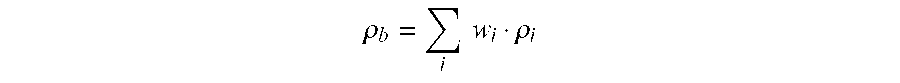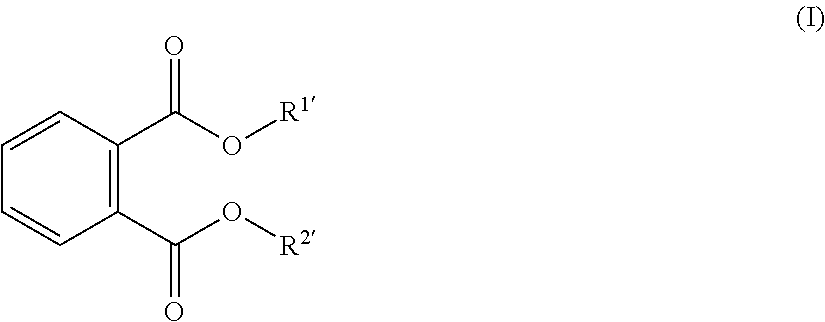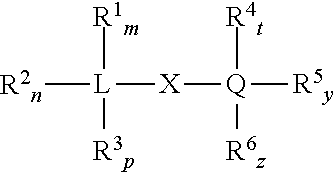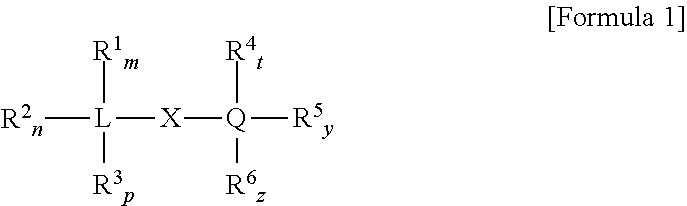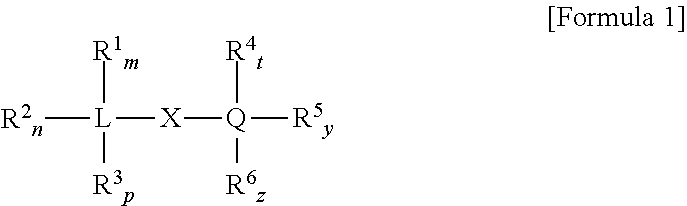Patents
Literature
197results about How to "Increased melt flow rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Thermoplastic elastomers having improved processing and physical property balance
InactiveUS6451915B1Without deleteriously sacrificing mechanical propertyEasy to processThermoplasticPolymer science
A thermoplastic elastomer formed by a process comprising the steps of dynamically vulcanizing a rubber within a mixture that includes the rubber, from about 10 to about 80 percent by weight of a thermoplastic resin based upon the total weight of the rubber and the thermoplastic combined, and from about 1 to about 25 percent by weight of a polymeric processing additive based upon the total weight of the rubber and the thermoplastic combined, where the polymeric processing additive is a linear polyolefin resin that has an melt flow rate that is greater than about 1,000 dg / min, a diene-modified polyolefin polymer that has an melt flow rate that is greater than about 1,000 dg / min, from about 0.005 to about 2.00 mole percent polymeric units deriving from dienes, and a viscosity average branching index that is from about 0.4 to about 0.95, or a mixture of the linear polyolefin resin and the diene-modified polyolefin polymer, where the step of dynamically vulcanizing the rubber results in vulcanized rubber having a crosslink density of about 40 to about 180 mole per milliliter of rubber.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
High flow, hydrogenated styrene-butadiene-styrene block copolymer and applications
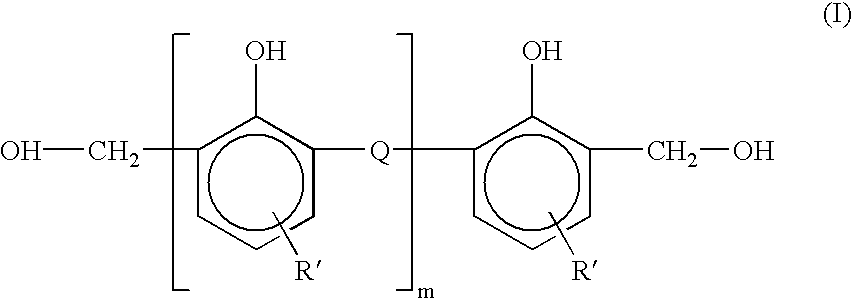
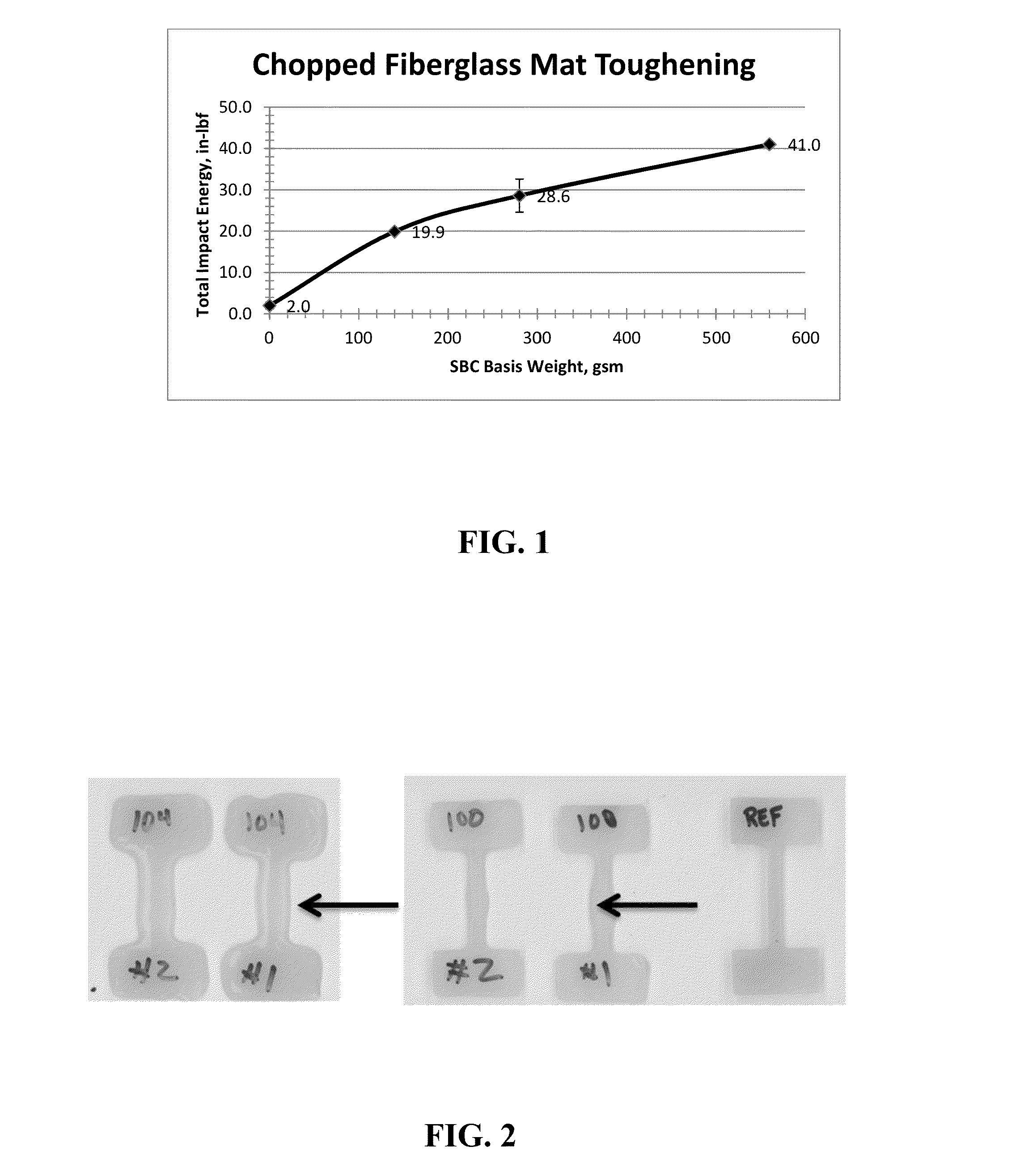
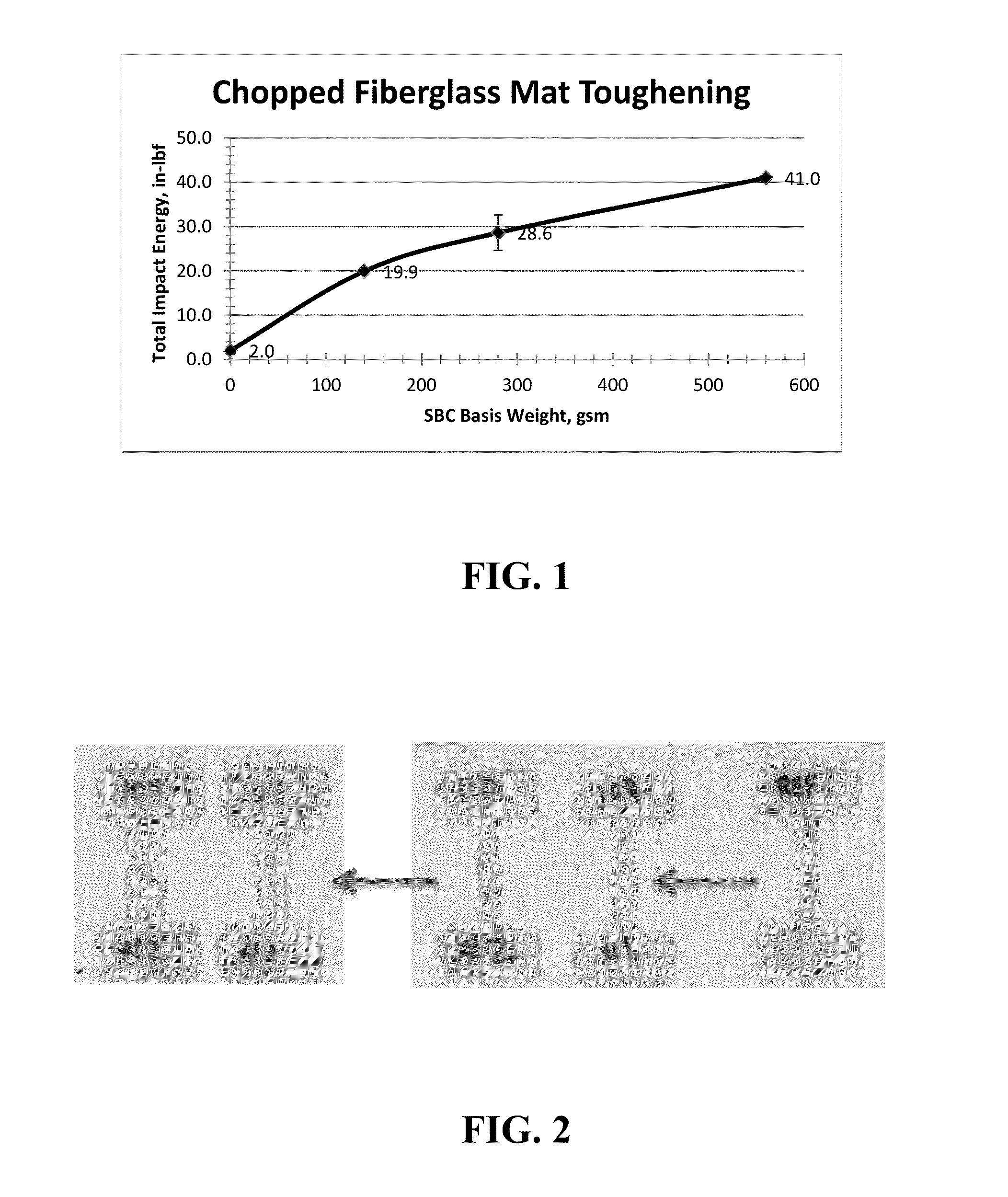
The invention relates to unique applications for the novel high melt flow, low viscosity, selectively hydrogenated styrene-butadiene-styrene (hSBS) or selectively hydrogenated controlled distribution styrene-butadiene / styrene-styrene (hSBSS) block copolymers, wherein the melt flow rate of said block copolymer is at least 100 g / 10 min at 230° C. under 2.16 kg mass according to ASTM D1238. These block copolymers are novel and have the highest melt flow rate of any styrenic block copolymer also possessing high strength and elasticity. It has applications that prior to the present invention were not normally possible due to the normal low melt flow rate of styrenic block copolymers. The present invention also encompasses various fields of use such as a fiberglass hSBS or hSBSS reinforced mat, low viscosity hSBS or hSBSS coatings for industrial uses, hot melt adhesives prepared from hSBS or hSBSS blended with polyalpha-olefins, and elastic film, fiber, and nonwoven constructions using hSBS or hSBSS.
Owner:KRATON POLYMERS US LLC
Gas phase olefin polymerizations using dual donor catalyst systems
InactiveUS6900281B2Wide molecular weight distributionImprove tactical performanceGas phaseElectron donor
A gas-phase olefin polymerization process in a plug flow reactor uses a catalyst system containing a magnesium halide supported titanium-containing component, an organoaluminum component, and at least one external electron donor component; in the process a first external donor component is added to the reactor at an injection point axially near an injection point for the supported transition metal containing component, and at least a second external donor component is added to the reactor axially downstream from the injection point for the first external donor component.
Owner:INEOS TECH USA
Matte biaxially oriented polylactic acid film
ActiveUS20100009208A1Minimize thermal shrinkage effectReduce internal stressBio-packagingSynthetic resin layered productsPolyolefinPolymer chemistry
A biaxially oriented laminate film including a core layer including a blend of crystalline polylactic acid polymer and a minority amount of polyolefin with a compatibilizing resin which is biaxially oriented such that a matte or opaque appearance is obtained. The laminate film may further have additional layers such as a heat sealable layer disposed on one side of the core layer including an amorphous polylactic acid resin and / or a polylactic acid resin-containing layer disposed on the side of the core layer opposite the heat sealable layer, a metal layer, or combinations thereof.
Owner:TORAY PLASTICS AMERICA
Glass reinforced nylon blend with improved knitline strength
The present invention provides a polymer alloy including from about 40% to about 75% by weight of at least one polyamide, from about 10% to about 50% by weight polypropylene, from about 0.01% to about 1.0% by weight of at least one block copolymer including a vinyl aromatic monomer and a conjugated diene, and also includes an unsaturated dicarboxylic reagent, from about 0.1% to about 5.0% by weight of at least one block copolymer or terpolymer, wherein the terpolymer may have an unsaturated dicarboxylic reagent grafted thereto, from about 0.01% to about 7.5% of a compatibilizing agent, and from about 5% to about 50% by weight of a filler. The alloy of the present invention exhibits improved knitline strength and improved drop impact results compared with prior art fiberglass-reinforced nylon blends.
Owner:LYONDELLBASELL ADVANCED POLYMERS INC
Thermoplastic polymers with thermally reversible and non-reversible linkages, and articles using same
InactiveUS20050037194A1Color stableHigh strengthMonocomponent polyurethanes artificial filamentMonocomponent polyethers artificial filamentPolymer chemistryChemistry
The invention provides a polymer adapted for use in melt processes, the polymer having thermally reversible and non-thermally reversible bonds which polymer is adapted to evanesce at an elevated temperature and revert to a thermally reversible bond upon cooling to ambient temperature so that the polymer is adapted, upon being heated to the elevated temperature, to dissociate into melt processable polymeric fragments and, upon being cooled to ambient temperature, to re-associate.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Polypropylene fibers and fabrics
InactiveUS7081299B2Improve featuresShot levelFixed capacitor dielectricSynthetic resin layered productsPolymer scienceNon-coordinating anion
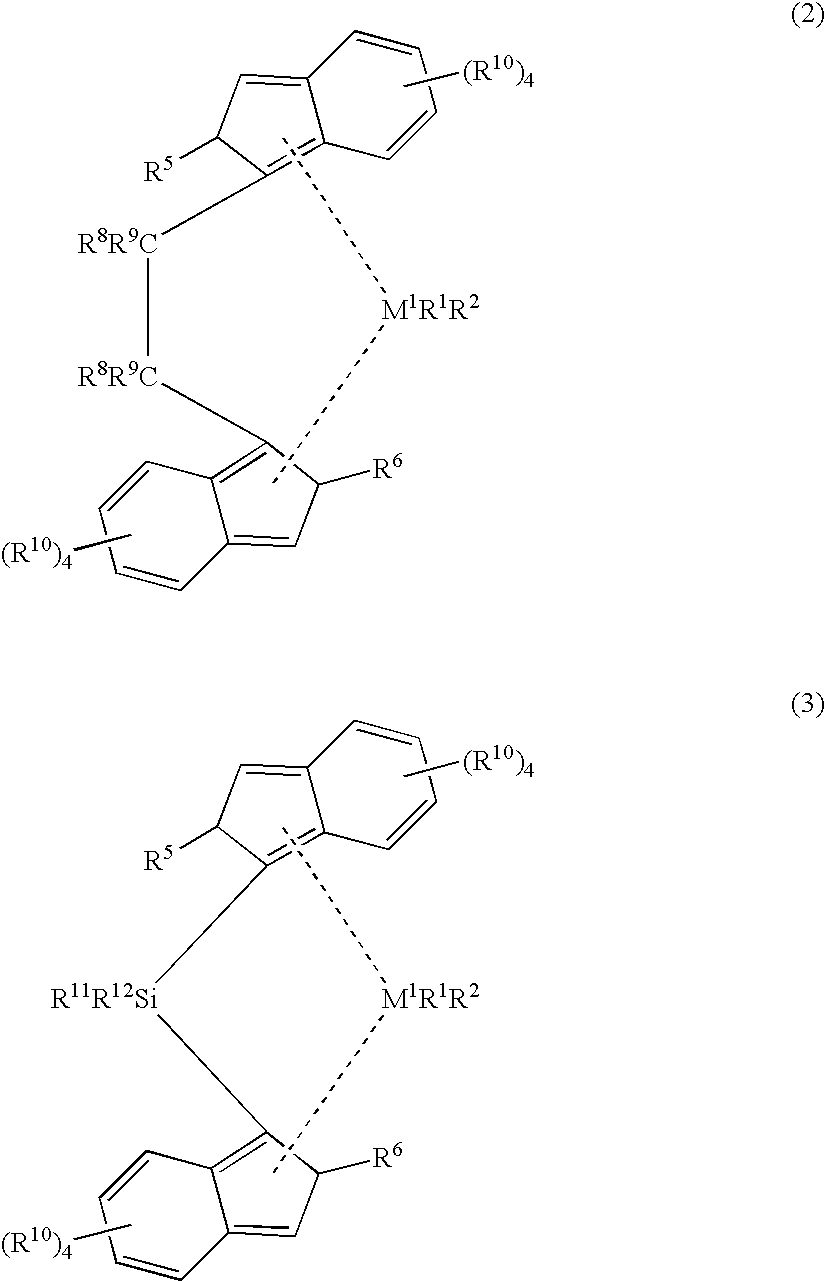
The present invention is a meltblown fiber and a fabric manufactured from the fiber comprising reactor grade polypropylene having a melt flow rate of from 100 to 5000 and having less than 50 stereo defects per 1000 units. Further, the polypropylene is typically produced from a metallocene catalyzed process, the metallocene being at least one bridged 2,4 di-substituted indenyl metallocene in one embodiment, and a bridged 4-phenyl indenyl metallocene in another embodiment. The metallocene is part of a system that can include a fluorided support and a non-coordinating anion activator.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Propylene Copolymers In Soft Thermoplastic Blends
ActiveUS20090270545A1Physical improvementImproved processing propertyPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsPolymer sciencePolyolefin
Thermoplastic polyolefins (TPOs) and / or thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPVs) are blended with low molecular weight propylene-dominated copolymers to provide polymeric compositions with an improved balance between processability and toughness. The compositions have improved processability by facilitating the ease with which a TPO or TPV, usually difficult to melt process, can be processed at high line speeds, which in turn improves the formation of the composition into articles.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Catalyst component for olefin polymerization and catalyst thereof
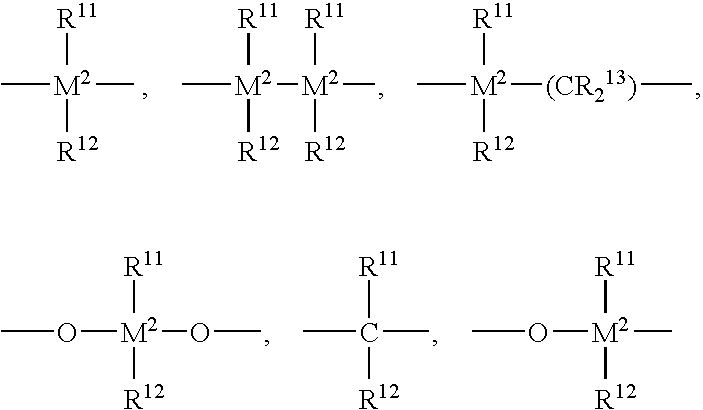
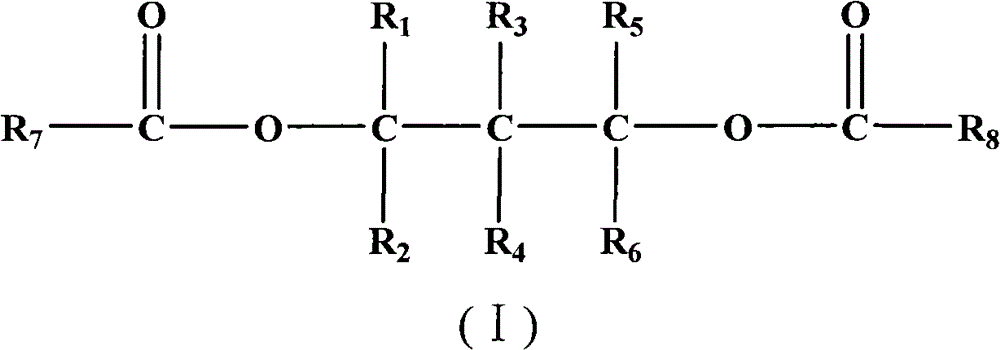
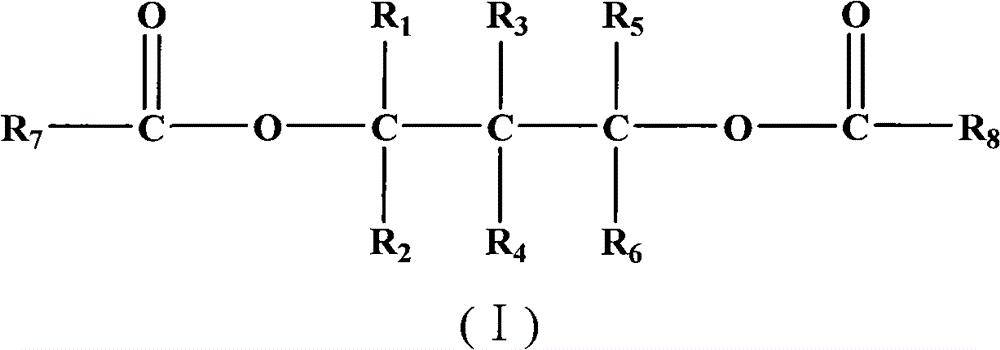
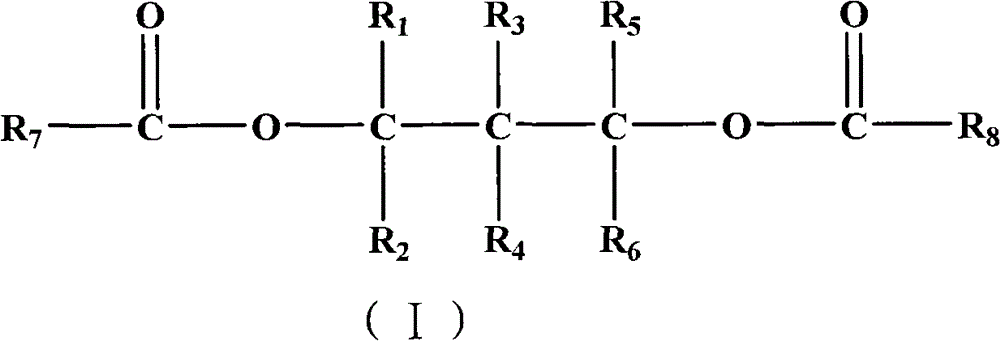
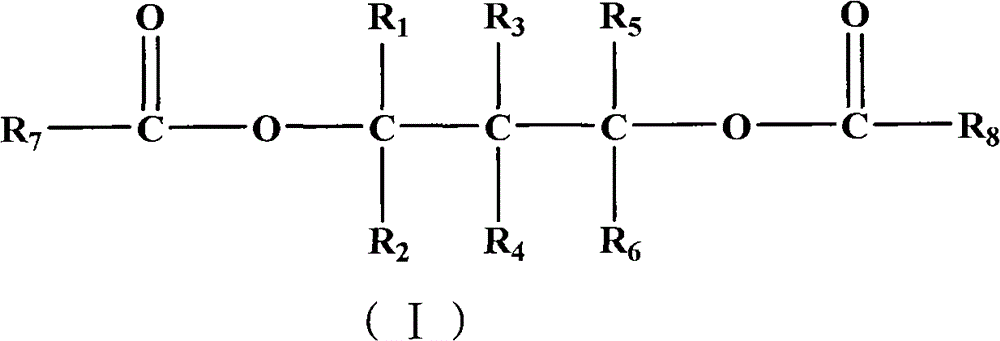
The invention provides a catalyst component for olefin polymerization. The catalyst component is prepared by: dispersing an alcohol adduct melt of magnesium halide in a dispersing agent system of white oil and silicone oil to form an emulsion, discharging the emulsion into a cooling liquid to perform cooling shaping, thus forming a magnesium halide alcohol adduct microsphere, washing and drying the magnesium halide alcohol adduct microsphere to form a spherical carrier; and then treating the spherical carrier through a titanium compound, raising the temperature gradually, adding an internal electron donor during treatment, and after treatment, carrying out washing with an inert solvent, and performing drying, thus obtaining the spherical catalyst component. Specifically, a phosphorus-containing compound is added during the steps, and the phosphorus content in the catalyst component is 0.2-3.0wt%. The internal electron donor compound contains at least one diol ester compound selected from the following general formula (I). When the catalyst is used for olefin polymerization, especially propylene polymerization, a polymer with a high isotactic index and a high melt flow rate can be obtained. Particularly under a high hydrogen concentration, a polymer with a high melt flow rate and a high isotactic index can be obtained.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
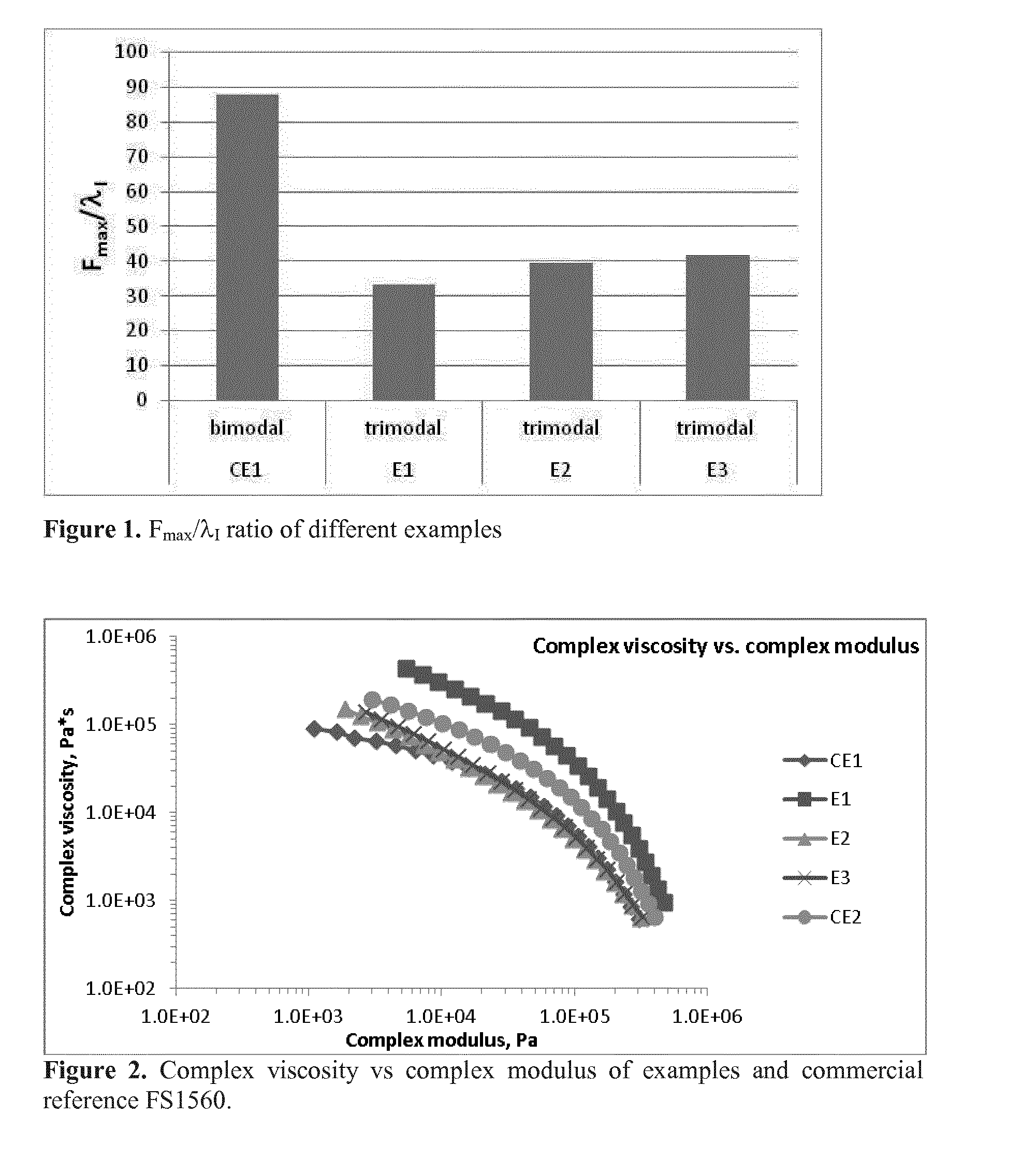
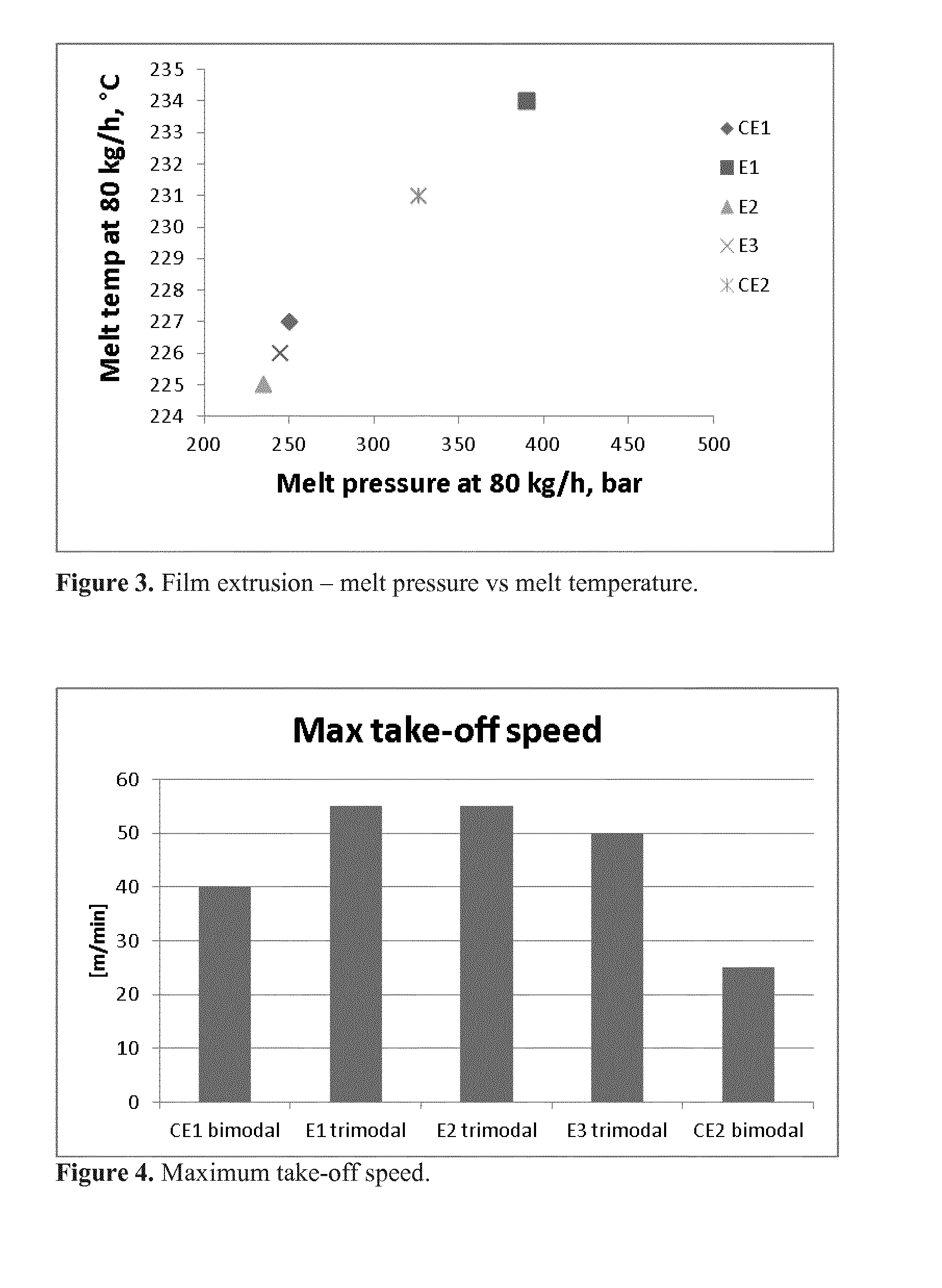
Multimodal polymer
A multimodal ethylene copolymer with a density of at least 940 kg / m3 having an MFR21 in the range of 1 to 30 g / 10 min and a Fmax / λ1 ratio of less than 60 cN / s; said ethylene copolymer comprising at least three components (I) an ethylene and optionally at least one C3-20 alpha olefin comonomer component forming 30 to 60 wt % of said ethylene copolymer; (II) an ethylene and optionally at least one C3-20 alpha olefin comonomer second component forming 30 to 60 wt % of said ethylene copolymer: and (III) an ethylene and optionally at least one C3-20 alpha olefin comonomer third component forming 3 to 20 wt % of said ethylene copolymer; wherein at least one of components (II) or (III) is a copolymer.
Owner:BOREALIS AG
Modified heterophasic polyolefin composition
A method of creating a modified heterophasic polyolefin composition is provided, whereby a polyolefin composition having at least two phases is melt mixed with a free radical generator, such as a peroxide, and a compatibilizing agent characterized by at least one nitroxide radical and at least one unsaturated bond capable of undergoing a radical addition reaction. Modified heterophasic polyolefin compositions with increased melt flow rates, impact strength, and clarity, which incorporate the compatibilizing agent, are also included within the scope of the invention.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Polyproylene bottles
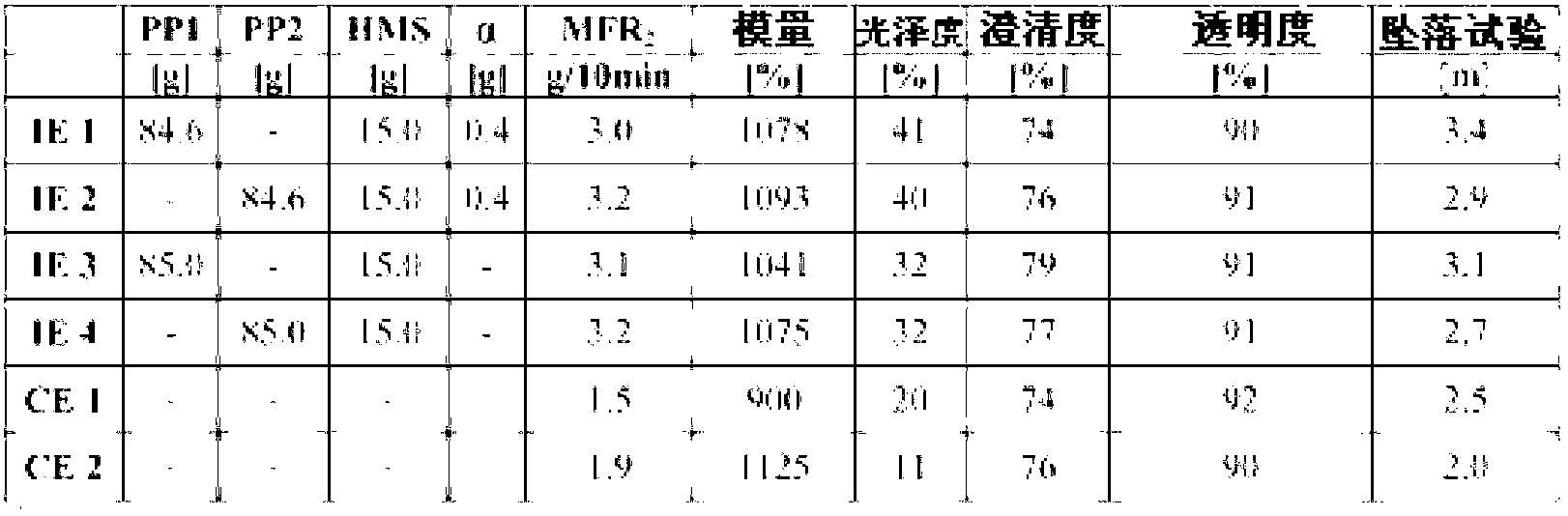
ActiveCN102869719AGood natureHigh glossDomestic articlesThin material handlingPolymer scienceFourier transform infrared spectroscopy
A polypropylene composition having a melt flow rate MFR2 (230 DEG C) measured according to according to ISO 1133 of at least 2.0 g / 10min, said polypropylene composition comprises a propylene copolymer (C-PP) and a high melt strength polypropylene (HMS-PP), wherein the propylene copolymer (C-PP) (a) has a comonomer content of equal or below 7.0 wt%, the comonmers are ethylene and / or at least one C4 to C12 alpha-olefin, and (b) fulfills the equation (I) R + 4.96 x C <= 95.66 wherein R is the randomness [%] measured by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and C is the comonomer content [wt%] measured by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR).
Owner:BOREALIS AG
High flow polyolefin composition with high stiffness and toughness
The present invention relates to a polyolefin composition comprising two heterophasic propylene copolymers which differ in the intrinsic viscosity of their xylene soluble fractions.
Owner:BOREALIS AG
Flame-proof ABS factory formula and its production method
InactiveCN1765985AImprove flame retardant performanceIncreased melt flow ratePolymer scienceDecabromobiphenyl ether
The invention relates to product formula and preparation method of a flame-proof ABS. Wherein, the formula comprises mainly: ABS resin, antimony trioxide, decabromodiphenyl oxide, coupling-treated aluminum hydroxide, anti-oxidant 168, tricresyl phosphate, chlorinated polyethylene (CPE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), EBS, magnesium stearate, SBS, nano-SiO2, and zinc borate. The preparation method comprises: mixing the ABS resin and tricresyl phosphate in high-speed mixer, adding other materials; putting into double screw extruder; cooling, granulating, screening, drying, and packaging. This product has well properties with low cost.
Owner:王崇高
High flow, hydrogenated styrene-butadiene-styrene block copolymer and applications
ActiveUS20130299731A1High strengthImprove toughnessFilm/foil adhesivesBuilding constructionsFiberGlass fiber
The invention relates to unique applications for the novel high melt flow, low viscosity, selectively hydrogenated styrene-butadiene-styrene (hSBS) or selectively hydrogenated controlled distribution styrene-butadiene / styrene-styrene (hSBSS) block copolymers, wherein the melt flow rate of said block copolymer is at least 100 g / 10 min. at 230° C. under 2.16 kg mass according to ASTM D1238. These block copolymers are novel and have the highest melt flow rate of any styrenic block copolymer also possessing high strength and elasticity. It has applications that prior to the present invention were not normally possible due to the normal low melt flow rate of styrenic block copolymers. The present invention also encompasses various fields of use such as a fiberglass hSBS or hSBSS reinforced mat, low viscosity hSBS or hSBSS coatings for industrial uses, hot melt adhesives prepared from hSBS or hSBSS blended with polyalpha-olefins, and elastic film, fiber, and nonwoven constructions using hSBS or hSBSS.
Owner:KRATON POLYMERS US LLC
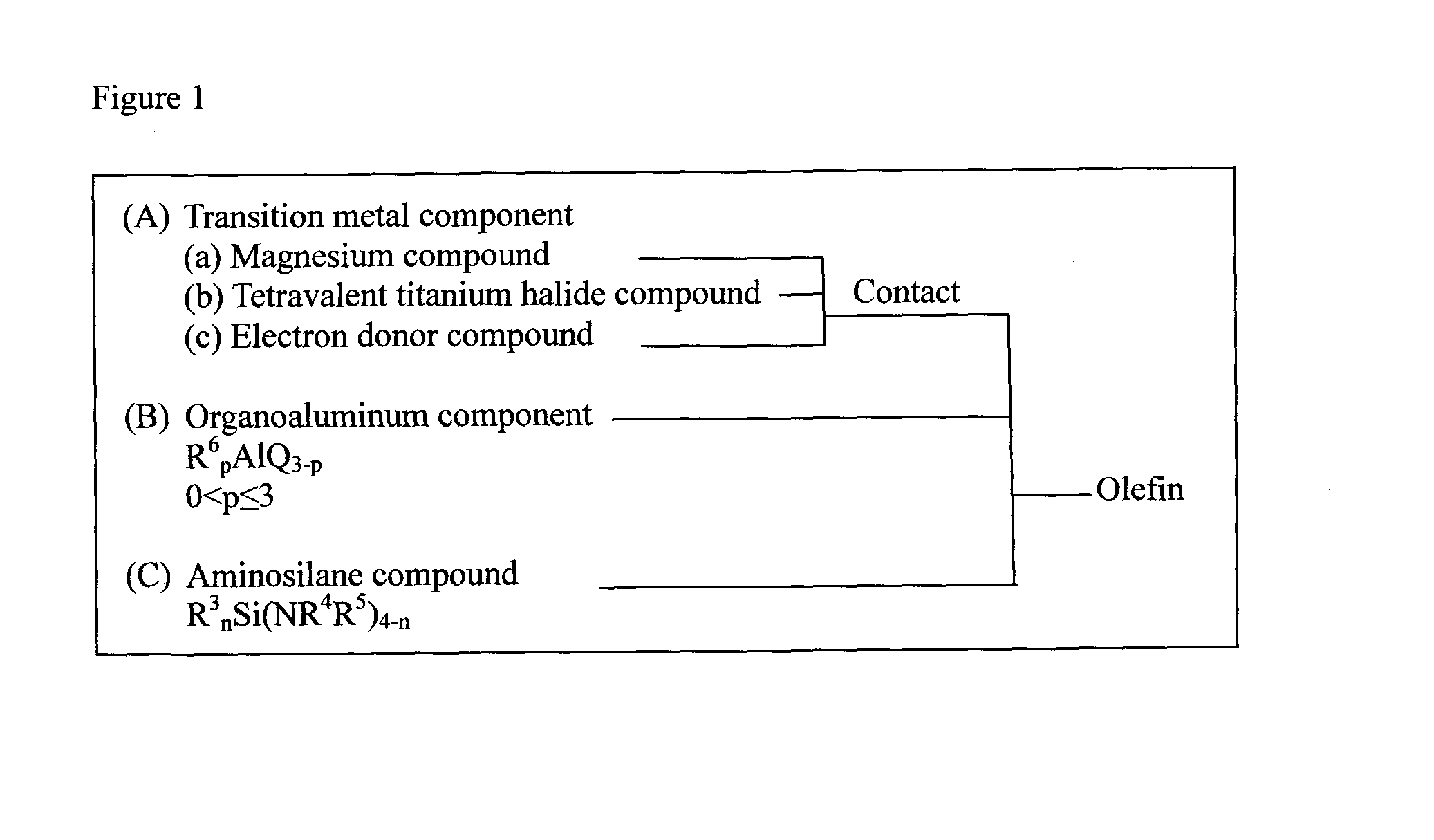
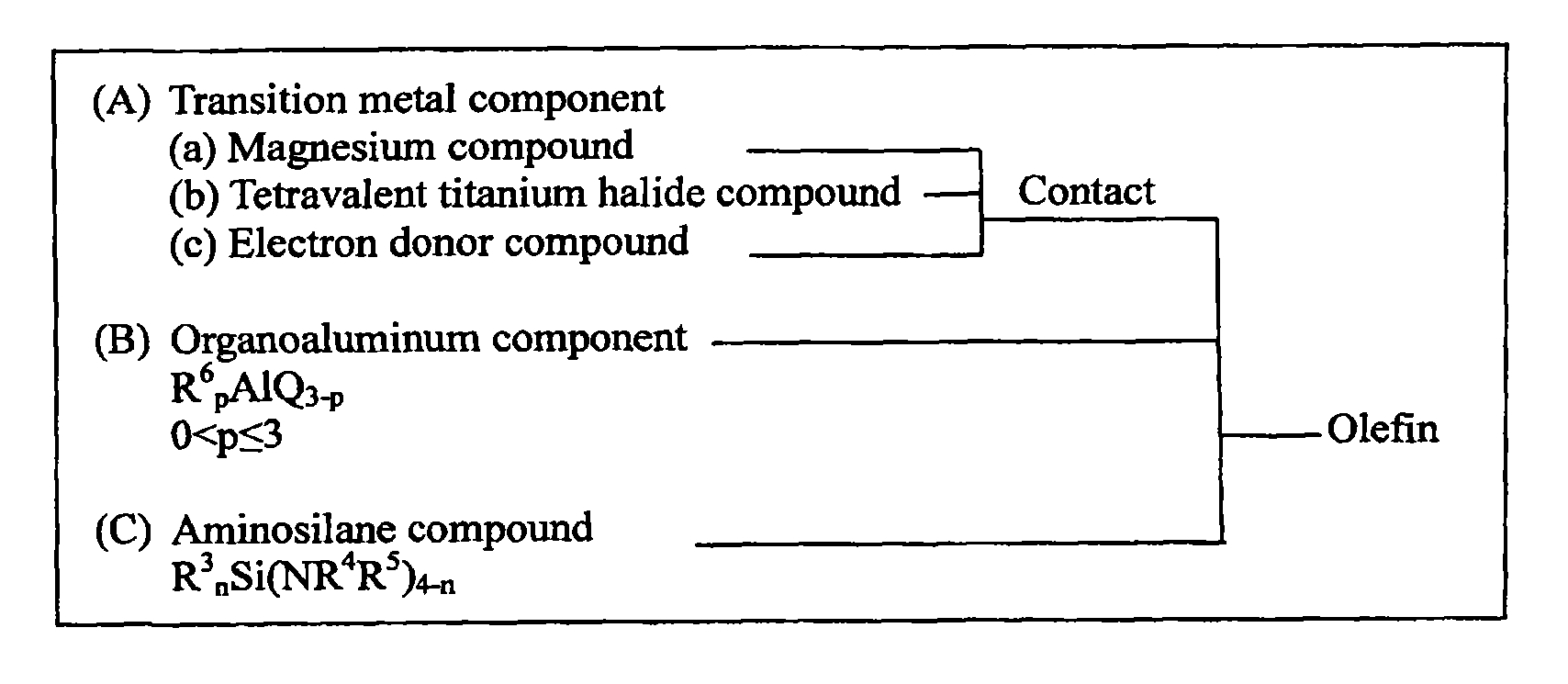
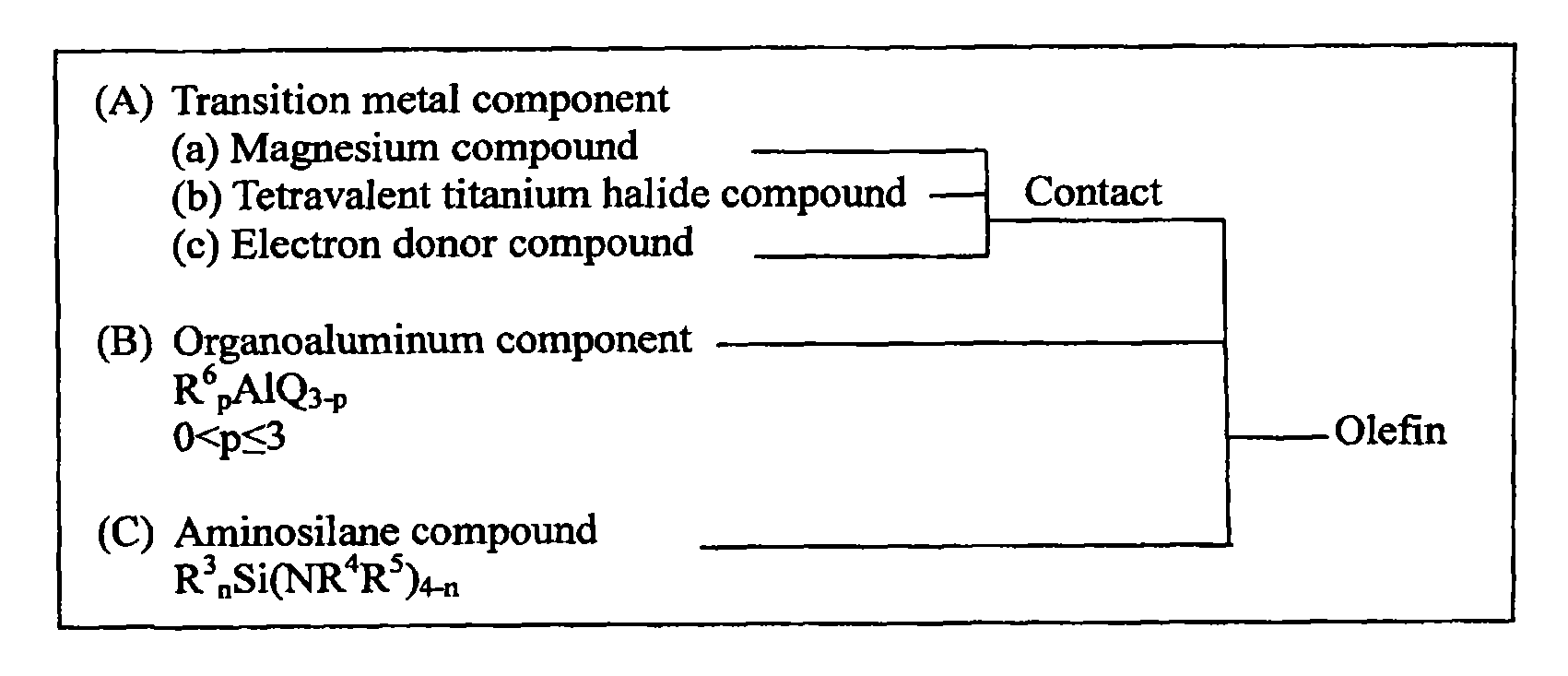
Aminosilane compounds, catalyst components and catalysts for olefin polymerization, and process for production of olefin polymers with the same
InactiveUS20100190942A1High stereoregularity and yieldLow costSilicon organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPolymer sciencePtru catalyst
A catalyst for polymerization of olefins formed from (A) a solid catalyst component containing magnesium, titanium, halogen, and an electron donor compound, (B) an organoaluminum compound shown by the formula, R6pAlQ3-p, and (C) an aminosilane compound shown by the formula, R3nSi(NR4R5)4-n; and a process for producing a catalyst for polymerization of olefins in the presence of the catalyst are provided. A novel aminosilane compound, a catalyst component for polymerization of olefins having a high catalytic activity, capable of producing polymers with high stereoregularity in a high yield, and exhibiting an excellent hydrogen response, a catalyst, and a process for producing olefin polymers using the catalyst are provided.
Owner:TOHO TITANIUM CO LTD
Thermoplastic olefin compositions
An in-reactor polymer blend including (a) a propylene-containing first polymer; and (b) propylene-containing second polymer having a different crystallinity from the first polymer. The polymer blend has a melting temperature, Tm, of at least 135° C., a melt flow rate of at least 70 dg / min, a tensile strength of at least 8 MPa, an elongation at break of at least 300%.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Optical fiber for single-mode operation
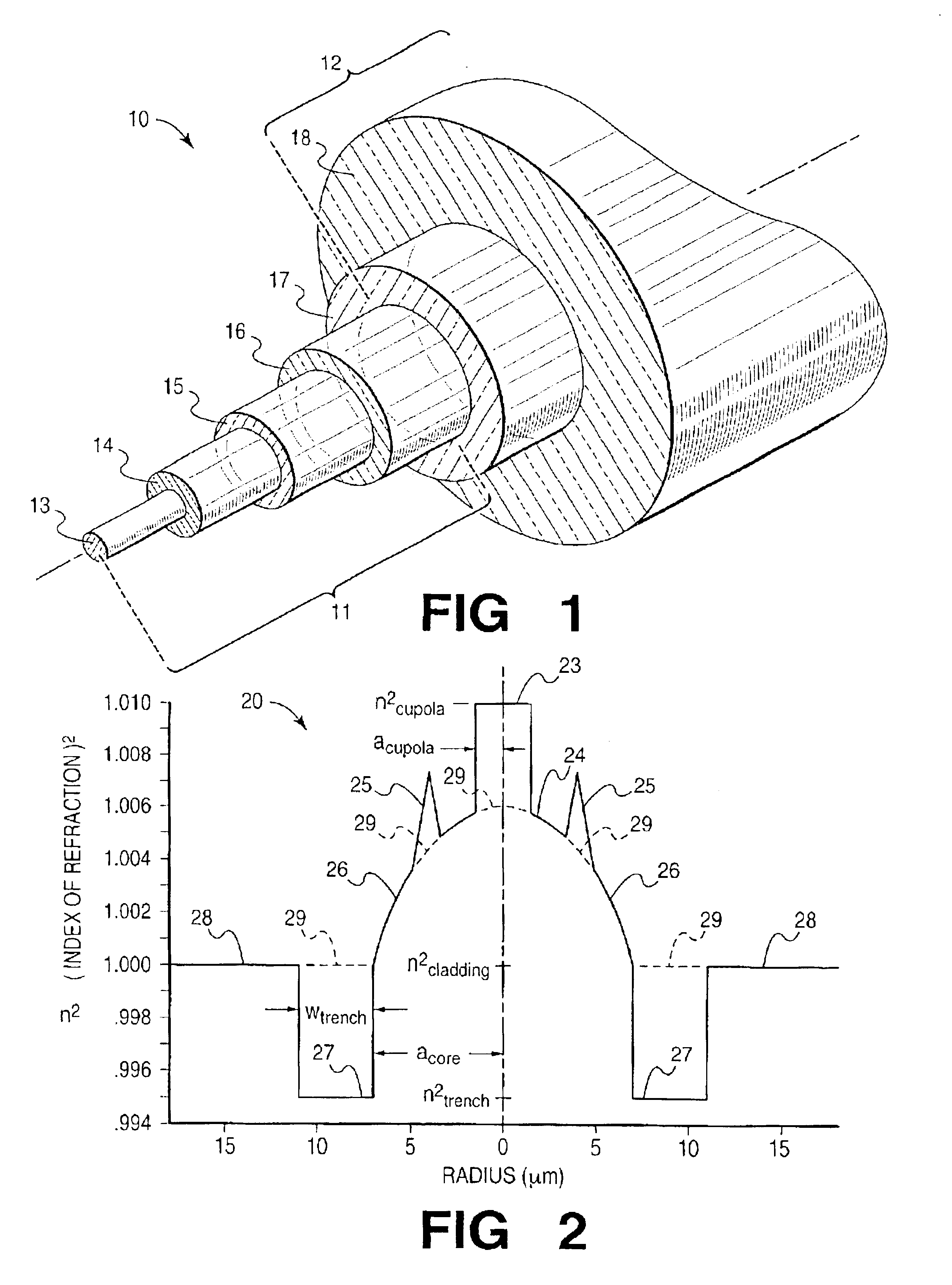
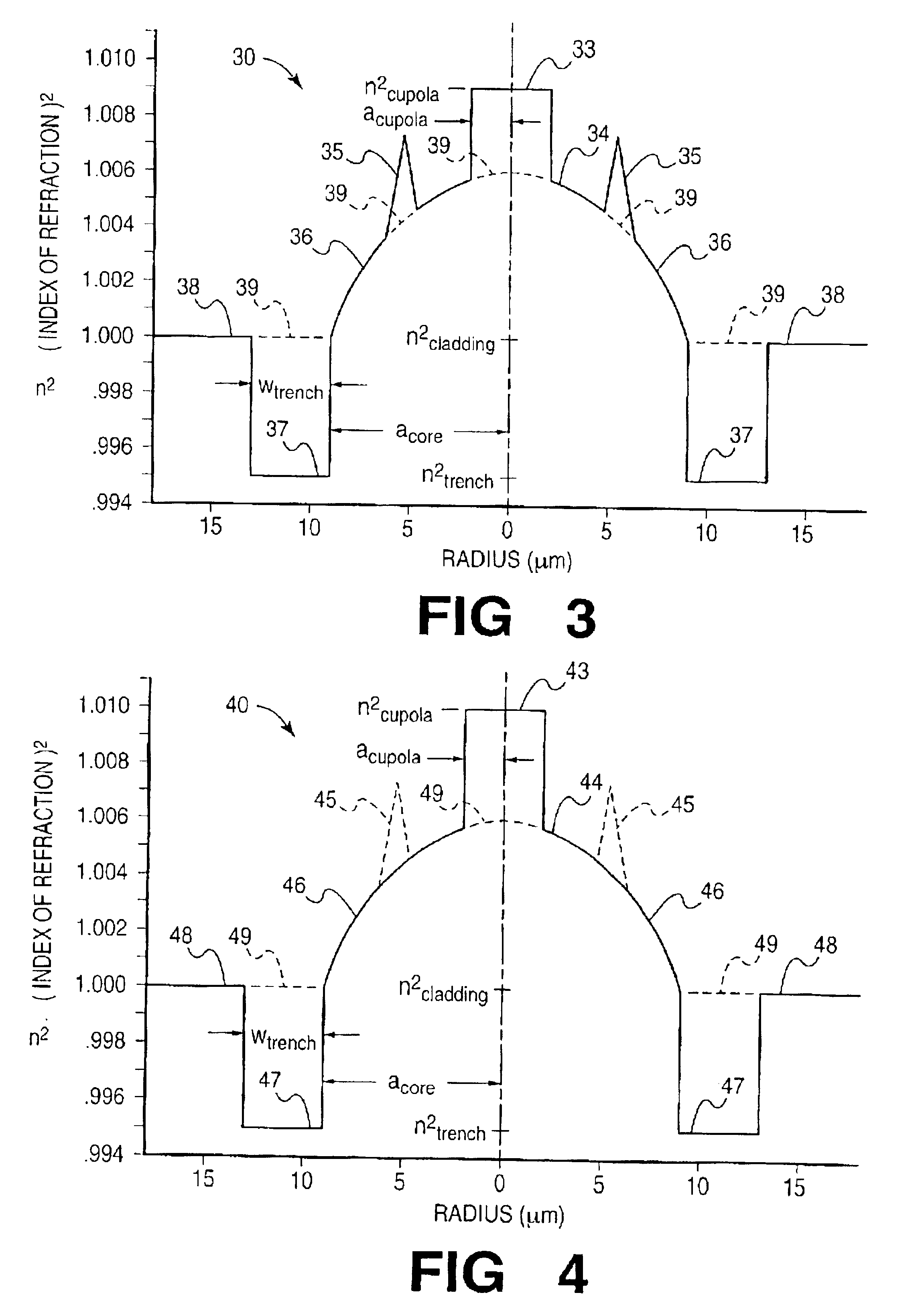
InactiveUS6839484B2Facilitate mode couplingReduce morbidityOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCouplingBasic mode
A single-mode fiber of increased core size consists of a “few-mode” fiber, of core size sufficient for guiding up to three high-order modes in addition to the fundamental mode, by interposing perturbations of such spacing along the fiber, as to selectively couple any such high-order modes to (unguided) cladding modes, thereby rejecting all but the fundamental mode. Unwanted coupling of the fundamental mode, leading to added fiber loss, is minimized by appropriate refractive index profile design.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Catalyst component for olefin polymerization and catalyst thereof
The invention provides a catalyst component for olefin polymerization. The catalyst component is prepared by: mixing a magnesium compound, an organic alcohol compound and an inert solvent, and adding an assistant precipitation agent to obtain an alcohol adduct; contacting the alcohol adduct with a titanium compound solution, then adding an internal electron donor compound and leaving them to react, conducting filtration to separate solid particles; adding the solid particles into the titanium compound solution, carrying out stirring and leaving them to react, and conducting filtration to separate solid particles; washing the solid particles by the inert solvent, and performing drying. Specifically, a phosphorus-containing compound is added during the steps. And the phosphorus content of the catalyst component is 0.2-3.0wt%. The internal electron donor compound contains at least one diol ester compound selected from the following general formula (I). When the catalyst is used for olefin polymerization, especially propylene polymerization, a polymer with a high isotactic index and a high melt flow rate can be obtained. Particularly under a high hydrogen concentration, a polymer with a high melt flow rate and a high isotactic index can be obtained.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Catalyst component and catalyst for olefin polymerization
ActiveCN103059171AStrong Stereotropic AbilityGood hydrogen sensitivityPhosphorous acidElectron donor
The invention provides a catalyst component for olefin polymerization. The catalyst component is prepared by: mixing a magnesium compound, an organic alcohol compound and an inert solvent, and adding an precipitation assistant to obtain an alcohol adduct; contacting the alcohol adduct with a titanium compound solution, then adding an internal electron donor compound and allowing them to react, conducting filtration to separate solid particles; adding the solid particles into the titanium compound solution, carrying out stirring and allowing them to react, and conducting filtration to separate solid particles; washing the solid particles by the inert solvent, and performing drying. Specifically, a phosphorus-containing compound, which can be alkyl ester or halogenated alkyl ester of orthophosphoric acid or phosphorous acid, an alkyl or aryl phosphine compound or a mixture thereof, is added during the steps. And the phosphorus content of the catalyst component is 0.2-3.0wt%. When the catalyst is used for olefin polymerization, especially propylene polymerization, a polymer with a high isotactic index and a high melt flow rate can be obtained.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Catalyst component for olefin polymerization, catalyst and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a catalyst component for olefin polymerization. The catalyst component contains the reaction product of a magnesium compound, a titanium compound, a phosphorus-containing compound and a phosphorus-free internal electron donor compound. The phosphorus-containing compound is added in a step except the step of magnesium compound dissolution, and the catalyst component has a phosphorus content of 0.4-3.0wt%. The involved catalyst has strong stereospecificity and good hydrogen regulation sensitivity. When the catalyst is used for olefin polymerization, especially propylene polymerization, a product with a high isotactic index, a high melt flow rate and a low dimethylbenzene soluble substance content can be obtained simultaneously. Especially when the catalyst is used for propylene polymerization under a high hydrogen concentration condition, the obtained polymer can have a high melt flow rate, a high isotactic index and a low dimethylbenzene soluble substance content, and at the same time, the polymer has a relatively narrow molecular weight distribution.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Water Pump Impeller
InactiveUS20080199319A1Enhance resistanceLow crack susceptibilityPropellersRotary propellersImpellerEngineering
Owner:SCHAEFFLER KG
Method for polymerizing polypropylene
The present disclosure relates to a method for polymerizing polypropylene, optionally with one or more additional comonomers in a gas phase reactor in the presence of a mixed electron donor system comprising at least one selectivity control agent and at least one activity limiting agent. The process involves controlling the polymerization process to ensure that the difference between the reactor temperature and the dew point temperature of the incoming monomer stream is 12° C. or greater.
Owner:WR GRACE & CO CONN
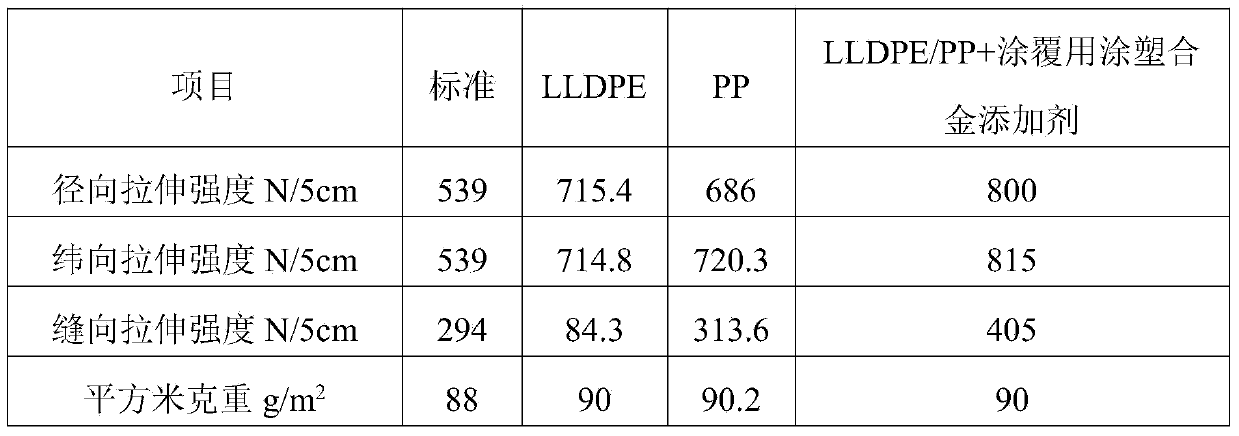
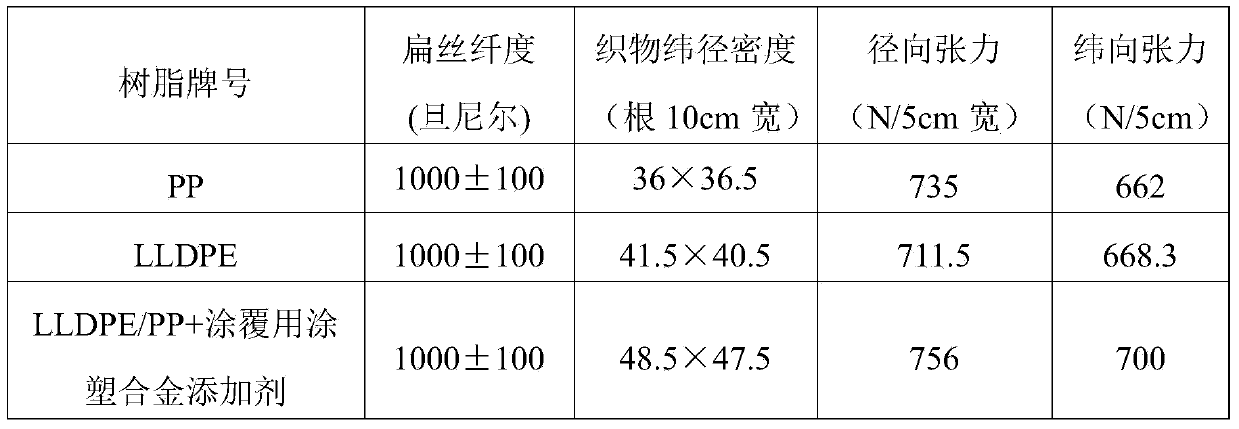
Preparation method of plastic woven bag
The invention relates to a preparation method of a plastic woven bag. The invention aims at solving the problems of poor bursting strength, poor tearing strength and poor tensile strength of an existing plastic woven bag taking a polypropylene material as a base fabric. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing a mixture from a coating plastic coated alloy additive, an LLDPE (linear low density polyethylene) resin, a PP (propene polymer) resin antioxidant and an ultraviolet light absorber; 2, extruding the mixture by using an extruder and cooling and forming to obtain a coating woven fabric used for producing the woven bag; 3, putting the coating woven fabric used for producing the woven bag into a screw extruder and extruding to obtain ribbon-like filaments of the coating fiber of the woven bag; 4, using a cylinder loom to woven the ribbon-like filaments of the coating fiber of the woven bag through a flat die method, and sequentially cutting, tailoring and sewing to obtain the plastic woven bag. The preparation method of the plastic woven bag is mainly used to prepare the plastic woven bag.
Owner:哈尔滨盛洋塑胶材料有限公司
Polypropylene impact copolymer compositions
The present invention relates to an impact-resistant olefin polymer composition including a polypropylene matrix having a weight average molecular weight and an ethylene-containing polymer including an ethylene-propylene copolymer having a molecular weight higher than the weight average molecular weight of the polypropylene matrix, the composition containing about 20 to 35 percent xylene solubles, and the xylene solubles fraction of the composition containing less than about 39 weight percent ethylene units, based on the combined weight of olefin monomers in the copolymer. The present invention further relates to impact copolymer compositions with a melt flow rate greater than about 8 that meet or exceed all pallet testing requirements. The compositions have superior stiffness-impact balance performance and excellent gloss and are useful for a number of applications including, but not limited to pallets, water-storm chambers, automotive compounding, septic tanks, bins, pales, crates, totes and plastic containers.
Owner:BRASKEM AMERICA
Aminosilane compounds, catalyst components and catalysts for olefin polymerization, and process for production of olefin polymers with the same
ActiveUS8648001B2High stereoregularity and yieldLow costGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPolymer sciencePtru catalyst
A catalyst for polymerization of olefins formed from (A) a solid catalyst component containing magnesium, titanium, halogen, and an electron donor compound, (B) an organoaluminum compound shown by the formula, R6pAlQ3-p, and (C) an aminosilane compound shown by the formula, R3nSi(NR4R5)4-n; and a process for producing a catalyst for polymerization of olefins in the presence of the catalyst are provided. A novel aminosilane compound, a catalyst component for polymerization of olefins having a high catalytic activity, capable of producing polymers with high stereoregularity in a high yield, and exhibiting an excellent hydrogen response, a catalyst, and a process for producing olefin polymers using the catalyst are provided.
Owner:TOHO TITANIUM CO LTD
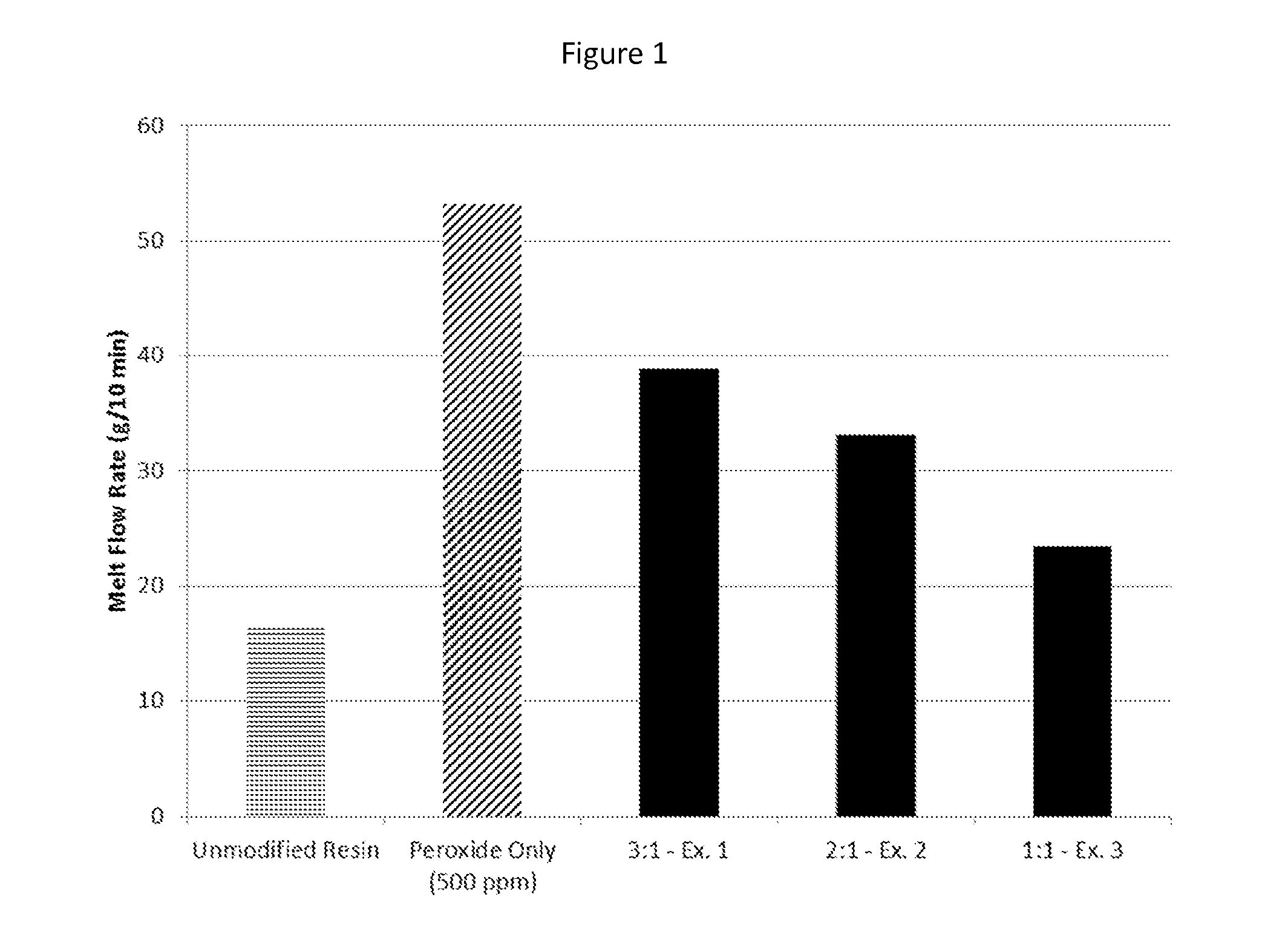
Method for improved melt flow rate fo filled polymeric resin
InactiveUS20060020056A1Increased melt flow rateImprove fusionPigment pastesPolymer resinPolymer chemistry
Fillers used in polymer applications are surface modified with an amine prior to compounding with a polymeric resin thus improving the melt flow rate and fusion times of the polymeric resin composition when compounded.
Owner:SPECIALITY MINERALS (MICHIGAN) INC
Glass fibre reinforced polyetherimide composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a glass fibre reinforced polyetherimide composite material and a preparation method thereof. The glass fibre reinforced polyetherimide composite material is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 27.4 to 93.8 parts of polyetherimide, 1 to 20 parts of thermotropic liquid crystal polymer, 5 to 50 parts of glass fibre, 0.05 to 0.6 part of antioxidant and 0.1 to 2 parts of lubricant. Compared with the prior art, the viscosity of a melt can be effectively lowered when the composite material is processed because the thermotropic liquid crystal polymer has very strong rheological property of shear thinning in the melt extrusion process of the thermotropic liquid crystal polymer and the polyetherimide, and the flow rate of the melt is enhanced so as to improve the processing performance of the material. In addition, the thermotropic liquid crystal polymer can form a microfibrillar structure in a polyetherimide matrix, and the strength of the composite material is enhanced. The production and preparation process of the composite material is simple and can be executed on a conventional melt extrusion machine without special equipment, and the operation process is simple and easy.
Owner:SHENZHEN KEJU NEW MATERIAL
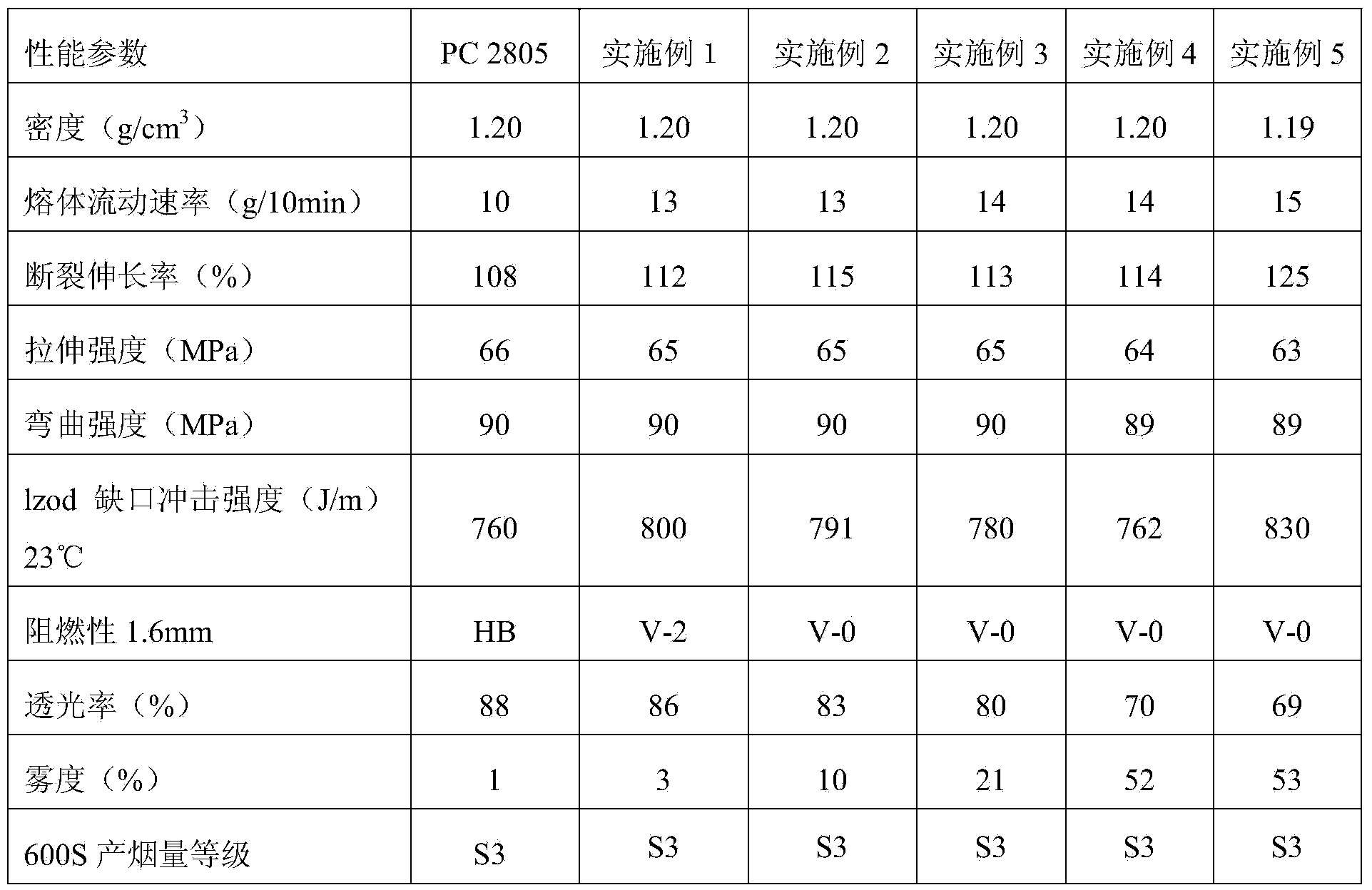
Transparent halogen-free low smoke antiflaming polycarbonate composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a transparent halogen-free low smoke antiflaming polycarbonate composite material and a preparation method thereof. The polycarbonate composite material comprises the following components in parts by weight: 900-980 parts of polycarbonate resin, 5-50 parts of polysiloxane fire retardant, 1-10 parts of sulfonate fire retardant, and 5-50 parts of additive. The preparation method comprises the following steps of mixing the polycarbonate resin, polysiloxane fire retardant, sulfonate fire retardant and additive in a highly mixing machine, then pelletizing through twin screw extrusion, drying and injection molding so as to obtain the transparent halogen-free low smoke antiflaming polycarbonate composite material. On one hand, the hazard that bromine antiflaming polycarbonate material generates carcinogen such as 4-bromo-dibenzdioxan and 4-bromo-dibenzofuran is avoided; on the other hand, the transparent halogen-free low smoke antiflaming polycarbonate composite material has excellent antiflaming performance, reaches the US standard of UL94V-0, also has high grade of transparency and excellent mechanical property, thermal property, low temperature performance and low smoke performance, and remarkably improves the processibility of the material.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGWEI JINCI ENG PLASTIC
Non-phthalate compounds as electron donors for polyolefin catalysts
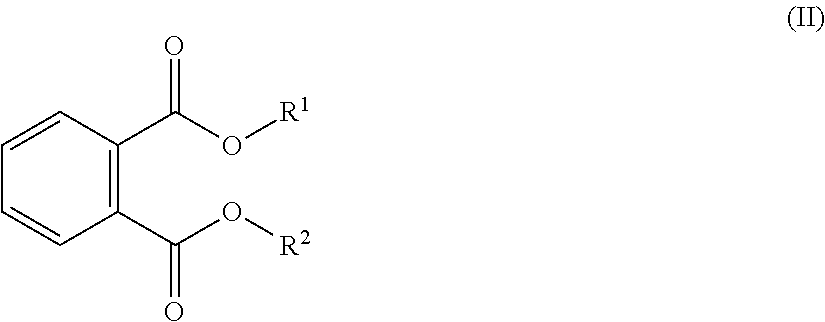
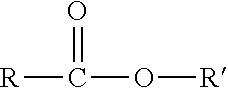
ActiveUS20140275456A1Improve responseIncreased melt flow rateOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationChemistryPolyolefin
Non-phthalate compounds having a structure represented by the general formulaand a method for using same are provided as electron donors in the Ziegler-Natta type catalyst system for the homopolymerization or copolymerization of alpha olefins. The non-phthalate compounds may be used in the preparation of the solid catalyst component, thus serving as “internal electron donors”, or employed during or prior to polymerization as “external electron donors,” and therefore they can be used to prepare phthalate-free polyolefins.
Owner:FORMOSA PLASTICS USA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com