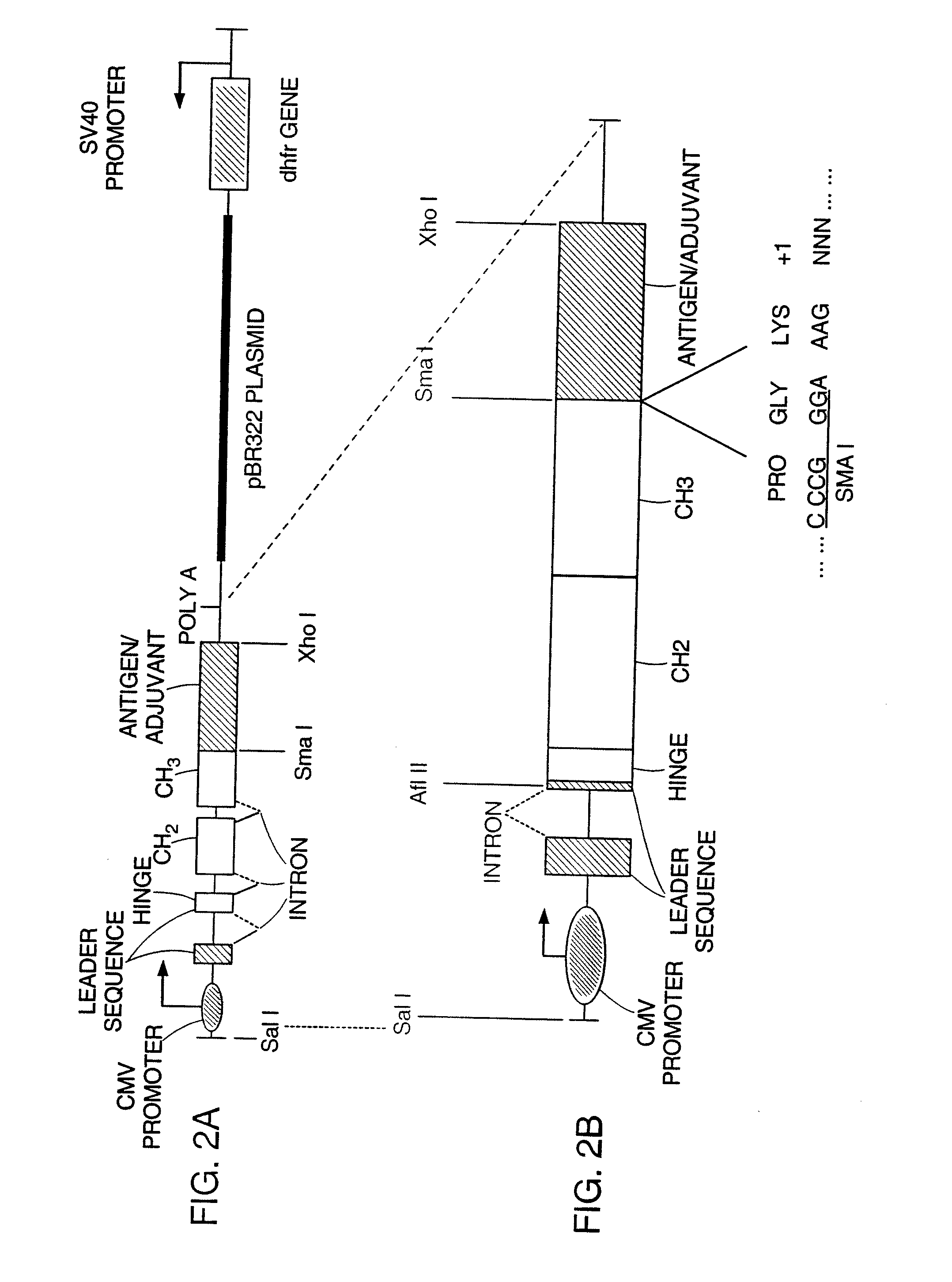
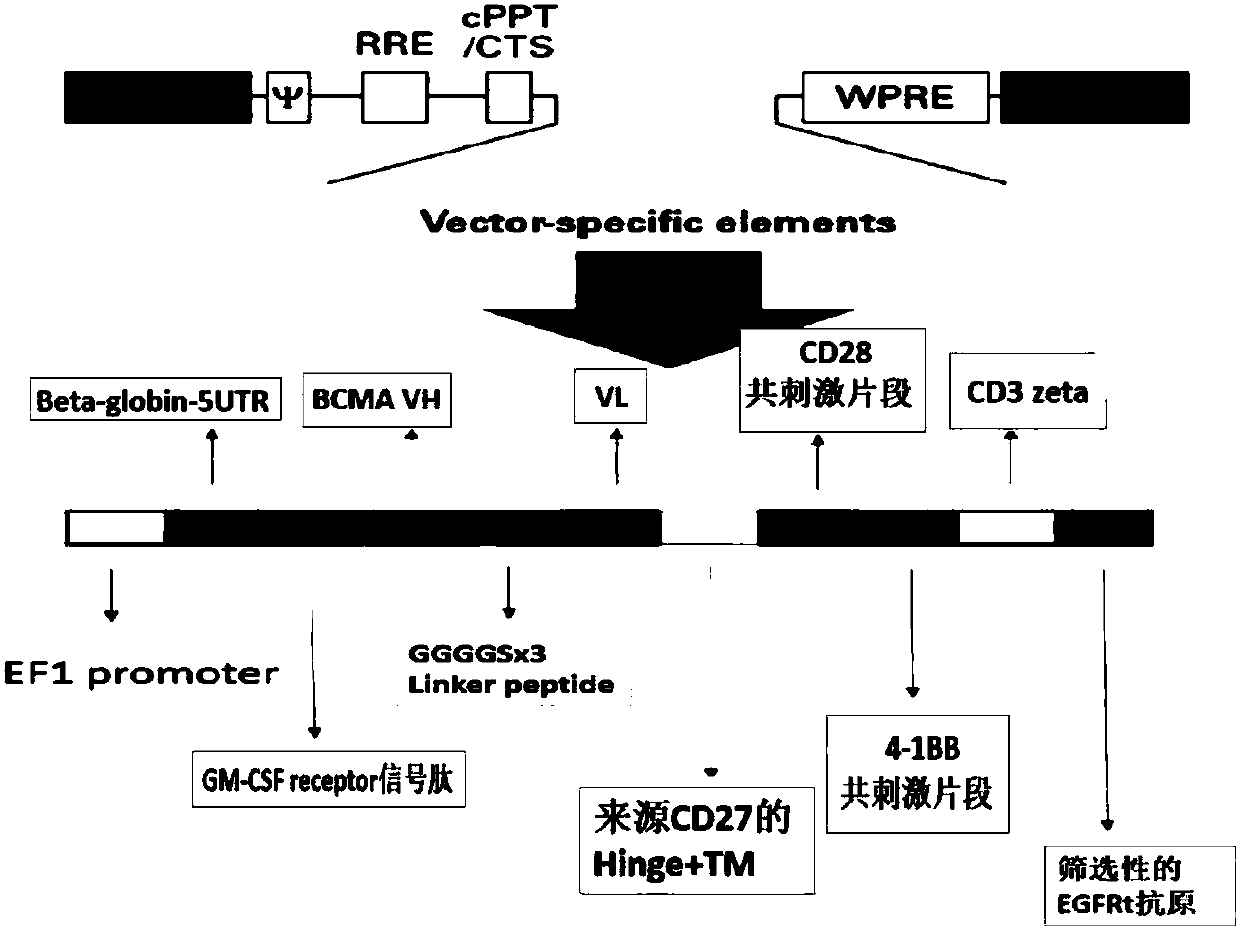
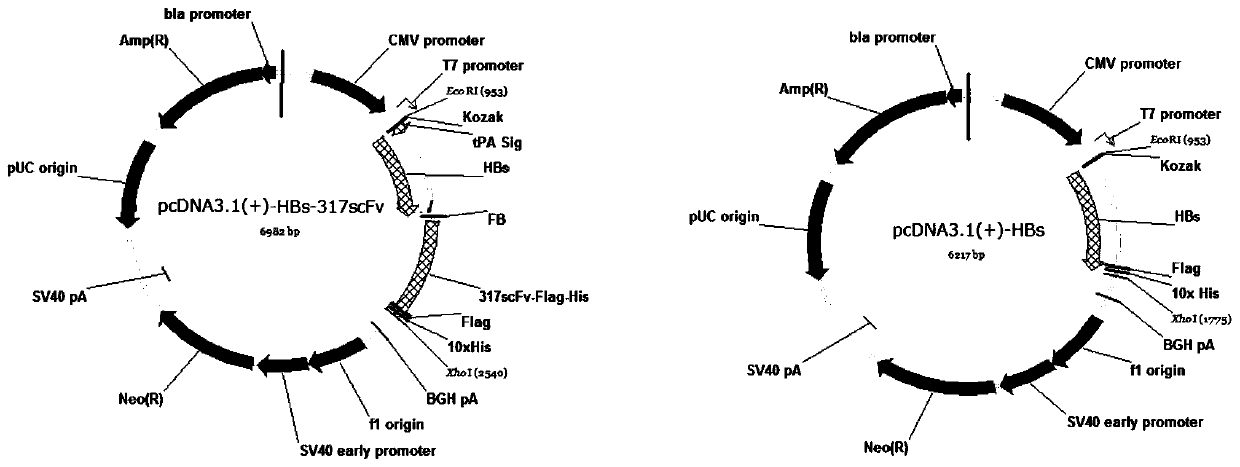
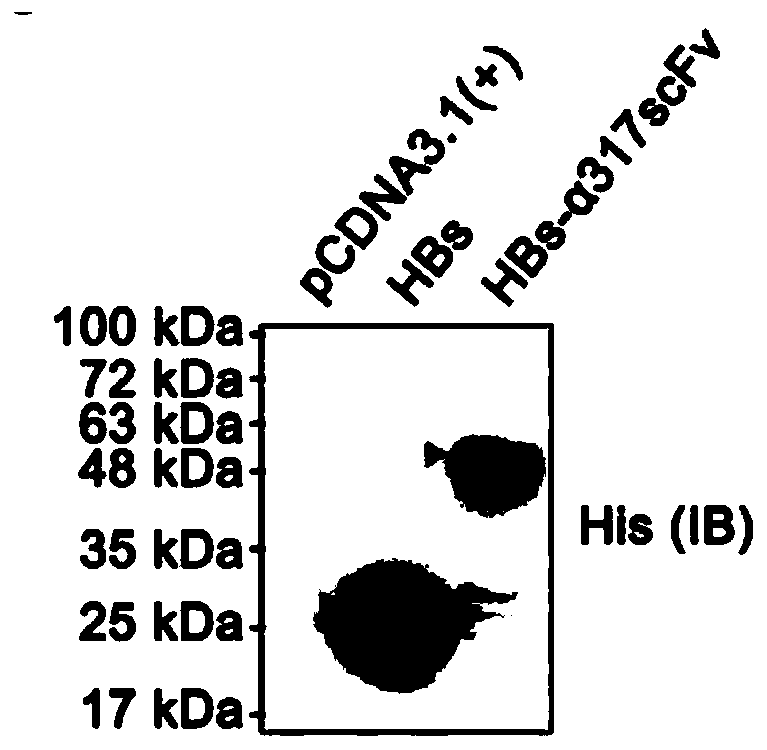
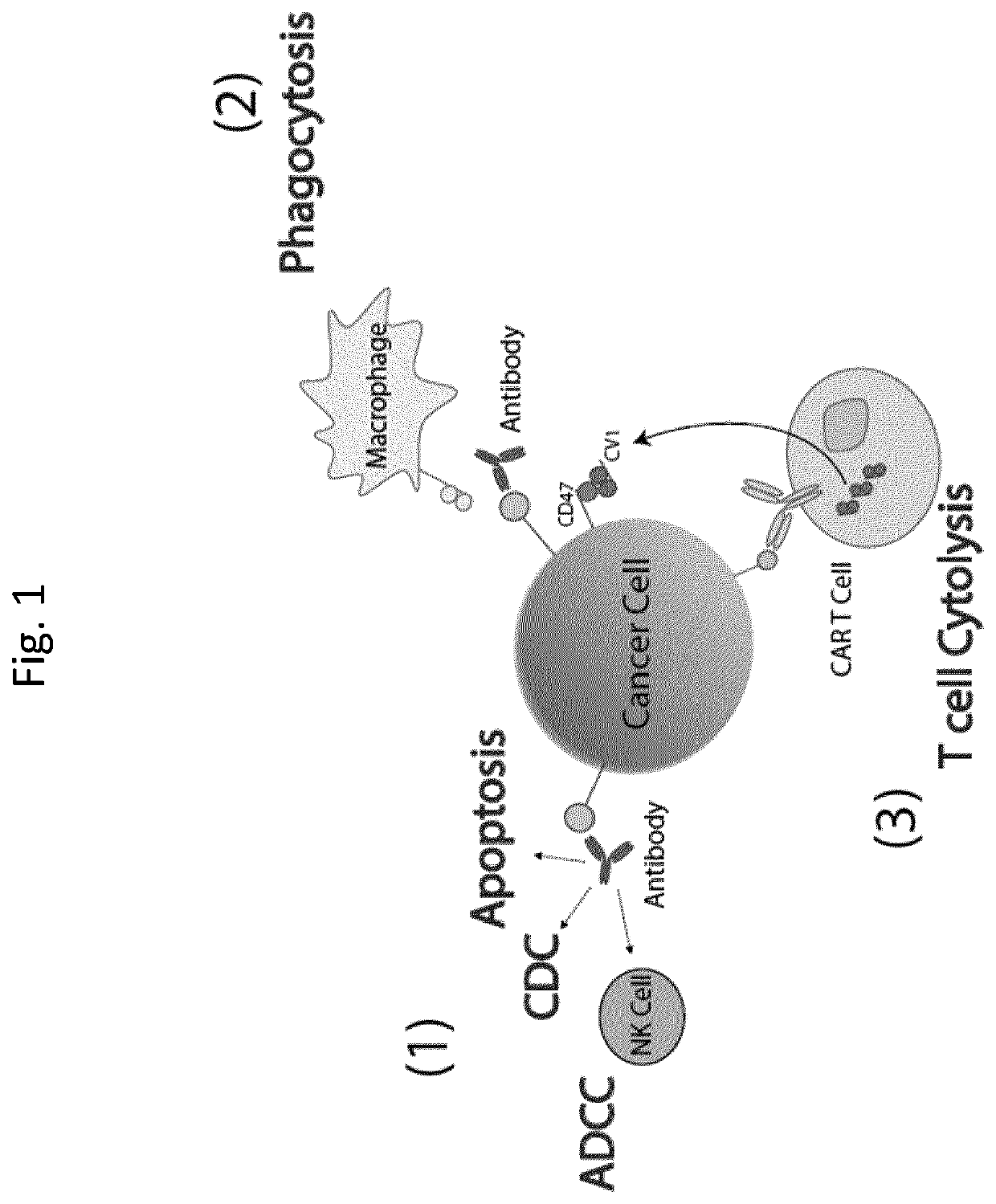
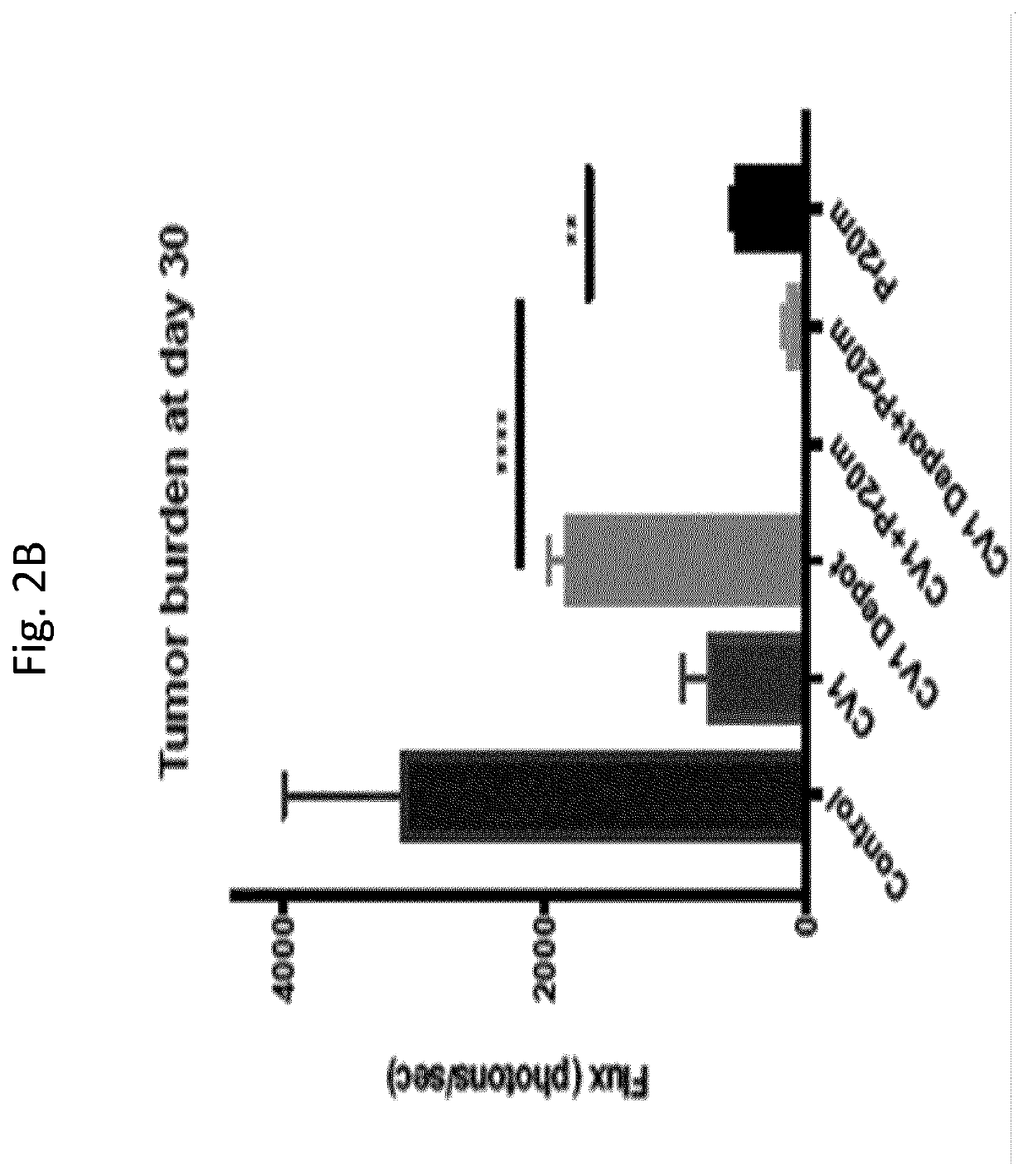
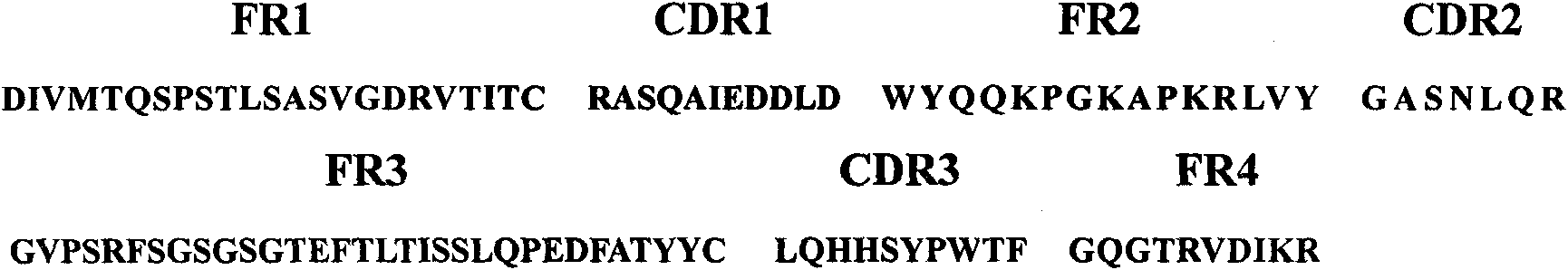Patents
Literature
100 results about "Antigen Targeting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Antigen Targeting involves specific and high affinity non-covalent interaction (binding) of an antibody reagent through intermolecular physical forces of attraction and spatial complementarity with a soluble or particulate substance (antigen) that induces an immune response. Using the keen specificity of antigen recognition by antibodies, targeting selectively localizes antibody-associated reagents to antigen sites for therapeutic or diagnostic effect.
DNA vaccines encoding antigen linked to a domain that binds CD40
InactiveUS20070025982A1Improve abilitiesEasy to demonstrateAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVirus peptidesPeptide antigenEukaryotic plasmids
Vaccines that target one or more antigens to a cell surface receptor improve the antigen-specific humoral and cellular immune response. Antigen(s) linked to a domain that binds to a cell surface receptor are internalized, carrying antigen(s) into an intracellular compartment where the antigen(s) are digested into peptides and loaded onto MHC molecules. T cells specific for the peptide antigens are activated, leading to an enhanced immune response. The vaccine may comprise antigen(s) linked to a domain that binds at least one receptor or a DNA plasmid encoding antigen(s) linked to a domain that binds at least one receptor. A preferred embodiment of the invention targets HIV-1 env antigen to the CD40 receptor, resulting in delivery of antigen to CD40 positive cells, and selective activation of the CD40 receptor on cells presenting HIV-1 env antigens to T cells.
Owner:LEDBETTER JEFFREY A +1
Compounds and Methods for Modulating an Immune Response
InactiveUS20120039806A1Recognition presentationRecognition processingOrganic active ingredientsFungiDendritic cellCell membrane
The present invention relates to the identification of proteins which bind the dendritic cell marker known as Clec9A. The present invention provides new compounds for targeting therapeutic agents such as antigens to dendritic cells. Also provided are methods of modulating a humoral and / or T cell mediated immune response to the antigen, methods of delivery of a cytotoxic agent to dendritic cells thereof involved in diseased states, methods of modulating the uptake and / or clearance of cells with a disrupted cell membrane, cells infected with a pathogen, dying cells or dead cells, or a portion thereof, and methods of modulating antigen recognition, processing and / or presentation, as well as immune responses to material derived from cells with a disrupted cell membrane, cells infected with a pathogen, dying cells or dead cells, or a portion thereof.
Owner:WALTER & ELIZA HALL INST OF MEDICAL RES +1
Preparation method of dendritic cell (DC) vaccine loaded with autologous tumor associated holoantigen
ActiveCN102091327ASignificant technological progressConvenient for clinical operationBlood/immune system cellsAntibody medical ingredientsCytotoxicityT lymphocyte
The invention belongs to preparation of biological cell formulations, and in particular relates to a preparation method of dendritic cell (DC) vaccine loaded with autologous tumor associated holoantigen. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing the autologous tumor associated holoantigen, collecting and separately culturing DCs, impacting the DCs by the autologous tumor associated holoantigen, maturing the DCs and preparing autologous tumor antigen specific DC vaccine. The invention solves the problems in the prior art that the immunogenicity of tumor antigen is not strong enough, the antigen target spots are incomplete, the tumor antigens of most tumor patients are difficult to acquire, and the like. The DC vaccine provided by the invention has the advantages of effectively inducing tumor antigen specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) in vitro and in vivo, efficiently generating specific cytotoxicity on tumors, having high overall effective rate and no obvious toxic side effects in clinical application, and the like.
Owner:玥特农生物科技河北有限责任公司
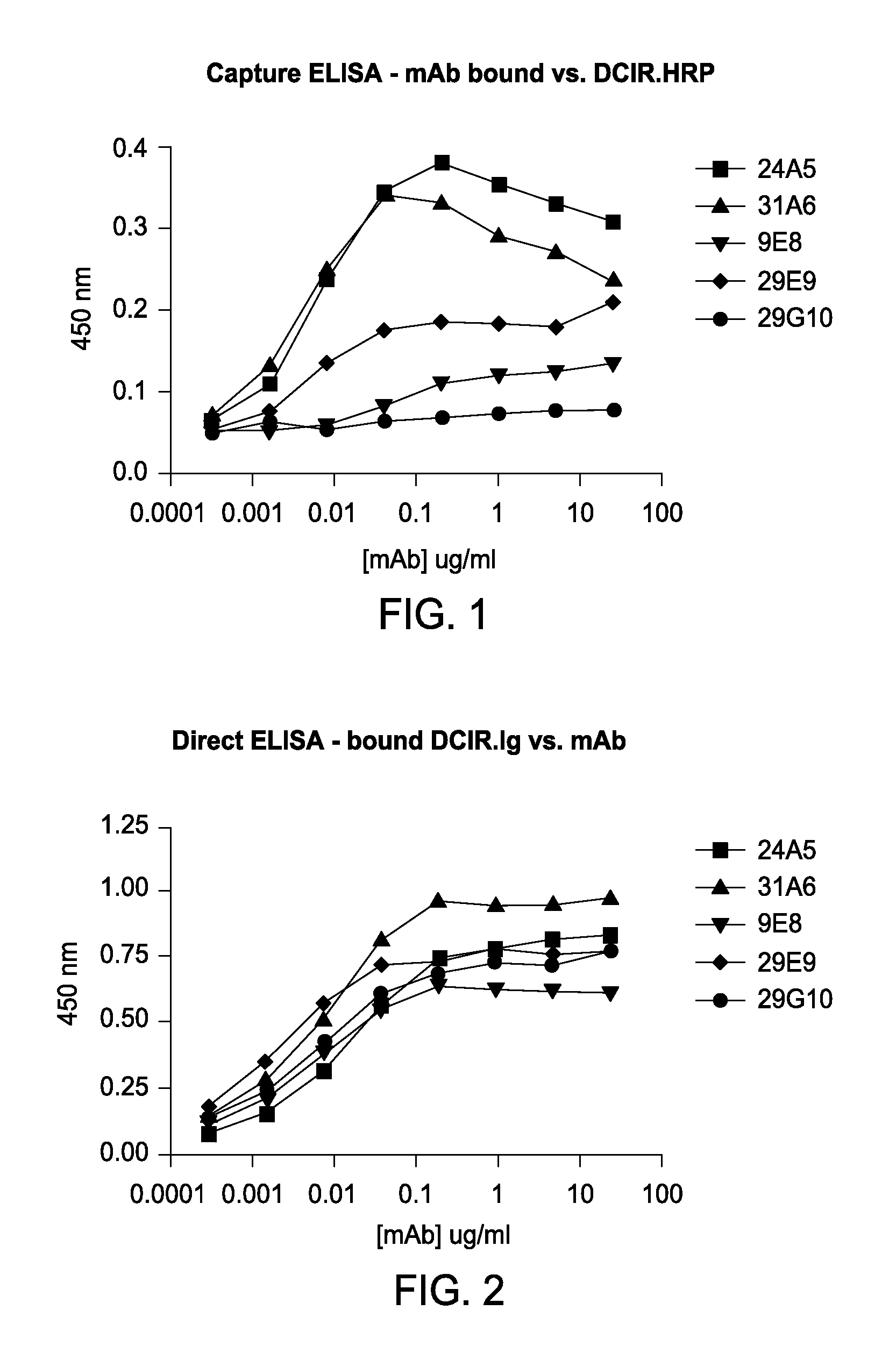
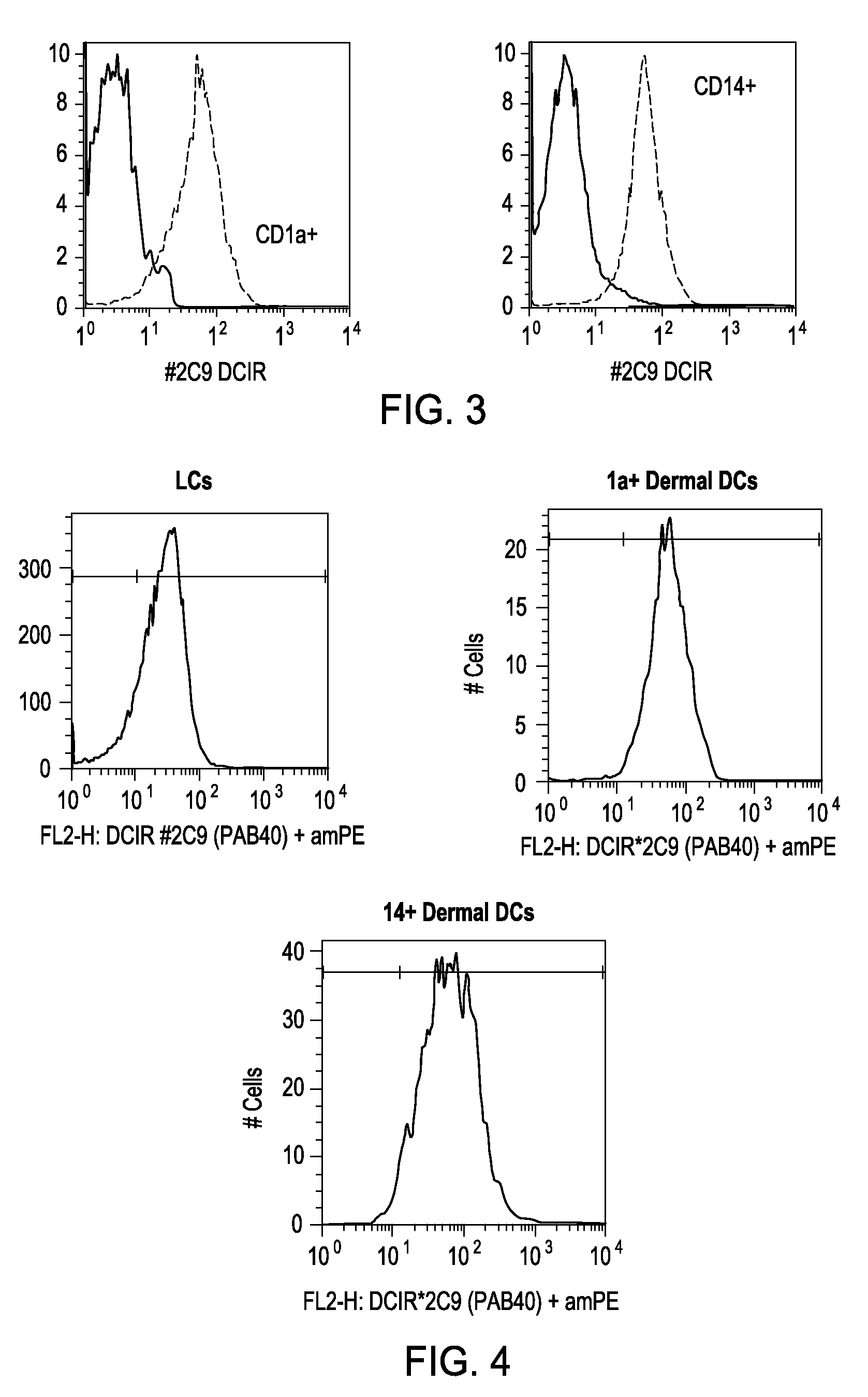
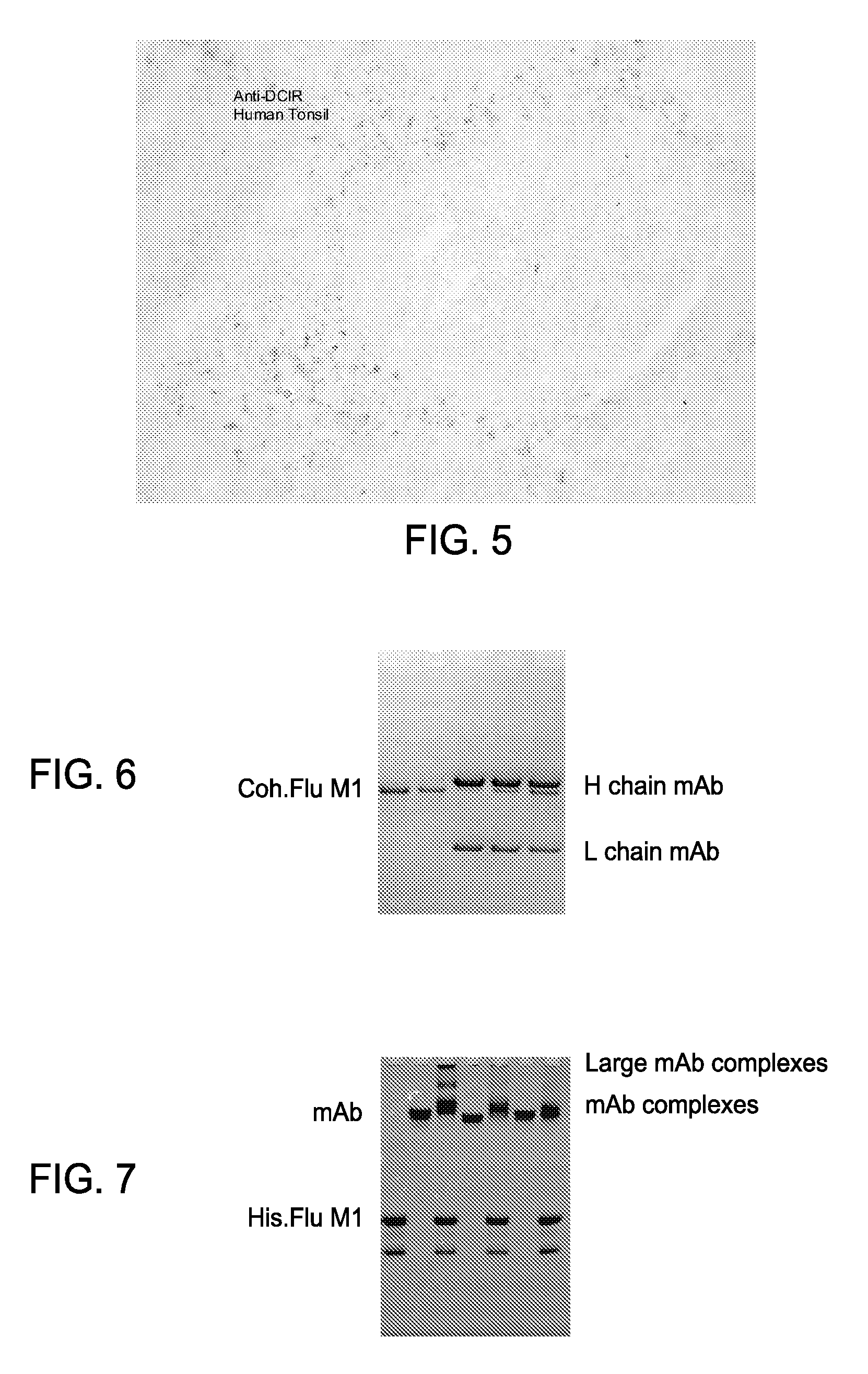
Vaccines based on targeting antigen to DCIR expressed on antigen-presenting cells
The present invention includes compositions and methods for increasing the effectiveness of antigen presentation using a DCIR-specific antibody or fragment thereof to which an antigen is attached that forms an antibody-antigen complex, wherein the antigen is processed and presented by a dendritic cell that has been contacted with the antibody-antigen complex.
Owner:BAYLOR RES INST
Detection kit for diagnosing tuberculosis
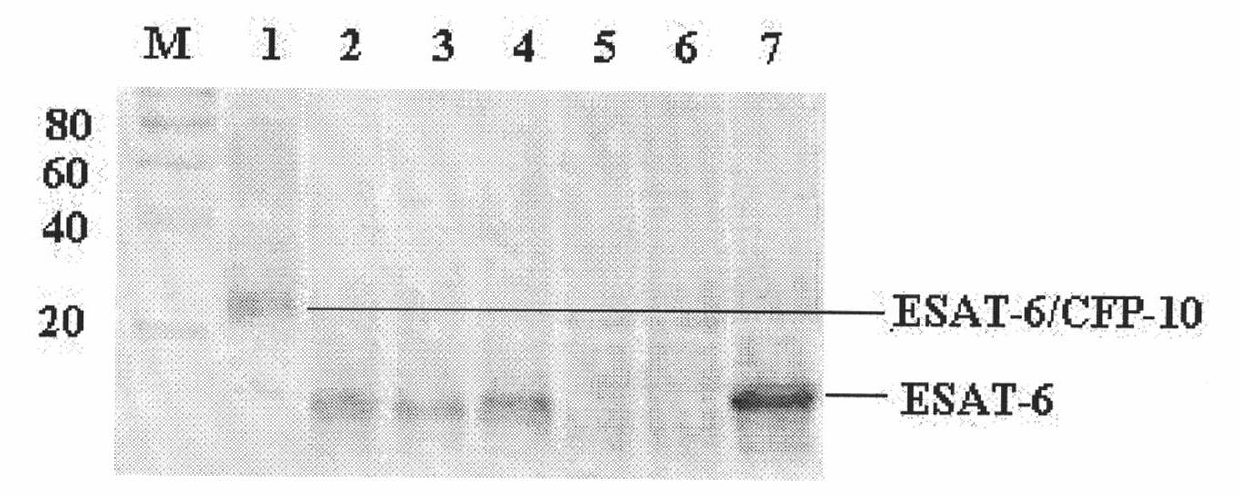
ActiveCN102175875ARapid diagnosisSpecific diagnosisBiological testingHybrid peptidesBiologyVaccine Immunogenicity
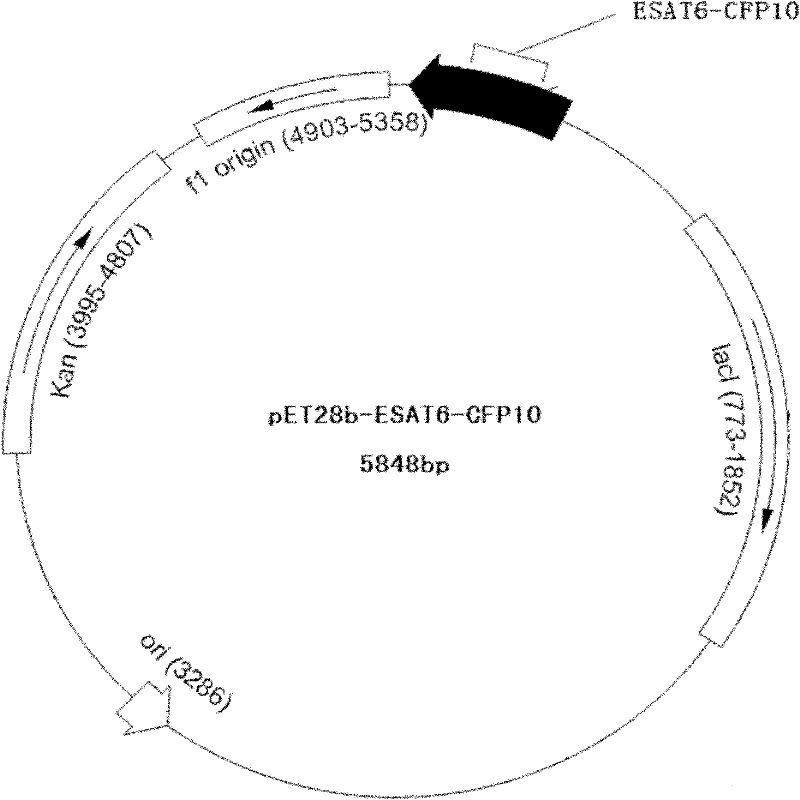
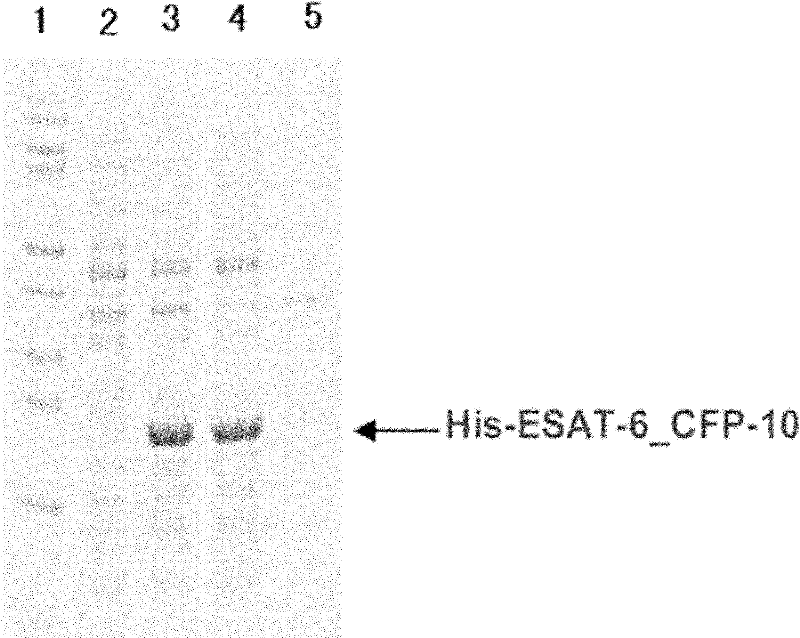
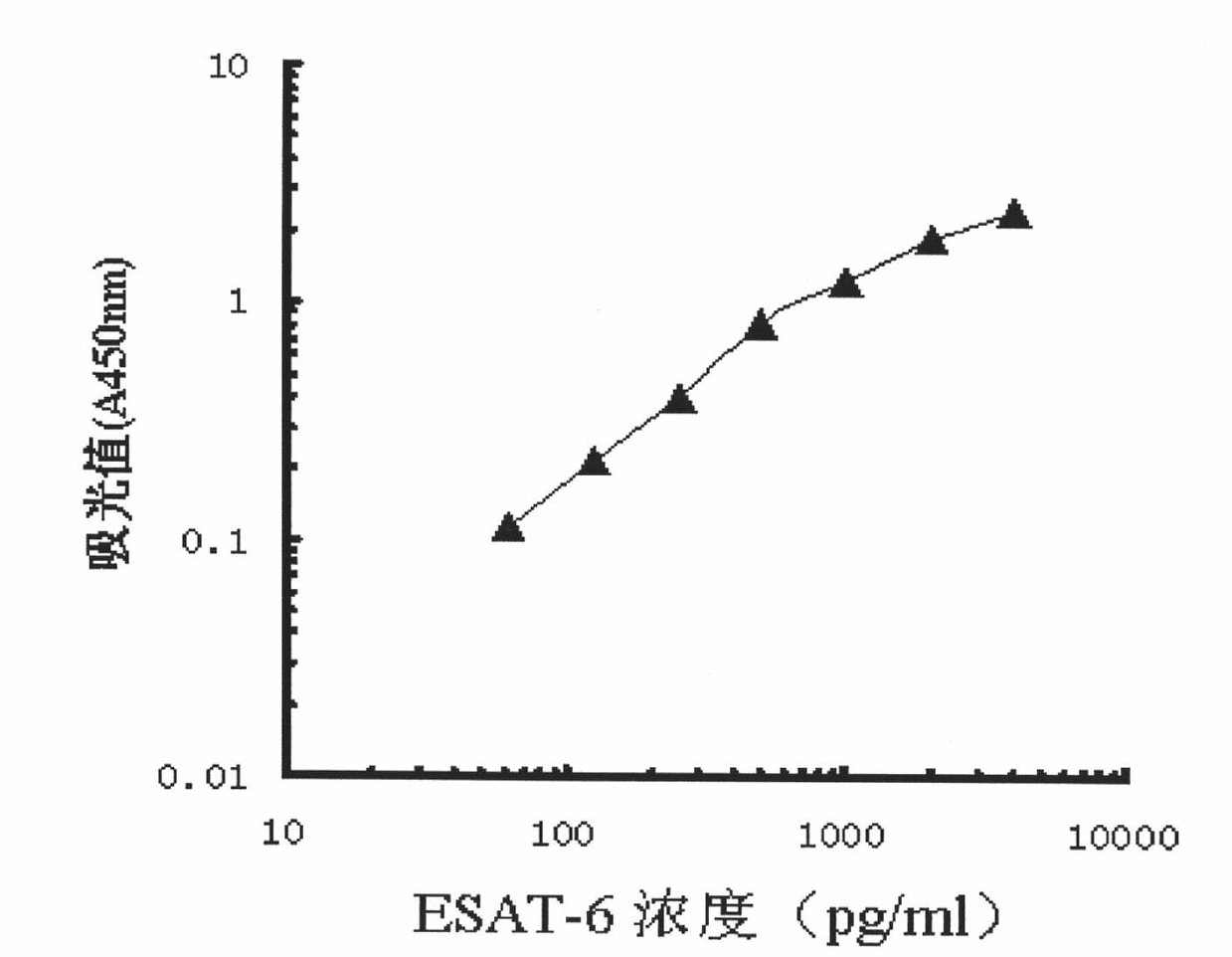
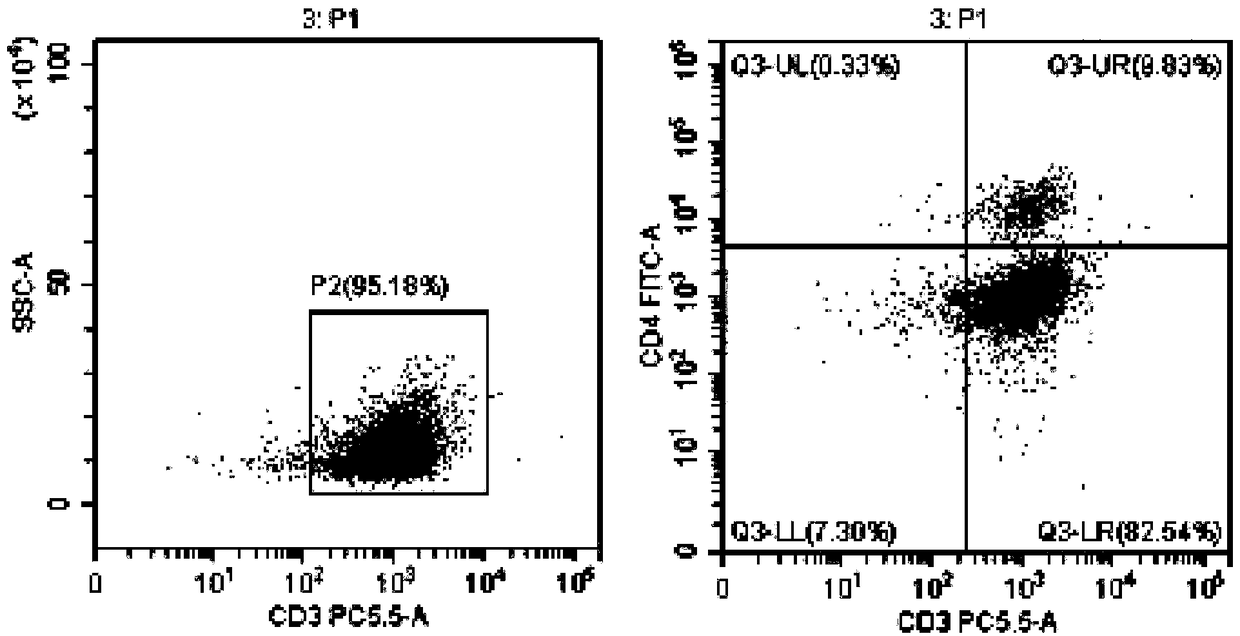
The invention relates to a detection kit for diagnosing tuberculosis, comprising a recombinant antigenic protein, wherein the recombinant antigenic protein is the fusion protein obtained by connecting ESAT-6 (early secreting antigen target 6KD), CFP-10 (cultufiltrate protein 10KD), and MPB64 (Mycobacterium bovis 64KD) by connecting peptides according to an arbitrary sequence, wherein the connecting peptides are short peptides which do not influence the immunogenicity of ESAT-6, CFP-10 and MPB64. Preferably, the recombinant antigenic protein in the detection kit for diagnosing tuberculosis is the antigenic protein with an amino acid sequence which is SEQ ID: No.1. When the detection kit in the invention is used for diagnosing tuberculosis, the diagnosis time is short, the diagnosis is fast, the sensitivity is strong, and the specificity is high; and the detection kit has an important significance on early diagnosis of tuberculosis.
Owner:武汉海吉力生物科技有限公司
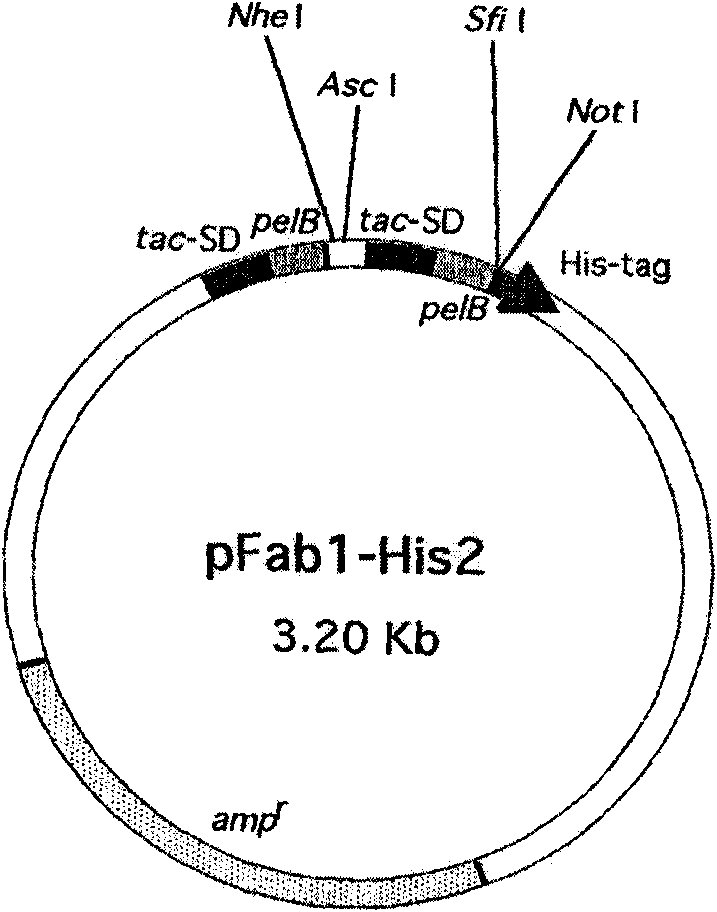
Preparation method for single-chain antibody based on hybridoma cell
ActiveCN103160515AAvoid distraction puzzlesEfficient and Accurate AcquisitionTissue cultureImmunoglobulinsSingle-Chain AntibodiesStructural homology
The invention discloses a preparation method for a single-chain antibody based on a hybridoma cell. The preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out inverse transcription with total mRNA of the hybridoma cell as a template to obtain cDNA and selecting and using universal primers with low degeneracy for amplification of a complete set of heavy chain variable region and light chain variable region genes of the antibody; inputting sequences of the amplified heavy chain and light chain variable region genes into an IMGT database for analysis and eliminating antibody genes and nonsense genes originated from the hybridoma cell so as to obtain candidate heavy chain and light chain variable region genes; translating the genes into amino acid sequences, carrying out three dimensional structural homology modeling to obtain a three dimensional simulation structure of the single-chain antibody and carrying out molecular docking analysis on the three dimensional simulation structure and a corresponding antigen target molecule; and splicing a candidate heavy chain and a candidate light chain with correct analysis results into a single-chain antibody gene by using an overlap extension PCR method and carrying out expression and identification of antibody activity. The preparation method provided by the invention is applicable to preparation of all the single-chain antibodies originated from monoclonal hybridoma cells; the process of the preparation method is simple and rapid, and a prepared product has high quality.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Methods of using Fc-Cytokine fusion proteins
InactiveUS20100068175A1Improving immunogenicityStrengthPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPeptide antigenImmunoglobulin heavy chain
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Myeloma BCMA antigen-targeted transgenic T cell, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107827989ADisinhibitionKnockout efficiency is lowHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigenAntigen receptors
The invention discloses a gene for encoding anti-BCMA chimeric antigen receptor. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is represented by SEQ ID NO:2. The invention also discloses a recombinant expression vector containing the gene, and a myeloma BCMA antigen-targeted transgenic T cell. The transgenic T-cell is a primitive cell containing the recombinant expression vector and knocked out of a PD1 gene or / and a CTLA4 gene, or is a primitive cell with the chromosome being integrated with the gene for encoding anti-BCMA chimeric antigen receptor and knocked out of tbe PD1 gene or / and the CTLA4 gene.A preparation method of the transgenic T-cell comprises the following steps: mixing of gRNA, CRISPR-cas9 mRNA and HDR mix, and electrotransformation recombination of the T cell. The invention furtherdiscloses an application of the myeloma BCMA antigen-targeted transgenic T cell in the preparation of drugs for treating multiple myeloma. In the construction process of carT of, a recognition sequence of EGFR is introduced, EGFR monoclonal antibody Cetuximab is used to eliminate a carT cell if necessary, and PD1 and CTLA4 genes are knocked out to relieve the inhibition effect of the PD1 and CTLA4 genes on the carT cell and enhance the overcoming effect of the carT cell on the inhibition of the tumor microenvironment on immune cell functions.
Owner:YINFENG BIOLOGICAL GRP +1
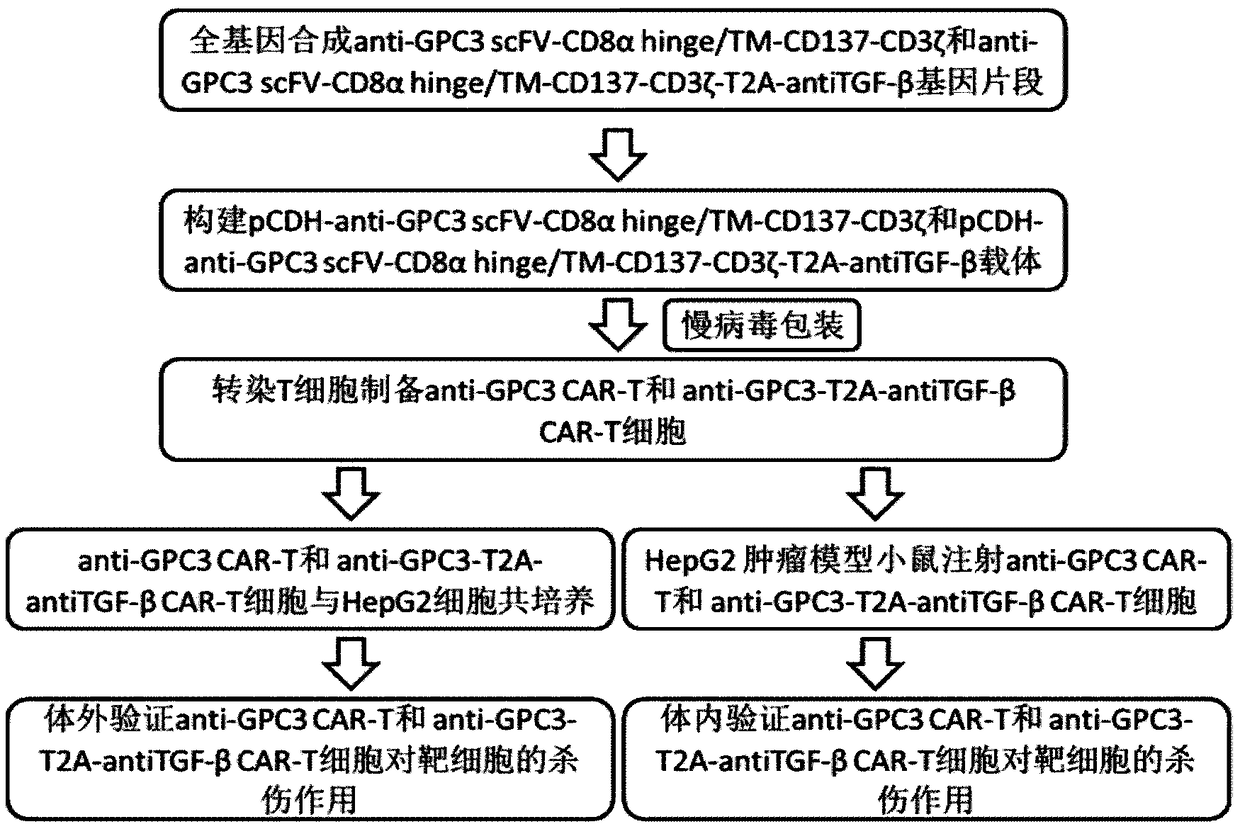
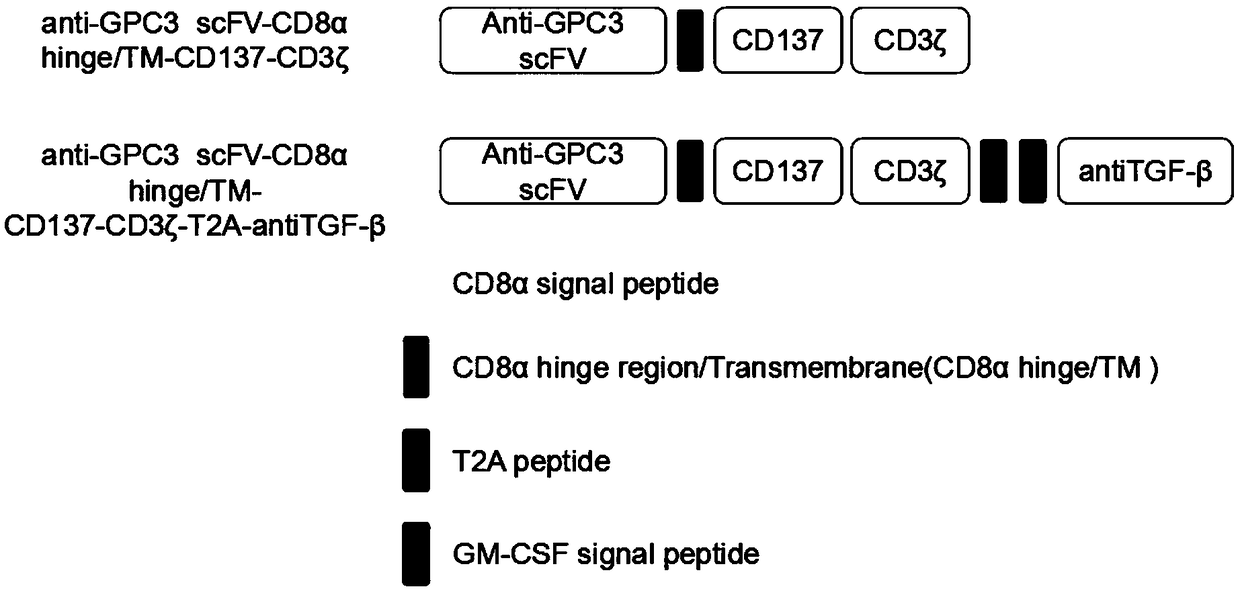
Construction method and application of lentiviral vector for expressing TGF-beta antibody as well as construction method and application of CAR-T cell
InactiveCN108949828AAchieve new breakthroughs in immunotherapySuppress immune responseGenetically modified cellsMammal material medical ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthAntigen
The invention discloses a construction method and an application of a lentiviral vector for expressing a TGF-beta antibody as well as a construction method and an application of a CAR-T cell based onthe problem that immunosuppression molecules and suppressor cells are the biggest barriers in the treatment of solid tumors in a tumor immunosuppression microenvironment, relating to the technical field of tumor immunotherapy. The invention discloses the lentiviral vector which carries a CAR gene of a solid tumor specific antigen target spot of the TGF-beta antibody as well as the CAR-T cell for expressing the solid tumor specific antigen target spot of the TGF-beta antibody. The construction methods and the application have the beneficial effects that the targeting effect on the tumor cells is realized, the suppressor cells in the tumor microenvironment are reduced, the solid tumors are killed to an extreme extend, and the new breakthrough on the immunotherapy of the solid tumors is realized.
Owner:安徽古一生物科技有限公司
B cell linear epitope of novel coronavirus S protein, antibody, identification method and application
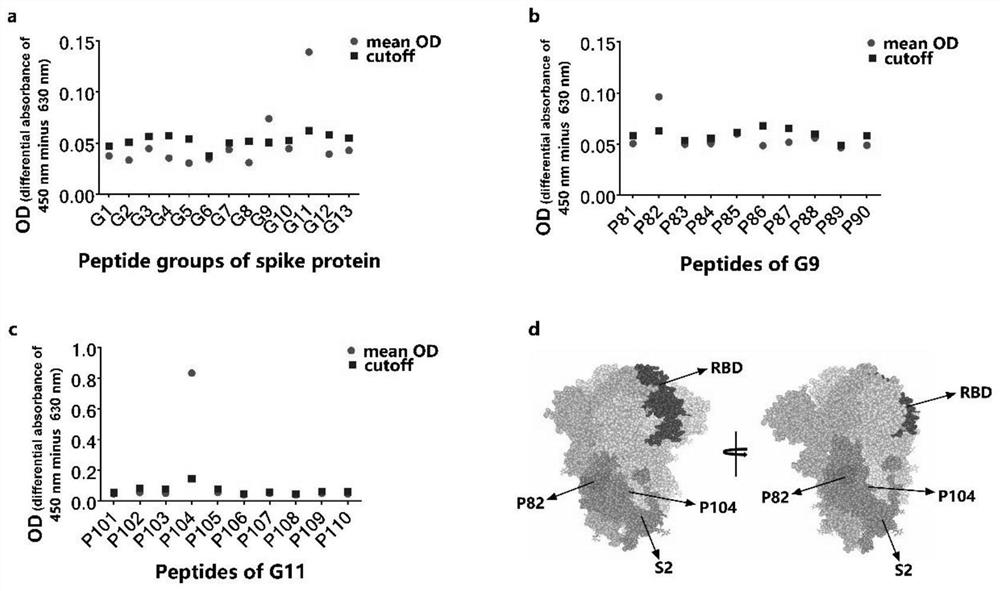
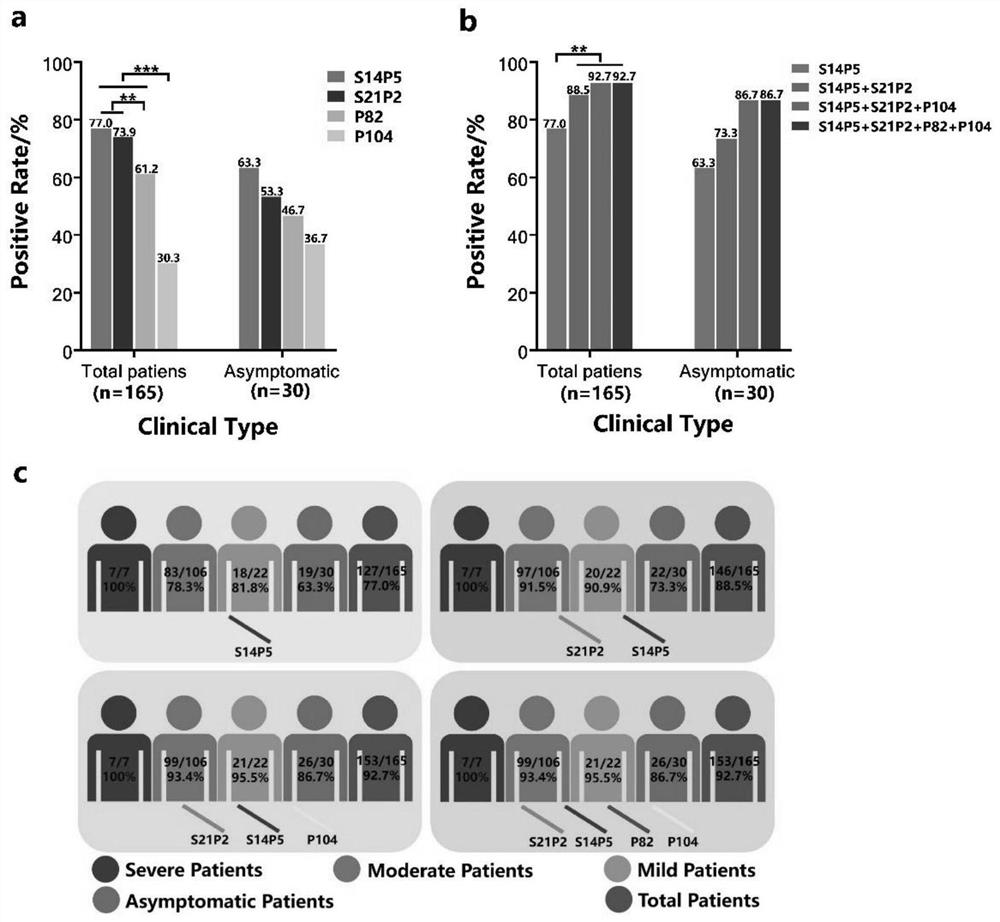
The invention is applicable to the technical field of biology, and provides a B cell linear epitope of a novel coronavirus S protein, an antibody, an identification method and an application, and theamino acid sequence of the B cell linear epitope of the S protein is shown as SEQ ID NO.104 or SEQ ID NO.82. The invention provides a brand-new B cell linear epitope of the novel coronavirus S protein, which can be used for detecting a specific antibody in blood of a COVID-19 patient, and can also be used for being inoculated into healthy people to induce generation of the specific antibody, so that an important antigen target is provided for design of an SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, research and development of the monoclonal antibody and research and development of an antibody detection kit.
Owner:SHENZHEN CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Three dimensional apparatus and method for integrating sample preparation and multiplex assays
InactiveUS20050136442A1Reduce crosstalkBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAntigenTarget capture
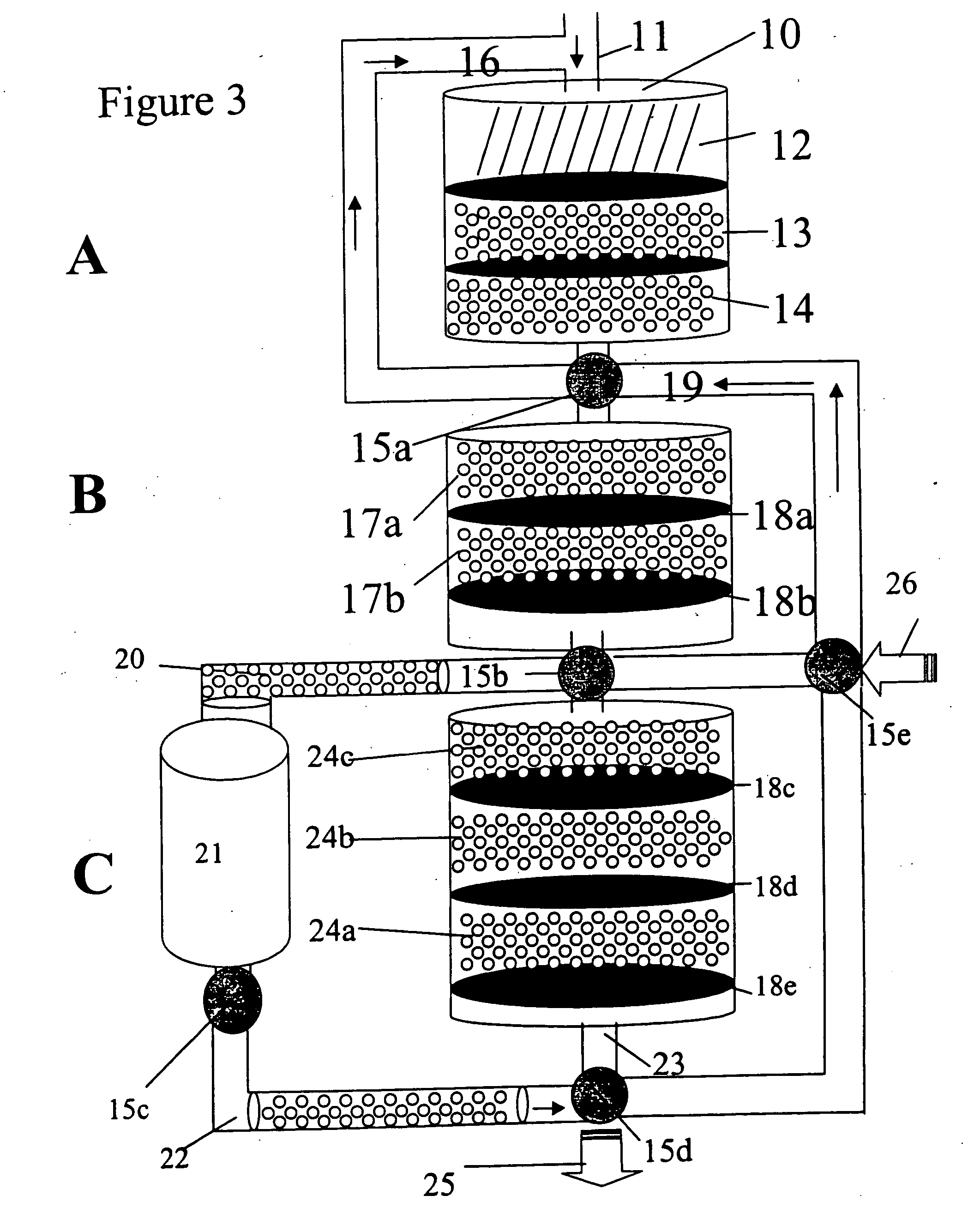
A method is provided for integrating sample preparation and multiplex assay of high volume samples for the presence of nucleic acid and antigen targets. The method uses a three dimensional platform, such as a column, for capturing desired targets out of the large volume sample. The column has a multiplicity of sample processing and target capture zones. The method further provides a simple and efficient sample pre-processing and testing methodology, as well as a simple and environmentally friendly detection methodology.
Owner:NANOGEN INC
Prostate-specific antigen targeting inhibitor of nuclide marker and preparation method of nuclide marker
PendingCN106075484AStable in natureImprove imaging effectRadioactive preparation carriersUrinary disorderAntigenTumor therapy
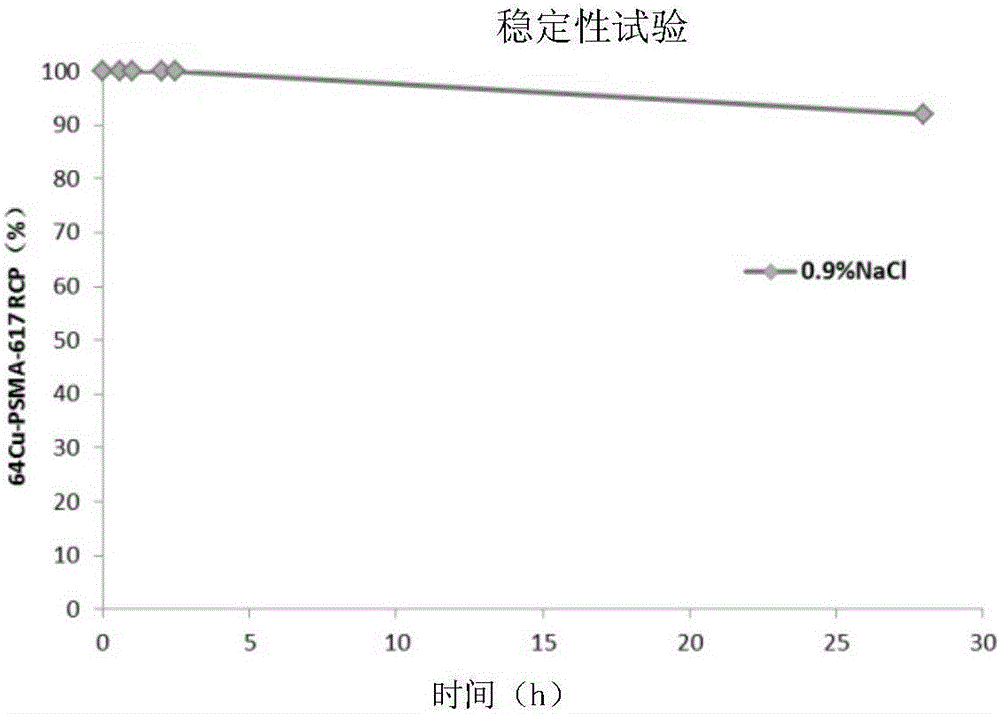
The invention provides a prostate-specific antigen targeting inhibitor of a nuclide marker. The targeting inhibitor is DKFZ-PSMA-617 of a radioactive nuclide marker. Radioactive nuclide includes at least one of 64Cu, 68Ga and 89Zr. The invention further provides a preparation method of the nuclide marker DKFZ-PSMA-617. The nuclide marker DKFZ-PSMA-617 is stable in property and good in development effect, has high affinity and functional activity on PSMA, is beneficial to diagnosis and accurate staging of early prostate cancer, and provides a new thought for diagnosis of breast cancer and gastric adenocarcinoma. Further preclinical animal level research proves that the inhibitor is expected to become a targeting PSMA developing agent and a tumor treatment agent with good application prospects.
Owner:BEIJING CANCER HOSPITAL PEKING UNIV CANCER HOSPITAL
Recombinant Newcastle disease virus vector containing novel coronavirus double-antigen target sequence combination and corresponding vaccine strain and vaccine
PendingCN113881704AImproving immunogenicitySmall toxicitySsRNA viruses negative-senseSsRNA viruses positive-senseReceptorSpecific immunity
Owner:ZHEJIAN DIFFERENCE BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
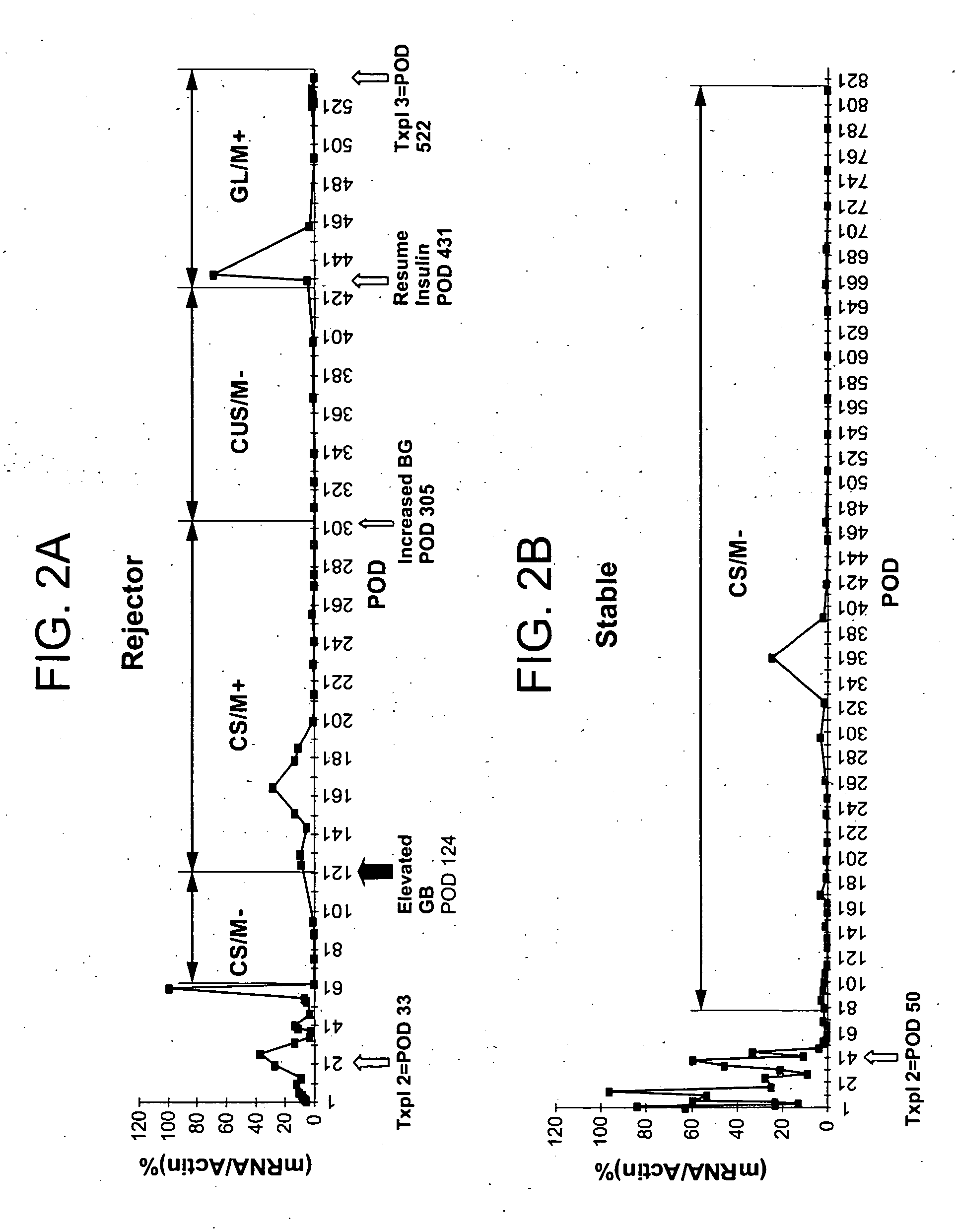
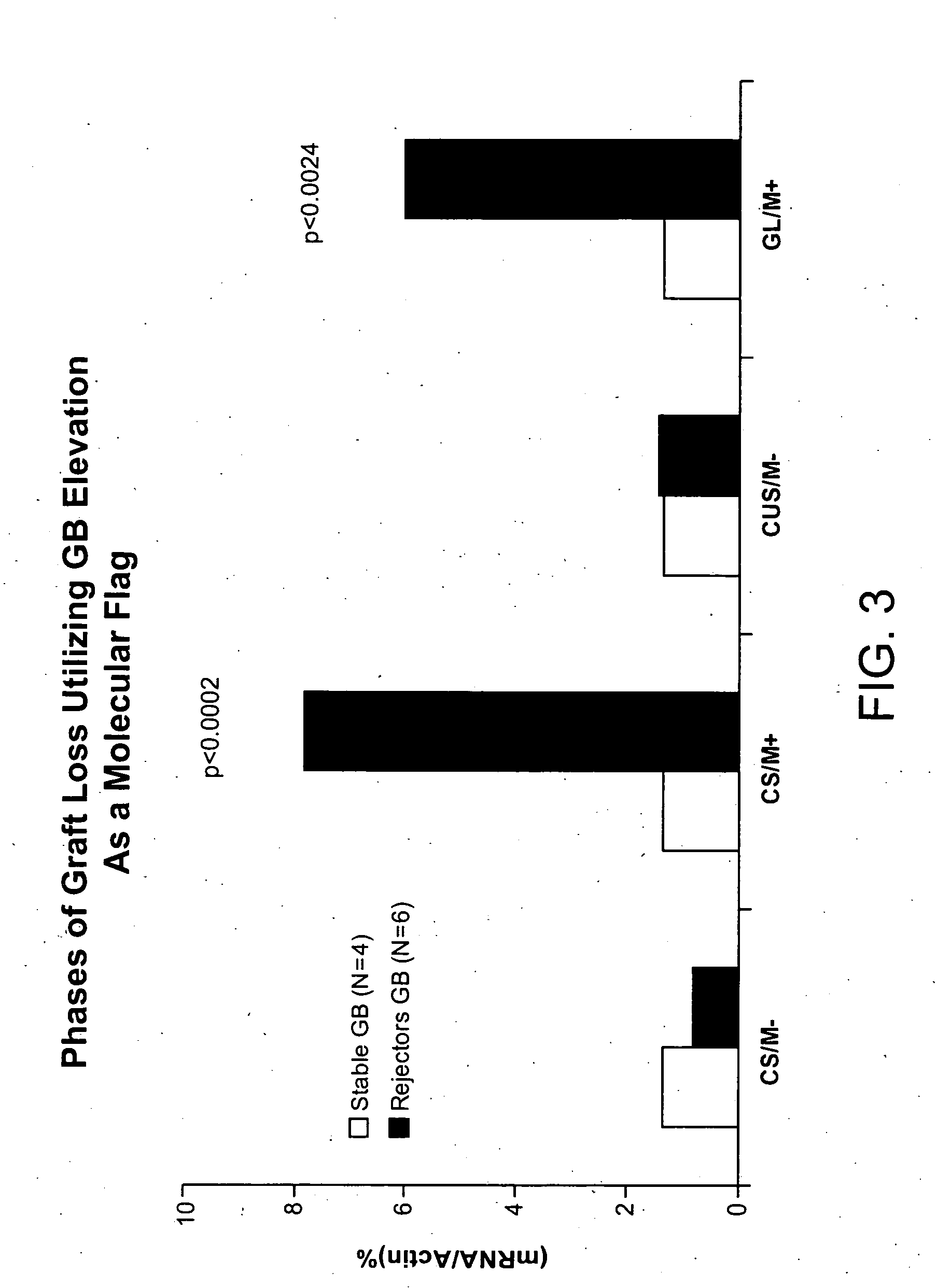
Molecular dissection of cellular responses to alloantigen or autoantigen in graft rejection and autoimmune disease
InactiveUS20060263343A1High expressionBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementAutoimmune conditionAuto antigen
An antigen-specific T-cell response to alloantigen, tissue-specific antigen (e.g., islet antigen or other autoantigens involved in autoimmune disease), or self (or host) antigen is detected at an early stage of graft rejection or recurrent autoimmunity. An increase in cytotoxic lymphocyte gene (CLG) expression in peripheral blood is a risk factor for development of deleterious immune responses, which may be confirmed by functional assays. For example, the distinction between production of regulatory or inflammatory cytokines by T cells may dissect the type of immune response which is being induced: the survival of transplanted islet cells used to treat type 1 diabetes may be monitored, loss of the transplant by graft rejection (i.e., an alloantigen target) may be distinguished from autoimmune disease (i.e., a self or host antigen target).
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC +1
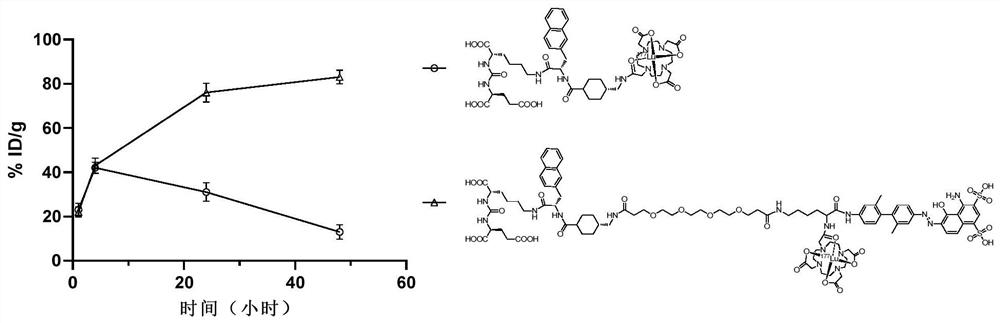
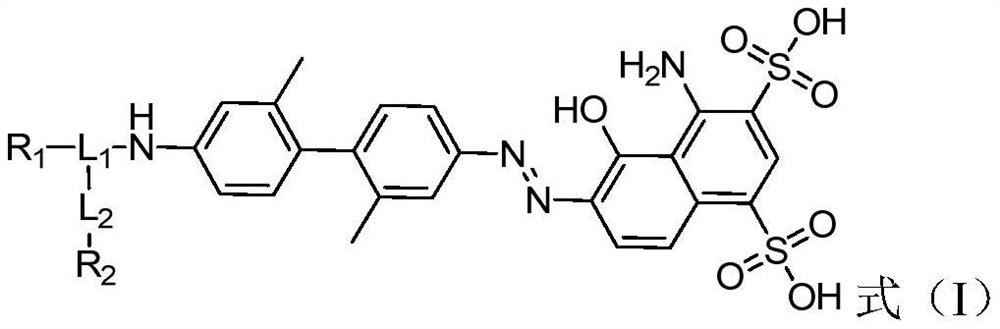
Prostate-specific membrane antigen targeting compound with long circulation half-life period as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN113004371AExtended retention timeProlong blood circulation half-lifeRadioactive preparation carriersPeptide preparation methodsAntigenProstate specific membrane
The invention provides a prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) targeting compound with a long circulation half-life period. The structure of the prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) targeting compound is represented by a formula (I), wherein R1 is a prostate specific membrane antigen targeting compound; -(X)n-(CH2)m-(Y)q-, wherein X and Y are independently selected from lysine, glutamic acid or a derivative structure containing lysine and glutamic acid, n is an integer from 0 to 12, m is an integer from 0 to 60, q is an integer from 0 to 12, and each CH2 can be replaced by -O-, -NH(CO)- or -(CO)-NH- alone; L2 is -(CH2)p-, wherein p is an integer from 0 to 30, each CH2 can be substituted individually with -O-, -NH(CO)- or -(CO)-NH-; and R2 is a nuclide chelating group. The invention further provides a radioactive marker based on the structure of the compound; the compound and the radioactive marker have remarkably prolonged blood circulation half-life period and enhanced tumor uptake enrichment and retention time, and are suitable for nuclide treatment and imaging of PSMA high-expression tumors.
Owner:YANTAI LANNACHENG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Double chimeric antigen receptor gene-modified immune cell based on CD19 and BCMA and application thereof
PendingCN109468283AEnhance long-term immunityPrevent escapeMammal material medical ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDiseaseTreatment effect
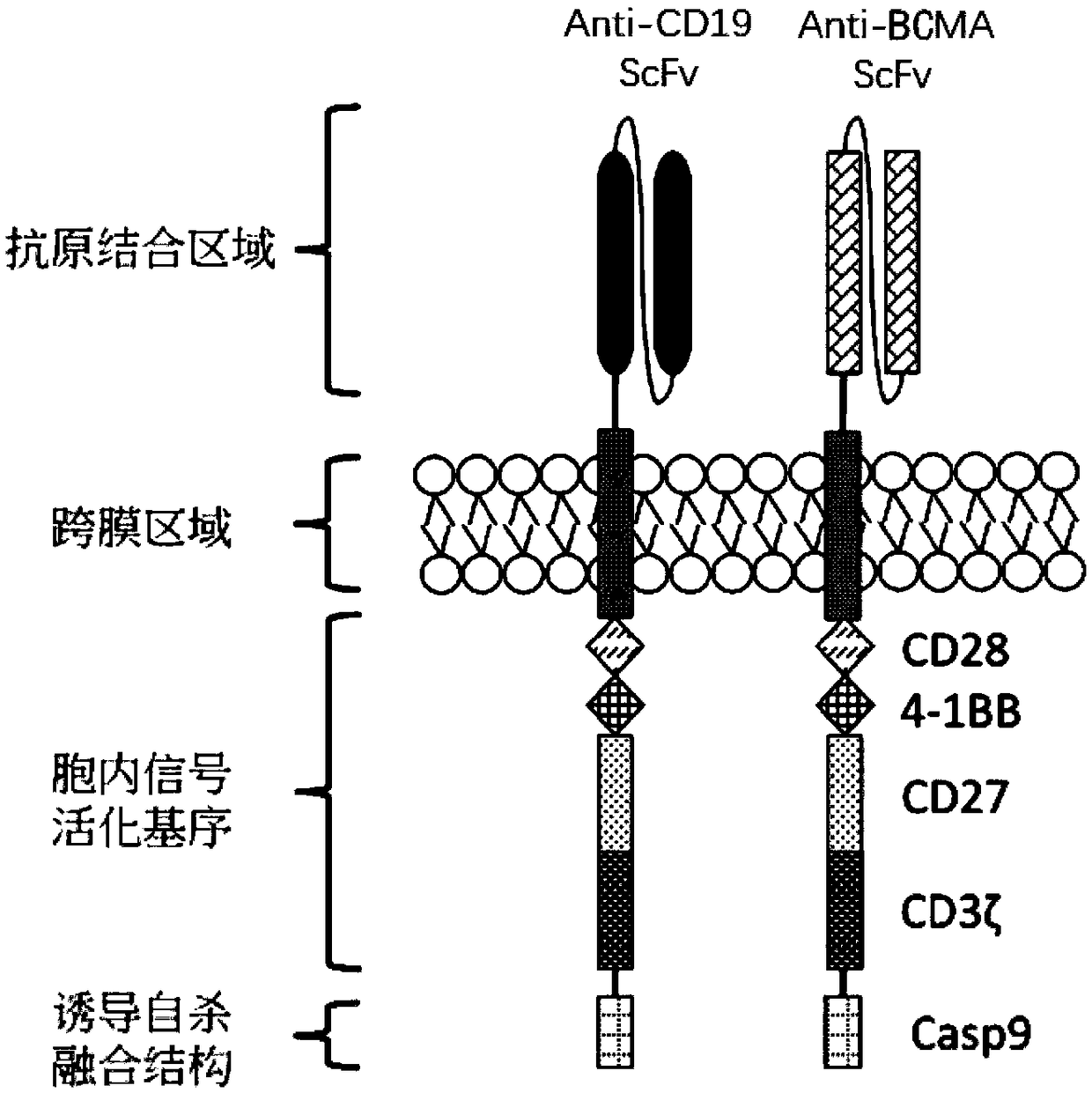
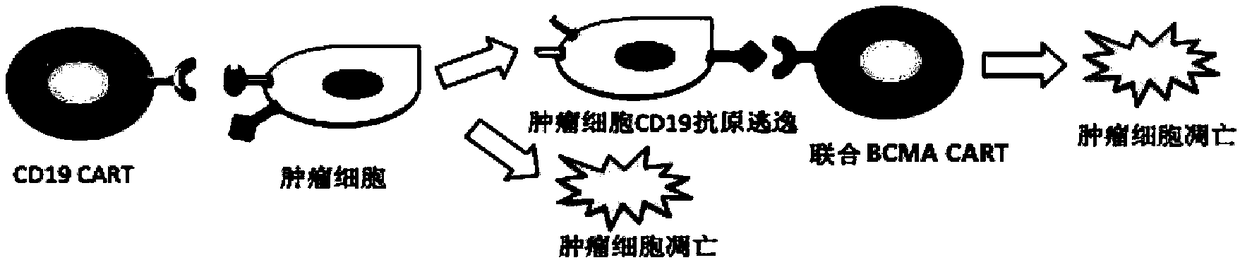
The invention relates to a double chimeric antigen receptor gene-modified immune cell based on CD19 and BCMA and application thereof. A double chimeric antigen receptor comprises a chimeric antigen receptor CD19 and a chimeric antigen receptor BCMA. The chimeric antigen receptor is formed by connecting an antigen binding domain, a trans-membrane domain, a co-stimulatory signal conduction region, aCD3 zeta signal conduction domain and an inducible suicide fusion domain in series. The chimeric antigen receptor can specifically recognize tumor surface antigens CD19 and BCMA; and compared with the use of other mono-chimeric antigen receptor T cells, the combined use of two antigen-targeted CAR-T cells ensures that the treatment effect is better, the CD19 escape is hard to occur, and diseasesare more easily alleviated.
Owner:BEIJING MEIKANG JIMIAN BIOTECH CO LTD
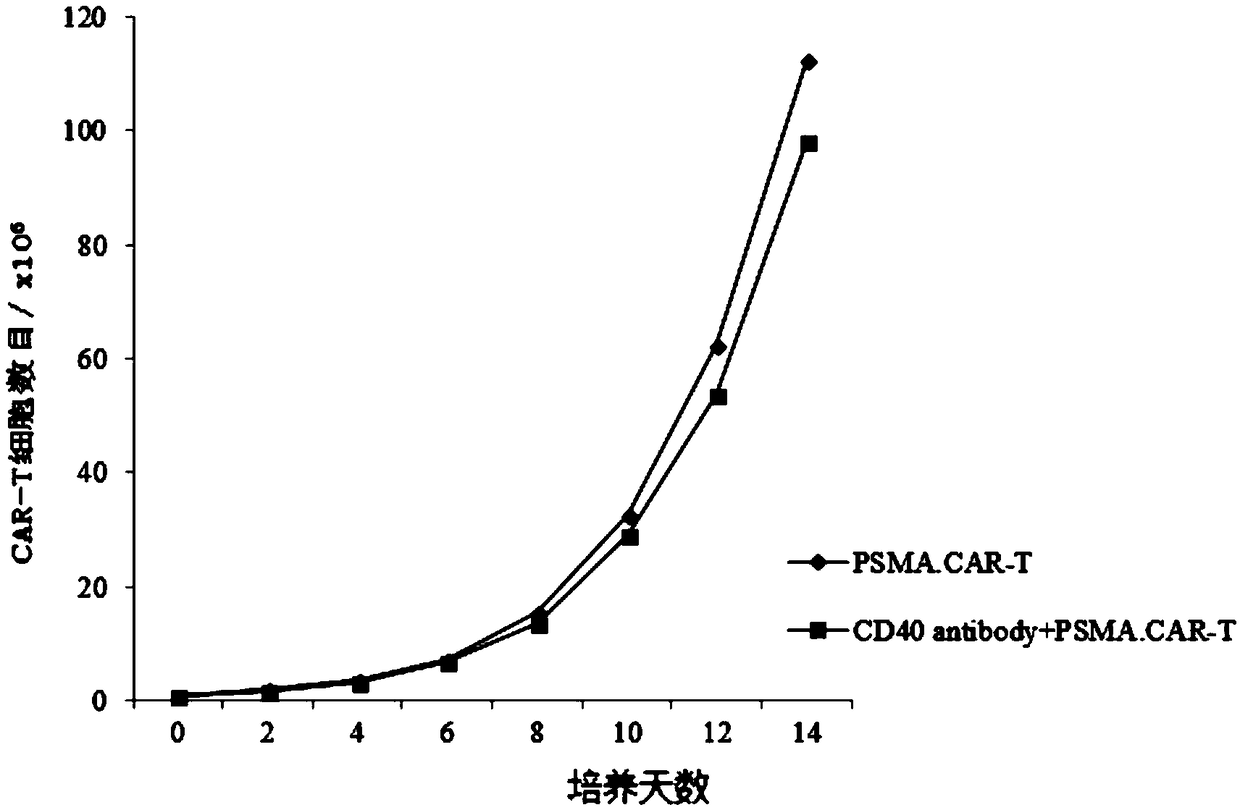
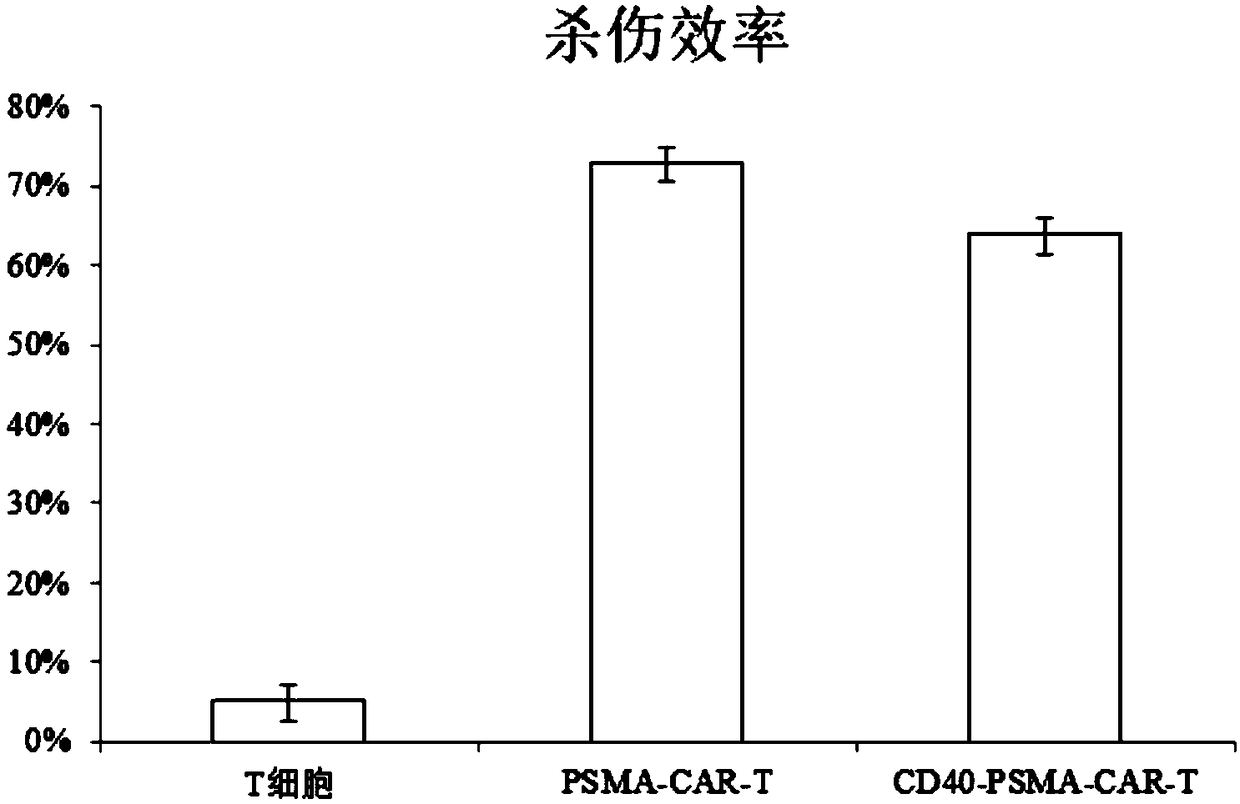
Lentiviral vector expressing CD40 antibody, and construction method and application of CAR-T cells
InactiveCN108913721APromote growthMammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsAntigenCancer research
The invention discloses a lentiviral vector expressing a CD40 antibody, and a construction method and application of CAR-T cells, and relates to the technical field of tumor immunotherapy. The lentiviral vector expressing the CD40 antibody, and the construction method and application of the CAR-T cells are put forward based on the problem that macrophages promote tumor deterioration. The lentiviral expression vector carrying CAR genes of solid tumor specific antigen target spots of the CD40 antibody, and the CAR-T cells expressing the solid tumor specific antigen target spots of the CD40 antibody are included. The lentiviral vector expressing the CD40 antibody, and the construction method and application of the CAR-T cells have the beneficial effects that the adverse effects that T cells for identifying a certain antigen by relying on TCR proliferate in quantity, and inflammation is likely to be caused are solved, and it is ensured that the CAR-T cells can exert the tumor killing capacity specifically and exclusively.
Owner:安徽古一生物科技有限公司
Surface antigen 1 of Toxoplasma gondii human antibody Fab fragment and encoded gene thereof
The present invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and relates to a surface antigen 1 (SAG1) of Toxoplasma gondii human antibody Fab fragment, encoded gene and use thereof. According to the invention, the surface antigen 1 (SAG1) of Toxoplasma gondii human antibody Fab fragment is filtered from a base through establishing a Toxoplasma gondii human immunoglobulin, ELISA, diluting the prothrombin time, sequencing analysis, etc. Through expression purifying and authenticating, the human antigen Fab fragment is authenticated to specifically identify the tachyzoite-bradyzoite recombination SAG1 of Toxoplasma gondii and have higher affinity with the tachyzoite-bradyzoite recombination SAG1 of Toxoplasma gondii, for being identified with the specificity of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoite-bradyzoite. The human antigen Fab fragment of the invention does not contain Fc segment and does not activate the alexin or cause the histopathological damages of human immune response, etc. when the function of restricting the invasion of Toxoplasma gondii to the host cell is exerted. The surface antigen 1 (SAG1) of Toxoplasma gondii human antibody Fab fragment is safe and reliable when applied for the human body. The antigen medicine for treating toxoplasmosis or the antigen targeted medicine can be prepared.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
A-type foot-and-mouth disease targeting composite epitope protein mediated by pig chemotactic factors and vaccine
ActiveCN105777909AEnhance humoral immunityEnhance cellular immunitySsRNA viruses positive-senseChemokinesDendritic cellTitin Antibody
The invention provides A-type foot-and-mouth disease targeting composite epitope protein mediated by pig chemotactic factors.The amino acid sequence of the protein is as shown in SEQ ID No.2 in a sequence list.The invention further provides a vaccine with the pig A-type foot-and-mouth disease targeting composite epitope protein.An FMDV specific antibody can be detected one week after an animal is immunized by the vaccine, and the valence of the antibody is continuously improved and reaches the highest four weeks after immunization.After 1000 pigs of the HNXX strain of the A / SEA / 97 series of the pig media infective dose (PID50) adapt to toxin attack, the pigs in the vaccine immunity group can all completely resist strong toxin attack, and no pigs present clinical symptoms within 10 days after toxin attack.It is shown that after an A8 antigen targets an XCR1 receptor through XCL1 and dendritic cells are activated by CpG, the body fluid immunity and cell immunity level of the antigen can be remarkably improved, and thus the vaccine is an effective vaccine with the A-type foot-and-mouth disease targeting composite epitope protein mediated by pig chemotactic factors.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Chimeric antigen receptor and application thereof in preparation of product for treatment of tumors
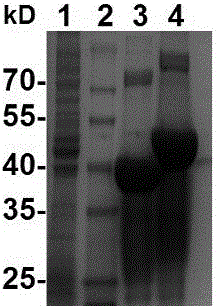
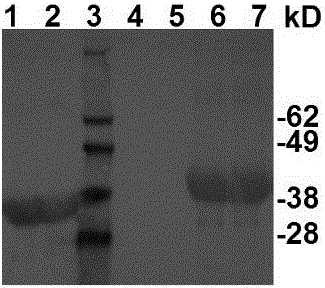
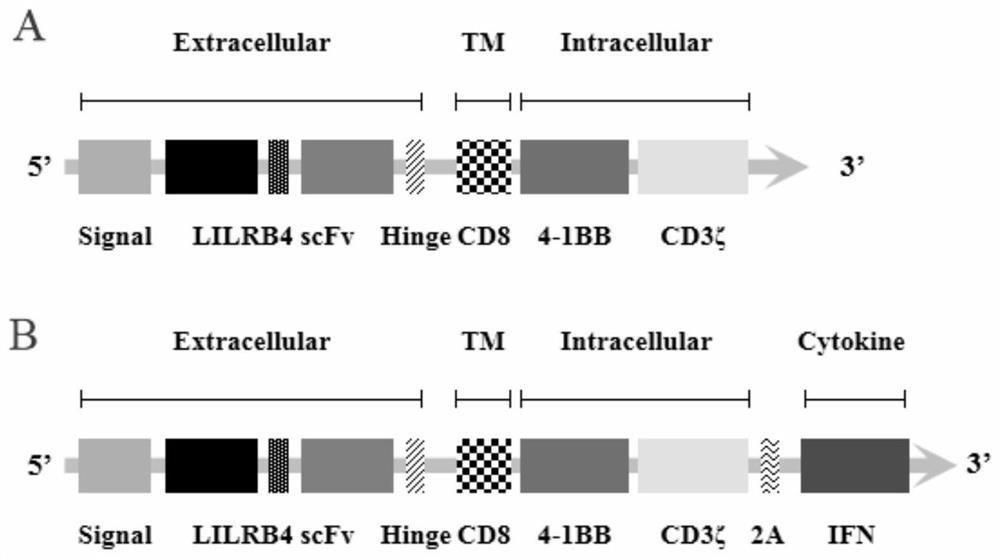
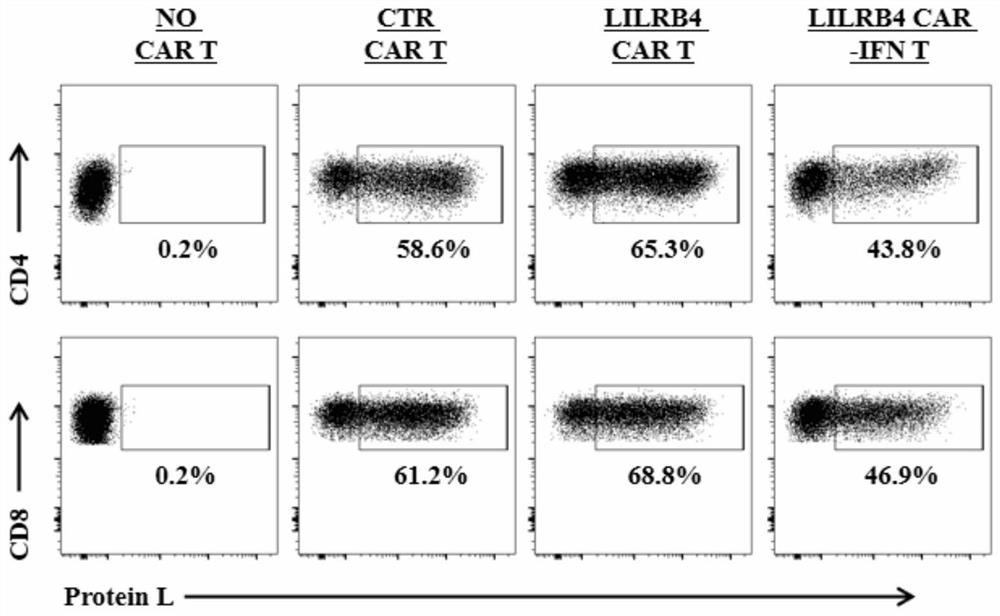
ActiveCN111892661APromote growthReduce the risk of inhibitionVirusesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigenSingle-Chain Antibodies
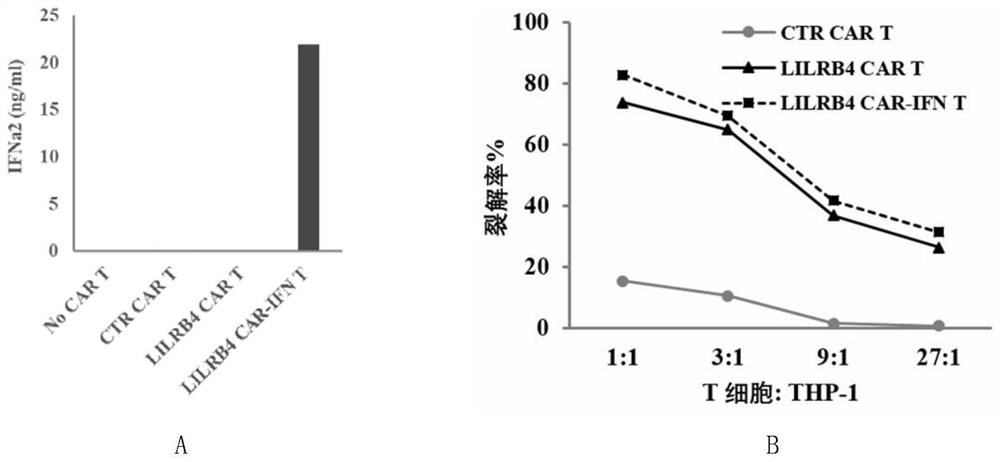
The invention discloses a chimeric antigen receptor and an application thereof in preparation of a product for treatment of tumors. The chimeric antigen receptor sequentially comprises a lead peptide,an anti-LILRB4 single-chain antibody, a human CD8 hinge transmembrane region, a human 4-1BB intracellular region, a human CD3 zeta intracellular region, a self-cleaving peptide and human IFN full length. A new generation of CAR-T cell treatment product is designed and developed by using LILRB4 as an antigen target for the first time, and a gene-optimized human full-length interferon (IFN) fragment is added to the C terminal of the LILRB4-CAR. Compared with a CAR-T cell which only expresses the LILRB4-CAR, the CAR-T cell which expresses the LILRB4-CAR-IFN has higher tumor killing capacity, andthe safety and effectiveness of the CAR-T cell in tumor treatment are further improved.
Owner:CARBIOGENE THERAPEUTICS CO LTD
Vectors And Methods For Genetic Immunization
ActiveUS20080145376A1High expressionImprove integritySnake antigen ingredientsNucleic acid vectorIntracellularTGE VACCINE
Improved DNA vaccine plasmids are disclosed. The improved plasmids eliminate all extraneous sequences, and have superior eukaryotic expression, improved yield and stability during bacterial production, facilitate flexible targeting of antigens to various intracellular destinations, and novel RNA-based functionality. These vectors are utilized in novel immunization methods wherein combinations of immunostimulatory DNA vaccine plasmids that target antigens to various intracellular destinations are used to elicit improved immune response.
Owner:ALDEVRON LLC
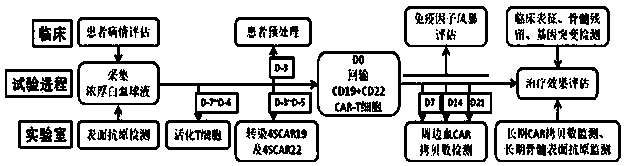
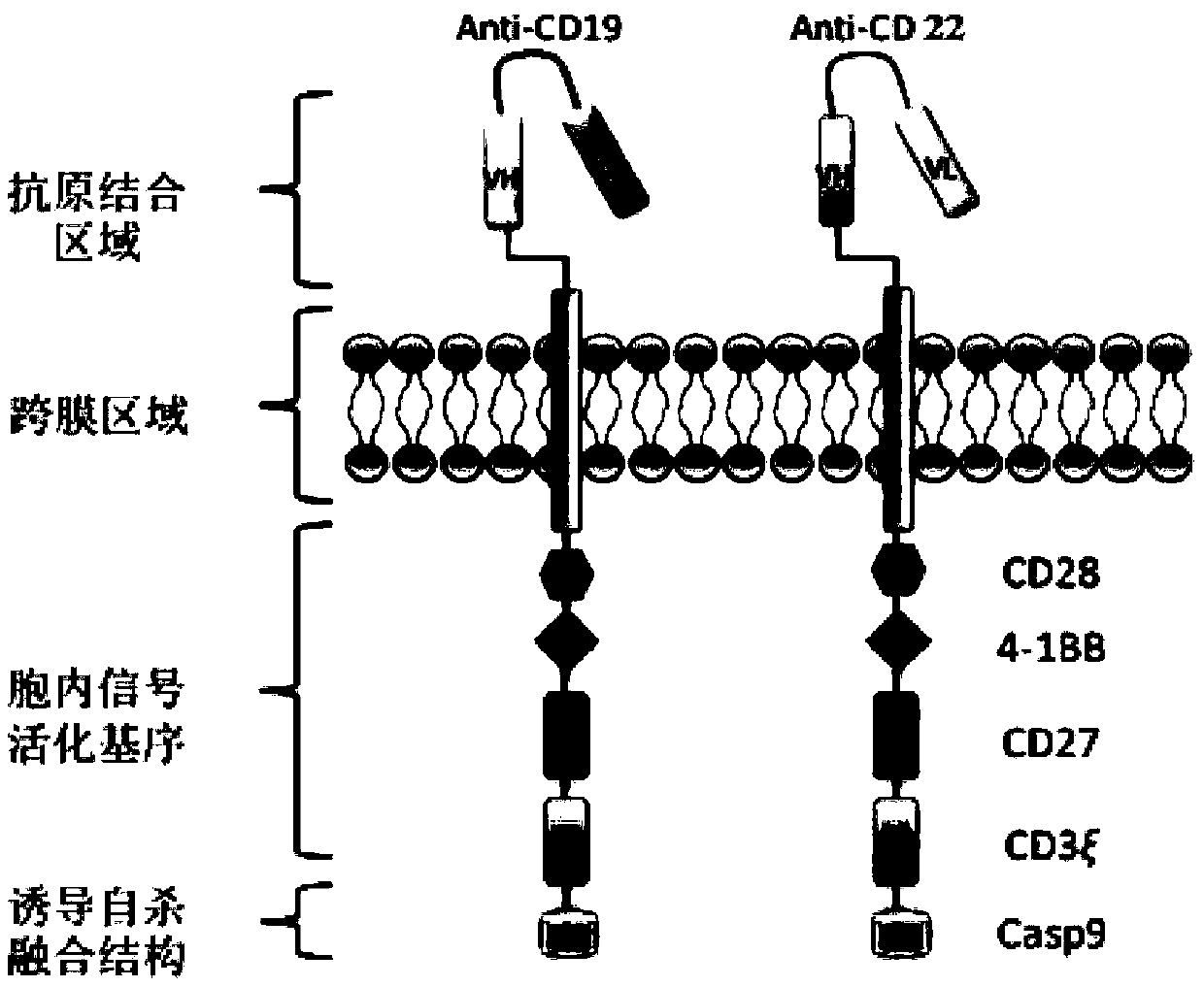
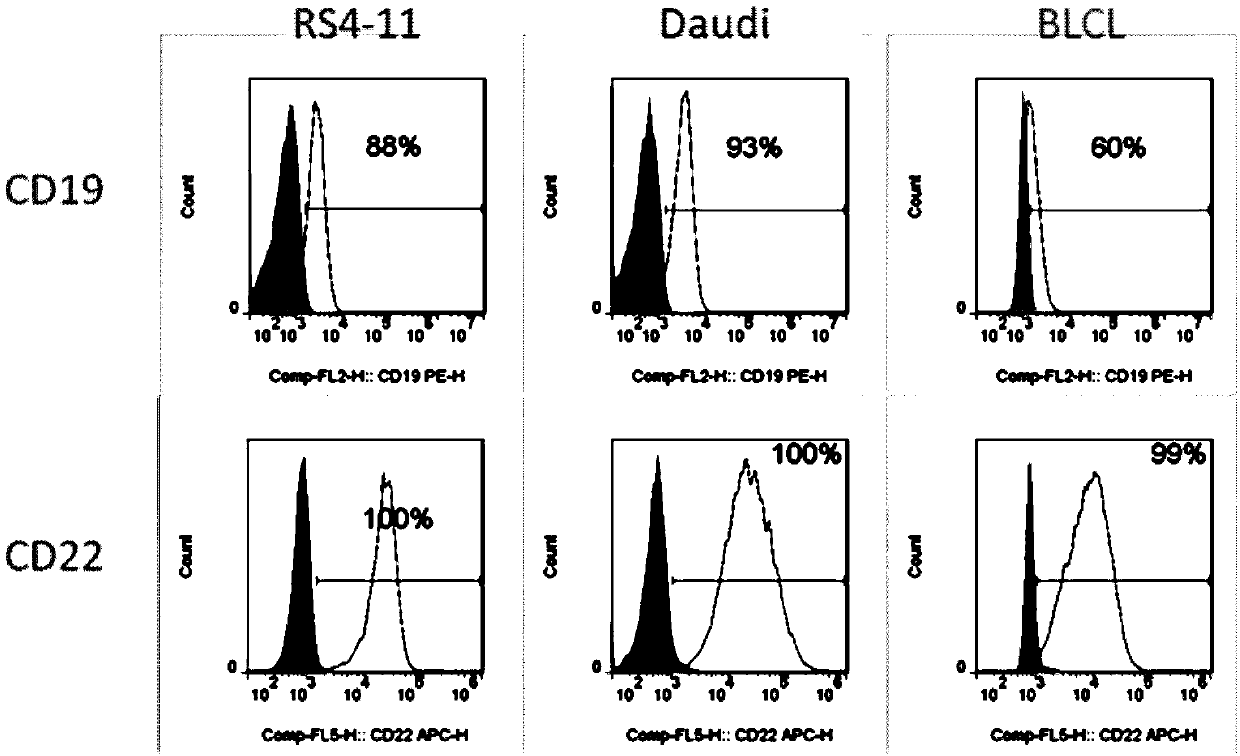
Dual chimeric antigen receptor gene modified immune cell based on CD19 and CD22 and application thereof
ActiveCN109517799AImprove anti-tumor effectThe effect of tumor shrinkage is obviousAnimal cellsVirusesTherapeutic effectAntigen binding
The invention relates to a dual chimeric antigen receptor gene modified immune cell based on CD19 and CD22 and application thereof. The dual chimeric antigen receptor comprises a chimeric antigen receptor CD19 and a chimeric antigen receptor CD22. The chimeric antigen receptor is composed of an antigen binding domain, a transmembrane domain, a co-stimulation signal transduction region and a CD3 zeta signal transduction domain, and an inducible suicide fusion domain, which are connected in series. The chimeric antigen receptor provided by the invention can be used for specifically identifying tumor surface antigens CD19 and CD22; and compared with the utilization of other single chimeric antigen receptor T cells, the combined utilization of two types of antigen targeting CAR-T cells has a better treatment effect and CD19 escaping is not easy to occur, so that diseases are easier to alleviate.
Owner:BEIJING MEIKANG JIMIAN BIOTECH CO LTD
Monoclonal antibody TBEF3 of tubercle bacillus-resistant ESAT-6 and application thereof
InactiveCN101985473AStable secretionNo decline in secretionImmunoglobulins against bacteriaMicroorganism based processesAntibody affinityCongenic
The invention provides a monoclonal antibody TBEF3 of tubercle bacillus-resistant secretory antigen target protein in early stage. The monoclonal antibody TBEF3 is prepared by the following steps: selecting a specific antigen peptide mouse; collecting sensitized mouse B lymphocyte and mouse myeloma cell to fuse; judging positive clones by using an enzyme linked immunosorbent assayelisa and an immunoblotting testing method; establishing a hybridoma cell line TBEF3 for secreting monoclonal antibody of tubercle bacillus-resistant secretory ESAT-6 in early stage; carrying out multiplication culturing on the positive cells and injecting to congenic mouse enterocoelia for induction of generation of ascitic fluid containing antibody; and carrying out collection and antibody affinity purification to obtain the monoclonal antibody TBEF3 of tubercle bacillus-resistant secretory antigen target protein in early stage. The invention also provides an application of the monoclonal antibody in testing the secretory antigen target protein of mycobacterium tuberculosis in early stage.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Efficient tumor antigen loaded DC vaccine and method for induced proliferation of tumor antigen specific CTL by same
ActiveCN108379569AImproving immunogenicityExpand sourceCancer antigen ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsSide effectPD-L1
The invention provides an efficient tumor antigen loaded DC vaccine and a method for induced proliferation of tumor antigen specific CTL by the same. The DC vaccine is prepared by steps: (1) tumor antigen preparation; (2) acquisition, separation and efficient culture and proliferation of DC cells; (3) adoption of a tumor antigen and an activator for sensitization and activation of the DC cells; (4) DC cell surface PD-L1 molecule closing. The invention further provides a sequential blood drawing method for in-vitro induced proliferation of CTL by the DC vaccine and closing of surface PD-1 molecules of CTL subjected to in-vitro induced proliferation. Problems of low immunogenicity of existing tumor antigens, incompleteness of antigen targets, difficulty in acquisition of tumor antigens of patients and insufficiency in DC and CTL in-vitro proliferation are solved. The DC vaccine is effective in in-vitro and in-vivo induction of tumor antigen specific CTL and capable of efficiently generating specific killing effects on tumors without evident toxic and side effects, and a promising clinical application prospect is achieved.
Owner:北京百益宁医学科技有限责任公司
Method for modifying bird flu virus through interferon inducible protein ESAT6
InactiveCN101792775ASignificant progressProminentlyMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionBird fluVirus Protein
The invention relates to a method for modifying a bird flu virus through interferon inducible protein ESAT6, which adopts an early secretory antigen target ESAT-6 gene of mycobacterium tuberculosis to modify the bird flu virus and is a method for splicing into an exogenous DNA on the basis of establishing a bird flu virus reverse genetic operating system. The selected ESAT-6 protein is secretory protein with a T cell multifunctional epiposition and has the main function of stimulating an organism to generate IFN, which has uniqueness in researching a virus anti-infective immune mechanism path. After a bird flu virus gene is modified through the DNA, when the modified virus is rescued, not only the transcription, the translation and the virus packaging of bird flu virus protein are not influenced, but also the ESAT-6 protein can be simultaneously generated.
Owner:GUANGDONG LAB ANIMALS MONITORING INST +1
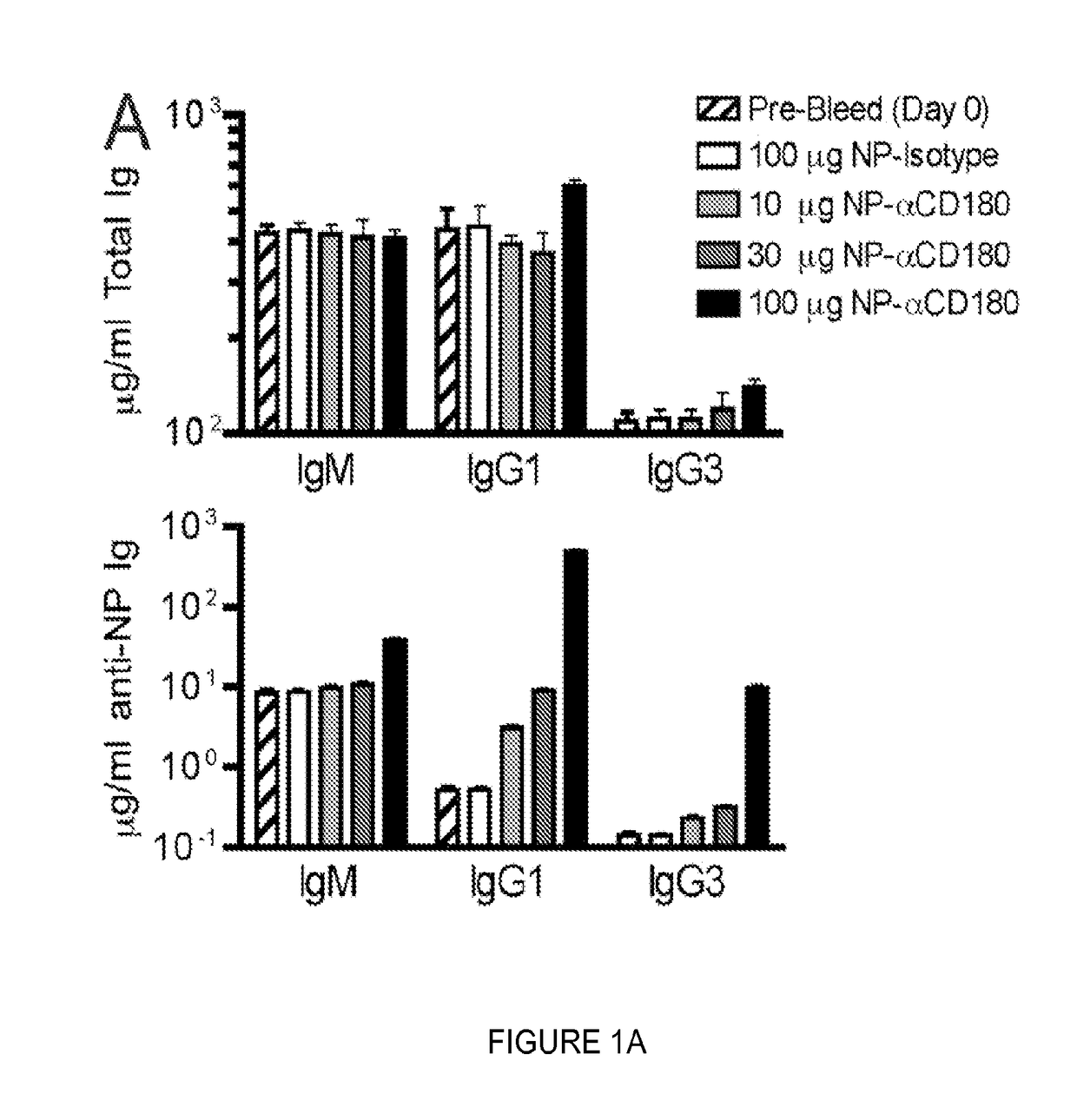
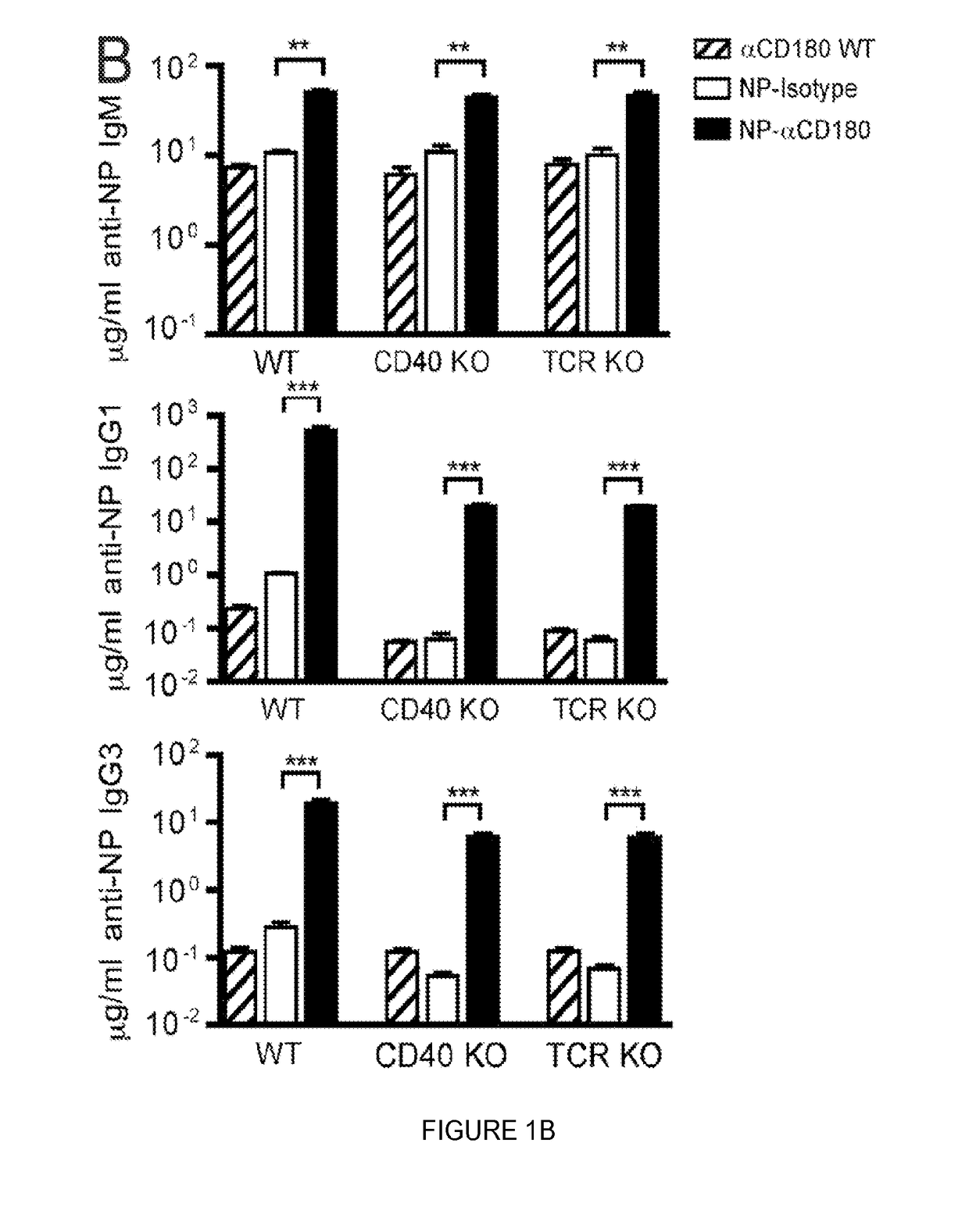
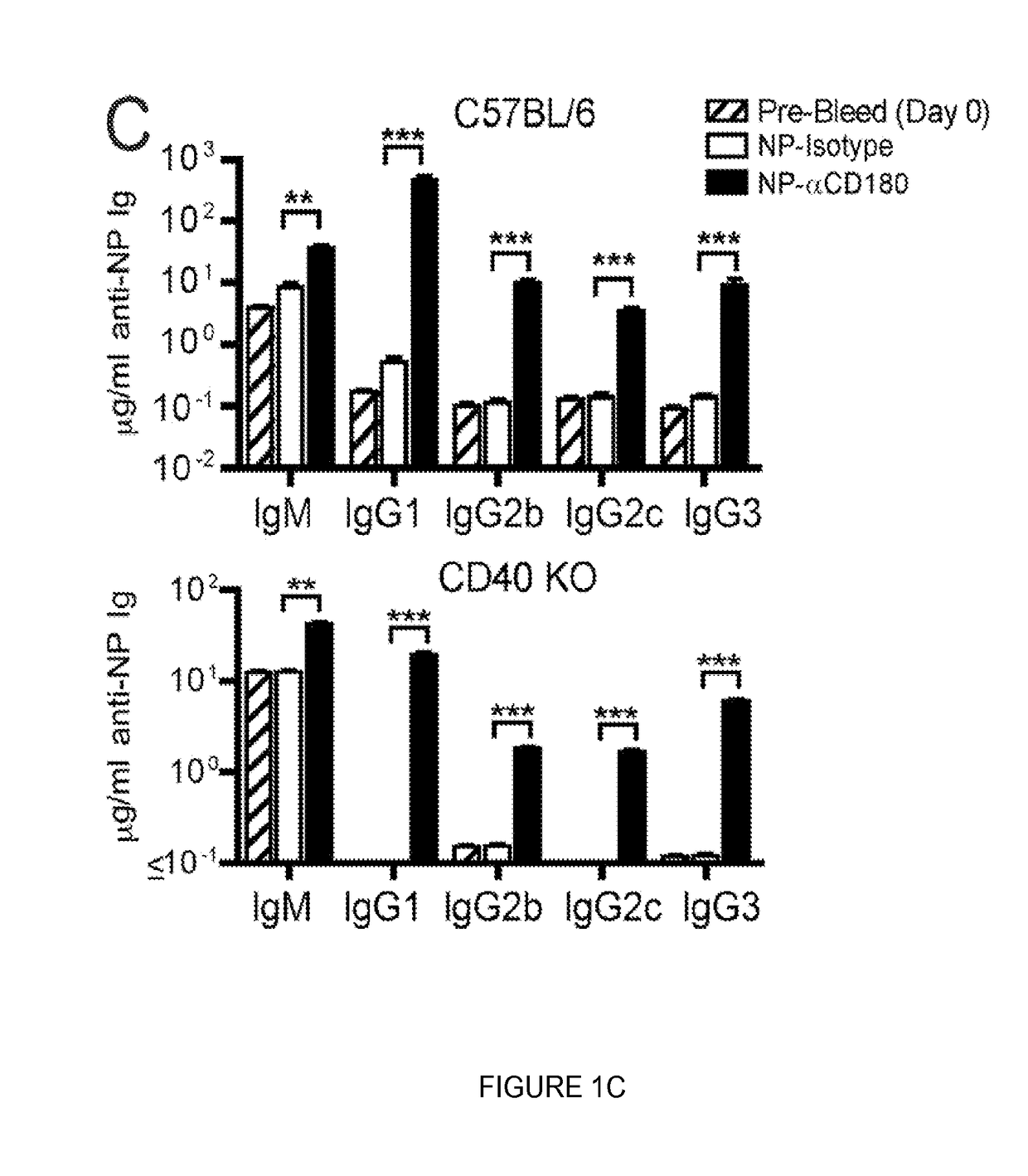
Compositions and methods for antigen targeting to CD180
The present limiting provides compositions of CD 180 targeting molecules coupled to heterologous antigens, and their use in treating and / or limiting disease.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
Fusion protein antibody, enhanced vaccine and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109705224AReduce usagePromote secretionAntiviralsCarrier-bound antigen/hapten ingredientsSpleen cellSpecific immunity
The invention relates to the technical field of immunization, and especially relates to a fusion protein antibody, an enhanced vaccine and a preparation method and an application thereof. The fusion protein antibody provided by the present invention comprises a secretion peptide, a targeting antigen, a connecting peptide, and a CD317-specific antibody. The CD317 as an antigen to target the delivery targets has more advantages that: 1) the expression level is higher and can be further induced up-regulated by IFN to form a benign feedback loop; and 2) the antigen presentation is more efficient and can activate the stronger specific immune response. Due to the high efficiency of antigen presentation, the amount of vaccine used can be reduced and the cost can be reduced. As the therapeutic vaccine, the ability to activate an immune response is stronger than that of a soluble non-targeting antigen under development. The experiments of the present invention show that the antibody provided bythe invention can significantly promote the division of spleen cells, promote the secretion of IFN-gamma, and improve the killing ability of mouse spleen cells to target cells.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Compositions and methods for adoptive cell therapy for cancer
PendingUS20210393692A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAdoptive cellular therapyAntigen receptors
Provided herein are compositions and methods for adoptive cell therapy comprising engineered immune cells that express a tumor antigen-targeted chimeric antigen receptor and a SIRPα polypeptide.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Chimeric receptor and application thereof
PendingCN113583139AHigh affinityEnhance ADCC effectPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntibody fragmentsTumor antigen
The invention provides a chimeric receptor. The chimeric receptor comprises (1) an extracellular recognition domain of an Fc fragment; (2) an extracellular spacer region; (3) a transmembrane area; (4) an intracellular signaling domain; optionally, the chimeric receptor further comprises (5) one or more co-stimulatory signaling domains and / or (6) one or more cytokine receptor signaling domains. The invention also provides an immune cell expressing the chimeric receptor. The invention also provides a combination comprising the immune cell and a tumor antigen targeting antibody or a viral antigen targeting antibody. The brand-new Fc fragment high-affinity chimeric receptor provided by the invention has higher antibody Fc fragment affinity, and can remarkably enhance ADCC effect when being used in combination with a tumor antigen targeting antibody or a virus antigen targeting antibody.
Owner:SHANGHAI SINOBAY BIOTECH CO LTD
Antigens Targeted by Prevalent Pathogennic T Cells in Type 1 Diabetes and Uses Thereof
The present invention is based on the identification of a predominant ligand of CD8+ T cells that are responsible eq for type 1 diabetes. That ligand is islet-specific glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit-related protein (IGRP). Several CD8+ T cell-binding peptides from IGRP are identified, including the peptide comprising amino acids 206-214 of the IGRP sequence, which has high avidity to the most prevalent T cell receptor of pathogenic CD8+ T cells in autoimmune diabetes. The invention thus provides oligopeptide and polypeptide compositions comprising YLKTN / A / I / L / V)FL, FLWSVFWLI, (T / A)YY / G / T)FLNFM, LR(LV)(F / L)(G / N)IDLL, KWCANPDWI, and SFCKSASIP. Also provided are oligopeptide compositions 8-10 amino acids in length and completely homologous with a mammalian IGRP, where the oligopeptide is capable of binding a human MHC class I molecule. Additionally, various methods of treating a mammal using the above compositions are provided, where the mammal is at risk for or has type 1 diabetes. Also provided are methods of preventing a CD8+ T cell that is cytotoxic to pancreatic islet β-cells from destroying a mammalian β-cell, where the methods also use the above compositions. Further provided are methods for determining whether a mammal is at risk for or has type 1 diabetes, where the methods use the above compositions.
Owner:UNIV TECH INT +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com