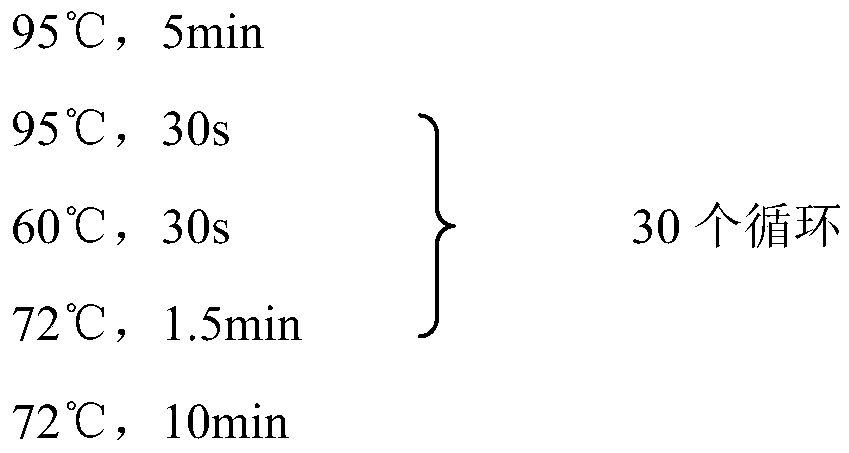
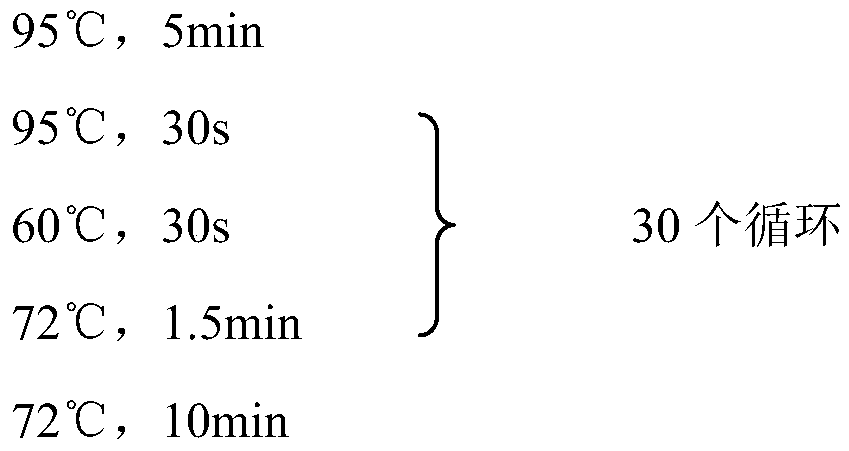
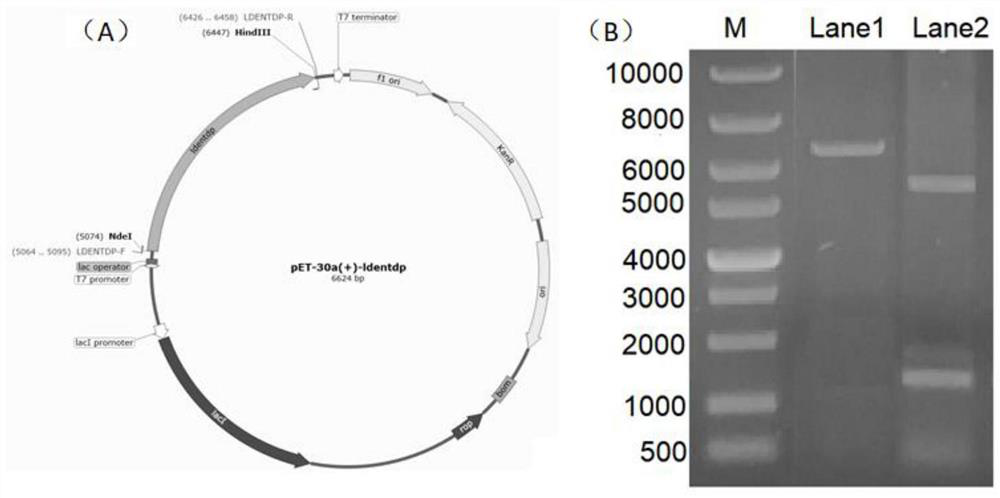
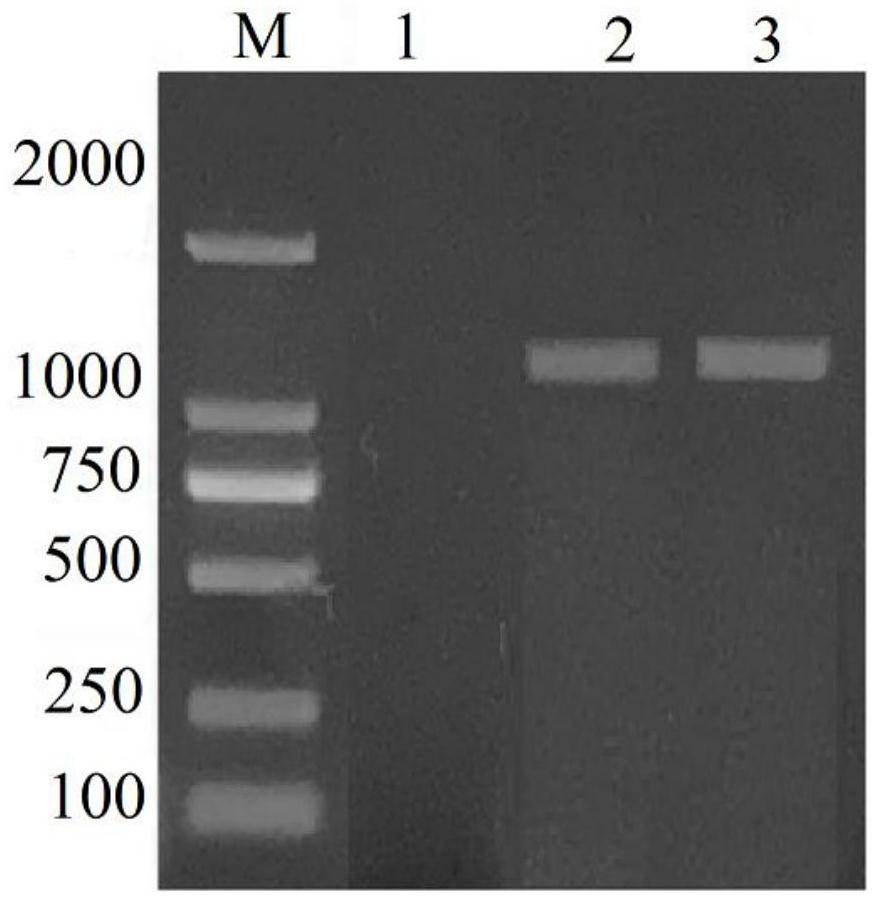
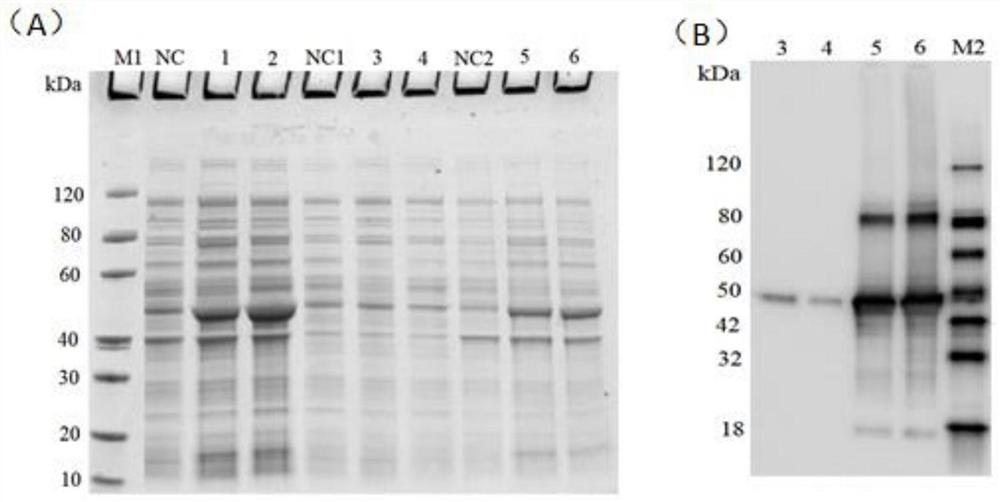
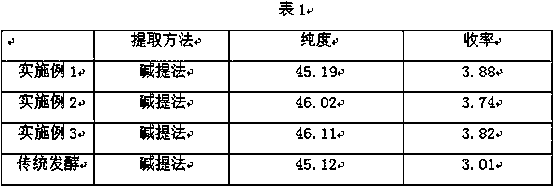
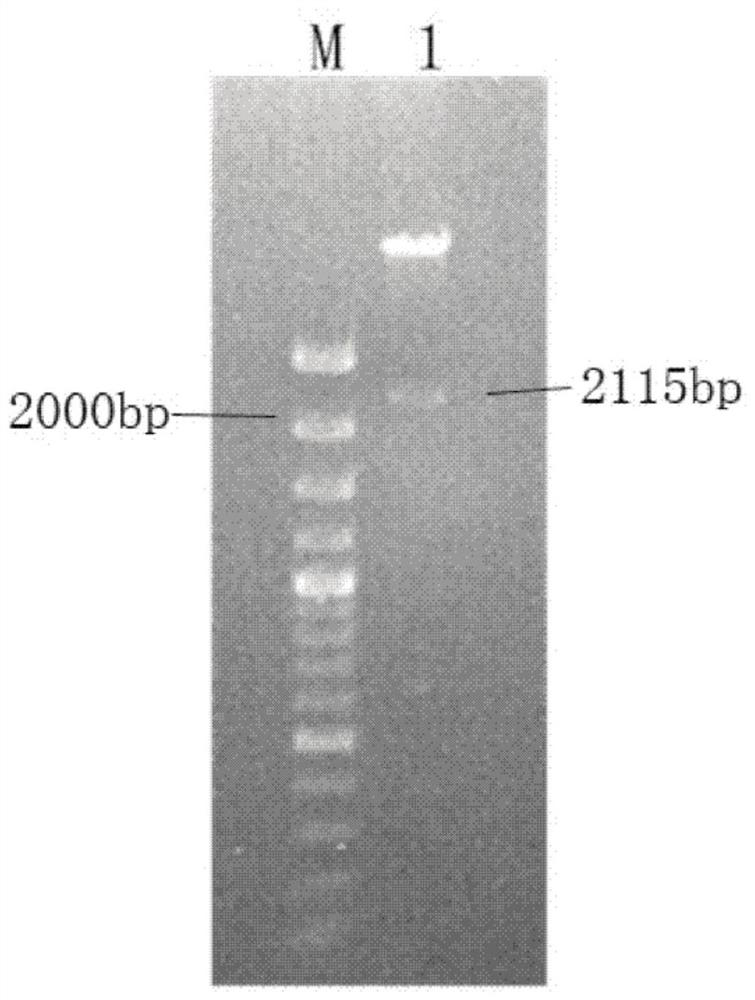
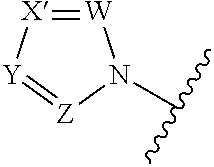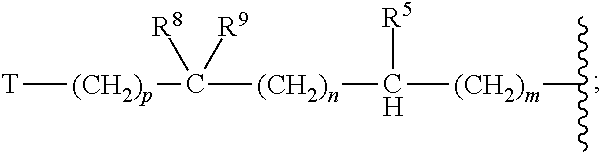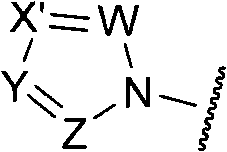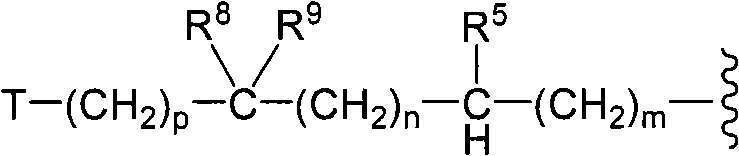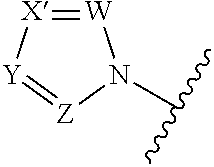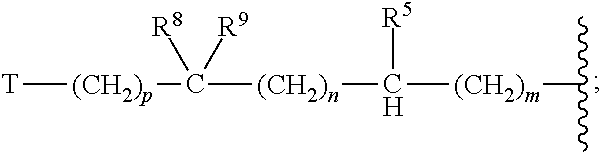Patents
Literature
47 results about "Glucan synthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
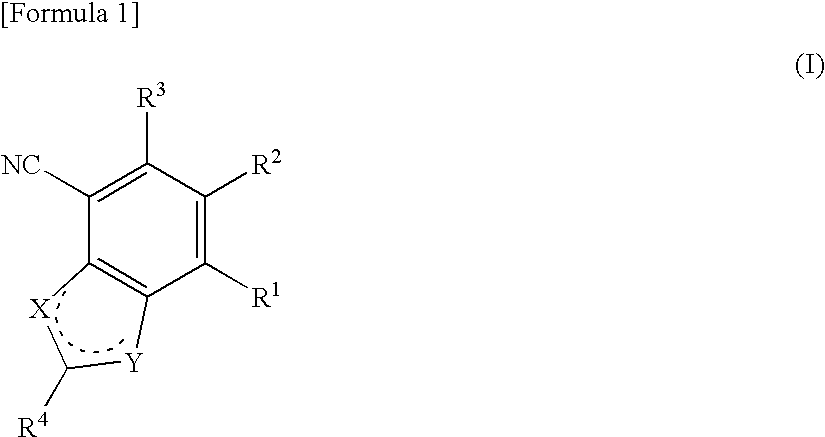
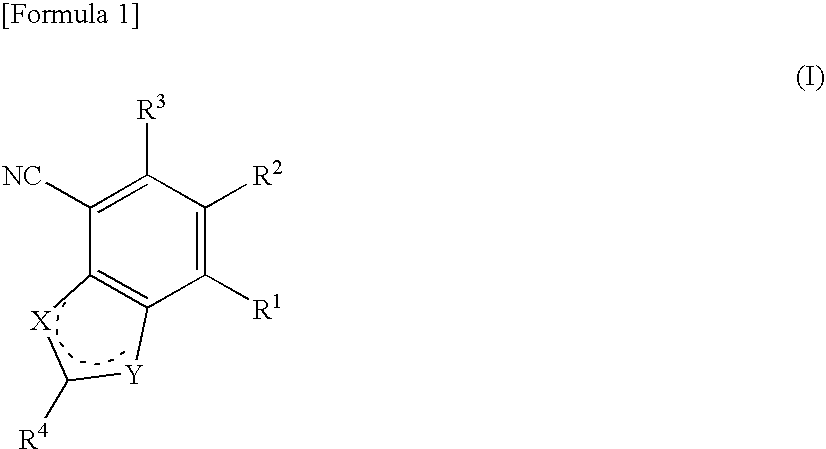
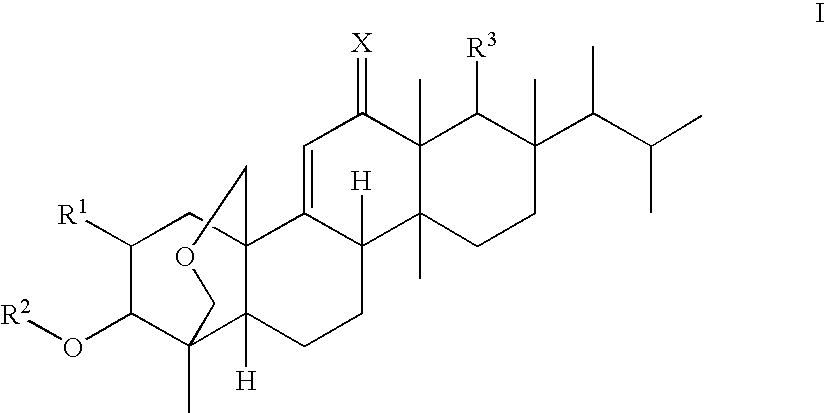
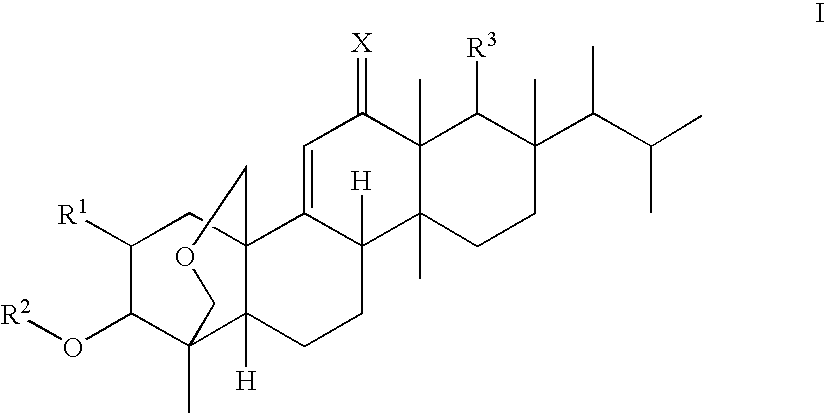
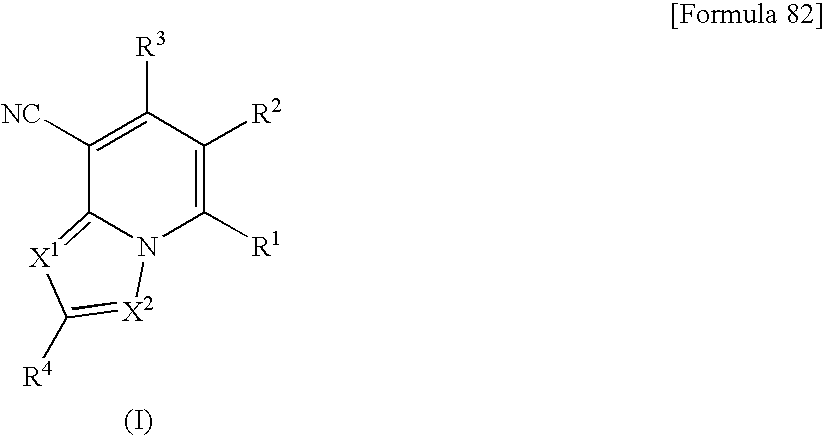
Heterocyclic compounds having antifungal activity
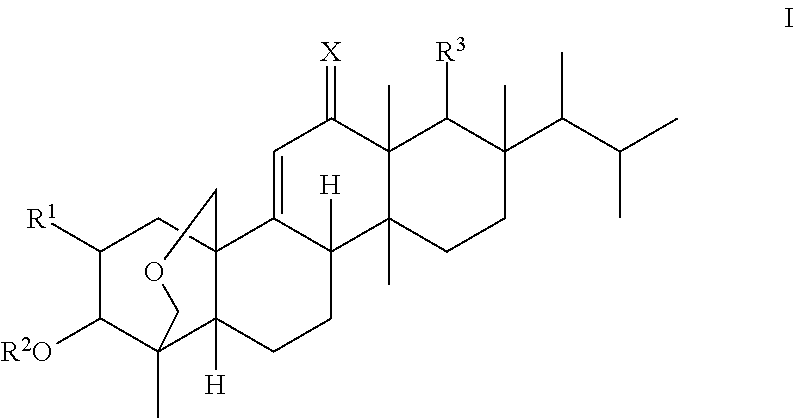
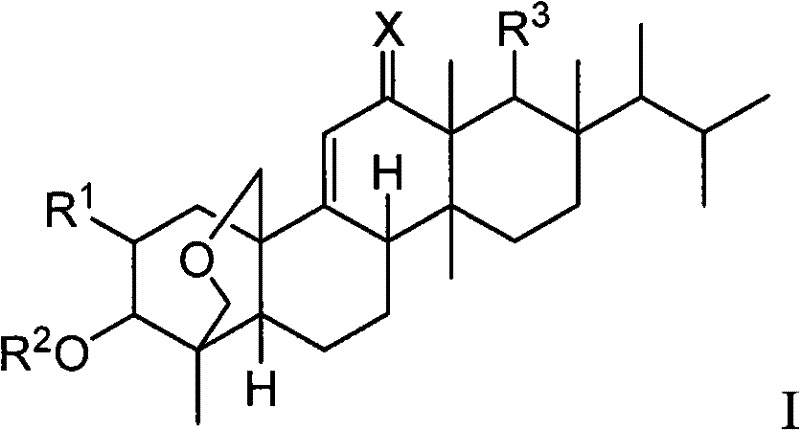
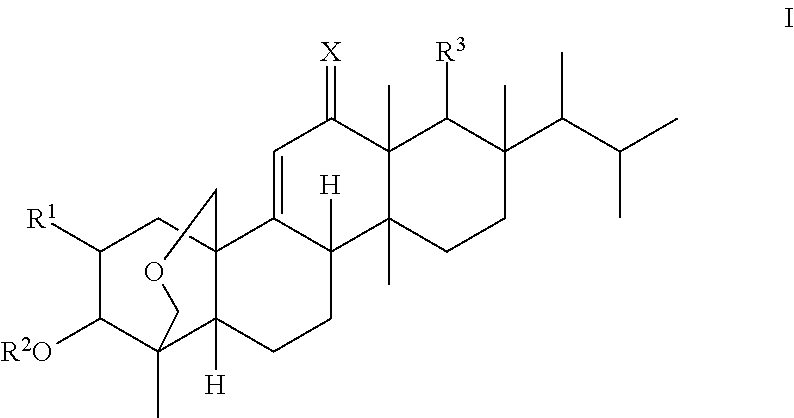
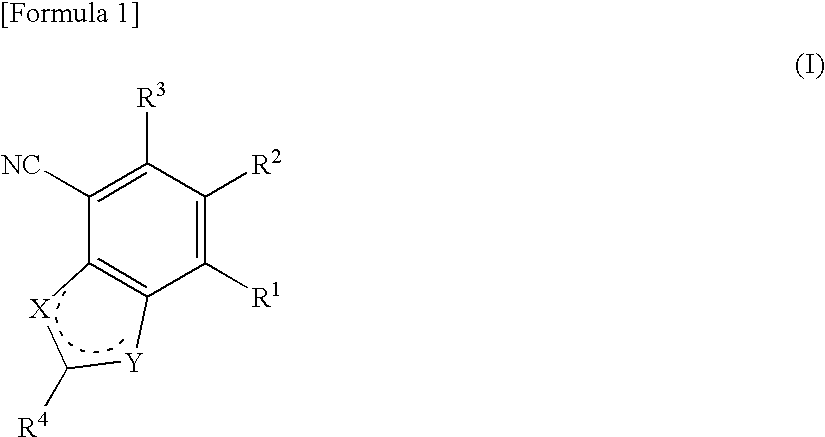
A compound which can specifically or selectively expresses an antifungal activity with a broad spectrum, based on the functional mechanism of 1,6-β-glucan synthesis inhibition, is provided, and an antifungal agent which comprises such a compound, a salt thereof or a solvate thereof is provided. A compound represented by the following formula (I), a salt thereof or a solvate thereof.
Owner:DAIICHI PHARMA CO LTD
Antifungal agents
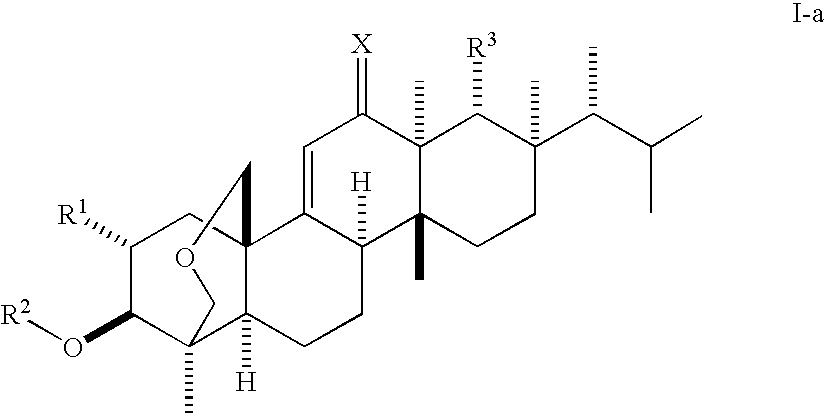
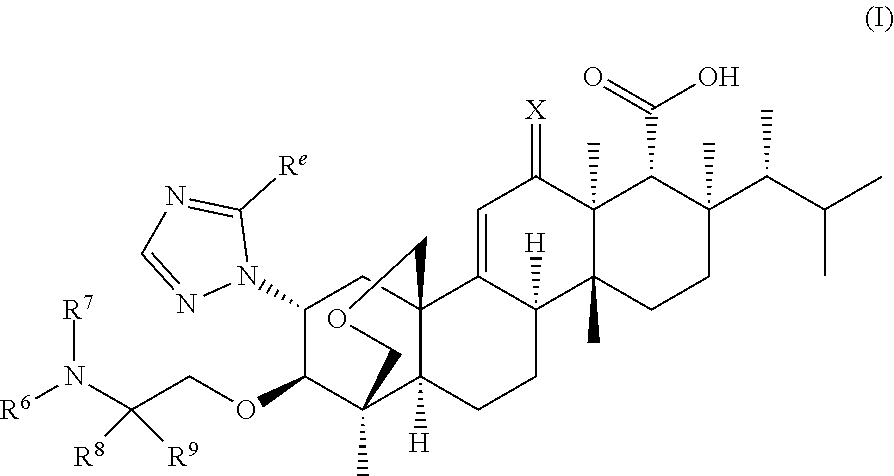
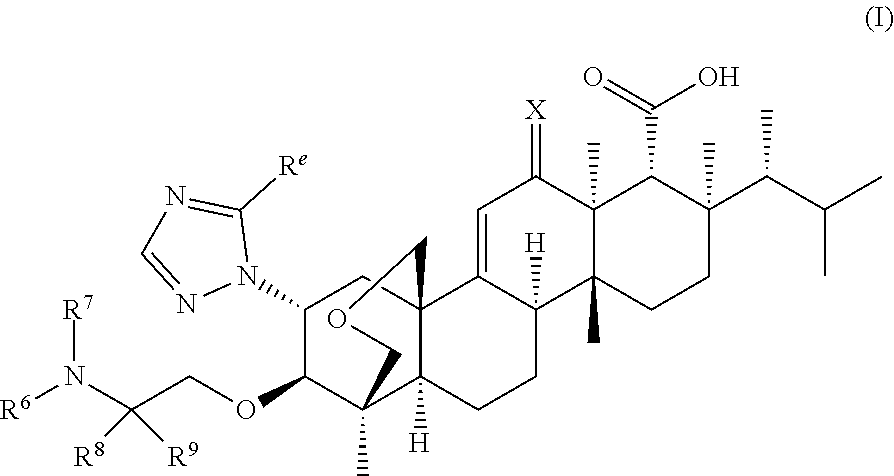
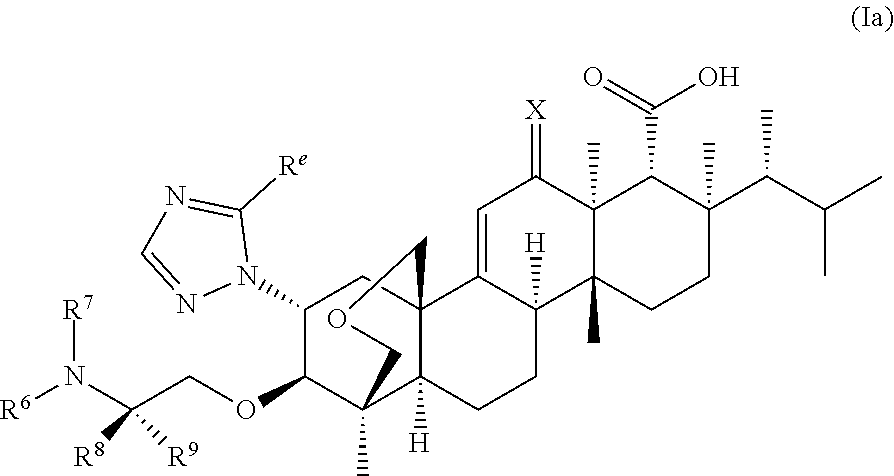
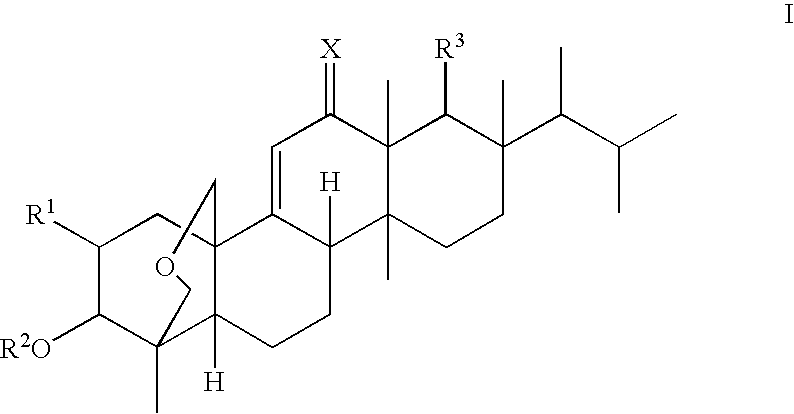
Novel derivatives of enfumafungin are disclosed herein, along with their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, hydrates and prodrugs. Also disclosed are compositions comprising such compounds, methods of preparing such compounds and methods of using such compounds as antifungal agents and / or inhibitors of (1,3)-β-D-glucan synthase. The disclosed compounds, their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, hydrates and prodrugs, as well as compositions comprising such compounds, salts, hydrates and prodrugs, are useful for treating and / or preventing fungal infections and associated diseases and conditions.
Owner:SCYNEXIS INC
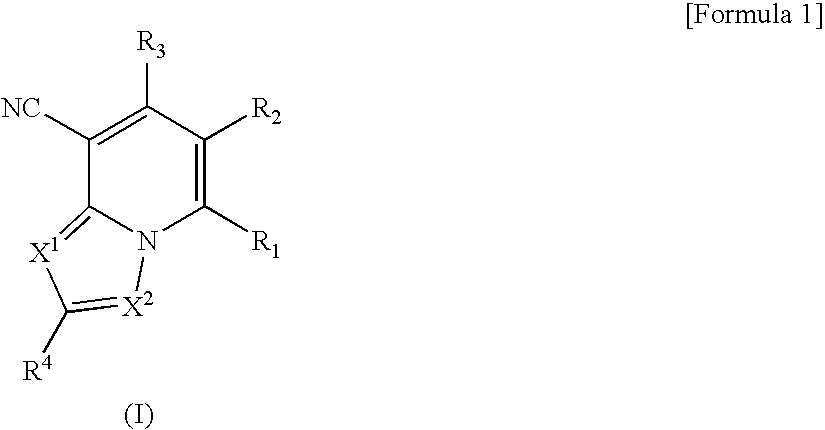
Antifungal bicyclic hetero ring compounds
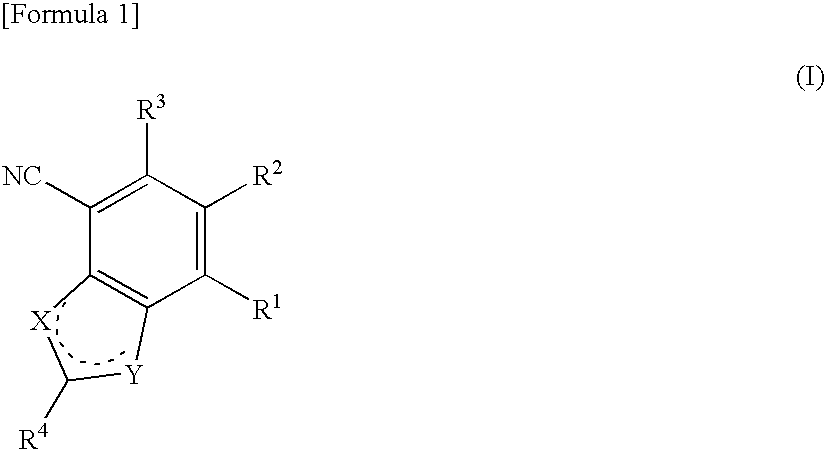
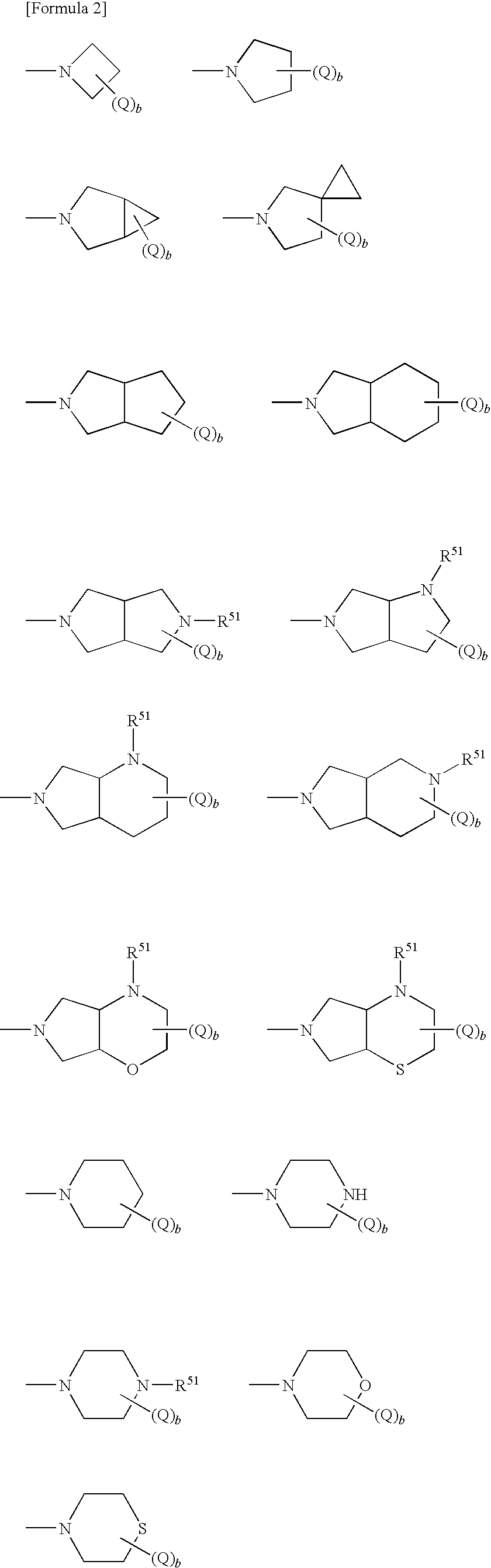
A 1,6-β-glucan synthetase inhibitor is provided, having potent growth inhibition and having excellent safety.A compound is provided, capable of expressing in a wide spectral range and specifically or selectively, an antifungal effect based on its functional mechanism of 1,6-β-glucan synthesis inhibition. Also provided is a drug, especially an antifungal that contains the compound, its salt or their hydrate. Concretely, provided are a compound of the following formula (I), its salt or their hydrate, and a drug or antifungal containing, as the active ingredient, the compound, its salt or their hydrate:
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
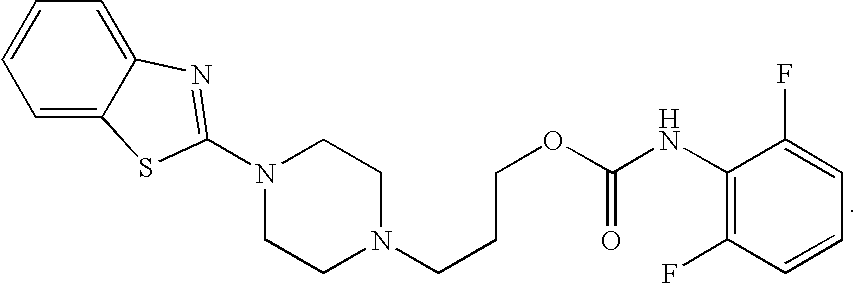
Imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine derivative
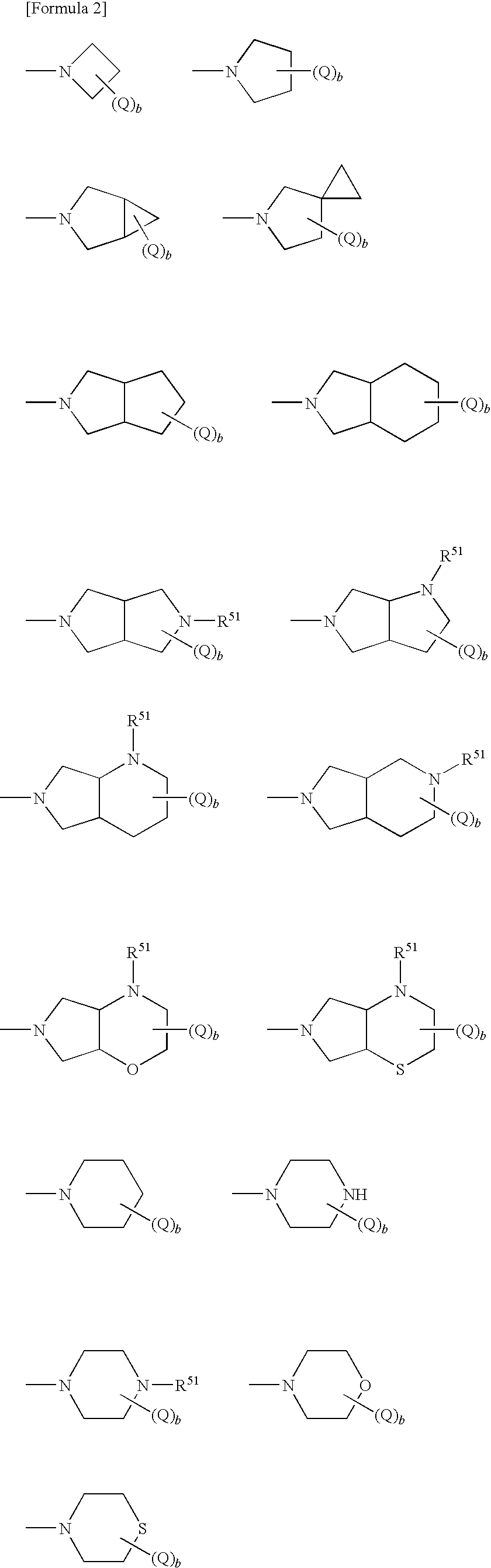
A compound reprsented by the following formula (I), its salts or nsolvates thereof capable of specifically or selectively expressig an antifungal activity in a broad spectrum based on the novel mechanism thereof of 1,6-β-glucan synthesis inhibition, and an antifungal agent containing any of them.
Owner:DAIICHI PHARMA CO LTD
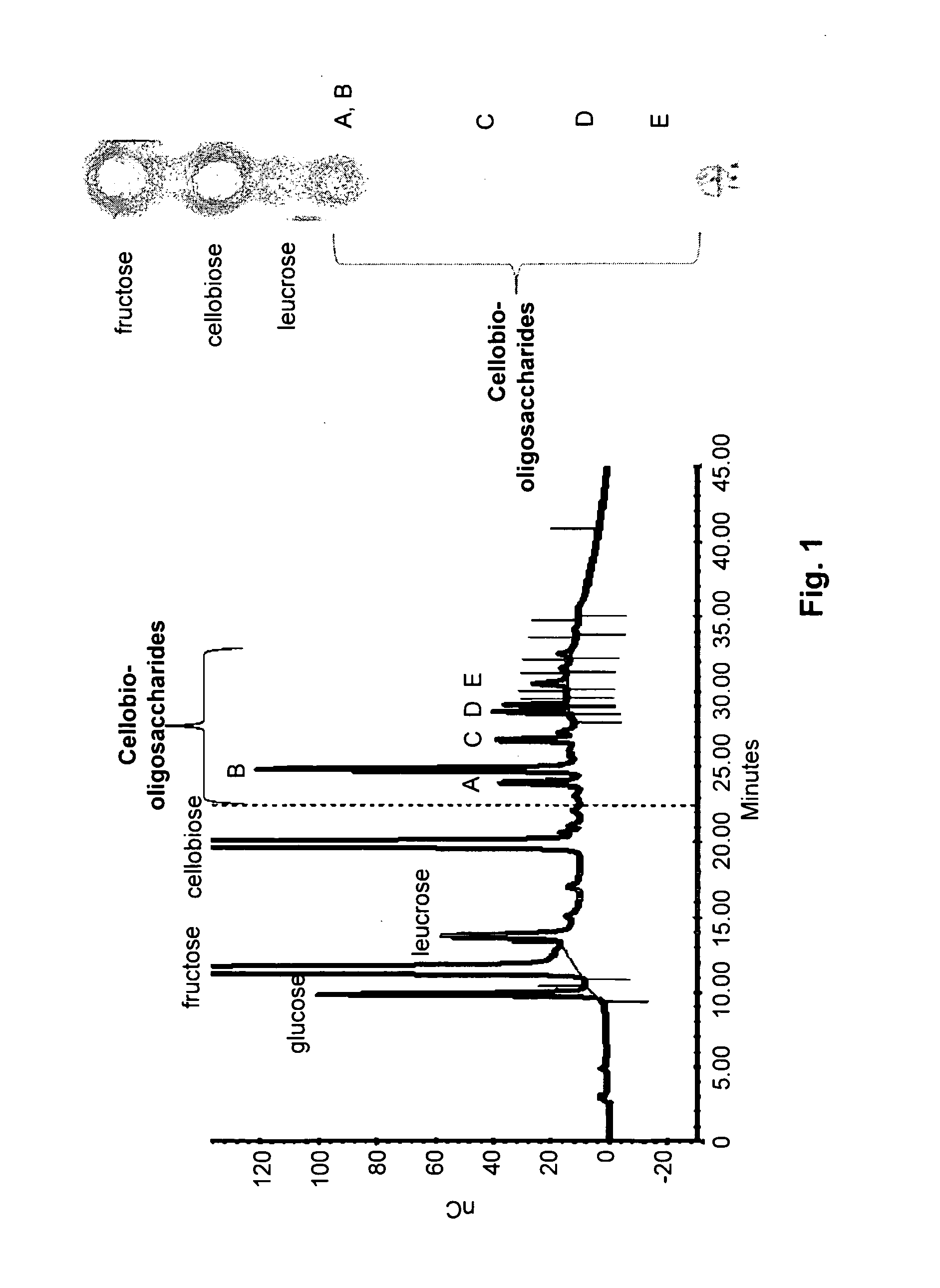
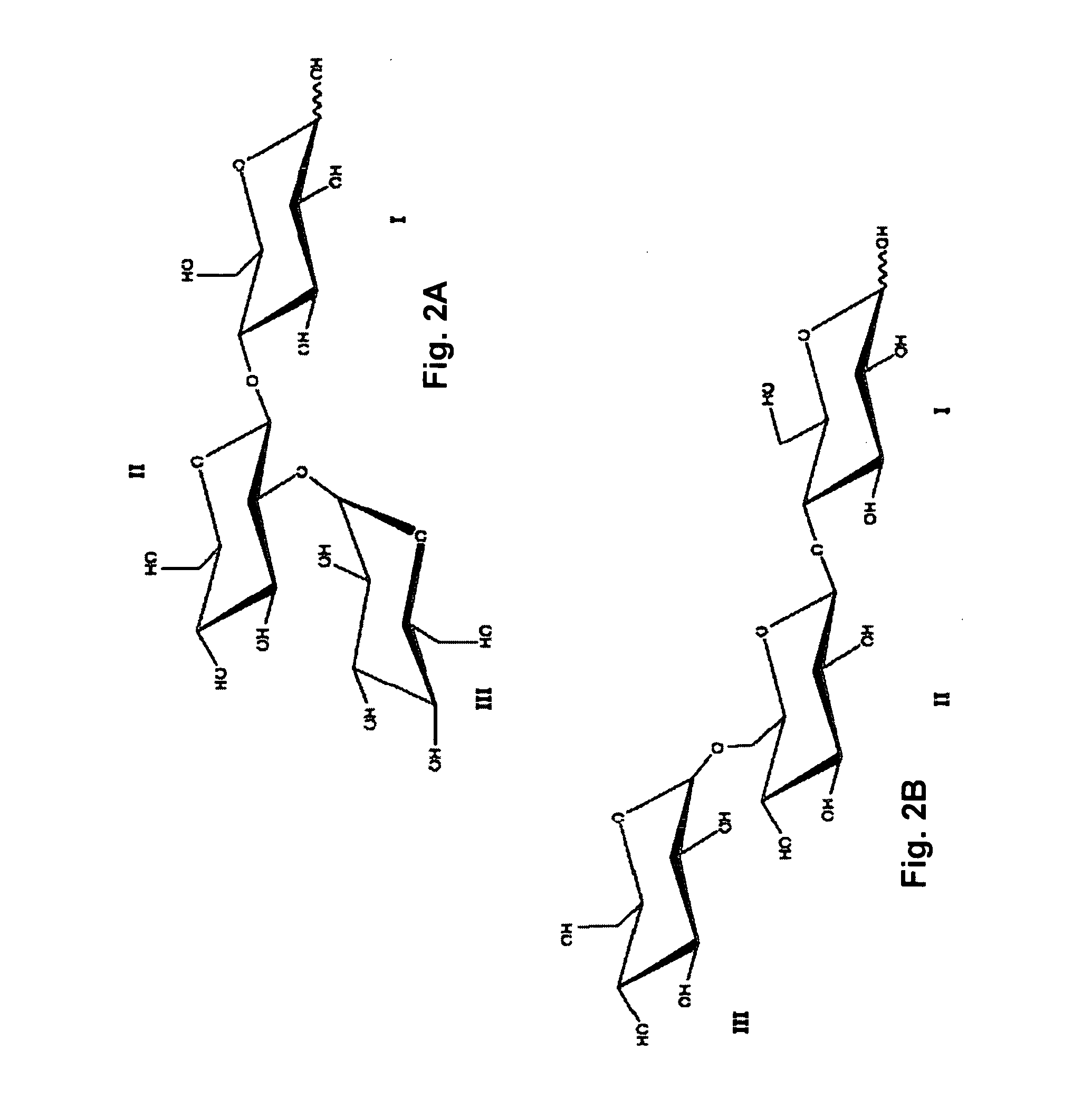
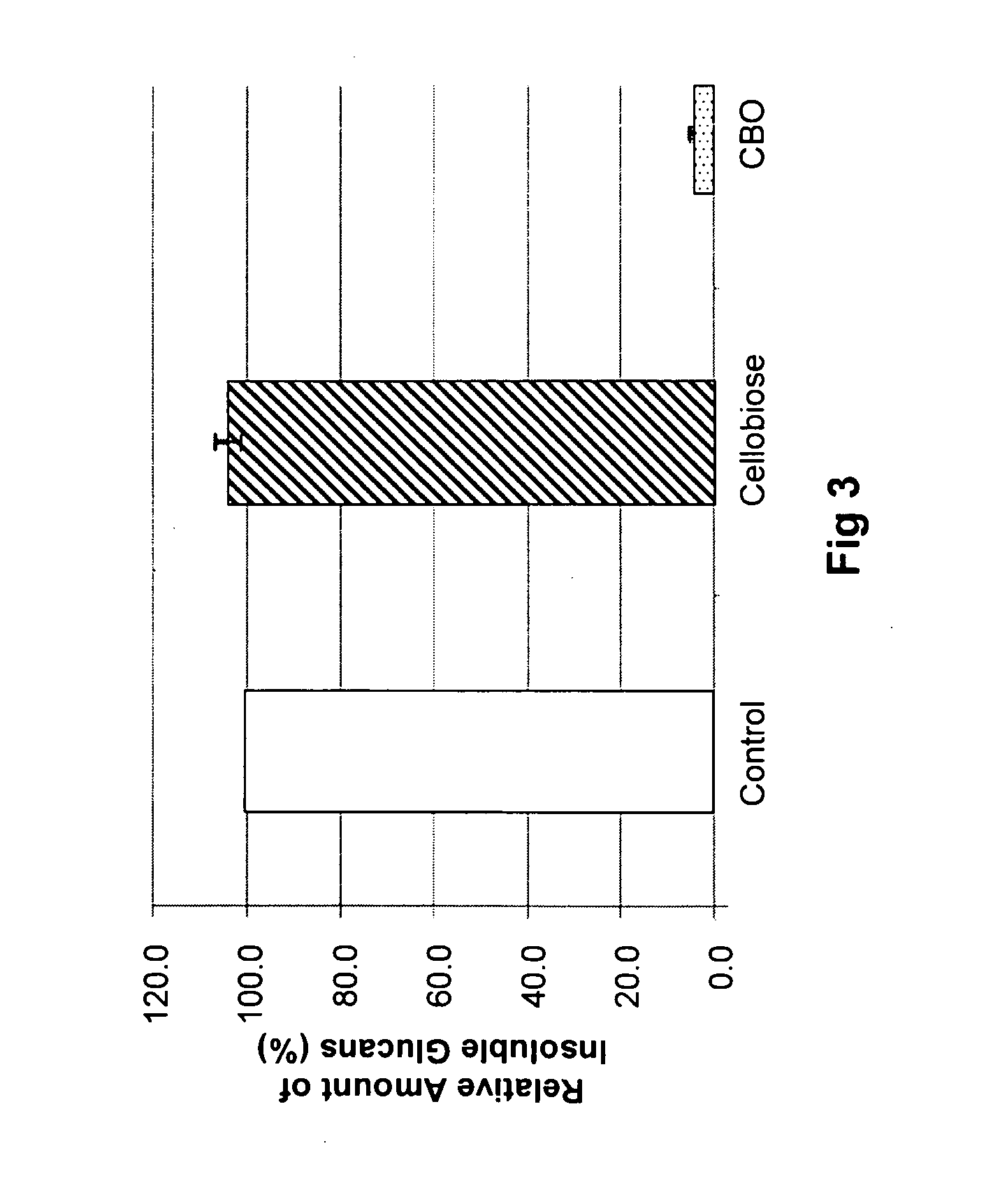
Antifungal and Anti-Cariogenic Cellobio-Oligosaccharides Produced by Dextransucrase
InactiveUS20110076240A1Avoid stickingInhibit productionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBacteroidesSucrose
Cellobio-oligosaccharides (CBO) produced by the dextransucrase-catalyzed transglycosylation reaction of sucrose and cellobiose were discovered to be effective as antifungal agents against dental caries and against fungi who rely on glucan as an integral part of the cell wall, e.g., A. terreus. The cellobio-oligosaccharides were found to be inhibitors of β-(1,3)-glucan synthase, an important enzyme involving in fungal cell wall component synthesis. The CBO caused structural changes in the growing fungal cells. In addition, the CBO were shown to be effective as anti-cariogenic agents in preventing bacterial adherence to teeth by inhibiting the formation of the bacterial plaque (glucans), e.g., that formed by Streptococcus mutans. Cellobio-oligosaccharides produced by dextransucrase were analyzed and shown to have a degree of polymerization (DP) ranging from 3 to 6 glucosyl groups. Examples of these cellobio-oligosaccharides produced by this method include, but are not limited to, trisaccharides such as α-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-D-glucopyranose and α-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-D-glucopyranose.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
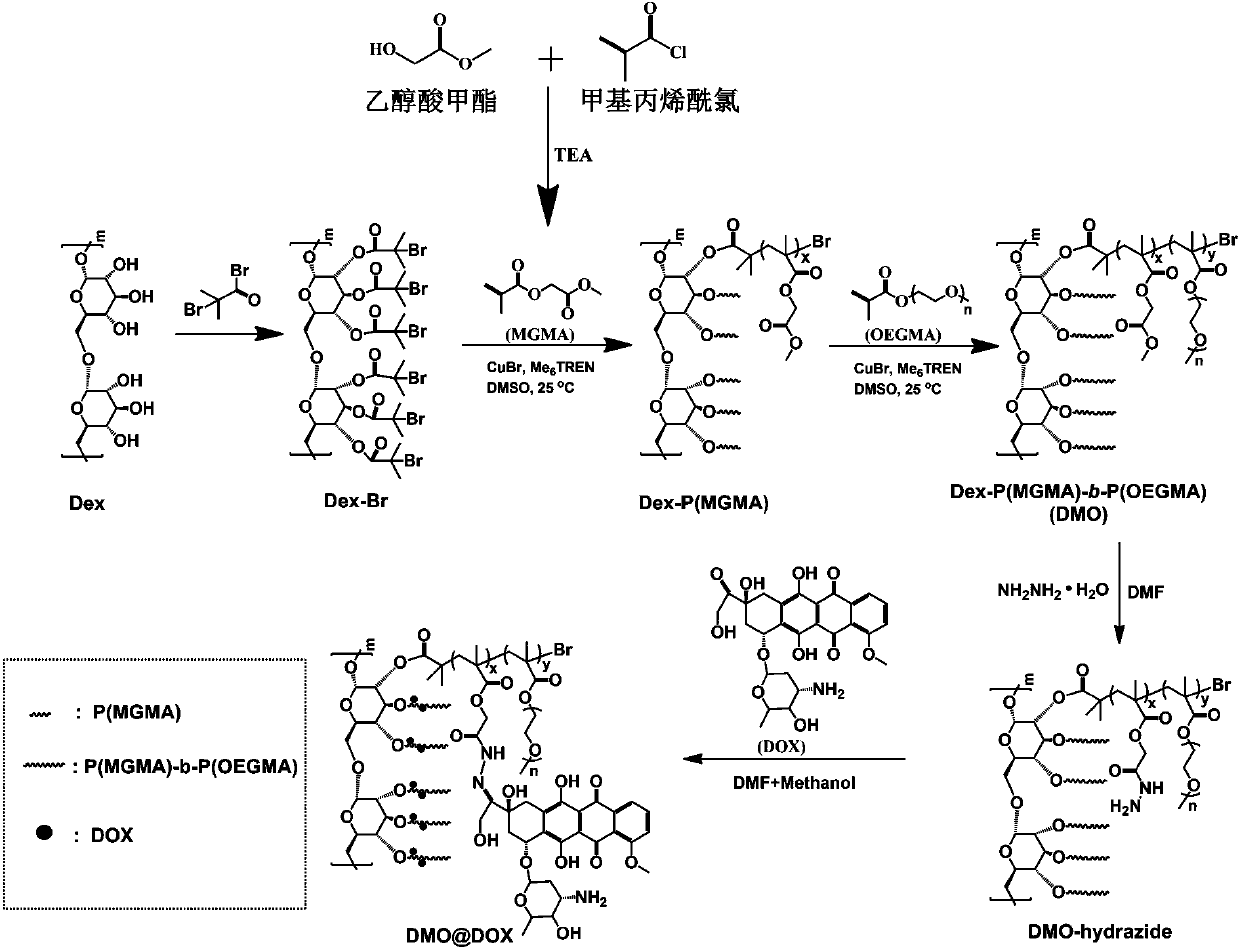
Preparation method of pH-responsive amphiphilic rod-like adriamycin polymer prodrug
ActiveCN107596383AEasily brokenEffective treatmentOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsChemical synthesisPolymeric prodrug
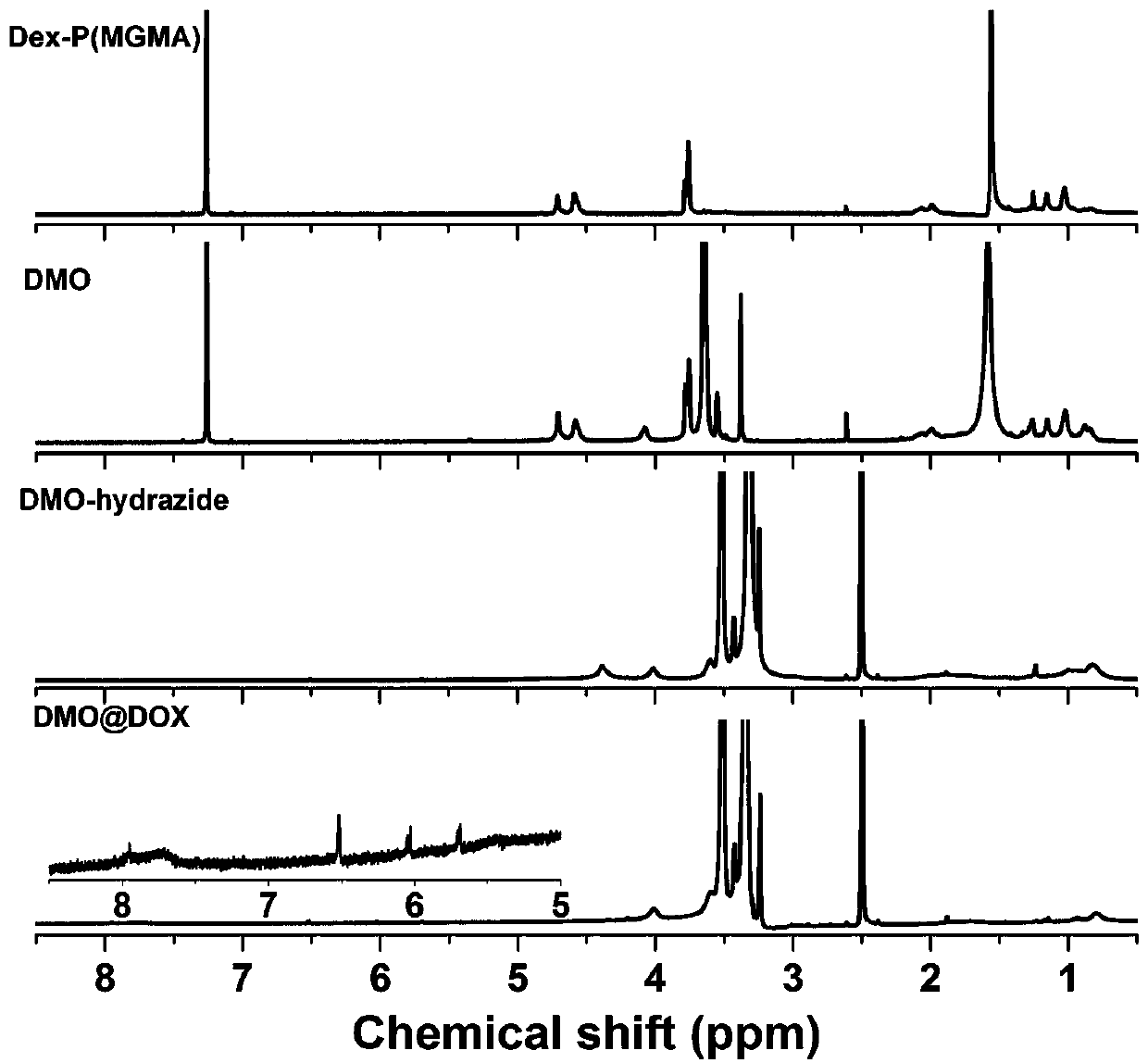
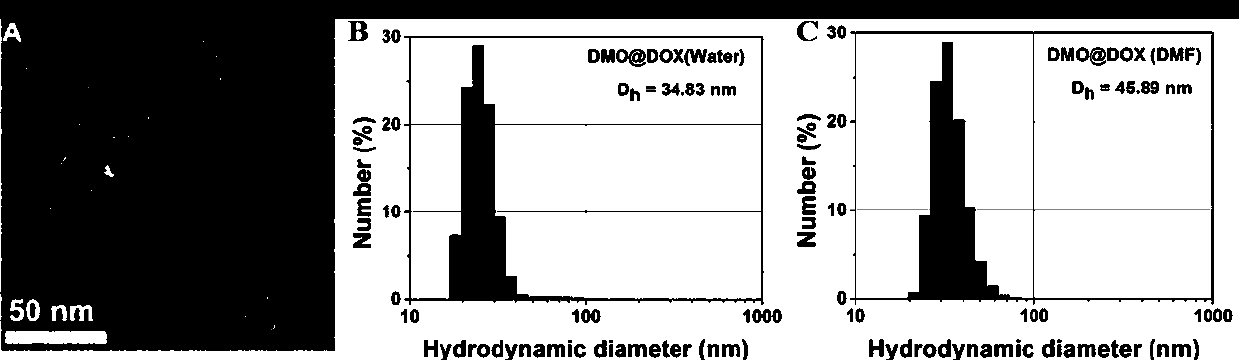
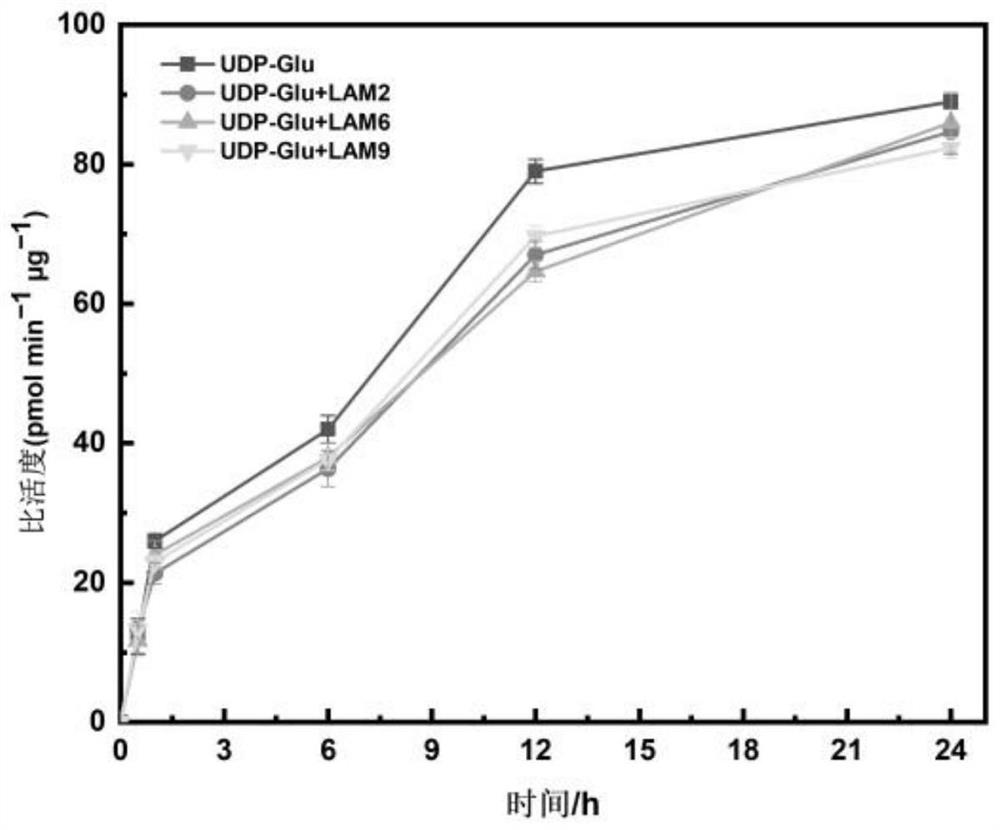
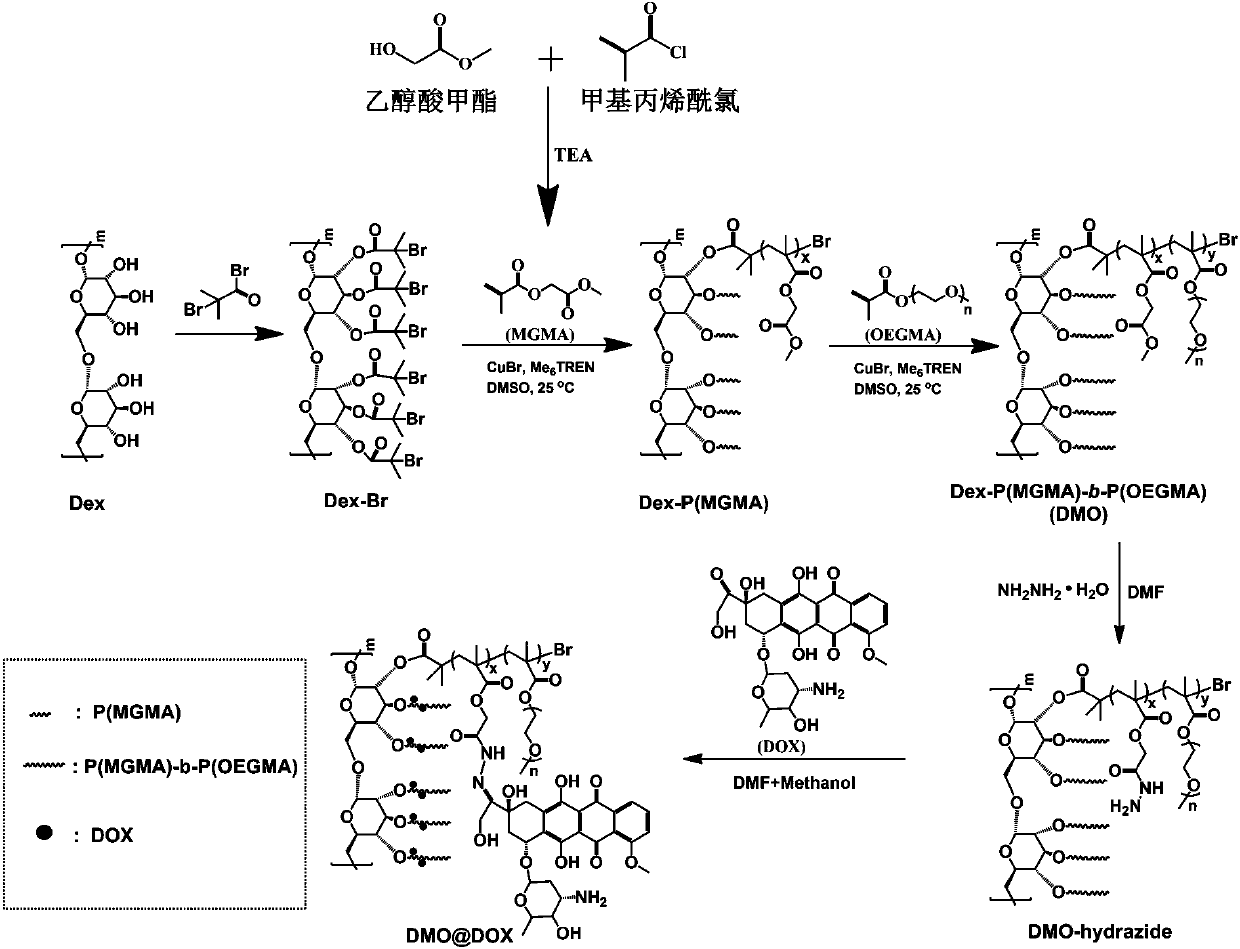
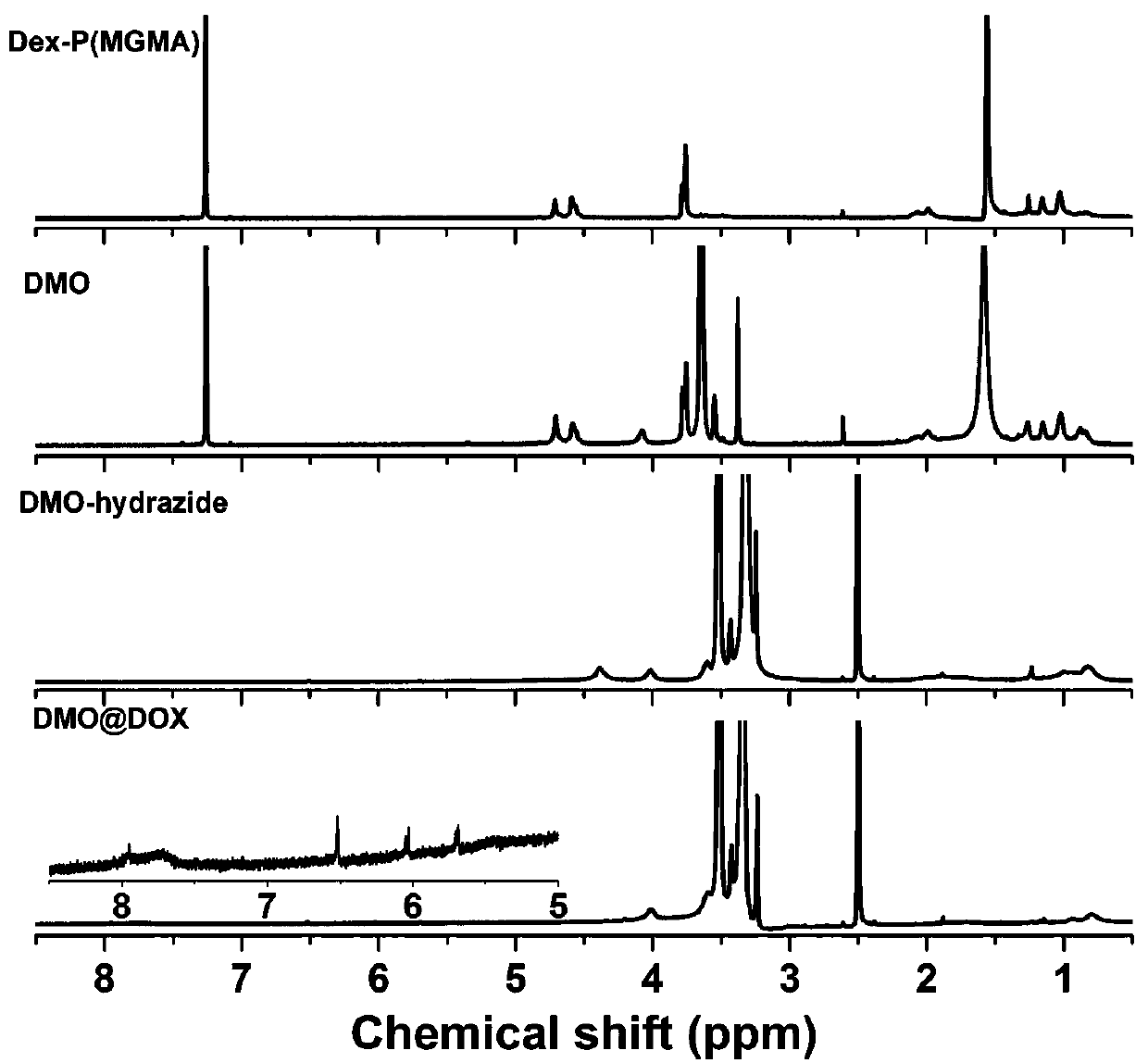
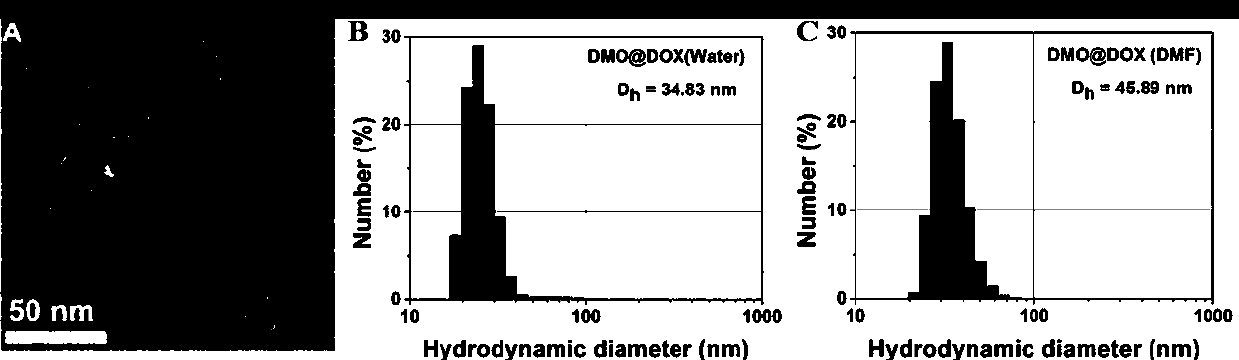
The invention relates to the fields of chemical synthesis and biological representation, and more particularly, provides a preparation method and an application of a pH-responsive amphiphilic rod-likepolymer prodrug, which is represented as the drawing in the specification. The preparation method of the amphiphilic rod-like polymer material includes the following steps: 1) synthesizing a rod-likeATRP initiator on the basis of glucan; 2) introducing a pH-responsive hydrophobic block on the basis of ATRP reaction; 3) introducing a hydrophilic block on the basis of ATRP reaction to obtain an amphiphilic polymer material; 4) substituting an ester group on the terminal of MGMA by means of hydrazine hydrate, thus producing a pH-responsive precursor; 5) forming a hydrazone bond by means of a carbonyl group on adriamycin and an amino group on the polymer material, thus producing the pH-responsive polymer prodrug. By means of weak acidity of interior of cancer cells, the amphiphilic rod-likepolymer prodrug can selectively release a drug by means of pH-stimulating response. The polymer prodrug is high in micelle stability, is high in drug carrying capacity and enables drug release to be under stimulating response control.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Piperazine-substituted pyridazinone derivatives useful as glucan synthase inhibitors
There is disclosed a method for treating or preventing fungal infections comprising the administration of at least one glucan synthase inhibitor of a formula as described above in the specification or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof; also claimed are methods of preparing pharmaceutical compositions comprising a compound as described above in the specification and a carrier, method of treating or preventing fungal infections comprising administration of combinations of glucan synthase inhibitor of a formula as described above in the specification and other antifungal agents, and method of treating or preventing fungal infections comprising administration of pharmaceutical compositions prepared according to a method described above in the specification, and a method of preparing a kit in a single package of the above described pharmaceutical composition and other antifungal agents.
Owner:SCHERING CORP
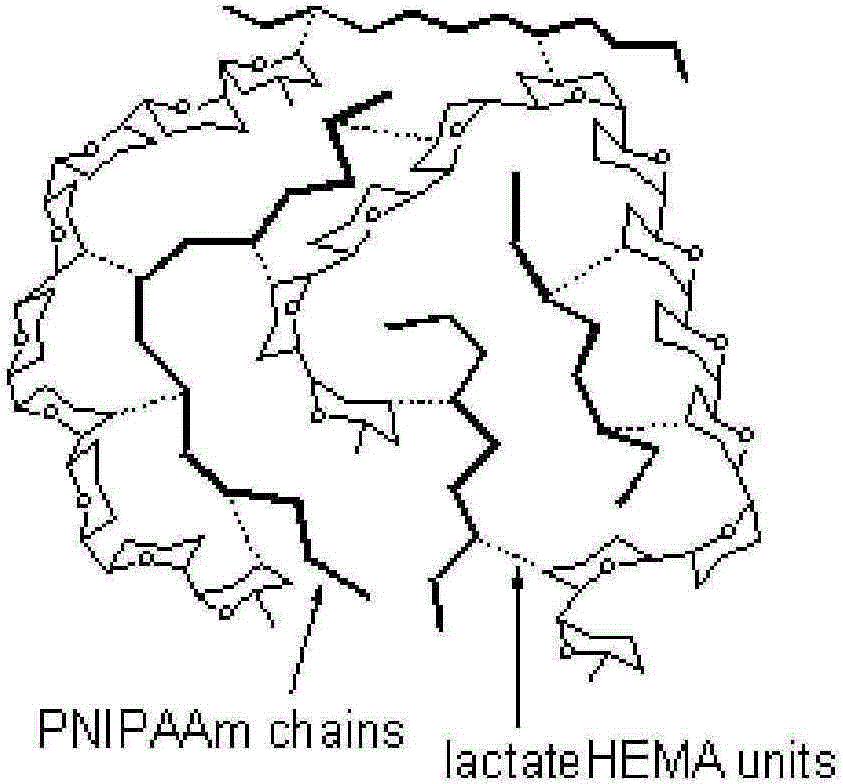
Method for synthesizing heat-sensitive and biodegradable hydrogel
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing heat-sensitive and biodegradable hydrogel. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a biodegradable cross-linking agent, namely polymerizing lactic acid dimmer lactide and hydroxyethyl methylacrylate to form an intermediate, introducing glucosan to synthesize the biodegradable cross-linking agent by virtue of a chemical reaction; and preparing the heat-sensitive and biodegradable hydrogel, namely dissolving N-isopropylacrylamide, an initiator and the biodegradable cross-linking agent in bovine serum albumin, adding a photoinitiator, performing light initiated polymerization, thereby obtaining the heat-sensitive and biodegradable hydrogel. The poly-N-isopropylacrylamide gel synthesized by the method is decomposed in a certain time due to the degradable structure of the cross-linking agent, and the decomposition products such as polylactic acid and glucosan can participate in human metabolism.
Owner:杨俊
Antifungal bicyclic hetero ring compounds
A 1,6-β-glucan synthetase inhibitor is provided, having potent growth inhibition and having excellent safety. A compound is provided, capable of expressing in a wide spectral range and specifically or selectively, an antifungal effect based on its functional mechanism of 1,6-β-glucan synthesis inhibition. Also provided is a drug, a salt or hydrate thereof, especially an antifungal that contains the compound. Concretely, provided is a compound of the following formula (I), its salt or hydrate, and a drug or antifungal containing, as the active ingredient, the compound, its salt or hydrate:
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
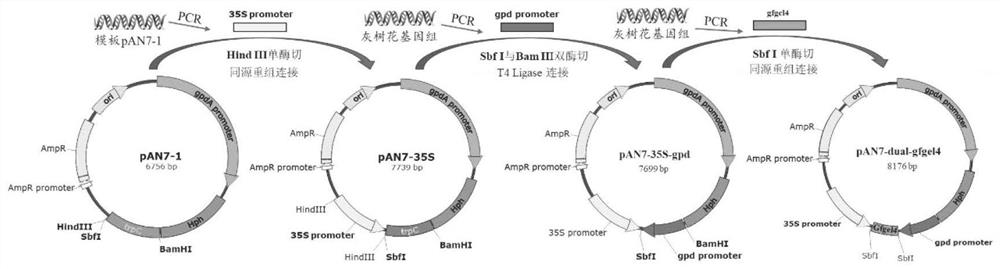
Grifola frondosa glucan synthase, and encoding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN109609525AEffective Resolution StrategiesEfficient methodFungiMicroorganism based processesMolecular levelGene silencing
The invention belongs to the technical fields of genetic breeding and genetic engineering of edible fungi, and specifically relates to grifola frondosa glucan synthase as well as an encoding gene andapplication thereof. The encoding gene of glucan synthesis key enzyme-glucan synthase is obtained for the first time from clones of grifola frondosa mycelium genome by the invention; key roles of thegene in grifola frondosa mycelium growth and glucan synthesis are demonstrated by gene silencing; and the glucan synthase is over-expressed in grifola frondosa by adopting an genetic engineering technology so as to have thallus growth of recombinant strains and synthesis yield of glucan significantly increased. The grifola frondosa glucan synthase as well as the encoding gene and the application thereof are helpful for understanding synthesis mechanism of edible and medicinal fungal polysaccharides at molecular level, developing metabolic engineering study on edible and medicinal fungal polysaccharide synthesis, and providing important technical support and reference for producing glucan with stable quality by performing high-efficiency fermentation.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Antifungal agents
Novel derivatives of enfumafungin are disclosed herein, along with' their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, hydrates and prodrugs. Also disclosed are compositions comprising such compounds, methods of preparing such compounds and method of using such compounds as antifungal agents and / or inhibitors of (1,3)-β-D-glucan synthase. The disclosed compounds, their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, hydrates and prodrugs, as well as compositions comprising such compounds, salts, hydrates and prodrugs, are useful for treating and / or preventing fungal infections and associated diseases and conditions.
Owner:SCYNEXIS INC
Novel nucleic acid sequences and their use in methods for achieving a pathogenic resistance in plants
InactiveCN101010431AVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsNucleic acid sequencingGlucan synthesis
The invention relates to a method for increasing the resistance to pathogens that penetrate mesophyll cells in a plant, or in an organ, tissue or cell of a plant. Said method is characterised in that the callose synthase activity in the plant, or in an organ, tissue or cell of said plant is reduced in comparison to control plants.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
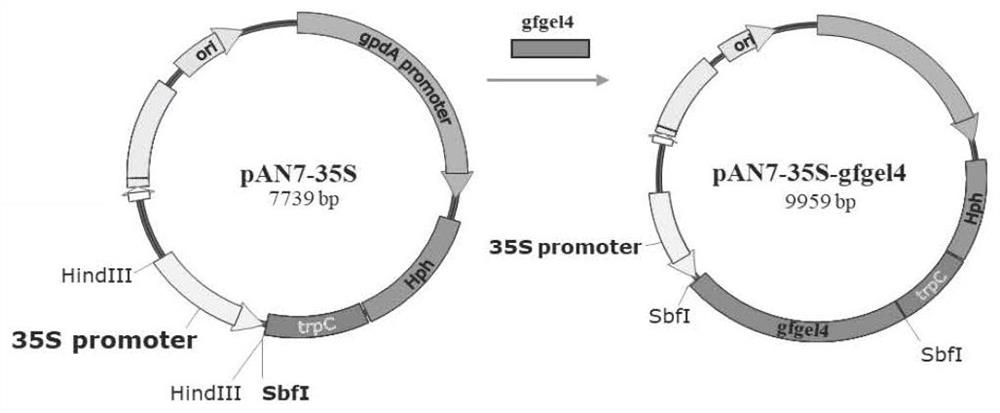
Grifola frondosa glucanyltransferase gfgel4 as well as encoding gene and application thereof
PendingCN113637691AIncrease the degree of branchingImprove solubilityFungiMicroorganism based processesGene silencingGenetic engineering
The invention discloses grifola frondosa glucanyltransferase gfgel4 as well as an encoding gene and application thereof, belongs to the technical field of edible mushroom inheritance and genetic engineering, and particularly relates to the grifola frondosa glucanyltransferase gfgel4 as well as the encoding gene and application thereof. The encoding gene of a key enzyme beta-1, 3 glucanyltransferase for forming a branch structure in the glucan synthesis process is cloned from a grifola frondosa mycelium genome for the first time, and the key role of the gene in the grifola frondosa mycelium growth process, the glucan synthesis process and the glucan branch structure forming process is proved through gene silencing; finally, through a genetic engineering technology, beta-1, 3 glucanyltransferase is overexpressed in grifola frondosa, so that the synthesis yield of glucan is increased, and meanwhile, the branching degree of glucan is increased; and according to the invention, the synthesis mechanism of edible and medicinal fungus polysaccharide can be understood from the molecular level, and a technical scheme and guidance are provided for modifying a glucan synthesis route of edible and medicinal fungi by utilizing the genetic engineering technology.
Owner:江苏康铂特医食品有限公司
Method for measuring activity of beta-glucan synthase
InactiveCN102443621AImprove securityReduce experiment costMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsBeta-glucan synthesisSalicylic acid
The invention discloses a method for measuring the activity of beta-glucan synthase. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantage that the activity of the beta-glucan synthase is determined by detecting the amount of glucan consumed by synthesizing the beta-glucan synthase into beta-glucan with the glucan as an enzymatic reaction substrate and 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid as a color developing agent under visible light. Compared with a traditional method for measuring the activity of the beta-glucan synthase by measuring the change of radioactive activity of UDP (Uridine Diphosphate)-[14C] glucan through a liquid scintillation counting instrument by using the UDP-[14C] glucan as a substrate, and the experiment cost is greatly reduced. In addition, no radioactive glucan is used as the substrate in the method, thus the safety of the experiment is high. The method has the advantages of high sensitivity, simpleness and safety in operation, convenience, quickness and convenience for large-scale popularization and application. The method disclosed by the invention can be widely used for researching and developing saccharide and enzyme products.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY +1
Antifungal agents
The present invention relates to novel enfumafungin derivatives of formula I and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, their synthesis, and their use as inhibitors of (1,3)-β-D-glucan synthase. The present compounds and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, as well as pharmaceutical compositions comprising the present compounds and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, are useful for treating or preventing antifungal infections and associated diseases and conditions.
Owner:SCYNEXIS INC
Novel nanometer drug carrier loaded with methyllprednisolone and preparation method of novel nanometer drug carrier
ActiveCN105727306AExtended half-lifeGood slow release functionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderMicrosphereHalf-life
The invention discloses a novel nanometer drug carrier loaded with methyllprednisolone. The novel nanometer drug carrier comprises methyllprednisolone and a carrier, wherein the carrier is an ibuprofen modified dextran nanometer microsphere, the particle diameter of the novel nanometer drug carrier loaded with methyllprednisolone is 120 to 160 nanometers, the preparation method of the novel nanometer drug carrier loaded with methyllprednisolone comprises two steps of synthesizing the ibuprofen modified dextran nanometer microsphere and preparing novel nanoparticles loaded with methyllprednisolone. The novel nanometer drug carrier loaded with methyllprednisolone disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the nanometer microsphere synthesized by ibuprofen modified dextran is taken as the carrier, so that methyllprednisolone can be effectively and targetedly delivered to injured parts, the half-life of methylprednisolone drugs can be effectively prolonged, and methyllprednisolone and ibuprofen can play a synergistic role on promotion of central nervous system injury repair.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF NANTONG UNIV
Aspergillus niger genetically engineered bacteria as well as construction method and application thereof
The invention discloses aspergillus niger genetically engineered bacteria. The aspergillus niger genetically engineered bacteria are aspergillus niger in which glucan synthesis regulating gene VosA isknocked out. The invention also discloses a construction method of the above genetically engineered bacteria, and further discloses an application of the genetically engineered bacteria in the production of citric acid through immobilized fermentation. The aspergillus niger genetically engineered bacteria in which the glucan synthesis regulating gene VosA is knocked out are constructed, so that the hydrophobicity of the aspergillus niger during the production of the citric acid through immobilized fermentation is reduced, the yield of a biological film is reduced, a vector agglomeration phenomenon is reduced, the citric acid yield and sugar conversion efficiency are improved, and the aspergillus niger genetically engineered bacteria are suitable for industrial production.
Owner:NANJING HIGH TECH UNIV BIOLOGICAL TECH RES INST CO LTD +1
Antifungal agents used in combination
The present invention relates to the use of enfumafungin derivative triterpenoid antifungal compounds in combination with other antifungal agents such azoles, polyenes, lipopeptides, and allylamides to treat fungal diseases. More particularly, the invention relates to antifungal combinations of enfumafungin derivative triterpenoids which are inhibitors of (1,3)-β-D-glucan synthesis, in combination with other antifungal agents such as mold-active agents that have activity against molds, including but not limited to voriconazole, isavuconazole, posaconazole, itraconazole and amphotericin B, for the treatment and / or prevention of infections caused by molds.
Owner:SCYNEXIS INC
Grifola frondosa glucan synthase and encoding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN110117601APromote growthGrow fastFungiMicroorganism based processesGene silencingGenetic engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of edible fungi hereditary and genetic engineering, and particularly relates to grifola frondosa glucan synthase and an encoding gene and application thereof. The glucan key synthetase-glucan synthetase encoding gene is cloned in grifola frondosa mycelium genome for the first time, and through gene silencing, it is proved that the gene plays a key rolein the grifola frondosa mycelium growth process and the glucan synthesis process; finally, through the genetic engineering technology, glucan synthetase is overexpressed in grifola frondosa, and the recombination strain cell growth and the glucan synthesis yield are significantly improved. The encoding gene is beneficial for understanding the edible and medical fungal polysaccharide synthesis mechanism at the molecular level, and by using the genetic engineering technology, a technical scheme and guidance are provided for modifying an edible and medical fungal polysaccharide synthesis route.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Antifungal agents
Novel derivatives of enfumafungin are disclosed herein, along with' their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, hydrates and prodrugs. Also disclosed are compositions comprising such compounds, methods of preparing such compounds and method of using such compounds as antifungal agents and / or inhibitors of (l,3)-beta-D-glucan synthase. The disclosed compounds, their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, hydrates and prodrugs, as well as compositions comprising such compounds, salts, hydrates and prodrugs, are useful for treating and / or preventing fungal infections and associated diseases and conditions.
Owner:SCYNEXIS INC
Antifungal agents
Novel derivatives of enfumafungin are disclosed herein, along with' their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, hydrates and prodrugs. Also disclosed are compositions comprising such compounds, methods of preparing such compounds and method of using such compounds as antifungal agents and / or inhibitors of (1,3)-β-D-glucan synthase. The disclosed compounds, their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, hydrates and prodrugs, as well as compositions comprising such compounds, salts, hydrates and prodrugs, are useful for treating and / or preventing fungal infections and associated diseases and conditions.
Owner:SCYNEXIS INC
Antifungal agents with enhanced activity in acidic ph
ActiveUS20200390751A1Reduced potencyHigh activityOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsEnfumafunginYeast
Owner:SCYNEXIS INC
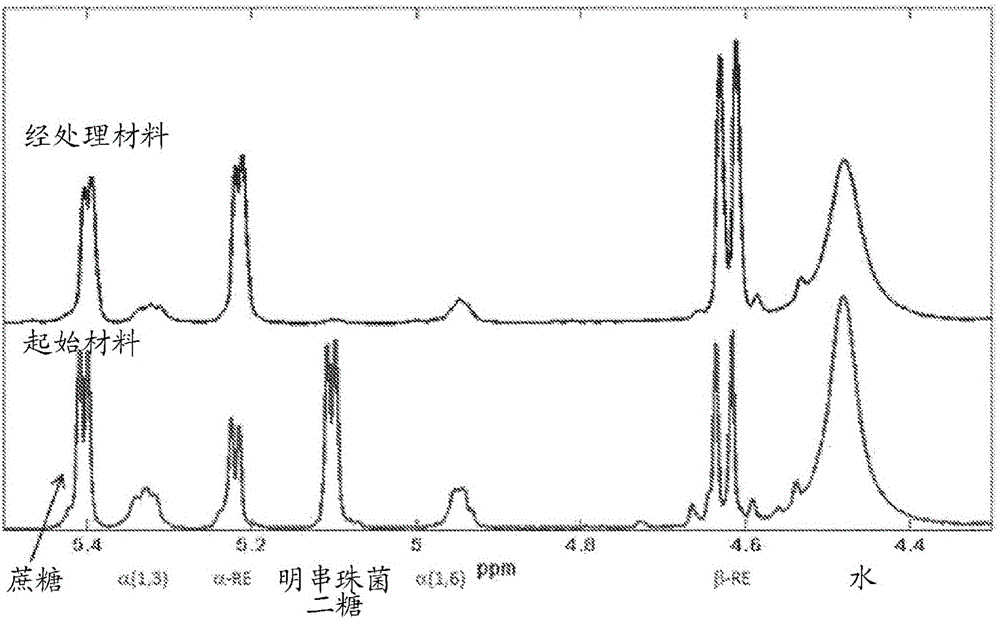
Enzymatic hydrolysis of disaccharides and oligosaccharides using alpha-glucosidase enzymes
A method is disclosed for hydro!yzing an alpha-1,5 giucosyl-fructose linkage in a saccharide (disaccharide or oligosaccharide) such as leucrose. This method comprises contacting the saccharide with an alpha-glucosidase enzyme such as transgiucosidase or glucoamylase under suitable conditions, during which contacting step the enzyme hydrolyzes at least one alpha-1,5 glucosyl-fructose linkage of the saccharide. This method is useful for reducing the amount of leucrose in a filtrate isolated from a glucan synthesis reaction, for example.
Owner:NUTRITION & BIOSCIENCE USA 4 INC
A kind of nanoscale drug carrier loaded with methylprednisolone and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105727306BExtended half-lifeGood slow release functionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderMicrosphereHalf-life
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF NANTONG UNIV
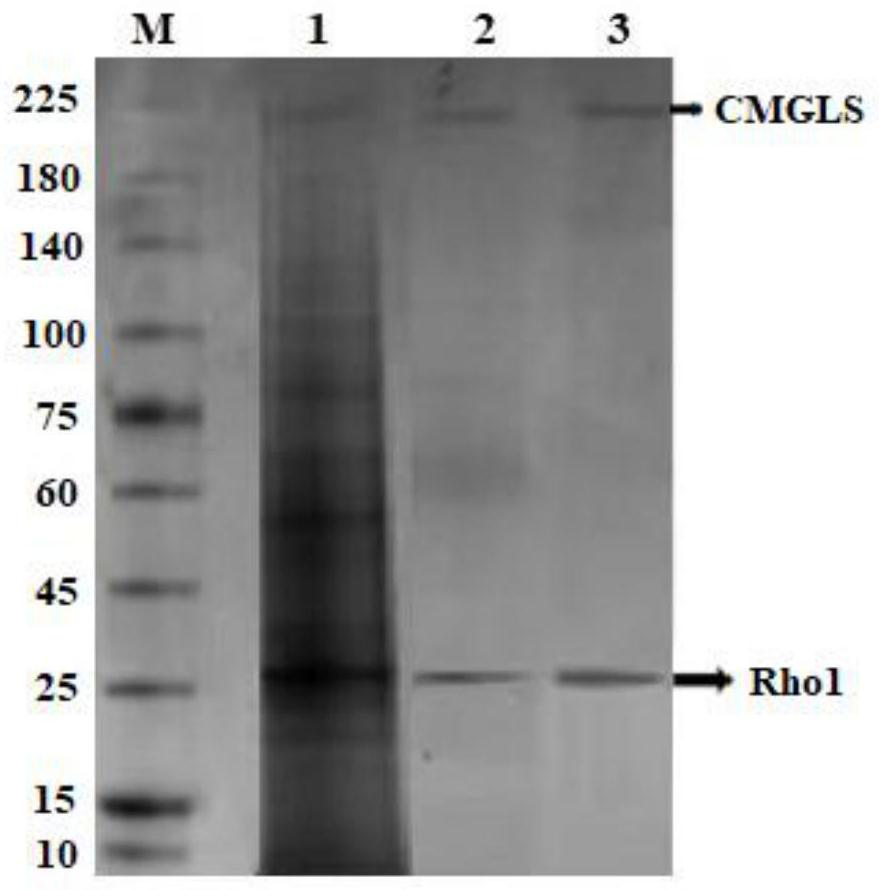
Cordyceps militaris membrane protein beta-1, 3-glucan synthetase as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses cordyceps militaris beta-1, 3-glucan synthetase as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of fungal biology and food biology. And a gene sequence for coding the cordyceps militaris beta-1, 3-glucan synthetase is as shown in SEQ ID No.3. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the cordyceps militaris beta-1, 3-glucan synthetase. Cordyceps militaris is used as a raw material, a detergent solubilizing membrane component extraction mode is combined with product trapping and Superdex10 / 300GL chromatographic column purification to obtain the high-purity cordyceps militaris beta-1, 3-glucan synthetase CMGLS, the enzyme catalyzes glucan chain synthesis by using UDP-glucose as a unique substrate, and the invention systematically provides the application of the cordyceps militaris beta-1, 3-glucan synthetase CMGLS in the preparation of the high-purity cordyceps militaris beta-1, 3-glucan synthetase CMGLS in the preparation of the high-purity cordyceps militaris beta-1, 3-glucan synthetase CMGLS. The catalytic characteristics of the 1, 3-glucan synthetase and the structural characteristics of the synthesized product provide important theoretical basis and necessary reference basis for the preparation of multiple transmembrane structures derived from other fungi and high-molecular-mass membrane proteins and the synthesis of glucan with different structures.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Preparation method of a class of pH-responsive amphiphilic rod-shaped doxorubicin polymer prodrug
ActiveCN107596383BIncrease upload volumeImprove stabilityOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsChemical synthesisPolymeric prodrug
The invention relates to the fields of chemical synthesis and biological representation, and more particularly, provides a preparation method and an application of a pH-responsive amphiphilic rod-likepolymer prodrug, which is represented as the drawing in the specification. The preparation method of the amphiphilic rod-like polymer material includes the following steps: 1) synthesizing a rod-likeATRP initiator on the basis of glucan; 2) introducing a pH-responsive hydrophobic block on the basis of ATRP reaction; 3) introducing a hydrophilic block on the basis of ATRP reaction to obtain an amphiphilic polymer material; 4) substituting an ester group on the terminal of MGMA by means of hydrazine hydrate, thus producing a pH-responsive precursor; 5) forming a hydrazone bond by means of a carbonyl group on adriamycin and an amino group on the polymer material, thus producing the pH-responsive polymer prodrug. By means of weak acidity of interior of cancer cells, the amphiphilic rod-likepolymer prodrug can selectively release a drug by means of pH-stimulating response. The polymer prodrug is high in micelle stability, is high in drug carrying capacity and enables drug release to be under stimulating response control.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
A recombinant bacterium utilizing dextran to synthesize 3-hydroxypropionic acid and its construction method and application
The invention provides recombinant bacteria capable of synthesizing 3-hydracrylic acid by using glucan as well as a construction method and application of the recombinant bacteria, and belongs to the field of gene engineering and fermentation engineering. Klebsiella pneumoniae is host bacteria for expressing a gene lgk capable of encoding levodextran kinase and a gene aldH capable of encoding aldehyde dehydrogenase. The construction method comprises the following steps: obtaining a recombinant carrier puC18-lgk-aldH, converting the recombinant carrier puC18-lgk-aldH into a competent cell of the host Klebsiella pneumoniae, and obtaining the recombinant bacteria. By use of the levodextran kinase gene lgk and the aldehyde dehydrogenase gene aldH which are optimized through a codon, in combination with the whole scheme, the substrate use rate is increased, and the yield is increased.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Beta-glucan synthase activity detection kit, detection method and application
PendingCN114486429AReduce experiment costLow costComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationUridine diphosphateHydrolysis
The invention provides a beta-glucan synthetase activity detection kit, a detection method and application, and belongs to the technical field of enzymes. In the invention, the kit for determining the activity of the beta-glucan synthetase mainly comprises exonucleoside triphosphate diphosphate hydrolase (ENTDP) capable of hydrolyzing uridine diphosphate (UDP) to release phosphate radicals and a reagent for determining the content of the released phosphate radicals, the kit for determining the activity of the beta-glucan synthetase can be used for rapidly and accurately determining the content of a by-product uridine diphosphate (UDP) formed in the process of synthesizing a beta-glucan sugar chain by the beta-glucan synthetase by taking UDP-glucose as a substrate, so that the activity of the beta-glucan synthetase is accurately calculated; the kit and the method for determining the activity of the beta-glucan synthetase have the obvious advantages of low equipment requirement, safety, simplicity and convenience in operation, high sensitivity, low cost and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Fermentation method for high-yield beta-glucan based on sparassis crispa
ActiveCN110777135AExpand the range of growthPromote growthFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyGastrodia Elata Extract
The invention discloses a fermentation method for high-yield beta-glucan based on sparassis crispa. According to the method, by means of multistage amplification treatment, the growth range of the sparassis crispa is expanded as far as possible, the external limit is reduced, and nutrients required by fermentation growth are provided sufficiently; the extraction rate of glucan is increased by gastrodia elata extract, due to the fact that the gastrodia elata extract contains a large amount of gastrodin, ethanolic extract of gastrodia elata and p-hydroxybenzaldehyde, the substances can promote growth of mycelia, and meanwhile, key components for glucan synthesis are provided; and content of protein and starch in a final product can be reduced through two-way fermentation, so that the purityof glucan is improved, meanwhile, the flora promotion effect can be achieved, and the growth of the sparassis crispa is further improved.
Owner:FUQING CITY FIRE KIRIN EDIBLE FUNGUS TECH DEV
Polysaccharogenic metastase MDOH gene and its application
The invention discloses a gene, namely a glucan glucosyltransferase gene MdoH, relates to xanthomonas pathopoiesis of rice bacterial leaf blight. The gene MdoH has a base sequence of SEQ ID. NO.1 in asequence table, and is composed of 1836 bases. The gene MdoH is one member of a glucan synthetic gene cluster. The protein coded by the gene contains 611 amino acids, and is noted as glucosyltransferase. Researches prove that, the pathogen virulence is reduced due to the function loss of the gene, and the gene can serve as a drug target to be used for researching and developing bio-pesticides forcontrolling the rice bacterial leaf blight. Therefore, the gene has an important application potential in control of rice diseases. The gene related to the pathopoiesis of rice bacterial leaf blighthas significances and values for deeply understanding the pathogenesis of pathogenic bacteria in rice, establishing a pathogenic model of the rice and pathogenic bacteria, and providing the drug control target and drug development platform.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

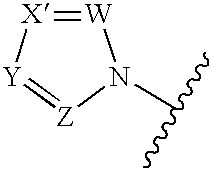
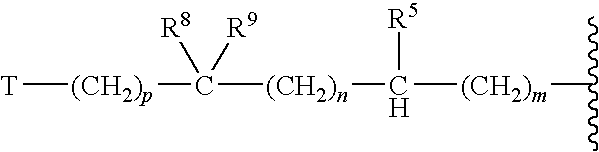
![Imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine derivative Imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine derivative](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/89a75cb9-4a7c-44a1-9630-5566b5210295/US20050113397A1-20050526-C00001.png)
![Imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine derivative Imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine derivative](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/89a75cb9-4a7c-44a1-9630-5566b5210295/US20050113397A1-20050526-C00002.png)
![Imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine derivative Imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine derivative](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/89a75cb9-4a7c-44a1-9630-5566b5210295/US20050113397A1-20050526-C00003.png)