Patents
Literature
59results about How to "Accurate and efficient testing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Automated test method
InactiveUS7020571B2Accurate and efficientQuality and safe operationResistance/reactance/impedenceCurrent/voltage measurementComputer hardwareElectrical devices
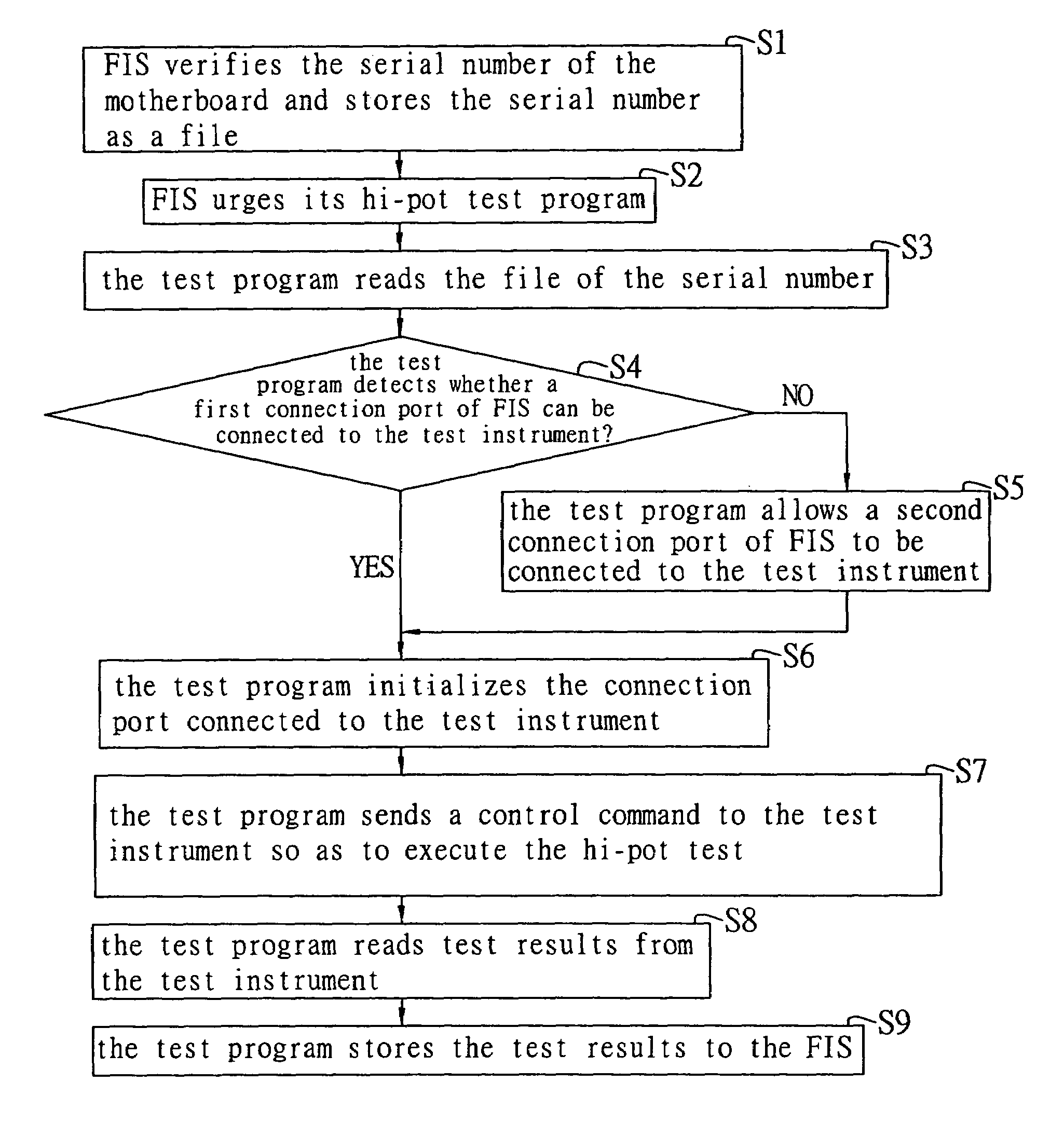
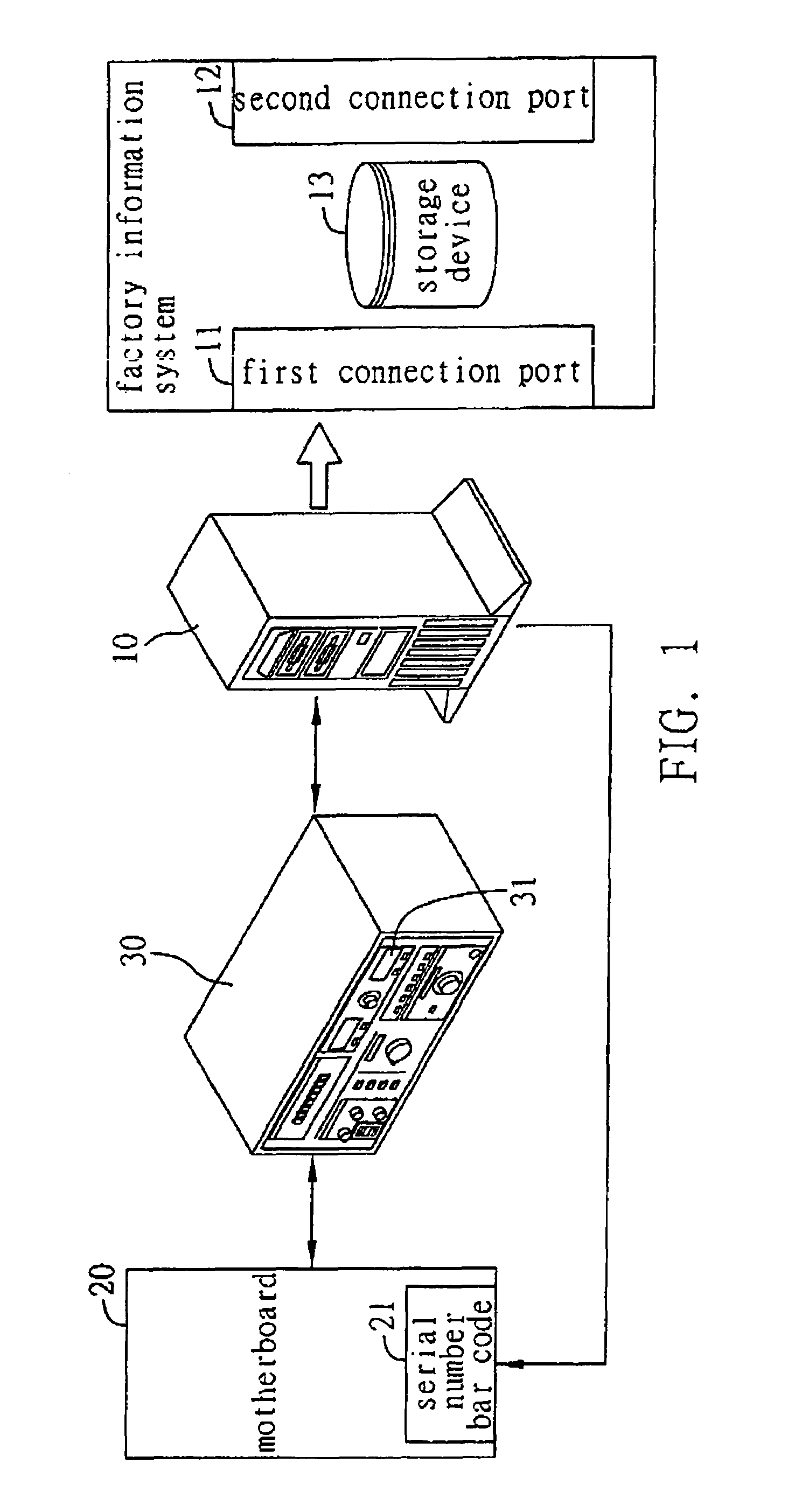
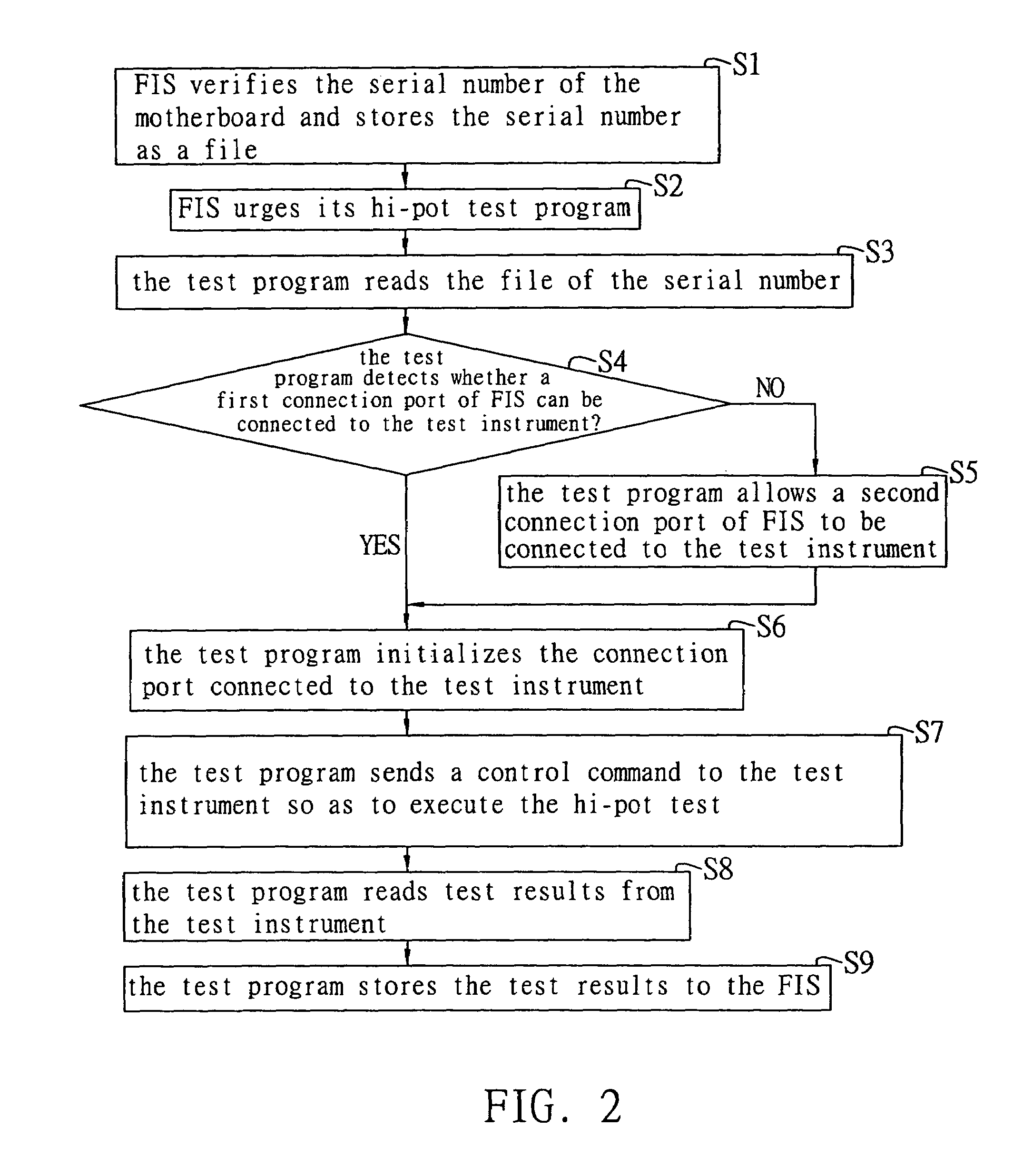
An automated test method for performing a hi-pot test procedure for an electrical device through the use of a test program installed in a factory information system (FIS) and a test instrument connected to the FIS. The test program sends a control command to the test instrument that in turn executes the hi-pot test for the electrical device. Test results are obtained by the test program from the test instrument and sent to the FIS. The test results are stored in the FIS for future reference.
Owner:INVENTEC CORP
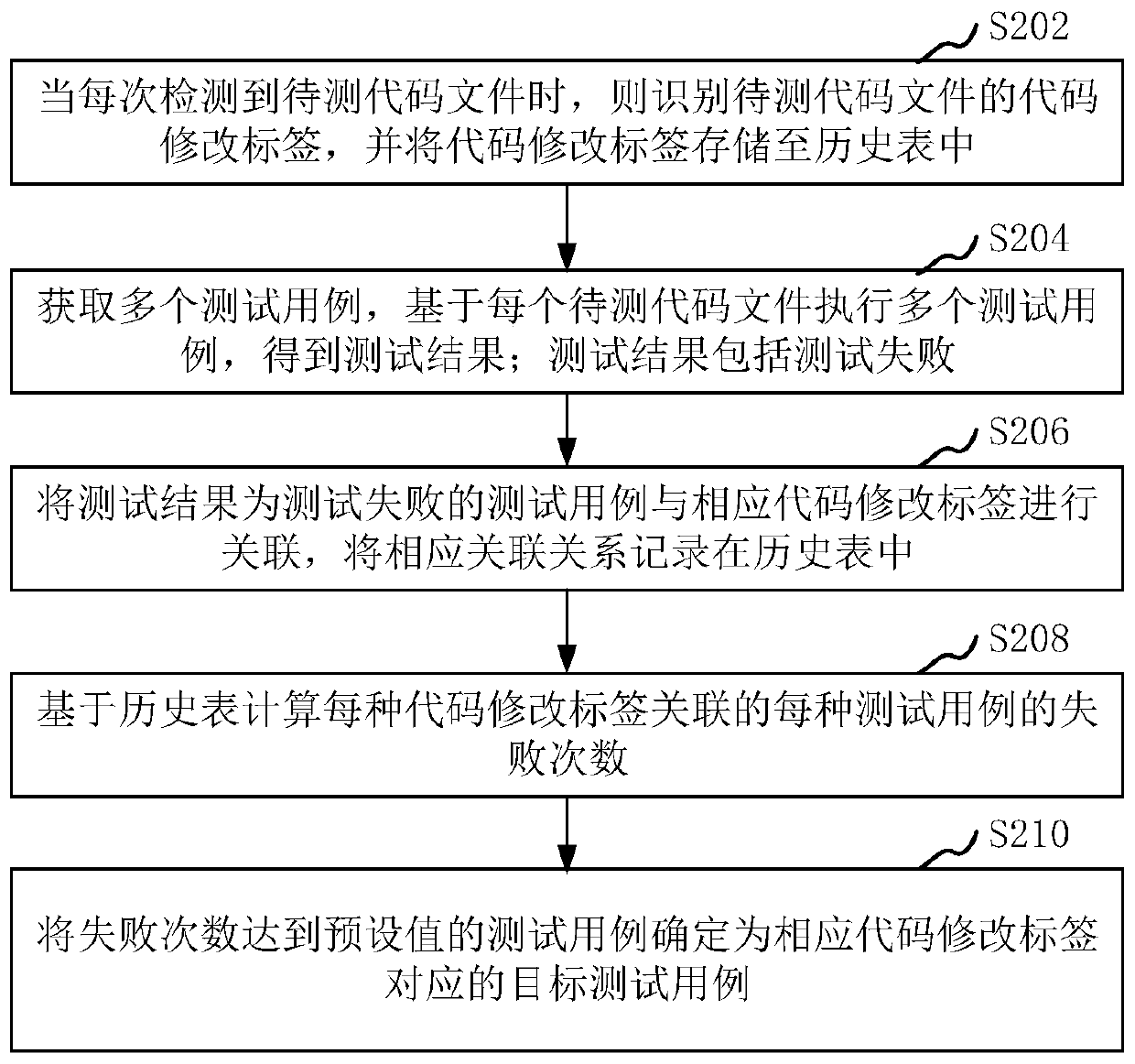
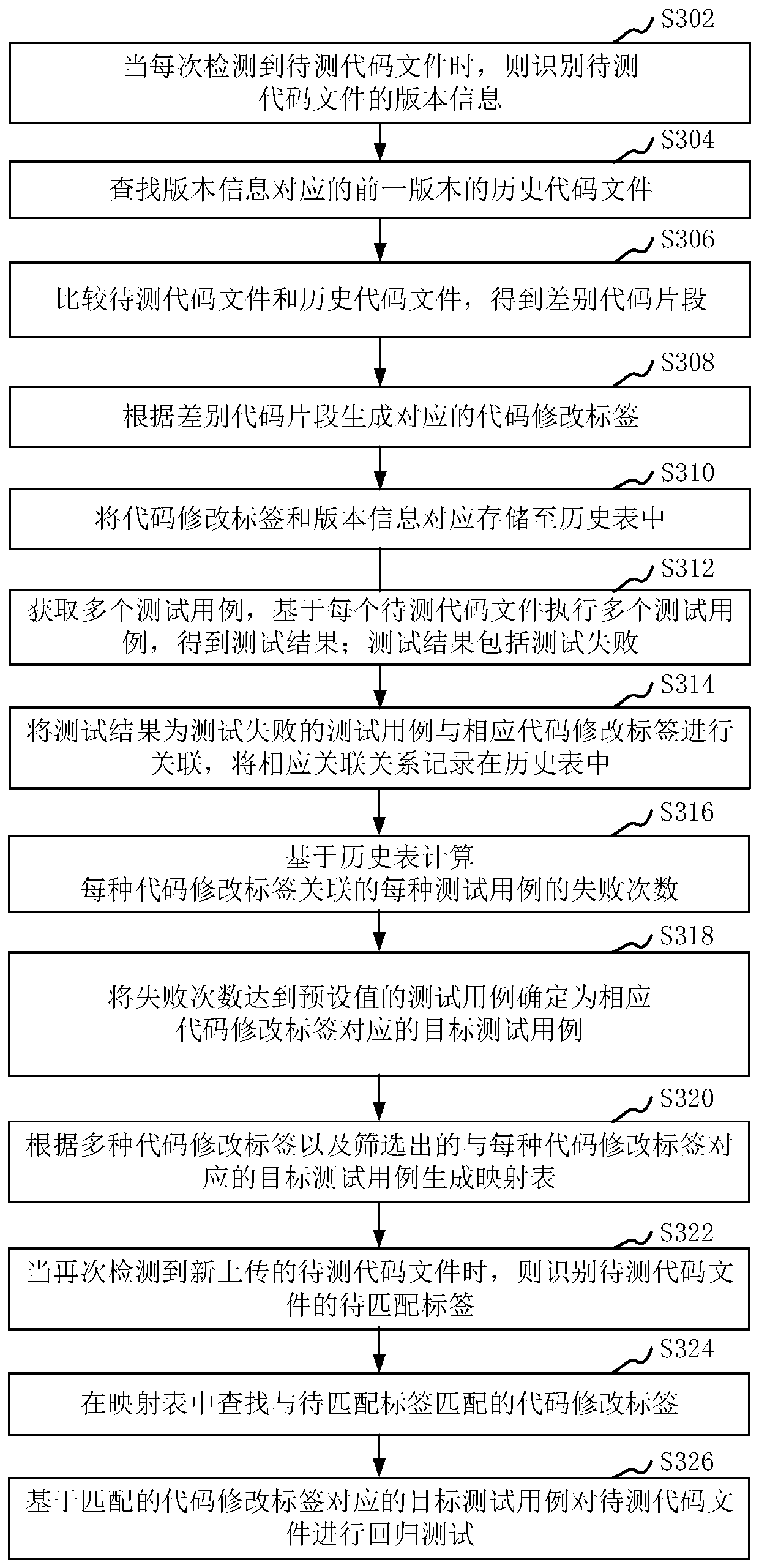
Test case screening method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
PendingCN110489321AAccurate and efficient testingPrecise screeningSoftware testing/debuggingService systemTest code
The invention relates to a test case screening method and device, computer equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of when a to-be-detected code file is detected each time, recognizing a code modification label of the to-be-detected code file, and storing the code modification label in a history table; obtaining a plurality of test cases, and executing the plurality of testcases based on the to-be-tested code file each time; associating the test cases of which the test results are test failure with the corresponding code modification tags, and recording corresponding association relationships in a historical table; calculating the failure times of each test case associated with each code modification tag based on the historical table; and determining a target test case corresponding to each code modification label according to each code modification label and the failure times of each associated test case. By adopting the method, the pertinence of the test casescan be improved when a service system after code modification is tested.
Owner:PING AN TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
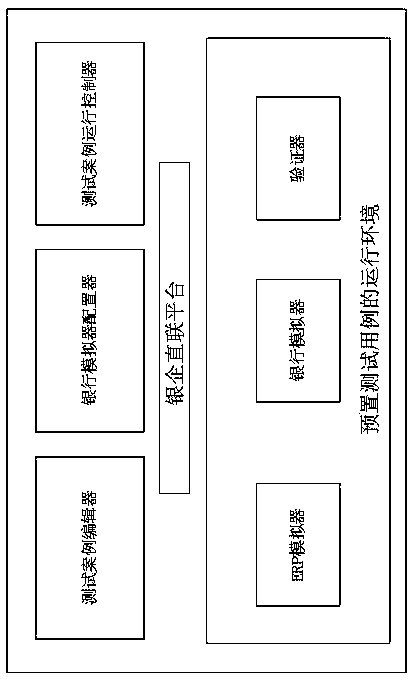
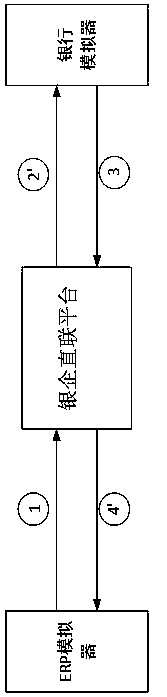
Real business-based financial transaction test system and method
InactiveCN108614777ARealize simulationEffectively detect defectsFinanceSoftware testing/debuggingFinancial transactionFinancial trading
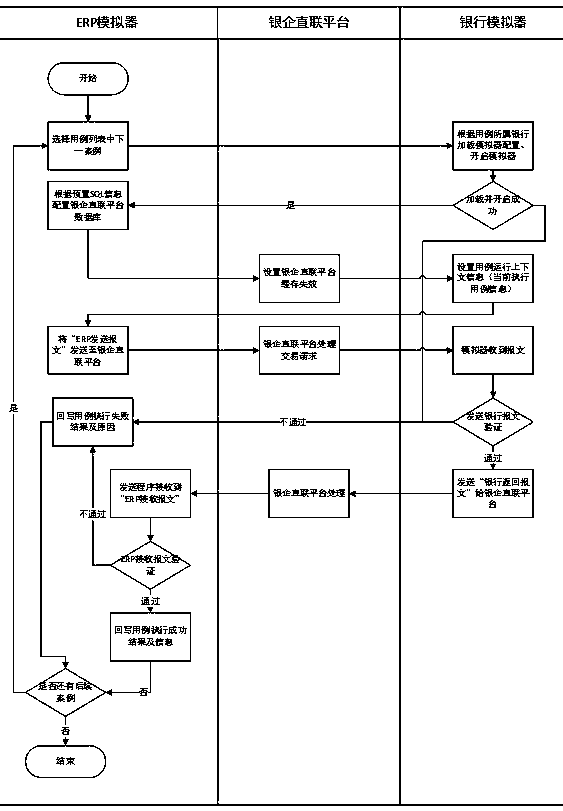
The invention discloses a real business-based financial transaction test system and method, belongs to the field of financial transaction simulation and test, and aims at carrying out modification byusing systems of ERP manufacturers so as to obtain effective and sufficient verification without influencing fund security of enterprise users. An adopted technical scheme is the real business-based financial transaction test system which comprises an ERP simulator, a bank simulator, a bank-enterprise direct connection platform, a verifier, a test case editor, a bank simulation configuration unitand a test case operation controller. The invention furthermore discloses the real business-based financial transaction test method.
Owner:SHANDONG INSPUR GENESOFT INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Chip stack device testing method, chip stack device rearranging unit, and chip stack device testing apparatus
ActiveUS20120126844A1Accurate and efficient testingLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringTest fixture
A plurality of chip stack devices having different external sizes can be tested accurately and efficiently with low cost. The present invention provides a chip stack device testing method testing a chip stack device configured by stacking a plurality of chips separated by dicing a substrate under test tested in a testing unit. A tray for chip stack devices having equal shape and external dimension to those of the undiced substrate under test is used, one or a plurality of the chip stack devices are attached and supported to an adhesive layer of the tray for chip stack devices to align the chip stack devices with positions of the respective chips of the undiced substrate under test, the tray for chip stack devices is installed in the testing unit in a similar manner to that in a test of the substrate under test, and the respective chip stack devices are tested.
Owner:NIHON MICRONICS
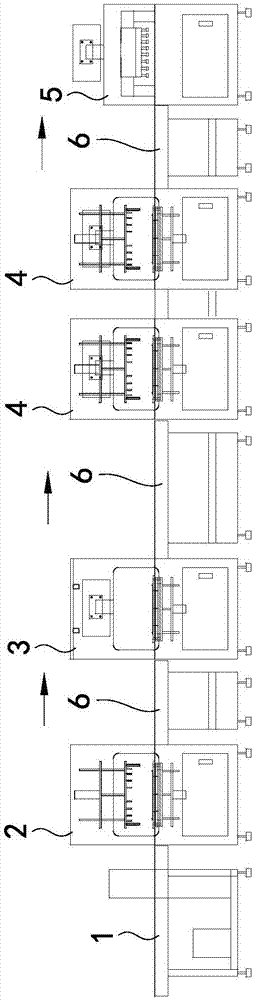
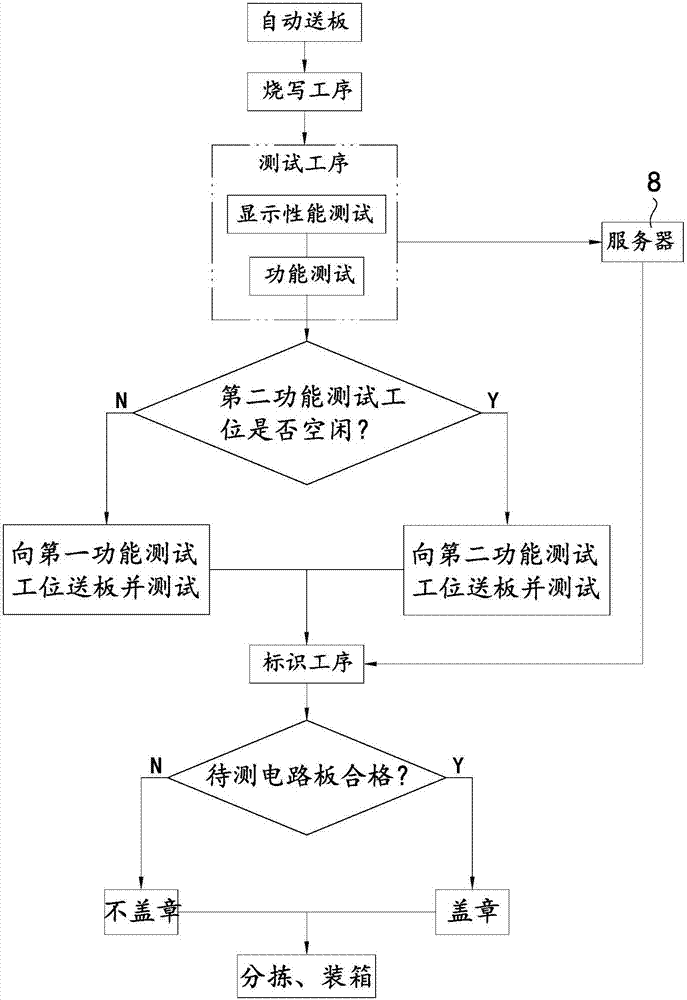
Intelligent test system and method for metering device circuit board
PendingCN106970318AMeet the needs of high-volume testingAvoid man-made damagePrinted circuit testingFunctional testingIdentification device
The invention discloses an intelligent test system and method for a metering device circuit board, belongs to the circuit board detection technology field and solves a problem of low efficiency caused by manual detection existing in a metering device circuit board in the prior art. The intelligent test system comprises a programming device used for realizing programming of function programs into a to-be-tested circuit board, a display performance test device used for testing display performance of the to-be-tested circuit board, a function test device used for testing functions of the to-be-tested circuit board, an identification device used for identifying the to-be-tested circuit board according to test results of the display performance test device and the function test device, a circuit board conveying mechanism which is connected with the programming device and is used for conveying the to-be-tested circuit board to the programming device, and a main control unit used for controlling operation of the programming device, the display performance test device, the function test device, the identification device and the circuit board conveying mechanism. The intelligent test system is advantaged in that the intelligent test system is applicable to circuit board tests of various types of intelligent gas meters.
Owner:GOLDCARD HIGH TECH
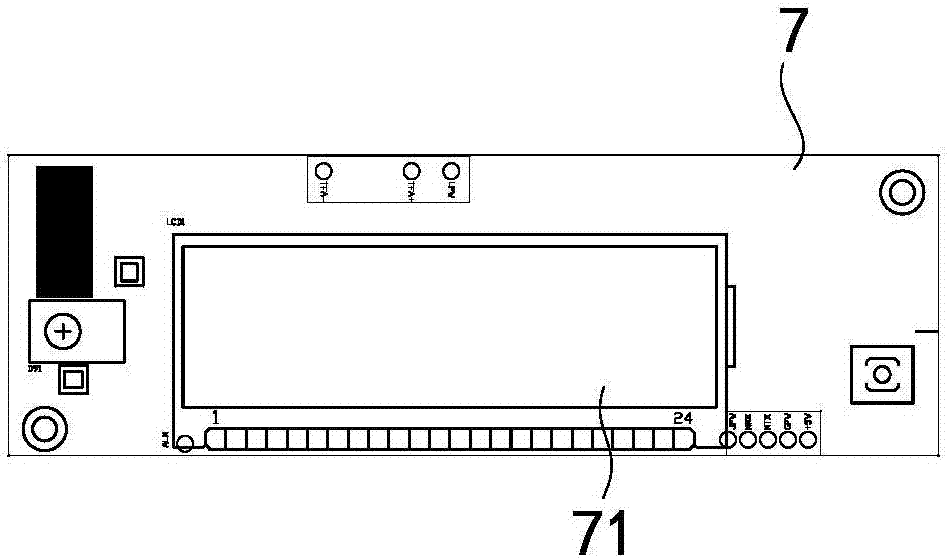
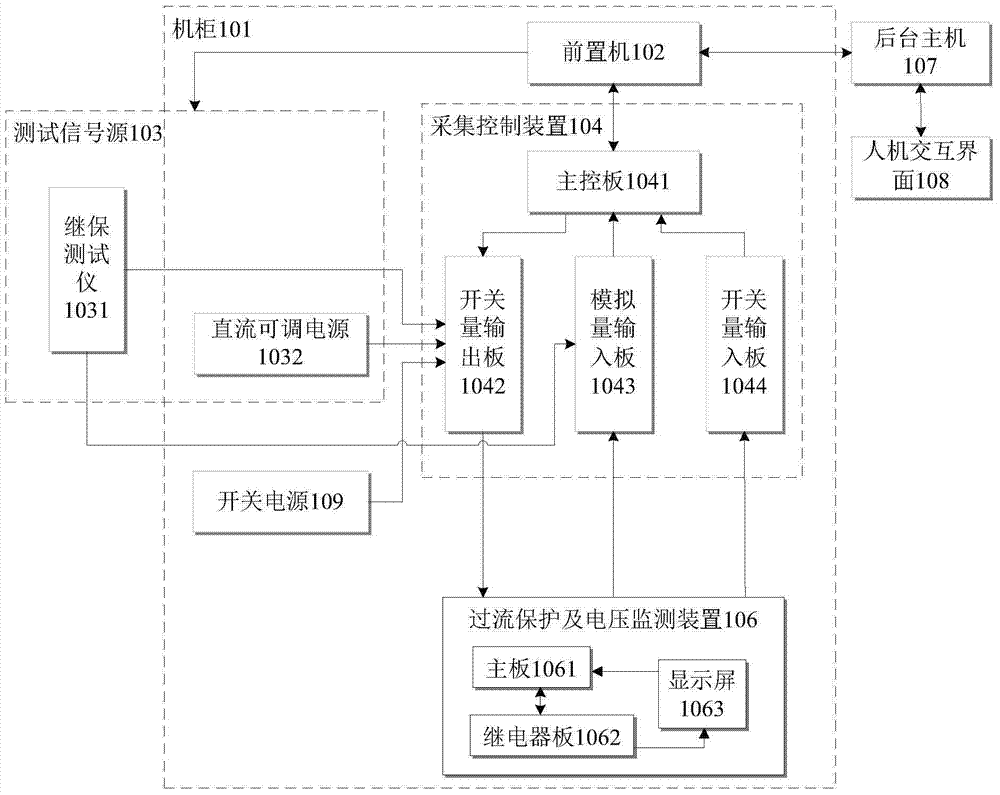
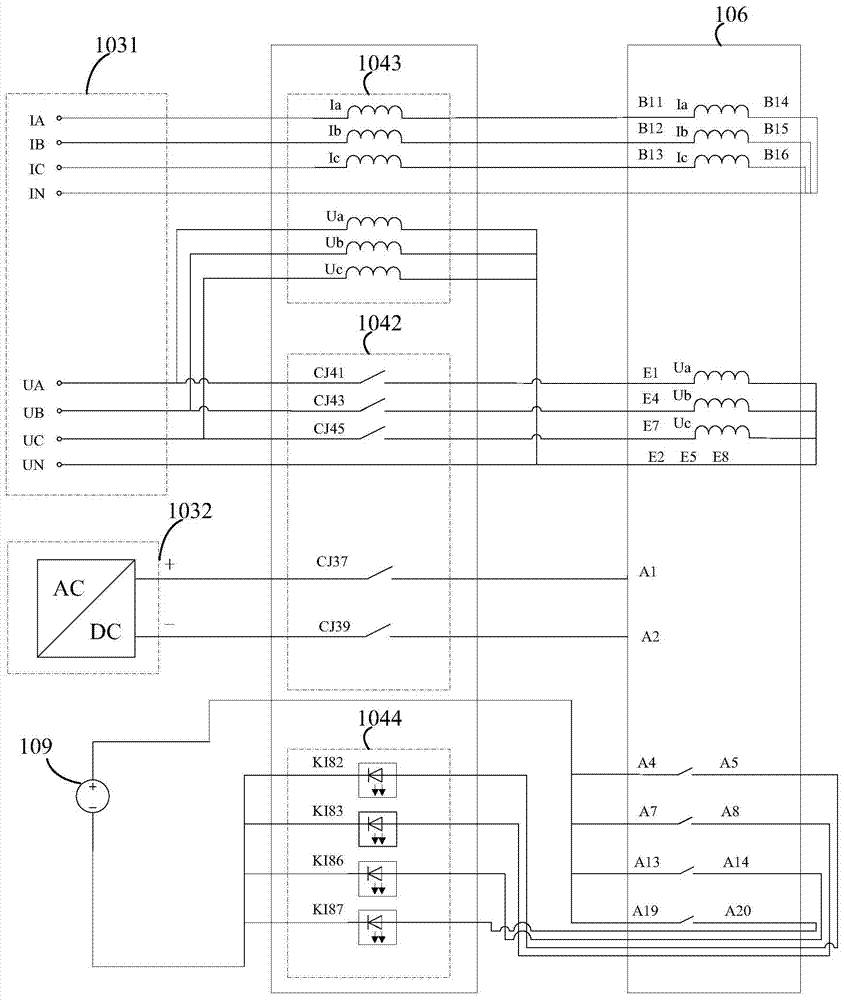
System and method for overcurrent protection and voltage monitoring device burn-in test
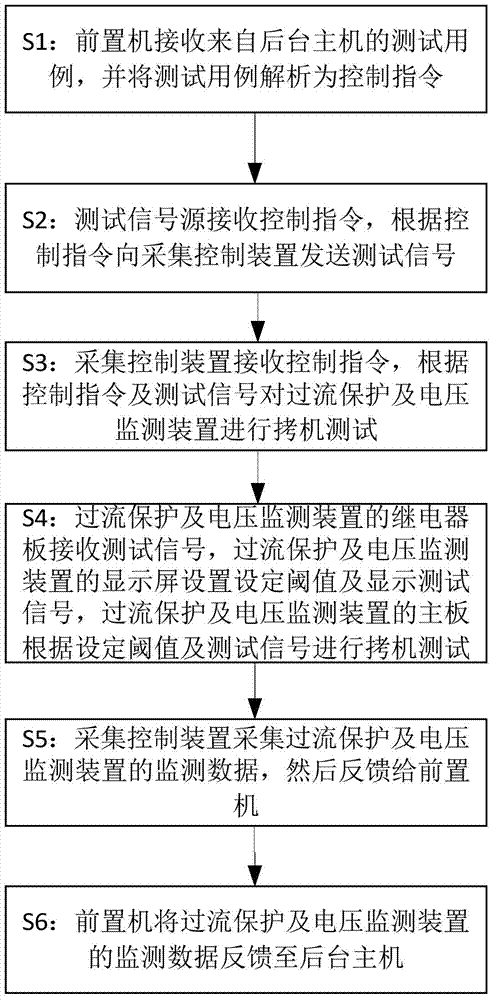
ActiveCN104849582AAccurate and efficient testingTimely detection of existing defectsElectrical testingEngineeringSwitching power
The invention discloses a system and a method for overcurrent protection and voltage monitoring device burn-in test. The system comprises a cabinet, a front-end processor, a test signal source, an acquisition control device, and a switching power supply. The method comprises: the front-end processor parsing a test case to a control command; the test signal source sending test signals to the acquisition control device; the acquisition control device receiving the control command, and acquiring monitored data of the overcurrent protection and voltage monitoring device, and feeding back to the front-end processor. The overcurrent protection and voltage monitoring device comprises a relay panel, a mainboard, and a display screen. The relay receives test signals. The display screen sets a given threshold value. The mainboard receives a burn-in test. The system and the method for overcurrent protection and voltage monitoring device burn-in test use automated, intelligent, and integrated online monitoring measures, and can accurately and efficiently test functions of the overcurrent protection and voltage monitoring device, and can find out defects of the overcurrent protection and voltage monitoring device, so as to effectively reduce fault risks of nuclear power station circuits.
Owner:CHINA GENERAL NUCLEAR POWER OPERATION +2
Communication equipment test device
InactiveCN102437885AImplement automated testingFast and flexible testingTransmission monitoringTest efficiencySERCOS interface
The invention relates to a communication equipment test device, which comprises a computer, a high-low-level controller, a test interface selection core module, a test module and a variable microwave module, wherein the computer is used for running test control software and for transmitting an interface control signal the high-low-level controller is provided with an input end and an output end, and the input end is connected with the computer and receives the interface control signal and generates a corresponding level signal; the test interface selection core module is connected with high-low-level controller and is provided with a plurality of test input interfaces and a plurality of test output interfaces, each test input interface is respectively connected with each test output interface, the high-low-level controller receives the interface control signal and selects a corresponding test input interface; the test module comprises a test part for testing each parameter of tested element; and the variable microwave module comprises multiple microwave parts. Due to the adoption of the communication equipment test device, the automatic test of each tested interface can be realized, different test parts can be selected according to different indexes to be tested, the test is flexible, rapid, high efficient and correct, the test cost can be reduced, and the test efficiency can be improved.
Owner:FILTRONIC SUZHOU TELECOMM PROD CO LTD
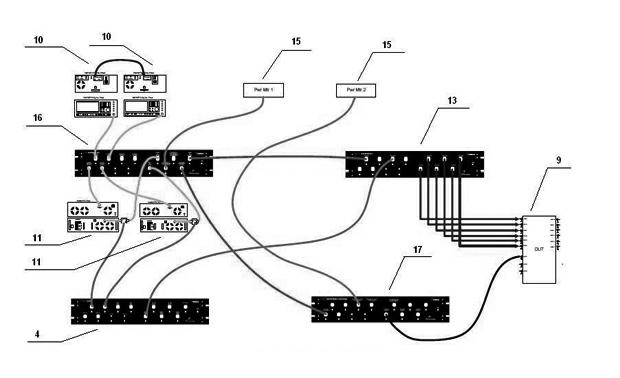
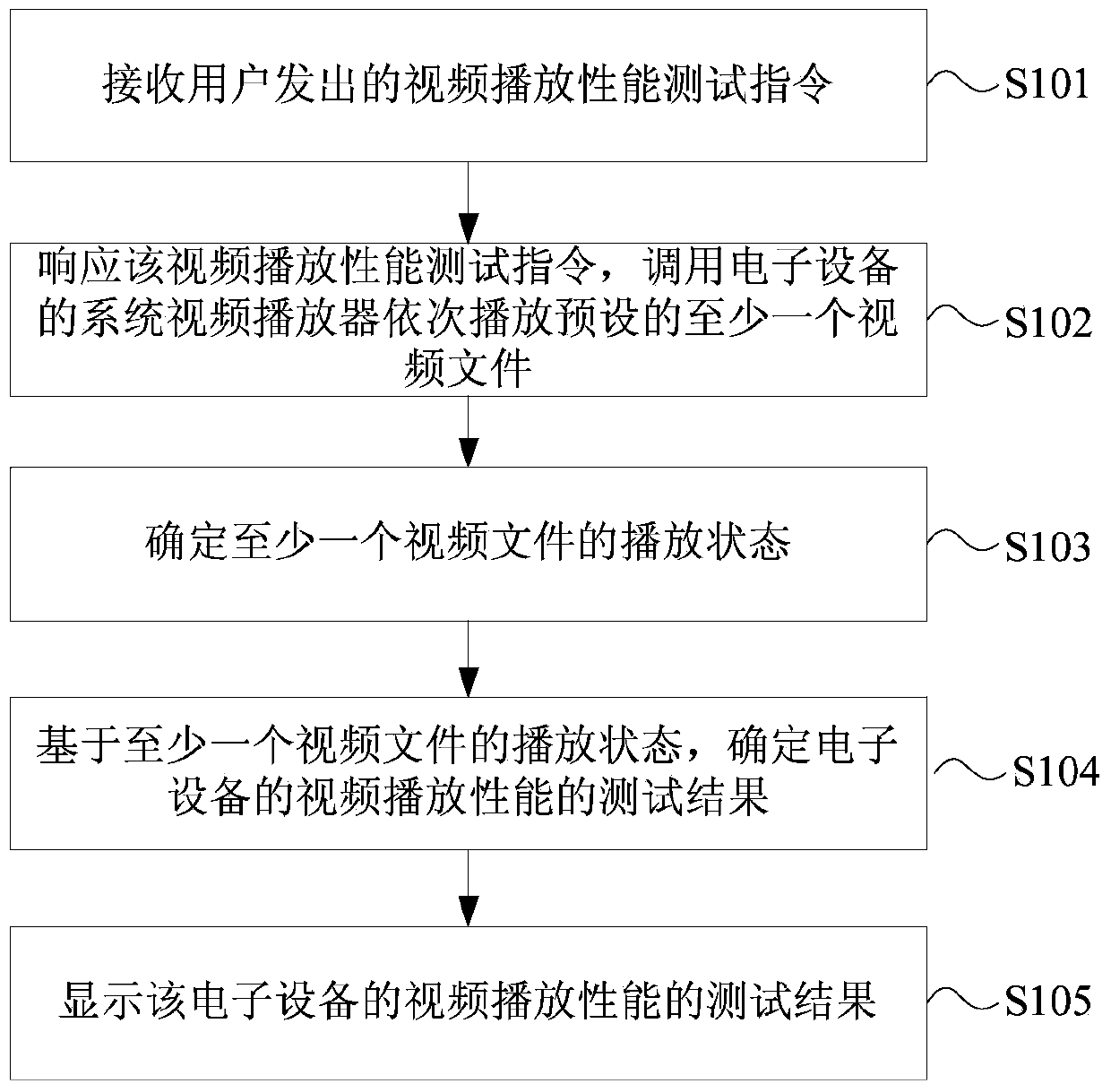
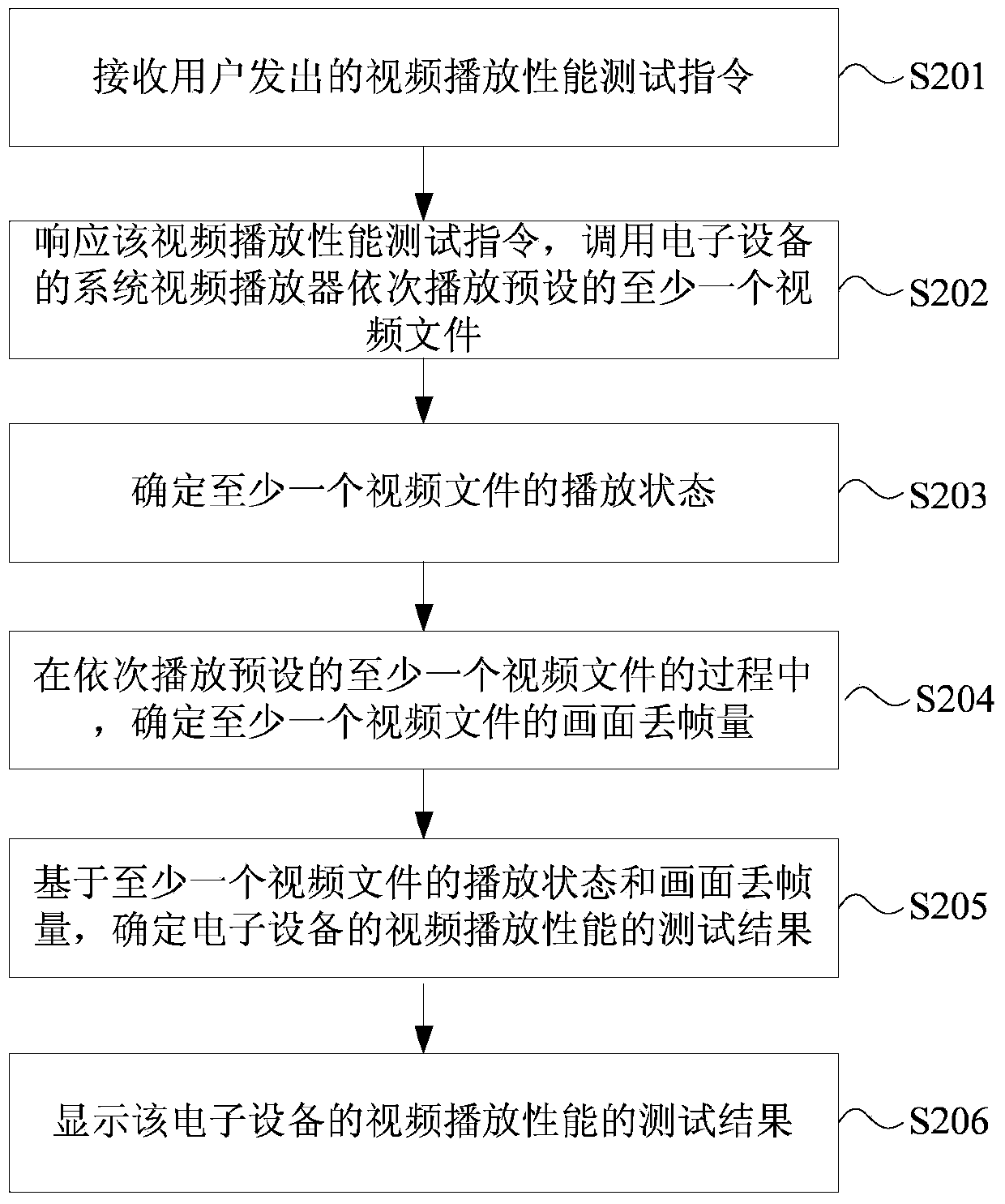
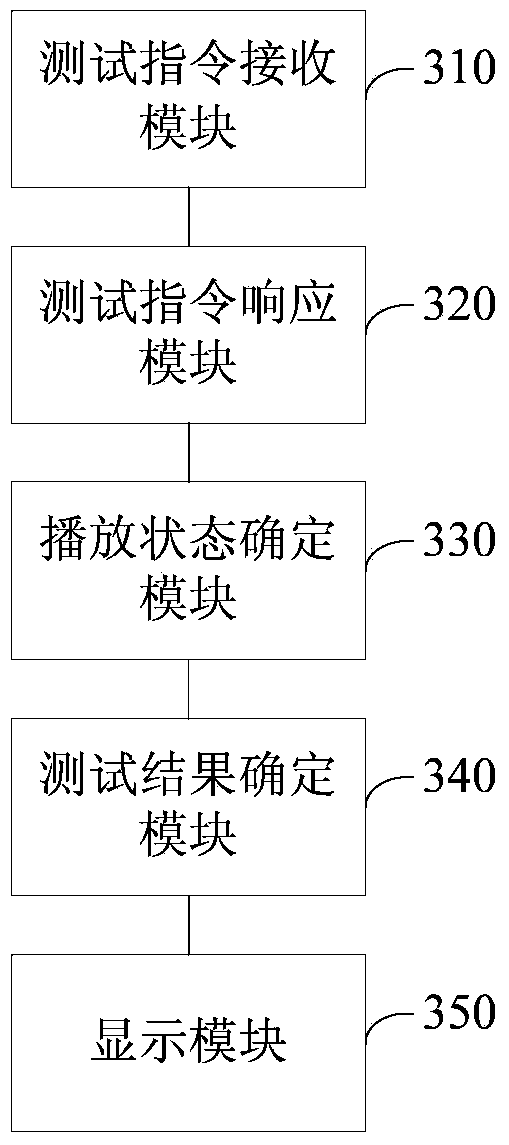
Method and device for testing video playing performance
ActiveCN103997643AAccurate and efficient testingTelevision systemsSelective content distributionComputer hardwareVideo player
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and device for testing the video playing performance. The method for testing the video playing performance is applied to an electronic device and includes the steps that a video playing performance test instruction sent by a user is received; a response to the video playing performance test instruction is generated, a system video player of the electronic device is called for sequentially playing at least one preset video file, and therefore the playing state of the video file is determined; based on the playing state of the video file, a test result of the video playing performance of the electronic device is determined; the test result of the video playing performance of the electronic device is displayed. Compared with the prior art, the video playing performance of the electronic device is accurately and efficiently tested through the scheme.
Owner:BEIJING ANTUTU TECH
Set of primers and probes to be used for identification of gene polymorphism and use thereof
InactiveUS20160053309A1Accurately and efficiently testSuperior flexibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningFluorescenceOligonucleotide
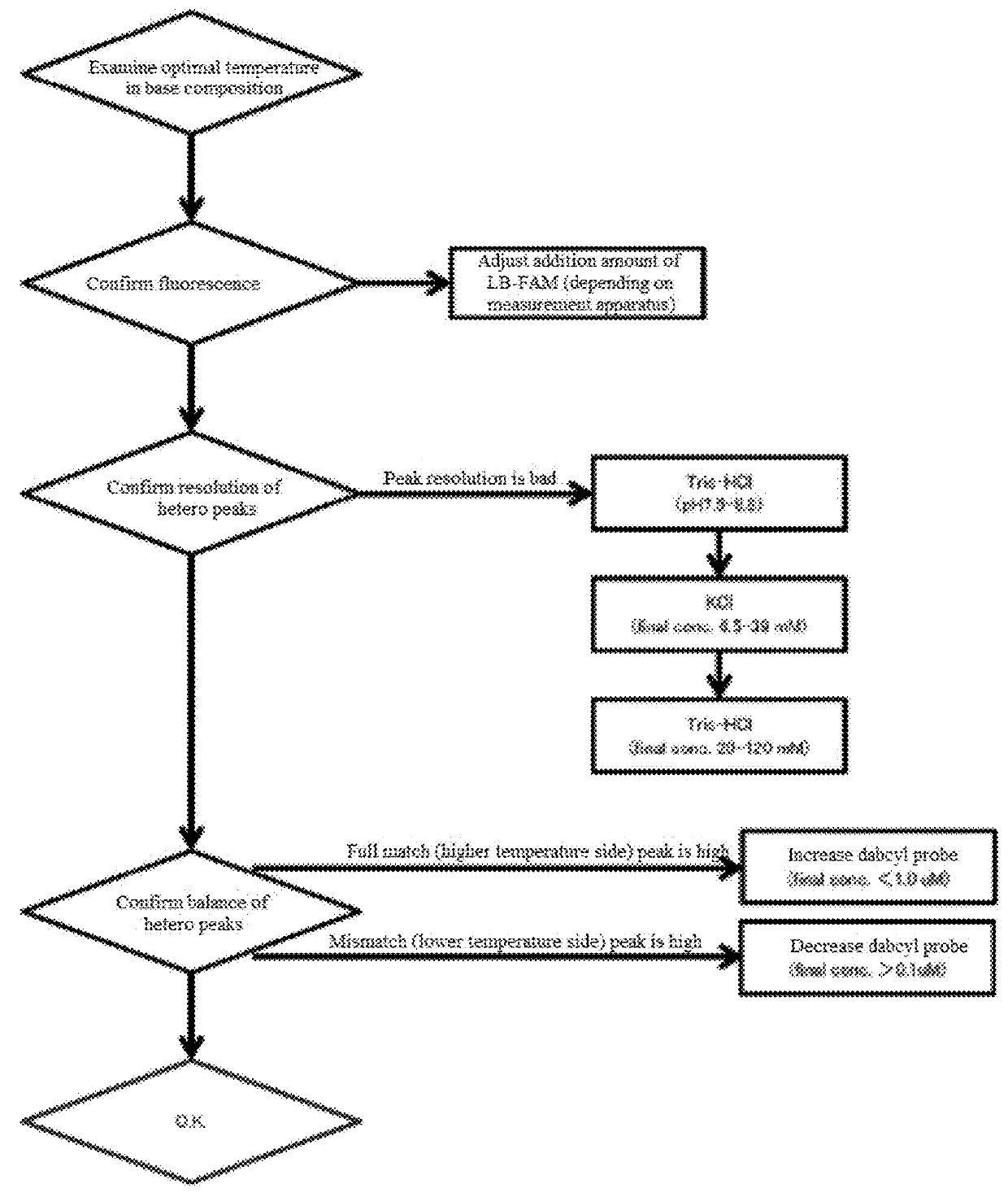
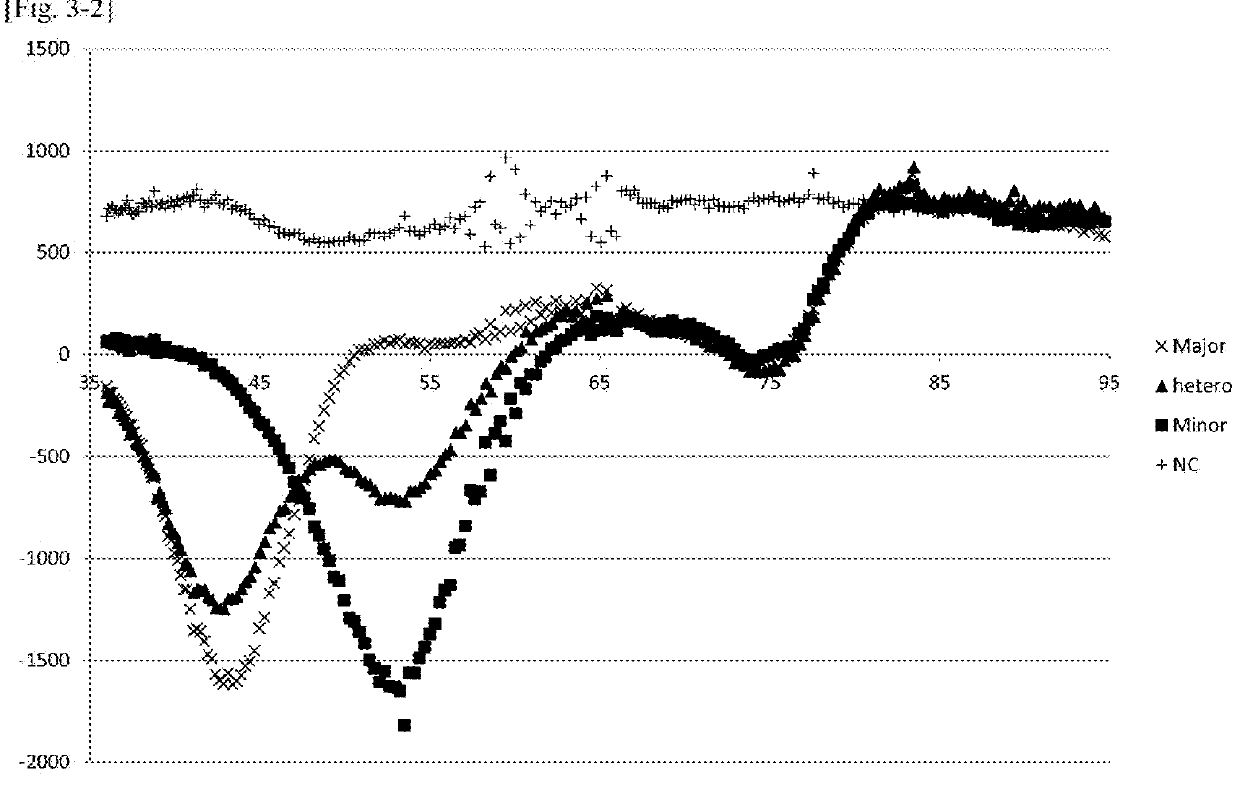
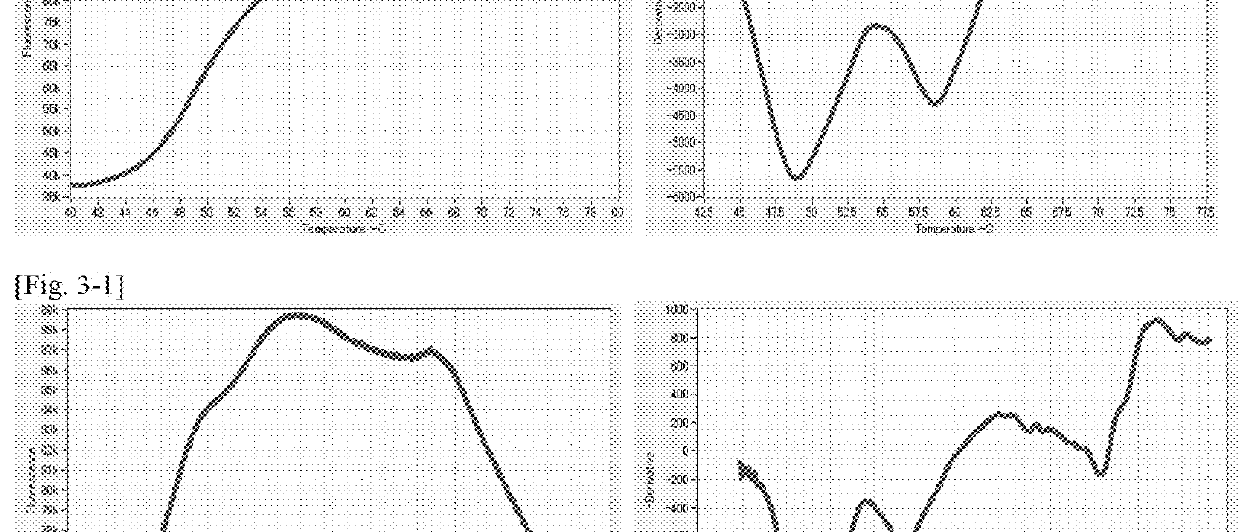
By establishing a simple method for extracting a nucleic acid from a human specimen, and using the LAMP method, which is an isothermal gene amplification method showing superior quickness and convenience, with a concept of measurement different from the conventional ones, there is established a test method including steps up to detection with a measurement apparatus. There is provided a method for detecting a target site, which is an LAMP method using four kinds of primers, FIP, F3 primer, BIP, and B3 primer, which are designed on the basis of six regions of a template polynucleotide, F1 region, F2 region, F3 region, B1 region, B2 region, and B3 region, wherein: the template polynucleotide contains the target site, the four kinds of primers are designed so that the target site exists between the F1 region and the F2 region, or between the B1 region and the B2 region; a loop primer designed on the basis of a region between the F1 region and the F2 region or between the B1 region and the B2 region on the side on which the target site exists, and an oligonucleotide probe that can associate with a region including the target site are used, the loop primer and the probe are designed so that the 5′ end of the loop primer and the 3′ end of the probe associate with the template polynucleotide at positions close to each other, one of the loop primer and the probe is modified with a fluorescent molecule around the 5′ end in the case of the loop primer or the 3′ end in the case of the probe, and the other is modified with a quenching molecule.
Owner:NIPPON GENE
Fluorescence immunoassay analysis system and testing method thereof
InactiveCN108318700AAccurate and efficient testingShorten test timeMaterial analysisReagent stripFluorescence immunoassay
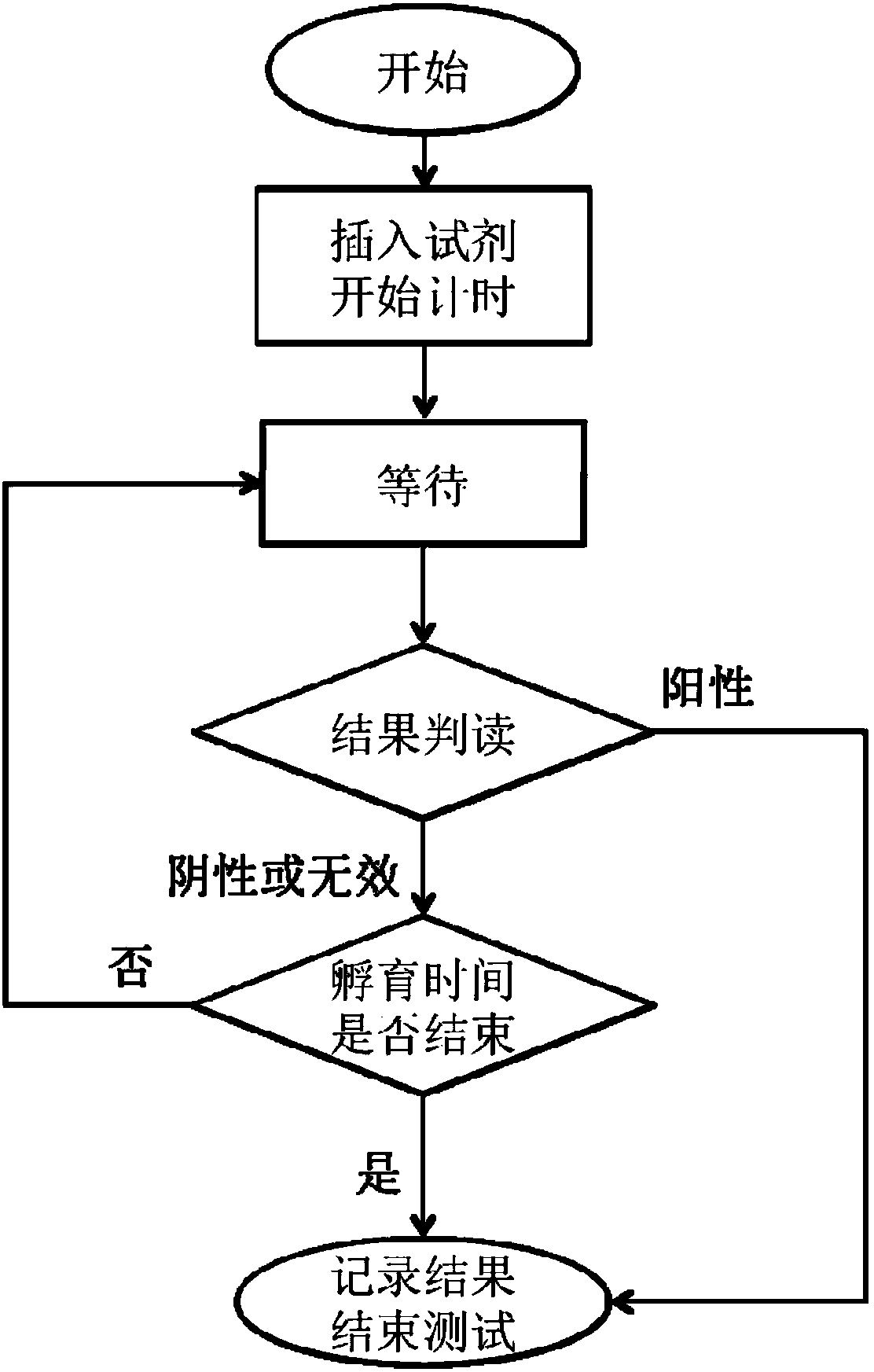
The invention discloses a fluorescence immunoassay analysis system and a testing method thereof. The system comprises a control module, a reagent channel, a code reader, a mobile unit and a fluorescence detection module, wherein the reagent channel comprises a plurality of reagent inserting positions and is used for clamping reagent strips and sending inserting information of the reagent strips tothe control module; the code reader is connected with the control module and is used for reading reagent types and sample number information; the mobile unit is connected with the control module andresponds to control signals of the control module to horizontally or vertically move to the inserting positions of the reagents to be detected; the fluorescence detection module is arranged on the mobile unit and is used for performing fluorescence detection on a sample to be detected and sending produced fluorescence detection signals to the control module. The system can wait and detect a plurality of fluorescence immunoassay chromatography reagents, and automatically end a testing process in advance after a positive result is interpreted, thereby improving the detection efficiency of qualitative screening reagents.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINGYAO MED TECH DEV CO LTD
Data testing method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
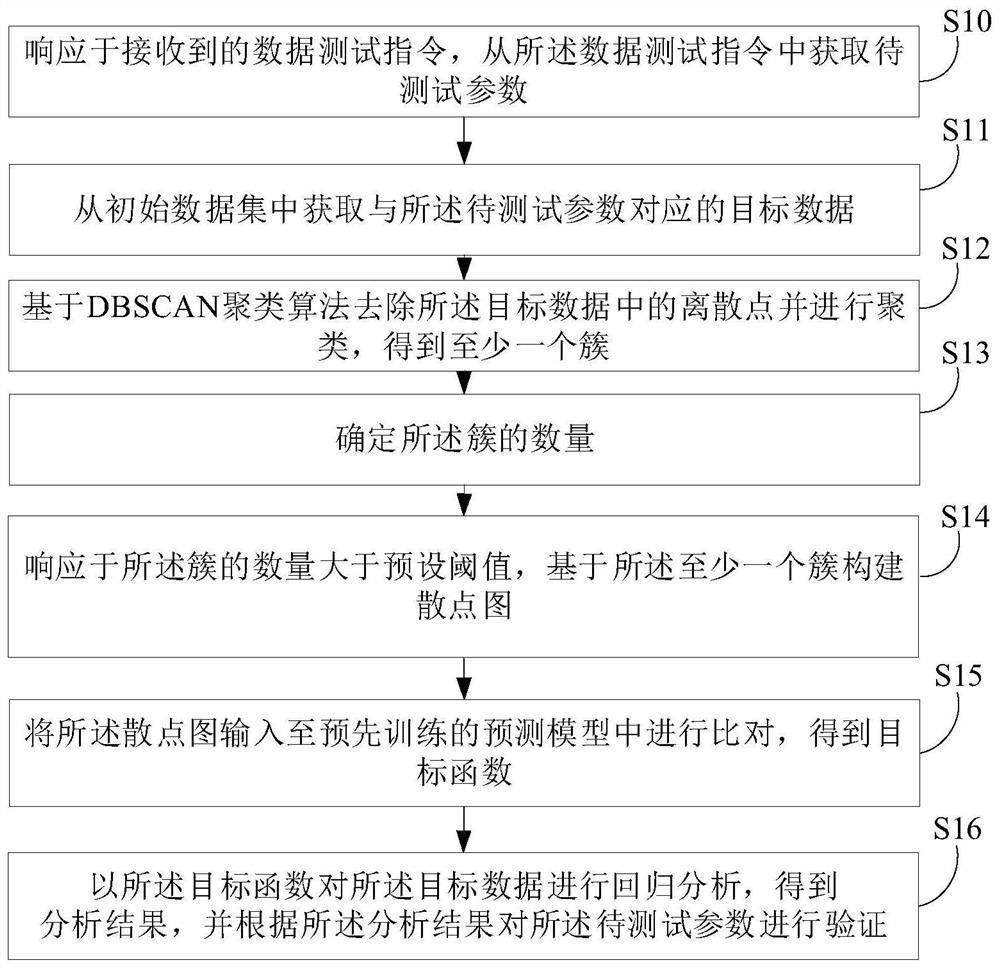
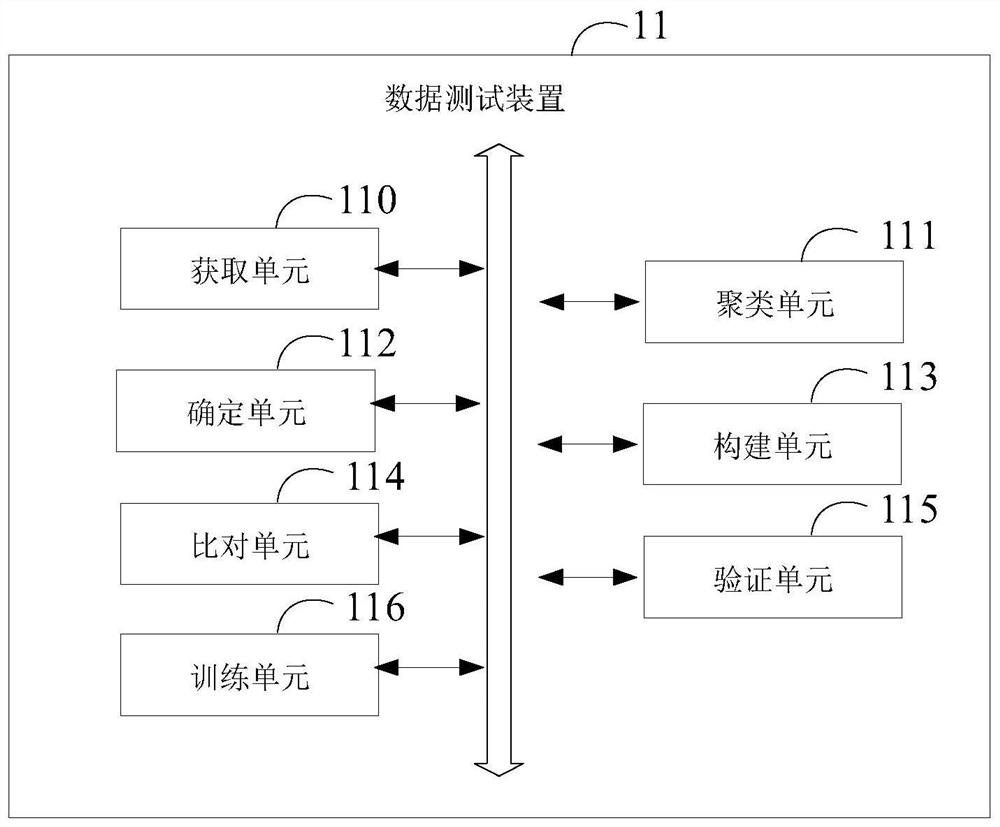
ActiveCN113780691AAccurate and efficient testingAchieving identifiabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionResourcesCluster algorithmData set
The invention provides a data testing method and device, electronic equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: in response to a received data test instruction, obtaining a to-be-tested parameter from the data test instruction; obtaining target data corresponding to the to-be-tested parameters from an initial data set; removing discrete points in the target data based on a DBSCAN clustering algorithm, carrying out clustering, and obtaining at least one cluster; determining the number of the clusters; in response to the fact that the number of the clusters is larger than a preset threshold value, constructing a scatter diagram based on the at least one cluster; inputting the scatter diagram into a pre-trained prediction model for comparison to obtain a target function; and performing regression analysis on the target data by using the target function to obtain an analysis result, and verifying the to-be-tested parameter according to the analysis result. According to the invention, the corresponding function can be automatically identified to test the to-be-tested parameter.
Owner:FU TAI HUA IND SHENZHEN +1
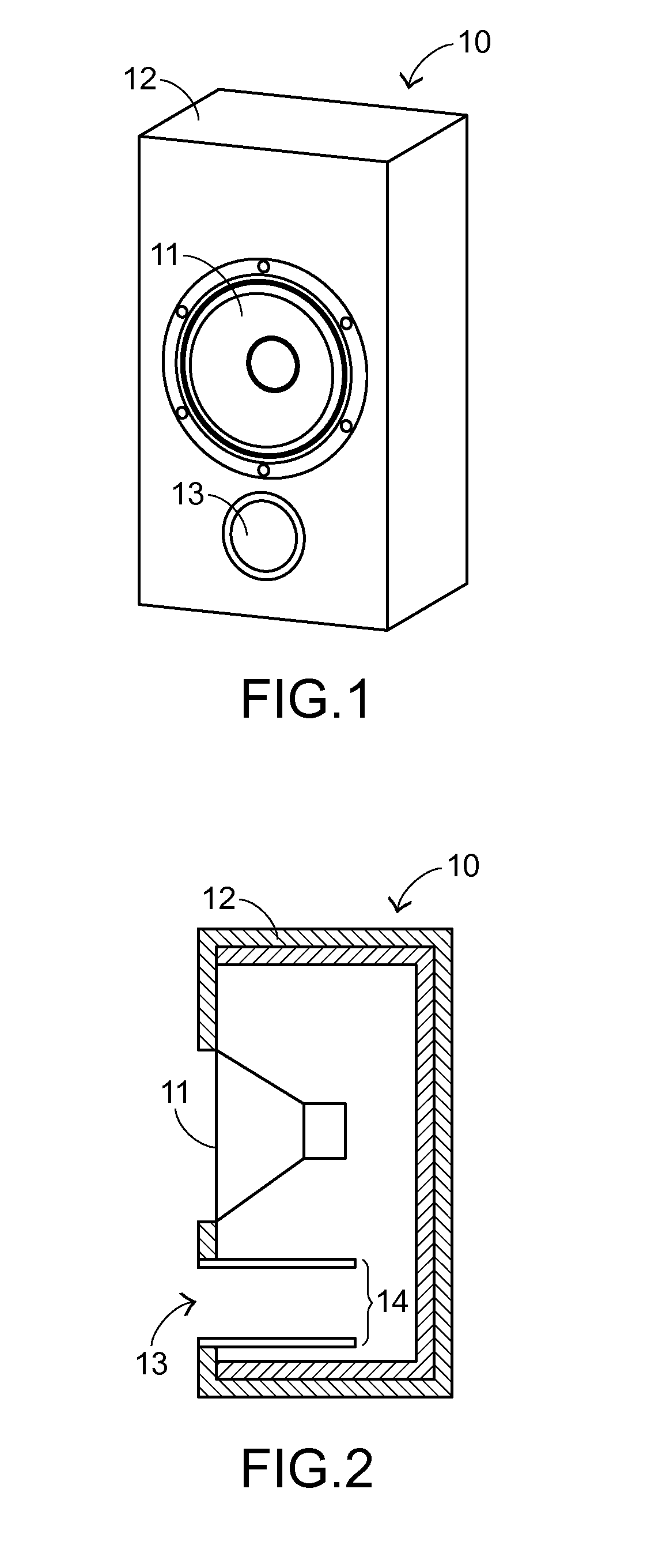
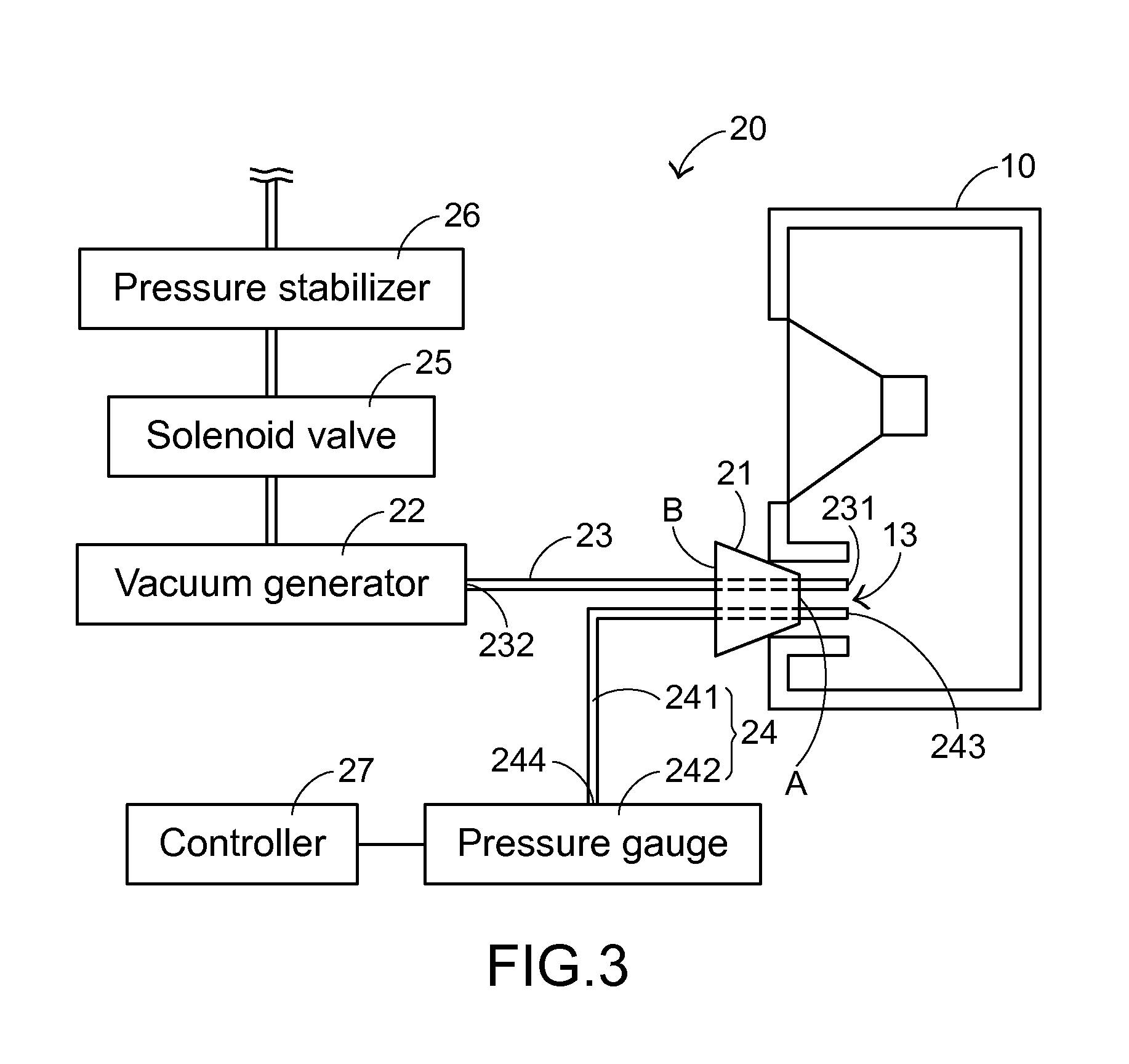
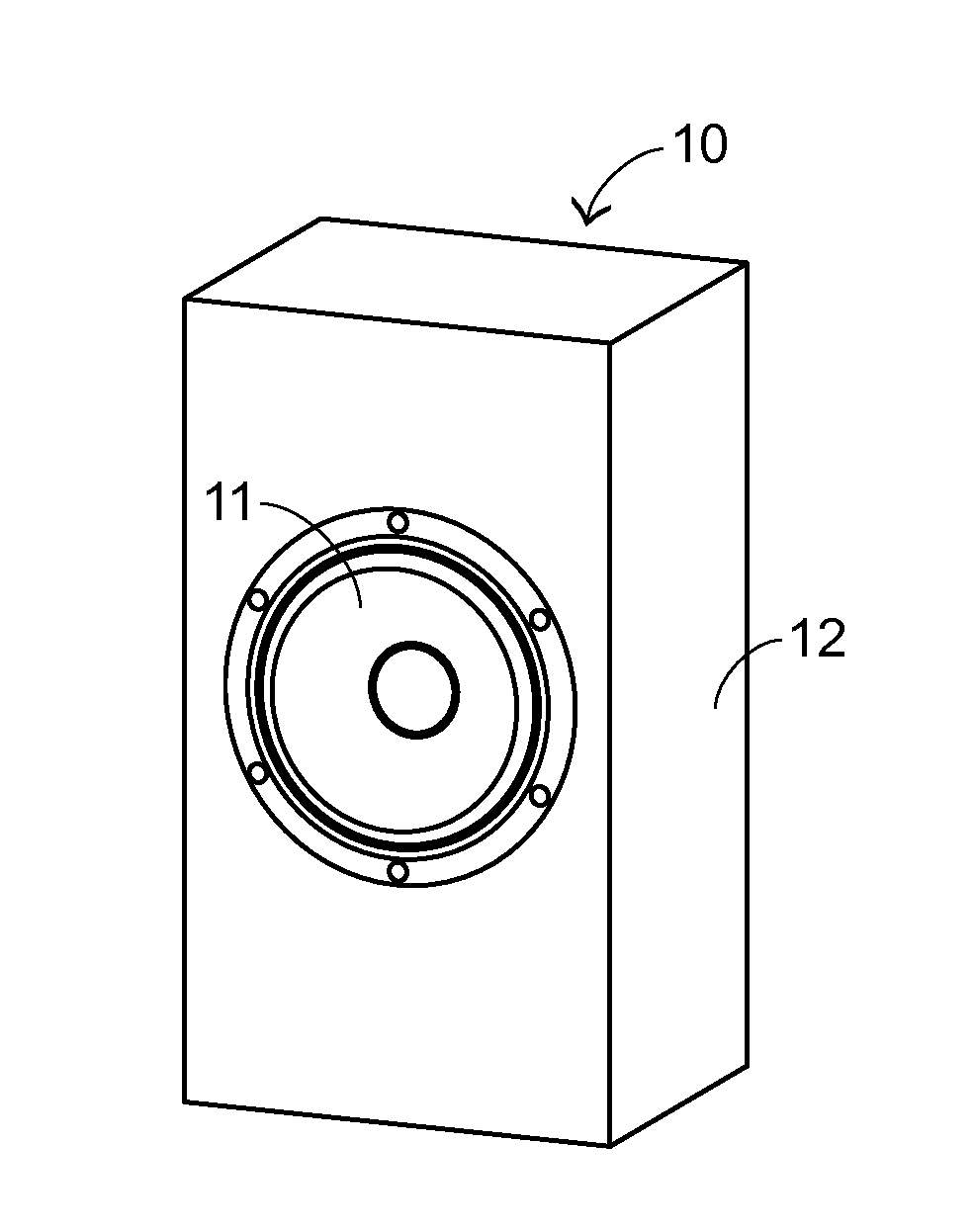
Open type speaker leak test system and method
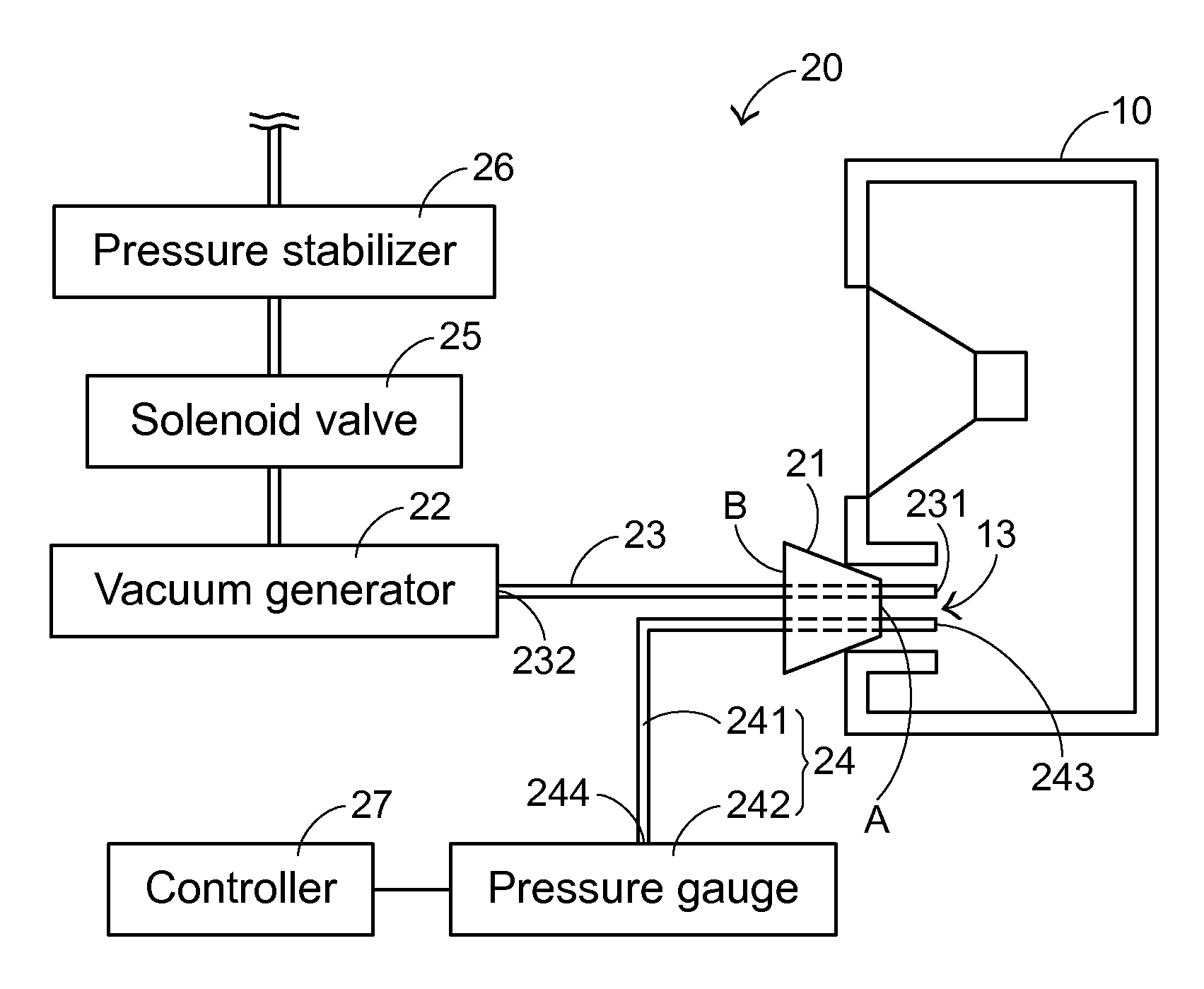
An open-type speaker leak test system and an open-type speaker leak test method are provided for testing whether an open-type speaker has a leak. The open-type speaker includes an enclosure with an opening. The open-type speaker leak test system includes a sealing element, a vacuum generator, a first communication tube, and a pressure measuring module. The sealing element is locked into the opening. A negative pressure value of the enclosure is generated by the vacuum generator. The first communication tube is penetrated through the sealing element and in communication with the open-type speaker and the vacuum generator. An equilibrium pressure value of the enclosure is measured by the pressure measuring module. If the equilibrium pressure value is lower than a default negative pressure value, the open-type speaker has the leak. Consequently, the misjudgment is reduced, and the testing efficiency is enhanced.
Owner:PRIMAX ELECTRONICS LTD
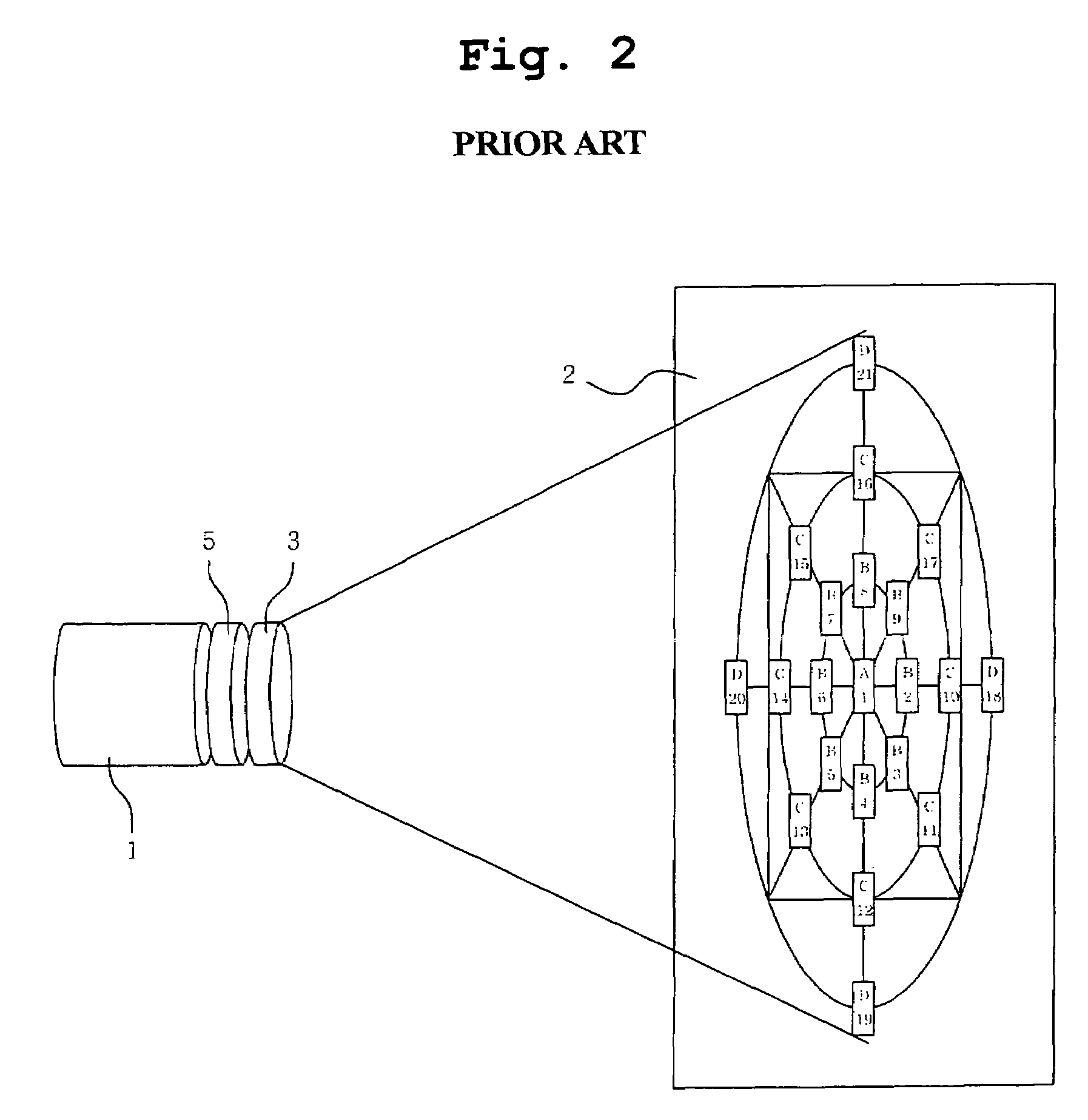
Image evaluation chart and performance test method using the same
InactiveUS7292266B2Accurate and efficient testingThe test data is reliableTelevision systemsTest performanceImage evaluation
An image evaluation chart and a method for testing performances of the video equipment using the same. The image evaluation chart includes a resolution inspection area. The resolution inspection area includes a center point located at a center part of the chart, a regular-squared outer line located at outside of the center point, and a plurality of resolution measurement lines symmetrically arranged at right and left sections and upper and lower sections on the basis of the center point. Therefore, the image evaluation chart accurately and efficiently tests all performances, for example, resolution, balance, view angle, distortion, and focus, etc., of video equipment such as a camera by means of one-shot image capture, and provides users with reliable test data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
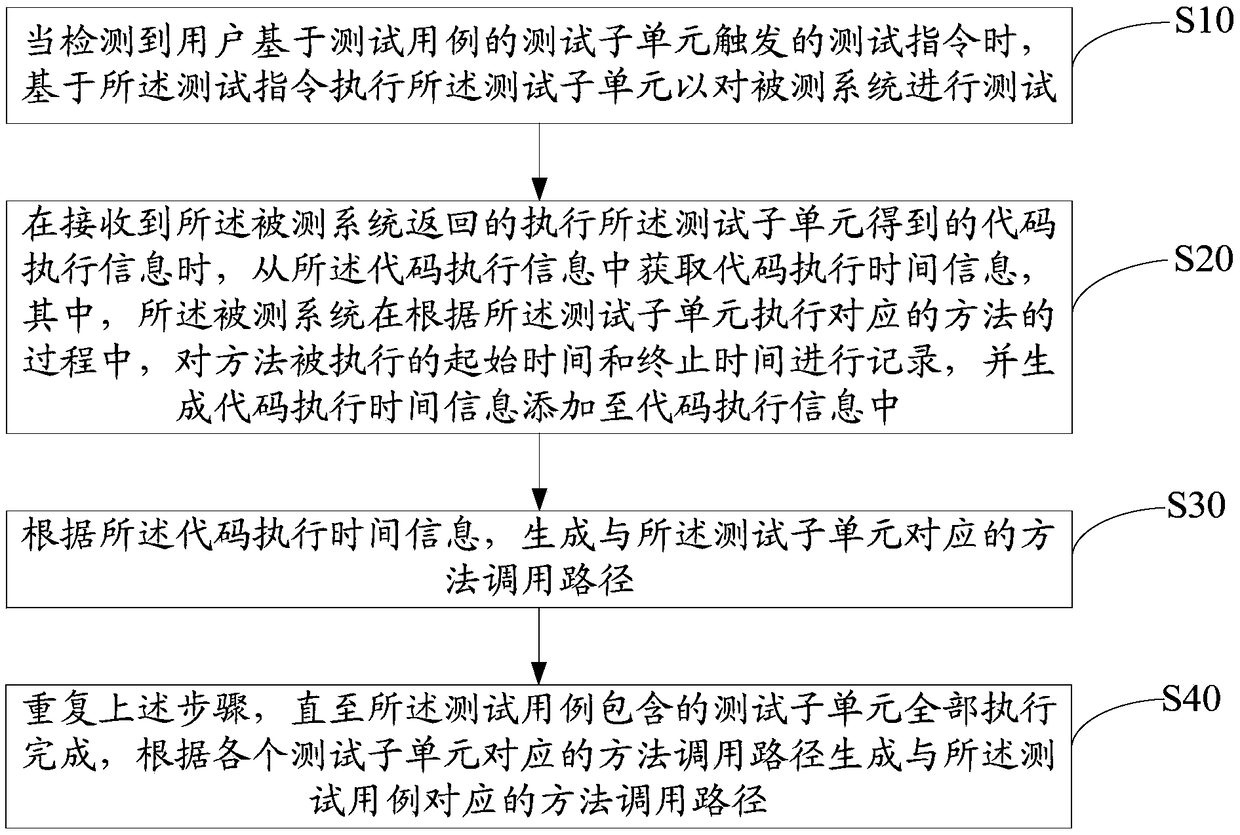
Monitoring device and method for testing process and computer readable storage medium
InactiveCN108664372AAccurate and efficient testingHardware monitoringSoftware testing/debuggingComputer hardwareTime information
The invention discloses a monitoring device of test process, comprises memory and processor, the memory has stored thereon a test monitoring program executable on a processor that, when executed by the processor, performs the following steps: When a test instruction triggered by the test subunit of the user based on the test case is detected, executing a test subunit on a basis of the test instruction to test the tested system; when receiving code execution information obtained by the execution test subunit returned by the system under test, executing a test subunit to test a system under testbased on a test instruction; when receiving code execution information obtained by the execution test subunit returned by the system under test, obtaining time information from the code execution information; Generating a method call path corresponding to the test subunit according to the time information; and repeating the above steps until all execution of a test subunits contained in a test case is completed, and generating a method call path corresponding to a test case according to method call path corresponding to each test subunit. The invention further provides a monitoring method ofa test process and a computer readable storage medium. According to the invention, accurate and efficient testing is realized.
Owner:PING AN TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Plate surface wear resistance testing device for building indoor decoration
ActiveCN112525746AEasy to useEasy to operateInvestigating abrasion/wear resistanceStructural engineeringWear resistance
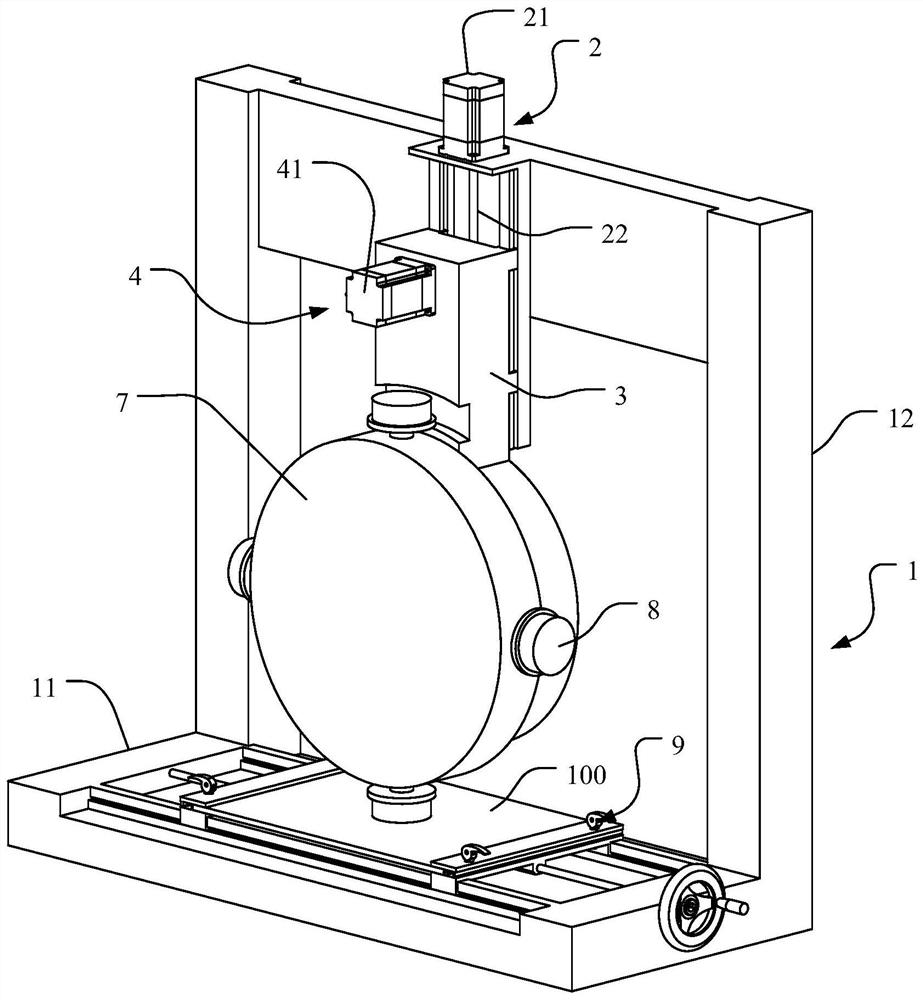
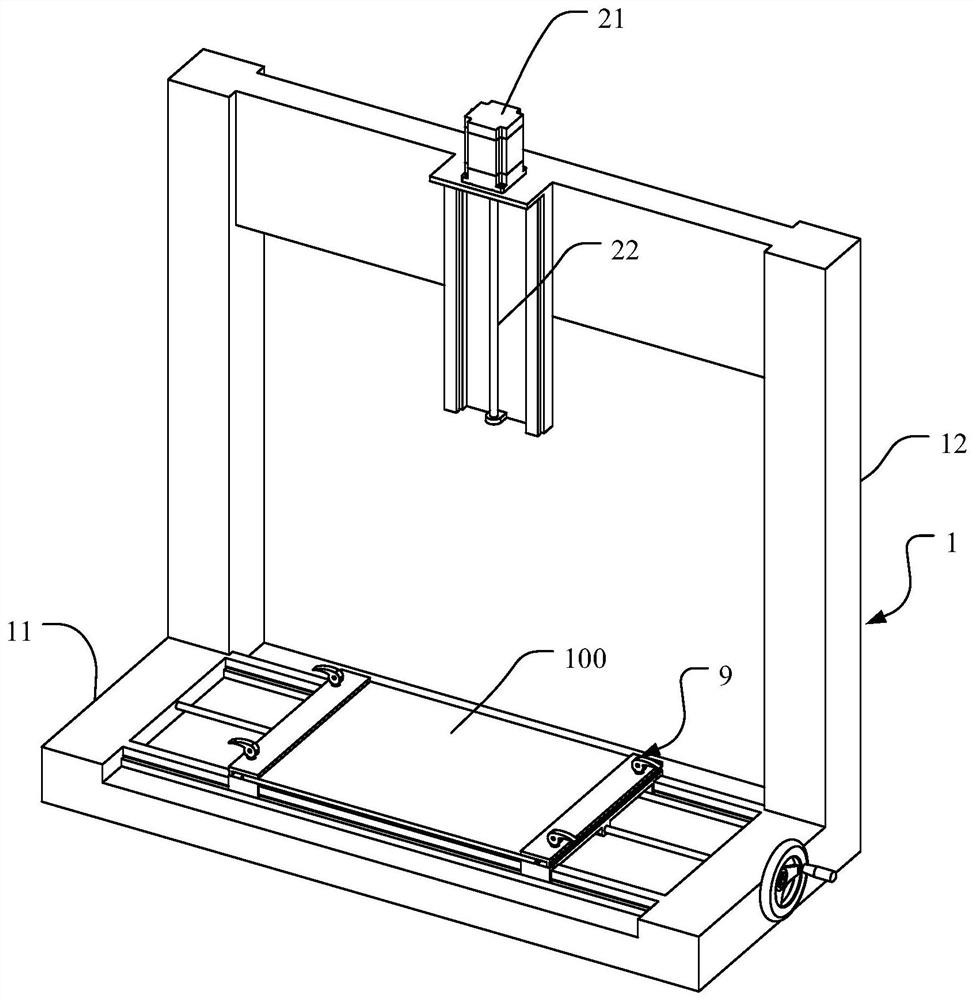
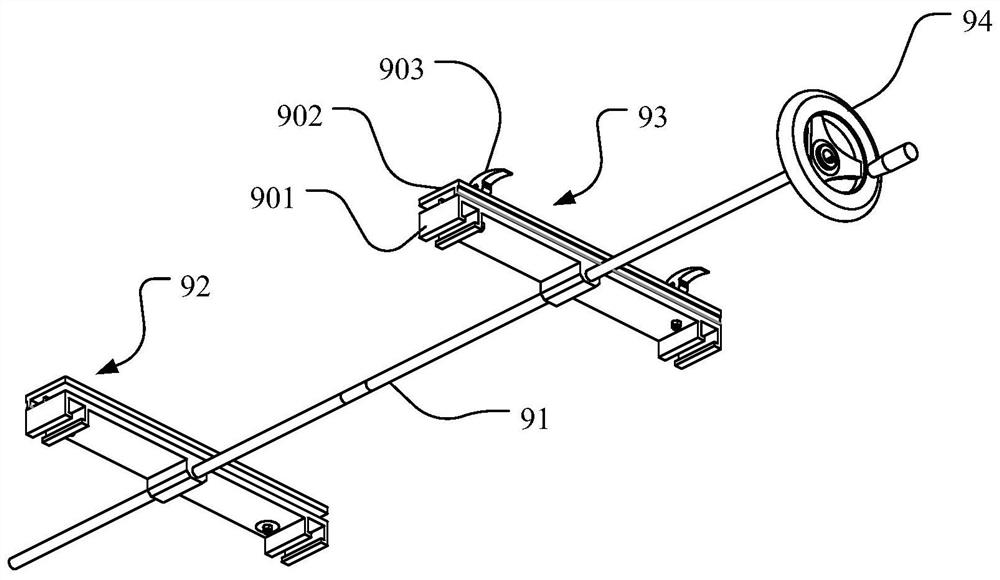
The invnetion discloses a plate surface abrasion resistance testing device for building interior decoration. The device comprises a supporting rack, a lifting driving piece, a lifting assembly, a mainmovement driving piece, a main movement middle transmission piece, a grinding head conversion driving piece, a grinding head mounting rotary disc and a plurality of abrasion resistance testing grinding head assemblies. The lifting driving piece is arranged on the supporting rack; the lifting assembly is connected to the lifting driving piece, the main motion driving piece is arranged on the lifting assembly, the main movement middle transmission piece is rotationally arranged on the lifting assembly, the grinding head conversion driving piece is arranged on the lifting assembly, and the grinding head mounting rotary disc is rotationally connected to the lower portion of the lifting assembly. A plurality of abrasion resistance testing grinding head assemblies are arranged on the outer peripheral wall of the grinding head mounting rotary disc, and a clamping assembly is arranged at the lower part of the supporting rack; the power input end of the main movement middle transmission pieceis in transmission connection with the main movement driving piece, and the power output end of the main movement middle transmission piece is in transmission connection with one of the abrasion resistance testing grinding head assemblies. The device greatly improves the test efficiency and applicability.
Owner:山东德才建设有限公司
Measuring system for measuring molecular electrical properties by consolidation method
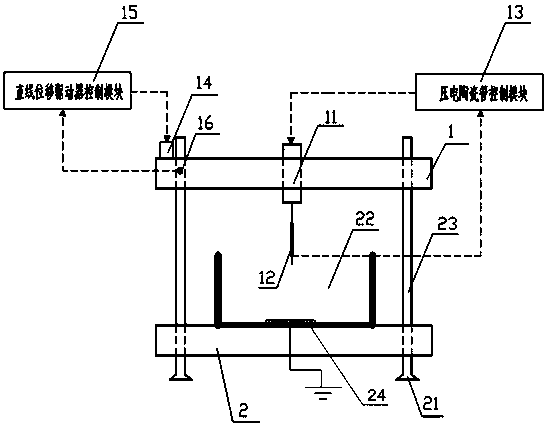
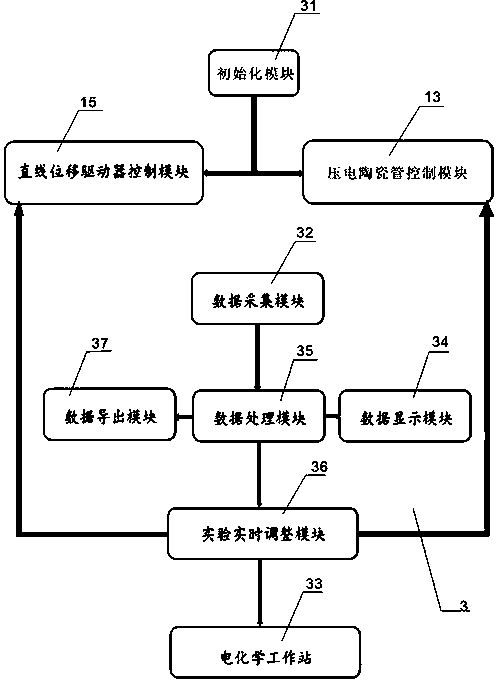
The invention discloses a measuring system for measuring molecular electrical properties by a consolidation method, wherein a piezoelectric ceramic tube in a vertical cylindrical shape is vertically fixed in the center of a lifting platform, the top and bottom ends of the piezoelectric ceramic tube respectively pass through the top surface and bottom surface of the lifting platform, and a gold probe electrode is disposed at the central position of the bottom end surface of the piezoelectric ceramic tube; a support rod lifts the lifting platform directly above a sample stage, the gold probe electrode is directly located above the sample stage, a rectangular sample slot is arranged at the center of the top surface of the sample stage, and a gold piece is placed in the sample slot. The modules in the system provided by the invention comprise a piezoelectric ceramic tube control module, a linear displacement driver control module, a data acquisition module, a data processing module, an experimental real-time adjustment module and an electrochemical workstation. The measuring system is simple in structure, low in cost, and simple in operation, has the advantages such as immediacy, accuracy, real-time, simple operation and easy learning, and can provide rich molecular internal information at a single molecular level through electrical measurement.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Testbed of hydraulic winches of drilling machine
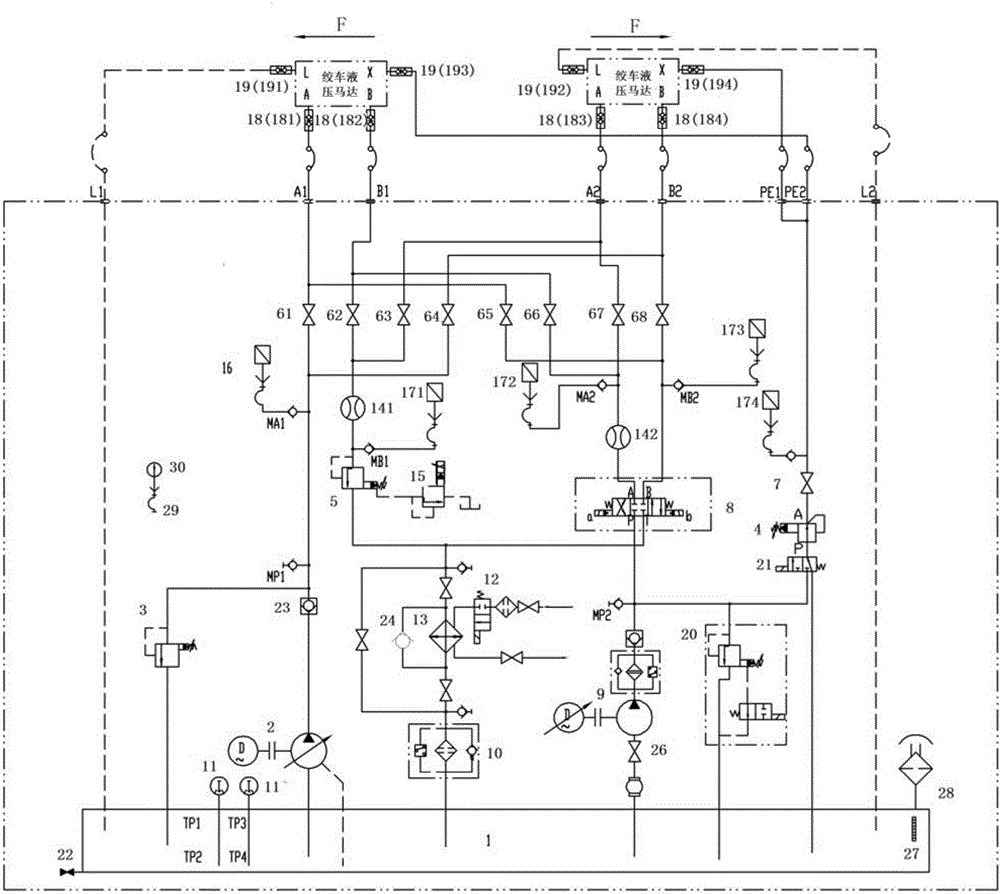
ActiveCN106593976AAccurate and efficient testingEasy to record and analyzeServomotorsStructural/machines measurementTest performanceTest requirements
The invention discloses a testbed of hydraulic winches of a drilling machine. The testbed comprises a PLC controller, an industrial personal computer, a hydraulic system and a test circuit, wherein the hydraulic system has two hydraulic winches which serve as a load winch and a tested winch, and the test circuit can test performances of the hydraulic winch as the tested winch and interchange the load winch and the tested winch according to a test requirement; the test circuit comprises a loading sub circuit which is connected to the load winch and can provide an adjustable loading force to the testbed, a driving sub circuit which is connected to the tested winch and can performing test driving on the tested winch, and an oil return pipeline for controlling medium cleanliness and system oil temperature of the hydraulic system and an auxiliary sub circuit which can interchange the load winch and the tested winch and open a parking brake corresponding to the hydraulic winch. The testbed disclosed by the invention not only can provide accurate and reliable test data, but also is simple in structure and easy to operate, and has the characteristics of being high in efficiency and working uninterruptedly for a long time.
Owner:DALIAN HUARUI HEAVY IND GRP CO LTD
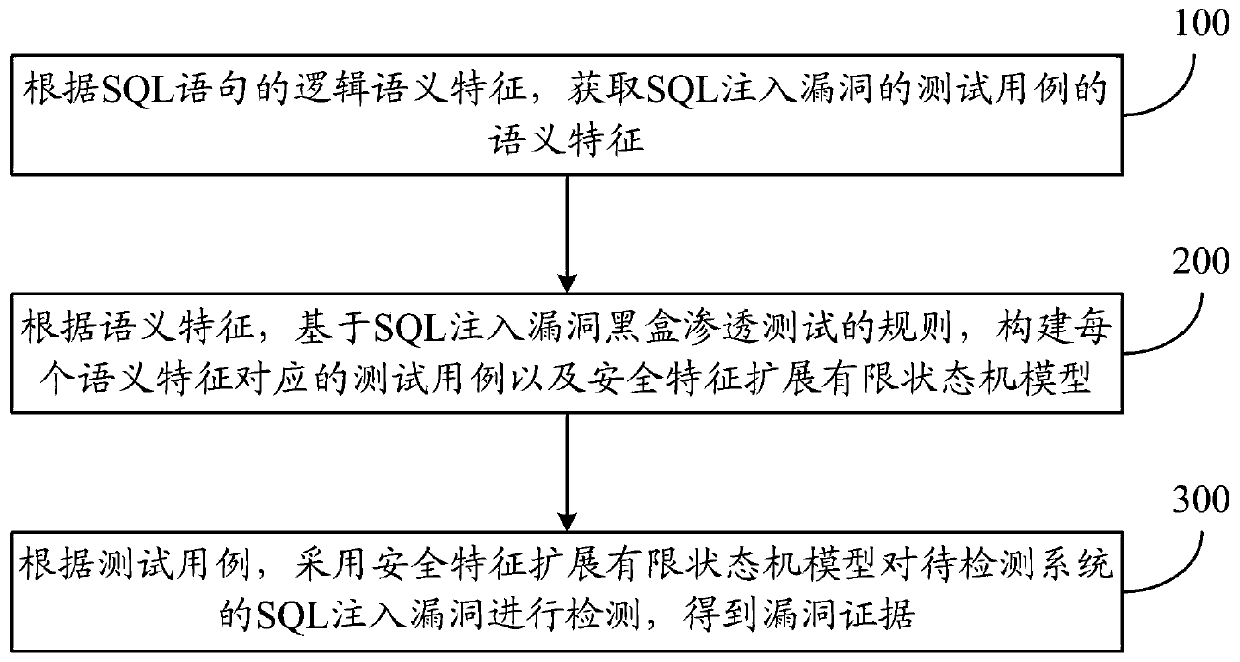
Method and system for detecting SQL injection vulnerabilities of power information system
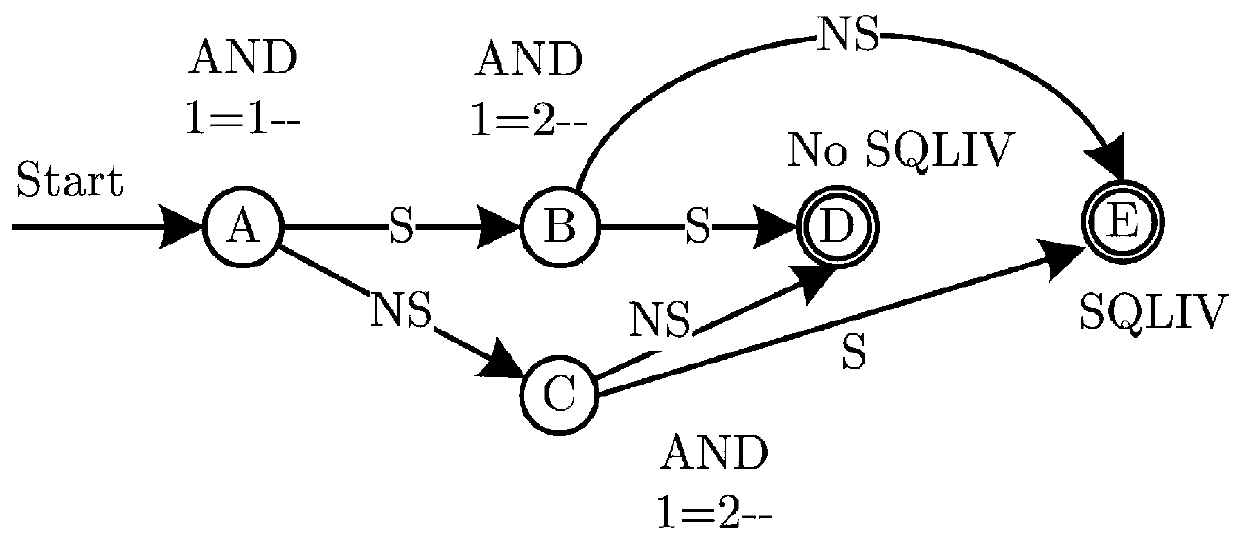
ActiveCN111064735AEfficient detectionImprove detection accuracyTransmissionSQL injectionSemantic feature
The invention relates to a method and a system for detecting SQL injection vulnerabilities of power information system. The detection method comprises the steps of obtaining semantic features of testcases of SQL injection vulnerabilities according to logic semantic features of SQL statements, different semantic features corresponding to different test actions; constructing a test case corresponding to each semantic feature and a security feature extension finite-state machine model based on SQL injection vulnerability black-box penetration test rules according to the semantic features, wherein the security feature extension finite-state machine model comprises a response state and a state conversion rule of each test case; and according to the test case, detecting an SQL injection vulnerability of a to-be-detected system by adopting the security feature extension finite-state machine model to obtain a vulnerability evidence. According to the invention, the detection precision of the SQL injection vulnerability can be improved.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV +2
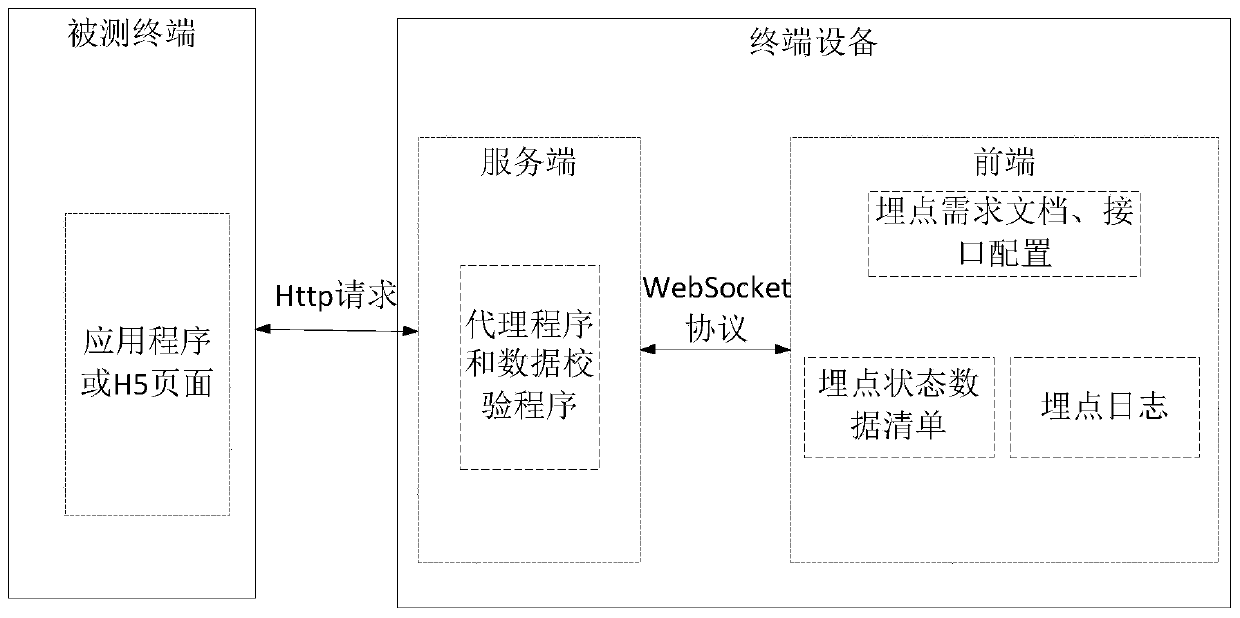
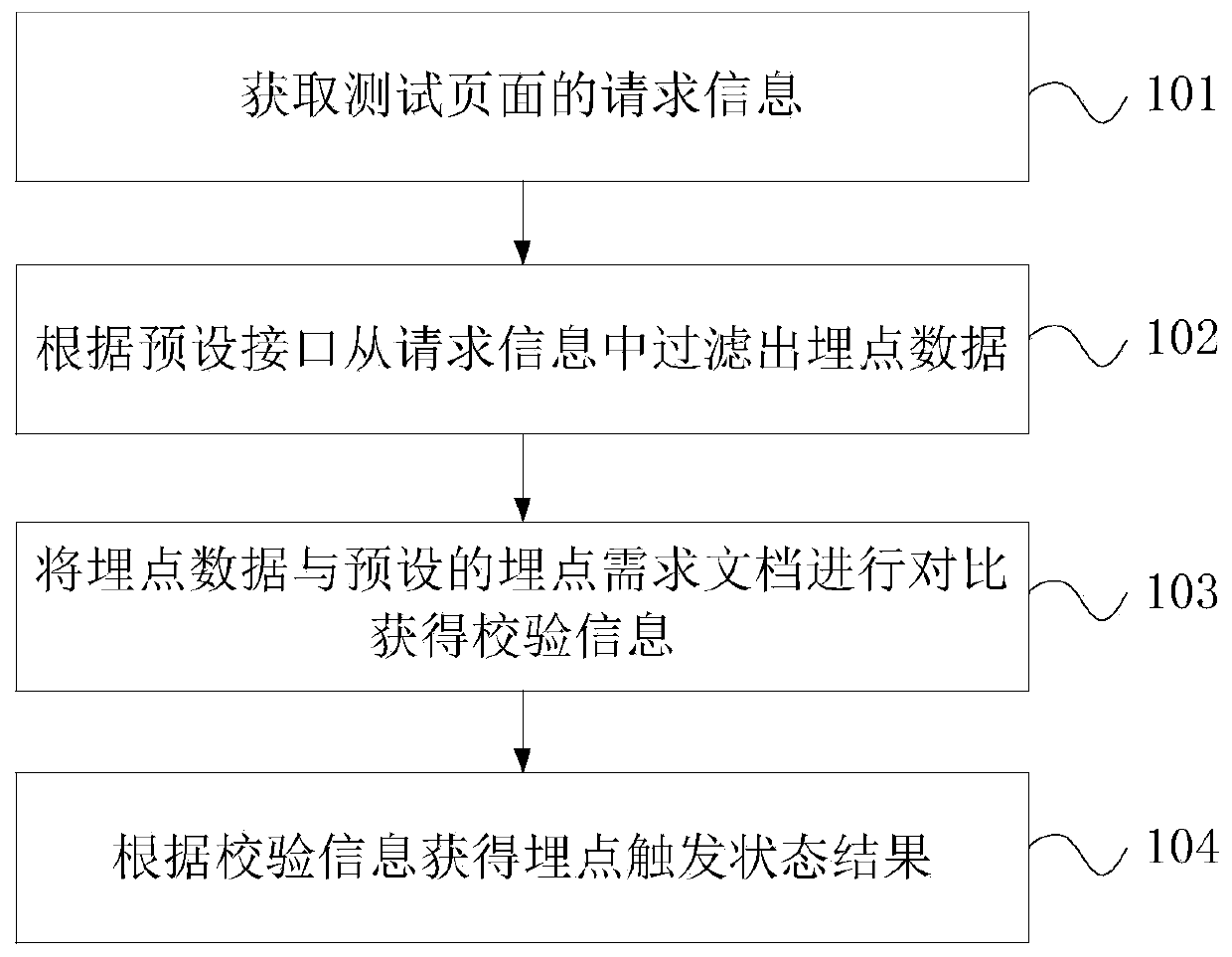
Buried point test method and device, terminal equipment and storage medium
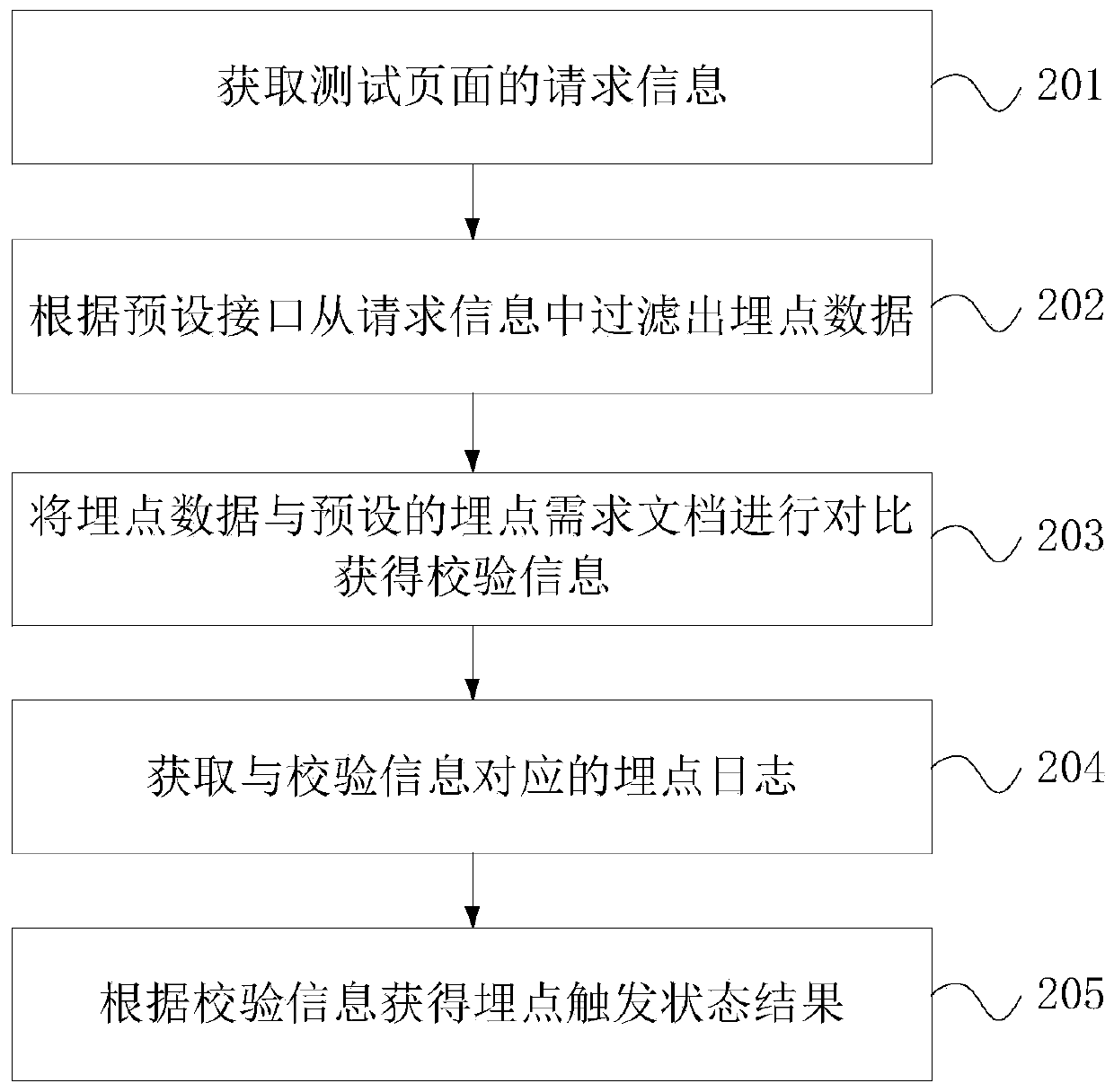
PendingCN111367814AAccurate and efficient testingSimplify the buried point testing processSoftware testing/debuggingWebsite content managementComputer hardwareTerminal equipment
The embodiment of the invention discloses a buried point test method and device, terminal equipment and a storage medium. The buried point test method comprises the steps of obtaining request information of a test page; filtering buried point data from the request information according to a preset interface; comparing the burying point data with a preset burying point demand document to obtain verification information, the preset burying point demand document comprising preset data corresponding to the burying point of each interface; and obtaining a buried point trigger state result accordingto the verification information. According to the embodiment of the invention, the terminal equipment can filter the buried point data from the request information of the test page; the buried pointdata is automatically compared with the preset buried point demand document to obtain the verification information, and the buried point trigger state result can be obtained according to the verification information, so that the buried point test process is simplified, and a user is assisted to realize accurate and efficient test of the buried point.
Owner:深圳市卡牛科技有限公司
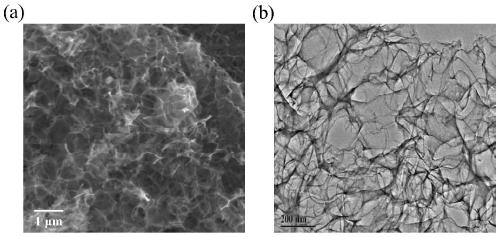
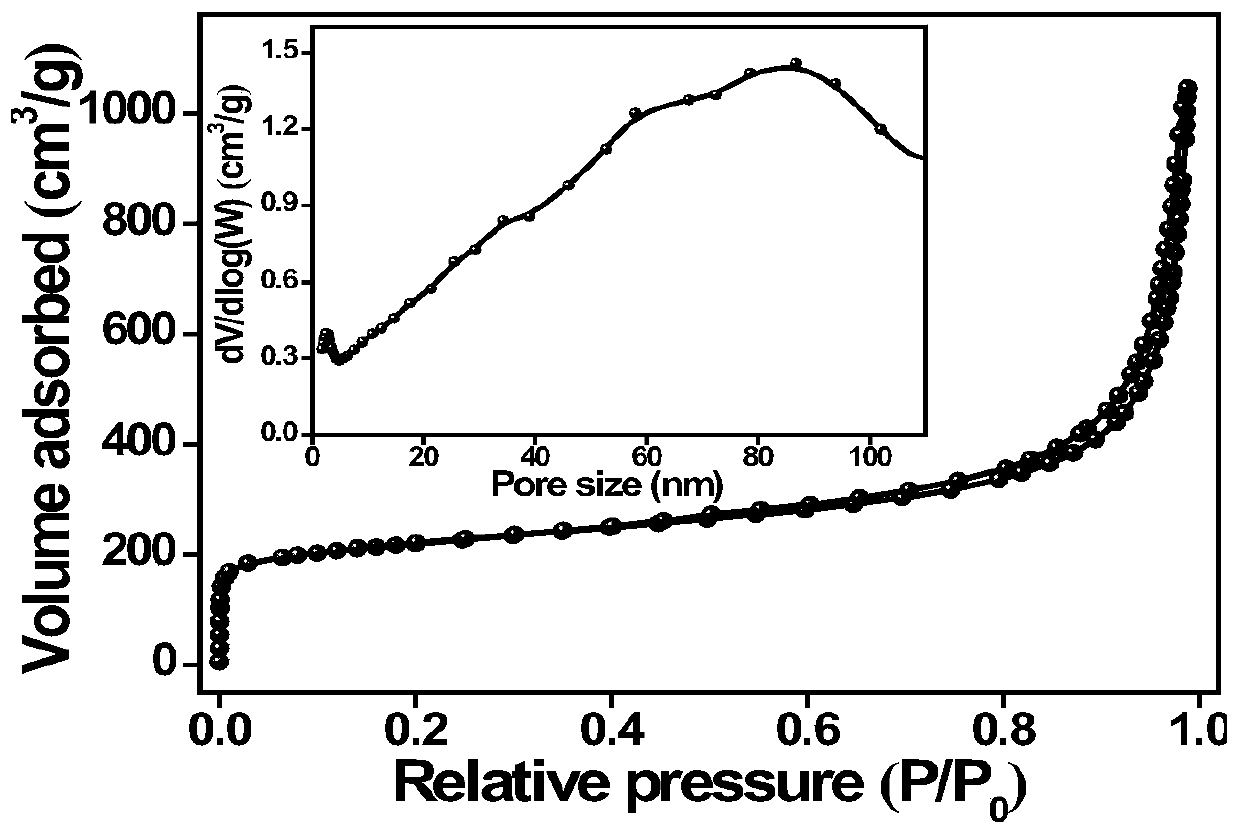
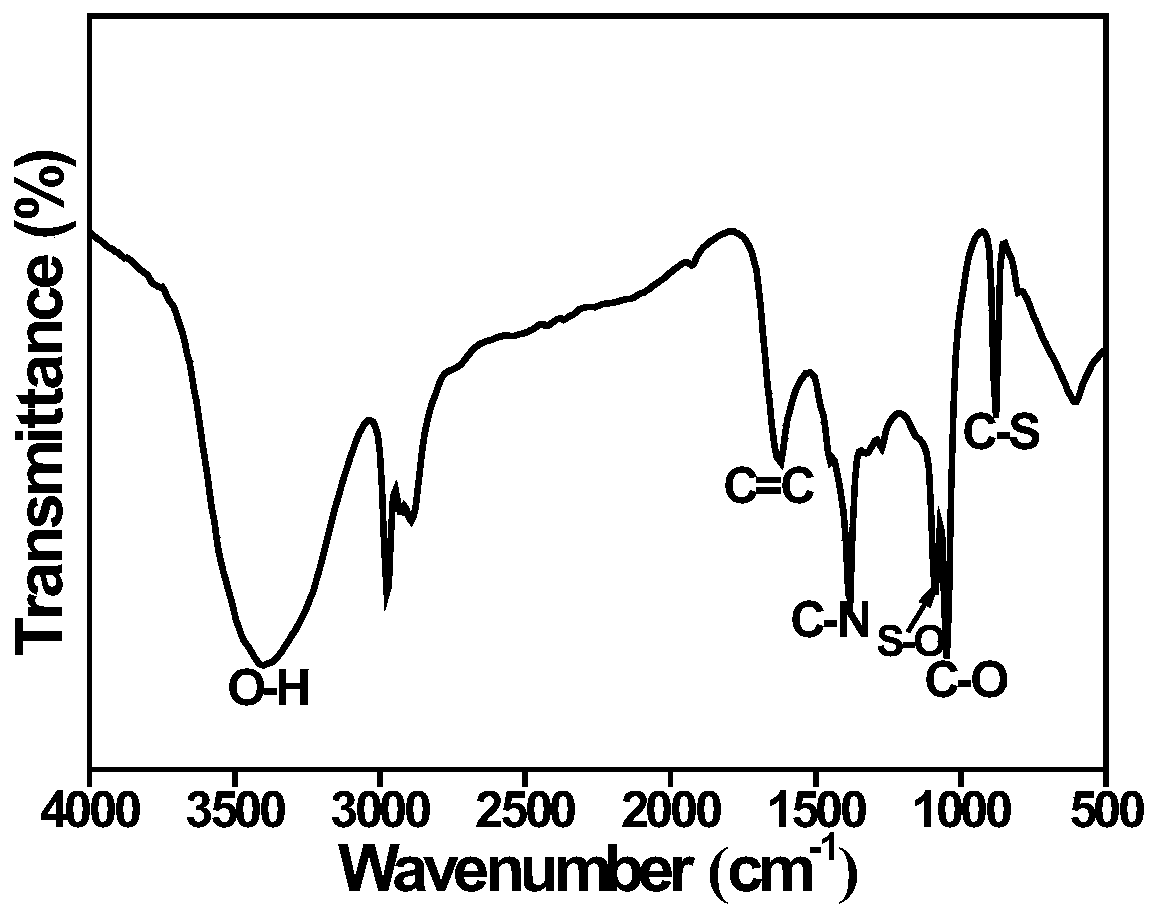
Preparation method and application of double-heteroatom doped porous graphene nano carbon sheet
ActiveCN111196602ALarge specific surface areaImprove conductivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGraphenePorous graphenePorous carbon
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a double-heteroatom doped porous graphene nano carbon sheet. First, through a sodium chloride template method, a heteroelement carbon source is regulated, and through heat treatment, a nitrogen and sulfur double-doped porous carbon nanometer sheet is prepared; then, the material is used as a novel carbon matrix for matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry, organic environmental pollutant small molecules (m / z is less than 700) are analyzed by mass spectrometry, and the novel matrix can also be used for analyzing the composition and content of the environmental pollutant small molecules in atmospheric haze (PM2.5). The method can also be used for analysis and quantitative detection of different kinds of amino acid biomolecules. When the double-heteroatom doped porous carbon material is used as a new matrix for detecting environmental pollutant molecules, the advantages of low background interference peak, high ion strength and the like are achieved.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
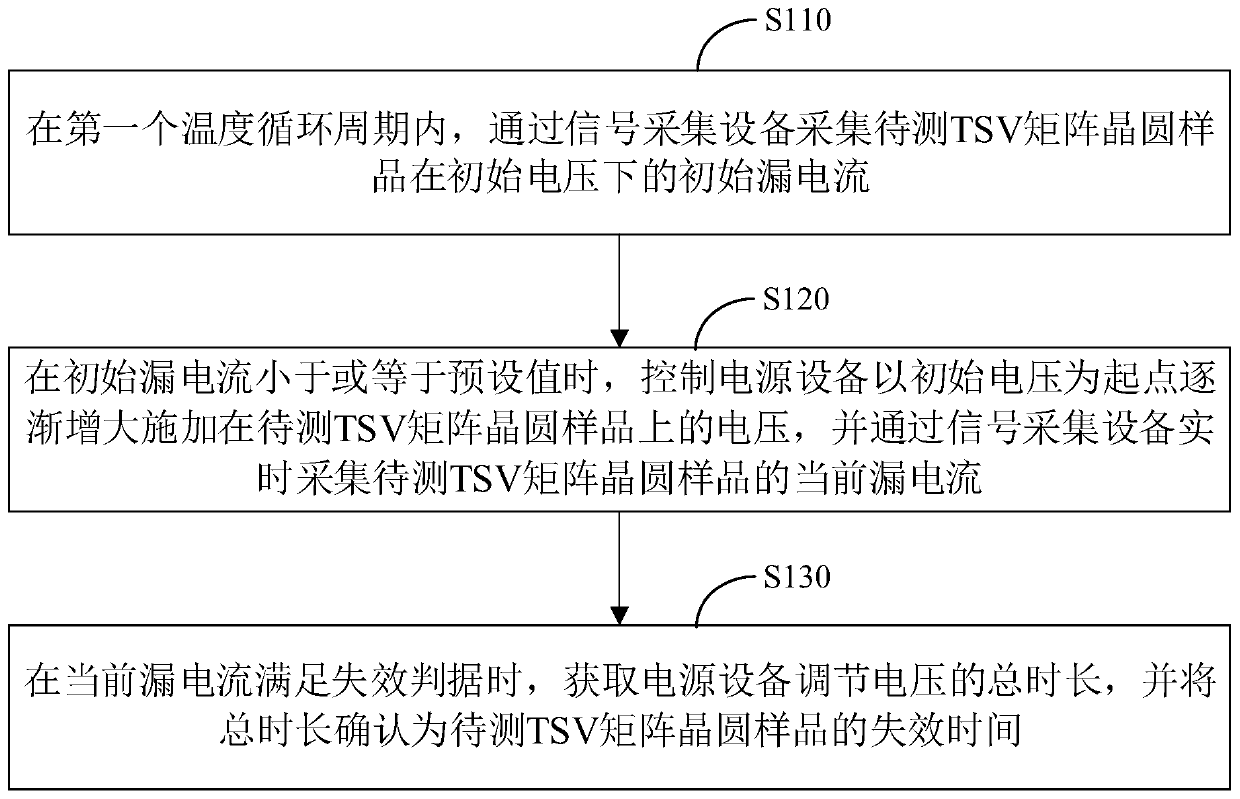
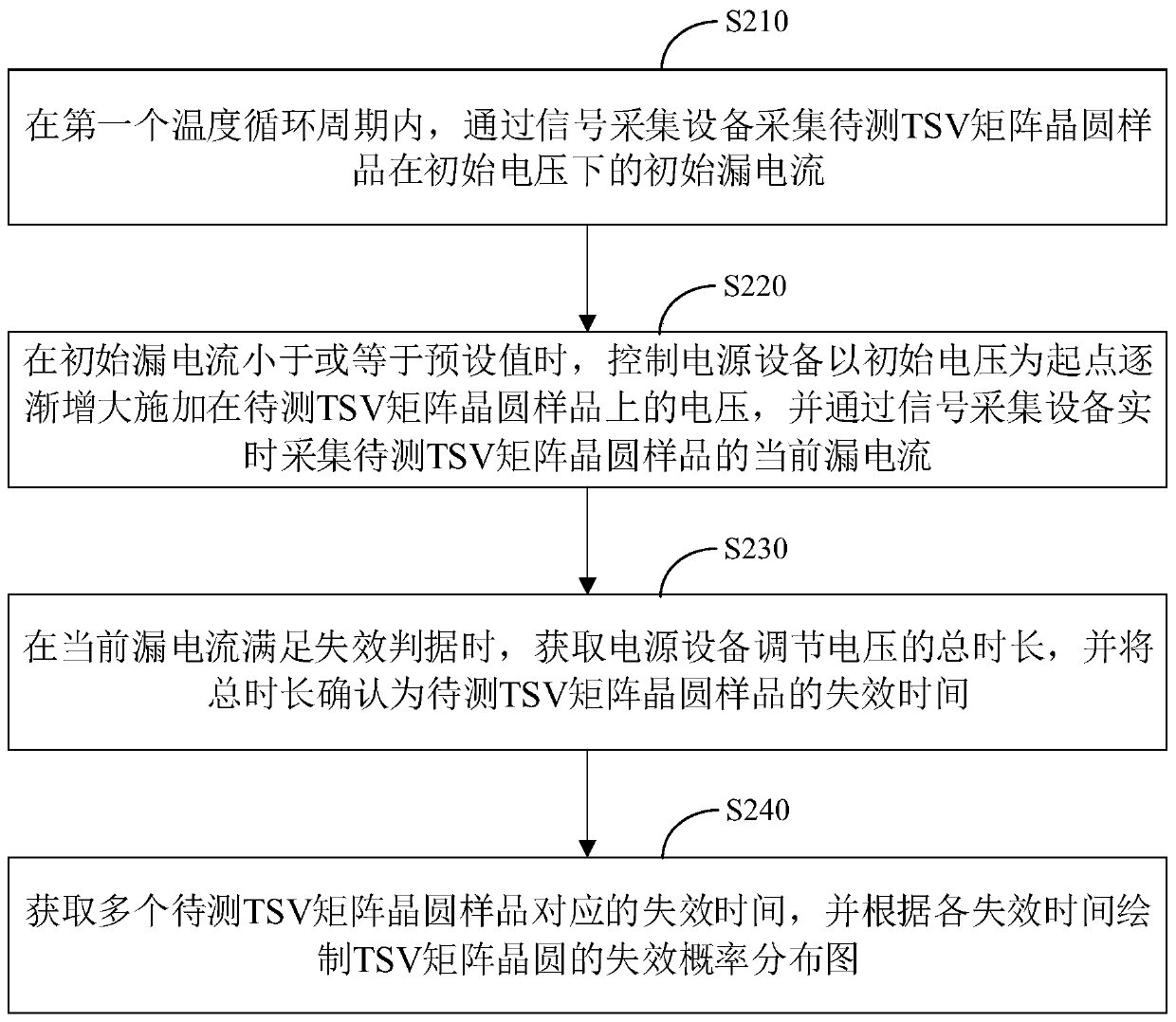
Electric breakdown life testing method, device and system of TSV structure and control equipment
ActiveCN110600390AAccurate and efficient testingSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectricityControl power
The invention relates to an electric breakdown life testing method, device and system of a TSV structure and control equipment. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring an initial leakagecurrent of a to-be-tested TSV matrix wafer sample under an initial voltage through signal acquisition equipment in a first temperature cycle period, wherein the first temperature cycle period is a first period of controlling temperature adjusting equipment to adjust the test environment temperature of the to-be-tested TSV matrix wafer sample to be changed cyclically; when the initial leakage current is lower than or equal to a preset value, controlling power supply equipment to gradually increase a voltage applied to the to-be-tested TSV matrix wafer sample by taking the initial voltage as astarting point, and acquiring a current leakage current of the to-be-tested TSV matrix wafer sample in real time through the signal acquisition equipment; and when the current leakage current meets failure criteria, obtaining a total voltage adjusting duration of the power supply equipment, and confirming the total duration as the failure time of the to-be-tested TSV matrix wafer sample. The service life performance of the TSV structure is efficiently and accurately tested, and the electric breakdown reliability of the TSV structure is efficiently and accurately tested.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS PROD RELIABILITY & ENVIRONMENTAL TESTING RES INST
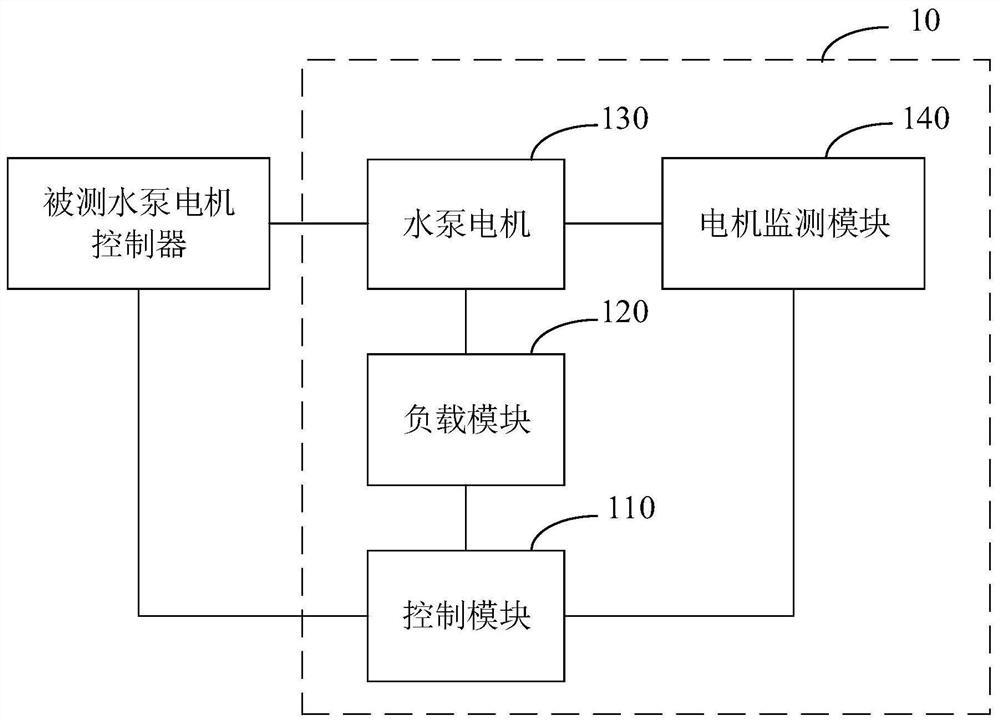
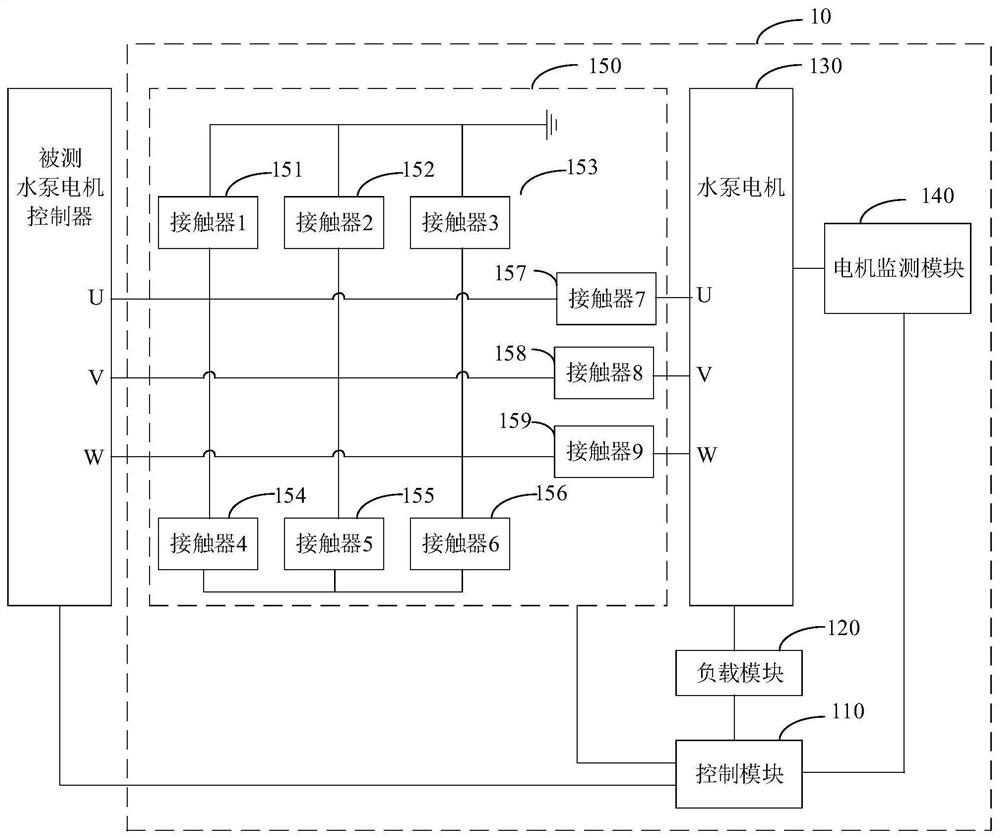
Water pump motor controller test system
ActiveCN113050592AAccurate and efficient testingElectric testing/monitoringControl engineeringElectric machinery
The invention is suitable for the technical field of motor controllers, and provides a water pump motor controller test system which comprises a control module, a water pump motor, a load module and a motor monitoring module, wherein the control module is used for controlling the operation of the tested water pump motor controller and generating and sending a load adjusting instruction to the load module; the water pump motor is used for running according to the driving of the tested water pump motor controller; the load module is used for adjusting self load according to the load adjusting instruction; the motor monitoring module is used for monitoring the water pump motor and generating and sending monitoring data to the control module; and the control module is also used for judging whether the tested water pump motor controller has a fault or not according to the monitoring data, the load data of the load module and a driving signal generated by the tested water pump motor controller. The test system provided by the invention can effectively simulate the load state of the water pump motor controller in actual work, thereby accurately and efficiently testing the tested water pump motor controller.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG TONHE ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
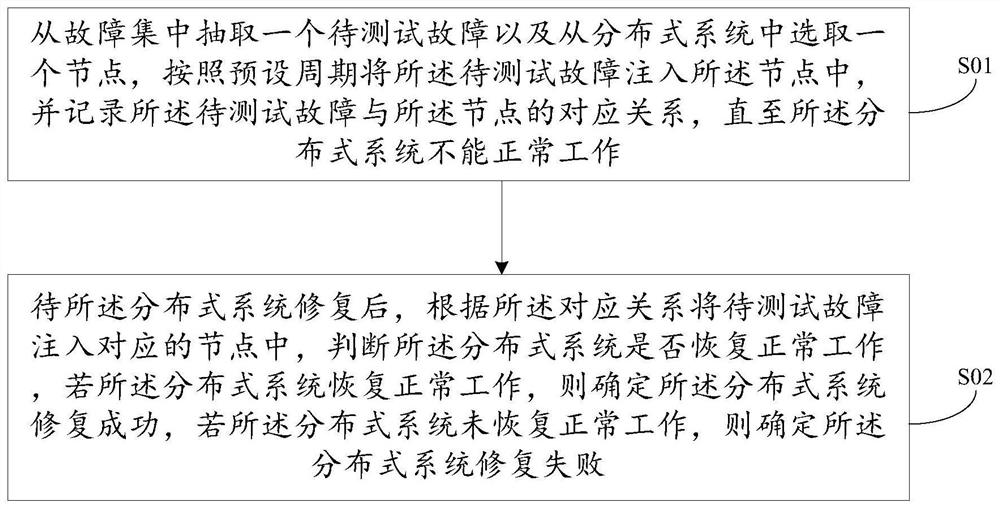
Fault test method and device
PendingCN112596934AAccurate and efficient testingHigh precisionReliability/availability analysisSoftware testing/debuggingSystem recoveryComputer science
The invention provides a fault test method and device, and the method comprises the steps: extracting a to-be-tested fault from a fault set, selecting a node from a distributed system, injecting the to-be-tested fault into the node in a preset period, and recording the corresponding relation between the to-be-tested fault and the node till the distributed system cannot work normally; and after thedistributed system is repaired, injecting the to-be-tested fault into the corresponding node according to the corresponding relationship, if the distributed system returns to normal work, indicatingthat the distributed system is successfully repaired, and if the distributed system cannot work normally, indicating that the distributed system fails to be repaired. The corresponding relation between the faults and the nodes is recorded, the faults are injected into the corresponding nodes through the corresponding relation, and whether the distributed system is successfully repaired or not is judged, so that the faults can be accurately and efficiently tested; and fault extraction and node selection are carried out randomly, so that the situations of fault generation and unknown node distribution are simulated more accurately, and the accuracy in verifying the availability of the distributed system is improved.
Owner:AGRICULTURAL BANK OF CHINA
Electrical test head used for keyboard key testing
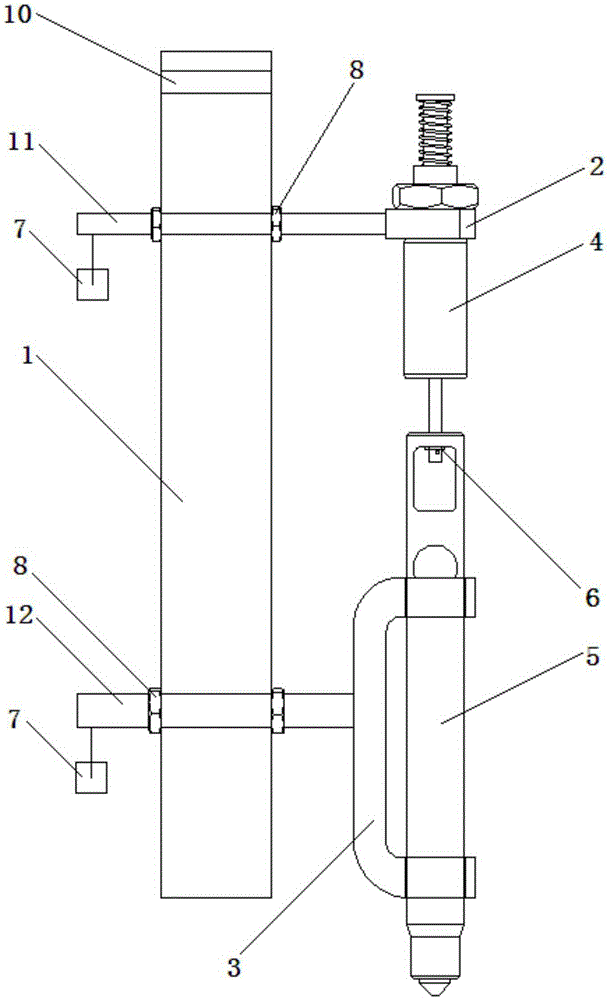
InactiveCN105277878AHighly integratedHigh degree of automationCircuit interrupters testingElectricityEngineering
The invention discloses an electrical test head used for keyboard key testing. The electrical test head comprises a holder which is vertically distributed, first and second expansion joints which are orderly arranged on the holder, fixation ring, a limiting ring and a test head assembly which is arranged on the fixation ring, wherein the fixation ring and the limiting ring are respectively arranged on first and second expansion joints. The test head assembly comprises an electromagnet and a weight from top to bottom, wherein the electromagnet and the weight are in lap connection. The electromagnet is fixed on the fixation ring. The top end of the electromagnet is a free end and is connected with a test wire. The bottom end of the electromagnet runs into the top end of the weight and is locked by a gasket. The weight is sleeved by the limiting ring. The top end of the weight is in sleeve joint with the bottom end of the electromagnet, and is hung on and in lap connection with the gasket. The bottom end of the weight is a free end, and acts on keys in a keyboard to be tested. The weight acts on the keys, is stressed upward, and moves upward along the bottom end of the electromagnet. The electrical test head has the advantages of compact structure, high practicability, high automation degree, accurate and efficient testing, flexible, smooth and precise adjustment, and high versatility, and is suitable for keyboard key layout of different products.
Owner:KUNSHAN HONGZHIXI AUTOMATION EQUIP
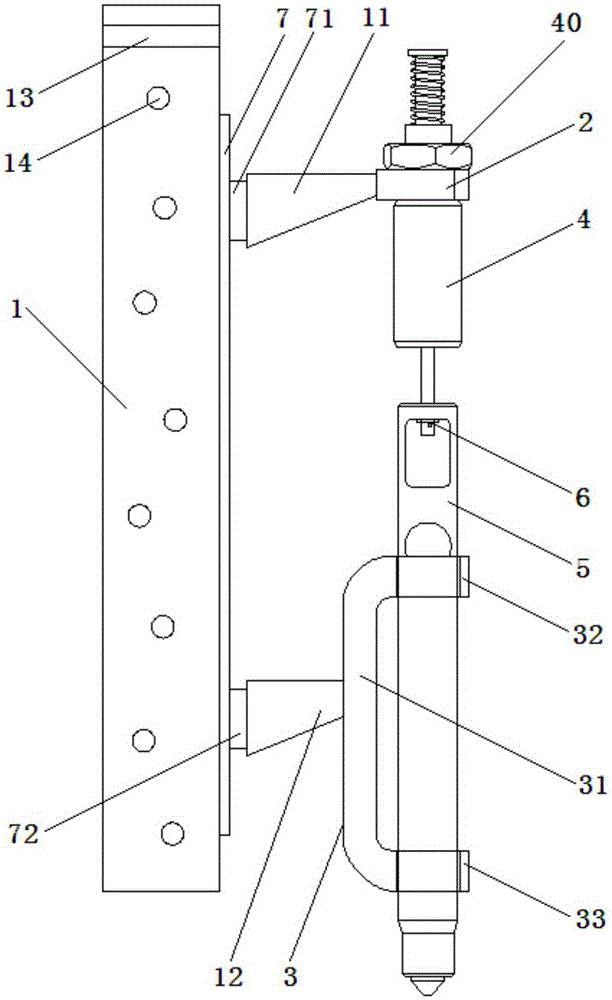
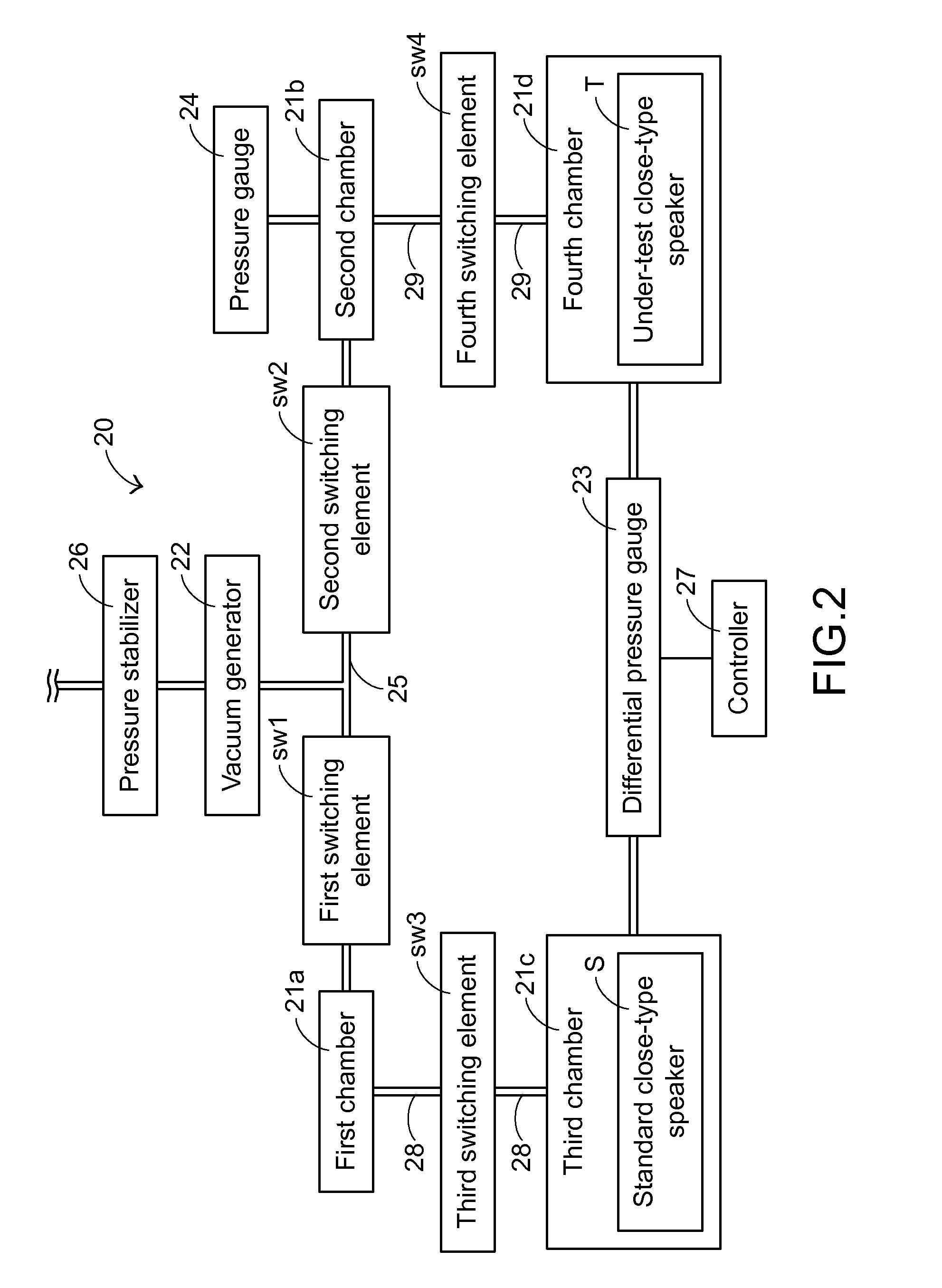
Close-type speaker leak test system and method
ActiveUS20150369692A1Accurate and efficient testingDetection of fluid at leakage pointMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateLoudspeakerEngineering
A close-type speaker leak test system includes a first chamber, a second chamber, a third chamber, a fourth chamber, a vacuum generator, and a differential pressure gauge. Firstly, a negative pressure value of the first chamber and the second chamber is generated by the vacuum generator. A standard close-type speaker is placed within the third chamber, and the first chamber and the third chamber are in communication with each other. An under-test close-type speaker is placed within a fourth chamber, and the second chamber and the fourth chamber are in communication with each other. A pressure difference value between the third chamber and the fourth chamber is measured by the differential pressure gauge. If the pressure difference value is larger than a predetermined value, the under-test close-type speaker has the leak. Consequently, the misjudgment is reduced, and the testing efficiency is enhanced.
Owner:TYMPHANY HK
Fault monitoring period test method and system and computer storage medium
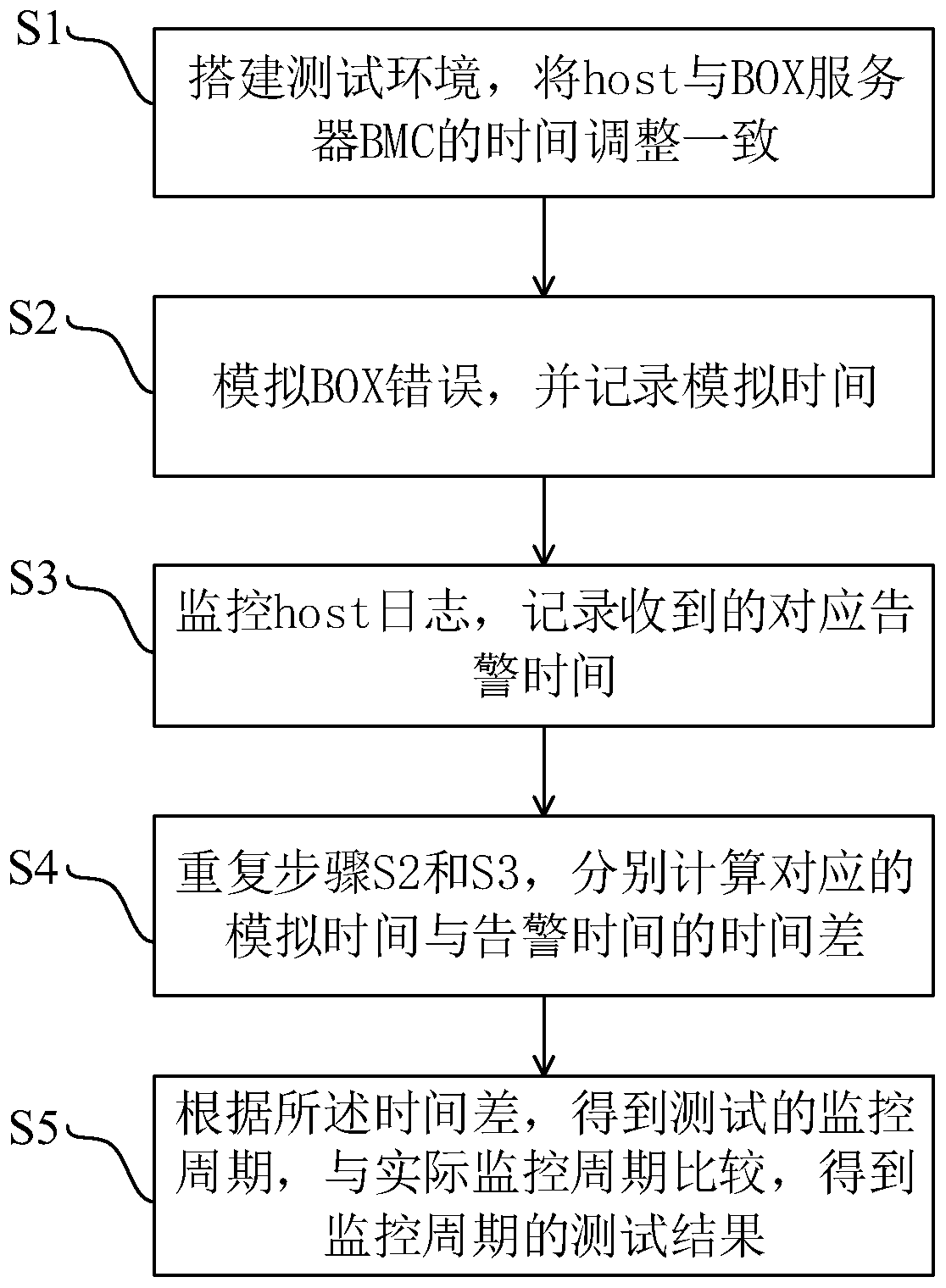
InactiveCN111459734AAccurate and efficient testingEfficient testingFaulty hardware testing methodsComputer scienceTime difference
The invention provides a fault monitoring period test method and system and a computer storage medium, and the test method comprises the steps: building a test environment, and enabling the time of ahost and the time of a BOX server BMC to be adjusted to be consistent; simulating BOX errors, and recording simulation time; monitoring the host log, and recording the received corresponding alarm time; repeating the test process, and respectively calculating the time difference between the corresponding simulation time and alarm time; and according to the time difference, obtaining a test monitoring period, and comparing the test monitoring period with an actual monitoring period to obtain a test result of the monitoring period. According to the method, the fault of the BOX server is simulated, the time is recorded, the fault log of the host is monitored, the alarm log corresponding to the simulated fault is screened, the alarm time is recorded, and whether the current monitoring period is abnormal or not is judged by comparing the time difference between the recorded time and the alarm time with the actual monitoring period. The whole process does not need human participation, and the abnormal condition of the monitoring period can be accurately and efficiently tested.
Owner:SUZHOU LANGCHAO INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
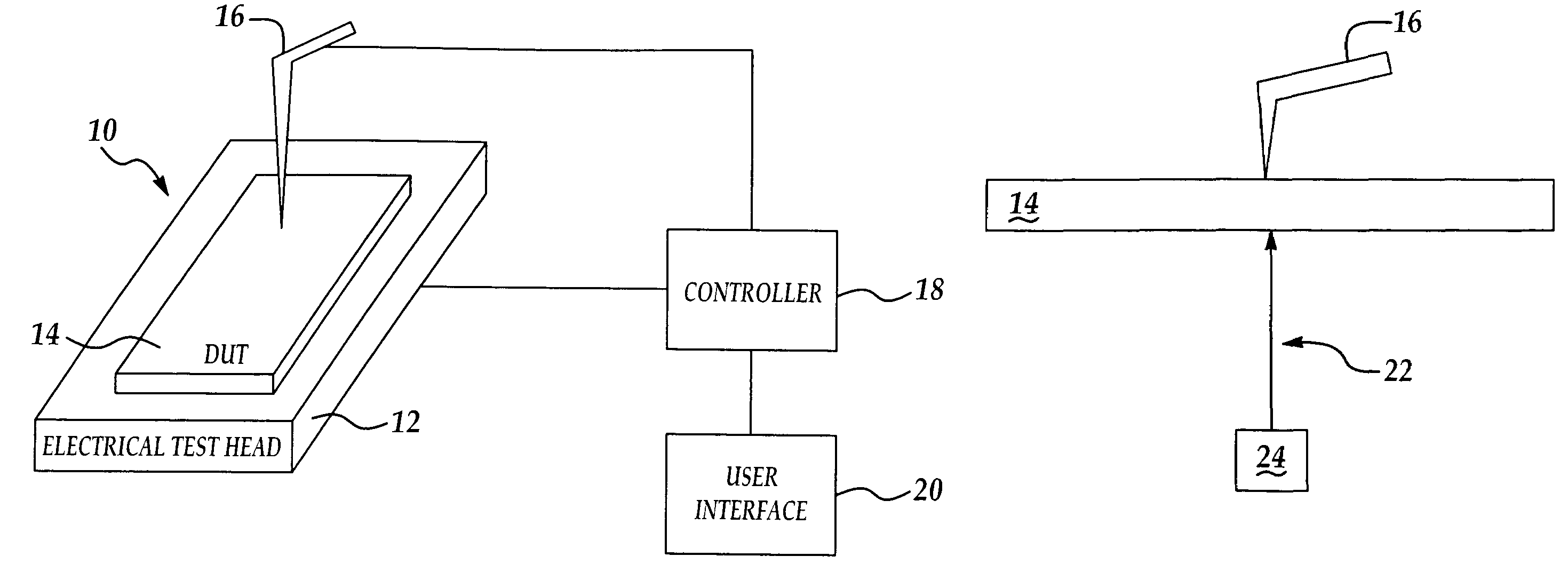
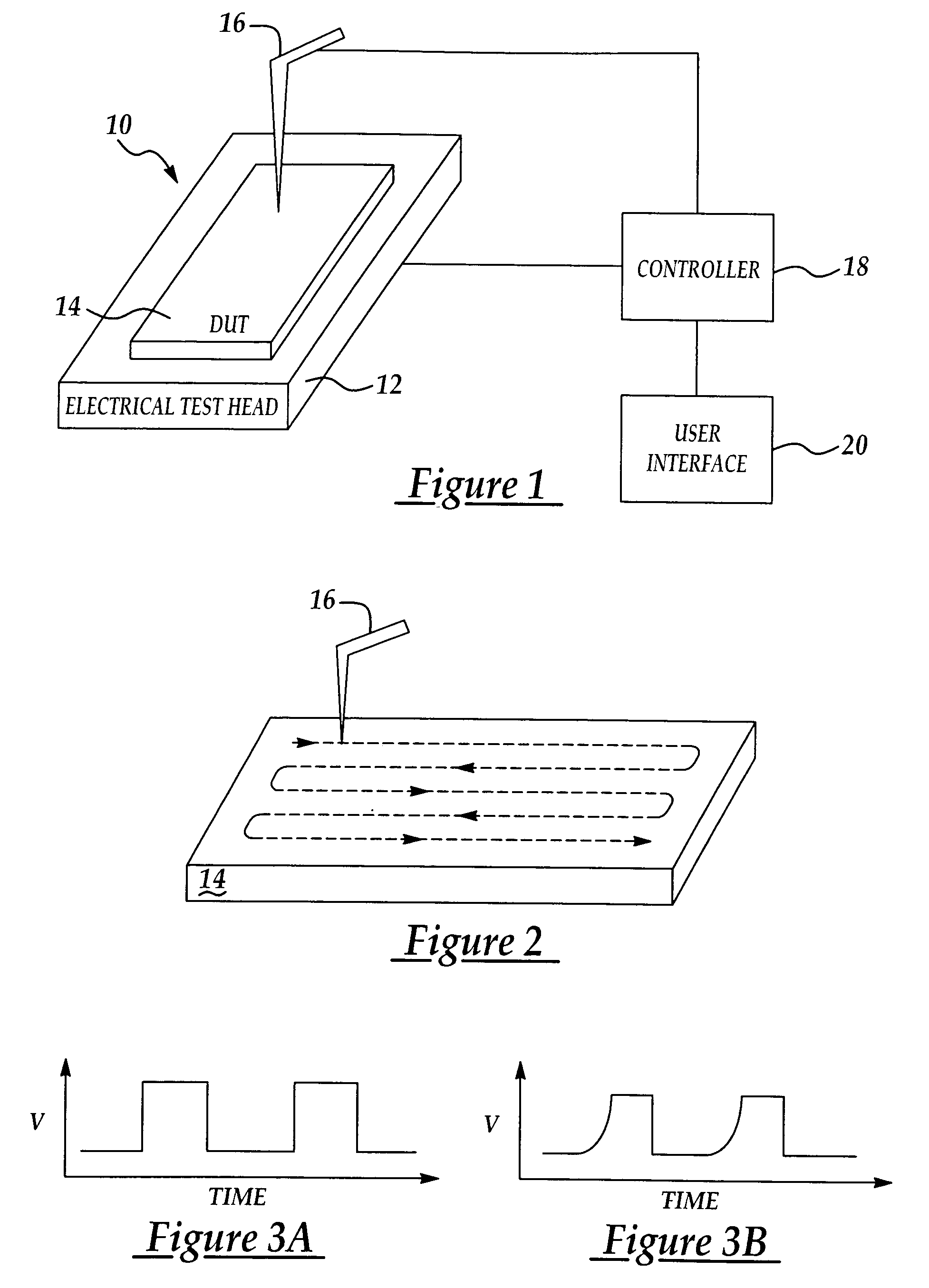
Electrical bias electrical test apparatus and method
InactiveUS7224173B2Accurate and efficient testingElectric discharge tubesIndividual semiconductor device testingElectricityElectrical testing
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Vehicle-mounted head-up displayer cover plate assembly and testing device and testing method of assembly
ActiveCN109682608AStable structureImprove performanceVehicle testingOptically investigating flaws/contaminationIn vehicleStructural engineering
The invention provides a vehicle-mounted head-up displayer cover plate assembly. The vehicle-mounted head-up displayer cover plate assembly comprises a cover plate frame, a sliding cover plate and adriving unit, wherein the sliding cover plate is arranged on the cover plate frame, the driving unit and the sliding cover plate is connected in linkage, the driving unit drives the sliding cover plate to slide on the cover plate frame. The invention also discloses a testing device of the vehicle-mounted head-up displayer cover plate assembly. The testing device comprises a base plate, a controlbox, a positioning column and a liner column, wherein the control box, the positioning post and the liner column are all arranged on the base plate, the cover plate frame is arranged on the positioning post and the liner column, and the control box and the driving unit are electrically connected. The vehicle-mounted head-up displayer cover plate assembly and the testing device for detecting the cover plate assembly have the advantage that the quality and performance of the cover plate assembly during delivery are ensured.
Owner:NINGBO SHUAITELONG GRP CO LTD
Electrical test head used for keyboard key electrical performance testing
InactiveCN105277879AHighly integratedHigh degree of automationCircuit interrupters testingElectricityKey pressing
The invention discloses an electrical test head used for keyboard key electrical performance testing. The electrical test head comprises a holder which is vertically distributed, first and second crossbars which vertically pass through and are locked on the holder, a fixation ring, a limiting ring and a test head assembly which is arranged on the fixation ring, wherein the fixation ring and the limiting ring are respectively arranged on the same side end of first and second crossbars. The test head assembly comprises an electromagnet and a weight from top to bottom, wherein the electromagnet and the weight are in lap connection. The electromagnet is fixed on the fixation ring. The top end of the electromagnet is a free end and is connected with a test wire. The bottom end of the electromagnet runs into the top end of the weight and is locked by a gasket. The weight is sleeved by the limiting ring. The top end of the weight is in sleeve joint with the bottom end of the electromagnet, and is hung on and in lap connection with the gasket. The bottom end of the weight is a free end, and acts on keys in a keyboard to be tested. The weight acts on the keys, is stressed upward, and moves upward along the bottom end of the electromagnet. The electrical test head has the advantages of high automation degree, accurate and efficient testing, flexible, smooth and precise adjustment, and high versatility, and is suitable for keyboard key layout of different products.
Owner:KUNSHAN HONGZHIXI AUTOMATION EQUIP
Product positioning test system and test method
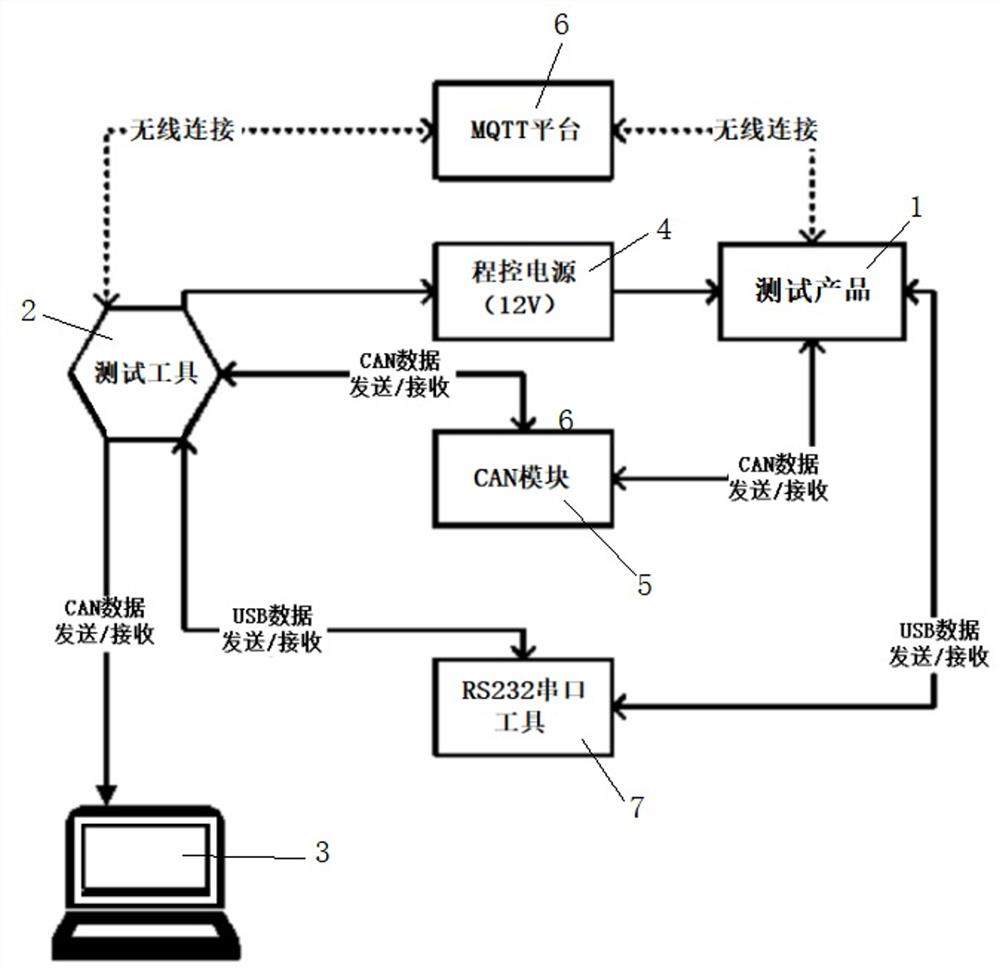
PendingCN113032276AStable data interactionSimple test stepsSoftware testing/debuggingEmbedded systemData transmission
The invention relates to the technical field of automatic information processing, and discloses a positioning product test system, which comprises a test product, a test tool and a terminal, and is characterized in that the test product is in communication connection with the test tool through a transmission protocol, and the test tool sends an instruction to the test product and receives feedback through the transmission protocol; The test tool is connected to a terminal for communication, and the transmission protocol comprises a CAN port protocol, an MQTT data transmission protocol and an RS-232 data transmission protocol. The invention further discloses a positioning product testing method. According to the invention, accurate and quick testing of data interaction and sending and receiving functions of a tested product is realized.
Owner:上海寰果信息科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com