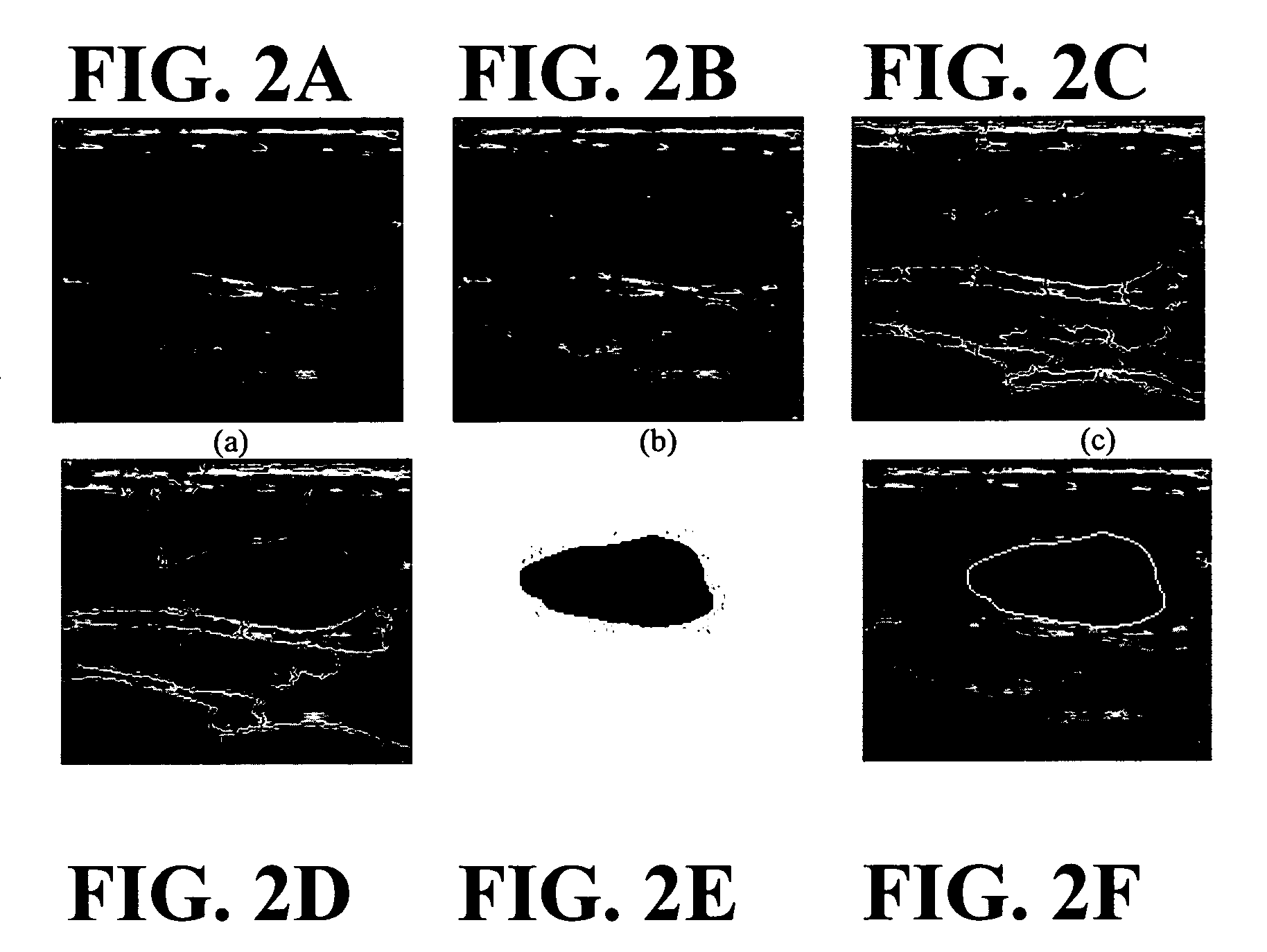
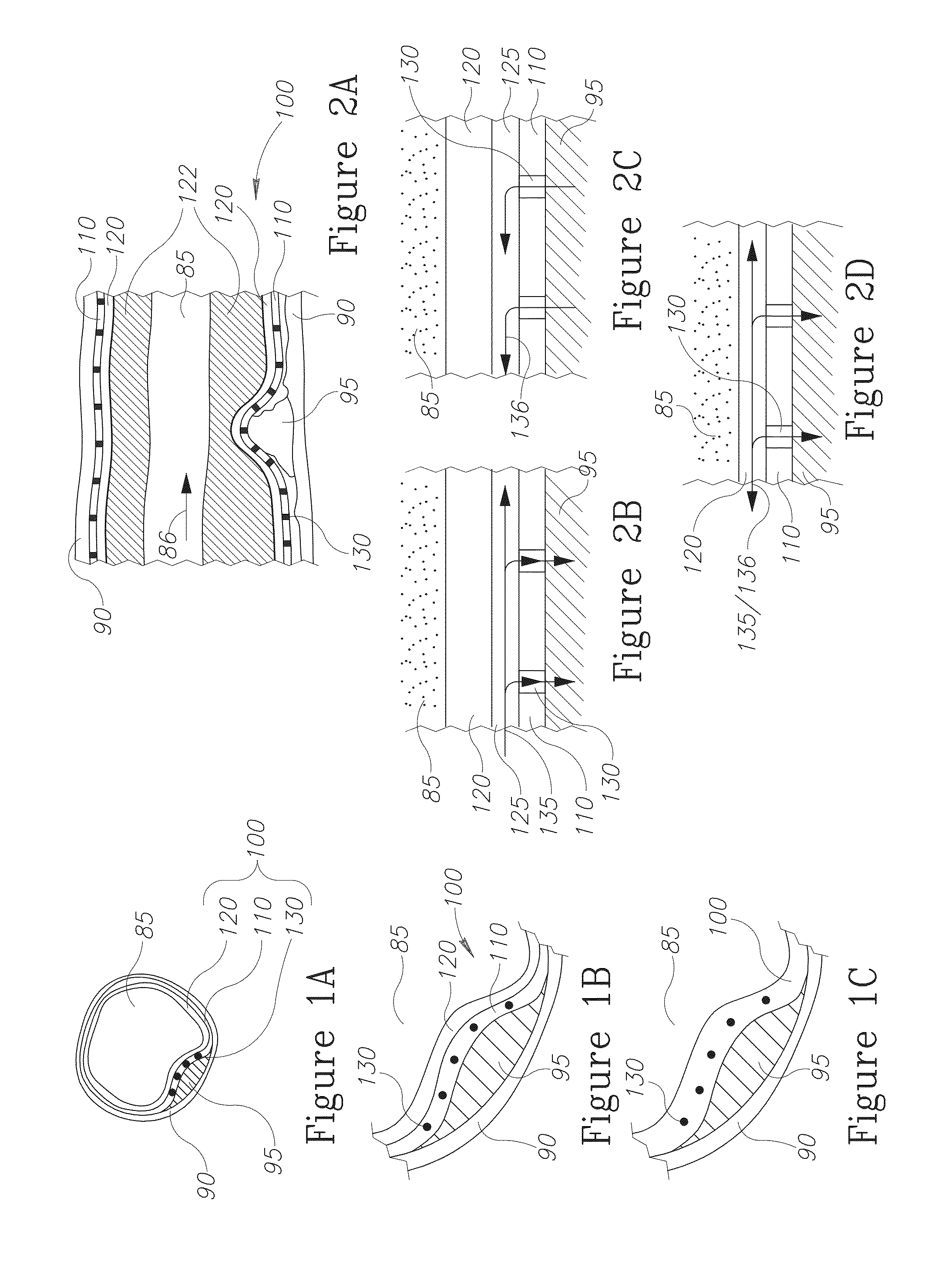
Patents
Literature
1061 results about "Circumscribed lesion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ulceration (lesion) Definition: a circumscribed inflammatory and often suppurating lesion on the skin or an internal mucous surface resulting in necrosis of tissue.
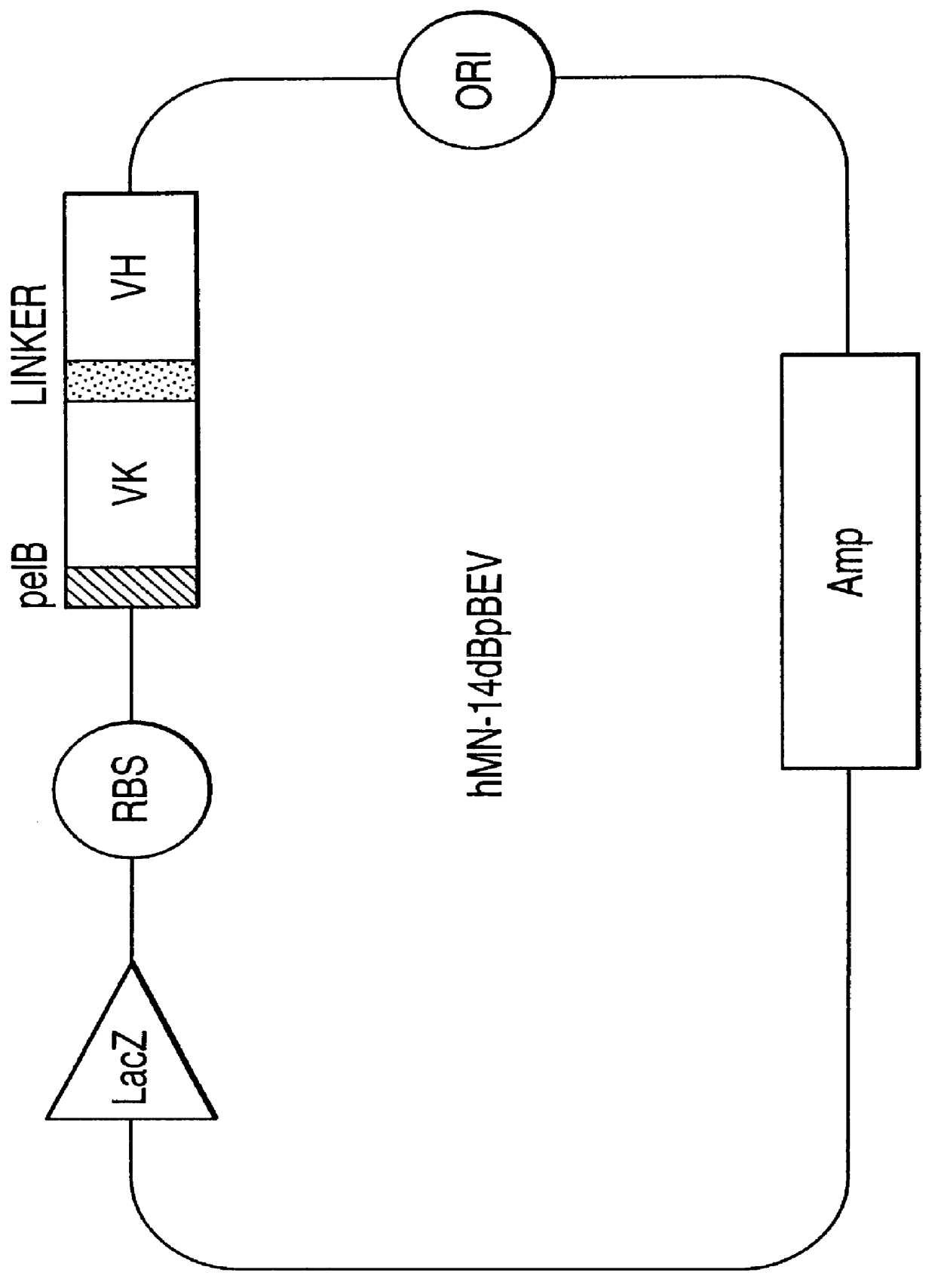
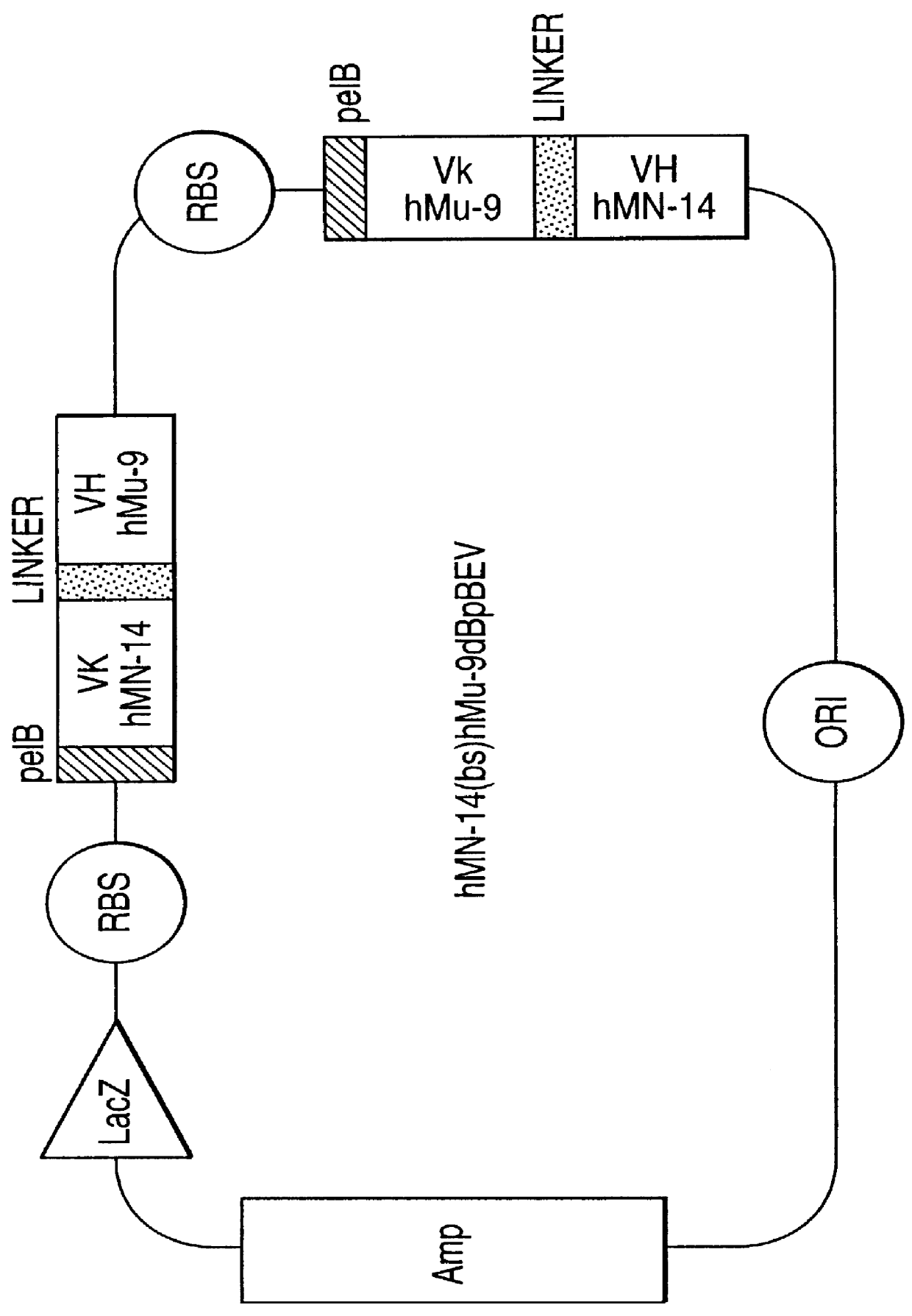
Intraoperative, intravascular, and endoscopic tumor and lesion detection, biopsy and therapy
InactiveUS6096289ADiscriminationImprove discriminationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryNon malignantAntibody fragments
Methods are provided for close-range intraoperative, endoscopic and intravascular deflection and treatment of lesions, including tumors and non-malignant lesions. The methods use antibody fragments or subfragments labeled with isotopic and non-isotopic agents. Also provided are methods for detection and treatment of lesions with photodynamic agents and methods of treating lesions with a protein conjugated to an agent capable of being activated to emit Auger electron or other ionizing radiation. Compositions and kits useful in the above methods are also provided.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
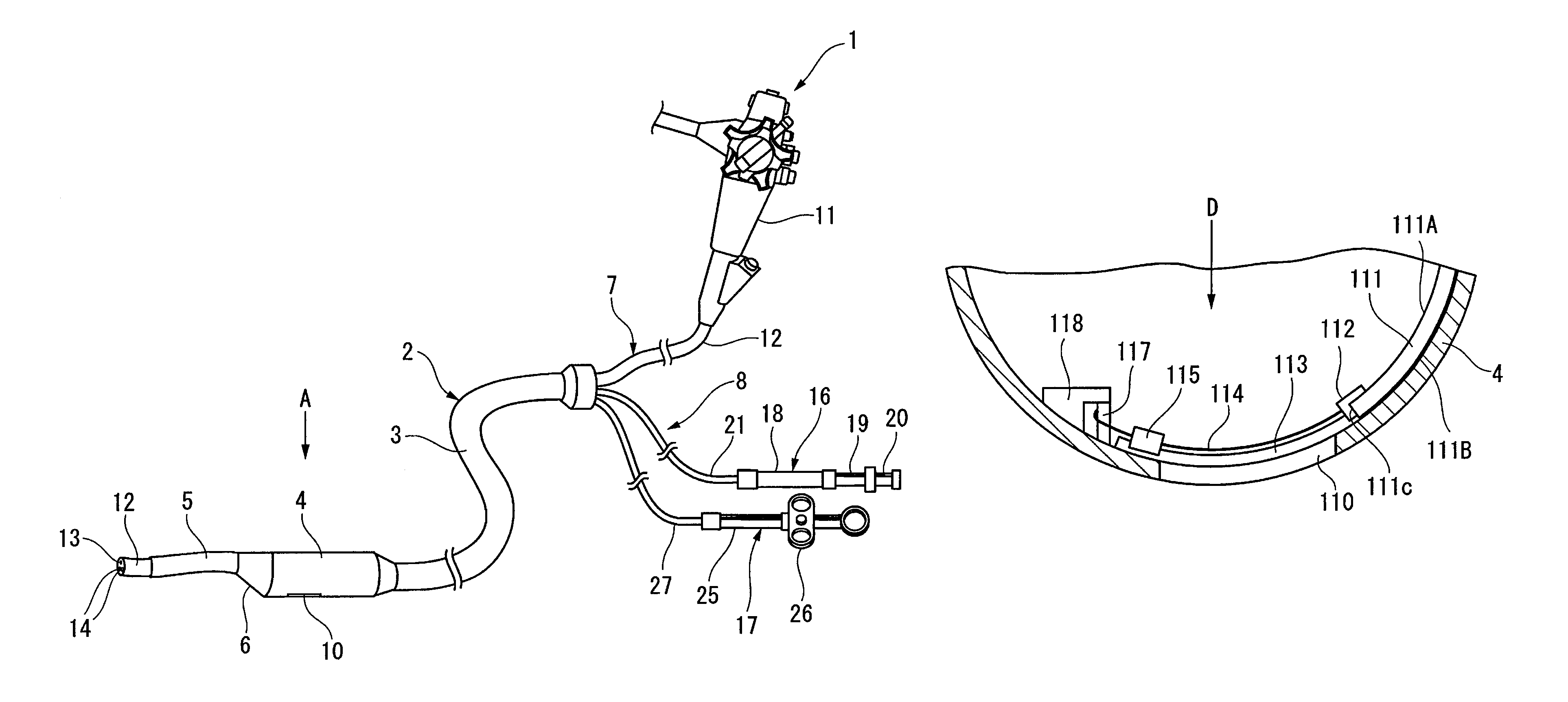
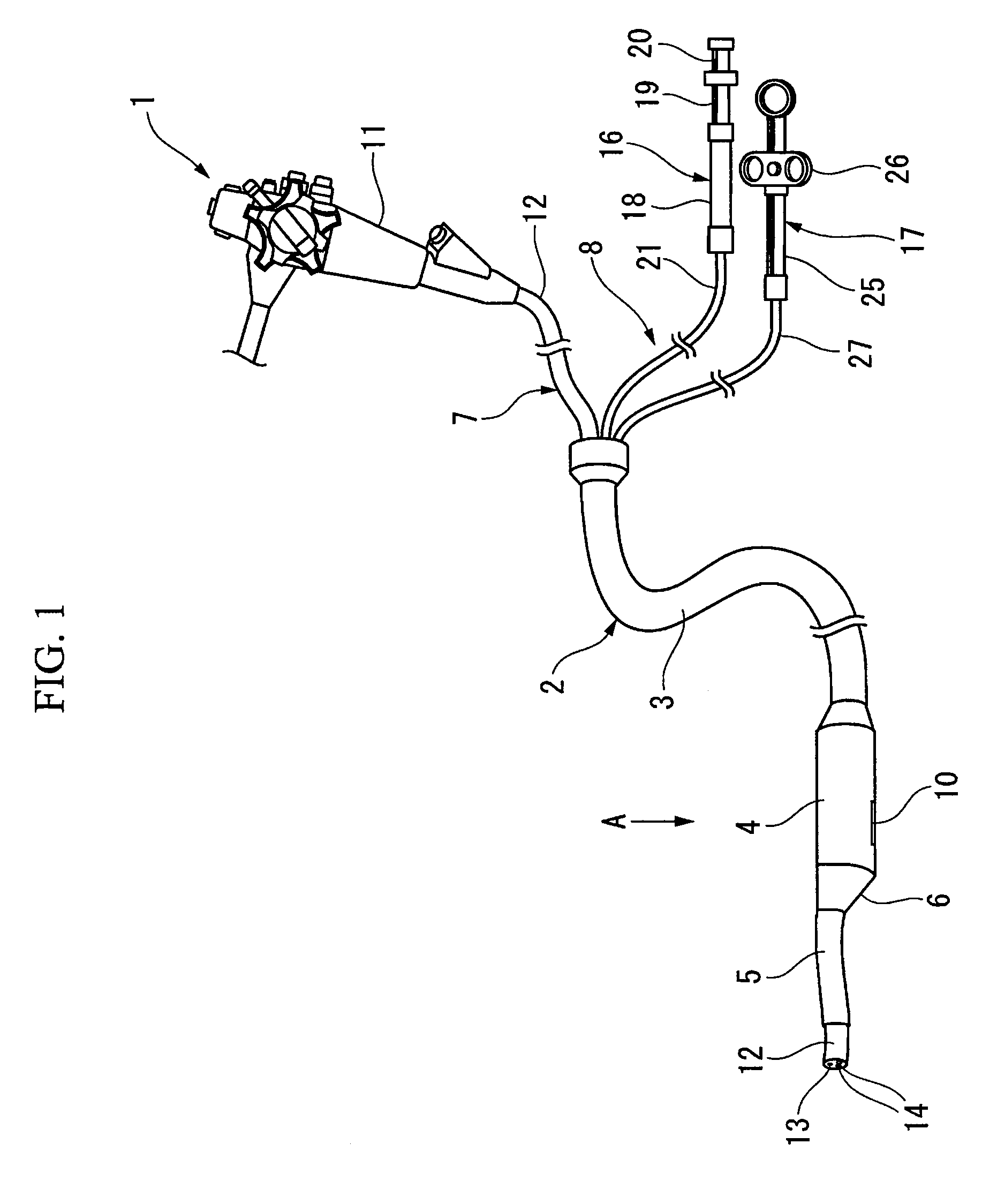
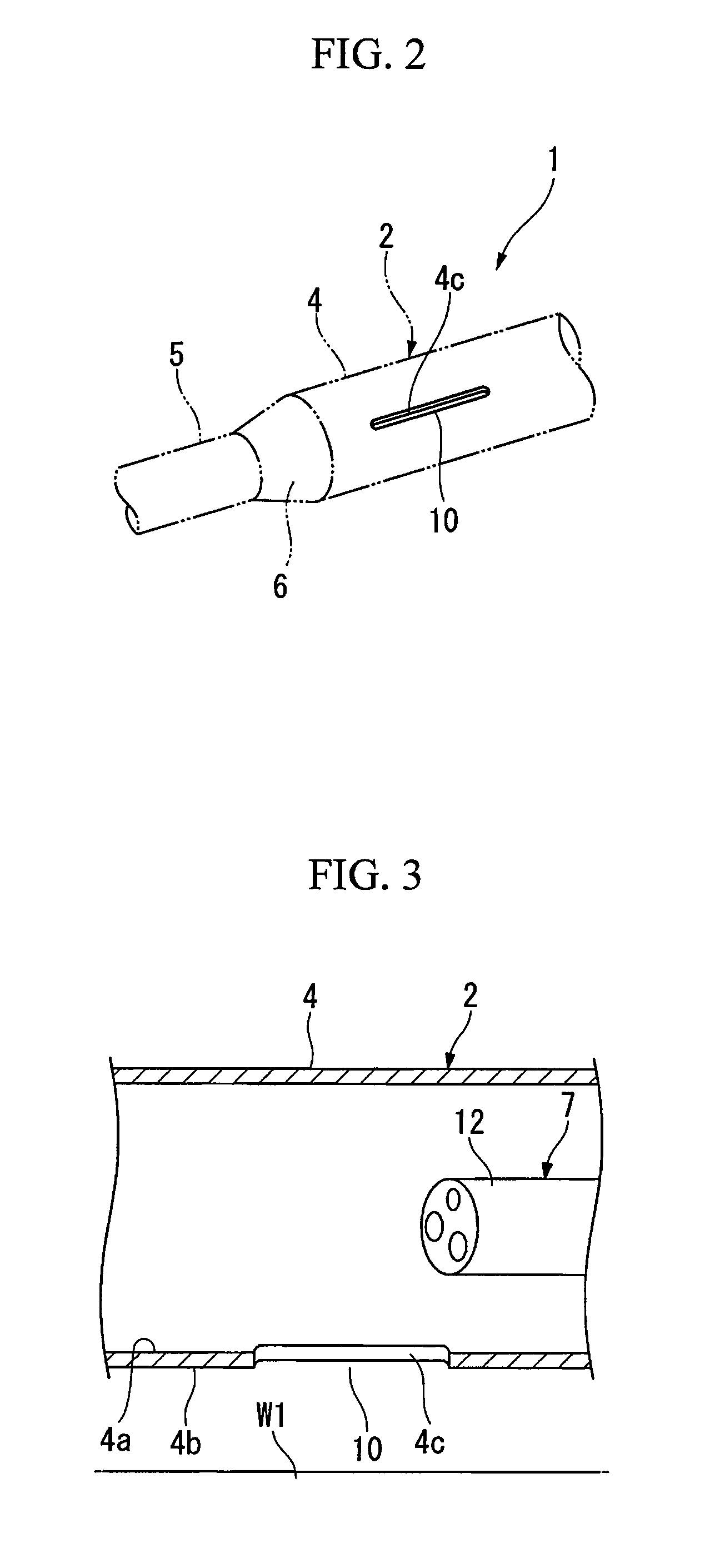
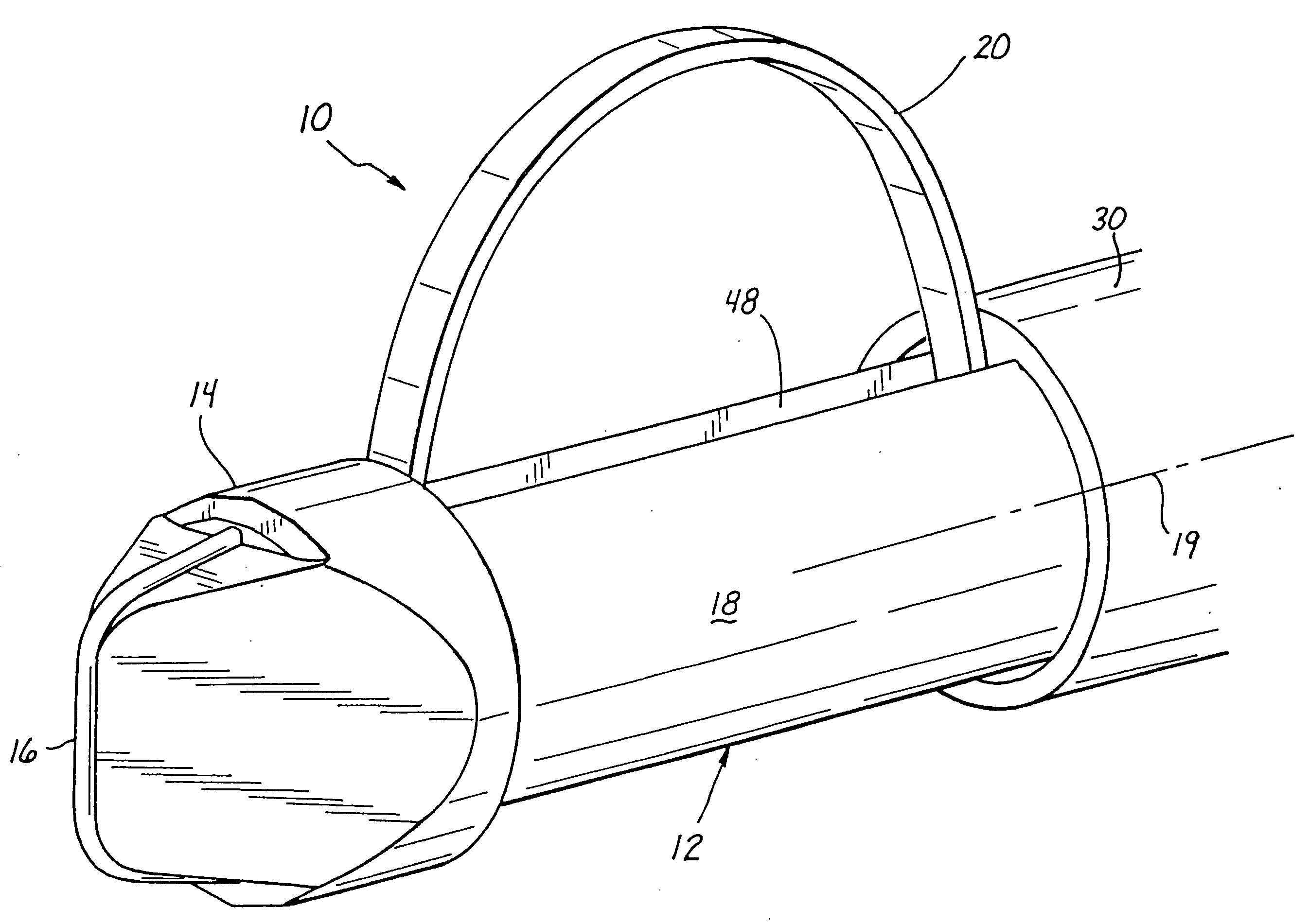
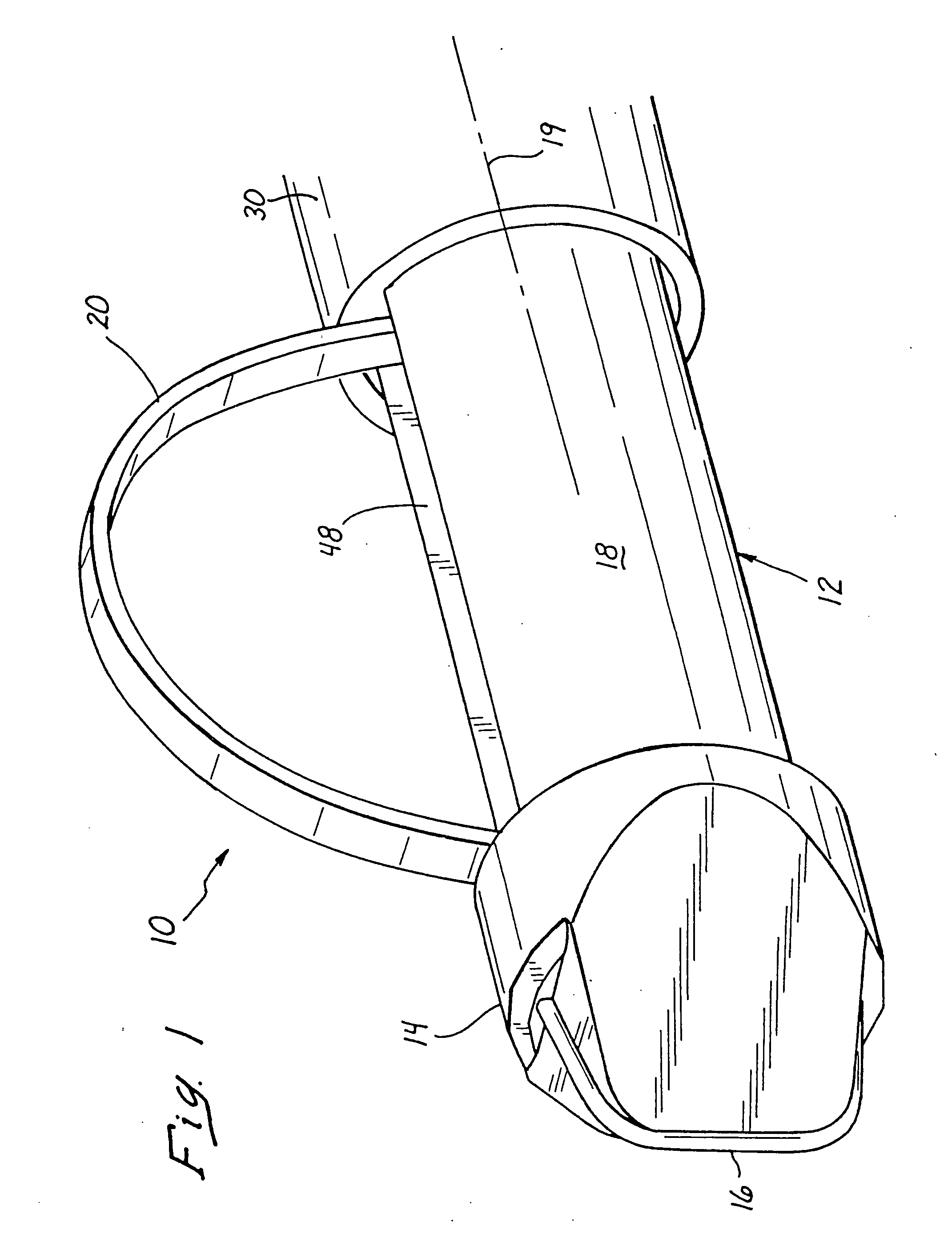
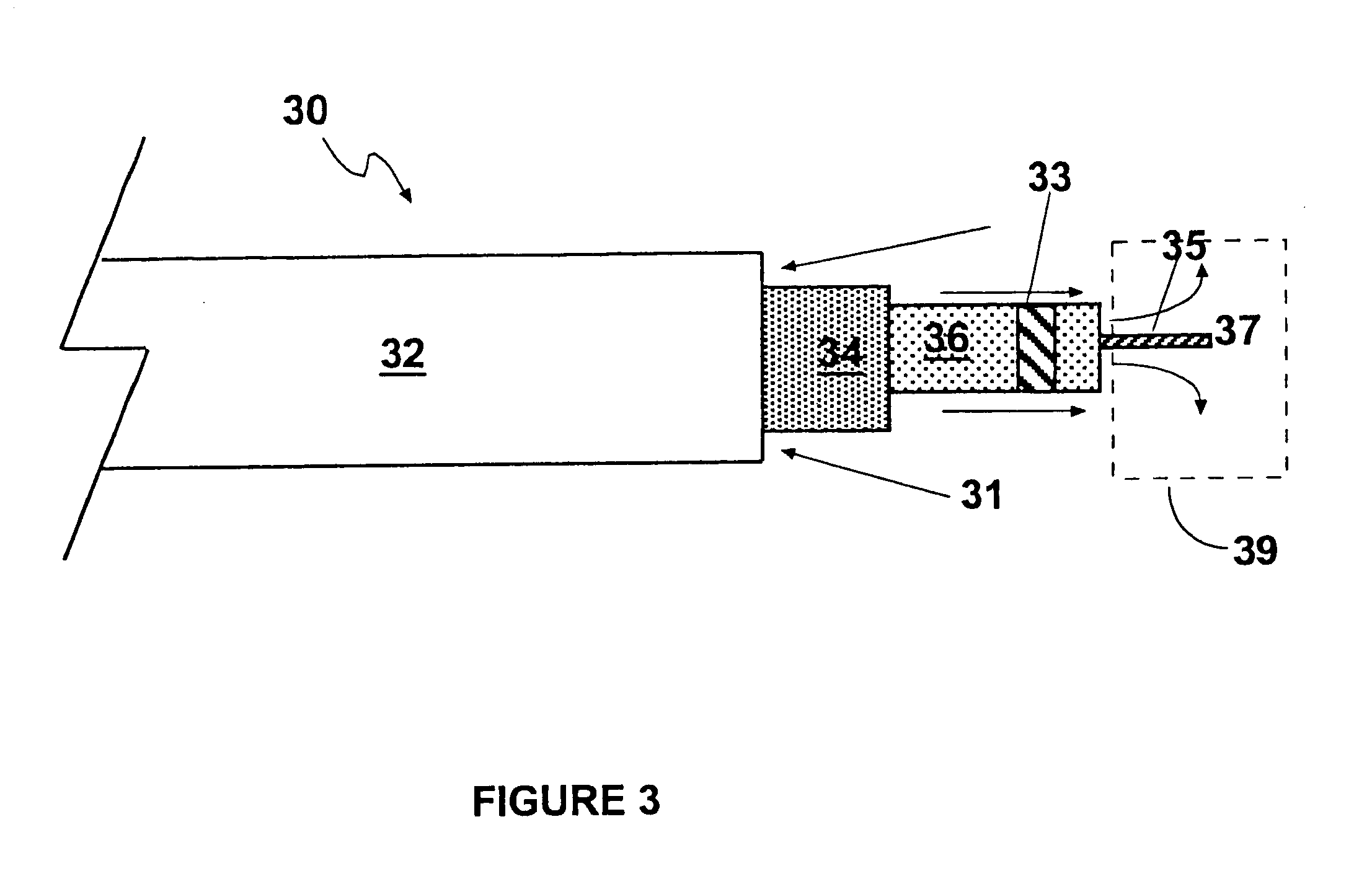
Pressing member, endoscopic treatment system, and endoscopic suturing device
An endoscopic treatment system 1 of the present invention includes an overtube 2 that is inserted into the body of a patient. An endoscope 7 and a suturing device 8 are inserted into the overtube 2. The overtube 2 has a long and flexible tube main body 3, and a chamber 4 is provided at the distal end of the tube main body 3. The chamber 4 has a lateral hole 10 formed on the lateral surface thereof. The width of the lateral hole 10 is set such that a lesion can be drawn into the lateral hole 10 while preventing other organs on the periphery of the lesion from being drawn into the lateral hole 10.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
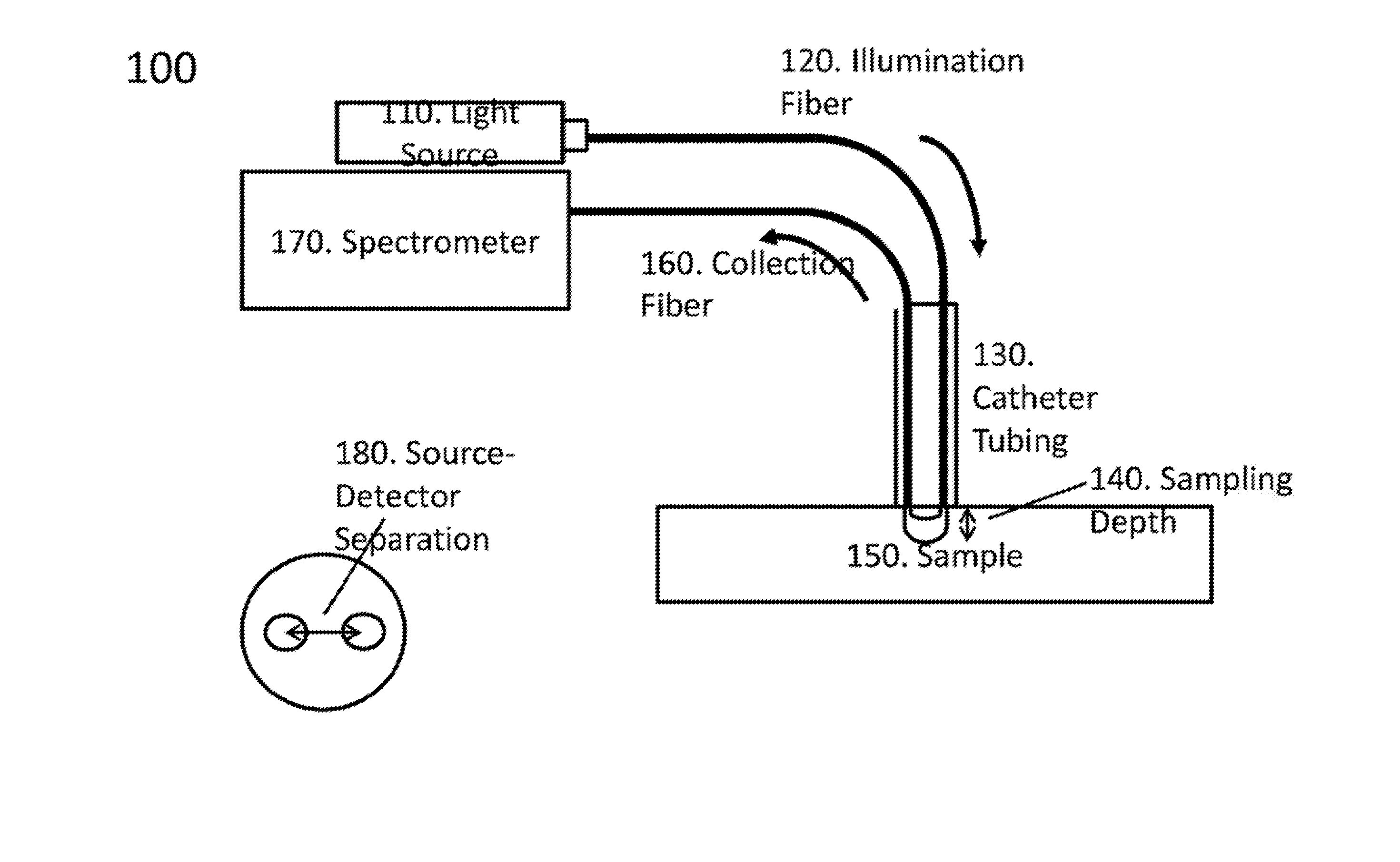
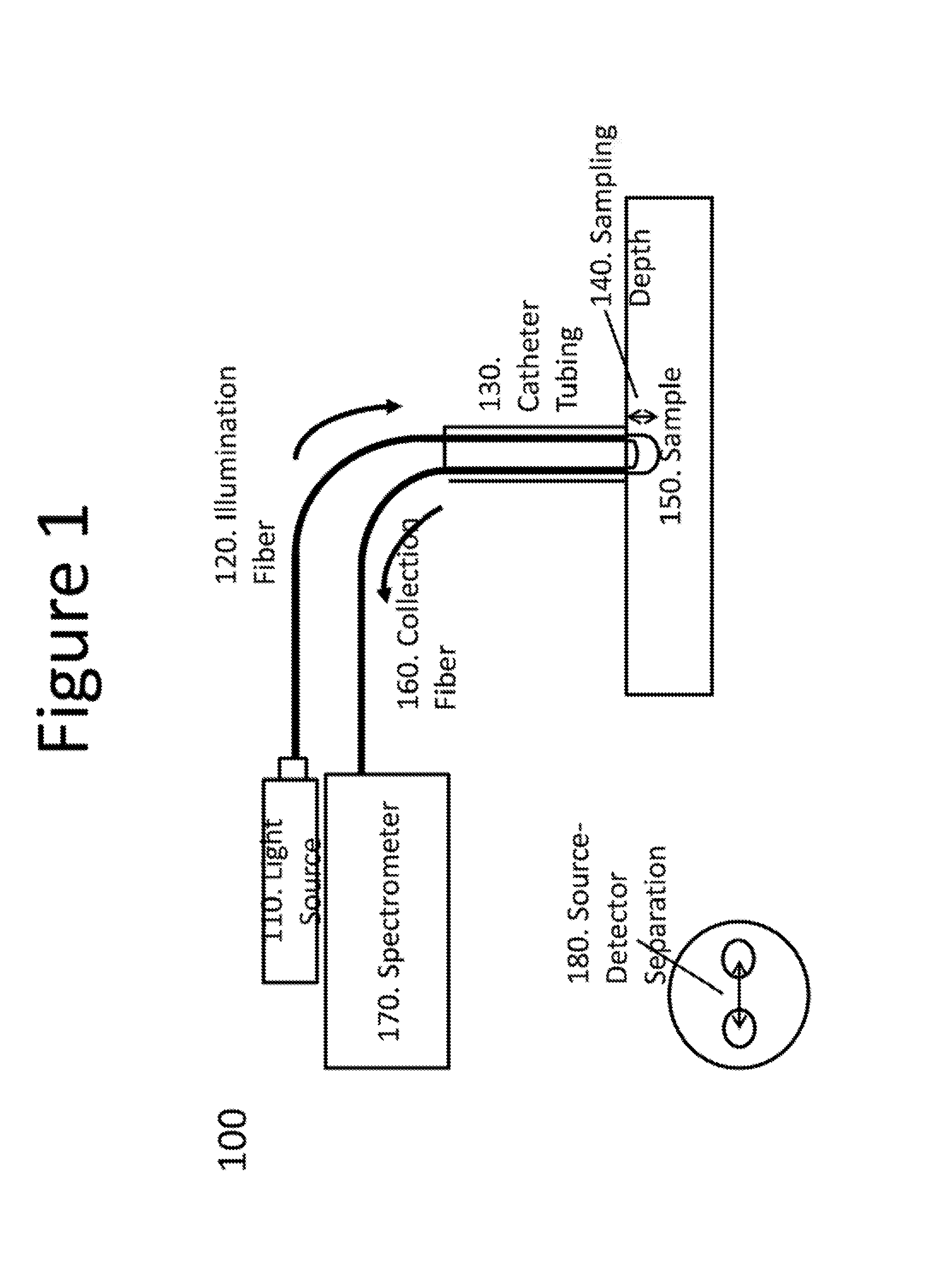
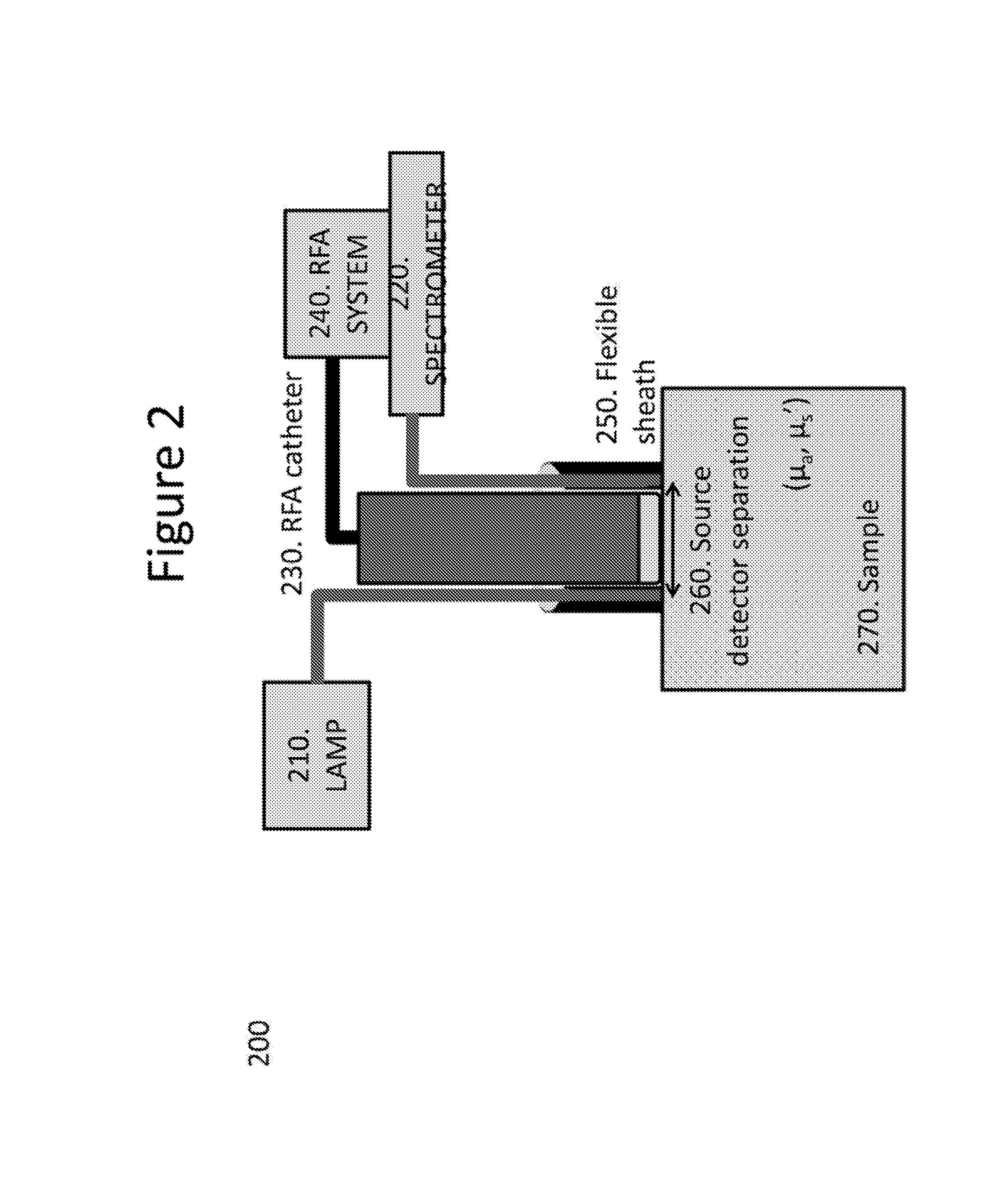
System, method and computer-accessible medium for characterization of tissue
InactiveUS20160235303A1Diagnostics using spectroscopyMedical automated diagnosisDiffuse reflectionNear infrared radiation
An exemplary system, method and computer-accessible medium for determining resultant information about a portion(s) of a tissue(s), can include, for example, receiving initial information which is based on a particular radiation that is returned from the portion(s), the particular radiation can be is based solely on an interaction between the portion(s) and a near-infrared radiation forwarded to the portion(s), and determining the resultant information about the portion(s) of the tissue(s) based on the initial information. The near-infrared radiation can be provided by a near-infrared light optical arrangement that can include a diffusely reflected near-infrared light arrangement. A depth of a lesion to be ablated can be determined by the near-infrared radiation based on the initial information. The initial information can include data corresponding to a reflectance spectrum(s) of the portion(s).
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Breast biopsy system and methods
InactiveUS20050004492A1Raise the possibilityMinimizing risk of migrationSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsCancer cellSurgical department
An apparatus and method are provided for precisely isolating a target lesion in a patient's body tissue, resulting in a high likelihood of “clean” margins about the lesion when it is removed for diagnosis and / or therapy. This approach advantageously will often result in the ability to both diagnose and treat a malignant lesion with only a single percutaneous procedure, with no follow-up percutaneous or surgical procedure required, while minimizing the risk of migration of possibly cancerous cells from the lesion to surrounding tissue or the bloodstream. In particular, the apparatus comprises a biopsy instrument having a distal end adapted for entry into the patient's body, a longitudinal shaft, and a cutting element disposed along the shaft. The cutting element is actuatable between a radially retracted position and a radially extended position. Advantageously, the instrument is rotatable about its axis in the radially extended position to isolate a desired tissue specimen from surrounding tissue by defining a peripheral margin about the tissue specimen. Once the tissue specimen is isolated, it may be segmented by further manipulation of the cutting element, after which the tissue segments are preferably individually removed from the patient's body through a cannula or the like. Alternatively, the specimen may be encapsulated and removed as an intact piece.
Owner:SENORX
Computerized detection of breast cancer on digital tomosynthesis mammograms
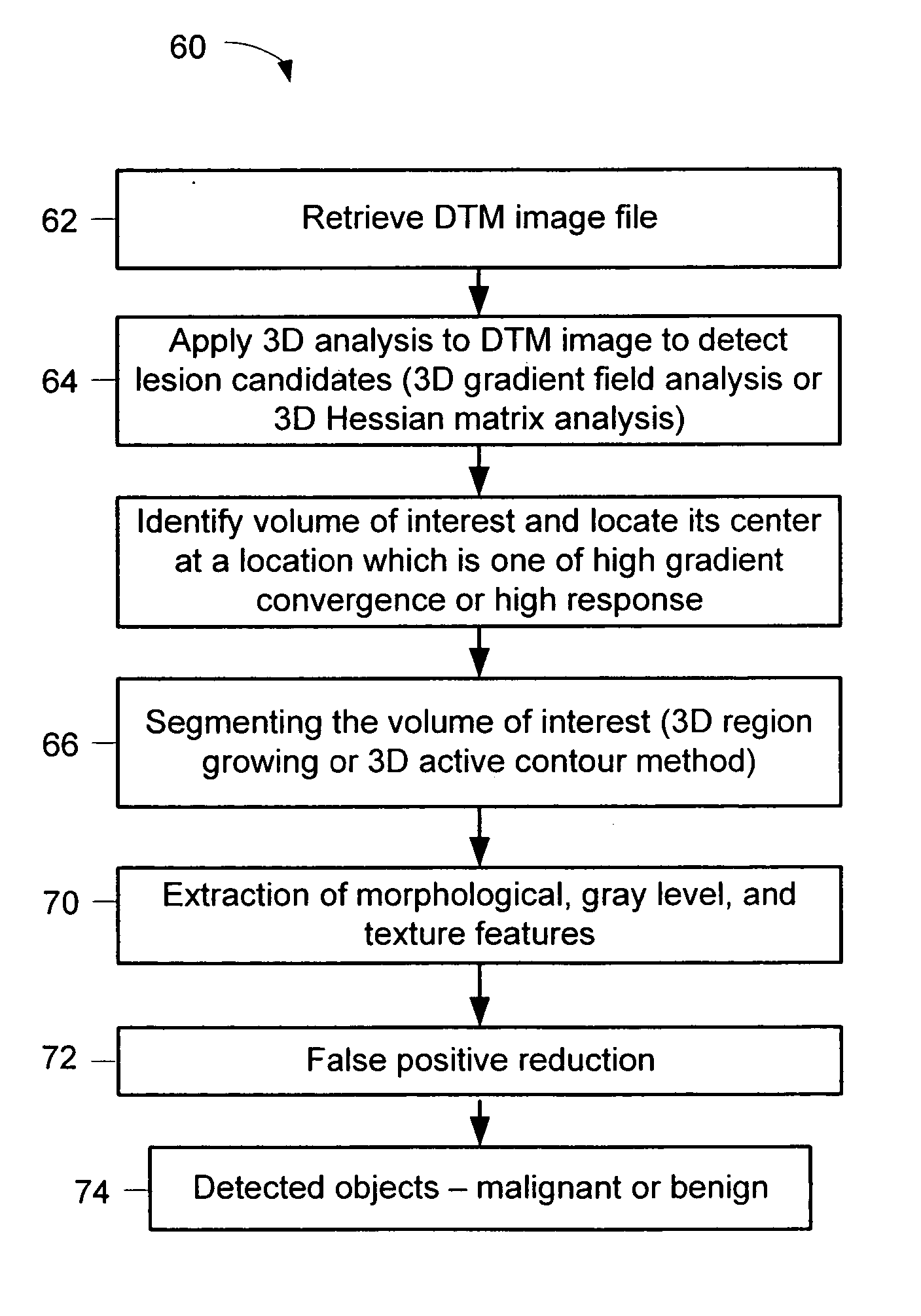
InactiveUS20060177125A1Improve breast cancer detectionExtension of timeImage enhancementImage analysisTomosynthesisGray level
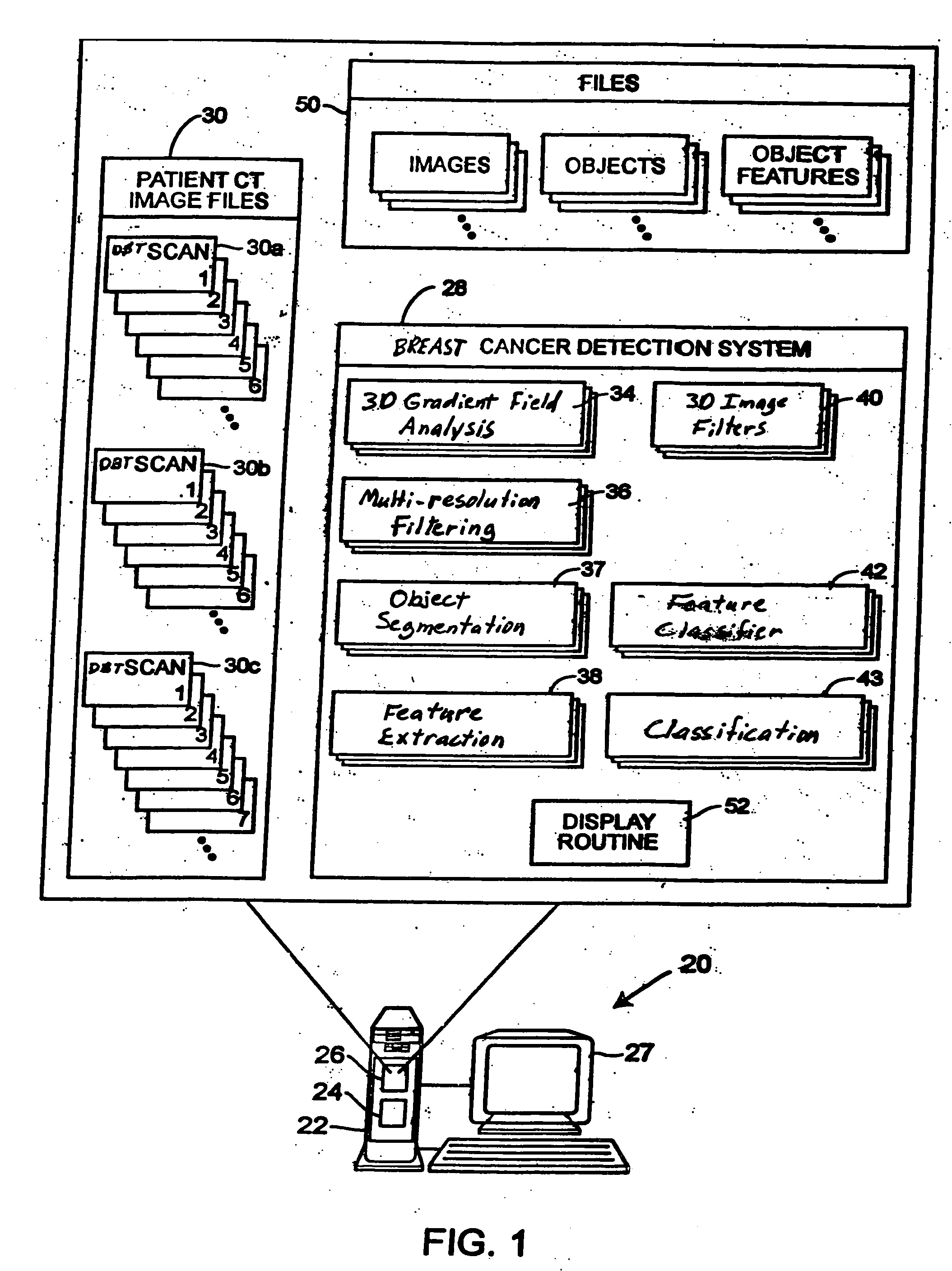
A method for using computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) for digital tomosynthesis mammograms (DTM) including retrieving a DTM image file having a plurality of DTM image slices; applying a three-dimensional gradient field analysis to the DTM image file to detect lesion candidates; identifying a volume of interest and locating its center at a location of high gradient convergence; segmenting the volume of interest by a three dimensional region growing method; extracting one or more three dimensional object characteristics from the object corresponding to the volume of interest, the three dimensional object characteristics being one of a morphological feature, a gray level feature, or a texture feature; and invoking a classifier to determine if the object corresponding to the volume of interest is a breast cancer lesion or normal breast tissue.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
System and method for predicting lesion size shortly after onset of RF energy delivery
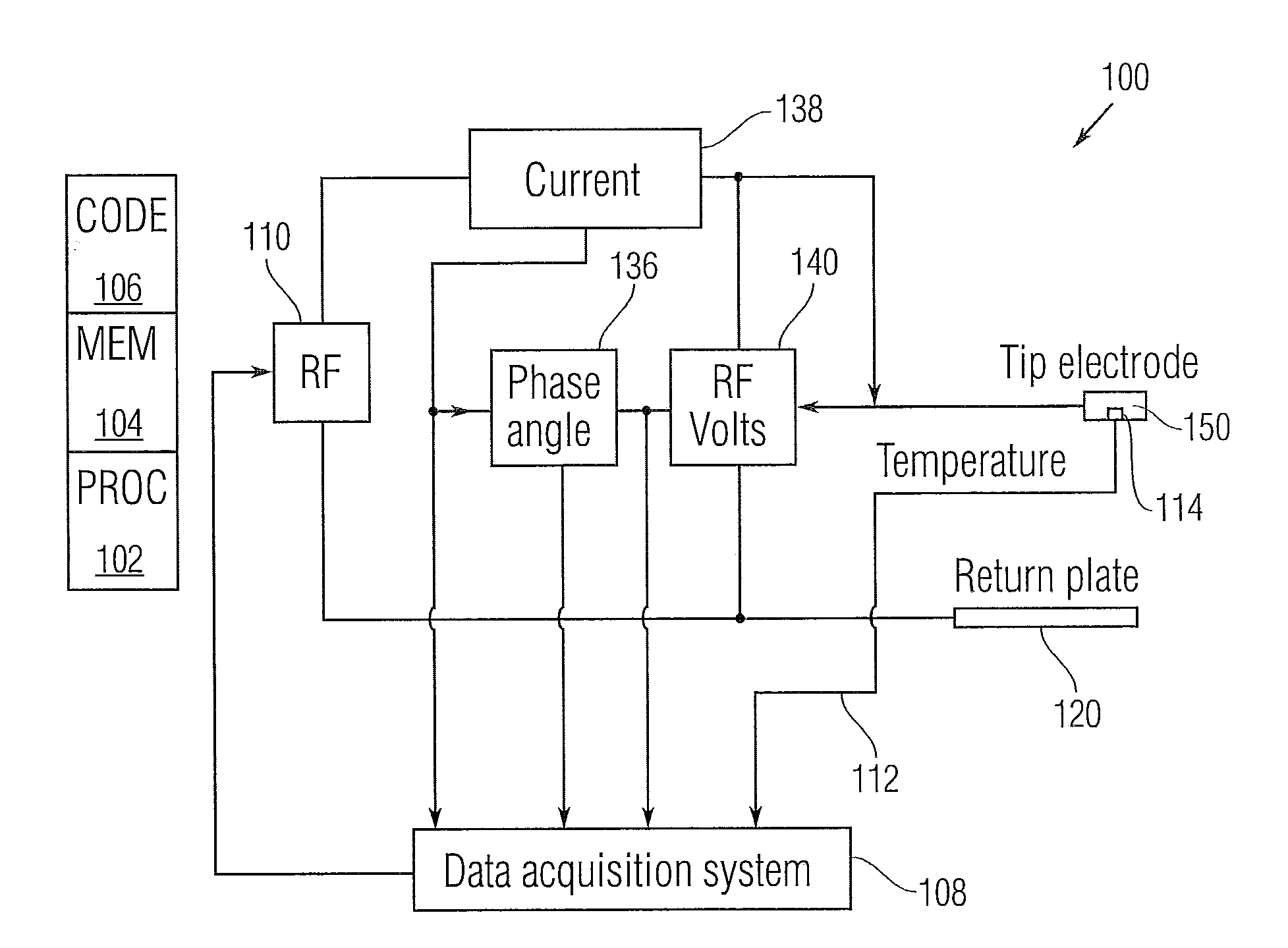
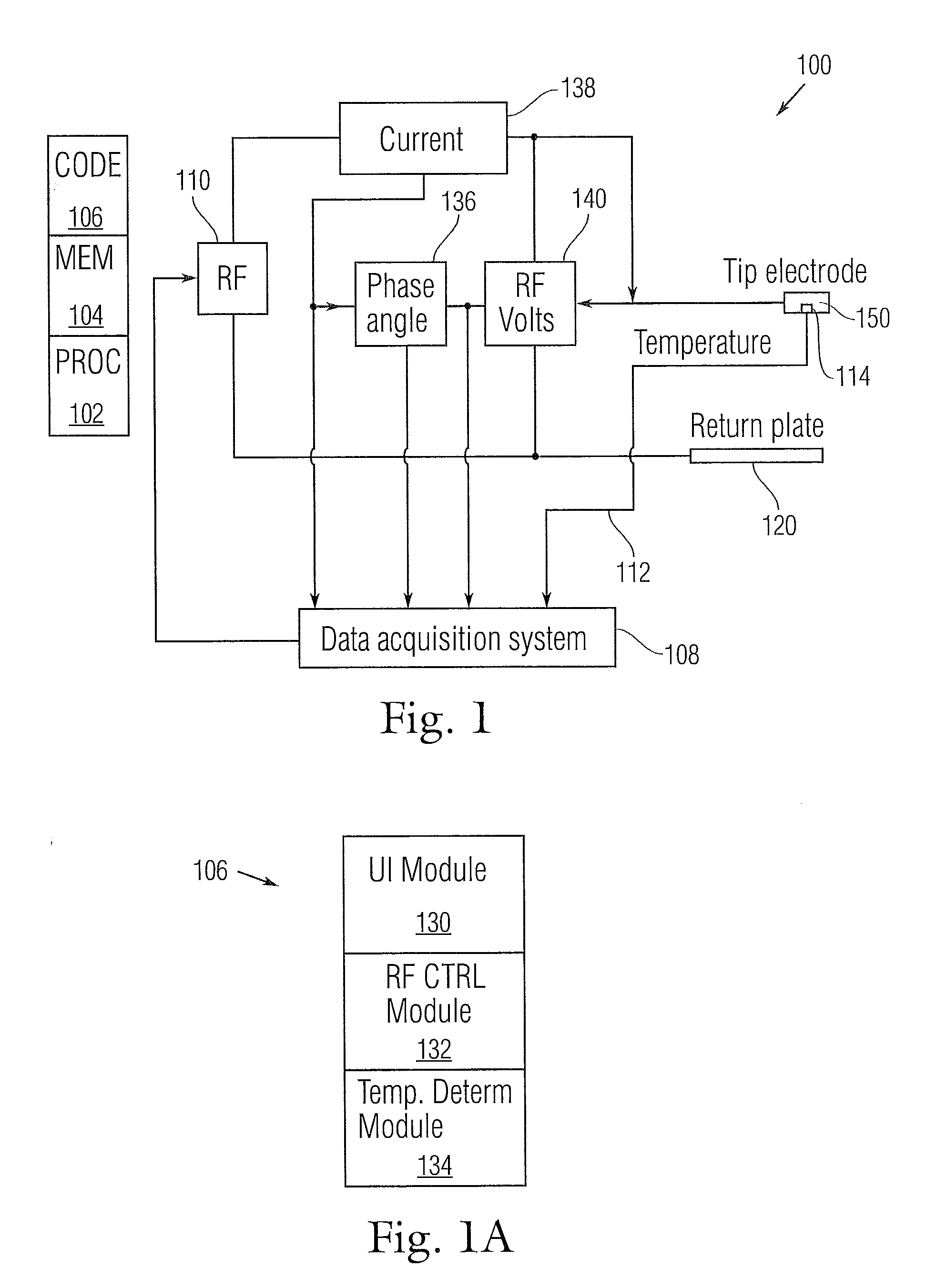
Lesion size or volume prediction shortly after the onset of an ablation procedure can inform or control the ablation procedure. The prediction and / or control is made without regard to an actual detected temperature in the vicinity of the ablation electrodes. As a consequence, the system has utility with irrigated catheter constructions and other situations in which local irrigation in the vicinity of an ablation site would otherwise interfere with a prediction or control scheme that solely relies upon temperature measurements.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA +1
Method for detecting X-ray mammary gland lesion image based on feature pyramid network under transfer learning
ActiveCN110674866AImprove robustnessImprove the extraction effectImage enhancementImage analysisData setImage detection
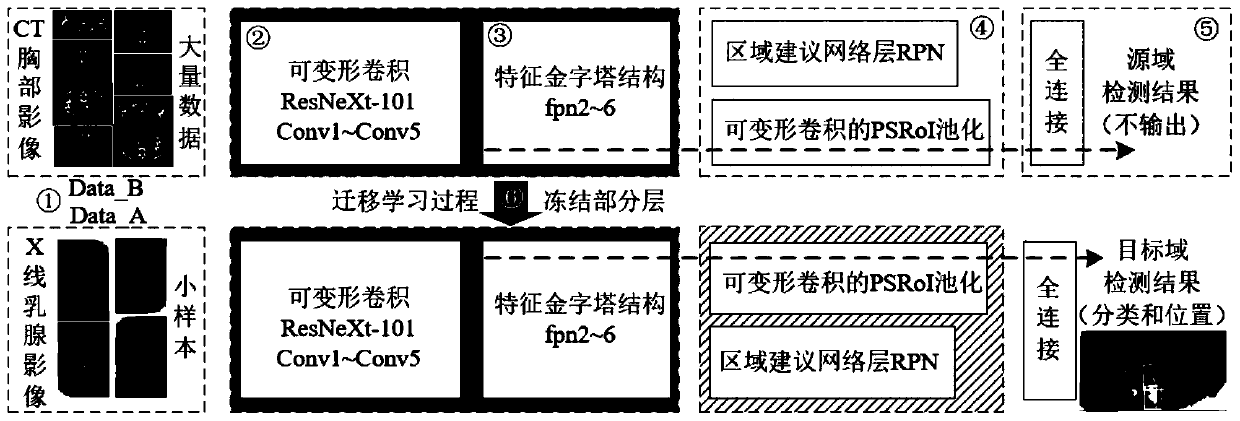
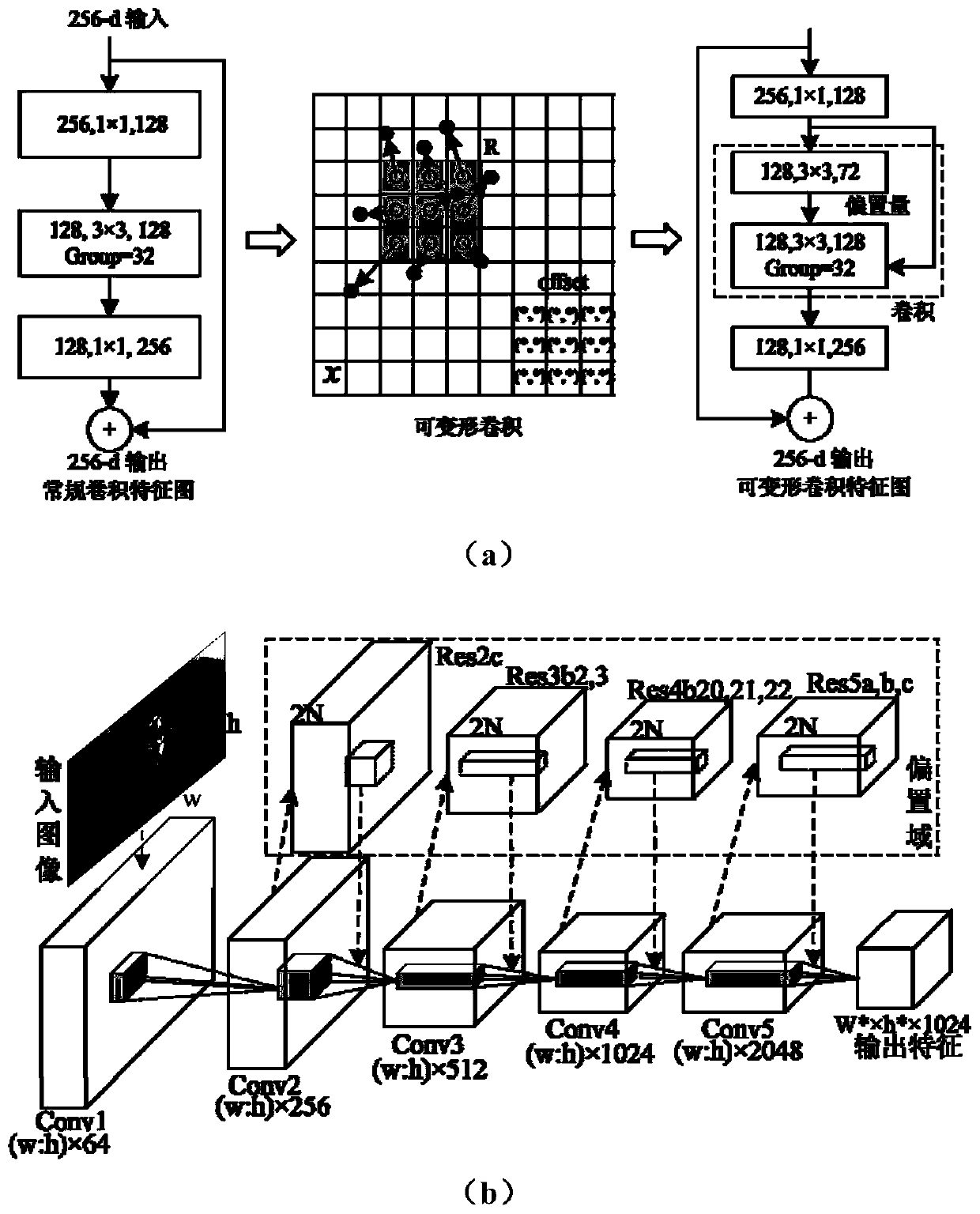
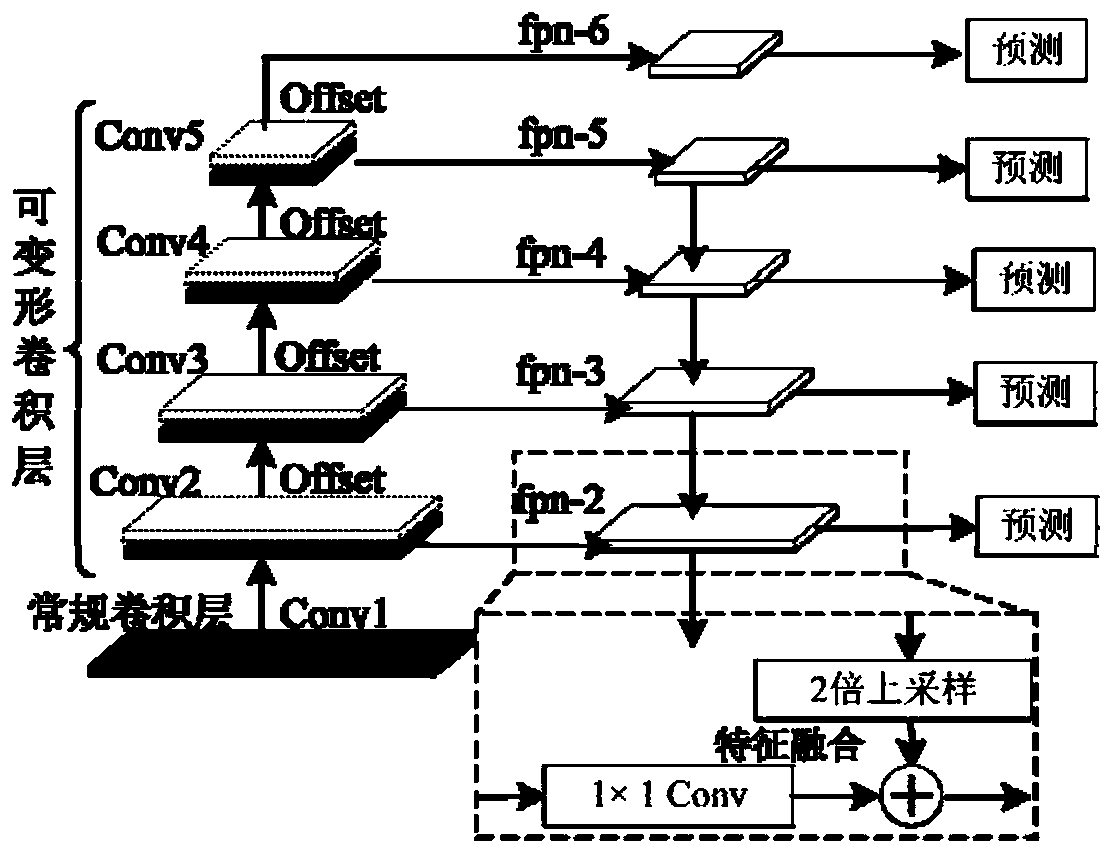
The invention provides a method for detecting an X-ray mammary gland lesion image based on feature pyramid network under transfer learning. The method comprises the steps: 1, establishing a source domain data set and a target domain data set; 2, establishing a deformable convolution residual network layer by a deformable convolution and extended residual network module; 3, establishing a multi-scale feature extraction sub-network based on a feature pyramid structure through a feature map up-sampling and feature fusion method in combination with a deformable convolution residual network layer;4, establishing a deformable pooling sub-network sensitive to the focus position; 5, establishing a post-processing network layer to optimize a prediction result and a loss function; and 6, migratingthe training model to a small sample molybdenum target X-ray mammary gland focus detection task so as to improve the detection precision of the network model on the focus in the small sample image. According to the method, a transfer learning strategy is combined to realize focus image processing in a small sample medical image.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
System and Method for Lesion Segmentation in Whole Body Magnetic Resonance Images
InactiveUS20080260221A1The result is accurateMinimal user interactionImage enhancementImage analysisWhole body mriVoxel
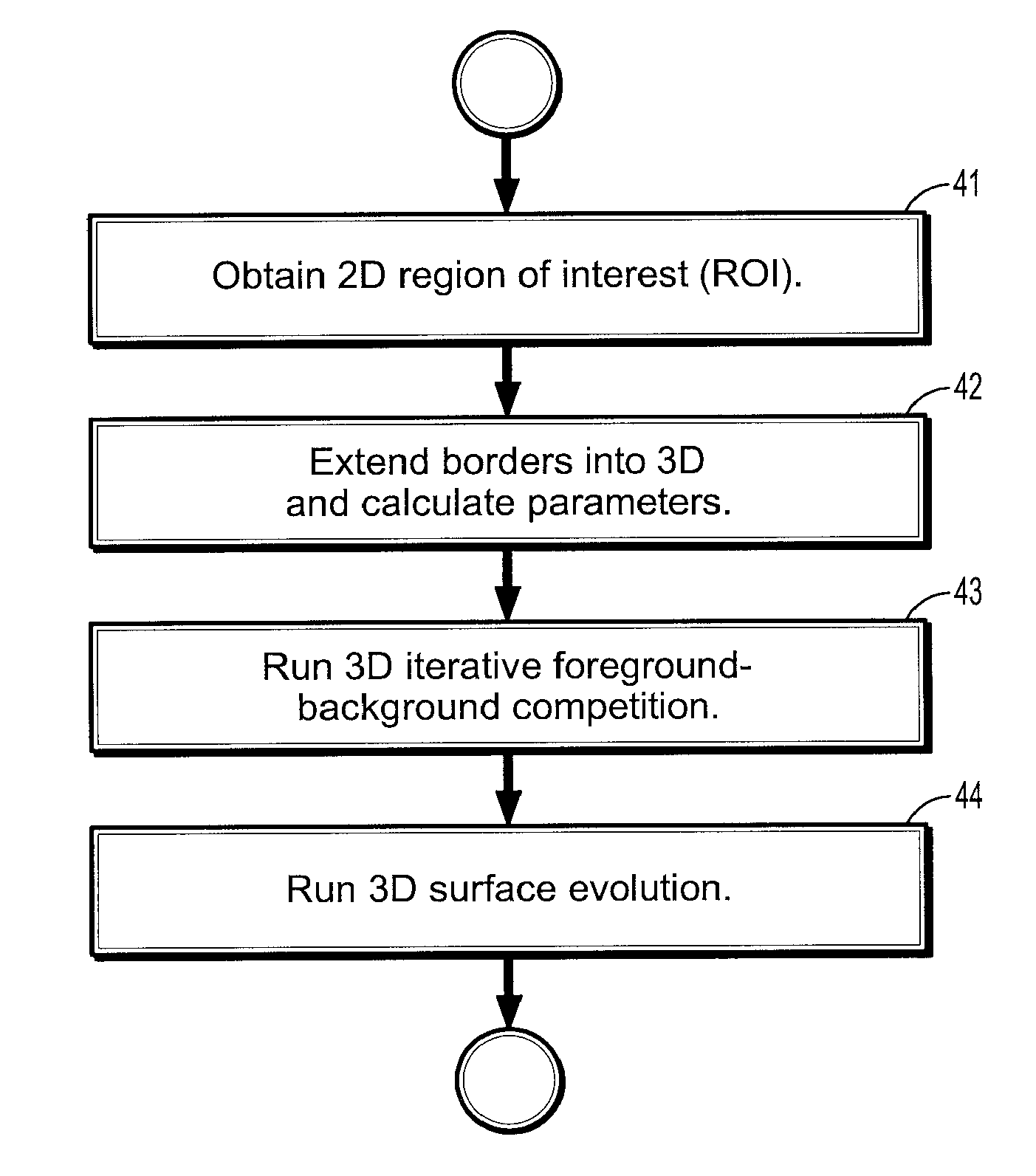
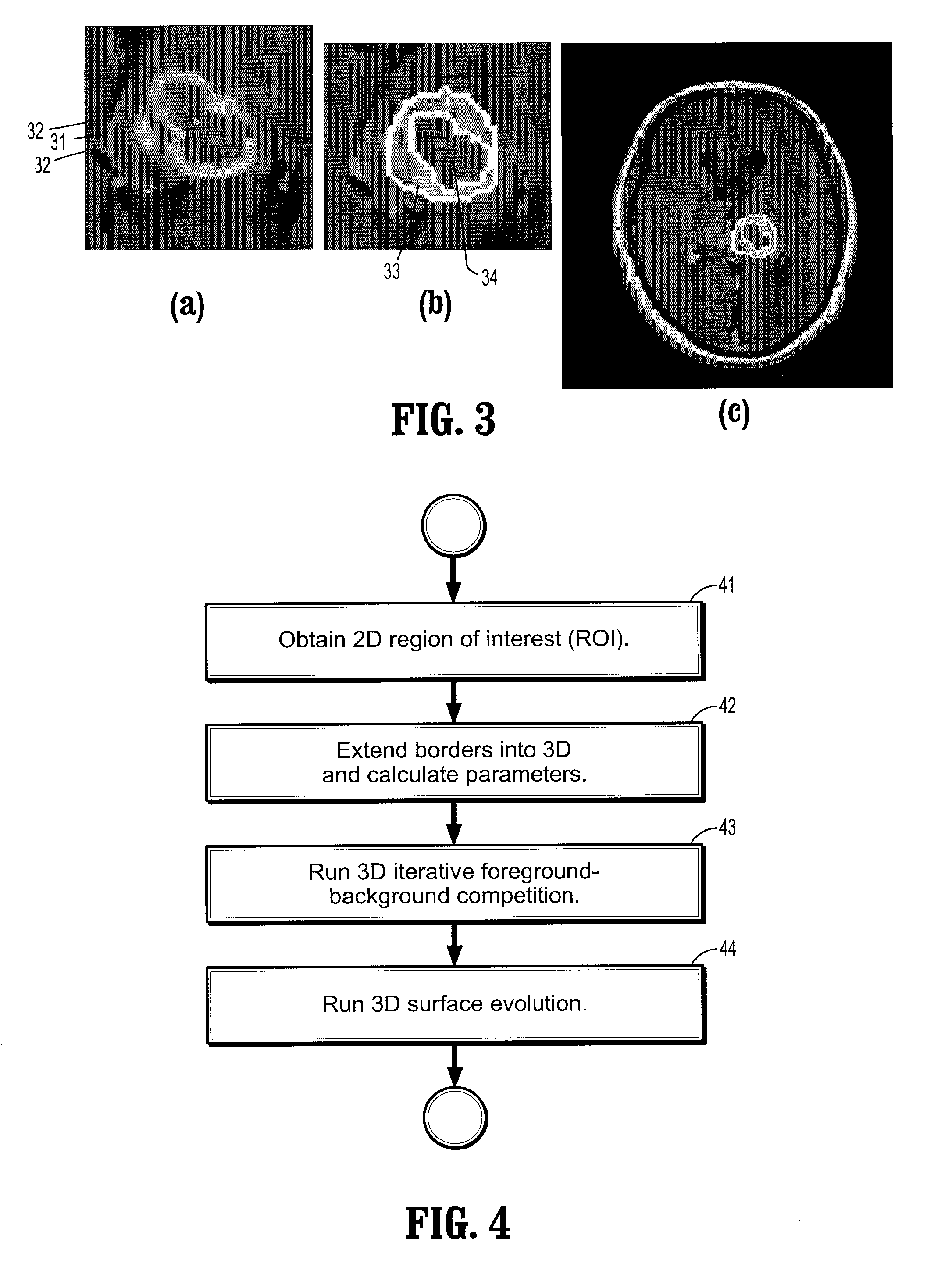
A method for lesion segmentation in 3-dimensional (3D) digital images, includes selecting a 2D region of interest (ROI) from a 3D image, the ROI containing a suspected lesion, extending borders of the ROI to 3D forming a volume of interest (VOI), where voxels on the borders of the VOI are initialized as background voxels and voxels in an interior of the VOI are initialized as foreground voxels, propagating a foreground and background voxel competition where for each voxel in the VOI, having each neighbor voxel in a neighborhood of the voxel attack the voxel, and, if the attack is successful, updating a label and strength of the voxel with that of the successful attacking voxel, and evolving a surface between the foreground and background voxels in 3D until an energy functional associated with the surface converges in value, where the surface segments the suspected lesion from the image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Hyperthermia treatment and probe therefor
InactiveUS7344529B2Prevent overheating cellsCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringLight beamPiezo electric
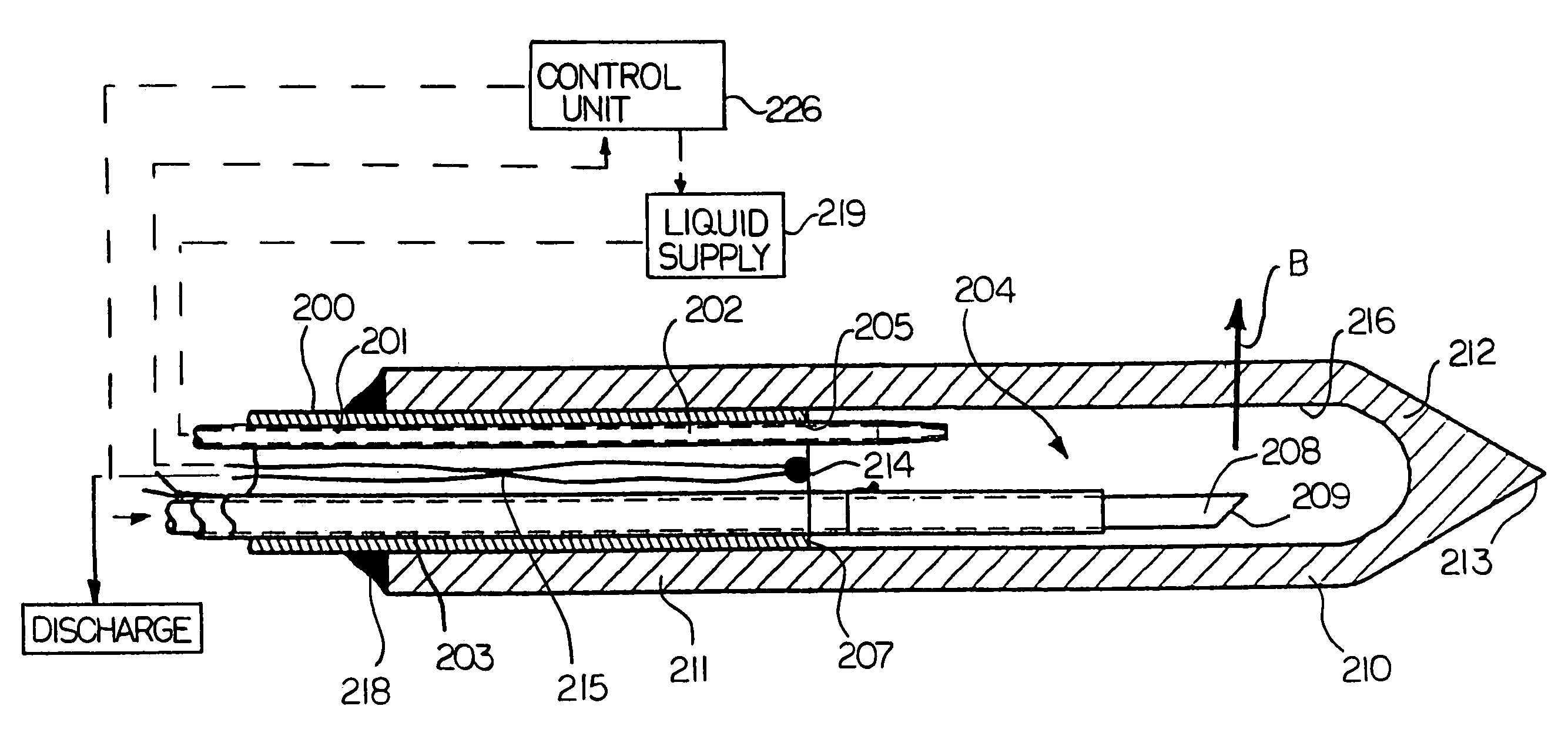
A method of using a probe that emits energy to coagulate lesions is disclosed. The probe is constructed and arranged to emit light from its distal end, either at an angle to its longitudinal axis, or along its longitudinal axis. Optionally, an end reflector may be used to direct the energy in a beam to one side of the fiber end. A reinforcing sleeve for the fiber is mounted to a shielded, Piezo-electric motor constructed and arranged to move the fiber both longitudinally and rotationally within an optional elongate cannula. An MRI system is arranged to generate a series of output signals indicative of temperature in the targeted area. The application of energy is stopped when the temperature at the boundary of the lesion reaches the required hyperthermic temperature. Cooling of the tip portion of the probe is effected by expansion of a supplied cooling fluid through a restrictive orifice into an expansion zone at the probe end. The fiber is encased in a stiff tubular titanium probe with a relatively small fluid supply duct inside the probe with the interior of the probe acting as a return duct for the expanded liquid. The temperature of the probe end is monitored by a sensor in the probe end and controlled by controlling the pressure in the supplied cooling fluid.
Owner:MONTERIS MEDICAL CORP
Proton generating catheters and methods for their use in enhancing fluid flow through a vascular site occupied by a calcified vascular occlusion
Catheter devices and methods are provided for enhancing fluid flow through a vascular site occupied by a calcified lesion. The catheter devices of the subject invention at least include, at their distal end, a proton generating means, and in many embodiments also include a flushing means. In using the subject devices, the distal end of the catheter is placed proximal to the vascular occlusion and protons are generated, e.g., via proton generation from water, in a manner sufficient to reduce the pH of the vascular site in the region proximal to the occlusion. The subphysiologic pH is maintained for a period of time sufficient for fluid flow through the vascular site to be enhanced. Also provided are kits comprising the subject catheter devices for use in the subject methods.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
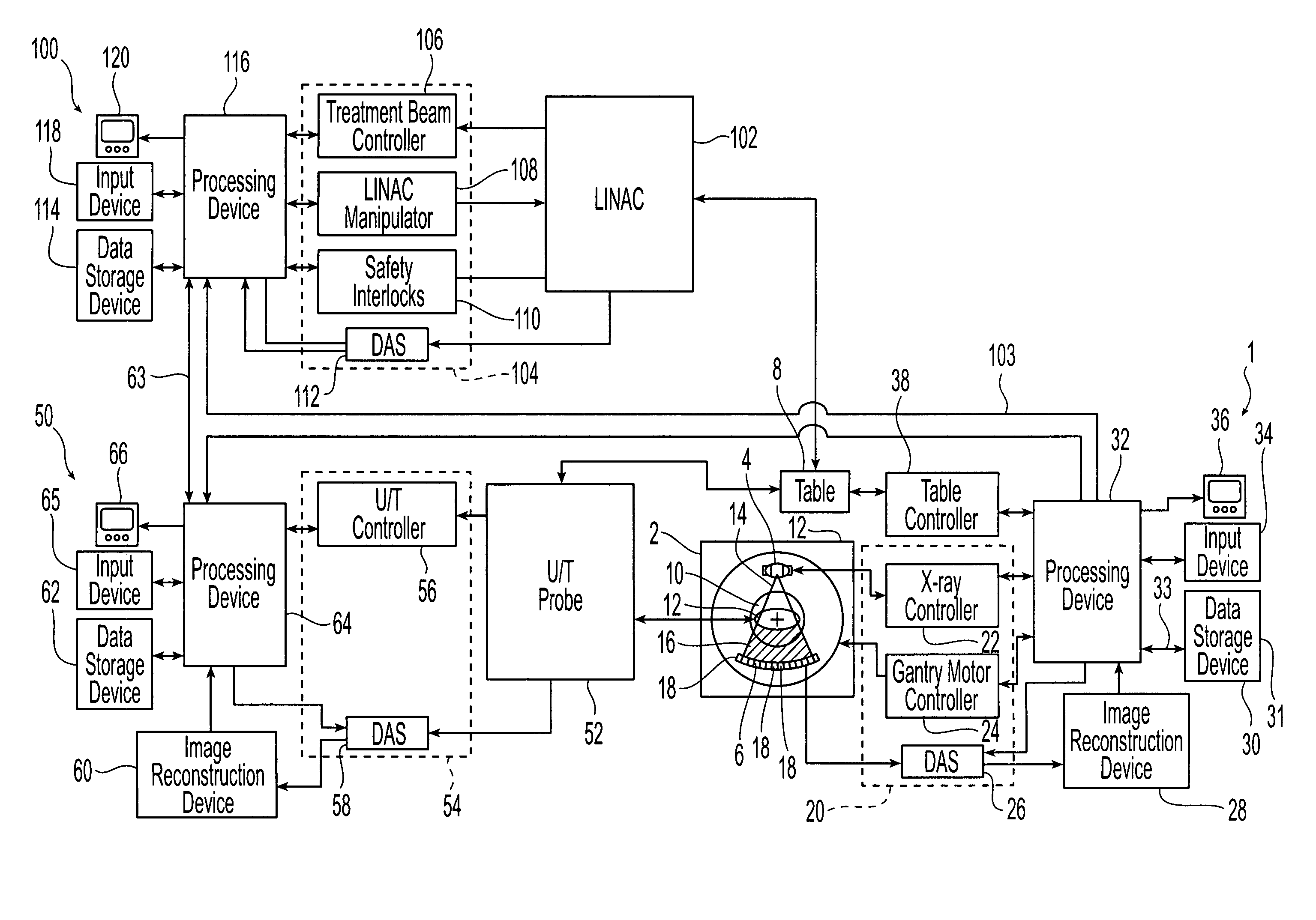
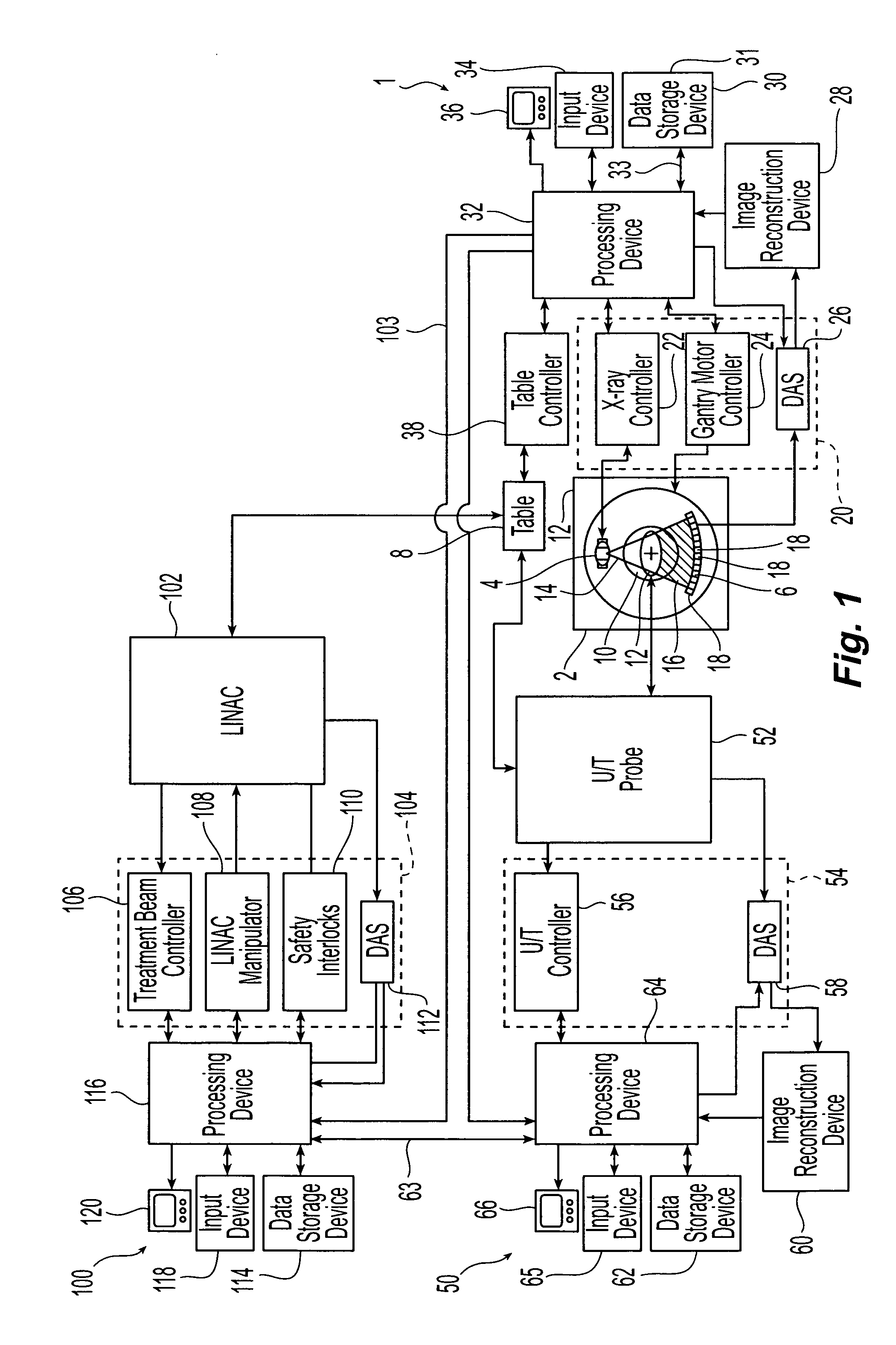
Real time ultrasound monitoring of the motion of internal structures during respiration for control of therapy delivery
InactiveUS20060241443A1Organ movement/changes detectionChiropractic devicesHelical computed tomographyReal time ultrasound
A method of targeting therapy such as radiation treatment to a patient includes: identifying a target lesion inside the patient using an image obtained from an imaging modality selected from the group consisting of computed axial tomography, magnetic resonance tomography, positron emission tomography, and ultrasound; identifying an anatomical feature inside the patient on a static ultrasound image; registering the image of the target lesion with the static ultrasound image; and tracking movement of the anatomical feature during respiration in real time using ultrasound so that therapy delivery to the target lesion is triggered based on (1) movement of the anatomical feature and (2) the registered images.
Owner:CIVCO MEDICAL INSTR CO
Antibodies against lesion tissue
Methods for isolating polynucleotides encoding antibodies against lesional tissues are provided, wherein the methods comprise the steps of: (a) isolating a B cell(s) that infiltrates into a lesional tissue of interest; and (b) obtaining an antibody-encoding polynucleotide from the isolated B cell(s). The lesions may be a cancer tissue or such. Antibody genes can be obtained without depending on B cell cloning. Accordingly, it is also possible to obtain genes encoding human-derived antibodies which are difficult to clone. Genes that encode antibodies against cancer can be obtained using cancer tissues as the lesion.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Segmentation of lesions in ultrasound images
InactiveUS20060247525A1Insensitive to in image noiseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementSonificationRadiology
A method for determining a candidate lesion region in a digital ultrasound medical image of anatomical tissue. The method includes the steps of: accessing the digital ultrasound medical image of anatomical tissue; applying an anisotropic diffusion filter to the ultrasound image to generate a filtered ultrasound image; performing a normalized cut operation on the filtered ultrasound image to partition the filtered ultrasound image into a plurality of regions; and selecting, from the plurality of regions, at least one region as a candidate lesion region.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
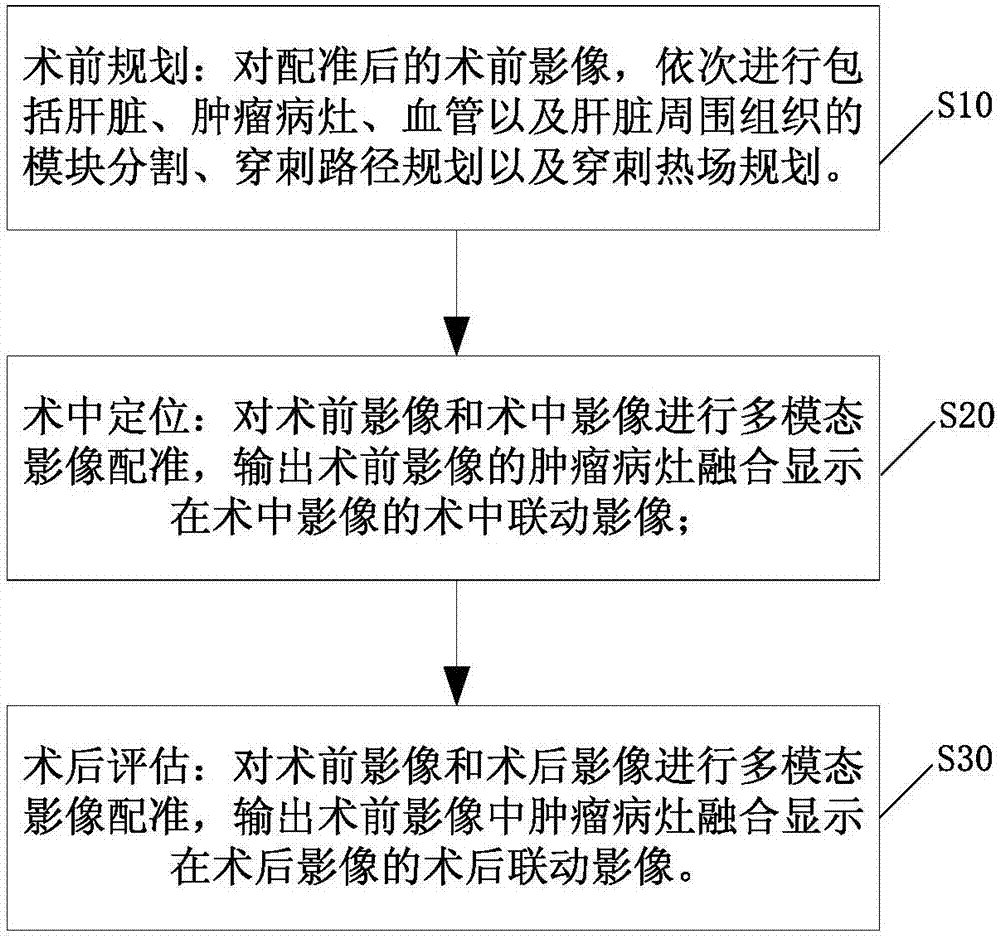
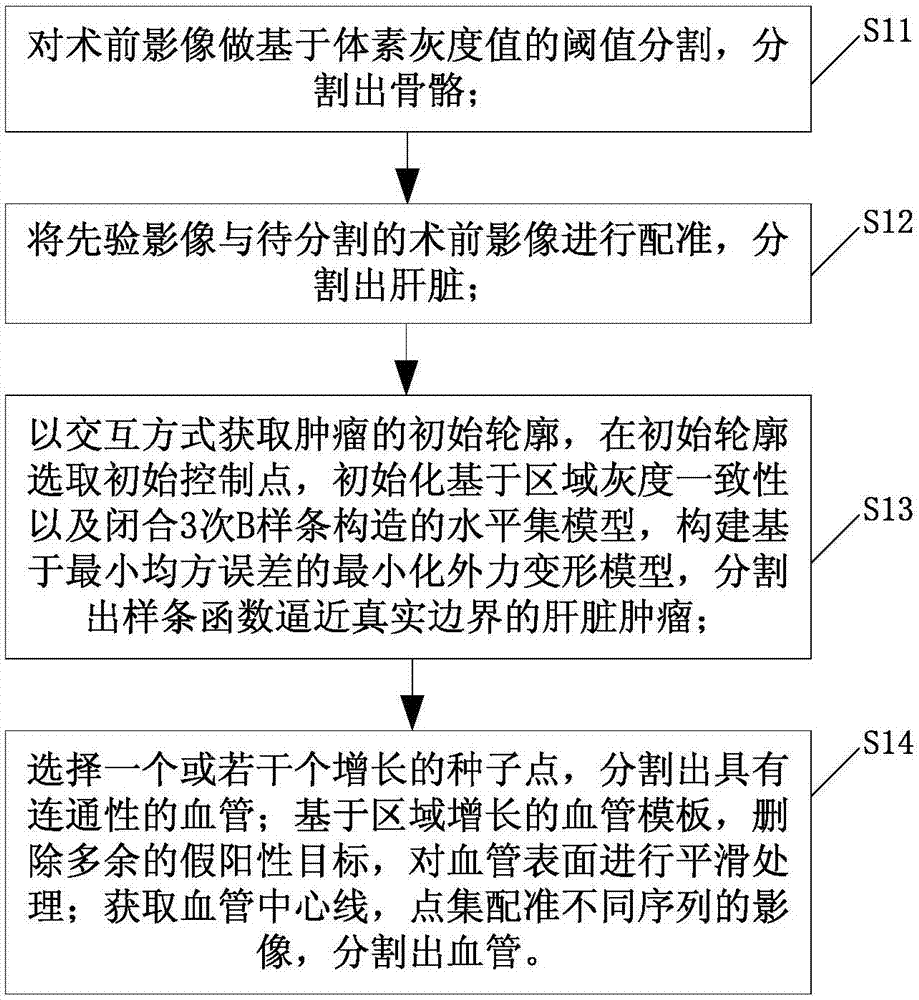
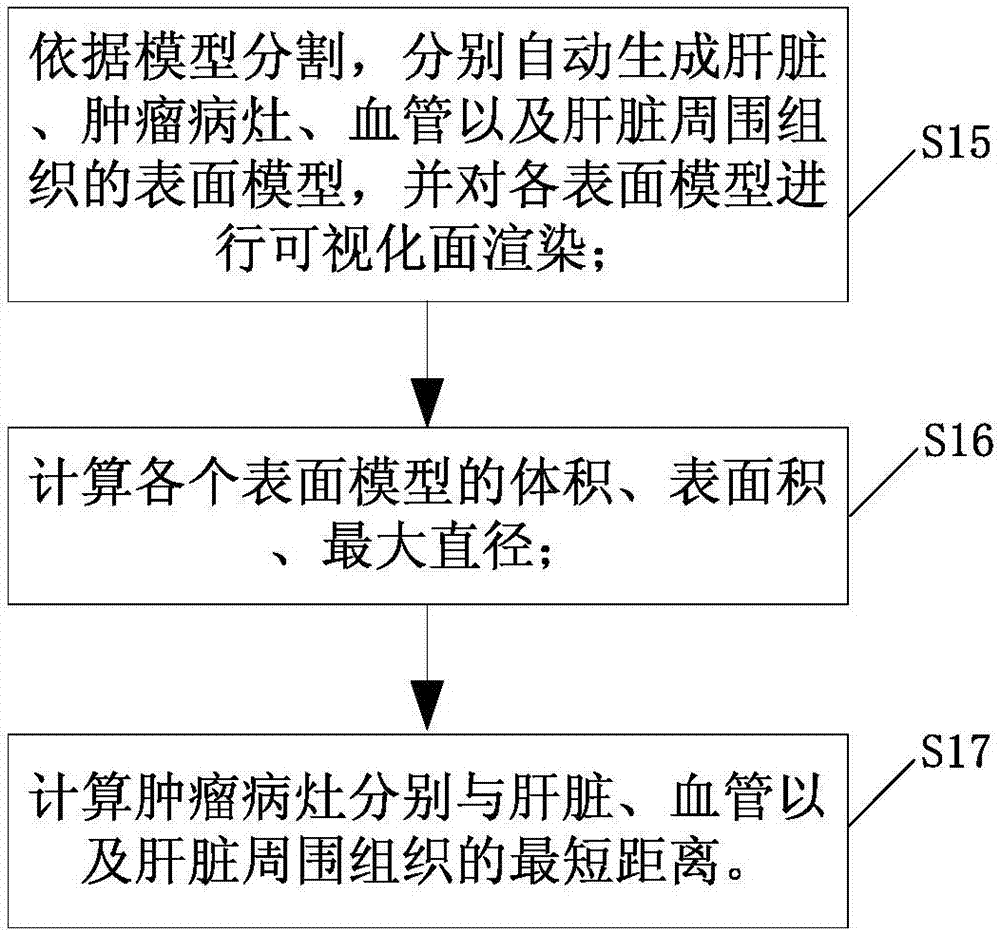
Local ablation method and system for liver cancer
InactiveCN107049475AThe display effect is intuitiveIntuitive navigationImage enhancementImage analysisDiagnostic Radiology ModalityTreatment experience
The invention discloses a local ablation method for liver cancer. The local ablation method comprises the following steps: carrying out modular partition including the liver, the tumor focus, the blood vessel and the tissue around the liver in sequence on the preoperative image after registration, and carrying out puncture path planning and puncture thermal field planning; carrying out multi-modal image registration on the preoperative image and an intra-operative image, outputting the tumor focus of the preoperative image, and displaying the tumor focus on the intra-operative image in a fusion manner; and carrying out multi-modal image registration on the preoperative image and a postoperative image, outputting the tumor focus in the preoperative image, and displaying the tumor focus in the preoperative image on the postoperative image in a fusion manner, wherein the preoperative image and the postoperative image respectively comprise the CT image and / or MR image of the time sequence, and the intra-operative image comprises the CT image. According to the method, the image registration step is added in preoperative planning, the intra-operative locating and postoperative assessment, thus the scientific planning for the tumor thermal ablation before the operation, the visual and effective information display in treatment during the operation, and the scientific assessment for the curative effects and the treatment experience feedback after the operation are realized, so that the preoperative planning is guided.
Owner:纪建松
Embolization coil delivery systems and methods
A system and method for ultrasonically guided endoscopic (EUS) delivery of one or more embolization coils to an internal body site. The embolization coil delivery devices are preferably ultrasonically guided to the selected internal body site after being advanced through the working channel of an endoscope with its distal end located near the selected internal body site. In one aspect, the system and method may be utilized to deploy an embolization coil into a lesion to promote thrombosis and / or prevent bleeding.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Method of recognizing abnormal tissue using the detection of early increase in microvascular blood content
InactiveUS20070179368A1Diagnostics using spectroscopyCatheterAbnormal tissue growthDevelopmental anomaly
The present invention, in one aspect, relates to a method for examining a target for tumors or lesions using what is referred to as “Early Increase in microvascular Blood Supply” (EIBS) that exists in tissues that are close to, but are not themselves, the abnormal tissue and in tissues that precede the development of such lesions or tumors. While the abnormal tissue can be a lesion or tumor, the abnormal tissue can also be tissue that precedes formation of a lesion or tumor, such as a precancerous adenoma, aberrant crypt foci, tissues that precede the development of dysplastic lesions that themselves do not yet exhibit dysplastic phenotype, and tissues in the vicinity of these lesions or pre-dysplastic tissues.
Owner:NORTHSHORE UNIV HEALTHSYST +1
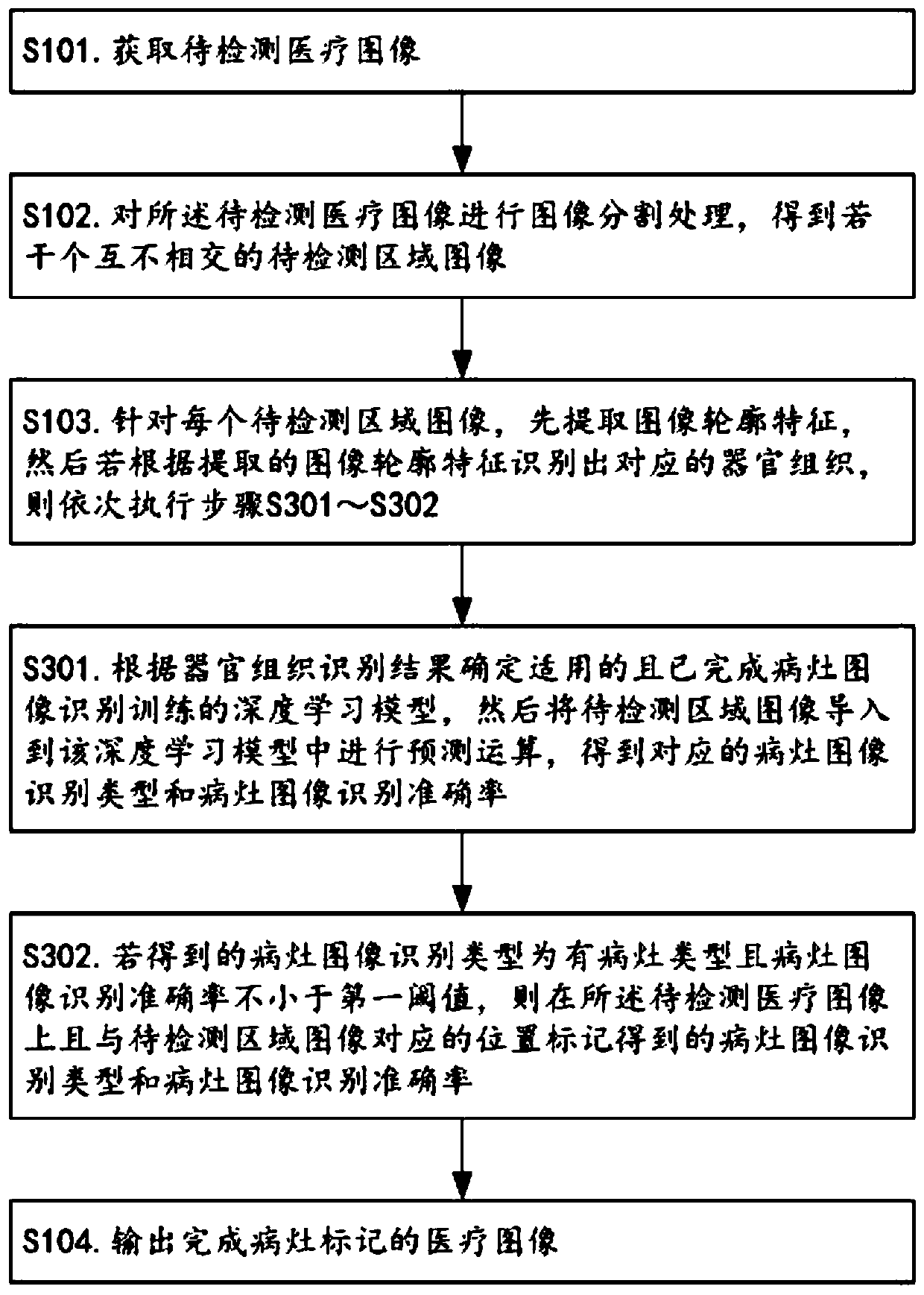
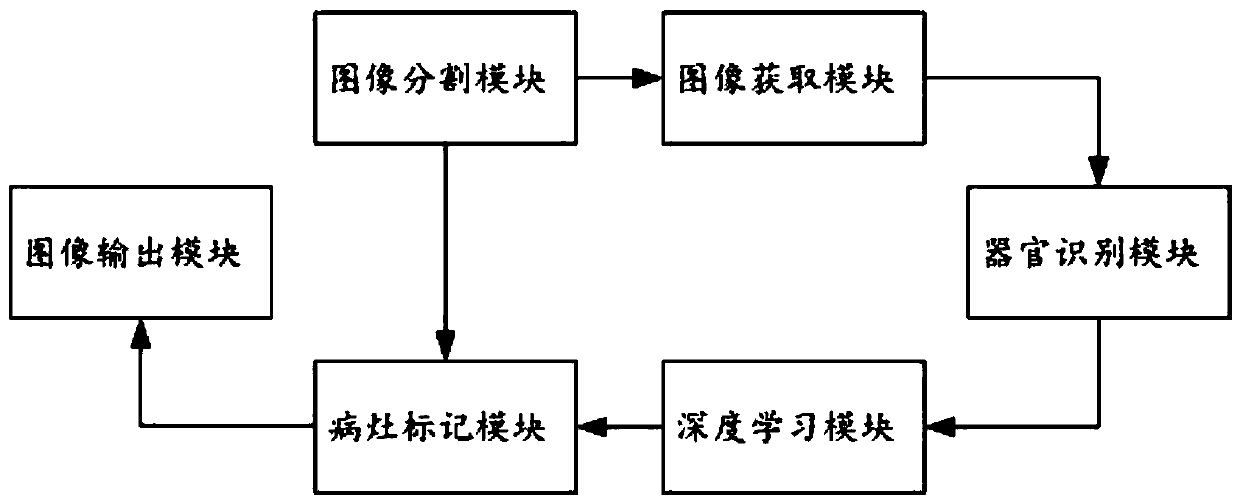
Focus image recognition method and focus image recognition system based on deep learning model
ActiveCN110232383AReduce work intensityAvoid delays in treatmentImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionMedical equipmentTreatment timing
The invention relates to the technical field of medical equipment, and discloses a focus image recognition method and a focus image recognition system based on a deep learning model. The invention provides a new method and a new system for automatically identifying conditions of medical images by replacing doctors based on the deep learning model. Regarding acquired to-be-detected medical images,Segmentation of a smallest organ tissue image and image recognition of a corresponding organ tissue, prediction of a deep learning model and marking on a predication result are carried out. The invention can replace doctors find out underlying conditions of medical images and automatically mark lesion tissues on the medical images. Therefore, a reminder is given to doctors for timely diagnosis. Working intensity of the doctors can be reduced. Whether diseases occur or not can be timely diagnosed. The treatment opportunity of conditions is prevented from being delayed, and the discovery of early-stage diseases is particularly facilitated.
Owner:HUNAN VATHIN MEDICAL INSTR CO LTD
Lesion treatment device and methods for treating lesions
Tissue and vessel treatment devices and respective methods are provided. Devices comprise a flexible treatment layer that comprises a plurality of operable elements configured to be activated to apply the treatment to the obstruction upon bending of the flexible treatment layer beyond a specified curvature threshold and to be de-activated upon a specified decrease of the bending. The treatment layer may comprise optical fiber(s) with the operable elements as emission regions that emit electromagnetic radiation from the core upon bending the optical fiber beyond a specified bending threshold. Devices may be configured as vessel sealing tips for surgical forceps, in which the treatment layer is configured to yield vessel welding and vessel cutting effects.
Owner:ASYMMETRIC MEDICAL
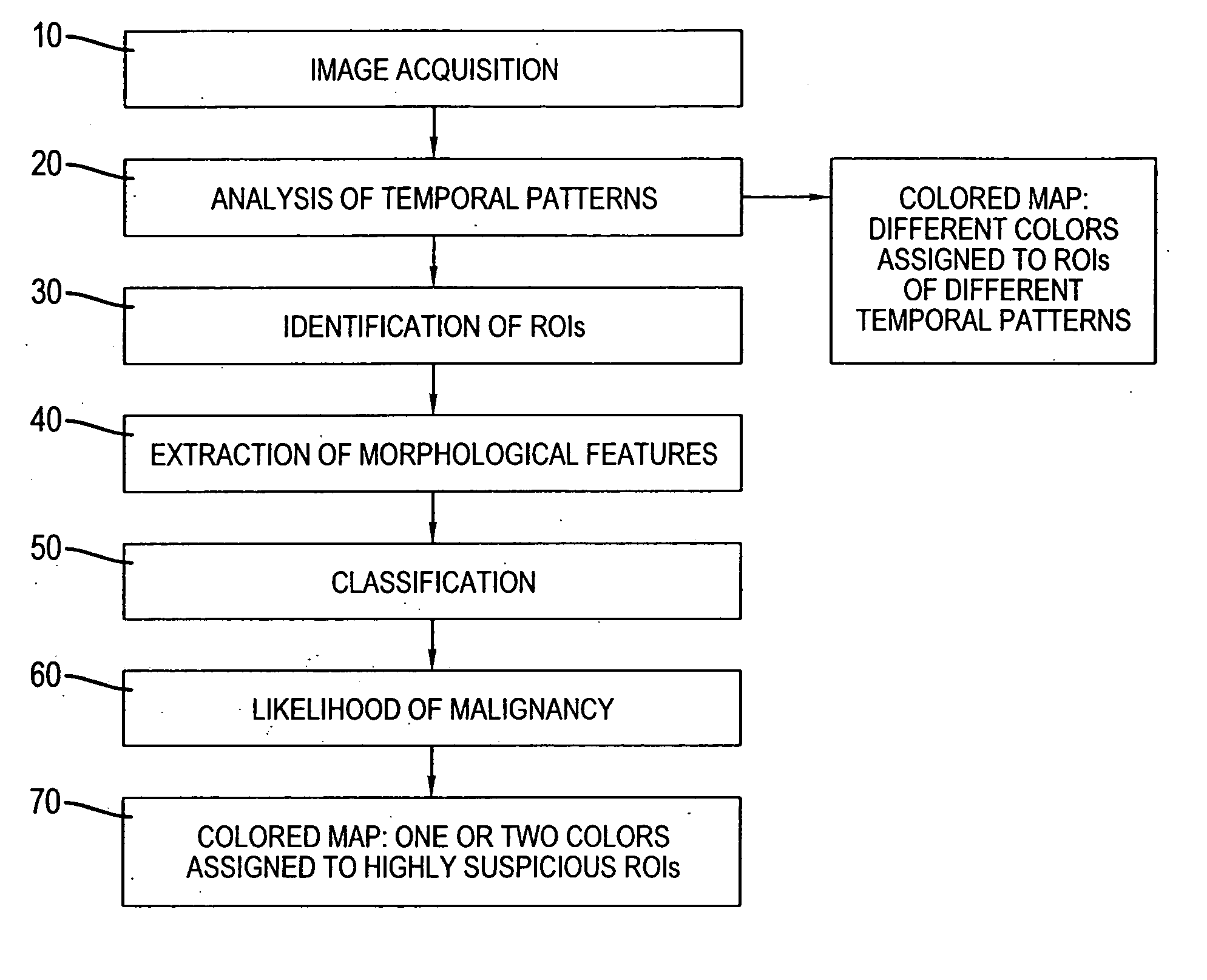
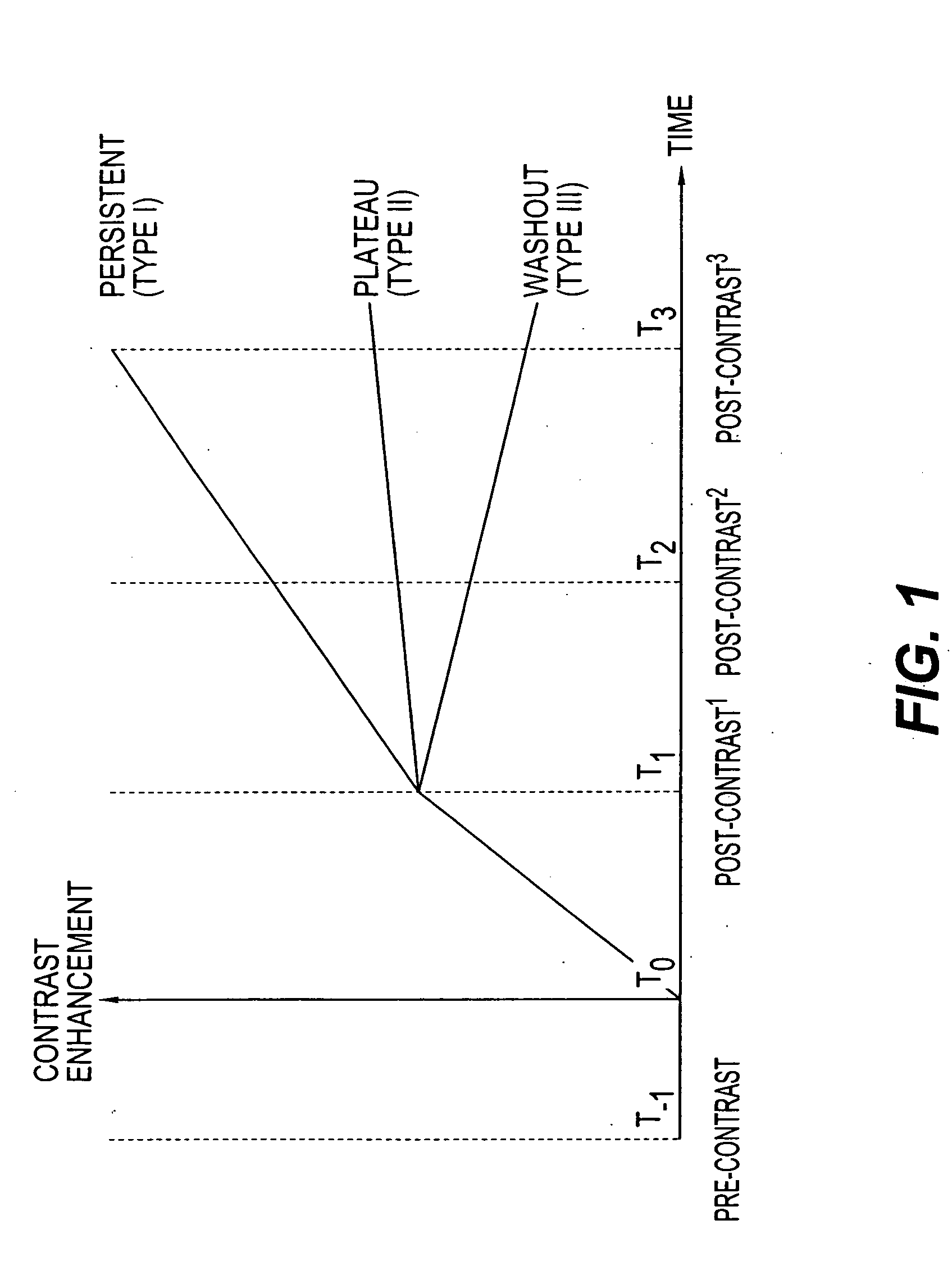
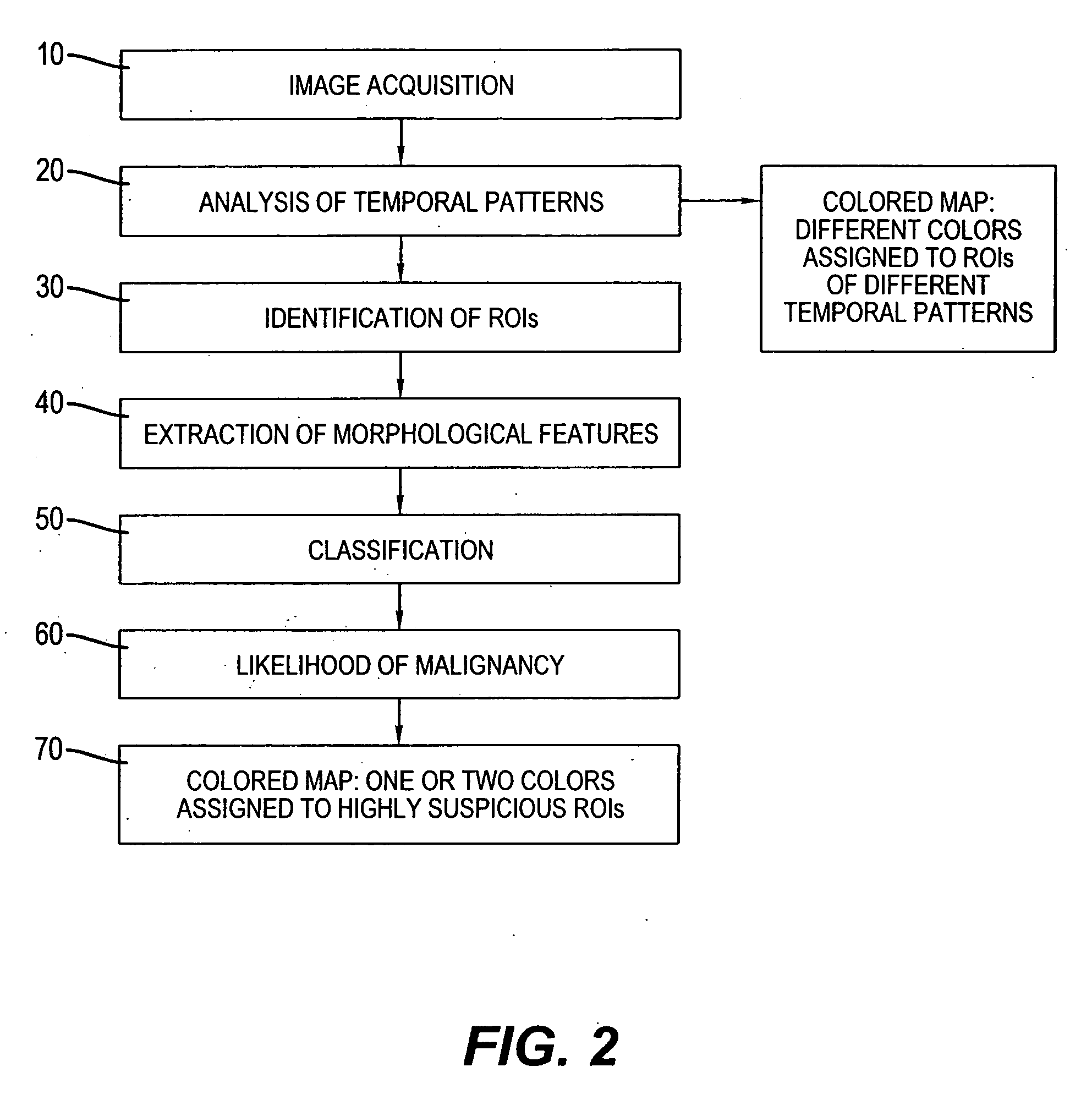
Methods and systems for automated detection and analysis of lesion on magnetic resonance images
A method for detecting and analyzing candidate lesions in a magnetic resonance image of a breast. The method includes the steps of: accessing a plurality of temporal magnetic resonance images of the breast; identifying candidate lesions by performing a temporal pattern analysis of the plurality of images to produce temporal features based on an uptake phase and a washout phase; performing a morphological operation on the candidate lesions to produce morphological features; and classifying the candidate lesions using the morphological features and temporal features to produce classified candidate lesions.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Photodynamic therapy with spatially resolved dual spectroscopic monitoring
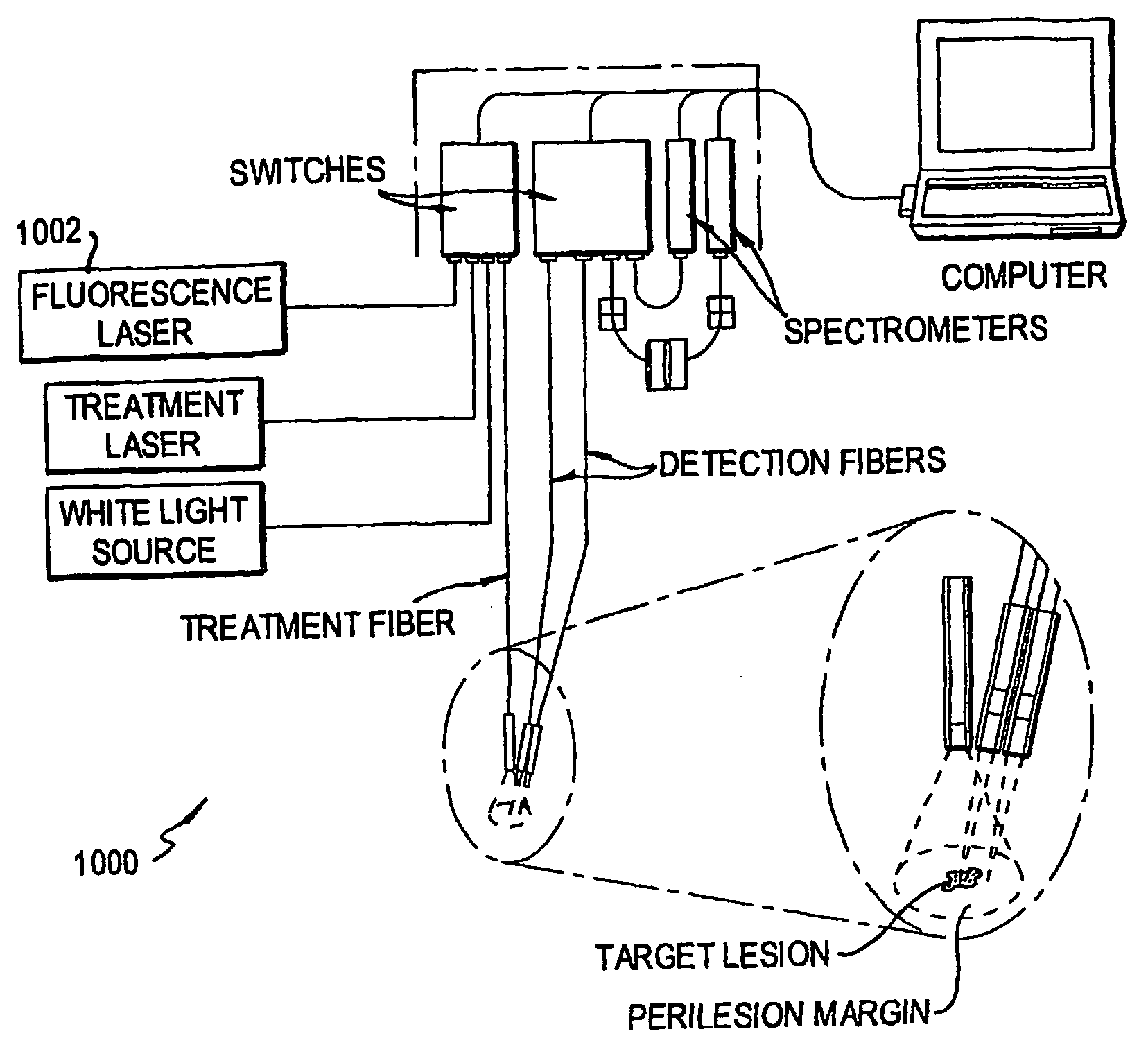
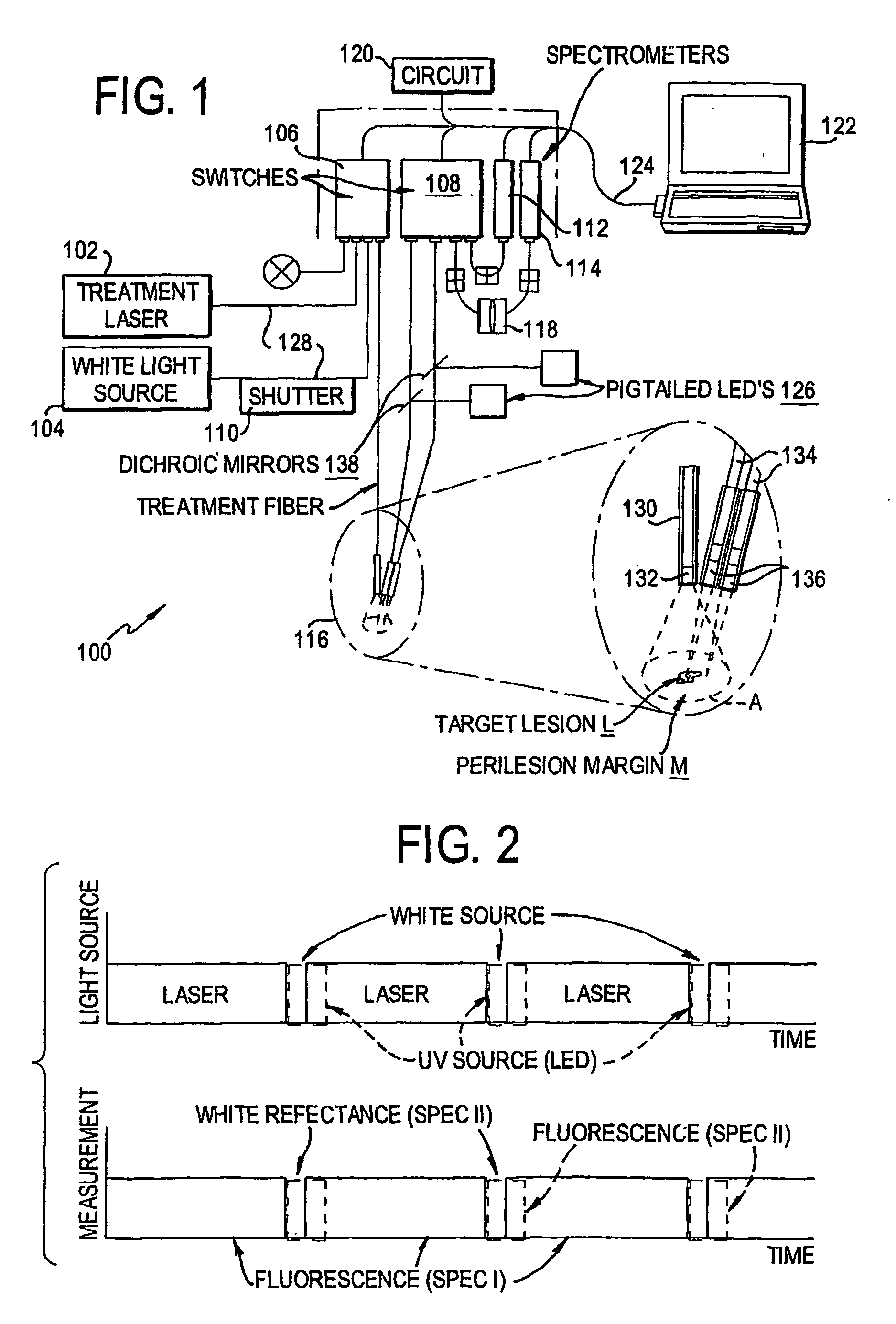
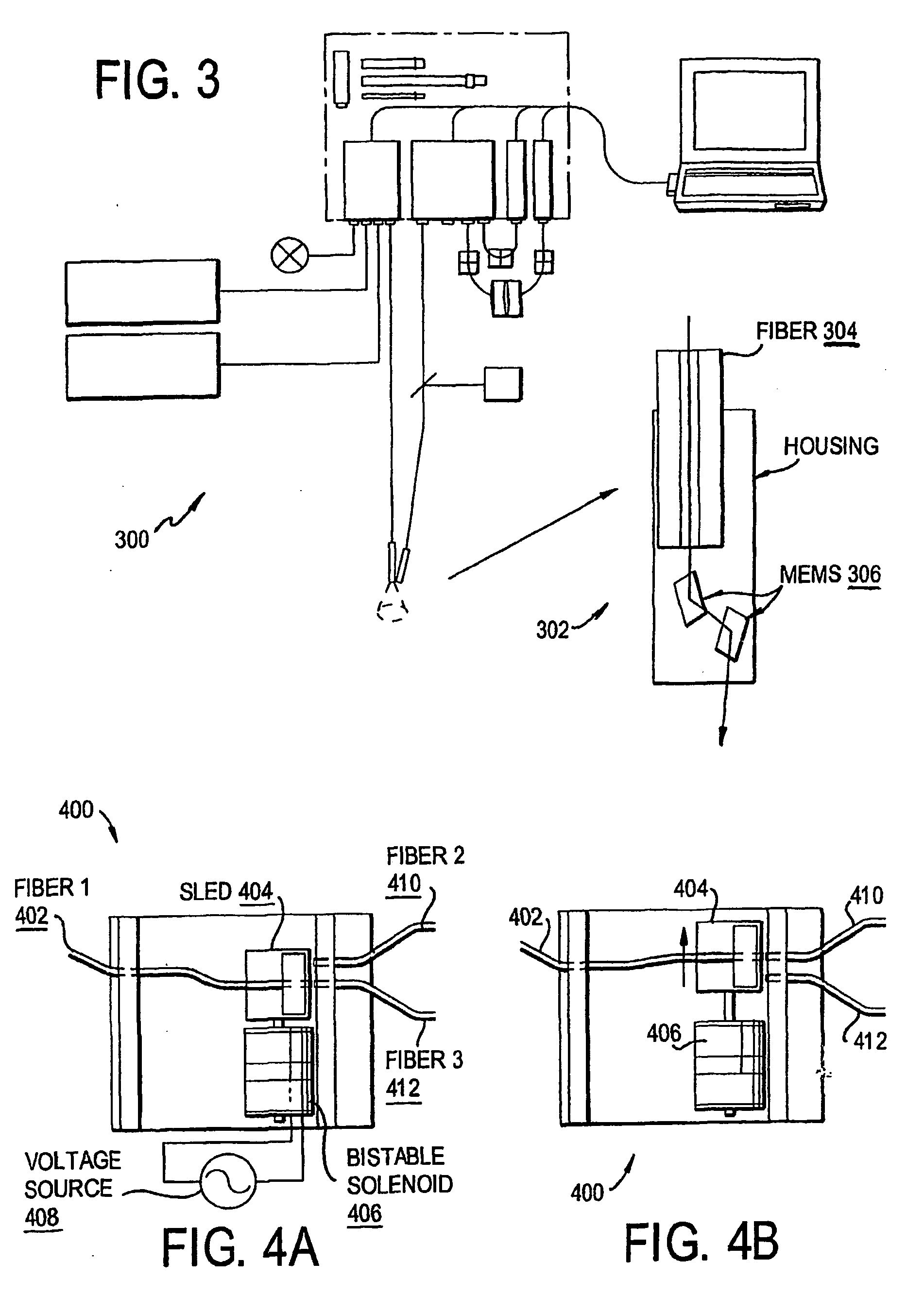
ActiveUS20090043296A1Accurate representationDiagnostics using lightSurgical instrument detailsUltraviolet fluorescenceSpectrometer
An instrument for photodynamic therapy applies treatment light from a dye laser, white light, and ultraviolet fluorescence excitation light from an LED onto a lesion and surrounding areas in a time-multiplexed manner. The reflected white light is analyzed in a spectrometer to determine a correction for the dynamic optical spectral properties of the patient's tissue. Light emitted by fluorescence from the lesion and the surrounding areas is analyzed in another spectrometer, and the results are corrected in a computer, using the correction. An optical switch has been developed for the instrument, using a bistable solenoid and a sled.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER +1
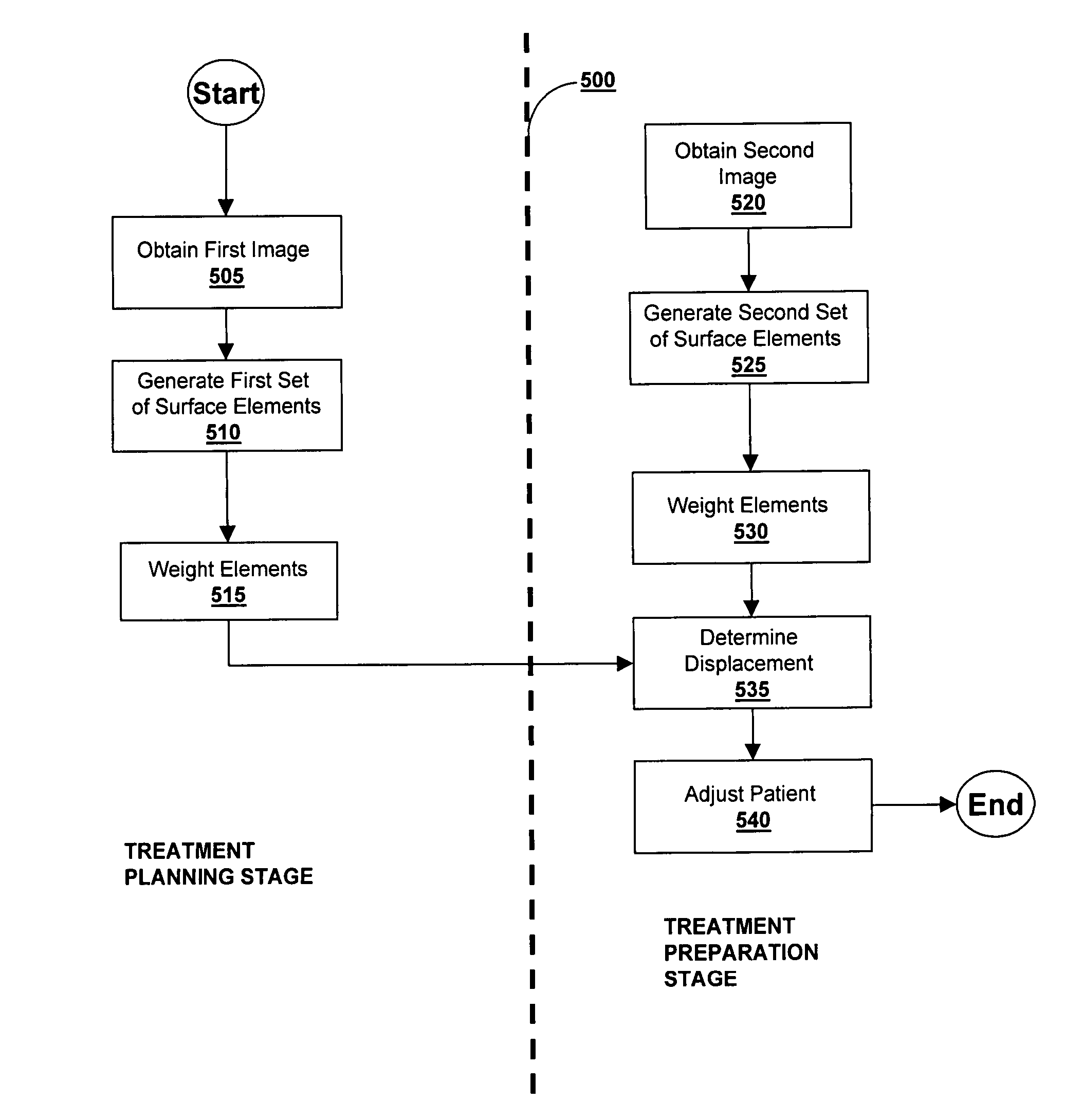
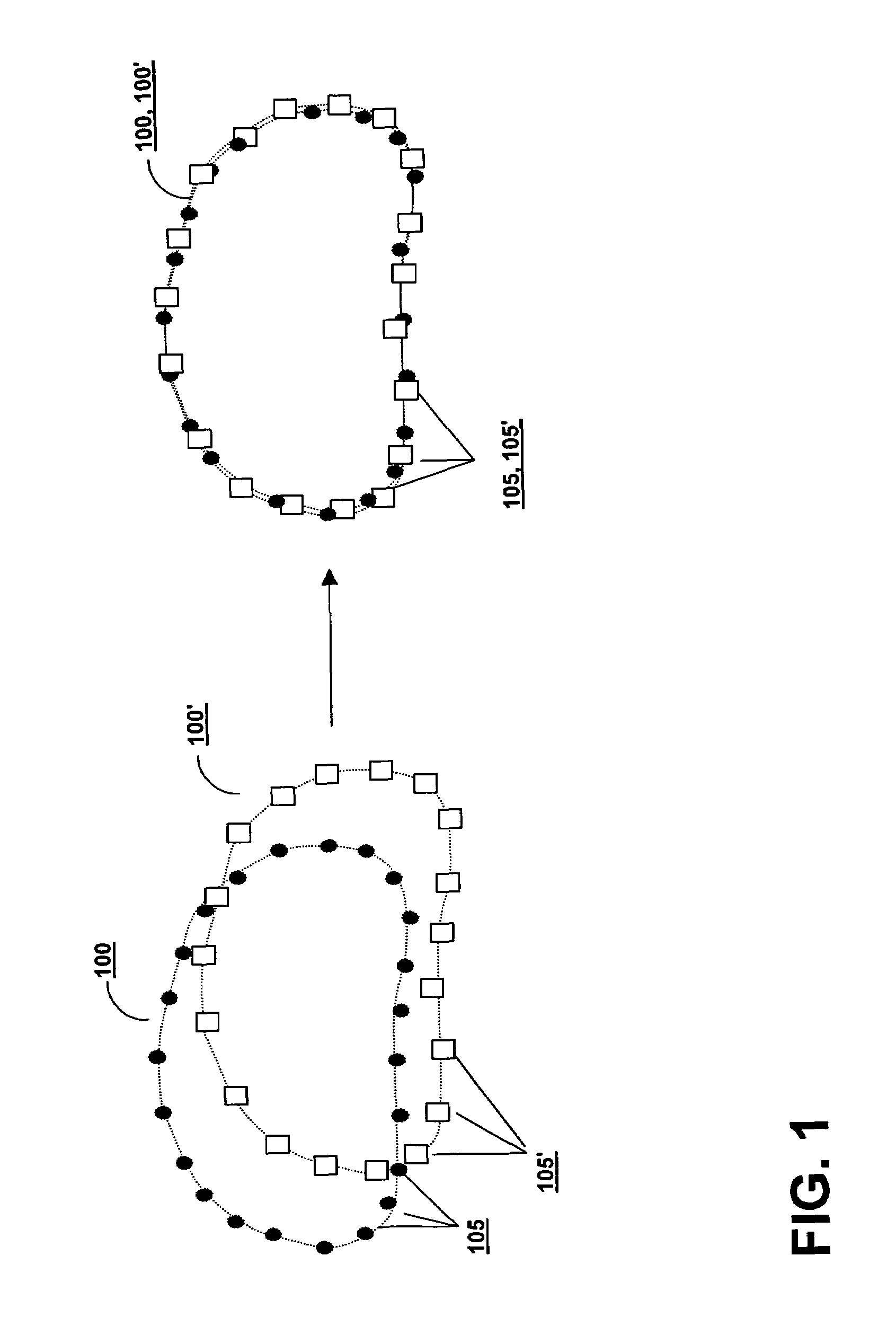
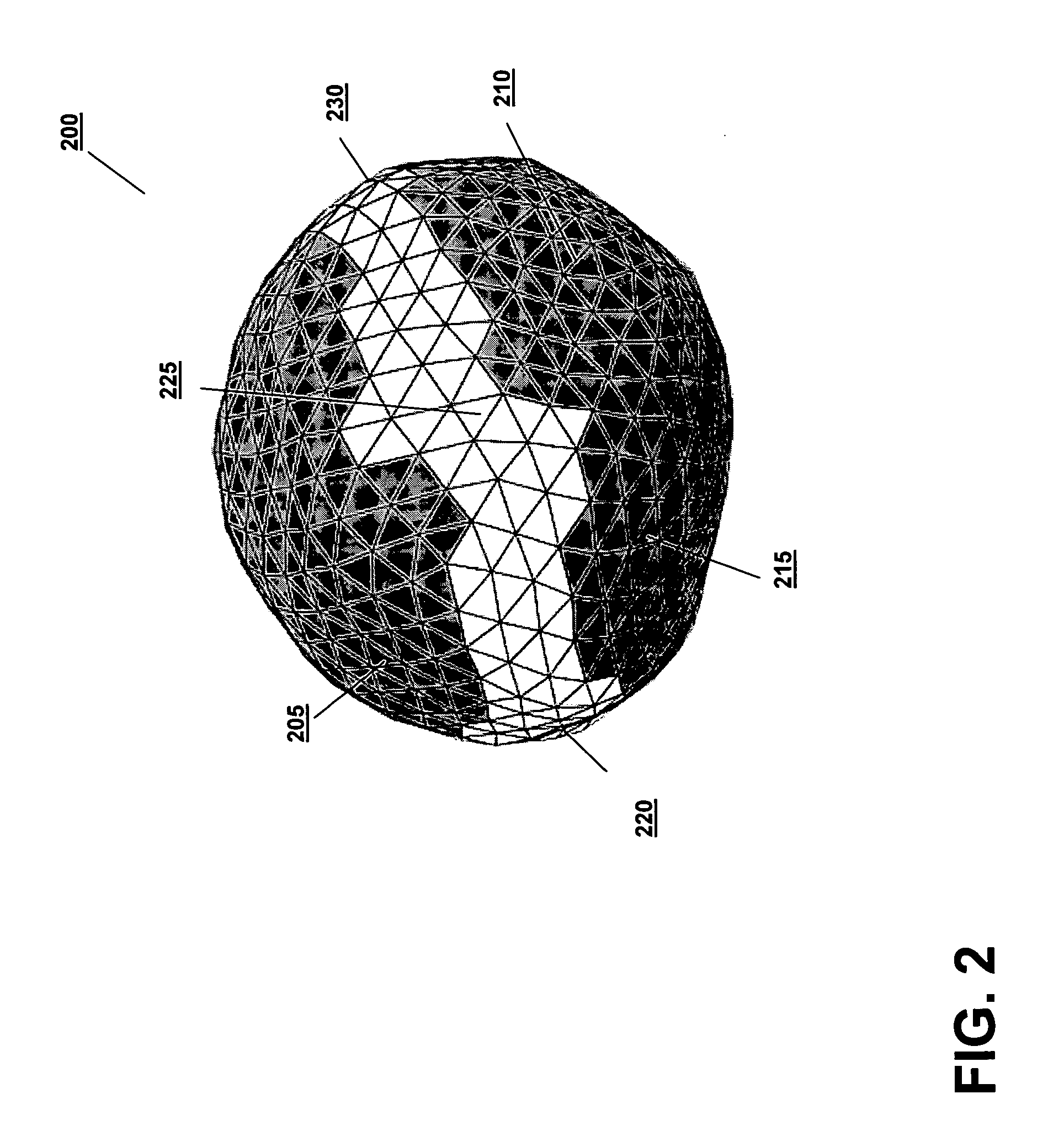
Weighted surface-to-surface mapping
ActiveUS7672705B2Facilitates rapid and accurate treatment position adjustmentImage enhancementImage analysis3d imageRadiology
A displacement of a lesion within a patient is determined for the purpose of administering radiation treatment by generating sets of surface elements from three-dimensional images of the lesion taken at different times. Weights are assigned to the surface elements, and based on weights and the proximity of corresponding elements in one set to elements in another set, a displacement is determined.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
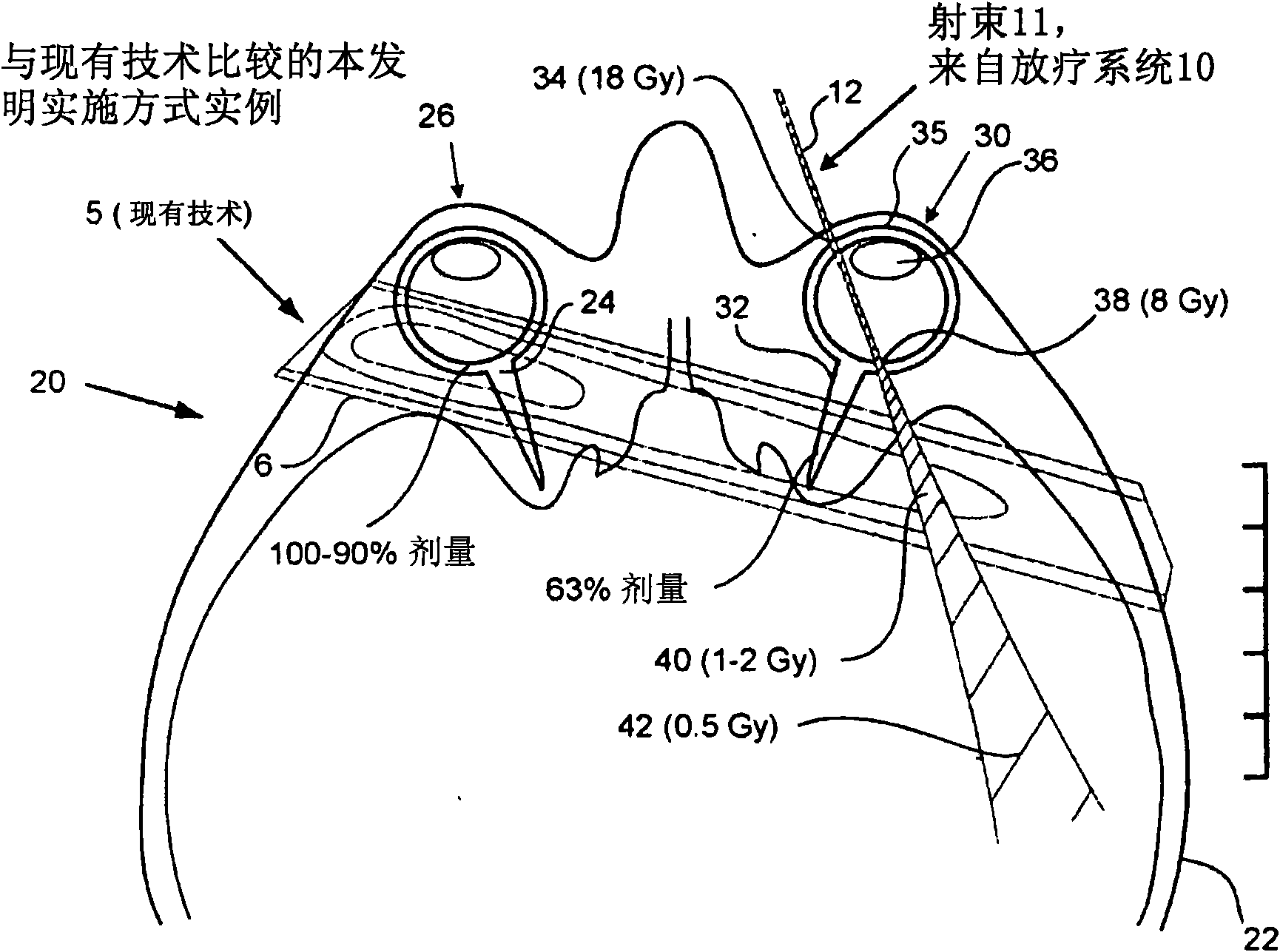
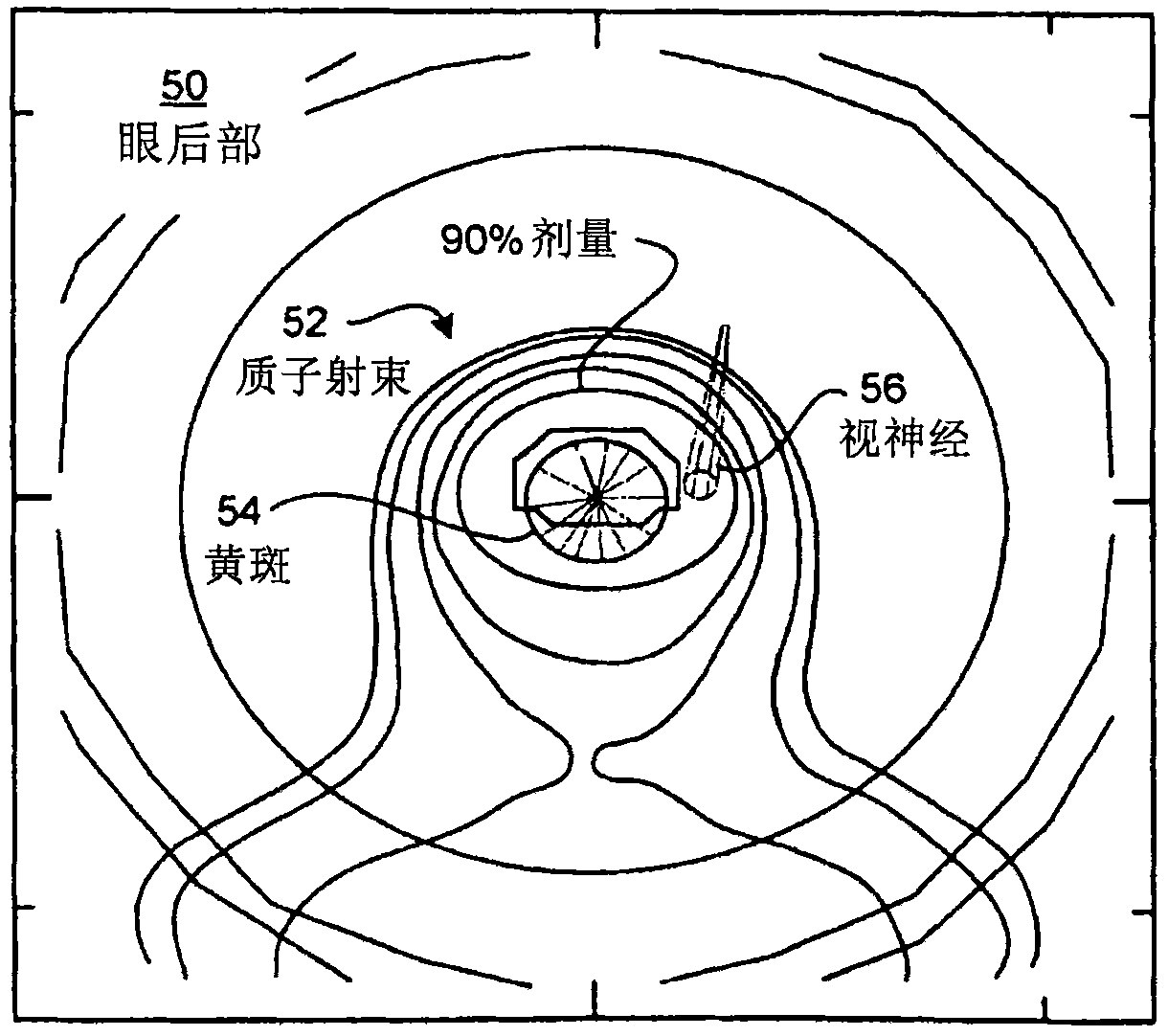
Methods and devices for orthovoltage ocular radiotherapy and treatment planning
A method, code and system for planning the treatment a lesion on or adjacent to the retina of an eye of a patient are disclosed. There is first established at least two beam paths along which x-radiation is to be directed at the retinal lesion. Based on the known spectral and intensity characteristics of the beam, a total treatment time for irradiation along each beam paths is determined. From the coordinates of the optic nerve in the aligned eye position, there is determined the extent and duration of eye movement away from the aligned patient-eye position in a direction that moves the patient's optic nerve toward the irradiation beam that will be allowed during treatment, while still maintaining the radiation dose at the patient optic nerve below a predetermined dose level.
Owner:ORAYA THERAPEUTICS
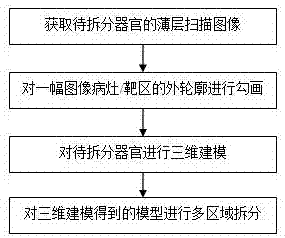
Three-dimensional imaging method and system of organ and lesion based on medical images
ActiveCN106887039AEasy to observeEasy to analyzeImage enhancementImage analysisImage segmentationComputer science
The invention discloses a three-dimensional imaging method and system of an organ and a lesion based on a medical image. The method comprises the steps of (S1) obtaining thin layer scan images of an organ to be split, (S2) sketching the contour of a lesion / target area of an image, (S3) carrying out 3D modeling on the organ to be split comprising the lesion / target area, and (S4) carrying out multi-area splitting on a model of the organ to be split obtained by the 3D modeling. According to the method and the system, medical image segmentation is not only stay in the segmentation of a whole organ and an external non-organ part, each area of the organ is segmented further and the lesion / target area is segmented, the observation of possible diseased organs of a patient in a later period is facilitated, and the analysis of a lesion / target area (tumor) position is facilitated.
Owner:CHENGDU GOLDISC UESTC MULTIMEDIA TECH
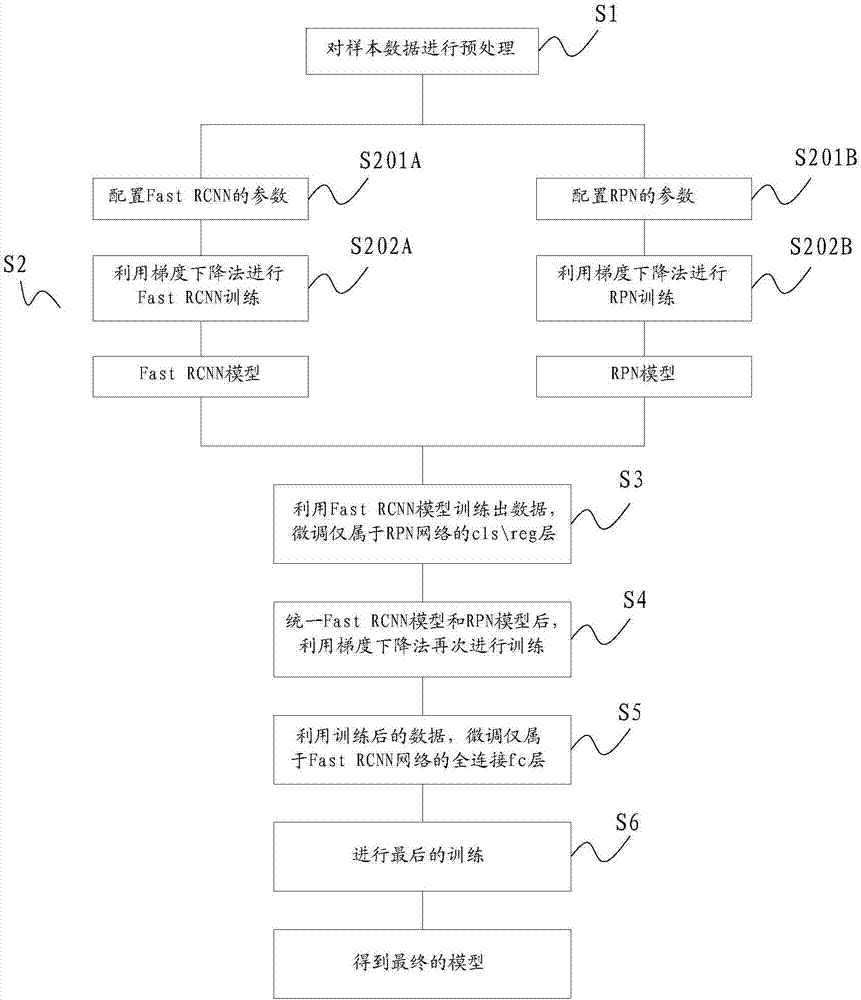
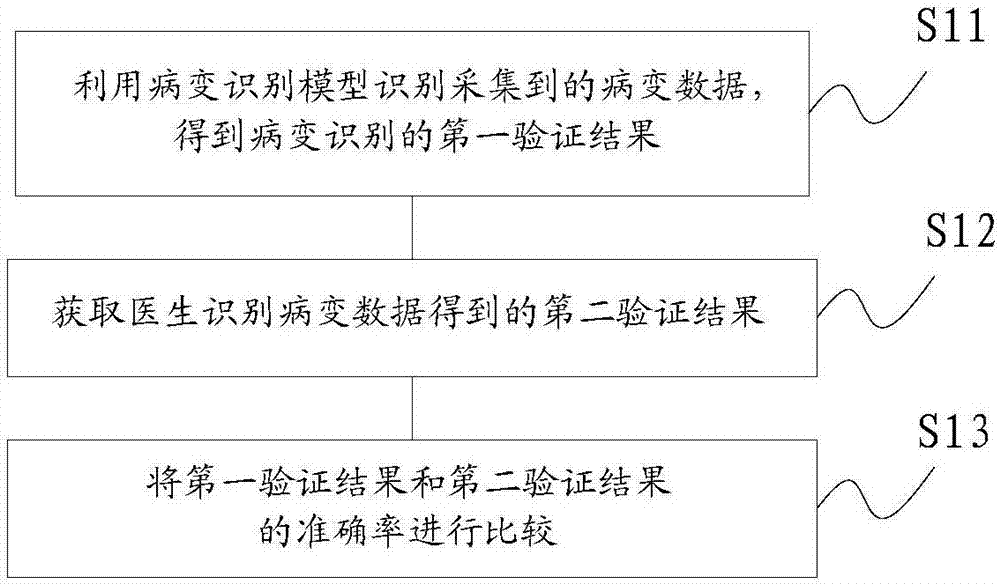
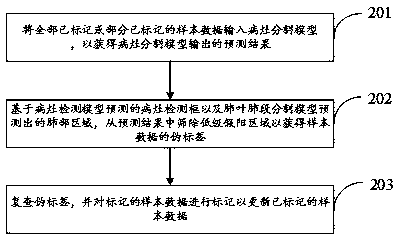
Training method and verification method for lesion identification model, and lesion image identification device
InactiveCN107368859AOvercoming subjectivityCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsIdentification deviceImage identification
The invention discloses a training method for a lesion identification model. The training method comprises the following step of utilizing an obtained lesion image sample to train a Faster RCNN (Recurrent Neural Network) to obtain the lesion identification model. The invention also correspondingly provides a lesion image device based on the lesion identification model and a verification method for the lesion identification mode. The training method for the lesion identification model is designed on the basis of a deep learning concept, and the position and the type of a focus can be accurately judged when the model is used for carrying out lesion identification.
Owner:BEIJING HOTWIRE MEDICAL TECH DEV CO LTD
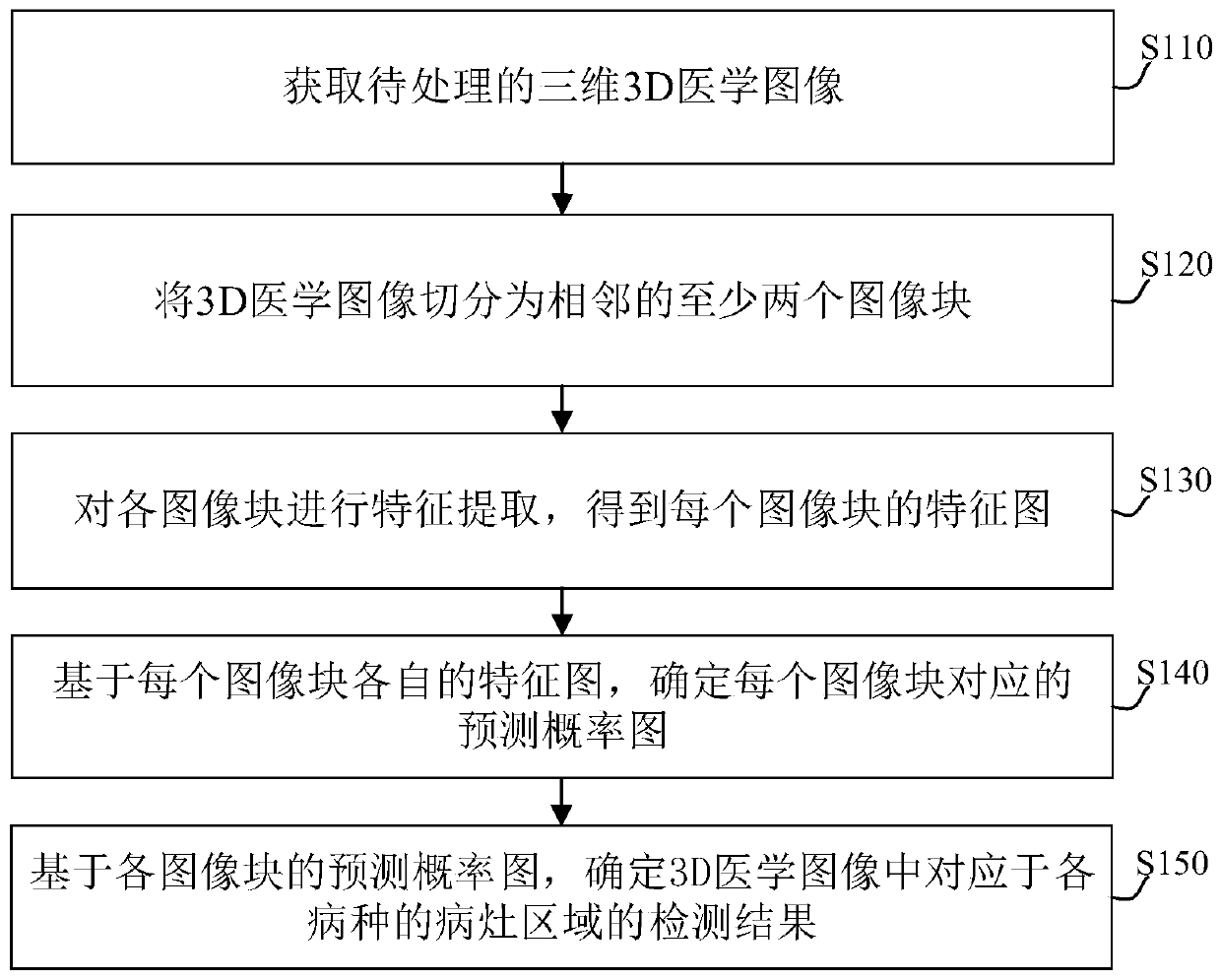
Medical image processing method and device, electronic equipment and computer storage medium
ActiveCN110807788AAccurate determination of test resultsImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingFeature extraction
The embodiment of the invention provides a medical image processing method and device, electronic equipment and a computer storage medium. The method can comprise the steps of obtaining a to-be-processed 3D medical image; segmenting the 3D medical image into at least two adjacent image blocks; performing feature extraction on each image block to obtain a feature map of each image block; determining a prediction probability graph corresponding to each image block based on the respective feature graph of each image block; and based on the prediction probability graph of each image block, determining a detection result of a lesion area corresponding to each disease in the 3D medical image. Through the scheme of the invention, the detection result corresponding to the same disease in the 3D medical image can be accurately determined based on the image blocks and the relevance among the image blocks.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
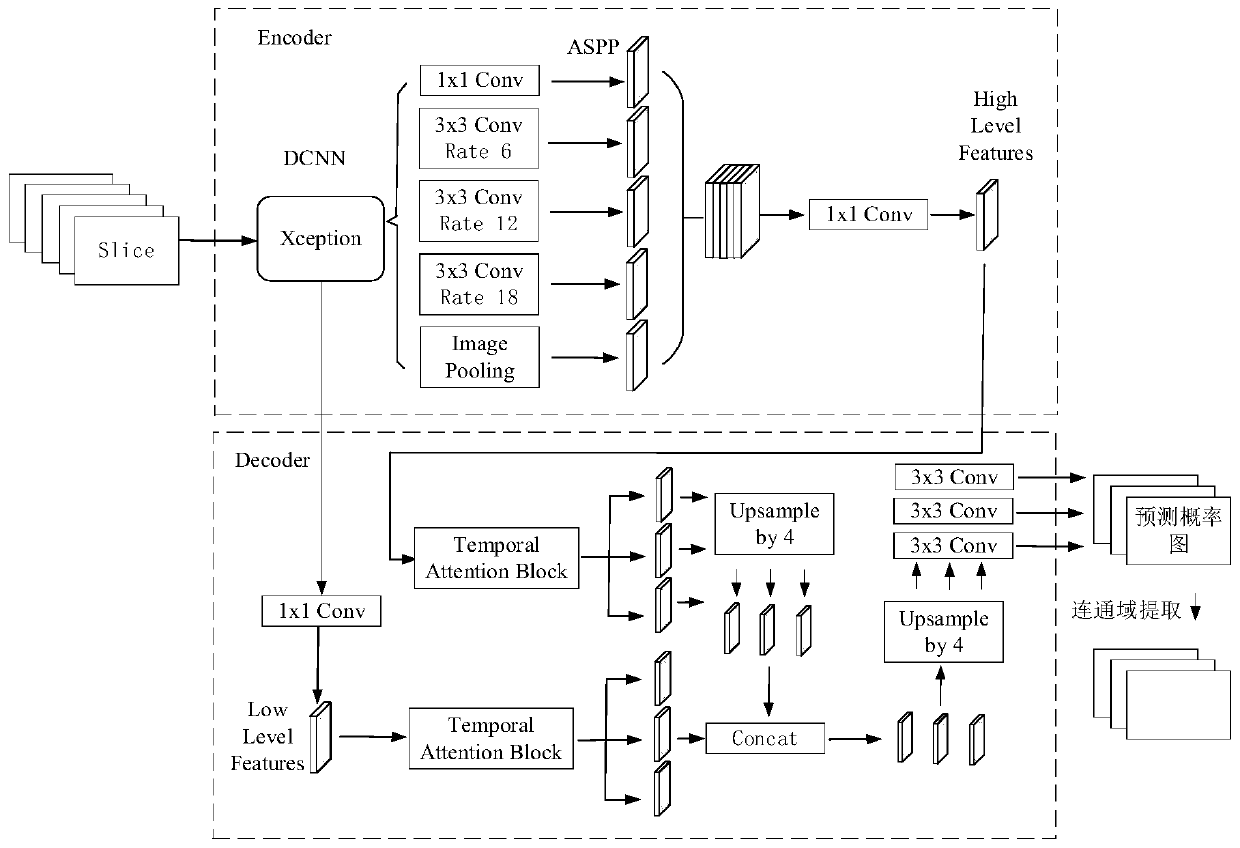
Pathological image processing method and model training method and device based on deep learning
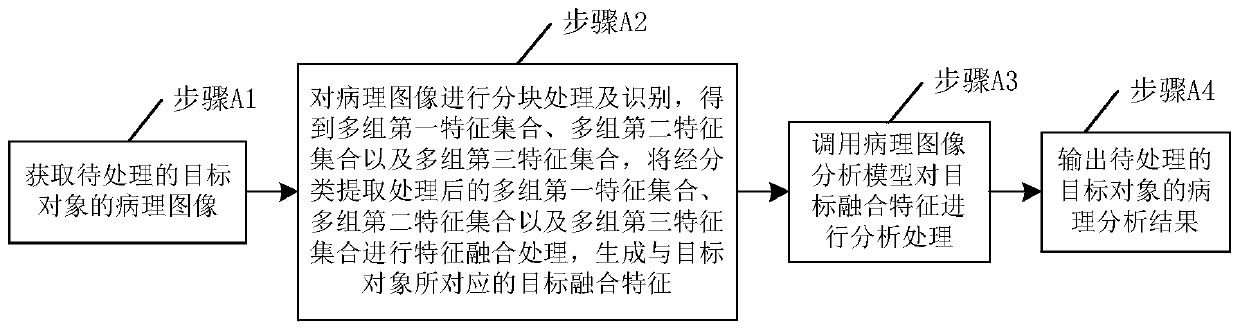
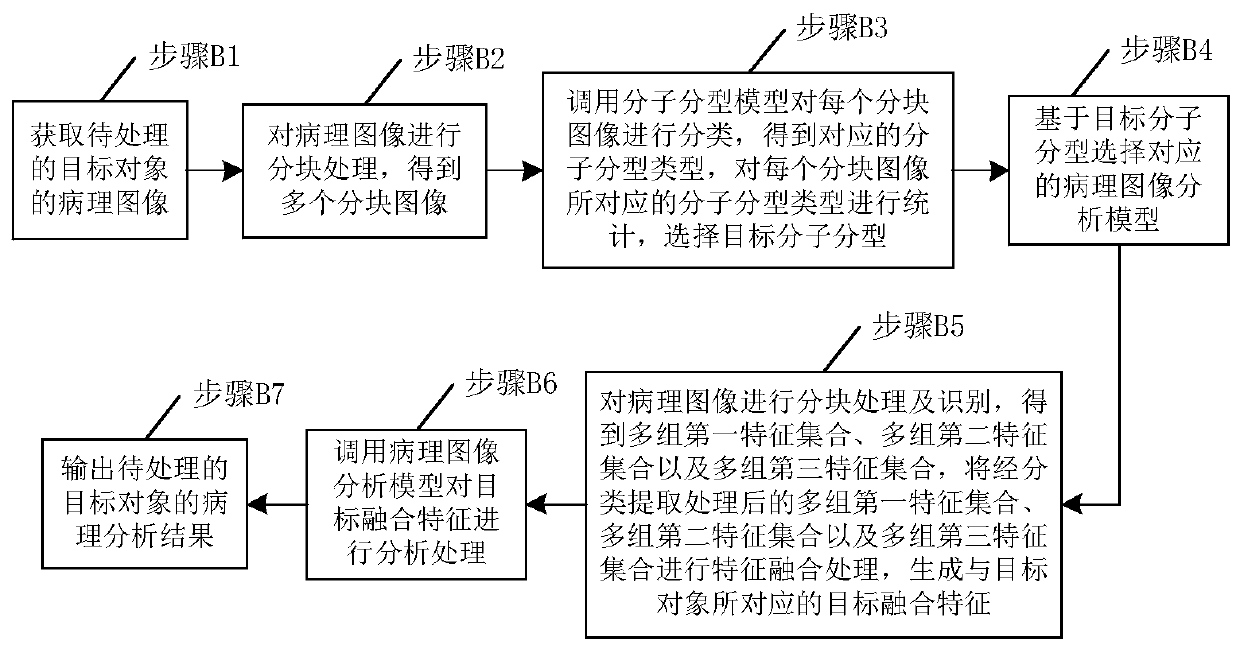
PendingCN111462036AShorten the timeImprove detection efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisFeature setImaging processing
The invention discloses a pathological image processing method based on deep learning. The pathological image processing method comprises: obtaining a pathological image of a to-be-processed target object; partitioning the pathological image of the target object to be processed to obtain a partitioned image set; performing feature classification extraction processing on the block image set to obtain N first feature sets, N second feature sets and N third feature sets; generating a target fusion feature corresponding to the target object; and calling the pathological image analysis model to analyze and process the target fusion features so as to output a pathological analysis result of the to-be-processed target object. The invention further discloses a model training method. The pathological image can be directly utilized to predict the risk of lesion metastasis. Compared with a biological detection technology, the method is advantageous in that the time for waiting for a detection result can be shortened, the detection efficiency can be improved, errors caused by uncontrollable factors such as experimental errors and operation errors can be avoided, and then a more accurate detection result is provided.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
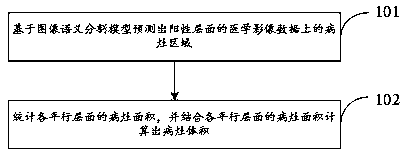
Pneumonia lesion segmentation method and device
ActiveCN111047609AEfficient use ofReduce the amount of calculationImage enhancementImage analysisLung lobeMedical imaging data
The embodiment of the invention provides a pneumonia lesion segmentation method and device, and solves the problems of low accuracy and low efficiency of an existing pneumonia lesion segmentation mode. The pneumonia lesion segmentation method comprises the following steps: predicting a lesion area on medical image data of a positive level based on an image semantic segmentation model; counting thelesion area of each parallel layer, and calculating the lesion volume by combining the lesion area of each parallel layer, wherein the image semantic segmentation model is established through the following training steps: inputting all or part of marked sample data into a focus segmentation model to obtain a prediction result output by the focus segmentation model; based on a focus detection frame predicted by a focus detection model and a lung region predicted by a lung lobe lung segment segmentation model, screening out a low-level false positive region from a prediction result to obtain afalse label of sample data, and adding unmarked sample data; and rechecking the pseudo label, and marking the marked sample data to update the marked sample data.
Owner:BEIJING SHENRUI BOLIAN TECH CO LTD +2
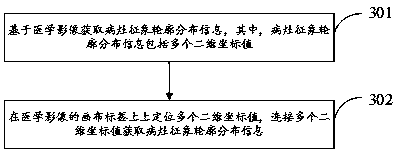
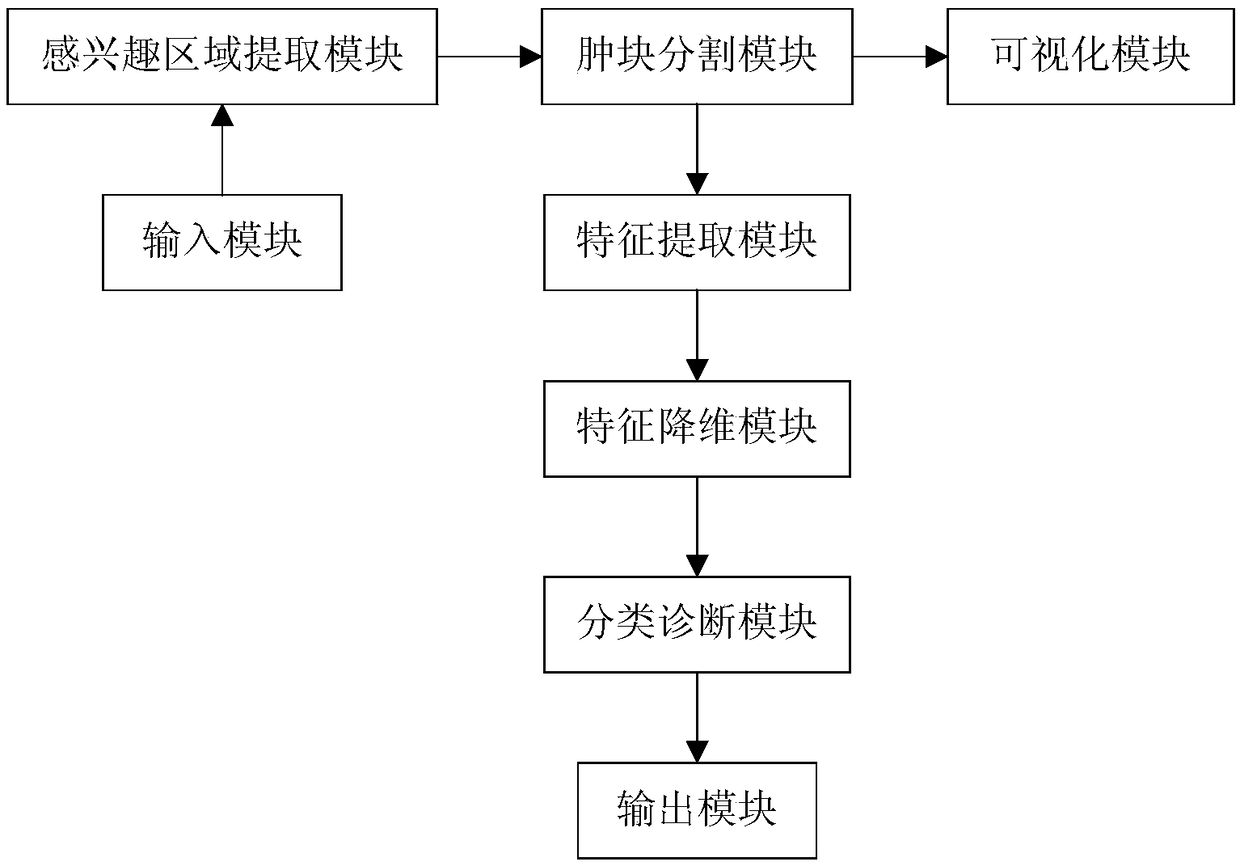
MRI image-based axillary lymph gland metastasis prediction system
InactiveCN109009110AImprove accuracyImprove efficiencyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFeature setLymphatic Spread
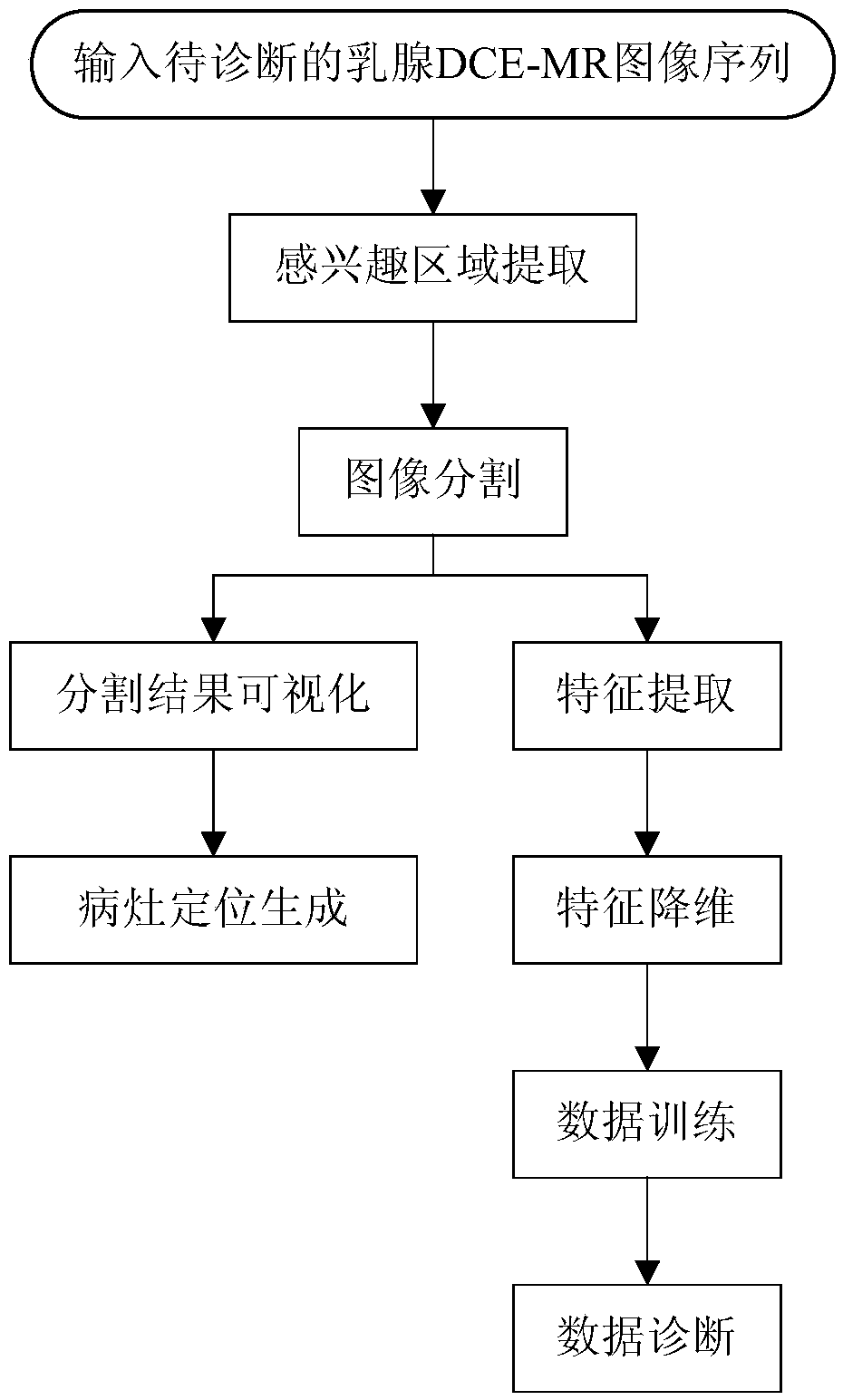
The invention provides an MRI image-based axillary lymph gland metastasis prediction system and relates to the technical field of computer aided diagnosis. The system comprises an input module, an area-of-interest extraction module, a lump segmentation module, a sub-visualization module, a feature extraction module, a feature dimensionality reduction module, a classification and diagnosis module,and an output module. The input module receives a to-be-diagnosed mammary gland DCE-MR image sequence input by a user. The area-of-interest extraction module extracts an area of interest from the mammary gland DCE-MR image sequence. The lump segmentation module segments a lump in the area of interest. The sub-visualization module carries out the visual display on each segmented image and extractsthe edge of a focus. The feature extraction module extracts relevant feature values according to the lump information and transmits the relevant feature values to the feature dimensionality reductionmodule. The feature dimensionality reduction module carries out feature dimensionality reduction on an extracted feature set. The classification and diagnosis module inputs each lump feature value into a classifier. After that, the automatic classification and recognition is carried out by a computer for judging whether a lymph gland has already been transferred or not. The output module displaysa transfer prediction result and a transfer probability. According to the invention, the accurate segmentation of breast lesions can be realized. The accurate diagnosis of mammary axillary lymph glandmetastasis can be effectively assisted.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Multi-modal fusion surgical navigation system and method based on three-dimensional reconstruction
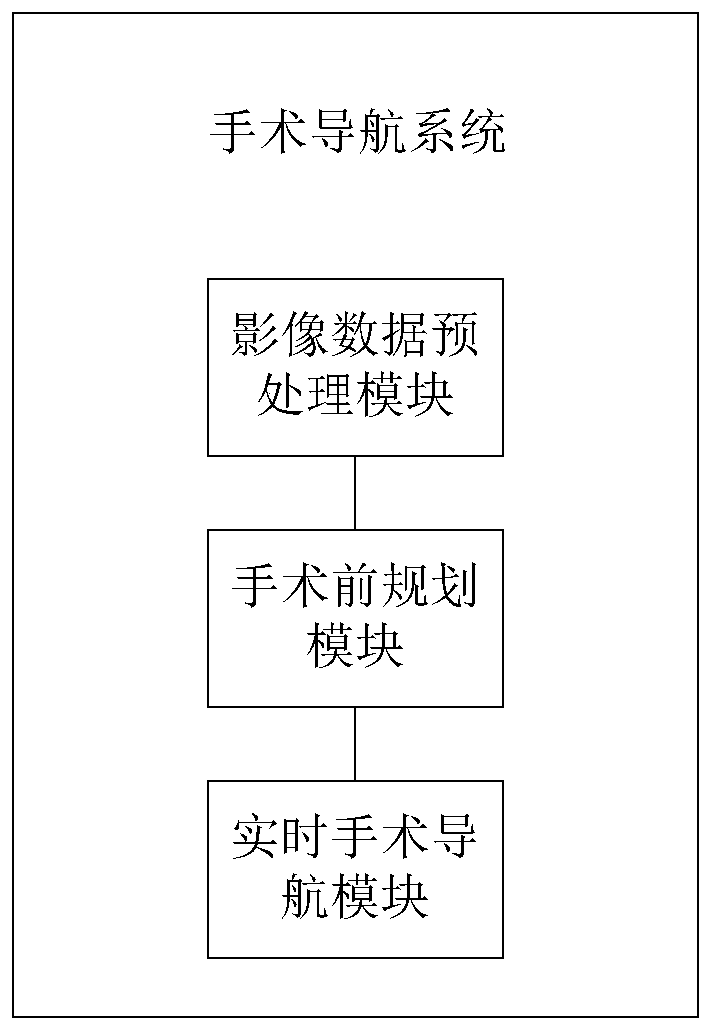
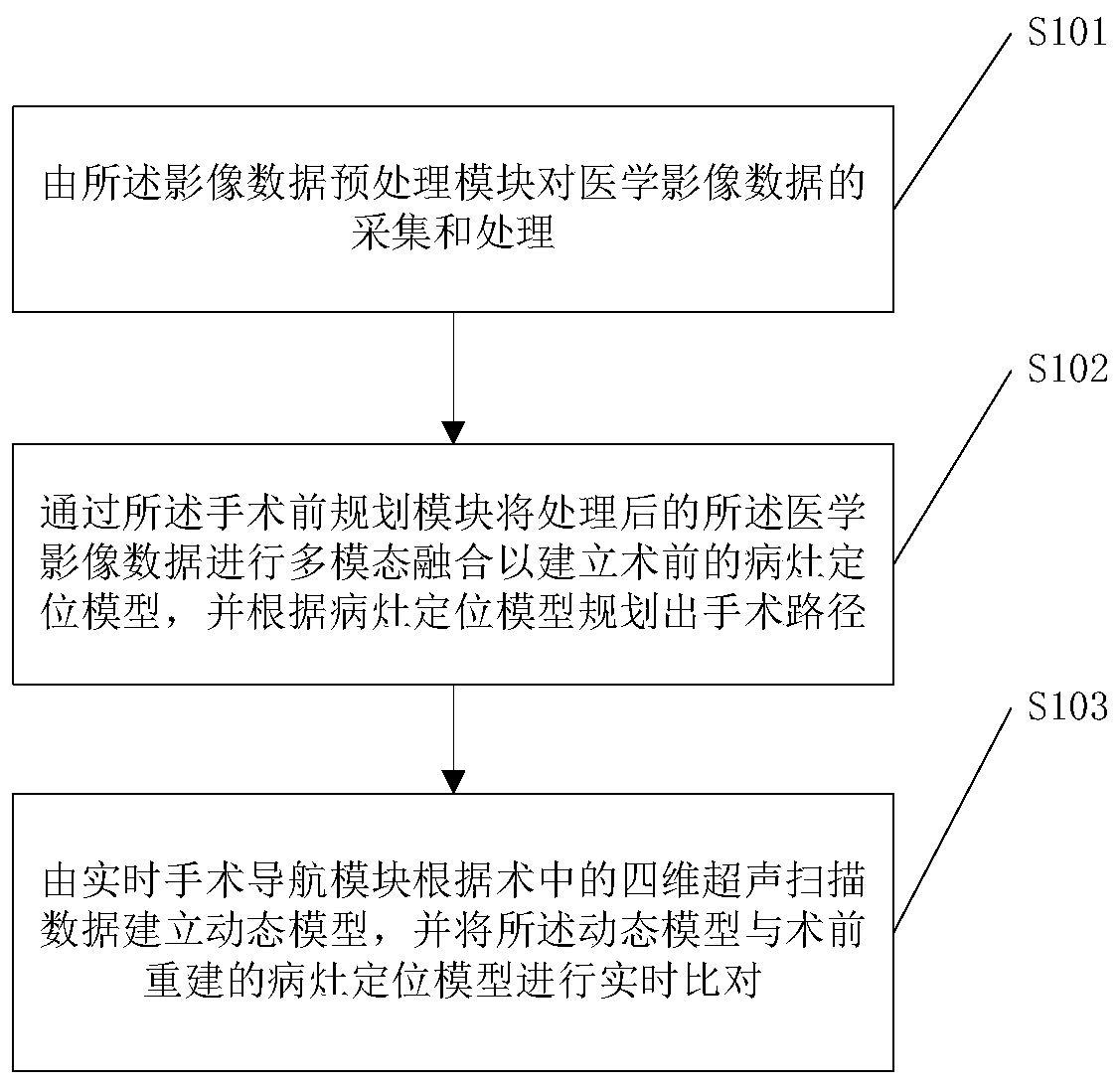
ActiveCN111529063AChange precision monitoringHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisMedical imaging dataDynamic models
The invention discloses a multi-modal fusion surgical navigation system and method based on three-dimensional reconstruction. The system comprises an image data preprocessing module, a pre-surgery planning module and a real-time surgical navigation module; the image data preprocessing module is used for the collection and processing of medical image data; the pre-surgery planning module performs multi-modal fusion of the processed medical image data to establish a pre-surgery lesion location model and plan a surgical path; and the real-time surgical navigation module establishes a dynamic model according to an intra-surgery four-dimensional ultrasound scan data, and compares the dynamic model with the pre-surgery lesion model to update the surgical path. The beneficial effects are: conducting fusion processing of different medical image data, integrating the advantages of each model, achieving information complementarity, and performing real-time comparison of the real-time establisheddynamic model with the pre-surgery lesion positioning navigation model, so as to make navigation more accurate. Accurate monitoring of the lesion changes is performed during the surgery process, so as to improve the accuracy and effect of interventional surgery.
Owner:广州狄卡视觉科技有限公司
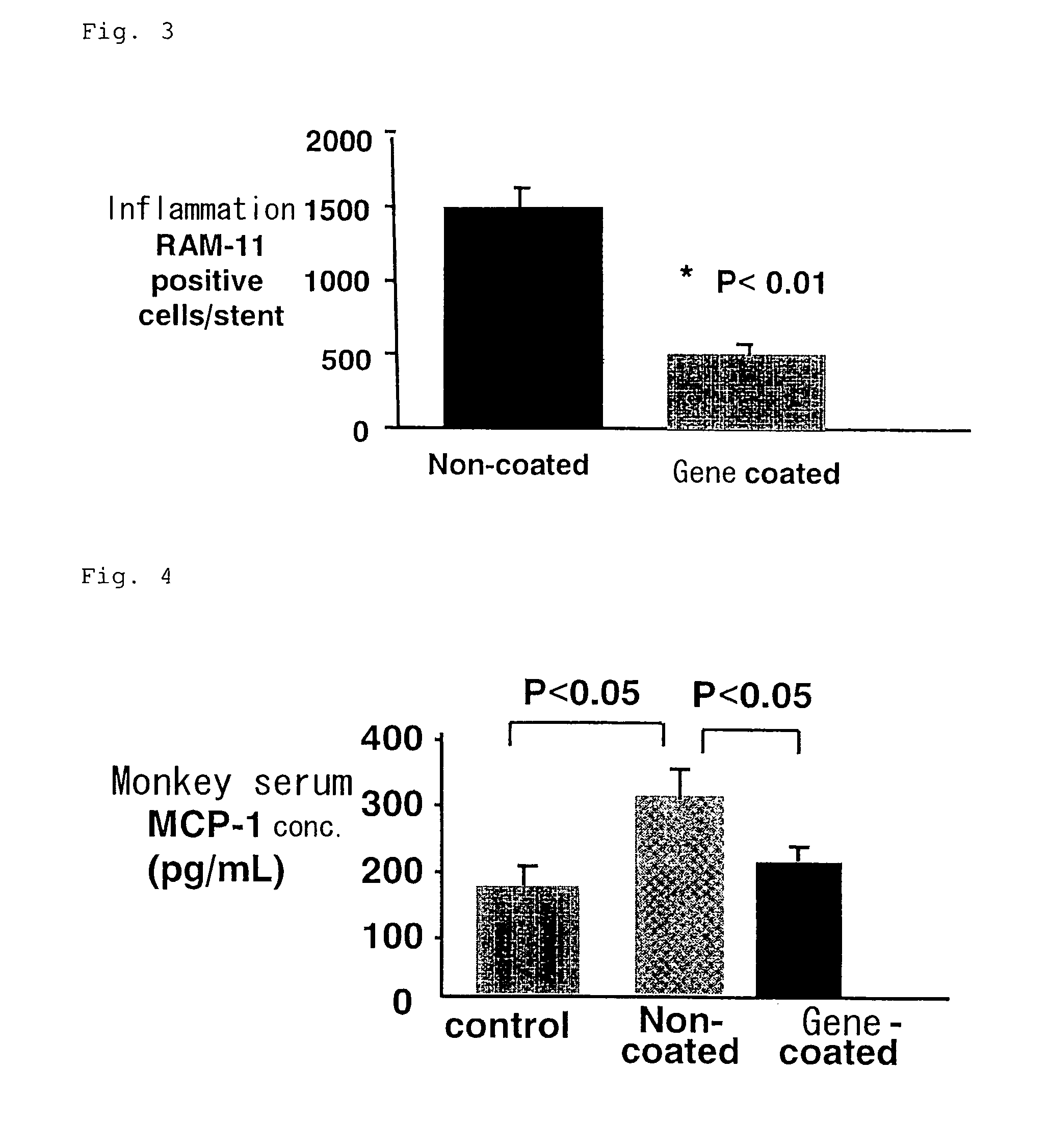
Drug/gene eluting stent
InactiveUS20070077266A1Improve gene transfer efficiencyReduce the given dosesPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsEndothelial regenerationThrombus
The present invention provides a more safe and highly effective stent having functions such as anti-inflammatory action, antithrombotic action, maintenance of tissue restoration response and maintenance of endothelial regeneration. More specifically, the drug / gene eluting stent has a layer containing a gene encoding a hybrid polypeptide on the surface. The hybrid polypeptide is preferably a bound of fibronectin-derived collagen binding domain (FNCBD) polypeptide and an anti-inflammatory factor or an angiogenic factor. The uniform fine particle size capsules can directly deliver the gene encoding the hybrid polypeptide to the lesion and have benefits of reducing the given doses, and thus improving safety and efficacy and further maintaining the efficacy for a long period.
Owner:EGASHIRA KENSUKE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com