Patents
Literature
66 results about "Deoxidized steel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Deoxidized steel is steel that has some or all of the oxygen removed from the melt during the steelmaking process. Liquid steels contain dissolved oxygen after their conversion from molten iron, but the solubility of oxygen in steel decreases with cooling. As steel cools, excess oxygen can cause blowholes or precipitate FeO. Therefore, several strategies have been developed for deoxidation. This may be accomplished by adding metallic deoxidizing agents to the melt either before or after it is tapped, or by vacuum treatment, in which carbon dissolved in the steel is the deoxidizer.
Vacuum treatment method of molten steel dephosphorus
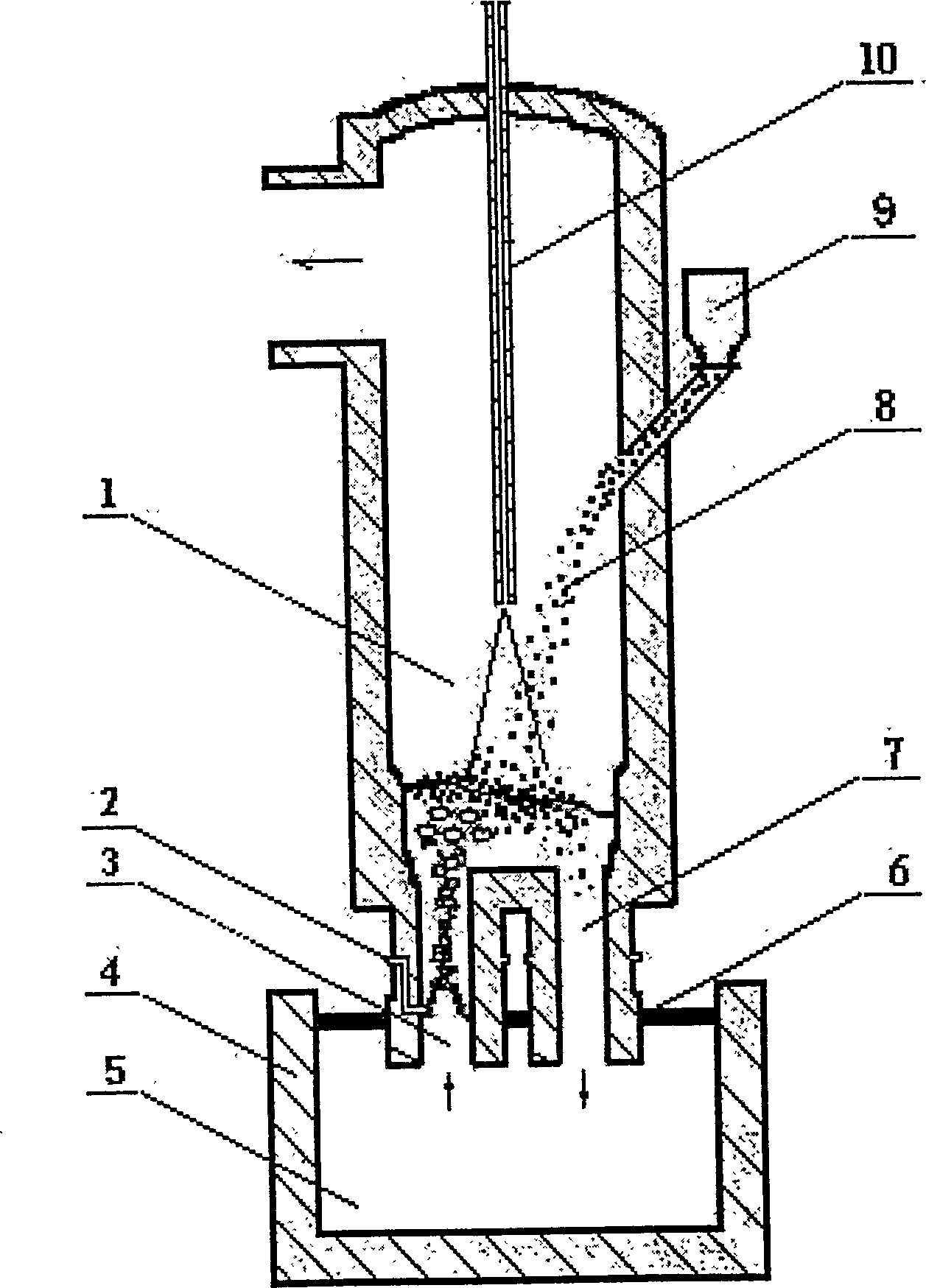
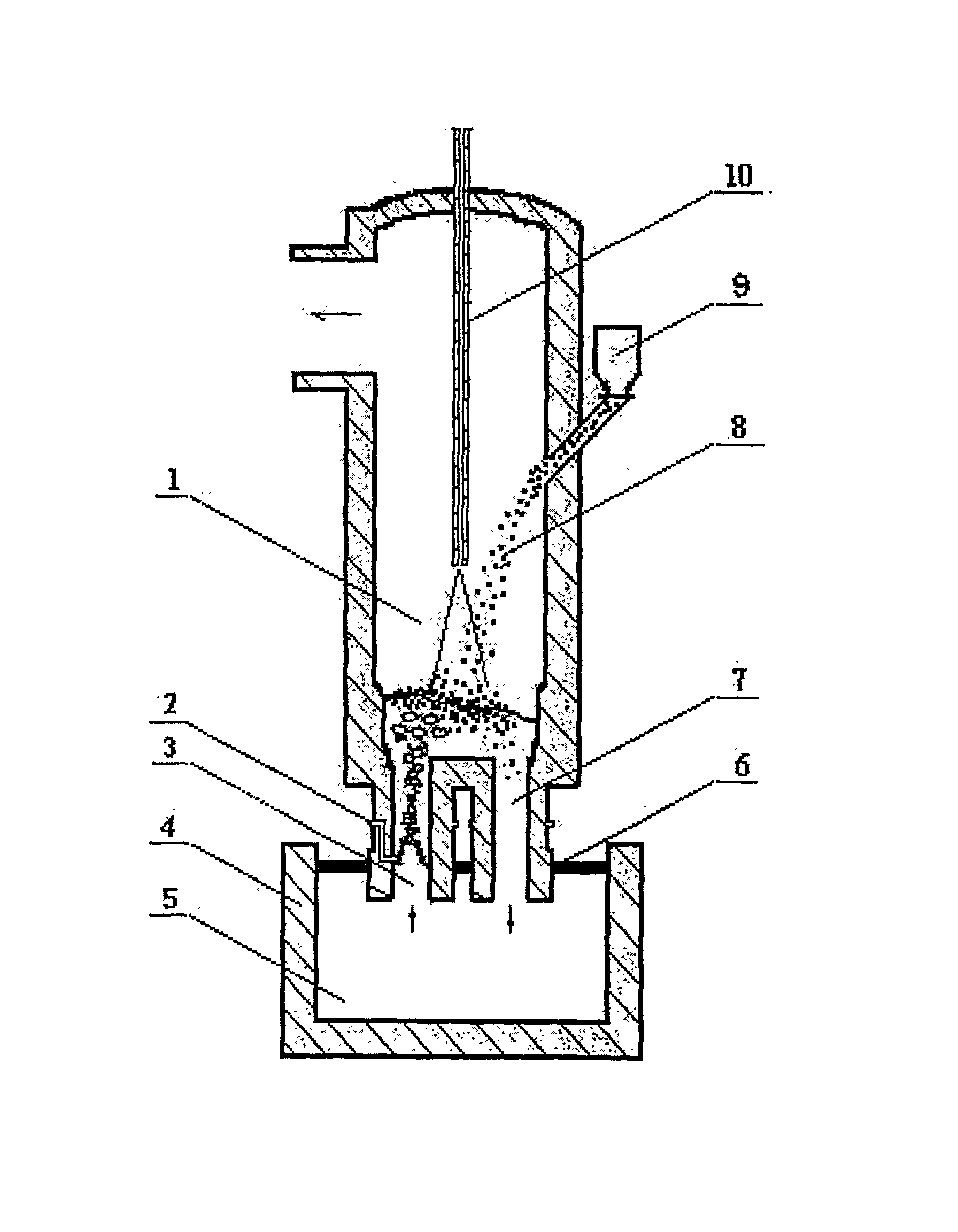
A vacuum treatment method for dephosphorizing molten steel to produce low-phosphorus (or ultralow-phosphorus) weakly-deoxidized steel or other steel features that in the vacuum carbon-oxygen reactionphase, the oxygen or iron oxide needed by dephosphorizing reaction is added to the molten steel pool in a vacuum chamber while the lime blocks or powder is added for quickly dephosphorizing, and thismethod can also prevent rephosphorization from the steel ladle slag.
Owner:武钢集团有限公司
White slag refining agent for LF (Ladle Furnace) refining furnace and preparation method thereof
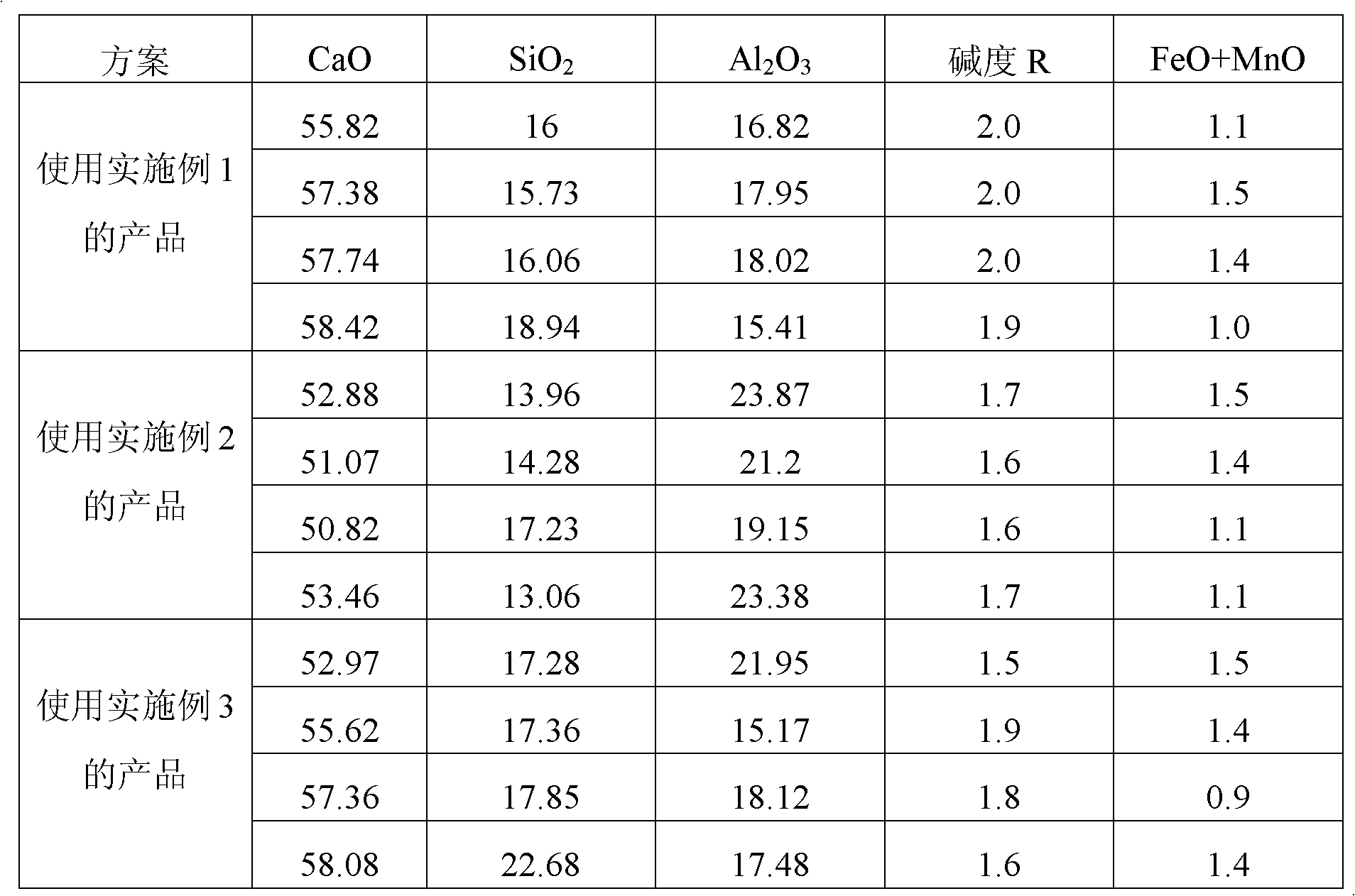
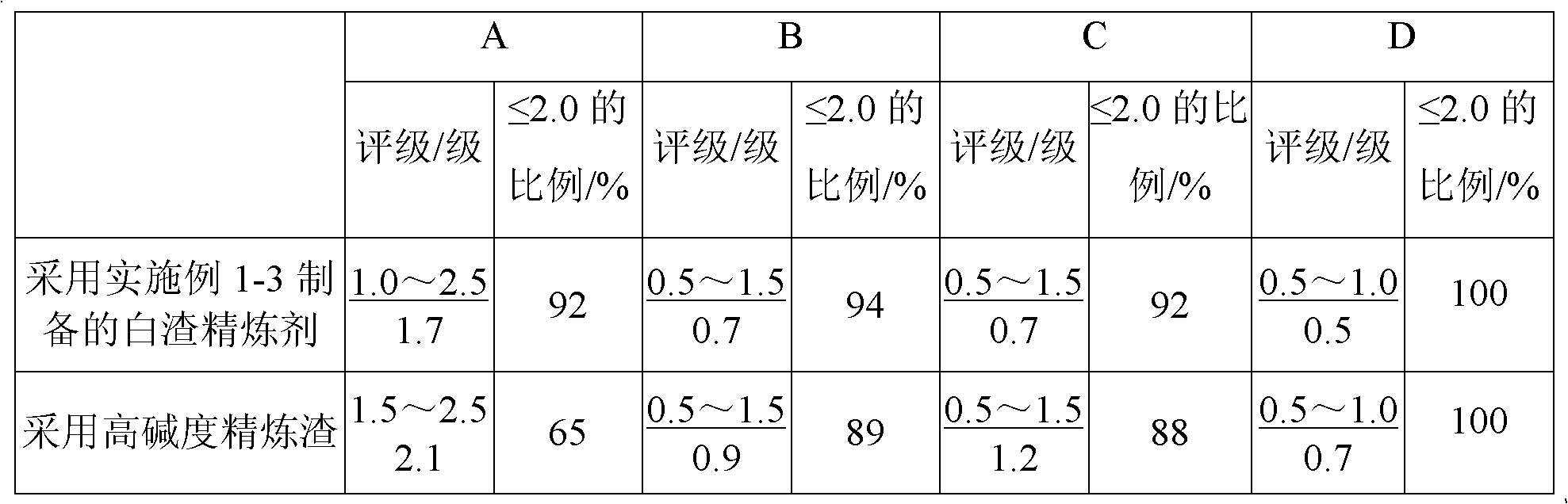
The invention relates to a white slag refining agent for an LF (Ladle Furnace) refining furnace, belonging to the technical field of steel making, in particular to the technical field of ladle slag modification treatment of the LF refining furnace. The invention aims to provide the white slag refining agent which has the advantages of low cost and strong inclusion adsorption capacity. The white slag refining agent for the LF refining furnace is characterized by comprising the following components in percentage by weight: 40-50 percent of calcium carbide, 8-14 percent of fluorite, 24-30 percent of limestone, 4-6 percent of bauxite and 4-12 percent of dolomite. The white slag refining agent has the advantages of low cost and wider application range and is suitable for a non Al deoxidized steel (a kind of steel, strictly controlling the aluminum content), for example. After being added into the LF refining furnace, the white slag refining agent can fulfill the functions of rapid deoxidation and white slag production and can enable the content of FeO and MnO in ladle slag to be no more than 1.5 percent to satisfy the smelting needs of high-grade steels.
Owner:PANZHIHUA GANGCHENG GROUP
High basicity fluorine-free RH (Ruhrstah-Heraeus) desulfurizer
The invention discloses a high basicity fluorine-free RH (Ruhrstah-Heraeus) desulfurizer, belonging to the technical field of steelmaking. The high basicity fluorine-free RH desulfurizer is characterized in that with a CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 slag system as a basic slag system, BaO is added to lower a melting point of the desulfurizer and enhance the optical basicity of the desulfurizer to reach 0.83; B2O3 is added to lower the melting point of the desulfurizer and enhance the melting speed of the desulfurizer, and therefore, under the flurorine-free condition, the desulfurizer can be rapidly molten without lowering the optical basicity of the RH desulfurizer; and fluoride which seriously influence the environment and seriously erodes equipment is not contained in a formula, thereby the corrosivity of the desulfurizer is reduced and the service life of the RH equipment is prolonged without the addition of the fluoride. Accordingly, the contradiction among high optical basicity, low melting point and rapid melting speed of the RH desulfurizer under the fluorine-free condition is solved and the efficiency of RH refinement to feeble deoxidized steel desulfurization treatment is enhanced.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Ti-Zr composite deoxidized steel used for ultrahigh-strength hull structure, and production process thereof
ActiveCN102199740AImprove performanceGood cold bending performanceHull structureChemical composition
The invention discloses Ti-Zr composite deoxidized steel used for an ultrahigh-strength hull structure, and a production process thereof. The Ti-Zr composite deoxidized steel comprises the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.05-0.14% of C, 0.10-0.35% of Si, 1.0-1.6% of Mn, 0.02-0.05% of Nb, 0.007-0.02% of Ti, 0.002-0.010% of Zr, 0.001-0.020% of Als, 0.15-0.5% of Mo, 0.2-0.6% of Cr, 0.2-0.8% of Ni, 0.2-0.8% of Cu and the balance of Fe and trace impurities. The production process provided by the invention comprises the following processes of smelting, heating, rough rolling, finish rolling, ACC (accelerated controlled cooling), quenching and tempering, and the obtained ultrahigh-strength ship plate has excellent comprehensive mechanical performance.
Owner:NANJING IRON & STEEL CO LTD +1
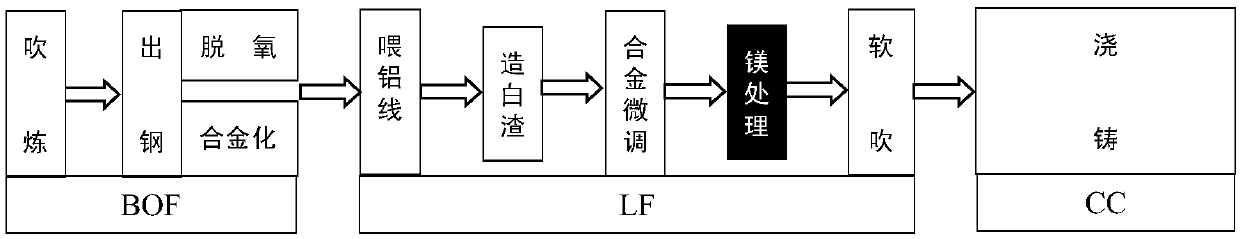
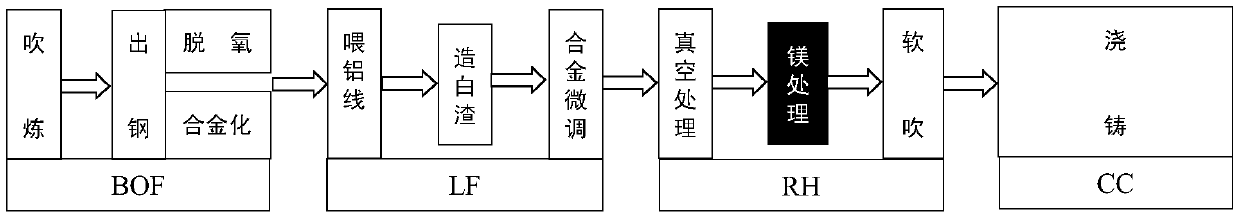
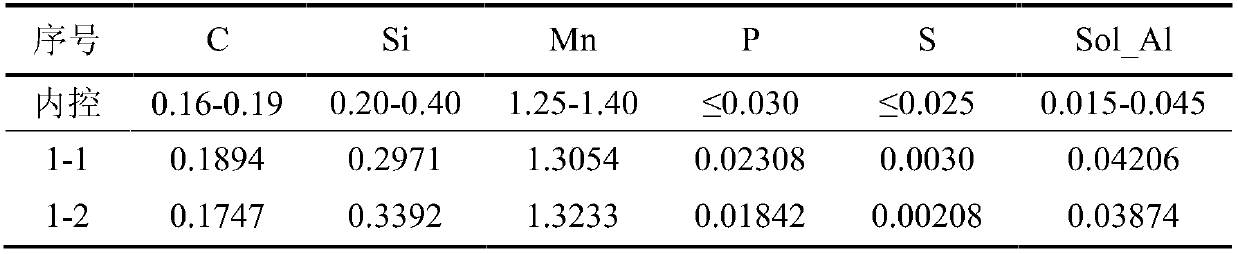
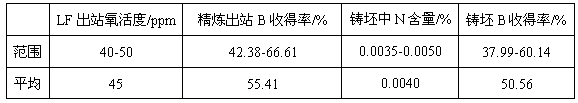
A kind of liquid magnesium treatment process for ship plate steel
A liquid magnesium treatment process for ship plate steel, which belongs to the field of clean steel smelting; the process is as follows: first, determine the station and timing of magnesium treatment: add Mg‑Al‑ after alloy fine-tuning in the LF process or after vacuum treatment in the RH process Fe alloy cored wire; secondly, according to the acid-soluble aluminum content of the steel type, on the premise of ensuring the magnesium treatment effect of Mg‑Al‑Fe alloy cored wire, coordinate the allocation of aluminum feeding amount and magnesium treatment wire feeding amount; then, carry out magnesium treatment Processing: In the LF or RH process, the cored wire feeding method is used to add Mg‑Al‑Fe alloy cored wire to the molten ship plate steel, and finally the finished molten steel is obtained. The ship plate rate deoxidized steel liquid magnesium treatment process of the present invention is used in the refining process of ship plate steel, and can control the cleanliness of the ship plate steel and the composition, quantity, particle size and distribution of inclusions in the steel; the method of the invention can improve the ship plate steel The cleanliness of plate steel and the control level of non-metallic inclusions can improve the mechanical properties and stability of ship plate steel.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
Smelting method for producing high-manganese steel used in low-temperature environment by means of LF refining furnace
The invention discloses a smelting method for producing high-manganese steel used in a low-temperature environment by mean of an LF refining furnace. The smelting method comprises the steps of stationary ladle argon blowing, molten steel deoxygenation, molten steel desulfurization, refining and slagging, alloy adding and fine adjustment of composition temperature. According to the smelting method,the technical problems such as high steelmaking production difficulty due to high manganese alloy content and low oxygen and sulfur content of the high-manganese steel used in the low-temperature environment are solved, a practical solution is provided for the LF refining production in large-scale production of the high-manganese steel used in the low-temperature environment, and the smelting method can be widely used in steelmaking production of the high-manganese steel. According to the high-manganese steel molten steel produced through the smelting method, the content of Mn is larger thanor equal to 22.5%, the content of O is less than or equal to 0.0030%, the content of S is less than or equal to 0.003%, the manganese alloy yield is larger than or equal to 96%, and the smelting method meets the technical requirements of high manganese alloy content, high yield and low oxygen sulfur impurity content.
Owner:HEBEI IRON AND STEEL
Boron-containing steel production method for reducing steel ladle lining refractory consumption
The invention relates to a boron-containing steel production method for reducing steel ladle lining refractory consumption, and belongs to the technical field of steel production. The technical scheme of the process flow comprises converter blowing, LF refining, ferroboron alloying and molding protection; each process is controlled as follows: converter blowing adopts hot metal containing 0.15-0.20% of Ti, steel tapping adopts Si-Al-Ba and Al-Mn-Ti-Mg to deoxidize, the whole operation process of steel ladle is protected by a protective cover, refined submerged arc slag is added into an LF Furnace adopting micro positive pressure operation, alloyed ferroboron is added before performing soft blowing, and crystallizer casting powder containing 5-10 % of TiO2 and 4-8% of B2O3 is adopted in the process of molten steel molding. By adopting the method, the yield of boron is improved and stabilized, and the magnesia steel ladle lining consumption rate is effectively reduced, so that the comprehensive smelting cost is reduced, and the service life of the steel ladle refractory material is prolonged by 8-12 times per bag; the lining erosion degree is reduced to form a reasonable bag throwing and injecting system, and the number of on-line baking steel ladles is reduced, so that the cost of gas consumption of 1 ton of steel is reduced by 13.3-17.8 Yuan; the yield of casting blank boron is improved by 8-10%; comprehensive benefit of 315.05 million each year is achieved.
Owner:HEBEI IRON AND STEEL
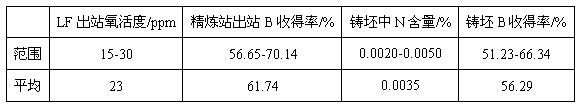
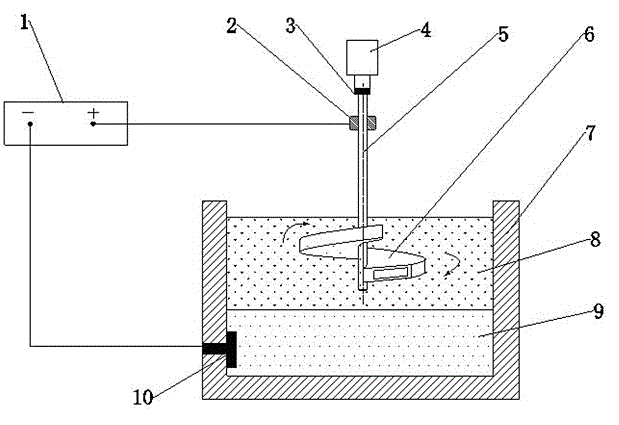
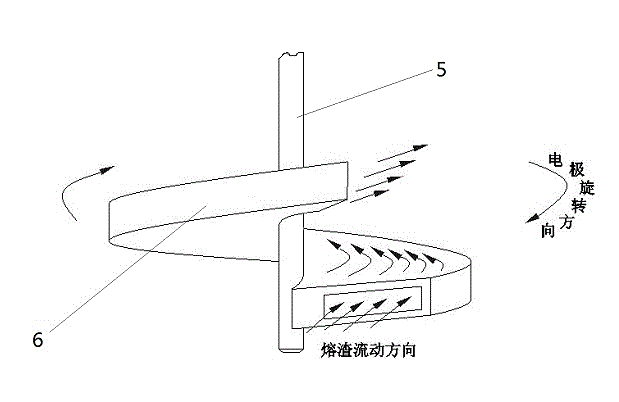
Rotating electrode device for external electric field deoxidation of metal and slag
InactiveCN103333992AIncrease contact areaIncreased deoxygenation reactionDeoxidized steelElectrode pair
The invention discloses a rotating electrode device for external electric field deoxidation of metal and slag. The device includes an anode electrode, a cathode electrode, a DC power supply and a metal wire. One end of the anode electrode is immersed in molten slag above a steel liquid to be deoxidized and filled in the furnace body; a stirring head and a rotating shaft of the anode electrode portion are integrally molded; the anode electrode can realize controllable spinning; the metal wire is connected with the rotary shaft part of the anode electrode through an electric brush; an electric spindle of a motor with adjustable speed coaxially drive the anode electrode; the electric spindle end of the motor with adjustable speed is fixedly connected with an end part of the anode electrode through an insulation material, so that the anode electrode can conduct axial rotation to further drive the stirring head part of the anode electrode to stir the molten slag; and the speed of the stirring head is adjusted according to the viscosity of the molten slag. The invention employs the electrodes to stir the steel liquid and molten slag, can increase the transfer rate of electrons as well as the transmission rate of the oxygen, thus greatly improving the deoxidation rate.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method for reducing B inclusions in aluminium-free deoxidized steel
The invention discloses a method for reducing B inclusions in aluminium-free deoxidized steel. The method comprises the following steps: 1) converter steelmaking: overoxidation tapping is avoided; deoxidation alloying is performed by adopting low-aluminium SiBaCa, ferrosilicon and mid-carbon ferromanganese during tapping, lime and fluorite are added, and silicon content of molten steel is controlled to be 0.55wt%-0.65wt%; (2) LF (ladle furnace) refining: lime and fluorite are added in batches in heating slagging of the LF, and final slag basicity is controlled to be 2.0-3.0; silicon content ofmolten steel is controlled to be 0.60wt%-0.70wt%, and vacuum treatment starts after soft blowing with argon at rate of 80-200 L / min for 10-20 min; 3) RH furnace refining: an RH furnace is kept at ultimate vacuum degree for 15-25 min and subjected to vacuum killing, then argon flow is regulated to 150-250 L / min, argon is blown for 1-3 min, then the argon flow is regulated to 80-200 L / min, soft blowing is performed for 8-15 min, and a product is discharged from the furnace and loaded to a casting machine. Over-standard rate of the B inclusions in steel products is reduced by process improvement.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
Composite diffusion deoxidizer and its application method
The present invention provides a AlCaC dcompound diffusion deoxidant for converter, and its application method incldues the following steps: 1). adding steel material into furnace; 2). after the steel material is molten, temp. is 1550-1650 deg.C, using oxygen-determining probe to point-measure dissolved oxygen in molten steel, taking out steel sample and slag sample, making spectral analysis of sample steel, 3). adding slag material, addition quantity is 5% of metal material; 4). after 7-15 min, adding AlCaC compound diffusion deoxidant and adding aluminium to make precipitation and deoxygenation; 5). refining for 40-50 min., timing taking out steel sample and making spectral analysis, at the same time measuring dissolved oxygen, finally tanking end slag sample.
Owner:上海梅山(集团)有限公司
Technological process for secondary refining desulphurization
The invention relates to an external refining technique used for various micro-alloyed steel and special steel, in particular to a technical method used for the external refining desulfurization, which is preferred in the refining desulfurization process of various micro-alloyed steel or the special steel. The technique comprises the following: a. a step of deoxidizing, in which the molten steel is deoxidized to realize that alpha [O] is less than or equal to 0.0003 percent; b. a step of feeding a core-spun yarn, in which the molten steel is refined at the position of LF, RH, VD or CAS-OB, the yarn feeding technique is adopted to feed the core-spun yarn into the molten steel at the positions; and c. a step of continuous casting, in which the continuous casting process is cast protectively in the whole process. The a technique shows that the technique has strong decarbolizing ability and the desulfurization degree between 60 and 90 percent by application, realizes that the molten steel is refined and decrabolized to the extent that the content of sulfur is lower than 0.0010 percent, greatly improves the degree of purity and lowers the smelting cost.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Aluminium manganess composite deoxidized alloy block for deoxidized contained manganess aluminium and its production technology
A composite deoxidizing Al-Mn alloy block for the deoxidized Mn-Al steel is prepared from Al and ferromanganese through smelting high-purity aluminium, pouring in a mould while adding preheated ferromanganese, and solidifying. Its advantages are high utilziation of aluminium.
Owner:张锡昌
Low-oxygen clean steel and low-oxygen clean steel product
ActiveUS20160053352A1Improve fatigue performanceHigh melting pointRare-earth elementNon-metallic inclusions
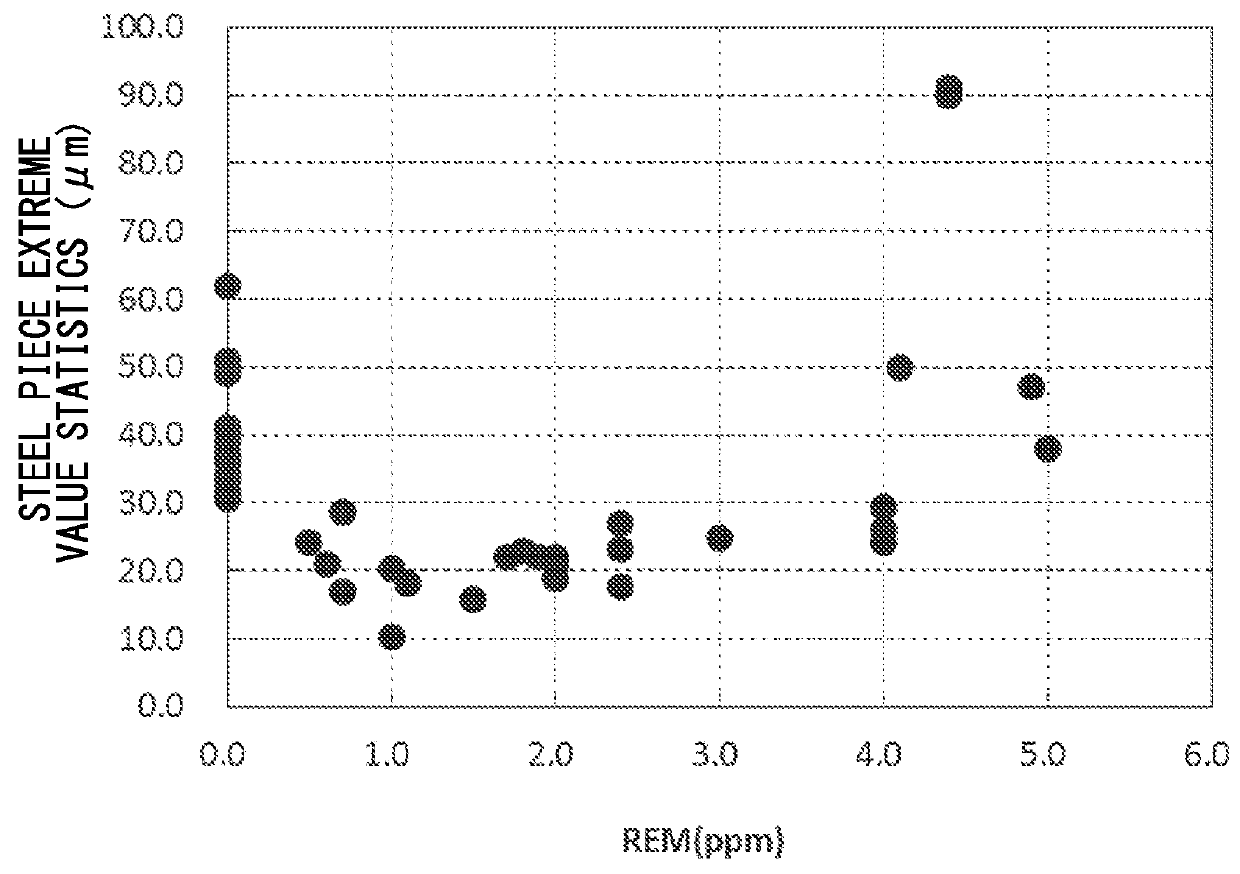
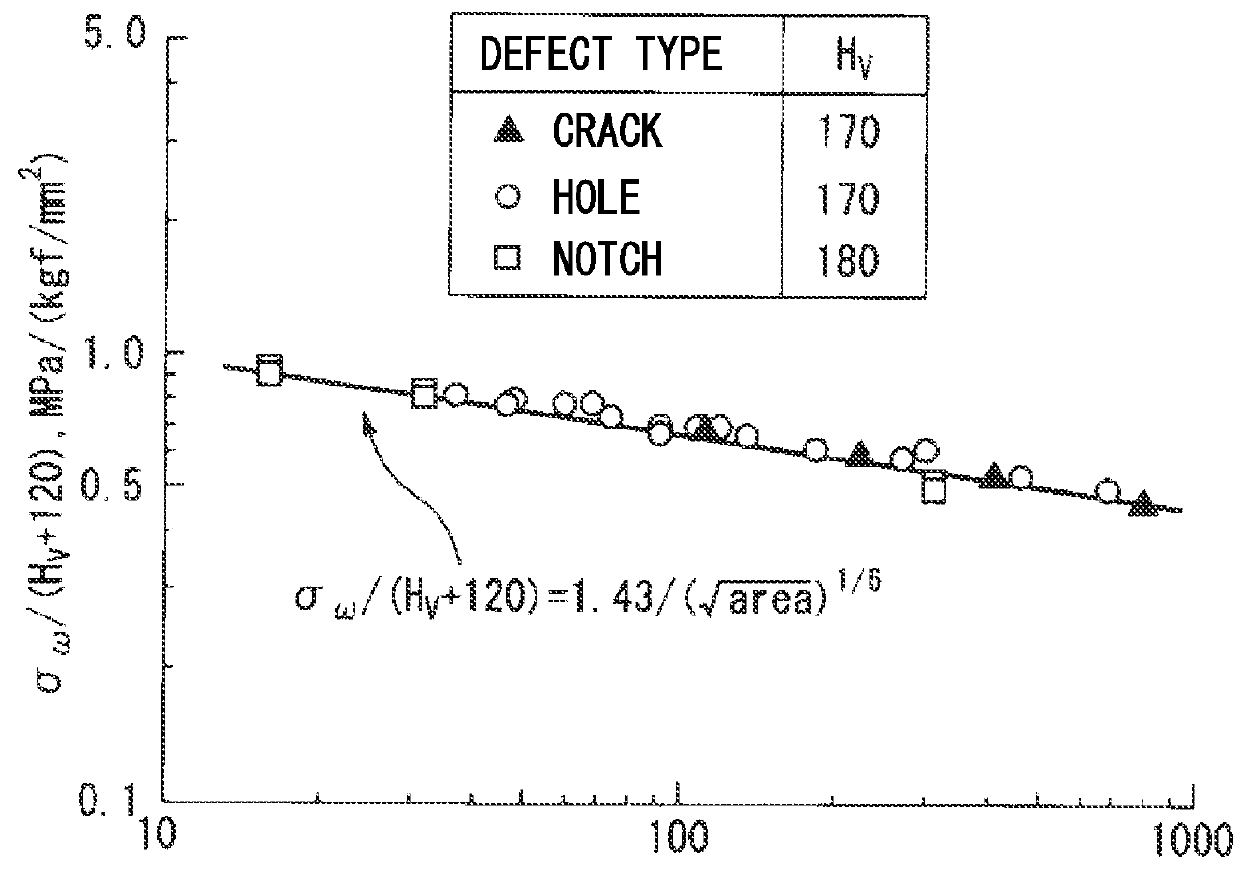
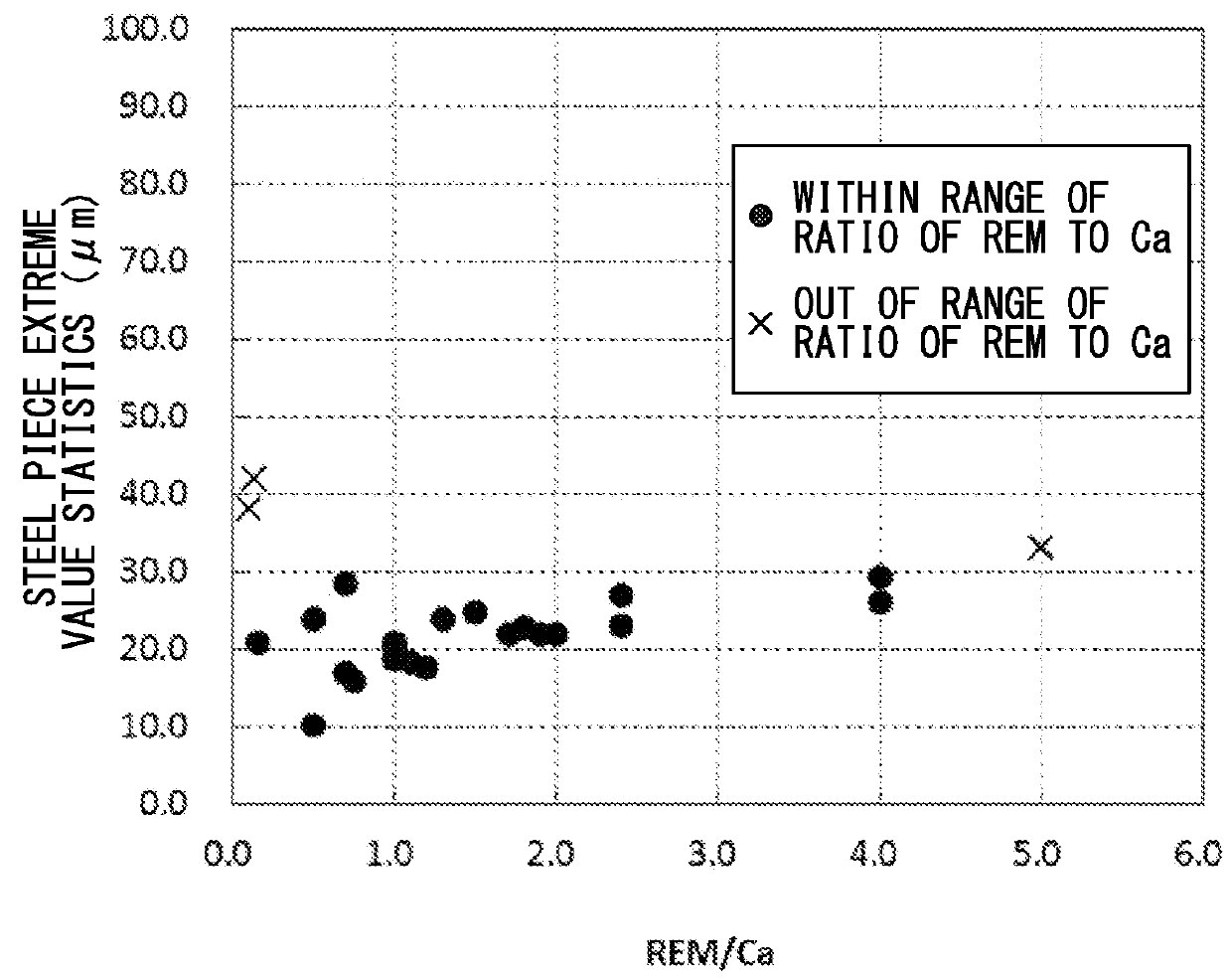
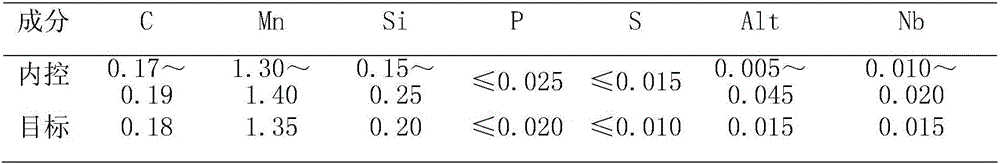
Low-oxygen clean steel is provided containing C, Si, Mn, P, and S as chemical components, and further containing, by mass %, 0.005% to 0.20% of Al, greater than 0% to 0.0005% of Ca, 0.00005% to 0.0004% of REM, and greater than 0% to 0.003% of T.O, wherein the REM content, the Ca content, and the T.O content satisfy 0.15≦REM / Ca≦4.00 and Ca / T.O≦0.50, nonmetallic inclusions which have a maximum predicted diameter of 1 μm to 30 μm measured using an extreme value statistical method under the condition in which a prediction area is 30,000 mm2, and contain Al2O3 and REM oxide are dispersed in the steel, an average proportion of the Al2O3 in the nonmetallic inclusions is greater than 50%, the REM is one or two or more of rare-earth elements La, Ce, Pr, and Nd, and the steel is Al-deoxidized steel or Al—Si-deoxidized steel.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Aluminium chromium composite deoxidized alloy block deoxidized contained chromium aluminium and its producing technology
A composite deoxidizing Al-Cr alloy block for the deoxidized Al-Cr contained steel is prepared from Al and ferrochromium through smelting Al, pouring the molten Al in a mould while proportionally adding the preheated ferrochromium blocks, and solidifying. Its advantages are high utilization of Al, high deoxidizing effect and high quality of steel.
Owner:山东鸿昌铁合金有限公司
Silicon carbide deoxidation steel production process
InactiveCN106676226AImprove desulfurization effectDeoxygenation stabilizationManufacturing convertersSmelting processEconomic benefits
The invention relates to a silicon carbide deoxidation steel production process, and relates to a process of not needing to use aluminum for deoxidation of a deep deoxidized steel in the whole process. Through optimization of the converter tapping deoxidation system and the slagging system, an LF furnace is added with silicon carbide for deoxidation and slagging, and is matched with a production process of feeding aluminum wires in the LF furnace to finely adjust aluminum in molten steel; the characteristics of silicon carbide and aluminum are used for fully and reasonably combining the dispersion deoxidation with the precipitation deoxidation in the smelting process; the process is stable in converter tapping deoxidation; the LF furnace is obvious in slagging and desulfurization effect; the casting blank quality is excellent; the steel plate flaw detection pass percent is stable; the aluminum consumption in one tonnage of steel for deep deoxidation steel production is reduced by about 0.42 kg; and the economic benefit in deep deoxidation steel production is greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Preparation method of iron-manganese-magnesium alloy deoxidizer for non-aluminum deoxidized steel
InactiveCN103981333AEasy to manufactureQuality improvementProcess efficiency improvementNon-metallic inclusionsIngot
The invention relates to a preparation method of an iron-manganese-magnesium alloy deoxidizer for non-aluminum deoxidized steel, which comprises the following steps: sequentially adding a magnesium-manganese interalloy, low-carbon ferromanganese and steel scrap into a line frequency furnace; after finishing adding all the raw materials, smelting until the melt is molten down, removing the scum, quickly casting an ingot in a water-cooled mold, cooling the cast ingot, and mechanically crushing into a 20-50mm block sample. The production process is simple and easy to control; the alloy product is free of aluminum, contains 5-10% of magnesium, has the advantages of high deoxidizing power, high specific gravity, stable chemical properties and high alloy yield; the addition of the molten steel can not result in acute rolling of the melting bath, and can not generate the phenomenon of splashing; and when being specially used for secondary treatment of non-aluminum deoxidized steel, the deoxidizer can effectively purify the molten steel, lower the size of the non-metallic inclusions in the steel and reduce the damage of the non-metallic inclusions on the properties of the steel, thereby being a high-grade molten steel deoxidizer and inclusion refiner.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
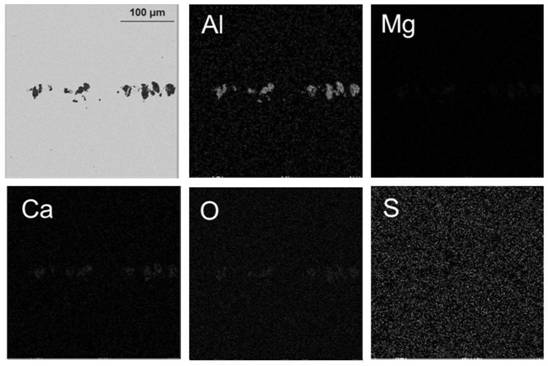
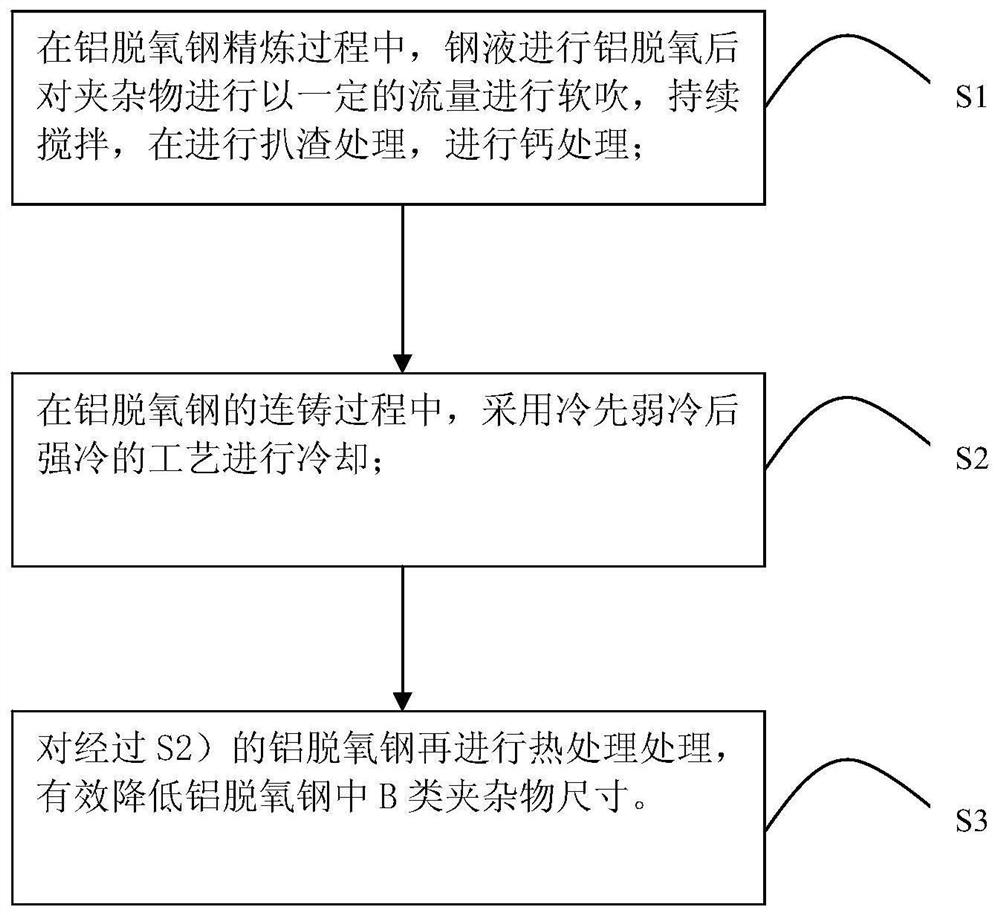
Method for reducing size of B-type inclusions in aluminum deoxidized steel
ActiveCN113106194AReduced deformabilityLower rating levelManufacturing convertersProcess efficiency improvementSteelmakingRefining (metallurgy)
The invention belongs to the field of ferrous metallurgy steelmaking, and particularly relates to a method for reducing the size of B-type inclusions in aluminum deoxidized steel. Through the method, during refining, molten steel is subjected to aluminum deoxidation firstly, then the inclusions are subjected to soft blowing stirring, large-size aluminum oxide inclusions are promoted to float upwards so as to be removed, the size of the inclusions is reduced, through calcium treatment or adding of calcium-containing silicon iron in combination with a controlled cooling and controlled heating method, the inclusions in the continuous casting and heat treatment process are promoted to be converted into composite inclusions with a CaS outer layer and an Al2O3-MgO core and with higher hardness, the deformability of the inclusions in the rolling process is reduced, the size of B-type inclusions in the aluminum deoxidized steel is effectively reduced, and the grade of the B-type inclusions in the aluminum deoxidized steel is lower than 1.5. The method has the beneficial effects that the length of the B-type inclusions in the aluminum deoxidized steel can be effectively avoided, the grade of the B-type inclusions is reduced, the strength, toughness and other properties of the aluminum deoxidized steel can be effectively improved, and the failure of a product in the service process is avoided.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING +2
Subway internal steel frame casting and production technology thereof
ActiveCN105149521AAvoid being overwhelmedGuaranteed temperatureFoundry mouldsFoundry coresElectric arc furnaceSteel frame
The invention relates to a subway internal steel frame casting and a production technology thereof. The production technology comprises the following steps: parting up and down by a symmetric point, adopting a gating system to enter from two ends of a casting mould so as to pour six pouring gates, and not arranging a flow gate in the middle section, wherein the cross section of a pouring ingate is smaller than that of the casting; arranging a plurality of risers, wherein the middle riser is a main riser, pouring from the first half part of a hole to increase the feeding capacity to a center plate thermal center, and arranging a riser runner in a rib plate; adopting an electric-arc furnace to smelt steel, adding aluminum, rare earth and silicozirconium alloy for forcible deoxidizing, blowing argon on a steel ladle, boiling the molten steel surface on the steel ladle, keeping for a few minutes, purifying to remove impurities, and moulding; controlling the pouring temperature to be within the range of from being equal to or smaller than 1560 to 1570 DEG C to ensure high-quality molten steel pouring, adopting ferrochromium resin sand for foundry sand, ensuring the heat preservation time equal to or greater than 24 hours, adopting an external iron chill auxiliary riser to realize progressive solidification, and after sand shakeout, cutting the riser, and feeding the casting in a furnace for thermal treatment; finally, finishing the casting subjected to the thermal treatment.
Owner:HUZHOU ZHONGLIAN MACHINERY EQUIP
Method for evaluating anti-stripping performance of refractory material for silicon deoxidized steel in using process
ActiveCN110987612AExacerbated harmEliminate distractionsMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesProcess efficiency improvementWire rodProduction line
The invention discloses a method for evaluating the anti-stripping performance of a refractory material for silicon deoxidized steel in the using process, and belongs to the field of ferrous metallurgy. The method is characterized in that a refractory material to be evaluated is used for smelting high-carbon silicon deoxidized steel. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, realizing lowmelting point of endogenous inclusions in the high-carbon silicon deoxidized steel through a refining process; carrying out plastic deformation on the endogenous inclusions by utilizing a high-temperature rolling process; secondly, controlling the final strength of the wire rod to be 1250 MPa or above by controlling the steel rolling process; wherein the diameter of the wire rod is 10-21 mm, immediately sampling and stretching the wire rod after the wire rod is discharged from a production line, the number of stretching samples being not less than 15, and analyzing and counting the fracture proportion caused by inclusion of corundum, magnesium aluminate spinel, zirconium oxide, forsterite and magnesium oxide by using a scanning electron microscope after stretching. The method can effectively evaluate the anti-stripping performance of the refractory material for deoxidized steel in the use process.
Owner:ZENITH STEEL GROUP CORP
Technological process for achieving size miniaturization of inclusion in Si deoxidized steel
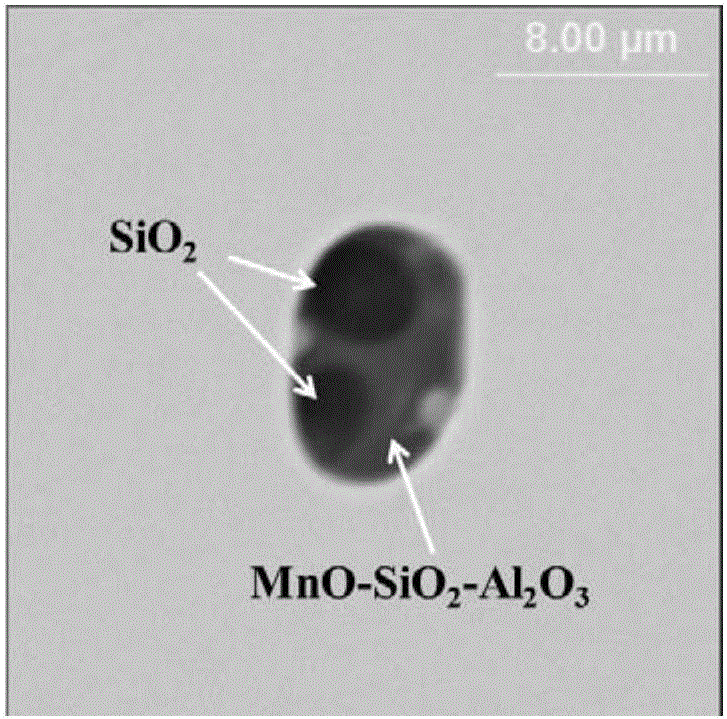
The invention belongs to the field of the metallurgical industry and discloses a technological process for achieving size miniaturization of an inclusion in Si deoxidized steel. The technological process comprises four steps of steelmaking, continuous casting, hot rolling and cold drawing; the inclusion is controlled in a low-melting-point spessartite inclusion and tridymite area in a centralized manner in the steelmaking step by controlling conditions in the four steps; and a two-phase inclusion comprising a MnO-SiO2-Al2O3 parent phase and a SiO2 quartz phase precipitated on the parent phase is generated afterwards; the two-phase inclusion is subjected to multiple passes of hot rolling to gradually extend and deform; phase separation between the MnO-SiO2-Al2O3 parent phase and the SiO2 quartz phase is gradually achieved by utilizing the differences of the deformation performance of the MnO-SiO2-Al2O3 parent phase and the deformation performance of the SiO2 quartz phase based on multiple passes of cold deformation machining; and the hard quartz phase is used for cutting the MnO-SiO2-Al2O3 parent phase, and size miniaturization of the inclusion is finally achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Aluminum deoxidized steel with tellurium-sulfur synergistic treatment and its preparation method and application
The present application provides an aluminum-deoxidized steel with tellurium-sulfur synergistic treatment and its preparation method and application, relating to the field of metal materials. Aluminum deoxidized steel with tellurium-sulfur synergistic treatment: C0.06%-0.09%, Al0.01%-0.02%, Si0.01%-0.03%, Mn1.0%-1.5%, S0.08%-0.1%, P0.045%‑0.055%, Te0.04%‑0.15%. The preparation method comprises: carrying out converter smelting of molten iron, carrying out deoxidation alloying in the steel tapping process; carrying out LF refining, adding sulfur-iron alloy and tellurium wire, and then continuously casting to obtain aluminum deoxidized steel with tellurium-sulfur synergistic treatment. Application of tellurium-sulfur co-processed aluminum-deoxidized steels as bearing steels, rail steels or wheel steels. The aluminum-deoxidized steel provided by the present application for the synergistic treatment of tellurium-sulfur limits the aggregation and growth of alumina, increases the cutting lubricity, and avoids the problem of nozzle nodules.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
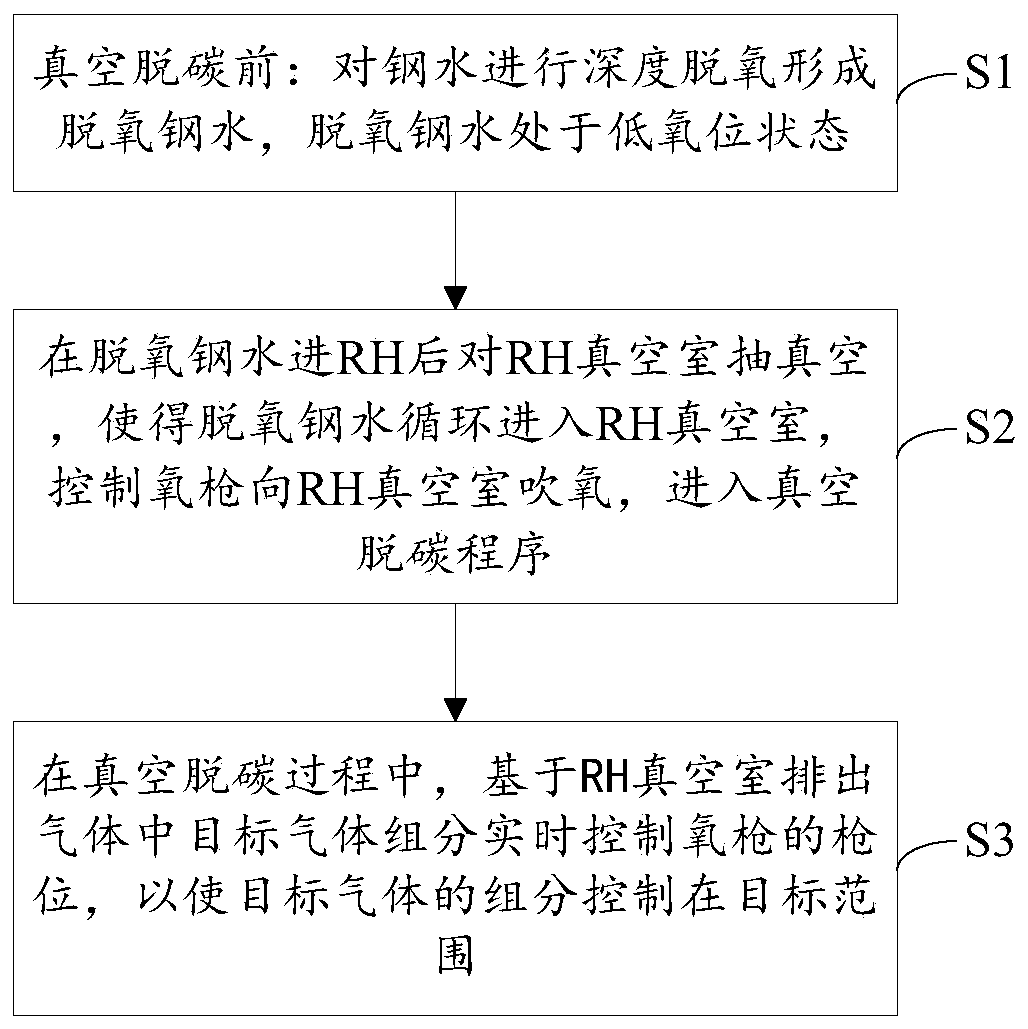
Method for increasing energy utilization rate for escaped carbon monoxide and hydrogen in vacuum decarburization process for molten steel
The invention discloses a method for increasing an energy utilization rate for escaped carbon monoxide and hydrogen in a vacuum decarburization process for molten steel. The method for increasing an energy utilization rate for the escaped carbon monoxide and hydrogen in the vacuum decarburization process for the molten steel comprises the following steps: S1, before vacuum decarburization, carrying out deep deoxidization on the molten steel to form deoxidized molten steel, and keeping the deoxidized molten steel to be in a low-oxygen-level state; S2, vacuumizing an RH vacuum chamber after thedeoxidized molten steel enters the RH vacuum chamber, enabling the deoxidized molten steel to cyclically enter the RH vacuum chamber, controlling an oxygen gun to blow oxygen to the RH vacuum chamber,and entering a vacuum decarburization program; and S3, in a vacuum decarburization process, controlling the gun position of the oxygen gun in real time on the basis of the components of target gas inexhausted gas of the RH vacuum chamber to control the components of the target gas to be in a target range. The deep deoxidization is carried out on the molten steel before decarburization, dissolvedoxygen is controlled to be under the condition that oxygen blowing is started at the beginning of vacuum establishment, and a concentrated carbon-oxygen reaction is basically not carried out before concentrated deoxidization is completed; a dehydrogenation process and a decarburization process are separated, a decarburization speed can be greatly controlled according to an oxygen blowing speed, and synchronous massive escape is avoided, so that serious splashing is avoided.
Owner:MAANSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
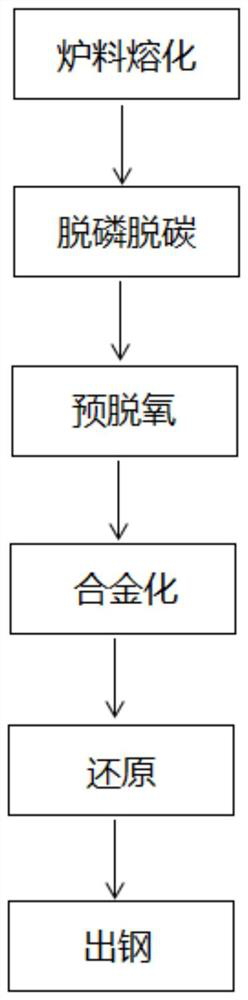
Smelting method of ZG06Cr13Ni4Mo steel and ZG06Cr13Ni4Mo steel
ActiveCN112662838AImprove purityReduce smelting costElectric furnaceProcess efficiency improvementElectric arc furnaceSmelting process
The invention discloses a smelting method of ZG06Cr13Ni4Mo steel. The smelting method comprises the following steps: S1, burdening calculation: total materials, furnace burden and alloy are calculated according to the amount of molten steel required by the product and are selected by taking 4 wt% of Ni as a target value, and the furnace burden comprises 25Cr2Ni4MoV return scraps, nickel-containing pig iron and high-quality scrap steel; S2, electric arc furnace rough smelting, specifically, furnace burden melting, dephosphorization and decarburization, pre-deoxidation, alloying, reduction and tapping are included, in the dephosphorization and decarburization step, when [C] is smaller than or equal to 0.02% and [P] is smaller than or equal to 0.003%, oxidizing slag is pulled away, and in the pre-deoxidation step, 5.0-6.0 kg / t steel of ferro-aluminum is added for pre-deoxidation after all oxidizing slag is pulled away; and S3, ladle refining, specifically, the total refining time is larger than or equal to 1 h, and hoisting-out pouring is conducted after refining. According to the method, the low-carbon stainless steel product with w (C) of 0.04-0.06% is produced through the electric arc furnace and the refining furnace, the technological process is simple, the smelting period is short, compared with VOD and AOD smelting processes, the equipment complexity is reduced, the smelting cost is low, the average oxygen content in the molten steel is 5.9 ppm, and the purity of the molten steel is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI ELECTRIC SHMP CASTING & FORGING CO LTD
Method for refining rare earth inclusions in steel through magnesium pretreatment
PendingCN114107601AStrong deoxygenation abilityReduce dissolved oxygen contentProcess efficiency improvementRefining (metallurgy)Slag
The invention relates to the technical field of ferrous metallurgy, in particular to a method for refining rare earth inclusions in steel through magnesium pretreatment, and solves the technical problem that the rare earth inclusions are large in size when aluminum deoxidized steel is subjected to rare earth treatment. After refining slag components and the content of aluminum, oxygen and sulfur in molten steel reach a control target, magnesium pretreatment is firstly carried out to modify large-size Al2O3 inclusions into fine and dispersed MgO inclusions, then rare earth treatment is carried out, the fine and dispersed MgO inclusions are converted to obtain rare earth inclusions, and the size of the rare earth inclusions is obviously refined compared with that of magnesium-free pretreatment. And meanwhile, the density of MgO inclusions is smaller than that of Al2O3 inclusions, and the MgO inclusions can float upwards and be discharged more easily according to the Stokes law, so that the cleanliness of the steel can be further improved by adopting magnesium pretreatment. The method is easy to operate, efficient, safe, low in steel grade limitation, suitable for refining processes such as LF, VD and RH and wide in application range.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
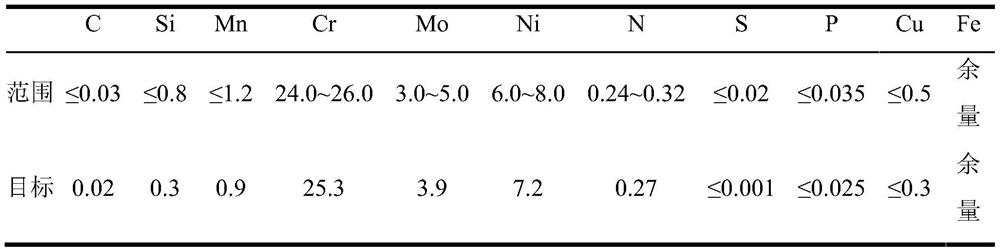
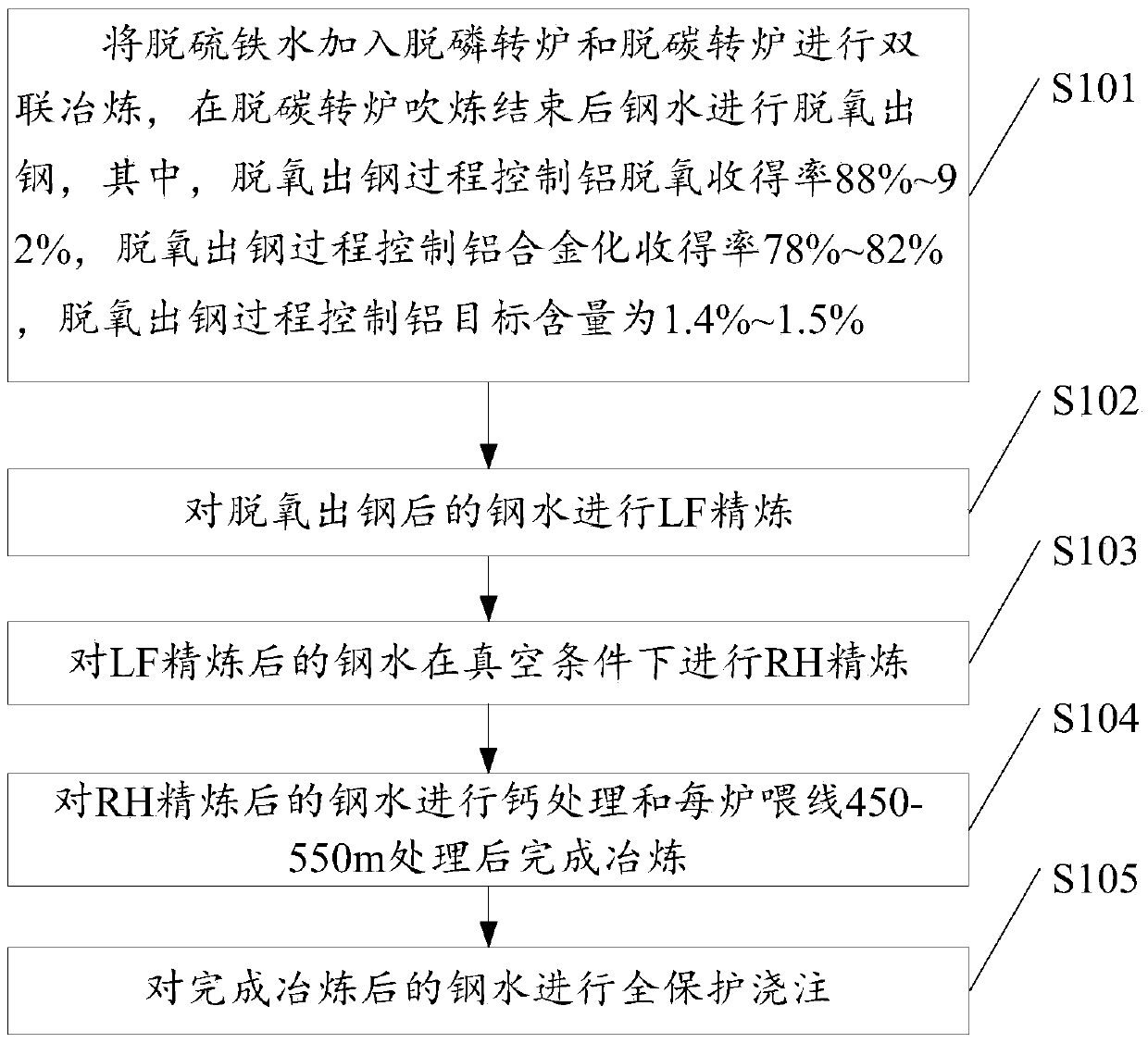
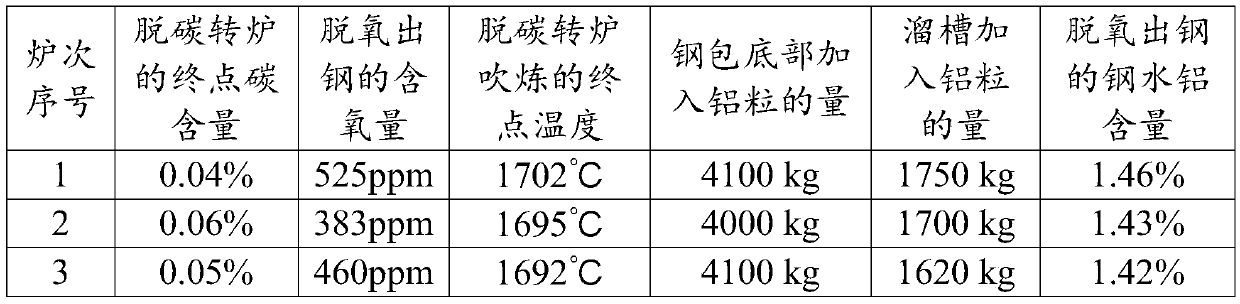
High-aluminum complex-phase steel and smelting method thereof
ActiveCN105506212AIncreased deoxygenation yieldIncreased target contentManufacturing convertersDeoxidized steelDecarburization
The invention discloses high-aluminum complex-phase steel and a smelting method thereof. The smelting method of the high-aluminum complex-phase steel comprises the following steps: adding desulfurized liquid iron into a dephosphorization converter and a decarburization converter for duplex smelting; performing deoxidation and tapping on liquid steel after blowing of the decarburization converter is ended, wherein the aluminum deoxidation yield of the deoxidation and tapping process is 88% to 92%, the aluminum alloying yield of the deoxidation and tapping process is 78% to 82%, and the target aluminum content of the deoxidation and tapping process is 1.4% to 1.5%; performing LF (Low-Frequency) refining on the deoxidized and tapped liquid steel; performing RH (Ruhrstahl Heraeus) refining on the LF-refined liquid steel at a vacuum condition; performing calcium treatment on the RH-refined liquid steel and feeding 450m to 550m of a wire into each furnace to finish the smelting; performing full-protective pouring on the smelted liquid steel. The high-aluminum complex-phase steel and the smelting method disclosed by the invention have the advantages of effectively solving the technical problems that the existing aluminum deoxidized steel is low in aluminum content and is incapable of containing target ingredients which are actually required by the high-aluminum complex-phase steel, realizing high aluminum alloying yield without reducing the production stability, and obtaining high-aluminum complex-phase steel of which the final aluminum content is 1.2% to 1.4% by smelting, wherein the high-aluminum complex-phase steel contains the target ingredients of an actual steel type required by a user.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
Tellurium-sulfur co-treated aluminum deoxidized steel as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides tellurium-sulfur co-treated aluminum deoxidized steel as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and relates to the field of metal materials. The tellurium-sulfur co-treated aluminum deoxidized steel comprises the following components of, in percentage by weight, 0.06%-0.09% of C, 0.01%-0.02% of Al, 0.01%-0.03% of Si, 1.0%-1.5% of Mn, 0.08%-0.1% of S, 0.045%-0.055% of P and 0.04%-0.15% of Te. The preparation method of the tellurium-sulfur co-treated aluminum deoxidized steel comprises the following steps that converter smelting is carried out on molten iron, and deoxidizing and alloying are carried out in a tapping process; and LF refining is carried out, a sulfur-iron alloy and a tellurium wire are added, and then continuous casting is carried out to obtain the tellurium-sulfur co-treated aluminum deoxidized steel. The tellurium-sulfur co-treated aluminum deoxidized steel is used as bearing steel, steel rail steel or wheel steel. According to the tellurium-sulfur co-treated aluminum deoxidized steel provided by the invention, aggregation and growth of aluminum oxide are limited, the cutting lubricity is improved, and the problem of nozzle clogging is avoided.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Slagging method for preventing high-silicon-aluminum deoxidized steel bale from adhering slag
PendingCN114737010AReduce burning lossReduce consumptionManufacturing convertersProcess efficiency improvementTemperature controlSlag
The invention discloses a slagging method for preventing a ladle of high-silicon-aluminum deoxidized steel from adhering slag, which comprises the following steps: controlling the tapping temperature of a converter to be 1625-1665 DEG C, and adding 0.25-0.60 kg of aluminum alloy to carry out semi-deoxidation after one fifth of the tapping; adding silicon-manganese alloy to further remove part of oxygen after one third of tapping; lime is added after two thirds of converter tapping, and the adding amount of the lime is 1.2-2.4 kg / t steel; after lime is added, argon is adopted for stirring at the bottom of a steel ladle, and argon blowing stirring continues to be conducted after tapping is finished; after the steel ladle is conveyed to an argon station, aluminum wires are fed into the molten steel for deoxidation alloying, and the addition amount of the aluminum wires is 0.4-0.7 kg / t steel; after aluminum feeding is finished, stirring by adopting moderate-strength argon quantity to promote slag steel interface reaction; according to the method, the content of Al2O3 in the high-silicon-aluminum deoxidized top slag can be reduced, the slag bonding problem caused by the high content of Al2O3 in the top slag is avoided, meanwhile, the consumption of deoxidized aluminum alloy and the consumption of slagging lime are reduced, the requirements for smooth production and molten steel quality are met, and the production cost is obviously reduced.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
Purification smelting process of wear-resistant castings
The invention discloses a purification smelting process of wear-resistant castings. The process comprises the steps that scrap steel, ferrochrome, ferromolybdenum, ferromanganese, ferrosilicon, ferrovanadium, ferrotungsten, ferro-nickel, ferro-hafnium and rare earth ferroalloy are selected as raw materials; the scrap steel is added into smelting equipment, after melting by 1 / 3-1 / 2, the ferrochromeand the ferromolybdenum are added for smelting, then the ferromanganese, the ferrosilicon, the ferrovanadium, the ferrotungsten, the ferro-nickel, the ferro-hafnium and the rare earth ferroalloy areadded for smelting, and a deoxidizing agent is added for purification and slagging-off; a diffusion deoxidizing agent is used for primary diffusion deoxidation, then ferrosilicon and ferromanganese are used for precipitation deoxidation, then the diffusion deoxidizing agent is used for secondary diffusion deoxidation, and the deoxidizing agent is used for final deoxidation to obtain deoxidized molten steel; the deoxidized molten steel is refined through an LF method to obtain refined molten steel; and the refined molten steel is discharged from a furnace and poured after the composition of therefined molten steel is adjusted. The purification smelting process of the wear-resistant castings is simple in operation and good in purification effect.
Owner:安徽中建材开源新材料科技有限公司
Steel slag modifier as well as preparation and use methods thereof
Owner:SICHUAN PAN YAN TECH
Compounded deoxidized material as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103614516AReduce oxidationAvoid secondary oxidationRecycling and recovery technologiesSteelmakingAlloy
The invention belongs to the technical field of steel making, and particularly relates to a compounded deoxidized material for the deoxidization of steel slag or molten steel as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The compounded deoxidized material is kalzium metal and comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 45-65% of Al, 15-30% of Ca, less than 3% of Si and the balance of aluminium oxide and calcium oxide mixture. The particle size of the kalzium metal is 10-40mm. The kalzium metal is the novel compounded deoxidized material which can be used for realizing the deoxidization and desulfurization of the steel slag and the molten steel and the inclusion adsorption and integrates the functions of deoxidization, purification and refinement; by adopting the compounded deoxidized material, the production cost of steel making is reduced under the condition of ensuring the quality.
Owner:XIXIA COUNTY SHUNFA NEW FURNACE CHARGE CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com