Patents
Literature
245results about "Refining by dialysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
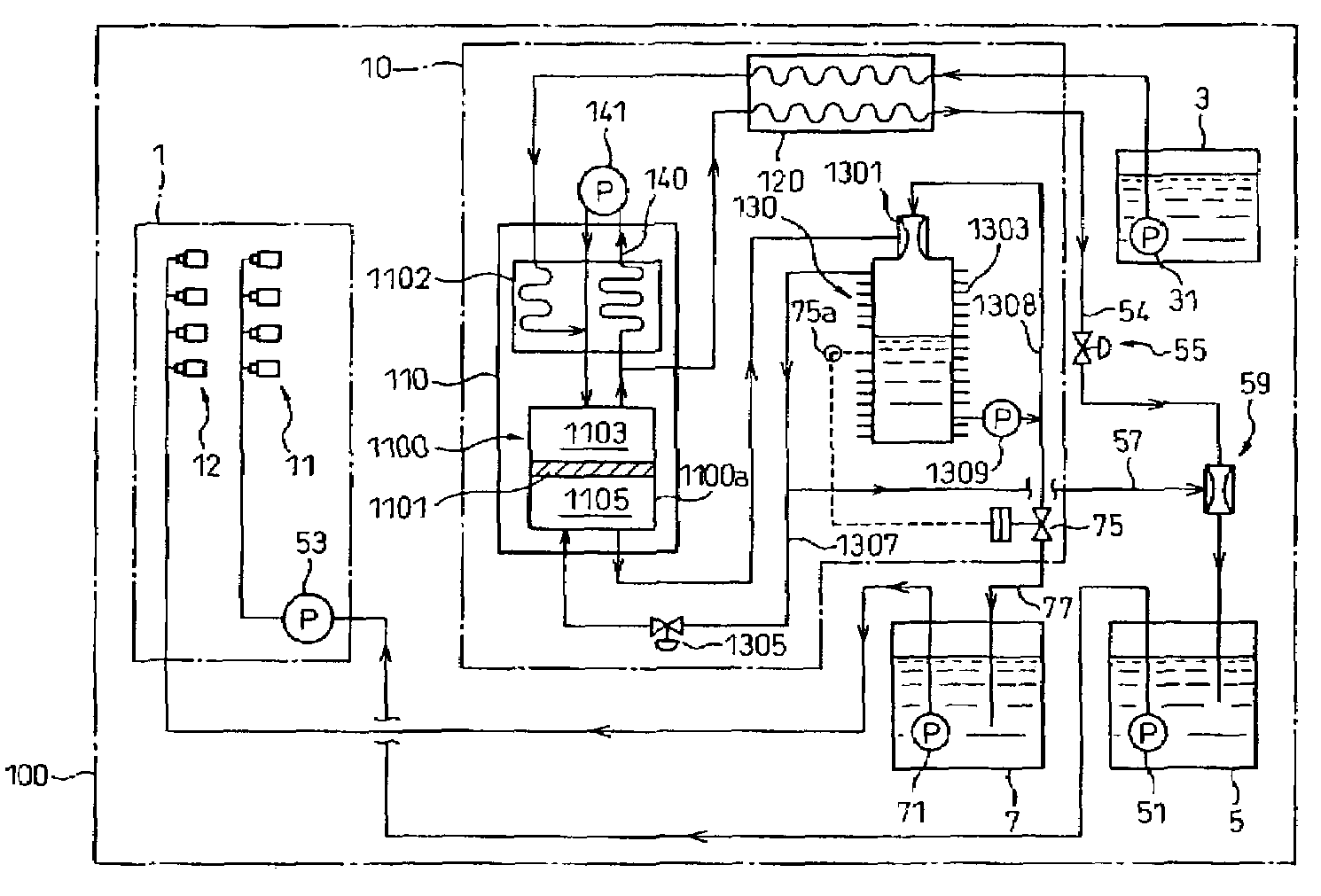
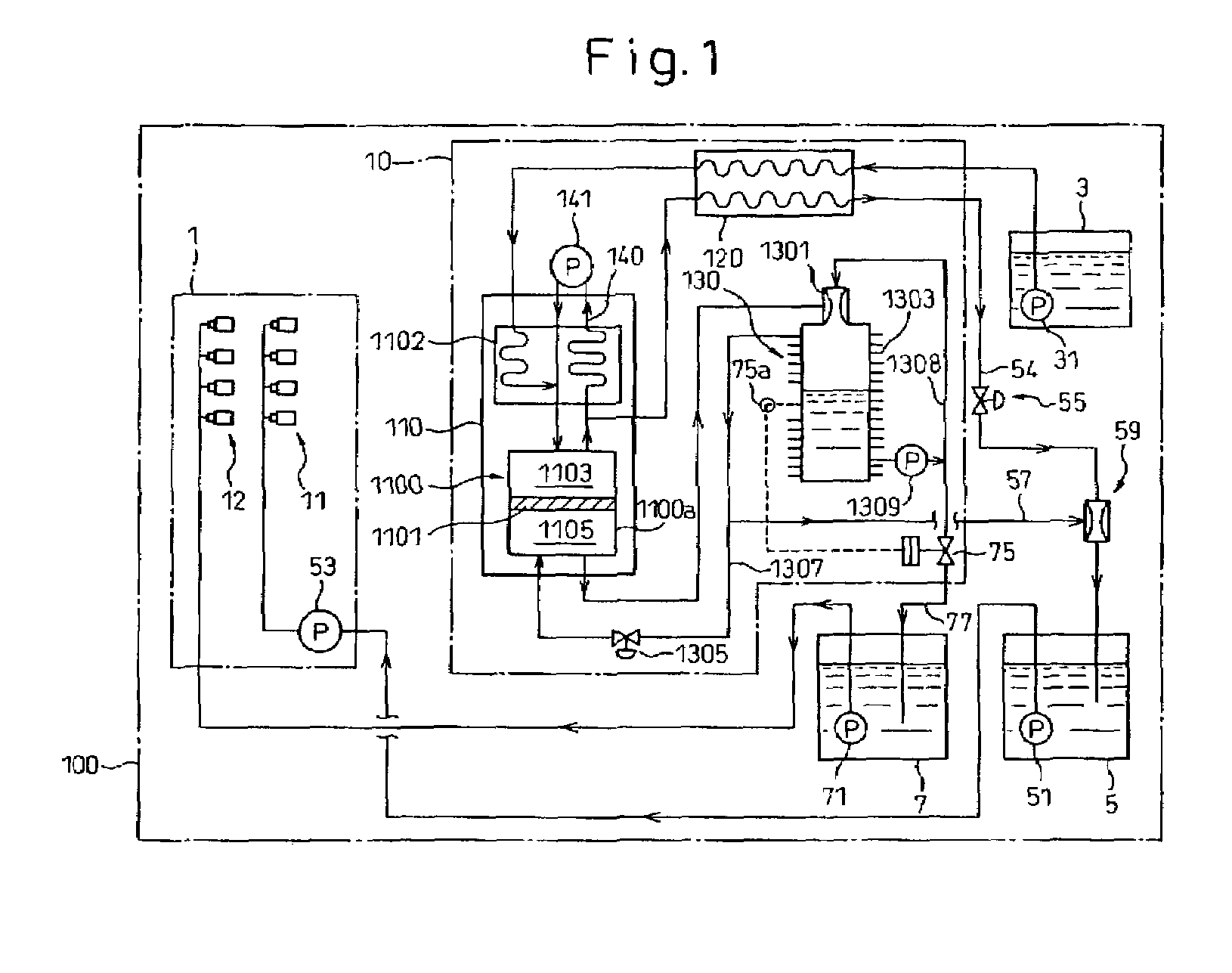
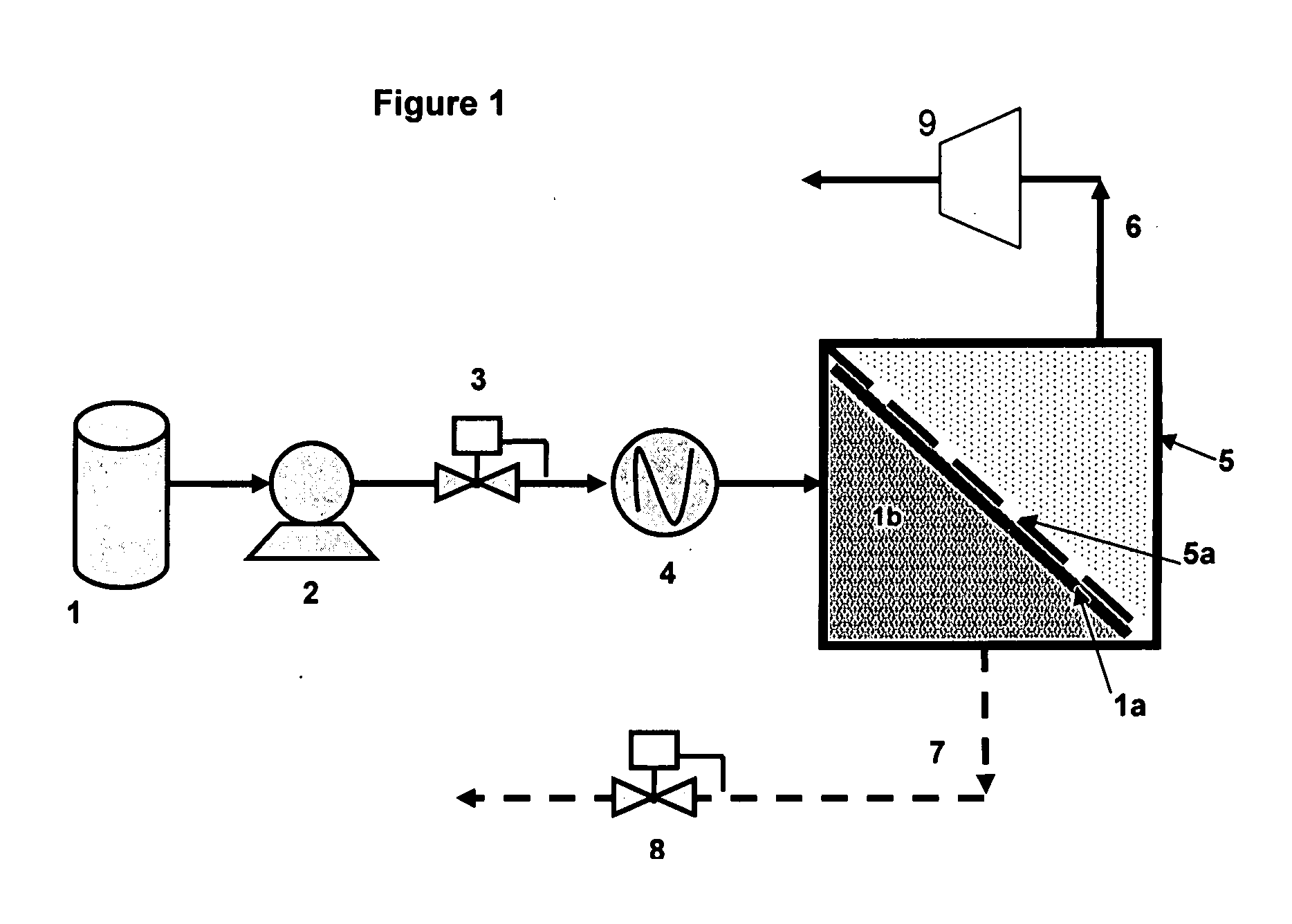
Onboard fuel separation apparatus for an automobile
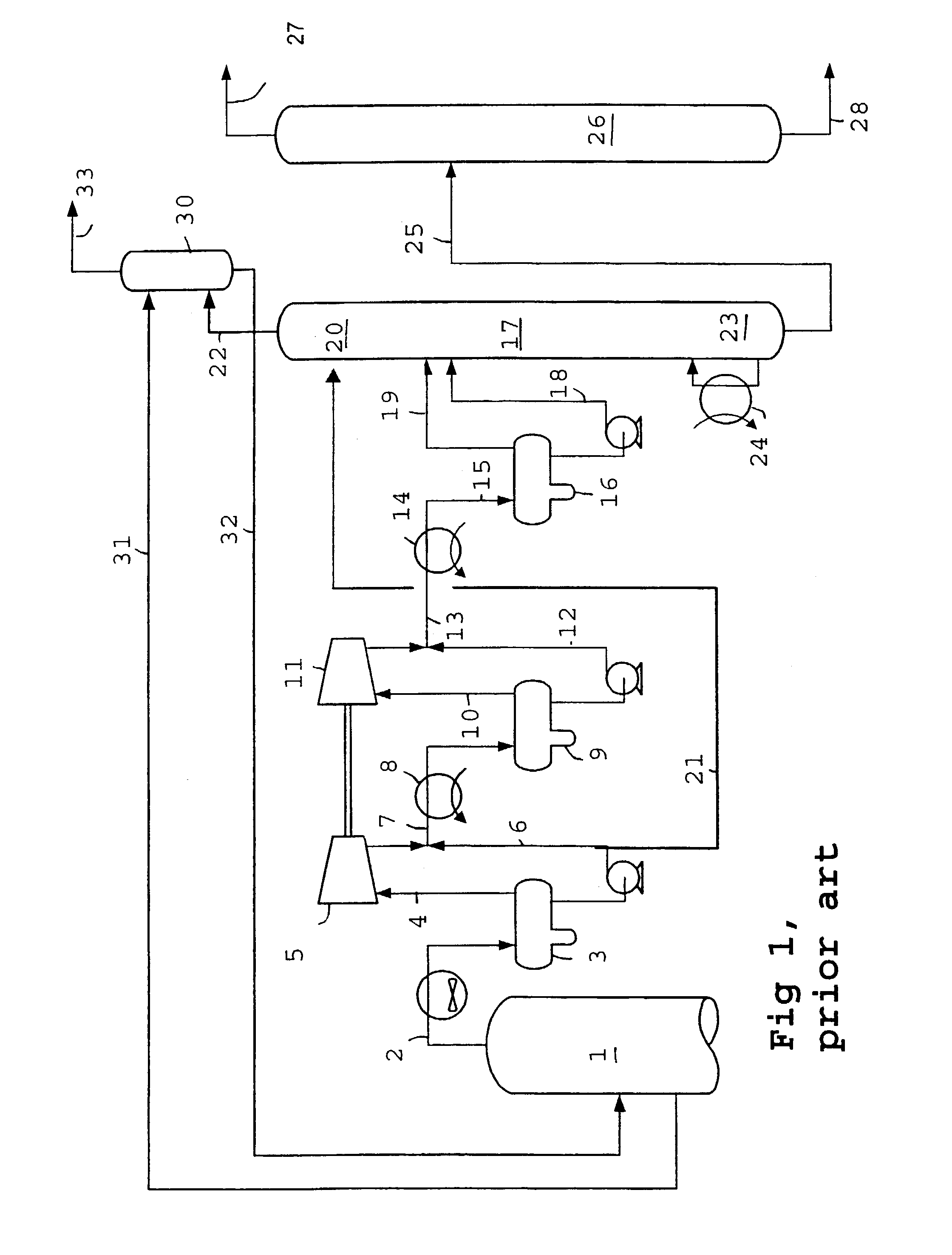
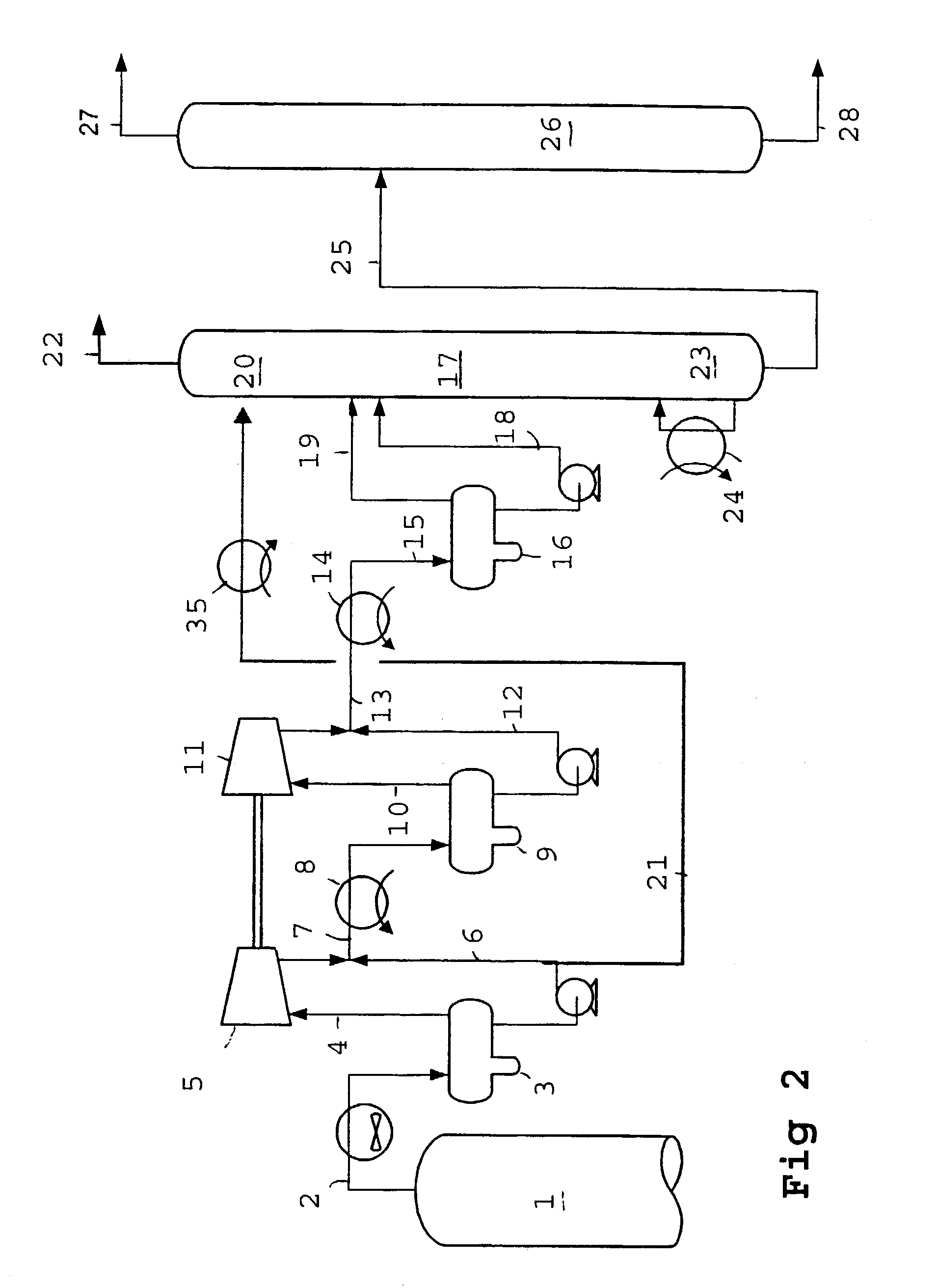
InactiveUS6972093B2Increase volumeBoost octaneInternal combustion piston enginesUsing liquid separation agentVolatilesEngineering
An onboard fuel separation apparatus separates a material fuel (gasoline) into a high-octane fuel having a higher octane value than the material fuel and a low-octane fuel having a lower octane value than the material fuel using a separation membrane which selectively allows high-octane value components (such as aromatic components) permeate through the membrane. The apparatus increases the ratio of the amount of the high-octane value components permeating through the membrane to the amount of the high-octane value components contained in the material fuel by, (A) Controlling the temperature of the material fuel supplied to the membrane (B) Increasing partial pressure of the low-octane value components on the high-octane fuel side of the membrane and removing volatiles from the permeate, and (C) Bypassing volatiles in the material feed around the membrane.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO +1
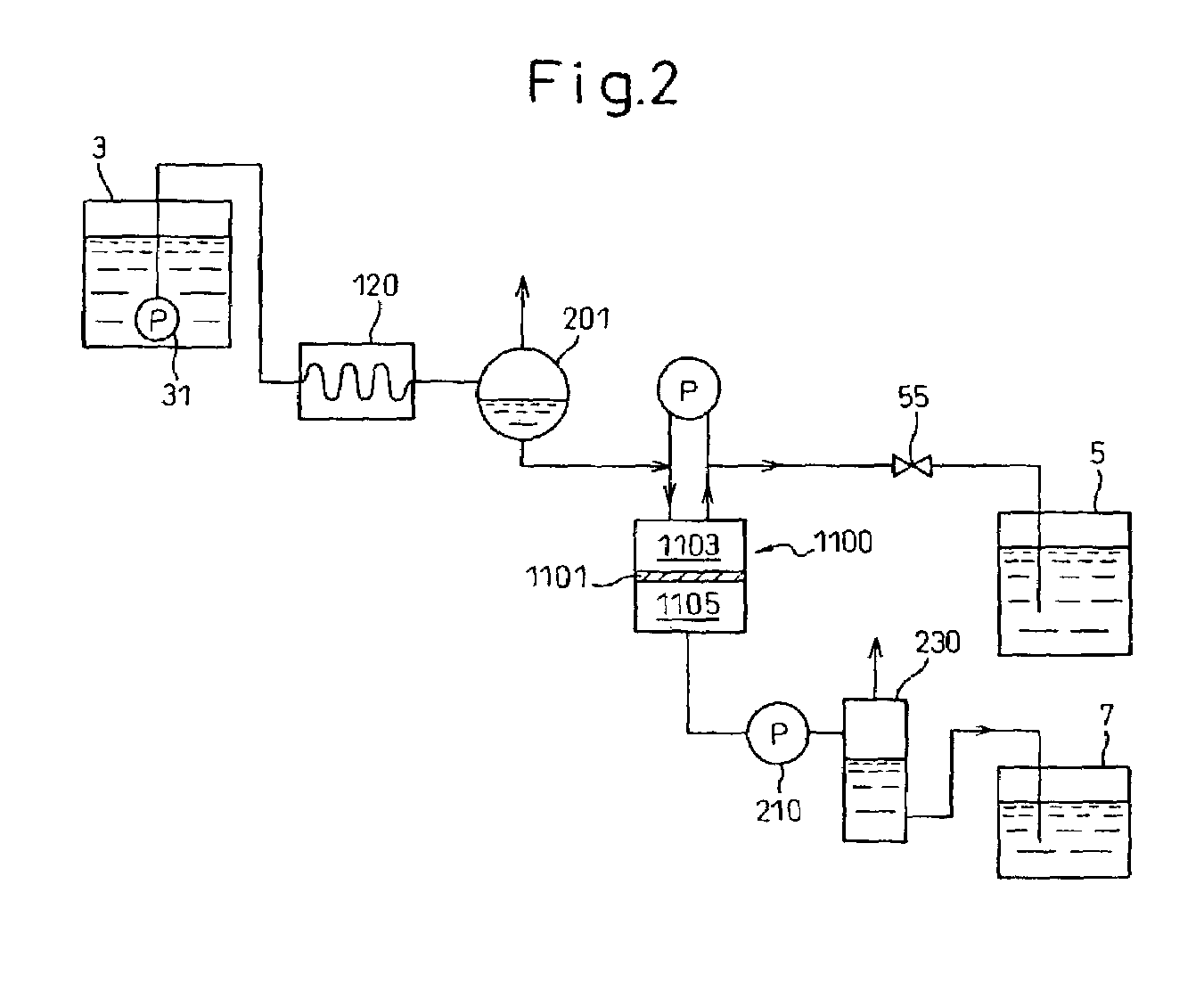
Membrane separation process using mixed vapor-liquid feed
ActiveUS20080011680A1Reduce the impactEfficient executionMembranesSemi-permeable membranesVapor liquidChemical physics
The present invention pertains to a process for the separation of aromatics from a feed stream, including aromatics and non-aromatics by selectively permeating the aromatics through a membrane comprising feeding a mixed phase vapor-liquid feed to a membrane wherein said liquid phase preferentially wets the surface of the membrane.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
High flux, microporous, sieving membranes and separators containing such membranes and processes using such membranes
InactiveUS20060201884A1Easy to implementReduced membrane surface areaSemi-permeable membranesMembranesHigh fluxChemistry
A sieving membrane comprises a thin, microporous barrier to provide a high flux. The membrane structure can tolerate defects yet still obtain commercially-attractive separations.
Owner:UOP LLC
UV-cross-linked membranes from polymers of intrinsic microporosity for liquid separations
ActiveUS7758751B1High selectivityEasy to processMembranesSemi-permeable membranesCross-linkPolymer science
The present invention is for high performance UV-cross-linked membranes from polymers of intrinsic microporosity (PIMs) and the use of such membranes for separations. More specifically, the invention involves the methods of making UV-cross-linked membranes from PIMs. These membranes were prepared by cross-linking the UV-cross-linkable membranes from PIMs by exposure to UV-radiation. Pure gas permeation test results demonstrate that the UV-cross-linked membranes from PIMs exhibit CO2 / CH4 performance well above the Robeson's polymer upper bound trade-off curve for CO2 / CH4 separation. They have more than doubled selectivity for CO2 / CH4 and extremely high permeability of CO2 compared to the original UV-cross-linkable membranes from PIMs. These membranes also show excellent separation performance for CO2 / N2, H2 / CH4, O2 / N2, and propylene / propane separations. These high performance UV-cross-linked membranes are very useful for gas and liquid separations such as CO2 / CH4, CO2 / N2, H2 / CH4, O2 / N2, olefin / paraffin, deep desulfurization of gasoline and diesel fuels, and ethanol / water separations.
Owner:UOP LLC
Petroleum Upgrading and Desulfurizing Process
ActiveUS20120181217A1Reduce dwell timeSmall sizeThermal non-catalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsSorbentWater flow
A petroleum feedstock upgrading method is provided. The method includes supplying a mixed stream that includes hydrocarbon feedstock and water to a hydrothermal reactor where the mixed stream is maintained at a temperature and pressure greater than the critical temperatures and pressure of water in the absence of catalyst for a residence time sufficient to convert the mixed stream into a modified stream having an increased concentration of lighter hydrocarbons and / or concentration of sulfur containing compounds. The modified stream is then supplied to an adsorptive reaction stage charged with a solid adsorbent operable to remove at least a portion of the sulfur present to produce a trimmed. The trimmed stream is then separated into a gas and a liquid streams, and the liquid stream is separated into a water stream and an upgraded hydrocarbon product stream.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
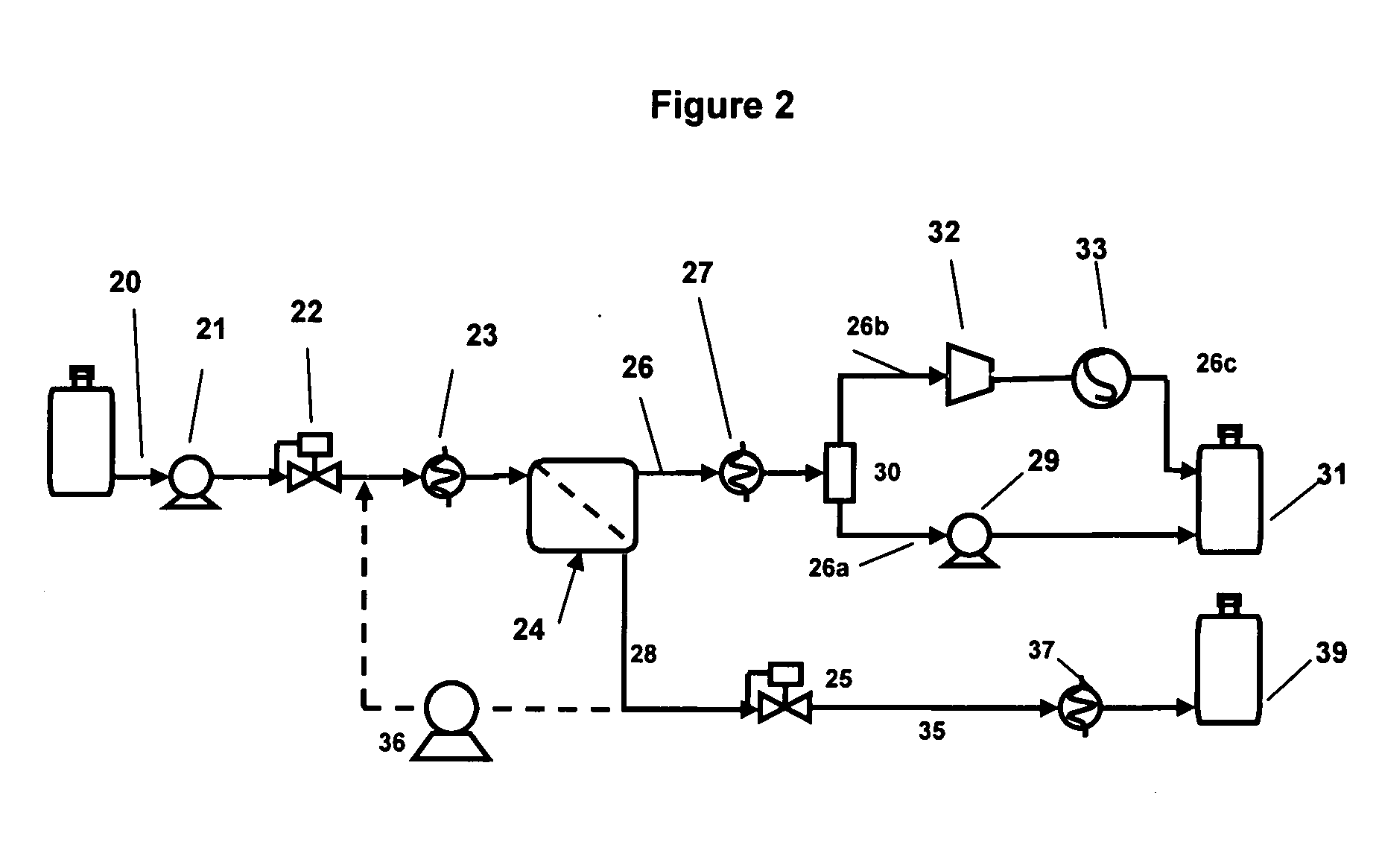
Transmix refining method
A transmix refining method comprises passing a transmix feed through a membrane to produce a permeate stream and a retentate stream without further processing the permeate stream and the retentate stream in a distillation device.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Liquid natural gas processing
ActiveUS6941771B2Avoid the needLower energy requirementsSolidificationLiquefactionRefluxNatural-gas processing
A process for the recovery of natural gas liquids (NGL) (ethane, ethylene, propane, propylene and heavier hydrocarbons) from liquefied natural gas (LNG) is disclosed. The LNG feed stream is split with at least one portion used as an external reflux, without prior treatment, to improve the separation and recovery of the natural gas liquids (NGL).
Owner:HOWE BAKER ENGINEERS LTD
Use of low pressure distillate as absorber oil in a FCC recovery section
InactiveUS7074323B2Less equipmentImprove throughputThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingNaphthaDistillation
A process for the recovery of gaseous products from the product mixture obtained by contacting a hydrocarbon feed with a catalyst in a fluid catalytic cracking process, wherein the liquid, obtained by separating the top product of main fractionators into gaseous and liquid fraction, when supplied to the absorber has a temperature of between about 8–25 DEG C. This liquid may be pre-saturated with gaseous top product from absorber; or also a high boiling fraction (cat cracker naphtha / light cycle oil) may be first separated from this liquid by distillation.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Two stage hydroprocessing with divided wall column fractionator
InactiveUS20120004478A1Low sulfurImprove propertiesCoke ovensHydrocarbon distillationFractionationReaction system
A divided wall column can allow for fractionation of multiple streams while maintaining separate product qualities. Effluents from multiple stages of a reaction system can be processed in a single divided wall column. The divided wall column can produce multiple cuts from each separated area, as well as at least one output from a common area. At least one reaction stage can advantageously have a continuous liquid phase environment.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
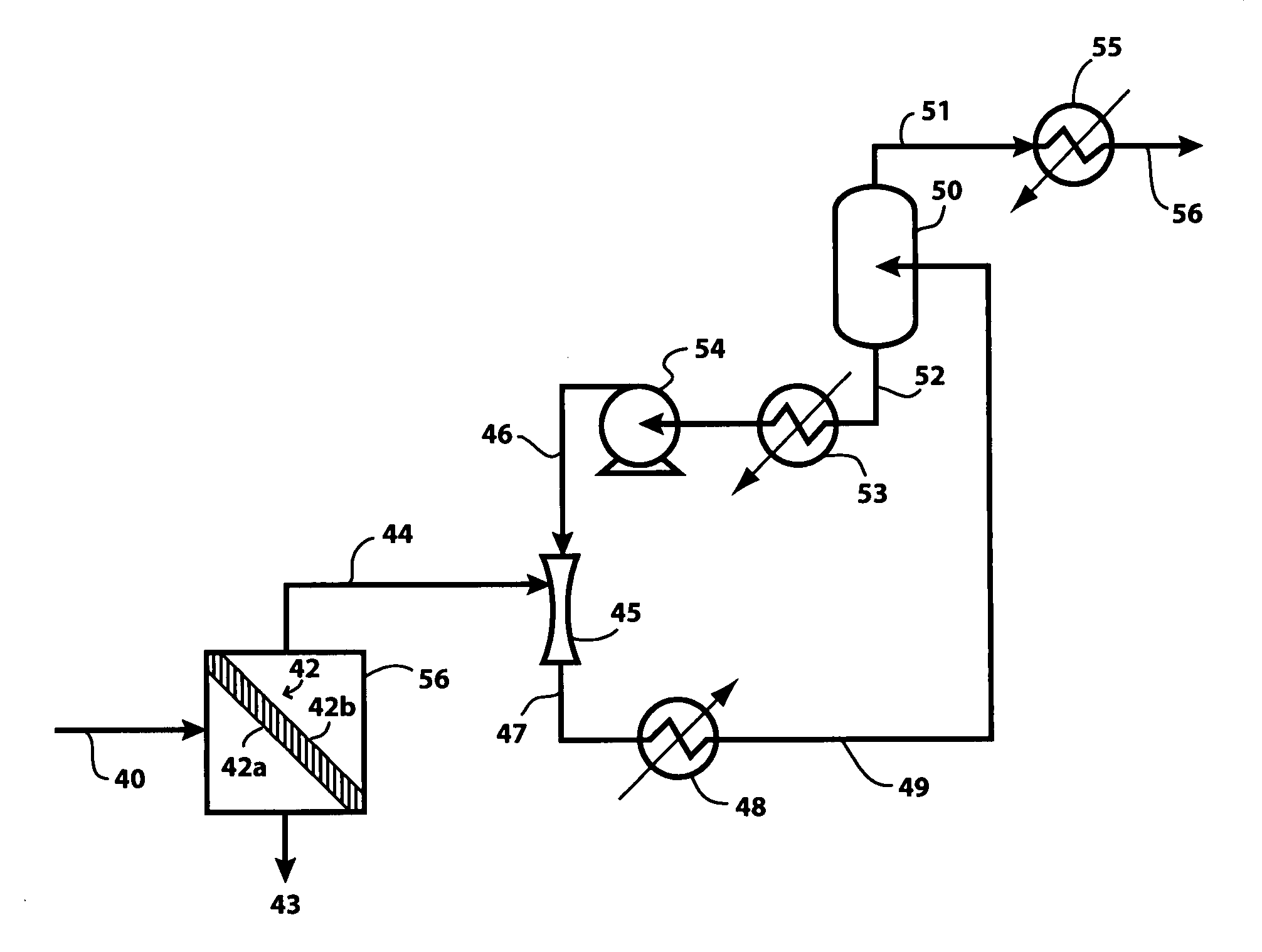
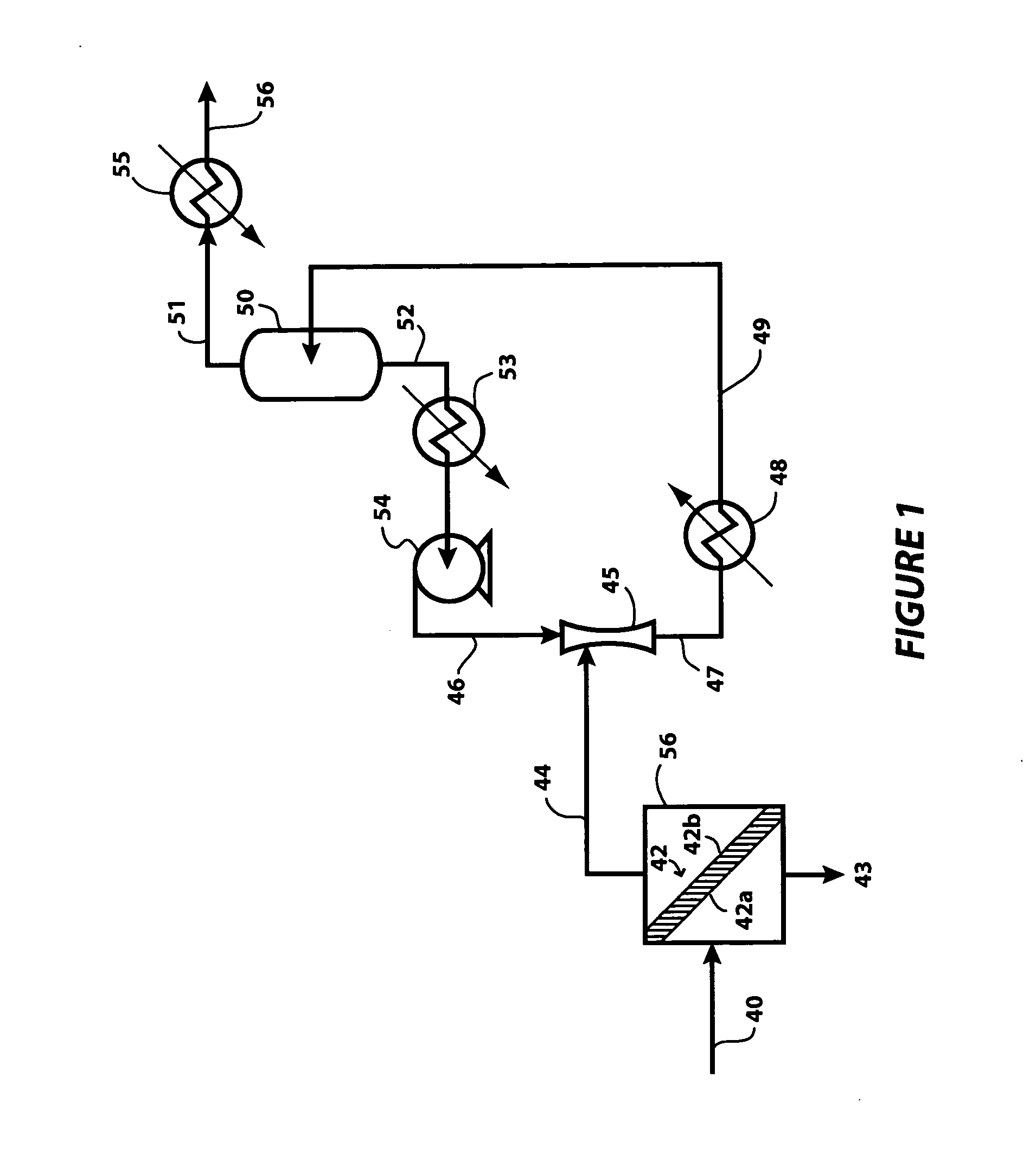
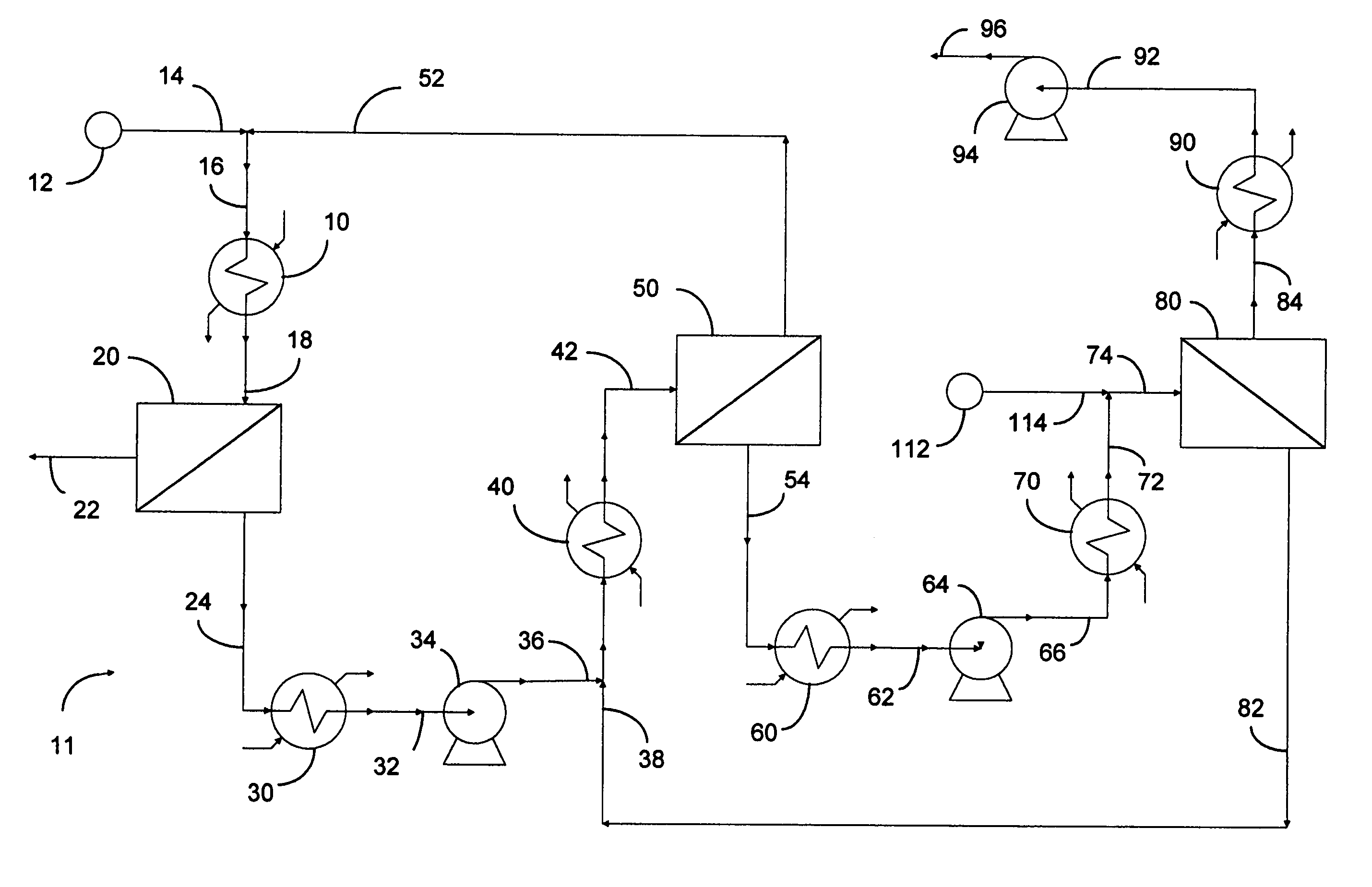
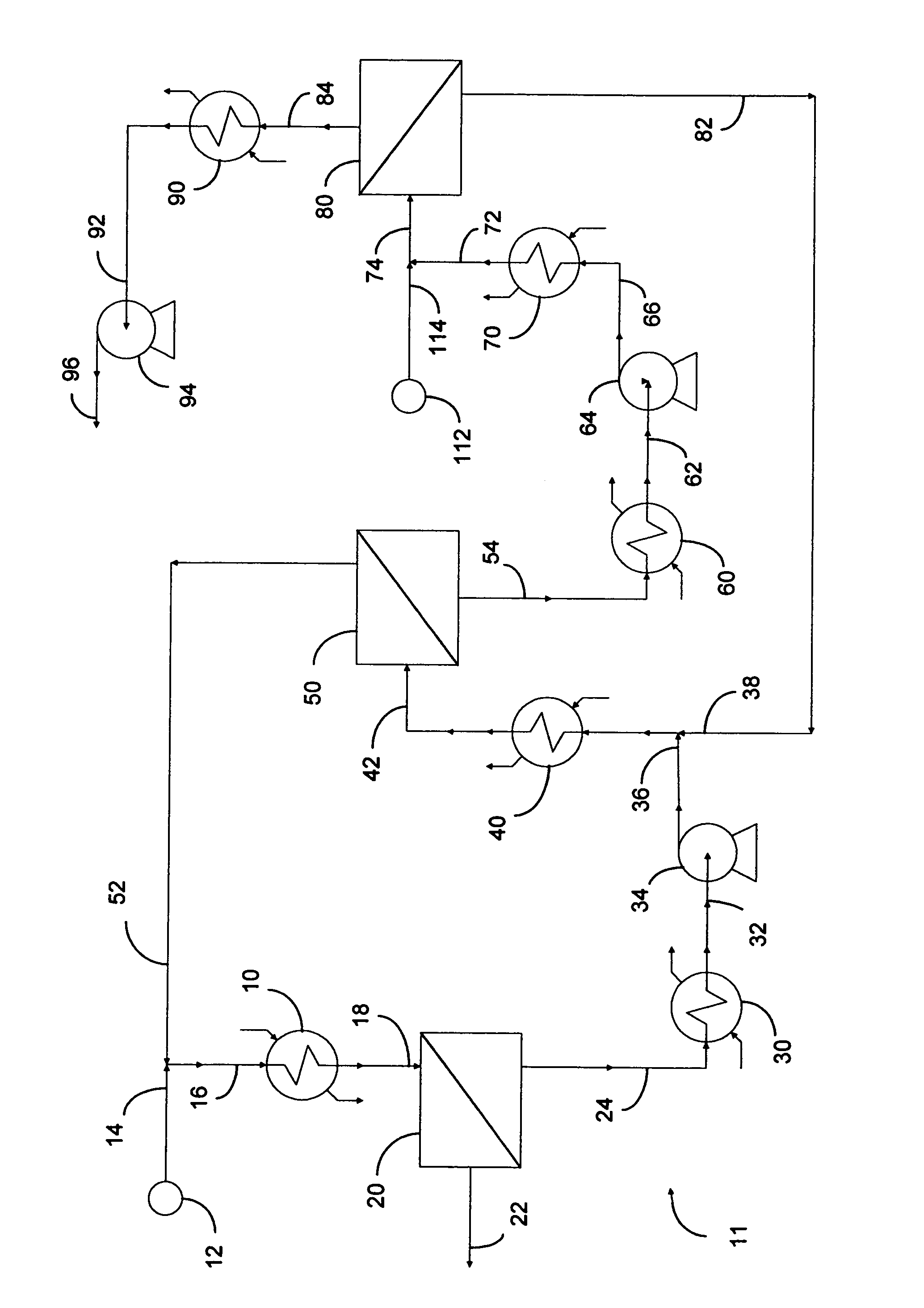
Membrane desulfurization of liquid hydrocarbons using an extractive liquid membrane contactor system and method
InactiveUS20110000823A1Transfer rate is not hinderedEasy to transportWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by selective extractionSolvent extractionOrganosulfur compoundsLiquid hydrocarbons
The process of the present invention is directed to the desulfurization of a sulfur-containing hydrocarbon stream with a membrane contactor, where sulfur compounds are concentrated in a sulfur-rich stream on a permeate side of the membrane using an extractive liquid, and a sulfur-lean stream is recovered as a retentate. The sulfur-rich stream, which has a small volume relative to the original hydrocarbon stream, is conveyed to a recovery zone to recover extractive liquid, and the remaining hydrocarbon stream having an increased concentration of sulfur compounds is passed to a downstream desulfurization apparatus or system, such as a hydrotreating system, to recover the hydrocarbons associated with the organosulfur compounds.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
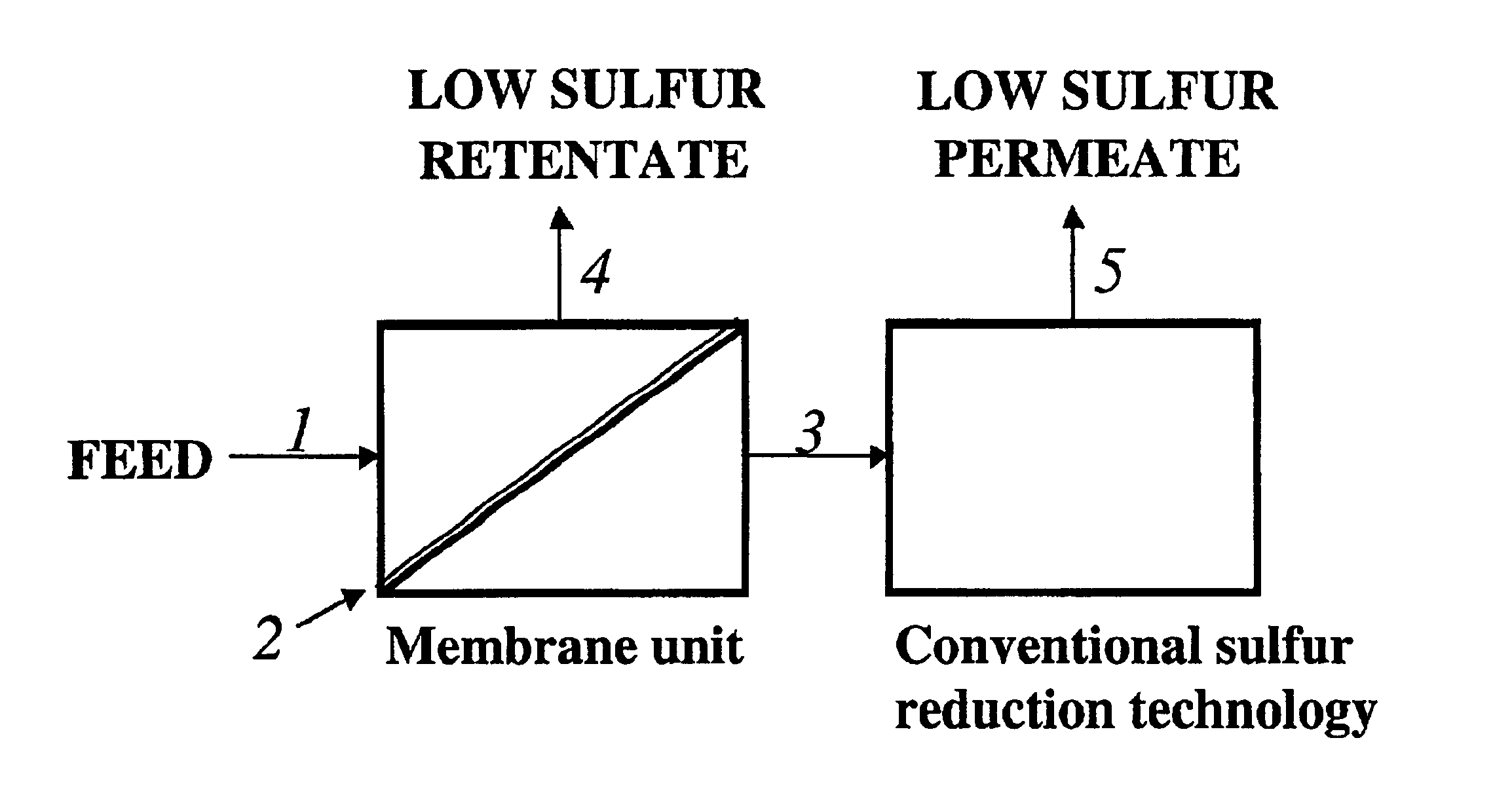
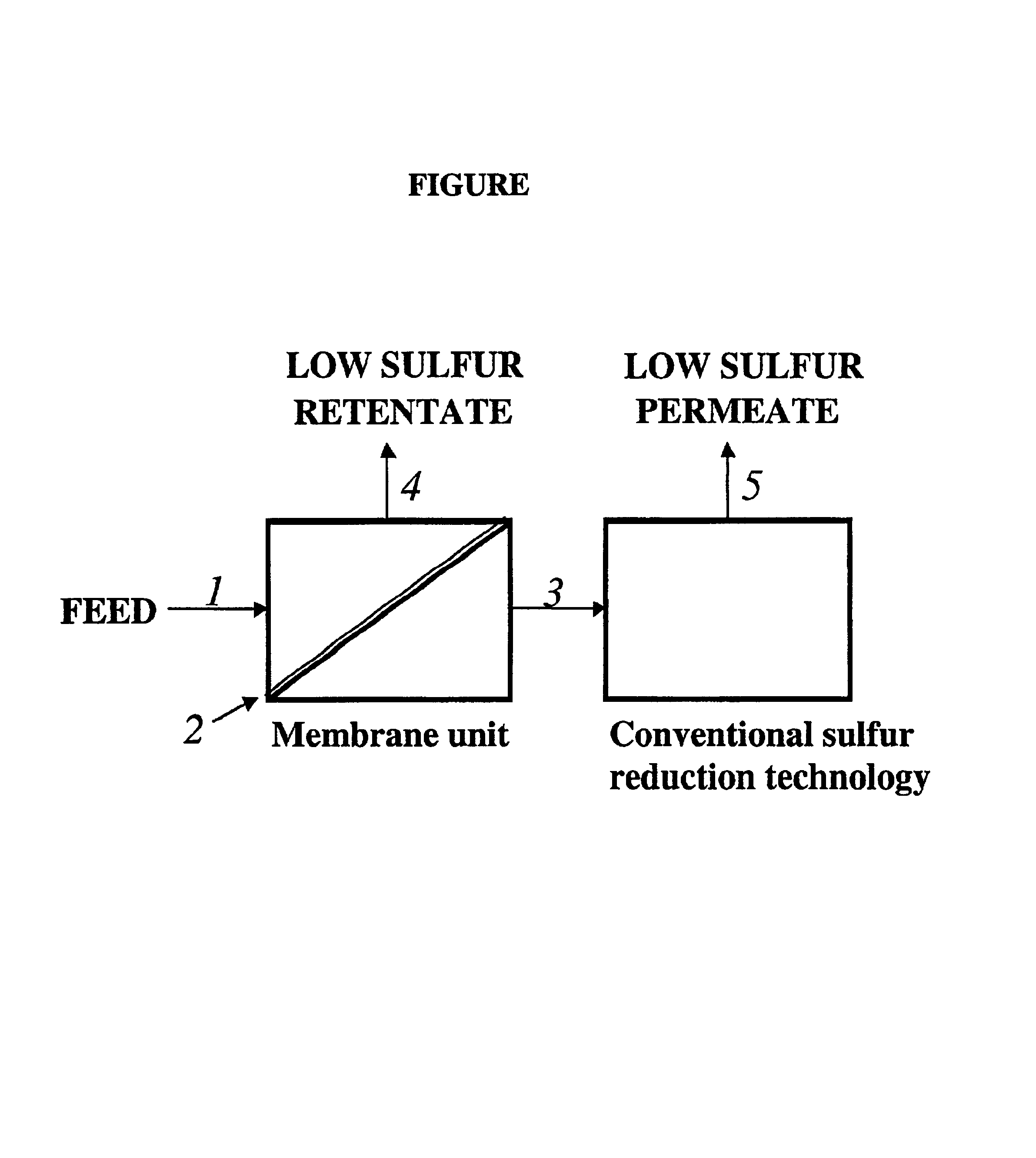
Membrane separation for sulfur reduction
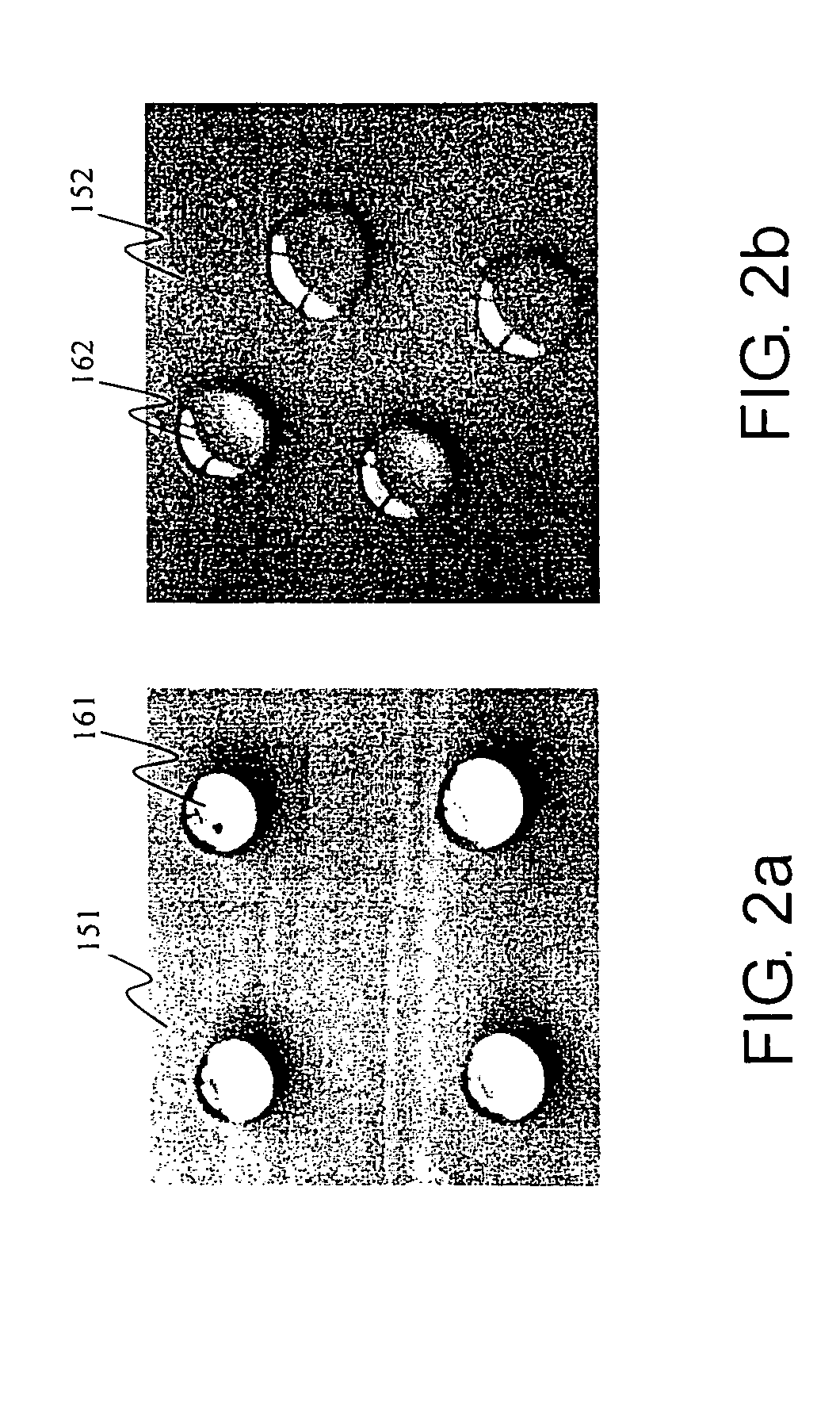
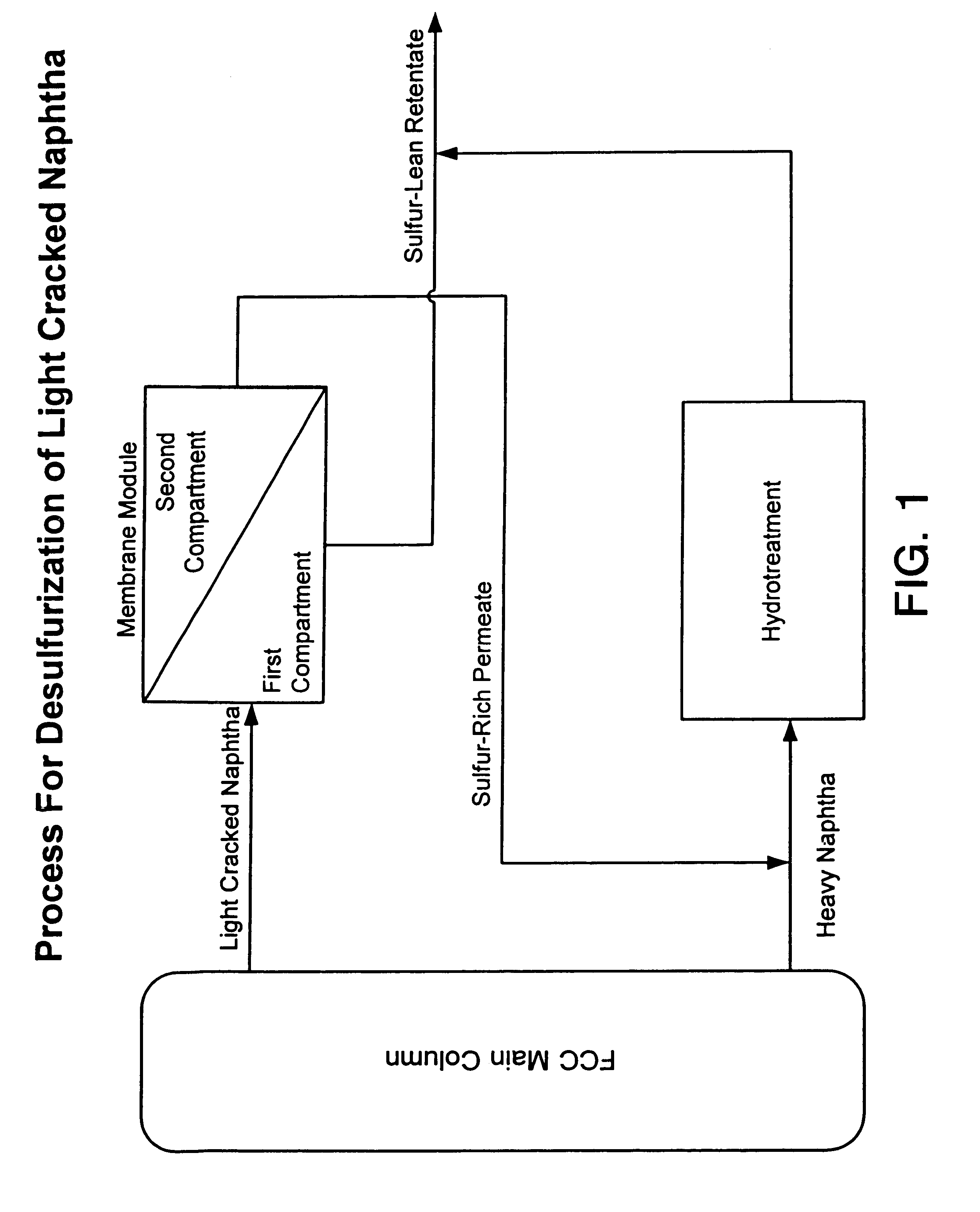
InactiveUS6896796B2Improve economyMinimized volumeDialysisTreatment with plural serial refining stagesNaphthaGasoline
A membrane process for the removal of sulfur species from a naphtha feed, in particular, a FCC light cat naphtha, without a substantial loss of olefin yield is disclosed. The process involves contacting a naphtha feed stream with a membrane having sufficient flux and selectivity to separate a sulfur deficient retentate fraction from a sulfur enriched permeate fraction, preferably, under pervaporation conditions. Sulfur deficient retentate fractions are useful directly into the gasoline pool. Sulfur-enriched permeate fractions are rich in sulfur containing aromatic and nonaromatic hydrocarbons and are further treated with conventional sulfur removal technologies, e.g. hydrotreating, to reduce sulfur content. The process of the invention provides high quality naphtha products having a reduced sulfur content and a high content of olefin compounds.
Owner:WR GRACE & CO CONN
Membrane separation process
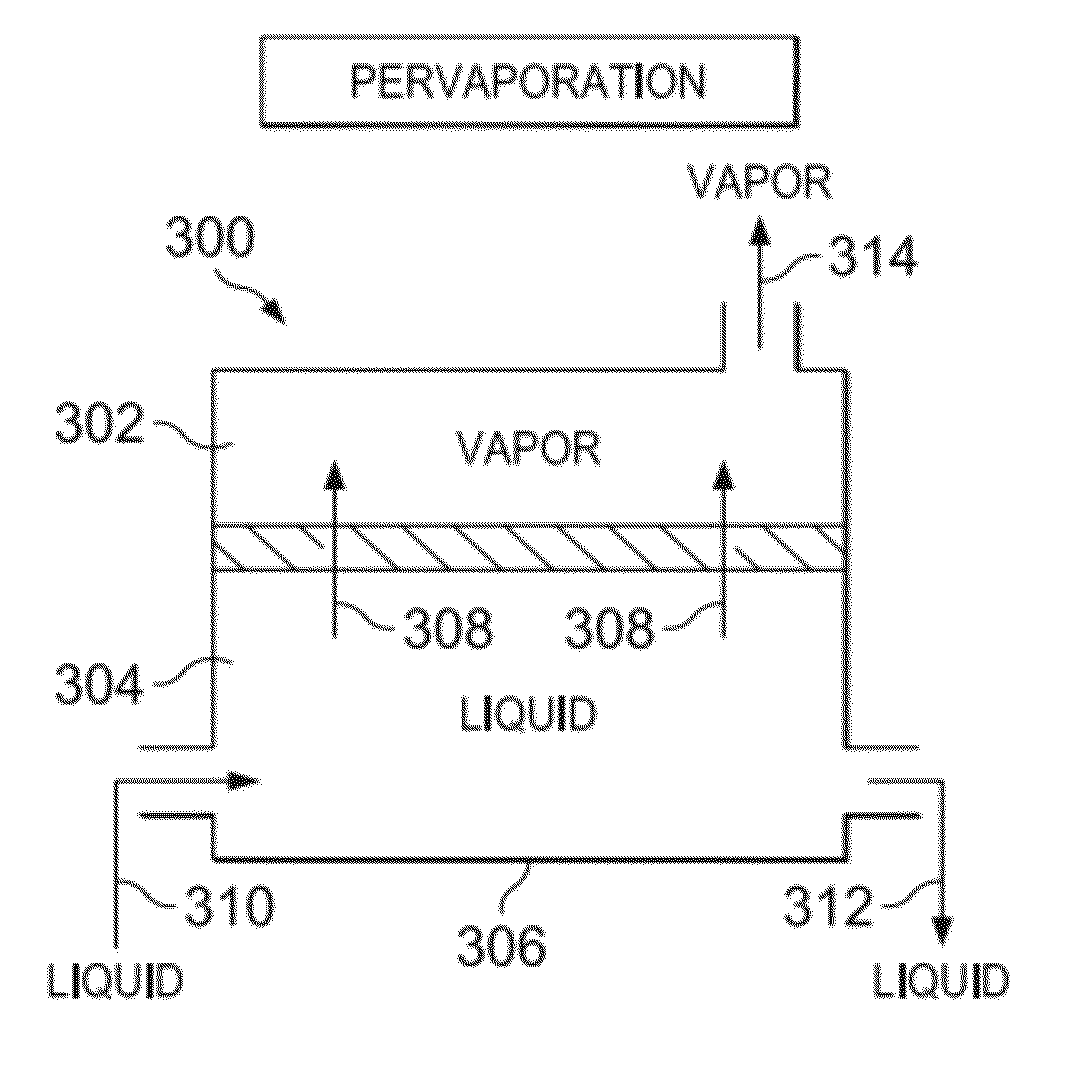
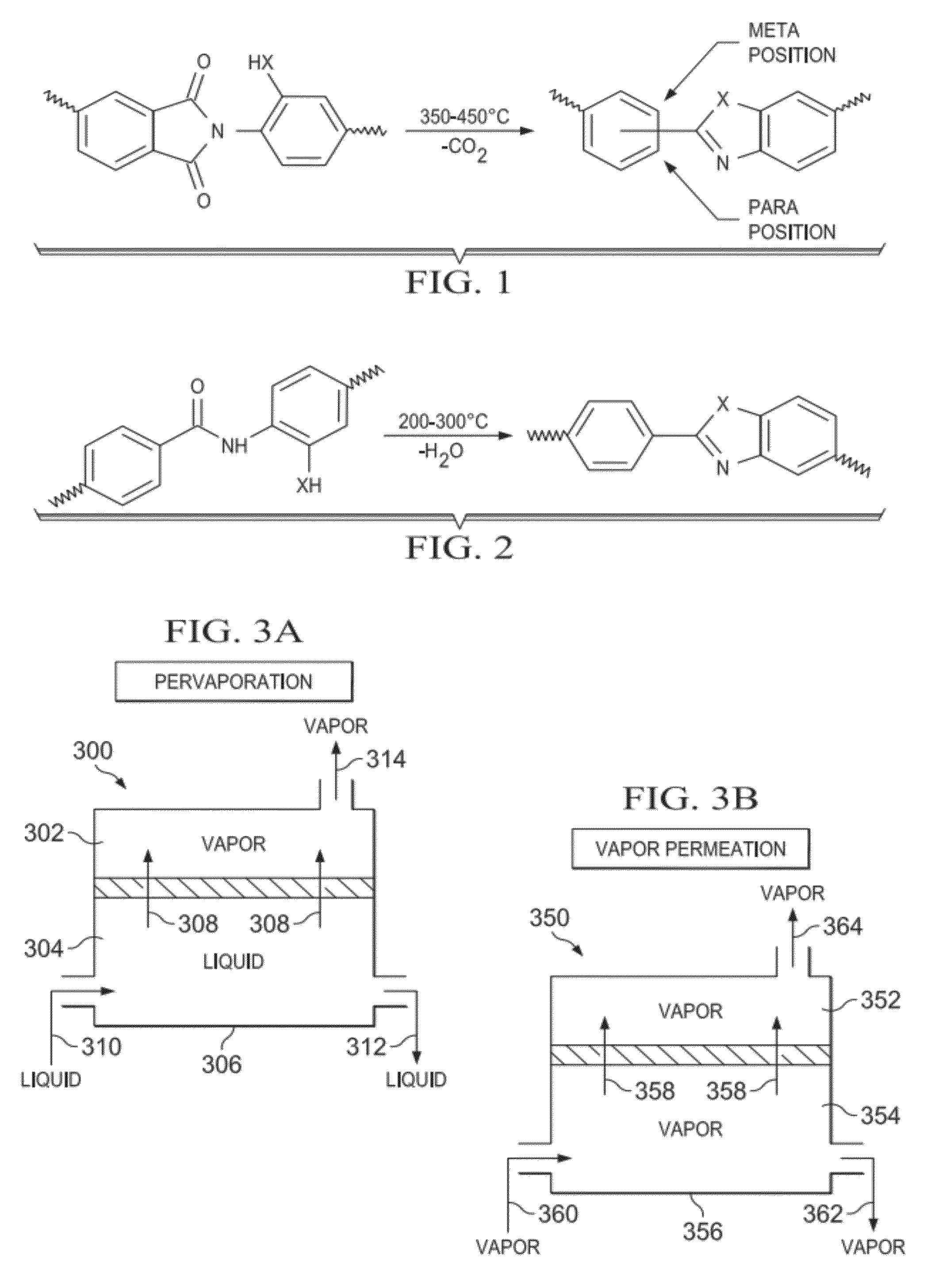
ActiveUS20070114177A1Organic compounds purification/separation/stabilisationMembranesSpray nozzlePervaporation
The invention relates to an improved membrane pervaporation and vapor permeation system in which the vacuum is produced by a fluid passing through a Venturi-type nozzle. The fluid is chosen from solvents that have little or no affinity for the permeate molecules. It is applicable over process feed rates, and can be used for the separation of aromatic species from hydrocarbon.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
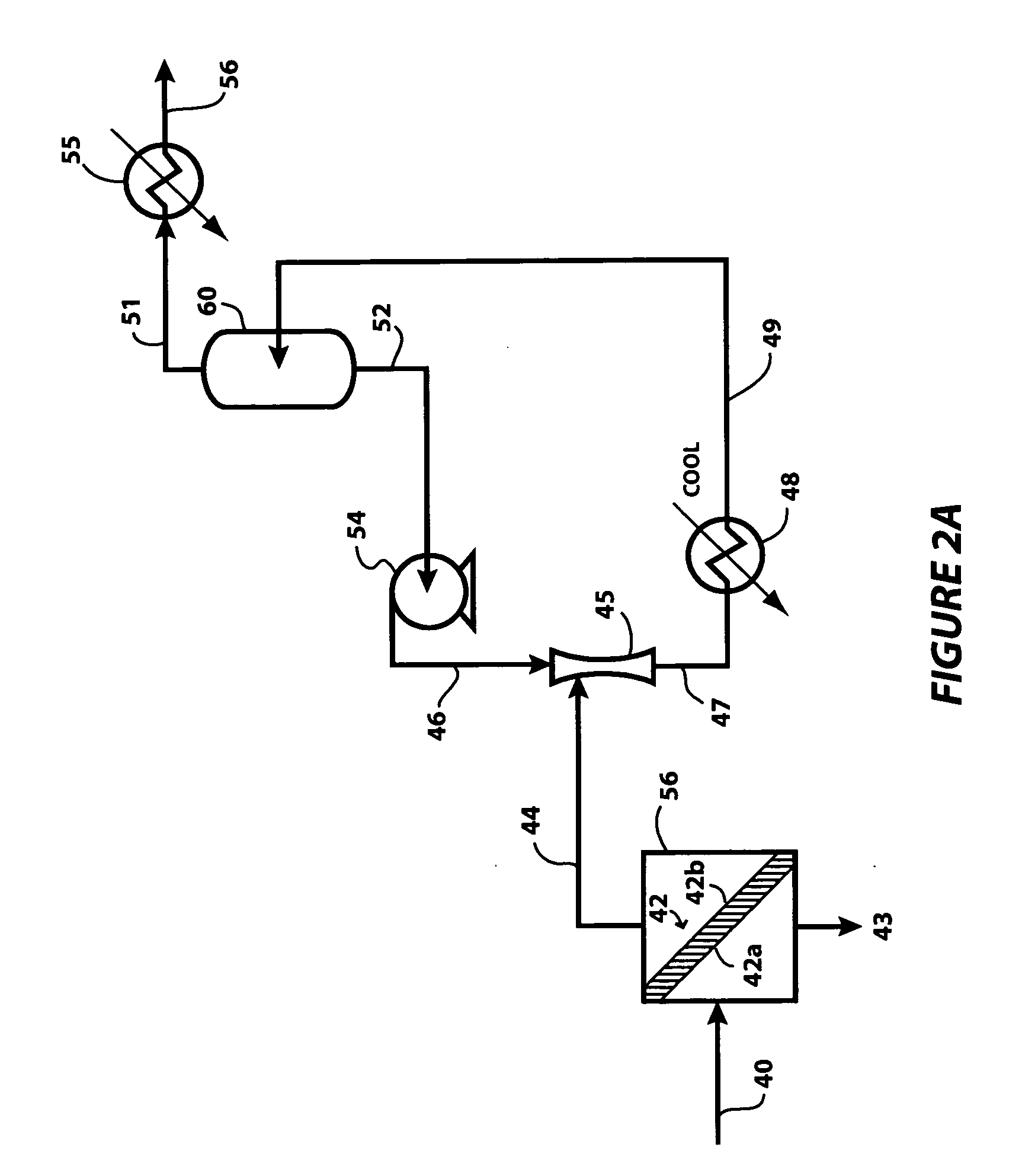
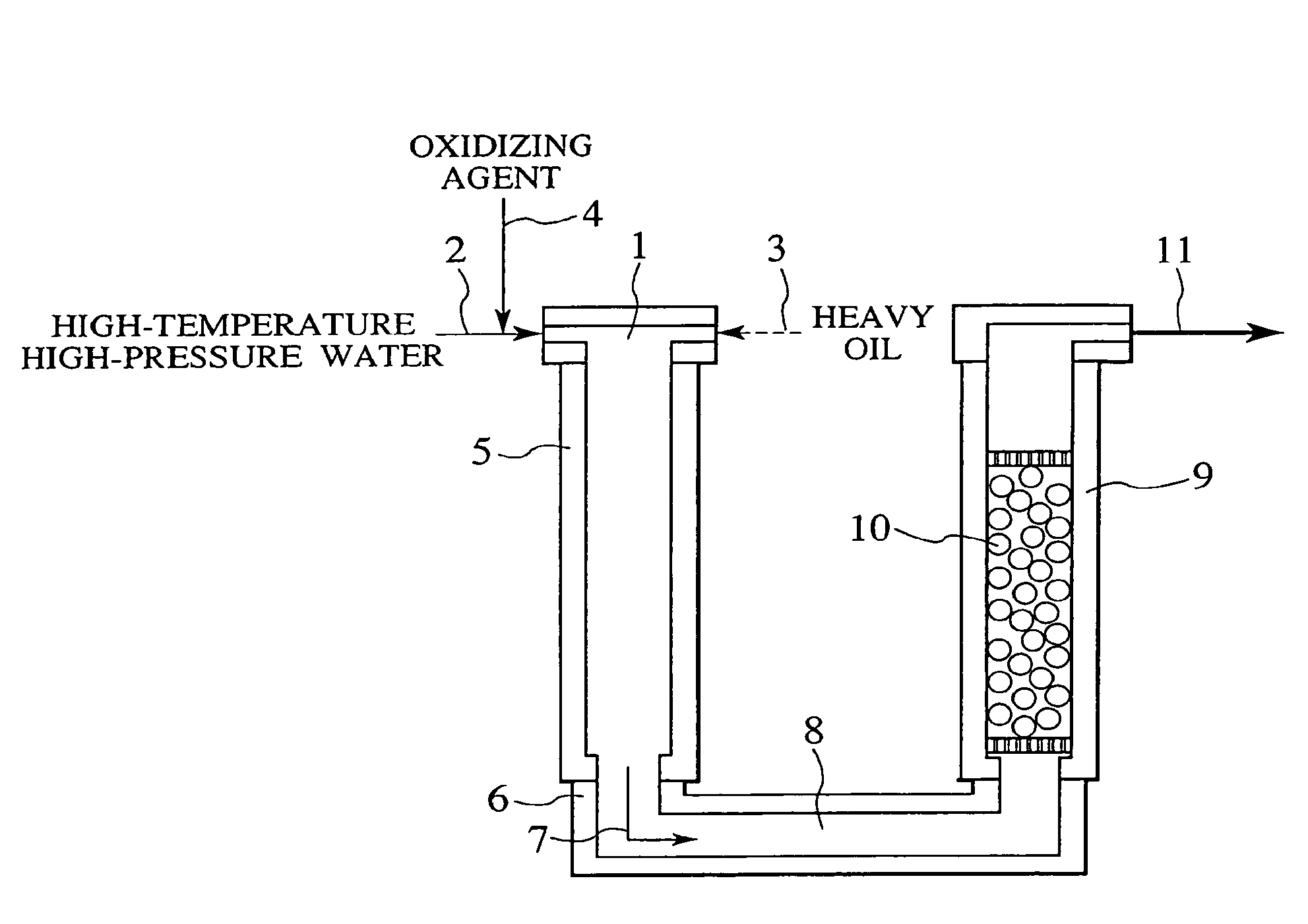
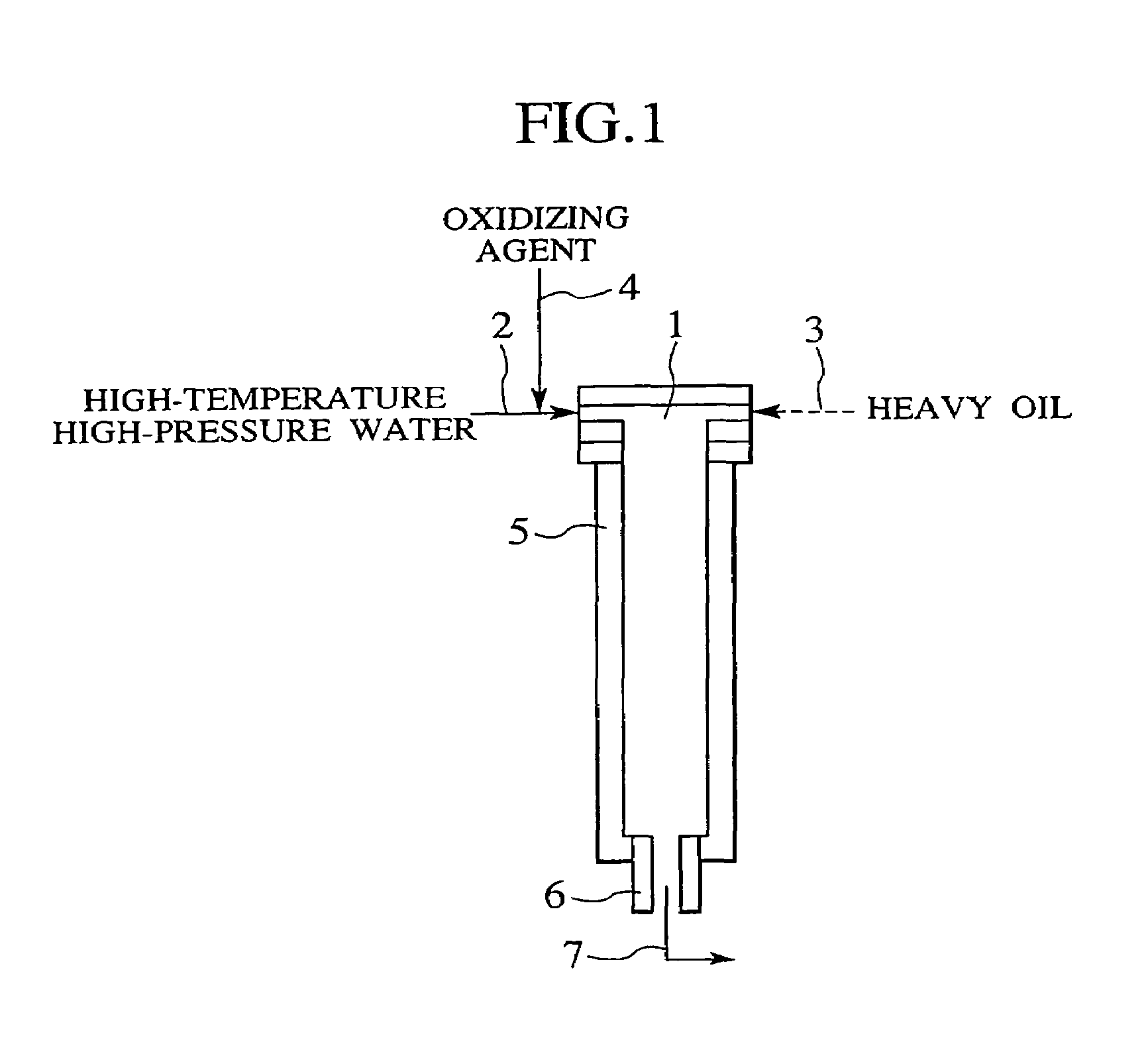
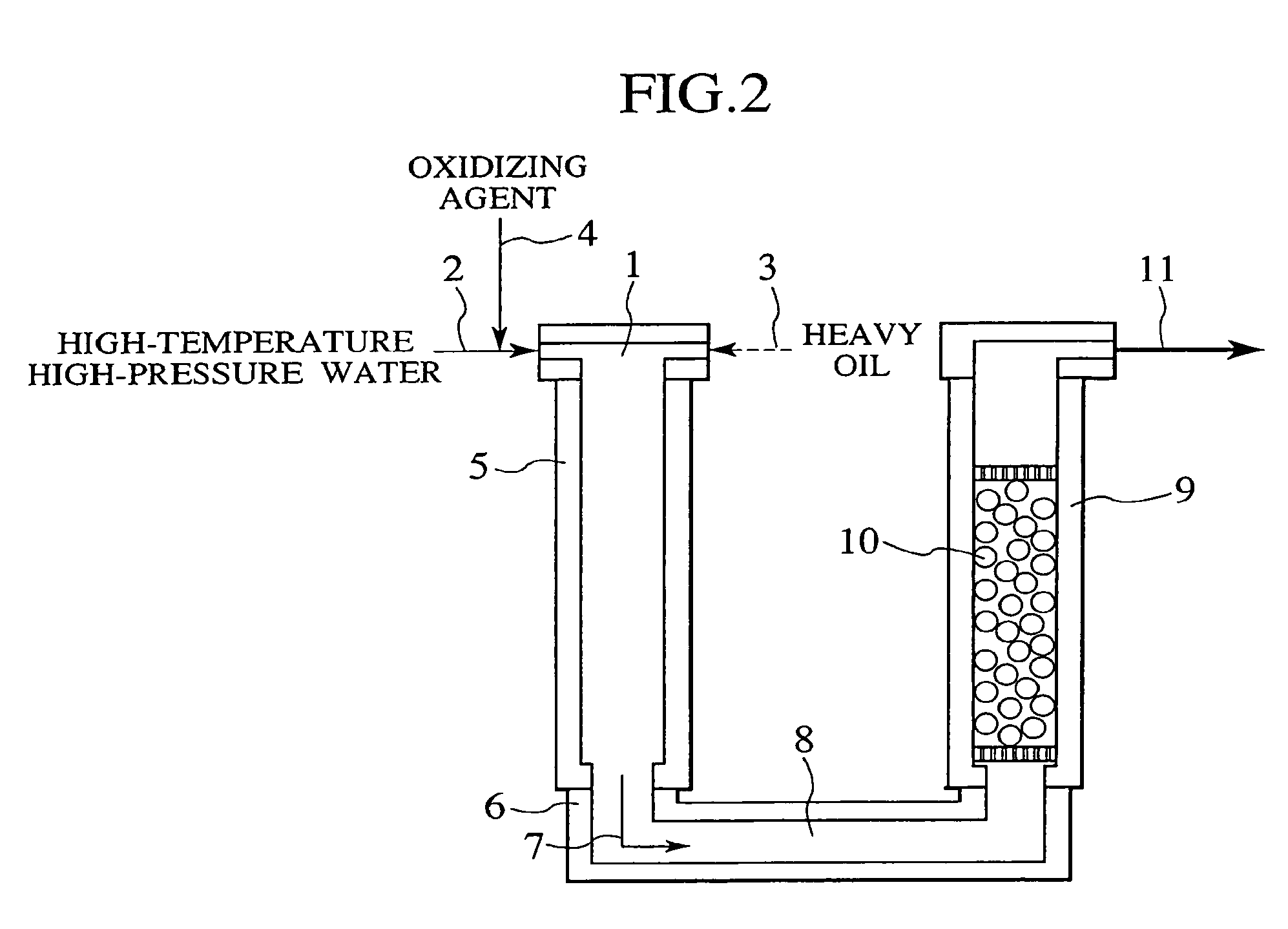
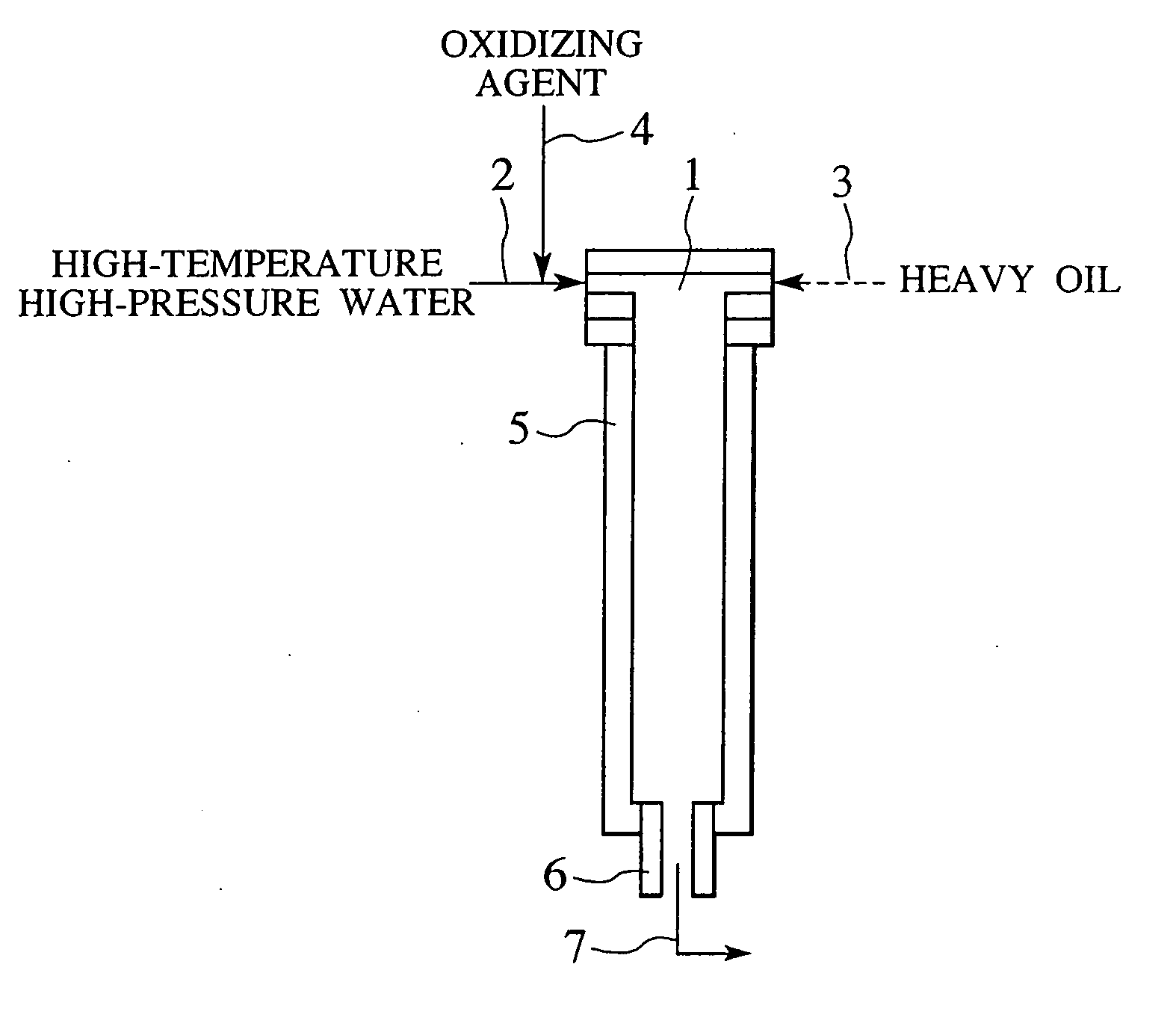
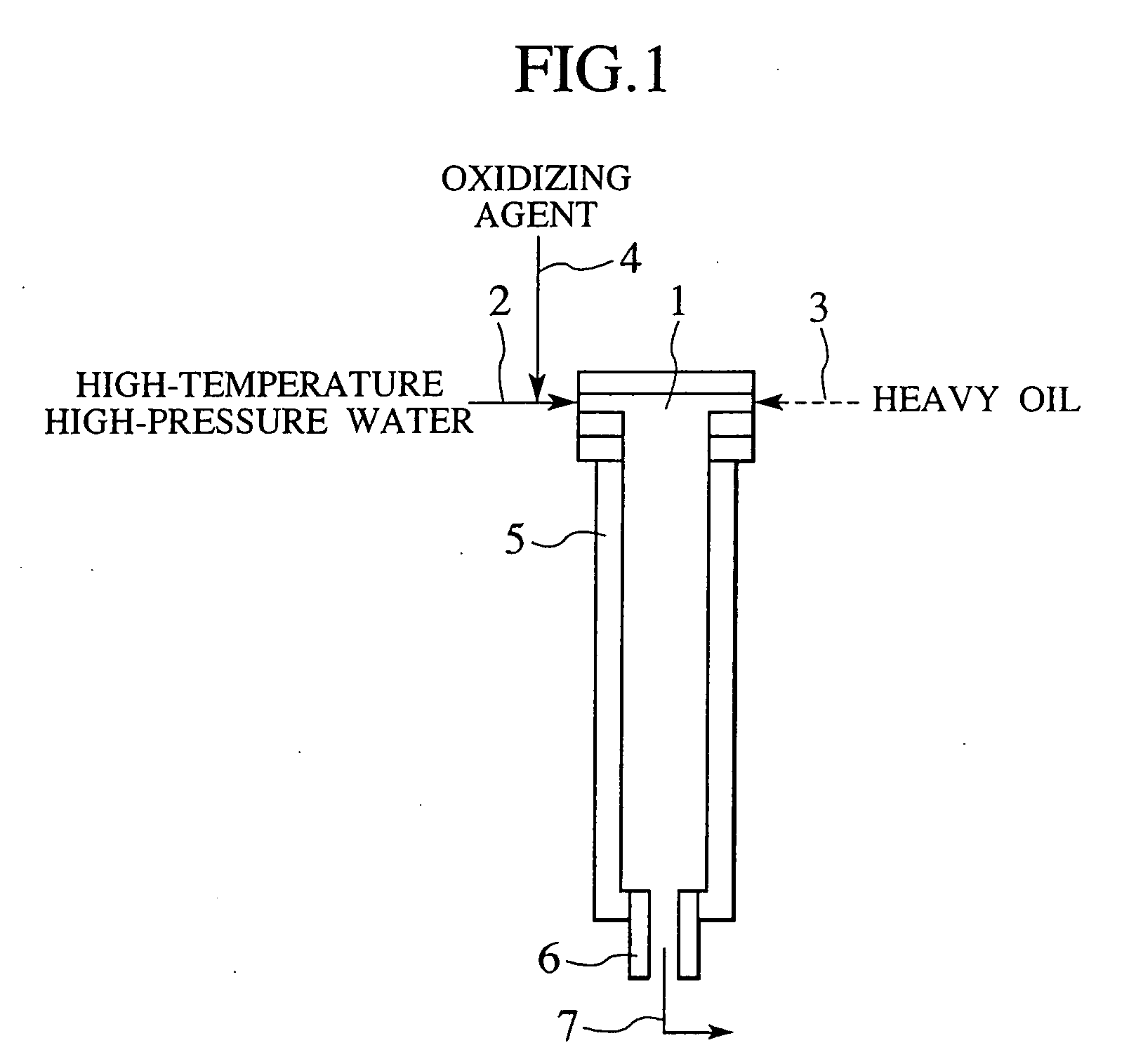
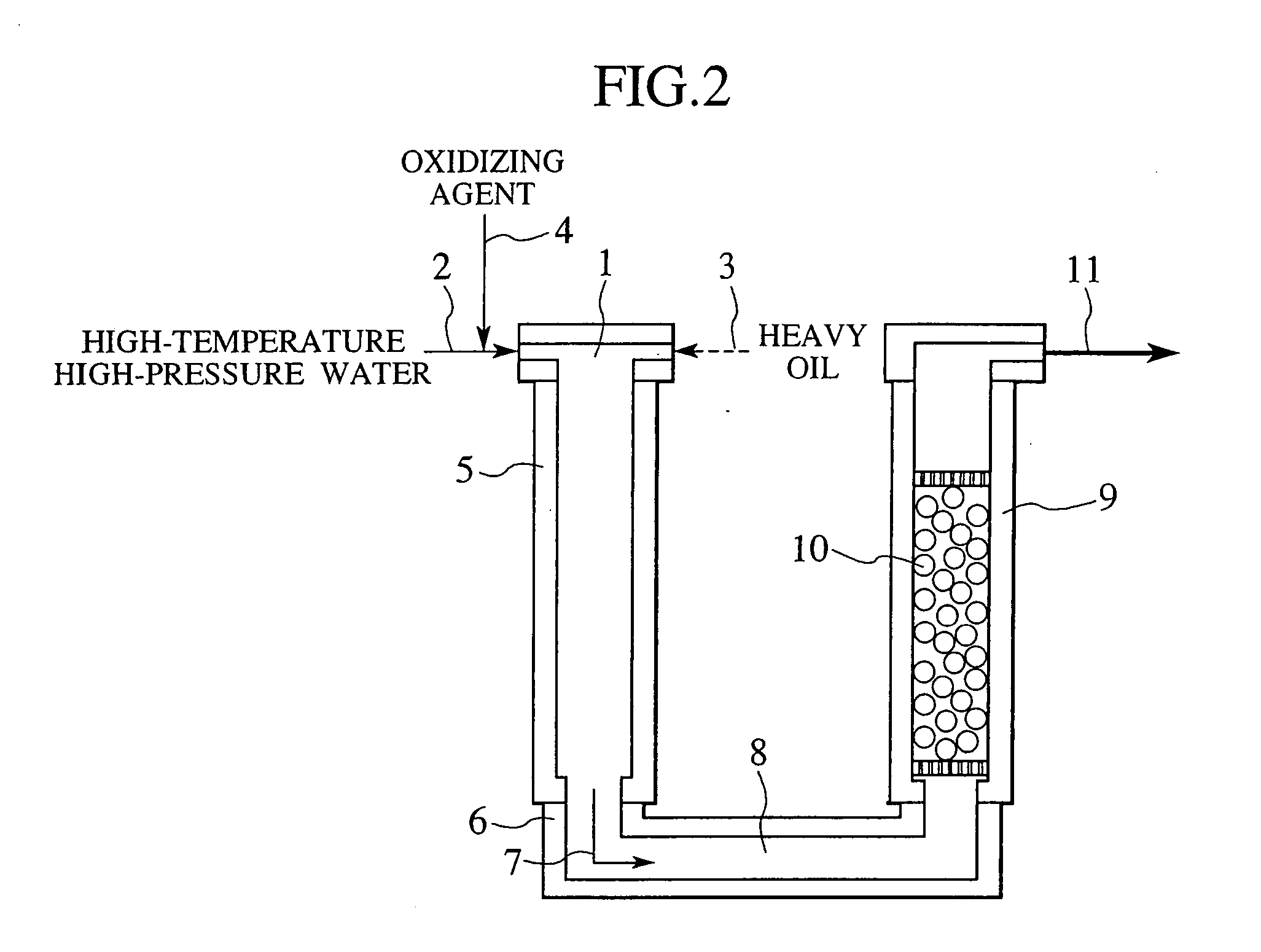
Process and apparatus for treating heavy oil with supercritical water and power generation system equipped with heavy oil treating apparatus
InactiveUS7264710B2Thermal non-catalytic crackingPressurized chemical processScavengerAfter treatment
The reforming of heavy oil with supercritical water or subcritical water is accomplished by mixing together supercriticai water, heavy oil, and oxidizing agent, thereby oxidizing vanadium in heavy oil with the oxidizing agent at the time of treatment with supercritical water and separate vanadium oxide. The separated vanadium oxide is removed by the scavenger after treatment with supercritical water. In this way it is possible to solve the long-standing problem with corrosion of turbine blades by vanadium which arises when heavy oil is used as gas turbine fuel.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Acoustic/pressure wave-driven separation device
InactiveUS8075786B2Thermal non-catalytic crackingGeneral water supply conservationConcentration gradientAcoustic wave
An acoustic / pressure wave-driven device for separating a first component from a mixture of the first component and a second fluid component. The device comprises a rich reservoir, a lean reservoir, a pump reservoir, a bridge structure, and an acoustic / pressure wave source. The rich reservoir is for containing a fluid mixture having an elevated concentration of the first component. The lean reservoir is for containing a fluid mixture having a lesser concentration of the first component that is leaner than the concentration of the first component in fluid mixture of the rich reservoir. The pump reservoir contains a fluid mixture of the first component and the second fluid component. The bridge structure has a sidewall defining a gradient channel in fluid communication with the rich reservoir and the lean reservoir and a length extending there between. The gradient channel is for containing a fluid having a concentration gradient of the first component along its length. A diffusion portion of the sidewall disposed between the gradient channel and the pump reservoir is adapted to permit diffusion of at least the first component between the gradient channel and the pump reservoir while preventing fluid flow there between. The acoustic / pressure wave source provides acoustic waves into the pump reservoir to cause pressure oscillations in the fluid mixture therein adjacent to the diffusion portion to move molecules of the target component against the concentration gradient from the lean reservoir into the rich reservoir.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Heat pipe for heating of gasoline for on-board octane segregation
InactiveUS20060037589A1OptimizationInternal combustion piston enginesEngine controllersOn boardExhaust fumes
In an internal combustion engine fuel system having a membrane separator for separating a primary fuel into a high octane fuel and a low octane fuel, and wherein the primary fuel is heated for separation in the membrane separator, the improvement comprising a heat pipe having an evaporator section positioned to be in the heat exchange relationship with exhaust gas from the internal combustion engine under conditions of use; and a heat output area in heat exchange relationship with a primary fuel as it is fed into the separator whereby the primary fuel is heated. In one embodiment the heat pipe is a variable conductance heat pipe having a top operating temperature not greater than about 160° C.
Owner:GUPTA RAMESH +4
Oil/gas separation membrane, its use in gas sensor and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20050086998A1Losing mechanical propertyLosing permeation efficiencyPreparing sample for investigationFuel testingAdhesiveHexafluoropropylene
An oil gas separation membrane combines a gas permeable yet oil and temperature resistant bulk polymer membrane such as poly(tetrafluoroethylene) and poly(tetrafluoroethylene-co-hexafluoropropylene); a porous metal support such as sintered metal frit disk made with stainless steel, bronze or nickel; and an highly gas permeable adhesive that bonds firmly the bulk polymer membrane and the metal frit surface together. The adhesive is either a homogenous polymer that has desirable gas permeability, or a coalescent porous polymer particulates network. A gas sensor employing the oil gas separation membrane for detecting and monitoring fault gases of oil filled electrical equipment requires no mechanical wearing or moving part such as pump and valve and the gas sensor is operated normally under various temperature and pressure conditions.
Owner:ASENSOR TECH
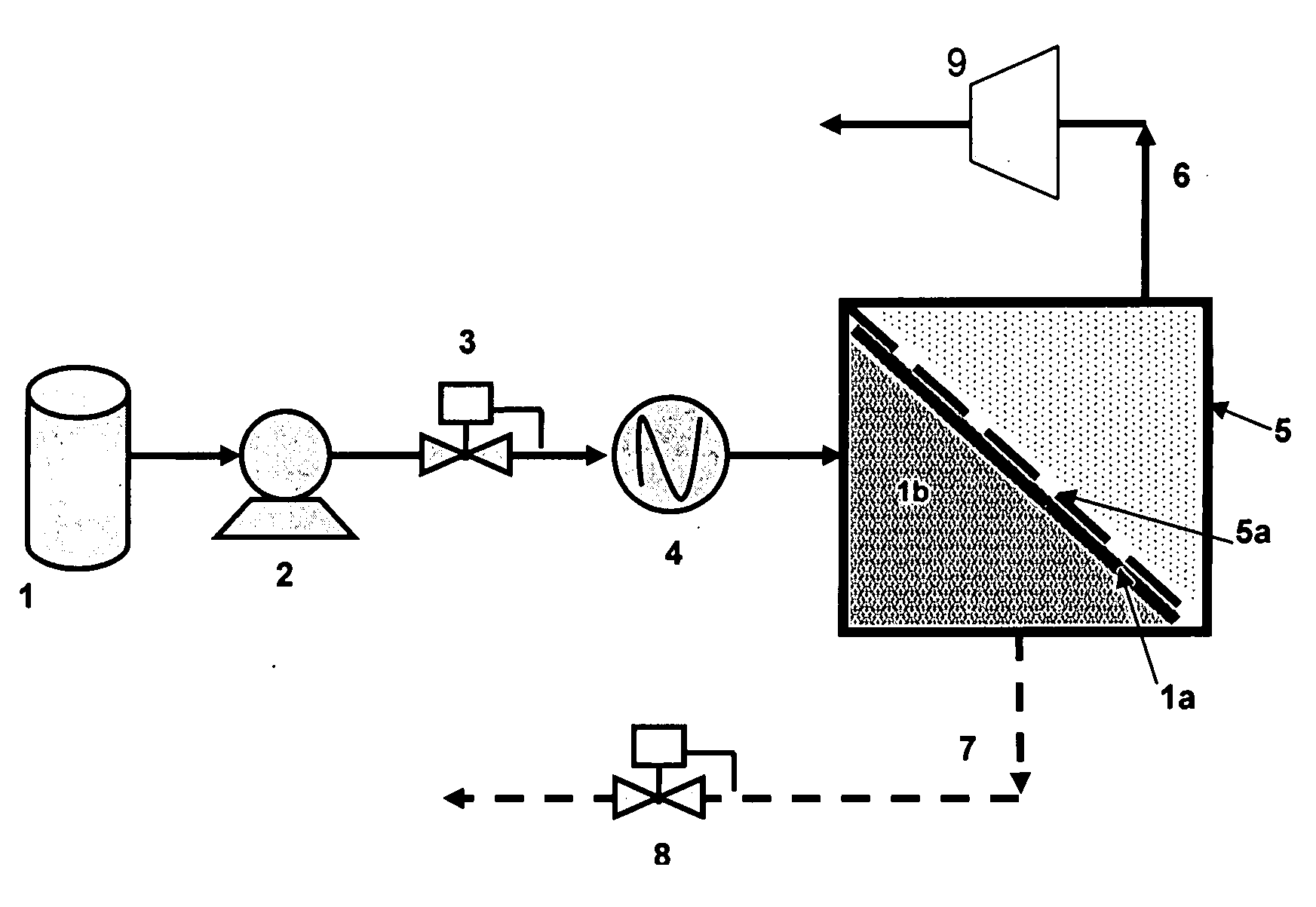
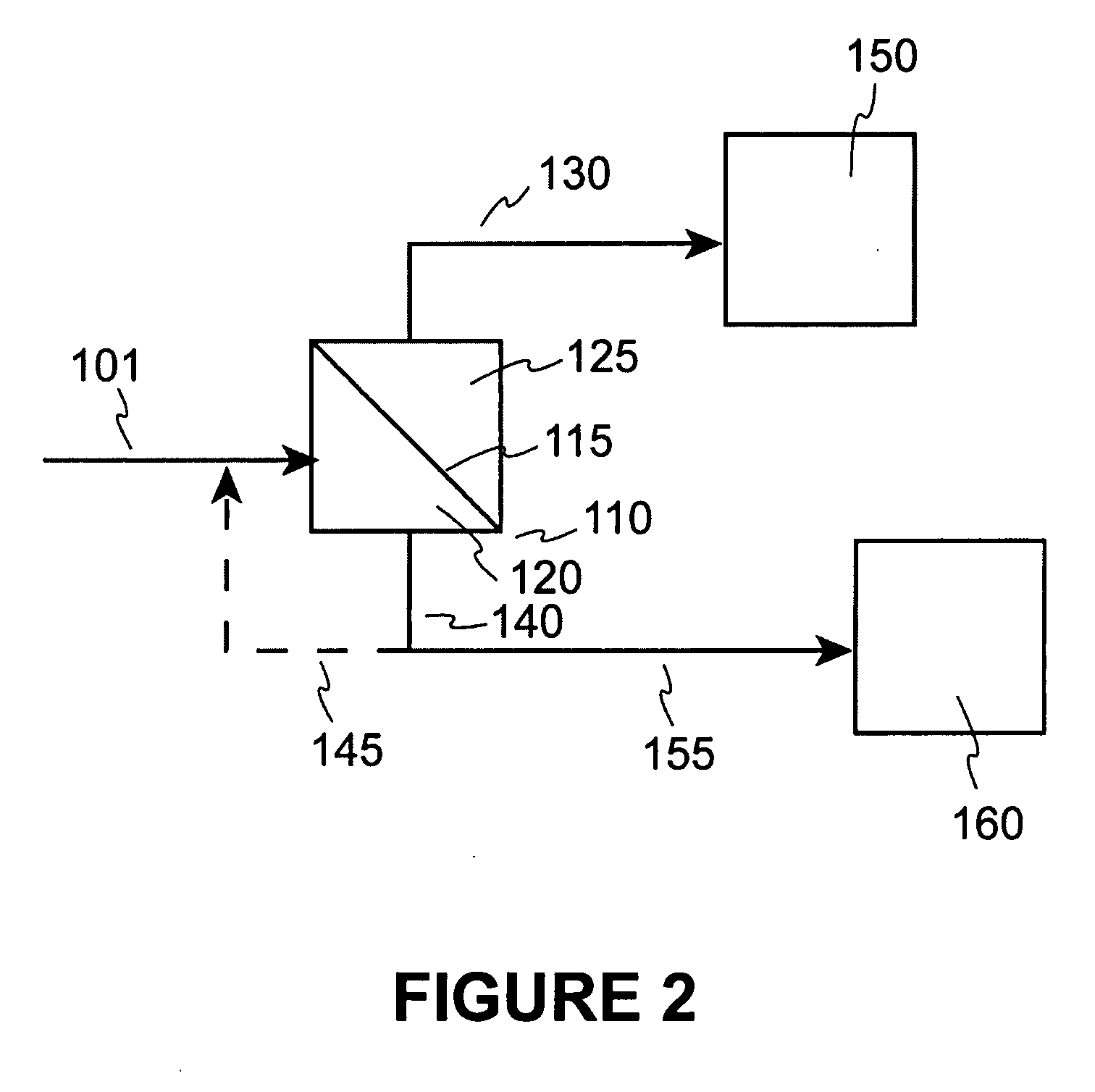
Selective separation of fluid compounds utilizing a membrane separation process
InactiveUS6986802B2Low costCost prohibitiveGas treatmentLiquid degasificationPermselective membraneControl equipment
Apparatus and processes are disclosed for economical separation of fluid mixtures utilizing perm-selective membranes. Broadly, apparatus of the invention comprises a plurality of membrane modules comprising a solid perm-selective membrane and equipment for controlling enthalpy of selected fluids within the apparatus. Advantageously, the membrane modules are disposed in a first product group, a second product group, and at least one intermediate group. Apparatus of the invention is particularly useful for simultaneous recovery of a very pure permeate product, and / or a desired non-permeate stream, from fluid mixtures of two or more compounds which when subjected to appropriately altered conditions of temperature and / or pressure exhibit a bubble point.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
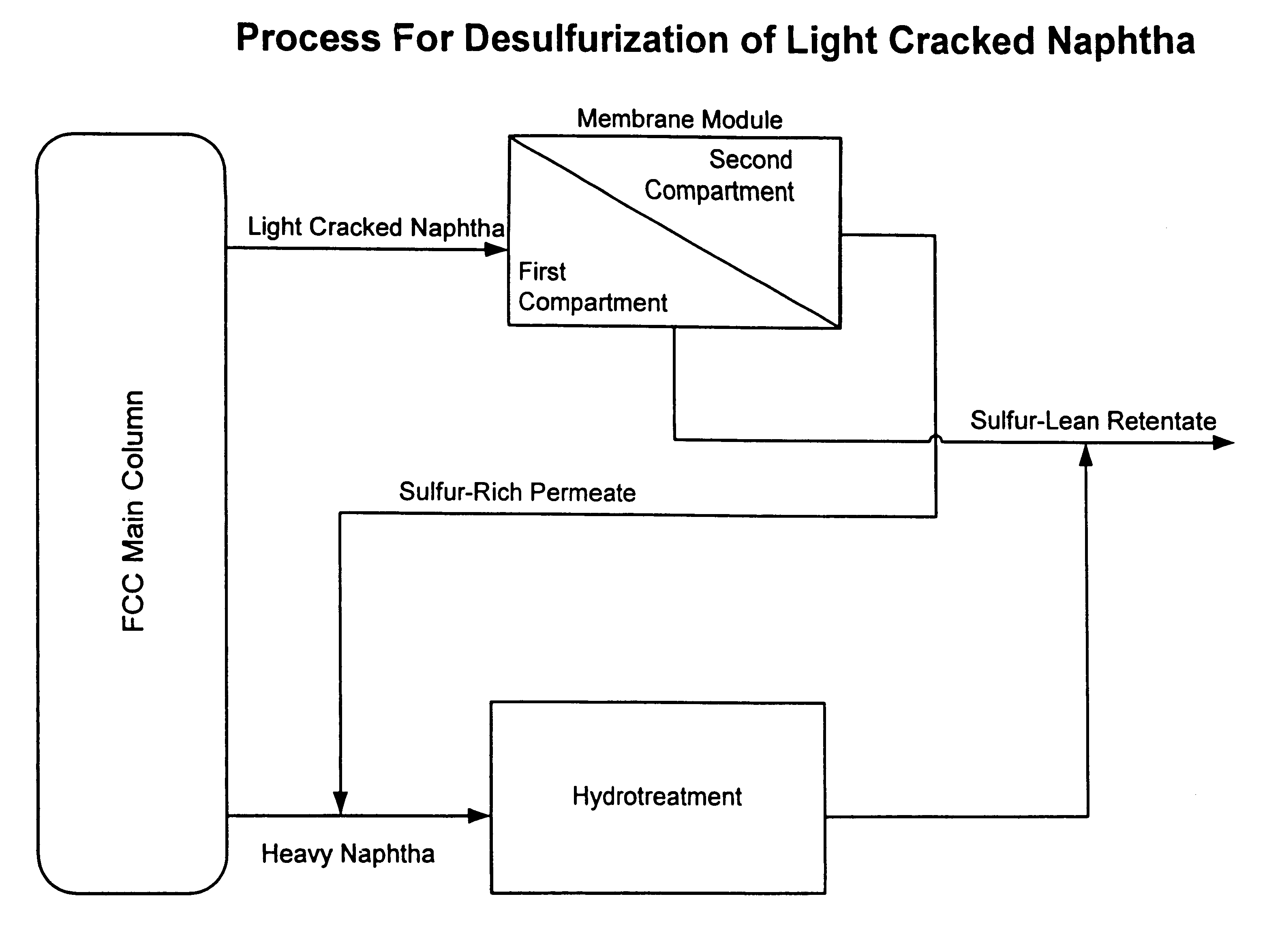
Membrane process for separating sulfur compounds from FCC light naphtha
InactiveUS6649061B2Ion-exchange process apparatusTreatment with plural serial stages onlyNaphthaHydrocarbon mixtures
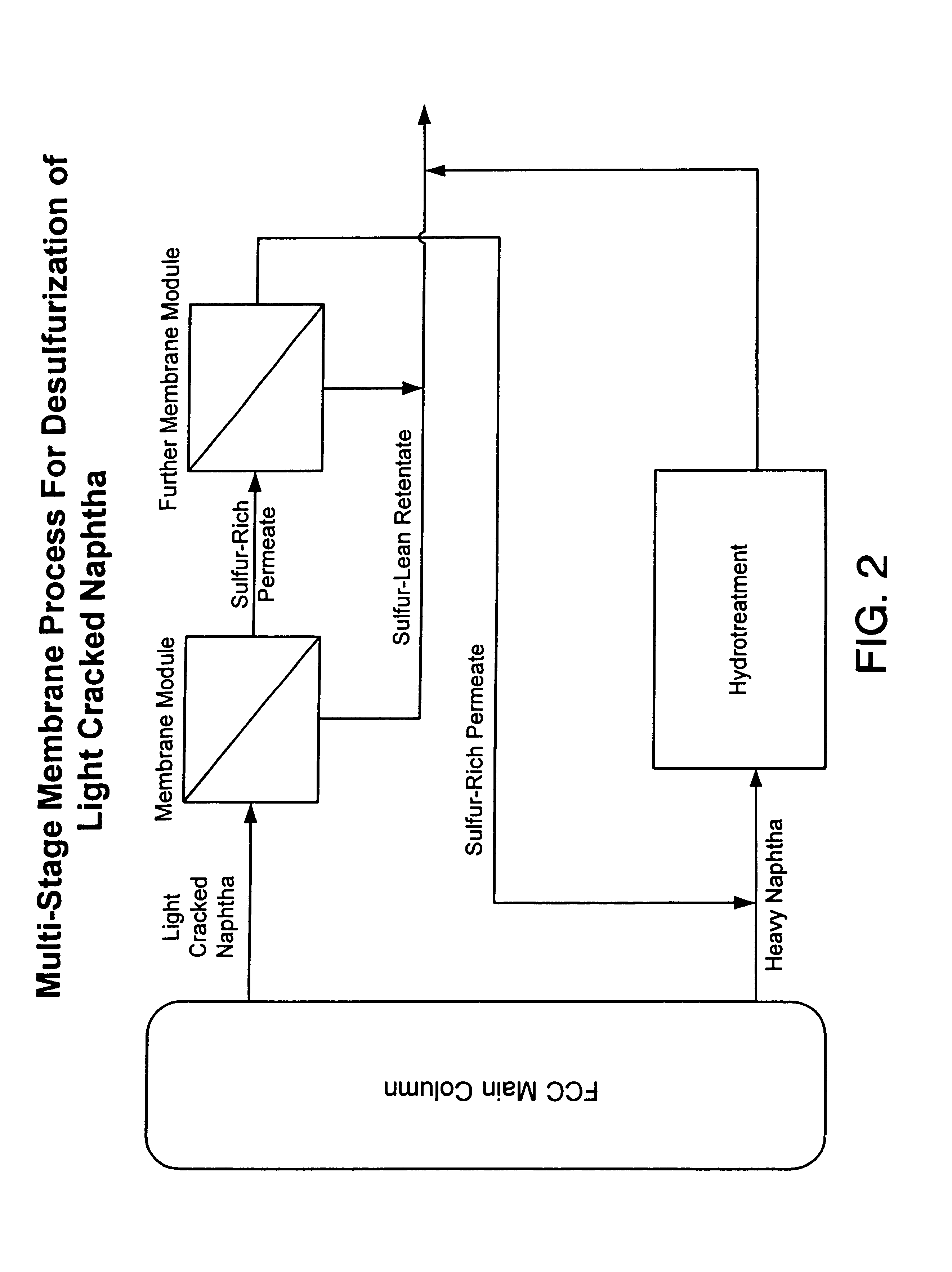
A process for the separation of sulfur compounds from a hydrocarbon mixture using a membrane is provided. Preferred hydrocarbon mixtures are oil refining fractions such as light cracked naphtha. Membranes are composed of either ionic or non-ionic materials and preferentially permeate sulfur compounds over other hydrocarbons. A single or multi-stage membrane system separates the hydrocarbon mixture into a sulfur-rich fraction and a sulfur-lean fraction. The sulfur-lean fraction may be used in fuel mixtures and the sulfur-rich fraction may be further treated for sulfur reduction.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
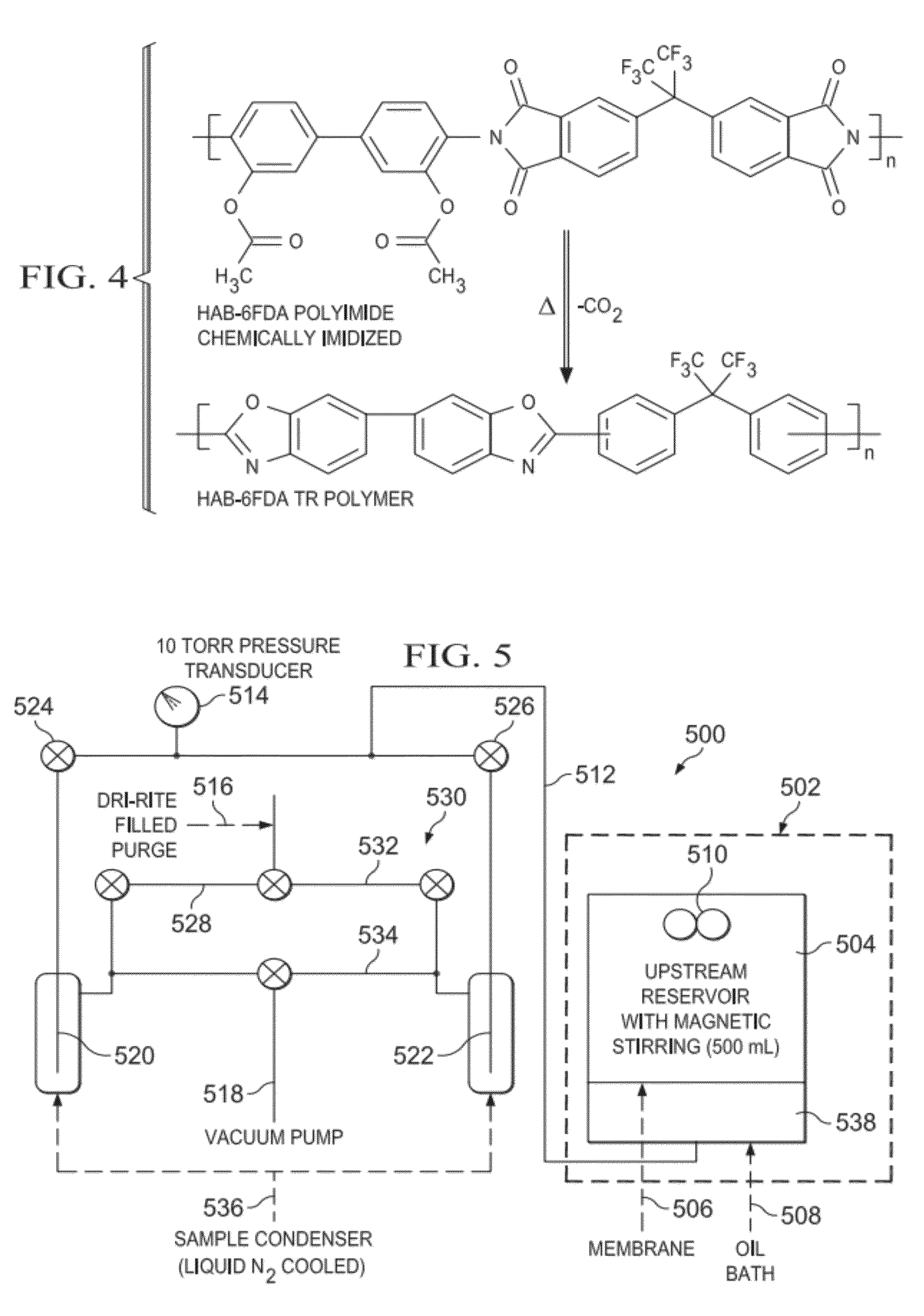
Thermally Rearranged (TR) Polymers as Membranes for Ethanol Dehydration
InactiveUS20120305484A1Improved separation propertiesGood chemical stabilityDewatering/demulsification with mechanical meansSolid sorbent liquid separationBiodieselOrganic solvent
Synthesis and use of a new class of polymeric materials with favorable separation characteristics for the dehydration of ethanol and other organic solvents is described herein. The thermally rearranged (TR) polybenzoxazole (PBO), polybenzimidazole (PBI) and polybenzothiazole (PBT) membranes of the present invention can be used for the dehydration of ethanol during processing to fuel grade biodiesel by either pervaporation or vapor permeation. The unique microstructure of the membranes provides excellent separation characteristics, and this, coupled with their inherent thermal and chemical stability, enables their usage in other separations, such as the dehydration of other organic solvents.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Membrane separation process
ActiveUS7497895B2Organic compounds purification/separation/stabilisationMembranesSpray nozzlePervaporation
The invention relates to an improved membrane pervaporation and vapor permeation system in which the vacuum is produced by a fluid passing through a Venturi-type nozzle. The fluid is chosen from solvents that have little or no affinity for the permeate molecules. It is applicable over process feed rates, and can be used for the separation of aromatic species from hydrocarbon.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
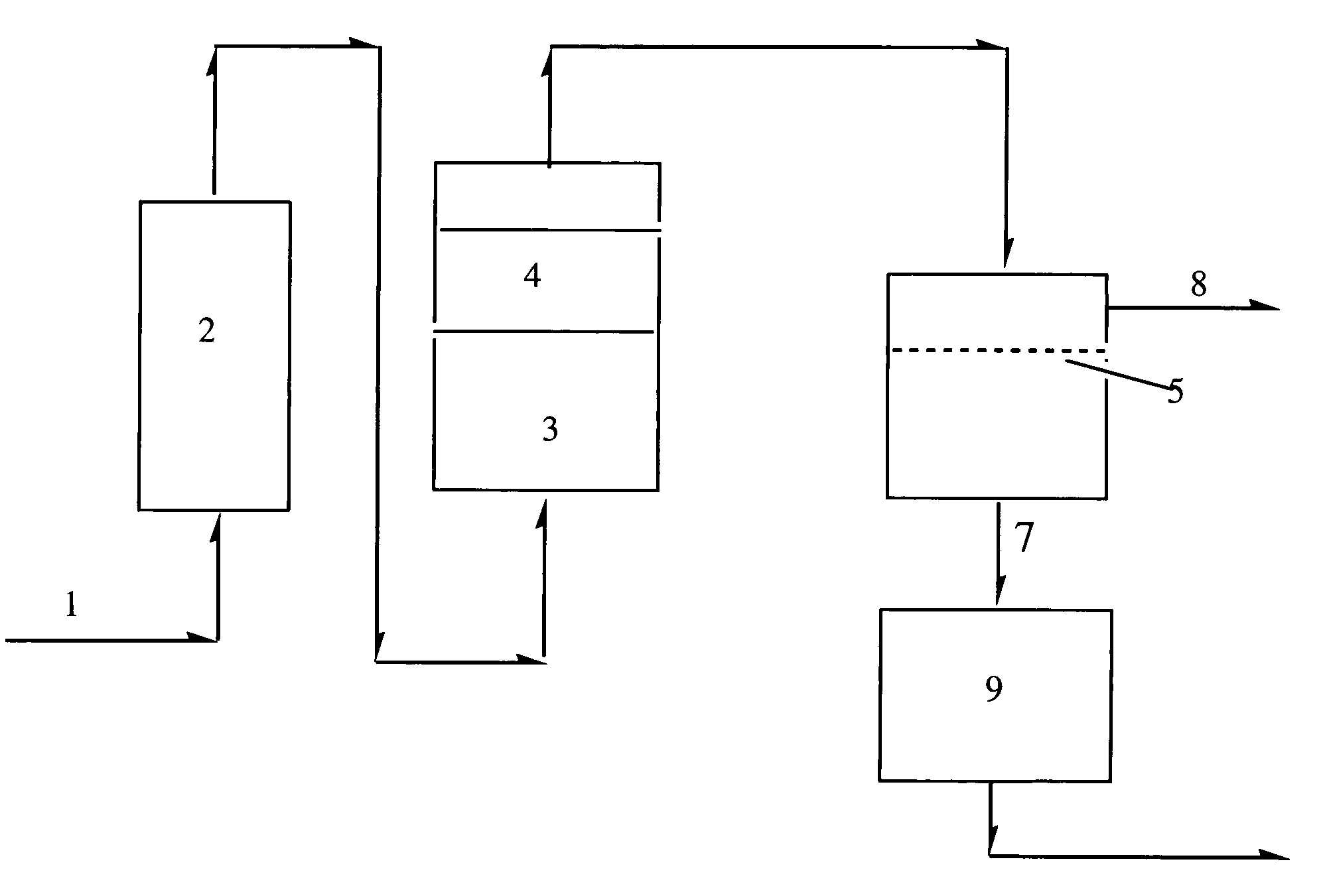
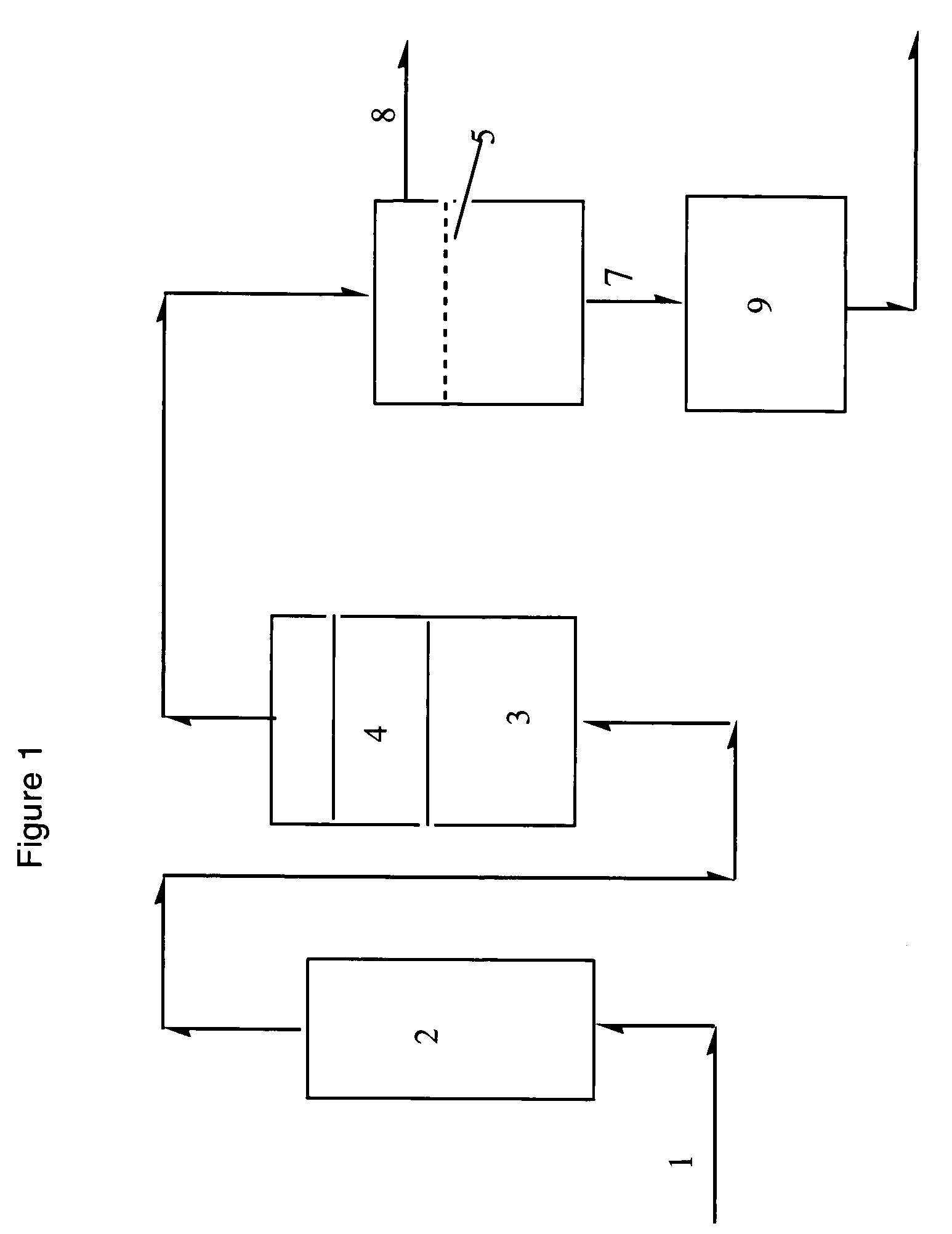
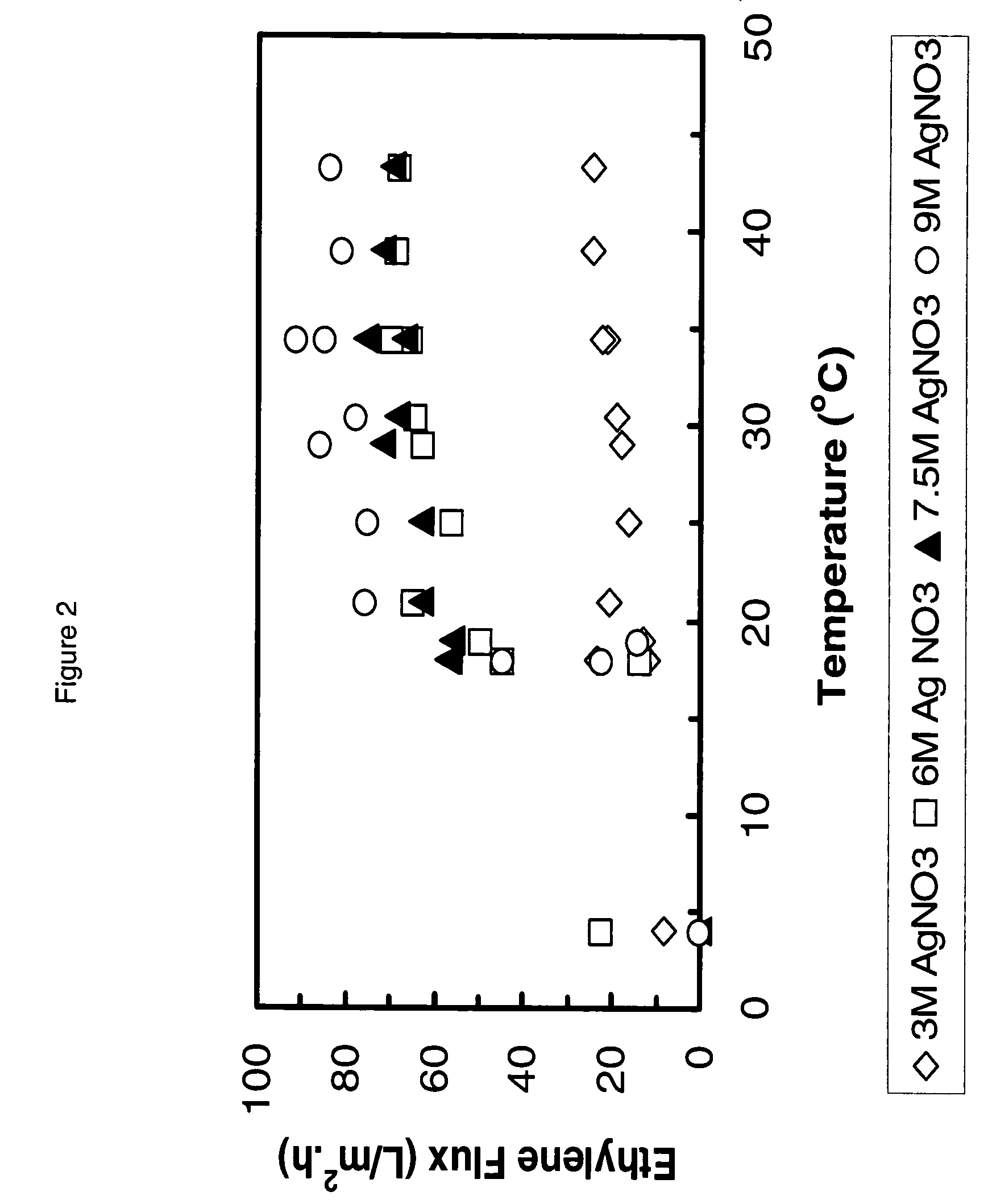
Process for the separation of olefins from paraffins using membranes
Chitosan membranes chelated with silver or cuprous material may be used to separate olefins from a mixture of olefins and paraffins. The feed stream is humidified, demisted, treated to remove sulfur compounds and passed to a cell having a chitosan membrane containing chelated silver or cuprous compounds. The process has a reasonable flux rate and is operable at reasonable temperatures and pressures. The process could be used in an olefin separation train.
Owner:IMTEX MEMBRANES CORP
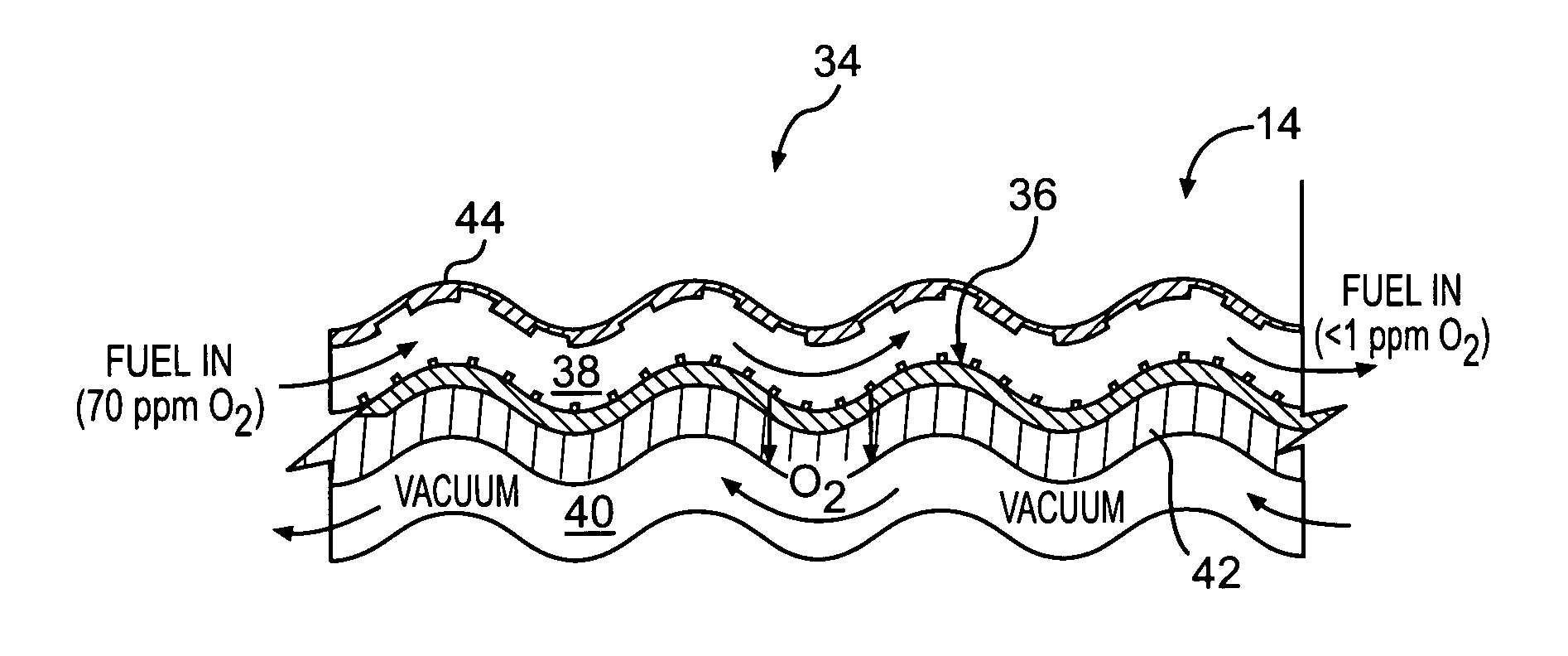
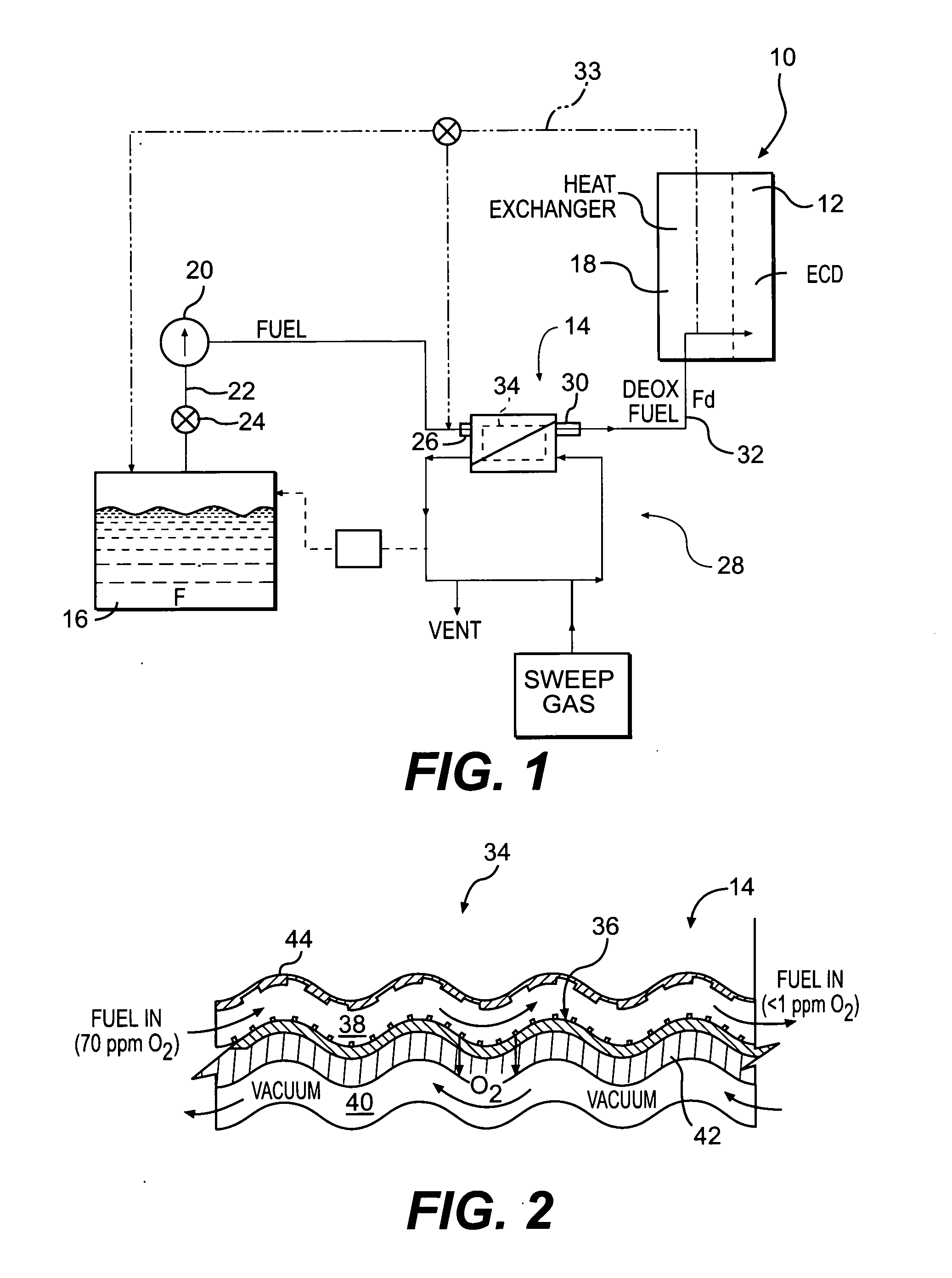
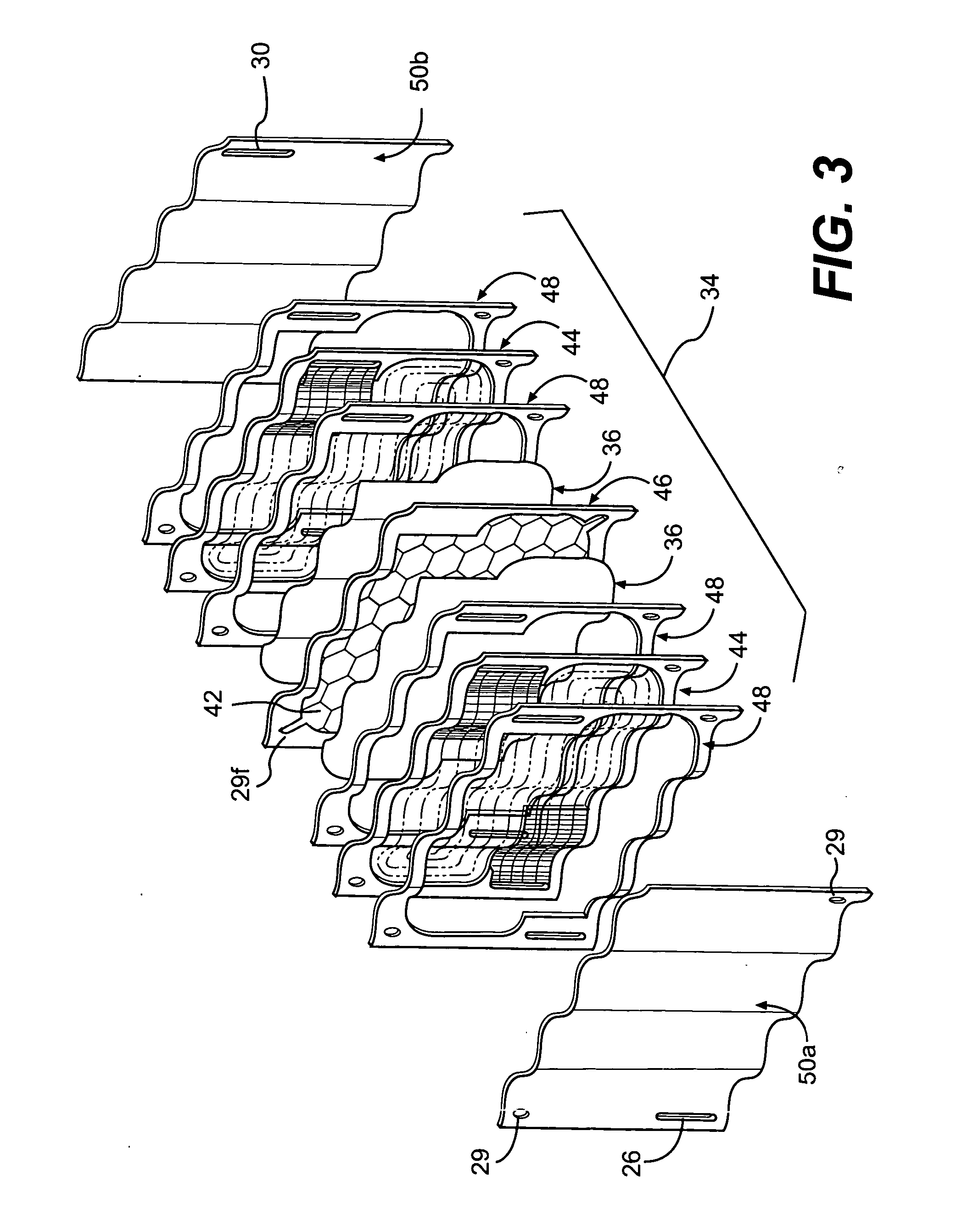
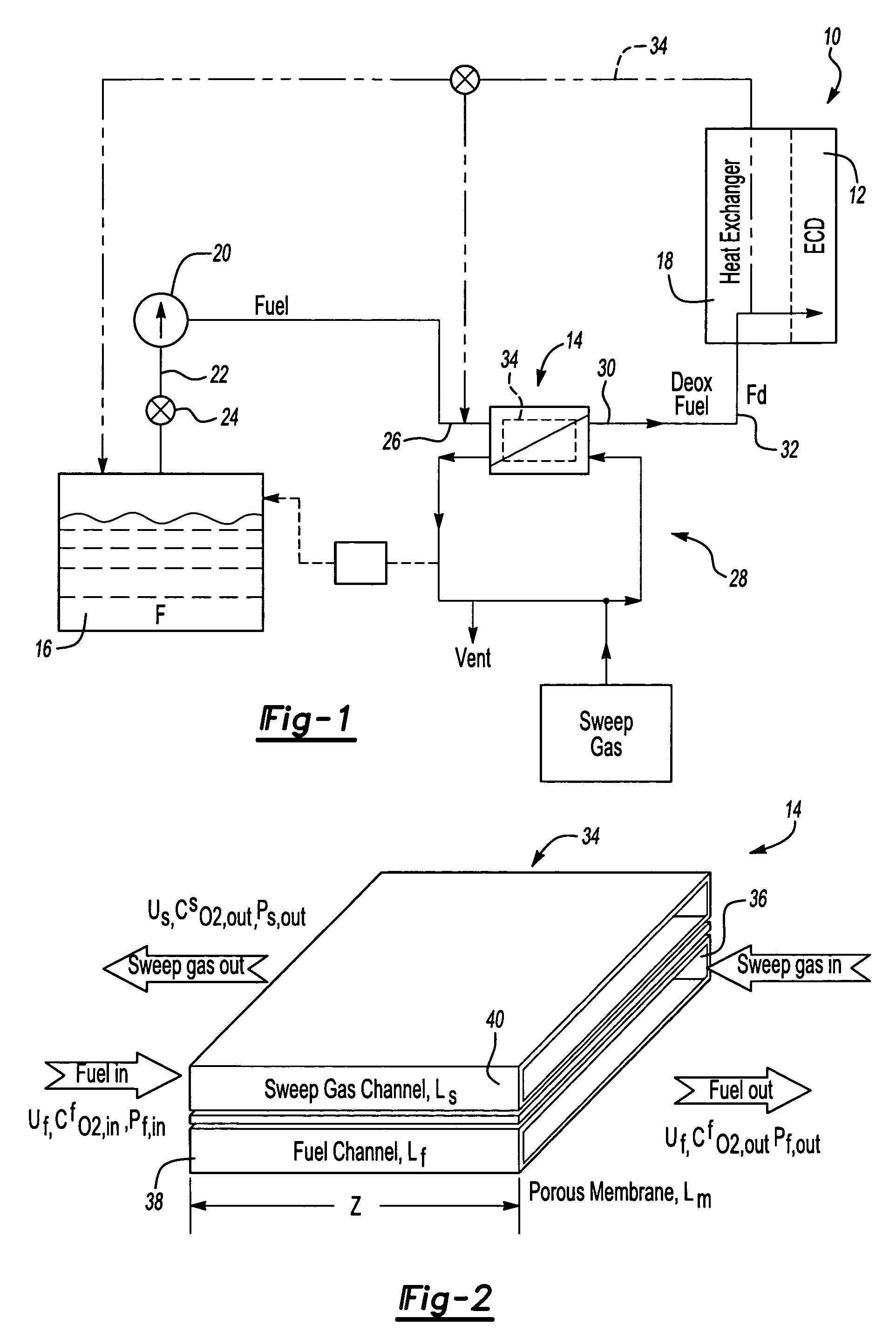
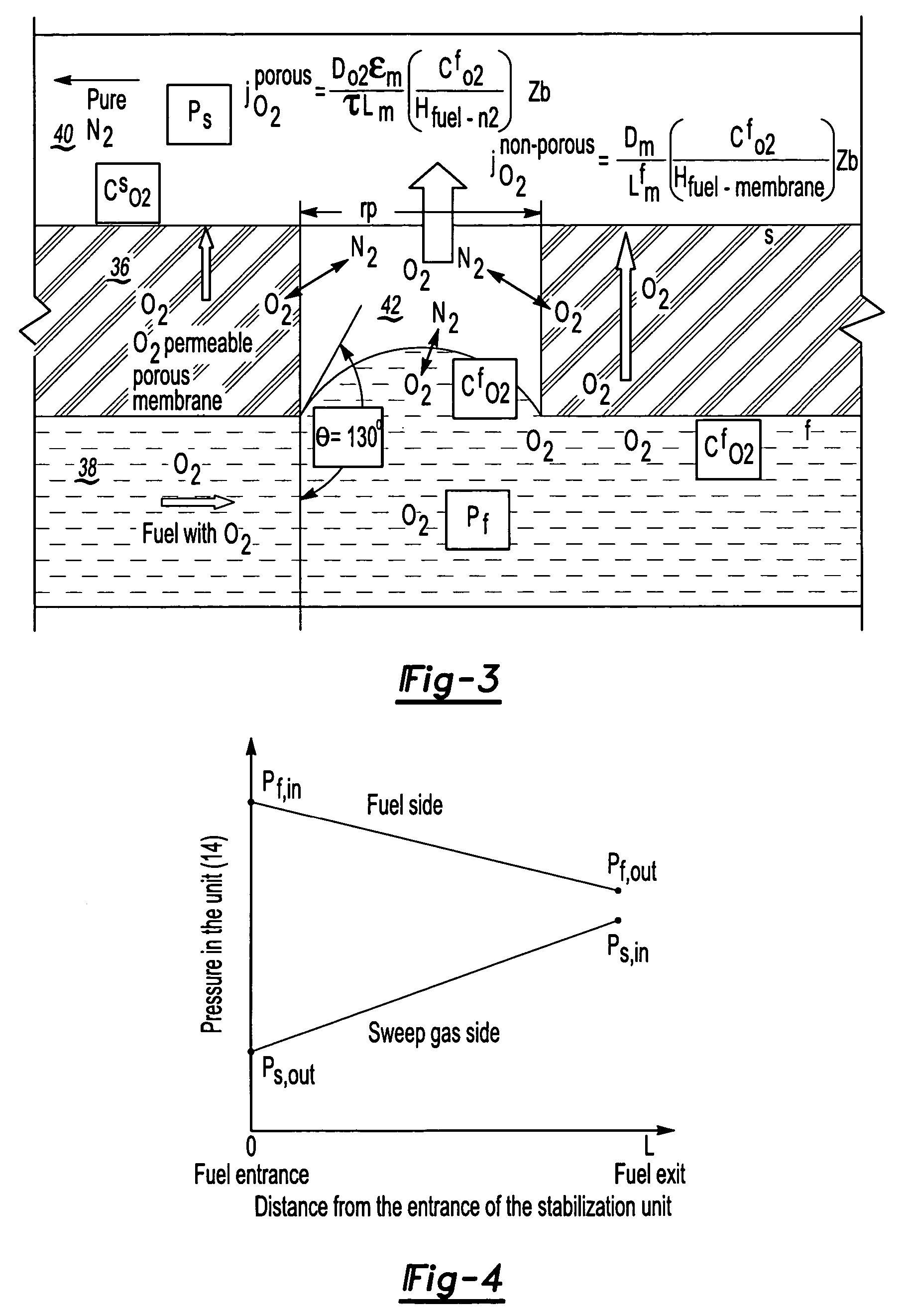
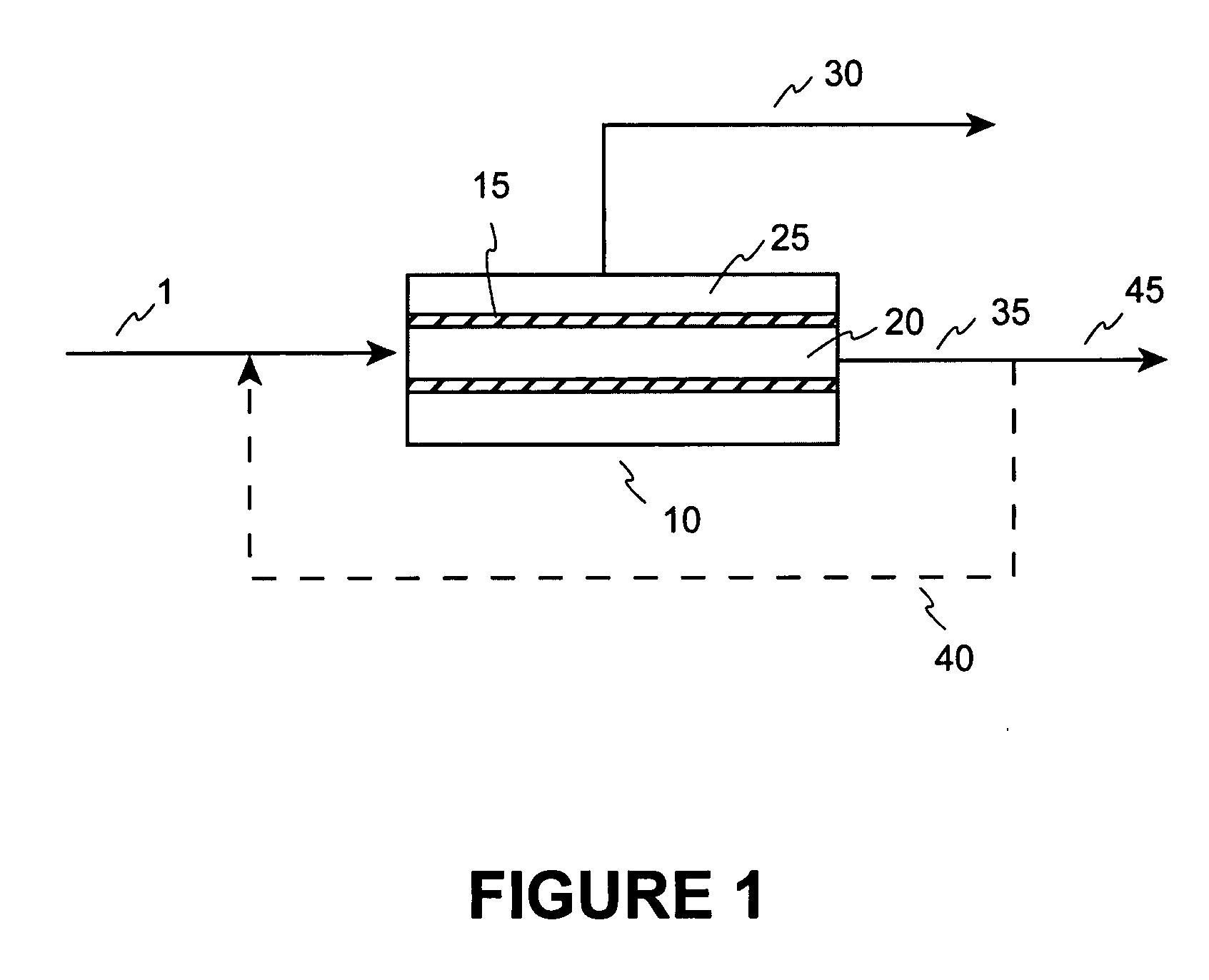
Fuel deoxygenation system with non-planar plate members
ActiveUS20060278073A1Enhances deoxygenationImprove efficiencyPower plant fuel tanksIsotope separationPorous substrateEngineering
A fuel system for an energy conversion device includes a multiple of fuel plates, oxygen permeable membranes, porous substrate plates, and vacuum frame plates which define a wave pattern configuration. The wave configuration enhances deoxygenation by increasing the efficiency and integrality due to higher surface volume ration, increase of flow turbulence, and minimal sharp edges which may otherwise damage the oxygen permeable membranes compared to other configurations.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
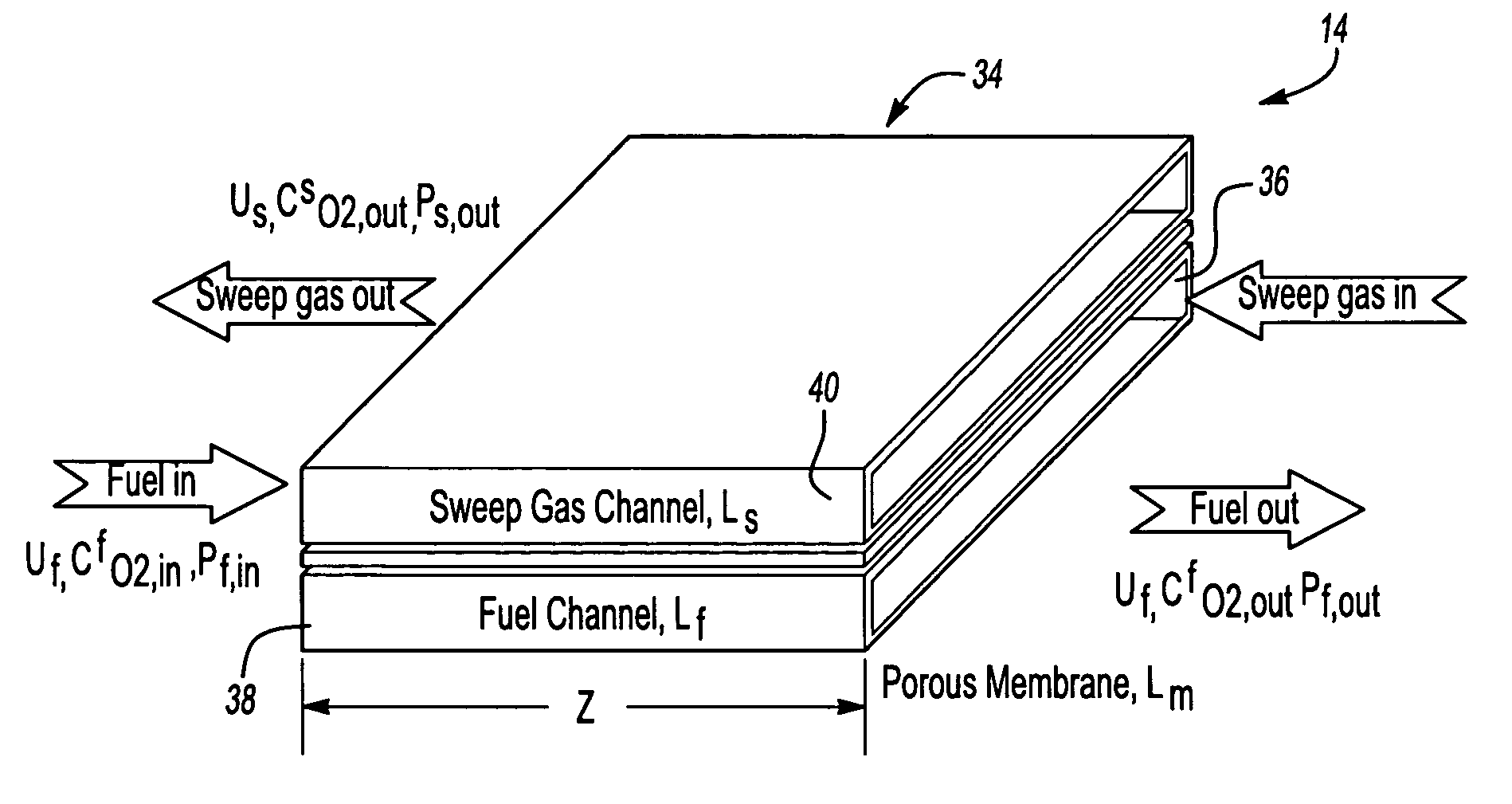
Fuel deoxygenation system
ActiveUS7153343B2Inexpensive sizeInexpensive weightLiquid fuel feeder/distributionSemi-permeable membranesPorous membraneEngineering
A fuel system for an energy conversion device includes a deoxygenator system with a porous membrane. The deoxygenator includes an oxygen receiving channel separated from the fuel channel by the porous membrane. The capillary forces counteract the pressure differential across the membrane, preventing any leakage of the fuel, while the oxygen concentration differential across the membrane allows for deoxygenation of the fuel through the porous membrane.
Owner:RTX CORP
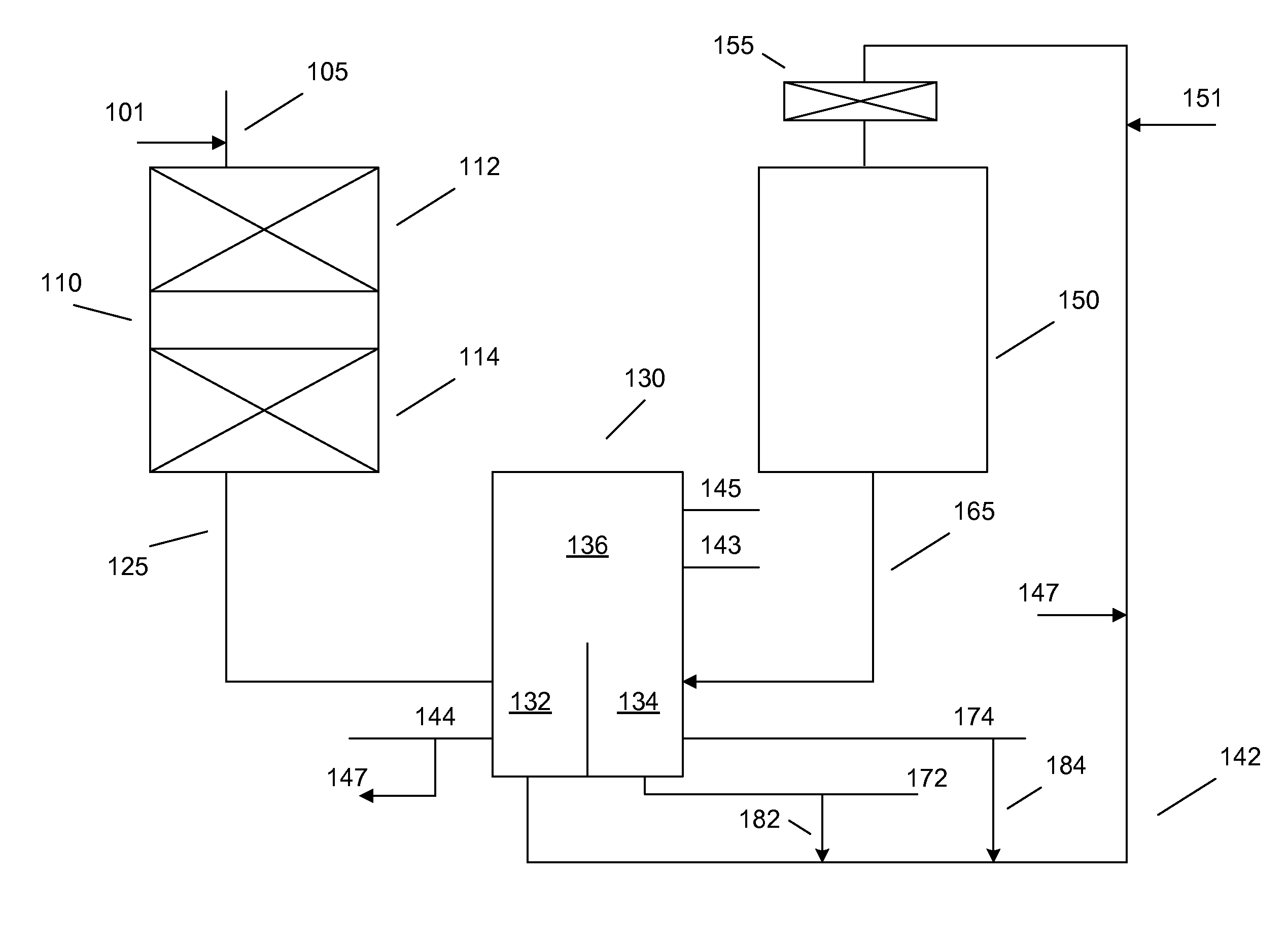
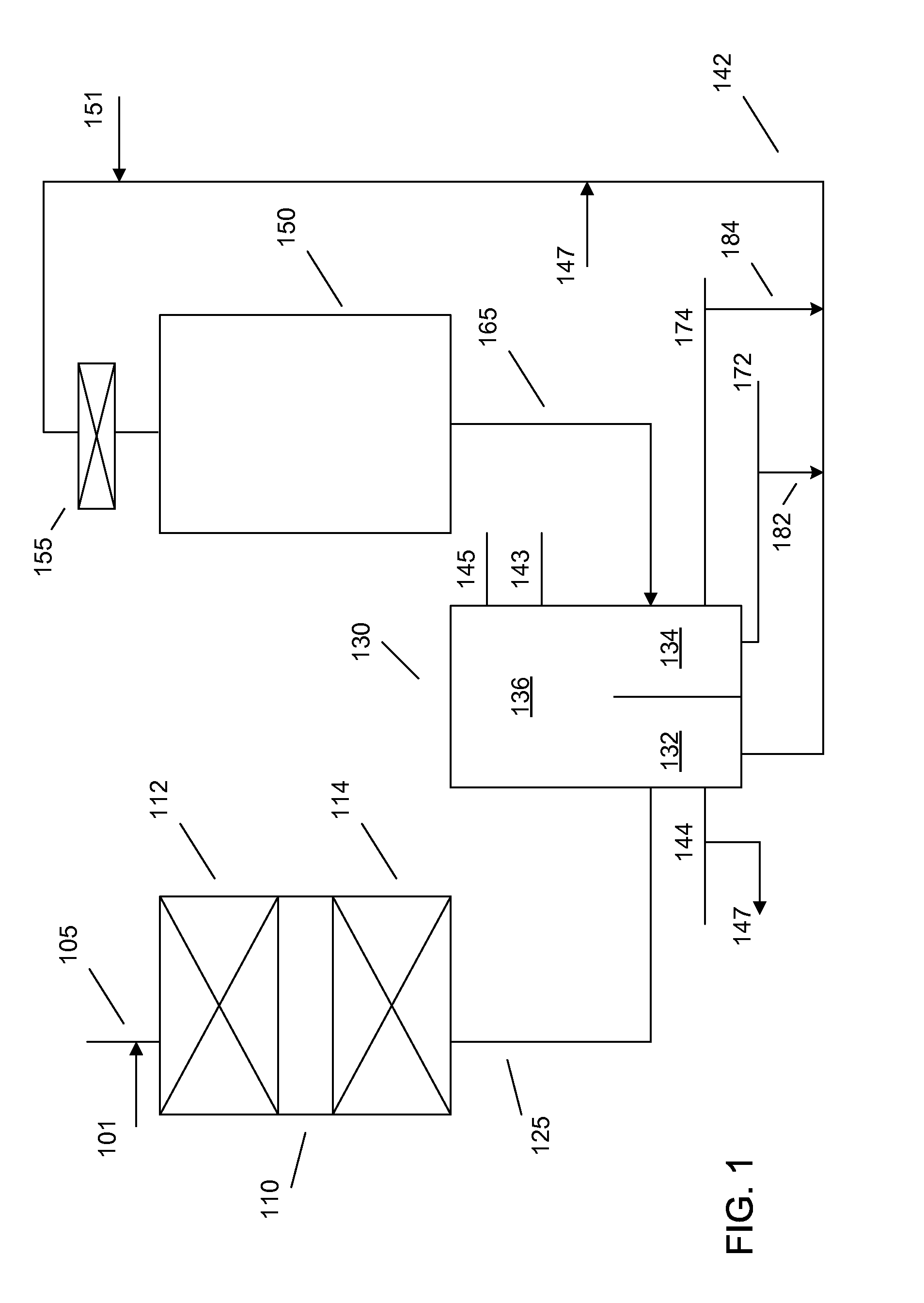
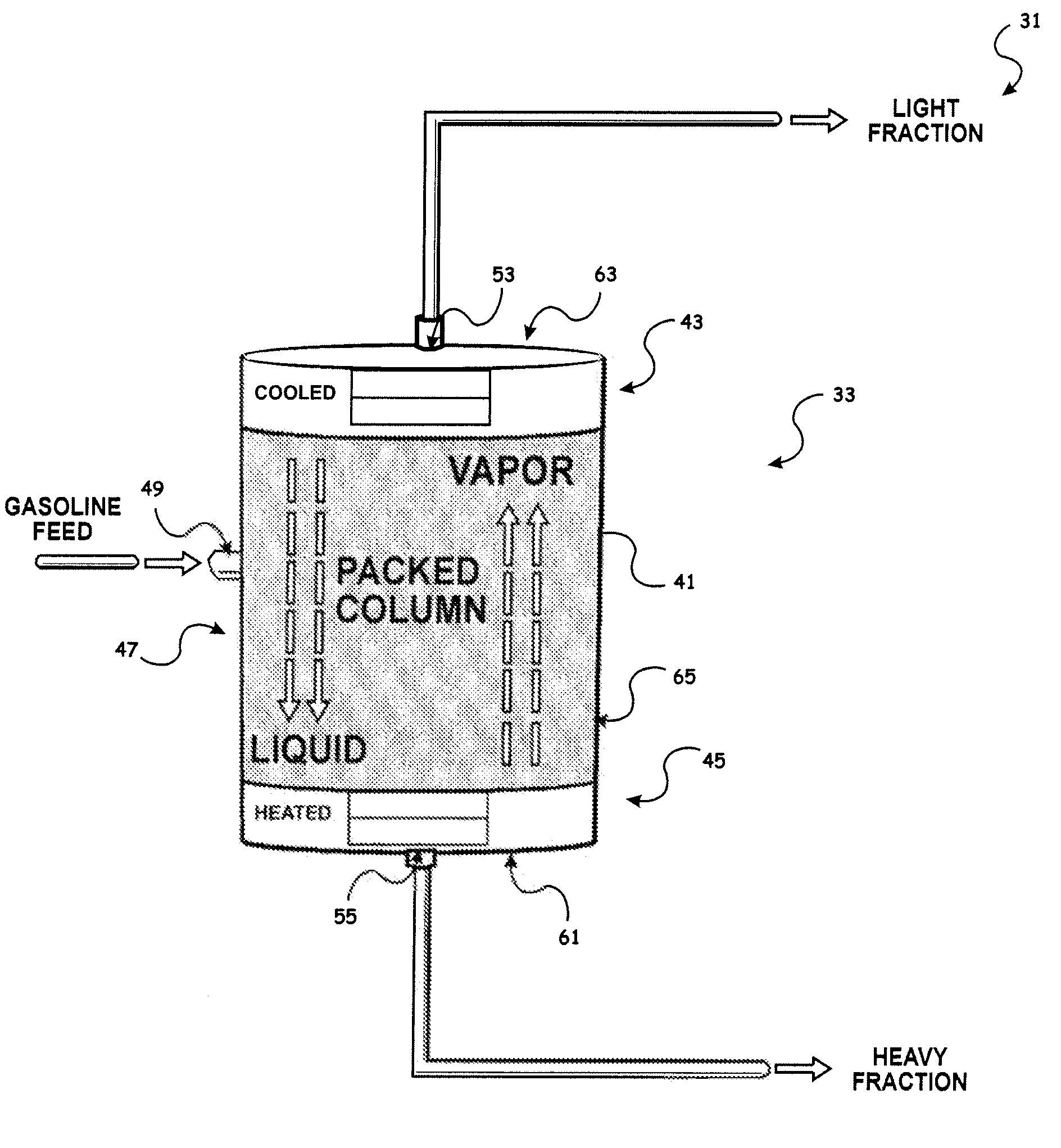
On-board fuel fractionation system and methods to generate an engine starting fuel
InactiveUS7370610B2Efficient separationAccelerate emissionsThermal non-catalytic crackingDistillation regulation/controlDistillationFractionation
A Fuel Fractionation System (FFS) and associated methods to generate and store a fuel for internal combustion engines is provided. FFS provides a distillation column assembly to distill liquid fuel to form a volatile light fraction secondary fuel. The distillation column assembly includes a vaporization module to vaporize a feed fuel in the distillation column and includes a condensation module to condense heavy fraction components of the vaporized feed fuel. FFS also provides a controller positioned to control the vaporization of feed fuel in the distillation column to thereby control the separation of the feed fuel into light fraction fuel and heavy fraction fuel components, and positioned to control the condensation of the heavy fraction components so that fuel exiting a light fraction output port in the distillation column is substantially light fraction fuel components by volume.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Process and apparatus for treating heavy oil with supercritical water and power generation system equipped with heavy oil treating apparatus
InactiveUS20070144941A1Thermal non-catalytic crackingPressurized chemical processScavengerAfter treatment
The reforming of heavy oil with supercritical water or subcritical water is accomplished by mixing together supercritical water, heavy oil, and oxidizing agent, thereby oxidizing vanadium in heavy oil with the oxidizing agent at the time of treatment with supercritical water and separate vanadium oxide. The separated vanadium oxide is removed by the scavenger after treatment with supercritical water. In this way it is possible to solve the long-standing problem with corrosion of turbine blades by vanadium which arises when heavy oil is used as gas turbine fuel.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
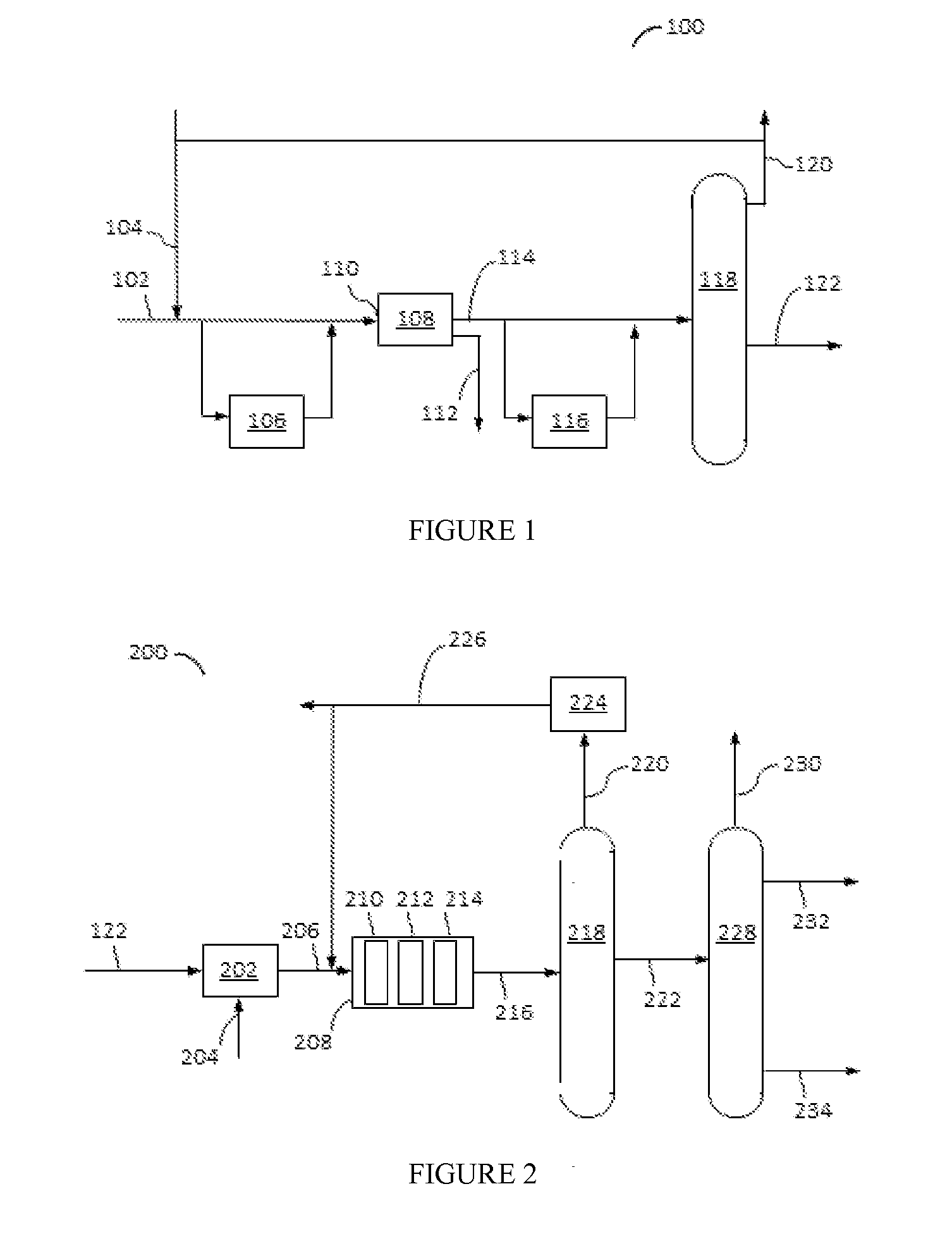
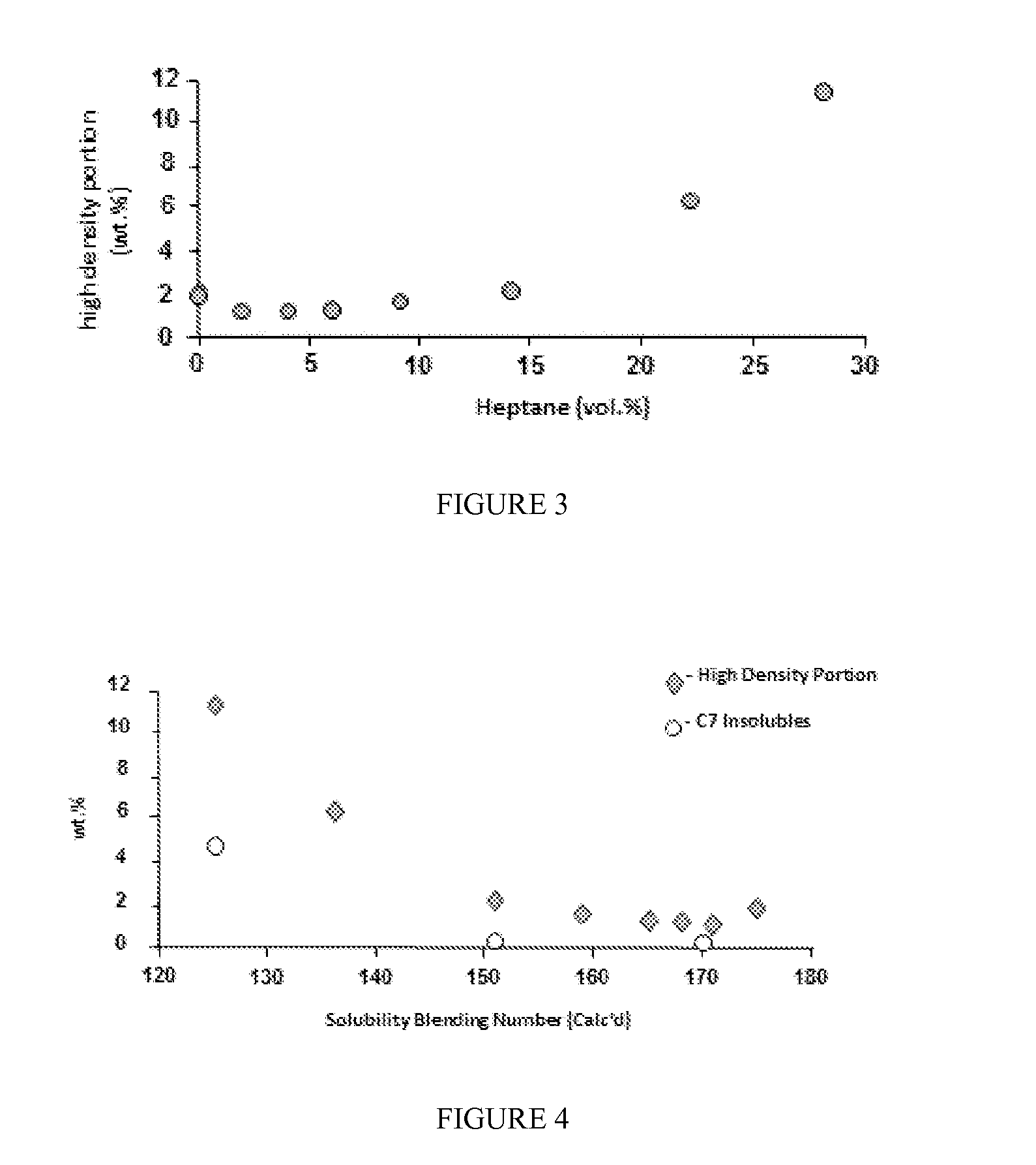
Method and Apparatus for Improving A Hydrocarbon Feed
ActiveUS20150361354A1Improve compatibilityImprove scalabilityTreatment with plural serial stages onlyRotary centrifugesHigh densityVolumetric Mass Density
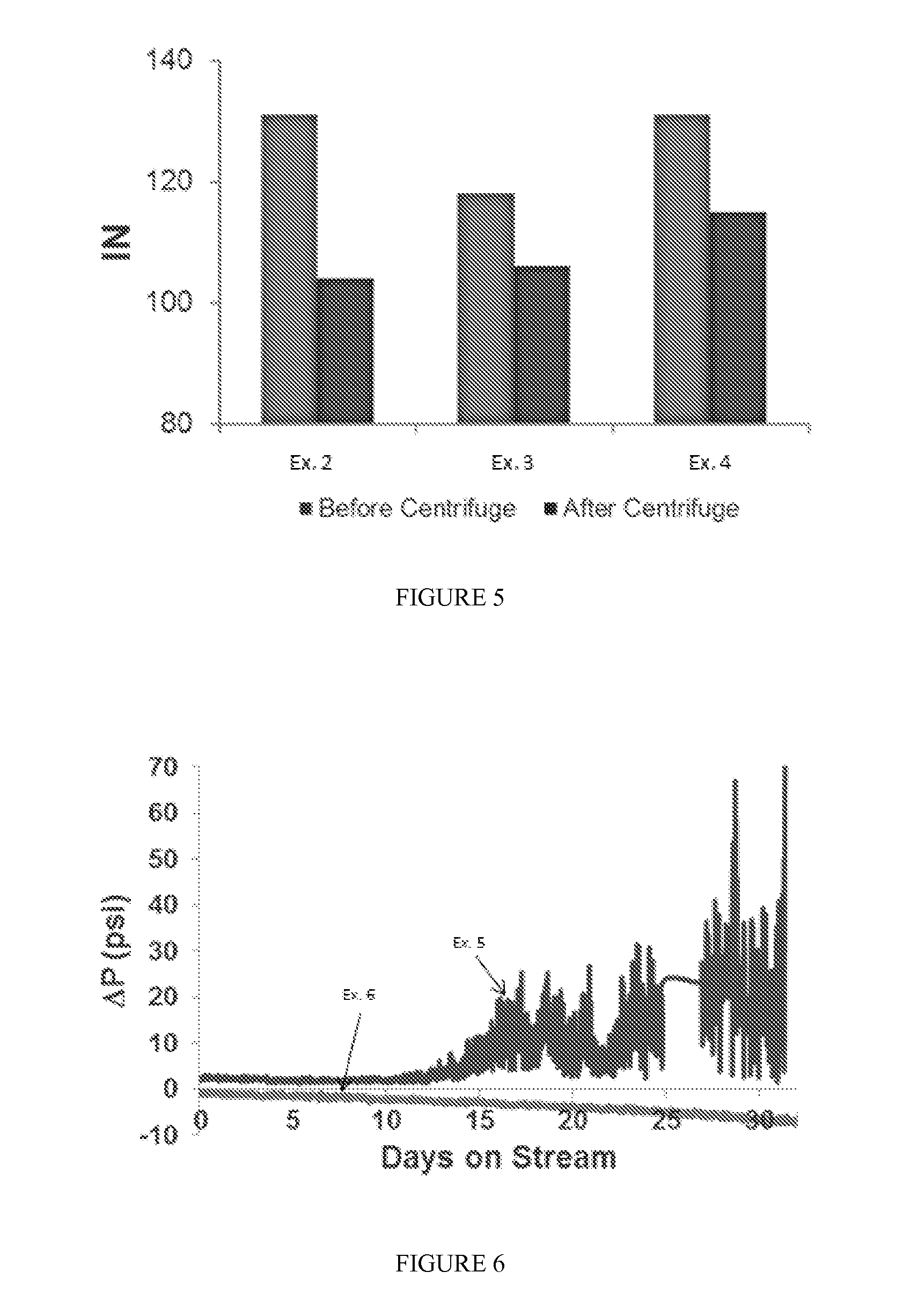
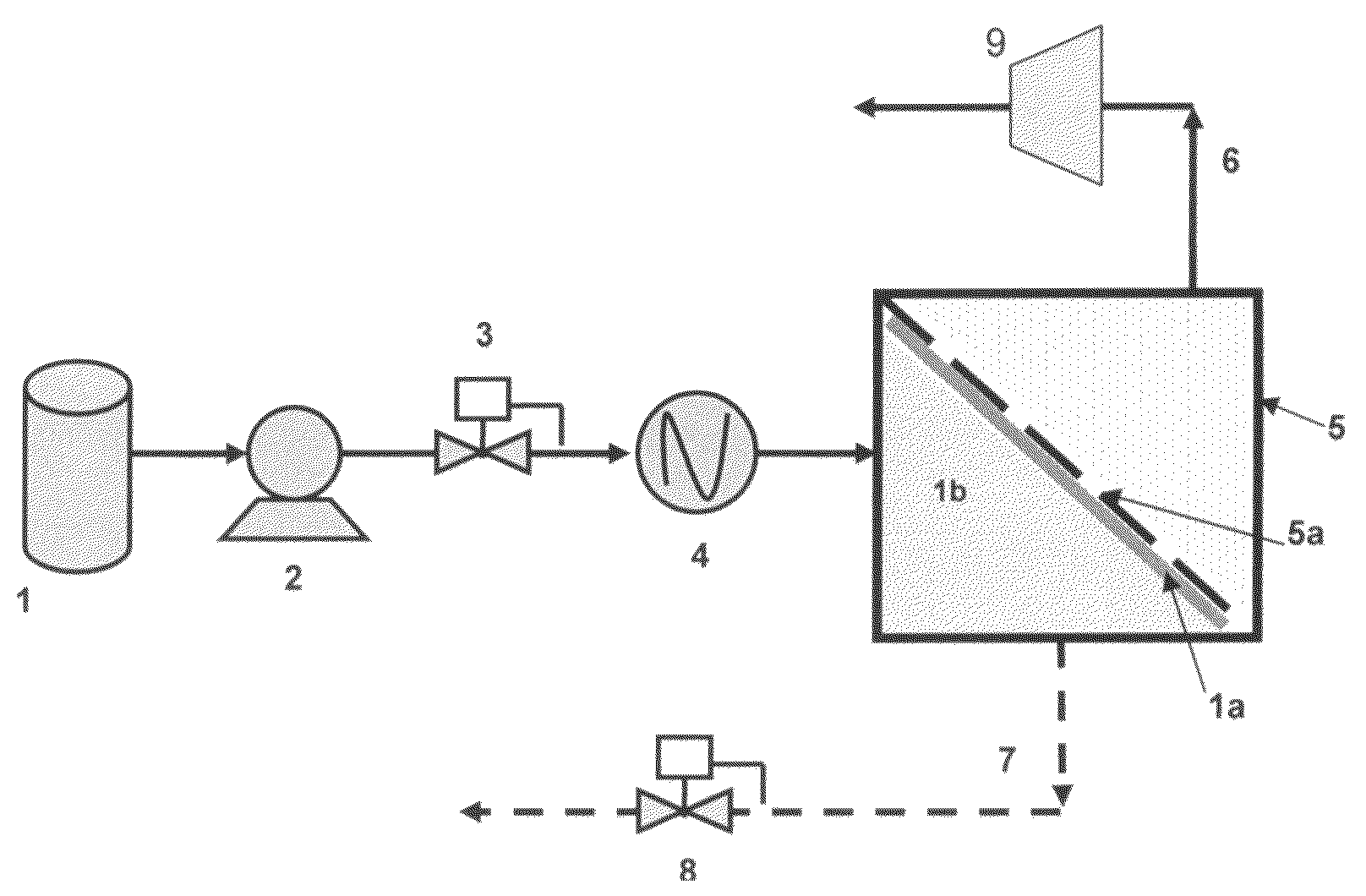
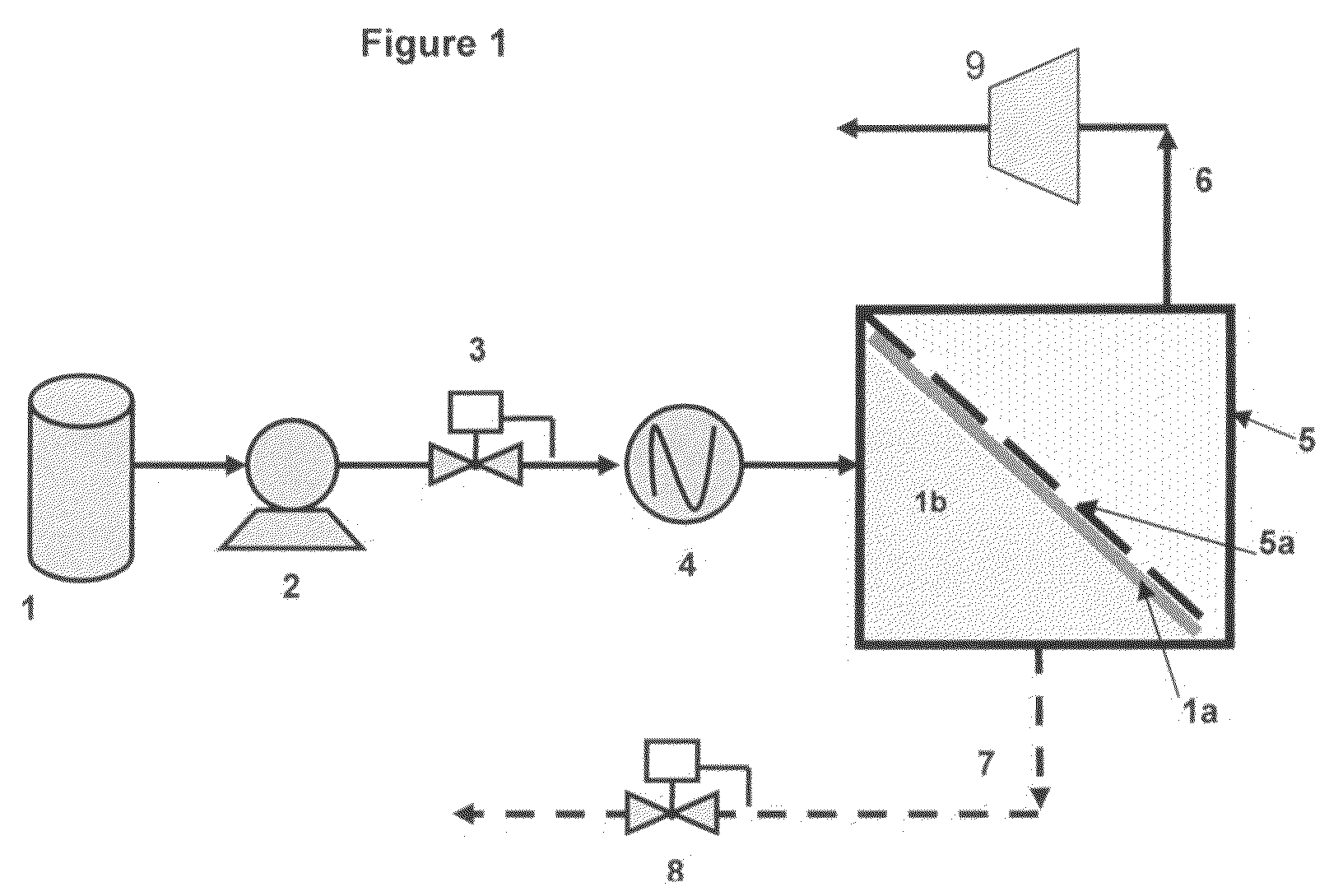
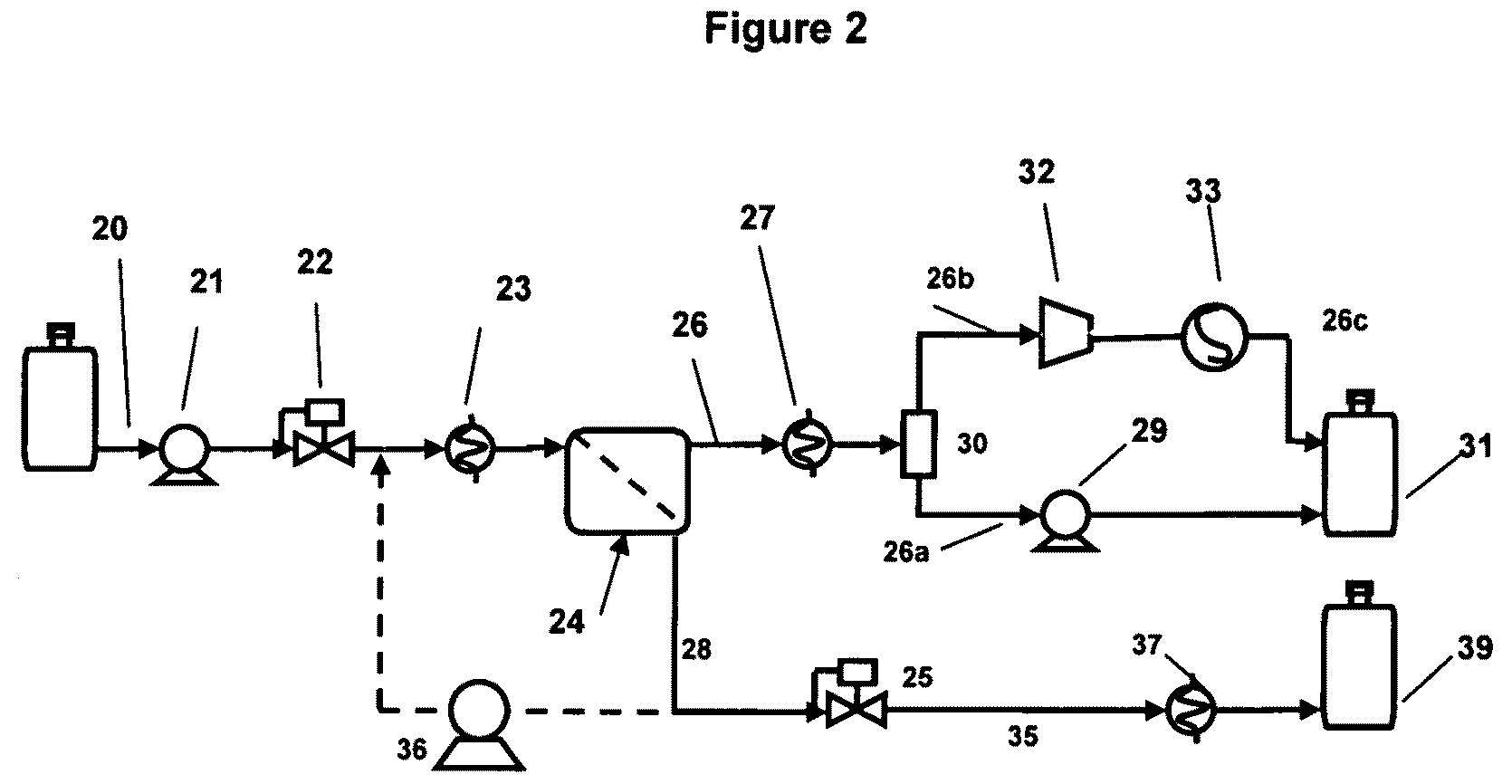
Methods for upgrading a hydrocarbon feed are disclosed. The methods include a hydrocarbon feed having an insolubility number, Ifeed, with at least a first fluid to form a fluid-feed mixture; and inducing a centrifugal force to the fluid-feed mixture sufficient to form at least a higher density portion and a lower density portion, said lower density portion having an insolubility number, ILD, wherein ILD / Ifeed≦0.95. Methods and apparatus for hydroprocessing the treated feed and blending with a fuel oil blend-stock are also described.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Membrane separation process using mixed vapor-liquid feed
ActiveUS7803275B2Reduce penetrationEfficient executionSemi-permeable membranesMembranesVapor liquidChemical physics
The present invention pertains to a process for the separation of aromatics from a feed stream, including aromatics and non-aromatics by selectively permeating the aromatics through a membrane comprising feeding a mixed phase vapor-liquid feed to a membrane wherein said liquid phase preferentially wets the surface of the membrane.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Polymer-coated inorganic membrane for separating aromatic and aliphatic compounds
InactiveUS20080035557A1Promotes uniform depositionMaximizing permeationMembranesDialysisSilicon dioxideMembrane composition
A membrane composition comprising an inorganic substrate which has a coating of an associating polymer. The membrane composition includes an inorganic substrate selected from the group consisting of a porous silica hollow tube, an alumina hollow tube and a ceramic monolith.
Owner:PARTRIDGE RANDALL D +3
Process for separating a heavy oil feedstream into improved products
This invention relates to a process for separating a heavy hydrocarbon stream to produce at least one permeate product stream and at least one retentate product stream. The process utilizes an ultrafiltration process to designed to maximize the quality of the permeate and retenate product streams as well as process embodiments which improve permeate production quantities as well as improve the quality of the product streams obtained by the separations process. In preferred embodiments, the process includes configuration and operational parameters to maximize permeate yield and selectivity.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Fuel deoxygenation system with textured oxygen permeable membrane
ActiveUS20060169138A1Increase surface areaMinimize barrier to diffusionSemi-permeable membranesMembranesOxygenDeoxygenation
A fuel system for an energy conversion device includes a deoxygenator system with an oxygen permeable membrane having a textured surface. A sweep gas and / or vacuum maintains an oxygen concentration differential across the membrane to deoxygenate the fuel. The textured surface increases the surface area of the oxygen permeable membrane. The textured surface of the oxygen permeable membrane is fabricated by pressing the textured surface into the oxygen permeable membrane with a microreplication-based tooling system. Another fabrication method presses the textured surface into a sacrificial film and the oxygen permeable membrane is then formed upon the sacrificial film to transfer the textured surface to the oxygen permeable membrane and the sacrificial film is then subsequently removed. Another fabrication method applies additional material to the oxygen permeable membrane through a porous sacrificial film.
Owner:RTX CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com