Patents
Literature
131 results about "Off resonance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for improving the start up of an ultrasonic system under zero load conditions
InactiveUS6898536B2Easy to startIncrease flexibilityNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementSurgical instrument detailsDriving currentPower flow
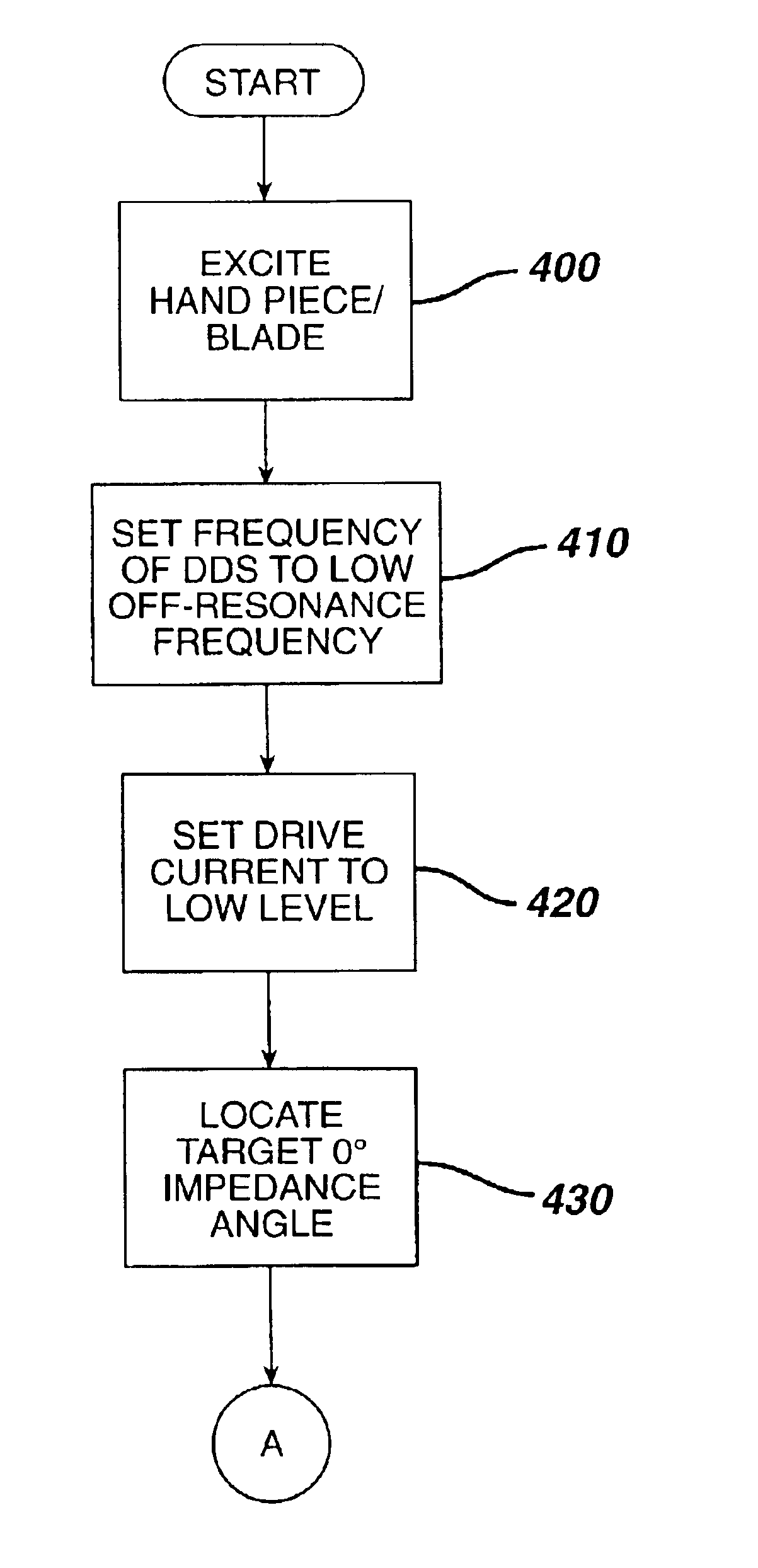
The start up performance of an ultrasonic system under zero load conditions is improved by setting a phase set point in a frequency control loop such that, at start up under zero load conditions, the phase set point intersects a point on a phase-frequency response curve which has a low positive slope. This intersection point on the phase-frequency response curve changes as the load is increased and the system Q is decreased. The controller “seeks” a target 0° impedance phase angle. The frequency of the ultrasonic generator is set to an off-resonance frequency which is lower than the resonance of any known hand piece / blade combination. In order for the drive voltage to not exceed the physical limit of the system, the drive current is set to a low level. The drive frequency is then smoothly increased in steps until the target 0° impedance phase delta is located.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Off-resonance photoacoustic spectrometric detection and analysis device
InactiveCN102661918AOptical signal enhancementImprove performanceMaterial analysis by optical meansGas concentrationNon coherent
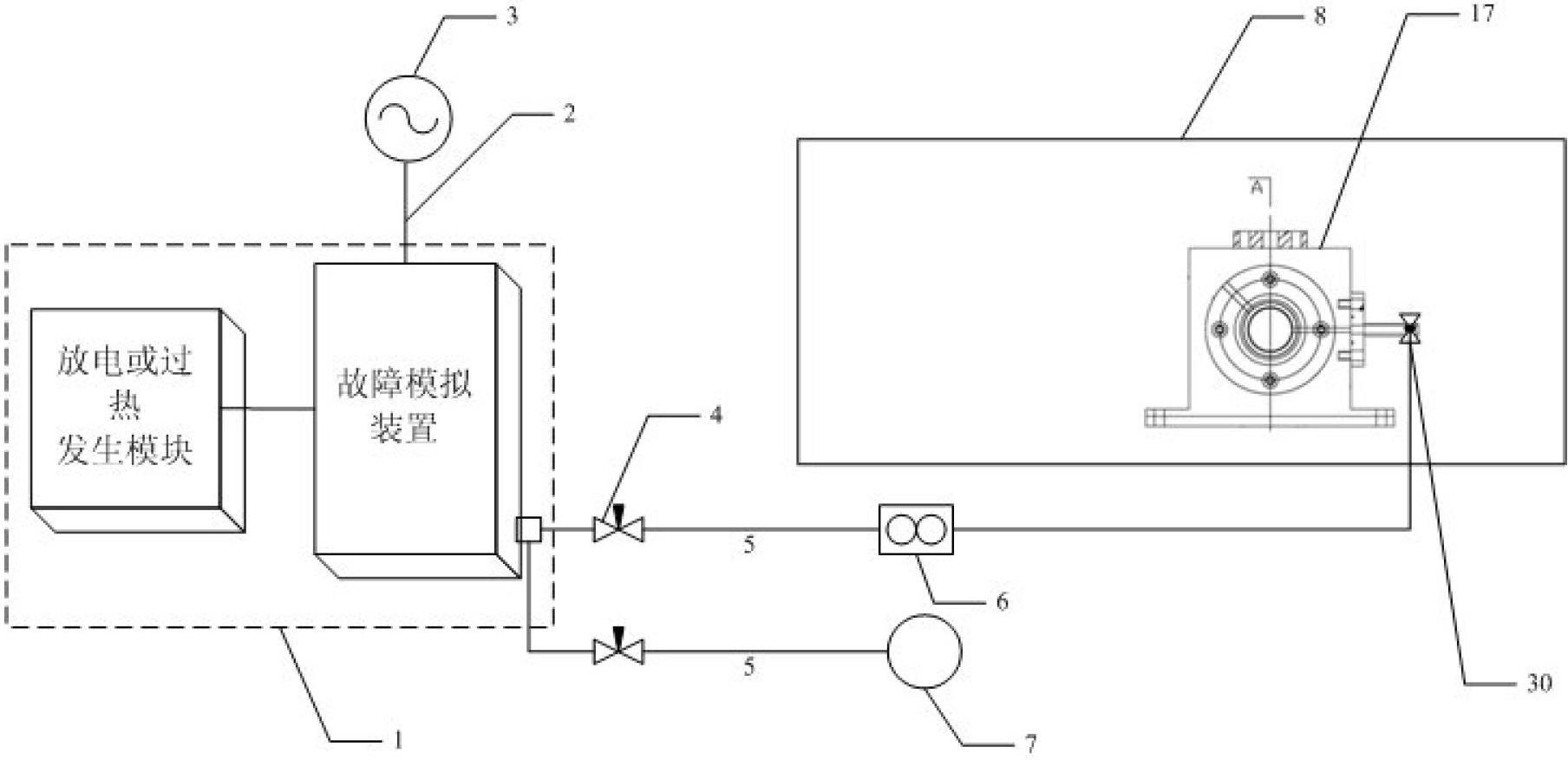
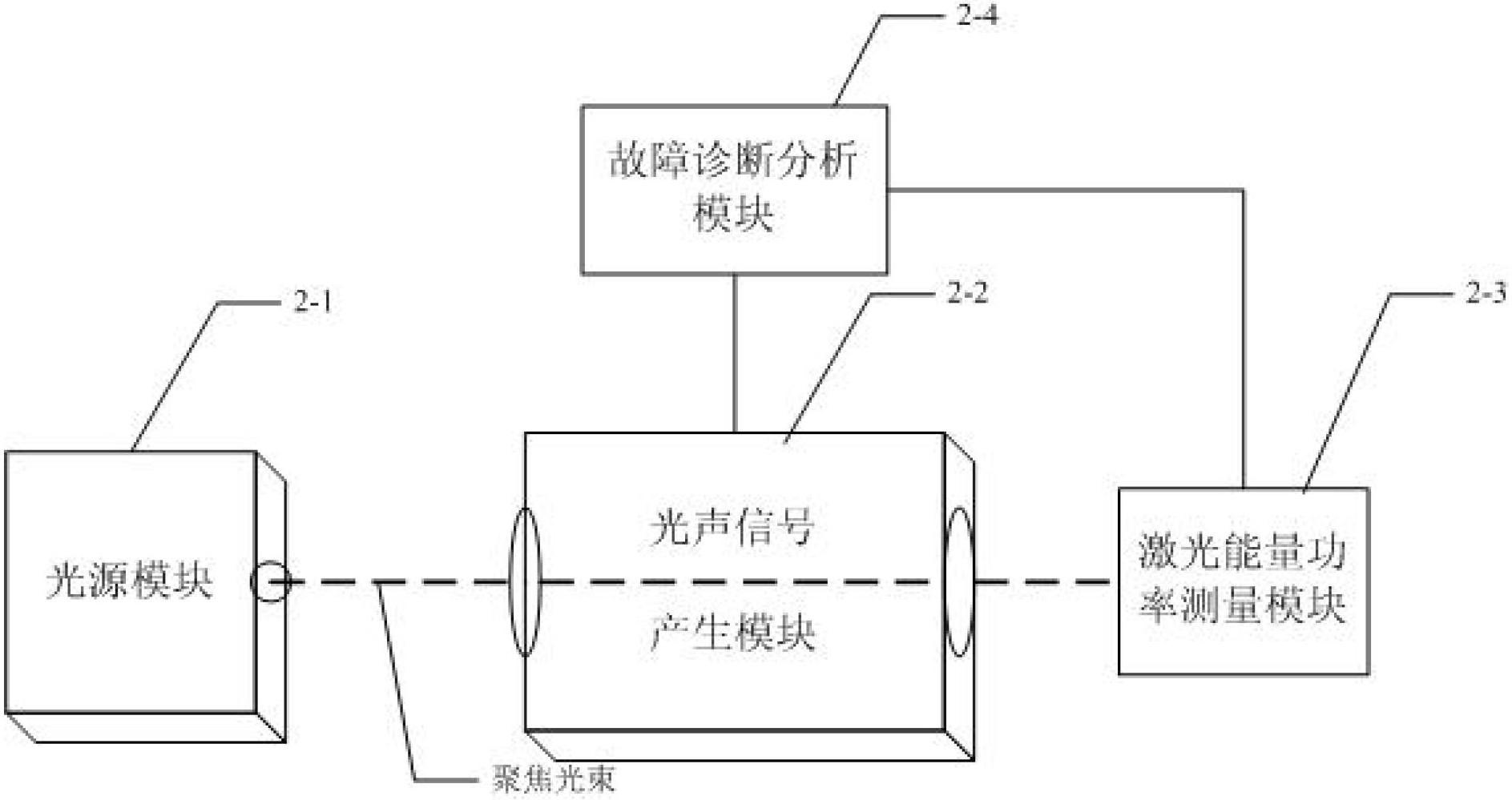
An off-resonance photoacoustic spectrometric detection and analysis device consists of a photoacoustic spectrometric module (8). The photoacoustic spectrometric module (8) comprises a light source module (2-1), a photoacoustic signal generation module (2-2), an optical power measurement module (2-3) and a fault diagnostic analysis module (2-4). Optical signals generated by an infrared incoherence light source in the light source module (2-1) are focused by an ellipsoidal reflector to form a focused light beam, the focused light beam is modulated into light of specific frequency and wavelength by chopping blades of an optical chopper and optical filters and then transmitted to the photoacoustic signal generation module (2-2), and the fault diagnostic analysis module (2-4) calculates each gas concentration according to to-be-tested gas photoacoustic signals generated by irradiation, diagnoses faults and alarms. The off-resonance photoacoustic spectrometric detection and analysis device can be used for quantitative detection of gases such as SF6, CF4, SO2F2, SOF2, SO2, SF4 and H2O and is applicable to onsite online monitoring.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Sensor apparatus and cantilever for it
InactiveUS20020092359A1Highly sensitive chemicalEasy to adaptNanotechForce measurementSelective excitationCondensed matter physics
A magnetically excited, resonant cantilever sensor apparatus has a cantilever as the transducer element. A static magnetic field is directed in the plane of the cantilever(s) cooperating with a current loop in / on the latter. Orienting the magnetic field along or perpendicular to the cantilever axis and controlling the current apprpriately allows for selective excitation of resonance or non-resonance modes and / or in a self-oscillation mode. The deflection of the cantilever is detected using piezoresistive or magnetic readout. The apparatus may be used as gas sensor, scanning force microscope, mechanical filter, temperature sensor or the like.
Owner:SWISS FEDERAL INST OF TECH ZURICH
Resonance type switching power source
InactiveUS7212415B2Stable output voltageImprove noiseApparatus with intermediate ac conversionPropulsion unit safety devicesEngineeringControl circuit
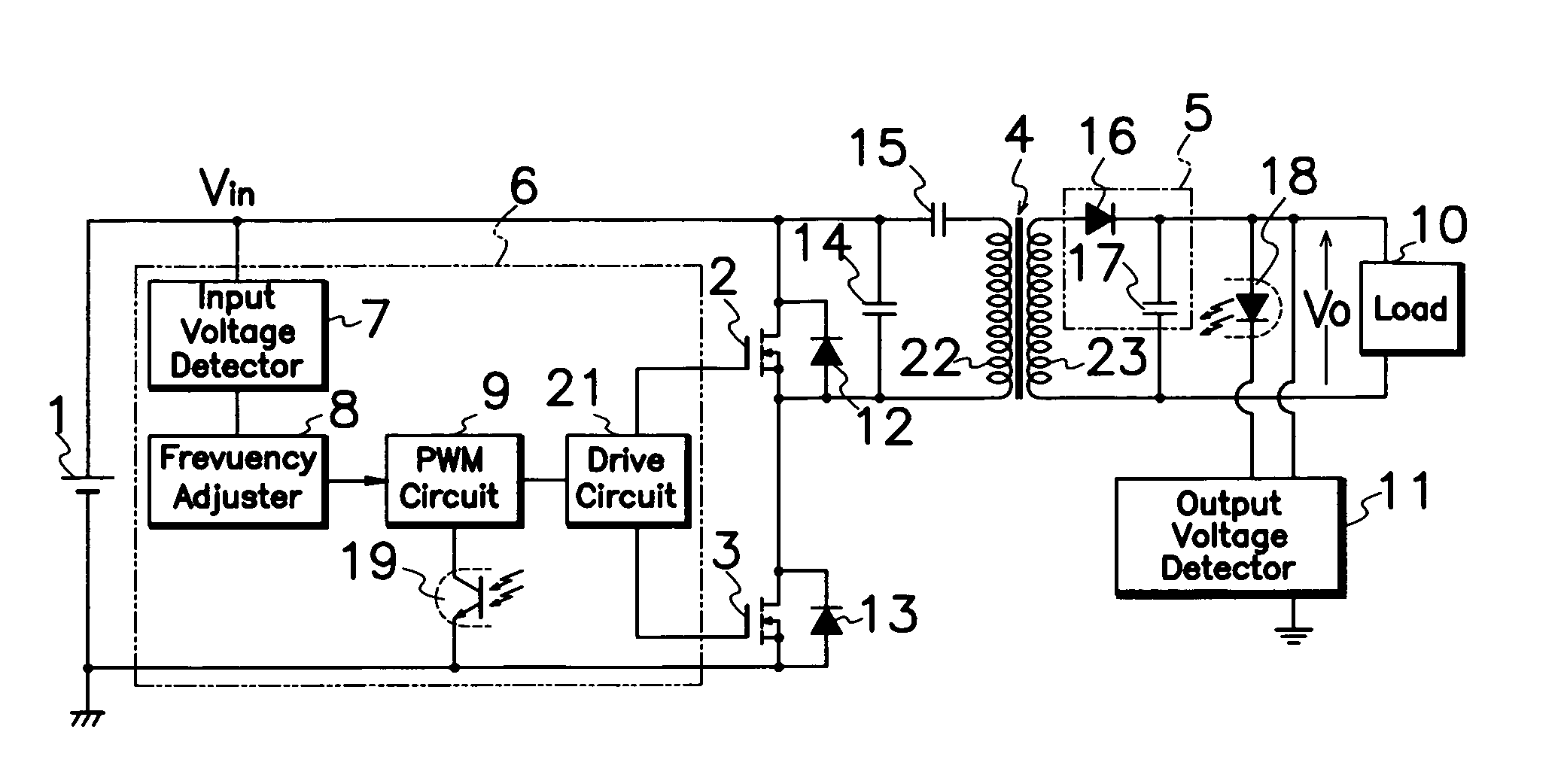
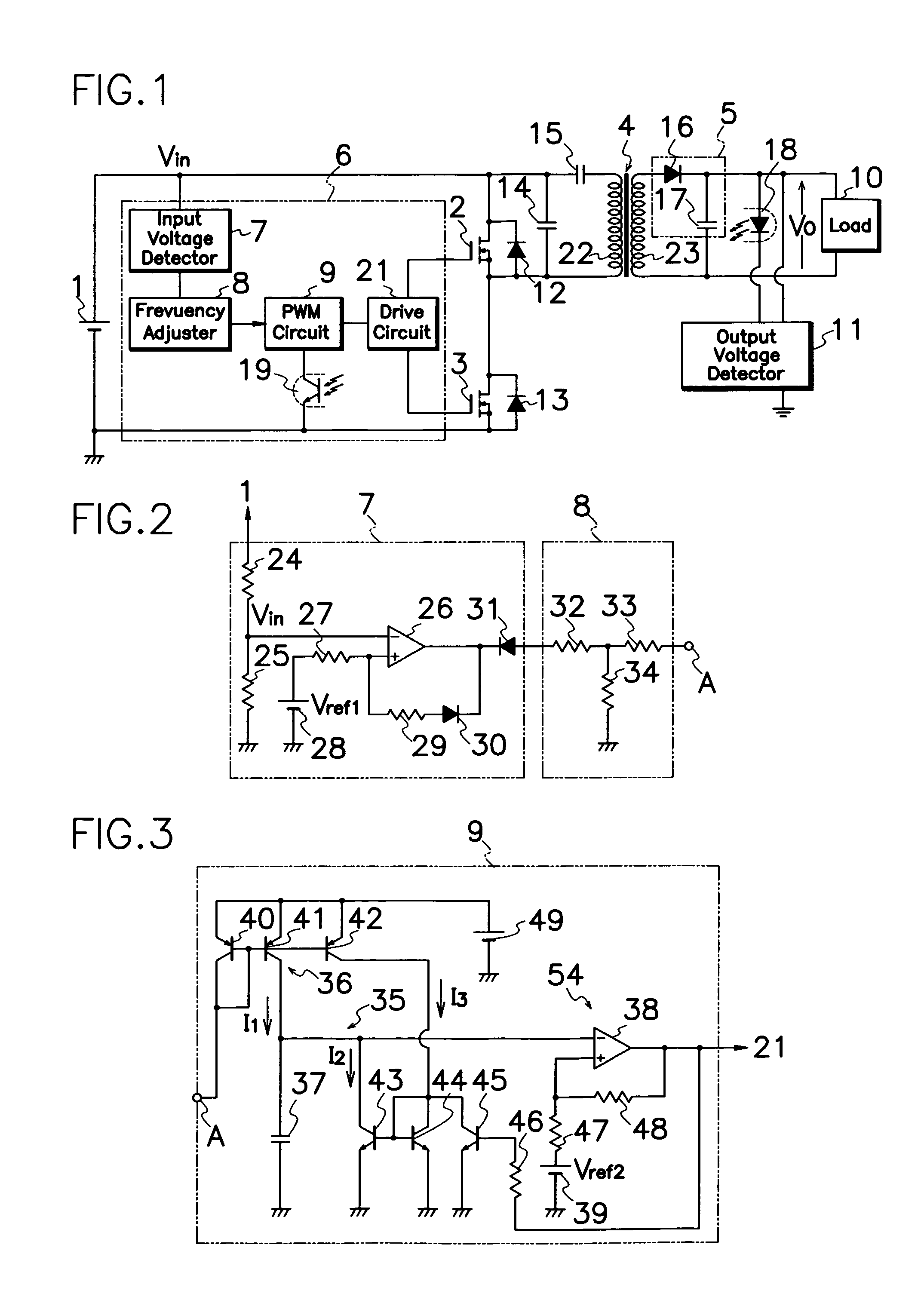
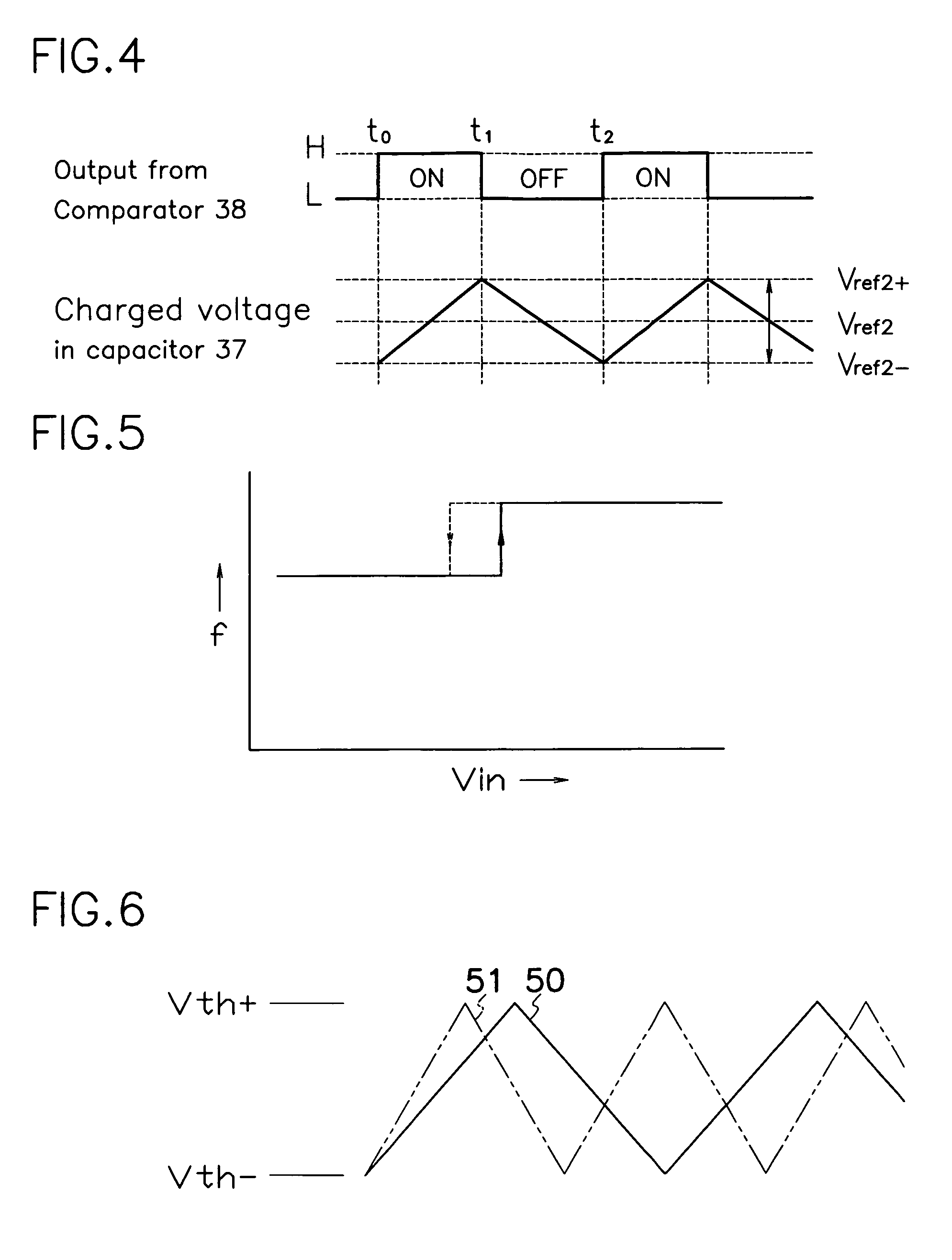
A control circuit 6 of a resonance type switching power source comprises a drive circuit 21 for supplying drive pulses to each gate terminal of first and second MOS-FETs 2,3; a PWM circuit 9 for causing drive circuit 21 to produce drive pulses; an input voltage detector 7 for detecting input voltage from DC power source 1 and comparing the input voltage and input reference voltage Vref1; and a frequency adjuster 8 for adjusting oscillation frequency of PWM circuit 9 in response to output level from the input voltage detector 7. With adjustment in oscillation frequency of PWM circuit 9 in response to input voltage Vin from DC power source 1, control circuit 6 can modify on-off timing of first and second MOS-FETs 2, 3 to keep good resonating action and prevent off-resonance although DC power source 1 produces fluctuating input voltages.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
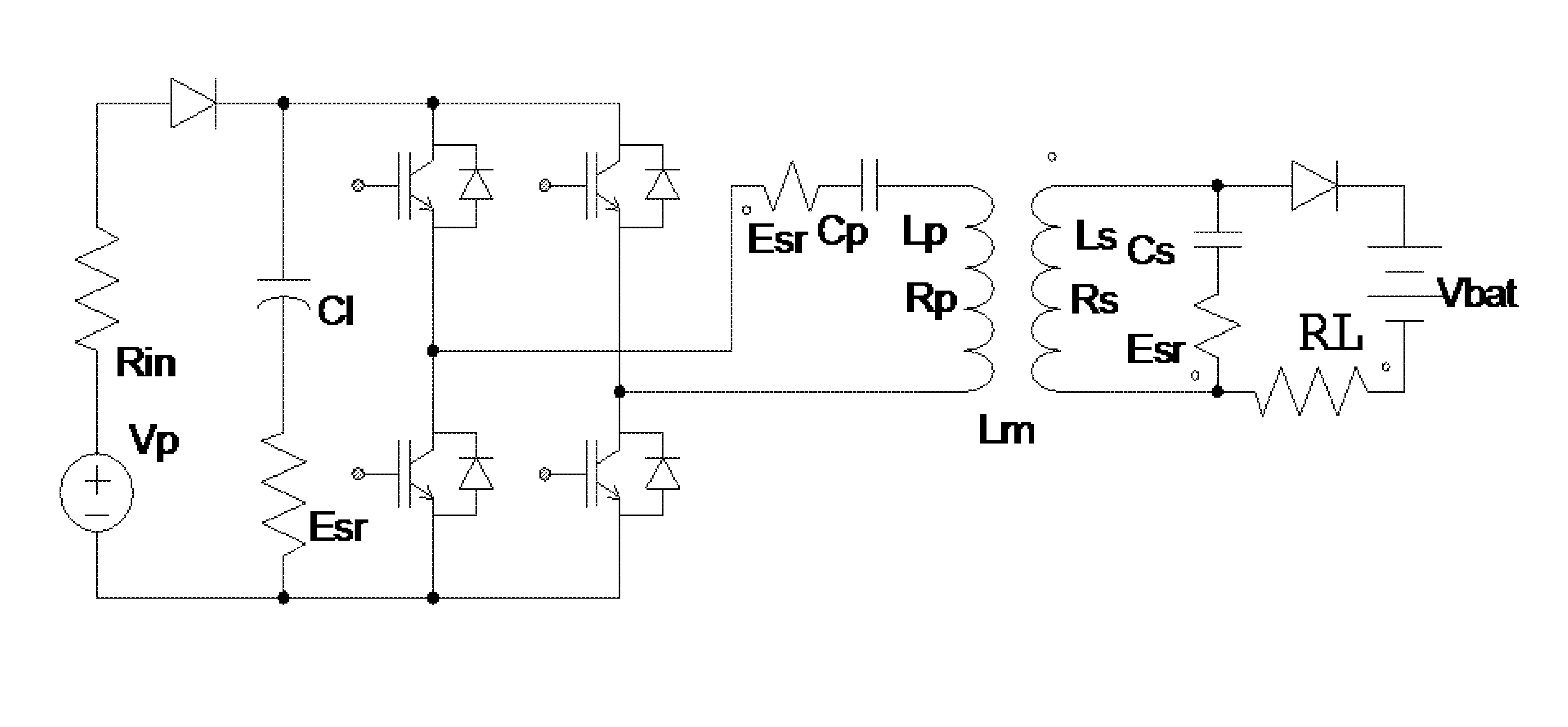
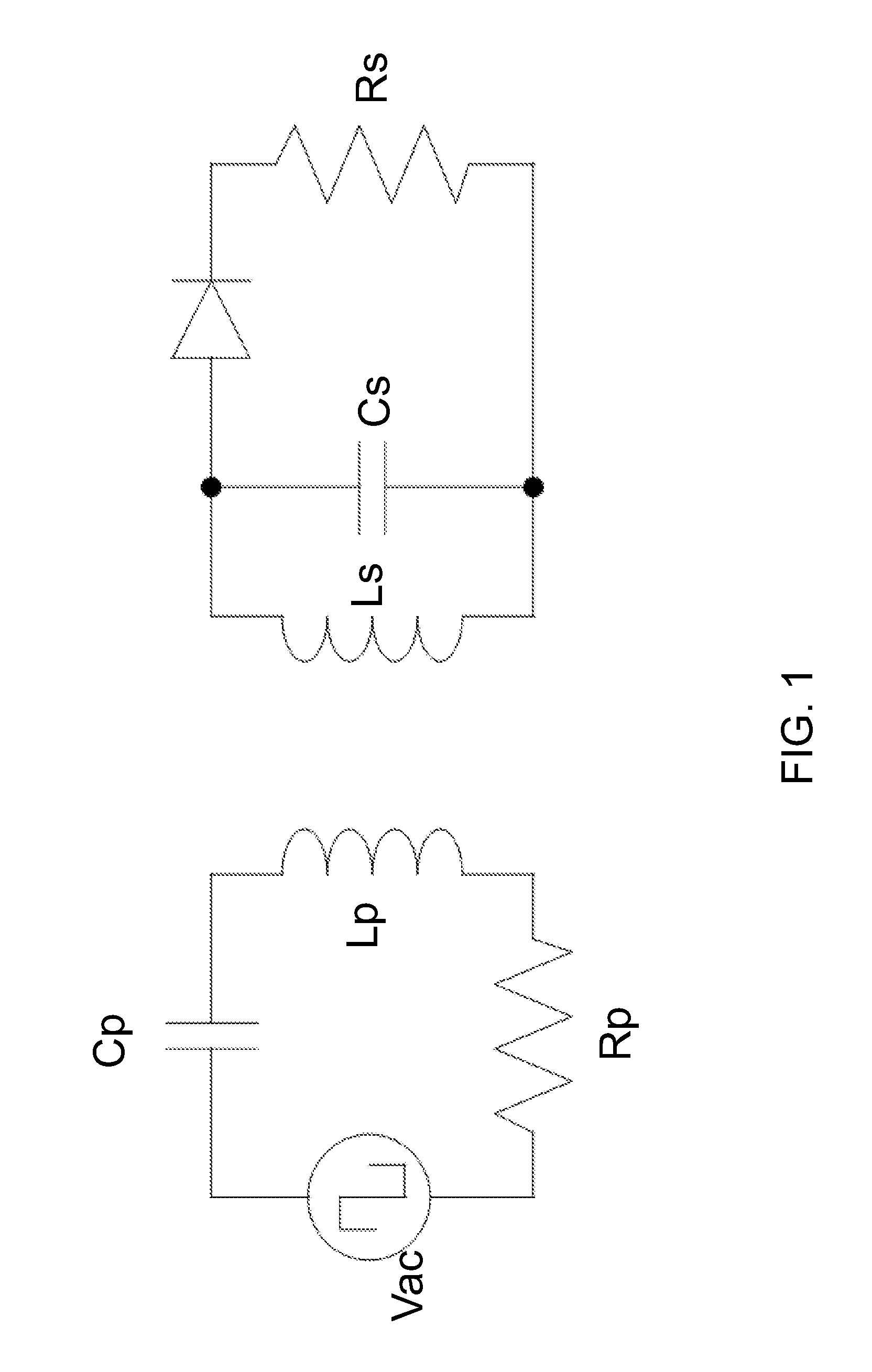
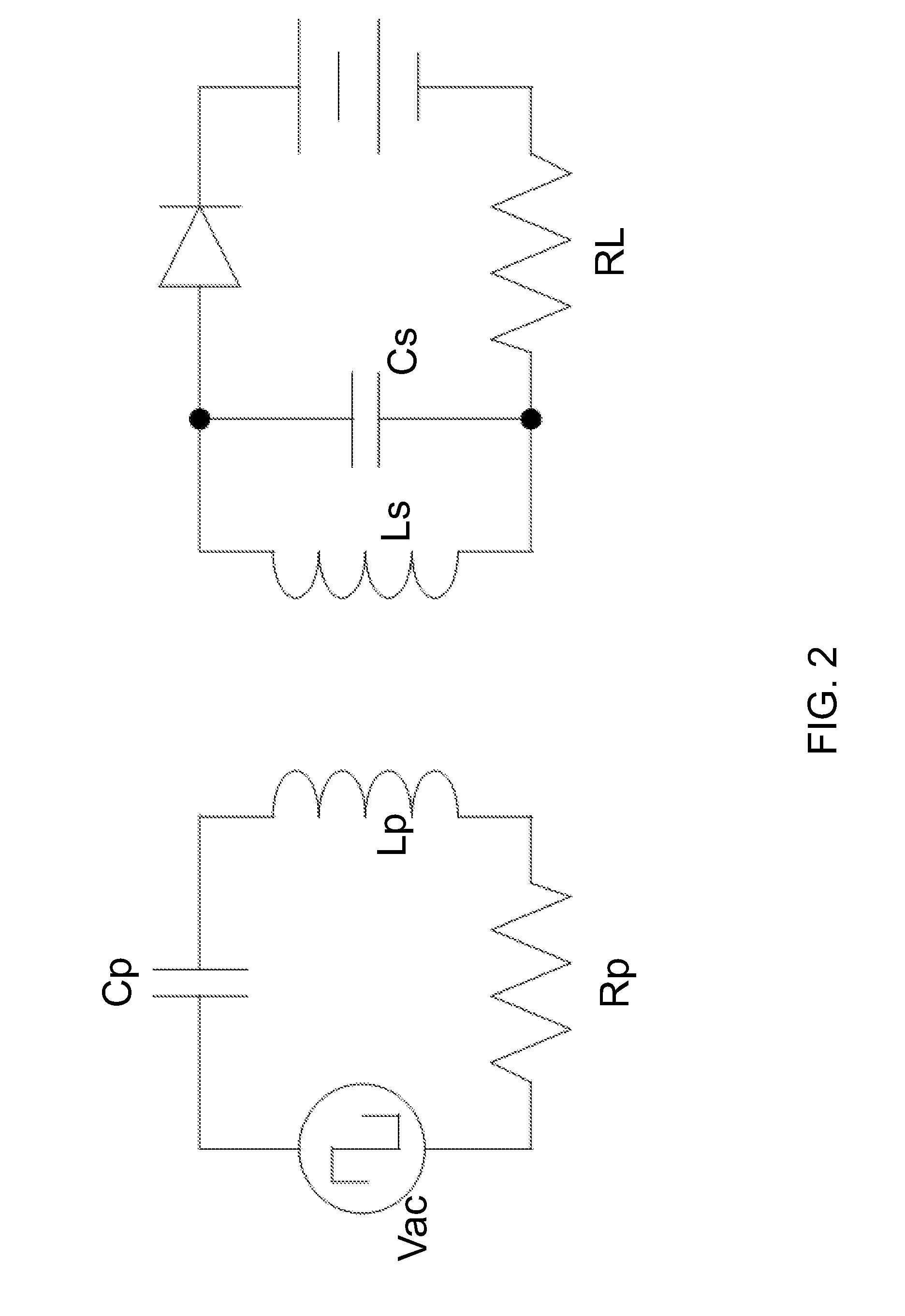
Off-resonance frequency operation for power transfer in a loosely coupled air core transformer
ActiveUS20120043930A1Near maximum transfer efficiencyImprove transmission efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric devicesCapacitanceDrivetrain
A power transmission system includes a loosely coupled air core transformer having a resonance frequency determined by a product of inductance and capacitance of a primary circuit including a primary coil. A secondary circuit is configured to have a substantially same product of inductance and capacitance. A back EMF generating device (e.g., a battery), which generates a back EMF with power transfer, is attached to the secondary circuit. Once the load power of the back EMF generating device exceeds a certain threshold level, which depends on the system parameters, the power transfer can be achieved at higher transfer efficiency if performed at an operating frequency less than the resonance frequency, which can be from 50% to 95% of the resonance frequency.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Spin locked balanced steady-state free precession (slssfp)
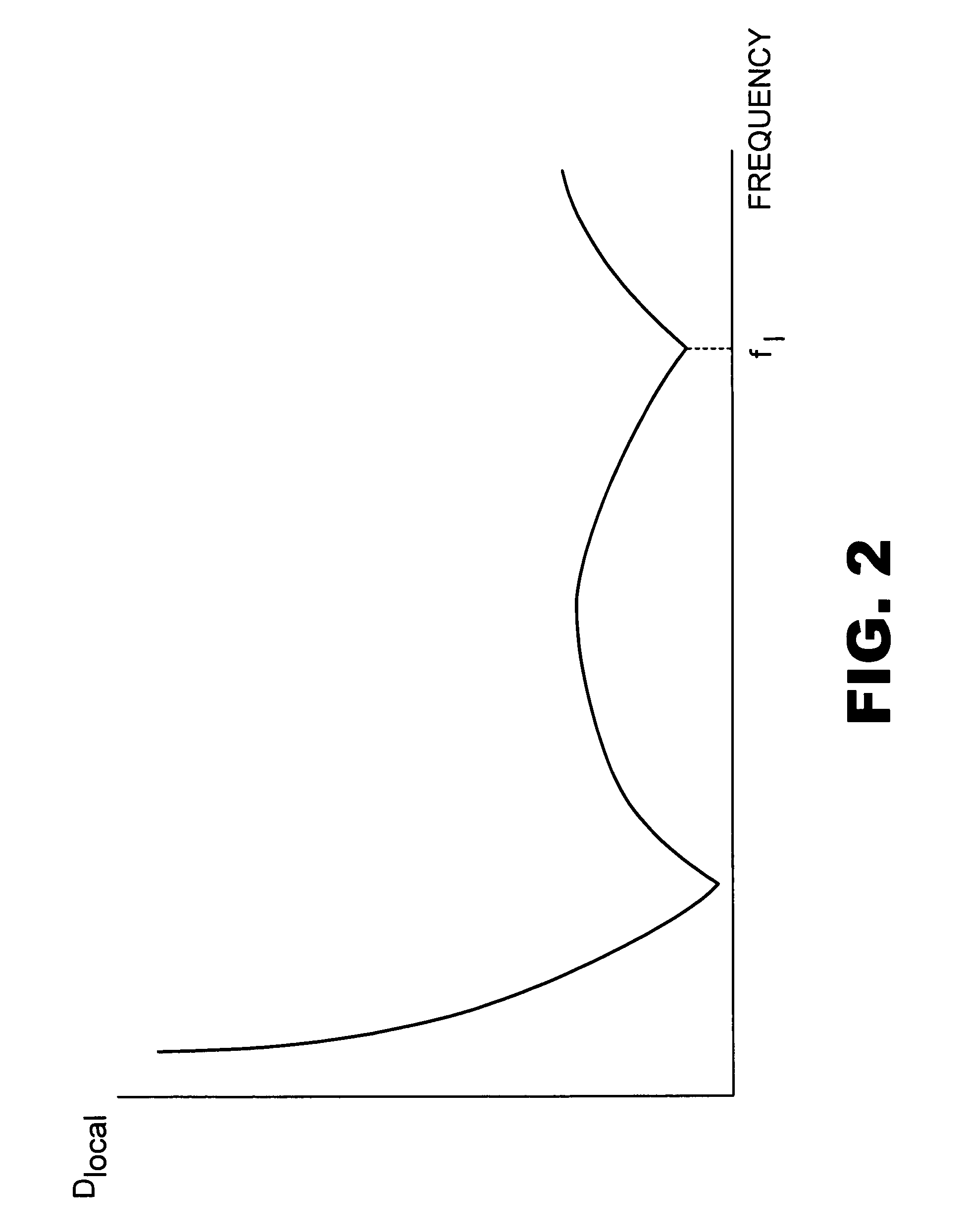
ActiveUS20100264920A1Improve contrast ratioShorten Image Acquisition TimeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionGradient echoOff resonance
A spin locked balanced steady-state free precession (slSSFP) pulse sequence combines a balanced gradient echo acquisition with an off-resonance spin lock pulse for fast MRI. The transient and steady-state magnetization trajectory is solved numerically using the Bloch equations and is shown to be similar to balanced steady-state free precession (bSSFP) for a range of T2 / T1 and flip angles, although the slSSFP steady-state could be maintained with considerably lower RF power. In both simulations and brain scans performed at 7 T, slSSFP is shown to exhibit similar contrast and SNR efficiency to bSSFP, but with significantly lower power.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Chemical species suppression for MRI imaging using spiral trajectories with off-resonance correction
ActiveUS6995560B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionChemical speciesComputer science
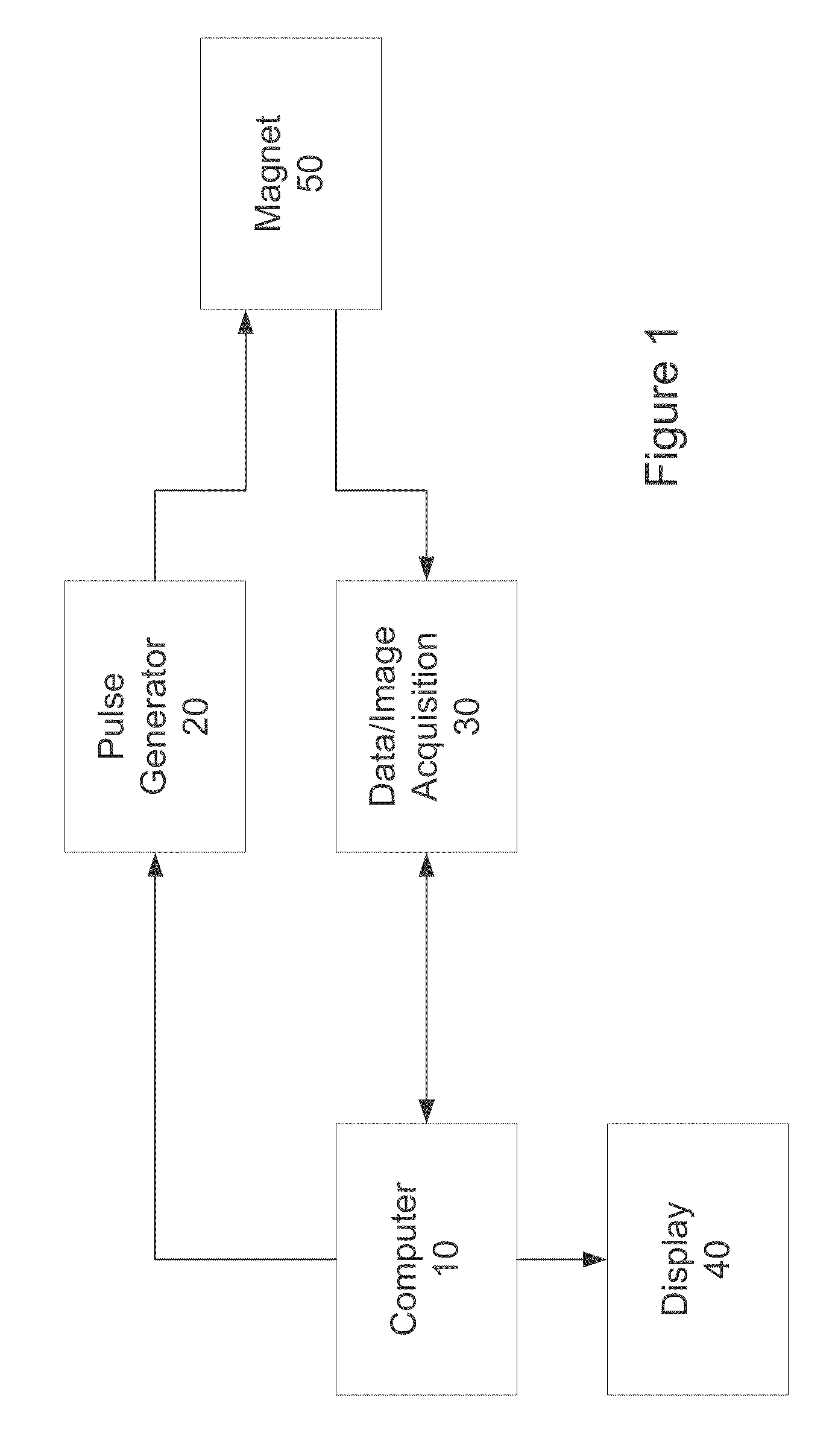
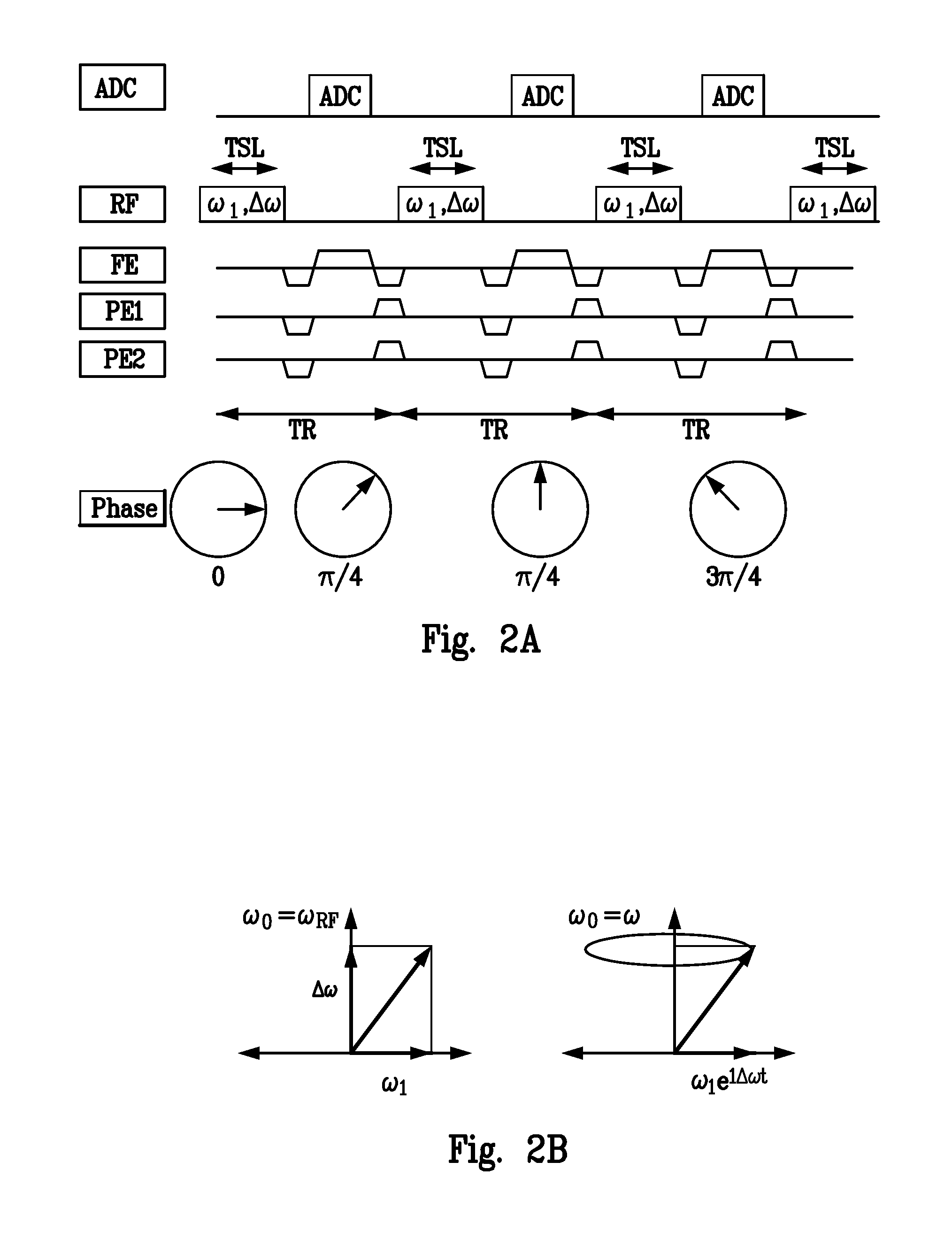
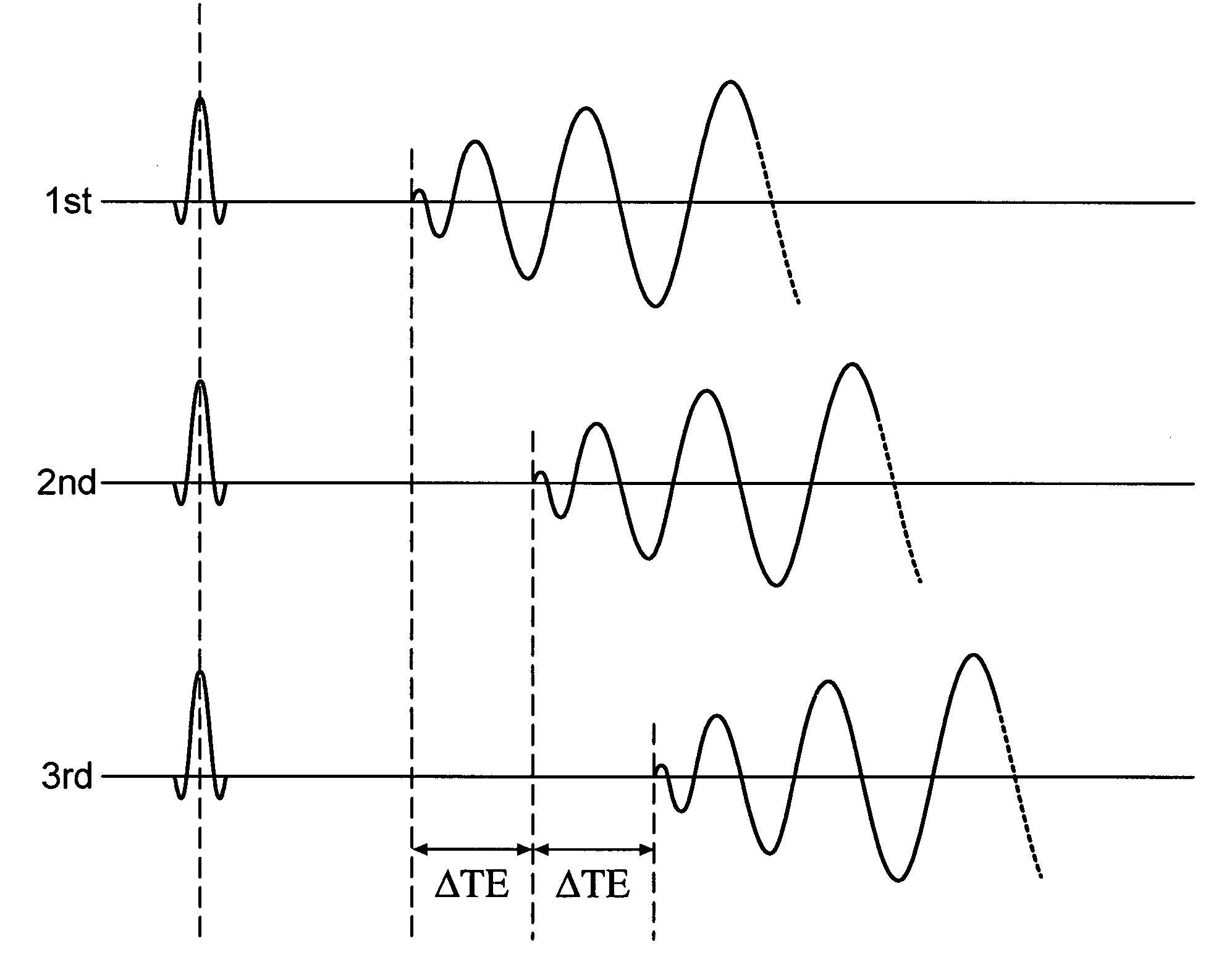
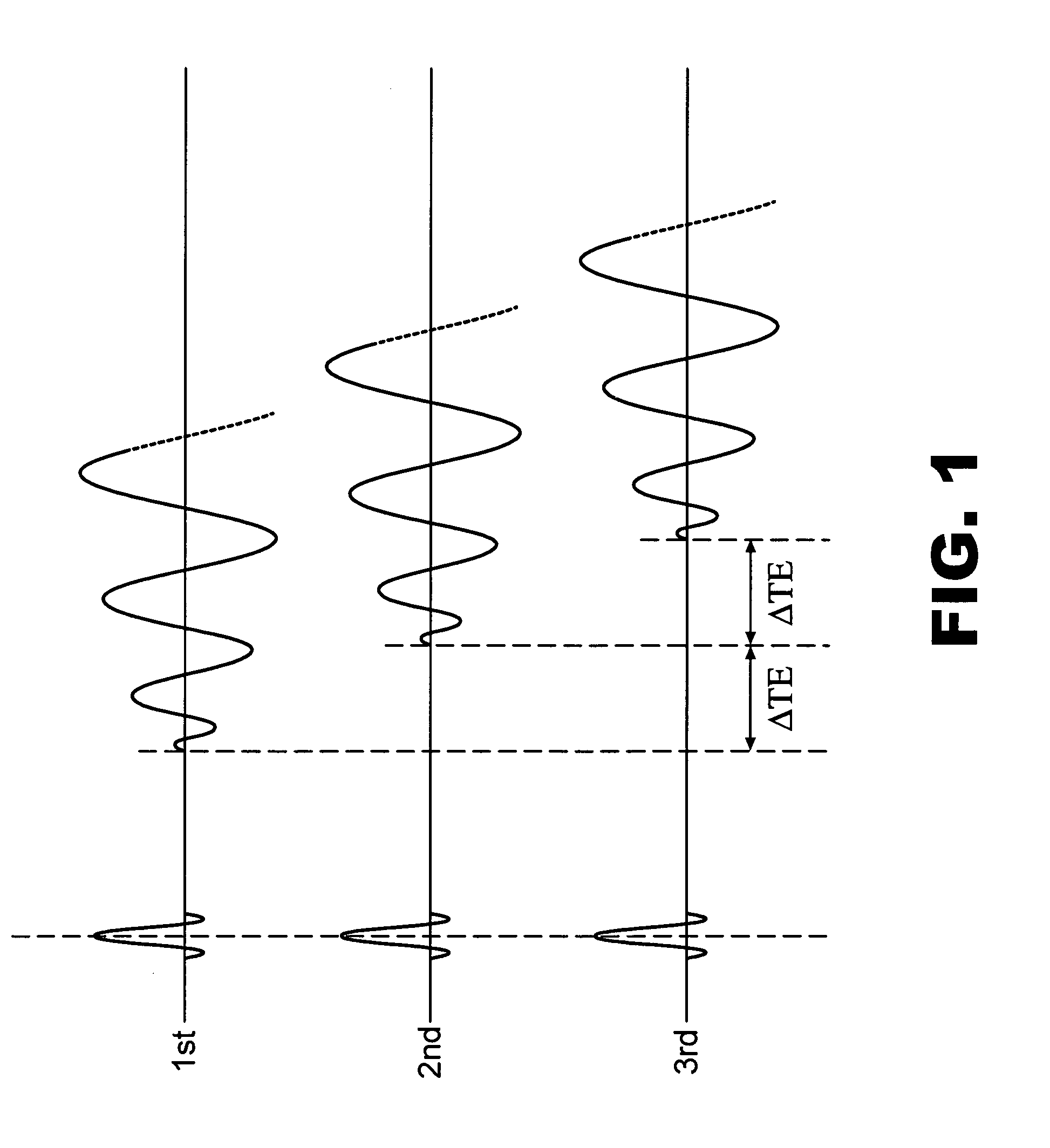
A method of chemical species suppression for MRI imaging of a scanned object region including acquiring K space data at a first TE, acquiring K space data at a second TE, reconstructing images having off resonance effects, estimating off resonance effects at locations throughout the reconstructed image, and determining the first and second chemical species signals at image locations of the scanned object from the acquired signals and correcting for blurring resulting from off resonance effects due to B0 inhomogeneity.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Multi-slice cerebral blood flow imaging with continuous arterial spin labeling MRI
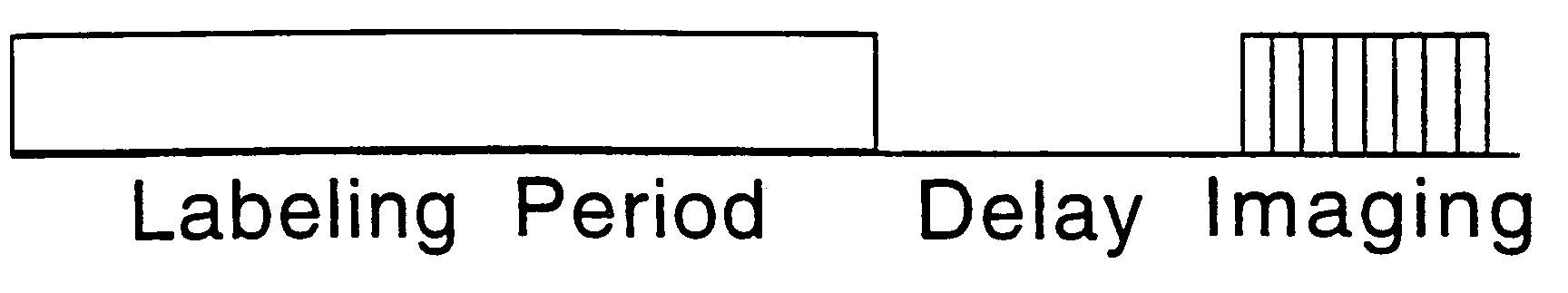
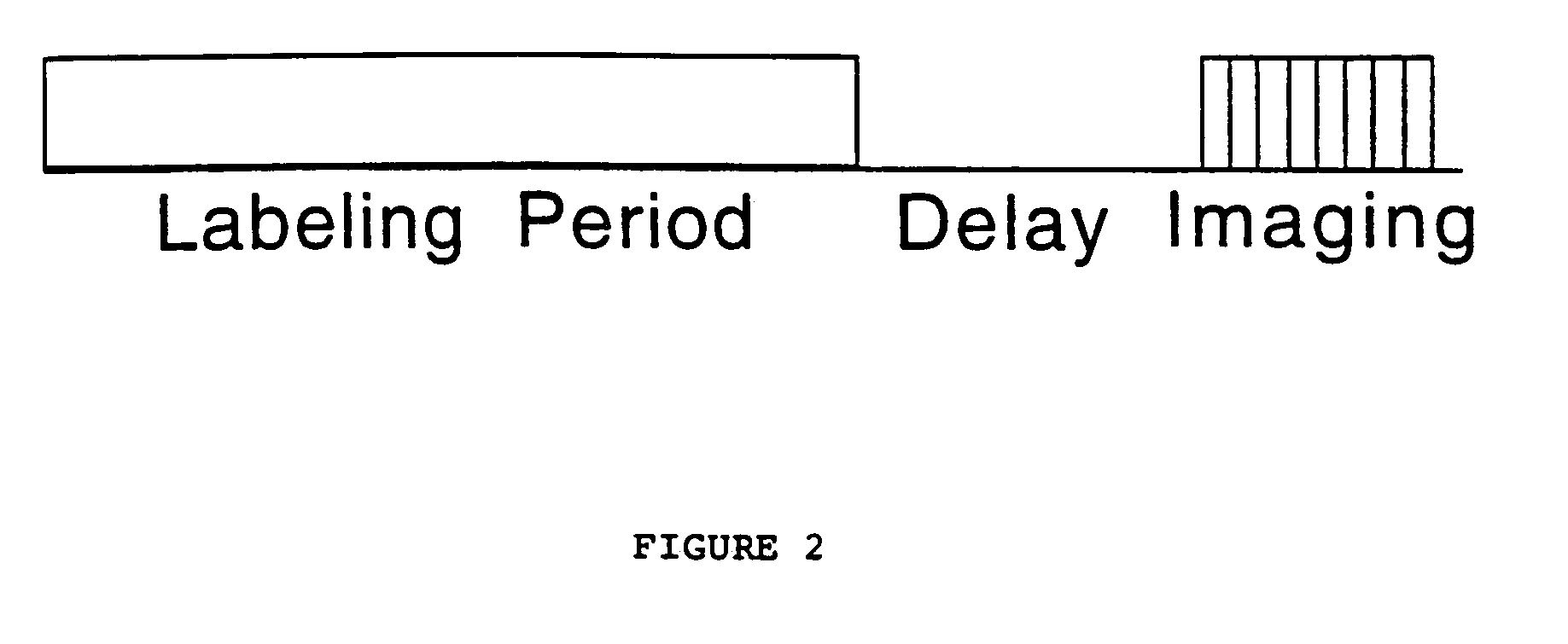
This invention is a method for multi-slice CBF imaging using continuous arterial spin labeling (CASL) with an amplitude modulated control which is both highly effective at controlling for off resonance effects, and efficient at doubly inverting inflow spins, thus retaining the signal advantages of CASL versus pulsed ASL techniques.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Efficient methods for reconstruction and deblurring of magnetic resonance images
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Dixon Techniques in spiral trajectories with off-resonance correction
ActiveUS20050033153A1Effective and more uniform fat signal suppressionMinimize angular relationshipDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDecompositionData acquisition
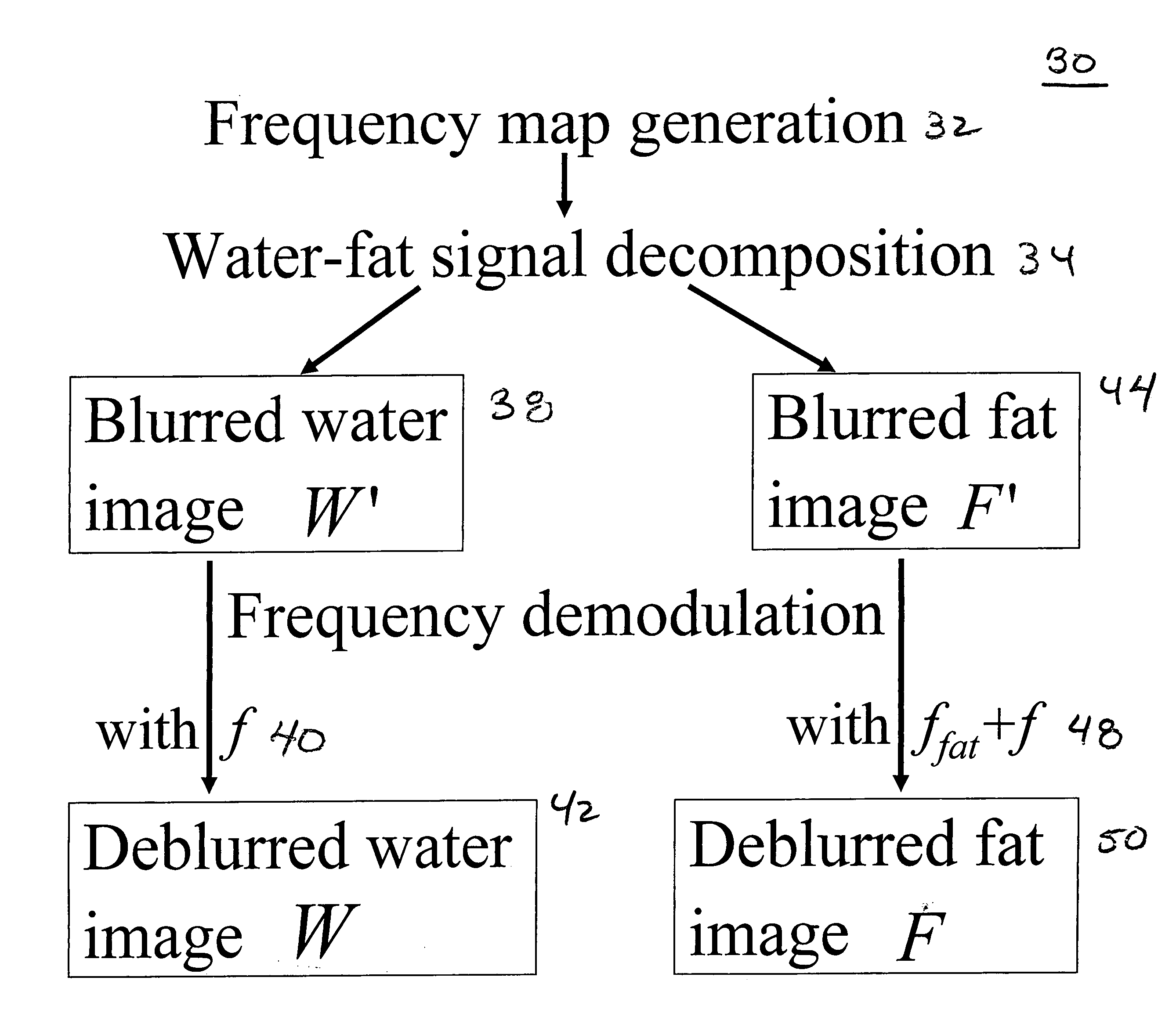
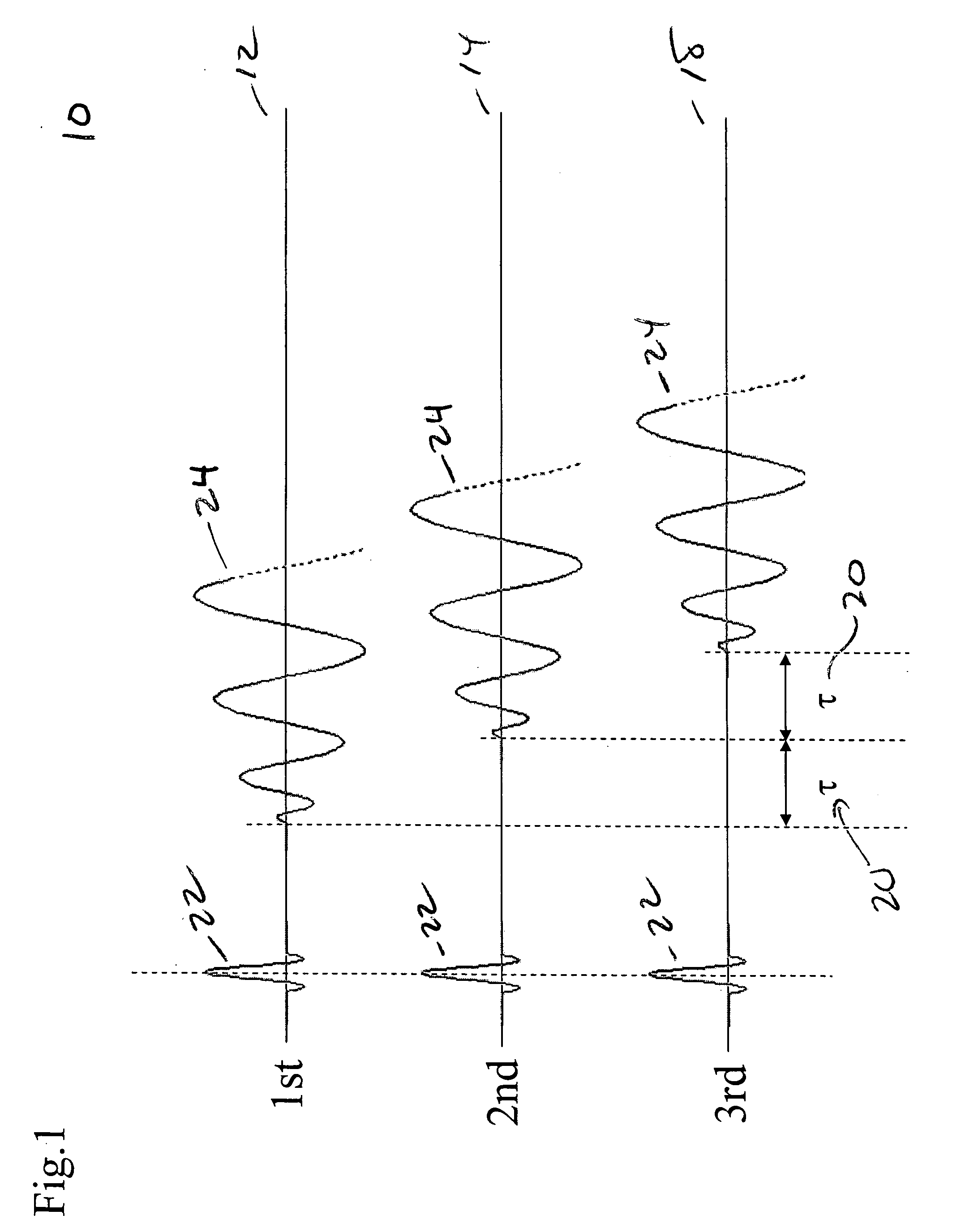
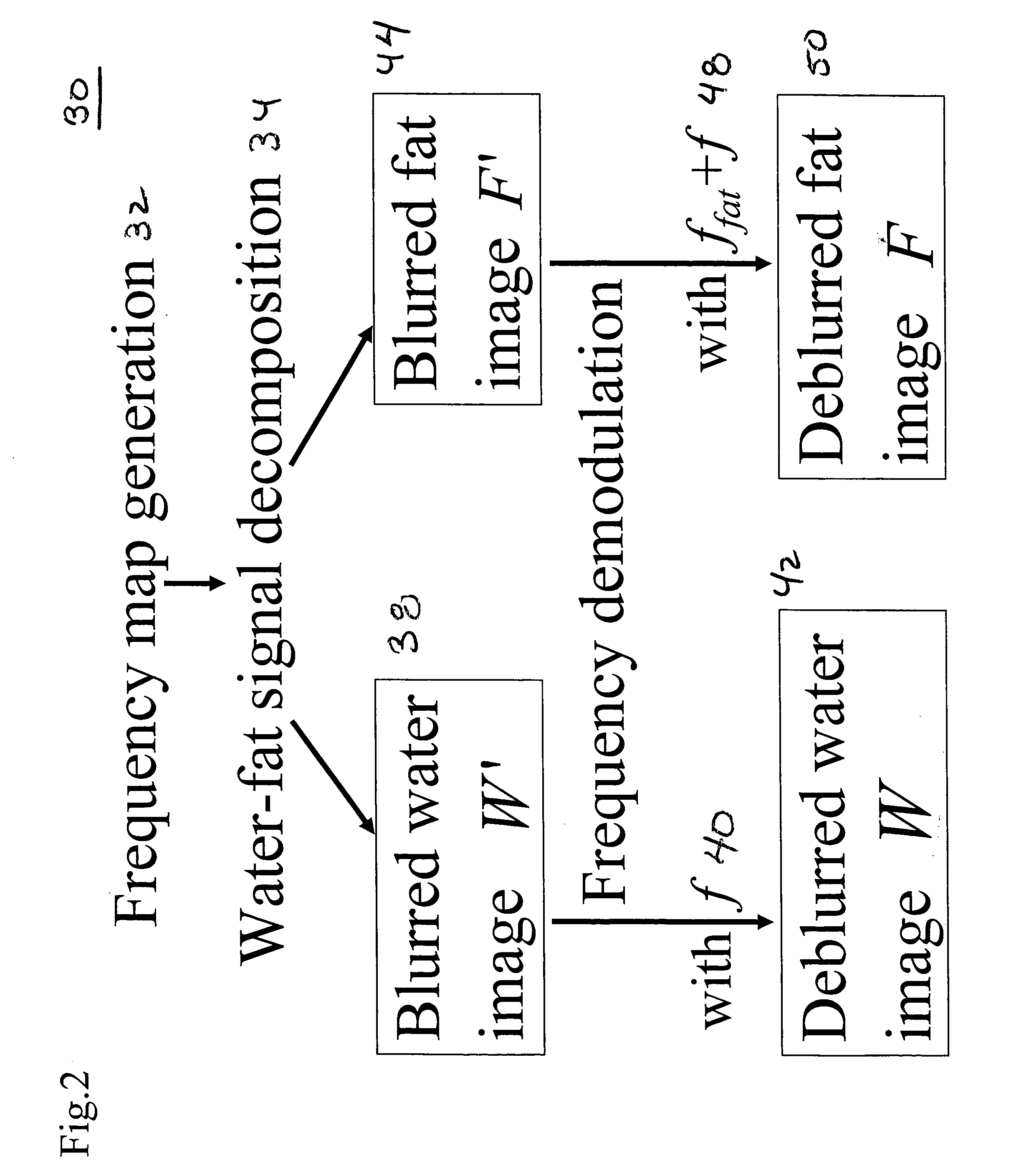
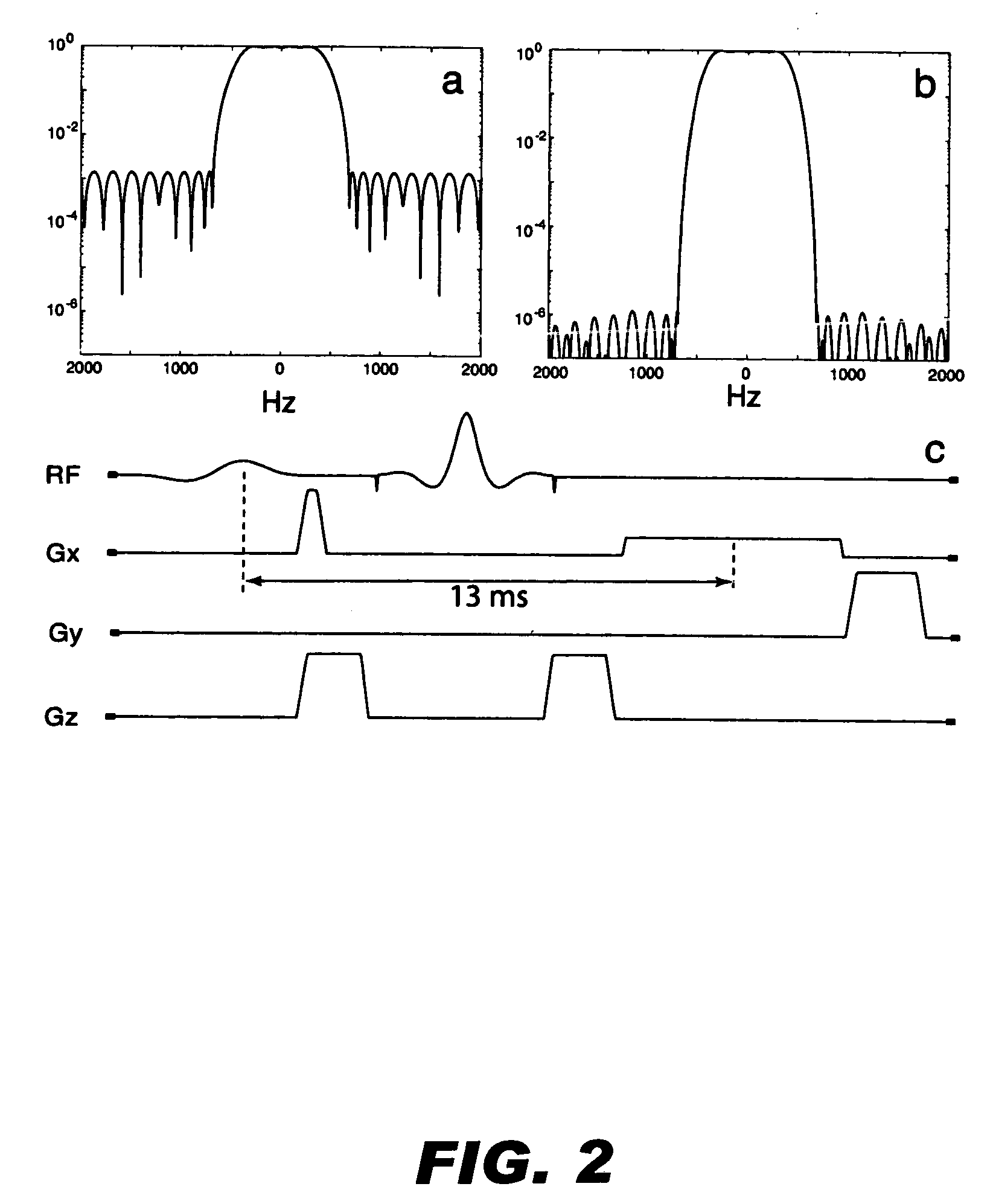
Spiral imaging has recently gained acceptance for rapid MR data acquisition. One of the main disadvantages of spiral imaging, however, is blurring artifacts due to off-resonance effects. Dixon techniques have been developed as methods of water-fat signal decomposition in rectilinear sampling schemes, and they can produce unequivocal water-fat signal decomposition even in the presence of B0 inhomogeneity. Three-point and two-point Dixon techniques can be extended to conventional spiral and variable-density spiral data acquisitions for unambiguous water-fat decomposition with off-resonance blurring correction. In the spiral three-point Dixon technique, water-fat signal decomposition and image deblurring are performed based on the frequency maps that are directly derived from the acquired images. In the spiral two-point Dixon technique, several predetermined frequencies are tested to create a frequency map. The techniques can achieve more effective and more uniform fat signal suppression when compared to the conventional spiral acquisition method with SPSP pulses.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Efficient methods for reconstruction and deblurring of magnetic resonance images
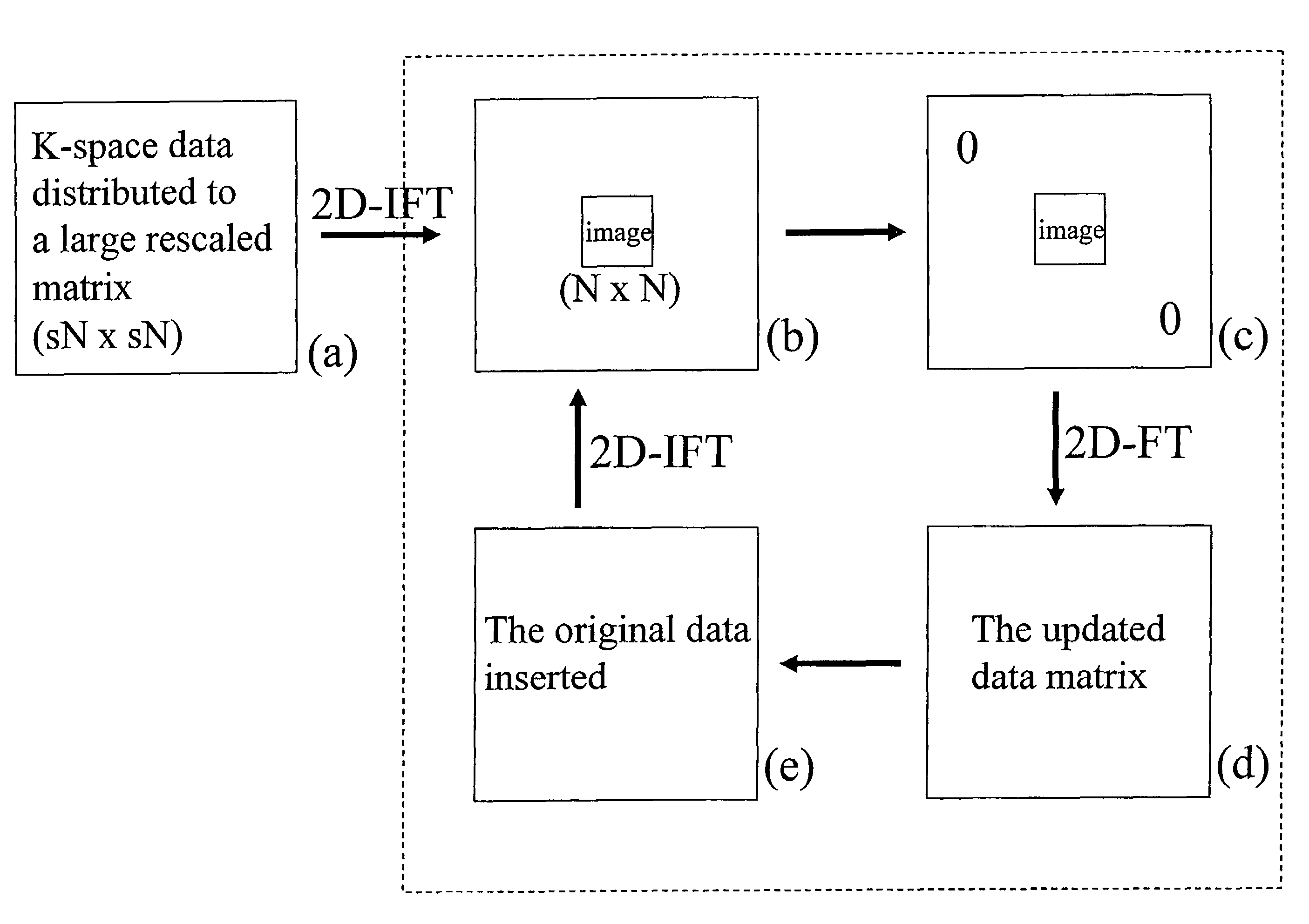
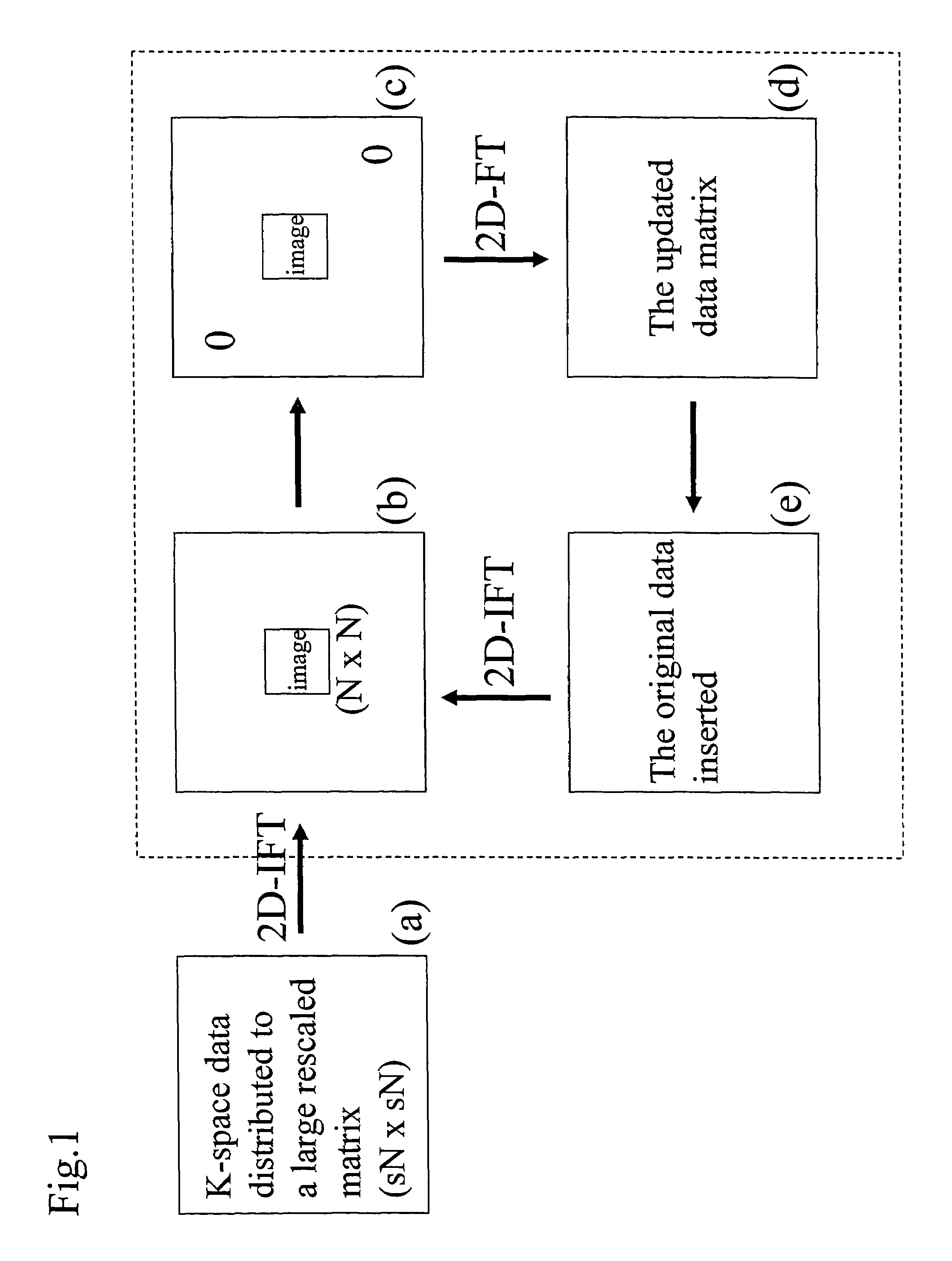
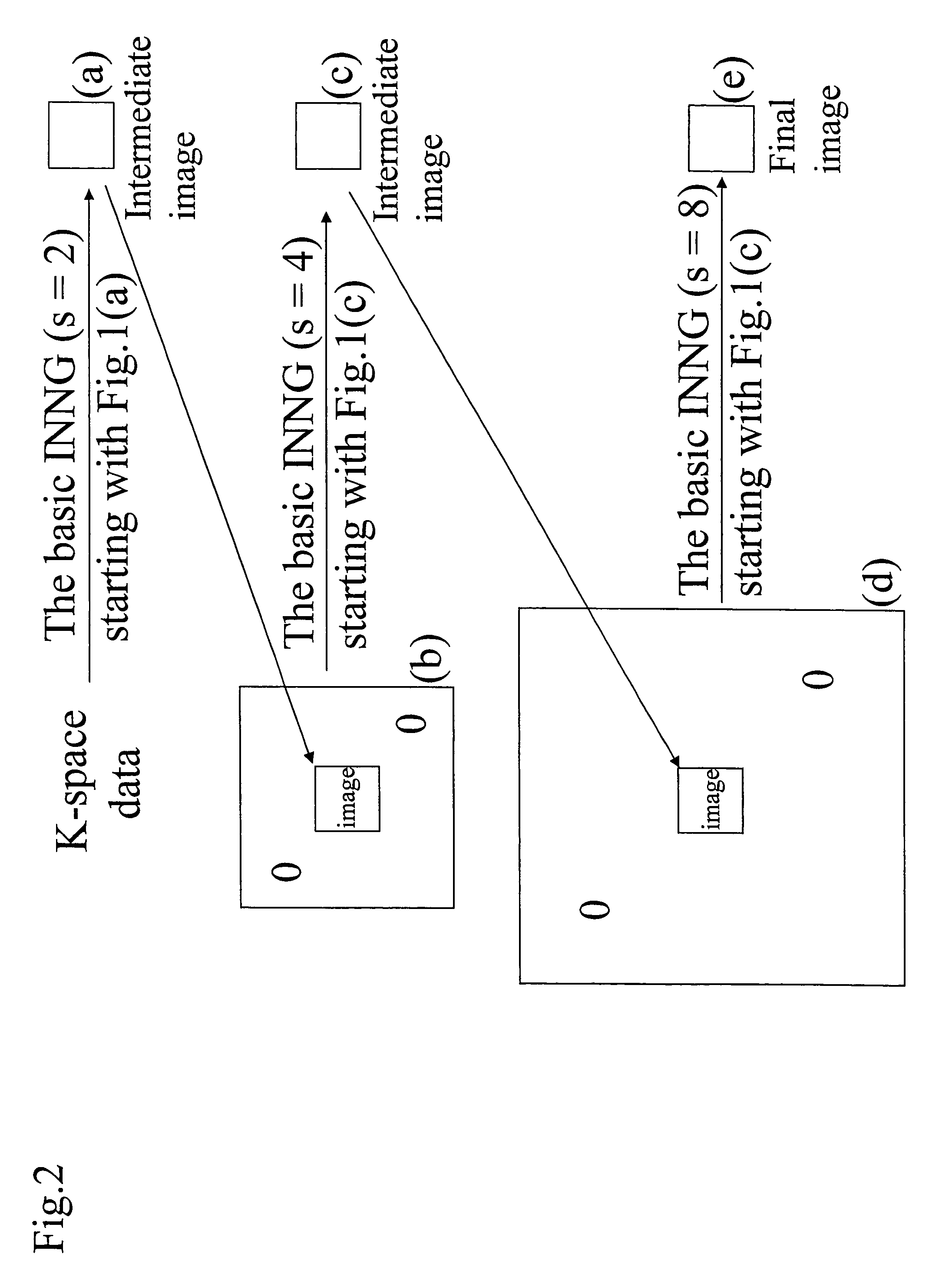
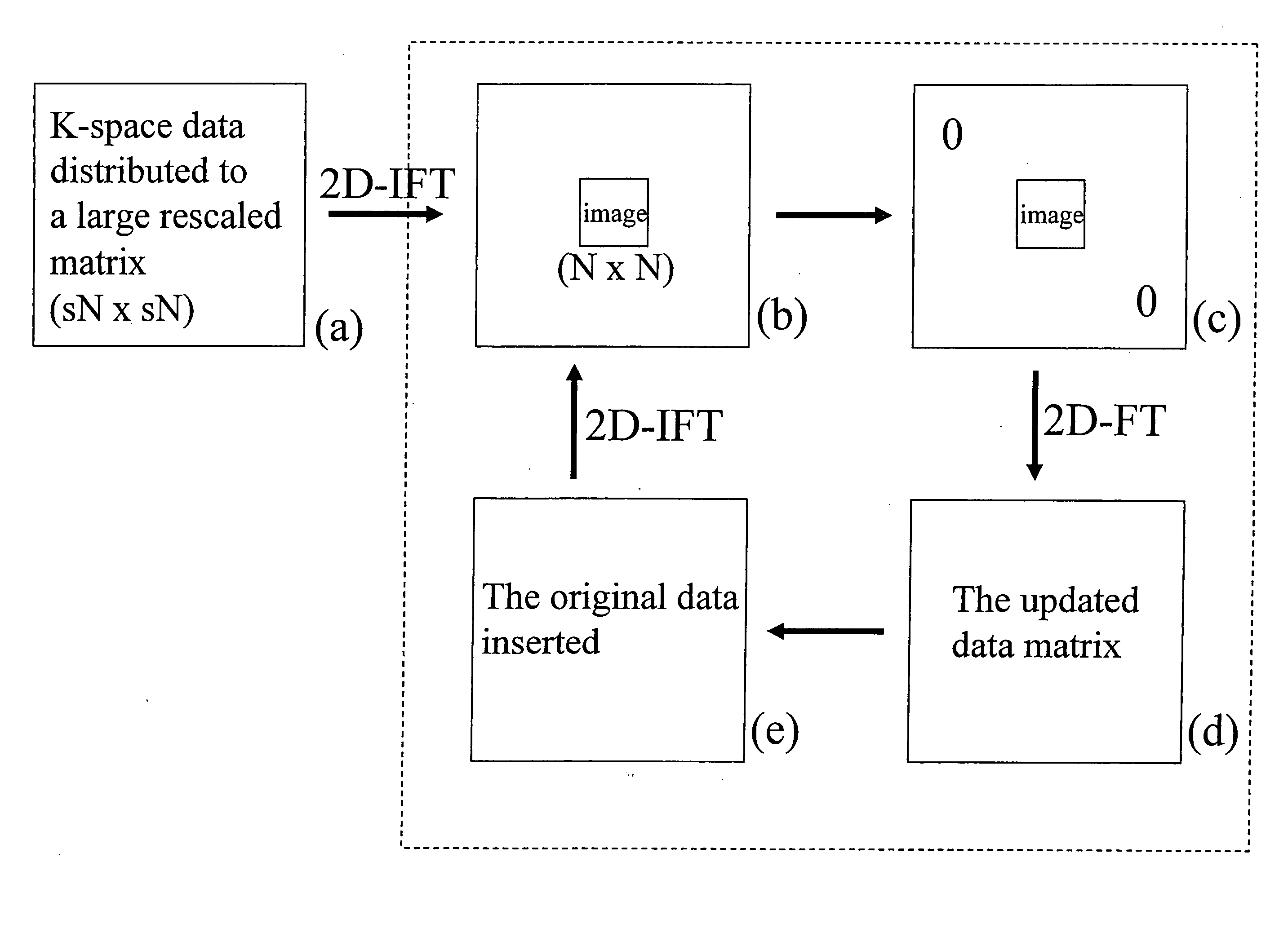
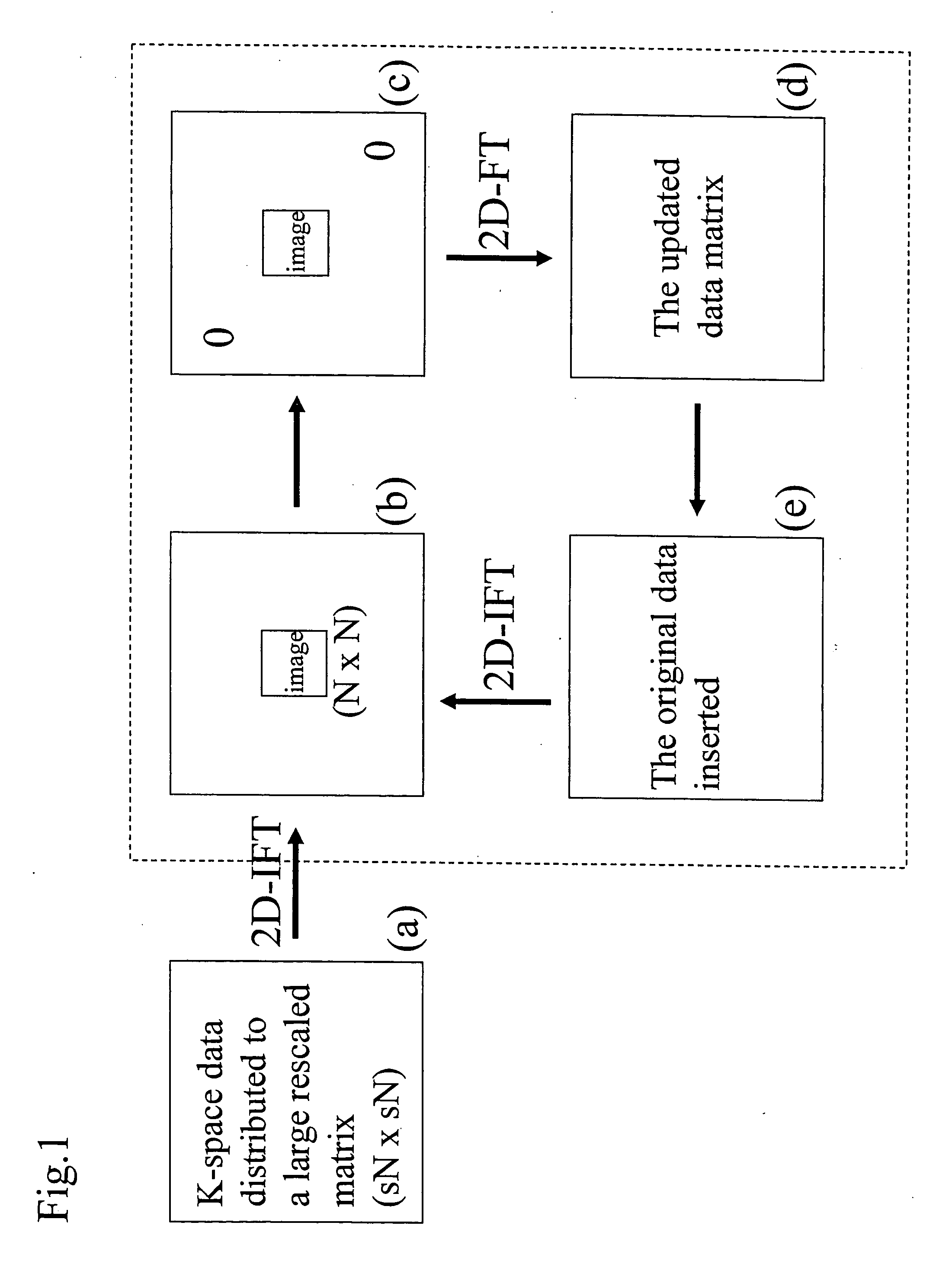
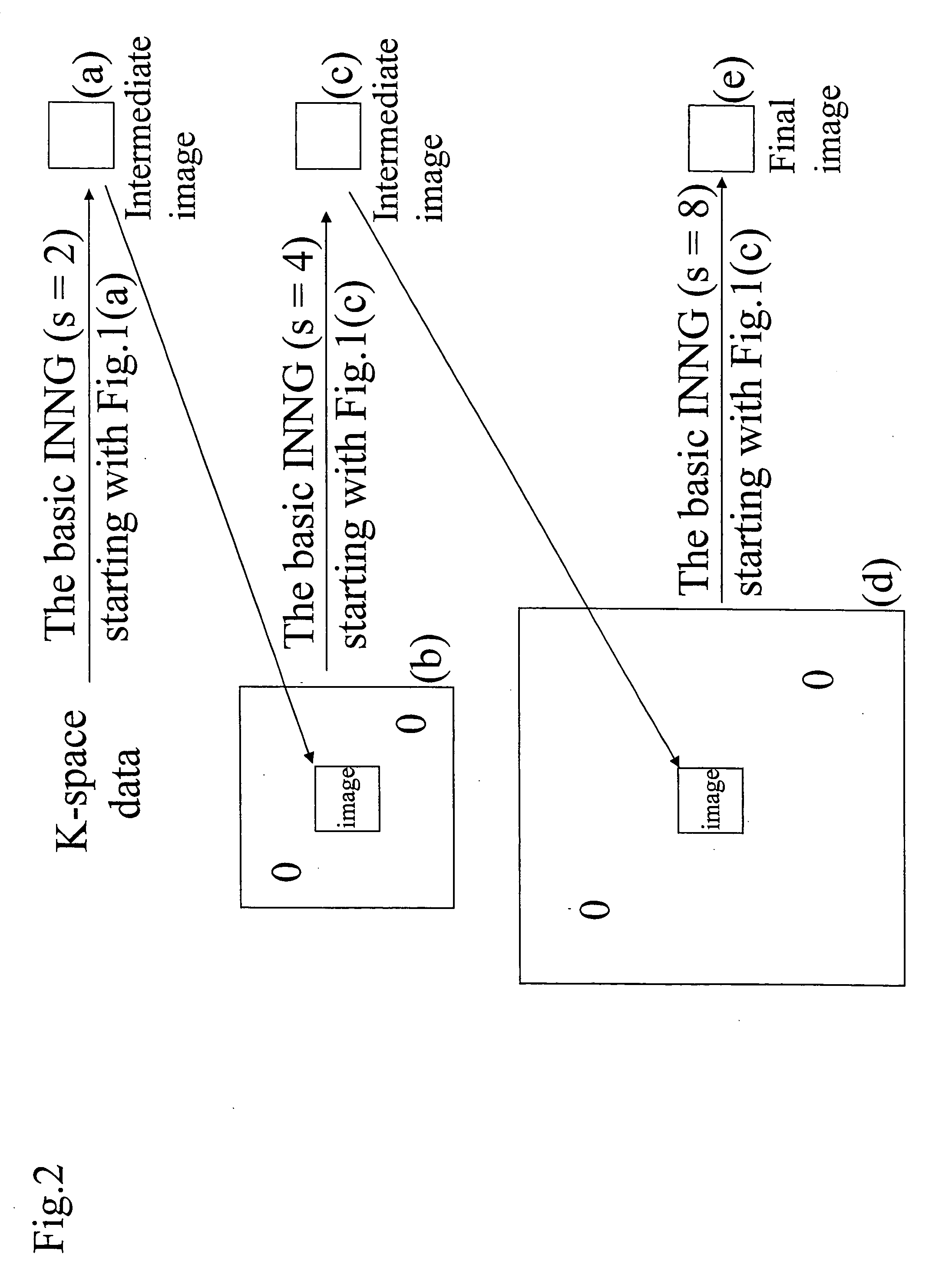
Methods are described for efficient reconstruction of MRI data. In one practice, new reconstruction algorithms for non-uniformly sampled k-space data are presented. In the disclosed algorithms, Iterative Next-Neighbor re-Gridding (INNG) and Block INNG (BINNG), iterative procedures are performed using larger rescaled matrices than the target grid matrix In BINNG algorithm, the sampled k-space region is partitioned into several blocks and the INNG algorithm is applied to each block. In another practice, a novel partial spiral reconstruction (PFSR) uses an estimated phase map from a low-resolution image reconstructed from the central k-space data and performs iterations, similar to the iterative procedures with INNG, with an imposed phase constraint. According to yet another practice, an off-resonance correction is performed on matrices that are smaller than the full image matrix. All these methods reduce the computational costs while rendering high-quality reconstructed images.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
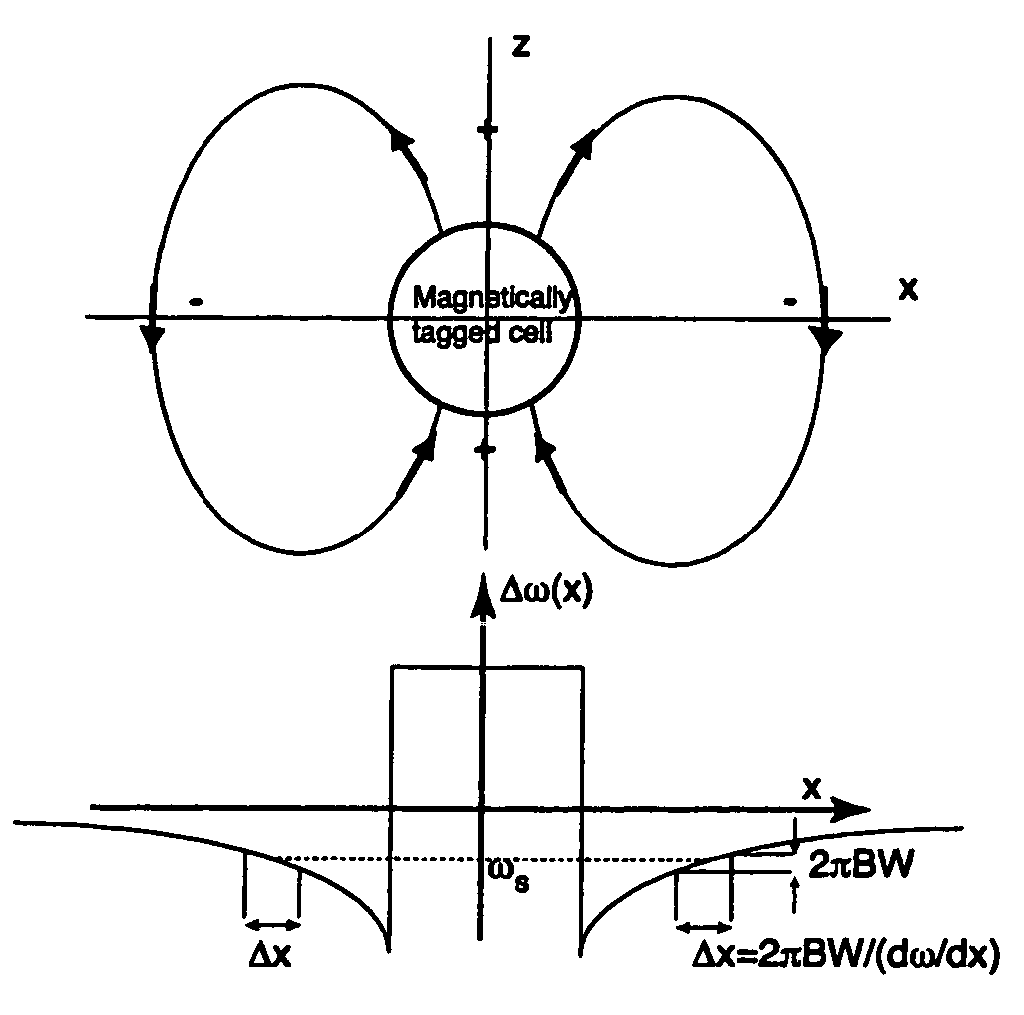
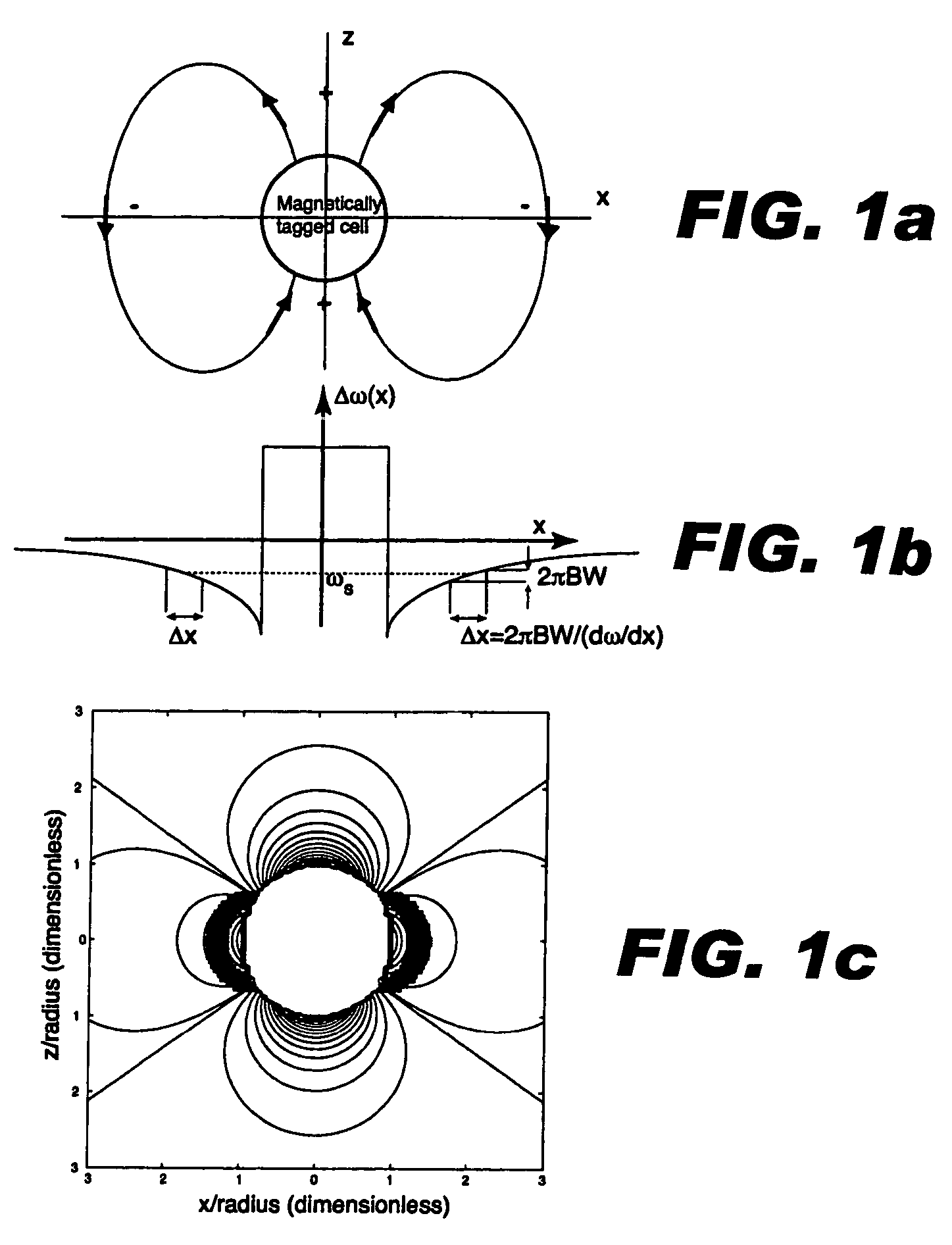
Positive contrast MRI of magnetically tagged cells, objects, tissues
ActiveUS20050261575A1Positive contrastReadily apparentDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsNegative Contrast AgentMagnetic marker
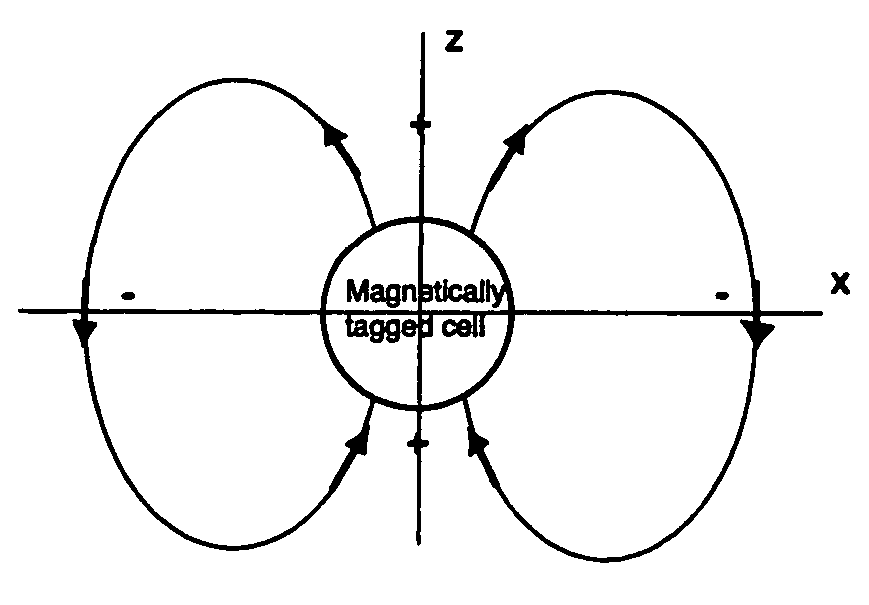
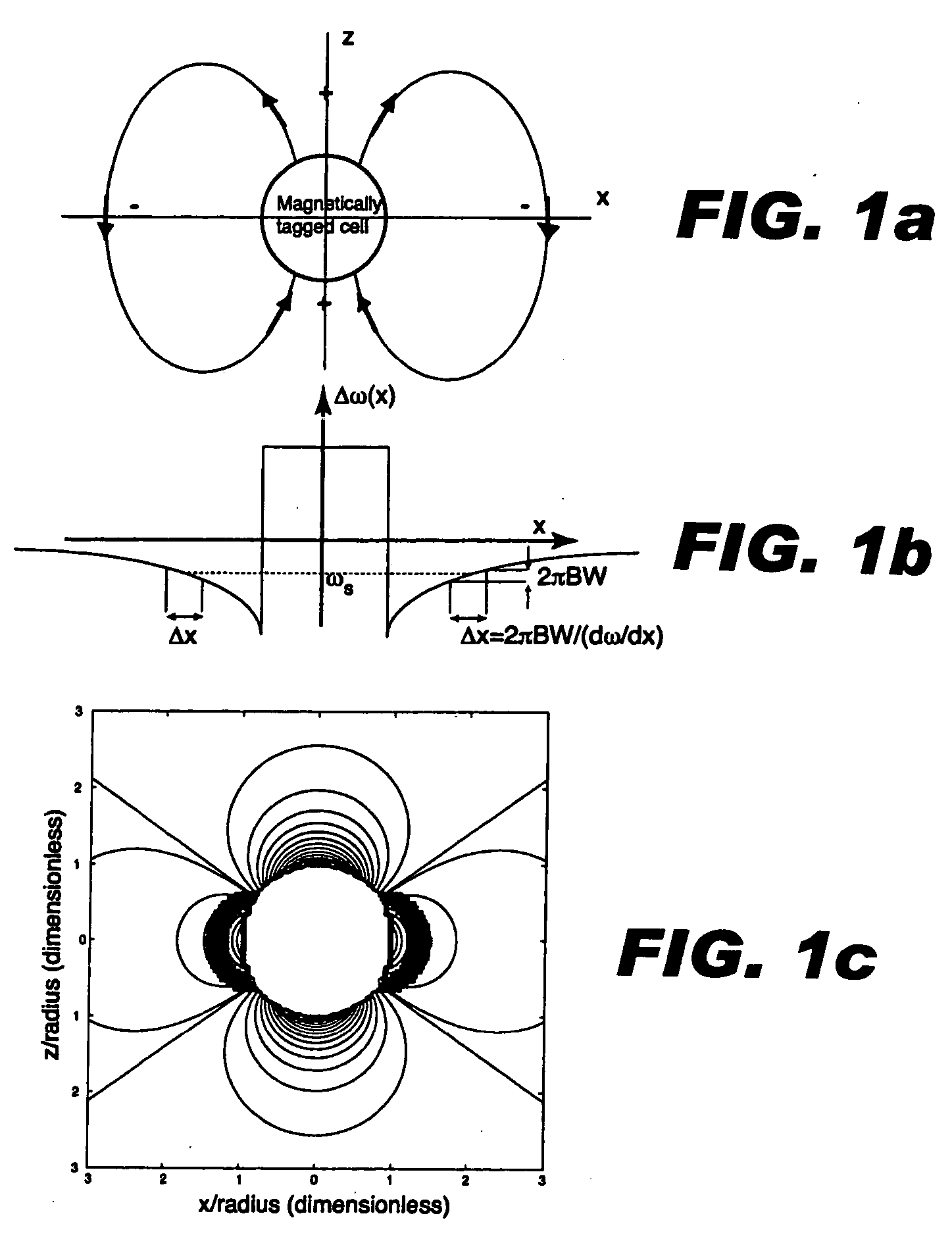
Contrast agents incorporating super-paramagnetic iron-oxide (SPIO) nanoparticles have shown promise as a means to visualize labeled cells using MRI. Labeled cells cause significant signal dephasing due to the magnetic field inhomogeneity induced in water molecules near the cell. With the resulting signal void as the means for detection, the particles are behaving as a negative contrast agent, which can suffer from partial-volume effects. Disclosed is a new method for imaging labeled cells with positive contrast. Spectrally-selective RF pulses are used to excite and refocus the off-resonance water surrounding the labeled cells so that only the fluid and tissue immediately adjacent to the labeled cells are visible in the image. Phantom, in vitro, and in vivo experiments show the feasibility of the new method. A significant linear correlation (r=0.87, p<0.005) between the estimated number of cells and the signal has been observed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Multi-slice cerebral blood flow imaging with continuous arterial spin labeling MRI
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Methods for fat signal suppression in magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20080218169A1Shorten the timeReduce acquisition timeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionData setFat suppression
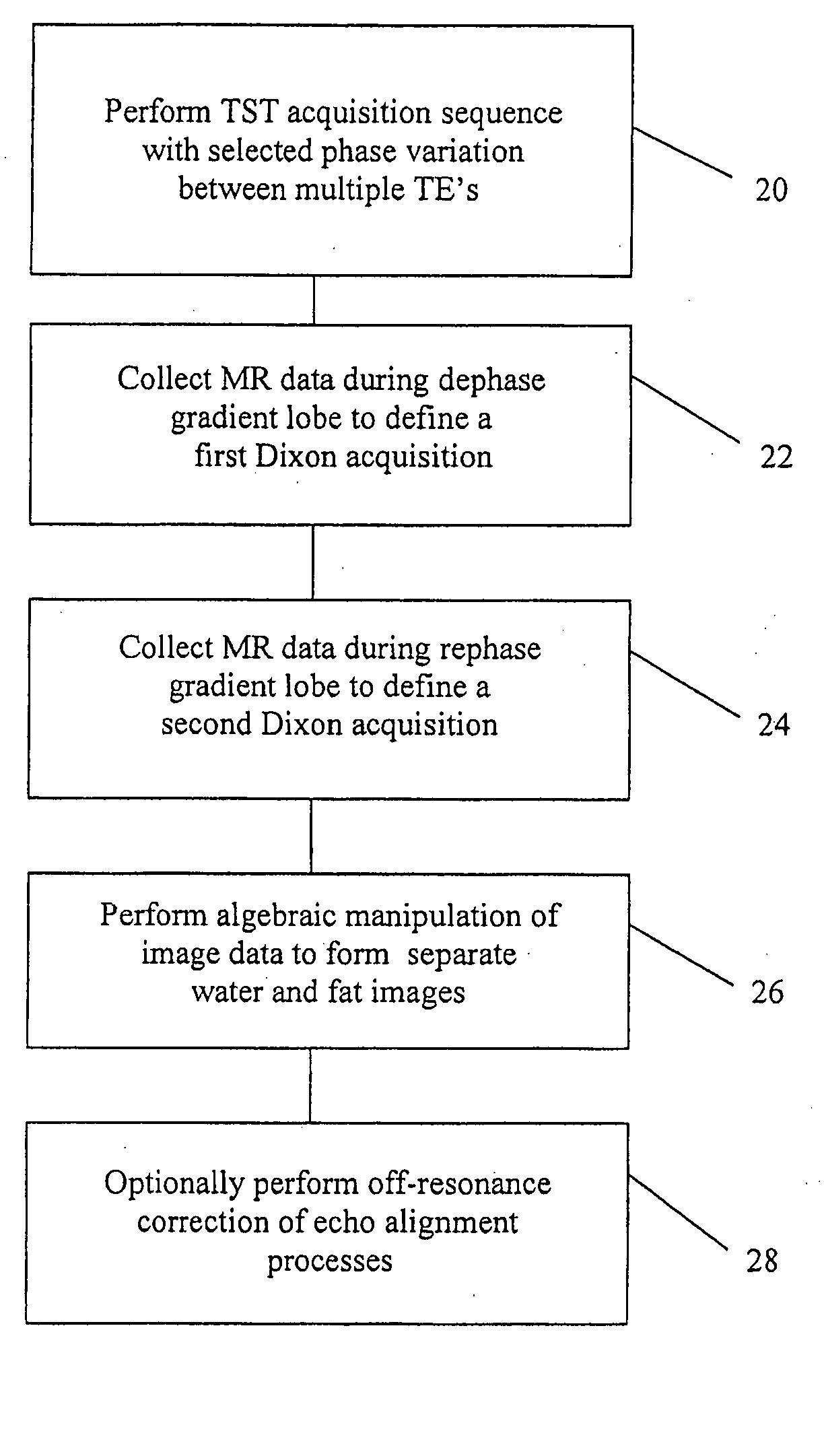
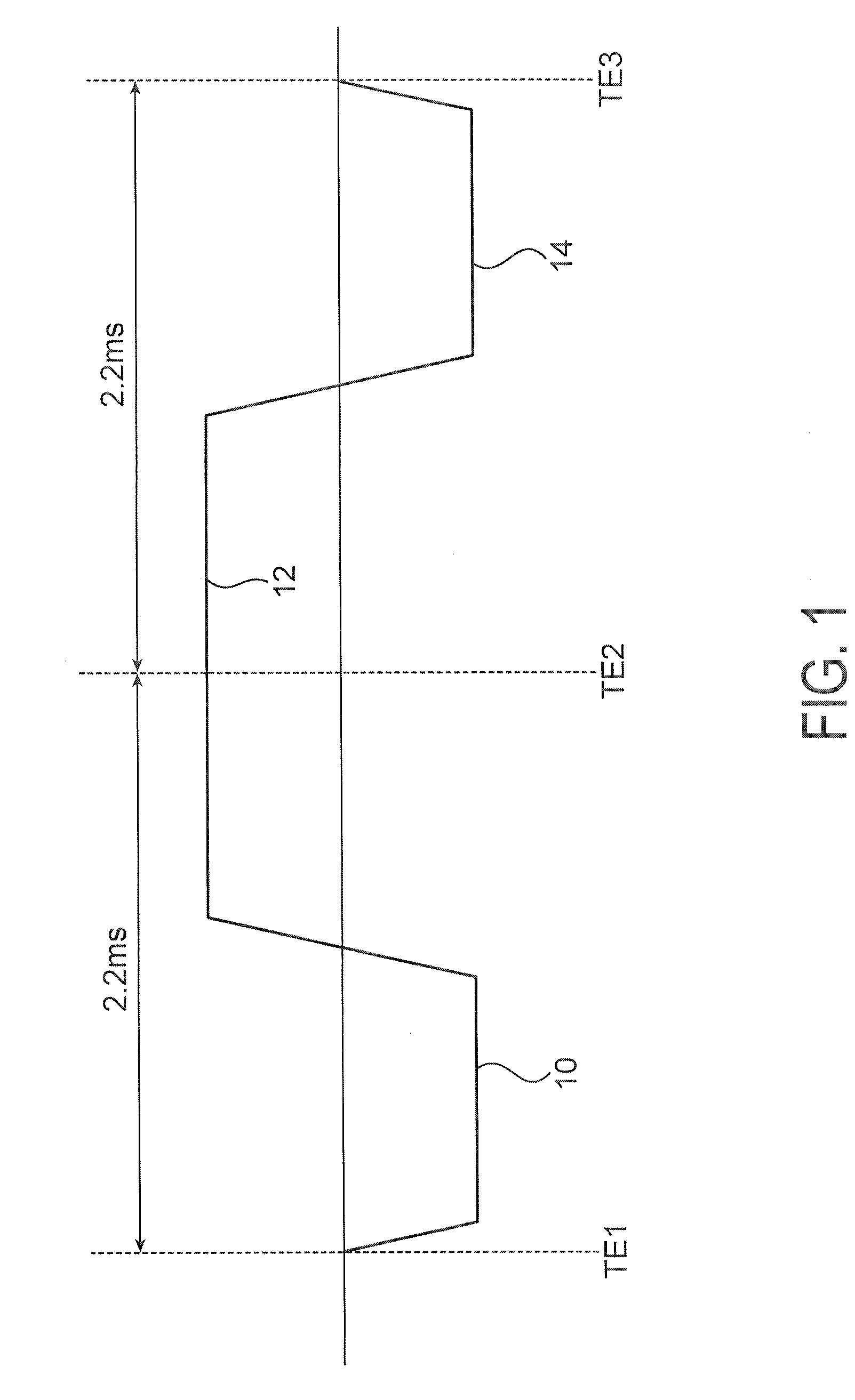
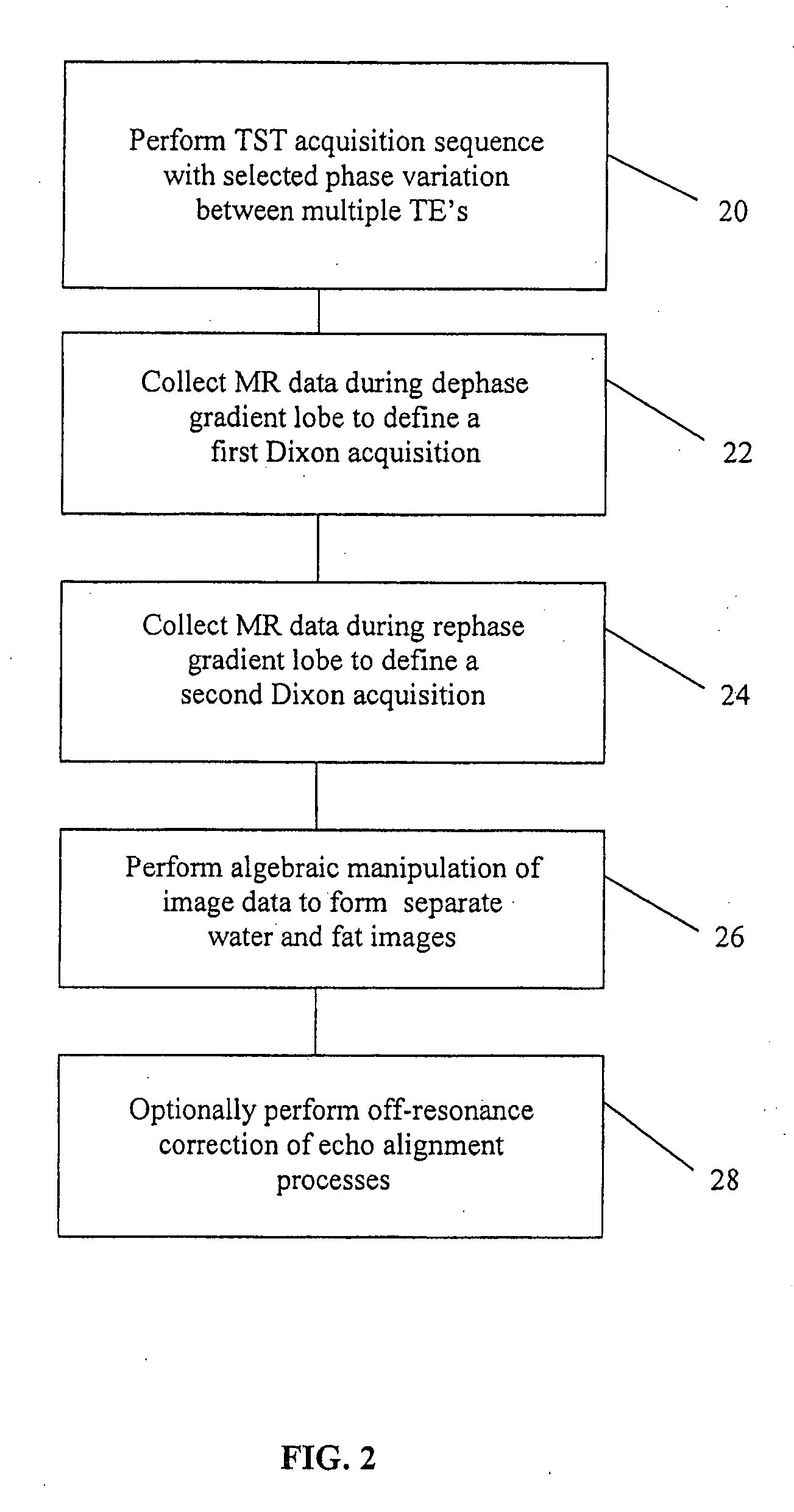
The present invention is directed to methods for chemical species signal suppression in magnetic resonance imaging procedures, wherein Dixon techniques are enhanced by continuously sampling techniques. In the invention, k-space data is acquired during the entire period of read gradient associated with a gradient echo pulse acquisition scheme. The invention utilizes a total sampling time (TST) acquisition during the entire read gradient, using three echoes of a TST data set to achieve chemical species separation in both homogenous fields as well as areas of field inhomogeneity. As an example, a continuously sampled rectilinearly FLASH pulse sequence is modified such that the time between echoes was configured to be 2.2 milliseconds, with TE selected to allow 180° phase variation in the fat magnetization between each of the three TE's (TE1, TE2, and TE3). Data collected during the dephase and rephase gradient lobes are defined as a first Dixon acquisition, with data collected by the read gradient lobe being defined as a second Dixon acquisition. Two point Dixon reconstruction techniques are used to form images for each chemical species, such as for generating water and fat images of the scanned object region. Other corrections, such as off-resonance correction may be applied on the image data.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Navigator-Based Data Correction For Simultaneous Multislice MR Imaging
ActiveUS20170089999A1Improve spatial resolutionEasy to correctImage enhancementImage analysisData setElectrical polarity
A magnetic resonance method and system are provided for providing improved simultaneous multislice echo planar imaging (EPI) with navigator-based correction of image data for B0 drift and N / 2 ghosting. The correction is based on two types of multi-echo phase-encoded navigator sequences having opposite readout gradient polarities, and optionally also uses a non-phase-encoded navigator sequence. One or more navigator sequences can be generated between each RF excitation pulse and the subsequent EPI readout sequence. A dynamic off-resonance in k-space technique can be used to correct for B0 drift, and a modified slice GRAPPA technique that is based on odd and even kernels can provide slice-specific correction for N / 2 ghosting effects for the EPI MR image data sets. Various patterns of navigator sequences and / or interpolation of navigator data can be used to improve accuracy of the image data corrections.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
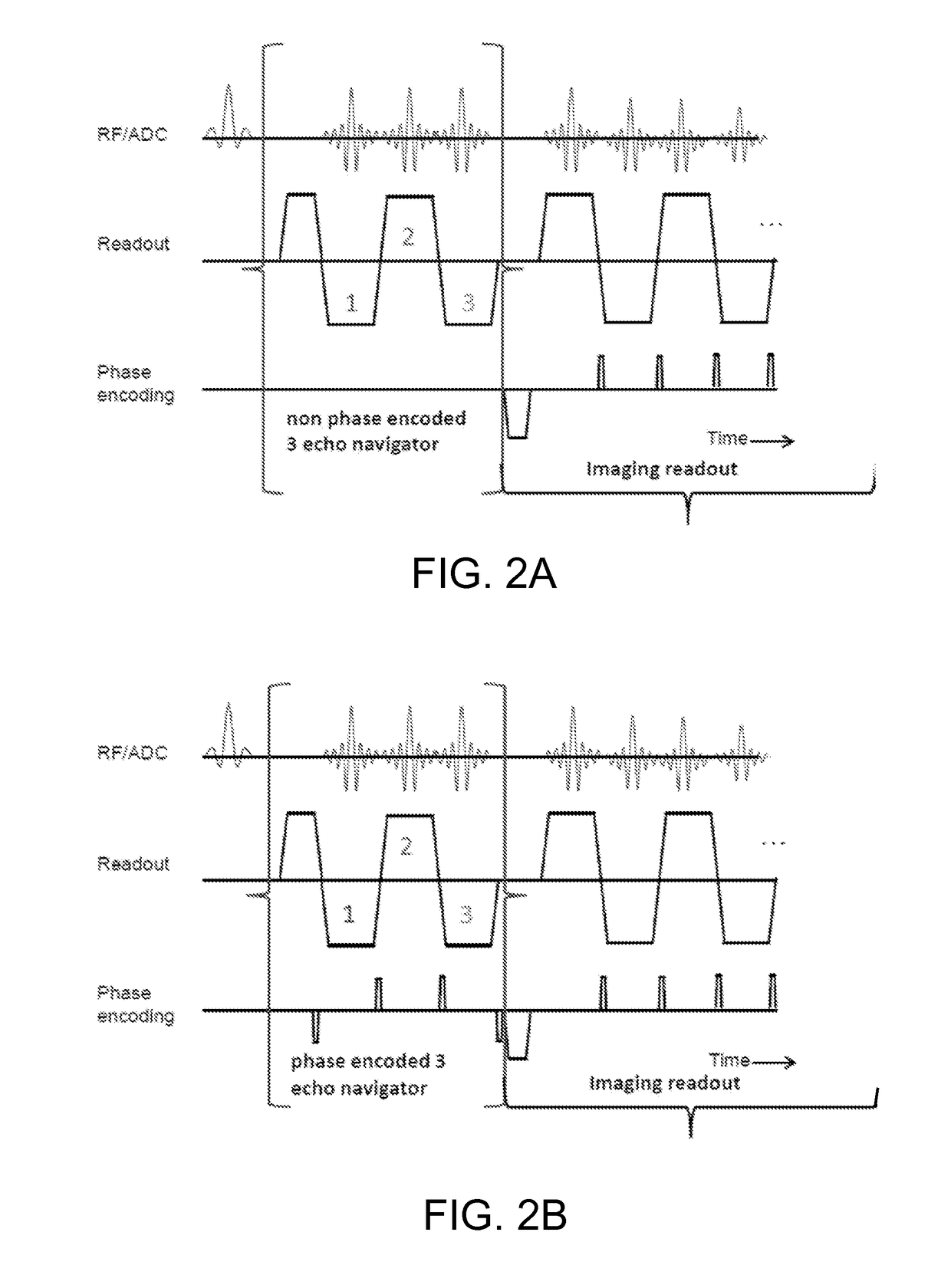
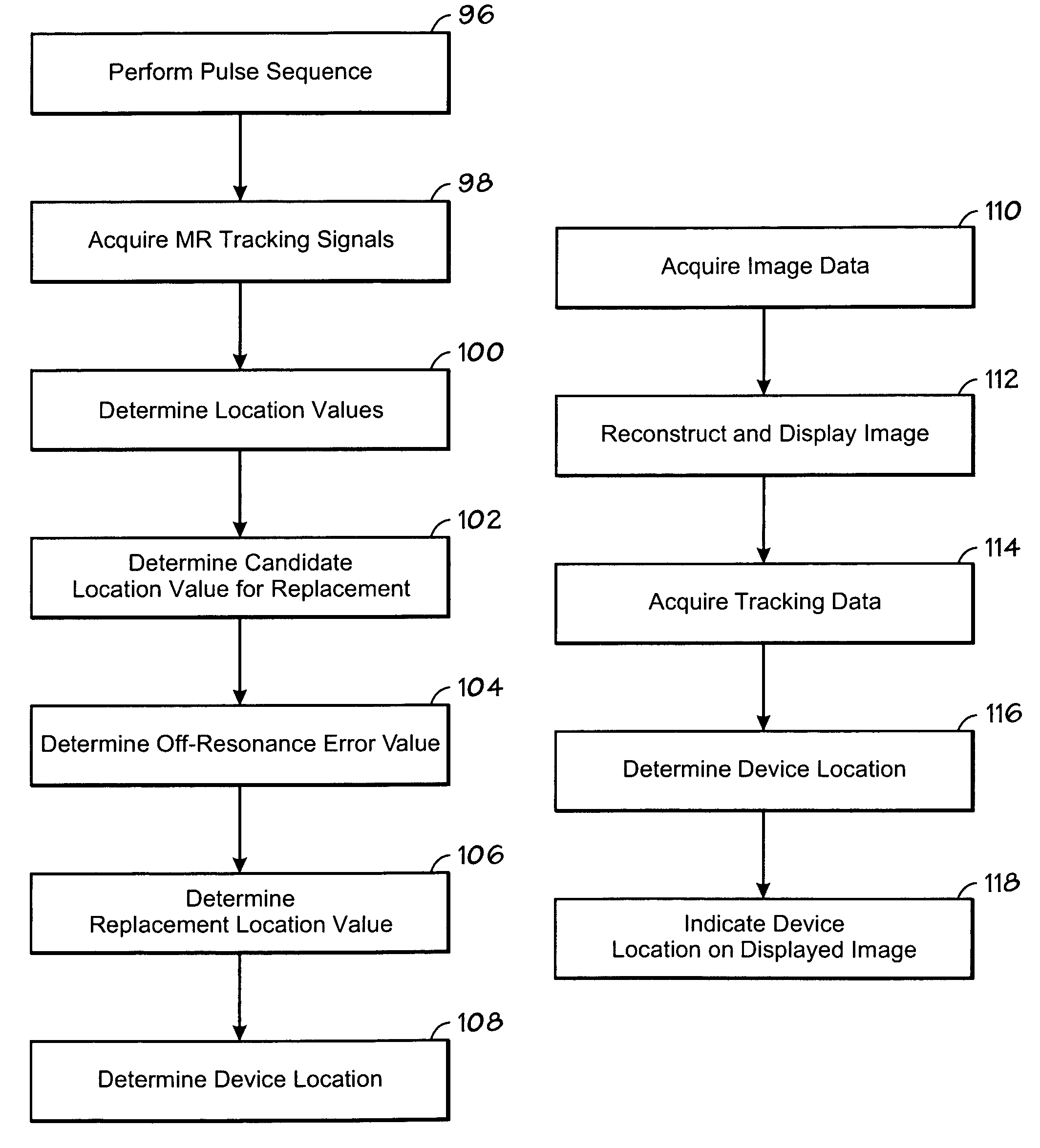
Method for multiplexed MR tracking
The present technique provides a novel method and apparatus for magnetic resonance device tracking. In one aspect of the present technique, a plurality of magnetic resonance tracking signals are acquired in response to a corresponding plurality of pulse sequences, wherein the plurality of magnetic resonance tracking signals are acquired from a tracking coil mounted in a device. A location value is also determined for each pulse sequence to produce a plurality of location values. Further, a candidate location value of the plurality of location values for replacement, an off-resonance error value for the plurality of magnetic resonance tracking signals, and a replacement location value based on the off-resonance error value are determined. The location of the device is also determined based on the plurality of location values, wherein the candidate location value was replaced in the plurality of location values with the replacement location value.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for nonlinear optical null ellipsometry
InactiveUS7336359B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsComputational physicsNonlinear optical
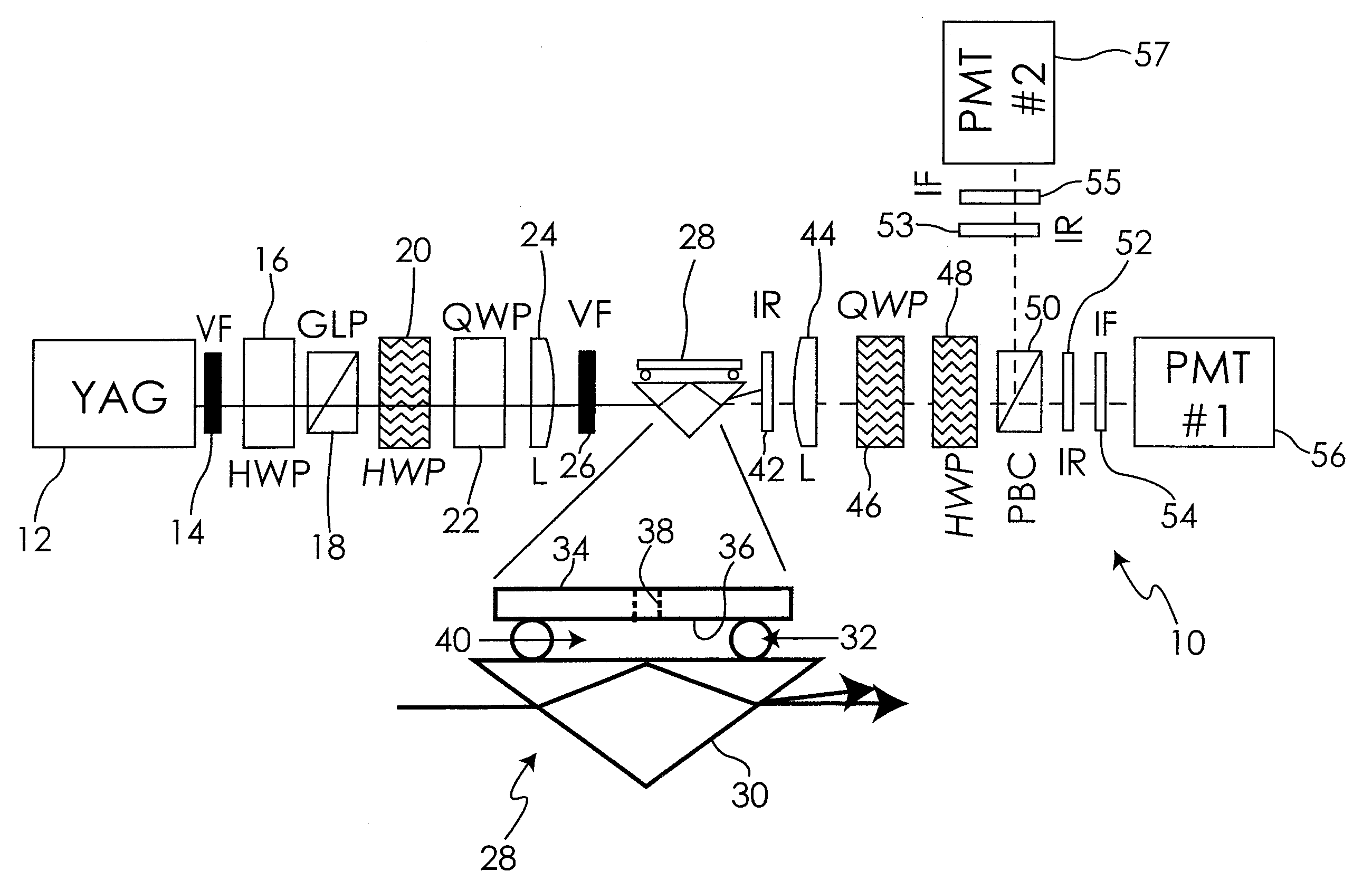
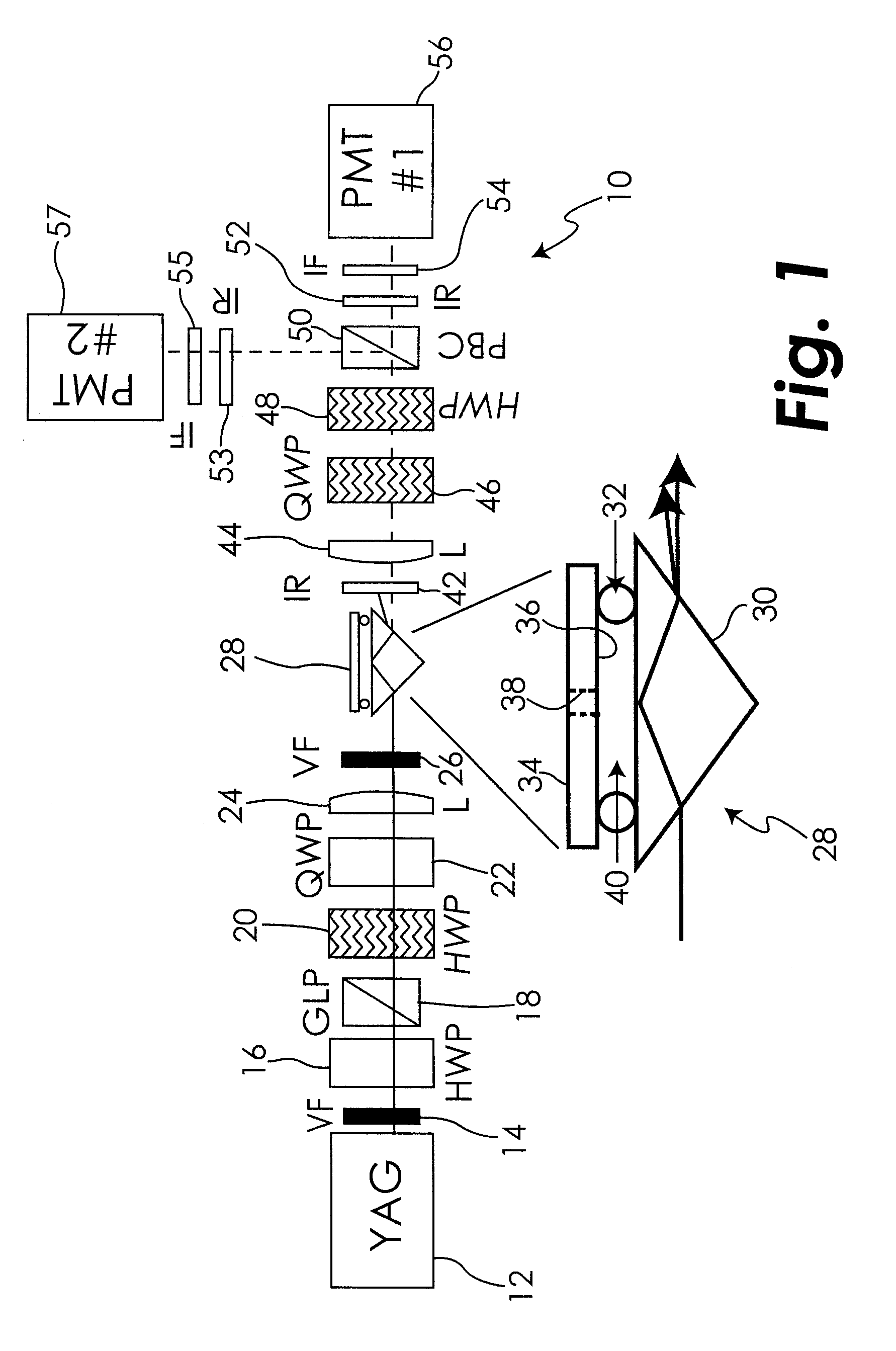
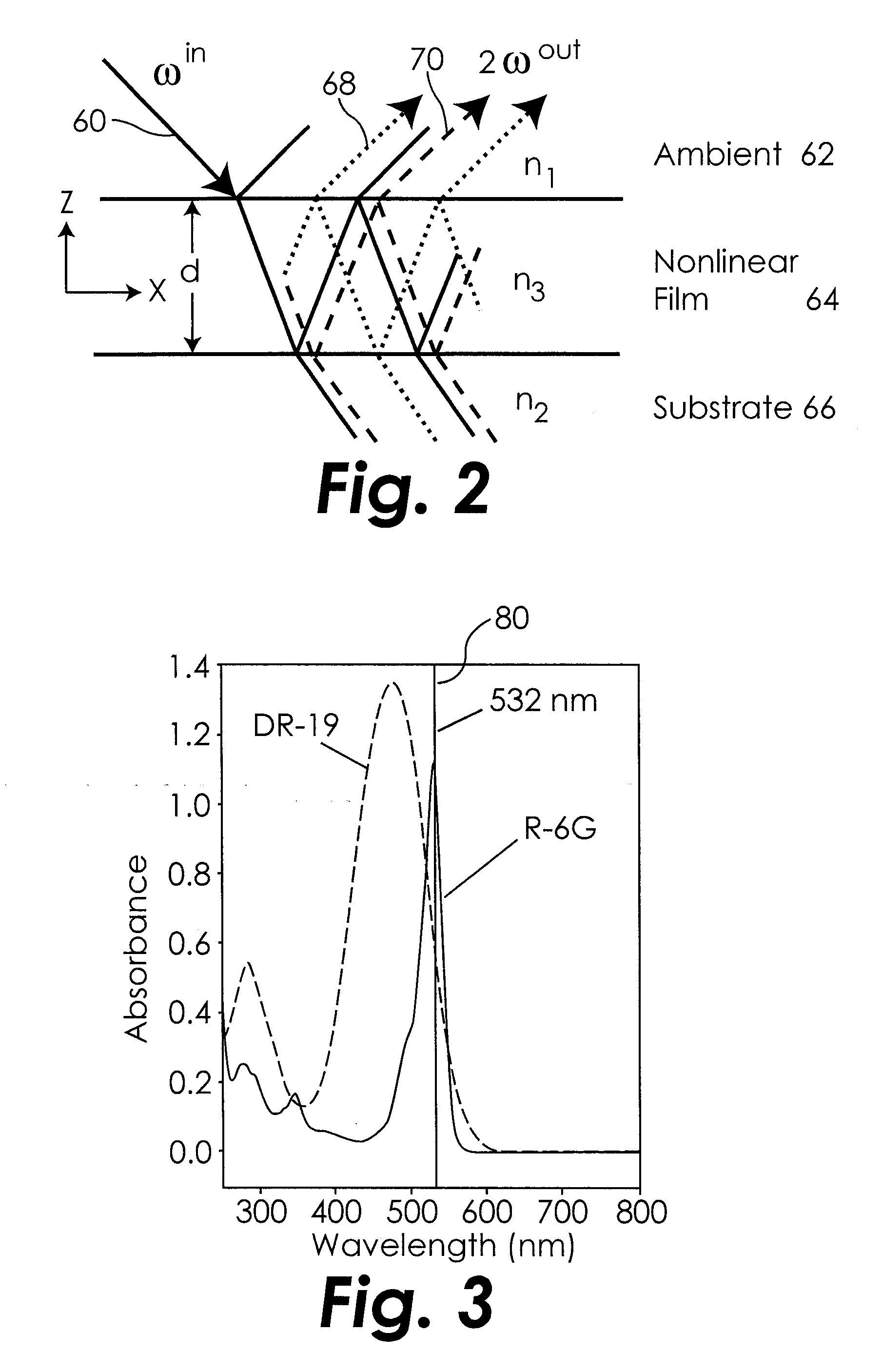
Nonlinear optical null ellipsometry is disclosed as a method to evaluate second-order nonlinearities on and off resonance in thin surface films and bulk materials.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
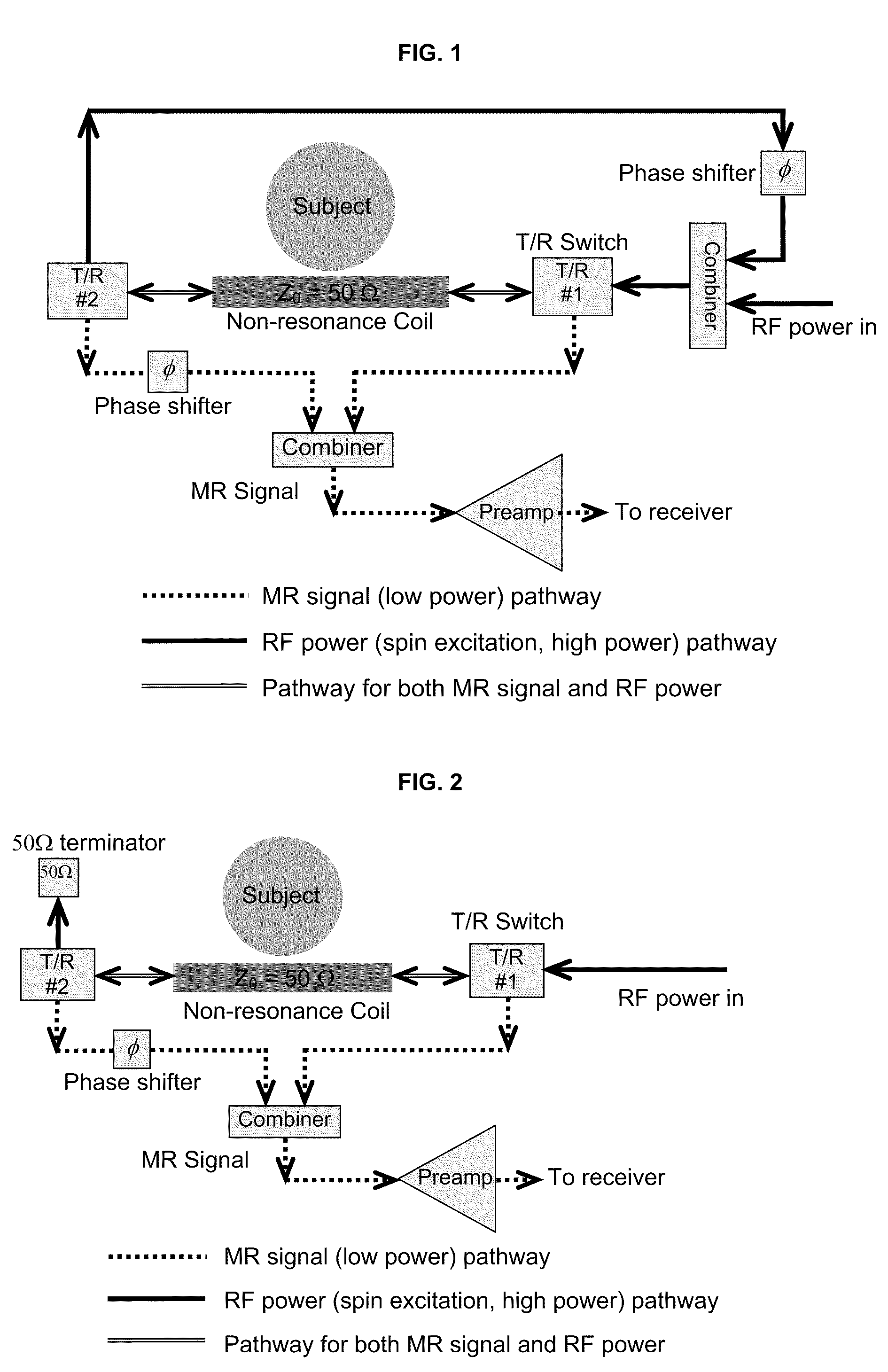
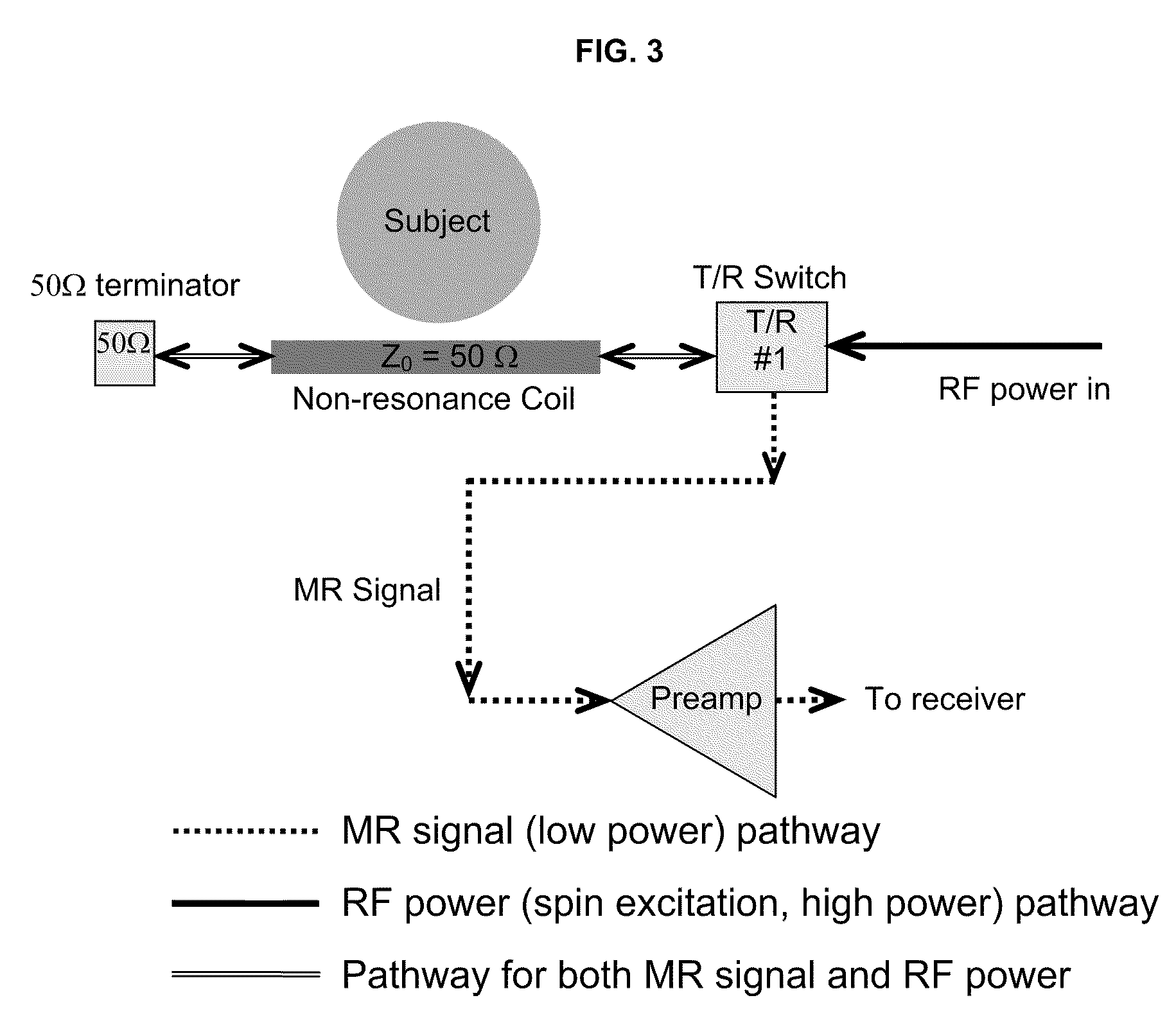
Method and apparatus for MRI signal excitation and reception using non-resonance RF method (NORM)
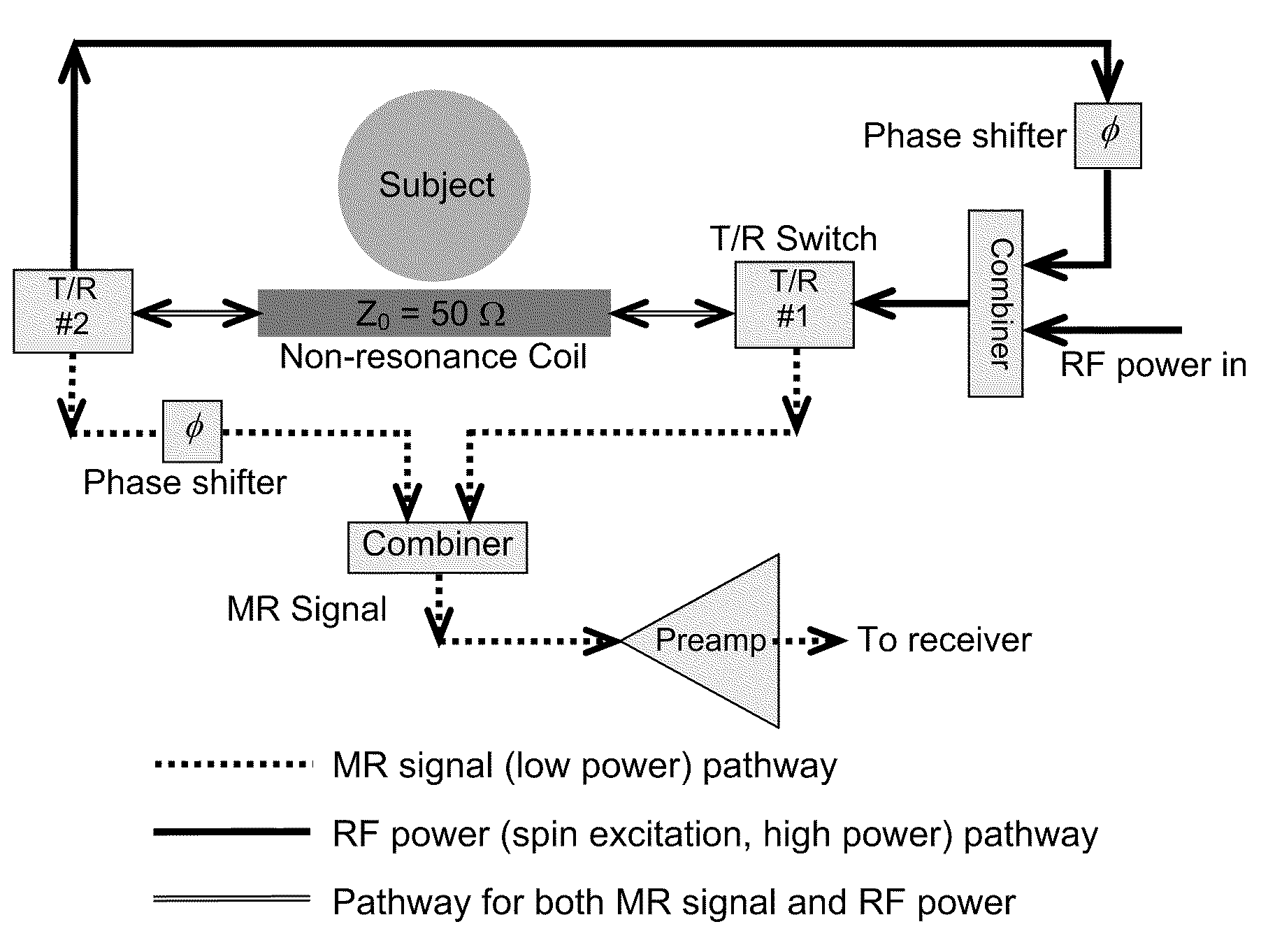
A system for MR signal excitation and reception and method which uses a non-resonant device or transmission line to perform MR imaging and spectroscopy. The system with non-resonant device is advantageous to parallel imaging due to the improved decoupling performance. Because the non-resonant RF coil is not generally sensitive to frequency, a MR system with the non-resonant RF coil is capable of multinuclear MR operation at varied magnetic field strength. The system comprises a non-resonant RF coil for connecting to an MR system, the conductor being configured to have a characteristic impedance matched to the MR system. The RF coil is configured to produce electromagnetic fields of differing strengths based on the constant characteristic impedance maintained in the system for exciting and receiving MR signals.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
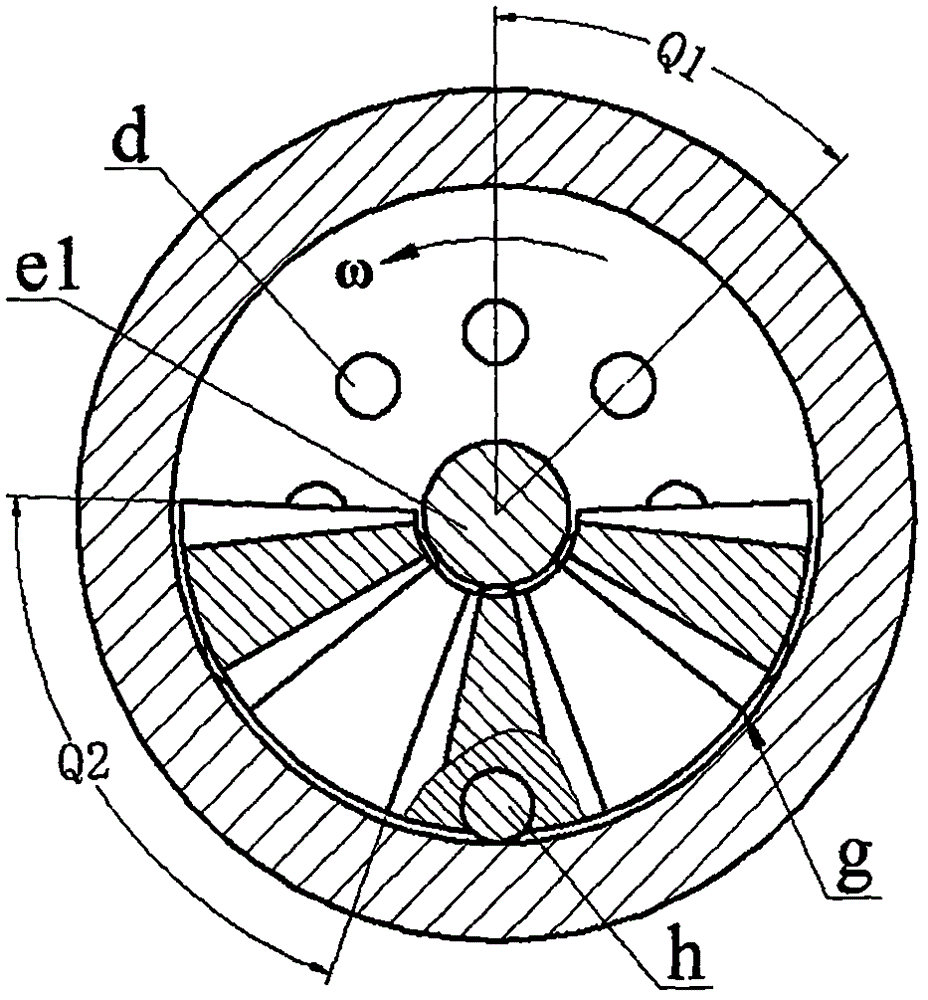
An off-resonance type wheel-type generator based on a cantilever beam piezoelectric vibrator
InactiveCN106160574ARealize real-time monitoringReasonable structurePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCantilevered beamStress point
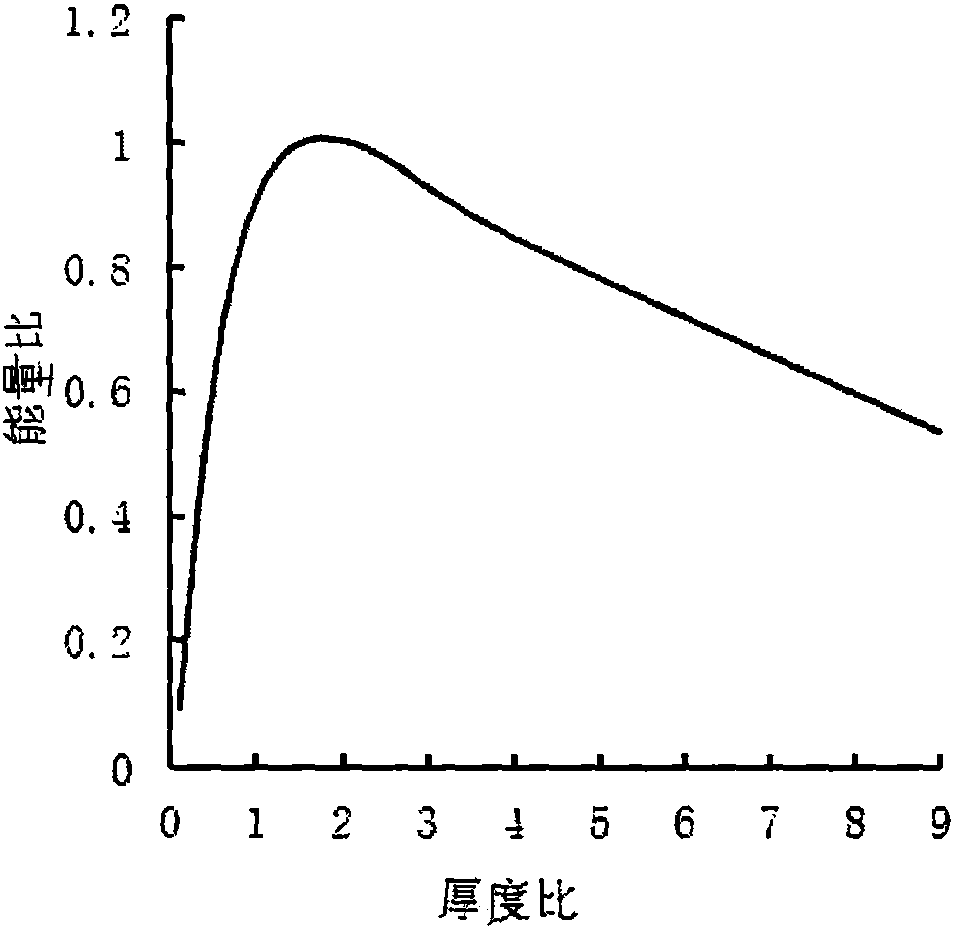
The invention relates to an off-resonance type wheel-type generator based on a cantilever beam piezoelectric vibrator, and belongs to the field of piezoelectric power generating. A rotary disc slide sink cavity is communicated with a central hole on the other side and communicated with an annular cavity through a guide hole; a cantilever shaft sleeved in the center hole is connected with a side plate installed on a side of the sink cavity; the side plate is provided with an annular cavity and a guide hole; extrusion balls are filled in the guide holes of the rotary disc and the side plate; a cantilever of a metal substrate pressed by the end cap in the annular cavities of the rotary disc and the side plate and a bonded piezoelectric wafer constitute a piezoelectric vibrator; an excitation disc is filled in a slide formed the slide sink cavity and the cantilever shaft; balls are embedded in the inner rim and the outer rim of the excitation disc; and a lift inclined plane, a convex surface, return inclined surface and a concave surface on the two sides of the excitation disc form an excitation unit. The advantages and characteristics of the off-resonance type wheel-type generator are that no fixed support is needed and no electromagnetic interference exists; the piezoelectric oscillator structure is reasonable; off-resonance power generation is realized and the deformation of the radius is determined by a limit surface; stress points are the same and only bear compressive stress, so that the electric power generation is large; the reliability is high; an effective frequency band width is large; and the off-resonance type wheel-type generator is especially suitable for a low rotating speed environment.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Polarization interference multi-element CARS (Coherent Anti-stokes Raman Scattering) microscopic imaging method
InactiveCN102540620AEliminates the effects of off-resonant background noiseMicroscopesNon-linear opticsMicroscopic imageFiber
The invention relates to a polarization interference multi-element CARS (Coherent Anti-stokes Raman Scattering) microscopic imaging method. The method comprises the steps that: high and heavy frequency polarization femtosecond laser is taken as a probe light of a CARS signal, and a part of the high and heavy frequency polarization femtosecond laser after beam splitting is taken as pump light pump PCF (Photon Crystal Fiber); and the output of a super continuous spectrum generated by the PCF is divided into two parts, a part is taken as a first Stokes exciting light, the other part is taken as a second Stokes exciting light after the polarization angle of the super continuous spectrum is changed by a half wave plate, and a CARS microscopic image is obtained through a confocal microscopic optical path and a spectrum analysis system. The polarization interference multi-element CARS microscopic imaging method provided by the invention has the advantages that: femtosecond CARS probe light and two beams of the super continuous spectrum Stokes exciting lights generated by the pump PCF after the beam splitting are subjected to polarization interference, and polarized component in some one direction is extracted and a peak-to-peak value after interference enhancement is selected through a polarization analyzer, thus the influence of off-resonance background noise of a sample can be eliminated, and the CARS microscopic image with high contrast and broad band is obtained.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
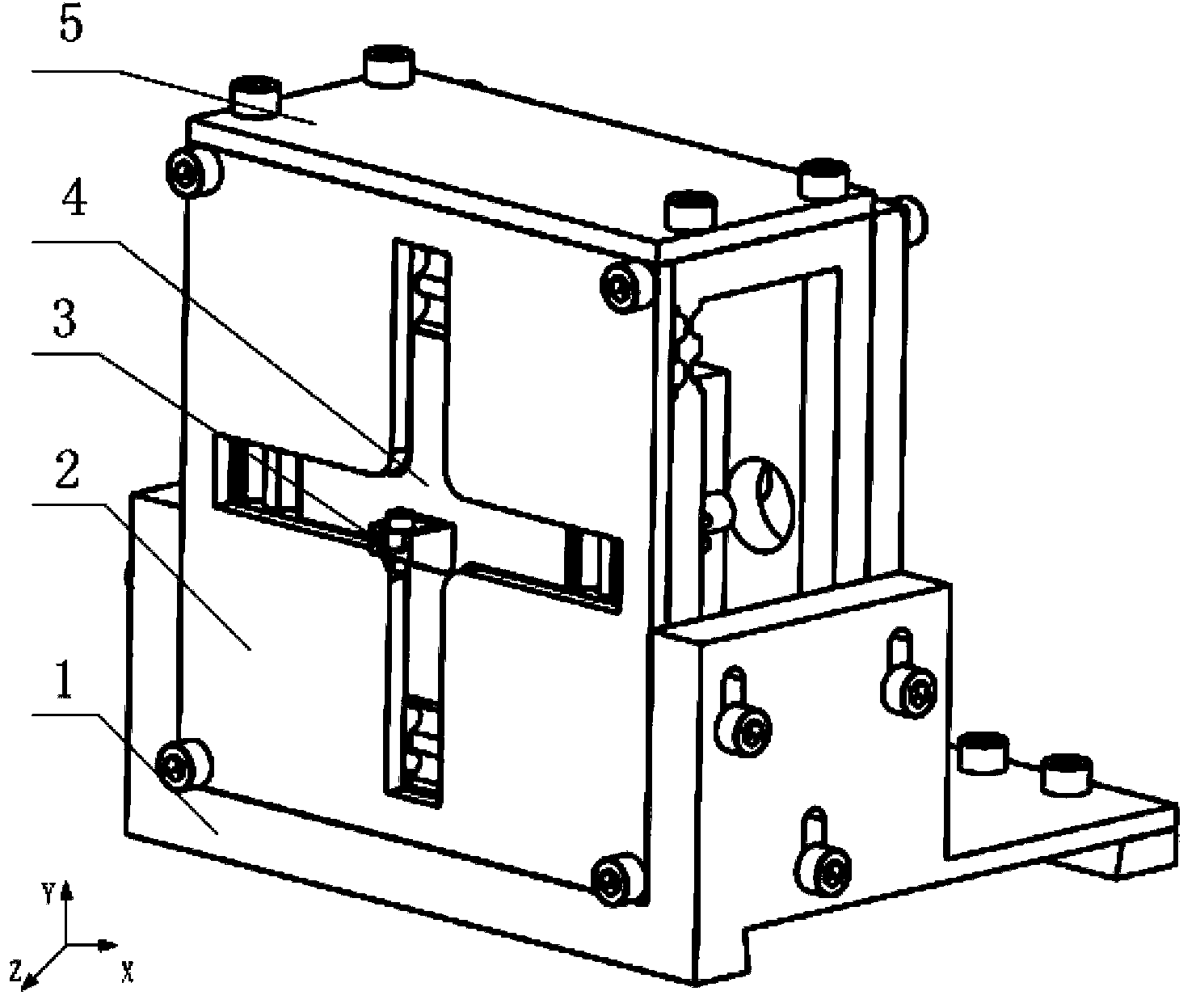
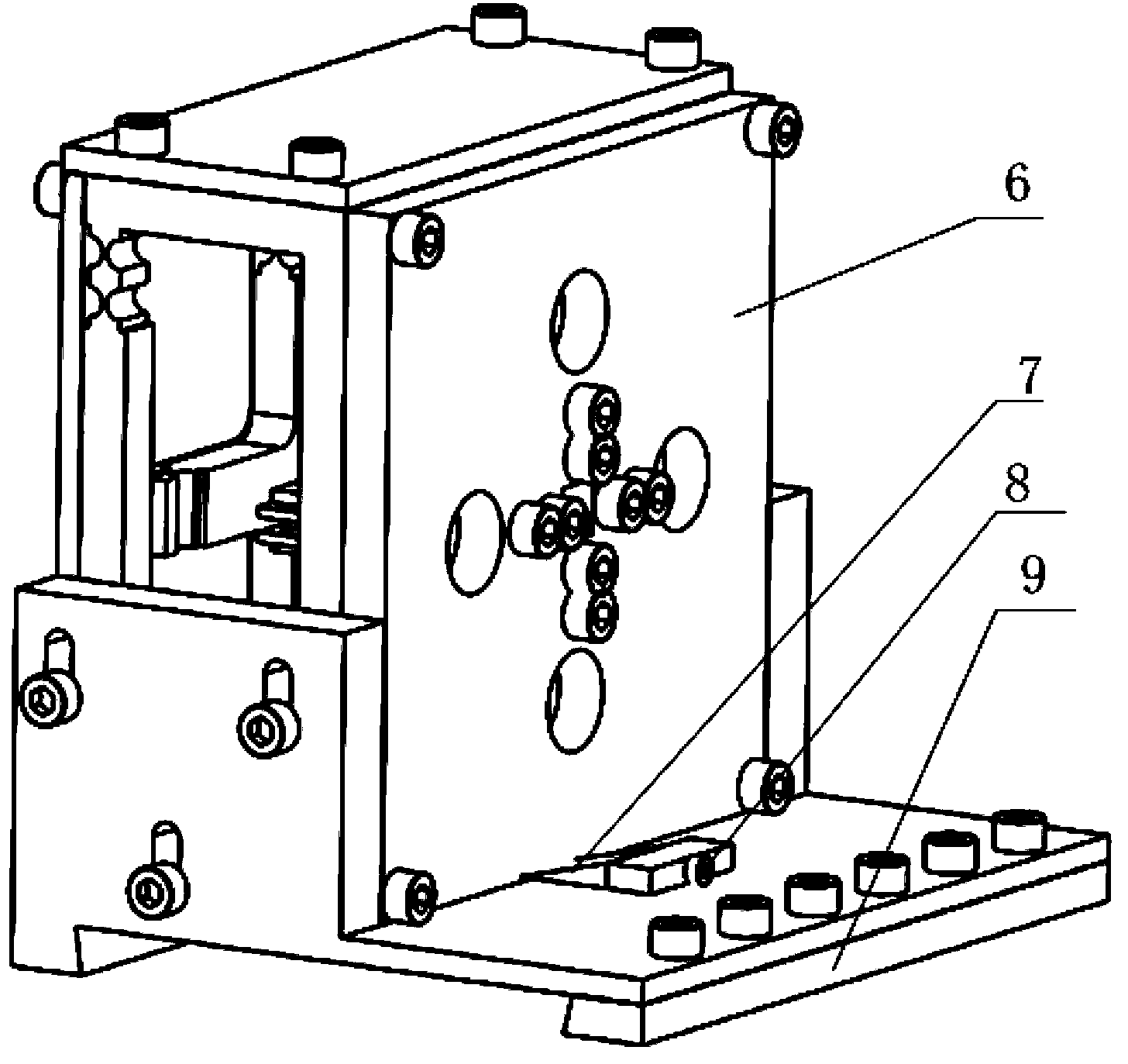
Off-resonance elliptical vibration cutting device
InactiveCN104117697AImprove cutting performanceCompact structureAuxillary equipmentMechanical vibrations separationButt jointEllipse
The invention relates to an off-resonance elliptical vibration cutting device, and belongs to the technical field of ultra-precision cutting and difficult-to-machine material cutting. A diamond cutter is fixedly connected with a cutter seat on the front portion of a base body through a fastening screw, and the tail ends of two piezoelectric stacks in the X direction are in contact with a lower wedge-shaped block. An upper wedge-shaped block and the lower wedge-shaped block are in contact to constitute a wedge-shaped block pre-tightening mechanism. A wedge-shaped block baffle is fixedly connected with a back plate of the base body through two fastening screws, a wedge-shaped block pre-tightening screw is in threaded connection with the wedge-shaped block baffle and is in butt joint with the upper wedge-shaped block. The free end of each piezoelectric stack is fixedly provided with a stainless steel spherical crown body, and the lower portion of the base body is connected with a wedge-shaped adjusting base through four fastening screws. The off-resonance elliptical vibration cutting device has the advantages that the best cutting performance of difficult-to-machine materials can be acquired, a driving part composed of the piezoelectric stacks and a flexible hinge is more compact in structure, the part, which achieves motion, of the cutter seat is smaller in size, a cutter can still achieve large displacement in the high-frequency cutting process, and the machining efficiency is guaranteed.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Positive contrast MRI of magnetically tagged cells, objects, tissues
Contrast agents incorporating super-paramagnetic iron-oxide (SPIO) nanoparticles have shown promise as a means to visualize labeled cells using MRI. Labeled cells cause significant signal dephasing due to the magnetic field inhomogeneity induced in water molecules near the cell. With the resulting signal void as the means for detection, the particles are behaving as a negative contrast agent, which can suffer from partial-volume effects. Disclosed is a new method for imaging labeled cells with positive contrast. Spectrally-selective RF pulses are used to excite and refocus the off-resonance water surrounding the labeled cells so that only the fluid and tissue immediately adjacent to the labeled cells are visible in the image. Phantom, in vitro, and in vivo experiments show the feasibility of the new method. A significant linear correlation (r=0.87, p<0.005) between the estimated number of cells and the signal has been observed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
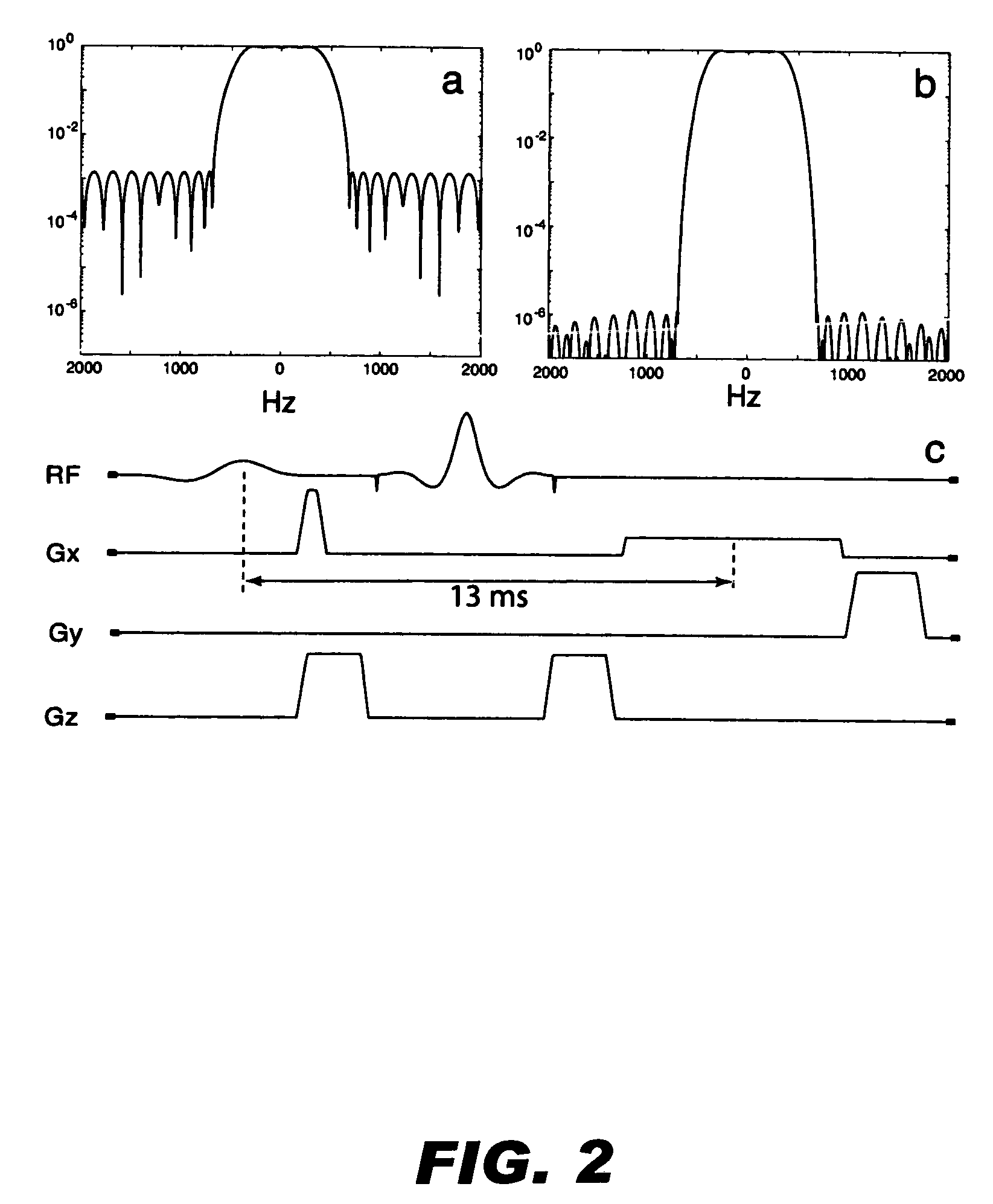
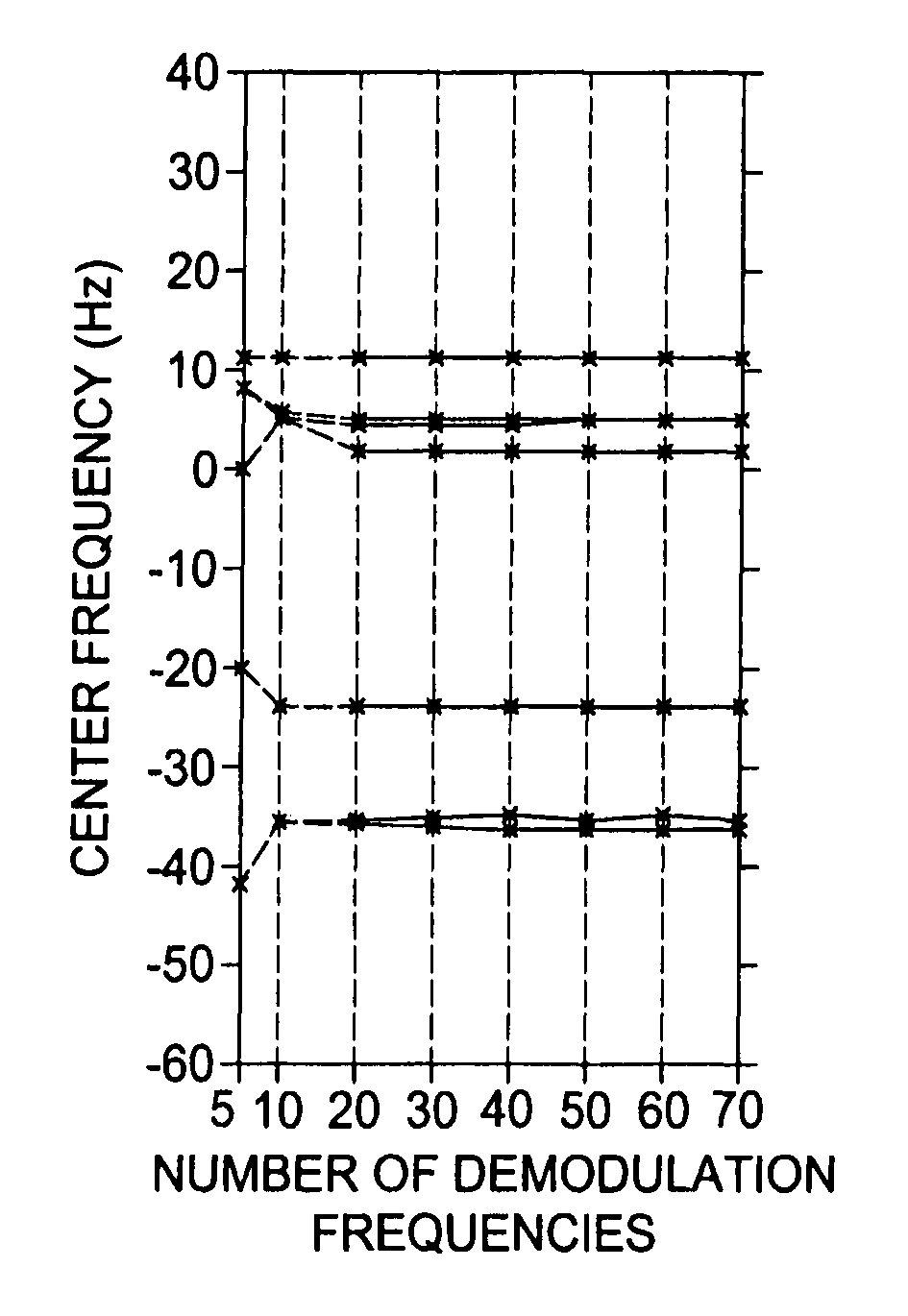
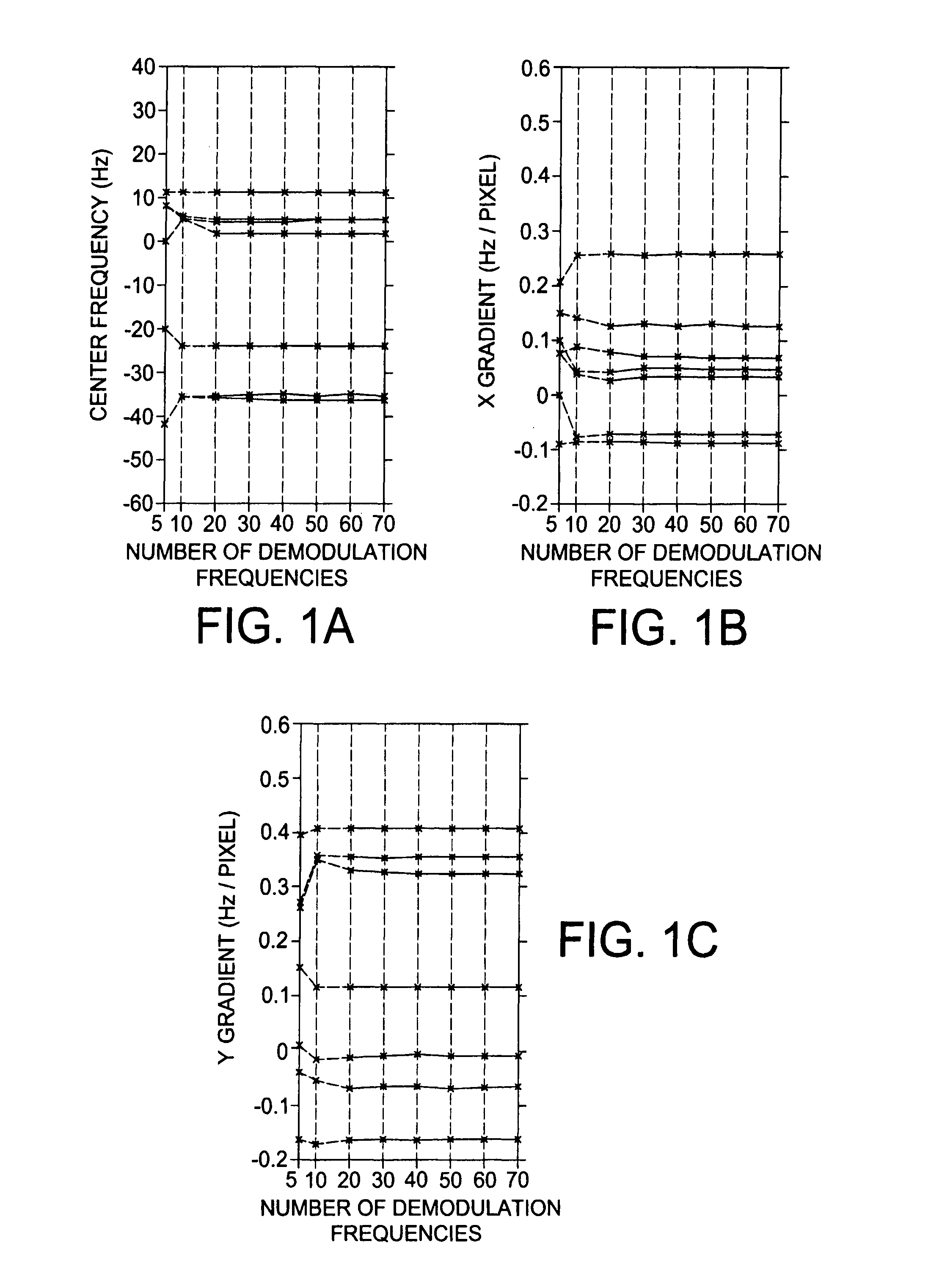
Fast automatic linear off-resonance correction method for spiral imaging
ActiveUS7642777B1Increasing estimation errorMore robustMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionImage resolutionAlgorithm
A fast automatic linear off-resonance correction method for MRI data uses a set of widely spaced demodulation frequencies to estimate a low-resolution field map from the image itself. A linear map is determined by fitting to this low-resolution map using a maximum-likelihood estimator with weights proportional to the pixel intensity.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
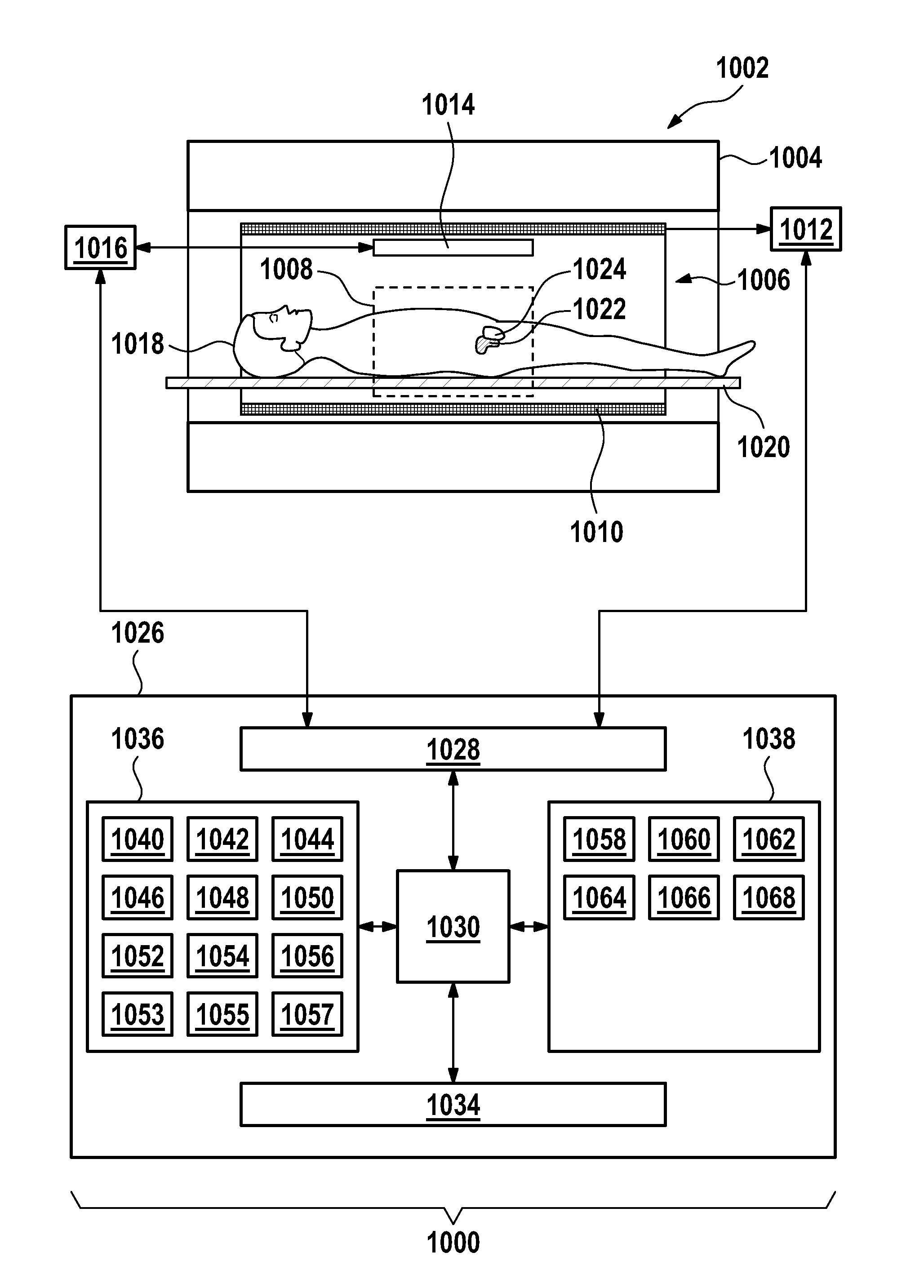
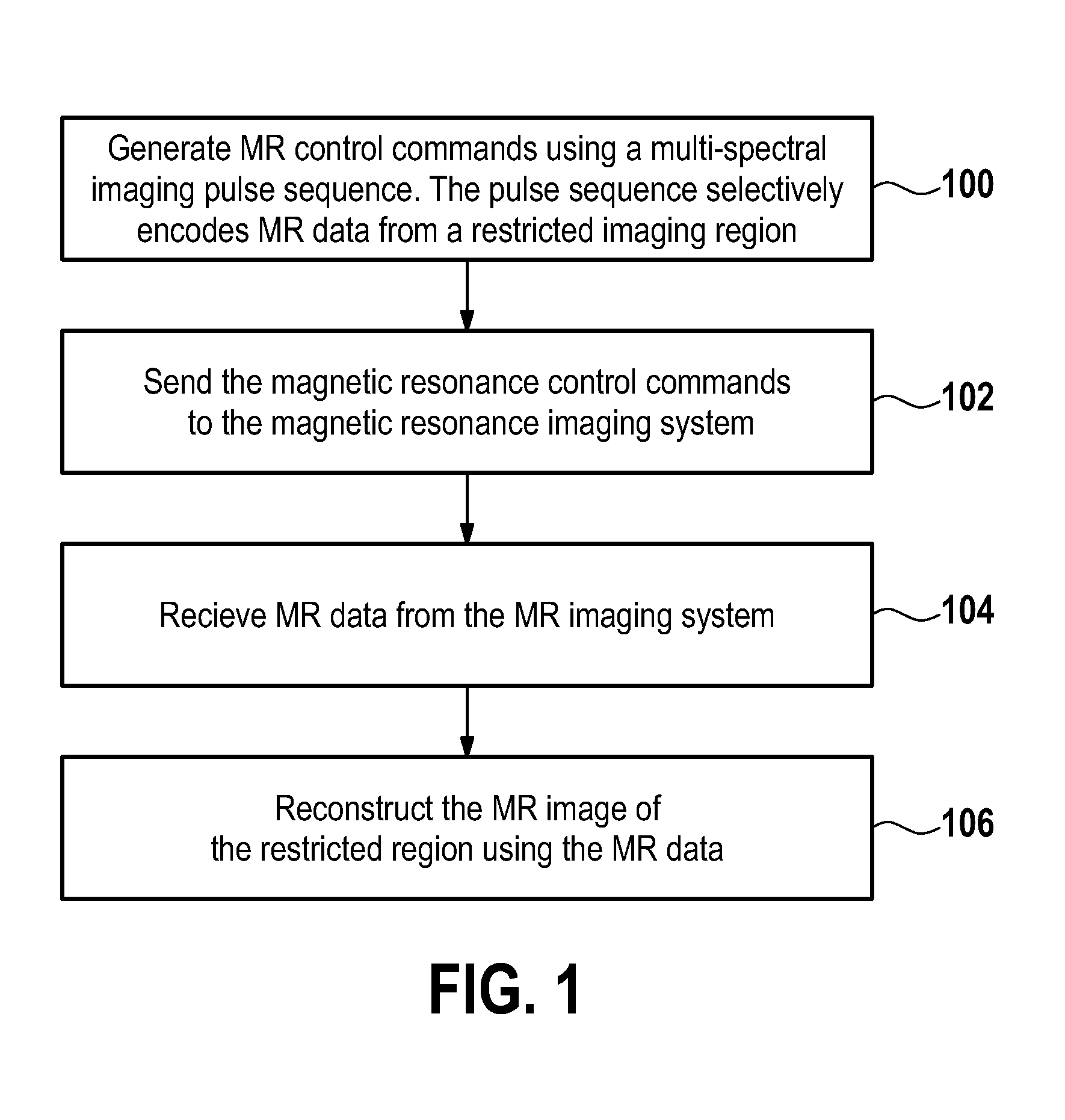
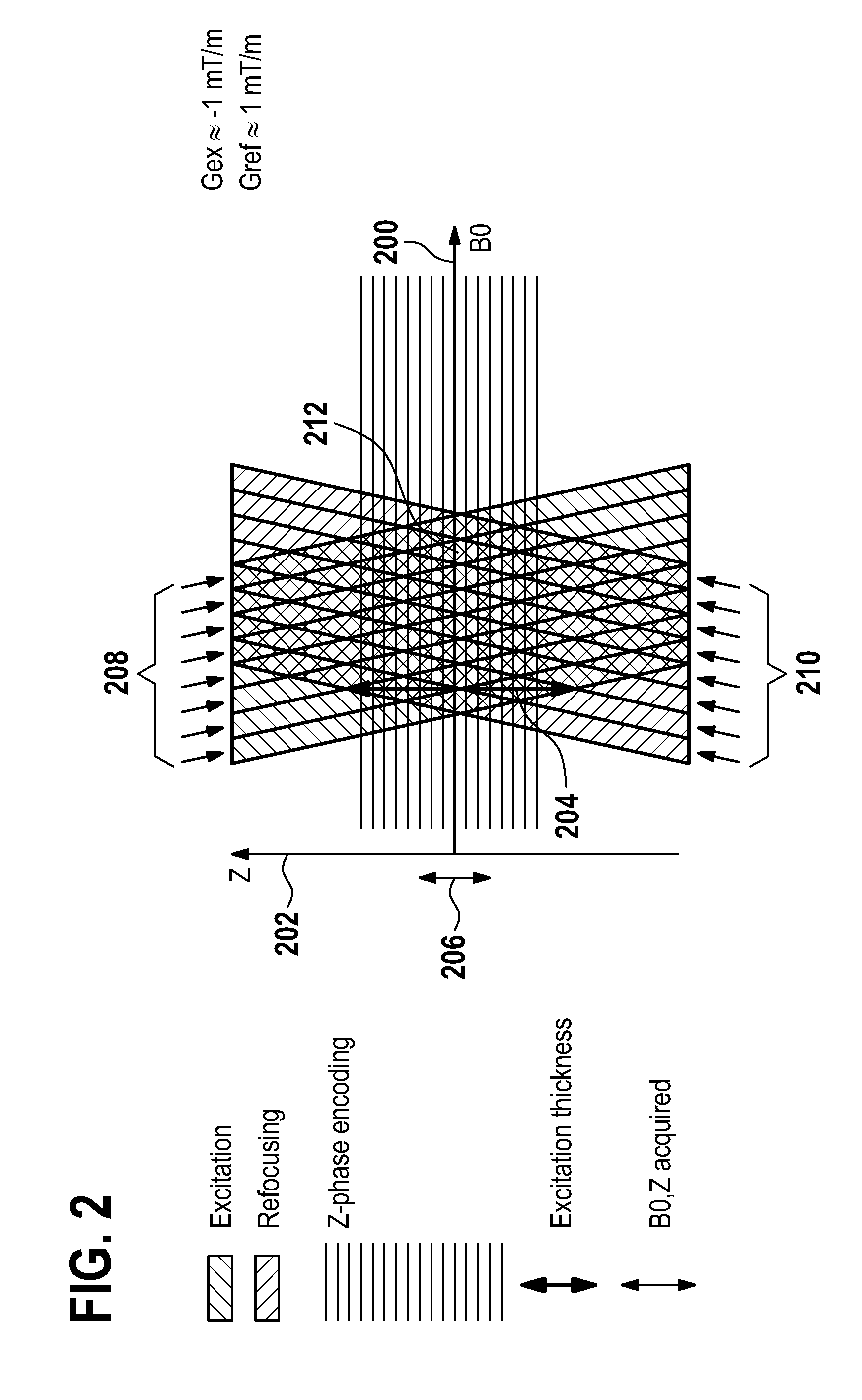
Restriction of the imaging region for MRI in an inhomogeneous magnetic field
ActiveUS20140002080A1Avoid distortionReduce noiseMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionFat suppressionParallel imaging
The invention relates to magnetic resonance imaging in the vicinity of a metallic object (like, for instance, a metal implant) where severe spatial perturbations of the static magnetic field occur. In order to suppress the back-folding of distant off-resonant signals into the region of interest, the imaging volume is spatially restricted by means of selection gradients applied concurrently with the excitation and the refocusing RF pulses in a spin echo sequence. The selection gradient applied during the excitation pulse has an amplitude and / or a polarity different from that of the selection gradient applied during the refocusing pulse so that the respectively selected slices in an off-resonance frequency versus spatial coordinate diagram become tilted with respect to one another. The applied imaging technique may of the SEMAC or MAVRIC type and may incorporate compressed sensing, parallel imaging, fat suppression and / or SVD-based noise reduction.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
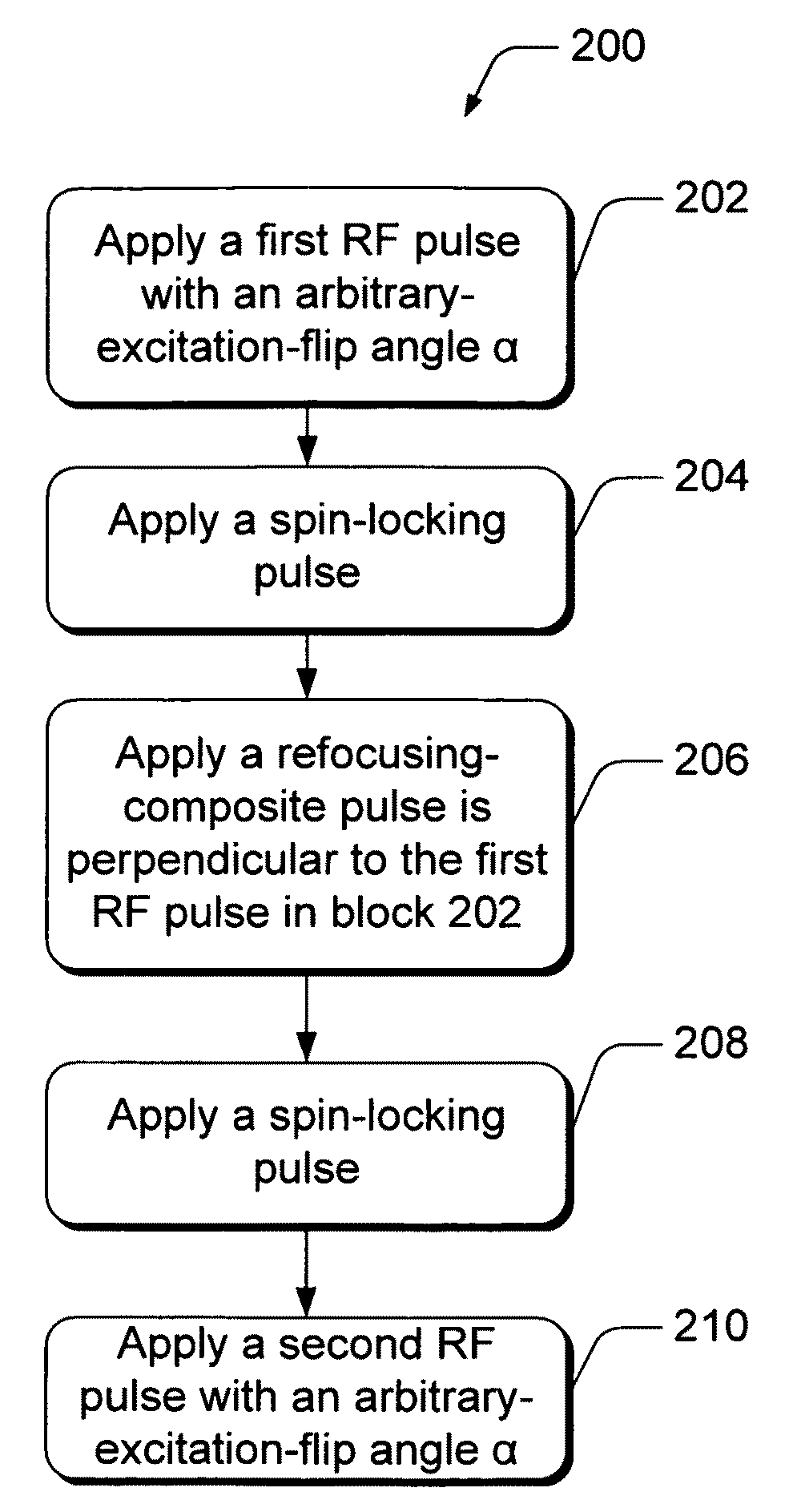
System and method for minimizing MRI-imaging artifacts
ActiveUS7705596B2Improve image qualityEliminate needMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionSpinsPulse sequence
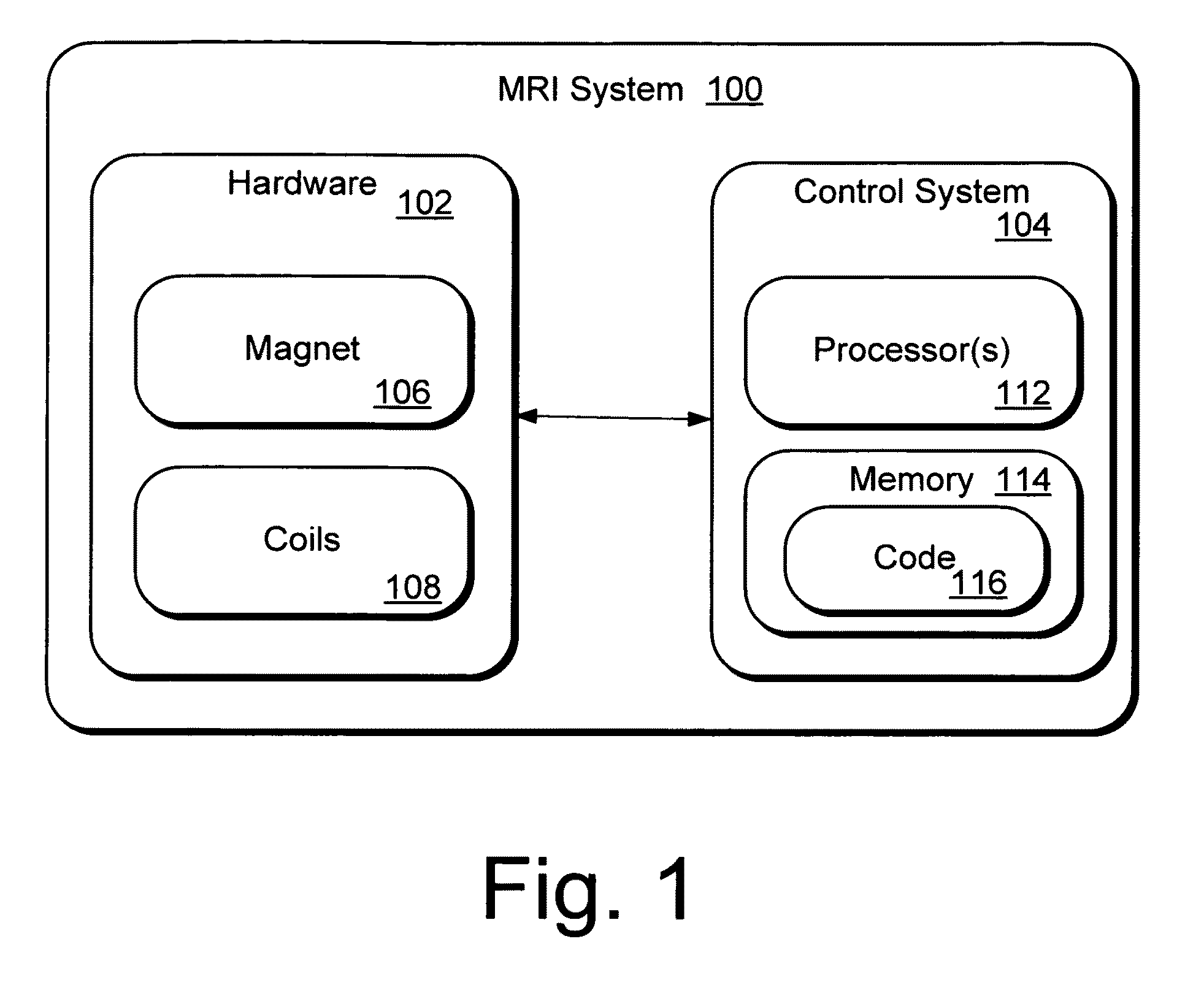
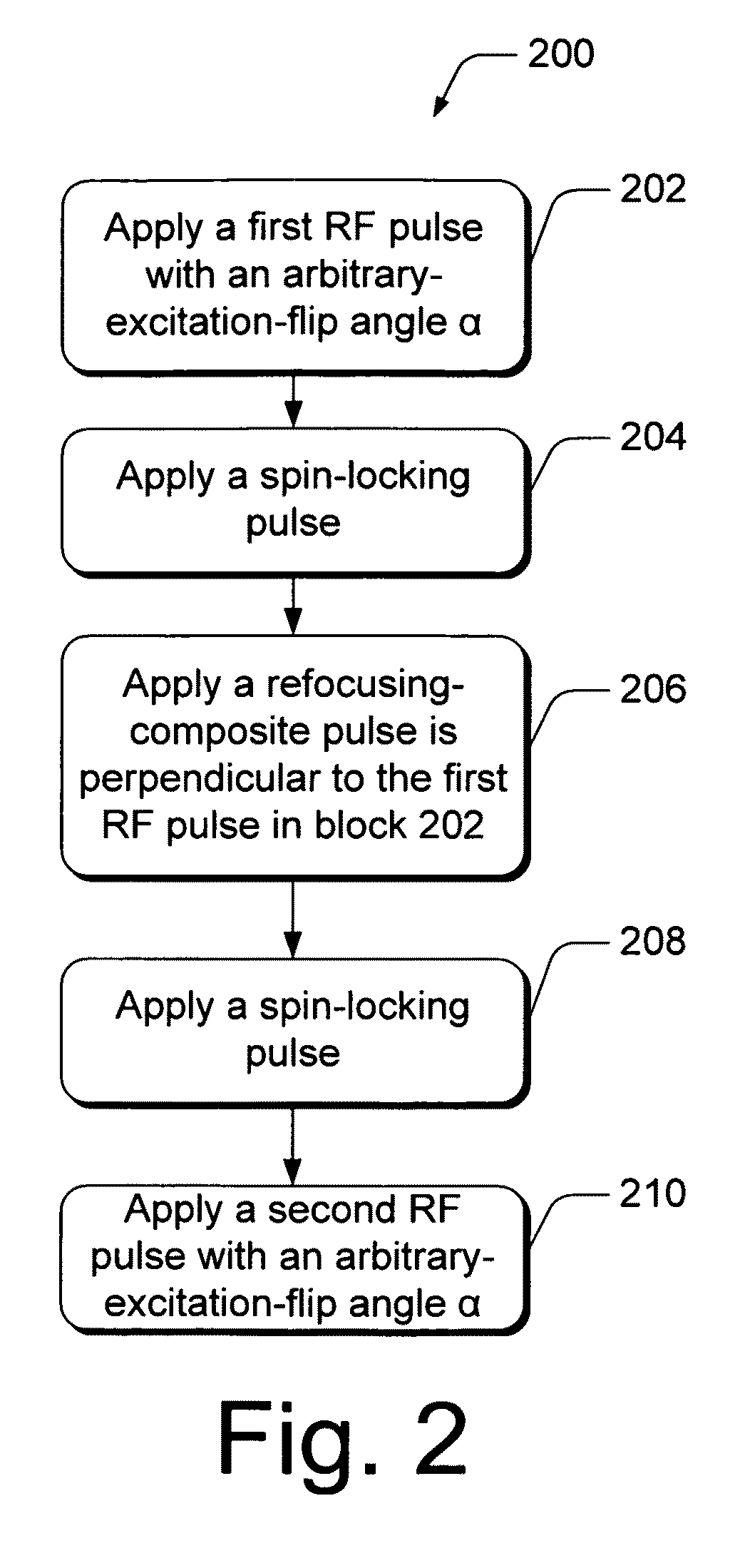
Methods of, and systems for, simultaneously compensating for external-magnetic-field inhomogeneity as well as radiofrequency magnetic-field inhomogeneity in an MRI system. In one method embodiment, a pulse sequence is applied when the transmitter-reference frequency is delivered on resonance. The pulse sequence includes radiofrequency pulses which may be applied at arbitrary-excitation-flip angles that are not necessarily 90° degrees. The pulse sequence also includes spin-locking pulses applied in concert with a refocusing-composite pulse. In another method embodiment, a pulse sequence is applied when the transmitter-reference frequency is delivered off resonance. This off-resonance-pulse sequence includes radiofrequency pulses which may be applied at arbitrary-excitation-flip angles that are not necessarily 90° degrees. Sandwiched between the excitation-flip angles are at least two off-resonance-spin-lock pulses applied at an inverse phase and frequency from each other.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Off-resonance three-dimensional elliptical diamond vibration cutting method and device
ActiveCN103394705AActive adjustment to achieveAdapt to the requirements of processing complex curved surfacesAutomatic control devicesAuxillary equipmentDiamond cuttingOff resonance
The invention relates to an off-resonance three-dimensional elliptical diamond vibration cutting method and device and belongs to a cutting method and device. Four piezoelectric stacks which are placed in parallel are driven according to input signals, and phase angles of the input signals are different in a two-to-two mode. The piezoelectric stacks push a pushing face on a tool apron hinge base body to enable various hinges to produce micrometric displacement, therefore a diamond cutter point three-dimensional elliptical movement track capable of being adjusted can be obtained, the track can be adjusted initiatively through frequency, amplitudes and phase differences of driving signals of the piezoelectric stacks and installation positions of the piezoelectric stacks. The off-resonance three-dimensional elliptical diamond vibration cutting method and device can meet requirements for various difficult-to-machine materials and different face types through diamond cutting, and obtains the best cutting machining performance.
Owner:HUAWEI TEHCHNOLOGIES CO LTD
Method for multiplexed MR tracking
The present technique provides a novel method and apparatus for magnetic resonance device tracking. In one aspect of the present technique, a plurality of magnetic resonance tracking signals are acquired in response to a corresponding plurality of pulse sequences, wherein the plurality of magnetic resonance tracking signals are acquired from a tracking coil mounted in a device. A location value is also determined for each pulse sequence to produce a plurality of location values. Further, a candidate location value of the plurality of location values for replacement, an off-resonance error value for the plurality of magnetic resonance tracking signals, and a replacement location value based on the off-resonance error value are determined. The location of the device is also determined based on the plurality of location values, wherein the candidate location value was replaced in the plurality of location values with the replacement location value.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
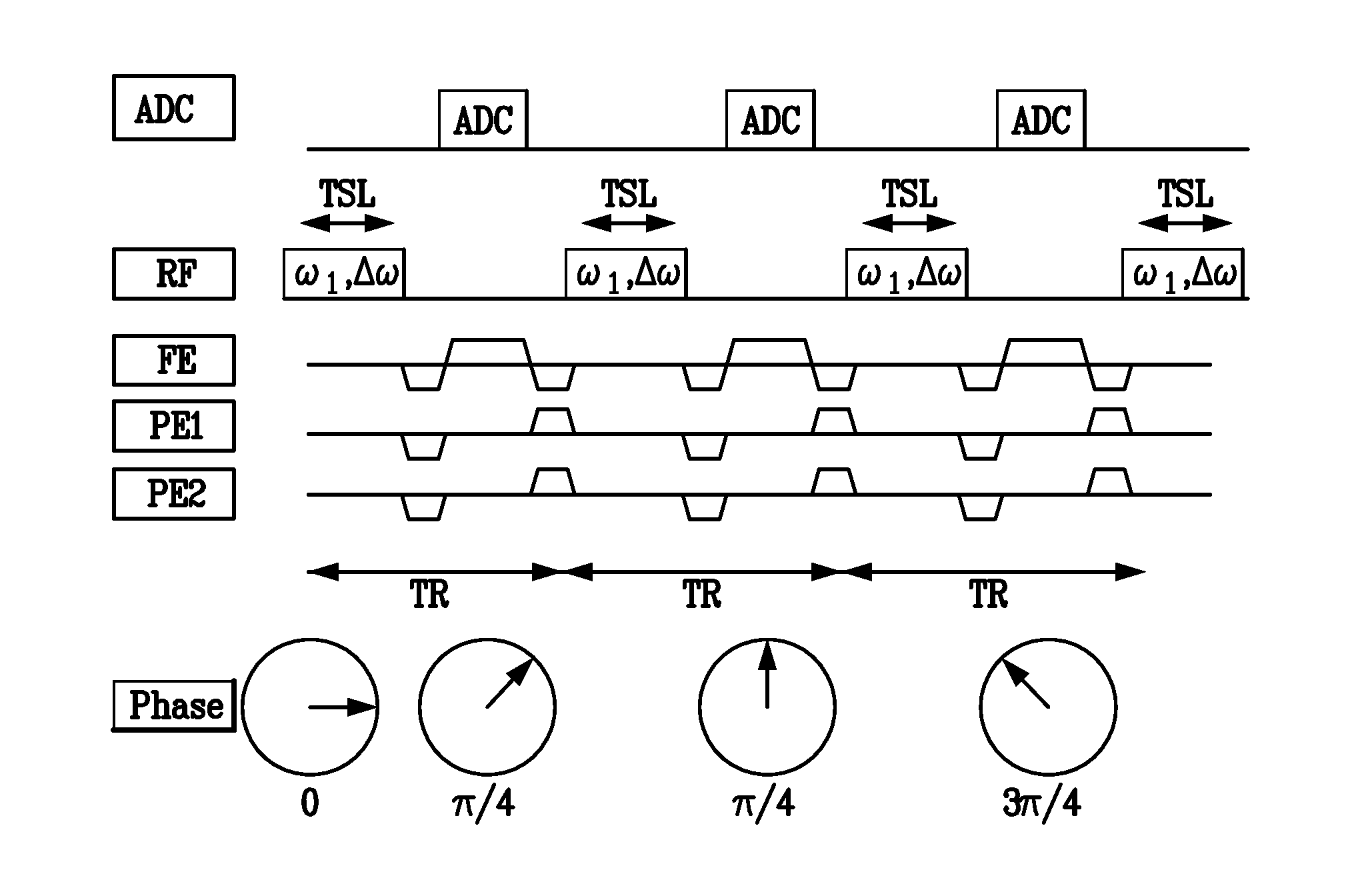
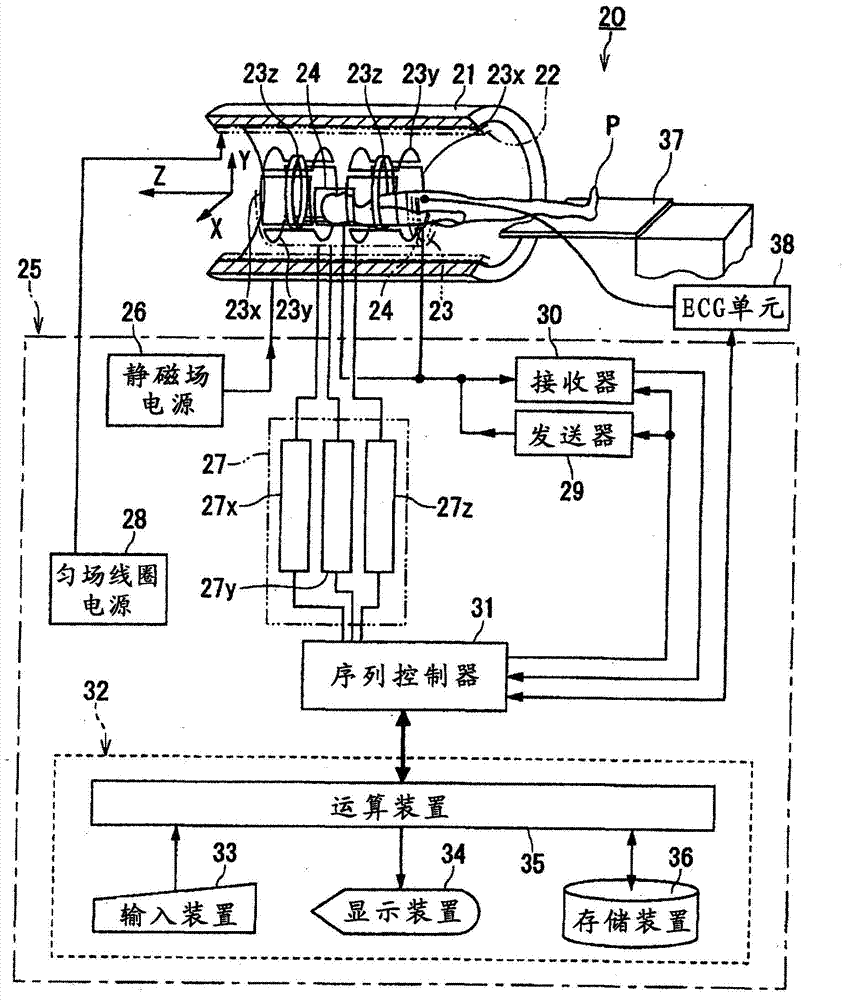
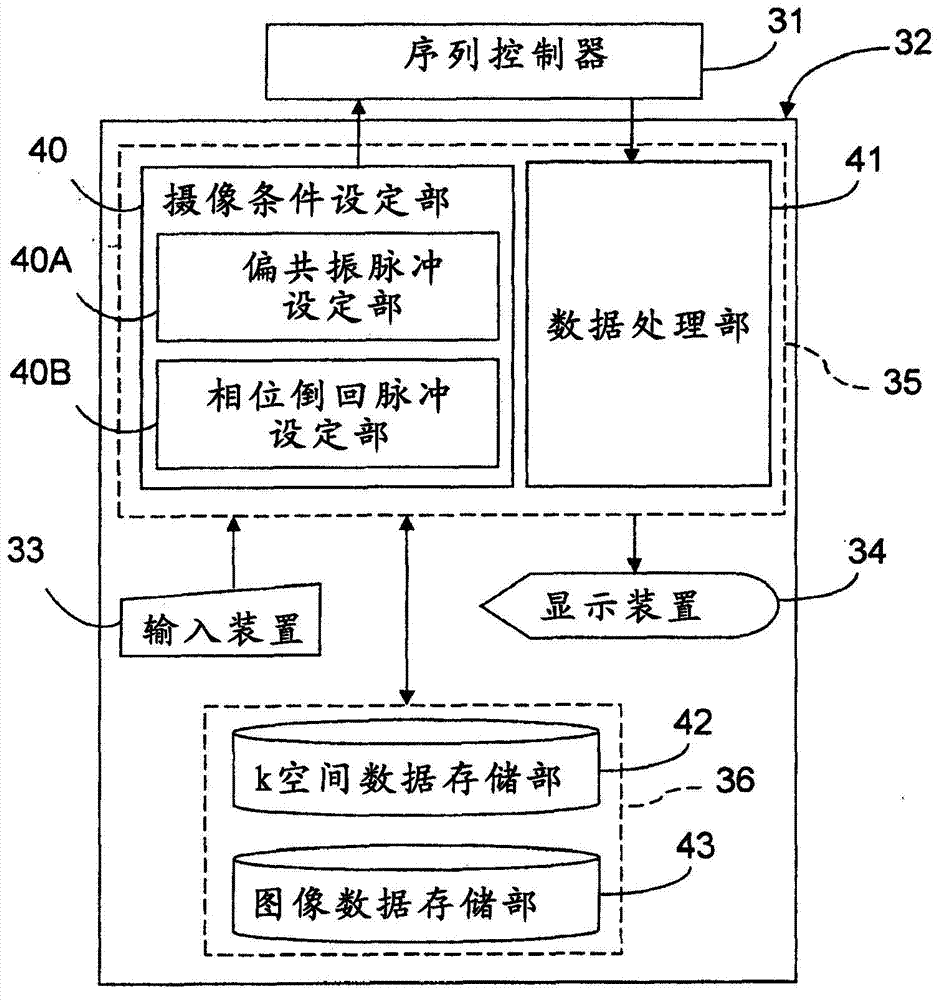
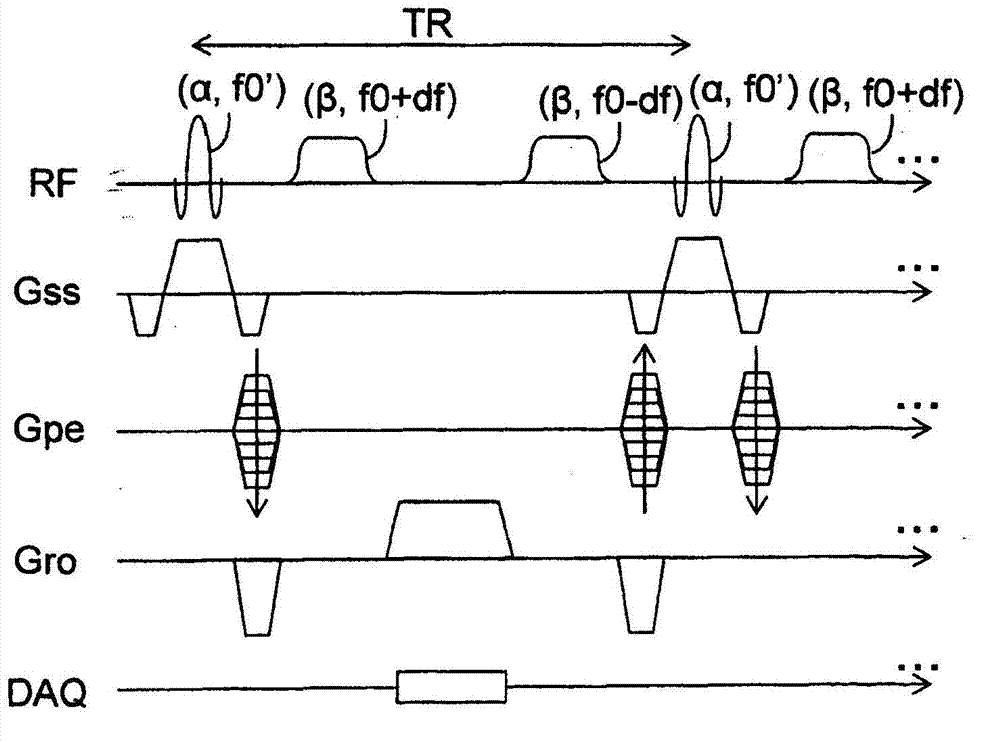
Magnetic resonance imaging device and magnetic resonance imaging method
ActiveCN103167829AIncrease contrastImprove picture qualityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsImaging conditionPhase shifted
The magnetic resonance imaging device according to an embodiment of the present invention is equipped with a data collection unit and a data processing unit. The data collection unit collects magnetic resonance signals in accordance with imaging conditions under which a first off-resonance high frequency pulse for generating a phase shift in a magnetic resonance signal is applied after the application of the excitation pulse but before the magnetic resonance signal is read, and a second off-resonance high frequency pulse is applied to compensate for the phase shift after the magnetic resonance signal is read but before the application of the next excitation pulse. The data processing unit acquires information to be acquired by processing the data regarding the magnetic resonance signal.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
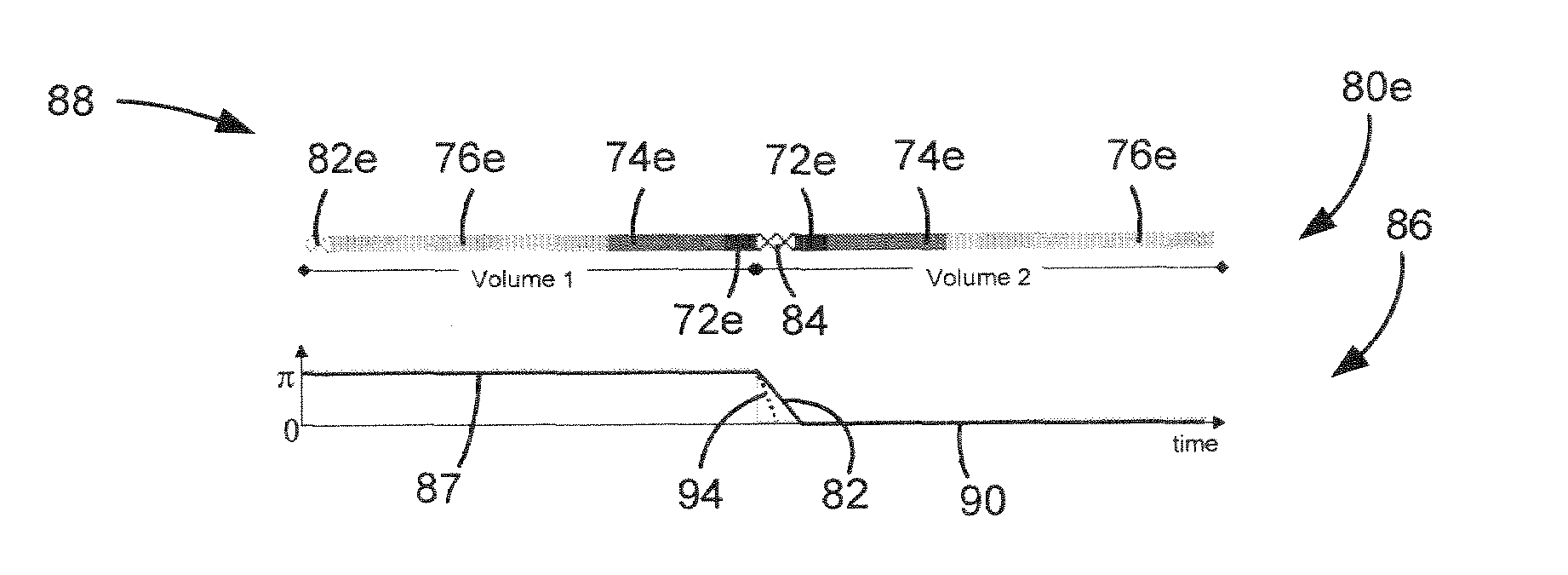
Method and apparatus of reducing artifacts in phase-cycled steady-state free precession imaging
InactiveUS7012428B1Magnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionSpinsSteady-state free precession imaging
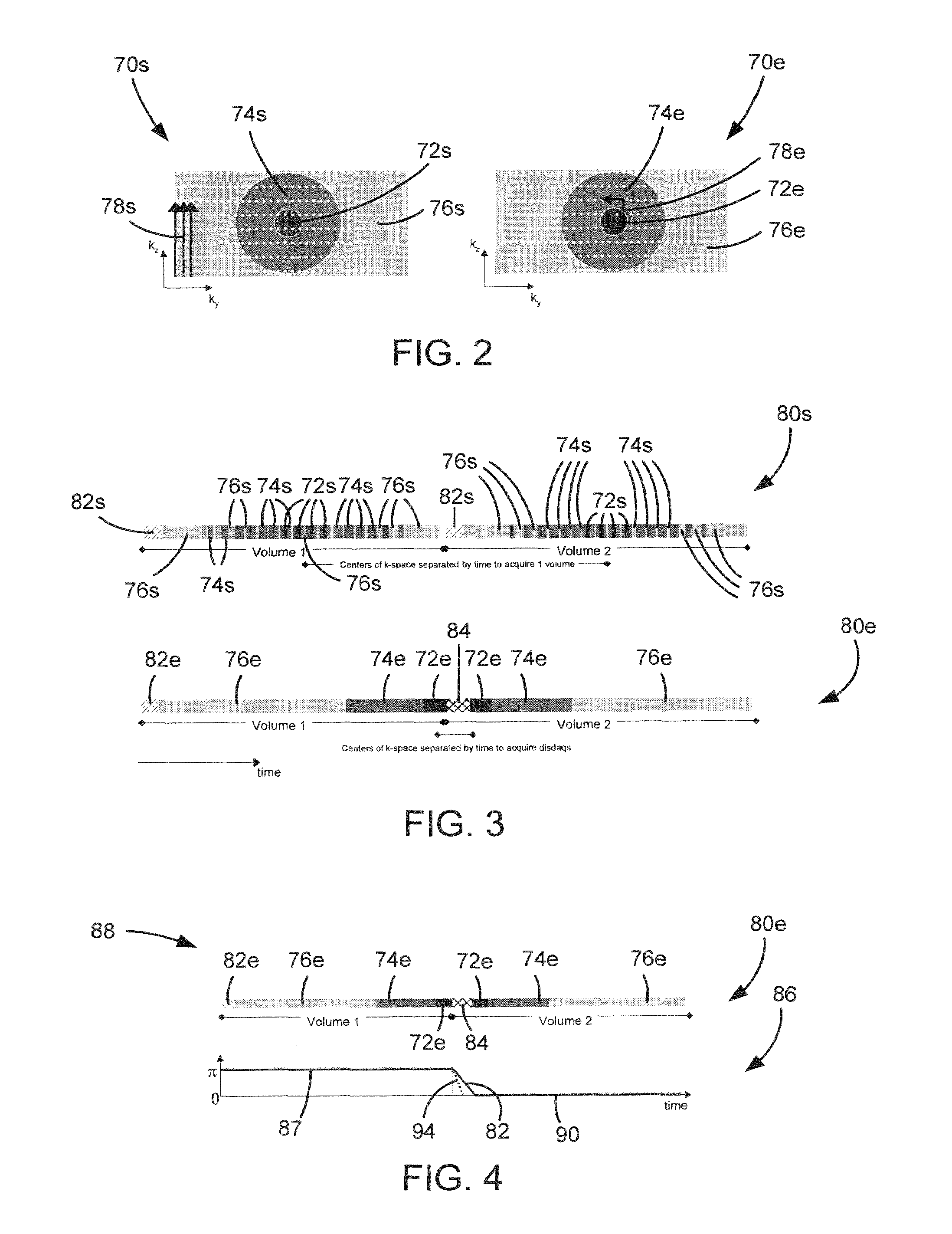
A method and apparatus of imaging multiple volumes of the anatomy of interest using a phase-cycled SSFP pulse sequence and a reverse elliptic centric view ordering to sample a first volume and an elliptic centric view ordering to sample a second volume is disclosed. Dummy acquisitions are played out between imaging of the first and second volumes, and the time to play out the dummy acquisitions is used to change the phase-cycling scheme of the RF pulses of the SSFP pulse sequence. Oscillations in signal are reduced as the spins in the anatomy of interest are brought to a new steady-state by gradually ramping the RF pulse phase increment for acquisition from the first volume to the RF pulse phase increment for acquisition from the second volume. The present invention is effective for reducing transient oscillations in MR signals from resonance and off-resonance spins, thus enabling the use of this technique for the reduction of motion artifacts in phase-cycled SSFP.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Tunable microwave photonic filter based on photoinjection semiconductor laser system
ActiveCN103018928AEnables tunabilityImprove reconfigurabilityNon-linear opticsNon linear dynamicOptoelectronics
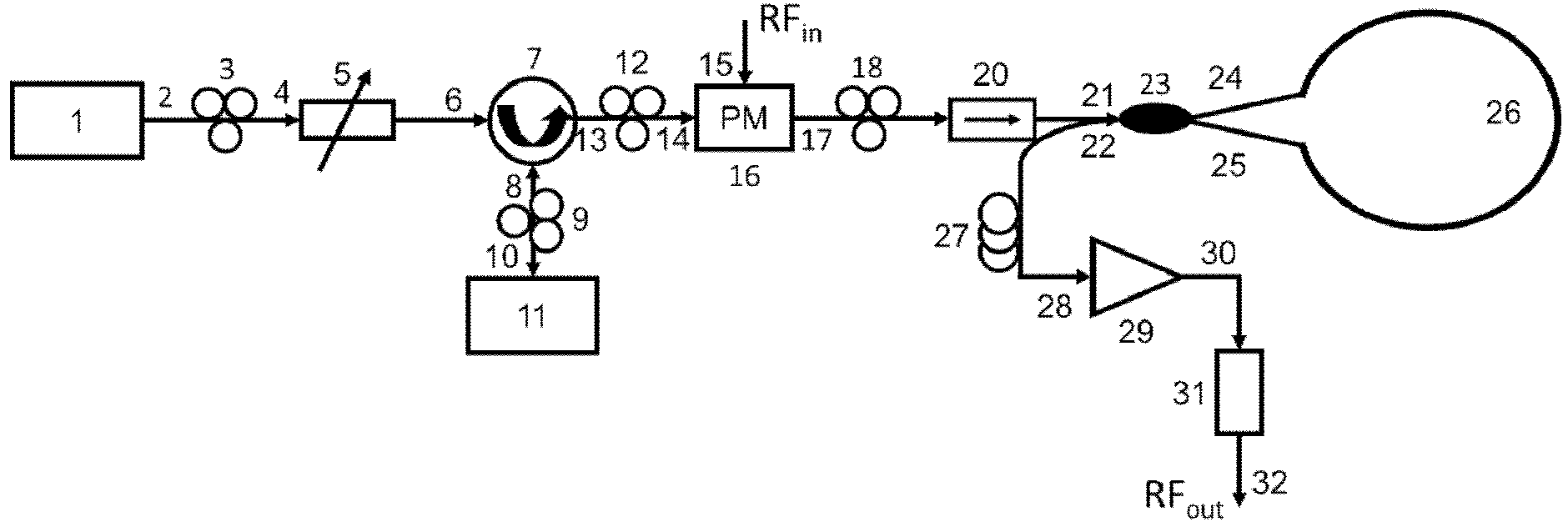
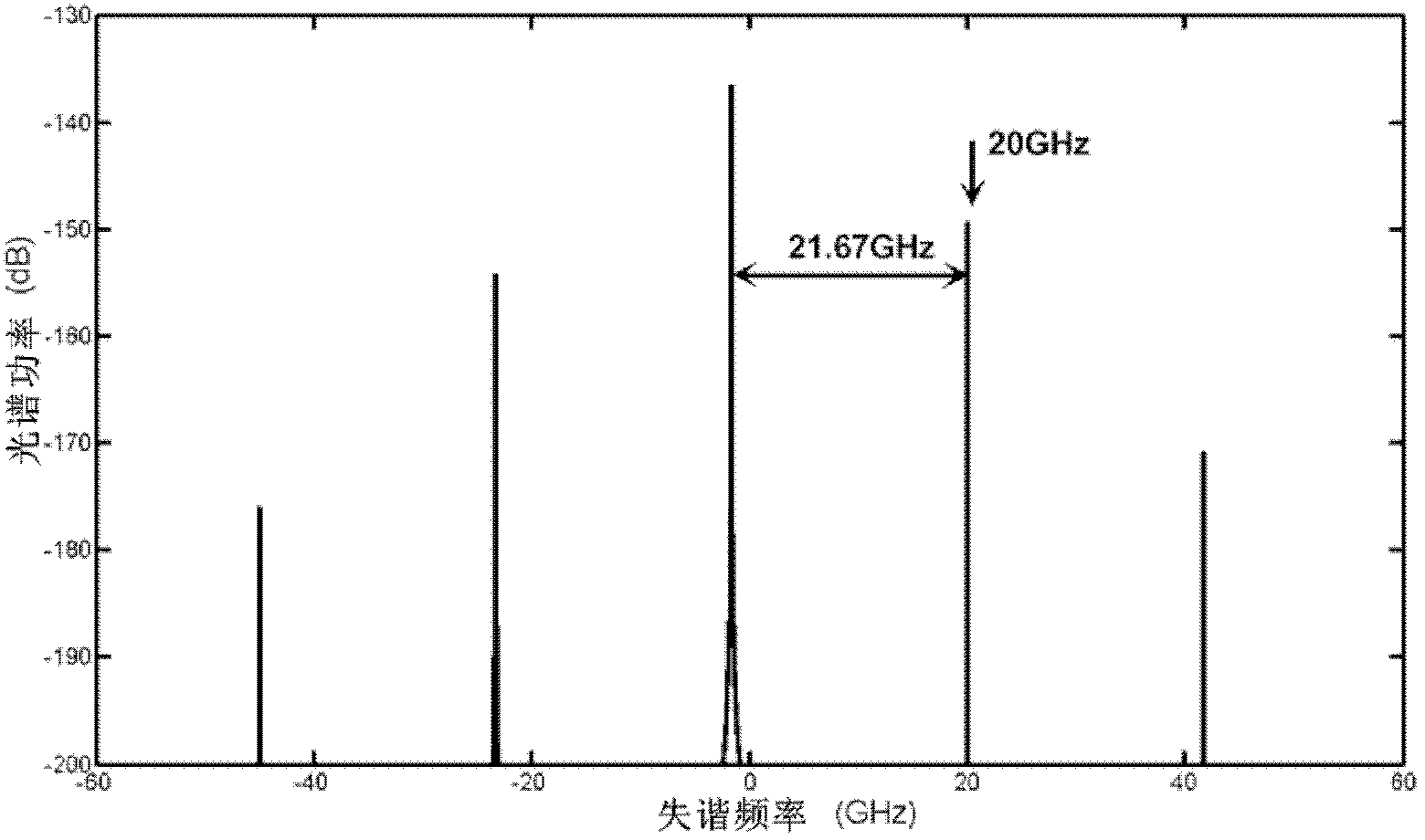
The invention discloses a tunable microwave photonic filter based on a photoinjection semiconductor laser system. The tunable microwave photonic filter comprises a master laser, a first polarization controller, a variable optical attenuator, an optical circulator, a slave laser, a second polarization controller, a third polarization controller, a phase modulator, a fourth polarization controller, an opto-isolator, a 3dB optical coupler, a Sagnac loop filter, single mode dispersion fiber, an optical amplifier and a photoelectric detector. By making use of the nonlinear dynamic behavior of light when the light enters the semiconductor laser system, by exciting the single-cycle oscillation effect P1 of the semiconductor lasers to generate similar beam-shaped spectra with variable frequency space, and by adjusting the intensity of injecting the master laser to the slave laser or the off-resonance frequency between the two lasers, the invention realizes the tunable microwave photonic filter with a tunable filtering window and at the same time the reconfigurability and multi-tap structure of the filters are realized.
Owner:HENAN SHIJIA PHOTONS TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com