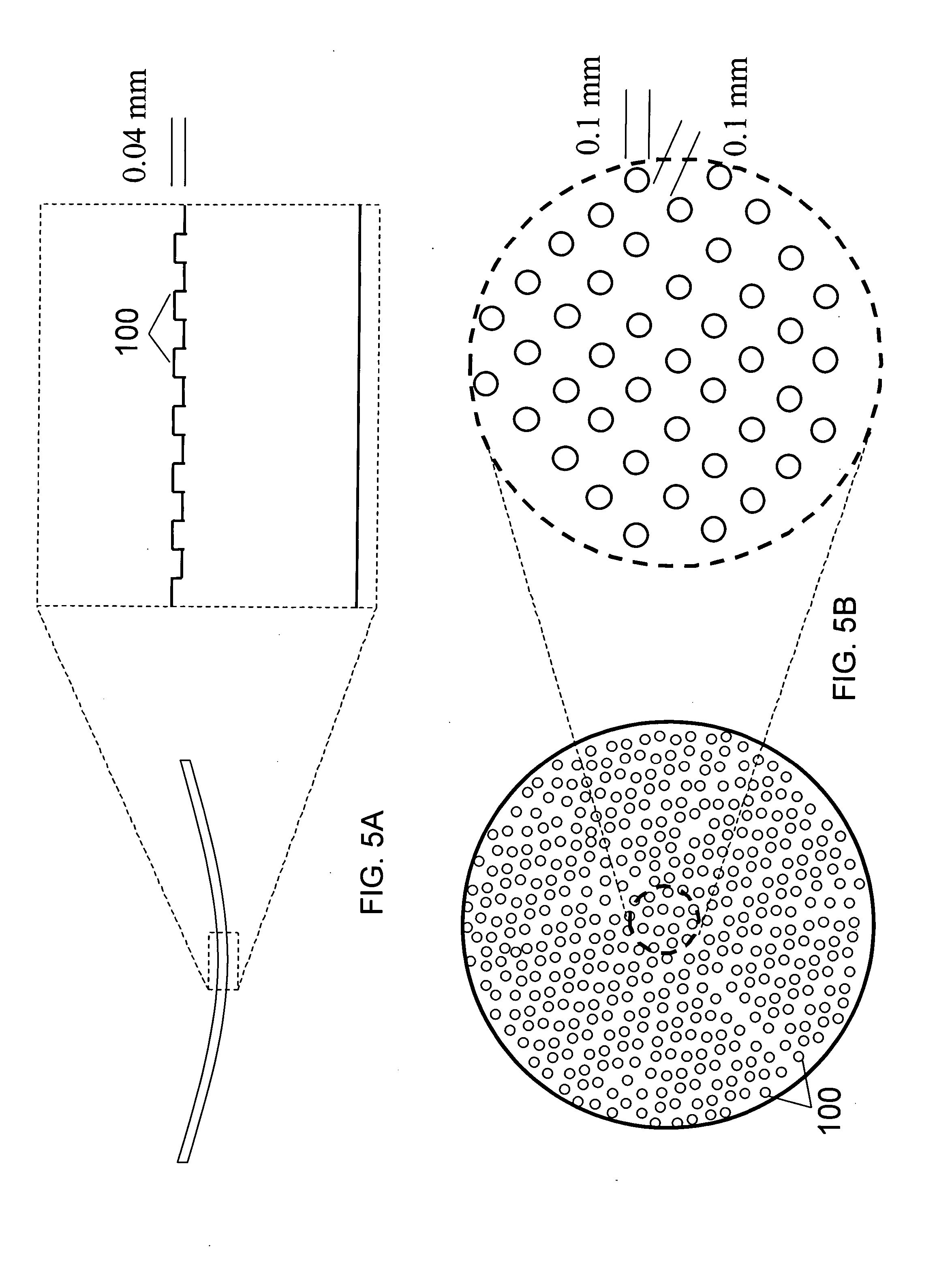
Patents
Literature
145 results about "Transplant cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
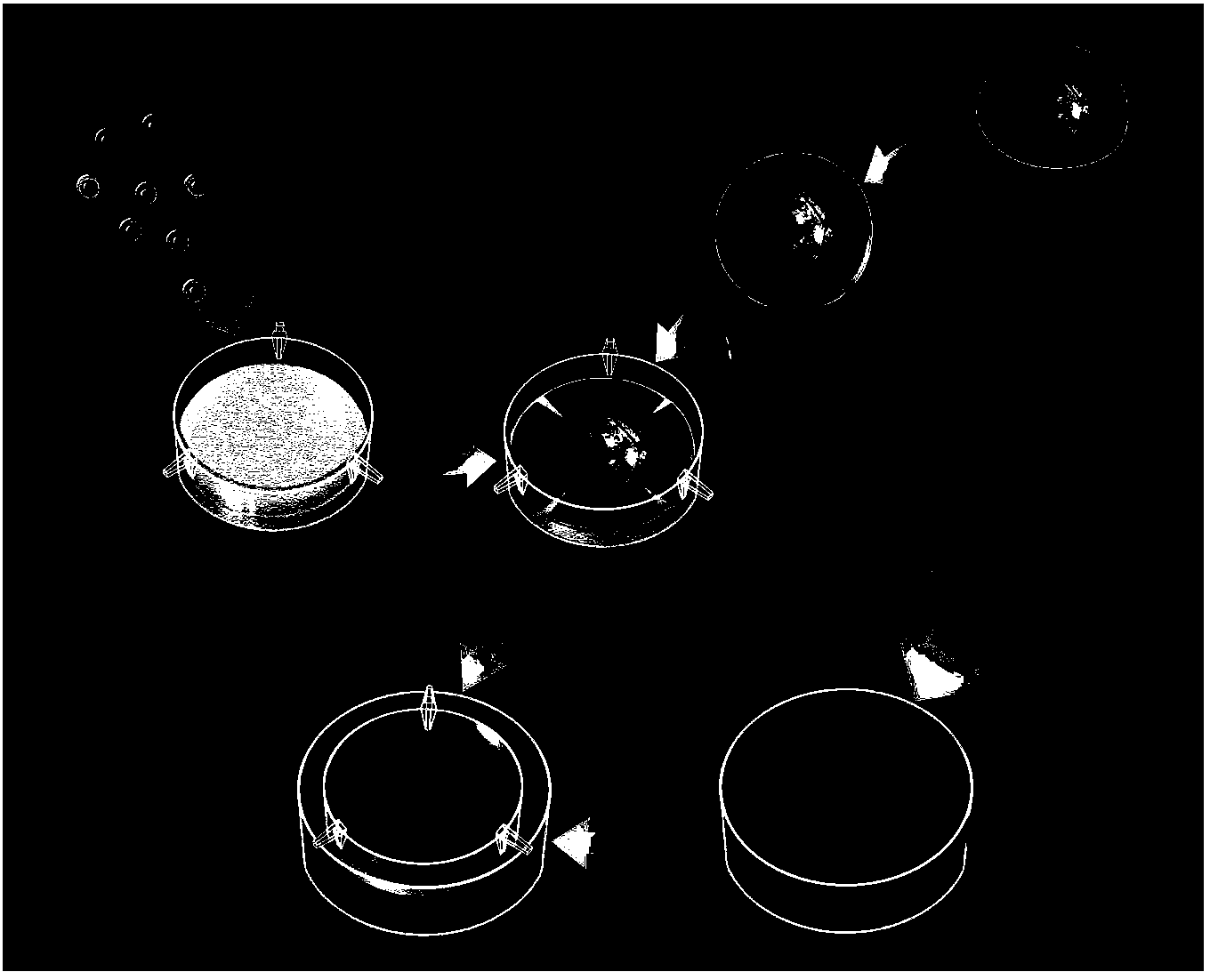
System and methods for treatment of alzheimer's and other deposition-related disorders of the brain
InactiveUS20040049134A1Slowing, stopping or avoiding a patient's cognitive lossesMinimal adverse side effectUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyDiseaseSide effect
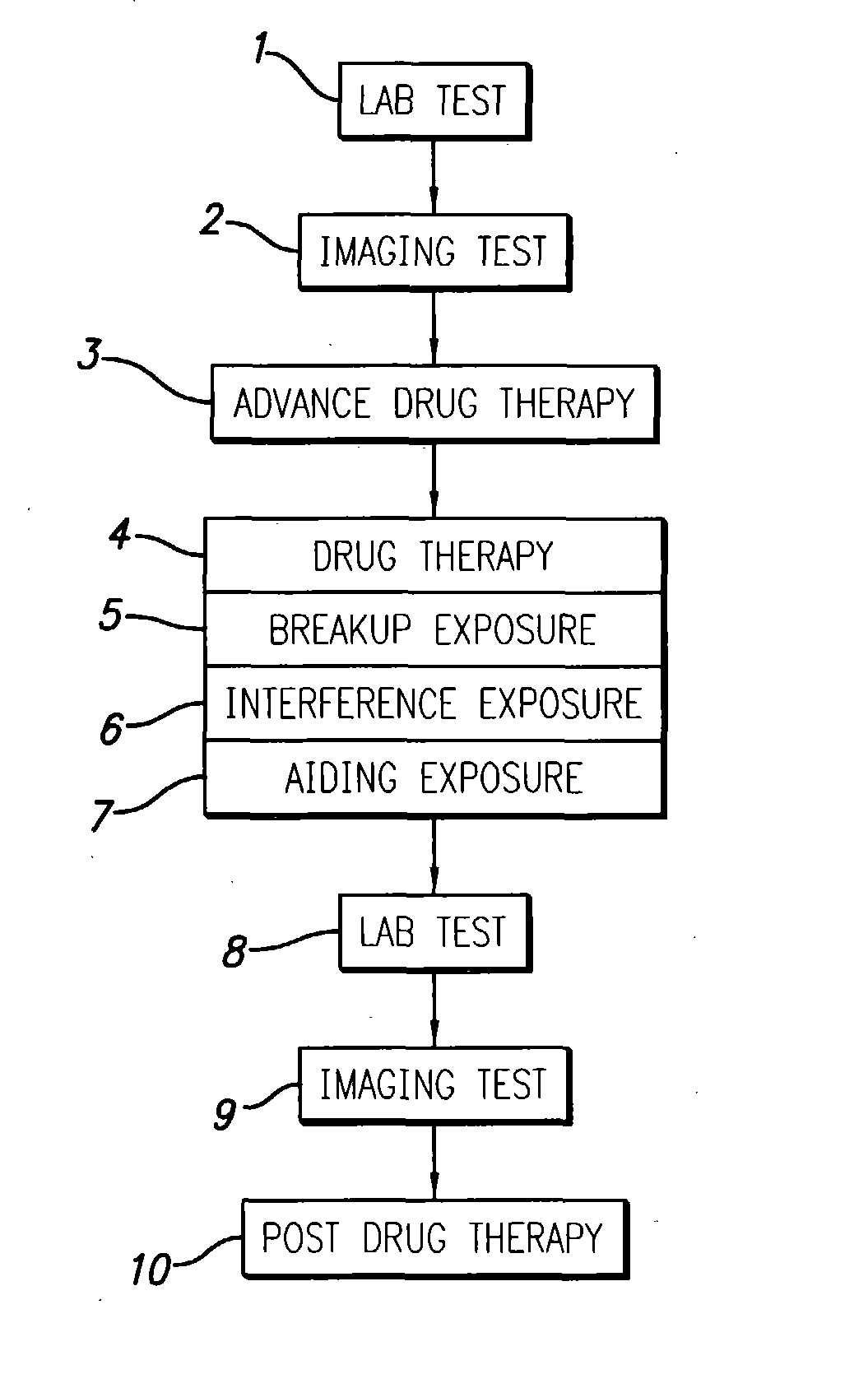
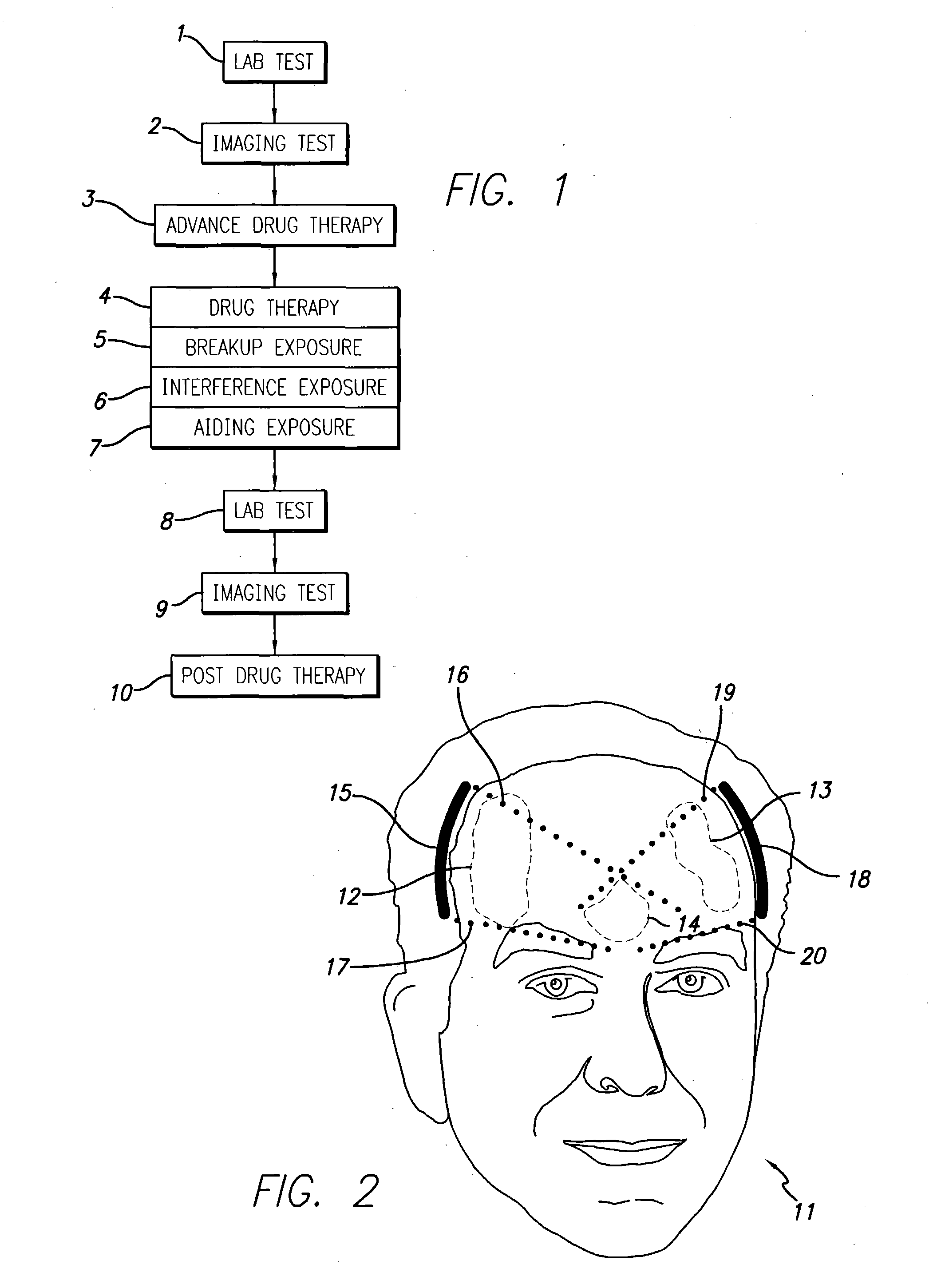
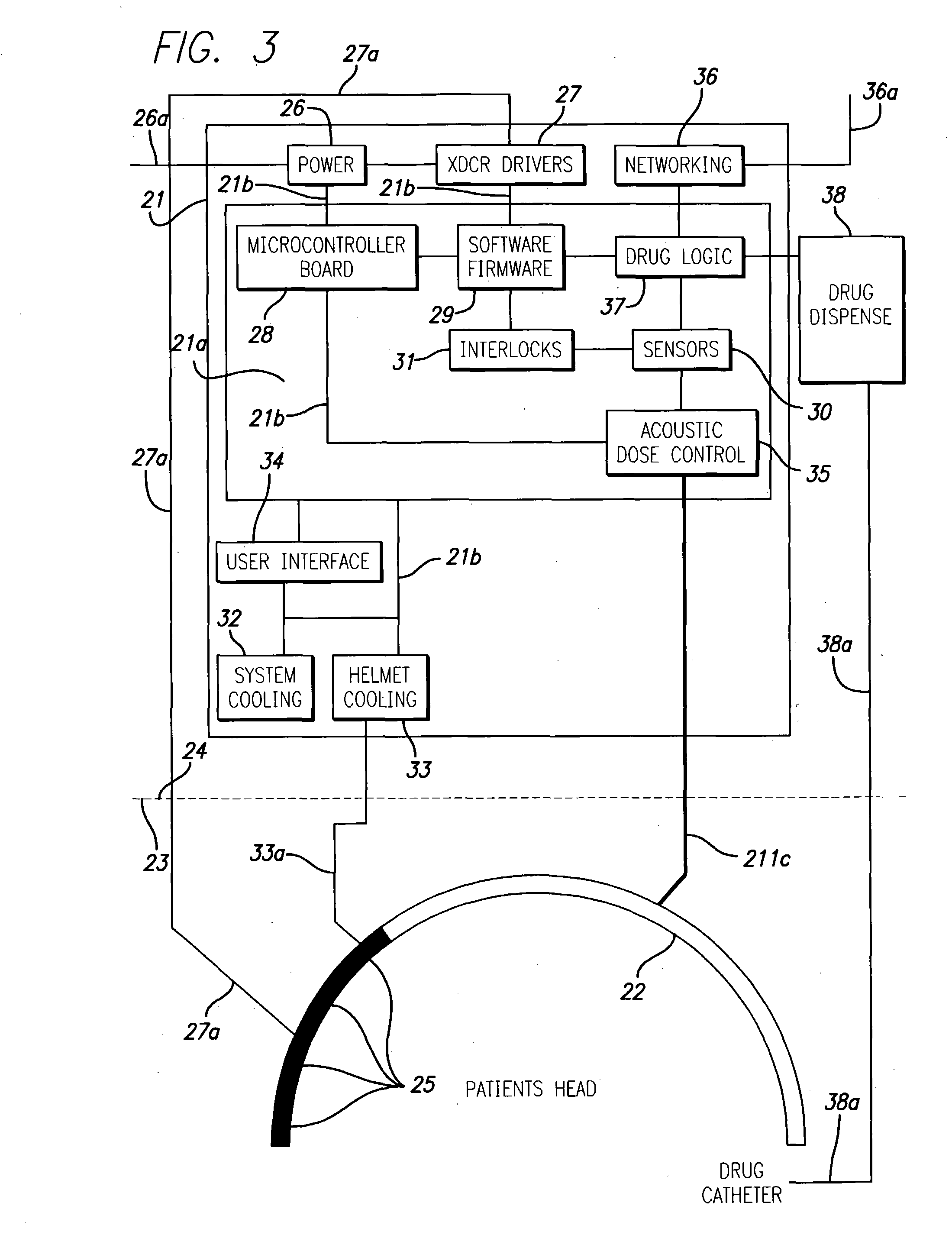
A system and methods are provided for the therapeutic treatment of brain-plaques, fibrils, abnormal-protein related or aggregation-prone protein related deposition-diseases. The system employs acoustic exposure therapy means for delivering therapeutic energy to at least one brain region. The therapy supports at least one of the following processes: (i) physical breakup, erosion, disentanglement, de-aggregation, dissolution, de-agglomeration, de-amalgamation or permeation of the deposits, (ii) interference in at least one deposit formation process, deposition related chemical reaction or biological or genetic pathway contributing to the deposits or deposition-related processes, and (iii) aiding the recovery, growth, regrowth or improved functionality of brain-related cells or functional pathways negatively impacted by, stressed by or disposed to the deposits, deposition-processes or deposition disease state, or supporting the growth of newly transplanted cells anywhere in the brain-related anatomy. The system and methods treat Alzheimer's and other deposition-related disorders of the brain, with minimal adverse side effects to the patient and may be used in cooperation with a drug.
Owner:TOSAYA CAROL A +1
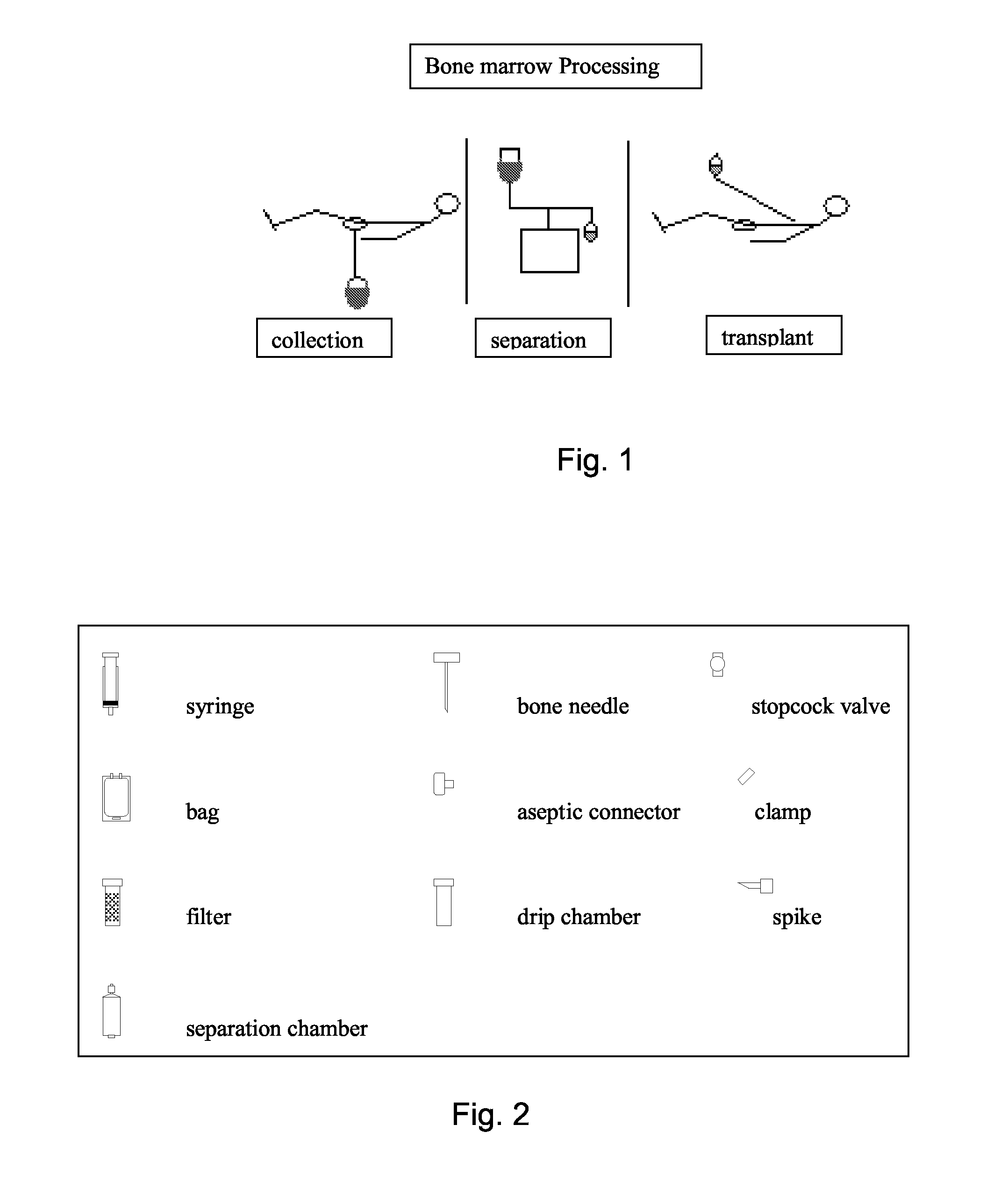
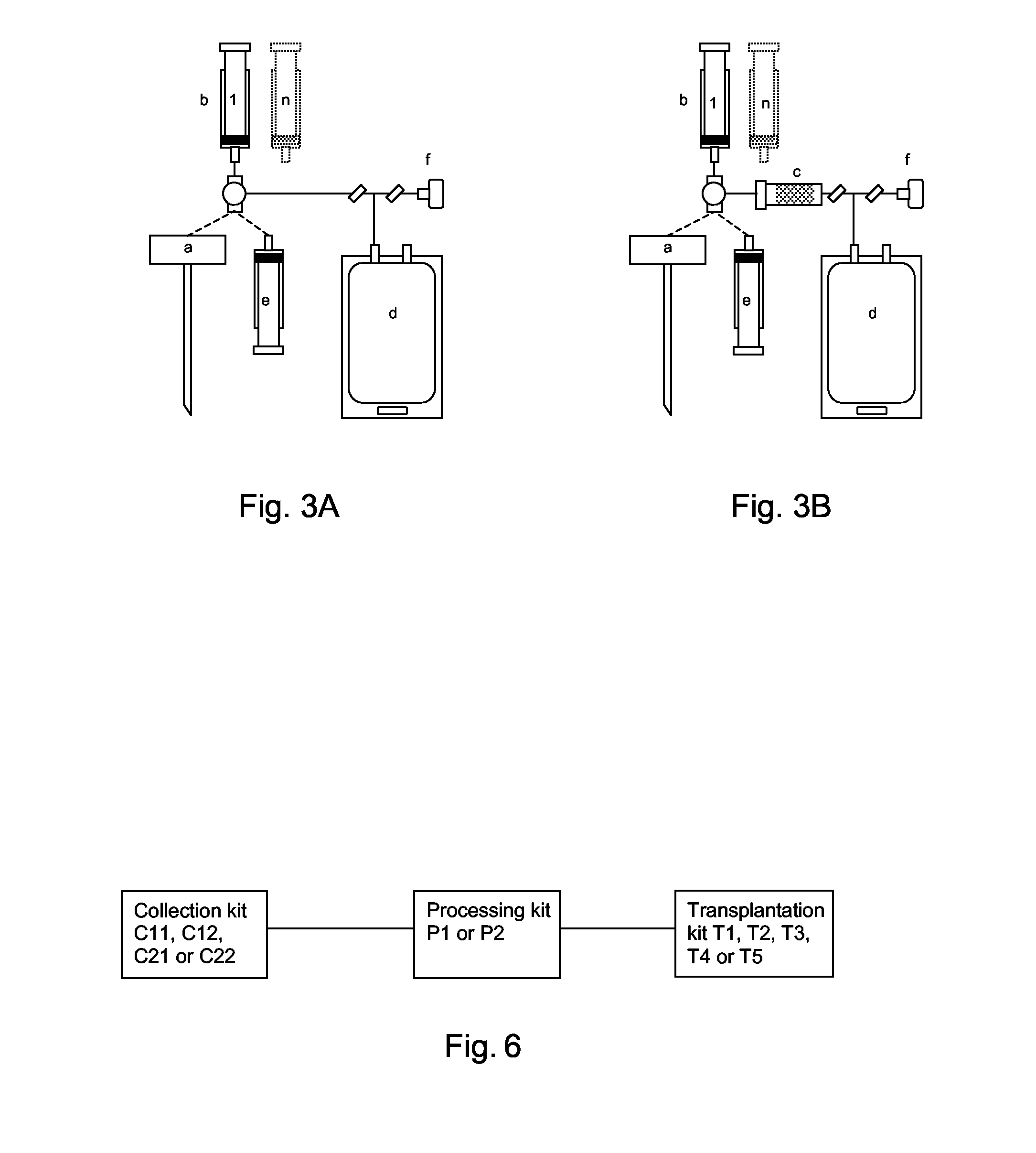
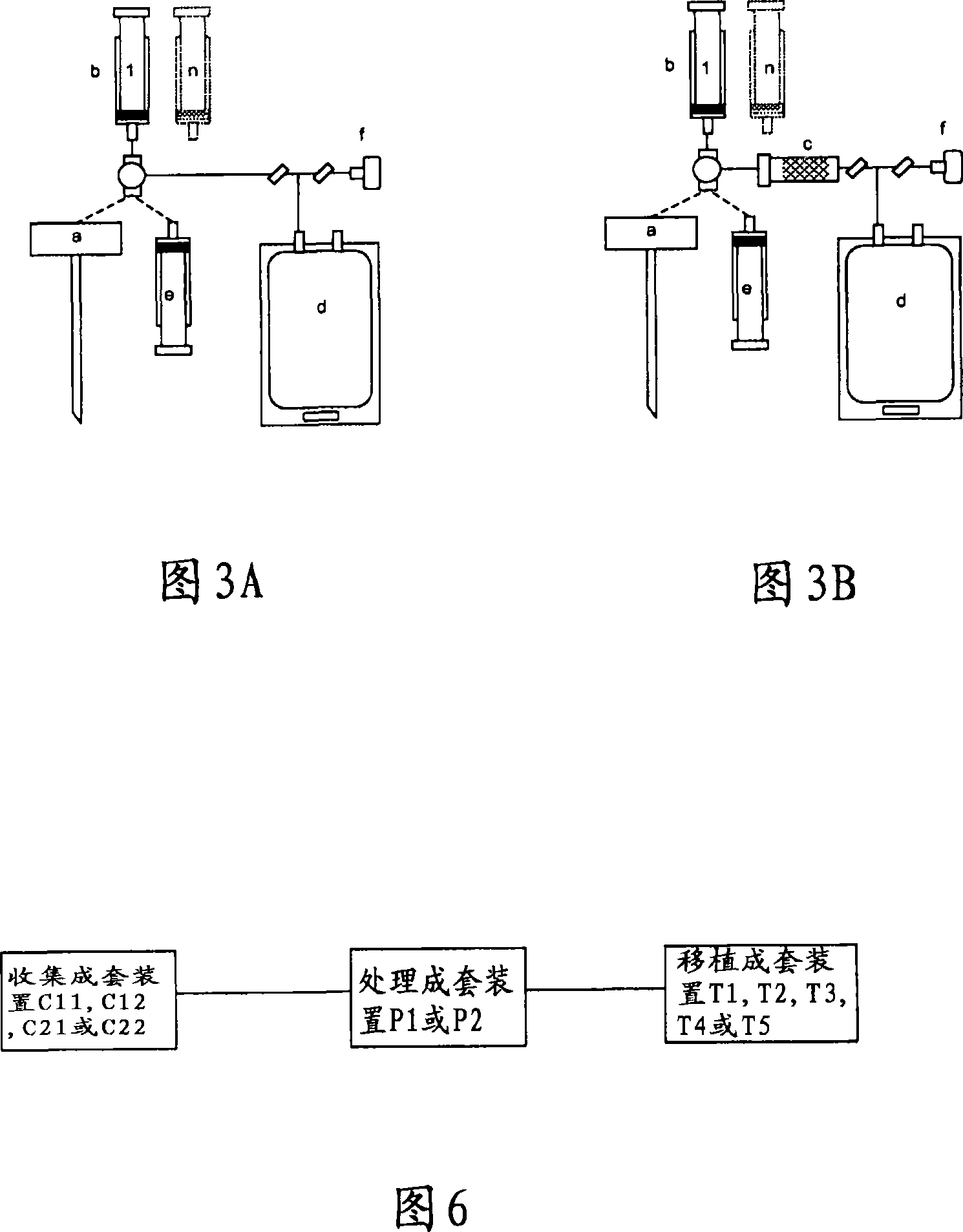
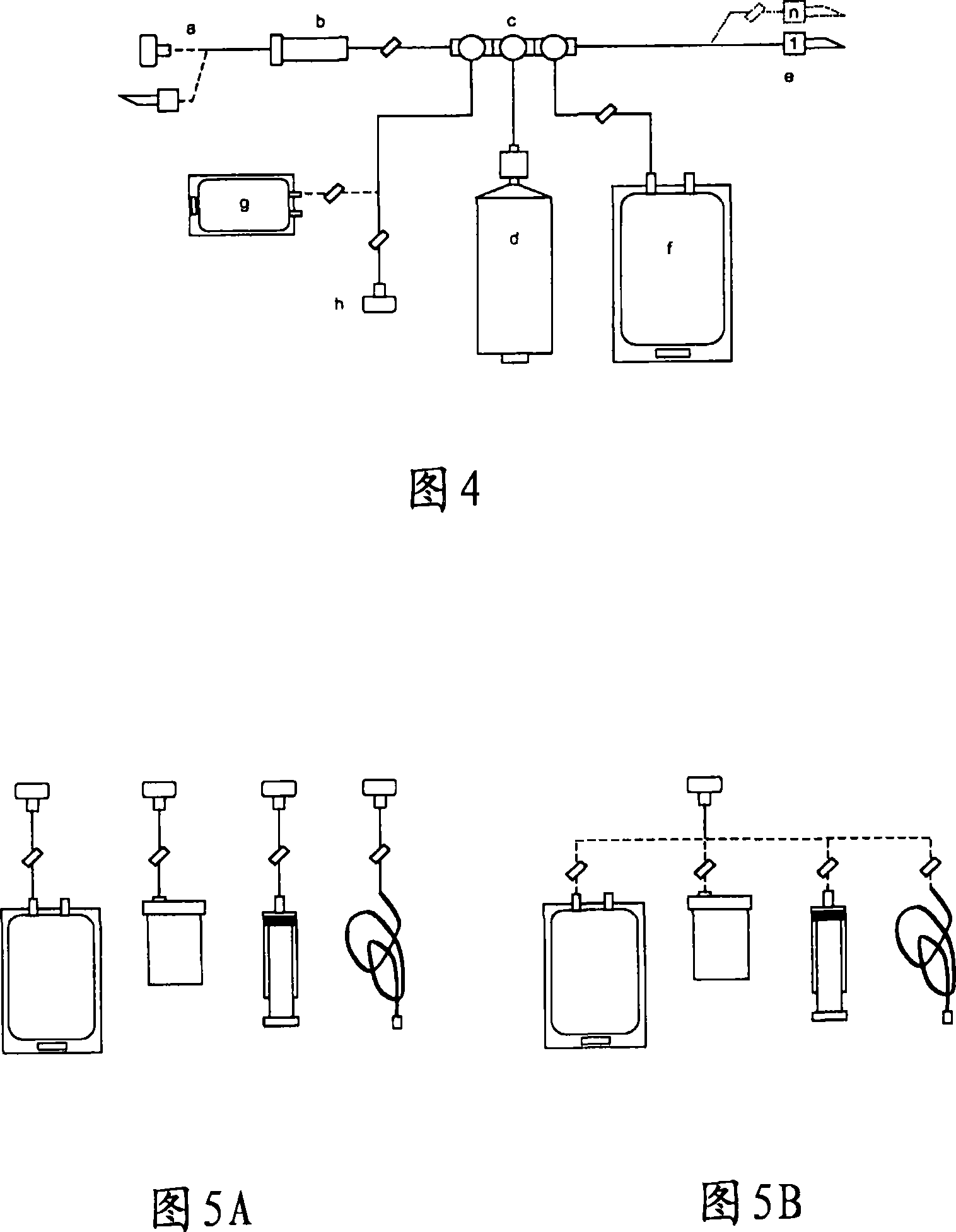
Integrated System for Collecting, Processing and Transplanting Cell Subsets, Including Adult Stem Cells, for Regenerative Medicine
InactiveUS20080171951A1Accurate collectionMinimize risk of contaminationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNervous disorderFluid transportTissue repair
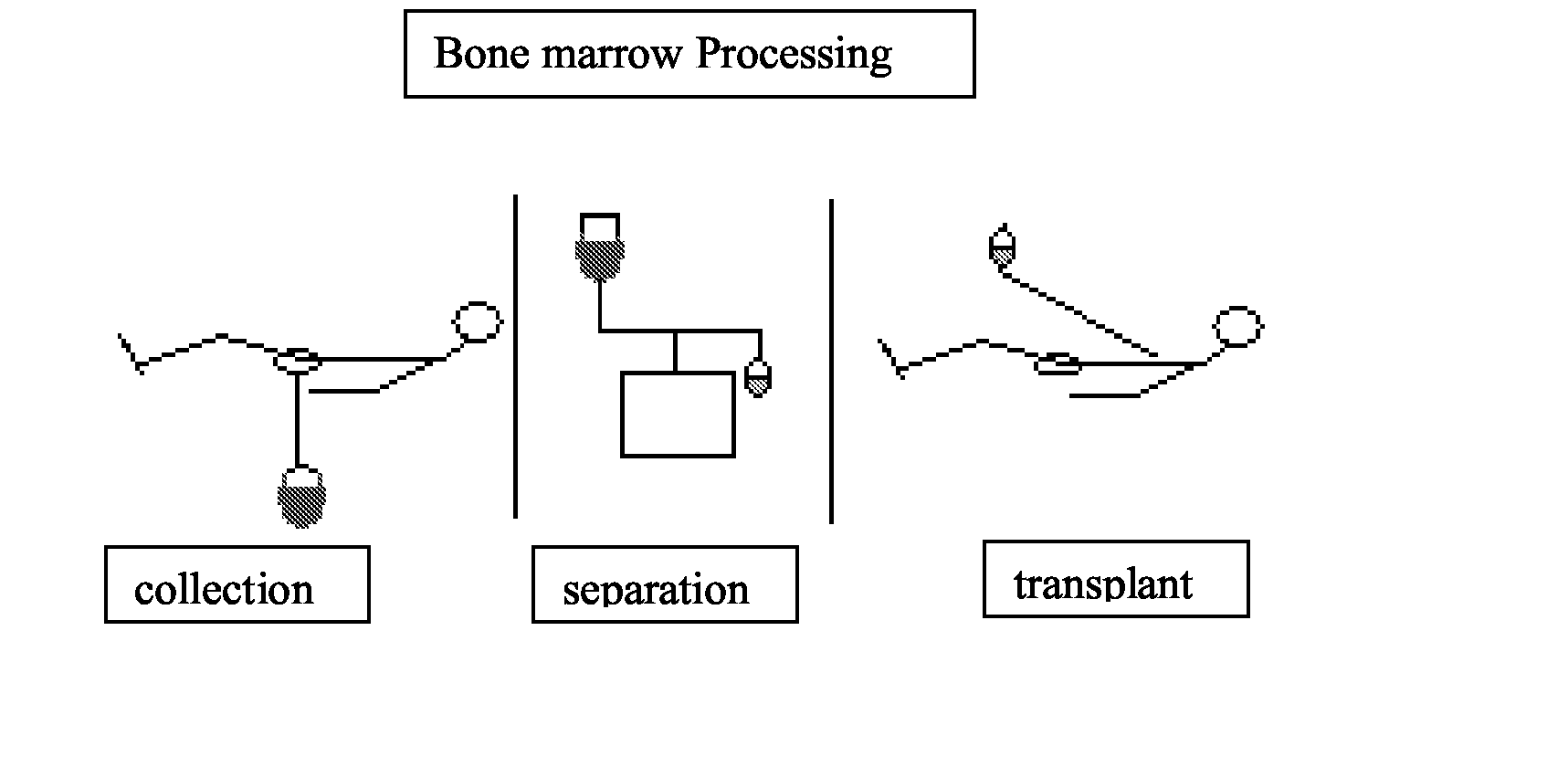
A system for the extraction, collection, processing and transplantation of cell subsets, including adult stem cells and platelets, in particular for tissue repair in regenerative medicine, comprises a set of disposable fluid-transport elements that are pre-connected or that include aseptic connectors for making interconnections between them in an aseptic manner or are adapted to be aseptically connected. The set usually includes three kits of disposable sterile elements, a collection kit, a processing kit, and a transplantation kit packaged in a blister pack on a support such as a tray, having one compartment for receiving each inter-connectable kit of the set. The set includes an extracting device, for example including a needle for bone puncture or vein puncture, for extracting bone marrow or other sources of cell subsets from a patient.
Owner:BIOSAFE SA
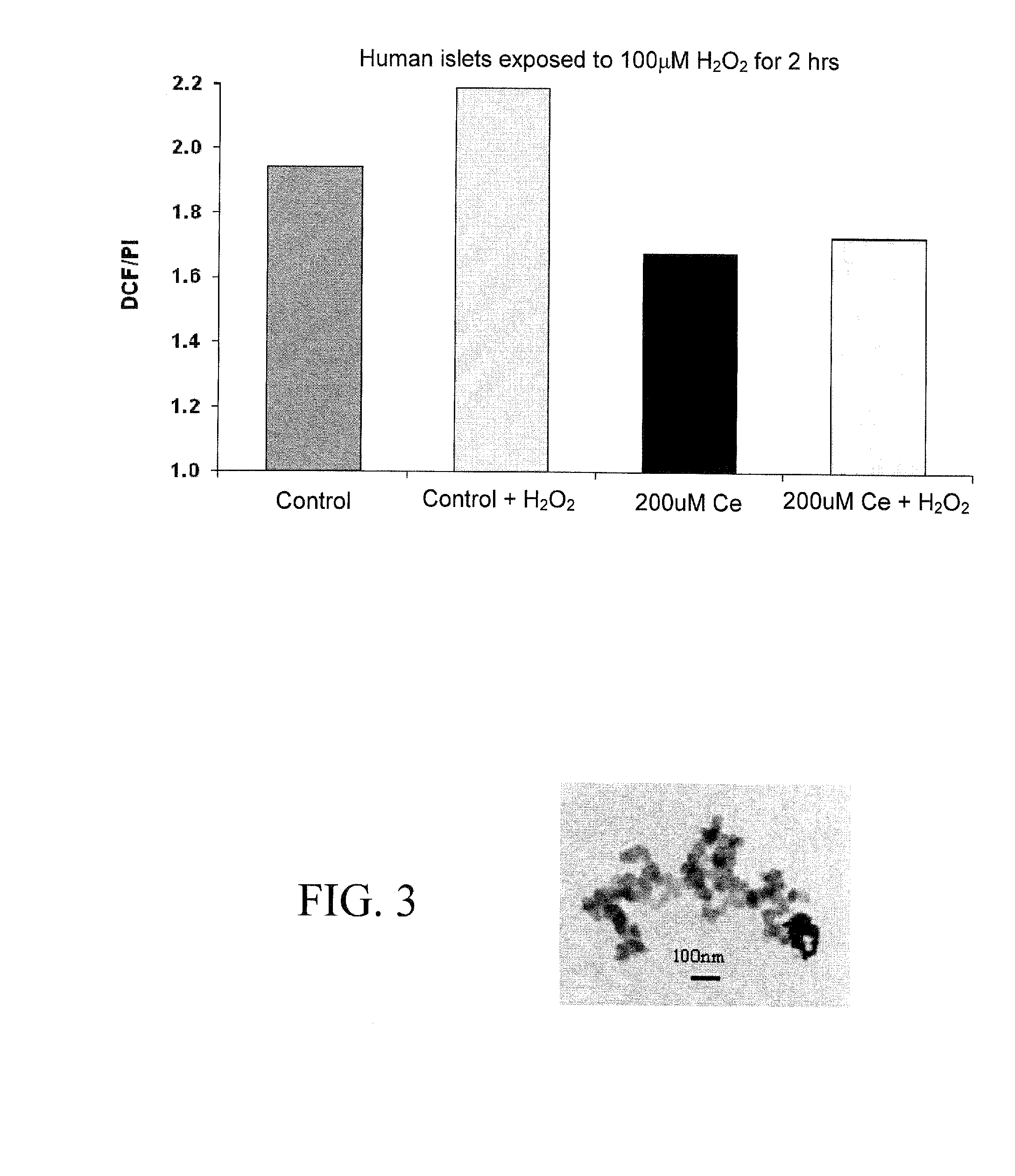
Nanoparticles for Protection of Cells from Oxidative Stress
InactiveUS20100172994A1Increase the number ofImprove survivabilityHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideMetal oxide nanoparticlesMedicine
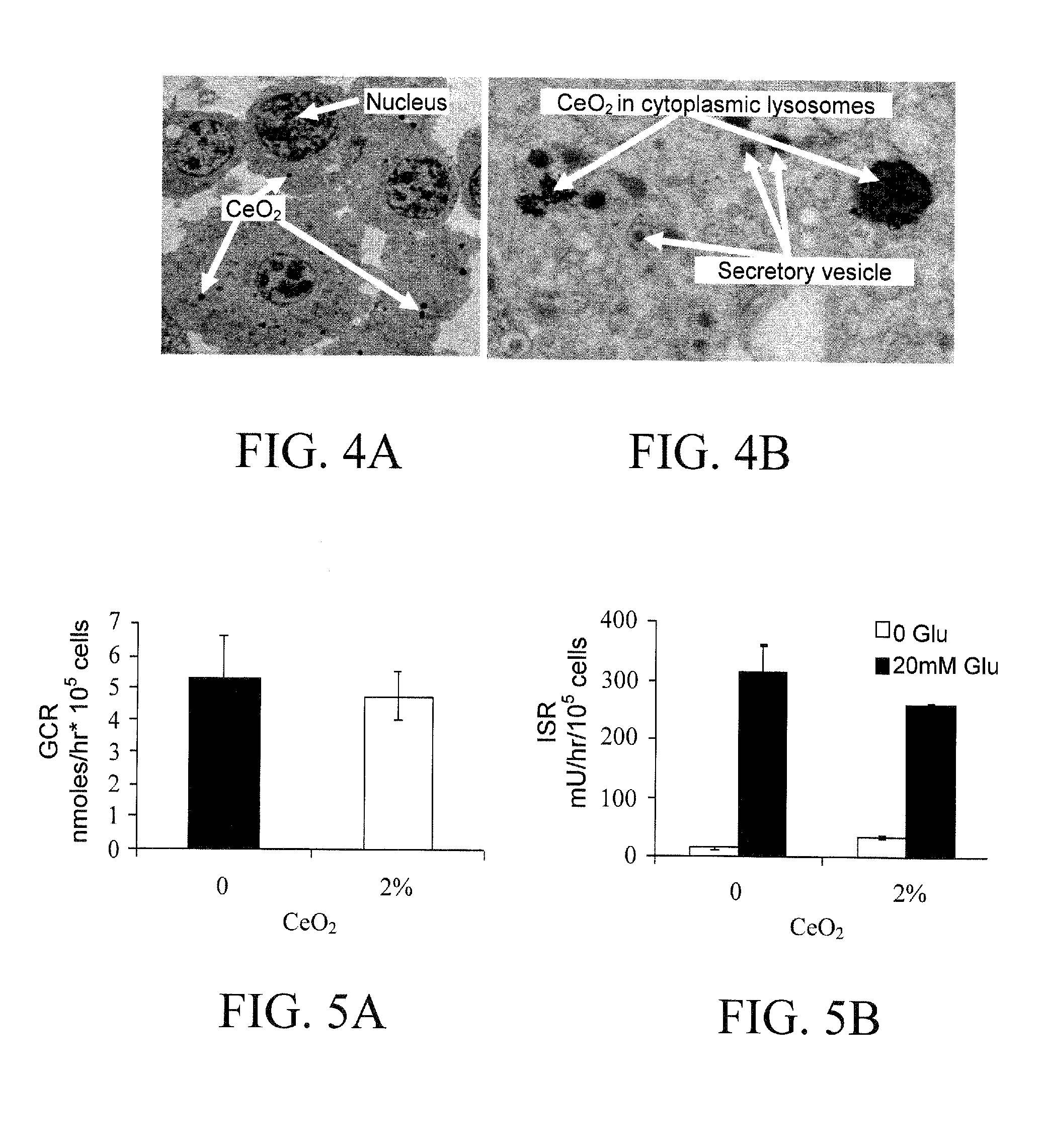
The present invention concerns metal oxide semiconductor nanoparticles with free radical scavenging activity, compositions comprising such nanoparticles, methods for their use, and methods for their production. In one aspect, the invention concerns a method for enhancing the survival or viability of transplanted cells, comprising administering an effective amount of metal oxide semiconductor nanoparticles to a target anatomical site of a subject before, during, or after administration of transplant cells to the subject. Preferably, the metal oxide nanoparticle is a cerium oxide (ceria) nanoparticle.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
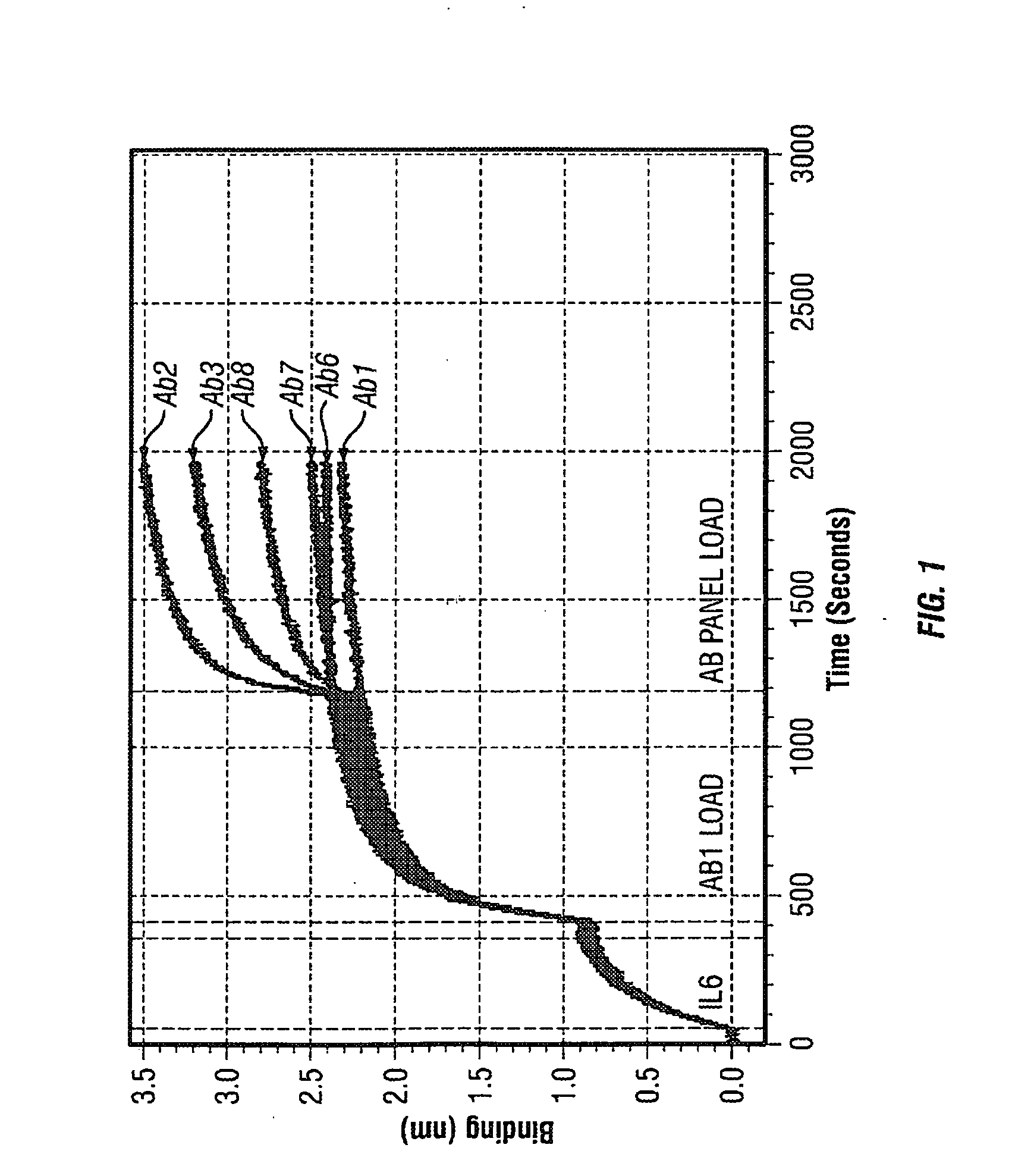
Antibodies to il-6 and use thereof
ActiveUS20130034554A1Reduce riskIncrease apoptosisCompounds screening/testingAntipyreticEGFR inhibitorsAnti-coagulants
Owner:VITAERIS INC +1
Method of providing a dynamic cellular cardiac support
The present invention provides a method for repairing damaged myocardium. The method comprises using a combination of cellular cardiomyoplasty and electrostimulation for myogenic predifferentiation of stem cells and to synchronize the contractions of the transplanted cells with the cardiac cells. The method comprises the steps of obtaining stem or myogenic cells from a donor, culturing and electrostimulating the isolated cells in vitro, and implanting the cells into the damaged myocardium.
Owner:BIOHEART
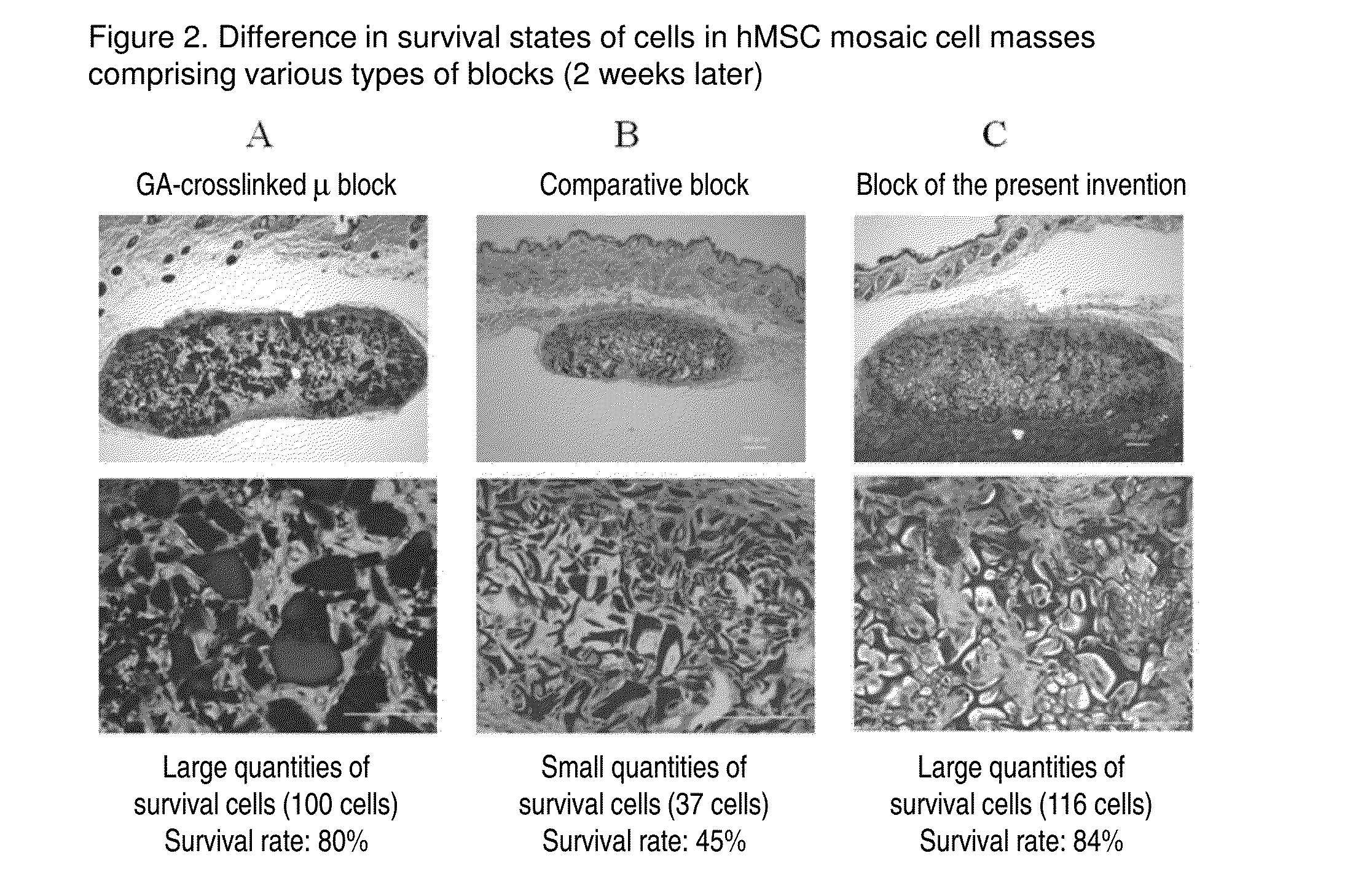
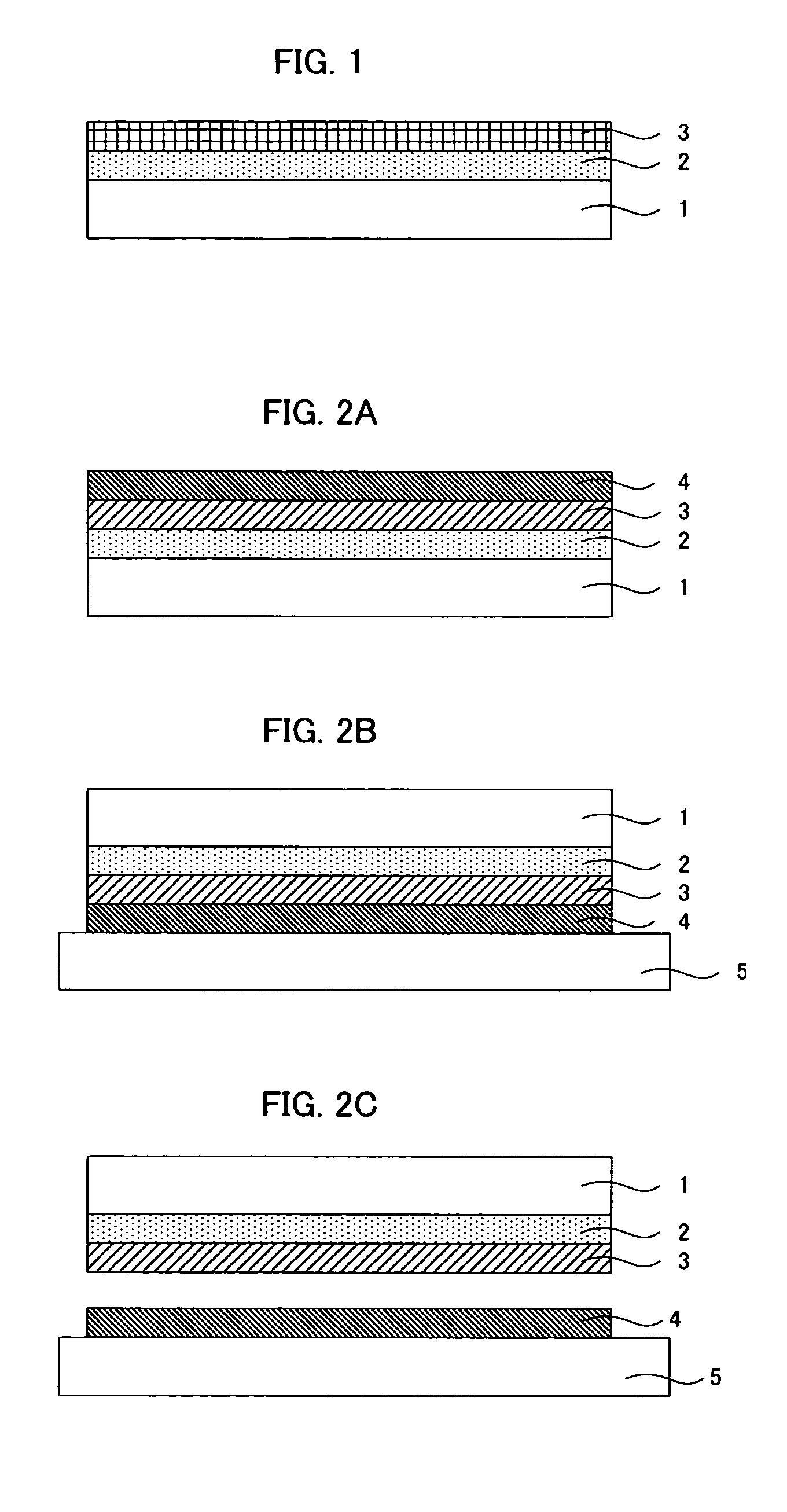
Cell construct for cell transplantation and cell aggregate for cell transplantation
An object of the present invention is to provide a cell construct for cell transplantation capable of having a thickness suitable for cell transplantation, preventing the necrosis of transplanted cells, and forming blood vessels in the transplantation site after transplantation. The present invention provides a cell construct for cell transplantation which comprises polymer blocks having biocompatibility and cells of at least one type, wherein the plural polymer blocks are arranged in spaces between the plural cells.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
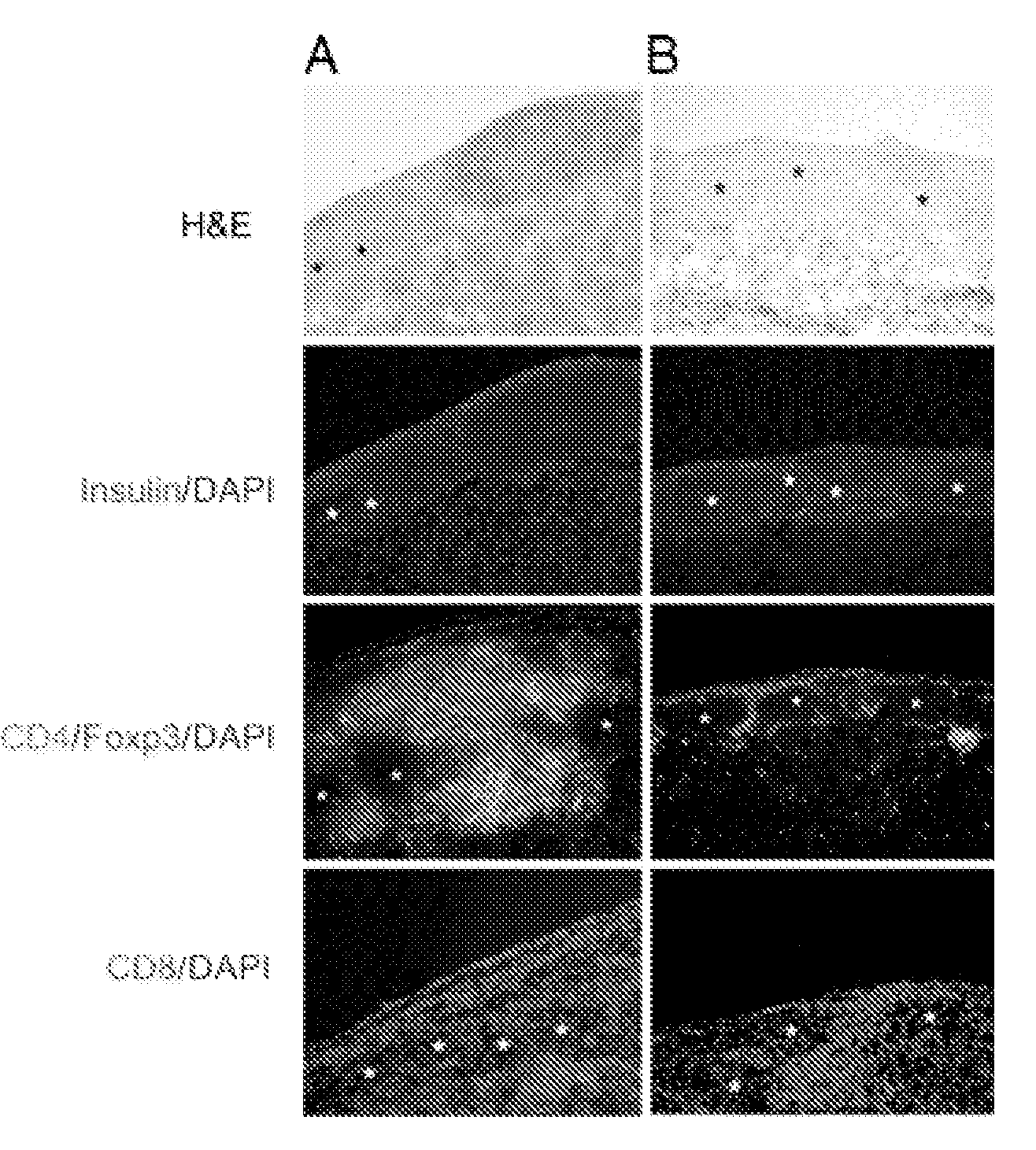
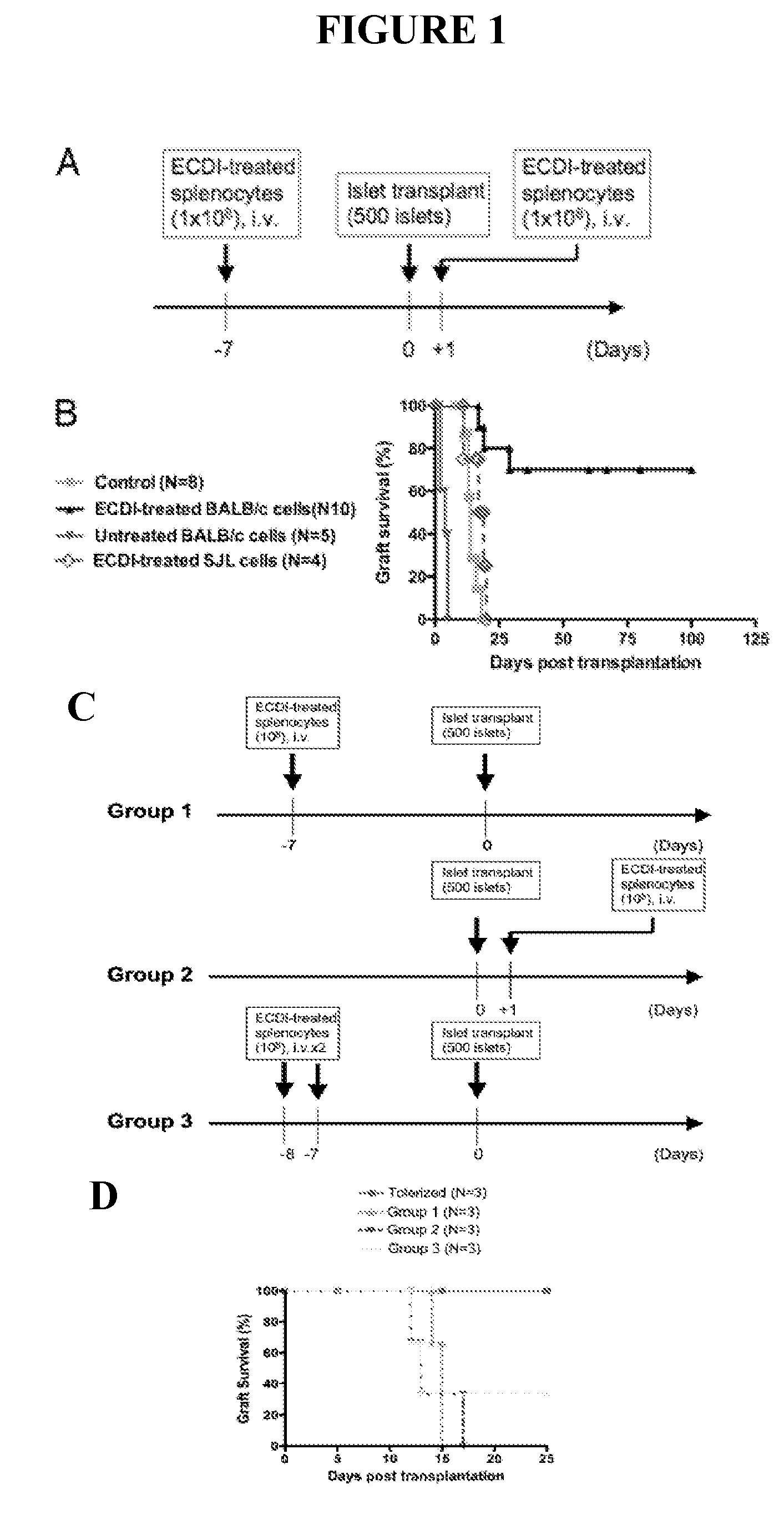
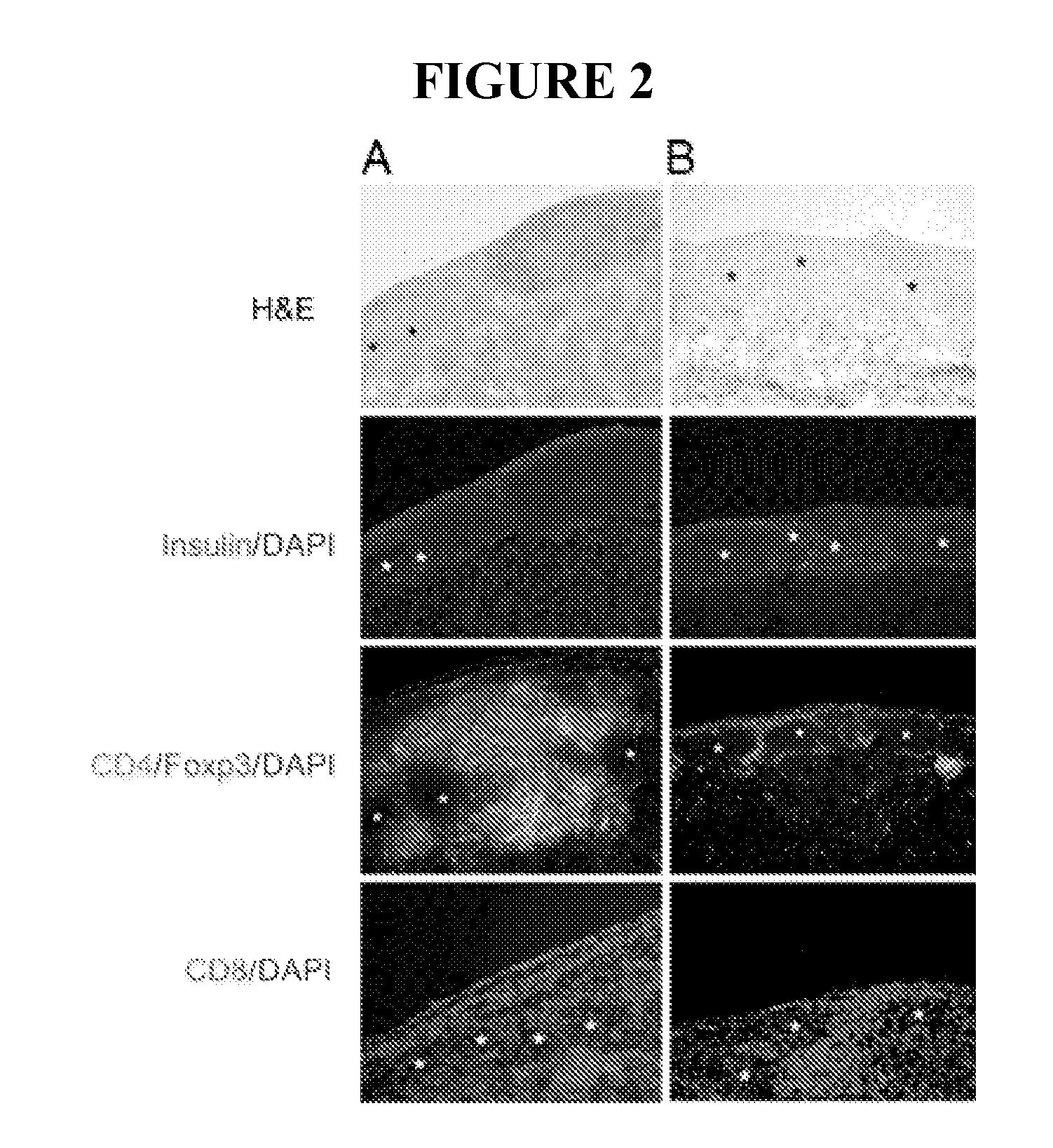
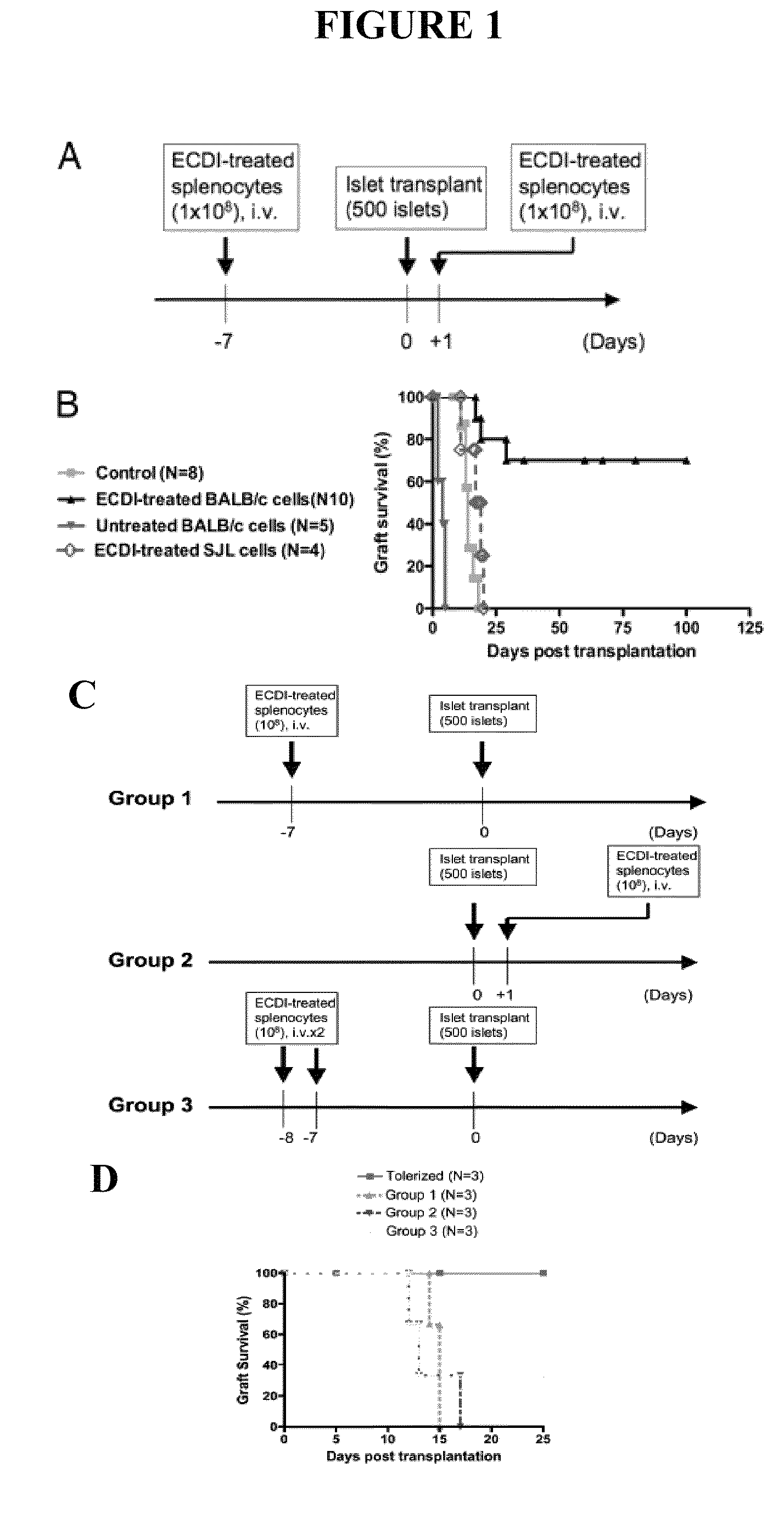
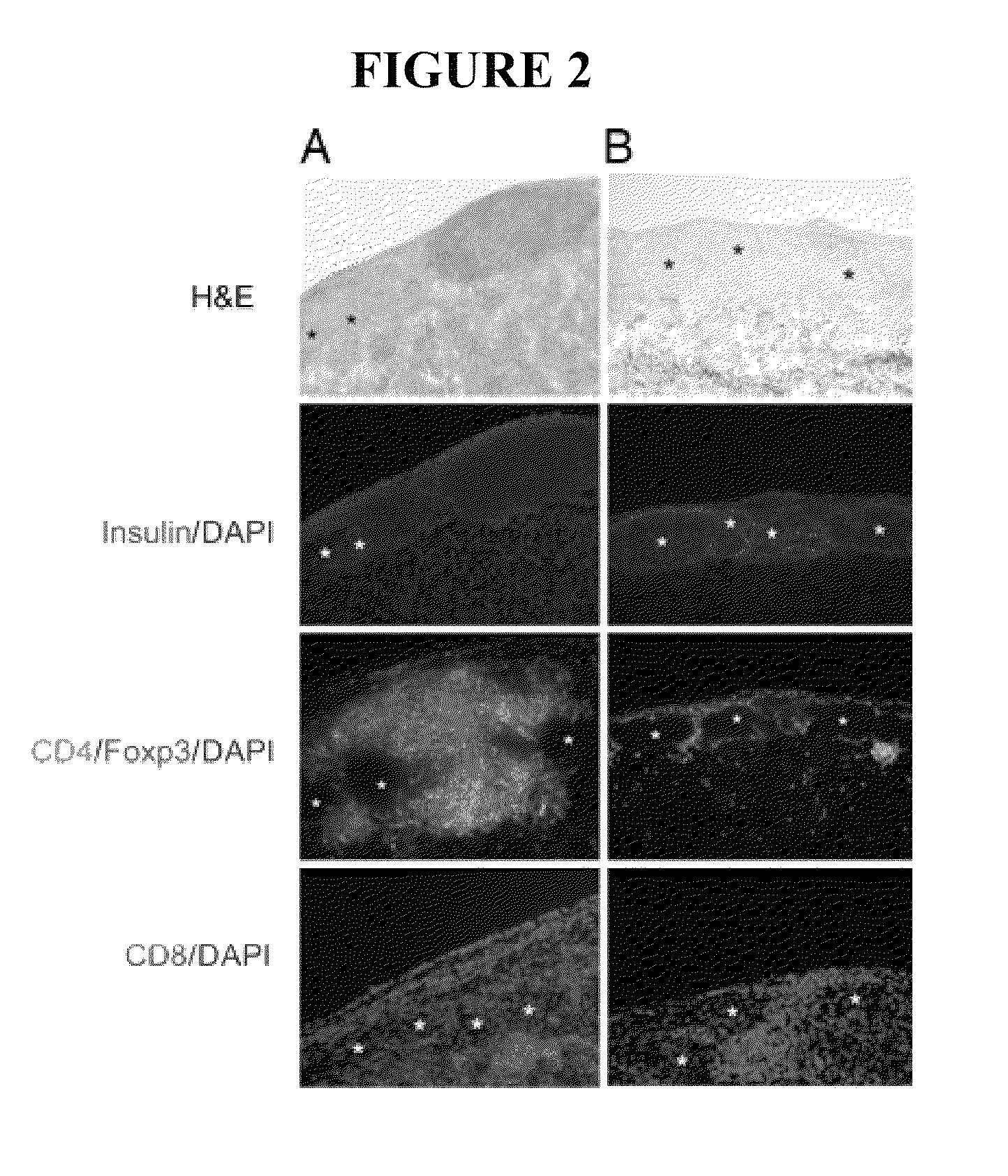
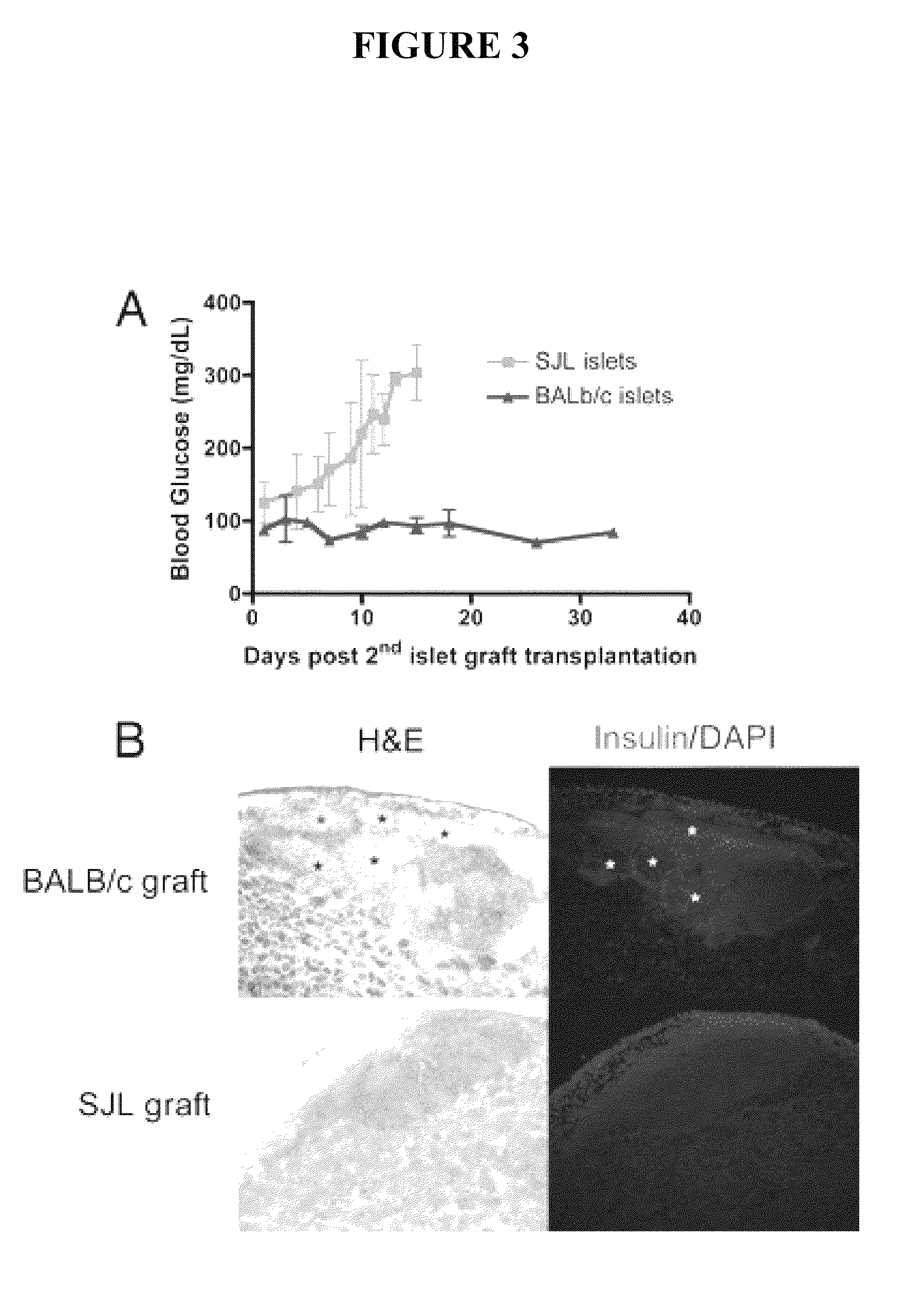
Use of ecdi-fixed cell tolerance as a method for preventing allograft rejection
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Formulation to improve survival of transplanted cells
The survival of cells during transplantation is enhanced. Cells to be transplanted are administered in a formulation that provides two ore more survival enhancing factors. Optionally, prior to administration, the cells are cultured in the presence of factors that enhance survival, and may be heat shocked prior to transplantation.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Tissur engineering blood vessel and method of construction in vitro
InactiveCN1718172AImprove adhesionAdjustable three-dimensional structureBlood vesselsBlood vessel featureBiology
A histoengineered blood vessel features that its internal and external layers are made of the composite superfine fibre membrane and different cells are transplanted in different layers. Said composite superfine fibre membrane is composed of a core made of natural or artificial biodegradable material and the shell layer made of natural biodegradable material. Its external construction method includes such steps as preparing scaffold step by step, transplanting cells layer by layer, and integrally shaping.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
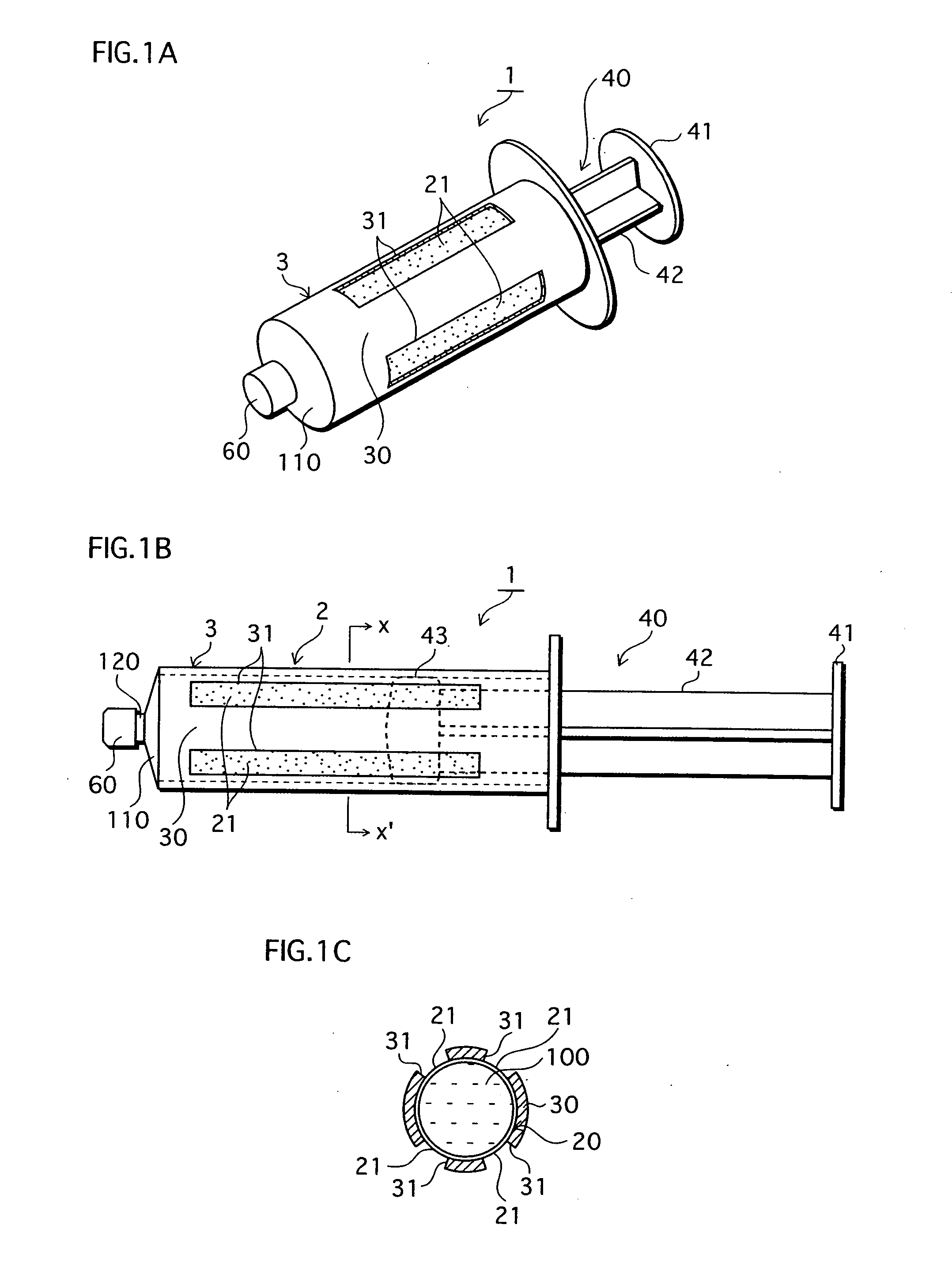
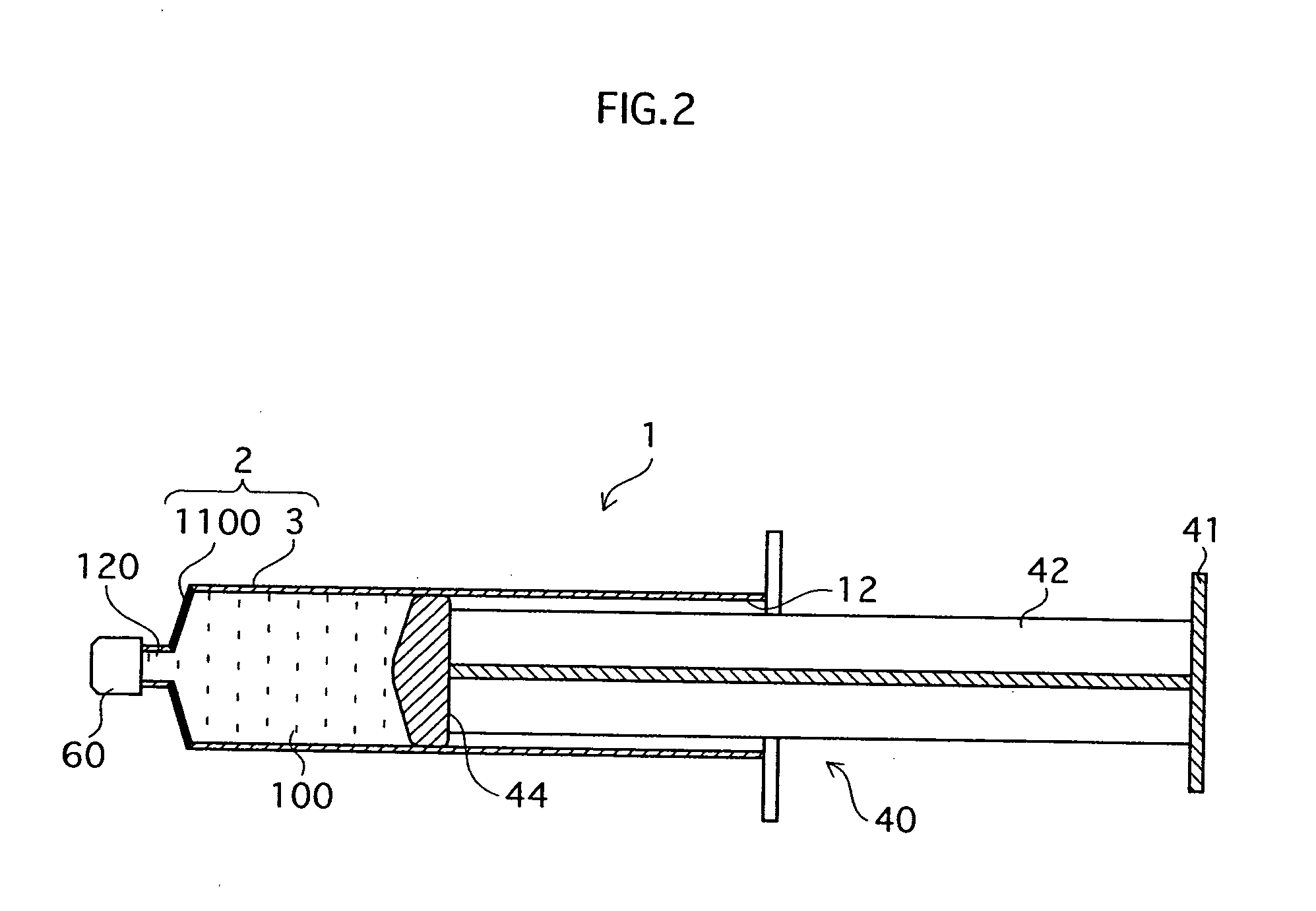
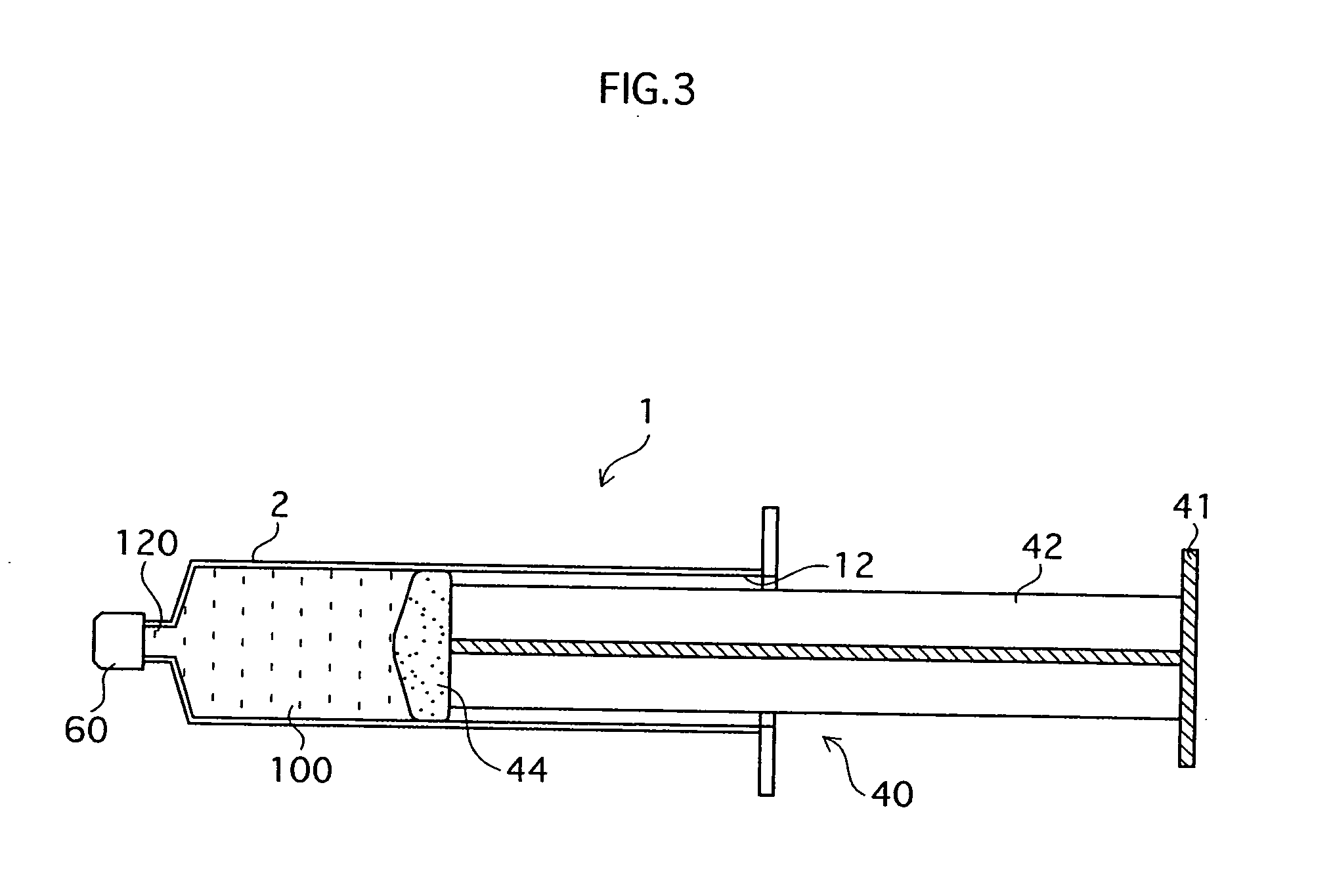
Cell handling device, human tissue regeneration composition, and human tissue regeneration method
InactiveUS20070020754A1Easy injectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNervous disorderHuman bodyCultured cell
The main objects of the present invention, which relates to regenerative medical treatments, are to enable (i) storage and conveyance of harvested or cultured cells without contamination occuring (ii) simple injection of the cells into a living body. To achieve these objects, cells harvested from a living body, or cells obtained by culturing harvested cells, are stored in a syringe-type storage vessel and subsequently transplanted into a living body. It is preferable that at least a part of the storage vessel inner wall in contact with the cells is formed from a cell non-adhesive material. Besides enabling cells in the vessel to take in the oxygen they require to survive, the present invention also enables cells quick and easy transplantation of cells into a living body without a cell detachment process, because cells are prevented from adhering to the inside of the vessel. Further, it is preferable that a stored tissue regeneration composition contains cell culture microcarriers floating in a fluidity medium, and that the cell culture microcarriers are composed of a bioabsorbable material and have cells adhering to their surfaces. Using this kind of tissue regeneration composition, a regenerative treatment can be carried out satisfactorily by simply and quickly transplanting cells from the syringe-type cell storage vessel into a living body without intricate scaffold-related procedures being required.
Owner:JMS CO LTD
Method of providing a dynamic cellular cardiac support
The present invention provides a method for repairing damaged myocardium. The method comprises using a combination of cellular cardiomyoplasty and electrostimulation for myogenic predifferentiation of stem cells and to synchronize the contractions of the transplanted cells with the cardiac cells. The method comprises the steps of obtaining stem or myogenic cells from a donor, culturing and electrostimulating the isolated cells in vitro, and implanting the cells into the damaged myocardium.
Owner:BIOHEART
Cellular transplantation for heart regeneration
InactiveUS20050244384A1Improved integration and survivalHighly integratedBiocideGenetically modified cellsProgenitorDisease
Myoblast cells obtained by culturing, particularly from satellite cells or other progenitor cells, are transplanted into tissue such as diseased heart tissue to form healthy repair tissue and reverse disease. This technique can be carried out in various ways and preferably includes a cellular integration factor to assist cellular survival, integration and longevity into the treated organ. Angiogenesis factors such as vascular endothelial growth factor are particularly preferred and may be transgenically expressed by the transplanted cell. Other factors that may be used to augment the procedure include migratory and scaffolding molecules. The methods and materials are particularly useful in combination with an automated cell processor and an automated catheter delivery system. The materials and methods for their use may be applied to the prophylaxis and therapy of damaged hearts, using cells originally obtained from the patient, another human, or another animal.
Owner:LAW
Systems and Methods for Tissue Processing and Preparation of Cell Suspension Therefrom
ActiveUS20160024450A1Accelerate tissue processing/disintegrationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEpitheliumMammalian tissue
The present invention provides for methods and at least partially automated devices suitable for producing a transplantable cellular suspension of living tissue suitable for promoting tissue regeneration in an epithelium-related procedure, as well as compositions produced therefrom. Tissue regeneration in humans is extremely limited and constitutes a major challenge to the repair of damaged organ function. Wound treatment is a typical area where tissue regeneration is required. Wounds (lacerations or openings) in mammalian tissue can result in tissue disruption and coagulation of the microvasculature at the wound face.
Owner:AVITA MEDICAL LTD
Method of increasing retention, survival and proliferation of transplanted cells in vivo
InactiveUS20080089867A1High retention rateConducive to survivalBiocideArtificial cell constructsOrgan systemTissues types
A method of increasing retention, survival and proliferation of transplanted cells in diseased or damaged tissue types or organ by providing transplanted cells with autologously-derived platelet cells and forming a autologously-derived platelet gel prior or during administration to the tissue type or organ through a delivery device and immobilizing the transplanted cells in the tissue type or organ system.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
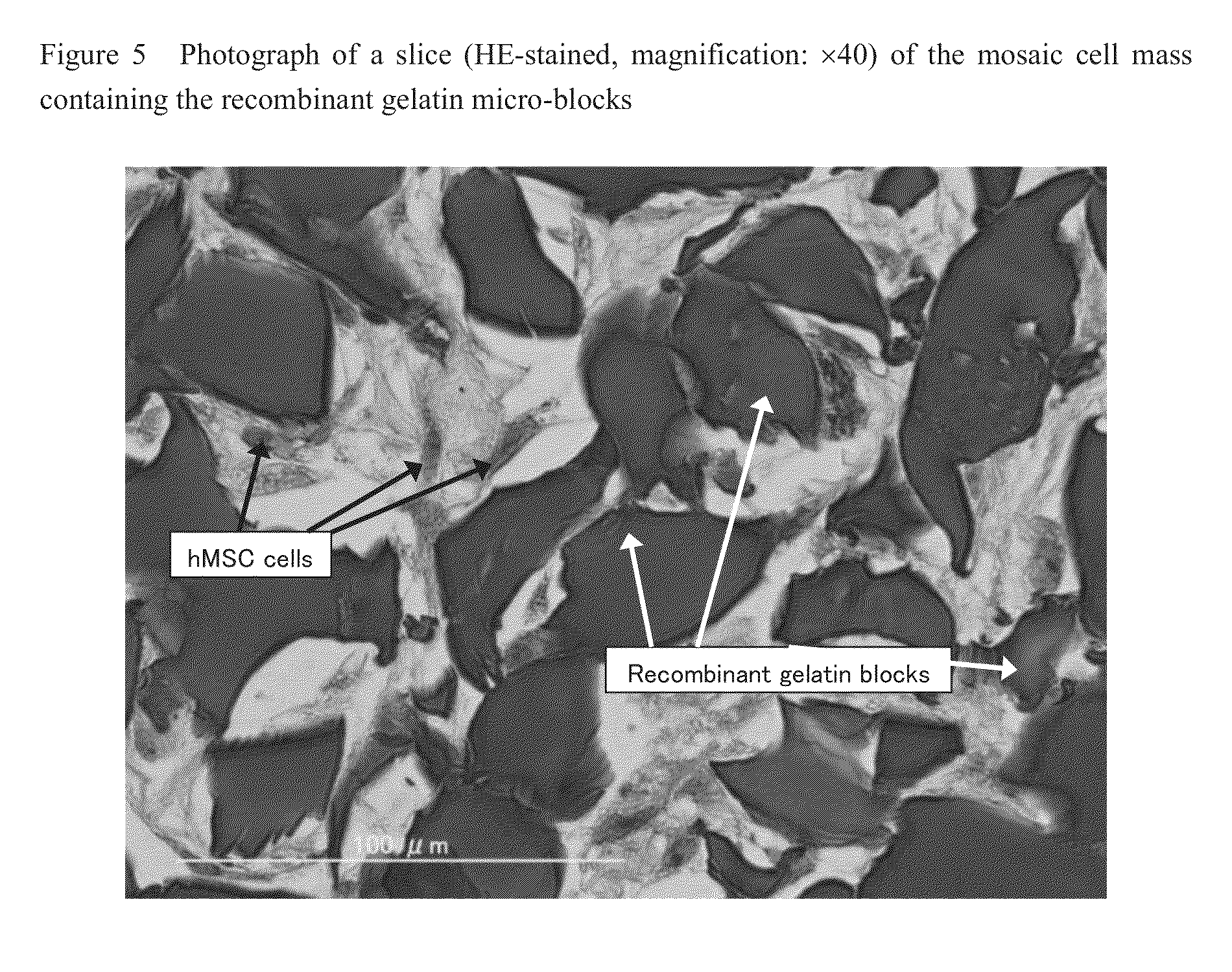
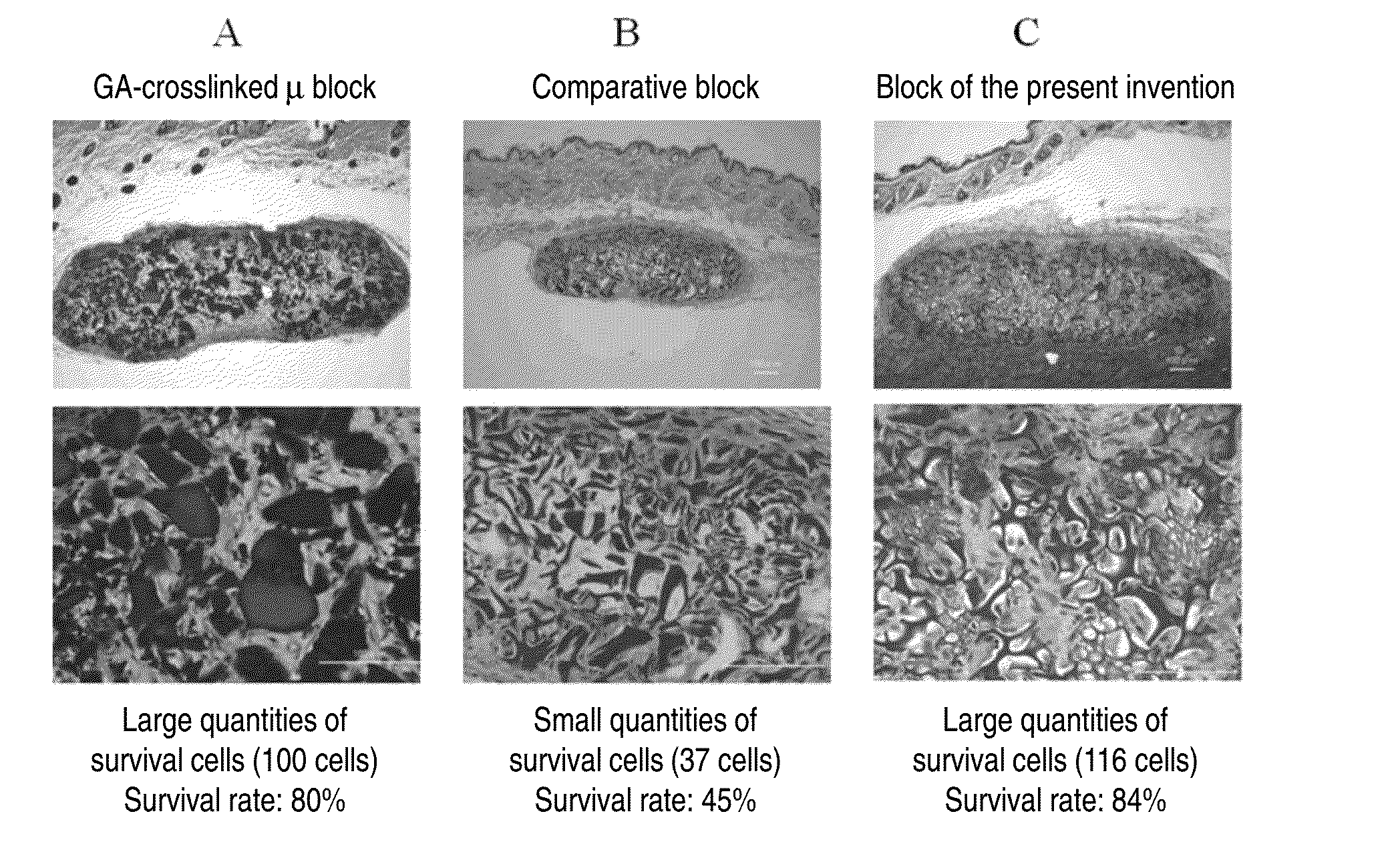
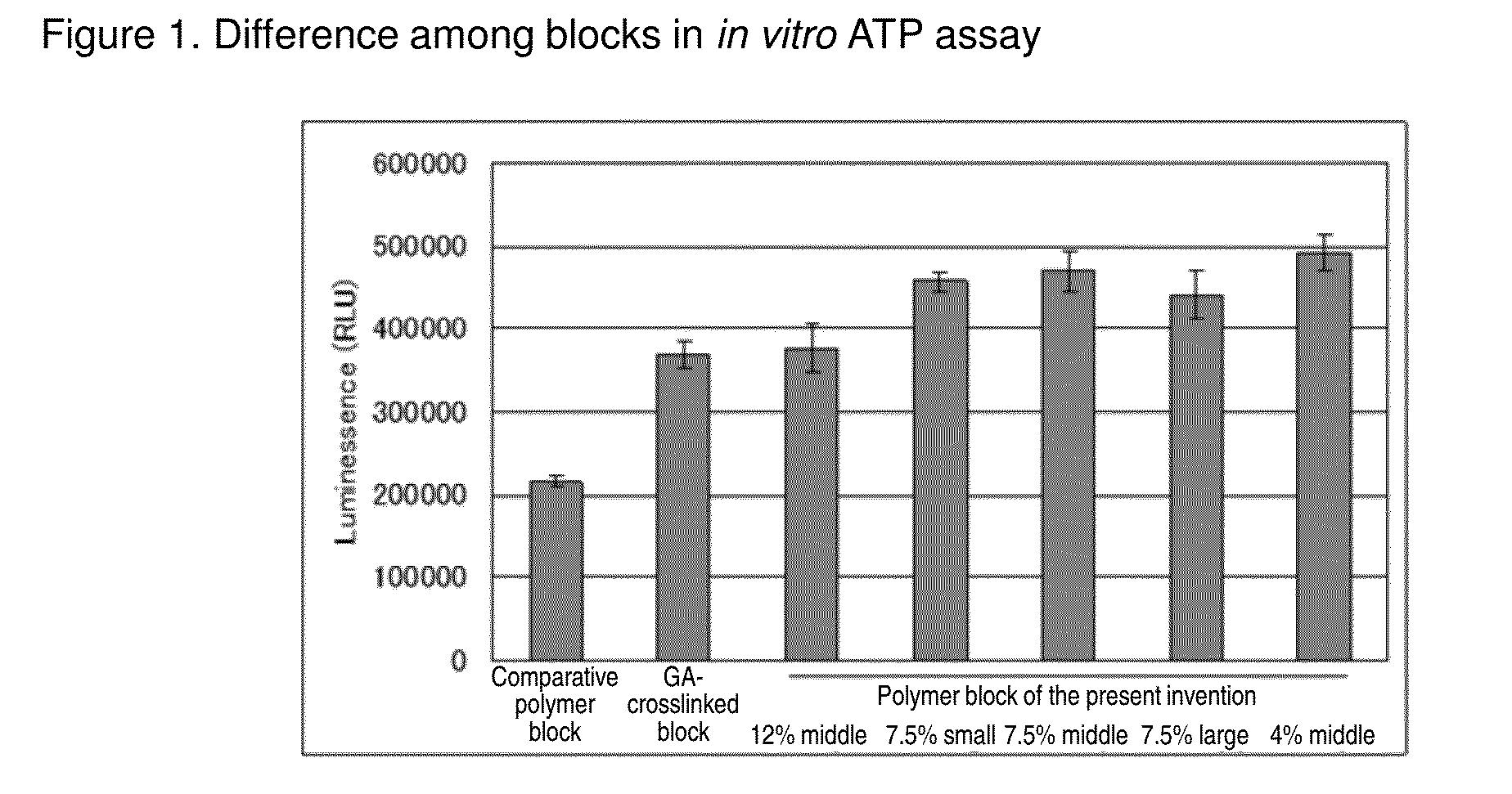
Cell construct for cell transplantation, biocompatible polymer block, and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20150352252A1Suppress the necrosis of the transplanted cellsConducive to survivalBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHigh cellCytotoxicity
It is an object of the present invention to provide a cell construct for cell transplantation that does not contain a substance having cytotoxicity, such as glutaraldehyde, and suppresses the necrosis of the transplanted cells in the construct (namely, having a high cell survival rate). The present invention provides a cell construct for cell transplantation comprising biocompatible polymer blocks that do not contain glutaraldehyde and at least one type of cells, wherein a plurality of biocompatible polymer blocks are disposed in gaps among a plurality of cells, and wherein the biocompatible polymer blocks have a tap density of 10 mg / cm3 or more and 500 mg / cm3 or less, or the value of the square root of the cross-sectional area / boundary length in the two-dimensional sectional image of the polymer block is 0.01 or more and 0.13 or less.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
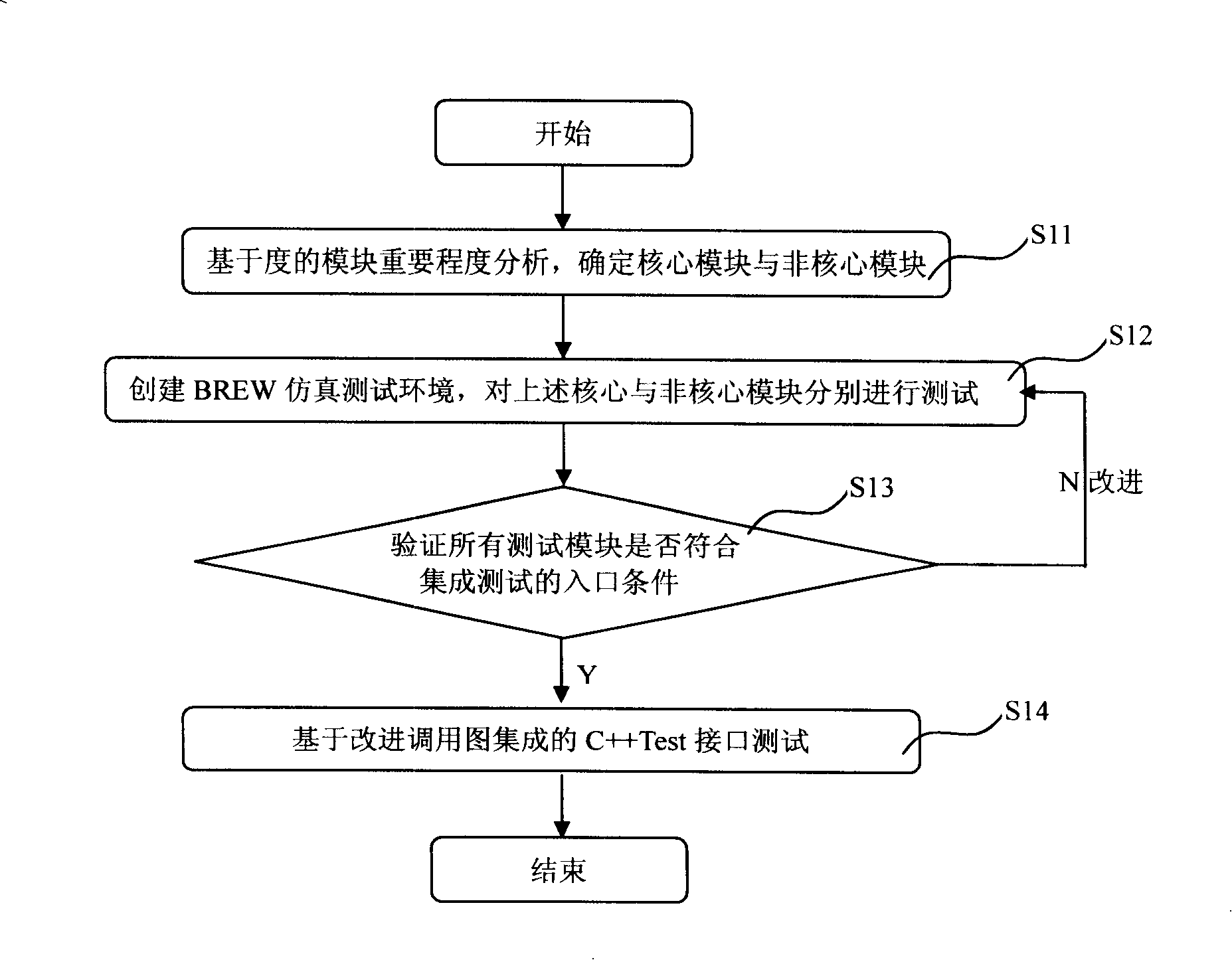
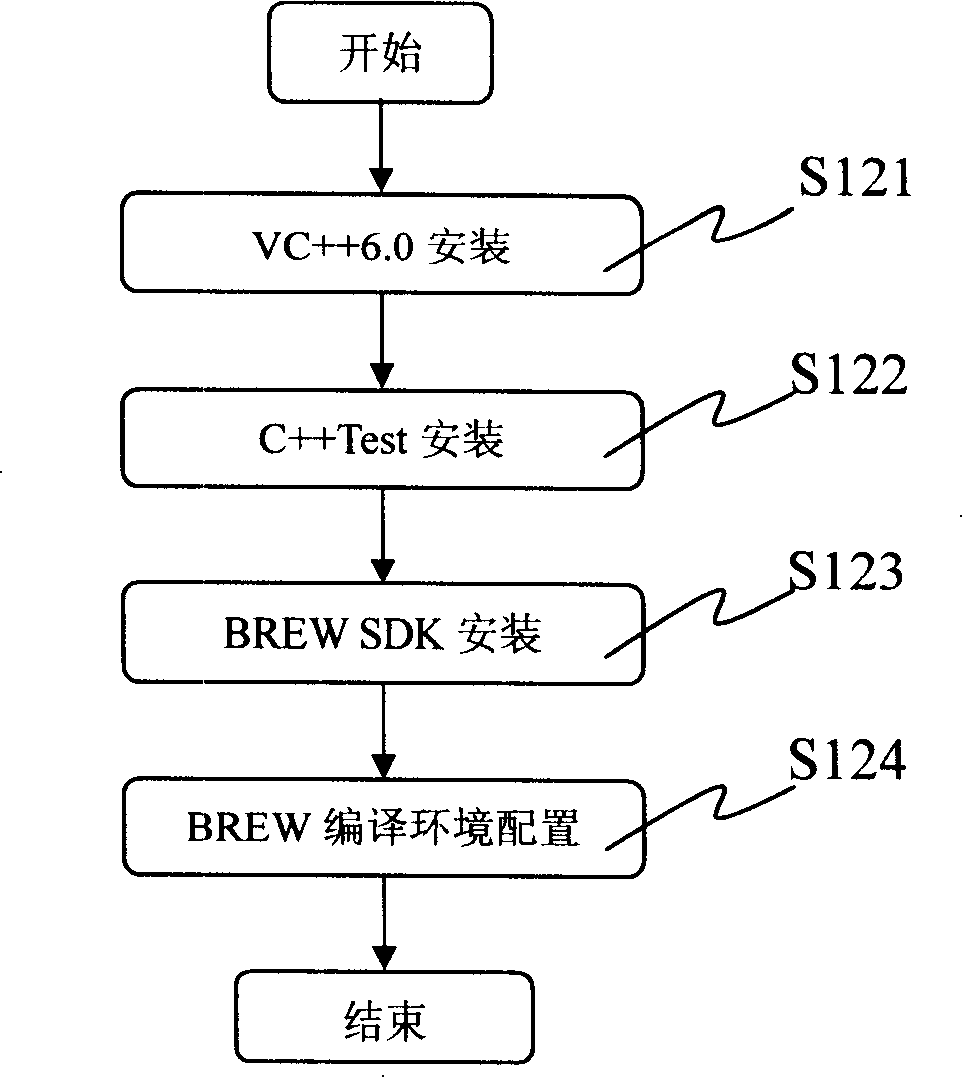
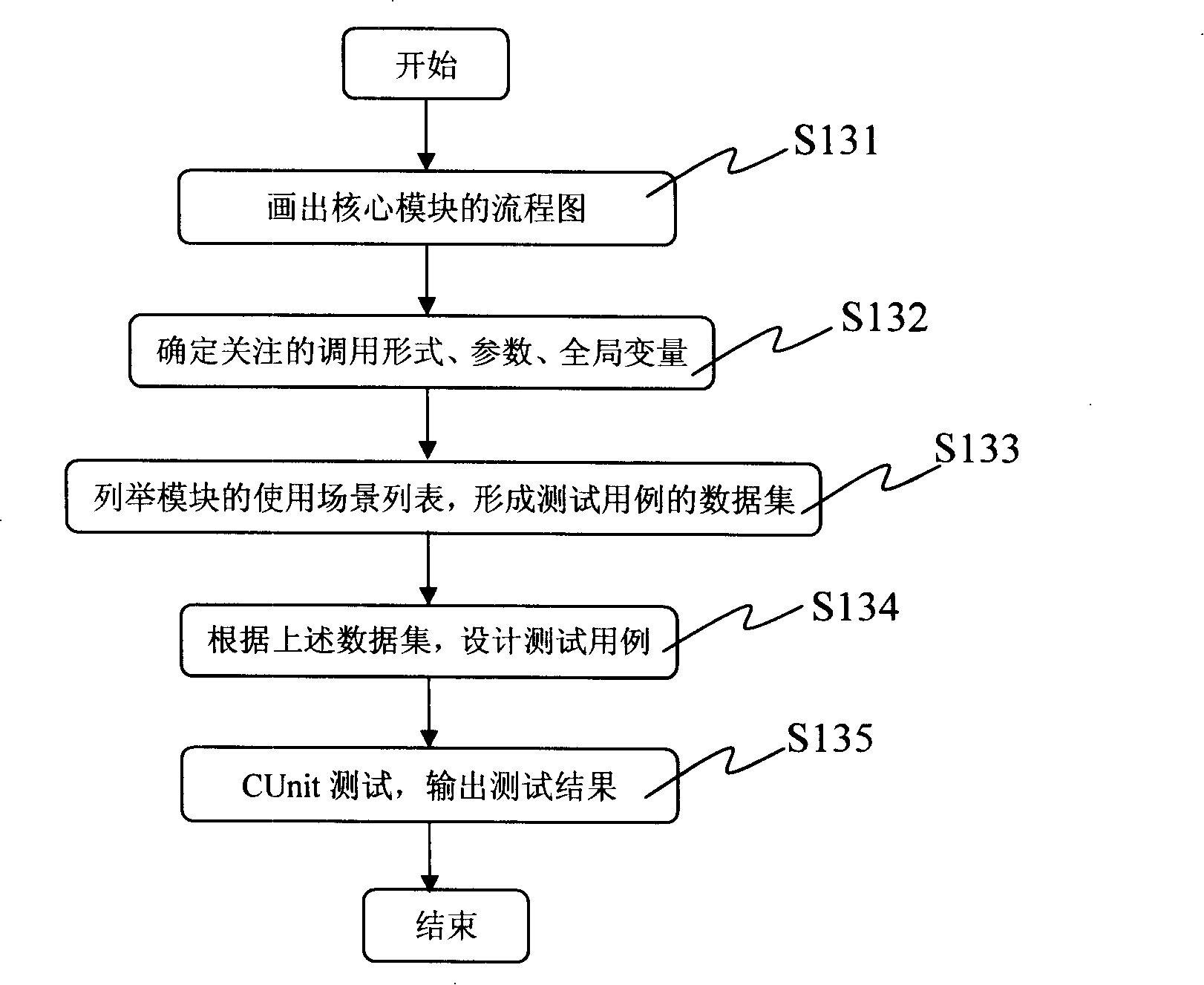
Integrated mobile telephone software test method
InactiveCN101212759AAvoiding the Difficulties of Integration TestingGuaranteed entry conditionsSoftware testing/debuggingRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsIntegration testingComputer module
The invention discloses a method for cell phone software integrated test, which is used for testing cell phone software based on BREW development platform and the invention comprises that: step 11, important degree of a module is analyzed based on degrees of functions of a software to be tested module so as to judge whether or not a module is a core module or a non-core module; step 12, in BREW emulating test environment, different test units are utilized to respectively test the core module and the non-core module; step 13, all the software to be tested modules are verified whether or not correspond to entry conditions of the integrated test according test results obtained in the step 12; step 14 is carried out to the software to be tested modules that are in line with the entry conditions; the software to be tested modules that are not in line with the entry conditions needs to be further promoted and the step 12 is carried out circularly; the step 14, the integrated test is carried out among the modules. The method of the invention properly changes and transplants cell phone software procedure that is only operated on an object machine into cell phone simulating procedure that can be operated in a computer, thus avoiding the difficulty of directly carrying out the integrated test on an embedded system of the cell phone.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Substrate for cell transfer
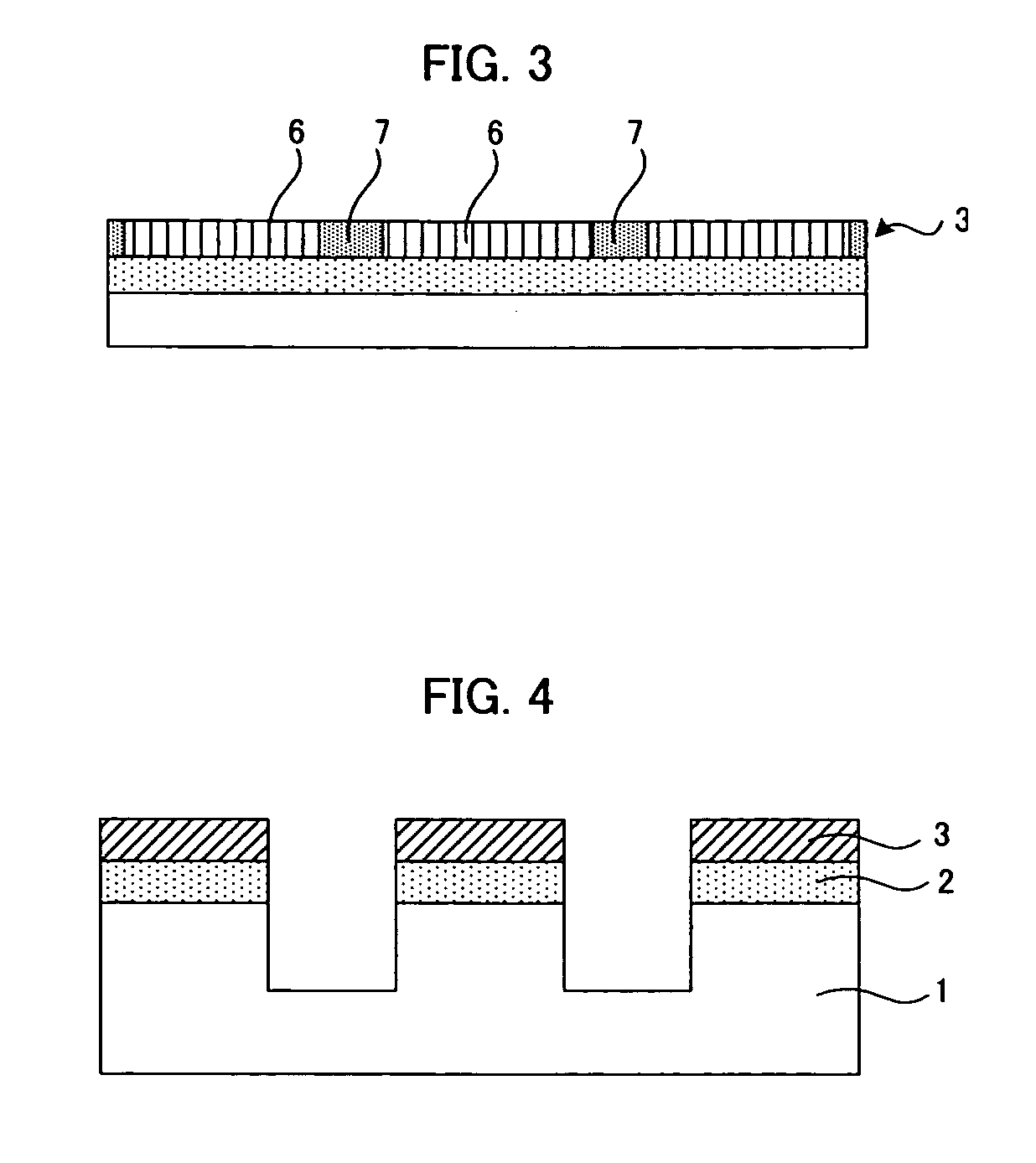
ActiveUS20070015277A1Form evenlyLow wettabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsVessel networkLymphatic vessel
A main object of the present invention is to provide a cell transfer substrate capable of transplanting cells, maintaining a pattern as it is, on a living body tissue or the like, even when: the size of the cell sheet is extremely small; the cells are cultured sparsely; the cells are in a form of a small colony; or the cells are cultured in a pattern, for example, as a blood vessel, a vessel network such as a lymphatic vessel, or a nerve network, and to provide a substrate for cell transfer to be used for the cell transfer substrate. In order to achieve the above-mentioned object, the present invention provides a substrate for cell transfer comprising: a polymer base material; an intermediate layer formed on the polymer base material; and a cell transfer layer formed on the intermediate layer.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Use of contact lens for corneal cell transplant
The present invention addresses the need for improved methods and apparatuses of transplanting cells to injured or diseased cornea. The methods disclosed provide for culture of cells on the concave surface of a contact lens, followed by application of the contact lens to the eye, thereby permitting repopulation of the corneal region by the cells. A particular use for the present invention involves the transfer of genetically altered cells.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
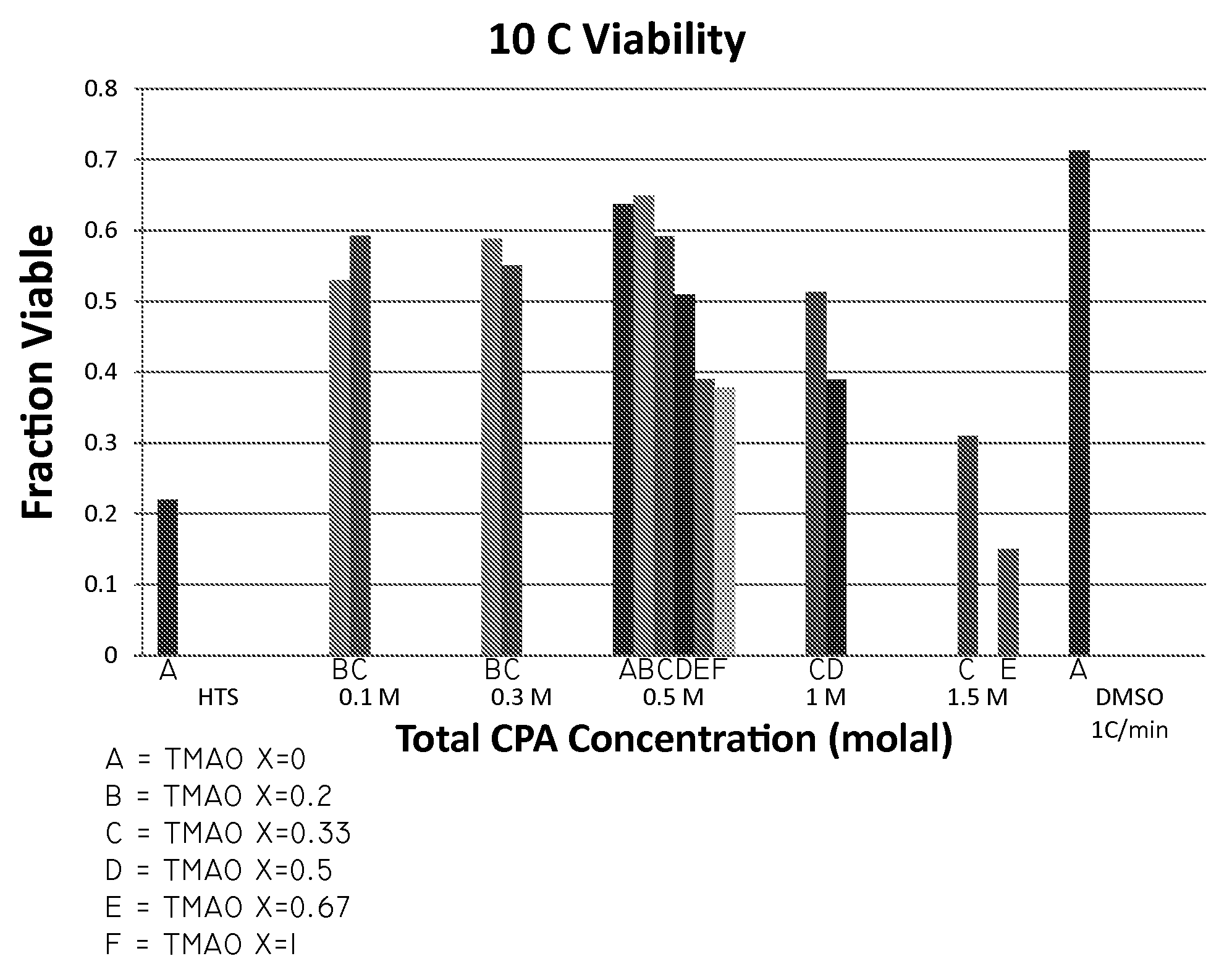
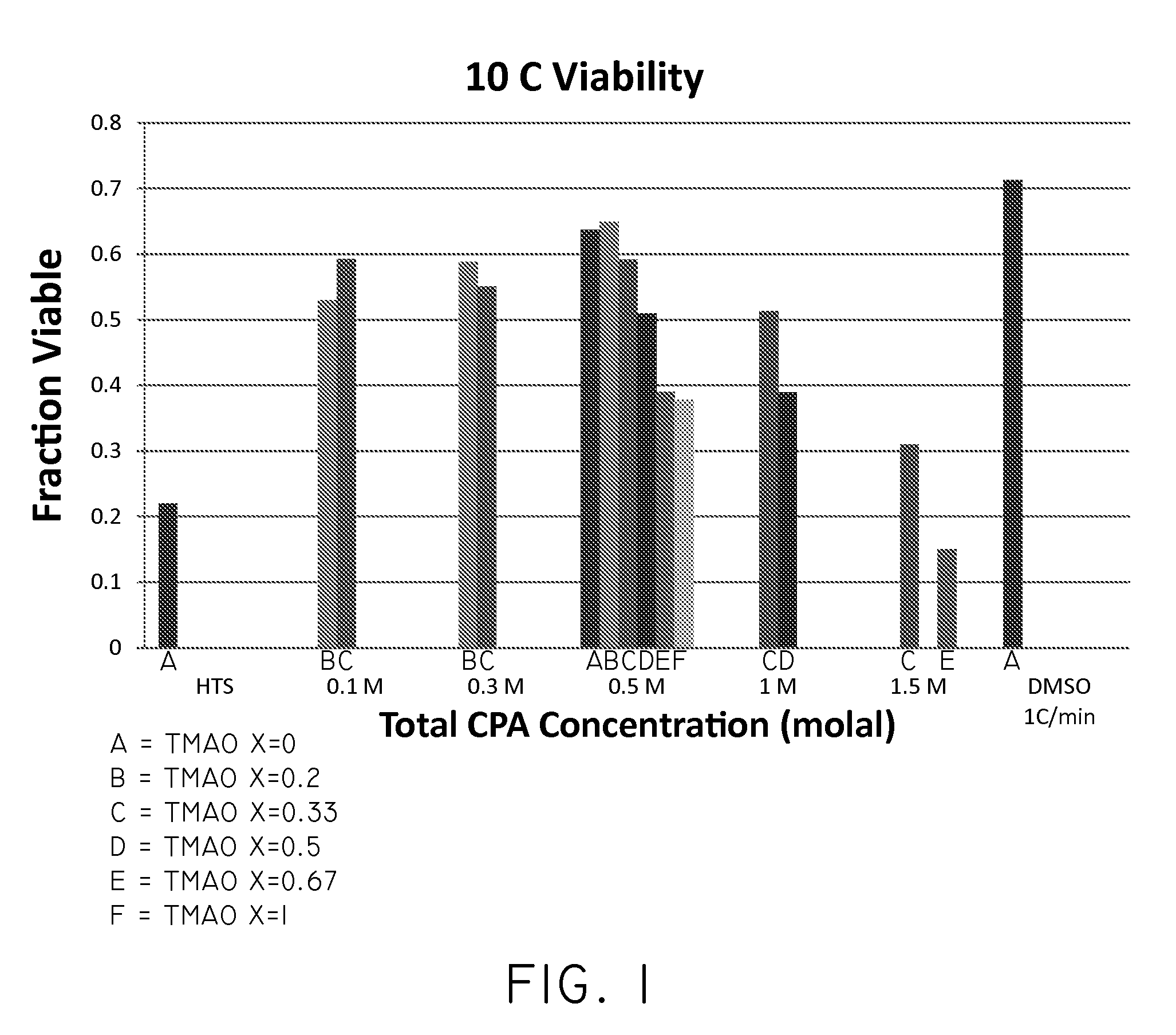
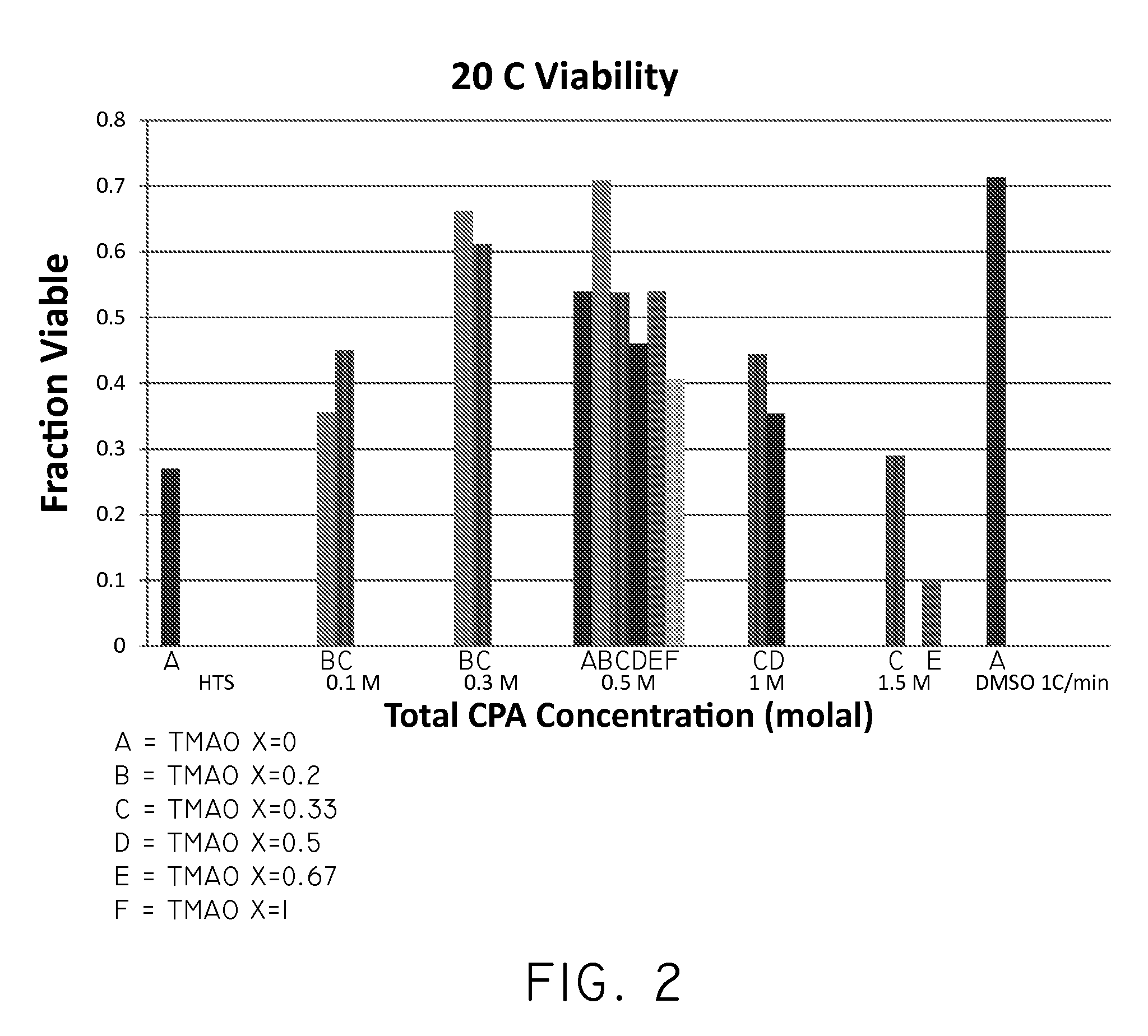
Cryopreservative compositions and methods
The invention relates to compositions for the cryogenic storage of biological materials and related methods. In an embodiment, the invention includes a cryopreservative composition including a chaotropic agent and a kosmotropic agent. In an embodiment, the invention includes a cryopreservative composition including urea and trimethylamine-N-oxide. In an embodiment, the invention includes a method of cryopreserving cells including contacting cells with a cryopreservative composition, the cryopreservative composition comprising a chaotropic agent and a kosmotropic agent. In an embodiment, the invention includes a method of transplanting cells into a subject, the method including administering a composition to the subject, the composition comprising an effective amount of a chaotropic agent, an effective amount of a kosmotropic agent, and cells. Other embodiments are also included herein.
Owner:SURMODICS INC
Method to determine an engrafting cell dose of hematopoietic stem cell transplant units
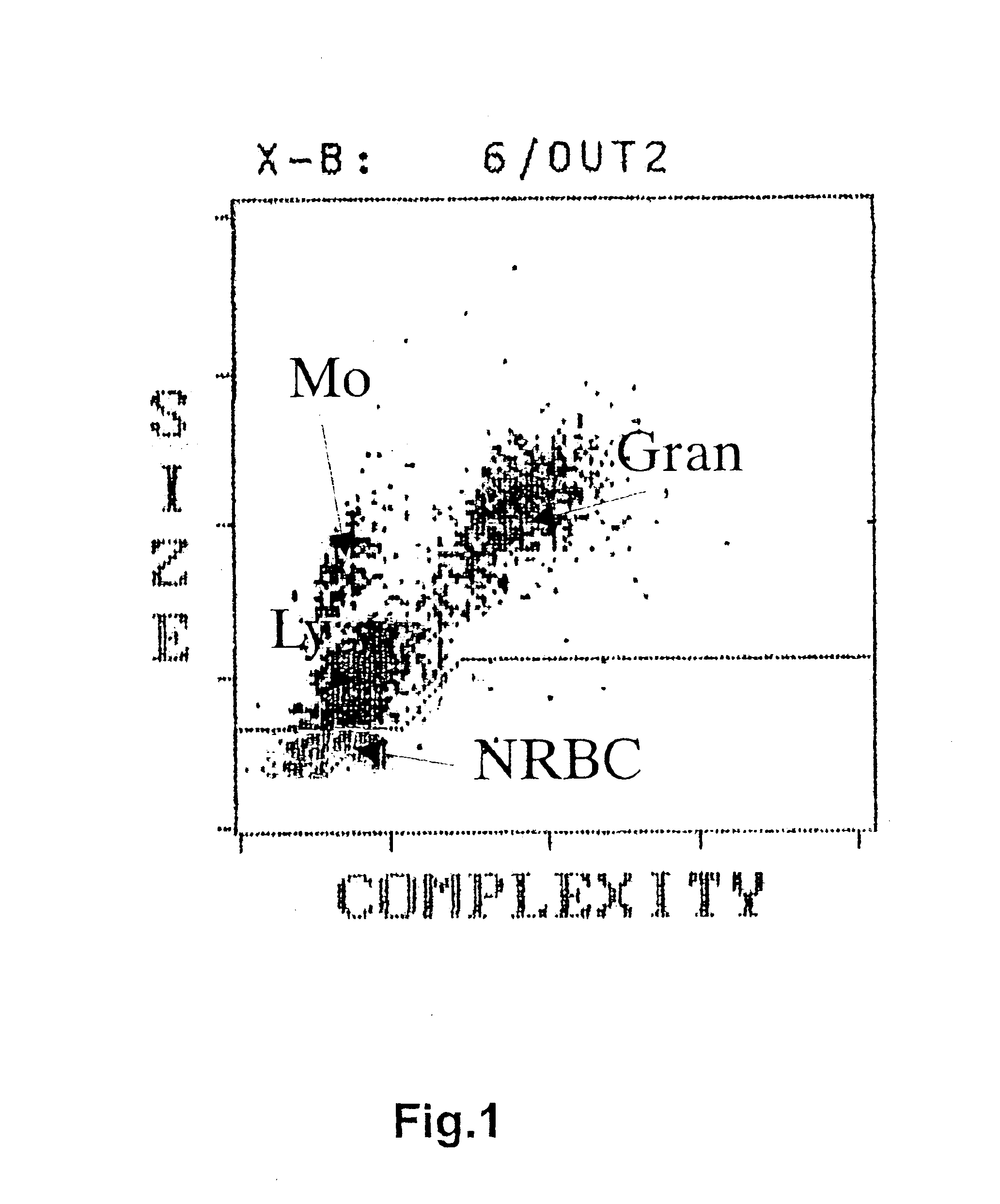
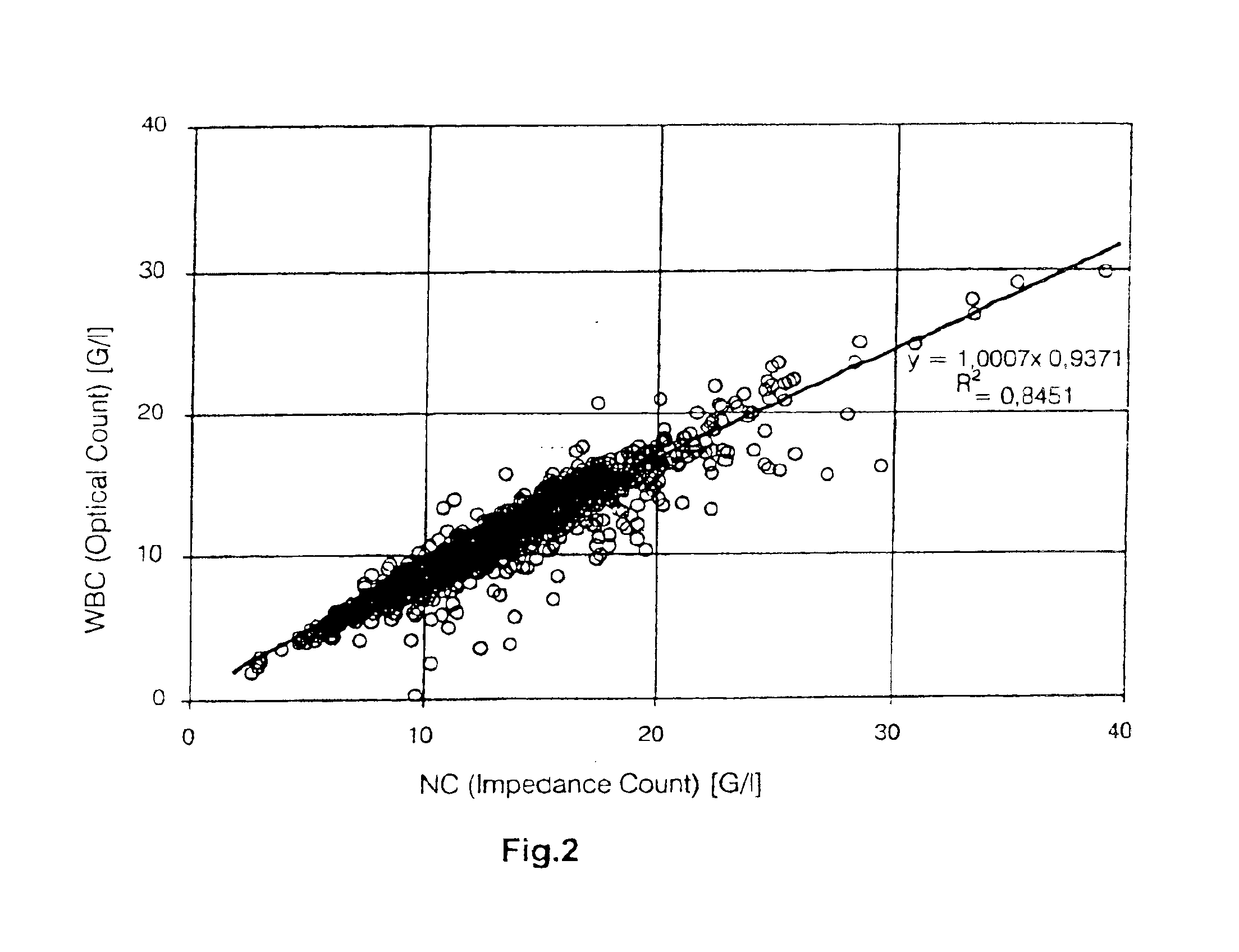
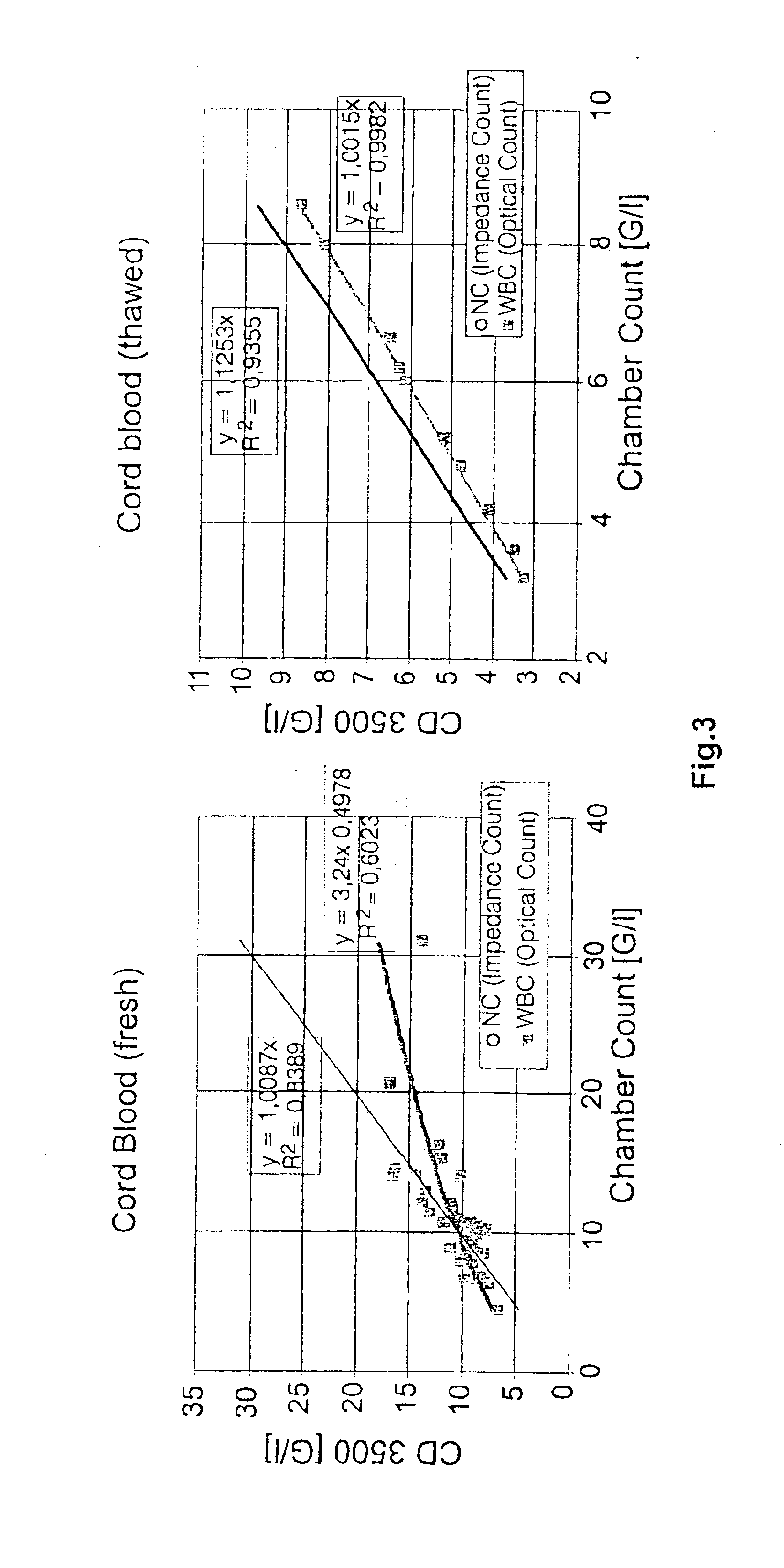
InactiveUS6852534B2Accurate assessmentAutomatically performBiocideDead animal preservationCord blood stem cellCell dose
A method to determine an engrafting cell dose of hematopoietic stem cell transplant units from transplant sources having nucleated cells selected from the group consisting of cord blood, bone marrow, peripheral blood comprising the steps of[0002]subjecting the source to a substantially complete erythrocyte lysis,[0003]measuring in a cell counter a signal corresponding selectively to white blood cells,[0004]assessing essentially quantitatively nucleated red blood cell (NRBC) count as part of the total nucleated cell (NC) count,[0005]and determining the number of white blood cells (WBCs) as transplant relevant cells.
Owner:KOURION THERAPEUTICS
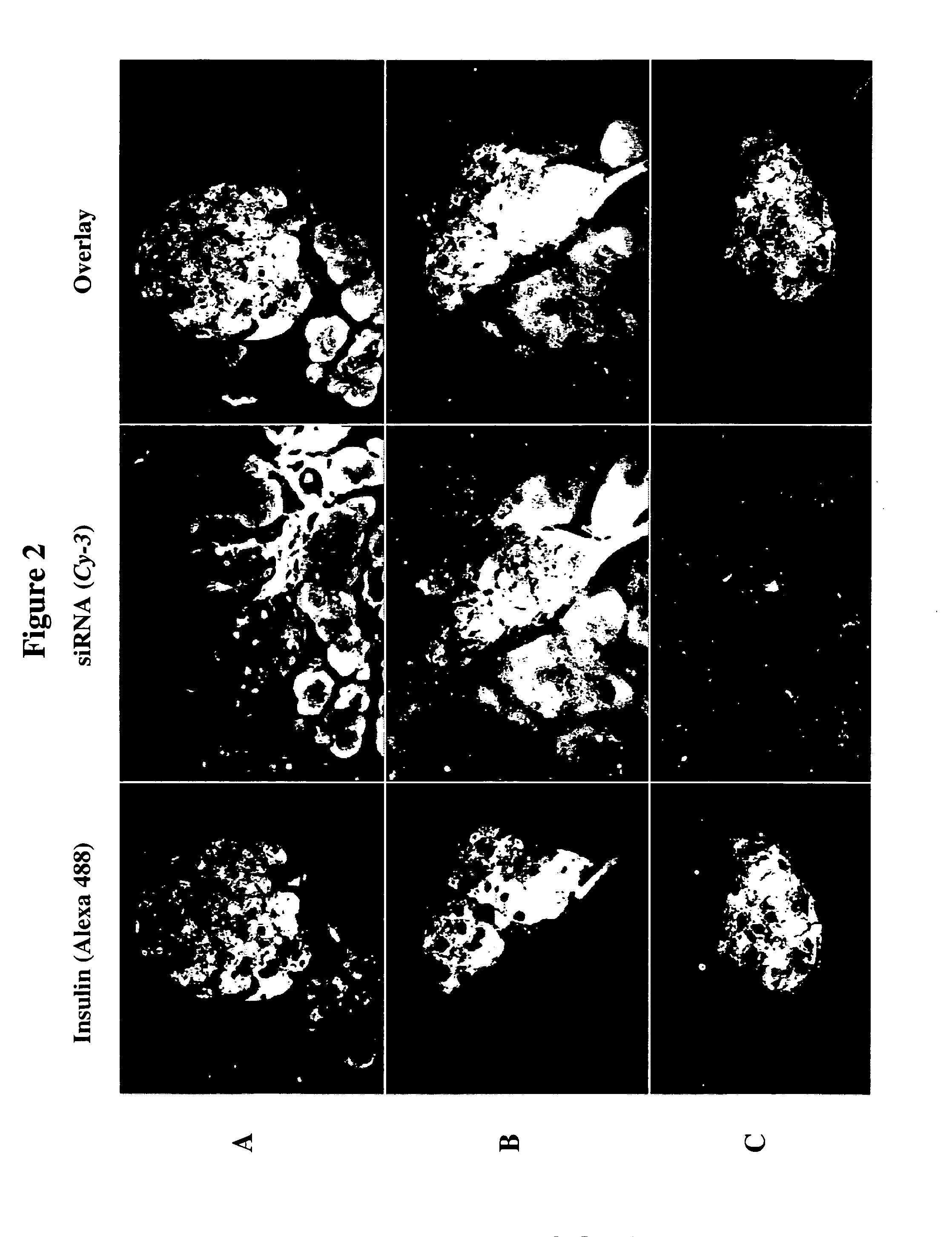
Therapeutic alteration of transplantable tissues through in situ or ex vivo exposure to RNA interference molecules
ActiveUS20060073127A1Prevent immune-mediated rejectionInhibit growthBiocideSugar derivativesApoptosisBiology
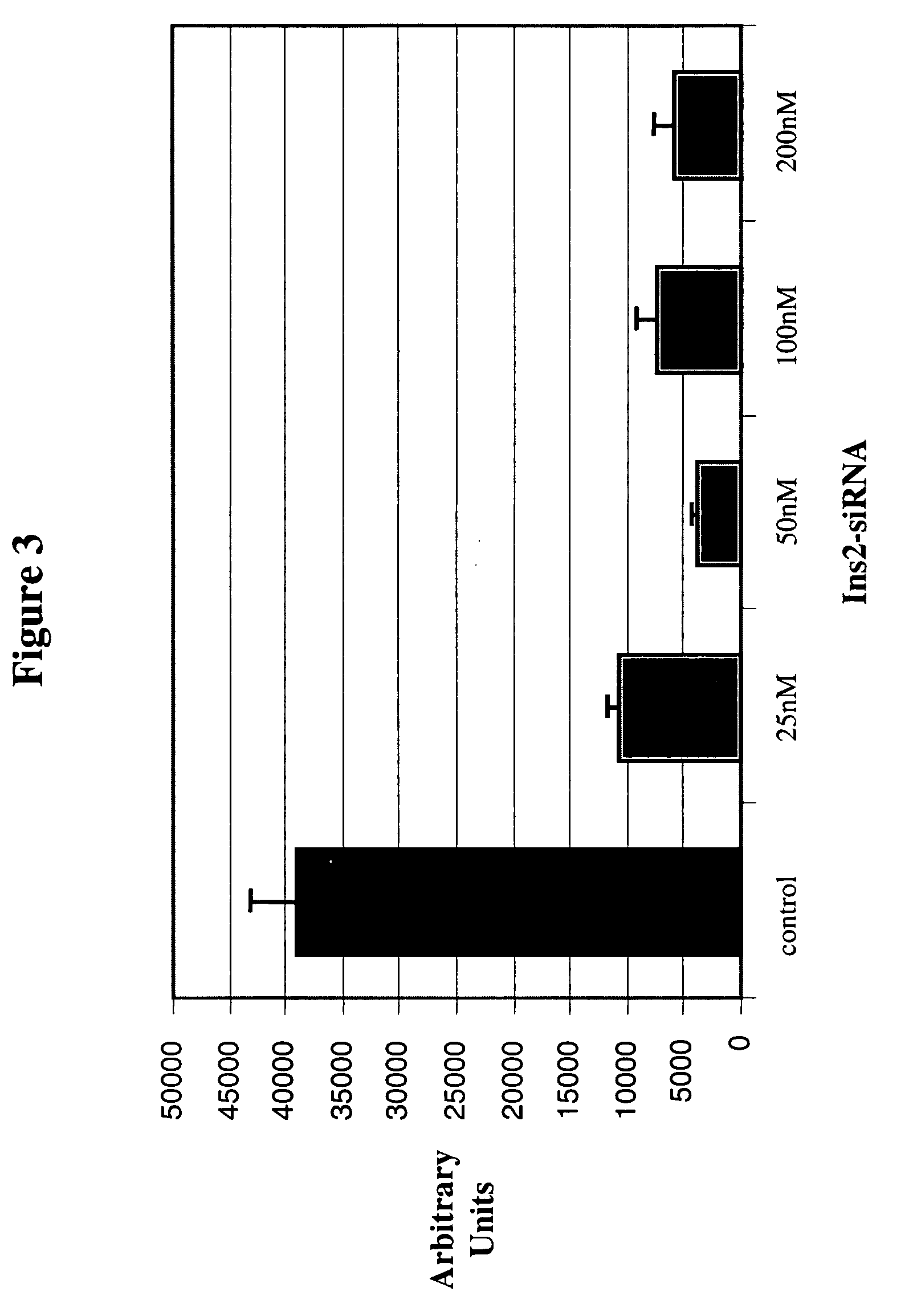
The present invention, at least in part, relates to the discovery of efficacious delivery of an RNAi agent (in preferred aspects of the invention, an siRNA) to a transplantable tissue. Organ rejection, transplantation-mediated transmission of viral infection, and triggering of apoptosis in transplanted tissues can each be minimized by the methods and compositions of the instant invention. The RNAi agent(s) of the instant invention can be delivered as “naked” molecules, or using liposomal and other modes of delivery, to transplantable tissues. Such delivery can occur via perfusion of the RNAi agent in solution through the vasculature of a whole or partial organ; or tissues including transplantable cells and cell lines may be bathed, injected or otherwise treated with RNAi agents. Preferred transplantable tissues include, for example, pancreas, liver, kidney, heart, lung, and all cells and cell lines derived from such tissues (e.g., pancreatic islet cells that may, e.g., be transplanted as a treated population).
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Imaging methods for visualizing implanted living cells
InactiveUS20090209831A1Reduce intensityUseful and rapid responseDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsNon destructiveLiving cell
A method is provided herein for indicating viability of cells grown on a rejection inert tissue cytoarchitecture or scaffolding with a medical device that supports at least one sensing function comprising:non-destructively observing a region of a patient to where cells have been transplanted;guiding the medical device to said region of a patient using the non-destructive observation;positioning said medical device within said region of a patient using the non-destructive observation to assist in the positioning;sensing a property within said region of a patient that is indicative of cell viability or nonviability; andusing data from sensing said property within said region to indicate cell viability from a transplant with the region. Magnetic Resonance Imaging is a particularly useful format for non-destructive observation of the region.
Owner:NEXGEN MEDICAL SYST
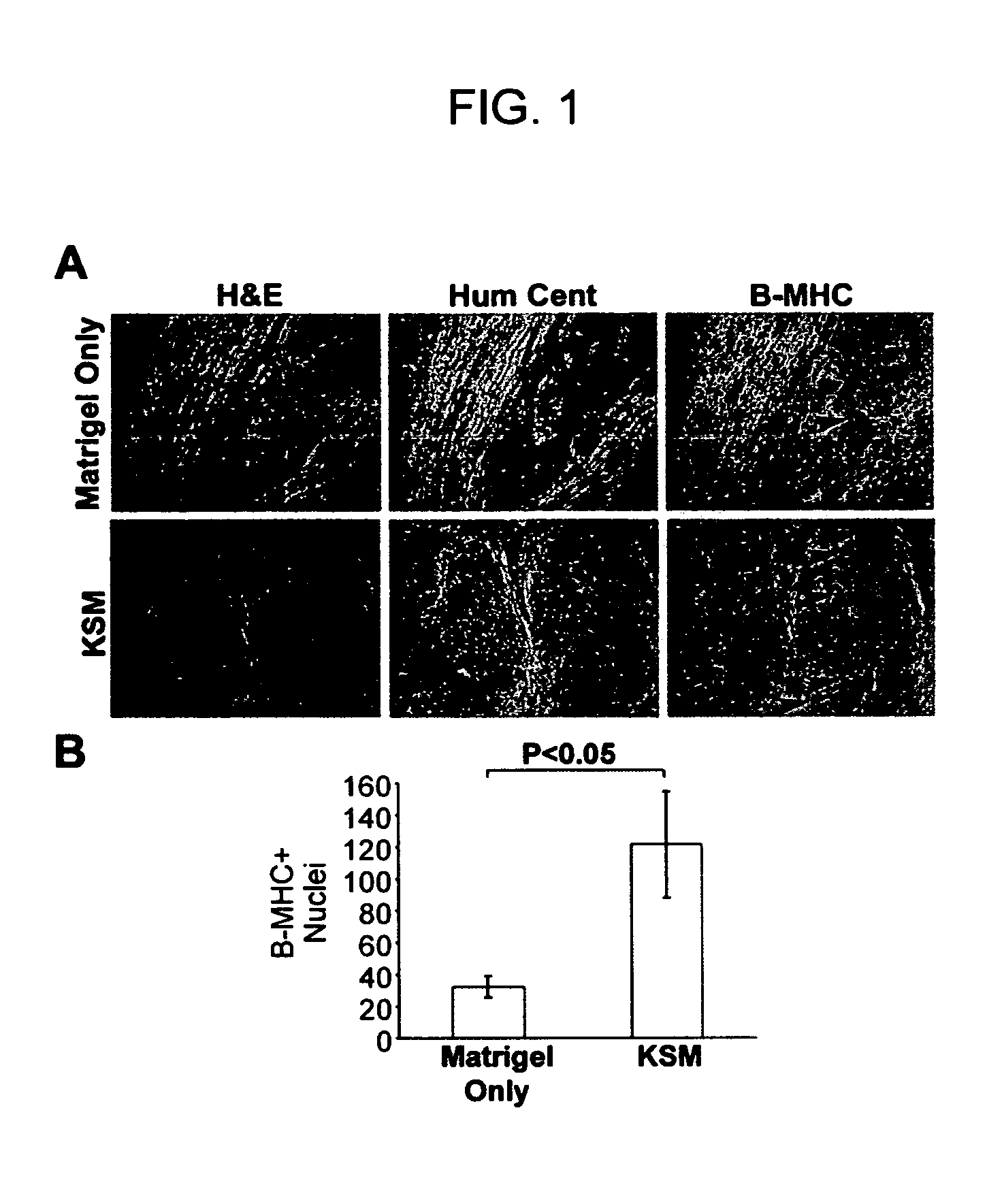
Use of ECDI-fixed cell tolerance as a method for preventing allograft rejection
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Bank of stem cells for producing cells for transplantation having HLA antigens matching those of transplant recipients, and methods for making and using such a stem cell bank
Methods for producing stem cell banks, preferably human, which optionally may be transgenic, e.g., comprised of homozygous MHC allele cell lines are provided. These cells are produced preferably from parthenogenic, IVF, or same-species or cross-species nuclear transfer embryos or by dedifferentiation of somatic cells by cytoplasm transfer. Methods for using these stem cell banks for producing stem and differentiated cells for therapy, especially acute therapies, and for screening for drugs for disease treatment are also provided.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
Integrated system for collecting, processing and transplanting cell subsets, including adult stem cells, for regenerative medicine
ActiveCN101146559AAccurate collectionReduce the risk of contaminationNervous disorderOther blood circulation devicesTissue repairAdult stem cell
A system for the extraction, collection, processing and transplantation of cell subsets, including adult stem cells and platelets, in particular for tissue repair in regenerative medicine, comprises a set of disposable fluid- transport elements that are pre-connected or that include aseptic connectors for making interconnections between them in an aseptic manner or are adapted to be aseptically connected. The set usually includes three kits of disposable sterile elements, a collection kit, a processing kit, and a transplantation kit packaged in a blister pack on a support such as a tray, having one compartment for receiving each inter-connectable kit of the set. The set includes an extracting device, for example including a needle for bone puncture or vein puncture, for extracting bone marrow or other sources of cell subsets from a patient.
Owner:BIOSAFE SA
Composition for Transplantation Comprising Adipose Stem Cells or Adipocytes
InactiveUS20100028310A1Increase volumePromote volumetric growthBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsMedicineThrombin activity
The present invention relates to a composition for transplantation in a physiologically compatible buffer solution comprising, (a) a transplant-cell selected among an adipose stem cell, an adipocyte, adipose tissues (fat tissue) and a mixture thereof; and (b) a semi-solid substance derived from a living body or a biodegradable substance selected among a hyaluronic acid, collagen, elastin, thrombin, chondroitin sulfate, albumin and a mixture thereof.
Owner:INFITRON +2
Biocompatible microfabricated macrodevices for transplanting cells
InactiveUS20180353650A1Easy to spreadFacilitated DiffusionPharmaceutical delivery mechanismProsthesisPorous membraneFibrosis
Macrodevices containing a micro-fabricated body having at least one or multiple compartments and a porous membrane, methods of making and using thereof, are described. The one or multiple compartments encapsulate one or more cells that secrete a therapeutic agent in cell-based therapy. The porous membrane provides immunoprotection the encapsulated cells. Further, the surface of the macrodevices is chemically modified using polymers and / or small molecules, reducing fibrosis of the macrodevices, thereby allowing in vivo delivery of the secreted therapeutic agents for extended periods of time.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Co-culture method of photosensory precursor cells and retinal tissue in vitro
The invention relates to a co-culture method of photosensory precursor cells and retinal tissue in vitro and aims to build a co-culture system for the photosensory precursor cells and denaturation retinal tissue of retina photoreceptor cells. The method comprises the following steps: a photosensory precursor cell layer of an embryonic eye source is prepared; a nerve cell layer of a denatured retina is prepared; the nerve cell layer of the denatured retina is placed on the photosensory precursor cell layer; an epithelial layer of retinochrome is prepared in the lower chamber of a plug-in type tissue culture dish; the co-culture system of the retinal tissue and cells is built in vitro, and the retinal tissue and cells are cultured in an incubator with 5% CO2 at the temperature of 37 DEG C. By adopting the method provided by the invention, the biological characteristics and cellular structure of host cells and transplanted cells, the synaptic contact of the transplanted cells and the host cells, and the chromatin conformation reconstruction of the transplanted cells and the host cells can be observed and detected directly in vitro, and the traces of survival, proliferation, differentiation and functional reconstruction of photosensory precursor cells of a transplanted embryonic eye source can be tracked.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
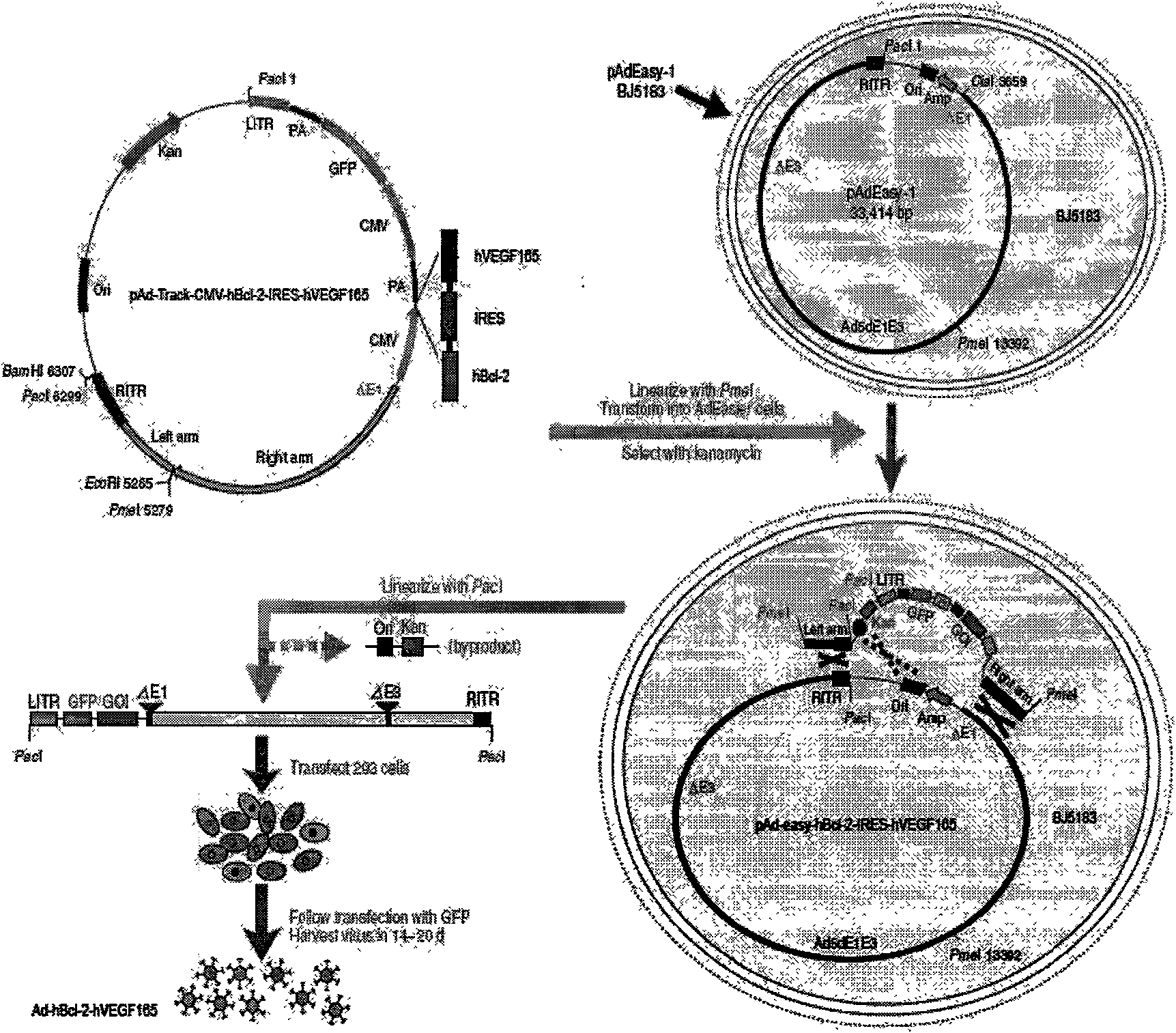
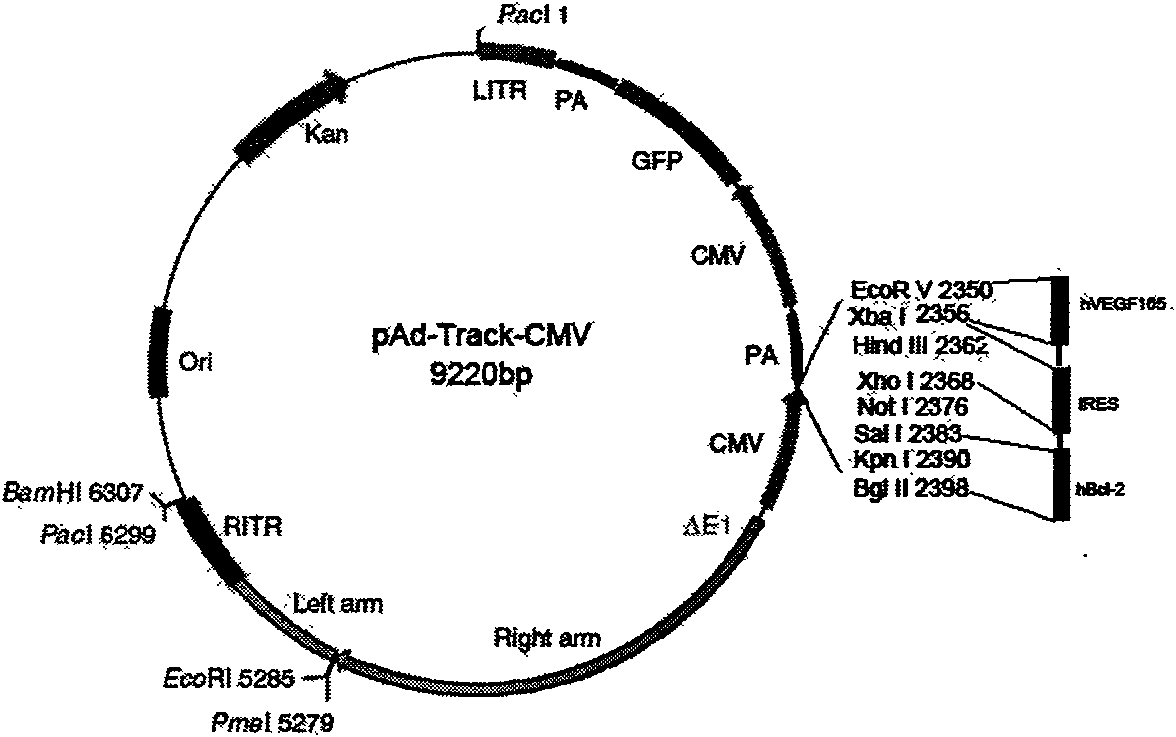
Human Bcl-2 and human VEGF165 double-gene co-expression recombinant vector and building method thereof
InactiveCN101654685APromote regenerationSolve the problem of low survival rateFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionAngiogenesis EffectAngiogenesis growth factor
The invention relates to a human Bcl-2 and human VEGF165 double-gene co-expression recombinant vector and a building method thereof, and is characterized in that IRES segment is utilized to connect an hBc1-2 gene and an hVEGF165 gene, and homologous recombination mechanisms in bacterium are utilized to recombine and build the human Bcl-2 and human VEGF165 double-gene co-expression recombinant vector according to an AdEasy system. The invention leads the Bcl-2 gene with anti-apoptosis capacity and the VEGF165 gene which currently promotes angiogenesis cytokine with strongest function to recombine on a same vector to be co-expressed, and solves the problem of low survival rate of transplanted cells under the condition of hypoxia and inflammation, simultaneously plays the function of promoting angiogenesis of VEGF165, plays an important part in the gene therapy of myocardial infarction and the cell transplantation research field, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Stem cells for modeling type 2 diabetes
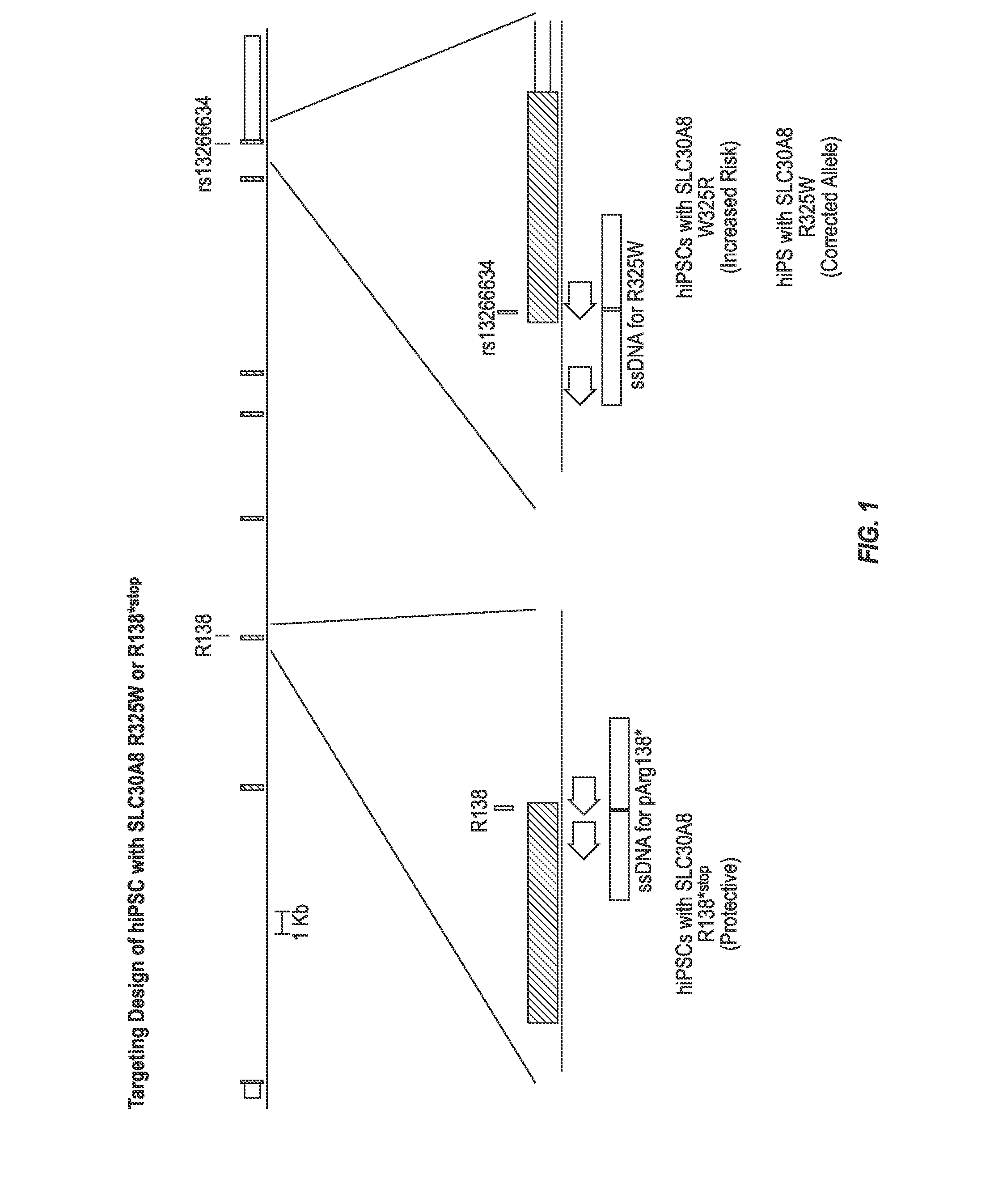
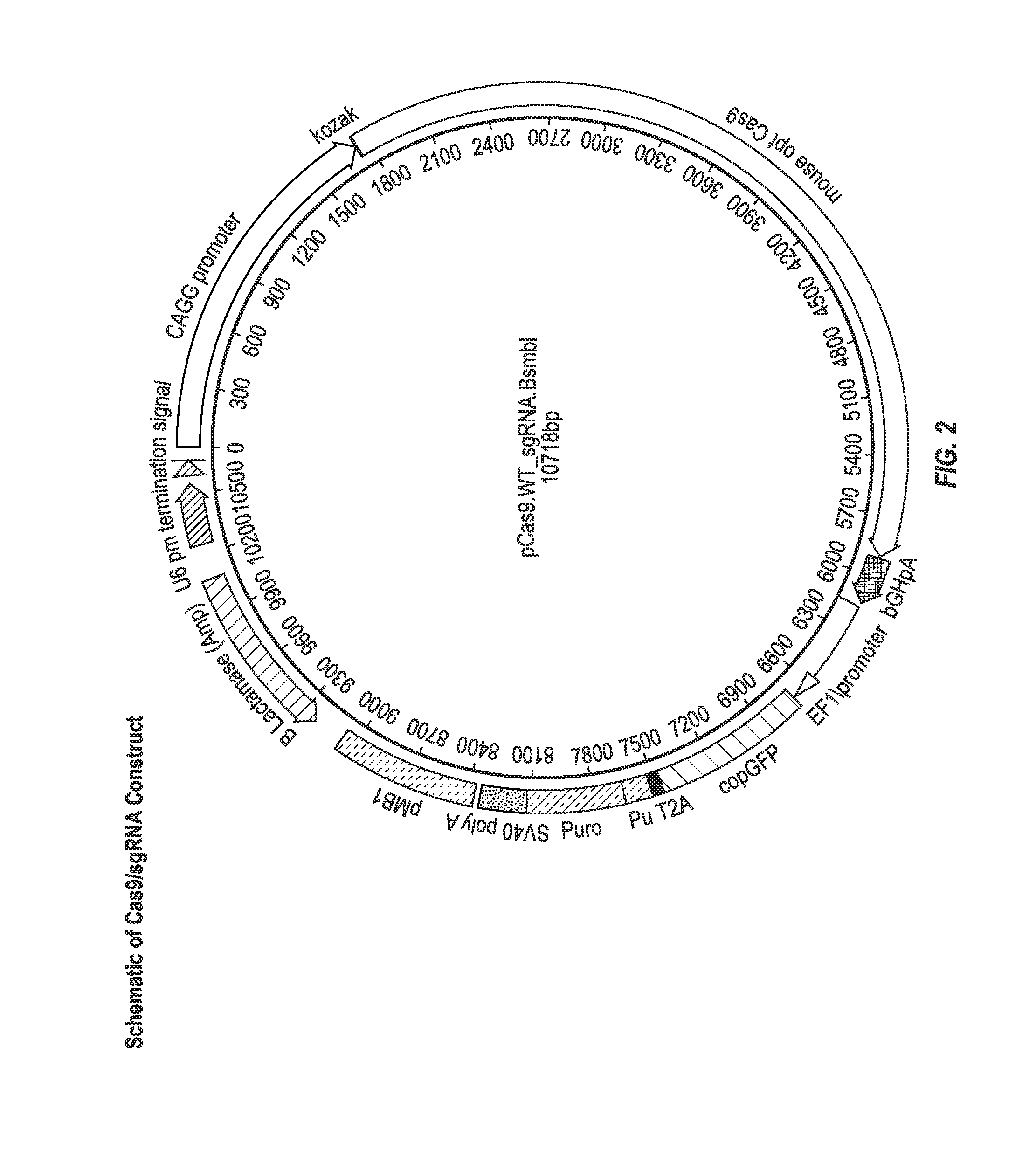
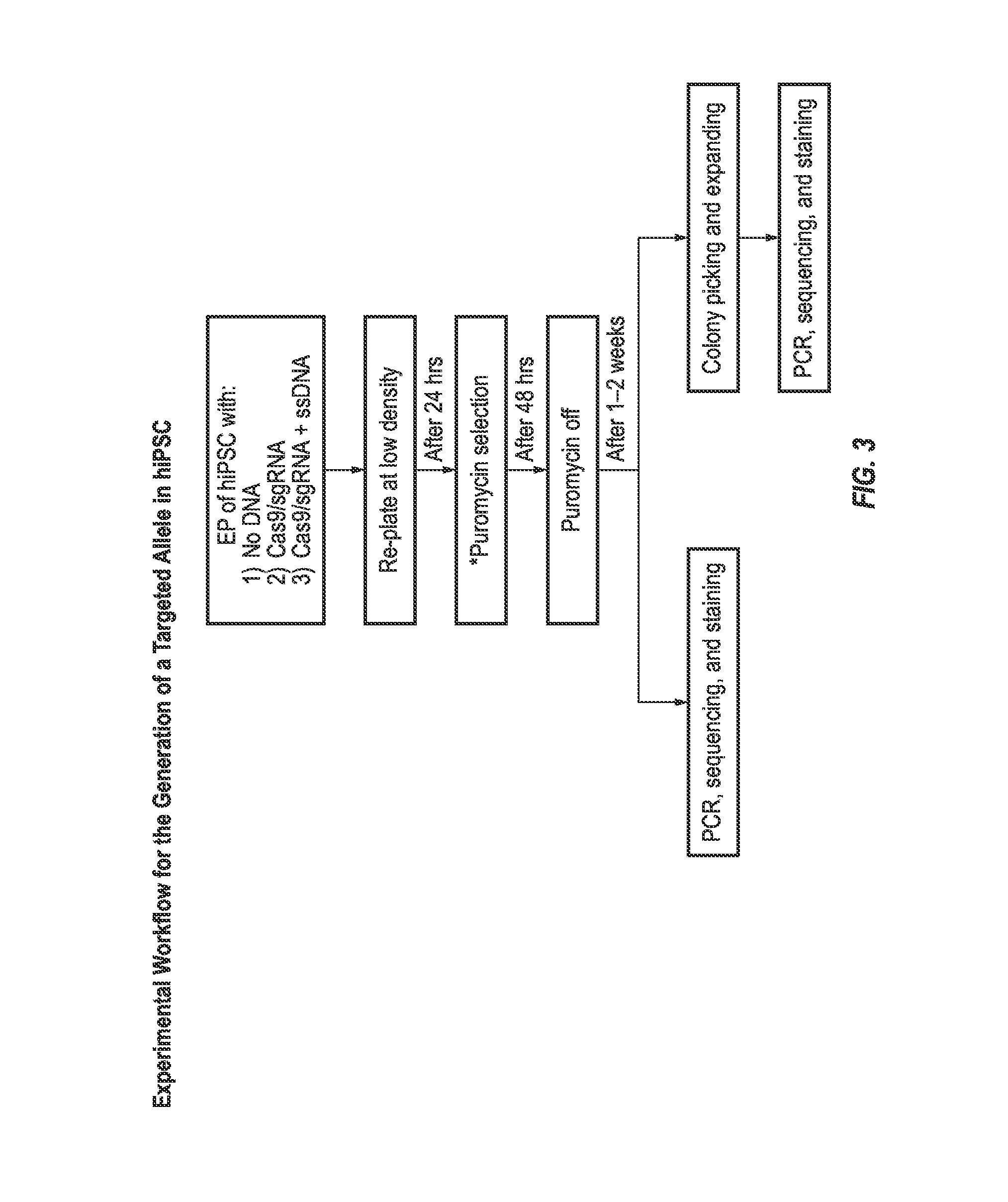
The invention provides stem cell derived beta-pancreatic cells and animal models of T2D in which cells have been grafted. The stem cells bear a mutated form of SLC30A8 conferring protection or susceptibility to T2D. The cells and animal models can be used for drug screening as well as to provide insights into the mechanism of T2D and potentially new therapeutic and diagnostic targets.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com