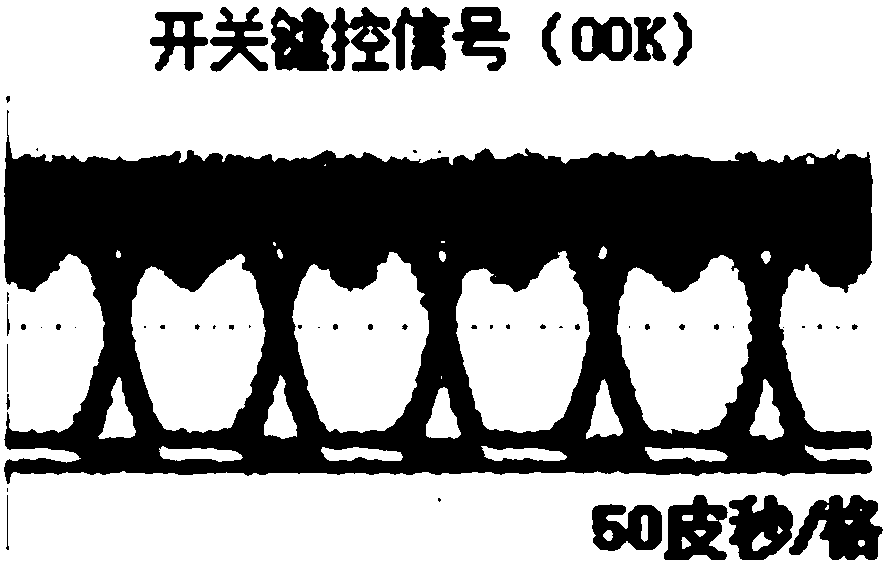
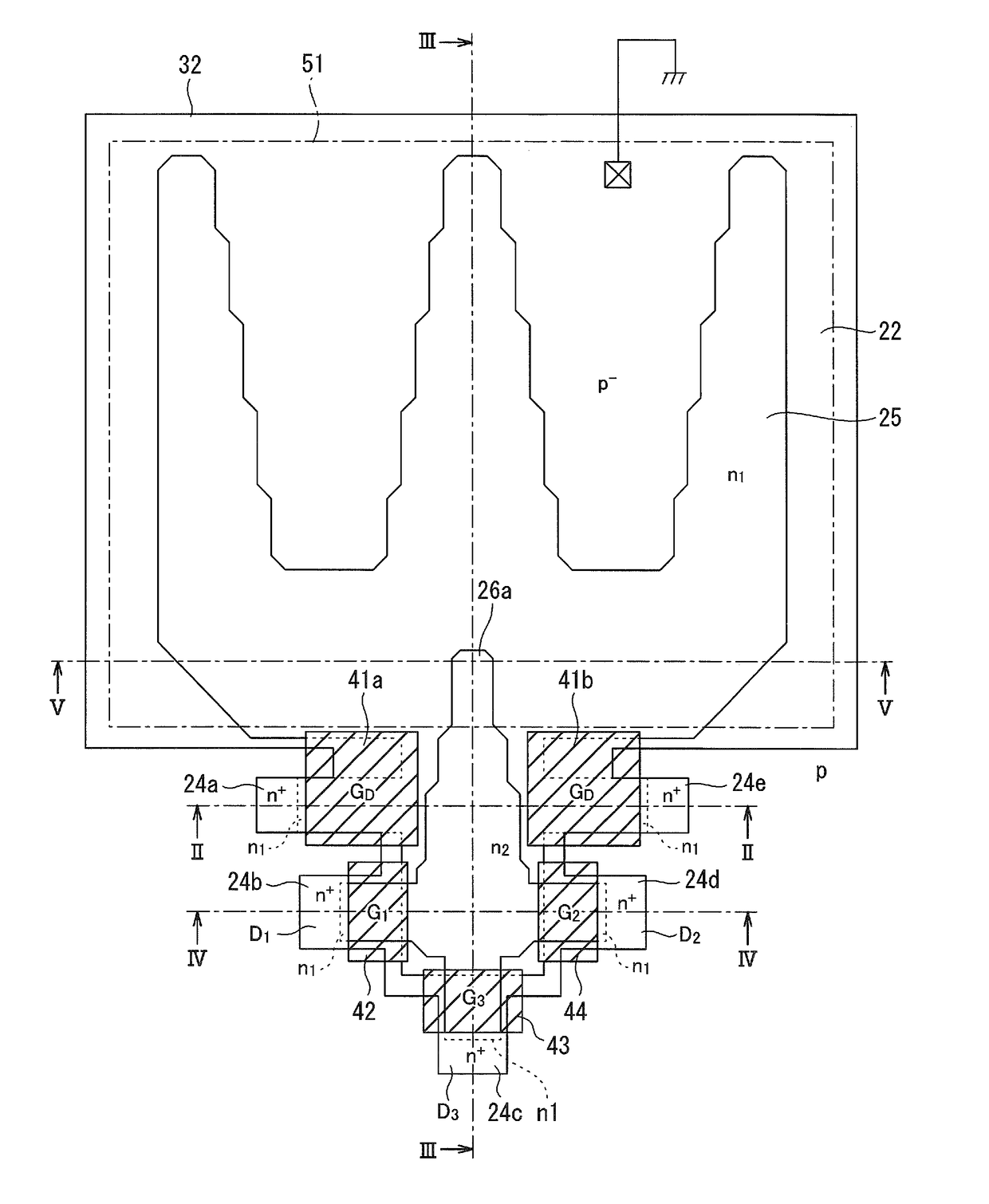
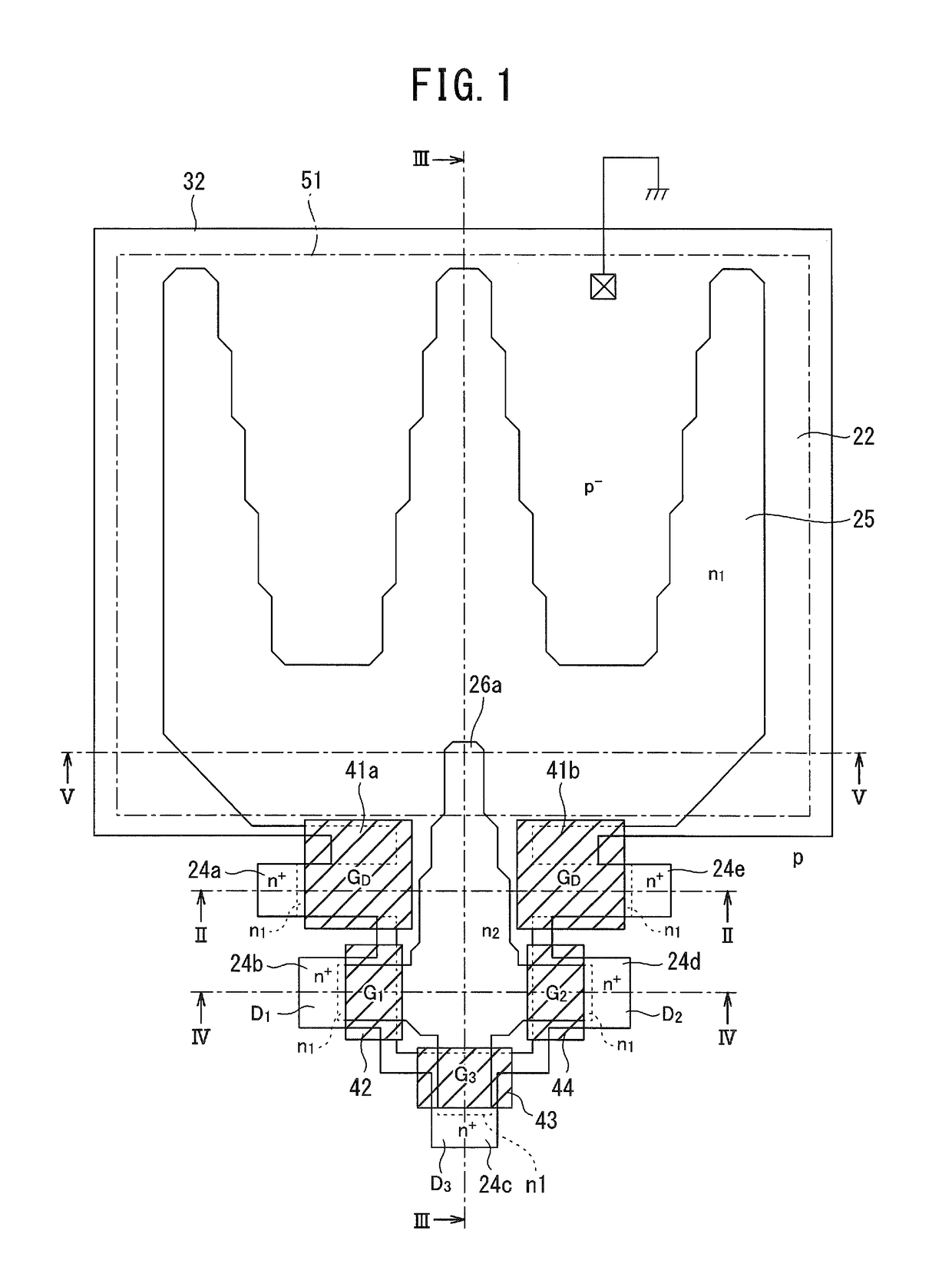
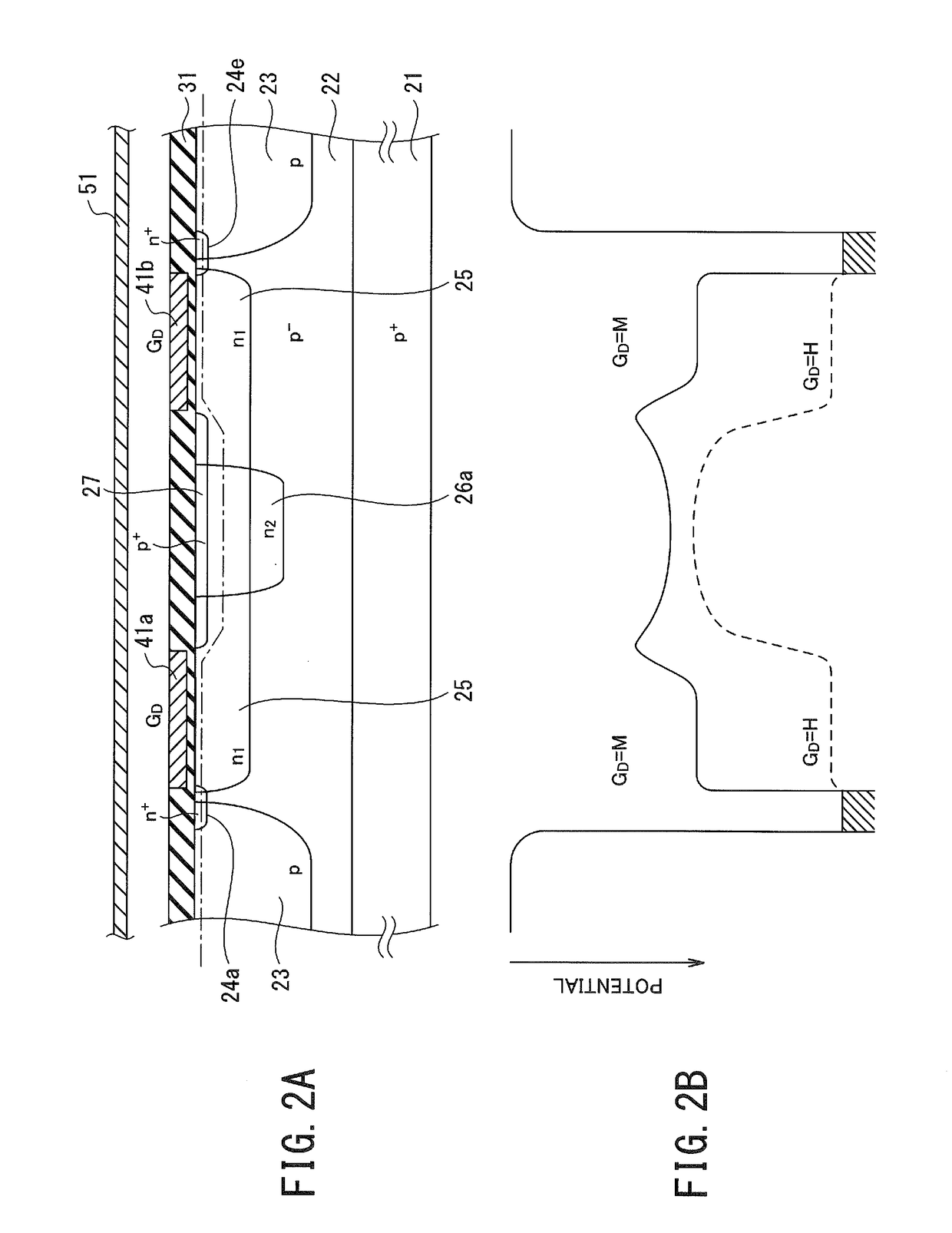
Patents
Literature
48results about How to "High-speed modulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
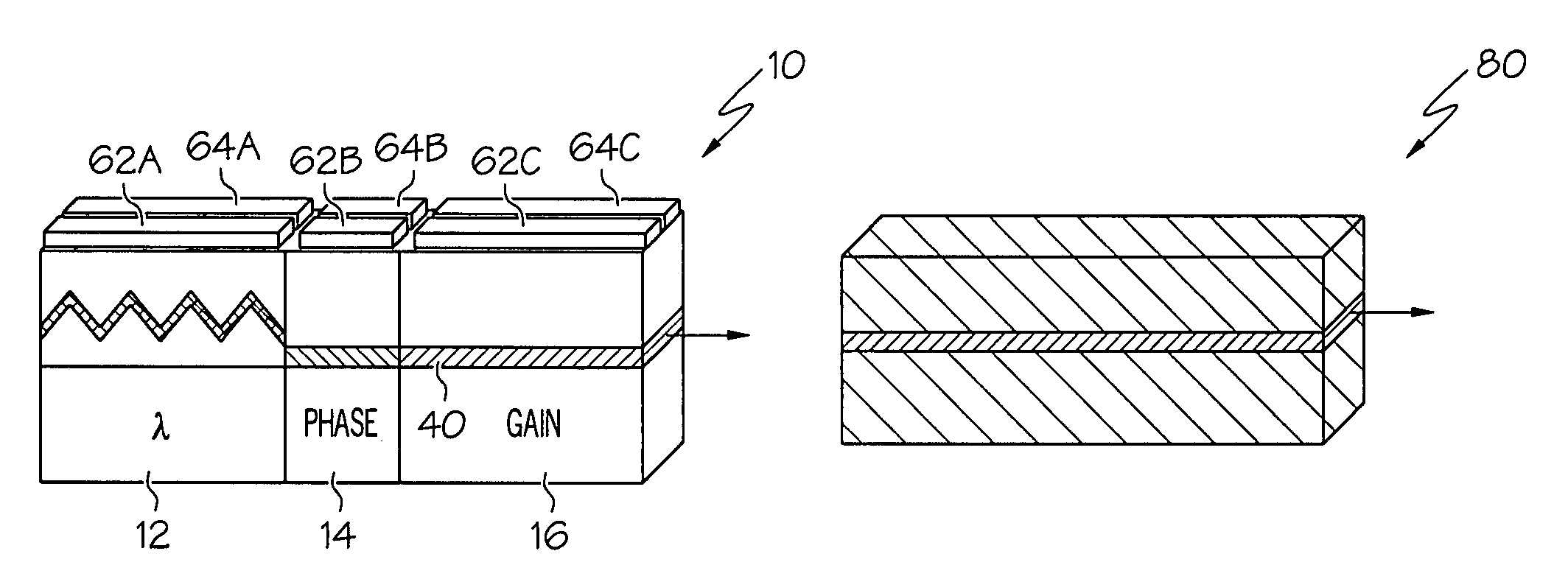
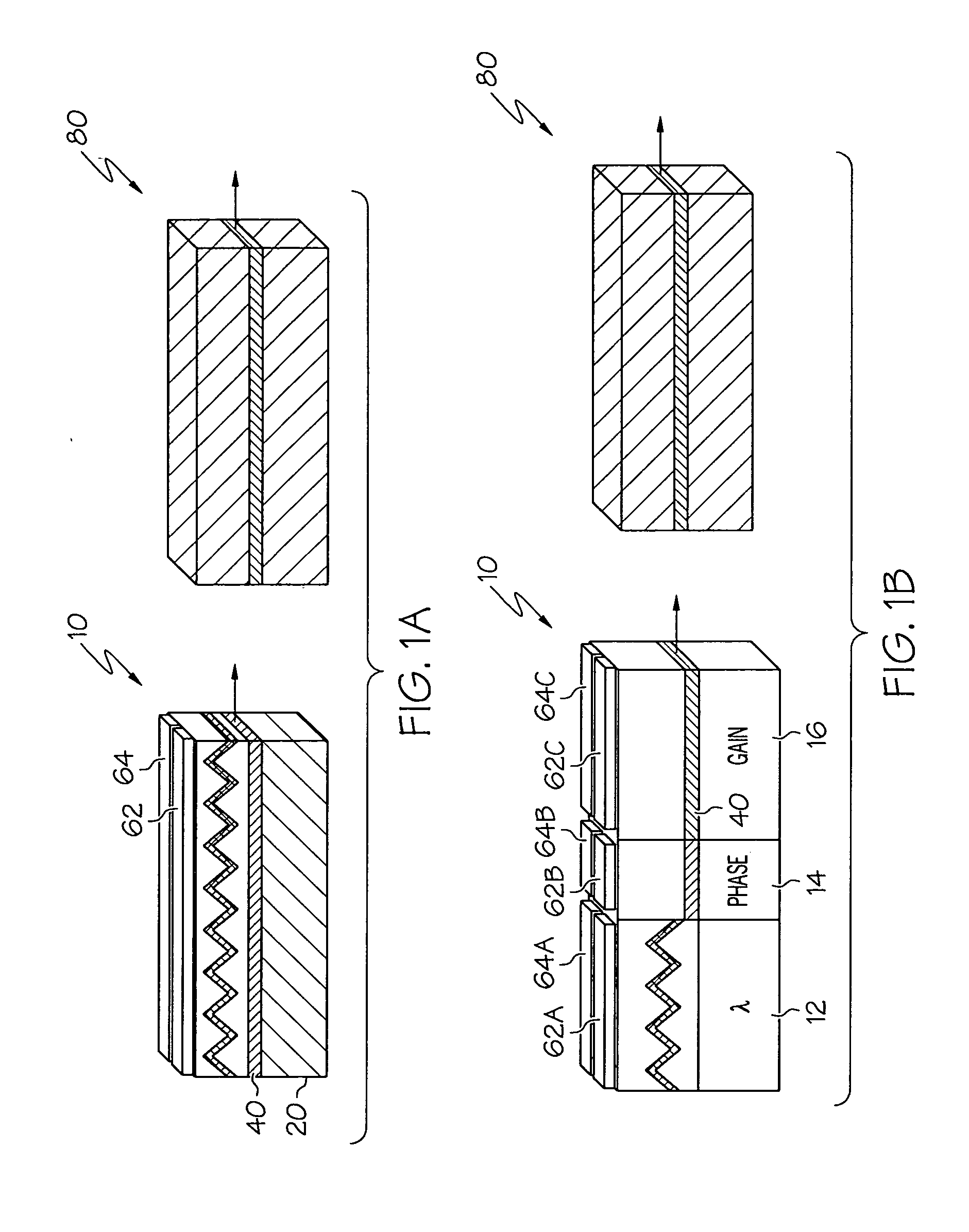
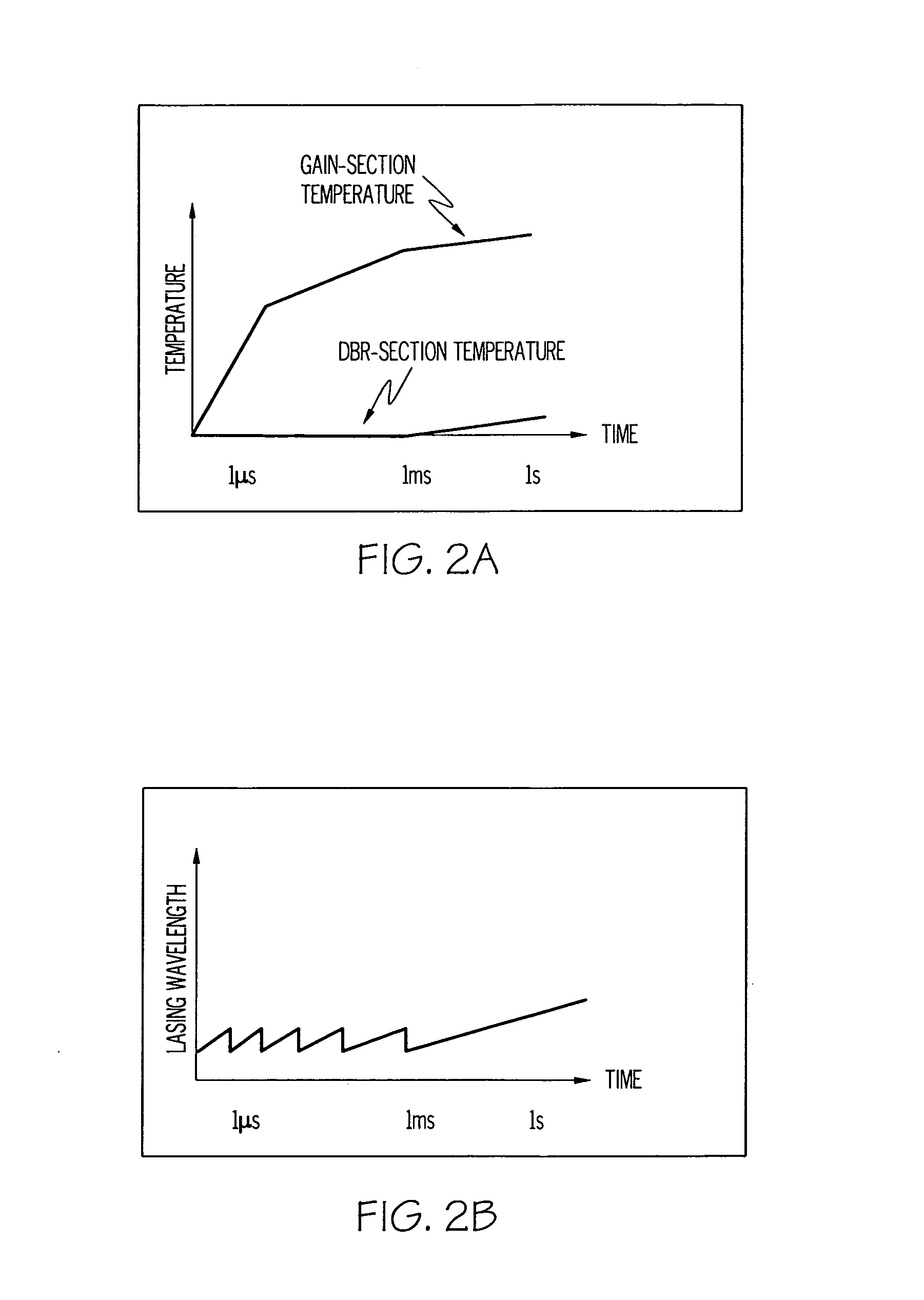
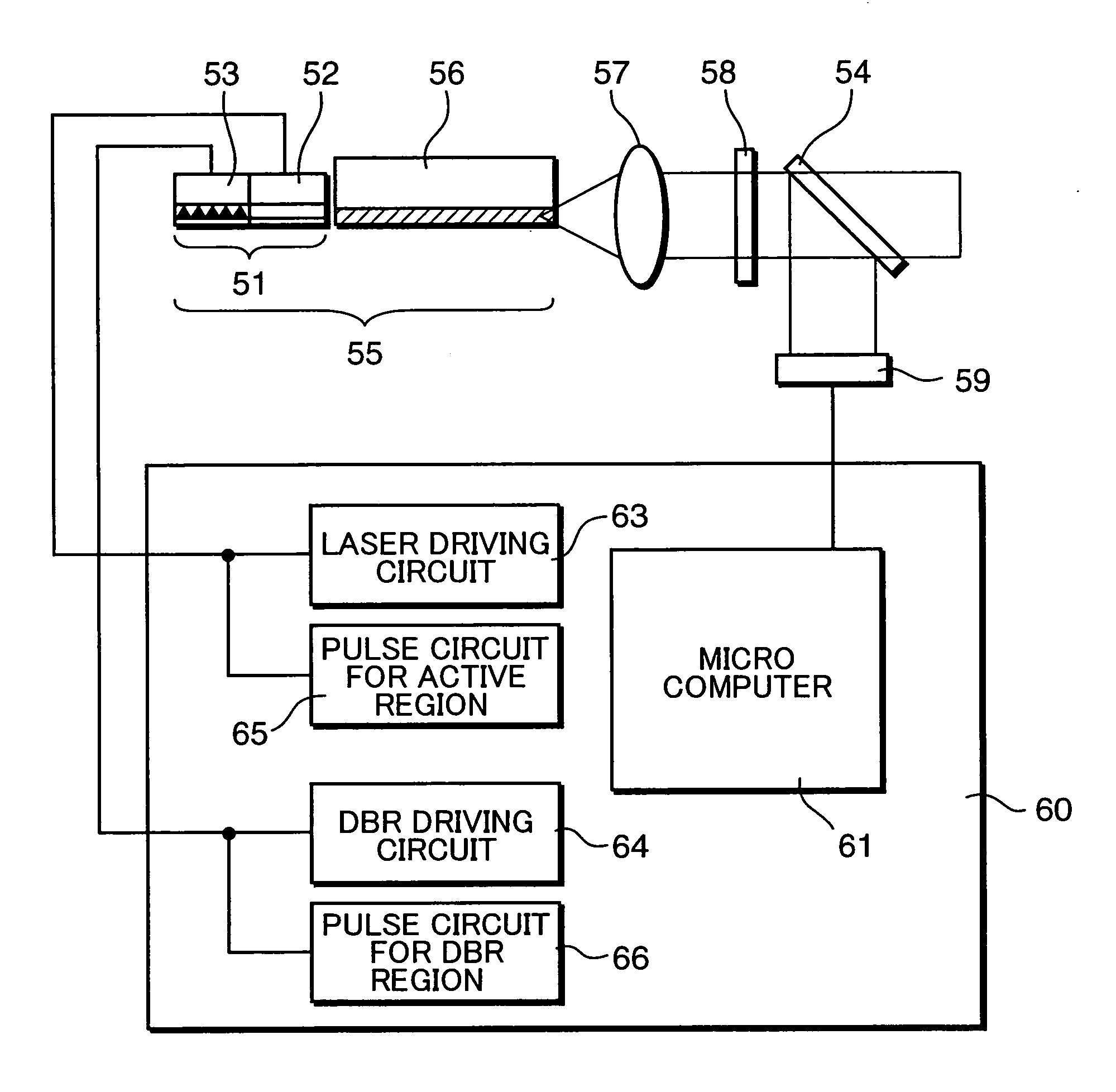
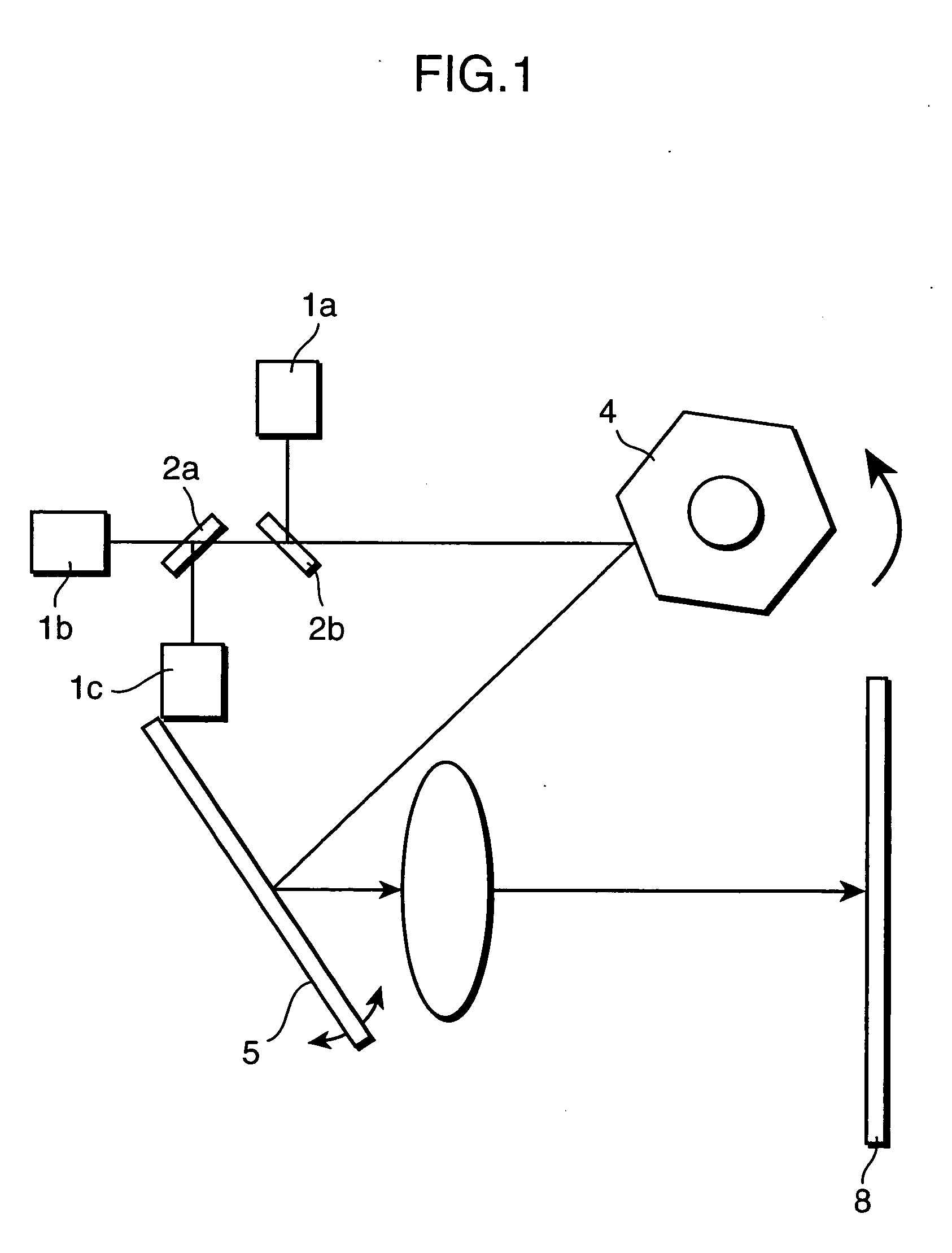
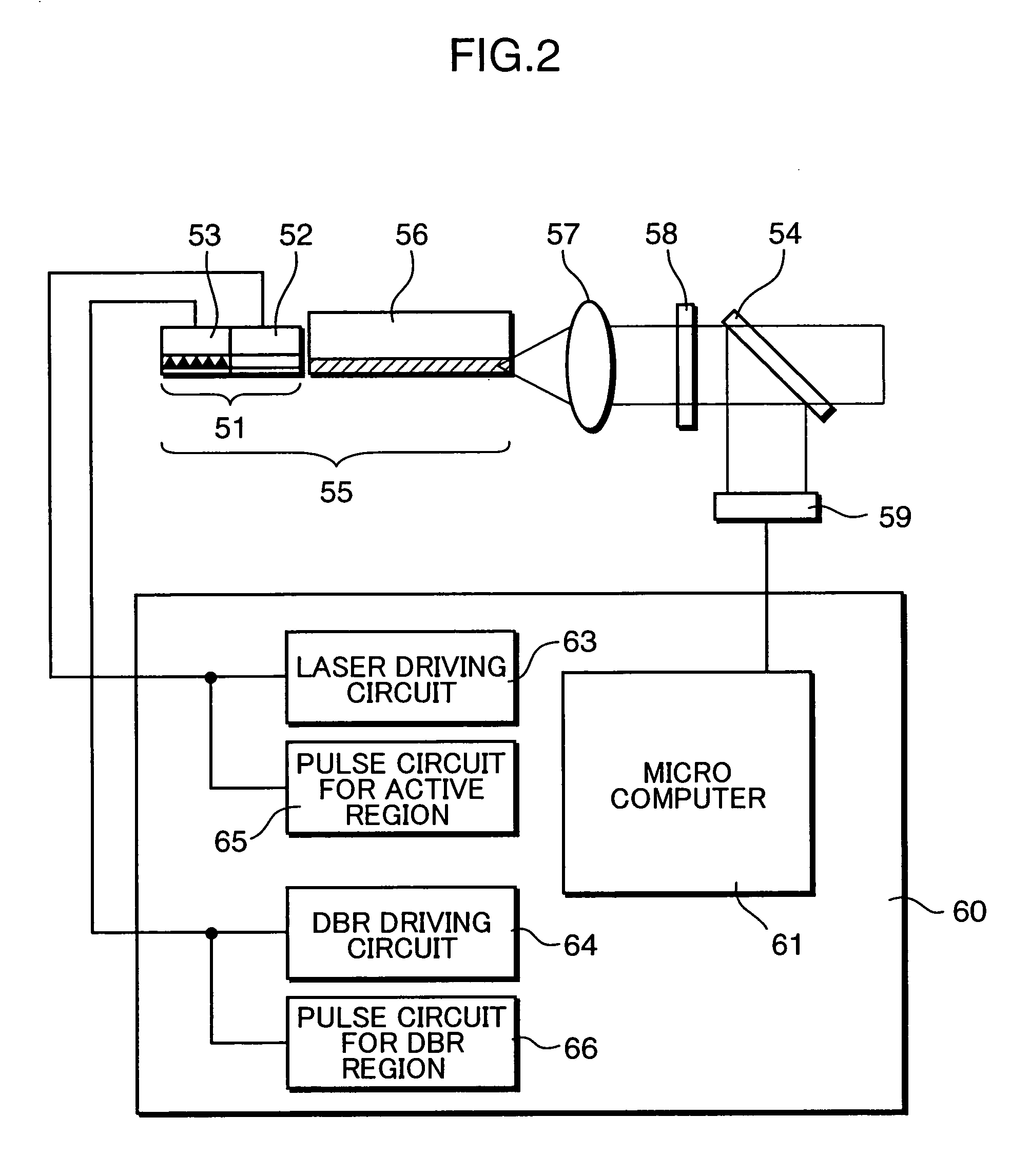
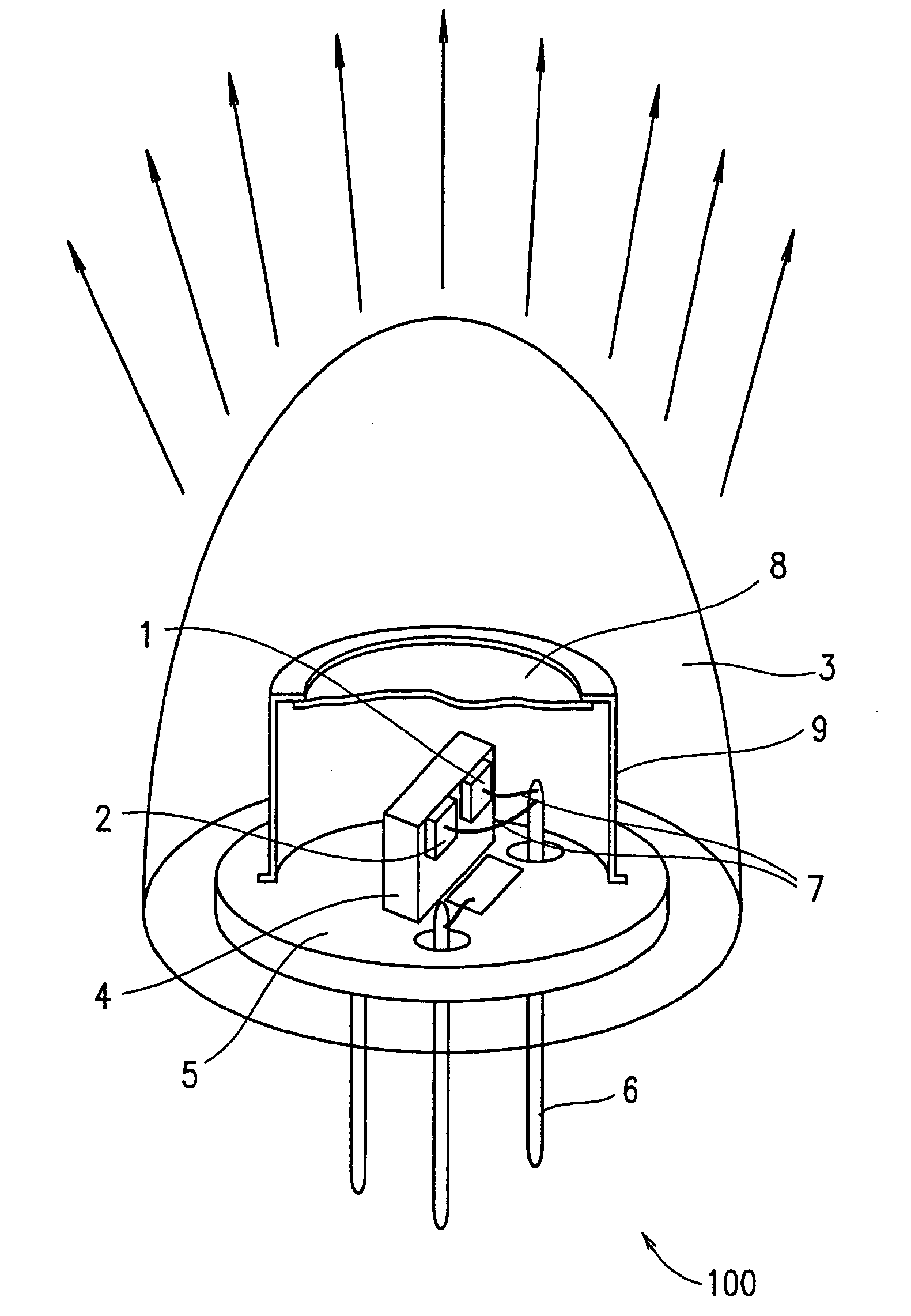
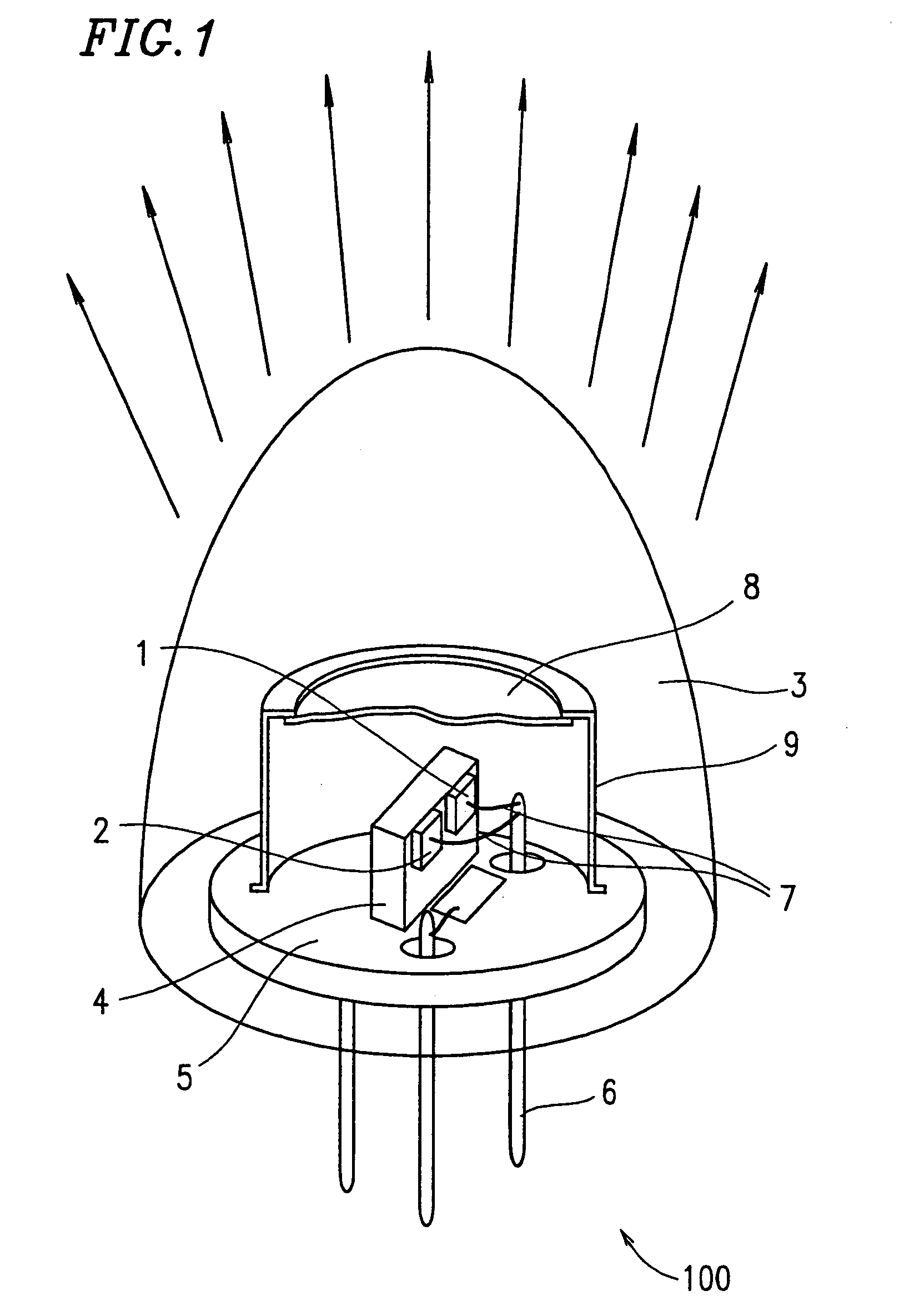
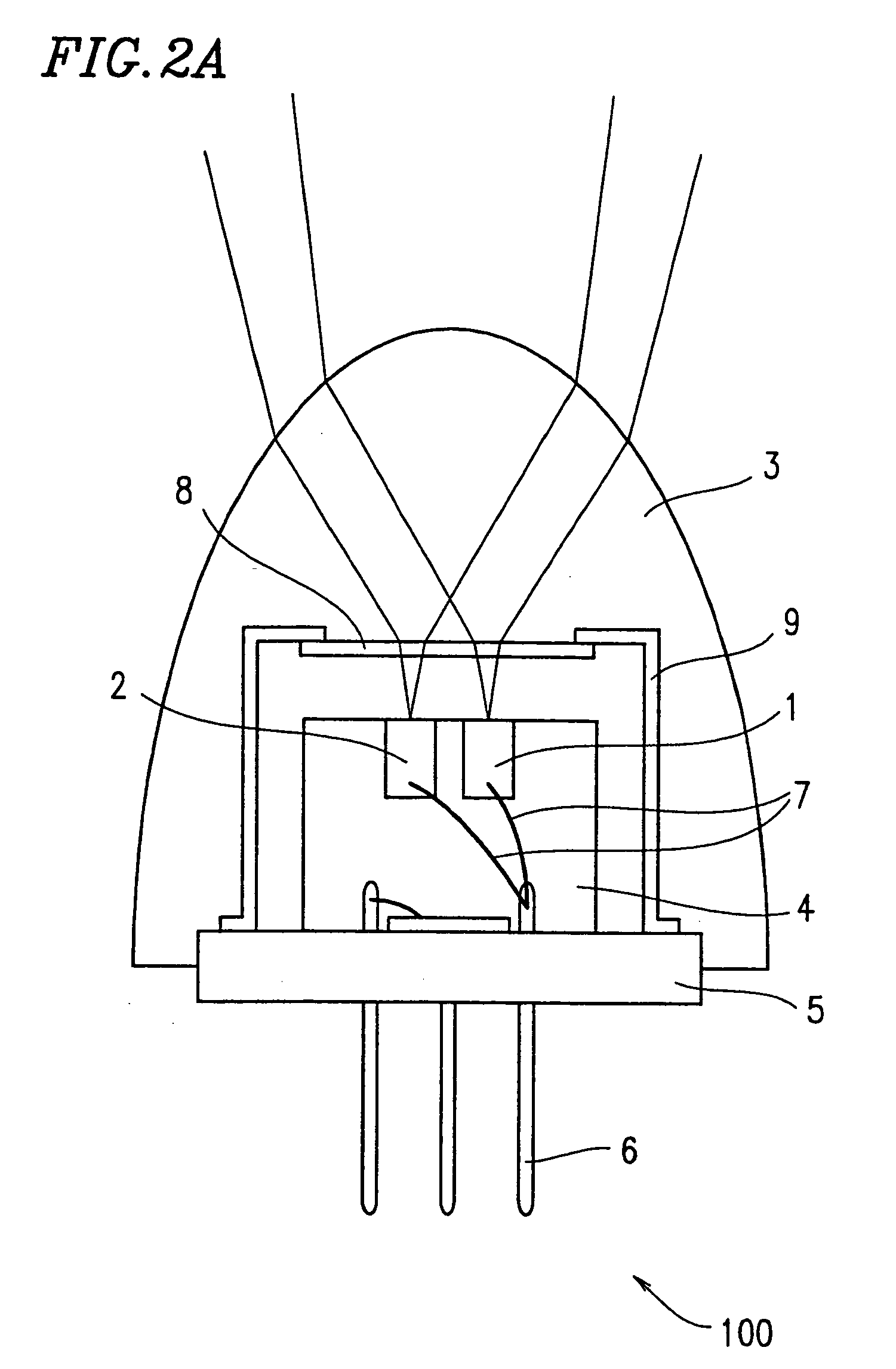
Thermal compensation in semiconductor lasers
InactiveUS20080063016A1High output powerWithout excessive noiseOptical wave guidanceLaser cooling arrangementsDriving currentHarmonic
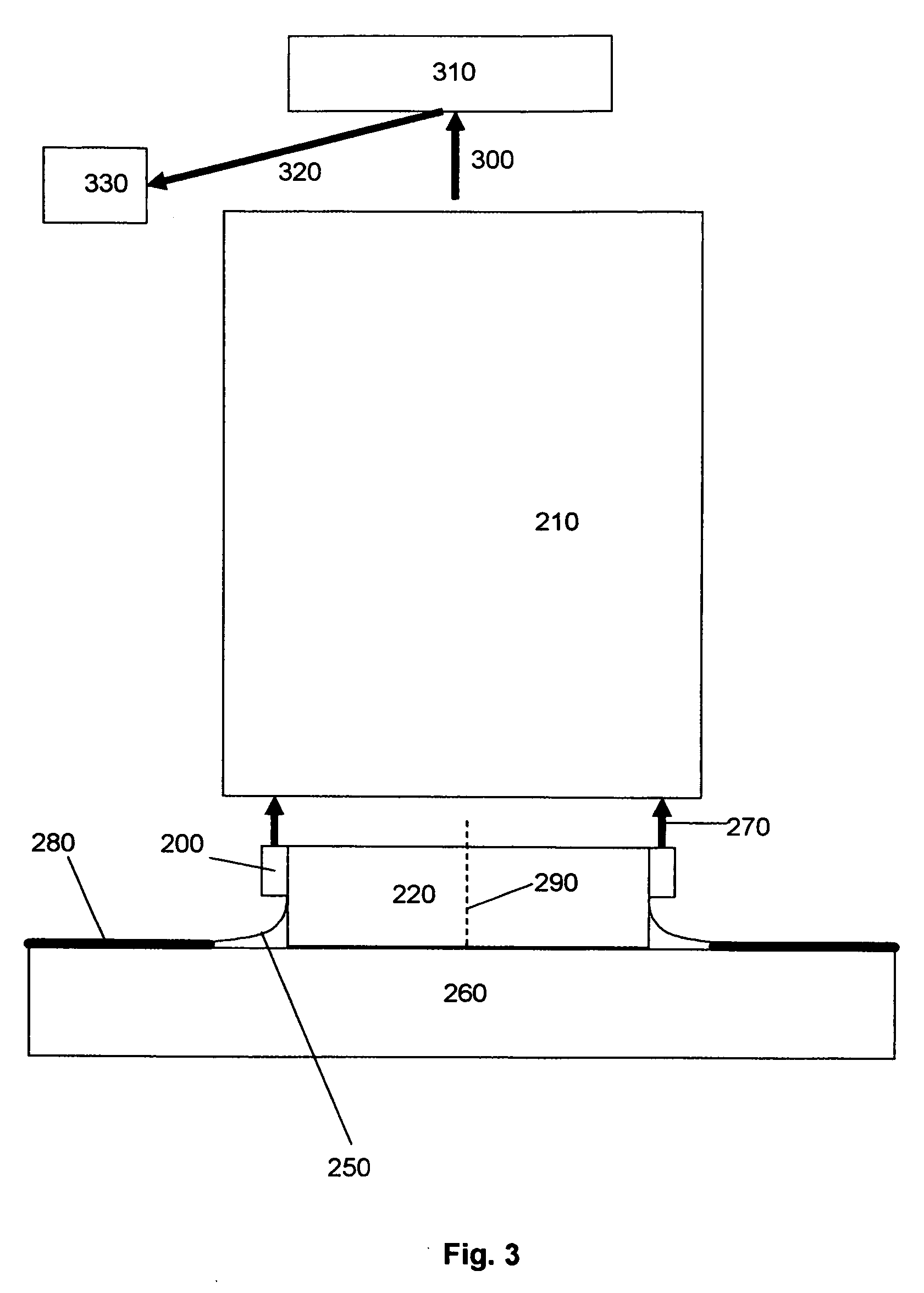
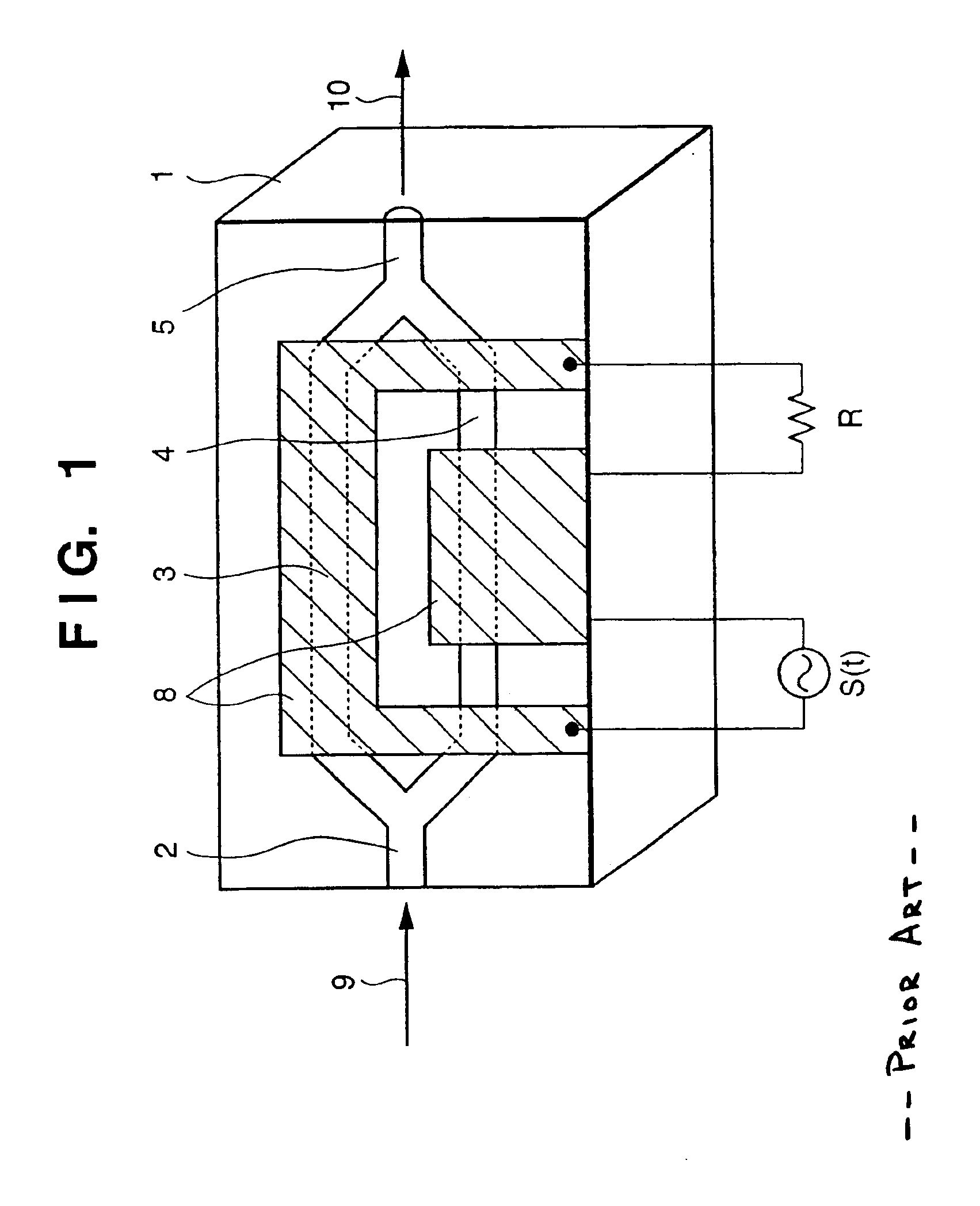
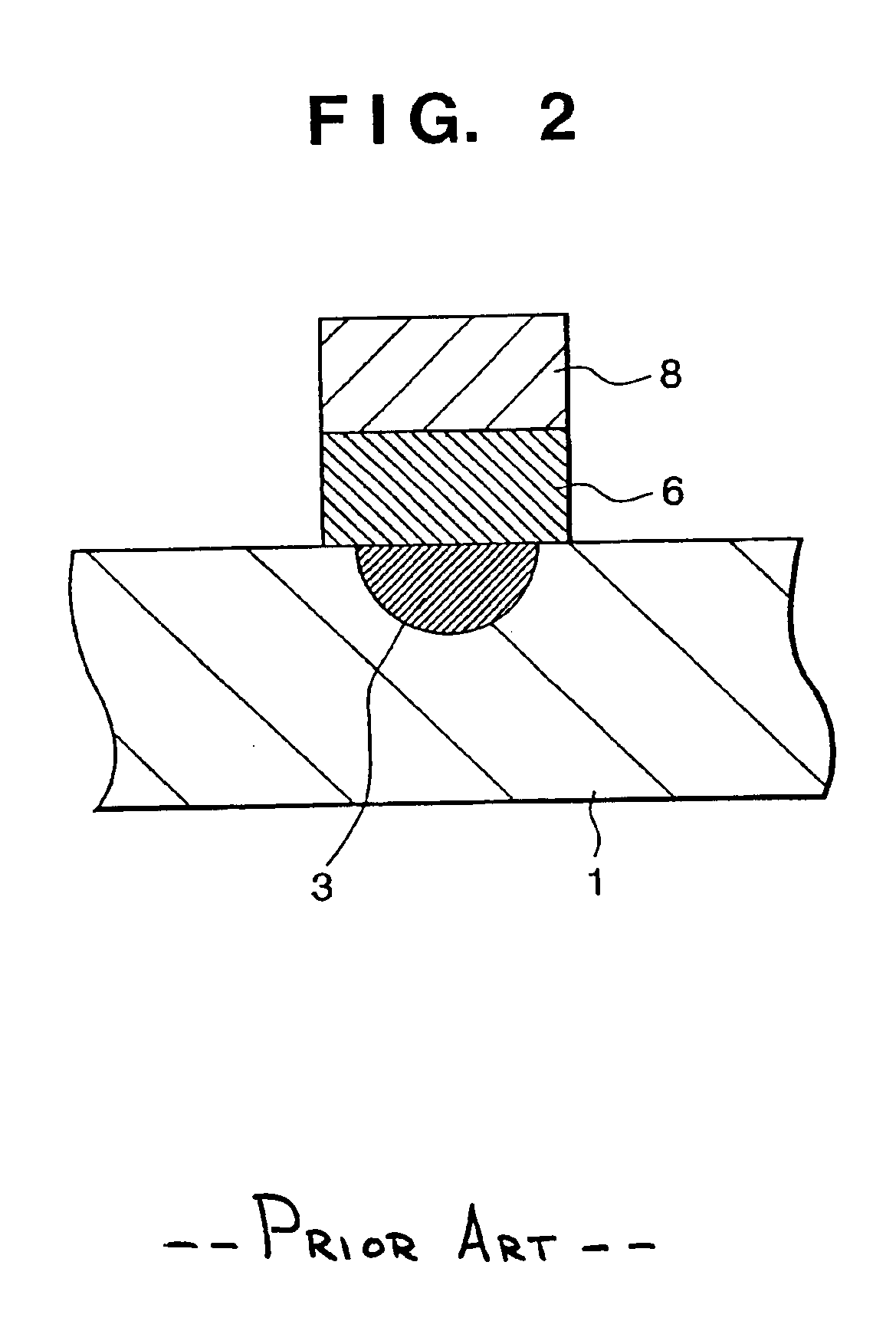
The present invention relates to methods for modulating a semiconductor laser and wavelength matching to a wavelength converter using monolithic micro-heaters integrated in the semiconductor laser. The present invention also relates to wavelength matching and stabilization in laser sources in general, without regard to whether the laser is modulated or whether second harmonic generation is utilized in the laser source. According to one embodiment of the present invention, a method of compensating for thermally induced patterning effects in a semiconductor laser is provided where the laser's heating element driving current IH is set to a relatively high magnitude when the laser's driving current ID is at a relatively low magnitude. Additional embodiments are disclosed and claimed.
Owner:CORNING INC
Surface-emission laser diode and surface-emission laser array, optical interconnection system, optical communication system, electrophotographic system, and optical disk system
InactiveUS20050147143A1High power operationIncrease speedOptical wave guidanceLaser cooling arrangementsSemiconductor materialsLaser array
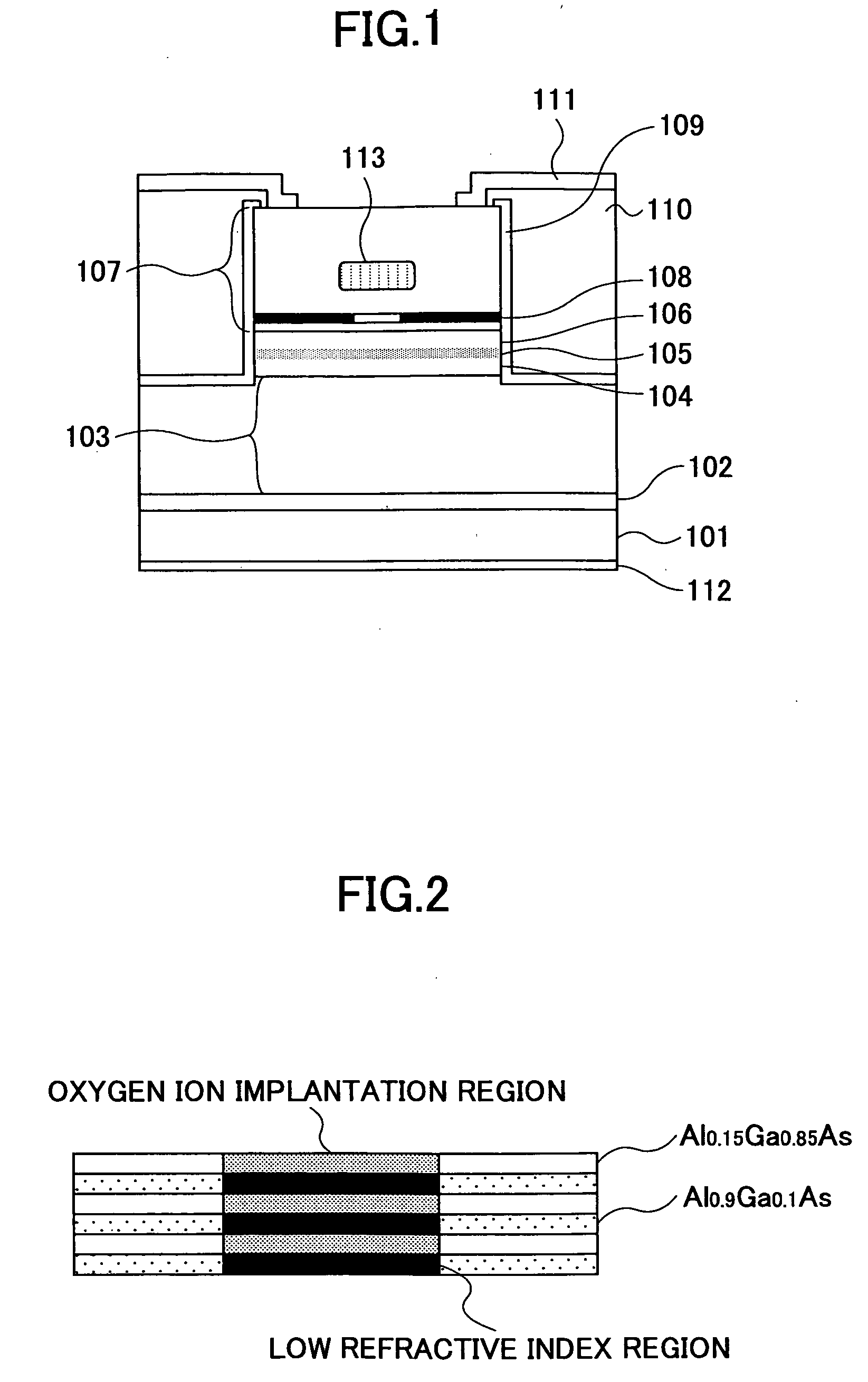
A surface-emission laser diode includes an active layer, a pair of cavity spacer layers formed at both sides of the active layer, a current confinement structure defining a current injection region into the active layer, and a pair of distributed Bragg reflectors opposing with each other across a structure formed of the active layer and the cavity spacer layers, the current confinement structure being formed by a selective oxidation process of a semiconductor layer, the pair of distributed Bragg reflectors being formed of semiconductor materials, wherein there is provided a region containing an oxide of Al and having a relatively low refractive index as compared with a surrounding region in any of the semiconductor distributed Bragg reflector or the cavity spacer layer in correspondence to a part spatially overlapping with the current injection region in a laser cavity direction.
Owner:RICOH KK
High-speed electrically regulated terahertz modulator
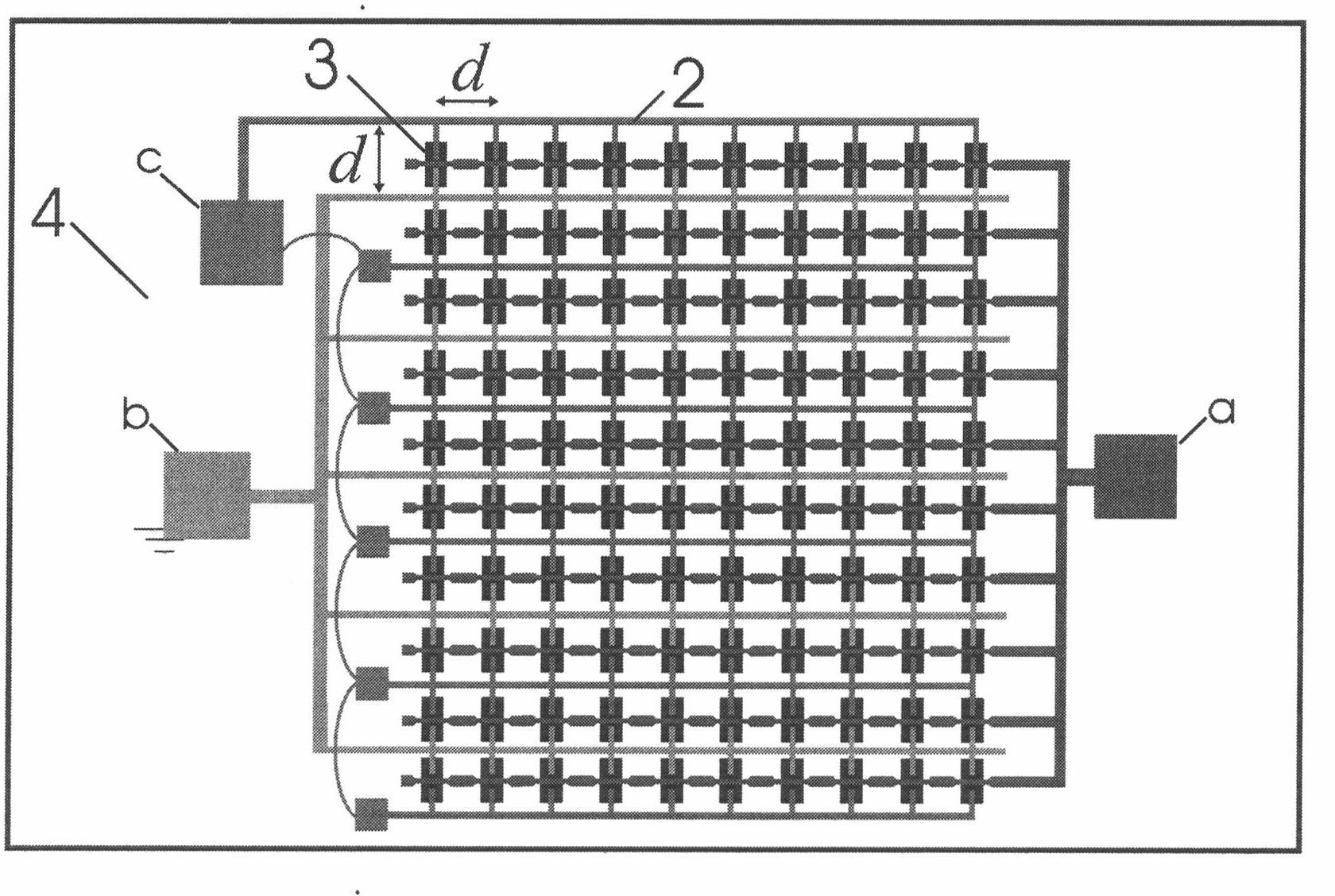
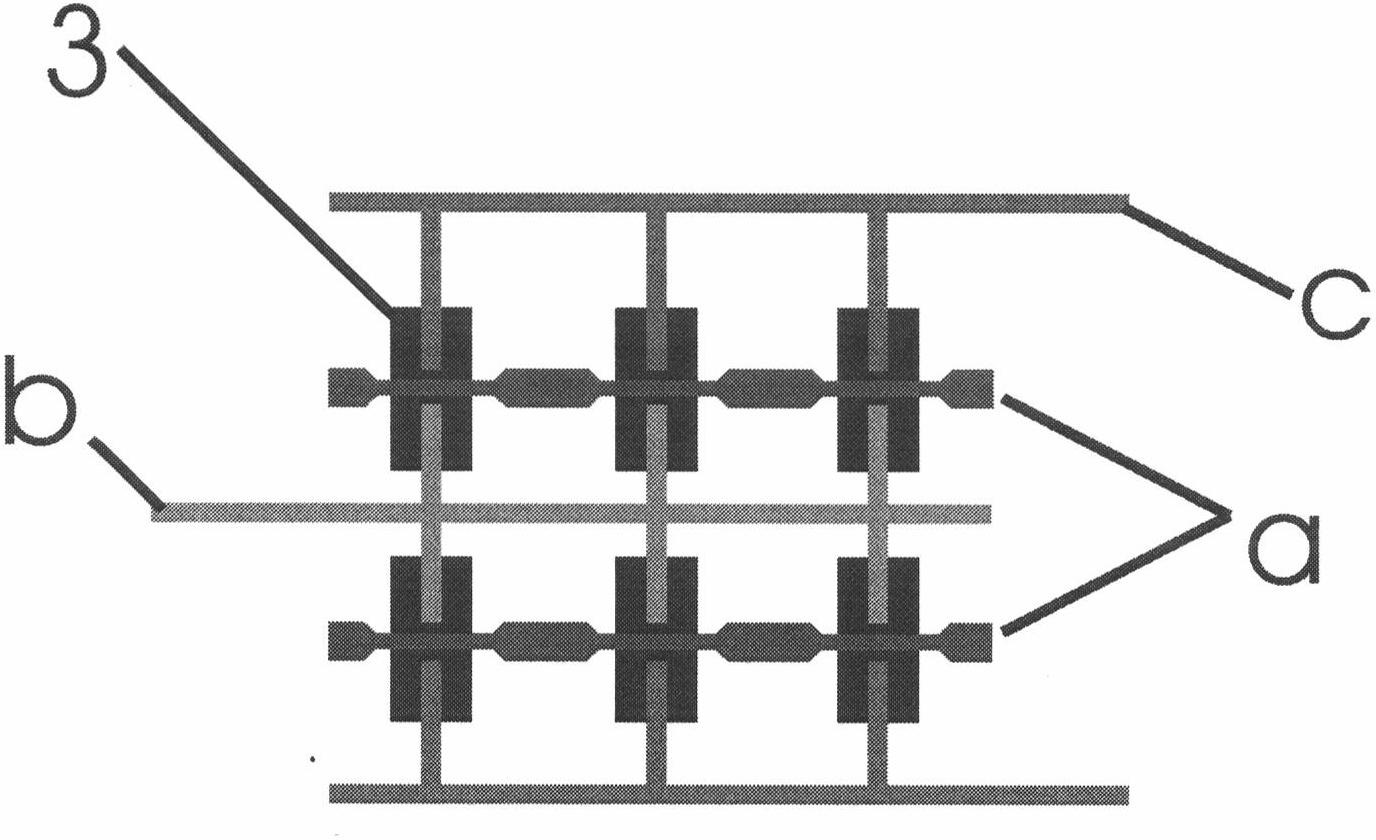
The invention discloses a high-speed electrically-modulating terahertz modulator. The high-speed electrically-modulating terahertz modulator comprises a medium substrate (4), wherein the medium substrate (4) is made of a material which is transparent to terahertz waves; an array which is formed by high electron mobility transistors (3) is distributed on the surface of the medium substrate (4); a frequency selecting surface structure (2) is attached to the surface of the medium substrate and the surface of the array of the high electron mobility transistors, and is a graphical conductive film with a bandpass filtering structure; the source electrode (b), the drain electrode (c) and the grid electrode (a) of each high electron mobility transistor are formed on the part of the conductive film, which corresponds to each high electron mobility transistor; and the electron mobility of the high electron mobility transistors is more than 1,500cm<2> / Vs. A high-speed modulation effect on the amplitude of the terahertz waves is achieved by the high-speed electrically-modulating terahertz modulator in an electrically modulating mode, a modulating speed can be more than 10MHz, and a relative modulating depth is over 50 percent.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
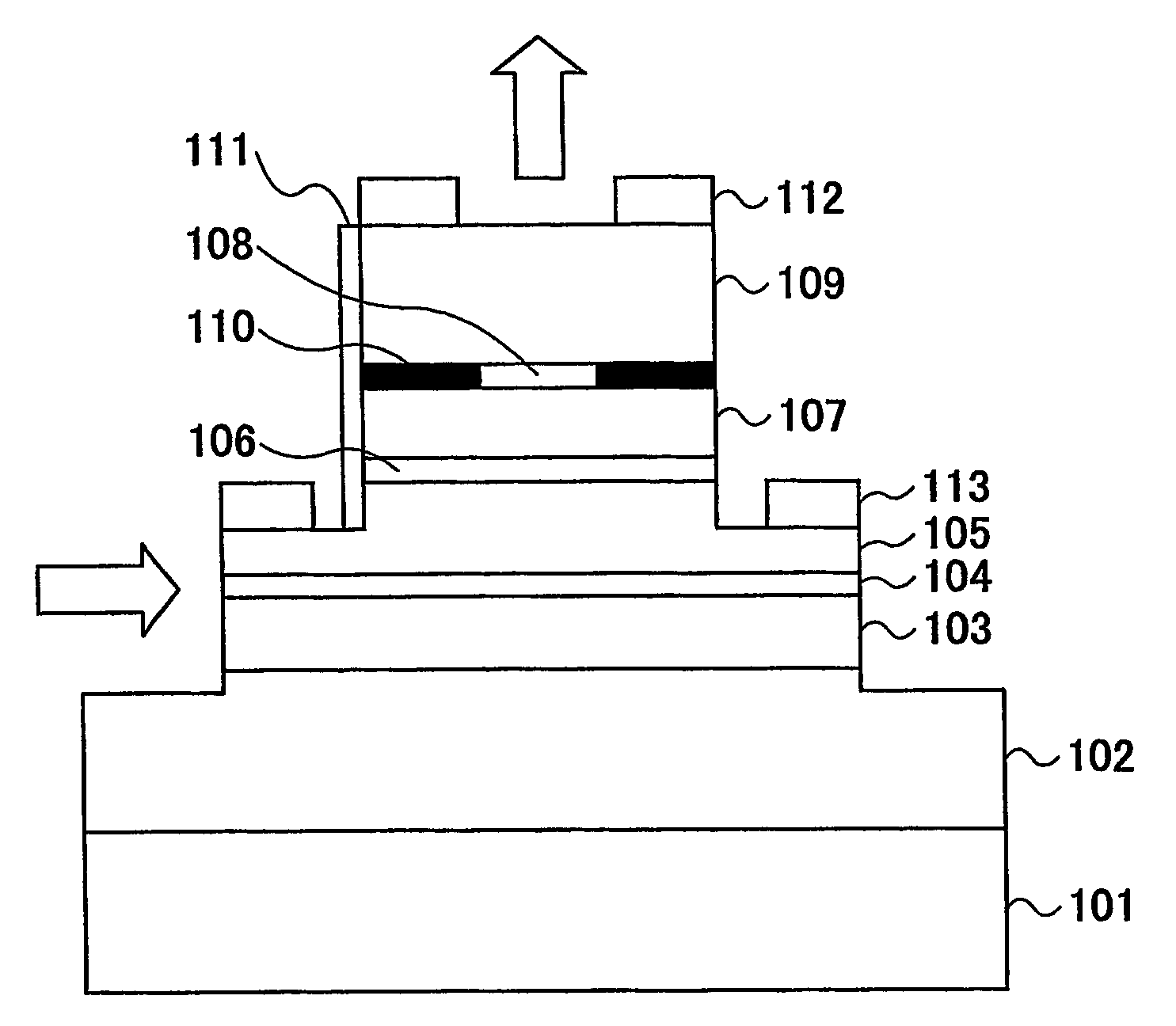
Optical semiconductor device
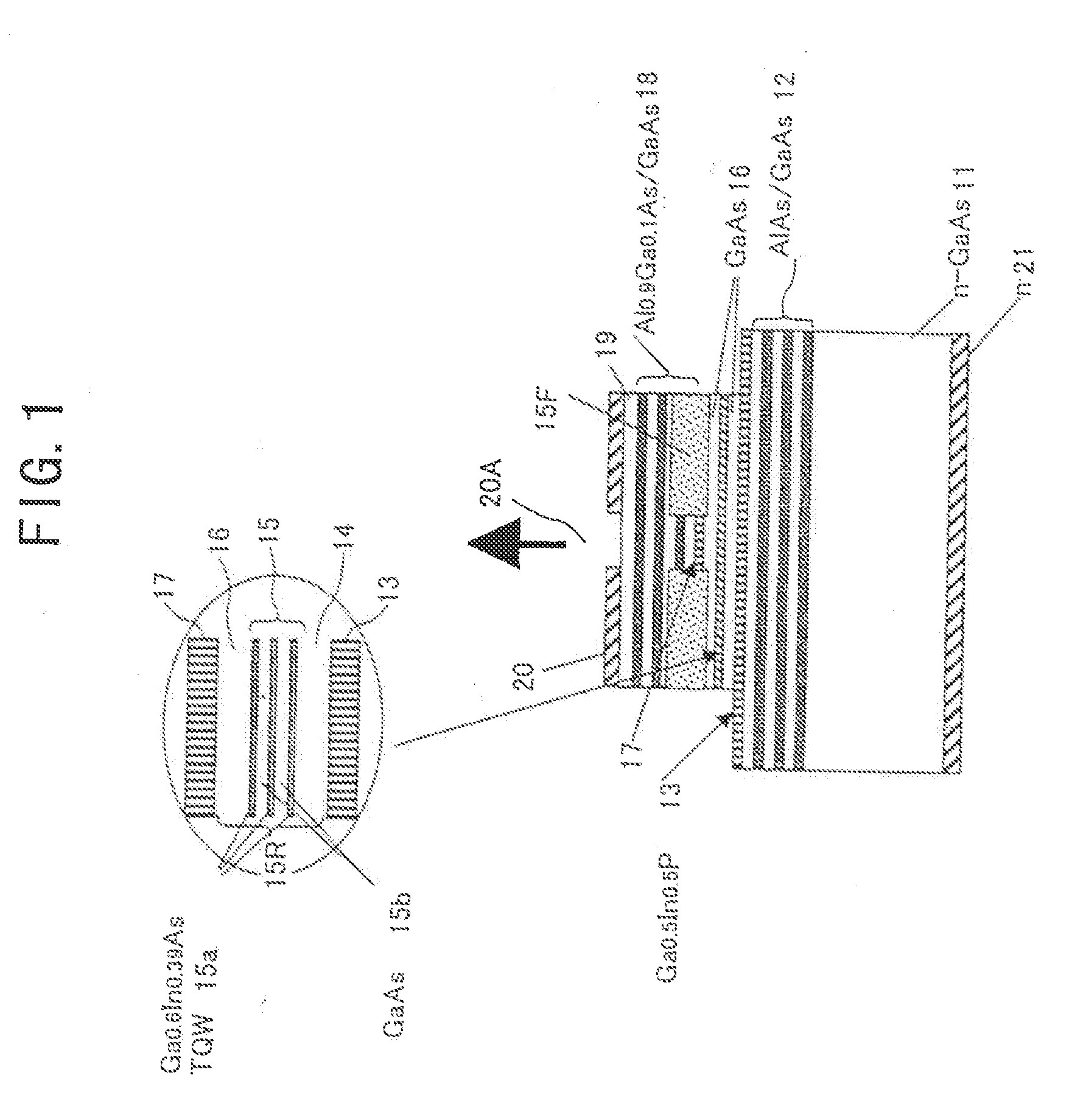
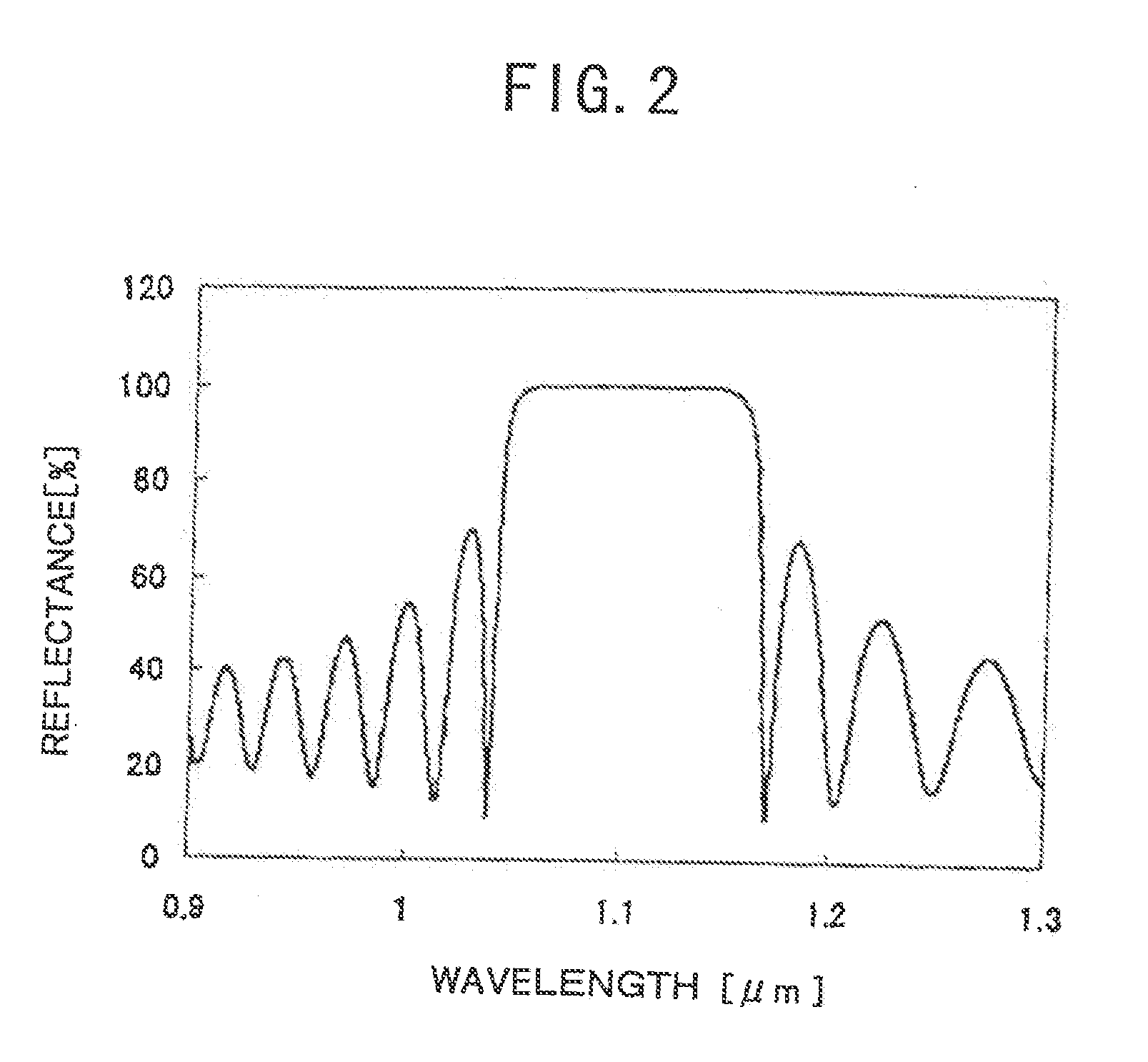
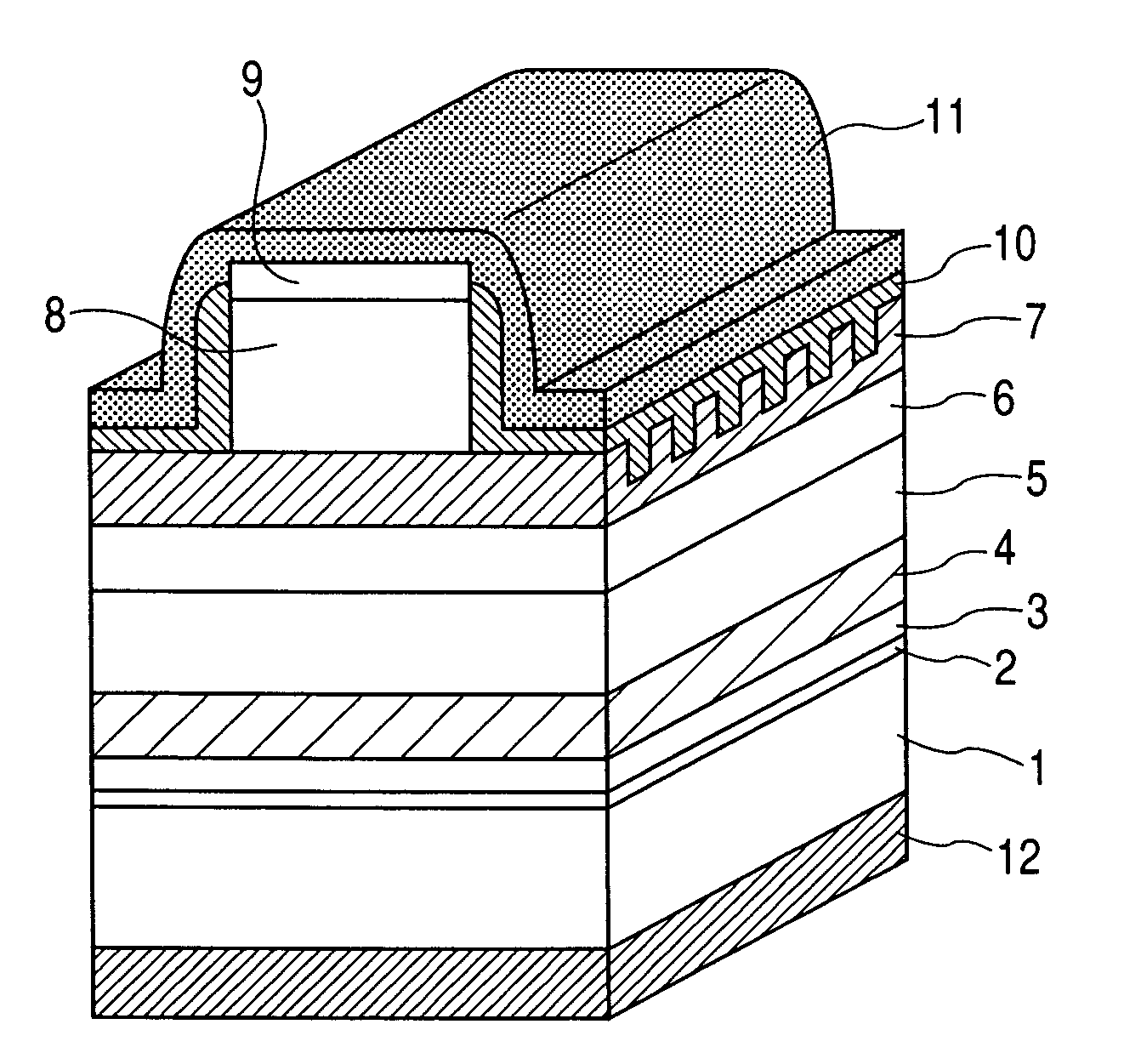
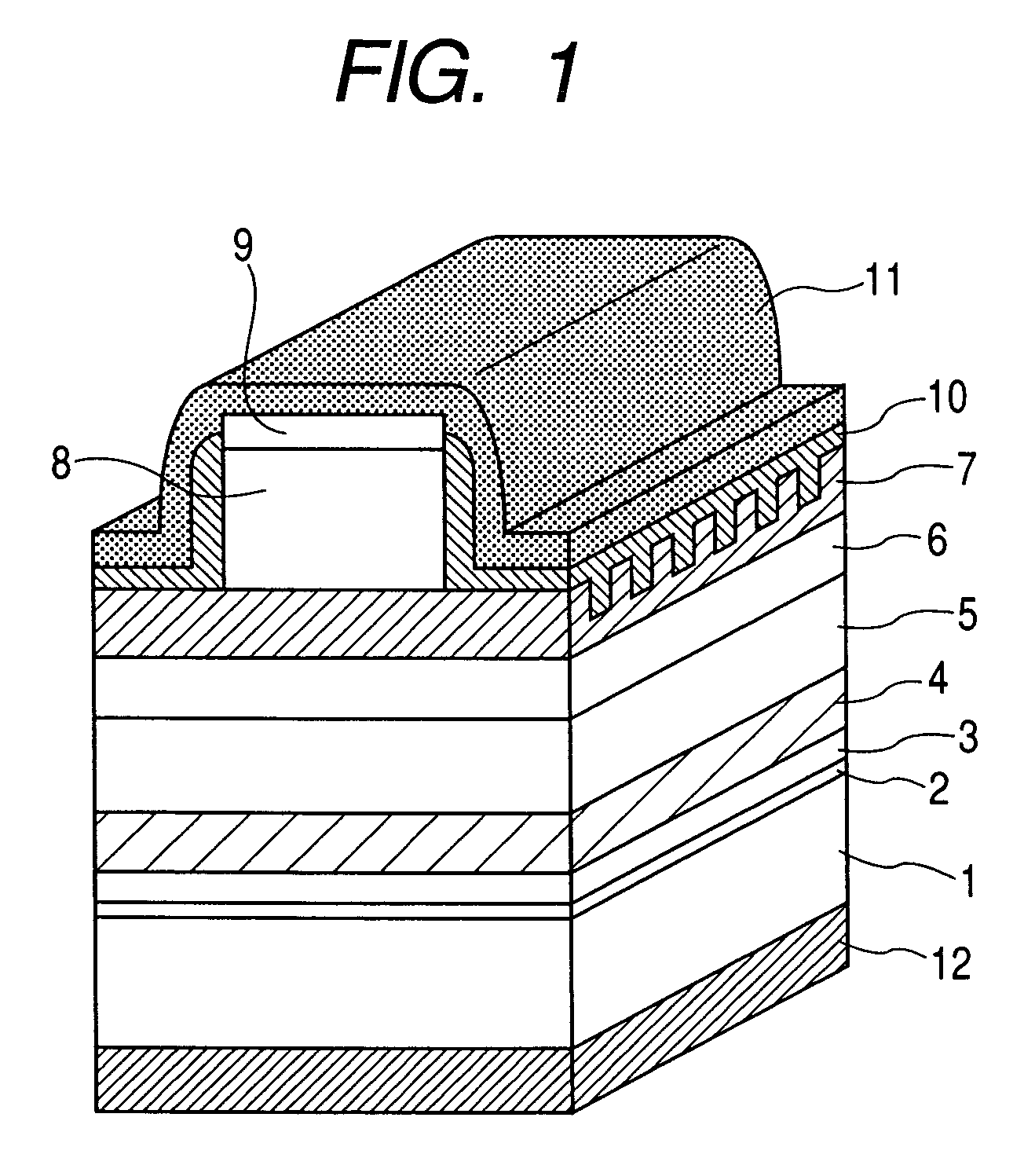
InactiveUS20070051939A1Improve reliabilityReduce driving voltageLaser optical resonator constructionNanoopticsElectronic band structureOptical modulator
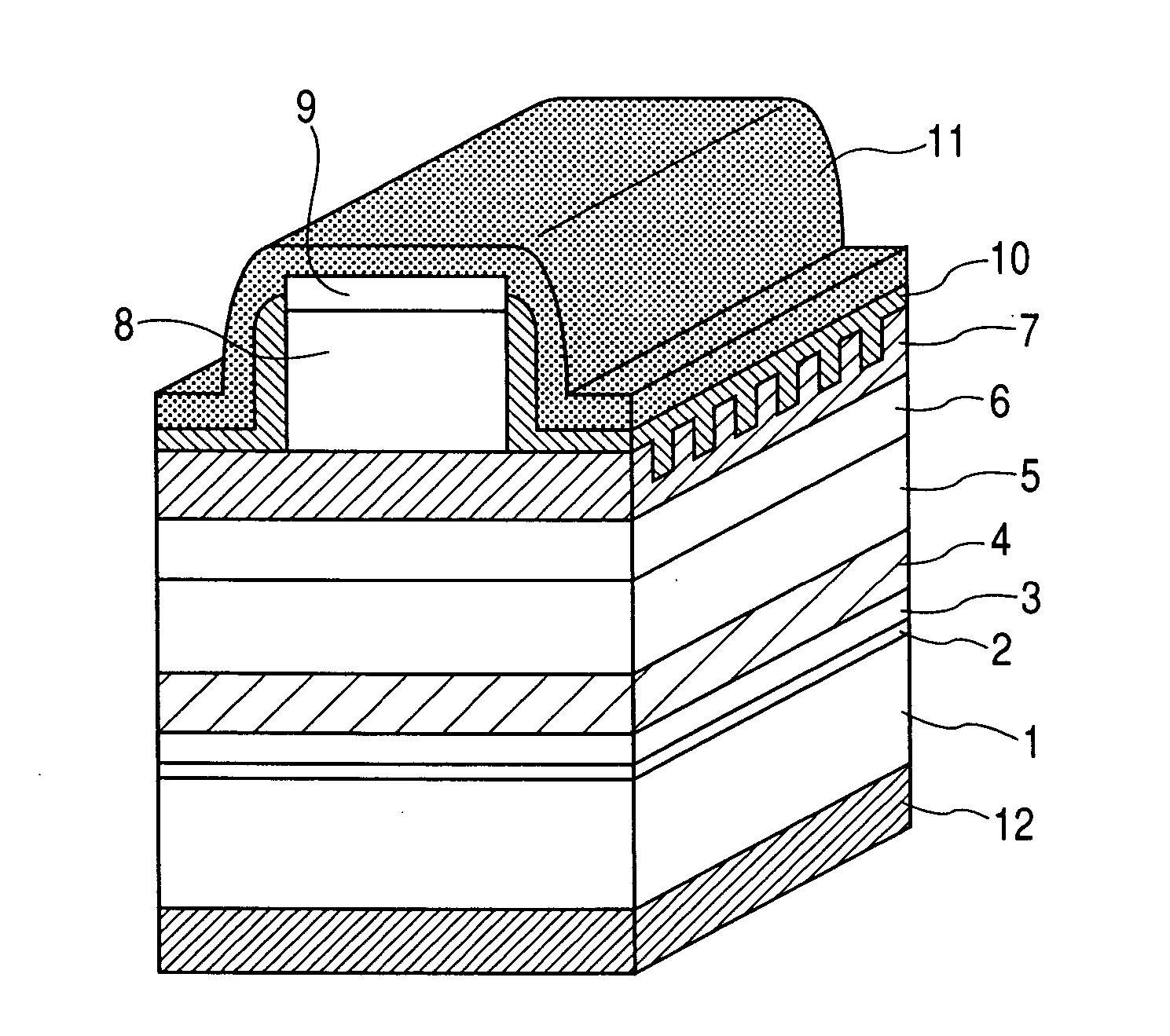
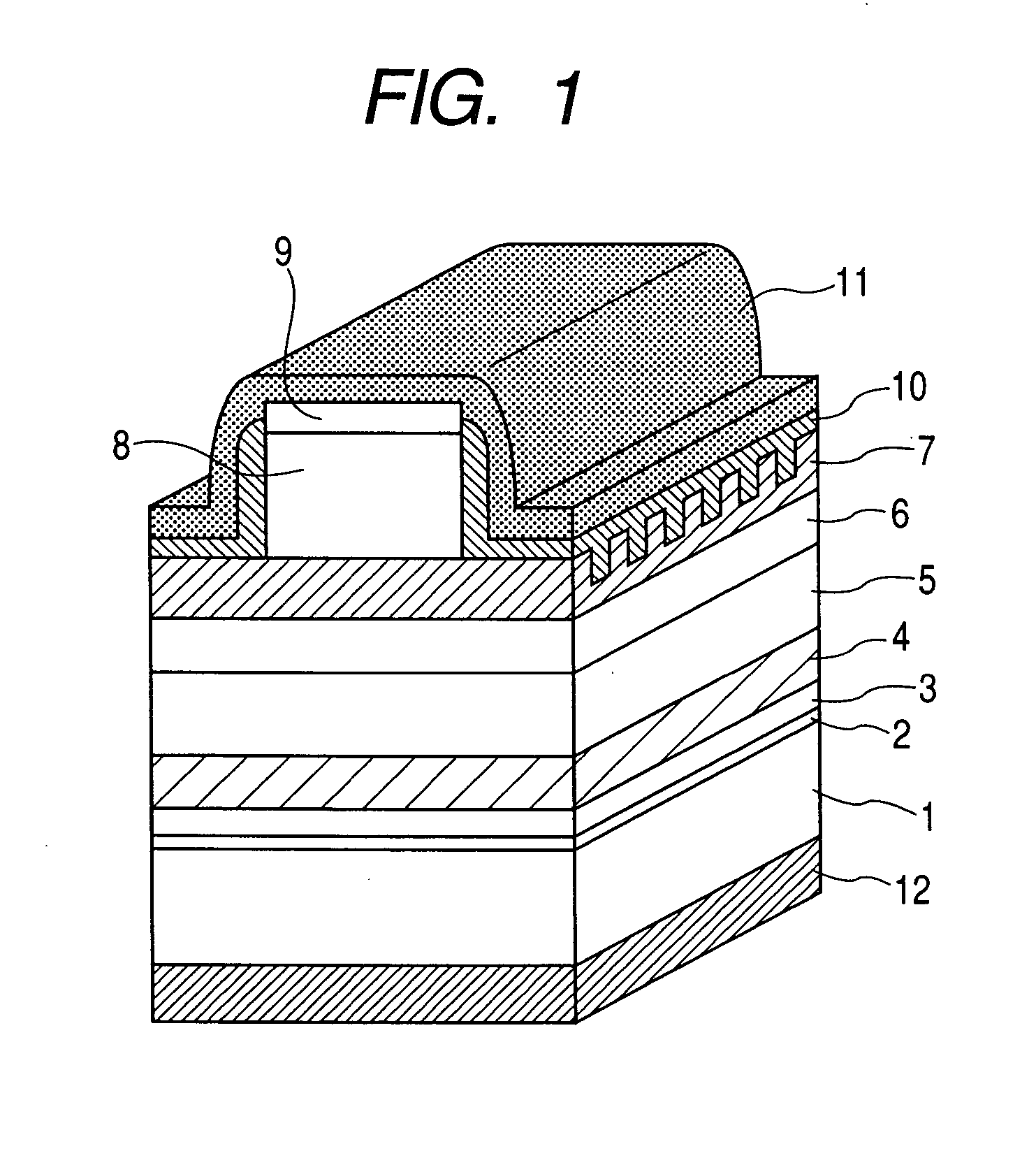
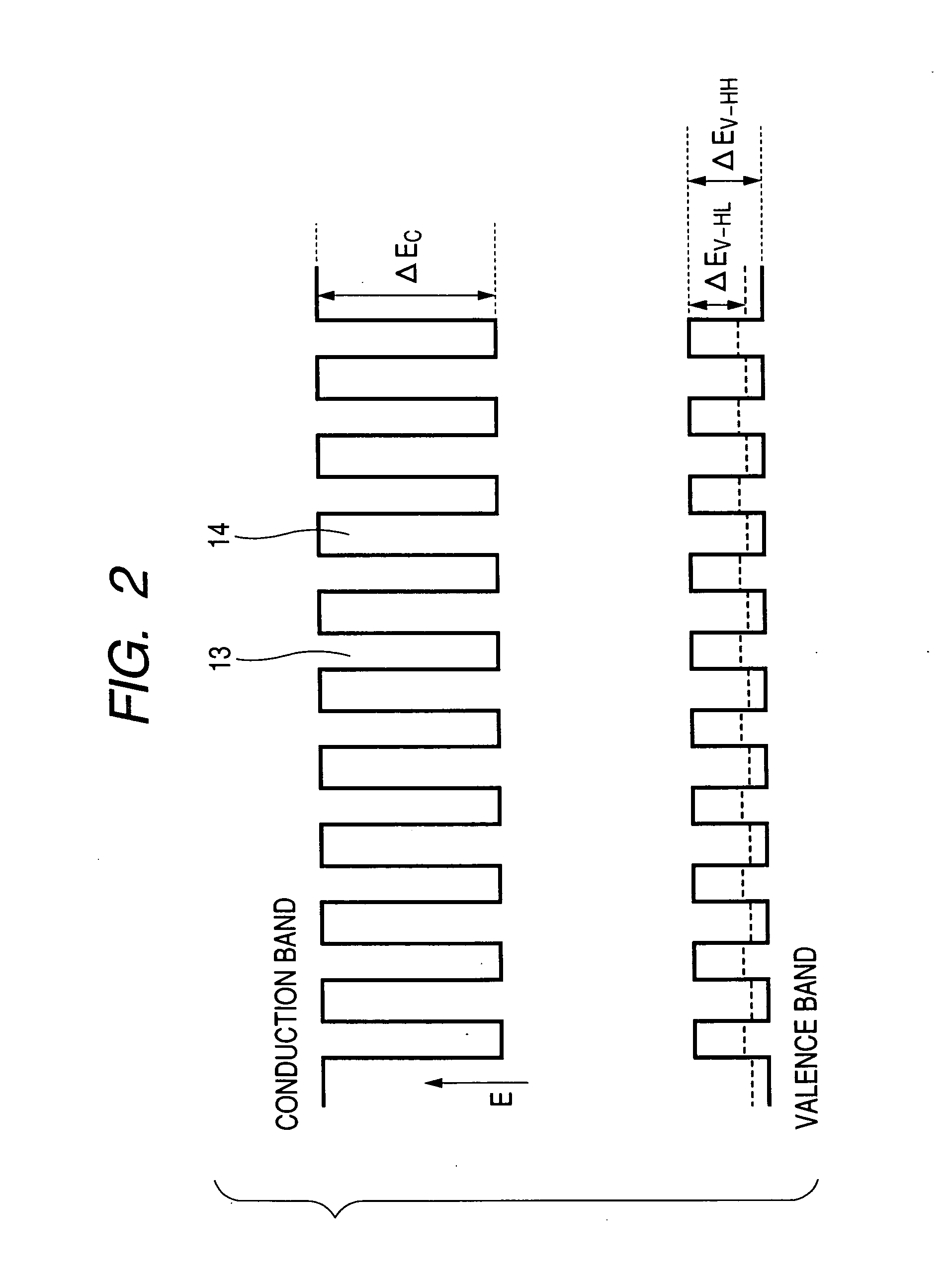
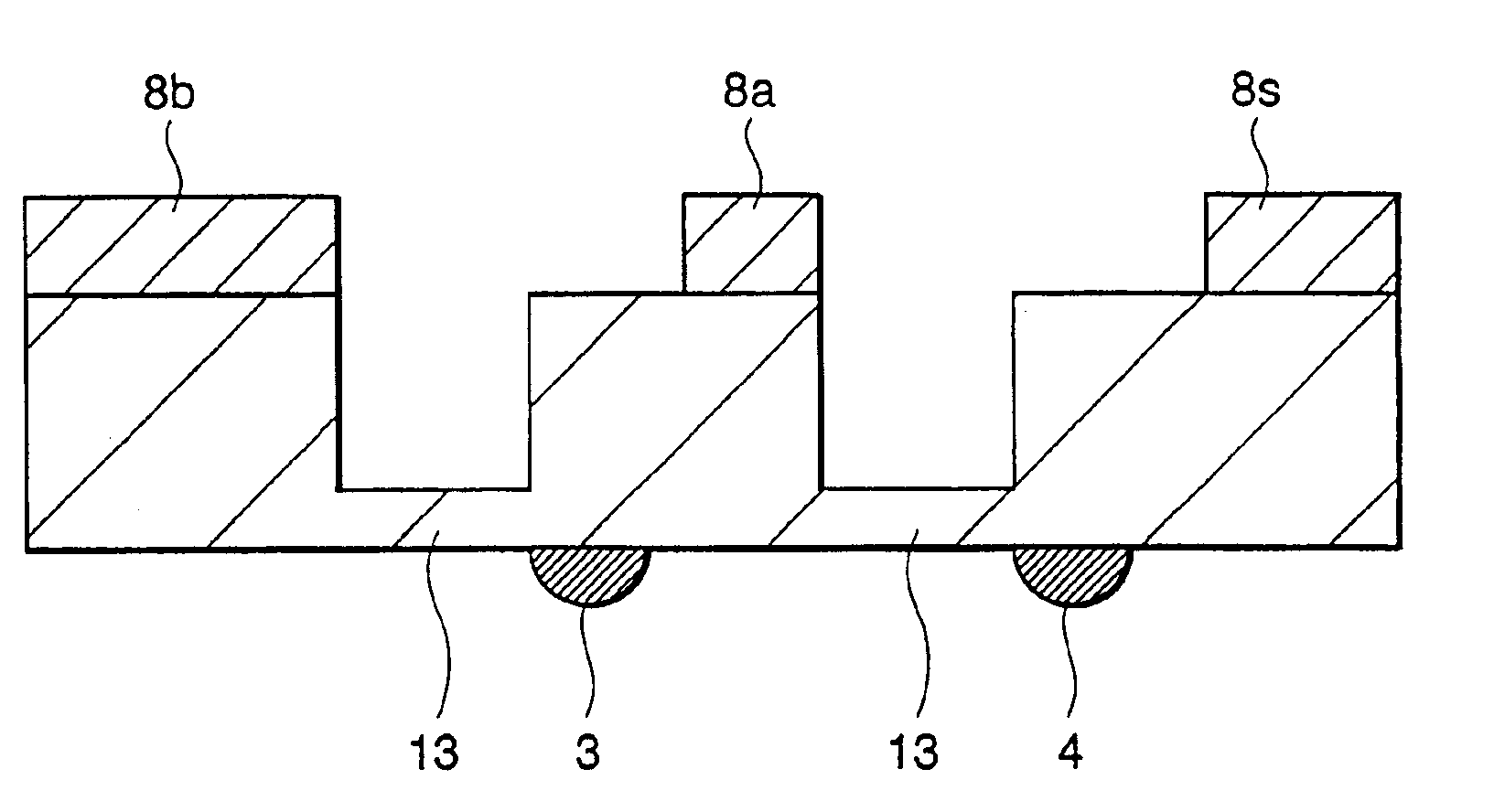
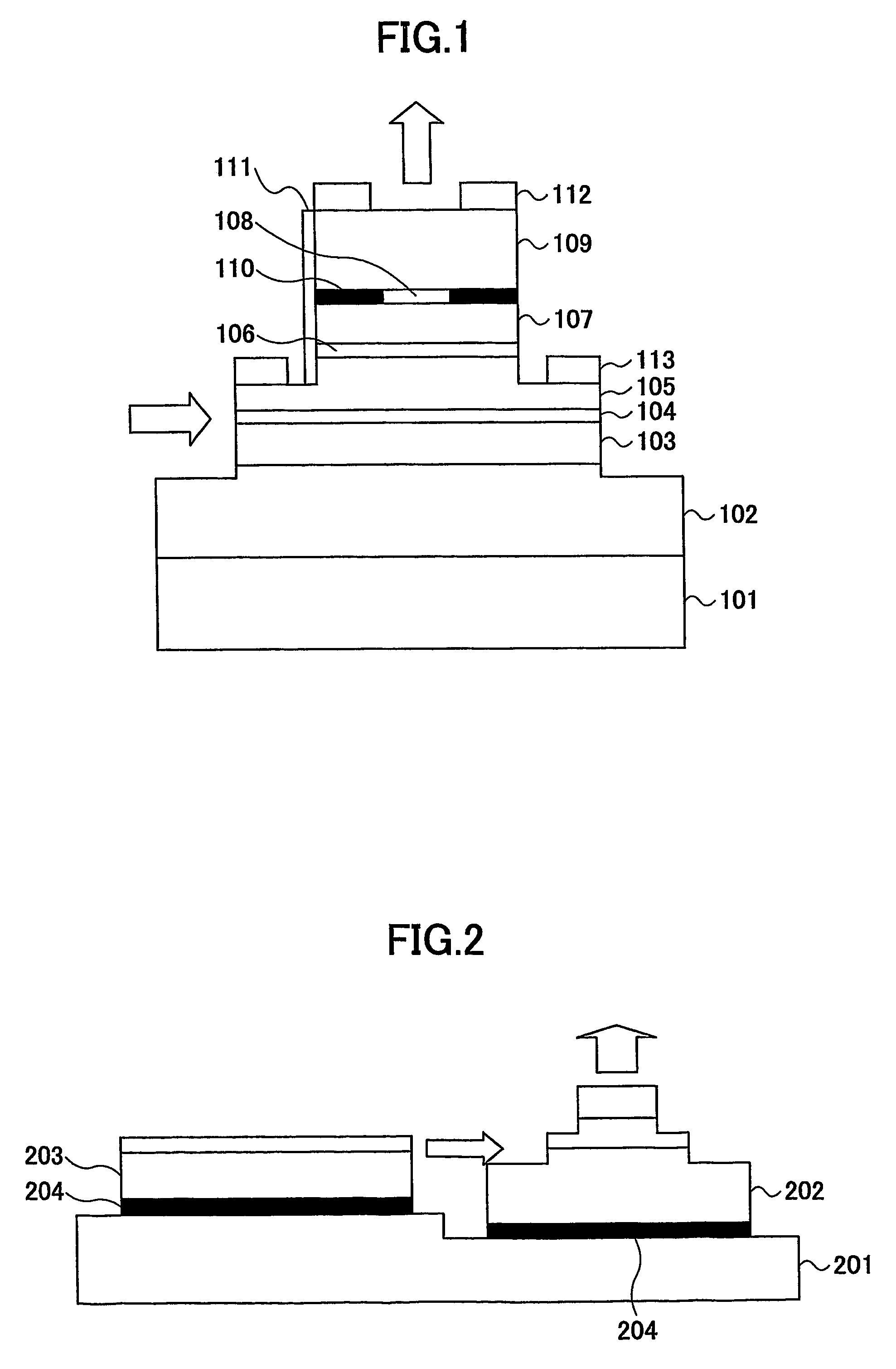
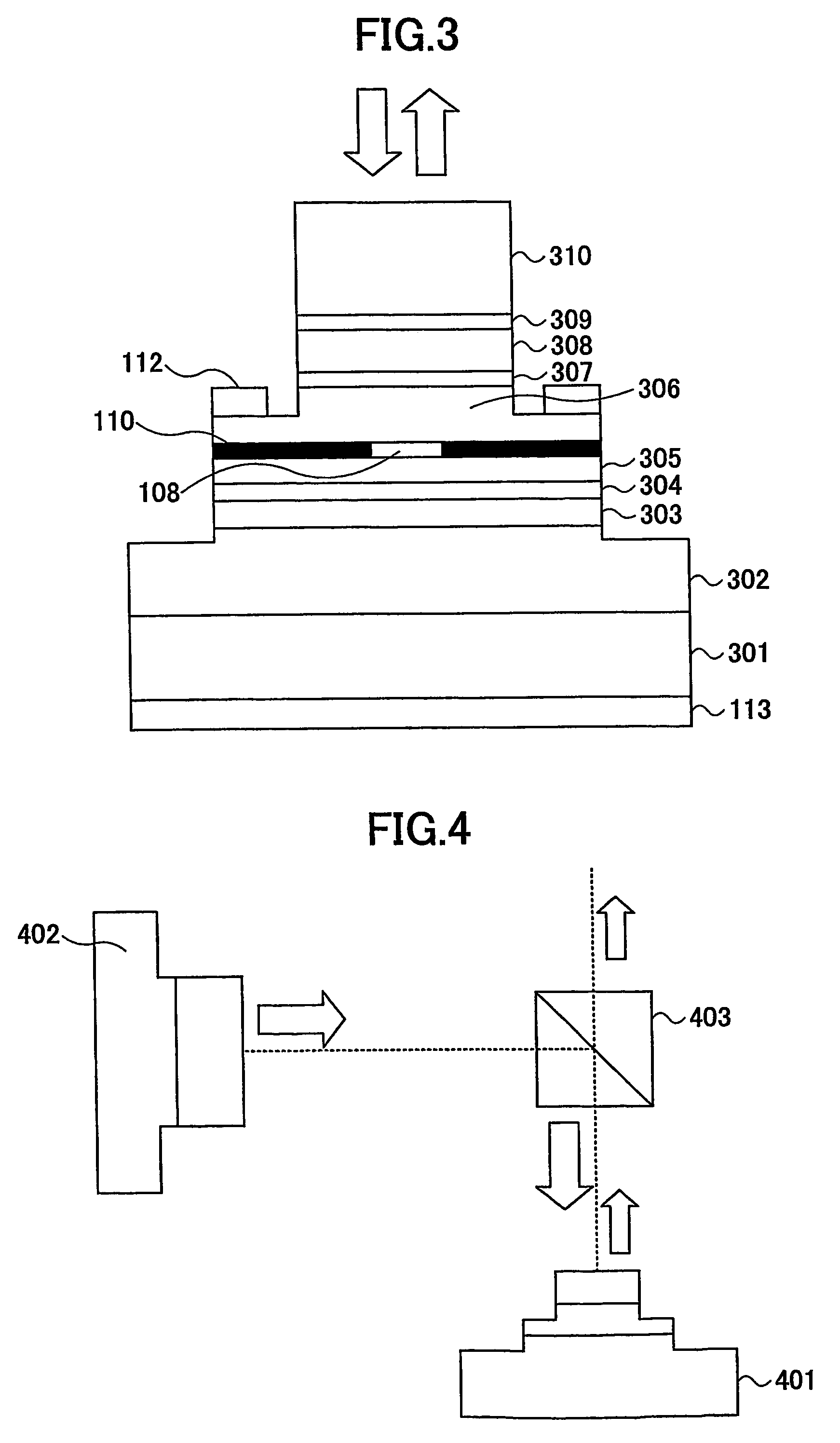
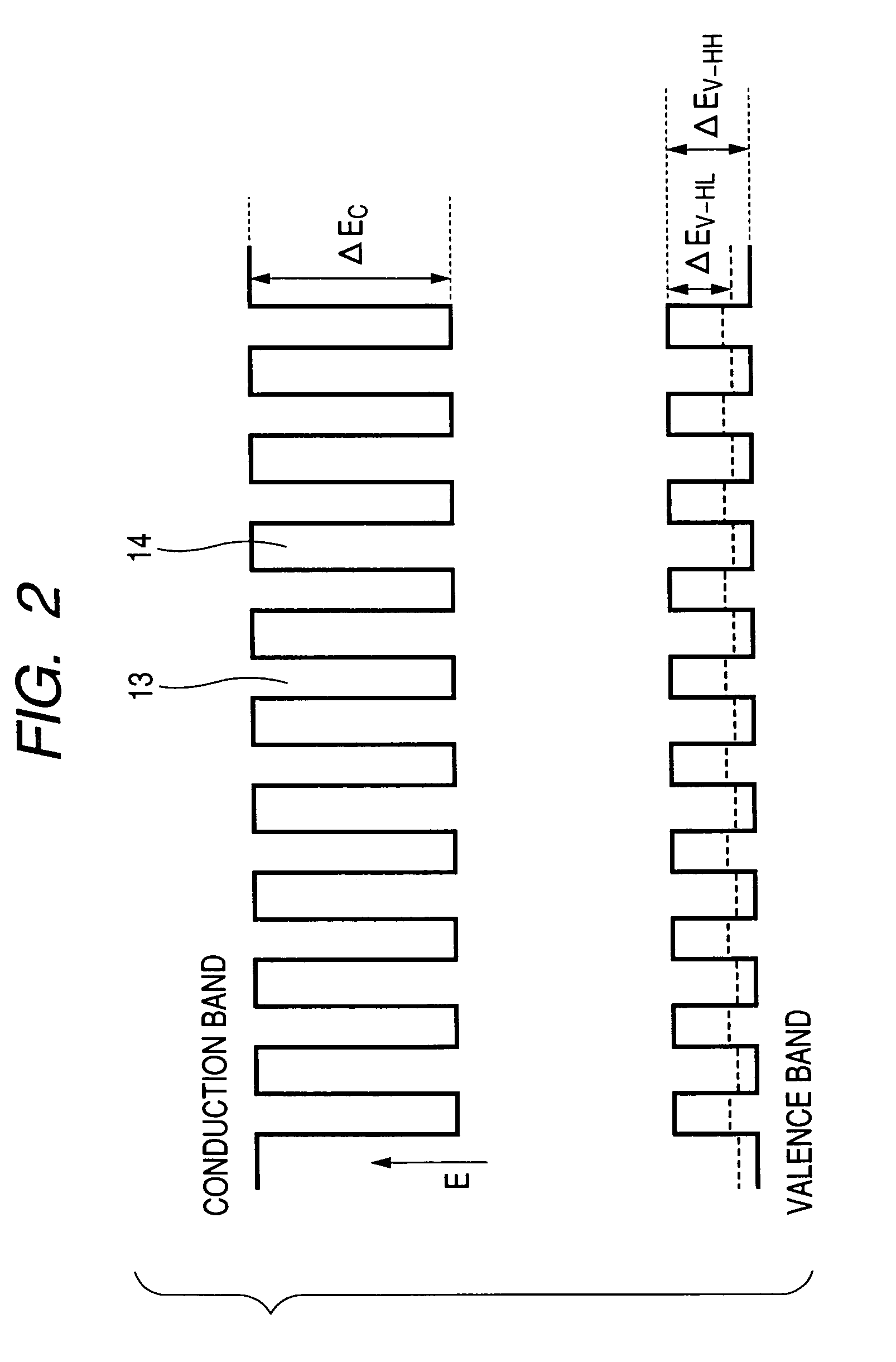
In the semiconductor laser or electro-absorption optical modulator that includes strained quantum well layers as active layers, making laser characteristics or modulator characteristics adequate has seen the respective limits since band structures, especially, ΔEc and ΔEv, have been unable to be adjusted independently. This invention is constructed by stacking an n-type InGaAlAs-GRIN-SCH layer 3, an MQW layer 4, a p-type InGaAlAs-GRIN-SCH layer 5, a p-type InAlAs electron-stopping layer 6, and others, in that order, on an n-type InP wafer 1; wherein the MQW layer 4 includes InGaAlAs-strained quantum well layers and InGaAlAsSb-formed barrier layers each having strain of an opposite sign to the strain applied to the quantum well layers.
Owner:OCLARO JAPAN INC
Compact laser spectrometer
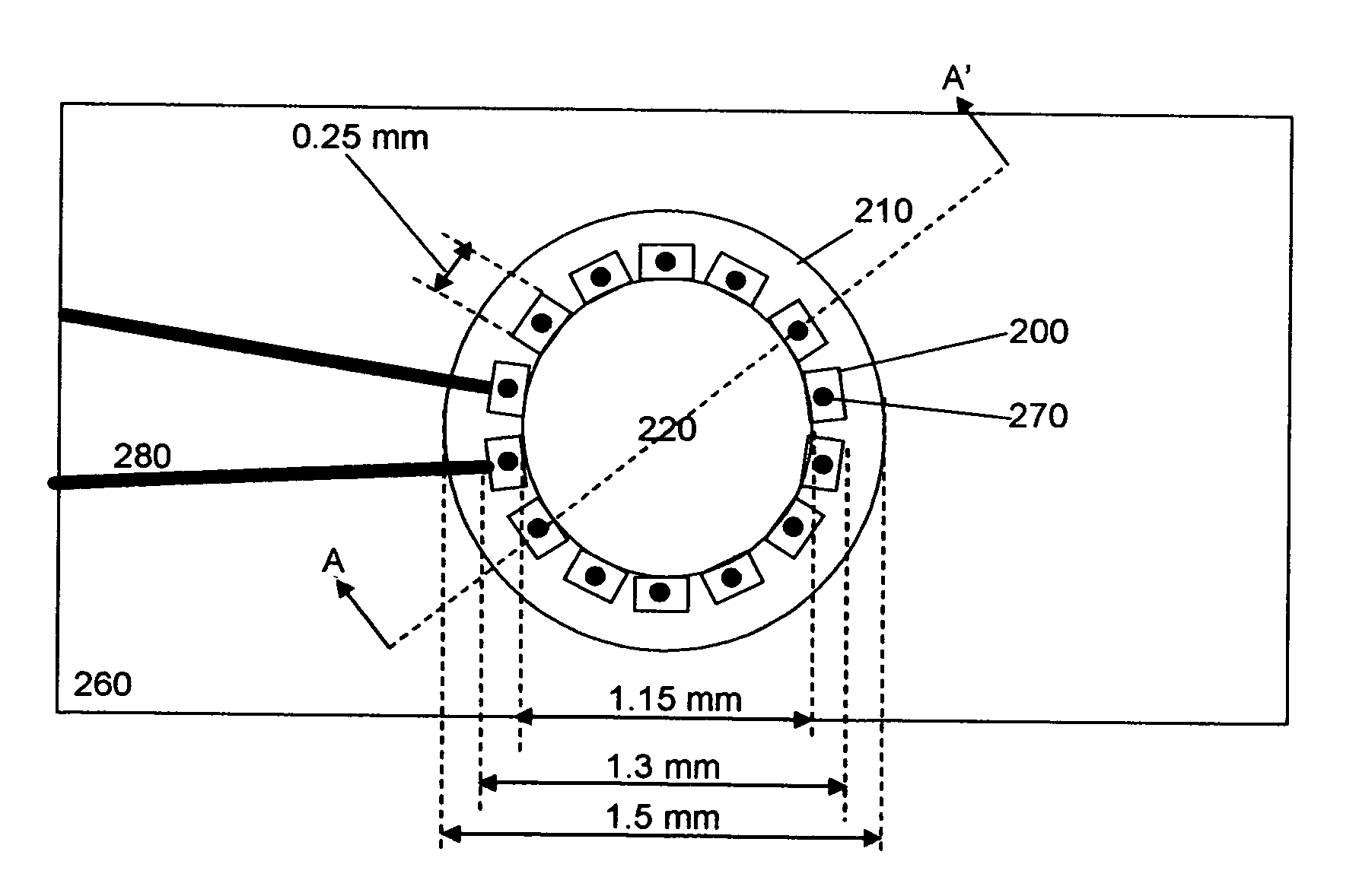
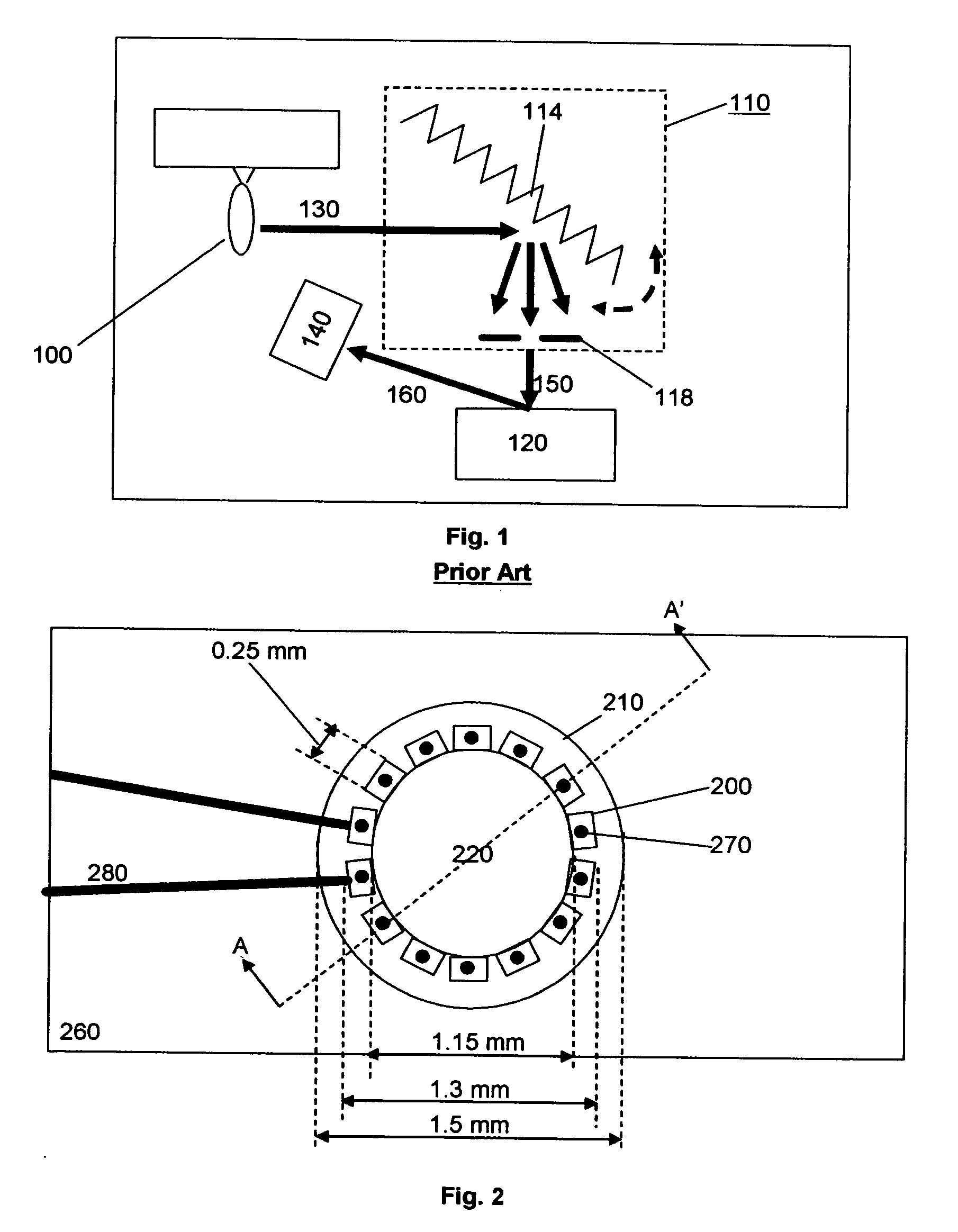
InactiveUS20070182960A1Fast measurement timeImprove signal-to-noise ratioRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserLinear arrays
A compact laser spectrometer according to the present invention includes a plurality of semiconductor lasers comprising a plurality of semiconductor gain medium compositions emitting a plurality of radiation components originating from an area having a maximum transverse dimension that is smaller than a minimum feature size of a sample. A broadband optical detector detects a diffuse reflectance. In one preferred embodiment of this invention the plurality of semiconductor lasers consists of Fabry-Perot edge-emitting lasers arranged around the perimeter of a cylindrical submount with a substantially circular cross-section. The plurality of radiation components is directly coupled to a multi-mode optical fiber, which presents radiation to a sample. In another preferred embodiment a linear array of Fabry-Perot edge-emitting lasers is directly coupled to a multi-mode fiber. In still another preferred embodiment, a two-dimensional array of vertical cavity surface-emitting lasers is directly coupled to a multi-mode optical fiber.
Owner:JAYARAMAN VIJAYSEKHAR
Surface-emission laser diode operable in the wavelength band of 1.1-1.7 micrometers and optical telecommunication system using such a laser diode
InactiveUS20080043796A1Reduce areaHigh speed modulationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor laser optical deviceMicrometerDistributed Bragg reflector
A surface-emission laser diode includes a distributed Bragg reflector tuned to wavelength of 1.1 μm or longer, wherein the distributed Bragg reflector includes an alternate repetition of a low-refractive index layer and a high-refractive index layer, with a heterospike buffer layer having an intermediate refractive index interposed therebetween with a thickness in the range of 5-50 nm.
Owner:RICOH KK
Optical modulator and method of manufacturing same
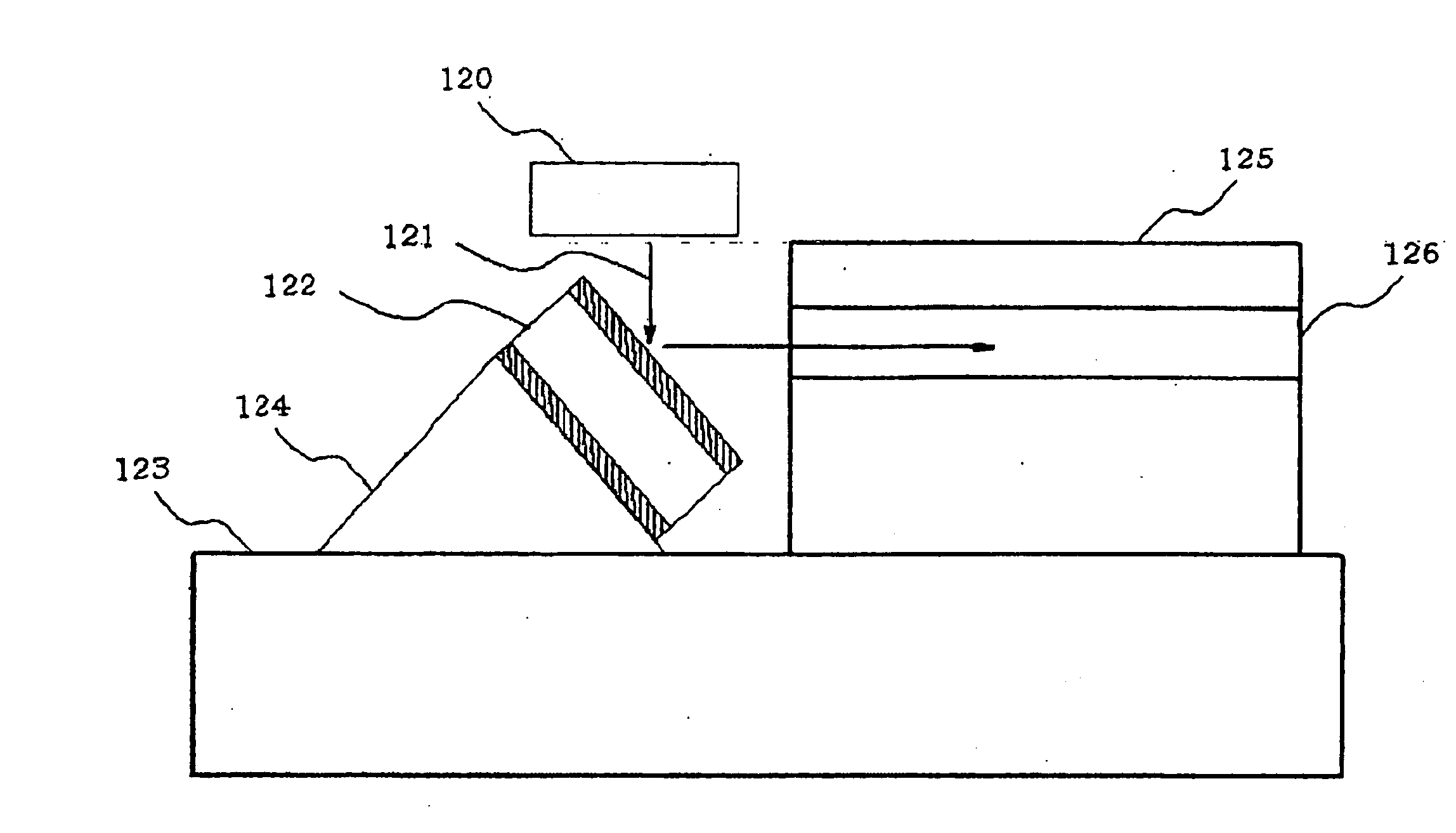
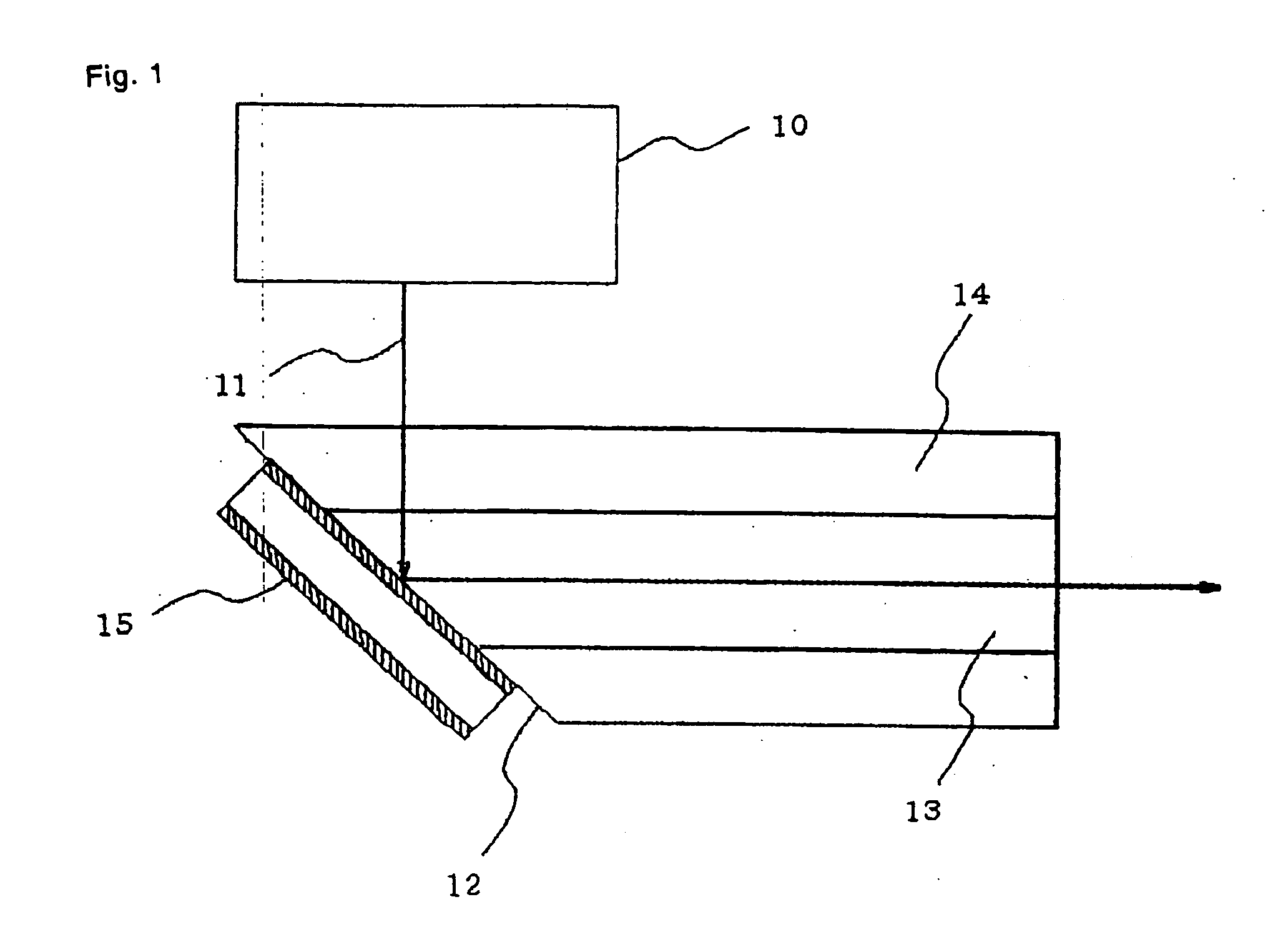
InactiveUS20050220386A1Improving Impedance MatchingReduce decreaseLaser detailsSemiconductor laser structural detailsAerosol depositionLaser light
Laser light emitted from a vertically confined surface emitting laser (VCSEL) is incident on a side surface near an end region of an optical waveguide. The end region of the optical waveguide is processed by polishing to taper at an angle of 45 degrees, and an optical modulator is formed on the polished surface. The optical modulator is a Fabry-Perot modulator using a linear electro-optical effect. The modulator has a thick transparent electro-optical layer which is deposited by using an aerosol deposition method.
Owner:NEC CORP
Vertical cavity surface emitting semiconductor laser, light emission device, and optical transmission system
InactiveUS20070071054A1Increase relaxation oscillation frequencyHigh speed modulationSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser active region structureResonatorTransmission system
A semiconductor laser is disclosed with which a VCSEL can be constituted with a simplified configuration for optical transmission at a transmission rate higher than 10 Gbps. The semiconductor laser includes a resonator including a first active region able to emit light in response to current injection and a second active region able to emit light in response to external excitation light. Multilayer film reflecting mirrors sandwich the resonator from two opposite sides. The first active region and the second active region generate light at a wavelength the same as the resonance mode of the resonator.
Owner:RICOH KK
Coherent light source and control method thereof, and display unit and laser display using them
InactiveUS20060209913A1High harmonic outputLow refractive indexLaser detailsSemiconductor laser optical deviceLaser displayLight source
In a display device that displays a video by scanning coherent light across a screen, modulation at high speeds and gradation are necessary for a coherent light source. An oscillation wavelength of a semiconductor laser outputting the fundamental wave is changed at high speeds through the plasma effect induced by applying a pulse current to the coherent light source. A change of the wavelength causes the output of a higher harmonic generated in a light wavelength conversion element to change, and gradation is produced using such a change.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
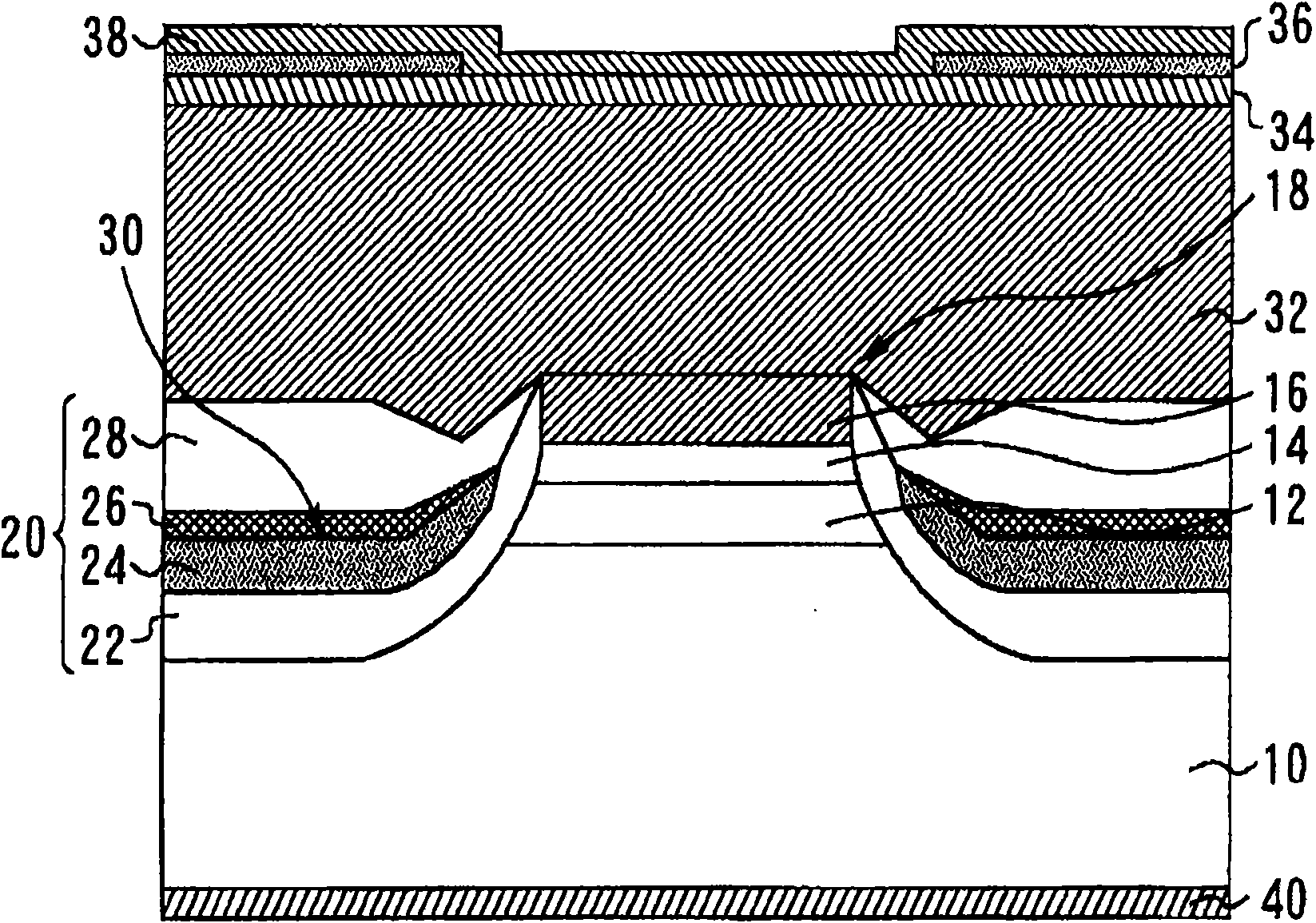
Semiconductor laser and manufacturing method therefor
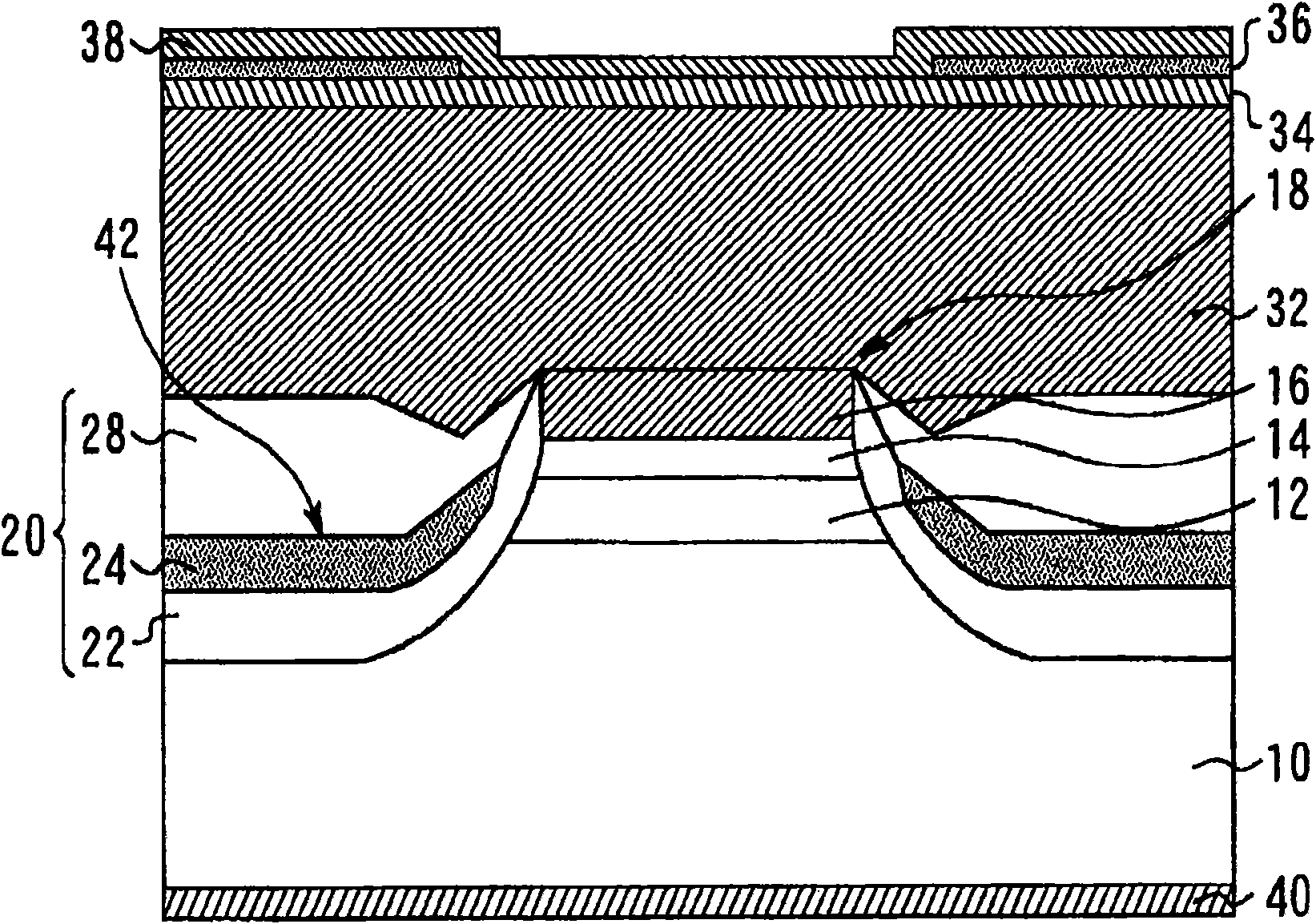
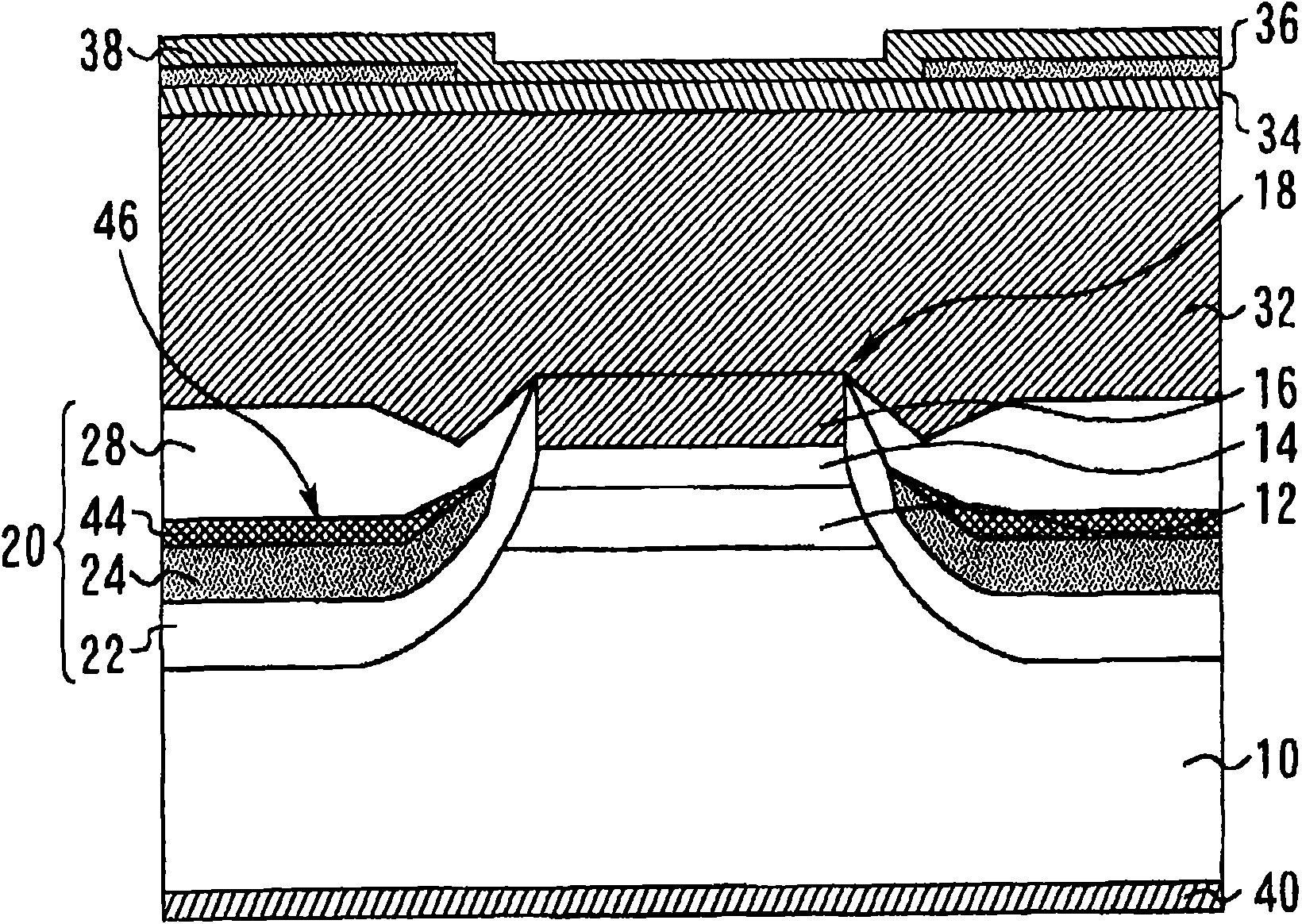
InactiveCN101593930AHigh speed modulationReduce leakage currentLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersQuantum wellCharge carrier
The present invention relates to a semiconductor laser and a manufacturing method therefor. The semiconductor laser can carry out high speed confection more than 10 Gbps, which comprises: a ridge structure (18) including a p-type InP cladding layer (12) (a p-type cladding layer), an AlGaInAs strained quantum well an active layer (14) (an active layer), and an n-type InP cladding layer (16) (an n-type cladding layer) stacked on one another; and a burying layer (20) burying sides of the ridge structure (18). The burying layer (20) includes a p-type InP layer (26) (a p-type semiconductor layer) and an n-type InP layer (24) (an n-type semiconductor layer) that form a pn junction; and one of the p-type semiconductor layer and the n-type semiconductor layer has a carrier concentration of 5x10cm or less near the pn junction.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Semiconductor laser-based spectrometer
InactiveUS20060280216A1Fast measurement timeImprove signal-to-noise ratioLaser detailsColor/spectral properties measurementsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Transmittance
A semiconductor laser-based spectrometer according to the present invention includes a plurality of semiconductor lasers comprising a plurality of semiconductor gain medium compositions directly coupled to a large-core multi-mode fiber with no intervening optics. An output radiation from the multi-mode fiber is tunable by switching the drive current amongst the lasers, and by thermal tuning of each laser in the array. In combination with presentation to a sample, and means for detection of a diffuse reflectance or transmittance, this assembly functions as a compact, high signal to noise ratio, fast measurement spectrometer. In one preferred embodiment of this invention the plurality of semiconductor lasers consists of Fabry-Perot edge-emitting lasers arranged around the perimeter of a cylindrical submount with a substantially circular cross-section. In another preferred embodiment a linear array of Fabry-Perot edge-emitting lasers is directly coupled to a multi-mode fiber. In still another preferred embodiment, a two-dimensional array of vertical cavity surface-emitting lasers is directly coupled to a multi-mode optical fiber.
Owner:JAYARAMAN VIJAYSEKHAR
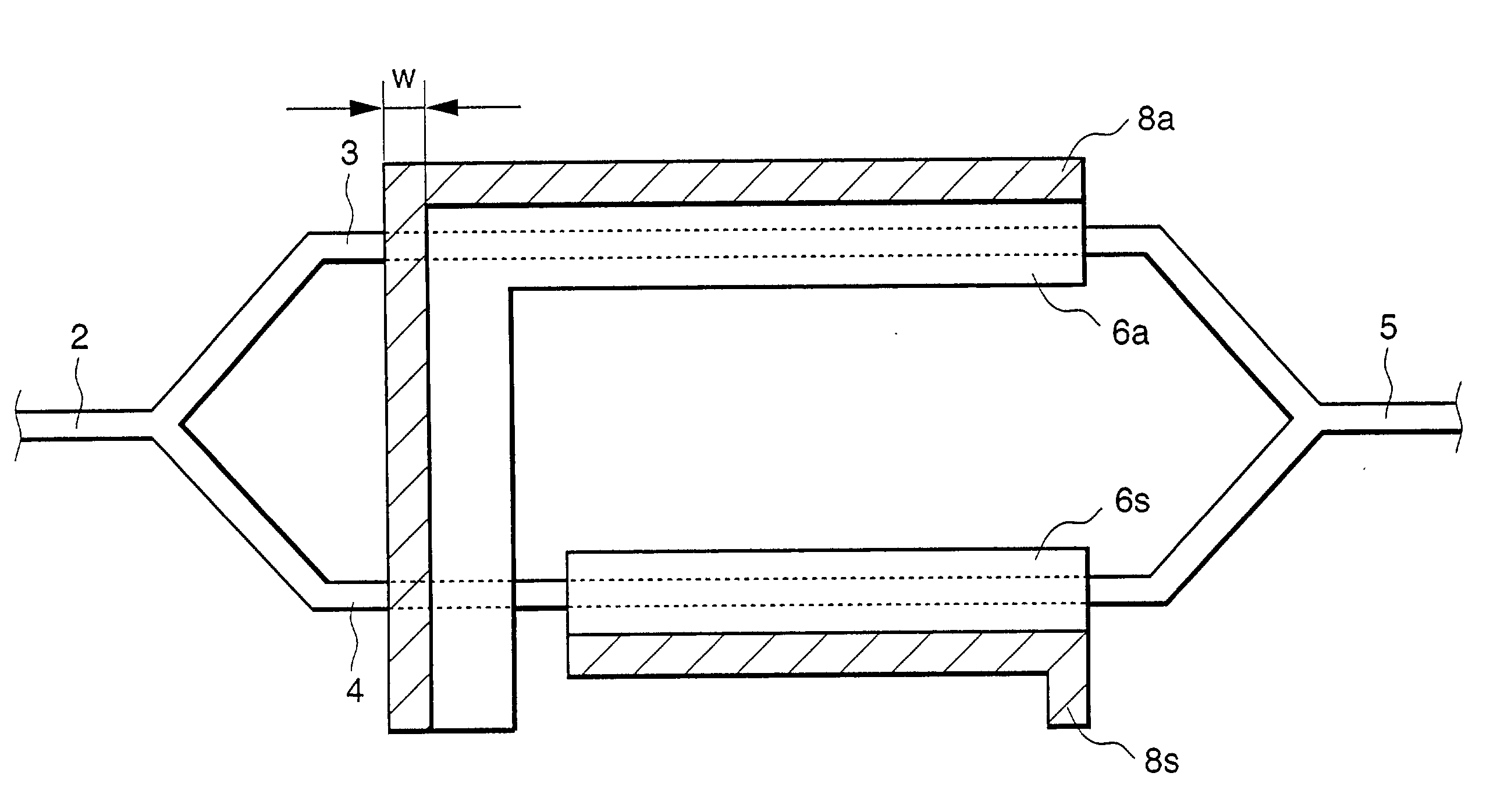
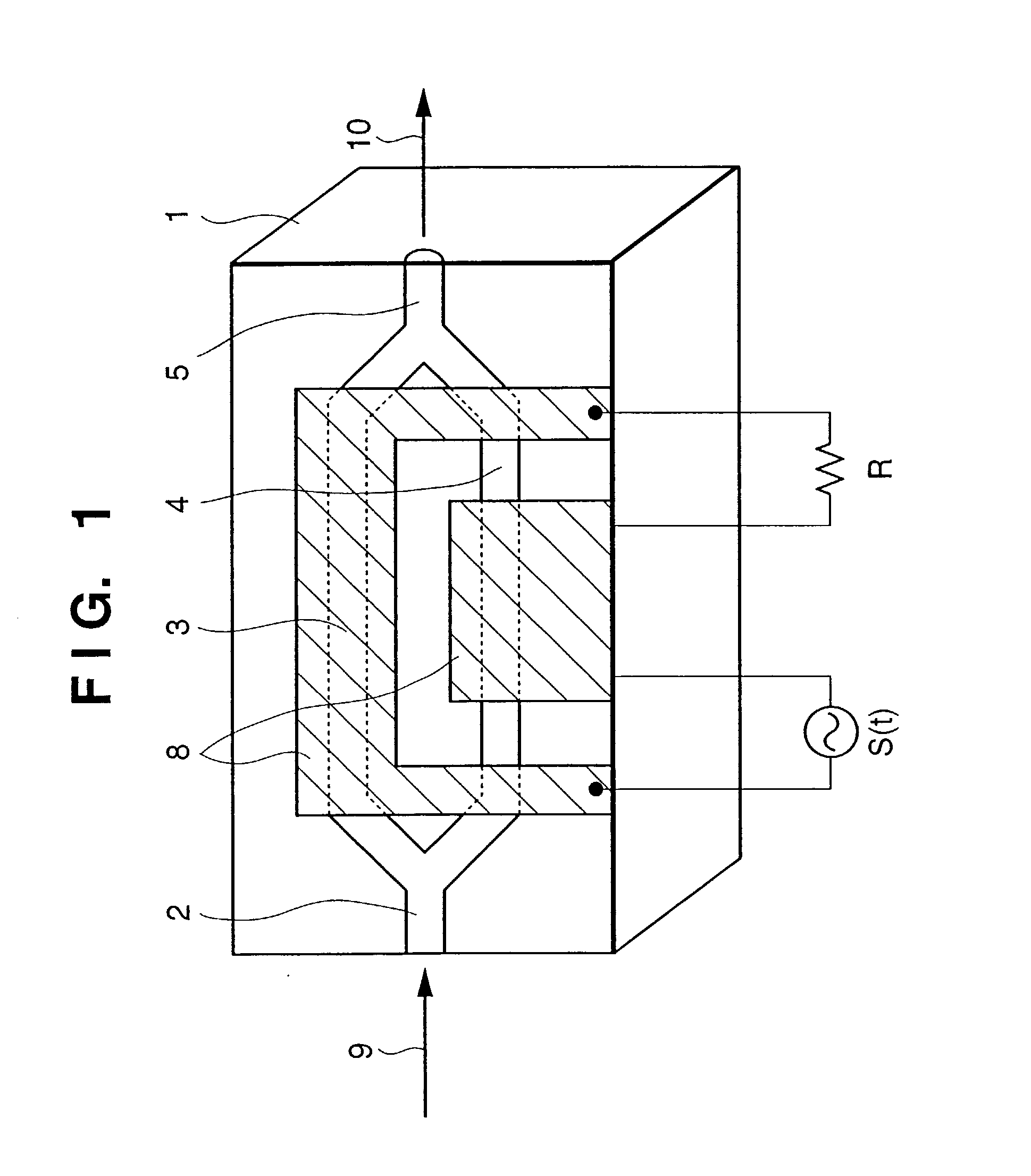
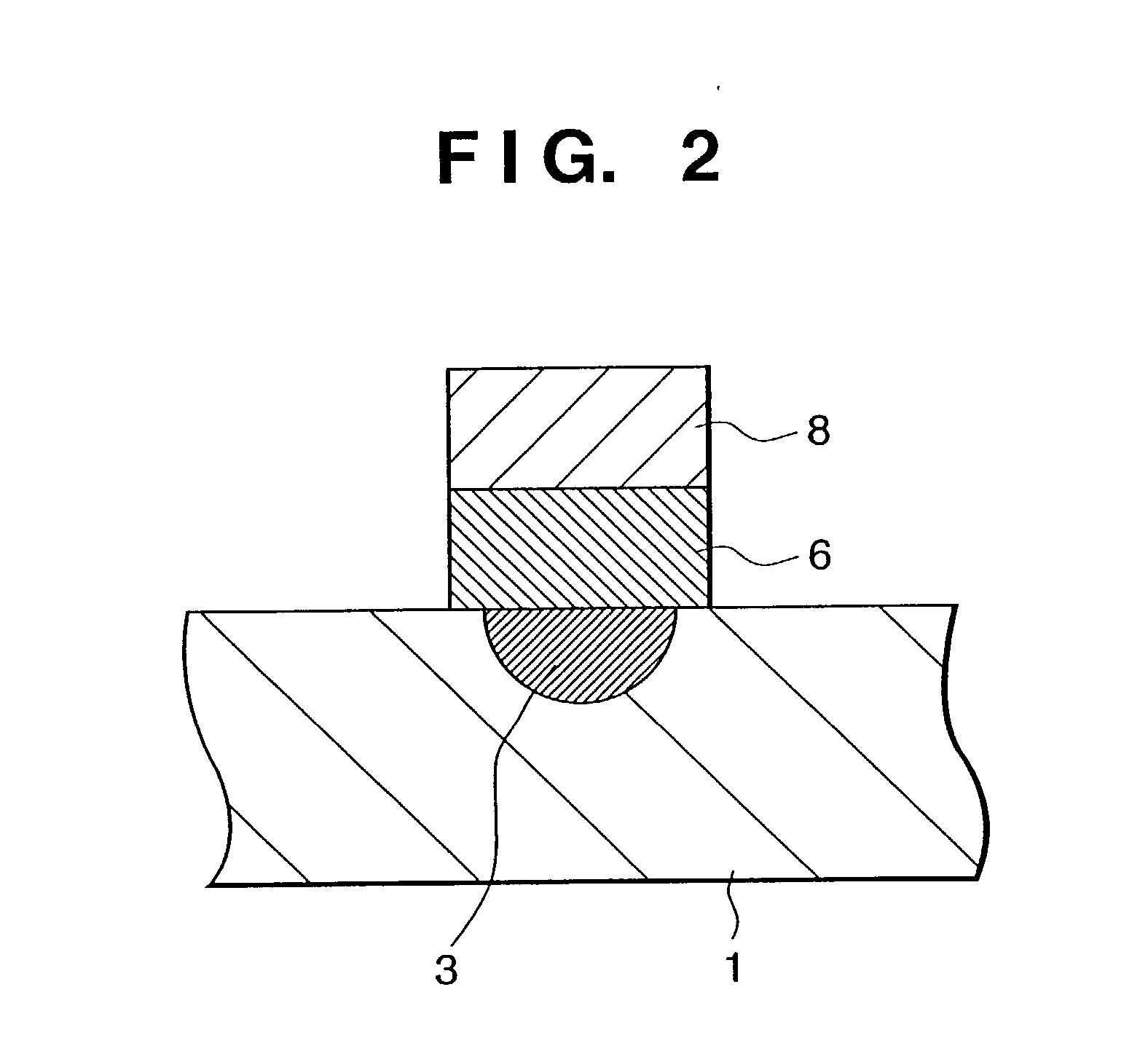
Arrangement method of metal electrode and transparent electrode in optical waveguide device and optical modulator using the optical waveguide
InactiveUS6853757B2High modulationAvoid light lossOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsElectricityWaveguide
The present disclosure relates to a device for modulating light emitted by a laser, including an optical substrate that has an electro-optical effect, at least one optical waveguide formed near a front face of the optical substrate, a first electrode that is formed with a conductive transparent film so that a part of the optical waveguide may be covered and is used for applying an electric field to the optical waveguide, a second electrode that is paired with the first electrode and is used for applying an electric field to the optical waveguide, and a third electrode that is formed with a metal film in a position that is shifted from a position just above the optical waveguide and is electrically connected with the first electrode.
Owner:CORLUX CORP
Arrangement method of metal electrode and transparent electrode in optical waveguide device and optical modulator using the optical waveguide
InactiveUS20030053730A1Avoid light lossHigh-speed modulationOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsMetal electrodesWaveguide
The present disclosure relates to a device for modulating light emitted by a laser, including an optical substrate that has an electro-optical effect, at least one optical waveguide formed near a front face of the optical substrate, a first electrode that is formed with a conductive transparent film so that a part of the optical waveguide may be covered and is used for applying an electric field to the optical waveguide, a second electrode that is paired with the first electrode and is used for applying an electric field to the optical waveguide, and a third electrode that is formed with a metal film in a position that is shifted from a position just above the optical waveguide and is electrically connected with the first electrode.
Owner:CORLUX CORP
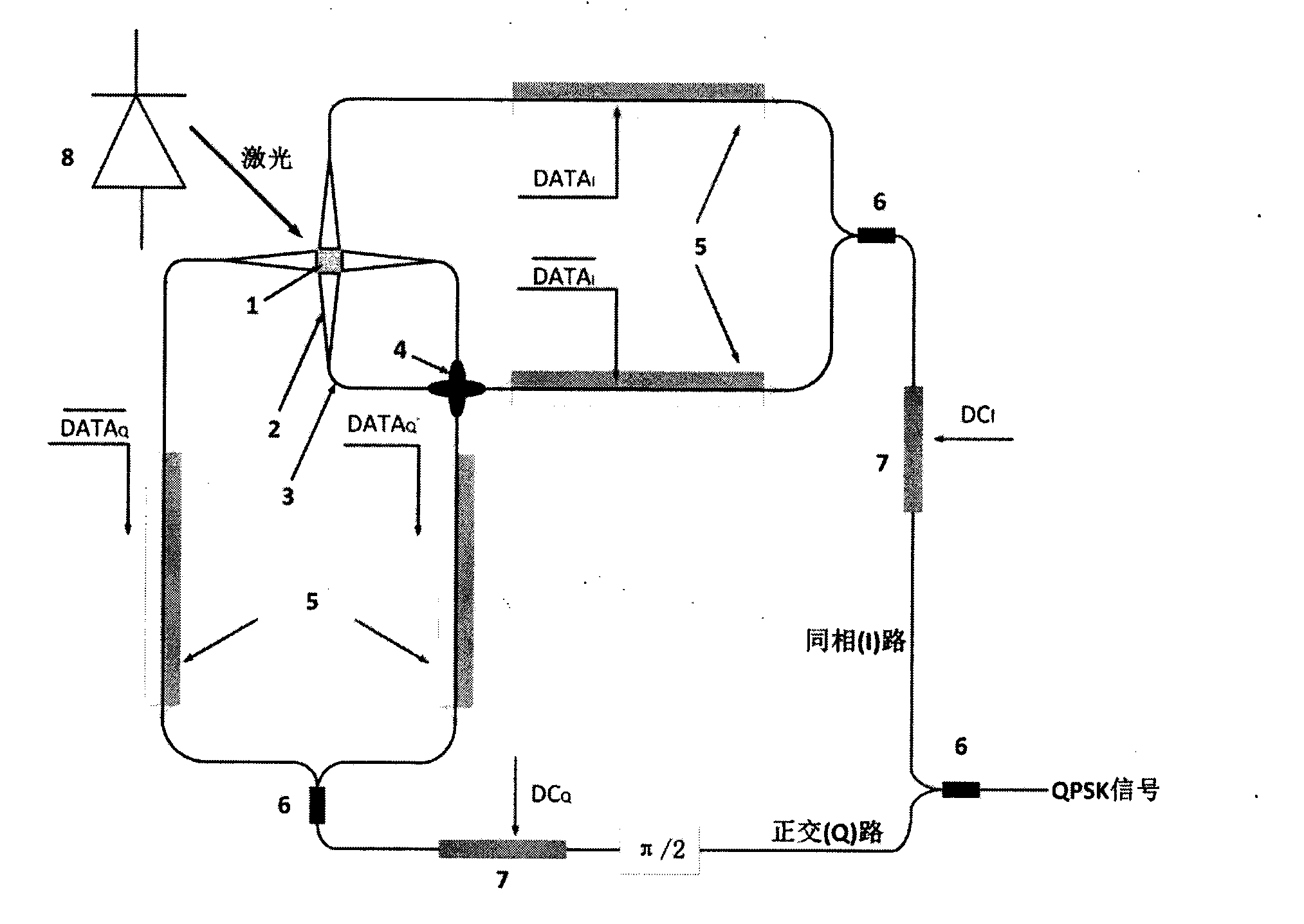
Two-dimensional grating coupling-based silicon-based QPSK (Quadrature Phase Shift Keying) photomodulator
ActiveCN104330905AImprove communication capacityHigh speed modulationNon-linear opticsGratingPhase difference
The invention discloses a two-dimensional grating coupling-based silicon-based QPSK (Quadrature Phase Shift Keying) photomodulator, comprising a two-dimensional grating coupler, four mode transducers, a single-mode waveguide, an optical cross and four radio frequency phase shifters, wherein the two-dimensional grating coupler, serving as a vertical optical coupling interface and a four-channel powder divider, averagely splits a coupling light into four channel waveguides; the four mode transducers are used for carrying out mode conversion and insulated optical transmission between the two-dimensional grating and the single-mode waveguide; the single-mode waveguide is used for carrying out low-loss single-mode transmission of an optical signal; the optical cross is used for carrying out non-crosstalk low-loss optical cross transmission between two waveguides; the four radio frequency phase shifters are used for loading electric signals of in-phase road data DATAI and quadrature road data DATAQ, thus achieving BPSK (Binary Phase Shift Keying) light phase modulation of two roads. Two of three MMI beam combiners are applied to light beam combination of two branch circuits in the in-phase road and the quadrature road; the other MMI beam combiner is applied to light beam combination of the in-phase road and the quadrature road; two thermal optical phase shifters are used for adjusting an optical wave phase difference between the in-phase road and the quadrature road by direct current, so as to meet pi / 2, and thus the optical signals of the in-phase road and the quadrature road are synthesized into a QPSK modulation signal.
Owner:苏州微光电子融合技术研究院有限公司
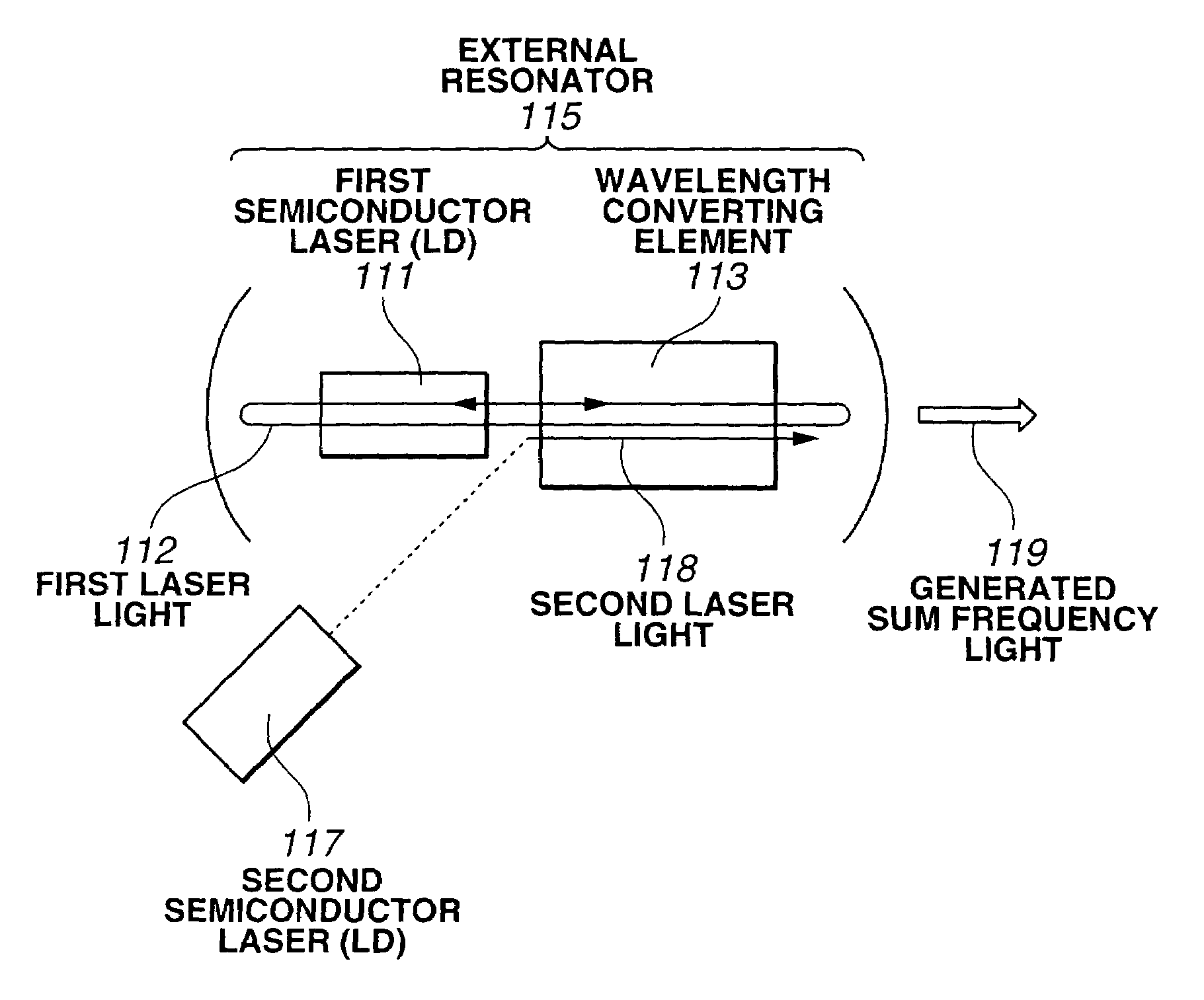
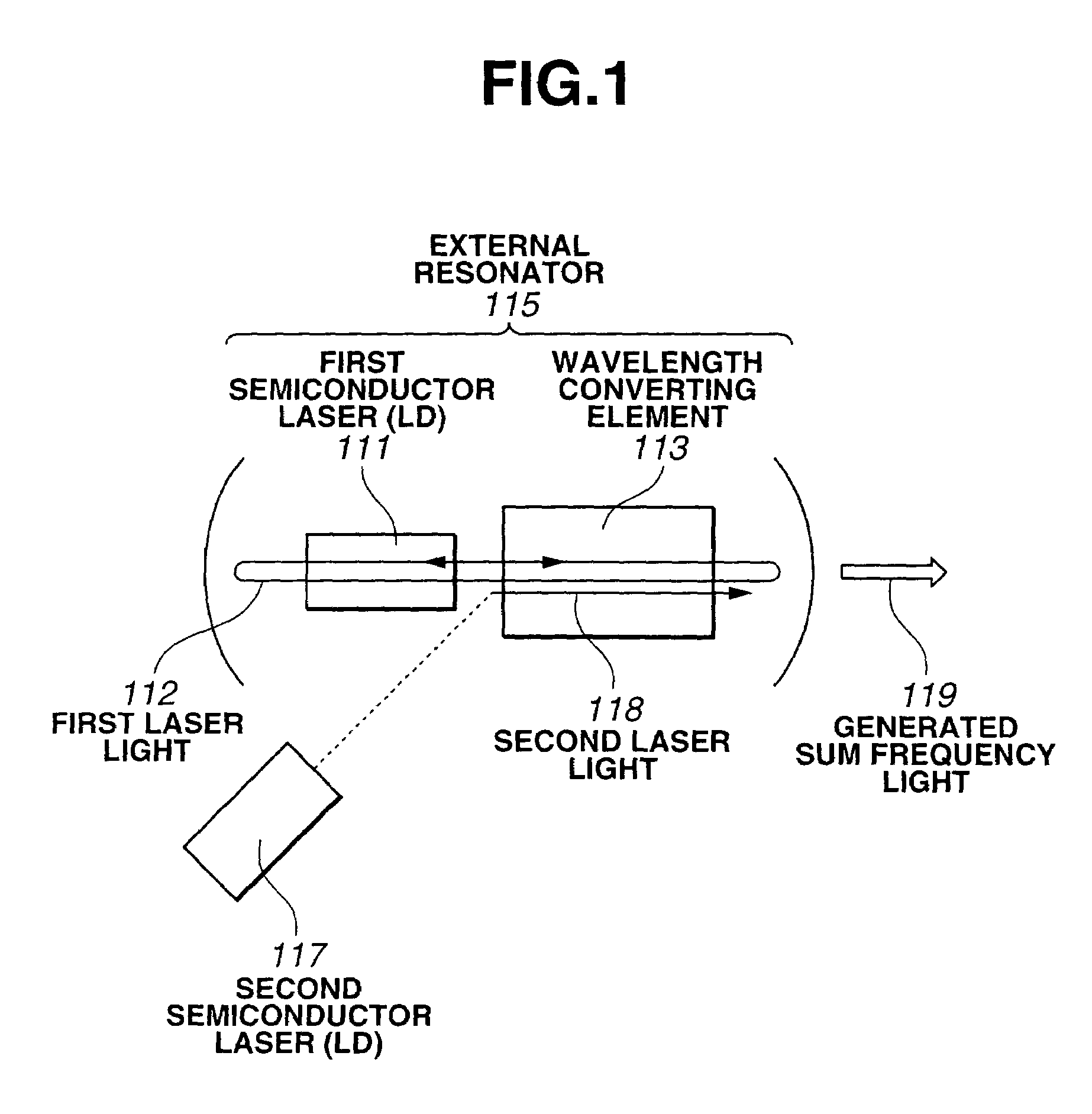
Optical wavelength converting apparatus, and optical wavelength converting method
InactiveUS7039077B2Improve conversion efficiencyHigh-speed modulationLaser detailsLight demodulationLaser lightLength wave
An optical wavelength converting apparatus includes a first semiconductor laser, a second semiconductor laser, and a wavelength converting element for converting first and second laser light from the first and second semiconductor lasers to sum frequency light. In this apparatus, the first semiconductor laser and the wavelength converting element are arranged so as to establish an external resonator structure in which the first laser light can be put under a resonant condition, and an optical path of the second laser light is so determined that the second laser light can propagate through the wavelength converting element.
Owner:CANON KK
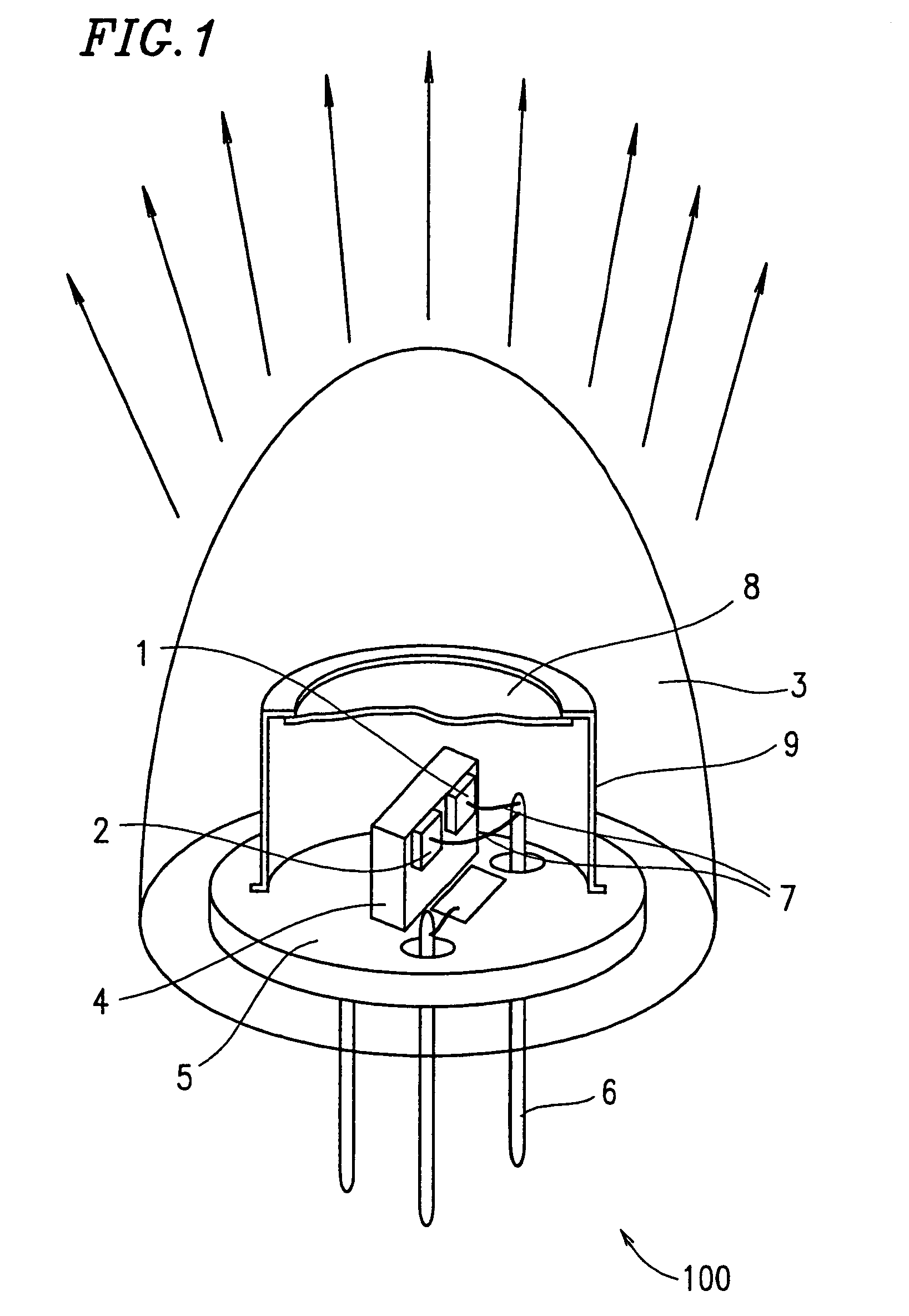
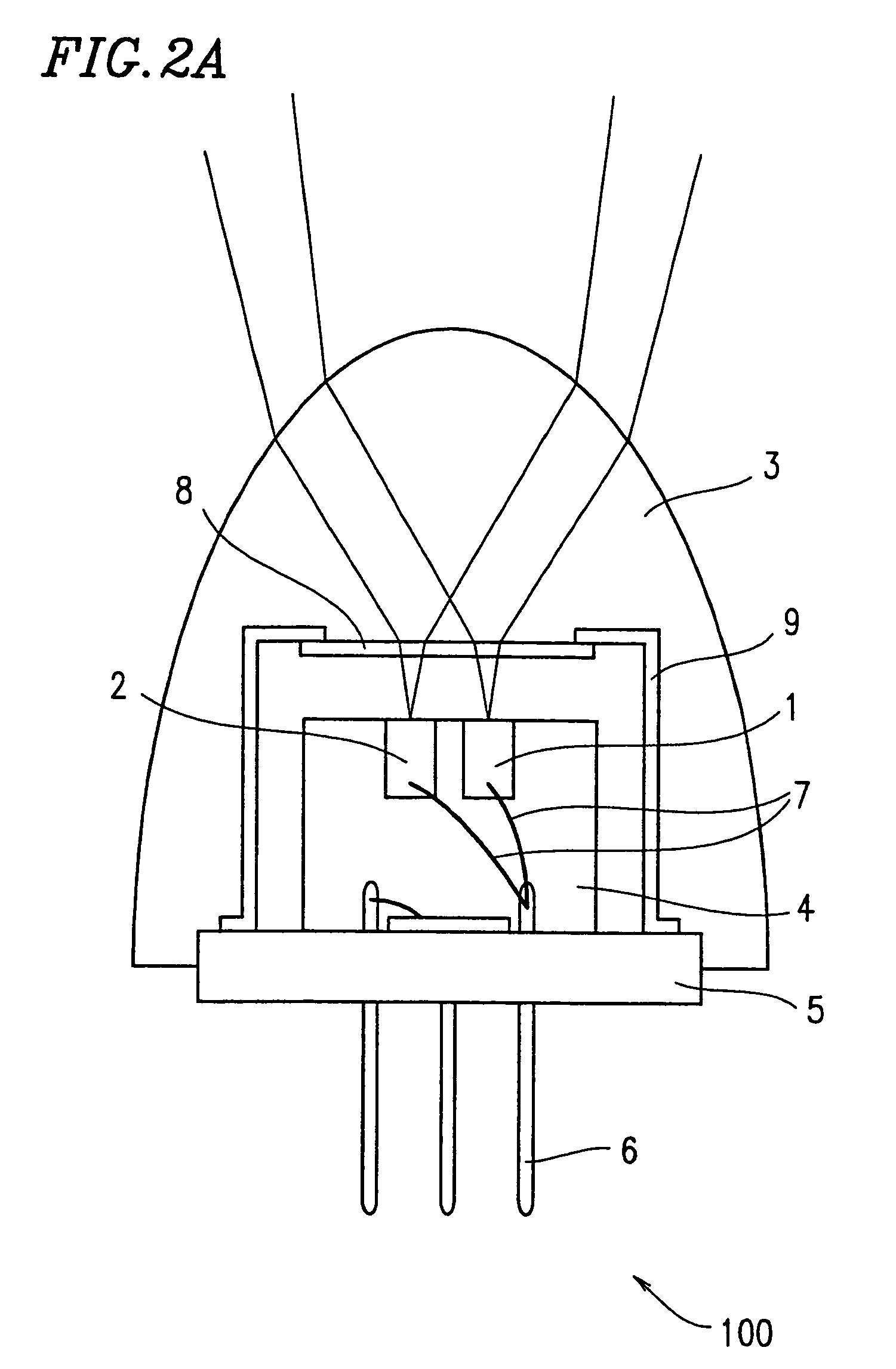
Semiconductor laser device, optical transmission device, optical transmission system, electronic device, control device, connector, communication device, and optical transmission method and data transmission and reception method
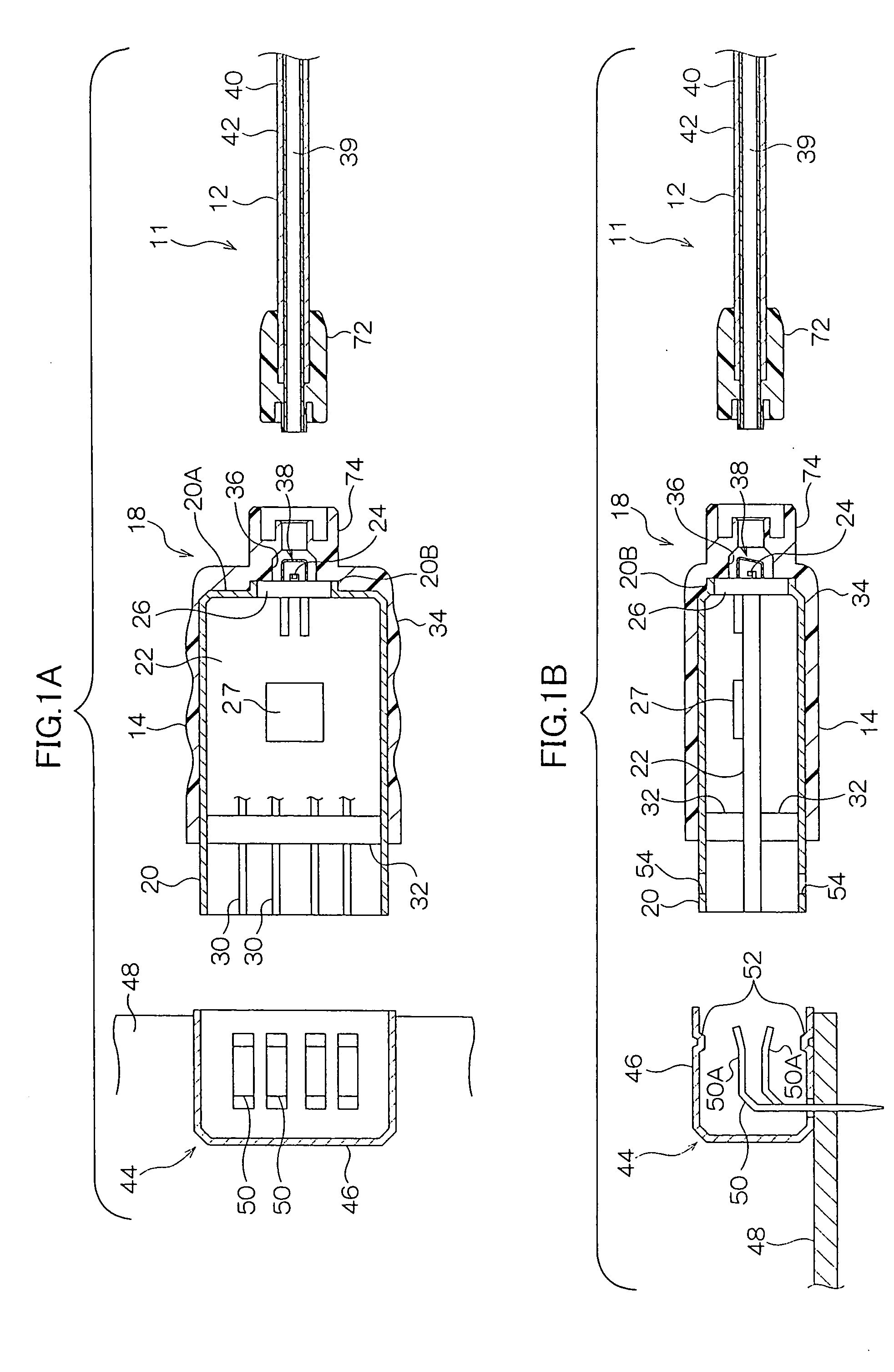
InactiveUS6888864B1Improve reliabilityLight diffusion capabilitySemiconductor laser arrangementsSemiconductor laser structural detailsData transmissionSemiconductor
A semiconductor laser device includes a semiconductor laser chip, and a molded resin having a light diffusion capability. The semiconductor laser chip is covered with the molded resin.
Owner:SHARP KK
Semiconductor laser device, optical transmission device, optical transmission system, electronic device, control device, connector, communication device, and optical transmission method and data transmission and reception method
InactiveUS20050163177A1High speed transmissionReduce power consumptionSemiconductor laser arrangementsSemiconductor laser structural detailsData transmissionCommunication device
A device including a semiconductor laser device having a semiconductor laser chip, and a molded resin having a light diffusion capability. The semiconductor laser chip is covered with the molded resin.
Owner:SHARP KK
Vertical cavity surface emitting semiconductor laser, light emission device, and optical transmission system
InactiveUS7376164B2Increase frequencyHigh densitySemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser active region structureResonanceSemiconductor package
A semiconductor laser is disclosed with which a VCSEL can be constituted with a simplified configuration for optical transmission at a transmission rate higher than 10 Gbps. The semiconductor laser includes a resonator including a first active region able to emit light in response to current injection and a second active region able to emit light in response to external excitation light. Multilayer film reflecting mirrors sandwich the resonator from two opposite sides. The first active region and the second active region generate light at a wavelength the same as the resonance mode of the resonator.
Owner:RICOH KK
Semiconductor laser element and electronic device using the same
InactiveUS6842472B1High speed modulationOptical wave guidanceSemiconductor laser arrangementsMultimode interferenceWaveguide
A semiconductor laser element includes: a semiconductor laser region in which at least one laser emission portion including an active layer for emitting light is provided; a multimode interference region including a first wave-guiding layer, one end of the first wave-guiding layer being optically coupled to the active layer of the at least one laser emission portion; and an output waveguide region including a second wave-guiding layer, the second wave-guiding layer being optically coupled to another end of the first wave-guiding layer, wherein the active layer of the at least one laser emission portion, the first wave-guiding layer, and the second wave-guiding layer are integrally formed.
Owner:SHARP KK
Surface-emission laser diode operable in the wavelength band of 1.1-1.7 micrometers and optical telecommunication system using such a laser diode
InactiveUS7590159B2Reduce areaElectrostatic capacitance of the device is reduced more effectivelySolid-state devicesSemiconductor laser optical deviceCommunications systemDistributed Bragg reflector
A surface-emission laser diode includes a distributed Bragg reflector tuned to wavelength of 1.1 μm or longer, wherein the distributed Bragg reflector includes an alternate repetition of a low-refractive index layer and a high-refractive index layer, with a heterospike buffer layer having an intermediate refractive index interposed therebetween with a thickness in the range of 5-50 nm.
Owner:RICOH KK
Reflection-type optical modulator module
InactiveUS20080137178A1Low production costHigh priceSemiconductor lasersNon-linear opticsCoupling lossCapacitance
Provided is a reflection-type optical modulation module. According to the reflection-type optical modulation module, an anti-reflective thin film is formed on the optical input / output side surface of a waveguide to reduce optical coupling loss, and also a high-reflective thin film is formed on the opposite side surface to feed back a modulated optical signal. Thus, even when the length of an absorption layer is shortened, a sufficient optical path length is available, and it is possible to obtain a sufficient extinction ratio. Since the optical path length is sufficiently long despite a reduction in the length of the device, capacitance is reduced, and high-speed operation is enabled. In addition, only one lensed optical fiber for optical input and output is used, and thus it is possible to reduce production cost and the number of installation processes. Furthermore, a small-sized and low-priced optical amplifier, instead of an external amplifier which is high priced and has a large volume, is integrated with an optical modulator so that production cost can be further reduced.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Range sensor and solid-state imaging device
ActiveUS10325953B2Increase the areaHigh-speed modulationTelevision system detailsWave based measurement systemsEngineeringPhotodiode
A range sensor includes: an n-type surface-buried region selectively buried in an upper portion of a pixel layer to implement a photodiode and extending from a light-receiving area toward plural portions shielded by a shielding plate along the upper portion of the pixel layer so as to provide a plurality of branches; n-type charge-accumulation regions having a higher impurity concentration than the surface-buried region; a plurality of transfer gate electrodes provided adjacent to the charge-accumulation regions; and an n-type guide region having a higher impurity concentration than the surface-buried region and a lower impurity concentration than the charge-accumulation regions, and provided with one end below an aperture of the shielding plate and other ends extending to a part of the respective transfer gate electrodes.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP SHIZUOKA UNIV
Single-mode high-speed modulation Fabry-Perot semiconductor laser based on coupled cavity
ActiveCN104868359AReduce the restrictionIncrease modulation bandwidthLaser optical resonator constructionLaser output parameters controlMode couplingLaser
The invention discloses a single-mode high-speed modulation Fabry-Perot semiconductor laser based on a coupled cavity, and the laser comprises a tube core which is in a stacked structure and comprises a lower electrode; a lower contact layer which is disposed on the lower electrode; and an N-type substrate which is disposed on the lower contact layer. The N-type substrate is divided into two parts: a Fabry-Perot type miniature cavity and an echo-wall type miniature cavity. The Fabry-Perot type miniature cavity is disposed on the N-type substrate, wherein one end of the Fabry-Perot type miniature cavity is aligned with one end of the N-type substrate. The echo-wall type miniature cavity is disposed on the N-type substrate, and is located at the other end of the Fabry-Perot type miniature cavity. The Fabry-Perot type miniature cavity and the echo-wall type miniature cavity have the same stacked structure. According to the invention, the high-power Fabry-Perot type miniature cavity and the single-mode high-speed modulation echo-wall type miniature cavity are combined together, and the mode coupling between the two cavities is adjusted so as to adjust the equivalent reflectivity of the Fabry-Perot type miniature cavity, thereby achieving high-power, single-mode lasing and better high-speed modulation characteristics.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical modulator and method of manufacturing same
InactiveUS20060269182A1Improving Impedance MatchingSensitive highLaser detailsSemiconductor laser structural detailsAerosol depositionLaser light
Laser light emitted from a vertically confined surface emitting laser (VCSEL) is incident on a side surface near an end region of an optical waveguide. The end region of the optical waveguide is processed by polishing to taper at an angle of 45 degrees, and an optical modulator is formed on the polished surface. The optical modulator is a Fabry-Perot modulator using a linear electro-optical effect. The modulator has a thick transparent electro-optical layer which is deposited by using an aerosol deposition method.
Owner:NEC CORP
Semiconductor laser device, optical transmission device, optical transmission system, electronic device, control device, connector, communication device, and optical transmission method and data transmission and reception method
InactiveUS7756181B2High speed transmissionReduce power consumptionSemiconductor laser arrangementsSemiconductor laser structural detailsData transmissionCommunication device
A device including a semiconductor laser device having a semiconductor laser chip, and a molded resin having a light diffusion capability. The semiconductor laser chip is covered with the molded resin.
Owner:SHARP KK
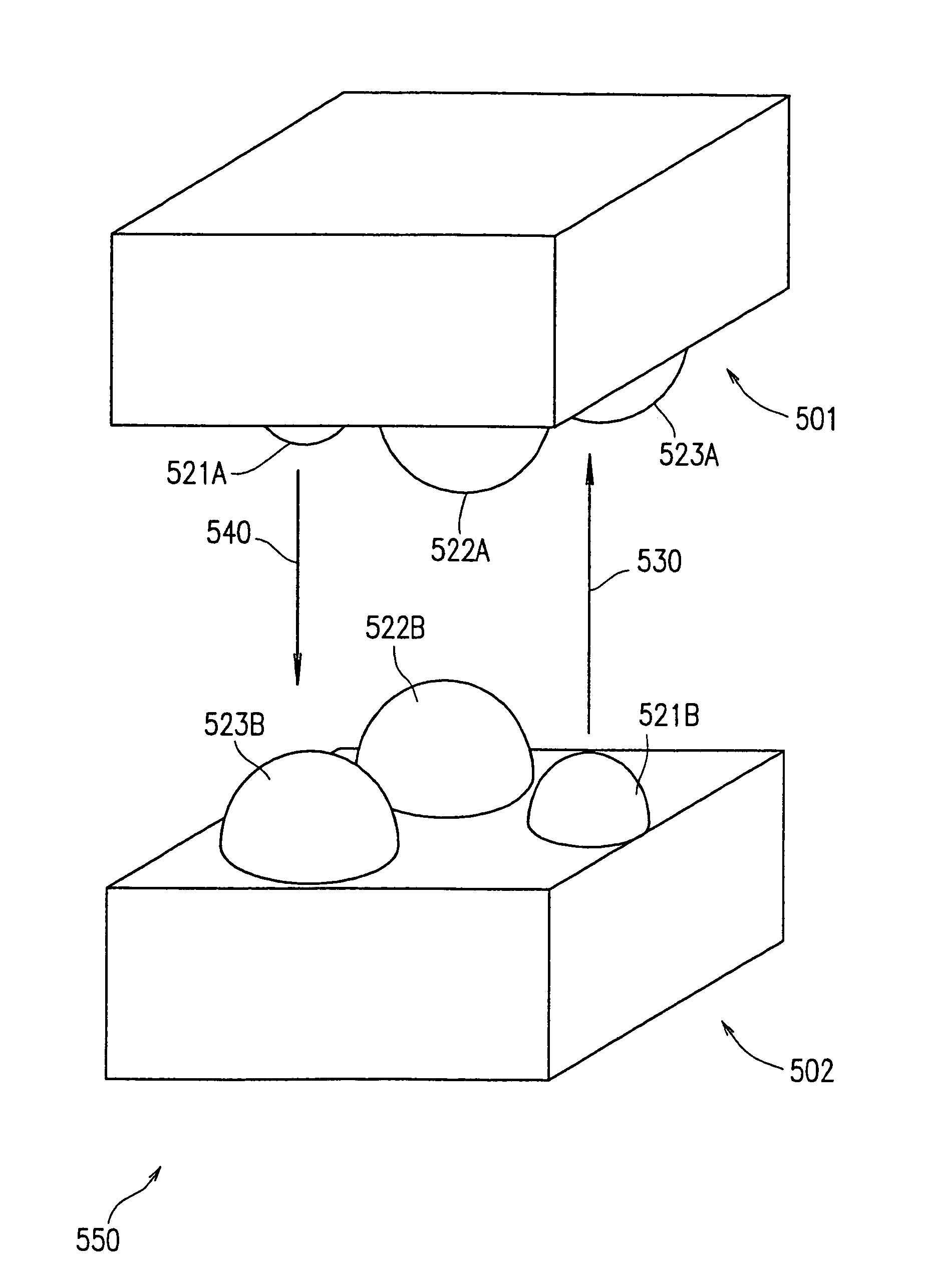
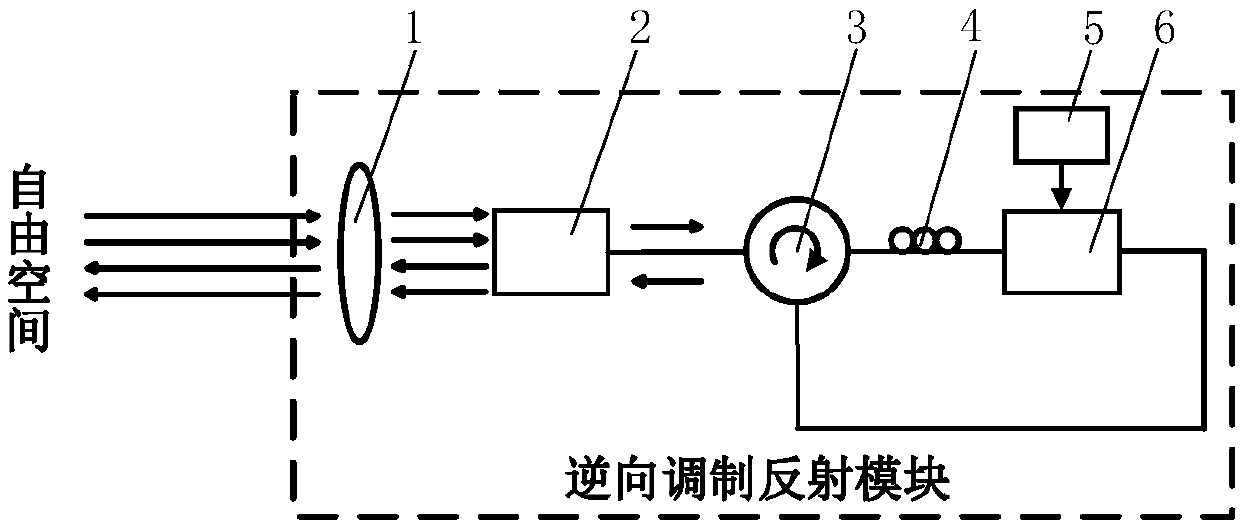
Modulator-based high-speed retro-modulation reflection module and reflection transmission method
ActiveCN107819523AHigh Speed Reverse Modulation ReflectionReduce volumeFree-space transmissionElectromagnetic receiversCommunications systemOptical antenna
The present invention discloses a modulator-based high-speed retro-modulation reflection module and a reflection transmission method. The modulator-based high-speed retro-modulation reflection modulecomprises an optical antenna, a space-to-fiber coupling apparatus, an optical circulator, a polarization controller, a signal source, and an electro-optic modulator. An optical carrier that is received by the optical antenna from free space is coupled by the space-to-fiber coupling apparatus, and is transmitted to the electro-optic modulator; an electric signal that is sent by the signal source ismodulated, by the electro-optic modulator, to the optical carrier that comes from the space-to-fiber coupling apparatus, to generate an optical signal; the optical signal is reflected back to the space-to-fiber coupling apparatus by the optical circulator, then is coupled back to the free space by the space-to-fiber coupling apparatus, and is retro-reflected by the optical antenna in a reverse direction, so as to implement high-speed long-distance free space communication. The modulator-based high-speed retro-modulation reflection module and the reflection transmission method are used for a high-speed retro-modulation reflection-type free space laser communication system, reduce a volume and power consumption of a retro-modulation terminal device, also significantly improve a transmissionrate of an uplink signal, and meet requirements of next-generation high-speed large-capacity long-distance free space optical signal transmission.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Range sensor and solid-state imaging device
ActiveUS20180114809A1Increase the areaHigh-speed modulationTelevision system detailsWave based measurement systemsPhotodiodeDistance sensors
A range sensor includes: an n-type surface-buried region selectively buried in an upper portion of a pixel layer to implement a photodiode and extending from a light-receiving area toward plural portions shielded by a shielding plate along the upper portion of the pixel layer so as to provide a plurality of branches; n-type charge-accumulation regions having a higher impurity concentration than the surface-buried region; a plurality of transfer gate electrodes provided adjacent to the charge-accumulation regions; and an n-type guide region having a higher impurity concentration than the surface-buried region and a lower impurity concentration than the charge-accumulation regions, and provided with one end below an aperture of the shielding plate and other ends extending to a part of the respective transfer gate electrodes.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP SHIZUOKA UNIV
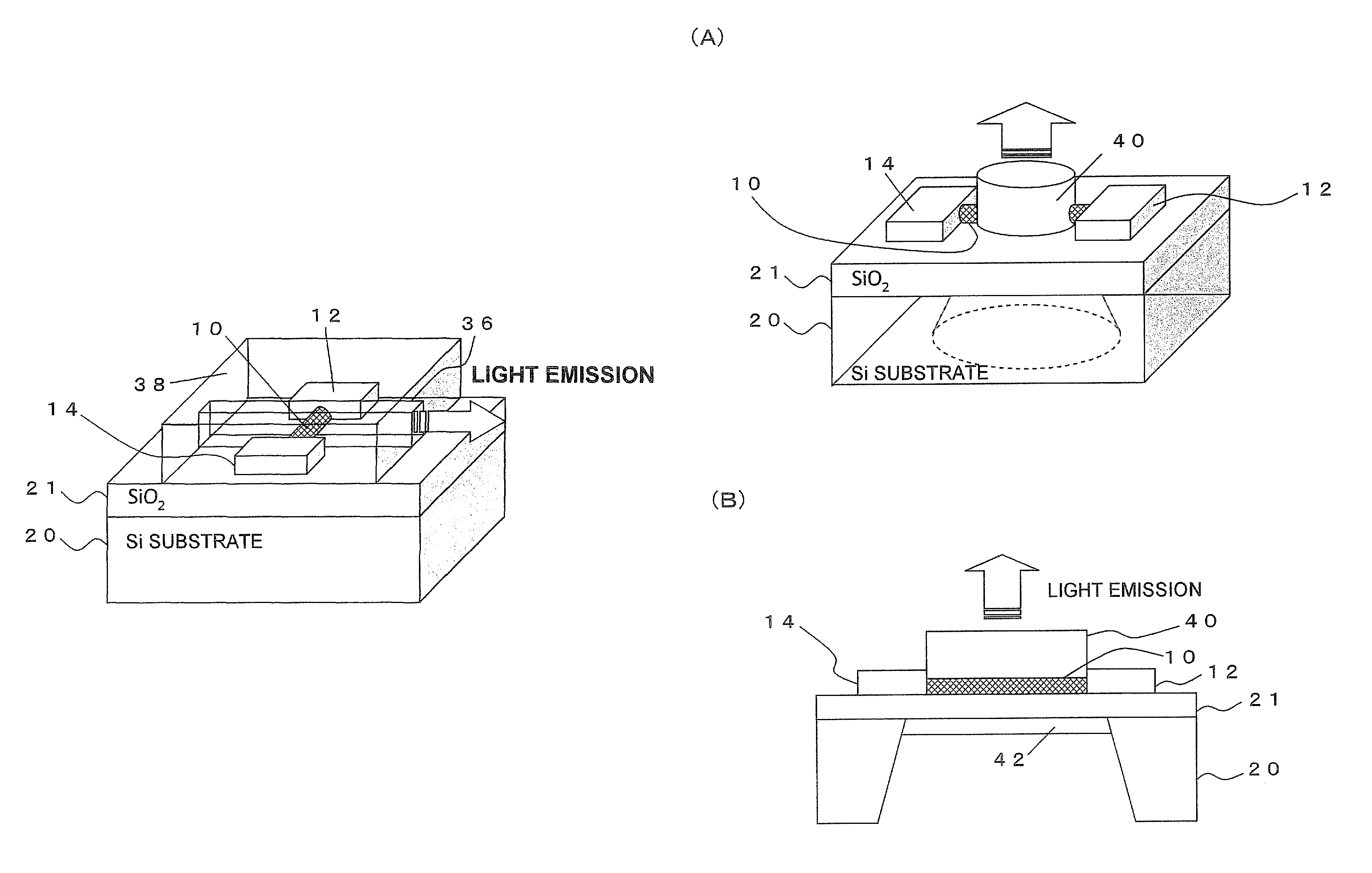
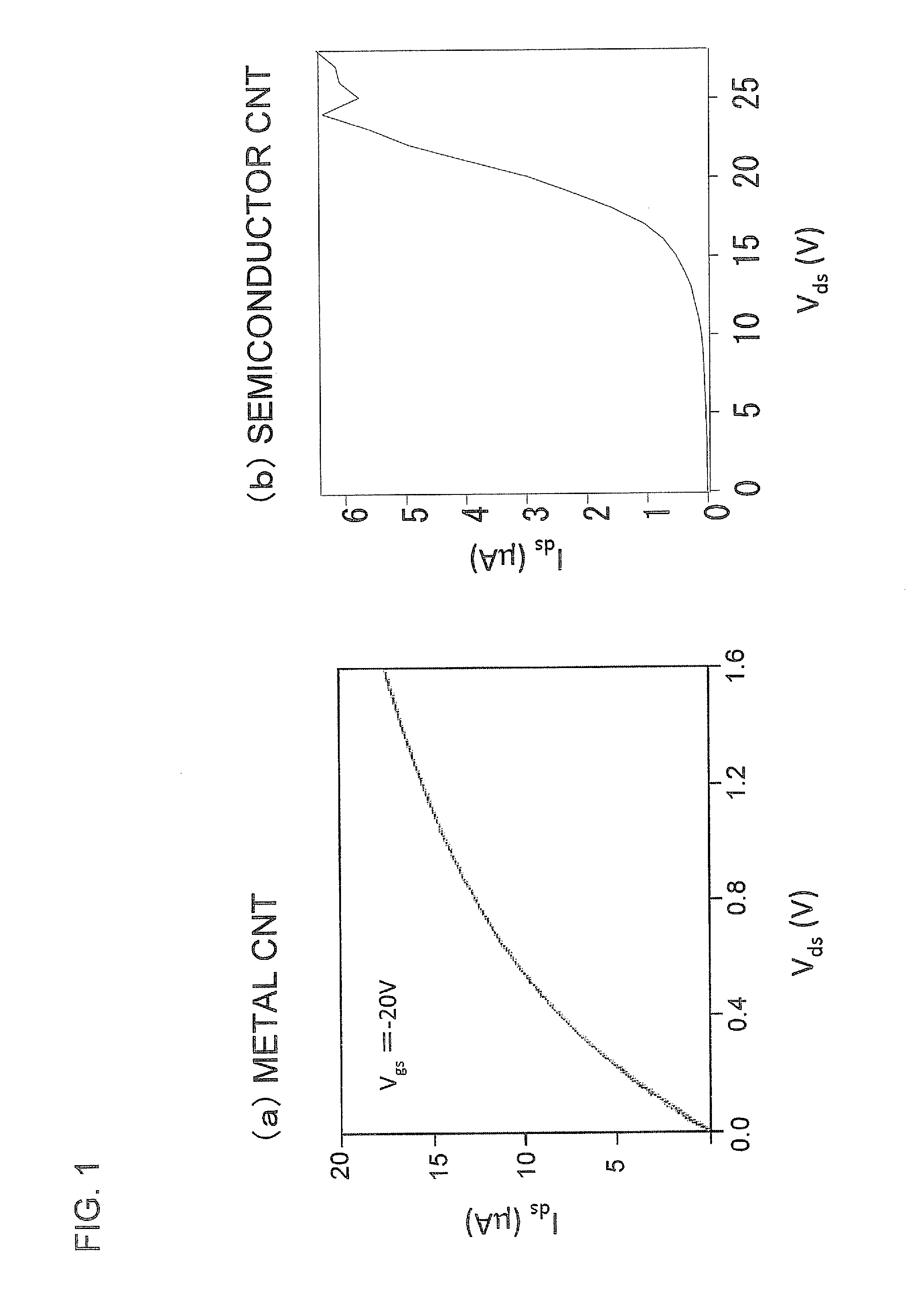
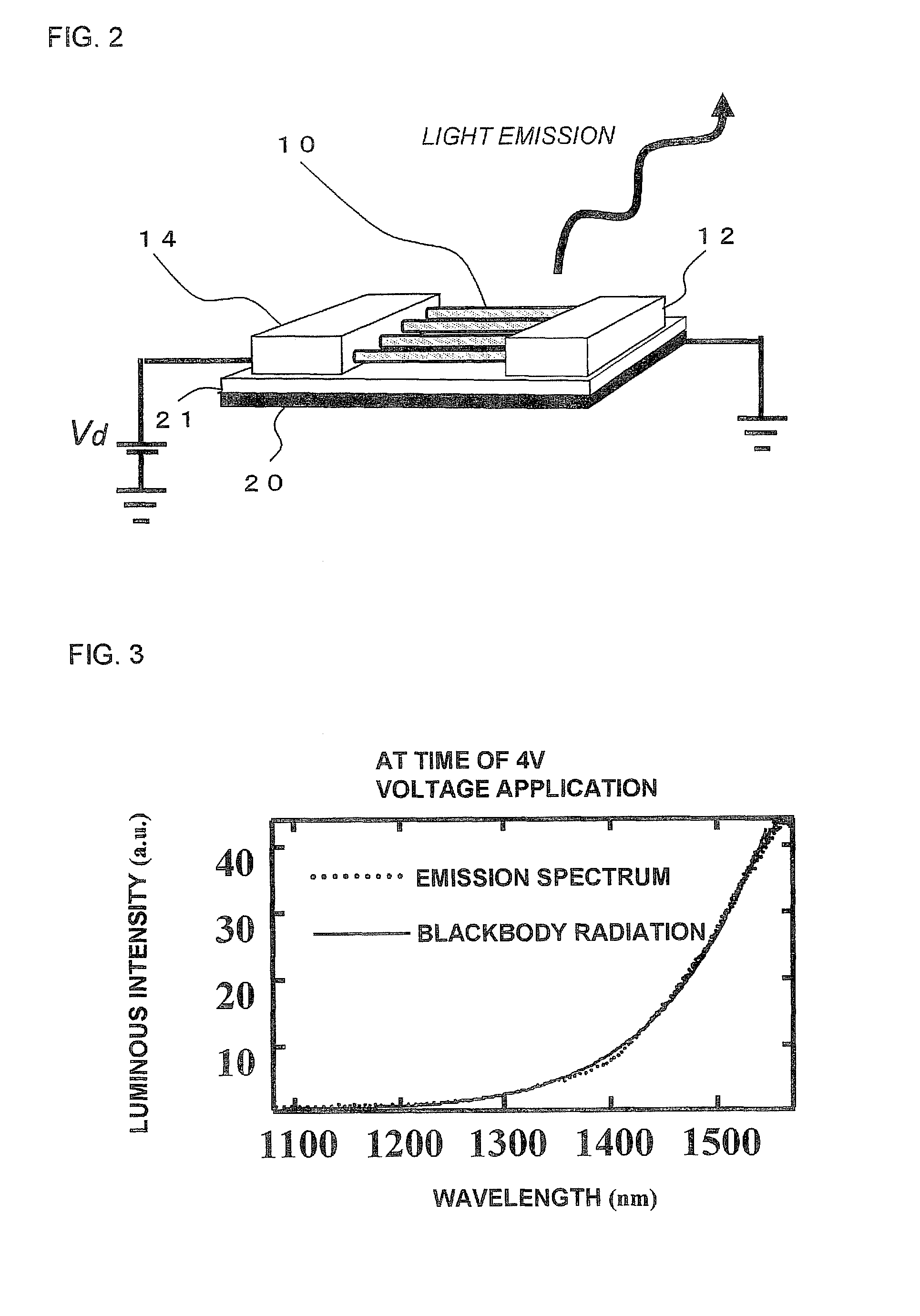
Carbon nanotube light emitting device, light source, and photo coupler
ActiveUS8895997B2Easy to makeHigh-speed modulationMaterial nanotechnologyLamp incadescent bodiesBlack-body radiationCarbon nanotube
A plurality of electrodes, and carbon nanotubes disposed between the electrodes, at least part of the carbon nanotubes including a metal carbon nanotube are provided. The metal carbon nanotube generates heat upon passing of current to the electrodes and emits light by blackbody radiation, so that the emitted light has a wide emission wavelength region and can be modulated at high speed. This makes it possible to implement a continuum spectrum light source that can be modulated at high speed, which is suitable for use in information communication, electrical and electronic fields.
Owner:KEIO UNIV
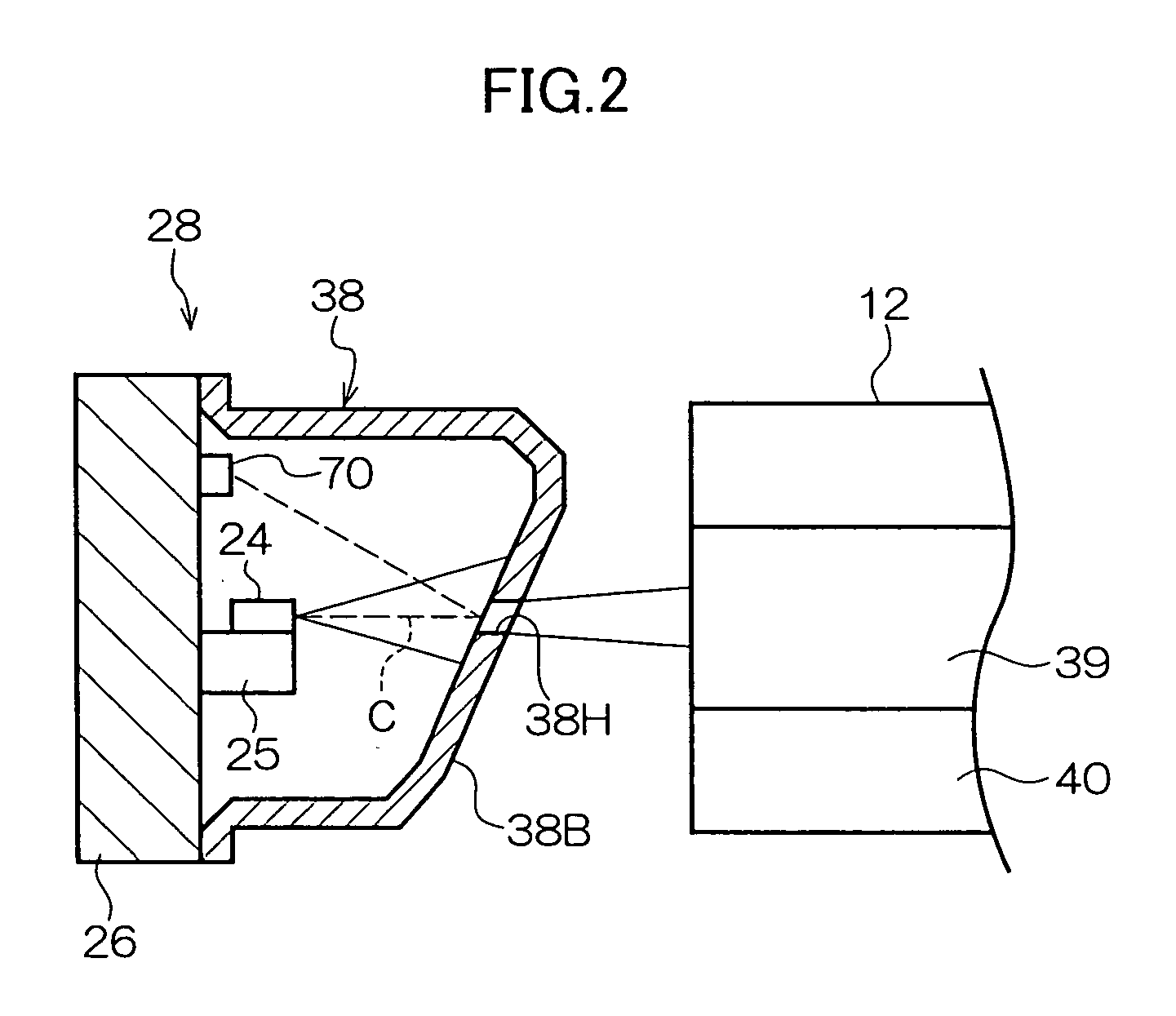
Optical signal transmitting device
InactiveUS20050169644A1Efficient couplingEnhanced couplingLaser detailsSemiconductor laser structural detailsDivergence angleLaser light
An optical signal transmitting device includes: a semiconductor laser diode that is disposed so that its periphery is covered by a laser package and which emits laser light in accordance with information to be transmitted; and a light limiting member that covers at least part of the periphery of the semiconductor laser diode and limits the light amount and divergence angle of the laser light emitted from the semiconductor laser diode. An opening is formed in a side wall of the light limiting member, and the laser light whose light amount and divergence angle have been limited by the light limiting member is guided to optical fiber connected to an optical signal device.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP +1
Optical semiconductor device
InactiveUS7223993B2Lower resistanceHigh-speed modulationLaser optical resonator constructionNanoopticsQuantum wellActive layer
In the semiconductor laser or electro-absorption optical modulator that includes strained quantum well layers as active layers, making laser characteristics or modulator characteristics adequate has seen the respective limits since band structures, especially, ΔEc and ΔEv, have been unable to be adjusted independently.This invention is constructed by stacking an n-type InGaAlAs-GRIN-SCH layer 3, an MQW layer 4, a p-type InGaAlAs-GRIN-SCH layer 5, a p-type InAlAs electron-stopping layer 6, and others, in that order, on an n-type InP wafer 1; wherein the MQW layer 4 includes InGaAlAs-strained quantum well layers and InGaAlAsSb-formed barrier layers each having strain of an opposite sign to the strain applied to the quantum well layers.
Owner:OCLARO JAPAN INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com