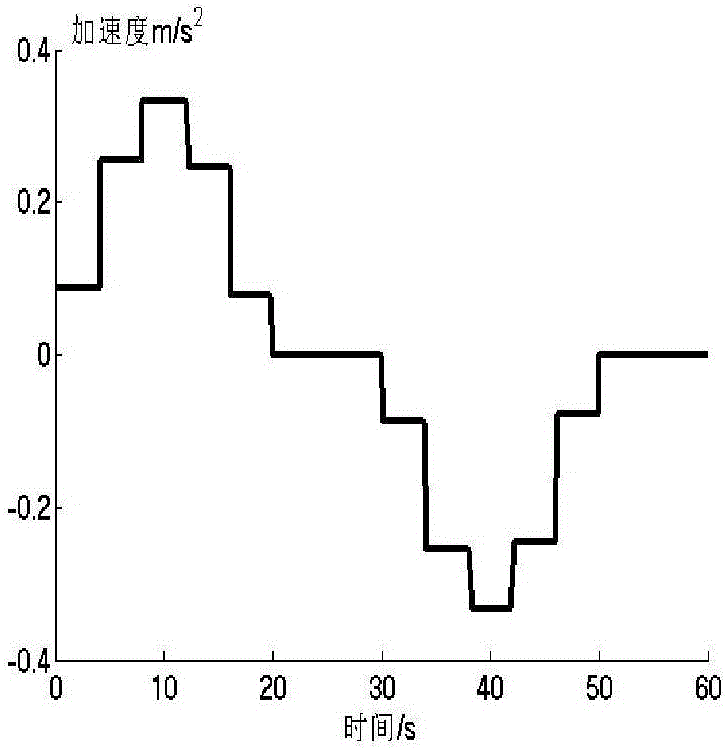
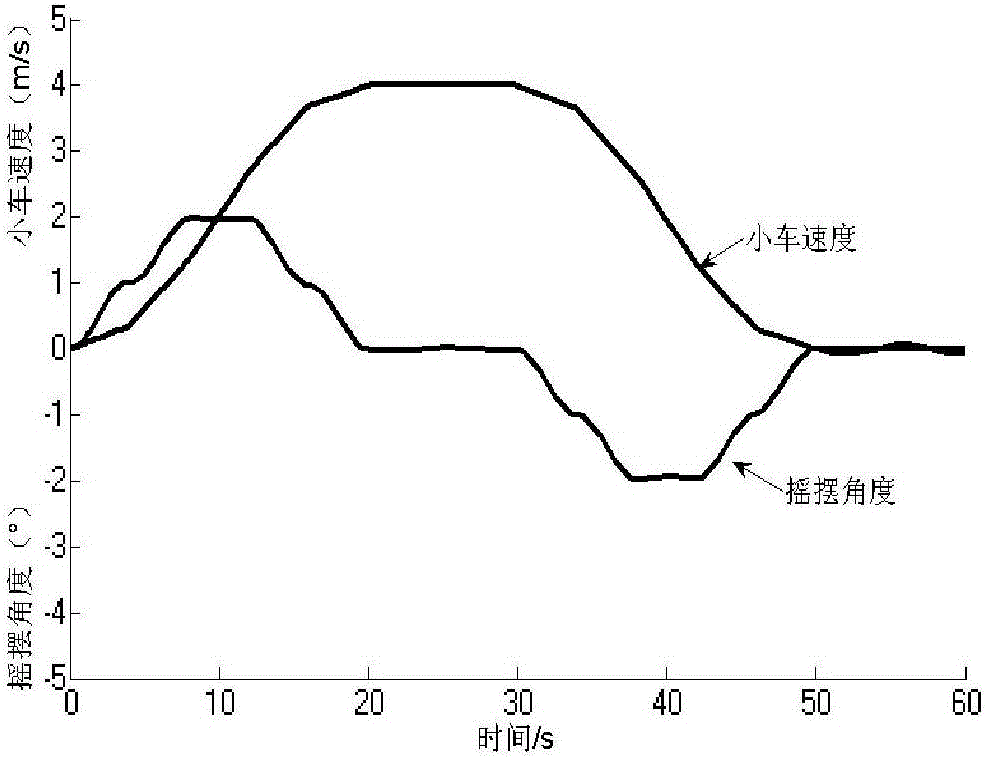
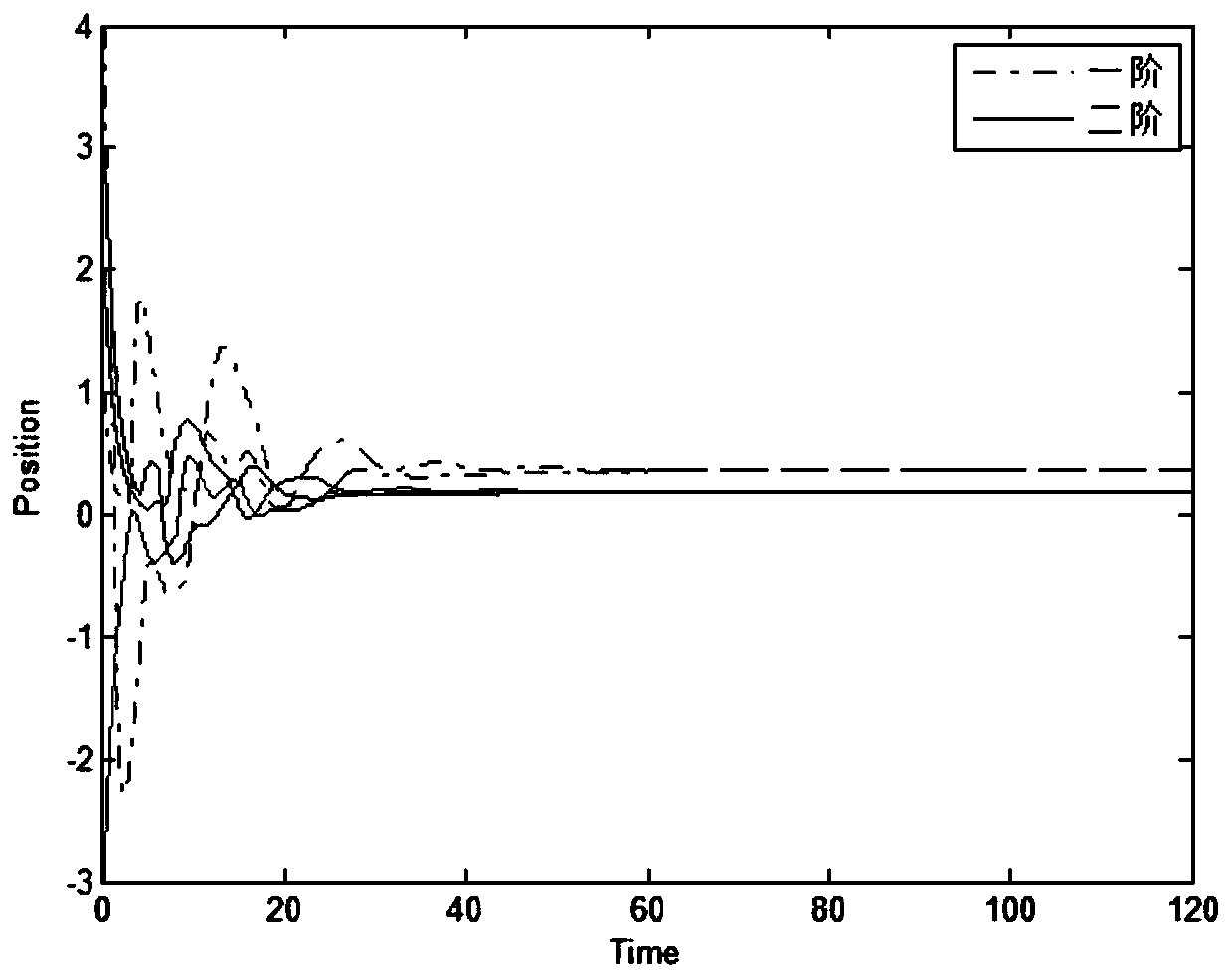
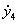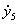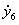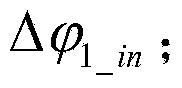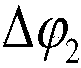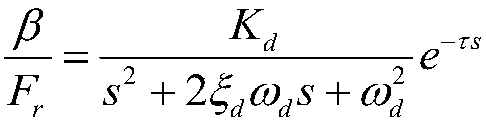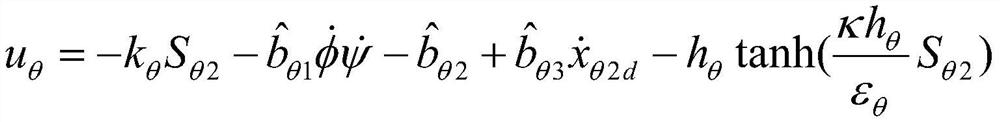Patents
Literature
98 results about "Second order systems" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
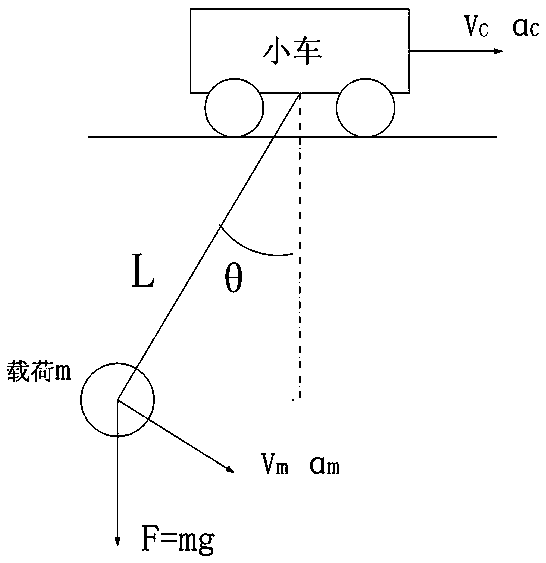
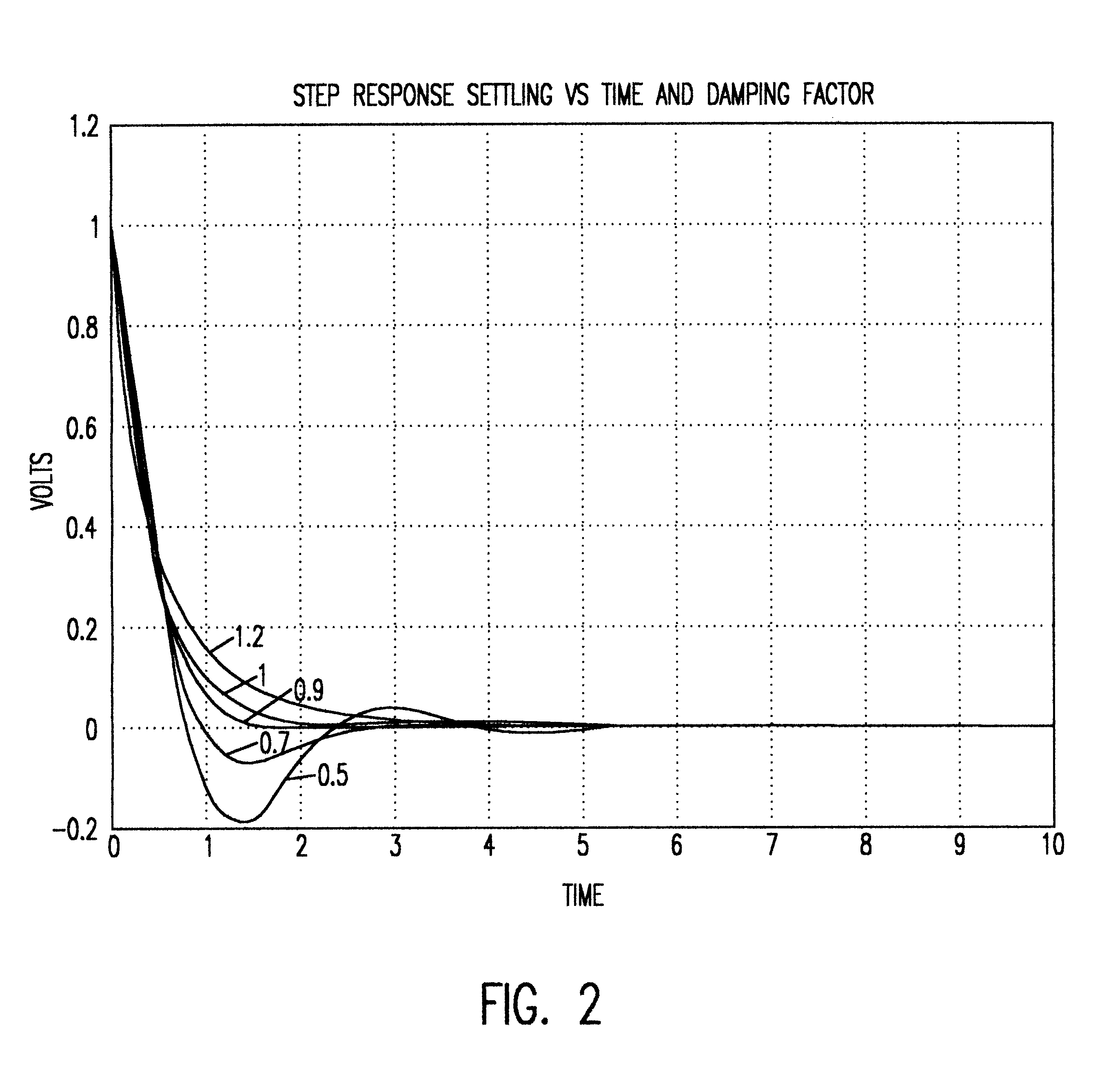
Second Order Systems. The order of a differential equation is the highest degree of derivative present in that equation. A system whose input-output equation is a second order differential equation is called Second Order System.
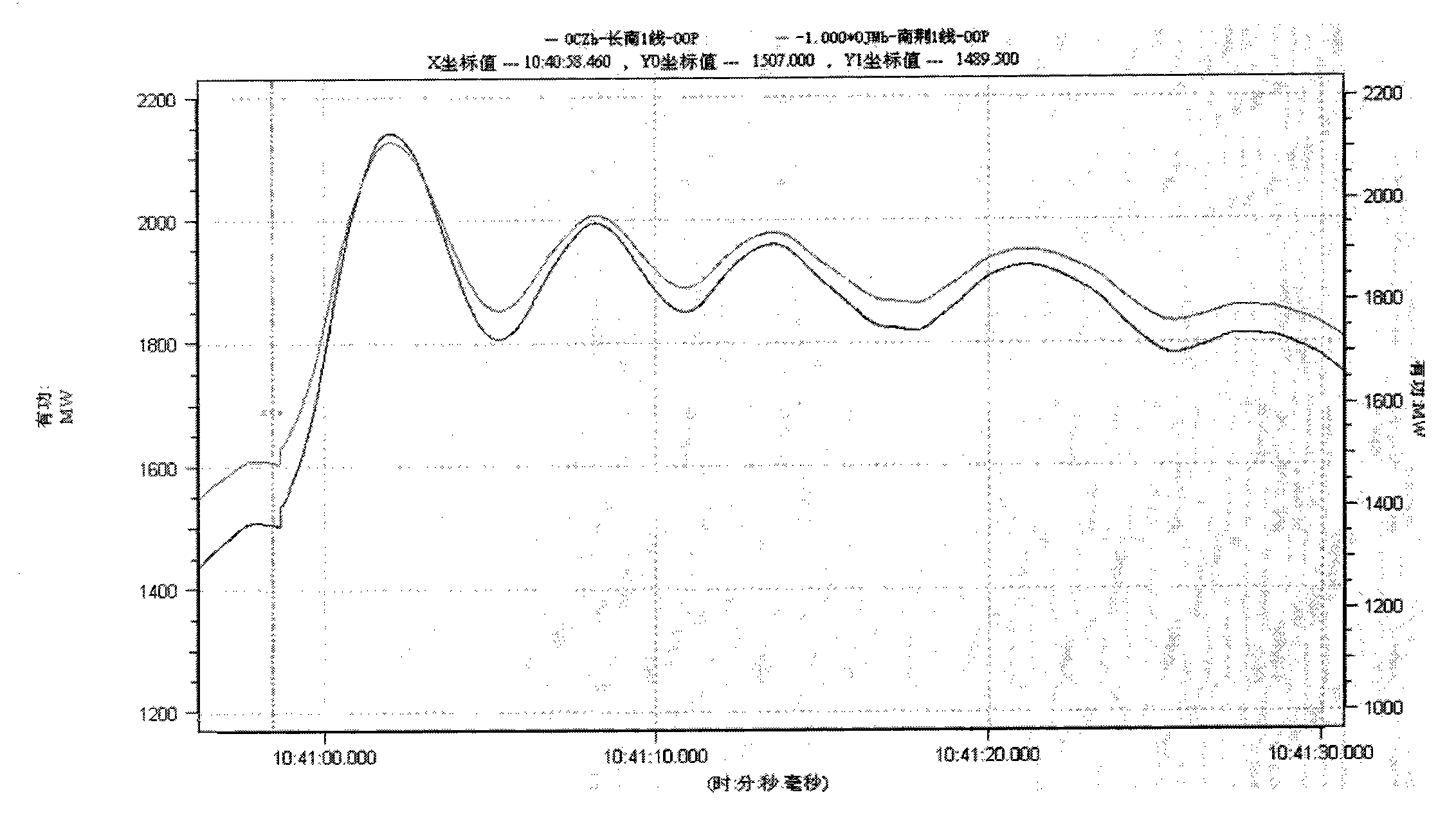
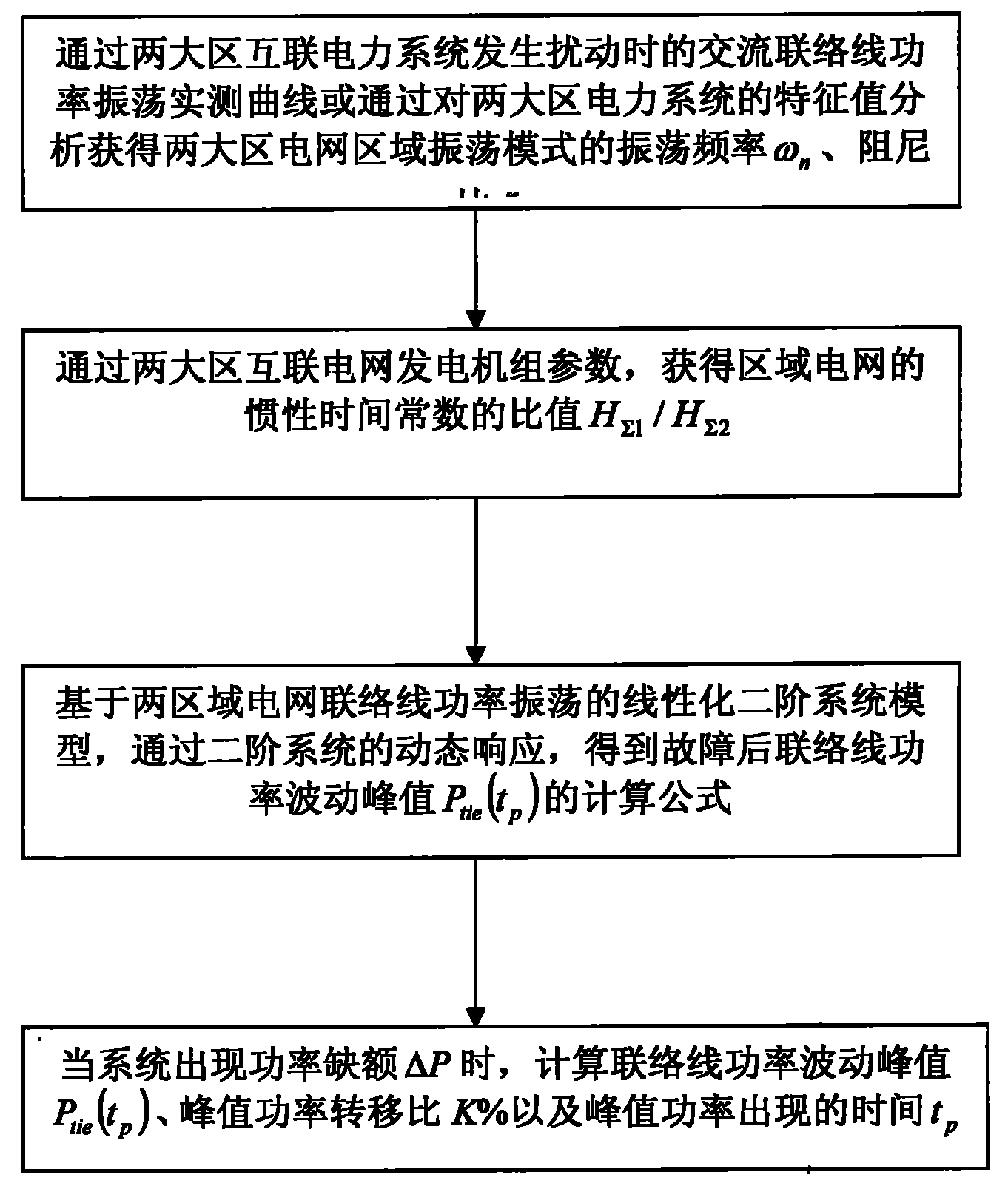
Two-region interconnected electric power system alternating current interconnection tie power fluctuation peak calculating method
ActiveCN101847872AHarmonic reduction arrangementAc network to reduce harmonics/ripplesElectric networkPeak value
The invention provides a two-region interconnected electric power system alternating current interconnection tie power fluctuation peak calculating method. When the electric power system is in power vacancy, large power vibration can be generated on interconnection tie. The invention is based on the linear second-order system model of two-region electric power system interconnection tie power oscillation and calculates interconnection tie power fluctuation peak after fault by dynamic response of the second-order system. The invention can be applied to simulation analysis of electric power system, grasps the dynamic characteristic of two-region interconnected electric power system, is beneficial to system operation and analysis personnel to timely take effective measures and improves safety steady operation level of electric power system.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Hypersonic aerocraft tracking control method with interference observer
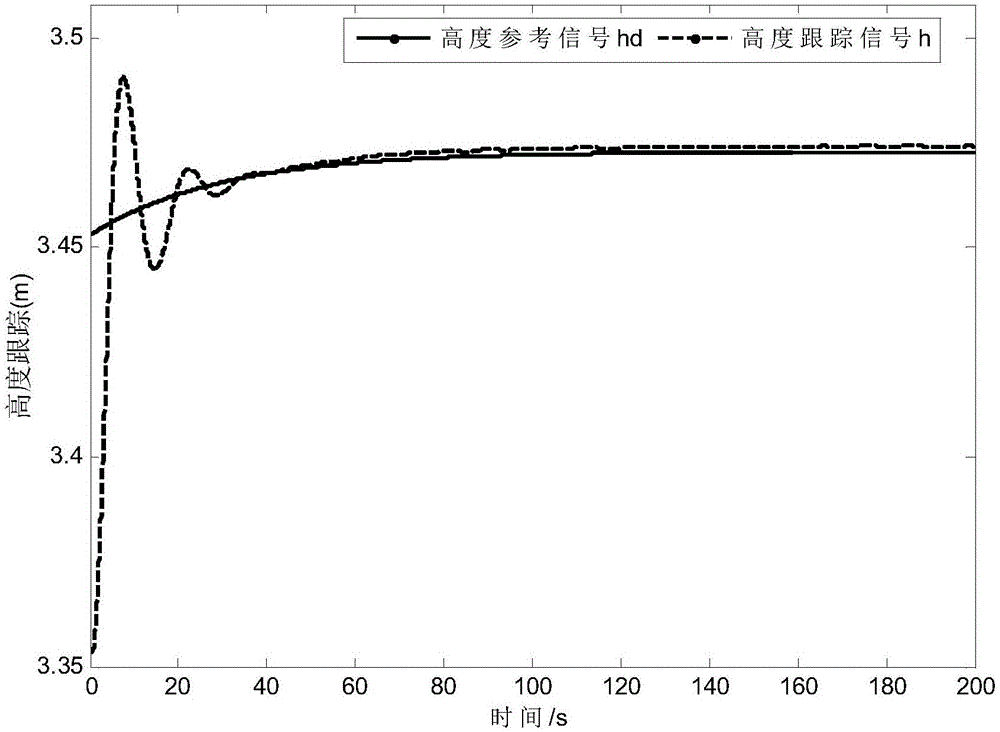
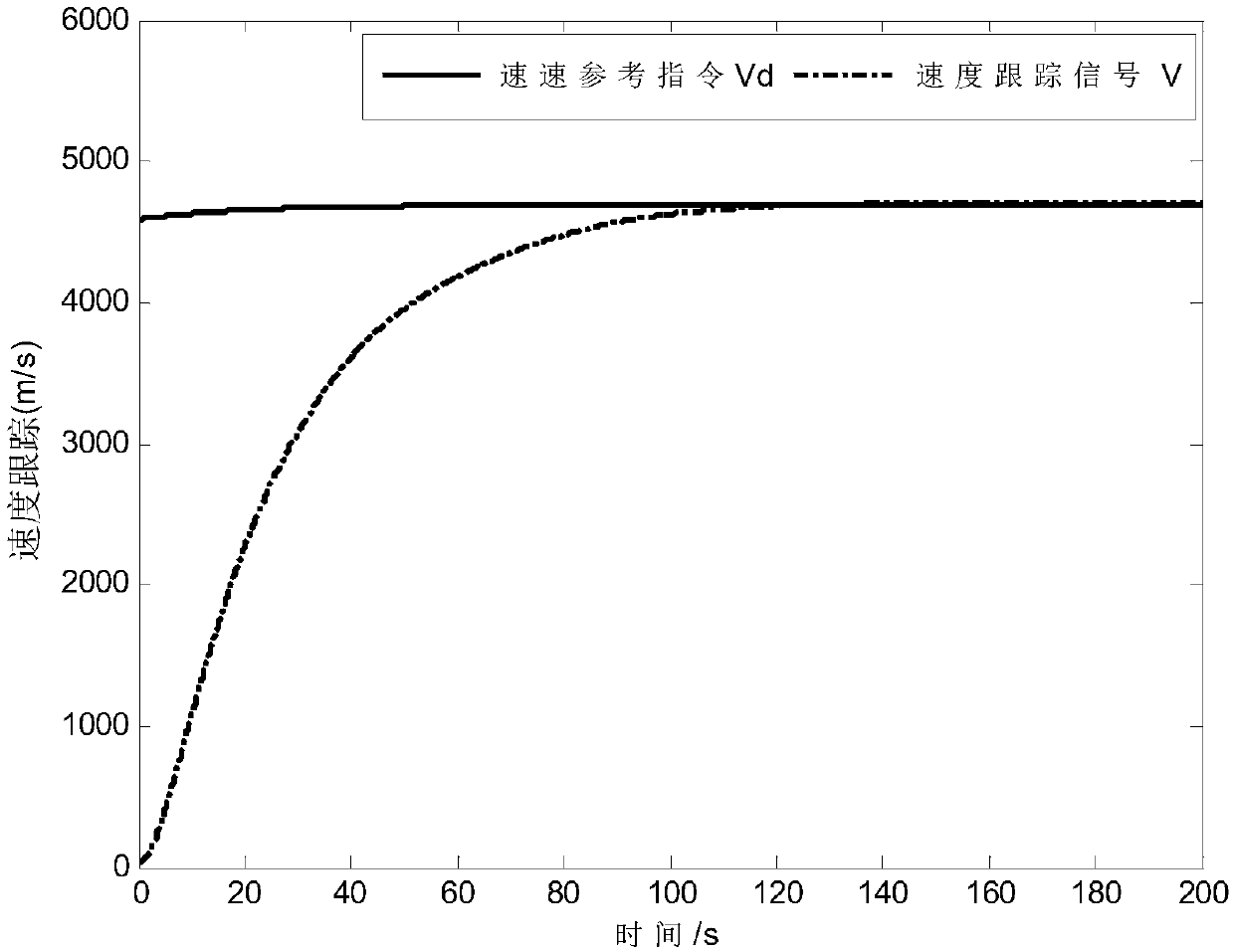
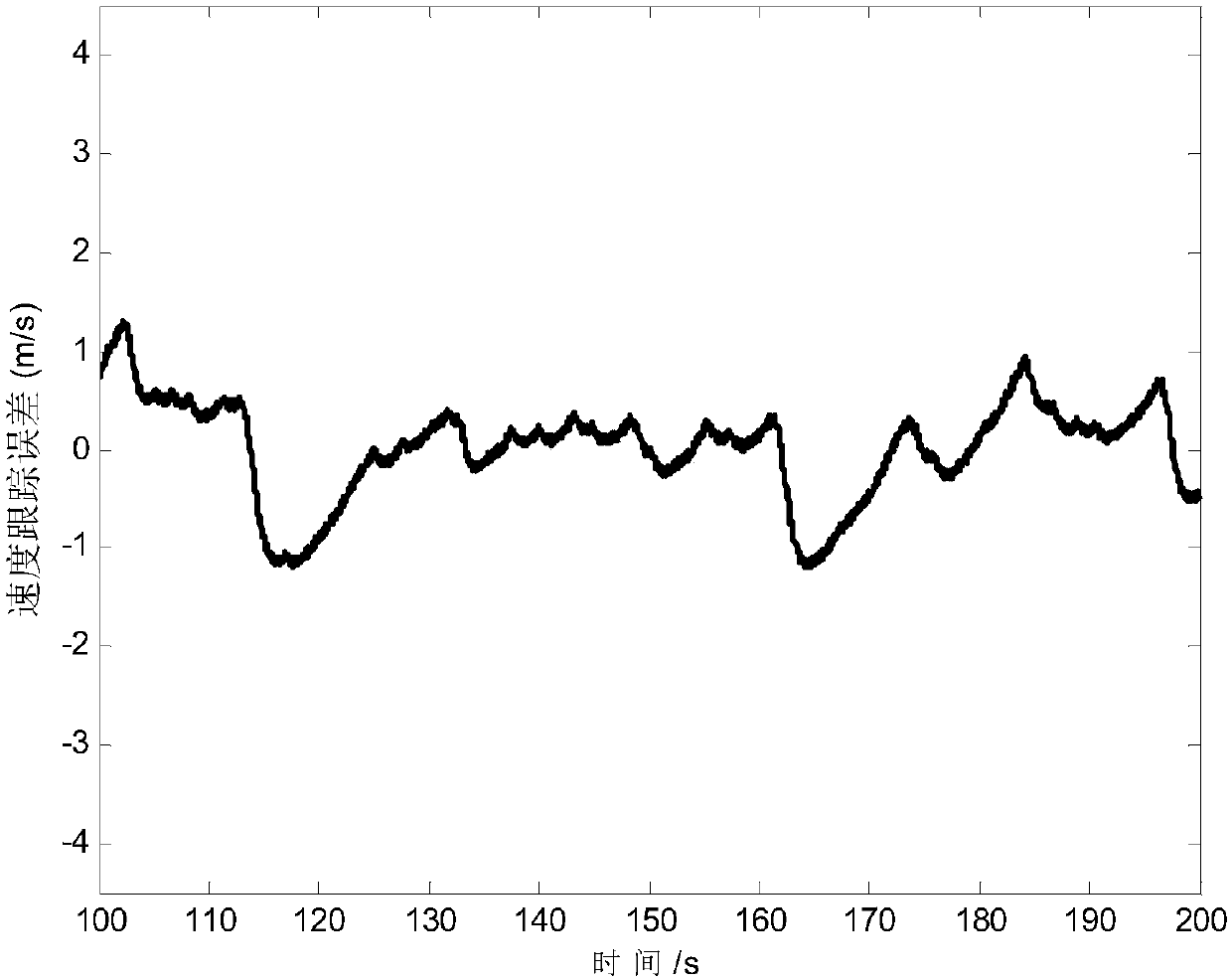
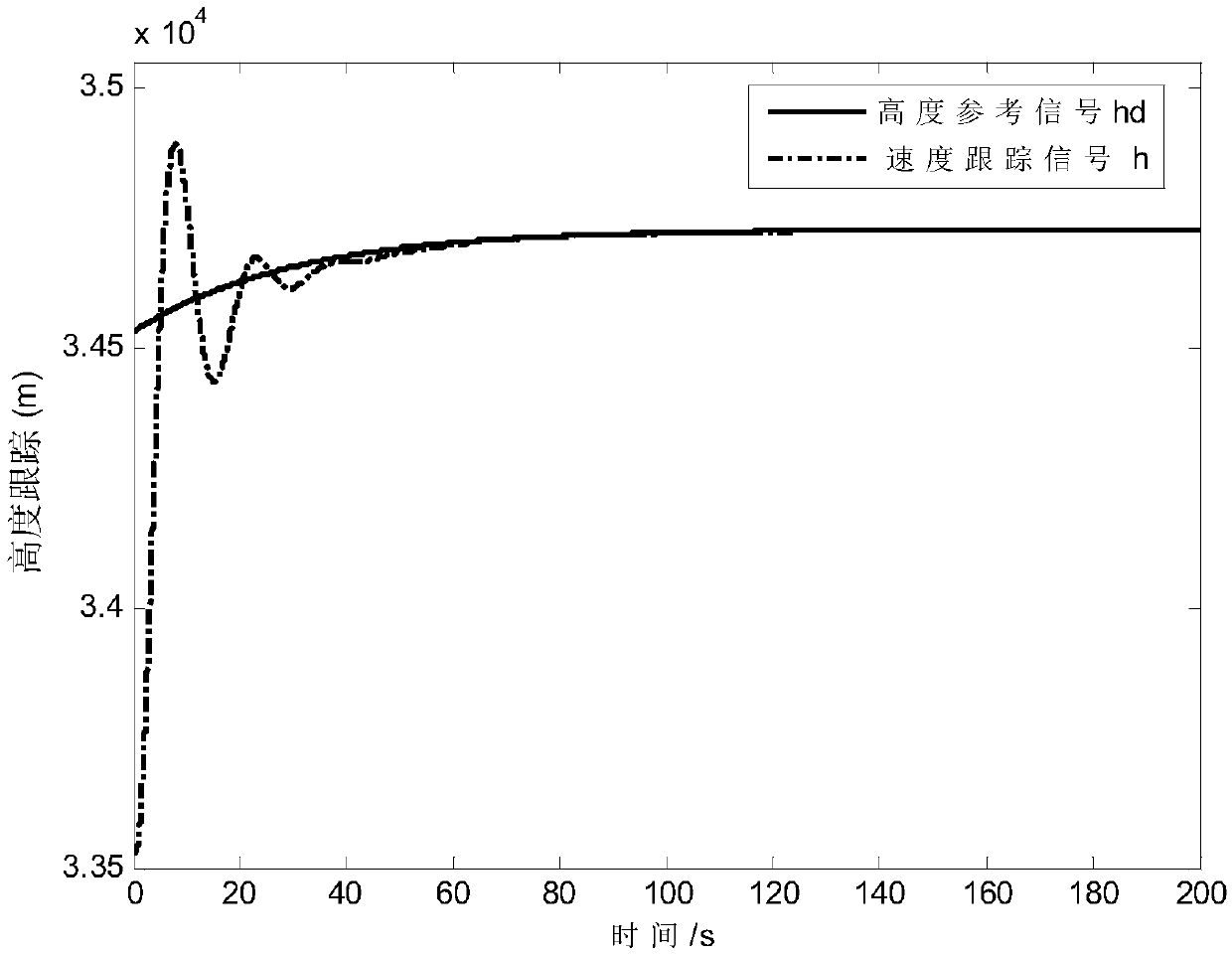
The invention relates to a hypersonic aerocraft tracking control method with an interference observer. The problem that the fact that the observer is bounded in the interference process of an observing system cannot be proved in the prior art is solved. The method provided by the invention comprises the steps that 1 a second-order system model with system interference is established according to the longitudinal input and output linearization model of a hypersonic aerocraft; 2 according to the second-order system model with system interference in the step 1, a finite time terminal sliding mode controller is designed based on a sliding mode control theory; and 3 system stability proving is carried out on the finite time terminal sliding mode controller designed in the Step 2. According to the method provided by the invention, the finite time of the sliding surface of the system is stable, and the system state is asymptotically convergent. The method provided by the invention is applied to the field of hypersonic aerocraft control.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Hypersonic aircraft robust tracking control method based on terminal sliding mode
The invention relates to a hypersonic aircraft robust tracking control method based on a terminal sliding mode, and solves the problems of complex control model, poor robustness and lack of consideration of controller input limitation of an existing aircraft. A hypersonic aircraft input / output linearization model is provided, and is converted into a second-order system model by introducing an error auxiliary variable; for the conditions that unknown upper bound exists in system interference and an actuator has no input saturation, an adaptive fast terminal sliding mode controller is designed based on a fast non-singular terminal sliding mode surface, thereby ensuring that the sliding mode surface is actually convergent in finite time; and by introducing a hyperbolic tangent function and astructural auxiliary system, an anti-saturation adaptive fast terminal sliding mode controller is designed, thereby meeting requirements of physical constraints of a hypersonic aircraft and meanwhile,ensuring that the system sliding mode surface is convergent in finite time. The method is applied to the aircraft field.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
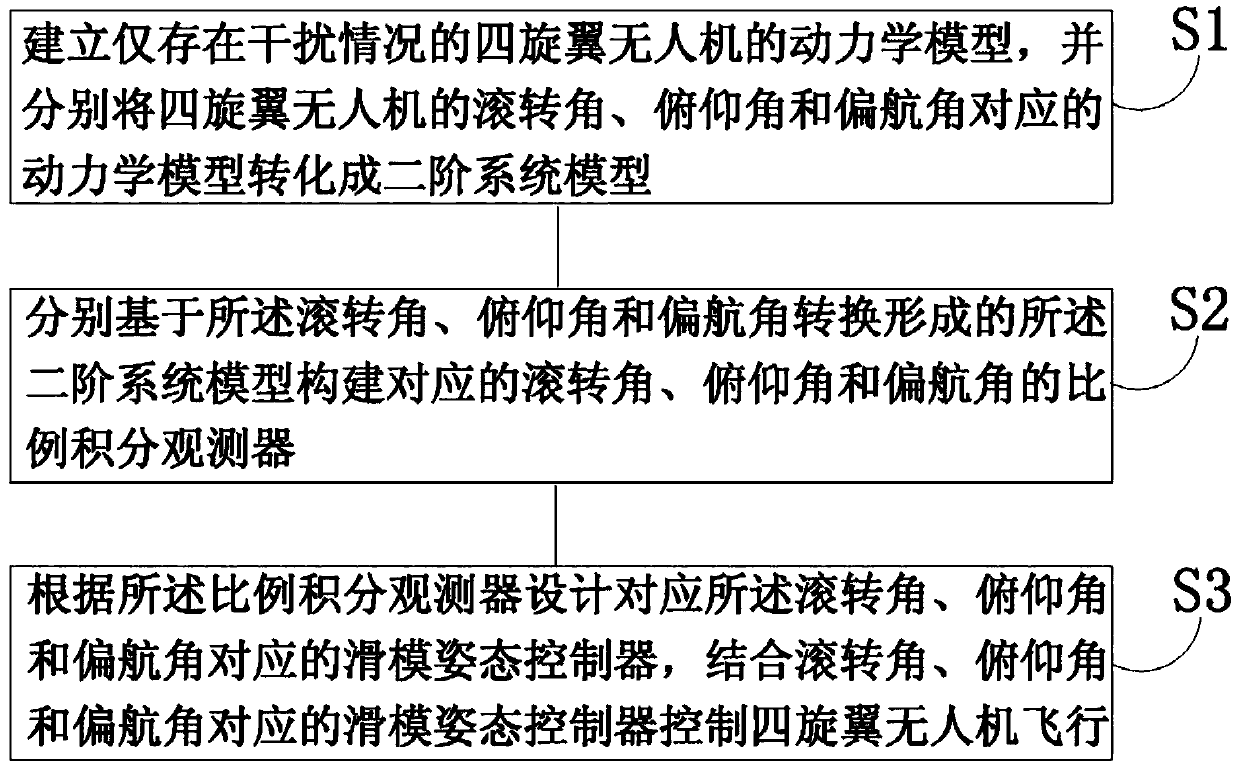
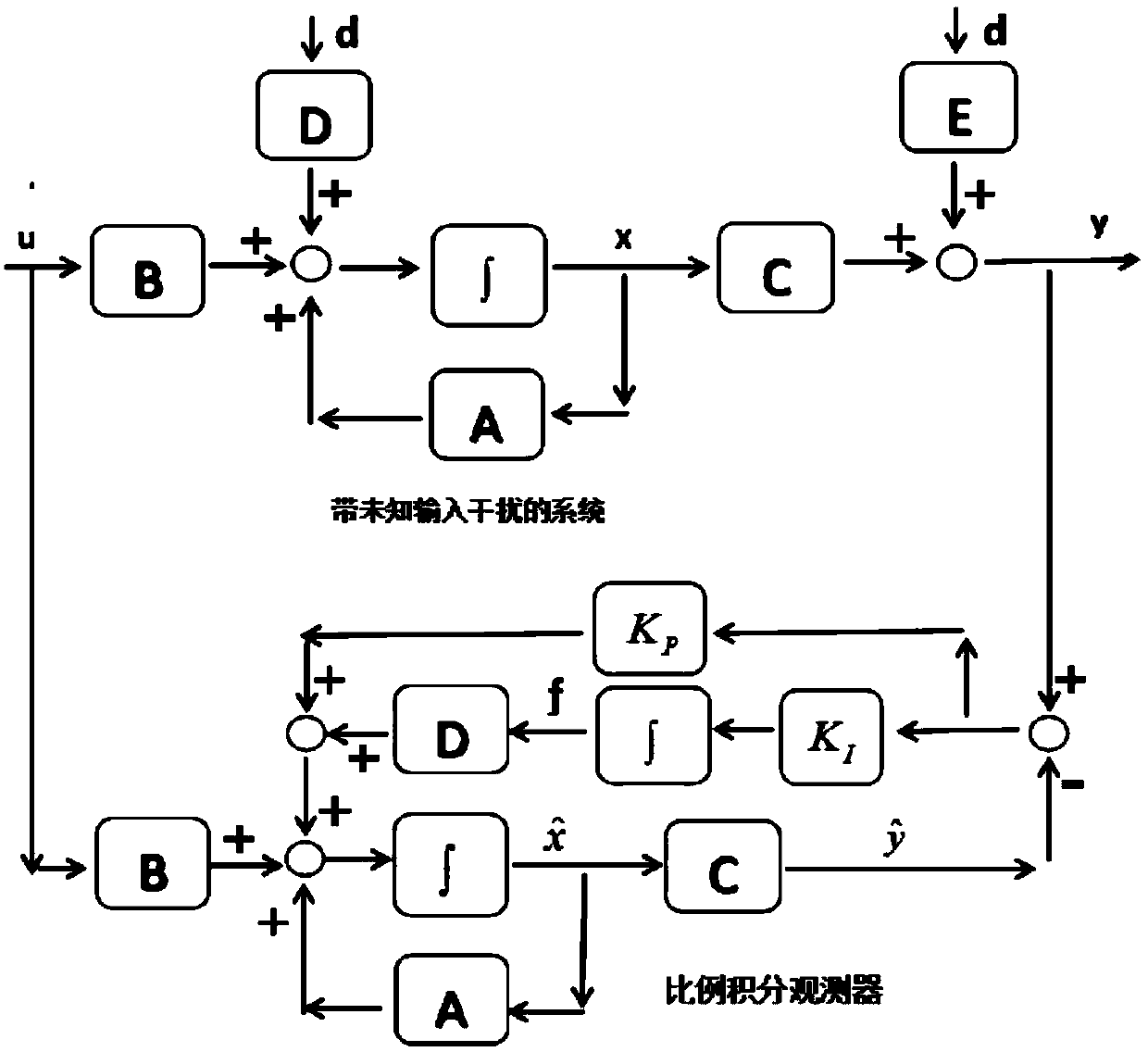
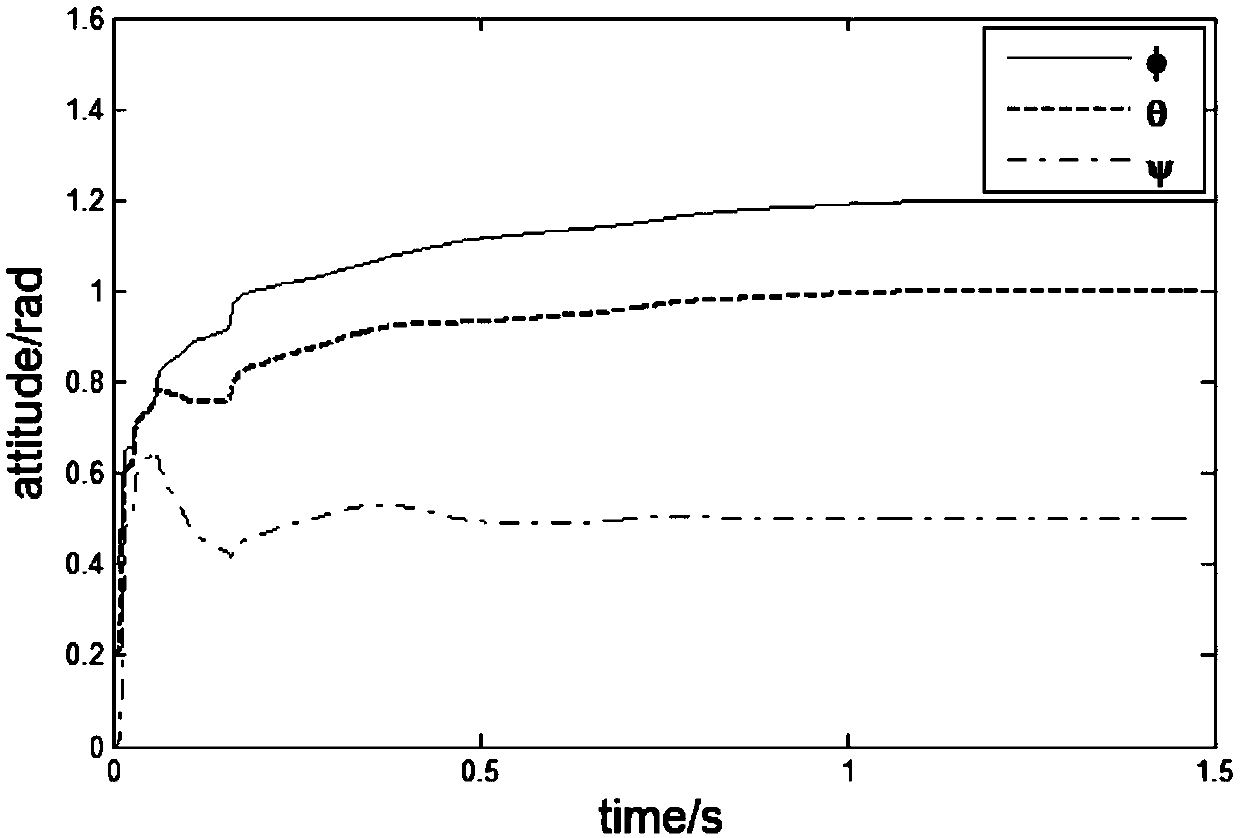
Sliding mode attitude control method for quadrotor UAV based on proportional integral observer
InactiveCN109521786AImproving Steady State Tracking AccuracyImprove robustnessAttitude controlAdaptive controlElevation angleDynamic models
The invention discloses a sliding mode attitude control method for a quadrotor UAV based on a proportional integral observer. The method comprises steps that a dynamic model of the quadrotor UAV withinterference only is established, and expressions of a rolling angle, an elevation angle and a yaw angle of the quadrotor UAV are transformed into second-order system models; the second-order system models are utilized to construct the corresponding proportional integral observer; a sliding mode attitude controller is designed according to the proportional integral observer, and the sliding mode attitude controller in combination with the rolling angle, the elevation angle and the yaw angle is utilized for flight control of the quadrotor UAV. The method is advantaged in that the proportional integral observer is combined with the sliding mode attitude controller, the partial feedback function of the proportional integral observer is utilized to estimate the shape and position input interference state of the quadrotor UAV, steady state tracking accuracy of the proportional integral state observer is improved, through the sliding mode attitude controller, relatively strong robustness andanti-interference to uncertain factors of the quadrotor UAV are achieved, and design and calculation are simple.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Crane anti-swinging control method based on positive and negative POSICAST input reshaping method
The invention relates to a crane anti-swinging control method based on a positive and negative POSICAST input reshaping method, which is applicable to any n time lag conditions. When the time lag of a designed reshaping device is shorter, the maximum value of a swinging angle is larger; when the time lag is longer, the maximum value of the swinging angle is smaller; meanwhile, when the jumping of an accelerated velocity is smaller, and the speed is gentler. A user can select freely according to actual conditions. The crane anti-swinging control method disclosed by the invention is applicable to a damping system and is also applicable to a non-damping second-order system. The method is an open loop control method, so that the method has the advantages that a measurement sensor for closed loop feedback is not needed. The crane anti-swinging control method utilizes phase step accelerated velocity input and aims at reshaping of phase step accelerated velocity output; compared with a pulse accelerated velocity input method, the speed is continuously changed, and a project is easy to realize. The crane anti-swinging control method is suitable for taking any phase step signal as input, and a damping second-order system is used for an anti-swinging system or a system for enabling certain output to finally return back to an original position.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
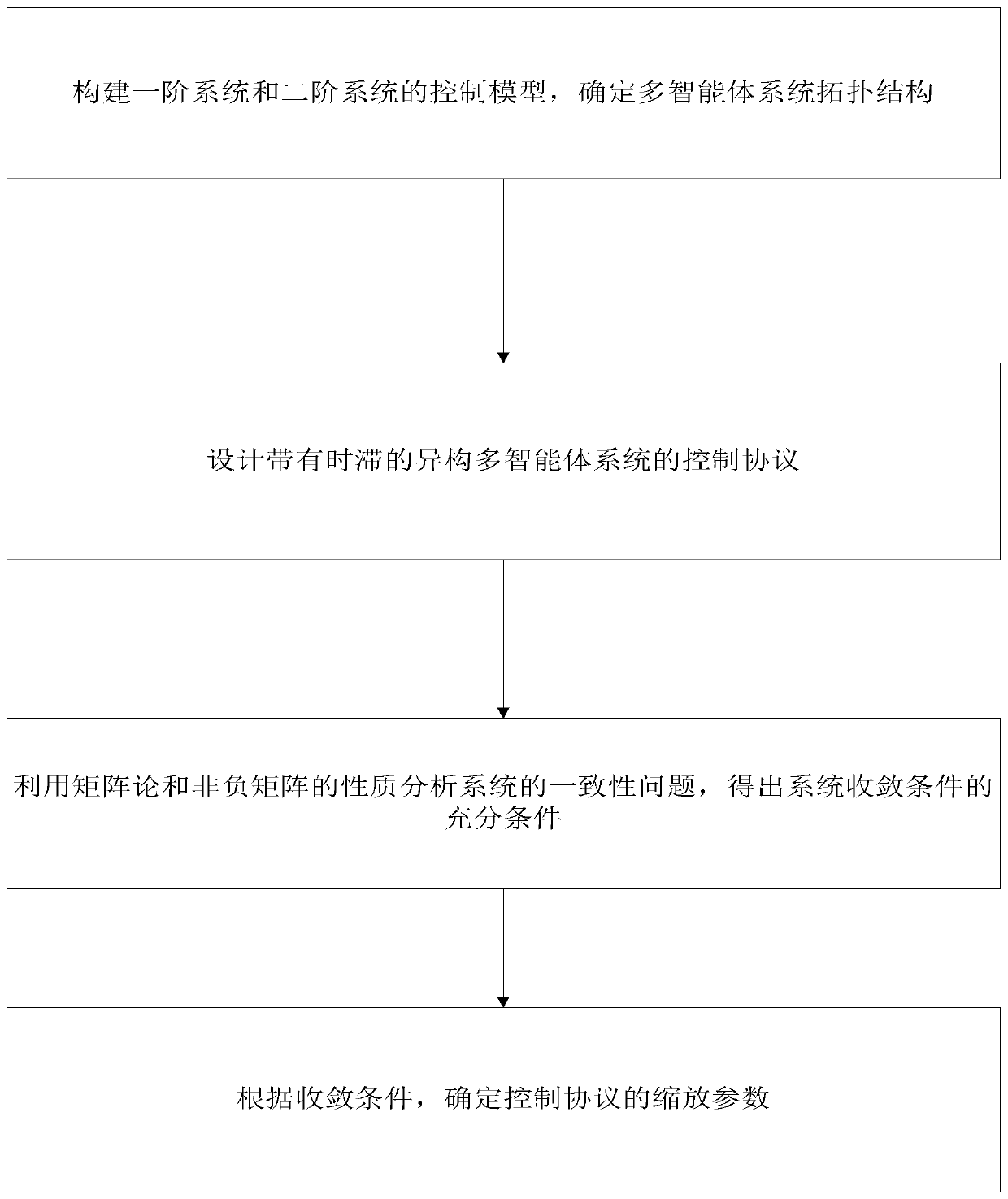
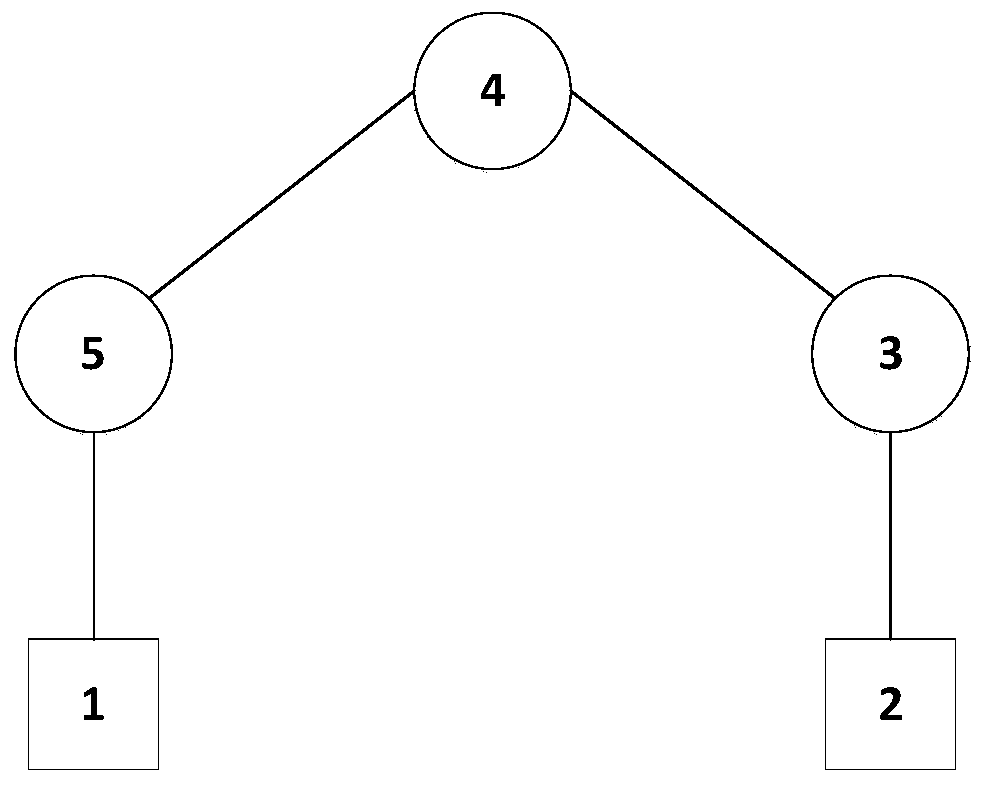
Group consistency control method for heterogeneous multi-agent system with time delay
ActiveCN110442022AAddressing Convergence EffectsTotal factory controlAdaptive controlAlgorithmTime delays
The invention discloses a group consistency control method for a heterogeneous multi-agent system with arbitrary bounded time delay, and the method comprises the following steps of constructing mathematical models of a first-order system and a second-order system, determining a topology of the multi-agent system, and describing its topological relationship by using graph theory knowledge; designing a control protocol of heterogeneous multi-agent system with time delay; analyzing the consistency problem of the system by using the properties of matrix theory and non-negative matrix to obtain a system convergence condition; determining a control protocol scaling parameter that meets the system convergence condition, and substituting the parameter into the system control protocol to implementthe group consistency control of the system. The invention provides the group consistency control method for the heterogeneous multi-agent system with arbitrary bounded time delay, and the method solves the global control problem by a distributed control method with no need of global information of the system, and only requires joint connection of topological graphs of the system at the same timewithout requiring their sub-graphs to be connected, thereby improving the robustness of the system and being suitable for group consistency control of heterogeneous multi-agent systems with arbitrarybounded delays.
Owner:COMP APPL RES INST CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Five-DOF (freedom of degree) bearingless synchronous reluctance motor decoupling controller and construction method thereof
ActiveCN102136822ALearnedAchieving the Curse of DimensionalityElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlHysteresisSynchronous reluctance motor
The invention discloses a five-DOF (freedom of degree) bearingless synchronous reluctance motor decoupling controller and a construction method thereof. Three expanded current hysteresis loop PWM (pulse width modulation) inverters, a switch power amplifier and a five-DOF bearingless synchronous reluctance motor form a compound controlled object; five support vector machine second-order systems, one support vector machine first-order system and eleven integrators are utilized to construct a support vector machine alpha-order inverse system and offline training is carried out, the support vector machine alpha-order inverse system is placed in front of the compound controlled object to form a pseudo linear system, and the pseudo linear system is equivalent to five position second-order integration subsystems and one position first-order integration subsystem; and five position controllers and one rotating speed controller are respectively designed for the six integration subsystems, thus a linear closed-loop controller is formed. In the invention, a least square support vector machine is adopted to approach an alpha-order inverse model of a nonlinear system, the dynamic decoupling control among all the controlled variables is realized, and the control performance of the overall system is effectively improved.
Owner:江阴智产汇知识产权运营有限公司
Positive and negative POSICAST input shaping method-based crane anti-swing control method
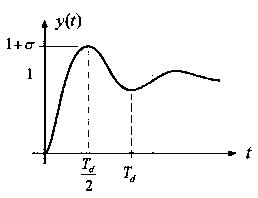
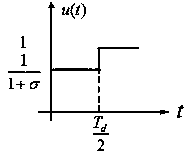
The invention relates to a positive and negative POSICAST input shaping method-based crane anti-swing control method. The method includes a positive and negative POSICAST method adopted when a swing angle returns to zero after a time point 3Td / 2, a positive and negative POSICAST method adopted when the swing angle returns to zero after a time point Td, and a positive and negative POSICAST method adopted when the swing angle returns to zero after a time point 3Td / 4, wherein Td is the damped oscillation period of a system. The method of the invention is either applicable to a damped system or an un-damped two-order system. The method of the invention is an open-loop control method. With the method adopted, a measuring sensor for closed-loop feedback is not required. According to the method of the invention, step acceleration input is utilized, and the shaping of step acceleration output is targeted. Compared with a pulse acceleration input method, the method has the advantages of continuous speed change and easiness in engineering realization. The method of the invention is applicable to any damped two-order systems adopting step signals as input, and is used for an anti-swing system or a system of which the output of a certain item is expected to return to an original position.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Digitization sampling time delay frequency conversion measuring method and measuring system
ActiveCN103812731AImprove running accuracyRun accuratelyData switching networksSmart substationTime delays
The invention discloses a digitization sampling time delay frequency conversion measuring method, and the method measures the non integer period time delay to the different frequency steady state analog quantity signals from an electronic transformer or analog inputting and merging unit to obtain the inertial time delay to all frequency signals from the digitization sampling process, including the non integer period time delay and integer period time delay, compensates the sending time difference for SV message based on the transmit frequency of the phaselock technique tracking SV message, reduces the influence caused by the sending time difference for SV message, and raises the digitization sampling time delay measuring precision. The invention also discloses a test system based on the method for ensuring the reliable application of the electronic transformer and the analog inputting and merging unit in the intelligent substation, eliminating the potential safety hazard of the electronic transformer and the analog inputting and merging unit on engineering application, raising the second-order system running veracity for the intelligent substation and having significance to the safe and reliable operation for the intelligent substation.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
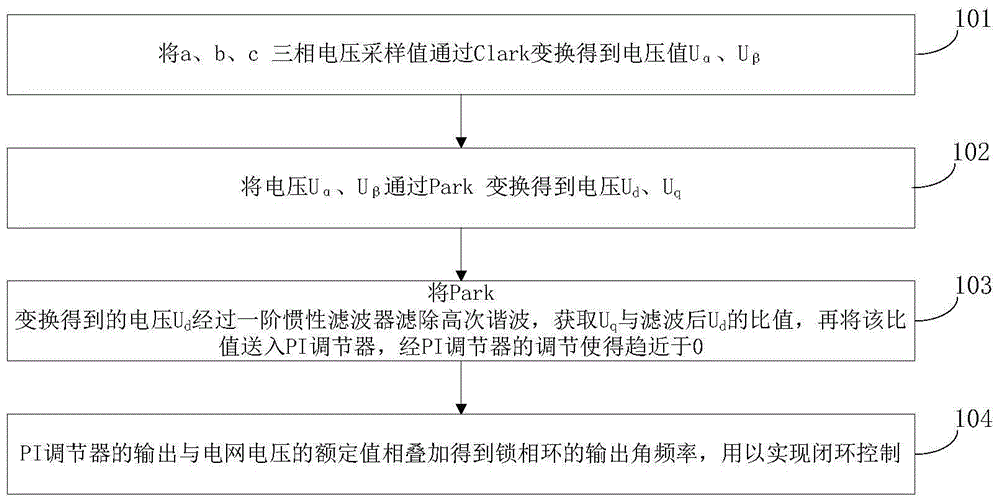
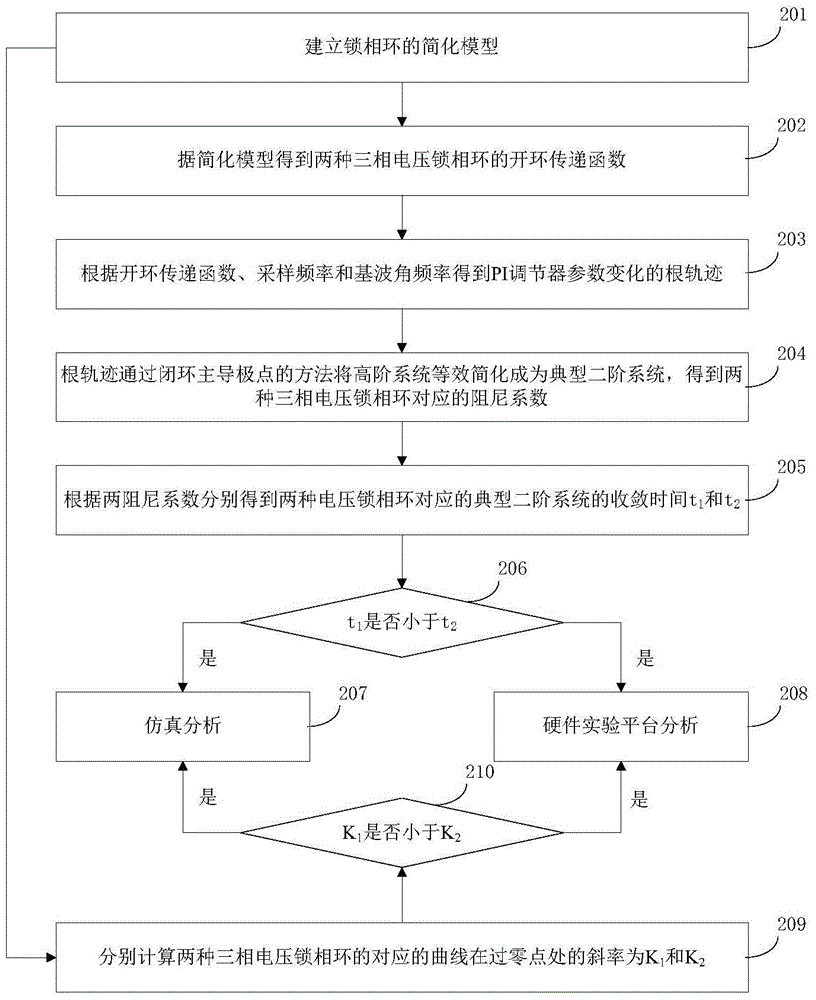
Rapid three-phase voltage phase-locked loop method and dynamic response performance analyzing method thereof
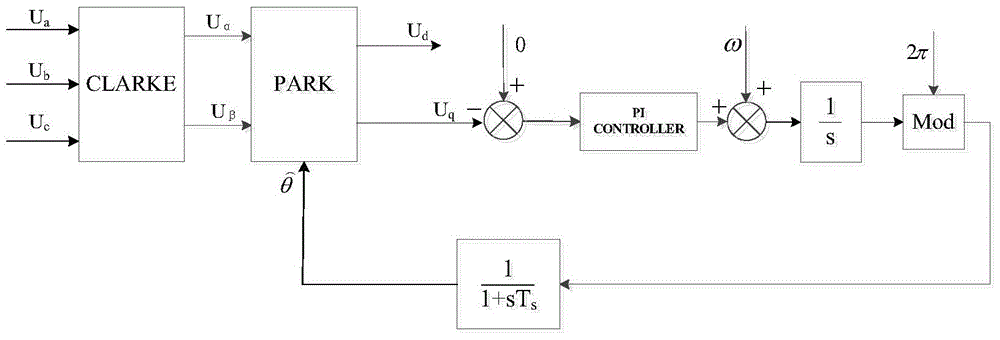
The invention discloses a rapid three-phase voltage phase-locked loop method and a dynamic response performance analyzing method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of electric power and electronic control. The analyzing method comprises the following steps: establishing a simplified model of a phase-locked loop, obtaining an open-loop transfer function of a traditional three-phase voltage phase-locked loop and a high-speed three-phase voltage phase-locked loop based on the simplified model, and obtaining a root locus of the changes of a PI regulator parameter Kp based on the open-loop transfer function, a sampling frequency and a fundamental wave angular frequency; drawing two root loci in the same coordinate system, performing equivalent simplification on a high-order system to a typical second order system through the method of closed loop dominant apices, and obtaining convergence time t1 and t2 of the typical second order system in correspondence to the traditional three-phase voltage phase-closed loop and the high-speed three phase voltage phase-locked loop. The analyzing method begins with a simplified mathematics model from a rapid three-phase voltage phase-closed loop structure, conducts separate and detailed discussion on time domain and frequency domain mathematics models, and at the same time demonstrates a theory analysis based on a relevant simulation platform and a hardware experiment platform.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Novel active-disturbance-rejection controller with embedded model
ActiveCN109507872AGood control effectGood setpoint trackingControllers with particular characteristicsIntegratorProportional differential
The invention discloses a novel active-disturbance-rejection controller with an embedded model. The novel active-disturbance-rejection controller comprises an extended state observer module arranged in the inner ring and a proportional differential feedback module arranged in the outer ring; model information is embedded in the extended state observer module and used for observing the total disturbance of a system outside a nominal model, and then transforming a controlled object into a series integrator standard type by compensating the part of the total disturbance and known dynamics in realtime in the inner ring; the proportional differential feedback module is based on the series integrator standard type and adjusts he output control amount through parameter setting according to a quantitative relationship between an outer ring controller differential parameter kd and a second-order system damping coefficient zeta to achieve the control of the controlled object; the system is thesystem of the controlled object. The novel active-disturbance-rejection controller with the embedded model can reduce the burden of an extended state observer, achieves the purposes of more accurate disturbance estimation and set value tracking and reduction of the influence of noise on the output control amount, and provides convenience for parameter setting and adjustment in an actual control process.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
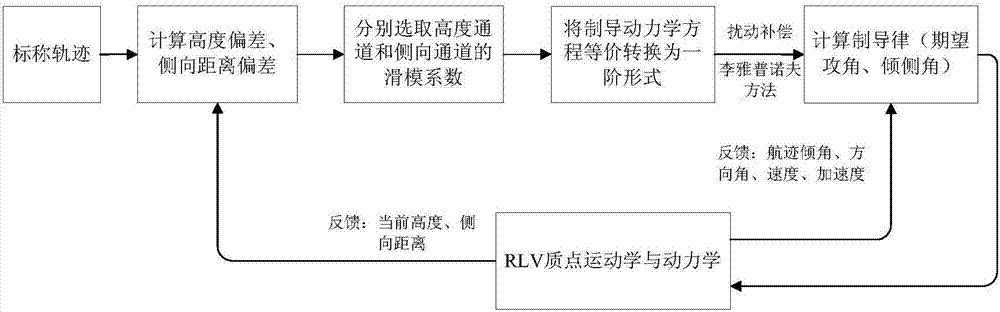
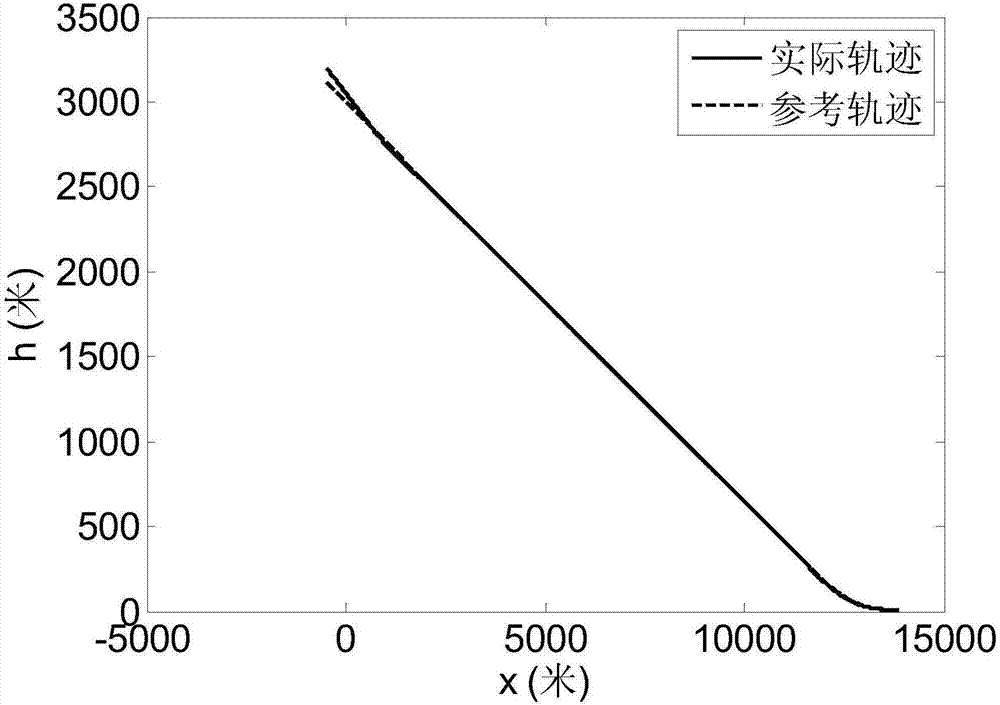
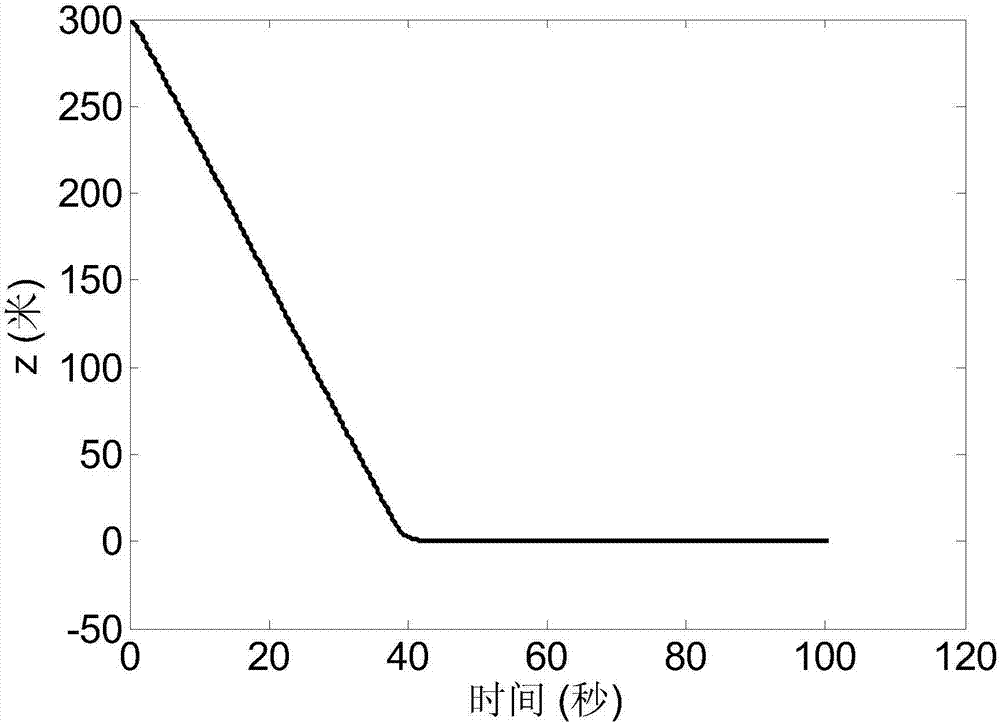
RLV landing section guidance law acquiring method based on sliding-mode control theory
ActiveCN107102547AImplement trackingSimplify the design processAdaptive controlGuidance systemThree degrees of freedom
A RLV landing section guidance law acquiring method based on a sliding-mode control theory comprises steps of: calculating a height deviation and a lateral distance deviation according to an RLV landing section nominal trajectory; then, selecting an appropriate sliding-mode surface according to the tracking deviation of the nominal trajectory, and equivalently converting a RLV three-degree-of-freedom kinetic equation into a form described by the sliding-mode surface; and finally, designing the guidance law by using a Lyapunov method. In the design process, by analyzing aerodynamic data, the uncertainty upper bound of a guidance circuit is obtained and a compensation term is introduced to suppress the uncertainty so that the guidance system has asymptotic stability to the uncertainties such as disturbance. The method can overcome the influence of the uncertainty of the RLV guidance system so as to improve guidance precision, converts an original second-order system into a first-order system by introducing the sliding-mode control method, thereby achieving a visual design process.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
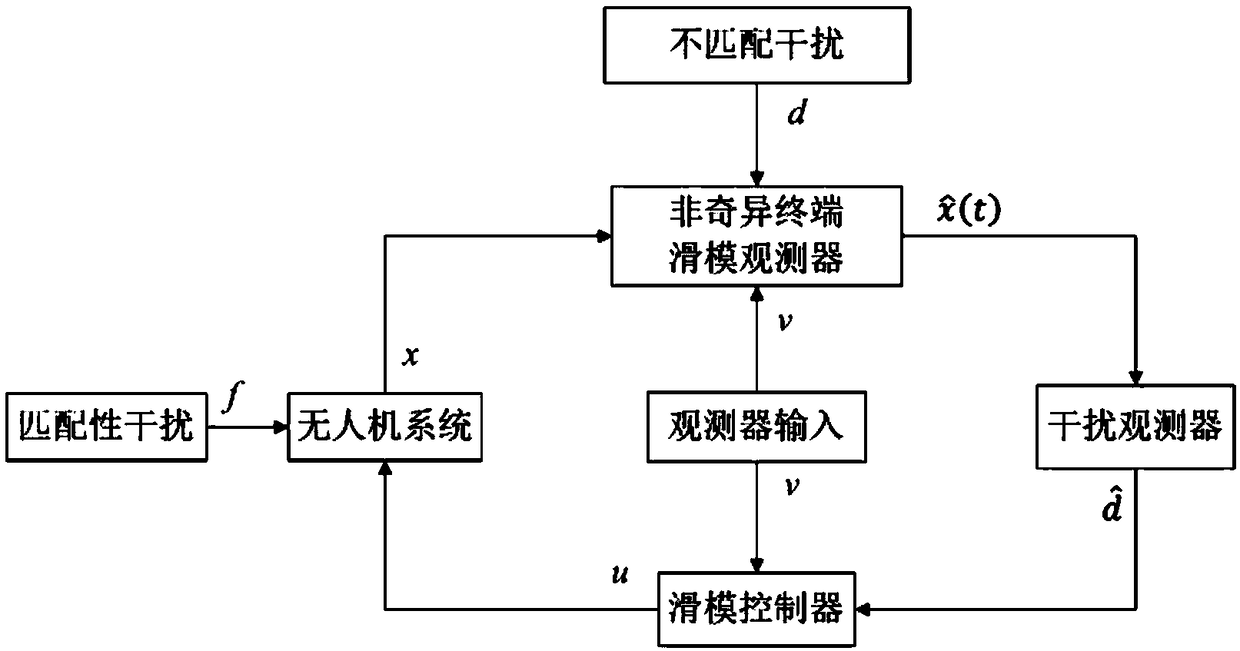
Robust control method for unmanned aerial vehicle attitude, and robust controller for achieving method
The invention provides a robust control method for unmanned aerial vehicle attitude, and a robust controller for achieving the method. The method comprises the following steps of building a second-order system mathematical model of an unmanned aerial vehicle; establishing a non-singular terminal sliding mode observer, and meanwhile, providing a sliding mode controller; and establishing an interference observer, and meanwhile, providing an interference controller. The robust controller comprises the non-singular terminal sliding mode observer and the sliding mode controller which are used for observing and controlling an unmanned aerial vehicle state and a matching interference condition, and the interference observer and the interference controller which are used for observing and controlling the unmanned aerial vehicle state and a non-matching interference condition. According to the method, in the presence of two kinds of interferences, the state of a four-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle system can be observed, and the two kinds of interferences can be compensated, so that the unmanned aerial vehicle system can reach the stable state, and the expected control goal of the attitude control of the four-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle system is achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
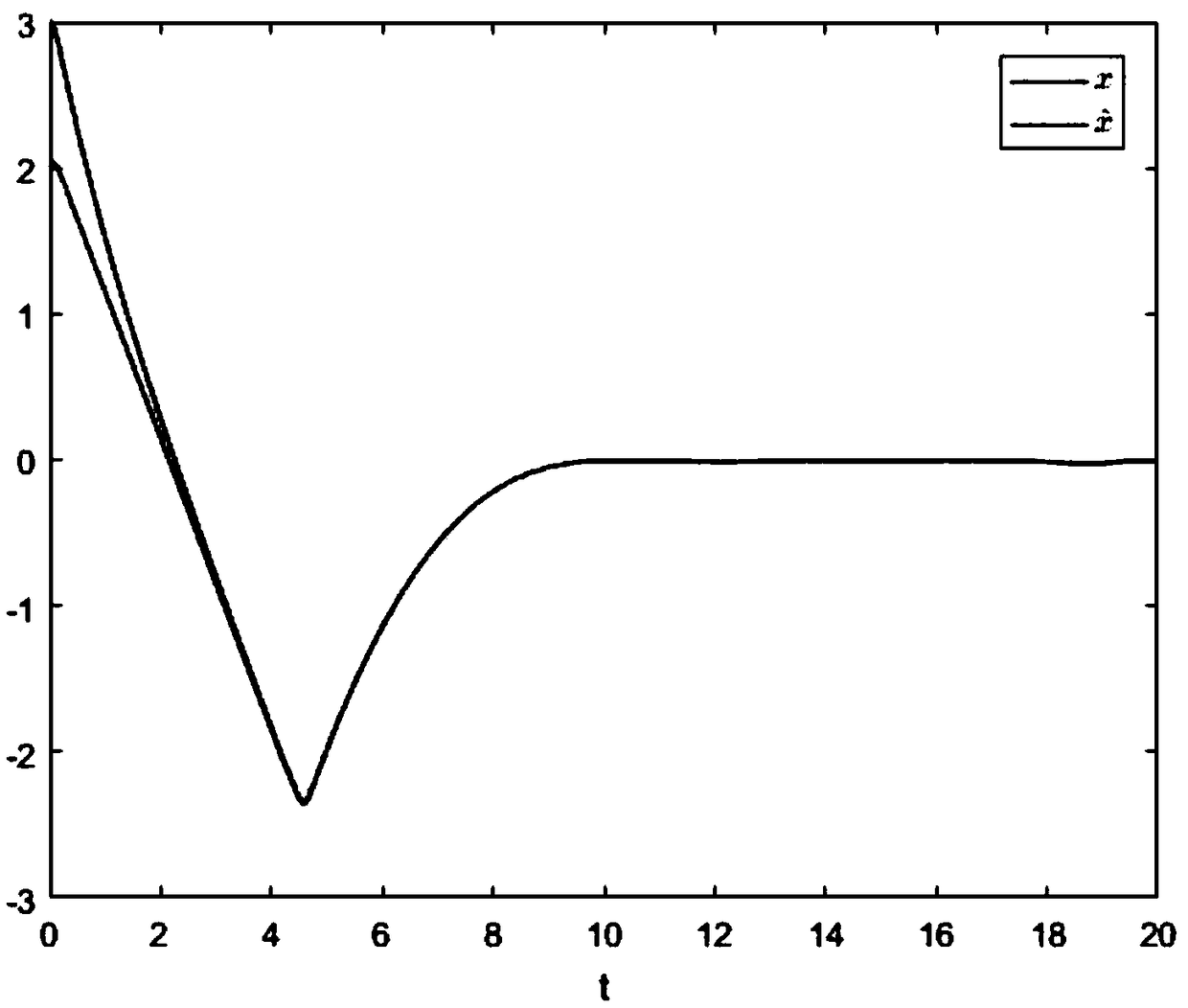
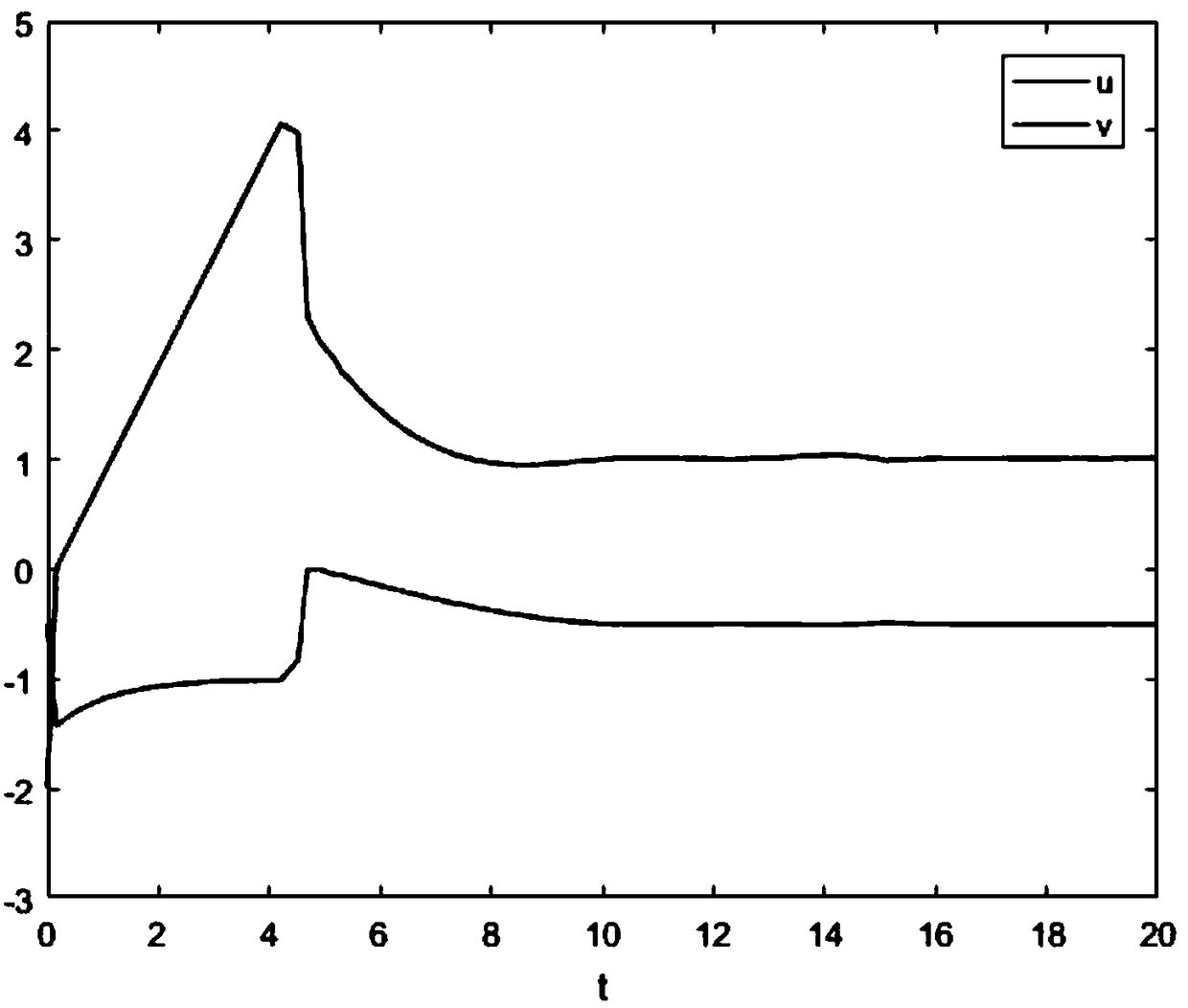
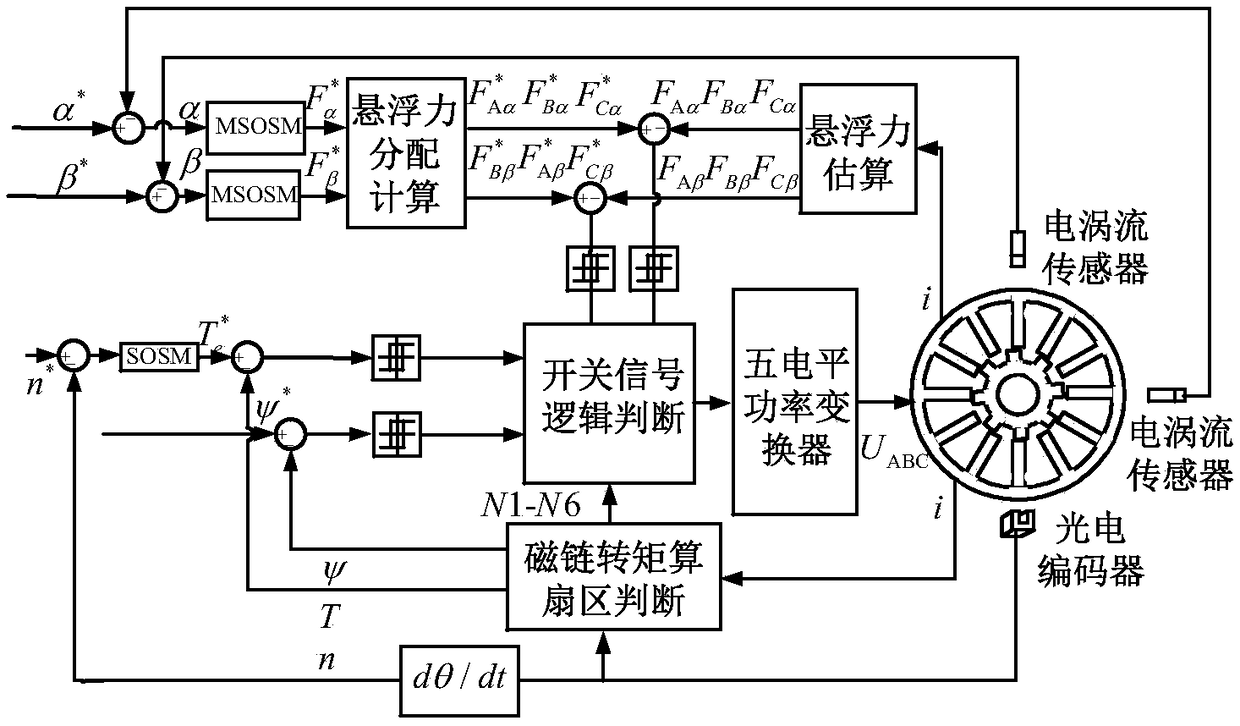
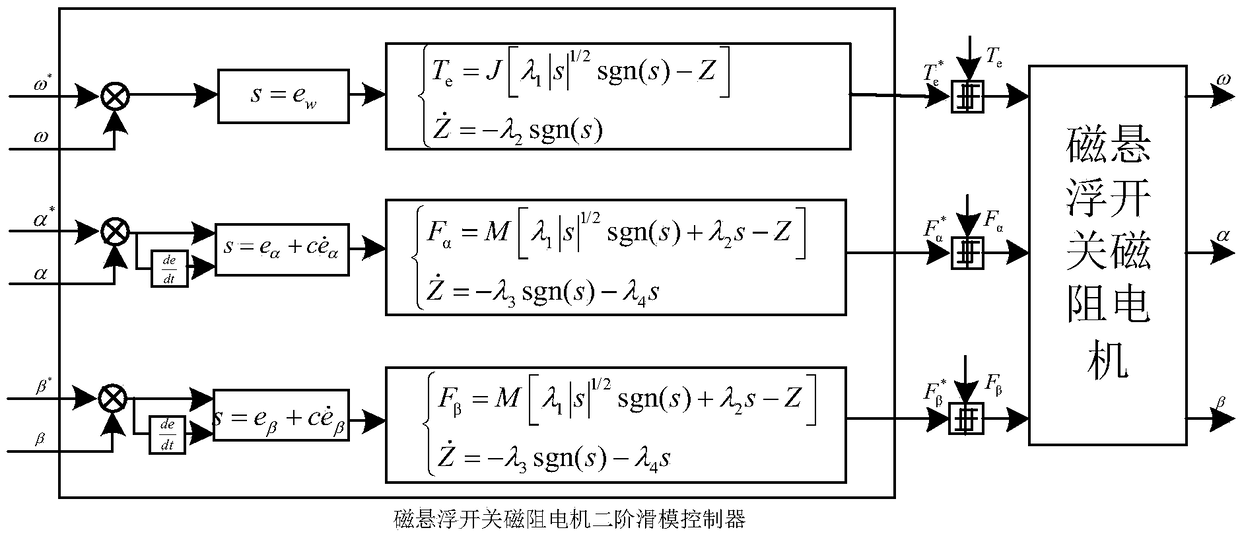
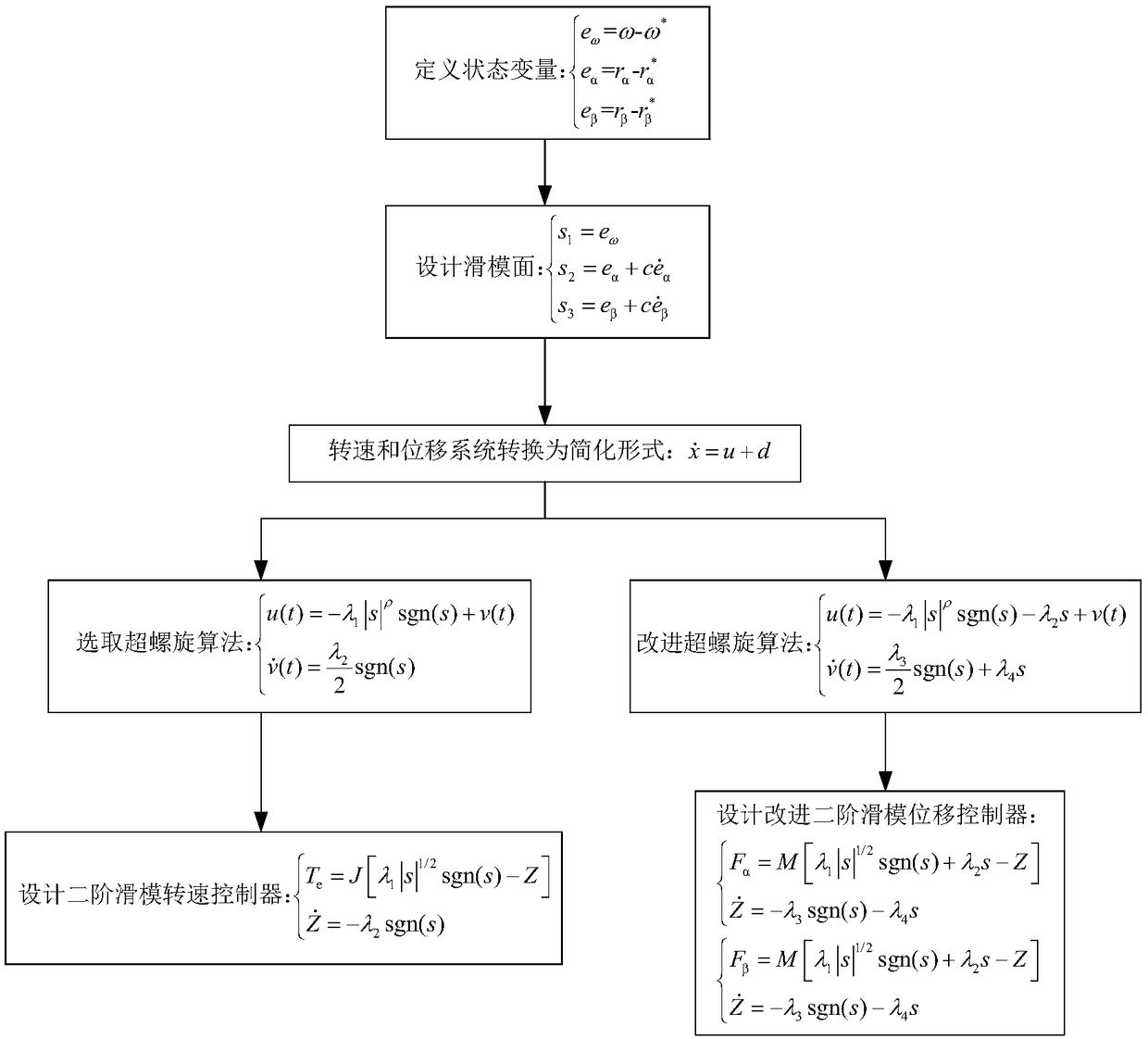
A second-order sliding mode control method for magnetically suspended switched reluctance motor
ActiveCN109194222AImprove robustnessImprove speed output accuracyElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlLevitationElectric machine
A second-order sliding mode control method for magnetically suspended switched reluctance motor is disclosed in the invention. The speed loop adopts the second-order sliding mode speed controller based on the superscrew algorithm, The reference torque is obtained by selecting the speed error to construct the sliding mode surface and combining with the mechanical equation of the maglev switched reluctance motor. The displacement loop adopts the second-order sliding mode displacement controller based on the improved superscrew algorithm, A high order error derivative of displacement is introduced to make the superhelix algorithm suitable for second order systems, The reference levitation force is obtained by improving the superscrew algorithm combined with linear compensation term. The invention adopts a second-order sliding mode speed controller based on a superscrew algorithm and a second-order sliding mode displacement controller based on an improved superscrew algorithm, The speed control precision and rotor suspension precision of SRM are improved, the problems of speed buffeting and displacement buffeting are solved, and the system has strong robustness to uncertain disturbance, which is easy to be realized in engineering.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
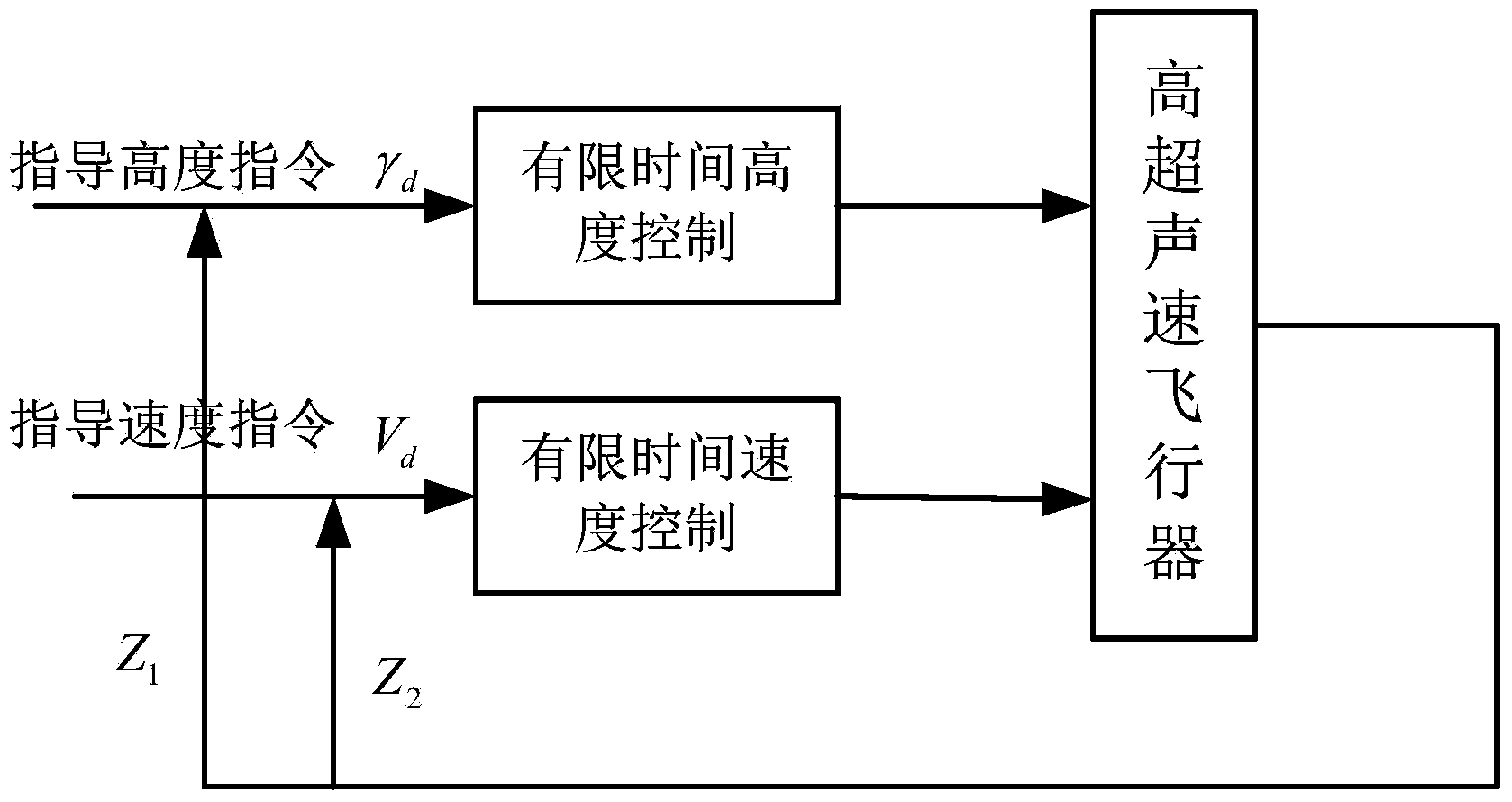
Motion control design method of hypersonic flight vehicle
InactiveCN103838237AAchieve convergenceVehicle position/course/altitude controlPosition/direction controlDynamic equationFlight vehicle
The invention discloses a control design method of a hypersonic flight vehicle. The method comprises the following steps that a longitudinal model of the hypersonic flight vehicle is given; finite time height control design to the hypersonic flight vehicle is achieved according to an engine dynamic equation described by a second-order system model; according to the sufficient condition of controller gain selecting, a flight speed and a flight path angle are converged to a given value within the finite time, and therefore the finite time speed control design to the hypersonic flight vehicle is achieved. According to the motion control design method of the hypersonic flight vehicle, based on the control method of a finite time control technology, the controller design method of dynamic inverse and the finite time control technology is combined, height control and speed control are seen as two sub systems for designing controllers respectively, and the difficult problems that the model order of the hypersonic flight vehicle is high and finite time control can not be achieved easily are solved.
Owner:湖北蔚蓝通用航空科技股份有限公司
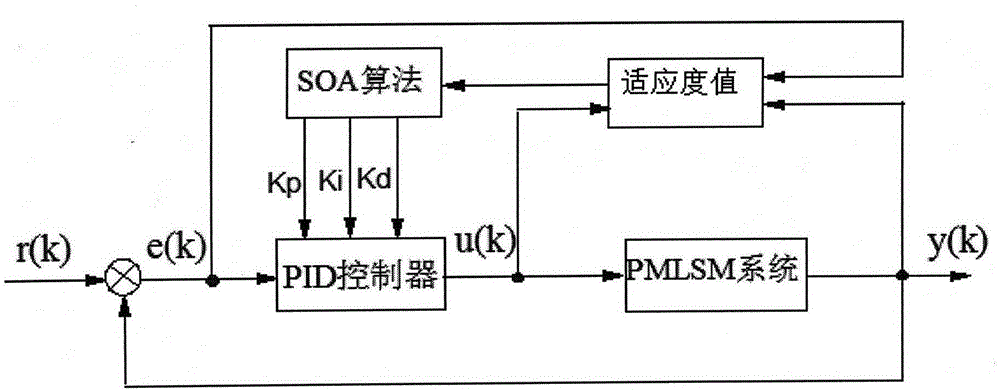
SOA-based PMLSM feed system PID parameter optimization method
The invention provides an SOA-based PMLSM feed system PID parameter optimization method and belongs to the numerical control technical field and swarm intelligent algorithm field. According to the method of the invention, as for defects existing in application of a traditional PID controller to a permanent magnet linear synchronous motor PMLSM feed system, a seeker optimization algorithm (SOA) and a traditional PID algorithm are combined together so as to be applied to a PMLSM feed system; a penalty controlled fitness function is introduced into the SOA to evaluate a solution, so that the response of an original second-order system is similar to the response of a first-order system, namely, overshoot will not occur on the system. The method has the advantages of simplicity, fast convergence speed, high robustness and flexible and adjustable fitness function. With the SOA-based PMLSM feed system PID parameter optimization method adopted, a new idea can be provided for the optimal design of the control parameters of the PMLSM feed system.
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF IND TECH
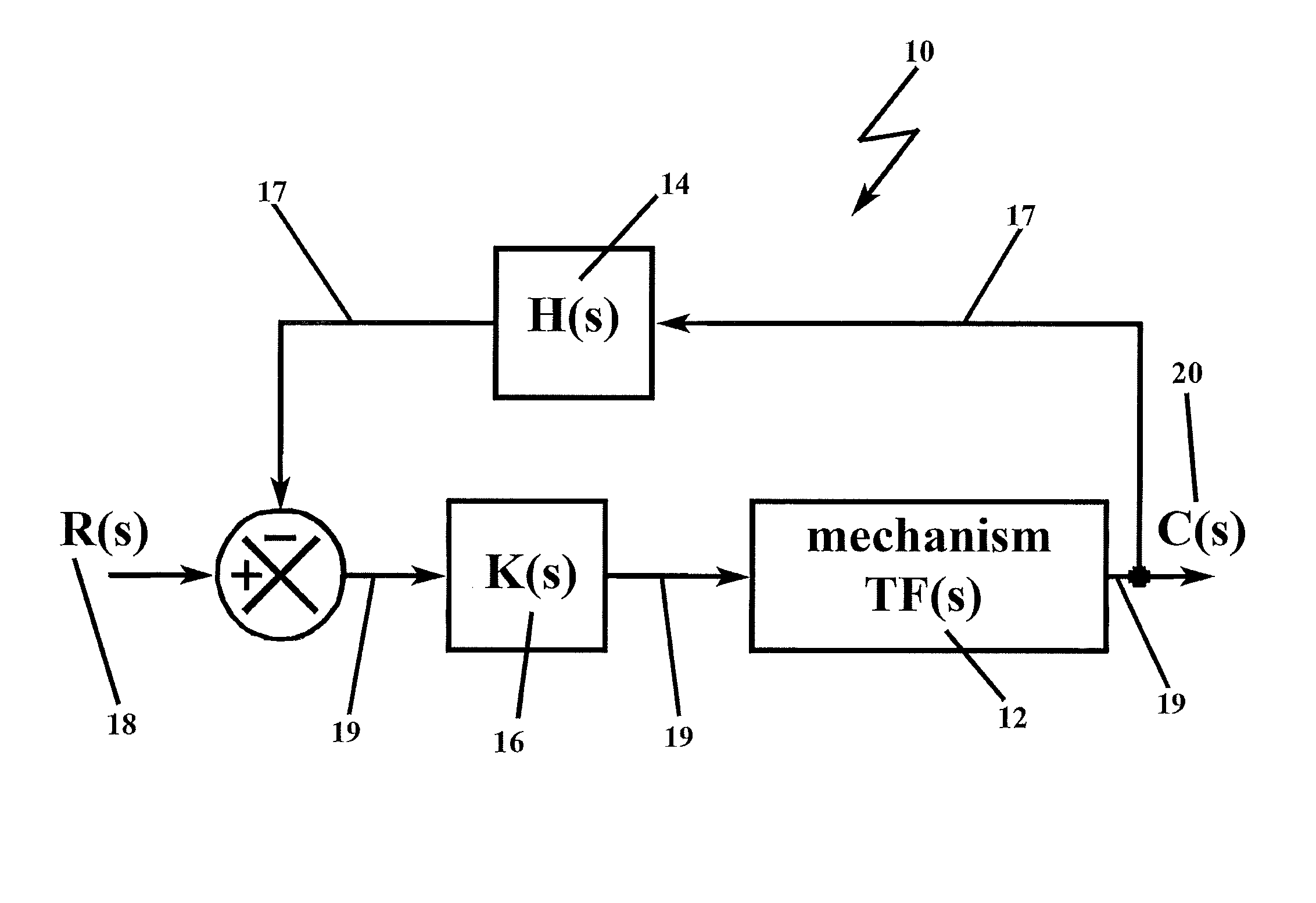
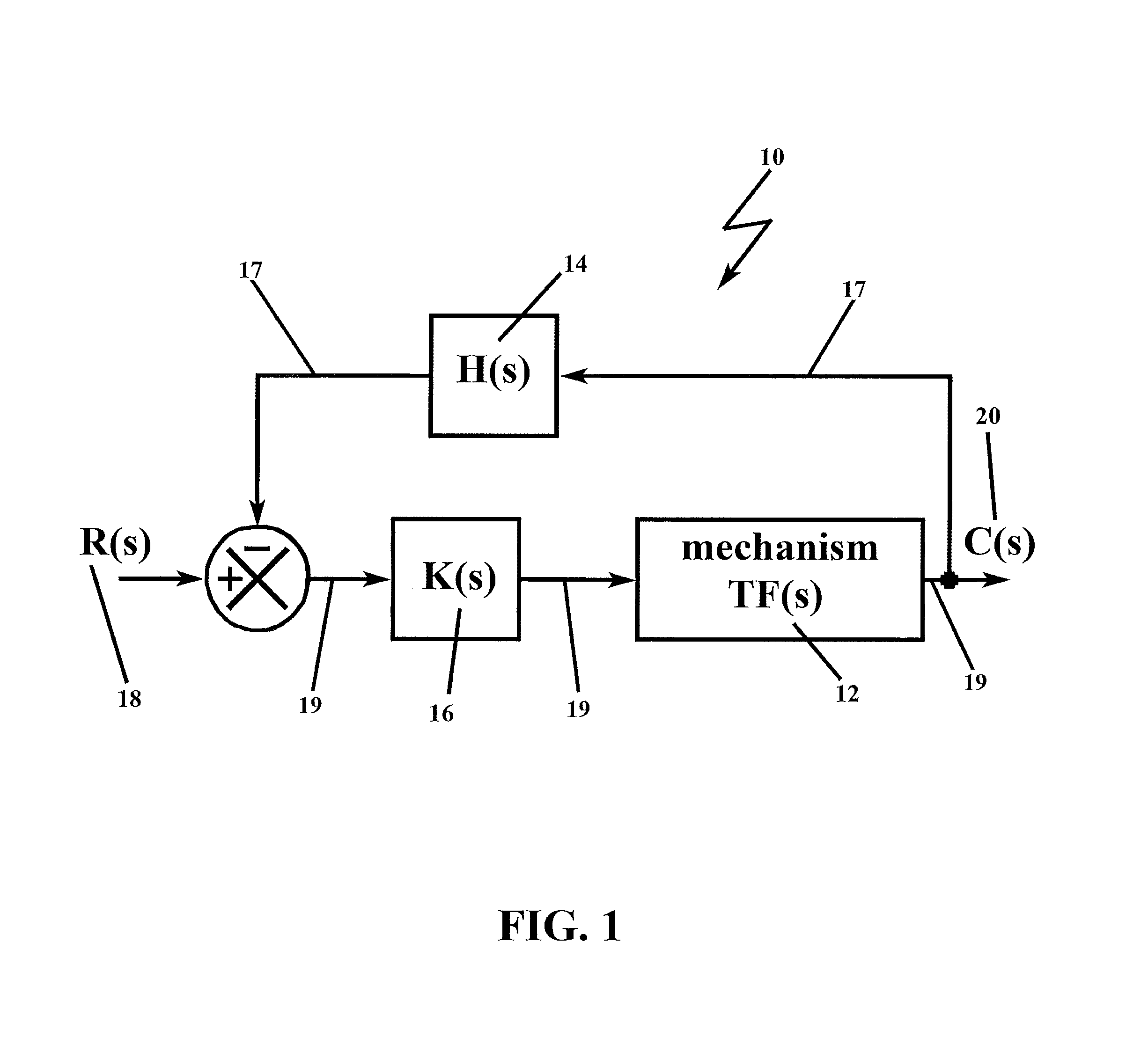
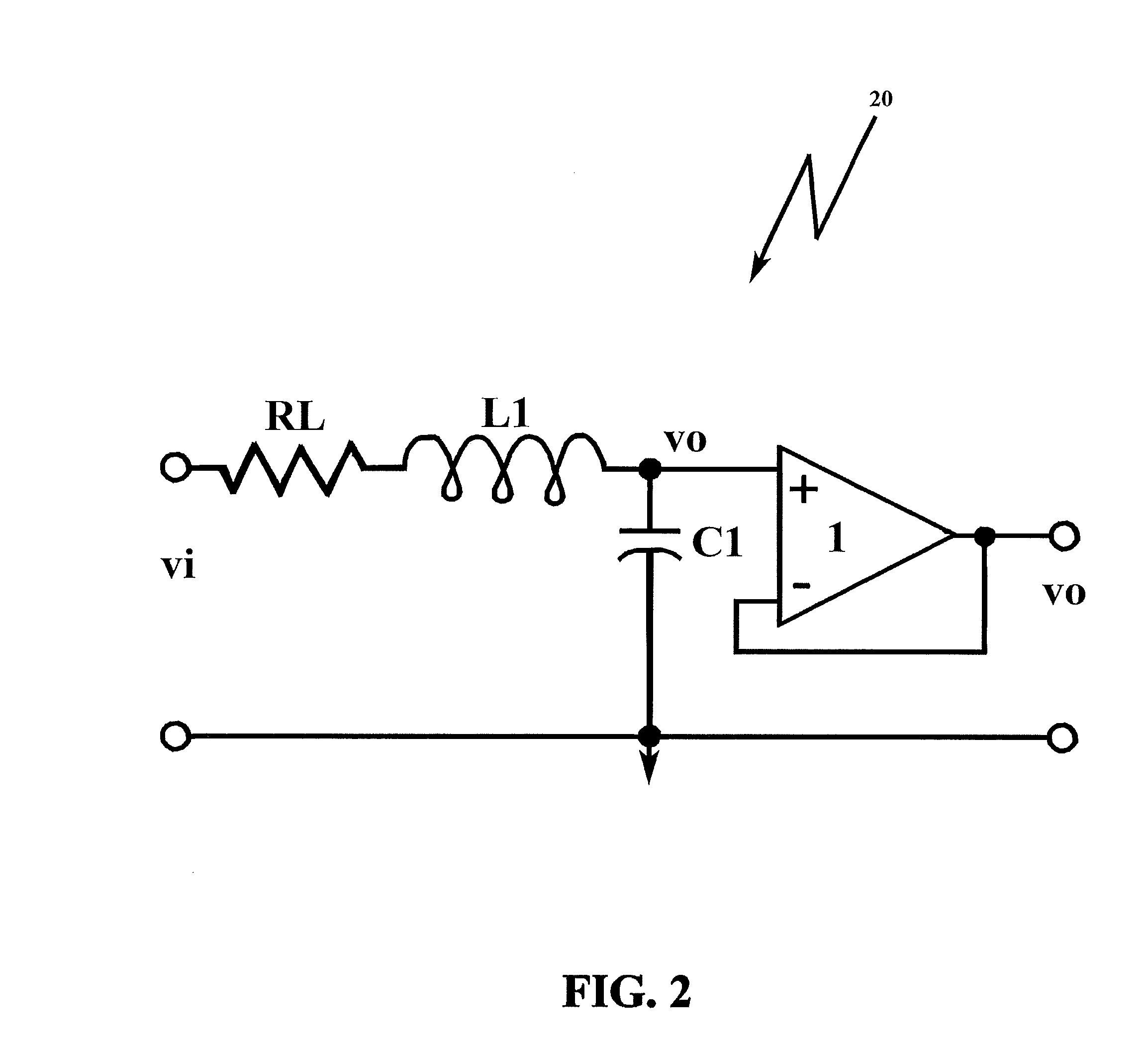
Compensation for canonical second order systems for eliminating peaking at the natural frequency and increasing bandwidth
ActiveUS20150101085A1Eliminate peaksHigh bandwidthAnti-hunting elementsScanning probe microscopyResonancePeak value
The present invention adds gain and phase into a canonical second order system in order to mitigate the adverse effects of unwanted resonance, where the gain is added to the forward path of a control loop of the system and is a ratio of the square of the system and mechanism frequencies, and the phase lead (H-factor) is added to the feedback path of the control loop of the system and is a complex ratio of these frequencies which includes a dc-component (Hdc) and a zero- or pole-component. By adding gain and phase lead, which is contrary to current approaches to addressing resonance, the present invention achieves the desired result of resonant free application in a canonical resonant-prone system of second order, and the methodology is applicable to higher order systems.
Owner:PAIGE NICHOLAS
Aircraft Dutch roll equivalent matching initial value selection method
ActiveCN108108523AMeet the equivalency fitting requirementsImprove work efficiencyGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsSystems designTime delays
The invention discloses an aircraft Dutch roll equivalent matching initial value selection method and belongs to the technical field of aircraft operation stabilization system design. The method comprises the steps that first, amplitude and phase data of a sideslip angle within the range of 0.1-10rad / s relative to a pedal force high-order system is obtained; second, a second-order system equivalent to a high-order transmission function in the first step is acquired based on a typical second-order system; third, a damping ratio initial value of a Dutch roll is determined according to a maximumvalue of an amplitude curve and an amplitude at the position of omega=0.1; fourth, a frequency initial value omega<d> of the Dutch roll is calculated; fifth, the amplitude at the position of omega=0.1and the frequency initial value are utilized to calculate a gain K initial value; and sixth, a time delay value tau is determined. According to the method, an initial value of equivalent matching isobtained according to the amplitude and phase data of the high-order system, the initial value is approximate to an exact solution, and it can be guaranteed that the equivalent matching requirement ismet in subsequent solving. Through the method, the work of repeatedly debugging the initial value is avoided, working efficiency is improved, and calculation difficulty is lowered.
Owner:XIAN AIRCRAFT DESIGN INST OF AVIATION IND OF CHINA
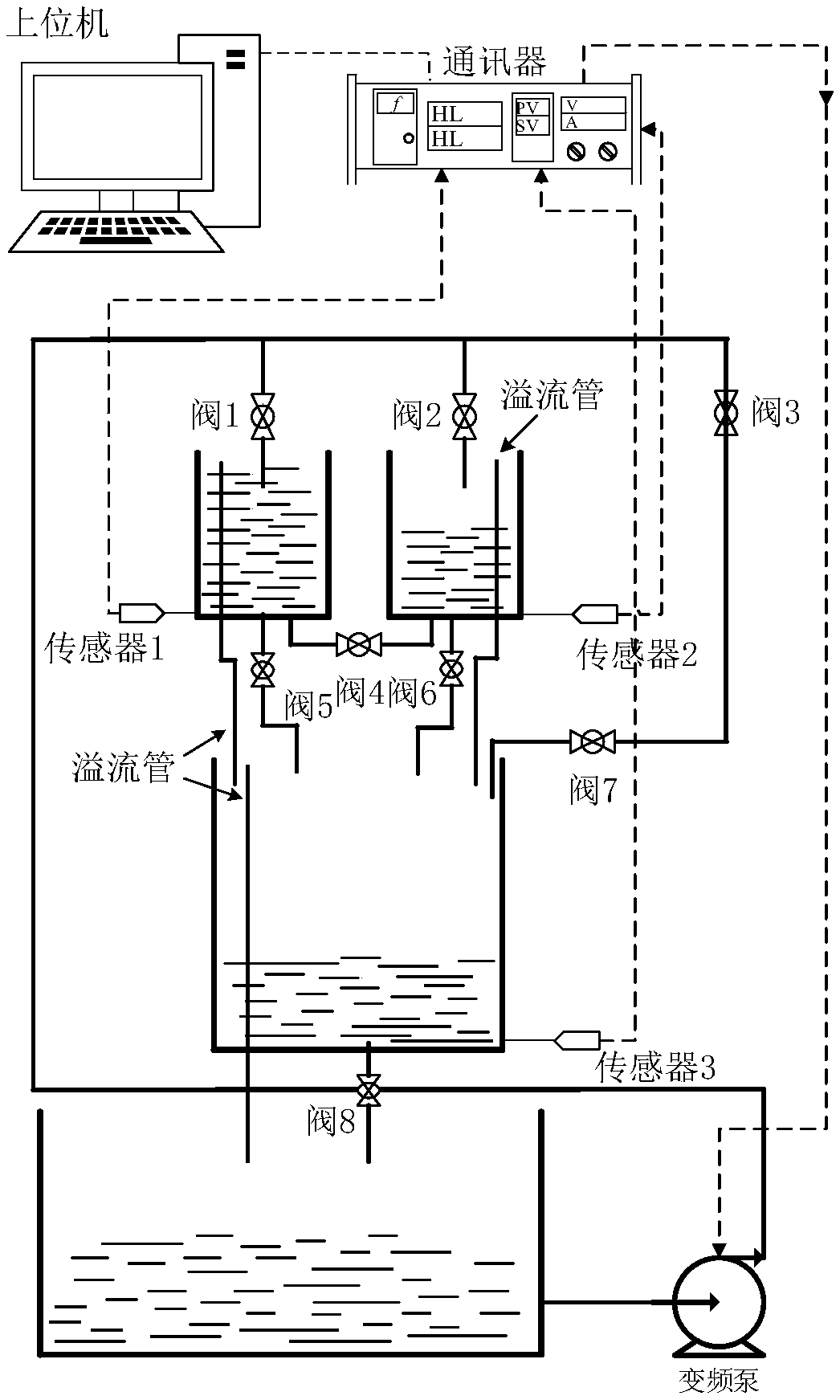
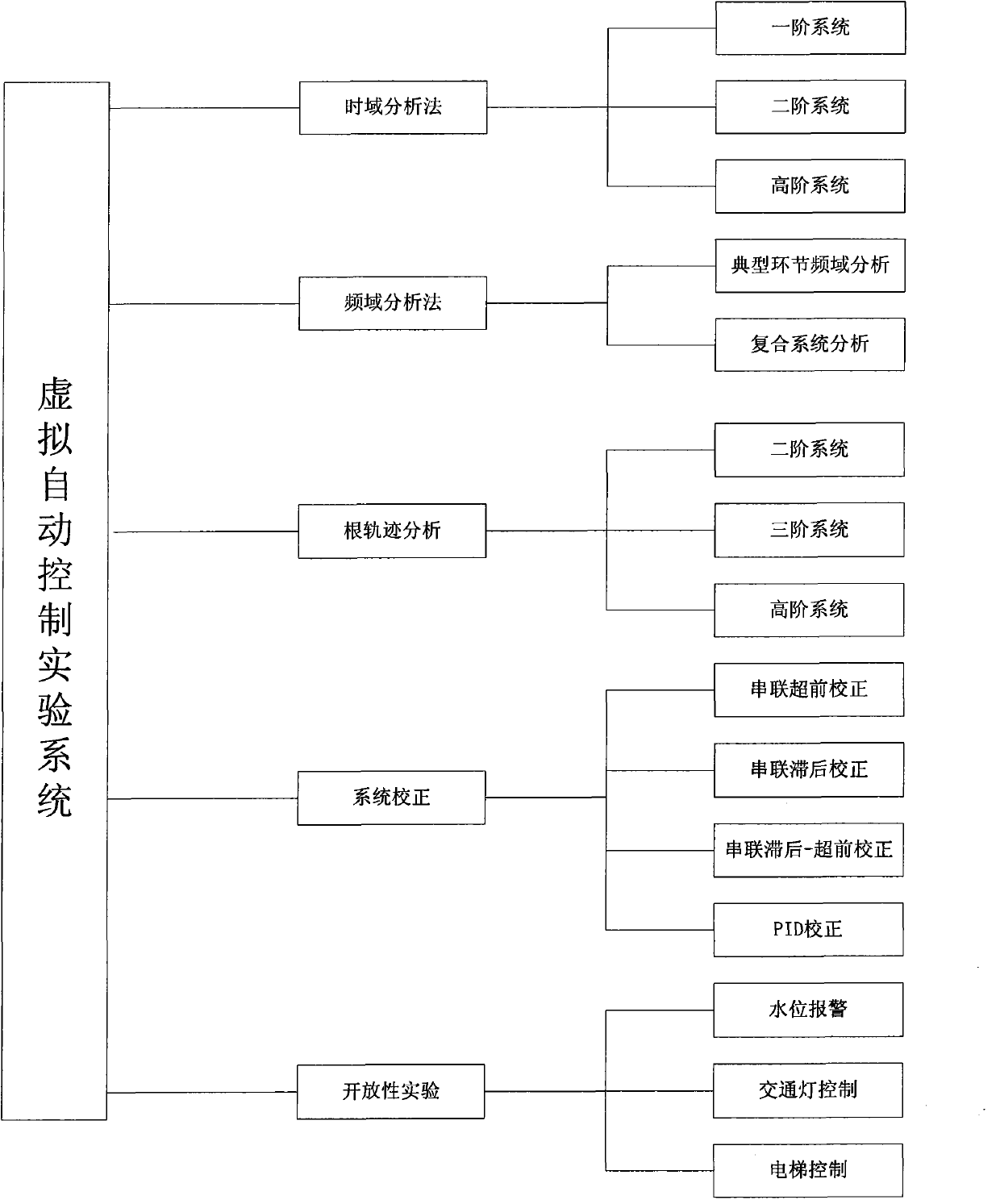
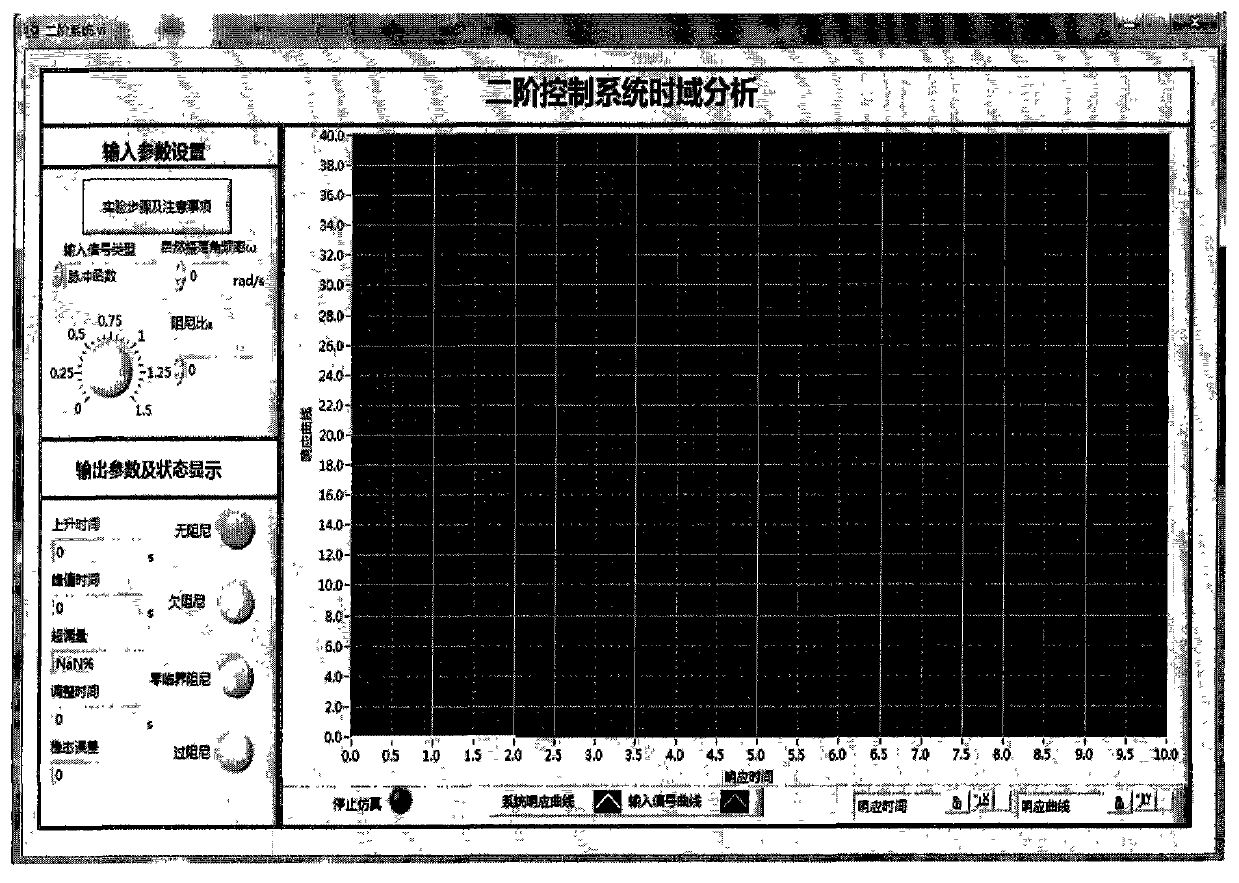
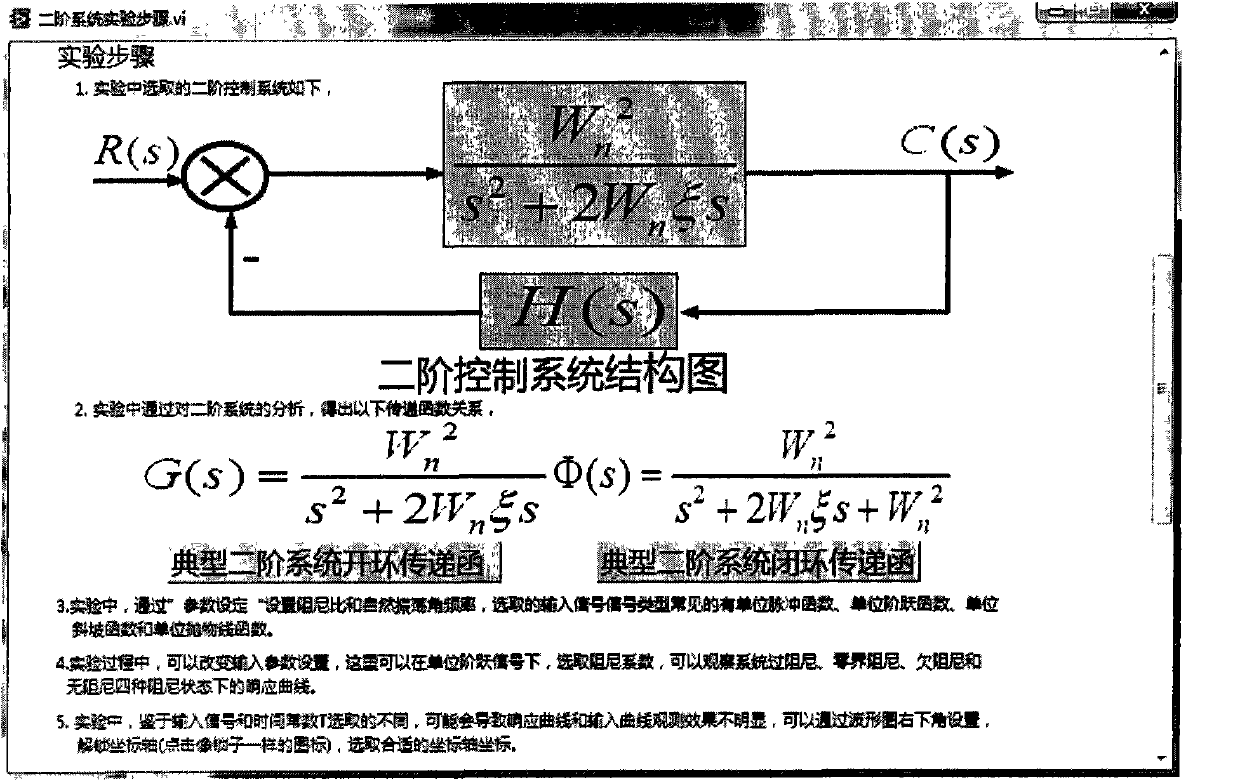
Virtual automatic control experimental system and design method of virtual automatic control experimental system
InactiveCN103995474AExperiment content is flexibleEasy to operateSimulator controlAutomatic controlSimulation
The invention discloses a virtual automatic control experimental system and a design method of the virtual automatic control experimental system. The virtual automatic control experimental system comprises a time domain analysis method experiment module, a root-locus method experiment module, a frequency domain analysis method experiment module, a system correction experiment module and an open experiment module, wherein the time domain analysis method experiment module comprises a first-order system time domain analysis module, a second-order system time domain analysis module and a high-order system time domain analysis module; the root-locus method experiment module comprises a second-order system root-locus analysis module, a third-order system root-locus analysis module and a high-order system root-locus analysis module; the frequency domain analysis method experiment module comprises a typical link frequency response characteristic analysis module and a composite system frequency response analysis module; the system correction experiment module comprises a series connection lead correction module, a series connection lag correction module, a series connection lag-lead correction module and a PID correction module; the open experiment module comprises a water level control module, an elevator control module and a traffic lamp control module. By means of the virtual automatic control experimental system and the design method, a user can design and simulate an automatic control experiment, the efficiency of the automatic control experiment is improved, limitation of hardware equipment is avoided, an experimenter can conveniently have a study, and shortcomings in a traditional experiment are overcome.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
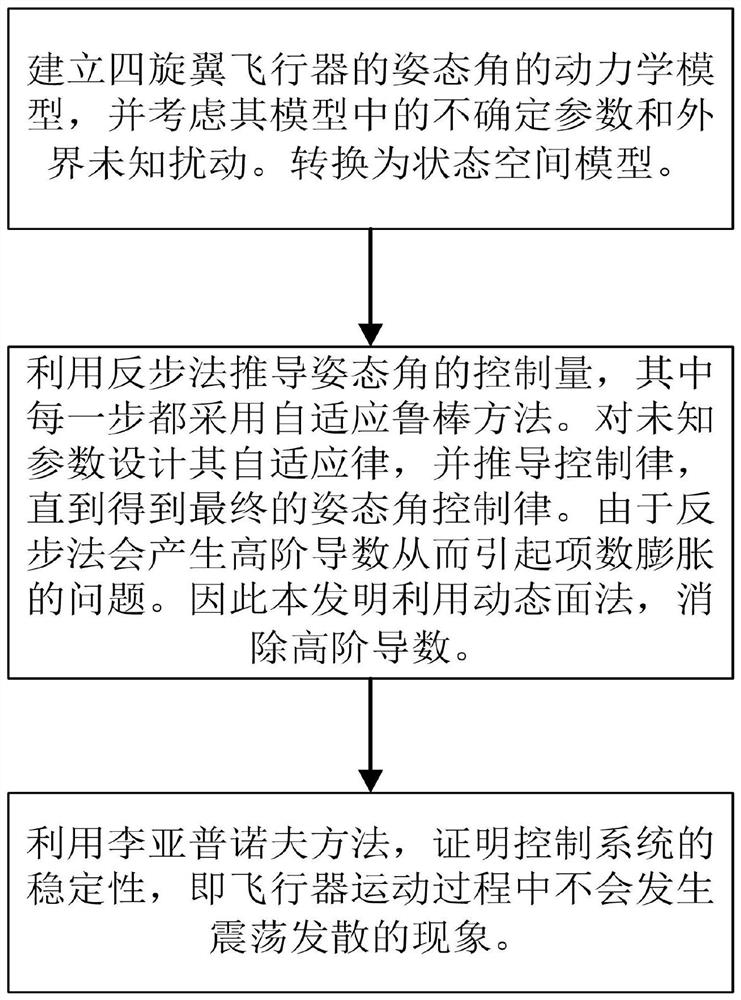
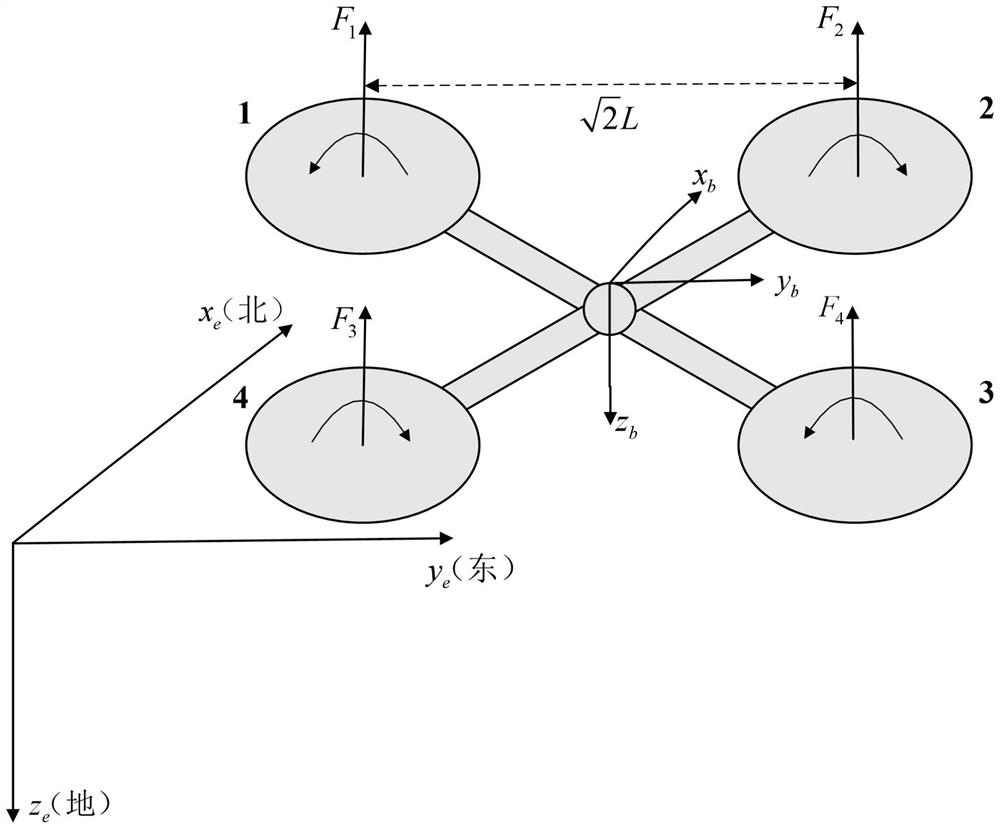
Attitude control method of rotorcraft
PendingCN112578805AEasy to adjustReduced accuracy requirementsAttitude controlSustainable transportationProportional integral differentialBackstepping
The invention relates to an attitude control method of a rotorcraft, which is used for controlling a pitch angle, a roll angle and a yaw angle of the rotorcraft, establishing a kinetic model of the attitude angle of the rotorcraft, estimating unknown parameters in the kinetic model in real time by using an adaptive method, compensating the uncertainty of the kinetic model, improving the robustnessof the control system by using a robustness method, and enhancing the anti-interference capability. Each attitude angle system is a second-order system, a backstepping method is adopted for derivation, derivation is sequentially carried out from the first order, a self-adaptive robust method is adopted for solving a result of each order, and finally the control law of the attitude angle is obtained. According to the method, the attitude angle is controlled by adopting a self-adaptive robust method, control parameters do not need to be accurately set like PID control (proportional-integral-derivative control), only the control parameters need to be large enough within a certain range, and parameter adjustment is simpler and more convenient; the requirement for the accuracy of the model isnot high, unknown parameters can be accurately estimated, and the tracking accuracy of expected signals is improved.
Owner:湖北航天飞行器研究所
Single input single output RCS interconnection circuit degradation method
InactiveCN1604092AHigh order reduction accuracyImprove numerical stabilitySpecial data processing applicationsNumerical stabilityInterconnection
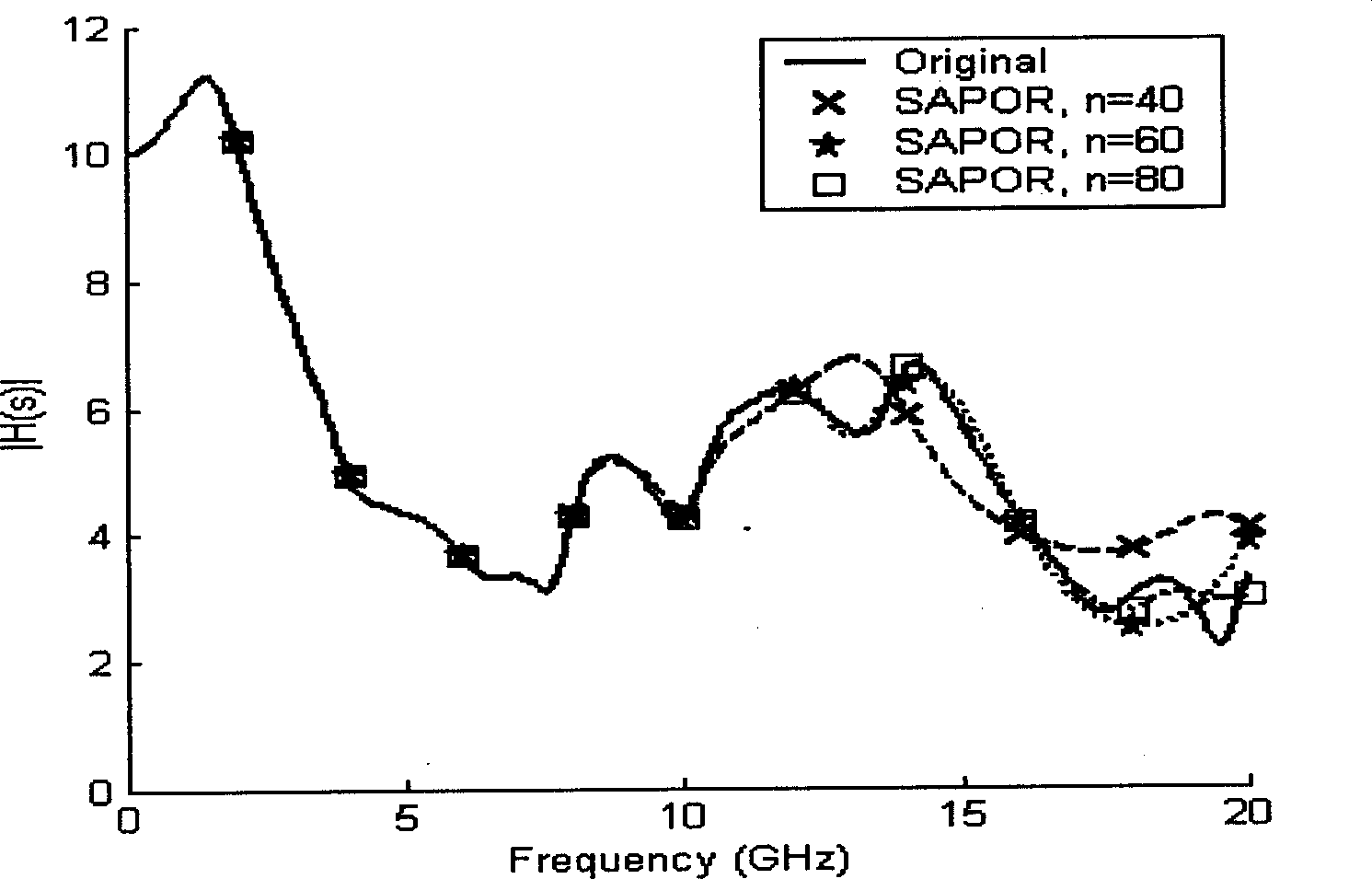
This invention belongs to electron technique field, which is in detail single input and output RCS connection circuit based on second order Arnoldi process. The method comprises the following steps: to form second order system, system frequency shift, system linearization, getting orthogonal matrix Q o f Krylov sub-space; finally to get N order deduction system. This invention is characterized by the following: it has high accuracy and ensures the data stability of the order deduction and has low computation and storage and ensures the passivity of the order deduction system.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
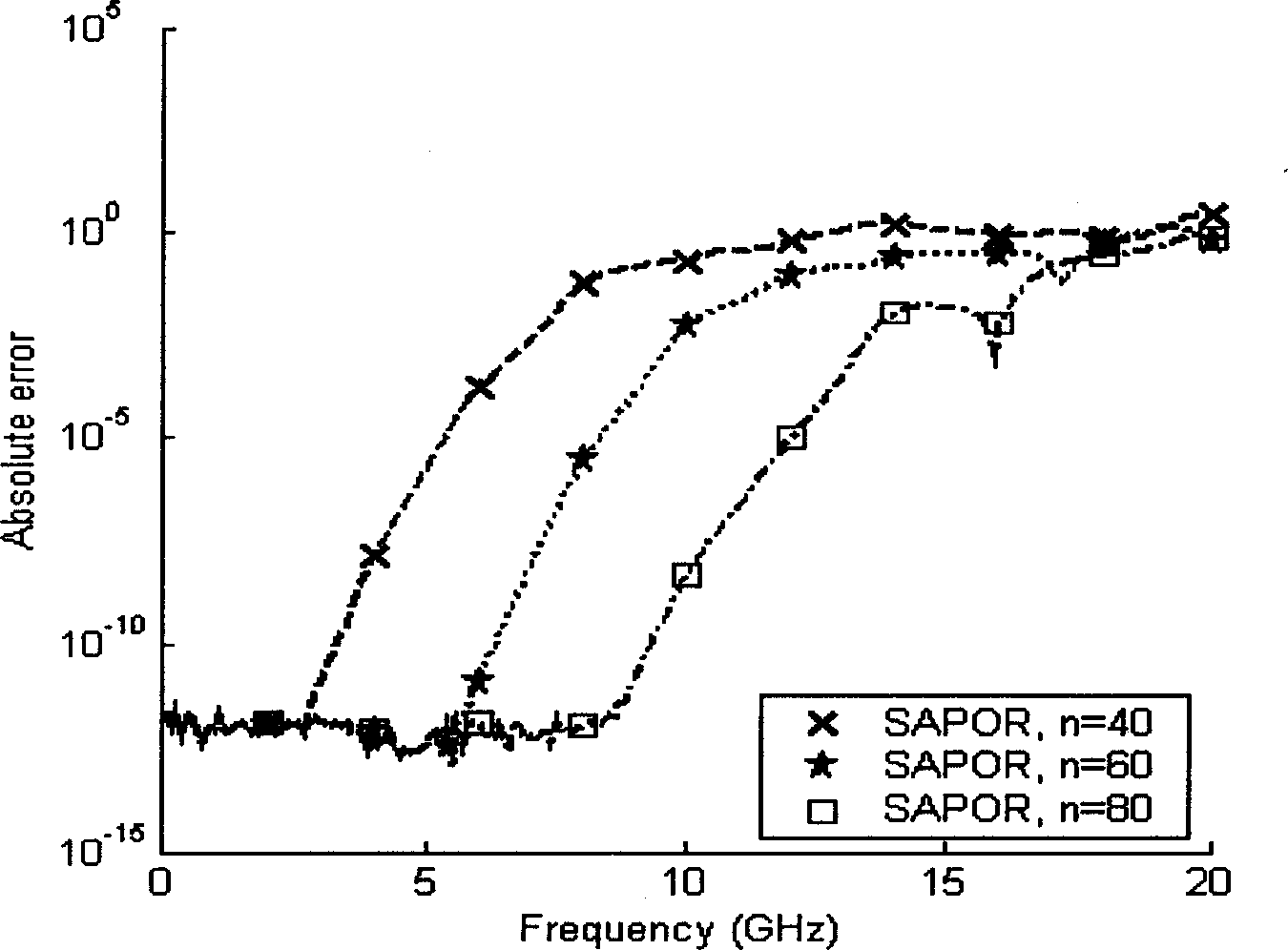
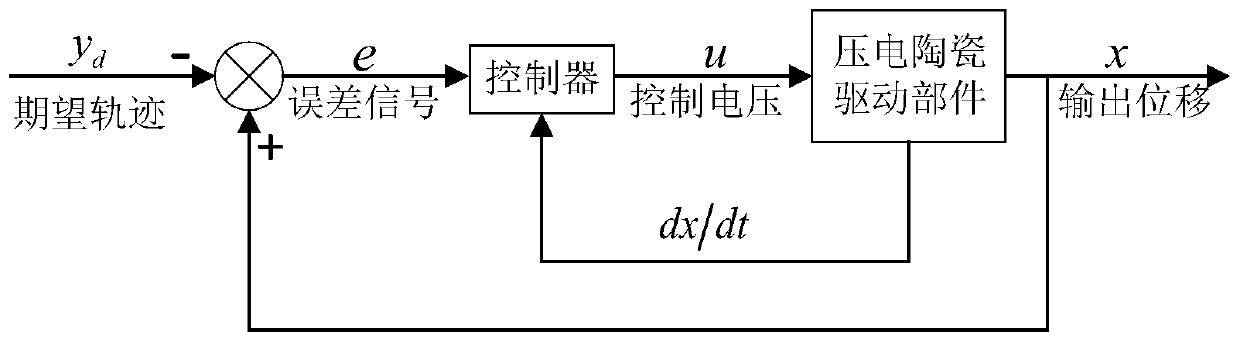
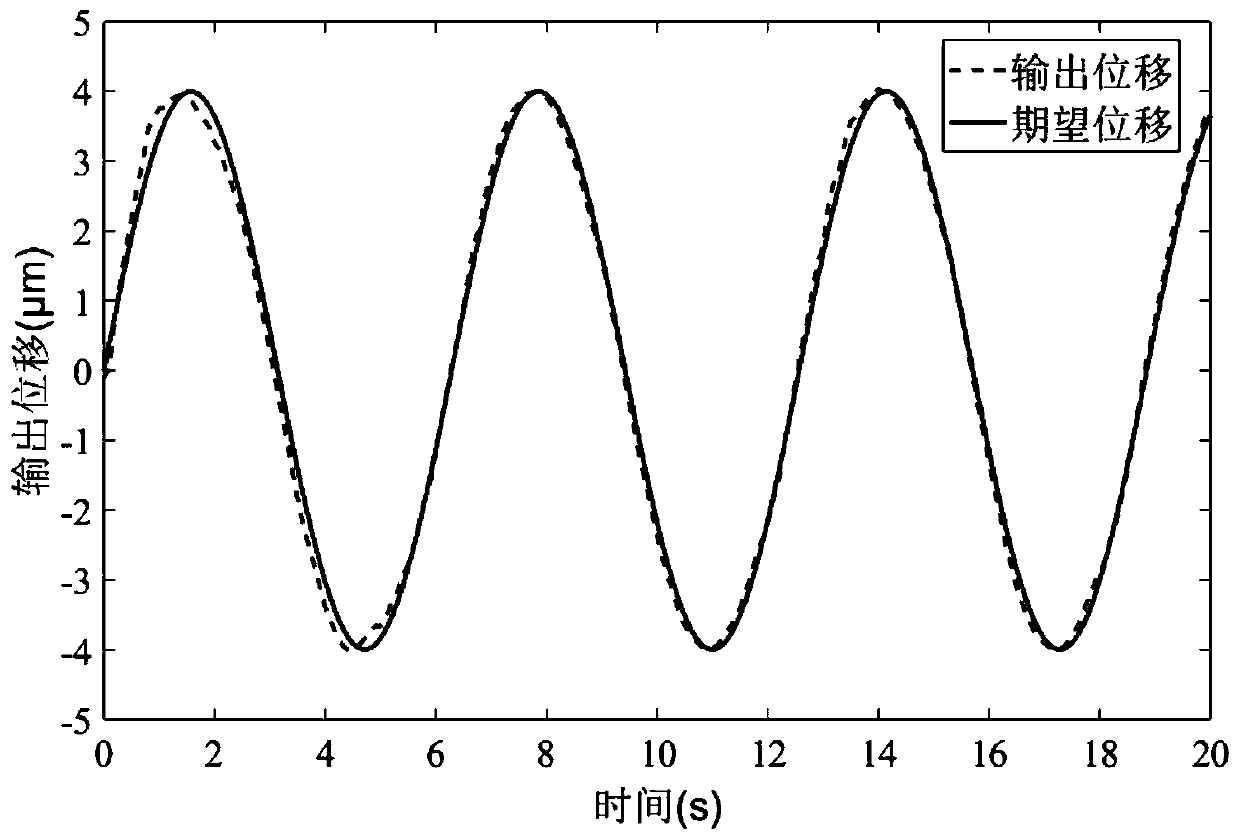
Robust adaptive control method for piezoelectric ceramic driving component in variable load environment
ActiveCN110045603AGuaranteed to be uniformly boundedSimple control structureAdaptive controlHysteresisElectricity
The invention discloses a robust adaptive control method for a piezoelectric ceramic driving component in a variable load environment; the method comprises the following steps as follows: establishinga piezoelectric ceramic driving system, setting a driven component to be a rigid load loaded in a vertical direction of the piezoelectric ceramic driving component, and measuring the output displacement by a laser displacement sensor, wherein the output displacement of the rigid load is consistent with the output displacement of the piezoelectric ceramic driving component; performing mathematicalmodel description on the variable-load piezoelectric ceramic driving component; and designing a robust adaptive controller. The robust adaptive control method considers uncertainties in the system and environmental disturbances, based on the mathematical model of the piezoelectric ceramic driving system in a loaded environment, a measurable-output second-order system with a hysteresis characteristic is used, a specified performance function is set to control system errors so as to achieve real-time adjustment of the robust adaptive controller output, so that high precision tracking driving accuracy of the piezoelectric ceramic driving platform to the input signal is ensured.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Precision high speed magnetic coil driver circuit
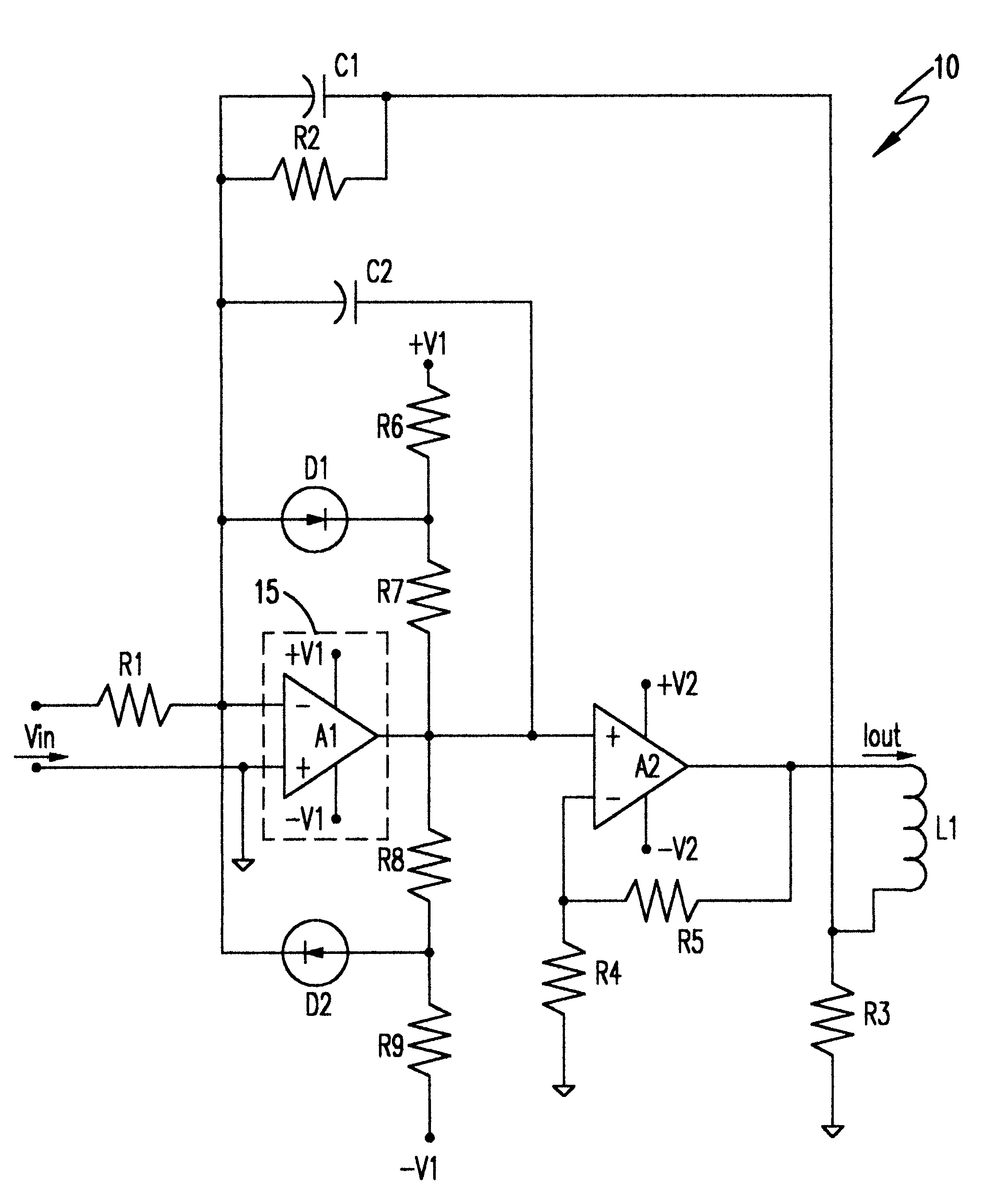
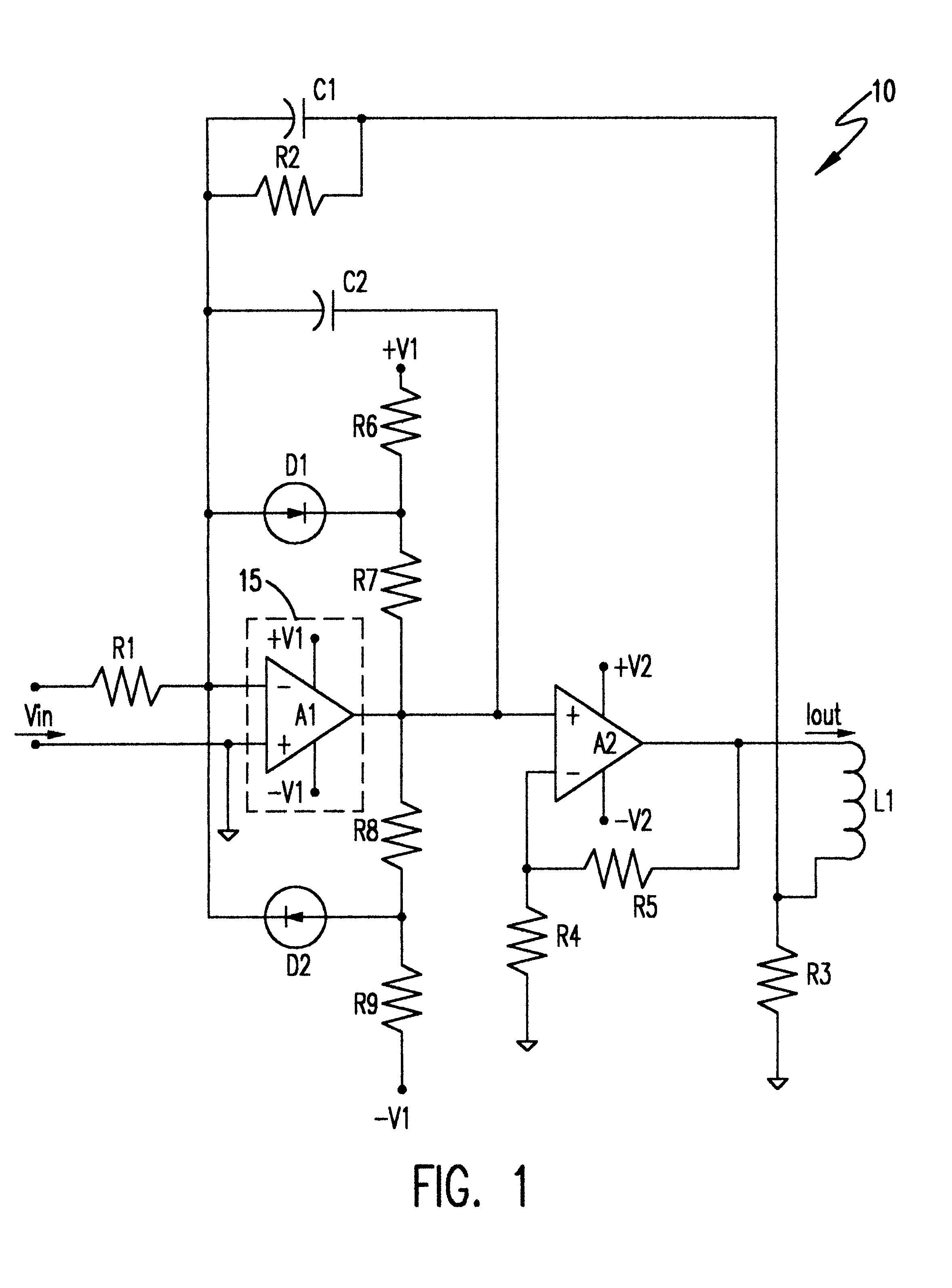
InactiveUS6388516B1Lower Level RequirementsShort timeNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsPulse automatic controlThermal isolationDriver circuit
Accuracy of correction of offset drift with temperature and noise are corrected in a high voltage, high current amplifier is improved by thermal isolation and / or temperature regulation of another amplifier having greater gain and connected to a different power supply in a closed loop feedback servo system. A clamping network connected to the higher gain amplifier to avoid hard saturation due to transient feedback signals from a reactive load, especially an inductive load, also prevents hard saturation of the high voltage, high current amplifier. An adjustable feedback circuit connected to the higher gain amplifier allows adjustment to obtain critical damping of a second order system and faster response to achieve proportionality of output current to input voltage with an accuracy of very few parts per million error and with minimum settling time.
Owner:IBM CORP
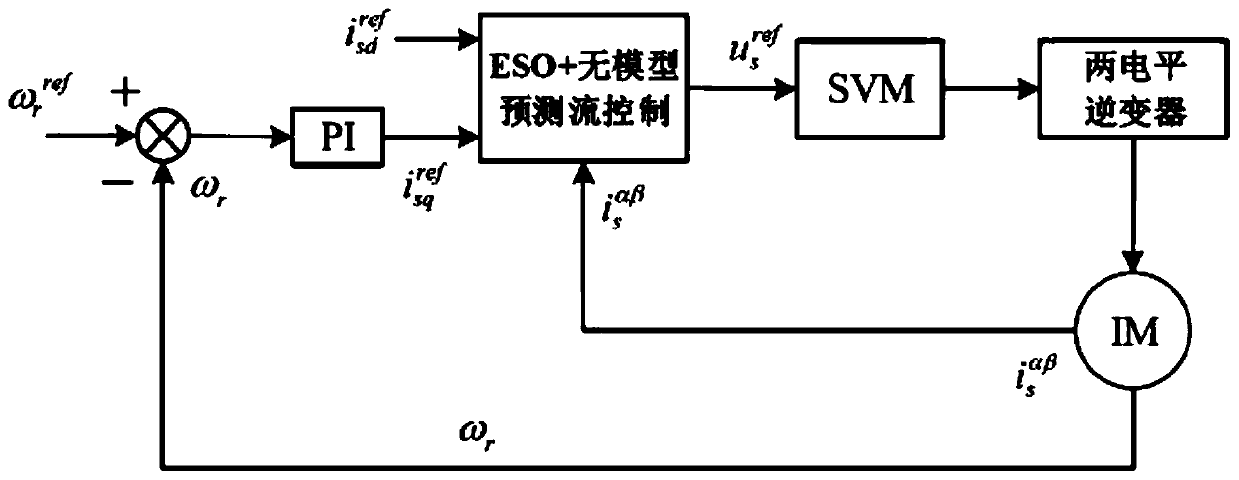
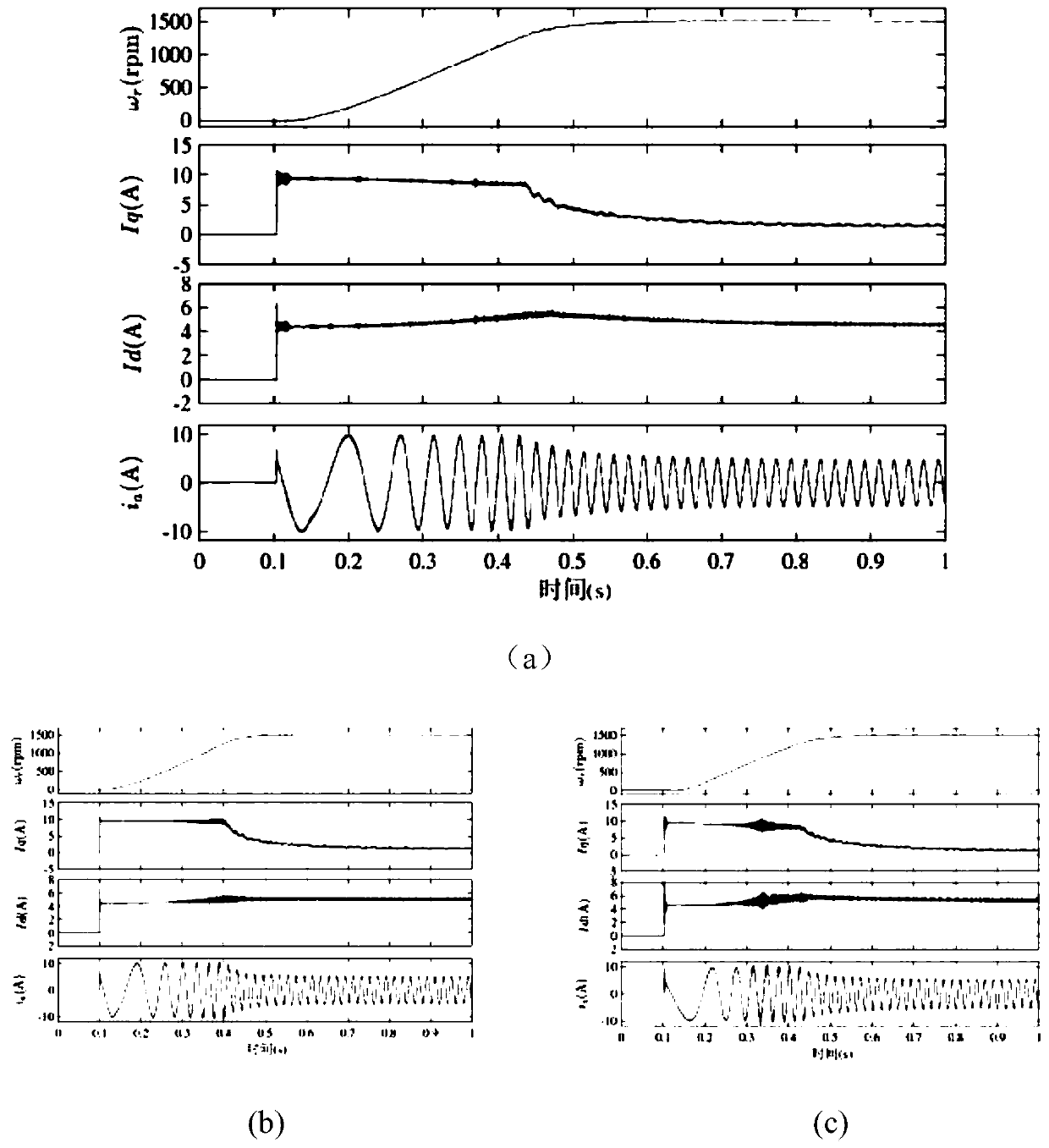
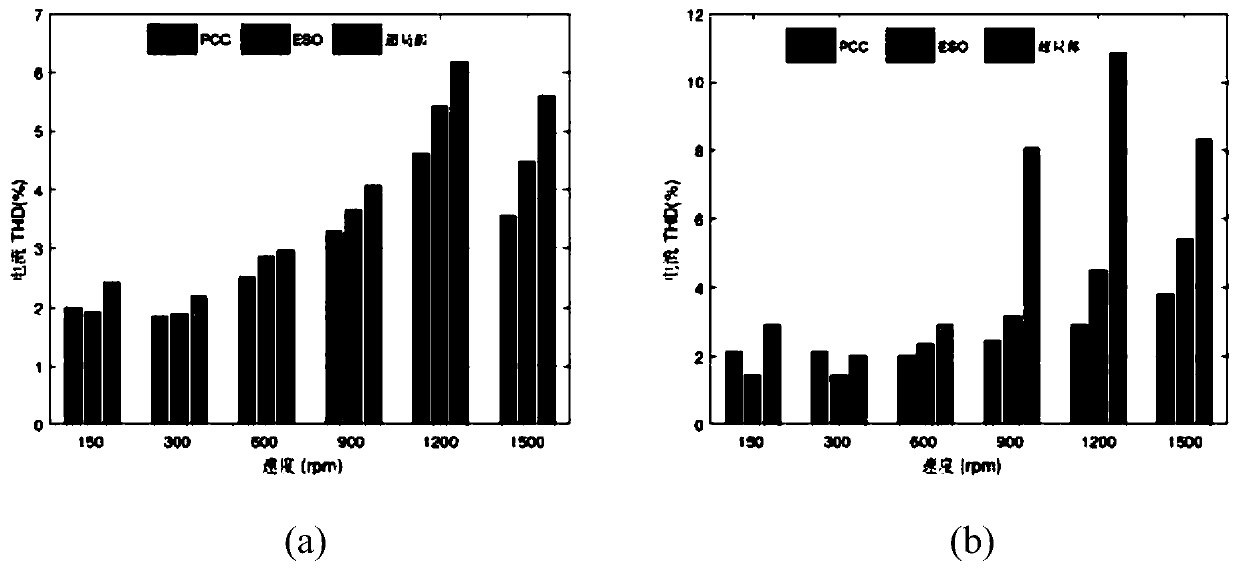
Model-free predictive current control method based on extended state observer
InactiveCN110601628AImprove robustnessImprove control performanceElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlState observerModel predictive control
A model-free predictive current control method based on an extended state observer is provided. The method comprises: writing a state equation of a second-order system, using a linear extended state observer and constructing a linear state observer equation; by combining a super-local model of current control of an asynchronous motor oriented based on the indirect magnetic field, designing a stator current linear extended state observer; discretizing the observer and choosing appropriate observation parameters to ensure the stability and good control performance of the observer; and writing the designed stator current linear extended state observer as the state equation to obtain an observation error of the observer, and obtaining a characteristic equation of the extended state observer soas to set reasonable observation parameters. According to the model-free predictive current control method based on an extended state observer provided by the present invention, current control without any motor parameter is realized, and the robustness of the model predictive control (MPC) to the motor parameters is greatly improved.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Stability distinguishing method of wide-area power system under influence of section variable-time delay
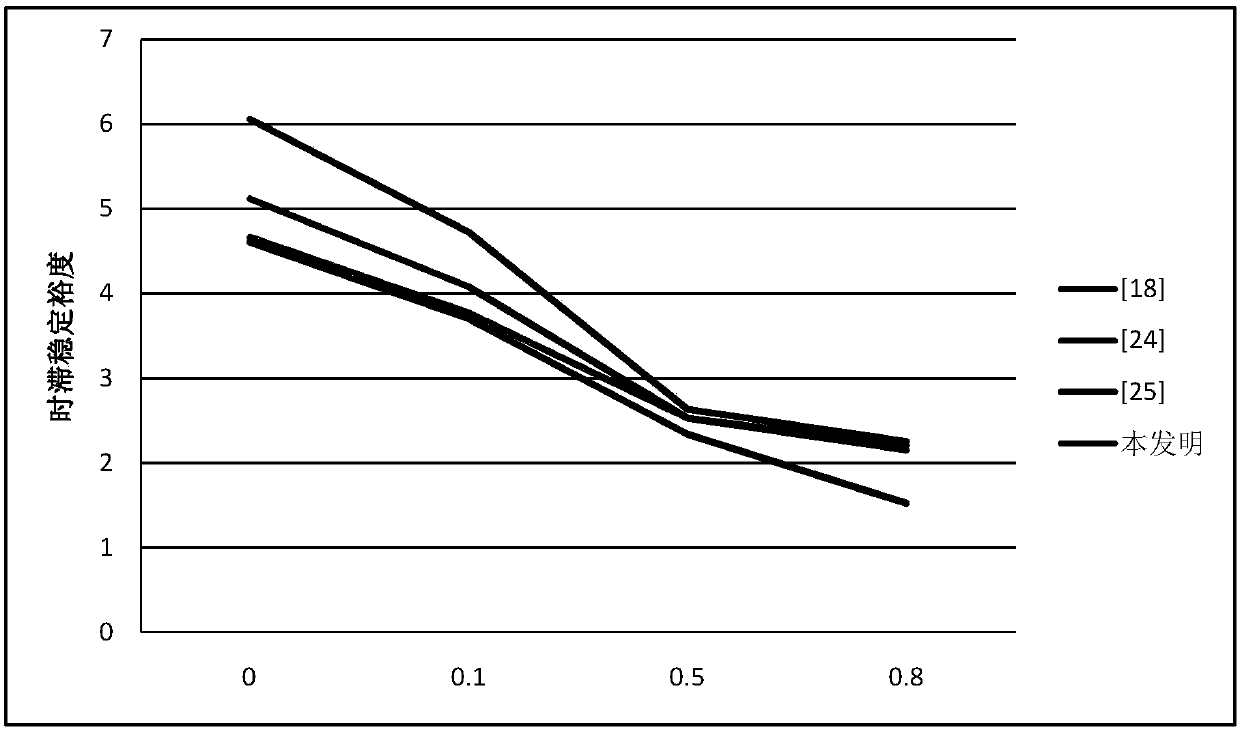
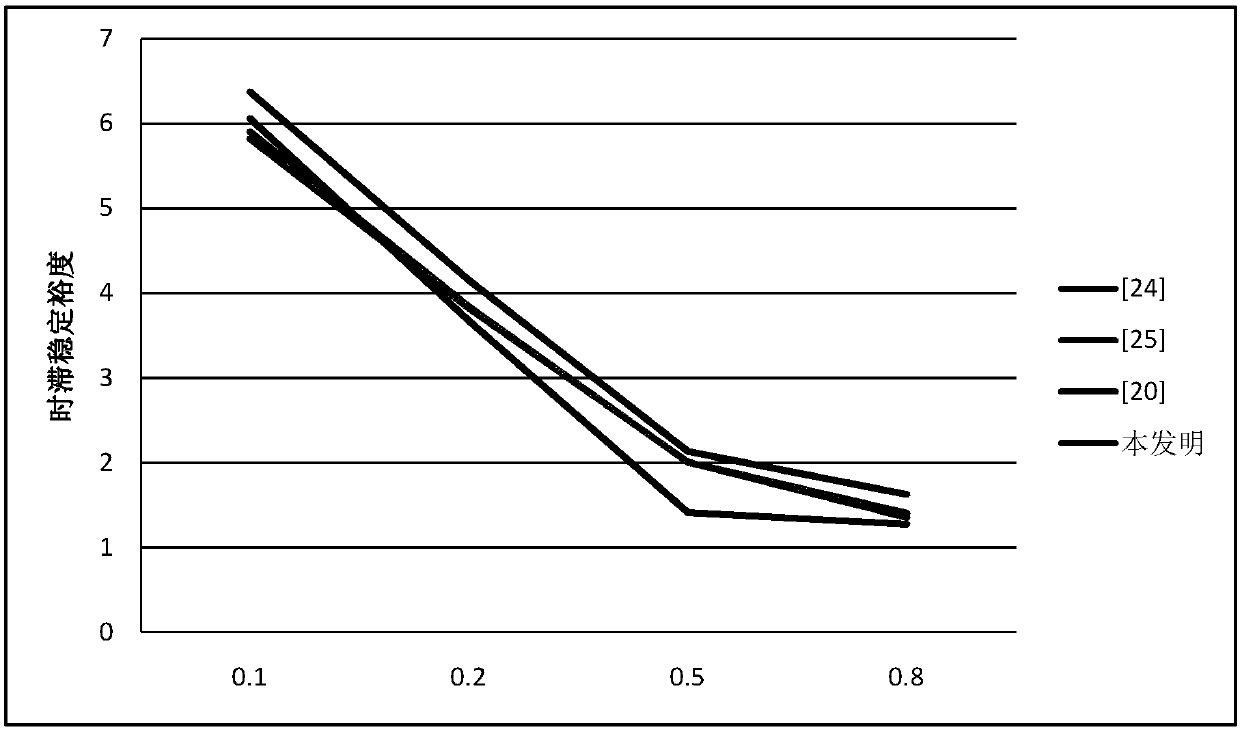
ActiveCN108092268ATake advantage ofReduce conservatismAc network circuit arrangementsSystem of imprimitivityWide area
The invention discloses a stability distinguishing method of a wide-area power system under influence of section variable-time delay. According to the stability distinguishing method, a novel augmentation vector and Lyapunov-Krasovskii functional construction method is proposed on the basis of building a wide-area section variable-time delay power system model with regard to serious influence of atime delay phenomenon on stable running of the wide-area power system; an error generated during the resolving process is reduced by employing methods of time delay partition, Wirtinger integral inequality, Free-matrix-based integral inequality and convex combination during resolving of a functional derivative to obtain a stability criterion with relatively low conservation property, and the stable running region of the system is expanded; and finally, compared with an existing method, the method has the advantage that the stable running region of the system is expanded by typical simulationanalysis of a second-order system, a single-machine infinite system and a four-machine eleven-node system.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Method and device for detecting ice thickness
InactiveCN110017800AFast solutionExtend working lifeUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansWork patternWorking life
The invention discloses a method and device for detecting ice thickness. The method comprises the following steps that a sensor is equivalent to an underdamped second-order system; only when it is required to detect the state information of the ice thickness, a pulse excitation signal is input to the sensor to detect and analyze an output response signal of the sensor system to the pulse input excitation signal; since the ice thickness of the surface of the sensor will change the basic parameters of the second-order system to varying degrees, a plurality of characteristics of the output response signal of the sensor system will change accordingly, and the information of the ice thickness can be obtained by detecting and analyzing the changes of these characteristics; and by applying the input pulse excitation signal to the sensor system, several different modes of operation can be selected. The method and device for detecting ice thickness can greatly prolong the working life of the sensor, realize accurate and reliable detection of the icing thickness by detecting various characteristics of the output response signal of the sensor, and have a plurality of different modes of operation available for selection such that the application of the sensor is more flexible and convenient.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Teaching experiment system for automatic control principle
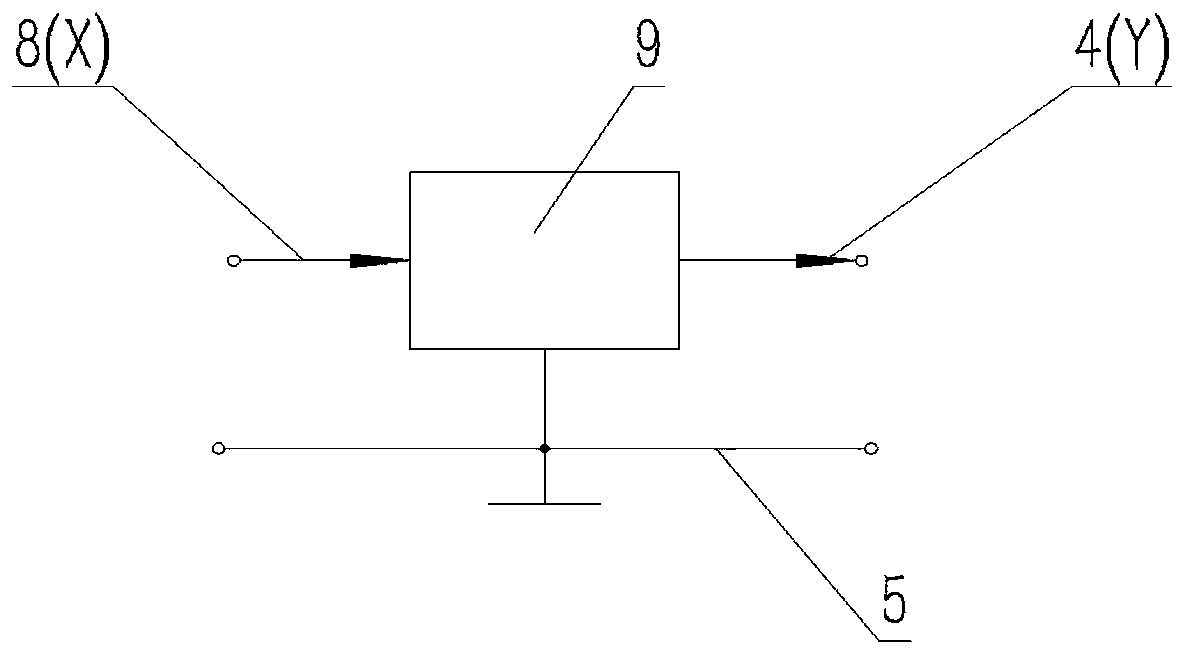
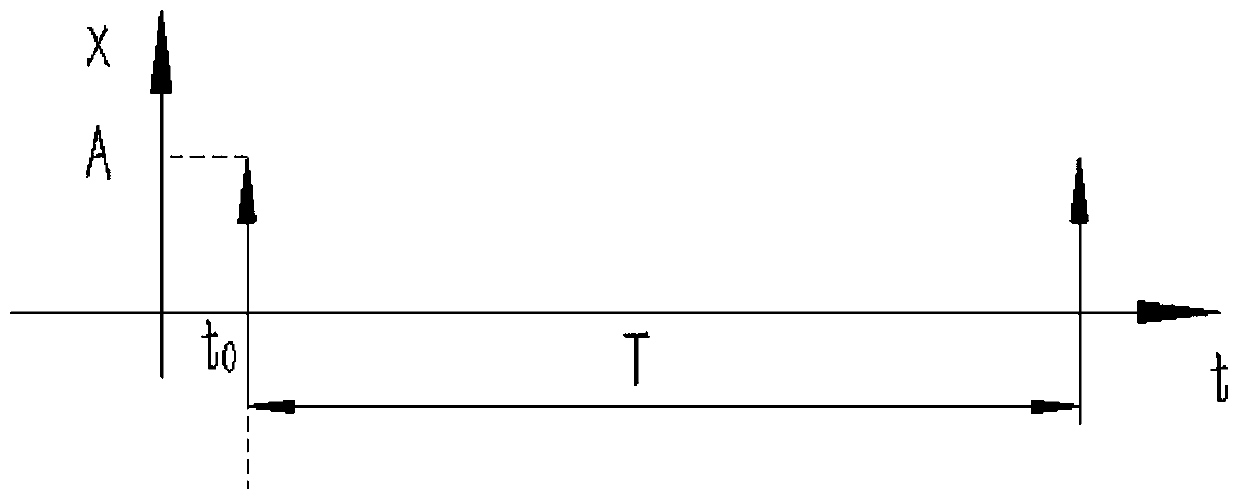
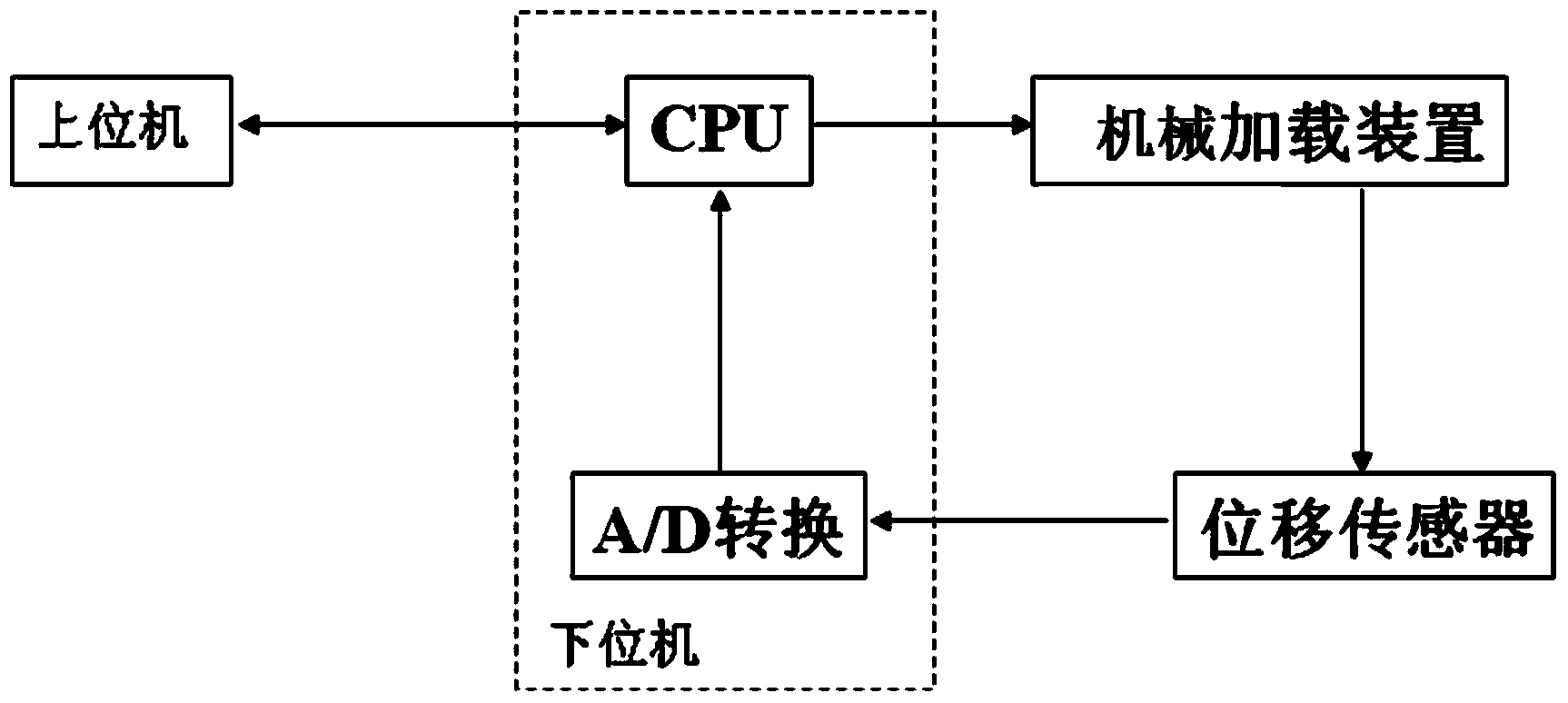
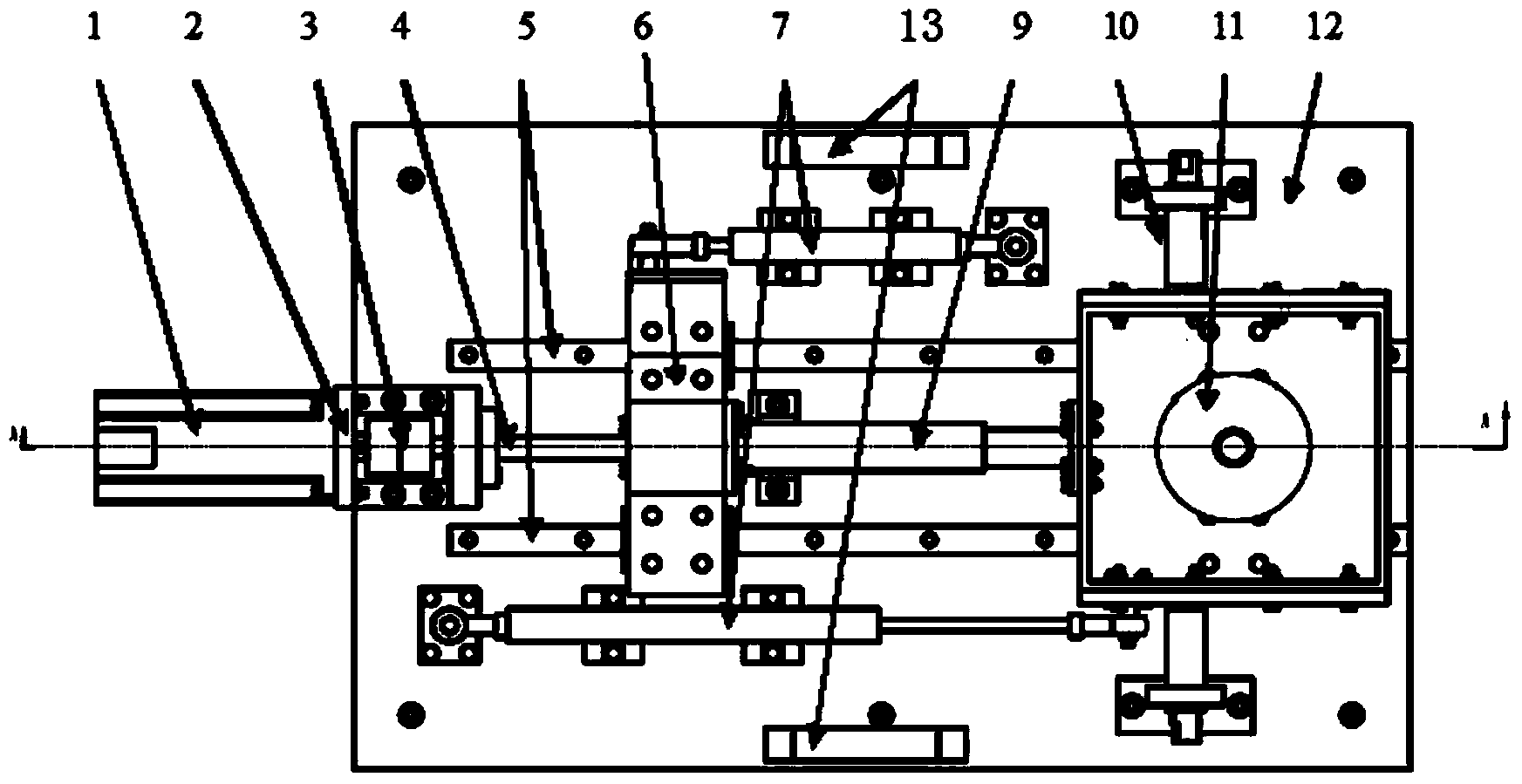
InactiveCN103854548AImprove teaching qualityImprove understandingEducational modelsSystems designAutomatic control
The invention discloses a teaching experiment system for the automatic control principle, and belongs to the field of teaching experiment system designing. The teaching experiment system comprises a mechanical loading device, a lower computer, two displacement sensors and an upper computer. The lower computer comprises a CPU and an A / D conversion module, wherein the upper computer, the CPU, the mechanical loading device, the two displacement sensors and the A / D conversion module are connected in sequence; the two displacement sensors and the CPU are respectively connected with the A / D conversion module. According to the teaching experiment system, as a mechanical device is adopted to form a typical second-order system serving as a controlled object, the operation state of an actual system under different controlled conditions can be observed by students, and intuitional instruction and theory and practice combination are facilitated. Besides, the teaching experiment system has important significance for improving laboratory teaching quality and strengthening understanding of the control theory and control engineering for the students.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Order reducing method of higher-order mathematical model for water turbine regulating system
ActiveCN104408330AEasy to implementThe de-escalation results are accurate and reliableSpecial data processing applicationsLoad stepMathematical model
The invention relates to an order reducing method of a higher-order mathematical model for a water turbine regulating system. The order reducing method comprises the following steps: a. simplifying the highest-order term of a system denominator, and achieving primary order reduction of the system to obtain a primary lower-order equivalent system formula; b. from the angle of fluctuation superposition, transforming the primary lower-order equivalent system formula into a form that two second-order subsystems are added; c. performing an Laplace inverse transform to obtain a unit rotating speed response wave equation of the primary lower-order equivalent system of the water turbine regulating system under load step disturbance; d. performing secondary order reduction on a complete fifth-order system formula; e. performing influence factor analysis of rotating speed response regulating quality of the water turbine regulating system by using a second-order system. The order reducing method has the advantages that compared with other order reducing methods, by the method, starting from the complete fifth-order system, all parameters and influence factors of the system are contained, and the later regulating quality analysis with reliable guarantee is provided.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Unmanned aerial vehicle flexible flight dynamics analysis method considering complex wind field
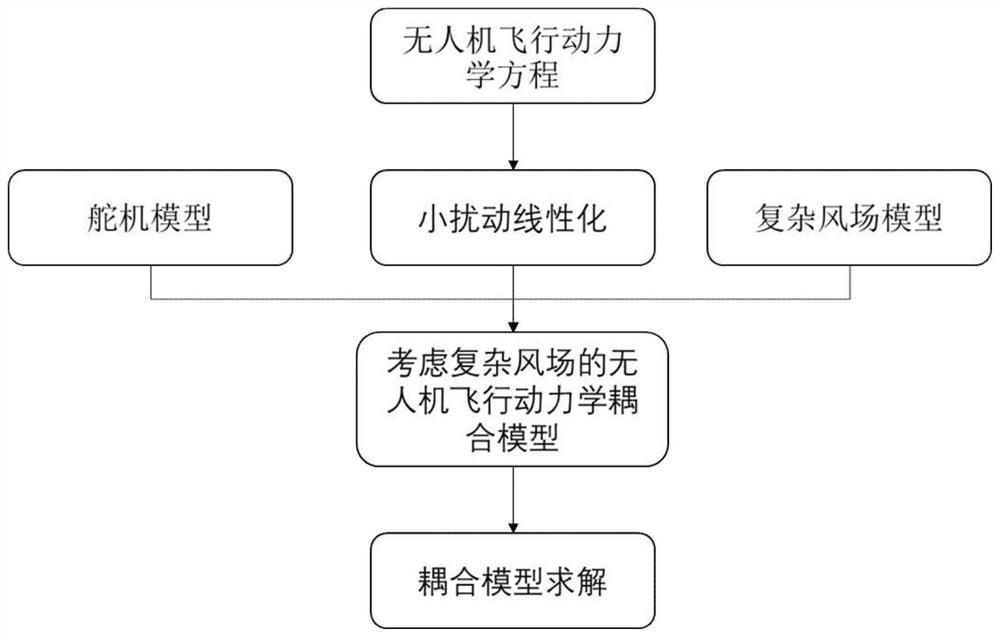
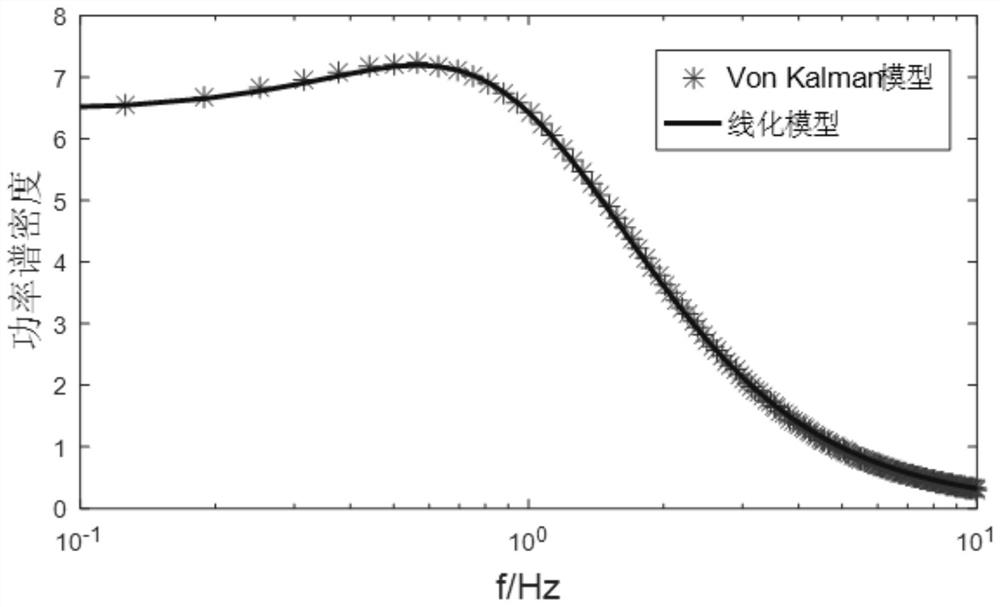
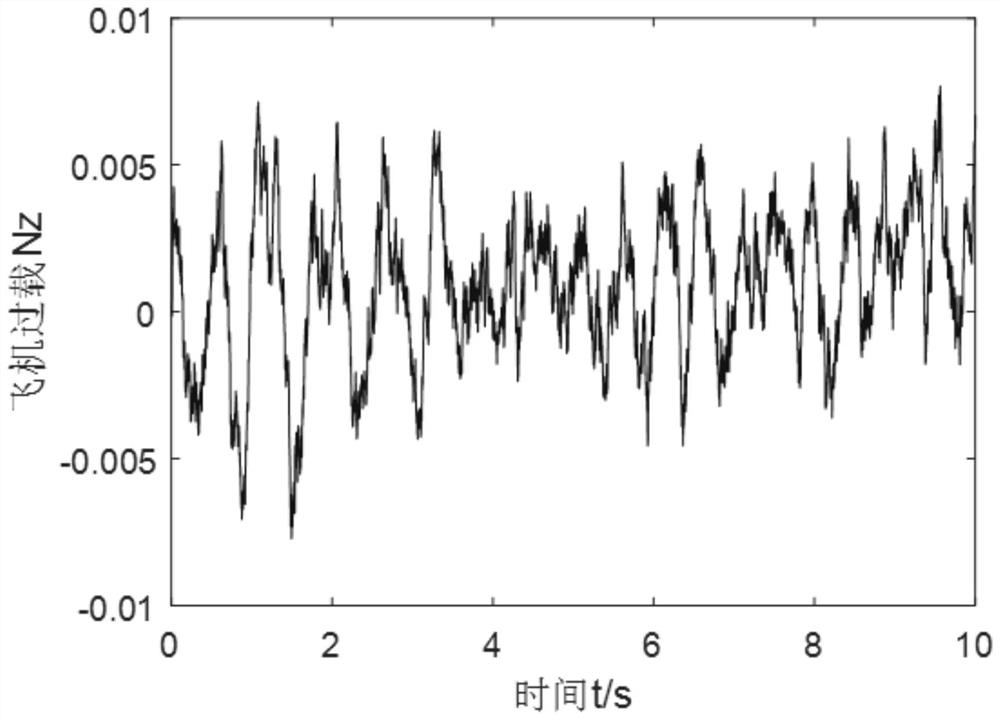
ActiveCN113761811ASustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationModal truncationClassical mechanics
The invention discloses an unmanned aerial vehicle flexible flight dynamics analysis method considering a complex wind field. The method comprises the following steps: establishing an unmanned aerial vehicle flight kinetic equation by using an average shafting theory; carrying out trimming linearization on the equation under the hypothesis of small disturbance, and establishing a wing elastic motion equation under modal coordinates based on a modal truncation method; utilizing a second-order system to simulate the reaction process of a steering engine to convert a transfer function of a steering engine model into a state space form, so that a flight dynamics model, an atmosphere model and the steering engine model in the state space form are coupled to obtain the gust response of the unmanned aerial vehicle.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Multi-agent system consistency achieving method based on cell decomposition
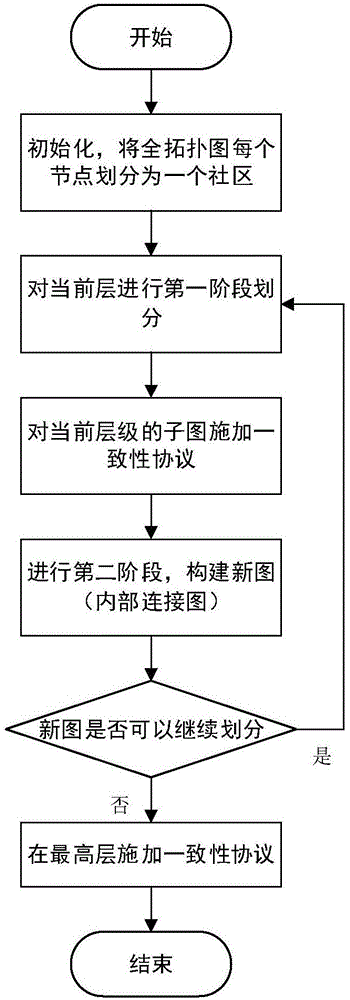
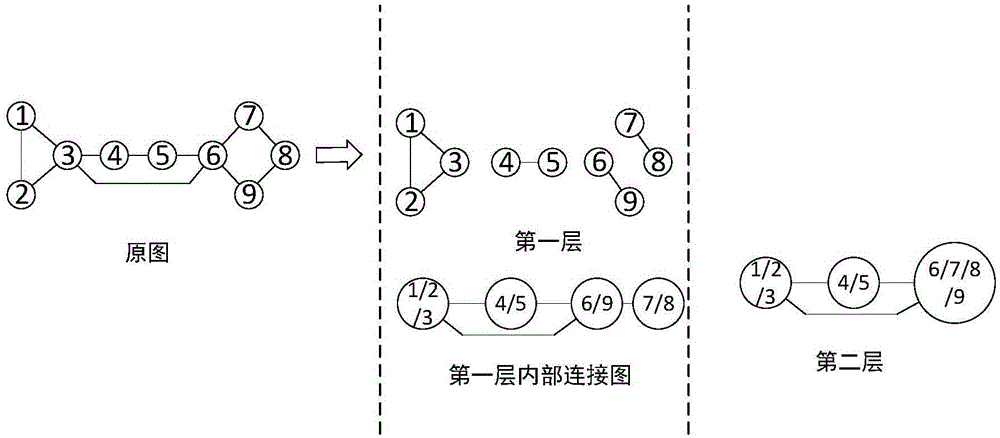
InactiveCN105138768ADo not change topologyDoes not change connection weightsSpecial data processing applicationsCommunity basedDecomposition
The invention discloses a multi-agent system consistency achieving method based on cell decomposition, and belongs to the technical field of multi-agent systems. By means of the multi-agent system consistency achieving method based on cell decomposition, the multi-agent system consistency convergence speed is increased, the problem that a consistency convergence speed increasing method is difficult to implement in actual application is solved, and the problem of a single-layer topology is converted to the problem on a multi-layer topology to be solved on the premise of neither changing a multi-agent topology relation nor changing connecting weight. Meanwhile, the method has the good improvement effect on a first-order system and a second-order system. The multi-agent system consistency achieving method is applied in wide-range engineering application based on a ground unmanned trolley system, an unmanned aerial vehicle system, a self-organization underwater fleet, a satellite group and the like, and has the practical significant in better application.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com