Patents
Literature
71results about How to "Sufficiently suppress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
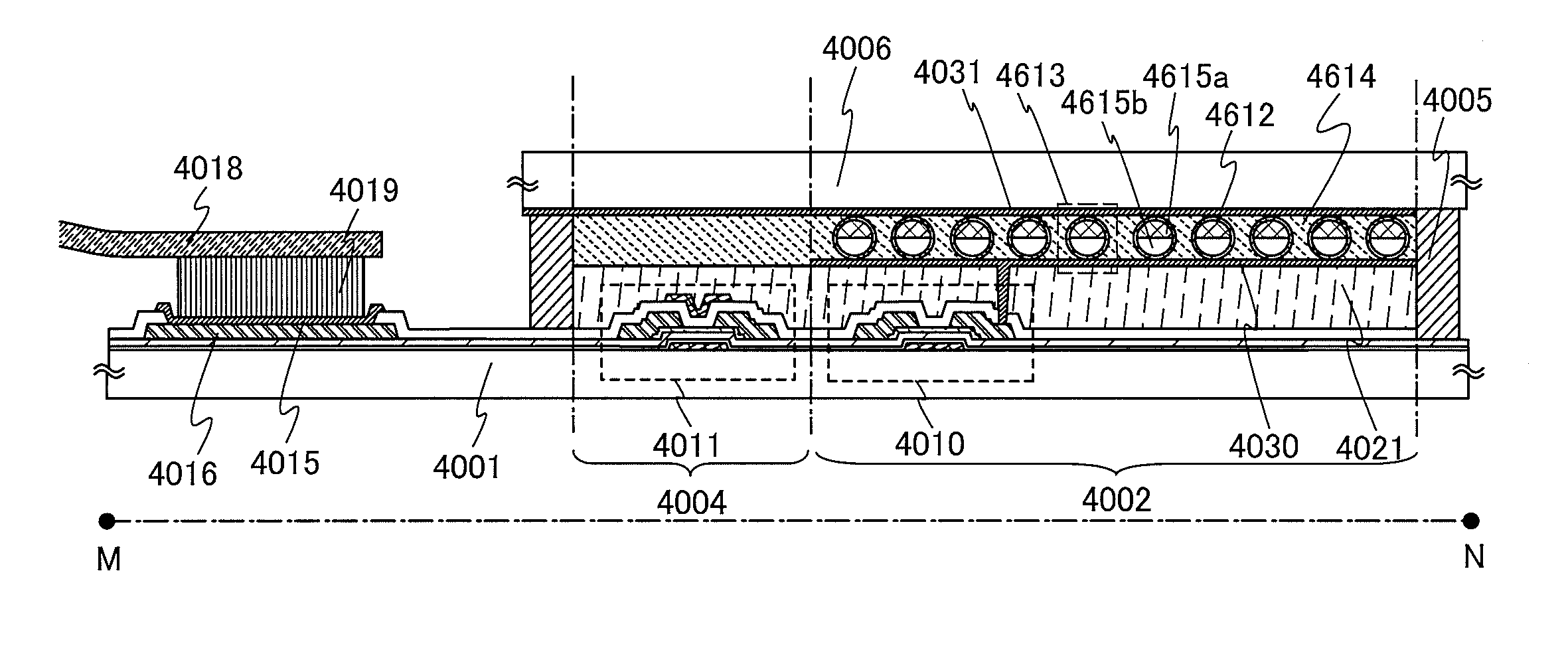
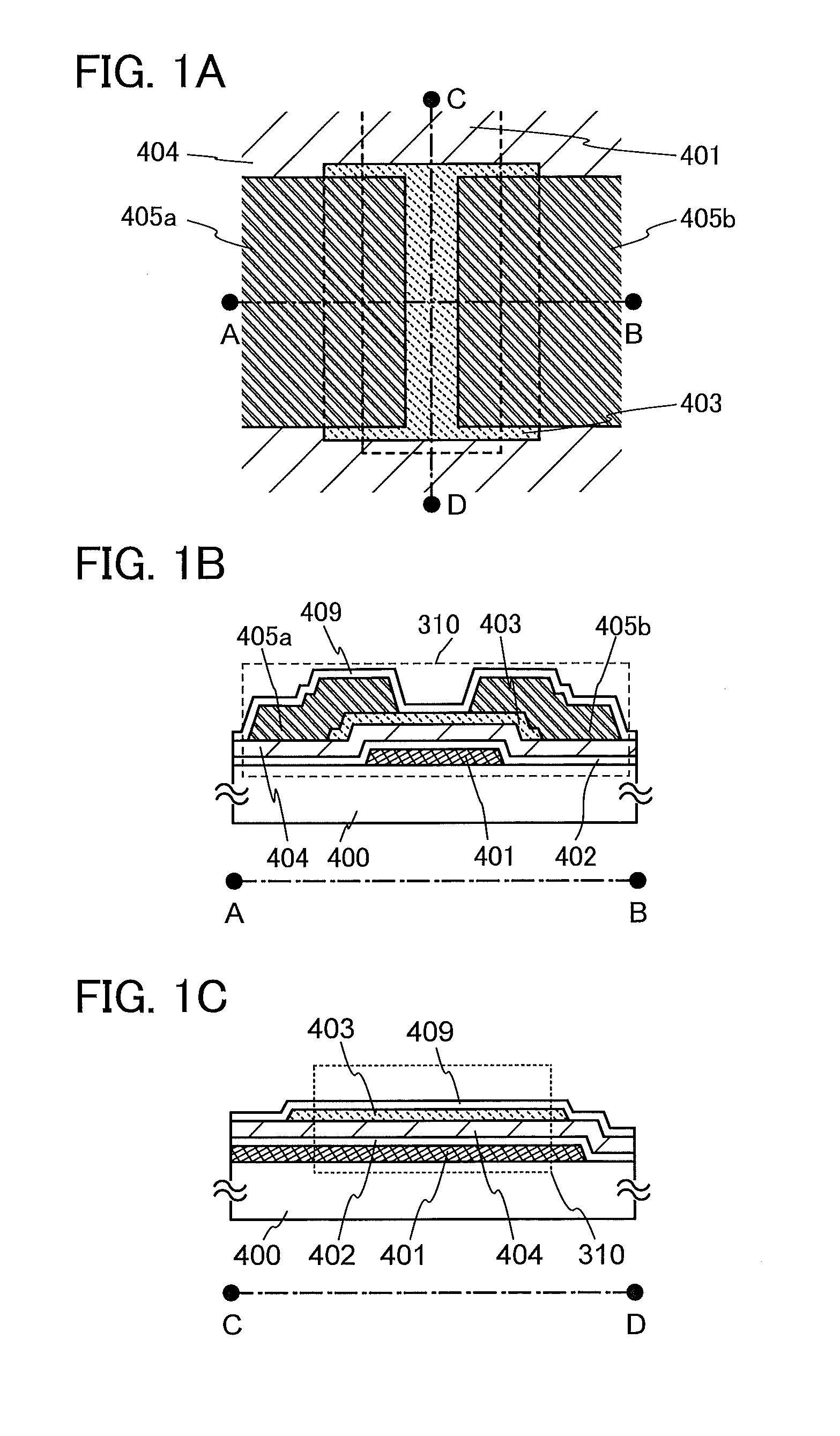
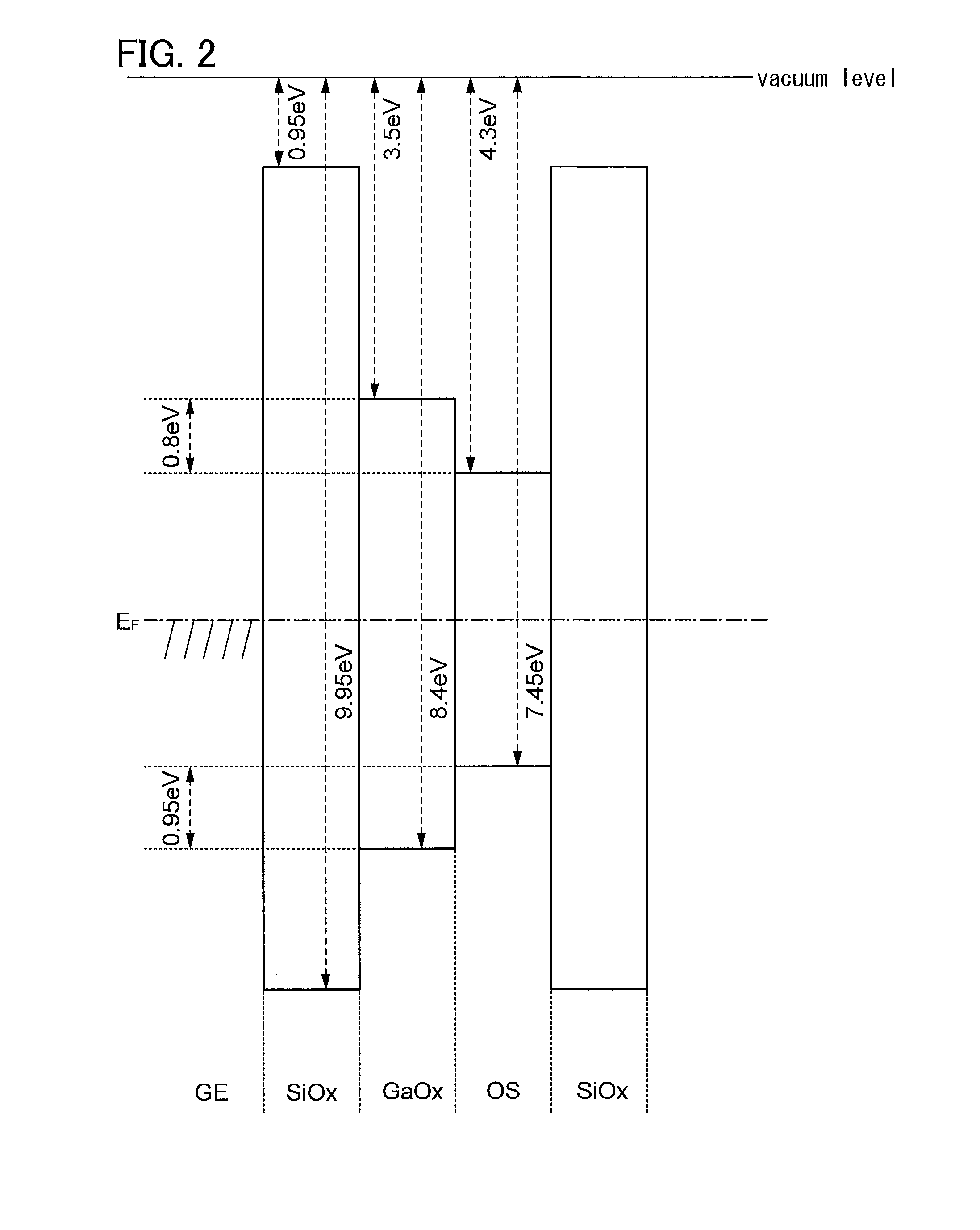
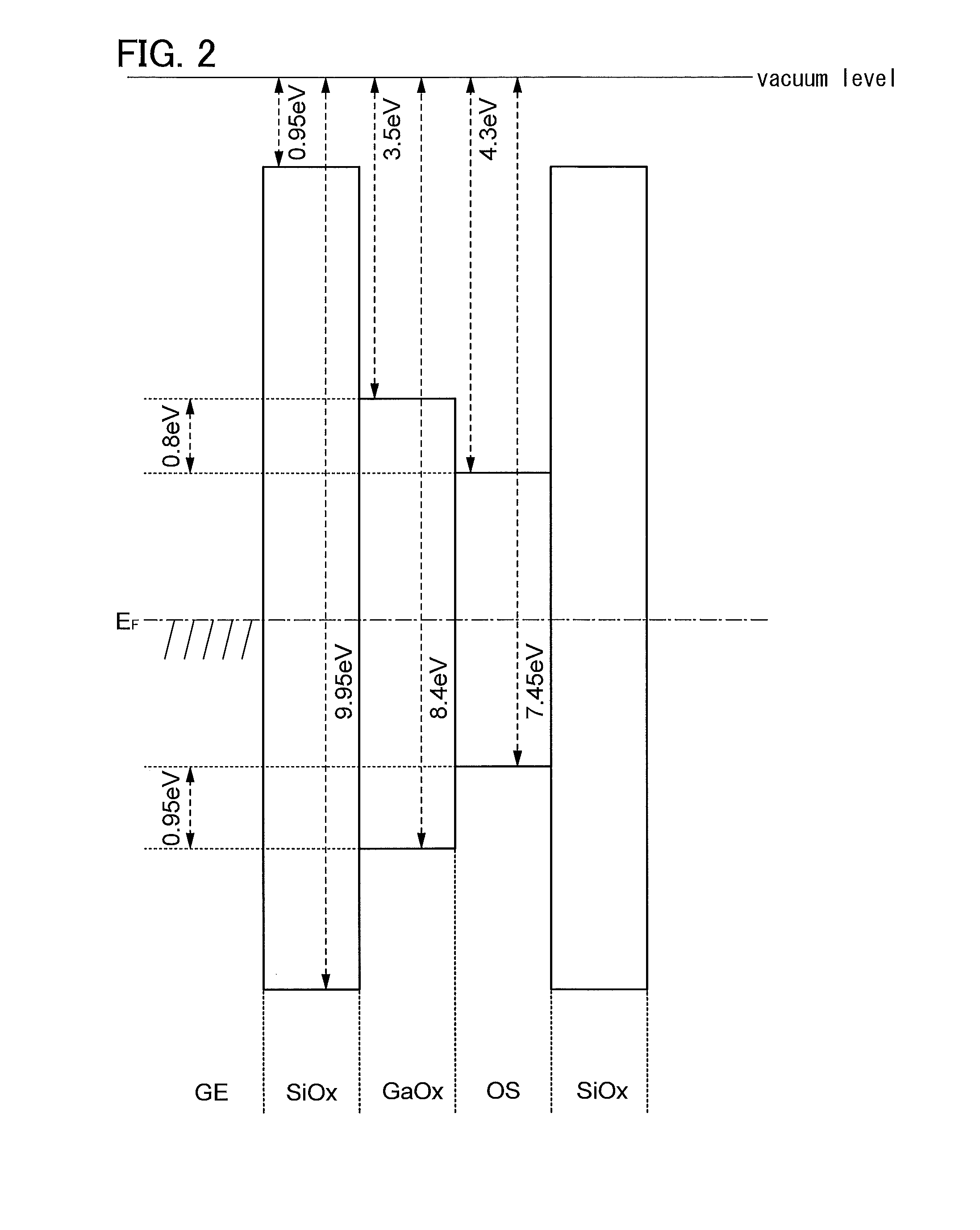
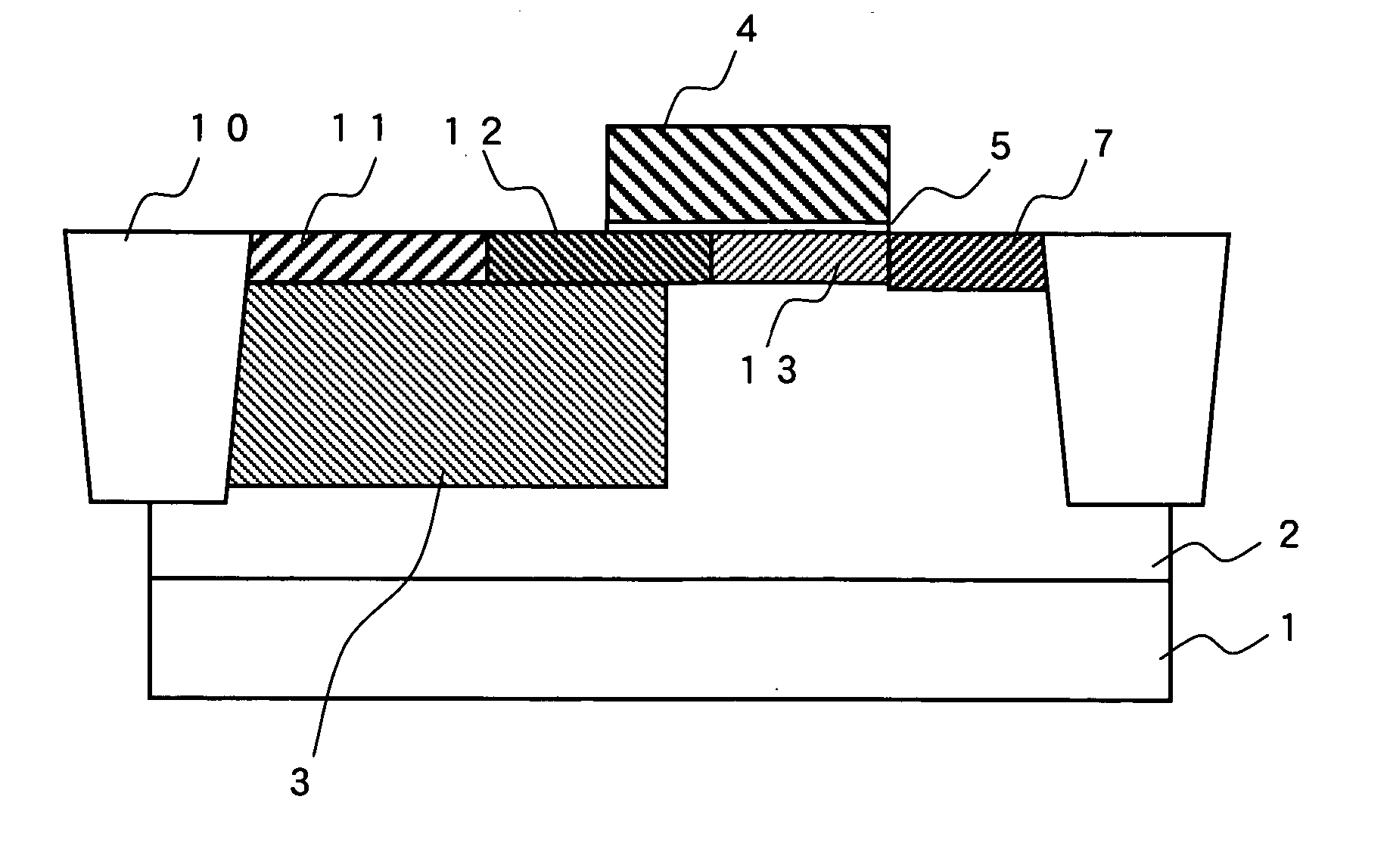
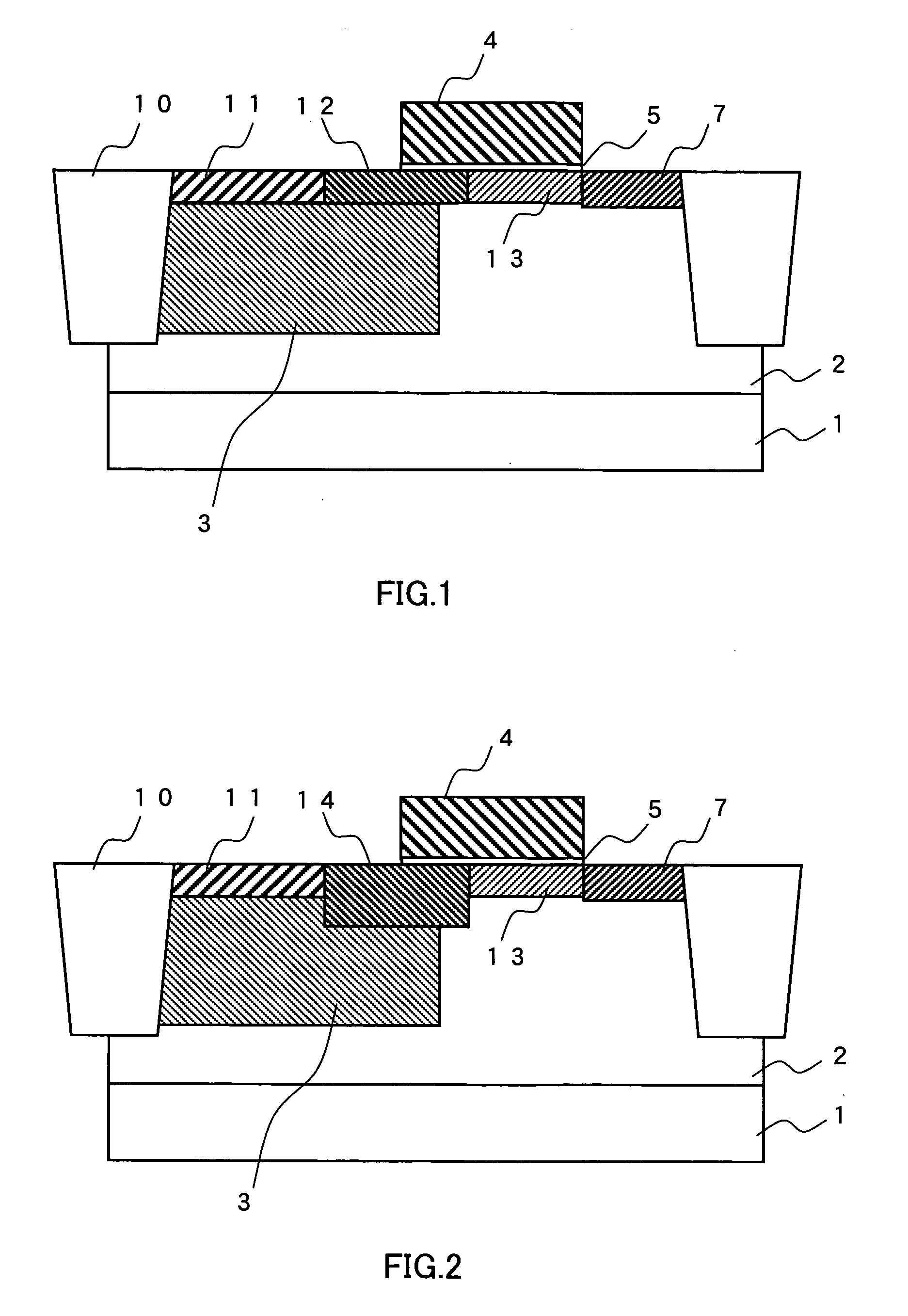
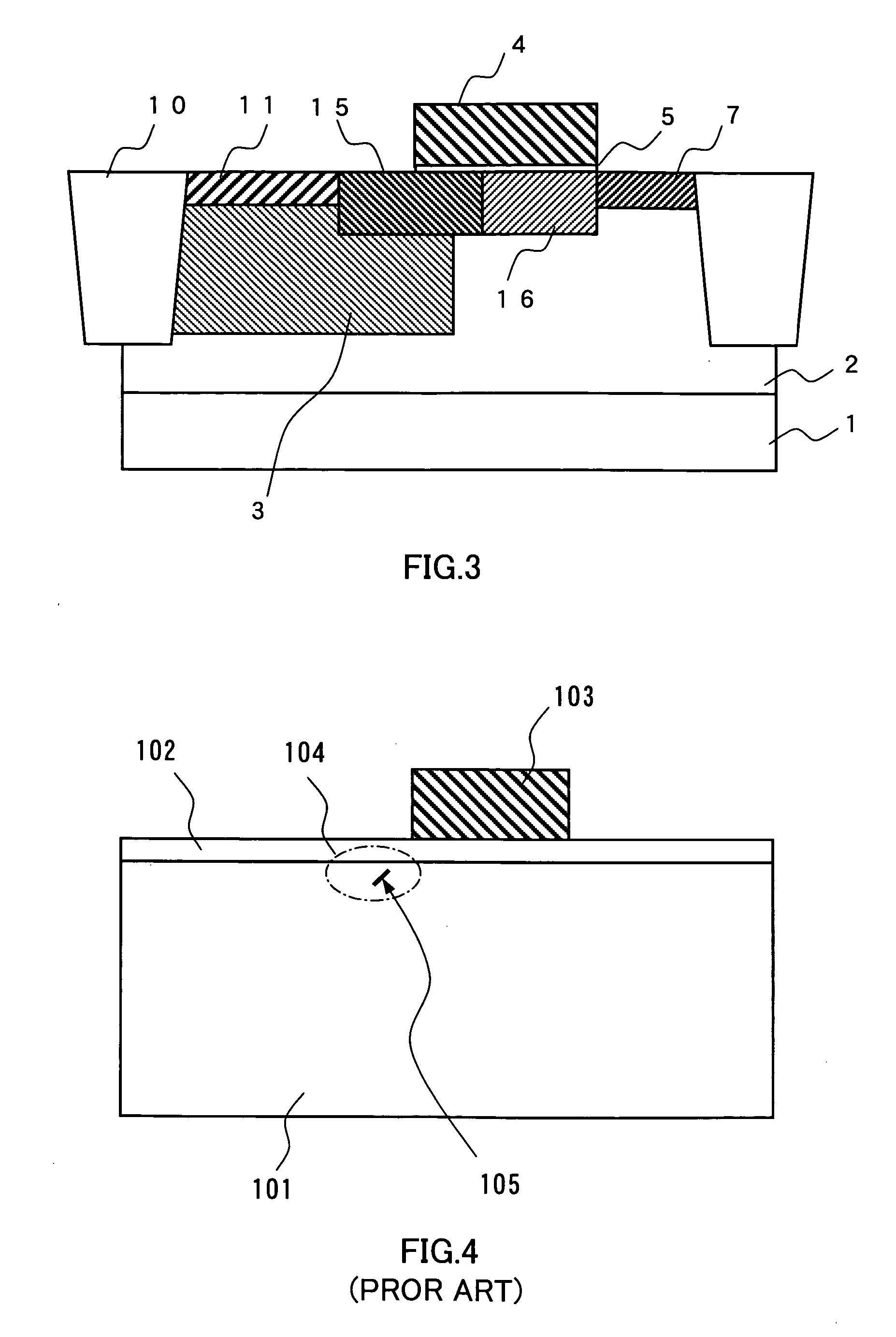
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20110240995A1Stable electrical characteristicsExcellent electrical propertiesTransistorPower semiconductor deviceOxygen
As a transistor including an oxide semiconductor film, a transistor in which a metal oxide film containing a constituent similar to that of an oxide semiconductor film is provided between the oxide semiconductor film and a gate insulating film and a gate insulating film containing a constituent different from that of the metal oxide film and that of the oxide semiconductor film is provided to be in contact with the metal oxide film is provided. The oxide semiconductor film used for an active layer of the transistor is a highly purified and electrically i-type (intrinsic) film which is formed by heat treatment through which an impurity such as hydrogen, moisture, a hydroxyl group or a hydride is removed and oxygen which is a main component of the oxide semiconductor and reduced together with the impurity removal step is supplied.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
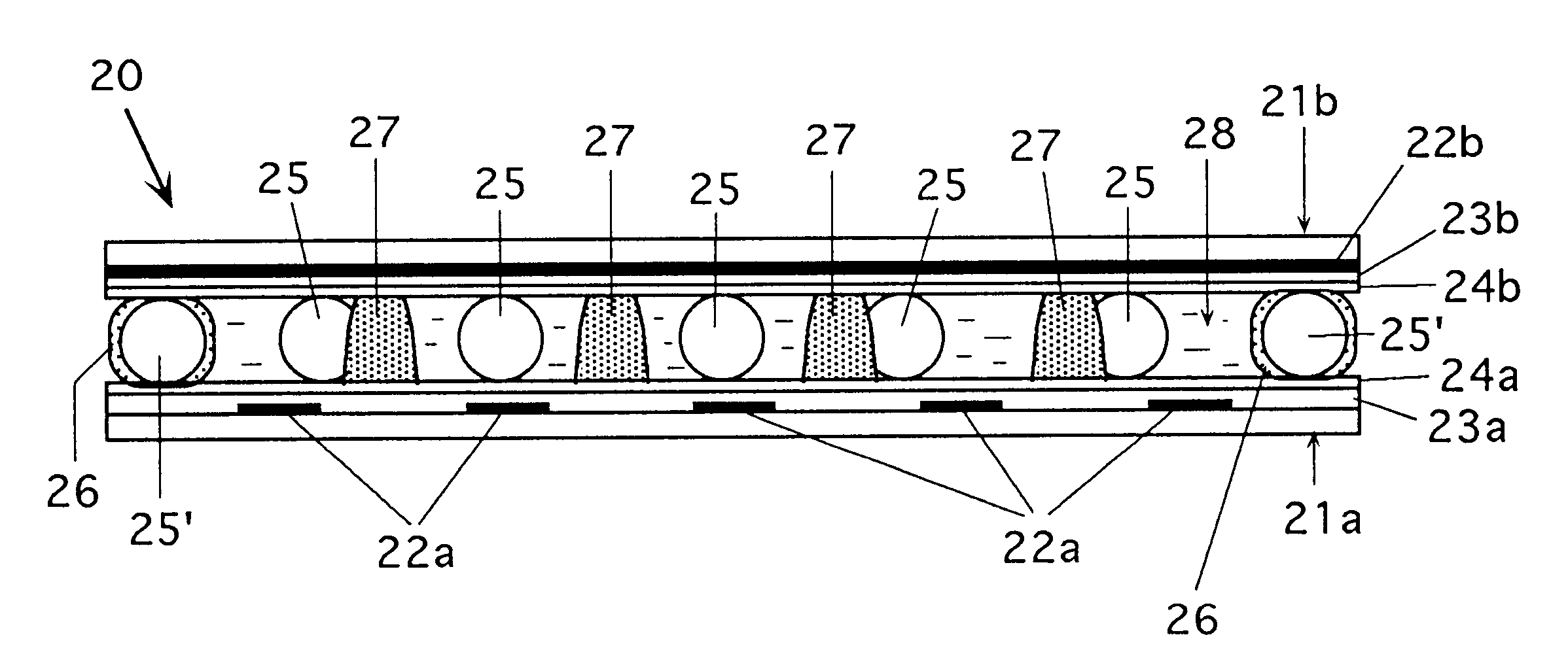
Method of manufacturing liquid crystal display element
InactiveUS6392736B1Simplify manufacturing stepsShort manufacturing timeStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
Method of manufacturing liquid crystal display element includes disposing adhesive on at least one of first and second substrates; disposing spacer particles on at least one substrate; supplying liquid crystal material onto at least one substrate; and fixing the substrates together with adhesive spacer particles and liquid crystal material therebetween. The substrates are fixed together by applying pressure and / or heat to the substrates from an end portion toward the other end portion thereof. An impulse applied to each spacer particle can be between 0.001 gf.sec and 0.1 gf.sec in substrate fixing step. Parameter X relating to heating in fixing step can satisfy 200<=X<=3000, where X=(T-20) / (V.D), T is temperature (°C), V is fixing speed (mm / sec) of substrates, and D is diameter of spacer particles (mm). The spacer particles can occupy an area ratio of 0.003 or more to unit area of the substrate.
Owner:MINOLTA CO LTD
Method of forming a protective film for a magnetic recording medium, a protective film formed by the method and a magnetic recording medium having the protective film
ActiveUS20100086808A1Improve relationshipSufficiently suppressPretreated surfacesRecord information storageTectorial membraneOptoelectronics
A method of forming a protective film of a magnetic recording medium is provided that achieves a good bonding characteristic with a lubricant film and at the same time, suppressing adhesion of contamination gases, to attain a reduced thickness of the magnetic recording medium. The method includes forming a protective film on a lamination including a substrate and a metallic film layer formed on the substrate, by means of a plasma CVD method using a raw material of a hydrocarbon gas, and performing a surface treatment on the protective film. The surface treatment includes a plasma treatment with argon gas, and a plasma treatment with a gas containing at least nitrogen gas.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
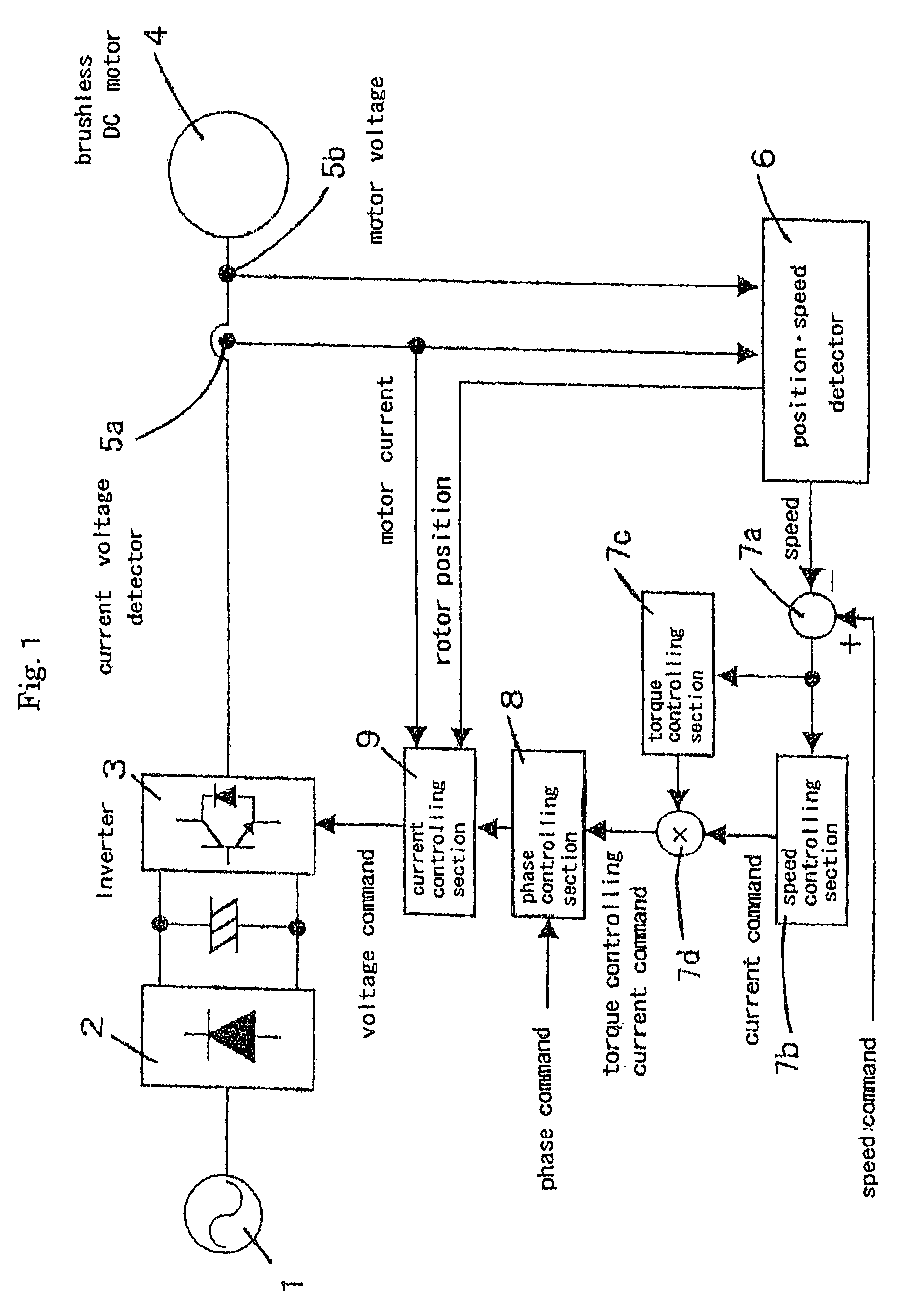
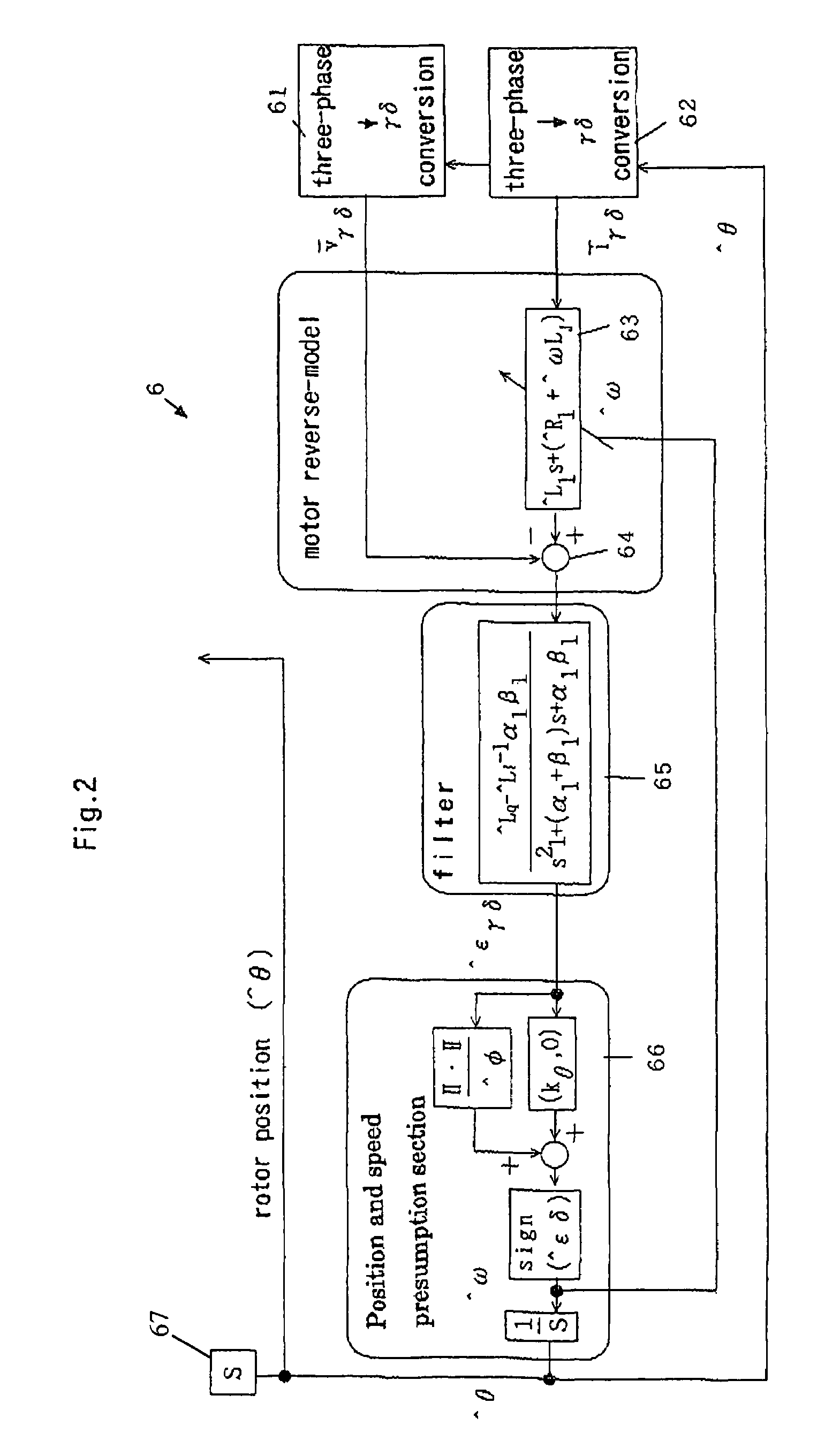
Synchronous motor control method and device
InactiveUS7180263B2Sufficiently follow high speed variationPrevent and greatly suppress speed variationSingle-phase induction motor startersTorque ripple controlSynchronous motorHarmonic
Synchronous motor controlling apparatus and method controls power applied to minimize or eliminate speed variations of a synchronous motor due to variations in load imposed the motor. The rotational position of a rotor of the synchronous motor based on the input terminal voltages and currents to the synchronous motor, and the power applied to the motor is adjusted accordingly. Higher harmonics of the input voltages and currents may also be used to detect the position of the rotor. In addition, the apparatus and method also accounts for the varying speed command inputs.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
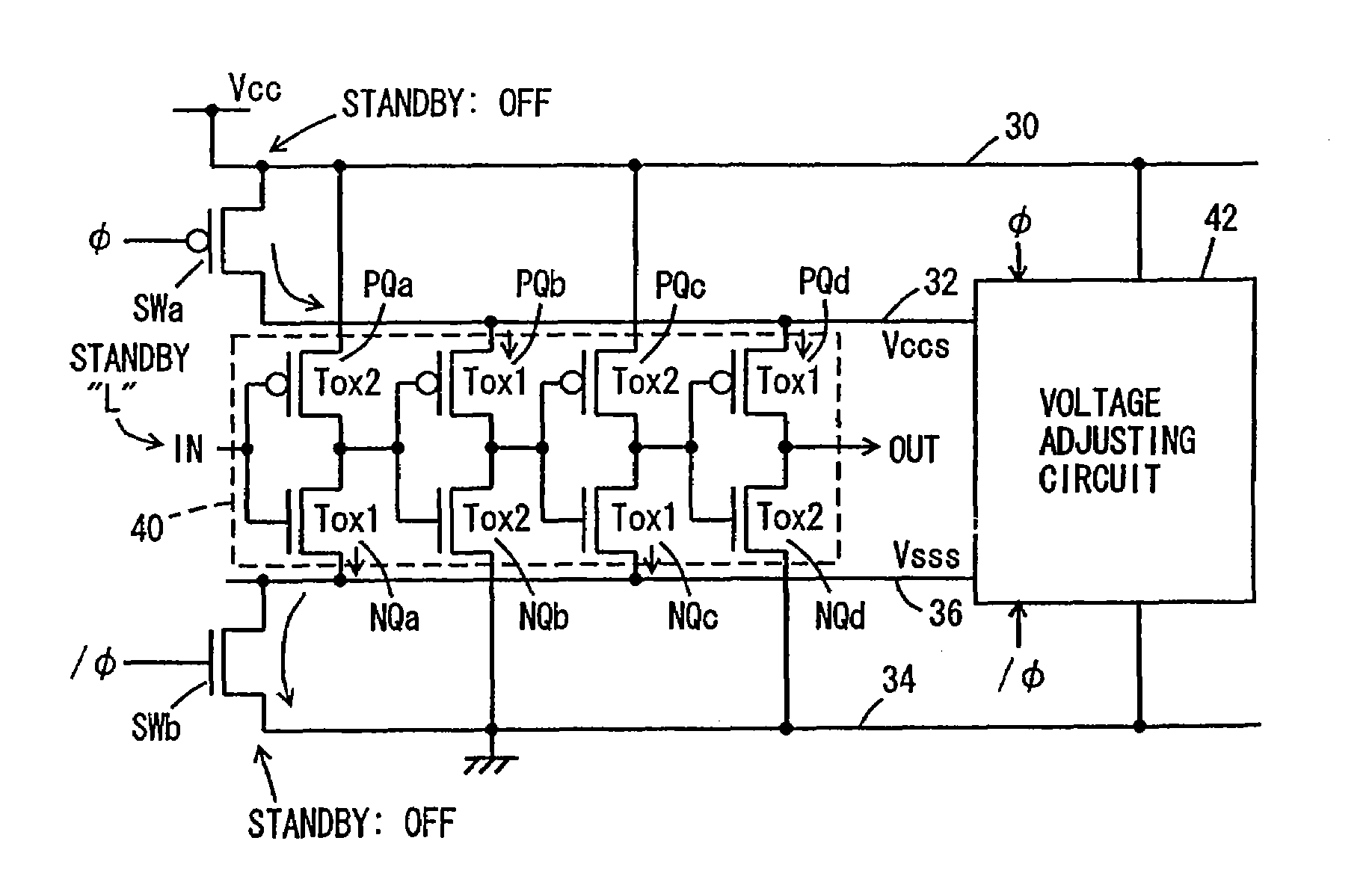
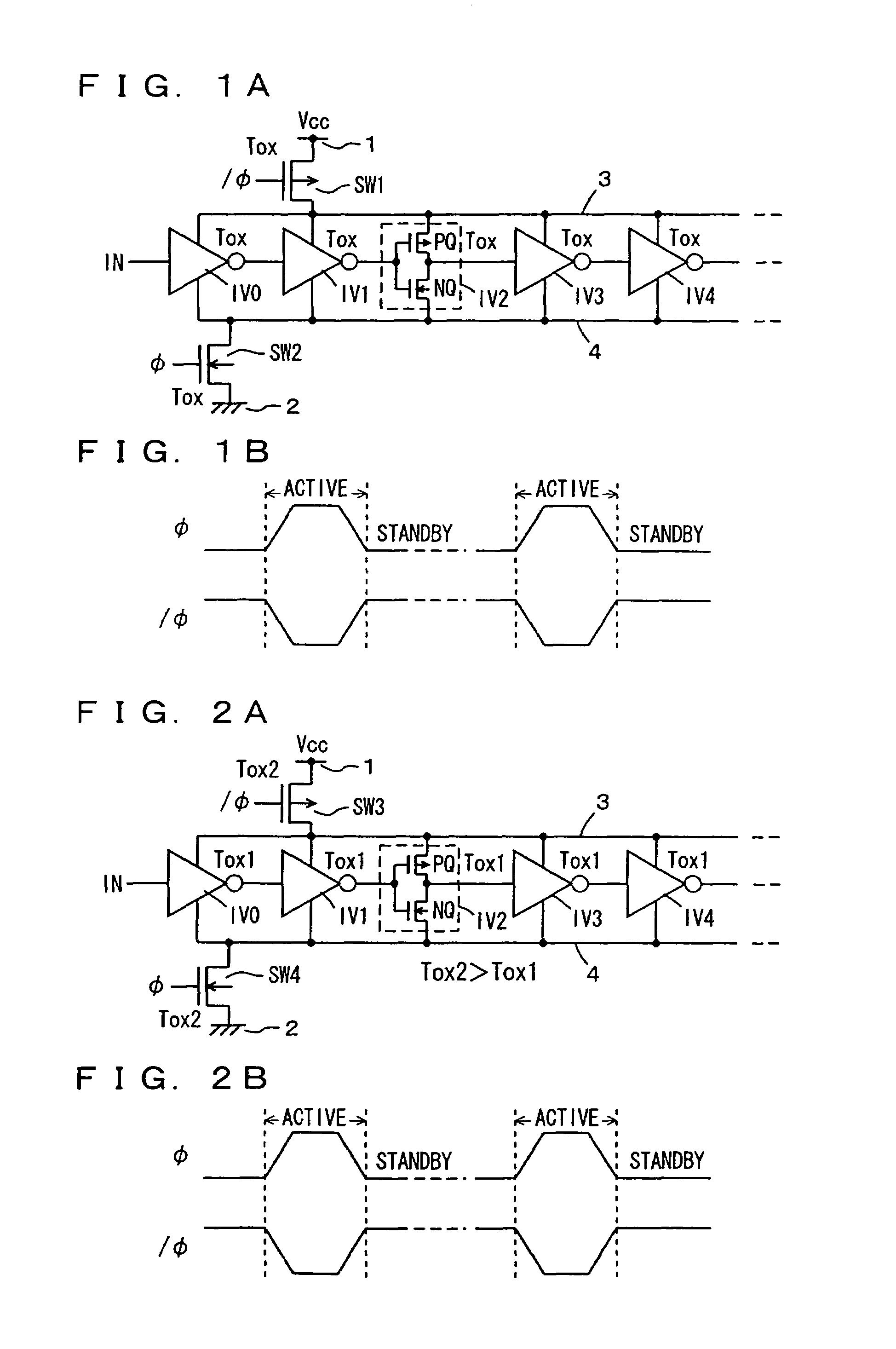
Semiconductor integrated circuit device operating with low power consumption
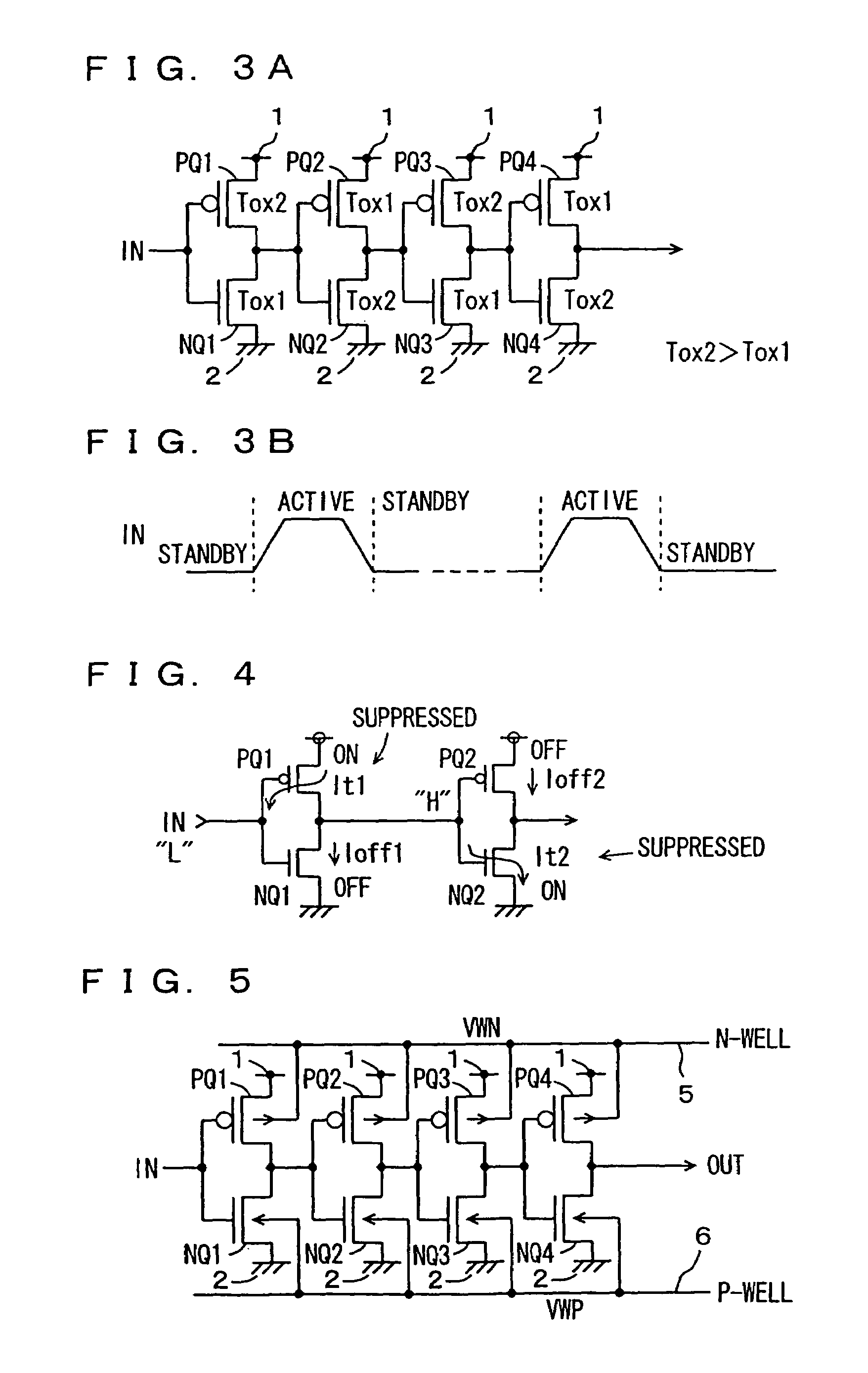
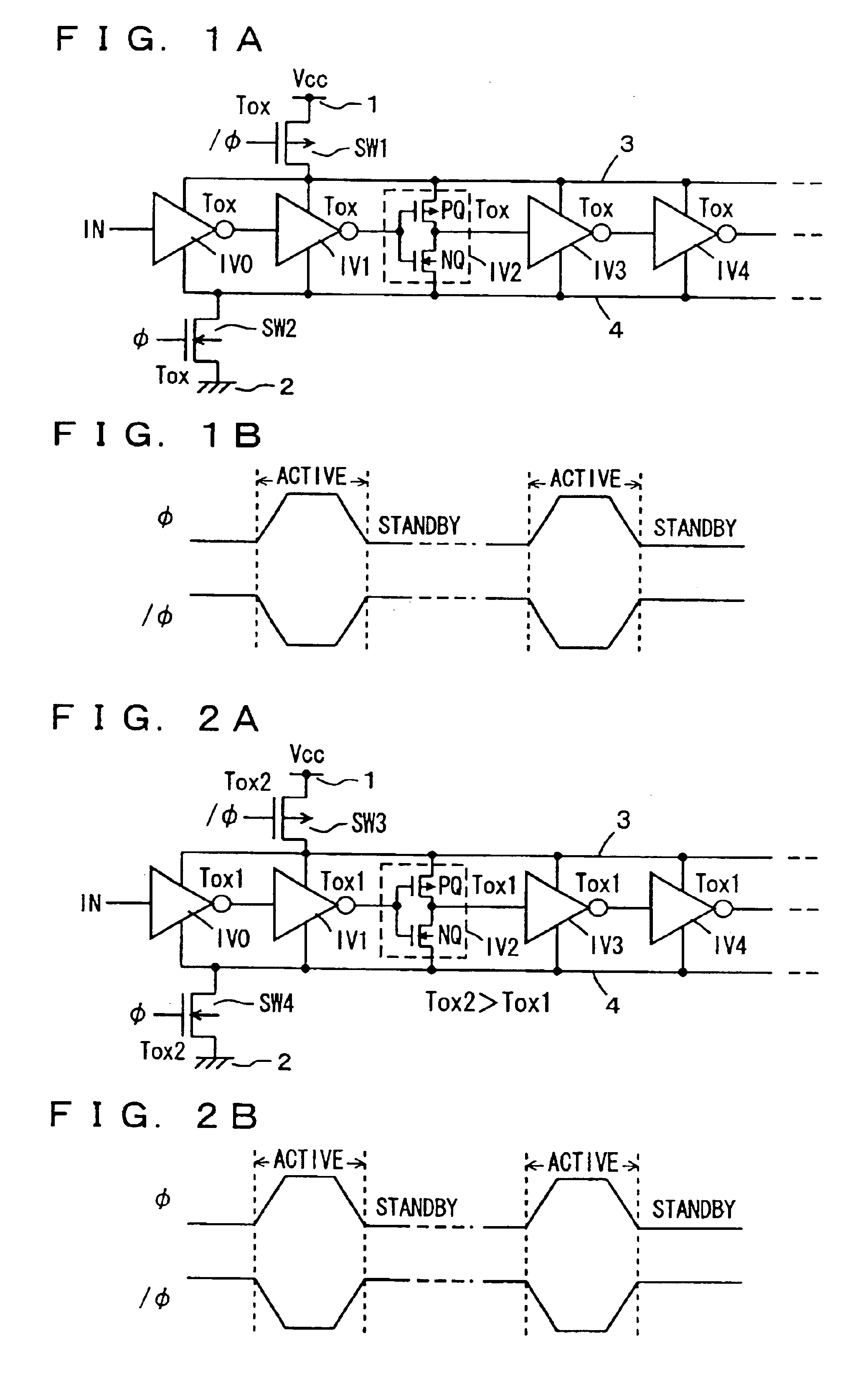
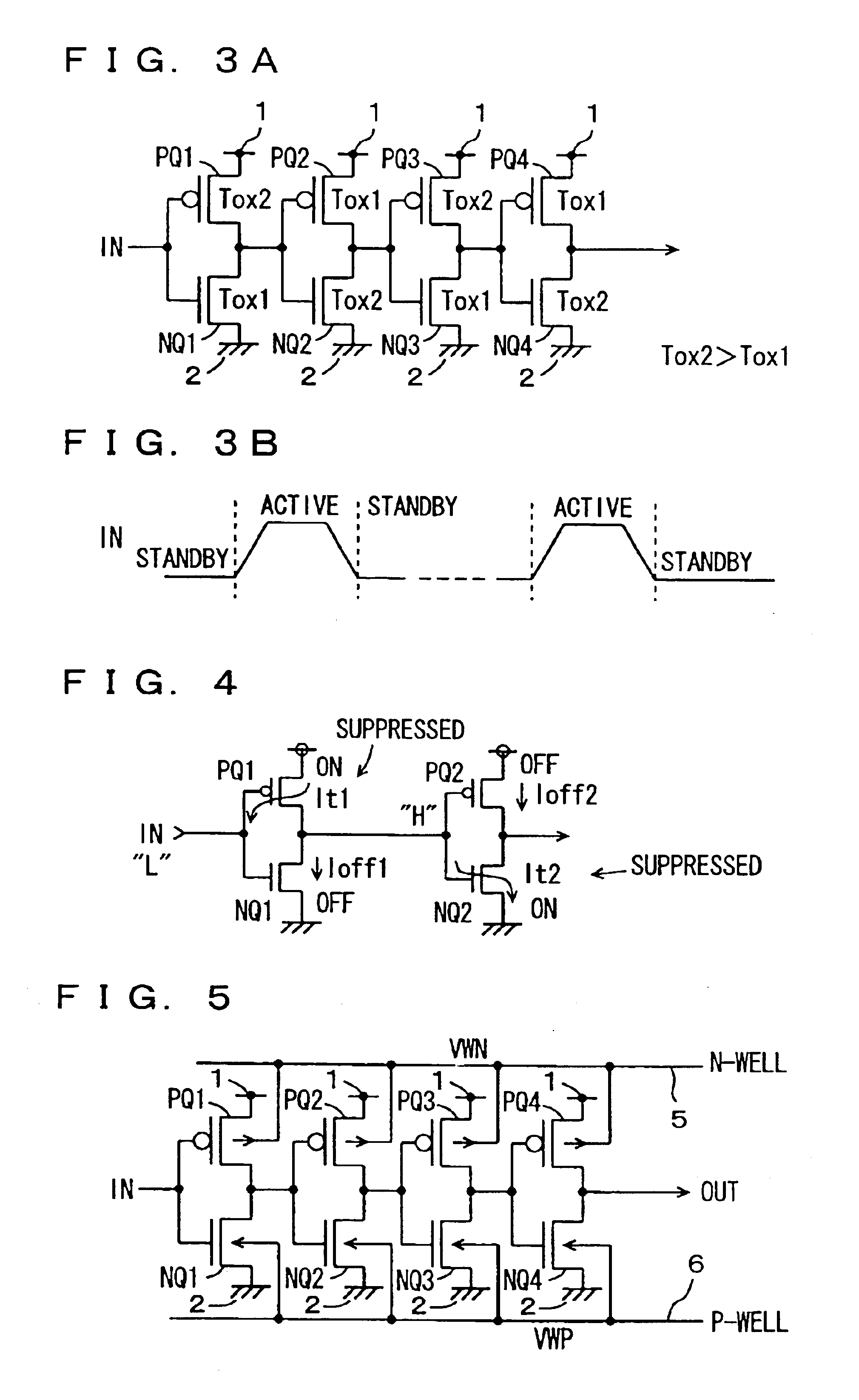
InactiveUS7521762B2Inhibit currentEasy to integrateTransistorReliability increasing modificationsActive stateGround line
Transistors having large gate tunnel barriers are used as transistors to be on in a standby state, MIS transistors having thin gate insulating films are used as transistors to be off in the standby state, and main and sub-power supply lines and main and sub-ground lines forming a hierarchical power supply structure are isolated from each other in the standby state so that a gate tunnel current is reduced in the standby state in which a low power consumption is required. In general, a gate tunnel current reducing mechanism is provided for any circuitry operating in a standby state and an active state, and is activated in the standby state to reduce the gate tunnel current in the circuitry in the standby state, to reduce power consumption in the standby state.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Method for using pulse compression in weather radar
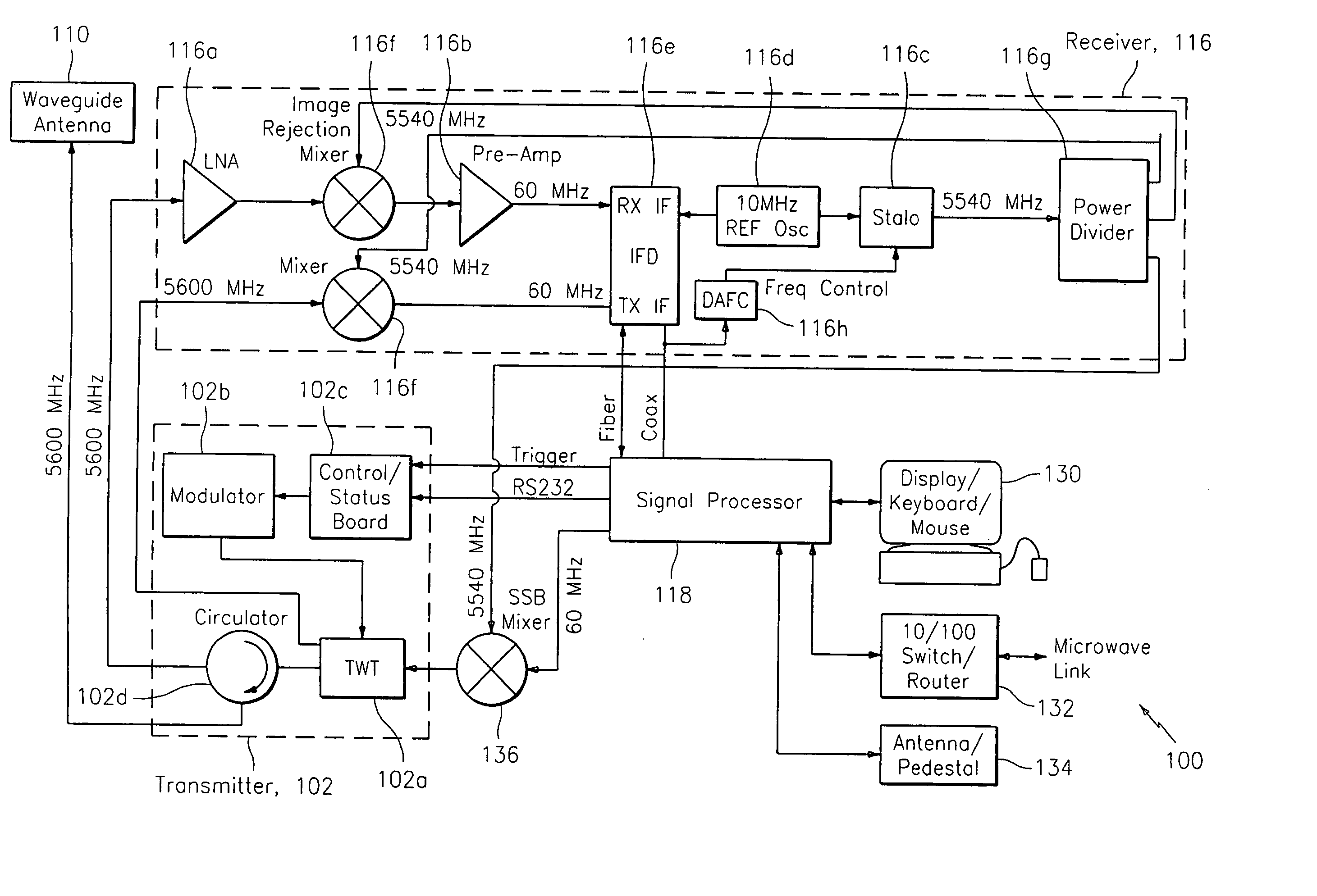
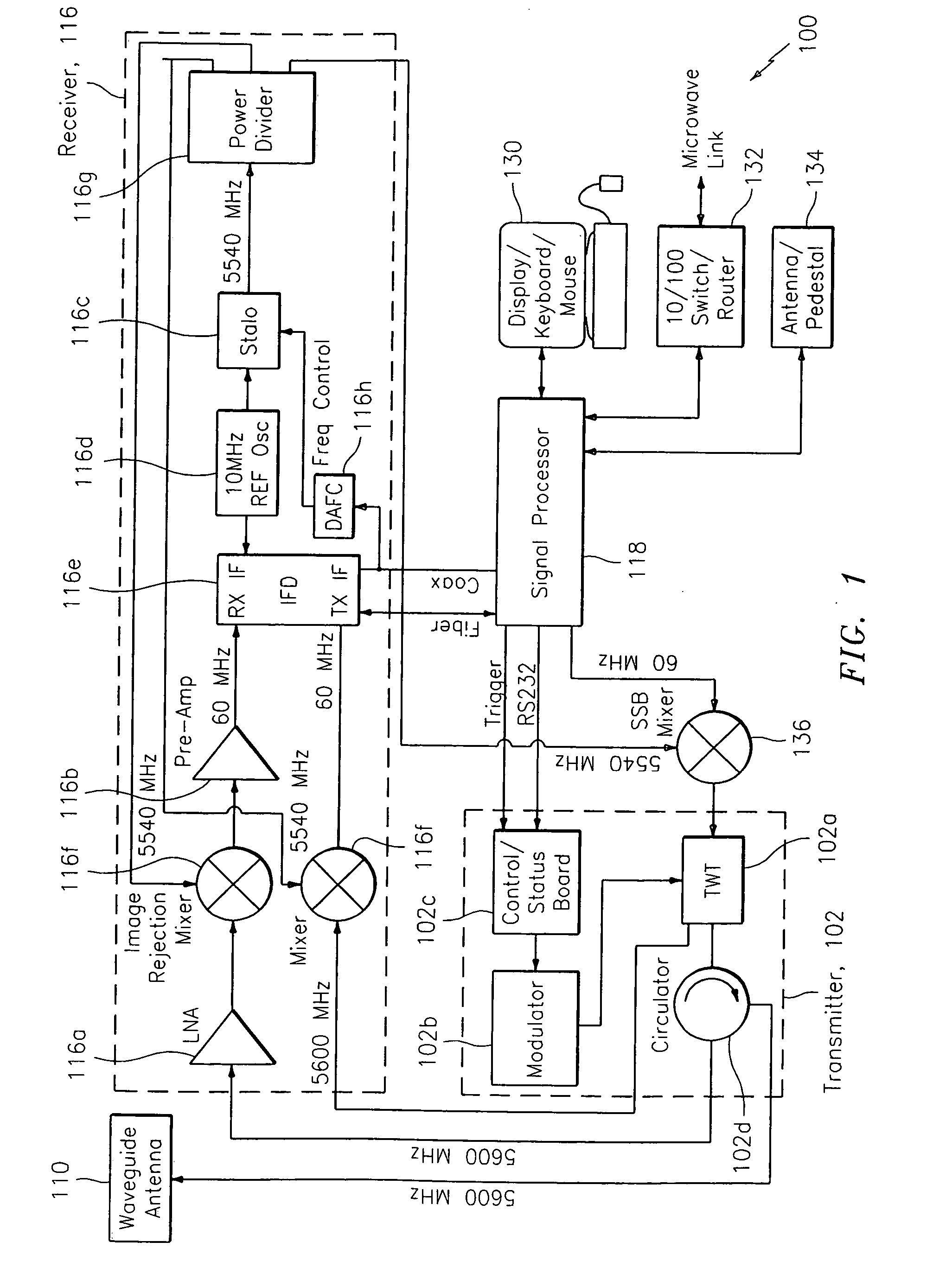
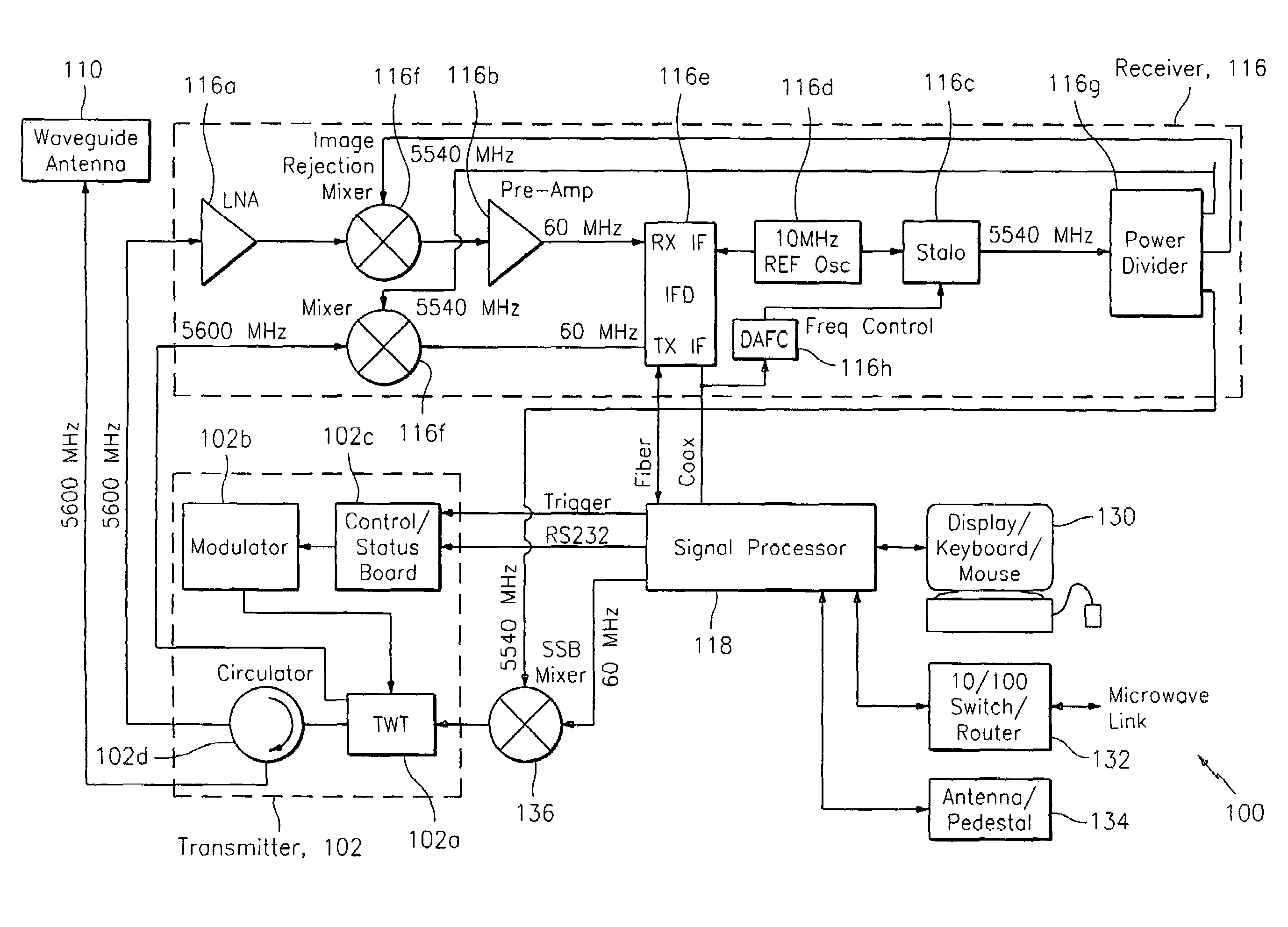
ActiveUS20070046526A1High sensitivityHigh quality meteorological radar imageryRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationWeather radarRadar systems
A system and method for processing data related to weather phenomena in a meteorological radar system. The method includes receiving an echo signal generated by transmitting a long pulse and employing a mismatched windowed filter on the echo signal such that the echo signal is compressed in time to achieve fine range resolution without substantially degrading sensitivity and while achieving low range time side lobes for Doppler velocities expected to be measured by the meteorological radar system.
Owner:VAISALA
Printed wiring board including power supply layer and ground layer
ActiveUS20070144770A1Reduce radiationReliably reducing power supply noisePrinted electric component incorporationCross-talk/noise/interference reductionCapacitorElectrical and Electronics engineering
A first power supply layer spreads over an insulating layer outside an island of a second power supply layer. A first ground layer spreads over an insulating layer outside an island of a second ground layer. First and second electrically-conductive pieces are interposed between the first and second power supply layers as well as between the first and second ground layers. A capacitor is interposed between the first and second electrically-conductive pieces. Power supply noise is forced to inevitably pass through the electrically-conductive pieces. The power supply noise thus reliably flows into the capacitor through the first and second electrically-conductive pieces. A printed wiring board is in this manner allowed to enjoy a sufficient suppression of the power supply noise.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Printed wiring board including power supply layer and ground layer
ActiveUS7428155B2Reliably reducing power supply noiseSufficiently suppressCross-talk/noise/interference reductionPrinted electric component incorporationEngineeringCapacitor
A first power supply layer spreads over an insulating layer outside an island of a second power supply layer. A first ground layer spreads over an insulating layer outside an island of a second ground layer. First and second electrically-conductive pieces are interposed between the first and second power supply layers as well as between the first and second ground layers. A capacitor is interposed between the first and second electrically-conductive pieces. Power supply noise is forced to inevitably pass through the electrically-conductive pieces. The power supply noise thus reliably flows into the capacitor through the first and second electrically-conductive pieces. A printed wiring board is in this manner allowed to enjoy a sufficient suppression of the power supply noise.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Electronic component package including heat spreading member
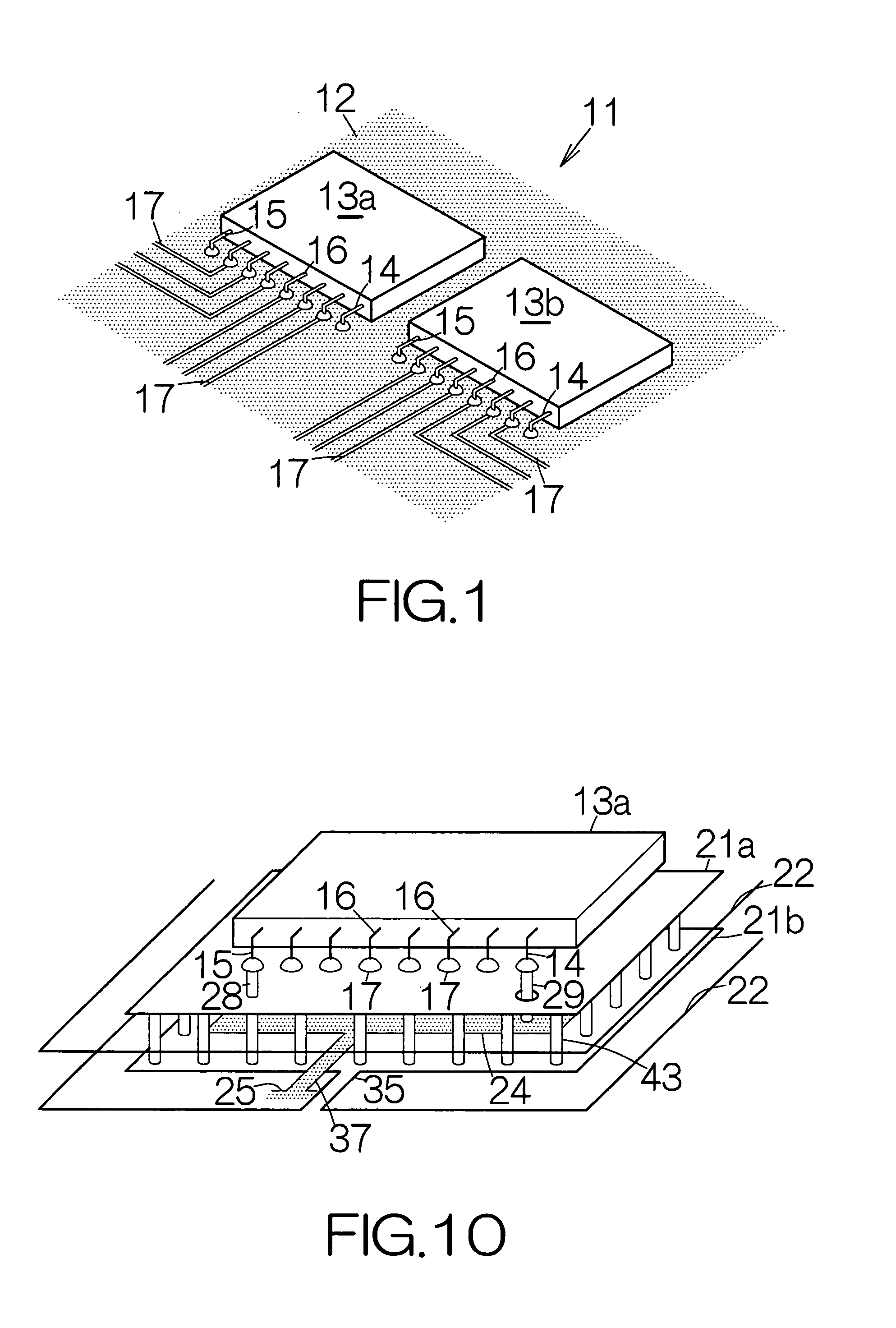
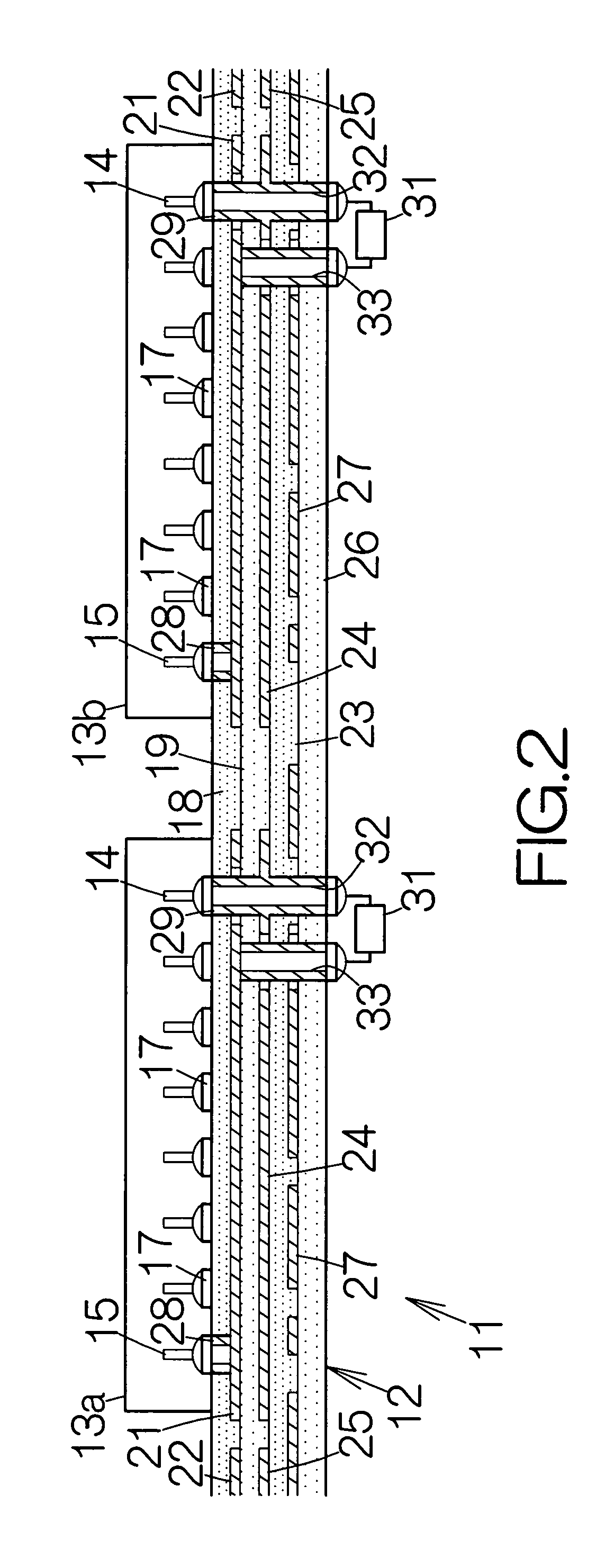
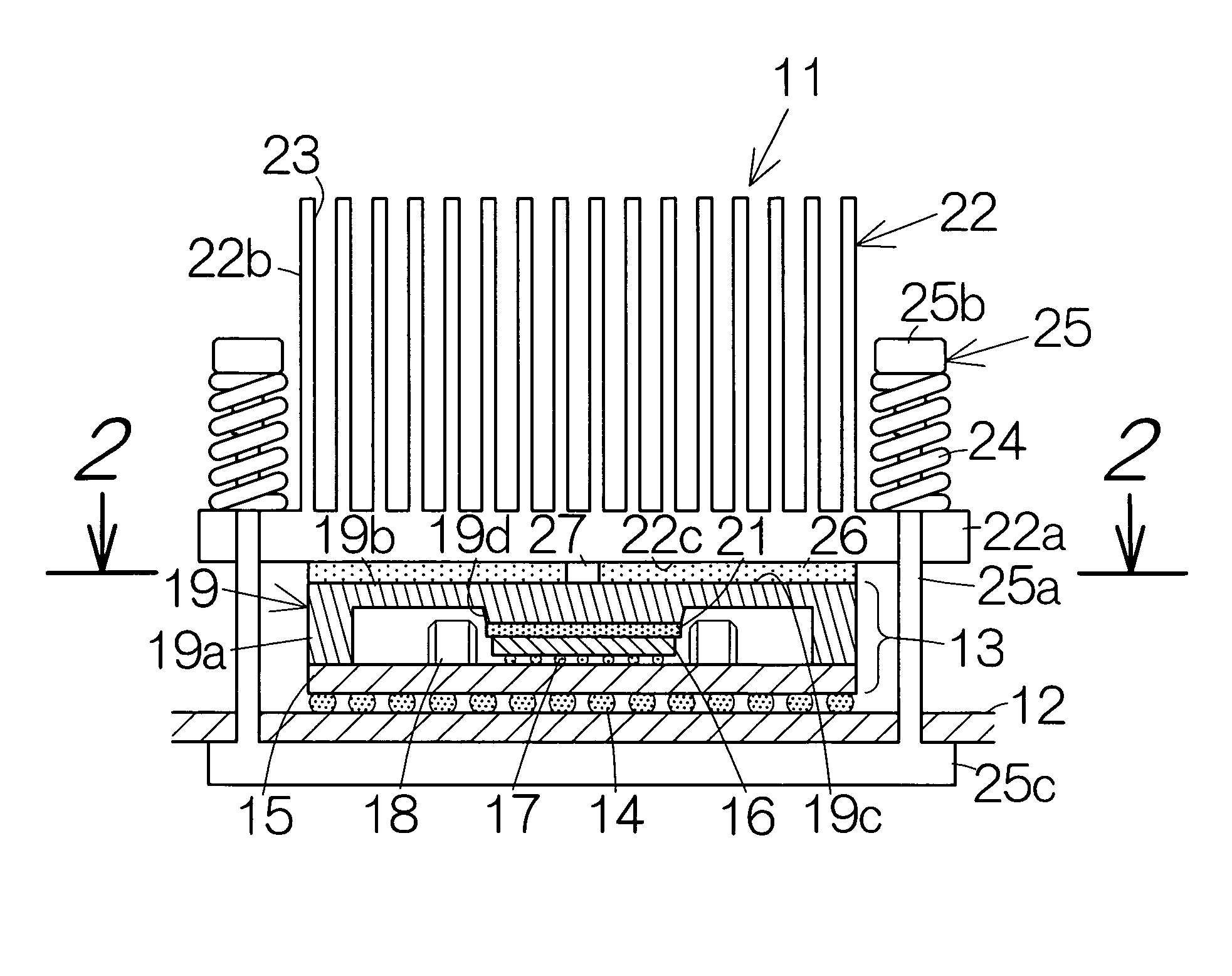
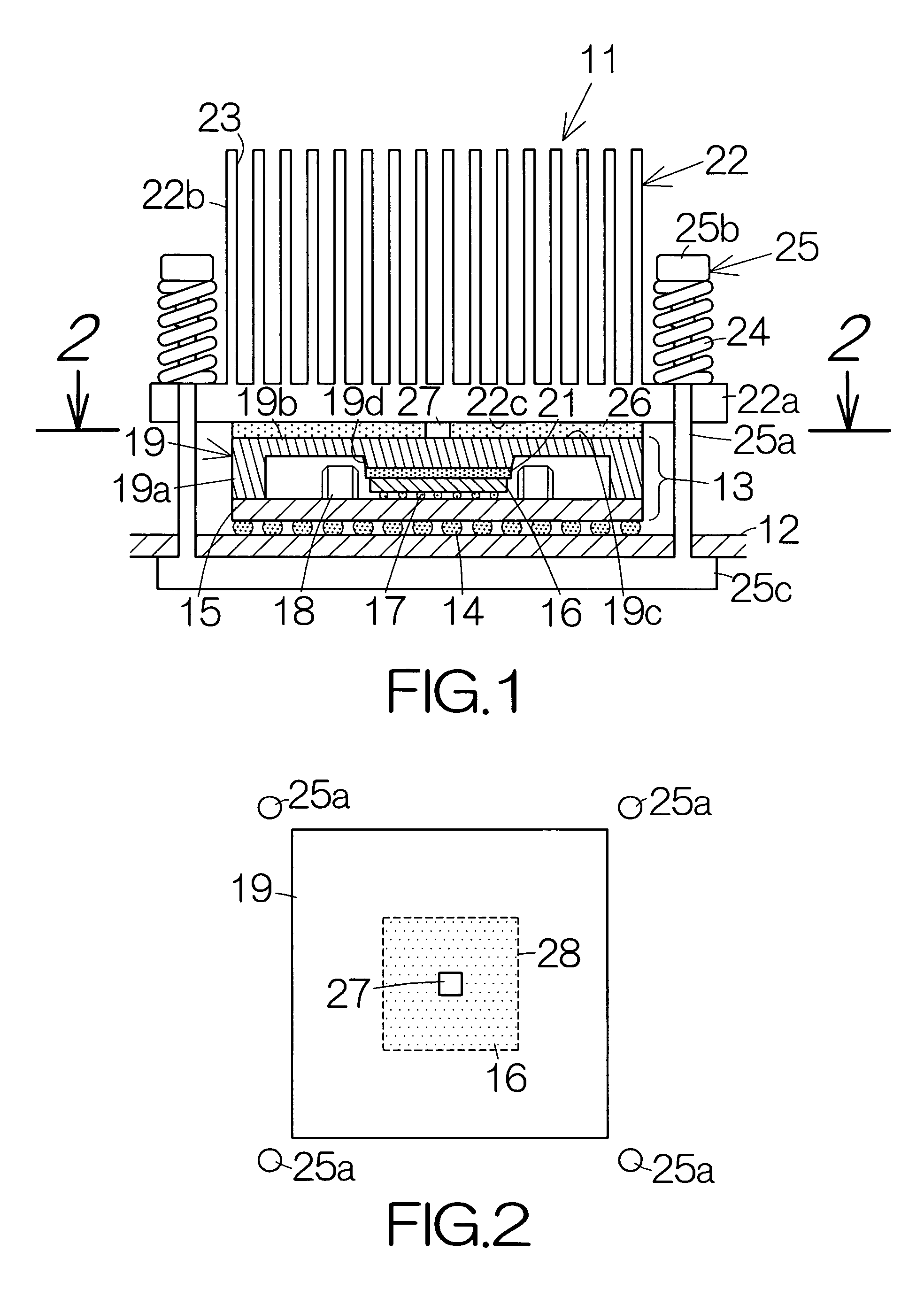
InactiveUS7477519B2Reliable heatingIncrease heat radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringThermal radiation
A heat spreading member is received on a predetermined surface of an electronic component. The heat spreading member extends larger than the predetermined surface. A contact piece is contacted with the heat spreading member over a contact area smaller than the predetermined surface. The contact piece serves to realize concentration of an urging force applied to the heat spreading member. The heat spreading member is thus reliably urged against the electronic component. The concentration of the urging force serves to prevent the heat spreading member and the electronic component from camber even if heat is applied to the heat spreading member and the electronic component. Separation is thus avoided between the heat spreading member and the electronic component. The heat spreading member reliably keeps contacting with the electronic component, so that the electronic component package is allowed to enjoy improvement in heat radiation.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
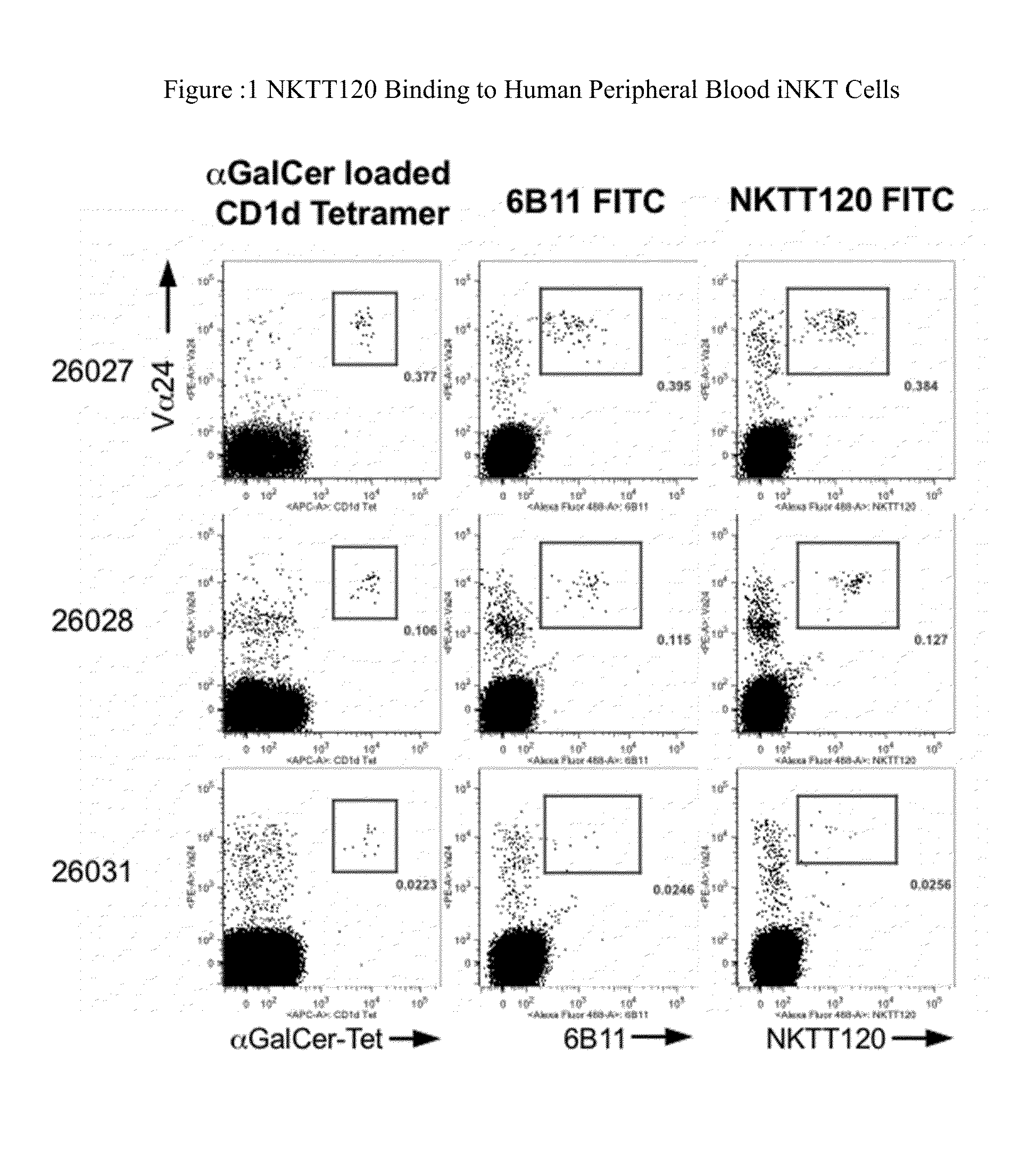
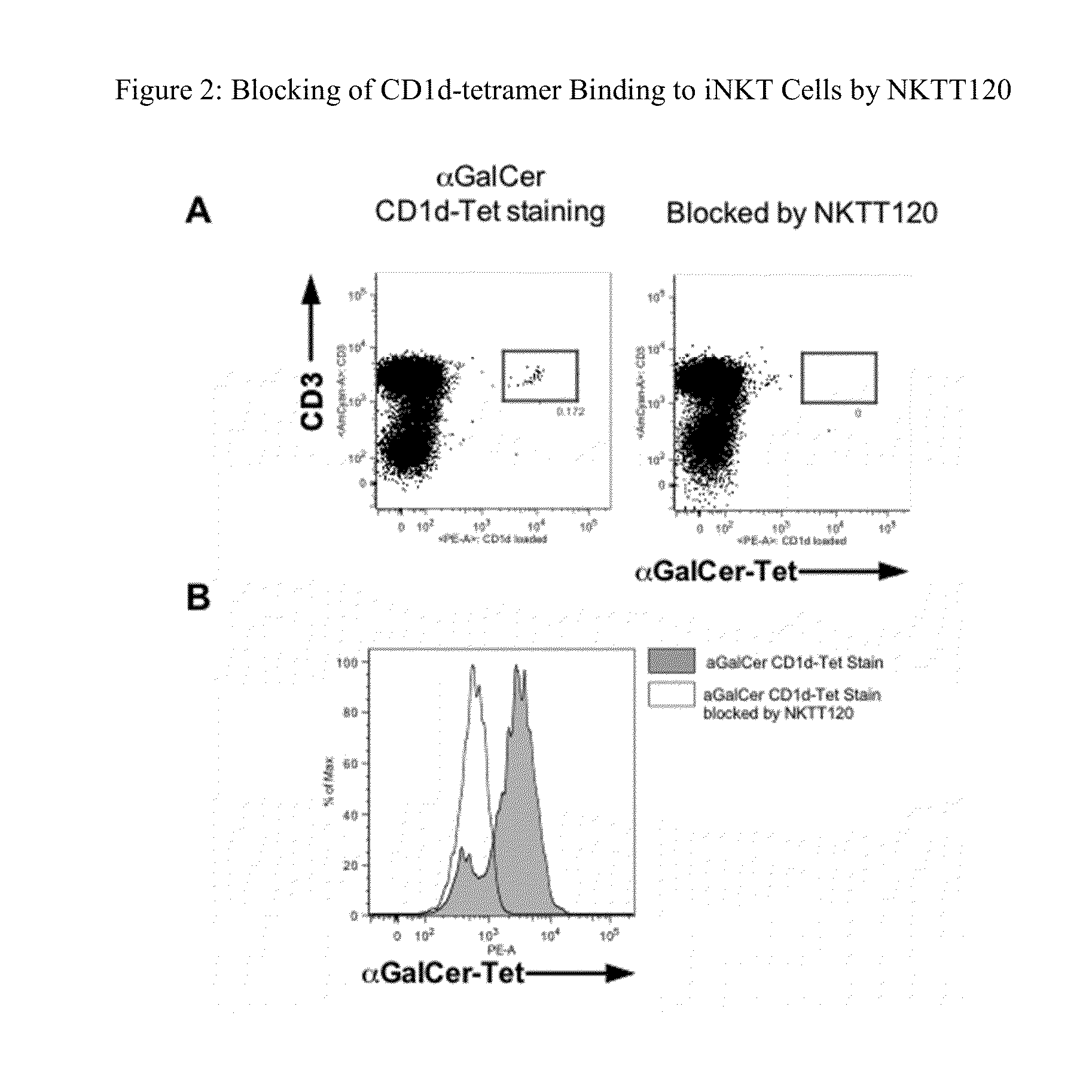
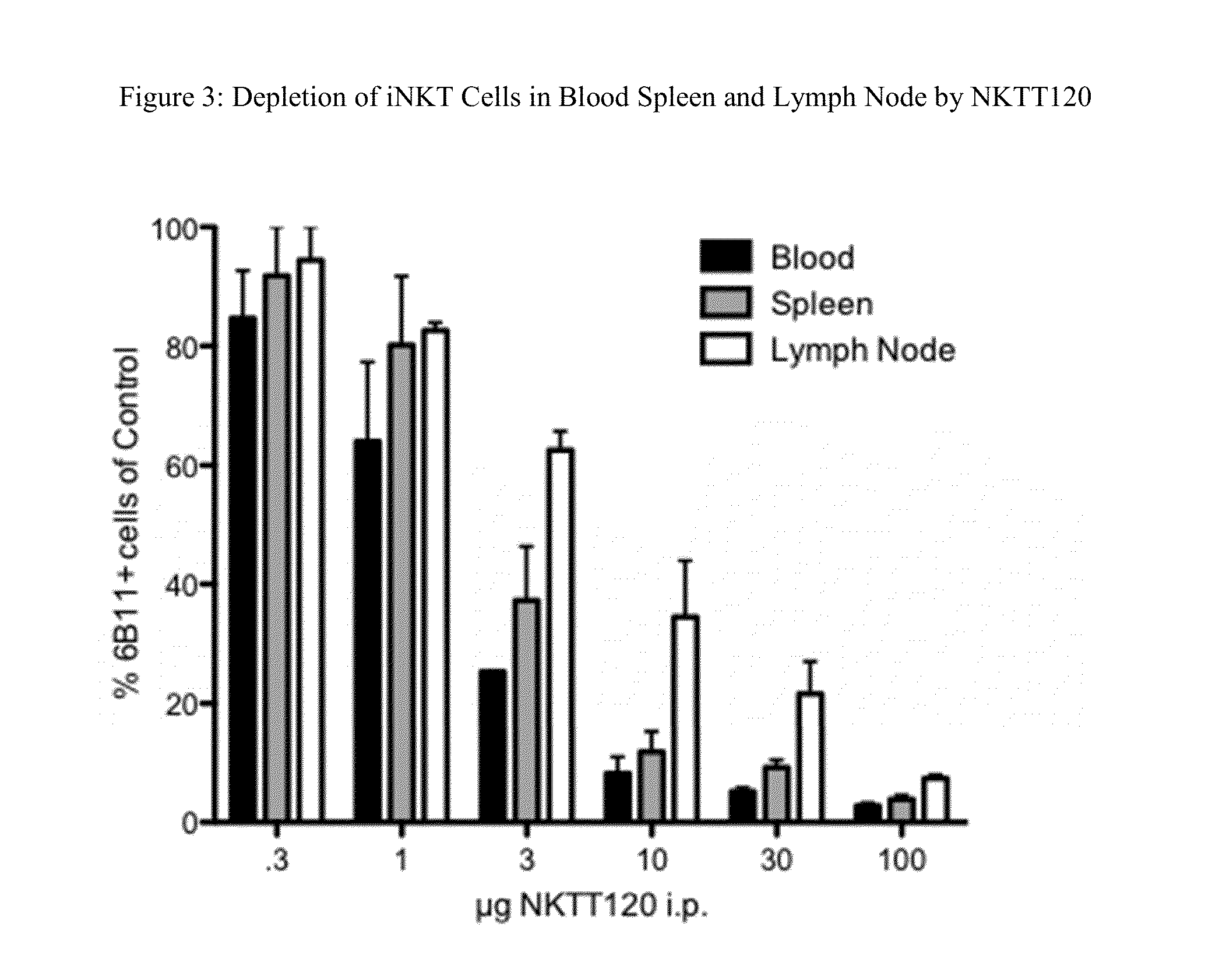
HUMANIZED ANTIBODIES TO iNKT
InactiveUS20130136735A1Suppress immune responseSufficiently suppressAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticBlocking antibodyHumanized antibody
Methods of treatment to suppress an immune response are provided. The method comprises administering to a subject in need of treatment a naked blocking antibody that binds selectively iNKT cells in an amount effective to suppress the subject's iNKT cell function. Compositions comprising, an isolated, humanized antibody that binds selectively iNKT cells are also provided.
Owner:NKT THERAPEUTICS
Transmitter and semiconductor integrated circuit for communication
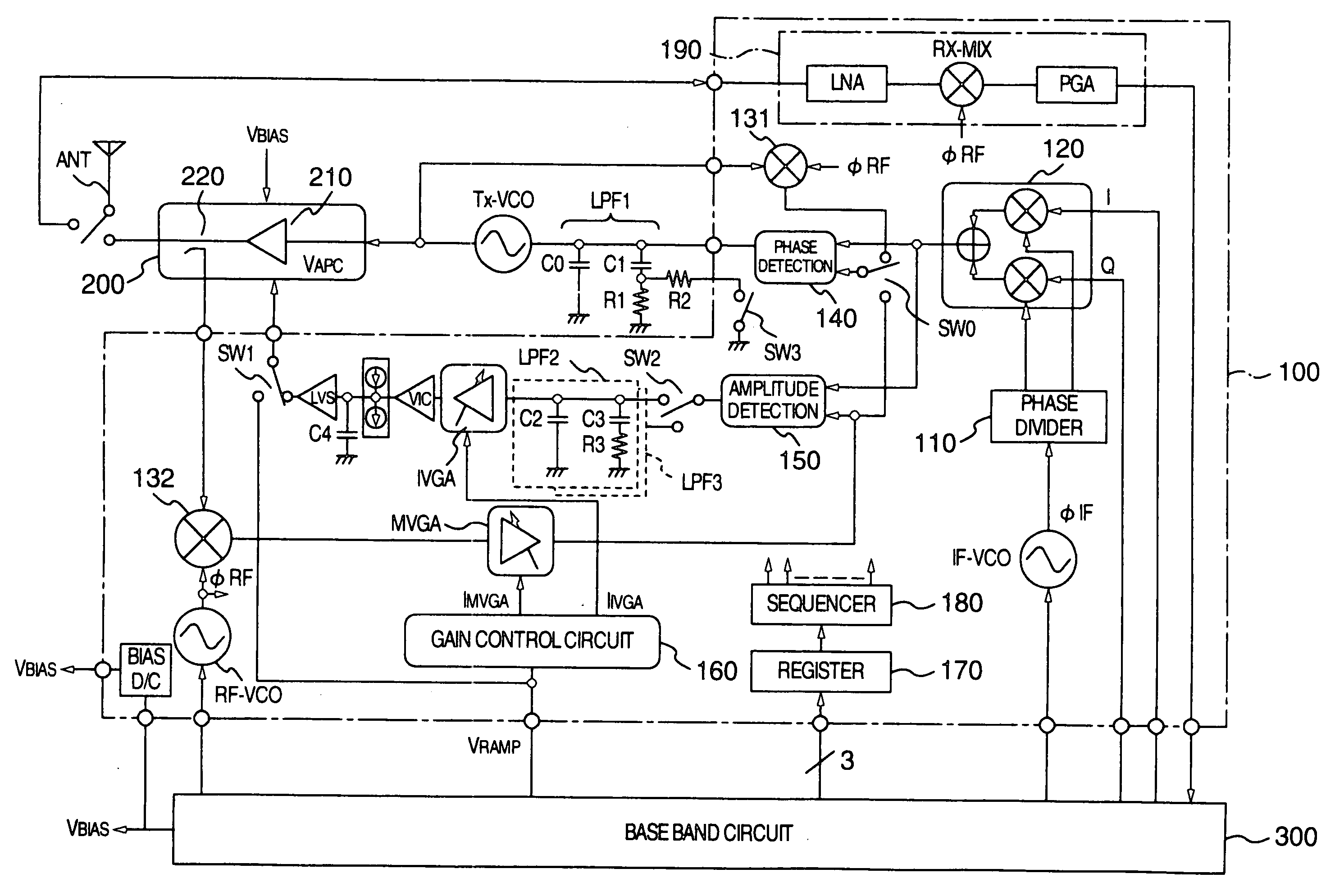
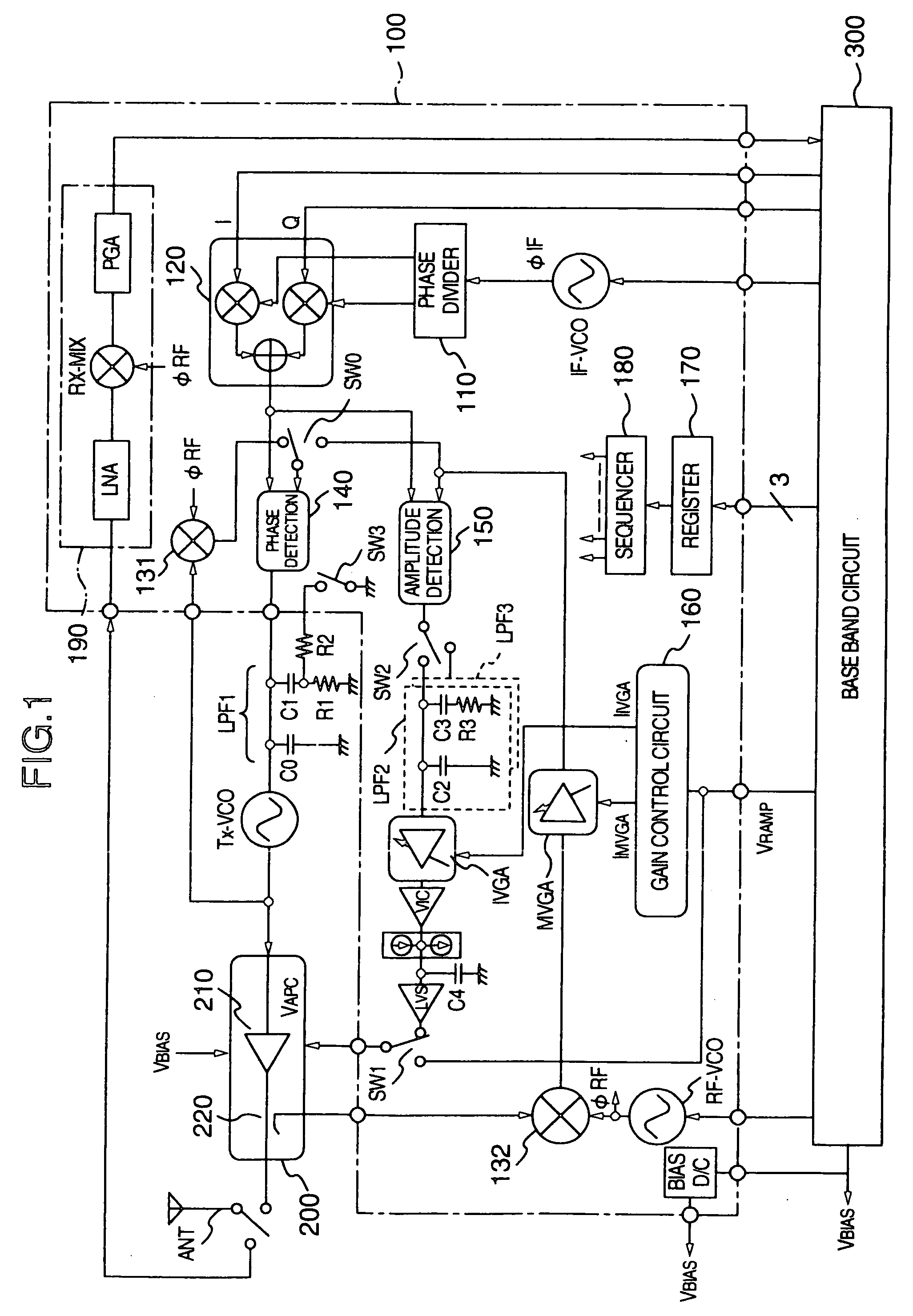
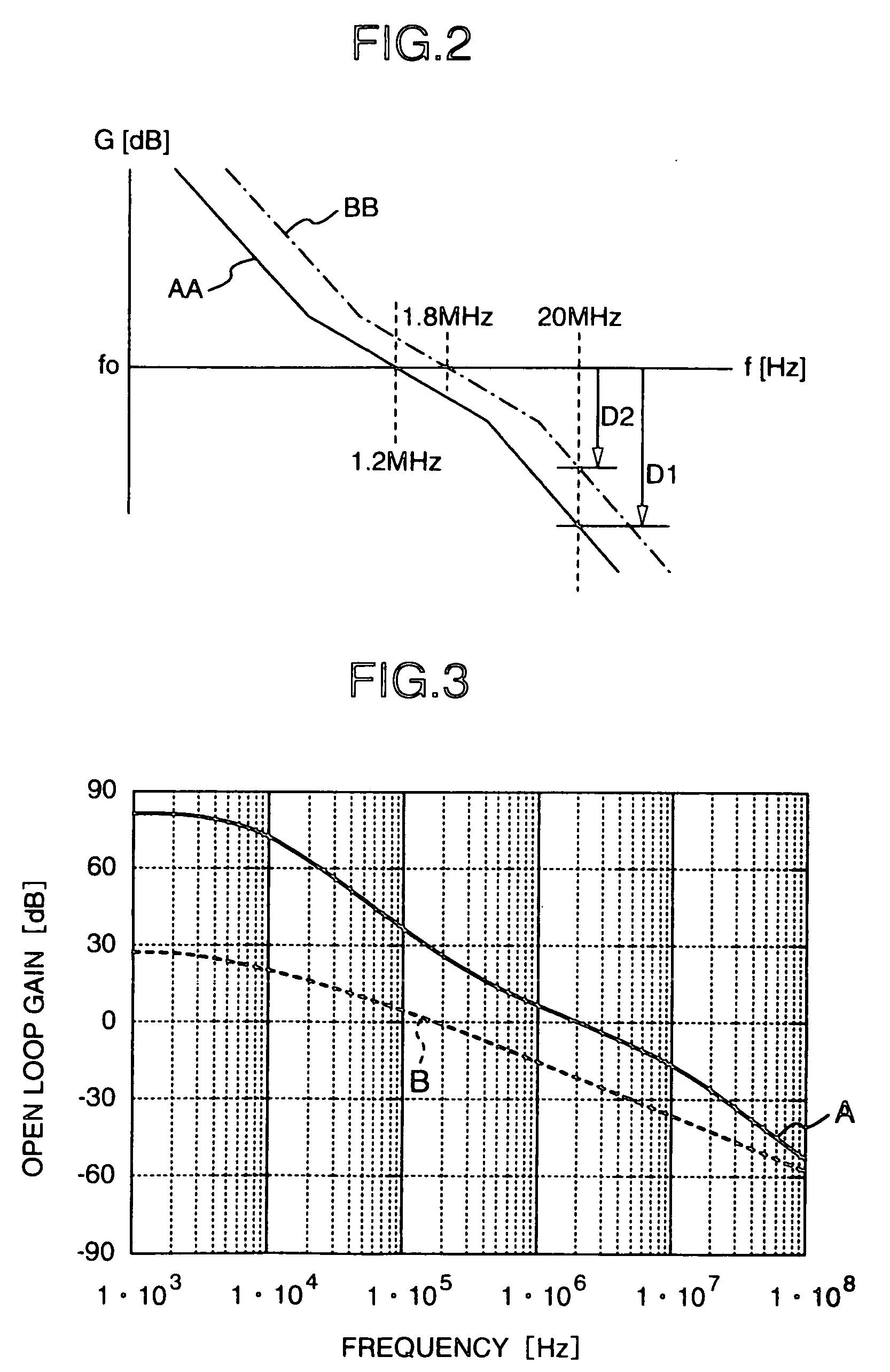
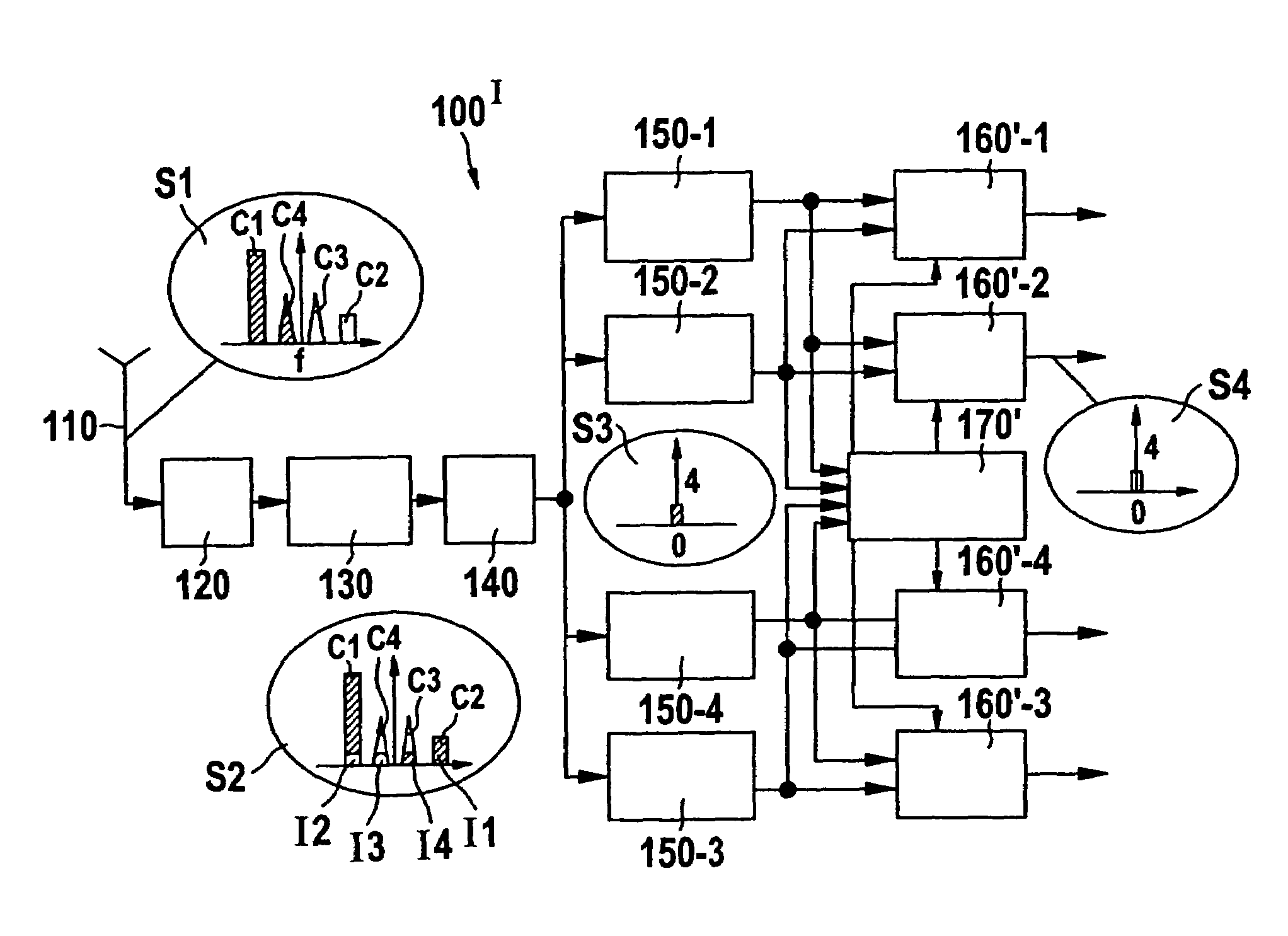
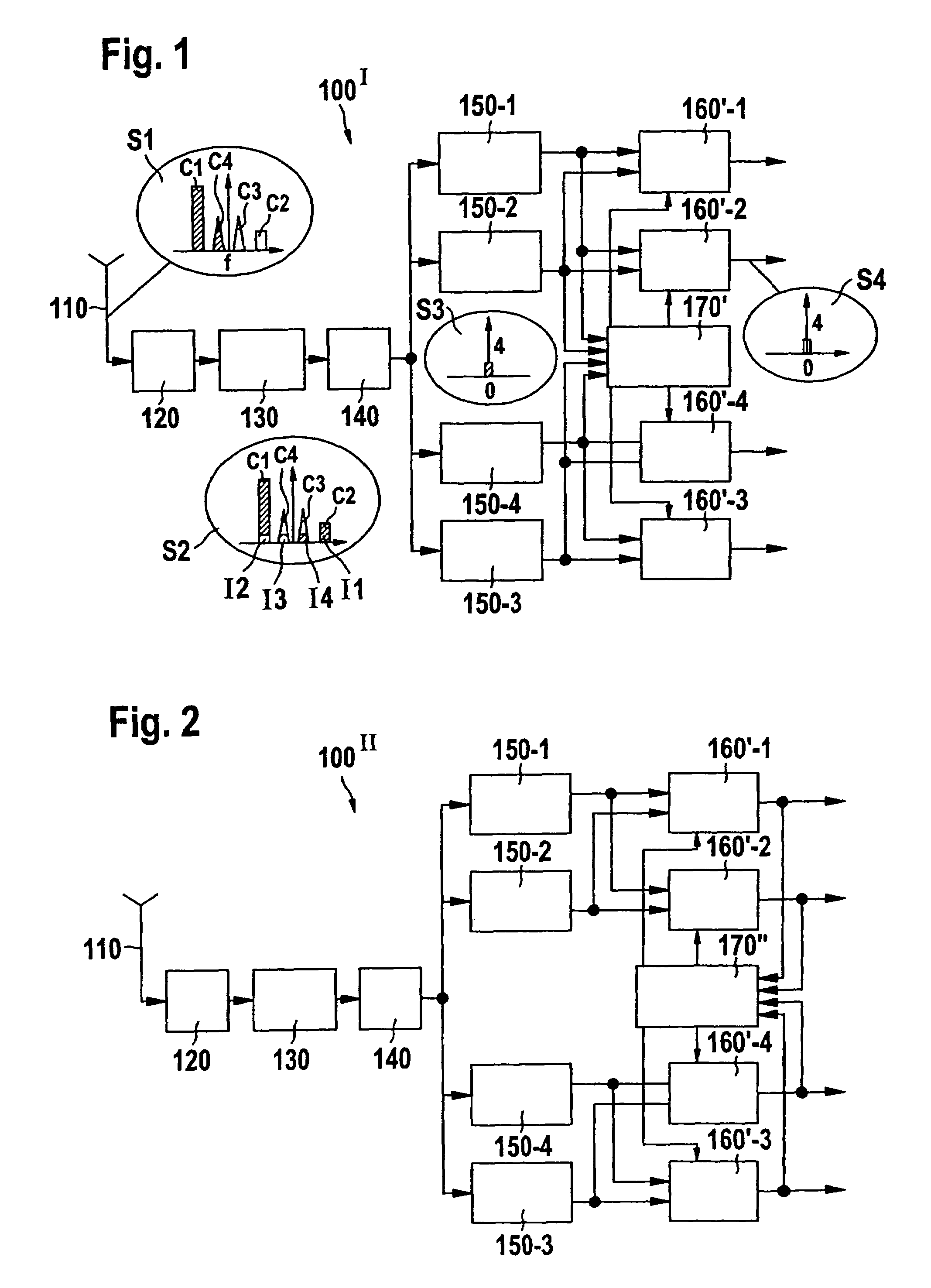
InactiveUS20060217081A1Improve errorNoise reaching the reception frequency band can be suppressed sufficientlySimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationResonant long antennasLoop filterAmplitude control
A transmitter adopting a polar loop system including a phase control loop for controlling the phase of a carrier signal outputted from a transmitting oscillator and an amplitude control loop for controlling the amplitude of a transmitting output signal outputted from a power amplification circuit, and designed to be capable of performing transmission using a GMSK modulation mode and transmission using an 8-PSK modulation mode. In the transmitter, the phase control loop is shared as a phase control loop for use in the GMSK modulation mode and a phase control loop for use in the 8-PSK modulation mode. A component similar to any one of components constituting a loop filter is provided in parallel therewith so that the component can be connected or disconnected in accordance with the modulation mode, for example, by use of a switching element.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC +1
Method for using pulse compression in weather radar
ActiveUS7583222B2High sensitivityShort rangeRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationDoppler velocityRadar systems
A system and method for processing data related to weather phenomena in a meteorological radar system. The method includes receiving an echo signal generated by transmitting a long pulse and employing a mismatched windowed filter on the echo signal such that the echo signal is compressed in time to achieve fine range resolution without substantially degrading sensitivity and while achieving low range time side lobes for Doppler velocities expected to be measured by the meteorological radar system.
Owner:VAISALA
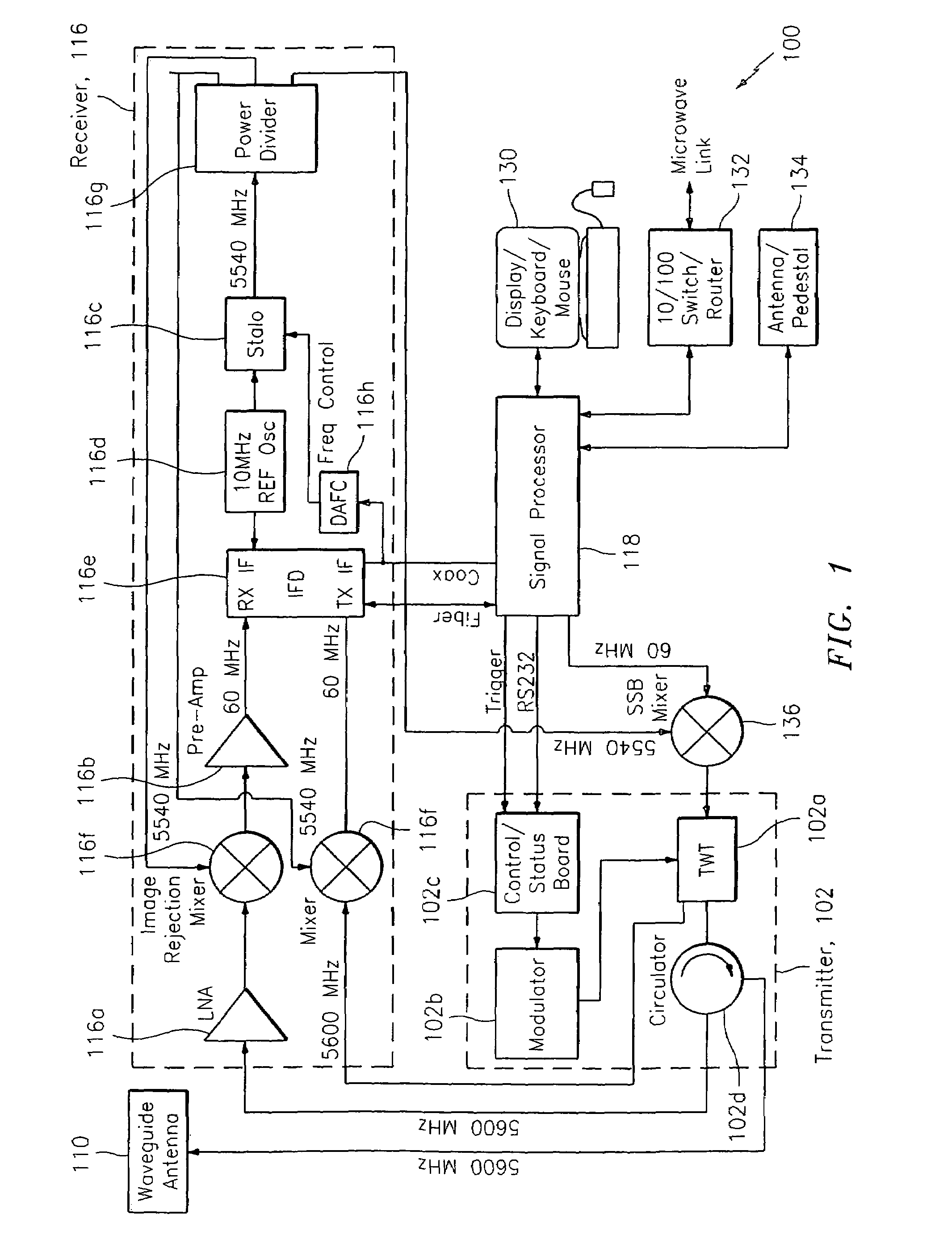
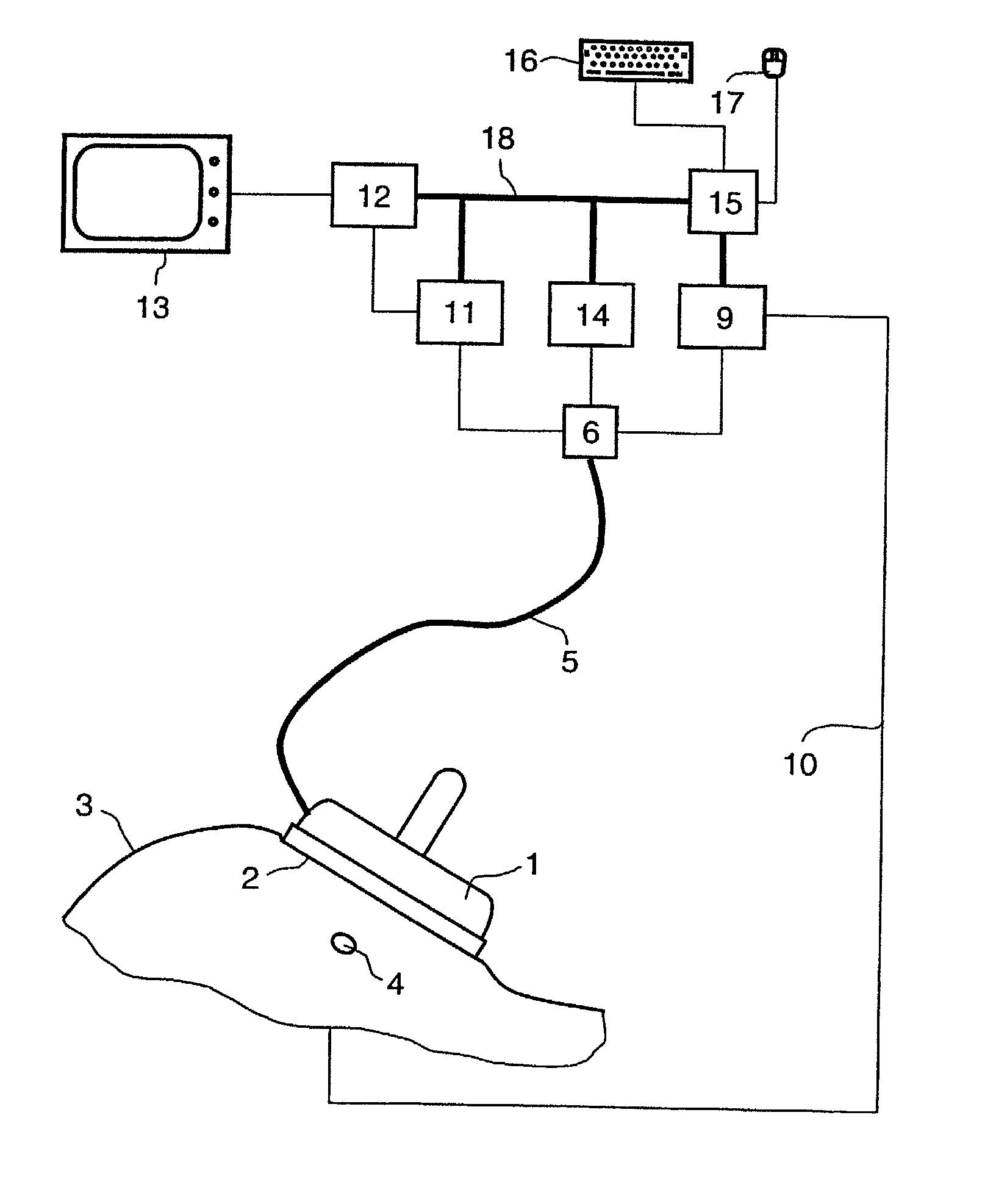
Measurement system for examining a section of tissue on a patient and the use of a measurement system of this type
InactiveUS7729756B2Undesired edge effect is avoidedImprove image qualityResistance/reactance/impedenceCatheterElectrical conductorPower flow
A measurement system for examining a section of tissue on a patient in which electric current and / or voltages are applied to a patient in at least one location and are measured on the section of tissue to be examined by at least one electrode of a contact surface of the measurement system. As a result, conclusions can be drawn about the interior of the section of tissue to be examined. The electrode is at least partially surrounded by a conductor element for contacting with a potential which deviates from that of the conductor element.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
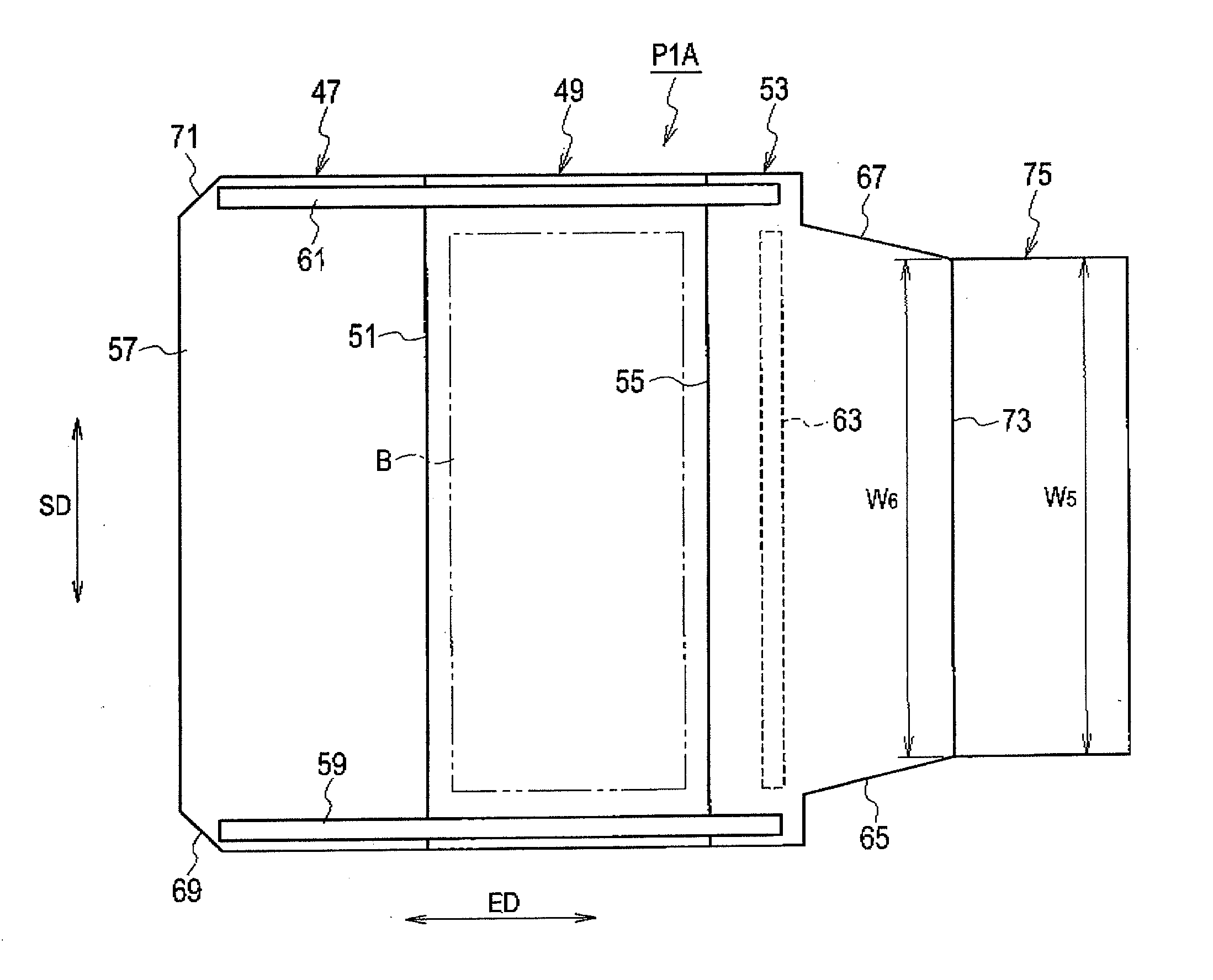
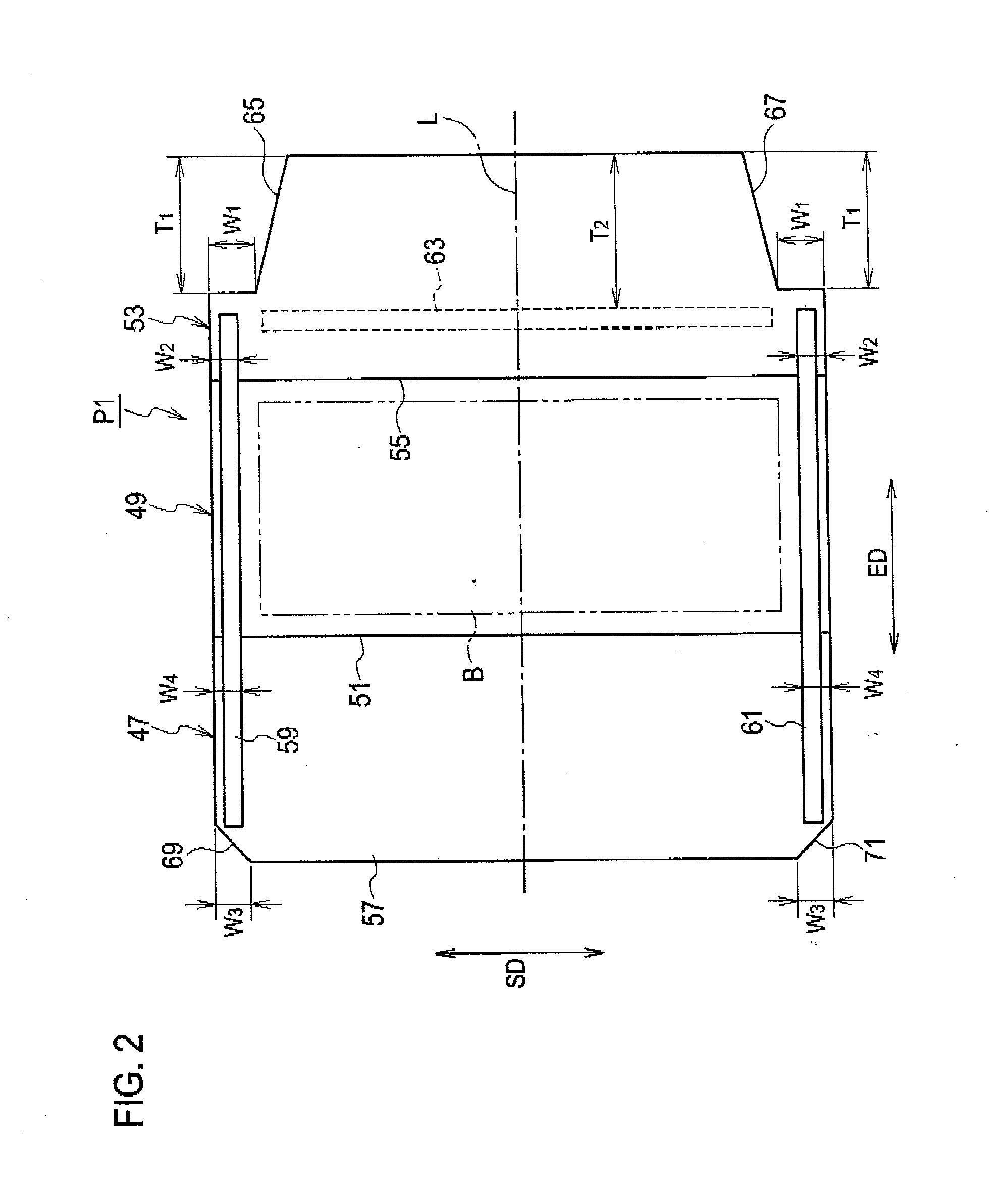
Envelope sheet
ActiveUS20130206824A1Correction of deformationReduce stiffnessEnvelopesEnvelope closersPaper sheetCoating
Another coating part is formed along a sheet short side direction, on a region which is a part of an envelope outer side of a third component sheet and which contacts a flap by folding along a second folding line. A first cutout part and a second cutout part which respectively extend in an extension direction of a first coating part and a second coating part, are respectively formed on both side fringes in the sheet short side direction in the third component sheet. The minimum width of each of the first cutout part and the second cutout part in the sheet short side direction is set longer than a length from the side fringe of the envelope sheet in the sheet short side direction to the inner side fringe of each of the first coating part and the second coating part.
Owner:RISO KAGAKU CORP
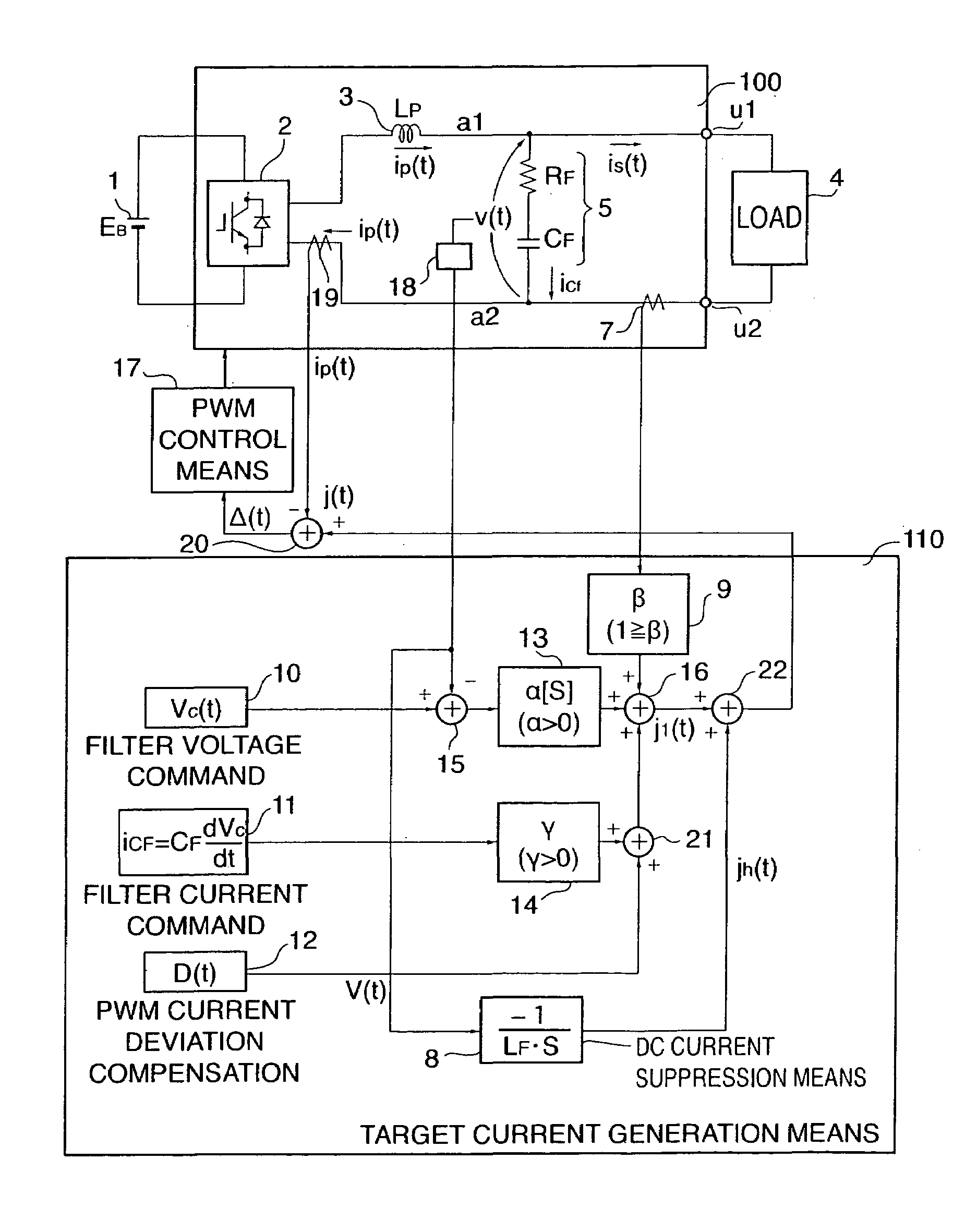
Single-phase power conversion device and three-phase power conversion device
InactiveUS7184282B2Sufficiently suppressBiased magnetization can be preventedEmergency protective circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversionTransformerTerminal voltage
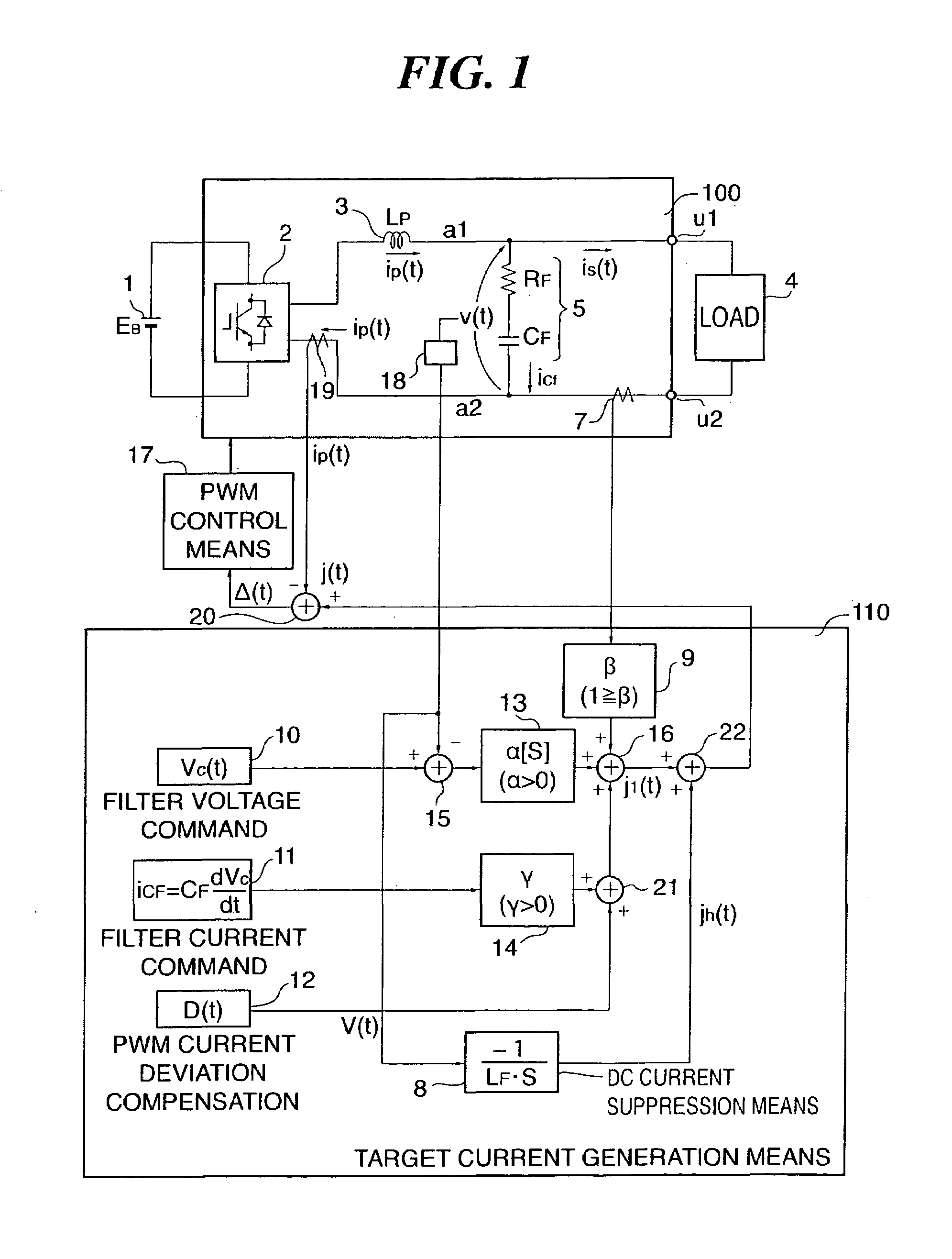
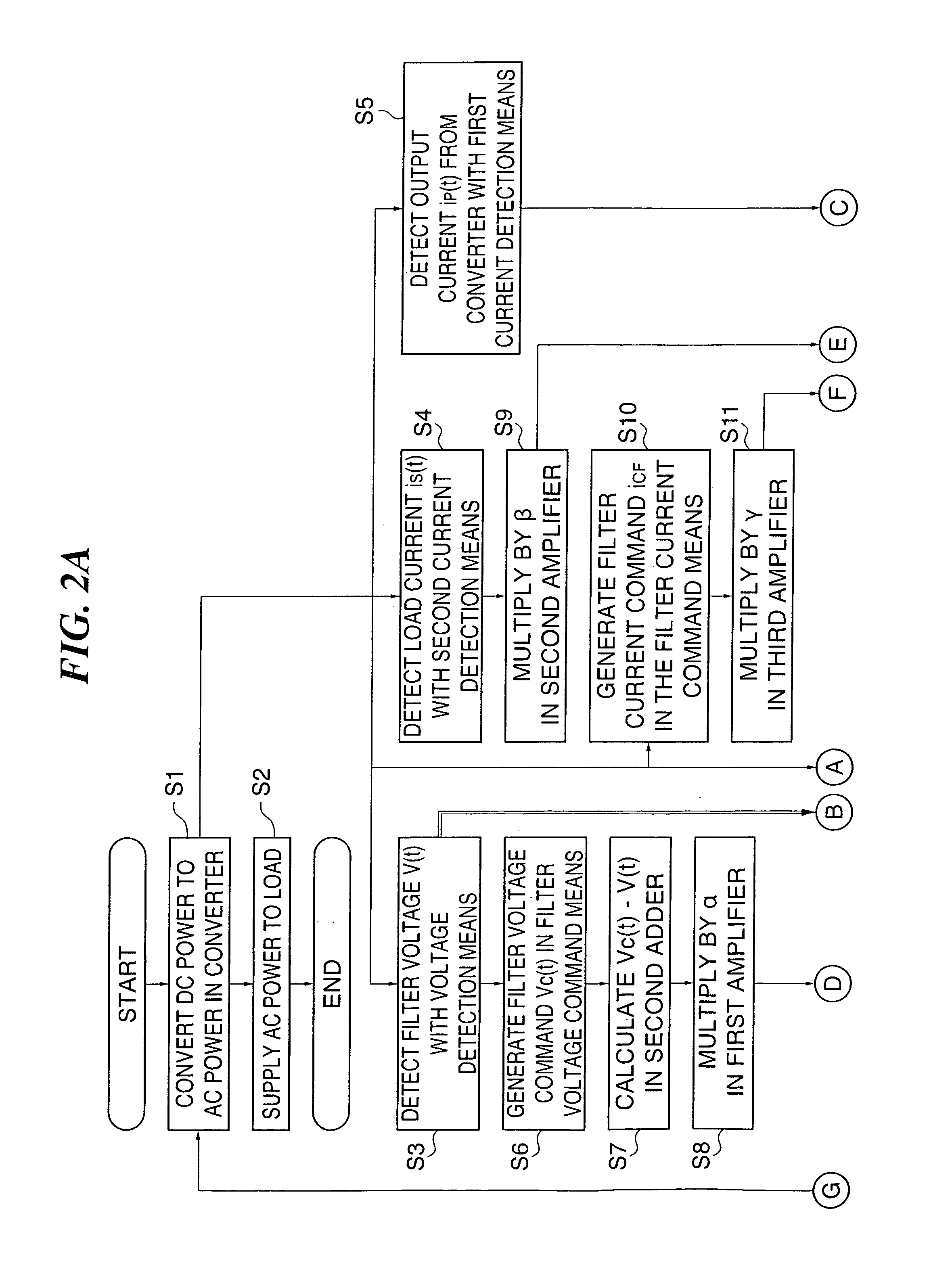
To suppress a DC component in AC power in a power converter for converting DC power to AC power. DC power is converted to AC power by a converter 2, and the AC power is supplied to output terminals u1 and u2 via an inductor 3. The converter 2 is controlled based on an error Δ(t) between an output current ip(t) outputted from the converter 2 and a target current j(t) outputted from a target current generation means 110 as a target value for the output current ip(t), and a DC component VD in an output terminal voltage v(t) is detected by a voltage detection means 18. A DC component ID is suppressed by correcting a target current j(t) by a DC component suppression means 8. Also, a DC component in the AC power is suppressed to prevent biased magnification of a transformer 4 by calculating a correction amount jh(t) for correcting the target current j(t) from the difference between a first instantaneous value d1 of a load current is(t) flowing to a load 4 at a first time point t1 and a second instantaneous value d2 of the load current is(t) at a second time point t2 that is a half cycle after the first time point to correct the target current j(t).
Owner:ORIGIN ELECTRIC CO LTD
Semiconductor device having an oxide semiconductor and a metal oxide film
ActiveUS9147768B2Stable electrical characteristicsImprove reliabilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor deviceActive layer
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Solid-state imaging device and method of manufacturing the same
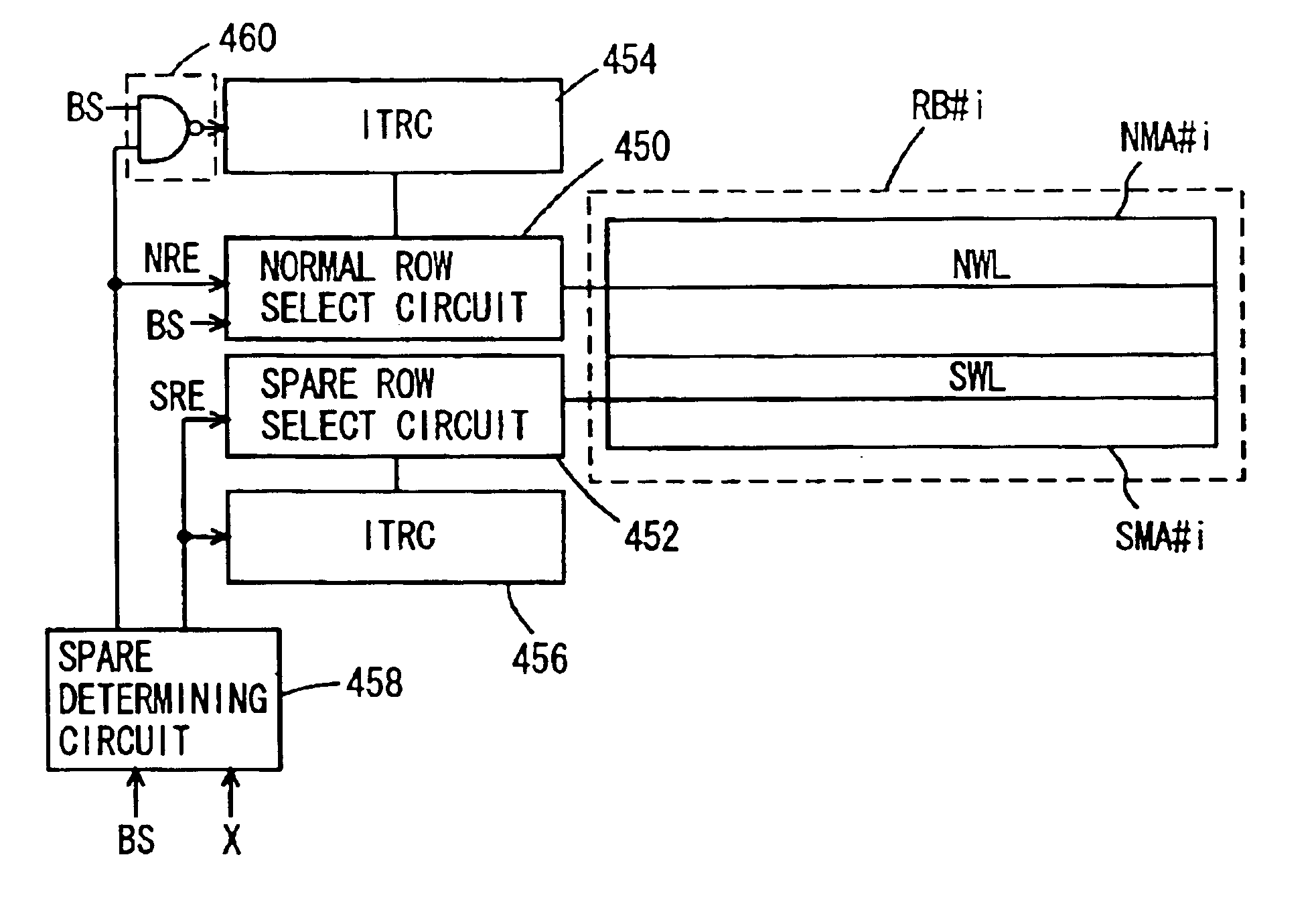
InactiveUS20050082631A1Improved readout characteristicSuppresses image defectsTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesLow voltageEngineering
A solid-state imaging device includes: a plurality of N-type photodiode regions formed inside a P-type well; a gate electrode having one edge being positioned adjacent to each of the photodiode regions; a N-type drain region positioned adjacent to the other edge of the gate electrode; an element-isolating portion having a STI structure, and a gate oxide film having a thickness of not more than 10 nm. One edge of the gate electrode overlaps the photodiode region. First, second and third regions are formed on a surface portion extending from the photodiode region to the drain region, in conditions such that the first region is disposed with a predetermined distance from one edge of the gate electrode and has a P-type first concentration C1, the second region is disposed with one edge positioned adjacent to the first region and the other edge overlapping the gate electrode and has a P-type second concentration C2, and the third region is disposed with one edge positioned adjacent to the second region and the other edge positioned adjacent to the drain region and has a P-type third concentration C3, wherein C1>C2>C3 or C1≈C2>C3. The readout characteristic at a low voltage is satisfactory, and image defects such as white flaws and dark current are suppressed sufficiently.
Owner:COLLABO INNOVATIONS INC
Direct conversion receiver
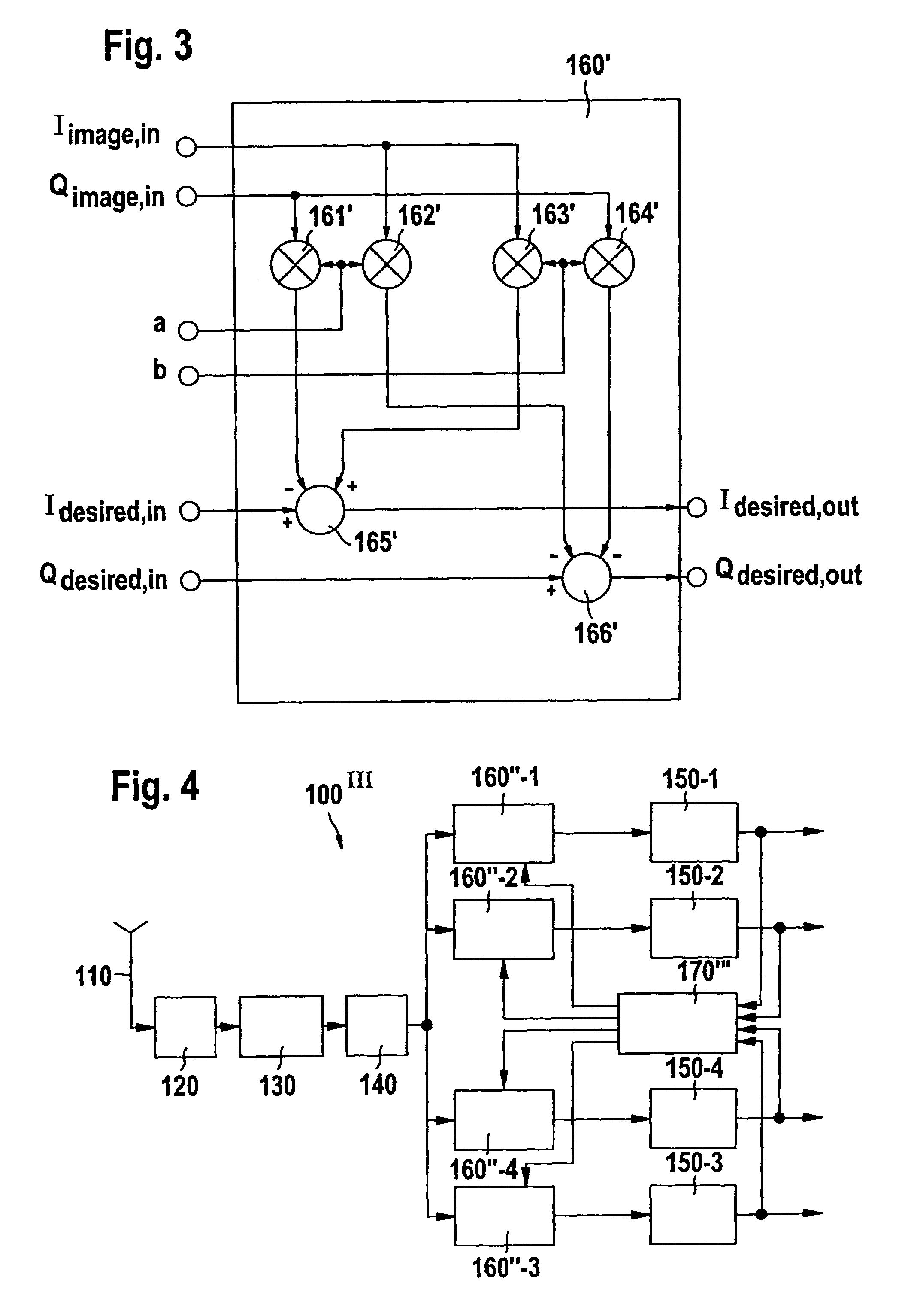
InactiveUS7292836B2For further processingSufficiently suppressMulti-frequency code systemsTransmission noise suppressionFrequency changerDigital down converter
The invention relates to a direct conversion receiver for down-converting a received multi-carrier signal comprising at least a first and a second carrier signal at image carrier frequencies to a base band resulting in that the first carrier signal includes an image signal of said second carrier signal. Further, the known direct conversion receiver comprises at least a first and a second digital down-converter unit for separating the first and the second carrier signal from the down-converted multi-carrier signal after digitization. In order to make such receivers less complex and adjust them for fast time varying szenarios it is proposed to provide an error estimating unit to said receivers for calculating a compensating coefficient representing the quota and / or the phase position of the image signal of the second carrier signal being included in the first carrier signal and to remove the undesired image signal in response to said compensating coefficient.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Semiconductor integrated circuit device operating with low power consumption
InactiveUS6911703B2Suppress current consumptionEasy to integrateTransistorPower reduction by control/clock signalEngineeringLow power dissipation
Transistors having large gate tunnel barriers are used as transistors to be on in a standby state, MIS transistors having thin gate insulating films are used as transistors to be off in the standby state, and main and sub-power supply lines and main and sub-ground lines forming a hierarchical power supply structure are isolated from each other in the standby state so that a gate tunnel current is reduced in the standby state in which a low power consumption is required. In general, a gate tunnel current reducing mechanism is provided for any circuitry operating in a standby state and an active state, and is activated in the standby state to reduce the gate tunnel current in the circuitry in the standby state, to reduce power consumption in the standby state.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Press-formed product
ActiveUS9718113B2Inexpensive materialsSufficiently suppressEngine componentsThin material handlingEngineeringWork hardening
A press-formed product includes a body having a transverse cross section including a bottom portion and a shoulder portion contiguous to the bottom portion through an R end. In the transverse cross section, a first region from the R end to a position a distance away in a bottom portion extending direction, and a second region which is part of the bottom portion and is contiguous to the first region have a work-hardening distribution introduced by press-forming. The work-hardening distribution has an average hardness Hv1 of an area of the first region from a steel sheet surface to a depth obtained by multiplying a steel sheet thickness by 0.2 and an average hardness Hv2 of an area of the second region from the steel sheet surface to a position obtained by multiplying the steel sheet thickness by 0.2 to satisfy a relationship of Hv1>1.05×Hv2.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP +1
Catalyst for purification of exhaust gas and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20090069174A1Suppresses the deterioration of RhImprove low temperature performanceInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusCatalyst supportExhaust gas
A catalyst for purification of exhaust gases, produced by use of a catalyst component A, a catalyst component B, and a binder, the catalyst component A being produced by supporting Rh on a catalyst support for Rh, having a CO2 adsorption amount per unit weight of from 25 μmol·g−1 to 60 μmol·g−1, and having a CO2 adsorption amount per unit specific surface area of from 0.2 μmol·m−2·g1 to 2.3 μmol·m−2·g1,the catalyst having a CO2 adsorption amount per unit weight of from 18 μmol·g−1 to 60 μmol·g−1 and a CO2 adsorption amount per unit specific surface area of from 0.2 μmol·m−2·g1 to 2.5 μmol·m−2·g1, anda ratio of the CO2 adsorption amount per unit weight of the catalyst to the CO2 adsorption amount per unit weight of the catalyst component A [(CO2 adsorption amount of the catalyst / CO2 adsorption amount of the catalyst component A)×100] being 75% or more.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
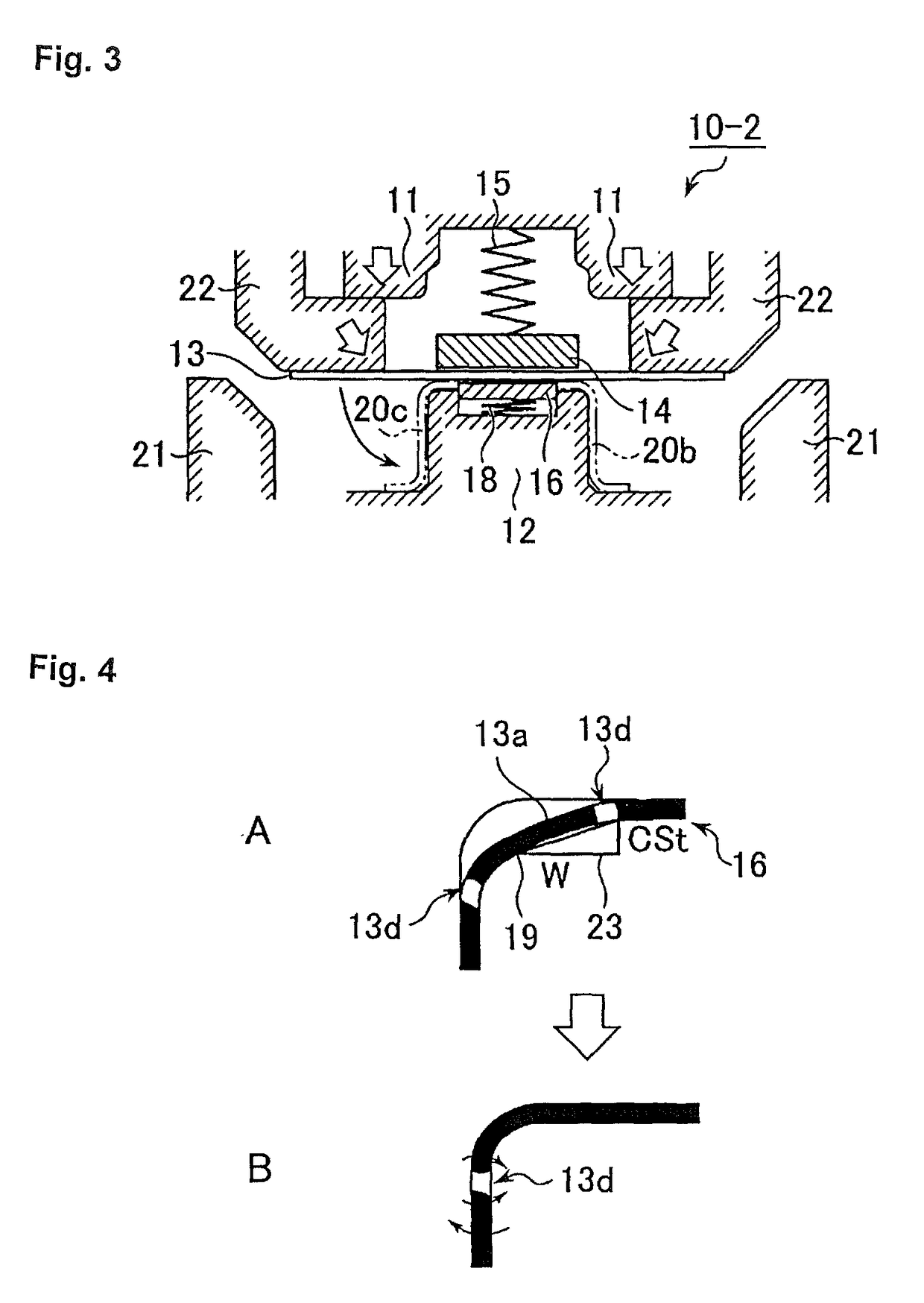
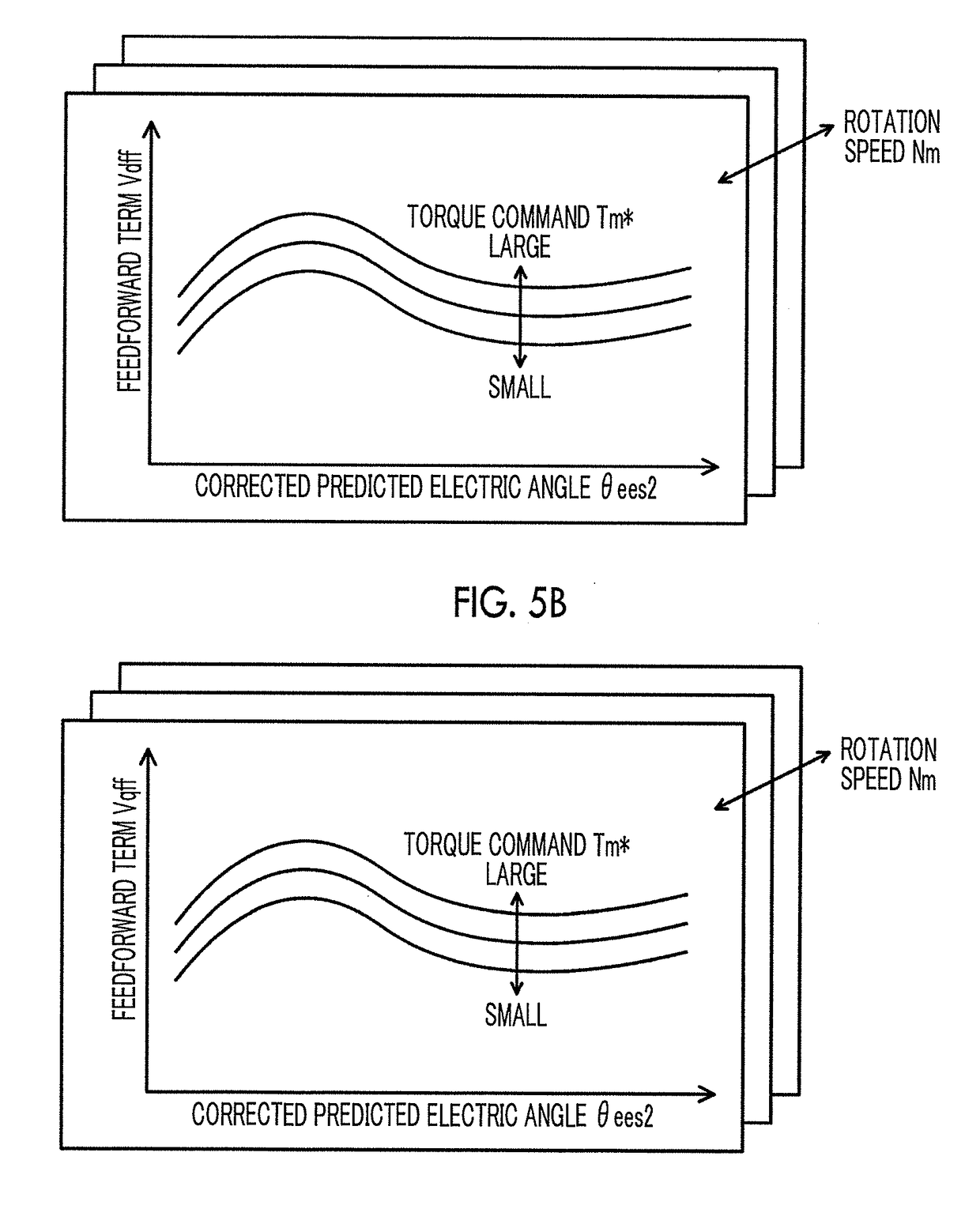
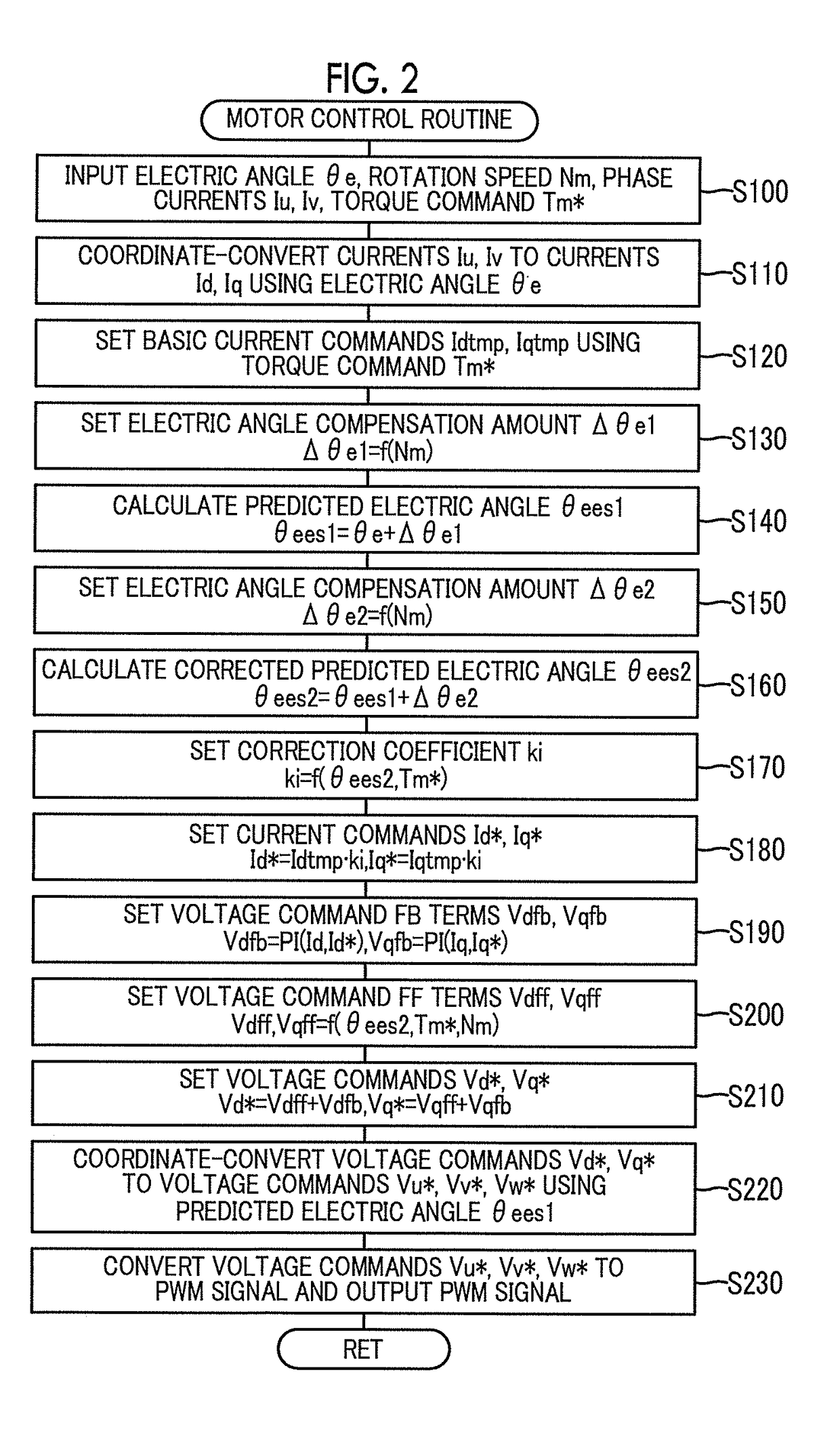
Drive device and control method for drive device
ActiveUS20170229984A1Suppress noiseReduce vibrationSpeed controllerTorque ripple controlElectricityPower inverter
Basic current commands of a d-axis and a q-axis are set based on a torque command of a motor. Subsequently, when the rotation speed of the motor is high, an electric angle compensation amount is set to be larger than that when the rotation speed of the motor is low, and a corrected predicted electric angle is set by adding the electric angle compensation amount to a predicted electric angle predicted from an electric angle based on a rotation position of a rotor of the motor from a rotation position detection sensor. Then, current commands of the d-axis and the q-axis are set by multiplying the basic current commands of the d-axis and the q-axis by a correction coefficient based on the corrected predicted electric angle, and an inverter is controlled using the current commands.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD +1
Coated fine particles containing drug for intrabuccally fast disintegrating dosage forms
InactiveUS20070231399A1Suppression of unpleasant tasteDissolve fastPill deliveryGranular deliveryWater soluble polymersDrug
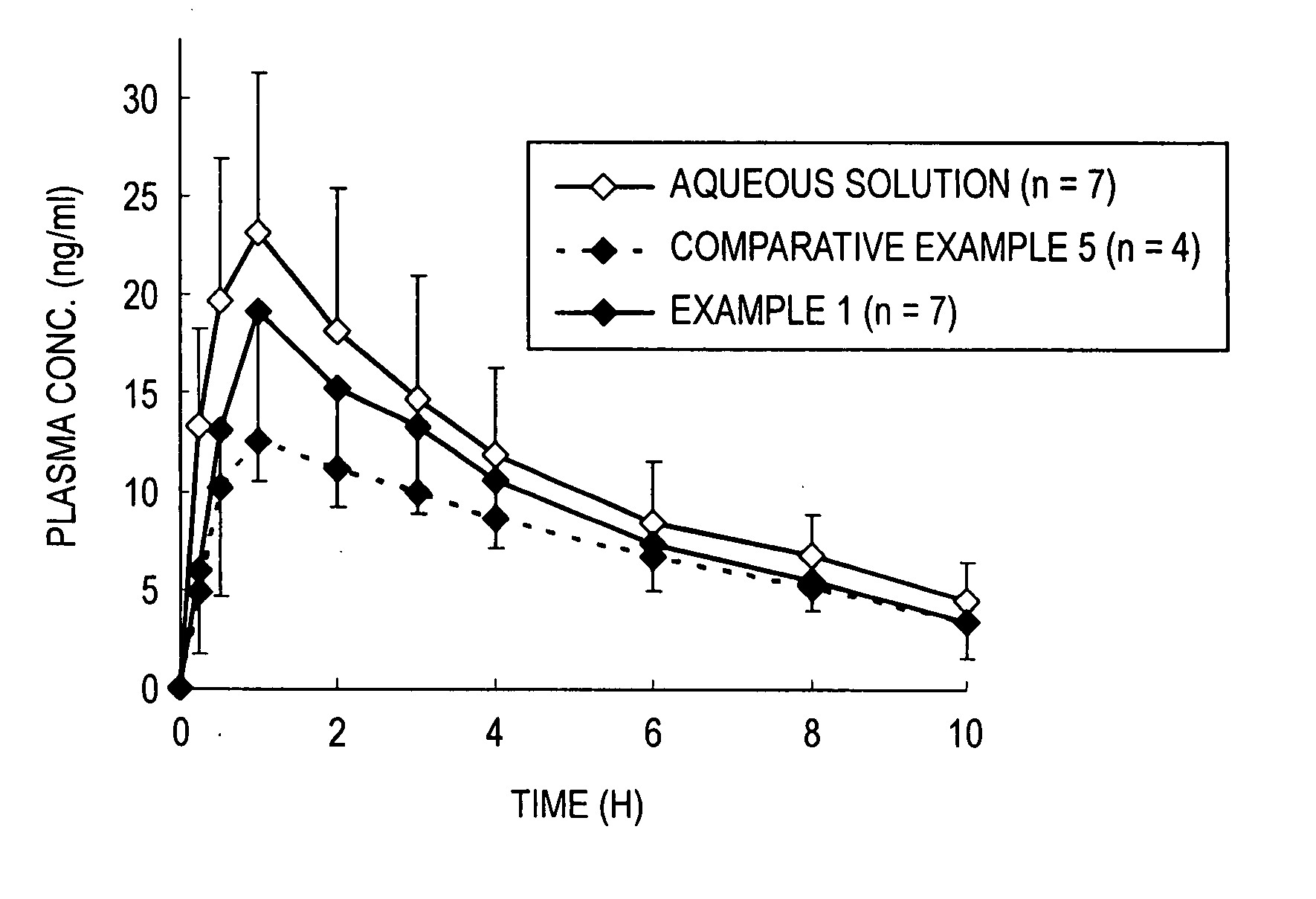
Regarding an object of sufficient suppression of unpleasant taste in the oral cavity and quick dissolution in the gastrointestinal tract, which is generated when a drug having a strong unpleasant taste such as bitterness, astringency and the like is applied to a quickly disintegrating preparations in the oral cavity, this invention has achieved the aforementioned object for the first time by employing a constitution of coating a coat of a water-soluble polymer and a specified ratio of a pH-independent water-insoluble polymer and hydroxypropylcellulose.
Owner:ASTELLAS PHARMA INC
Solid-state imaging device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7030433B2Improved readout characteristicSuppresses image defectsTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesLow voltageEngineering
A solid-state imaging device includes: a plurality of N-type photodiode regions formed inside a P-type well; a gate electrode having one edge being positioned adjacent to each of the photodiode regions; a N-type drain region positioned adjacent to the other edge of the gate electrode; an element-isolating portion having a STI structure, and a gate oxide film having a thickness of not more than 10 nm. One edge of the gate electrode overlaps the photodiode region. First, second and third regions are formed on a surface portion extending from the photodiode region to the drain region, in conditions such that the first region is disposed with a predetermined distance from one edge of the gate electrode and has a P-type first concentration C1, the second region is disposed with one edge positioned adjacent to the first region and the other edge overlapping the gate electrode and has a P-type second concentration C2, and the third region is disposed with one edge positioned adjacent to the second region and the other edge positioned adjacent to the drain region and has a P-type third concentration C3, wherein C1>C2>C3 or C1≈C2>C3. The readout characteristic at a low voltage is satisfactory, and image defects such as white flaws and dark current are suppressed sufficiently.
Owner:COLLABO INNOVATIONS INC
Electronic component package including heat spreading member
InactiveUS20060146503A1Reliably transferring heatIncrease heat radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringThermal radiation
A heat spreading member is received on a predetermined surface of an electronic component. The heat spreading member extends larger than the predetermined surface. A contact piece is contacted with the heat spreading member over a contact area smaller than the predetermined surface. The contact piece serves to realize concentration of an urging force applied to the heat spreading member. The heat spreading member is thus reliably urged against the electronic component. The concentration of the urging force serves to prevent the heat spreading member and the electronic component from camber even if heat is applied to the heat spreading member and the electronic component. Separation is thus avoided between the heat spreading member and the electronic component. The heat spreading member reliably keeps contacting with the electronic component, so that the electronic component package is allowed to enjoy improvement in heat radiation.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Electronic component
ActiveUS20190164696A1Inhibit the generation of cracksInhibition of volume increaseFixed capacitor electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricElectronic componentElectrode
An element body of a rectangular parallelepiped shape includes a pair of principal surfaces opposing each other in a first direction, a pair of side surfaces opposing each other in a second direction, and a pair of end surfaces opposing each other in a third direction. An external electrode disposed on an end portion of the element body in the third direction. When viewed from the third direction, a width of the element body in the second direction is the largest at a central position in the first direction, and gradually decreases from the central portion in the first direction. When viewed from the third direction, a position in which a length from one end to another end of the conductive resin layer in the second direction is the largest is located closer to the one principal surface than the central position.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
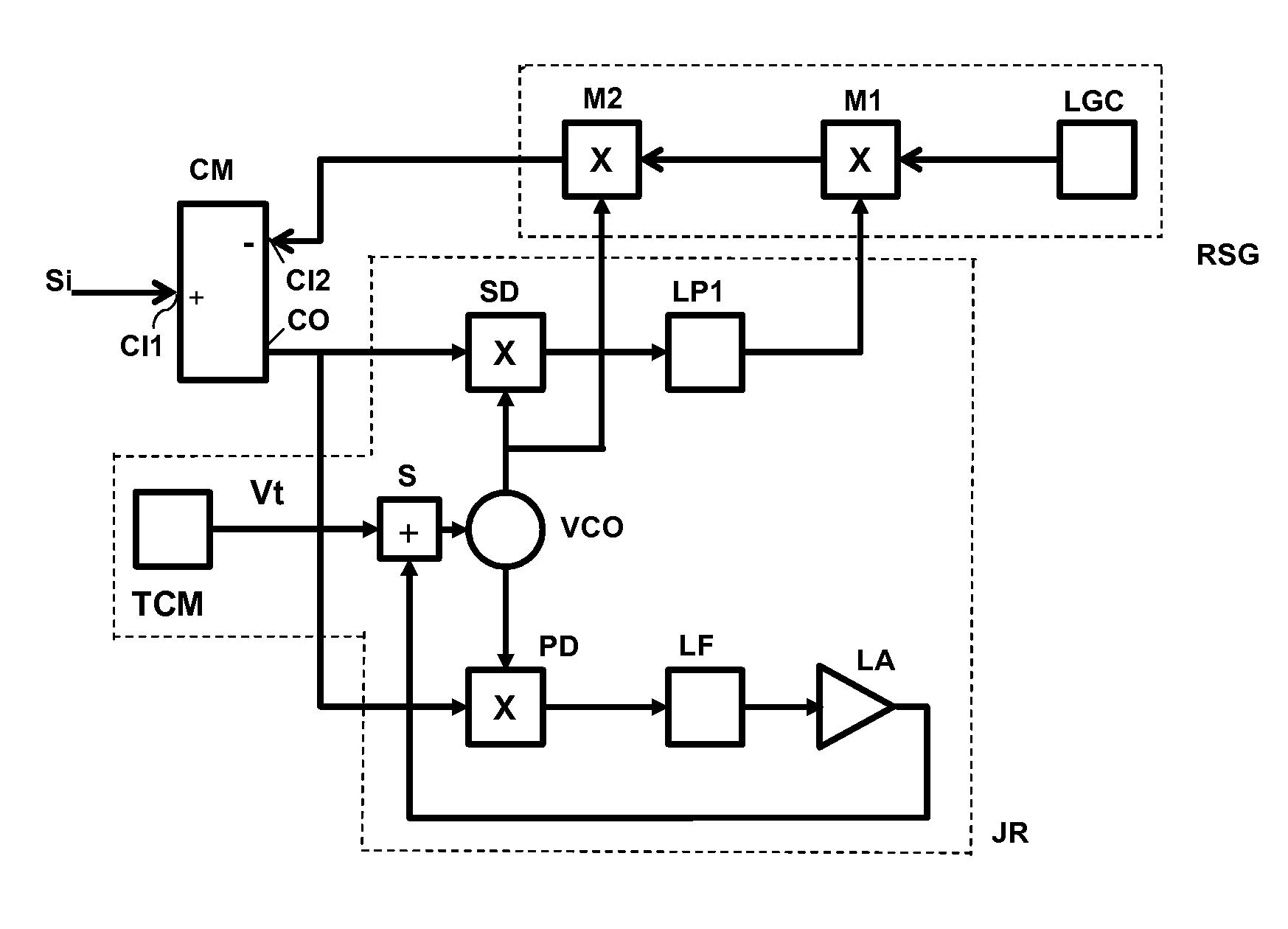
Anti-jamming system
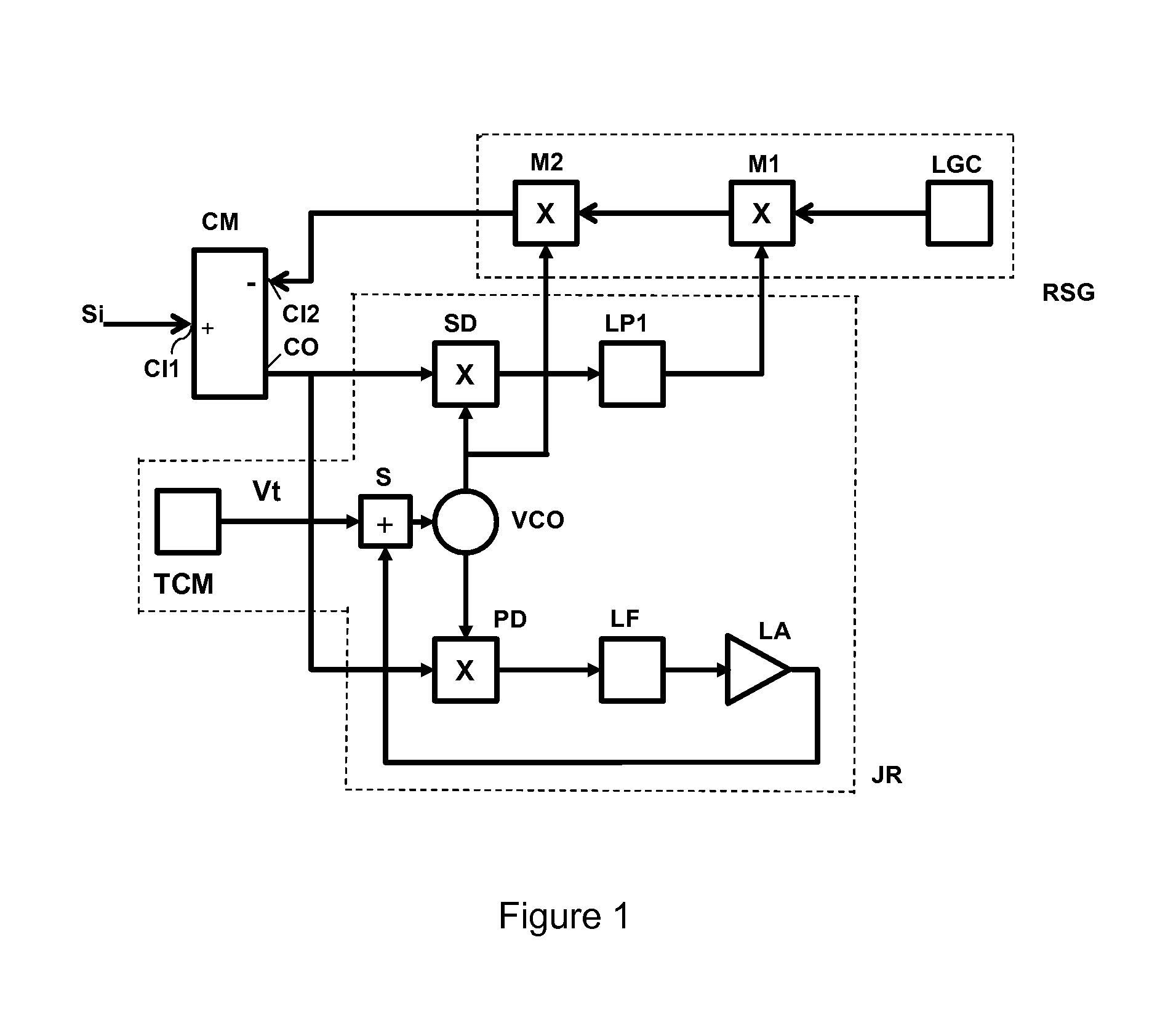
ActiveUS20140141737A1Robust implementationReduce signal to noise ratioCommunication jammingRadio transmissionLoop filterPhase detector
An anti-jamming system includes a tunable negative jamming signal feedback loop for feedback suppression of a received jamming signal. The system includes a zero IF phase locked loop (PLL) jamming signal receiver having a synchronous demodulator and a phase detector. A VCO is included in the PLL, as well as a phase detector and a loop filter. A replica jamming signal generator includes a tracking modulator with a baseband signal input coupled to an output of a synchronous demodulator in the receiver and a carrier input provided by the VCO. An output of the tracking modulator is negatively fed back to the input of the receiver to suppress the jamming signal in the received input.
Owner:SEMICON IDEAS TO MARKET ITOM
XY stage
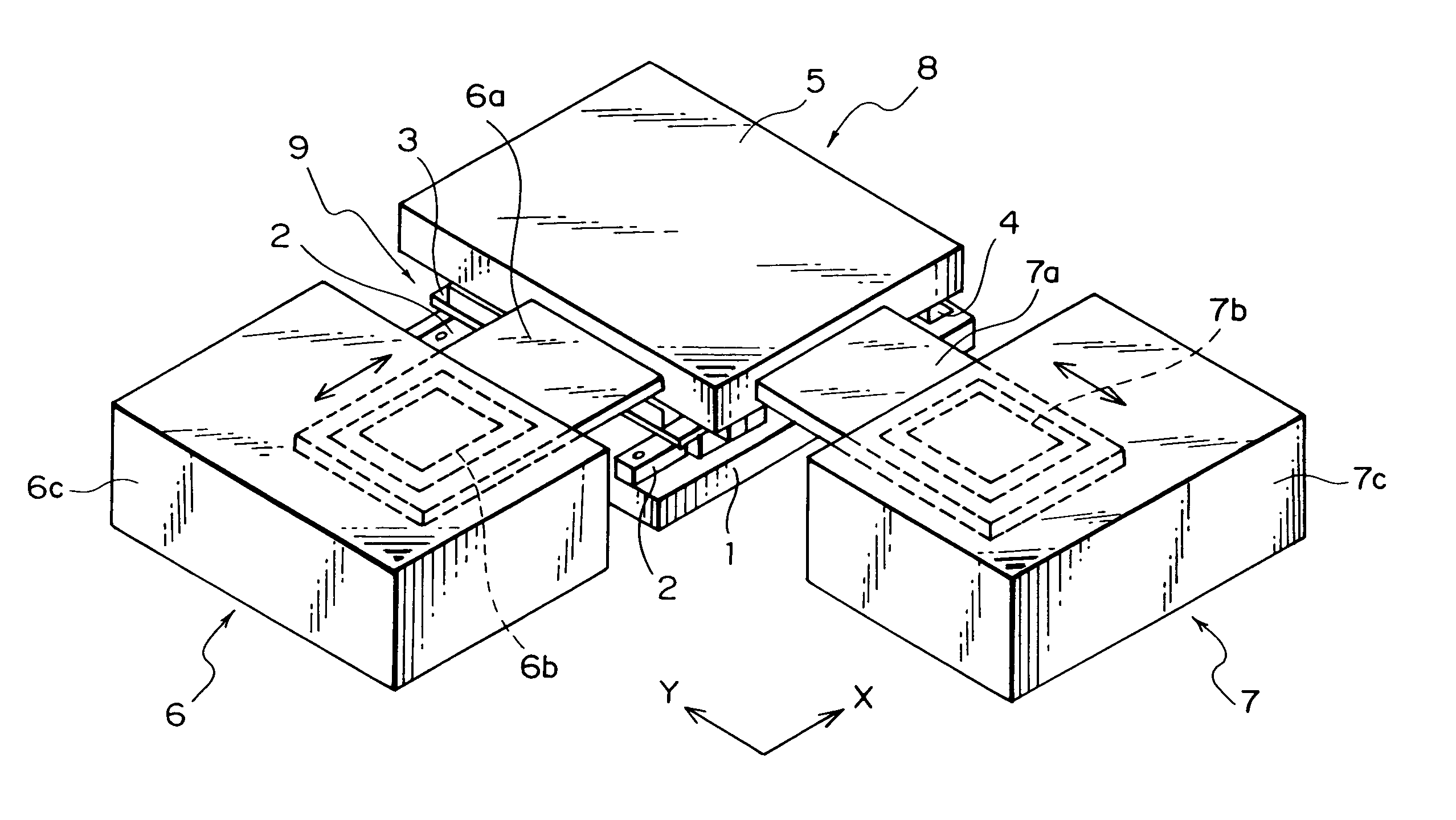
InactiveUS7654207B1Sufficiently suppressEasy to move and controlAutomatic control devicesSolid-state devicesLinear motorGravitation
An XY stage comprises a base, a movable table which is disposed on the base so as to be movable in an X direction and a Y direction in an X-Y plane, and a work member which is provided on the movable table. The XY stage further comprises: a first linear motor for giving a driving force in the X direction to the movable table at the same height as the center of gravity of a movable section composed of the movable table and the work member; and a second linear motor for giving a driving force in the Y direction to the movable table at the same height as the center of gravity of the movable section.
Owner:NEC CORP
Pneumatic Tire
InactiveUS20080230164A1Increase rectilinear propagation stabilityControl generationTyre tread bands/patternsNon-skid devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A pneumatic tire in which a tread surface is provided with a main groove extending as a straight shape in a tire circumferential direction, and a block row formed by arranging a plurality of blocks facing to the main groove in the tire circumferential direction, the block row has a plurality of first blocks in which a wall surface facing to the main groove is chamfered, and a plurality of second blocks arranged between the first blocks and in which a position in a tire width direction of an edge portion of a wall surface facing to the main groove is differentiated from the first block.
Owner:TOYO TIRE & RUBBER CO LTD
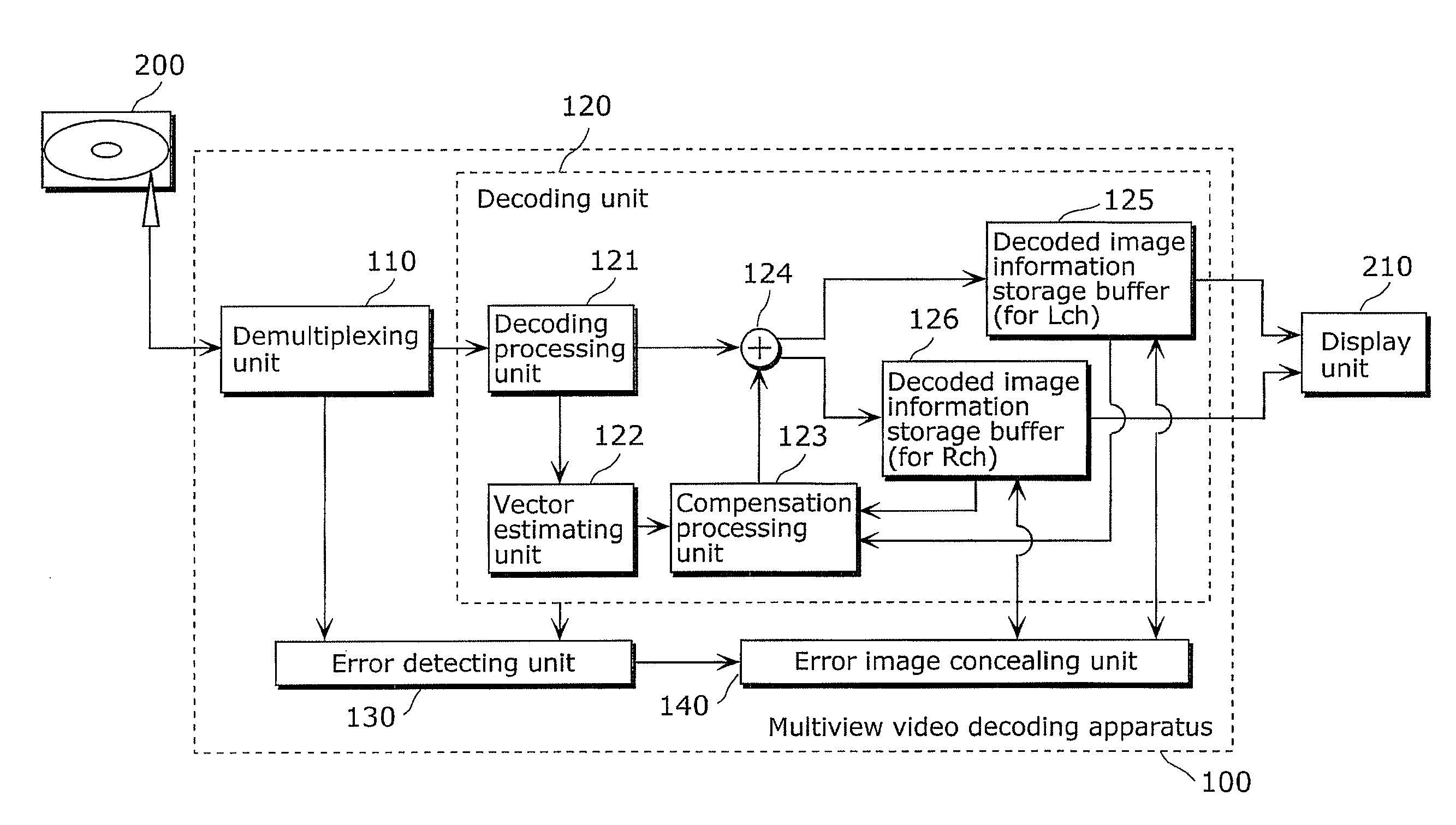
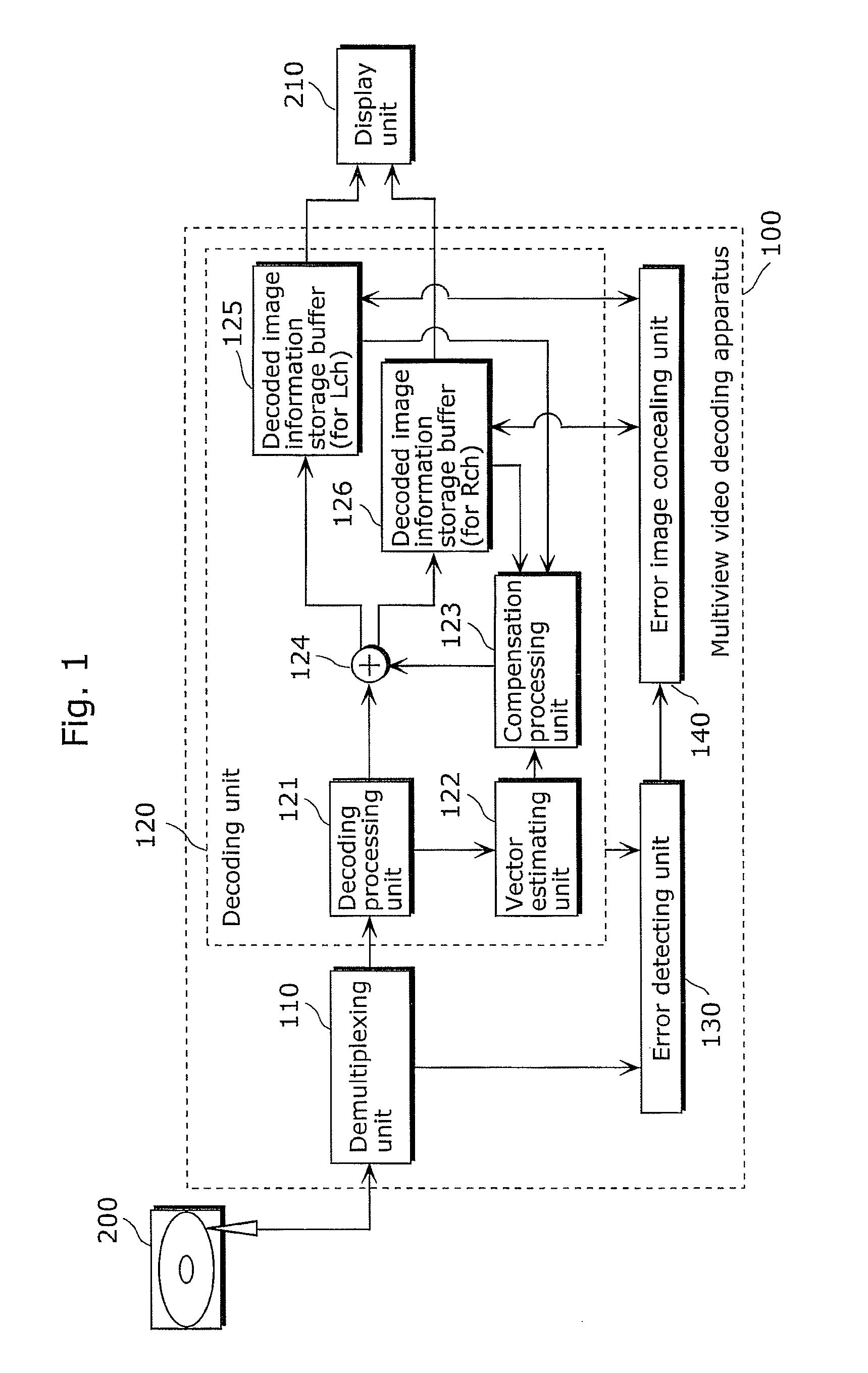
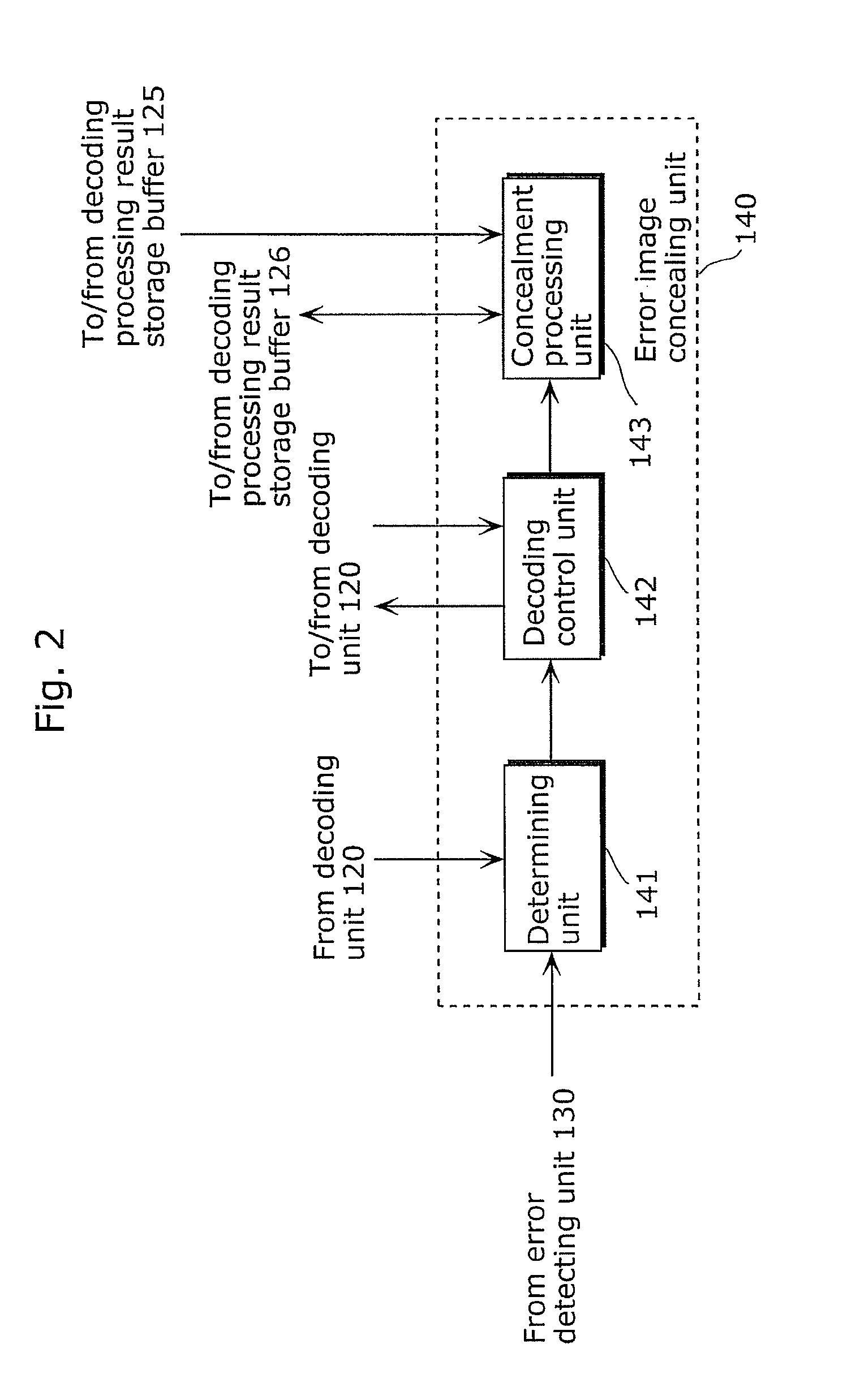
Multiview video decoding apparatus and multiview video decoding method
InactiveUS20110280318A1Suppress artifactsMore natural imageColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionViewpointsError concealment
A multiview video decoding apparatus which sufficiently suppresses artifact in a decoded image even when an error occurs in the to-be-decoded image. It decodes a video stream including first coded video information of a first viewpoint and second coded video information of a second viewpoint, and includes: a decoding unit which decodes the video stream; and an error detecting unit which detects an error in the video stream; and an error concealing unit which conceals the error and includes (i) a decoding control unit which, when the error is in first coded image information in the first coded video information, causes said decoding unit to decode second coded image information included in the second coded video information and to be decoded after the first coded image information and (ii) a concealment processing unit which conceals the detected error, using decoded image information generated by decoding the second coded image information.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com