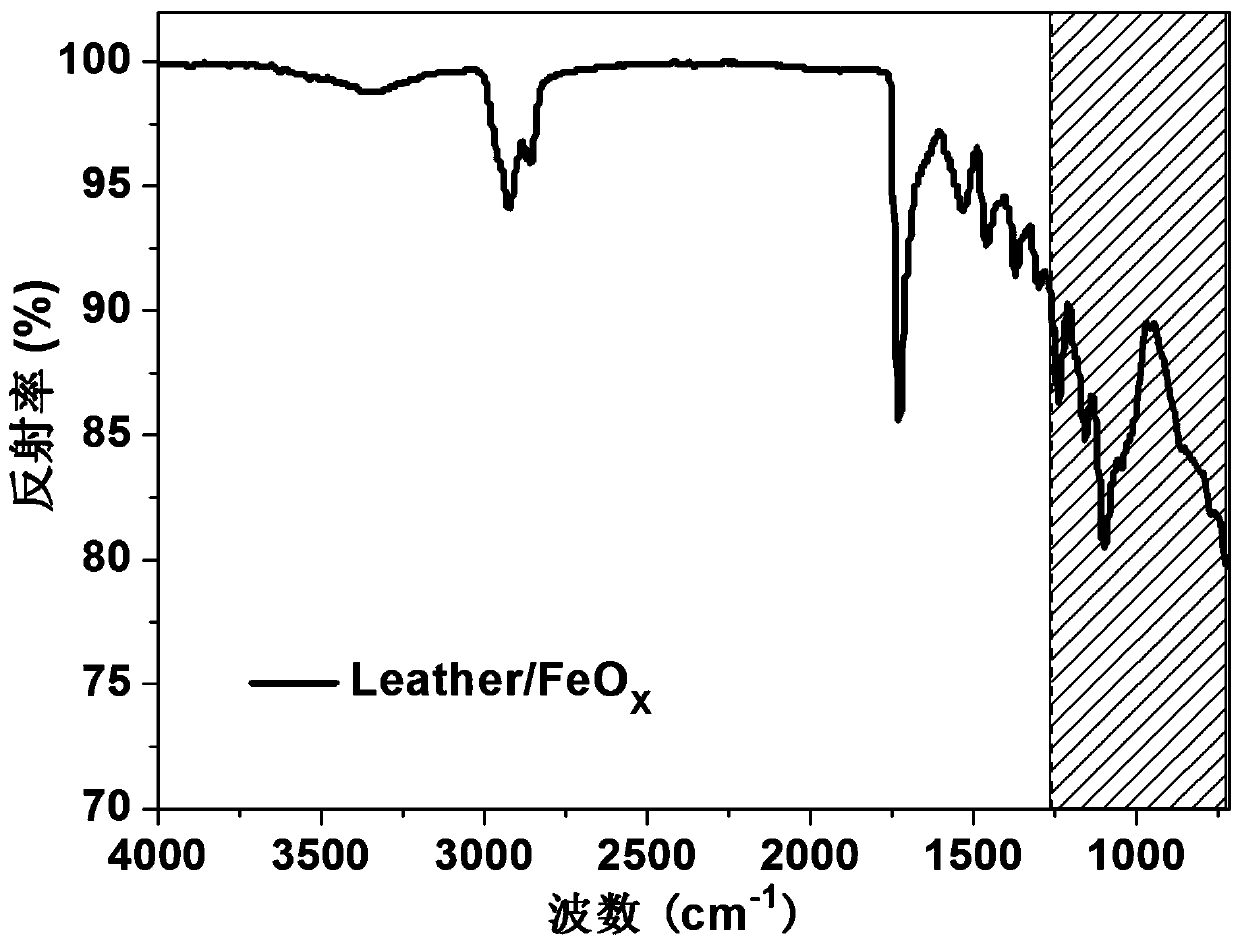
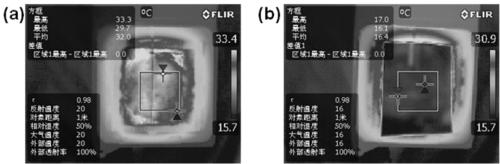
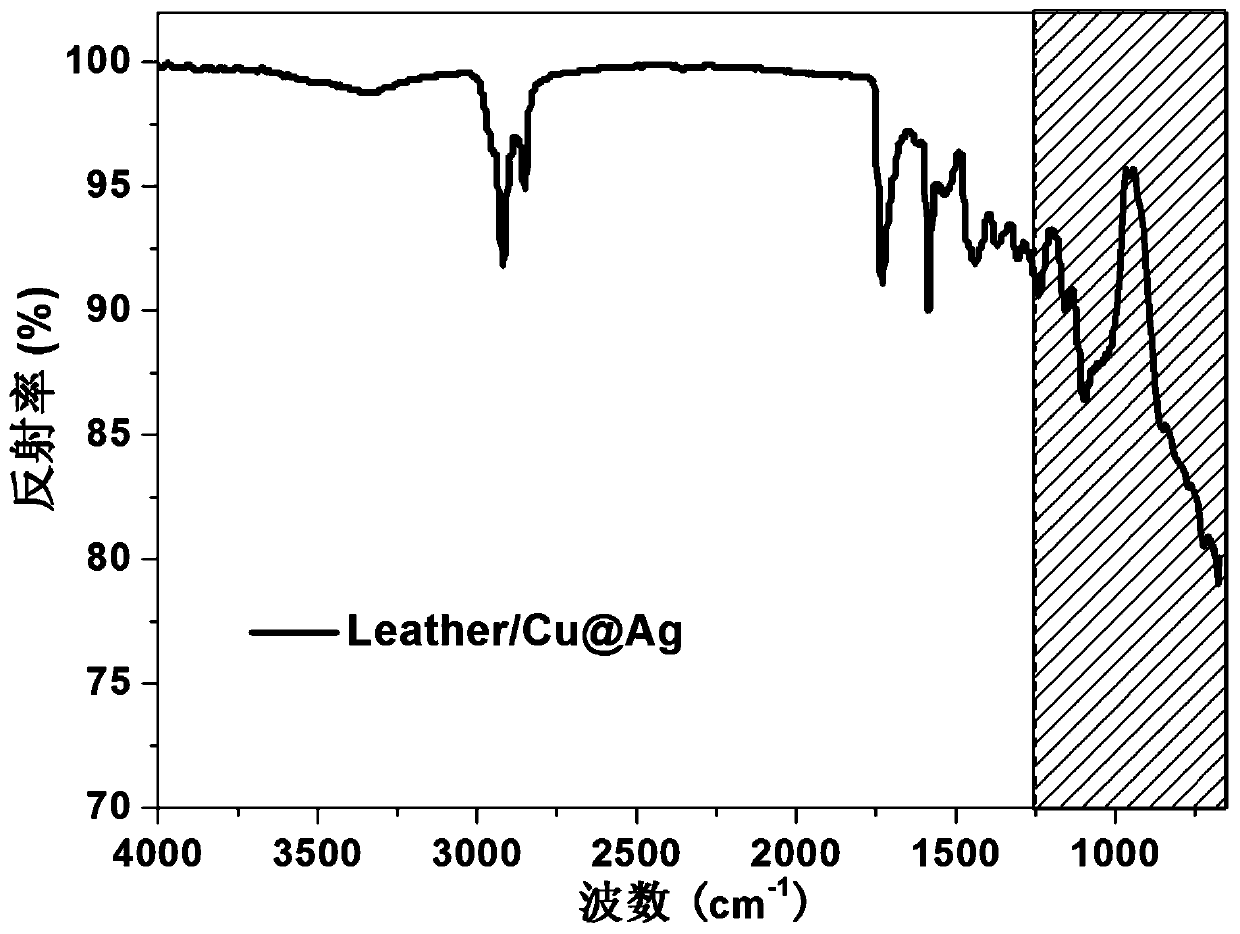
Infrared stealth material taking leather as base material, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111286562AIncrease reflectivity rReduces infrared radiation absorptionTanning treatmentPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsLow emittanceMetallic materials
The invention provides an infrared stealth leather material, which has low emissivity and controllable temperature under a normal-temperature infrared atmospheric window of 8-14 [mu]m, and is characterized in that natural leather prepared from livestock skin is used as a base material, and the surface of the base material is coated with a low-emissivity metal material, or after the natural leatheris dehydrated and added into a phase change material, the natural leather is coated with the low-emissivity metal material, so that the infrared stealth material which is low in emissivity, controllable in temperature, soft, foldable and wearable is prepared. The leather material with dual functions of infrared stealth and radar stealth can be prepared by regulating and controlling the metal variety and proportion of the coating.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com