Patents
Literature
426results about How to "Bonded firmly" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
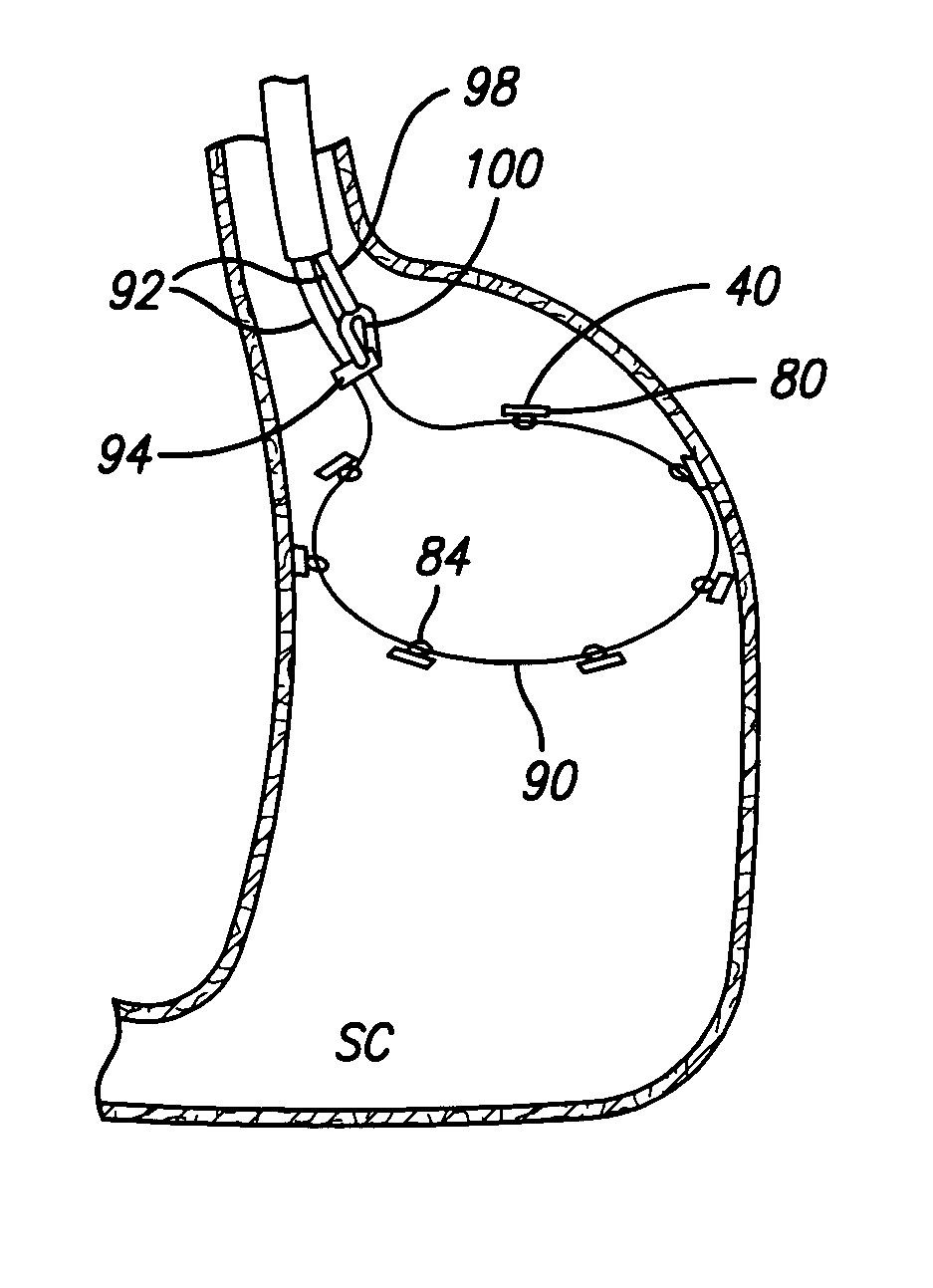
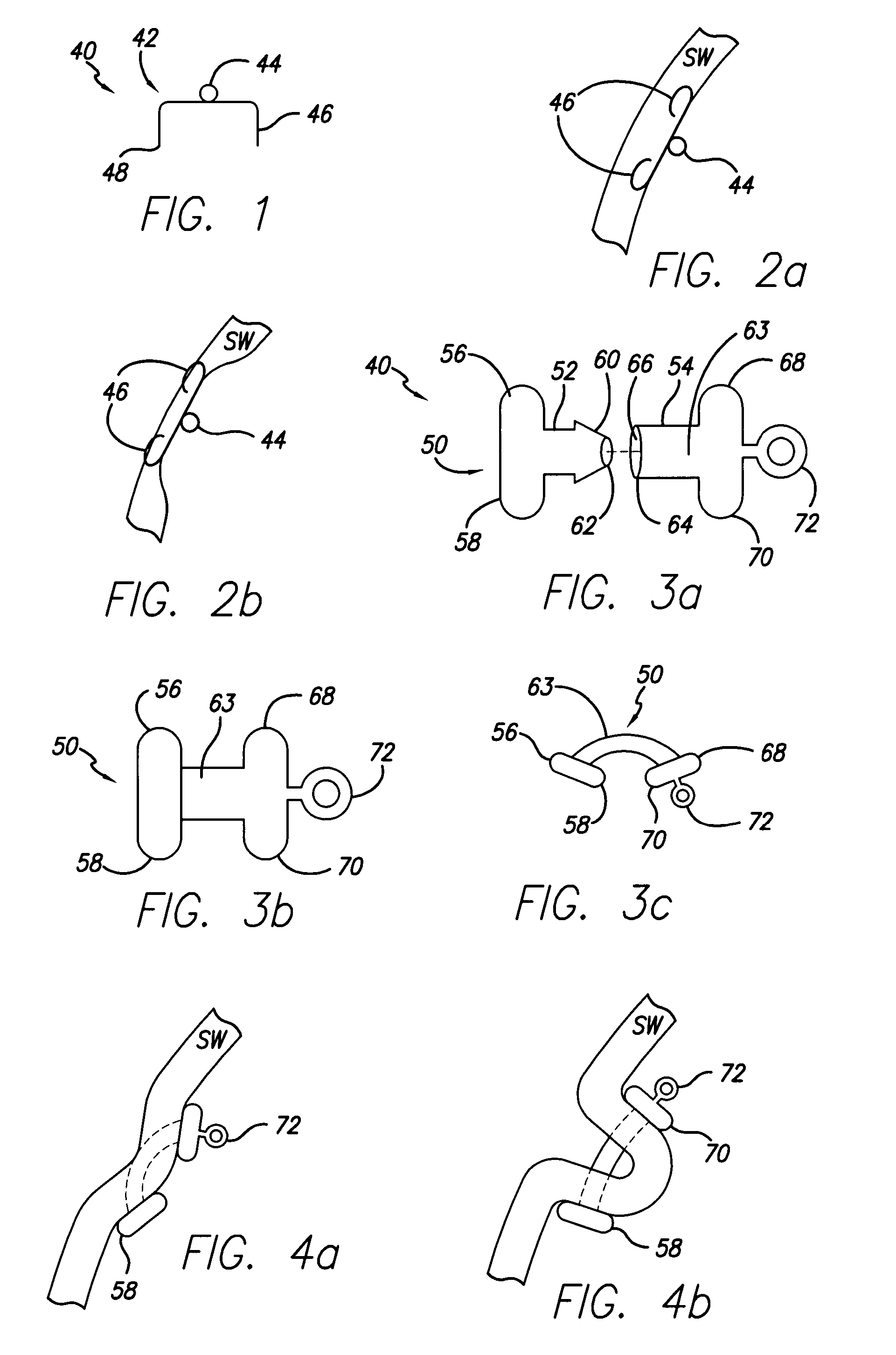
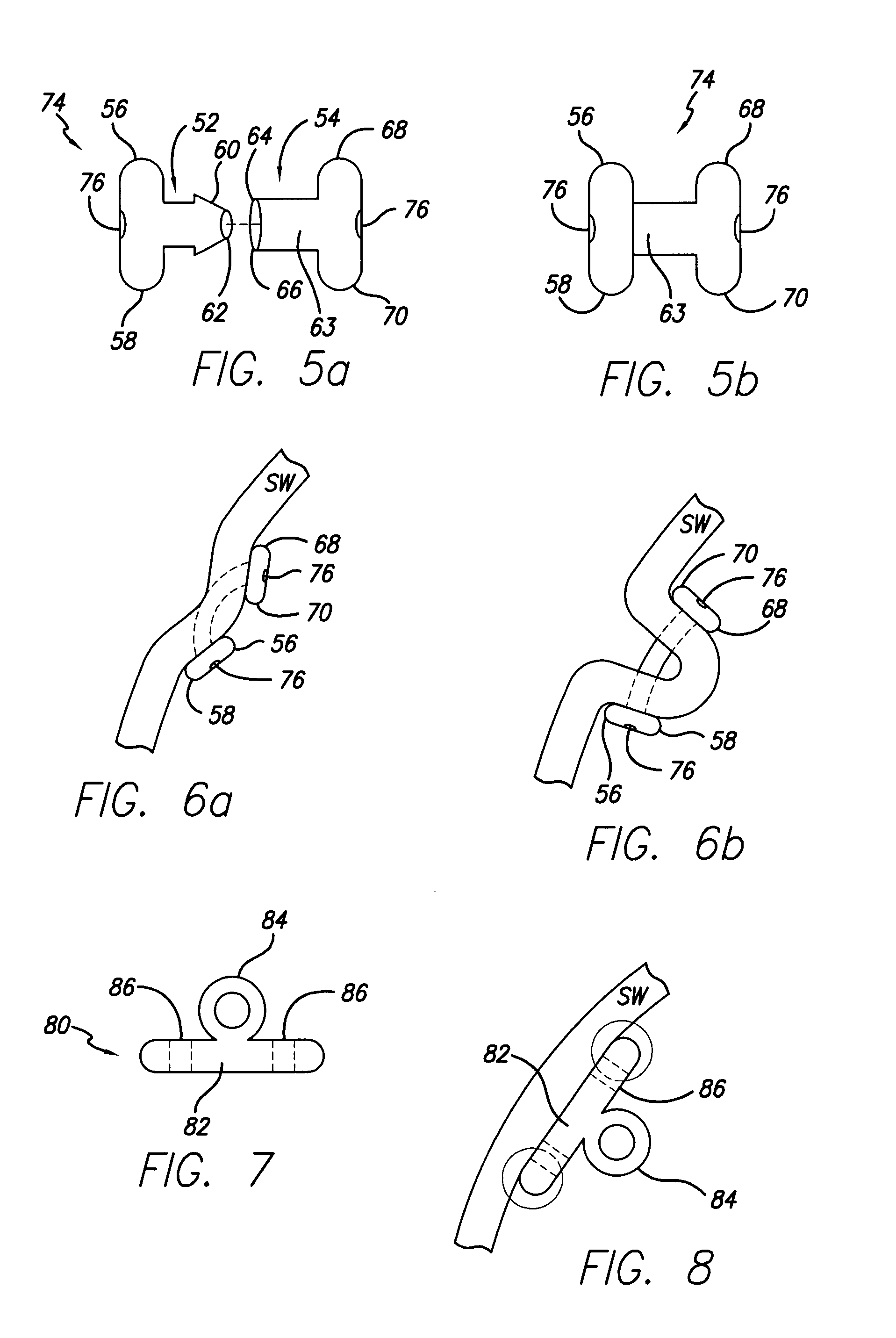
Methods for reducing hollow organ volume
ActiveUS20050192599A1Reducing stomach volumeLarge anchor surface areaStaplesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesOrgan VolumeBody organs
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Arrangement of building elements with connecting means
InactiveUS7377081B2Potential savingAccurately processStrutsWallsArchitectural engineeringInterconnection
An arrangement of building elements capable of a snap-fastening interconnection comprises an element, especially the tongue, consisting of a different material from the other building elements. An MDF / HDF panel, is initially milled along the longitudinal and / or transverse sides, and the resulting groove is then provided and / or foam-filled with extrudates. Finally, the free ends of the extrudates are milled to form the profile of the tongue. Alternatively, or additionally, a groove may also be milled into the extrudates.
Owner:KAINDL FLOORING GMBH
Thermoplastic elastomer composition, process for the preparation there of, hose made by using the composition, and process for the production thereof
InactiveUS6179008B1Improvement of hose flexibilityLow production costSynthetic resin layered productsFlexible pipesElastomerVulcanization
A thermoplastic elastomer composition which, when used for the inner tube and / or outer cover of a hose, can improve the hose flexibility at an ordinary temperature and low temperature, oil resistance, and cold resistance and can reduce the production costs since it does not require a vulcanization step and a hose having said properties using this elastomer composition for its inner tube and / or outer cover and a process and apparatus for the production thereof.
Owner:YOKOHAMA RUBBER CO LTD
Composite structures containing tissue webs and other nonwovens
InactiveUS20050136772A1Resists effect of waterMaintain stiffnessPersonal careCarpet cleanersEngineeringPolymer
The present invention discloses a disposable scrubbing product for use in household cleaning or personal care applications. In one embodiment, the present invention is directed to a cleaning tool including a handle and a rigid base to which the scrubbing product of the present invention may be attached to form a convenient cleaning tool. The scrubbing product of the invention is a multi-layer laminate product and generally includes at least two distinct layers, an abrasive layer and an absorbent fibrous layer such as a tissue layer made from papermaking fibers. The abrasive layer is formed primarily of polymeric fibers in a disordered or random distribution as is typical of fibers deposited in meltblown or spunbond processes so as to form an open, porous structure. In one embodiment, an anchoring agent, such as synthetic fibers, are incorporated into the tissue layer that form a bond with the abrasive layer when forming a laminate in accordance with the present invention.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Methods and devices for reducing hollow organ volume
ActiveUS20070208360A1Reduce volumeOvercomes shortcomingStaplesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesBody organsOrgan Volume
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Capillary for wire bonding and method of wire bonding using it
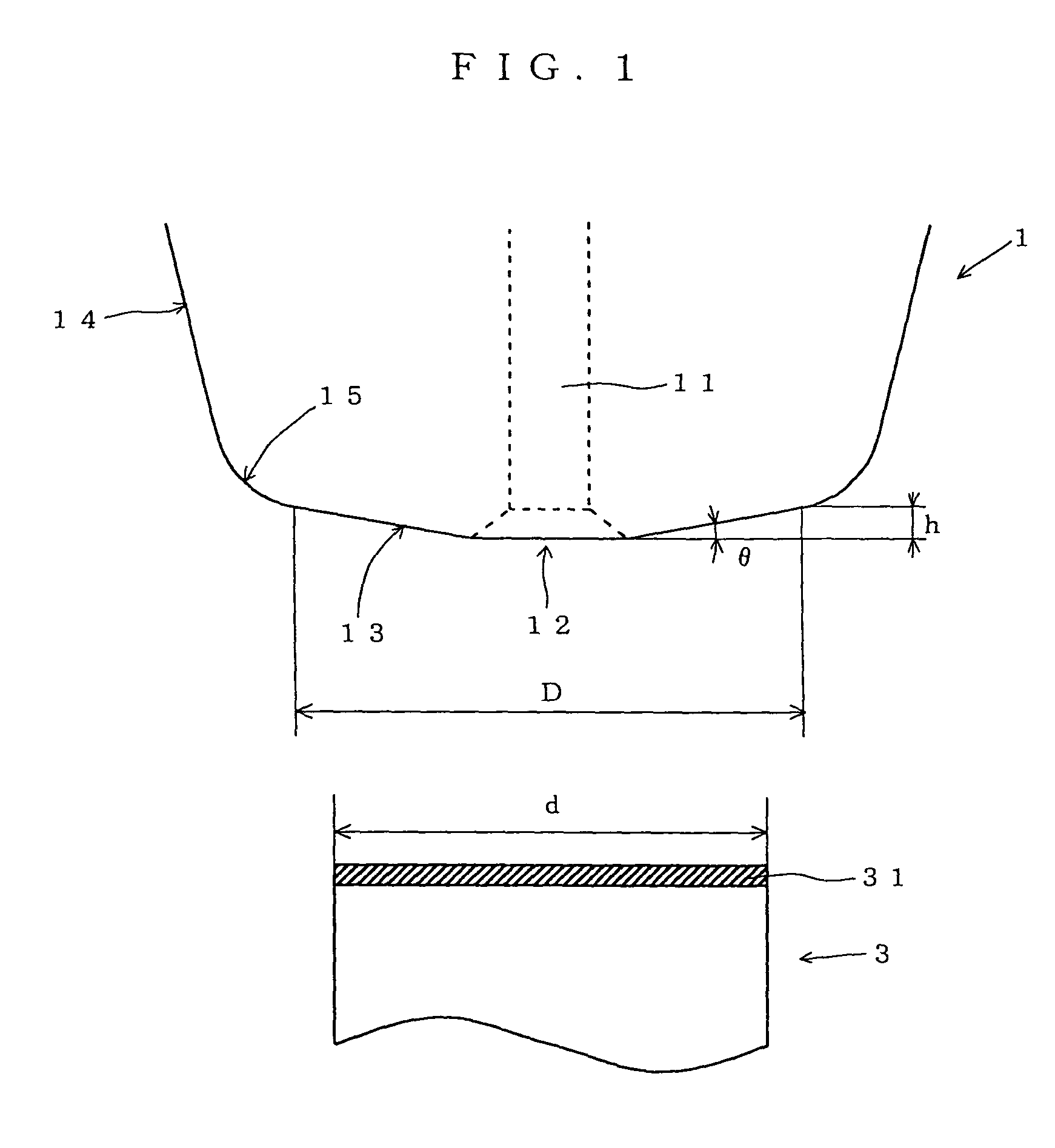
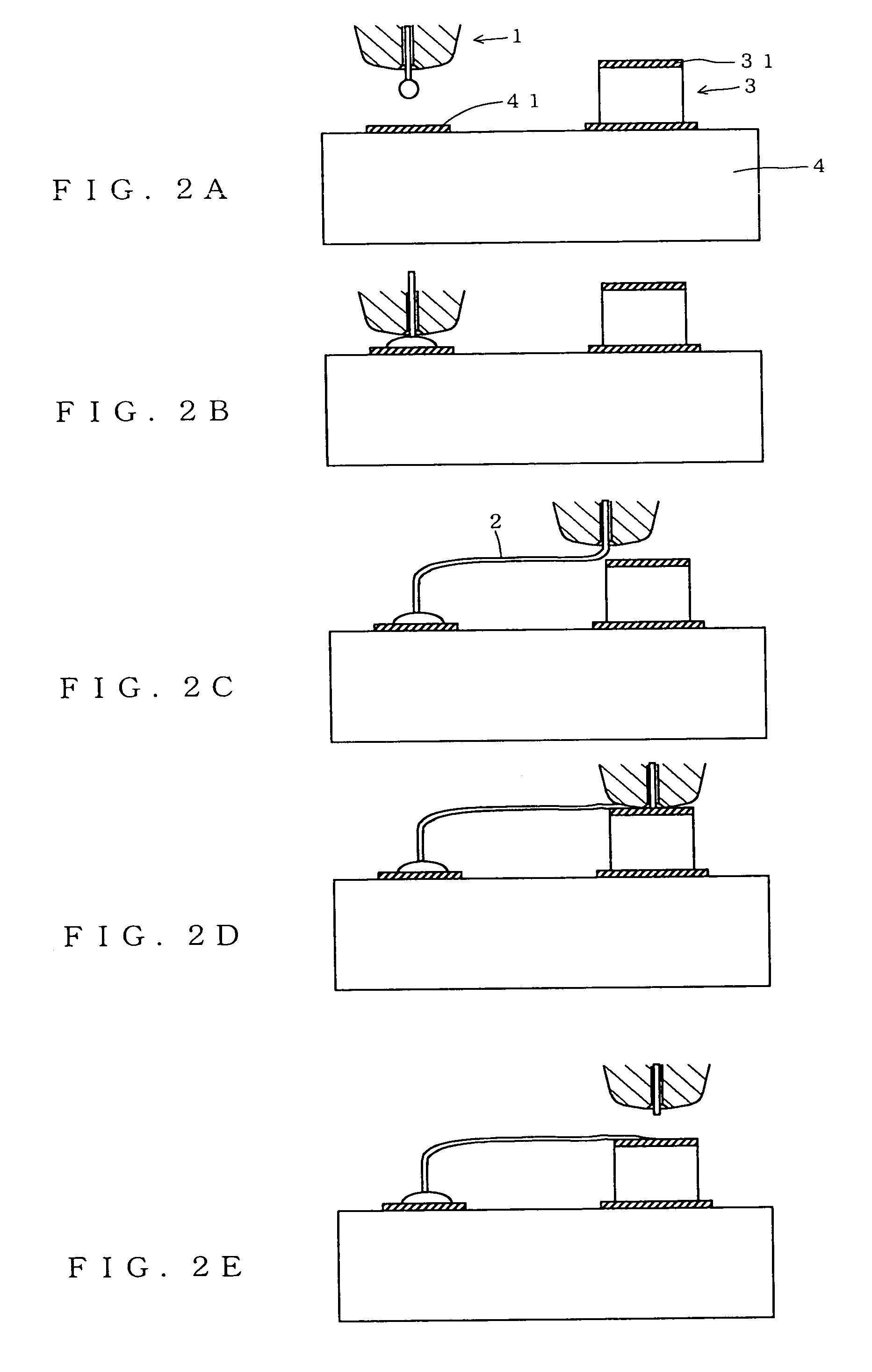
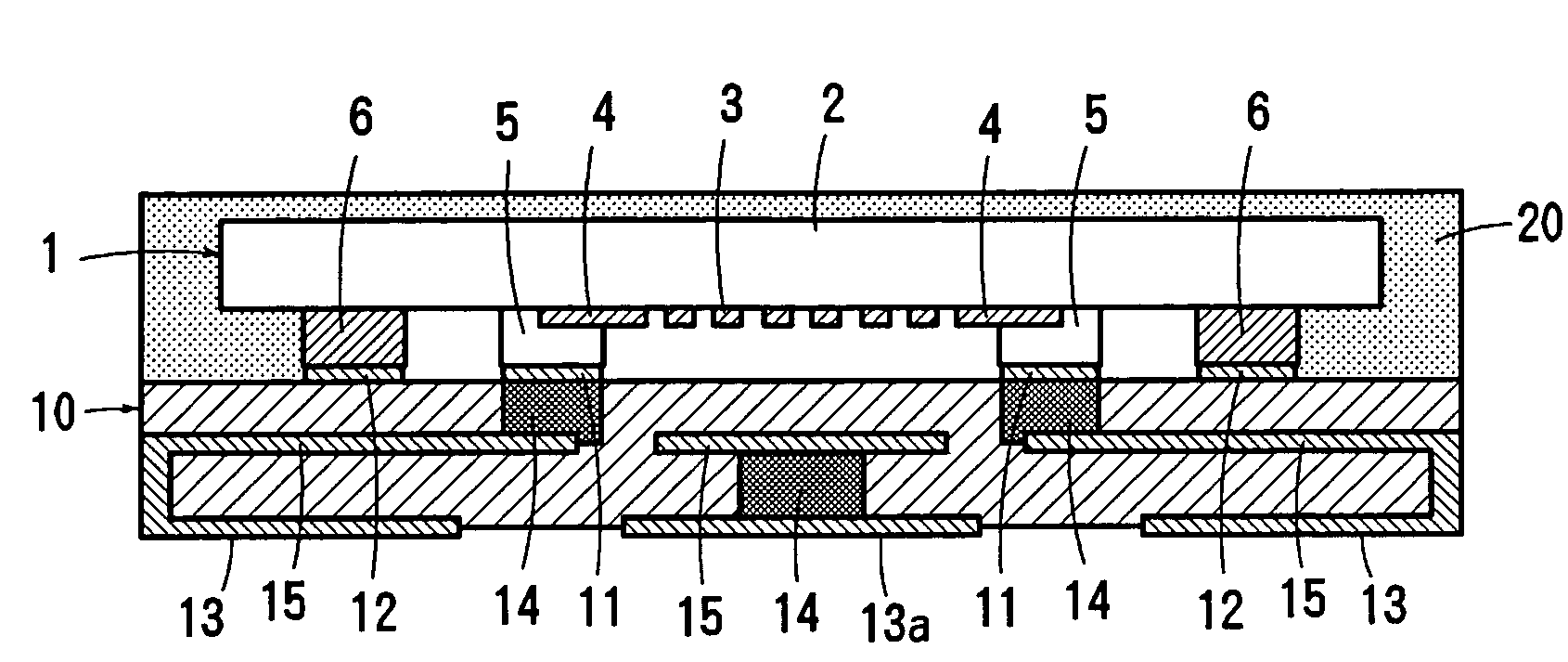
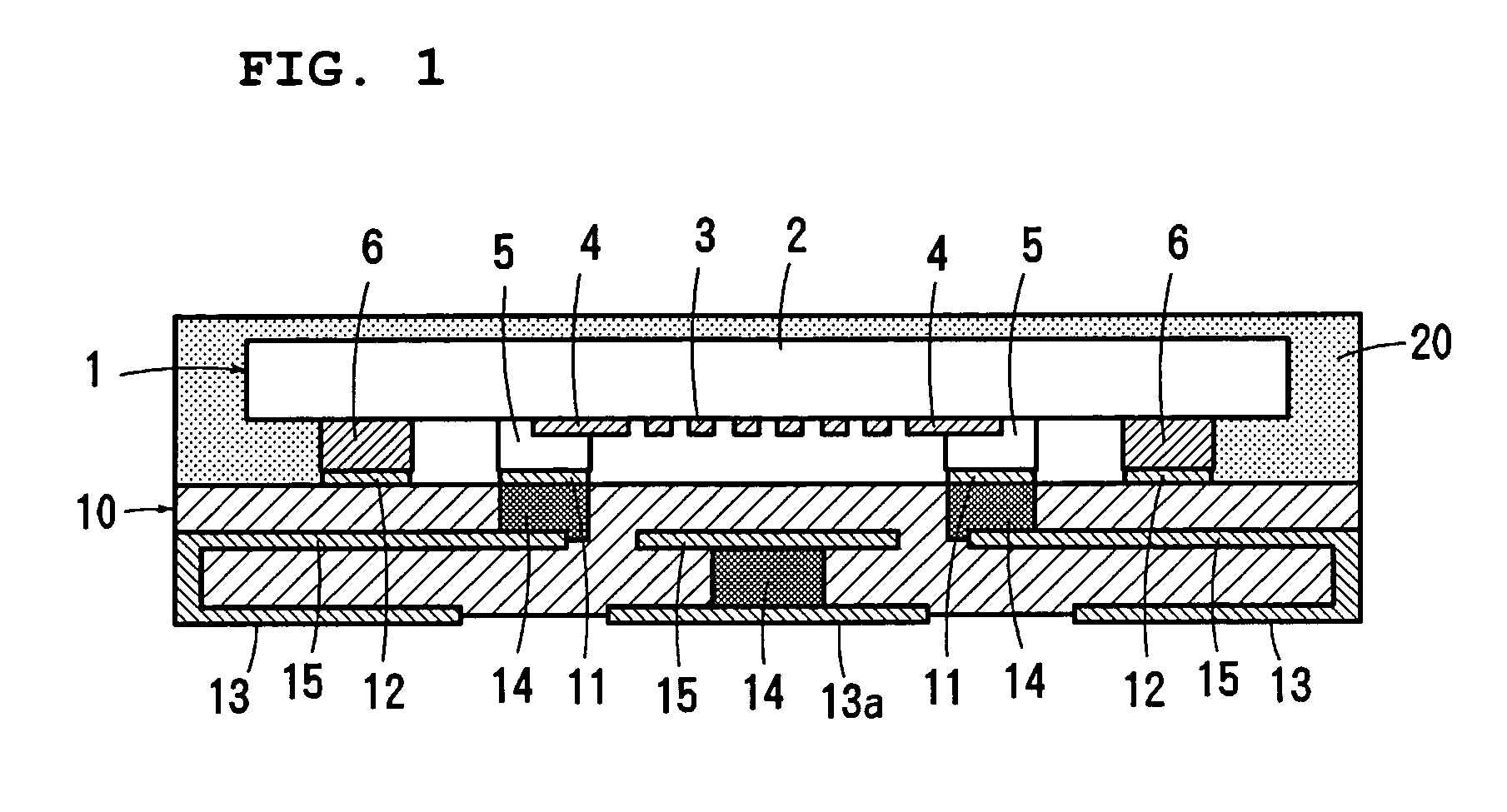
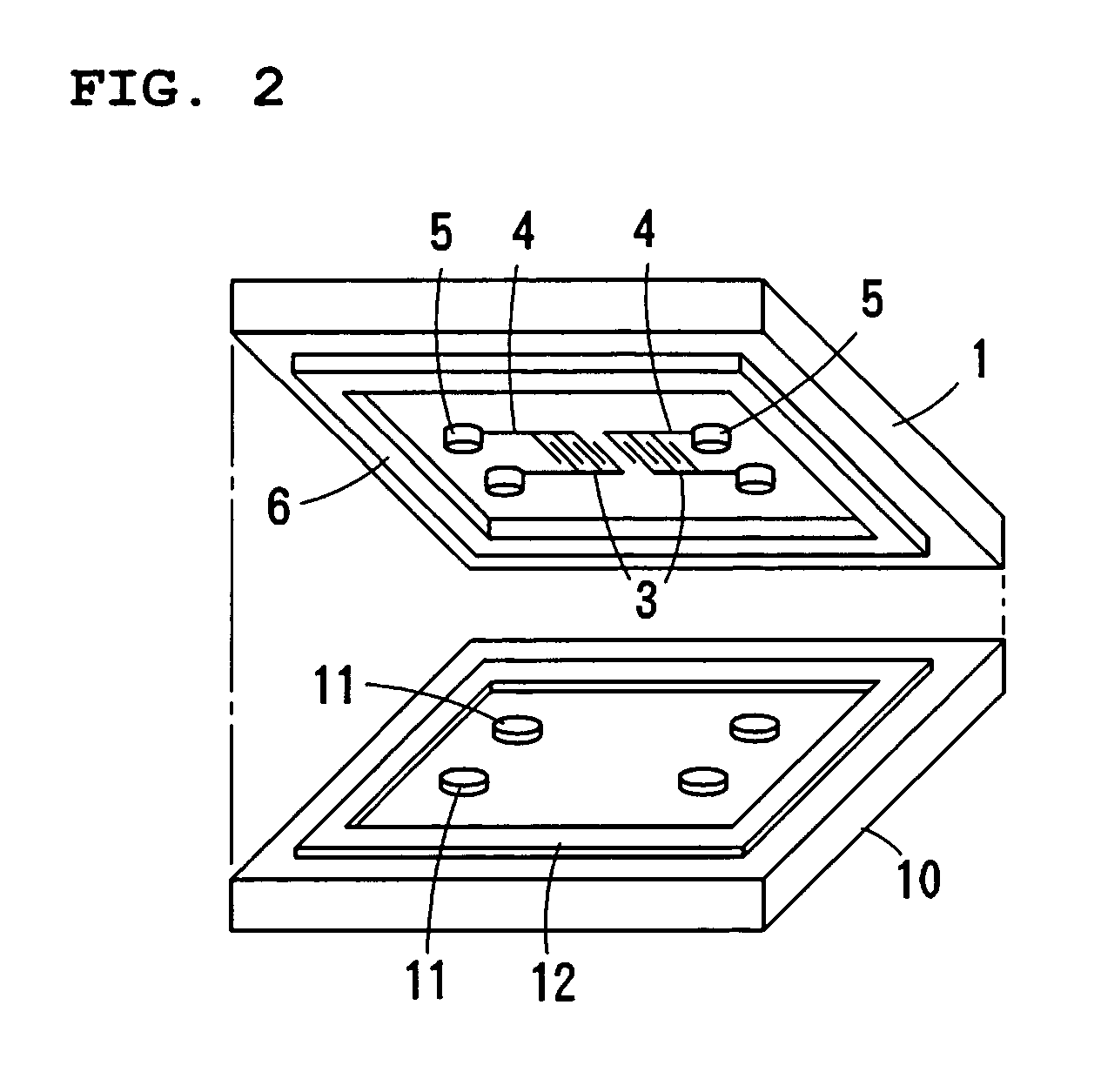
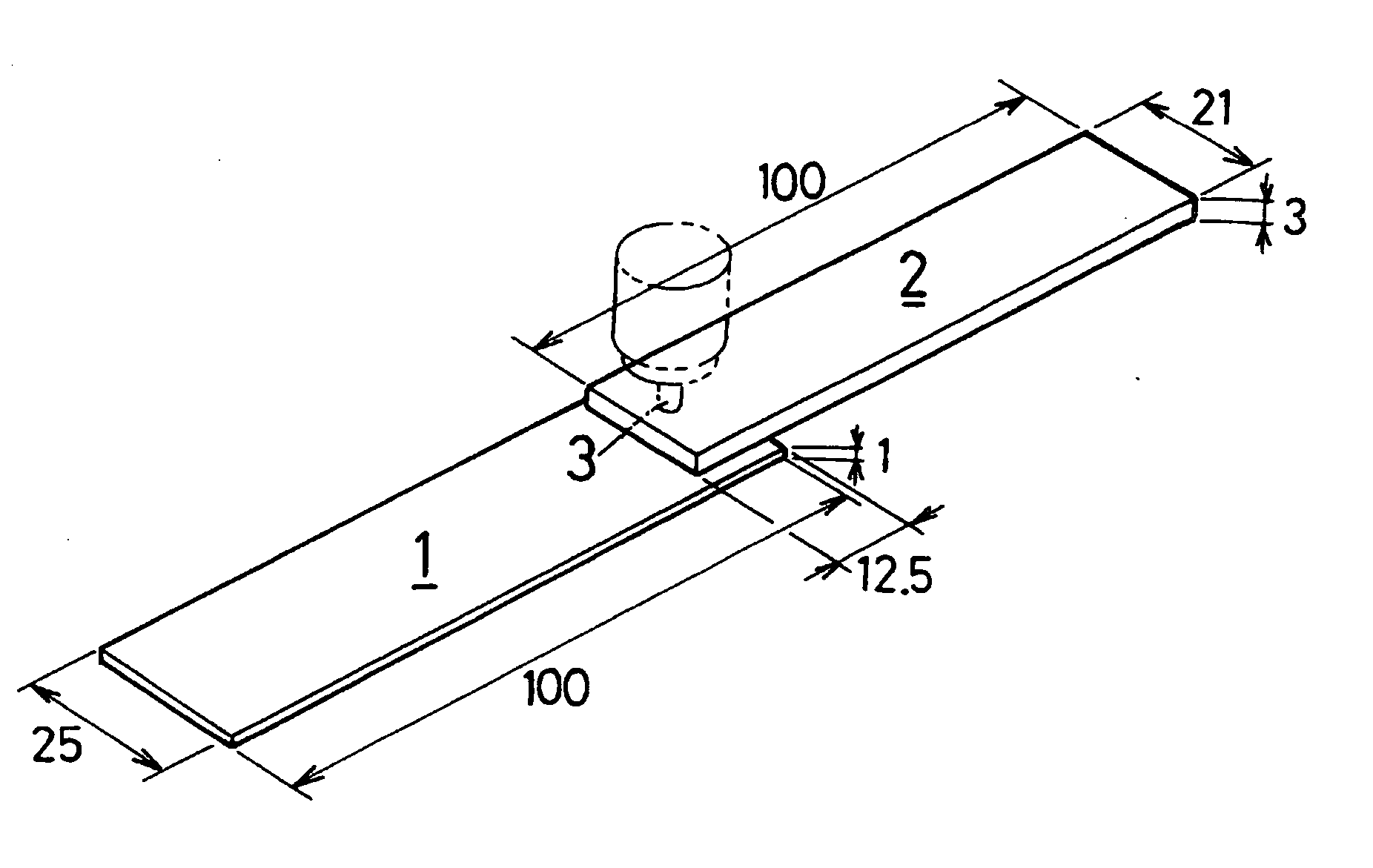
ActiveUS7051915B2Preventing breakage and peeling-offBonded firmlySolid-state devicesWelding/cutting auxillary devicesEngineeringWire bonding
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Bonding apparatus and bonding method
InactiveUS20120247664A1Improve reliabilityReduce gapSolid-state devicesLaminationAdhesiveIncrease temperature
The bonding apparatus is capable of effectively increasing temperature of a substrate and reducing occurrence of position gaps and poor connection in a process of flip-chip-bonding semiconductor devices to the substrate. The bonding apparatus comprises: a supporting unit for supporting the substrate, on which the semiconductor devices have been adhered by a non-conductive; and a heating / pressing unit for heating and pressing the substrate, the heating / pressing unit having a built-in heat source and a clamping face, onto which the substrate supported by the supporting unit is pressed. The substrate supported by the supporting unit is moved toward the clamping face of the heating / pressing unit so as to preheat the substrate and the semiconductor devices by radiation heat. Then, the semiconductor devices are pressed onto the clamping face of the heating / pressing unit so as to cure the non-conductive adhesive and bond bumps of the semiconductor devices to terminal sections of the substrate.
Owner:APIC YAMADA CORP
Metal stent with surface layer of noble metal oxide and method of fabrication
In a process for producing a biocompatible stent, a tubular substrate of the stent adapted for diametric expansion has a layer of a noble metal oxide formed over at least the outer surface of greater diameter of the substrate, the substrate being composed of a metal or an alloy thereof that is non-noble or less-noble than the layer's noble metal. An interface region adapted to prevent corrosion and to provide a firm bond between the surface of the substrate and the noble metal oxide layer is established, at least in part, by forming the noble metal oxide layer with a progressively varying concentration of noble metal-to-oxide with depth of the layer such that a surface of pure noble metal and negligible oxide of the layer is in closest proximity to the surface of the substrate. In one embodiment of the process, the interface region is established by forming the surface of pure noble metal and negligible oxide thereof in direct contact with the metal or alloy of the substrate surface. In another, the interface region is established by first creating an oxide of the substrate metal or alloy thereof at the substrate surface, and then forming the noble metal oxide layer as above, but in contact with the substrate metal or alloy oxide. Alternatively, the noble metal oxide layer has no progressively varying concentration but simply overlies an oxide of the substrate metal or alloy.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Reinforcing members
ActiveUS20040256888A1Satisfactory performanceEfficient coatingVehicle seatsSuperstructure subunitsEngineeringAdhesive materials
A structural reinforcement for a hollow section at least part of at least one of whose surfaces is the internal surface of an external panel comprising a rigid reinforcing member having a shape that substantially conforms to the cross section to be reinforced. An expandable adhesive material is provided over a portion of the surface of the rigid reinforcing member and the shape of the rigid reinforcing member and the amount and location of the expandable adhesive is such that upon foaming the foam contacts and bonds to the internal surfaces of the hollow section other than the interior surface of the external panel. In this way deformation of the external body panel during the foaming and / or cooling of the foamed expandable material is reduced or prevented.
Owner:ZEPHYROS INC
Image graphic adhesive system and method for using same
InactiveUS6482288B1Bonded firmlyPredictive performanceLamination ancillary operationsPicture framesGraphicsAdhesive system
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Adhesive film and image display device
InactiveUS20070031660A1Improve bindingImprove adhesionSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationAntistatic agentWater dispersible
An adhesive film prevents static charge on peeling generated when removed from an adherend and also improves adhesion between a base material and an adhesive layer, where an under coat layer containing an organometallic is formed on the base material and then an adhesive layer is formed on the base material. Alternatively, an adhesive film showing high adhesion with a glass substrate, and including an antistatic layer, which prevents static charge on peeling generated when the surface protective film is removed, and improves adhesion between a base material and an adhesive layer, where the adhesive film includes a base material, an adhesive layer made of a water dispersible adhesive including, and an antistatic layer, containing a water soluble or water dispersible conductive material, interposed between them, and the adhesive film is stuck onto an image display device.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Thermoplastic elastomer composition and process of production thereof and hose using thermoplastic elastomer composition and process of production thereof
InactiveUS6526859B1Increase flexibilityLow production costFlexible pipesCoatingsElastomerVulcanization
A thermoplastic elastomer composition which, when used for the inner tube and / or outer cover of a hose, can improve the hose flexibility at an ordinary temperature and low temperature, oil resistance, and cold resistance and can reduce the production costs since it does not require a vulcanization step and a hose having said properties using this elastomer composition for its inner tube and / or outer cover and a process and apparatus for the production thereof.
Owner:THE YOKOHAMA RUBBER CO LTD
Thermosetting flux and solder paste
InactiveUS20050056687A1Improve bindingBonded firmlyPrinted circuit assemblingPrinted circuit aspectsRosinSolder paste
The invention aims to provide a thermosetting flux suitable for solder bonding of a semiconductor element and an electronic part and making solder bonding with a high bonding strength and a high heat resistant strength at a high temperature possible and a paste containing the flux and a non-lead type solder paste and with respect to the thermosetting flux, an epoxy resin, a hardening agent, and at least one of rosin derivatives having functional groups reactive on the epoxy resin and selected from maleic acid-modified rosin, a fumaric acid-modified rosin, and acrylic acid-modified rosin are used. The flux can be used in form of a solder paste while being mixed and kneaded with the non-lead type solder alloy powder.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Composite punching film and its producing method
InactiveCN1943530AImprove breathabilityHigh porositySynthetic resin layered productsLaminationPunchingVolumetric Mass Density
A compound punching film and preparation thereof, said punching film consisting of a layer of plastic film and one or two side compound non-woven fabrics. On plastic film is of evenly spread tiny mesh, density thereof is 170-500 mesh / C sqm ,perforating rate is 10-35%. Said whole compound film is perforated of evenly big mesh , aperture thereof greater than that of tiny mesh two times, the shape of big mesh is of funnel, thereof protruding to one side and on the surface of awl is of tiny mesh. Said invention combines PE film technique and punching one, making compound of a layer of non-woven fabric and cast film with the help of high melting temp. of cast film, also making use of mesh cage through vacuum suction nozzle punching tiny mesh, thereafter punching big mesh by pressure roller machine, thus to prepare new compound punching film with good permeability, softness and strong third dimension.
Owner:蔡子辛 +1
Hermetically sealing a package to include a barrier metal
ActiveUS7259032B2Good adhesionReliable sealing propertyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksResistHermetic packaging
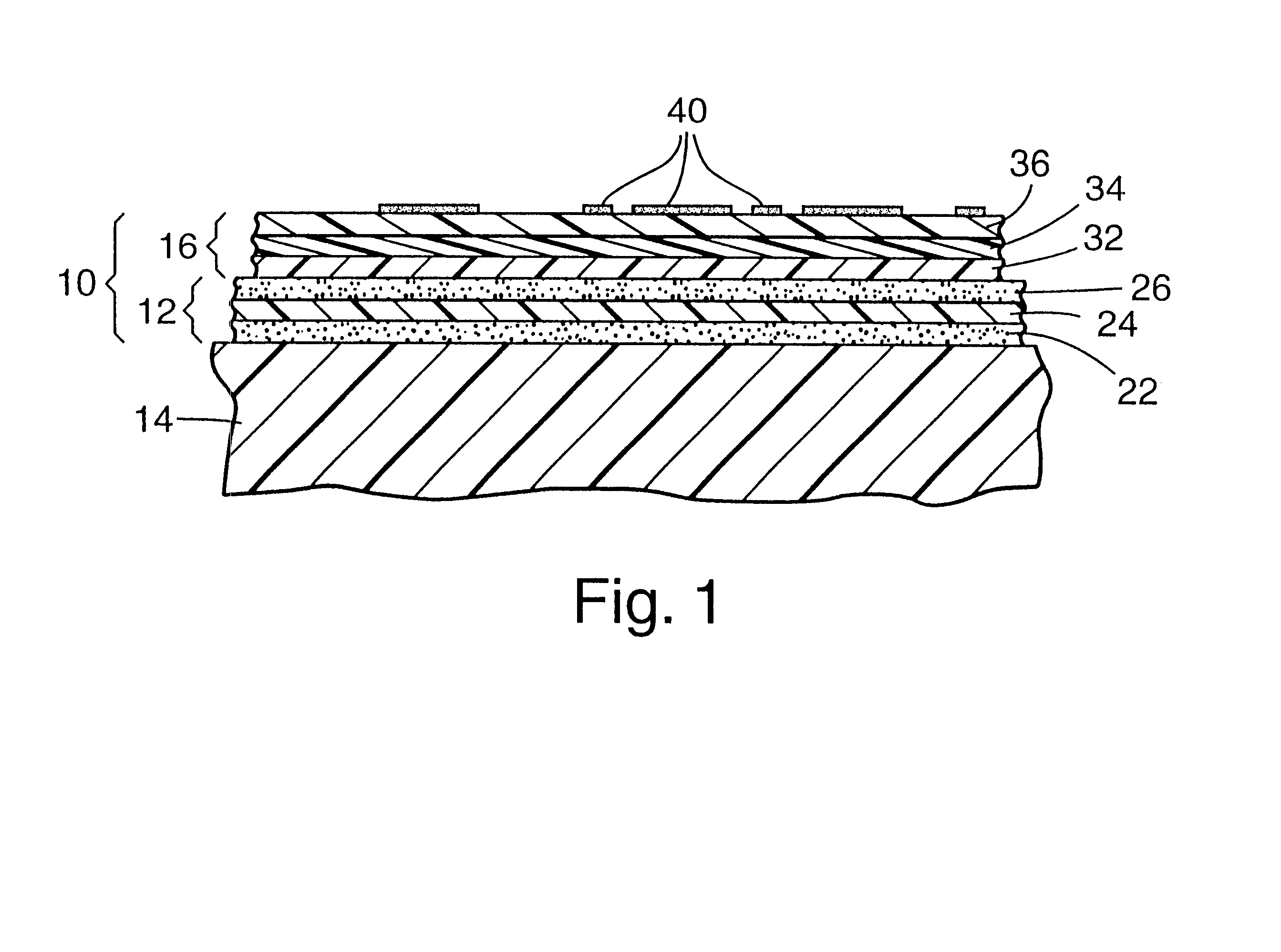
A method for manufacturing an electronic device includes the steps of forming a first resist pattern on a primary surface of a SAW element, the first resist pattern having openings at positions corresponding to those at which bumps and a sealing frame are to be formed, sequentially forming metals over the first resist pattern, the metals being formed into adhesion layers, barrier metal layers, and solder layers, removing the first resist pattern on the SAW element such that the bumps and the sealing frame are simultaneously formed. When the bumps and the sealing frame of the SAW element are bonded to bond electrodes of the bond substrate, the solder layers are melted and alloyed by heating.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Composite article of aluminum alloy with resin and method for production thereof
ActiveUS20060127684A1Effective combinationExhibit some effectSynthetic resin layered productsPaper/cardboard layered productsHydrazine compoundElectrical devices
The present invention allows both the advantages of a metallic housing and those of a synthetic resin structure to be exhibited in electronic devices, home electrical devices, etc., and achieves high productivity and mass productivity and further enables a desired configuration and structure to be designed freely. As a pretreatment, a shaped aluminum alloy material is dipped in an aqueous solution of at least one selected from the group consisting of ammonia, hydrazine, and a water-soluble amine compound. A thermoplastic resin composition containing polyphenylene sulfide as a component is integrally bonded to the surface of the treated shaped aluminum alloy material by injection molding or other method. The molded article is a product made of the shaped aluminum alloy material and the thermoplastic resin composition containing PPS. Thus, the characteristic features of metal can be utilized in terms of mechanical strength and external appearance design. Moreover, a complicated configuration and structure can be formed inside the housing.
Owner:TAISEI PLAS CO LTD
Soft and durable tissue products containing a softening agent
InactiveUS20060137842A1Reduce hydrophobicityHigh retention rateNatural cellulose pulp/paperMechanical working/deformationCellulose fiberAcid anhydride
Fibrous products containing a durable softening agent are disclosed. The softening agent generally comprises a polysiloxane containing a plurality of first functional groups. In order to improve the wet retention of the softening agent on cellulosic fibers, the softening agent is reacted with a retention agent. The retention agent generally comprises a cationic polymer having a second functional group. In one embodiment, for instance, the softening agent contains epoxy groups or anhydride groups, while the retention agent contains amine groups. Products that may be made according to the present invention include tissue products, wipes and other absorbent articles.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Bracket for camera die set and camera die set
InactiveCN104749858AGood imaging effectSpeed up the flowMountingsCamera body detailsCamera lensAdhesive
The invention discloses a bracket for a camera die set and the camera die set. The bracket comprises a bracket body; the bracket body comprises a first surface and a second surface which are oppositely arranged; a first concave groove and an annular boss are arranged on the first surface, wherein the annular boss is arranged around the outer side of the first concave groove; a second concave groove is formed in the second surface; through holes which pass through the first concave groove and the second concave groove are formed in the bracket body. According to the bracket for the camera die set, when a lens driving assembly is adhered on the part of the first surface, positioned at the outer side of the annular boss through an adhesive, excessive adhesive is difficult to flow to the first concave groove and a lens, so that the adhering firmness of the bracket and the lens driving assembly can be ensured, the adhesive can be prevented from adhering to a light filter and glass, and as a result, the light filtering performance of the light filter and the light transmission performance of the glass can be ensured, and the good imaging effect of the camera die set can be ensured; in addition, the lens is difficult to be adhered and fixed through excessive adhesive, and the focus of the lens can be normally adjusted.
Owner:NANCHANG O FILM OPTICAL ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD +3
Porous nonwoven scrims in acoustical panels
ActiveUS20110147119A1Reduce lossesReduce airflow resistanceCeilingsLamination ancillary operationsAdhesiveEngineering
An acoustical building panel and method of manufacturing it are disclosed. Embodiments of the panel include a porous nonwoven scrim, a coating deposited on the scrim, a base mat, and an adhesive deposited on either the base mat or the scrim in a discrete form such as in droplets. Embodiments of the method of manufacture include steps of perforating the base mat, applying the adhesive to the base mat in the discrete form, laminating the scrim onto the base mat, and applying the coating to the scrim surface.
Owner:USG INTERIORS LLC
Anodic bonding method and electronic device having anodic bonding structure
InactiveUS7153758B2Good close adhesionBond be not deteriorateLamination ancillary operationsLaminationAnodic bondingElectrical conductor
In anodic bonding between a conductor or semiconductor and glass, in order to attain good adhesion at a lower bonding temperature than usual and improve the toughness at its boundary to obtain higher reliability for a bonded portion even in a case where bonded members are warped or dust is present at the bonding boundary, a soft metal film is formed on the surface of a conductor or semiconductor on which an active metal film having high reactivity with oxygen is formed, whereby a warp or dust, if any, can be absorbed by the deformation of the soft metal film, thereby to improve the adhesion at the boundary. Adhesion at the bonding boundary is improved even at a low bonding temperature of, e.g., about 200° C. Further, the toughness at the bonding boundary can be improved to increase reliability by roughening the bonded surface on the side of the glass.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Ceramic electronic component and wiring board
ActiveUS20120018204A1Improve reliabilityBonded firmlyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectronic componentMaterials science
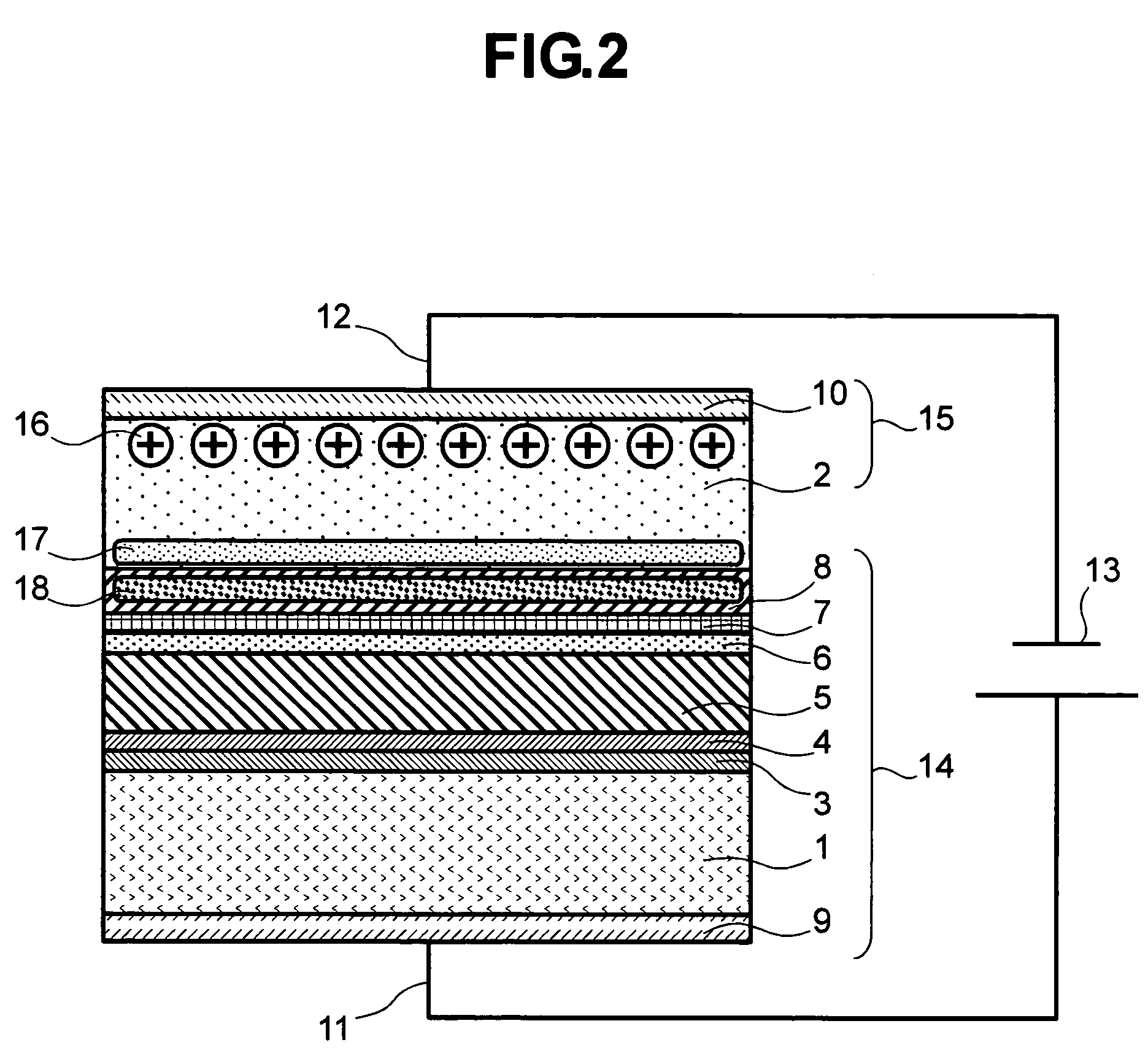
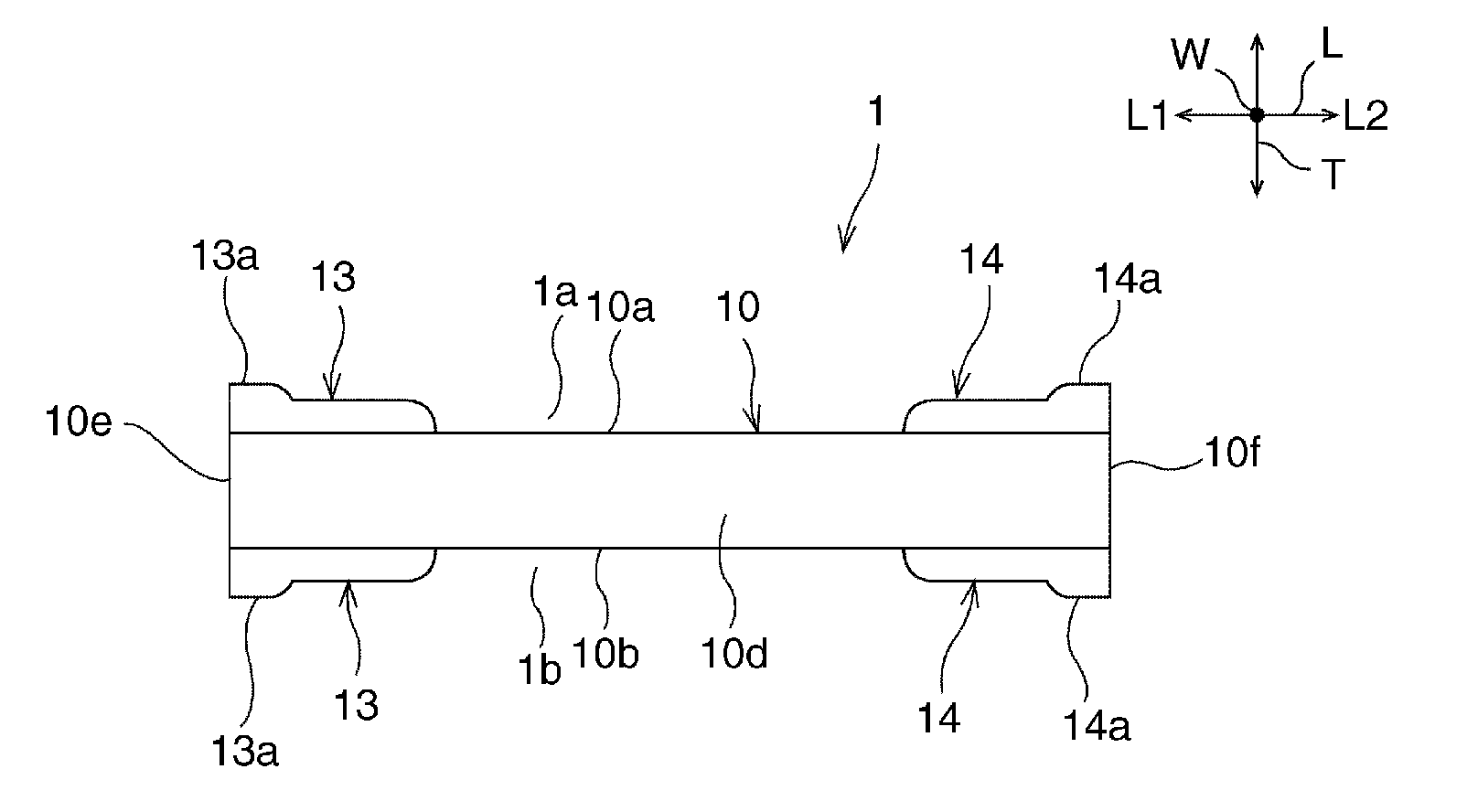
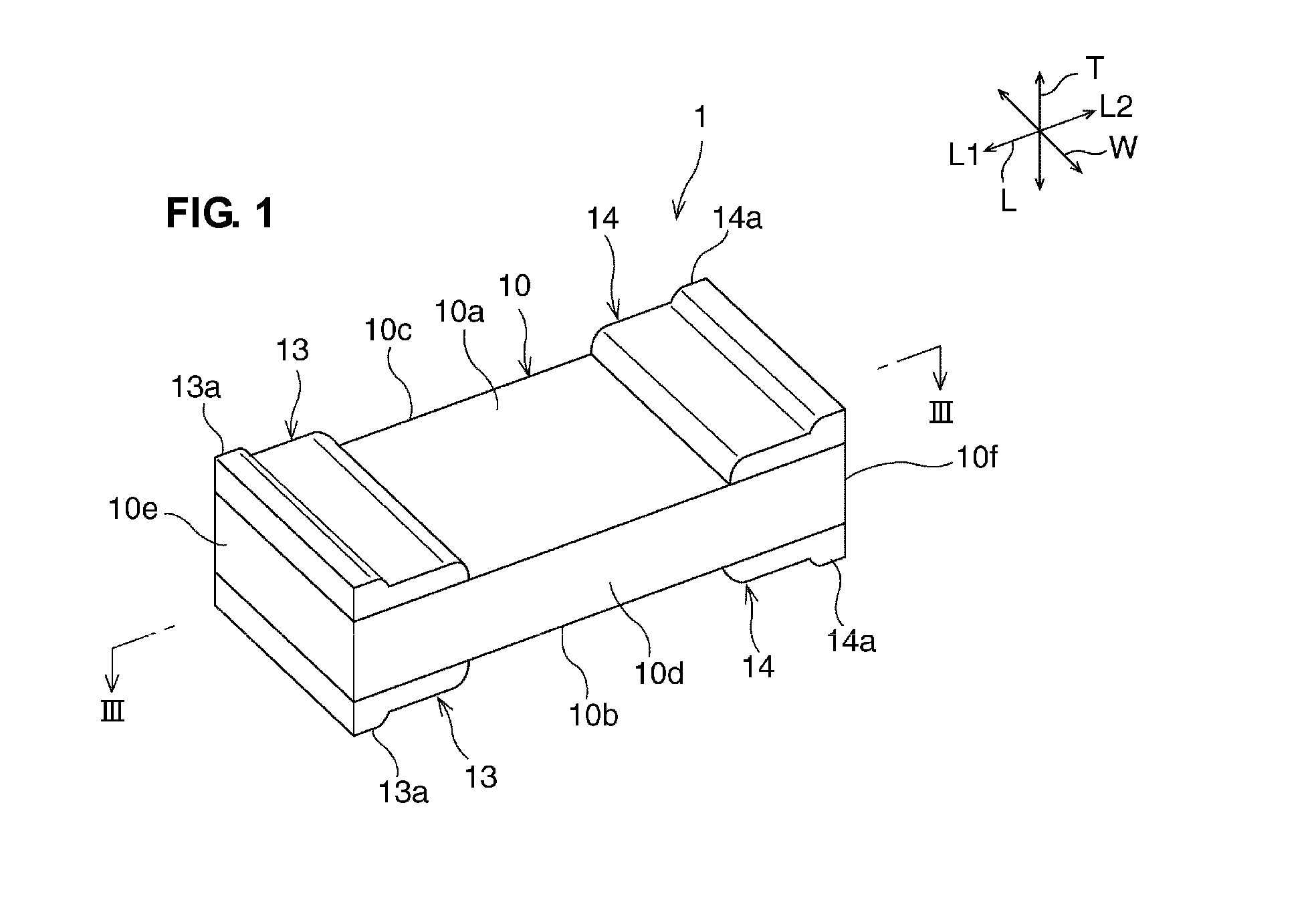
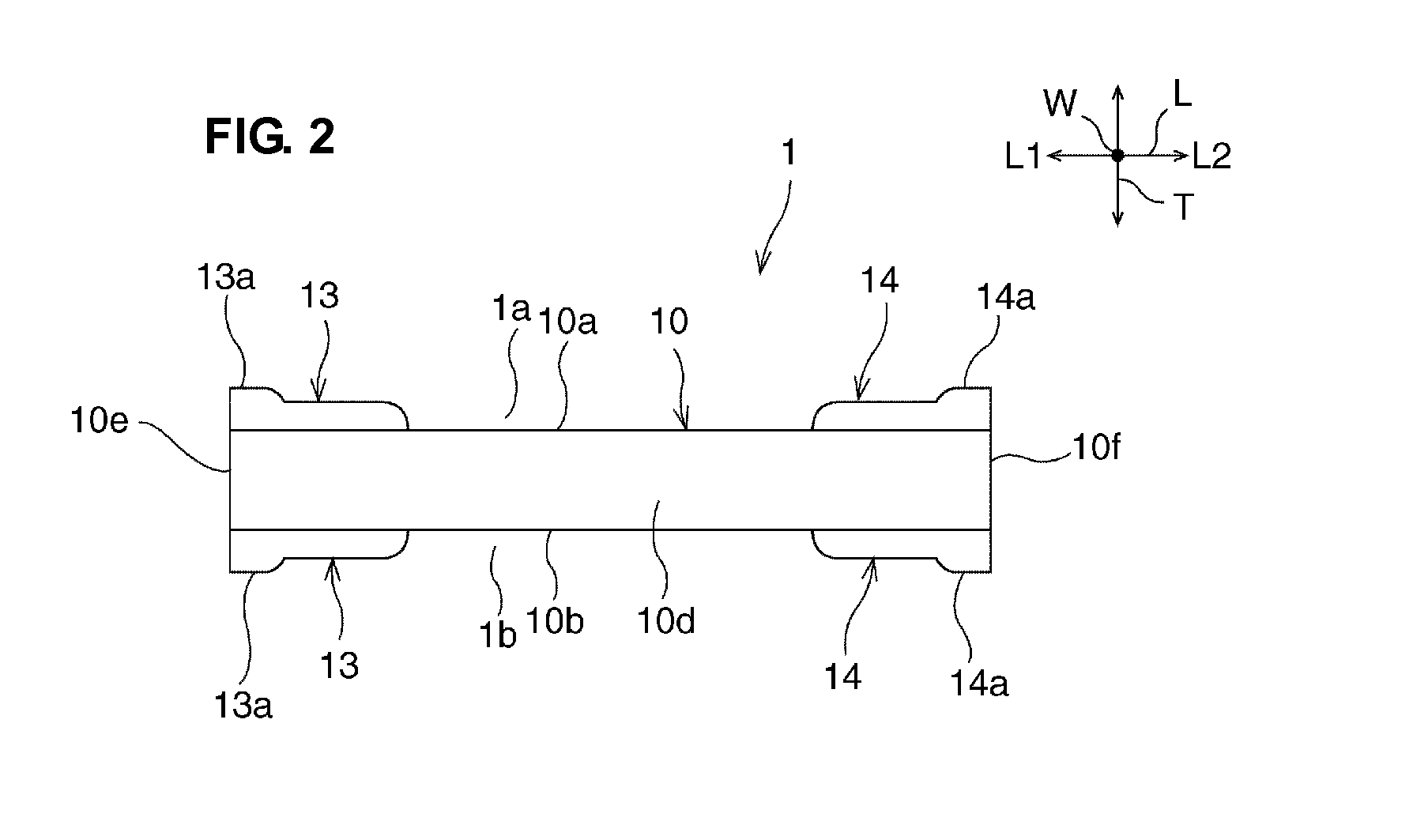
A ceramic electronic component includes a ceramic element body having a substantially rectangular parallelepiped shape, and first and second external electrodes. The first and second external electrodes are provided on a first principal surface. Portions of the first and second external electrodes project further than the other portions in a thickness direction. A projecting portion of the first external electrode is provided at one end of the first external electrode in a length direction and a second projecting portion of the second external electrode is provided at another end of the second external electrode in the length direction. Thus, a concave portion is provided between the projecting portions, and a portion of the first principal surface provided between the first and second external electrodes is exposed.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Partially crosslinked adhesive-supported porous film for battery separator and its use
InactiveUS20040101757A1Suitable for productionBonded firmlyLayered productsFilm/foil adhesivesEngineeringAdhesive
A partially crosslinked adhesive-supported porous film for battery separator, which in producing a battery, can effectively produce a battery as an electrode / separator laminate in which an electrode and a separator are temporarily bonded to each other without causing mutual slip movement between the electrode and the separator and which after producing a battery, functions itself as a separator having a small heat shrinkage factor even at high temperatures, and a process of producing a battery using such a partially crosslinked adhesive-supported porous film. The partially crosslinked adhesive-supported porous film for battery separator, includes a porous film substrate having supported thereon a partially crosslinked adhesive that is partially crosslinked by preparing a reactive polymer having a functional group in the molecule and capable of being crosslinked upon reaction with a polyfunctional compound having reactivity with the functional group and then reacting the reactive polymer with a polyfunctional compound.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Bonding method, device formed by such method, surface activating unit and bonding apparatus comprising such unit
InactiveUS20070110917A1High bonding strengthReduce the impactSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesChemical treatmentDevice form
In a method of bonding objects to be bonded together in a solid phase at low temperature after subjecting bonding surfaces of the objects to be bonded to a hydrophilic treatment using a plasma, the objects to be bonded are conventionally handled in the atmospheric air for bonding, so that adhesion of organic substances in the atmospheric air leads to a reduction in bonding strength. Therefore, diffusion bonding needs to be performed at a temperature of as high as 1100° C. in the conventional art. According to the present invention, firm bond can be achieved at low temperature. In a method for bonding objects to be bonded together in a solid phase after subjecting bonding surfaces of the objects to be bonded to a hydrophilic treatment using a plasma, a chemical treatment step of subjecting both the objects to be bonded to the hydrophilic treatment using the plasma without exposure to the atmospheric air is performed after a physical treatment step of subjecting both the objects to be bonded to a physical treatment using an energy wave, such as an atom beam, an ion beam or a plasma, thereby bonding both the objects to be bonded together. Therefore, satisfactory bonding can be achieved without adhesion of organic substances or the like, thereby making it possible to achieve firm bond at a low temperature of 500° C. or less.
Owner:BONDTECH
Heatable Media Line
InactiveUS20100263740A1Prevent freezingHigh degreeValve members for heating/coolingExhaust apparatusLine tubingPlastic molding
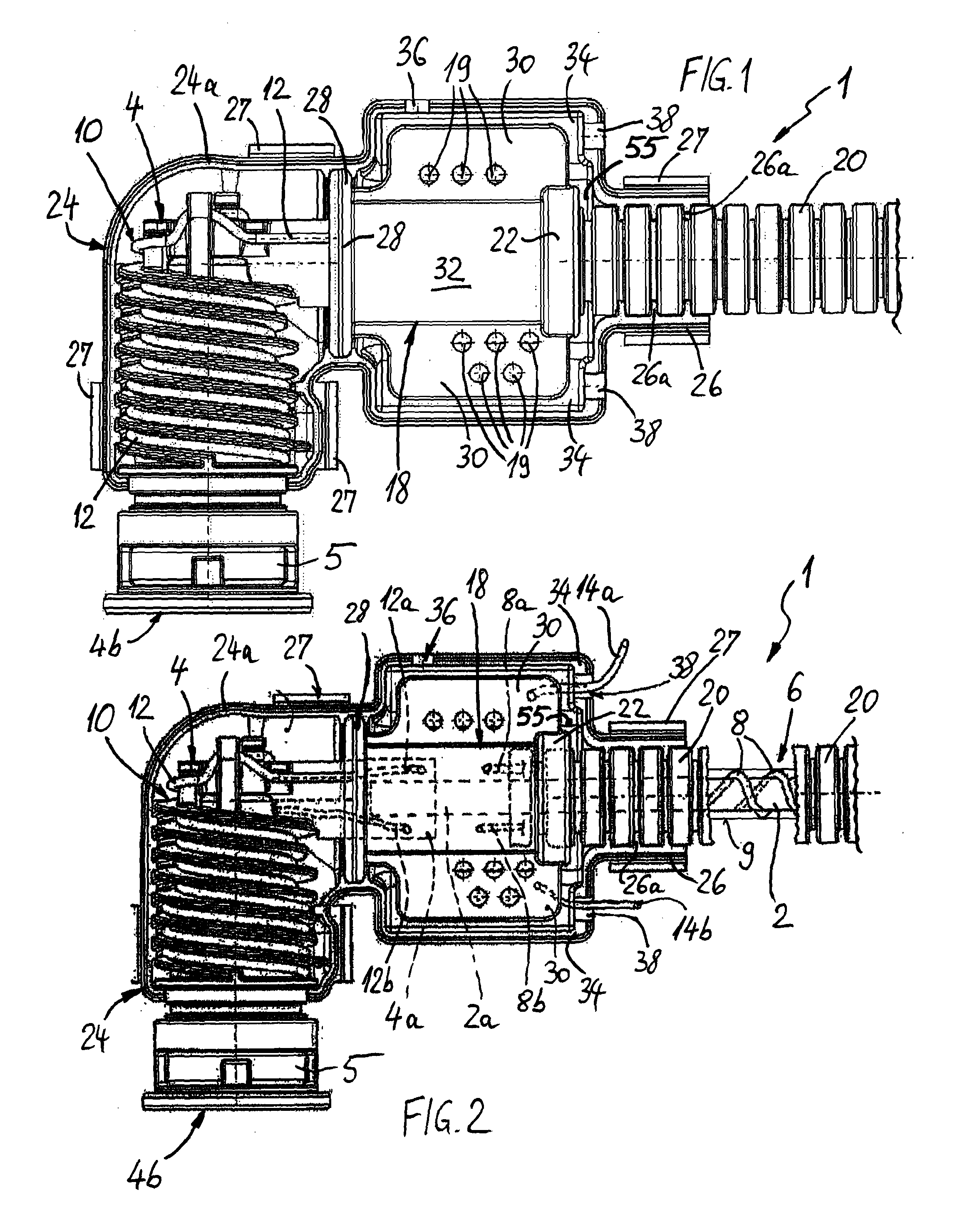
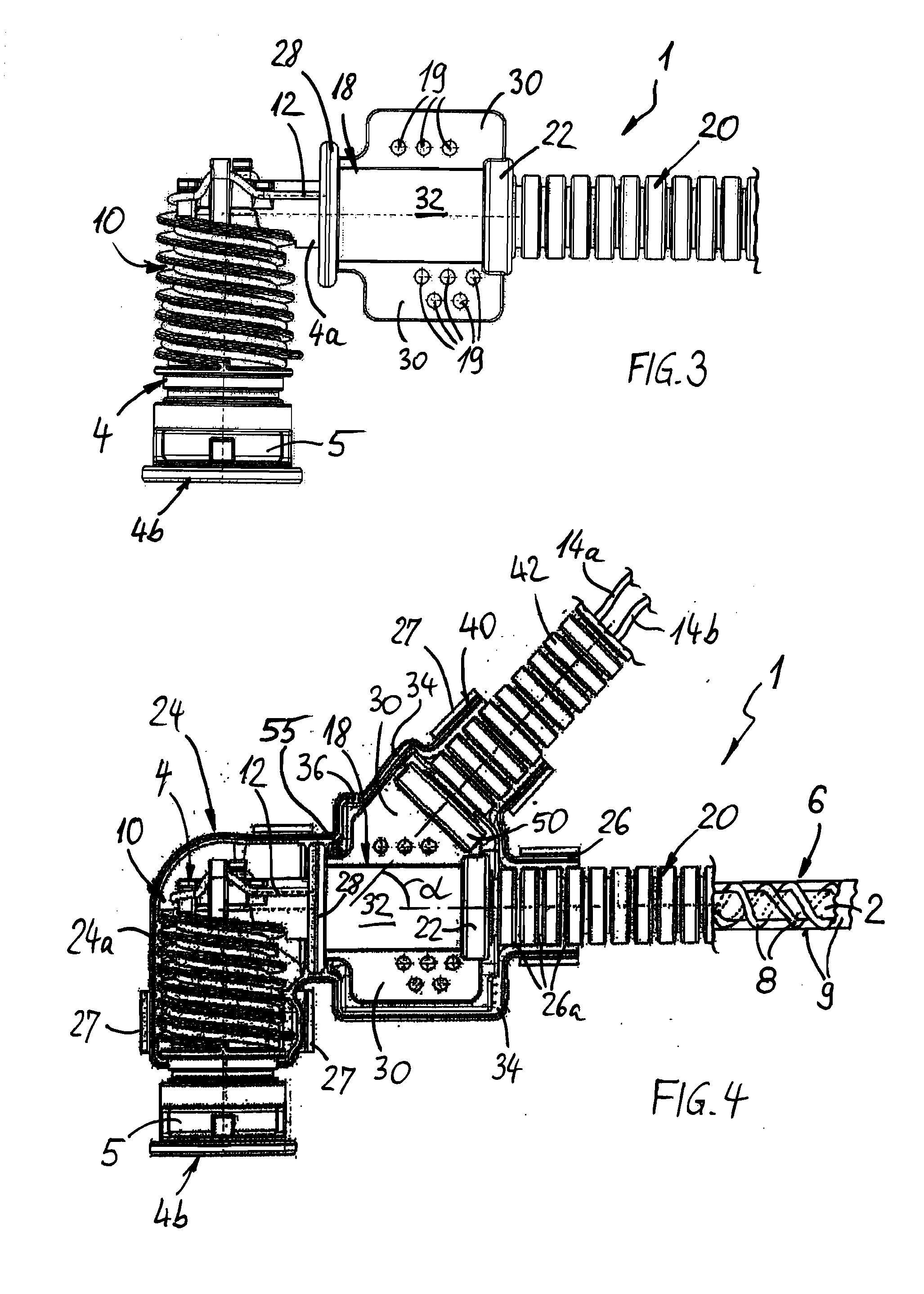
The present invention relates to an electrically heatable media line (1), comprising a fluid line (2) and at least one fluid connector (4) connected to a line end (2a). The fluid line (2) and the fluid connector (4) respectively have electric heating means (6, 10), wherein the fluid line (2) and / or the fluid connector (4) including electric connections (16) of the heating means (6, 10) are / is enclosed by a plastic molding compound.
Owner:VOSS AUTOMOTIVE
Substrate and semiconductor device
InactiveUS20070164445A1Easy to adjustSuppress bonding failureFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSemiconductorSemiconductor device
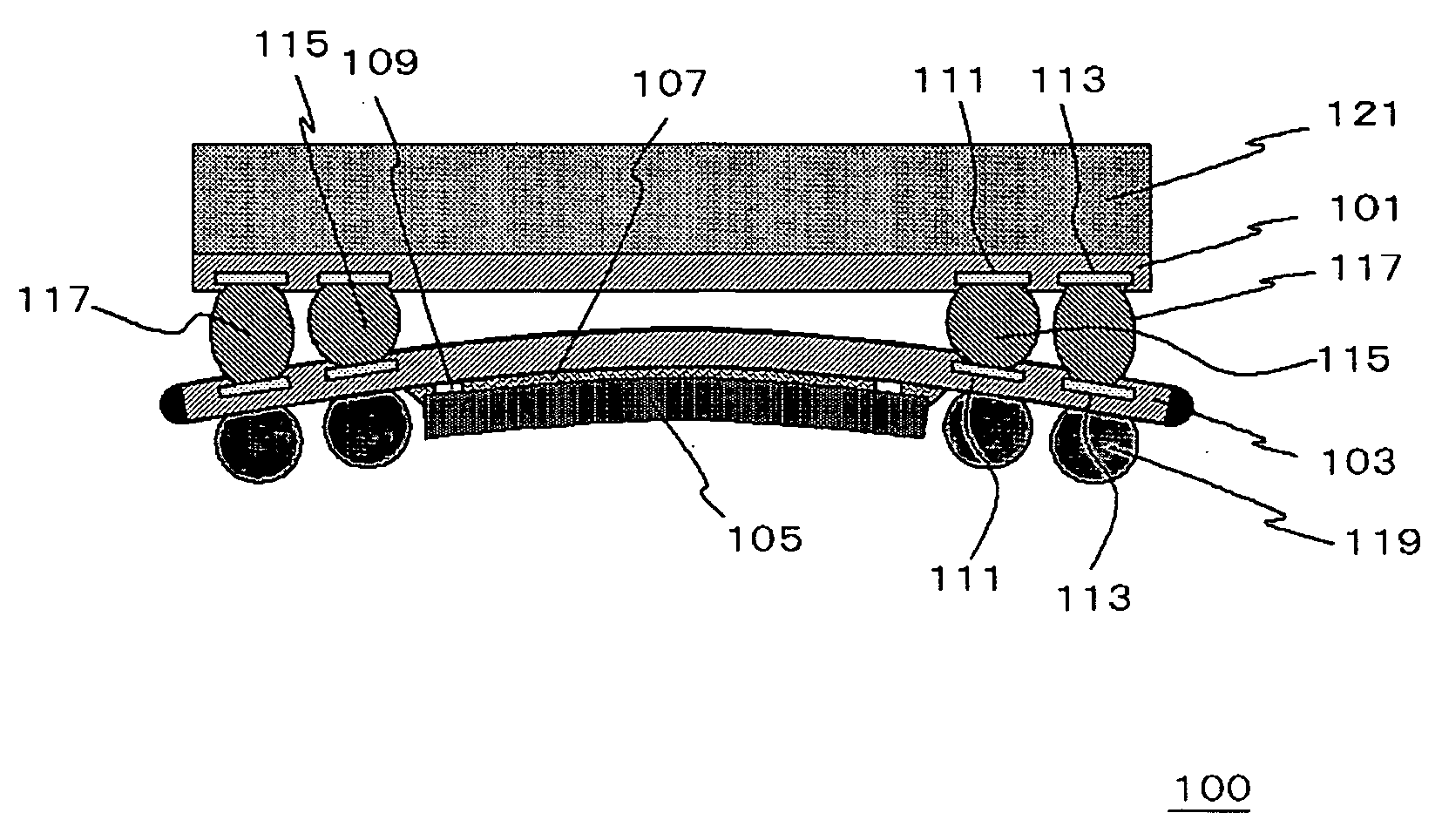
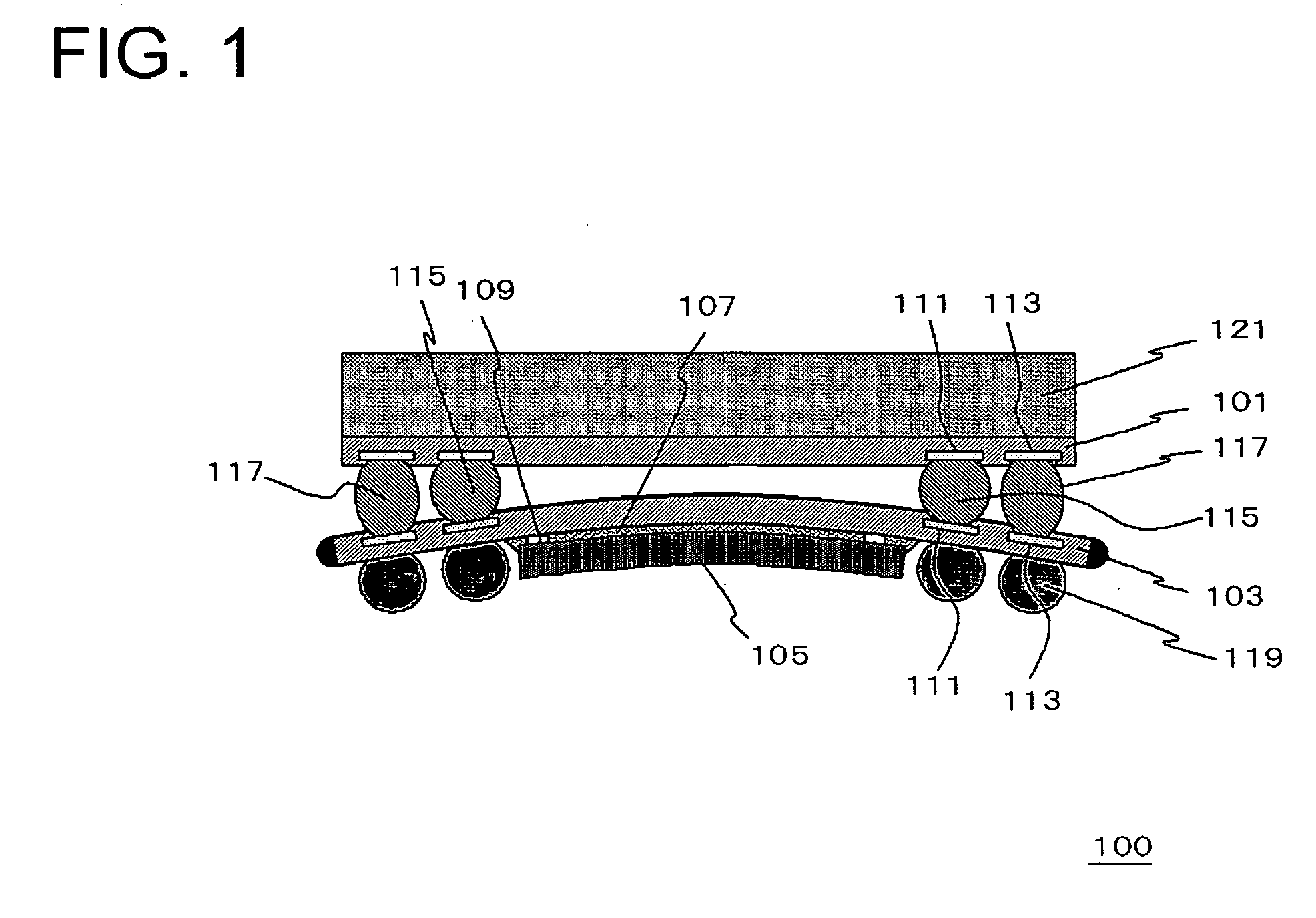
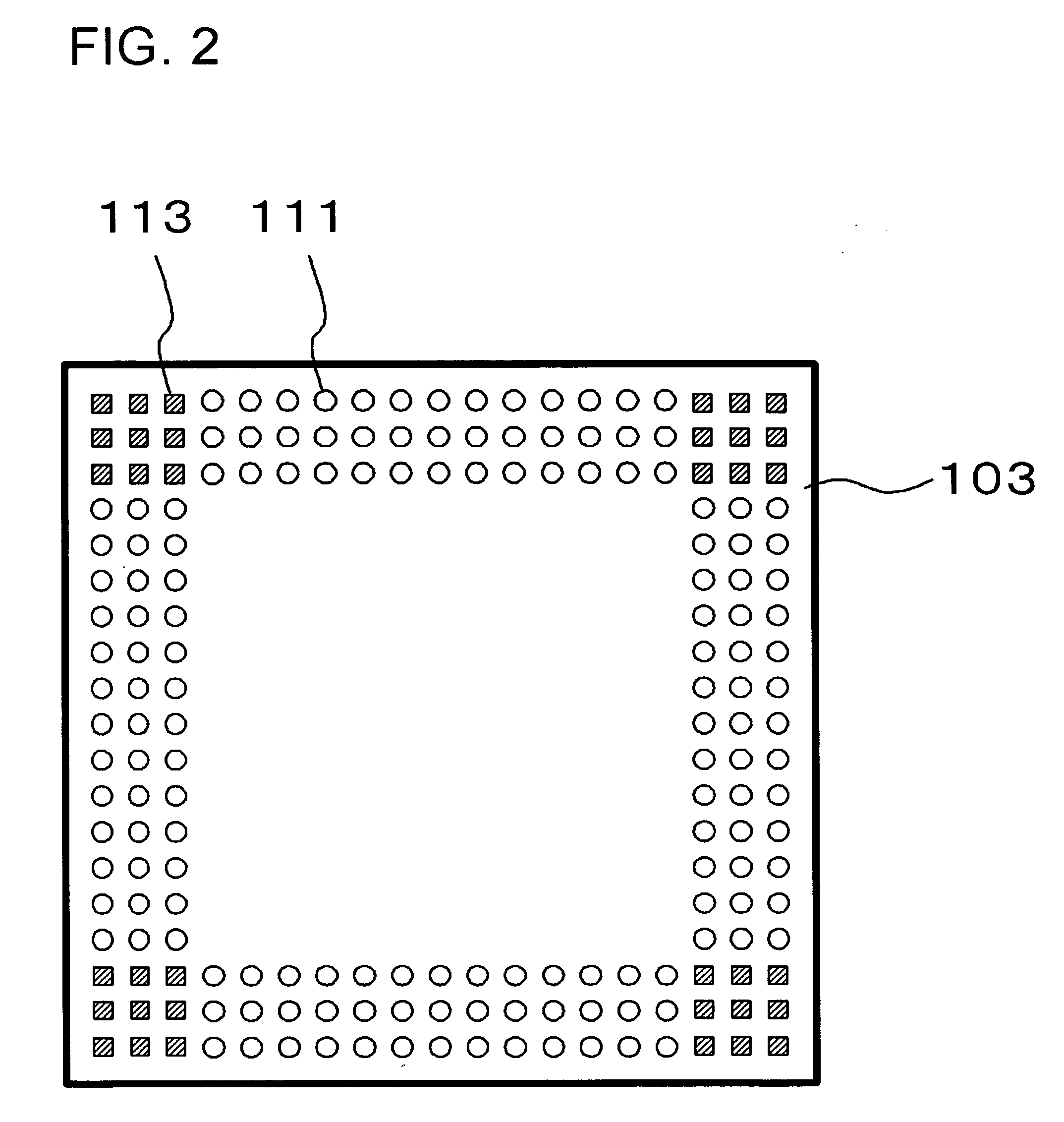
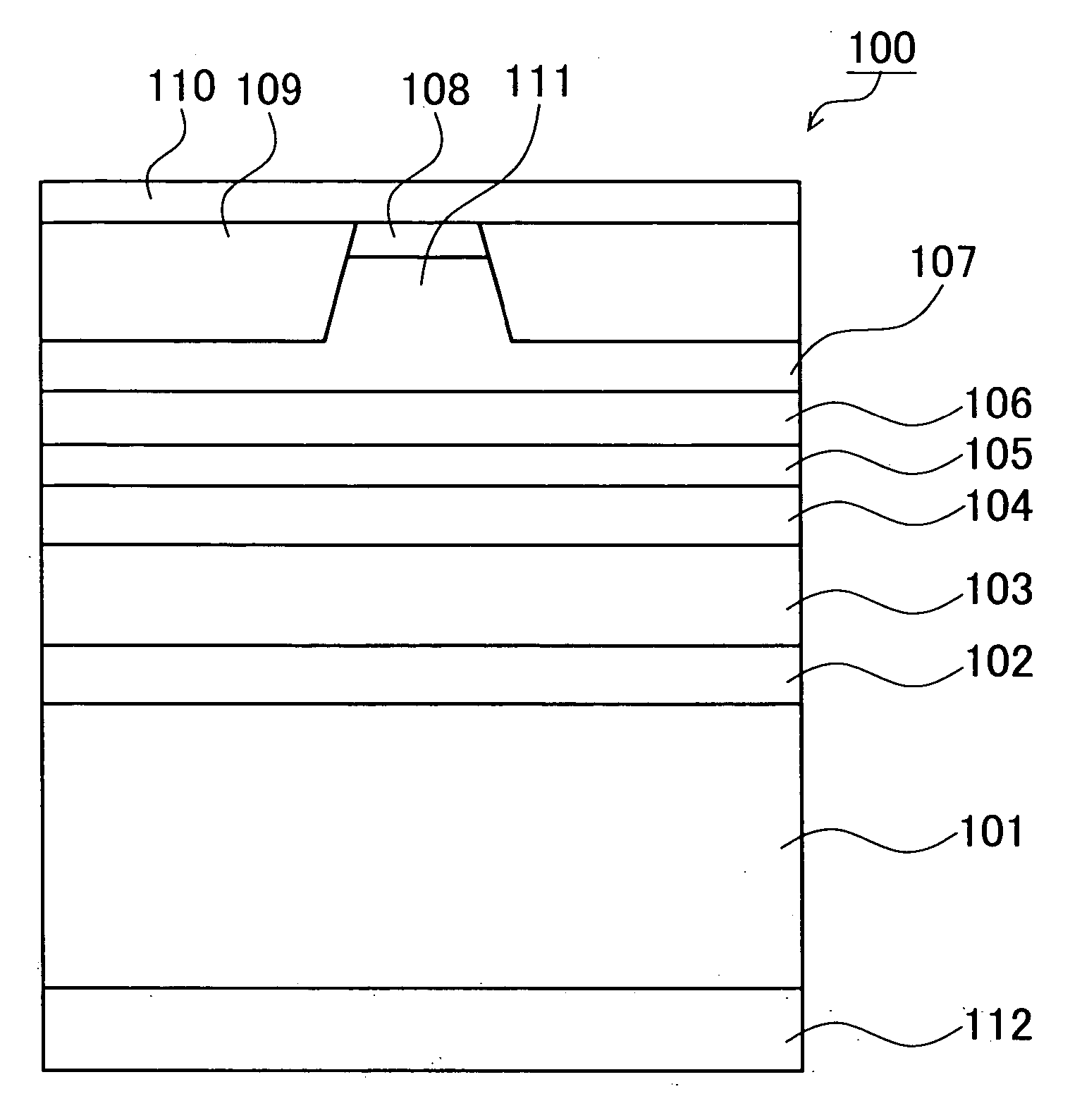
Aiming at adjusting the height of bump electrodes connected to lands on a substrate, a semiconductor device 100 has a first interconnect substrate 103 and a second interconnect substrate 101. On one surface of these substrates, first lands 111 and second lands 113 are provided. The plane geometry of the second lands 113 is a polygon characterized by the inscribed circle thereof having an area smaller than the area of the inscribed circle of the first land.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Nitride semiconductor light-emitting device and method of manufacture thereof
ActiveUS20070080368A1Improve adhesionImprove reliabilityLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight emitting deviceNitride semiconductors
In a nitride semiconductor laser bar including a group III-V nitride semiconductor layer, on the front-side cavity end face, a separation layer of aluminum nitride is laid, and further on the separation layer, an end face coating film of aluminum oxide is laid. Likewise, on the rear-side cavity end face, a separation layer of aluminum nitride is laid, and further on the separation layer, an end face coating film of an aluminum oxide / TiO2 multilayer film is laid.
Owner:SHARP FUKUYAMA LASER CO LTD
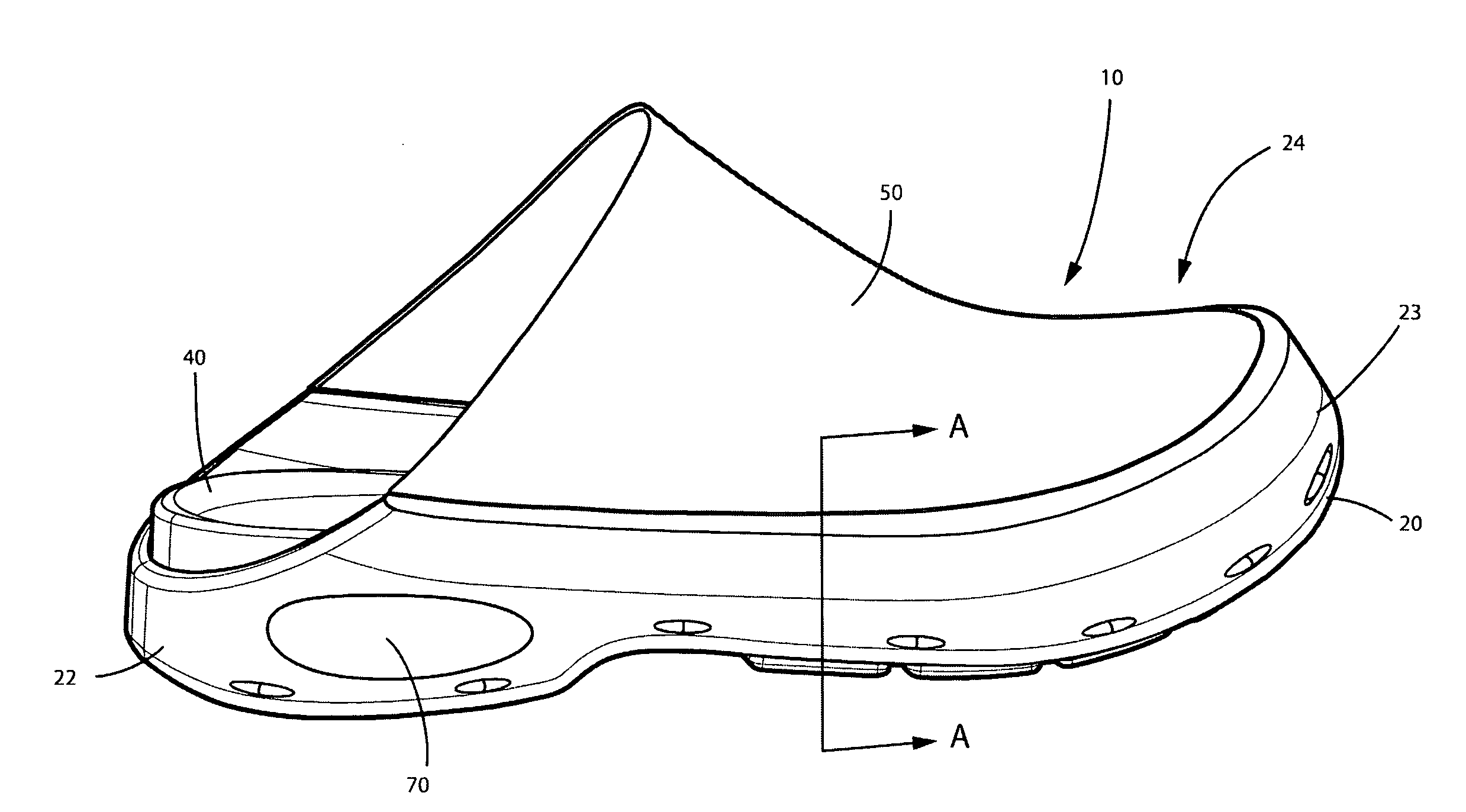
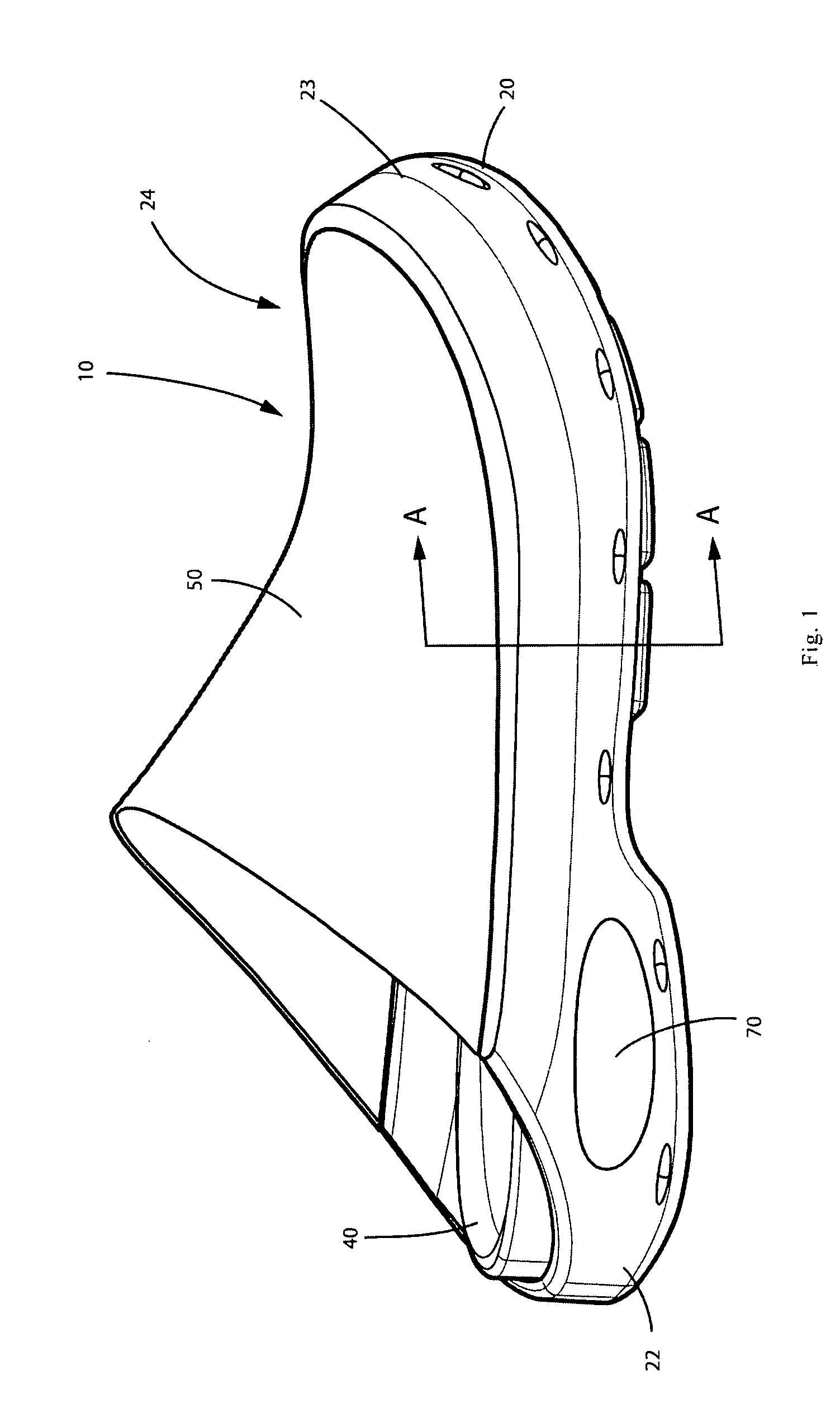
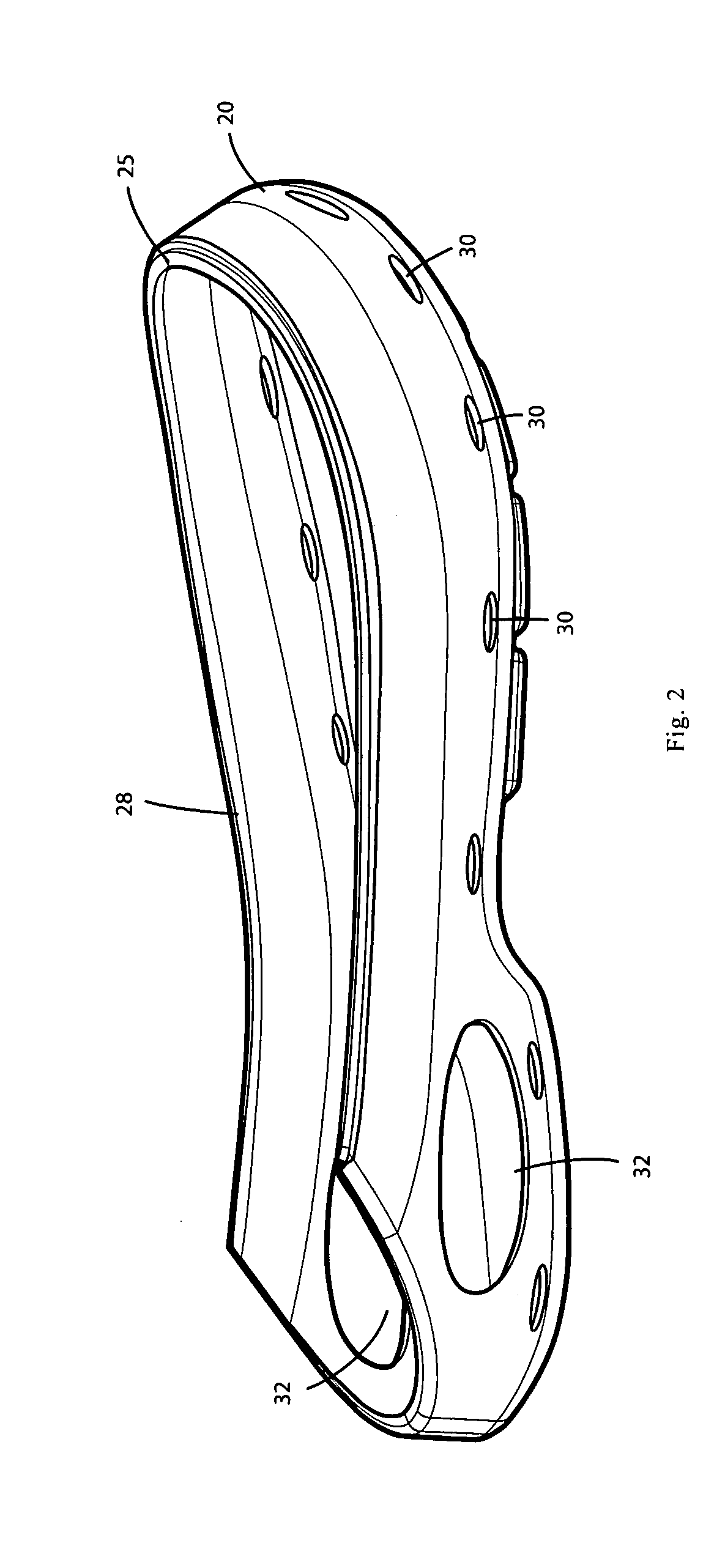
Melded footwear
ActiveUS20080168684A1Reduce and eliminate needLabor cost and cost of manufacturingSolesInsolesAdhesiveEngineering
Melded footwear and process for manufacture of footwear. This enhanced shoe can be formed and assembled with a limited number of steps and without the need for much stitching. The shoe has a durable polyurethane shell, which is an integrated upper and outsole. The shoe contains a textile upper portion which is attached by direct injection molded. Molding the textile to the outsole eliminates the need for the use of adhesives. A locking plug element is provided that serves the dual function of providing cushioning around the heel and locking certain elements together.
Owner:GAMILA
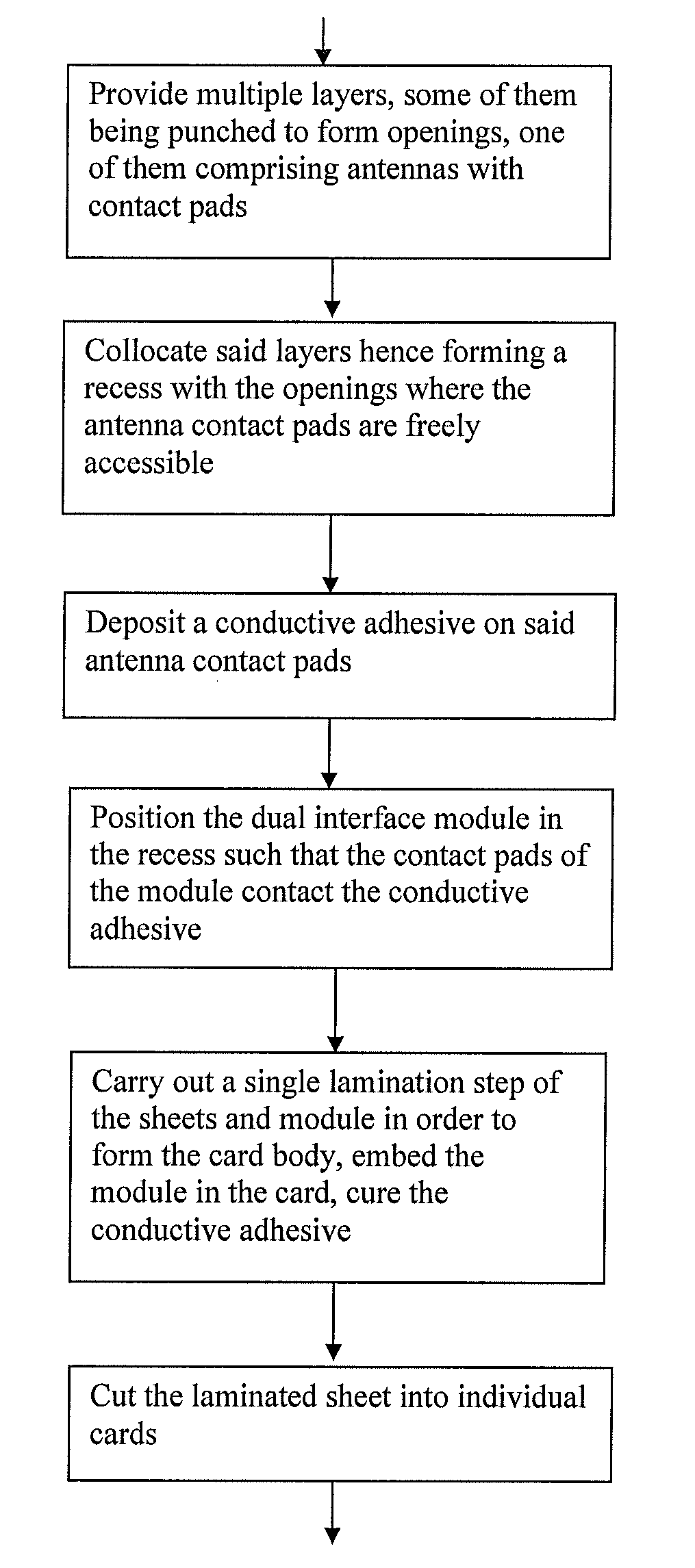
Manufacturing method for a card and card obtained by said method
InactiveUS20090151150A1Speed up the processEasy to carryPrinted circuit aspectsSolid-state devicesContact padIsotropic conductive adhesives
A method for manufacturing a dual interface card includes at least the following step:collocating multiple card support sheets one onto the other, some of these sheets showing holes, in order to form a recess adapted to receive the dual interface module, one of the sheets supporting the antenna having solid metallic contact pads at least partially freely accessible in the recessdepositing a conductive adhesive onto the contact padspositioning the dual interface module in the recess such that the pads of the module are contacting the conductive adhesiveexecuting one single lamination step of the sheets with the module in order to:laminate the multiple layers together in order to form the card bodyembed the dual interface module in the recess andachieve the curing of the isotropic conductive adhesive and the permanent electrical contact between the antenna and the dual interface module.
Owner:ASSA ABLOY AB
Preparation of semiconductor device
InactiveUS20060205237A1Improve reliabilityBonded firmlyCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsEngineeringSealant
In the preparation of a semiconductor device comprising a semiconductor member, the semiconductor member is subjected to plasma treatment and then primer treatment, prior to the encapsulation thereof with an encapsulant. The semiconductor device, typically LED package, is highly reliable in that a firm bond is established between the semiconductor member and the encapsulant resin.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Ceramic joint body
InactiveUS6921881B2Occurrence can be suppressedAvoid warpingLayered product treatmentLaminationBond interfaceElectrical conductor
A ceramic joint body including a ceramic substrate and a ceramic body such as a cylindrical body firmly bonded to each other and excellent in corrosion resistance in the ceramic substrate for use for a semiconductor product producing / examining the step. The ceramic bonded body includes a ceramic substrate in which a conductor is provided, and a ceramic body bonded to a bottom face of the ceramic substrate. The ceramic bonded body has a region, where no conductor is formed, in at least a part of a region above a bonding interface between the ceramic substrate and the ceramic body.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com