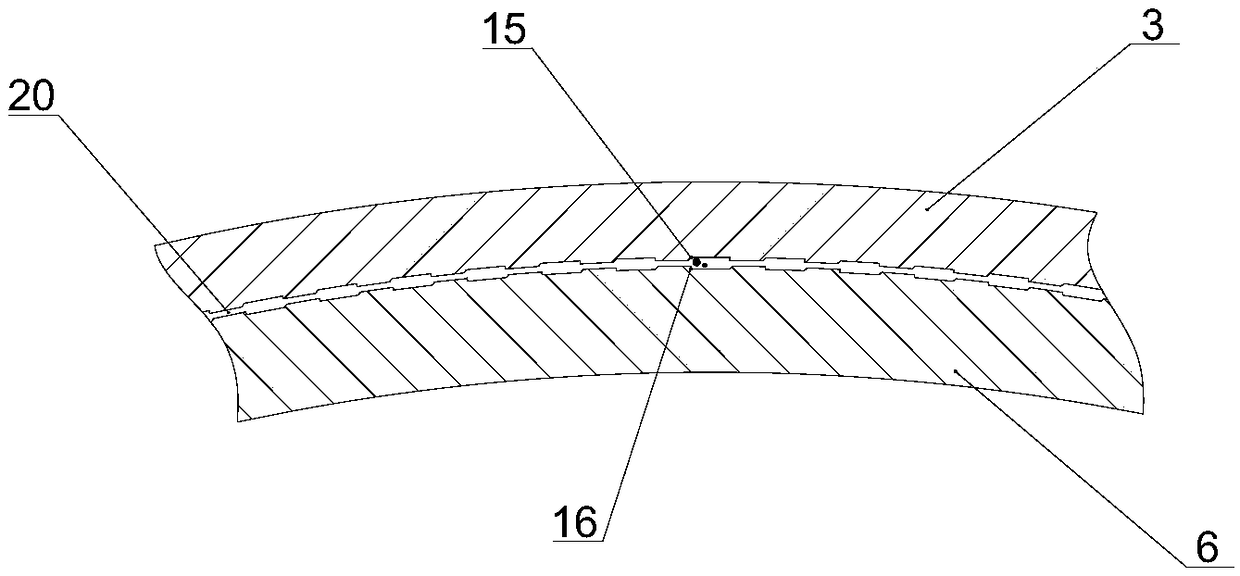
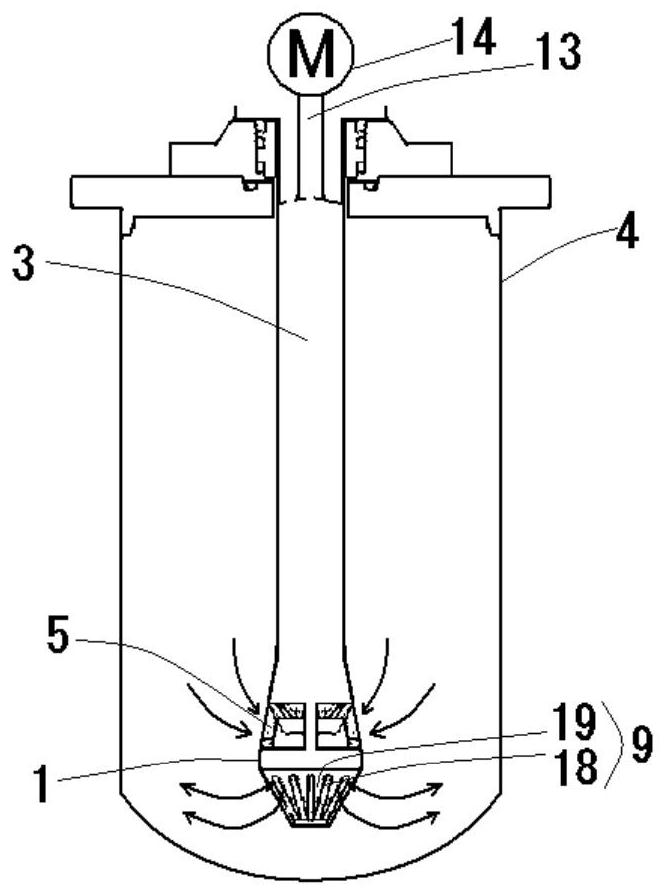
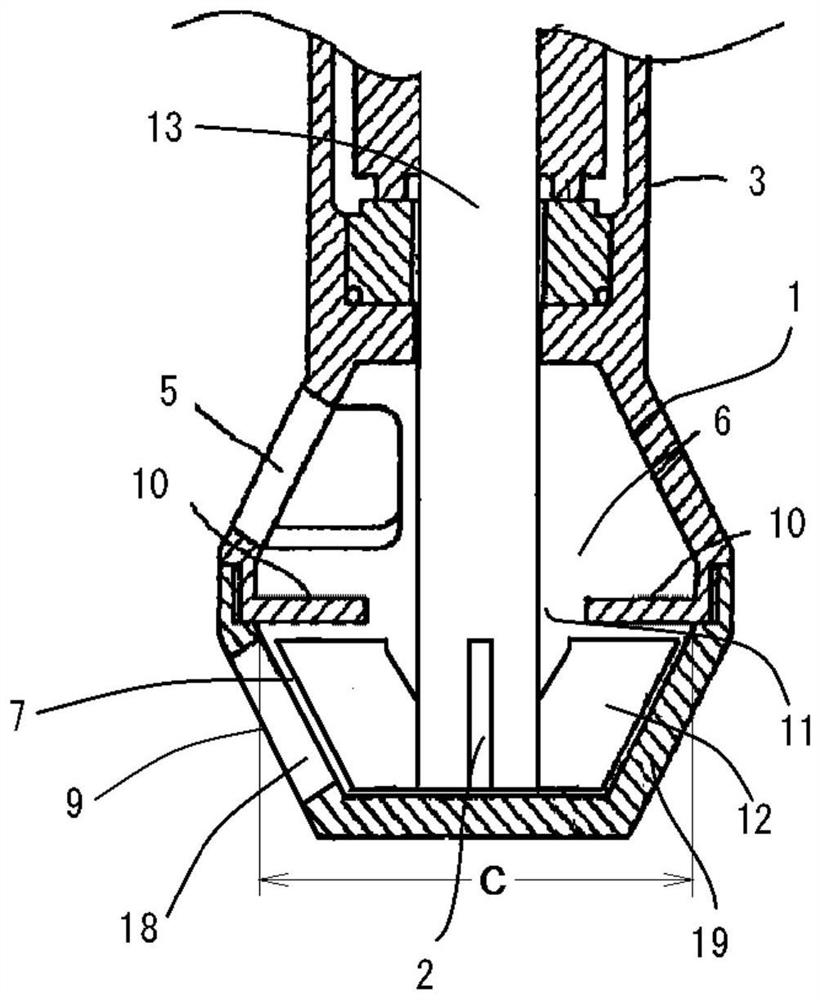
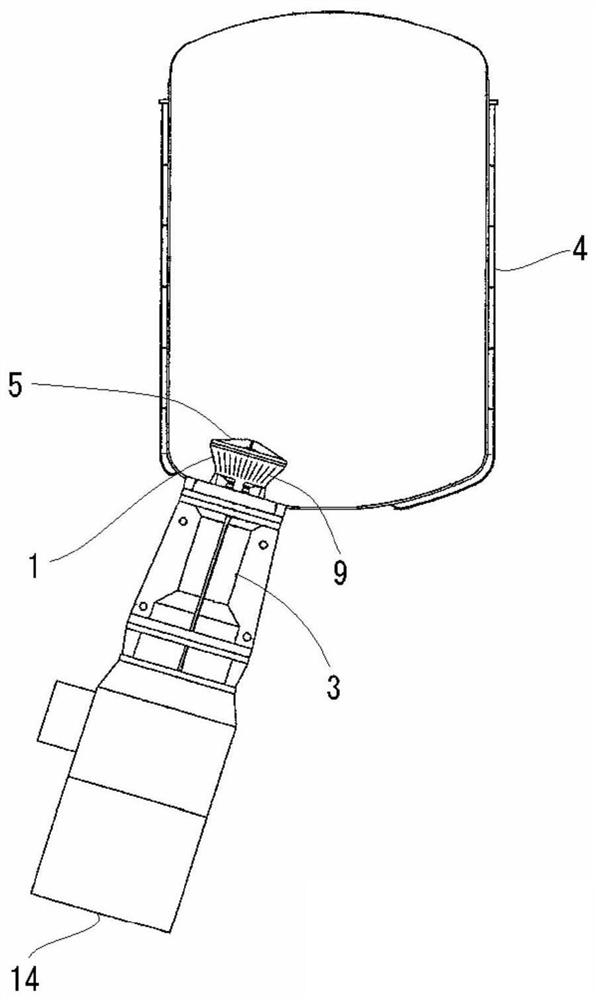
Patents
Literature
45results about How to "Effective shear" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Preparation method of animal peptone by double-enzyme enzymolysis
ActiveCN102827911AVitality is stable and easy to controlIncrease the depth of hydrolysisFermentationLaboratory cultureChemistry
The invention provides a preparation method of animal peptone by double-enzyme enzymolysis and belongs to the technical field of biological products. Fresh ox bone and animal tissue and entrails are taken as the raw materials and are subjected to deep hydrolysis by adopting pancreatin and compound protease under a weak base condition, and then the technical measures of separation and purification and the like are carried out to obtain a peptone of which the molecular weight is steadily kept between 2000 and 2500 and of which the amino acid content is balanced. The characteristics of high efficiency, specifity, distribution cooperativity, environment friendliness and the like obtained through catalytic hydrolysis by pancreatin and compound protease are fully utilized, so that stability and the high quality of various performance indexes of products are effectively ensured. The obtained peptone does not precipitate and is not muddy in the presence of acid and base and the peptone is not solidified and keeps completely clear at a high temperature. The peptone can be used as the main raw material of high-grade microorganism mediums and can completely replace imported products.
Owner:PINGLIANG HUAKE BIOLOGICAL TECH
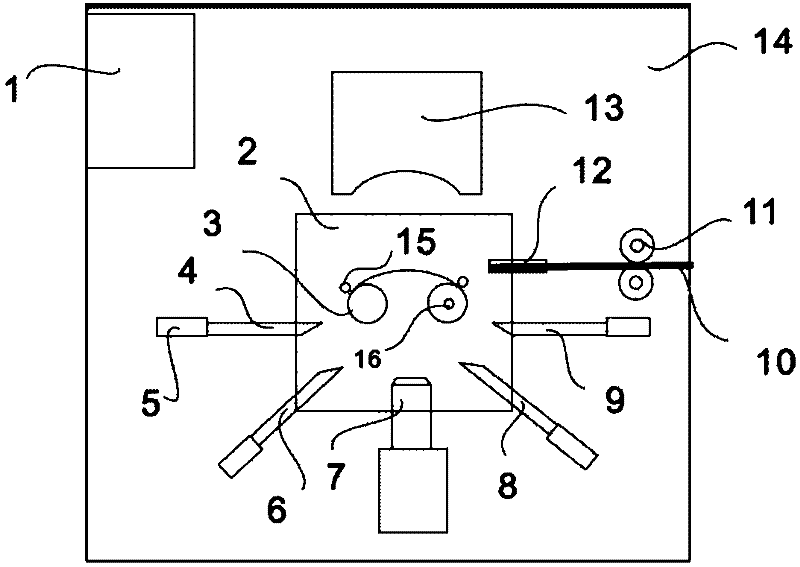
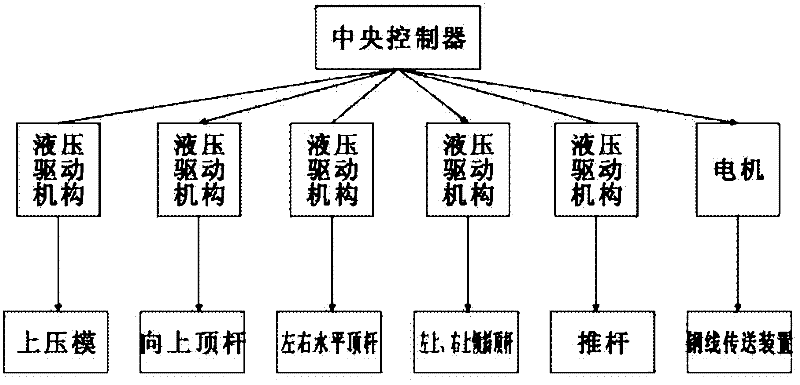
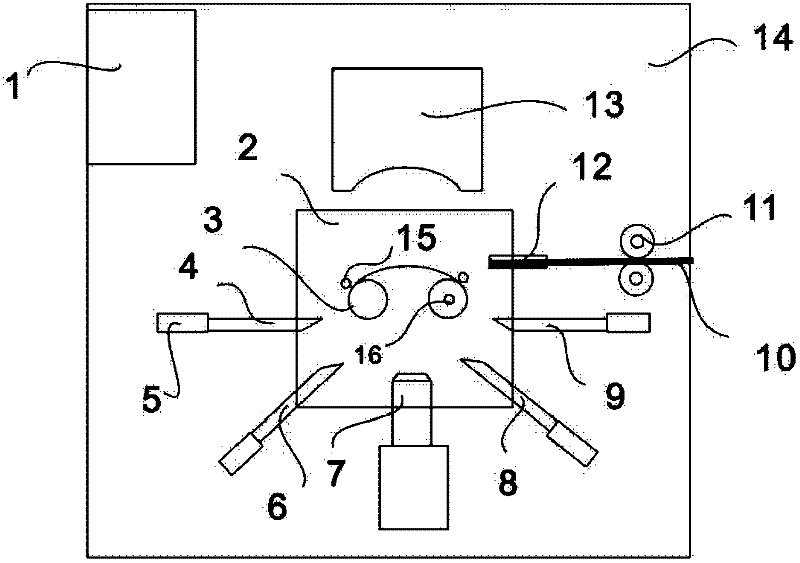
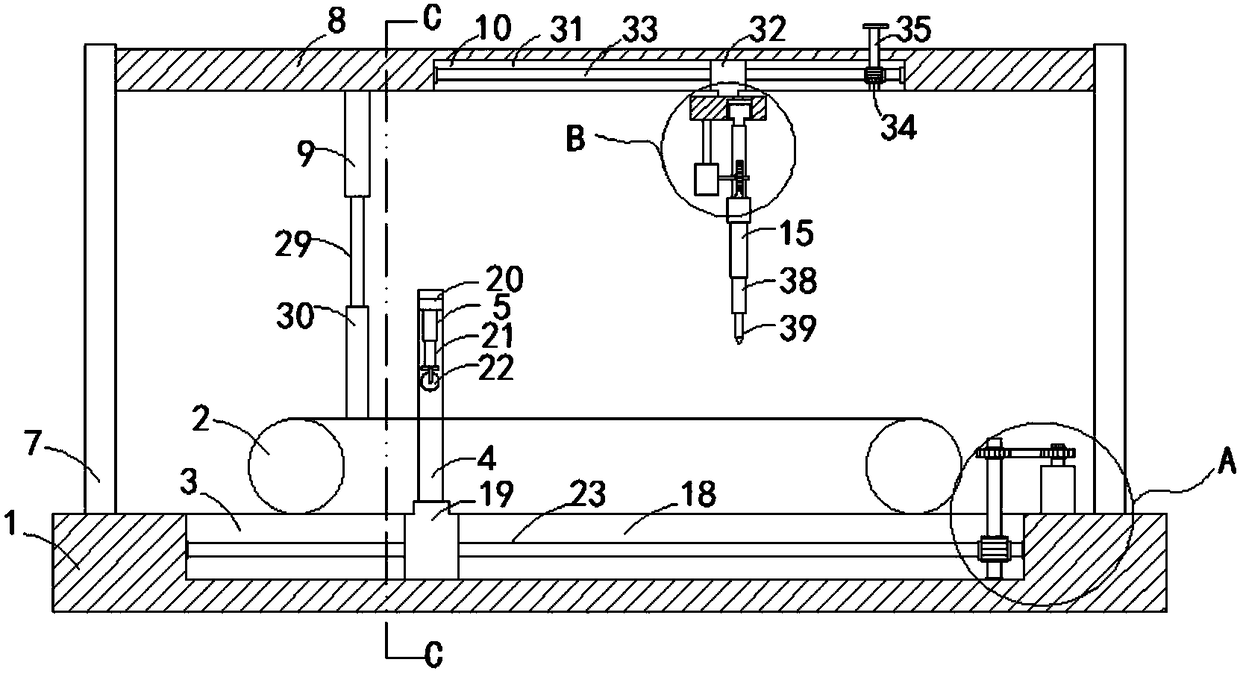
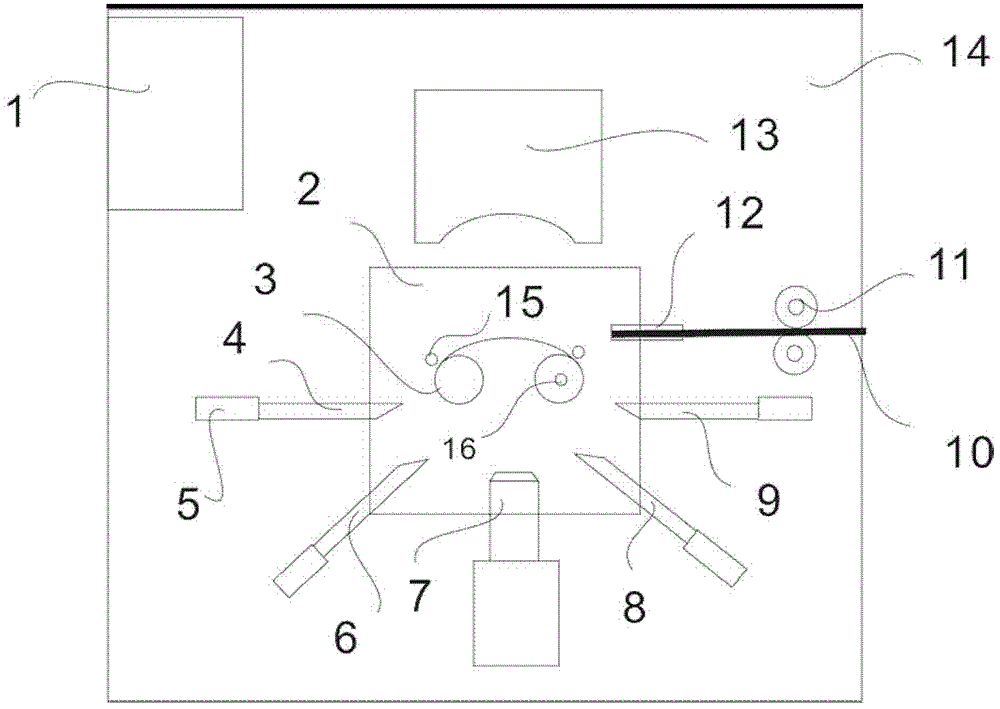
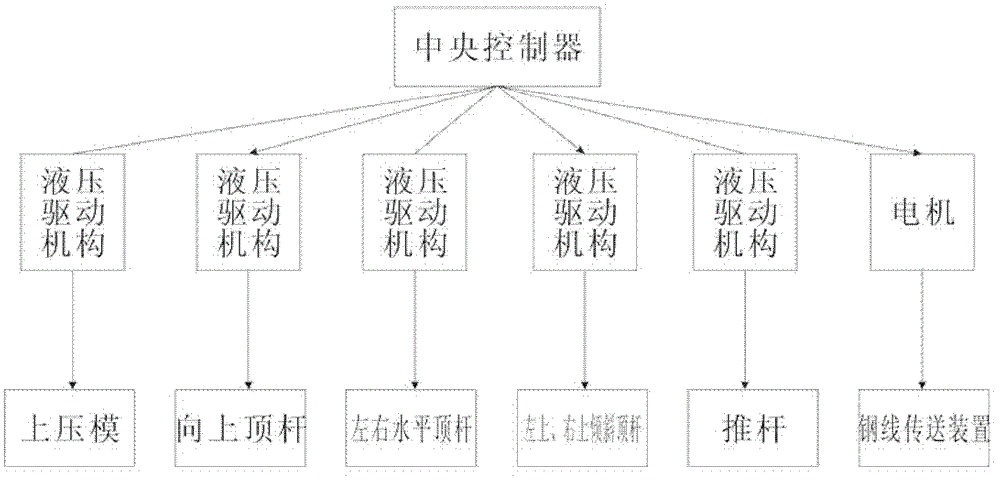
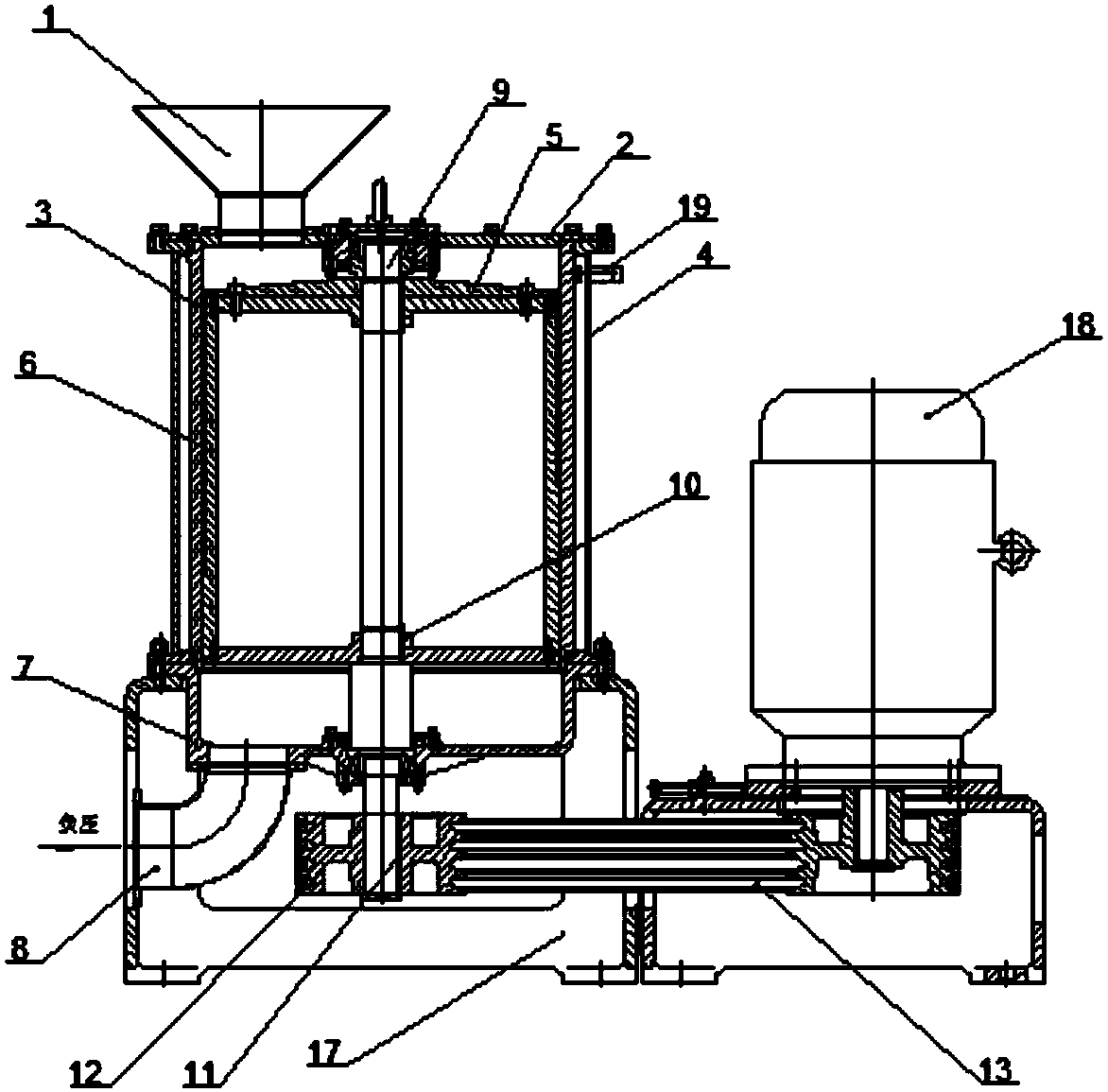
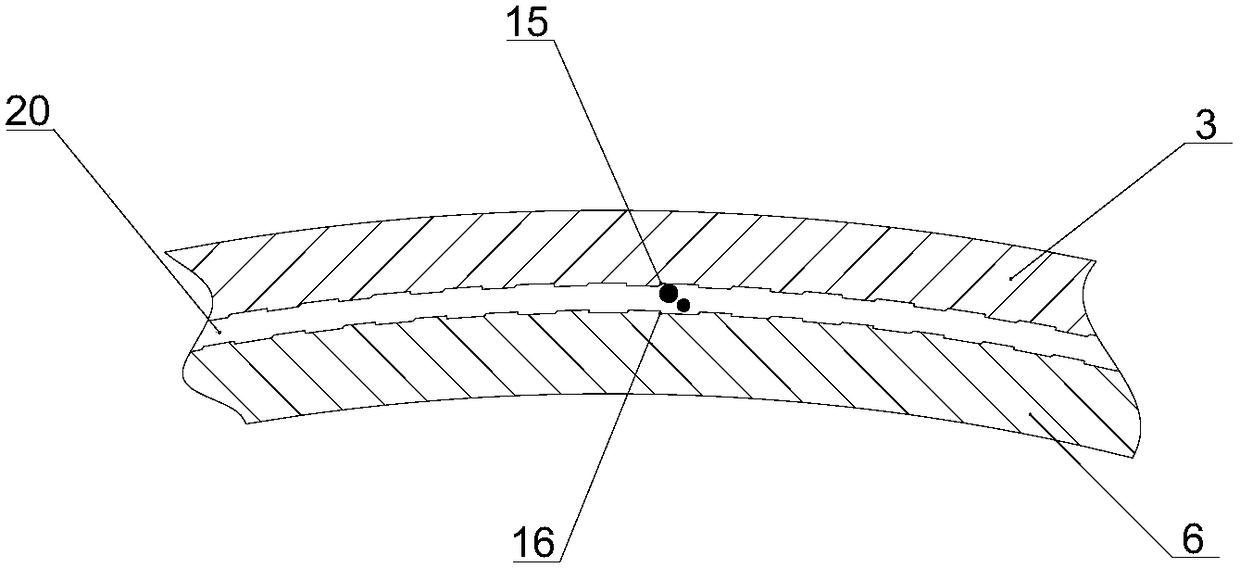
A device for making steel wire gardening hooks
The invention relates to equipment for manufacturing gardening products, in particular to equipment for manufacturing a steel wire gardening hook. The equipment comprises a working platform, a working base, a lug boss-shaped core mould and a steel wire conveying device, wherein an upper compression mould is arranged right above the core mould; a forming mandril group composed of mandrils is arranged below the core mould; hydraulic driving mechanisms of the upper compression mould and each mandril as well as a driving mechanism of the steel wire conveying device are respectively connected to acentral controller internally installed with a steel wire gardening hook forming program by means of electric execution units. By adopting the structure, a steel wire can be effectively sheared, and gradually pressed and reshaped into a qualified steel wire gardening hook, and no heating treatment is required; and the steel wire is subjected to one-step machining and shaping, so that the labour efficiency is improved and the danger is reduced; and a discharging conductor used for penetrating through and hanging the gardening hook is fixedly arranged on the surface of core mould parallel to the working platform, and a push rod is arranged on the working base close to the edge of the periphery of the core mould; and the equipment is capable of continuously processing material and discharging the products.
Owner:TIANJIN FANYAMEI HORTICULTURAL ORNAMENT
Automatic textile cloth cutting device
ActiveCN108203875AEffective levelingEffective shearSevering textilesTextile shapingEngineeringAutomation
The invention belongs to the technical field of textile equipment, and particularly relates to an automatic textile cloth cutting device. The automatic textile cloth cutting device comprises a base, the base is provided with a conveying belt and a first sliding mechanism which is parallel to the conveying belt, the upper end of the first sliding mechanism is provided with a support rod, the side wall of the support rod is provided with a leveling device, and the leveling device is located over the conveying belt; the base is provided with a first rotating device meshed with the first sliding mechanism and two vertical plates arranged on the portions, at the left and right ends of the conveying belt, of the base respectively, a horizontal plate is arranged between the two vertical plate andlocated over the conveying belt, the lower end of the horizontal plate is provided with a pressing mechanism, and the lower end of the horizontal plate is provided with a second sliding mechanism. The automatic textile cloth cutting device has the advantages that not only can the automation degree of the cloth cutting device be improved, but also cloth can be effectively fixed, and the effect ofcutting the cloth is improved.
Owner:大连聿力玩具有限公司
Preparation method and separation performance research of polymer-covalent organic framework material (polyCOF) composite films
InactiveCN109012243AHigh yieldIncrease water fluxSemi-permeable membranesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisComposite filmCrystallinity
Novel polymer-covalent organic framework (polyCOF) film materials with a high machinability, a high chemical stability and a high crystallinity are creatively designed and synthesized against the problems of poor chemical stability and uneven pore size of traditional polymeric films and the problems of poor machinability and poor chemical stability of covalent organic framework films. A series ofpolyCOF films are prepared by introducing a polymer containing a construction monomer, and the polyCOF films integrates the advantages (such as high crystallinity, high porosity and high stability) ofa covalent organic framework material with the advantages (such as easy film formability, high flexibility and high machinability) of a linear polymer. The amount of polymeric reactants is adjusted to adjust the crystallinity, the porosity and the mechanical performances of the polyCOF films, and the concentration of reaction raw materials can be adjusted to adjust the thickness of the films. More importantly, the polyCOF films can be used for separating and purifying mixed gases, all organic molecules and biological pollutants.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Preparation method of animal peptone by double-enzyme enzymolysis
ActiveCN102827911BEffective shearIncrease the depth of hydrolysisFermentationPerformance indexBiologic Products
The invention provides a preparation method of animal peptone by double-enzyme enzymolysis and belongs to the technical field of biological products. Fresh ox bone and animal tissue and entrails are taken as the raw materials and are subjected to deep hydrolysis by adopting pancreatin and compound protease under a weak base condition, and then the technical measures of separation and purification and the like are carried out to obtain a peptone of which the molecular weight is steadily kept between 2000 and 2500 and of which the amino acid content is balanced. The characteristics of high efficiency, specifity, distribution cooperativity, environment friendliness and the like obtained through catalytic hydrolysis by pancreatin and compound protease are fully utilized, so that stability and the high quality of various performance indexes of products are effectively ensured. The obtained peptone does not precipitate and is not muddy in the presence of acid and base and the peptone is not solidified and keeps completely clear at a high temperature. The peptone can be used as the main raw material of high-grade microorganism mediums and can completely replace imported products.
Owner:PINGLIANG HUAKE BIOLOGICAL TECH
Ultrafine maize straw grinding device
The invention relates to an ultrafine maize straw grinding device. The ultrafine maize straw grinding device comprises a machine frame. The machine frame is provided with a grinding assembly and a motor assembly. The grinding assembly comprises a rotating shaft, a movable grinding sleeve and a fixed grinding sleeve. The movable grinding sleeve and the fixed grinding sleeve are columnar and installed with the rotating shaft as the axis. The movable grinding sleeve is fixed to the rotating shaft through a first key. The fixed grinding sleeve is fixed to the machine frame. An upper cover is fixed to the upper end of the fixed grinding sleeve. A hopper is fixed to the upper cover. A discharging bin is fixed to the lower end of the fixed grinding sleeve. A discharging pipe is fixed to the lower end of the discharging bin. The ultrafine maize straw grinding device further comprises a transmission assembly. The grinding assembly is connected with the motor assembly through the transmission assembly. The ultrafine maize straw grinding device can effectively cut and grind fiber straw materials to needed fineness, and the problem that after the straw achieves certain fineness, discharging is difficult is solved. The ultrafine maize straw grinding device can achieve ultrafine grinding of maize straw in a large-flux, high-efficiency and low-energy-consumption manner.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Gate cutting device
The invention discloses a gate cutter comprising a base, a motor, a cutter mechanism and a roller shaft mechanism. The gate cutting device is characterized in that a motor base is disposed on the right of the base, the motor is fixed on the motor base, a motor rotating shaft is disposed at the left end of the motor, the cutter mechanism is fixed on the motor rotating shaft, a guide rail carrier is disposed on the left of the base, the roller shaft mechanism is arranged above the guide rail carrier and fixed through a roller shaft fixing mechanism, and universal wheels are disposed below the base. The gate cutting device has the advantages that cast gates can be cut effectively, workpieces rarely shake, machining errors are reduced effectively, and the gate cutting device is simple in structure and convenient and flexible to use.
Owner:中发输配电设备(平湖)有限公司
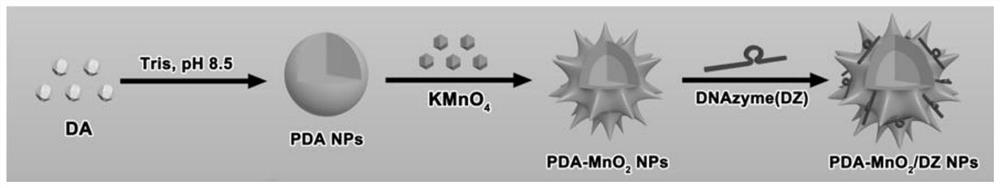
DNA/nano-composite as well as preparation method and application thereof
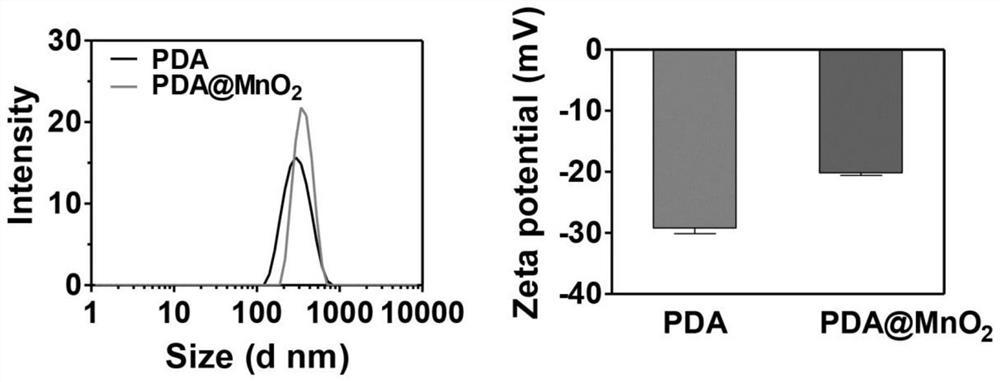
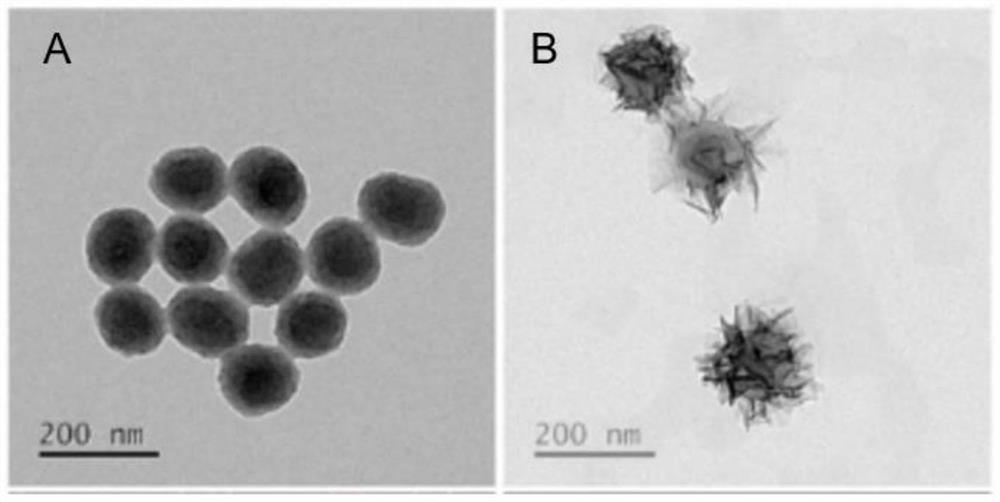
ActiveCN112741903AImprove light-to-heat conversion efficiencyLow heat resistancePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsNanoparticleA-DNA
The invention discloses a DNA / nano-composite as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The DNA / nano-composite comprises a polydopamine nanoparticle, a manganese dioxide nanoparticle and DNAzyme. The DNA / nano-composite is a core-shell nanoparticle, the polydopamine nanoparticle is taken as a core, the manganese dioxide nanoparticle is taken as a shell, and the DNAzyme is adsorbed on the surface of the shell, wherein the DNAzyme is DNAzyme designed for mRNA of HSP70 protein. In the DNA / nano-composite, the polydopamine core is a good photothermal reagent and can be used for photothermal therapy, and manganese dioxide on the surface of the polydopamine core can be degraded into Mn<2+> under the action of glutathione highly expressed in tumor cells, so that the DNAzyme is activated, the expression of the HSP70 protein is down-regulated, the sensitivity of the tumor cells to the photothermal therapy is improved, and the photothermal therapy is enhanced.
Owner:CHANGSHA MEDICAL UNIV
In-situ self-assembled slapper ignition component and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104387216ASimple processImprove manufacturing efficiencyDetonatorsPhotoresistAlumina ceramic
The invention discloses an in-situ self-assembled slapper ignition component and a preparation method thereof. Specifically, the in-situ self-assembled slapper ignition component comprises a pin equipped alumina ceramic substrate, a metal copper exploding foil, a Parylene C slapper layer, a photoresist structural layer and an acceleration chamber. The metal copper exploding foil is disposed on the alumina ceramic substrate, the Parylene C slapper layer is arranged on the metal copper exploding foil, the photoresist structural layer is disposed on the Parylene C slapper layer, and the acceleration chamber is disposed in the photoresist structural layer. The component provided by the invention has the characteristics of self-assembly and flexibility, and can meet the production needs of various slapper ignition components with different specifications. According to the invention, photoresist is applied to preparation of the acceleration chamber and tempering modification treatment thereon so as to further strengthen the mechanical properties. Thus, the acceleration chamber can effectively shear slappers.
Owner:INST OF CHEM MATERIAL CHINA ACADEMY OF ENG PHYSICS
Integrated Radix Puerariae crushing device
The invention provides an integrated Radix Puerariae crushing device. The device comprises a crushing cylinder, a motor is arranged at the left side of the crushing cylinder, a first belt pulley is fixedly arranged on the output shaft of the motor, the first belt pulley is connected with a second belt pulley through a belt, the second belt pulley is fixedly connected with a third rotating shaft, the third rotating shaft is connected with a first circular gear through a spline, the first circular gear is engaged with a second circular gear, the second circular gear is connected with a fourth rotating shaft through a spline, and the third rotating shaft and the fourth rotating shaft respectively penetrate through the left sidewall of the crushing cylinder and then are fixedly connected withthreaded rods. A double-helix crushing structure composed of the two threaded rods is used to effectively shear large Radix Puerariae blocks to form small blocks, the small blocks are screened by a sieve plate and are crushed through helical blade to form small granules, so the crushing process is simple to operate, and the crushed Radix Puerariae granules have a uniform particle size, and are suitable for producing slurry.
Owner:CHONGQING RADIX PUERARIAE CULTURAL COMM CO LTD
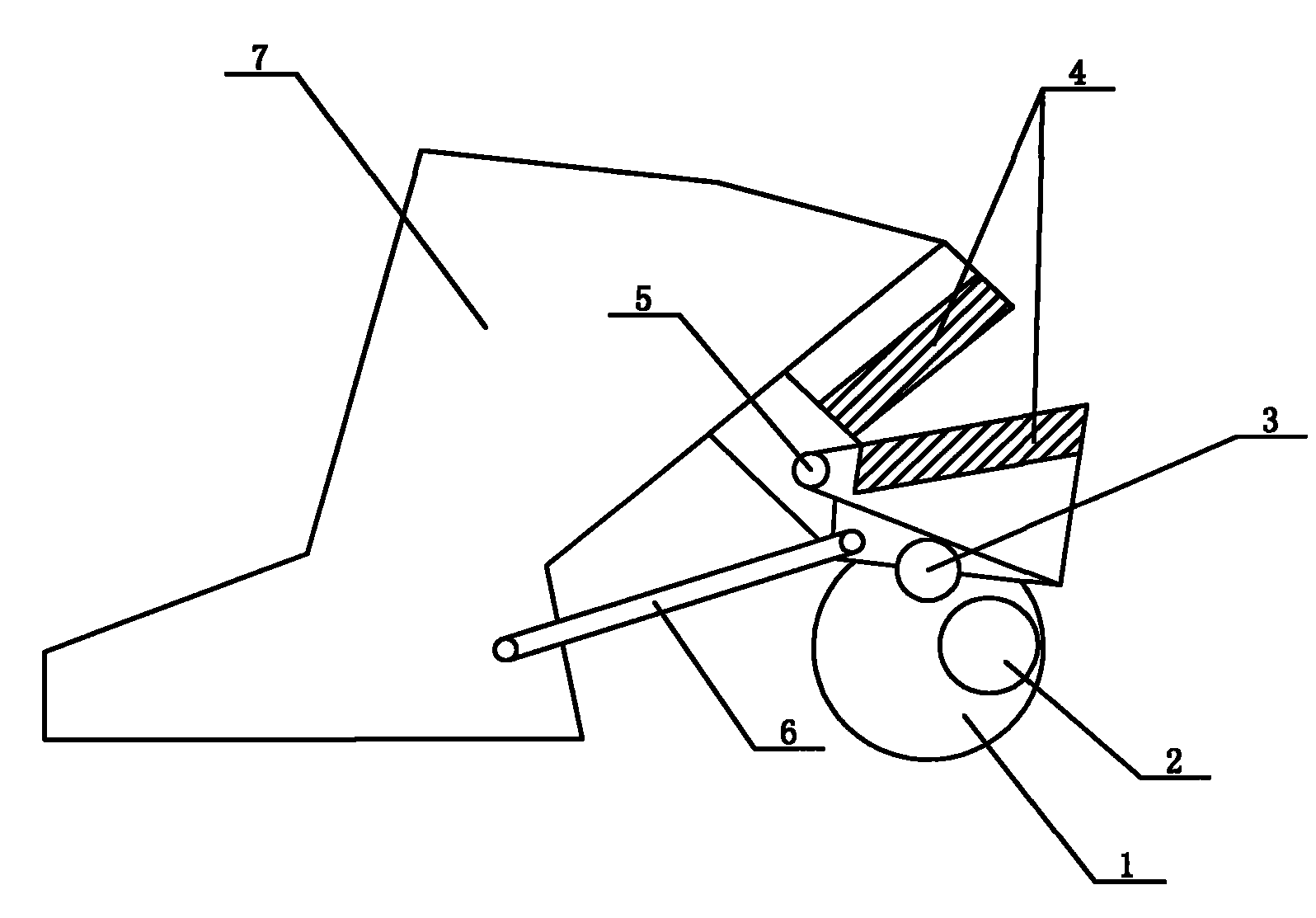
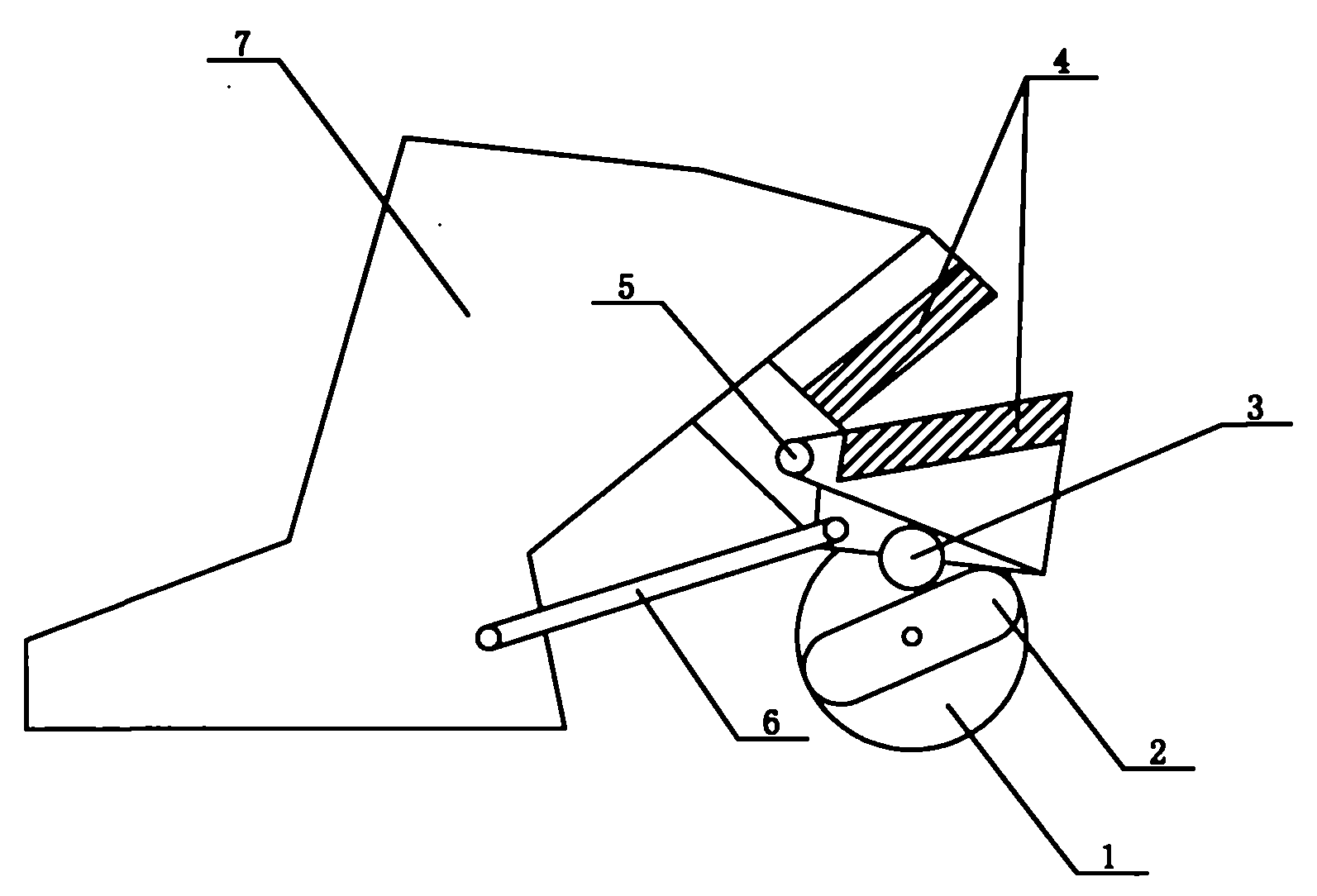
Novel selvage scissors of weaving machine
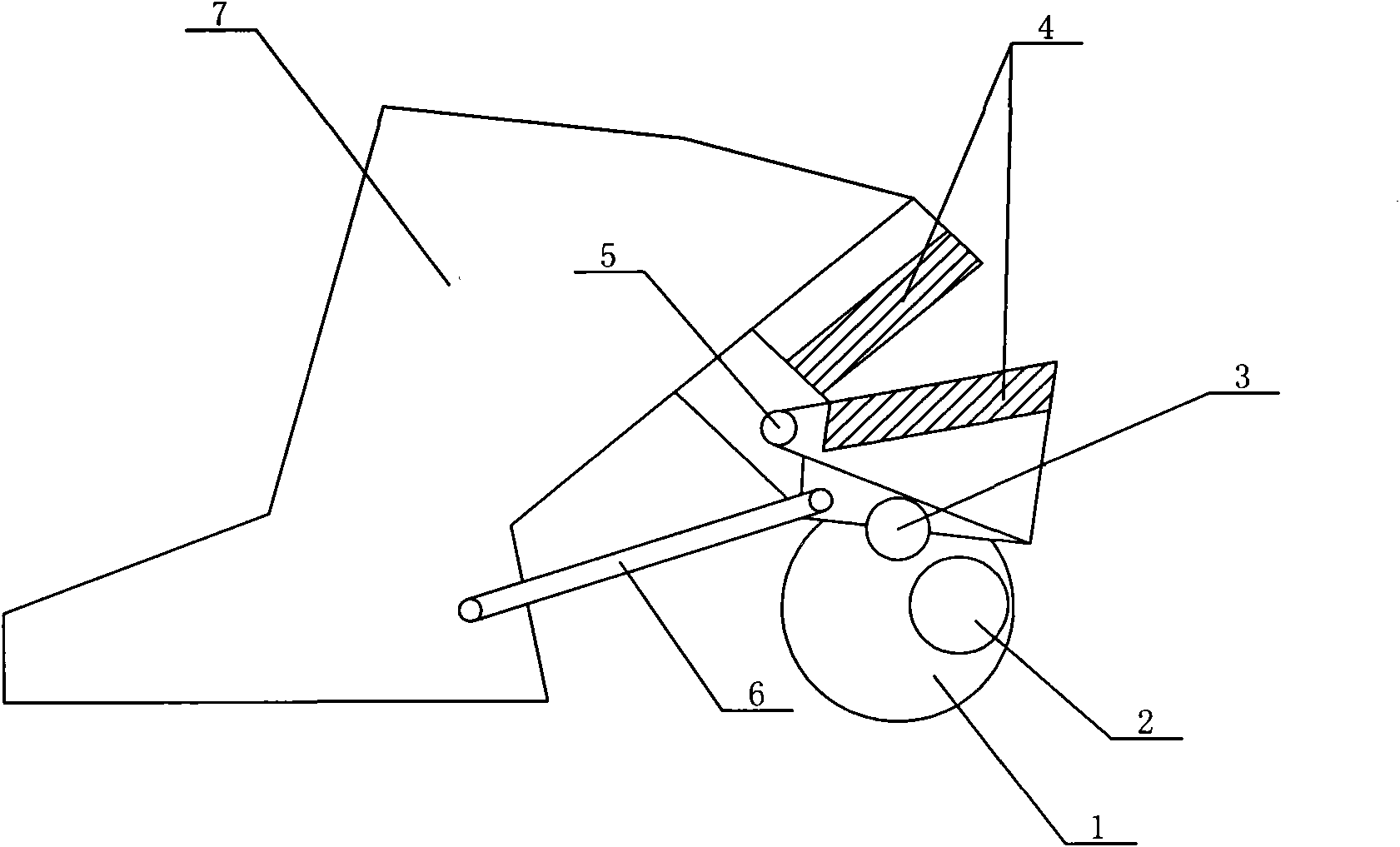
InactiveCN102400270ASimple structureHigh transmission efficiencyAuxillary apparatusEngineeringTextile
The invention provides novel selvage scissors of a weaving machine, and relates to the field of the manufacture of machines, in particular to the field of the manufacture of weaving machines. The novel selvage scissors consist of a rotating wheel (1), an eccentric wheel (2), a roller wheel (3), blades (4), a small shaft (5), a connecting and stretching device (6) and a tool rest (7), wherein the rotating wheel (1) is connected with the eccentric wheel (2), the roller wheel (3) is arranged at the lower ends of the blades (4), the blades (4) are connected with each other through the small shaft (5), and two ends of the connecting and stretching device (6) are respectively connected with the blades (4) and the tool rest (7). The novel selvage scissors have the advantages of simple structure, high transmission efficiency and lower mechanical failure rate; and all assemblies are connected together to form a whole, and can be linked effectively so as to realize effective cutting.
Owner:包建红
Reusable back wall for pipeline water pressure test
The invention discloses a reusable back wall for pipeline water pressure test, comprising a plurality of prefabricated reinforced concrete stoplog blocks (1) stacked; the prefabricated reinforced concrete stoplog blocks (1) are serially inserted via multiple steel bars (2), a plurality of back beams (4) are abutted to the front of the stoplog blocks (1), and the rear of each stoplog block (1) is filled and tamped with earthwork. The reusable back wall is used for pipeline water pressure test.
Owner:惠州市水电建筑工程有限公司
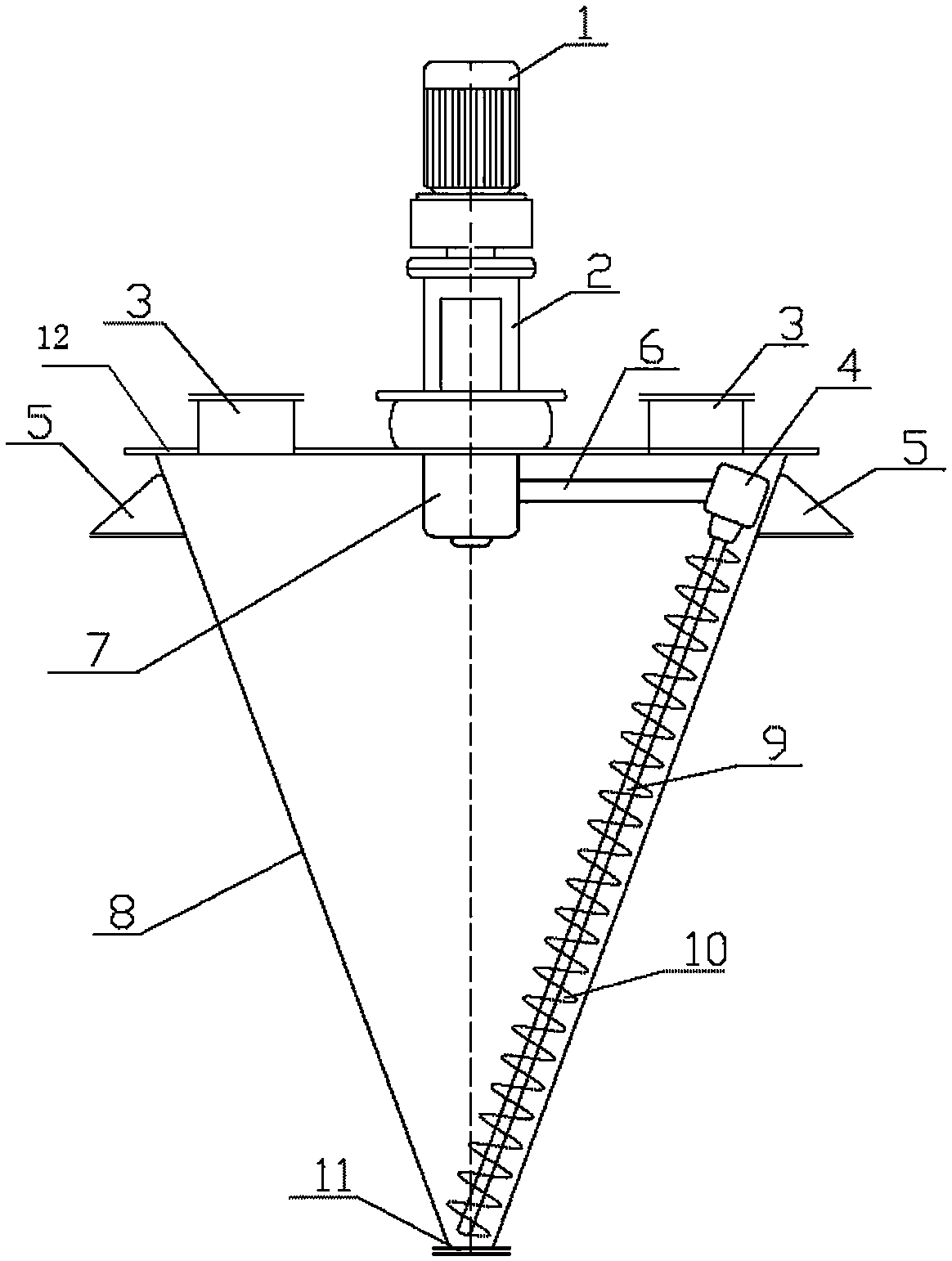
Screw type conical reaction kettle
InactiveCN104258802AEffective shearFacilitated releaseRotary stirring mixersChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsDrive shaftReducer
The invention belongs to the field of chemical engineering equipment, and relates to a reaction kettle, in particular to a single screw type conical reaction kettle. The screw type conical reaction kettle comprises a kettle body, a kettle cover and a stirring rod, and is characterized in that the kettle body adopts an inverted cone structure, a motor is mounted at the center part of the kettle cover, the lower end of the motor is connected with a speed reducer, a main drive box is mounted at the lower part of the speed reducer, one end of the main drive box is connected with a transverse drive shaft which is connected with an auxiliary turning box, the auxiliary turning box is connected with the stirring rod, and the stirring rod is parallel to the kettle body and is mounted close to the wall of the kettle; a spiral filament is welded on the outer wall of the stirring rod, and a manhole is formed in the kettle cover; and bracket bases are arranged on the kettle body, and a discharge valve is arranged at the bottom of the kettle body. The stirring rod can revolve under the drive of the main drive shaft and can perform autoroatation under the drive of the auxiliary turning box, and the spiral filament on the stirring rod can effectively shear a viscous material in the autoroatation and revolution process, so that the material around the spiral filament turns to be uniformly mixed, and the reaction kettle is particularly suitable for producing the viscous material.
Owner:HENAN ACADEMY OF SCI CHEM RES INST CO LTD
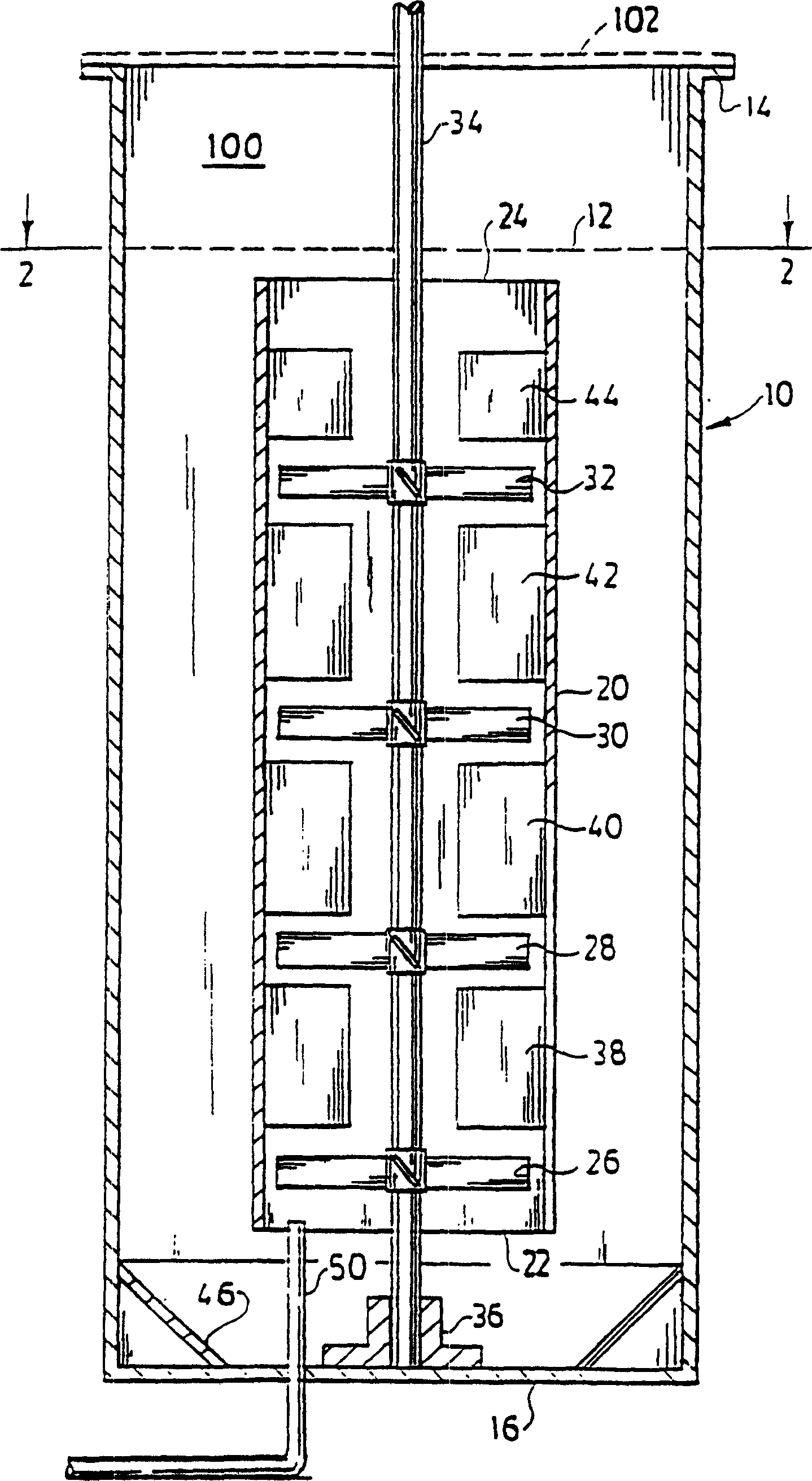
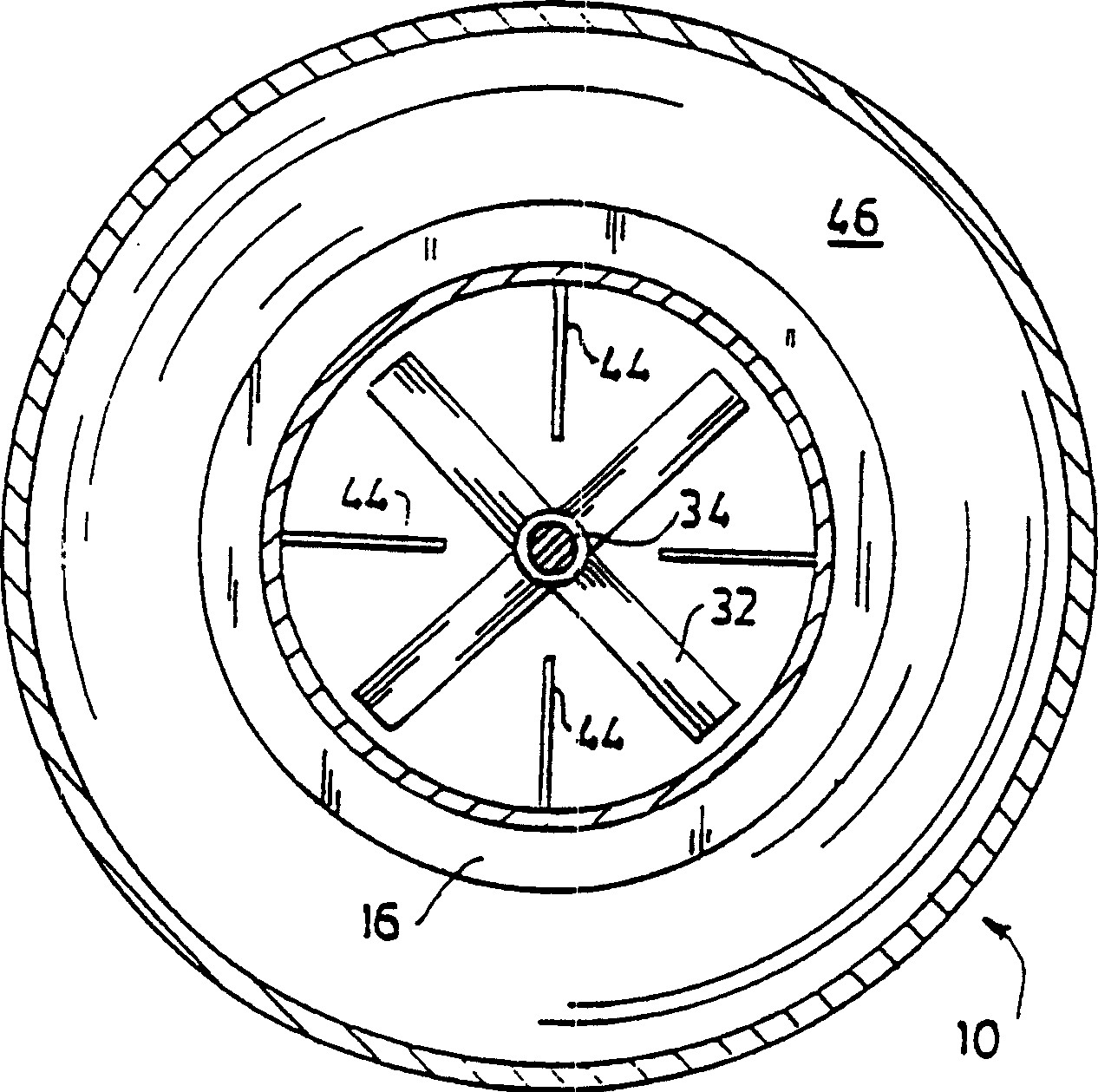
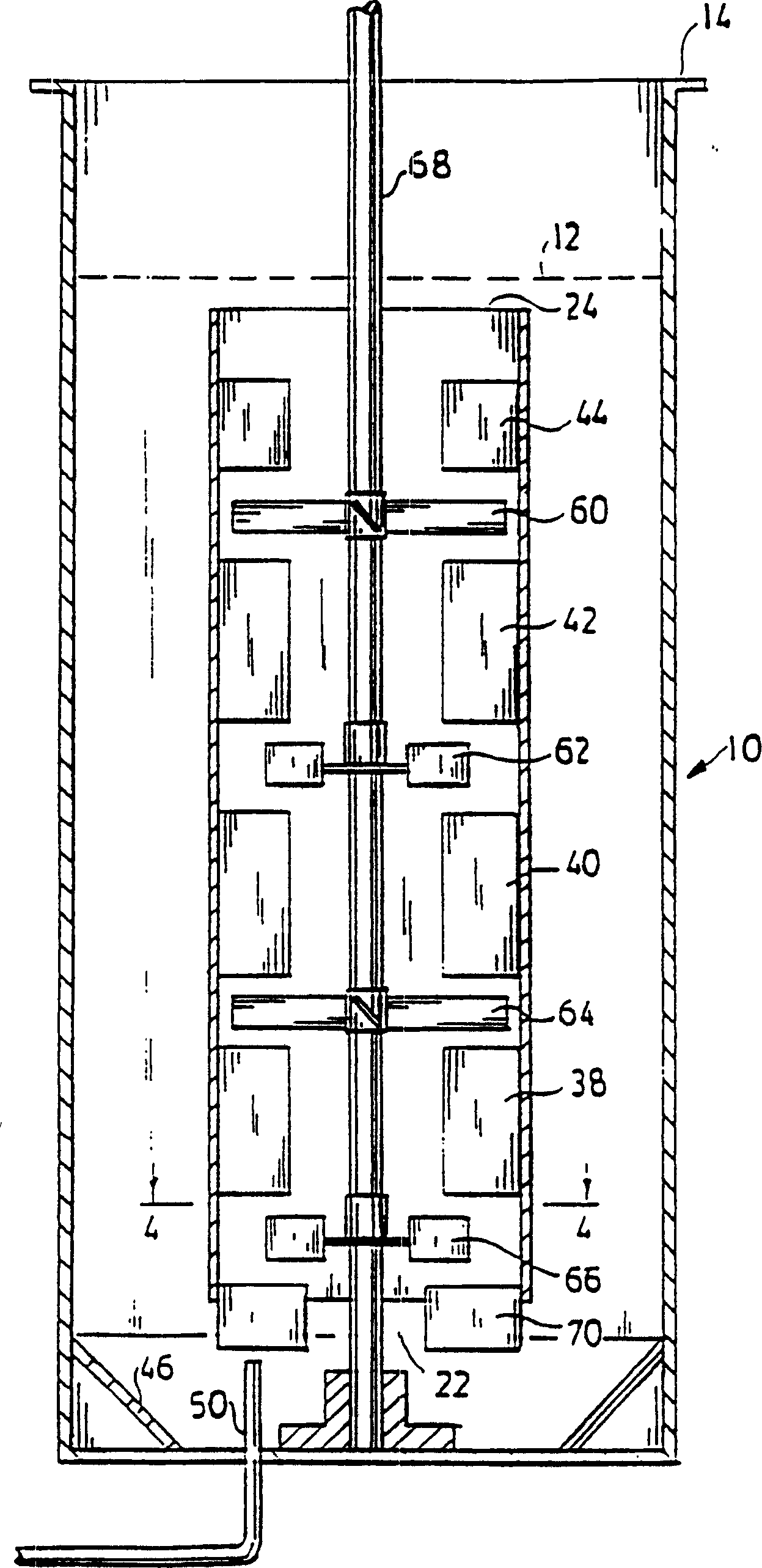
Mixer systems
InactiveCN1195867CHigh viscosityEffective shearBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsImpellerTest sample
A system for providing improved bulk liquid mixing and effective gas-liquid contacting for mass transfer of the gas to the liquid, especially a non-Newtonian liquid, the viscosity of which decreases when under shearing conditions (shear thinning), in an upright tank. A process, such as fermentation which produces commercial quantities of polysaccharides such as xanthan gum, may be carried out in the tank. An upright draft tube is mounted within the tank and has a lower end spaced from the tank bottom and an upper end spaced below the surface of the liquid in the tank. A plurality of mixing impellers in the draft tube are sufficiently close to each other to establish a field or pattern of agitation to cause shear thinning and upflow throughout the draft tube and which may produce turbulence at the liquid surface. A plurality of radially inwardly projecting circumferentially spaced baffles extend from the draft tube and are proximate the mixing impellers to prevent swirling of the liquid within the draft tube. Gas may be sparged into the vessel in or adjacent to the lower end of the draft tube. A circulating co-current flow of gas and liquid, with intimate gas-liquid contact, is induced up through the draft tube and out the upper end of the draft tube so as to provide a high rate of mass transfer from the gas to the liquid. The flow including entrained gas turns down through the annular region between the tank wall and the draft tube for recirculation of the liquid and gas above the surface of the liquid, resulting in high gas holdup and gas-liquid contact in the downflow annular region and in the upflow draft tube region, without gas flooding of the impellers. The concentration of dissolved gas and the effectiveness of the system for gas-phase mass transfer is determined by reaeration of a test sample of the liquid.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Straw compressing machine
InactiveCN107962807AEfficient extrusionEffective shearShaping pressDrive shaftAgricultural engineering
The invention discloses a straw compressing machine. The straw compressing machine comprises a lower pressing plate, wedge blocks, an upper pressing plate and an extrusion device, wherein the wedge blocks which are uniformly distributed circularly are arranged between the upper pressing plate and the lower pressing plate; the lower pressing plate, the wedge blocks and the upper pressing plate arefixedly connected through fixing bolts; the extrusion device is arranged in the lower pressing plate and the upper pressing plate and is driven by a driving shaft; a protection shield is arranged on the top of the upper pressing plate; a material inlet is formed in the top of the protection shield; and a material outlet is formed between every adjacent wedge blocks, the upper pressing plate and the lower pressing plate; and a material guiding device is arranged on the bottom of the lower pressing plate. The straw compressing machine has the advantages that defects of a traditional compressingmachine are overcome; simple maintenance and adjustment are realized; requirement on plant straws is low; adaptability is high; use is convenient; and efficiency is high.
Owner:曹燕燕
Sewage biochemical treatment device
PendingCN111233139AAvoid running mudAvoid mud runningSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentSewageActivated sludge
The invention relates to the technical field of sewage treatment, in particular to a sewage biochemical treatment device, which comprises a sewage tank; a blocking member which is installed in the sewage pool and divides the sewage pool into a main aeration area, a gas stripping / membrane water outlet area and an auxiliary aeration area which are communicated in sequence, wherein a sewage inlet isformed in the main aeration area, and sewage circularly flows in the sewage pool by the sequence of the main aeration area, the gas stripping / membrane water outlet area, the auxiliary aeration area and the main aeration area; a membrane filtration assembly, which is arranged in the gas stripping / membrane water outlet area and used for filtering activated sludge to separate mud from water, and a water outlet of the membrane filtration assembly is a purified water outlet; and a gas stripping device which is arranged in the sewage pool and is used for providing power for the circular flow of thesewage. The biochemical reaction tank is combined with a membrane filtration water outlet technology, so that the problems of large occupied area and easiness in mud leakage of a clarification area are effectively solved.
Owner:恩格拜(武汉)生态科技有限公司
Signboard shearing device
The invention relates to the technical field of signboards, in particular to a signboard shearing device. The problem that an existing device cannot complete shearing at a time is solved. The signboard shearing device comprises a cutting device, a direction dividing mechanism is arranged on one side of the cutting device, a rotating platform used for positioning a workpiece is arranged on the other side of the cutting device, a visual detector is arranged on the cutting device, a conveying device is arranged on the rotating platform, and the conveying device is used for clamping the workpiece and enabling the workpiece to move towards the cutting device. According to the signboard shearing device, an aluminum plate is placed on the rotating platform, the size of the aluminum plate is detected through the visual detector, the rotating platform is combined to control rotation of the aluminum plate till the four edges are aligned, then the conveying device clamps the aluminum plate and enables the aluminum plate to move towards the cutting device, the aluminum plate is conveyed out through the direction dividing mechanism after being cut by the cutting device, the four edges of the aluminum plate can be effectively sheared at a time, then the aluminum plate is conveyed out through the direction dividing mechanism, manpower is effectively reduced, and the production efficiency is remarkably improved.
Owner:新疆丝路六合电气科技有限公司
Equipment for manufacturing steel wire gardening hook
The invention relates to equipment for manufacturing gardening products, in particular to equipment for manufacturing a steel wire gardening hook. The equipment comprises a working platform, a working base, a lug boss-shaped core mould and a steel wire conveying device, wherein an upper compression mould is arranged right above the core mould; a forming mandril group composed of mandrils is arranged below the core mould; hydraulic driving mechanisms of the upper compression mould and each mandril as well as a driving mechanism of the steel wire conveying device are respectively connected to acentral controller internally installed with a steel wire gardening hook forming program by means of electric execution units. By adopting the structure, a steel wire can be effectively sheared, and gradually pressed and reshaped into a qualified steel wire gardening hook, and no heating treatment is required; and the steel wire is subjected to one-step machining and shaping, so that the labour efficiency is improved and the danger is reduced; and a discharging conductor used for penetrating through and hanging the gardening hook is fixedly arranged on the surface of core mould parallel to the working platform, and a push rod is arranged on the working base close to the edge of the periphery of the core mould; and the equipment is capable of continuously processing material and discharging the products.
Owner:TIANJIN FANYAMEI HORTICULTURAL ORNAMENT
Corn straw ultrafine grinding device
ActiveCN105149048BUltra-fine crushing achievedEffective shearGrain treatmentsFiberAgricultural engineering
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Stirrer
PendingCN112203755AEffective shearAchieve decentralizationFlow mixersRotary stirring mixersJet flowMechanical engineering
Provided is a stirrer that can more efficiently achieve shearing applied, by an action of an intermittent jet flow, to a fluid to be processed. The stirrer is characterized by concentrically comprising a rotor 2 including a blade 12, a partition wall 10, and a screen 9, wherein: the screen 9 includes a plurality of slits 18 in a circumferential direction thereof and screen members 19 located between the adjacent slits 18; by rotating at least the rotor 2 of the two components, the fluid to be processed is discharged from the inside to the outside of the screen 9 as the intermittent jet flow through the slits 18 of the screen 9; the screen 9 has a cylindrical shape having a circular cross section; an opening of the slit 18 provided on the inner wall surface of the screen 9 is used as an inflow opening 28; openings of the plurality of slits 18 provided on the outer wall surface of the screen 9 are used as outflow openings 29; and the width (So) of the outflow openings 29 in the circumferential direction is set to be smaller than the width (Si) of the inflow opening 28 in the circumferential direction.
Owner:M TECH CO LTD
A shredder suitable for ultra-high speed cigarette making machine
The invention relates to a shredder suitable for ultra-high-speed cigarette making machines, which includes a shredding device and a motor. The shredding device includes a support frame, a hob and a base. The first blade is fixed, and the two ends of one side of the fixing seat are respectively provided with protrusions, and the protrusions are provided with through holes for accommodating the bearings, and the knife holder is provided with a gap corresponding to the protrusions, and the protrusions are inserted into the gaps. The rotating shaft pin is inserted in the bearing and the knife rest, so that the knife rest is rotated around the rotating shaft pin, and a plurality of springs are arranged at intervals on one side of the fixed seat, and the springs are offset against the other side of the knife rest. The pulverizer of the present invention adopts a spring-type base design, which can enhance the stability of the pulverizer, prolong the life cycle of the equipment to one year, and the damage of foreign matter to the blade is close to zero. At the same time, the daily maintenance and fault repair time of the pulverizer The cost is reduced to within 10 minutes, which can effectively cut the cigarette paper and prevent the cigarette paper from fluttering to shutdown or quality problems.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO ZHEJIANG IND
Shear rotary valve and oil immersion type shear rotary valve plunger pump comprising same
The invention relates to a shear rotary valve comprising a valve body and a valve element arranged in a valve cavity of the valve body. The valve body is provided with a discharging opening communicating with the valve cavity, a first feeding opening and a second feeding opening, the valve element is provided with a cutting edge, the discharging opening and the first feeding opening are alternatively opened and closed when the valve element rotates in the valve cavity, and the cutting edge is driven to shear materials flowing through the discharging opening and the first feeding opening. An oil immersion type shear rotary valve plunger pump comprises a material cylinder, a driving device and the shear rotary valve, a piston is arranged in the material cylinder and divides an inner cavity of the material cylinder into a first cavity and a second cavity, the first cavity of the material cylinder communicates with the second feeding opening of the shear rotary valve, the driving device isarranged at the end, close to the second cavity, of the material cylinder, and the output end of the driving device is connected with the piston. During reversing of the valve element, the cutting edge can shear particles in the materials through power of reversing of the valve element, blocking or stalling of the valve element due to the particles in the materials is avoided, and the feeding accuracy is improved.
Owner:WUHAN HI TECH WEICHUANG TECH CO LTD
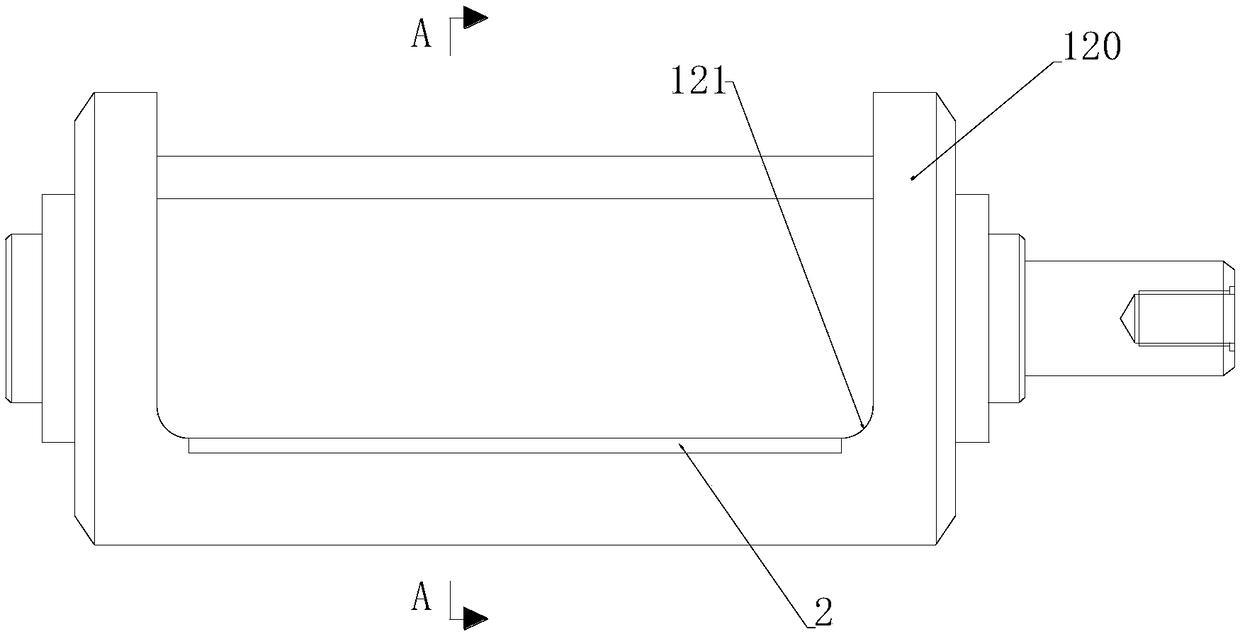
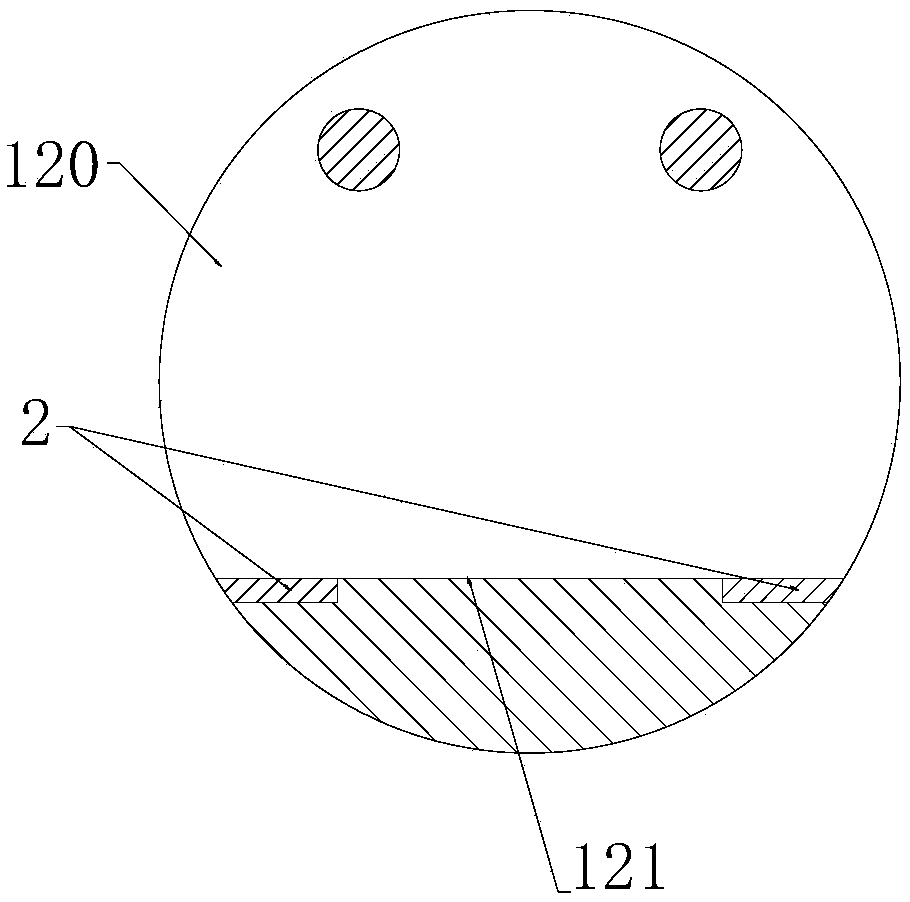
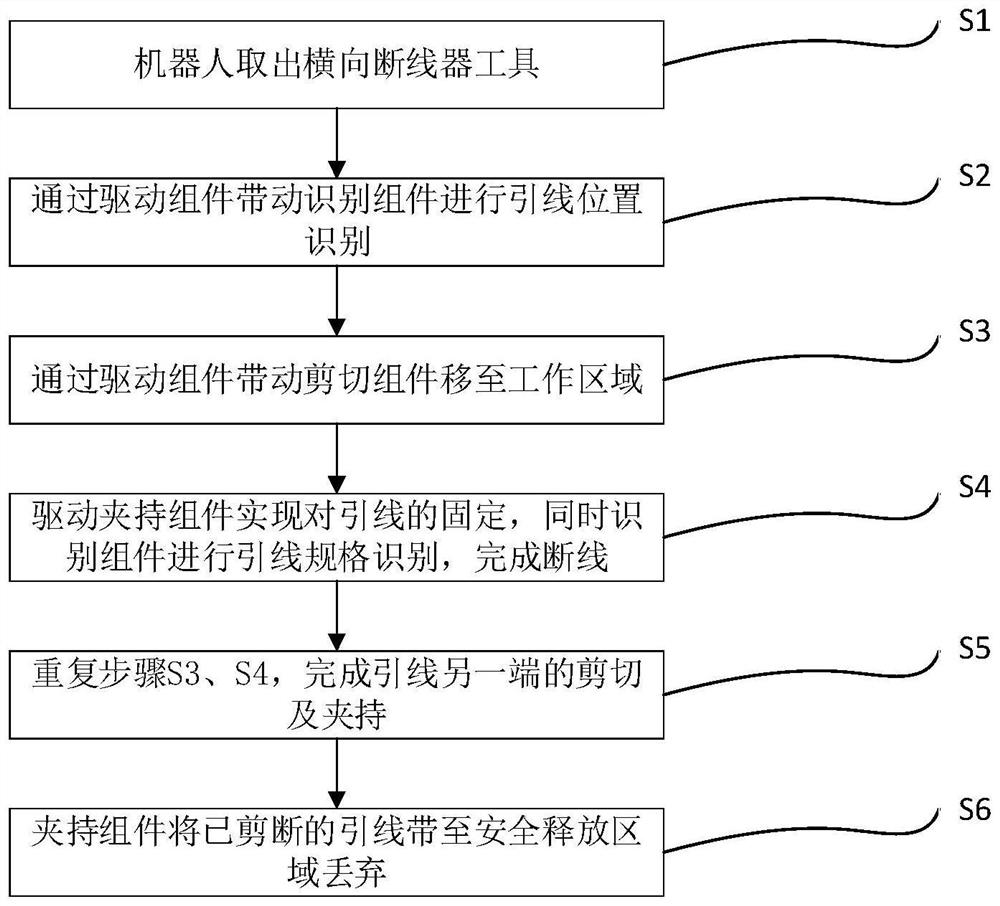
Automatic control method for operating robot to break lead
PendingCN114552478AEffective shearGuaranteed accuracyApparatus for cutting/splicing cablesApparatus for overhead lines/cablesAutomatic controlControl engineering
The invention discloses an automatic control method for operating a robot to break a lead. The automatic control method comprises the following steps that the robot takes out a transverse wire breaker tool; the driving assembly drives the identification assembly to identify the position of the lead; the shearing assembly is driven by the driving assembly to move to a working area; the clamping assembly is driven to fix the lead, and meanwhile, the identification assembly identifies the specification of the lead to complete wire breaking; repeating the steps to complete shearing and clamping of the other end of the lead; the clamping assembly brings the cut-off lead to a safety release area to be discarded. According to the technical scheme, the lead is fixed through the clamping assembly, meanwhile, the specification of the lead is determined through the recognition assembly, the movable cutter is controlled by the driving assembly to be matched with the fixed cutter to achieve effective shearing of the lead, manual participation is not needed, and the work efficiency is greatly improved while the work completion accuracy is guaranteed.
Owner:丽水正好电力实业集团有限公司 +1
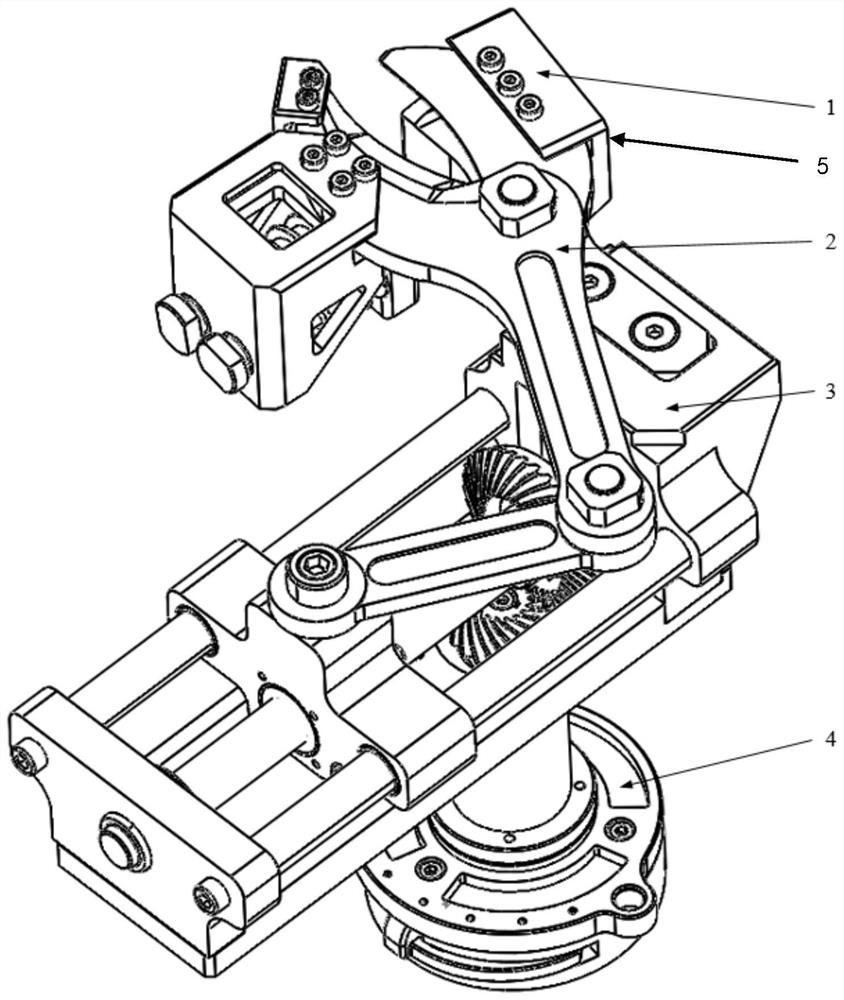
Shearing device for branches near power transmission lines in power system and method of use
ActiveCN105746189BEffective shearAvoid interferenceCuttersCutting implementsGear wheelElectric power system
The invention relates to a shearing saw device for branches near power transmission lines in a power system, which is characterized in that: it includes a support rod and the like; the cross section of the support rod is a hollow chord-cut circular ring; the bearing seat is provided with a bearing, A hollow disk and an elastic element; the scissor arm includes a rear plate, a bending section, a front plate, a clamping block, and a chain saw slot; the chain saw includes a driven gear, a chain saw blade, and a sprocket; the scissor arm drives The device includes a connecting rod, a slider, a first slideway, a pull rod, and a second slideway; the chain saw transmission device includes a transmission chain, a driving gear, and a power device; the broken branch holding device includes a first splint, a second A splint; a method of using a scissors saw device for a branch near a power transmission line in a power system, including wearing and fixing, adjusting the position of the scissor arm, cutting, holding and taking off the branch, the present invention can drive the chain saw through the power device. Branches can be cut and clamped; they can also be attached to the operator by means of belts and guards.
Owner:国网山东省电力公司庆云县供电公司
Tooling assembly, blanking tool therefor and associated method
Owner:STOLLE MACHINERY CO LLC
Novel selvedge scissors for weaving machine
InactiveCN102400269ASimple structureHigh transmission efficiencyAuxillary apparatusKnife bladesKnife holder
The invention relates to novel selvedge scissors for a weaving machine, and relates to the field of mechanical manufacturing, in particular to the field of the manufacturing of textile machines. The selvedge scissors consist of a turning wheel (1), a stirring sheet (2), a roller (3), a blade (4), a small shaft (5), a connection stretching device (6) and a knife rest (7), wherein the turning wheel (1) is connected with the stirring sheet (2); the roller (3) is arranged at the lower end of the blade (4); the blade (4) is connected with the small shaft (5); and two ends of the connection stretching device (6) are connected with the blade (4) and the knife rest (7). The novel selvedge scissors have a simple structure, high transmission efficiency and low mechanical failure rate; and each assembly is connected, so the selvedge scissors can be subjected to linkage effectively to shear effectively.
Owner:包建红
A kind of sealing ring bonding pliers and using method
ActiveCN112622289BPrecise dockingImprove bonding qualityDomestic articlesMechanical engineeringBonding strength
The invention provides a sealing ring bonding pliers and a using method, which comprises a first clamp arm and a second clamp arm, and the middle parts of the second clamp arm of the first clamp arm are hingedly connected by a pin shaft , between the tail of the first clamp arm and the second clamp arm is provided with an automatic clamping mechanism for driving the two to realize the clamping action, and the end of the first clamp arm is fixed with a first clamp table The end of the second clamp arm is fixed with a second clamp structure, and the first clamp structure and the second clamp structure are respectively installed with the same structure for compressing the end of the sealing strip. A pressing mechanism, wherein a shearing device for shearing the sealing strip is installed on the first jaw structure. It can solve the problems of poor fit of O-ring incision, dislocation of bonding and poor bonding strength.
Owner:CHINA YANGTZE POWER
A torsional impact screw drilling tool
ActiveCN111577120BDoes not affect bend pointBending point will not increaseEarth drilling toolsDrill bitsDrive shaftClassical mechanics
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH +1
Crusher suitable for ultrahigh-speed cigarette making machine
The invention relates to a crusher suitable for an ultrahigh-speed cigarette making machine. The crusher comprises a crushing device and a motor, the crushing device comprises a supporting frame, a hob and a base, the base comprises a rotating shaft pin, a tool rest and a fixed seat, a first blade is fixed to one side of the tool rest, convex blocks are arranged at the two ends of one side of thefixed seat correspondingly, through holes for accommodating bearings are formed in the convex blocks, notches corresponding to the convex blocks are formed in the tool rest, the convex blocks are inserted into the notches, and the rotating shaft pin is inserted into the bearings and the tool rest so that the tool rest can rotate around the rotating shaft pin, a plurality of springs are further arranged on one side of the fixed seat at intervals, and the springs abut against the other side of the tool rest. The crusher adopts the spring-type base design, the working stability of the crusher canbe enhanced, the life cycle of equipment is prolonged to one year, damage of foreign matter to blades is nearly zero, meanwhile, the daily maintenance and fault repair time of the crusher is shortened within ten minutes, cigarette paper can be effectively cut, and the shutdown or quality problem caused by floating of the cigarette paper is prevented.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO ZHEJIANG IND
Natural rubber primary processing wet stirring and extrusion washing all-in-one machine
The invention discloses a natural rubber primary processing wet stirring and extrusion washing all-in-one machine. The machine comprises is characterized by comprising a base; a coupling is mounted between a motor and an input shaft of a speed reducer, and a coupling is arranged behind an output shaft of the speed reducer; and for security consideration, a protective cover is mounted at the external of the coupling. A main shaft is mounted in a main machine shell; a tail bearing base and a head bearing base are mounted on the main machine shell; and bearings are mounted in the bearing bases for enabling the main shaft to perform a rotating motion. The main shaft is provided with a feeding movable cutter, a pushing movable cutter, a wet stirring discharge movable cutter, a spiral cutting movable cutter, a pushing spiral and a discharge cutting movable cutter, which are fixed with the main shaft by keys; spacing sleeves are arranged between the adjacent movable cutters to guarantee the distances between the adjacent movable cutters; certain angles are formed between the adjacent movable cutters; and inclined surface edges of all the movable cutters are spirally arranged. A cavity separation plate is mounted at the middle part of the main machine shell for dividing the shell into two working cavities. A discharge outer screening plate and a discharge inner screening plate are mounted at the tail part of the main machine shell, and are both provided with discharge holes. A certain amount of fixed cutters are mounted in the peripheral direction of the main machine shell, and arefixed with the main machine shell as a whole. The upper part of the main machine shell is a feed port; and glue enters a wet stirring cavity through the feed port.
Owner:西双版纳绿恒橡胶机械设备有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com