Patents
Literature
34 results about "Argon ion laser" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
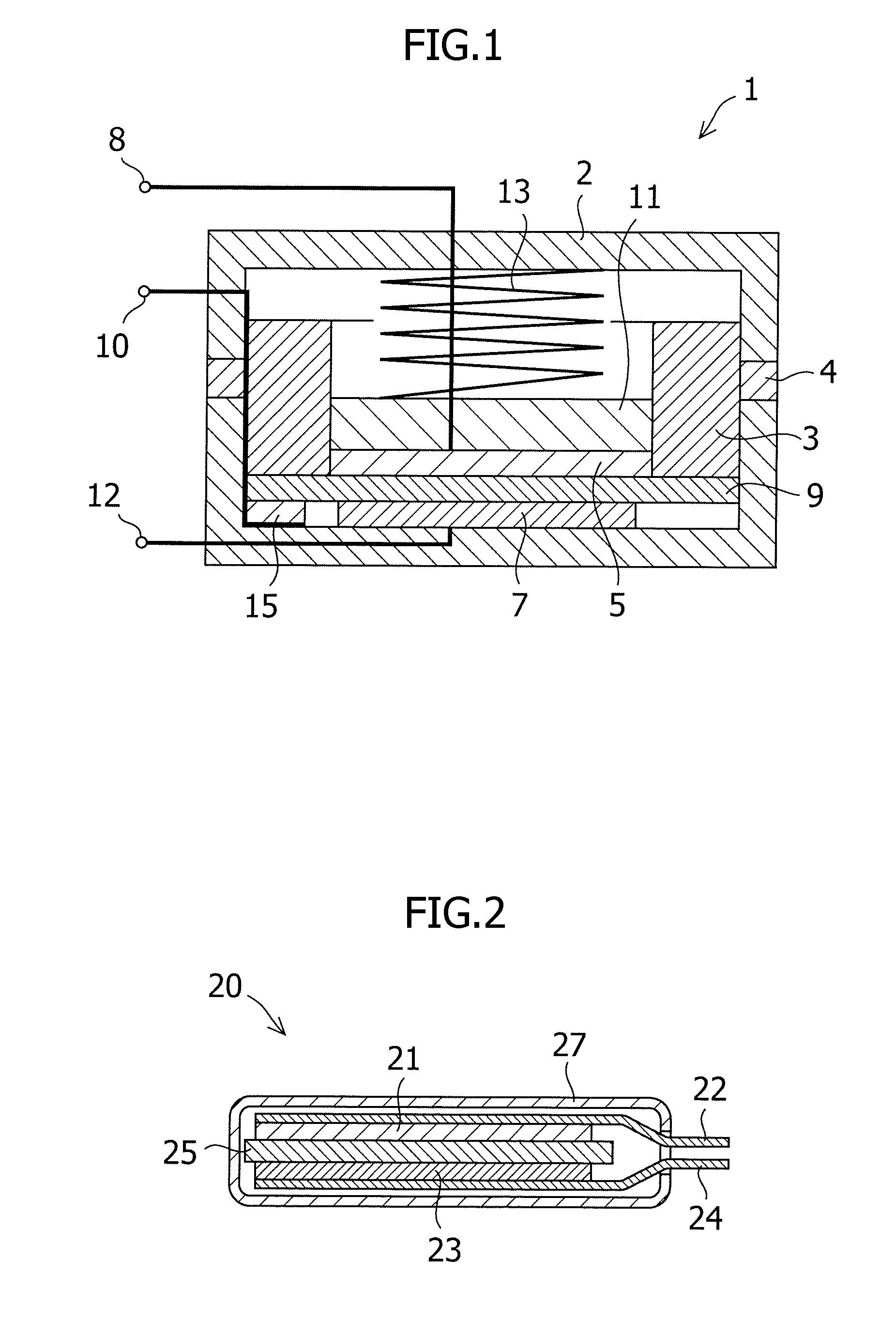
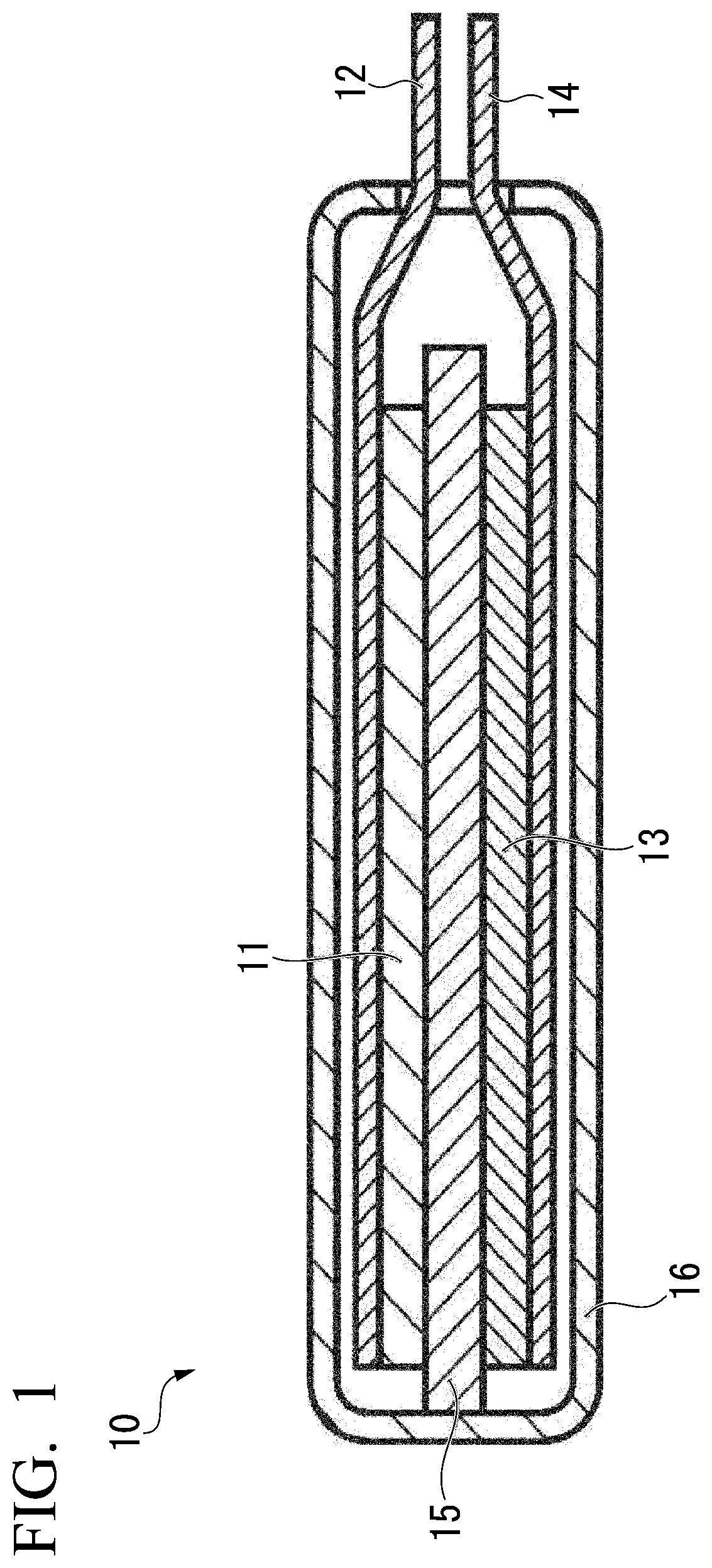
The core component of an argon ion laser is an argon-filled tube, made e.g. of beryllium oxide ceramics, in which an intense electrical discharge between two hollow electrodes generates a plasma with a high density of argon (Ar+) ions.
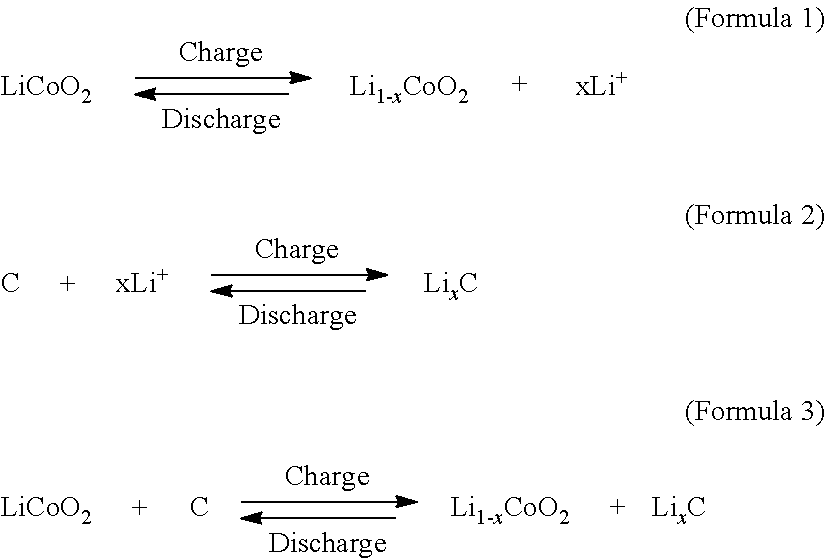
Carbonaceous material for electrode and non-aqueous solvent secondary battery using this material
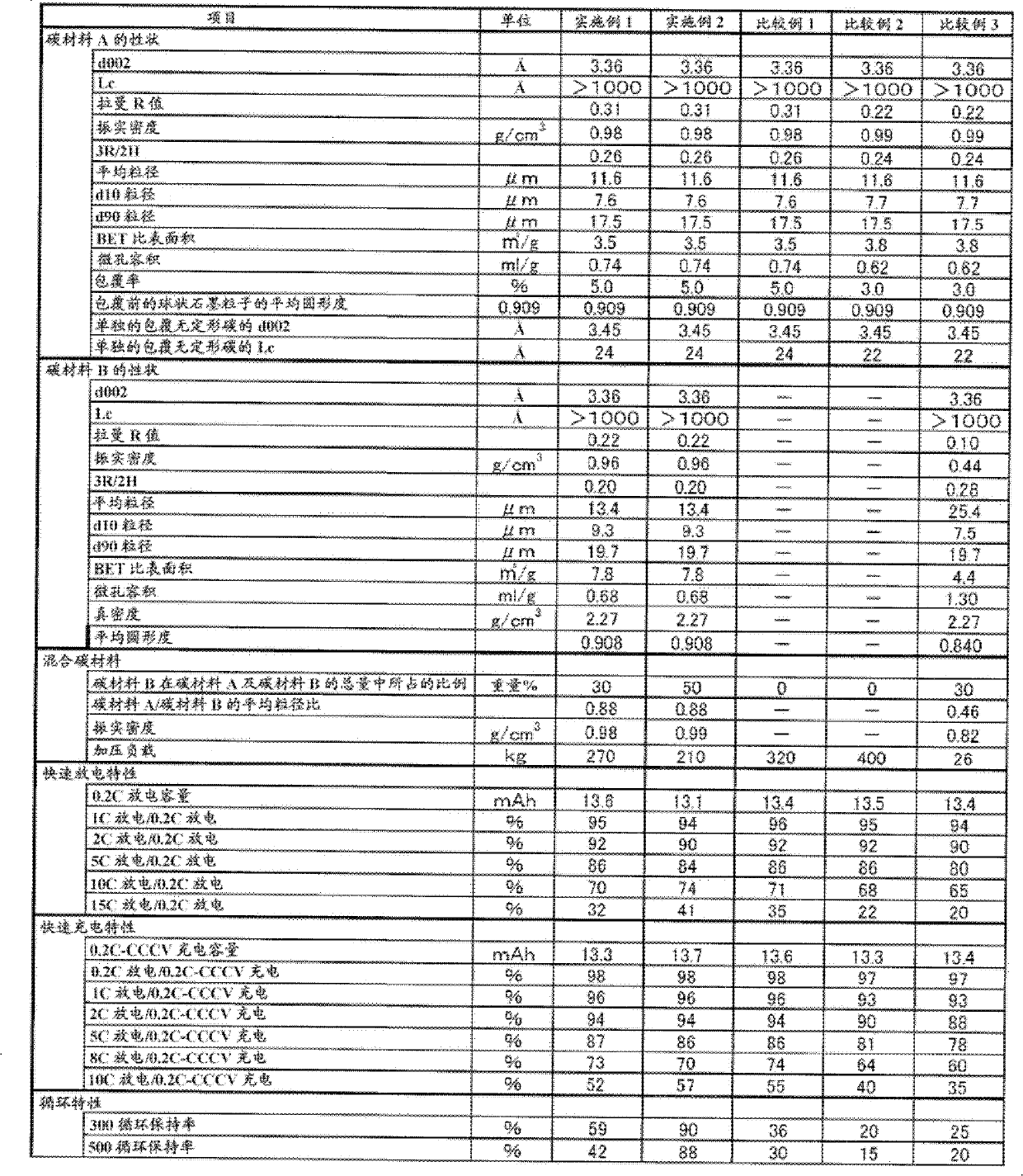
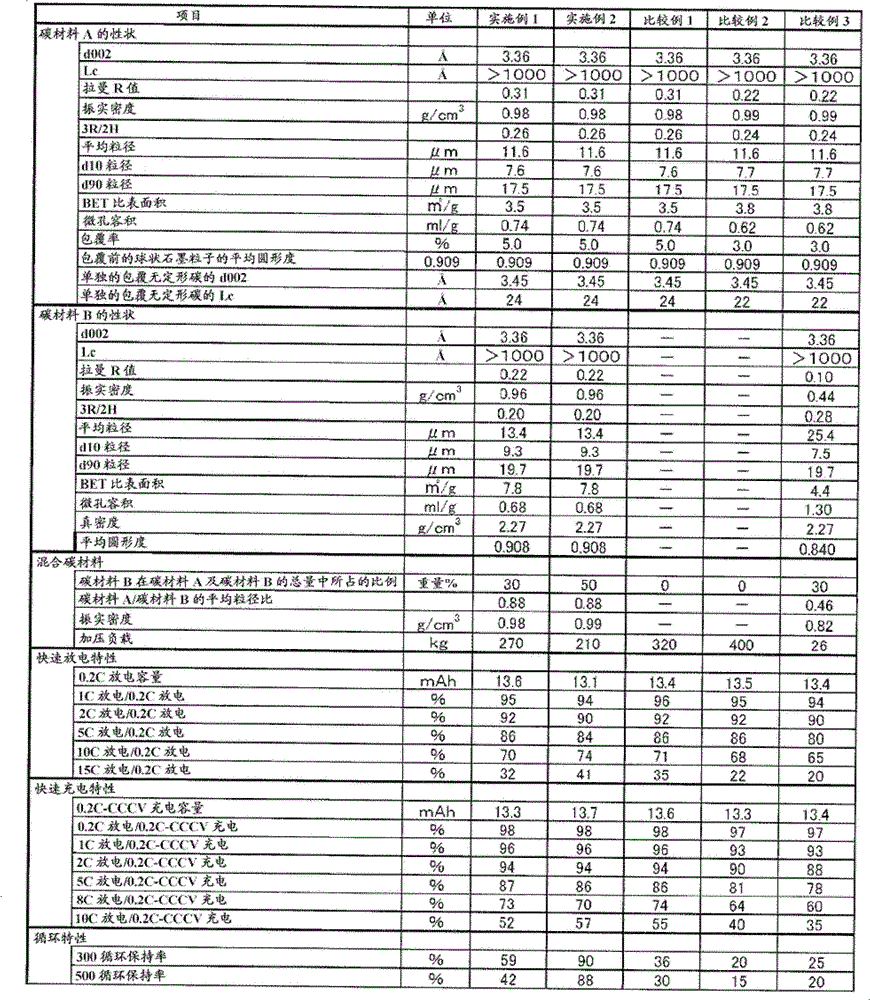
InactiveUS6632569B1Large discharge capacityImprove propertiesAlkaline accumulatorsConductive materialX-rayPeak value
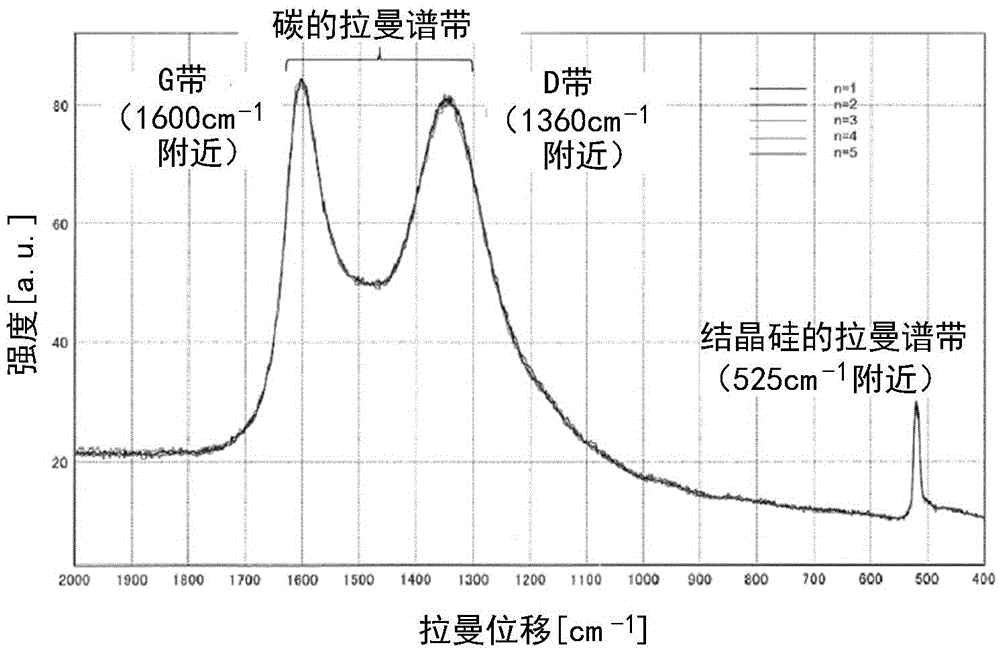
A carbonaceous material has a plane space d002 of a (002) plane less than 0.337 nm in an X-ray wide angle diffraction method, a crystallite size (Lc) of 90 nm or higher, an R value, as a peak intensity ratio of a peak intensity of 1360 cm<HIL><−1 < / SP><PDAT>to a peak intensity of 1580 cm<HIL><−1 < / SP><PDAT>in a Raman spectrum in use of an argon ion laser, of 0.20 or higher, and a tap density of 0.75 g / cm<HIL><3 < / SP><PDAT>or higher. Also disclosed is a multilayer structure carbonaceous material for electrode, which is manufactured by carbonizing some organic compounds where the carbonaceous material for electrode is mixed with the organic compounds. The battery using the carbonaceous material for electrode or the multilayer structure carbonaceous material for electrode has a large capacity, a small irreversible capacity admitted in the initial cycle, excellent capacity maintaining rate of the cycle, and particularly, largely improved quick charging and discharging characteristics.< / PTEXT>
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Negative electrode material for non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery and non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery using same
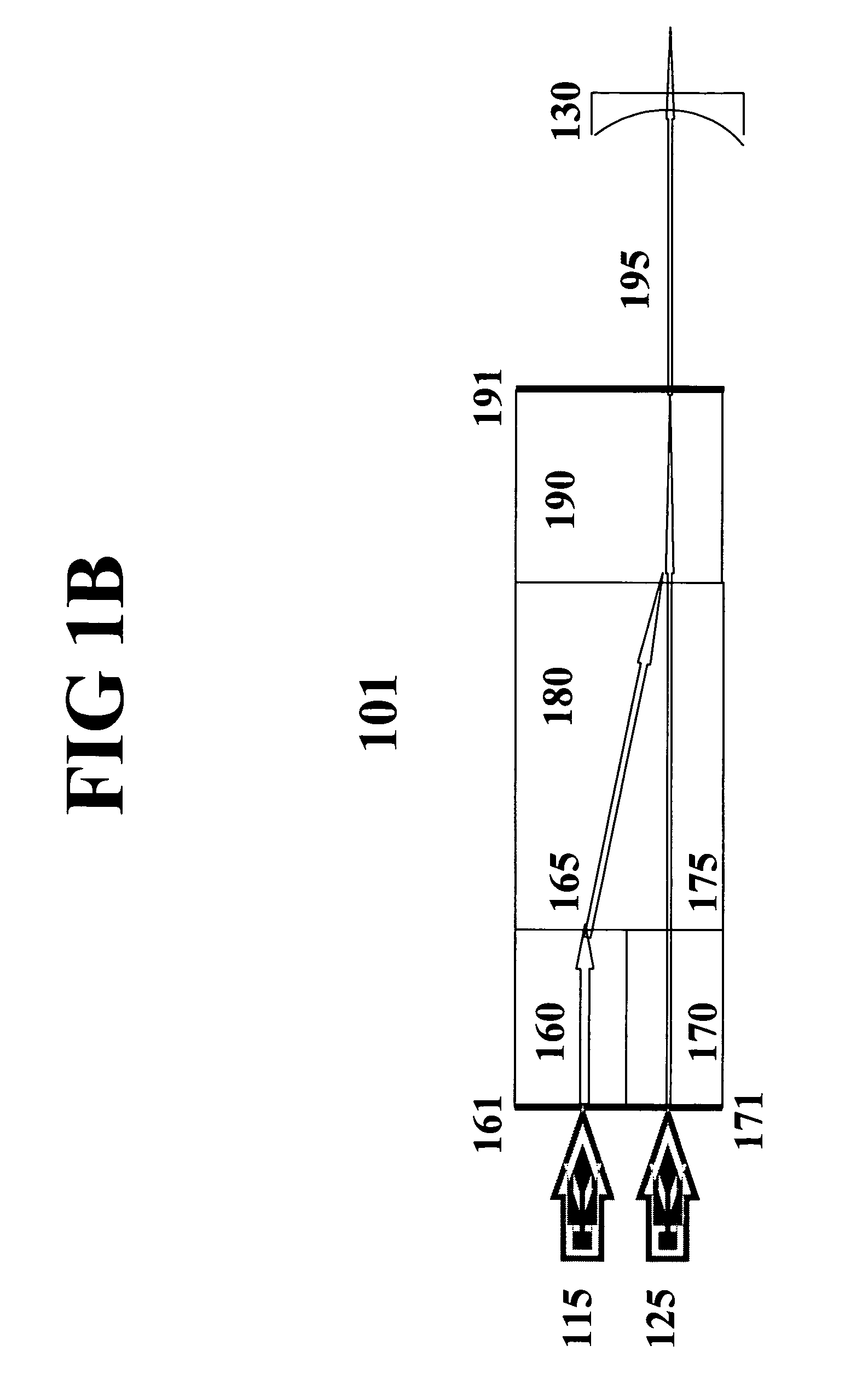
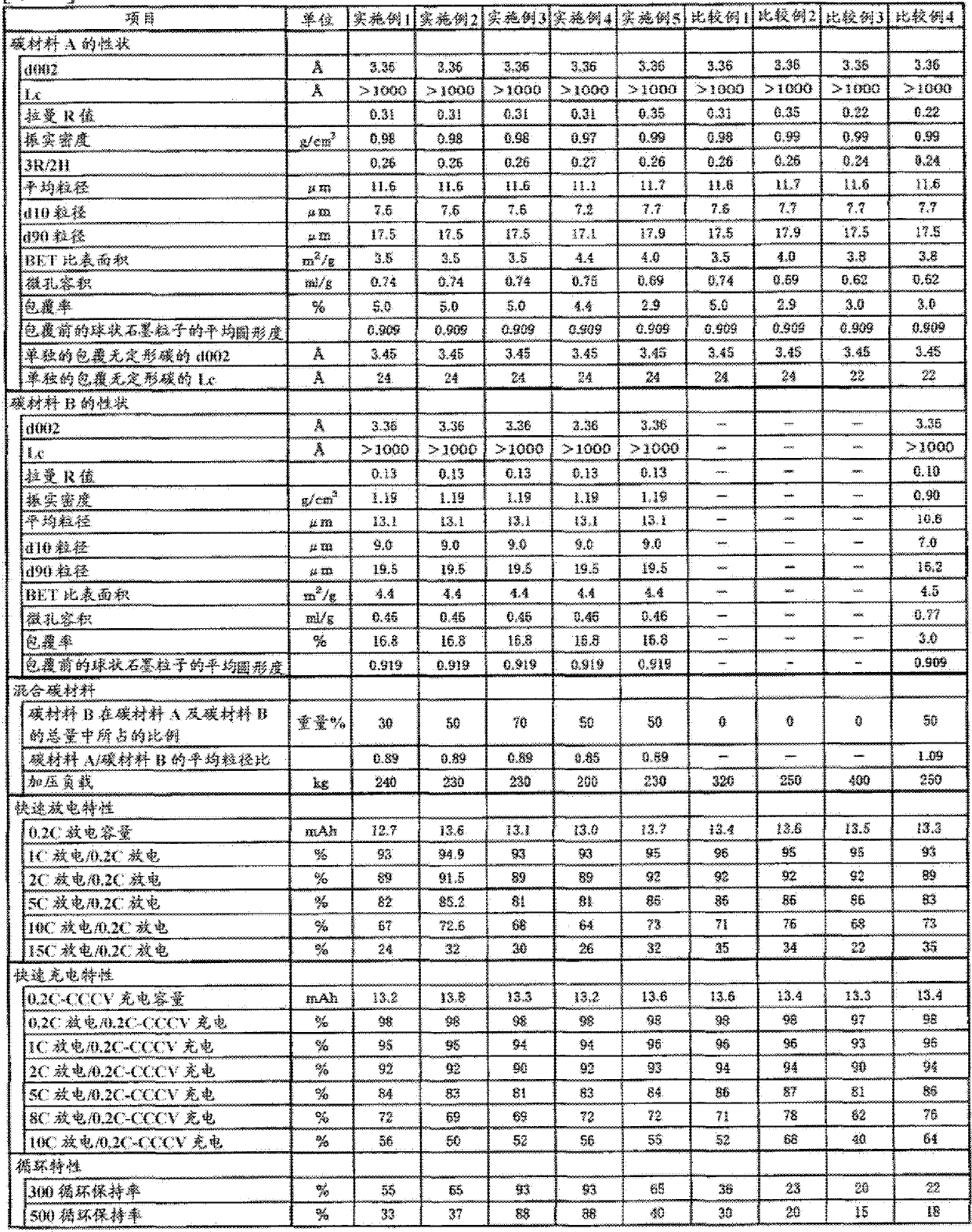
ActiveCN102362381AFast charge and discharge characteristicsExcellent cycle characteristicsGraphiteNegative electrodesElectrical batteryX-ray
Disclosed is a mixed carbon material for use in an electrode of a non-aqueous secondary battery showing excellent characteristics having rapid charge-discharge characteristics and high cycle characteristics. More particularly, disclosed is a negative electrode material for non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery comprising the following carbon material A and carbon material B, wherein the carbon material A is a multilayer-structured carbon material which contains graphite particles and amorphous carbon covering the surfaces of the particles, and in which a 002 plane spacing (d002) measured by X-ray wide angle diffraction is 3.37Angstrom or less, Lc is 900Angstrom or more, a tap density is 0.8 g / cm<3> or more, and a Raman R value, which is the ratio of a peak intensity at around 1360 cm<-1> to a peak intensity at around 1580 cm<-1> in an argon ion laser Raman spectrum, is 0.25 to 0.6; and the carbon material B is graphite particles in which a 002 plane spacing (d002) measured by X-ray wide angle diffraction is 3.37Angstrom or less, Lc is 900Angstrom or more, a tap density is 0.8 g / cm<3> or more, a Raman R value, which is the ratio of a peak intensity at around 1360 cm<-1> to a peak intensity at around 1580 cm<-1> in an argon ion laser Raman spectrum, is 0.2 to 0.5, and an average circularity measured by a flow-type particle analyzer is 0.9 or more.
Owner:MITSUBISHI RAYON CO LTD
Monolithic microchip laser with intracavity beam combining and sum frequency or difference frequency mixing
ActiveUS20060209912A1Avoid polarizationLasing suppressionOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionLow noiseNonlinear optical crystal
A method for producing low-noise laser output at various wavelengths and / or in various operation modes in a monolithic microchip laser comprises schemes of generating two fundamental beams in separate cavities, precise intracavity beam combination based on the walk-off effect in birefringent crystal, and wavelength conversion in nonlinear optical crystals. The fundamental beams are produced from light sources selected upon the desired wavelengths, polarizations, and other features related to the laser output. Low-noise laser devices operated in SLM or with spectra of flat-top or desired bandwidths are constructed according to the method. High-volume fabrication is feasible. Apparatus of compact size and efficient frequency conversion is demonstrated with various configurations including those for generating low-noise 491 nm laser, as a replacement of Argon ion laser.
Owner:PAVILION INTEGRATION
Method and apparatus realizing quasi confocal fluorescent microscopic with dynamic speckle illumination
InactiveCN101303302AGood value for moneySimple structureScattering properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicroscopic imageEffect light
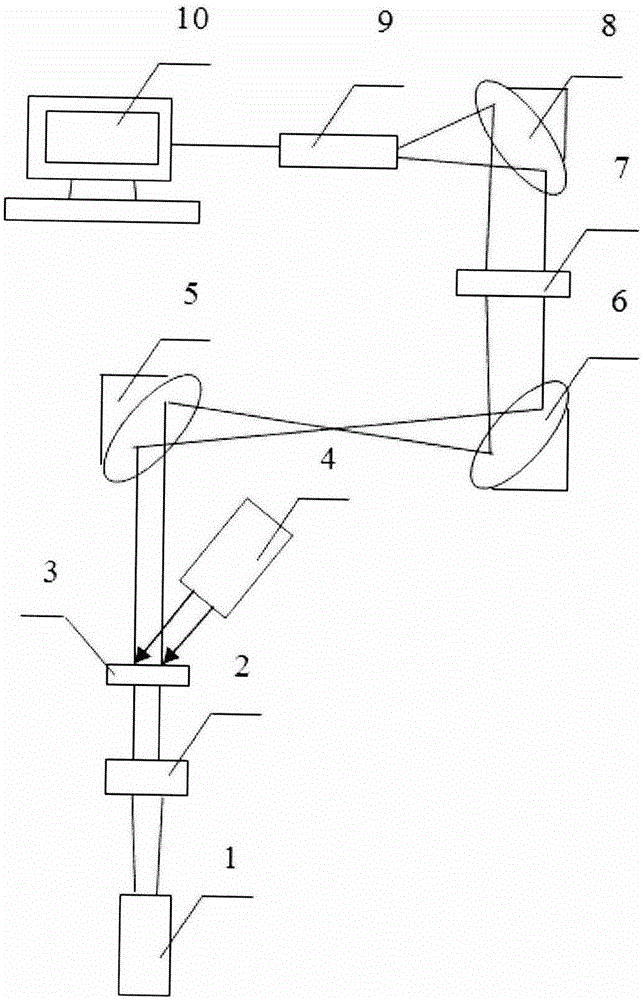
The present invention relates to a novel method and a novel device, incorporating dynamic speckle lighting with a conventional wide field fluorescence microscope organically to implement approximately confocal fluorescence microscopy (i.e., quasi-confocal fluorescence microscopy). The present invention employs an argon ion laser as the light source; the exciting light passes through a scattering object, a relay light path system for expanding and shaping, and then is coupled to the fluorescence microscope and focused to the sample. The stepping and revolution of the scattering object is controlled with a computer to produce a dynamic speckle pattern on the sample. The received fluorescent images are processed to obtain high-resolution spatial chromatographic images under no need to scan condition. The method can be used to obtain high-resolution three-dimensional chromatographic and microscopic image information of biological tissue samples in a non-intrusive manner. The device has simple structure, high cost-performance ratio, and is favorable for post data processing, easy to operate and apply; therefore, the device and method have a wide market application prospect and great significance for clinical diagnosis and life science research.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Monolithic microchip laser with intracavity beam combining and sum frequency or difference frequency mixing
ActiveUS7535937B2Enhances efficiency and compactnessLow intracavity lossOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionNonlinear optical crystalLow noise
A method for producing low-noise laser output at various wavelengths and / or in various operation modes in a monolithic microchip laser comprises schemes of generating two fundamental beams in separate cavities, precise intracavity beam combination based on the walk-off effect in birefringent crystal, and wavelength conversion in nonlinear optical crystals. The fundamental beams are produced from light sources selected upon the desired wavelengths, polarizations, and other features related to the laser output. Low-noise laser devices operated in SLM or with spectra of flat-top or desired bandwidths are constructed according to the method. High-volume fabrication is feasible. Apparatus of compact size and efficient frequency conversion is demonstrated with various configurations including those for generating low-noise 491 nm laser, as a replacement of Argon ion laser.
Owner:PAVILION INTEGRATION
Negative electrode material for non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery and non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery using same
ActiveCN102362380AFast charge and discharge characteristicsExcellent cycle characteristicsNegative electrodesSecondary cellsX-rayCharge discharge
Disclosed is a mixed carbon material for use in an electrode of a non-aqueous secondary battery showing excellent characteristics having rapid charge-discharge characteristics and high cycle characteristics. More particularly, disclosed is a negative electrode material for non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery comprising the following carbon material A and carbon material B: (carbon material A) a multilayer-structured carbon material which contains graphite particles and amorphous carbon covering the surfaces of the particles, and in which a 002 plane spacing (d002) measured by X-ray wide angle diffraction is 3.37Angstrom or less, Lc is 900Angstrom or more, a tap density is 0.8 g / cm<3> or more, and a Raman R value, which is the ratio of a peak intensity at around 1360 cm<-1> to a peak intensity at around 1580 cm<-1> in an argon ion laser Raman spectrum, is 0.25 to 0.6; and (carbon material B) a carbon material in which a 002 plane spacing (d002) measured by X-ray wide angle diffraction is 3.37Angstrom or less, Lc is 900Angstrom or more, a tap density is 0.8 g / cm<3> or more, and a Raman R value, which is the ratio of a peak intensity at around 1360 cm<-1> to a peak intensity at around 1580 cm<-1> in an argon ion laser Raman spectrum, is 0.11 to 0.2.
Owner:MITSUBISHI RAYON CO LTD
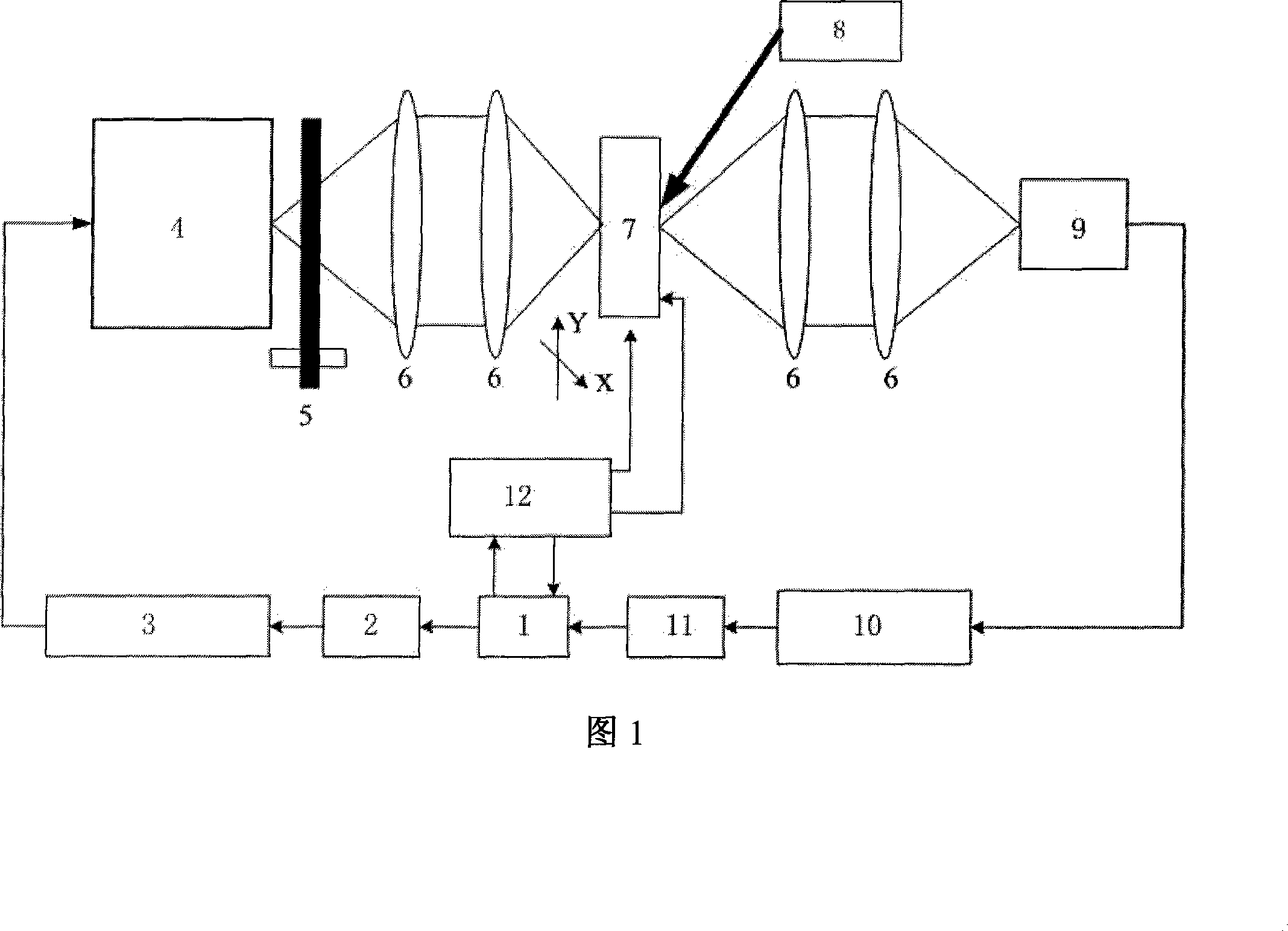
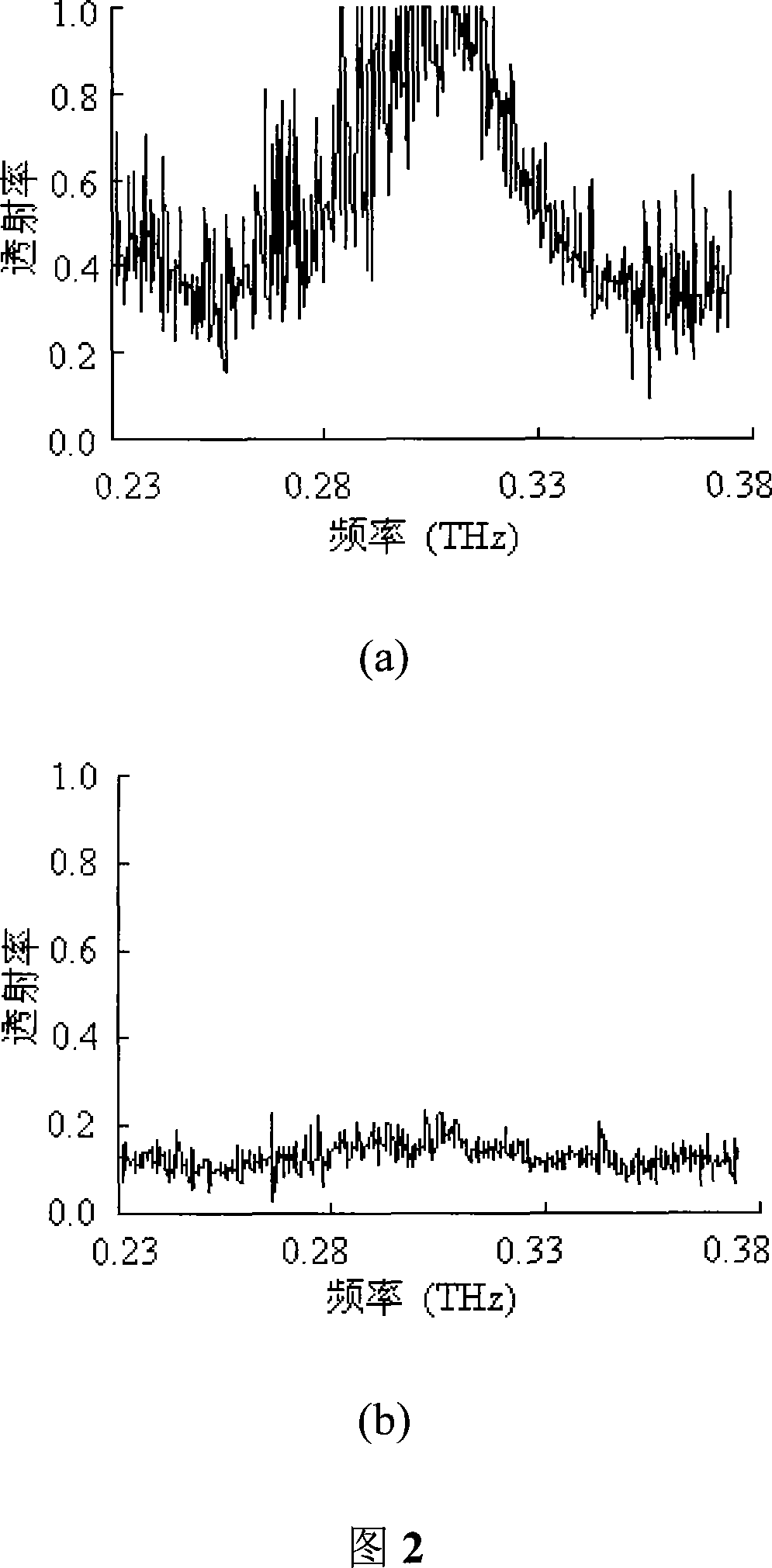
Controllable terahertz wave attenuator device and its method
InactiveCN101187733AImprove the attenuation effectAttenuation spectrum is flatLaser detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHigh resistanceCharge carrier
The invention discloses a controllable terahertz wave attenuator device and a method. The device is that a computer is connected respectively with a D / A converter and a two-dimensional moving platform, the D / A converter is connected with a direct current high voltage amplifier, a terahertz wave source device, a chopper, a piece of focusing lens, a high resistance silicon, a piece of focusing lens, a terahertz wave detector, a locking phase amplifier, an A / D converter, and the computer, the high-resistance silicon is connected respectively with an argon ion laser and the two-dimensional moving platform. The method is that lasers which are issued by the argon ion laser are used by the controllable terahertz wave attenuator device to excite photo-generated carriers; terahertz waves can be decreased through the absorbing effect of the photo-generated carriers to the terahertz waves. The controllable terahertz wave attenuator device of the invention has large decrement, smooth attenuating spectra ray, compact structure, convenient adjustment, low cost, and can satisfy the requirements of the terahertz waves for applying in the fields of imaging, medical diagnosis, safety check, information communication, space astronomy, and the like.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
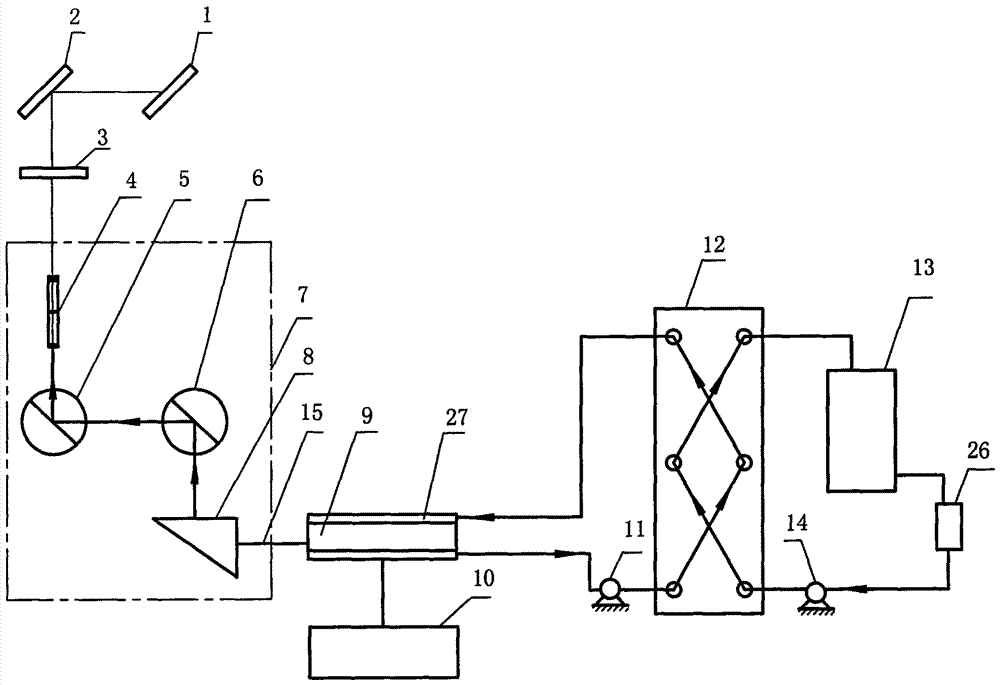
Sheet type light source system of laser beam
InactiveCN104950433AEnsure normal conductionGuaranteed low lossFluorescence/phosphorescenceOptical elementsResonant cavityHigh power lasers
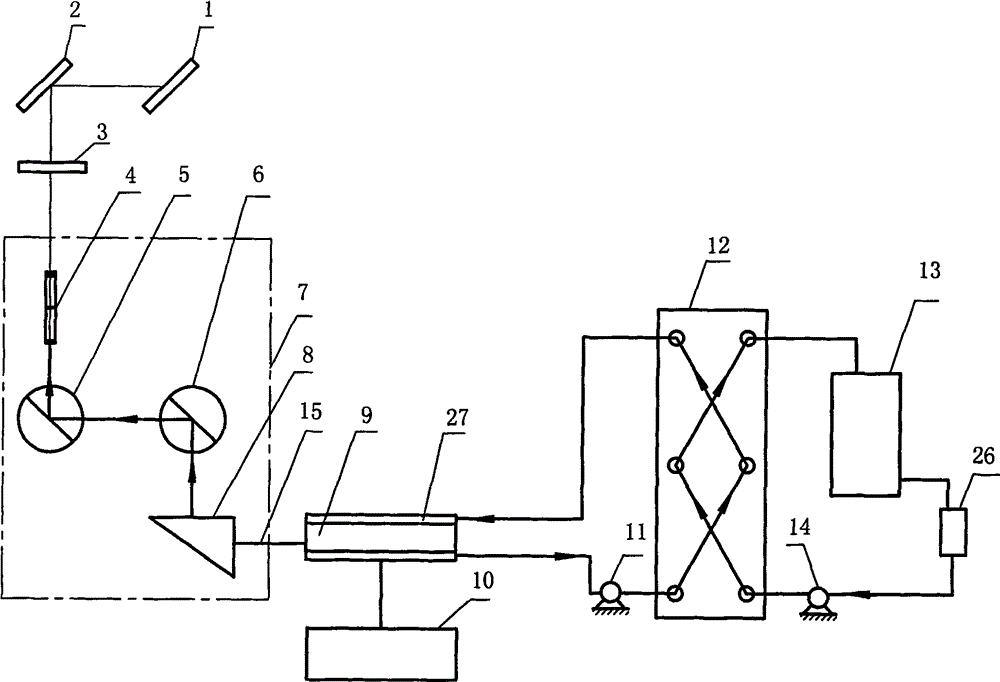
The invention relates to a sheet type light source system of a laser beam. The system is composed of a first reflection mirror, second reflection mirror, a Finel lens, a grid fine tuning device, an argon ion laser, a heat exchanger, and a cooling tower. One end of the heat exchanger and the cooling tower to form an external circulation loop; and the other end of the heat exchanger and a resonance cooling chamber of the argon ion laser form an internal circulation loop. Cooling water circulates in the external circulation loop and the internal circulation loop. A laser beam transmitted by the argon ion laser passes through the grid fine tuning device, the Finel lens, the second reflection mirror, and the first reflection mirror successively. The grid fine tuning device, the argon ion laser, the Finel lens, the second reflection mirror, and the first reflection mirror are respectively installed on a sheet light steering device. According to the invention, with the heat exchange system, security operation of the laser can be guaranteed; the transmission orientation of the high-power laser beam can be adjusted flexibly by using the grid fine tuning device and the transmission height and orientation of the sheet light can be adjusted flexibly by using the sheet light steering device, so that the user can change the measurement section conveniently.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES +1
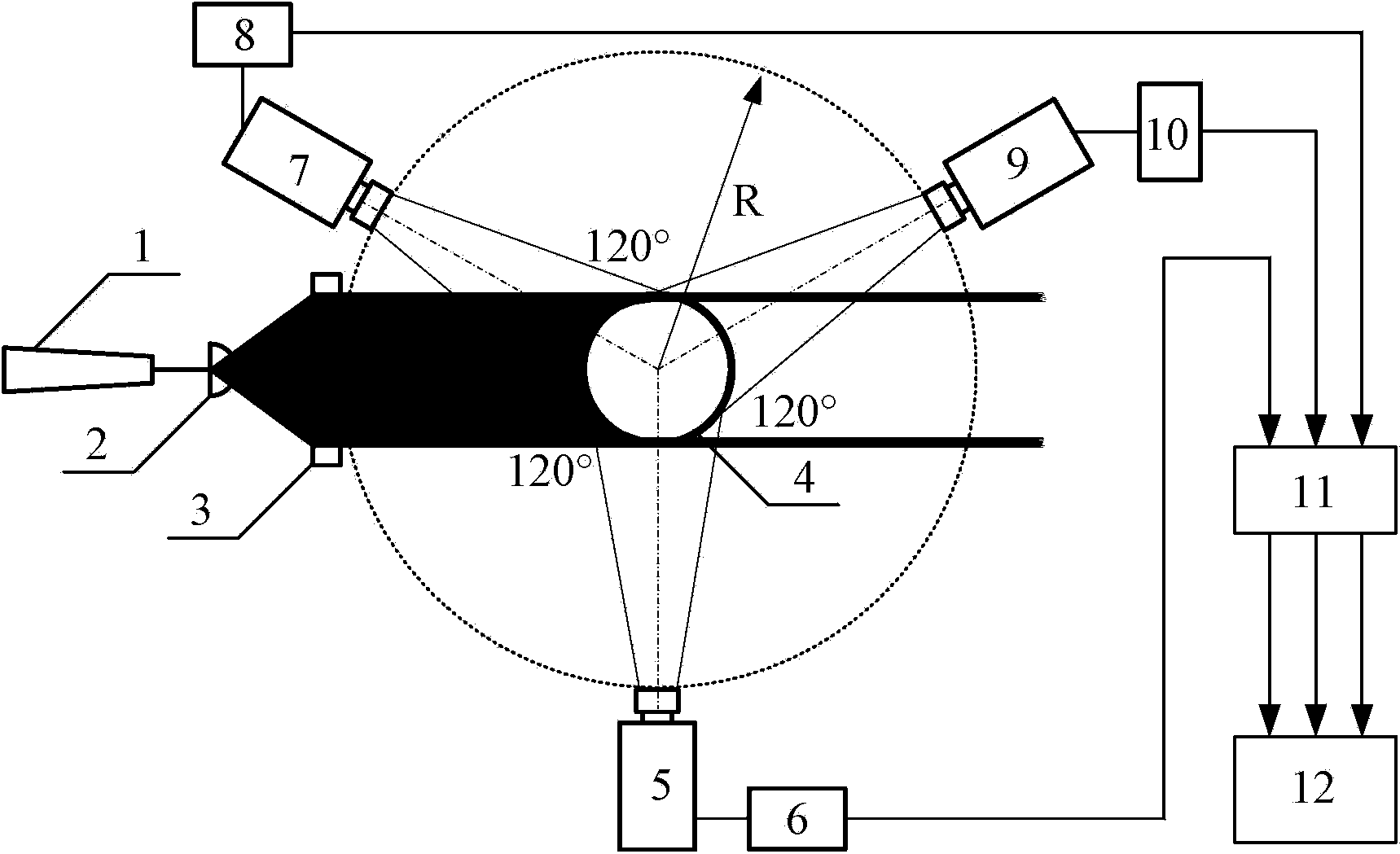
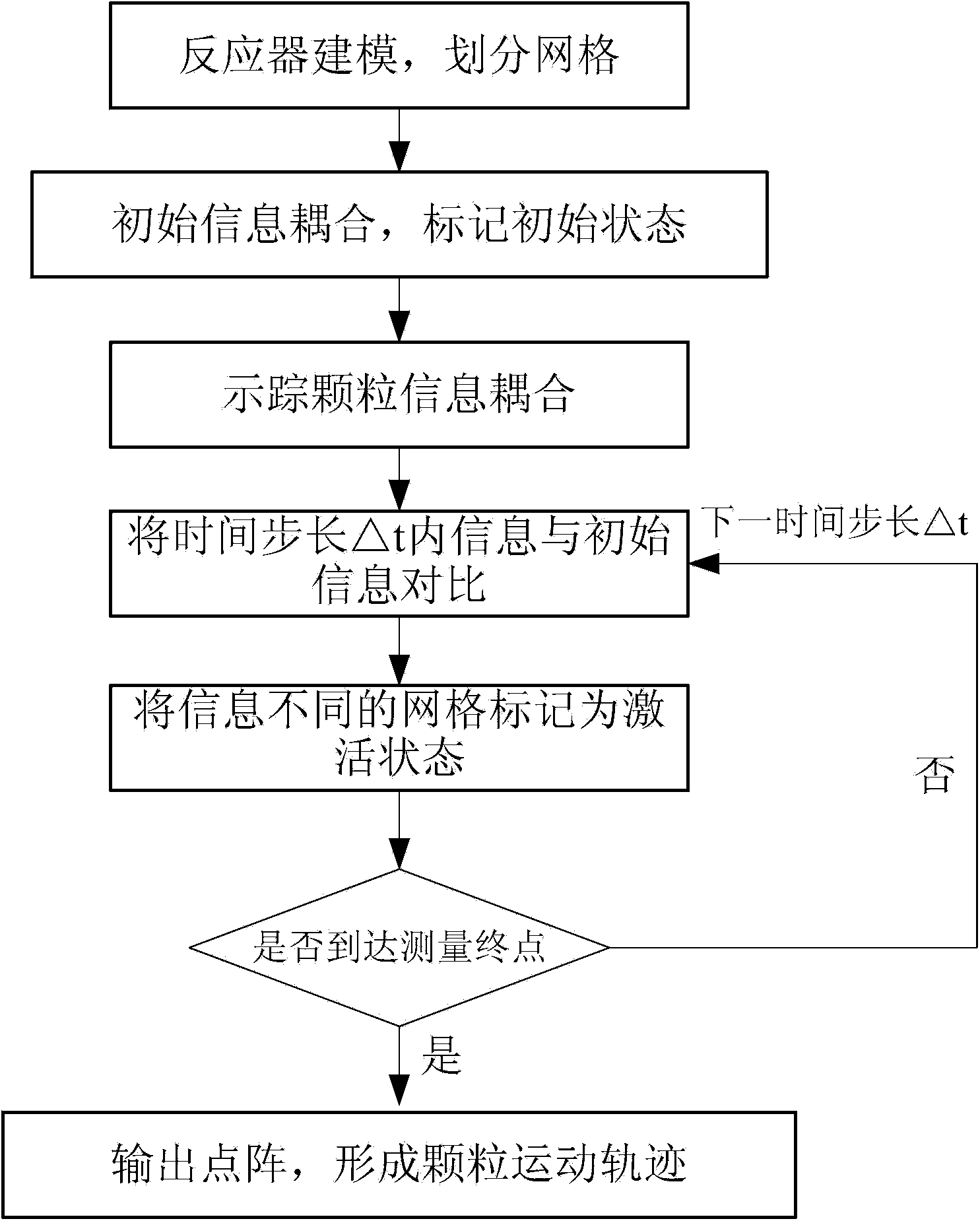
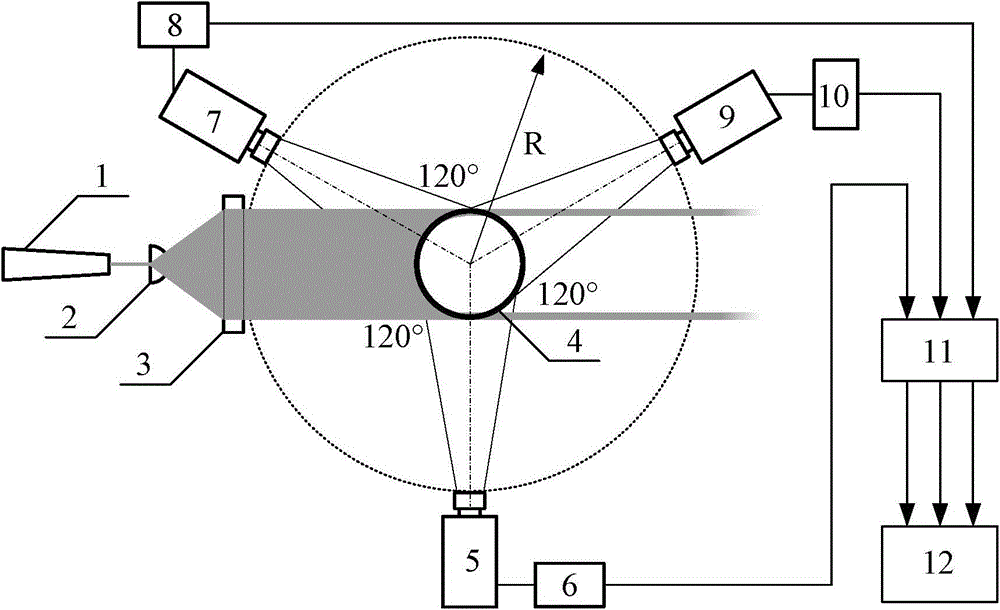
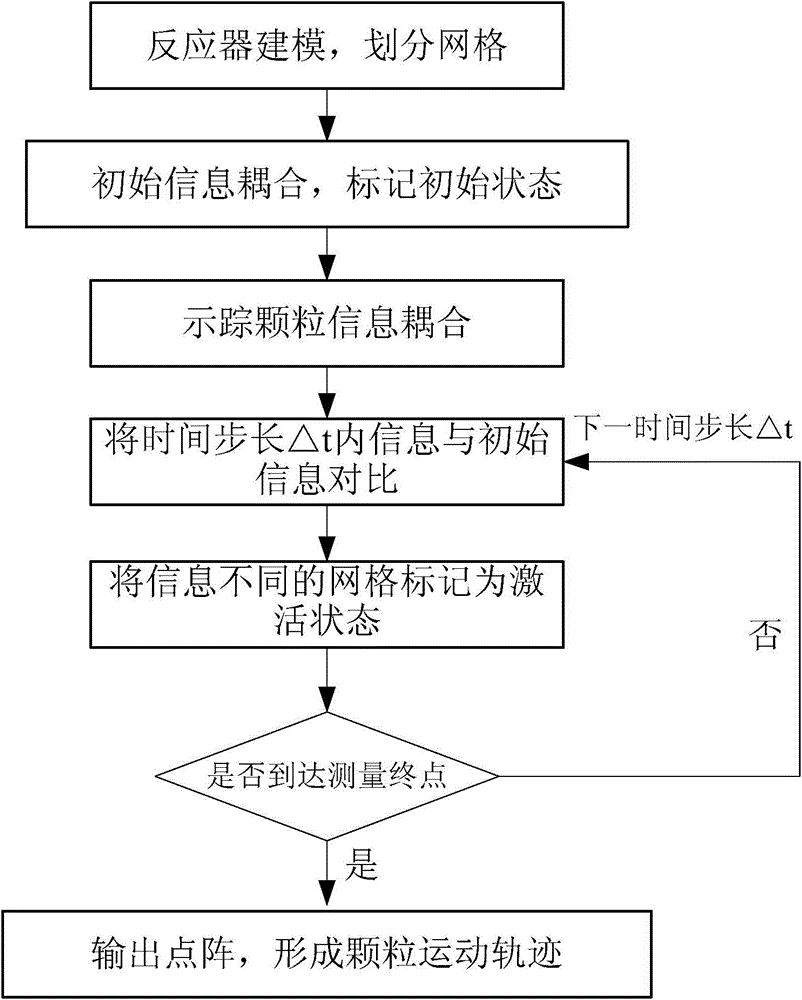
Measuring device and method for two-phase flow system internal particle motion trajectory
The invention discloses a measuring device and method for a two-phase flow system internal particle motion trajectory. The measuring device comprises a laser emission system and a photovoltaic conversion detection system, wherein the laser emission system is composed of an argon ion laser, a first cylindrical lens, a second cylindrical lens and a reactor, and the photovoltaic conversion detection system is composed of three optical receivers, three photomultiplier tubes, a filter and a computer. The three optical receivers are evenly arranged around the peripheral side of the reactor by using the reactor as a circle center. According to the measuring method, non-immersive measurement is included, the measuring device does not need to be placed into the reactor, the influence of the measuring device on two-phase flow inside the reactor is avoided, measuring accuracy is improved, and the measuring result is precise and reliable; the argon ion laser is used as a light source and replaces an X-ray source, the cost of an X-ray detector is omitted, and the measuring device is economical, practical, safe and reliable.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Photosensitive planography printing plate
ActiveCN1519649AHigh sensitivityExcellent developabilityElectrolysis componentsPhotomechanical coating apparatusExposure latitudeImage formation
The object of the invention is to solve the problems in the related art, and to provide a photosensitive lithographic printing plate which is processable for image formation thereon with argon ion laser, FD-YAG laser, violet laser or the like, which has high sensitivity, which satisfies both the requirement of staining resistance in printing and the requirement of printing durability, and which has good developability, good ink acceptability, good image formability and broad exposure latitude.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Thin disk 515nm all-solid-state green laser
InactiveCN102437502ASimple structureReduce volumeOptical resonator shape and constructionAll solid stateResonant cavity
The invention provides a thin disk 515nm all-solid-state green laser. The laser comprises a pumping source, a first spherical coupling mirror, an output coupling mirror, a second spherical coupling mirror, a gain medium and a heat sink, wherein the gain medium is welded on the heat sink via a welding layer; the rear surface of the gain medium and the concave surface of the output coupling mirror form a plano-concave resonant cavity; the output coupling mirror is arranged on the emergent light path of the gain medium; the pumping source, the first spherical coupling mirror and the second spherical coupling mirror form a four-pass pumped optical coupling system; the first spherical coupling mirror and the pumping source are arranged at the same side of the plano-concave resonant cavity; the first spherical coupling mirror is arranged on the path of the pumping light transmitted by the pumping source; and the second spherical coupling mirror is arranged on the path of the pumping light reflected by the gain medium. The miniaturized thin disk all-solid-state green laser can realize 515nm of wavelength and can replace the dye laser and argon ion laser.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH
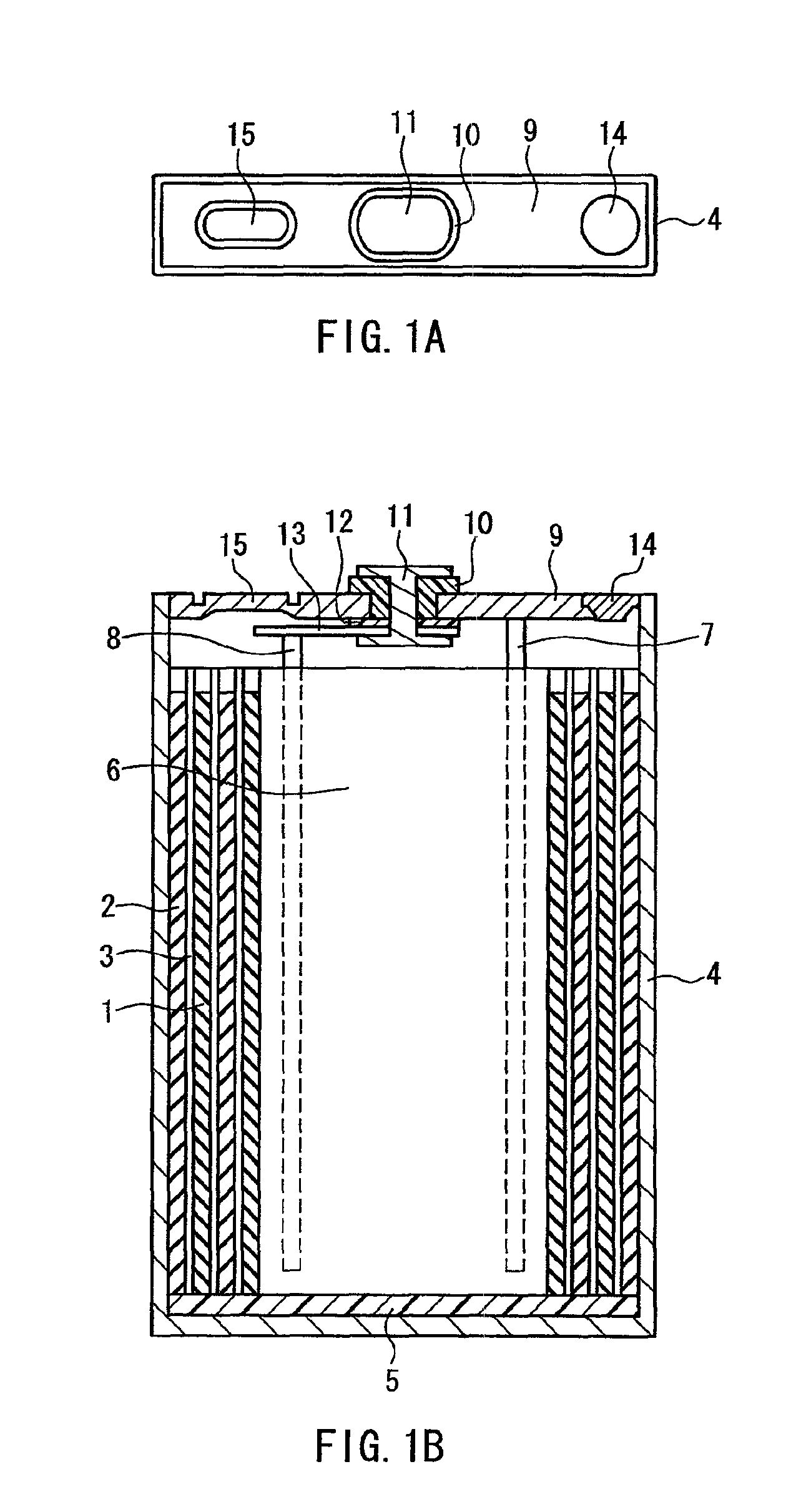
Electrochemical device
ActiveUS8637177B2Improve the level ofImprove storabilityHybrid capacitor separatorsHybrid capacitor electrolytesPorous layerGraphite
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
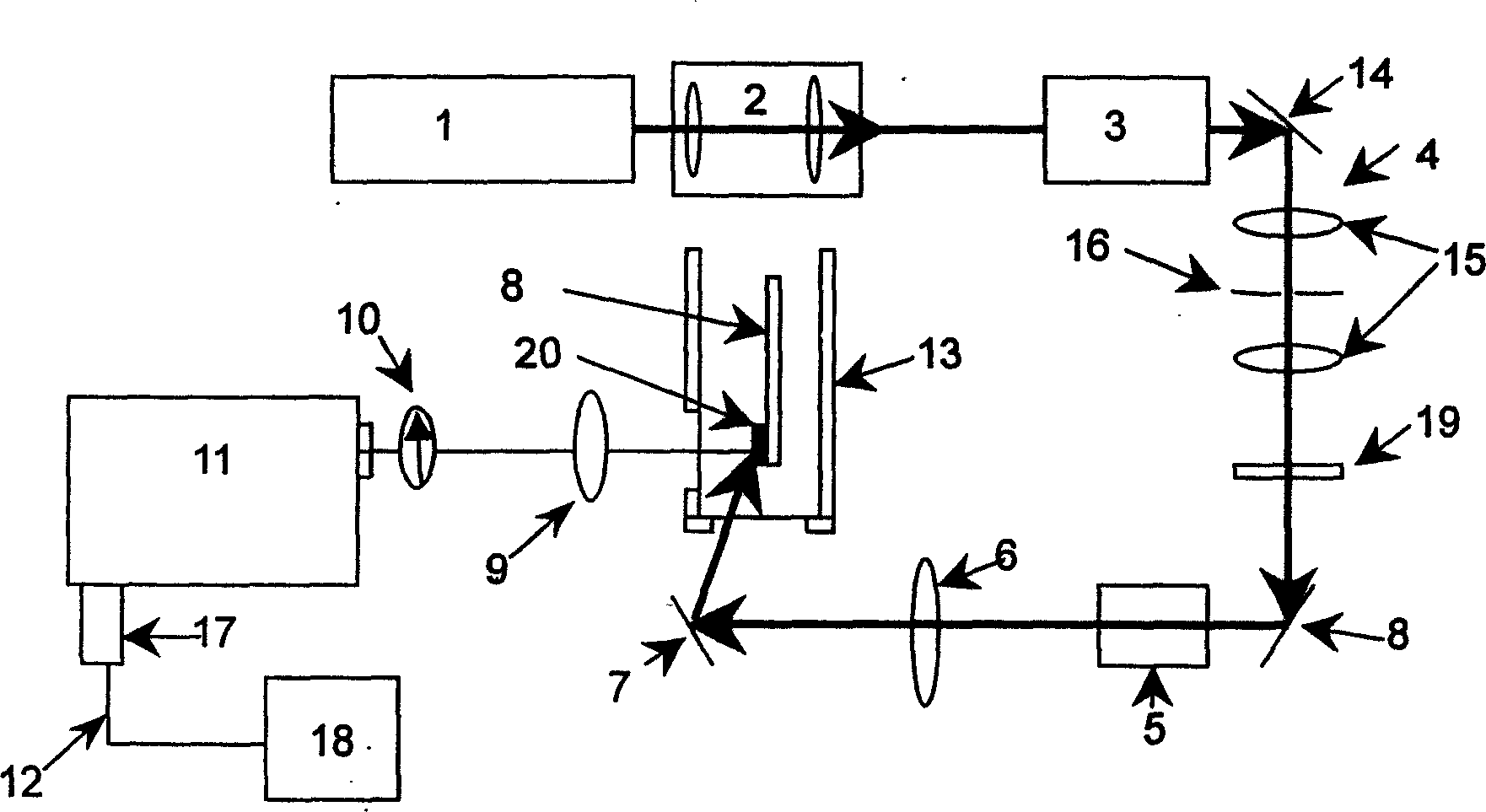
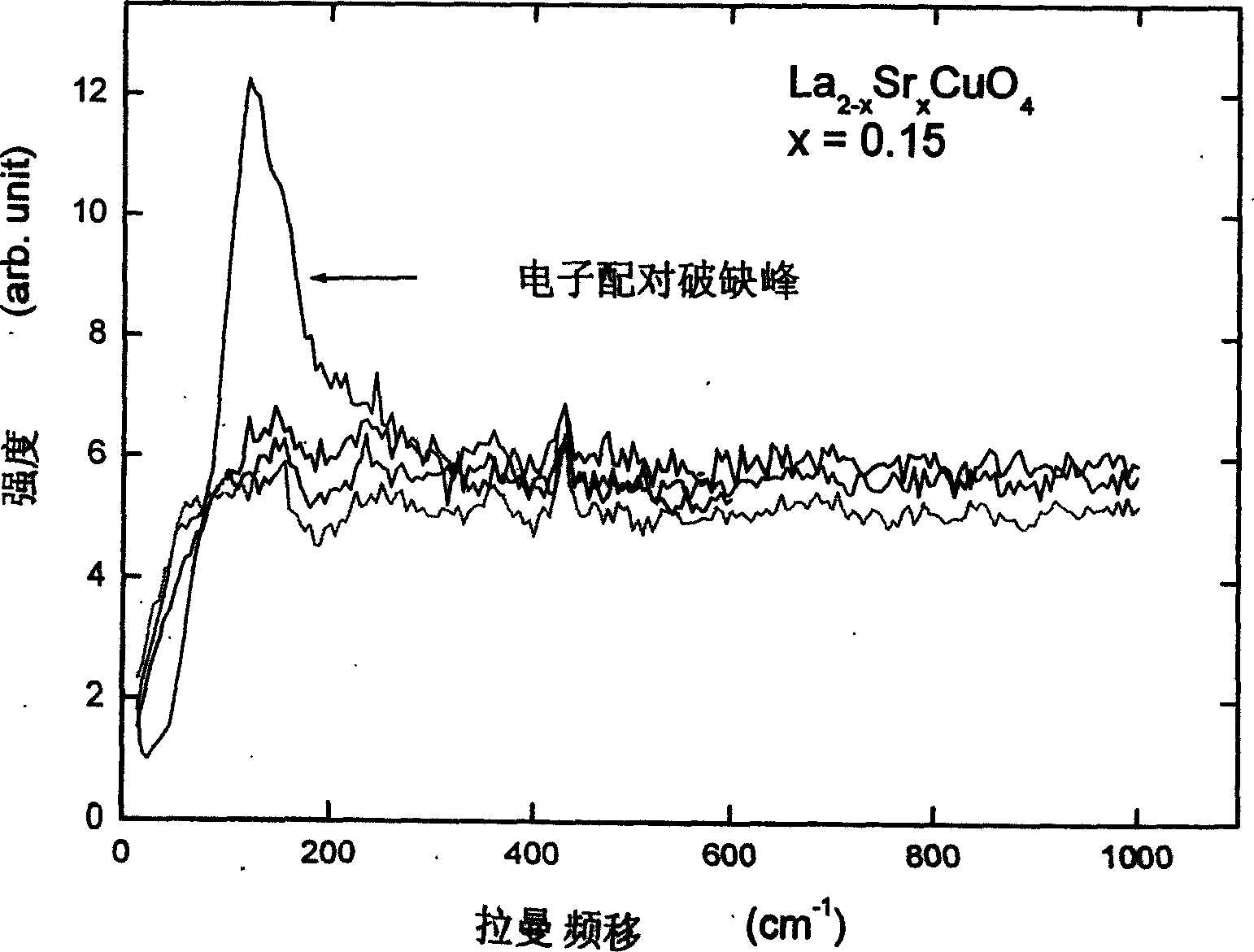
Low-temperature polarizing electronic Raman scattering apparatus
A Raman scattering device of low temperature polarization electron is featured as setting collimation lens set, plasma filter, space filter, polarization rotator and focal lens in sequence along operation path of argon ion laser; setting reflector behind focal lens to reflect laser beam on sample seat; having objective lens for collecting sample scattering light and polarization plate for selecting direction, setting spectrograph behind the polarization plate and connecting the spectrograph to monitor.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Detecting device and method for continuous wave terahertz real-time watermark imaging
InactiveCN105181697AControl the number of displayed image framesHigh detection sensitivityPaper-money testing devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansHigh resistanceNon destructive
The invention discloses a detecting device and method for continuous wave terahertz real-time watermark imaging. The detecting device comprises a continuous wave terahertz radiation source, a collimating beam-expanding system, a high-resistance silicon wafer, an argon ion laser, an off-axis parabolic lens, a sample platform, a terahertz wave detector and a computer. According to the detecting device provided by the invention, the collimating beam-expanding system is utilized to collimate the terahertz wave into parallel beams; the off-axis parabolic lens is used for expanding the beams for the second time; after the beams penetrate through a sample, the beams are focused on the terahertz wave detector; the computer is used for performing real-time imaging display on the image; the turning-on / off control on the detecting device is realized by utilizing a fact that whether the argon ion laser beam illuminates on the high-resistance silicon wafer or not. The detecting device for continuous wave terahertz real-time watermark imaging provided by the invention has the advantages of compact structure, high response speed, convenient switching, real-time watermark imaging and significant practical application value, and is also capable of performing non-destructive detection on the hazardous metal hidden in the packaging articles such as newspaper, fabrics and plastics.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Active material for nonaqueous electrolyte battery, electrode for nonaqueous electrolyte battery, nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery and battery pack
An active material for a non-aqueous electrolyte battery according to the embodiment is a composite including at least: a carbonaceous substance; and silicon-containing particles dispersed in the carbonaceous substance, the silicon-containing particles including at least one of silicon, a silicon alloy and a silicon oxide, wherein in an argon ion laser Raman spectrum, the half-width ([Delta]G) of a peak having a maximum intensity I1 in the range of 1575 cm-1 or more and 1625 cm-1 or less is 100 cm-1 or more and 150 cm-1 or less, and the intensity ratio of a peak having a maximum intensity I2 in the range of 500 cm-1 or more and 550 cm-1 or less to the peak having the maximum intensity I1 in the range of 1575 cm-1 or more and 1625 cm-1 or less (I2 / I1) is 0.25 or more and 0.50 or less.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Preparation of distributed optical fiber sensor reflector
InactiveCN1908707ASimple organizationEasy to operateDiffraction gratingsOptical light guidesUv laserGrating
The disclosed manufacture method for new distributed optical fiber sensor reflector comprises: a 139nm argon-ion UV laser or 248nm quasi-molecular laser, two column lenses vertical with each other and parallel with a phase template, and a slit made of well-conductive metal to be regulated as requirement on width. This invention can reduce cost without chirp template for industrial production.
Owner:天津爱天光电子科技有限公司
Negative electrode material for non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery and non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery using same
ActiveCN102362381BFast charge and discharge characteristicsExcellent cycle characteristicsGraphiteNegative electrodesX-rayCharge discharge
To provide a mixed carbon material used for an electrode of a nonaqueous secondary battery with excellent characteristics satisfying both rapid charge-discharge characteristics and high cycle characteristics. A negative electrode material for nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery, comprising the following carbon material A and carbon material B: (Carbon material A) a multilayer-structure carbon material containing a graphitic particle and an amorphous carbon covering the surface of the graphitic particle, which is a carbon material where the interplanar spacing (d002) of 002 planes by the wide-angle X-ray diffraction method is 3.37 Å or less, Lc is 900 Å or more, the tap density is 0.8 g / cm 3 or more, and the Raman R value that is a ratio of the peak intensity near 1,360 cm -1 to the peak intensity near 1,580 cm -1 in the argon ion laser Raman spectrum, is from 0.25 to 0.6, (Carbon material B) a graphitic particle where the interplanar spacing (d002) of 002 planes by the wide-angle X-ray diffraction method is 3.37 Å or less, Lc is 900 Å or more, the tap density is 0.8 g / cm 3 or more, the Raman R value that is a ratio of the peak intensity near 1,360 cm -1 to the peak intensity near 1,580 cm -1 in the argon ion laser Raman spectrum, is from 0.2 to 0.5, and the average degree of circularity as determined by a flaw-type particle analyzer is 0.9 or more.
Owner:MITSUBISHI RAYON CO LTD
Laser dynamic analysing method for making accurate measurement to construction and city space
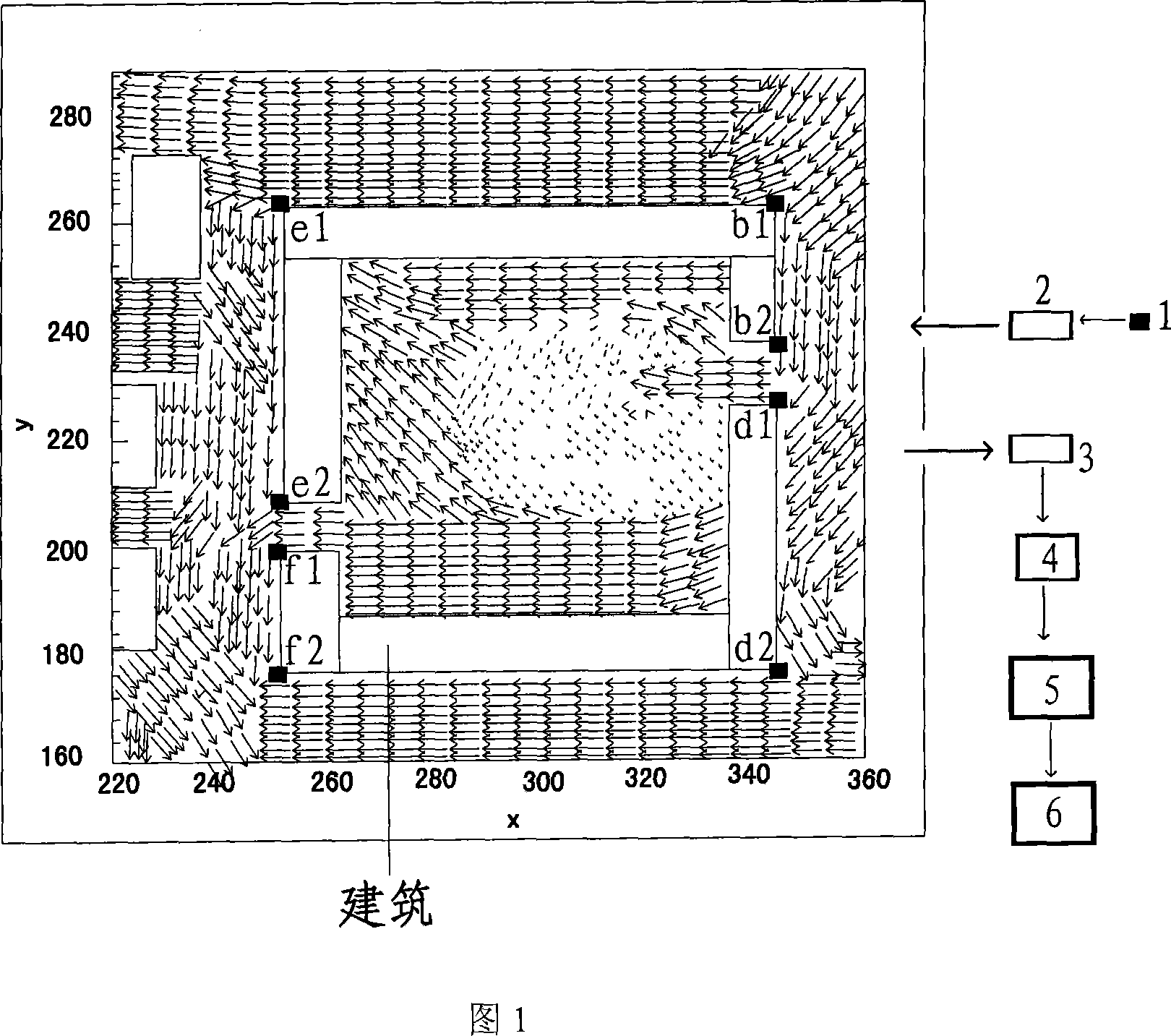
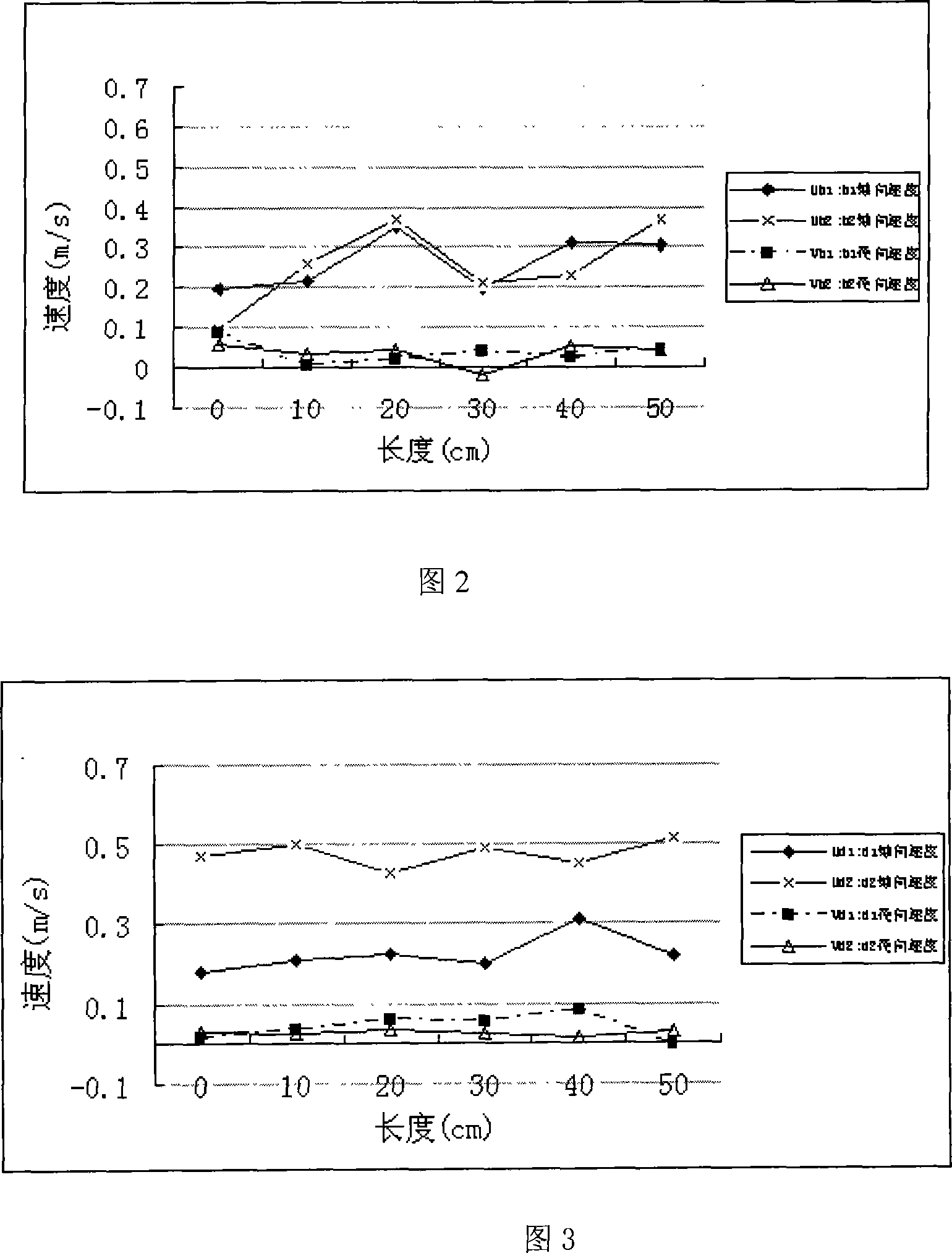
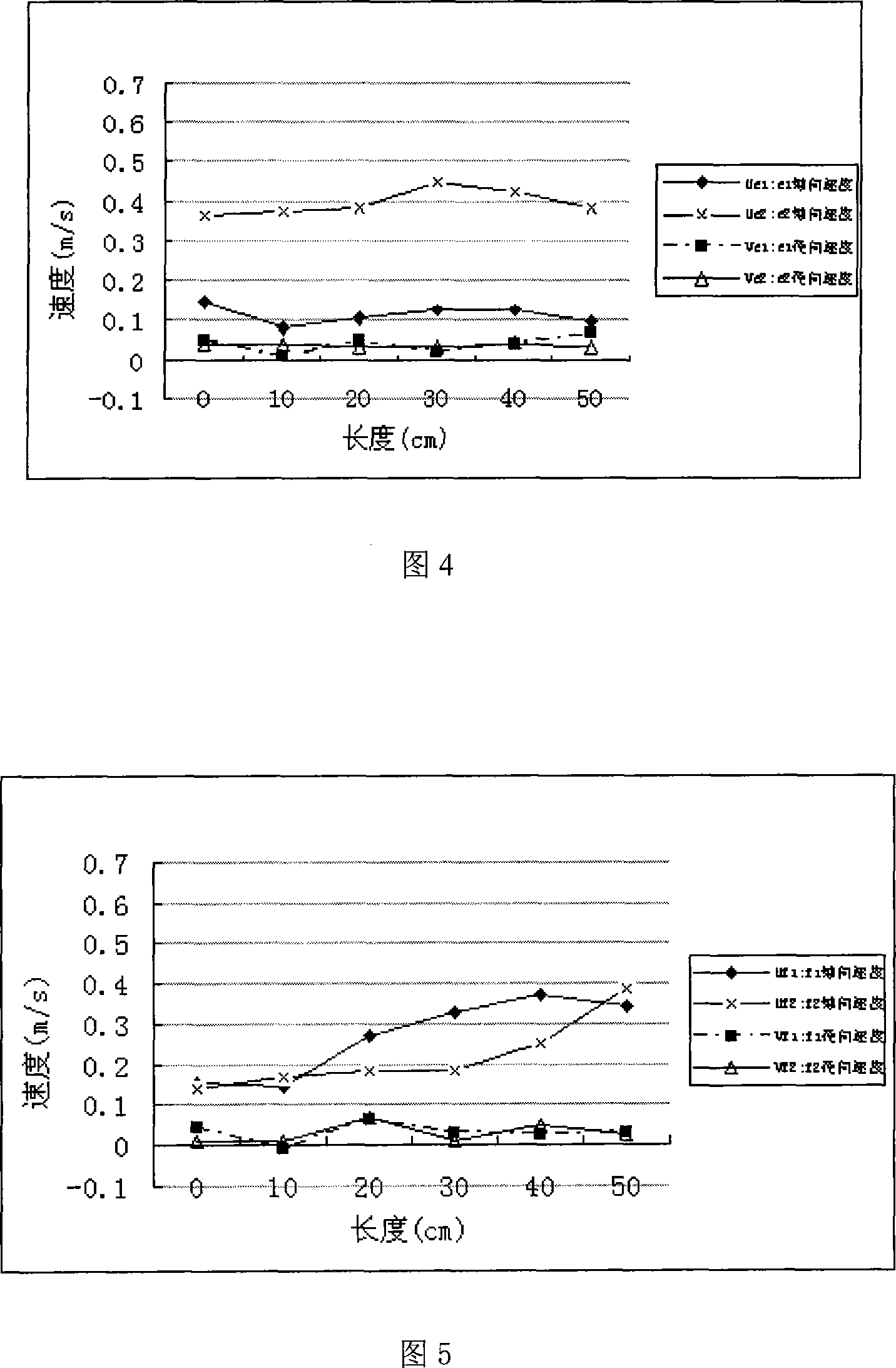
InactiveCN101021430AEfficient designEfficient analysisStructural/machines measurementFluid speed measurementFiberLaser beams
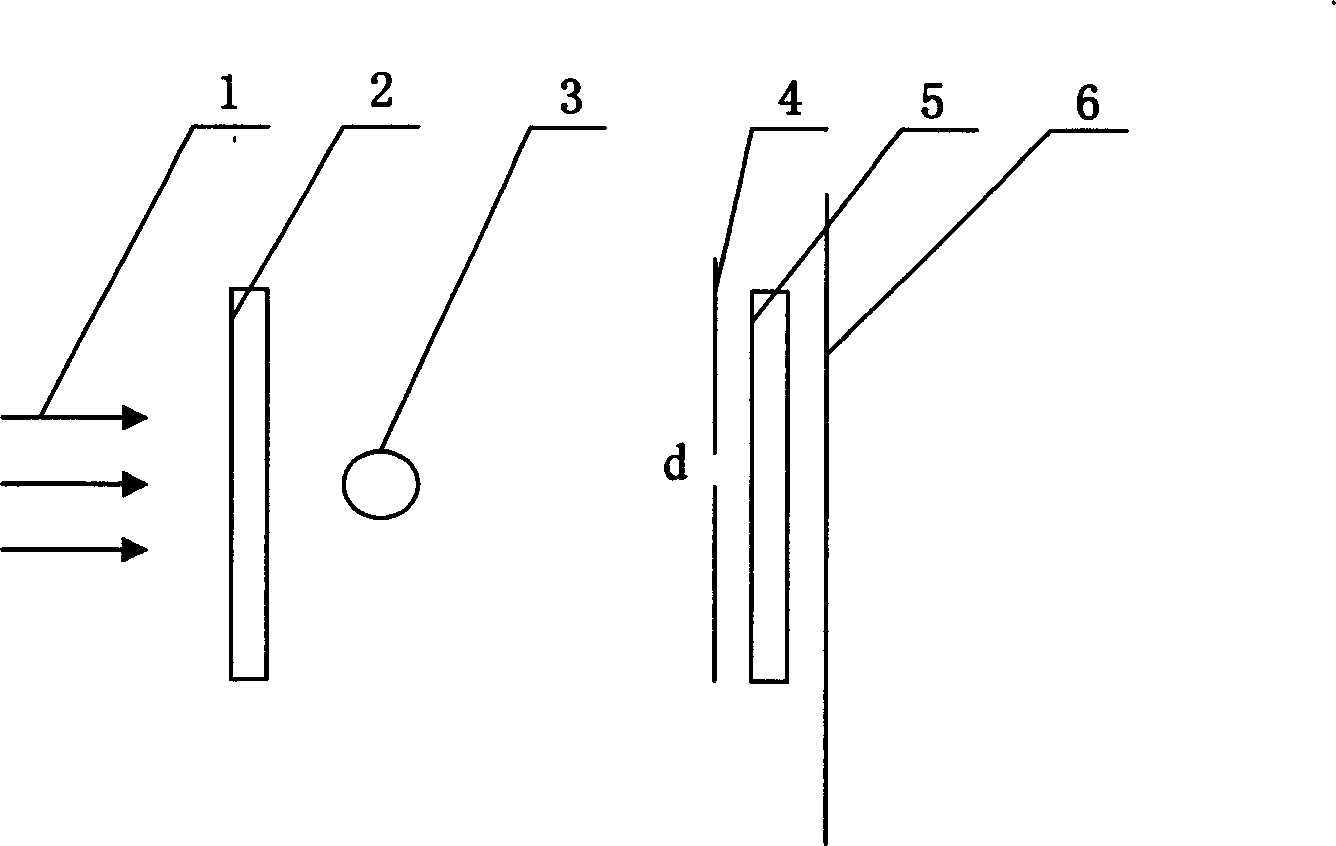
The invention discloses a laser dynamic analysis method (PDA) which can measure architecture and city space accurately. Its steps are: Build a model configuration of architecture and city space and minimize then into a fixed flow field in proportion. Insufflate natural air (tracer particle) into flow field. Blend laser beam radiated by argon ion laser is divided to two or more beam by incidence optical system, which is induced into flow field by focusing lens to form multi-beam converged measuring control system. Utilize receiving optical system to collect scattered beam radiated by tracer particles and transfer optical signal to electric signal which is transformed to readable digital signal by signal processor. Velocity of particles is achieved by autocorrelation technique. Realization device of the method is composed of an argon ion laser, an incidence optical system, a receiving optical system, a multimode fiber, an optic probe, a signal processor and an auxiliary device.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium and method of manufacturing the same
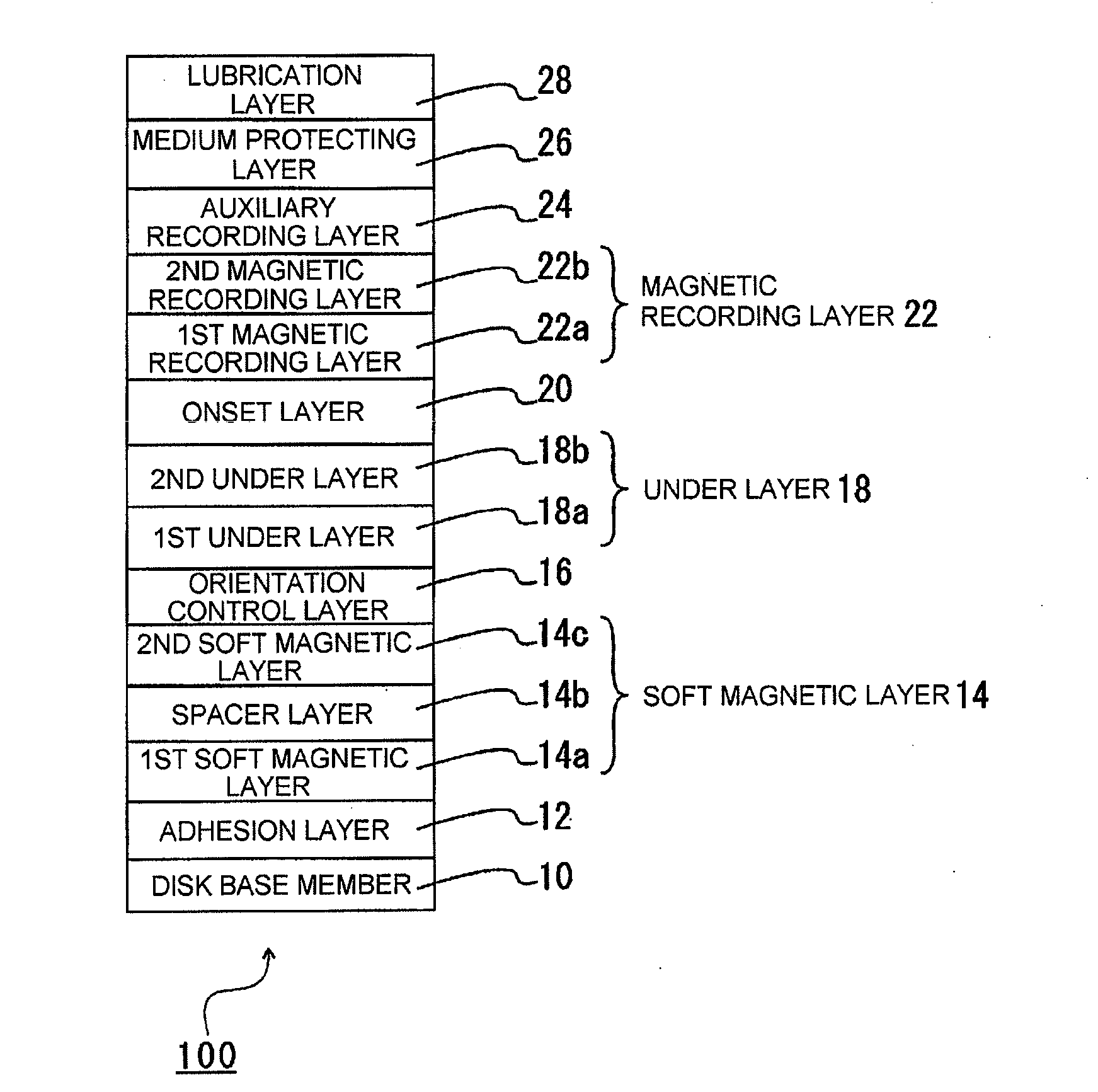
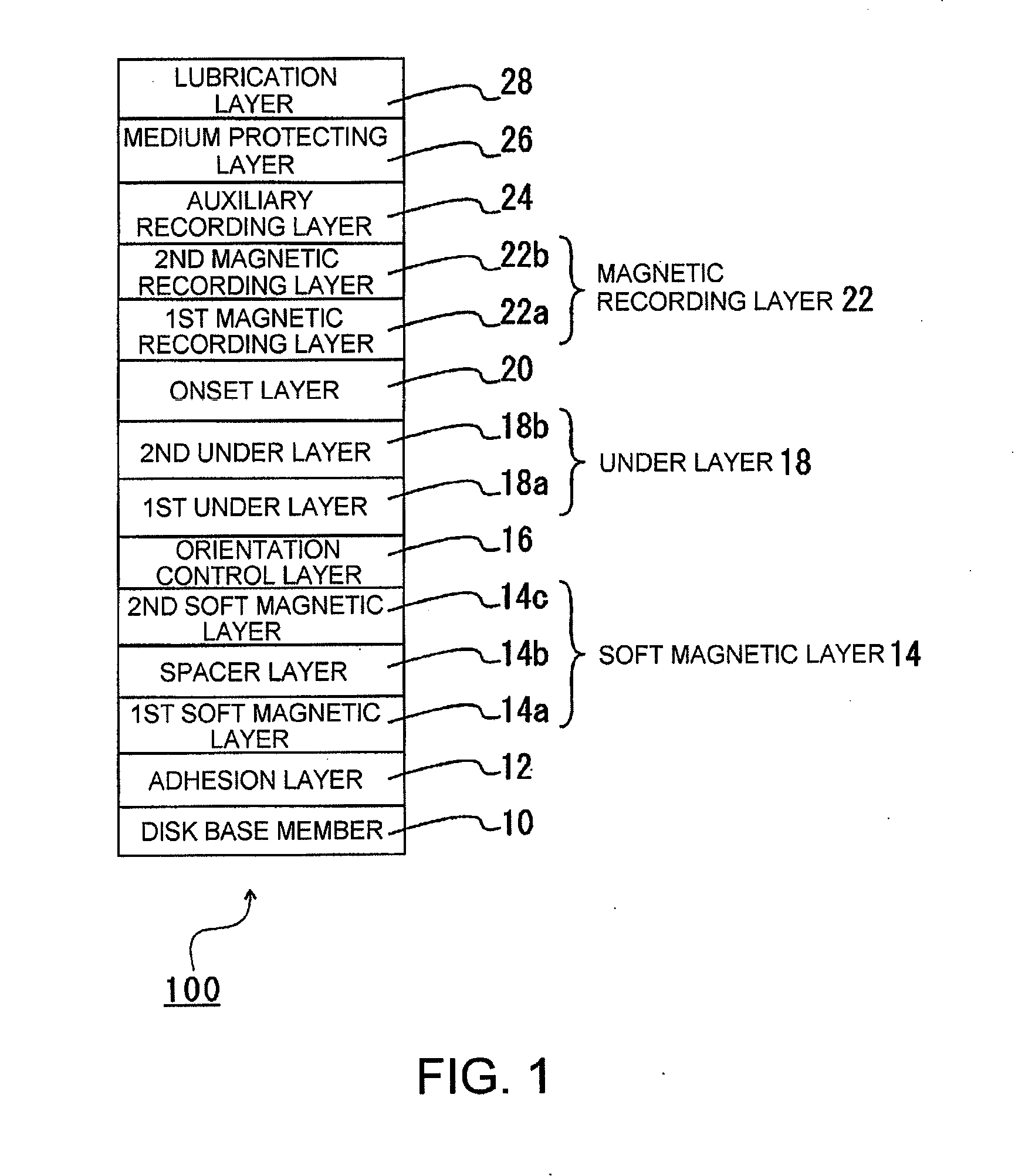
ActiveUS20100112379A1Protective coatings for layersMagnetic materials for record carriersFluorescenceRecording layer
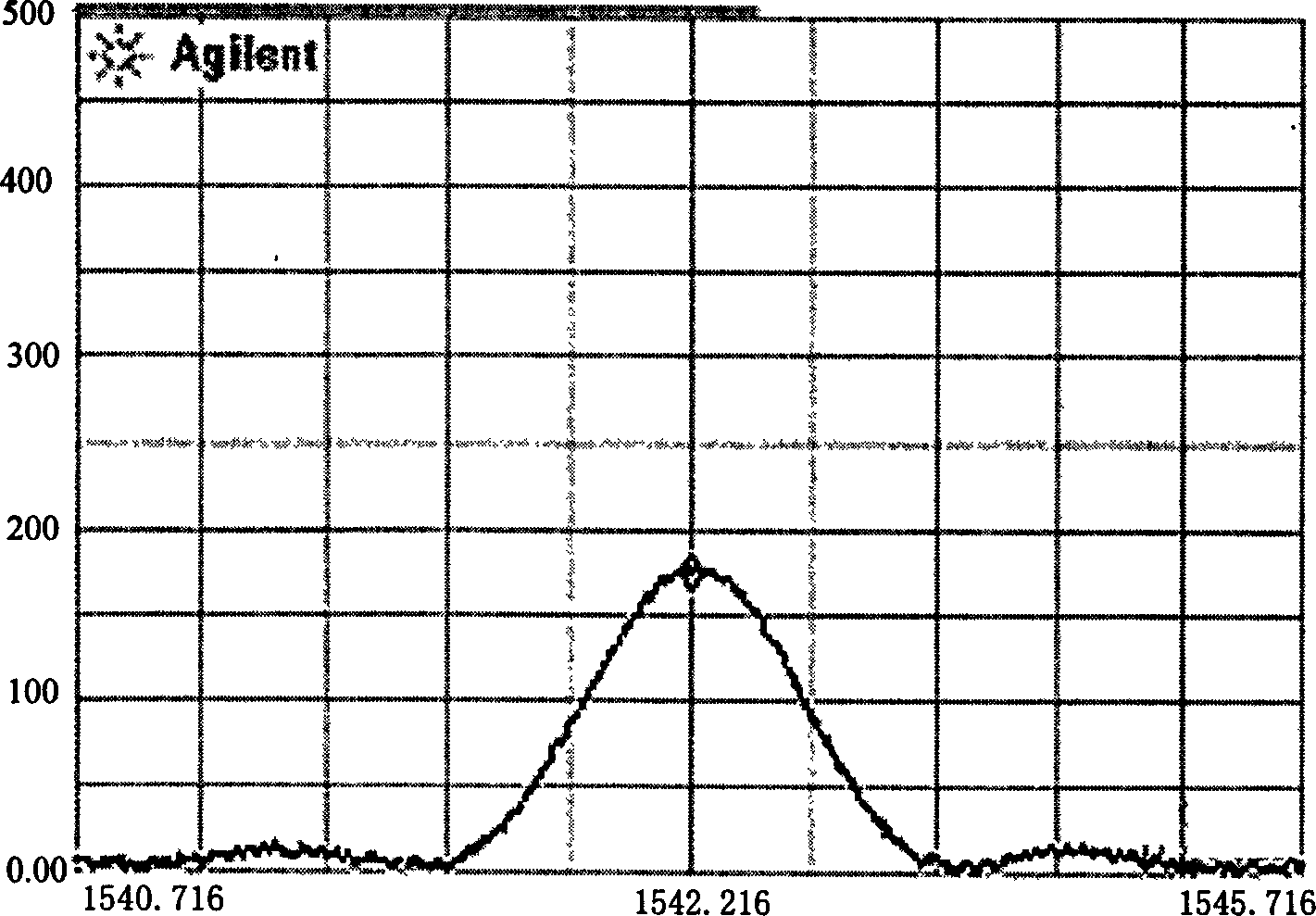
A vertical magnetic recording disc (100) includes a base (10), a magnetic recording layer (22), and a medium protection layer (26). The magnetic recording layer (22) is a ferromagnetic layer having a granular structure where a granular portion is formed. The medium protection layer (26) contains nitrogen (N) atoms and carbon (C) atoms with a number ratio (N / C) in a range from 0.050 to 0.150. In a Raman spectrum obtained by exciting the medium protection layer (26) by argon ion laser light of wavelength 514.5 nm, from which a fluorescence is removed, the peak ratio Dh / Gh is in a range from 0.70 to 0.95, when a D peak Dh appearing in the vicinity of 1350 cm−1 is separated from G peak Gh appearing in the vicinity of 1520 cm−1 by the Gauss function.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Carbon material for negative electrode of lithium secondary battery and method for producing the same
To provide a negative electrode carbon material capable of suppressing capacity degradation which will occur due to repetition of a charge / discharge cycle, storage under a charged state, float charging, or the like. An artificial graphite for a negative electrode of a lithium secondary battery having a c-axis crystallite size L (112) of from 2.0 to 4.2 nm as calculated from a (112) diffraction line obtained by X-ray wide-angle diffractometry and having a half-value width ΔνG of from 15 to 19 cm−1 for a peak appearing in a wavelength region of from 1580 cm−1±100 cm−1 in the Raman spectroscopy using an argon ion laser light having a wavelength of 5145 angstrom.
Owner:JX NIPPON OIL & ENERGY CORP
Lithium battery
InactiveCN1531124AImprove permeabilityAvoid decompositionNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsOrganic electrolyte cellsFull width at half maximumLength wave
A lithium cell includes a positive electrode, a negative electrode employing a carbon material as an active material, and a non-aqueous electrolyte including a solute dissolved in a non-aqueous solvent, and is characterized in that the carbon material in the negative electrode has an RA value (IA / IG) of 0.05 or more, the RA value calculated from a peak intensity (IA) of a broad peak PA having a full width at half maximum of 100 cm<-1 >or more and a peak intensity (IG) in the vicinity of 1580 cm<-1 >as determined by laser Raman spectroscopy using an argon ion laser having a wavelength of 514.5 nm, the peak intensity (IA) determined from a peak PD in the vicinity of 1360 cm<-1>, as determined by the aforesaid laser Raman spectroscopy, which is separated into the broad peak PA having the full width at half maximum of 100 cm<-1 >or more and a peak PB having a full width at half maximum of less than 100 cm<-1>.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Laser beam sheet light source system
InactiveCN104950433BEnsure normal conductionGuaranteed low lossFluorescence/phosphorescenceOptical elementsCooling towerCooling chamber
The laser sheet light source system of the present invention comprises: a first reflector, a second reflector, a Fresnel lens, a grid fine-tuning device, an argon ion laser, a heat exchanger and a cooling tower. One end of the heat exchanger forms an outer circulation loop with the cooling tower, and the other end of the heat exchanger forms an inner circulation loop with the resonant cavity cooling chamber of the argon ion laser, and the cooling water circulates in the outer circulation loop and the inner circulation loop respectively. The laser beam emitted by the argon ion laser passes through the grid fine-tuning device, the Fresnel lens, the second reflector and the first reflector in sequence. The grid fine-tuning device, the argon ion laser, the Fresnel lens, the second reflector and the first reflector are respectively installed on the sheet light turning device. The heat exchange system of the present invention ensures the safe operation of the laser; the grid fine-tuning device can flexibly adjust the transmission orientation of the high-power laser beam, and at the same time, the sheet light steering device can flexibly adjust the transmission height and orientation of the sheet light, which greatly facilitates users Change the measurement section.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES +1
Preparation method of nano inorganic-organic nano-filtration membrane
InactiveCN104511245AEmbody stabilityReduce frictionSemi-permeable membranesCellulose acetatePhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a preparation method of a nano inorganic-organic nano-filtration membrane, and belongs to the technical field of nano-filtration membrane preparation. The preparation method comprises the following steps: putting cellulose acetate into dichloromethane, stirring to obtain a casting solution; painting the casting solution on a glass plate to form a wet membrane with a thickness of 280 [mu]m, allowing the wet membrane to stand still for 20-23 minutes, then soaking the glass plate in deionized water with a temperature of 20-23 DEG C for 10 to 15 minutes so as to obtain an asymmetric membrane; subjecting the asymmetric membrane to exchange treatments in a methanol solution and cyclohexane in sequence so as to obtain a cellulose acetate nano-filtration flat wet membrane; soaking the obtained wet membrane in a silver nitrate solution for 20 to 30 minutes, washing so as to obtain a composite wet membrane; paving the composite wet membrane on an insulation surface, radiating the upper surface of the composite wet membrane by argon ion laser beams for 15 to 25 minutes so as to obtain the target product. The permeation flux of the membrane prepared by the provided preparation method will increase when the temperature is rising.
Owner:曹福宝
Laser scanning confocal microscope-based hair imaging method
InactiveCN102095705ASimple and fast operationLow costAnalysis by material excitationIon laserLaser scanning
The invention provides a laser scanning confocal microscope-based hair imaging method, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: marking hairs by using 0.5 percent acridine orange, and washing the hairs by using deionized water for 1 minute; and scanning a hair sample by using 488nm-wavelength laser of an argon ion laser of a laser scanning confocal microscope, and acquiring an image by using an XYZ scanning program. The method is easy to operate and the flaky structure of the hairs can be observed.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
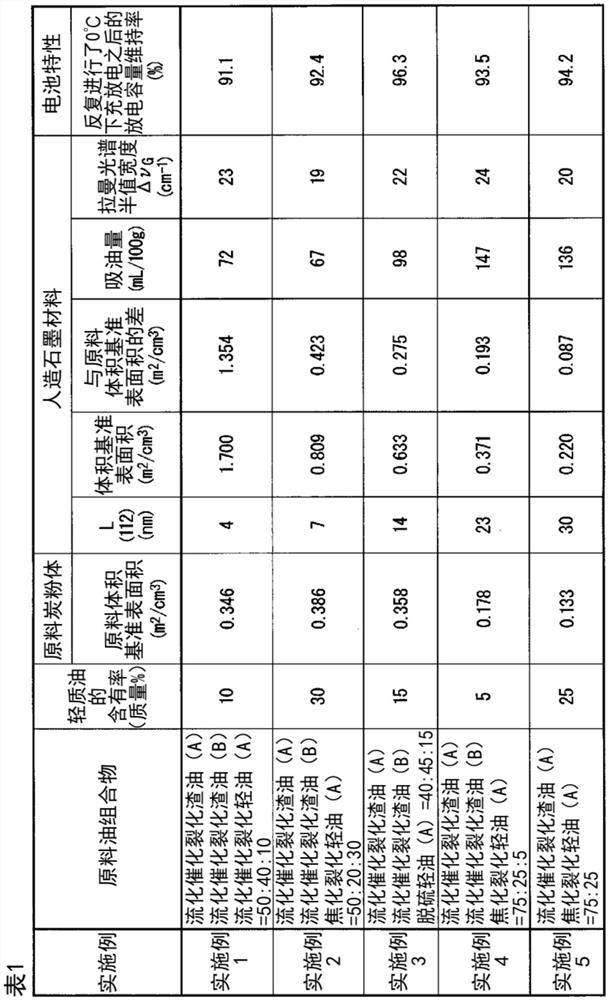
Synthetic graphite material, synthetic graphite material production method, negative electrode for lithium ion secondary battery, and lithium ion secondary battery
Provided is a synthetic graphite material, in which a size L (112) of a crystallite in a c-axis direction as calculated from a (112) diffraction line obtained by an X-ray wide angle diffraction method is in a range of 4 to 30 nm, a surface area based on a volume as calculated by a laser diffraction type particle size distribution measuring device is in a range of 0.22 to 1.70 m2 / cm3, an oil absorption is in a range of 67 to 147 mL / 100 g, and a half width ΔvG of a peak present in a wavelength range of 1580 cm−1±100 cm−1 is in a range of 19 to 24 cm−1 in Raman spectrum analysis using argon ion laser light having a wavelength of 514.5 nm.
Owner:ENEOS CORP
Lithium battery
InactiveCN100355129CImprove permeabilityAvoid decompositionNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsOrganic electrolyte cellsFull width at half maximumSolvent
A lithium cell includes a positive electrode, a negative electrode employing a carbon material as an active material, and a non-aqueous electrolyte including a solute dissolved in a non-aqueous solvent, and is characterized in that the carbon material in the negative electrode has an RA value (IA / IG) of 0.05 or more, the RA value calculated from a peak intensity (IA) of a broad peak PA having a full width at half maximum of 100 cm<-1 >or more and a peak intensity (IG) in the vicinity of 1580 cm<-1 >as determined by laser Raman spectroscopy using an argon ion laser having a wavelength of 514.5 nm, the peak intensity (IA) determined from a peak PD in the vicinity of 1360 cm<-1>, as determined by the aforesaid laser Raman spectroscopy, which is separated into the broad peak PA having the full width at half maximum of 100 cm<-1 >or more and a peak PB having a full width at half maximum of less than 100 cm<-1>.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Double-color laser system for replacing argon ion laser
PendingCN114498301AReduced stabilityGood bundle effectSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser arrangementsLight beamErbium lasers
The invention provides a double-color laser system for replacing an argon ion laser, which comprises an assembly shell and an upper cover arranged at the upper end of the assembly shell, and is characterized by further comprising two semiconductor thermal control devices which emit laser and are symmetrically distributed; the light beam shaping element is used for straightening the laser beam; the laser beam combining device overcomes the defects in the prior art, is reasonable in design and compact in structure, can combine two lasers with different wavelengths, is good in beam combining effect, can control the stability of the combined laser through the light taking detection element, and is simple in structure and high in energy conversion efficiency.
Owner:无锡增意光电有限公司
Measuring device and method for particle movement trajectory in two-phase flow system
The invention discloses a measuring device and method for a two-phase flow system internal particle motion trajectory. The measuring device comprises a laser emission system and a photovoltaic conversion detection system, wherein the laser emission system is composed of an argon ion laser, a first cylindrical lens, a second cylindrical lens and a reactor, and the photovoltaic conversion detection system is composed of three optical receivers, three photomultiplier tubes, a filter and a computer. The three optical receivers are evenly arranged around the peripheral side of the reactor by using the reactor as a circle center. According to the measuring method, non-immersive measurement is included, the measuring device does not need to be placed into the reactor, the influence of the measuring device on two-phase flow inside the reactor is avoided, measuring accuracy is improved, and the measuring result is precise and reliable; the argon ion laser is used as a light source and replaces an X-ray source, the cost of an X-ray detector is omitted, and the measuring device is economical, practical, safe and reliable.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Synthetic graphite material, synthetic graphite material production method, negative electrode for lithium ion secondary battery, and lithium ion secondary battery
A synthetic graphite material wherein the crystal grain size L(112) in the c-axis direction as calculated from a (112) diffraction line obtained by wide-angle X-ray diffraction is 4-30 nm, the surface area based on volume as calculated by a laser diffraction-type particle size distribution measurement device is 0.22-1.70 m2 / cm3, the oil absorption is 67-147 mL / 100g, and the half-value width [delta][nu]G is 19-24 cm-1 for a peak appearing in the wavelength region of 1580 cm-1+ / -100 cm-1 in Raman spectroscopy using argon ion laser light having a wavelength of 514.5 nm.
Owner:JXTJ NIPPON OIL & ENERGY CORP
Carbon material for electrode and non-aqueous secondary battery using said electrode carbon material
InactiveCN1199303CImprove the preservation effectImprove reliabilityCell electrodesSecondary cellsX-rayPeak value
Disclosed is a carbon material for electrode. The carbonaceous material has a plane space d002 of a (002) plane less than 0.337 nm in an X-ray wide angle diffraction method, a crystallite size (Lc) of 90 nm or higher, an R value, as a peak intensity ratio of a peak intensity of 1360 cm<-1> to a peak intensity of 1580 cm<-1> in a Raman spectrum in use of an argon ion laser, of 0.20 or higher, and a tap density of 0.75 g / cm<3> or higher. Also disclosed is a multilayer structure carbonaceous material for electrode, which is manufactured by carbonizing some organic compounds where the carbonaceous material for electrode is mixed with the organic compounds. The battery using the carbonaceous material for electrode or the multilayer structure carbonaceous material for electrode has a large capacity, a small irreversible capacity admitted in the initial cycle, excellent capacity maintaining rate of the cycle, and particularly, largely improved quick charging and discharging characteristics.
Owner:MITSUBISHI RAYON CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com