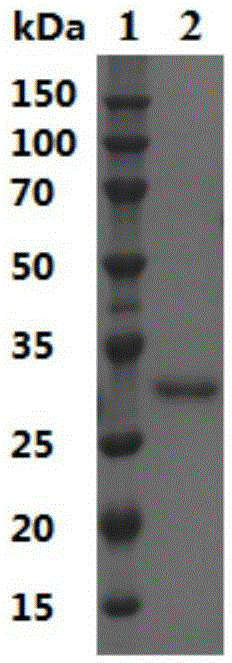
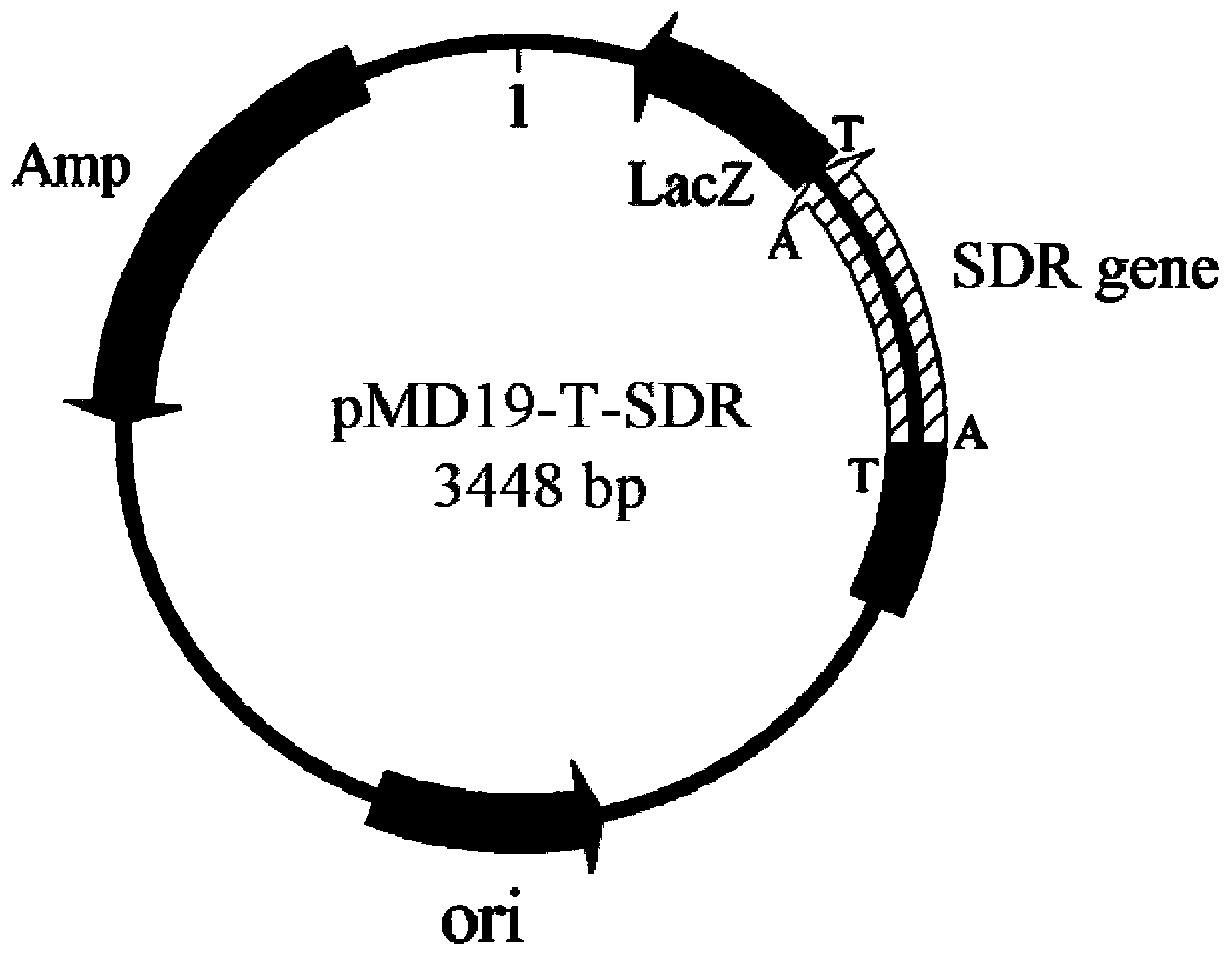
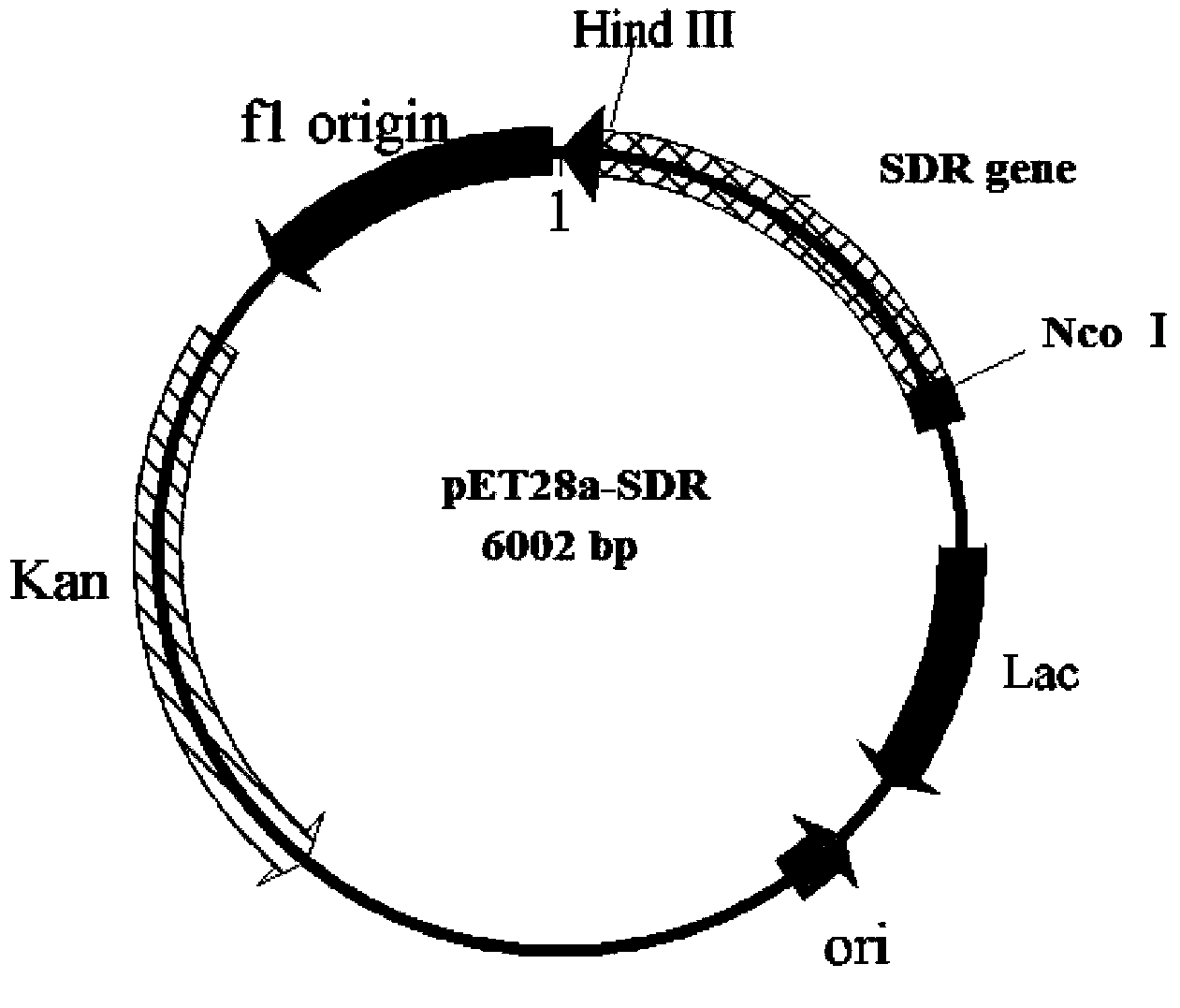
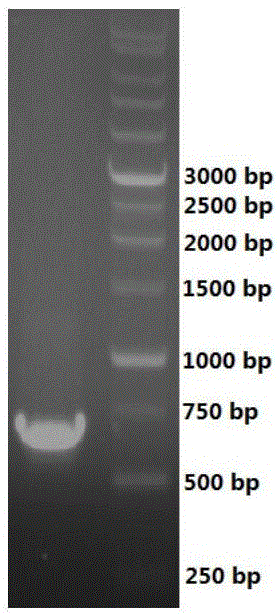
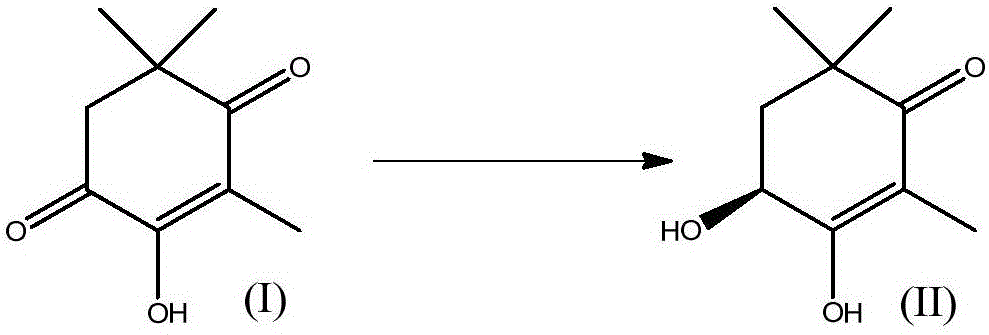
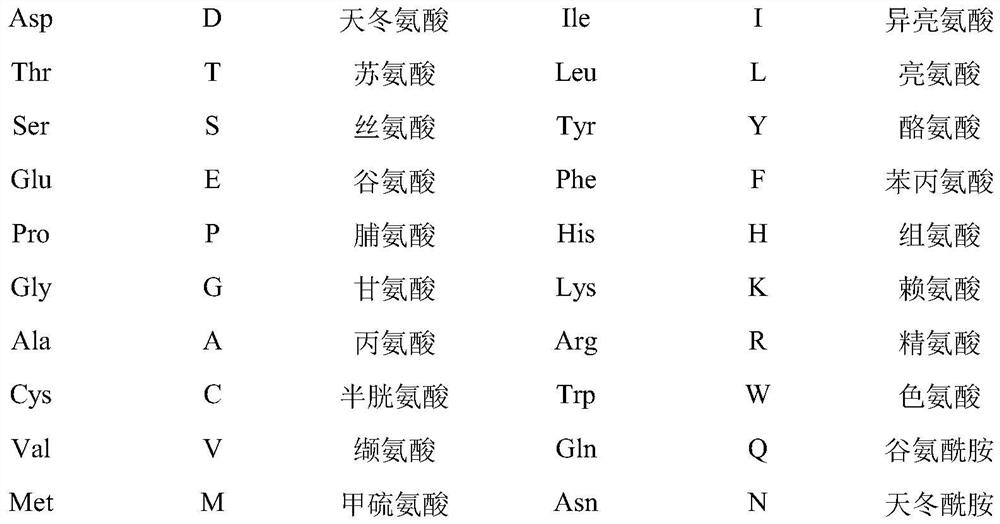
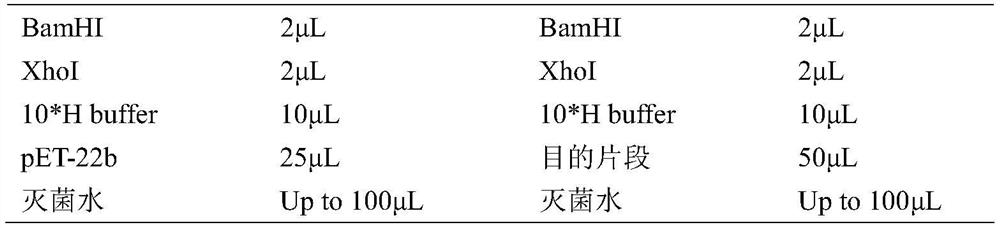
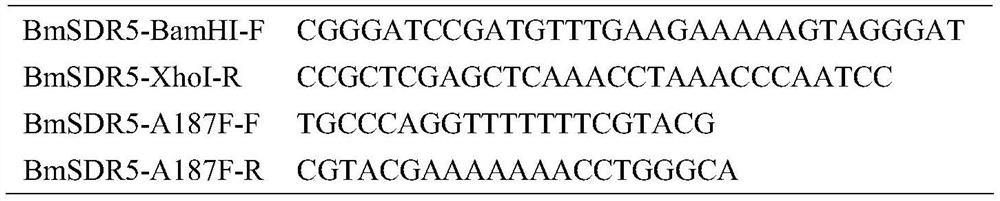
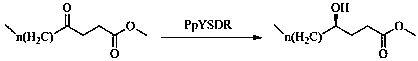Patents
Literature
33 results about "Short-chain dehydrogenase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
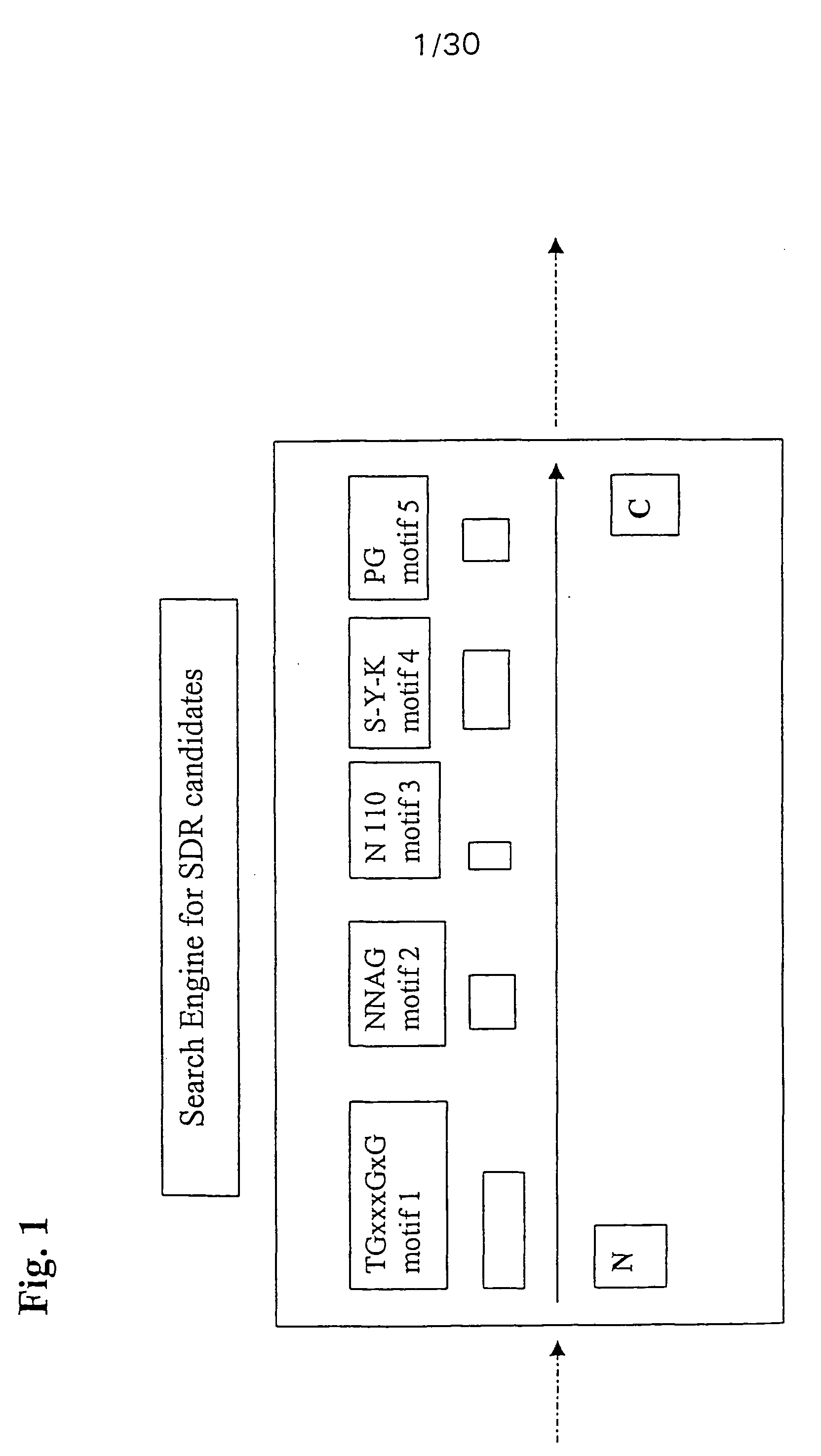
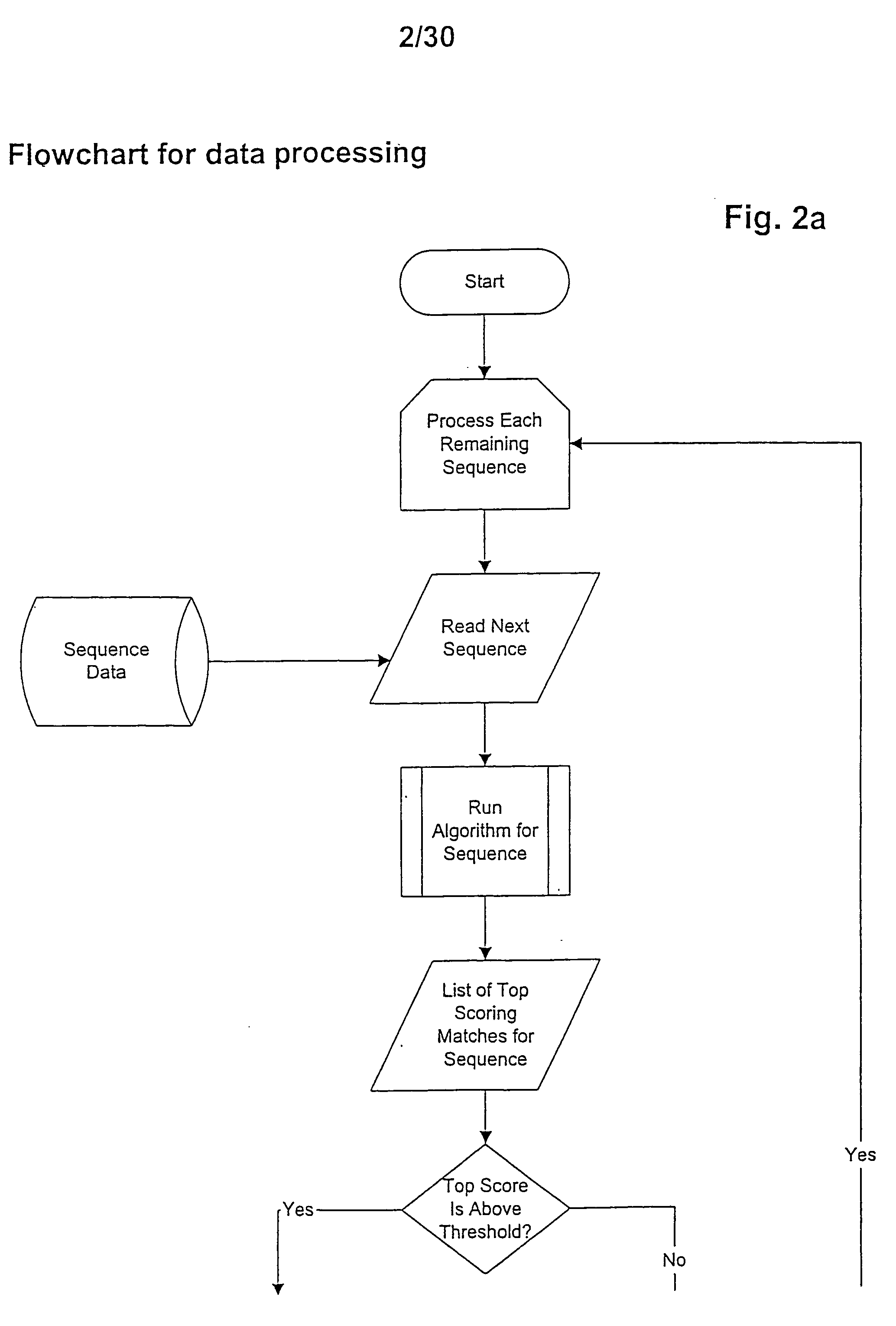
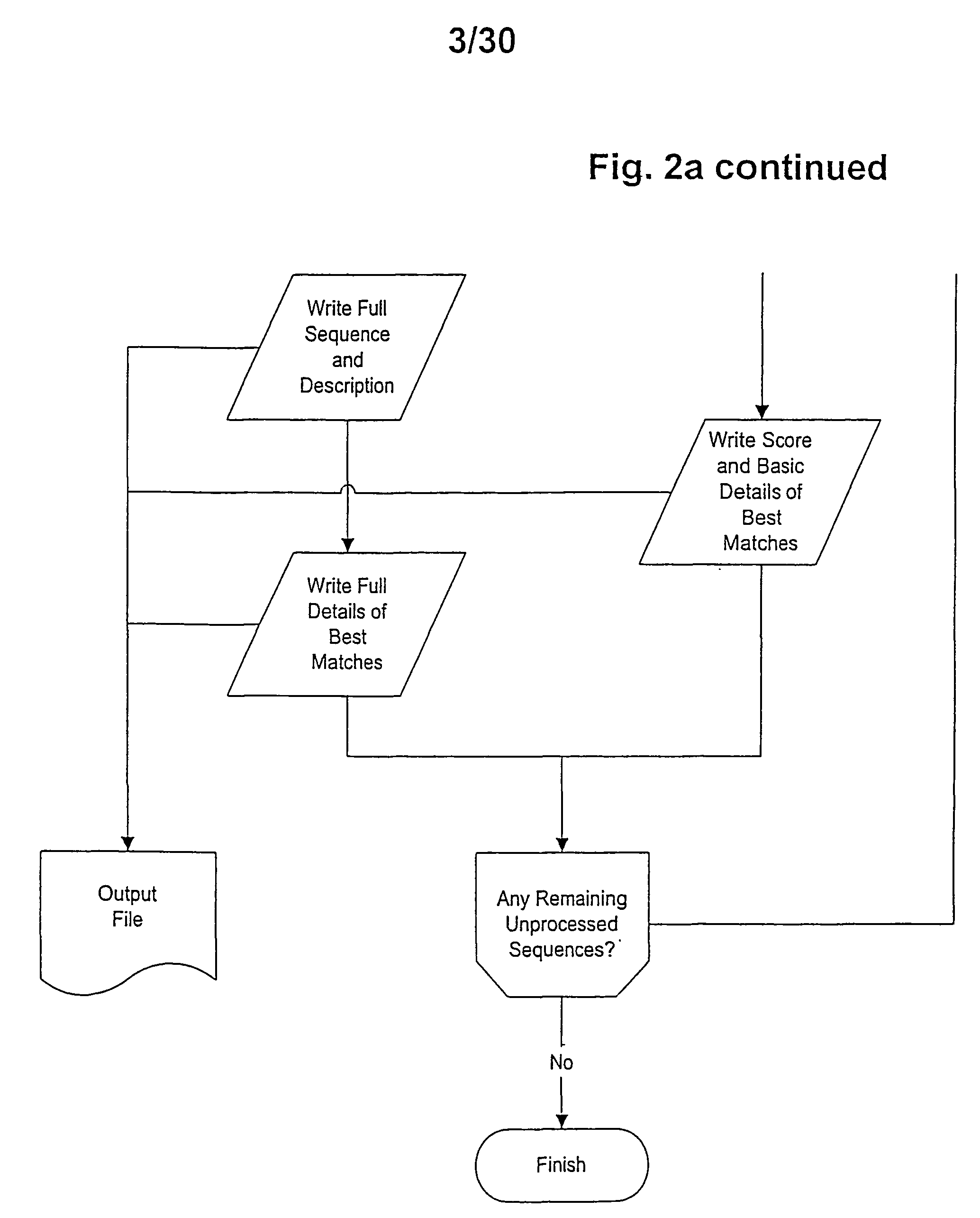
The short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases family (SDR) is a very large family of enzymes, most of which are known to be NAD- or NADP-dependent oxidoreductases. As the first member of this family to be characterised was Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase, this family used to be called 'insect-type', or 'short-chain' alcohol dehydrogenases. Most members of this family are proteins of about 250 to 300 amino acid residues. Most dehydrogenases possess at least 2 domains, the first binding the coenzyme, often NAD, and the second binding the substrate. This latter domain determines the substrate specificity and contains amino acids involved in catalysis. Little sequence similarity has been found in the coenzyme binding domain although there is a large degree of structural similarity, and it has therefore been suggested that the structure of dehydrogenases has arisen through gene fusion of a common ancestral coenzyme nucleotide sequence with various substrate specific domains.
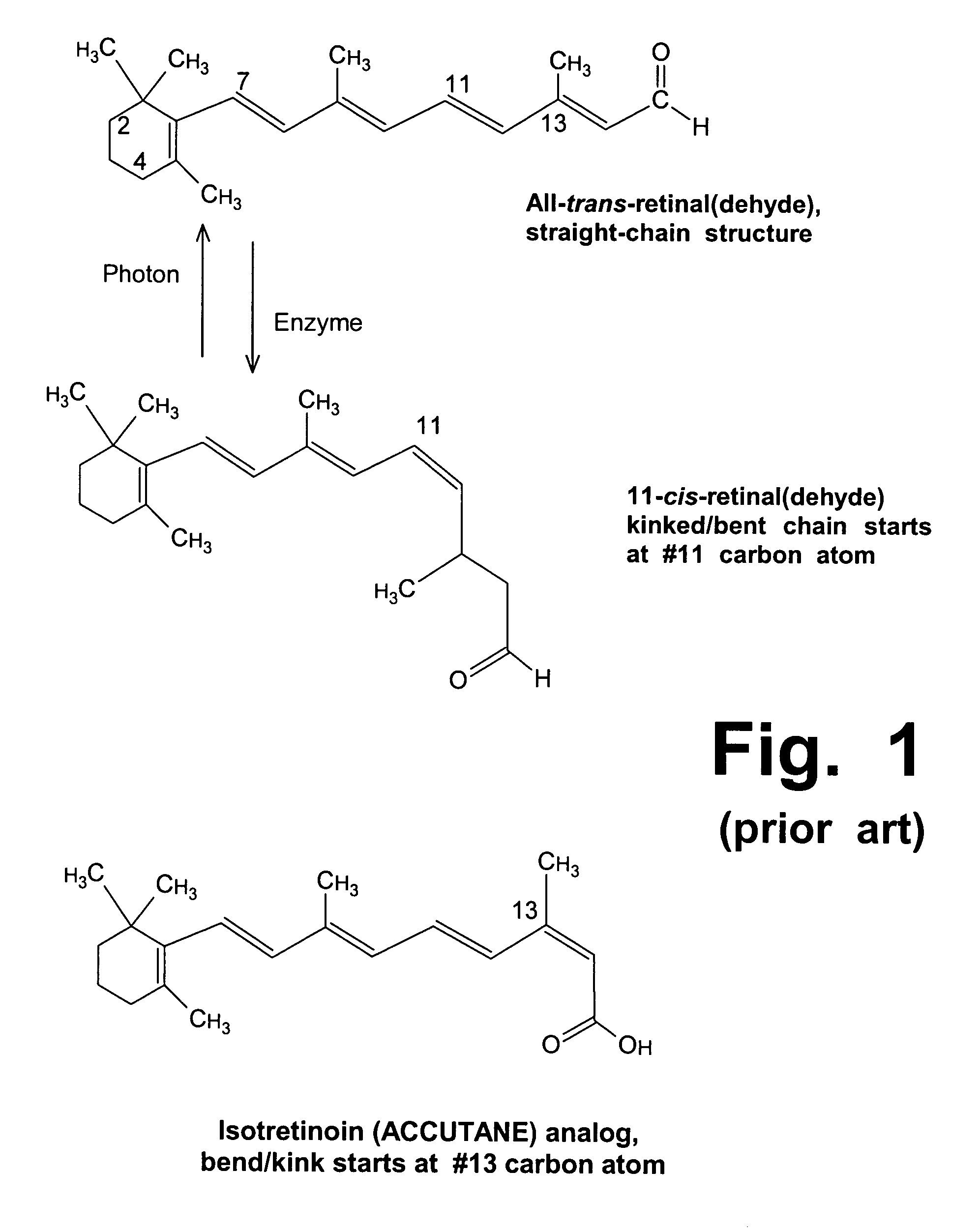
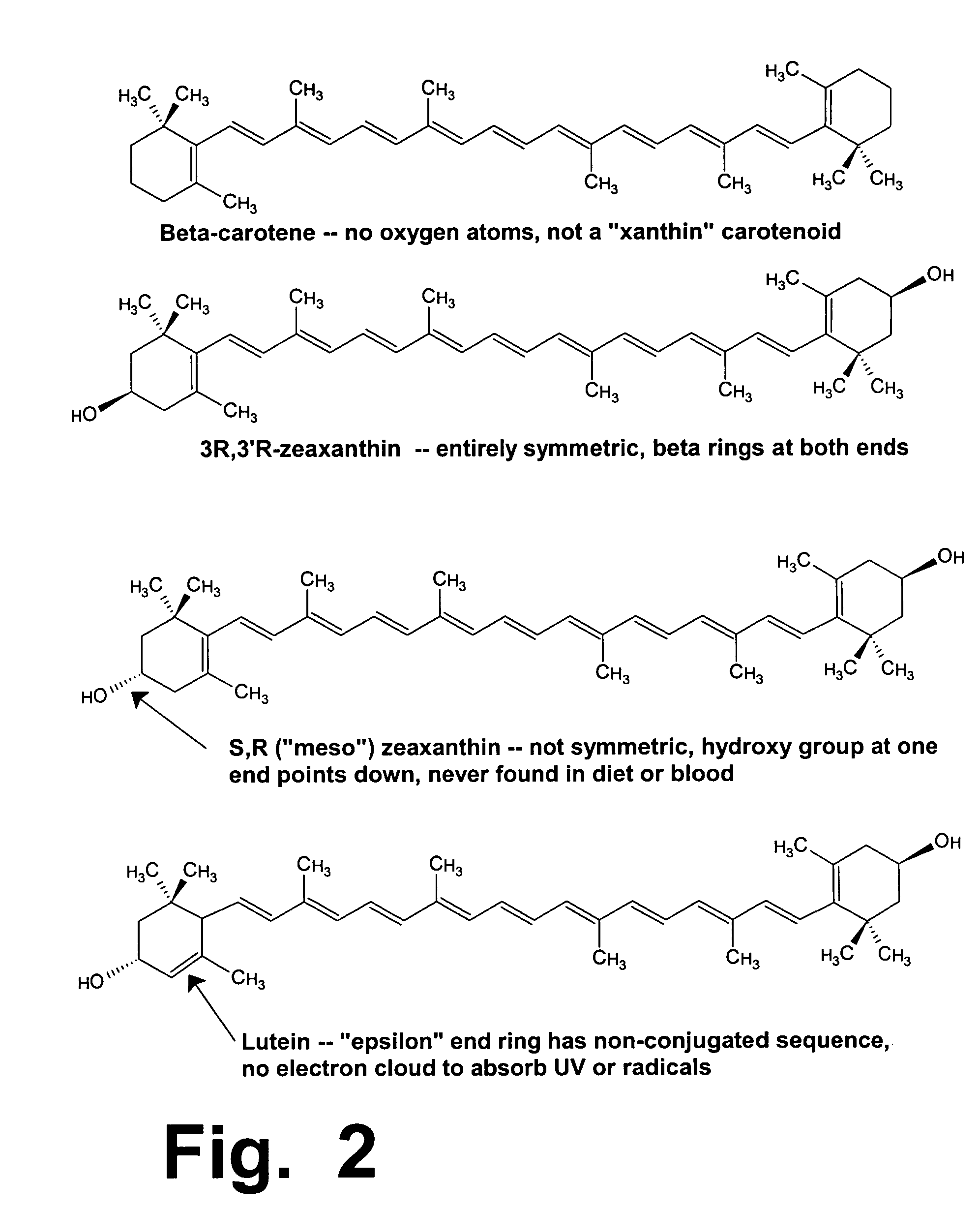
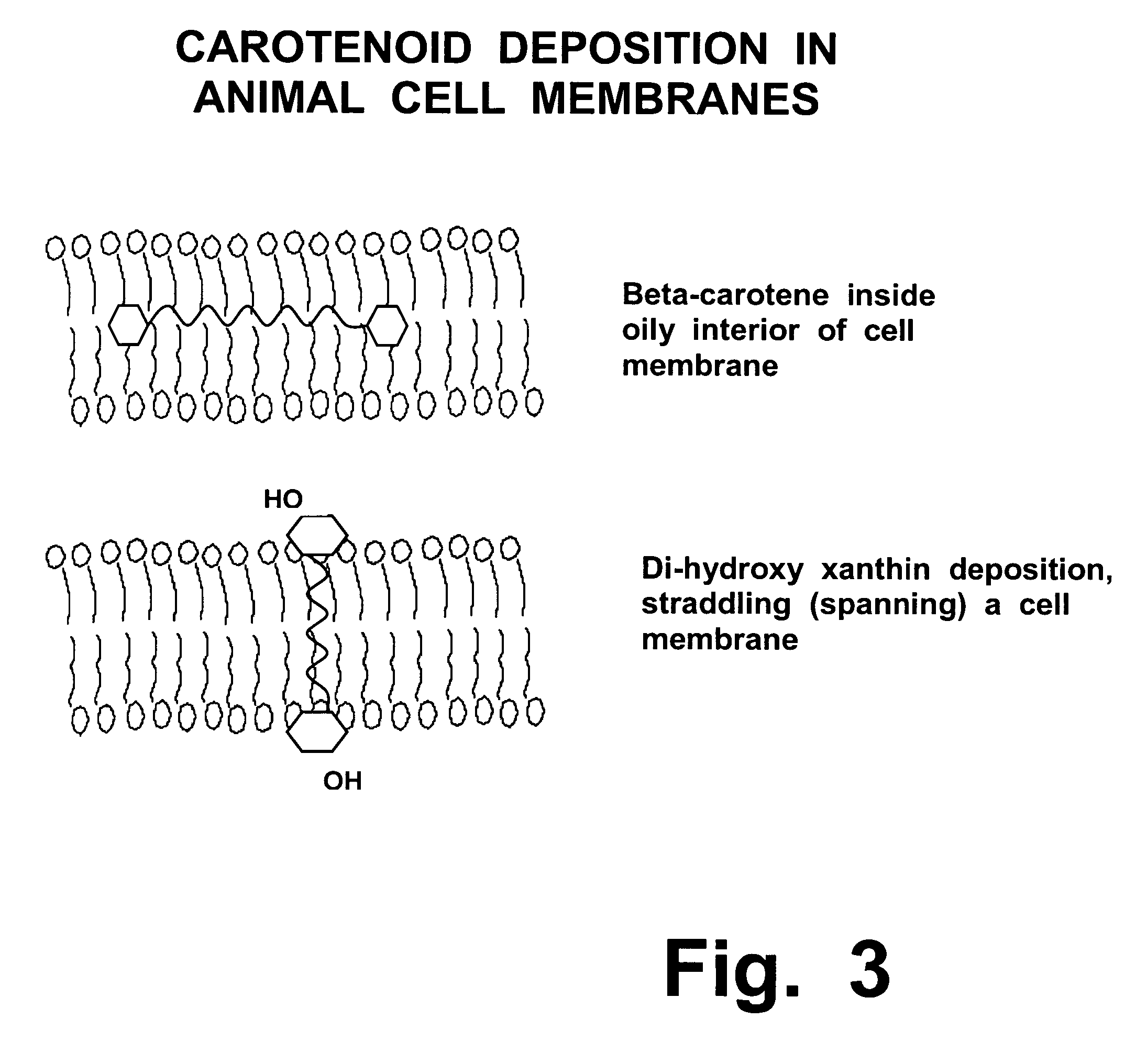
Treatment of Stargardt's disease and other lipofuscin disorders with combined retinaldehyde inhibitor and zeaxanthin
InactiveUS20060089411A1Slow downImprove abilitiesBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsMetaboliteRetinoid
Zeaxanthin, a natural carotenoid, can improve and increase the ability of enzyme inhibitors that can slow down certain enzymes that are contributing to toxic metabolite accumulation in people who suffer from Stargardt's disease or other lipofuscin disorders. Such enzyme inhibitors include retinoid analogs such as isotretinoin, commonly known by the trademark, ACCUTANE. This drug binds to and inhibits at least two retinal enzymes, known as RPE65 and short chain dehydrogenase, which create surplus metabolites that feed into a pathway that eventually creates toxic metabolites in people with Stargardt's disease. However, isotretinoin treatment alone is not highly effective; therefore, use of zeaxanthin as an adjunctive treatment can improve the efficacy and outcomes of such treatments.
Owner:ZEAVISION LLC
Mutant short-chain dehydrogenase, recombinant expression vector, genetic engineering bacterium and application
InactiveCN106636020AHigh catalytic activityEasy to manufactureOxidoreductasesFermentationAlcoholKetone
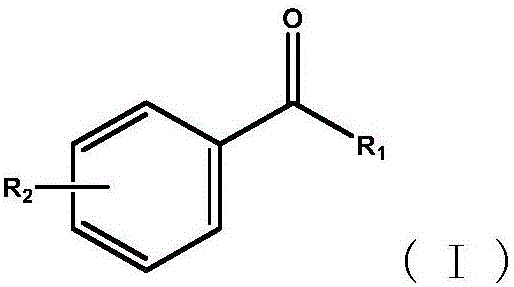
The invention provides a mutant of short-chain dehydrogenase, a recombinant expression vector, a genetic engineering bacterium, a preparation method of the mutant and application of the mutant or the genetic engineering bacterium generating the mutant in asymmetrically reducing a series of prochiral ketones to prepare optical homochiral alcohol. The chiral alcohol prepared by asymmetric reduction of the mutant of the short-chain dehydrogenase or the genetic engineering bacterium containing the mutant has high catalytic activity, and high-optical-purity chiral alcohol (ee>99%) can be synthesized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Short-chain dehydrogenase, gene of short-chain dehydrogenase, recombinant expression vector, genetically engineered bacterium and application
InactiveCN105238768AAsymmetric reductionHigh optical purityBacteriaOxidoreductasesPtru catalystKetone
The invention provides short-chain dehydrogenase obtained from Empedobacter brevis, a gene of the short-chain dehydrogenase, recombinant short-chain dehydrogenase, a recombinant expression vector with the gene, a genetically engineered bacterium, a preparation method of the recombinant short-chain dehydrogenase and application of the short-chain dehydrogenase or the genetically engineered bacterium containing the short-chain dehydrogenase to asymmetric reduction of prochiral ketones for preparation of optical pure chiral alcohols. The short-chain dehydrogenase for preparation of the chiral alcohols by asymmetric reduction has remarkable advantages and can be used for synthesis of high-optical-purity chiral alcohols (ee>99%). Moreover, easiness in preparation of catalysts, mild reaction conditions, high substrate adaptability and environment friendliness are realized, asymmetric reduction of the prochiral ketones can be efficiently catalyzed by recombinant cells in an isopropanol-containing reaction system without any coenzymes, and industrial application and development prospect is promising.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
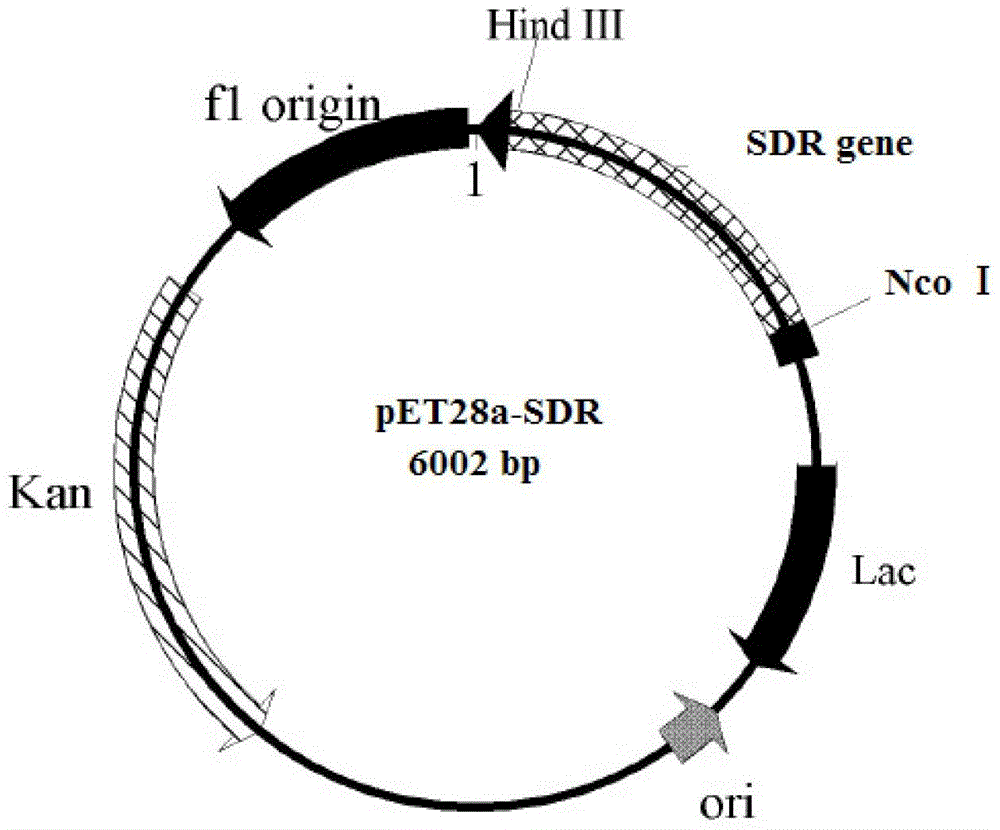
Leifsonia xyli HSO904-based short chain dehydrogenase, and encoding gene, carrier, engineering bacteria and application thereof
The invention discloses a leifsonia xyli HSO904-based short chain dehydrogenase, and an encoding gene, a carrier, engineering bacteria and application thereof. A gene of the leifsonia xyli HSO904-based short chain dehydrogenase has more than 90% of homology of a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. A colon bacillus BL21 / pET28a (+)-SDR prepared by the recombination of the short chain dehydrogenase is used as an enzyme source, 3, 5-bis-trifluoro methyl acetophenone, trifluoromethyl acetophenone, 4-hydroxyl-2-butanone, acetoacetic ester, 4-chloro ethyl acetoacetate, acetoacetic acid tert-butyl acetate and the like are used as substrates to prepare corresponding chiral compounds such as (R)-3, 5-bis-trifluoromethyl phenethyl alcohol, trifluoromethyl benzaldehyde ethanol, 2-hydroxyl-butyl alcohol, 3-hydroxy ethyl butyrate, 4-chloro-3-hydroxy ethyl butyrate and 3-hydroxy butyric acid tert-butyl acetate through a catalytic asymmetric reduction reaction.
Owner:艾吉泰康(嘉兴)生物科技有限公司
Short-chain dehydrogenase and gene thereof, recombinant expression vector, genetically engineered bacterium and application thereof in astaxanthin chiral intermediate synthesis
ActiveCN106520715AHigh stereoselectivityEasy to manufactureOxidoreductasesFermentationAlcoholAstaxanthin
The invention provides a short-chain dehydrogenase and a gene thereof, a recombinant short-chain dehydrogenase, a recombinant expression vector containing the gene, a genetically engineered bacterium, a preparation method of the recombinant short-chain dehydrogenase, and an application of the short-chain dehydrogenase or the genetically engineered bacterium containing the short-chain dehydrogenase in astaxanthin chiral intermediate synthesis through asymmetric reduction for prochiral ketones. In the application provided by the invention, asymmetric reduction preparation of the short-chain dehydrogenase for chiral alcohols has remarkable advantages, and an astaxanthin chiral intermediate (having an enantiomeric excess (ee) of greater than 99%) with a high optical purity can be synthesised. A catalyst is easy to prepare, the reaction conditions are moderate, a substrate is wide in adaptability, and the short-chain dehydrogenase is environment-friendly; and moreover, the recombinant cell of the short-chain dehydrogenase is capable of efficiently catalyzing the asymmetric reduction for prochiral ketones in an isopropanol-containing reaction system without any coenzyme, and has a great industrialized application and development prospect.
Owner:杭州馨海酶源生物科技有限公司
Short-chain dehydrogenase CPE (Cytopathic Effect) gene, coding enzyme, carrier, recombination engineering bacteria and application
The invention discloses a short-chain dehydrogenase CPE (Cytopathic Effect) gene, a gene coding enzyme, a carrier, a recombination engineering bacteria and an application of the engine coding enzyme in an asymmetric reductive carbonylation compound. The short-chain dehydrogenase CPE has relatively high conversion rate and e.e. value; and the reductase with relatively low Km value can keep enzyme activity for a longer time under a condition that the concentration of substrate is relatively low; and the quantity of added enzyme can be reduced in the actual industrial production; and the cost can also be reduced; and moreover, the maximum reaction speed can be reached when the substrate with low concentration is added, so that the production period of unit weight products can be reduced in the actual industrial production, and the energy consumption and the labor cost can be decreased.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Short-chain dehydrogenase and mutant thereof as well as preparation of gene and application of short-chain dehydrogenase
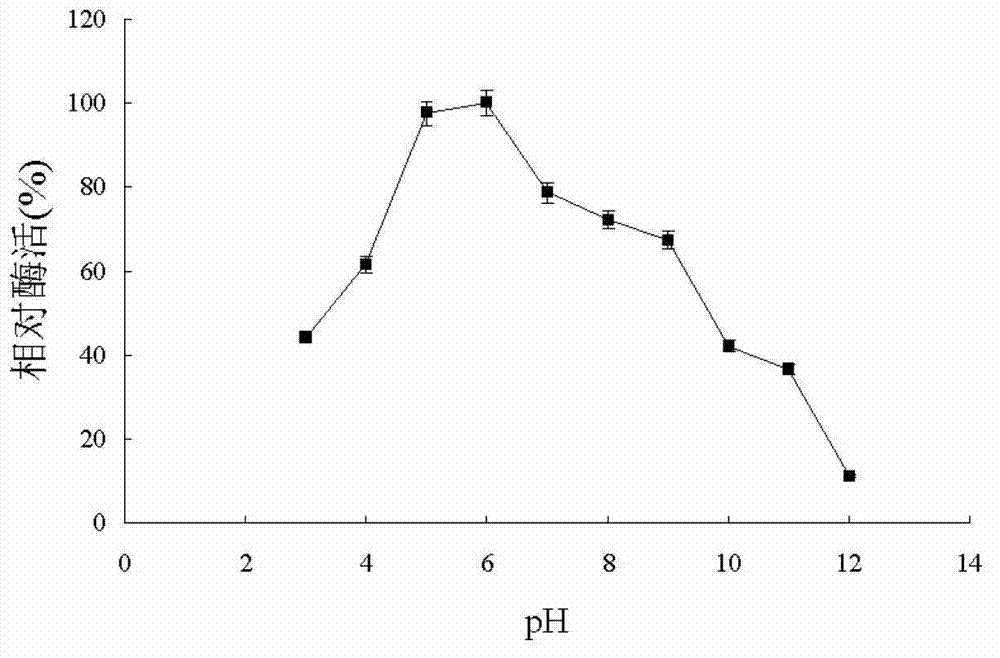
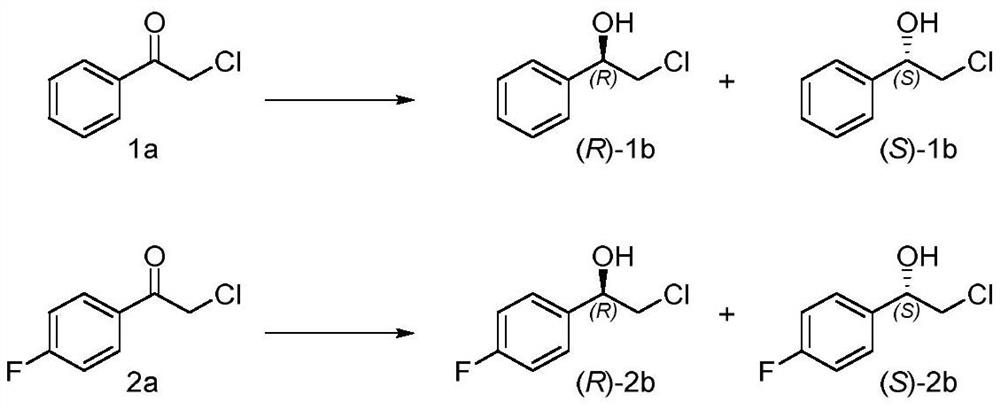
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and relates to wild type short-chain dehydrogenase LfSDR1 and a gene of mutant enzyme of the short-chain dehydrogenase, construction of a recombinant expression vector containing the gene, preparation of recombinant expression transformant, recombinase and a preparation method of the recombinase. Through mutation of the wild type short-chaindehydrogenase LfSDR1, the mutant enzyme having two stereoselectivities (R or S stereoselectivities) is obtained, and catalytic asymmetrical reduction on prochiral ketone is carried out by utilizing the mutant enzyme, such as asymmetrical reduction of catalytic 1-phenyl ethanone compounds. Compared with the wild type short-chain dehydrogenase, the mutant disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the stereoselectivities is improved or reversed, a substrate is catalyzed so as to obtain chiral alcohol having two types (R or S type), such as optical pure (R)- or (S)-2-chloro-1-phenylethanol; moreover, the mutant has a good application value in the field of preparation of chiral alcohol.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
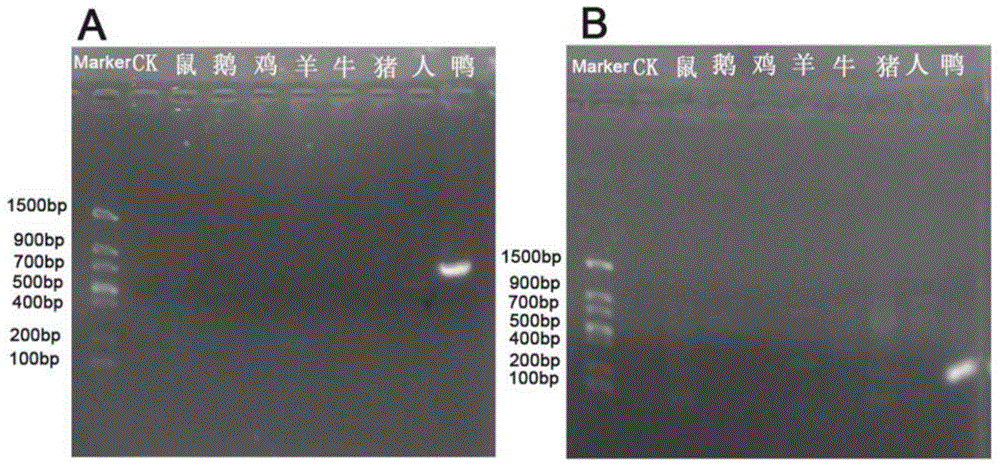
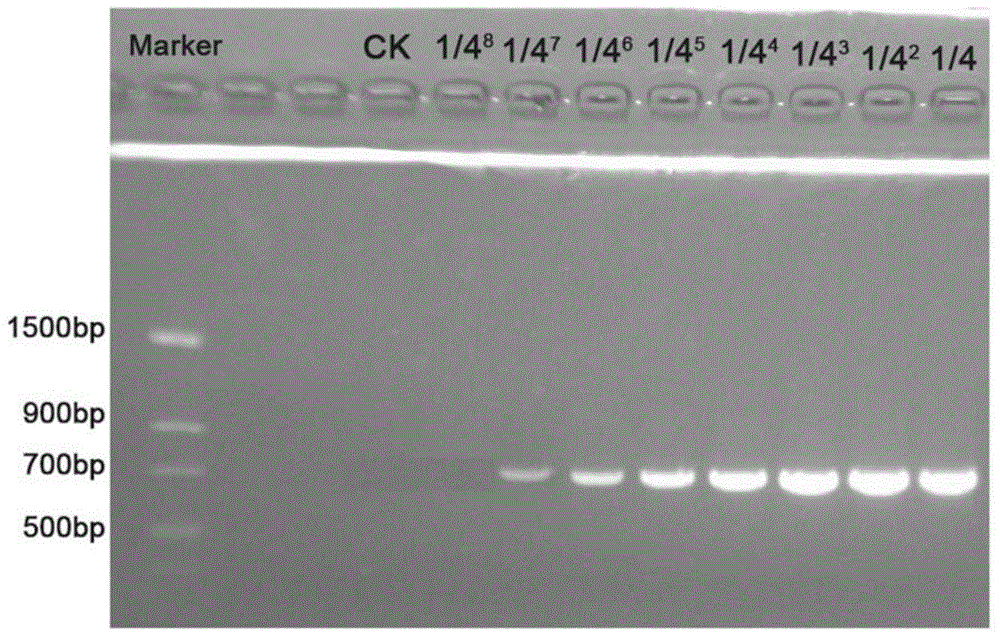
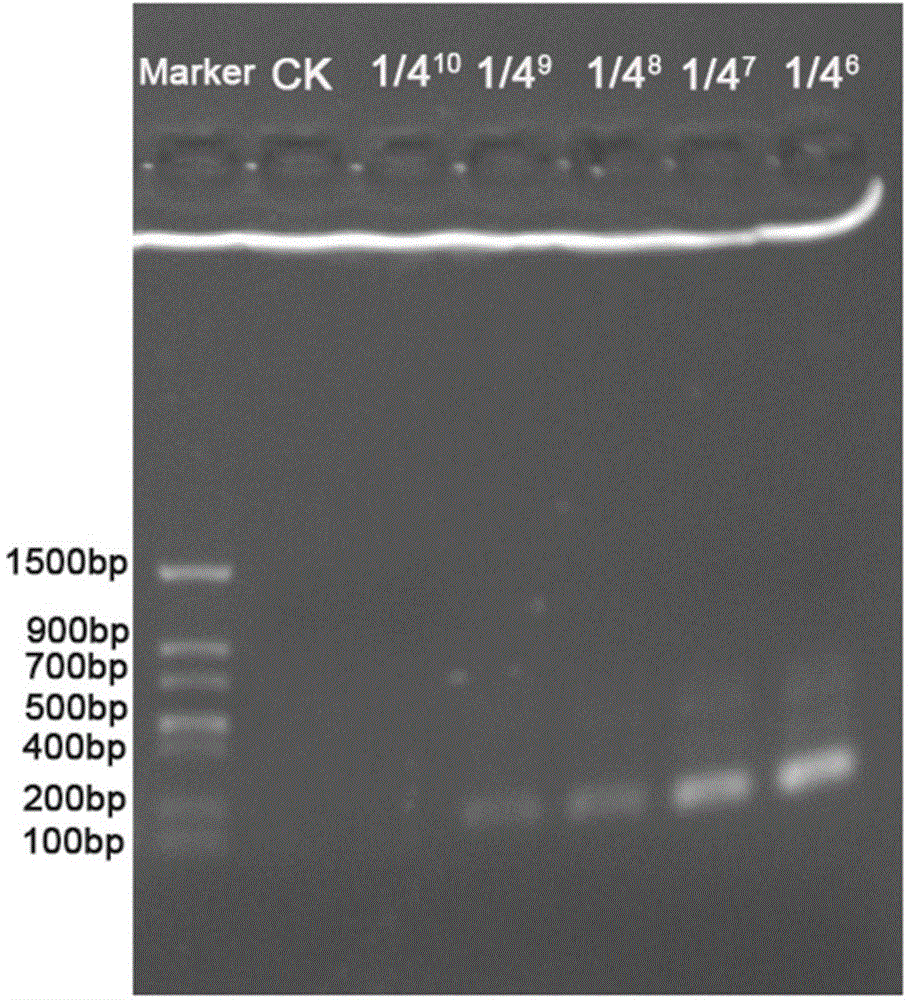
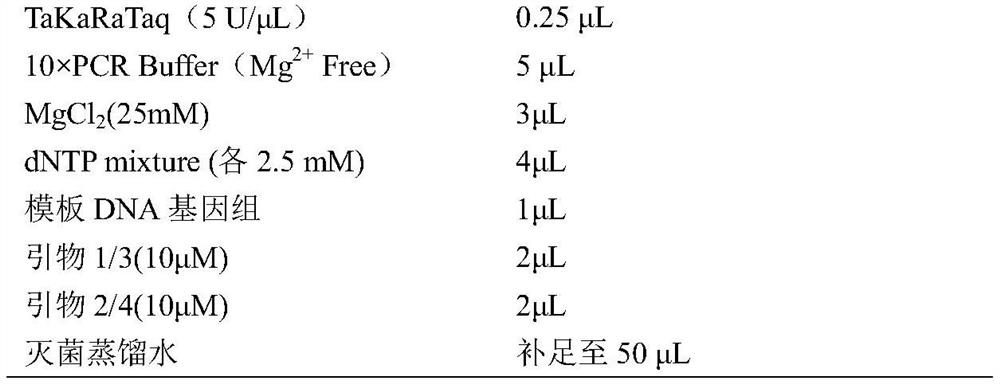
Nested PCR (polymerase chain reaction) kit for detecting duck-manure pollution in water body and detection method thereof
ActiveCN104878002AReduce misjudgmentStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNeutral Detergent FiberA-DNA
The invention discloses a nested PCR (polymerase chain reaction) kit for detecting duck-manure pollution in a water body and a detection method thereof, and belongs to the field of the detection of pollution in water bodies. The nested PCR kit for detecting the duck-manure pollution in the water body comprises two pairs of nested PCR primers, dNTP (deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate), a PCR buffer, a Taq polymerase, a Mg<2+> solution and ddH2O (double distilled water). Two rounds of PCR amplification are used by a nested PCR method. The detection method comprises the following steps of extracting a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) in a to-be-detected water sample, and carrying out a first round of PCR amplification by using the DNA in the to-be-detected water sample as a template, wherein the primers are an SDF (stroma derived factor) and SDR (short-chain dehydrogenase / reductase); after a first reaction is terminated, carrying out a second round of PCR amplification by using a product of the first round of PCR amplification as a template, wherein the primers are an NDF (neutral detergent fiber)and NDR, and after a second reaction is terminated, detecting the existence of a 158bp strip, which shows that the water body is subjected to the duck-manure pollution, through agarose gel electrophoresis. According to the method, the detection sensitivity is greatly increased through nested PCR amplification; a little duck-manure pollution which exists in water can be detected; moreover, the method has a favorable specificity, and can be directly applied to the detection and the preventive treatment work of fecal pollution in the water body.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
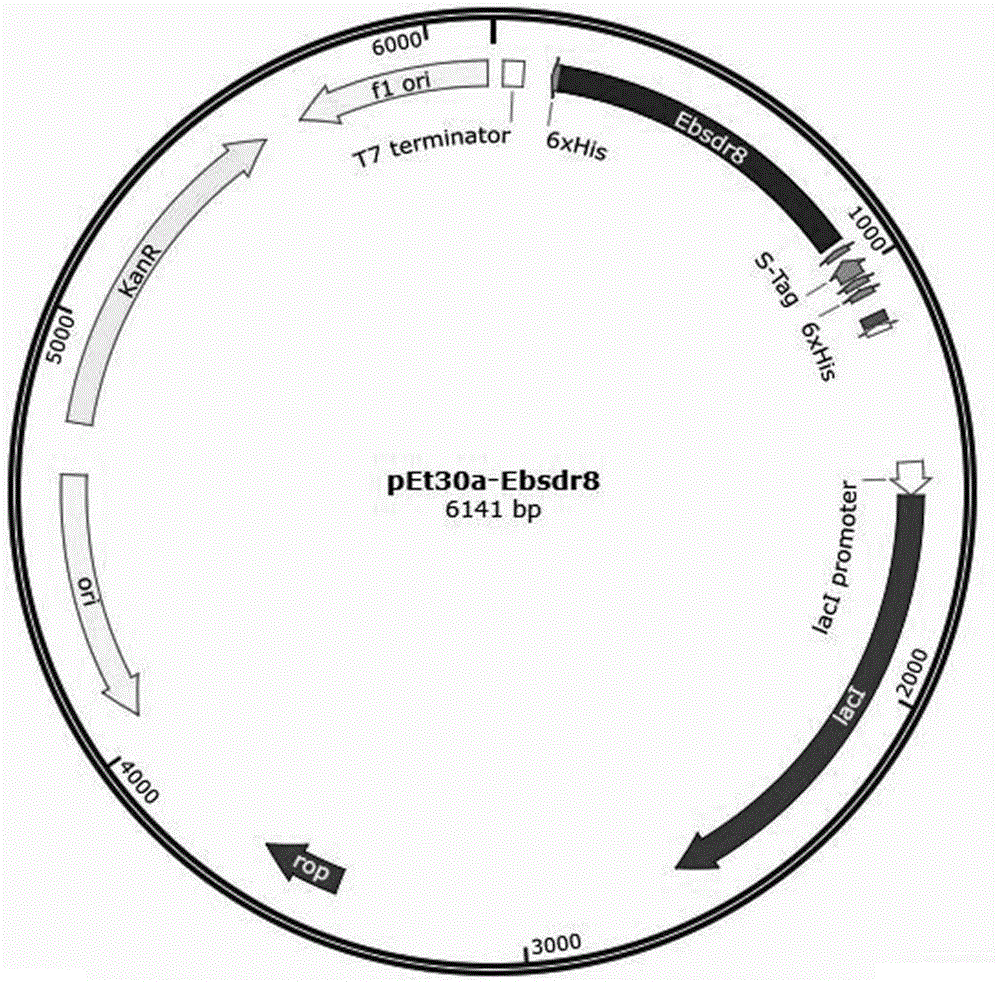
Short-chain dehydrogenase and mutant thereof, and preparation and applications of gene
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and relates to short-chain dehydrogenase and a mutant thereof, and preparation and applications of a gene, specifically to a wild type C=C double bond reductase OYE1 derived from Saccharomyces pastoris, and a mutant thereof, short-chain dehydrogenases LfSDR1, BmSDR5 and BsSDR8 respectively derived from Lactobacillus fermentum, Bacillus megaterium and Bacillus subtilis, mutants thereof, C=C double bond reductase and C=O double bond reductase with stereoselectivity complementation, genes of C=C double bond reductase and C=O double bond reductase, construction and preparation of a recombinant expression vector containing the gene, expression of recombinase, an enzyme catalytic two-step asymmetric reduction reaction of carvone, the conditions of the reaction, and a detection method of the product dihydrocarveol. Compared with the existing chemical method, the method of the invention has the advantages of being easy to operate, mild in reaction condition, environmentally friendly and the like.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Biological preparation method of chiral hydroxy acid ester
ActiveCN111454998AHigh activityImprove efficiencyOxidoreductasesFermentationEnzymatic synthesisChiral selectivity
The invention discloses a biological preparation method of a chiral hydroxy acid ester. The method comprises the following steps: (1) oxidizing a fatty acid by ketolase spheroidene monooxygenase to generate a 4-oxo fatty acid; and (2) asymmetrically reducing the 4-oxo fatty acid by short-chain dehydrogenase PpYSDR-M85Q / L136A to obtain an R-hydroxy acid ester. In the biological preparation method of a chiral hydroxy acid ester of the invention, a short-chain dehydrogenase mutant is constructed, the short-chain dehydrogenase mutant greatly improves the activity and chiral selectivity for keto acids compared with the wild type, the efficiency of the enzyme in catalyzing keto acids to prepare chiral lactones can be improved, and thereby an application value of the enzyme is fully explored. Atthe same time, the enzymatic synthesis of the chiral hydroxy acid ester has the characteristics such as simple process, environmental friendliness, and high benefit.
Owner:黄山科宏生物香料股份有限公司
Short chain dehydrogenases/reductases(sdr)
InactiveUS20050089847A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingBiologyShort-chain dehydrogenase
The present invention relates to a method for identifying or verifying members of the short chain dehydrogenase (SDR) family, to a method for providing modulators for members of the SDR family and to the preparation of pharmaceutical agents using these modulators.
Owner:BIONETWORKS GMBH
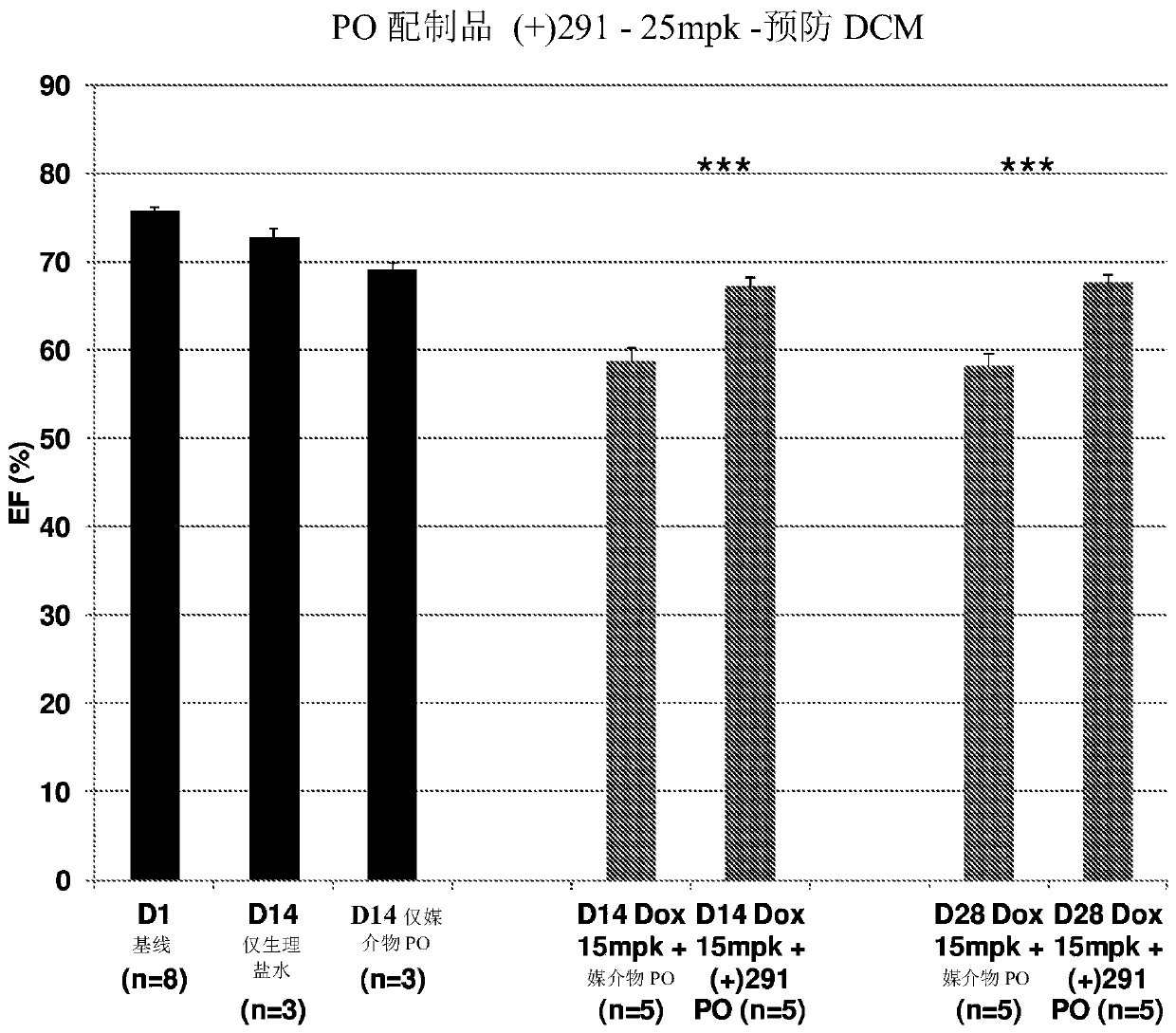
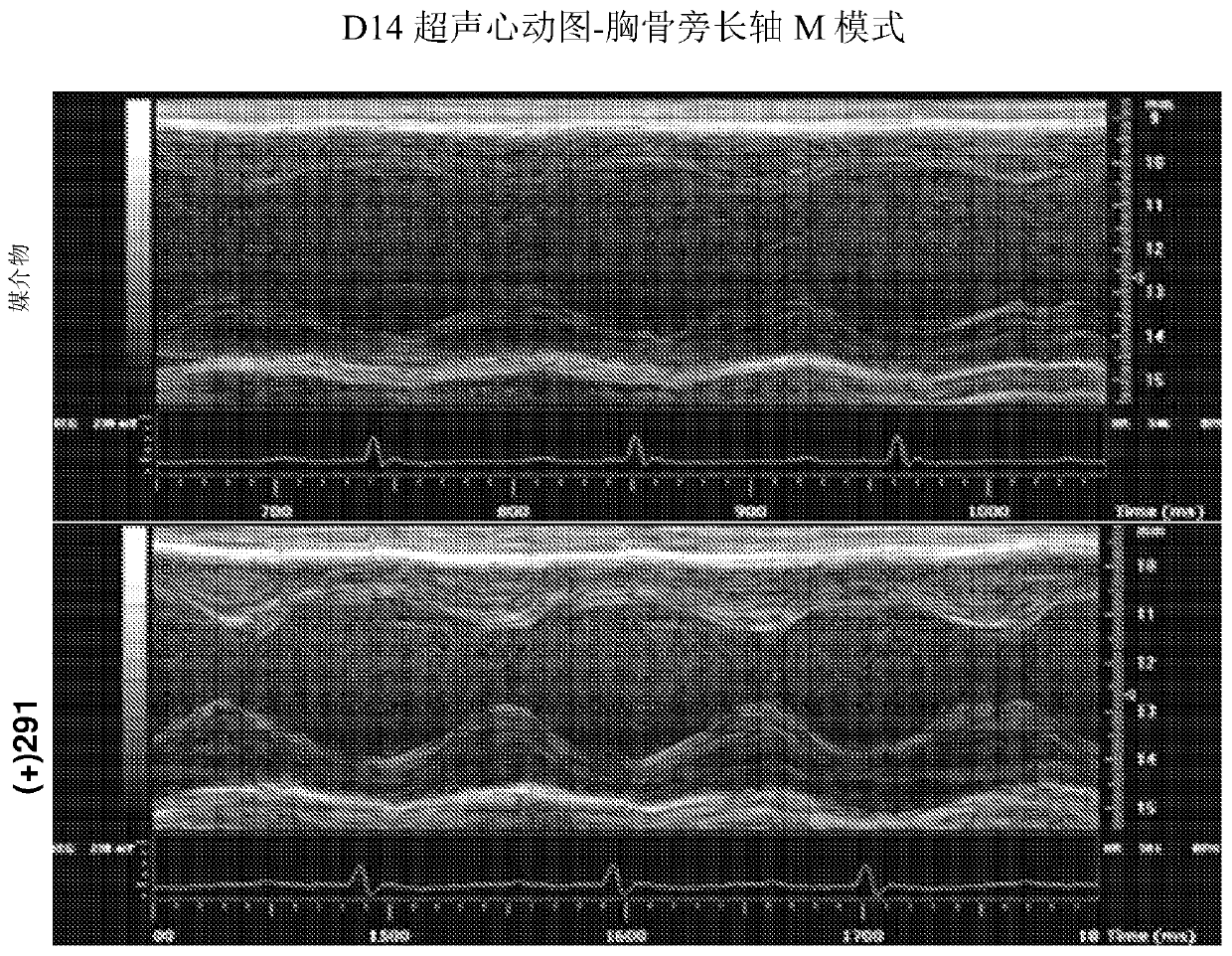
Inhibitors of short-chain dehydrogenase activity for treating coronary disorders
PendingCN110891568AInhibit enzyme activityOrganic active ingredientsImmunoglobulinsCoronary arteriesRat heart
A method of treating preventing, minimizing, and / or reversing congestive heart failure, cardiomyopathy, and / or reduction of cardiac ejection fraction in a subject in need thereof includes administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a 15-PGDH inhibitor.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV +1
Functions and application of short chain dehydrogenase TsrU
ActiveCN103205470AImprove toleranceHigh catalytic efficiencyOxidoreductasesFermentationSide chainStructural analog
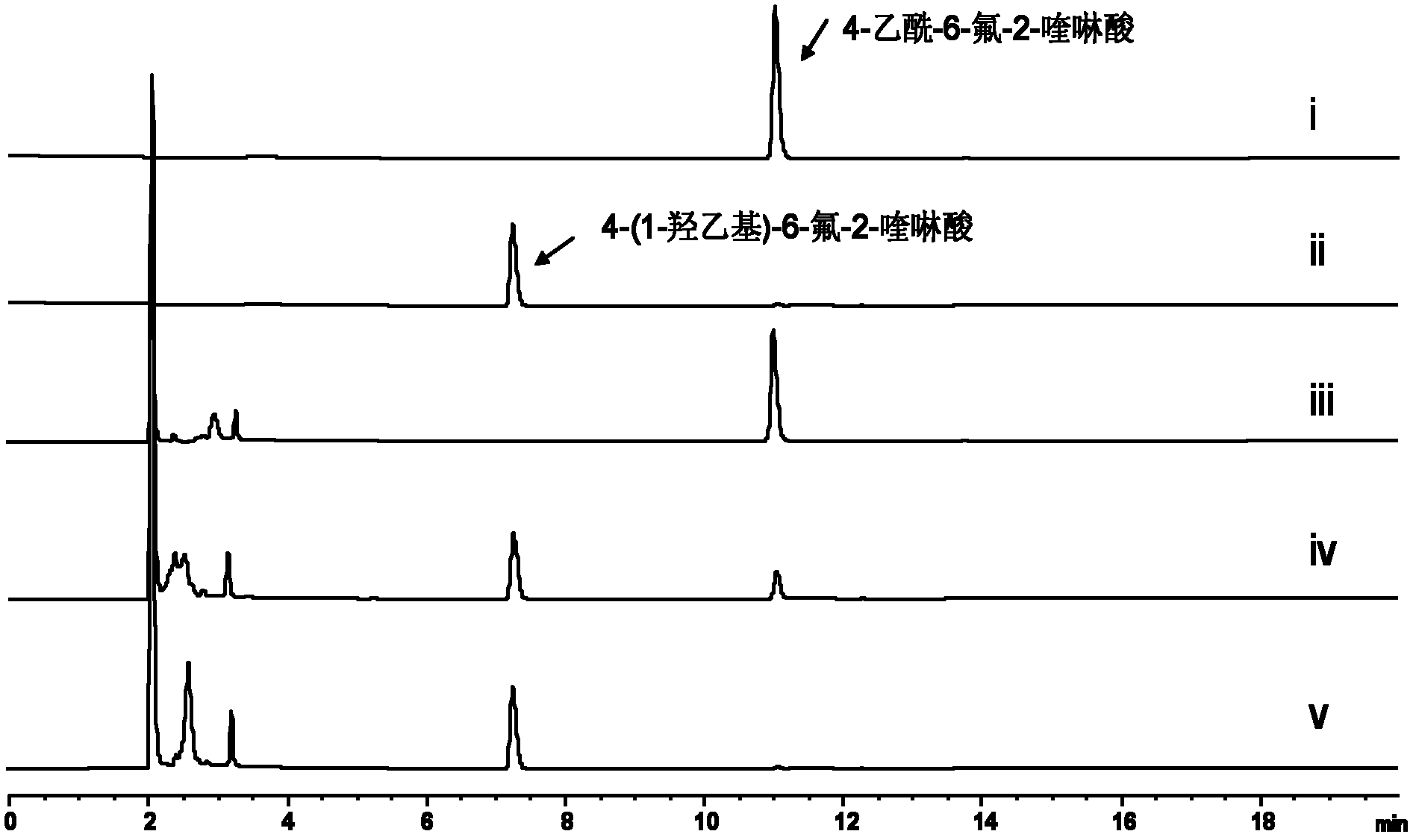
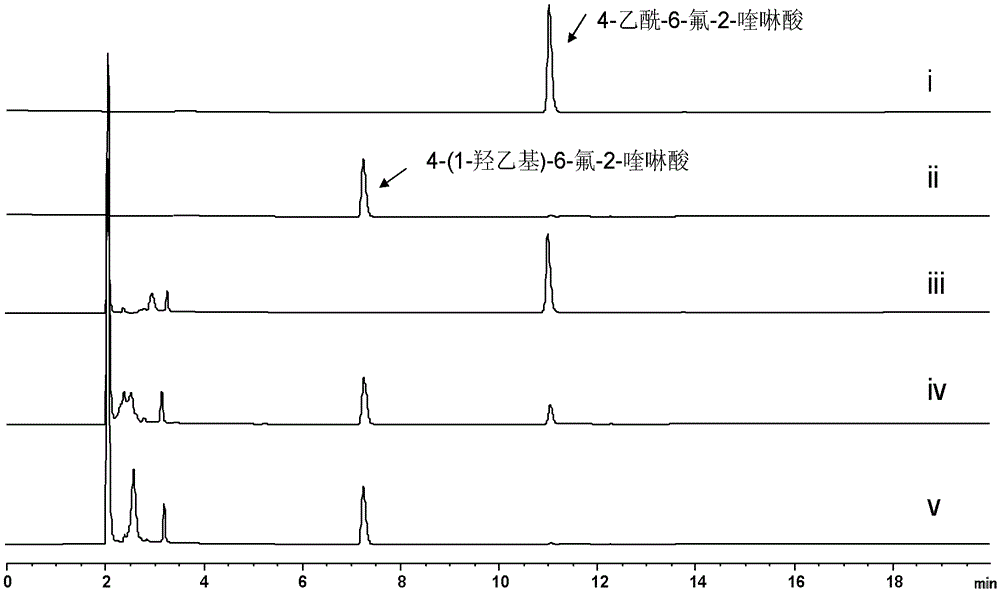
The invention discloses functions and application of a short chain dehydrogenase TsrU. Specifically, the short chain dehydrogenase TsrU can catalyze the carbonyl chiral single reduction reaction of 4-acetyl-2-quinolinic acid or its analogues, can be used for in-vitro efficient production of 4-(1-hydroxymethyl)-2-quinolinic acid or its structural analogues, and in a side chain reaction of thiostrepton biosynthesis, the enzyme has a high tolerance to a substrate, so that the short chain dehydrogenase TsrU can be widely applied to chiral reduction reactions of other similar substrates.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Short-chain dehydrogenase mutant and applications thereof,
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and relates to short-chain dehydrogenase, a mutant and applications thereof, particularly to a stereoselective complementary short-chain dehydrogenase mutant, wherein the mutant is obtained by mutation of wild type short chain dehydrogenase (LfSDR1) excavated from Lactobacillus fermentum. The invention specifically relates to a short-chain dehydrogenase mutant and a preparation method thereof, and applications of the short-chain dehydrogenase mutant as a catalyst in catalysis of asymmetric reduction of 4R / S-carvone to prepare stereodiverse carveol. Compared with the existing chemical method, the method of the invention has the advantages of easy operation, mild reaction condition, environmentally friendly and the like.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Corrosion-inhibiting combustion-supporting coke cleaning agent
InactiveCN102220174AReach clear dust and clear cokeSave energyLiquid carbonaceous fuelsFuel additivesAlkaline earth metalCleansing Agents
The invention relates to a corrosion-inhibiting combustion-supporting coke cleaning agent and particularly relates to short-chain dehydrogenase (SDR)-4# corrosion-inhibiting combustion-supporting coke cleaning agent which is applicable to different types of boilers and heating furnaces, which use residual oil, thickened oil and mashgas as fuel, and can support combustion and clean coke agglomerate. The SDR-4# corrosion-inhibiting combustion-supporting coke cleaning agent is prepared by weighing zinc oxide, alkaline earth element, zeolite catalyst, potassium nitrate, manganese dioxide, magnesium nitrate, and corrosion inhibitor in a ratio, mixing, placing in a grinding machine, grinding, drying and stirring and has the characteristics of multiple functions of inhibiting corrosion, supporting combustion, cleaning coke and saving energy.
Owner:马中胜
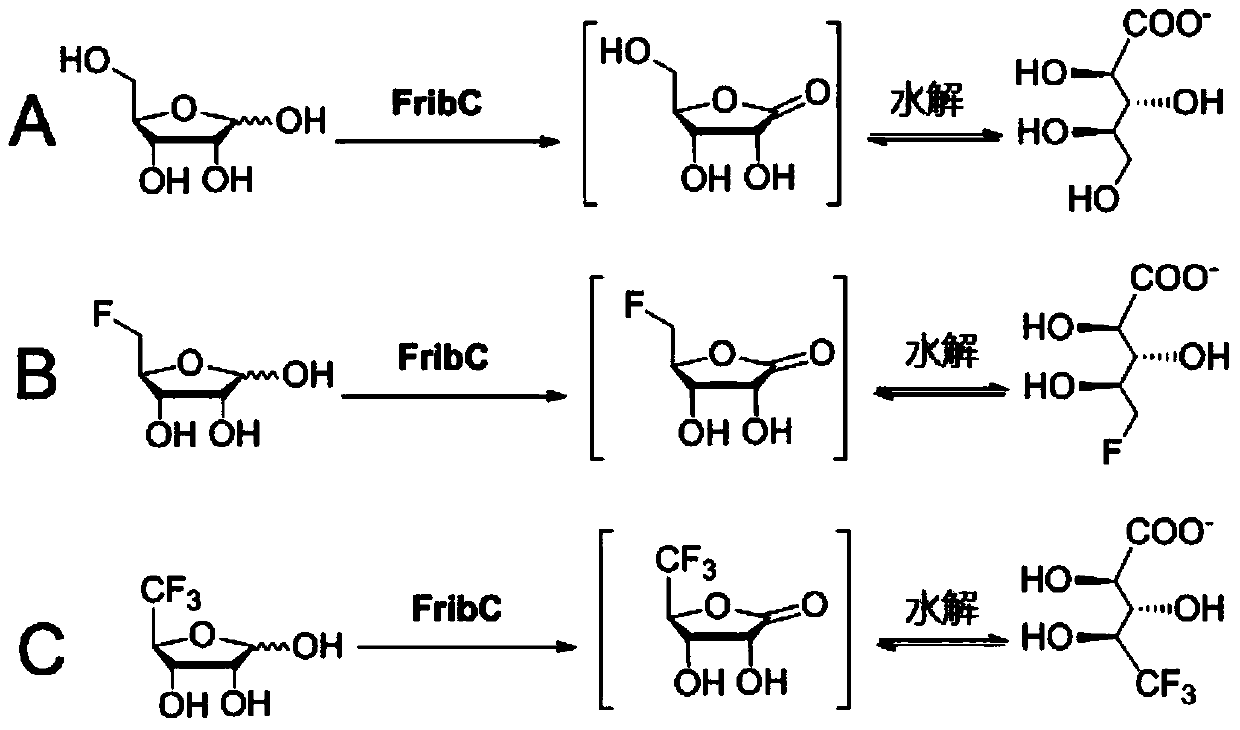
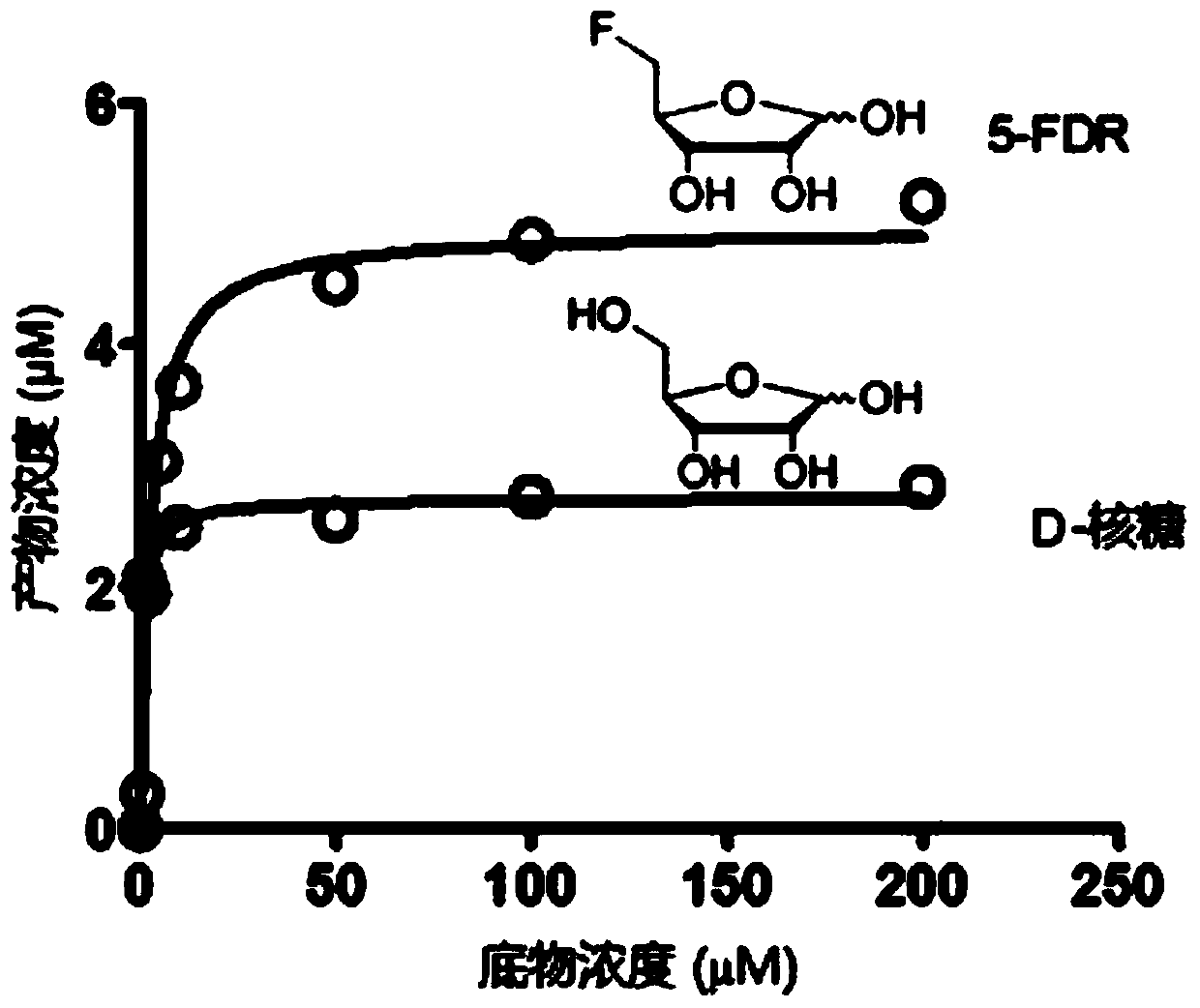
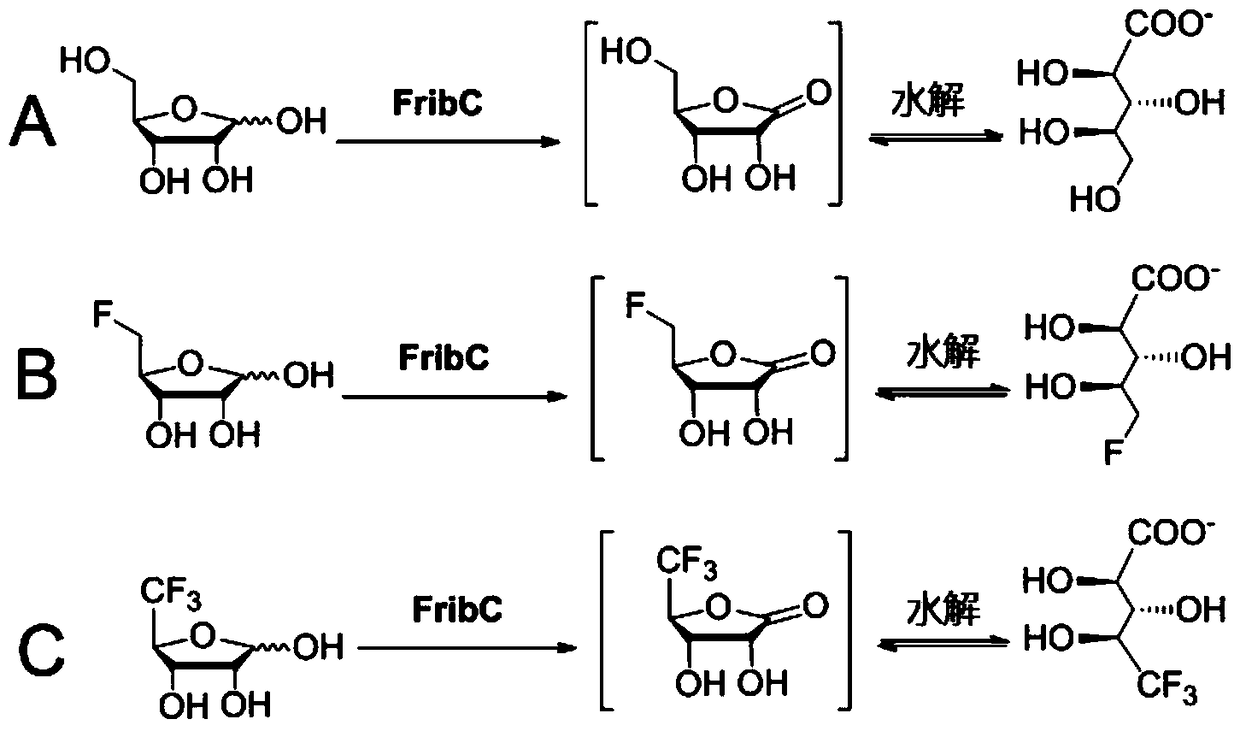
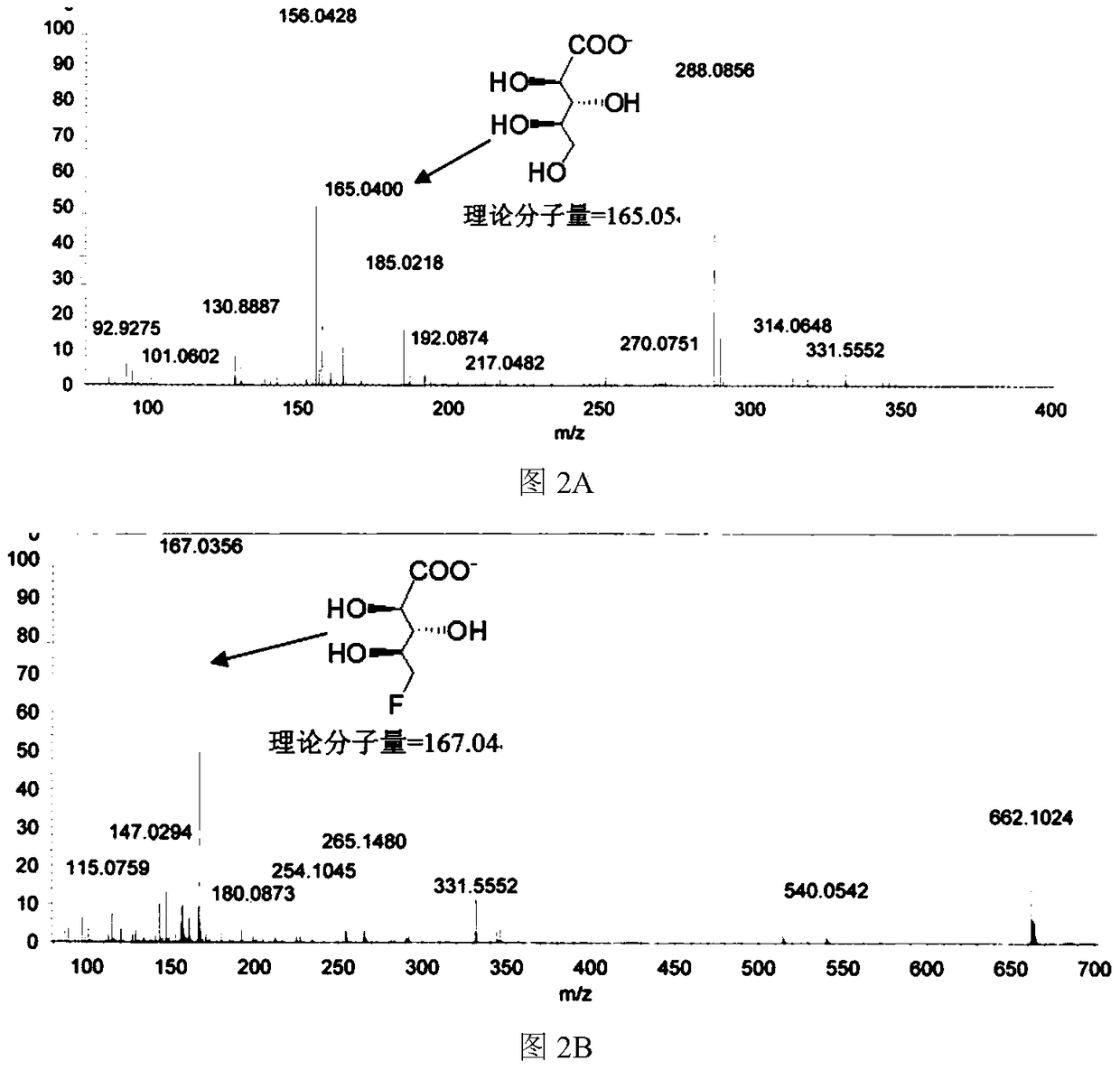
Short-chain dehydrogenase capable of hydrolyzing ribose and variety of fluorinated ribose
The invention relates to short-chain dehydrogenase FribC capable of hydrolyzing ribose and a variety of fluorinated ribose and application thereof. The short-chain dehydrogenase is characterized in that a coding gene of the dehydrogenase is a gene sequence shown in a sequence 1 or an amino acid sequence shown in a sequence 2; a substrate of the dehydrogenase is D-ribose or modified D-ribose, and the modified D-ribose comprises 5-fluoro-5-deoxy-D-ribose, 4-difluoromethyl-5-deoxy-D-ribose or 4-trifluoromethyl-5-deoxy-D-ribose. The FribC provided by the invention can be prepared into a biocatalyst and is applied to the biotransformation of a variety of ribose; the FribC can also be prepared into a radiotracer used for positron emission tomography (PET).
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Short-chain dehydrogenase, coding gene, vector, engineering bacterium and application derived from Refsonia
The invention discloses a leifsonia xyli HSO904-based short chain dehydrogenase, and an encoding gene, a carrier, engineering bacteria and application thereof. A gene of the leifsonia xyli HSO904-based short chain dehydrogenase has more than 90% of homology of a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. A colon bacillus BL21 / pET28a (+)-SDR prepared by the recombination of the short chain dehydrogenase is used as an enzyme source, 3, 5-bis-trifluoro methyl acetophenone, trifluoromethyl acetophenone, 4-hydroxyl-2-butanone, acetoacetic ester, 4-chloro ethyl acetoacetate, acetoacetic acid tert-butyl acetate and the like are used as substrates to prepare corresponding chiral compounds such as (R)-3, 5-bis-trifluoromethyl phenethyl alcohol, trifluoromethyl benzaldehyde ethanol, 2-hydroxyl-butyl alcohol, 3-hydroxy ethyl butyrate, 4-chloro-3-hydroxy ethyl butyrate and 3-hydroxy butyric acid tert-butyl acetate through a catalytic asymmetric reduction reaction.
Owner:艾吉泰康(嘉兴)生物科技有限公司
Short-chain dehydrogenase capable of hydrolyzing ribose and various fluororibose and its application
The invention relates to short-chain dehydrogenase FribC capable of hydrolyzing ribose and a variety of fluorinated ribose and application thereof. The short-chain dehydrogenase is characterized in that a coding gene of the dehydrogenase is a gene sequence shown in a sequence 1 or an amino acid sequence shown in a sequence 2; a substrate of the dehydrogenase is D-ribose or modified D-ribose, and the modified D-ribose comprises 5-fluoro-5-deoxy-D-ribose, 4-difluoromethyl-5-deoxy-D-ribose or 4-trifluoromethyl-5-deoxy-D-ribose. The FribC provided by the invention can be prepared into a biocatalyst and is applied to the biotransformation of a variety of ribose; the FribC can also be prepared into a radiotracer used for positron emission tomography (PET).
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing calcipotriol key chiral intermediate based on short-chain carbonyl reductase
ActiveCN114591991AHigh ee valueHigh optical purityMicroorganism based processesNucleic acid vectorPtru catalystFreeze-drying
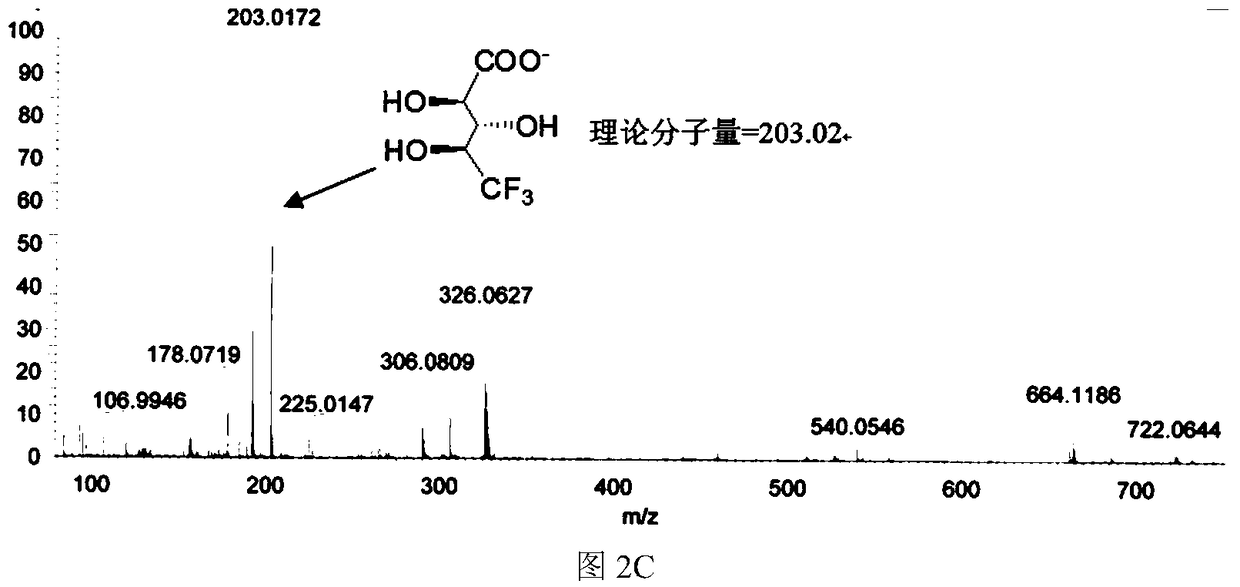
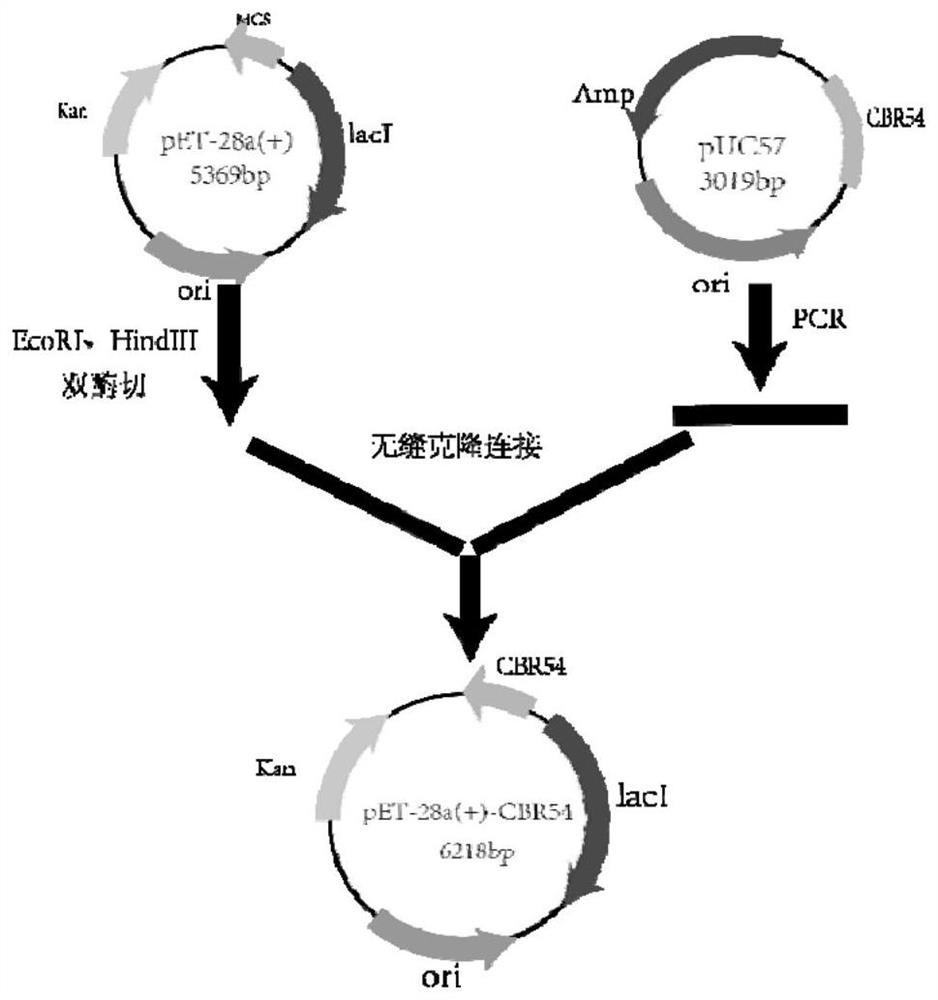
The invention provides a method for preparing a key chiral intermediate of calcipotriol based on short-chain carbonyl reductase, which comprises the following steps: constructing a first genetically engineered bacterium for expressing CBR54 by using short-chain dehydrogenase SR03 of underground neosphingobium; the method comprises the following steps: performing separation, purification and culture on a first genetically engineered bacterium for expressing CBR54 to obtain a second genetically engineered bacterium for expressing short-chain carbonyl reductase, performing freeze drying on the second genetically engineered bacterium to obtain CBR54 crude enzyme powder, taking the CBR54 crude enzyme powder, GDH enzyme powder and NADH coenzyme as catalysts, taking cyclopropylcarbonyl methyl-benzothiazole-2-thioether as a substrate, adding a buffer solution, performing catalytic reaction for 8-24 hours, and performing separation and purification to obtain the short-chain carbonyl reductase. 2-[(S)-2-hydroxy-2-cyclopropyl)-1-ethylthio]-benzothiazole is obtained, and the calcipotriol key chiral intermediate is obtained; the method can solve the technical problems of high cost, large substrate loss and low product purity of the existing chiral body preparation.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Short-chain dehydrogenase mutant and its application
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, relates to short-chain dehydrogenase and its mutants and applications, in particular to stereoselective complementary short-chain dehydrogenase mutants, and the mutants are excavated from Lactobacillus fermentum The wild-type short-chain dehydrogenase (LfSDR1) mutation obtained, specifically relates to the short-chain dehydrogenase mutant and its preparation method and its use as a catalyst to catalyze the asymmetric reduction of 4R / S-carvone to prepare stereodiversity carveol. Compared with the existing chemical methods, the method has the advantages of simple operation, mild reaction conditions, and environmental friendliness.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
A kind of short-chain dehydrogenase and its application
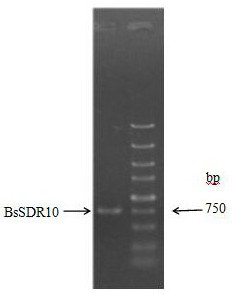
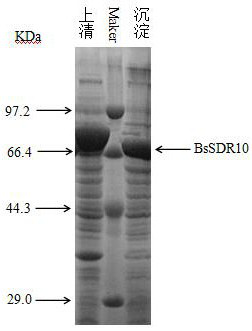
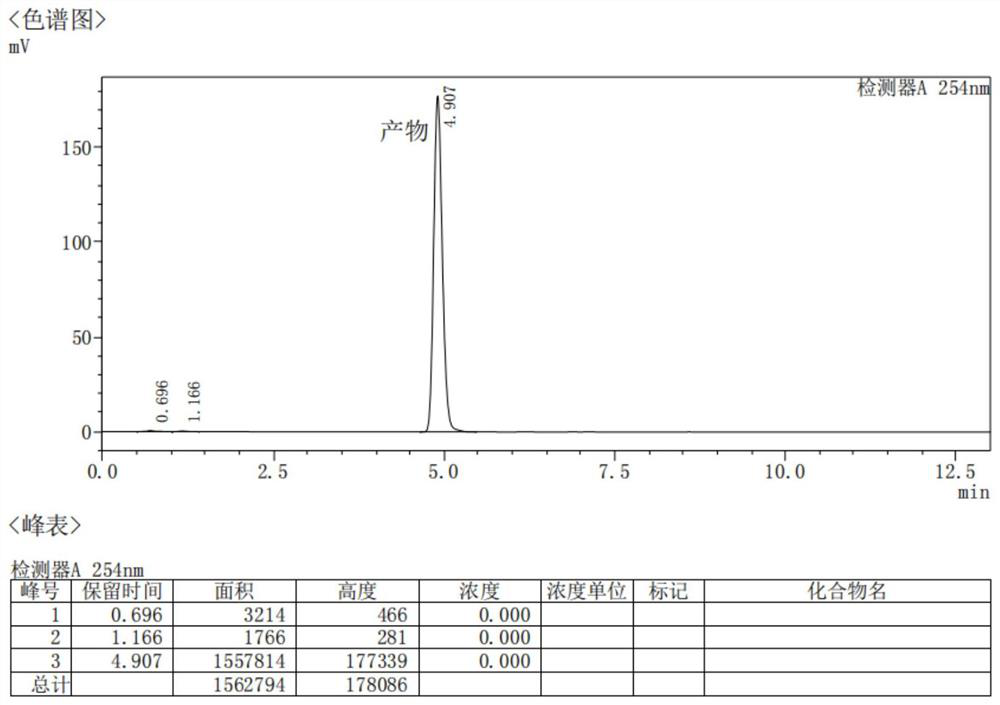
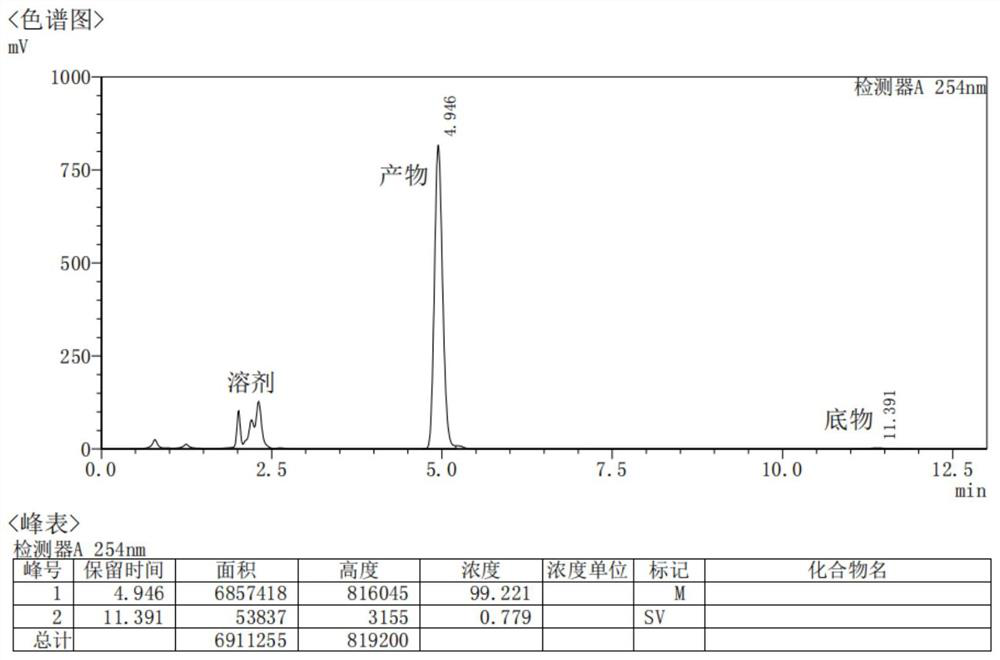
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and discloses a short-chain dehydrogenase gene, a short-chain dehydrogenase BsSDR10, and an engineered bacteria excavated from Bacillus subtilis (Bacillus subtilis). Carbonyl compounds to prepare optically active chiral alcohols. The enzyme has the advantages of stereospecificity, mild reaction conditions and simple operation, and has a good application prospect in the production of chiral pharmaceutical intermediates.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
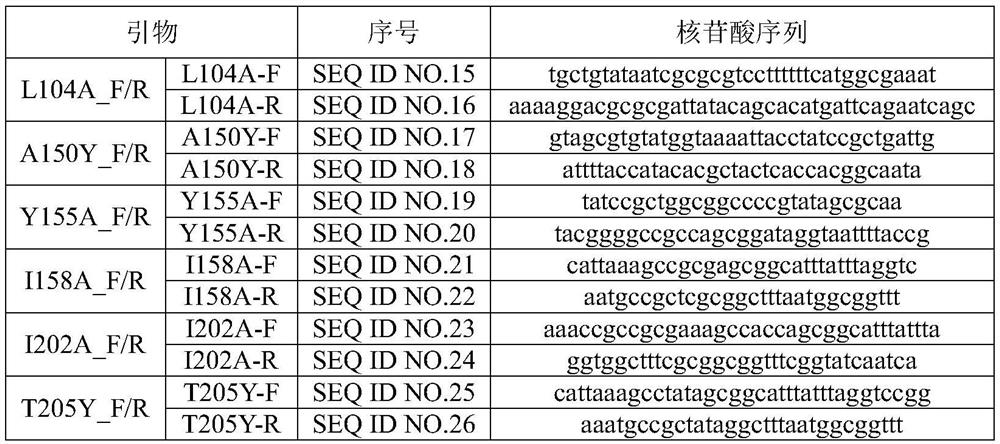
Mutant of short-chain dehydrogenase, encoding gene, encoding gene obtaining method and application of mutant
PendingCN114875003AIncrease enzyme activityImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEthylic acidBio engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological engineering, and particularly relates to a mutant of short-chain dehydrogenase, and the mutant is a mutant L104A, a mutant A150Y, a mutant Y155A, a mutant I158A, a mutant I202A or a mutant T205A. The amino acid sequence of the short-chain dehydrogenase is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. Compared with wild type short-chain dehydrogenase, the short-chain dehydrogenase mutant has higher enzyme activity, prednisolone can be prepared from prednisone or prednisone acetate matched with hydrolase as a substrate, the conversion rate of the substrate is high, the yield of the product is high, no by-product is generated, the reaction can be carried out at a higher substrate concentration level, and the method is suitable for industrial production. The method is suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Short-chain dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN113293151AChange or even reverse selectivityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhenethyl alcoholAcetophenone
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to short-chain dehydrogenase mutants and application thereof, wherein the mutants are obtained by mutating wild types of various short-chain dehydrogenase. The invention particularly relates to the short-chain dehydrogenase mutant, a preparation method thereof and a method for preparing a phenethyl alcohol derivative with optical activity through reduction of an acetophenone derivative compound by using the short-chain dehydrogenase mutant.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Short-chain dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN113293152AChange or even reverse selectivityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhenethyl alcoholAcetophenone
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
A short-chain dehydrogenase and its gene, recombinant expression vector, genetically engineered bacteria and its application in the synthesis of astaxanthin chiral intermediates
ActiveCN106520715BHigh stereoselectivityEasy to manufactureOxidoreductasesFermentationAstaxanthinBetaxanthins
The invention provides a short-chain dehydrogenase and a gene thereof, a recombinant short-chain dehydrogenase, a recombinant expression vector containing the gene, a genetically engineered bacterium, a preparation method of the recombinant short-chain dehydrogenase, and an application of the short-chain dehydrogenase or the genetically engineered bacterium containing the short-chain dehydrogenase in astaxanthin chiral intermediate synthesis through asymmetric reduction for prochiral ketones. In the application provided by the invention, asymmetric reduction preparation of the short-chain dehydrogenase for chiral alcohols has remarkable advantages, and an astaxanthin chiral intermediate (having an enantiomeric excess (ee) of greater than 99%) with a high optical purity can be synthesised. A catalyst is easy to prepare, the reaction conditions are moderate, a substrate is wide in adaptability, and the short-chain dehydrogenase is environment-friendly; and moreover, the recombinant cell of the short-chain dehydrogenase is capable of efficiently catalyzing the asymmetric reduction for prochiral ketones in an isopropanol-containing reaction system without any coenzyme, and has a great industrialized application and development prospect.
Owner:杭州馨海酶源生物科技有限公司
Polypeptide human rudder chain dehydrogenase 9.46 and polynucleotide for encoding polypeptide
A novel polypeptide-human short-chain dehydrogenase 9.46, the polynucleotide for coding it, the process for preparing said polypeptide by DNA recombination, the application of said polypeptide in treating diseases, such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, immunopathy, etc. the antagon of said polypeptide and its medical action, and the application of said polynucleotide are disclosed.
Owner:BIOWINDOW GENE DEV INC
Short-chain dehydrogenase as well as mutant and application thereof
PendingCN114574454AHigh stereoselectivityHigh yieldOxidoreductasesChemical recyclingEnzymatic synthesisChemical synthesis
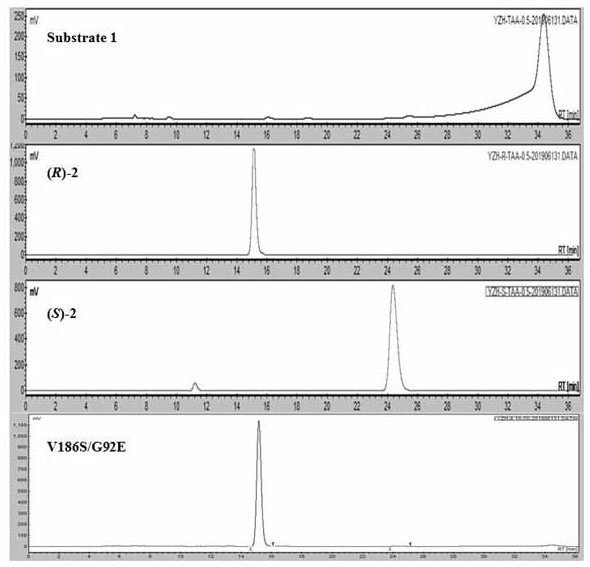
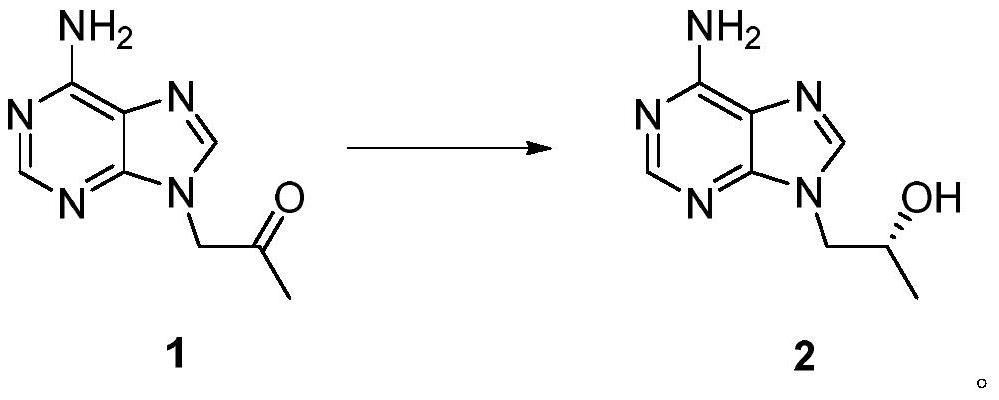
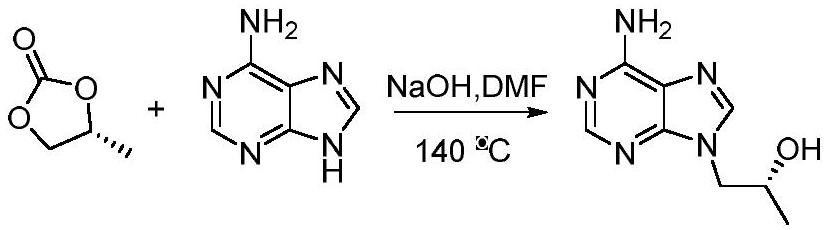
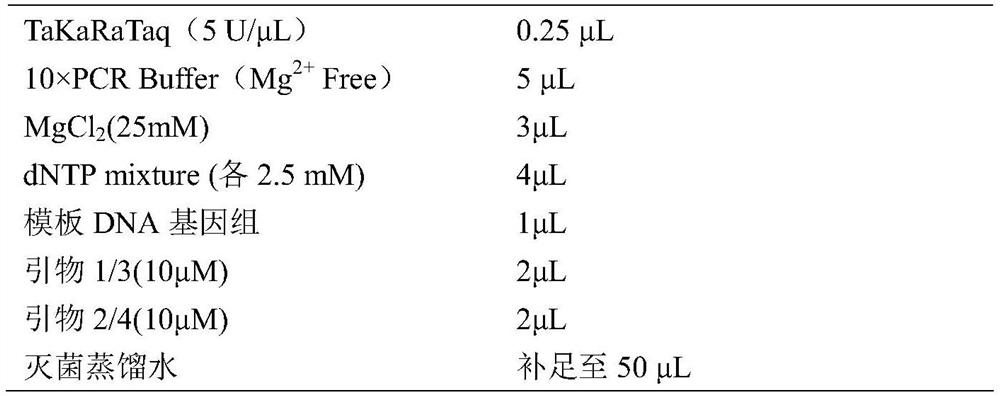
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines, relates to short-chain dehydrogenase as well as a mutant and application thereof, in particular to application of the short-chain dehydrogenase and the mutant thereof in synthesis of (R)-(+)-9-(2-hydroxypropyl) adenine, and particularly relates to application of the short-chain dehydrogenase and the mutant thereof in catalytic reduction of a substrate 6-amino-9-(2-acetonyl) purine, synthesis of (R)-(+)-9-(2-hydroxypropyl) adenine and synthesis of (R)-(+)-9-(2-hydroxypropyl) adenine. The invention also relates to the application of the compound in the preparation of (R)-(+)-9-(2-hydroxypropyl) adenine with extremely high chiral purity. The amino acid sequence of the short-chain dehydrogenase is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, and mutants of the short-chain dehydrogenase are as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2-34. The short-chain dehydrogenase and the mutant thereof are used as biocatalysts, 6-amino-9-(2-acetonyl) purine (1) is used as a substrate, a coenzyme regeneration system is carried, and NAD (P) < + > is used as a coenzyme to realize enzymatic synthesis of (R)-(+)-9-(2-hydroxypropyl) adenine (2). Compared with the existing chemical synthesis process of (R)-(+)-9-(2-hydroxypropyl) adenine, the method has the advantages of high product yield, good stereoselectivity and environmental protection. The conversion rate and stereoselectivity of the compound are high, and the highest conversion rate and stereoselectivity can reach 99%.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Short-chain dehydrogenase mutants and uses thereof
The present invention relates to the field of biotechnology, and relates to short-chain dehydrogenase mutants and applications thereof. Such mutants are obtained through mutation from wild-type short-chain dehydrogenases, and specifically relate to short-chain dehydrogenase mutants and The preparation method thereof and the method for preparing optically active phenethyl alcohol derivatives by utilizing short-chain dehydrogenase mutants through the reduction of acetophenone derivative compounds.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Function and application of a short-chain dehydrogenase tsru
ActiveCN103205470BImprove toleranceHigh catalytic efficiencyOxidoreductasesFermentationSide chainStructural analog
The invention discloses functions and application of a short chain dehydrogenase TsrU. Specifically, the short chain dehydrogenase TsrU can catalyze the carbonyl chiral single reduction reaction of 4-acetyl-2-quinolinic acid or its analogues, can be used for in-vitro efficient production of 4-(1-hydroxymethyl)-2-quinolinic acid or its structural analogues, and in a side chain reaction of thiostrepton biosynthesis, the enzyme has a high tolerance to a substrate, so that the short chain dehydrogenase TsrU can be widely applied to chiral reduction reactions of other similar substrates.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Short-chain dehydrogenase BLSDR1 as well as coding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses short-chain dehydrogenase BLSDR1 as well as a coding gene and application thereof. The protein provided by the invention is a protein coded by an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ NO.2. A new short-chain dehydrogenase gene blsdr1 is cloned from bacillus coagulans NL01, the gene can be expressed in a host cell to produce the short-chain dehydrogenase, and the short-chain dehydrogenase has a wide substrate spectrum in the aspect of reducing carbonyl compounds, has certain organic solvent tolerance and can be used for removal and reduction of various ketoaldehyde compounds.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com