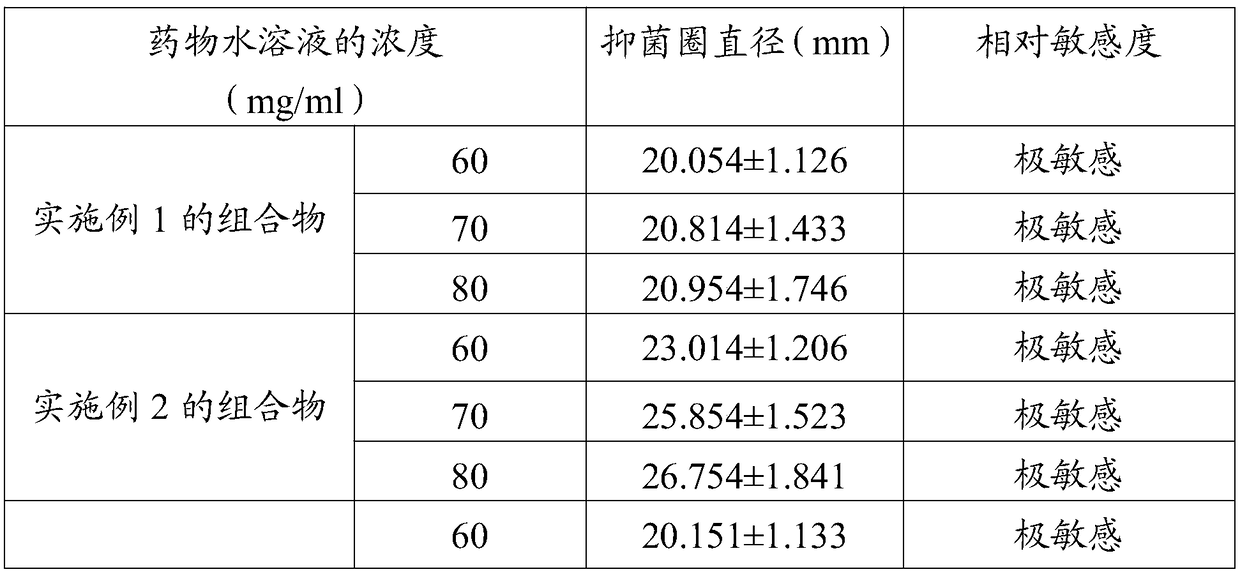
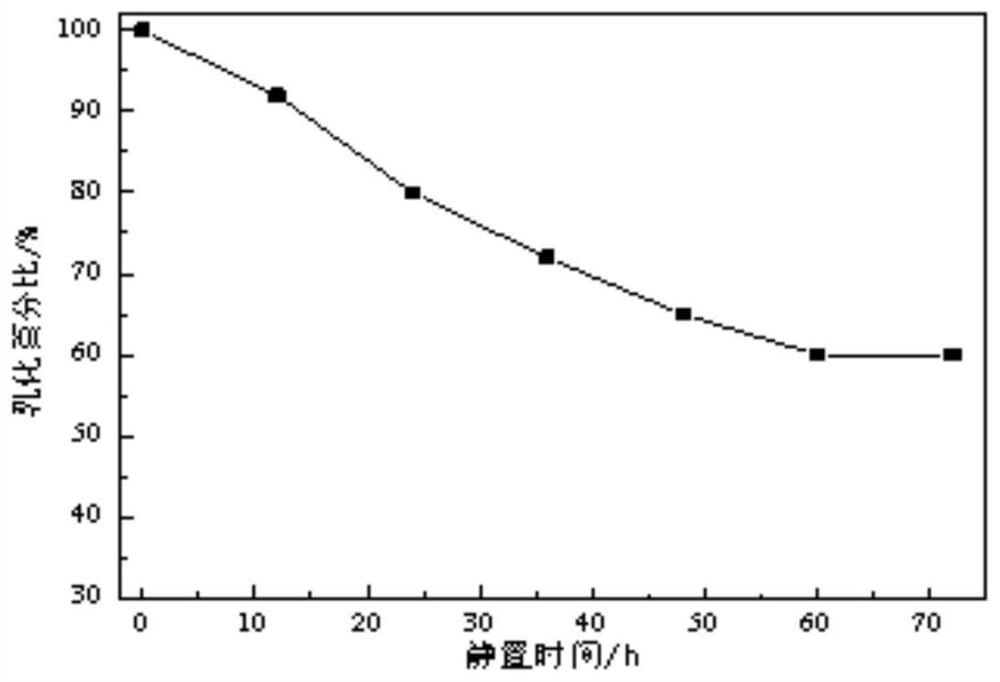
Patents
Literature
30 results about "Pseudomonas plecoglossicida" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
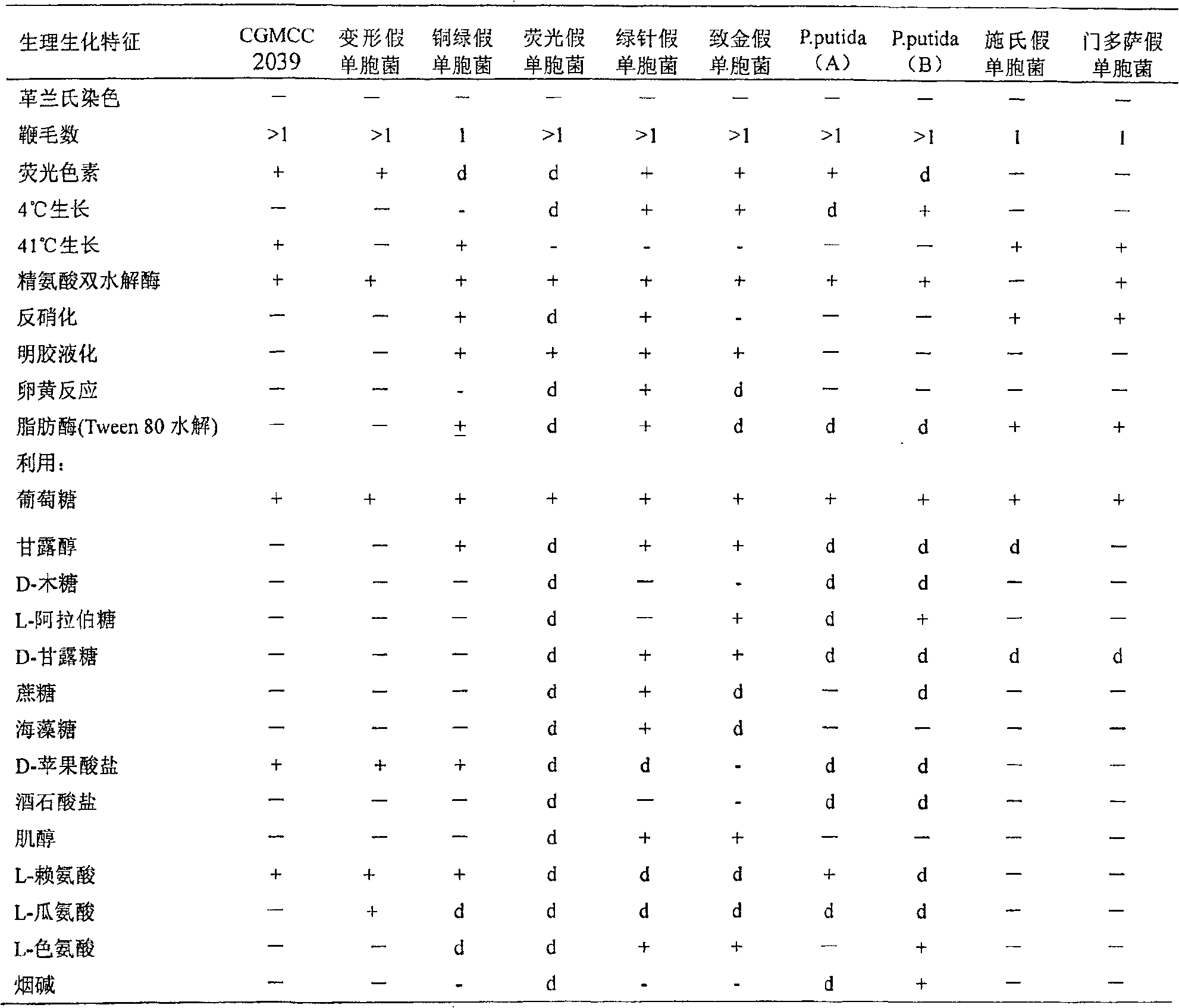
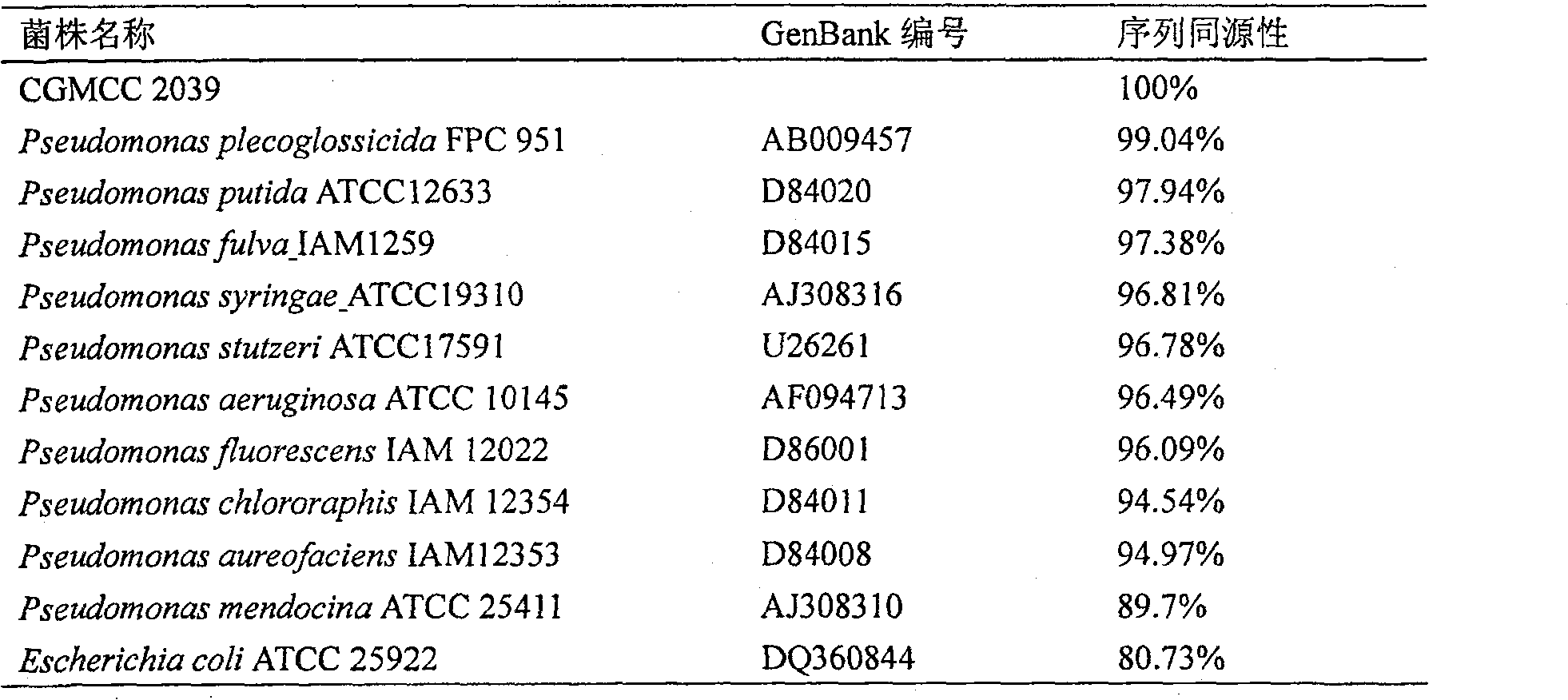
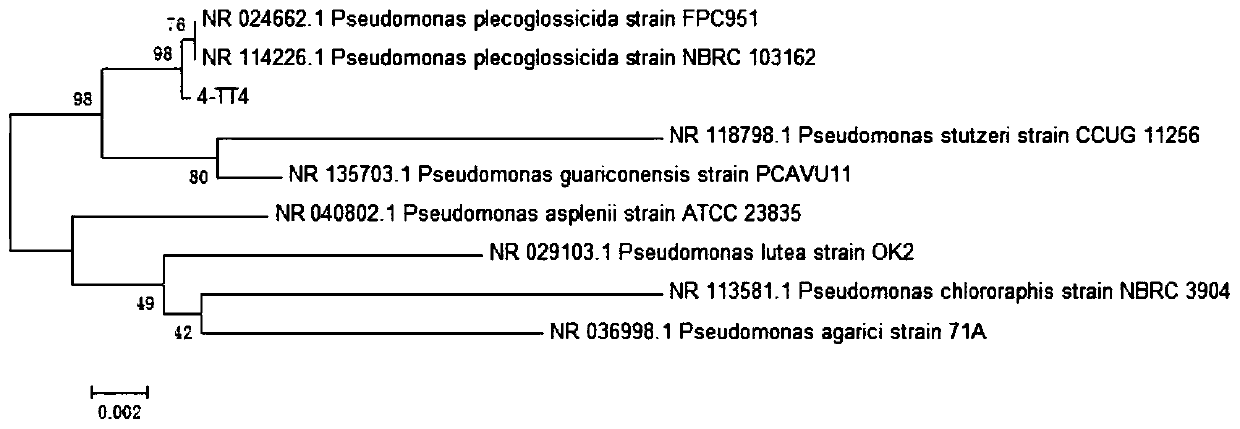
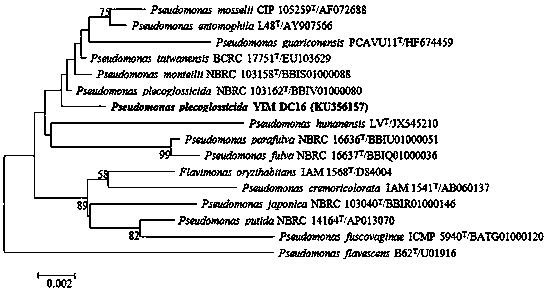
Pseudomonas plecoglossicida is a non-fluorescent, Gram-negative, rod-shaped, motile bacterium that causes hemorrhagic ascites in the ayu fish (Plecoglossus altivelis), from which it derives its name. Based on 16S rRNA analysis, P. plecoglossicida has been placed in the P. putida group.
Construction of recombinant strain capable of producing arginine deiminase and directional modification method thereof
InactiveCN102061283AIncrease enzyme activityIncreased specific enzyme activityBacteriaHydrolasesBio engineeringRecombinase
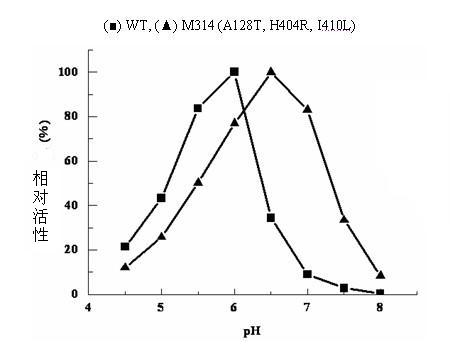
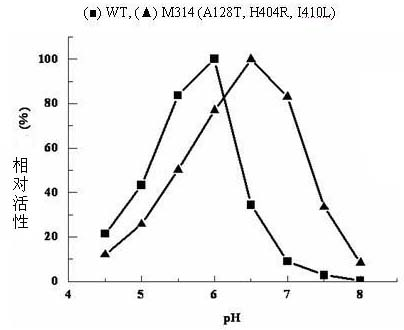
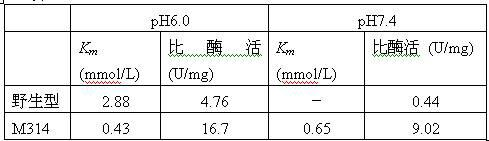
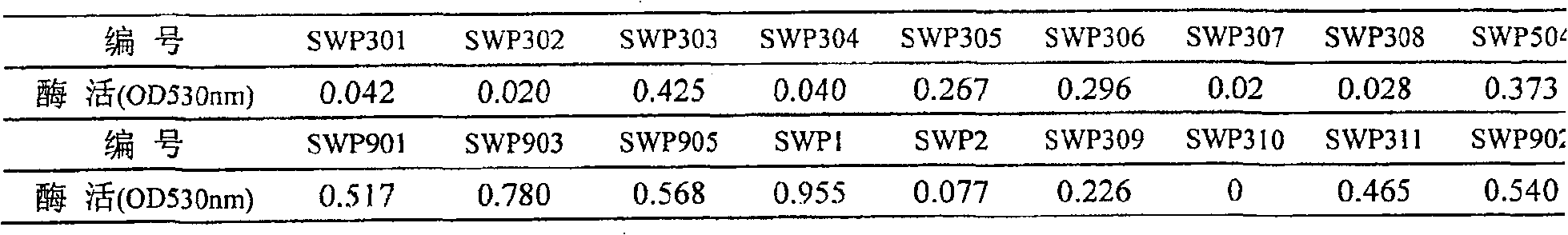
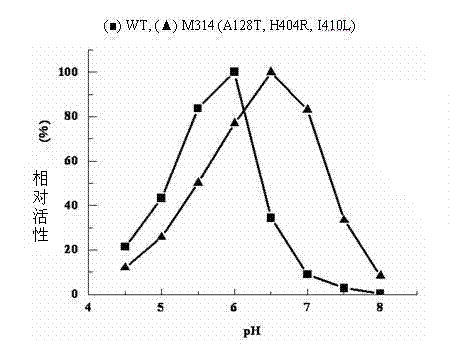
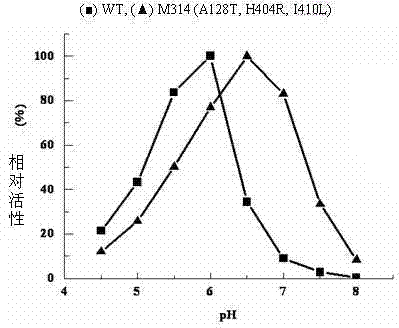
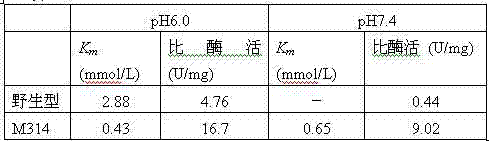
The invention relates to construction of a recombinant strain capable of producing arginine deiminase (ADI) and a directional modification method thereof, belonging to the technical field of medical biological engineering. The method comprises the following steps of: amplifying the ADI coding gene arcA of a pseudomonas plecoglossicida CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No. 2039 by adopting a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method, and constructing an ADI recombination expression strain, researching the enzymology properties of the recombinant ADI enzyme, wherein Km is 2.88mmol / L (pH is 6.0), the optimal pH is 6.0, the enzyme activity is 20.85U / mg, and the enzyme activity is reduced by more than 90% when the pH is increased to the physiological pH (7.4). The directional modification is carried out on the recombinant ADI enzyme by adopting a prone PCR mutation technology, so as to improve the activity and substrate affinity of the enzyme under the physiological pH condition. An excellent mutant strain ADIM314 is obtained by screening through the directional modification. Compared with a wild enzyme, the activity of the ADIM314 enzyme under the physiological pH condition is improved by more than 20 times, the Km value is reduced to 0.65mmol / L (pH is 7.4), and the optimal pH is improved to 6.5 from 6.0.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Strain for producing arginine deiminase and application thereof
InactiveCN101121925AIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsBacteroides speciesArginine deiminase
The invention discloses a method to produce ADI strain by screening and the application of the method, pertaining to the field of bioengineering technology. The invention particularly relates to a rapid method to screen ADI strain and produce Pseudomonas plecoglossicida (CGMCC No.2039) of ADI, as well as a method to produce ADI by using the microorganism. Under an aerobic condition and an environment maintained at pH6.5-8.0, enzyme activity can achieve 1.6U / mL fermentation broth after 20-24h fermentation culture. ADI produced with such microorganism has very strong inhabitation agaisnt liver cancer cell strain (HepG2). ADI genes can be obtained from the chromosome DNA of such microorganism, and the gene order can be achieved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Pseudomonas plecoglossicida and application thereof
ActiveCN107400650AReduce CODLower biochemical oxygen demandBacteriaWater contaminantsAcrylonitrileEnergy source
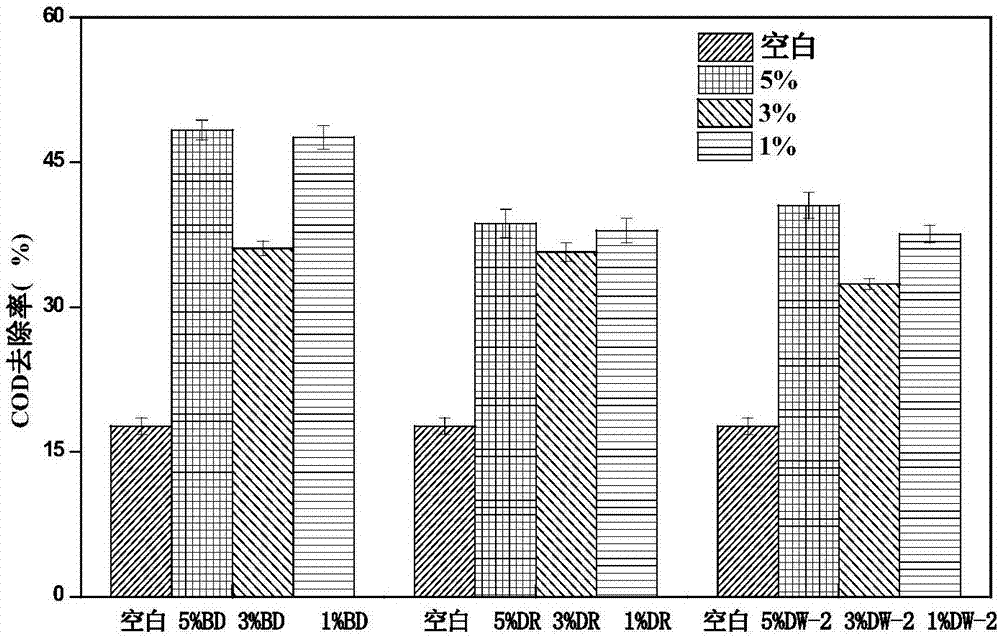
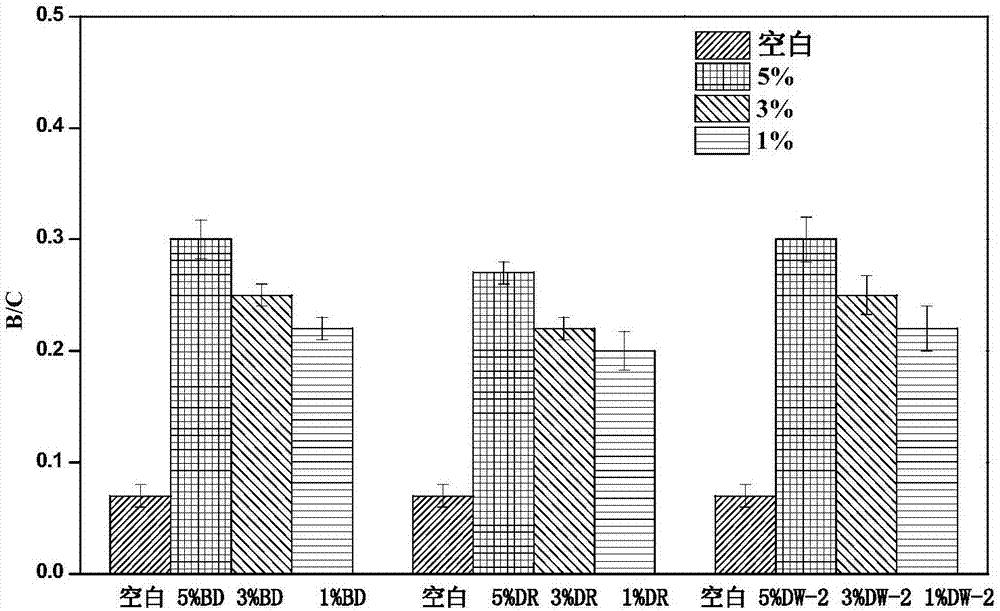
The invention discloses pseudomonas plecoglossicida and application thereof and particularly provides pseudomonas plecoglossicida BD with the preservation number being CGMCC No.14205. The provided pseudomonas plecoglossicida BD can grow and propagate with nitrile compounds as the only energy source, can degrade contaminants such as the nitrile compounds in acrylonitrile waste water and reduces the chemical oxygen demand and the biochemical oxygen demand of the acrylonitrile waste water, and accordingly the biodegradability of the acrylonitrile waste water is improved.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +2
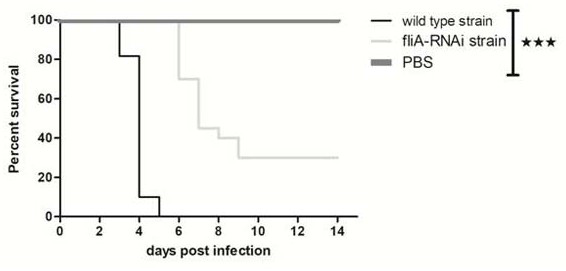
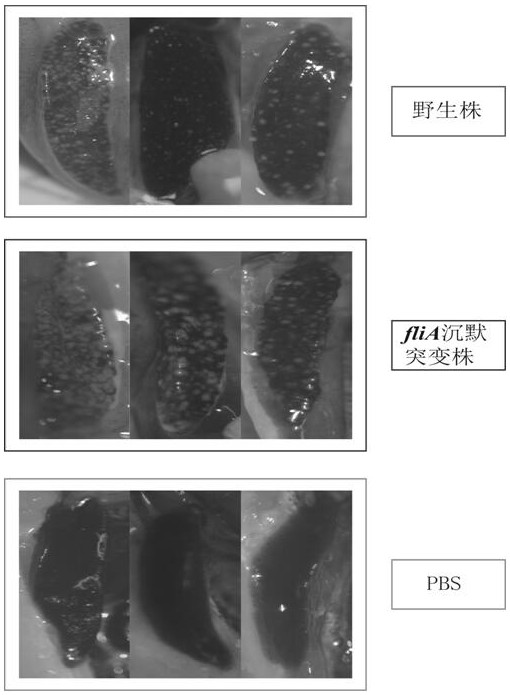
Pseudomonas plecoglossicida fliA gene silenced strain
ActiveCN109706105AReduced toxicityReduce mortalityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaMicrobiologyGene silencing
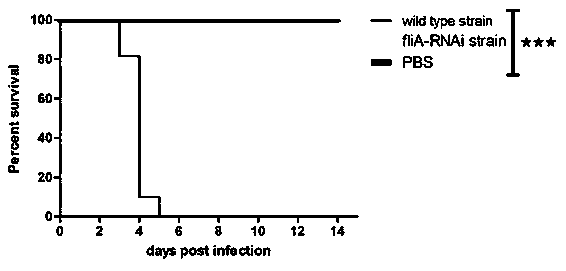
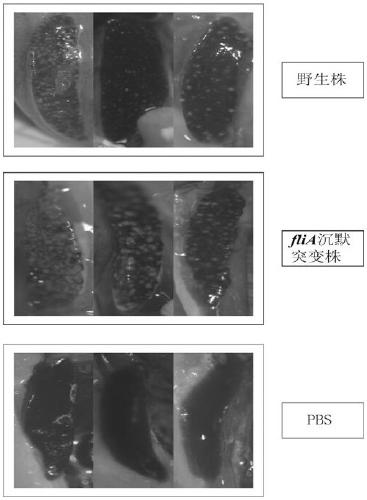
The invention provides a Pseudomonas plecoglossicida fliA gene silenced strain that is Pseudomonas plecoglossicida fliA-RNAi and deposited in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on November 12th, 2018 with an accession number of CCTCC NO:M 2018770. The constructed Pseudomonas plecoglossicida fliA gene silenced strain has virulence significantly lower than that of a Pseudomonas plecoglossicida wild strain, time of death caused by same infection conditions is delayed, and the death rate is greatly reduced, thus laying a theoretical foundation for development of an attenuated Pseudomonasplecoglossicida vaccine.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Method for analyzing root domain soil microbial community structure of soft-rot diseased amorphophallus konjac plant
The invention discloses a method for analyzing a root domain soil microbial community structure of a soft-rot diseased amorphophallus konjac plant. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring and treating a test sample, preparing a culture medium, performing microorganism isolation and enumeration, identifying dominant strains, testing the pH and the nutrition of soil, and processing data. By adopting the method for analyzing the root domain soil microbial community structure of the soft-rot diseased amorphophallus konjac plant, the change of the soil microbial community structure with the amorphophallus konjac soft-rot disease is studied, relevant micro-ecology mechanisms of the amorphophallus konjac soft-rot disease can be studied for a first time, and great significance is achieved. The study of the method for analyzing the root domain soil microbial community structure of the soft-rot diseased amorphophallus konjac plant shows that 9 dominant microorganisms, namely, 3 dominant bacteria including pseudomonas plecoglossicida, pseudomonas chlororaphis subsp.aureofaciens and stenotrophomonas pavanii, 4 dominant bacteria including fusarium solani, fusarium oxysporum, penicillium canescens and penucillium, and 2 dominant actionmycetes including streptomyces scabiei and streptomyces cellulosae, massively exist at the root domain of the soft-rot diseased amorphophallus konjac plant.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Pseudomonas plecoglossicida ExoU gene knockout mutant strain and application thereof
InactiveCN106047783AEffective prevention and controlReduced toxicityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaPseudocardium sachalinenseGenetic engineering
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and relates to a pseudomonas plecoglossicida ExoU gene knockout mutant strain and an application thereof. The mutant strain NB2011[delta]ExoU is preserved with preservation number of CGMCC No.12430; and a preparation method of the mutant strain comprises the following steps: conducting gene knocking-out on the ExoU gene of the pseudomonas plecoglossicida wild strain NB2011 by virtue of a homologous recombinant gene knockout technology, and conducting screening and identification by virtue of a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technology, so that an obtained strain is determined as the gene knockout mutant strain. By researching pathogenicity of the mutant strain disclosed by the invention through animal experiments, results show that the toxicity of the mutant strain on experimental animals is significantly reduced; therefore, the mutant strain can be applicable to pseudomonas plecoglossicida hypo-toxic vaccines.
Owner:ZHEJIANG WANLI UNIV
Multiple PCR detection kit for rapidly identifying pathogenic Pseudomonas plecoglossicida, and method thereof
InactiveCN103993072ARapid determinationSensitive assayMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPseudomonadaceaePolymerase L
The present invention discloses a multiple PCR detection kit for rapidly identifying pathogenic Pseudomonas plecoglossicida, and a method thereof. The kit comprises TaqDNA polymerase, a PCR buffer, a deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate mixture, double distilled water, and primer pairs of Pseudomonadaceae, Pseudomonas plecoglossicida and pathogenic Pseudomonas plecoglossicida. The multiple PCR detection method for rapidly identifying pathogenic Pseudomonas plecoglossicida by using the kit comprises: primary separation of Pseudomonadaceae, and multiple PCR amplifications. Compared with the kit and the method in the prior art, the kit and the method of the present invention have the following advantages that: with application of the kit of the present invention to detect, Pseudomonadaceae, Pseudomonas plecoglossicida and pathogenic Pseudomonas plecoglossicida corresponding to the DNA primer pairs of the three Pseudomonadaceae can be rapidly detected, and with the detection method of the present invention, the presence of the Pseudomonadaceae can be rapidly, sensitively and specifically determined by using the kit, and the pathogenic stain and the non-virulent environment isolation strain can be distinguished.
Owner:ZHEJIANG WANLI UNIV
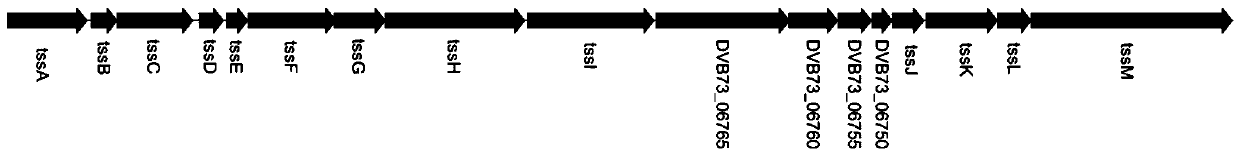
Pseudomonas plecoglossicida attenuated vaccine for fish with T6SS-1 gene cluster knocked out
ActiveCN109825464AAnimal safeImproving immunogenicityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaEscherichia coliAnimals vaccines
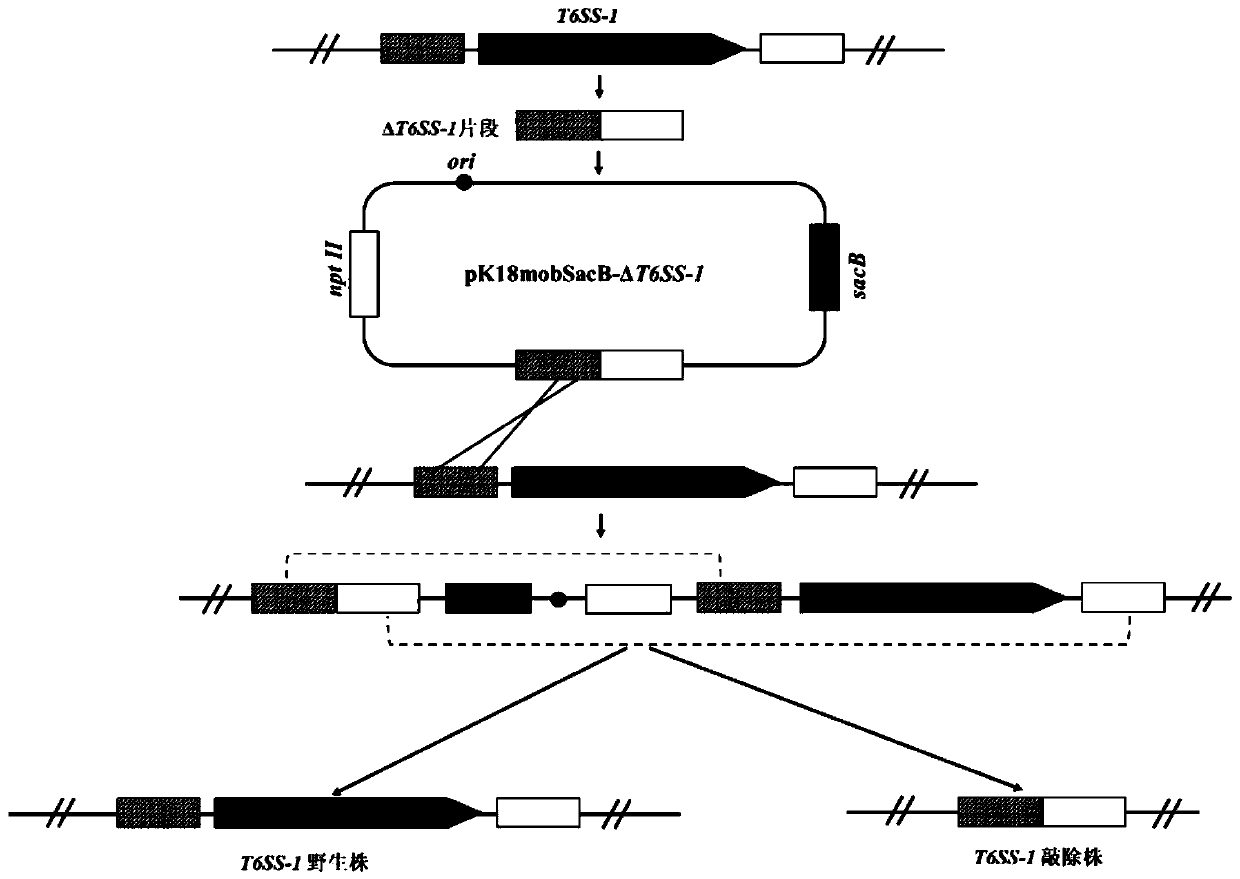
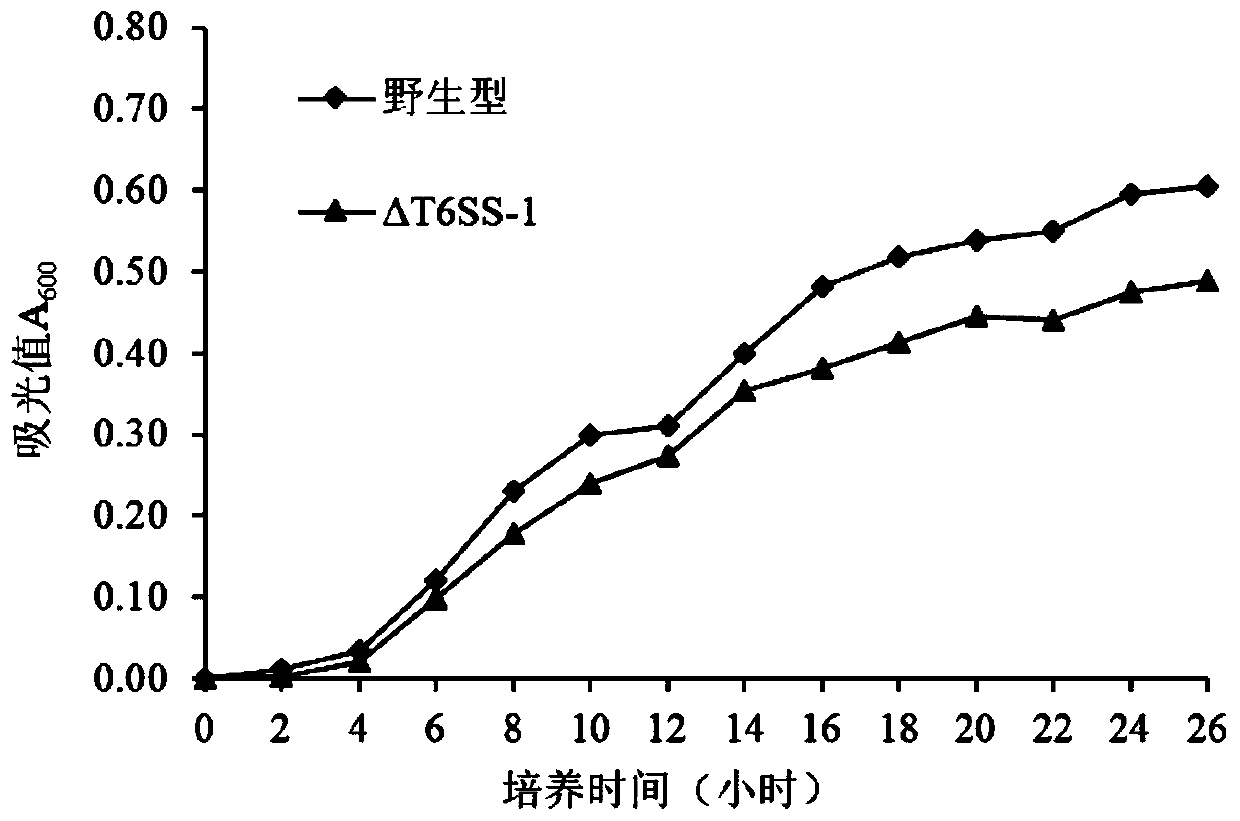
The invention provides a pseudomonas plecoglossicida attenuated vaccine for fish with a T6SS-1 gene cluster knocked out, and belongs to the technical field of animal vaccines. The vaccine comprises aknockout strain of one set of VI-secreting system gene clusters of a pseudomonas plecoglossicida genome. A construction method includes adopting an overlapped PCR way to obtain a splicing fragment ofupstream and downstream sequences of the T6SS-1 gene cluster; connecting the splicing fragment to pK18mobSacB to construct a knockout vector and transferring the knockout vector to the competent escherichia coli, transferring the knockout vector to pseudomonas plecoglossicida cells by conjugation and conducting homologous recombination exchange twice to achieve knockout of a target gene. The T6SS-1 gene cluster is knocked out to achieve the pseudomonas plecoglossicida attenuated vaccine with the virulence significantly weakened relative to a wild strain while good immunogenicity is maintained.The vaccine has a good immune protection effect on a host of inoculated fish, and the virulence of the knockout strain does not recover.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Strain for producing arginine deiminase and application thereof
InactiveCN100584940CIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsBio engineeringChromosomal dna
The invention discloses a method to produce ADI strain by screening and the application of the method, pertaining to the field of bioengineering technology. The invention particularly relates to a rapid method to screen ADI strain and produce Pseudomonas plecoglossicida (CGMCC No.2039) of ADI, as well as a method to produce ADI by using the microorganism. Under an aerobic condition and an environment maintained at pH6.5-8.0, enzyme activity can achieve 1.6U / mL fermentation broth after 20-24h fermentation culture. ADI produced with such microorganism has very strong inhabitation agaisnt liver cancer cell strain (HepG2). ADI genes can be obtained from the chromosome DNA of such microorganism, and the gene order can be achieved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Pesticide omethoate degrading microorganism compound bacterial agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110591979AEasy to operateEasy constructionBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationPseudocardium sachalinenseMixing ratio
The invention relates to a pesticide omethoate degrading microorganism compound bacterial agent and a preparation method thereof. The compound bacterial agent is prepared from Pseudomonas graminis ZZY-C13-1-8 or a mixture of the Pseudomonas graminis ZZY-C13-1-8 and Pseudomonas plecoglossicida, glycerin, activated carbon and kaoline with a mixing ratio being 1 to 1 to (1.5-2) to 3 to (2.5-3). A thallus involved by the invention is cultured by a special fluid nutrient medium, the obtained compound bacterial agent can degrade omethoate residual in agricultural soils in situ with the degrading ratio of the omethoate residual in the soils reaching 75 percent or above, and the pesticide omethoate degrading microorganism compound bacterial agent and the preparation method have the advantages of low treatment cost, simpleness in construction, no influence on production and operation, no secondary pollution, small influence on environment and the like.
Owner:MICROBIOLOGY INST OF SHAANXI
Pseudomonas plecoglossicida and application thereof
ActiveCN110055187APromote degradationEfficient degradationBacteriaExcrement fertilisersMicroorganismMicrobial agent
The invention relates to pseudomonas plecoglossicida and application thereof. The preservation number of the pseudomonas plecoglossicida is CGMCC No.14475. The invention also provides a microbial agent containing the pseudomonas plecoglossicida as an active ingredient. The invention further provides application of the pseudomonas plecoglossicida and the microbial agent in degrading sulfamethazine,treating poultry breeding wastes and repairing antibiotic contamination. By means of the technical scheme, the sulfamethazine can be removed more efficiently.
Owner:INST OF ENVIRONMENT & SUSTAINABLE DEV IN AGRI CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
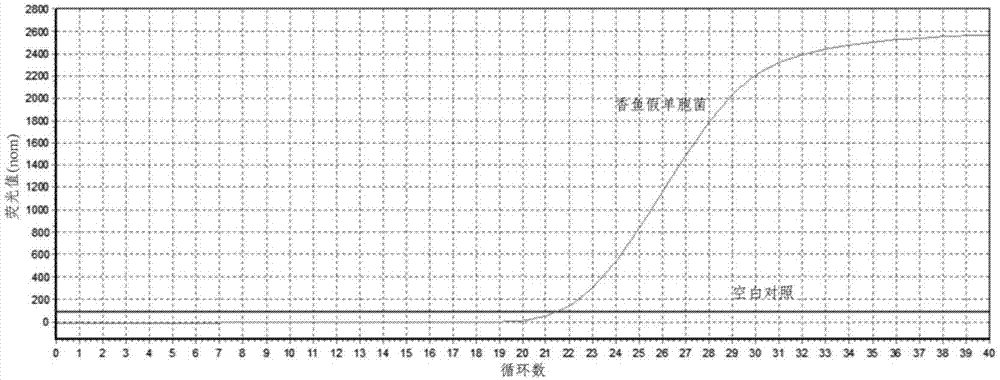
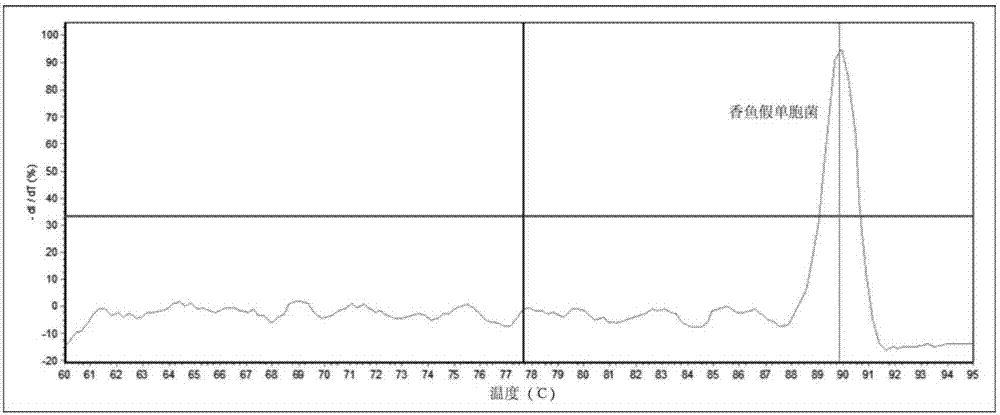
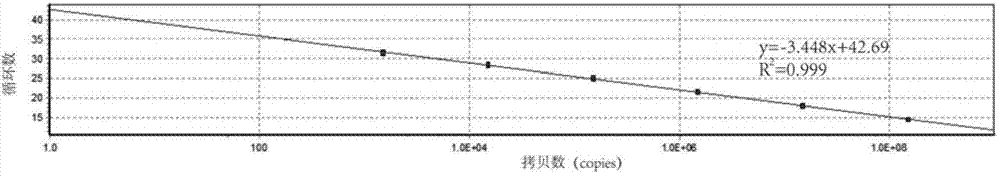
Fluorescent quantitative PCR detection kit of Pseudomonas plecoglossicida, and detection method thereof
InactiveCN103276093BQuantitatively sensitiveSensitive quantitative PCR detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesEnzymatic hydrolysis
The invention discloses a fluorescent quantitative PCR detection kit of Pseudomonas plecoglossicida, and a detection method thereof. The kit comprises 10.0mul of an SYBR Premix Ex TaqTMII reagent, 0.8mul of an upstream primer solution having a concentration f 10muM, and 0.8mul of a downstream primer solution having a concentration of 1.0muM. The detection method comprises the steps of bacterium extraction, bacterium enzymatic hydrolysis, DNA crude extract preparation, DNA crude extract purification and detection. The detection kit can sensitively, rapidly, quantitatively and specifically detect early-stage Pseudomonas plecoglossicida, and the qualitative and quantitative sensitivities can reach 10<3>copies; and the detection kit can detect whether aquatic farming animals are infected with the Pseudomonas plecoglossicida nor not, the content of the Pseudomonas plecoglossicida in the farming water environment, whether a farming feed and a fresh bait are polluted by the Pseudomonas plecoglossicida or not, and the like.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Phenol-degrading bacterium strain capable of producing biological surfactant and application thereof
ActiveCN109837227AImprove degradation efficiencyStrong emulsifying abilityBacteriaWater contaminantsAlkanePhenol
The present invention relates to a phenol-degrading bacterium strain capable of producing a biological surfactant and an application thereof. A technical solution is as follows: the provided bacteriumstrain is pseudomonas plecoglossicida BPH-3 which is preserved by the China Center for Type Culture Collection, a preservation number is: CCTCC NO:M 2019144, and a preservation date is March 14, 2019. A GenBank accession number of 16S rDNA of the pseudomonas plecoglossicida BPH-3 is MK575471, the pseudomonas plecoglossicida BPH-3 is a Gram-negative bacterium strain, and colony is milky white andround, smooth in surface and neat in edges; and after Gram staining, the pseudomonas plecoglossicida BPH-3 is negative under a microscope and presents a short-rod shape. During fermentation degradation, the phenol-degrading bacterium strain forms a glycolipid biological surfactant which can promote solubilization, emulsification, wetting and osmosis of long-chain alkanes and can effectively degrade phenol in coking wastewater and petrochemical wastewater.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR detection kit for deformed pseudomonas plecoglossicida TaqMan and preparation method thereof
PendingCN111440887AOptimizationImprove responseMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDiseaseMicrobiology
The invention provides a real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR detection kit for a deformed pseudomonas plecoglossicida TaqMan and a preparation method thereof. The kit comprises a primer and a probe for specifically detecting the deformed pseudomonas plecoglossicida, wherein the sequence is as follows: a formula as shown in the specification. The kit provided by the invention is complete in reagents and simple to operate, and provides a detection tool for the scale detection and control of the disease.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
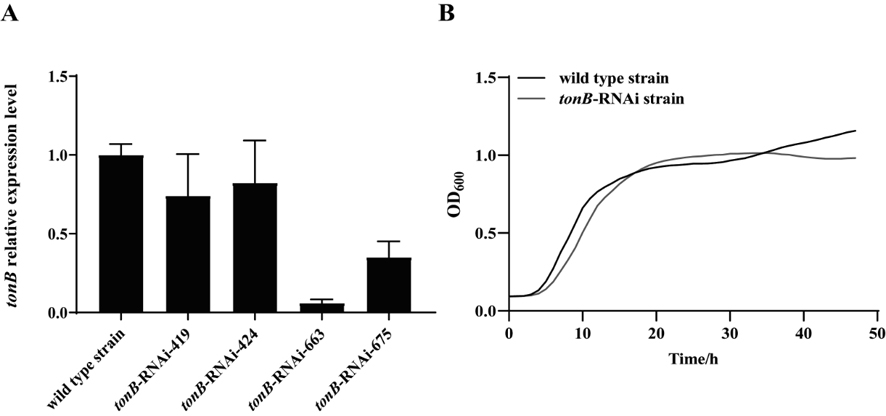
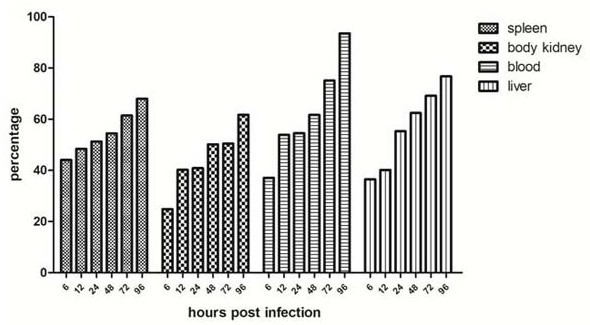
Pseudomonas plecoglossicida tonB gene silencing strain and application thereof
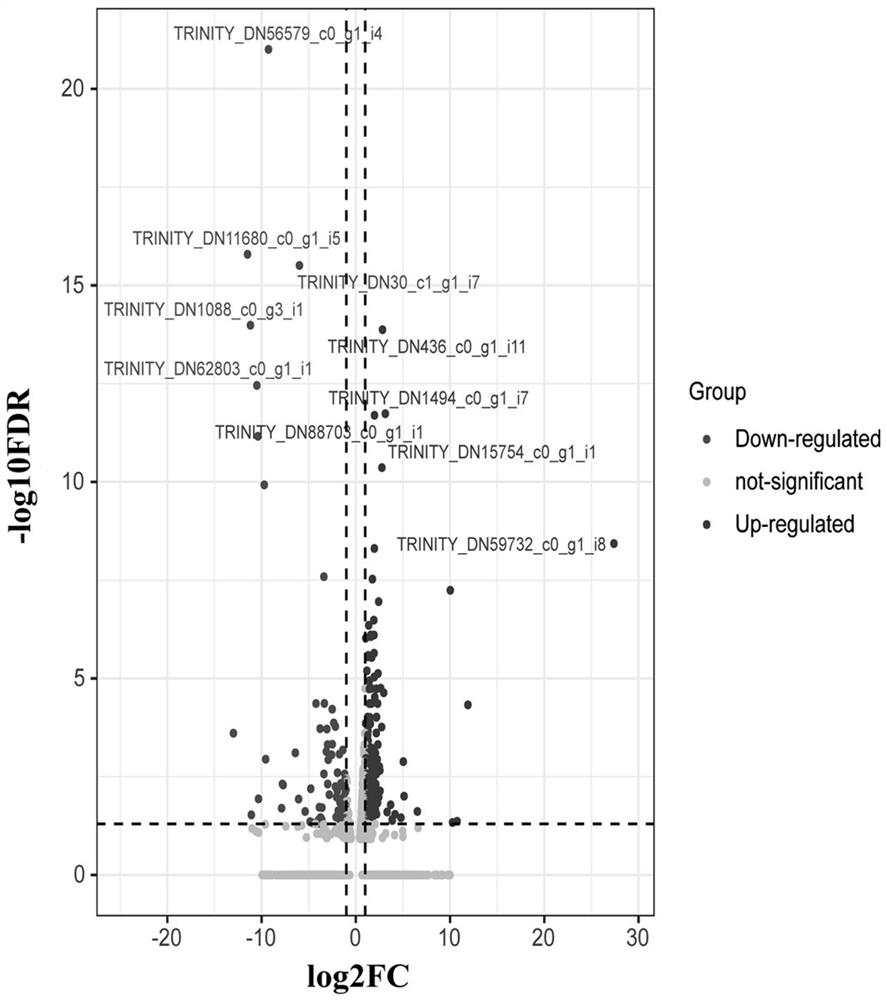
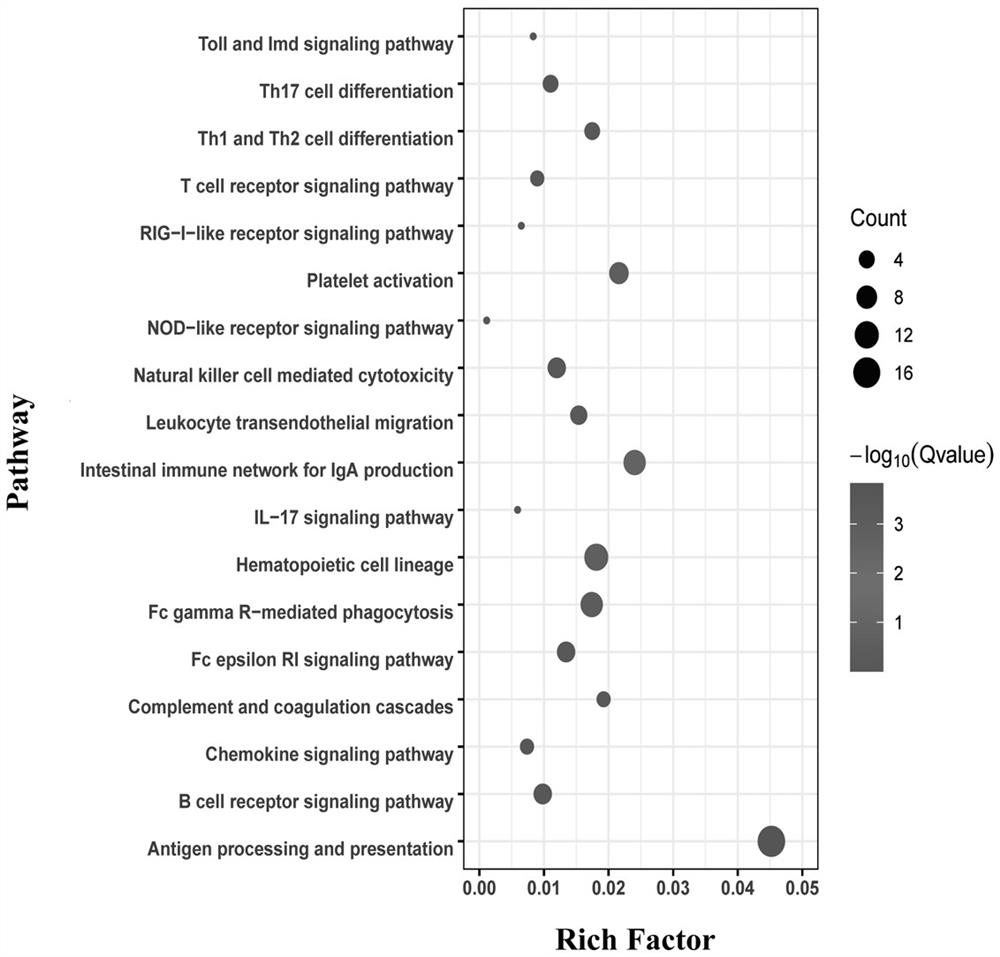
The invention provides a Pseudomonas plecoglossicida tonB gene silencing strain and application of the Pseudomonas plecoglossicida tonB gene silencing strain. The bacterial strain is Pseudomonas plecoglossicida tonB-RNAi, the bacterial strain is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on December 18, 2020, and the preservation number is CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection) NO: M 2020919. Compared with a wild strain, the strain for silencing the Pseudomonas plecoglossicida tonB gene has the advantages that the pathogenicity of the strain to the epinephelus coioides is remarkably reduced, and a spleen transcriptome of the epinephelus coioides can be remarkably changed, so that the strain can be used for researching the pathogenesis of the pseudomonas deformation, and particularly, the Pseudomonas plecoglossicida tonB gene silencing strain has unique advantages in studying the pathogenesis of pseudomonas deformation from the perspective of Epinephelus coioides infection and material transportation.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Ayucidal Pseudomonas exou gene knockout mutant strain and application thereof
InactiveCN106047783BLow toxicityEffective prevention and controlAntibacterial agentsBacteriaGenetic engineeringTGE VACCINE
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and relates to a pseudomonas plecoglossicida ExoU gene knockout mutant strain and an application thereof. The mutant strain NB2011[delta]ExoU is preserved with preservation number of CGMCC No.12430; and a preparation method of the mutant strain comprises the following steps: conducting gene knocking-out on the ExoU gene of the pseudomonas plecoglossicida wild strain NB2011 by virtue of a homologous recombinant gene knockout technology, and conducting screening and identification by virtue of a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technology, so that an obtained strain is determined as the gene knockout mutant strain. By researching pathogenicity of the mutant strain disclosed by the invention through animal experiments, results show that the toxicity of the mutant strain on experimental animals is significantly reduced; therefore, the mutant strain can be applicable to pseudomonas plecoglossicida hypo-toxic vaccines.
Owner:ZHEJIANG WANLI UNIV
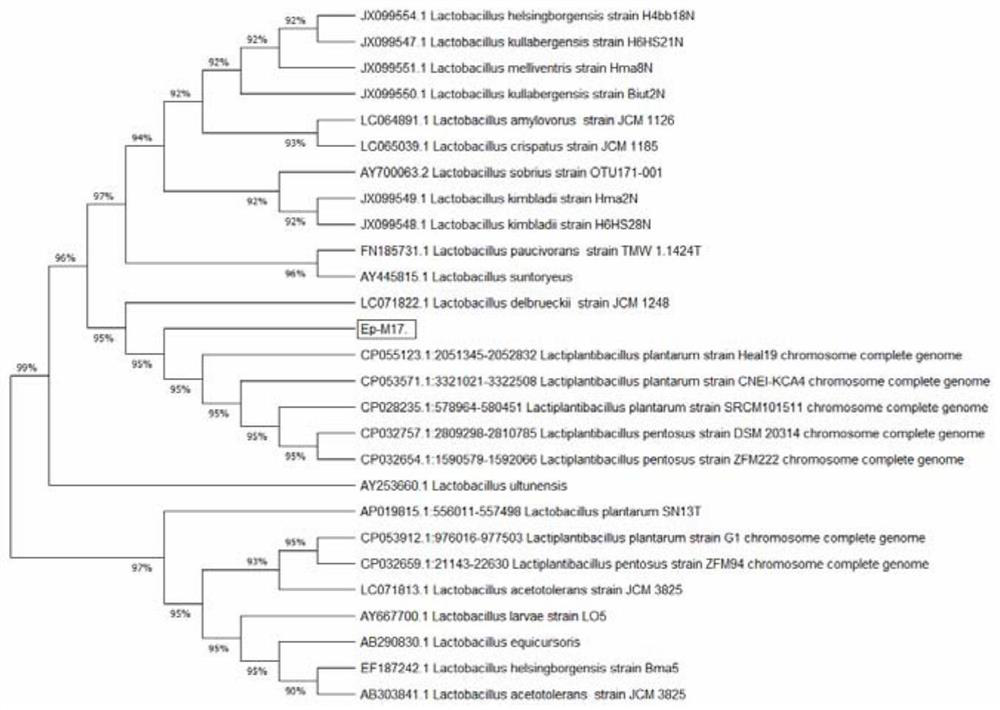
Lactobacillus plantarum and application thereof in preparation of probiotic preparation for prawn culture
ActiveCN114874934APromote growthImprove survival rateBacteriaClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyStaphyloccocus aureus
The invention discloses lactobacillus plantarum and application thereof in preparing a probiotic preparation for prawn culture, and is characterized in that the strain is an Ep-M17 strain, is classified and named as lactobacillus plantarum, is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on March 21, 2022, and has a preservation number of CGMCC No.24559; the lactobacillus plantarum is applied to preparation of a probiotic preparation for prawn culture, a vibrio parahaemolyticus inhibitor, a vibrio alginolyticus inhibitor, edwardsiella tarda, staphylococcus aureus, a pseudomonas plecoglossicida inhibitor, a plesiomonas shigelloides inhibitor, an aeromonas hydrophila inhibitor and an aeromonas veronii inhibitor. The compound has the advantages that the compound has an inhibition effect on edwardsiella tarda, staphylococcus aureus, vibrio parahaemolyticus, vibrio alginolyticus, pseudomonas plecoglossicida, plesiomonas shigelloides, aeromonas hydrophila and aeromonas veronii pathogens.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
A strain of Pseudomonas mutans flia gene silencer
ActiveCN109706105BLow toxicityReduce mortalityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaMicrobiologyAttenuated vaccine
The invention provides a Pseudomonas plecoglossicida fliA gene silenced strain that is Pseudomonas plecoglossicida fliA-RNAi and deposited in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on November 12th, 2018 with an accession number of CCTCC NO:M 2018770. The constructed Pseudomonas plecoglossicida fliA gene silenced strain has virulence significantly lower than that of a Pseudomonas plecoglossicida wild strain, time of death caused by same infection conditions is delayed, and the death rate is greatly reduced, thus laying a theoretical foundation for development of an attenuated Pseudomonasplecoglossicida vaccine.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Pseudomonas plecoglossicida DNA vaccine and preparing method and application thereof
InactiveCN108498793AHigh protection rateWeakened immune protectionAntibacterial agentsPeptidesMicrobiologyPseudocardium sachalinense
The invention discloses a pseudomonas plecoglossicida DNA vaccine and a preparing method and application thereof. The pseudomonas plecoglossicida DNA vaccine is characterized in that the pseudomonas plecoglossicida DNA vaccine is pCI-pcrV; pseudomonas plecoglossicida NB2011 genome DNA serves as a template, and is subjected to PCR amplification through a primer P1 / P2, the amplified products are purified to be connected with plasmid pCI-neo, and recombinant plasmid pCI-pcrV is obtained, and is the pseudomonas plecoglossicida DNA vaccine, wherein the sequence of a target gene pcrV is shown in SEQID NO:1. According to the pseudomonas plecoglossicida DNA vaccine, the immune protective rate of pseudomonas plecoglossicida infection is 70% or above, and therefore the high protective rate is achieved. The immune protective rate of the pseudomonas plecoglossicida DNA vaccine in 8 weeks after immunization is not obviously reduced, and therefore the pseudomonas plecoglossicida DNA vaccine has thelong-acting advantage.
Owner:ZHEJIANG WANLI UNIV
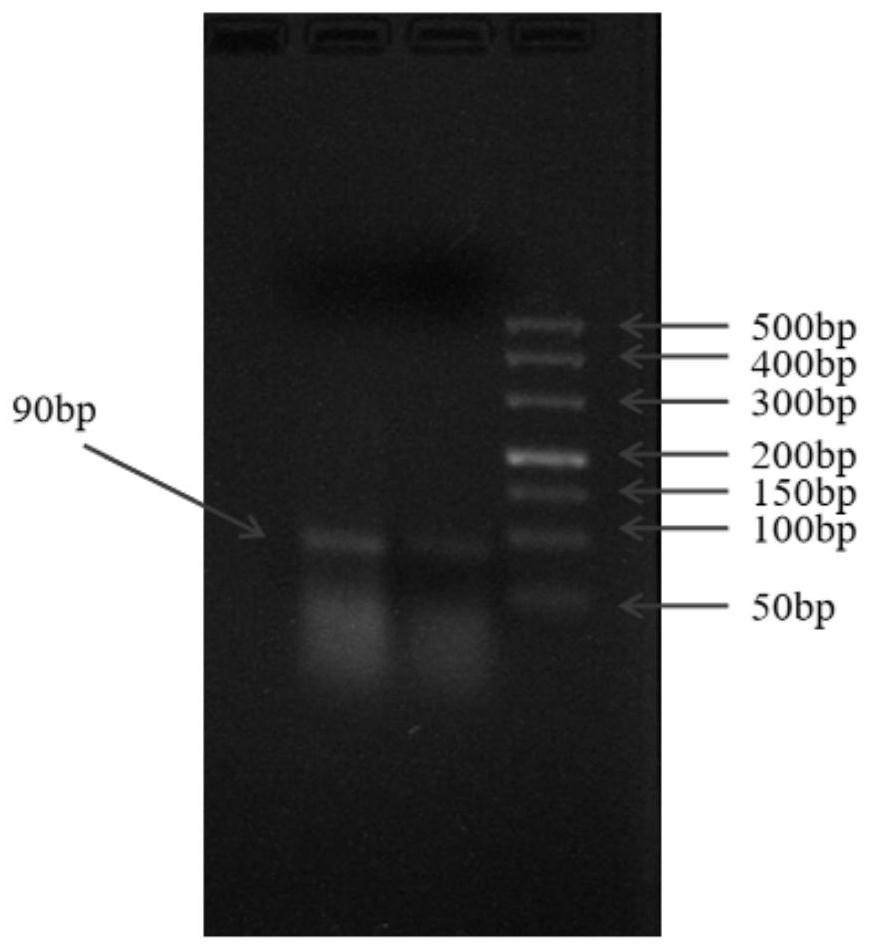
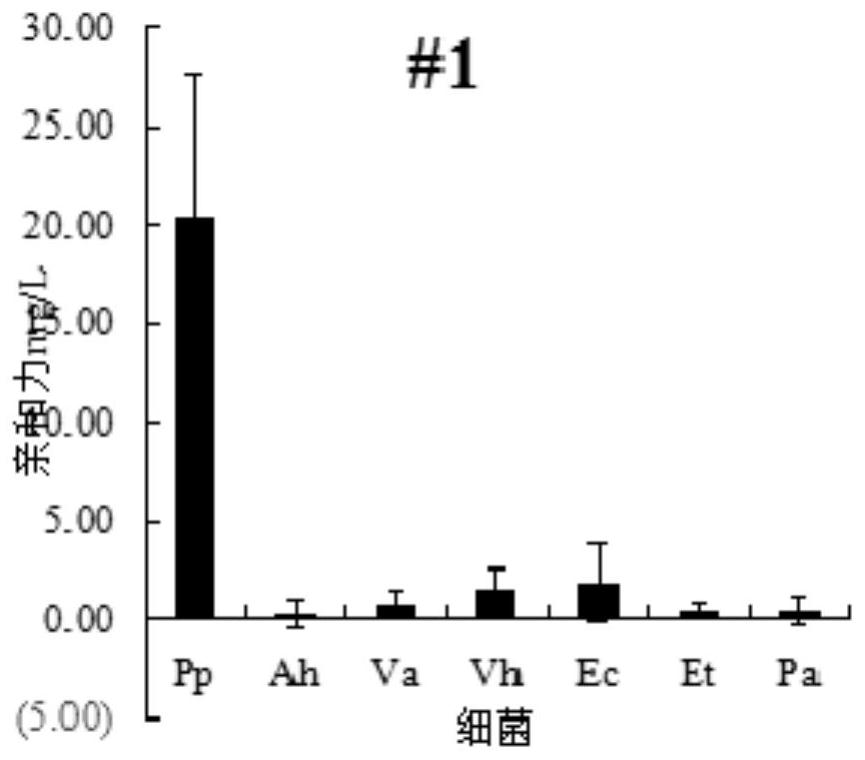
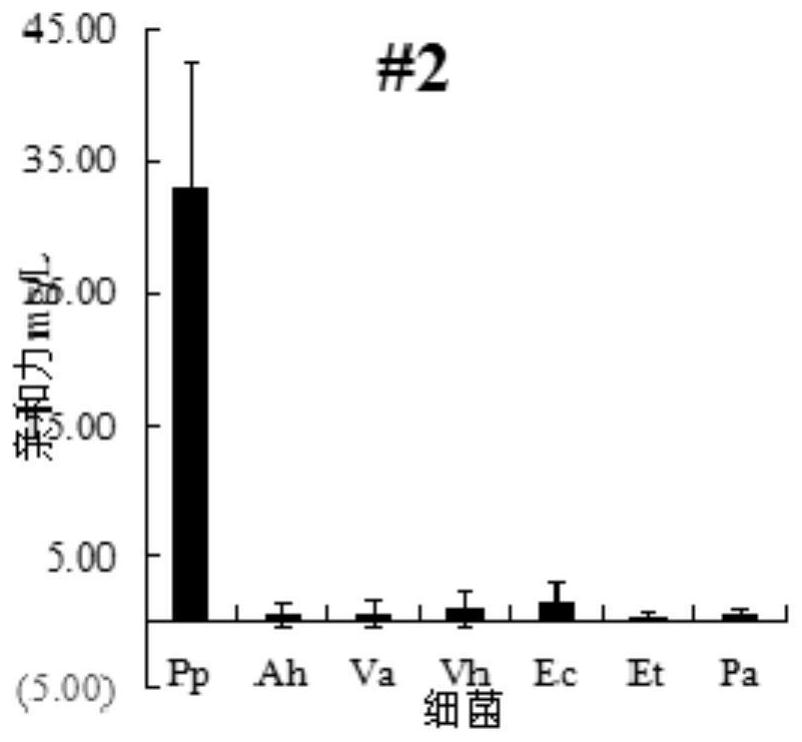
Pseudomonas plecoglossicida aptamers and screening method therefor
PendingCN113278622AHigh affinitySimple methodDNA preparationDNA/RNA fragmentationAptamerMicrobiology
The invention relates to aptamers and particularly relates to Pseudomonas plecoglossicida aptamers and a screening method therefor. Sequences of the aptamers are represented by SEQ. NO. 1-5, the aptamers capable of specifically identifying and inhibiting the growth of Pseudomonas plecoglossicida are screened by employing SELEX technologies such as inverse screening, and the influence on the Pseudomonas plecoglossicida caused by the aptamers is characterized through measuring affinity. According to the Pseudomonas plecoglossicida aptamers and the screening method therefor, high-frequency sequences can be objectively and effectively classified, and thus, an objective and effective basis is provided for subsequent accurate selection and verification on the aptamers; and the method is simple and is convenient in operation, so that the blindness of verification is lowered greatly, and the screening efficiency is increased. Five aptamers #1, #2, #3, #4 and #5 with highest relative important indexes are picked from a screened result, the affinity of these aptamers to 28-DEG-C Pseudomonas plecoglossicida is higher than that of other bacteria, and thus, these aptamers have relatively good affinity and specificity to the 28-DEG-C Pseudomonas plecoglossicida.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
A kind of Pseudomonas mutans and application thereof
ActiveCN110055187BPromote degradationEfficient degradationBacteriaExcrement fertilisersBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The present disclosure relates to a pseudomonas mutans and application thereof. The deposit number of Pseudomonas plecoglossicida of the present disclosure is CGMCC No.14475. The present disclosure also provides a microbial bacterial agent, which contains the above-mentioned Pseudomonas mutans as an active ingredient. The present disclosure also provides the application of the above-mentioned Pseudomonas mutans and the above-mentioned microbial bacterial agent in degrading sulfamethazine, treating poultry and livestock breeding waste and remediating antibiotic pollution. Through the above technical solution, the present disclosure can remove sulfamethazine more effectively.
Owner:INST OF ENVIRONMENT & SUSTAINABLE DEV IN AGRI CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
An aerobic denitrifying bacteria and its application
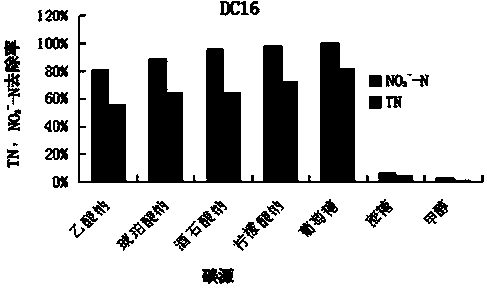
The invention discloses a strain of aerobic denitrifying bacterium Pseudomonas plecoglossicida YIM DC16, which has been preserved in the General Microorganism Center of the China Microorganism Culture Collection and Management Committee on July 14, 2015, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.11077; it is a microbial strain with aerobic denitrification ability; the strain of the present invention can utilize a variety of carbon sources such as glucose, sodium succinate, sodium citrate, sodium acetate, sodium tartrate and the like under aerobic or oxygen-limited conditions. Aerobic denitrification; the strain was cultured at 20°C, 100 rpm, initial pH 7.5, and C / N=15 in a liquid medium with glucose as the carbon source and KNO3 as the sole nitrogen source for 36 h. The removal rate of nitrate nitrogen can reach 90.07%, and the removal rate of total nitrogen can also reach 76.99%, which has a good market application prospect.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
A kind of Pseudomonas mutans and application thereof
ActiveCN107400650BReduce CODImprove biodegradabilityBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyAcrylonitrile
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +2
Ayucidal Pseudomonas dna vaccine, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108498793BHigh protection rateWeakened immune protectionAntibacterial agentsPeptidesMicrobiologyTGE VACCINE
Owner:ZHEJIANG WANLI UNIV
Mutant strain with deletion of type VI secretion systems of pseudomonas plecoglossicida and application of mutant strain
PendingCN112063551AFree from harmImprove immunityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaMicrobiologyTGE VACCINE
The invention relates to a marker-free gene deletion attenuated mutant strain of a pseudomonas plecoglossicida wild virulent strain. The marker-free gene deletion attenuated mutant strain of the pseudomonas plecoglossicida wild strain can be used as an attenuated live vaccine for preventing pseudomonas plecoglossicida infection, and the marker-free gene deletion attenuated mutant strain of the pseudomonas plecoglossicida wild strain lacks partial effect element genes of three sets of type VI secretion systems of pseudomonas plecoglossicida, including T6SS1, T6SS2 and T6SS3. The pseudomonas plecoglossicida virulent strain is a pseudomonas plecoglossicida virulent strain NB2011, the preservation number of the pseudomonas plecoglossicida virulent strain NB2011 is CGMCC No.8985, the marker-free gene deletion attenuated mutant strain of the pseudomonas plecoglossicida wild virulent strain is delta T6SS1-3, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.20416. The invention also provides an application of the marker-free gene deletion attenuated mutant strain. The attenuated mutant strain provided by the invention eliminates the potential toxicity return environment and product safety risk ubiquitous in the traditional attenuated live vaccine, and is a safe, effective and economic vaccine for the visceral white spot disease of bred large yellow croaker.
Owner:ZHEJIANG WANLI UNIV
Traditional Chinese medicine composition used for treating grouper pseudomonas plecoglossicida and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108815280AImprove efficacyReduce dosageAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryDiseaseCure rate
The invention relates to a traditional Chinese medicine composition used for treating grouper pseudomonas plecoglossicida and a preparation method and an application thereof, which belong to the technical field of aquatic product culture. The traditional Chinese medicine composition comprises coptis, radix astragali and phellodendron amurense with mass ratio being 0.9-1.3:0.9-1.3:0.9-1.3. The traditional Chinese medicine composition can greatly increase the drug effect, and the survival rate by using the traditional Chinese medicine composition is increased by 60% and above by comparing with that of non-feeding of the traditional Chinese medicine composition. The traditional Chinese medicine composition has the advantages of scientific compatibility, low cost, short treatment course, fasteffectiveness, and high cure rate, and provides support for preventing and treating fish disease in culture production.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
A phenol-degrading bacterium producing biosurfactant and its application
ActiveCN109837227BImprove degradation efficiencyStrong emulsifying abilityBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyStaining
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A multiplex PCR detection kit and method for rapidly identifying pathogenic Pseudomonas ayumi
InactiveCN103993072BRapid determinationSensitive assayMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPseudomonadaceaePolymerase L
Owner:ZHEJIANG WANLI UNIV
Construction of recombinant strain capable of producing arginine deiminase and directional modification method thereof
InactiveCN102061283BIncrease enzyme activityIncreased specific enzyme activityBacteriaHydrolasesBio engineeringRecombinase
The invention relates to construction of a recombinant strain capable of producing arginine deiminase (ADI) and a directional modification method thereof, belonging to the technical field of medical biological engineering. The method comprises the following steps of: amplifying the ADI coding gene arcA of a pseudomonas plecoglossicida CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No. 2039 by adopting a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method, and constructing an ADI recombination expression strain, researching the enzymology properties of the recombinant ADI enzyme, wherein Km is 2.88mmol / L (pH is 6.0), the optimal pH is 6.0, the enzyme activity is 20.85U / mg, and the enzyme activity is reduced by more than 90% when the pH is increased to the physiological pH (7.4). The directional modification is carried out on the recombinant ADI enzyme by adopting a prone PCR mutation technology, so as to improve the activity and substrate affinity of the enzyme under the physiological pH condition. An excellent mutant strain ADIM314 is obtained by screening through the directional modification. Compared with a wild enzyme, the activity of the ADIM314 enzyme under the physiological pH condition is improved by more than 20 times, the Km value is reduced to 0.65mmol / L (pH is 7.4), and the optimal pH is improved to 6.5 from 6.0.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Pseudomonas plecoglossicida HtpG antigen and preparation method of polyclonal antibody of Pseudomonas plecoglossicida HtpG antigen
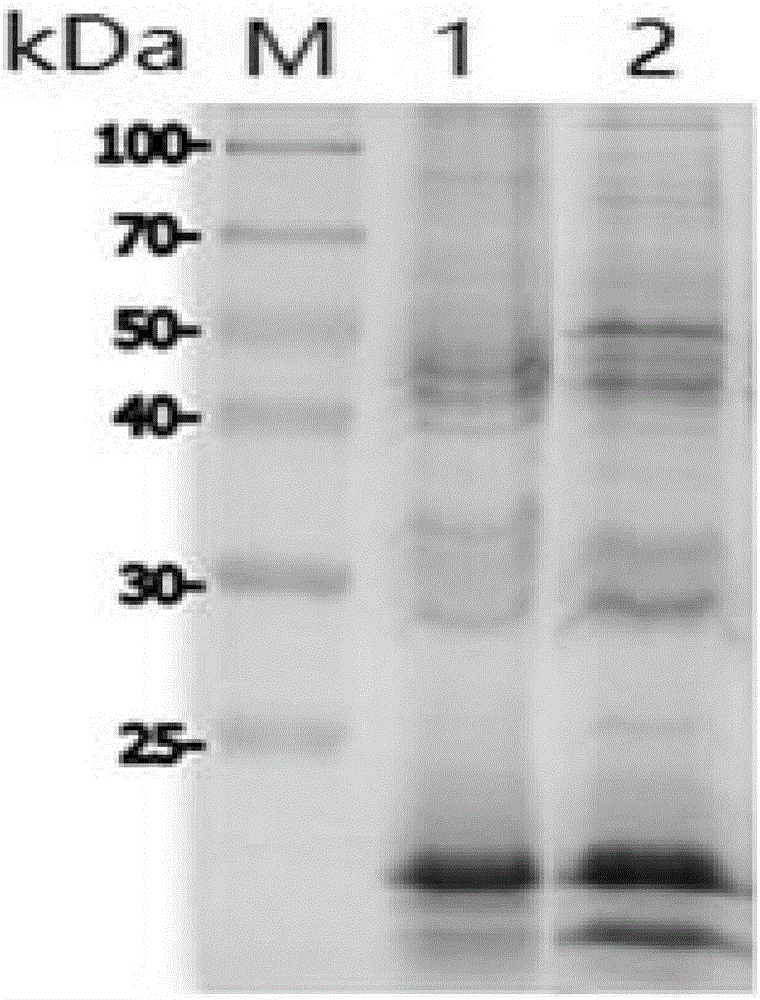
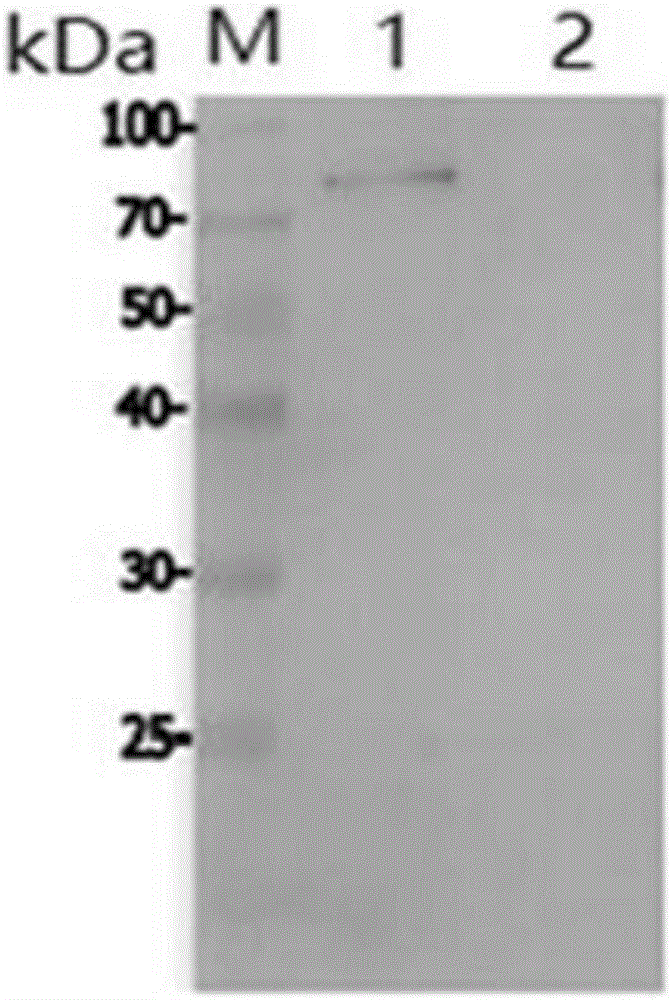
PendingCN112831515AImproving immunogenicityNormal yieldSerum immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaEscherichia coliAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention discloses a Pseudomonas plecoglossicida H tpG antigen and a preparation method of a polyclonal antibody of the Pseudomonas plecoglossicida H tpG antigen. The method includes: the following steps: firstly, artificially synthesizing an H tpG gene according to codon preference of escherichia coli, inserting the H tpG gene into a pET-32 expression vector, and selecting positive clone for sequencing verification; then, transforming the constructed plasmid into BL21DE3 competent cells, performing culturing, inducing, splitting and centrifuging to obtain protein, and detecting the expression condition of the protein by SDS-PAGE; further, selecting a strain with good sample expression for inoculation, culture, induction, splitting decomposition and purification, obtaining protein, and identifying the molecular weight, purity and concentration of the protein through SDS-PAGE; furthermore, taking the obtained H tpG protein as an antigen for animal immunization, collecting and purifying antiserum, and obtaining the H tpG antibody. The HtpG antigen of pseudomonas proteinans is obtained, and the corresponding HtpG polyclonal antibody is prepared. The titer of the antiserum and the affinity purification antibody is detected by an indirect ELISA method, and the result shows that the yield of the affinity purification antibody is normal. The method is simple, and the prepared antibody is high in immunogenicity.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com