Patents
Literature
123 results about "Secondary bonding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
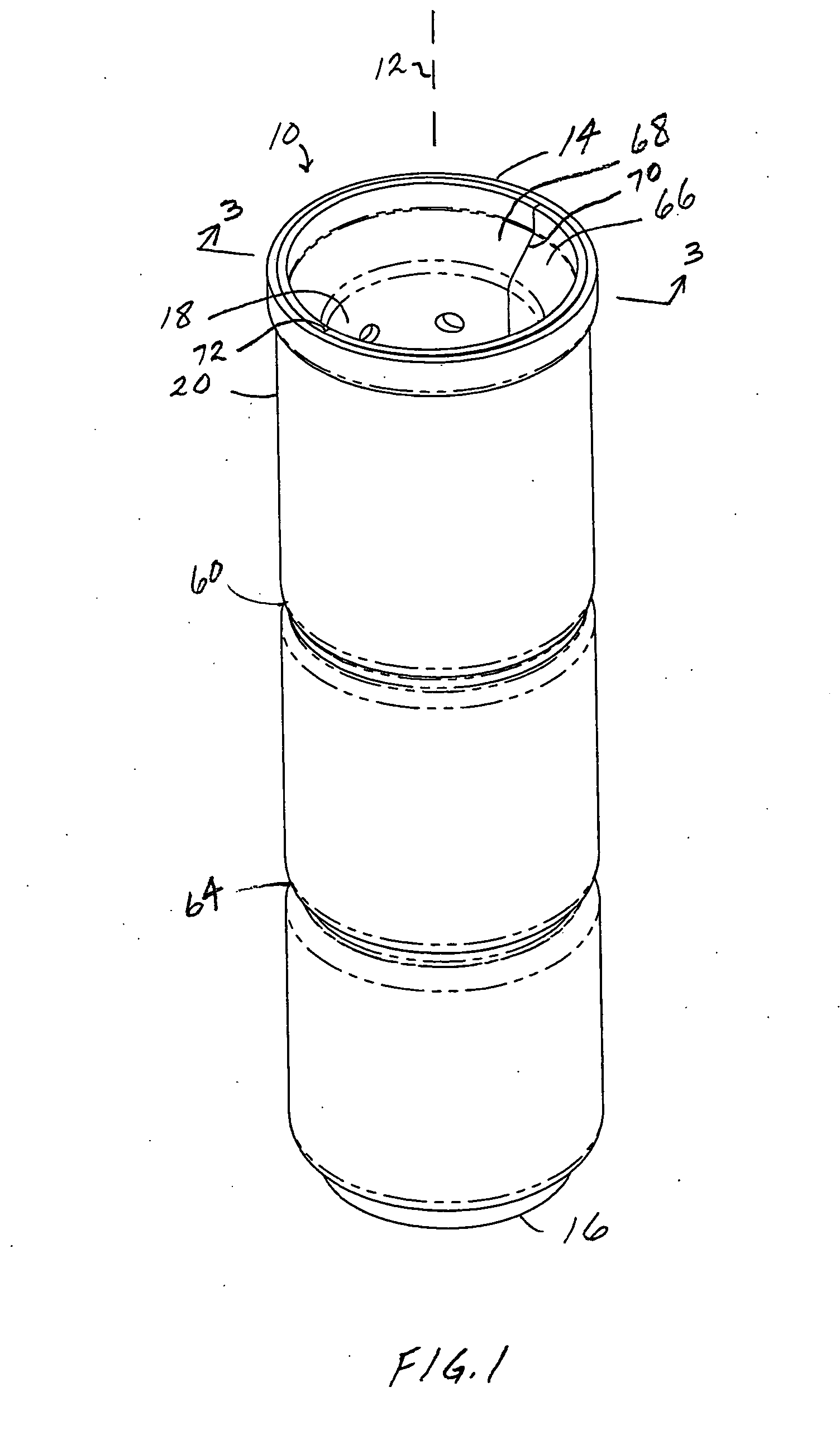
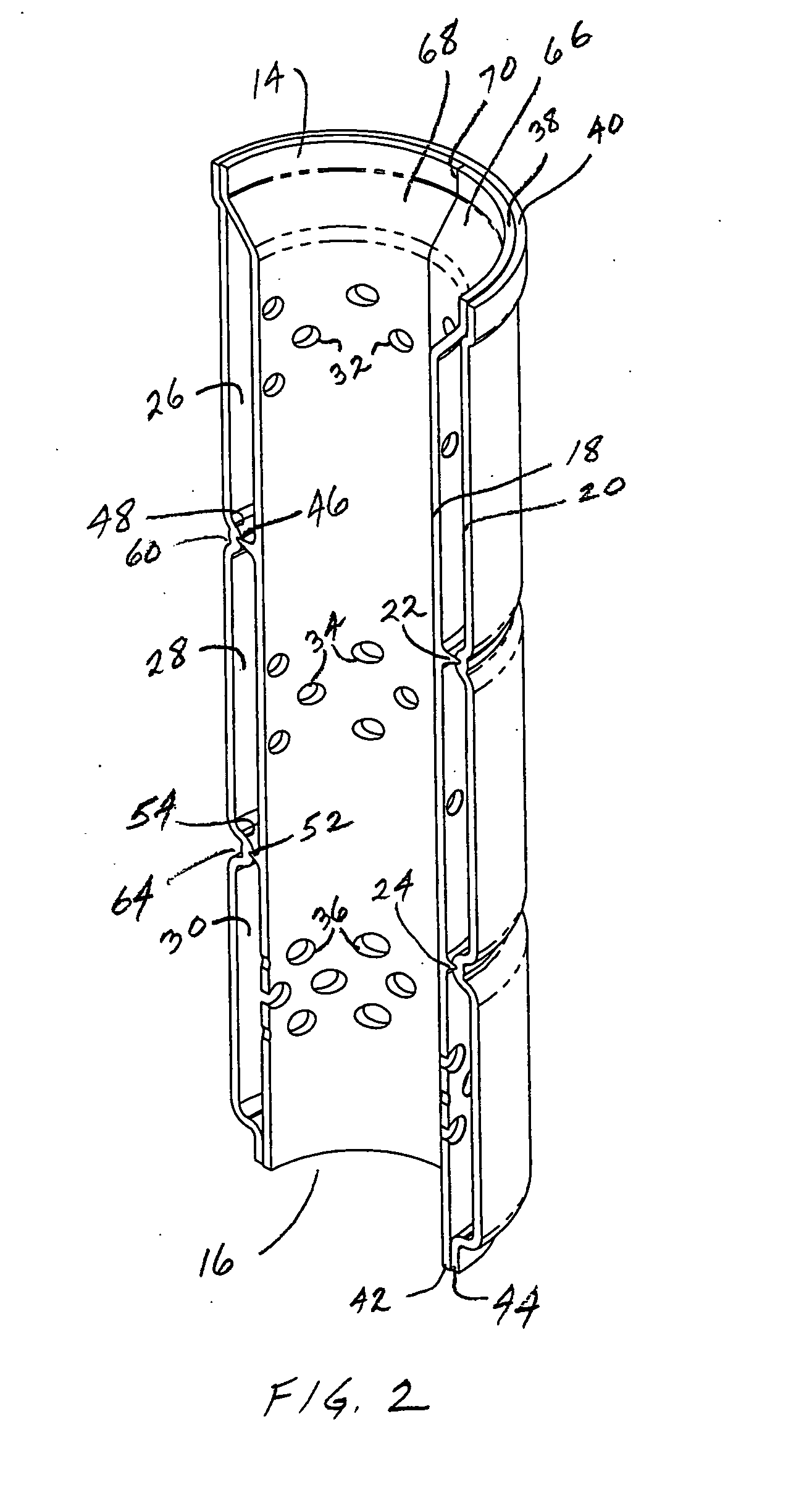
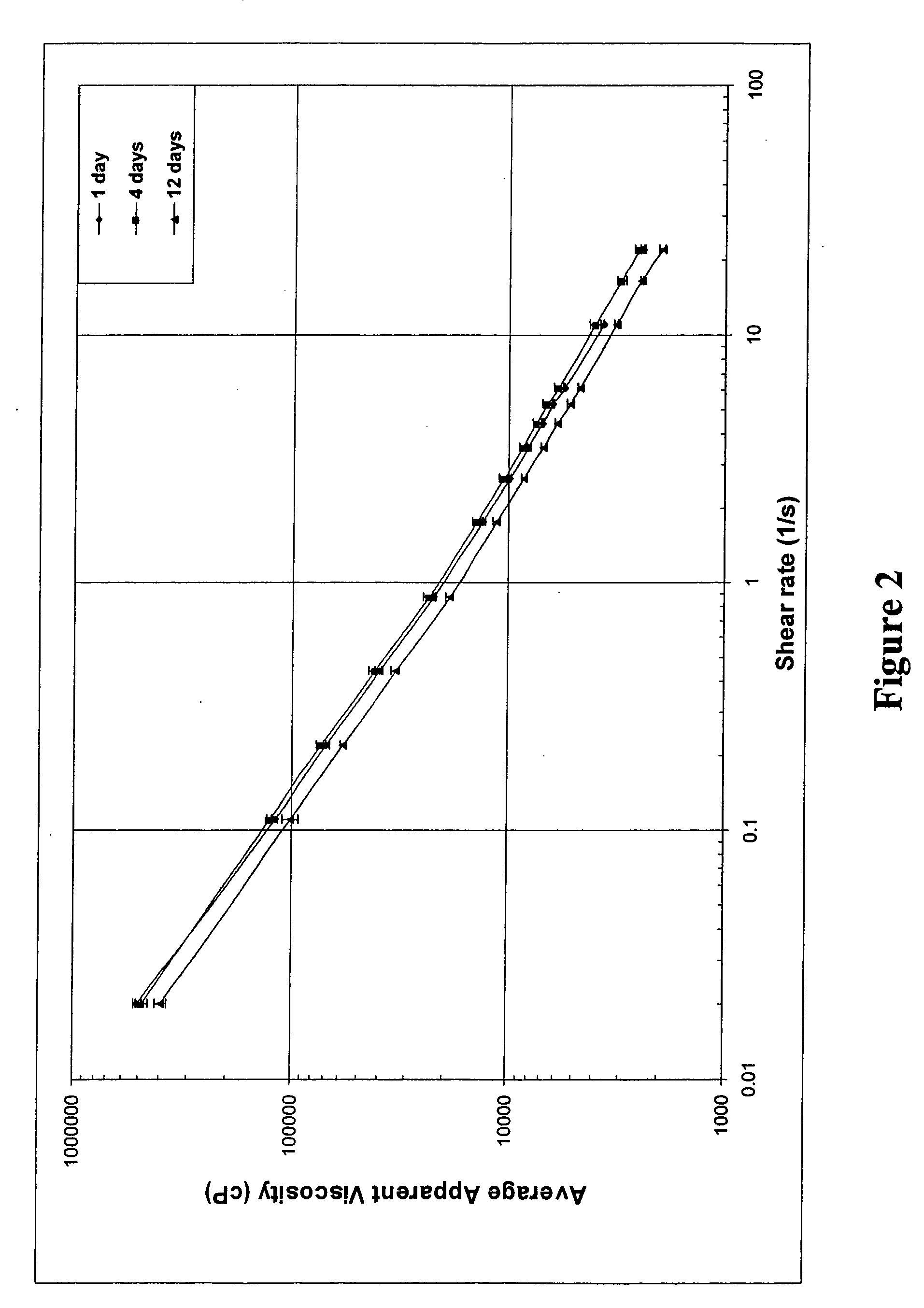
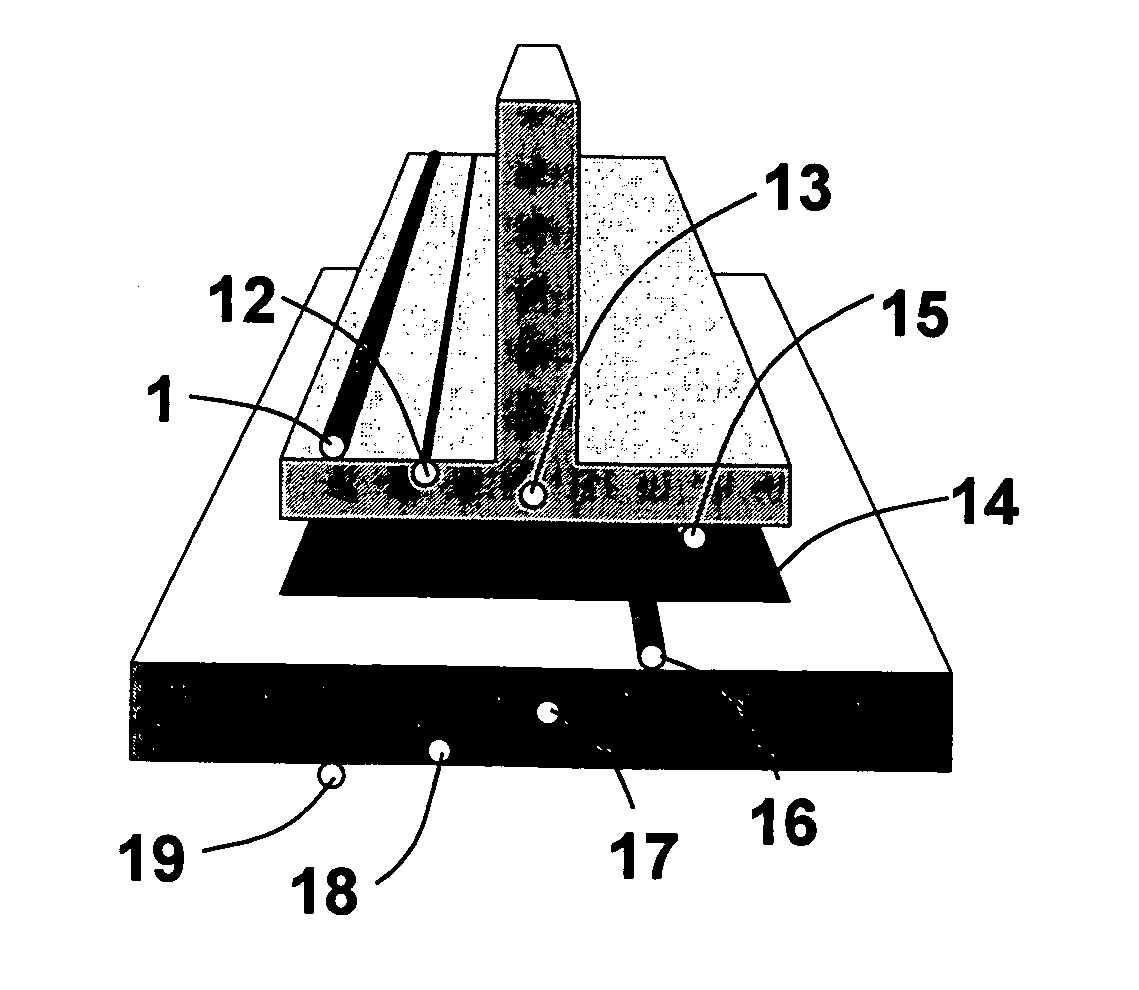
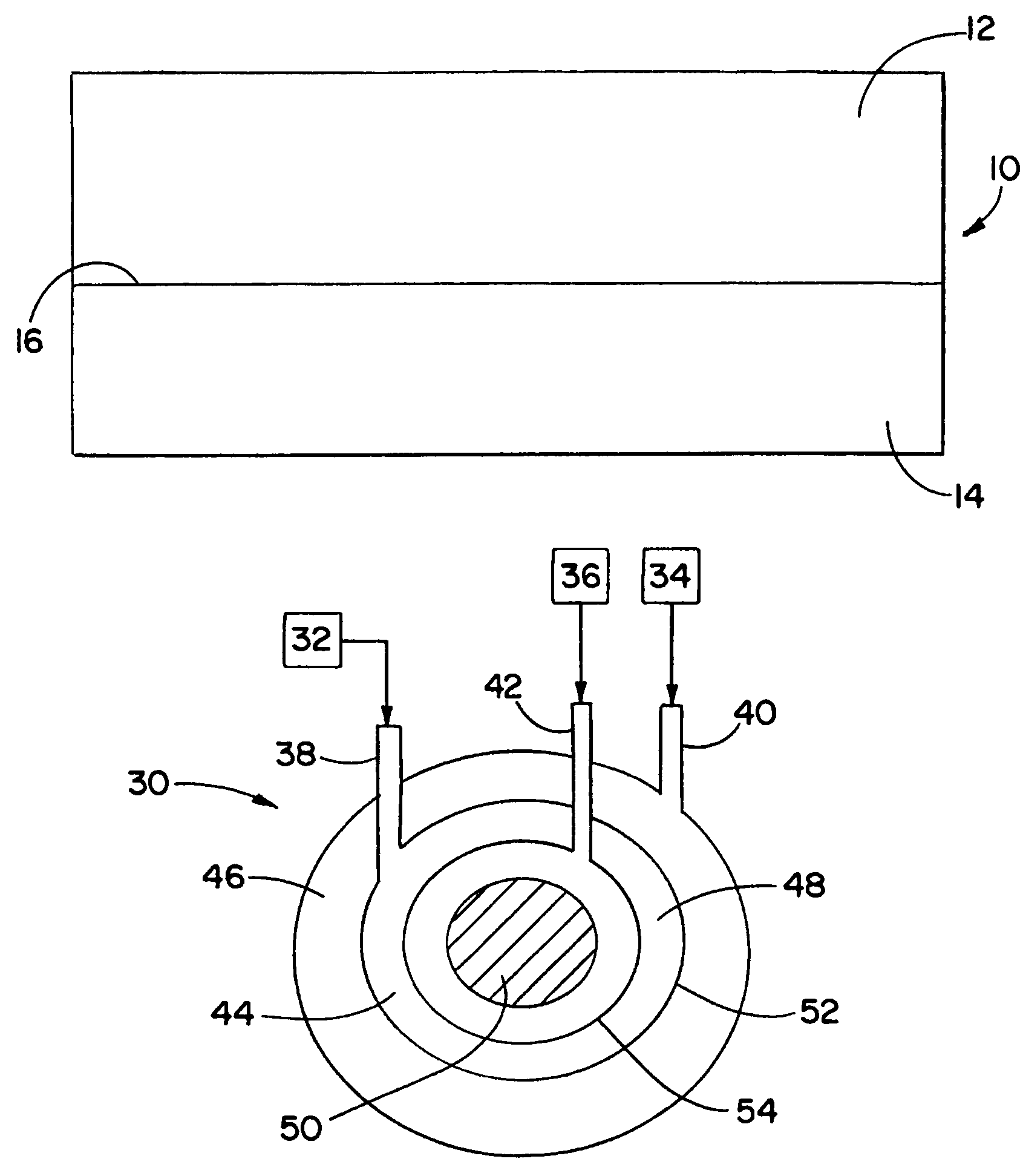
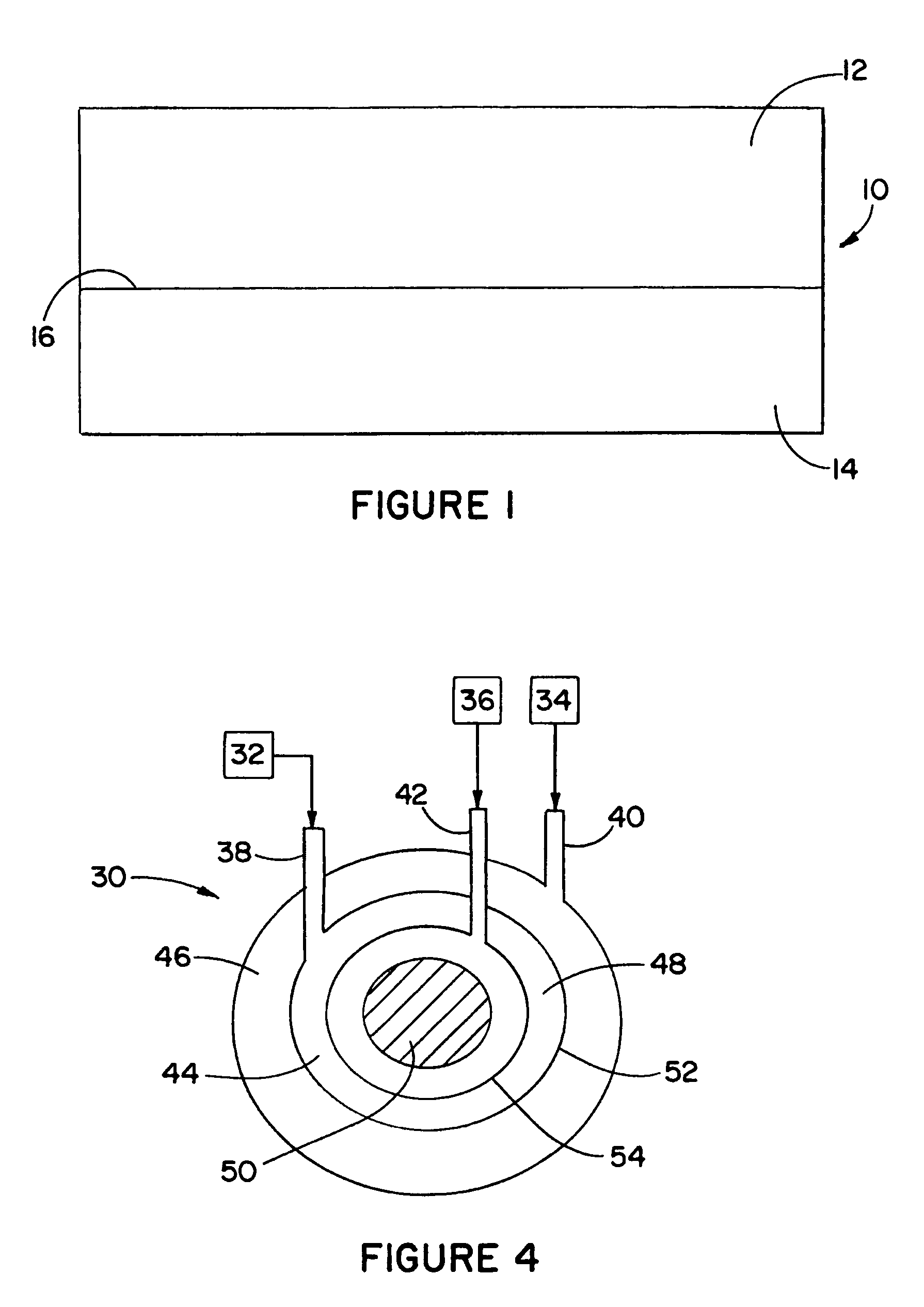
Printable Elastic Composite
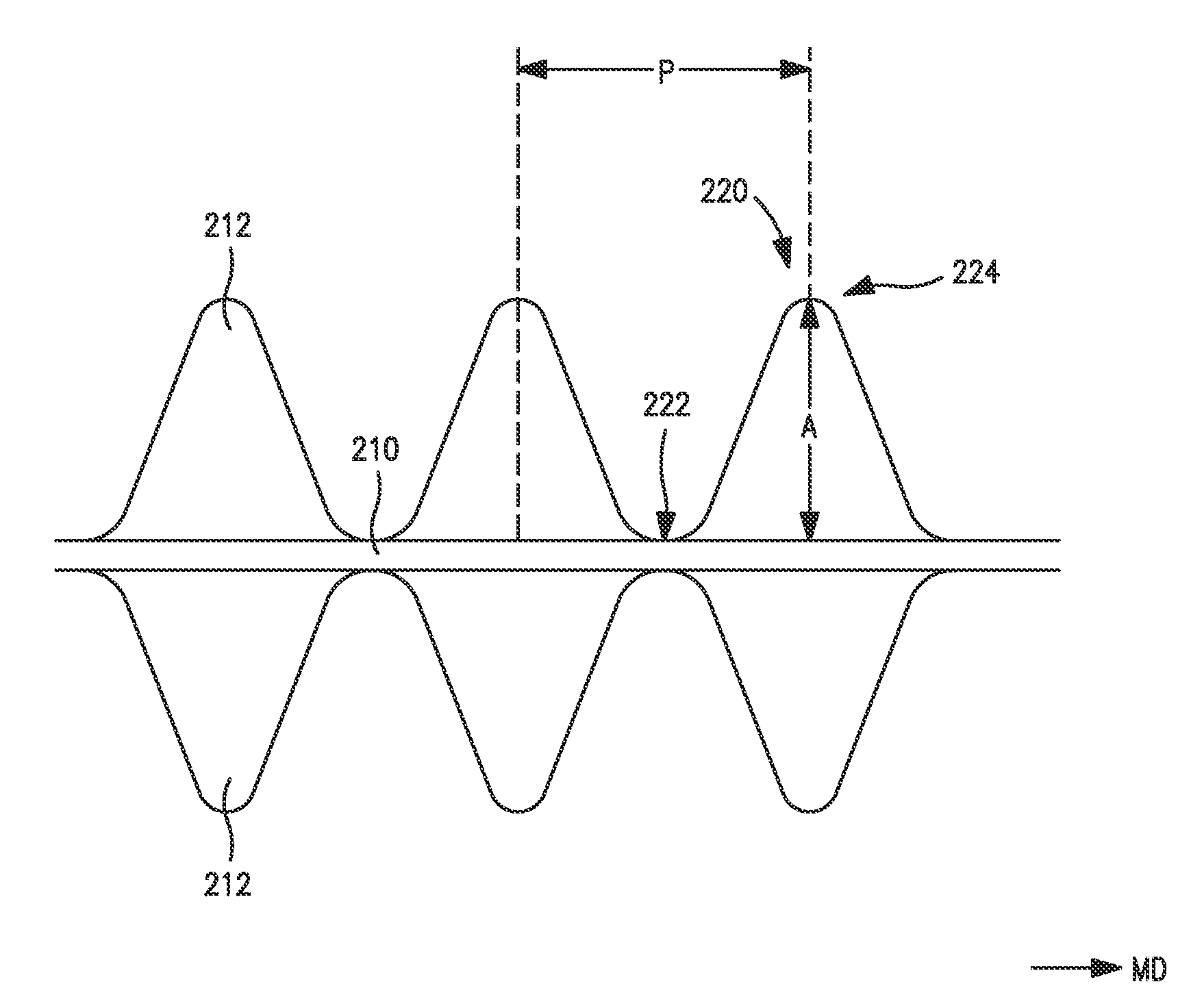
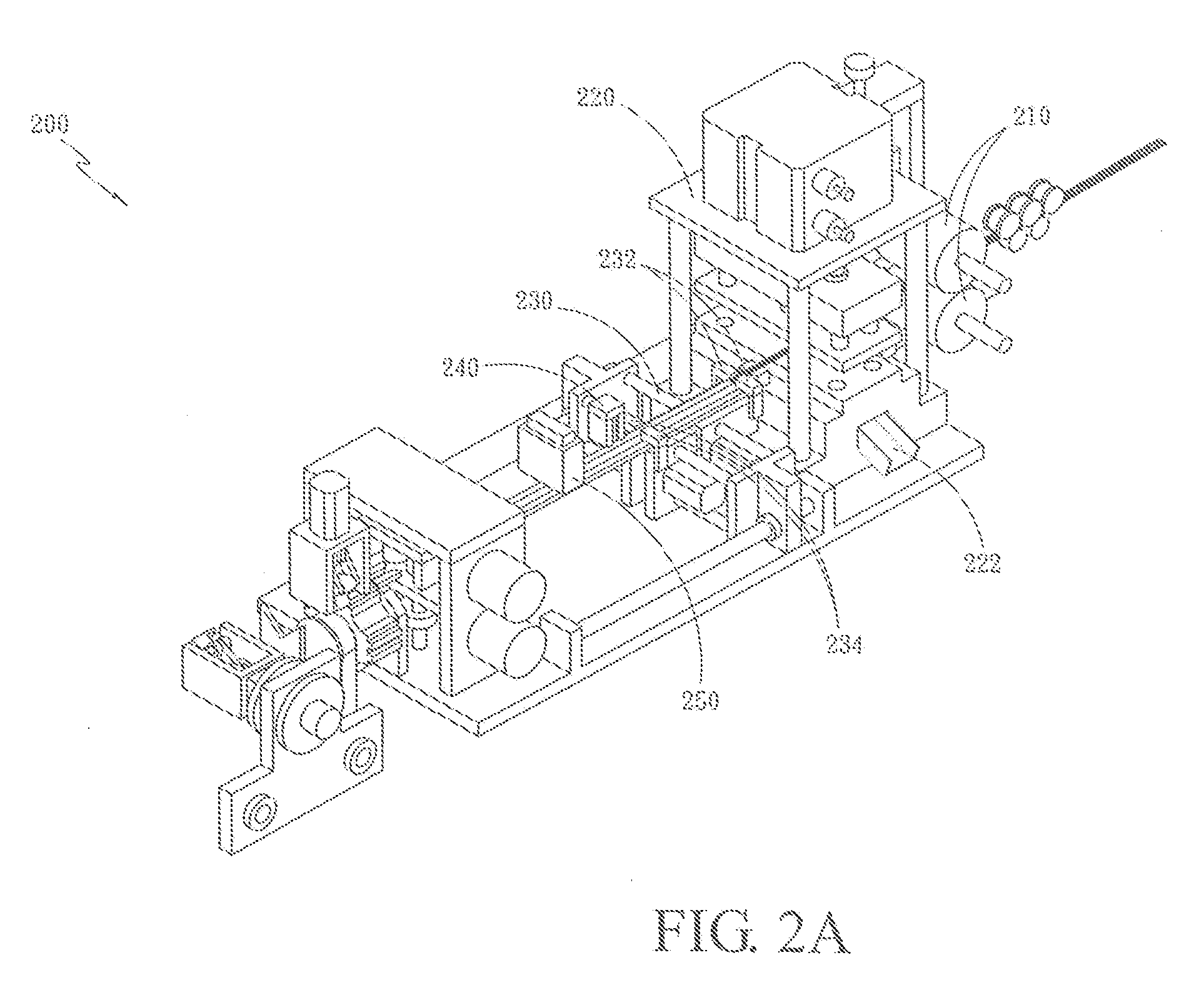
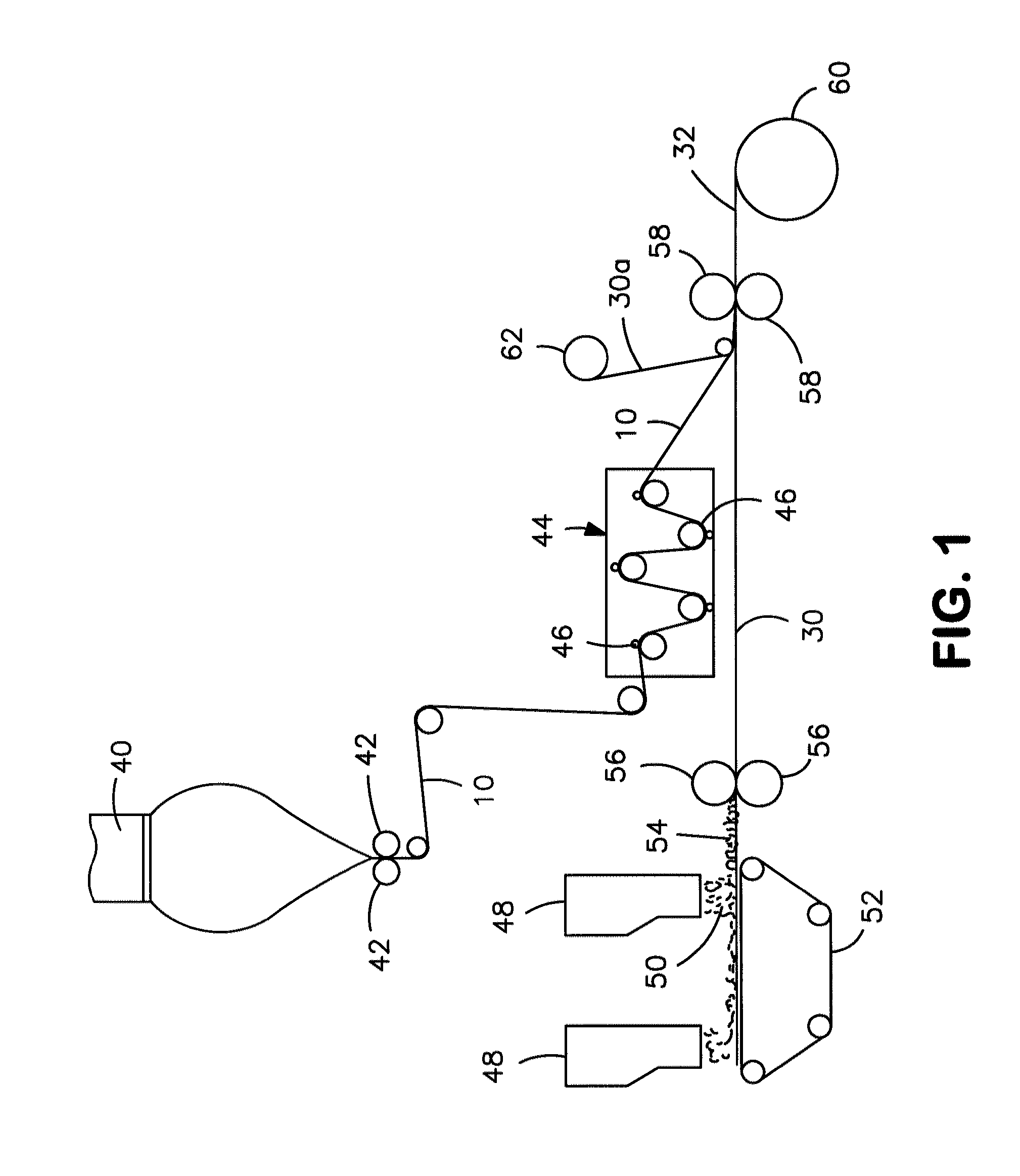
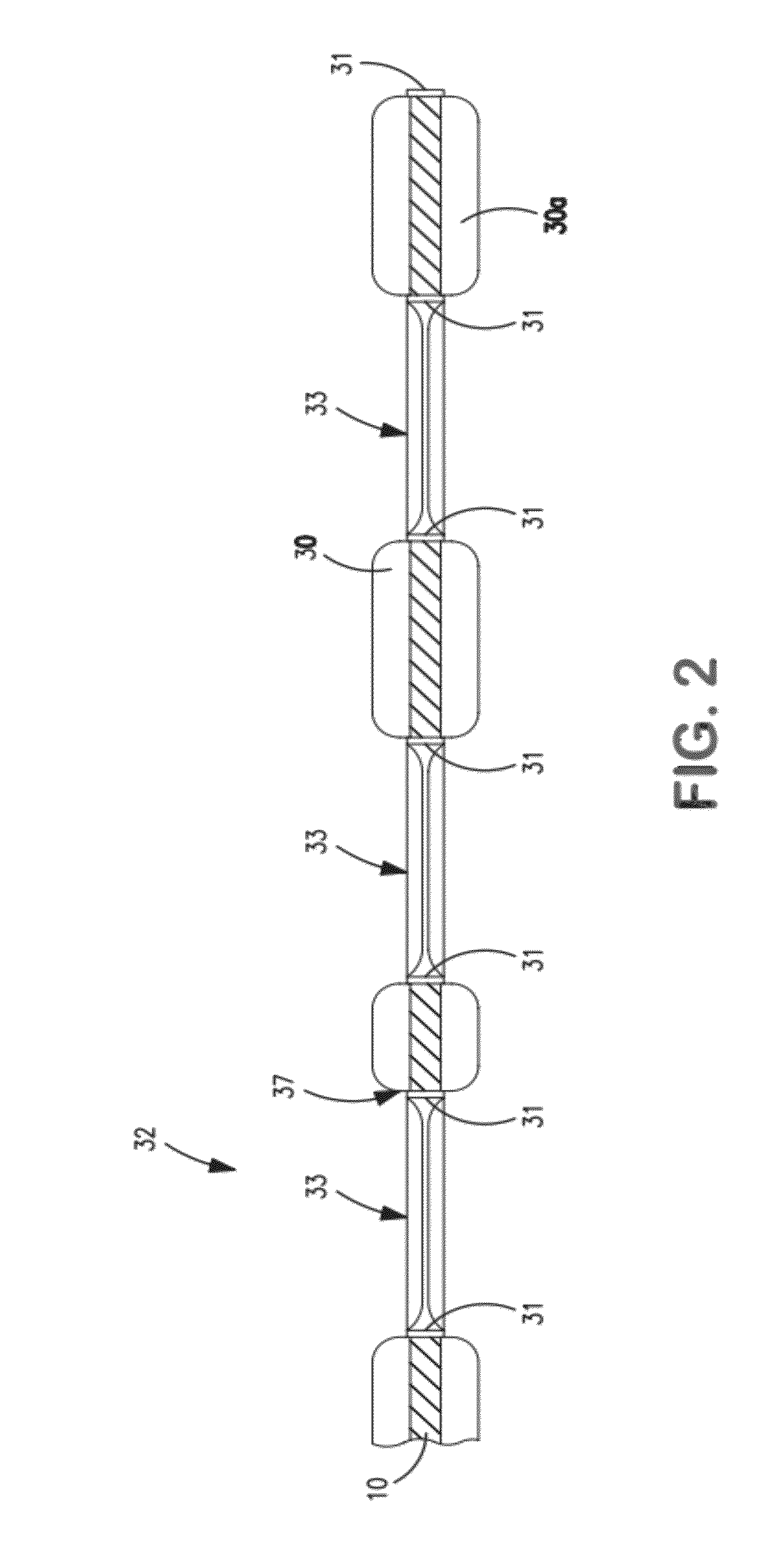
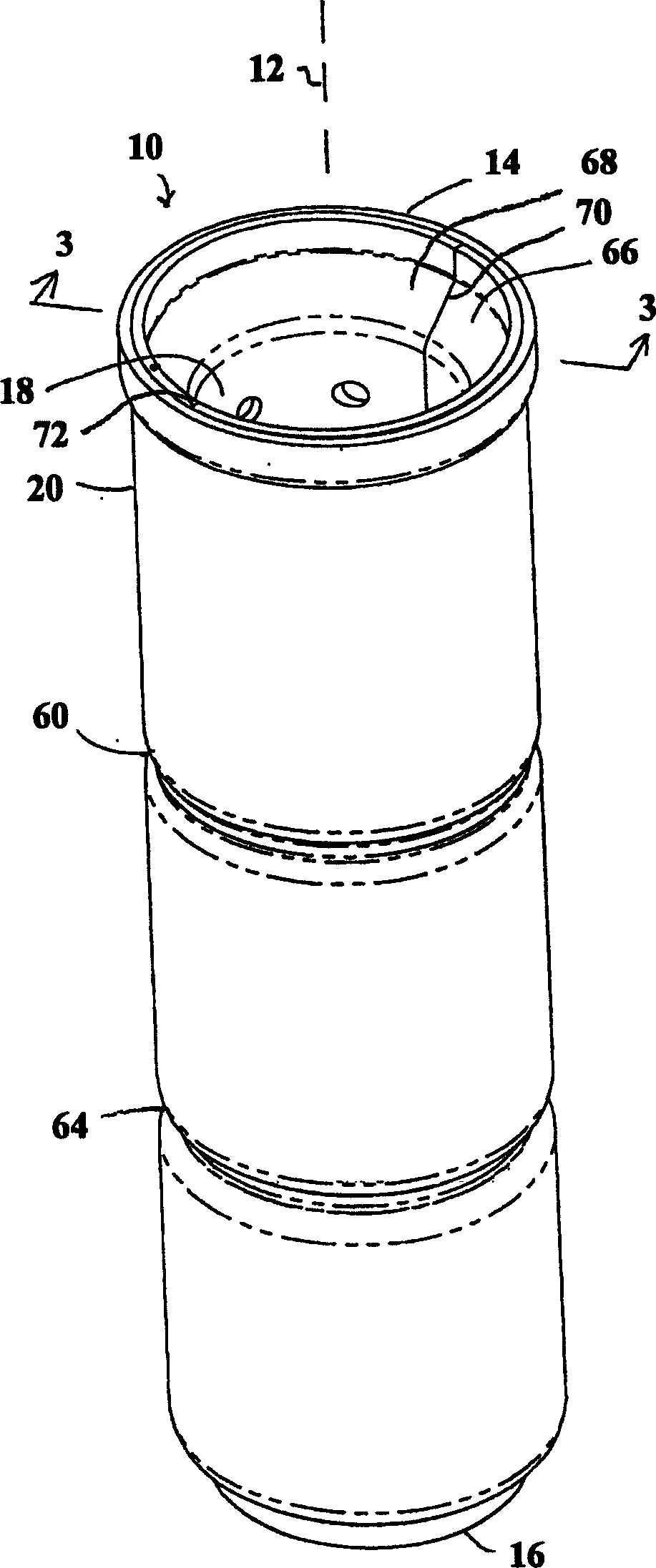
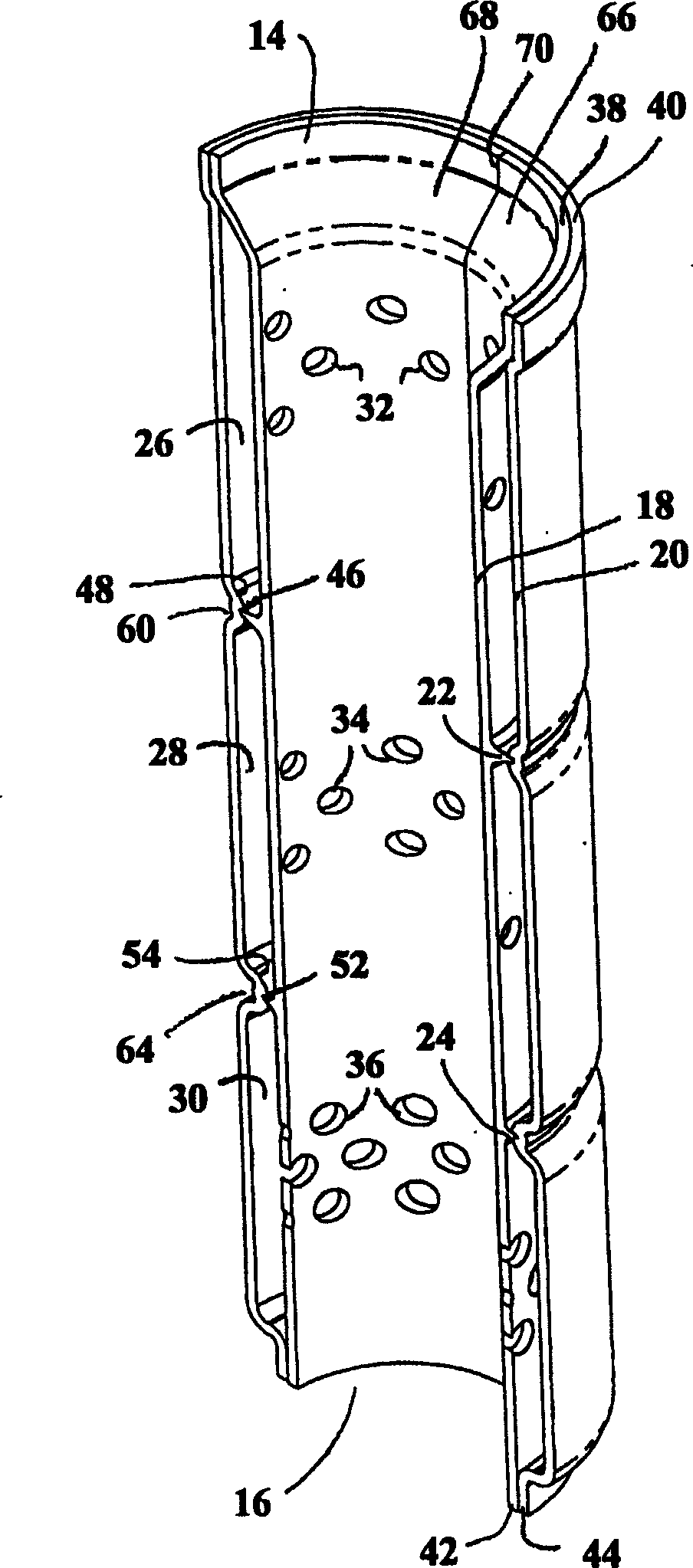
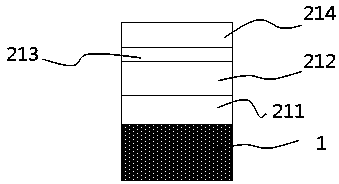
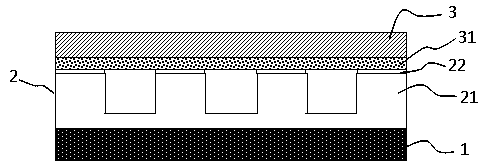
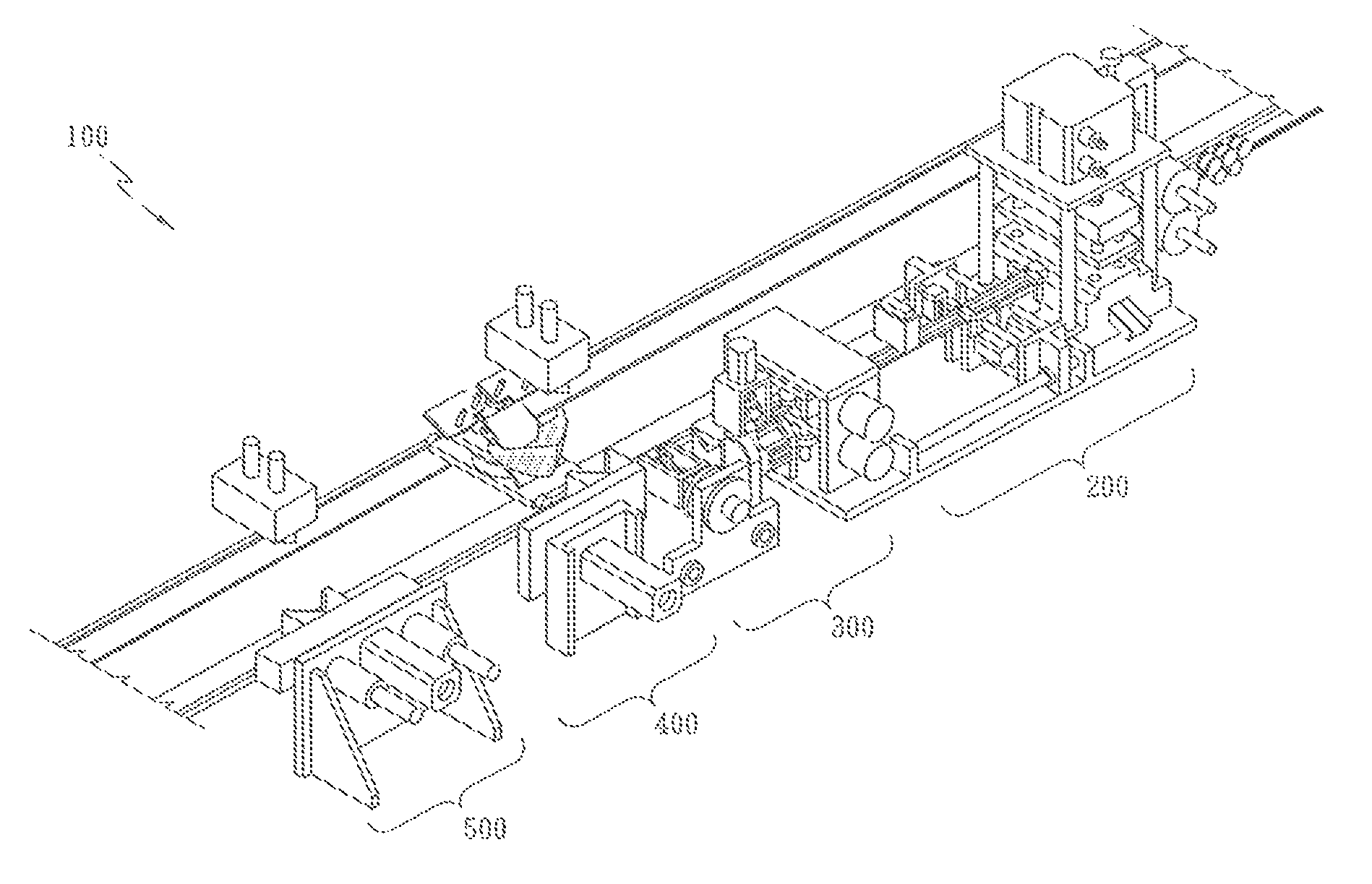
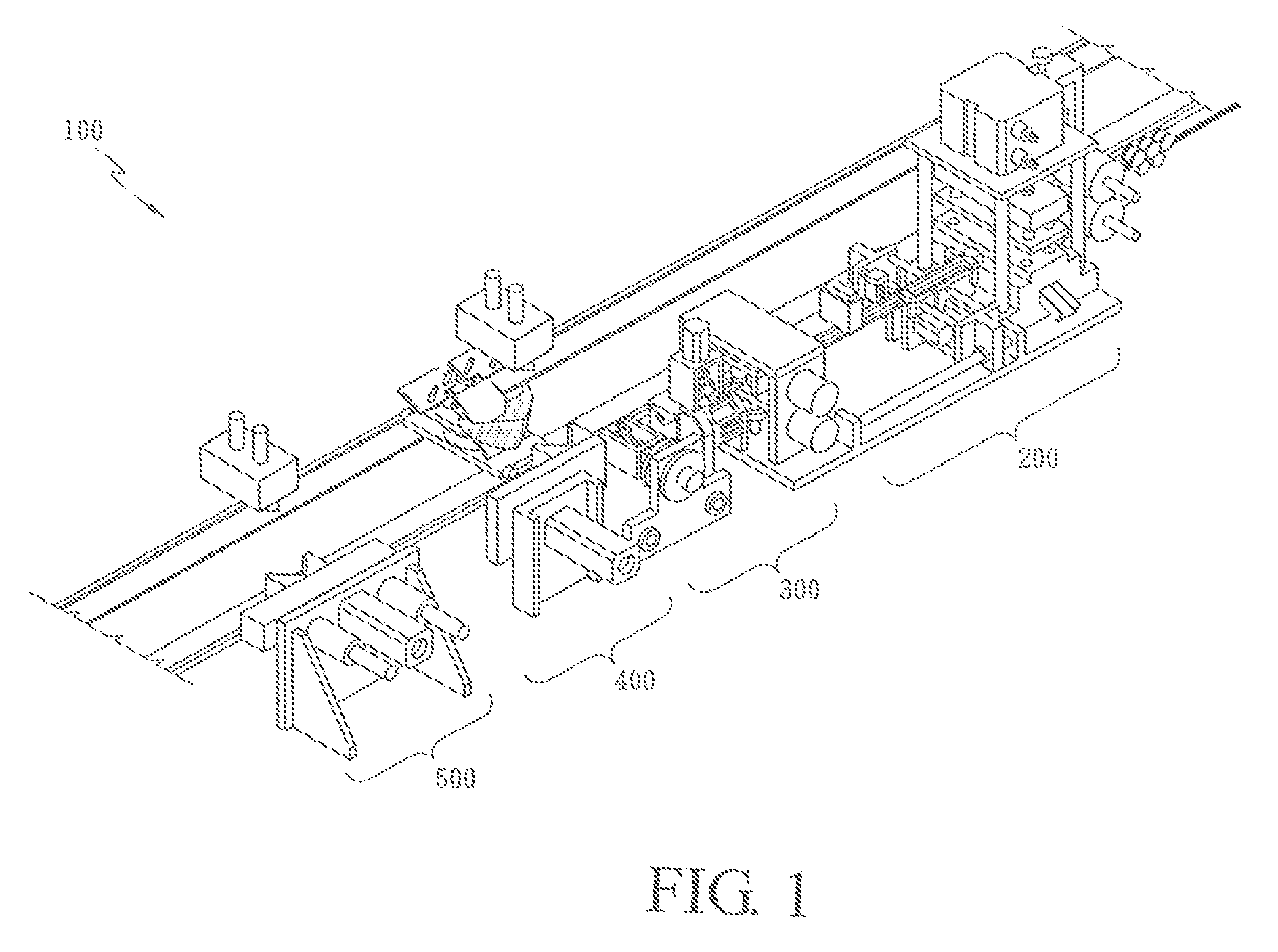
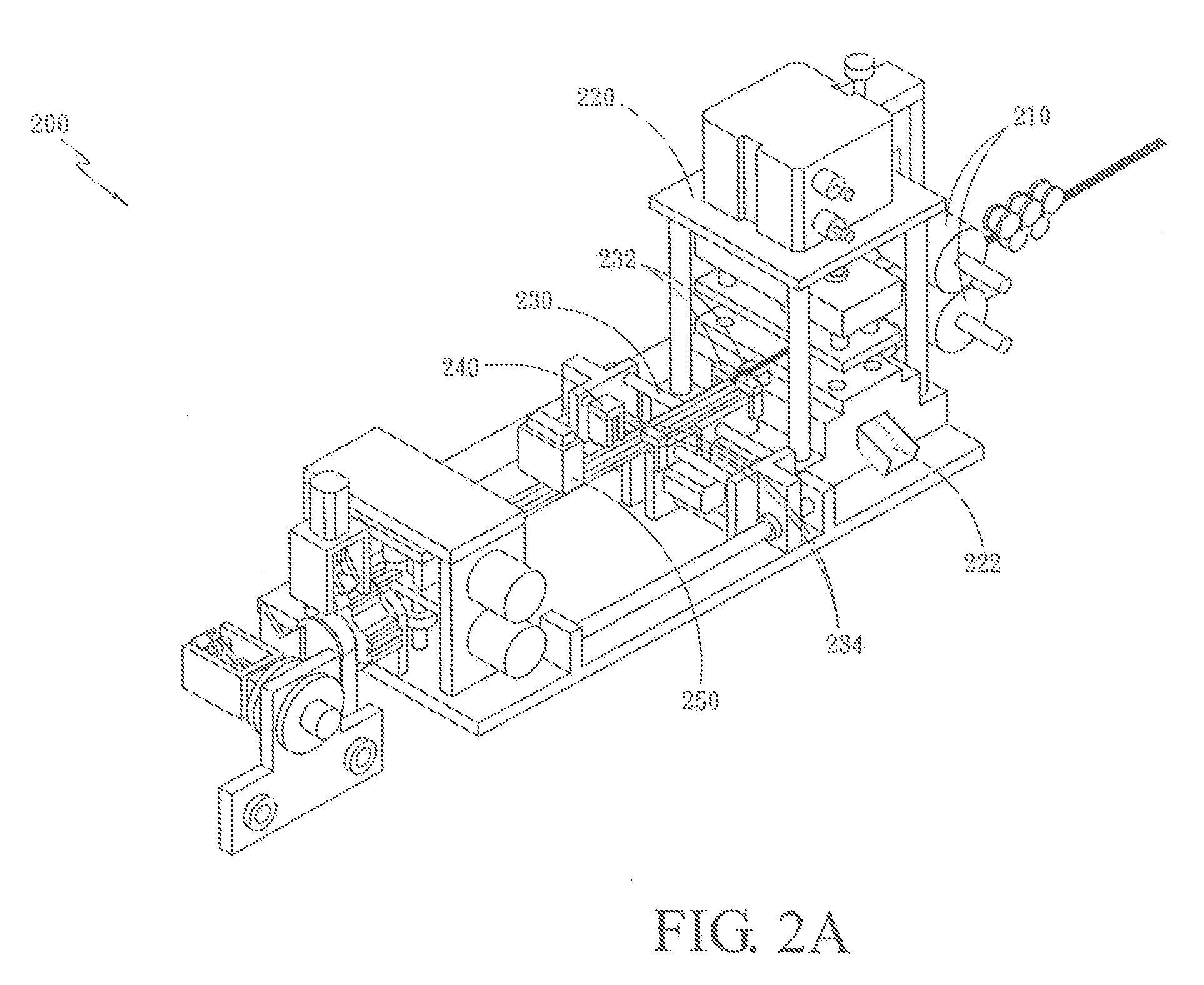
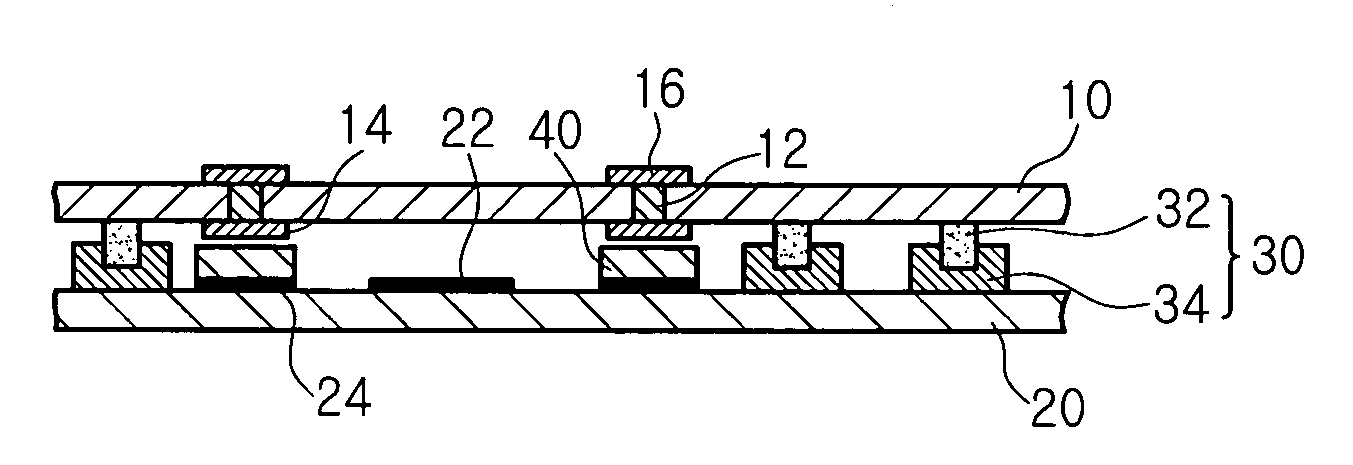
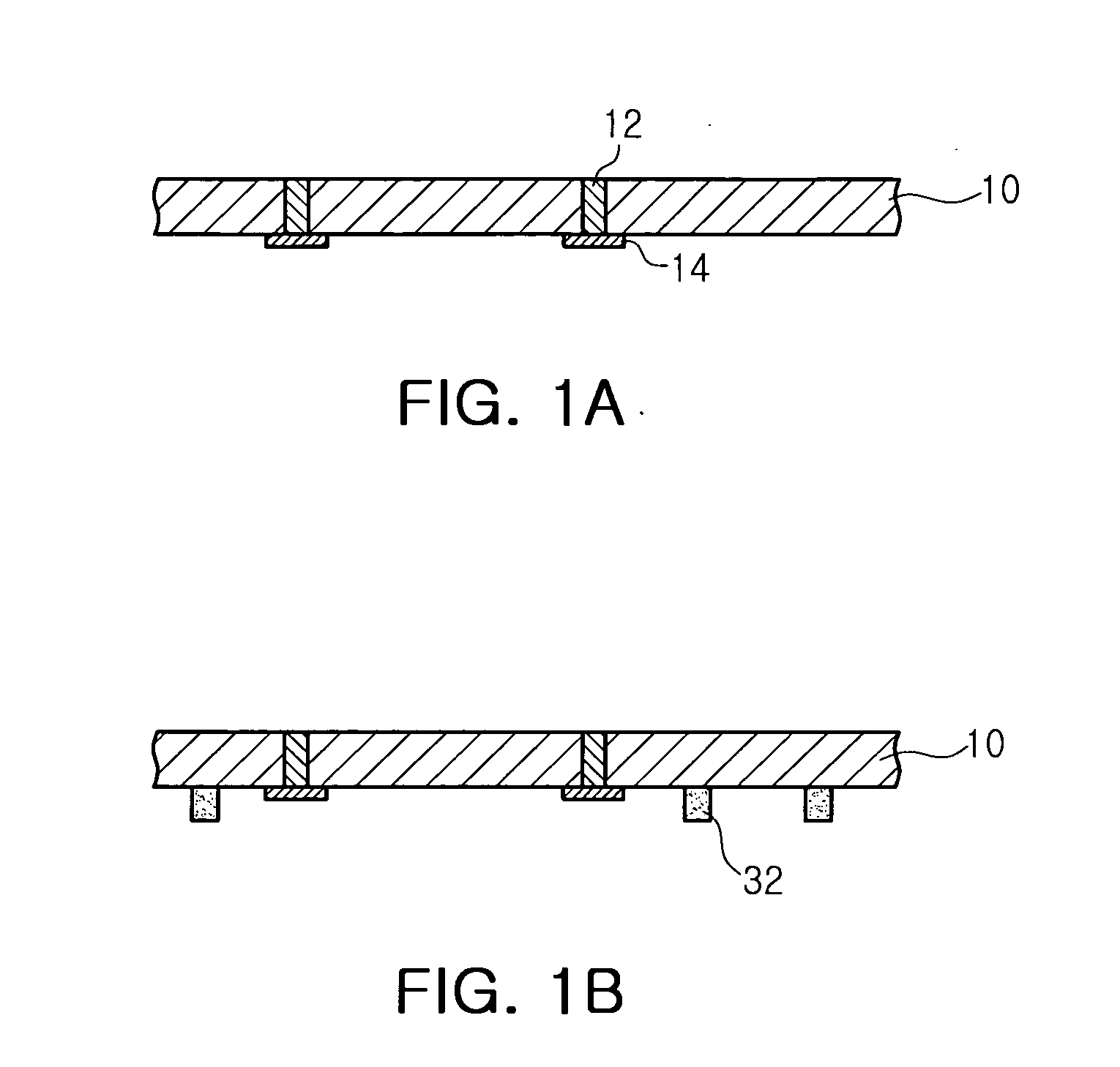
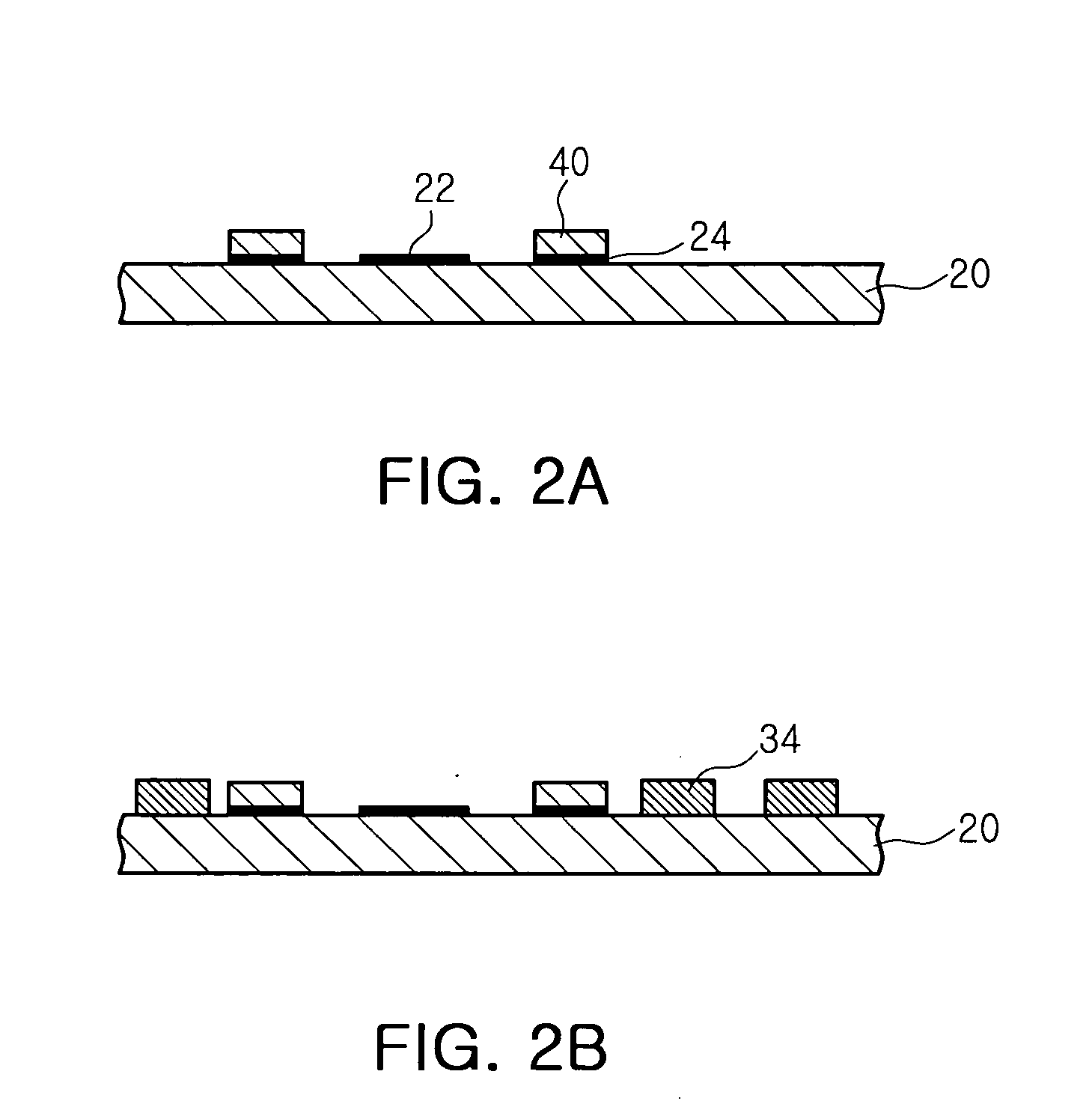
ActiveUS20090197041A1Lamination ancillary operationsDuplicating/marking methodsSmall amplitudeSecondary bonding
A composite that contains an elastic film laminated to a meltblown facing is provided. During lamination, apertures and discrete bond sites may be concurrently formed in the elastic film. The discrete bond sites may be located proximate (adjacent or near to) a perimeter defined by corresponding apertures formed by displacement of the film. The location of the bond sites adjacent to or near the apertures may enhance the durability of the meltblown facing by strengthening the area surrounding the apertures. Furthermore, the content of the elastic film and the temperature / pressure of lamination may be selected to that the film possesses a sufficient tack for adhering to the facing at regions other than those fused together by the bonding elements of the patterned roll. Such secondary bonding further stabilizes the meltblown facing and renders it suitable for printing. Further, the film is under tension in the machine direction during lamination. Subsequent to lamination, however, the film is retracted so that the facing retracts toward its original machine direction length, thereby gathering and forming pleats. It has been discovered that these pleats have a relatively small amplitude (height), as well as a substantially uniform frequency across the surface of the facing. Such a small height and increased regularity improves the ability to transfer an ink to “peaks” of the pleats, thereby improving print quality and uniformity.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Resonator with retention ribs
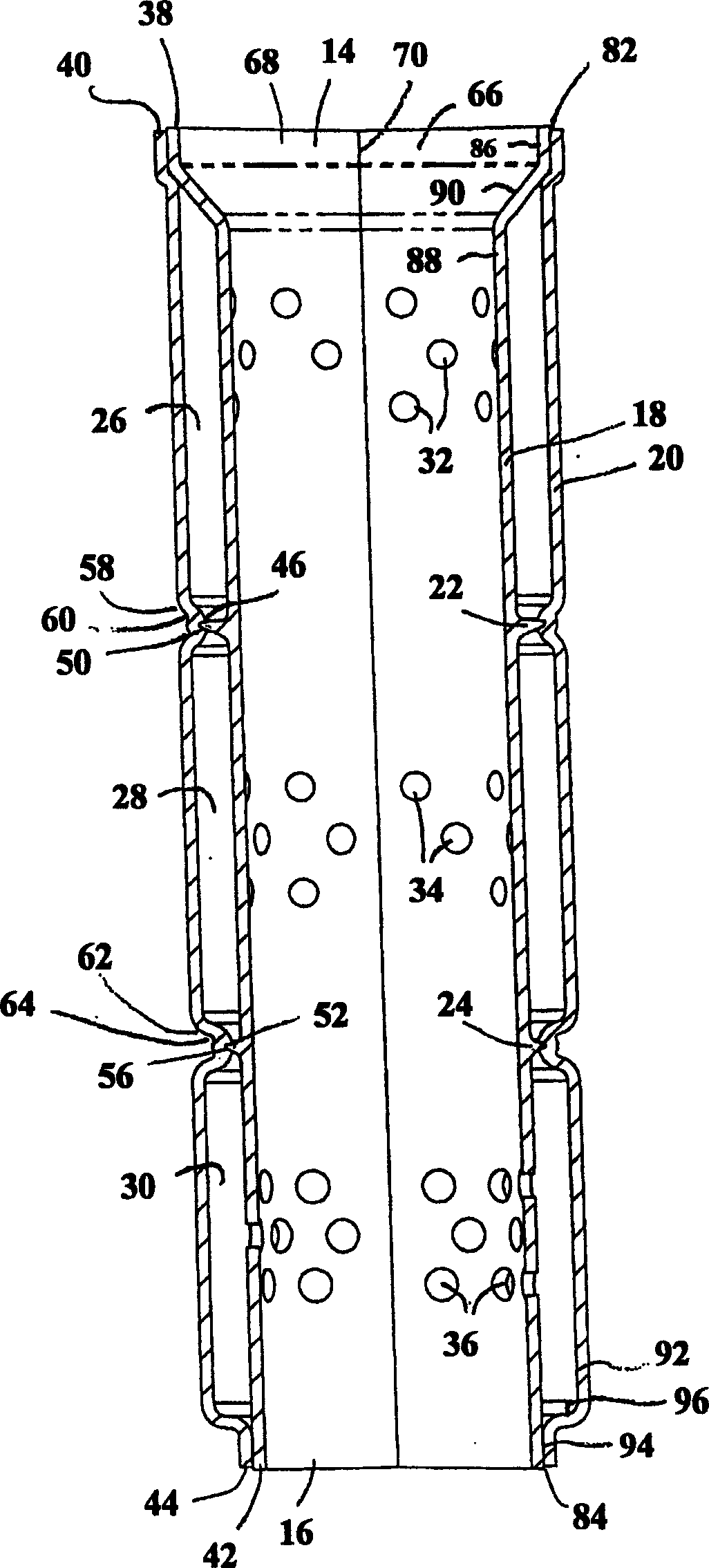
InactiveUS20050150718A1Simple and cost-effectiveSilencing apparatusCombustion enginesEngineeringSecondary bonding
A resonator includes an inner perforated tube, an outer shell, and a plurality of annular ribs extending radially therebetween and defining resonant chambers. Progressive stepping of ribs and grooves enables axial insertion assembly with minimal cost. The need for welding or secondary bonding operations is eliminated.
Owner:FLEETGUARD INC
Automatic nose strip bonding apparatus for face mask
InactiveUS20080251210A1Improve manufacturing speedImprove product qualityLiquid surface applicatorsLamination ancillary operationsNoseSecondary bonding
An automatic nose strip bonding apparatus for a face mask is disclosed, including a nose strip providing mechanism, a nose strip turnover mechanism, and a press-to-bond device. The nose strip providing mechanism drives a nose strip forward and carries out stamping operation on the nose strip, and applies a bonding agent to the nose strip. The nose strip turnover mechanism serves to turn over the nose strip that has already been applied with the bonding agent to allow the surface of the nose strip on which the bonding agent is applied to face a face mask. The press-to-bond device includes a first bonding device and a second bonding device to attach the nose strip to the face mask and to carry out a secondary bonding operation, respectively, to ensure firm bonding of the nose strip to the face mask.
Owner:CHEN HUNG HO
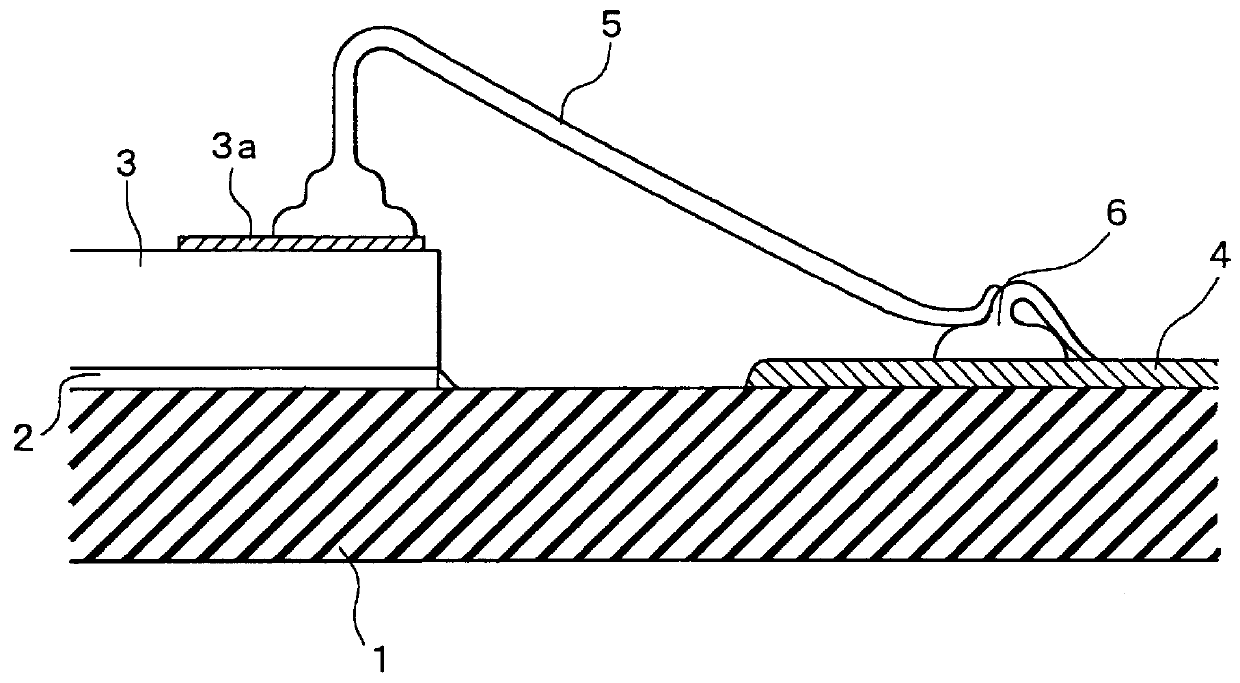
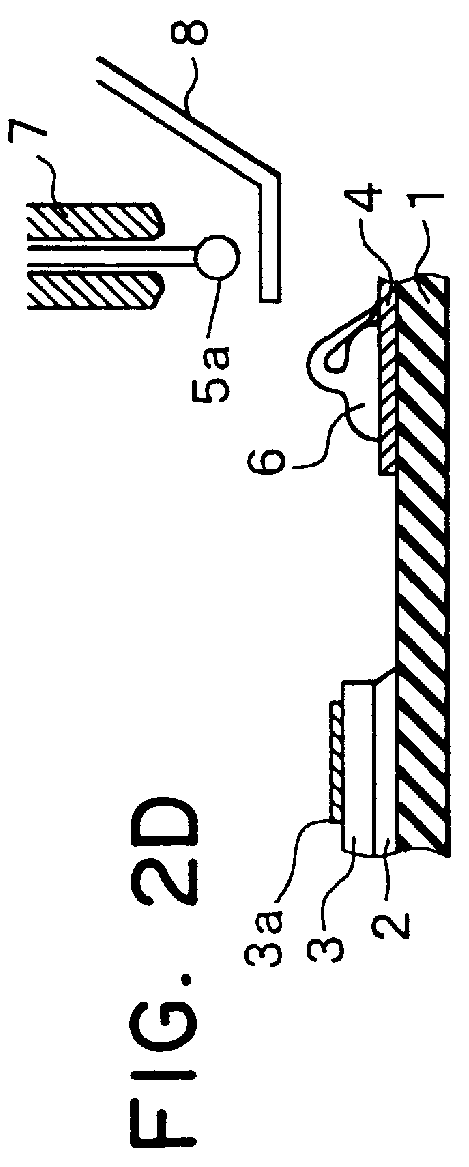
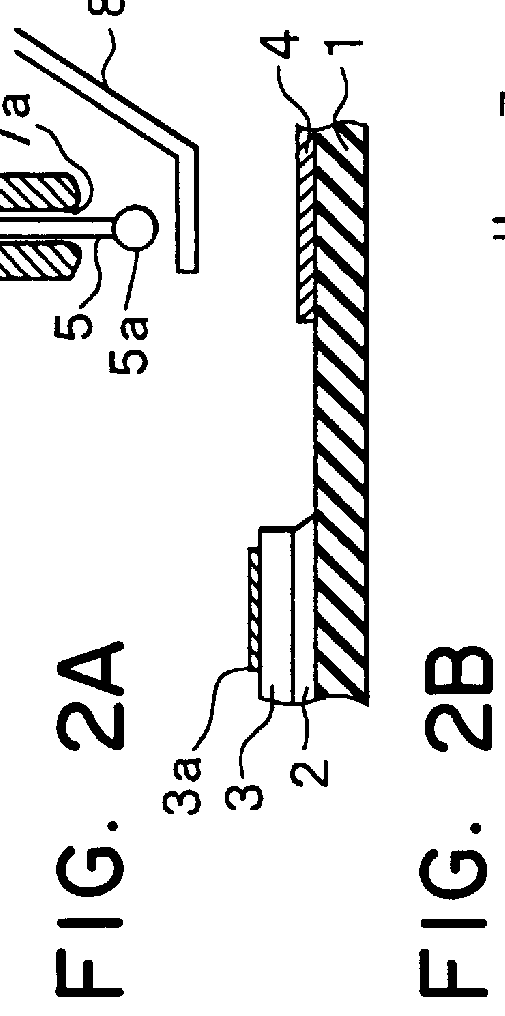
Wire bonding method
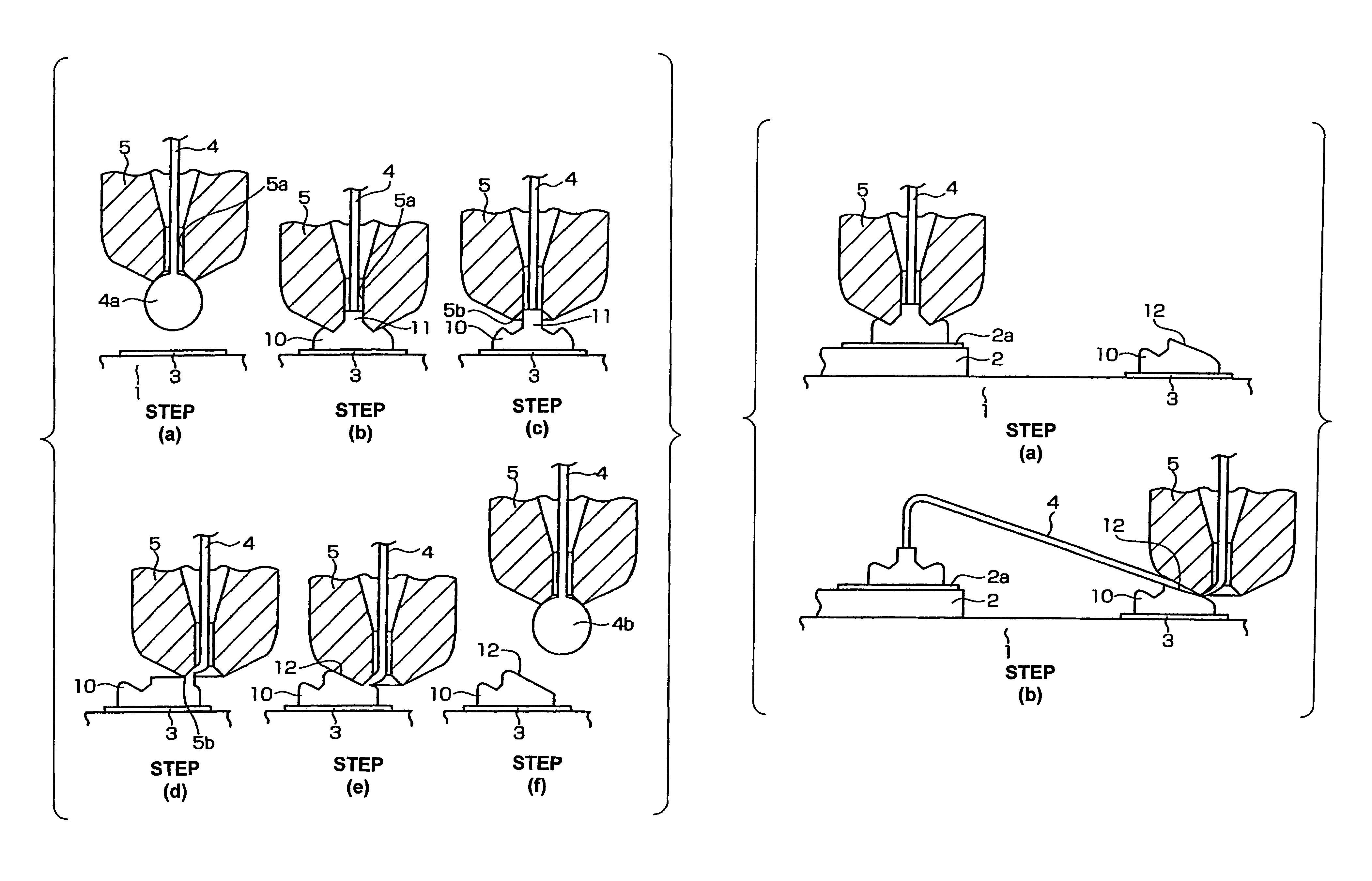
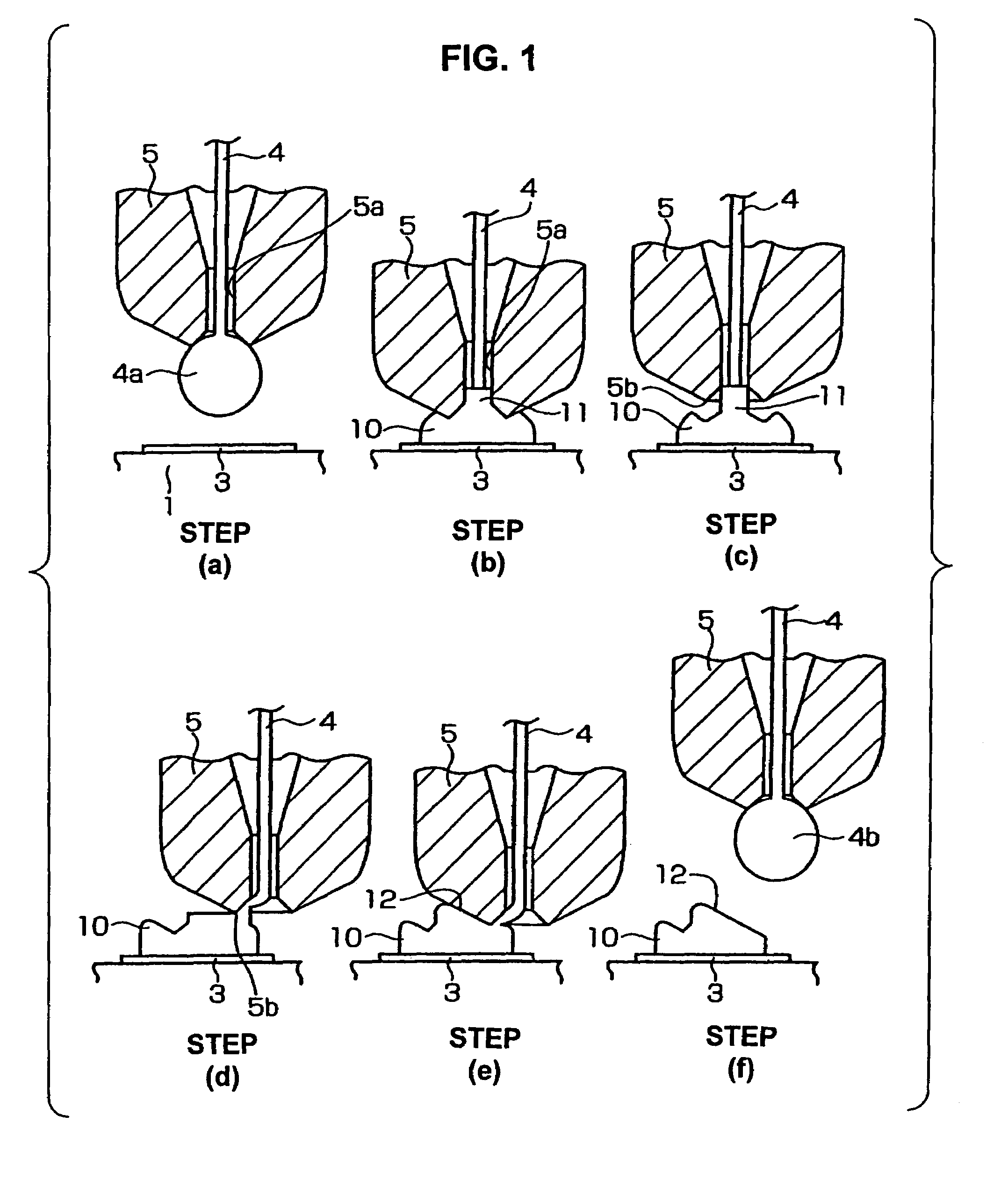
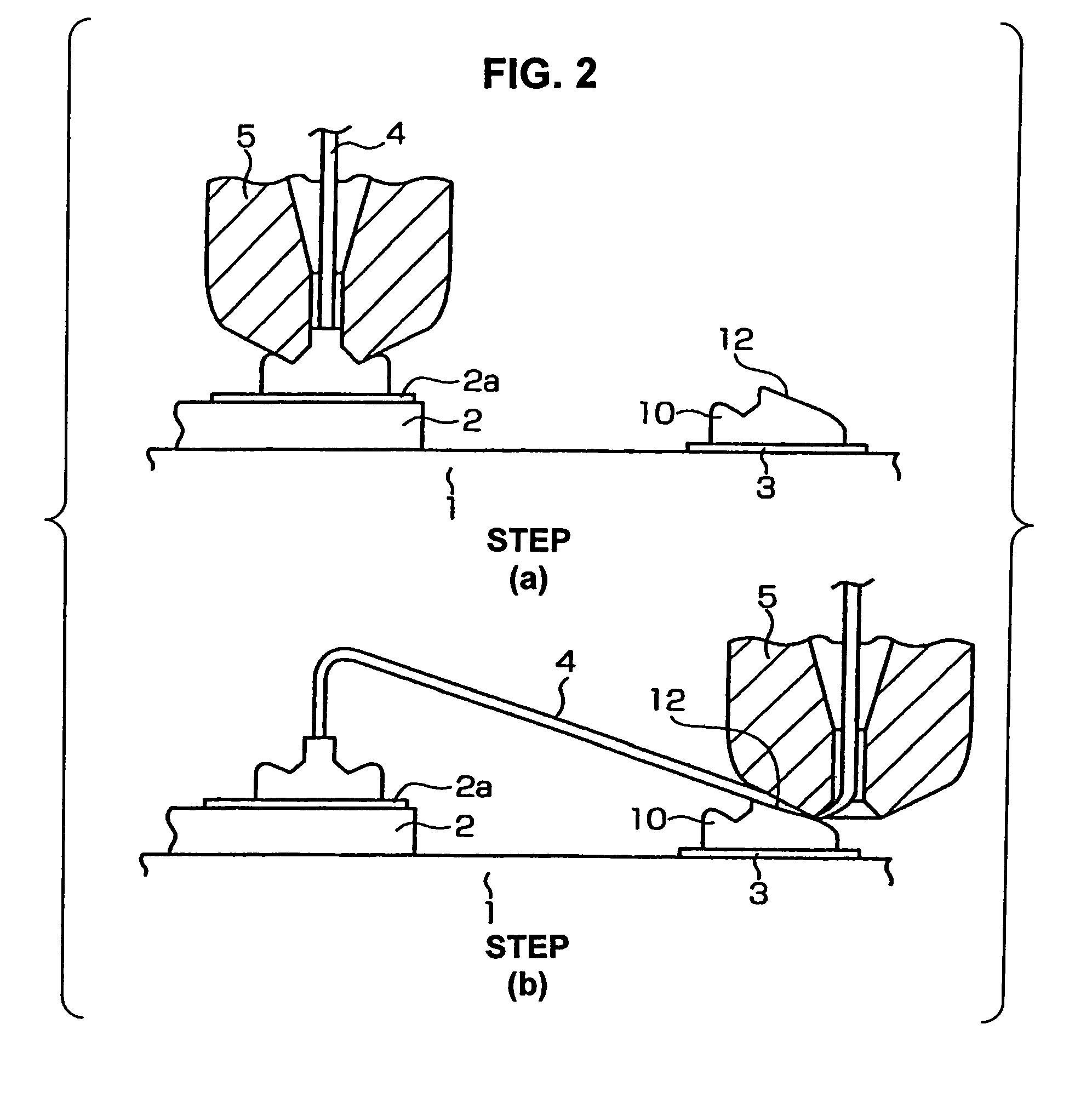
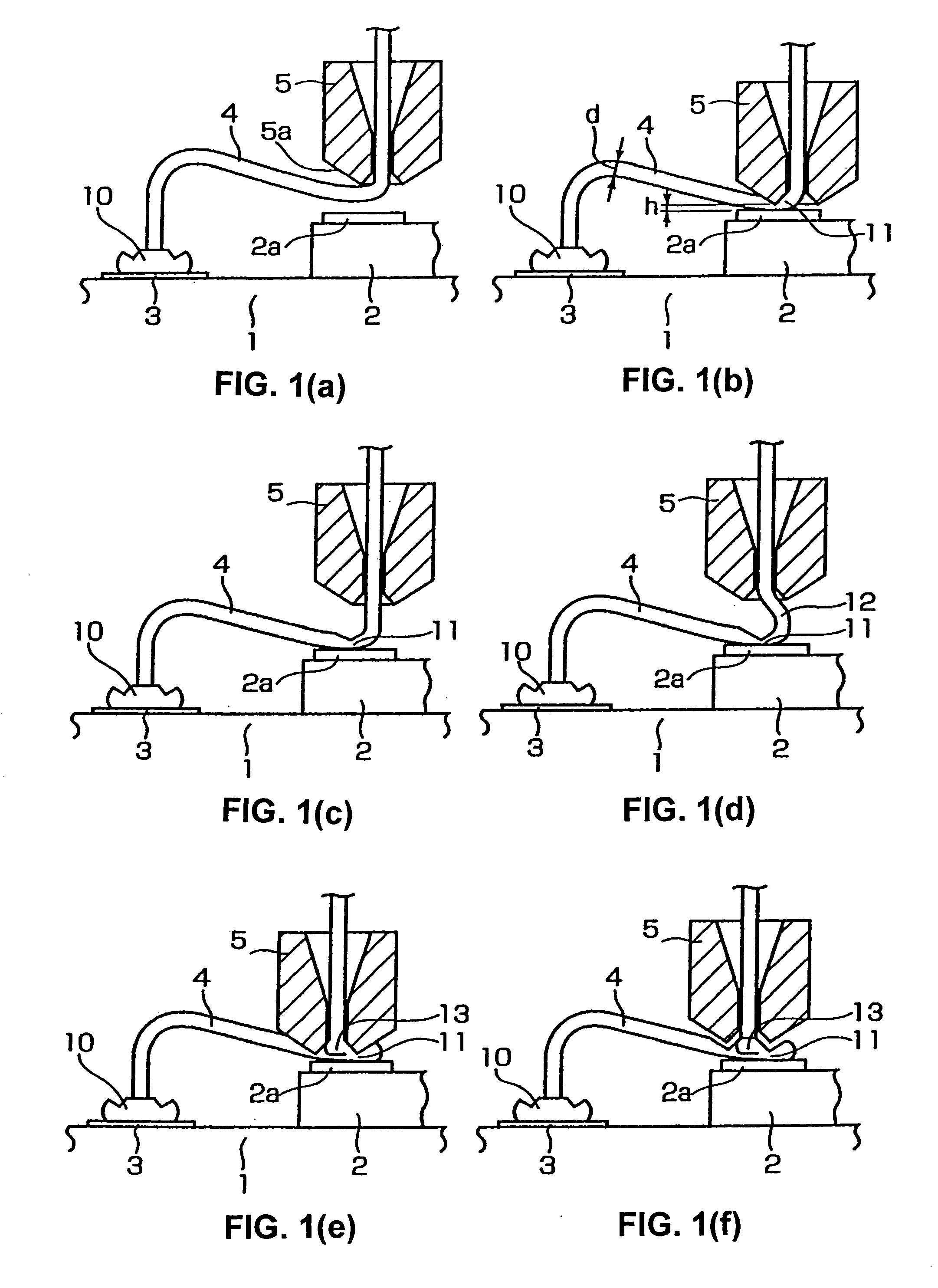
A ball is formed at the tip of a wire projecting from a capillary. The capillary is positioned above an interconnection, and ball bonding forms a bump on the interconnection. The capillary is then moved next to the bump and wedge bonding is carried out. Next, the capillary is moved upward and another ball is formed at the tip of the wire, and the wire is primary bonded to a bonding pad of a semiconductor chip. The wire is then looped and the capillary is positioned above the bump, and secondary bonding is carried out. As a result, the formation of tails on the bump is prevented.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Bonding apparatus and bonding method
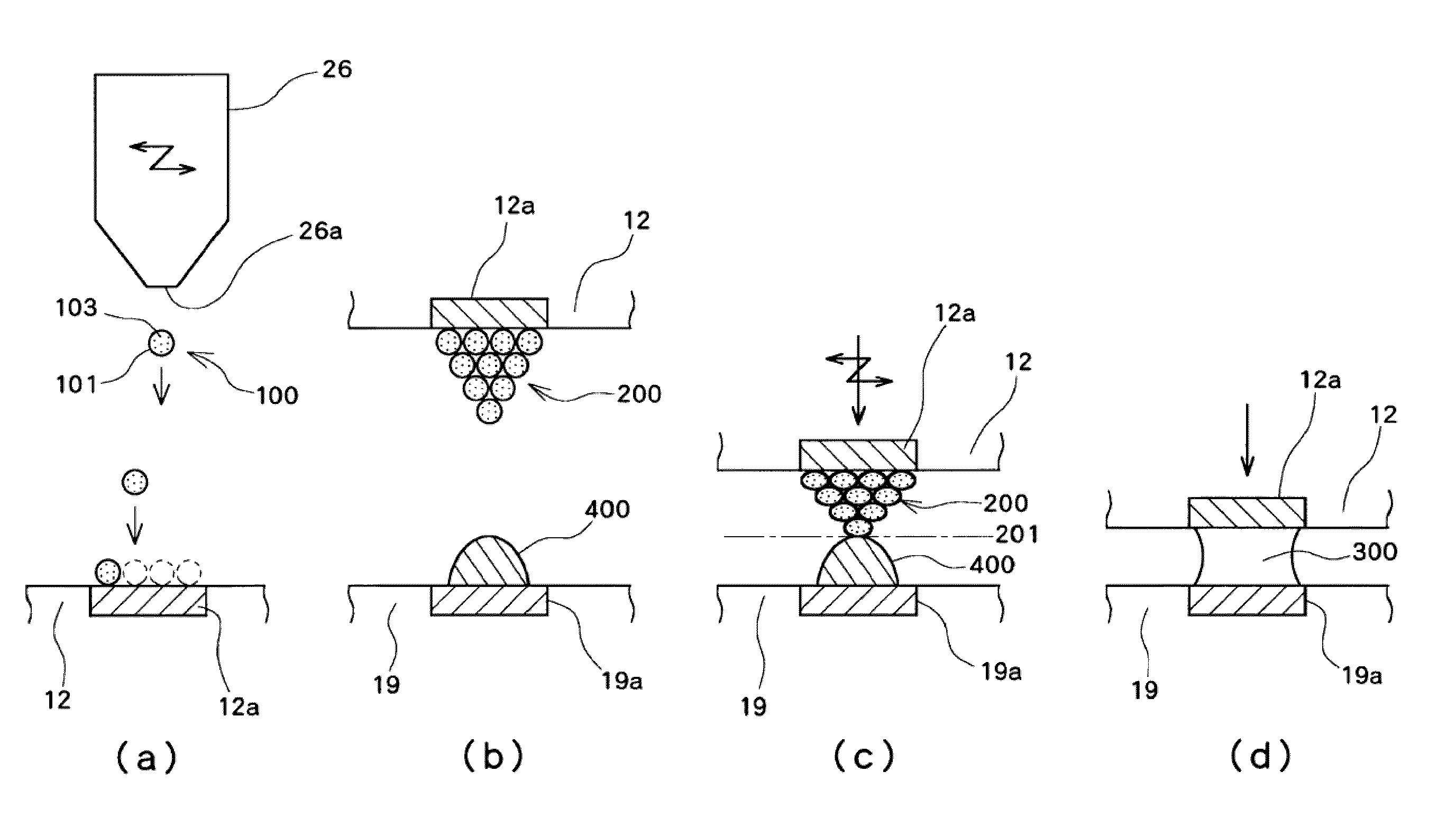
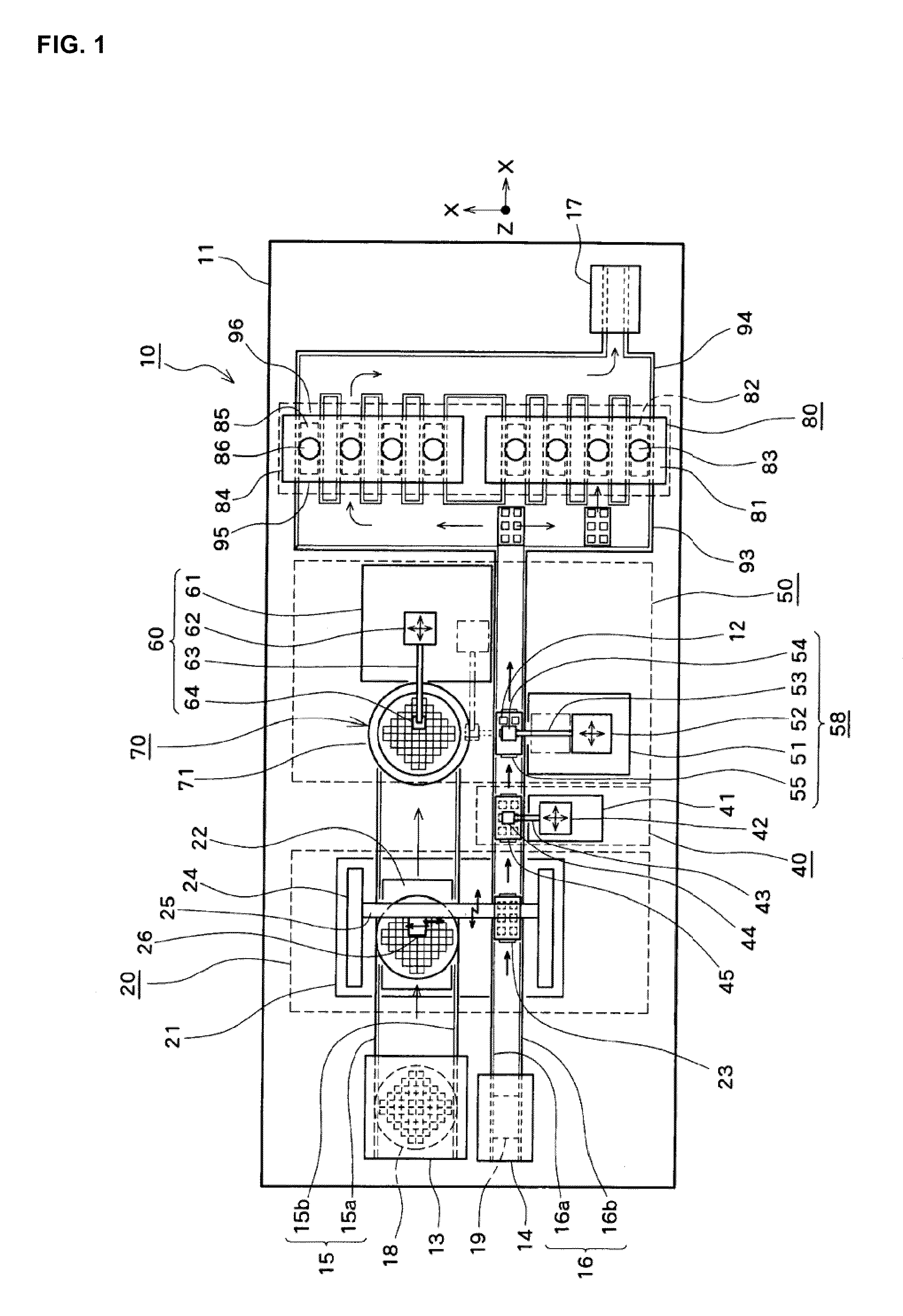
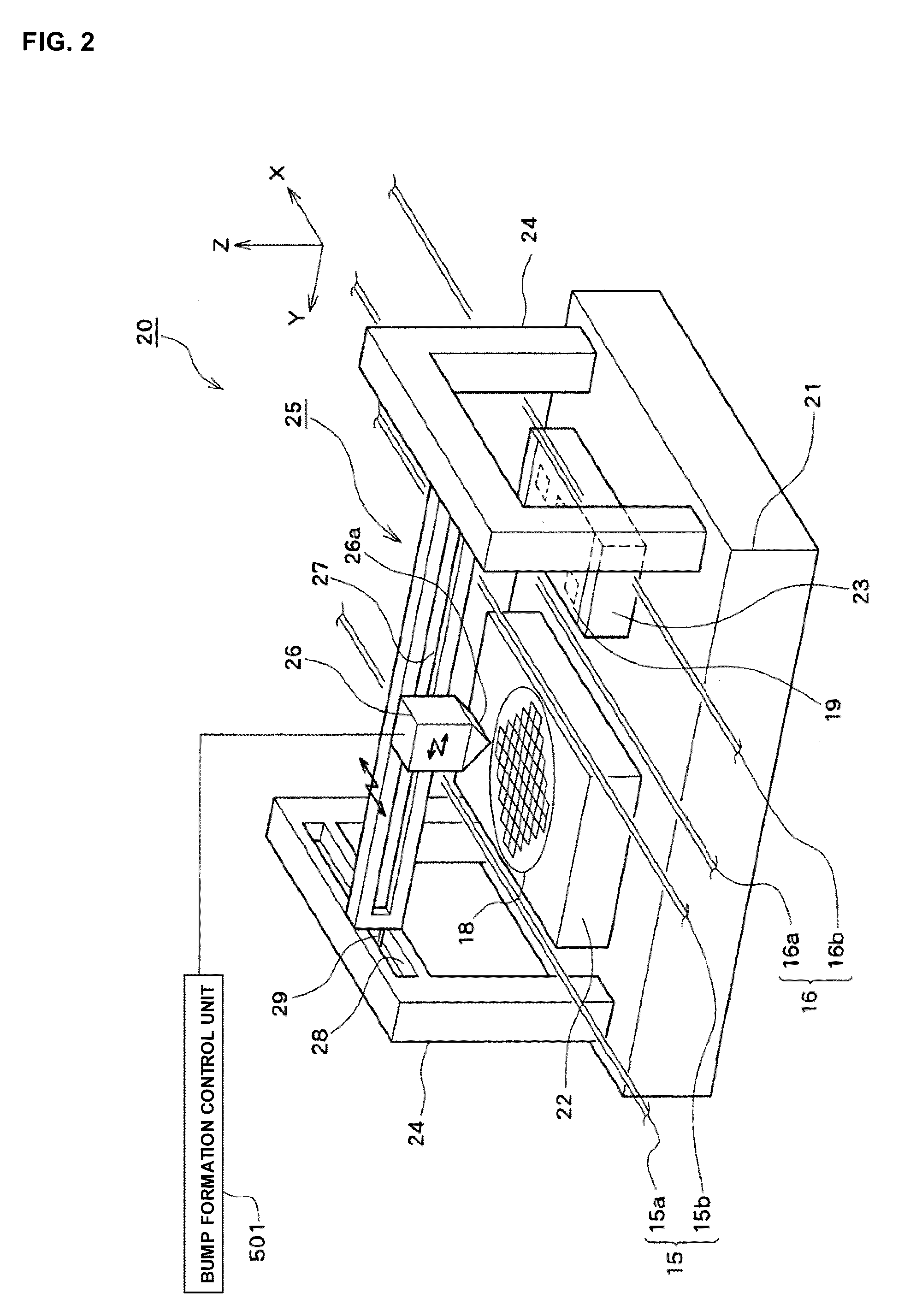
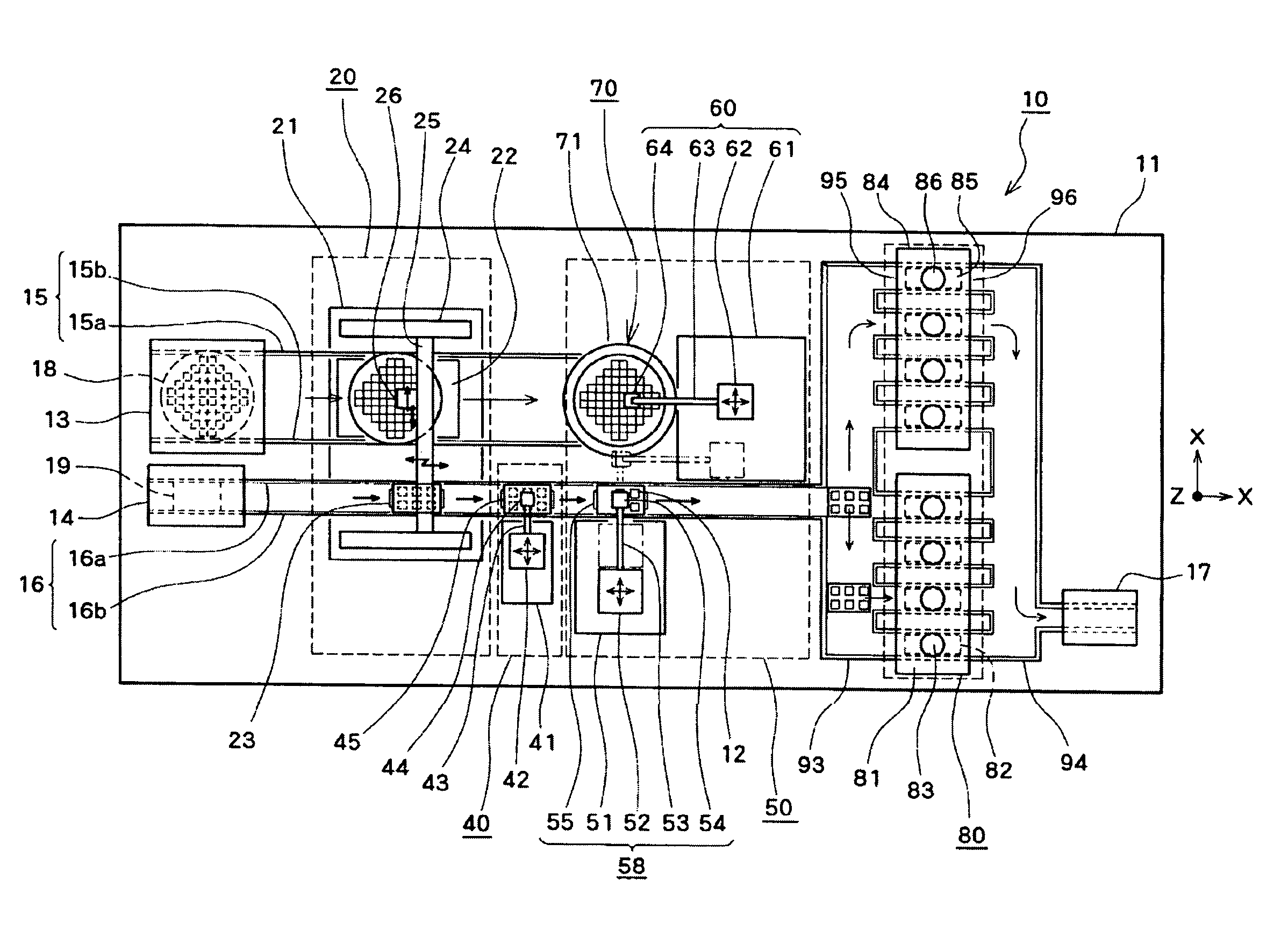
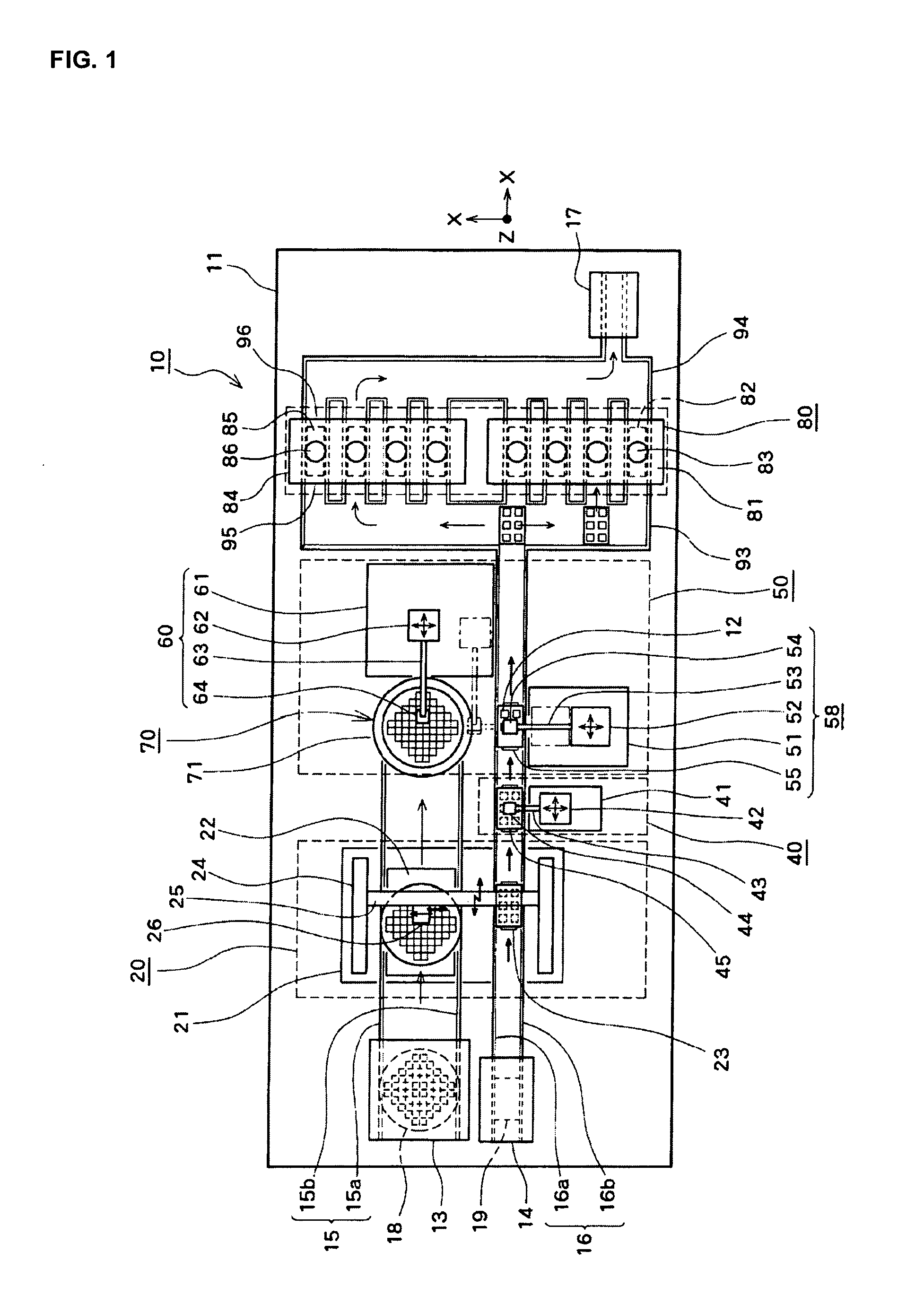
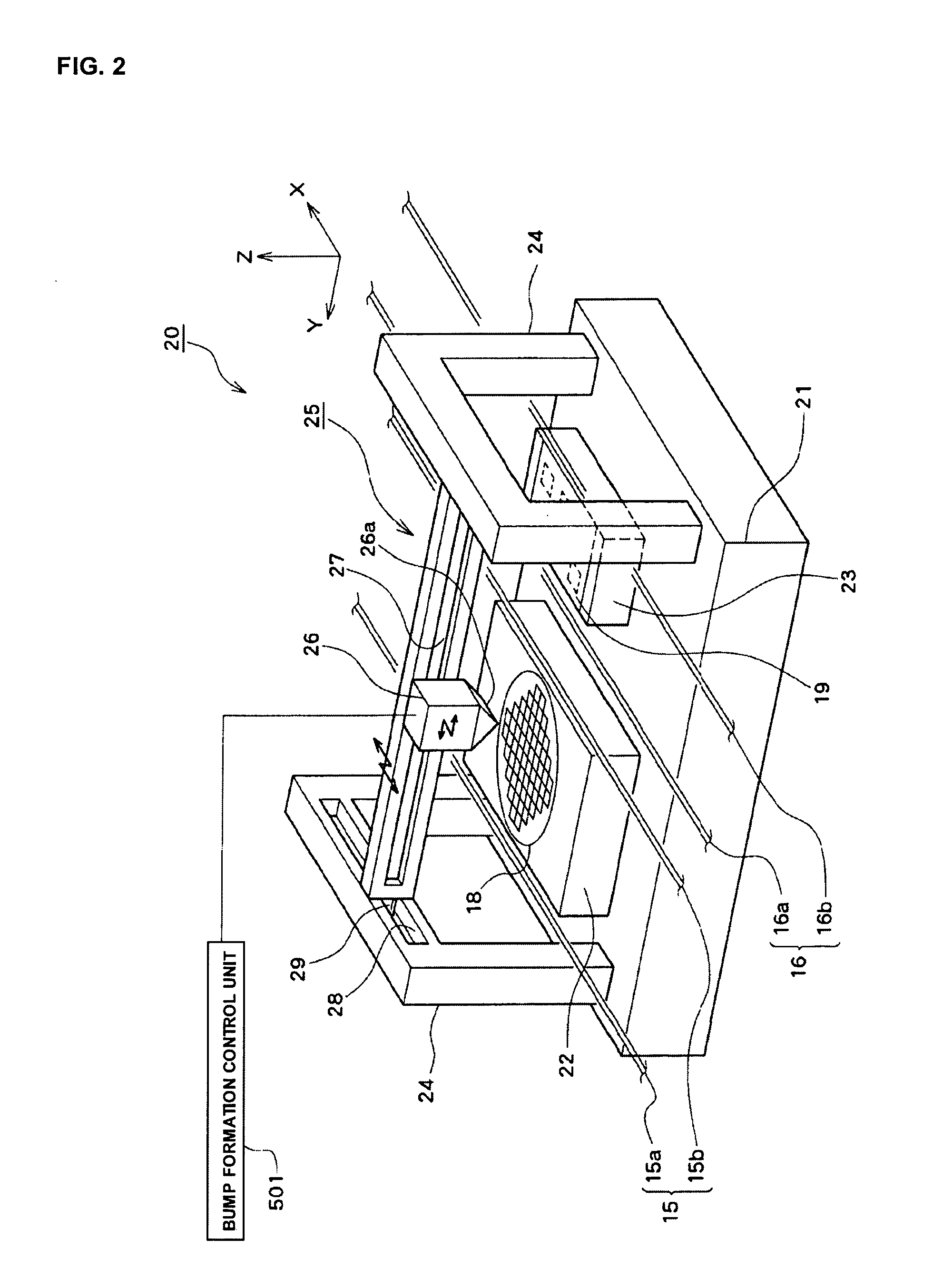
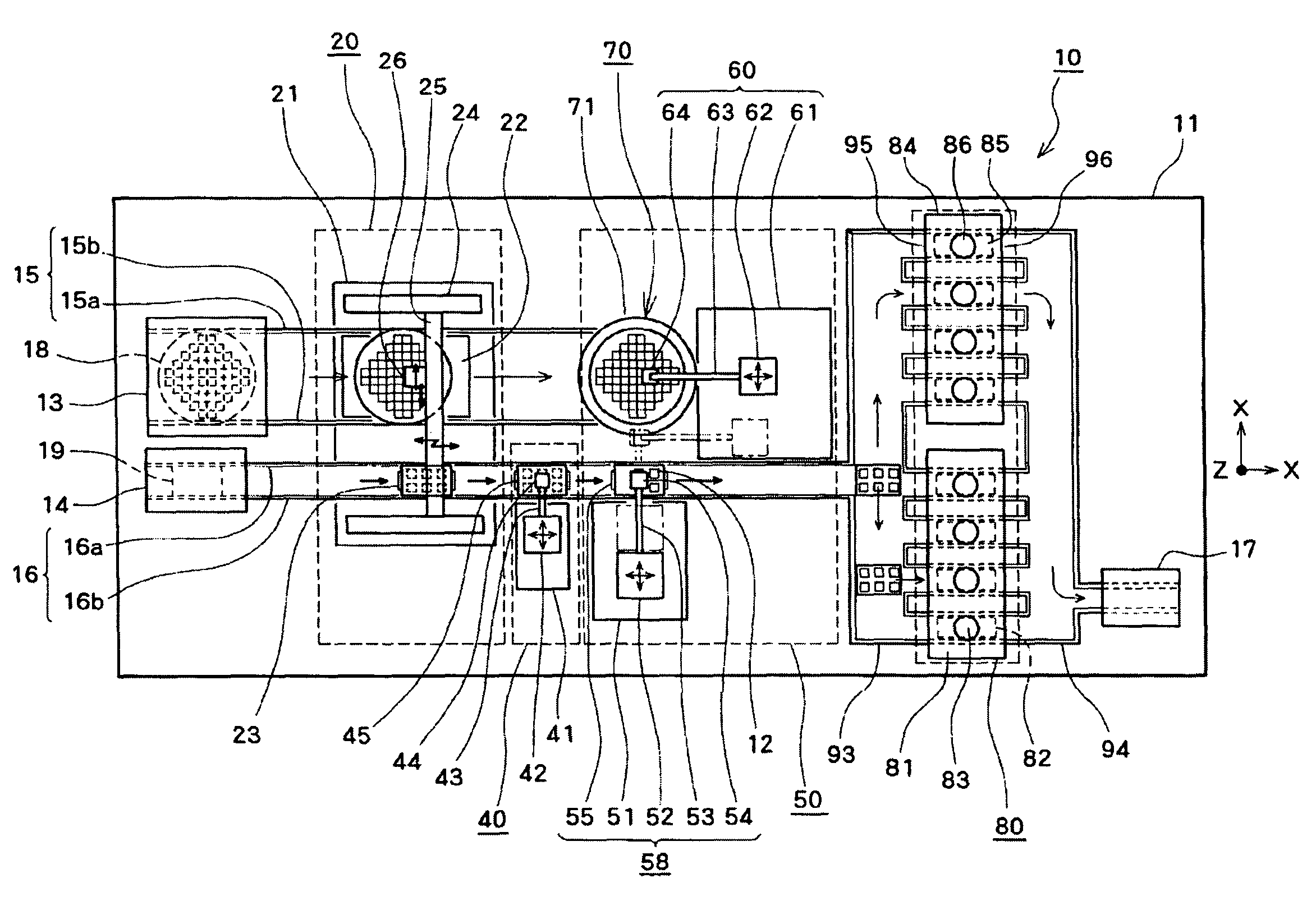
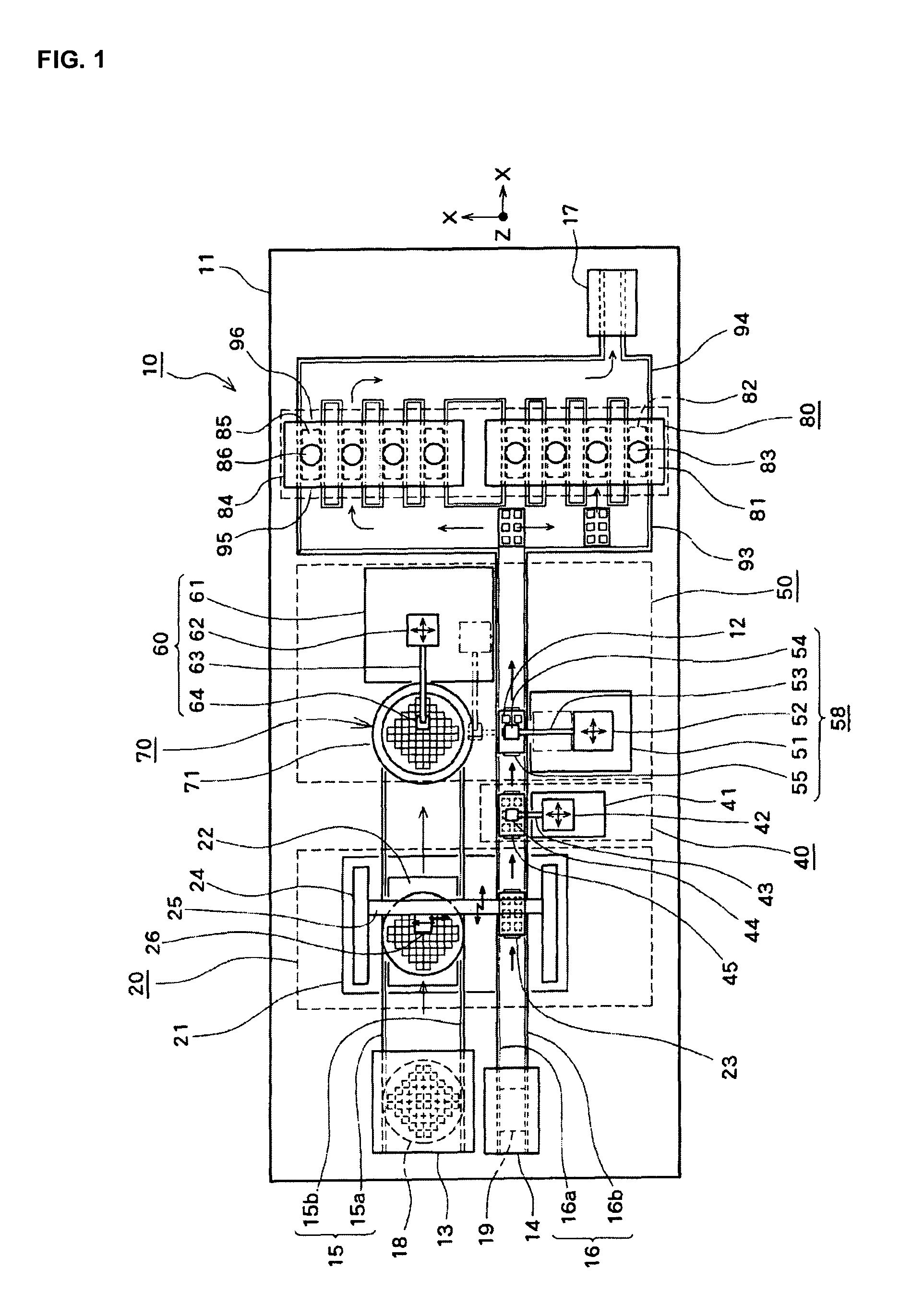
InactiveUS20100093131A1Improve bindingEffective combinationMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringSecondary bonding
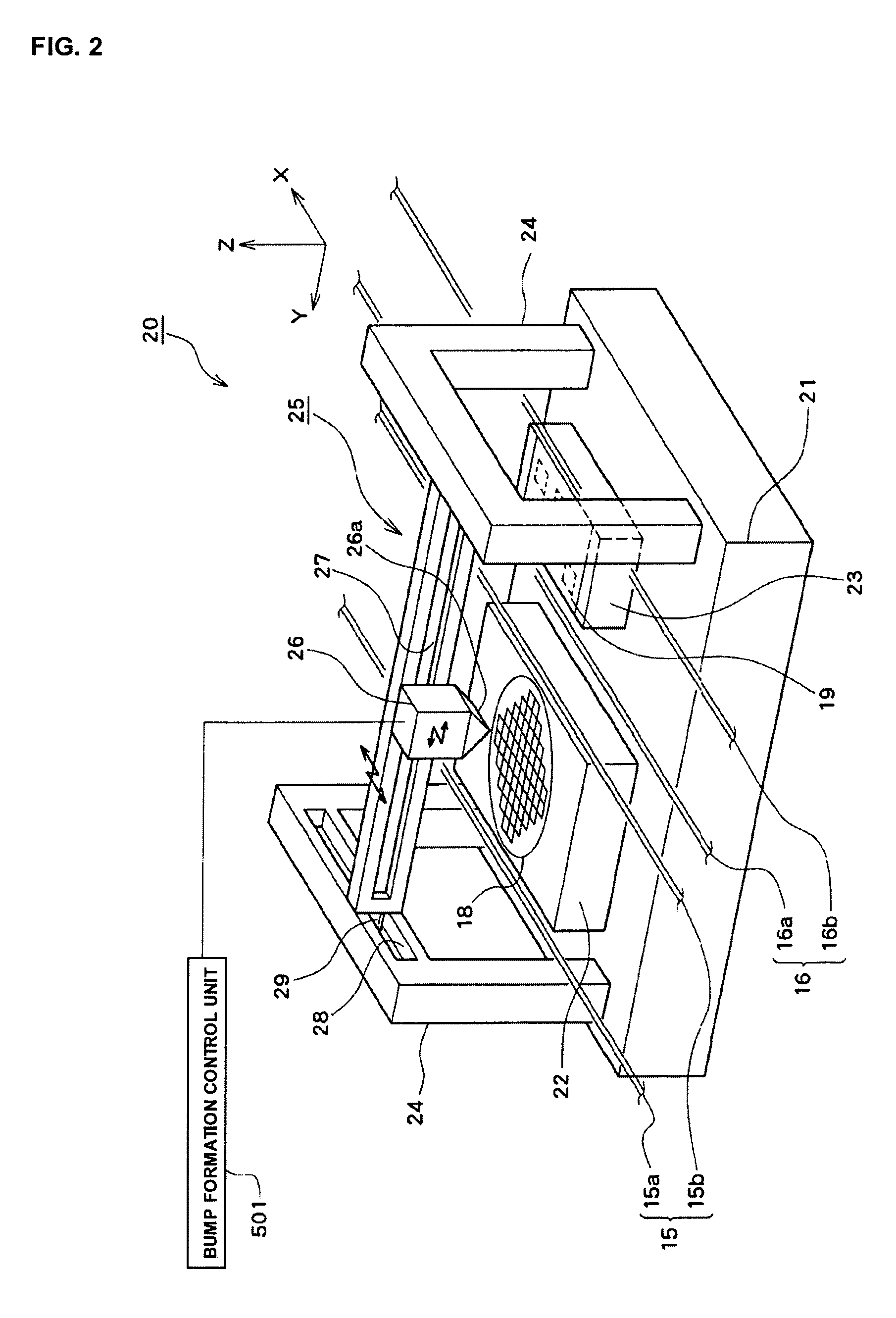
A bonding apparatus (10) that bonds an electrode of a semiconductor die (12) and an electrode of a circuit board (19) using a metal nano paste includes a bump formation mechanism (20) that forms bump by injecting microdroplets of a metal nano paste on each electrode, a primary bonding mechanism (50) that carries out primary bonding to the electrodes in a non-conductive state by pressing the bump of the semiconductor die (12) against the bump of the circuit board (19), and a secondary bonding mechanism (80) that carries out secondary bonding so that the electrodes become conductive by pressurizing the primary bonded bump in bonding direction and by heating the bump to pressurize and sinter the metal nanoparticles in the bump. With this, it is possible to efficiently bond the electrodes with a simple and easy way while reducing a bonding load.
Owner:SHINKAWA CO LTD
Printable elastic composite
ActiveUS8287677B2Lamination ancillary operationsDuplicating/marking methodsSmall amplitudeEngineering
A composite that contains an elastic film laminated to a meltblown facing is provided. During lamination, apertures and discrete bond sites may be concurrently formed in the elastic film. The discrete bond sites may be located proximate (adjacent or near to) a perimeter defined by corresponding apertures formed by displacement of the film. The location of the bond sites adjacent to or near the apertures may enhance the durability of the meltblown facing by strengthening the area surrounding the apertures. Furthermore, the content of the elastic film and the temperature / pressure of lamination may be selected to that the film possesses a sufficient tack for adhering to the facing at regions other than those fused together by the bonding elements of the patterned roll. Such secondary bonding further stabilizes the meltblown facing and renders it suitable for printing. Further, the film is under tension in the machine direction during lamination. Subsequent to lamination, however, the film is retracted so that the facing retracts toward its original machine direction length, thereby gathering and forming pleats. It has been discovered that these pleats have a relatively small amplitude (height), as well as a substantially uniform frequency across the surface of the facing. Such a small height and increased regularity improves the ability to transfer an ink to “peaks” of the pleats, thereby improving print quality and uniformity.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Resonator with retention ribs
A resonator includes an inner porous tube, a housing and a plurality of annular ribs extending radially between the inner porous tube and the housing and defining a resonant cavity. The progressive step of the ribs and grooves enables an axially inserted assembly with a minimum of effort. This eliminates the need for welding or secondary bonding operations.
Owner:FLEETGUARD INC
Bonding apparatus and bonding method
InactiveUS20100089980A1Effective combinationReduce loadMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringSecondary bonding
A bonding apparatus (10) that bonds an electrode of a semiconductor die (12) and an electrode of a circuit board (19) using a metal nano paste includes a bump formation mechanism (20) that forms bump by injecting microdroplets of a metal nano paste on each electrode, a primary bonding mechanism (50) that carries out primary bonding to the electrodes in a non-conductive state by pressing the bump of the semiconductor die (12) against the bump of the circuit board (19), and a secondary bonding mechanism (80) that includes a pressurizing unit that pressurizes the primary bonded bump in bonding direction, and that carries out secondary bonding so that the electrodes become conductive by heating the bump up to a temperature higher than a binder removal temperature of the metal nano paste and a dispersant removal temperature of the metal nano paste, removing the binder and the dispersant, and pressurizing and sintering the metal nanoparticles in the bump. With this, it is possible to efficiently bond the electrodes with a simple and easy way while reducing a bonding load.
Owner:SHINKAWA CO LTD
Semiconductor device and wire bonding method
InactiveUS20050092815A1Not to damageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialLead bonding
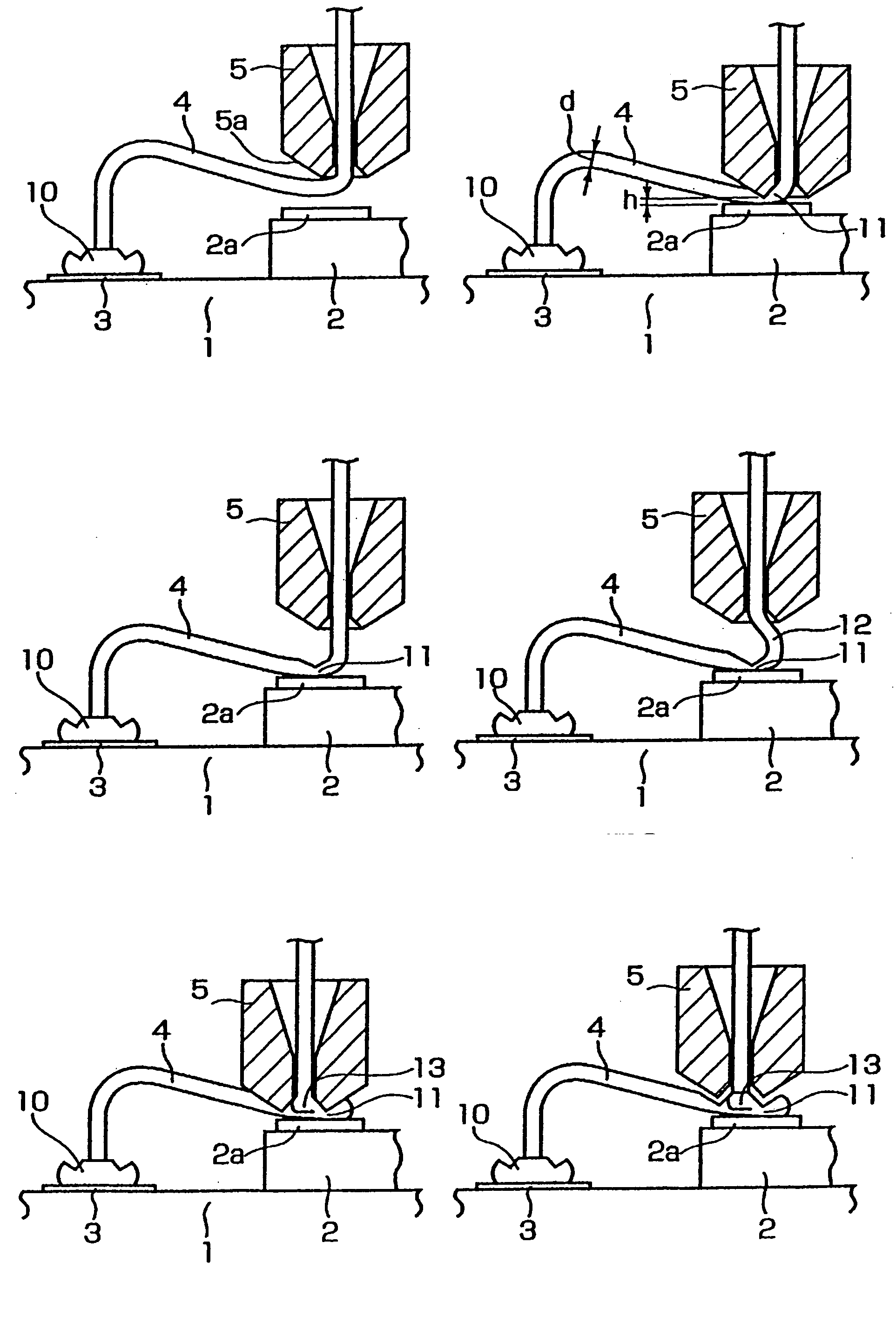
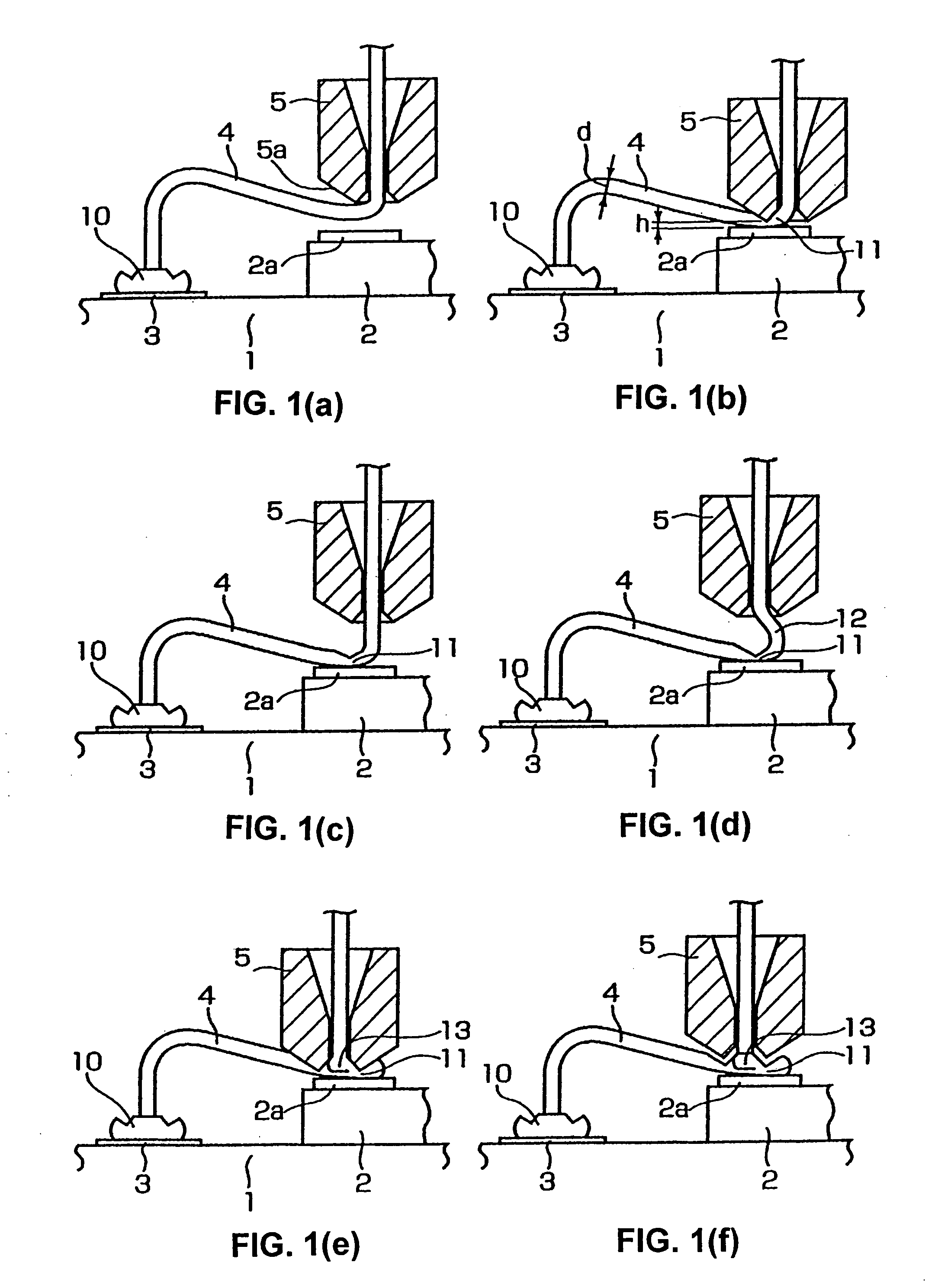
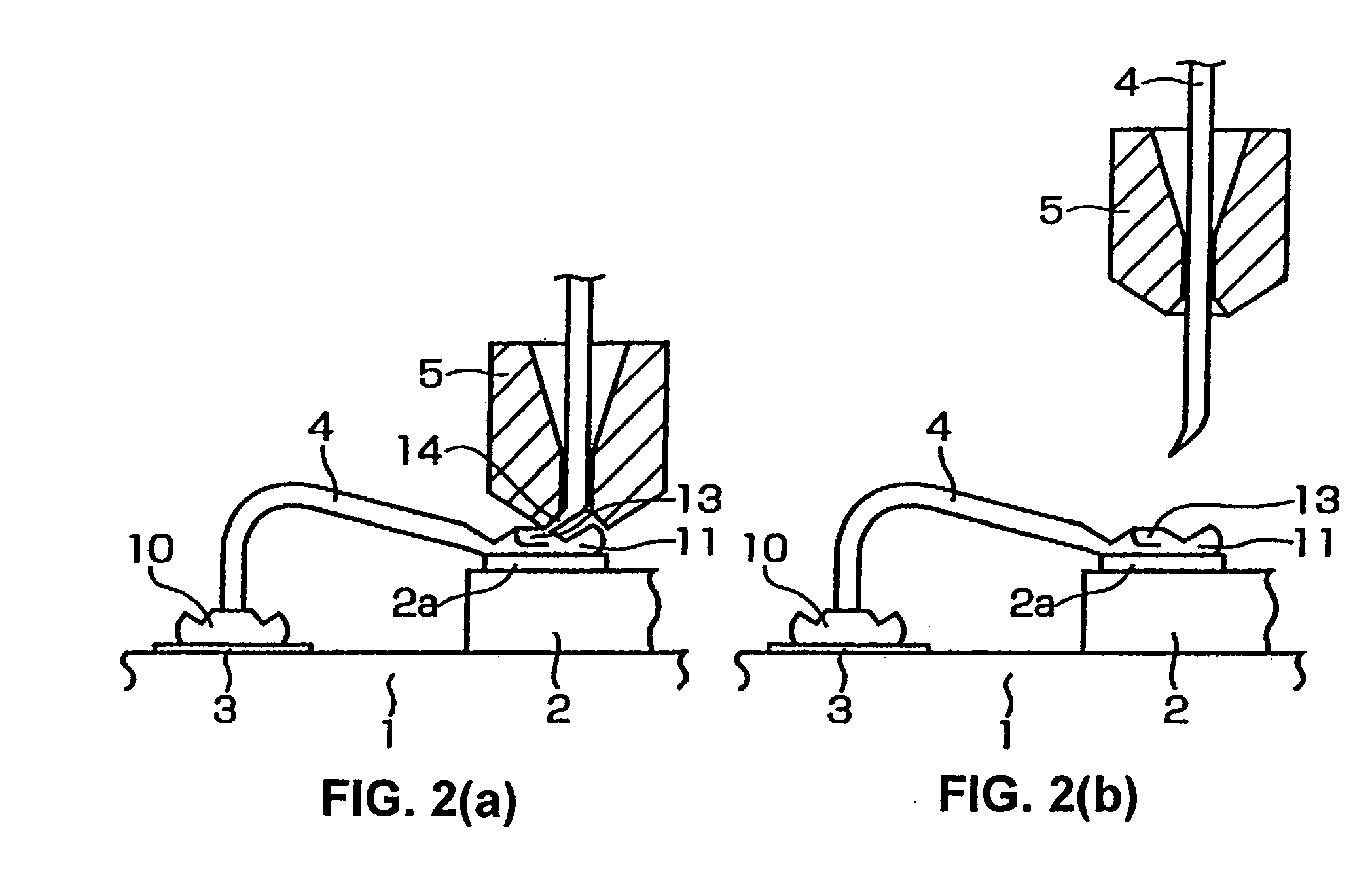
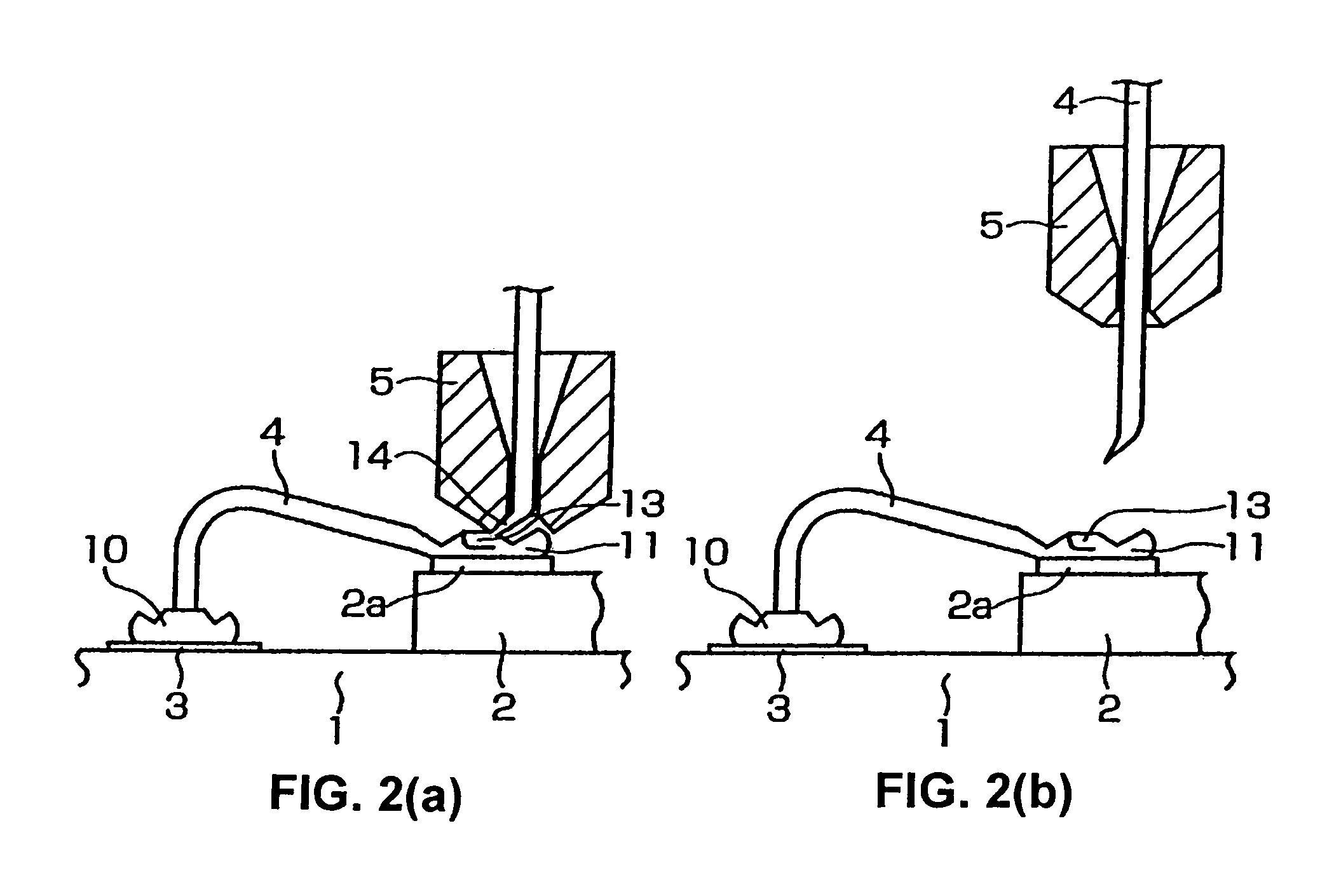
A wire bonding method that performs a primary bonding of wire on a first bonding point and performs a secondary bonding of the wire on a second bonding point, thus connecting the first and second bonding points with the wire, the secondary bonding including: a first bonding step that forms a first bonding part by bonding the wire to the second bonding point, a second bonding step that forms a second bonding part by raising a capillary through which the wire passes and moving the capillary toward the first bonding point, and then lowering the capillary and overlapping the wire to connect the wire to the first bonding part, and a ting step that cuts the wire.
Owner:SHINKAWA CO LTD
Micro LED transfer method
InactiveCN109802019AImprove transfer success rateAvoid pullingSemiconductor devicesSuction forceLed array
The invention provides a micro LED transfer method, belonging to the technical field of light emitting display. A semi-etched LED structure is firstly formed, turning over is carried out through one-time transfer, a buffer layer is removed, a separate LED array is formed, a metal layer is formed on an LED, the metal layer is broken on the side wall of the LED at the time, through secondary bonding, the LED is sucked by a transfer suction head and placed on a metal electrode corresponding to a receiving substrate, and after bonding, micro LED transfer is completed. The problem of film breakagecaused by laser lift-off stress release can be improved, and the problem that transfer of a thick metal layer needs a large suction force for pulling can be solved.
Owner:NANJING CEC PANDA LCD TECH
Composite components with integral protective casings
InactiveUS20080237922A1Avoid the needHigh strengthMouldsThin material handlingPorositySecondary bonding
Methods and compositions for fabricating composite parts including at least one structural material and at least one protective material that are integrally bonded without the use of secondary bonding operations. One or more of the materials forming the layers of the composite parts may be a ceramic composition with or without porosity and one or more of the materials may be a polymer composition. Methods including co-injection processes also are provided for fabricating multi-layered structures in which each layer serves a desired function while still being integrated into the overall structure.
Owner:ADVANCED CERAMICS
Method for bonding carbon fiber/phenolic-nitrile rubber materials
ActiveCN104861884AComplete structureMeet the design requirementsAdhesive processes with surface pretreatmentAdhesive processes with adhesive heatingStructural reliabilityFiber
The invention discloses a method for bonding carbon fiber / phenolic-nitrile rubber materials, and belongs to the field of the manufacturing of a solid rocket engine insulator, and aims at solving the bonding problems of an engine housing, a first EPDM insulation material, a carbon fiber / phenolic-nitrile rubber materials and a second EPDM insulation material and improving the structural reliability. The method mainly comprises the steps of preparation, coating, prefabrication, cleaning, glue coating, setting, thermal pre-pressing, flaw detection, curing and the like. The structural integrity of the engine housing, a first EPDM insulation material, the carbon fiber / phenolic-nitrile rubber materials and the second EPDM insulation material are ensured by using a secondary bonding method, a secondary curing mode, a prefabrication forming method, a stepped temperature rising / dropping mode and other methods; the method has no de-bonding, air-entraining air hole and other quality problems, completely can meet the design requirements, and ensures the safety and reliability of a system.
Owner:HUBEI SANJIANG AEROSPACE JIANGHE CHEM TECH +1
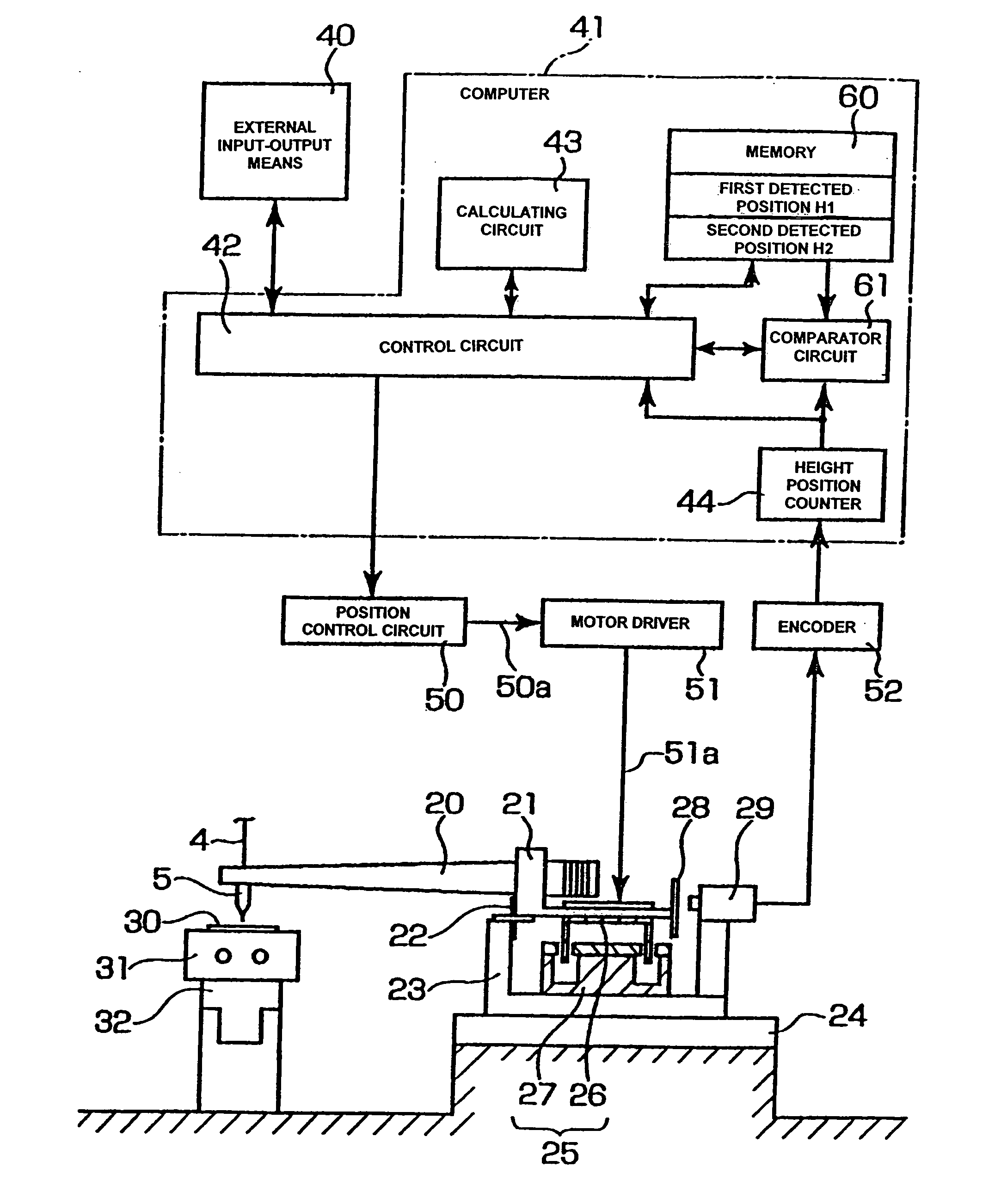
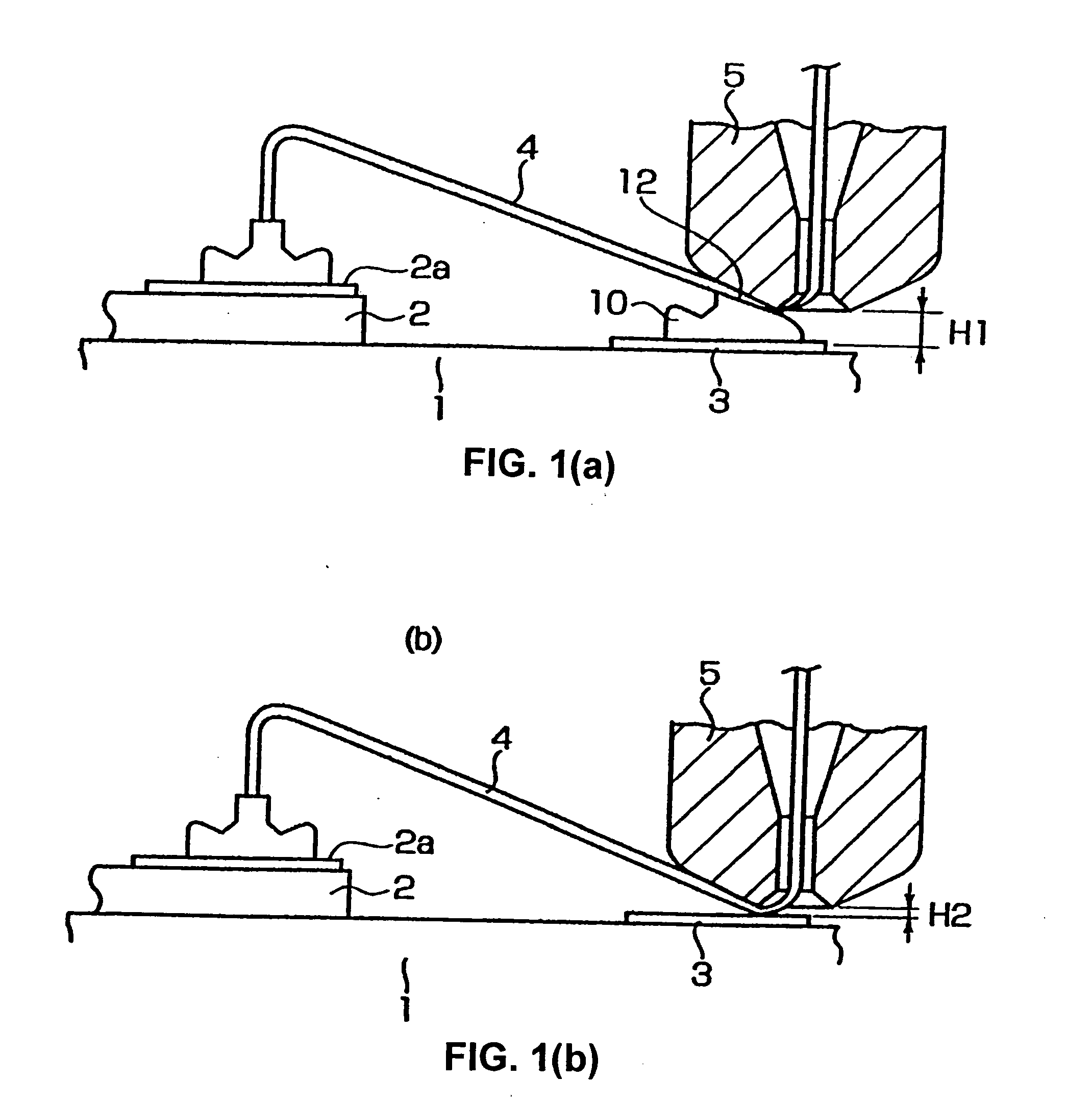
Wire bonding method and apparatus
ActiveUS20050061849A1Improve productivitySolid-state devicesWelding/cutting auxillary devicesElectrical conductorComparators circuits
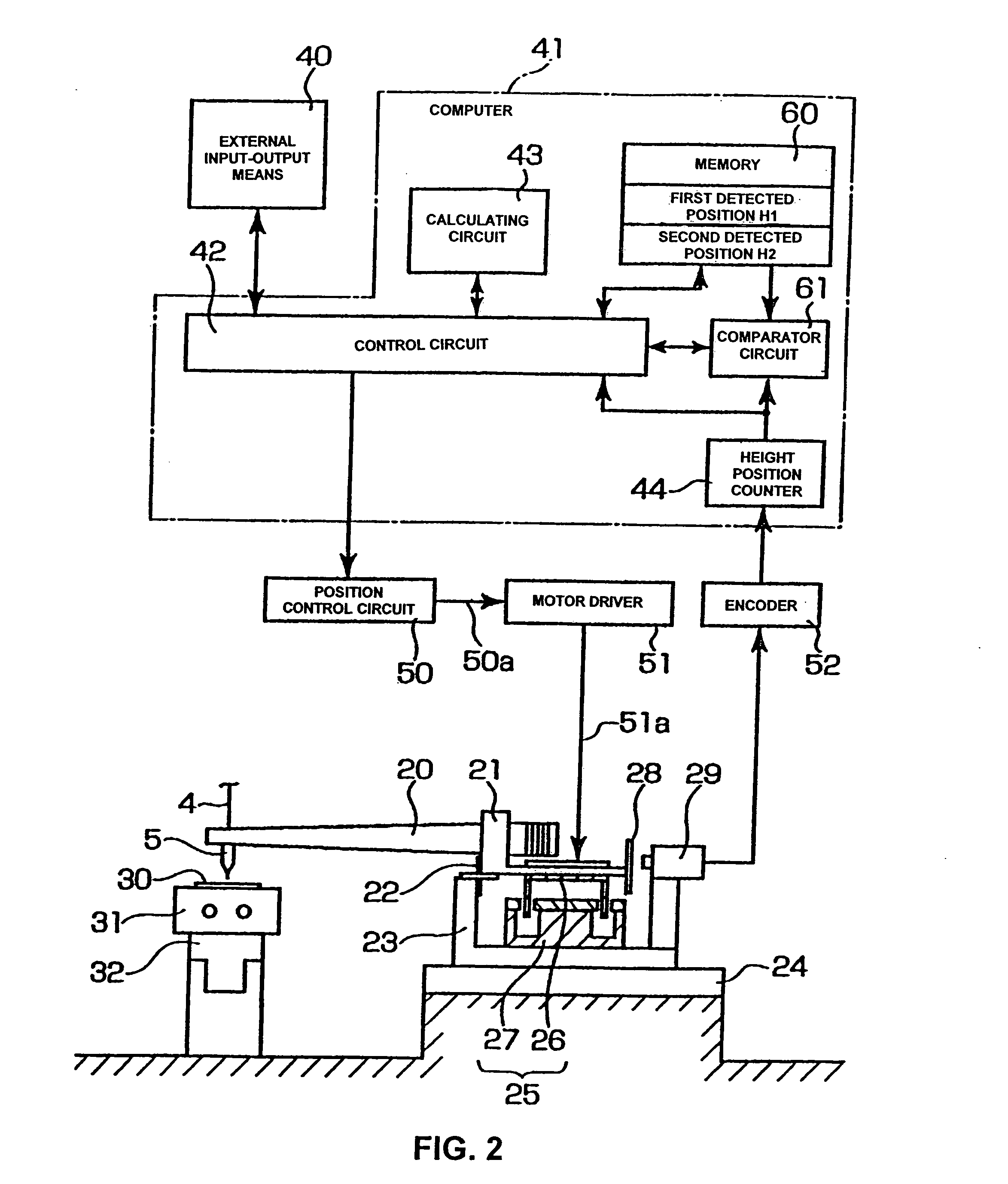
A wire bonding apparatus and method involving a computer 41 that has a height position counter 44 that produces height position signals for a capillary 5 by processing signals from a position sensor 29 that detects the position of the bonding arm 20 in the vertical direction. This computer 41 includes a memory 60, which stores the detected position of the capillary 5 at the time that secondary bonding is performed on a bump that is formed in a normal manner on the second conductor, and a comparator circuit 61, which outputs a “bump not-adhered” signal in cases where the output value of the height position counter 44 is outside the permissible error range of the detected position that is stored in the memory 60.
Owner:SHINKAWA CO LTD
Liquid phase diffusion welding method for metallic machine part and metallic machine part
ActiveUS20060163321A1Improve joint qualityShorten bonding timeCamsValve arrangementsProduction rateElectrical resistance and conductance
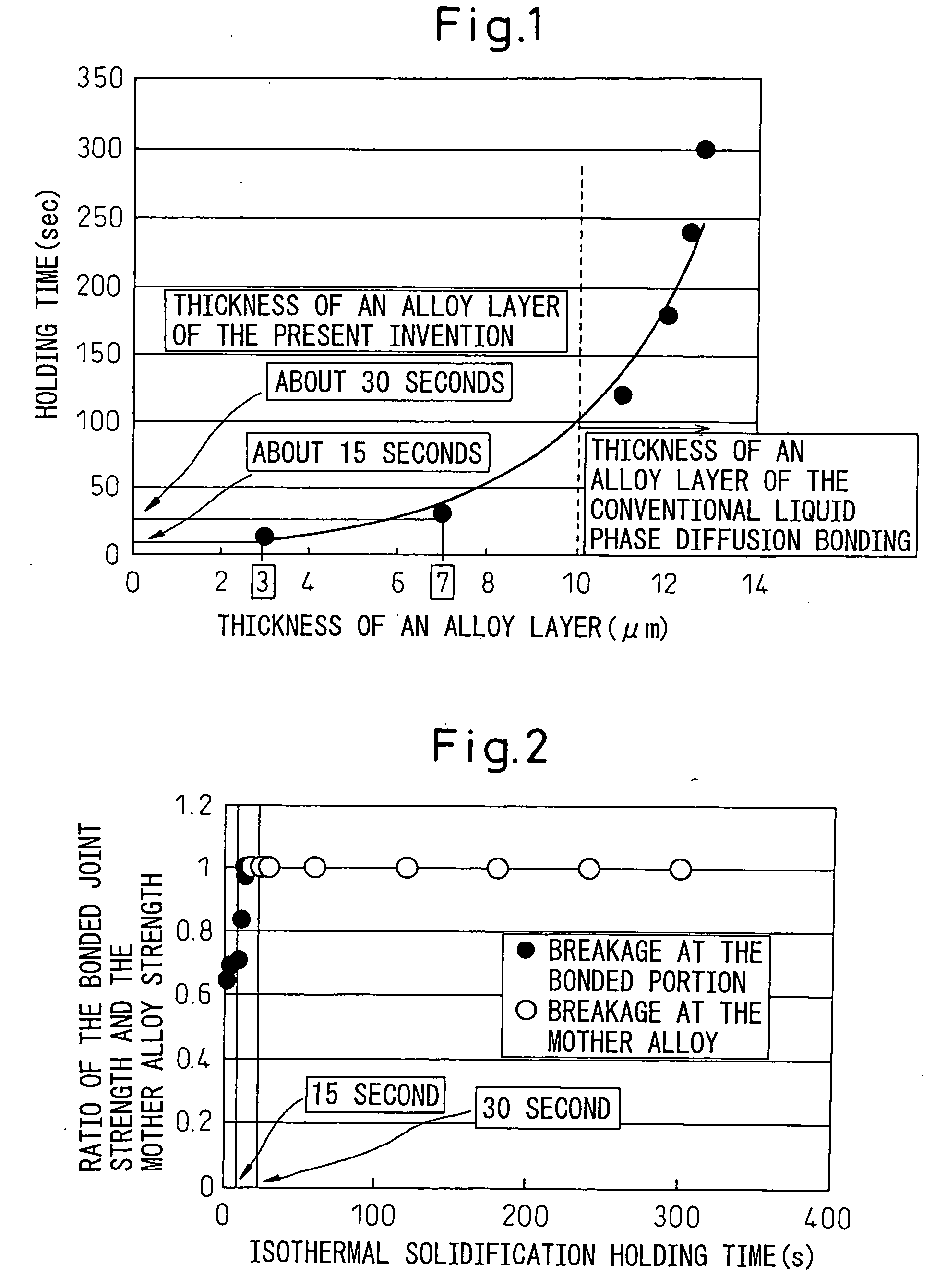
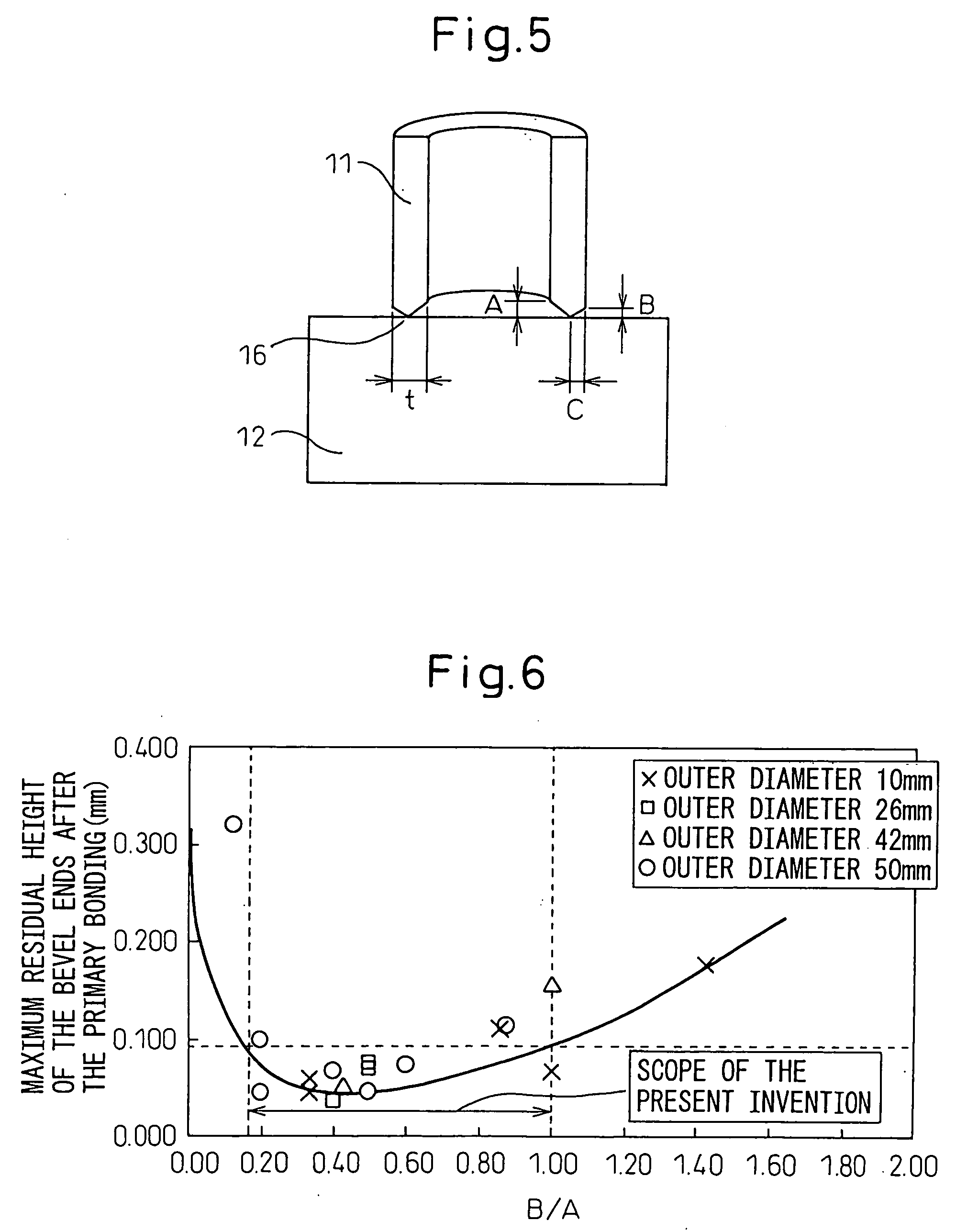
A liquid phase diffusion bonding method for a metal machine part superior in the quality of the joint and the productivity enabling the bonding time to be shortened, achieving homogenization of the bonding structure and improving the tensile strength, fatigue strength, and joint quality and reliability. This liquid phase diffusion bonding method of a metal machine part is characterized interposing an amorphous alloy foil for liquid phase diffusion bonding at bevel faces of metal materials, performing primary bonding by melt bonding said amorphous alloy foil and said metal material by resistance welding to form a joint, then performing secondary bonding by liquid phase diffusion bonding by reheating said joint to at least the melting point of said amorphous alloy foil, then holding it there to complete the solidification process of said joint.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP +1
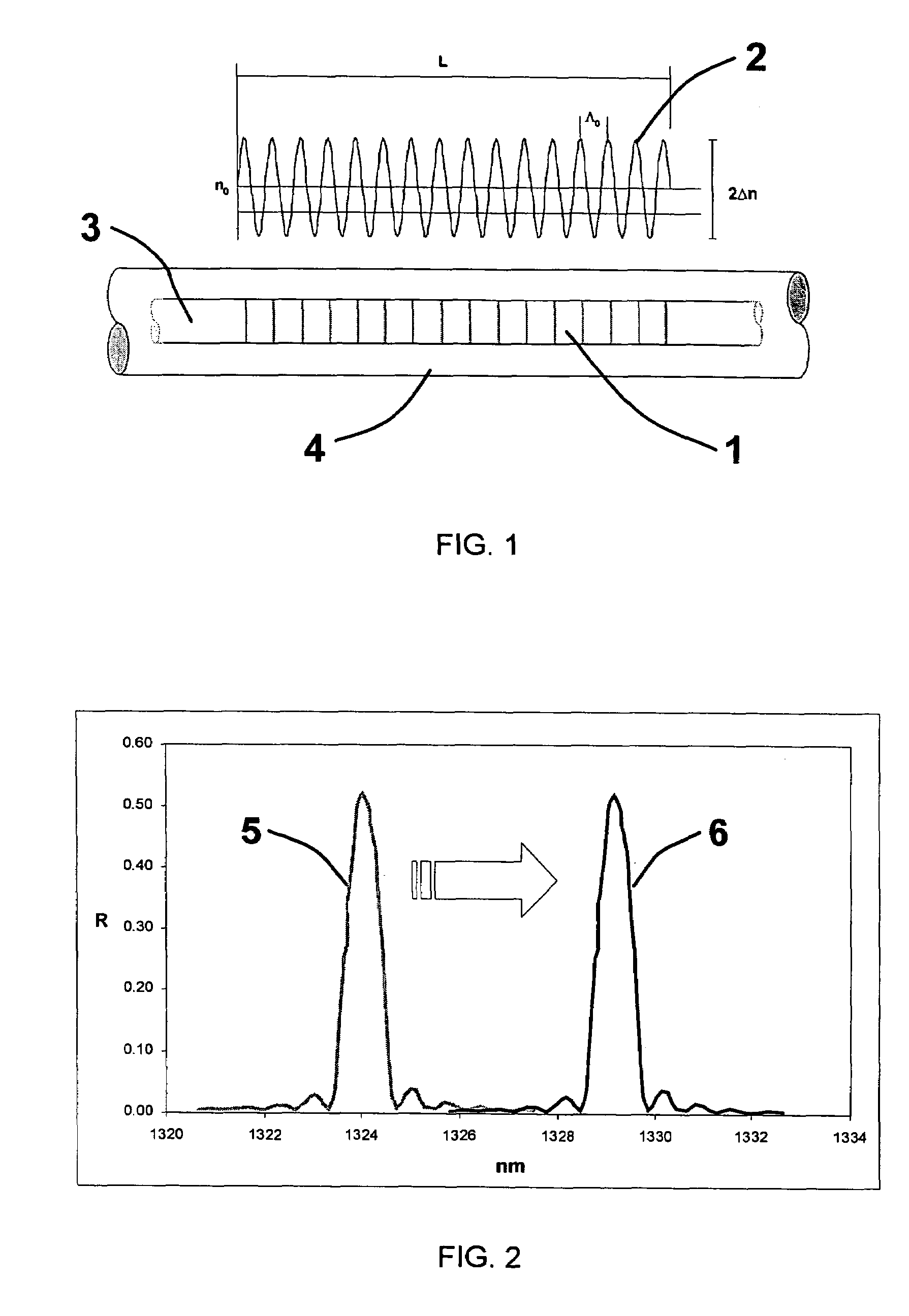
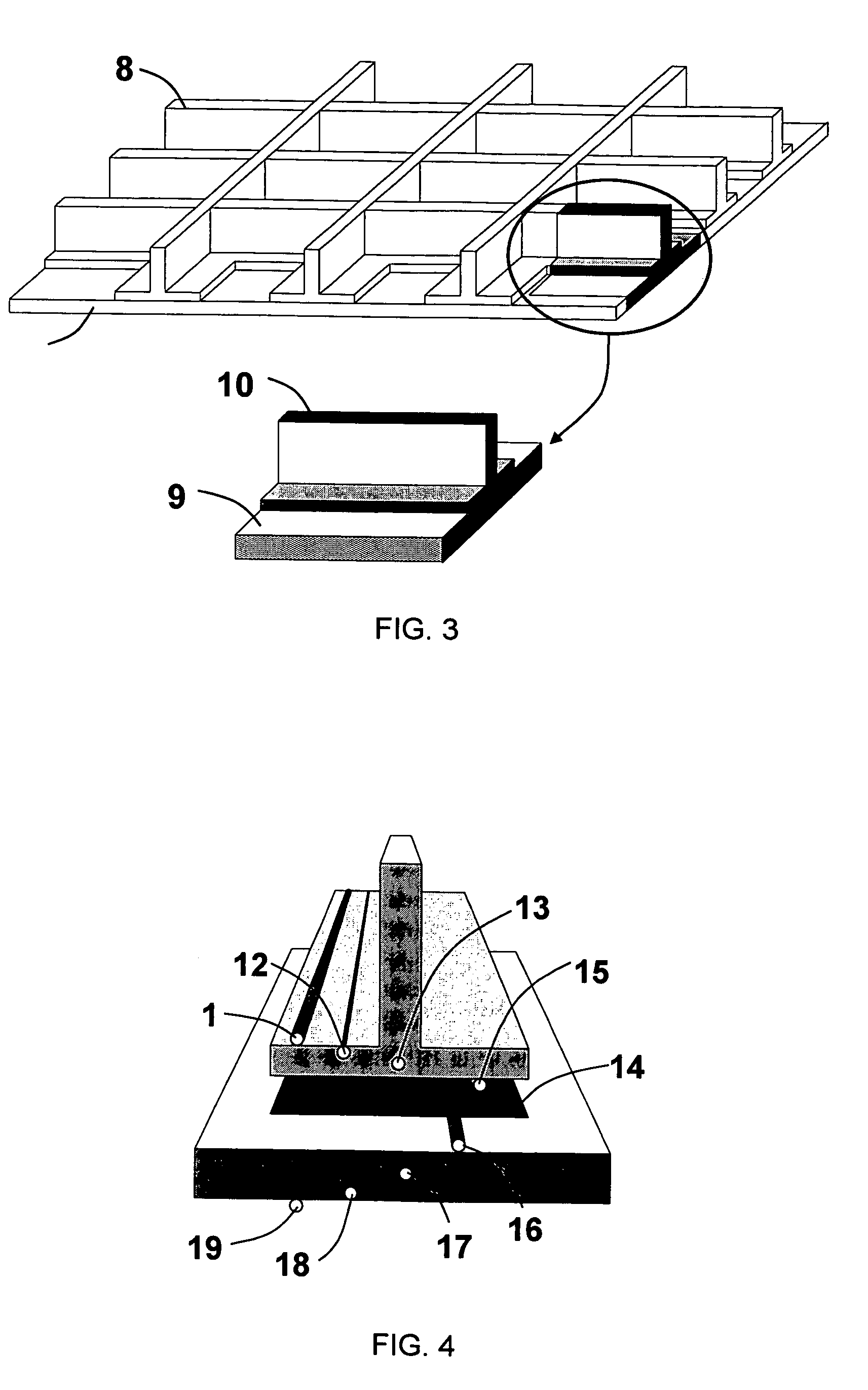
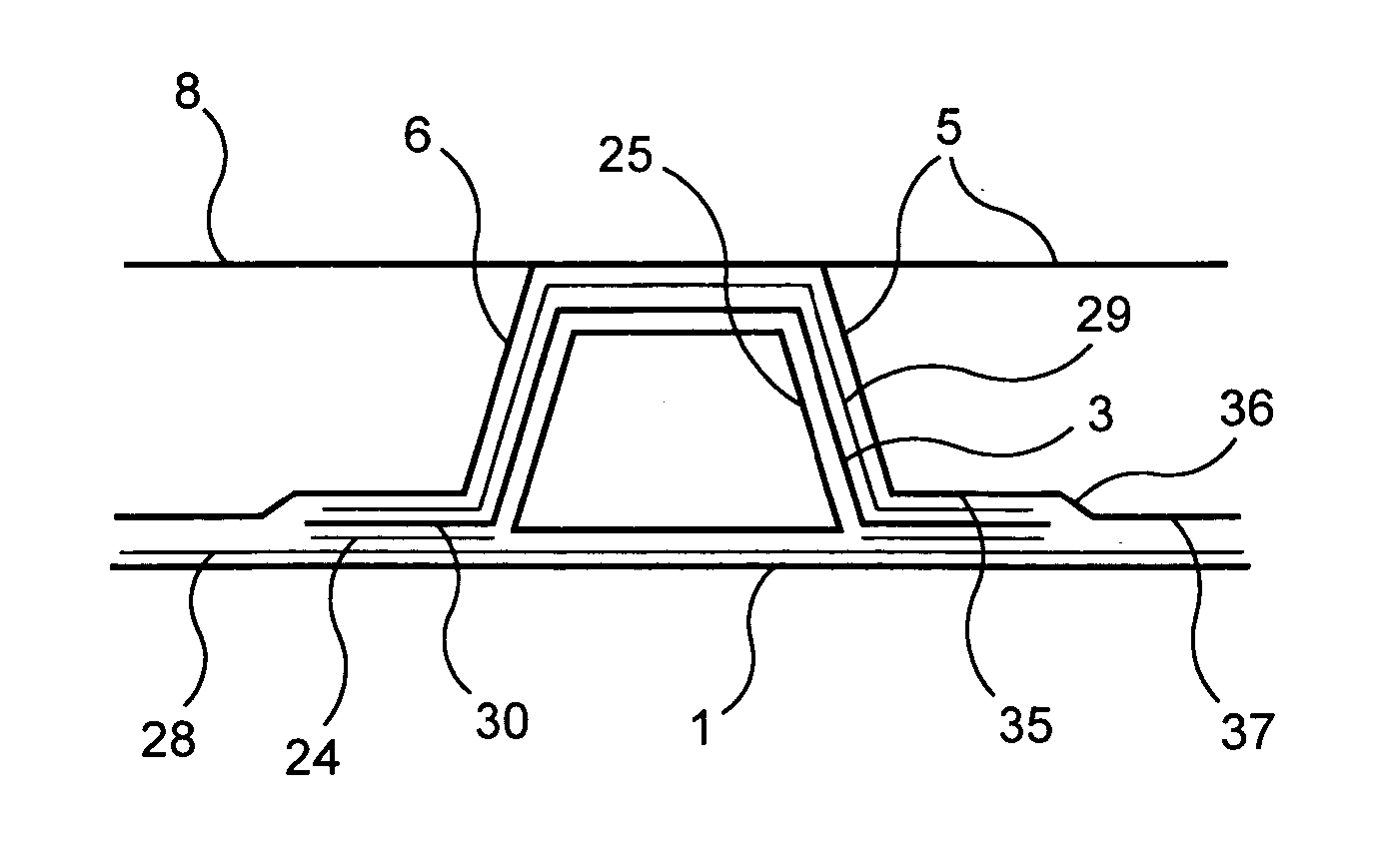
Method to monitor structural damage occurrence and progression in monolithic composite structures using fibre Bragg grating sensors
A method of monitoring structural damage in a composite structure manufactured by co-curing, co-bonding or secondary bonding of several sub-components (7, 8), using fibre optic Bragg grating sensors attached or embedded to or between (in the bonding line) said sub-components, comprising a first step of measuring the wavelength spectra (31, 33, 40) of said Bragg grating sensors at the end of the manufacturing of the part, and in a known load condition, considered as reference and a second step of identifying the occurrence of a failure of the structure and the progress of said failure detecting the release of the residual stresses / strains stored during the curing process by measuring changes (31 to 32, 33 to 34, 40 to 41) with respect to said reference wavelength spectra.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS SL
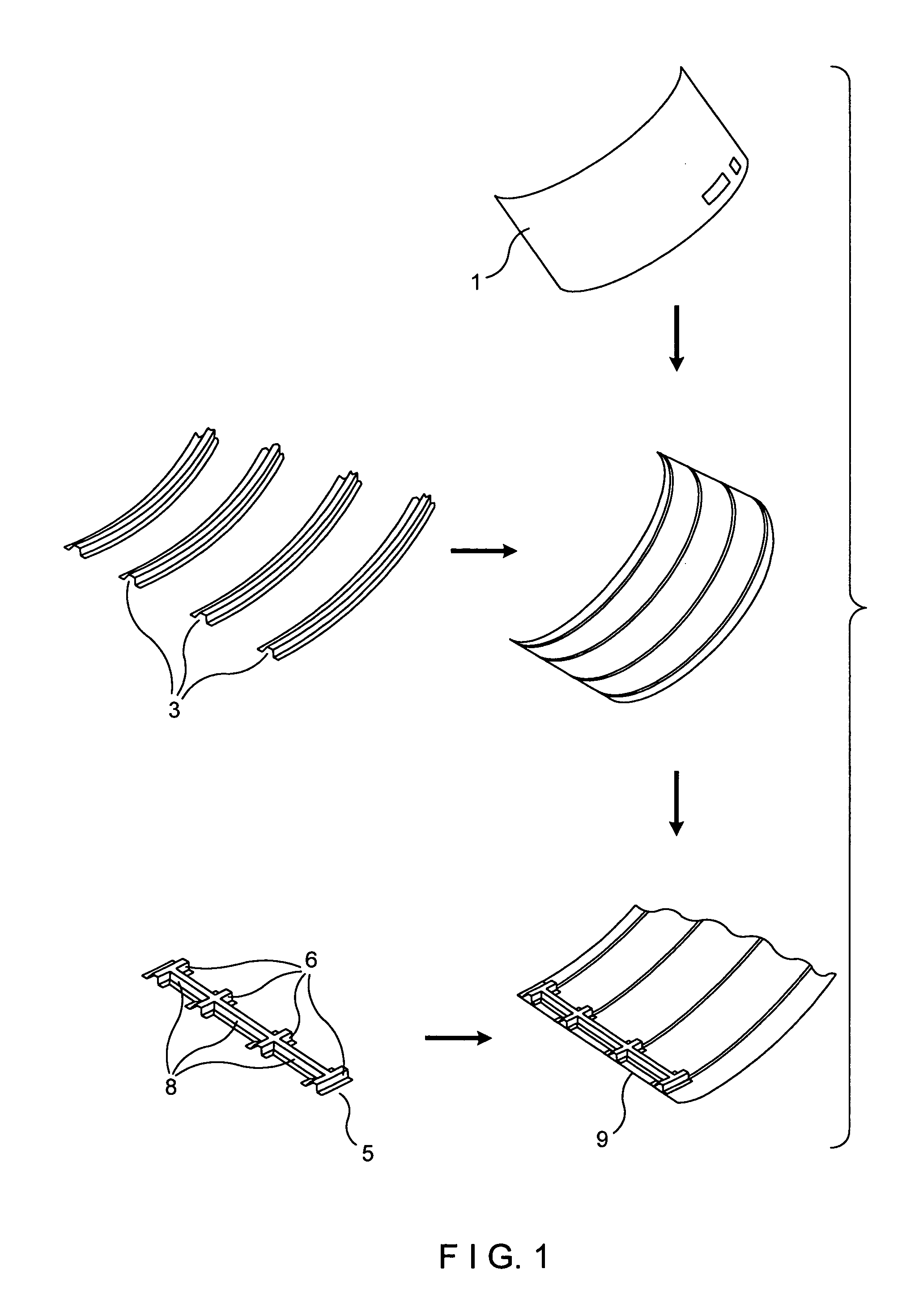
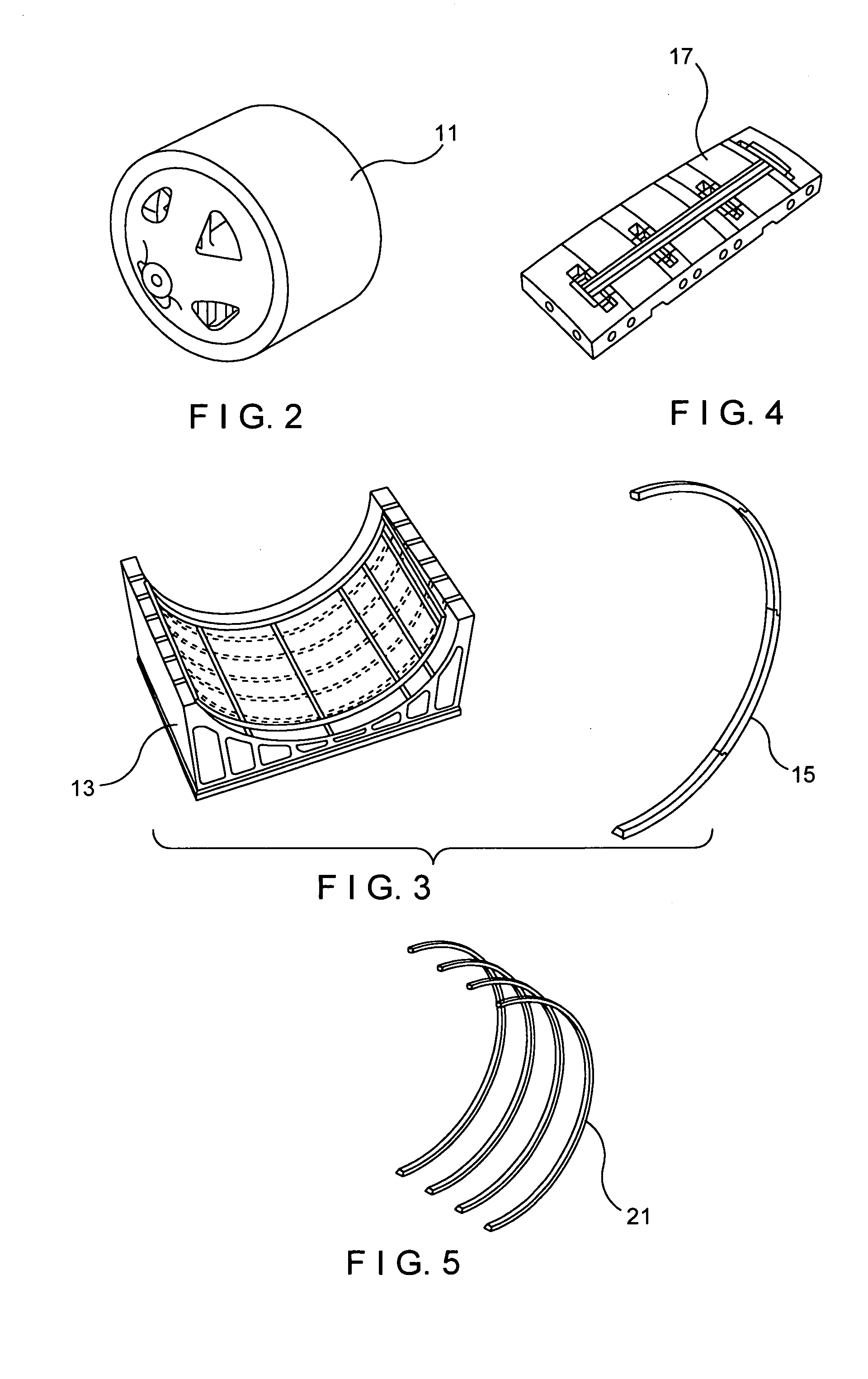
Process for manufacturing a monolithic fan cowl
Process for manufacturing a monolithic fan cowl (9) of curvilinear shape for aircraft engines comprising the following steps: a) providing a skin (1) cured, several longitudinal hat frames (3) uncured and several transversal hat frames (5) cured; b) placing said longitudinal hat frames (3) on the skin (1) c) placing said transversal hat frames (5) over the longitudinal frames (3) and the skin (1); d) covering the assembly with a vacuum bag; e) performing an autoclave cycle under high temperature and pressure conditions for co-bonding the skin (1) and the longitudinal hat frames (3), and for a secondary bonding of the transversal hat frames (5) to the skin (1) and the longitudinal hat frames (3).
Owner:EADS CONSTRS AERONAUTICAS
Bonding apparatus and bonding method
InactiveUS7726546B2Effective combinationReduce loadMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringSecondary bonding
A bonding apparatus (10) that bonds an electrode of a semiconductor die (12) and an electrode of a circuit board (19) using a metal nano paste includes a bump formation mechanism (20) that forms bump by injecting microdroplets of a metal nano paste on each electrode, a primary bonding mechanism (50) that carries out primary bonding to the electrodes in a non-conductive state by pressing the bump of the semiconductor die (12) against the bump of the circuit board (19), and a secondary bonding mechanism (80) that includes a pressurizing unit that pressurizes the primary bonded bump in bonding direction, and that carries out secondary bonding so that the electrodes become conductive by heating the bump up to a temperature higher than a binder removal temperature of the metal nano paste and a dispersant removal temperature of the metal nano paste, removing the binder and the dispersant, and pressurizing and sintering the metal nanoparticles in the bump. With this, it is possible to efficiently bond the electrodes with a simple and easy way while reducing a bonding load.
Owner:SHINKAWA CO LTD
Surface-modified separation membrane and method for modifying surface of separation membrane
ActiveUS20160199788A1Increase resistanceImprove stabilitySemi-permeable membranesMembranesOxygenPermeation
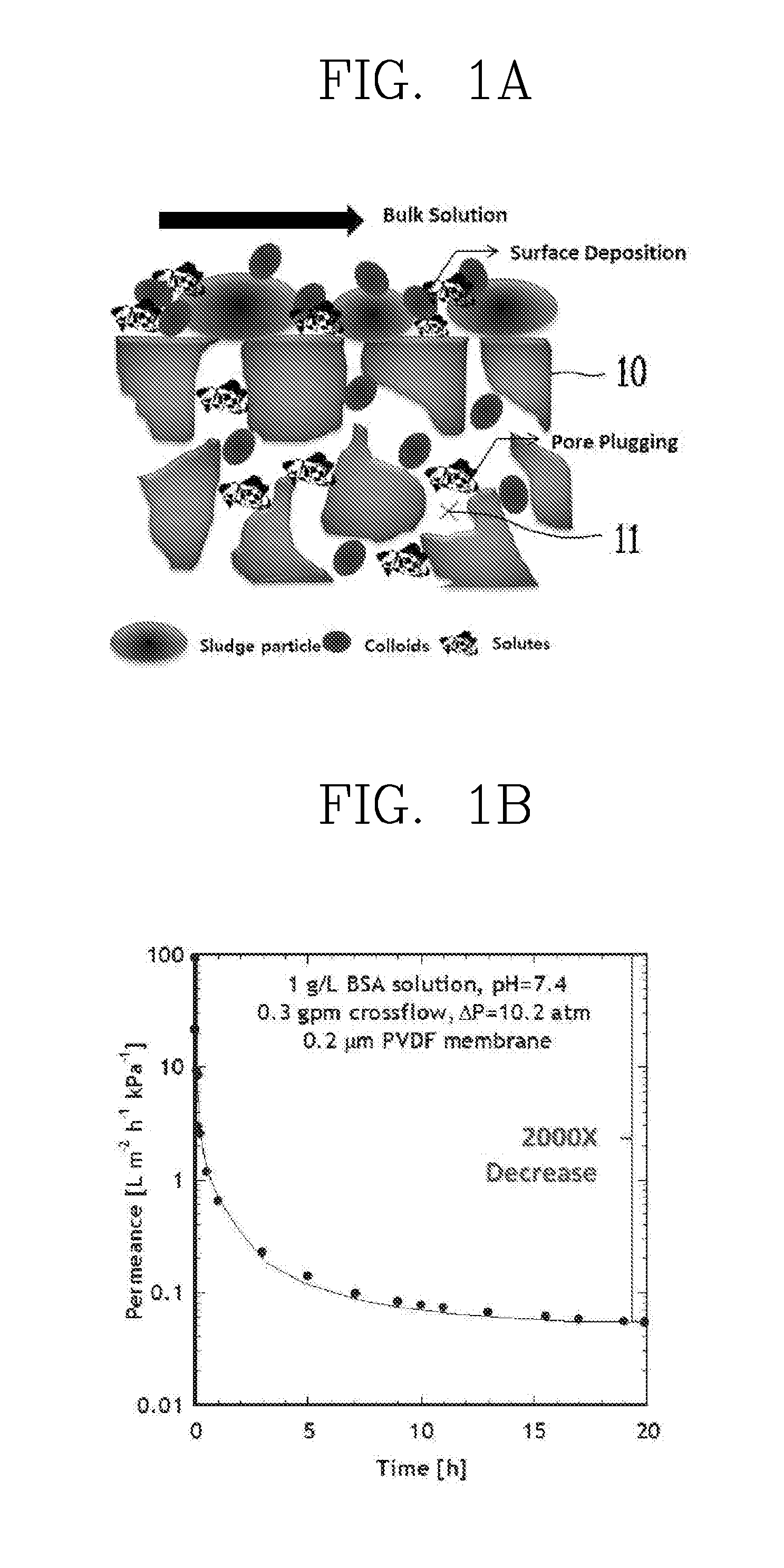
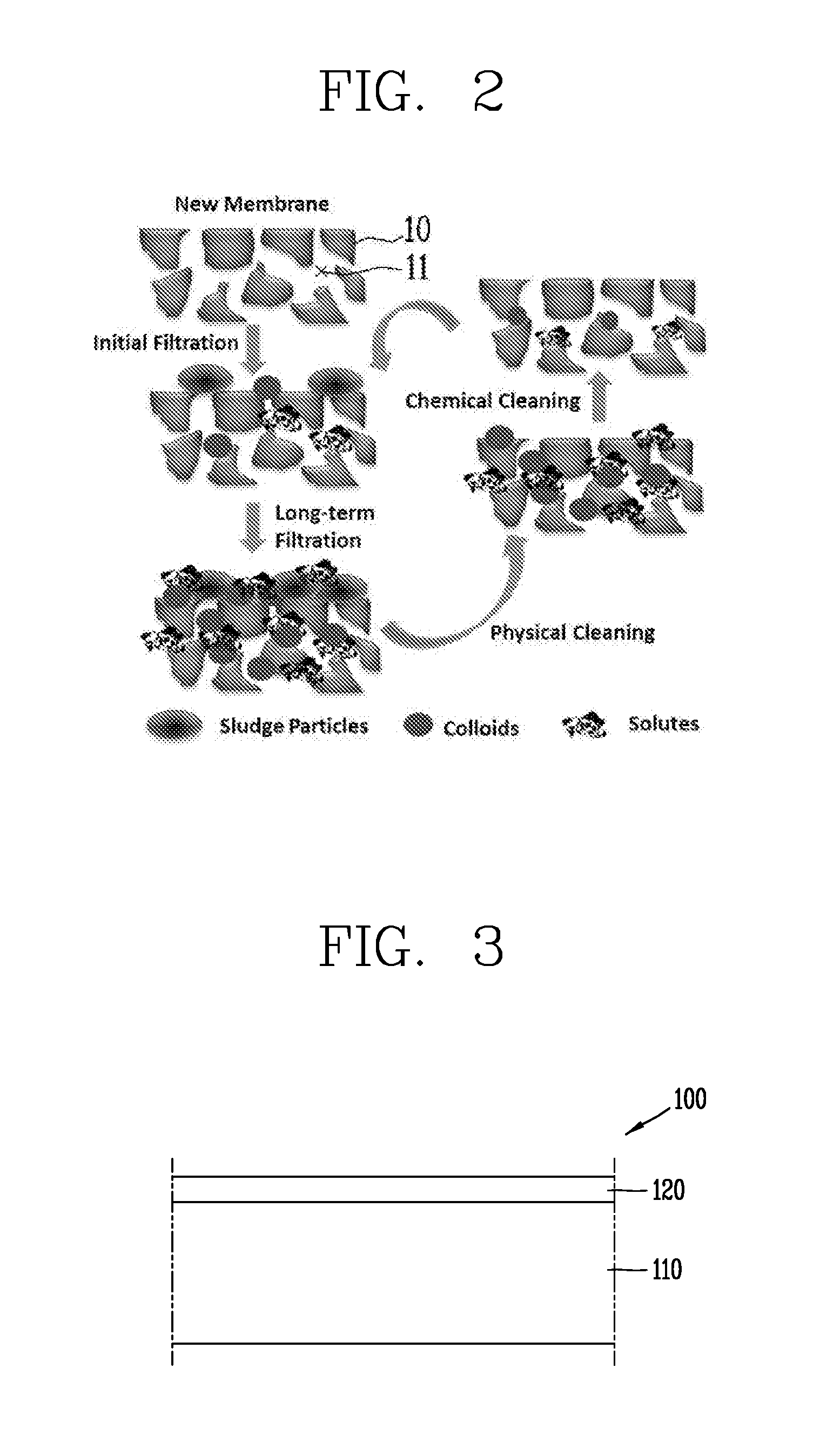
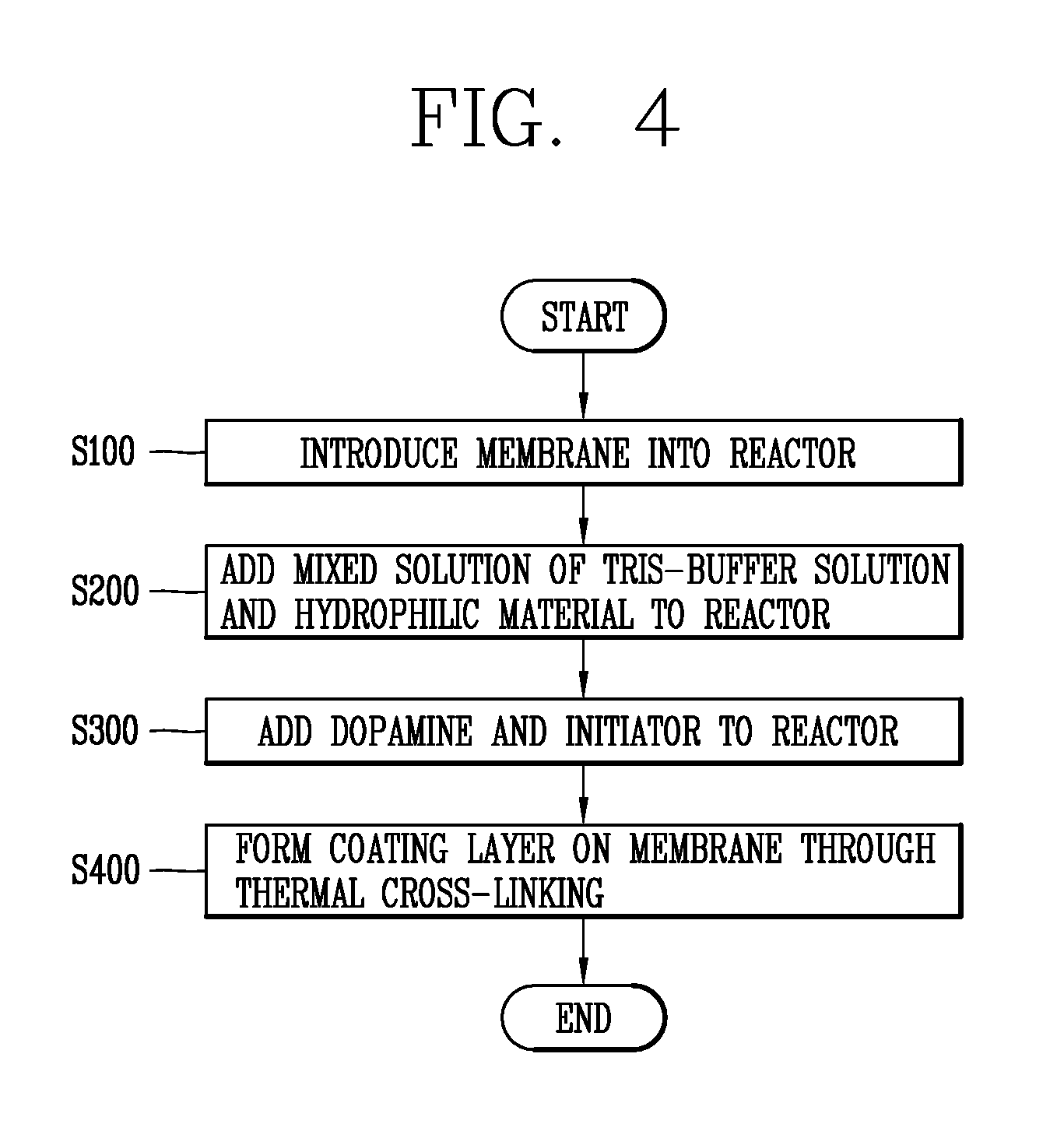
A surface-modified separation membrane of the present invention comprises a separation membrane, and a coating layer formed on the surface of the separation membrane for improving the contamination resistance and chemical resistance of the separation membrane, wherein the coating layer is implemented with a nanoscale thickness of the coating layer in order to inhibit a decrease in permeation flux of the separation membrane before and after coating the coating layer, and comprises: dopamine for providing, to the coating layer, an adsorption force to be bound stably with the separation membrane; and a hydrophilic material which is bound to the dopamine through secondary bonding or cross-linking containing a hydrogen bond in order to inhibit the deterioration of the durability of the coating layer, and provides hydrophilicity to the surface of the separation membrane in order to protect the separation membrane from hydrophobic contaminants. A method for modifying the surface of a separation membrane of the present invention comprises the steps of: injecting a separation membrane to be surface-modified into a reactor; adding a mixture solution, which is formed by adding a hydrophilic material to a Tris-buffer solution having an adjusted pH range at which dopamine reacts and stirring the same, to the reactor; adding dopamine and an initiator, which induces the cross-linking of the hydrophilic material and dopamine, to the reactor at a predetermined temperature range; and forming a coating layer comprising dopamine and the hydrophilic material on the separation membrane through thermal cross-linking at the predetermined temperature range while injecting oxygen into the reactor.
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUND HANYANG UNIV) +1
Secondary bonding forming method of structural part with curvature
The invention belongs to the technical field of structural bonded assembly forming, and relates to a secondary bonding forming method of a structural part with curvature. According to the invention, various assemblies are connected without adopting a riveting mode, and various bonded assemblies are integrally formed after being subjected to secondary curing and bonded through the curing of an expanded adhesive film J-99B; and the problem that a butt seam is easy to recess in the pressurizing and curing process of a product is solved through a butt seam unilateral beehive balance discharge process method, so that the product weight is reduced, and the product stability is enhanced.
Owner:HARBIN
Composite material plate with folding sandwich structure and forming method thereof
InactiveCN102756531AGood adhesionSimple preparation processLaminationLamination apparatusWhole bodyEngineering
The invention relates to a composite material plate with a folding sandwich structure and a forming method thereof and belongs to the fields of composite materials and forming technology thereof. A composite material plate or a curved plate with lightweight, adjustable three-dimensional rigidity and a permeable whole body is formed by co-curing a pre-curing folding sandwich structure and pre-curing upper and lower panels, or co-bonding the cured folding sandwich structure and the pre-cured upper and lower panels, or performing secondary bonding on the cured folding sandwich structure and the cured upper and lower panels. The composite material plate has a simple preparation process and high shape adaptability, and can be widely applied to structures with lightweight and capable of resisting shock damage.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
Wire bonding method
InactiveUS7025247B2Stable reliabilitySolid-state devicesWelding/cutting auxillary devicesElectrical conductorEngineering
A wire bonding method including the steps of forming a bump by performing ball bonding of a ball by wire on a second conductor, raising a capillary to a height that is equal to or lower than the height of a ball portion that rises into a through-hole of the capillary during formation of the bump, moving the capillary in a direction that is opposite from the first conductor, lowering the capillary so as to form an inclined wedge on the bump, cutting the wire, performing the primary bonding on the first conductor, and making a loop with the wire with respect to the bump from the first conductor, thus performing the secondary bonding on the inclined wedge on the bump.
Owner:SHINKAWA CO LTD
Machining method for circuit board drilling
InactiveCN103857208AAvoid damageReduce processing stepsElectrical connection printed elementsMultilayer circuit manufactureSecondary bondingCopper
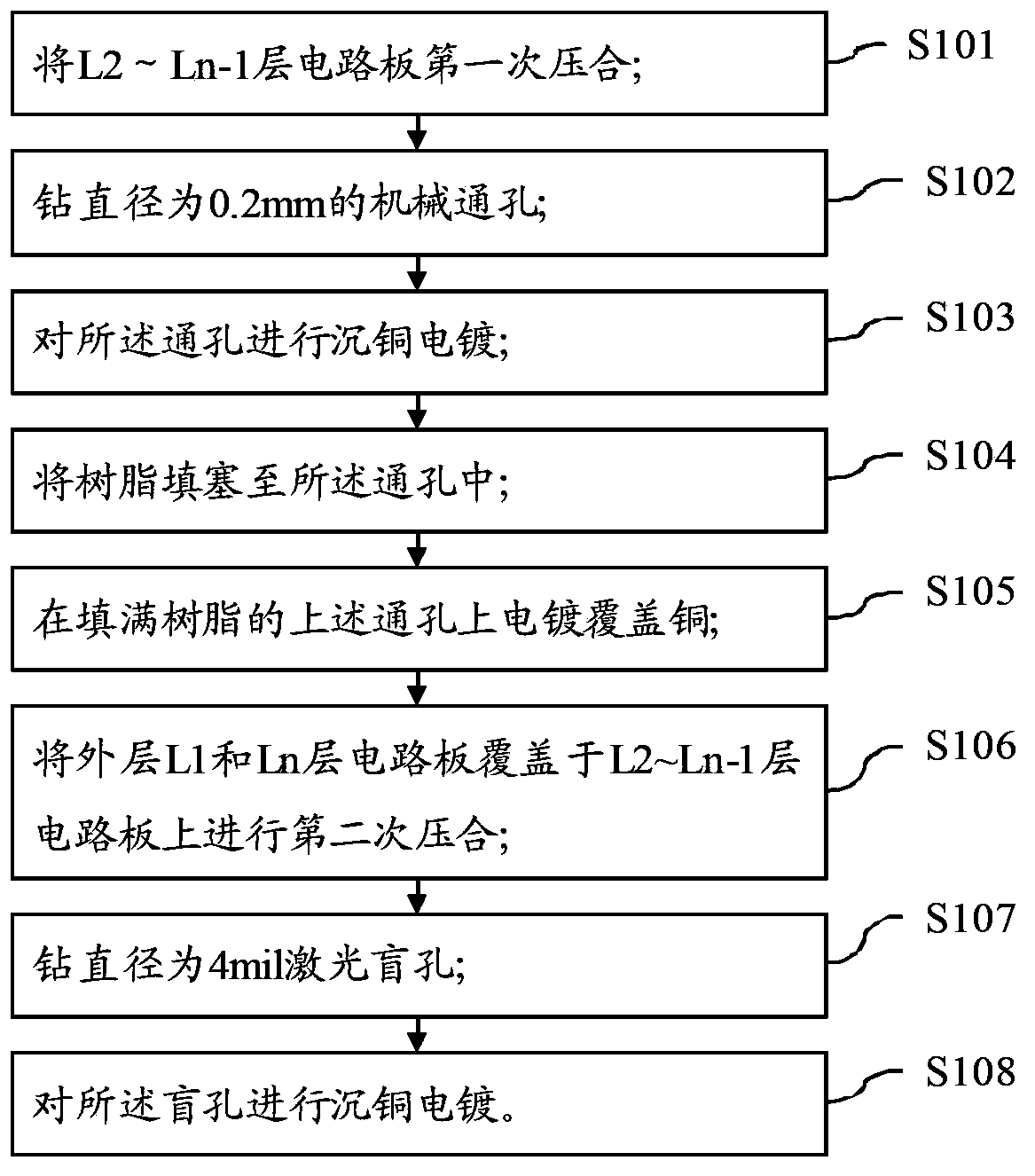
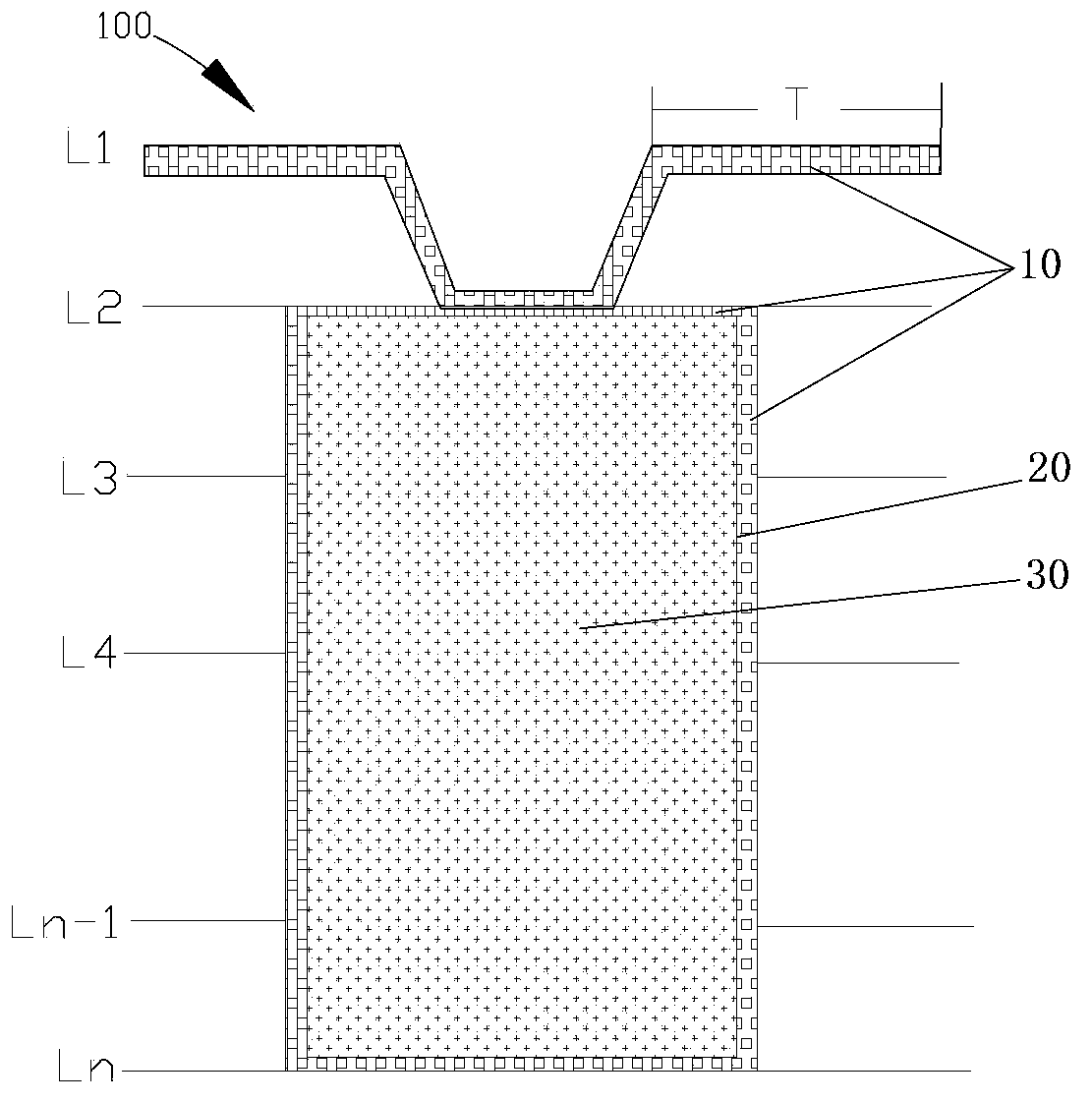
The invention relates to the field of circuit board processing, and provides a machining method for circuit board drilling. The method aims to solve the problem that due to wiring of a ball grid array (BGA) PCB with the diameter of 0.6 mm, the yield of a circuit board is difficult to guarantee. The machining method for circuit board drilling includes the following steps that primary bonding is carried out on L2 to Ln-1 layers of circuit boards; mechanical through holes with the diameter of 0.2 mm are drilled; copper electroplating is carried out on the through holes; the through holes are filled with resin; copper is electroplated and covers the through holes filled with the resin; the L1 layer of circuit board and the Ln layer of circuit board cover the L2-Ln-1 layers of the circuit boards for secondary bonding; laser blind holes with the diameter of 4 mil are drilled; copper electroplating is carried out on the blind holes. The invention further provides a circuit board formed through the method. By means of combination of the electroless copper technology processing method and HDI, drilling in the BGA PCB is achieved, so that conducting and wiring functions are achieved, good use performance of products is guaranteed, and the defective rate of the products is lowered.
Owner:SHENNAN CIRCUITS
Novel metal-free connector composite material sandwiched plate connecting structure and design method thereof
ActiveCN105500867AReduce weightGuarantee the effectiveness of electromagnetic wave stealthSynthetic resin layered productsGlass/slag layered productsGlass fiberIndustrial equipment
The invention discloses a novel metal-free connector composite material sandwiched plate connecting structure and a design method thereof. The novel metal-free connector composite material sandwiched plate connecting structure is characterized by comprising glass fiber cloth (1A), a PVC foam core (1B), a composite material sandwiched plate (1), a composite material connector (2) and a composite material reinforcing rib (3), wherein the glass fiber cloth (1A) is layered in a crossed mode respectively at 0 degree and 90 degrees by surrounding the PVC foam core (1B) to prepare the composite material sandwiched plate (1), the composite material connector (2) and the composite material reinforcing rib (3), and a composite material sandwiched plate connecting structure is prepared by secondary bonding. The novel metal-free connector composite material sandwiched plate connecting structure can be used for structures with special requirements, such as high rigidity, high strength, and electromagnetic wave invisibility. Compared with a traditional connecting structure, the novel connecting structure disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of high connecting efficiency, compact structure, capability of meeting the electromagnetic invisibility requirement, simple and flexible molding technology and the like, and has wide application prospect in national defense and industrial equipment.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Automatic nose strip bonding apparatus for face mask
InactiveUS7784516B2Improve manufacturing speedImprove product qualityLiquid surface applicatorsLamination ancillary operationsNoseEngineering
An automatic nose strip bonding apparatus for a face mask is disclosed, including a nose strip providing mechanism, a nose strip turnover mechanism, and a press-to-bond device. The nose strip providing mechanism drives a nose strip forward and carries out stamping operation on the nose strip, and applies a bonding agent to the nose strip. The nose strip turnover mechanism serves to turn over the nose strip that has already been applied with the bonding agent to allow the surface of the nose strip on which the bonding agent is applied to face a face mask. The press-to-bond device includes a first bonding device and a second bonding device to attach the nose strip to the face mask and to carry out a secondary bonding operation, respectively, to ensure firm bonding of the nose strip to the face mask.
Owner:CHEN HUNG HO
Method for manufacturing semiconductor package
InactiveUS20080286904A1Reduce manufacturing costSimple manufacturing processImpedence networksSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsAdhesiveSemiconductor package
Provided is a method for manufacturing a semiconductor package. In the method, a wafer for a cap substrate is provided. The wafer for the cap substrate includes a plurality of vias and via electrodes on a lower surface. A wafer for a device substrate is provided. The wafer for the device substrate includes a circuit unit and a connection electrode on an upper surface. The wafer for the cap substrate and the wafer for the device substrate are primarily bonded by a medium of a primary adhesive. A trench is formed to expose the upper surface of the wafer for the device substrate to an outside along an outer edge of the primary adhesive. A secondary bonding operation is performed by a medium of a secondary adhesive to electrically connect the via electrode and the connection electrode. The wafer for the device substrate is diced along a virtual cut line.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
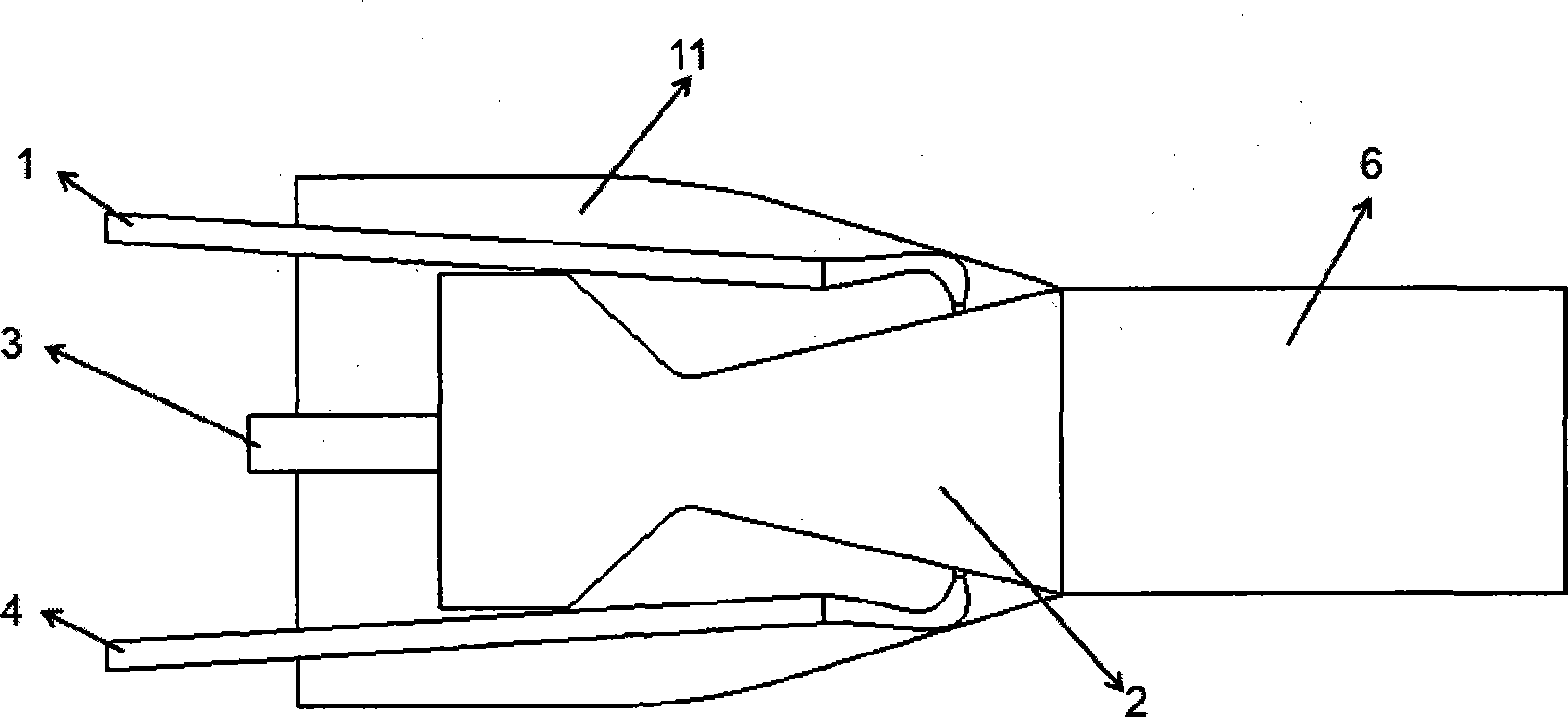
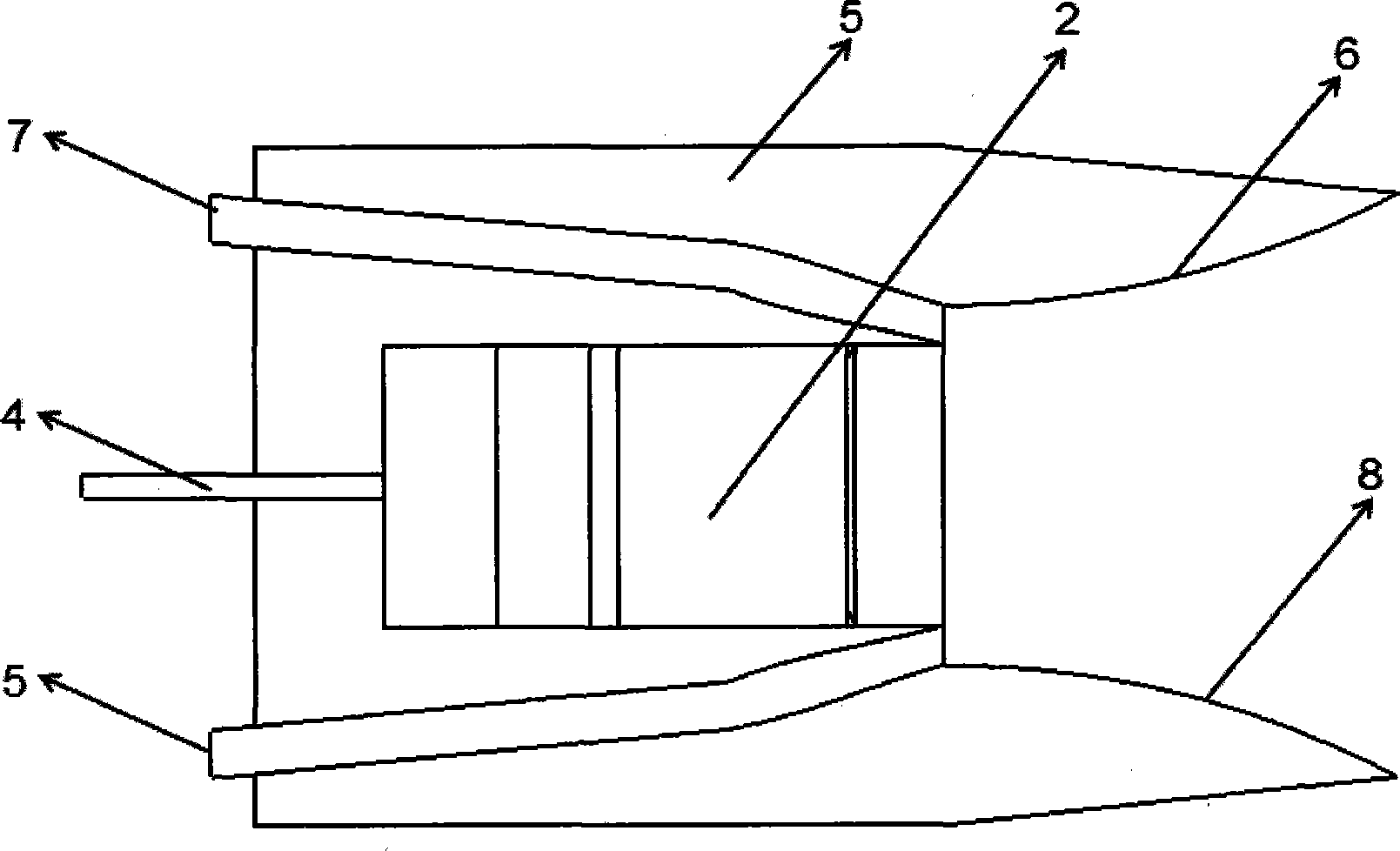
Multi-axial fixed geometrical pneumatic vectoring nozzle structure
Disclosed is a multi-axial fixed geometrical pneumatic vectoring nozzle structure. The multi-axial fixed geometrical pneumatic vectoring nozzle structure is composed of an upper high-pressure secondary flow injection pipe, a lower high-pressure secondary flow injection pipe, a rectangular convergent-divergent nozzle, a left secondary flow suction pipe, a right secondary flow suction pipe, a left Coanda curved surface, a right Coanda curved surface and a skin connected with the nozzle and an airframe. A thrust vectoring state and a non-thrust vectoring state exist during normal operation, and only the high-pressure secondary flow injection pipes and the secondary flow suction pipes need to be closed at the same time for the non-thrust vectoring state. For vectoring conditions, if pitch thrust vectoring needs to be realized, only the high-pressure secondary flow injection pipes are opened, and pitch thrust vectoring angles can be controlled by means of control on flow and pressure of high-pressure secondary flow entering the pipes; if yaw thrust vectoring needs to be realized, the secondary flow suction pipes need to be connected with a vacuum suction device, and different yaw vectoring angles are realized by control on vacuum degree of the vacuum suction device; if pitch control and yaw control are needed at the same time, the two above processed need to be combined.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Composite components with integral protective casings
InactiveUS6935594B1Avoid the needHigh strengthLayered productsMilitary adjustmentPorositySecondary bonding
Methods and compositions for fabricating composite parts including at least one structural material and at least one protective material that are integrally bonded without the use of secondary bonding operations. One or more of the materials forming the layers of the composite parts may be a ceramic composition with or without porosity and one or more of the materials may be a polymer composition. Methods including co-injection processes also are provided for fabricating multi-layered structures in which each layer serves a desired function while still being integrated into the overall structure.
Owner:ADVANCED CERAMICS
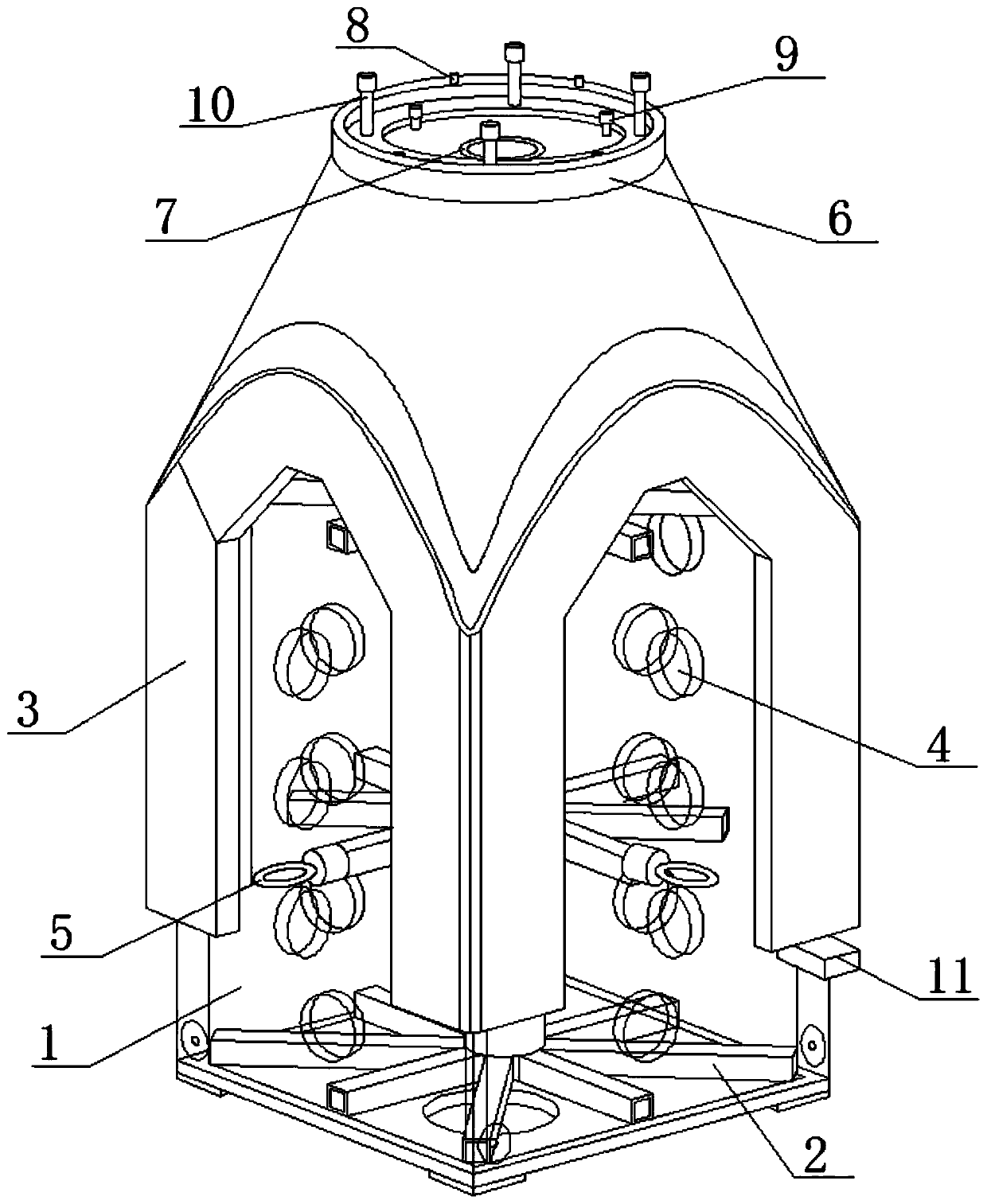
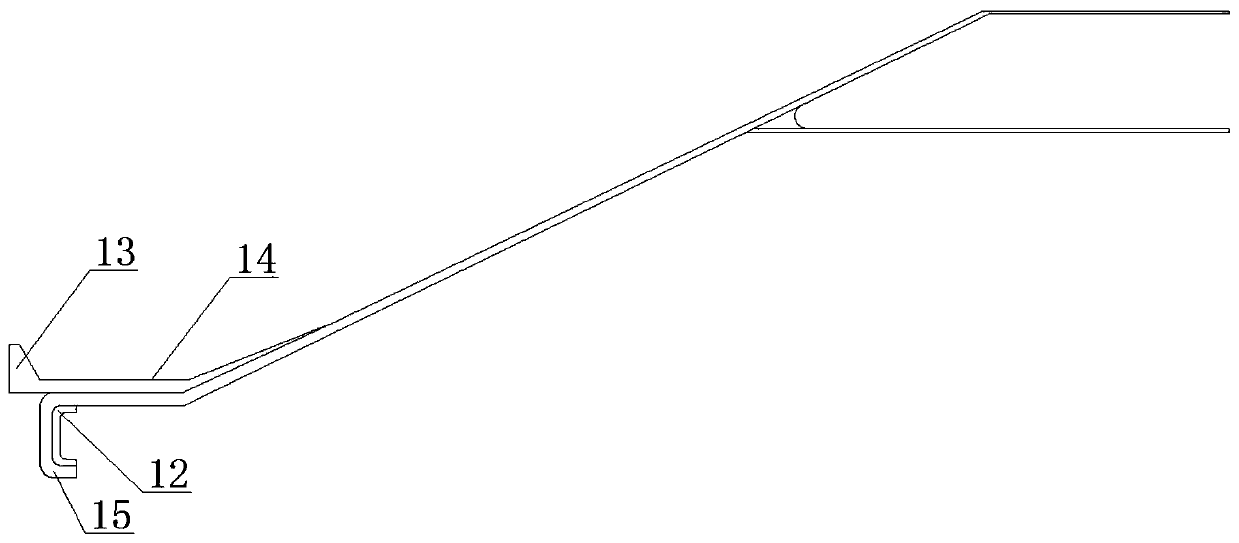
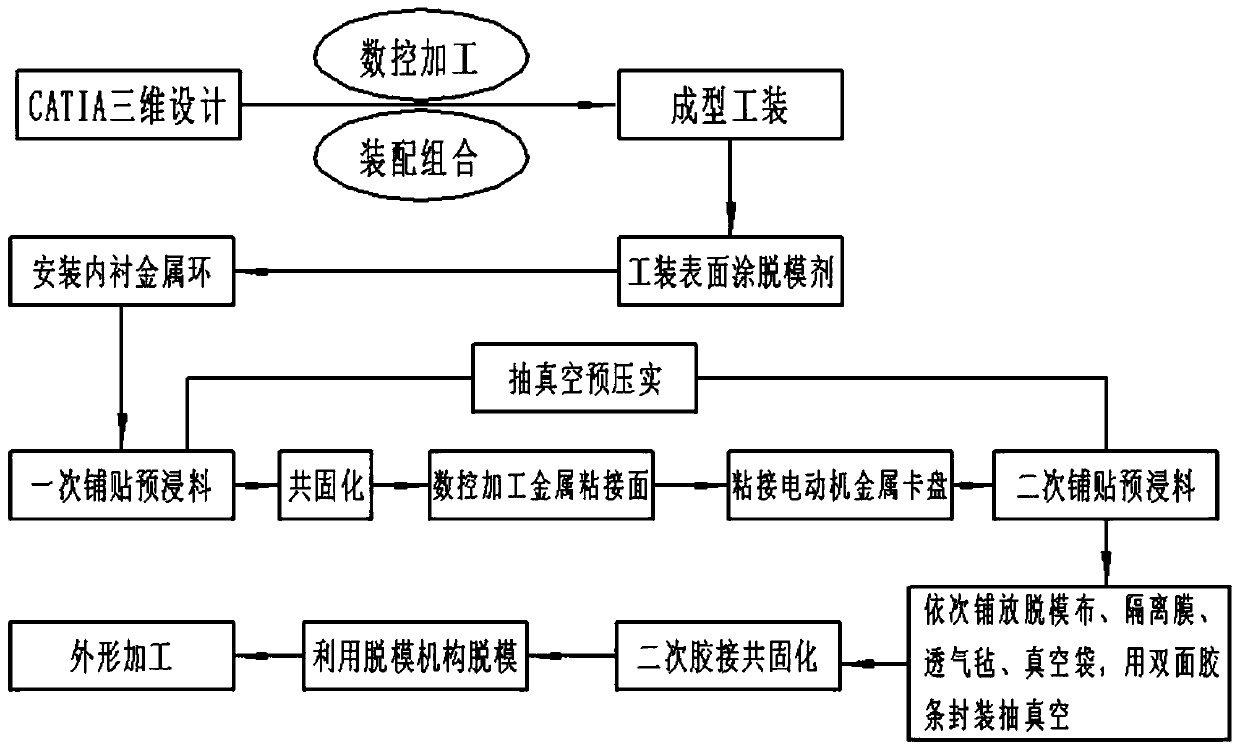
Unmanned aerial vehicle electric cabin composite cephalic cone integrated forming tool and process
ActiveCN111186143ALow costGuaranteed assembly accuracyDomestic articlesCircular discUncrewed vehicle
The invention provides an unmanned aerial vehicle electric cabin composite cephalic cone integrated forming tool and process. The unmanned aerial vehicle electric cabin composite cephalic cone integrated forming tool comprises a male molded surface, internal square pipe supports, a blocked metal core model, a metal moving disc, internal center circular pipe supports, positioning pins, fastening bolts, demolding bolts and demolding blocks, four swivels are mounted on the outer side wall of the male molded surface, a vacuum bag area is formed in the surface of the male molded surface, the blocked metal core model sleeves the top of the male molded surface, and the blocked metal core model and the male molded surface are in positioning butt-joint through the positioning pins. According to theunmanned aerial vehicle electric cabin composite cephalic cone integrated forming tool and process, design is reasonable, the assembly accuracy can be guaranteed, it is guaranteed that secondary bonding co-curing forming of a composite cephalic cone and a motor mounting metal clamping disc meets the requirements, and meanwhile the equipment cost can be lowered.
Owner:AEROSPACE SHENZHOU AIRCRAFT
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20070029367A1Not to damageCooking-vessel materialsSolid-state devicesDevice materialSecondary bonding
A wire bonding method that performs a primary bonding of wire on a first bonding point and performs a secondary bonding of the wire on a second bonding point, thus connecting the first and second bonding points with the wire, the secondary bonding including: a first bonding step that forms a first bonding part by bonding the wire to the second bonding point, a second bonding step that forms a second bonding part by raising a capillary through which the wire passes and moving the capillary toward the first bonding point, and then lowering the capillary and overlapping the wire to connect the wire to the first bonding part, and a ting step that cuts the wire.
Owner:SHINKAWA CO LTD
Diamond-based gallium nitride composite wafer and bonding preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111900200AReduce pollutionReduced bond qualitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCarbide siliconWafering
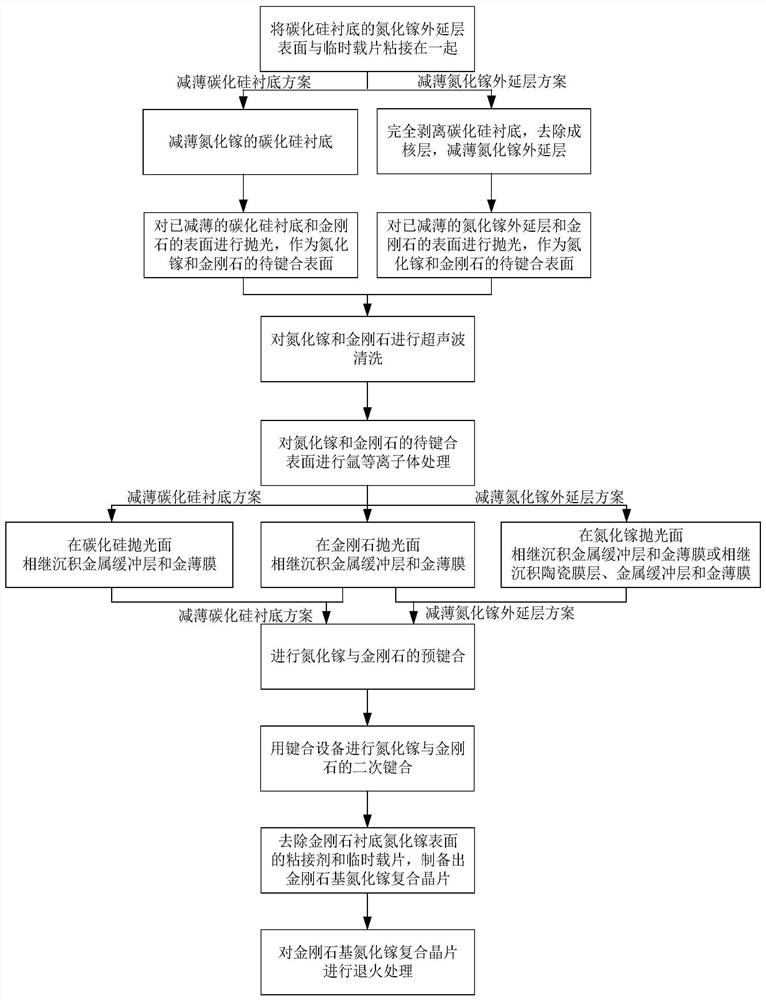
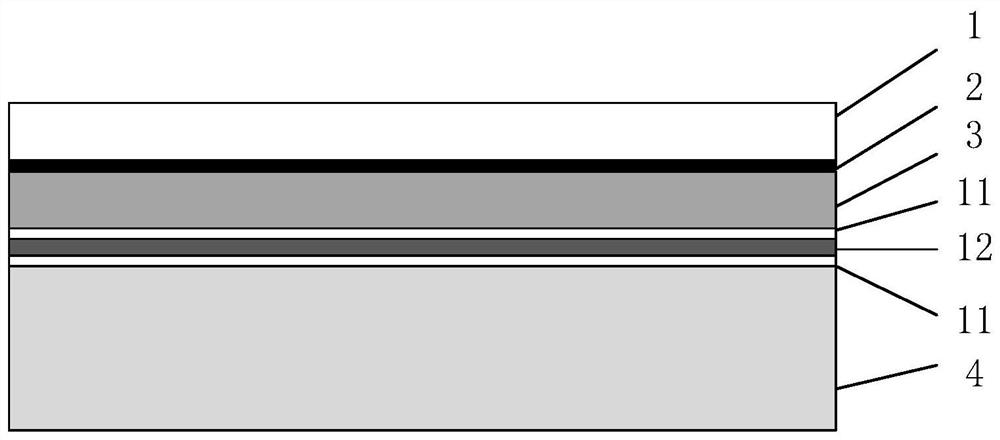
The invention discloses a diamond-based gallium nitride composite wafer and a bonding preparation method thereof. The wafer is provided with a gallium nitride / nucleating layer / silicon carbide / metal intermediate layer / diamond substrate, a gallium nitride / metal intermediate layer / diamond substrate, a gallium nitride / ceramic film layer / metal intermediate layer / diamond substrate and other structures.The method mainly comprises the following steps of thinning a silicon carbide substrate of gallium nitride, or completely stripping the silicon carbide substrate and thinning a gallium nitride layer,carrying out polishing and argon plasma treatment on the silicon carbide substrate or the gallium nitride layer and the to-be-bonded surface of the diamond, depositing a metal buffer layer and a goldfilm on the to-be-bonded surface of the silicon carbide substrate, or depositing a metal buffer layer and a gold film on the to-be-bonded surface of the gallium nitride layer, or depositing a ceramicfilm layer, a metal buffer layer and a gold film, and depositing a metal buffer layer and a gold film on the to-be-bonded surface of the diamond, enabling gallium nitride and diamond to be pre-bondedat first, and then conducting secondary bonding, and carrying out annealing treatment on the diamond-based gallium nitride composite wafer. The bonding strength can be improved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com