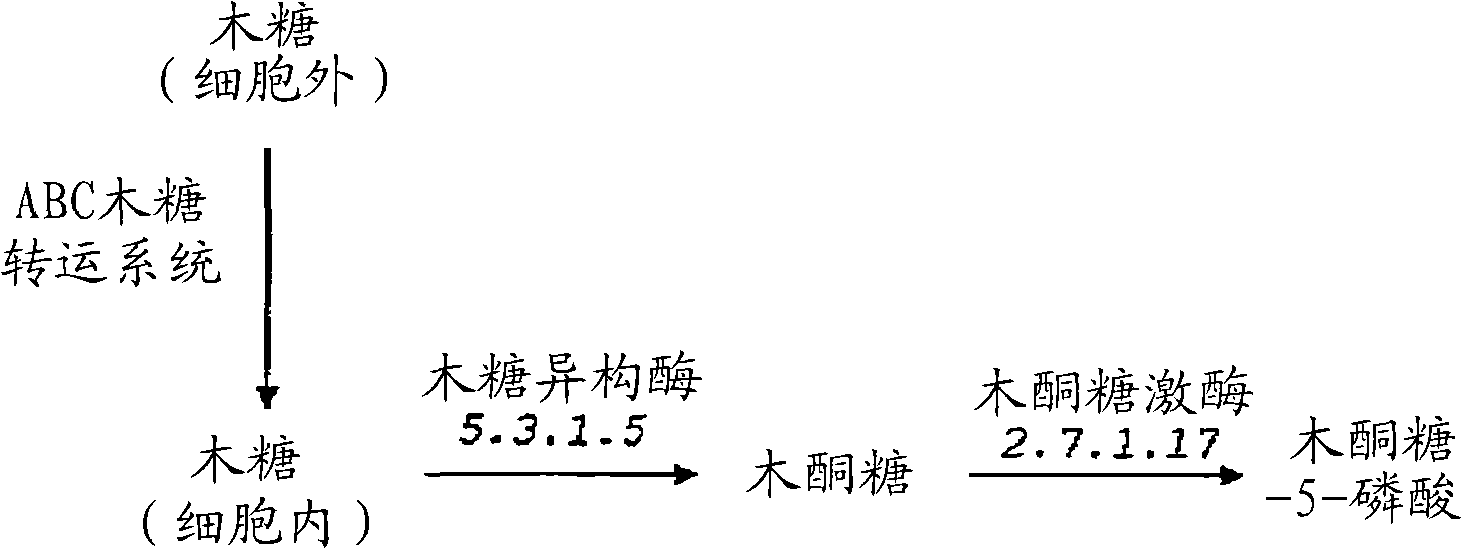
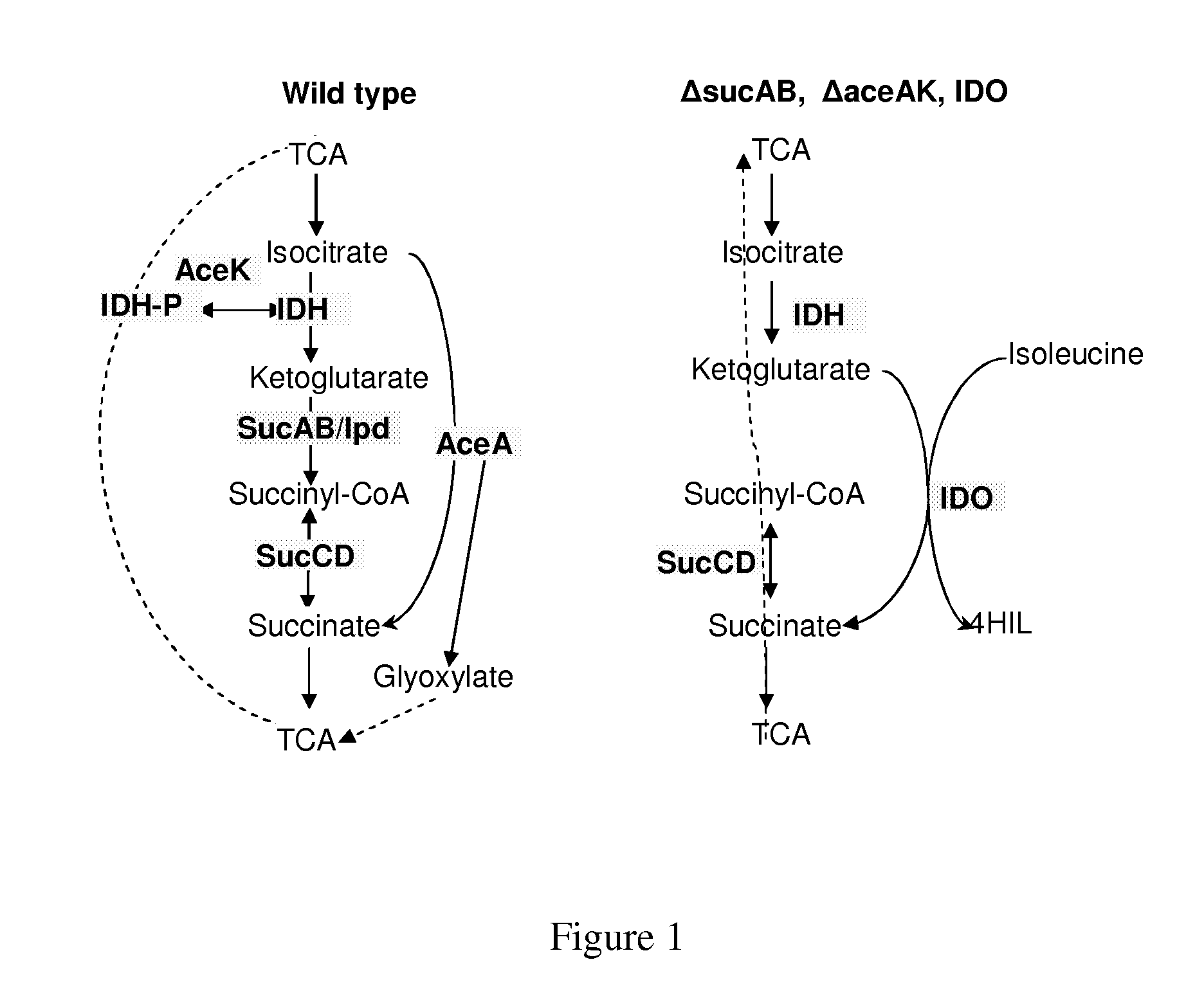
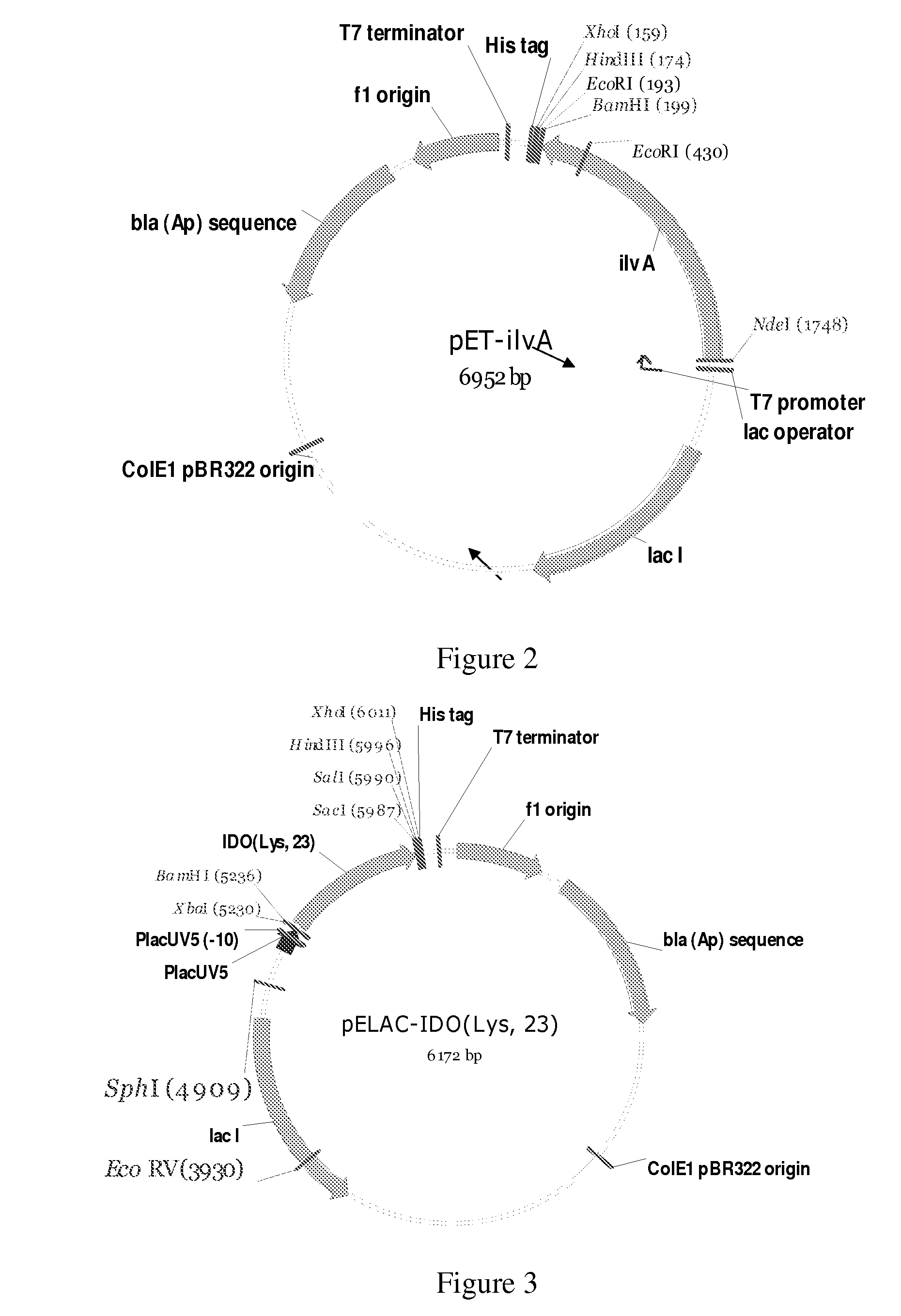
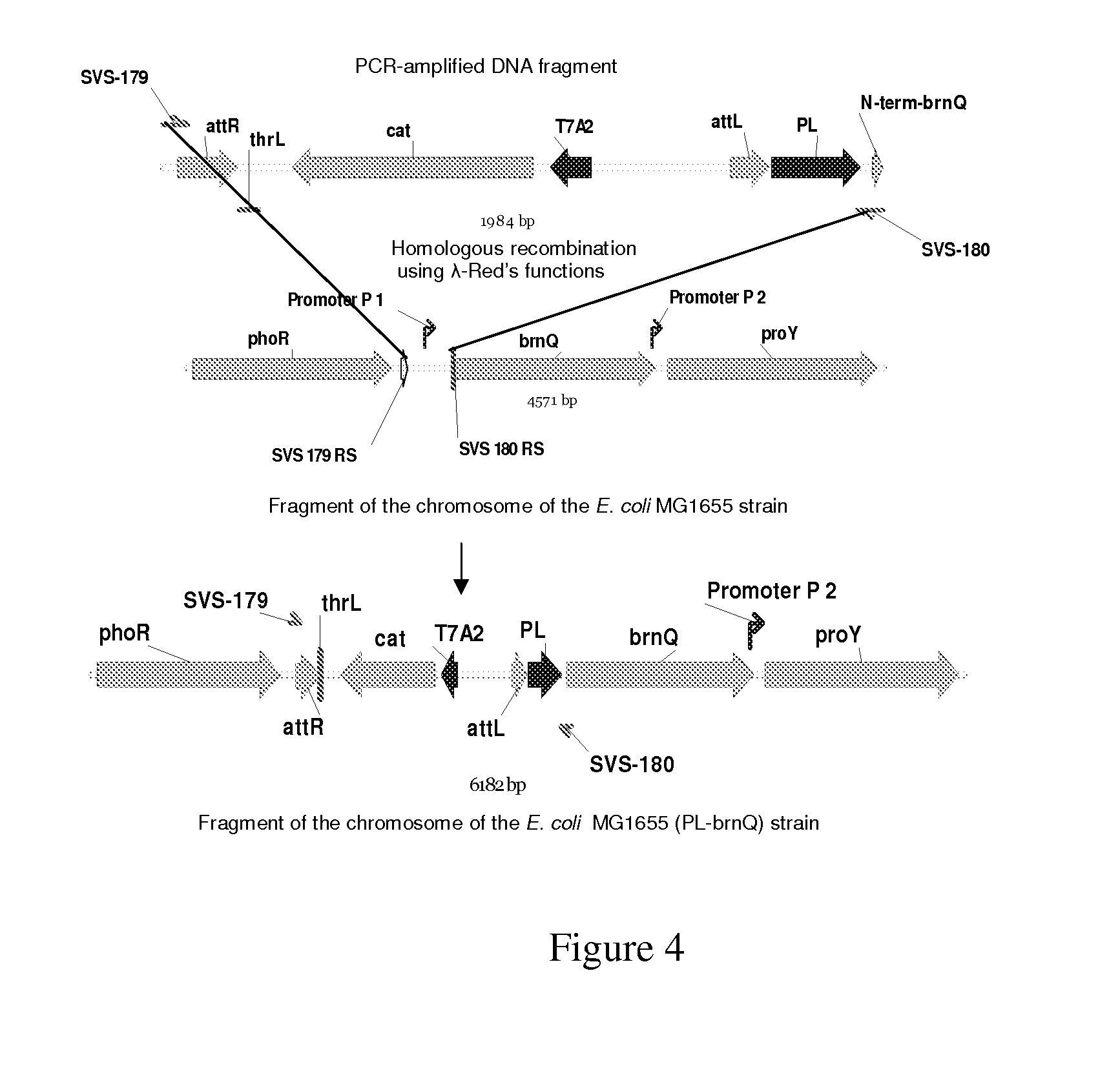
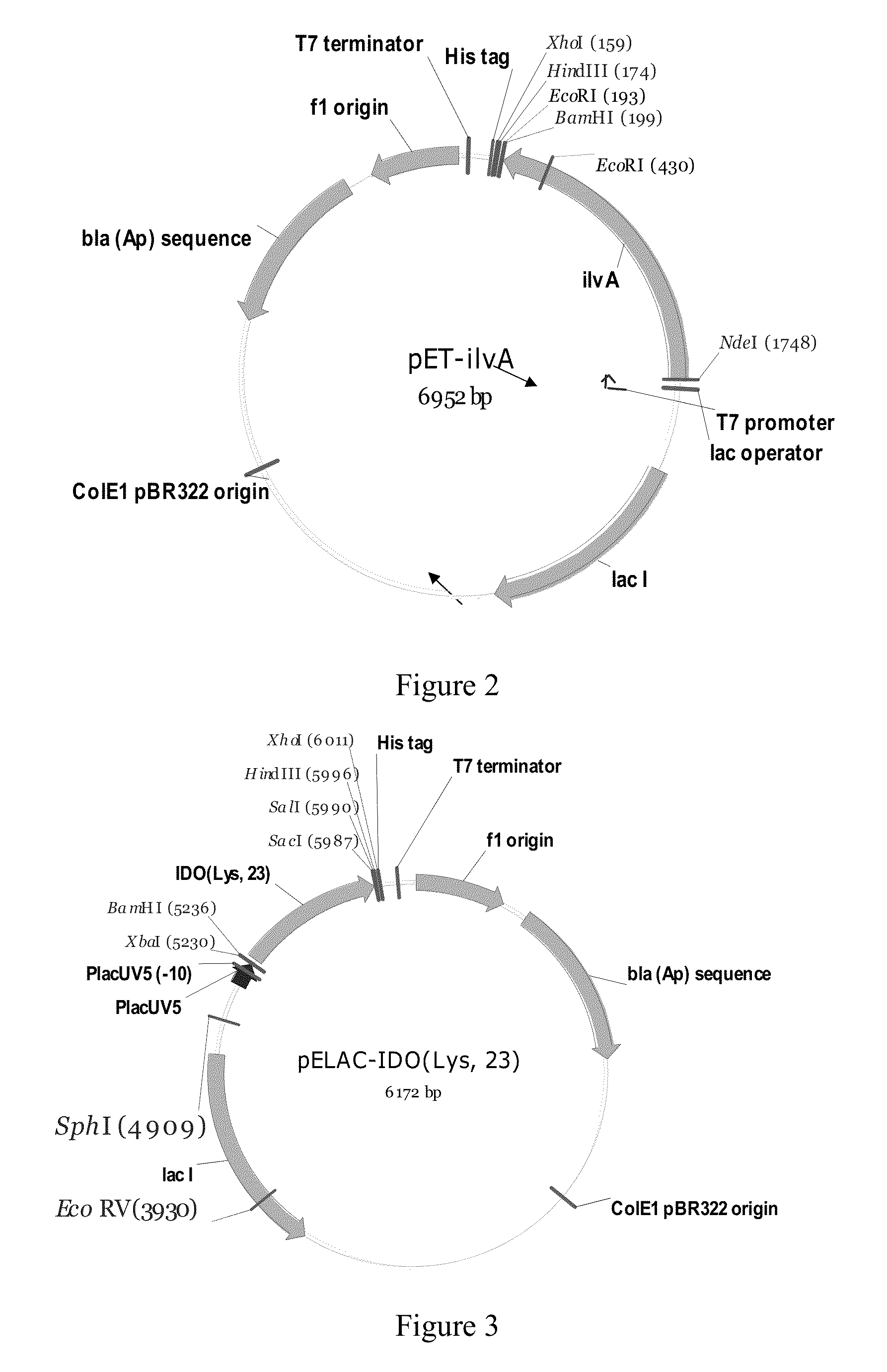
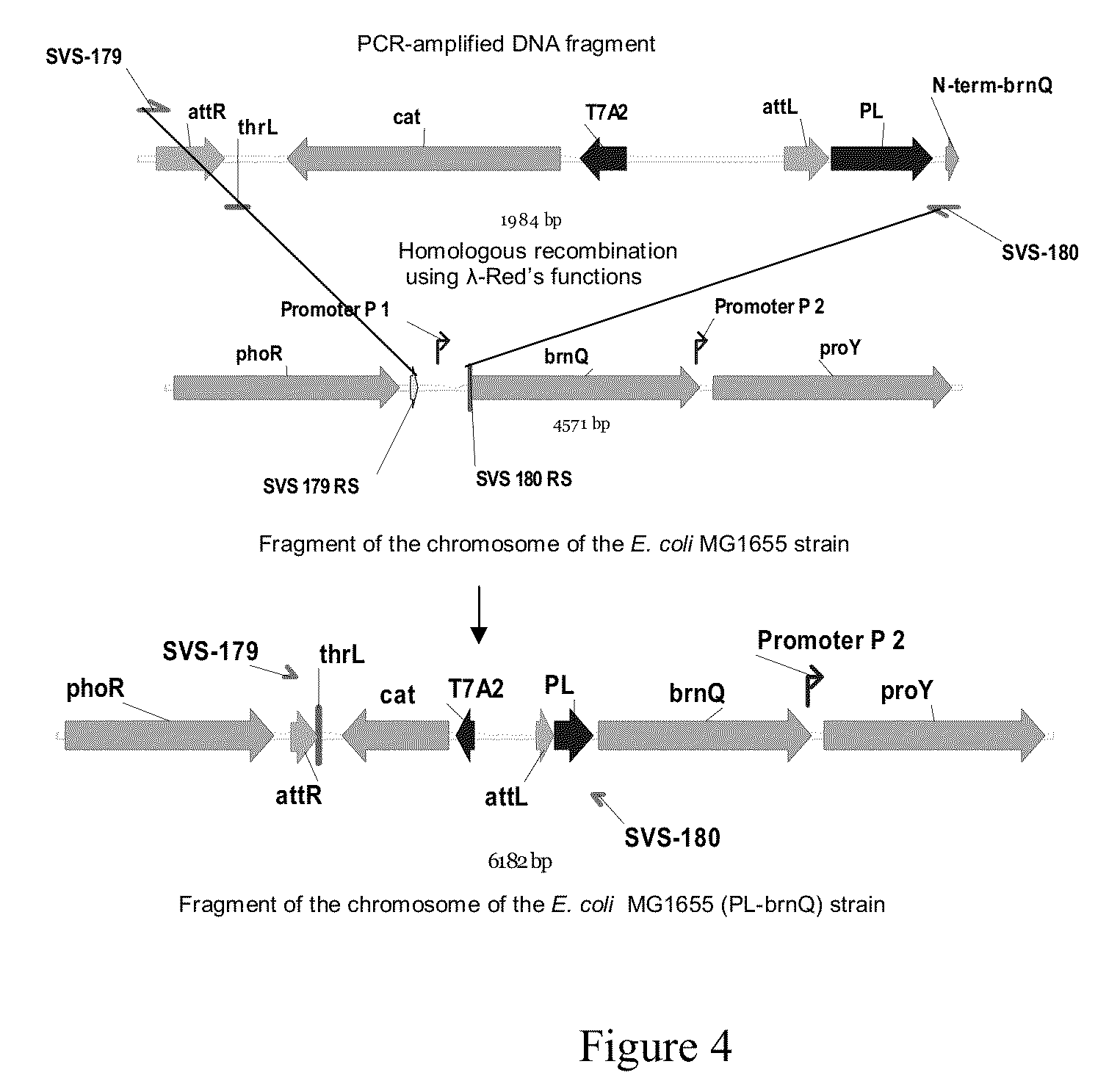
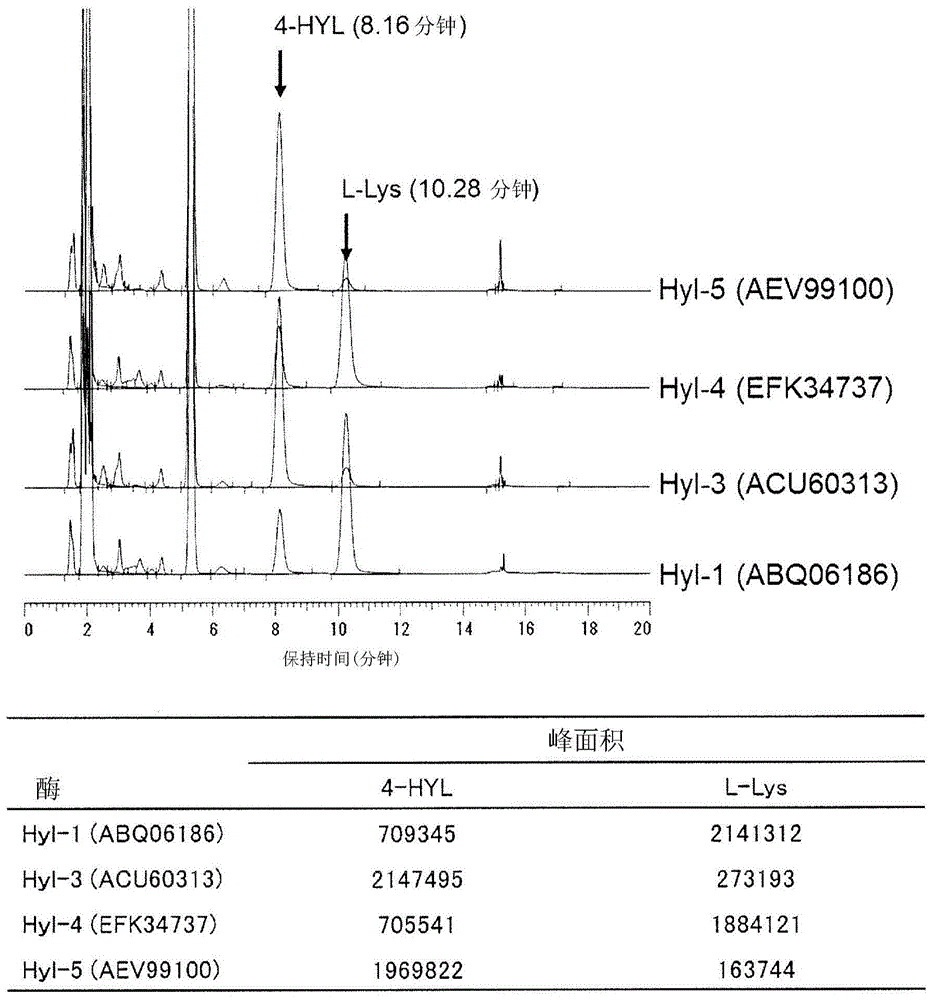
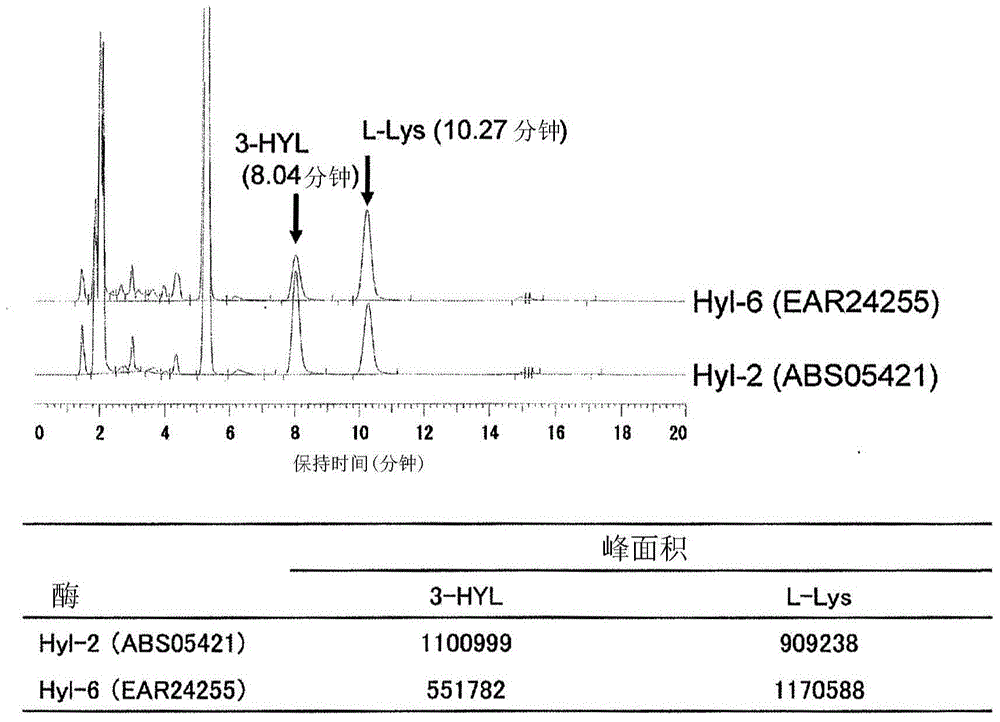
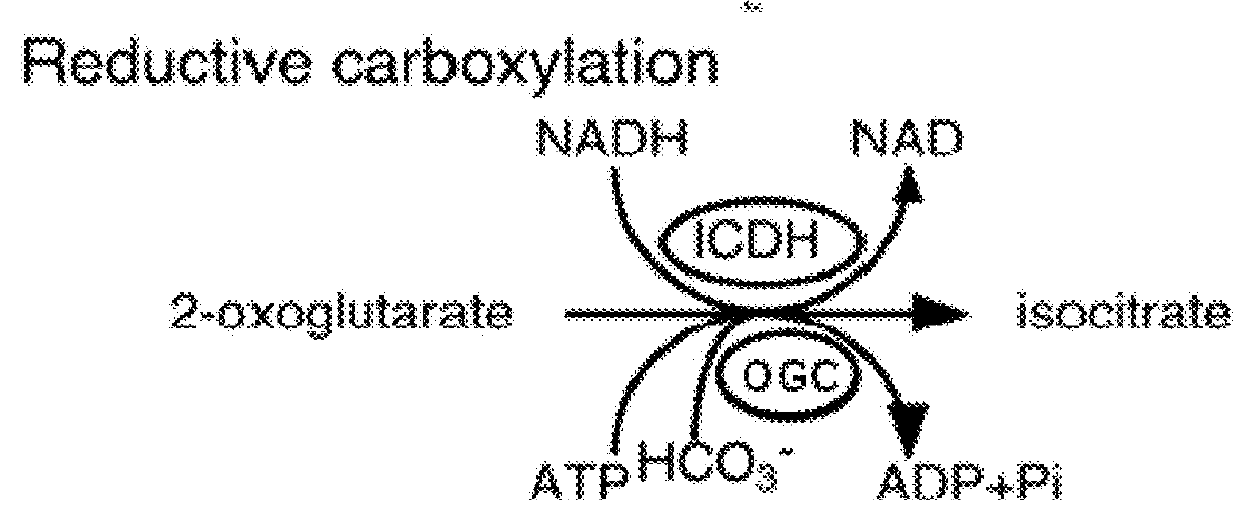
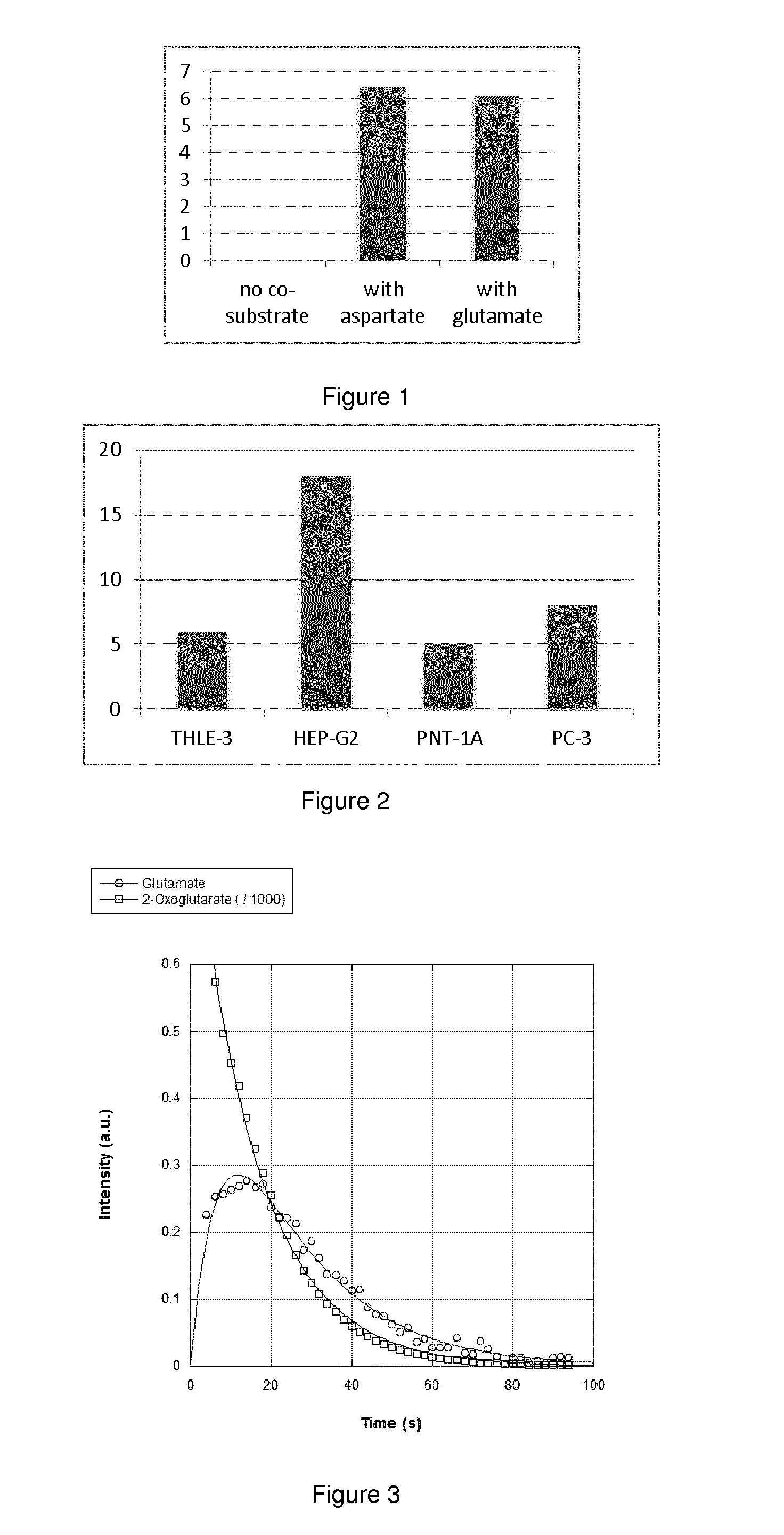
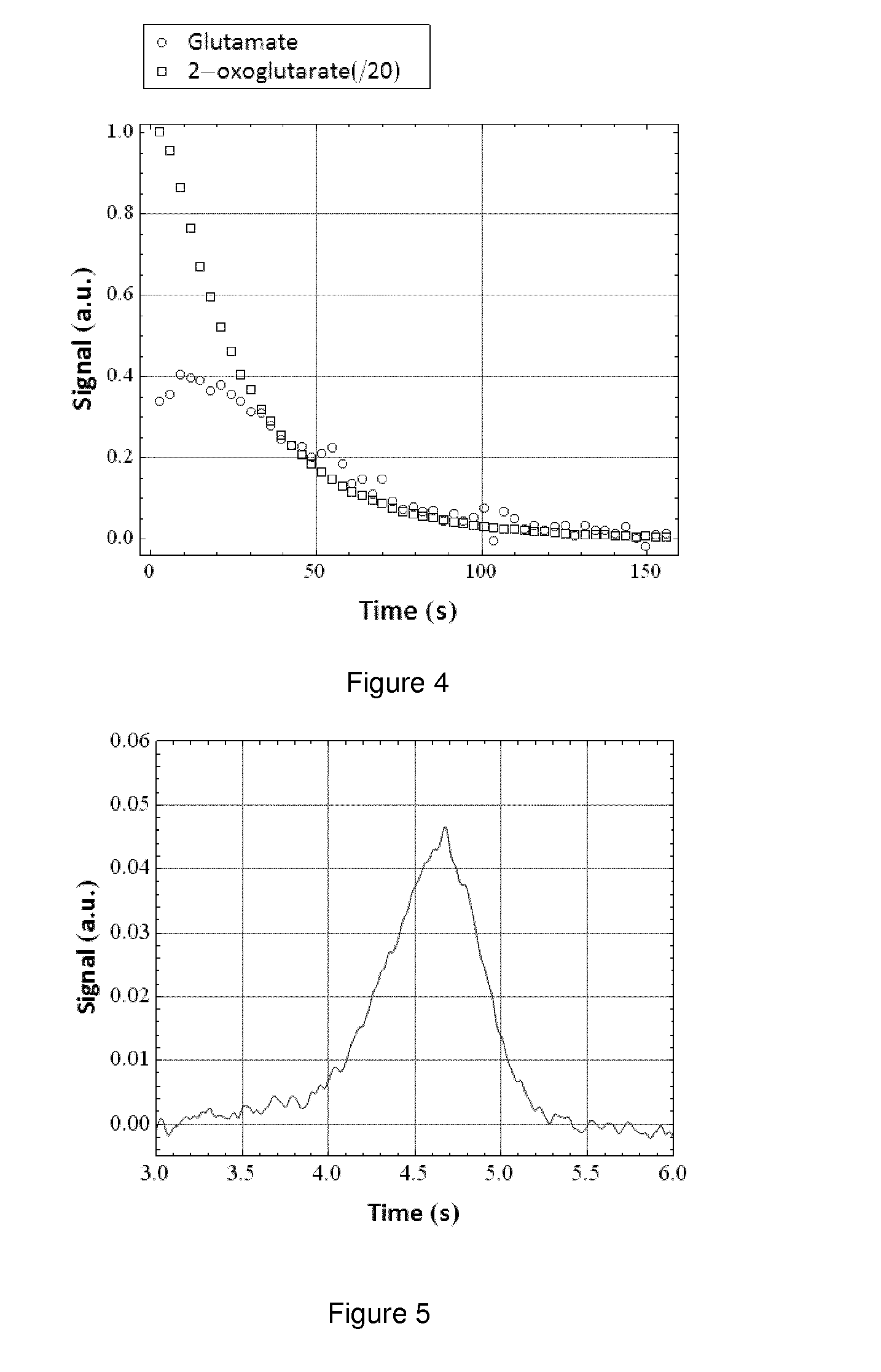
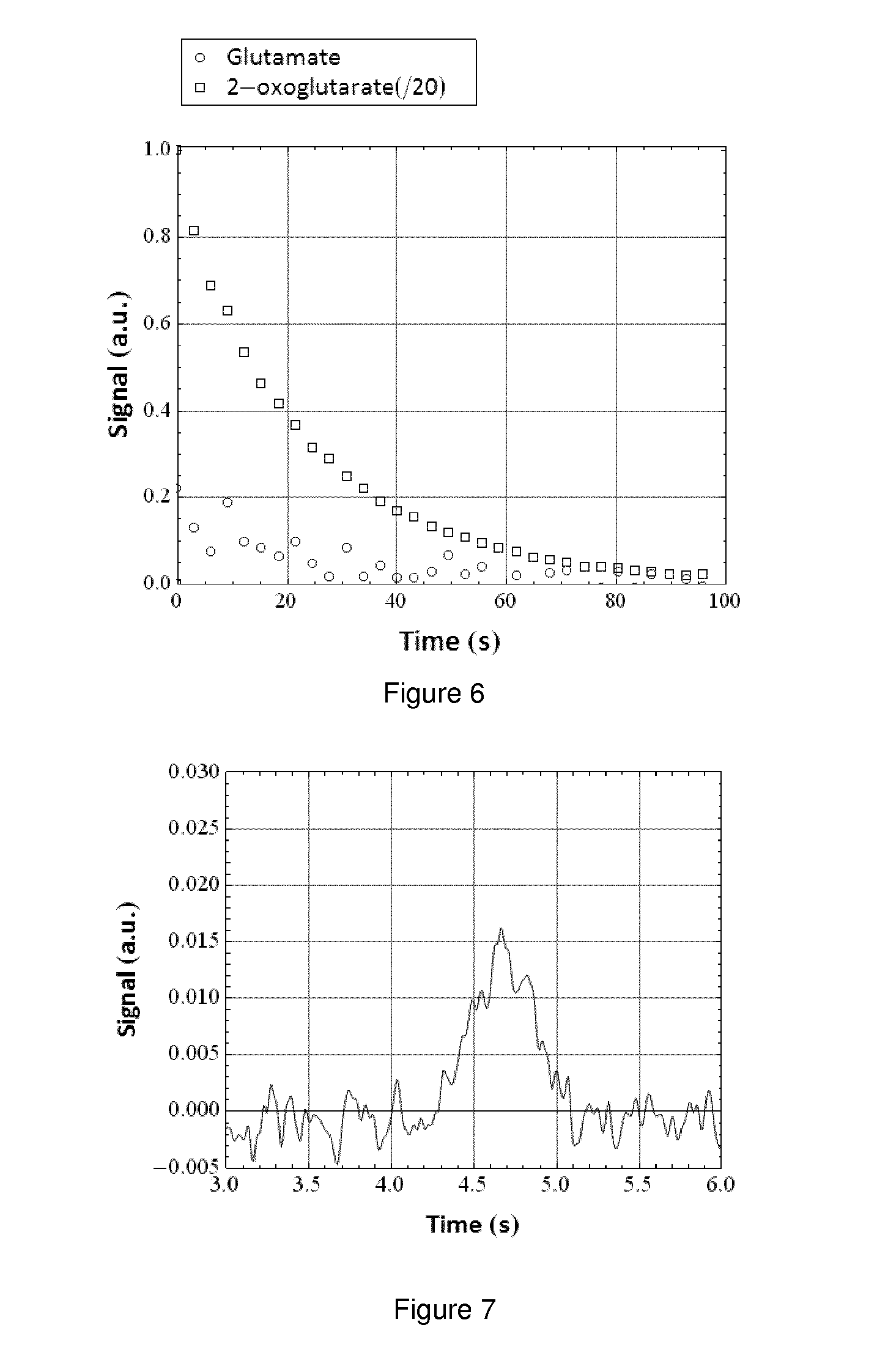
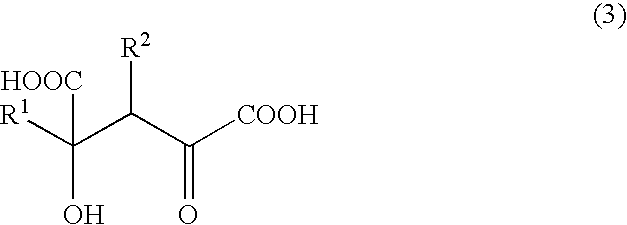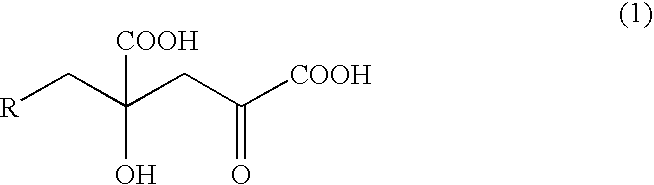Patents
Literature
35 results about "2-Oxoglutarate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
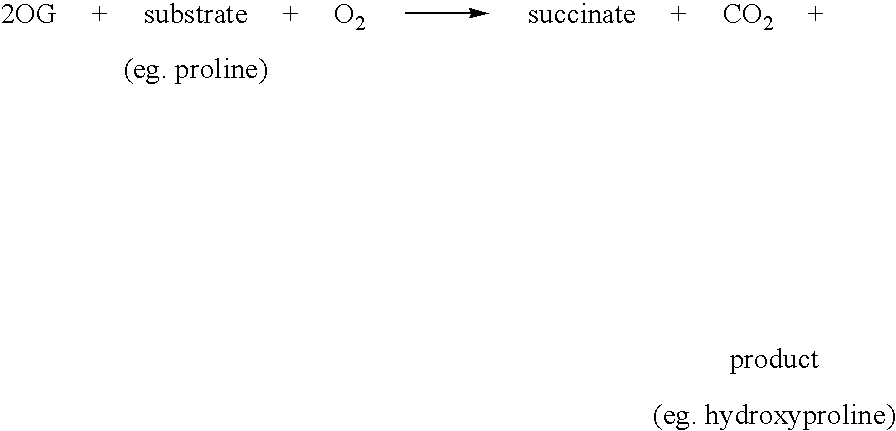
Β-Ketoglutaric acid varies only by the position of the ketone functional group, and is much less common. Its anion , α-ketoglutarate ( α-KG , also called 2-oxoglutarate , or 2OG ) is an important biological compound.
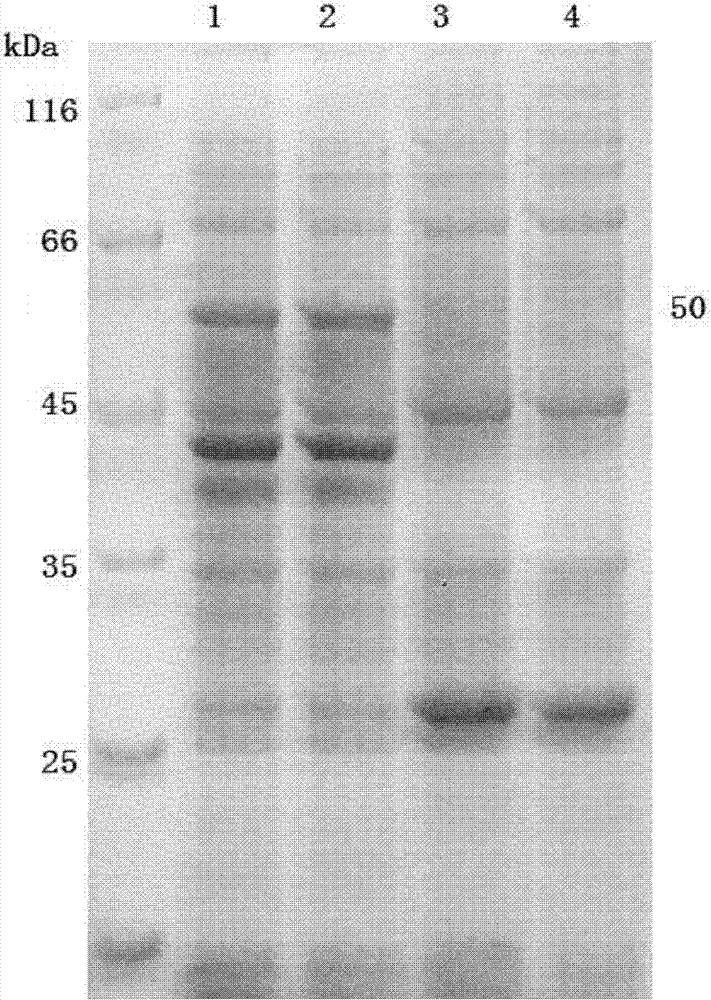
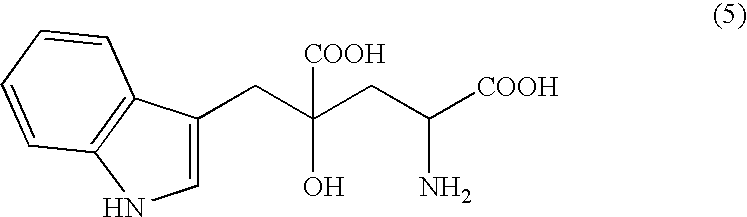
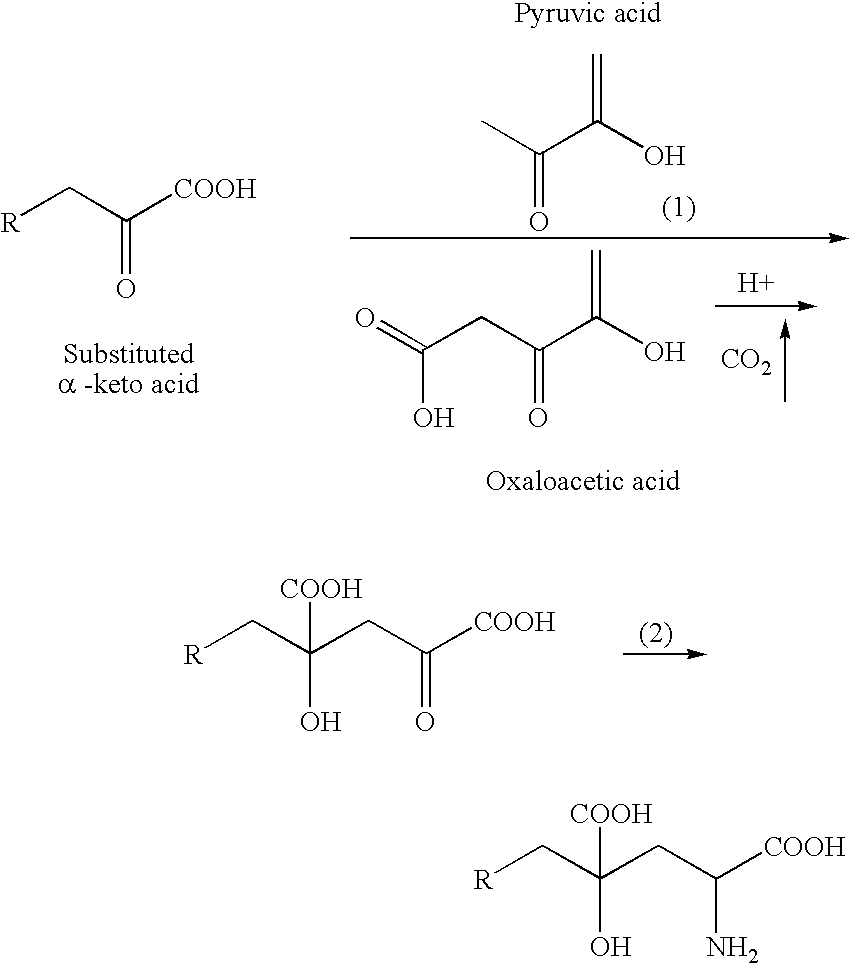
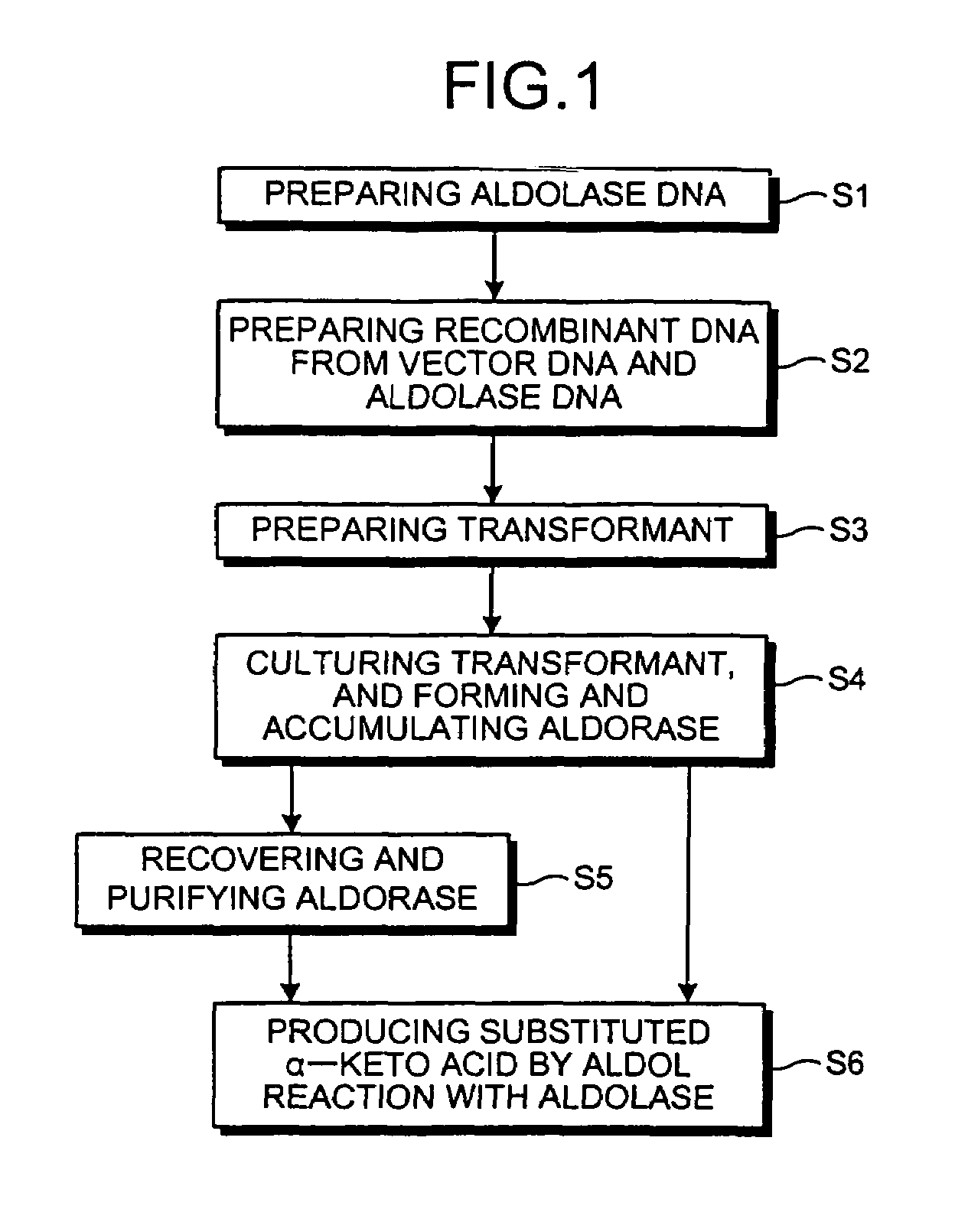
Novel aldolase and production process of substituted alpha-keto acids
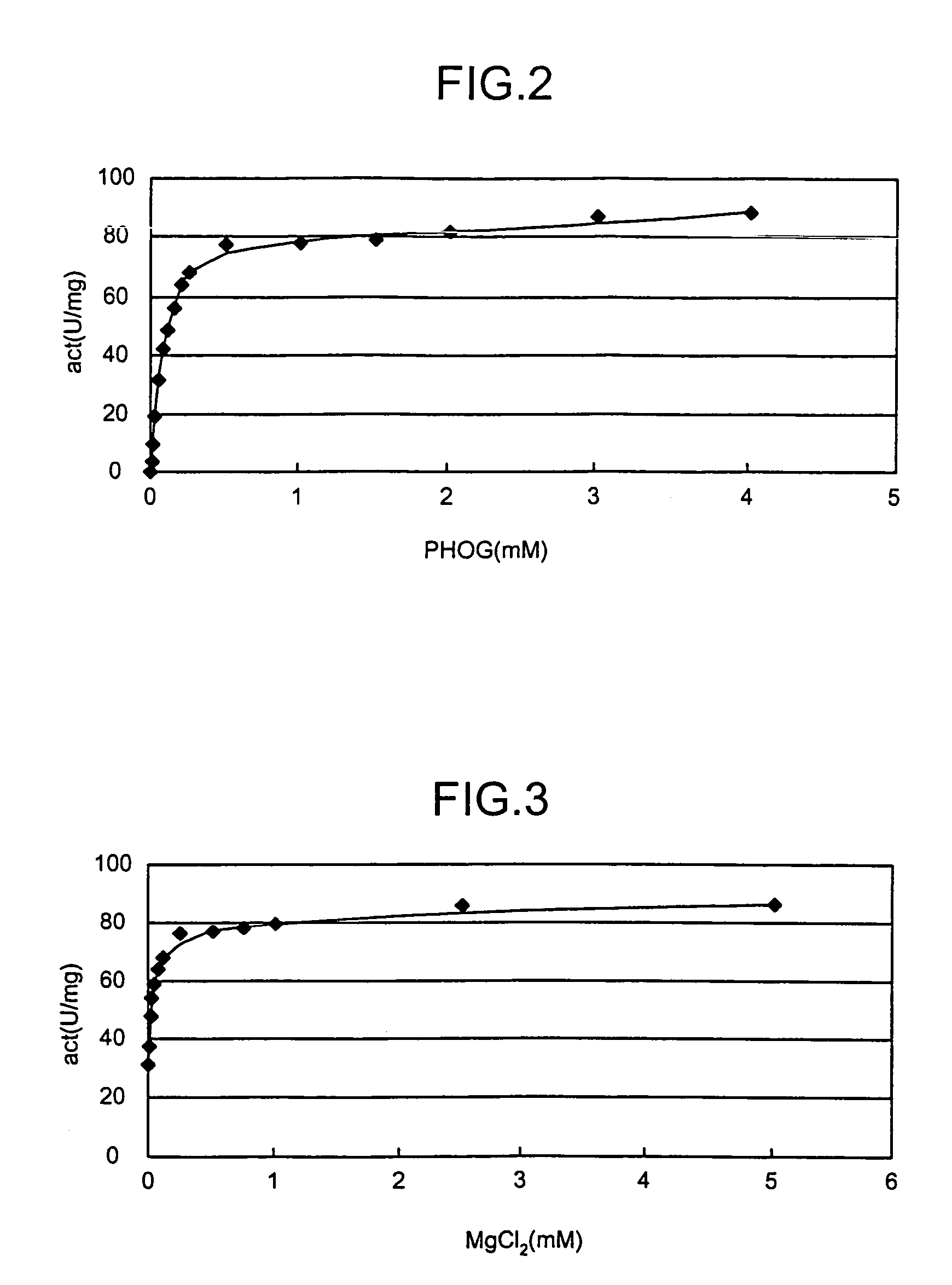
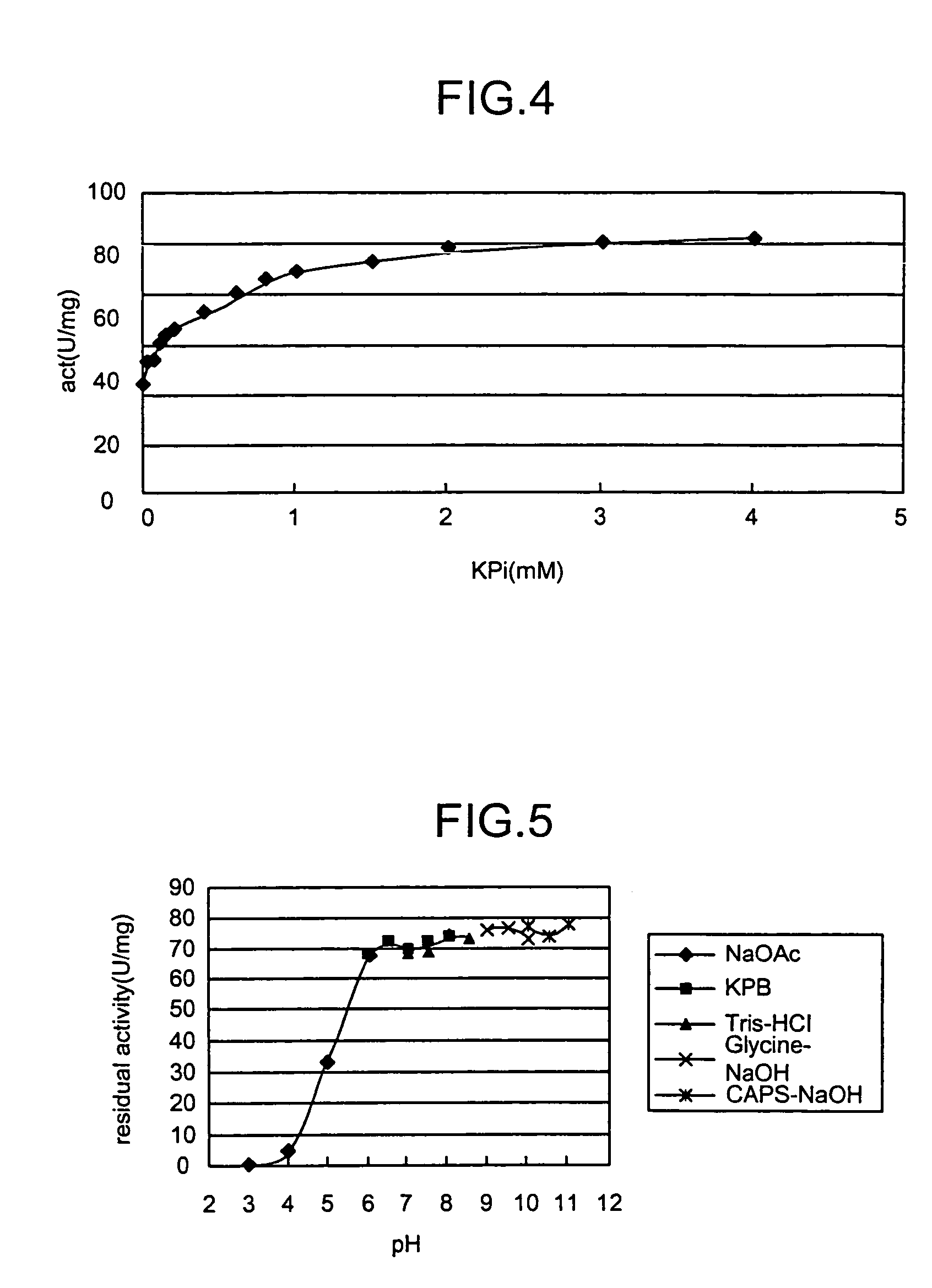
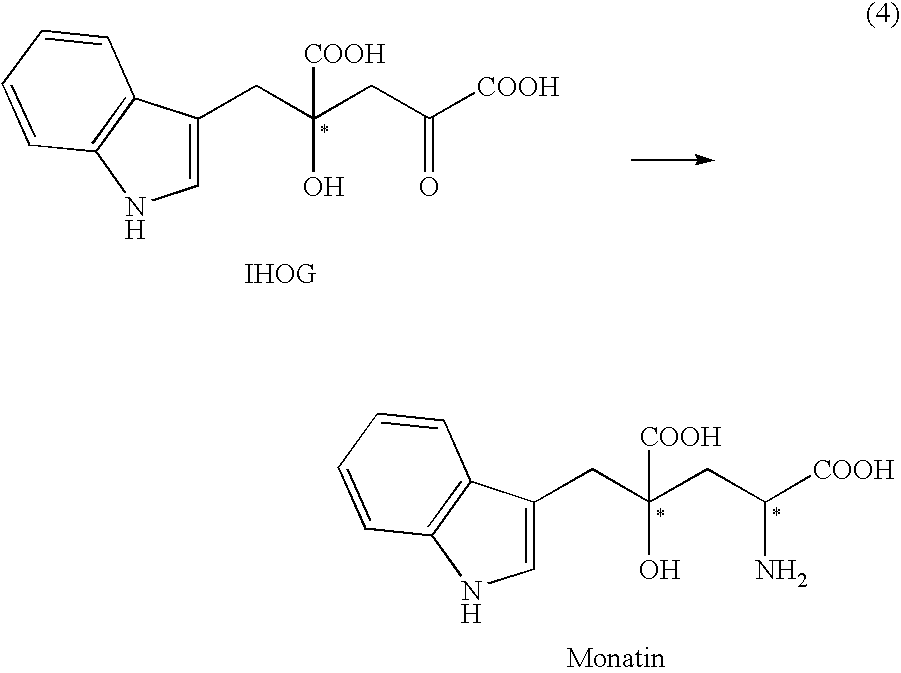
4-(Indol-3-ylmethyl)-4-hydroxy-2-oxoglutarate, which is useful as an intermediate in the synthesis of monatin, may be synthesized from indole pyruvic acid and pyruvic acid (and / or oxaloacetic acid) by using a novel aldolase derived from the genus Pseudomonas, Erwinia, Flavobacterium, or Xanthomonas.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Aldolase and production process of substituted alpha-keto acids
4-(Indol-3-ylmethyl)-4-hydroxy-2-oxoglutarate, which is useful as an intermediate in the synthesis of monatin, may be synthesized from indole pyruvic acid and pyruvic acid (and / or oxaloacetic acid) by using a novel aldolase derived from the genus Pseudomonas, Erwinia, Flavobacterium, or Xanthomonas.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Mutated D-aminotransferase and method for producing optically active glutamic acid derivatives using the same
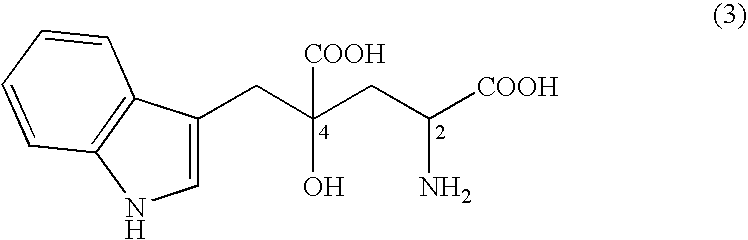
A D-aminotransferase can be modified so as to efficiently produce (2R, 4R)-monatin having high sweetness intensity from 4-(indol-3-ylmethyl)-4-hydroxy-2-oxoglutaric acid by substituting an amino acid at least at one of positions (positions 100, 180 to 183, 243 and 244) involved in efficiently producing the (2R, 4R)-monatin in an amino acid sequence of a wild-type D-aminotransferase represented in SEQ ID NO:2.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Plants with Increased Yield
InactiveUS20120227134A1MicroorganismsVector-based foreign material introductionUbiquitin-Protein LigasesSerine hydroxymethyltransferase
A method for producing a plant with increased yield as compared to a corresponding wild type plant whereby the method comprises at least the following step: increasing or generating in a plant or a part thereof one or more activities of a polypeptide selected from the group consisting of 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase, 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase, 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphate phosphatase, 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase, 5OS chloroplast ribosomal protein L21, 57972199. R01.1-protein, 60952769. R01.1-protein, 60S ribosomal protein, ABC transporter family protein, AP2 domain-containing transcription factor, argonaute protein, AT1 G29250.1-protein, AT1 G53885-protein, AT2G35300-protein, AT3G04620-protein, AT4G01870-protein, AT5G42380-protein, AT5G47440-protein, CDS5394-protein, CDS5401_TRUNCATED-protein, cold response protein, cullin, Cytochrome P450, delta-8 sphingolipid desaturase, galactinol synthase, glutathione-S-transferase, GTPase, haspin-related protein, heat shock protein, heat shock transcription factor, histone H2B, jasmonate-zim-domain protein, mitochondrial asparaginyl-tRNA synthetase, Oligosaccharyltransferase, OS02G44730-protein, Oxygen-evolving enhancer protein, peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase, peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase family protein, plastid lipid-associated protein, Polypyrimidine tract binding protein, PRLI-interacting factor, protein kinase, protein kinase family protein, rubisco subunit binding-protein beta subunit, serine acetyltransferase, serine hydroxymethyltransferase, small heat shock protein, S-ribosylhomocysteinase, sugar transporter, Thioredoxin H-type, ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, ubiquitin-protein ligase, universal stress protein family protein, and Vacuolar protein.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
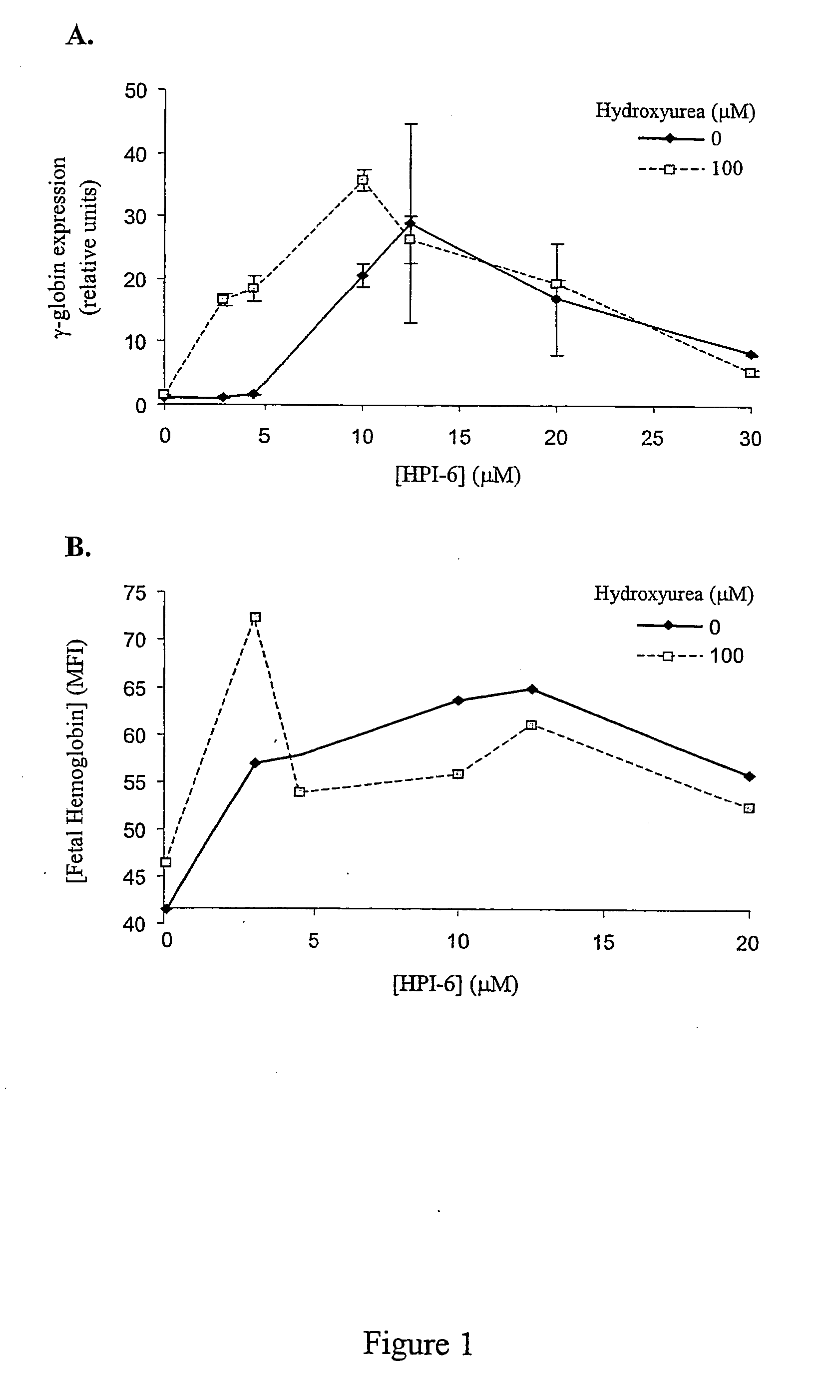
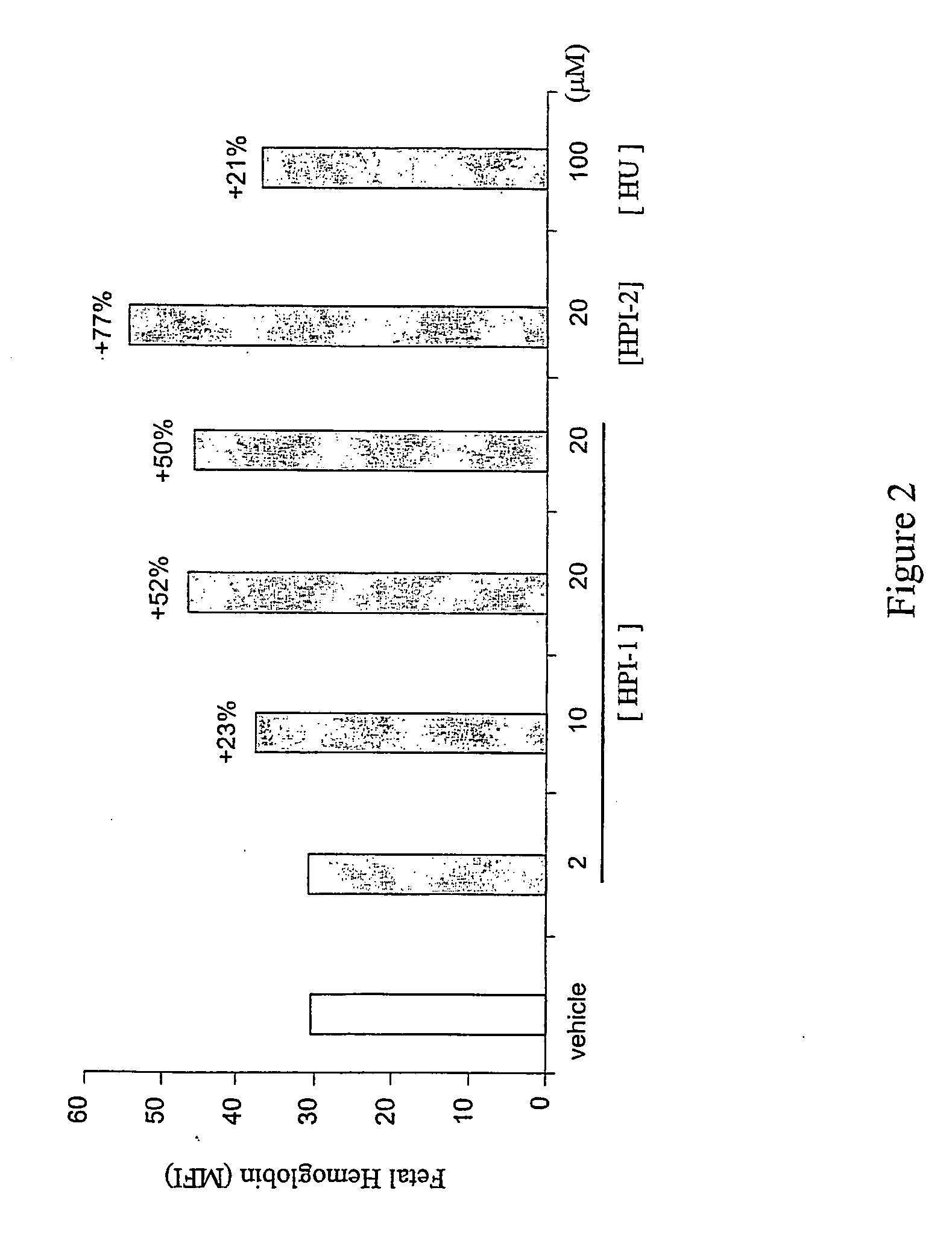
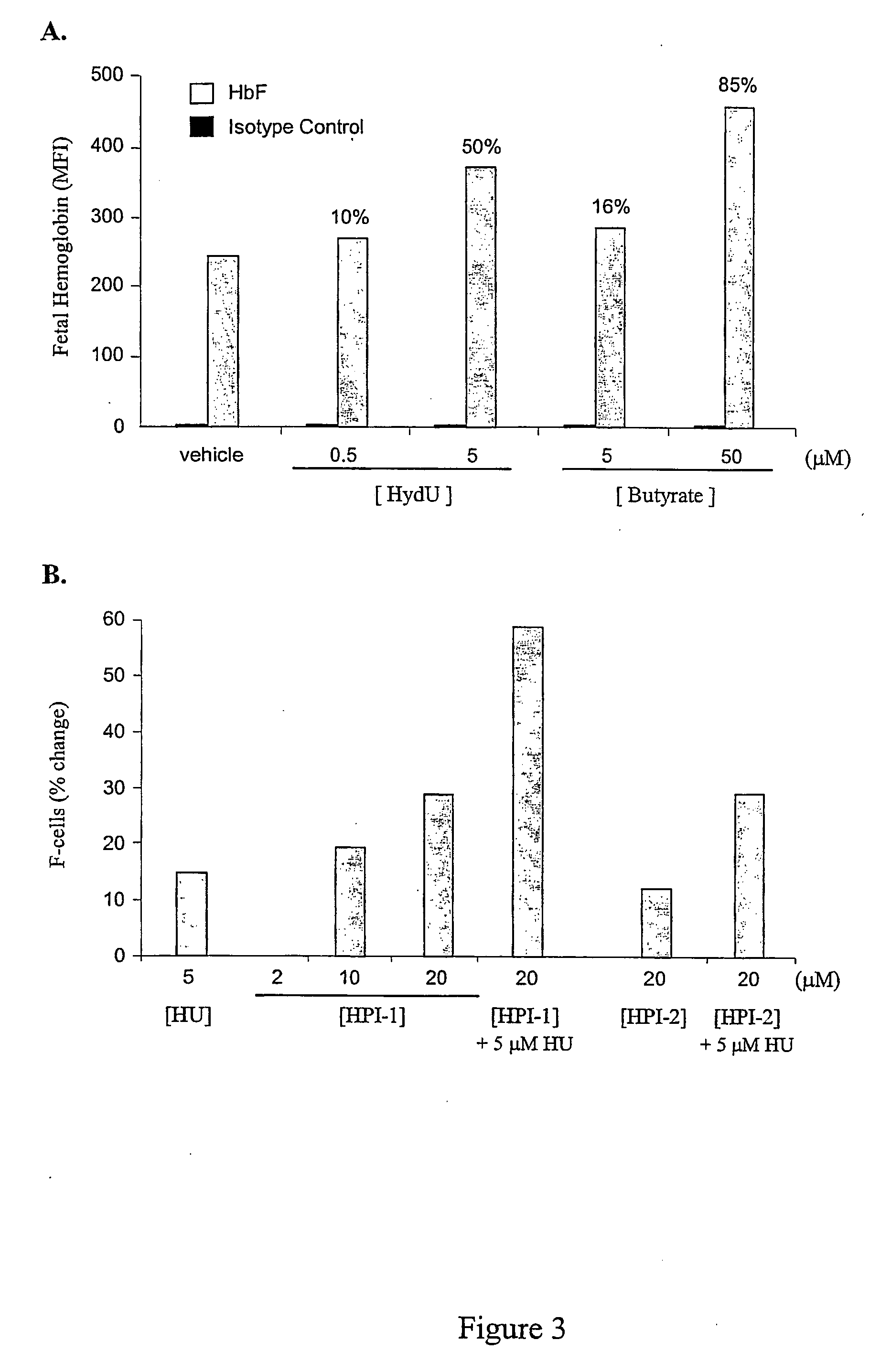
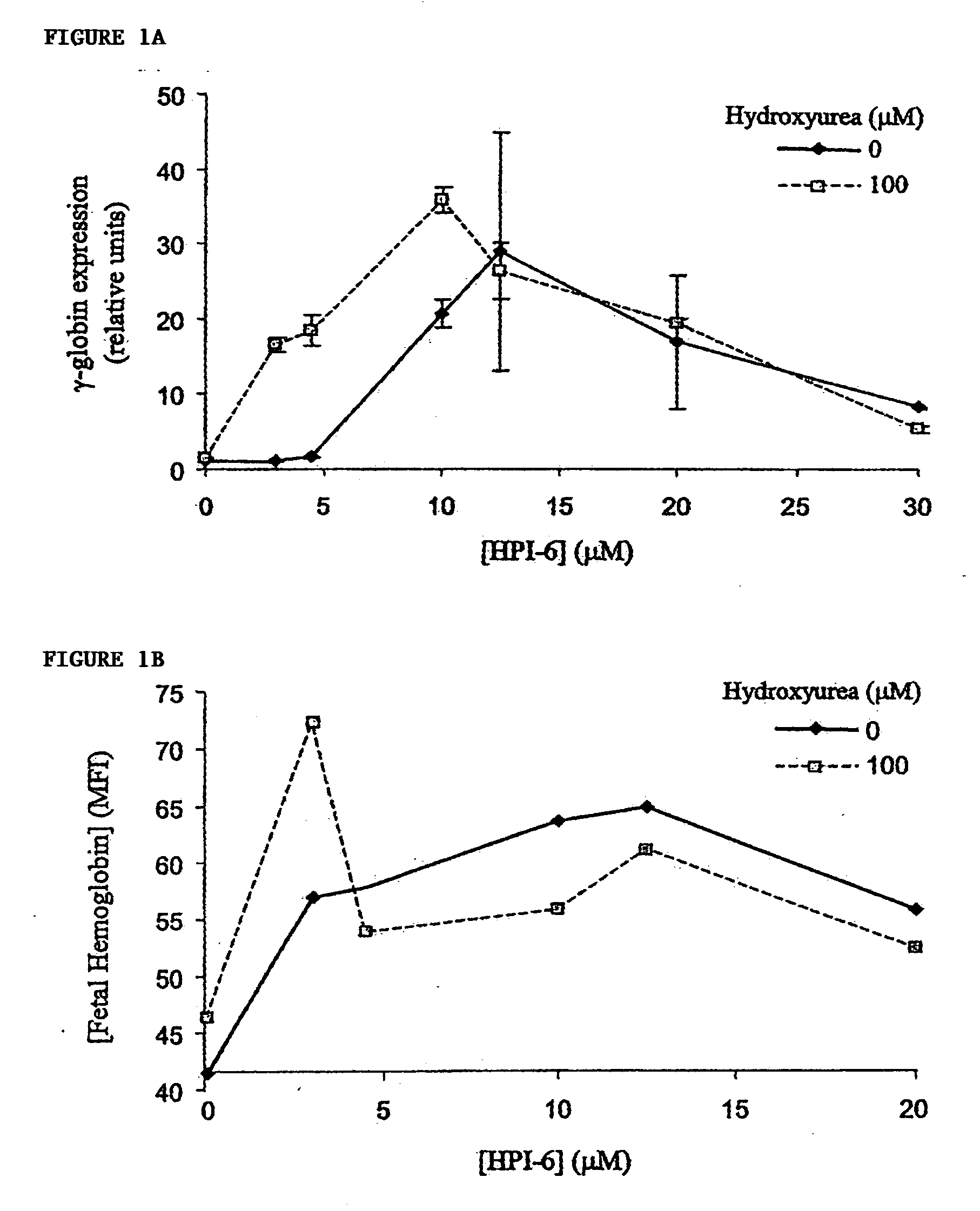
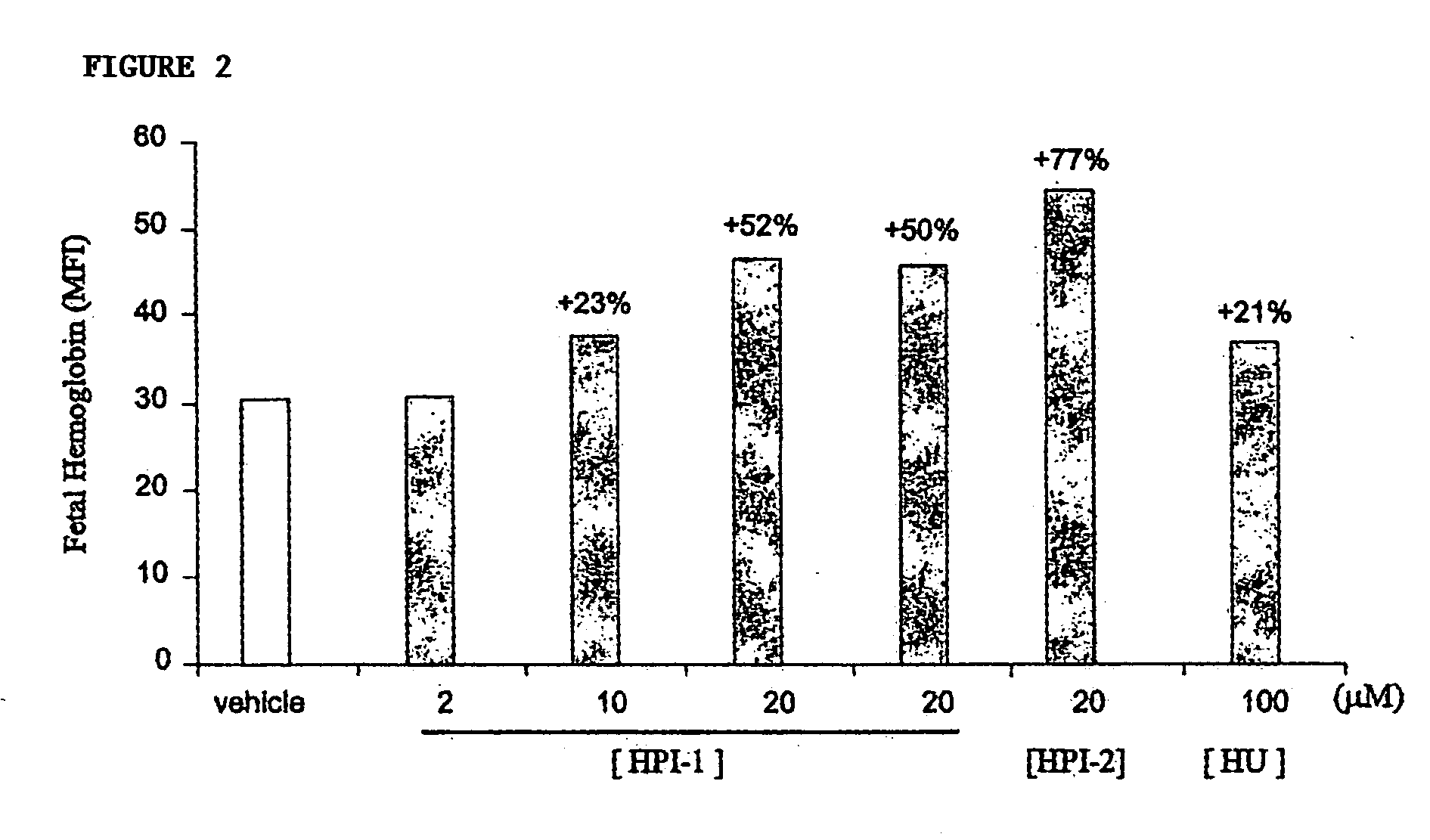
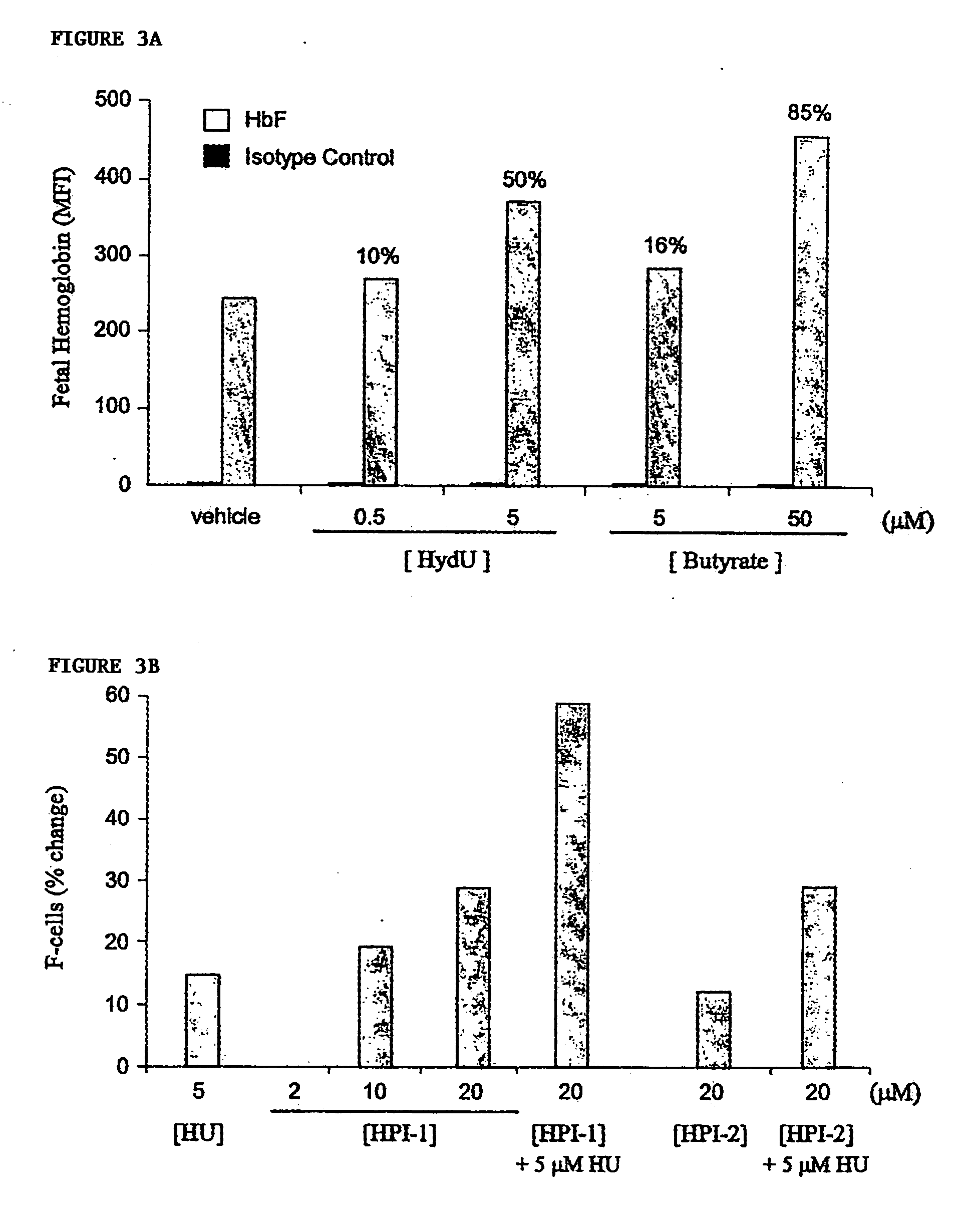
Inhibitors of 2-oxoglutarate dioxygenase as gamma globin inducers
InactiveUS20070042937A1Increase gene expressionInhibit hydroxylationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseThalassemia
The present invention provides methods for increasing endogenous globin expression in a subject, specifically γ-globin expression. The invention also provides compounds and medicaments for use in the methods. The methods are particularly useful for increasing fetal hemoglobin production in a subject, and can be used to treat various disorders, e.g., β thalassemia and sickle cell disease.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD +1
High throughput assay
InactiveUS20050214894A1Safe and efficientMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingFluorescenceOxygenase activity
A method for detecting 2-oxoglutarate oxygenase activity, which method comprises: (i) contacting a 2-oxoglutarate oxygenase and a substrate of the 2-oxoglutarate oxygenase in the presence of 2-oxoglutarate; (ii) adding a derivatisation reagent capable of forming a fluorescent product with 2-oxoglutarate; (iii) detecting the fluorescent product produced by the reaction between the derivatisation reagent and 2-oxoglutarate, if any, thereby detecting 2-oxoglutarate oxgenase activity.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
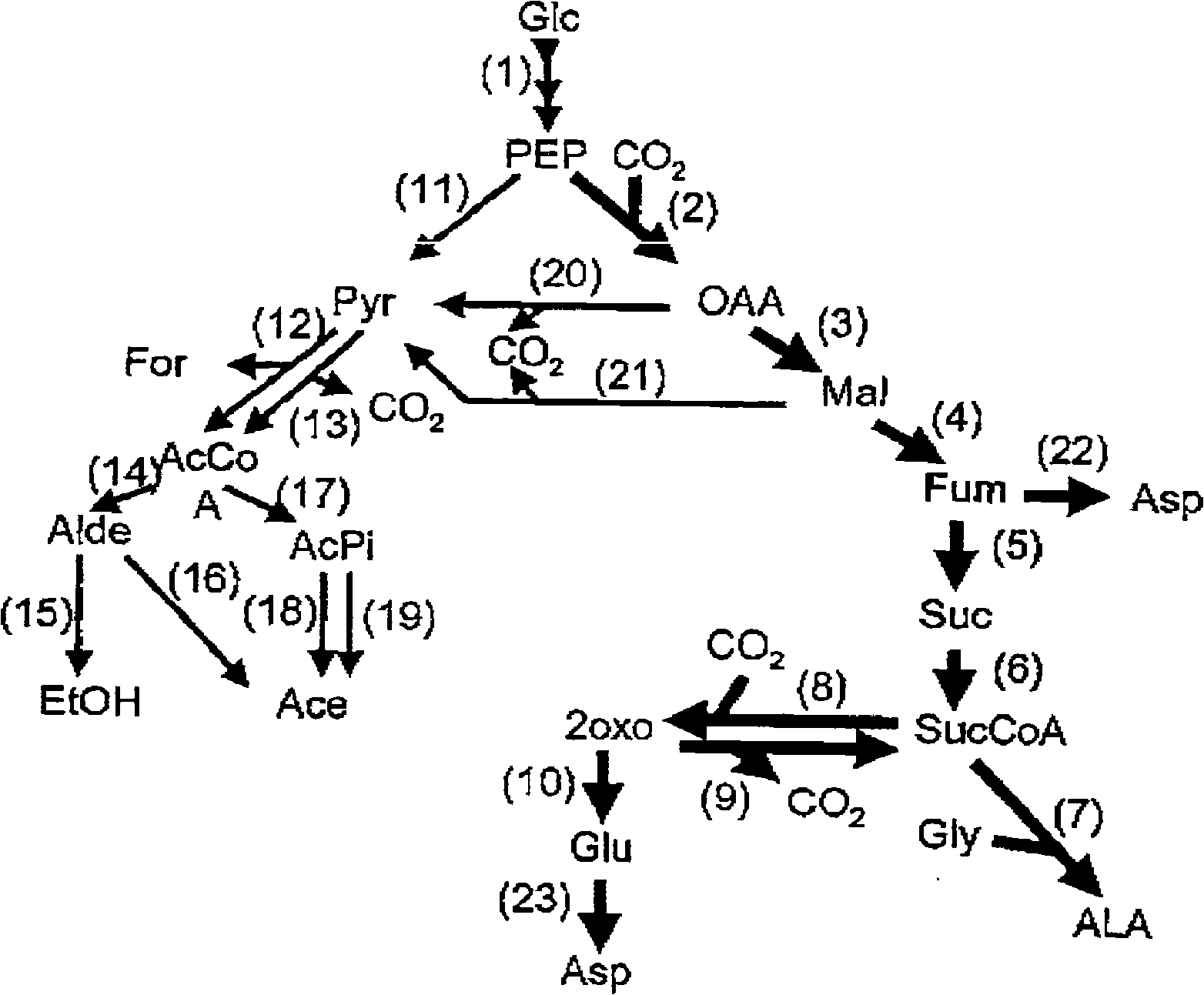
Genes from actinobacillus succinogenes 13oz (atcc 55618) for production of chemicals from the a. succinogenes C4-pathway
InactiveCN101278041AIncrease intakeBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaBiotechnology5-aminolevulinate
Actinobacillus succinogenes genes and methods of using the genes in genetically engineered A. succinogenes so as to improve production of chemicals such as succinate, fumarate, malate, 5-aminolevulinate, 2-oxoglutarate, glutamate, and aspartate. The genetically engineered A. succinogenes strains are capable of overexpressing C4 enzymes. The genetically engineered A. succinogenes can have one or more gene knockouts or modifications that inhibit C3 enzymes. The fluxes supplying substrate to the C4 pathway can also be improved in some of the genetically engineered A. succinogenes.
Owner:MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Bacterium producing a product of a reaction catalyzed by a protein having 2-oxoglutarate-dependent enzyme activity and a method for manufacturing the product
ActiveUS20100330622A1Increase productionHigh activityBacteriaSugar derivativesDioxygenase activityDNA fragmentation
A method for manufacturing a product of a reaction catalyzed by a protein having 2-oxoglutarate-dependent enzyme activity such as (2S,3R,4S)-4-hydroxy-L-isoleucine or a salt thereof using a bacterium transformed with a DNA fragment containing a gene coding for a protein having 2-oxoglutarate-dependent enzyme activity such as L-isoleucine dioxygenase activity; and wherein said bacterium has the ability to produce a product such as (2S,3R,4S)-4-hydroxy-L-isoleucine.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Inhibitors of 2-oxoglutarate dioxygenase as gamma globin inducers
InactiveUS20070185045A1Increase gene expressionInhibit hydroxylationCompound screeningBiocideThalassemiaΓ globin
The present invention provides methods for increasing endogenous globin expression in a subject, specifically γ-globin expression. The invention also provides compounds and medicaments for use in the methods. The methods are particularly useful for increasing fetal hemoglobin production in a subject, and can be used to treat various disorders, e.g., β thalassemia and sickle cell disease.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
Method for extracting alpha-ketoglutaric acid from fermentation liquor
InactiveCN105198732AEmission reductionEfficient emissionsOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound separation/purificationHigh concentrationMycoprotein
The invention discloses a method for extracting alpha-ketoglutaric acid from fermentation liquor. The method comprises the following steps: heating fermentation liquor containing the alpha-ketoglutaric acid for sterilization and decolorization, and drying mycoprotein; adding Ca(OH)2 into a filtration liquid, and performing centrifugal separation to obtain calcium 2-oxoglutarate and Ca(OH)2; adding H2SO4 into the calcium 2-oxoglutarate and Ca(OH)2, and performing centrifugal separation to obtain CaSO4 sediments; enabling the filtration liquid to flow into an ion exchange column for adsorption, and adding activated carbon into eluant for decolorization for 30 min; performing pressure reduction evaporation on the high-concentration alpha-ketoglutaric acid solution to obtain alpha-ketoglutaric acid crystals, and performing centrifugal separation to obtain an alpha-ketoglutaric acid crude product, washing the alpha-ketoglutaric acid crude product with methanol, removing impurities through washing, and performing centrifugation to remove methanol, so as to obtain the alpha-ketoglutaric acid, wherein the volume ratio of the alpha-ketoglutaric acid crude product to the methanol is 5:1. Through the adoption of the method, the problems in the prior art that pyruvic acid as a by-product during the extraction process of the alpha-ketoglutaric acid cannot be effectively separated and the discharge amount of waste liquid is high are solved.
Owner:SHANDONG YANGCHENG BIOLOGY TECH CO LTD
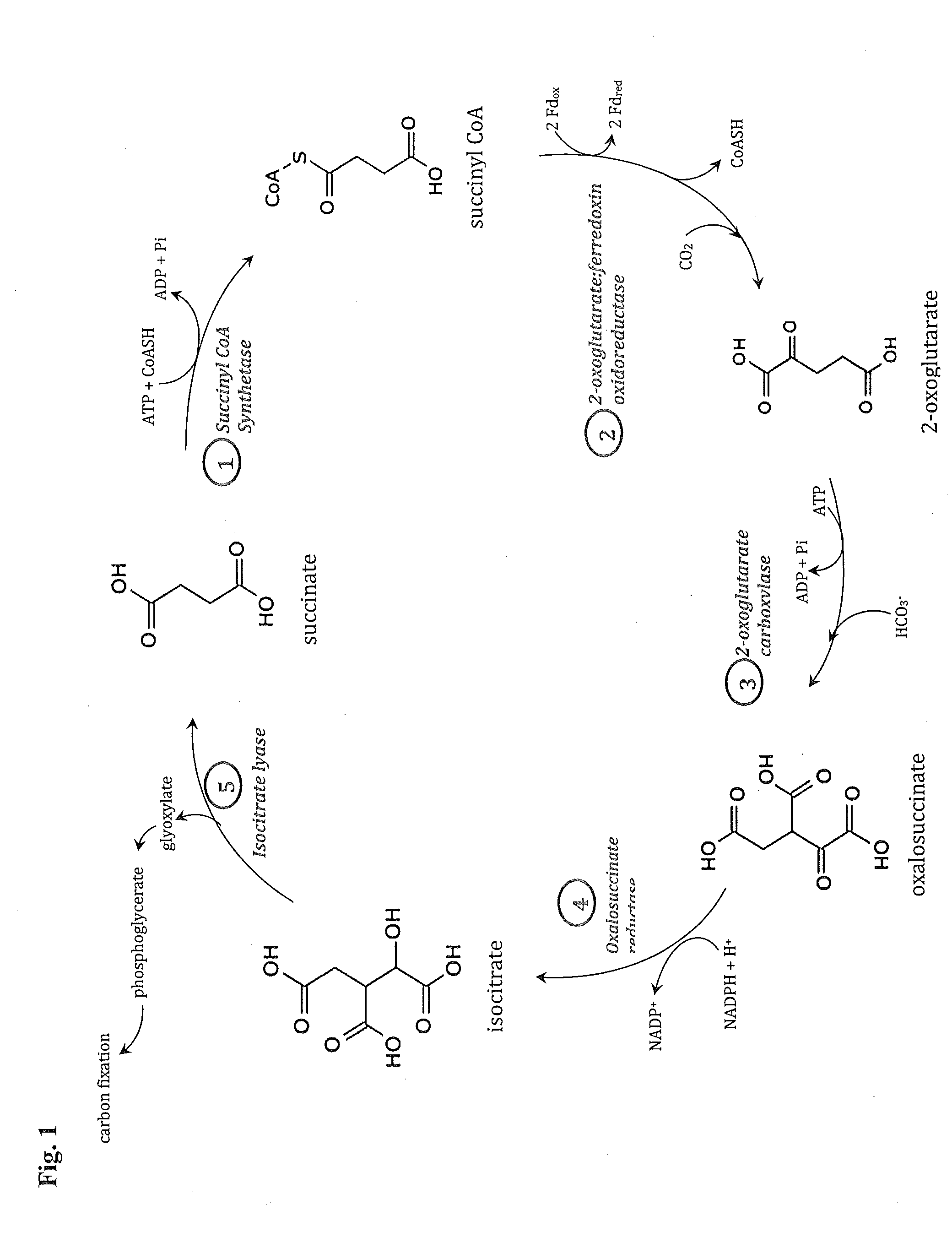
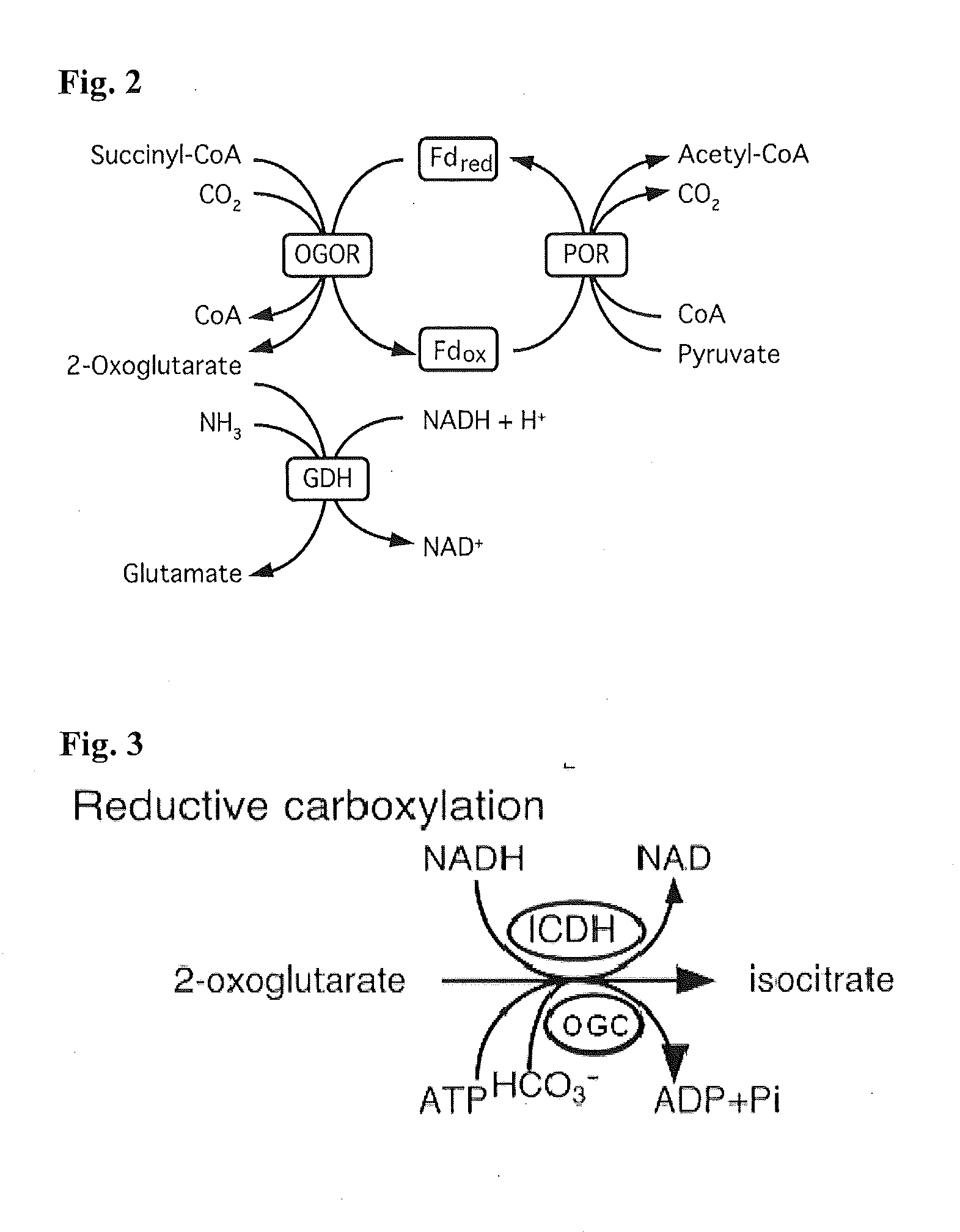
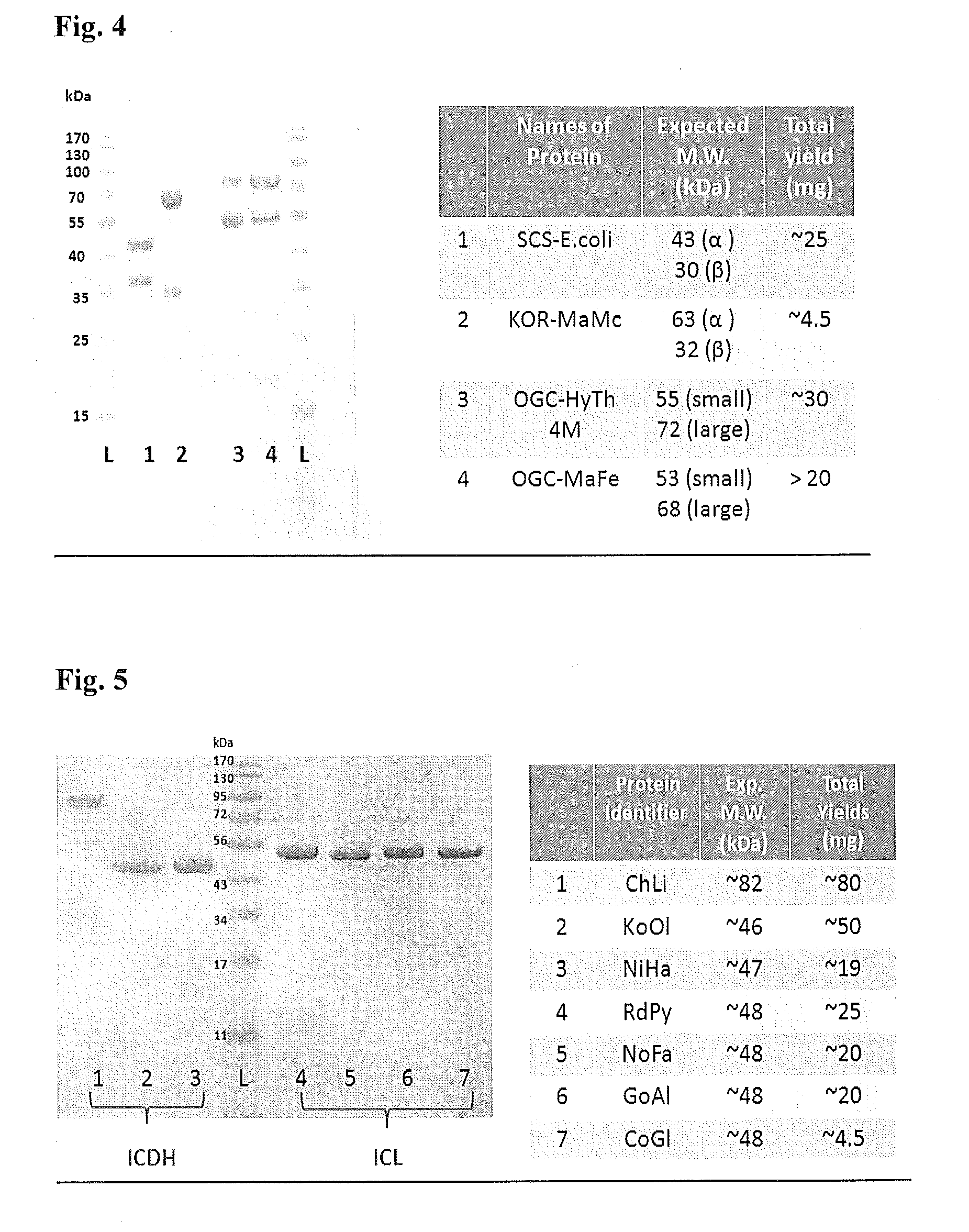
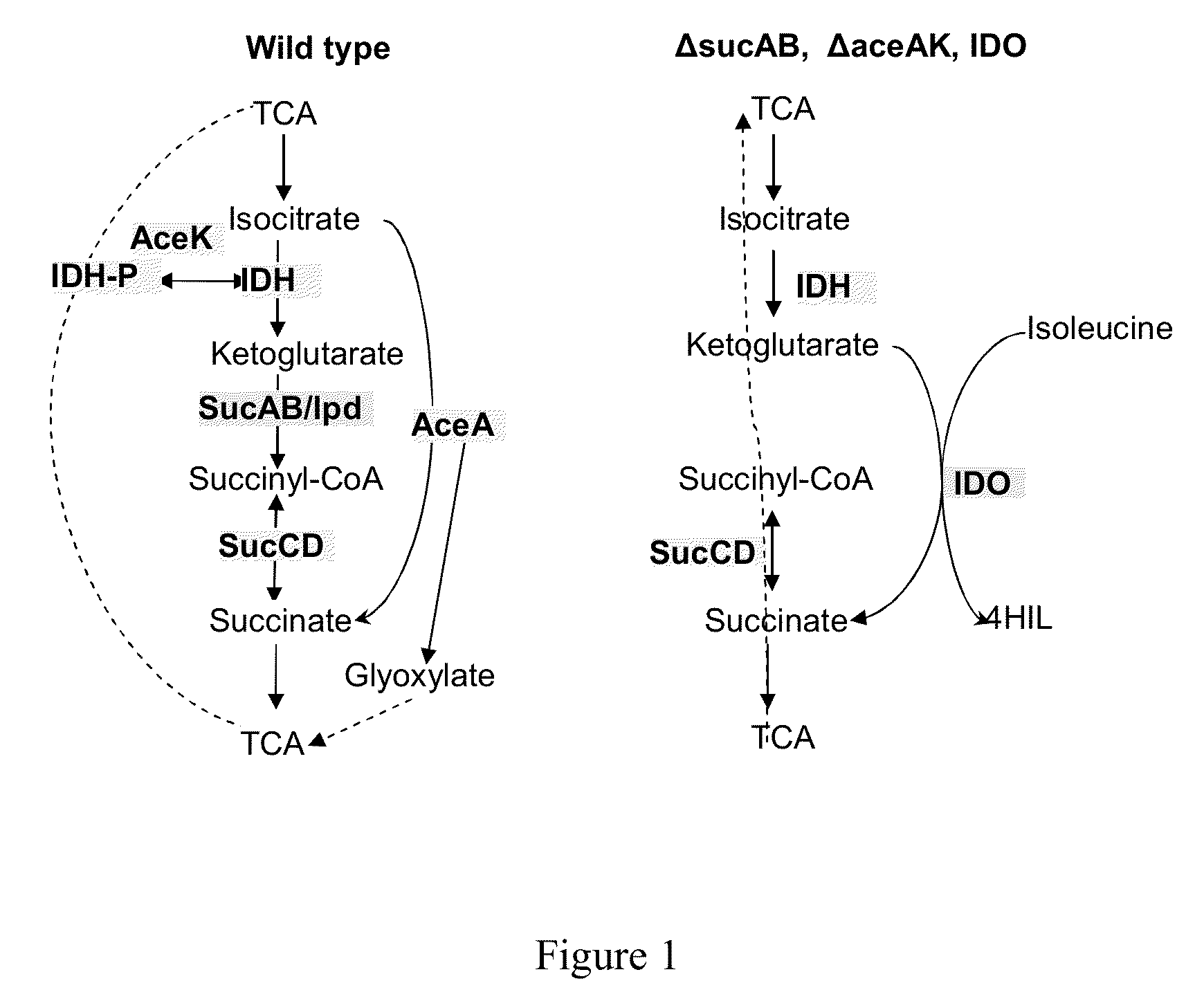
Synthetic Pathway for Biological Carbon Dioxide Sequestration
InactiveUS20140150135A1Improve efficiencyIncreased biomass productionBiocideOrganic chemistryHeterologousNucleotide
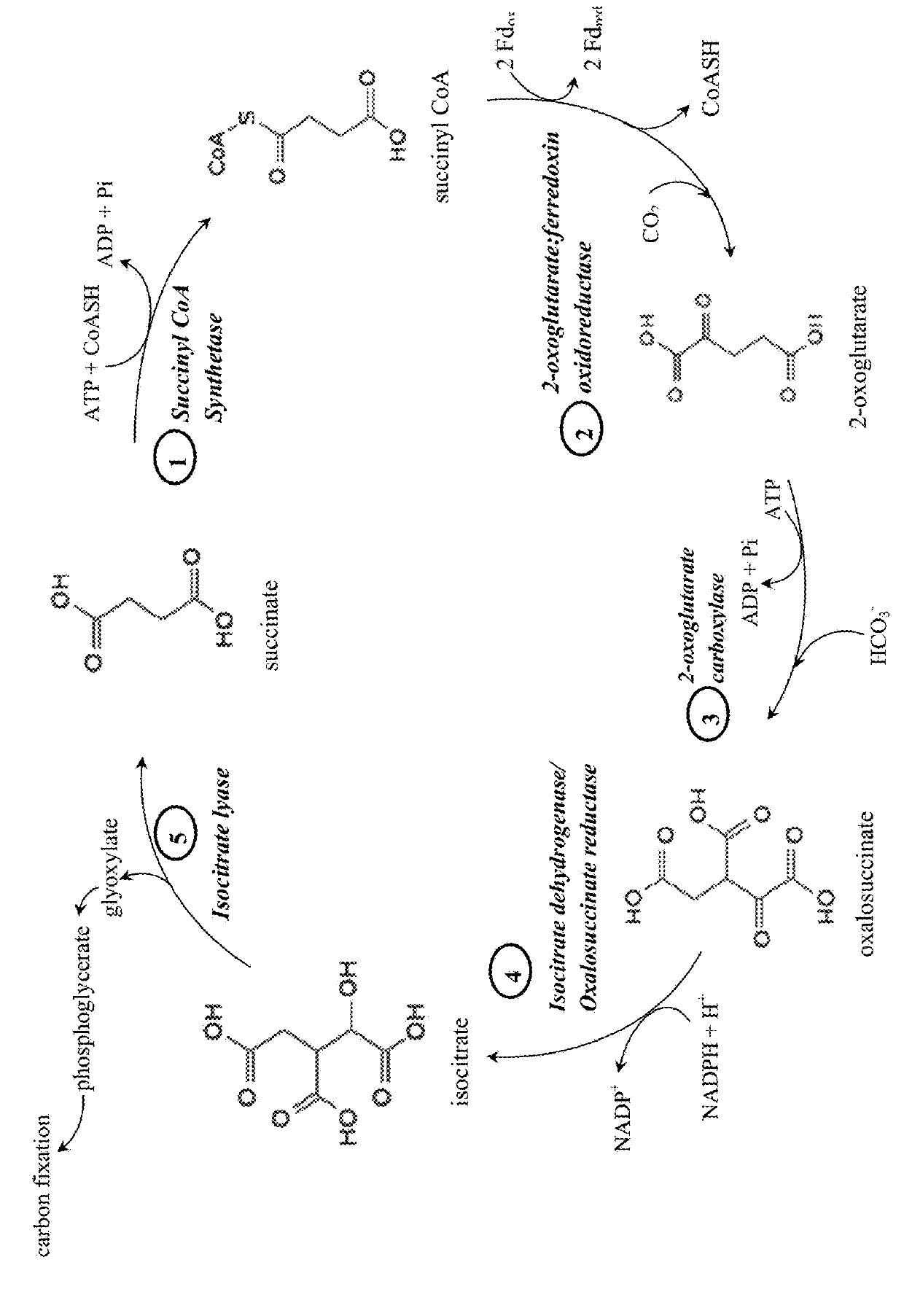
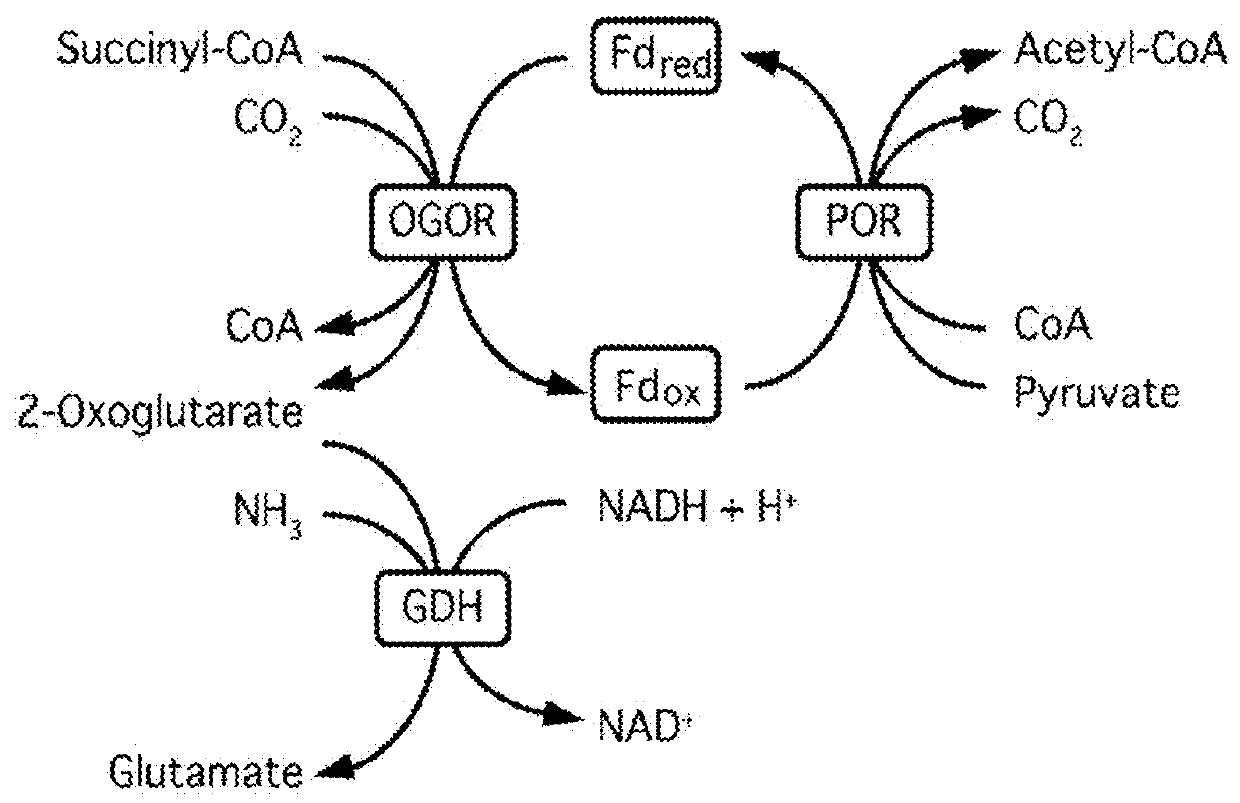
This invention relates to methods for increasing carbon fixation and / or increasing biomass production in a plant, comprising: introducing into a plant, plant part, and / or plant cell one or more heterologous polynucleotides encoding polypeptides having the enzyme activity of succinyl CoA synthetase, 2-oxoglutarate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase, 2-oxoglutarate carboxylase, oxalosuccinate reductase and isocitrate lyase to produce a stably transformed plant, plant part, and / or plant cell expressing the one or more heterologous polynucleotides. The methods further comprise introducing into a plant, plant part or plant cell heterologous polynucleotides encoding polypeptides having the enzyme activity of glyoxylate carboligase and tartronic semialdehyde reductase, and / or heterologous polynucleotides encoding a superoxide reductase from an archaeon species, an aquaporin and / or an inhibitor of cell wall invertase inhibitor. Additionally, transformed plants, plant parts, and / or plant cells are provided as well as products produced from the transformed plants, plant parts, and / or plant cells.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
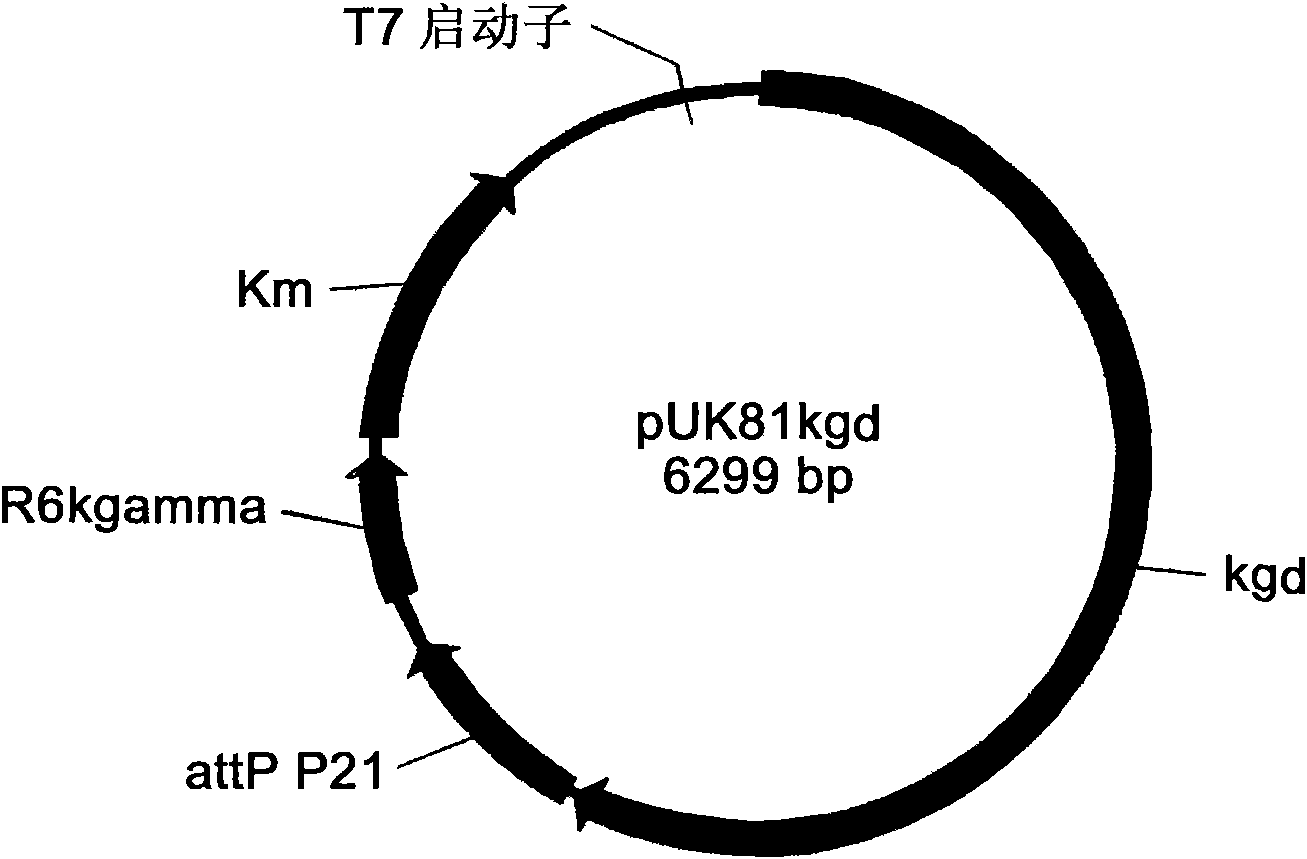
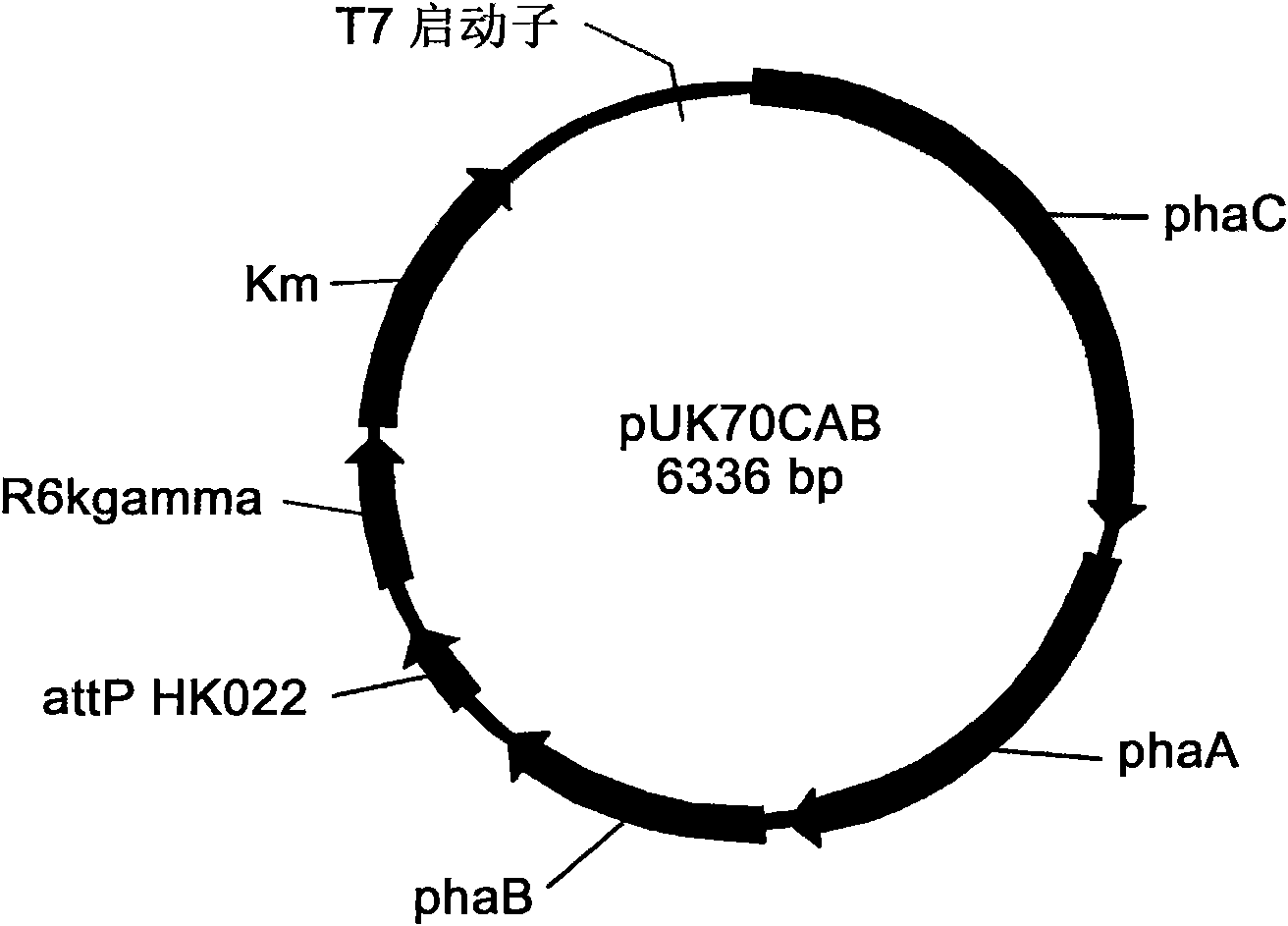
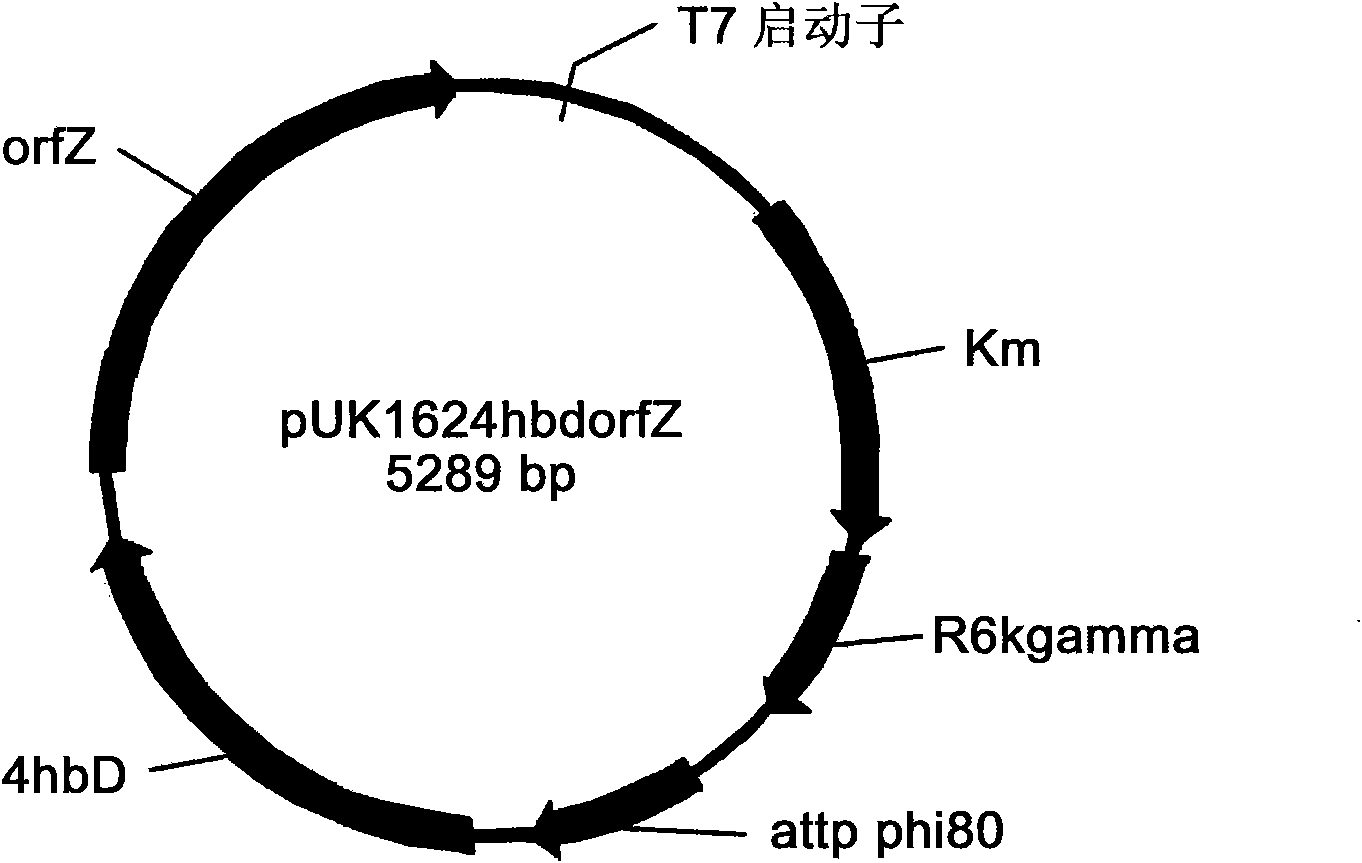
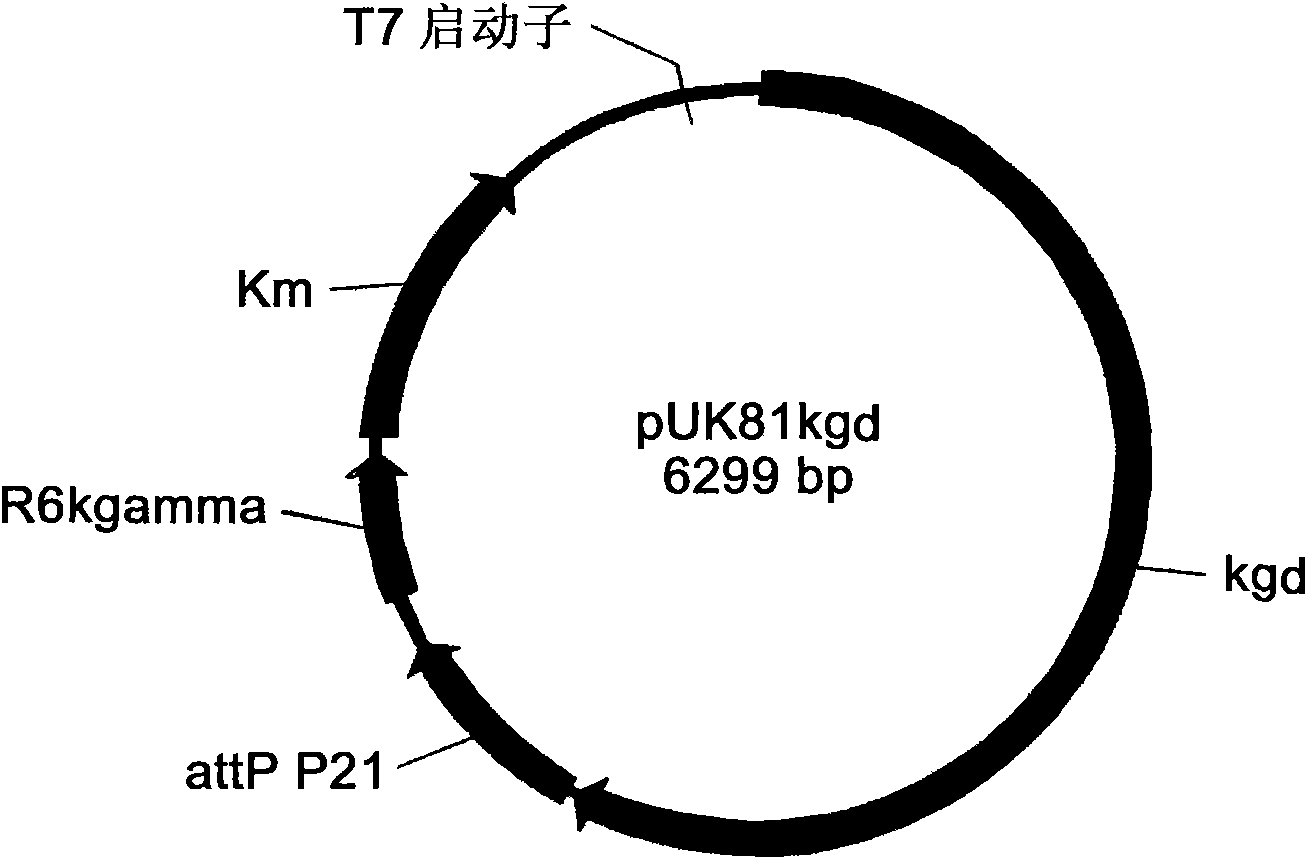
Engineering bacterium containing 2-oxoglutarate decarboxylase gene kgd and applications thereof
InactiveCN102382789AReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCoenzyme A biosynthesis2-Oxoglutarate Dehydrogenase
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and fermentation, and particularly discloses an engineering bacterium for producing 3-hydroxybutyric acid and 4-hydroxybutyric acid copolyester (P3HB4HB) by utilizing a sugar carbon source. Exogenous genes needed for combining the P2HB4HB are recombined and integrated on the genome of the engineering bacterium and comprise poly-3-hydroxybutyrate synthetic gene phaCAB and 4-hydroxybutyryl coenzyme A which is transferase gene orfZ, 4-hydroxybutyric acid dehydrogenase gene 4hbD and 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase gene kgd. By utilization of the engineering bacterium, the P3HB4HB can be produced by using the sugar carbon source with relatively cheap price, the production cost is effectively reduced, and the large-scale industrial production and the commercial application and development are pushed.
Owner:TIANJIN GREENBIO MATERIAL CO LTD
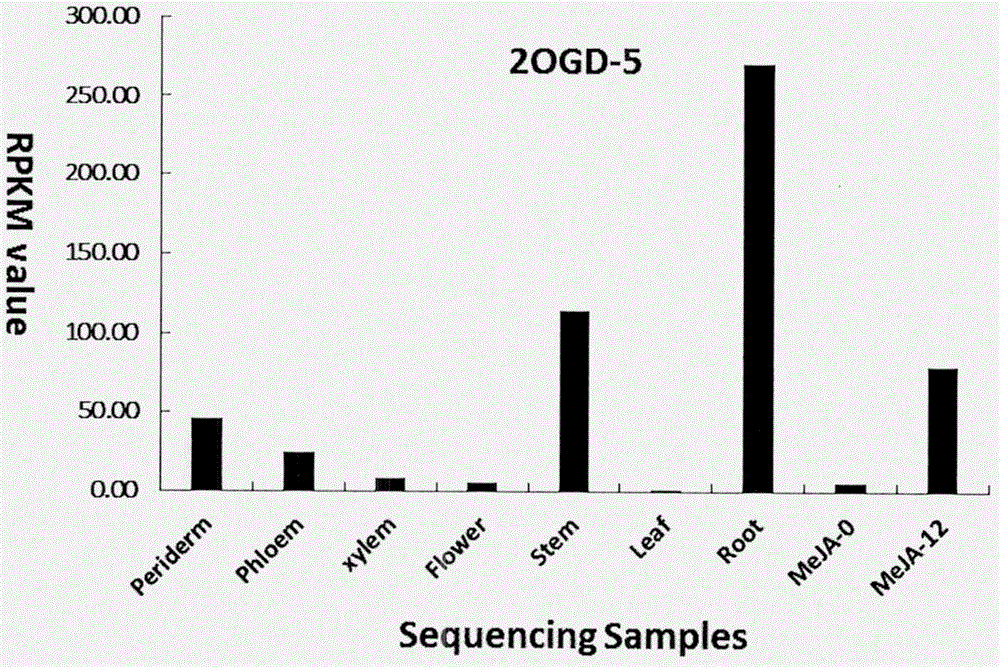
Clone identification and application of 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase (2OGD-5) gene participating in tanshinone synthesis
The invention discloses an encoding gene sequence of 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase (2OGD-5) gene participating in tanshinone synthesis. The provided 2OGD-5 gene has a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No.1, and protein encoded by the gene has an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No.2. Hairy roots of salvia miltiorrhiza bunge are subjected to genetic transformation by constructing a 2OGD-5-RNAi vector, and compared with the contrast, the content of miltirone, cryptotanshinone and tanshinone is remarkably reduced. The provided 2OGD-5 has the capability of producing tanshinone compounds under catalysis. The compounds have the function of treating cardiovascular disease. The research thought of tanshinone synthesis is innovated, and the encoding gene sequence lays a foundation for artificial synthesis of tanshinone compounds and has huge research and application prospect.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
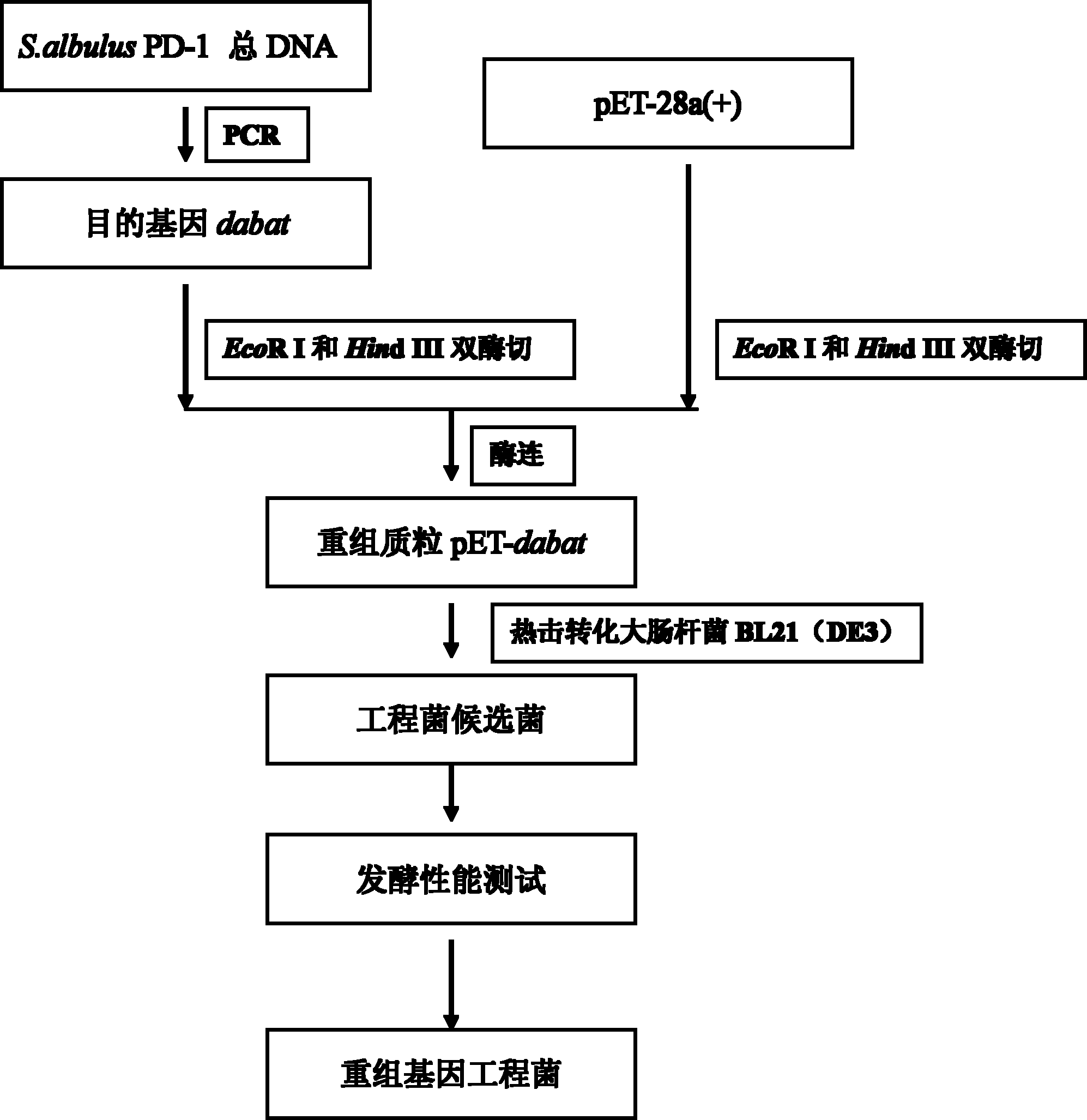
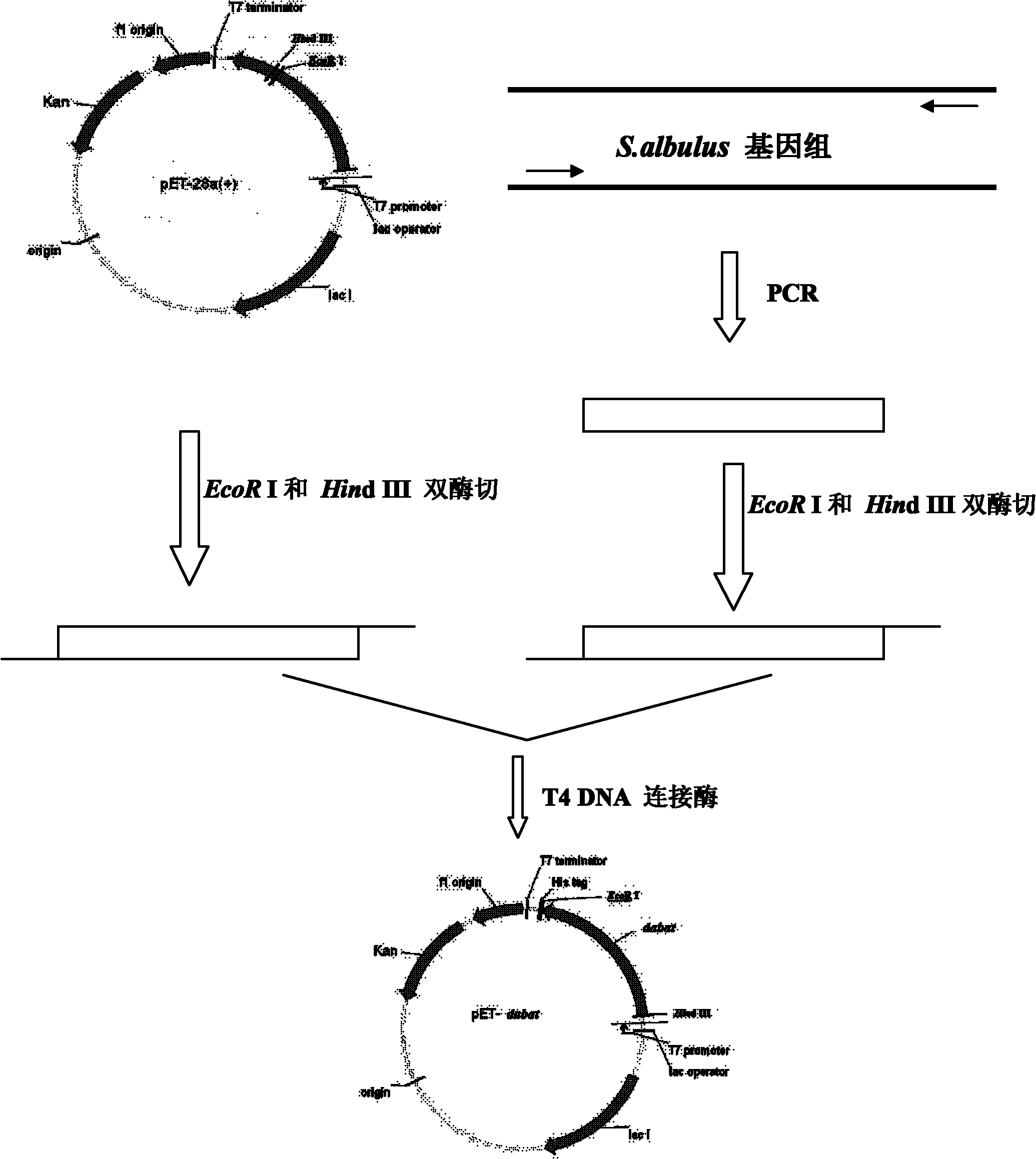
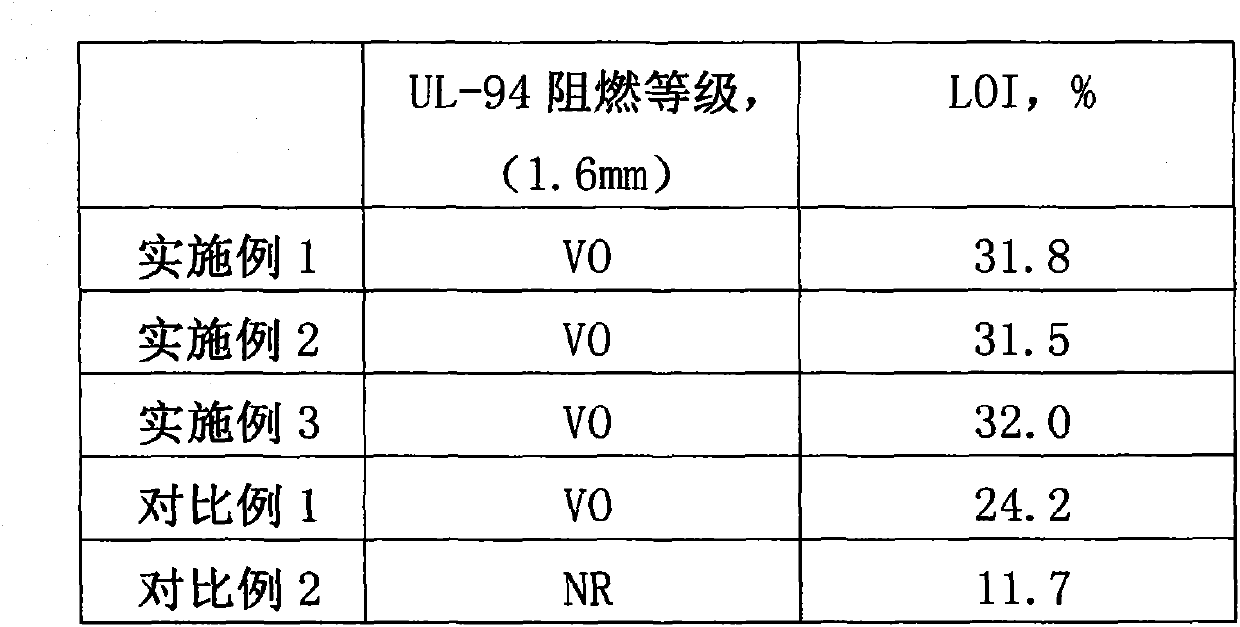
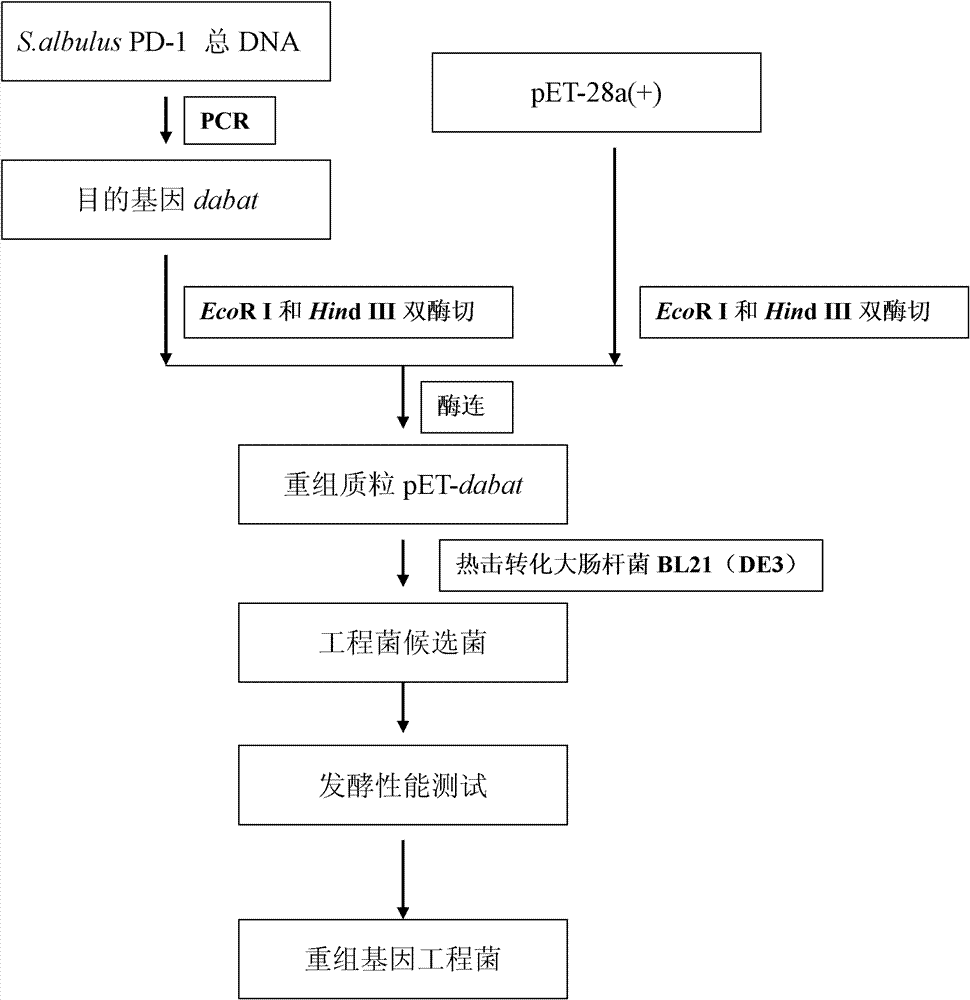
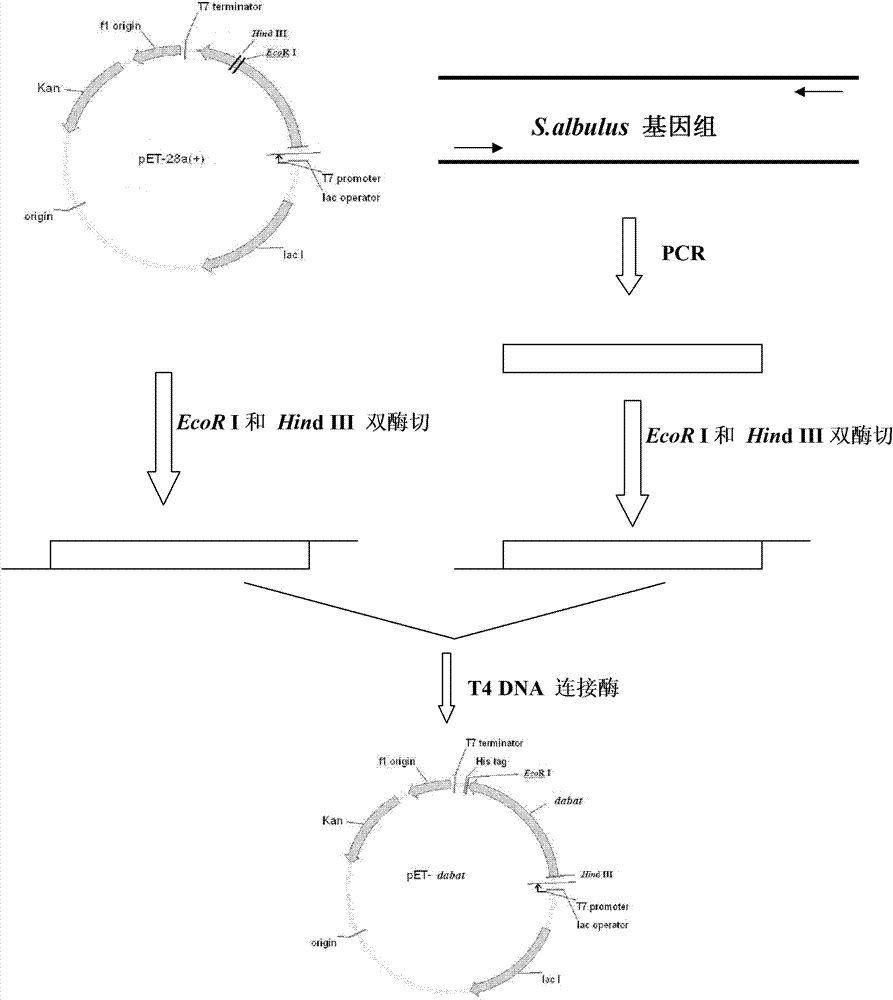
Diaminobutyrate-2-oxoglutarate transaminase and application thereof
The invention discloses diaminobutyrate-2-oxoglutarate transaminase and application thereof. The diaminobutyrate-2-oxoglutarate transaminase has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2. The invention also discloses an encoding gene of the diaminobutyrate-2-oxoglutarate transaminase, wherein the encoding gene has a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The invention also discloses an expression vector containing the encoding gene of the diaminobutyrate-2-oxoglutarate transaminase, a genetic engineering strain and a construction method thereof. In the invention, an expressed diaminobutyrate-2-oxoglutarate transaminase gene is extracted, sequenced and cloned from Streptomyces albulus for the first time; and the genetic engineering strain is constructed and L-2,4-diaminobutyrate is fermented and produced by utilizing the genetic engineering strain, so that a novel L-2,4-diaminobutyrate acquisition way is opened up.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Bacterium producing a product of a reaction catalyzed by a protein having 2-oxoglutarate-dependent enzyme activity and a method for manufacturing the product
A method for manufacturing a product of a reaction catalyzed by a protein having 2-oxoglutarate-dependent enzyme activity such as (2S,3R,4S)-4-hydroxy-L-isoleucine or a salt thereof using a bacterium transformed with a DNA fragment containing a gene coding for a protein having 2-oxoglutarate-dependent enzyme activity such as L-isoleucine dioxygenase activity; and wherein said bacterium has the ability to produce a product such as (2S,3R,4S)-4-hydroxy-L-isoleucine.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
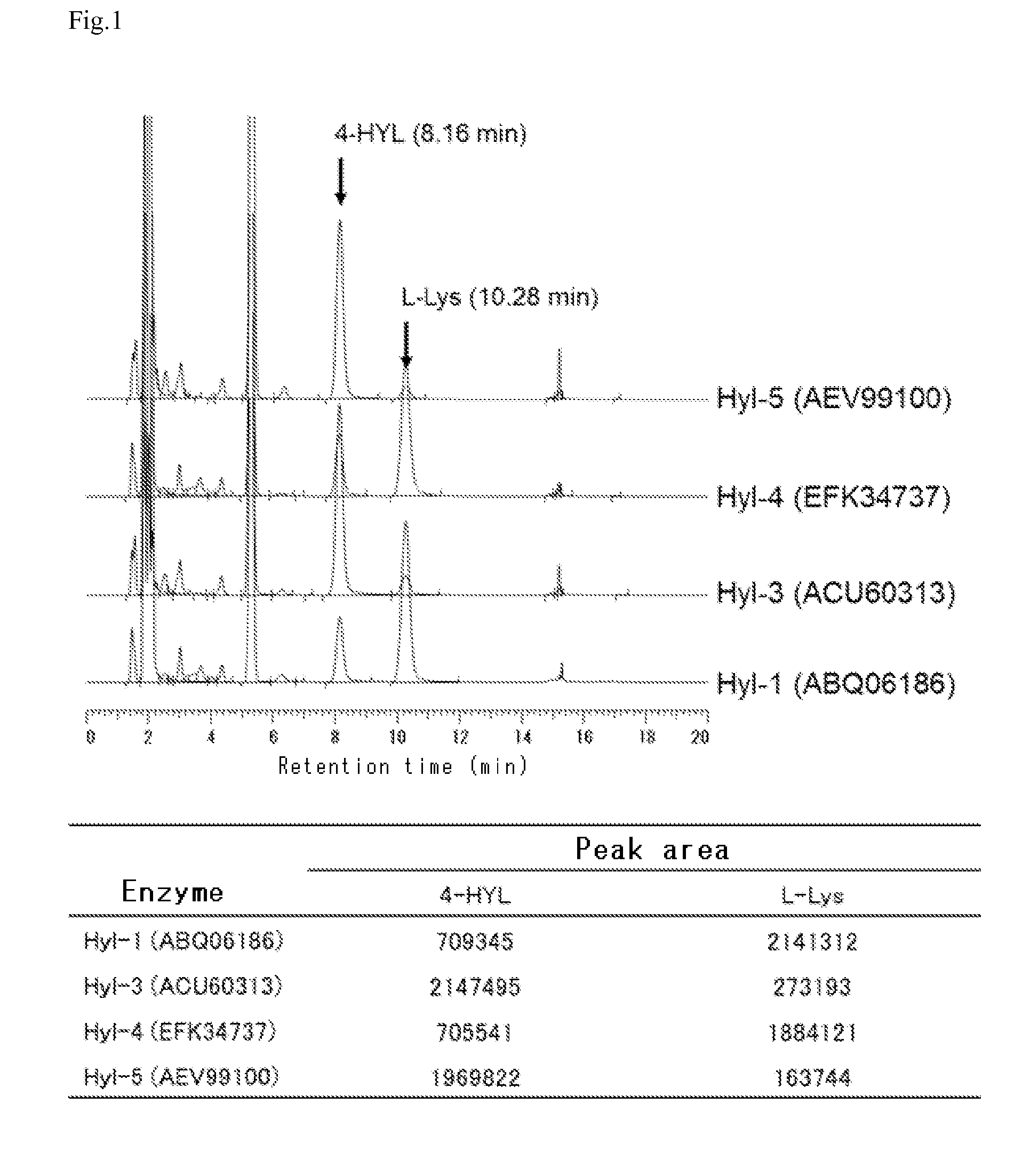
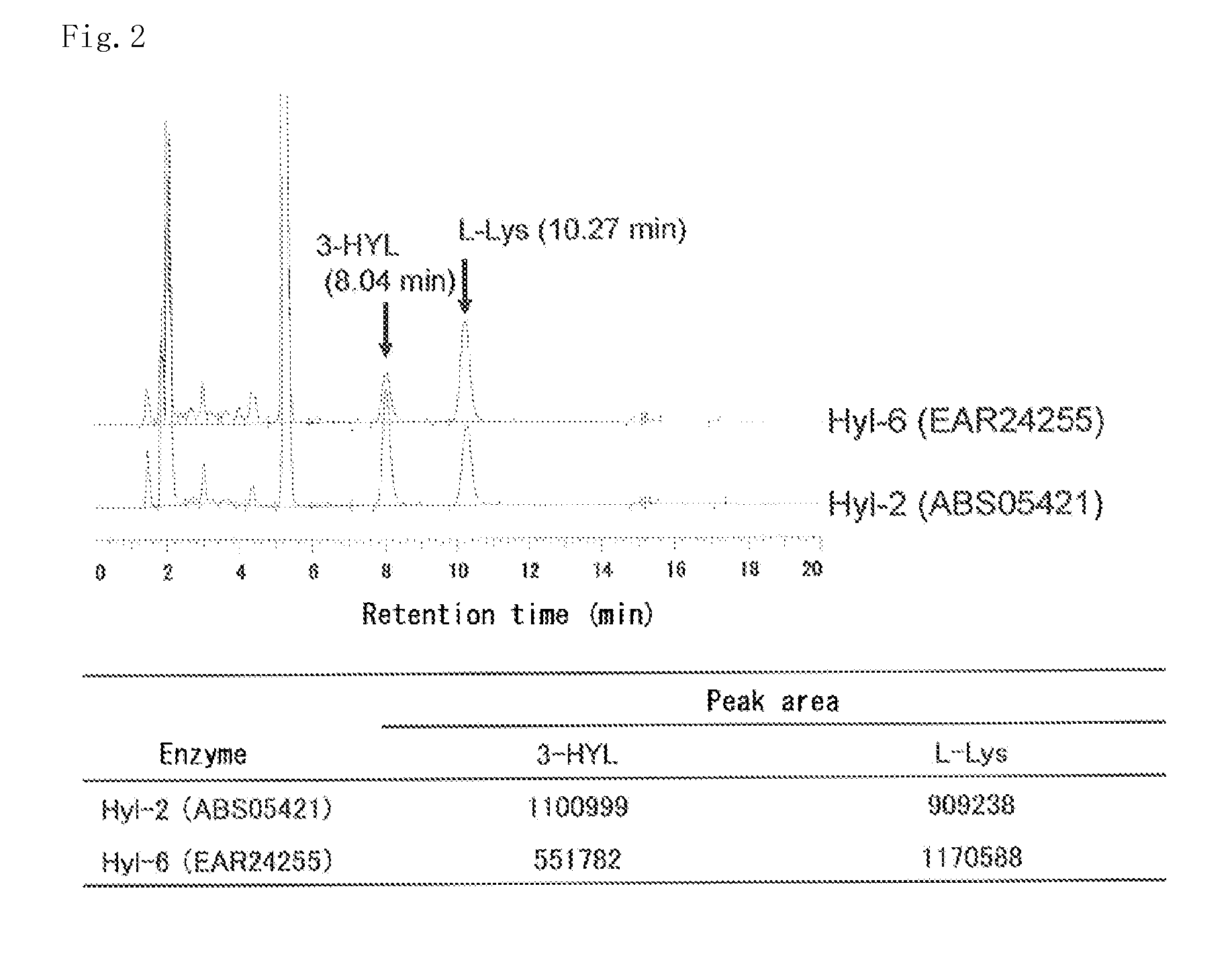
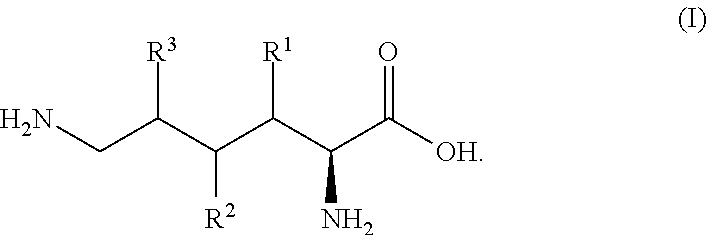
Production method for l-lysine hydroxylase and hydroxy-l-lysine using same, and production method for hydroxy-l-pipecolic acid
ActiveCN104685061AEfficient preparationRecombinant DNA-technologyOxidoreductasesHydrogen atomCulture fluid
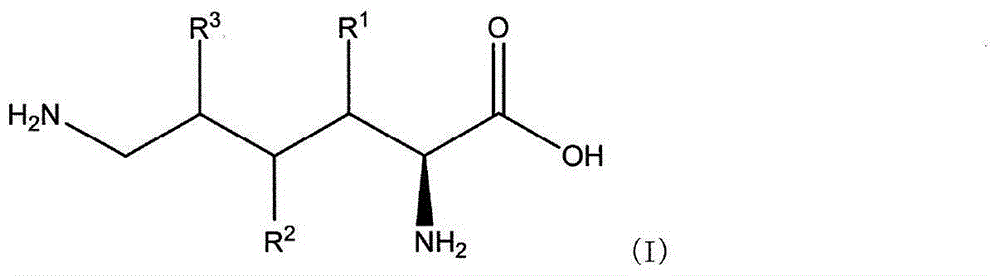
The present invention addresses the issue of providing a method whereby hydroxy-L-lysine can be efficiently produced. The present invention provides a production method for hydroxy-L-lysine, characterized by: causing a 2-oxoglutarate-dependent L-lysine hydroxylase, cells including same, a preparation of said cells, or a culture fluid obtained by cultivating said cells, to act on L-lysine; and generating the hydroxy-L-lysine indicated in general formula (I) (in the formula, R1, R2, and R3 each indicate a hydrogen atom or a hydroxyl group and at least one among R1, R2, and R3 indicates a hydroxyl group.)
Owner:API CO LTD
Method for Assaying FTO (2-Oxoglutarate Dependent Oxygenase) Activity
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD
Methods, reagents and cells for biosynthesizing compounds
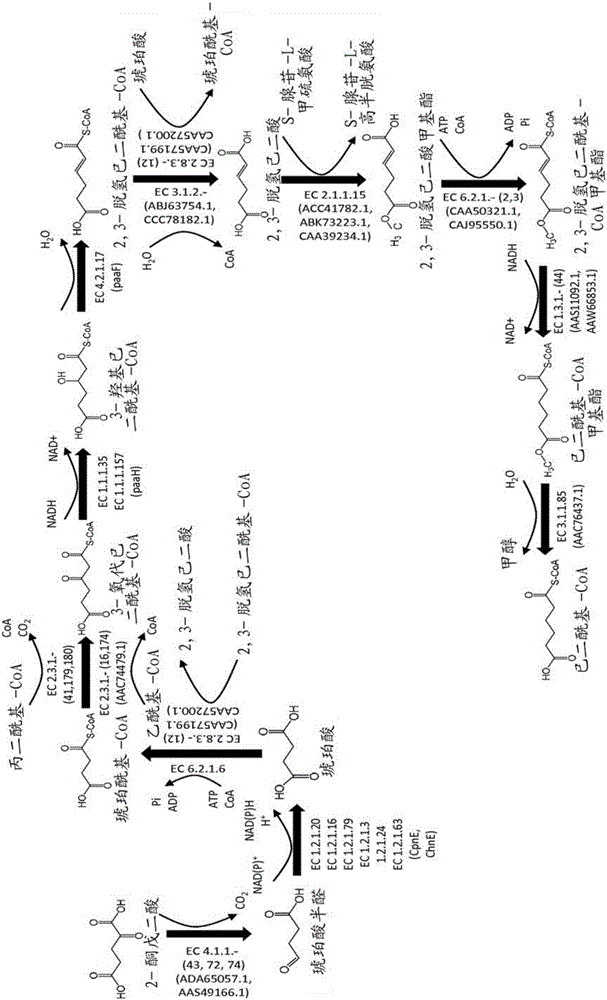
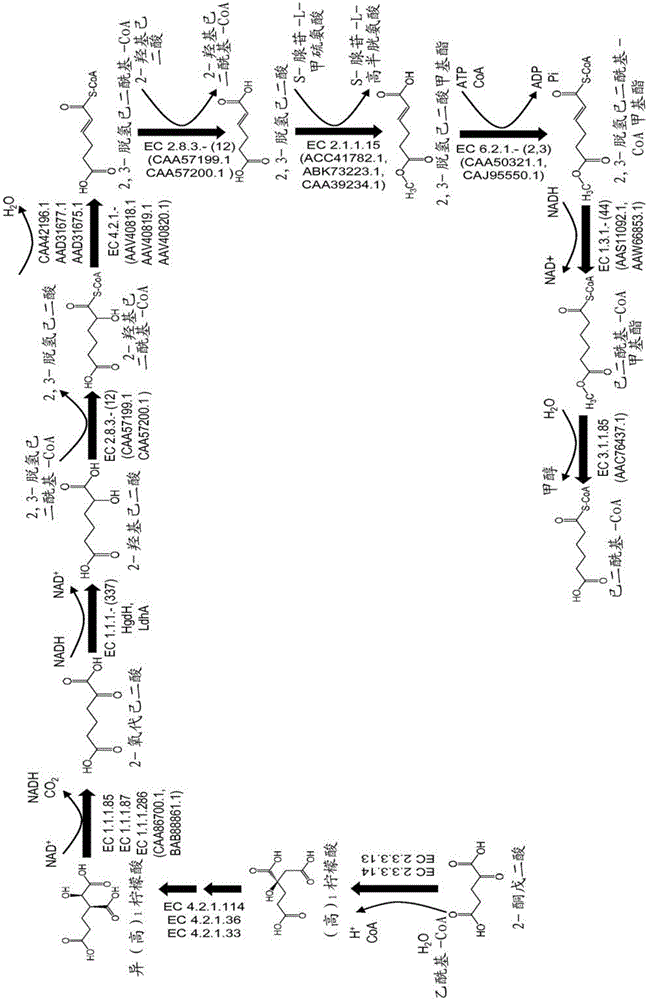
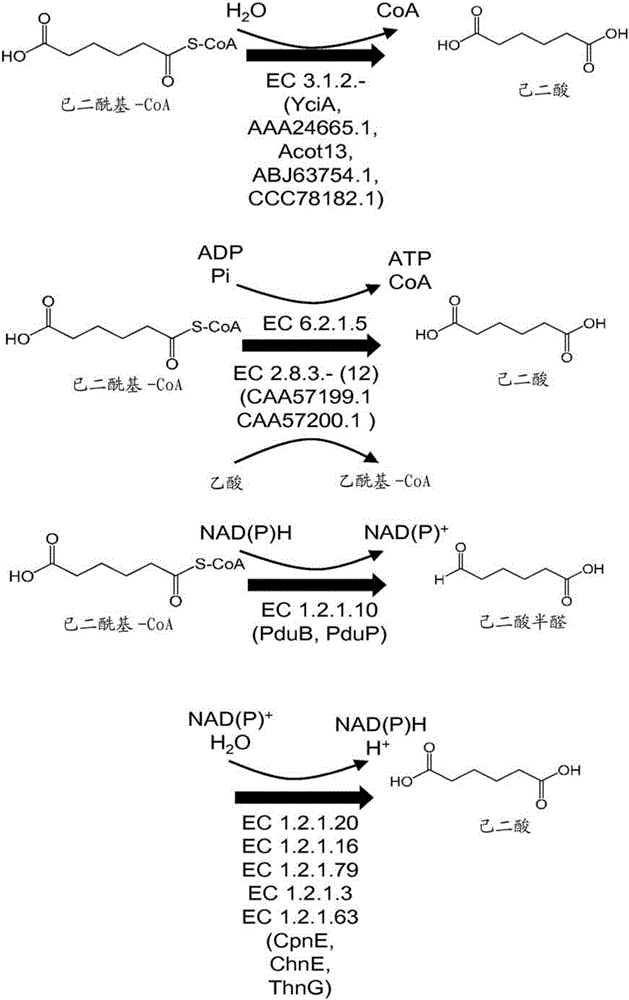
This document describes biochemical pathways for producing 2,3-dehydroadipyl-CoA methyl ester from precursors such as 2-oxoglutarate using one or more of a fatty acid O-methyltransferase, a thioesterase, a CoA-transferase and a CoA ligase, as well as recombinant hosts expressing one or more of such enzymes. 2,3-dehydroadipyl-CoA methyl ester can be enzymatically converted to adipyl-CoA using a trans-2-enoyl-CoA reductase, and a methylesterase, which in turn can be enzymatically converted to adipic acid, 6-aminohexanoate, 6-hydroxyhexanoate, caprolactam, hexamethylenediamine, or 1,6-hexanediol.
Owner:INVISTA TEXTILES (U K) LTD
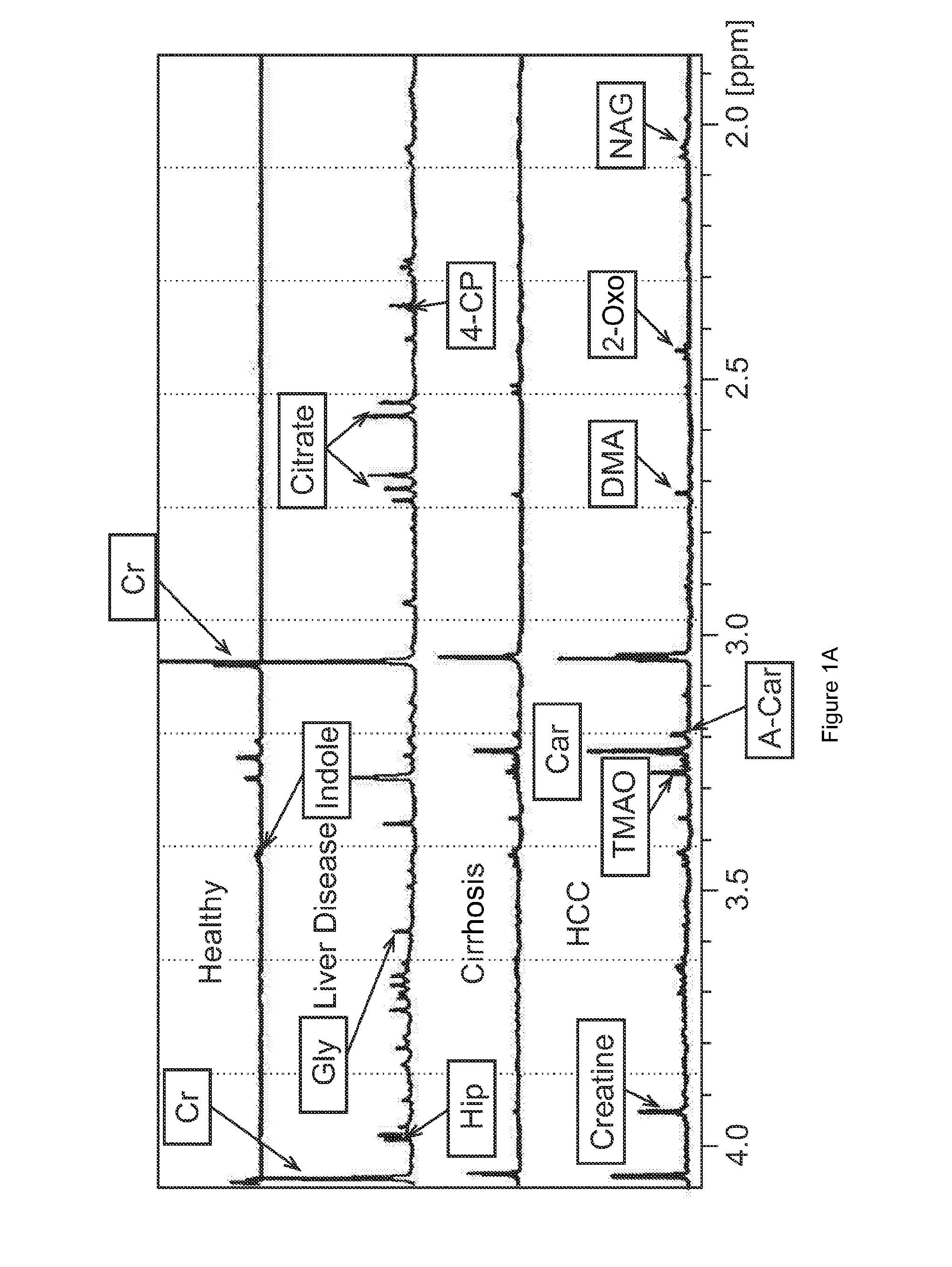
Diagnostic method for hepatic cancer
Methods and kits for analysing a sample from a test subject. The methods involve determining the level of at least one compound selected from the group consisting of N-acetylglutamate, methionine, acetylcarnitine, indole-3-acetate, 2-oxoglutarate, anserine, aspartate and butyrate in the sample from the test subject; and comparing the level of the at least one compound determined to at least one control level, wherein the levels of the at least one compound are indicative of whether the subject has hepatic cancer.
Owner:IMPERIAL INNOVATIONS LTD
Synthetic pathway for biological carbon dioxide sequestration
ActiveUS20180163220A1Improve efficiencyIncreased biomass productionVectorsClimate change adaptationPlant cellFerredoxin
This invention relates to methods for increasing carbon fixation and / or increasing biomass production in a plant, comprising: introducing into a plant, plant part, and / or plant cell heterologous polynucleotides encoding (1) a succinyl CoA synthetase, (2) a 2-oxoglutarate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase, (3) a 2-oxoglutarate carboxylase, (4) an oxalosuccinate reductase, or (5) an isocitrate lyase, or (6) a succinyl CoA synthetase and a 2-oxoglutarate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase, (7) a 2-oxoglutarate carboxylase and an oxalosuccinate reductase polypeptide, and / or (8) a 2-oxoglutarate carboxylase polypeptide, an oxalosuccinate reductase polypeptide and an isocitrate lyase polypeptide to produce a stably transformed plant, plant part, and / or plant cell, wherein said heterologous polynucleotides are from a bacterial and / or an archaeal species. Additionally, transformed plants, plant parts, and / or plant cells are provided as well as products produced from the transformed plants, plant parts, and / or plant cells.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Control of metabolism with human 2-oxoglutarate carrier
The present invention is directed to compositions and methods related to the use of human OGC as an uncoupling protein.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Hyperpolarized 2-oxoglutarate as metabolic agent in mr
InactiveUS20150273086A1Information can be usedHigh sensitivityIn-vivo radioactive preparationsMicrobiological testing/measurementMedicineResonance
Hyperpolarized 1-13C-2-oxoglutarate as contrast agent in 13C Magnetic Resonance diagnostic technique (13C-MRI) for use in the diagnosis of cancer. In particular, upon administration of said 1-13C-2-oxoglutarate, signals of 1-13C-glutamate are detected. More in particular, different MR signals from 13C nuclei are detected and compared, said comparison being useful to determine a difference between tumor and non-tumor tissues, to determine the aggressiveness of a tumor or the efficacy of an anti-tumor therapy.
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
Engineering bacterium containing 2-oxoglutarate decarboxylase gene kgd and applications thereof
InactiveCN102382789BReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCoenzyme A biosynthesis2-Oxoglutarate Dehydrogenase
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and fermentation, and particularly discloses an engineering bacterium for producing 3-hydroxybutyric acid and 4-hydroxybutyric acid copolyester (P3HB4HB) by utilizing a sugar carbon source. Exogenous genes needed for combining the P2HB4HB are recombined and integrated on the genome of the engineering bacterium and comprise poly-3-hydroxybutyrate synthetic gene phaCAB and 4-hydroxybutyryl coenzyme A which is transferase gene orfZ, 4-hydroxybutyric acid dehydrogenase gene 4hbD and 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase gene kgd. By utilization of the engineering bacterium, the P3HB4HB can be produced by using the sugar carbon source with relatively cheap price, the production cost is effectively reduced, and the large-scale industrial production and the commercial application and development are pushed.
Owner:TIANJIN GREENBIO MATERIAL CO LTD
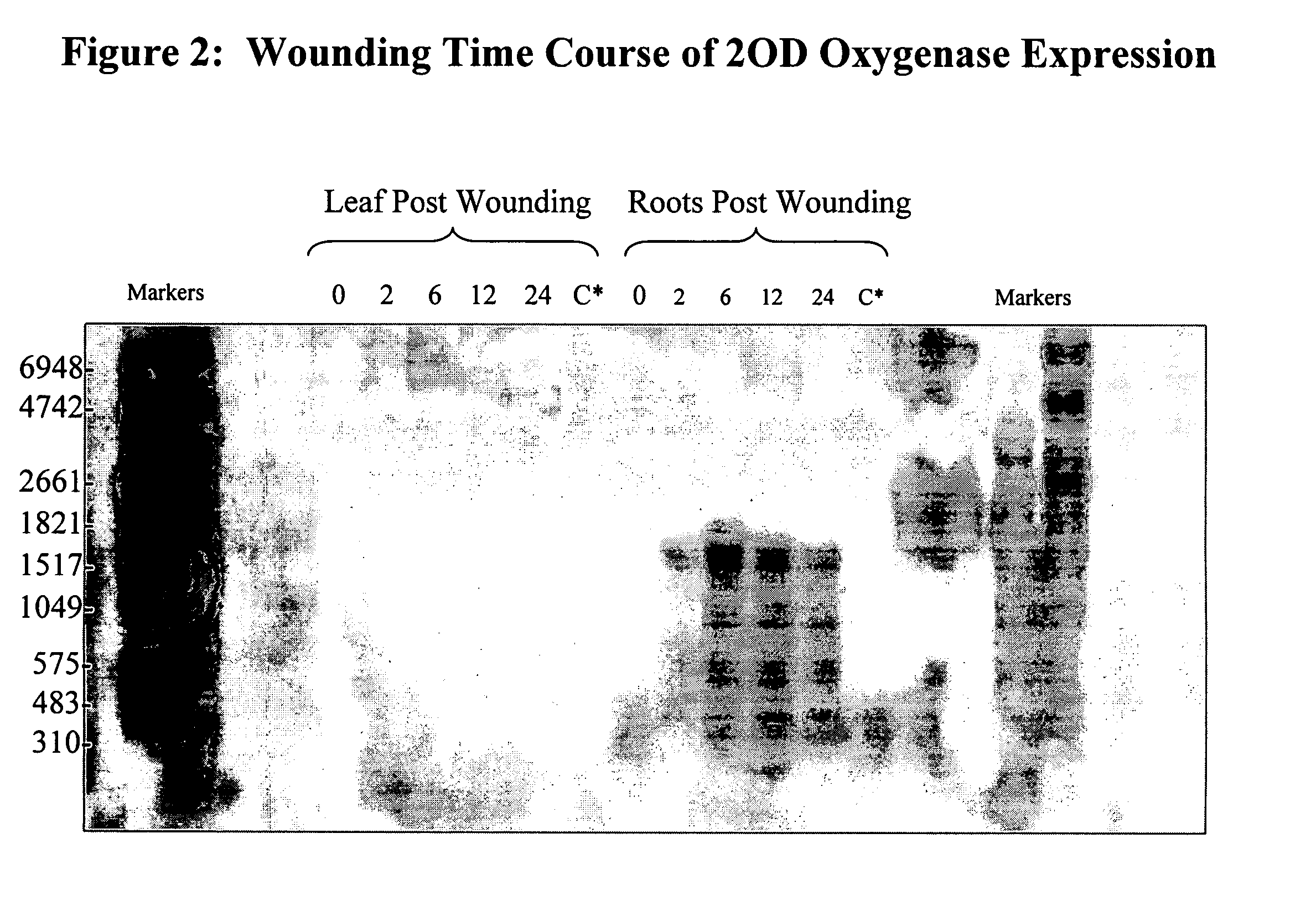
Root-preferred, wound- and insect-inducible 2-oxoglutarate-dependent oxygenase promoter from maize and its use
The present invention provides compositions and methods for regulating expression of heterologous nucleotide sequences in a plant. Compositions include a novel nucleotide sequence for an inducible promoter for the gene encoding a maize 2-oxoglutarate-dependent oxygenase. A method for expressing a heterologous nucleotide sequence in a plant using the promoter sequences disclosed herein is provided. The method comprises stably incorporating into the genome of a plant cell a nucleotide sequence operably linked to the root-preferred promoter of the present invention and regenerating a stably transformed plant that expresses the nucleotide sequence.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +1
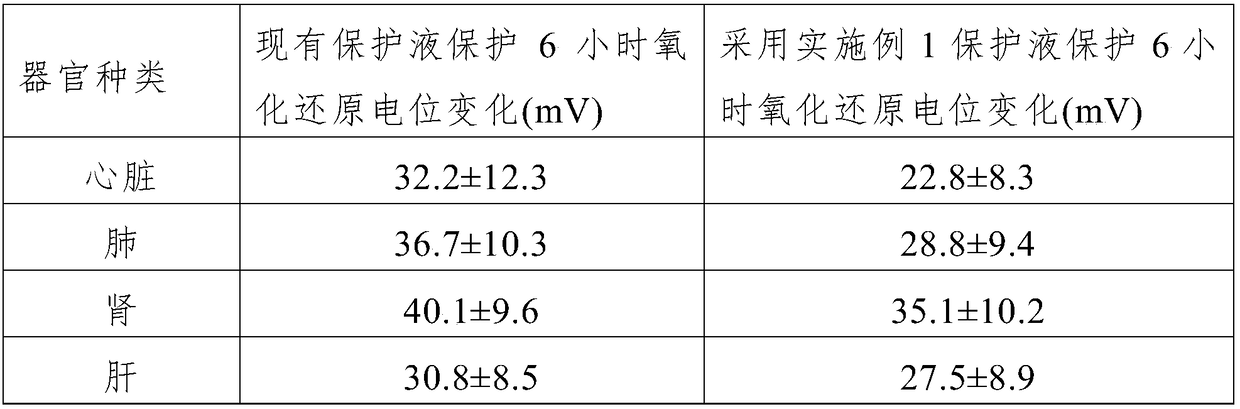
Hydrogen-containing organ transplantation protective liquid and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109275658AImprove the preservation effectLittle side effectsDead animal preservationSide effectPotassium
The invention relates to a hydrogen-containing organ transplantation protective liquid and a preparation method thereof. Each liter of a water solution of the protective liquid contains 14-16 mmol ofNaCl, 8-10 mmol of KCl, 3-5 mmol of MgCl2.6H2O, 16-20 mmol of histidine.HCl.H2O, 170-190 mmol of histidine, 1-3 mmol of tryptophan, 10-20 mmol of mannitol, 0.015 mmol of CaCl2.2H2O, 0.8-1.2 mmol of potassium hydrogen 2-oxoglutarate and 9-11 mmol of hydrogen. The hydrogen-containing organ transplantation protective liquid provided by the invention effectively enhances the in-vitro organ preservation effect. According to the invention, the hydrogen is adopted, and the hydrogen and the mannitol act on oxygen free radicals at a same time, so that the effect of anti-oxidation free radicals is enhanced, and side effects of the mannitol are reduced.
Owner:韩城维康水科技有限公司
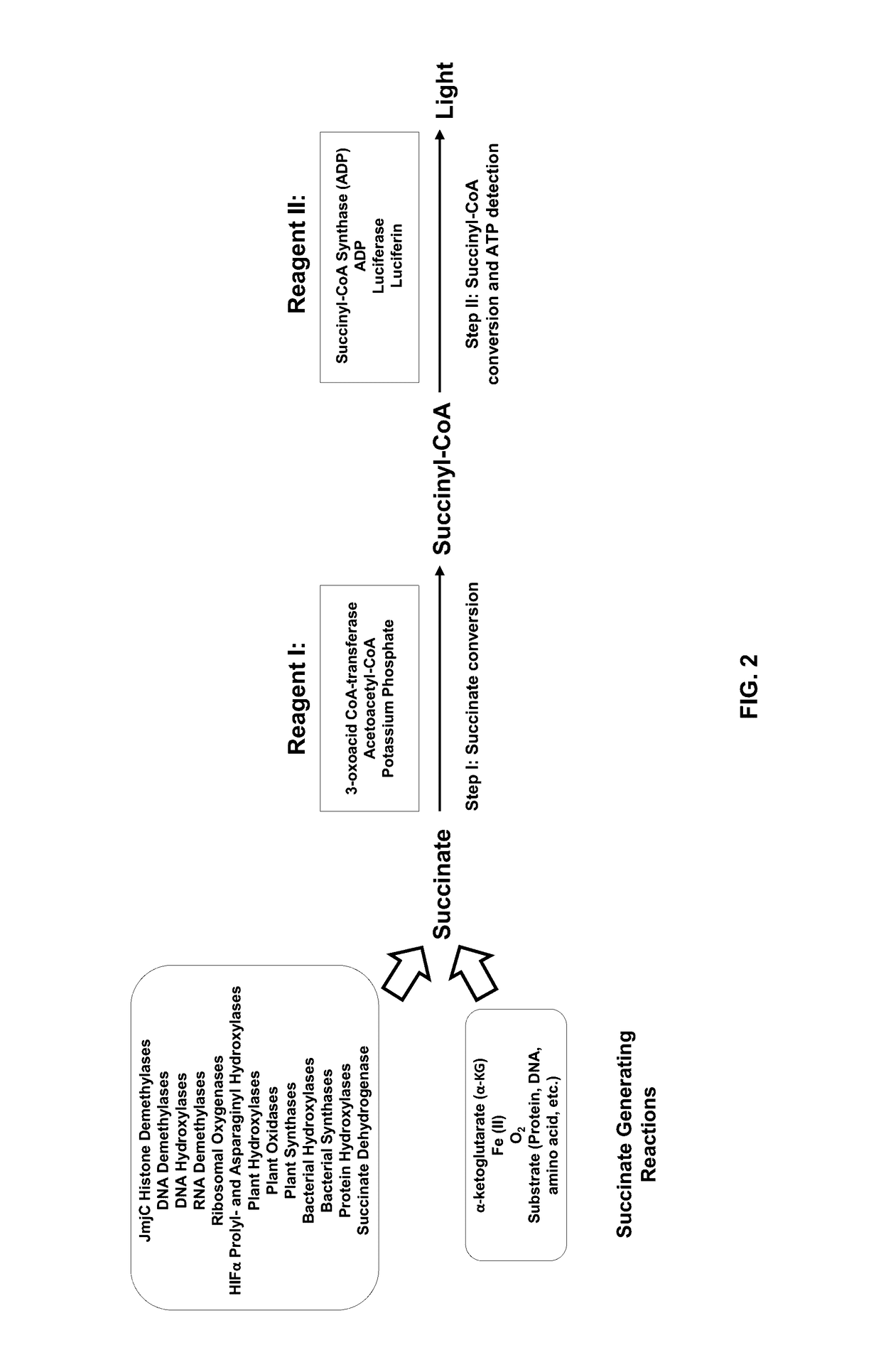
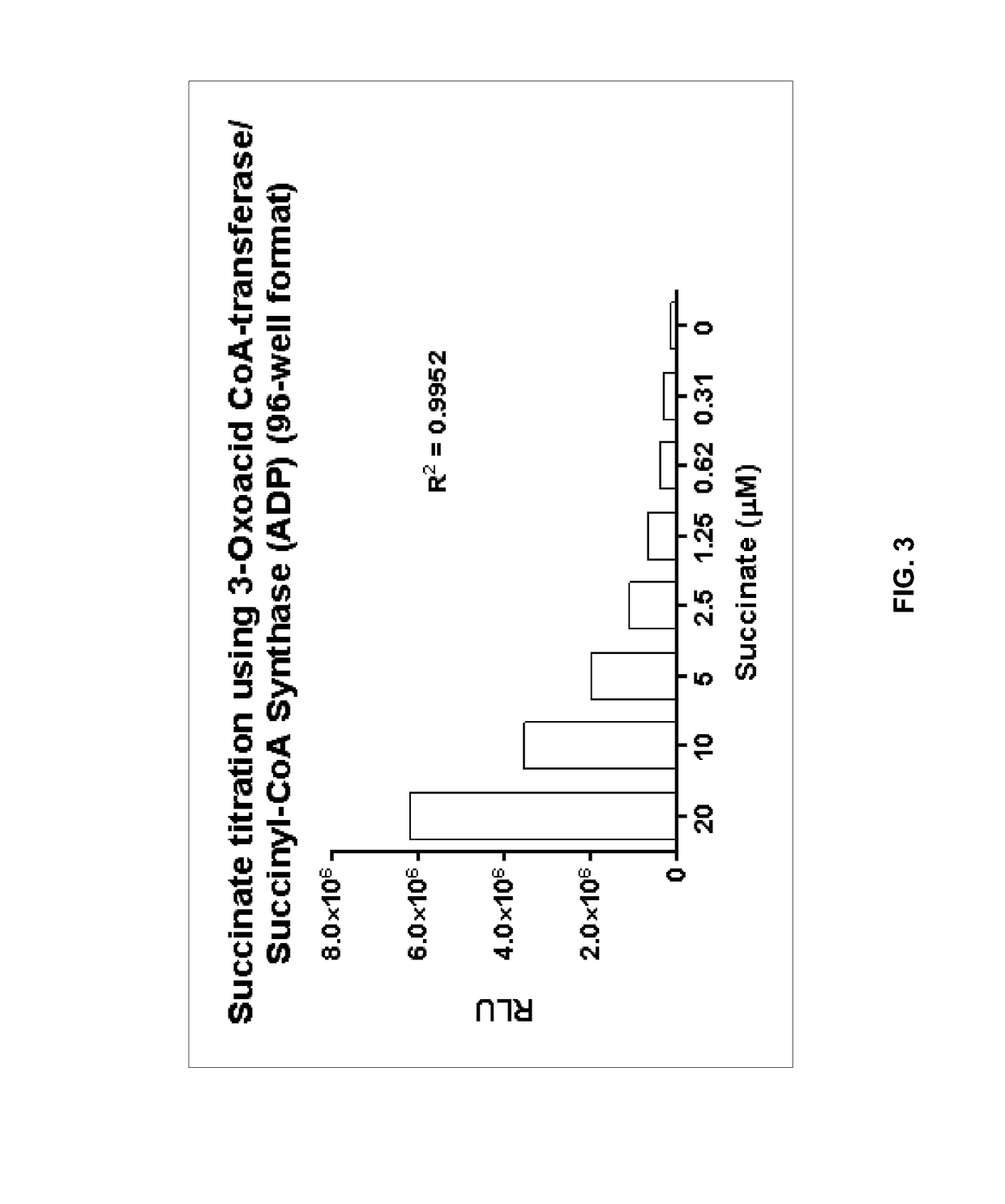
Bioluminescent succinate detection assay
ActiveUS9677117B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisOxygenase activityMicrobiology
Owner:PROMEGA CORP
A flame retardant for car seats
The invention relates to fire retardant for a car seat and belongs to the field of flame retardant products. The fire retardant for the car seat is prepared from the following raw materials: water, tetraethylene glycol dimethacrylate, endo-1,7,7-trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-alcohol acetate, all-cis-6,9,12-octadecartrienoic acid, disodium 2-oxoglutarate dehydrate, 2-amino-2-hydroxymethyl-1,3-propylene glycol, 2-propargyl-3-methyl-4-hydroxyl-2-cyclopentene-1-ketone and trans-4-Hydroxycinnamic acid. The fire retardant for the car seat is formed by interreaction on material components, is stable in chemical properties, hardly decomposes at high temperature, attaches on the fabric or leather surface without influencing the properties of the fire retardant product, also can effectively prevent a flame from spreading and avoid a fire of the car seat, has excellent flame retardant efficiency and is applicable to popularization and application in the field of car seats.
Owner:YANCHENG SILU INFORMATION TECH SERVICE CO LTD
L-lysine hydroxylase and production method for hydroxy-L-lysine and hydroxy-L-pipecolic acid using same
ActiveUS9512452B2Efficient productionHighly optically pure hydroxy-L-lysineOxidoreductasesFermentationHydrogen atomL-pipecolic acid
Owner:API CORP (JP)
Fire retardant for car seat
The invention relates to fire retardant for a car seat and belongs to the field of flame retardant products. The fire retardant for the car seat is prepared from the following raw materials: water, tetraethylene glycol dimethacrylate, endo-1,7,7-trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-alcohol acetate, all-cis-6,9,12-octadecartrienoic acid, disodium 2-oxoglutarate dehydrate, 2-amino-2-hydroxymethyl-1,3-propylene glycol, 2-propargyl-3-methyl-4-hydroxyl-2-cyclopentene-1-ketone and trans-4-Hydroxycinnamic acid. The fire retardant for the car seat is formed by interreaction on material components, is stable in chemical properties, hardly decomposes at high temperature, attaches on the fabric or leather surface without influencing the properties of the fire retardant product, also can effectively prevent a flame from spreading and avoid a fire of the car seat, has excellent flame retardant efficiency and is applicable to popularization and application in the field of car seats.
Owner:YANCHENG SILU INFORMATION TECH SERVICE CO LTD
Diaminobutyrate-2-oxoglutarate transaminase and application thereof
The invention discloses diaminobutyrate-2-oxoglutarate transaminase and application thereof. The diaminobutyrate-2-oxoglutarate transaminase has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2. The invention also discloses an encoding gene of the diaminobutyrate-2-oxoglutarate transaminase, wherein the encoding gene has a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The invention also discloses an expression vector containing the encoding gene of the diaminobutyrate-2-oxoglutarate transaminase, a genetic engineering strain and a construction method thereof. In the invention, an expressed diaminobutyrate-2-oxoglutarate transaminase gene is extracted, sequenced and cloned from Streptomyces albulus for the first time; and the genetic engineering strain is constructed and L-2,4-diaminobutyrate is fermented and produced by utilizing the genetic engineering strain, so that a novel L-2,4-diaminobutyrate acquisition way is opened up.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com